Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-32.2 - CERTIFICATION - China Green Agriculture, Inc. | f10k2017a2ex32-2_chinagreen.htm |
| EX-32.1 - CERTIFICATION - China Green Agriculture, Inc. | f10k2017a2ex32-1_chinagreen.htm |
| EX-31.2 - CERTIFICATION - China Green Agriculture, Inc. | f10k2017a2ex31-2_chinagreen.htm |
| EX-31.1 - CERTIFICATION - China Green Agriculture, Inc. | f10k2017a2ex31-1_chinagreen.htm |
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K/A
(Amendment No.2)
☒ ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the fiscal year ended June 30, 2017
or
☐ TRANSITION REPORT UNDER SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the transition period from _________ to _____________
Commission file number: 001-34260
CHINA GREEN AGRICULTURE, INC.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| Nevada | 36-3526027 | |
| (State
or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) |
(I.R.S.
Employer Identification No.) |
Third floor, Borough A, Block A. No. 181, South Taibai Road
Xi’an, Shaanxi Province, PRC 710065
(Address of principal executive offices) (Zip Code)
Registrant’s telephone number: +86-29-88266368
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| Title of each class | Name of each exchange on which registered | |
| Common Stock, $0.001 Par Value Per Share | NYSE |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None.
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Exchange Act. Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such report(s)), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§ 232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of Registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company,” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| Large accelerated filer ☐ | Accelerated filer ☐ | |
| Non-accelerated filer ☐ | Smaller reporting company ☒ | |
| Do not check if a smaller reporting company | Emerging growth company ☐ |
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes ☐ No ☒
The aggregate market value of the voting and non-voting common equity held by non-affiliates computed by reference to the price at which the common equity was last sold, or the average bid and asked price of such common equity, as of the last business day of the registrant’s most recently completed second fiscal quarter: $31,605,055 as of December 31, 2016, based on the closing price $1.20 of the Company’s common stock on such date.
The number of outstanding shares of the registrant’s common stock on October 19, 2017, was 38,551,265.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
None.
Explanatory Note
This Amendment No. 2 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K/A is filed as an amendment to the Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2017 filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”) by China Green Agriculture, Inc. (the "Company") on October 19, 2017. The purpose of this Amendment No. 2 is to revise certain disclosures pursuant to the comment letter received from the SEC in connection with our filing of the Form 10-K/A on March 16, 2018.
In this Amendment, the following changes were included:
| ● | We marked the 2017 column in the statement of cash flows as “Restated.”, and added note 20, restatement of financial statements |
| ● | The Company's independent registered public accounting firm had performed necessary procedures as a result of the restatement and the audit report was updated; |
| ● | As we reclassified certain cash outflows from operating activities to investing activities, we conclude that the Disclosure Controls and Procedures were not effective as of June 30, 2017 and Internal Controls over Financial Reporting were not effective as of June 30, 2017. We revised the conclusion in Item 9a. |
This Form 10-K/A does not reflect events that may have occurred subsequent to the original filing date of October 19, 2017 and does not modify or update in any other way disclosures made in the Form 10-K. Accordingly, this Form 10-K/A should be read in conjunction with the Form 10-K and other filings made with the Commission subsequent to the filing of the Form 10-K, including any amendments to those filings.
Pursuant to Rule 12b-15 under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, this Form 10-K/A contains the complete text of Item 8, Item 9, Item 9a, Item 9b, the financial statements, and the currently dated certifications of our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer. Capitalized terms not otherwise defined have the meanings ascribed to them in the Form 10-K.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
| i |
| Item 8. | Financial Statements and Supplementary Data |
Balance sheets, as of June 30, 2017 and 2016, and statements of operations, stockholders’ equity and cash flows for each of the two years in the period ended June 30, 2017 and 2016, together with the related notes and the reports of independent registered public accounting firms, are set forth on the “F” pages of this report.
| Item 9. | Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants On Accounting and Financial Disclosure |
Not applicable.
| Item 9a. | Controls and Procedures |
| (a) | Disclosure Controls and Procedures |
Pursuant to Rule 13a-15(b) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 ("Exchange Act"), at the conclusion of the fiscal year ended June 30, 2017 we carried out an evaluation, under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, of the effectiveness of the design and operation of our disclosure controls and procedures (as such term is defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 (the “Exchange Act”)). In March 2018, we reevaluated the effectiveness of the design and operation of our disclosure controls and procedures. Based upon the additional evaluation, our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer concluded that as of June 30, 2017, our disclosure controls and procedures were not effective to satisfy the objectives for which they are intended due to the material weakness in our internal control over financial reporting discussed below.
| (b) | Management Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting |
Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of our financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles. Internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (i) pertain to the maintenance of records that in reasonable detail accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the Company; (ii) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the Company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the Company; and (iii) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the Company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
| 1 |
Any system of internal control, no matter how well designed, has inherent limitations, including the possibility that a control can be circumvented or overridden and misstatements due to error or fraud may occur and not be detected in a timely manner. Also, because of changes in conditions, internal control effectiveness may vary over time. Accordingly, even an effective system of internal control will provide only reasonable assurance with respect to financial statement preparation. In addition, the design of any system of controls is based in part on certain assumptions about the likelihood of future events, and there can be no assurance that any design will succeed in achieving its stated goals under all potential future conditions. Over time, controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions or deterioration in the degree of compliance with policies or procedures. Therefore, any current evaluation of controls cannot and should not be projected to future periods.
Management assessed our internal control over financial reporting as of the year ended June 30, 2017. In making this assessment, management used the criteria set forth by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission 2013 framework (COSO) in the report entitled "Internal Control-Integrated Framework." The COSO framework summarizes each of the components of a company’s internal control system, including (i) the control environment, (ii) risk assessment, (iii) control activities, (iv) information and communication, and (v) monitoring. Our management has implemented and tested our internal control over financial reporting based on these criteria and noted the existence of a material weakness as of June 30, 2017. Such material weakness in internal control over our financial reporting was primarily related to our ability to properly record and classify payments we made in acquisitions. Our inability to properly record and classify such acquisition payments may result in inadequate or deficient financial reporting. Our management has considered it as material weakness and determined that as of June 30, 2017, the internal control over financial reporting was not effective to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external reporting purposes in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
In an effort to remedy the material weakness in the future, we have commenced to do the following:
| ● | Develop a comprehensive training and development plan, for our finance, accounting and internal audit personnel, including our Chief Financial Officer, Financial Manager, and others, in the principles and rules of U.S. GAAP, SEC reporting requirements and the application thereof. |
| ● | Design and implement a program to provide ongoing company-wide training regarding the Company’s internal controls, with particular emphasis on our finance and accounting staff. |
| ● | Implement an internal review process over financial reporting to review all recent accounting pronouncements and to verify that the accounting treatment identified in such report have been fully implemented and confirmed by our internal control department. In the future, we will continue to improve our ongoing review and supervision of our internal control over financial reporting. |
We are not required to have our internal control over financial reporting as of June 30, 2017 audited by our auditors because we are a smaller reporting company.
| (c) | Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting |
There were no changes in the Company’s internal control over financial reporting that occurred during our last fiscal quarter ended June 30, 2017 that has materially affected or is reasonably likely to materially affect our internal control over financial reporting.
| Item 9b. | Other Information |
There is no other information required to be disclosed under this item which was not previously disclosed.
| 2 |
| Item 15. | Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules |
| (a) | The following documents are filed as part of this report: |
| (1) | Financial Statements |
The following financial statements of China Green Agriculture, Inc. and Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm are presented in the “F” pages of this Report:
| (2) | Financial Schedules |
| None. | |
Financial statement schedules have been omitted because they are either not applicable or the required information is included in the financial statements or notes hereto.
| (3) | Exhibits |
The exhibits listed in the accompanying index to exhibits are filed or incorporated by reference as part of this Report.
| (b) | Exhibits |
See the Exhibit Index following the signature page of this report, which Index is incorporated herein by reference.
| 3 |
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the Registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| China Green Agriculture, Inc. | ||
| Date: April 13, 2018 | By: | /s/ Zhuoyu Li |
| Zhuoyu Li, CEO | ||
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this Report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the Registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| April 13, 2018 | /s/ Zhuoyu Li | |
| Zhuoyu Li, Chairman of the Board of Directors and | ||
| CEO (principal executive officer) | ||
| April 13, 2018 | /s/ Yongcheng Yang | |
| Yongcheng Yang, Chief Financial Officer | ||
| (principal financial officer and | ||
| principal accounting officer) | ||
| April 13, 2018 | /s/ Ale Fan | |
| Ale Fan, Director | ||
| April 13, 2018 | /s/ Lianfu Liu | |
| Lianfu Liu, Director | ||
| April 13, 2018 | /s/ Daqing Zhu | |
| Daqing Zhu, Director | ||
| April 13, 2018 | /s/ Jinjun Lu | |
| Jinjun Lu, Director |
| 4 |
China Green Agriculture, Inc.
Exhibit Index to Annual Report on Form 10-K/A
For the Year Ended June 30, 2017
| 5 |
| 101.INS | XBRL Instance Document. |
| 101.SCH | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document. |
| 101.CAL | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document. |
| 101.LAB | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document. |
| 101.PRE | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document. |
| 101.DEF | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document. |
* Filed herewith
+ In accordance with SEC Release 33-8238, Exhibit 32.1 and 32.2 are being furnished and not filed.
| 6 |
FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
CHINA GREEN AGRICULTURE, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Index to Consolidated Financial Statements
TABLE OF CONTENTS
| F-1 |
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors of
China Green Agriculture, Inc. and its subsidiaries
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of China Green Agriculture, Inc. and its subsidiaries (the “Company”) as of June 30, 2017 and 2016, and the related consolidated statements of income and comprehensive income (loss), stockholders’ equity, and cash flows for each of the years in the two-year period ended June 30, 2017. The Company’s management is responsible for these financial statements. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements and schedules are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of China Green Agriculture, Inc. and its subsidiaries as of June 30, 2017 and 2016, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the years in the two-year period ended June 30, 2017 in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
As discussed in note 20, the Company restated its financial statements for the year ended June 30, 2017
/s/ KSP Group, INC.
CERTIFIED PUBLIC ACCOUNTANTS
Los Angeles, CA
April 13, 2018
| F-2 |
CHINA GREEN AGRICULTURE,
INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
AS OF JUNE 30, 2017 AND 2016
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| ASSETS | ||||||||
| Current Assets | ||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 123,050,548 | $ | 102,896,486 | ||||
| Accounts receivable, net | 140,252,335 | 116,573,490 | ||||||
| Inventories | 78,013,891 | 87,436,315 | ||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | 4,201,782 | 1,310,709 | ||||||
| Amount due from related parties | 1,412,844 | 481,886 | ||||||
| Advances to suppliers, net | 24,023,062 | 24,606,459 | ||||||
| Total Current Assets | 370,954,462 | 333,305,345 | ||||||
| Plant, Property and Equipment, Net | 34,191,332 | 37,569,739 | ||||||
| Deferred Asset, Net | 864,070 | 13,431,621 | ||||||
| Other Assets | 279,031 | 379,047 | ||||||
| Other Non-current Assets | 17,829,621 | 0 | ||||||
| Intangible Assets, Net | 22,911,876 | 23,840,048 | ||||||
| Goodwill | 8,651,238 | 7,980,838 | ||||||
| Total Assets | $ | 455,681,630 | $ | 416,506,638 | ||||
| LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | ||||||||
| Current Liabilities | ||||||||
| Accounts payable | $ | 19,643,897 | $ | 5,246,153 | ||||
| Customer deposits | 7,046,570 | 6,320,841 | ||||||
| Accrued expenses and other payables | 9,135,313 | 16,396,003 | ||||||
| Amount due to related parties | 3,071,102 | 2,473,004 | ||||||
| Taxes payable | 2,690,407 | 4,104,218 | ||||||
| Short term loans | 7,678,111 | 4,665,500 | ||||||
| Interest payable | 256,904 | 0 | ||||||
| Derivative liability | 195,812 | 144,818 | ||||||
| Total Current Liabilities | 49,718,116 | 39,350,537 | ||||||
| Long-term Liabilities | ||||||||
| Long-term loan | 3,549 | 0 | ||||||
| Convertible notes payable | 8,431,912 | 6,671,769 | ||||||
| Total Liabilities | $ | 58,153,577 | $ | 46,022,306 | ||||
| Stockholders’ Equity | ||||||||
| Preferred Stock, $.001 par value, 20,000,000 shares authorized, zero shares issued and outstanding | - | - | ||||||
| Common stock, $.001 par value, 115,197,165 shares authorized, 38,535,161 and 36,978,605 shares issued and outstanding as of June 30, 2017 and June 30, 2016, respectively | 38,551 | 37,648 | ||||||
| Additional paid-in capital | 128,915,651 | 127,593,932 | ||||||
| Statutory reserve | 28,962,302 | 27,203,861 | ||||||
| Retained earnings | 244,738,993 | 221,345,279 | ||||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive income | (5,127,444 | ) | (5,696,388 | ) | ||||
| Total Stockholders’ Equity | 397,528,052 | 370,484,332 | ||||||
| Total Liabilities and Stockholders’ Equity | $ | 455,681,629 | $ | 416,506,638 | ||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
| F-3 |
CHINA GREEN AGRICULTURE, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF INCOME AND COMPREHENSIVE INCOME (LOSS)
FOR THE YEARS ENDED JUNE 30, 2017 AND 2016
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Sales | ||||||||
| Jinong | $ | 106,642,032 | $ | 125,716,937 | ||||
| Gufeng | 104,446,239 | 134,661,420 | ||||||
| Yuxing | 8,517,231 | 8,406,663 | ||||||
| VIEs - others | 65,607,538 | 0 | ||||||
| Net sales | 285,213,040 | 268,785,020 | ||||||
| Cost of goods sold | ||||||||
| Jinong | 48,056,379 | 53,515,169 | ||||||
| Gufeng | 89,913,446 | 116,427,052 | ||||||
| Yuxing | 6,872,878 | 5,813,468 | ||||||
| VIEs - others | 56,598,252 | 0 | ||||||
| Cost of goods sold | 201,440,955 | 175,755,689 | ||||||
| Gross profit | 83,772,085 | 93,029,331 | ||||||
| Operating expenses | ||||||||
| Selling expenses | 32,472,315 | 48,596,184 | ||||||
| General and administrative expenses | 19,321,999 | 11,841,228 | ||||||
| Total operating expenses | 51,794,314 | 60,437,412 | ||||||
| Income from operations | 31,977,771 | 32,591,919 | ||||||
| Other income (expense) | ||||||||
| Other income (expense) | (82,491 | ) | (5,473 | ) | ||||
| Interest income | 318,404 | 485,673 | ||||||
| Interest expense | (549,650 | ) | (995,959 | ) | ||||
| Total other income (expense) | (313,737 | ) | (515,759 | ) | ||||
| Income before income taxes | 31,664,034 | 32,076,160 | ||||||
| Provision for income taxes | 6,511,880 | 7,371,967 | ||||||
| Net income | 25,152,154 | 24,704,193 | ||||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss) | ||||||||
| Foreign currency translation gain (loss) | 568,944 | (31,404,626 | ) | |||||
| Comprehensive income (loss) | $ | 25,721,098 | $ | (6,700,433 | ) | |||
| Basic weighted average shares outstanding | 38,093,028 | 36,703,576 | ||||||
| Basic net earnings per share | $ | 0.66 | $ | 0.67 | ||||
| Diluted weighted average shares outstanding | 38,093,028 | 36,703,576 | ||||||
| Diluted net earnings per share | 0.66 | 0.67 | ||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
| F-4 |
CHINA GREEN AGRICULTURE, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
STATEMENTS OF STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
FOR THE YEARS ENDED JUNE 30, 2017 AND 2016
| Additional | Accumulated Other | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number | Common | Paid In | Statutory | Retained | Comprehensive | Stockholders’ | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Of Shares | Stock | Capital | Reserve | Earnings | Income | Equity | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| BALANCE, JUNE 30, 2015 | 35,905,198 | 35,905 | 123,360,384 | 25,030,688 | 198,814,259 | 25,708,238 | 372,949,474 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 24,704,193 | 24,704,193 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of stock for consulting services | 73,407 | 73 | 114,690 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 114,763 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock based compensation | 1,670,000 | 1,670 | 4,118,858 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4,120,528 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Transfer to statutory reserve | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2,173,173 | (2,173,173 | ) | 0 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive income | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | (31,404,626 | ) | (31,404,626 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
| BALANCE, JUNE 30, 2016 | 37,648,605 | $ | 37,648 | $ | 127,593,932 | $ | 27,203,861 | $ | 221,345,279 | $ | (5,696,388 | ) | $ | 370,484,332 | ||||||||||||||
| Net income | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 25,152,154 | 25,152,154 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of stock for consulting services | 32,660 | 33 | 41,179 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 41,212 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock based compensation | 870,000 | 870 | 1,280,539 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1,281,409 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Transfer to statutory reserve | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1,758,441 | (1,758,441 | ) | 0 | 0 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive income | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 568,944 | 568,944 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| BALANCE, June 30, 2017 | 38,551,265 | $ | 38,551 | $ | 128,915,651 | $ | 28,962,302 | $ | 244,738,993 | $ | (5,127,444 | ) | $ | 397,528,052 | ||||||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
| F-5 |
CHINA GREEN AGRICULTURE, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
FOR THE YEARS ENDED JUNE 30, 2017 AND 2016
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Restated | ||||||||
| Cash flows from operating activities | ||||||||
| Net income | $ | 25,152,154 | $ | 24,704,193 | ||||
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities | ||||||||
| Issuance of common stock and stock options for compensation | 1,323,292 | 4,235,291 | ||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 17,408,120 | 40,311,189 | ||||||
| Gain (Loss) on disposal of property, plant and equipment | 108,309 | 1,368 | ||||||
| Amortization of debt discount | 228,292 | |||||||
| Change in fair value of derivative liability | 29,457 | |||||||
| Changes in operating assets | ||||||||
| Accounts receivable | (22,327,119 | ) | (48,730,250 | ) | ||||
| Amount due from related parties | (910,622 | ) | (481,886 | ) | ||||
| Other current assets | (2,791,737 | ) | (88,636 | ) | ||||
| Inventories | 10,031,596 | 13,933,090 | ||||||
| Advances to suppliers | 527,953 | 15,300,685 | ||||||
| Other assets | (17,116,355 | ) | 64,449 | |||||
| Changes in operating liabilities | ||||||||
| Accounts payable | 13,362,022 | (945,055 | ) | |||||
| Customer deposits | 279,605 | (15,242,740 | ) | |||||
| Tax payables | (1,374,636 | ) | (55,805 | ) | ||||
| Accrued expenses and other payables | (2,467,431 | ) | 1,352,762 | |||||
| Interest payable | 251,064 | 0 | ||||||
| Net cash provided by operating activities | 21,713,964 | 34,358,655 | ||||||
| Cash flows from investing activities | ||||||||
| Purchase of plant, property, and equipment | (42,283 | ) | (19,192 | ) | ||||
| Cash paid for acquisition, net | (5,560,350 | ) | 708,737 | |||||
| Change in construction in process | (210,873 | ) | 0 | |||||
| Net cash used in investing activities | (5,813,506 | ) | 689,545 | |||||
| Cash flows from financing activities | ||||||||
| Proceeds from loans | 5,948,021 | 3,110,000 | ||||||
| Repayment of loans | (3,154,956 | ) | (20,712,600 | ) | ||||
| Advance from related party | 600,000 | 500,000 | ||||||
| Net cash provided by financing activities | 3,393,065 | (17,102,600 | ) | |||||
| Effect of exchange rate change on cash and cash equivalents | 860,540 | (8,031,678 | ) | |||||
| Net increase in cash and cash equivalents | 20,154,063 | 9,913,922 | ||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents, beginning balance | 102,896,486 | 92,982,564 | ||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents, ending balance | $ | 123,050,548 | $ | 102,896,486 | ||||
| Supplement disclosure of cash flow information | ||||||||
| Interest expense paid | $ | 289,869 | $ | 995,959 | ||||
| Income taxes paid | $ | 6,899,600 | $ | 7,217,789 | ||||
| Supplement non-cash activities | ||||||||
| Convertible note issued for acquisitions | $ | 1,503,277 | $ | 6,671,769 | ||||
| Derivative liability issued for acquisitions | $ | 20,626 | $ | 144,818 | ||||
| Nonmonetary sales and purchases | $ | 58,205,497 | $ | - | ||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
| F-6 |
CHINA GREEN AGRICULTURE, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
JUNE 30, 2017
NOTE 1 – ORGANIZATION AND DESCRIPTION OF BUSINESS
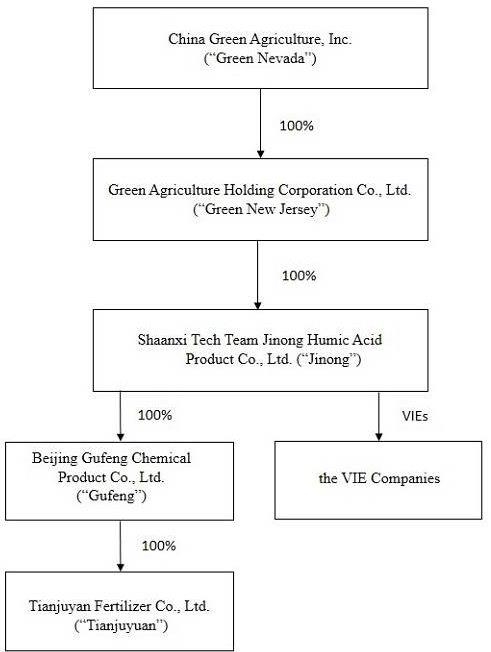
China Green Agriculture, Inc. (the “Company”, “Parent Company” or “Green Nevada”), through its subsidiaries, is engaged in the research, development, production, distribution and sale of humic acid-based compound fertilizer, compound fertilizer, blended fertilizer, organic compound fertilizer, slow-release fertilizers, highly-concentrated water-soluble fertilizers and mixed organic-inorganic compound fertilizer and the development, production and distribution of agricultural products.
Unless the context indicates otherwise, as used in the notes to the financial statements of the Company, the following are the references herein of all the subsidiaries of the Company (i) Green Agriculture Holding Corporation (“Green New Jersey”), a wholly-owned subsidiary of Green Nevada, incorporated in the State of New Jersey; (ii) Shaanxi TechTeam Jinong Humic Acid Product Co., Ltd. (“Jinong”), a wholly-owned subsidiary of Green New Jersey organized under the laws of the PRC; (iii) Xi’an Hu County Yuxing Agriculture Technology Development Co., Ltd. (“Yuxing”), a Variable Interest Entity (“VIE”) in the in the People’s Republic of China (the “PRC”) controlled by Jinong through a series of contractual agreements; (iv) Beijing Gufeng Chemical Products Co., Ltd., a wholly-owned subsidiary of Jinong in the PRC (“Gufeng”), and (v) Beijing Tianjuyuan Fertilizer Co., Ltd., Gufeng’s wholly-owned subsidiary in the PRC (“Tianjuyuan”).
On June 30, 2016 the Company, through its wholly-owned subsidiary Jinong, entered into strategic acquisition agreements and a series of contractual agreements with the shareholders of the following six companies that are organized under the laws of the PRC and would be deemed VIEs: Shaanxi Lishijie Agrochemical Co., Ltd. (“Lishijie”), Songyuan Jinyangguang Sannong Service Co., Ltd. (“Jinyangguang”), Shenqiu County Zhenbai Agriculture Co., Ltd. (“Zhenbai”), Weinan City Linwei District Wangtian Agricultural Materials Co., Ltd. (“Wangtian”), Aksu Xindeguo Agricultural Materials Co., Ltd. (“Xindeguo”), and Xinjiang Xinyulei Eco-agriculture Science and Technology co., Ltd. (“Xinyulei”). On January 1, 2017, the Company, through its wholly-owned subsidiary Jinong, entered into strategic acquisition agreements and a series of contractual agreements with the shareholders of the following six companies that are organized under the laws of the PRC and would be deemed VIEs Sunwu County Xiangrong Agricultural Materials Co., Ltd. (“Xiangrong”), and Anhui Fengnong Seed Co., Ltd. (“Fengnong”).
Yuxing, Lishijie, Jinyangguang, Zhenbai, Wangtian, Xindeguo, Xinyulei, Xiangrong and Fengnong may also collectively be referred to as the “the VIE Companies”; Lishijie, Jinyangguang, Zhenbai, Wangtian, Xindeguo, Xinyulei, Xiangrong and Fengnong may also collectively be referred to as “the sales VIEs”.
| F-7 |
CHINA GREEN AGRICULTURE, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
JUNE 30, 2017
The Company’s current corporate structure as of is set forth in the diagram below:
| F-8 |
CHINA GREEN AGRICULTURE, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
JUNE 30, 2017
NOTE 2 – BASIS OF PRESENTATION AND SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Principle of consolidation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company and its wholly-owned subsidiaries, Green New Jersey, Jinong, Gufeng, Tianjuyuan, and the VIE Companies. All significant inter-company accounts and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
Effective June 16, 2013, Yuxing was converted from being a wholly-owned foreign enterprise 100% owned by Jinong to a domestic enterprise 100% owned one natural person, who is not affiliated to the Company (“Yuxing’s Owner”). Effective the same day, Yuxing’s Owner entered into a series of contractual agreements with Jinong pursuant to which Yuxing became the VIE of Jinong.
VIE assessment
A VIE is an entity (1) that has total equity at risk that is not sufficient to finance its activities without additional subordinated financial support from other entities, (2) where the group of equity holders does not have the power to direct the activities of the entity that most significantly impact the entity’s economic performance, or the obligation to absorb the entity’s expected losses or the right to receive the entity’s expected residual returns, or both, or (3) where the voting rights of some investors are not proportional to their obligations to absorb the expected losses of the entity, their rights to receive the expected residual returns of the entity, or both, and substantially all of the entity’s activities either involve or are conducted on behalf of an investor that has disproportionately few voting rights. To determine if an entity is considered a VIE, the Company first perform a qualitative analysis, which requires certain subjective decisions regarding its assessments, including, but not limited to, the design of the entity, the variability that the entity was designed to create and pass along to its interest holders, the rights of the parties, and the purpose of the arrangement. If the Company cannot conclude after a qualitative analysis whether an entity is a VIE, it performs a quantitative analysis. The qualitative analysis considered the design of the entity, the risks that cause variability, the purpose for which the entity was created, and the variability that the entity was designed to pass along to its variable interest holders. When the primary beneficiary could not be identified through a qualitative analysis, we used internal cash flow models to compute and allocate expected losses or expected residual returns to each variable interest holder based upon the relative contractual rights and preferences of each interest holder in the VIE’s capital structure.
Use of estimates
The preparation of consolidated financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the consolidated financial statements and the amount of revenues and expenses during the reporting periods. Management makes these estimates using the best information available at the time the estimates are made. However, actual results could differ materially from those results.
Cash and cash equivalents and concentration of cash
For statement of cash flows purposes, the Company considers all cash on hand and in banks, certificates of deposit with state owned banks in the Peoples Republic of China (“PRC”) and banks in the United States, and other highly-liquid investments with maturities of three months or less, when purchased, to be cash and cash equivalents. The Company maintains large sums of cash in three major banks in China. The aggregate cash in such accounts and on hand as of June 30, 2017 and 2016 was $122,907,629 and $102,728,991, respectively. There is no insurance securing these deposits in China. In addition, the Company also had $142,919 and $167,495 in cash in two banks in the United States as of June 30, 2017 and 2016, respectively. Cash overdraft as of balance sheet date will be reflected as liabilities in the balance sheet. The Company has not experienced any losses in such accounts and believes it is not exposed to any significant risks on its cash in bank accounts.
Accounts receivable
The Company’s policy is to maintain reserves for potential credit losses on accounts receivable. Management regularly reviews the composition of accounts receivable and analyzes customer credit worthiness, current economic trends and changes in customer payment patterns to evaluate the adequacy of these reserves at each year-end. Accounts considered uncollectible are written off through a charge to the valuation allowance. As of June 30, 2017, and 2016, the Company had accounts receivable of $149,709,758 and $117,936,342, net of allowance for doubtful accounts of $9,457,423 and $1,362,852, respectively. The Company adopts no policy to accept product returns post to the sales delivery.
| F-9 |
CHINA GREEN AGRICULTURE, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
JUNE 30, 2017
Other receivable
Other receivable relates to the amount due from party other than the counterparties of the business contracts and trades that the Company and the subsidiaries entered. The Company had none other receivable during the year ended Jun 30, 2017 and the year ended June 30, 2016.
Inventories
Inventory is valued at the lower of cost (determined on a weighted average basis) or market. Inventories consist of raw materials, work in process, finished goods and packaging materials. The Company reviews its inventories regularly for possible obsolete goods and establishes reserves when determined necessary. At June 30, 2017 and 2016, the Company had no reserve for obsolete goods.
Property, plant and equipment
Property, plant and equipment are recorded at cost. Gains or losses on disposals are reflected as gain or loss in the year of disposal. The cost of improvements that extend the life of plant, property, and equipment are capitalized. These capitalized costs may include structural improvements, equipment, and fixtures. All ordinary repair and maintenance costs are expensed as incurred.
Depreciation for financial reporting purposes is provided using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the assets:
| Estimated Useful Life | ||
| Building | 10-25 years | |
| Agricultural assets | 8 years | |
| Machinery and equipment | 5-15 years | |
| Vehicles | 3-5 years |
Construction in Progress
Construction in progress represents the costs incurred relating to the construction of buildings or new additions to the Company’s plant facilities. Costs classified to construction in progress include all costs of obtaining the asset and bringing it to the location and condition necessary for its intended use. No depreciation is provided for construction in progress until the assets are completed and are placed into service. Interest incurred during construction is capitalized into construction in progress.
| F-10 |
CHINA GREEN AGRICULTURE, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
JUNE 30, 2017
Long-Lived Assets
The Company tests long-lived assets for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable through the estimated undiscounted cash flows expected to result from the use and eventual disposition of the assets. Whenever any such impairment exists, an impairment loss will be recognized for the amount by which the carrying value exceeds the fair value. At June 30, 2017 and 2016, the Company determined that there were no impairments of its long-lived assets.
Deferred asset
Deferred assets represent amounts that the distributors owed to the Company in their marketing efforts and developing standard stores to expand the Company’s products’ competitiveness and market shares. The amount owed to the Company to assist its distributors will be expensed over three years which is the term as stated in the cooperation agreement, if the distributors are actively selling the Company’s products. For the years ended June 30, 2017 and 2016, the Company amortized $12,567,551 and $35,068,272, respectively, of the deferred assets. If a distributor breaches, defaults, or terminates the agreement with the Company within the three-year period, the outstanding unamortized portion of the amount owed will become payable to the Company immediately. The Company’s Chairman, Mr. Li, guaranteed to the Company of amounts remaining unpaid due from distributors. These deferred assets are subject to annual impairment testing. The estimated amortization expense of the deferred assets for the twelve months ending June 30, 2018 is $864,070.
The deferred assets consist of items inside the distributors’ stores such as furniture, racks, cabinets, and display units, and items outside or attached to the distributors’ stores such as signage and billboards. These types of assets would be capitalized as fixed assets if the Company owned the stores or utilized the assets for its own operations. These assets would also be capitalized as leasehold improvements if the Company leased these stores from the distributors. Therefore, the Company believes that under the U.S. generally accepted accounting principles, these types of assets purchases are properly capitalized. In addition, the Company believes that these assets are properly classified as deferred assets because if a distributor breaches, defaults, or terminates the agreement with the Company within a three-year period, a proportionate amount expended by the Company is to be repaid by the distributor. The Chairman of the Board of directors of the Company guaranteed to the Company of amounts remaining unpaid due from distributors.
The assets inside the distributors’ stores are custom made to fit the layout of each individual store and the signage and billboards are also custom designed to fit the specific location. The assets were purchased by the Company directly from the manufacturers and installed in the distributors’ stores. The Company wants to maintain control over the quality of the items being purchased as well as making them uniform among all the distributor locations.
| June 30, | June 30, | |||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Total Deferred Assets | $ | 11,580,304 | $ | 130,086,315 | ||||
| Less: accumulated amortization | $ | (10,716,234 | ) | $ | (116,654,694 | ) | ||
| Total | $ | 864,070 | $ | 13,431,621 | ||||
Intangible Assets
The Company records intangible assets acquired individually or as part of a group at fair value. Intangible assets with definitive lives are amortized over the useful life of the intangible asset, which is the period over which the asset is expected to contribute directly or indirectly to the entity’s future cash flows. The Company evaluates intangible assets for impairment at least annually and more often whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying value may not be recoverable. Whenever any such impairment exists, an impairment loss will be recognized for the amount by which the carrying value exceeds the fair value. The Company has not recorded impairment of intangible assets as of June 30, 2017 and 2016 respectively.
Goodwill
Goodwill represents the excess of purchase price over the underlying net assets of businesses acquired. Goodwill is reviewed for impairment on an annual basis, or more frequently if events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of goodwill may be impaired. The goodwill impairment test is a two-step test. Under the first step, the fair value of the reporting unit is compared with its carrying value including goodwill. If the fair value of the reporting unit exceeds its carrying value, step two does not need to be performed. If the fair value of the reporting unit is less than its carrying value, an indication of goodwill impairment exists for the reporting unit and the enterprise must perform step two of the impairment test. Under step two, an impairment loss is recognized for any excess of the carrying amount of the reporting unit’s goodwill over the implied fair value of that goodwill. The implied fair value of goodwill is determined by allocating the fair value of the reporting unit in a manner comparable to a purchase price allocation. The residual fair value after this allocation is the implied fair value of the reporting unit goodwill. As of June 30, 2017, and 2016, the Company performed the required impairment review which resulted in no impairment adjustment.
| F-11 |
CHINA GREEN AGRICULTURE, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
JUNE 30, 2017
Summary of changes in goodwill by reporting segments is as follows:
| Balance at | Foreign | Balance at | ||||||||||||||
| June 30, | Currency | June 30, | ||||||||||||||
| Segment | 2016 | Additions | Adjustment | 2017 | ||||||||||||
| Gufeng | $ | 4,822,659 | $ | (8,460 | ) | 4,814,199 | ||||||||||
| Acquisition of VIE Companies | 3,158,179 | 684,399 | (5,540 | ) | 3,837,038 | |||||||||||
| $ | 7,980,838 | $ | 684,399 | $ | (14,000 | ) | $ | 8,651,237 | ||||||||
Fair Value Measurement and Disclosures
Our accounting for Fair Value Measurement and Disclosures, defines fair value as the exchange price that would be received for an asset or paid to transfer a liability (an exit price) in the principal or most advantageous market for the asset or liability in an orderly transaction between market participants on the measurement date. This topic also establishes a fair value hierarchy which requires classification based on observable and unobservable inputs when measuring fair value. The fair value hierarchy distinguishes between assumptions based on market data (observable inputs) and an entity’s own assumptions (unobservable inputs). The hierarchy consists of three levels:
Level one — Quoted market prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities;
Level two — Inputs other than level one inputs that are either directly or indirectly observable; and
Level three — Unobservable inputs developed using estimates and assumptions, which are developed by the reporting entity and reflect those assumptions that a market participant would use.
Determining which category an asset or liability falls within the hierarchy requires significant judgment. The Company evaluates its hierarchy disclosures each quarter.
The following table presents the Company’s assets and liabilities required to be reflected within the fair value hierarchy as of June 30, 2017.
| Fair Value | Fair Value Measurements at | |||||||||||||||
| As of June 30, | June 30, 2017 | |||||||||||||||
| Description | 2017 | Using Fair Value Hierarchy | ||||||||||||||
| Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | ||||||||||||||
| Derivative liability | $ | 195,812 | $ | $ | 195,812 | $ | - | |||||||||
The carrying values of cash and cash equivalents, trade and other receivables, trade and other payables approximate their fair values due to the short maturities of these instruments.
Derivative financial instruments
The Company evaluates its financial instruments to determine if such instruments are derivatives or contain features that qualify as embedded derivatives. For derivative financial instruments that are accounted for as liabilities, the derivative instrument is initially recorded at its fair value and is then re-valued at each reporting date, with changes in the fair value reported in the statements of operations. The Company uses a binomial option pricing model to value the derivative instruments. The classification of derivative instruments, including whether such instruments should be recorded as liabilities or as equity, is evaluated at the end of each reporting period.
At June 30, 2017, the only derivative financial instrument is the variable conversion feature embedded in the convertible notes payable (See Note 9). The fair value of the embedded conversion of $195,812 is recorded as a derivative liability at June 30, 2017. The fair value was determined using a binomial option pricing model with the following assumptions:
| Risk-free rate | 2.5 | % | ||
| Volatility | 51.2 | % | ||
| Dividend yield | 0.0 | % | ||
| Country risk premium | 90.0 | % | ||
| Liquidity risk premium | 3.0 | % |
| F-12 |
CHINA GREEN AGRICULTURE, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
JUNE 30, 2017
Revenue recognition
Sales revenue is recognized on the date of shipment to customers when a formal arrangement exists, the price is fixed or determinable, the delivery is completed, no other significant obligations of the Company exist and collectability is reasonably assured.
The Company’s revenue consists of invoiced value of goods, net of a value-added tax (VAT). No product return or sales discount allowance are made as products delivered and accepted by customers are not returnable and sales discounts are not granted after products are delivered.
Customer deposits
Payments received before all the relevant criteria for revenue recognition are satisfied are recorded as customer deposits. When all revenue recognition criteria are met, the customer deposits are recognized as revenue. As of June 30, 2017, and 2016, the Company had customer deposits of $7,046,570 and $8,578,341, respectively.
Stock-Based Compensation
The costs of all employee stock options, as well as other equity-based compensation arrangements, are reflected in the consolidated financial statements based on the estimated fair value of the awards on the grant date. That cost is recognized over the period during which an employee is required to provide service in exchange for the award—the requisite service period (usually the vesting period). Stock compensation for stock granted to non-employees is determined as the fair value of the consideration received or the fair value of equity instruments issued, whichever is more reliably measured.
Income taxes
The Company accounts for income taxes using an asset and liability approach which allows for the recognition and measurement of deferred tax assets based upon the likelihood of realization of tax benefits in future years. Under the asset and liability approach, deferred taxes are provided for the net tax effects of temporary differences between the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities for financial reporting purposes and the amounts used for income tax purposes. A valuation allowance is provided for deferred tax assets if it is more likely than not these items will either expire before the Company is able to realize their benefits, or that future deductibility is uncertain.
Under ASC 740, a tax position is recognized as a benefit only if it is “more likely than not” that the tax position would be sustained in a tax examination, with a tax examination being presumed to occur. The evaluation of a tax position is a two-step process. The first step is to determine whether it is more-likely-than-not that a tax position will be sustained upon examination, including the resolution of any related appeals or litigations based on the technical merits of that position. The second step is to measure a tax position that meets the more-likely-than-not threshold to determine the amount of benefit to be recognized in the financial statements. A tax position is measured at the largest amount of benefit that is greater than 50 percent likely of being realized upon ultimate settlement. Tax positions that previously failed to meet the more-likely-than-not recognition threshold should be recognized in the first subsequent period in which the threshold is met. Previously recognized tax positions that no longer meet the more-likely-than-not criteria should be de-recognized in the first subsequent financial reporting period in which the threshold is no longer met. Penalties and interest incurred related to underpayment of income tax are classified as income tax expense in the year incurred. No significant penalties or interest relating to income taxes have been incurred during the years ended June 30, 2017, and 2016. GAAP also provides guidance on de-recognition, classification, interest and penalties, accounting in interim periods, disclosures and transition.
Foreign currency translation
The reporting currency of the Company is the US dollar. The functional currency of the Company and Green New Jersey is the US dollar. The functional currency of the Chinese subsidiaries is the Chinese Yuan or Renminbi (“RMB”). For the subsidiaries whose functional currencies are other than the US dollar, all asset and liability accounts were translated at the exchange rate on the balance sheet date; stockholders’ equity is translated at the historical rates and items in the income statement and cash flow statements are translated at the average rate in each applicable period. Translation adjustments resulting from this process are included in accumulated other comprehensive income in the statement of shareholders’ equity. The resulting translation gains and losses that arise from exchange rate fluctuations on transactions denominated in a currency other than the functional currency is included in the results of operations as incurred.
| F-13 |
CHINA GREEN AGRICULTURE, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
JUNE 30, 2017
Segment reporting
The Company utilizes the “management approach” model for segment reporting. The management approach model is based on the way a company’s management organizes segments within the company for making operating decisions and assessing performance. Reportable segments are based on products and services, geography, legal structure, management structure, or any other way management disaggregates a company.
As of June 30, 2017, the Company, through its subsidiaries is engaged into four main business segments based on location and product: Jinong (fertilizer production), Gufeng (fertilizer production) and Yuxing (agricultural products production) and the eight sales VIEs that the Company acquired on June 30, 2016 and January 1, 2017. As of June 30, 2017, the Company maintained four main business segments.
Fair values of financial instruments
Fair value is the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. Assets and liabilities measured at fair value are categorized based on whether the inputs are observable in the market and the degree that the inputs are observable. The categorization of financial assets and liabilities within the valuation hierarchy is based upon the lowest level of input that is significant to the fair value measurement.
The Company’s financial instruments primarily consist of cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable, other receivables, advances to suppliers, accounts payable, other payables, tax payable, and related party advances and borrowings.
As of the balance sheet dates, the estimated fair values of the financial instruments were not materially different from their carrying values as presented on the balance sheets. This is attributed to the short maturities of the instruments and that interest rates on the borrowings approximate those that would have been available for loans of similar remaining maturity and risk profile at respective balance sheet dates.
Statement of cash flows
The Company’s cash flows from operations are calculated based on the local currencies. As a result, amounts related to assets and liabilities reported on the statement of cash flows may not necessarily agree with changes in the corresponding balances on the balance sheets.
Earnings per share
Basic earnings per share is computed based on the weighted average number of shares of common stock outstanding during the period. Diluted earnings per share is computed based on the weighted average number of shares of common stock plus the effect of dilutive potential common shares outstanding during the period using the treasury stock method. Dilutive potential common shares include outstanding stock options and stock awards.
The components of basic and diluted earnings per share consist of the following:
| Years Ended June 30, | ||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Net Income for Basic Earnings Per Share | $ | 25,152,154 | $ | 24,704,193 | ||||
| Basic Weighted Average Number of Shares | 38,093,028 | 36,703,576 | ||||||
| Net Income Per Share – Basic | $ | 0.66 | $ | 0.67 | ||||
| Net Income for Diluted Earnings Per Share | $ | 25,152,154 | $ | 24,704,193 | ||||
| Diluted Weighted Average Number of Shares | 38,093,028 | 36,703,576 | ||||||
| Net Income Per Share – Diluted | $ | 0.66 | $ | 0.67 | ||||
Reclassification
Certain reclassifications have been made to the prior year consolidated financial statements to conform to the 2017 consolidated financial statement presentation. Such reclassifications did not affect total revenues, operating income or net income or cash flows as previously reported.
Recent accounting pronouncements
Revenue Recognition: In May 2014, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update No. 2014-09, Revenue from Contracts with Customers: Topic 606 (ASU 2014-09), to supersede nearly all existing revenue recognition guidance under U.S. GAAP. The core principle of ASU 2014-09 is to recognize revenues when promised goods or services are transferred to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration that is expected to be received for those goods or services. ASU 2014-09 defines a five step process to achieve this core principle and, in doing so, it is possible more judgment and estimates may be required within the revenue recognition process than are required under existing U.S. GAAP, including identifying performance obligations in the contract, estimating the amount of variable consideration to include in the transaction price and allocating the transaction price to each separate performance obligation. ASU 2014-09 is effective for us in our first quarter of fiscal 2018 using either of two methods: (i) retrospective to each prior reporting period presented with the option to elect certain practical expedients as defined within ASU 2014-09 (full retrospective method); or (ii) retrospective with the cumulative effect of initially applying ASU 2014-09 recognized at the date of initial application and providing certain additional disclosures as defined per ASU 2014-09 (modified retrospective method). We are currently assessing the impact to our consolidated financial statements, and have not yet selected a transition approach.
| F-14 |
CHINA GREEN AGRICULTURE, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
JUNE 30, 2017
Disclosure of Going Concern Uncertainties: In August 2014, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) issued Accounting Standards Update No. 2014-15, Disclosure of Uncertainties about an Entity’s Ability to Continue as a Going Concern (ASU 2014-15), to provide guidance on management’s responsibility in evaluating whether there is substantial doubt about a company’s ability to continue as a going concern and to provide related footnote disclosures. ASU 2014-15 is effective for us in our fourth quarter of fiscal 2017 with early adoption permitted. We do not believe the impact of our pending adoption of ASU 2014-15 on the Company’s financial statements will be material.
Financial instrument: In January 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-01, “Financial Instruments - Overall (Subtopic 825-10): Recognition and Measurement of Financial Assets and Financial Liabilities” (“ASU 2016-01”). The standard addresses certain aspects of recognition, measurement, presentation, and disclosure of financial instruments. ASU 2016-01 is effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those years, beginning after December 15, 2017, and early adoption is not permitted. Accordingly, the standard is effective for us on September 1, 2018. We are currently evaluating the impact that the standard will have on our consolidated financial statements.
Leases: In February 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-02, Leases (Topic 842) (“ASU 2016-2”), which provides guidance on lease amendments to the FASB Accounting Standard Codification. This ASU will be effective for us beginning in May 1, 2019. We are currently in the process of evaluating the impact of the adoption of ASU 2016-2 on our consolidated financial statements.
Stock-based Compensation: In March 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-09, Compensation—Stock Compensation (Topic 718): Improvements to Employee Share-Based Payment Accounting (ASU 2016-09). ASU 2016-09 changes how companies account for certain aspects of stock-based awards to employees, including the accounting for income taxes, forfeitures, and statutory tax withholding requirements, as well as classification in the statement of cash flows. ASU 2016-09 is effective for us in the first quarter of 2018, and earlier adoption is permitted. We are still evaluating the effect that this guidance will have on our consolidated financial statements and related disclosures.
Financial Instruments - Credit Losses: In June 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-13, Financial Instruments - Credit Losses (Topic 326): The amendments in this Update require a financial asset (or a group of financial assets) measured at amortized cost basis to be presented at the net amount expected to be collected. The amendments broaden the information that an entity must consider in developing its expected credit loss estimate for assets measured either collectively or individually. The use of forecasted information incorporates more timely information in the estimate of expected credit loss, which will be more decision useful to users of the financial statements. ASU 2016-13 is effective for the Company for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2019, including interim periods within those fiscal years. Early adoption is allowed as of the fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2018, including interim periods within those fiscal years. The Company is still evaluating the effect that this guidance will have on the Company’s consolidated financial statements and related disclosures.
Statement of Cash Flows: In August 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-15, Statement of Cash Flows (Topic 230): The amendments in this Update apply to all entities, including both business entities and not-for-profit entities that are required to present a statement of cash flows under Topic 230. The amendments in this Update provide guidance on the following eight specific cash flow issues. The amendments are an improvement to GAAP because they provide guidance for each of the eight issues, thereby reducing the current and potential future diversity in practice described above. ASU 2016-15 is effective for the Company for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, including interim periods within those fiscal years. Early adoption is permitted, including adoption in an interim period. The Company is still evaluating the effect that this guidance will have on the Company’s consolidated financial statements and related disclosures.
Statement of Cash Flows: In November 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-18, Statement of Cash Flows (Topic 230): “Restricted Cash”(“ASU 2016-18”). ASU 2016-18 requires that a statement of cash flows explain the change during the period in the total of cash, cash equivalents, and amounts generally described as restricted cash or restricted cash equivalents. This update is effective in fiscal years, including interim periods, beginning after December 15, 2017 and early adoption is permitted. The adoption of this guidance will result in the inclusion of the restricted cash balances within the overall cash balance and removal of the changes in restricted cash activity, which are currently recognized in Other financing activities, on the Statements of Consolidated Cash Flows. Furthermore, an additional reconciliation will be required to reconcile Cash and cash equivalents and restricted cash reported within the Consolidated Balance Sheets to sum to the total shown in the Statements of Consolidated Cash Flows. The Company anticipates adopting this new guidance effective January 1, 2018. The Company is currently evaluating this guidance and the impact it will have on the Consolidated Financial Statements and disclosures.
Business Combination: In January 2017, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update No. 2017-01, Business Combinations (Topic 805): Clarifying the Definition of a Business (ASU 2017-01), which revises the definition of a business and provides new guidance in evaluating when a set of transferred assets and activities is a business. This guidance will be effective for us in the first quarter of 2018 on a prospective basis, and early adoption is permitted. We do not expect the standard to have a material impact on our consolidated financial statements.
| F-15 |
CHINA GREEN AGRICULTURE, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
JUNE 30, 2017
Stock-based Compensation: In May 2017, the FASB issued ASU No. 2017-09, “Compensation—Stock compensation (Topic 718): Scope of modification accounting” (“ASU 2017-09”). The purpose of the amendment is to clarify which changes to the terms or condition of a share-based payment award require an entity to apply modification accounting. For all entities that offer share based payment awards, ASU 2017-09 are effective for interim and annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2017. The Company is currently assessing the impact of ASU 2017-09 on its condensed consolidated financial statements.
Other recent accounting pronouncements issued by the FASB, including its Emerging Issues Task Force, the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants, and the Securities and Exchange Commission did not or are not believed by management to have a material impact on the Company’s present or future financial statements.
NOTE 3 – INVENTORIES
Inventories consisted of the following:
| June 30, | June 30, | |||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Raw materials | $ | 39,397,711 | $ | 29,926,762 | ||||
| Supplies and packing materials | $ | 540,151 | $ | 444,373 | ||||
| Work in progress | $ | 421,496 | $ | 408,820 | ||||
| Finished goods | $ | 37,655,533 | $ | 56,656,360 | ||||
| Total | $ | 78,013,891 | $ | 87,436,315 | ||||
During the year ended June 30, 2017, the Company sold compound fertilizers (finished goods) to certain parties at market price, and purchased equivalent amount of simple fertilizers (raw material) from the same parties also at market price. The simple fertilizers purchased, along with other materials were used in the Company’s production facility to manufacture compound fertilizers. While nonmonetary, the sales and purchase transactions were consummated independently under separate agreements at different times, and measured at the prevailing market value. The total amount of nonmonetary sales and purchases amounted to $58,205,442 during the year ended June 30, 2017. No gain or loss incurred as the result of the nonmonetary transactions.
NOTE 4 – PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT
Property, plant and equipment consisted of the following:
| June 30, | June 30, | |||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Building and improvements | $ | 40,113,868 | $ | 42,489,975 | ||||
| Auto | 3,473,352 | 937,642 | ||||||
| Machinery and equipment | 18,760,880 | 19,015,420 | ||||||
| Agriculture assets | 764,660 | 765,983 | ||||||
| Total property, plant and equipment | 63,111,079 | 63,209,020 | ||||||
| Less: accumulated depreciation | (28,919,747 | ) | (25,639,281 | ) | ||||
| Total | $ | 34,191,332 | $ | 37,569,739 | ||||
NOTE 5 – INTANGIBLE ASSETS
Intangible assets consisted of the following:
| June 30, | June 30, | |||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Land use rights, net | $ | 10,121,591 | $ | 10,381,215 | ||||
| Technology patent, net | - | - | ||||||
| Customer relationships, net | 5,578,641 | 6,403,343 | ||||||
| Non-compete agreement | 1,092,584 | 925,678 | ||||||
| Trademarks | 6,119,875 | 6,129,812 | ||||||
| Total | $ | 22,911,876 | $ | 23,840,048 | ||||
LAND USE RIGHT
On September 25, 2009, Yuxing was granted a land use right for approximately 88 acres (353,000 square meters or 3.8 million square feet) by the People’s Government and Land & Resources Bureau of Hu County, Xi’an, Shaanxi Province. The fair value of the related intangible asset was determined to be the respective cost of RMB73,184,895 (or $10,995,299). The intangible asset is being amortized over the grant period of 50 years using the straight-line method.
| F-16 |
CHINA GREEN AGRICULTURE, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
JUNE 30, 2017
On August 13, 2003, Tianjuyuan was granted a certificate of Land Use Right for a parcel of land of approximately 11 acres (42,726 square meters or 459,898 square feet) at Ping Gu District, Beijing. The purchase cost was recorded at RMB1,045,950 (or $157,144). The intangible asset is being amortized over the grant period of 50 years.
On August 16, 2001, Jinong received a land use right as a contribution from a shareholder, which was granted by the People’s Government and Land& Resources Bureau of Yangling District, Shaanxi Province. The fair value of the related intangible asset at the time of the contribution was determined to be RMB7,285,099 (or $1,094,513). The intangible asset is being amortized over the grant period of 50 years.
The Land Use Rights consisted of the following:
| June 30, | June 30, | |||||||||||||||
| 2016 | Additions | Amortization | 2017 | |||||||||||||
| Land use rights | $ | 12,268,150 | - | $ | 12,246,630 | |||||||||||
| Less: accumulated amortization | (1,886,935 | ) | (238,104 | ) | (2,125,039 | ) | ||||||||||
| Total land use rights, net | $ | 10,381,215 | $ | 10,121,591 | ||||||||||||
TECHNOLOGY PATENT
On August 16, 2001, Jinong was issued a technology patent related to a proprietary formula used in the production of humid acid. The fair value of the related intangible asset was determined to be the respective cost of RMB 5,875,068 (or $884,198) and is being amortized over the patent period of 10 years using the straight-line method. This technology patent has been fully amortized.
On July 2, 2010, the Company acquired Gufeng and its wholly-owned subsidiary Tianjuyuan. The fair value on the acquired technology patent was estimated to be RMB9,200,000 (or $1,384,600) and is amortized over the remaining useful life of six years using the straight-line method. As of June 30, 2016, this technology patent is fully amortized.
The technology know-how consisted of the following:
| June 30, | June 30, | |||||||||||||||
| 2016 | Additions | Amortization | 2017 | |||||||||||||
| Technology know-how | $ | 2,268,798 | - | $ | 2,264,818 | |||||||||||
| Less: accumulated amortization | (2,268,798 | ) | (2,264,818 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Total technology know-how, net | $ | - | $ | - | ||||||||||||
CUSTOMER RELATIONSHIP
On July 2, 2010, the Company acquired Gufeng and its wholly-owned subsidiary Tianjuyuan. The fair value on the acquired customer relationships was estimated to be RMB65,000,000 (or $9,765,600) and is amortized over the remaining useful life of ten years. On June 30, 2016, and January 1, 2017 the Company acquired the eight sales VIEs. The fair value of the acquired customer relationships was estimated to be RMB19,917,253 (or $2,992,368) and is amortized over the remaining useful life of from three years up to ten years.
| June 30, | June 30, | |||||||||||||||
| 2016 | Additions | Amortization | 2017 | |||||||||||||
| Customer relationships | $ | 12,257,101 | 522,028 | $ | 12,757,628 | |||||||||||
| Less: accumulated amortization | (5,853,758 | ) | (1,325,229 | ) | (7,178,987 | ) | ||||||||||
| Total customer relationships, net | $ | 6,403,343 | $ | 5,578,641 | ||||||||||||
NON-COMPETE AGREEMENT
On July 2, 2010, the Company acquired Gufeng and its wholly-owned subsidiary Tianjuyuan. The fair value on the acquired non-compete agreement was estimated to be RMB1,320,000 (or $198,264) and is amortized over the remaining useful life of five years using the straight-line method. On June 30, 2016, the Company acquired the sales VIEs. The fair value on the acquired non-compete agreements were estimated to be RMB8,765,582 (or $1,316,906) and is amortized over the remaining useful life of five years using the straight-line method.
| June 30, | June 30, | |||||||||||||||
| 2016 | Additions | Amortization | 2017 | |||||||||||||
| Non-compete agreement | $ | 1,124,338 | 390,080 | $ | 1,124,338 | |||||||||||
| Less: accumulated amortization | (198,660 | ) | (422,634 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Total non-compete agreement, net | $ | 925,678 | $ | 1,092,584 | ||||||||||||
TRADEMARKS
On July 2, 2010, the Company acquired Gufeng and its wholly-owned subsidiary Tianjuyuan. The preliminary fair value on the acquired trademarks was estimated to be RMB40,700,000 (or $6,119,059) and is subject to an annual impairment test.
| F-17 |
CHINA GREEN AGRICULTURE, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
JUNE 30, 2017
AMORTIZATION EXPENSE
Estimated amortization expenses of intangible assets for the next five twelve months periods ended June 30, are as follows:
| Years Ending June 30, | Expense ($) | |||
| 2018 | 1,894,275 | |||
| 2019 | 1,894,275 | |||
| 2020 | 1,855,439 | |||
| 2021 | 747,663 | |||
| 2022 | 576,687 | |||
NOTE 6 – OTHER NON-CURRENT ASSETS
Other non-current assets mainly include advance payments related to lease the land use for the Company. As of June 30, 2017, the balance of other non-current assets was $17,829,621, which was the lease fee advances for agriculture lands that the Company engaged in Shiquan County from 2018 to 2027.
In March 2017, Jinong entered into the lease agreement for approximately 3,400 mu, and 2600 hectare agriculture lands in Shiquan County, Shaanxi Province. The lease was from April 2017 and was renewable for every ten-year period up to 2066. The aggregate leasing fee was approximately RMB 13 million per annum, The Company had made 10-year advances of leasing fee per lease terms. The Company has amortized $0.5 million as expenses for the three months ended June 30, 2017.
Estimated amortization expenses of the lease advance payments herein for the next four twelve-month periods ended June 30 and thereafter are as follows:
| Years ending June 30, | ||||
| 2018 | $ | 2,016,918 | ||
| 2019 | $ | 2,016,918 | ||
| 2020 | $ | 2,016,918 | ||
| 2021 | $ | 2,016,918 | ||
| 2022 and thereafter | $ | 11,778,867 | ||
NOTE 7 – RELATED PARTIES TRANSACTIONS
At the end of December 2015, Yuxing entered into a sales agreement with the Company’s affiliate, 900LH.com Food Co., Ltd. (“900LH.com”, previously announced as Xi’an Gem Grain Co., Ltd) pursuant to which Yuxing is to supply various vegetables to 900LH.com for its incoming seasonal sales at the holidays and year ends (the “Sales Agreement”). The contingent contracted value of the Sales Agreement is RMB 25,500,000 (approximately $3,965,250). During the year ended June 30, 2017 and 2016, Yuxing has sold approximately $2,472,165 and $1,383,787 products to 900LH.com.
The amount due from 900LH.com to Yuxing was $1,412,844 and $481,886 as of June 30, 2017 and 2016, respectively.
As of June 30, 2017, and 2016, the amount due to related parties was $3,071,102 and $2,473,004, respectively. As of June 30, 2017, and 2016, $1,051,652 and $1,092,243, respectively were amounts that Gufeng borrowed from a related party, Xi’an Techteam Science & Technology Industry (Group) Co. Ltd., a company controlled by Mr. Tao Li, Chairman and CEO of the Company, representing unsecured, non-interest-bearing loans that are due on demand. These loans are not subject to written agreements. As of June 30, 2017, the Company owed Mr. Tao Li, Chairman and CEO of the Company unsecured, non-interest-bearing advances of $1,950,000. These advances are not subject to written agreements.
As of June 30, 2017, the Company’s subsidiary, Jinong, owed 900LH.com. $30,707.
On June 29, 2016, Jinong signed an office lease with Kingtone Information Technology Co., Ltd. (“Kingtone Information”), where Mr. Tao Li, Chairman and CEO of the Company, serves as its Chairman. Pursuant to the lease, Jinong rented 612 square meters (approximately 6,588 square feet) of office space from Kingtone Information. The lease provided for a two-year term effective as of July 1, 2016 with monthly rent of RMB24,480 (approximately $3,678).
| F-18 |
CHINA GREEN AGRICULTURE, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
JUNE 30, 2017
NOTE 8 – ACCRUED EXPENSES AND OTHER PAYABLES
Accrued expenses and other payables consisted of the following:
| June 30, | June 30, | |||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Payroll payable | $ | 103,412 | $ | 58,704 | ||||
| Welfare payable | 154,239 | 154,510 | ||||||
| Accrued expenses | 4,863,988 | 4,450,306 | ||||||
| Acquisitions payable | - | 5,568,500 | ||||||
| Other payables | 3,887,676 | 6,037,764 | ||||||
| Other levy payable | 125,998 | 126,219 | ||||||
| Total | $ | 9,135,312 | $ | 16,396,003 | ||||
NOTE 9 – LOAN PAYABLES
As of June 30, 2017, the short-term loan payables consisted of three loans which mature on dates ranging from July 28, 2017 through June 8, 2018 with interest rates ranging from 5.22% to 6.31%. The loans No. 1 to 3 are guaranteed with parent company’s credit from Jinong; the loans No. 2 and 3 4 below are collateralized by Tianjuyan’s land use right and building ownership right.
| No. | Payee | Loan period per agreement | Interest Rate | June 30, 2017 | ||||||||
| 1 | Bank of Beijing-Pinggu Branch | June 28, 2016 -July 28, 2017 | 5.22 | % | $ | 1,502,360 | ||||||
| 2 | Postal Saving Bank of China - Pinggu Branch | March 24, 2017 – March 5, 2018 | 6.31 | % | 4,507,080 | |||||||
| 3 | Bank of Beijing - Pinggu Branch | June 9, 2017-June 8, 2018 | 5.22 | % | 1,502,360 | |||||||
| 4 | Bank of China-Anhui | November 25, 2016-October25, 2017 | LPR | * | $ | 166,311 | ||||||
| Total | $ | 7,678,111 | ||||||||||
*LPR stands for Loan Prime Rate. The LPR rate is a 1-year lending rate used by commercial banks to their top grade borrowers whose credit are comparable to the interbank borrowing credit worthiness in China. The LPR rate is a variable rate and was published along with Shanghai Interbank Offer Rates daily.
As of June 30, 2016, the short-term loan payables consisted of three loans which mature on dates ranging from May 18, 2016 through March 17, 2017 with interest rates ranging from 4.87% to 5.82%. The loans No. 1 and 3 below are collateralized by Tianjuyan’s land use right and building ownership right. The loans No. 2 is guaranteed by Jinong’s credit.
| No. | Payee | Loan period per agreement | Interest Rate | June 30, 2016 | ||||||||
| 1 | Agriculture Bank of China-Pinggu Branch | May. 18, 2016 - Mar. 17, 2017 | 4.87 | % | $ | 1,953,068 | ||||||
| 2 | Beijing Bank - Pinggu Branch | Aug. 11, 2015- Aug. 2, 2016 | 5.82 | % | 1,502,360 | |||||||
| 3 | Agriculture Bank of China-Pinggu Branch | Jan. 19, 2016 – Jan. 17, 2017 | 5.00 | % | 1,201,888 | |||||||
| Total | $ | 4,657,316 | ||||||||||
The interest expense from short-term loans was $549,650 and $995,959 for the years ended June 30, 2017 and 2016, respectively.
NOTE 10 – CONVERTIBLE NOTES PAYABLE
Relating to the acquisition of the VIE Companies, the Company subsidiary, Jinong, issued to the VIE Companies shareholders convertible notes payable twice, in the aggregate notional amount of RMB 63,000,000 ($9,462,600) with a term of three years and an annual interest rate of 3%.
| No. | Related Acquisitions of Sales VIEs | Issuance Date | Maturity Date | Notional Interest Rate | Conversion Price | Notional Amount (in RMB) | ||||||||||||
| 1 | Wangtian, Lishijie, Shenqiu, Xindeguo, Xinyulei, Jinyangguang | June 30, 2016 | June 30, 2019 | 3 | % | $ | 5.00 | 51,000,000 | ||||||||||
| 2 | Fengnong, Xiangrong | January 1, 2017 | December 31, 2019 | 3 | % | $ | 5.00 | 12,000,000 | ||||||||||
| F-19 |
CHINA GREEN AGRICULTURE, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
JUNE 30, 2017
The convertible notes take priority over the preferred stock and common stock of Jinong, and any other class or series of capital stocks Jinong issues in the future in terms of interests and payments in the event of any liquidation, dissolution or winding up of Jinong. On or after the third anniversary of the issuance date of the note, noteholders may request Jinong to process the note conversion to convert the note into shares of the Company’s common stock. The notes cannot be converted prior to the mature date. The per share conversion price of the notes is the higher of the following: (i) $5.00 per share or (ii) 75% of the closing price of the Company’s common stock on the date the noteholder delivers the conversion notice.
The Company determined that the fair value of the convertible notes payable was RMB 56,124,446 ($8,431,912) and RMB 44,330,692 ($6,671,769) as of June 30, 2017 and June 30, 2016, respectively, which was mainly due to the additional issuance of RMB 12,000,000 in the Xiangrong and Fengnong acquisition on Jan 1, 2017. The difference between the fair value of the notes and the face amount of the notes will be amortized to accretion interest expense over the three-year life of the notes. As of June 30, 2017, the amortization of this discount into accretion interest expenses was $369,401. As these notes were issued on and after June 30, 2016, there was no amortization of this discount into interest expense in fiscal year 2016.
NOTE 11 – TAXES PAYABLE
Enterprise Income Tax
Effective January 1, 2008, the Enterprise Income Tax (“EIT”) law of the PRC replaced the tax laws for Domestic Enterprises (“DEs”) and Foreign Invested Enterprises (“FIEs”). The EIT rate of 25% replaced the 33% rate that was applicable to both DEs and FIEs. The two-year tax exemption and three-year 50% tax reduction tax holiday for production-oriented FIEs was eliminated. Since January 1, 2008, Jinong became subject to income tax in China at a rate of 15% as a high-tech company, because of the expiration of its tax exemption on December 31, 2007. Accordingly, it made provision for income taxes for the years ended June 30, 2017 and 2016 of $3,521,978 and $3,592,823, respectively, which is mainly due to the operating income from Jinong. Gufeng is subject to 25% EIT rate and thus it made provision for income taxes of $2,148,326 and $3,584,006 for the year ended June 30, 2017 and 2016, respectively.
Value-Added Tax
Certain fertilizer products that are produced and sold in the PRC were subject to a Chinese Value-Added Tax (VAT) of 13% of the gross sales price. On April 29, 2008, the PRC State of Administration of Taxation (SAT) released Notice #56, “Exemption of VAT for Organic Fertilizer Products”, which allows certain fertilizer products to be exempt from VAT beginning June 1, 2008. The Company submitted the application for exemption in May 2009, which was granted effective September 1, 2009, continuing through December 31, 2015.
Income Taxes and Related Payables
Taxes payable consisted of the following:
| June 30, | June 30, | |||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| VAT provision | $ | (575,872 | ) | $ | 2,218 | |||
| Income tax payable | 2,229,735 | 3,445,480 | ||||||
| Other levies | 1,036,544 | 656,520 | ||||||
| Total | $ | 2,690,407 | $ | 4,104,218 | ||||
The provision for income taxes consists of the following:
| Years Ended June 30, | ||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Current tax - foreign | $ | 6,511,880 | $ | 7,371,967 | ||||
| Deferred tax | - | - | ||||||
| $ | 6,511,880 | $ | 7,371,967 | |||||
The components of deferred income tax assets and liabilities are as follows:
| June 30, | June 30, | |||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Deferred tax assets: | ||||||||
| Net operating loss | $ | 14,607,802 | $ | 13,803,943 | ||||
| Total deferred tax assets | 14,607,802 | 13,803,943 | ||||||
| Less valuation allowance | (14,607,802 | ) | (13,803,943 | ) | ||||
| $ | - | $ | - | |||||
| F-20 |
CHINA GREEN AGRICULTURE, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
JUNE 30, 2017
The Company periodically evaluates the likelihood of the realization of deferred tax assets, and adjusts the carrying amount of the deferred tax assets by the valuation allowance to the extent the future realization of the deferred tax assets is not judged to be more likely than not. The Company considers many factors when assessing the likelihood of future realization of its deferred tax assets, including its recent cumulative earnings experience by taxing jurisdiction, expectations of future taxable income or loss, the carryforward periods available to the Company for tax reporting purposes, and other relevant factors.
At June 30, 2017, based on the weight of available evidence, including cumulative losses in recent years and expectations of future taxable income, the Company determined that it was more likely than not that its deferred tax assets would not be realized and have a $14.6 million valuation allowance associated with its deferred tax assets.
Tax Rate Reconciliation
Our effective tax rates were approximately 20.6% and 21.6% for years ended June 30, 2017 and 2016, respectively. Substantially all the Company’s income before income taxes and related tax expense are from PRC sources. Actual income tax benefit reported in the consolidated statements of income and comprehensive income differ from the amounts computed by applying the US statutory income tax rate of 34% to income before income taxes for the years ended June 30, 2017 and 2016 for the following reasons:
June 30, 2017
| Tax Rate Reconciliation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| China | United States | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 15% - 25% | 34% | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pretax income (loss) | $ | 34,028,617 | $ | (2,364,584 | ) | $ | 31,664,033 | |||||||||||||||||
| Expected income tax expense (benefit) | 8,507,154 | 25 | % | (803,958 | ) | 34 | % | 7,703,196 | ||||||||||||||||
| High-tech income benefits on Jinong | (2,033,489 | ) | -6.0 | % | (2,033,489 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Gains from subsidiaries in which additional benefit is recognized | 38,215 | 0.1 | % | 38,215 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Change in valuation allowance on deferred tax asset from US tax benefit | 0 | 803,958 | (34 | )% | 803,958 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Actual tax expense | $ | 6,511,880 | 19.1 | % | $ | 0 | 0 | % | $ | 6,511,880 | 20.6 | % | ||||||||||||
| June 30, 2016 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| China | United States | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 15% - 25% | 34% | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pretax income (loss) | $ | 32,076,160 | (5,768,770 | ) | $ | 26,307,390 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Expected income tax expense (benefit) | 8,019,040 | 25.0 | % | (1,961,382 | ) | 34.0 | % | 6,062,571 | ||||||||||||||||
| High-tech income benefits on Jinong | (2,214,672 | ) | (5.7 | )% | - | - | (2,214,672 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Losses from subsidiaries in which no benefit is recognized | 1,567,599 | ) | (0.8 | )% | - | - | 1,567,599 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Change in valuation allowance on deferred tax asset from US tax benefit | - | 1,961,382 | (34.0 | )% | 1,961,382 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Actual tax expense | $ | 7,371,967 | 23 | % | $ | - | - | % | $ | 7,371,967 | 21.6 | % | ||||||||||||
| F-21 |
CHINA GREEN AGRICULTURE, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
JUNE 30, 2017
NOTE 12 – STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
Common Stock
On September 30, 2014, the Company granted an aggregate of 1,750,000 shares of restricted stock under the 2009 Plan to certain executive officers, directors and employees, among which were (i) 240,000 shares of restricted stock to Mr. Tao Li, the CEO; (ii) 100,000 shares of restricted stock to Mr. Ken Ren, the CFO, (iii) 40,000 shares of restricted stock to Mr. Yizhao Zhang, (iv) 30,000 shares of restricted stock to Ms. Yiru Shi, and (v) 20,000 shares of restricted stock to Mr. Lianfu Liu, each an independent director of the Company; and (vi) 1,320,000 shares of restricted stock to key employees. The stock grants are subject to time-based vesting schedules, vesting in various installments until March 31, 2015 for the CFO and the three independent directors, until June 30, 2015 for the CEO and until March 31, 2017 for the employees. The value of the restricted stock awards was $3,675,000 and is based on the fair value of the Company’s common stock on the grant date. This amount has been amortized to compensation expense over the vesting periods for the various awards.
On September 28, 2015, the Company granted an aggregate of 1,000,000 shares of restricted stock under the 2009 Plan to certain key employees. The stock grants are subject to time-based vesting schedules, vesting in various installments until June 30, 2016. The value of the restricted stock awards was $1,660,000 and is based on the fair value of the Company’s common stock on the grant date. This amount is being amortized to compensation expense over the vesting periods for the various awards.
On June 26, 2016, the Company granted an aggregate of 670,000 shares of restricted stock under the 2009 Plan to certain key employees. The stock grants vest immediately. The value of the restricted stock awards was $897,800 and is based on the fair value of the Company’s common stock on the grant date.
On December 30, 2016, the Company granted an aggregate of 870,000 shares of restricted stock under the 2009 Plan to certain key employees. The stock grants vest immediately. The value of the restricted stock awards was $1,044,000 and is based on the fair value of the Company’s common stock on the grant date.
The following table sets forth changes in compensation-related restricted stock awards during the twelve-month periods ended June 2017 and 2016:
| Fair | Grant Date | |||||||||||
| Number of | Value of | Fair Value | ||||||||||
| Shares | Shares | Per share | ||||||||||
| Outstanding (unvested) at June 30, 2016 | - | $ | - | |||||||||
| Granted | - | - | $ | - | ||||||||
| Forfeited | - | |||||||||||
| Vested | - | - | ||||||||||
| Outstanding (unvested) at June 30, 2017 | - | $ | - | |||||||||
As of June 30, 2017, the unamortized expense related to the grant of restricted shares of common stock was nil. The fair value of the restricted common stock awards was based on the closing price of the Company’s common stock on the grant date. The fair value of the common stock awarded is amortized over the various vesting terms of each grant.
The following table sets forth changes in compensation-related restricted stock awards during years ended June 30, 2017 and 2016:
| Fair | Grant Date | |||||||||||
| Number of | Value of | Fair Value | ||||||||||
| Shares | Shares | Per share | ||||||||||
| Outstanding (unvested) at June 30, 2015 | 1,708,000 | $ | 1,797,992 | |||||||||
| Granted | 1,000,000 | 1,660,000 | $ | 1.66 | ||||||||
| Granted | 670,000 | 897,800 | $ | 1.34 | ||||||||
| Forfeited | - | - | ||||||||||
| Vested | (2,790,000 | ) | (4,120,528 | ) | ||||||||
| Outstanding (unvested) at June 30, 2016 | 588,000 | $ | 235,264 | |||||||||
| Granted | 870,000 | 1,044,000 | $ | 1.20 | ||||||||
| Forfeited | - | - | ||||||||||
| Vested | (1,458,000 | ) | (1,279,264 | ) | ||||||||
| Outstanding (unvested) at June 30, 2017 | - | - | ||||||||||
| F-22 |
CHINA GREEN AGRICULTURE, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
JUNE 30, 2017
During the year ended June 30, 2017, the Company issued 32,660 shares of common stock for consulting services valued at $41,212. The shares were valued at the market price on the date of issuance.
During the year ended June 30, 2016, the Company issued 73,407 shares of common stock for consulting services valued at $114,763. The shares were valued at the market price on the date of issuance.
Preferred Stock
Under the Company’s Articles of Incorporation, the Board has the authority, without further action by stockholders, to designate up to 20,000,000 shares of preferred stock in one or more series and to fix the rights, preferences, privileges, qualifications and restrictions granted to or imposed upon the preferred stock, including dividend rights, conversion rights, voting rights, rights and terms of redemption, liquidation preference and sinking fund terms, any or all of which may be greater than the rights of the common stock. If the Company sells preferred stock under its registration statement on Form S-3, it will fix the rights, preferences, privileges, qualifications and restrictions of the preferred stock of each series in the certificate of designation relating to that series and will file the certificate of designation that describes the terms of the series of preferred stock the Company offers before the issuance of the related series of preferred stock.
As of June 30, 2017, the Company has 20,000,000 shares of preferred stock authorized, with a par value of $.001 per share, of which no shares are issued or outstanding.
NOTE 13 – STOCK OPTIONS
There were no issuances of stock options during the years ended June 30, 2017 and 2016.
Options outstanding and related weighted average price and intrinsic value are as follows:
| Weighted | ||||||||||||
| Average | Aggregate | |||||||||||
| Number | Exercise | Intrinsic | ||||||||||
| of Shares | Price | Value | ||||||||||
| Outstanding, June 30, 2014 | 115,099 | $ | 14.66 | $ | - | |||||||
| Granted | - | |||||||||||
| Forfeited/Canceled | (115,099 | ) | ||||||||||
| Exercised | - | |||||||||||
| Outstanding, June 30, 2015 | - | $ | - | $ | - | |||||||
| Granted | - | |||||||||||
| Forfeited/Canceled | - | |||||||||||
| Exercised | - | |||||||||||
| Outstanding, June 30, 2016 | - | $ | - | $ | - | |||||||
| Granted | - | |||||||||||
| Forfeited/Canceled | - | |||||||||||
| Exercised | - | |||||||||||
| Outstanding, June 30, 2017 | - | $ | - | $ | - | |||||||
| F-23 |
CHINA GREEN AGRICULTURE, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
JUNE 30, 2017
NOTE 14 – CONCENTRATIONS AND LITIGATION
Market Concentration
All the Company’s revenue-generating operations are conducted in the PRC. Accordingly, the Company’s business, financial condition and results of operations may be influenced by the political, economic and legal environments in the PRC, and by the general state of the PRC’s economy.
The Company’s operations in the PRC are subject to specific considerations and significant risks not typically associated with companies in North America and Western Europe. These include risks associated with, among other things, the political, economic and legal environment and foreign currency exchange. The Company’s results may be adversely affected by, among other things, changes in governmental policies with respect to laws and regulations, anti-inflationary measures, currency conversion and remittance abroad, and rates and methods of taxation.
Vendor and Customer Concentration
There were two vendors, from which the Company purchased 14.1% and 12.2% of its raw materials for fertilizer manufacturing during the year ended June 30, 2017. Total purchase from these two vendors was amounted to $21,033,713 as June 30, 2017.
There were two vendors, , from which the Company purchased 18.8% and 17.4% of its raw materials for fertilizer manufacturing during the year ended June 30, 2016. Total purchase from these two venders amounted to $52,241,454 as June 30, 2016.
Two customers, accounted for an aggregated amount of $31,379,821 or 7.1% and 7.0% of the Company’s manufactured fertilizer sales for the year ended June 30, 2017.
One customer, Sino-agri Holding Co., Ltd., accounted for $59,696,999, or 23.0% of the Company’s manufactured fertilizer sales for the year ended June 30, 2016.
NOTE 15 – SEGMENT REPORTING
As of June 30, 2017, the Company was organized into four main business segments based on location and product: Jinong (fertilizer production), Gufeng (fertilizer production), Yuxing (agricultural products production) and the sales VIEs. Each of the four operating segments referenced above has separate and distinct general ledgers. The chief operating decision maker (“CODM”) receives financial information, including revenue, gross margin, operating income and net income produced from the various general ledger systems to make decisions about allocating resources and assessing performance; however, the principal measure of segment profitability or loss used by the CODM is net income by segment.
| Years Ended June 30, | ||||||||
| Revenues from unaffiliated customers: | 2017 | 2016 | ||||||
| Jinong | $ | 106,642,032 | $ | 125,716,937 | ||||
| Gufeng | 104,446,239 | 134,661,420 | ||||||
| Yuxing | 8,517,231 | 8,406,663 | ||||||
| Sales VIEs | 65,607,538 | 0 | ||||||
| Consolidated | $ | 285,213,040 | $ | 268,785,020 | ||||
| Operating income : | ||||||||
| Jinong | $ | 22,562,310 | $ | 22,942,976 | ||||
| Gufeng | 8,286,761 | 13,952,983 | ||||||
| Yuxing | (2,376,007 | ) | 1,464,728 | |||||
| Sales VIEs | 5,869,291 | 0 | ||||||
| Reconciling item (1) | 0 | 0 | ||||||
| Reconciling item (2) | (1,082,505 | ) | (1,648,240 | ) | ||||
| Reconciling item (2) --stock compensation | (1,282,079 | ) | (4,120,528 | ) | ||||
| Consolidated | $ | 31,977,771 | $ | 32,591,919 | ||||
| F-24 |
CHINA GREEN AGRICULTURE, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
JUNE 30, 2017
| Net income: | ||||||||
| Jinong | $ | 18,699,889 | $ | 19,637,155 | ||||
| Gufeng | 6,264,392 | 9,364,364 | ||||||
| Yuxing | (2,375,961 | ) | 1,471,412 | |||||
| Sales VIEs | 4,925,927 | - | ||||||
| Reconciling item (1) | 15 | 30 | ||||||
| Reconciling item (2) | (2,364,598 | ) | (5,768,768 | ) | ||||
| Consolidated | $ | 25,152,153 | $ | 24,704,193 | ||||
| Depreciation and Amortization: | ||||||||
| Jinong | $ | 13,358,370 | $ | 35,924,393 | ||||
| Gufeng | 2,302,047 | 2,920,960 | ||||||
| Yuxing | 1,366,840 | 1,465,836 | ||||||
| Sales VIEs | 380,863 | - | ||||||
| Consolidated | $ | 17,408,120 | $ | 40,311,189 | ||||
| Interest expense: | ||||||||
| Gufeng | 290,126 | 995,959 | ||||||
| Gufeng | 251,064 | - | ||||||
| Sales VIEs | 8,460 | |||||||
| Consolidated | $ | 549,650 | $ | 995,959 | ||||
| Capital Expenditure: | ||||||||
| Jinong | $ | 9,582 | $ | 7,894 | ||||
| Gufeng | 12,273 | 3,239 | ||||||
| Yuxing | 6,210 | 8,059 | ||||||
| Sales VIEs | 14,217 | - | ||||||
| Consolidated | $ | 42,283 | $ | 19,192 | ||||
| As of | ||||||||
| June 30, | June 30, | |||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Identifiable assets: | ||||||||
| Jinong | $ | 213,355,900 | $ | 198,599,977 | ||||
| Gufeng | 156,648,924 | 149,891,328 | ||||||
| Yuxing | 40,965,345 | 45,448,157 | ||||||
| Sales VIEs | 45,063,273 | 24,675,497 | ||||||
| Reconciling item (1) | 142,919 | 170,444 | ||||||
| Reconciling item (2) | (2,879 | ) | (2,876 | ) | ||||
| Consolidated | $ | 456,173,481 | $ | 418,782,527 | ||||
(1) Reconciling amounts refer to the unallocated assets or expenses of Green New Jersey.
(2) Reconciling amounts refer to the unallocated assets or expenses of the Parent Company.
Total revenues from exported products currently accounted for less than 1% of the Company’s total fertilizer revenues for the years ended June 30, 2017 and 2016, respectively.
| F-25 |
CHINA GREEN AGRICULTURE, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
JUNE 30, 2017
NOTE 16 – COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
On June 29, 2016, Jinong signed an office lease with Kingtone Information. Pursuant to the lease, Jinong rented 612 square meters (approximately 6,588 square feet) of office space from Kingtone Information. The lease provided for a two-year term effective as of July 1, 2016 with monthly rent of $3,678 (approximately RMB 24,480).
In January 2008, Jintai signed a ten-year land lease with Xi’an Jinong Hi-tech Agriculture Demonstration Zone for a monthly rent of $781 (RMB 5,200).
In February 2004, Tianjuyuan signed a fifty-year lease with the village committee of Dong Gao Village and Zhen Nan Zhang Dai Village in the Beijing Ping Gu District, at a monthly rent of $444 (RMB 2,958).
Accordingly, the Company recorded an aggregate of $641,330 and $176,796 as rent expenses for the years ended June 30, 2017 and 2016, respectively. The contingent rent expenses herein for the next five years ended June 30, are as follows:
| Years ending June 30, | ||||
| 2018 | 148,632 | |||
| 2019 | 58,841 | |||
| 2020 | 58,841 | |||
| 2021 | 58,841 | |||
| 2022 | 58,841 | |||
NOTE 17 – BUSINESS COMBINATIONS
On June 30, 2016, the Company, through its wholly-owned subsidiary Jinong, entered into strategic acquisition agreements and also into a series of contractual agreements to qualify as VIEs with the shareholders of Shaanxi Lishijie Agrochemical Co., Ltd., Songyuan Jinyangguang Sannong Service Co., Ltd., Shenqiu County Zhenbai Agriculture Co., Ltd., Weinan City Linwei District Wangtian Agricultural Materials Co., Ltd., Aksu Xindeguo Agricultural Materials Co., Ltd., and Xinjiang Xinyulei Eco-agriculture Science and Technology Co., Ltd.
Subsequently, on January 1, 2017, Jinong entered into similar strategic acquisition agreements and a series of contractual agreements to qualify as VIEs with the shareholders of Sunwu County Xiangrong Agricultural Materials Co., Ltd., and Anhui Fengnong Seed Co., Ltd..
The series of contractual agreements for the VIE Companies to qualify as VIEs (the “VIE Agreements”) that Jinong, the VIE Companies, and the shareholders of VIE Companies entered into, are as follows:
Entrusted Management Agreements
Pursuant to the terms of certain Entrusted Management Agreements dated June 30, 2016 and January 1, 2017, between Jinong and the shareholders of the VIE Companies (the “Entrusted Management Agreements”), the VIE Companies and their shareholders agreed to entrust the operations and management of its business to Jinong. According to the Entrusted Management Agreement, Jinong possesses the full and exclusive right to manage the VIE Companies’ operations, assets and personnel, has the right to control all the VIE Companies’ cash flows through an entrusted bank account, is entitled to the VIE Companies’ net profits as a management fee, is obligated to pay all the VIE Companies’ payables and loan payments, and bears all losses of the VIE Companies. The Entrusted Management Agreements will remain in effect until (i) the parties mutually agree to terminate the agreement; (ii) the dissolution of the VIE Companies; or (iii) Jinong acquires all the assets or equity of the VIE Companies (as more fully described below under “Exclusive Option Agreements”).
Exclusive Technology Supply Agreements
Pursuant to the terms of certain Exclusive Technology Supply Agreements dated June 30, 2016 and January 1, 2017, between Jinong and the VIE Companies (the “Exclusive Technology Supply Agreements”), Jinong is the exclusive technology provider to the VIE Companies. The VIE Companies agreed to pay Jinong all fees payable for technology supply prior to making any payments under the Entrusted Management Agreement. The Exclusive Technology Supply Agreements shall remain in effect until (i) the parties mutually agree to terminate the agreement; (ii) the dissolution of the VIE Companies; or (iii) Jinong acquires the VIE Companies (as more fully described below under “Exclusive Option Agreements”).
| F-26 |
CHINA GREEN AGRICULTURE, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
JUNE 30, 2017
Shareholder’s Voting Proxy Agreements
Pursuant to the terms of certain Shareholder’s Voting Proxy Agreements dated June 30, 2016 and January 1, 2017, among Jinong and the shareholders of the VIE Companies (the “Shareholder’s Voting Proxy Agreements”), the shareholders of the VIE Companies irrevocably appointed Jinong as their proxy to exercise on such shareholders’ behalf all of their voting rights as shareholders pursuant to PRC law and the Articles of Association of the VIE Companies, including the appointment and election of directors of the VIE Companies. Jinong agreed that it shall maintain a board of directors, the composition and appointment of which shall be approved by the Board of the Company. The Shareholder’s Voting Proxy Agreements will remain in effect until Jinong acquires all the assets or equity of the VIE Companies.
Exclusive Option Agreements
Pursuant to the terms of certain Exclusive Option Agreements dated June 30, 2016 and January 1, 2017, among Jinong, the VIE Companies, and the shareholders of the VIE Companies (the “Exclusive Option Agreements”), the shareholders of the VIE Companies granted Jinong an irrevocable and exclusive purchase option (the “Option”) to acquire the VIE Companies’ equity interests and/or remaining assets, but only to the extent that the acquisition does not violate limitations imposed by PRC law on such transactions. The Option is exercisable at any time at Jinong’s discretion so long as such exercise and subsequent acquisition of the VIE Companies does not violate PRC law. The consideration for the exercise of the Option is to be determined by the parties and memorialized in the future by definitive agreements setting forth the kind and value of such consideration. Jinong may transfer all rights and obligations under the Exclusive Option Agreements to any third parties without the approval of the shareholders of the VIE Companies so long as a written notice is provided. The Exclusive Option Agreements may be terminated by mutual agreements or by 30 days written notice by Jinong.
Equity Pledge Agreements
Pursuant to the terms of certain Equity Pledge Agreements dated June 30, 2016 and January 1, 2017, among Jinong and the shareholders of the VIE Companies (the “Pledge Agreements”), the shareholders of the VIE Companies pledged all of their equity interests in the VIE Companies to Jinong, including the proceeds thereof, to guarantee all of Jinong’s rights and benefits under the Entrusted Management Agreements, the Exclusive Technology Supply Agreements, the Shareholder’ Voting Proxy Agreements and the Exclusive Option Agreements. Prior to termination of the Pledge Agreements, the pledged equity interests cannot be transferred without Jinong’s prior written consent. The Pledge Agreements may be terminated only upon the written agreement of the parties.
Non-Compete Agreements
Pursuant to the terms of certain Non-Compete Agreements dated June 30, 2016 and January 1, 2017, among Jinong and the shareholders of the VIE Companies (the “Non-Compete Agreements”), the shareholders of the VIE Companies agreed that during the period beginning on the initial date of their services with Jinong, and ending five (5) years after termination of their services with Jinong, without Jinong’s prior written consent, they will not provide services or accept positions including but not limited to partners, directors, shareholders, managers, proxies or consultants, provided by any profit making organizations with businesses that may compete with Jinong. They will not solicit or interfere with any of the Jinong’s customers, or solicit, induce, recruit or encourage any person engaged or employed by Jinong to terminate his or her service or engagement. If the shareholders of the VIE Companies breach the non-compete obligations contained therein, Jinong is entitled to all loss and damages; if the damages are difficult to determine, remedies bore the shareholders of the VIE Companies shall be no less than 50% of the salaries and other expenses Jinong provided in the past.
| F-27 |
CHINA GREEN AGRICULTURE, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
JUNE 30, 2017
The Company entered into these VIE Agreements as a way for the Company to have more control over the distribution of its products. The transactions are accounted for as business combinations in accordance with ASC 805. A summary of the purchase price allocations at fair value is below:
For acquisitions made on June 30, 2016:
| Cash | $ | 708,737 | ||
| Accounts receivable | 6,422,850 | |||
| Advances to suppliers | 1,803,180 | |||
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | 807,645 | |||
| Inventories | 7,787,043 | |||
| Machinery and equipment | 140,868 | |||
| Intangible assets | 270,900 | |||
| Other assets | 3,404,741 | |||
| Goodwill | 3,158,179 | |||
| Accounts payable | (3,962,670 | ) | ||
| Customer deposits | (3,486,150 | ) | ||
| Accrued expenses and other payables | (4,653,324 | ) | ||
| Taxes payable | (16,912 | ) | ||
| Purchase price | $ | 12,385,087 |
A summary of the purchase consideration paid is below:
| Cash | $ | 5,568,500 | ||
| Convertible notes | 6,671,769 | |||
| Derivative liability | 144,818 | |||
| $ | 12,385,087 |
The cash component of the purchase price for these acquisitions made on June 30, 2016 was paid in July and August 2016.
For acquisitions made on January 1, 2017:
| Working Capital | $ | 941,192 | ||
| Machinery and equipment | 222,875 | |||
| Intangible assets | 1440 | |||
| Goodwill | 684,400 | |||
| Customer Relationship | 522,028 | |||
| Non-compete Agreement | 392,852 | |||
| Purchase price | $ | 2,764,787 |
A summary of the purchase consideration paid is below:
| Cash | $ | 1,201,888 | ||
| Assumed liability | 3,549 | |||
| Convertible notes | 1,538,244 | |||
| Derivative liability | 21,106 | |||
| $ | 2,764,787 |
The cash component of the purchase price for these acquisitions made on January 1, 2017 was paid during March 2017.
| F-28 |
CHINA GREEN AGRICULTURE, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
JUNE 30, 2017
NOTE 18 – VARIABLE INTEREST ENTITIES
Because of these contractual arrangements, with Yuxing and the VIE Companies the Company is entitled to substantially all the economic benefits of Yuxing and the VIE Companies. The following financial statement amounts and balances of the VIEs were included in the accompanying consolidated financial statements as of June 30, 2017 and 2016:
| June 30, | June 30, | |||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| ASSETS | ||||||||
| Current Assets | ||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 374,587 | $ | 1,017,841 | ||||
| Accounts receivable, net | 30,687,859 | 7,050,201 | ||||||
| Inventories | 21,314,940 | 26,370,202 | ||||||
| Other current assets | 2,195,156 | 1,839,523 | ||||||
| Advances to suppliers | 2,380,812 | 4,900,524 | ||||||
| Total Current Assets | 56,953,354 | 41,196,291 | ||||||
| Plant, Property and Equipment, Net | 12,418,906 | 13,377,817 | ||||||
| Other assets | 225,508 | 334,264 | ||||||
| Intangible Assets, Net | 13,002,818 | 12,913,776 | ||||||
| Goodwill | 3,837,038 | 3,158,179 | ||||||
| Total Assets | $ | 86,437,624 | $ | 70,980,327 | ||||
| LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | ||||||||
| Current Liabilities | ||||||||
| Short-term loan | $ | 166,311 | 0 | |||||
| Accounts payable | $ | 18,355,921 | $ | 3,840,052 | ||||
| Customer deposits | 1,375,785 | 3,486,150 | ||||||
| Accrued expenses and other payables | 3,833,868 | 5,562,253 | ||||||
| Amount due to related parties | 42,741,043 | 43,478,158 | ||||||
| Total Current Liabilities | 66,472,928 | 56,366,613 | ||||||
| Long-term Loan | 3,549 | 0 | ||||||
| Total Liabilities | $ | 66,476,477 | 0 | |||||
| Stockholders’ equity | 19,961,147 | 14,613,714 | ||||||
| Total Liabilities and Stockholders’ Equity | $ | 86,437,624 | $ | 70,980,327 | ||||
| Years Ended June 30, | ||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Revenue | $ | 74,124,754 | $ | 8,406,663 | ||||
| Expenses | 71,572,295 | 6,935,251 | ||||||
| Net income | $ | 2,552,459 | $ | 1,471,412 | ||||
| F-29 |
CHINA GREEN AGRICULTURE, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
JUNE 30, 2017
NOTE 19 – RESTRICTED NET ASSETS
The Company’s operations are primarily conducted through its PRC subsidiaries, which can only pay dividends out of their retained earnings determined in accordance with the accounting standards and regulations in the PRC and after it has met the PRC requirements for appropriation to statutory reserves. In addition, the Company’s businesses and assets are primarily denominated in RMB, which is not freely convertible into foreign currencies. All foreign exchange transactions take place either through the People’s Bank of China or other banks authorized to buy and sell foreign currencies at the exchange rates quoted by the People’s Bank of China. Approval of foreign currency payments by the People’s Bank of China or other regulatory institutions requires submitting a payment application form together with suppliers’ invoices, shipping documents and signed contracts. These currency exchange control procedures imposed by the PRC government authorities may restrict the ability of the Company’s PRC subsidiaries to transfer their net assets to the Parent Company through loans, advances or cash dividends.
The Company’s PRC subsidiaries net assets as of June 30, 2017 and 2016 exceeded 25% of the Company’s consolidated net assets. Accordingly, condensed Parent Company financial statements have been prepared in accordance with Rule 5-04 and Rule 12-04 of SEC Regulation S-X, and are as follows.
Parent Company Financial Statements
PARENT COMPANY FINANCIAL INFORMATION OF CHINA GREEN AGRICULTURE, INC.
| Condensed Balance Sheets | As of June 30, | |||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| ASSETS | ||||||||
| Current Assets: | ||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 139,969 | $ | 167,495 | ||||
| Other current assets | 71 | 70 | ||||||
| Total Current Assets | 140,040 | 167,565 | ||||||
| Long-term equity investment | 404,406,925 | 376,321,912 | ||||||
| Total long-term assets | 404,406,925 | 376,321,912 | ||||||
| Total Assets | $ | 404,546,965 | $ | 376,489,477 | ||||
| LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | ||||||||
| Current Liabilities: | ||||||||
| Accounts payable | $ | 214,520 | $ | 214,520 | ||||
| Amount due to related parties | 1,988,743 | 1,388,743 | ||||||
| Other payables and accrued expenses | 4,815,649 | 4,401,882 | ||||||
| Total Current Liabilities | 7,018,913 | 6,005,145 | ||||||
| Stockholders’ Equity | ||||||||
| Common stock, $.001 par value, 115,197,165 shares authorized, 37,648,605 and 35,905,198, shares issued and outstanding as of June 30, 2016 and 2015, respectively | 38,551 | 37,648 | ||||||
| Additional paid in capital | 128,915,651 | 127,593,932 | ||||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive income | (5,127,444 | ) | (5,696,388 | ) | ||||
| Retained earnings | 273,701,295 | 248,549,140 | ||||||
| Total Stockholders’ Equity | 397,528,052 | 370,484,332 | ||||||
| Total Liabilities and Stockholders’ Equity | $ | 404,546,965 | $ | 376,489,477 | ||||
| F-30 |
CHINA GREEN AGRICULTURE, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
JUNE 30, 2017
| Condensed Statements of Operations | Year ended June 30, | |||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Revenue | $ | - | $ | - | ||||
| General and administrative expenses | 2,364,598 | 5,768,770 | ||||||
| Interest income | 15 | 30 | ||||||
| Equity investment in subsidiaries | 27,516,737 | 30,472,933 | ||||||
| Net income | $ | 25,152,153 | $ | 24,704,193 | ||||
| Condensed Statements of Cash Flows | Year Ended June 30, | |||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities | $ | (627,526 | ) | $ | (138,881 | ) | ||
| Net cash provided by investing activities | - | - | ||||||
| Net cash provided by financing activities | 600,000 | - | ||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents, beginning balance | 167,495 | 306,376 | ||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents, ending balance | $ | 139,969 | $ | 167,495 | ||||
Notes to Condensed Parent Company Financial Information
As of June 30, 2017, and 2016, there were no material contingencies, significant provisions for long-term obligations, or guarantees of the Company, except as separately disclosed in the Consolidated Financial Statements, if any. Certain information and footnote disclosures normally included in financial statements prepared in accordance with U.S. GAAP have been condensed or omitted.
NOTE 20 – RESTATEMENT OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
On April 13, 2018, the management of China Green Agriculture, Inc. (the “Company”) concluded, after consultation with our independent registered public accounting firm, the previous issued financial statements contained in the Company’s annual Report on Form 10K for the year ended June 30, 2017 should not be relied upon due primarily to the computation errors in the connection with the allocation of cash payment for VIE acquisitions. The company made two rounds of acquisitions in June 2016 and January 2017 respectively. For the acquisitions made in June 2016, the purchase consideration included RMB 37,000,000 in cash, which was originally recorded as $5.6 million acquisition payable in “Accrued Expenses and Other Payables” as of June 30, 2016. After paying it off this acquisition payable in fiscal year 2017, the Company recorded its payment of $5.4 million (using average exchange rate) in the “Cash Flows from Operating Activities” section in the Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows, which includes “Accrued Expenses and Other Payables”. As these cash outflows were related to the payment for business combinations, the payment should be included in the investing activities section of the statement of cash flow in the amended Form 10-K.
For the acquisitions made in January 2017, the purchase consideration included RMB 8,000,000 million in cash. The Company recorded a net payment in cash of $0.14 million in the “Cash Flows from Investing Activities” net of the effects from the RMB 7,100,000 cash acquired in the target companies’ working capital. The net payment $5.4 million for June 2016 acquisitions should be included in the investing activities section of the statement of cash flow in the amended Form 10-K.
| F-31 |
