Attached files
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
[x] | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2016
OR
[ ] | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from __________ to __________
Commission file number 000-54755
CĪON Investment Corporation | ||
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter) | ||
Maryland | 45-3058280 | |
(State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) | |
3 Park Avenue, 36th Floor New York, New York | 10016 | |
(Address of principal executive offices) | (Zip Code) | |
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code (212) 418-4700
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
Title of each class | Name of each exchange on which registered | |
None | Not applicable | |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act:
Common Stock, par value $0.001 per share | ||
(Title of class) | ||
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act.
Yes [ ] No [x]
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act.
Yes [ ] No [x]
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days.
Yes [x] No [ ]
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Website, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files).
Yes [ ] No [ ]
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K (§229.405 of this chapter) is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K.
[ ]
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
Large accelerated filer [ ] | Accelerated filer [ ] | |
Non-accelerated filer [x] (Do not check if a smaller reporting company) | Smaller reporting company [ ] | |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act).
Yes [ ] No [x]
There is no established market for the Registrant’s shares of common stock. The Registrant is currently conducting an ongoing follow-on public offering of its shares of common stock pursuant to a Registration Statement on Form N-2, as amended (File No. 333-203683), which shares are being sold at $9.65 per share, with discounts available for certain categories of purchasers, or at a price necessary to ensure that shares are not sold at a price below net asset value per share.
The number of shares of the Registrant’s common stock, $0.001 par value, outstanding as of March 9, 2017 was 110,720,587.
Documents Incorporated by Reference
Portions of the Registrant’s definitive Proxy Statement relating to the Registrant’s 2017 Annual Meeting of Shareholders, to be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission within 120 days following the end of the Registrant’s fiscal year, are incorporated by reference in Part III of this Annual Report on Form 10-K as indicated herein.
CĪON INVESTMENT CORPORATION
FORM 10-K
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page | ||
PART I
Forward-Looking Statements
Some of the statements within this Annual Report on Form 10-K constitute forward-looking statements because they relate to future events or our future performance or financial condition. The forward-looking statements contained in this Annual Report on Form 10-K may include statements as to:
• | our future operating results; |
• | our business prospects and the prospects of our portfolio companies; |
• | the impact of the investments that we expect to make; |
• | the ability of our portfolio companies to achieve their objectives; |
• | our current and expected financings and investments; |
• | the adequacy of our cash resources, financing sources and working capital; |
• | the use of borrowed money to finance a portion of our investments; |
• | the timing of cash flows, if any, from the operations of our portfolio companies; |
• | our contractual arrangements and relationships with third parties; |
• | the actual and potential conflicts of interest with CION Investment Management, LLC, or CIM, and Apollo Global Management, LLC, or Apollo, and their respective affiliates; |
• | the ability of CIM and Apollo Investment Management, L.P., or AIM, a subsidiary of Apollo and a registered investment adviser under the Investment Advisers Act of 1940, as amended, or the Advisers Act, to locate suitable investments for us and the ability of CIM to monitor and administer our investments; |
• | the ability of CIM and AIM and their respective affiliates to attract and retain highly talented professionals; |
• | the dependence of our future success on the general economy and its impact on the industries in which we invest; |
• | the effects of a changing interest rate environment; |
• | our ability to source favorable private investments; |
• | our tax status; |
• | the effect of changes to tax legislation and our tax position; |
• | the tax status of the companies in which we invest; and |
• | the timing and amount of distributions and dividends from the companies in which we invest. |
In addition, words such as “anticipate,” “believe,” “expect” and “intend” indicate a forward-looking statement, although not all forward-looking statements include these words. The forward-looking statements contained in this Annual Report on Form 10-K involve risks and uncertainties. Our actual results could differ materially from those implied or expressed in the forward-looking statements for any reason, including the factors set forth in “Risk Factors” in Item 1A of Part I of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Other factors that could cause actual results to differ materially include:
• | changes in the economy; |
• | risks associated with possible disruption in our operations or the economy generally due to terrorism or natural disasters; and |
• | future changes in laws or regulations and conditions in our operating areas. |
We have based the forward-looking statements on information available to us on the date of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Except as required by the federal securities laws, we undertake no obligation to revise or update any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise. You are advised to review any additional disclosures that we may make directly to you or through reports that we in the future may file with the Securities and Exchange Commission, or SEC, including annual reports on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q and current reports on Form 8-K. The forward-looking statements contained in this Annual Report on Form 10-K are excluded from the safe harbor protection provided by Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, or the Securities Act, and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, or the Exchange Act.
1
Amounts and percentages presented herein may have been rounded for presentation and all dollar amounts, excluding share and per share amounts, are presented in thousands unless otherwise noted.
Item 1. Business
CĪON Investment Corporation, or the Company, was incorporated under the general corporation laws of the State of Maryland on August 9, 2011. When used in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, the terms “we,” “us,” “our” or similar terms refer to the Company and its consolidated subsidiaries. In addition, the term “portfolio companies” refers to companies in which we have invested, either directly or indirectly through our total return swap, or TRS (described in further detail under “Item 1. Business – Financing Arrangements – Total Return Swap” below).
We are an externally managed, non-diversified closed-end management investment company that has elected to be regulated as a business development company, or BDC, under the Investment Company Act of 1940, as amended, or the 1940 Act. We elected to be treated for federal income tax purposes as a regulated investment company, or RIC, as defined under Subchapter M of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended, or the Code.
We are managed by CIM, our affiliate and a registered investment adviser under the Advisers Act. CIM oversees the management of our activities and is responsible for making investment decisions for our portfolio. We and CIM engaged AIM to act as our investment sub-adviser. AIM assists us with identifying investment opportunities and making investment recommendations for approval by CIM, according to pre-established investment guidelines. All of our investment decisions are the sole responsibility of, and are made at the sole discretion of, CIM. Pursuant to the terms of the investment sub-advisory agreement among us, CIM and AIM, AIM is not responsible or liable for any such investment decision, only provides the investment advisory services expressly set forth in the investment sub-advisory agreement and is not responsible or liable for the provision of any other service.
Our investment objective is to generate current income and, to a lesser extent, capital appreciation for investors. We seek to meet our investment objective by utilizing the experienced management teams of both CIM and AIM, which includes their access to the relationships and human capital of Apollo and CION Investment Group, LLC, or CIG, in sourcing, evaluating and structuring transactions, as well as monitoring and servicing our investments. Our portfolio is comprised primarily of investments in senior secured debt, including first lien loans, second lien loans and unitranche loans, and, to a lesser extent, collateralized securities, structured products and other similar securities, unsecured debt, including corporate bonds and long-term subordinated loans, referred to as mezzanine loans, and equity, of private and thinly-traded U.S. middle-market companies. See “Item 1. Business – Investment Types” below for a detailed description of the types of investments that may comprise our portfolio. We define middle-market companies as companies that generally possess annual earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization, or EBITDA, of $50 million or less, with experienced management teams, significant free cash flow, strong competitive positions and potential for growth.
In addition, we may from time to time invest up to 30% of our assets opportunistically in other types of investments, including collateralized securities, structured products and other similar securities and the securities of larger public companies and foreign securities, which may be deemed “non-qualifying assets” for the purpose of complying with investment restrictions under the 1940 Act. This treatment extends to the TRS, as we treat each loan underlying the TRS as a qualifying asset if the obligor on such loan is an eligible portfolio company and as a non-qualifying asset if the obligor is not an eligible portfolio company. We may, however, accord different treatment to the TRS in the future in accordance with any applicable new rules or interpretations adopted by the staff of the SEC. See “Item 1. Business – Qualifying Assets” below.
In connection with our debt investments, we may receive equity interests such as warrants or options as additional consideration. We may also purchase minority interests in the form of common or preferred equity in our target companies, typically in conjunction with one of our debt investments or through a co-investment with a financial sponsor. We expect that our investments will generally range between $5 million and $50 million each, although investments may vary as the size of our capital base changes and will ultimately be at the discretion of CIM subject to oversight by our board of directors. We have made and intend to make smaller investments in syndicated loan opportunities, which typically include investments in companies with annual EBITDA of greater than $50 million, subject to liquidity and diversification constraints.
To enhance our opportunity for gain, we employ leverage as market conditions permit and at the discretion of CIM, but in no event can leverage employed exceed 50% of the value of our total assets as required by the 1940 Act. For purposes of the asset coverage ratio test applicable to us as a BDC, we treat the outstanding notional amount of the TRS, less the total amount of cash collateral posted by Flatiron Funding, LLC, or Flatiron, under the TRS, as a senior security for the life of that instrument. We may, however, accord different treatment to the TRS in the future in accordance with any applicable new rules or interpretations adopted by the staff of the SEC.
Portfolio and Investment Activity
As of December 31, 2016, our investment program primarily consisted of two components. First, we engage in the direct purchase of debt securities primarily issued by portfolio companies and lend directly to portfolio companies. Second, by entering into a TRS and directing the creation of a portfolio of underlying corporate loans that serve as reference assets under the TRS, we have obtained economic exposure to additional portfolio companies, although there may be overlap between such additional portfolio companies and our direct lending portfolio companies. The following table summarizes the composition of our investment portfolio at amortized cost and fair value and our underlying TRS loans portfolio at notional amount and fair value as of December 31, 2016:
2
December 31, 2016 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Investment Portfolio | Total Return Swap | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Investments Cost(1) | Investments Fair Value | Percentage of Investment Portfolio | Notional Amount of Underlying TRS Loans | Fair Value of Underlying TRS Loans | Percentage of Underlying TRS Loans | Cost/ Notional Amount(1) | Fair Value | Percentage | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Senior secured first lien debt | $ | 489,904 | $ | 489,913 | 48.1 | % | $ | 351,747 | $ | 341,194 | 86.9 | % | $ | 841,651 | $ | 831,107 | 58.9 | % | |||||||||||||||
Senior secured second lien debt | 437,240 | 434,347 | 42.6 | % | 56,100 | 51,251 | 13.1 | % | 493,340 | 485,598 | 34.4 | % | |||||||||||||||||||||
Collateralized securities and structured products - debt | 39,471 | 38,114 | 3.7 | % | — | — | — | 39,471 | 38,114 | 2.7 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Collateralized securities and structured products - equity | 37,713 | 34,648 | 3.4 | % | — | — | — | 37,713 | 34,648 | 2.5 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Unsecured debt | 17,290 | 16,851 | 1.7 | % | — | — | — | 17,290 | 16,851 | 1.1 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Equity | 4,832 | 5,107 | 0.5 | % | — | — | — | 4,832 | 5,107 | 0.4 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Subtotal/total percentage | 1,026,450 | 1,018,980 | 100.0 | % | 407,847 | 392,445 | 100.0 | % | 1,434,297 | 1,411,425 | 100.0 | % | |||||||||||||||||||||
Short term investments(2) | 70,498 | 70,498 | — | — | 70,498 | 70,498 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total investments | $ | 1,096,948 | $ | 1,089,478 | $ | 407,847 | $ | 392,445 | $ | 1,504,795 | $ | 1,481,923 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Number of portfolio companies | 103 | 49 | 141(3) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Purchased at a weighted average price of par | 95.87 | % | 98.96 | % | 96.73 | % | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Gross annual portfolio yield based upon the purchase price(4) | 9.99 | % | 6.73 | % | 9.07 | % | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(1) | Represents amortized cost for debt investments and cost for equity investments. Amortized cost represents the original cost adjusted for the amortization of premiums and/or accretion of discounts, as applicable, on our investments. |
(2) | Short term investments represent an investment in a fund that invests in highly liquid investments with average original maturity dates of three months or less. |
(3) | The sum of investment portfolio and TRS portfolio companies does not equal the total number of portfolio companies. This is due to 11 portfolio companies being in both the investment and TRS portfolios. |
(4) | The gross annual portfolio yield does not represent and may be higher than an actual investment return to shareholders because it excludes our expenses and all sales commissions and dealer manager fees and does not consider the cost of leverage. |
We do not currently intend to list our securities on an exchange and do not expect a public market to develop for them in the foreseeable future. We believe that an unlisted structure is appropriate for the long-term nature of the assets in which we invest. In addition, because our common stock will not be listed on a national securities exchange, we will be able to pursue our investment objective without subjecting our investors to the daily share price volatility associated with the public markets. To provide our shareholders with limited liquidity, we conduct quarterly tender offers pursuant to our share repurchase program. In connection with that program, we intend, but are not required, to continue conducting quarterly repurchase offers. This is the only method of liquidity that we will offer prior to a liquidity event. Until we complete a liquidity event, it is unlikely that shareholders will be able to sell their common stock when desired or at a desired price.
Although we do not currently intend to list our common stock on an exchange and do not expect a public market to develop for it in the foreseeable future, we intend to seek to complete a liquidity event within three to five years following the completion of our offering stage or at such earlier time as our board of directors may determine, taking into consideration market conditions and other factors; however, our offering of common stock may extend for an indefinite period. We will view our offering stage as complete as of the termination date of our most recent public equity offering if we have not conducted a public equity offering in any continuous two-year period. However, there can be no assurance that we will be able to complete a liquidity event.
As a BDC, we are subject to certain regulatory restrictions in negotiating or investing in certain investments with entities with which we may be restricted from doing so under the 1940 Act, such as CIM and its affiliates, unless we obtain an exemptive order from the SEC or co-invest alongside such affiliates in accordance with existing regulatory guidance. Furthermore, we are subject to certain regulatory restrictions on investing with AIM and its affiliates in transactions where AIM or its affiliates negotiate terms other than price on our behalf, unless such transactions occur pursuant to an exemptive order from the SEC. We are currently seeking exemptive relief from the SEC to engage in co-investment transactions with CIM and its affiliates. However, there can be no assurance that we will obtain such exemptive relief. Even if we receive exemptive relief, neither CIM nor its affiliates will be obligated to offer us the right to participate in any transactions originated by them.
3
Status of Our Continuous Public Offerings
On December 17, 2012, we met our minimum offering requirement of $2,500 in capital raised from persons not affiliated with us, admitted our initial public investors as shareholders and officially commenced operations. Our initial continuous public offering ended on December 31, 2015 and our follow-on continuous public offering commenced on January 25, 2016. Since commencing our initial continuous public offering on July 2, 2012 and through March 9, 2017, we received and accepted subscriptions for 110,720,587 shares of common stock for corresponding net proceeds of $1,126,475 at an average price per share of $10.17, including shares purchased by our affiliates. The net proceeds received include gross proceeds received from reinvested shareholder distributions of $91,354 pursuant to our distribution reinvestment plan, as amended and restated, for which we issued 10,036,822 shares of common stock, and gross proceeds paid for shares of common stock tendered for repurchase of $32,784 pursuant to our share repurchase program, for which we repurchased 3,641,315 shares of common stock.
Distributions
In January 2013, we began authorizing monthly distributions to our shareholders. On February 1, 2014, we changed from semi-monthly closings to weekly closings for the sale of our shares. As a result, our board of directors authorizes and declares on a monthly basis a weekly distribution amount per share of our common stock. Subject to our board of directors’ discretion and applicable legal restrictions, our board of directors intends to continue to authorize and declare on a monthly basis a weekly distribution amount per share of our common stock.
Our board of directors declared distributions for 52, 52 and 49 record dates during the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. Declared distributions are paid monthly. The following table presents cash distributions per share that were declared during the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014:
Distributions | ||||||||
Three Months Ended | Per Share | Amount | ||||||
2014 | ||||||||
March 31, 2014 (nine record dates) | $ | 0.1679 | $ | 3,315 | ||||
June 30, 2014 (thirteen record dates) | 0.1829 | 5,120 | ||||||
September 30, 2014 (fourteen record dates) | 0.1969 | 7,396 | ||||||
December 31, 2014 (thirteen record dates) | 0.1829 | 8,716 | ||||||
Total distributions for the year ended December 31, 2014 | $ | 0.7306 | $ | 24,547 | ||||
2015 | ||||||||
March 31, 2015 (thirteen record dates) | $ | 0.1829 | $ | 10,767 | ||||
June 30, 2015 (thirteen record dates) | 0.1829 | 13,223 | ||||||
September 30, 2015 (thirteen record dates) | 0.1829 | 15,517 | ||||||
December 31, 2015 (thirteen record dates) | 0.1829 | 17,761 | ||||||
Total distributions for the year ended December 31, 2015 | $ | 0.7316 | $ | 57,268 | ||||
2016 | ||||||||
March 31, 2016 (thirteen record dates) | $ | 0.1829 | $ | 19,004 | ||||
June 30, 2016 (thirteen record dates) | 0.1829 | 19,167 | ||||||
September 30, 2016 (thirteen record dates) | 0.1829 | 19,480 | ||||||
December 31, 2016 (thirteen record dates) | 0.1829 | 19,808 | ||||||
Total distributions for the year ended December 31, 2016 | $ | 0.7316 | $ | 77,459 | ||||
On December 13, 2016, our board of directors declared five weekly cash distributions of $0.014067 per share, which were paid on February 1, 2017 to shareholders of record on January 3, January 10, January 17, January 24, and January 31, 2017. On January 17, 2017, our board of directors declared four weekly cash distributions of $0.014067 per share, which were paid on March 1, 2017 to shareholders of record on February 7, February 14, February 21, and February 28, 2017. On February 21, 2017, our board of directors declared four weekly cash distributions of $0.014067 per share, payable on March 29, 2017 to shareholders of record on March 7, March 14, March 21, and March 28, 2017.
About CIM
CIM is a registered investment adviser. CIM is a subsidiary of CIG and part of the CION Investments group of companies, or CION Investments. We believe that CION Investments is a leading asset manager that provides innovative alternative investment products to individual and institutional investors through publicly-registered programs, private funds and separately managed accounts. CION Investments is headquartered in New York, with an office in Boston.
4
Mark Gatto and Michael A. Reisner, together with Keith S. Franz, Gregg A. Bresner and Stephen Roman, form the senior management team of CIM. Both Messrs. Gatto and Reisner have significant managerial and investing experience and serve as our co-chairmen, co-presidents and co-chief executive officers.
CIM’s senior management team has extensive experience in lending to private U.S. middle-market companies and has developed an expertise in using all levels of a firm’s capital structure to produce income-generating investments, focusing on risk management and delivering risk-adjusted returns that typically are collateralized by a company’s business-essential equipment or corporate infrastructure.
About CION Investments
With more than 30 years of experience in the alternative asset management industry, CION Investments has managed investments for more than 82,000 investors and made approximately $5.5 billion in total investments. CION Investments, through its managed funds, provides direct secured financing to private and public companies worldwide primarily in industries such as marine, manufacturing, transportation, automotive, energy and power, telecommunications, industrial and mining. CION Investments provides distribution services as well through CION Securities, LLC, or CION Securities, one of our affiliates.
Pursuant to an administration agreement, ICON Capital, LLC, or ICON Capital, furnishes us with office facilities and equipment, and clerical, bookkeeping and record keeping services. ICON Capital also oversees our financial records and prepares our reports to shareholders and reports filed with the SEC. ICON Capital also performs the calculation and publication of our net asset value, and oversees the preparation and filing of our tax returns, the payment of our expenses and the performance of various third party service providers. Furthermore, ICON Capital will provide on our behalf managerial assistance to those portfolio companies to which we are required to provide such assistance.
About AIM
We and CIM have engaged AIM to act as our investment sub-adviser as we believe that AIM possesses skills that will aid us in achieving our investment objective. AIM is a subsidiary of Apollo (NYSE: APO) and is the investment adviser to Apollo Investment Corporation (NASDAQ: AINV), or AINV. AINV is a publicly traded BDC that invests primarily in various forms of debt investments, including secured and unsecured loan investments and/or equity in private U.S. middle-market companies. AINV may also invest in the securities of public companies and structured products and other investments such as collateralized loan obligations and credit-linked notes.
AIM assists CIM in identifying investment opportunities and makes investment recommendations for approval by CIM, according to pre-established investment guidelines. AIM is not responsible or liable for any such investment decision. Further, AIM only provides the investment advisory services expressly set forth in the investment sub-advisory agreement among AIM, CIM and us. Investment recommendations made by AIM are made in a manner that we expect to be consistent with the investment processes developed for the advisory services provided to AINV since its inception in 2004.
Market Opportunity
We believe that the market for lending to private U.S. middle-market companies is underserved and presents a compelling investment opportunity. CIM’s management team has witnessed significant demand for debt capital among middle-market companies that have the characteristics we target. We believe that this demand, coupled with the limited and fragmented availability of funding within our target market, will enable us to achieve favorable transaction pricing. We continue to raise funds in an attempt to capitalize on what we believe is a favorable environment. We believe that the following characteristics and market trends support our belief:
•The middle-market is a large addressable market. According to GE Capital’s National Center for the Middle Market 4th Quarter 2016 Middle Market Indicator, there are approximately 200,000 U.S. middle-market companies, which represent approximately $6 trillion in aggregate revenue and approximately 48 million aggregate employees. The U.S. middle-market accounts for approximately one-third of private sector gross domestic product, or GDP, which, measured on a global scale, would be the third largest global economy. GE defines middle-market companies as those with $10 million to $1 billion in annual revenue, which we believe has significant overlap with our definition of middle-market companies that generally possess EBITDA of $50 million or less.
•Greater demand for non-traditional sources of debt financing. We believe that commercial banks in the U.S., which have traditionally been the primary source of capital to middle-market companies, have experienced consolidation, unprecedented loan losses, capital impairments and stricter regulatory scrutiny. These factors have led to substantially reduced loan volume to middle-market companies. For example, according to the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, Assets and Liabilities of Commercial Banks in the United States (Release Date – January 4, 2013), commercial banks in the U.S. reduced their commercial and industrial loans by approximately $105 billion from 2008 to 2012. Consequently, we believe there is an increasing trend for middle-market companies to seek financing from other sources, such as us.
•Disruptions within the credit markets have reduced middle-market companies’ access to the capital markets for senior debt. While many middle-market companies were previously able to raise senior debt financing through traditional large financial institutions, we believe this approach to financing will become more difficult as implementation of U.S. and international financial reforms, such as Basel 3, are expected to limit the capacity of large financial institutions to hold loans of middle-market companies on their balance sheets.
5
•There is a large pool of uninvested private equity capital likely to seek additional senior debt capital to finance strategic transactions. We expect that middle-market private equity firms will continue to invest the approximately $653 billion raised since 2010 in middle-market companies, as reported in Pitchbook’s 2016 Annual U.S. PE Middle Market Report, and that these private equity firms will seek to support their investments with senior loans from other sources, such as us.
•General reduction in supply of corporate debt. Recent market events have significantly impacted traditional sources of credit, reducing the ability of such sources to provide financing. We believe that the disruption in the credit markets has created an environment where liquidity and capital resources are scarce while the financing requirements of companies remain high. We believe that the scarcity of capital and the continuing need for financing will allow us to pursue more favorable economic terms, governance terms and covenants in comparison to those that existed in other periods.
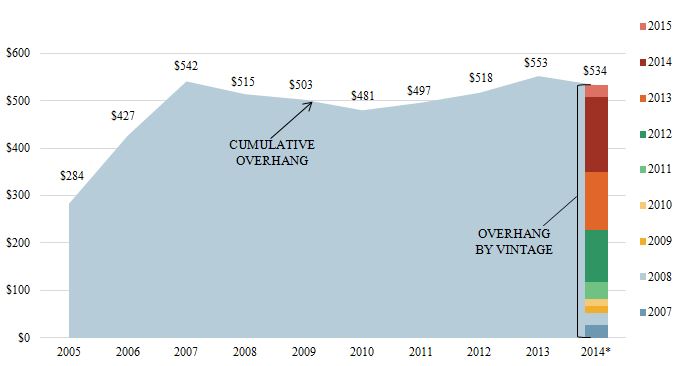
•Specialized lending and unfunded private equity commitments drive demand for debt capital. Lending to small- and middle-market companies requires in-depth diligence, credit expertise, structuring experience and active portfolio management. In addition, middle-market companies may require more active monitoring and participation on the lender’s part. As such, we believe that, of the U.S. financial institutions that are not liquidity constrained, few are capable of pursuing a sustained lending strategy successfully. We believe this creates a significant supply/demand imbalance for small and middle-market credit. We also expect that private equity firms will continue to pursue acquisitions and will seek to leverage their equity investments with debt financing, including senior debt, unitranche debt, and mezzanine loans provided by companies such as ours. Historically, according to the S&P LCD Leveraged Lending Review, such leverage has represented approximately 62% of a private equity acquisition. Therefore, adding to the imbalance in the availability of credit is the significant amount of unallocated private equity capital raised since 2010 described above, much of which will require debt financing in the coming years. As depicted in the chart below, almost $534 billion of unfunded private equity commitments were outstanding through the end of 2015. Based upon the historical proportion of leverage to total investment size, this represents potential demand of approximately $865 billion.
U.S. PE Capital Overhang ($B) by Year
•Active private equity focus on small- and middle-market firms. Private equity firms have continued their active roles investing in small- and middle-market companies, and CIM expects this trend to continue. Private equity funds often seek to leverage their investments by combining equity capital with senior secured and mezzanine loans from other sources. Thus, we believe that significant private equity investment in middle-market firms will create substantial investment opportunities for us to fill the role of leverage provider. We believe that the network of relationships between CIM’s senior management team, Apollo’s management team and the private equity community will be a key channel through which we will seek to access significant investment opportunities.
•Middle-market companies compared to larger companies. We believe that middle-market companies compare favorably to larger companies with respect to our investment objective and strategy. According to the GE Capital 2012 National Middle Market Summit Report, almost 70% of middle-market companies have been in business for more than 20 years and are, on average, less financially leveraged than large companies. During the economic downturn from 2007 to 2010, surviving middle-market companies created more than two million jobs, as compared to nearly four million jobs eliminated by larger companies.
6
•Attractive market segment. We believe that the underserved nature of such a large segment of the market can at times create a significant opportunity for investment. In particular, we believe that middle-market companies are more likely to offer attractive economics in terms of transaction pricing (including higher debt yields), upfront and ongoing fees, prepayment penalties and more attractive security features in the form of stricter covenants and quality collateral. In addition, as compared to larger companies, middle-market companies often have simpler capital structures and carry less leverage, thus aiding the structuring and negotiation process and allowing us greater flexibility in structuring favorable transactions.
Average Nominal Spread of Leveraged Loans1
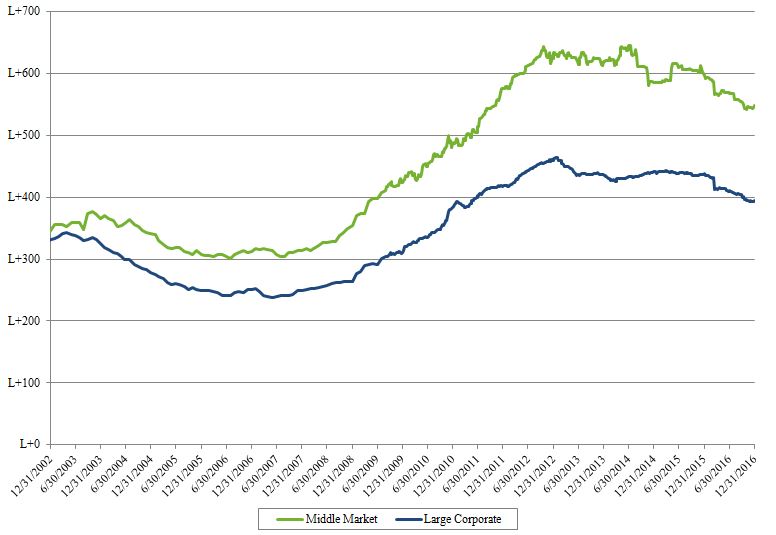
1 Excludes all facilities in default.
Source: S&P Capital IQ LCD and S&P/LSTA Leveraged Loan Index.
7
Average Discounted Spread of Leveraged Loans2
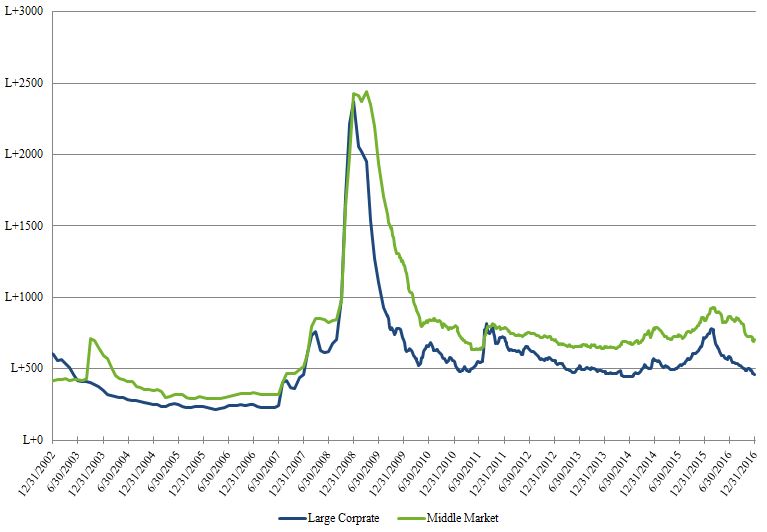
2 Excludes all facilities in default.
Spread calculations have been adjusted to be based off of the bid rather than par (that is assuming that the discounted margin is as a percent of the current market value rather than the par amount of the loan).
Source: S&P Capital IQ LCD and S&P/LSTA Leveraged Loan Index.
Characteristics of and Risks Related to Investments in Private Companies
We have invested and continue to invest primarily in the debt of privately held companies. Investments in private companies pose significantly greater risks as compared to investments in public companies. First, private companies have reduced access to the capital markets, resulting in diminished capital resources and ability to withstand financial distress. Second, the investments themselves are often illiquid. As such, we may have difficulty exiting an investment promptly or at a desired price prior to maturity or outside of a normal amortization schedule. In addition, little public information generally exists about private companies. Finally, these companies often do not have third-party debt ratings or audited financial statements. We must therefore rely on the ability of CIM and/or AIM to obtain adequate information through their due diligence efforts to evaluate the creditworthiness of, and risks involved with, investing in these companies. These companies and their financial information will also generally not be subject to the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, as amended, or the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, and other rules and regulations that govern public companies that are designed to protect investors.
Investment Strategy
When evaluating an investment, we use the resources of CIM and AIM to develop an investment thesis and a proprietary view of a potential company’s value. When identifying prospective portfolio companies, we focus primarily on the following attributes, which we believe will help us generate higher total returns with an acceptable level of risk. These attributes are:
•Leading, defensible market positions that present attractive growth opportunities. We seek to invest in companies that we believe possess advantages in scale, scope, customer loyalty, product pricing or product quality versus their competitors, minimizing sales risk and protecting profitability.
•Companies with leading market positions and strong free cash flows. We seek to invest in the debt of companies that have a leading market position or other significant competitive advantages and significant free cash flow. We believe that such companies are able to maintain consistent cash flow to service and repay our loans and maintain growth or market share.
8
•Investing in middle-market, private companies. We seek to invest in middle-market, private companies that generally possess annual EBITDA of $50 million or less at the time of investment. We do not intend to invest in start-up companies, turnaround situations or companies with speculative business plans.
•Proven management teams with meaningful equity ownership. We focus on investments in which the target company has an experienced management team with an established track record of success. We typically require the portfolio companies to have in place proper incentives to align management’s goals with ours. Generally, we focus on companies in which the management teams have significant equity interests.
•Private equity sponsorship. Often we seek to participate in transactions sponsored by what we believe to be high-quality private equity firms. CIM’s management team believes that a private equity sponsor’s willingness to invest significant sums of equity capital into a company provides an additional level of due diligence investigation and is an implicit endorsement of the quality of the investment. Further, by co-investing with quality private equity firms that commit significant sums of equity capital with junior priority to our debt investments, we may benefit from having due diligence on our investments performed by both parties. Further, strong private equity sponsors with significant investments at risk have the ability and a strong incentive to contribute additional capital in difficult economic times should operational or financial issues arise.
•Broad portfolio. We seek to create a portfolio of portfolio companies engaged in a variety of industries and located in a variety of geographic locations, thereby potentially reducing the risk of a downturn in any one industry or geographic location having a disproportionate impact on the value of our portfolio. We are not a “diversified company” as such term is defined under the 1940 Act. Because we are a BDC, we focus on and invest at least 70% of our total assets in U.S. companies, but seek to maintain investments across the various geographic regions of the U.S. To the extent that we invest in foreign companies, we intend to do so in accordance with the limitations under the 1940 Act and only in jurisdictions with established legal frameworks and a history of respecting creditor rights, including countries that are members of the European Union, as well as Canada, Australia and Japan. We cannot assure investors that we will be successful in our efforts to maintain a broad portfolio of investments.
•Viable exit strategy. We focus our investment activity primarily in companies whose business models and growth prospects offer attractive exit possibilities, including repayment of our investments, with the potential for capital gain on any equity interest we hold through an initial public offering of common stock, a merger, a sale or other recapitalization.
Moreover, we may acquire investments in the secondary loan market, and, in analyzing such investments, we will employ the same analytical process that we use for our primary investments.
Potential Competitive Advantages
We believe that we offer to our investors the following potential competitive advantages over other capital providers to private U.S. middle-market companies:
•Proven ability to invest in middle-market companies. With AIM as our sub-adviser, we are partnered with a team that we believe has proven its ability to source, structure and manage private investments for a publicly-traded BDC, AINV. In addition to its ability to call on its resources, AIM is able to draw upon Apollo’s team of 376 investment professionals that have approximately $192 billion of total assets under management as of December 31, 2016. Apollo has developed an expertise in sourcing and investing in debt issued by middle-market companies. We leverage this expertise, which we believe enables us to make investments that offer the most favorable risk/reward characteristics.
•Global platform with seasoned investment professionals. CIM’s senior management team believes that the breadth and depth of its experience, together with the wider resources of the Apollo investment team, who source, structure, execute, monitor and realize upon a broad range of private investments on behalf of Apollo, as well as the specific expertise of Apollo in the BDC arena, provides us with a significant competitive advantage in sourcing attractive investment opportunities worldwide.
•Long-term investment horizon. We believe that our flexibility to make investments with a long-term view provides us with the opportunity to generate favorable returns on invested capital and expands the types of investments that we may consider. The long-term nature of our capital structure helps us avoid disposing of assets at unfavorable prices and we believe makes us a better partner for portfolio companies.
•Transaction sourcing capability. CIM and AIM seek to identify attractive investment opportunities both through active origination channels and through their long-term relationships with numerous corporate and fund management teams, members of the financial community and potential corporate partners. We also have access to the experience of CIM’s officers in sourcing middle-market transactions through such persons’ network of originators and underwriters. In addition, CIM seeks to leverage Apollo’s significant access to transaction flow. We believe that the broad networks of CIM and Apollo and their respective affiliates will produce a significant amount of investment opportunities for us.
•Disciplined, income-oriented investment philosophy. CIM employs a defensive investment approach focused on long-term credit performance and principal protection. This investment approach involves a multi-stage selection process for each investment opportunity as well as ongoing monitoring by CIM of each investment made, with particular emphasis on early detection of credit deterioration. This strategy is designed to maximize current yield and minimize the risk of capital loss while maintaining potential for long-term capital appreciation.
•Ability to utilize a wide range of transaction structures. We believe that each of CIM’s and Apollo’s broad expertise and experience in transaction structuring at all levels of a company’s capital structure affords us numerous tools to manage risk while preserving the opportunity for returns
9
on investments. We attempt to capitalize on this expertise in an effort to produce an investment portfolio that will perform in a broad range of economic conditions. In addition, we believe that the ability to offer several forms of financing makes us an attractive provider of capital to prospective portfolio companies. Such flexible transaction structuring allows a prospective portfolio company to forego the substantial cost of conducting multiple negotiations and undergoing multiple due diligence processes to secure the different types of capital it requires.
Investment Types
There are a number of investment types corresponding to a company’s capital structure. Typically, investors determine the appropriate type of investment based upon their risk and return requirements. Below is a diagram illustrating where these investments lie in a typical target company’s capital structure. First lien debt is situated at the top of the capital structure, and typically has the first claim on the assets and cash flows of the company, followed by second lien debt, mezzanine debt, preferred equity and finally common equity. Due to this priority of cash flows and claims on assets, an investment’s risk increases as it moves further down the capital structure. Investors are usually compensated for this risk associated with junior status in the form of higher returns, either through higher interest payments or potentially higher capital appreciation.
We focus primarily on investments in senior secured debt, including first lien loans, second lien loans and unitranche loans, and, to a lesser extent, collateralized securities, structured products and other similar securities, unsecured debt, including corporate bonds and long-term subordinated loans, referred to as mezzanine loans, and equity. The mix of investments in our portfolio and other aspects regarding the implementation of our strategy may change materially over time.
CIM seeks to tailor our investment focus as market conditions evolve. Depending on market conditions and other factors, we may, as noted above, increase or decrease our exposure to less senior portions of the capital structure, where returns tend to be stronger in a more stable or growing economy, but less secure in weak economic environments. We rely on CIM’s and AIM’s experience to structure investments, potentially using all levels of the capital structure, which we believe will perform in a broad range of economic environments.
Typical Leveraged Capital Structure Diagram
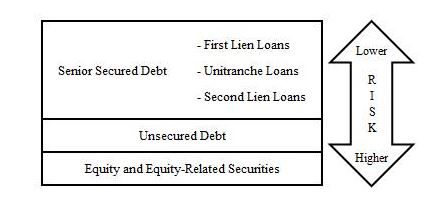
Senior Secured Debt
First Lien Loans
First lien secured loans are situated at the top of the capital structure. Because these loans have priority in payment, they carry the least risk among all investments in a company. Generally, our first lien secured loans are expected to have maturities of three to seven years, offer some form of amortization, and have first priority security interests in the assets of the borrower. We expect that our first lien secured loans typically will have variable interest rates ranging between 4.0% and 9.0% over a standard benchmark, such as the prime rate or the London InterBank Offered Rate, or LIBOR. In some cases, a portion of the total interest may accrue or be paid in kind.
Unitranche Loans
Unitranche loans provide all of the debt needed to finance a leveraged buyout or other corporate transaction, both senior and subordinated, but generally in a first lien position, while the borrower generally pays a blended, uniform interest rate rather than different rates for different tranches. Unitranche loans generally require payments of both principal and interest throughout the life of the loan. Unitranche loans generally have contractual maturities of five to six years and interest is generally paid quarterly. Generally, we expect these securities to carry a blended yield that is between first lien secured and subordinated debt interest rates. Unitranche loans provide a number of advantages for borrowers, including the following: simplified documentation, greater certainty of execution and reduced decision-making complexity throughout the life of the loan. In addition, we may receive additional returns from any warrants we may receive in connection with these investments. In some cases, a portion of the total interest may accrue or be paid in kind.
10
Second Lien Loans
Second lien secured loans are immediately junior to first lien secured loans and have substantially the same maturities, collateral and covenant structures as first lien secured loans. Second lien secured loans, however, are granted a second priority security interest in the assets of the borrower. In return for this junior ranking, second lien secured loans generally offer higher returns compared to first lien secured debt. These higher returns come in the form of higher interest and in some cases the potential for equity participation through warrants, though to a lesser extent than with mezzanine loans. Generally, we expect these loans to carry a fixed rate of 8.0% to 13.0% or a floating current yield of 7.0% to 12.0% over the prime rate or LIBOR. In addition, we may receive additional returns from any warrants we may receive in connection with these investments. In some cases, a portion of the total interest may accrue or be paid in kind.
Unsecured Debt
In addition to first lien loans and second lien loans, we also may invest a portion of our assets in unsecured debt, including corporate bonds and subordinated debt. Unsecured debt investments usually rank junior in priority of payment to first lien loans and second lien loans, but are situated above preferred equity and common stock in the capital structure. In return for their junior status compared to first lien loans and second lien loans, unsecured debt investments typically offer higher returns through both higher interest rates and possible equity ownership in the form of warrants, enabling the lender to participate in the capital appreciation of the borrower. These warrants typically require only a nominal cost to exercise. We intend to generally target unsecured debt with interest-only payments throughout the life of the security, with the principal due at maturity. Typically, unsecured debt investments have maturities of five to ten years. Generally, we expect these securities to carry a fixed rate of 10% to 15%. In addition, we may receive additional returns from any warrants we may receive in connection with these investments. In some cases, a portion of the total interest may accrue or be paid in kind.
Collateralized Securities, Structured Products and Other
We may also invest in collateralized securities, structured products and other similar securities, which may include collateralized debt obligations, or CDOs, collateralized bond obligations, or CBOs, collateralized loan obligations, or CLOs, structured notes and credit-linked notes. These investments may be structured as trusts or other types of pooled investment vehicles. They may also involve the deposit with or purchase by an entity of the underlying investments and the issuance by that entity of one or more classes of securities backed by, or representing interests in, the underlying investments or referencing an indicator related to such investments. CDOs, CBOs and CLOs are types of asset-backed securities issued by special purpose vehicles created to reapportion the risk and return characteristics of a pool of assets. The underlying pool for a CLO, for example, may include domestic and foreign senior loans, senior unsecured loans and subordinate corporate loans.
Equity and Equity-Related Securities
While we intend to maintain our focus on investments in debt securities, from time to time, when we see the potential for significant gains, or in connection with securing particularly favorable terms in a debt investment, we may make non-control investments in preferred or common equity, typically in conjunction with a private equity sponsor we believe to be of high quality. Alternatively, we may hold equity-related securities consisting primarily of warrants or other equity interests generally obtained in connection with our unsecured debt investments. In the future, we may achieve liquidity through a merger or acquisition of a portfolio company, a public offering of a portfolio company’s stock or by exercising our right, if any, to require a portfolio company to repurchase the equity-related securities we hold. With respect to any preferred or common equity investments, we expect to target an annual investment return of at least 20%.
Non-U.S. Securities
We may invest in non-U.S. securities, which may include securities denominated in U.S. dollars or in non-U.S. currencies, to the extent permitted by the 1940 Act.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
We may maintain a certain level of cash or equivalent instruments to make follow-on investments if necessary in existing portfolio companies or to take advantage of new opportunities.
Comparison of Targeted Debt Investments to Corporate Bonds
Loans to private companies are debt instruments that can be compared to corporate bonds to aid an investor’s understanding. As with corporate bonds, loans to private companies can range in credit quality depending on security-specific factors, including total leverage, amount of leverage senior to the security in question, variability in the issuer’s cash flows, the quality of assets securing debt and the degree to which such assets cover the subject company’s debt obligations. As is the case in the corporate bond market, we will require greater returns for securities that we perceive to carry increased risk. The companies in which we invest may be leveraged, often as a result of leveraged buyouts or other recapitalization transactions, and, in certain cases, will not be rated by national rating agencies. We believe that our targeted debt investments typically will carry ratings from a nationally recognized statistical ratings organization, or NRSRO, and that such ratings generally will be below investment grade (rated lower than “Baa3” by Moody’s or lower than “BBB-” by S&P). To the extent we make unrated investments, we believe that such investments would likely receive similar ratings if they were to be examined by an NRSRO. Compared to below-investment grade corporate bonds that are typically available to the public, our targeted first
11
lien secured and second lien secured loan investments are higher in the capital structure, have priority in receiving payment, are secured by the issuer’s assets, allow the lender to seize collateral if necessary, and generally exhibit higher rates of recovery in the event of default. Corporate bonds, on the other hand, are often unsecured obligations of the issuer.
The market for loans to private companies possesses several key differences compared to the corporate bond market. For instance, due to a possible lack of debt ratings for certain middle market firms, and also due to the reduced availability of information for private companies, investors must conduct extensive due diligence investigations before committing to an investment. This intensive due diligence process gives the investor significant access to management, which is often not possible in the case of corporate bondholders, who rely on underwriters, debt rating agencies and publicly available information for due diligence reviews and monitoring of corporate issuers. While holding these investments, private debt investors often receive monthly or quarterly updates on the portfolio company’s financial performance, along with possible representation on the company’s board of directors, which allows the investor to take remedial action quickly if conditions happen to deteriorate. Due to reduced liquidity, the relative scarcity of capital and extensive due diligence and expertise required on the part of the investor, we believe that private debt securities typically offer higher returns than corporate bonds of equivalent credit quality.
Operating and Regulatory Structure
Our investment activities are managed by CIM and supervised by our board of directors, a majority of whom are independent. Pursuant to our investment advisory agreement, we pay CIM an annual base management fee based on our gross assets as well as incentive fees based on our performance.
Pursuant to an administration agreement, ICON Capital provides us with general ledger accounting, fund accounting, investor relations, employee compensation and benefit-related expenses, and other expenses associated with performing administrative services. In addition, we have contracted with U.S. Bancorp Fund Services, LLC to provide additional accounting and administrative services.
As a BDC, we are required to comply with certain regulatory requirements. Also, while we are permitted to finance investments using debt, our ability to use debt is limited in certain significant respects pursuant to the 1940 Act. Within the limits of existing regulation, we will adjust our use of debt, according to market conditions, to the level we believe will allow us to generate maximum risk-adjusted returns. We elected to be treated for federal income tax purposes, and intend to qualify annually, as a RIC under Subchapter M of the Code.
Sources of Income
The primary means through which our shareholders will receive a return of value is through interest income, dividends and capital gains generated by our investments. In addition to these sources of income, we may receive fees paid by our portfolio companies, including one-time closing fees paid at the time an investment is made and/or monitoring fees paid throughout the term of our investments. Closing fees typically range from 1.0% to 2.0% of the purchase price of an investment, while annual monitoring fees generally range from 0.25% to 1.0% of the purchase price of an investment. In addition, we may generate revenue in the form of commitment, structuring or diligence fees, monitoring fees, fees for providing managerial assistance and possibly consulting fees and performance-based fees.
Risk Management
We seek to limit the downside potential of our investment portfolio by:
• | applying our investment strategy guidelines for portfolio investments; |
• | requiring a total return on investments (including both interest and potential appreciation) that adequately compensates us for credit risk; |
• | creating and maintaining a broad portfolio of investments, size permitting, with an adequate number of companies, across different industries, with different types of collateral; and |
• | negotiating or seeking debt investments with covenants or features that protect us while affording portfolio companies flexibility in managing their businesses consistent with preservation of capital. |
Such restrictions may include affirmative and negative covenants, default penalties, lien protection, change of control provisions and board rights. We may also enter into interest rate hedging transactions at the sole discretion of CIM. Such transactions will enable us to selectively modify interest rate exposure as market conditions dictate. Furthermore, our ability to engage in hedging transactions may be adversely affected by recent rules adopted by the U.S. Commodity Futures Trading Commission, or CFTC.
Affirmative Covenants
Affirmative covenants require borrowers to take actions that are meant to ensure the solvency of the company, facilitate the lender’s monitoring of the borrower, and ensure payment of interest and loan principal due to lenders. Examples of affirmative covenants include covenants requiring the borrower to maintain adequate insurance, accounting and tax records, and to produce frequent financial reports for the benefit of the lender.
12
Negative Covenants
Negative covenants impose restrictions on the borrower and are meant to protect lenders from actions that the borrower may take that could harm the credit quality of the lender’s investment. Examples of negative covenants include restrictions on the payment of distributions and restrictions on the issuance of additional debt without the lender’s approval. In addition, certain covenants restrict a borrower’s activities by requiring it to meet certain earnings interest coverage ratio and leverage ratio requirements. These covenants are also referred to as financial or maintenance covenants.
Investment Process
The investment professionals employed by CIM and AIM have spent their careers developing the resources necessary to make investments in private companies. Our transaction process is highlighted below.
Our Transaction Process
Sourcing
CIM utilizes its access to transaction flow and seeks to leverage AIM’s significant access to transaction flow as well to source transactions. With respect to CIM’s origination channel, CIM seeks to leverage CION Investments' significant industry relationships and investment personnel that actively source new investments. With respect to AIM’s origination channel, CIM seeks to leverage the global presence of Apollo to generate access to originated transactions with attractive investment characteristics. We believe that CIM’s and AIM’s broad networks have and will continue to produce a significant pipeline of investment opportunities for us.
Evaluation
Initial Review. In its initial review of an investment opportunity to present to us, CIM’s or AIM’s transaction team, as applicable, examines information furnished by the target company and external sources, including rating agencies, if applicable, to determine whether the investment meets our basic investment criteria and other guidelines, within the context of creating and maintaining a broad portfolio of investments, and offers an acceptable probability of attractive returns with identifiable downside risk.
Credit Analysis/Due Diligence. Before undertaking an investment, the transaction team from CIM and AIM conduct a thorough due diligence review of the opportunity to ensure the company fits our investment strategy, which may include:
• | a full operational analysis to identify the key risks and opportunities of the target’s business, including a detailed review of historical and projected financial results; |
• | a detailed analysis of industry dynamics, competitive position, regulatory, tax and legal matters; |
• | on-site visits, if deemed necessary, as well as telephone calls and meetings with management and other key personnel; |
• | background checks to further evaluate management and other key personnel; |
• | a review by legal and accounting professionals, environmental or other industry consultants, if necessary; |
• | financial sponsor due diligence, including portfolio company and lender reference checks, if necessary; and |
• | a review of management’s experience and track record. |
When possible, our advisory team seeks to structure transactions in such a way that our target companies are required to bear the costs of due diligence, including those costs related to any outside consulting work we may require.
Execution
Recommendation. We and CIM have engaged AIM to identify and recommend investment opportunities for CIM’s approval. We believe that AIM seeks to maintain a defensive approach toward its investment recommendations by emphasizing risk control in its transaction process, which includes (1) the pre-review of each opportunity by one of its portfolio managers to assess the general quality, value and fit relative to our portfolio, (2)
13
where possible, transaction structuring with a focus on preservation of capital in varying economic environments and (3) ultimate approval of investment recommendations by AIM’s investment committee.
Approval. After completing its internal transaction process, subject to the terms of the investment sub-advisory agreement, the applicable CIM or AIM transaction team makes formal recommendations for review and approval by CIM. In connection with its recommendation, it transmits any relevant underwriting material and other information pertinent to the decision-making process. In addition, AIM makes its staff available to answer inquiries by CIM in connection with its recommendations. Each new investment that we make requires the unanimous approval of a quorum of members of CIM’s investment committee. A quorum consists of at least two investment committee members.
Monitoring
Portfolio Monitoring. CIM, with the help of AIM, closely monitors our portfolio companies on an ongoing basis, as well as monitors the financial trends of each portfolio company to determine if each is meeting its respective business plans and to assess the appropriate course of action for each company. In addition, depending on the size, nature and performance of the transaction, senior investment professionals of CIM may take board seats or obtain board observation rights for our portfolio companies.
CIM and AIM have several methods of evaluating and monitoring the performance and fair value of our investments, which includes, but are not limited to, the assessment of success in adhering to a portfolio company’s business plan and compliance with covenants; periodic and regular contact with portfolio company management and, if appropriate, the financial or strategic sponsor, to discuss financial position, requirements and accomplishments; comparisons to other portfolio companies in the industry; attendance at and participation in board meetings; and review of monthly and quarterly financial statements and financial projections for portfolio companies.
CIM uses an investment rating system to characterize and monitor our expected level of returns on each investment in our portfolio. These ratings are just one of several factors that CIM uses to monitor our portfolio, are not in and of themselves determinative of fair value or revenue recognition and are presented for indicative purposes. CIM rates the credit risk of all investments on a scale of 1 to 5 no less frequently than quarterly. This system is intended primarily to reflect the underlying risk of a portfolio investment relative to our initial cost basis in respect of such portfolio investment (i.e., at the time of acquisition), although it may also take into account under certain circumstances the performance of the portfolio company’s business, the collateral coverage of the investment and other relevant factors.
The following is a description of the conditions associated with each investment rating used in this ratings system:
Investment Rating | Description | |
1 | Indicates the least amount of risk to our initial cost basis. The trends and risk factors for this investment since origination or acquisition are generally favorable, which may include the performance of the portfolio company or a potential exit. | |
2 | Indicates a level of risk to our initial cost basis that is similar to the risk to our initial cost basis at the time of origination or acquisition. This portfolio company is generally performing in accordance with our analysis of its business and the full return of principal and interest or dividend is expected. | |
3 | Indicates that the risk to our ability to recoup the cost of such investment has increased since origination or acquisition, but full return of principal and interest or dividend is expected. A portfolio company with an investment rating of 3 requires closer monitoring. | |
4 | Indicates that the risk to our ability to recoup the cost of such investment has increased significantly since origination or acquisition, including as a result of factors such as declining performance and noncompliance with debt covenants, and we expect some loss of interest, dividend or capital appreciation, but still expect an overall positive internal rate of return on the investment. | |
5 | Indicates that the risk to our ability to recoup the cost of such investment has increased materially since origination or acquisition and the portfolio company likely has materially declining performance. Loss of interest or dividend and some loss of principal investment is expected, which would result in an overall negative internal rate of return on the investment. | |
For investments rated 3, 4 or 5, CIM enhances its level of scrutiny over the monitoring of such portfolio company.
CIM monitors and, when appropriate, changes investment ratings assigned to each investment in our portfolio. In connection with our valuation process, CIM reviews these investment ratings on a quarterly basis.
The following table summarizes the composition of our investment portfolio and our underlying TRS loans portfolio based on the 1 to 5 investment rating scale at fair value as of December 31, 2016 and 2015, excluding short term investments of $70,498 and $18,892, respectively:
14
December 31, 2016 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Investment Portfolio | Total Return Swap | Total | |||||||||||||||||||
Investment Rating | Investments Fair Value | Percentage of Investment Portfolio | Fair Value of Underlying TRS Loans | Percentage of Underlying TRS Loans | Fair Value | Percentage | |||||||||||||||
1 | $ | — | — | $ | — | — | $ | — | — | ||||||||||||
2 | 963,477 | 94.6 | % | 342,620 | 87.3 | % | 1,306,097 | 92.5 | % | ||||||||||||
3 | 50,942 | 5.0 | % | 34,657 | 8.8 | % | 85,599 | 6.1 | % | ||||||||||||
4 | 4,561 | 0.4 | % | 12,798 | 3.3 | % | 17,359 | 1.2 | % | ||||||||||||
5 | — | — | 2,370 | 0.6 | % | 2,370 | 0.2 | % | |||||||||||||
$ | 1,018,980 | 100.0 | % | $ | 392,445 | 100.0 | % | $ | 1,411,425 | 100.0 | % | ||||||||||
December 31, 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Investment Portfolio | Total Return Swap | Total | |||||||||||||||||||
Investment Rating | Investments Fair Value | Percentage of Investment Portfolio | Fair Value of Underlying TRS Loans | Percentage of Underlying TRS Loans | Fair Value | Percentage | |||||||||||||||
1 | $ | — | — | $ | — | — | $ | — | — | ||||||||||||
2 | 624,097 | 95.9 | % | 652,073 | 95.5 | % | 1,276,170 | 95.7 | % | ||||||||||||
3 | 24,180 | 3.7 | % | 23,047 | 3.4 | % | 47,227 | 3.5 | % | ||||||||||||
4 | 2,630 | 0.4 | % | 6,845 | 1.0 | % | 9,475 | 0.7 | % | ||||||||||||
5 | — | — | 1,160 | 0.1 | % | 1,160 | 0.1 | % | |||||||||||||
$ | 650,907 | 100.0 | % | $ | 683,125 | 100.0 | % | $ | 1,334,032 | 100.0 | % | ||||||||||
The amount of the investment portfolio and underlying TRS loans in each rating category may vary substantially from period to period resulting primarily from changes in the composition of each portfolio as a result of new investment, repayment and exit activities. In addition, changes in the rating of investments may be made to reflect our expectation of performance and changes in investment values.
Valuation Process. Each quarter, we value investments in our portfolio, and such values are disclosed each quarter in reports filed with the SEC. Investments for which market quotations are readily available are recorded at such market quotations. With respect to investments for which market quotations are not readily available, our board of directors determines the fair value of investments in good faith utilizing the input of our audit committee, CIM, AIM, and any other professionals or materials that our board of directors deems worthy and relevant, including independent third-party valuation firms, if applicable.
Managerial Assistance. As a BDC, we must offer, and provide upon request, managerial assistance to certain of our portfolio companies. This assistance could involve, among other things, monitoring the operations of our portfolio companies, participating in board and management meetings, consulting with and advising officers of portfolio companies and providing other organizational and financial guidance. Depending on the nature of the assistance required, CIM will provide such managerial assistance on our behalf to portfolio companies that request this assistance. To the extent fees are paid for these services, we, rather than CIM, will retain any fees paid for such assistance.
Exit
Exit Transactions. We seek to invest in companies that can generate consistent cash flow to repay their loans while maintaining growth in their businesses. We expect this internally generated cash flow to be a key means through which we will receive timely payment of interest and loan principal. Additionally, we attempt to invest in portfolio companies whose business models and growth prospects offer attractive exit possibilities via third-party transactions, including sales to strategic or other buyers and initial public offerings of common stock. Such third-party transactions may be particularly important in realizing capital gains through the equity portions of our investments. We also seek to exit investments in secondary market transactions when price targets are achieved or circumstances otherwise warrant.
Financing Arrangements
Total Return Swap
On December 17, 2012, Flatiron, our wholly-owned consolidated financing subsidiary, entered into a TRS with Citibank, N.A., or Citibank. A TRS is a contract in which one party agrees to make periodic payments to another party based on the change in the market value of and interest payments from the assets underlying the TRS in return for periodic payments based on a fixed or variable interest rate. A TRS effectively adds leverage to a portfolio by providing investment exposure to a security or market without owning or taking physical custody of such security or investing directly
15
in such market. Because of the unique structure of a TRS, a TRS typically offers lower financing costs than are offered through more traditional borrowing arrangements.
Effective December 9, 2013, Flatiron and Citibank amended the TRS to, among other things, increase the maximum aggregate market value of the portfolio of loans subject to the TRS (determined at the time each such loan becomes subject to the TRS) from $150,000 to $225,000, and increase the interest rate payable by Flatiron to Citibank with respect to each loan included in the TRS by increasing the spread over the floating rate index specified for each such loan from 1.25% to 1.35% per year. Flatiron and Citibank further amended the TRS to increase the maximum aggregate market value of the portfolio of loans subject to the TRS to $275,000 effective February 18, 2014, to $325,000 effective April 30, 2014, to $375,000 effective July 30, 2014, to $475,000 effective September 5, 2014, to $600,000 effective January 20, 2015, to $750,000 effective March 4, 2015 and to $800,000 effective March 22, 2016. Effective October 2, 2015, Flatiron and Citibank further amended the TRS to extend the termination or call date from December 17, 2015 to March 17, 2016 and to provide that the floating rate index specified for each loan included in the TRS will not be less than zero. On December 22, 2015, Flatiron and Citibank further amended the TRS to reduce the ramp-down period from 90 days to 30 days prior to the termination date, which represents the period when reinvestment is no longer permitted under the terms of the TRS. Effective February 18, 2016, Flatiron and Citibank further amended the TRS to extend the termination or call date from March 17, 2016 to February 18, 2017, and increase the interest rate payable by Flatiron to Citibank with respect to each loan included in the TRS by increasing the spread over the floating rate index specified for each such loan from 1.35% to 1.40% per year. Effective February 18, 2017, Flatiron and Citibank further amended the TRS to extend the termination or call date from February 18, 2017 to April 18, 2017. The agreements between Flatiron and Citibank, which collectively establish the TRS, are referred to herein as the TRS Agreement.
The TRS with Citibank enables us, through our ownership of Flatiron, to obtain the economic benefit of owning the loans subject to the TRS, without actually owning them, in return for an interest-type payment to Citibank. As such, the TRS is analogous to Flatiron borrowing funds to acquire loans and incurring interest expense to a lender.
In connection with the TRS, Flatiron is required to comply with various covenants and reporting requirements as defined in the TRS Agreement. As of and for the year ended December 31, 2016, Flatiron was in compliance with these covenants and reporting requirements.
JPM Credit Facility
On August 26, 2016, 34th Street Funding, LLC, or 34th Street, our newly-formed, wholly-owned, consolidated, special purpose financing subsidiary, entered into a senior secured credit facility with JPMorgan Chase Bank, National Association, or JPM. The senior secured credit facility with JPM, or the JPM Credit Facility, provides for delayed-draw borrowings in an aggregate principal amount of $150,000, of which $25,000 may be funded as a revolving credit facility, each subject to conditions described in the JPM Credit Facility. On August 26, 2016, 34th Street drew down $57,000 of borrowings under the JPM Credit Facility.
On September 30, 2016, 34th Street amended and restated the JPM Credit Facility, or the Amended JPM Credit Facility, with JPM. Under the Amended JPM Credit Facility, the aggregate principal amount available for delayed-draw borrowings was increased from $150,000 to $225,000, of which $25,000 may be funded as a revolving credit facility, each subject to conditions described in the Amended JPM Credit Facility. On September 30, 2016, 34th Street drew down $167,423 of additional borrowings under the Amended JPM Credit Facility, a portion of which was used to purchase the portfolio of loans from Credit Suisse Park View BDC, Inc., or CS Park View. For a detailed discussion of the acquisition of CS Park View, refer to Note 6 to our consolidated financial statements included in this report.
Advances under the Amended JPM Credit Facility bear interest at a floating rate equal to the three-month LIBOR, plus a spread of 3.50% per year. Interest is payable quarterly in arrears. All advances under the Amended JPM Credit Facility will mature, and all accrued and unpaid interest thereunder will be due and payable, by no later than August 23, 2020. 34th Street may prepay advances pursuant to the terms and conditions of the Amended JPM Credit Facility, subject to a 1% premium in certain circumstances. In addition, 34th Street will be subject to a non-usage fee of 0.5% and 1.0% per year on the amount, if any, of the aggregate principal amount available under the Amended JPM Credit Facility that has not been borrowed during the period from the closing date and ending on, but excluding, May 23, 2017, or the Ramp-Up Period, and from the termination of the Ramp-Up Period and ending on, but excluding, August 23, 2019, respectively. The non-usage fees, if any, are payable quarterly in arrears.
We contributed loans and other corporate debt securities to 34th Street in exchange for 100% of the membership interests of 34th Street, and may contribute additional loans and other corporate debt securities to 34th Street in the future. 34th Street’s obligations to JPM under the Amended JPM Credit Facility are secured by a first priority security interest in all of the assets of 34th Street. The obligations of 34th Street under the Amended JPM Credit Facility are non-recourse to us, and our exposure under the Amended JPM Credit Facility is limited to the value of our investment in 34th Street.
In connection with the Amended JPM Credit Facility, 34th Street has made certain representations and warranties and is required to comply with various covenants, reporting requirements and other customary requirements for similar facilities. As of and from August 26, 2016 to December 31, 2016, 34th Street was in compliance with all covenants and reporting requirements.
East West Bank Credit Facility
On April 30, 2015, we entered into a revolving credit facility, or the EWB Credit Facility, with East West Bank, or EWB. The EWB Credit Facility provides for borrowings in an aggregate principal amount of up to $40,000, subject to certain conditions, and we are required to maintain $2,000 in a demand deposit account with EWB at all times.
16
Advances under the EWB Credit Facility bear interest at a floating rate equal to (i) the greater of 3.25% per year or the variable rate of interest per year announced by EWB as its prime rate, which was 3.75% at December 31, 2016, plus (ii) a spread of 0.75%. Interest is payable quarterly in arrears. Each advance under the EWB Credit Facility will be due and payable on the earlier of 90 days from the date such advance was made by EWB, or April 27, 2017. We may prepay any advance without penalty or premium. We will be subject to a non-usage fee of 0.50% per year on the average amount, if any, of the aggregate principal amount available under the EWB Credit Facility that has not been borrowed, payable at the end of each quarter. The non-usage fee, if any, is payable quarterly in arrears. Our obligations to EWB under the EWB Credit Facility are secured by a first priority security interest in certain eligible investments in which we have a beneficial interest, as updated from time to time.
On January 28, 2016, we entered into the first amendment to the EWB Credit Facility with EWB. Under the original EWB Credit Facility, the borrowing base was the lesser of (i) the average monthly net proceeds received by us from the sale of our equity securities during the trailing three month period ending on the last day of the immediately preceding calendar month; or (ii) 50% of collateral securing the EWB Credit Facility. Under the first amendment, during the period commencing on January 30, 2016 through July 31, 2016, (i) the trailing equity component of the borrowing base was removed; (ii) the borrowing base was decreased to 40% of the collateral securing the EWB Credit Facility; and (iii) the required minimum fair market value of the collateral securing the EWB Credit Facility was increased from two to two and one-half times all outstanding advances under the EWB Credit Facility. Prior to entering into the second amendment to the EWB Credit Facility (as described below), these amended provisions were scheduled to revert back to their original terms on July 31, 2016.
On April 21, 2016, we entered into the second amendment to the EWB Credit Facility with EWB. Under the second amendment, the date after which the amended provisions of the first amendment will revert back to their original terms was extended from July 31, 2016 to September 30, 2016 and the maturity date of the EWB Credit Facility was extended from April 29, 2016 to April 27, 2017.
At December 31, 2016, we had no outstanding borrowings under the EWB Credit Facility and we were in compliance with all covenants and reporting requirements under the EWB Credit Facility.
Determination of Net Asset Value
The value of our assets is determined quarterly and at such other times that an event occurs that materially affects the valuation. The valuation is made pursuant to Section 2(a)(41) of the 1940 Act, which requires that we value our assets as follows: (i) the market price for those securities for which a market quotation is readily available, and (ii) for all other securities and assets, at fair value, as determined in good faith by our board of directors. As a BDC, Section 2(a)(41) of the 1940 Act requires the board of directors to determine in good faith the fair value of portfolio securities for which a market price is not readily available, and it does so in conjunction with the application of our valuation procedures by CIM.
There is no single standard for determining fair value in good faith. As a result, determining fair value requires that judgment be applied to the specific facts and circumstances of each asset while employing a valuation process that is consistently followed. Determinations of fair value involve subjective judgments and estimates. Accordingly, the notes to our consolidated financial statements refer to the uncertainty with respect to the possible effect of such valuations, and any change in such valuations in our consolidated financial statements.
Regulation
We have elected to be regulated as a BDC under the 1940 Act. A BDC is a special category of investment company under the 1940 Act that was added by Congress to facilitate the flow of capital to private companies and small public companies that do not have efficient or cost-effective access to public capital markets or other conventional forms of corporate financing. BDCs make investments in private or thinly-traded public companies in the form of long-term debt and/or equity capital, with the goal of generating current income or capital growth.
BDCs are closed-end funds that elect to be regulated as BDCs under the 1940 Act. As such, BDCs are subject to only certain provisions of the 1940 Act, as well as the Securities Act and the Exchange Act. BDCs are provided greater flexibility under the 1940 Act than are other investment companies in dealing with their portfolio companies, issuing securities, and compensating their managers. BDCs can be internally or externally managed and may qualify to elect to be taxed as RICs for federal tax purposes. The 1940 Act contains prohibitions and restrictions relating to transactions between BDCs and their affiliates, principal underwriters, and affiliates of those affiliates or underwriters. The 1940 Act requires that a majority of a BDC’s directors be persons other than “interested persons,” as that term is defined in the 1940 Act. In addition, the 1940 Act provides that we may not change the nature of our business so as to cease to be, or withdraw our election as a BDC unless approved by a majority of our outstanding voting securities.
The 1940 Act defines “a majority of the outstanding voting securities” as the lesser of (i) 67% or more of the voting securities present at a meeting if the holders of more than 50% of our outstanding voting securities are present or represented by proxy or (ii) 50% of our voting securities.
We are generally not able to issue and sell our common stock at a price below net asset value per share. We may, however, sell our common stock, or warrants, options or rights to acquire our common stock, at a price below the then-current net asset value of our common stock if our board of directors determines that such sale is in our best interests and the best interests of our shareholders, and our shareholders approve such sale. In addition, we may generally issue new shares of our common stock at a price below net asset value in rights offerings to existing shareholders, in payment of distributions and in certain other limited circumstances.
As a BDC, we are subject to certain regulatory restrictions in negotiating or investing in certain investments. For example, we generally are not permitted to co-invest with certain entities affiliated with CIM in transactions originated by CIM or its affiliates unless we obtain an exemptive order
17
from the SEC. Furthermore, we are subject to certain regulatory restrictions on investing with AIM and its affiliates in transactions where AIM or its affiliates negotiate terms other than price on our behalf, unless such transactions occur pursuant to an exemptive order from the SEC. We are currently seeking exemptive relief from the SEC to engage in co-investment transactions with CIM and its affiliates. However, there can be no assurance that we will obtain such exemptive relief. Under the investment sub-advisory agreement, AIM assists CIM in identifying investment opportunities and making investment recommendations for approval by CIM. AIM is not responsible or liable for any such investment decision.
We may invest up to 100% of our assets in securities acquired directly from issuers in privately negotiated transactions. With respect to such securities, we may, for the purpose of public resale, be deemed an “underwriter” as that term is defined in the Securities Act. We do not intend to acquire securities issued by any investment company that exceed the limits imposed by the 1940 Act. Under these limits, except for registered money market funds, we generally cannot acquire more than 3% of the voting stock of any investment company, invest more than 5% of the value of our total assets in the securities of one investment company or invest more than 10% of the value of our total assets in the securities of more than one investment company. With regard to that portion of our portfolio invested in securities issued by investment companies, it should be noted that such investments might indirectly subject our shareholders to additional expenses as they will indirectly be responsible for the costs and expenses of such companies. None of our investment policies are fundamental and any may be changed without shareholder approval.
Qualifying Assets
Under the 1940 Act, a BDC may not acquire any asset other than assets of the type listed in Section 55(a) of the 1940 Act, which are referred to as qualifying assets, unless, at the time the acquisition is made, qualifying assets represent at least 70% of the company’s total assets. The principal categories of qualifying assets relevant to our business are any of the following:
1. | Securities purchased in transactions not involving any public offering from the issuer of such securities, which issuer (subject to certain limited exceptions) is an eligible portfolio company, or from any person who is, or has been during the preceding 13 months, an affiliated person of an eligible portfolio company, or from any other person, subject to such rules as may be prescribed by the SEC. An eligible portfolio company is defined in the 1940 Act as any issuer that: |
a. | is organized under the laws of, and has its principal place of business in, the U.S.; |
b. | is not an investment company (other than a small business investment company wholly-owned by the BDC) or a company that would be an investment company but for certain exclusions under the 1940 Act; and |
c. | satisfies any of the following: |
i. | does not have any class of securities that is traded on a national securities exchange; |
ii. | has a class of securities listed on a national securities exchange, but has an aggregate market value of outstanding voting and non-voting common equity of less than $250 million; |
iii. | is controlled by a BDC or a group of companies including a BDC and the BDC has an affiliated person who is a director of the eligible portfolio company; or |
iv. | is a small and solvent company having total assets of not more than $4.0 million and capital and surplus of not less than $2.0 million. |
2. | Securities of any eligible portfolio company that we control. |
3. | Securities purchased in a private transaction from a U.S. issuer that is not an investment company or from an affiliated person of the issuer, or in transactions incident thereto, if the issuer is in bankruptcy and subject to reorganization or if the issuer, immediately prior to the purchase of its securities, was unable to meet its obligations as they came due without material assistance other than conventional lending or financing arrangements. |
4. | Securities of an eligible portfolio company purchased from any person in a private transaction if there is no ready market for such securities and we already own 60% of the outstanding equity of the eligible portfolio company. |
5. | Securities received in exchange for or distributed on or with respect to securities described in (1) through (4) above, or pursuant to the exercise of warrants or rights relating to such securities. |
6. | Cash, cash equivalents, U.S. government securities or high-quality debt securities maturing in one year or less from the time of investment. |
In addition, a BDC must have been organized and have its principal place of business in the U.S. and must be operated for the purpose of making investments in the types of securities described in (1), (2) or (3) above.
Managerial Assistance to Portfolio Companies
In order to count portfolio securities as qualifying assets for the purpose of the 70% test, we must either control the issuer of the securities or must offer to make available to the issuer of the securities (other than small and solvent companies described above) significant managerial assistance; except that, where we purchase such securities in conjunction with one or more other persons acting together, one of the other persons in the group may
18
make available such managerial assistance. Making available managerial assistance means, among other things, any arrangement whereby the BDC, through its directors, officers or employees, offers to provide, and, if accepted, does so provide, significant guidance and counsel concerning the management, operations or business objectives and policies of a portfolio company. Depending on the nature of the assistance required, CIM will provide such managerial assistance on our behalf to portfolio companies that request this assistance. To the extent fees are paid for these services, we, rather than CIM, will retain any fees paid for such assistance.
Temporary Investments
Pending investment in other types of “qualifying assets,” as described above, our investments may consist of cash, cash equivalents, U.S. government securities or high-quality debt securities maturing in one year or less from the time of investment, which we refer to, collectively, as temporary investments, so that 70% of our assets are qualifying assets. Typically, we will invest in U.S. Treasury bills or in repurchase agreements, provided that such agreements are fully collateralized by cash or securities issued by the U.S. government or its agencies. A repurchase agreement involves the purchase by an investor, such as us, of a specified security and the simultaneous agreement by the seller to repurchase it at an agreed-upon future date and at a price that is greater than the purchase price by an amount that reflects an agreed-upon interest rate. There is no percentage restriction on the proportion of our assets that may be invested in such repurchase agreements. However, if more than 25% of our total assets constitute repurchase agreements from a single counterparty, we may not meet the RIC diversification tests, as further defined in the “Taxation as a Regulated Investment Company” section below, in order to qualify as a RIC for federal income tax purposes. Thus, we do not intend to enter into repurchase agreements with a single counterparty in excess of this limit. CIM will monitor the creditworthiness of the counterparties with which we enter into repurchase agreement transactions.
Senior Securities
We are permitted, under specified conditions, to issue multiple classes of debt and one class of stock senior to our common stock if our asset coverage, as defined in the 1940 Act, is at least equal to 200% immediately after each such issuance. In addition, while any senior securities remain outstanding, we must make provisions to prohibit any distribution to our shareholders or the repurchase of such securities or shares unless we meet the applicable asset coverage ratios at the time of the distribution or repurchase. We may also borrow amounts up to 5% of the value of our total assets for temporary or emergency purposes without regard to asset coverage. See “Item 1A. Risk Factors - Risks Related to Business Development Companies - Regulations governing our operation as a BDC and RIC will affect our ability to raise, and the way in which we raise, additional capital or borrow for investment purposes, which may have a negative effect on our growth.”
Code of Ethics
We and CIM have adopted a code of ethics pursuant to Rule 17j-1 under the 1940 Act that establishes procedures for personal investments and restricts certain personal securities transactions. Personnel subject to the code may invest in securities for their personal investment accounts, including securities that may be purchased or held by us, so long as such investments are made in accordance with the code’s requirements. Shareholders may read and copy the code of ethics at the SEC’s Public Reference Room in Washington, D.C. Shareholders may obtain information on the operation of the Public Reference Room by calling the SEC at (202) 551-8090. In addition, the code of ethics is attached as an exhibit to our Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on May 11, 2016, which is available on the EDGAR Database on the SEC’s Internet site at http://www.sec.gov. Shareholders may also obtain copies of the code of ethics, after paying a duplicating fee, by electronic request at the following e-mail address: publicinfo@sec.gov, or by writing the SEC’s Public Reference Section, 100 F Street, N.E., Washington, D.C. 20549.
Compliance Policies and Procedures
We and CIM have adopted and implemented written policies and procedures reasonably designed to prevent violation of the federal securities laws and are required to review these compliance policies and procedures annually for their adequacy and the effectiveness of their implementation. Our Chief Compliance Officer, or CCO, is responsible for administering our policies and procedures and CIM’s chief compliance officer is responsible for administering its policies and procedures.
Proxy Voting Policies and Procedures
We have delegated our proxy voting responsibility to CIM. The proxy voting policies and procedures of CIM are set forth below. The guidelines are reviewed periodically by CIM and our non-interested directors, and, accordingly, are subject to change.
Introduction
As an investment adviser registered under the Advisers Act, CIM has a fiduciary duty to act solely in the best interests of its clients. As part of this duty, it recognizes that it must vote client securities in a timely manner free of conflicts of interest and in the best interests of its clients. These policies and procedures for voting proxies for the investment advisory clients of CIM are intended to comply with Section 206 of, and Rule 206(4)-6 under, the Advisers Act.
Proxy Policies
CIM will vote proxies relating to our securities in a manner that it believes, in its discretion, to be in the best interest of our shareholders. It will review on a case-by-case basis each proposal submitted for a shareholder vote to determine its impact on the portfolio securities held by its clients.
19
Although CIM will generally vote against proposals that may have a negative impact on its clients’ portfolio securities, it may vote for such a proposal if there exists compelling long-term reasons to do so.
The proxy voting decisions of CIM are made by the senior officers who are responsible for monitoring each of its clients’ investments. To ensure that its vote is not the product of a conflict of interest, it will require that: (a) anyone involved in the decision-making process disclose to the chief compliance officer any potential conflict that he or she is aware of and any contact that he or she has had with any interested party regarding a proxy vote and (b) officers and employees involved in the decision making process or vote administration are prohibited from revealing how CIM intends to vote on a proposal in order to reduce any attempted influence from interested parties. The CCO of CIM will work with the appropriate senior officers to resolve any conflict that may arise.
Proxy Voting Records
Shareholders may obtain information, without charge, regarding how CIM voted proxies with respect to our portfolio securities by making a written request for proxy voting information to: Chief Compliance Officer, c/o CĪON Investment Corporation, 3 Park Avenue, 36th Floor, New York, NY 10016.
Election to be Taxed as a Regulated Investment Company
We elected to be treated as a RIC under Subchapter M of the Code. As a RIC, we generally will not be subject to corporate-level federal income taxes on any income that we distribute to our shareholders from our tax earnings and profits. To qualify as a RIC, we must, among other things, meet certain source-of-income and asset diversification requirements (as described below). In addition, in order to maintain RIC tax treatment, we must distribute to our shareholders, for each taxable year, at least 90% of our “investment company taxable income,” which is generally our net ordinary income plus the excess, if any, of realized net short-term capital gains over realized net long-term capital losses and determined without regard to any deduction for distributions paid. We refer to this as the Annual Distribution Requirement.
Taxation as a Regulated Investment Company
If we:
• | qualify as a RIC; and |
• | satisfy the Annual Distribution Requirement, |
then we will not be subject to federal income tax on the portion of our income we distribute (or are deemed to distribute) to shareholders. We will be subject to U.S. federal income tax at the regular corporate rates on any income or capital gains not distributed (or deemed distributed) to our shareholders.
We will be subject to a 4.0% nondeductible federal excise tax on certain undistributed income unless we distribute in a timely manner an amount at least equal to the sum of (1) 98.0% of our net ordinary income (taking into account certain deferrals and elections) for each calendar year, (2) 98.2% of our capital gain net income (adjusted for certain ordinary losses) for the one-year period ending October 31 in that calendar year and (3) any ordinary income and capital gain net income recognized, but not distributed, in preceding years and on which we paid no federal income tax, or the Excise Tax Avoidance Requirement.
In order to qualify as a RIC for federal income tax purposes, we must, among other things:
• | continue to qualify as a BDC under the 1940 Act at all times during each taxable year; |
• | derive in each taxable year at least 90% of our gross income from dividends, interest, payments with respect to certain securities, loans, gains from the sale of stock or other securities, net income from certain “qualified publicly traded partnerships,” or other income derived with respect to our business of investing in such stock or securities, or the 90% Income Test; and |
• | diversify our holdings so that at the end of each quarter of the taxable year: |
• | at least 50% of the value of our assets consists of cash, cash equivalents, U.S. Government securities, securities of other RICs, and other securities if such other securities of any one issuer do not represent more than 5% of the value of our assets or more than 10% of the outstanding voting securities of the issuer; and |
• | no more than 25% of the value of our assets is invested in the securities, other than U.S. government securities or securities of other RICs, of one issuer, of two or more issuers that are controlled, as determined under applicable Code rules, by us and that are engaged in the same or similar or related trades or businesses or of certain “qualified publicly traded partnerships,” or the Diversification Tests. |
For federal income tax purposes, we may be required to recognize taxable income in circumstances in which we do not receive a corresponding payment in cash. For example, if we hold debt obligations that are treated under applicable tax rules as having original issue discount (such as debt instruments with contractual “payment-in-kind,” or PIK, interest or, in certain cases, increasing interest rates or debt instruments that were issued with warrants), we must include in income each taxable year a portion of the original issue discount that accrues over the life of the obligation, regardless of whether cash representing such income is received by us in the same taxable year. We may also have to include in income other amounts that we have not yet received in cash, such as deferred loan origination fees that are paid after origination of the loan or are paid in non-cash compensation such as
20
warrants or stock. We anticipate that a portion of our income may constitute original issue discount or other income required to be included in taxable income prior to receipt of cash.
Because any original issue discount or other amounts accrued will be included in our investment company taxable income for the year of the accrual, we may be required to make a distribution to our shareholders in order to satisfy the Annual Distribution Requirement, even though we will not have received any corresponding cash amount. As a result, we may have difficulty meeting the annual distribution requirement necessary to qualify for and maintain RIC tax treatment under the Code. We may have to sell some of our investments at times and/or at prices we would not consider advantageous, raise additional debt or equity capital or forego new investment opportunities for this purpose. If we are not able to obtain cash from other sources, we may fail to qualify for RIC tax treatment and thus become subject to corporate-level income tax. Our ability to dispose of assets to meet our distribution requirements may be limited by (1) the illiquid nature of our portfolio and/or (2) other requirements relating to our status as a RIC, including the Diversification Tests. If we dispose of assets in order to meet the Annual Distribution Requirement or the Excise Tax Avoidance Requirement, we may make such dispositions at times that, from an investment standpoint, are not advantageous.
Under the 1940 Act, we are not permitted to make distributions to our shareholders while our debt obligations and other senior securities are outstanding unless certain “asset coverage” tests are met. As a result, we may be prohibited from making distributions necessary to satisfy the Annual Distribution Requirement. Even if we are not prohibited from making distributions, our ability to raise additional capital to satisfy the Annual Distribution Requirement may be limited. If we are not able to make sufficient distributions to satisfy the Annual Distribution Requirement, we may fail to qualify for RIC tax treatment and thus become subject to corporate-level income tax.
Certain of our investment practices may be subject to special and complex federal income tax provisions that may, among other things, (1) treat dividends that would otherwise constitute qualified dividend income as non-qualified dividend income, (2) disallow, suspend or otherwise limit the allowance of certain losses or deductions, (3) convert lower-taxed long-term capital gain into higher-taxed short-term capital gain or ordinary income, (4) convert an ordinary loss or a deduction into a capital loss (the deductibility of which is more limited), (5) cause us to recognize income or gain without receipt of a corresponding distribution of cash, (6) adversely affect the time as to when a purchase or sale of stock or securities is deemed to occur, (7) adversely alter the characterization of certain complex financial transactions and (8) produce income that will not be qualifying income for purposes of the 90% Income Test. We intend to monitor our transactions and may make certain tax elections to mitigate the potential adverse effect of these provisions, but there can be no assurance that any adverse effects of these provisions will be mitigated.
If we purchase shares in a passive foreign investment company, or a PFIC, we may be subject to federal income tax on its allocable share of a portion of any “excess distribution” received on, or any gain from the disposition of, such shares even if our allocable share of such income is distributed as a taxable dividend to our shareholders. Additional charges in the nature of interest generally will be imposed on us in respect of deferred taxes arising from any such excess distribution or gain. If we invest in a PFIC and elect to treat the PFIC as a “qualified electing fund” under the Code, or a QEF, in lieu of the foregoing requirements, we will be required to include in income each year our proportionate share of the ordinary earnings and net capital gain of the QEF, even if such income is not distributed by the QEF. Alternatively, we may be able to elect to mark-to-market at the end of each taxable year our shares in a PFIC; in this case, we will recognize as ordinary income our allocable share of any increase in the value of such shares, and as ordinary loss our allocable share of any decrease in such value to the extent that any such decrease does not exceed prior increases included in our income. Under either election, we may be required to recognize in a year income in excess of distributions from PFICs and proceeds from dispositions of PFIC stock during that year, and such income will nevertheless be subject to the Annual Distribution Requirement and will be taken into account for purposes of the 4% excise tax.
Exchange Act and Sarbanes-Oxley Act Compliance
We are subject to the reporting and disclosure requirements of the Exchange Act, including the filing of quarterly, annual and current reports, proxy statements and other required items. In addition, we are subject to the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, which imposes a wide variety of regulatory requirements on publicly-held companies and their insiders. Many of these requirements affect us. For example:
• | pursuant to Rule 13a-14 of the Exchange Act, our co-chief executive officers and our chief financial officer are required to certify the accuracy of the financial statements contained in our periodic reports; |
• | pursuant to Item 307 of Regulation S-K, our periodic reports are required to disclose our conclusions about the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures; and |
• | pursuant to Rule 13a-15 of the Exchange Act, our management is required to prepare a report regarding its assessment of our internal control over financial reporting. |
The Sarbanes-Oxley Act requires us to review our current policies and procedures to determine whether we comply with the Sarbanes-Oxley Act and the regulations promulgated thereunder. We intend to monitor our compliance with all regulations that are adopted under the Sarbanes-Oxley Act and will take actions necessary to ensure that we are in compliance therewith.
Under the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act, or JOBS Act, we are exempt from the provisions of Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, which would require that our independent registered public accounting firm provide an attestation report on the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting. This may increase the risk that material weaknesses or other deficiencies in our internal control over financial reporting go undetected.
21
Other
We expect to be periodically examined by the SEC for compliance with the 1940 Act.
We are required to provide and maintain a bond issued by a reputable fidelity insurance company to protect us against larceny and embezzlement. Furthermore, as a BDC, we are prohibited from protecting any director or officer against any liability to us or our shareholders arising from willful misconduct, bad faith, gross negligence or reckless disregard of the duties involved in the conduct of such person’s office.
Employees
We do not currently have any employees and we do not currently intend to hire any in the future. The compensation of our chief financial officer and treasurer, Keith S. Franz, and our chief compliance officer and secretary, Stephen Roman, is paid by CIM. We reimburse CIM for the compensation paid to our chief financial officer and his staff and our chief compliance officer and his staff. In the future, CIM may retain additional investment personnel based upon its needs.
Available Information
Within 60 days after the end of each fiscal quarter, we distribute our quarterly report on Form 10-Q to all shareholders of record. In addition, we distribute our annual report on Form 10-K to all shareholders within 120 days after the end of each fiscal year. These reports are available on our website at www.cioninvestments.com and on the SEC’s website at www.sec.gov. Information contained on our website is not incorporated by reference into this Annual Report on Form 10-K and shareholders should not consider information contained on our website to be part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
We file with or submit to the SEC annual, quarterly and current reports, proxy statements and other information meeting the informational requirements of the Exchange Act. Shareholders may inspect and copy these reports, proxy statements and other information, as well as related exhibits and schedules, at the Public Reference Room of the SEC at 100 F Street, N.E., Washington, DC 20549. Shareholders may obtain information on the operation of the Public Reference Room by calling the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330. The SEC maintains an Internet site that contains reports, proxy and information statements and other information filed electronically by us with the SEC, which are available on the SEC’s website at www.sec.gov. Copies of these reports, proxy and information statements and other information may be obtained, after paying a duplicating fee, by electronic request at the following e-mail address: publicinfo@sec.gov, or by writing the SEC’s Public Reference Section, 100 F Street, N.E., Washington, DC 20549.
22
Item 1A. Risk Factors
Investing in our common stock involves a number of significant risks. In addition to the other information contained in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, investors should consider carefully the following information before making an investment in our common stock. If any of the following events occur, our business, financial condition and results of operations could be materially and adversely affected. In such case, the net asset value of our common stock could decline, and investors may lose all or part of their investment.
Risks Relating to Our Business and Structure
Our board of directors may change our operating policies and strategies without prior notice or shareholder approval, the effects of which may be adverse to our results of operations and financial condition.
Our board of directors has the authority to modify or waive our current operating policies, investment criteria and strategies without prior notice and without shareholder approval. We cannot predict the effect any changes to our current operating policies, investment criteria and strategies would have on our business, net asset value, operating results and value of our stock. However, the effects might be adverse, which could negatively impact our ability to pay investors distributions and cause investors to lose all or part of their investment. Moreover, we have significant flexibility in investing the net proceeds from our continuous offering and may use the net proceeds from our continuous offering in ways with which investors may not agree or for purposes other than those contemplated in our prospectus.
Price declines in the medium- and large-sized U.S. corporate debt market may adversely affect the fair value of our portfolio, reducing our net asset value through increased net unrealized depreciation.
Conditions in the medium- and large-sized U.S. corporate debt market may deteriorate, as seen during the recent financial crisis, which may cause pricing levels to similarly decline or be volatile. During the financial crisis, many institutions were forced to raise cash by selling their interests in performing assets in order to satisfy margin requirements or the equivalent of margin requirements imposed by their lenders and/or, in the case of hedge funds and other investment vehicles, to satisfy widespread redemption requests. This resulted in a forced deleveraging cycle of price declines, compulsory sales, and further price declines, with falling underlying credit values, and other constraints resulting from the credit crisis generating further selling pressure. If similar events occurred in the medium- and large-sized U.S. corporate debt market, our net asset value could decline through an increase in unrealized depreciation and incurrence of realized losses in connection with the sale of our investments, which could have a material adverse impact on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Economic activity in the U.S. was adversely impacted by the global financial crisis that began in 2007 and has yet to fully recover.
Economic activity continues to be somewhat subdued since the 2007 financial crisis. As a result, corporate interest rate risk premiums, otherwise known as credit spreads, declined significantly throughout most of 2009 and 2010. However, credit spreads remain slightly above historical averages, particularly in the loan market. The improving economic and market conditions that have driven these declines in credit spreads may reverse themselves if uncertainty returns to the markets. Such a reversal could negatively impact credit spreads as well as our ability to obtain financing, particularly from the debt markets.
The downgrade in the U.S. credit rating and the economic crisis in Europe could materially adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
In August 2011, Standard and Poor’s lowered its long-term sovereign credit rating on the U.S. from “AAA” to “AA+,” which was affirmed by Standard and Poor’s in June 2016. Moody’s and Fitch Ratings, Inc., or Fitch, have also warned that they may downgrade the U.S. federal government’s credit rating. In addition, the economic downturn and the significant government interventions into the financial markets and fiscal stimulus spending over the last several years have contributed to significantly increased U.S. budget deficits. The U.S. government has on several occasions adopted legislation to suspend the federal debt ceiling to allow the U.S. Treasury Department to issue additional debt. Further downgrades or warnings by Standard and Poor’s or other rating agencies, and the U.S. government’s credit and deficit concerns in general, including issues around the federal debt ceiling, could cause interest rates and borrowing costs to rise, which may negatively impact both the perception of credit risk associated with our debt portfolio and our ability to access the debt markets on favorable terms. Furthermore, in February 2014, the Federal Reserve began scaling back its bond-buying program, or quantitative easing, which it ended in October 2014. Quantitative easing was designed to stimulate the economy and expand the Federal Reserve’s holdings of long-term securities until key economic indicators, such as the unemployment rate, showed signs of improvement. The Federal Reserve also raised interest rates during the fourth quarter of 2016. It is unclear what effect, if any, the end of quantitative easing, future interest rate raises, if any, and the pace of any such raises will have on the value of our investments or our ability to access the debt markets on favorable terms.
The impact of the current crisis in Europe with respect to the ability of certain European Union countries to continue to service their sovereign debt obligations is inherently unpredictable and could adversely affect the U.S. and global financial markets and economic conditions. These events could adversely affect our business in many ways, including, but not limited to, adversely impacting our portfolio companies’ ability to obtain financing, or obtaining financing but at significantly lower valuations than the preceding financing rounds. If any of these events were to occur, it could materially adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations. On June 23, 2016, citizens of the United Kingdom, or the U.K., voted in favor of the exit of the U.K. from the European Union, or Brexit. The uncertainty in the wake of the referendum could have negative impacts on both the U.K. economy and the economies of other countries in Europe. The Brexit process also may lead to greater volatility in the global currency and financial markets, which could adversely affect our investments.
23
Our ability to achieve our investment objective depends on the ability of CIM and AIM to manage and support our investment process. If either CIM or AIM were to lose any members of their respective senior management teams, our ability to achieve our investment objective could be significantly harmed.
Since we have no employees, we depend on the investment expertise, skill and network of business contacts of the broader networks of CIM and Apollo and their affiliates. CIM, with the assistance of AIM, evaluates, negotiates, structures, executes, monitors and services our investments. Our future success depends to a significant extent on the continued service and coordination of CIM and its senior management team. The departure of any members of CIM’s senior management team could have a material adverse effect on our ability to achieve our investment objective. Likewise, the departure of any key employees of AIM may impact its ability to render services to us under the terms of its sub-advisory agreement with CIM and us.
Our ability to achieve our investment objective depends on CIM’s ability, with the assistance of AIM, to identify and analyze, and to invest in, finance and monitor companies that meet our investment criteria. CIM’s capabilities in structuring the investment process, providing competent, attentive and efficient services to us, and facilitating access to financing on acceptable terms depend on the employment of investment professionals in an adequate number and of adequate sophistication to match the corresponding flow of transactions. To achieve our investment objective, CIM may need to hire, train, supervise and manage new investment professionals to participate in our investment selection and monitoring process. CIM may not be able to find investment professionals in a timely manner or at all. Failure to support our investment process could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Both the investment advisory agreement between CIM and us and the investment sub-advisory agreement that we and CIM have entered into with AIM have been approved pursuant to Section 15 of the 1940 Act. In addition, both the investment advisory agreement and the investment sub-advisory agreement have termination provisions that allow the parties to terminate the agreements. The investment advisory agreement may be terminated at any time, without penalty, by us or by CIM, upon 60 days notice. The investment sub-advisory agreement may be terminated at any time, upon 60 days’ written notice by AIM or, if a majority of the independent directors of our board of directors or the holders of a majority of our outstanding voting securities determine that the investment sub-advisory agreement with AIM should be terminated, by us. If either agreement is terminated, it may adversely affect the quality of our investment opportunities. In addition, in the event such agreements are terminated, it may be difficult for us to replace CIM and/or AIM.
The investment sub-advisory agreement provides that if AIM terminates the agreement other than for good reason or the agreement is not renewed or is terminated for cause (as defined in the investment sub-advisory agreement), then (x) AIM will be entitled to receive all amounts and any accrued, but unreimbursed, expenses payable to it and not yet paid pursuant to the investment sub-advisory agreement and (y) CIM may elect to subject AIM to an exclusivity restriction contained in the investment sub-advisory agreement, which survives until three years from the date that we met our minimum offering requirement. The term “good reason,” as used in the investment sub-advisory agreement, is defined to include any of the following: (A) those instances in which CIM would be prohibited from acting as an investment adviser to us under Section 9(a) of the 1940 Act on account of action by itself or a person subject to its supervision in the absence of receiving an exemptive order under Section 9(c) of the 1940 Act; (B) those instances in which CIM becomes subject to a prohibition under Section 9(a) or (b) of the 1940 Act; or (C) CIM or we breach the investment sub-advisory agreement in any material respect and fail to cure such breach within 30 days after notice by AIM.
The investment sub-advisory agreement also provides that if the agreement is terminated by AIM for good reason or the agreement is not renewed or is terminated otherwise without cause by us or our shareholders, as applicable, AIM will be entitled to the payment of all amounts and any accrued but unreimbursed expenses payable to it and not yet paid, as well as an amount equal to 37.5% of the gross amount of management fees and incentive fees paid by us over the three year period commencing in the calendar quarter following the calendar quarter in which such termination occurs. Pursuant to the terms of the investment sub-advisory agreement, CIM is obligated to make all such payments to AIM and we are not obligated to pay in the event that CIM is unable or unwilling to pay. In addition, the restriction on the ability of CIM and its affiliates from directly or indirectly acting as an investment adviser or sub-adviser and/or as a sponsor (or engaging any other person for the purpose of acting as an investment adviser or sub-adviser) to any other business development company that engages primarily in the business of providing senior, unitranche and/or mezzanine financing to private, U.S. businesses, and (other than us) whose securities are listed on a public securities exchange will survive indefinitely.
Because our business model depends to a significant extent upon relationships with private equity sponsors, investment banks and commercial banks, the inability of CIM and AIM to maintain or develop these relationships, or the failure of these relationships to generate investment opportunities, could adversely affect our business.
CIM and AIM depend on their broader organizations’ relationships with private equity sponsors, investment banks and commercial banks, and we rely to a significant extent upon these relationships to provide us with potential investment opportunities. If CIM or Apollo or their organizations, as applicable, fail to maintain their existing relationships or develop new relationships with other sponsors or sources of investment opportunities, we may not be able to grow our investment portfolio. In addition, individuals with whom CIM and Apollo or their respective broader organizations have relationships are not obligated to provide us with investment opportunities, and, therefore, there is no assurance that such relationships will generate investment opportunities for us.
24
We may face increasing competition for investment opportunities, which could delay deployment of our capital, reduce returns and result in losses.
We compete for investments with other BDCs and investment funds (including private equity funds, mezzanine funds and funds that invest in CLOs, structured notes, derivatives and other types of collateralized securities and structured products), as well as traditional financial services companies such as commercial banks and other sources of funding. Moreover, alternative investment vehicles, such as hedge funds, have begun to invest in areas in which they have not traditionally invested, including making investments in small to mid-sized private U.S. companies. As a result of these new entrants, competition for investment opportunities in small and middle-market private U.S. companies may intensify. Many of our competitors are substantially larger and have considerably greater financial, technical and marketing resources than we do. For example, some competitors may have a lower cost of capital and access to funding sources that are not available to us. In addition, some of our competitors may have higher risk tolerances or different risk assessments than we have. These characteristics could allow our competitors to consider a wider variety of investments, establish more relationships and offer better pricing and more flexible structuring than we are able to do. We may lose investment opportunities if we do not match our competitors’ pricing, terms or structure. If we are forced to match our competitors’ pricing, terms or structure, we may not be able to achieve acceptable returns on our investments or may bear substantial risk of capital loss. A significant part of our competitive advantage stems from the fact that the market for investments in small and middle-market private U.S. companies is underserved by traditional commercial banks and other financial sources. A significant increase in the number and/or the size of our competitors in this target market could force us to accept less attractive investment terms. Furthermore, many of our competitors have greater experience operating under, or are not subject to, the regulatory restrictions that the 1940 Act imposes on us as a BDC.
As required by the 1940 Act, a significant portion of our investment portfolio is and will be recorded at fair value as determined in good faith by our board of directors and, as a result, there is and will be uncertainty as to the value of our portfolio investments.
Under the 1940 Act, we are required to carry our portfolio investments at market value or, if there is no readily available market value, at fair value as determined by our board of directors. There is not a public market for the securities of the privately-held companies in which we invest. Most of our investments will not be publicly traded or actively traded on a secondary market. As a result, we value these securities quarterly at fair value as determined in good faith by our board of directors as required by the 1940 Act.
Certain factors that may be considered in determining the fair value of our investments include investment dealer quotes for securities traded on the secondary market for institutional investors, the nature and realizable value of any collateral, the portfolio company’s earnings and its ability to make payments on its indebtedness, the markets in which the portfolio company does business, comparison to comparable publicly-traded companies, discounted cash flow and other relevant factors. As a result, our determinations of fair value may differ materially from the values that would have been used if a ready market for these non-traded securities existed. Due to this uncertainty, our fair value determinations may cause our net asset value on a given date to materially differ from the value that we may ultimately realize upon the sale of one or more of our investments.
There is a risk that investors in our common stock may not receive distributions or that our distributions may not grow over time.
We may not achieve investment results that will allow us to make a specified level of cash distributions or year-to-year increases in cash distributions. In addition, due to the asset coverage test applicable to us as a BDC, we may be limited in our ability to make distributions.
The amount of any distributions we may make is uncertain and our distributions may exceed our earnings. Therefore, portions of the distributions that we make may represent a return of capital to shareholders that will lower their tax basis in their common stock and reduce the amount of funds we have for investment in targeted assets.
We may fund our cash distributions to shareholders from any sources of funds available to us, including offering proceeds, borrowings, net investment income from operations, capital gains proceeds from the sale of assets, non-capital gains proceeds from the sale of assets, dividends or other distributions paid to us on account of preferred and common equity investments in portfolio companies, and expense support from CIG and AIM, which is subject to recoupment. In addition, through December 31, 2014, a portion of our distributions resulted from expense support from CIG, and future distributions may result from expense support from CIG and AIM. Our ability to pay distributions might be adversely affected by, among other things, the impact of one or more of the risk factors described in this section. In addition, the inability to satisfy the asset coverage test applicable to us as a BDC may limit our ability to pay distributions. All distributions are and will be paid at the discretion of our board of directors and will depend on our earnings, our financial condition, maintenance of our RIC status, compliance with applicable BDC regulations and such other factors as our board of directors may deem relevant from time to time. We cannot assure investors that we will continue to pay distributions to our shareholders in the future. In the event that we encounter delays in locating suitable investment opportunities, we may pay all or a substantial portion of our distributions from the proceeds of our public offering or from borrowings in anticipation of future cash flow, which may constitute a return of shareholders’ capital. A return of capital is a return of shareholders’ investment, rather than a return of earnings or gains derived from our investment activities. A shareholder will not be subject to immediate taxation on the amount of any distribution treated as a return of capital to the extent of the shareholder’s basis in its shares; however, the shareholder's basis in its shares will be reduced (but not below zero) by the amount of the return of capital, which will result in the shareholder recognizing additional gain (or a lower loss) when the shares are sold. To the extent that the amount of the return of capital exceeds the shareholder's basis in its shares, such excess amount will be treated as gain from the sale of the shareholder’s shares. A shareholder’s basis in the investment will be reduced by the nontaxable amount, which will result in additional gain (or a lower loss) when the shares are sold. Distributions from the proceeds of our public offering or from borrowings also could reduce the amount of capital we ultimately invest in our portfolio companies.
25
We have not established any limit on the amount of funds we may use from available sources, such as borrowings, if any, or proceeds from our offering, to fund distributions (which may reduce the amount of capital we ultimately invest in assets).
Through December 31, 2014, a portion of our distributions resulted from expense support from CIG, and future distributions may result from expense support from CIG and AIM, each of which is subject to repayment by us within three years. The purpose of this arrangement is to reduce our operating expenses and to avoid such distributions being characterized as a return of capital. Shareholders should understand that any such distributions are not based on our investment performance, and can only be sustained if we achieve positive investment performance in future periods and/or CIG and AIM continue to provide such expense support. Shareholders should also understand that our future repayments of expense support to CIG and AIM will reduce the distributions that they would otherwise receive. There can be no assurance that we will achieve such performance in order to sustain these distributions, or be able to pay distributions at all. CIG and AIM have no obligation to provide expense support to us in future periods.
Changes in laws or regulations governing our operations may adversely affect our business or cause us to alter our business strategy.
We and our portfolio companies are subject to regulation at the local, state and federal level. New legislation may be enacted or new interpretations, rulings or regulations could be adopted, including those governing the types of investments we are permitted to make, any of which could harm us and our shareholders, potentially with retroactive effect.
Additionally, any changes to the laws and regulations governing our operations relating to permitted investments may cause us to alter our investment strategy to avail ourselves of new or different opportunities. Such changes could result in material differences to our strategies and plans as set forth herein and may result in our investment focus shifting from the areas of expertise of CIM and AIM to other types of investments in which CIM and AIM may have less expertise or little or no experience. Thus, any such changes, if they occur, could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations and the value of a shareholder’s investment.
As a public company, we are subject to regulations not applicable to private companies, such as provisions of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act. Efforts to comply with such regulations will involve significant expenditures, and non-compliance with such regulations may adversely affect us.
As a public company, we are subject to the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, and the related rules and regulations promulgated by the SEC. Our management is required to report on our internal control over financial reporting pursuant to Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act. We are required to review on an annual basis our internal control over financial reporting, and on a quarterly and annual basis to evaluate and disclose changes in our internal control over financial reporting. As a relatively new company, developing and maintaining an effective system of internal controls may require significant expenditures, which may negatively impact our financial performance and our ability to make distributions. This process also will result in a diversion of our management’s time and attention. We cannot be certain of when our evaluation, testing, and remediation actions will be completed or the impact of the same on our operations. In addition, we may be unable to ensure that the process is effective or that our internal controls over financial reporting are or will be effective in a timely manner. In the event that we are unable to develop or maintain an effective system of internal controls and maintain or achieve compliance with the Sarbanes-Oxley Act and related rules, we may be adversely affected.
The impact of financial reform legislation on us is uncertain.
In light of recent conditions in the U.S. and global financial markets and the U.S. and global economy, legislators, the presidential administration and regulators have increased their focus on the regulation of the financial services industry. The Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, or the Dodd-Frank Act, institutes a wide range of reforms that will have an impact on all financial institutions. Many of the requirements called for in the Dodd-Frank Act will be implemented over time, most of which will be subject to implementing regulations over the course of the next several years. Given the uncertainty associated with the manner in which the provisions of the Dodd-Frank Act will be implemented by the various regulatory agencies and through regulations, the full impact such requirements will have on our business, results of operations or financial condition is unclear. The changes resulting from the Dodd-Frank Act may require us to invest significant management attention and resources to evaluate and make necessary changes in order to comply with new statutory and regulatory requirements. Failure to comply with any such laws, regulations or principles, or changes thereto, may negatively impact our business, results of operations and financial condition. While we cannot predict what effect any changes in the laws or regulations or their interpretations would have on us as a result of the Dodd-Frank Act, these changes could be materially adverse to us and our shareholders.
We may experience fluctuations in our quarterly results.
We could experience fluctuations in our quarterly operating results due to a number of factors, including our ability or inability to make investments in companies that meet our investment criteria, the interest rate payable on the debt securities we acquire, the level of our expenses (including our borrowing costs), variations in and the timing of the recognition of realized and unrealized gains or losses, the degree to which we encounter competition in our markets and general economic conditions. As a result of these factors, results for any previous period should not be relied upon as being indicative of performance in future periods.
26
Any unrealized losses we experience on our portfolio may be an indication of future realized losses, which could reduce our income available for distribution.
As a BDC, we are required to carry our investments at market value or, if no market value is ascertainable, at the fair value as determined in good faith by our board of directors. Decreases in the market value or fair value of our investments relative to amortized cost will be recorded as unrealized depreciation. Any unrealized losses in our portfolio could be an indication of a portfolio company’s inability to meet its repayment obligations to us with respect to the affected loans. This could result in realized losses in the future and ultimately in reductions of our income available for distribution in future periods. In addition, decreases in the market value or fair value of our investments will reduce our net asset value.
Pending legislation may allow us to incur additional leverage.
As a BDC, we are generally not permitted to incur indebtedness unless immediately after such borrowing we have an asset coverage for total borrowings of at least 200% (i.e., the amount of debt may not exceed 50% of the value of our assets). Recent legislation introduced in the U.S. House of Representatives, if passed, would modify this section of the 1940 Act and increase the amount of debt that BDCs may incur by modifying the percentage from 200% to 150%. Even if this legislation does not pass, similar legislation may pass that permits us to incur additional leverage under the 1940 Act. As a result, we may be able to incur additional indebtedness in the future, and, therefore, your risk of an investment in us may increase.
Risks Related to CIM and its Affiliates; Risks Related to AIM and its Affiliates
CIM has limited prior experience managing a BDC or a RIC.
CIM has limited experience managing a BDC or a RIC and may not be able to successfully operate our business or achieve our investment objective. As a result, an investment in our shares of common stock may entail more risk than the shares of common stock of a comparable company with a substantial operating history.
The 1940 Act and the Code impose numerous constraints on the operations of BDCs and RICs that do not apply to the other types of investment vehicles previously managed by CIM’s management team. For example, under the 1940 Act, BDCs are required to invest at least 70% of their total assets primarily in securities of qualifying U.S. private or thinly-traded public companies. Moreover, qualification for RIC tax treatment under Subchapter M of the Code requires, among other things, satisfaction of source-of-income and other requirements. The failure to comply with these provisions in a timely manner could prevent us from qualifying as a BDC or RIC or could force us to pay unexpected taxes and penalties, which could be material. CIM’s limited experience in managing a portfolio of assets under such constraints may hinder its ability to take advantage of attractive investment opportunities and, as a result, achieve our investment objective.
CIM and its affiliates, including our officers and some of our directors, face conflicts of interest caused by compensation arrangements with us and our affiliates, which could result in actions that are not in the best interests of our shareholders.
CIM and its affiliates receive substantial fees from us in return for their services, and these fees could influence the advice provided to us. Among other matters, the compensation arrangements could affect their judgment with respect to public offerings of equity by us, which allow the dealer manager to earn additional dealer manager fees and CIM to earn increased asset management fees. In addition, the decision to utilize leverage will increase our assets and, as a result, will increase the amount of management fees payable to CIM and may increase the amount of subordinated income incentive fees payable to CIM.
We may be obligated to pay CIM incentive compensation even if we incur a net loss due to a decline in the value of our portfolio.
Our investment advisory agreement entitles CIM to receive incentive compensation on income regardless of any capital losses. In such case, we may be required to pay CIM incentive compensation for a fiscal quarter even if there is a decline in the value of our portfolio or if we incur a net loss for that quarter.
Any incentive fee payable by us that relates to our net investment income may be computed and paid on income that may include interest that has been accrued, but not yet received, including original issue discount, which may arise if we receive warrants in connection with the origination of a loan or possibly in other circumstances, or contractual PIK interest, which represents contractual interest added to the loan balance and due at the end of the loan term. To the extent we do not distribute accrued PIK interest, the deferral of PIK interest has the simultaneous effects of increasing the assets under management and increasing the base management fee at a compounding rate, while generating investment income and increasing the incentive fee at a compounding rate. In addition, the deferral of PIK interest would also increase the loan-to-value ratio at a compounding rate if the issuer’s assets do not increase in value, and investments with a deferred interest feature, such as PIK interest, may represent a higher credit risk than loans on which interest must be paid in full in cash on a regular basis.
For example, if a portfolio company defaults on a loan that is structured to provide accrued interest, it is possible that accrued interest previously included in the calculation of the incentive fee will become uncollectible. CIM is not under any obligation to reimburse us for any part of the incentive fee it received that was based on accrued income that we never received as a result of a default by an entity on the obligation that resulted in the accrual of such income, and such circumstances would result in our paying an incentive fee on income we never received.
27
There may be conflicts of interest related to obligations that CIM’s and Apollo’s respective senior management and investment teams have to other clients.
The members of the senior management and investment teams of both CIM and Apollo serve or may serve as officers, directors or principals of entities that operate in the same or a related line of business as we do, or of investment funds managed by the same personnel. In serving in these multiple capacities, they may have obligations to other clients or investors in those entities, the fulfillment of which may not be in our best interests or in the best interest of our shareholders. Our investment objective may overlap with the investment objectives of such investment funds, accounts or other investment vehicles. In particular, we rely on CIM to manage our day-to-day activities and to implement our investment strategy. CIM and certain of its affiliates are presently, and plan in the future to continue to be, involved with activities that are unrelated to us. As a result of these activities, CIM, its officers and employees and certain of its affiliates will have conflicts of interest in allocating their time between us and other activities in which they are or may become involved, including the management of its affiliated equipment funds. CIM and its officers and employees will devote only as much of its or their time to our business as CIM and its officers and employees, in their judgment, determine is reasonably required, which may be substantially less than their full time.
We rely, in part, on AIM to assist with identifying investment opportunities and making investment recommendations to CIM. AIM, its affiliates and their respective members, partners, officers and employees will devote as much of their time to our activities as they deem necessary and appropriate. Apollo and its affiliates are not restricted from forming additional investment funds, entering into other investment advisory relationships, except in certain limited circumstances as set forth in the investment sub-advisory agreement, or engaging in other business activities, even though such activities may be in competition with us and/or may involve substantial time and resources of AIM. These activities could be viewed as creating a conflict of interest in that the time and effort of the members of AIM, its affiliates and their officers and employees will not be devoted exclusively to our business, but will be allocated between us and such other business activities of Apollo and its affiliates in a manner that Apollo deems necessary and appropriate.
AIM currently acts as investment adviser to AINV, which is also a BDC and is authorized to invest in the same kinds of securities we invest or may invest in, although AINV primarily focuses on providing senior and subordinated debt to companies that are expected to have greater EBITDA than those that are our primary focus. Also, in connection with such business activities, AIM and its affiliates may have existing business relationships or access to material, non-public information that may prevent it from recommending investment opportunities that would otherwise fit within our investment objective. These activities could be viewed as creating a conflict of interest in that the time, effort and ability of the members of AIM, its affiliates and their officers and employees will not be devoted exclusively to our business, but will be allocated between us and such other accounts managed by AIM and its affiliates as AIM deems necessary and appropriate.
It is possible that conflicts of interest will arise from time to time in connection with our prospective and existing investments and AINV or other funds or accounts managed or advised by Apollo, including, without limitation, in circumstances giving rise to the restructuring of an issuer in which we and AINV are investors, as well as follow-on investments or dispositions with respect to such issuer. In such circumstance, it is likely that we and CIM, on the one hand, will be walled off from Apollo and AINV, on the other hand, and accordingly the parties will not collectively discuss or participate in, for example, the restructuring with respect to such issuer. Further, there may also arise instances in which we and AINV are invested in the same issuer and we and/or AINV seeks to dispose of such investment in a transaction that may otherwise require exemptive relief, in which case the parties may need to obtain an exemptive order, the receipt of which cannot be assured.
In addition, there are no information barriers amongst AIM and certain of its affiliates. If AIM or its affiliates were to receive material non-public information about a particular company, or have an interest in investing in a particular company, we may be prevented from investing in such company.
Furthermore, it is possible that AINV or other funds managed or advised by Apollo may own or make investments in the same or similar securities at different times and on different terms than we do. From time to time, we and AINV or other funds managed or advised by Apollo may make investments at different levels of an issuer’s capital structure or otherwise in different classes of an issuer’s securities. Such investments may inherently give rise to conflicts of interest or perceived conflicts of interest between or among the various classes of securities that may be held by such entities. Conflicts may also arise because portfolio decisions regarding us may benefit AINV or other funds managed or advised by Apollo. Apollo and its managed funds may pursue or enforce rights with respect to an issuer in which we have invested, and those activities may have an adverse effect on us. As a result, prices, availability, liquidity, and terms of our investments may be negatively impacted by the activities of Apollo or its managed funds, and transactions for us may be impaired or effected at prices or terms that may be less favorable than would otherwise have been the case.
The time and resources that individuals employed by CIM and Apollo devote to us may be diverted and we may face additional competition due to the fact that individuals employed by CIM and Apollo are not prohibited from raising money for or managing other entities that make the same types of investments that we target.
Neither CIM nor AIM, nor individuals employed by CIM or AIM, are generally prohibited from raising capital for and managing other investment entities that make the same types of investments as those we target. As a result, the time and resources that these individuals may devote to us may be diverted. In addition, we may compete with any such investment entity for the same investors and investment opportunities. We will be unable to participate in certain transactions originated by CIM or its affiliates unless we receive exemptive relief from the SEC. We are currently seeking exemptive relief from the SEC to engage in co-investment transactions with CIM and its affiliates. However, there can be no assurance that we will obtain such exemptive relief. Even if we receive exemptive relief, neither CIM nor its affiliates will be obligated to offer us the right to participate in any transactions originated by them. Affiliates of Apollo, whose primary business includes the origination of investments, engage in investment advisory
28
business with accounts that compete with us. Affiliates of AIM have no obligation to make their originated investment opportunities available to AIM or to us.
Our base management and incentive fees may induce CIM to make, and AIM to recommend, speculative investments or to incur leverage.
The incentive fee payable by us to CIM may create an incentive for it to make investments on our behalf that are risky or more speculative than would be the case in the absence of such compensation arrangement. The way in which the incentive fee payable to CIM is determined may encourage it to use leverage to increase the return on our investments. The part of the management and incentive fees payable to CIM that relates to our net investment income is computed and paid on income that may include interest income that has been accrued but not yet received in cash, such as market discount, debt instruments with PIK interest, preferred stock with PIK dividends and zero coupon securities. This fee structure may be considered to involve a conflict of interest for CIM to the extent that it may encourage CIM to favor debt financings that provide for deferred interest, rather than current cash payments of interest. In addition, the fact that our base management fee is payable based upon our gross assets, which would include any borrowings for investment purposes, may encourage CIM to use leverage to make additional investments. Under certain circumstances, the use of leverage may increase the likelihood of default, which would disfavor holders of our common stock. Such a practice could result in our investing in more speculative securities than would otherwise be in our best interests, which could result in higher investment losses, particularly during cyclical economic downturns. In addition, since AIM will receive a portion of the incentive fees paid to CIM, AIM may have an incentive to recommend investments that are riskier or more speculative.
Shares of our common stock may be purchased by CIM, Apollo or their affiliates.
CIM, Apollo and their respective affiliates may purchase shares of our common stock for any reason deemed appropriate; provided, however, that it is intended that neither CIM, Apollo nor their respective affiliates will hold 5% or more of our outstanding shares of common stock. CIM, Apollo and their respective affiliates will not acquire any shares of our common stock with the intention to resell or re-distribute such shares. The purchase of common stock by CIM, Apollo and their respective affiliates could create certain risks, including, but not limited to, the following:
• | CIM, Apollo and their respective affiliates may have an interest in disposing of our assets at an earlier date so as to recover their investment in our common stock; and |
• | substantial purchases of shares by CIM, Apollo and their respective affiliates may limit CIM’s or AIM’s ability to fulfill any financial obligations that it may have to us or incurred on our behalf. |
CIM relies on key personnel, the loss of any of whom could impair its ability to successfully manage us.
Our future success depends, to a significant extent, on the continued services of the officers and employees of CIM or its affiliates. The loss of services of one or more members of CIM’s management team, including members of our investment committee, could adversely affect our financial condition, business and results of operations.
The compensation we pay to CIM was determined without independent assessment on our behalf, and these terms may be less advantageous to us than if such terms had been the subject of arm’s-length negotiations.
The compensation we pay to CIM was not entered into on an arm’s-length basis with an unaffiliated third party. As a result, the form and amount of such compensation may be less favorable to us than they might have been had these been entered into through arm’s-length transactions with an unaffiliated third party.
CIM’s influence on conducting our operations gives it the ability to increase its fees, which may reduce the amount of cash flow available for distribution to our shareholders.
CIM is paid a base management fee calculated as a percentage of our gross assets and unrelated to net income or any other performance base or measure. CIM may advise us to consummate transactions or conduct our operations in a manner that, in CIM’s reasonable discretion, is in the best interests of our shareholders. These transactions, however, may increase the amount of fees paid to CIM. CIM’s ability to influence the base management fee paid to it by us could reduce the amount of cash flow available for distribution to our shareholders.
Risks Related to Business Development Companies
The requirement that we invest a sufficient portion of our assets in qualifying assets could preclude us from investing in accordance with our current business strategy; conversely, the failure to invest a sufficient portion of our assets in qualifying assets could result in our failure to maintain our status as a BDC.
As a BDC, we may not acquire any assets other than “qualifying assets” unless, at the time of and after giving effect to such acquisition, at least 70% of our total assets are qualifying assets. See “Item 1. Business – Regulation.” Therefore, we may be precluded from investing in what we believe are attractive investments if such investments are not qualifying assets. Conversely, if we fail to invest a sufficient portion of our assets in qualifying assets, we could lose our status as a BDC, which would have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations. Similarly, these rules could prevent us from making additional investments in existing portfolio companies, which could result in the dilution
29
of our position, or could require us to dispose of investments at an inopportune time to comply with the 1940 Act. If we were forced to sell non-qualifying investments in the portfolio for compliance purposes, the proceeds from such sale could be significantly less than the current value of such investments.
Failure to maintain our status as a BDC would reduce our operating flexibility.
If we do not remain a BDC, we might be regulated as a registered closed-end investment company under the 1940 Act, which would subject us to substantially more regulatory restrictions under the 1940 Act and correspondingly decrease our operating flexibility.
Regulations governing our operation as a BDC and RIC will affect our ability to raise, and the way in which we raise, additional capital or borrow for investment purposes, which may have a negative effect on our growth.
As a result of the annual distribution requirement to qualify as a RIC, we may need to periodically access the capital markets to raise cash to fund new investments. We may issue “senior securities,” as defined under the 1940 Act, including borrowing money from banks or other financial institutions only in amounts such that our asset coverage, as defined in the 1940 Act, equals at least 200% after such incurrence or issuance. Our ability to issue different types of securities is also limited. Compliance with these requirements may unfavorably limit our investment opportunities and reduce our ability in comparison to other companies to profit from favorable spreads between the rates at which we can borrow and the rates at which we can lend. As a BDC, therefore, we intend to continuously issue equity at a rate more frequent than our privately owned competitors, which may lead to greater shareholder dilution.
We have borrowed for investment purposes. If the value of our assets declines, we may be unable to satisfy the asset coverage test, which would prohibit us from paying distributions and could prevent us from qualifying as a RIC. If we cannot satisfy the asset coverage test, we may be required to sell a portion of our investments and, depending on the nature of our debt financing, repay a portion of our indebtedness at a time when such sales may be disadvantageous.
Under the 1940 Act, we generally are prohibited from issuing or selling our common stock at a price per share, after deducting selling commissions and dealer manager fees, that is below our net asset value per share, which may be a disadvantage as compared with other public companies. We may, however, sell our common stock, or warrants, options or rights to acquire our common stock, at a price below the current net asset value of our common stock if our board of directors, including our independent directors, determine that such sale is in our best interests and the best interests of our shareholders, and our shareholders, as well as those shareholders that are not affiliated with us, approve such sale. In any such case, the price at which our securities are to be issued and sold may not be less than a price that, in the determination of our board of directors, closely approximates the fair value of such securities.
Our ability to enter into transactions with our affiliates is restricted.
We are prohibited under the 1940 Act from participating in certain transactions with certain of our affiliates without the prior approval of a majority of the independent members of our board of directors and, in some cases, the SEC. Any person that owns, directly or indirectly, 5% or more of our outstanding voting securities will be our affiliate for purposes of the 1940 Act and generally we will be prohibited from buying or selling any securities from or to such affiliate, absent the prior approval of our board of directors. The 1940 Act also prohibits certain “joint” transactions with certain of our affiliates, which could include investments in the same portfolio company (whether at the same or closely related times), without prior approval of our board of directors and, in some cases, the SEC. If a person acquires more than 25% of our voting securities, we will be prohibited from buying or selling any security from or to such person or certain of that person’s affiliates, or entering into prohibited joint transactions with such persons, absent the prior approval of the SEC. Similar restrictions limit our ability to transact business with our officers, directors, investment advisers, sub-advisers or their affiliates. As a result of these restrictions, we may be prohibited from buying or selling any security from or to any fund or any portfolio company of a fund managed by CIM or Apollo, or entering into joint arrangements such as certain co-investments with these companies or funds without the prior approval of the SEC, which may limit the scope of investment opportunities that would otherwise be available to us.
We are uncertain of our sources for funding our future capital needs; if we cannot obtain debt or equity financing on acceptable terms, our ability to acquire investments and to expand our operations will be adversely affected.
The net proceeds from the sale of common stock will be used for our investment opportunities, operating expenses and for payment of various fees and expenses such as base management fees, incentive fees and other expenses. Any working capital reserves we maintain may not be sufficient for investment purposes, and we may require debt or equity financing to operate. Accordingly, in the event that we develop a need for additional capital in the future for investments or for any other reason, these sources of funding may not be available to us. Consequently, if we cannot obtain debt or equity financing on acceptable terms, our ability to acquire investments and to expand our operations will be adversely affected. As a result, we would be less able to create and maintain a broad portfolio of investments and achieve our investment objective, which may negatively impact our results of operations and reduce our ability to make distributions to our shareholders.
We are a non-diversified investment company within the meaning of the 1940 Act, and therefore we are not limited with respect to the proportion of our assets that may be invested in securities of a single issuer.
We are classified as a non-diversified investment company within the meaning of the 1940 Act, which means that we are not limited by the 1940 Act with respect to the proportion of our assets that we may invest in securities of a single issuer. Under the 1940 Act, a “diversified” investment company is required to invest at least 75% of the value of its total assets in cash and cash items, government securities, securities of other investment
30
companies and other securities limited in respect of any one issuer to an amount not greater than 5% of the value of the total assets of such company and no more than 10% of the outstanding voting securities of such issuer. As a non-diversified investment company, we are not subject to this requirement. To the extent that we assume large positions in the securities of a small number of issuers, or within a particular industry, our net asset value may fluctuate to a greater extent than that of a diversified investment company as a result of changes in the financial condition or the market’s assessment of the issuer. We may also be more susceptible to any single economic or regulatory occurrence than a diversified investment company or to a general downturn in the economy. However, we will be subject to the diversification requirements applicable to RICs under Subchapter M of the Code.
Risks Related to Our Investments
Our investments in prospective portfolio companies may be risky, and we could lose all or part of our investment.
We invest or intend to invest in the following types of loans of private and thinly-traded U.S. middle-market companies.
Senior Secured Debt.
First Lien Loans and Second Lien Loans. When we invest in senior secured term debt, including first lien loans and second lien loans, we will generally take a security interest in the available assets of these portfolio companies, including the equity interests of their subsidiaries. We expect this security interest to help mitigate the risk that we will not be repaid. However, there is a risk that the collateral securing our loans may decrease in value over time or lose its entire value, may be difficult to sell in a timely manner, may be difficult to appraise and may fluctuate in value based upon the success of the business and market conditions, including as a result of the inability of the portfolio company to raise additional capital. Also, in some circumstances, our security interest could be subordinated to claims of other creditors. In addition, deterioration in a portfolio company’s financial condition and prospects, including its inability to raise additional capital, may be accompanied by deterioration in the value of the collateral for the loan. Consequently, the fact that a loan is secured does not guarantee that we will receive principal and interest payments according to the loan’s terms, or at all, or that we will be able to collect on the loan should we be forced to enforce our remedies.
Unitranche Loans. We also expect to invest in unitranche loans, which are loans that combine both senior and subordinated financing, generally in a first-lien position. Unitranche loans provide all of the debt needed to finance a leveraged buyout or other corporate transaction, both senior and subordinated, but generally in a first lien position, while the borrower generally pays a blended, uniform interest rate rather than different rates for different tranches. Unitranche debt generally requires payments of both principal and interest throughout the life of the loan. Unitranche debt generally has contractual maturities of five to six years and interest is typically paid quarterly. Generally, we expect these securities to carry a blended yield that is between senior secured and subordinated debt interest rates. Unitranche loans provide a number of advantages for borrowers, including the following: simplified documentation, greater certainty of execution and reduced decision-making complexity throughout the life of the loan. In addition, we may receive additional returns from any warrants we may receive in connection with these investments. In some cases, a portion of the total interest may accrue or be paid in kind. Because unitranche loans combine characteristics of senior and subordinated financing, unitranche loans have risks similar to the risks associated with senior secured debt, including first lien loans and second lien loans, and subordinated debt in varying degrees according to the combination of loan characteristics of the unitranche loan.
Unsecured Debt. Our unsecured debt, including corporate bonds and subordinated, or mezzanine, investments will generally rank junior in priority of payment to senior debt. This may result in a heightened level of risk and volatility or a loss of principal, which could lead to the loss of the entire investment. These investments may involve additional risks that could adversely affect our investment returns. To the extent interest payments associated with such debt are deferred, such debt may be subject to greater fluctuations in valuations, and such debt could subject us and our shareholders to non-cash income, including PIK interest and original issue discount. Loans structured with these features may represent a higher level of credit risk than loans that require interest to be paid in cash at regular intervals during the term of the loan. Since we generally will not receive any principal repayments prior to the maturity of some of our unsecured debt investments, such investments will have greater risk than amortizing loans.
Collateralized Securities, Structured Products and Other. We may also invest in collateralized securities, structured products and other similar securities, which may include CDOs, CBOs, CLOs, structured notes and credit-linked notes. Investments in such securities and products involve risks, including, without limitation, credit risk and market risk. Certain of these securities and products may be thinly traded or have a limited trading market. Where our investments in collateralized securities, structured products and other similar securities are based upon the movement of one or more factors, including currency exchange rates, interest rates, reference bonds (or loans) and stock indices, depending on the factor used and the use of multipliers or deflators, changes in interest rates and movement of any factor may cause significant price fluctuations. Additionally, changes in the reference instrument or security may cause the interest rate on such a security or product to be reduced to zero, and any further changes in the reference instrument may then reduce the principal amount payable on maturity of the security or product. Collateralized securities, structured products and other similar securities may be less liquid than other types of securities and more volatile than the reference instrument or security underlying the product.
Equity Investments. We expect to make selected equity investments. In addition, when we invest in senior secured debt, including first and second lien loans, or unsecured debt, we may acquire warrants to purchase equity securities. Our goal is ultimately to dispose of these equity interests and realize gains upon our disposition of such interests. However, the equity interests we receive may not appreciate in value and, in fact, may decline in value. Accordingly, we may not be able to realize gains from our equity interests, and any gains that we do realize on the disposition of any equity interests may not be sufficient to offset any other losses we experience.
Non-U.S. Securities. We may invest in non-U.S. securities, which may include securities denominated in U.S. dollars or in non-U.S. currencies, to the extent permitted by the 1940 Act. Because evidence of ownership of such securities usually are held outside the United States, we would be subject
31
to additional risks if we invested in non-U.S. securities, which include possible adverse political and economic developments, seizure or nationalization of foreign deposits and adoption of governmental restrictions which might adversely affect or restrict the payment of principal and interest on the non-U.S. securities to investors located outside the country of the issuer, whether from currency blockage or otherwise. Since non-U.S. securities may be purchased with and payable in foreign currencies, the value of these assets as measured in U.S. dollars may be affected unfavorably by changes in current rates and exchange control regulations.
In addition, we invest in debt securities that are rated below investment grade by rating agencies or that would be rated below investment grade if they were rated. Debt securities rated below investment grade quality are generally regarded as having predominantly speculative characteristics and may carry a greater risk with respect to a borrower’s capacity to pay interest and repay principal. They may also be difficult to value and illiquid.
To the extent original issue discount constitutes a portion of our income, we will be exposed to risks associated with the deferred receipt of cash representing such income.
Our investments may include original issue discount instruments. To the extent original issue discount constitutes a portion of our income, we will be exposed to typical risks associated with such income being required to be included in taxable and accounting income prior to receipt of cash, including the following:
• | Original issue discount instruments may have unreliable valuations because the accruals require judgments about collectability. |
• | Original issue discount instruments may create heightened credit risks because the inducement to trade higher rates for the deferral of cash payments typically represents, to some extent, speculation on the part of the borrower. |
• | For accounting purposes, cash distributions to shareholders representing original issue discount income do not come from paid-in capital, although they may be paid from the offering proceeds. Thus, although a distribution of original issue discount income comes from the cash invested by shareholders, the 1940 Act does not require that shareholders be given notice of this fact. |
• | In the case of PIK “toggle” debt, the PIK election has the simultaneous effects of increasing the assets under management, thus increasing the base management fee, and increasing the investment income, thus increasing the potential for realizing incentive fees. |
• | Since original issue discount will be included in our investment company taxable income for the year of the accrual, we may be required to make a distribution to our shareholders in order to satisfy the annual distribution requirement applicable to RICs, even if we will not have received any corresponding cash amount. As a result, we may have difficulty meeting such annual distribution requirement necessary to obtain and maintain RIC tax treatment under the Code. If we are not able to obtain cash from other sources, and choose not to make a qualifying share distribution, we may fail to qualify for RIC tax treatment and thus become subject to corporate-level income tax. |
• | Original issue discount creates risk of non-refundable cash payments to the advisor based on non-cash accruals that may never be realized. |
Our portfolio companies may incur debt that ranks equally with, or senior to, our investments in such companies.
We intend to invest primarily in senior secured debt, including first lien loans, second lien loans and unitranche loans of private and thinly-traded U.S. middle-market companies. Our portfolio companies may have, or may be permitted to incur, other debt that ranks equally with, or senior to, the debt in which we invest. By their terms, such debt instruments may entitle the holders to receive payment of interest or principal on or before the dates on which we are entitled to receive payments with respect to the debt instruments in which we invest. Also, in the event of insolvency, liquidation, dissolution, reorganization or bankruptcy of a portfolio company, holders of debt instruments ranking senior to our investment in that portfolio company would typically be entitled to receive payment in full before we receive any payment or distribution. After repaying such senior creditors, such portfolio company may not have any remaining assets to use for repaying its obligation to us. In the case of debt ranking equally with debt instruments in which we invest, we would have to share on an equal basis any payments or distributions with other creditors holding such debt in the event of an insolvency, liquidation, dissolution, reorganization or bankruptcy of the relevant portfolio company.
There may be circumstances where our debt investments could be subordinated to claims of other creditors or we could be subject to lender liability claims.
If one of our portfolio companies were to file for bankruptcy, depending on the facts and circumstances, including the extent to which we actually provided managerial assistance to that portfolio company, a bankruptcy court might recharacterize our debt investment and subordinate all or a portion of our claim to that of other creditors. We may also be subject to lender liability claims for actions taken by us with respect to a borrower’s business or instances where we exercise control over the borrower.
We generally will not control our portfolio companies.
We do not expect to control most of our portfolio companies, even though we may have board representation or board observation rights, and our debt agreements with such portfolio companies may contain certain restrictive covenants. As a result, we are subject to the risk that a portfolio company in which we invest may make business decisions with which we disagree and the management of such company, as representatives of the holders of the company’s common equity, may take risks or otherwise act in ways that do not serve our interests as debt investors. Due to the lack of liquidity for our investments in non-traded companies, we may not be able to dispose of our interests in our portfolio companies as readily as we would like or at an appropriate valuation. As a result, a portfolio company may make decisions that could decrease the value of our portfolio holdings.
32
We will be exposed to risks associated with changes in interest rates.
We are subject to financial market risks, including changes in interest rates. General interest rate fluctuations may have a substantial negative impact on our investments and investment opportunities and, accordingly, have a material adverse effect on our ability to achieve our investment objective and our target rate of return on invested capital. In addition, an increase in interest rates would make it more expensive to use debt for our financing needs, if any.
International investments create additional risks.
We have made, and expect to continue to make, investments in portfolio companies that are domiciled outside of the United States. We anticipate that up to 30% of our investments may be in assets located in jurisdictions outside the United States. Our investments in foreign portfolio companies are deemed “non-qualifying assets,” which means, as required by the 1940 Act, they may not constitute more than 30% of our total assets at the time of our acquisition of any asset, after giving effect to the acquisition. Notwithstanding that limitation on our ownership of foreign portfolio companies, those investments subject us to many of the same risks as our domestic investments, as well as certain additional risks including the following:
• | foreign governmental laws, rules and policies, including those restricting the ownership of assets in the foreign country or the repatriation of profits from the foreign country to the United States; |
• | foreign currency devaluations that reduce the value of and returns on our foreign investments; |
• | adverse changes in the availability, cost and terms of investments due to the varying economic policies of a foreign country in which we invest; |
• | adverse changes in tax rates, the tax treatment of transaction structures and other changes in operating expenses of a particular foreign country in which we invest; |
• | the assessment of foreign-country taxes (including withholding taxes, transfer taxes and value added taxes, any or all of which could be significant) on income or gains from our investments in the foreign country; |
• | adverse changes in foreign-country laws, including those relating to taxation, bankruptcy and ownership of assets; |
• | changes that adversely affect the social, political and/or economic stability of a foreign country in which we invest; |
• | high inflation in the foreign countries in which we invest, which could increase the costs to us of investing in those countries; |
• | deflationary periods in the foreign countries in which we invest, which could reduce demand for our assets in those countries and diminish the value of such investments and the related investment returns to us; and |
• | legal and logistical barriers in the foreign countries in which we invest that materially and adversely limit our ability to enforce our contractual rights with respect to those investments. |
In addition, we may make investments in countries whose governments or economies may prove unstable. Certain of the countries in which we may invest may have political, economic and legal systems that are unpredictable, unreliable or otherwise inadequate with respect to the implementation, interpretation and enforcement of laws protecting asset ownership and economic interests. In some of the countries in which we may invest, there may be a risk of nationalization, expropriation or confiscatory taxation, which may have an adverse effect on our portfolio companies in those countries and the rates of return we are able to achieve on such investments. We may also lose the total value of any investment which is nationalized, expropriated or confiscated. The financial results and investment opportunities available to us, particularly in developing countries and emerging markets, may be materially and adversely affected by any or all of these political, economic and legal risks.
We have entered into the TRS Agreement that exposes us to certain risks, including market risk, liquidity risk and other risks similar to those associated with the use of leverage.
A TRS is a contract in which one party agrees to make periodic payments to another party based on the change in the market value of the assets underlying the TRS, which may include a specified security, basket of securities or securities indices during the specified period, in return for periodic payments based on a fixed or variable interest rate. A TRS is typically used to obtain exposure to a security or market without owning or taking physical custody of such security or investing directly in such market. A TRS may effectively add leverage to our portfolio because, in addition to our total net assets, we would be subject to investment exposure on the amount of securities subject to the TRS. A TRS is also subject to the risk that a counterparty will default on its payment obligations thereunder or that we will not be able to meet our obligations to the counterparty. In addition, because a TRS is a form of synthetic leverage, such arrangements are subject to risks similar to those associated with the use of leverage. See “Risks Relating to Debt Financing” below and “Item 1. Business – Financing Arrangements – Total Return Swap.”
Second priority liens on collateral securing debt investments that we make to our portfolio companies may be subject to control by senior creditors with first priority liens. If there is a default, the value of the collateral may not be sufficient to repay in full both the first priority creditors and us.
Certain debt investments that we make to portfolio companies may be secured on a second priority basis by the same collateral securing first priority debt of such companies. The first priority liens on the collateral will secure the portfolio company’s obligations under any outstanding senior debt and may secure certain other future debt that may be permitted to be incurred by the company under the agreements governing the loans. The holders of obligations secured by the first priority liens on the collateral will generally control the liquidation of and be entitled to receive proceeds from
33
any realization of the collateral to repay their obligations in full before us. In addition, the value of the collateral in the event of liquidation will depend on market and economic conditions, the availability of buyers and other factors. There can be no assurance that the proceeds, if any, from the sale or sales of all of the collateral would be sufficient to satisfy the debt obligations secured by the second priority liens after payment in full of all obligations secured by the first priority liens on the collateral. If such proceeds are not sufficient to repay amounts outstanding under the debt obligations secured by the second priority liens, then we, to the extent not repaid from the proceeds of the sale of the collateral, will only have an unsecured claim against the company’s remaining assets, if any.
The rights we may have with respect to the collateral securing the debt investments we make to our portfolio companies with senior debt outstanding may also be limited pursuant to the terms of one or more intercreditor agreements that we enter into with the holders of senior debt. Under such an intercreditor agreement, at any time that obligations that have the benefit of the first priority liens are outstanding, any of the following actions that may be taken in respect of the collateral will be at the direction of the holders of the obligations secured by the first priority liens: the ability to cause the commencement of enforcement proceedings against the collateral; the ability to control the conduct of such proceedings; the approval of amendments to collateral documents; releases of liens on the collateral; and waivers of past defaults under collateral documents. We may not have the ability to control or direct such actions, even if our rights are adversely affected.
Economic recessions or downturns could impair our portfolio companies and adversely affect our operating results.
Many of our portfolio companies may be susceptible to economic recessions or downturns and may be unable to repay our debt investments during these periods. Therefore, our non-performing assets are likely to increase, and the value of our portfolio is likely to decrease during these periods. Adverse economic conditions may also decrease the value of any collateral securing our senior secured debt. A prolonged recession may further decrease the value of such collateral and result in losses of value in our portfolio and a decrease in our revenues, net income and net asset value. Unfavorable economic conditions also could increase our funding costs, limit our access to the capital markets or result in a decision by lenders not to extend credit to us on terms we deem acceptable. These events could prevent us from increasing investments and adversely affect our operating results.
A covenant breach or other defaults by our portfolio companies may adversely affect our operating results.
A portfolio company’s failure to satisfy financial or operating covenants imposed by us or other lenders could lead to defaults and, potentially, termination of its loans and foreclosure on its secured assets, which could trigger cross-defaults under other agreements and jeopardize a portfolio company’s ability to meet its obligations under the debt or equity securities that we hold. We may incur expenses to the extent necessary to seek recovery upon default or to negotiate new terms, which may include the waiver of certain financial covenants, with a defaulting portfolio company.
Investing in middle-market companies involves a number of significant risks, any one of which could have a material adverse effect on our operating results.
Investments in middle-market companies involve the same risks that apply generally to investments in larger, more established companies. However, such investments have more pronounced risks in that middle-market companies:
• | may have limited financial resources and may be unable to meet their obligations under their debt securities that we hold, which may be accompanied by a deterioration in the value of any collateral and a reduction in the likelihood of us realizing on any guarantees we may have obtained in connection with our investment; |
• | have shorter operating histories, narrower product lines and smaller market shares than larger businesses, which tends to render them more vulnerable to competitors’ actions and changing market conditions, as well as general economic downturns; |
• | are more likely to depend on the management talents and efforts of a small group of persons; therefore, the death, disability, resignation or termination of one or more of these persons could have a material adverse impact on our portfolio company and, in turn, on us; |
• | generally have less predictable operating results, may from time to time be parties to litigation, may be engaged in rapidly changing businesses with products subject to a substantial risk of obsolescence, and may require substantial additional capital to support their operations, finance expansion or maintain their competitive position. In addition, our executive officers, directors and members of CIM may, in the ordinary course of business, be named as defendants in litigation arising from our investments in the portfolio companies; and |
• | may have difficulty accessing the capital markets to meet future capital needs, which may limit their ability to grow or to repay their outstanding indebtedness upon maturity. |
We may not realize gains from our equity investments.
Certain investments that we may make could include warrants or other equity securities. In addition, we may make direct equity investments in portfolio companies. Our goal is ultimately to realize gains upon our disposition of such equity interests. However, the equity interests we receive may not appreciate in value and, in fact, may decline in value. Accordingly, we may not be able to realize gains from our equity interests, and any gains that we do realize on the disposition of any equity interests may not be sufficient to offset any other losses we experience. We also may be unable to realize any value if a portfolio company does not have a liquidity event, such as a sale of the business, recapitalization or public offering, which would allow us to sell the underlying equity interests. We intend to seek puts or similar rights to give us the right to sell our equity securities back to the portfolio company issuer. We may be unable to exercise these put rights for the consideration provided in our investment documents if the issuer is in financial distress.
34
An investment strategy focused primarily on privately-held companies presents certain challenges, including, but not limited to, the lack of available information about these companies.
We have invested and continue to invest primarily in privately-held companies. Investments in private companies pose significantly greater risks than investments in public companies. First, private companies have reduced access to the capital markets, resulting in diminished capital resources and the ability to withstand financial distress. Second, the depth and breadth of experience of management in private companies tends to be less than that at public companies, which makes such companies more likely to depend on the management talents and efforts of a smaller group of persons and/or persons with less depth and breadth of experience. Therefore, the decisions made by such management teams and/or the death, disability, resignation or termination of one or more of these persons could have a material adverse impact on our investments and, in turn, on us. Third, the investments themselves tend to be less liquid. As such, we may have difficulty exiting an investment promptly or at a desired price prior to maturity or outside of a normal amortization schedule. As a result, the relative lack of liquidity and the potential diminished capital resources of our target portfolio companies may affect our investment returns. Fourth, little public information generally exists about private companies. Further, these companies may not have third-party debt ratings or audited financial statements. We must therefore rely on the ability of CIM and/or AIM to obtain adequate information through due diligence to evaluate the creditworthiness and potential returns from investing in these companies. These companies and their financial information will generally not be subject to the Sarbanes-Oxley Act and other rules that govern public companies. If we are unable to uncover all material information about these companies, we may not make a fully informed investment decision, and we may lose money on our investments.
A lack of liquidity in certain of our investments may adversely affect our business.
We have invested and continue to invest in certain companies whose securities are not publicly traded or actively traded on the secondary market, and whose securities are subject to legal and other restrictions on resale or will otherwise be less liquid than publicly-traded securities. The illiquidity of certain of our investments may make it difficult for us to sell these investments when desired. In addition, if we are required to liquidate all or a portion of our portfolio quickly, we may realize significantly less than the value at which we had previously recorded these investments. The reduced liquidity of our investments may make it difficult for us to dispose of them at a favorable price, and, as a result, we may suffer losses.
We may not have the funds or ability to make additional investments in our portfolio companies or to fund our unfunded debt commitments.
We may not have the funds or ability to make additional investments in our portfolio companies or to fund our unfunded debt commitments. After our initial investment in a portfolio company, we may be called upon from time to time to provide additional funds to such company or have the opportunity to increase our investment through the exercise of a warrant to purchase common stock. There is no assurance that we will make, or will have sufficient funds to make, follow-on investments. Any decisions not to make a follow-on investment or any inability on our part to make such an investment may have a negative impact on a portfolio company in need of such an investment, may result in a missed opportunity for us to increase our participation in a successful operation or may reduce the expected return on the investment.
We may acquire various financial instruments for purposes of “hedging” or reducing our risks, which may be costly and ineffective and could reduce our cash available for distribution to our shareholders.
We may seek to hedge against interest rate and currency exchange rate fluctuations and credit risk by using financial instruments such as futures, options, swaps and forward contracts, subject to the requirements of the 1940 Act. These financial instruments may be purchased on exchanges or may be individually negotiated and traded in over-the-counter markets. Use of such financial instruments for hedging purposes may present significant risks, including the risk of loss of the amounts invested. Defaults by the other party to a hedging transaction can result in losses in the hedging transaction. Hedging activities also involve the risk of an imperfect correlation between the hedging instrument and the asset being hedged, which could result in losses both on the hedging transaction and on the instrument being hedged. Use of hedging activities may not prevent significant losses and could increase our losses. Further, hedging transactions may reduce cash available to pay distributions to our shareholders.
Prepayments of our debt investments by our portfolio companies could adversely impact our results of operations and reduce our return on equity.
We are subject to the risk that the investments we make in our portfolio companies may be repaid prior to maturity. When this occurs, we will generally reinvest these proceeds in temporary investments, pending their future investment in new portfolio companies. These temporary investments will typically have substantially lower yields than the debt being prepaid and we could experience significant delays in reinvesting these amounts. Any future investment in a new portfolio company may also be at lower yields than the debt that was repaid. As a result, our results of operations could be materially adversely affected if one or more of our portfolio companies elect to prepay amounts owed to us. Additionally, prepayments, net of prepayment fees, could negatively impact our return on equity.
Risks Relating to Debt Financing
Since we have borrowed money, the potential for loss on amounts invested in us is magnified and may increase the risk of investing in us. Borrowed money may also adversely affect the return on our assets, reduce cash available for distribution to our shareholders, and result in losses.
The use of borrowings, also known as leverage, increases the volatility of investments by magnifying the potential for loss on invested equity capital. Since we have used leverage to partially finance our investments, through borrowing from banks, shareholders experience increased risks of
35
investing in our common stock. If the value of our assets decreases, leveraging would cause net asset value to decline more sharply than it otherwise would have had we not leveraged. Similarly, any decrease in our income would cause net income to decline more sharply than it would have had we not borrowed. Such a decline could negatively affect our ability to make distributions to our shareholders. In addition, our shareholders bear the burden of any increase in our expenses as a result of our use of leverage, including interest expenses and any increase in the management or incentive fees payable to CIM.
We may continue to use leverage to finance our investments. The amount of leverage that we employ will depend on CIM’s and our board of directors’ assessment of market and other factors at the time of any proposed borrowing. There can be no assurance that leveraged financing will be available to us on favorable terms or at all. However, to the extent that we continue to use leverage to finance our assets, our financing costs will reduce cash available for distributions to shareholders. Moreover, we may not be able to meet our financing obligations and, to the extent that we cannot, we risk the loss of some or all of our assets to liquidation or sale to satisfy the obligations. In such an event, we may be forced to sell assets at significantly depressed prices due to market conditions or otherwise, which may result in losses.
As a BDC, we generally are required to meet a coverage ratio of total assets to total borrowings and other senior securities, which include all of our borrowings and any preferred stock that we may issue in the future, of at least 200%. If this ratio declines below 200%, we cannot incur additional debt and could be required to sell a portion of our investments to repay some debt when it is disadvantageous to do so. This could have a material adverse effect on our operations and investment activities. Moreover, our ability to make distributions to shareholders may be significantly restricted or we may not be able to make any such distributions whatsoever. The amount of leverage that we will employ will be subject to oversight by our board of directors, a majority of whom are independent directors with no material interests in such transactions.
At December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, our borrowings for the BDC coverage ratio were $488,936, $491,708 and $326,703, respectively, which included the non-collateralized TRS notional amount, unfunded commitments (solely at December 31, 2014) and the financing arrangement in connection with our directors and officers insurance and resulted in coverage ratios of 304%, 284% and 252%, respectively. For a detailed discussion on the coverage ratio calculation, refer to Note 13 to our consolidated financial statements included in this report.
Illustration. The following table illustrates the effect of leverage on returns from an investment in our common stock assuming various annual returns, net of expenses. The calculations in the table below are hypothetical and actual returns may be higher or lower than those appearing below. The calculation assumes (i) we sell approximately $150 million of our common stock during 2017, (ii) our net offering proceeds from such sales equal $140 million, (iii) resulting in estimated net assets of approximately $1.14 billion as of December 31, 2017 and average net assets of approximately $1.07 billion during 2017, (iv) we borrow funds equal to 60% of our average net assets during such period, or $650 million, and (v) a weighted average cost of funds of 4.80%. Actual expenses will depend on the number of shares of common stock we sell in the offering and the amount of leverage we employ. For example, if we were to raise proceeds significantly less than this amount during 2017, our expenses as a percentage of our average net assets would be significantly higher. There can be no assurance that we will sell an aggregate of $150 million worth of our common stock during 2017. In order to compute the “Corresponding return to shareholders,” the “Assumed Return on Our Portfolio (net of expenses)” is multiplied by the assumed total assets to obtain an assumed return to us. From this amount, the interest expense is calculated by multiplying the assumed weighted average cost of funds times the assumed debt outstanding, and the product is subtracted from the assumed return to us in order to determine the return available to shareholders. The return available to shareholders is then divided by our shareholders’ equity to determine the “Corresponding return to shareholders.” Actual interest payments may be different.
Assumed Return on Our Portfolio (net of expenses) | -10% | -5% | —% | 5% | 10% | ||||
Corresponding return to shareholders | (18.28)% | (10.43)% | (2.58)% | 5.27% | 13.12% | ||||
Similarly, assuming (i) $1.14 billion in net assets as of December 31, 2017 and average net assets of $1.07 billion during 2017, (ii) a weighted average cost of funds of 4.80% and (iii) $650 million in debt outstanding, our assets would need to yield an annual return (net of expenses) of approximately 1.64% in order to cover the annual interest payments on our outstanding debt.
Changes in interest rates may affect our cost of capital and net investment income.
Since we have used debt to finance a portion of our investments, our net investment income will depend, in part, upon the difference between the rate at which we borrow funds and the rate at which we invest those funds. As a result, we can offer no assurance that a significant change in market interest rates will not have a material adverse effect on our net investment income. In periods of rising interest rates when we have debt outstanding, our cost of funds will increase, which could reduce our net investment income. We expect that our long-term fixed-rate investments will be financed primarily with equity and long-term debt. We may use interest rate risk management techniques in an effort to limit our exposure to interest rate fluctuations. These techniques may include various interest rate hedging activities to the extent permitted by the 1940 Act. These activities may limit our ability to participate in the benefits of lower interest rates with respect to the hedged portfolio. Adverse developments resulting from changes in interest rates or hedging transactions could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations. Also, we have limited experience in entering into hedging transactions, and we will initially have to purchase or develop such expertise.
A rise in the general level of interest rates can be expected to lead to higher interest rates applicable to our debt investments. Accordingly, an increase in interest rates would make it easier for us to meet or exceed the incentive fee hurdle rate and may result in a substantial increase in the amount of incentive fees payable to CIM with respect to pre-incentive fee net investment income.
36
Federal Income Tax Risks
We will be subject to corporate-level income tax if we are unable to qualify as a RIC under Subchapter M of the Code or to satisfy RIC distribution requirements.
To qualify for and maintain RIC tax treatment under Subchapter M of the Code, we must, among other things, meet the following annual distribution, income source and asset diversification requirements.
• | The annual distribution requirement for a RIC will be satisfied if we distribute to our shareholders on an annual basis at least 90% of our net ordinary income and realized net short-term capital gains in excess of realized net long-term capital losses, if any. Because we use debt financing, we are subject to an asset coverage ratio requirement under the 1940 Act and are subject to certain financial covenants under loan and credit agreements that could, under certain circumstances, restrict us from making distributions necessary to satisfy the distribution requirement. If we are unable to obtain cash from other sources, we could fail to qualify for RIC tax treatment and thus become subject to corporate-level income tax. |
• | The income source requirement will be satisfied if we obtain at least 90% of our income for each taxable year from dividends, interest, gains from the sale of common stock or securities or similar sources. |
• | The asset diversification requirement will be satisfied if we meet certain asset diversification requirements at the end of each quarter of our taxable year. To satisfy this requirement, at least 50% of the value of our assets must consist of cash, cash equivalents, U.S. government securities, securities of other RICs, and other securities if such other securities of any one issuer do not represent more than 5% of the value of our assets or more than 10% of the outstanding voting securities of the issuer; and no more than 25% of the value of our assets can be invested in the securities, other than U.S. government securities or securities of other RICs, of one issuer, of two or more issuers that are controlled, as determined under applicable Code rules, by us and that are engaged in the same or similar or related trades or businesses or of certain “qualified publicly-traded partnerships.” Failure to meet these requirements may result in our having to dispose of certain investments quickly in order to prevent the loss of RIC status. Because most of our investments will be in private companies, and therefore will be relatively illiquid, any such dispositions could be made at disadvantageous prices and could result in substantial losses. |
If we fail to qualify for or maintain RIC tax treatment for any reason and are subject to corporate income tax, the resulting corporate taxes could substantially reduce our net assets, the amount of income available for distribution and the amount of our distributions.
We may have difficulty paying our required distributions if we recognize income before or without receiving cash representing such income.
For federal income tax purposes, we may be required to recognize taxable income in circumstances in which we do not receive a corresponding payment in cash. For example, if we hold debt obligations that are treated under applicable tax rules as having original issue discount (such as debt instruments with PIK interest or, in certain cases, increasing interest rates or debt instruments that were issued with warrants), we must include in income each year a portion of the original issue discount that accrues over the life of the obligation, regardless of whether cash representing such income is received by us in the same taxable year. We may also have to include in income other amounts that we have not yet received in cash, such as deferred loan origination fees that are paid after origination of the loan or are paid in non-cash compensation such as warrants or stock. We anticipate that a portion of our income may constitute original issue discount or other income required to be included in taxable income prior to receipt of cash. Further, we may elect to amortize market discounts and include such amounts in our taxable income in the current year, instead of upon disposition, as an election not to do so would limit our ability to deduct interest expenses for tax purposes.
Because any original issue discount or other amounts accrued will be included in our investment company taxable income for the year of the accrual, we may be required to make a distribution to our shareholders in order to satisfy the annual distribution requirement, even though we will not have received any corresponding cash amount. As a result, we may have difficulty meeting the annual distribution requirement necessary to qualify for and maintain RIC tax treatment under Subchapter M of the Code. We may have to sell some of our investments at times and/or at prices we would not consider advantageous, raise additional debt or equity capital or forgo new investment opportunities for this purpose. If we are not able to obtain cash from other sources, we may fail to qualify for or maintain RIC tax treatment and thus become subject to corporate-level income tax.
Deferred PIK interest instruments may have less reliable valuations because these instruments have continuing accruals that require continuing judgment about the collectability of the deferred payments and the value of any associated collateral. In addition, deferred PIK interest instruments create the risk of non-refundable cash payments to our investment adviser based on non-cash accruals that ultimately may not be realized. For accounting purposes, any cash distributions to shareholders representing deferred PIK interest income are not treated as coming from paid-in capital, even though the cash to pay these distributions may come from offering proceeds. Thus, although a distribution of deferred PIK interest may come from the cash invested by shareholders, the 1940 Act does not require that shareholders be given notice of this fact by reporting it as a return of capital.
If we do not qualify as a “publicly offered regulated investment company,” as defined in the Code, shareholders will be taxed as though they received a distribution of some of our expenses.
A “publicly offered regulated investment company” is a RIC whose shares are either (i) continuously offered pursuant to a public offering within the meaning of Section 4 of the Securities Act, (ii) regularly traded on an established securities market or (iii) held by at least 500 persons at all times during the taxable year. If we are not a publicly offered RIC for any period, a non-corporate shareholder’s allocable portion of our affected expenses, including our management fees, will be treated as an additional distribution to the shareholder and will be deductible by such shareholder only to the
37
extent permitted under the limitations described below. For non-corporate shareholders, including individuals, trusts, and estates, significant limitations generally apply to the deductibility of certain expenses of a non-publicly offered RIC, including advisory fees. In particular, these expenses, referred to as miscellaneous itemized deductions, are deductible to an individual only to the extent they exceed 2% of such a shareholder’s adjusted gross income, and are not deductible for alternative minimum tax purposes. While we anticipate that we will constitute a publicly offered RIC, there can be no assurance that we will in fact so qualify for any of our taxable years.
Risks Relating to an Investment in our Common Stock
Investors will not know the purchase price per share at the time they submit their subscription agreements and could receive fewer shares of common stock than anticipated if our board of directors determines to increase the offering price to comply with the requirement that we avoid selling shares at a net offering price below our net asset value per share.
The purchase price at which shareholders purchase common stock will be determined at each weekly closing date to ensure that the sales price, after deducting selling commissions and dealer manager fees, is equal to or greater than the net asset value of our common stock. As a result, in the event of an increase in our net asset value per share, an investor’s purchase price may be higher than the prior weekly closing price per share, and therefore an investor may receive a smaller number of shares than if such investor had subscribed at the prior weekly closing price.
Our offering is a “best efforts” offering, and if we are unable to continue to raise substantial funds, then we will be more limited in the number and type of investments we may make, and the value of a shareholder’s investment in us may be reduced in the event our assets under-perform.
Our offering is being made on a “best efforts” basis, whereby the dealer manager and selected broker-dealers participating in the offering are only required to use their best efforts to sell our common stock and have no firm commitment or obligation to purchase any of our common stock. Amounts that we raise may not be sufficient for us to purchase a broad portfolio of investments. To the extent that less than the maximum number of shares of common stock is subscribed for, the opportunity for us to purchase a broad portfolio of investments may be decreased and the returns achieved on those investments may be reduced as a result of allocating all of our expenses among a smaller capital base.
The common stock sold in our offering will not be listed on an exchange or quoted through a quotation system for the foreseeable future, if ever. Therefore, if shareholders purchase common stock in our offering, shareholders will have limited liquidity and may not receive a full return of shareholder invested capital if shareholders sell their common stock. We are not obligated to complete a liquidity event by a specified date; therefore, until we complete a liquidity event, it is unlikely that shareholders will be able to sell their common stock.
The common stock offered by us are illiquid assets for which there is not expected to be any secondary market nor is it expected that any will develop in the foreseeable future. Prior to the completion of a liquidity event, our share repurchase program provides a limited opportunity for investors to achieve liquidity, subject to certain restrictions and limitations, at a price which may reflect a discount from the purchase price paid for the common stock being repurchased. However, there can be no assurance that we will complete a liquidity event. See “Item 5. Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Shareholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities – Share Repurchase Program” for a detailed description of our share repurchase program.
In making the decision to apply for listing of our common stock, our board of directors will try to determine whether listing our common stock or liquidating our assets will result in greater value for our shareholders. In making a determination of what type of liquidity event is in the best interest of our shareholders, our board of directors, including our independent directors, may consider a variety of criteria, including, but not limited to, maintaining a broad portfolio of investments, portfolio performance, our financial condition, potential access to capital as a listed company, the investment advisory experience of CIM and market conditions for the sale of our assets or listing of our common stock and the potential for shareholder liquidity. If we determine to pursue a listing of our common stock on a national securities exchange in the future, at that time we may consider either an internal or an external management structure. There can be no assurance that we will complete a liquidity event. Until we complete a liquidity event, it is unlikely that shareholders will be able to sell their shares. If our common stock is listed, we cannot assure shareholders that a public trading market will develop. Further, even if we do complete a liquidity event, shareholders may not receive a return of all of their invested capital.
The dealer manager in our continuous follow-on offering may be unable to sell a sufficient number of shares of common stock for us to achieve our investment objective.
The dealer manager for our continuous follow-on offering is CION Securities, LLC, or CION Securities, one of our affiliates. There is no assurance that it will be able to sell a sufficient number of shares of common stock to allow us to have adequate funds to purchase a broad portfolio of investments and generate income sufficient to cover our expenses. As a result, we may be unable to achieve our investment objective, and shareholders could lose some or all of the value of their investment.
Because the dealer manager is one of our affiliates, shareholders will not have the benefit of an independent due diligence review of us, which is customarily performed in firm commitment underwritten offerings; the absence of an independent due diligence review increases the risks and uncertainty faced as a shareholder.
As a result of CION Securities being one of our affiliates, its due diligence review and investigation of us and our prospectus cannot be considered to be an independent review. Therefore, shareholders do not have the benefit of an independent review and investigation of our offering of the type normally performed by an unaffiliated, independent underwriter in a firm commitment underwritten public securities offering. A shareholder
38
may be able to rely on his or her own broker-dealer to make an independent review and investigation of the terms of the offering. If a shareholder is unable to so rely on his or her broker-dealer, however, he or she will not have the benefit of any independent review and evaluation of the terms of the offering by the dealer manager. In addition, we do not, and do not expect to, have research analysts reviewing our performance or our securities on an ongoing basis. Therefore, shareholders will not have an independent review of our performance and the value of our common stock relative to other publicly-traded companies.
Our ability to successfully conduct our continuous follow-on offering is dependent, in part, on the ability of the dealer manager to successfully establish, operate and maintain a network of selected broker-dealers.
The success of our continuous follow-on offering, and correspondingly our ability to implement our business strategy, is dependent upon the ability of the dealer manager to establish, operate and maintain a network of licensed securities broker-dealers and other agents to sell our common stock. If the dealer manager fails to perform, we may not be able to raise adequate proceeds through our follow-on public offering to implement our investment strategy. If we are unsuccessful in implementing our investment strategy, shareholders could lose all or a part of their investment.
Beginning in the first quarter of 2014, we began offering to repurchase shares of our common stock on a quarterly basis. As a result, shareholders have limited opportunities to sell their shares of our common stock and, to the extent they are able to sell their shares of our common stock under the program, they may not be able to recover the amount of their investment in our common stock.
Beginning in the first quarter of 2014, we commenced tender offers to allow shareholders to tender their shares of common stock on a quarterly basis at a price equal to 90% of our public offering price in effect on the date of repurchase; provided that, solely for our quarterly repurchase offer for the fourth quarter of 2015, we repurchased shares from tendering shareholders at a price that was (i) not less than the net asset value per share and (ii) not more than 2.5% greater than the net asset value per share. Commencing with our quarterly repurchase offer for the fourth quarter of 2016 and on a quarterly basis thereafter, we repurchase shares from tendering shareholders at a price equal to the estimated net asset value per share on the date of repurchase. The share repurchase program includes numerous restrictions that limit shareholders’ ability to sell their shares of common stock. We limit the number of shares of common stock repurchased pursuant to our share repurchase program as follows: (1) we currently limit the number of shares of common stock to be repurchased during any calendar year to the number of shares of common stock we can repurchase with the proceeds we receive from the issuance of shares of our common stock pursuant to our fifth amended and restated distribution reinvestment plan, although at the discretion of our board of directors, we may also use cash on hand, cash available from borrowings and cash from liquidation of securities investments as of the end of the applicable period to repurchase shares of common stock; (2) we will not repurchase shares of common stock in any calendar year in excess of 15% of the weighted average number of shares of common stock outstanding in the prior calendar year, or 3.75% in each quarter; (3) unless a shareholder tenders all of his or her shares of common stock, he or she must tender at least 25% of the amount of common stock the shareholder purchased in the offering and must generally maintain a minimum balance of $5,000 subsequent to submitting a portion of his or her shares of common stock for repurchase by us; and (4) to the extent that the number of shares of common stock put to us for repurchase exceeds the number of shares of common stock that we are able to purchase, we will repurchase shares of common stock on a pro rata basis, not on a first-come, first-served basis. Further, we will have no obligation to repurchase shares of common stock if the repurchase would violate the restrictions on distributions under federal law or Maryland law.
Although we have adopted a share repurchase program, we have discretion to not repurchase shares of common stock, to suspend the program, and to cease repurchases.
Our board of directors may amend, suspend or terminate the share repurchase program upon 30 days’ notice. Shareholders may not be able to sell their shares at all in the event our board of directors amends, suspends or terminates the share repurchase program, absent a liquidity event. We will notify shareholders of such developments (1) in our quarterly reports or (2) by means of a separate mailing to shareholders, accompanied by disclosure in a current or periodic report under the Exchange Act. The share repurchase program has many limitations and should not be relied upon as a method to sell shares of common stock promptly or at a desired price.
The timing of our repurchase offers pursuant to our share repurchase program may be at a time that is disadvantageous to our shareholders.
When we make quarterly repurchase offers pursuant to the share repurchase program, the repurchase price will be lower than the price that investors paid for common stock in our offering, unless we experience substantial capital appreciation and capital gains. As a result, to the extent investors have the ability to sell their common stock to us as part of our share repurchase program, the price at which an investor may sell common stock, which will be the estimated net asset value per share on the date of repurchase, may be lower than what an investor paid in connection with the purchase of common stock in our offering.
In addition, in the event an investor chooses to participate in our share repurchase program, the investor will be required to provide us with notice of intent to participate prior to knowing what the estimated net asset value per share will be on the repurchase date. Although an investor will have the ability to withdraw a repurchase request prior to the repurchase date, to the extent an investor seeks to sell common stock to us as part of our periodic share repurchase program, the investor will be required to do so without knowledge of what the repurchase price of our common stock will be on the repurchase date.
39
We may be unable to invest a significant portion of the net proceeds of our offering on acceptable terms in an acceptable timeframe.
Delays in investing the net proceeds of our offering may impair our performance. We cannot assure shareholders that we will be able to identify any investments that meet our investment objective or that any investment that we make will produce a positive return. We may be unable to invest the net proceeds of our offering on acceptable terms within the time period that we anticipate or at all, which could adversely affect our financial condition and operating results.
In addition, even if we are able to raise significant proceeds, we will not be permitted to use such proceeds to co-invest with certain entities affiliated with CIM in transactions originated by CIM or its affiliates unless we first obtain an exemptive order from the SEC or co-invest alongside CIM or its affiliates in accordance with existing regulatory guidance. However, we will be permitted to and may co-invest in syndicated deals and secondary loan market transactions where price is the only negotiated point. Furthermore, we will not be permitted to use such proceeds to co-invest with Apollo or its affiliates unless (i) we co-invest alongside Apollo or its affiliates in accordance with existing regulatory guidance or (ii) in transactions where Apollo or its affiliates negotiate terms other than price on our behalf, such transactions occur pursuant to an exemptive order from the SEC. We are currently seeking exemptive relief from the SEC to engage in co-investment transactions with CIM and its affiliates. However, there can be no assurance that we will obtain such exemptive relief. Even if we receive exemptive relief, neither CIM nor its affiliates will be obligated to offer us the right to participate in any transactions originated by them.
Before making investments, we will invest the net proceeds of our offering primarily in cash, cash equivalents, U.S. government securities, repurchase agreements and high-quality debt instruments maturing in one year or less from the time of investment, which may produce returns that are significantly lower than the returns that we expect to achieve when our portfolio is fully invested in securities meeting our investment objective. As a result, any distributions that we pay while our portfolio is not fully invested in securities meeting our investment objective may be lower than the distributions that we may be able to pay when our portfolio is fully invested in securities meeting our investment objective.
A shareholder’s interest in us will be diluted if we issue additional shares of common stock, which could reduce the overall value of an investment in us.
Potential investors will not have preemptive rights to any common stock we issue in the future. Our articles of incorporation authorize us to issue 500,000,000 shares of common stock. Pursuant to our articles of incorporation, a majority of our entire board of directors may amend our articles of incorporation to increase the number of authorized shares of common stock without shareholder approval. After an investor purchases shares of common stock, we intend to continuously sell additional shares of common stock in our follow-on offering and any additional follow-on offering or issue equity interests in private offerings. To the extent that we issue additional shares of common stock at or below net asset value after an investor purchases shares of our common stock, an investor’s percentage ownership interest in us will be diluted. In addition, depending upon the terms and pricing of any additional offerings and the value of our investments, an investor may also experience dilution in the book value and fair value of his or her shares of common stock.
Certain provisions of our articles of incorporation and bylaws could deter takeover attempts and have an adverse impact on the value of our common stock.
Our bylaws exempt us from the Maryland Control Share Acquisition Act, which significantly restricts the voting rights of control shares of a Maryland corporation acquired in a control share acquisition. If our board of directors were to amend our bylaws to repeal this exemption from the Maryland Control Share Acquisition Act, that statute may make it more difficult for a third party to obtain control of us and increase the difficulty of consummating such a transaction. There can be no assurance, however, that we will not so amend our bylaws in such a manner at some time in the future. We will not, however, amend our bylaws to make us subject to the Maryland Control Share Acquisition Act without our board of directors determining that doing so would not conflict with the 1940 Act and obtaining confirmation from the SEC that it does not object to such determination.
Our articles of incorporation and bylaws, as well as certain statutory and regulatory requirements, contain certain provisions that may have the effect of discouraging a third party from attempting to acquire us. Our board of directors may, without shareholder action, authorize the issuance of shares in one or more classes or series, including preferred shares; and our board of directors may, without shareholder action, amend our articles of incorporation to increase the number of our shares, of any class or series, that we have authority to issue. These anti-takeover provisions may inhibit a change of control in circumstances that could give the holders of our common stock the opportunity to realize a premium over the value of our common stock.
Investing in our common stock involves a high degree of risk.
The investments we make in accordance with our investment objective may result in a higher amount of risk than alternative investment options and volatility or loss of principal. Our investments in portfolio companies may be highly speculative and aggressive and, therefore, an investment in our common stock may not be suitable for someone with lower risk tolerance.
40
The net asset value of our common stock may fluctuate significantly.
The net asset value and liquidity, if any, of the market for shares of our common stock may be significantly affected by numerous factors, some of which are beyond our control and may not be directly related to our operating performance. These factors include:
• | changes in regulatory policies or tax guidelines, particularly with respect to RICs or BDCs; |
• | loss of RIC or BDC status; |
• | changes in earnings or variations in operating results; |
• | changes in the value of our portfolio of investments; |
• | changes in accounting guidelines governing valuation of our investments; |
• | any shortfall in revenue or net income or any increase in losses from levels expected by investors; |
• | departure of either of our adviser, our sub-adviser or certain of their respective key personnel; |
• | general economic trends and other external factors; and |
• | loss of a major funding source. |
41
Item 1B. Unresolved Staff Comments
Not applicable.
Item 2. Properties
We do not own any real estate or other physical properties materially important to our operation. Our executive offices are located at 3 Park Avenue, 36th Floor, New York, NY 10016. We believe that our current office facilities are adequate for our business as it is presently conducted.
Item 3. Legal Proceedings
We are not currently subject to any material legal proceedings, nor, to our knowledge, is any material legal proceeding threatened against us. From time to time, we may be party to certain legal proceedings in the ordinary course of business, including proceedings relating to the enforcement of our rights under contracts with our portfolio companies and other third parties. While the outcome of these legal proceedings cannot be predicted with certainty, we do not expect that any such proceedings will have a material effect upon our financial condition or results of operations.
Item 4. Mine Safety Disclosures
Not applicable.
42
PART II
Item 5. Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Shareholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
Our shares are not listed on an exchange or quoted through a quotation system. There is currently no market for our common stock, and we do not expect that a market for our shares will develop in the future. No shares have been authorized for issuance under any equity compensation plans. Under Maryland law, our shareholders generally will not be personally liable for our debts or obligations.
We are currently selling our shares on a continuous basis at our latest public offering price of $9.65 per share; however, to the extent that our net asset value per share increases, we will sell at a price necessary to ensure that shares are not sold at a price, after deduction of selling commissions and dealer manager fees, that is below net asset value per share. In the event of a material decline in our net asset value per share, which we consider to be a 2.5% decrease below our current net offering price, we will reduce our offering price in order to establish a new net offering price that is not more than 2.5% above our net asset value per share. Therefore, persons who tender subscriptions for shares of our common stock in the offering must submit subscriptions for a certain dollar amount, rather than a number of shares of common stock and, as a result, may receive fractional shares of our common stock. In connection with each weekly closing on the sale of shares of our common stock, our board of directors has delegated to one or more of its directors the authority to conduct such closings so long as there is no change to our public offering price or to establish a new net offering price that is not more than 2.5% above our net asset value per share. In connection with each weekly closing, we will, in each case if necessary, update the information contained in our prospectus by filing a prospectus supplement with the SEC, and we will also post any updated information to our website.
Set forth below is a chart describing the classes of our securities outstanding as of March 9, 2017:
Title of Class | Amount Authorized | Amount Held by Us or for Our Account | Amount Outstanding Exclusive of Amount Held by Us or for Our Account | |||
Common stock | 500,000,000 | — | 110,720,587 | |||
As of March 9, 2017, we had 22,397 record holders of our common stock.
Share Repurchase Program
We do not currently intend to list our common stock on any securities exchange and do not expect a public market for them to develop in the foreseeable future. It is unlikely that shareholders will be able to sell their common stock when desired or at a desired price. No shareholder will have the right to require us to repurchase his or her common stock or any portion thereof. Because no public market will exist for our common stock, and none is expected to develop, shareholders will not be able to liquidate their investment prior to our liquidation or other liquidity event, other than through our share repurchase program, or, in limited circumstances, as a result of transfers of common stock to other eligible investors.
Beginning in the first quarter of 2014, we began offering, and on a quarterly basis thereafter we intend to continue offering, to repurchase common stock on such terms as may be determined by our board of directors in its complete and absolute discretion unless, in the judgment of the independent directors of our board of directors, such repurchases would not be in the best interests of our shareholders or would violate applicable law. We conduct such repurchase offers in accordance with the requirements of Rule 13e-4 of the Exchange Act and the 1940 Act. In months in which we repurchase common stock, we generally conduct repurchases on the same date that we hold the first weekly closing in a calendar month for the sale of common stock in our offering. The offer to repurchase common stock is conducted solely through tender offer materials made available to each shareholder.
The board also considers the following factors, among others, in making its determination regarding whether to cause us to continue offering to repurchase shares and under what terms:
· the effect of such repurchases on our qualification as a RIC (including the consequences of any necessary asset sales);
· the liquidity of our assets (including fees and costs associated with disposing of assets);
· our investment plans and working capital requirements;
· the relative economies of scale with respect to our size;
· our history in repurchasing shares or portions thereof; and
· the condition of the securities markets.
On November 2, 2015, we amended the terms of the share repurchase program, effective as of our quarterly repurchase offer for the fourth quarter of 2015, which commenced in November 2015 and was completed in January 2016. Under the amended share repurchase program, we offered to repurchase shares of common stock at a price per share of $8.96, which was (i) not less than the net asset value per share immediately prior to January 4, 2016 and (ii) not more than 2.5% greater than the net asset value per share as of such date. On January 22, 2016, we further amended the terms of
43
the share repurchase program, effective as of our quarterly repurchase offer for the first quarter of 2016, which commenced in February 2016 and was completed in April 2016. Under the further amended share repurchase program, we offered to repurchase shares of common stock at a price equal to 90% of the public offering price in effect on each date of repurchase. On December 8, 2016, we further amended the terms of the share repurchase program, effective as of our quarterly repurchase offer for the fourth quarter of 2016, which commenced in November 2016 and was completed in January 2017. Under the further amended share repurchase program, we will offer to repurchase shares of common stock at a price equal to the estimated net asset value per share determined on each date of repurchase.
We currently limit the number of shares of common stock to be repurchased during any calendar year to the number of shares of common stock we can repurchase with the proceeds we receive from the issuance of shares of our common stock pursuant to our fifth amended and restated distribution reinvestment plan. At the discretion of our board of directors, we may also use cash on hand, cash available from borrowings and cash from liquidation of securities investments as of the end of the applicable period to repurchase common stock. In addition, we limit the number of shares of common stock to be repurchased in any calendar year to 15% of the weighted average number of shares of common stock outstanding in the prior calendar year, or 3.75% in each quarter, though the actual number of shares of common stock that we offer to repurchase may be less in light of the limitations noted above. We offer to repurchase such common stock on each date of repurchase at a price equal to the estimated net asset value per share on each date of repurchase.
We do not repurchase common stock, or fractions thereof, if such repurchase causes us to be in violation of the securities or other laws of the U.S., Maryland or any other relevant jurisdiction.
While we have conducted quarterly tender offers as described above, we are not required to do so and may suspend or terminate the share repurchase program at any time, upon 30 days’ notice.
The table below provides information concerning our repurchases of shares of our common stock during the quarter ended December 31, 2016 pursuant to our share repurchase program.
Period | Total Number of Shares Purchased | Average Price Paid per Share | Total Number of Shares Purchased as Part of Publicly Announced Plans or Programs | Maximum Number of Shares That May Yet Be Purchased Under the Plans or Programs | ||||||||||
October 1 to October 31, 2016 | 619,240 | $ | 9.05 | 619,240 | (1 | ) | ||||||||
November 1 to November 30, 2016 | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||
December 1 to December 31, 2016 | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||
Total | 619,240 | $ | 9.05 | 619,240 | (1 | ) | ||||||||
(1) | See above for a description of the maximum number of shares of our common stock that may be repurchased under our share repurchase program. |
In the event that CIM or any of its affiliates holds common stock in the capacity of a shareholder, any such affiliates may tender common stock for repurchase in connection with any repurchase offer we make on the same basis as any other shareholder. CIG will not tender its common stock for repurchase as long as CIM remains our investment adviser.
Distributions
We did not declare or pay any distributions during 2012. In January 2013, we began authorizing monthly distributions to our shareholders. Subject to our board of directors’ discretion and applicable legal restrictions, our board of directors intends to continue to authorize and declare on a monthly basis a weekly distribution amount per share of our common stock. We will calculate each shareholder’s specific distribution amount for the period using record and declaration dates and each shareholder’s distributions will begin to accrue on the date we accept each shareholder’s subscription for shares of our common stock. From time to time, we may also pay interim special distributions in the form of cash or shares of common stock at the discretion of our board of directors. Each year, information regarding the sources of our distributions (i.e., paid from ordinary income, paid from net capital gains on the sale of securities, and/or a return of capital, the latter of which is a nontaxable distribution) will be provided to our shareholders. Our distributions may exceed our earnings, especially during the period before we have substantially invested the proceeds from our offering. As a result, a portion of the distributions we make may represent a return of capital.
We elected to be treated for federal income tax purposes as a RIC, as defined under Subchapter M of the Code, beginning in 2012.
To qualify for and maintain RIC tax treatment, we must, among other things, distribute in respect of each taxable year at least 90% of our net ordinary income and realized net short-term capital gains in excess of realized net long-term capital losses, if any. In order to avoid certain excise taxes imposed on RICs, we currently intend to distribute in respect of each calendar year an amount at least equal to the sum of (1) 98.0% of our net ordinary income (taking into account certain deferrals and elections) for the calendar year, (2) 98.2% of our capital gains in excess of capital losses, or capital gain net income (adjusted for certain ordinary losses), for the one-year period ending on October 31 of the calendar year and (3) any net ordinary income and capital gain net income for preceding years that were not distributed during such years and on which we paid no federal income tax. We can offer no assurance that we will achieve results that will permit the payment of any cash distributions and, if we issue senior securities, we will be prohibited
44
from making distributions if doing so causes us to fail to maintain the asset coverage ratios stipulated by the 1940 Act or if distributions are limited by the terms of any of our borrowings.
Our board of directors declared distributions for 52, 52 and 49 record dates during the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. Declared distributions are paid monthly. The following table presents cash distributions per share that were declared during the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014:
Distributions | ||||||||
Three Months Ended | Per Share | Amount | ||||||
2014 | ||||||||
March 31, 2014 (nine record dates) | $ | 0.1679 | $ | 3,315 | ||||
June 30, 2014 (thirteen record dates) | 0.1829 | 5,120 | ||||||
September 30, 2014 (fourteen record dates) | 0.1969 | 7,396 | ||||||
December 31, 2014 (thirteen record dates) | 0.1829 | 8,716 | ||||||
Total distributions for the year ended December 31, 2014 | $ | 0.7306 | $ | 24,547 | ||||
2015 | ||||||||
March 31, 2015 (thirteen record dates) | $ | 0.1829 | $ | 10,767 | ||||
June 30, 2015 (thirteen record dates) | 0.1829 | 13,223 | ||||||
September 30, 2015 (thirteen record dates) | 0.1829 | 15,517 | ||||||
December 31, 2015 (thirteen record dates) | 0.1829 | 17,761 | ||||||
Total distributions for the year ended December 31, 2015 | $ | 0.7316 | $ | 57,268 | ||||
2016 | ||||||||
March 31, 2016 (thirteen record dates) | $ | 0.1829 | $ | 19,004 | ||||
June 30, 2016 (thirteen record dates) | 0.1829 | 19,167 | ||||||
September 30, 2016 (thirteen record dates) | 0.1829 | 19,480 | ||||||
December 31, 2016 (thirteen record dates) | 0.1829 | 19,808 | ||||||
Total distributions for the year ended December 31, 2016 | $ | 0.7316 | $ | 77,459 | ||||
On December 13, 2016, our board of directors declared five weekly cash distributions of $0.014067 per share, which were paid on February 1, 2017 to shareholders of record on January 3, January 10, January 17, January 24, and January 31, 2017. On January 17, 2017, our board of directors declared four weekly cash distributions of $0.014067 per share, which were paid on March 1, 2017 to shareholders of record on February 7, February 14, February 21, and February 28, 2017. On February 21, 2017, our board of directors declared four weekly cash distributions of $0.014067 per share, payable on March 29, 2017 to shareholders of record on March 7, March 14, March 21, and March 28, 2017.
On February 1, 2014, we changed from semi-monthly closings to weekly closings for the sale of our shares. As a result, our board of directors authorizes and declares on a monthly basis a weekly distribution amount per share of our common stock.
We have adopted an “opt in” distribution reinvestment plan for our shareholders. As a result, if we make a distribution, our shareholders will receive distributions in cash unless they specifically “opt in” to the fifth amended and restated distribution reinvestment plan so as to have their cash distributions reinvested in additional shares of our common stock.
We have made and intend to make our distributions in the form of cash, out of assets legally available for such purpose, unless shareholders elect to receive their distributions in the form of additional shares of common stock pursuant to our fifth amended and restated distribution reinvestment plan. Any distributions reinvested under the plan will nevertheless remain taxable to U.S. shareholders. We may fund our cash distributions to shareholders in the future from any sources of funds available to us, including offering proceeds, borrowings, net investment income from operations, capital gains proceeds from the sale of assets, non-capital gains proceeds from the sale of assets, dividends or other distributions paid to us on account of preferred and common equity investments in portfolio companies and expense support from CIG and AIM. Through December 31, 2014, a portion of our distributions resulted from expense support from CIG, and future distributions may result from expense support from CIG and AIM, each of which is subject to repayment by us. The amount of the distribution for shareholders receiving our common stock will be equal to the fair market value of the stock received. If shareholders hold common stock in the name of a broker or financial intermediary, they should contact the broker or financial intermediary regarding their election to receive distributions in the form of additional common stock.
The following table reflects the sources of cash distributions on a GAAP basis that were declared during the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014:
45
Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Source of Distribution | Per Share | Amount | Percentage | Per Share | Amount | Percentage | Per Share | Amount | Percentage | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net investment income(1) | $ | 0.4302 | $ | 45,549 | 58.8 | % | $ | 0.3164 | $ | 24,762 | 43.2 | % | $ | 0.1792 | $ | 6,020 | 24.5 | % | |||||||||||||||
Net realized gain on total return swap | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net interest and other income from TRS portfolio | 0.2480 | 26,273 | 33.9 | % | 0.3868 | 30,281 | 52.9 | % | 0.4360 | 14,650 | 59.7 | % | |||||||||||||||||||||
Net gain on TRS loan sales | 0.0277 | 2,916 | 3.8 | % | 0.0060 | 472 | 0.8 | % | 0.0696 | 2,339 | 9.5 | % | |||||||||||||||||||||
Net realized gain on investments | 0.0257 | 2,721 | 3.5 | % | 0.0143 | 1,121 | 2.0 | % | 0.0458 | 1,538 | 6.3 | % | |||||||||||||||||||||
Distributions in excess of net investment income(2) | — | — | — | 0.0081 | 632 | 1.1 | % | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Total distributions | $ | 0.7316 | $ | 77,459 | 100.0 | % | $ | 0.7316 | $ | 57,268 | 100.0 | % | $ | 0.7306 | $ | 24,547 | 100.0 | % | |||||||||||||||
(1) | Distributions from net investment income include expense support from CIG of $1,880 for the year ended December 31, 2014. |
(2) | Distributions in excess of net investment income represent certain expenses, which are not deductible on a tax-basis. Unearned capital gains incentive fees and certain offering expenses reduce GAAP basis net investment income, but do not reduce tax basis net investment income. These tax-related adjustments represent additional net investment income available for distribution for tax purposes. See Note 14 for the sources of our cash distributions on a tax basis. |
46
Item 6. Selected Financial Data
The following selected financial data for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015, 2014 and 2013, and for the period from January 31, 2012 (Inception) through December 31, 2012, is derived from our audited consolidated financial statements. The data for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014 should be read in conjunction with our consolidated financial statements and related notes thereto and “Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” included elsewhere in this report.
Years Ended December 31, | For the Period from January 31, 2012 (Inception) through December 31, 2012 | |||||||||||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||||||||||
Statement of operations data: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Total investment income | $ | 80,590 | $ | 52,809 | $ | 17,713 | $ | 1,863 | $ | 3 | ||||||||||
Operating expenses | ||||||||||||||||||||
Total operating expenses | 32,212 | 23,380 | 12,451 | 5,873 | 117 | |||||||||||||||
Expense support from CIG | — | — | (1,880 | ) | (3,959 | ) | (117 | ) | ||||||||||||
Recoupment of expense support from CIG | 667 | 4,667 | 622 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Net operating expenses | 32,879 | 28,047 | 11,193 | 1,914 | — | |||||||||||||||
Net investment income (loss) | 47,711 | 24,762 | 6,520 | (51 | ) | 3 | ||||||||||||||
Net realized and unrealized gain (loss) on investments, foreign currency and total return swap | 71,962 | (26,204 | ) | 9,815 | 6,153 | 22 | ||||||||||||||
Net increase (decrease) in net assets resulting from operations | $ | 119,673 | $ | (1,442 | ) | $ | 16,335 | $ | 6,102 | $ | 25 | |||||||||
Weighted average shares of common stock outstanding(1) | 105,951,017 | 78,501,760 | 33,630,690 | 5,522,797 | 500,338 | |||||||||||||||
Per share data:(1) | ||||||||||||||||||||
Net investment income (loss)(2) | $ | 0.45 | $ | 0.32 | $ | 0.19 | $ | (0.01 | ) | $ | 0.01 | |||||||||
Net increase (decrease) in net assets resulting from operations | $ | 1.13 | $ | (0.02 | ) | $ | 0.49 | $ | 1.10 | $ | 0.05 | |||||||||
Distributions declared | $ | 0.73 | $ | 0.73 | $ | 0.73 | $ | 0.72 | $ | — | ||||||||||
Balance sheet data: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Net assets at the beginning of period | $ | 904,326 | $ | 496,389 | $ | 144,571 | $ | 4,487 | $ | — | ||||||||||
Net assets at end of period | $ | 999,763 | $ | 904,326 | $ | 496,389 | $ | 144,571 | $ | 4,487 | ||||||||||
Net asset value per share of common stock at beginning of period | $ | 8.71 | $ | 9.22 | $ | 9.32 | $ | 8.97 | $ | — | ||||||||||
Net asset value per share of common stock at end of period | $ | 9.11 | $ | 8.71 | $ | 9.22 | $ | 9.32 | $ | 8.97 | ||||||||||
Other data: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Distributions declared | $ | 77,459 | $ | 57,268 | $ | 24,547 | $ | 3,974 | $ | — | ||||||||||
Total investment return - net asset value(3) | 13.51 | % | 2.13 | % | 6.92 | % | 11.96 | % | (0.35 | )% | ||||||||||
Number of investments at period end | 123 | 86 | 59 | 42 | 2 | |||||||||||||||
Total portfolio investment purchases during the period(4) | $ | 569,893 | $ | 438,217 | $ | 403,742 | $ | 94,332 | $ | 1,973 | ||||||||||
Total portfolio investment sales and prepayments during the period(4) | $ | 229,075 | $ | 113,433 | $ | 144,492 | $ | 4,335 | $ | 3 | ||||||||||
(1) | The per share data was derived by using the weighted average shares of common stock outstanding for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015, 2014 and 2013 and from the commencement of operations on December 17, 2012 through December 31, 2012, respectively. |
(2) | Net investment income (loss) per share includes expense support from CIG of $0.06 and $0.72 per share for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively, and $0.23 per share for the period from January 31, 2012 (Inception) through December 31, 2012. There was no expense support from CIG or AIM for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015. Net investment income (loss) per share also includes expense support recoupments by CIG of $0.01, $0.06 and $0.02 per share for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. There were no expense support recoupments by CIG for the year ended December 31, 2013 or for the period from January 31, 2012 (Inception) through December 31, 2012. |
47
(3) | Total investment return-net asset value is a measure of the change in total value for shareholders who held our common stock at the beginning and end of the period, including distributions paid or payable during the period. Total investment return-net asset value is based on (i) the beginning period net asset value per share on the first day of the period, (ii) the net asset value per share on the last day of the period of (A) one share plus (B) any fractional shares issued in connection with the reinvestment of monthly distributions, and (iii) the value of distributions payable, if any, on the last day of the period. The total investment return-net asset value calculation assumes that monthly cash distributions are reinvested in accordance with our distribution reinvestment plan then in effect as described in Note 5 to our consolidated financial statements included in this report. The total investment return-net asset value does not consider the effect of the sales load from the sale of our common stock. The total investment return-net asset value includes the effect of the issuance of shares at a net offering price that is greater than net asset value per share, which causes an increase in net asset value per share. Total returns covering less than a full year are not annualized. |
(4) | Excludes our short term investments. |
48
Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
The following discussion should be read in conjunction with our consolidated financial statements and related notes and other financial information appearing elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. In addition to historical information, the following discussion and other parts of this Annual Report on Form 10-K contain forward-looking information that involves risks and uncertainties.
Overview
We were incorporated under the general corporation laws of the State of Maryland on August 9, 2011 and commenced operations on December 17, 2012 upon raising proceeds of $2,500 from persons not affiliated with us, CIM or Apollo. We are an externally managed, non-diversified closed-end management investment company that has elected to be regulated as a BDC under the 1940 Act. We elected to be treated for federal income tax purposes as a RIC, as defined under Subchapter M of the Code.
Our investment objective is to generate current income and, to a lesser extent, capital appreciation for investors. Our portfolio is comprised primarily of investments in senior secured debt, including first lien loans, second lien loans and unitranche loans, and, to a lesser extent, collateralized securities, structured products and other similar securities, unsecured debt, including corporate bonds and long-term subordinated loans, referred to as mezzanine loans, and equity, of private and thinly traded U.S. middle-market companies. In connection with our debt investments, we may receive equity interests such as warrants or options as additional consideration. We may also purchase minority interests in the form of common or preferred equity in our target companies, either in conjunction with one of our debt investments or through a co-investment with a financial sponsor.
We are managed by CIM, our affiliate and a registered investment adviser. CIM oversees the management of our activities and is responsible for making investment decisions for our portfolio. We and CIM have engaged AIM to act as our investment sub-adviser. On November 1, 2016, our board of directors, including a majority of directors who are not interested persons, approved the renewal of the investment advisory agreement with CIM and the investment sub-advisory agreement with AIM, each for a period of twelve months commencing December 17, 2016.
We seek to meet our investment objective by utilizing the experienced management teams of both CIM and AIM, which includes their access to the relationships and human capital of Apollo, CIG and ICON Capital, in sourcing, evaluating and structuring transactions, as well as monitoring and servicing our investments. We focus primarily on the senior secured debt of private and thinly-traded U.S. middle-market companies, which we define as companies that generally possess annual EBITDA of $50 million or less, with experienced management teams, significant free cash flow, strong competitive positions and potential for growth.
Revenue
We primarily generate revenue in the form of interest income on the debt securities that we hold and capital gains on debt or other equity interests that we acquire in portfolio companies. The majority of our senior debt investments bear interest at a floating rate. Interest on debt securities is generally payable quarterly or monthly. In some cases, some of our investments may provide for deferred interest payments or PIK interest. The principal amount of the debt securities and any accrued, but unpaid, interest generally will become due at the maturity date. In addition, we may generate revenue in the form of commitment, structuring or diligence fees, monitoring fees, fees for providing managerial assistance and possibly consulting fees and performance-based fees. Any such fees generated in connection with our investments will be recognized when earned.
Operating Expenses
Our primary operating expenses are the payment of advisory fees and other expenses under the investment advisory and administration agreements. Our investment advisory fee compensates CIM for its work in identifying, evaluating, negotiating, executing, monitoring and servicing our investments. CIM is responsible for compensating AIM for its services pursuant to the investment sub-advisory agreement. We bear all other expenses of our operations and transactions, including, without limitation:
• | corporate expenses relating to borrowings and costs associated with the offering of our common stock, subject to limitations included in the investment advisory and administration agreements; |
• | the costs of calculating our net asset value, including the cost of any third-party valuation services; |
• | investment advisory fees; |
• | fees payable to third parties relating to, or associated with, making, monitoring and disposing of investments and valuing investments and enforcing our contractual rights, including fees and expenses associated with performing due diligence reviews of prospective investments; |
• | transfer agent and custodial fees; |
• | fees and expenses associated with our marketing efforts; |
• | interest payable on debt, if any, incurred to finance our investments; |
• | federal and state registration fees; |
• | federal, state and local taxes; |
• | independent directors’ fees and expenses; |
• | costs of proxy statements, tender offer materials, shareholders’ reports and notices; |
49
• | fidelity bond, directors and officers/errors and omissions liability insurance and other insurance premiums; |
• | direct costs such as printing, mailing, long distance telephone and staff; |
• | fees and expenses associated with independent audits and outside legal costs, including compliance with the Sarbanes-Oxley Act; |
• | costs associated with our reporting and compliance obligations under the 1940 Act and applicable federal and state securities laws; |
• | brokerage commissions for our investments; and |
• | all other expenses incurred by CIM, AIM or us in connection with administering our business, including expenses incurred by CIM or AIM in performing its obligations, and the reimbursement of the compensation of our chief financial officer and chief compliance officer and their respective staffs paid by CIM or its affiliates, to the extent that they are not a person with a controlling interest in CIM or any of its affiliates, in each case subject to the limitations included in the investment advisory and administration agreements, as applicable. |
Portfolio Investment Activity for the Years Ended December 31, 2016 and 2015
The following table summarizes our investment activity, excluding short term investments and PIK securities, for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015:
Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Net Investment Activity | Investment Portfolio | Total Return Swap | Total | Investment Portfolio | Total Return Swap | Total | ||||||||||||||||||
Purchases and drawdowns | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Senior secured first lien debt | $ | 423,262 | $ | 28,993 | $ | 452,255 | $ | 82,147 | $ | 499,475 | $ | 581,622 | ||||||||||||
Senior secured second lien debt | 124,281 | — | 124,281 | 261,022 | 22,011 | 283,033 | ||||||||||||||||||
Collateralized securities and structured products - debt | — | — | — | 15,500 | — | 15,500 | ||||||||||||||||||
Collateralized securities and structured products - equity | 10,000 | — | 10,000 | 24,914 | — | 24,914 | ||||||||||||||||||
Unsecured debt | 5,832 | — | 5,832 | 54,634 | — | 54,634 | ||||||||||||||||||
Equity | 6,518 | 171 | 6,689 | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
Derivatives | 229 | — | 229 | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
Sales and principal repayments | (229,075 | ) | (341,258 | ) | (570,333 | ) | (113,433 | ) | (235,891 | ) | (349,324 | ) | ||||||||||||
Net portfolio activity | $ | 341,047 | $ | (312,094 | ) | $ | 28,953 | $ | 324,784 | $ | 285,595 | $ | 610,379 | |||||||||||
The following table summarizes the composition of our investment portfolio at amortized cost and fair value and our underlying TRS loans portfolio at notional amount and fair value as of December 31, 2016 and 2015:
50
December 31, 2016 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Investment Portfolio | Total Return Swap | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Investments Cost(1) | Investments Fair Value | Percentage of Investment Portfolio | Notional Amount of Underlying TRS Loans | Fair Value of Underlying TRS Loans | Percentage of Underlying TRS Loans | Cost/ Notional Amount(1) | Fair Value | Percentage | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Senior secured first lien debt | $ | 489,904 | $ | 489,913 | 48.1 | % | $ | 351,747 | $ | 341,194 | 86.9 | % | $ | 841,651 | $ | 831,107 | 58.9 | % | |||||||||||||||
Senior secured second lien debt | 437,240 | 434,347 | 42.6 | % | 56,100 | 51,251 | 13.1 | % | 493,340 | 485,598 | 34.4 | % | |||||||||||||||||||||
Collateralized securities and structured products - debt | 39,471 | 38,114 | 3.7 | % | — | — | — | 39,471 | 38,114 | 2.7 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Collateralized securities and structured products - equity | 37,713 | 34,648 | 3.4 | % | — | — | — | 37,713 | 34,648 | 2.5 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Unsecured debt | 17,290 | 16,851 | 1.7 | % | — | — | — | 17,290 | 16,851 | 1.1 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Equity | 4,832 | 5,107 | 0.5 | % | — | — | — | 4,832 | 5,107 | 0.4 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Subtotal/total percentage | 1,026,450 | 1,018,980 | 100.0 | % | 407,847 | 392,445 | 100.0 | % | 1,434,297 | 1,411,425 | 100.0 | % | |||||||||||||||||||||
Short term investments(2) | 70,498 | 70,498 | — | — | 70,498 | 70,498 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total investments | $ | 1,096,948 | $ | 1,089,478 | $ | 407,847 | $ | 392,445 | $ | 1,504,795 | $ | 1,481,923 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Number of portfolio companies | 103 | 49 | 141(3) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Average annual EBITDA of portfolio companies | $49.9 million | $200.7 million | $94.7 million | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Median annual EBITDA of portfolio companies | $42.7 million | $66.0 million | $50.4 million | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Purchased at a weighted average price of par | 95.87 | % | 98.96 | % | 96.73 | % | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Gross annual portfolio yield based upon the purchase price(4) | 9.99 | % | 6.73 | % | 9.07 | % | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(1) | Represents amortized cost for debt investments and cost for equity investments. Amortized cost represents the original cost adjusted for the amortization of premiums and/or accretion of discounts, as applicable, on our investments. |
(2) | Short term investments represent an investment in a fund that invests in highly liquid investments with average original maturity dates of three months or less. |
(3) | The sum of investment portfolio and TRS portfolio companies does not equal the total number of portfolio companies. This is due to 11 portfolio companies being in both the investment and TRS portfolios. |
(4) | The gross annual portfolio yield does not represent and may be higher than an actual investment return to shareholders because it excludes our expenses and all sales commissions and dealer manager fees and does not consider the cost of leverage. |
51
December 31, 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Investment Portfolio | Total Return Swap | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Investments Amortized Cost(1) | Investments Fair Value | Percentage of Investment Portfolio | Notional Amount of Underlying TRS Loans | Fair Value of Underlying TRS Loans | Percentage of Underlying TRS Loans | Amortized Cost/ Notional Amount(1) | Fair Value | Percentage | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Senior secured first lien debt | $ | 106,147 | $ | 104,187 | 16.0 | % | $ | 661,055 | $ | 634,597 | 92.9 | % | $ | 767,202 | $ | 738,784 | 55.4 | % | |||||||||||||||
Senior secured second lien debt | 468,899 | 453,713 | 69.7 | % | 56,970 | 48,528 | 7.1 | % | 525,869 | 502,241 | 37.7 | % | |||||||||||||||||||||
Collateralized securities and structured products - debt | 44,361 | 41,663 | 6.4 | % | — | — | — | 44,361 | 41,663 | 3.1 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Collateralized securities and structured products - equity | 31,184 | 24,604 | 3.8 | % | — | — | — | 31,184 | 24,604 | 1.8 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Unsecured debt | 29,553 | 26,740 | 4.1 | % | — | — | — | 29,553 | 26,740 | 2.0 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Subtotal/total percentage | 680,144 | 650,907 | 100.0 | % | 718,025 | 683,125 | 100.0 | % | 1,398,169 | 1,334,032 | 100.0 | % | |||||||||||||||||||||
Short term investments(2) | 18,892 | 18,892 | — | — | 18,892 | 18,892 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total investments | $ | 699,036 | $ | 669,799 | $ | 718,025 | $ | 683,125 | $ | 1,417,061 | $ | 1,352,924 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Number of portfolio companies | 82 | 87 | 142(3) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Average annual EBITDA of portfolio companies | $80.4 million | $266.4 million | $181.1 million | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Median annual EBITDA of portfolio companies | $64.2 million | $91.0 million | $74.9 million | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Purchased at a weighted average price of par | 97.16 | % | 99.02 | % | 98.10 | % | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Gross annual portfolio yield based upon the purchase price(4) | 9.42 | % | 6.47%(5) | 7.91 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(1) | Amortized cost represents the original cost adjusted for the amortization of premiums and/or accretion of discounts, as applicable, on our investments. |
(2) | Short term investments represent an investment in a fund that invests in highly liquid investments with average original maturity dates of three months or less. |
(3) | The sum of investment portfolio and TRS portfolio companies does not equal the total number of portfolio companies. This is due to 27 portfolio companies being in both the investment and TRS portfolios. |
(4) | The gross annual portfolio yield does not represent and may be higher than an actual investment return to shareholders because it excludes our expenses and all sales commissions and dealer manager fees. |
(5) | The gross annual portfolio yield for underlying TRS loans is determined without giving consideration to leverage. |
The following table summarizes the composition of our investment portfolio and our underlying TRS loans portfolio by the type of interest rate as of December 31, 2016 and 2015, excluding short term investments of $70,498 and $18,892, respectively:
December 31, 2016 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Investment Portfolio | Total Return Swap | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Interest Rate Allocation | Investments Cost | Investments Fair Value | Percentage of Investment Portfolio | Notional Amount of Underlying TRS Loans | Fair Value of Underlying TRS Loans | Percentage of Underlying TRS Loans | Cost/ Notional Amount | Fair Value | Percentage | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Floating interest rate investments | $ | 936,846 | $ | 931,214 | 91.4 | % | $ | 407,847 | $ | 392,445 | 100.0 | % | $ | 1,344,693 | $ | 1,323,659 | 93.8 | % | |||||||||||||||
Fixed interest rate investments | 47,059 | 48,011 | 4.7 | % | — | — | — | 47,059 | 48,011 | 3.4 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Other income producing investments | 37,713 | 34,648 | 3.4 | % | — | — | — | 37,713 | 34,648 | 2.4 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Non-income producing equity | 4,832 | 5,107 | 0.5 | % | — | — | — | 4,832 | 5,107 | 0.4 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Total investments | $ | 1,026,450 | $ | 1,018,980 | 100.0 | % | $ | 407,847 | $ | 392,445 | 100.0 | % | $ | 1,434,297 | $ | 1,411,425 | 100.0 | % | |||||||||||||||
52
December 31, 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Investment Portfolio | Total Return Swap | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Interest Rate Allocation | Investments Amortized Cost | Investments Fair Value | Percentage of Investment Portfolio | Notional Amount of Underlying TRS Loans | Fair Value of Underlying TRS Loans | Percentage of Underlying TRS Loans | Amortized Cost/ Notional Amount | Fair Value | Percentage | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Floating interest rate investments | $ | 606,286 | $ | 585,873 | 90.0 | % | $ | 718,025 | $ | 683,125 | 100.0 | % | $ | 1,324,311 | $ | 1,268,998 | 95.1 | % | |||||||||||||||
Fixed interest rate investments | 42,674 | 40,430 | 6.2 | % | — | — | — | 42,674 | 40,430 | 3.0 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Other income producing investments | 31,184 | 24,604 | 3.8 | % | — | — | — | 31,184 | 24,604 | 1.9 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Total investments | $ | 680,144 | $ | 650,907 | 100.0 | % | $ | 718,025 | $ | 683,125 | 100.0 | % | $ | 1,398,169 | $ | 1,334,032 | 100.0 | % | |||||||||||||||
The following table shows the composition of our investment portfolio and our underlying TRS loans portfolio by industry classification and the percentage, by fair value, of the total assets in such industries as of December 31, 2016 and 2015:
December 31, 2016 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Investment Portfolio | Total Return Swap | Total | |||||||||||||||||||
Industry Classification | Investments Fair Value | Percentage of Investment Portfolio | Fair Value of Underlying TRS Loans | Percentage of Underlying TRS Loans | Fair Value | Percentage | |||||||||||||||
High Tech Industries | $ | 217,339 | 21.3 | % | $ | 45,351 | 11.6 | % | $ | 262,690 | 18.6 | % | |||||||||
Services: Business | 126,869 | 12.5 | % | 66,733 | 17.0 | % | 193,602 | 13.7 | % | ||||||||||||
Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals | 118,337 | 11.6 | % | 70,176 | 17.9 | % | 188,513 | 13.4 | % | ||||||||||||
Diversified Financials | 72,762 | 7.1 | % | — | — | 72,762 | 5.2 | % | |||||||||||||
Media: Advertising, Printing & Publishing | 54,354 | 5.3 | % | 7,328 | 1.9 | % | 61,682 | 4.4 | % | ||||||||||||
Beverage, Food & Tobacco | 53,658 | 5.3 | % | — | — | 53,658 | 3.8 | % | |||||||||||||
Construction & Building | 39,137 | 3.8 | % | 14,269 | 3.6 | % | 53,406 | 3.8 | % | ||||||||||||
Chemicals, Plastics & Rubber | 27,253 | 2.7 | % | 25,701 | 6.5 | % | 52,954 | 3.7 | % | ||||||||||||
Capital Equipment | 51,155 | 5.0 | % | — | — | 51,155 | 3.6 | % | |||||||||||||
Hotel, Gaming & Leisure | 28,974 | 2.8 | % | 21,071 | 5.4 | % | 50,045 | 3.5 | % | ||||||||||||
Retail | 18,852 | 1.9 | % | 30,801 | 7.8 | % | 49,653 | 3.5 | % | ||||||||||||
Telecommunications | 35,411 | 3.5 | % | 13,775 | 3.5 | % | 49,186 | 3.5 | % | ||||||||||||
Automotive | 39,192 | 3.9 | % | — | — | 39,192 | 2.8 | % | |||||||||||||
Services: Consumer | 9,477 | 0.9 | % | 26,278 | 6.7 | % | 35,755 | 2.5 | % | ||||||||||||
Media: Diversified & Production | 23,100 | 2.3 | % | 7,277 | 1.8 | % | 30,377 | 2.1 | % | ||||||||||||
Banking, Finance, Insurance & Real Estate | 17,636 | 1.7 | % | 11,547 | 2.9 | % | 29,183 | 2.1 | % | ||||||||||||
Aerospace & Defense | 21,780 | 2.1 | % | 5,564 | 1.4 | % | 27,344 | 1.9 | % | ||||||||||||
Media: Broadcasting & Subscription | 9,776 | 1.0 | % | 10,013 | 2.6 | % | 19,789 | 1.4 | % | ||||||||||||
Energy: Oil & Gas | 12,803 | 1.3 | % | 4,570 | 1.2 | % | 17,373 | 1.2 | % | ||||||||||||
Consumer Goods: Durable | 1,000 | 0.1 | % | 15,942 | 4.1 | % | 16,942 | 1.2 | % | ||||||||||||
Metals & Mining | 11,349 | 1.1 | % | 3,528 | 0.9 | % | 14,877 | 1.1 | % | ||||||||||||
Energy: Electricity | 13,715 | 1.3 | % | — | — | 13,715 | 1.0 | % | |||||||||||||
Forest Products & Paper | — | — | 12,521 | 3.2 | % | 12,521 | 0.9 | % | |||||||||||||
Consumer Goods: Non-Durable | 8,611 | 0.8 | % | — | — | 8,611 | 0.6 | % | |||||||||||||
Containers, Packaging & Glass | 3,845 | 0.4 | % | — | — | 3,845 | 0.3 | % | |||||||||||||
Environmental Industries | 2,595 | 0.3 | % | — | — | 2,595 | 0.2 | % | |||||||||||||
Subtotal/total percentage | 1,018,980 | 100.0 | % | 392,445 | 100.0 | % | 1,411,425 | 100.0 | % | ||||||||||||
Short term investments | 70,498 | — | 70,498 | ||||||||||||||||||
Total investments | $ | 1,089,478 | $ | 392,445 | $ | 1,481,923 | |||||||||||||||
53
December 31, 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Investment Portfolio | Total Return Swap | Total | |||||||||||||||||||
Industry Classification | Investments Fair Value | Percentage of Investment Portfolio | Fair Value of Underlying TRS Loans | Percentage of Underlying TRS Loans | Fair Value | Percentage | |||||||||||||||
Services: Business | $ | 124,412 | 19.1 | % | $ | 94,924 | 13.9 | % | $ | 219,336 | 16.4 | % | |||||||||
Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals | 54,122 | 8.3 | % | 121,889 | 17.8 | % | 176,011 | 13.2 | % | ||||||||||||
High Tech Industries | 86,848 | 13.3 | % | 77,663 | 11.4 | % | 164,511 | 12.3 | % | ||||||||||||
Diversified Financials | 66,267 | 10.2 | % | — | — | 66,267 | 5.0 | % | |||||||||||||
Chemicals, Plastics & Rubber | 27,161 | 4.2 | % | 37,270 | 5.5 | % | 64,431 | 4.8 | % | ||||||||||||
Banking, Finance, Insurance & Real Estate | 32,224 | 5.0 | % | 31,160 | 4.6 | % | 63,384 | 4.8 | % | ||||||||||||
Beverage, Food & Tobacco | 62,314 | 9.6 | % | — | — | 62,314 | 4.7 | % | |||||||||||||
Construction & Building | 24,099 | 3.7 | % | 35,443 | 5.2 | % | 59,542 | 4.5 | % | ||||||||||||
Hotel, Gaming & Leisure | 26,839 | 4.1 | % | 32,079 | 4.7 | % | 58,918 | 4.4 | % | ||||||||||||
Retail | 8,623 | 1.4 | % | 49,276 | 7.2 | % | 57,899 | 4.3 | % | ||||||||||||
Telecommunications | 9,148 | 1.4 | % | 29,943 | 4.4 | % | 39,091 | 2.9 | % | ||||||||||||
Services: Consumer | 13,154 | 2.0 | % | 25,003 | 3.7 | % | 38,157 | 2.9 | % | ||||||||||||
Forest Products & Paper | — | — | 32,697 | 4.8 | % | 32,697 | 2.5 | % | |||||||||||||
Media: Advertising, Printing & Publishing | 24,627 | 3.8 | % | 7,740 | 1.1 | % | 32,367 | 2.4 | % | ||||||||||||
Consumer Goods: Durable | — | — | 28,803 | 4.2 | % | 28,803 | 2.2 | % | |||||||||||||
Media: Broadcasting & Subscription | 9,952 | 1.5 | % | 16,642 | 2.4 | % | 26,594 | 2.0 | % | ||||||||||||
Consumer Goods: Non-Durable | 13,974 | 2.1 | % | 12,347 | 1.8 | % | 26,321 | 2.0 | % | ||||||||||||
Automotive | 19,766 | 3.0 | % | 5,100 | 0.8 | % | 24,866 | 1.9 | % | ||||||||||||
Media: Diversified & Production | 10,153 | 1.6 | % | 14,287 | 2.1 | % | 24,440 | 1.8 | % | ||||||||||||
Containers, Packaging & Glass | 11,851 | 1.8 | % | 8,366 | 1.2 | % | 20,217 | 1.5 | % | ||||||||||||
Energy: Electricity | 13,677 | 2.1 | % | 2,194 | 0.3 | % | 15,871 | 1.2 | % | ||||||||||||
Aerospace & Defense | — | — | 13,975 | 2.0 | % | 13,975 | 1.0 | % | |||||||||||||
Energy: Oil & Gas | 6,274 | 1.0 | % | 3,286 | 0.5 | % | 9,560 | 0.7 | % | ||||||||||||
Mining & Metals | — | — | 3,038 | 0.4 | % | 3,038 | 0.2 | % | |||||||||||||
Environmental Industries | 2,850 | 0.4 | % | — | — | 2,850 | 0.2 | % | |||||||||||||
Capital Equipment | 2,572 | 0.4 | % | — | — | 2,572 | 0.2 | % | |||||||||||||
Subtotal/total percentage | 650,907 | 100.0 | % | 683,125 | 100.0 | % | 1,334,032 | 100.0 | % | ||||||||||||
Short term investments | 18,892 | — | 18,892 | ||||||||||||||||||
Total investments | $ | 669,799 | $ | 683,125 | $ | 1,352,924 | |||||||||||||||
Except for CION / Capitala Senior Loan Fund I, LLC, or CCSLF, we do not “control” and are not an “affiliate” of any of our portfolio companies or any of the companies of the loans underlying the TRS, each as defined in the 1940 Act. In general, under the 1940 Act, we would be presumed to “control” a portfolio company or issuer if we owned 25% or more of its voting securities and would be an “affiliate” of a portfolio company or issuer if we owned 5% or more of its voting securities.
Our investment portfolio may contain senior secured investments that are in the form of lines of credit, revolving credit facilities, or unfunded commitments, which may require us to provide funding when requested in accordance with the terms of the underlying agreements. As of December 31, 2016 and 2015, our unfunded commitments amounted to $65,096 and $43,404, respectively. As of March 9, 2017, our unfunded commitments amounted to $85,986. Since these commitments may expire without being drawn upon, unfunded commitments do not necessarily represent future cash requirements or future earning assets for us. Refer to the section “Commitments and Contingencies and Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements” for further details on our unfunded commitments.
Investment Portfolio Asset Quality
CIM uses an investment rating system to characterize and monitor our expected level of returns on each investment in our portfolio. These ratings are just one of several factors that CIM uses to monitor our portfolio, are not in and of themselves determinative of fair value or revenue recognition and are presented for indicative purposes. CIM rates the credit risk of all investments on a scale of 1 to 5 no less frequently than quarterly. This system is intended primarily to reflect the underlying risk of a portfolio investment relative to our initial cost basis in respect of such portfolio investment (i.e., at the time of acquisition), although it may also take into account under certain circumstances the performance of the portfolio company’s business, the collateral coverage of the investment and other relevant factors.
54
The following is a description of the conditions associated with each investment rating used in this ratings system:
Investment Rating | Description | |
1 | Indicates the least amount of risk to our initial cost basis. The trends and risk factors for this investment since origination or acquisition are generally favorable, which may include the performance of the portfolio company or a potential exit. | |
2 | Indicates a level of risk to our initial cost basis that is similar to the risk to our initial cost basis at the time of origination or acquisition. This portfolio company is generally performing in accordance with our analysis of its business and the full return of principal and interest or dividend is expected. | |
3 | Indicates that the risk to our ability to recoup the cost of such investment has increased since origination or acquisition, but full return of principal and interest or dividend is expected. A portfolio company with an investment rating of 3 requires closer monitoring. | |
4 | Indicates that the risk to our ability to recoup the cost of such investment has increased significantly since origination or acquisition, including as a result of factors such as declining performance and noncompliance with debt covenants, and we expect some loss of interest, dividend or capital appreciation, but still expect an overall positive internal rate of return on the investment. | |
5 | Indicates that the risk to our ability to recoup the cost of such investment has increased materially since origination or acquisition and the portfolio company likely has materially declining performance. Loss of interest or dividend and some loss of principal investment is expected, which would result in an overall negative internal rate of return on the investment. | |
For investments rated 3, 4, or 5, CIM enhances its level of scrutiny over the monitoring of such portfolio company.
The following table summarizes the composition of our investment portfolio and our underlying TRS loans portfolio based on the 1 to 5 investment rating scale at fair value as of December 31, 2016 and 2015, excluding short term investments of $70,498 and $18,892, respectively:
December 31, 2016 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Investment Portfolio | Total Return Swap | Total | |||||||||||||||||||
Investment Rating | Investments Fair Value | Percentage of Investment Portfolio | Fair Value of Underlying TRS Loans | Percentage of Underlying TRS Loans | Fair Value | Percentage | |||||||||||||||
1 | $ | — | — | $ | — | — | $ | — | — | ||||||||||||
2 | 963,477 | 94.6 | % | 342,620 | 87.3 | % | 1,306,097 | 92.5 | % | ||||||||||||
3 | 50,942 | 5.0 | % | 34,657 | 8.8 | % | 85,599 | 6.1 | % | ||||||||||||
4 | 4,561 | 0.4 | % | 12,798 | 3.3 | % | 17,359 | 1.2 | % | ||||||||||||
5 | — | — | 2,370 | 0.6 | % | 2,370 | 0.2 | % | |||||||||||||
$ | 1,018,980 | 100.0 | % | $ | 392,445 | 100.0 | % | $ | 1,411,425 | 100.0 | % | ||||||||||
December 31, 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Investment Portfolio | Total Return Swap | Total | |||||||||||||||||||
Investment Rating | Investments Fair Value | Percentage of Investment Portfolio | Fair Value of Underlying TRS Loans | Percentage of Underlying TRS Loans | Fair Value | Percentage | |||||||||||||||
1 | $ | — | — | $ | — | — | $ | — | — | ||||||||||||
2 | 624,097 | 95.9 | % | 652,073 | 95.5 | % | 1,276,170 | 95.7 | % | ||||||||||||
3 | 24,180 | 3.7 | % | 23,047 | 3.4 | % | 47,227 | 3.5 | % | ||||||||||||
4 | 2,630 | 0.4 | % | 6,845 | 1.0 | % | 9,475 | 0.7 | % | ||||||||||||
5 | — | — | 1,160 | 0.1 | % | 1,160 | 0.1 | % | |||||||||||||
$ | 650,907 | 100.0 | % | $ | 683,125 | 100.0 | % | $ | 1,334,032 | 100.0 | % | ||||||||||
The amount of the investment portfolio and underlying TRS loans in each rating category may vary substantially from period to period resulting primarily from changes in the composition of each portfolio as a result of new investment, repayment and exit activities. In addition, changes in the rating of investments may be made to reflect our expectation of performance and changes in investment values.
55
Current Investment Portfolio
As of March 9, 2017, our investment portfolio, excluding our short term investments and TRS, consisted of interests in 101 portfolio companies (51% in senior secured first lien debt, 41% in senior secured second lien debt, 6% in collateralized securities and structured products (comprised of 1% invested in rated debt, 2% invested in non-rated debt and 3% invested in non-rated equity of such securities and products), 1% in unsecured debt and 1% in equity) with a total fair value of $1,038,216 with an average and median portfolio company annual EBITDA of $49.7 million and $42.2 million, respectively, at initial investment. As of March 9, 2017, investments in our portfolio, excluding our short term investments and TRS, were purchased at a weighted average price of 95.81% of par value. Our estimated gross annual portfolio yield was 9.84% based upon the purchase price of such investments. The estimated gross portfolio yield does not represent and may be higher than an actual investment return to shareholders because it excludes our expenses and all sales commissions and dealer manager fees. For the year ended December 31, 2016, our total investment return-net asset value was 13.51%. Total investment return-net asset value does not represent and may be higher than an actual investment return to shareholders because it excludes all sales commissions and dealer manager fees. Total investment return-net asset value is a measure of the change in total value for shareholders who held our common stock at the beginning and end of the period, including distributions paid or payable during the period, and is described further in Note 13 of our consolidated financial statements.
As of March 9, 2017, our only short term investment was an investment in a U.S. Treasury Obligations Fund of $76,443.
Further, as of March 9, 2017, through a TRS (described further in Note 7 of our consolidated financial statements), we obtained the economic benefit of owning investments in first and second lien senior secured floating-rate loans of 48 portfolio companies. We also held one credit default swap with a notional amount of €22,000 and a fair value of $4 as of March 9, 2017.
Results of Operations
Comparison of the Years Ended December 31, 2016 and 2015
Our results of operations for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015 were as follows:
Years Ended December 31, | |||||||
2016 | 2015 | ||||||
Investment income | $ | 80,590 | $ | 52,809 | |||
Net operating expenses | 32,879 | 28,047 | |||||
Net investment income | 47,711 | 24,762 | |||||
Net realized gain on investments and foreign currency | 2,721 | 1,121 | |||||
Net change in unrealized appreciation (depreciation) on investments | 21,584 | (27,587 | ) | ||||
Net realized gain on total return swap | 28,159 | 30,753 | |||||
Net change in unrealized appreciation (depreciation) on total return swap | 19,498 | (30,491 | ) | ||||
Net increase (decrease) in net assets resulting from operations | $ | 119,673 | $ | (1,442 | ) | ||
Investment Income
For the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, we generated investment income of $80,590 and $52,809, respectively, consisting primarily of interest income on investments in senior secured debt, collateralized securities, structured products, and unsecured debt of 131 and 91 portfolio companies held during each respective period. Our average investment portfolio size, excluding our short term investments and TRS, increased $333,708, from $501,236 during the year ended December 31, 2015 to $834,944 during the year ended December 31, 2016, as we deployed the net proceeds from the JPM Credit Facility and the net proceeds from our follow-on continuous public offering, which commenced on January 25, 2016. We expect our investment portfolio to continue to grow due to the anticipated equity available to us for investment from our follow-on continuous public offering. As a result, we believe that reported investment income for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015 is not representative of our stabilized or future performance. Interest income earned by loans underlying the TRS is not included in investment income in the consolidated statements of operations, but rather it is recorded as part of net realized gain on total return swap. Currently, the TRS is scheduled to terminate on April 18, 2017. We expect to either extend the TRS or convert the TRS into a traditional credit facility. In the event that we convert the TRS into a traditional credit facility, we would expect an increase in investment income.
Operating Expenses
The composition of our operating expenses for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015 was as follows:
56
Years Ended December 31, | |||||||
2016 | 2015 | ||||||
Management fees | $ | 20,092 | $ | 14,827 | |||
Administrative services expense | 1,834 | 1,900 | |||||
General and administrative | 6,717 | 6,248 | |||||
Interest expense | 3,569 | 405 | |||||
Total operating expenses | 32,212 | 23,380 | |||||
Recoupment of expense support from CIG | 667 | 4,667 | |||||
Net operating expenses | $ | 32,879 | $ | 28,047 | |||
During the year ended December 31, 2016, the increase in management fees was a direct result of the increase in our net assets, while the increase in interest expense was a result of entering into the JPM Credit Facility on August 26, 2016. The decrease in recoupment of expense support from CIG was a result of our reimbursement of all previously provided expense support from CIG as of December 31, 2016.
The composition of our general and administrative expenses for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015 was as follows:
Years Ended December 31, | |||||||
2016 | 2015 | ||||||
Professional fees | $ | 1,623 | $ | 1,044 | |||
Transfer agent expense | 1,272 | 1,144 | |||||
Dues and subscriptions | 775 | 505 | |||||
Valuation expense | 625 | 310 | |||||
Printing and marketing expense | 553 | 755 | |||||
Due diligence fees | 470 | 1,006 | |||||
Insurance expense | 376 | 297 | |||||
Director fees and expenses | 274 | 296 | |||||
Filing fees | 53 | 478 | |||||
Other expenses | 696 | 413 | |||||
Total general and administrative expense | $ | 6,717 | $ | 6,248 | |||
Expense Support and Recoupment of Expense Support
Our affiliate, CIG, agreed to provide expense support to us commencing with the quarter ended December 31, 2012 for certain expenses pursuant to the expense support and conditional reimbursement agreement. We further amended and restated the expense support and conditional reimbursement agreement on December 16, 2015 and December 14, 2016 for purposes of including AIM as a party to the expense support and conditional reimbursement agreement and extending the termination date from December 31, 2016 to December 31, 2017, respectively. Commencing with the quarter beginning January 1, 2016, CIG and AIM each agrees to provide expense support to us for 50% of certain expenses pursuant to the expense support and conditional reimbursement agreement. Refer to the discussion under “Related Party Transactions” below for further details about the expense support and conditional reimbursement agreement. Also, see Note 4 to our consolidated financial statements for additional disclosure regarding expense support from CIG and AIM.
For the year ended December 31, 2016, CIG recouped $667 of expense support made during the three months ended December 31, 2014 in connection with the expense support and conditional reimbursement agreement. For the year ended December 31, 2015, CIG recouped $4,667 of expense support made during each of the three months ended March 31, 2013, June 30, 2013, September 30, 2013, December 31, 2013, March 31, 2014, and December 31, 2014 in connection with the expense support and conditional reimbursement agreement. We did not receive any expense support from CIG or AIM for the years ended December 31, 2016 or 2015.
Recoupment of such support will be determined as appropriate to meet the objectives of the expense support and conditional reimbursement agreement. As a result, we may or may not be requested to reimburse CIG and AIM for any expense support that may be received from CIG and AIM in the future.
Net Investment Income
Our net investment income totaled $47,711 and $24,762 for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively. The increase in net investment income was primarily due to an increase in the size of our investment portfolio relative to our expenses as we continued to achieve economies of scale due to proceeds received from our continuous public offerings and our credit facilities.
57
Net Realized Gain on Investments and Foreign Currency
Our net realized gain on investments and foreign currency totaled $2,721 and $1,121 for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively. The increase in net realized gain on investments and foreign currency was primarily due to an increase in sales and principal repayment activity during the year ended December 31, 2016 compared to the year ended December 31, 2015. During the year ended December 31, 2016, we received sale proceeds of $34,951 and principal repayments of $194,124, resulting in net realized gains of $2,721. During the year ended December 31, 2015, we received sale proceeds of $71,605 and principal repayments of $41,828, resulting in net realized gains of $1,121.
Net Change in Unrealized Appreciation (Depreciation) on Investments
The net change in unrealized appreciation (depreciation) on our investments totaled $21,584 and ($27,587) for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively. This change was driven primarily by a tightening of credit spreads during the year ended December 31, 2016 that positively impacted the fair value of certain investments.
Net Realized Gain on TRS
Our net realized gain on the TRS totaled $28,159 and $30,753 for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively. The components of net realized gain on the TRS are summarized below:
Years Ended December 31, | |||||||
2016 | 2015 | ||||||
Interest and other income from TRS portfolio | $ | 39,746 | $ | 40,499 | |||
Interest and other expense from TRS portfolio | (13,473 | ) | (10,218 | ) | |||
Net gain on TRS loan sales | 1,886 | 472 | |||||
Total | $ | 28,159 | $ | 30,753 | |||
Net Change in Unrealized Appreciation (Depreciation) on TRS
The net change in unrealized appreciation (depreciation) on the TRS totaled $19,498 and ($30,491) for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively. This change was driven primarily by a tightening of credit spreads during the year ended December 31, 2016 that positively impacted the fair value of certain investments.
Net Increase (Decrease) in Net Assets Resulting from Operations
For the year ended December 31, 2016, we recorded a net increase in net assets resulting from operations of $119,673 compared to a net decrease in net assets resulting from operations of ($1,442) for the year ended December 31, 2015, as a result of our operating activity for the respective periods.
Results of Operations
Comparison of the Years Ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
Our results of operations for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 were as follows:
Years Ended December 31, | |||||||
2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Investment income | $ | 52,809 | $ | 17,713 | |||
Net operating expenses | 28,047 | 11,193 | |||||
Net investment income | 24,762 | 6,520 | |||||
Net realized gain on investments | 1,121 | 1,538 | |||||
Net change in unrealized depreciation on investments | (27,587 | ) | (2,754 | ) | |||
Net realized gain on total return swap | 30,753 | 16,989 | |||||
Net change in unrealized depreciation on total return swap | (30,491 | ) | (5,958 | ) | |||
Net (decrease) increase in net assets resulting from operations | $ | (1,442 | ) | $ | 16,335 | ||
58
Investment Income
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, we generated investment income of $52,809 and $17,713, respectively, consisting primarily of interest income on investments in senior secured debt, collateralized securities, structured products, and unsecured debt of 91 portfolio companies held during each respective period. Our average investment portfolio size, excluding our short term investments and TRS, increased $278,886, from $222,350 during the year ended December 31, 2014 to $501,236 during the year ended December 31, 2015, as we continued to deploy the net proceeds from our initial continuous public offering, which ended on December 31, 2015. We expect our investment portfolio to continue to grow due to the anticipated equity available to us for investment from our follow-on continuous public offering, which commenced on January 25, 2016. As a result, we believe that reported investment income for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 is not representative of our stabilized or future performance. Interest income earned by loans underlying the TRS is not included in investment income in the consolidated statements of operations, but rather it is recorded as part of net realized gain on total return swap.
Operating Expenses
The composition of our operating expenses for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 was as follows:
Years Ended December 31, | |||||||
2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Management fees | $ | 14,827 | $ | 6,132 | |||
Administrative services expense | 1,900 | 1,792 | |||||
Capital gains incentive fee | — | (757 | ) | ||||
Offering, organizational and other costs - CIG | — | 1,012 | |||||
General and administrative | 6,248 | 4,272 | |||||
Interest expense | 405 | — | |||||
Total operating expenses | 23,380 | 12,451 | |||||
Expense support from CIG | — | (1,880 | ) | ||||
Recoupment of expense support from CIG | 4,667 | 622 | |||||
Net operating expenses | $ | 28,047 | $ | 11,193 | |||
The composition of our general and administrative expenses for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 was as follows:
Years Ended December 31, | |||||||
2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Transfer agent expense | $ | 1,144 | $ | 627 | |||
Professional fees | 1,044 | 849 | |||||
Due diligence fees | 1,006 | 967 | |||||
Printing and marketing expense | 755 | 681 | |||||
Dues and subscriptions | 505 | 230 | |||||
Filing fees | 478 | 113 | |||||
Valuation expense | 310 | 136 | |||||
Insurance expense | 297 | 235 | |||||
Director fees and expenses | 296 | 162 | |||||
Other expenses | 413 | 272 | |||||
Total general and administrative expense | $ | 6,248 | $ | 4,272 | |||
Expense Support and Recoupment of Expense Support
For the year ended December 31, 2015, CIG recouped $4,667 of expense support made during each of the three months ended March 31, 2013, June 30, 2013, September 30, 2013, December 31, 2013, March 31, 2014, and December 31, 2014 in connection with the expense support and conditional reimbursement agreement. We did not receive any expense support from CIG for the year ended December 31, 2015. For the year ended December 31, 2014, we received expense support from CIG of $1,880 and CIG recouped $622 of expense support made during each of the three months ended December 31, 2012 and March 31, 2013 in connection with the expense support and conditional reimbursement agreement.
Refer to the section “Results of Operations – Comparison of the Years Ended December 31, 2016 and 2015 – Expense Support and Recoupment of Expense Support” above for further details on our expense support from CIG and AIM.
59
Net Investment Income
Our net investment income totaled $24,762 and $6,520 for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively. The increase in net investment income was primarily due to an increase in the size of our investment portfolio relative to our expenses as we continued to achieve economies of scale due to proceeds received from our initial continuous public offering.
Net Realized Gain on Investments
Our net realized gain on investments totaled $1,121 and $1,538 for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively. The decrease in net realized gain on investments was primarily due to a decrease in sales and principal repayment activity during the year ended December 31, 2015 compared to the year ended December 31, 2014. During the year ended December 31, 2015, we received sale proceeds of $71,605 and principal repayments of $41,828, resulting in net realized gains of $1,121. During the year ended December 31, 2014, we received sale proceeds of $94,182 and principal repayments of $50,310, resulting in net realized gains of $1,538.
Net Change in Unrealized Depreciation on Investments
The net change in unrealized depreciation on our investments totaled $27,587 and $2,754 for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively. This change was driven primarily by a widening of credit spreads during the year ended December 31, 2015 that negatively impacted the fair value of certain investments.
Net Realized Gain on TRS
Our net realized gain on the TRS totaled $30,753 and $16,989 for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively. The components of net realized gain on the TRS are summarized below:
Years Ended December 31, | |||||||
2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Interest and other income from TRS portfolio | $ | 40,499 | $ | 19,081 | |||
Interest and other expense from TRS portfolio | (10,218 | ) | (4,431 | ) | |||
Net gain on TRS loan sales | 472 | 2,339 | |||||
Total | $ | 30,753 | $ | 16,989 | |||
Net Change in Unrealized Depreciation on TRS
The net change in unrealized depreciation on the TRS totaled $30,491 and $5,958 for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively. This change was driven primarily by a widening of credit spreads during the year ended December 31, 2015 that negatively impacted the fair value of certain investments.
Net (Decrease) Increase in Net Assets Resulting from Operations
For the year ended December 31, 2015, we recorded a net decrease in net assets resulting from operations of ($1,442) compared to a net increase in net assets resulting from operations of $16,335 for the year ended December 31, 2014, as a result of our operating activity for the respective periods.
60
Net Asset Value per Share, Annual Investment Return and Total Return Since Inception
Our net asset value per share was $9.11 and $8.71 on December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively. After considering (i) the overall changes in net asset value per share, (ii) paid distributions of approximately $0.7316 per share during the year ended December 31, 2016, and (iii) the assumed reinvestment of those distributions in accordance with our distribution reinvestment plan then in effect, the total investment return-net asset value was 13.51% for the twelve-month period ended December 31, 2016. Total investment return-net asset value does not represent and may be higher than an actual return to shareholders because it excludes all sales commissions and dealer manager fees. Total investment return-net asset value is a measure of the change in total value for shareholders who held our common stock at the beginning and end of the period, including distributions paid or payable during the period, and is described further in Note 13 to our consolidated financial statements included in this report.
Initial shareholders who subscribed to the offering in December 2012 with an initial investment of $10,000 and an initial purchase price equal to $9.00 per share (public offering price net of sales load) have seen an annualized return of 8.36% and a cumulative total return of 38.35% through December 31, 2016 (see chart below). Initial shareholders who subscribed to the offering in December 2012 with an initial investment of $10,000 and an initial purchase price equal to $10.00 per share (the initial public offering price including sales load) have seen an annualized return of 5.57% and a cumulative total return of 24.52% through December 31, 2016. Over the same time period, the S&P/LSTA Leveraged Loan Index, a primary measure of senior debt covering the U.S. leveraged loan market, which currently consists of approximately 1,000 credit facilities throughout numerous industries, recorded an annualized return of 4.15% and a cumulative total return of 17.86%. In addition, the BofA Merrill Lynch US High Yield Index, a primary measure of short-term US dollar denominated below investment grade corporate debt publicly issued in the US domestic market, recorded an annualized return of 5.37% and a cumulative total return of 23.56% over the same period.
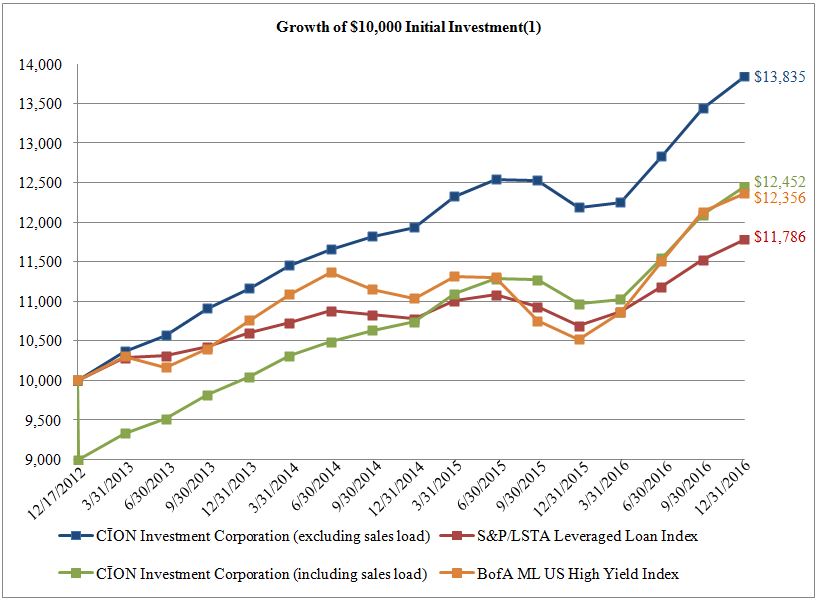
(1) Cumulative performance: December 17, 2012 to December 31, 2016
The calculations for the Growth of $10,000 Initial Investment are based upon (i) an initial investment of $10,000 in our common stock at the beginning of the period, at a share price of $10.00 per share (including sales load) and $9.00 per share (excluding sales load), (ii) assumes reinvestment of monthly distributions in accordance with our distribution reinvestment plan then in effect, (iii) the sale of the entire investment position at the net asset value per share on the last day of the period, and (iv) the distributions declared and payable to shareholders, if any, on the last day of the period.
61
Financial Condition, Liquidity and Capital Resources
We generate cash primarily from the net proceeds from our follow-on continuous public offering and from cash flows from interest, fees and dividends earned from our investments as well as principal repayments and proceeds from sales of our investments. We also employ leverage to seek to enhance our returns as market conditions permit and at the discretion of CIM, but in no event will leverage employed exceed 50% of the value of our total assets, as required by the 1940 Act. We are engaged in a follow-on continuous public offering of shares of our common stock. Our initial continuous public offering commenced on July 2, 2012 and ended on December 31, 2015. Our follow-on continuous public offering commenced on January 25, 2016. We accept subscriptions on a continuous basis and issue shares at weekly closings at prices that, after deducting selling commissions and dealer manager fees, are at or above our net asset value per share.
We will sell our shares on a continuous basis at our latest public offering price of $9.65 per share; however, to the extent that our net asset value fluctuates, we will sell at a price necessary to ensure that shares are sold at a price, after deduction of selling commissions and dealer manager fees, that is above and within 2.5% of net asset value per share.
As of December 31, 2016, we sold 109,787,557 shares for net proceeds of $1,117,566 at an average price per share of $10.18. The net proceeds received include reinvested shareholder distributions of $84,473, for which we issued 9,281,664 shares of common stock, and gross proceeds paid for shares of common stock tendered for repurchase of $25,414, for which we repurchased 2,827,092 shares of common stock. Since commencing our initial continuous public offering on July 2, 2012 and through December 31, 2016, sales commissions and dealer manager fees related to the sale of our common stock were $63,255 and $30,994, respectively.
As of March 9, 2017, we sold 110,720,587 shares of common stock for net proceeds of $1,126,475 at an average price per share of $10.17. The net proceeds received include reinvested shareholder distributions of $91,354, for which we issued 10,036,822 shares of common stock, and gross proceeds paid for shares of common stock tendered for repurchase of $32,784, for which we repurchased 3,641,315 shares of common stock. Since commencing our initial continuous public offering on July 2, 2012 and through March 9, 2017, sales commissions and dealer manager fees related to the sale of our common stock were $63,442 and $31,165, respectively.
The net proceeds from our follow-on continuous public offering will be invested primarily in cash, cash equivalents, U.S. government securities, repurchase agreements and high-quality debt instruments maturing in one year or less prior to being invested in debt securities of private U.S. companies.
As of December 31, 2016 and 2015, we had $70,498 and $18,892 in short term investments, respectively, invested in a fund that primarily invests in U.S. government securities.
Total Return Swap
As of December 31, 2016 and March 9, 2017, the notional amount available under the TRS was $392,153 and $399,093, respectively. Currently, the TRS is scheduled to terminate on April 18, 2017. We expect to either extend the TRS or convert the TRS into a traditional credit facility. For a detailed discussion of our TRS, refer to Note 7 to our consolidated financial statements included in this report.
JPM Credit Facility
As of December 31, 2016 and March 9, 2017, our outstanding borrowings under the JPM Credit Facility were $224,423 and the aggregate principal amount available in connection with the JPM Credit Facility was $577.
For a detailed discussion of our JPM Credit Facility, refer to Note 8 to our consolidated financial statements included in this report.
East West Bank Credit Facility
As of December 31, 2016, we had no outstanding borrowings under the EWB Credit Facility and the aggregate principal amount available in connection with the EWB Credit Facility was $7,254. As of March 9, 2017, we had no outstanding borrowings under the EWB Credit Facility and the aggregate principal amount available in connection with the EWB Credit Facility was $6,788.
For a detailed discussion of our EWB Credit Facility, refer to Note 8 to our consolidated financial statements included in this report.
Unfunded Commitments
As of December 31, 2016 and March 9, 2017, our unfunded commitments amounted to $65,096 and $85,986, respectively.
For a detailed discussion of our unfunded commitments, refer to Note 11 to our consolidated financial statements included in this report.
62
RIC Status and Distributions
Our total investment portfolio includes loans and other securities on our consolidated balance sheets and loans underlying the TRS. Accordingly, we treat net interest and other income earned on all investments, including the loans underlying the TRS, as a component of investment company taxable income when determining our sources of distributions. The sources of our distributions for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015 were as follows:
Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Investment Portfolio | Total Return Swap Portfolio | Total Investment Portfolio | Percentage | Investment Portfolio | Total Return Swap Portfolio | Total Investment Portfolio | Percentage | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Net investment income | $ | 45,549 | $ | 26,273 | $ | 71,822 | 92.7 | % | $ | 24,762 | $ | 30,281 | $ | 55,043 | 96.1 | % | ||||||||||||||
Capital gains from the sale of assets(1)(2) | 2,721 | 2,916 | 5,637 | 7.3 | % | 1,121 | 472 | 1,593 | 2.8 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||
Distributions in excess of net investment income(3) | — | — | — | — | 632 | — | 632 | 1.1 | % | |||||||||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 48,270 | $ | 29,189 | $ | 77,459 | 100.0 | % | $ | 26,515 | $ | 30,753 | $ | 57,268 | 100.0 | % | ||||||||||||||
(1) | For the year ended December 31, 2016, we distributed long-term capital gains of $906. We distributed no long-term capital gains for the year ended December 31, 2015. |
(2) | During the year ended December 31, 2016, we realized losses of $1,030 in our total return swap portfolio, which are not currently deductible on a tax-basis. |
(3) | Distributions in excess of net investment income represent certain expenses, which are not deductible on a tax-basis. Unearned capital gains incentive fees and certain offering expenses reduce GAAP basis net investment income, but do not reduce tax basis net investment income. These tax-related adjustments represent additional net investment income available for distribution for tax purposes. See Note 14 for the sources of our cash distributions on a tax basis. |
For an additional discussion of our RIC status and distributions, refer to Note 2 and Note 5, respectively, to our consolidated financial statements included in this report.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
See Note 2 to our consolidated financial statements included in this report for a discussion of certain recent accounting pronouncements that are applicable to us.
Critical Accounting Policies
Our consolidated financial statements are prepared in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles, or GAAP, which requires us to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities at the date of the consolidated financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting periods. Critical accounting policies are those that require the application of management’s most difficult, subjective or complex judgments, often because of the need to make estimates about the effect of matters that are inherently uncertain and that may change in subsequent periods. In preparing the consolidated financial statements, we also utilize available information, including our past history, industry standards and the current economic environment, among other factors, in forming our estimates and judgments, giving due consideration to materiality. Actual results may differ from these estimates. In addition, other companies may utilize different estimates, which may impact the comparability of our results of operations to those of companies in similar businesses.
Valuation of Portfolio Investments
The value of our assets is determined quarterly and at such other times that an event occurs that materially affects the valuation. The valuation is made pursuant to Section 2(a)(41) of the 1940 Act, which requires that we value our assets as follows: (i) the market price for those securities for which a market quotation is readily available, and (ii) for all other securities and assets, at fair value, as determined in good faith by our board of directors. As a BDC, Section 2(a)(41) of the 1940 Act requires the board of directors to determine in good faith the fair value of portfolio securities for which a market price is not readily available, and it does so in conjunction with the application of our valuation procedures by CIM.
There is no single standard for determining fair value in good faith. As a result, determining fair value requires that judgment be applied to the specific facts and circumstances of each asset while employing a valuation process that is consistently followed. Determinations of fair value involve subjective judgments and estimates. Accordingly, the notes to our consolidated financial statements refer to the uncertainty with respect to the possible effect of such valuations, and any change in such valuations in our consolidated financial statements.
63
Valuation Methods
With respect to investments for which market quotations are not readily available, we undertake a multi-step valuation process each quarter, as described below:
• | our quarterly valuation process begins with each portfolio company or investment being initially valued by certain of CIM’s investment professionals and certain members of its management team, with such valuation taking into account information received from various sources, including independent valuation firms and AIM, if applicable; |
• | preliminary valuation conclusions are then documented and discussed with CIM’s valuation committee; |
• | CIM’s valuation committee reviews the preliminary valuation, and, if applicable, delivers such preliminary valuation to an independent valuation firm for its review; |
• | CIM’s valuation committee, or its designee, and, if appropriate, the relevant investment professionals meet with the independent valuation firm to discuss the preliminary valuation; |
• | designated members of CIM’s management team respond and supplement the preliminary valuation to reflect any comments provided by the independent valuation firm; |
• | our audit committee meets with members of CIM’s management team and the independent valuation firm to discuss the assistance provided and the results of the independent valuation firm’s review; and |
• | our board of directors discusses the valuation and determines the fair value of each investment in our portfolio in good faith based on various statistical and other factors, including the input and recommendation of CIM, the audit committee and any third-party valuation firm, if applicable. |
In addition to the foregoing, certain investments for which a market price is not readily available are evaluated on a quarterly basis by an independent valuation firm and certain other investments are on a rotational basis reviewed once over a twelve-month period by an independent valuation firm. Finally, certain investments are not evaluated by an independent valuation firm unless the net asset value and other aspects of such investments in the aggregate exceed certain thresholds.
Given the expected types of investments, excluding short term investments that are classified as Level 1, management expects our portfolio holdings to be classified as Level 3. Due to the uncertainty inherent in the valuation process, particularly for Level 3 investments, such fair value estimates may differ significantly from the values that would have been used had an active market for the investments existed. In addition, changes in the market environment and other events that may occur over the life of the investments may cause the gains or losses that we ultimately realize on these investments to materially differ from the valuations currently assigned. Inputs used in the valuation process are subject to variability in the future and can result in materially different fair values.
For an additional discussion of our investment valuation process, refer to Note 2 to our consolidated financial statements included in this report.
Related Party Transactions
For a discussion of our relationship with related parties including CION Securities, CIM, ICON Capital, and CIG and amounts incurred under agreements with such related parties, refer to Note 4 to our consolidated financial statements included in this report.
Contractual Obligations
On December 17, 2012, Flatiron entered into a TRS with Citibank. Flatiron and Citibank have amended the TRS on numerous occasions including the most recent thirteenth amendment on February 18, 2017. See Note 7 to our consolidated financial statements for a more detailed description of the TRS.
On August 26, 2016, 34th Street entered into the JPM Credit Facility with JPM, as amended and restated on September 30, 2016. See Note 8 to our consolidated financial statements for a more detailed description of the JPM Credit Facility.
On April 30, 2015, we entered into the EWB Credit Facility with EWB, as amended on January 28, 2016 and April 21, 2016. See “Financial Condition, Liquidity and Capital Resources - East West Bank Credit Facility” above for a more detailed description of the EWB Credit Facility.
Commitments and Contingencies and Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
Commitments and Contingencies
We have entered into certain contracts with other parties that contain a variety of indemnifications. Our maximum exposure under these arrangements is unknown. However, we have not experienced claims or losses pursuant to these contracts and believe the risk of loss related to such indemnifications to be remote.
64
Our investment portfolio may contain debt investments that are in the form of lines of credit, revolving credit facilities, or other unfunded commitments, which may require us to provide funding when requested in accordance with the terms of the underlying agreement. For further details on such debt investments, refer to Note 11 to our consolidated financial statements included in this report.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
We currently have no off-balance sheet arrangements except for those discussed in “Financial Condition, Liquidity and Capital Resources - Total Return Swap” and “Commitments and Contingencies and Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements - Commitments and Contingencies” above.
65
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
We are subject to financial market risks, including changes in interest rates. As of December 31, 2016, 93.8% of our portfolio investments and underlying loans subject to the TRS paid variable interest rates. A rise in the general level of interest rates can be expected to lead to higher interest rates applicable to our debt investments, especially to the extent that we hold variable rate investments, and to declines in the value of any fixed rate investments we may hold. To the extent that a majority of our investments may be in variable rate investments, an increase in interest rates could make it easier for us to meet or exceed our incentive fee hurdle rate, as defined in our investment advisory agreement, and may result in a substantial increase in our net investment income, and also to the amount of incentive fees payable to CIM with respect to our pre-incentive fee net investment income.
Under the terms of the TRS with Citibank, we pay fees to Citibank at a floating rate based primarily on LIBOR (and in limited cases the prime rate), plus a spread of 1.40% per year, in exchange for the right to receive the economic benefit of a pool of loans. Pursuant to the terms of the EWB Credit Facility, borrowings are at a floating rate of 0.75% plus the greater of 3.25% or the variable rate of interest per year announced by EWB as its prime rate, which was 3.75% at December 31, 2016. Under the terms of the JPM Credit Facility, advances bear interest at a floating rate equal to the three-month LIBOR, plus a spread of 3.50% per year. In addition, in the future we may seek to borrow funds in order to make additional investments. Our net investment income will depend, in part, upon the difference between the rate at which we borrow funds and the rate at which we invest those funds. As a result, we would be subject to risks relating to changes in market interest rates. In periods of rising interest rates when we have debt outstanding, our cost of funds would increase, which could reduce our net investment income, especially to the extent we hold fixed rate investments. We expect that our long-term investments will be financed primarily with equity and long-term debt. Our interest rate risk management techniques may include various interest rate hedging activities to the extent permitted by the 1940 Act. Adverse developments resulting from changes in interest rates could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
The following table shows the effect over a twelve month period of changes in interest rates on our net interest income, excluding short term investments, assuming no changes in our investment portfolio, the TRS Agreement, the EWB Credit Facility or the JPM Credit Facility in effect as of December 31, 2016:
Change in Interest Rates | Increase in Net Interest Income(1) | Percentage Change in Net Interest Income | ||||||
Down 50 basis points(2) | $ | 2,845 | 2.8 | % | ||||
Current base interest rate | — | — | ||||||
Up 50 basis points | 2,593 | 2.6 | % | |||||
Up 100 basis points | 6,265 | 6.2 | % | |||||
Up 200 basis points | 13,679 | 13.5 | % | |||||
Up 300 basis points | 21,097 | 20.9 | % | |||||
(1) | Pursuant to the TRS, we receive from Citibank all interest payable in respect of the loans subject to the TRS and pay to Citibank interest at a rate equal to the floating rate index specified for each loan (typically LIBOR of varying maturities), which will not be less than zero, plus 1.40% per year on the full notional amount of the loans subject to the TRS. As of December 31, 2016, all of the loans subject to the TRS paid variable interest rates. This table assumes no change in defaults or prepayments by portfolio companies over the next twelve months. |
(2) | With respect to the TRS, while we pay interest to Citibank based on the floating rate index specified for each loan, which will not be less than zero, we receive interest from Citibank based on the floating rate index specified for each loan, which is typically not less than 1%. |
The interest rate sensitivity analysis presented above does not consider the potential impact of the changes in fair value of our fixed rate debt investments and the net asset value of our common stock in the event of sudden increases in interest rates. Approximately 3.4% of our portfolio investments and none of our underlying loans subject to the TRS paid fixed interest rates as of December 31, 2016. Rising market interest rates will most likely lead to fair value declines for fixed interest rate investments and a decline in the net asset value of our common stock, while declining market interest rates will most likely lead to an increase in the fair value of fixed interest rate investments and an increase in the net asset value of our common stock.
In addition, we may have risk regarding portfolio valuation. See “Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Critical Accounting Policies—Valuation of Portfolio Investments” and Note 2 to our consolidated financial statements included in this report.
66
Item 8. Consolidated Financial Statements and Supplementary Data
Page | |
67
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
The Board of Directors and Shareholders
CĪON Investment Corporation
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of CÎON Investment Corporation (the Company), including the consolidated schedules of investments, as of December 31, 2016 and 2015, and the related consolidated statements of operations, changes in net assets, and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2016. These consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these consolidated financial statements based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the consolidated financial statements are free of material misstatement. We were not engaged to perform an audit of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Our audits included consideration of internal control over financial reporting as a basis for designing audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion. An audit also includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the consolidated financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, and evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. Our procedures included confirmation of investments owned as of December 31, 2016 and 2015, by correspondence with the custodian and others, or by other appropriate auditing procedures where replies from others were not received. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the consolidated financial position of CÎON Investment Corporation at December 31, 2016 and 2015, and the consolidated results of its operations, changes in its net assets, and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2016, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
/s/ Ernst & Young LLP
New York, New York
March 15, 2017
68
CĪON Investment Corporation
Consolidated Balance Sheets
(in thousands, except share and per share amounts)
December 31, 2016 | December 31, 2015 | |||||||
Assets | ||||||||
Investments, at fair value (amortized cost of $1,096,948 and $699,036, respectively) | $ | 1,089,478 | $ | 669,799 | ||||
Derivative assets (cost of $229) | 46 | — | ||||||
Cash | 15,046 | 39,741 | ||||||
Restricted cash | 2,000 | 2,000 | ||||||
Due from counterparty(1) | 143,335 | 226,316 | ||||||
Receivable for common stock purchased | — | 5,459 | ||||||
Interest receivable on investments | 6,689 | 5,973 | ||||||
Receivable due on investments sold | — | 50 | ||||||
Receivable due on total return swap(1) | 4,187 | 6,175 | ||||||
Prepaid expenses and other assets | 282 | 243 | ||||||
Total assets | $ | 1,261,063 | $ | 955,756 | ||||
Liabilities and Shareholders' Equity | ||||||||
Liabilities | ||||||||
Payable for investments purchased | $ | 15,837 | $ | 9,800 | ||||
Credit facility payable (net of unamortized debt issuance costs of $3,212) | 221,211 | — | ||||||
Accounts payable and accrued expenses | 1,476 | 692 | ||||||
Interest payable | 864 | — | ||||||
Commissions payable for common stock purchased ($0 and $171 to CION Securities, LLC, respectively) | 2 | 474 | ||||||
Accrued management fees | 5,781 | 4,430 | ||||||
Accrued administrative services expense | 682 | 617 | ||||||
Accrued recoupment of expense support from CIG(2) | — | 480 | ||||||
Due to CIG - offering, organizational and other costs(3) | 45 | 37 | ||||||
Unrealized depreciation on total return swap(1) | 15,402 | 34,900 | ||||||
Total liabilities | 261,300 | 51,430 | ||||||
Commitments and contingencies (Note 4 and Note 11) | ||||||||
Shareholders' Equity | ||||||||
Common stock, $0.001 par value; 500,000,000 shares authorized; | ||||||||
109,787,557 and 103,814,361 shares issued and outstanding, respectively | 110 | 104 | ||||||
Capital in excess of par value | 1,021,280 | 968,359 | ||||||
Undistributed net investment income | 1,428 | — | ||||||
Accumulated net unrealized depreciation on investments | (7,653 | ) | (29,237 | ) | ||||
Accumulated net unrealized depreciation on total return swap(1) | (15,402 | ) | (34,900 | ) | ||||
Total shareholders' equity | 999,763 | 904,326 | ||||||
Total liabilities and shareholders' equity | $ | 1,261,063 | $ | 955,756 | ||||
Net asset value per share of common stock at end of period | $ | 9.11 | $ | 8.71 | ||||
(1) | See Note 7 for a discussion of the Company’s total return swap agreement. |
(2) | See Note 4 for a discussion of expense support from CION Investment Group, LLC (formerly, ICON Investment Group, LLC), or CIG, and recoupment of expense support. |
(3) | See Note 2 for a discussion of offering, organizational and other costs submitted to the Company for reimbursement by CIG and its affiliates. |
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
69
CĪON Investment Corporation
Consolidated Statements of Operations
(in thousands, except share and per share amounts)
Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
Investment income | ||||||||||||
Interest income | $ | 79,892 | $ | 51,994 | $ | 17,314 | ||||||
Fee and other income | 698 | 815 | 399 | |||||||||
Total investment income | 80,590 | 52,809 | 17,713 | |||||||||
Operating expenses | ||||||||||||
Management fees | 20,092 | 14,827 | 6,132 | |||||||||
Administrative services expense | 1,834 | 1,900 | 1,792 | |||||||||
Capital gains incentive fee(1) | — | — | (757 | ) | ||||||||
Offering, organizational and other costs - CIG(2) | — | — | 1,012 | |||||||||
General and administrative(3) | 6,717 | 6,248 | 4,272 | |||||||||
Interest expense | 3,569 | 405 | — | |||||||||
Total operating expenses | 32,212 | 23,380 | 12,451 | |||||||||
Expense support from CIG(4) | — | — | (1,880 | ) | ||||||||
Recoupment of expense support from CIG(4) | 667 | 4,667 | 622 | |||||||||
Net operating expenses | 32,879 | 28,047 | 11,193 | |||||||||
Net investment income | 47,711 | 24,762 | 6,520 | |||||||||
Realized and unrealized gains (losses) | ||||||||||||
Net realized gain on investments | 2,725 | 1,121 | 1,538 | |||||||||
Net realized loss on foreign currency | (4 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
Net change in unrealized appreciation (depreciation) on investments | 21,584 | (27,587 | ) | (2,754 | ) | |||||||
Net realized gain on total return swap(5) | 28,159 | 30,753 | 16,989 | |||||||||
Net change in unrealized appreciation (depreciation) on total return swap(5) | 19,498 | (30,491 | ) | (5,958 | ) | |||||||
Total net realized and unrealized gains (losses) | 71,962 | (26,204 | ) | 9,815 | ||||||||
Net increase (decrease) in net assets resulting from operations | $ | 119,673 | $ | (1,442 | ) | $ | 16,335 | |||||
Per share information—basic and diluted | ||||||||||||
Net increase (decrease) in net assets per share resulting from operations | $ | 1.13 | $ | (0.02 | ) | $ | 0.49 | |||||
Weighted average shares of common stock outstanding | 105,951,017 | 78,501,760 | 33,630,690 | |||||||||
(1) | See Note 2 and Note 4 for a discussion of the methodology employed by the Company in calculating the capital gains incentive fee. |
(2) | See Note 2 for a discussion of offering, organizational and other costs submitted to the Company for reimbursement by CIG and its affiliates. |
(3) | See Note 10 for details of the Company’s general and administrative expenses. |
(4) | See Note 4 for a discussion of expense support from CIG and recoupment of expense support. |
(5) | See Note 7 for a discussion of the Company’s total return swap agreement. |
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
70
CĪON Investment Corporation
Consolidated Statements of Changes in Net Assets
(in thousands, except share and per share amounts)
Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
Changes in net assets from operations: | ||||||||||||
Net investment income | $ | 47,711 | $ | 24,762 | $ | 6,520 | ||||||
Net realized gain on investments | 2,725 | 1,121 | 1,538 | |||||||||
Net realized loss on foreign currency | (4 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
Net change in unrealized appreciation (depreciation) on investments | 21,584 | (27,587 | ) | (2,754 | ) | |||||||
Net realized gain on total return swap(1) | 28,159 | 30,753 | 16,989 | |||||||||
Net change in unrealized appreciation (depreciation) on total return swap(1) | 19,498 | (30,491 | ) | (5,958 | ) | |||||||
Net increase (decrease) in net assets resulting from operations | 119,673 | (1,442 | ) | 16,335 | ||||||||
Changes in net assets from shareholders' distributions:(2) | ||||||||||||
Net investment income | (45,549 | ) | (24,762 | ) | (6,020 | ) | ||||||
Net realized gain on total return swap | ||||||||||||
Net interest and other income from TRS portfolio | (26,273 | ) | (30,281 | ) | (14,650 | ) | ||||||
Net gain on TRS loan sales | (2,916 | ) | (472 | ) | (2,339 | ) | ||||||
Net realized gain on investments and foreign currency | (2,721 | ) | (1,121 | ) | (1,538 | ) | ||||||
Distributions in excess of net investment income(3) | — | (632 | ) | — | ||||||||
Net decrease in net assets from shareholders' distributions | (77,459 | ) | (57,268 | ) | (24,547 | ) | ||||||
Changes in net assets from capital share transactions: | ||||||||||||
Issuance of common stock, net of issuance costs of $2,823, $43,746 and $33,965, respectively | 32,008 | 443,858 | 346,518 | |||||||||
Reinvestment of shareholders' distributions | 39,047 | 29,886 | 13,997 | |||||||||
Repurchase of common stock | (17,832 | ) | (7,097 | ) | (485 | ) | ||||||
Net increase in net assets resulting from capital share transactions | 53,223 | 466,647 | 360,030 | |||||||||
Total increase in net assets | 95,437 | 407,937 | 351,818 | |||||||||
Net assets at beginning of period | 904,326 | 496,389 | 144,571 | |||||||||
Net assets at end of period | $ | 999,763 | $ | 904,326 | $ | 496,389 | ||||||
Net asset value per share of common stock at end of period | $ | 9.11 | $ | 8.71 | $ | 9.22 | ||||||
Shares of common stock outstanding at end of period | 109,787,557 | 103,814,361 | 53,818,629 | |||||||||
Undistributed net investment income at end of period | $ | 1,428 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||
(1) | See Note 7 for a discussion of the Company’s total return swap agreement. |
(2) | This table presents changes in net assets from shareholders' distributions on a GAAP basis. See Note 5 for a discussion of the sources of distributions paid by the Company and Note 14 for the sources of distributions paid by the Company on a tax basis. |
(3) | Distributions in excess of net investment income represent certain expenses, which are not deductible on a tax-basis. Unearned capital gains incentive fees and certain offering expenses reduce GAAP basis net investment income, but do not reduce tax basis net investment income. These tax-related adjustments represent additional net investment income available for distribution for tax purposes. |
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
71
CĪON Investment Corporation
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
(in thousands)
Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
Operating activities: | |||||||||||
Net increase (decrease) in net assets resulting from operations | $ | 119,673 | $ | (1,442 | ) | $ | 16,335 | ||||
Adjustments to reconcile net increase (decrease) in net assets resulting from | |||||||||||
operations to net cash used in operating activities: | |||||||||||
Net accretion of discount on investments | (2,763 | ) | (1,025 | ) | (395 | ) | |||||
Proceeds from principal repayment of investments | 194,124 | 41,828 | 50,310 | ||||||||
Purchase of investments | (569,003 | ) | (438,217 | ) | (403,742 | ) | |||||
(Increase) decrease in short term investments, net | (51,606 | ) | (8,542 | ) | 1,034 | ||||||
Paid-in-kind interest | (1,255 | ) | — | — | |||||||
Proceeds from sale of investments | 34,951 | 71,605 | 94,182 | ||||||||
Net realized gain on investments | (2,725 | ) | (1,121 | ) | (1,538 | ) | |||||
Net unrealized (appreciation) depreciation on investments | (21,584 | ) | 27,587 | 2,754 | |||||||
Net unrealized (appreciation) depreciation on total return swap(1) | (19,498 | ) | 30,491 | 5,958 | |||||||
Amortization of debt issuance costs | 529 | 186 | — | ||||||||
(Increase) decrease in due from counterparty(1) | 82,981 | (97,928 | ) | (87,684 | ) | ||||||
(Increase) decrease in expense support from CIG, net(2) | — | — | 545 | ||||||||
(Increase) decrease in interest receivable on investments | (580 | ) | (3,789 | ) | (1,769 | ) | |||||
(Increase) decrease in receivable due on investments sold | 50 | (50 | ) | 535 | |||||||
(Increase) decrease in receivable due on total return swap(1) | 1,988 | (1,618 | ) | (2,755 | ) | ||||||
(Increase) decrease in prepaid expenses and other assets | 134 | (26 | ) | (26 | ) | ||||||
Increase (decrease) in payable for investments purchased | 6,037 | 5,694 | 644 | ||||||||
Increase (decrease) in accounts payable and accrued expenses | 777 | 177 | (94 | ) | |||||||
Increase (decrease) in interest payable | 864 | — | — | ||||||||
Increase (decrease) in accrued management fees | 1,351 | 3,399 | 1,031 | ||||||||
Increase (decrease) in accrued administrative services expense | 65 | 47 | 570 | ||||||||
Increase (decrease) in due to CIG - offering, organizational and other costs(3) | 8 | (447 | ) | (66 | ) | ||||||
Increase (decrease) in accrued recoupment of expense support from CIG(2) | (480 | ) | 480 | — | |||||||
Increase (decrease) in accrued capital gains incentive fee | — | — | (530 | ) | |||||||
Net cash used in operating activities | (225,962 | ) | (372,711 | ) | (324,701 | ) | |||||
Financing activities: | |||||||||||
Gross proceeds from issuance of common stock | 40,290 | 483,604 | 379,024 | ||||||||
Commissions and dealer manager fees paid | (3,295 | ) | (43,869 | ) | (33,368 | ) | |||||
Repurchase of common stock | (17,832 | ) | (7,097 | ) | (485 | ) | |||||
Shareholders' distributions paid(4) | (38,412 | ) | (27,382 | ) | (11,446 | ) | |||||
Borrowings under credit facilities(5) | 242,423 | 32,000 | — | ||||||||
Repayment of credit facilities(5) | (18,000 | ) | (32,000 | ) | — | ||||||
Debt issuance costs paid | (3,907 | ) | (278 | ) | — | ||||||
Net cash provided by financing activities | 201,267 | 404,978 | 333,725 | ||||||||
Net (decrease) increase in cash and restricted cash | (24,695 | ) | 32,267 | 9,024 | |||||||
Cash and restricted cash, beginning of period | 41,741 | 9,474 | 450 | ||||||||
Cash and restricted cash, end of period | $ | 17,046 | $ | 41,741 | $ | 9,474 | |||||
Supplemental disclosure of cash flow information | |||||||||||
Cash paid for interest | $ | 2,175 | $ | 219 | $ | — | |||||
Supplemental non-cash financing activities: | |||||||||||
Reinvestment of shareholders' distributions(4) | $ | 39,047 | $ | 29,886 | $ | 13,997 | |||||
(1) | See Note 7 for a discussion of the Company’s total return swap agreement. |
(2) | See Note 4 for a discussion of expense support from CIG and recoupment of expense support. |
(3) | See Note 2 for a discussion of offering, organizational and other costs submitted to the Company for reimbursement by CIG and its affiliates. |
(4) | See Note 5 for a discussion of the sources of distributions paid by the Company. |
(5) | See Note 8 for a discussion of the Company's credit facilities. |
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
72
CĪON Investment Corporation
Consolidated Schedule of Investments
December 31, 2016
(in thousands)
Portfolio Company(a) | Index Rate(b) | Industry | Principal/ Par Amount/ Units(d) | Cost(p) | Fair Value(c) | |||||||||||
Senior Secured First Lien Debt - 49.0% | ||||||||||||||||
AbelConn, LLC / Atrenne Computing Solutions, LLC / Airco Industries, LLC, L+850, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 7/17/2019(j) | 3 Month LIBOR | Aerospace & Defense | $ | 22,112 | $ | 21,702 | $ | 21,780 | ||||||||
Adams Publishing Group, LLC, L+700, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 11/3/2020(n) | 3 Month LIBOR | Media: Advertising, Printing & Publishing | 3,892 | 3,818 | 3,833 | |||||||||||
American Clinical Solutions LLC, L+950, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 6/11/2020 | 3 Month LIBOR | Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals | 9,034 | 8,908 | 8,492 | |||||||||||
American Media, Inc., L+750, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 8/24/2020(n) | 3 Month LIBOR | Media: Advertising, Printing & Publishing | 11,467 | 11,150 | 11,123 | |||||||||||
American Media, Inc., 0.50% Unfunded, 8/24/2020(e) | None | Media: Advertising, Printing & Publishing | 505 | (15 | ) | (15 | ) | |||||||||
American Media, Inc., 7.50%, 8/24/2020(e) | None | Media: Advertising, Printing & Publishing | 206 | (6 | ) | (6 | ) | |||||||||
American Teleconferencing Services, Ltd., L+650, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 12/8/2021(n) | 3 Month LIBOR | Telecommunications | 19,248 | 17,475 | 18,863 | |||||||||||
AMPORTS, Inc., L+500, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 5/19/2020(j) | 3 Month LIBOR | Automotive | 19,100 | 18,743 | 18,718 | |||||||||||
Blue Ribbon, LLC, L+400, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 11/15/2021(i) | 3 Month LIBOR | Beverage, Food & Tobacco | 9,975 | 9,975 | 9,972 | |||||||||||
CF Entertainment Inc., L+1100, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 6/26/2020(n) | 3 Month LIBOR | Media: Diversified & Production | 17,094 | 17,057 | 17,094 | |||||||||||
Dodge Data & Analytics, LLC / Skyline Data News and Analytics, LLC, L+875, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 10/31/2019(n) | 3 Month LIBOR | Construction & Building | 10,387 | 10,241 | 10,218 | |||||||||||
ECI Acquisition Holdings, Inc., L+625, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 3/11/2019(n) | 3 Month LIBOR | High Tech Industries | 8,517 | 8,493 | 8,517 | |||||||||||
Elemica, Inc., L+800, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 7/7/2021(n) | 1 Month LIBOR | High Tech Industries | 17,413 | 17,005 | 16,977 | |||||||||||
Elemica, Inc., 0.50% Unfunded, 7/7/2021(e) | None | High Tech Industries | 2,500 | (57 | ) | (62 | ) | |||||||||
EnTrans International, LLC, L+750, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 6/4/2020 | 3 Month LIBOR | Capital Equipment | 13,594 | 9,977 | 10,331 | |||||||||||
F+W Media, Inc., L+950, 1.25% LIBOR Floor, 6/30/2019(n) | 3 Month LIBOR | Media: Diversified & Production | 7,280 | 7,092 | 6,006 | |||||||||||
Forbes Media LLC, L+675, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 9/12/2019(j) | 1 Month LIBOR | Media: Advertising, Printing & Publishing | 15,000 | 14,621 | 14,400 | |||||||||||
Ignite Restaurant Group, Inc., L+700, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 2/13/2019(n) | 3 Month LIBOR | Beverage, Food & Tobacco | 10,482 | 10,400 | 10,167 | |||||||||||
Infinity Sales Group, LLC, L+1050, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 11/21/2018(n) | 1 Month LIBOR | Services: Business | 8,214 | 7,550 | 7,372 | |||||||||||
Infogroup Inc., L+550, 1.50% LIBOR Floor, 5/26/2018(n) | 3 Month LIBOR | Media: Advertising, Printing & Publishing | 15,578 | 15,277 | 15,451 | |||||||||||
InterGen N.V., L+450, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 6/12/2020(h)(i) | 3 Month LIBOR | Energy: Electricity | 1,182 | 1,156 | 1,153 | |||||||||||
Intertain Group Ltd., L+650, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 4/8/2022(h)(n) | 3 Month LIBOR | Hotel, Gaming & Leisure | 1,765 | 1,736 | 1,780 | |||||||||||
Ipsen International GmbH, L+800, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 9/30/2019(h)(j) | 1 Month LIBOR | Capital Equipment | 1,422 | 1,429 | 1,429 | |||||||||||
Ipsen, Inc., L+700, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 9/30/2019(j) | 1 Month LIBOR | Capital Equipment | 8,095 | 8,002 | 8,035 | |||||||||||
ITC Service Group Acquisition LLC, L+950, 0.50% LIBOR Floor, 5/26/2021(j) | 1 Month LIBOR | High Tech Industries | 11,250 | 11,035 | 11,081 | |||||||||||
KPC Health Care, Inc., L+925, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 8/28/2020(n) | 3 Month LIBOR | Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals | 7,544 | 7,401 | 7,809 | |||||||||||
Labvantage Solutions Inc., L+800, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 12/29/2020(n) | 3 Month LIBOR | High Tech Industries | 4,875 | 4,829 | 4,863 | |||||||||||
Labvantage Solutions Ltd., E+800, 1.00% EURIBOR Floor, 12/29/2020(h) | 3 Month EURIBOR | High Tech Industries | € | 4,495 | 5,005 | 4,728 | ||||||||||
Lift Brands, Inc., L+800, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 12/23/2019(n) | 3 Month LIBOR | Services: Consumer | 9,548 | 9,438 | 9,477 | |||||||||||
Ministry Brands, LLC, L+500, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 12/2/2022(e) | 3 Month LIBOR | Services: Business | 9,994 | 9,587 | 9,894 | |||||||||||
Nathan's Famous Inc., 10.00%, 3/15/2020(h)(n) | None | Beverage, Food & Tobacco | 6,000 | 6,000 | 6,540 | |||||||||||
Nextech Systems, LLC, L+725, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 6/22/2021(j)(n) | 1 Month LIBOR | High Tech Industries | 15,642 | 15,062 | 15,330 | |||||||||||
NWN Acquisition Holding Company LLC, L+1000, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 10/16/2020(j) | 3 Month LIBOR | High Tech Industries | 13,717 | 13,357 | 13,271 | |||||||||||
Pacific Coast Holding Investment LLC, L+970, 2.00% LIBOR Floor, 2/14/2017 | 1 Month LIBOR | Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals | 5,250 | 5,242 | 5,250 | |||||||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
73
CĪON Investment Corporation
Consolidated Schedule of Investments
December 31, 2016
(in thousands)
Portfolio Company(a) | Index Rate(b) | Industry | Principal/ Par Amount/ Units(d) | Cost(p) | Fair Value(c) | ||||||||
Petroflow Energy Corporation, L+800, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 6/29/2019(q) | 3 Month LIBOR | Energy: Oil & Gas | 4,895 | 4,618 | 4,601 | ||||||||
Plano Molding Company, LLC, L+700, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 5/12/2021(n) | 2 Month LIBOR | Consumer Goods: Non-Durable | 8,840 | 8,772 | 8,611 | ||||||||
Rimini Street, Inc., 15.00%, 6/24/2020(m)(q) | None | High Tech Industries | 19,822 | 19,556 | 19,426 | ||||||||
Sequoia Healthcare Management, LLC, 16.00%, 7/17/2019(n)(q) | None | Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals | 6,511 | 6,405 | 6,397 | ||||||||
Shift PPC LLC, L+600, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 12/22/2021 | 3 Month LIBOR | High Tech Industries | 9,500 | 9,266 | 9,265 | ||||||||
SmartBear Software Inc., L+750, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 12/30/2020(n) | 3 Month LIBOR | High Tech Industries | 18,588 | 18,271 | 18,727 | ||||||||
Southcross Holdings Borrower LP, 9.00%, 4/13/2023(q) | None | Energy: Oil & Gas | 172 | 151 | 135 | ||||||||
Spinal USA, Inc. / Precision Medical Inc., L+950, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 1/21/2020(n) | 3 Month LIBOR | Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals | 12,281 | 12,194 | 12,158 | ||||||||
Spinal USA, Inc. / Precision Medical Inc., L+950, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 7/21/2020(q) | 3 Month LIBOR | Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals | 128 | 126 | 127 | ||||||||
Sprint Industrial Holdings, LLC, L+575, 1.25% LIBOR Floor, 5/14/2019(n) | 3 Month LIBOR | Energy: Oil & Gas | 7,306 | 6,849 | 5,406 | ||||||||
Studio Movie Grill Holdings, LLC, L+725, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 9/30/2020(e)(n) | 1 Month LIBOR | Hotel, Gaming & Leisure | 15,143 | 15,004 | 15,143 | ||||||||
Telestream Holdings Corp., L+677, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 1/15/2020(j)(n) | 3 Month LIBOR | High Tech Industries | 7,154 | 7,027 | 7,011 | ||||||||
Tenere Inc., L+1000, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 12/23/2021 | 3 Month LIBOR | Capital Equipment | 32,000 | 31,219 | 31,199 | ||||||||
Therapure Biopharma Inc., L+875, 0.50% LIBOR Floor, 12/1/2021(h) | 1 Month LIBOR | Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals | 15,000 | 14,925 | 14,925 | ||||||||
WD Wolverine Holdings, LLC, L+550, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 10/17/2023(i) | 1 Month LIBOR | Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals | 2,000 | 1,960 | 1,946 | ||||||||
Worley Claims Services, LLC, L+800, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 10/31/2020(n) | 1 Month LIBOR | Services: Business | 20,115 | 19,925 | 20,015 | ||||||||
Zywave Inc., L+500, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 11/17/2022 | 3 Month LIBOR | High Tech Industries | 5,000 | 4,951 | 4,950 | ||||||||
Total Senior Secured First Lien Debt | 489,904 | 489,913 | |||||||||||
Senior Secured Second Lien Debt - 43.4% | |||||||||||||
ABG Intermediate Holdings 2 LLC, L+850, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 5/27/2022(e)(m)(n) | 3 Month LIBOR | Retail | 18,666 | 18,365 | 18,852 | ||||||||
Access CIG, LLC, L+875, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 10/17/2022(m) | 3 Month LIBOR | Services: Business | 16,030 | 15,460 | 15,549 | ||||||||
ALM Media, LLC, L+800, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 7/30/2021(n) | 3 Month LIBOR | Media: Advertising, Printing & Publishing | 10,344 | 10,205 | 9,568 | ||||||||
American Residential Services LLC, L+800, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 12/31/2021(n) | 3 Month LIBOR | Construction & Building | 4,933 | 4,889 | 4,983 | ||||||||
AmWINS Group, LLC, L+850, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 9/4/2020(n) | 1 Month LIBOR | Banking, Finance, Insurance & Real Estate | 3,825 | 3,852 | 3,878 | ||||||||
Confie Seguros Holding II Co., L+900, 1.25% LIBOR Floor, 5/8/2019 | 1 Month LIBOR | Banking, Finance, Insurance & Real Estate | 13,827 | 13,365 | 13,758 | ||||||||
Conisus, LLC, L+875, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 6/23/2021 | 3 Month LIBOR | Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals | 11,750 | 9,604 | 9,517 | ||||||||
Drew Marine Group, Inc., L+700, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 5/19/2021(h) | 3 Month LIBOR | Chemicals, Plastics & Rubber | 9,500 | 9,460 | 9,120 | ||||||||
EISI LLC, L+850, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 9/23/2020(m)(n) | 3 Month LIBOR | High Tech Industries | 20,000 | 19,761 | 19,400 | ||||||||
Elements Behavioral Health, Inc., L+1200, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 2/11/2020(q) | 3 Month LIBOR | Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals | 5,701 | 5,668 | 4,561 | ||||||||
Emerald 3 Ltd., L+700, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 5/16/2022(h)(n) | 3 Month LIBOR | Environmental Industries | 3,000 | 2,978 | 2,595 | ||||||||
Flexera Software LLC, L+700, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 4/2/2021 | 1 Month LIBOR | High Tech Industries | 9,385 | 9,128 | 9,291 | ||||||||
Genex Holdings, Inc., L+775, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 5/30/2022(n) | 1 Month LIBOR | Services: Business | 11,410 | 11,331 | 11,011 | ||||||||
Global Tel*Link Corp., L+775, 1.25% LIBOR Floor, 11/23/2020 | 3 Month LIBOR | Telecommunications | 9,500 | 9,488 | 9,254 | ||||||||
Infiltrator Water Technologies, LLC, L+875, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 5/26/2023(n) | 3 Month LIBOR | Construction & Building | 13,917 | 13,732 | 13,986 | ||||||||
Institutional Shareholder Services Inc., L+850, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 4/30/2022(i)(n) | 2 Month LIBOR | Services: Business | 10,648 | 10,534 | 10,542 | ||||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
74
CĪON Investment Corporation
Consolidated Schedule of Investments
December 31, 2016
(in thousands)
Portfolio Company(a) | Index Rate(b) | Industry | Principal/ Par Amount/ Units(d) | Cost(p) | Fair Value(c) | ||||||||
Mergermarket USA, Inc., L+650, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 2/4/2022(n) | 3 Month LIBOR | Services: Business | 3,380 | 3,328 | 3,304 | ||||||||
Ministry Brands, LLC, L+925, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 6/2/2023(e) | 3 Month LIBOR | Services: Business | 5,488 | 5,385 | 5,406 | ||||||||
Mississippi Sand, LLC, L+1000, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 11/21/2019 | 3 Month LIBOR | Metals & Mining | 13,196 | 10,899 | 11,349 | ||||||||
Mitchell International, Inc., L+750, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 10/11/2021(m)(n) | 1 Month LIBOR | High Tech Industries | 14,909 | 14,476 | 14,825 | ||||||||
MSC.Software Corp., L+750, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 6/1/2021(m) | 3 Month LIBOR | High Tech Industries | 15,000 | 14,832 | 15,019 | ||||||||
MWI Holdings, Inc., L+925, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 12/28/2020(n) | 3 Month LIBOR | Construction & Building | 10,000 | 9,773 | 9,950 | ||||||||
Navex Global, Inc., L+875, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 11/18/2022(m)(n) | 12 Month LIBOR | High Tech Industries | 16,245 | 16,031 | 15,920 | ||||||||
Onex TSG Holdings II Corp., L+850, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 7/31/2023(n) | 3 Month LIBOR | Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals | 12,249 | 12,136 | 12,065 | ||||||||
Patterson Medical Supply, Inc., L+850, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 8/28/2023(n) | 2 Month LIBOR | Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals | 13,500 | 13,378 | 13,095 | ||||||||
Pelican Products, Inc., L+825, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 4/11/2021(m) | 3 Month LIBOR | Chemicals, Plastics & Rubber | 3,469 | 3,478 | 3,396 | ||||||||
PetroChoice Holdings, Inc., L+875, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 8/21/2023(n) | 1 Month LIBOR | Chemicals, Plastics & Rubber | 15,000 | 14,729 | 14,737 | ||||||||
PetVet Care Centers, LLC, L+850, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 6/17/2021 | 3 Month LIBOR | Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals | 13,500 | 13,097 | 13,095 | ||||||||
Pike Corp., L+850, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 6/22/2022(n) | 1 Month LIBOR | Energy: Electricity | 12,500 | 12,354 | 12,562 | ||||||||
Premiere Global Services, Inc., L+950, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 6/6/2022 | 3 Month LIBOR | Telecommunications | 3,000 | 2,882 | 2,895 | ||||||||
PSC Industrial Holdings Corp., L+825, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 12/5/2021(n) | 3 Month LIBOR | Services: Business | 10,000 | 9,842 | 9,450 | ||||||||
Securus Technologies Holdings, Inc., L+775, 1.25% LIBOR Floor, 4/30/2021 | 3 Month LIBOR | Telecommunications | 4,500 | 4,479 | 4,399 | ||||||||
SMG, L+825, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 2/27/2021(n) | 3 Month LIBOR | Hotel, Gaming & Leisure | 6,142 | 6,142 | 6,126 | ||||||||
Sterling Midco Holdings, Inc., L+775, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 6/19/2023(n) | 3 Month LIBOR | Services: Business | 10,462 | 10,432 | 10,226 | ||||||||
STG-Fairway Acquisitions, Inc., L+925, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 6/30/2023(n) | 3 Month LIBOR | Services: Business | 10,000 | 9,869 | 9,400 | ||||||||
Survey Sampling International, LLC, L+900, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 12/16/2021(m) | 3 Month LIBOR | Services: Business | 15,000 | 14,763 | 14,700 | ||||||||
Telecommunications Management, LLC, L+800, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 10/30/2020(n) | 3 Month LIBOR | Media: Broadcasting & Subscription | 1,606 | 1,573 | 1,564 | ||||||||
TexOak Petro Holdings LLC, 8.00%, 12/29/2019(q) | None | Energy: Oil & Gas | 6,728 | 1,549 | 2,590 | ||||||||
TMK Hawk Parent, Corp., L+750, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 10/1/2022(n) | 3 Month LIBOR | Beverage, Food & Tobacco | 15,000 | 14,880 | 14,925 | ||||||||
TouchTunes Interactive Networks, Inc, L+825, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 5/29/2022 | 3 Month LIBOR | Hotel, Gaming & Leisure | 6,000 | 5,943 | 5,925 | ||||||||
U.S. Renal Care, Inc., L+800, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 12/29/2023(n) | 3 Month LIBOR | Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals | 10,000 | 9,819 | 8,900 | ||||||||
Wand Intermediate I LP, L+725, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 9/19/2022(n) | 3 Month LIBOR | Automotive | 16,000 | 15,881 | 15,680 | ||||||||
Winebow Holdings, Inc., L+750, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 1/2/2022(n) | 1 Month LIBOR | Beverage, Food & Tobacco | 12,823 | 12,544 | 12,054 | ||||||||
Zywave Inc., L+900, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 11/17/2023 | 3 Month LIBOR | High Tech Industries | 5,000 | 4,926 | 4,925 | ||||||||
Total Senior Secured Second Lien Debt | 437,240 | 434,347 | |||||||||||
Collateralized Securities and Structured Products - Debt - 3.8% | |||||||||||||
Deutsche Bank AG Frankfurt CRAFT 2013-1A Class Credit Linked Note, L+925, 4/17/2020(h) | 3 Month LIBOR | Diversified Financials | 2,000 | 2,022 | 1,980 | ||||||||
Deutsche Bank AG Frankfurt CRAFT 2013-1X Class Credit Linked Note, L+925, 4/17/2020(h) | 3 Month LIBOR | Diversified Financials | 610 | 616 | 604 | ||||||||
Deutsche Bank AG Frankfurt CRAFT 2014-1 Class Credit Linked Note, L+965, 5/15/2019(h) | 3 Month LIBOR | Diversified Financials | 5,400 | 5,400 | 5,292 | ||||||||
Deutsche Bank AG Frankfurt CRAFT 2015-2 Class Credit Linked Note, L+925, 1/16/2022(h) | 3 Month LIBOR | Diversified Financials | 15,500 | 15,500 | 14,880 | ||||||||
Great Lakes CLO 2014-1, Ltd. Class E Notes, L+525, 4/15/2025(g)(h) | 3 Month LIBOR | Diversified Financials | 5,000 | 4,615 | 4,484 | ||||||||
Ivy Hill Middle Market Credit Fund VII, Ltd. Class E Notes, L+565, 10/20/2025(g)(h) | 3 Month LIBOR | Diversified Financials | 2,000 | 1,879 | 1,799 | ||||||||
JFIN CLO 2014, Ltd. Class E Notes, L+500, 4/20/2025(g)(h) | 3 Month LIBOR | Diversified Financials | 2,500 | 2,345 | 2,303 | ||||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
75
CĪON Investment Corporation
Consolidated Schedule of Investments
December 31, 2016
(in thousands)
Portfolio Company(a) | Index Rate(b) | Industry | Principal/ Par Amount/ Units(d) | Cost(p) | Fair Value(c) | ||||||||||
NXT Capital CLO 2014-1, LLC Class E Notes, L+550, 4/23/2026(g)(h) | 3 Month LIBOR | Diversified Financials | 7,500 | 7,094 | 6,772 | ||||||||||
Total Collateralized Securities and Structured Products - Debt | 39,471 | 38,114 | |||||||||||||
Collateralized Securities and Structured Products - Equity - 3.5% | |||||||||||||||
Anchorage Capital CLO 2012-1, Ltd. Subordinated Notes, 4.57% Estimated Yield, 1/13/2025(h) | (f) | Diversified Financials | 4,000 | 2,882 | 2,622 | ||||||||||
APIDOS CLO XVI Subordinated Notes, 3.28% Estimated Yield, 1/19/2025(h) | (f) | Diversified Financials | 9,000 | 4,704 | 3,099 | ||||||||||
CENT CLO 19 Ltd. Subordinated Notes, 8.68% Estimated Yield, 10/29/2025(h) | (f) | Diversified Financials | 2,000 | 1,330 | 1,182 | ||||||||||
Dryden XXIII Senior Loan Fund Subordinated Notes, 1.40% Estimated Yield, 7/17/2023(h) | (f) | Diversified Financials | 9,250 | 4,726 | 4,135 | ||||||||||
Galaxy XV CLO Ltd. Class A Subordinated Notes, 8.72% Estimated Yield, 4/15/2025(h) | (f) | Diversified Financials | 4,000 | 2,424 | 2,323 | ||||||||||
Ivy Hill Middle Market Credit Fund VII, Ltd. Subordinated Notes, 8.80% Estimated Yield, 10/20/2025(h) | (f) | Diversified Financials | 2,000 | 1,654 | 1,478 | ||||||||||
Ivy Hill Middle Market Credit Fund VIII, Ltd. Subordinated Loan, 10.35% Estimated Yield, 2/2/2026(e)(h) | (f) | Diversified Financials | 10,000 | 9,940 | 9,773 | ||||||||||
Ivy Hill Middle Market Credit Fund IX, Ltd. Subordinated Notes, 14.59% Estimated Yield, 10/18/2025(h) | (f) | Diversified Financials | 8,146 | 6,106 | 6,239 | ||||||||||
Ivy Hill Middle Market Credit Fund X, Ltd. Subordinated Notes, 11.50% Estimated Yield, 7/24/2027(h) | (f) | Diversified Financials | 4,760 | 3,947 | 3,797 | ||||||||||
Total Collateralized Securities and Structured Products - Equity | 37,713 | 34,648 | |||||||||||||
Unsecured Debt - 1.7% | |||||||||||||||
American Tire Distributors, Inc., 10.25%, 3/1/2022 | None | Automotive | 5,000 | 4,871 | 4,794 | ||||||||||
Flex Acquisition Company, Inc., L+700, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 12/29/2017 | 1 Month LIBOR | Containers, Packaging & Glass | 3,833 | 3,814 | 3,845 | ||||||||||
Radio One, Inc., 9.25%, 2/15/2020 | None | Media: Broadcasting & Subscription | 9,000 | 8,605 | 8,212 | ||||||||||
Total Unsecured Debt | 17,290 | 16,851 | |||||||||||||
Equity - 0.5% | |||||||||||||||
Mooregate ITC Acquisition, LLC, Class A Units(o) | High Tech Industries | 500 Units | 563 | 538 | |||||||||||
NS NWN Acquisition, LLC(o) | High Tech Industries | 346 Units | 393 | 337 | |||||||||||
NSG Co-Invest (Bermuda), LP(h)(o) | Consumer Goods: Durable | 1,575 Units | 1,000 | 1,000 | |||||||||||
Southcross Holdings GP, LLC, Units(o) | Energy: Oil & Gas | 188 Units | — | — | |||||||||||
Southcross Holdings LP, Class A-II Units(o) | Energy: Oil & Gas | 188 Units | 75 | 71 | |||||||||||
Speed Commerce Investment Part, LLC(o) | High Tech Industries | 629 Units | 2,640 | 3,000 | |||||||||||
Tenere Inc. Warrant(o) | Capital Equipment | N/A | 161 | 161 | |||||||||||
TexOak Petro Holdings, LLC(o) | Energy: Oil & Gas | 60,000 Units | — | — | |||||||||||
Total Equity | 4,832 | 5,107 | |||||||||||||
Short Term Investments - 7.1%(k) | |||||||||||||||
First American Treasury Obligations Fund, Class Z Shares, 0.39%(l) | 70,498 | 70,498 | |||||||||||||
Total Short Term Investments | 70,498 | 70,498 | |||||||||||||
TOTAL INVESTMENTS - 109.0% | $ | 1,096,948 | 1,089,478 | ||||||||||||
LIABILITIES IN EXCESS OF OTHER ASSETS - (9.0%) | (89,715 | ) | |||||||||||||
NET ASSETS - 100% | $ | 999,763 | |||||||||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
76
CĪON Investment Corporation
Consolidated Schedule of Investments
December 31, 2016
(in thousands)
Counterparty | Instrument | Maturity Date | Notional Amount(d) | Cost(p) | Fair Value(c) | |||||||||||
Derivative Asset - 0.0% | ||||||||||||||||
Credit Default Swap | ||||||||||||||||
JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A. | Deutsche Bank AG Credit Default Swap | 3/20/2017 | € | 22,000 | $ | 229 | $ | 46 | ||||||||
Derivative Liability - (1.5%) | ||||||||||||||||
Total Return Swap | ||||||||||||||||
Citibank, N.A. | See Note 7 | 2/18/2017 | $ | 407,847 | N/A | $ | (15,402 | ) | ||||||||
a. | All of the Company’s investments are issued by eligible U.S. portfolio companies, as defined in the Investment Company Act of 1940, as amended, or the 1940 Act, except for investments specifically identified as non-qualifying per note h. below. Except for CION / Capitala Senior Loan Fund I, LLC, or CCSLF, the Company does not control and is not an affiliate of any of the portfolio companies in its investment portfolio. Unless specifically identified in note q. below, investments do not contain a paid-in-kind, or PIK, interest provision. |
b. | The 1, 2, 3 and 12 month London Interbank Offered Rate, or LIBOR, rates were 0.77%, 0.82%, 1.00% and 1.69%, respectively, as of December 31, 2016. The actual LIBOR rate for each loan listed may not be the applicable LIBOR rate as of December 31, 2016, as the loan may have been priced or repriced based on a LIBOR rate prior to or subsequent to December 31, 2016. The 3 month Euro Interbank Offered Rate, or EURIBOR, rate was (0.34%) as of December 31, 2016. |
c. | Fair value determined in good faith by the Company’s board of directors (see Note 9). |
d. | Denominated in U.S. dollars unless otherwise noted. |
e. | As discussed in Note 11, the Company was committed, upon the satisfaction of certain conditions, to fund an additional $1,119, $711, $2,500, $1,111, $5,274 and $4,127 as of December 31, 2016 to ABG Intermediate Holdings 2 LLC, American Media, Inc., Elemica Holdings, Inc., Ivy Hill Middle Market Credit Fund VIII, Ltd., Ministry Brands, LLC and Studio Movie Grill Holdings, LLC, respectively. As of March 9, 2017, the Company was committed, upon the satisfaction of certain conditions, to fund an additional $1,119, $415, $10,000, $2,500, $1,111 and $4,127 to ABG Intermediate Holdings 2 LLC, American Media, Inc., CF Entertainment Inc., Elemica Holdings, Inc., Ivy Hill Middle Market Credit Fund VIII, Ltd. and Studio Movie Grill Holdings, LLC, respectively. |
f. | The CLO subordinated notes are considered equity positions in the CLO vehicles and are not rated. Equity investments are entitled to recurring distributions, which are generally equal to the remaining cash flow of the payments made by the underlying vehicle's securities less contractual payments to debt holders and expenses. The estimated yield indicated is based upon a current projection of the amount and timing of these recurring distributions and the estimated amount of repayment of principal upon termination. Such projections are periodically reviewed and adjusted, and the estimated yield may not ultimately be realized. |
g. | Great Lakes CLO 2014-1 Class E Notes, Ivy Hill Middle Market Credit Fund VII Class E Notes and NXT Capital CLO 2014-1 Class E Notes were rated Ba2 on Moody's credit scale as of December 31, 2016. JFIN CLO 2014 Class E Notes were rated BB on S&P's credit scale as of December 31, 2016. |
h. | The investment is not a qualifying asset under the 1940 Act. A business development company may not acquire any asset other than qualifying assets, unless, at the time the acquisition is made, qualifying assets represent at least 70% of the company’s total assets as defined under Section 55 of the 1940 Act. As of December 31, 2016, 90.5% of the Company’s total assets represented qualifying assets. In addition, as described in Note 7, the Company calculates its compliance with the qualifying asset test on a “look through” basis by treating each loan underlying the total return swap as either a qualifying asset or non-qualifying asset based on whether the obligor is an eligible portfolio company. On this basis, 89.1% of the Company’s total assets represented qualifying assets as of December 31, 2016. |
i. | Position or a portion thereof unsettled as of December 31, 2016. |
j. | In addition to the interest earned based on the stated interest rate of this loan, which is the amount reflected in this schedule, the Company may be entitled to receive additional amounts as a result of an arrangement between the Company and other lenders in the syndication in exchange for lower payment priority. |
k. | Short term investments represent an investment in a fund that invests in highly liquid investments with average original maturity dates of three months or less. |
l. | 7-day effective yield as of December 31, 2016. |
m. | Investment or a portion thereof was pledged as collateral supporting the amounts outstanding, if any, under the revolving credit facility with East West Bank as of December 31, 2016 (see Note 8). |
n. | Investment or a portion thereof held within the Company’s wholly-owned consolidated subsidiary, 34th Street Funding, LLC, or 34th Street, and was pledged as collateral supporting the amounts outstanding under the credit facility with JPMorgan Chase Bank, National Association, or JPM, as of December 31, 2016 (see Note 8). |
o. | Non-income producing security. |
p. | Represents amortized cost for debt investments, cost for equity investments and premium paid for derivatives. |
77
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
CĪON Investment Corporation
Consolidated Schedule of Investments
December 31, 2016
(in thousands)
q. | For the year ended December 31, 2016, the following investments contain a PIK interest provision whereby the issuer has either the option or the obligation to make interest payments with the issuance of additional securities: |
Interest Rate | Interest Amount | |||||||||||||||||||
Portfolio Company | Investment Type | Cash | PIK | All-in-Rate | Cash | PIK | All-in-Rate | |||||||||||||
Elements Behavioral Health, Inc. | Senior Secured Second Lien Debt | — | 13.00% | 13.00% | $ | — | $ | 700 | $ | 700 | ||||||||||
Petroflow Energy Corp. | Senior Secured First Lien Debt | 3.00% | 6.00% | 9.00% | $ | 14 | $ | 99 | $ | 113 | ||||||||||
Rimini Street, Inc. | Senior Secured First Lien Debt | 12.00% | 3.00% | 15.00% | $ | 1,286 | $ | 164 | $ | 1,450 | ||||||||||
Sequoia Healthcare Management, LLC | Senior Secured First Lien Debt | 12.00% | 4.00% | 16.00% | $ | 206 | $ | 68 | $ | 274 | ||||||||||
Smile Brands Group, Inc.(r) | Senior Secured First Lien Debt | 7.50% | 1.50% | 9.00% | $ | 187 | $ | 34 | $ | 221 | ||||||||||
Southcross Holdings Borrower LP(s) | Senior Secured First Lien Debt | 3.50% | 5.50% | 9.00% | $ | 2 | $ | 6 | $ | 8 | ||||||||||
Spinal USA, Inc. / Precision Medical Inc. | Senior Secured First Lien Debt | — | 10.50% | 10.50% | $ | — | $ | 3 | $ | 3 | ||||||||||
TexOak Petro Holdings LLC | Senior Secured Second Lien Debt | — | 8.00% | 8.00% | $ | — | $ | 181 | $ | 181 | ||||||||||
r. | Outstanding principal and accrued interest of the underlying loan was fully repaid on August 17, 2016. |
s. | Prior to December 31, 2016, the underlying loan was assigned to the Company and removed from the TRS. |
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
78
CĪON Investment Corporation
Consolidated Schedule of Investments
December 31, 2015
(in thousands)
Portfolio Company(a) | Index Rate(b) | Industry | Principal/Par Amount | Amortized Cost | Fair Value(c) | |||||||||||
Senior Secured First Lien Debt - 11.5% | ||||||||||||||||
Accruent, LLC, L+625, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 11/25/2019 | 3 Month LIBOR | High Tech Industries | $ | 2,962 | $ | 2,957 | $ | 2,933 | ||||||||
ECI Acquisition Holdings, Inc., L+625, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 3/11/2019(d) | 3 Month LIBOR | High Tech Industries | 8,583 | 8,548 | 8,497 | |||||||||||
F+W Media, Inc., L+725, 1.25% LIBOR Floor, 6/30/2019 | 3 Month LIBOR | Media: Diversified & Production | 10,414 | 10,090 | 10,153 | |||||||||||
Ignite Restaurant Group, Inc., L+700, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 2/13/2019 | 3 Month LIBOR | Beverage, Food & Tobacco | 11,639 | 11,510 | 11,522 | |||||||||||
Infogroup Inc., L+550, 1.50% LIBOR Floor, 5/26/2018 | 3 Month LIBOR | Media: Advertising, Printing & Publishing | 15,743 | 15,242 | 14,956 | |||||||||||
Intertain Group Ltd., L+650, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 4/8/2022(g) | 3 Month LIBOR | Hotel, Gaming & Leisure | 1,993 | 1,956 | 1,963 | |||||||||||
Nathan's Famous Inc., 10.00%, 3/15/2020(g) | None | Beverage, Food & Tobacco | 6,000 | 6,000 | 6,248 | |||||||||||
Panda Sherman Power, LLC, L+750, 1.50% LIBOR Floor, 9/14/2018 | 3 Month LIBOR | Energy: Electricity | 4,243 | 4,215 | 3,840 | |||||||||||
Plano Molding Company, LLC, L+600, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 5/12/2021 | 3 Month LIBOR | Consumer Goods: Non-Durable | 10,945 | 10,842 | 10,726 | |||||||||||
Smile Brands Group, Inc., L+775, 1.25% LIBOR Floor, 8/16/2019(l) | 3 Month LIBOR | Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals | 3,678 | 3,623 | 2,630 | |||||||||||
Sprint Industrial Holdings, LLC, L+575, 1.25% LIBOR Floor, 5/14/2019 | 3 Month LIBOR | Energy: Oil & Gas | 7,381 | 6,785 | 6,274 | |||||||||||
Studio Movie Grill Holdings, LLC, L+725, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 9/10/2018(d) | 3 Month LIBOR | Hotel, Gaming & Leisure | 18,625 | 18,538 | 18,625 | |||||||||||
TOPPS Company, Inc., L+600, 1.25% LIBOR Floor, 10/2/2018 | 3 Month LIBOR | Consumer Goods: Non-Durable | 3,310 | 3,273 | 3,248 | |||||||||||
US Joiner Holding Company, L+600, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 4/16/2020 | 3 Month LIBOR | Capital Equipment | 2,598 | 2,568 | 2,572 | |||||||||||
Total Senior Secured First Lien Debt | 106,147 | 104,187 | ||||||||||||||
Senior Secured Second Lien Debt - 50.2% | ||||||||||||||||
ABG Intermediate Holdings 2 LLC, L+850, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 5/27/2022(d) | 3 Month LIBOR | Retail | 8,788 | 8,721 | 8,623 | |||||||||||
Access CIG, LLC, L+875, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 10/17/2022 | 3 Month LIBOR | Services: Business | 16,030 | 15,382 | 15,629 | |||||||||||
ALM Media, LLC, L+800, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 7/30/2021 | 3 Month LIBOR | Media: Advertising, Printing & Publishing | 10,344 | 10,174 | 9,671 | |||||||||||
American Residential Services LLC, L+800, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 12/31/2021 | 3 Month LIBOR | Construction & Building | 3,700 | 3,669 | 3,672 | |||||||||||
AmWINS Group, LLC, L+850, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 9/4/2020 | 3 Month LIBOR | Banking, Finance, Insurance & Real Estate | 3,075 | 3,104 | 3,052 | |||||||||||
Blue Ribbon, LLC, L+825, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 11/13/2022(k) | 3 Month LIBOR | Beverage, Food & Tobacco | 18,000 | 17,846 | 17,640 | |||||||||||
C.H.I. Overhead Doors, Inc., L+775, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 7/31/2023 | 3 Month LIBOR | Construction & Building | 7,000 | 6,965 | 6,580 | |||||||||||
Concentra Inc., L+800, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 6/1/2023 | 3 Month LIBOR | Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals | 5,714 | 5,659 | 5,657 | |||||||||||
Deltek, Inc., L+850, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 6/26/2023 | 3 Month LIBOR | Services: Business | 11,245 | 11,080 | 11,105 | |||||||||||
Drew Marine Group, Inc., L+700, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 5/19/2021(g) | 3 Month LIBOR | Chemicals, Plastics & Rubber | 9,500 | 9,452 | 9,120 | |||||||||||
EISI LLC, L+850, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 9/23/2020(k) | 3 Month LIBOR | High Tech Industries | 20,000 | 19,709 | 19,400 | |||||||||||
Elements Behavioral Health, Inc., L+1075, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 2/11/2020(l) | 3 Month LIBOR | Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals | 5,018 | 4,978 | 4,918 | |||||||||||
Emerald 3 Ltd., L+700, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 5/16/2022(g) | 3 Month LIBOR | Environmental Industries | 3,000 | 2,974 | 2,850 | |||||||||||
Flexera Software LLC, L+700, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 4/2/2021 | 3 Month LIBOR | High Tech Industries | 9,385 | 9,081 | 8,834 | |||||||||||
GCA Services Group, Inc., L+800, 1.25% LIBOR Floor, 11/1/2020 | 3 Month LIBOR | Services: Consumer | 3,361 | 3,353 | 3,319 | |||||||||||
Genex Holdings, Inc., L+775, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 5/30/2022 | 1 Month LIBOR | Services: Business | 11,410 | 11,331 | 10,754 | |||||||||||
Global Tel*Link Corp., L+775, 1.25% LIBOR Floor, 11/23/2020 | 3 Month LIBOR | Telecommunications | 9,500 | 9,486 | 6,650 | |||||||||||
GTCR Valor Companies, Inc., L+850, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 11/30/2021 | 3 Month LIBOR | High Tech Industries | 5,000 | 4,960 | 4,806 | |||||||||||
Hilex Poly Co. LLC, L+875, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 6/5/2022 | 3 Month LIBOR | Containers, Packaging & Glass | 12,409 | 12,176 | 11,851 | |||||||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
79
CĪON Investment Corporation
Consolidated Schedule of Investments
December 31, 2015
(in thousands)
Portfolio Company(a) | Index Rate(b) | Industry | Principal/Par Amount | Amortized Cost | Fair Value(c) | ||||||||
Infiltrator Water Technologies, LLC, L+875, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 5/26/2023 | 3 Month LIBOR | Construction & Building | 13,916 | 13,714 | 13,847 | ||||||||
Institutional Shareholder Services Inc., L+750, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 4/30/2022 | 3 Month LIBOR | Services: Business | 7,860 | 7,777 | 7,506 | ||||||||
Landslide Holdings, Inc., L+725, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 2/25/2021 | 3 Month LIBOR | Services: Business | 9,830 | 9,826 | 9,044 | ||||||||
Lanyon Solutions, Inc., L+850, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 11/15/2021 | 3 Month LIBOR | High Tech Industries | 2,273 | 2,264 | 2,103 | ||||||||
Learfield Communications, Inc., L+775, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 10/9/2021 | 3 Month LIBOR | Media: Broadcasting & Subscription | 1,350 | 1,339 | 1,343 | ||||||||
Mergermarket USA, Inc., L+650, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 2/4/2022 | 3 Month LIBOR | Services: Business | 3,380 | 3,319 | 3,076 | ||||||||
Mitchell International, Inc., L+750, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 10/11/2021 | 3 Month LIBOR | High Tech Industries | 7,509 | 7,491 | 7,190 | ||||||||
MSC.Software Corp., L+750, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 5/29/2021 | 3 Month LIBOR | High Tech Industries | 15,000 | 14,801 | 13,200 | ||||||||
Navex Global, Inc., L+875, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 11/18/2022(k) | 3 Month LIBOR | High Tech Industries | 16,245 | 16,006 | 15,757 | ||||||||
Onex TSG Holdings II Corp., L+850, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 7/31/2023 | 1 Month LIBOR | Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals | 12,249 | 12,129 | 12,187 | ||||||||
Patterson Medical Supply, Inc., L+775, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 8/28/2023 | 3 Month LIBOR | Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals | 13,500 | 13,370 | 13,230 | ||||||||
Pelican Products, Inc., L+825, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 4/11/2021 | 3 Month LIBOR | Chemicals, Plastics & Rubber | 3,469 | 3,481 | 3,304 | ||||||||
PetroChoice Holdings, Inc., L+875, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 8/21/2023 | 1 Month LIBOR | Chemicals, Plastics & Rubber | 15,000 | 14,707 | 14,737 | ||||||||
Pike Corp., L+850, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 6/22/2022 | 3 Month LIBOR | Energy: Electricity | 10,000 | 9,843 | 9,837 | ||||||||
PODS, LLC, L+825, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 2/2/2023 | 3 Month LIBOR | Services: Consumer | 9,984 | 9,927 | 9,835 | ||||||||
PSC Industrial Holdings Corp., L+825, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 12/5/2021 | 3 Month LIBOR | Services: Business | 10,000 | 9,824 | 9,450 | ||||||||
RP Crown Parent, LLC, L+1000, 1.25% LIBOR Floor, 12/21/2019 | 3 Month LIBOR | High Tech Industries | 5,000 | 4,746 | 4,128 | ||||||||
Securus Technologies Holdings, Inc., L+775, 1.25% LIBOR Floor, 4/30/2021 | 3 Month LIBOR | Telecommunications | 4,500 | 4,476 | 2,498 | ||||||||
SI Organization, Inc., L+800, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 5/23/2020 | 3 Month LIBOR | Services: Business | 1,511 | 1,499 | 1,473 | ||||||||
SMG, L+825, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 2/27/2021 | 3 Month LIBOR | Hotel, Gaming & Leisure | 6,220 | 6,220 | 6,251 | ||||||||
Sterling Midco Holdings, Inc., L+775, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 6/19/2023 | 3 Month LIBOR | Services: Business | 10,462 | 10,430 | 10,383 | ||||||||
STG-Fairway Acquisitions, Inc., L+925, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 6/30/2023 | 3 Month LIBOR | Services: Business | 10,000 | 9,855 | 9,600 | ||||||||
Surgery Center Holdings, Inc., L+750, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 11/3/2021 | 1 Month LIBOR | Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals | 6,037 | 6,050 | 5,675 | ||||||||
Survey Sampling International, LLC, L+900, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 12/16/2021 | 3 Month LIBOR | Services: Business | 15,000 | 14,729 | 14,700 | ||||||||
TASC, Inc., 12.00%, 5/23/2021(g) | None | Services: Business | 7,332 | 7,121 | 7,442 | ||||||||
Telecommunications Management, LLC, L+800, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 10/30/2020 | 3 Month LIBOR | Media: Broadcasting & Subscription | 1,606 | 1,566 | 1,566 | ||||||||
TMK Hawk Parent, Corp., L+750, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 10/1/2022(k) | 3 Month LIBOR | Beverage, Food & Tobacco | 15,000 | 14,865 | 14,850 | ||||||||
TransFirst Inc., L+800, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 11/11/2022 | 1 Month LIBOR | Banking, Finance, Insurance & Real Estate | 14,368 | 14,309 | 14,081 | ||||||||
U.S. Renal Care, Inc., L+800, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 12/29/2023(h) | 3 Month LIBOR | Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals | 10,000 | 9,800 | 9,825 | ||||||||
Vestcom International, Inc., L+775, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 9/30/2022(k) | 3 Month LIBOR | Services: Business | 15,000 | 14,935 | 14,250 | ||||||||
Wand Intermediate I LP, L+725, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 9/19/2022 | 3 Month LIBOR | Automotive | 16,000 | 15,875 | 15,160 | ||||||||
Winebow Holdings, Inc., L+750, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 1/2/2022 | 1 Month LIBOR | Beverage, Food & Tobacco | 12,823 | 12,505 | 12,054 | ||||||||
Total Senior Secured Second Lien Debt | 468,899 | 453,713 | |||||||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
80
CĪON Investment Corporation
Consolidated Schedule of Investments
December 31, 2015
(in thousands)
Portfolio Company(a) | Index Rate(b) | Industry | Principal/Par Amount | Amortized Cost | Fair Value(c) | |||||||||||
Collateralized Securities and Structured Products - Debt - 4.6% | ||||||||||||||||
Deutsche Bank AG Frankfurt CRAFT 2013-1A Class Credit Linked Note, L+925, 4/17/2020(g) | 3 Month LIBOR | Diversified Financials | 2,000 | 2,029 | 1,940 | |||||||||||
Deutsche Bank AG Frankfurt CRAFT 2013-1X Class Credit Linked Note, L+925, 4/17/2020(g) | 3 Month LIBOR | Diversified Financials | 610 | 618 | 592 | |||||||||||
Deutsche Bank AG Frankfurt CRAFT 2014-1 Class Credit Linked Note, L+965, 5/15/2019(g) | 3 Month LIBOR | Diversified Financials | 5,400 | 5,400 | 5,238 | |||||||||||
Deutsche Bank AG Frankfurt CRAFT 2015-2 Class Credit Linked Note, L+925, 1/16/2022(g) | 3 Month LIBOR | Diversified Financials | 15,500 | 15,500 | 15,190 | |||||||||||
Great Lakes CLO 2014-1, Ltd. Class E Notes, L+525, 4/15/2025(f)(g) | 3 Month LIBOR | Diversified Financials | 5,000 | 4,568 | 3,950 | |||||||||||
Ivy Hill Middle Market Credit Fund VII, Ltd. Class E Notes, L+565, 10/20/2025(f)(g) | 3 Month LIBOR | Diversified Financials | 2,000 | 1,869 | 1,673 | |||||||||||
JFIN CLO 2014, Ltd. Class E Notes, L+500, 4/20/2025(f)(g) | 3 Month LIBOR | Diversified Financials | 2,500 | 2,326 | 2,031 | |||||||||||
JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A. Credit Linked Note, L+1225, 12/20/2021(g) | 3 Month LIBOR | Diversified Financials | 5,000 | 5,000 | 4,940 | |||||||||||
NXT Capital CLO 2014-1, LLC Class E Notes, L+550, 4/23/2026(f)(g) | 3 Month LIBOR | Diversified Financials | 7,500 | 7,051 | 6,109 | |||||||||||
Total Collateralized Securities and Structured Products - Debt | 44,361 | 41,663 | ||||||||||||||
Collateralized Securities and Structured Products - Equity - 2.7% | ||||||||||||||||
Anchorage Capital CLO 2012-1, Ltd. Subordinated Notes, 16.00% Estimated Yield, 1/13/2025(g) | (e) | Diversified Financials | 4,000 | 3,209 | 2,480 | |||||||||||
APIDOS CLO XVI Subordinated Notes, 16.00% Estimated Yield, 1/19/2025(g) | (e) | Diversified Financials | 9,000 | 5,238 | 3,578 | |||||||||||
CENT CLO 19 Ltd. Subordinated Notes, 16.00% Estimated Yield, 10/29/2025(g) | (e) | Diversified Financials | 2,000 | 1,407 | 1,055 | |||||||||||
Dryden XXIII Senior Loan Fund Subordinated Notes, 16.00% Estimated Yield, 7/17/2023(g) | (e) | Diversified Financials | 9,250 | 5,740 | 4,077 | |||||||||||
Galaxy XV CLO Ltd. Class A Subordinated Notes, 16.00% Estimated Yield, 4/15/2025(g) | (e) | Diversified Financials | 4,000 | 2,626 | 2,178 | |||||||||||
Ivy Hill Middle Market Credit Fund VII, Ltd. Subordinated Notes, 17.00% Estimated Yield, 10/20/2025(g) | (e) | Diversified Financials | 2,000 | 1,798 | 1,416 | |||||||||||
Ivy Hill Middle Market Credit Fund IX, Ltd. Subordinated Notes, 17.00% Estimated Yield, 10/18/2025(g) | (e) | Diversified Financials | 8,146 | 6,931 | 6,202 | |||||||||||
Ivy Hill Middle Market Credit Fund X, Ltd. Subordinated Notes, 17.00% Estimated Yield, 7/24/2027(g) | (e) | Diversified Financials | 4,760 | 4,235 | 3,618 | |||||||||||
Total Collateralized Securities and Structured Products - Equity | 31,184 | 24,604 | ||||||||||||||
Unsecured Debt - 3.0% | ||||||||||||||||
Alliant Holdings I, L.P., 8.25%, 8/1/2023 | None | Banking, Finance, Insurance & Real Estate | 7,255 | 7,238 | 6,856 | |||||||||||
American Tire Distributors, Inc., 10.25%, 3/1/2022 | None | Automotive | 5,000 | 4,852 | 4,606 | |||||||||||
NFP Corp., 9.00%, 7/15/2021 | None | Banking, Finance, Insurance & Real Estate | 9,000 | 8,958 | 8,235 | |||||||||||
Radio One, Inc., 9.25%, 2/15/2020 | None | Media: Broadcasting & Subscription | 9,000 | 8,505 | 7,043 | |||||||||||
Total Unsecured Debt | 29,553 | 26,740 | ||||||||||||||
Short Term Investments - 2.1%(i) | ||||||||||||||||
First American Treasury Obligations Fund, Class Z Shares(j) | 18,892 | 18,892 | ||||||||||||||
Total Short Term Investments | 18,892 | 18,892 | ||||||||||||||
TOTAL INVESTMENTS - 74.1% | $ | 699,036 | 669,799 | |||||||||||||
OTHER ASSETS IN EXCESS OF LIABILITIES - 25.9% | 234,527 | |||||||||||||||
NET ASSETS - 100% | $ | 904,326 | ||||||||||||||
TOTAL RETURN SWAP - (3.9)% | Notional Amount | Unrealized Depreciation | ||||||||||||||
Citibank TRS Facility (see Note 7) | $ | 718,025 | $ | (34,900 | ) | |||||||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
81
CĪON Investment Corporation
Consolidated Schedule of Investments
December 31, 2015
(in thousands)
a. | All of the Company’s investments are issued by eligible U.S. portfolio companies, as defined in the 1940 Act, except for investments specifically identified as non-qualifying per note g. below. Except for CCSLF, the Company does not control and is not an affiliate of any of the portfolio companies in its investment portfolio. Unless specifically identified in note l. below, investments do not contain a PIK interest provision. |
b. | The 1 and 3 month LIBOR rates were 0.43% and 0.61%, respectively, as of December 31, 2015. The actual LIBOR rate for each loan listed may not be the applicable LIBOR rate as of December 31, 2015, as the loan may have been priced or repriced based on a LIBOR rate prior to or subsequent to December 31, 2015. |
c. | Fair value determined in good faith by the Company’s board of directors (see Note 9). |
d. | As discussed in Note 11, the Company was committed, upon the satisfaction of certain conditions, to fund an additional $1,207, $1,069 and $1,128 as of December 31, 2015 and March 11, 2016 to ECI Acquisition Holdings, Inc., Studio Movie Grill Holdings, LLC and ABG Intermediate Holdings 2 LLC, respectively. |
e. | The CLO subordinated notes are considered equity positions in the CLO vehicles and are not rated. Equity investments are entitled to recurring distributions, which are generally equal to the remaining cash flow of the payments made by the underlying vehicle's securities less contractual payments to debt holders and expenses. The estimated yield indicated is based upon a current projection of the amount and timing of these recurring distributions and the estimated amount of repayment of principal upon termination. Such projections are periodically reviewed and adjusted, and the estimated yield may not ultimately be realized. |
f. | Great Lakes CLO 2014-1 Class E Notes, Ivy Hill Middle Market Credit Fund VII Class E Notes and NXT Capital CLO 2014-1 Class E Notes were rated Ba2 on Moody's credit scale as of December 31, 2015. JFIN CLO 2014 Class E Notes were rated BB on S&P's credit scale as of December 31, 2015. |
g. | The investment is not a qualifying asset under the 1940 Act. A business development company may not acquire any asset other than qualifying assets, unless, at the time the acquisition is made, qualifying assets represent at least 70% of the Company’s total assets as defined under Section 55 of the 1940 Act. As of December 31, 2015, 90.0% of the Company’s total assets represented qualifying assets. In addition, as described in Note 7, the Company calculates its compliance with the qualifying asset test on a “look through” basis by treating each loan underlying the total return swap as either a qualifying asset or non-qualifying asset based on whether the obligor is an eligible portfolio company. On this basis, 87.2% of the Company’s total assets represented qualifying assets as of December 31, 2015. |
h. | Position or a portion thereof unsettled as of December 31, 2015. |
i. | Short term investments represent an investment in a fund that invests in highly liquid investments with average original maturity dates of three months or less. |
j. | Effective yield as of December 31, 2015 was <0.01%. |
k. | Investment or a portion thereof was pledged as collateral supporting the amounts outstanding, if any, under the revolving credit facility with East West Bank as of December 31, 2015 (See Note 8). |
l. | For the year ended December 31, 2015, the following investments contain a PIK interest provision whereby the issuer has either the option or the obligation to make interest payments with the issuance of additional securities: |
Interest Rate | Interest Amount | |||||||||||||||||||
Portfolio Company | Investment Type | Cash | PIK | All-in-Rate | Cash | PIK | All-in-Rate | |||||||||||||
Elements Behavioral Health, Inc.(m) | Senior Secured Second Lien Debt | 9.75% | 2.00% | 11.75% | $ | 495 | $ | 32 | $ | 527 | ||||||||||
Smile Brands Group, Inc. | Senior Secured First Lien Debt | 7.50% | 1.50% | 9.00% | $ | 328 | $ | 11 | $ | 339 | ||||||||||
m. | Subsequent to December 31, 2015, Elements Behavioral Health, Inc. notified the Company that it would not make its scheduled interest payment due on February 12, 2016. As a result, the Company entered into a new Forbearance Agreement and Eighth Amendment to Second Lien Credit Agreement, which, among other things, modified the interest rate to LIBOR plus 12% and specified that all interest shall be paid-in-kind on each interest payment date through the earlier of the forbearance period termination or June 30, 2017. The investment has not been placed on non-accrual status as the Company believes that all principal and interest is likely to be collected. |
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
82
CĪON Investment Corporation
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
December 31, 2016
(in thousands, except share and per share amounts)
Note 1. Organization and Principal Business
CĪON Investment Corporation, or the Company, was incorporated under the general corporation laws of the State of Maryland on August 9, 2011. On December 17, 2012, the Company successfully raised gross proceeds from unaffiliated outside investors of at least $2,500, or the minimum offering requirement, and commenced operations. The Company is an externally managed, non-diversified closed-end management investment company that has elected to be regulated as a business development company, or BDC, under the 1940 Act. The Company elected to be treated for federal income tax purposes as a regulated investment company, or RIC, as defined under Subchapter M of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended, or the Code.
The Company’s investment objective is to generate current income and, to a lesser extent, capital appreciation for investors. The Company’s portfolio is comprised primarily of investments in senior secured debt, including first lien loans, second lien loans and unitranche loans, and, to a lesser extent, collateralized securities, structured products and other similar securities, unsecured debt, including corporate bonds and long-term subordinated loans, referred to as mezzanine loans, and equity, of private and thinly traded U.S. middle-market companies.
The Company is managed by CION Investment Management, LLC, or CIM, a registered investment adviser and an affiliate of the Company. CIM oversees the management of the Company’s activities and is responsible for making investment decisions for the Company’s investment portfolio. The Company and CIM have engaged Apollo Investment Management, L.P., or AIM, a subsidiary of Apollo Global Management, LLC, or, together with its subsidiaries, Apollo, a leading global alternative investment manager, to act as the Company’s investment sub-adviser. On November 1, 2016, the board of directors of the Company, including a majority of the board of directors who are not interested persons, approved the renewal of the investment sub-advisory agreement with AIM for a period of twelve months commencing December 17, 2016.
Note 2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Basis of Presentation and Consolidation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements of the Company have been prepared in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles, or GAAP, and include the accounts of the Company and its wholly-owned subsidiaries. In the opinion of management, all adjustments (consisting of normal recurring adjustments) considered necessary for a fair presentation have been included. All intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation. The Company does not consolidate its interest in CCSLF.
The Company is considered an investment company as defined in Accounting Standards Update Topic 946, Financial Services – Investment Companies, or ASU 946. Accordingly, the required disclosures as outlined in ASU 946 are included in the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
The Company evaluates subsequent events through the date that the consolidated financial statements are issued.
Recently Adopted Accounting Standards
In August 2014, the Financial Accounting Standards Board, or the FASB, issued ASU 2014-15, Presentation of Financial Statements - Going Concern, which requires that entities evaluate whether there are conditions or events, considered in the aggregate, that raise substantial doubt about the entity’s ability to continue as a going concern within the one year period subsequent to the date that the financial statements are issued or within the one year period subsequent to the date that the financial statements are available to be issued. This guidance was adopted by the Company during the three months ended March 31, 2016. As a result of management's evaluation, no conditions present were identified that raise substantial doubt about the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern and no additional disclosure is required.
In February 2015, the FASB issued ASU 2015-02, Consolidation: Amendments to the Consolidation Analysis, or ASU 2015-02, which amends the criteria for determining which entities are considered variable interest entities, or VIEs, amends the criteria for determining if a service provider possesses a variable interest in a VIE and ends the deferral granted to investment companies for application of the VIE consolidation model. This guidance was adopted by the Company during the three months ended March 31, 2016, which did not have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements. In addition, no prior-period information was retrospectively adjusted as a result of the adoption of ASU 2015-02.
In April 2015, the FASB issued ASU 2015-03, Interest - Imputation of Interest: Simplifying the Presentation of Debt Issuance Costs, or ASU 2015-03, which requires that loan costs related to a recognized debt liability be presented in the balance sheet as a direct deduction from the carrying amount of that debt liability, consistent with debt discounts or premiums. ASU 2015-03 requires retrospective application and represents a change in accounting principle. In August 2015, the FASB issued ASU No. 2015-15, Interest - Imputation of Interest: Presentation and Subsequent Measurement of Debt Issuance Costs Associated with Line-of-Credit Arrangements, or ASU 2015-15, which allows an entity to continue to present line of credit issuance costs as an asset, regardless of whether there are any outstanding borrowings on the line of credit. This guidance was adopted by the Company during the three months ended March 31, 2016. No prior-period information was retrospectively adjusted as a result of the adoption of this guidance. As a result, unamortized debt issuance costs of $64 are presented as prepaid expenses and other assets in the consolidated balance sheet as of December 31, 2016 as the Company has no recognized debt liability associated with these costs. In addition, unamortized debt issuance costs of $3,212 were directly deducted from the carrying amount of the associated debt liability in the consolidated balance sheet as of December 31, 2016.
In November 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-18, Statement of Cash Flows: Restricted Cash, or ASU 2016-18, which requires that a statement of cash flows explain the change during the period in the total of cash, cash equivalents and amounts generally described as restricted cash. The purpose of this guidance is to eliminate diversity in practice in the classification and presentation of changes in restricted cash on the statement of cash flows. As a result, amounts generally described as restricted cash should be included within cash and cash equivalents when reconciling the beginning and
83
CĪON Investment Corporation
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
December 31, 2016
(in thousands, except share and per share amounts)
ending total amounts shown on the statement of cash flows. This guidance is effective for interim and annual periods beginning after December 15, 2017 and early adoption is permitted. The Company adopted this guidance during the three months ended December 31, 2016, which had no material impact on the Company's consolidated financial statements.
Recently Announced Accounting Standards
In August 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-15, Statement of Cash Flows: Classification of Certain Cash Receipts and Cash Payments (a consensus of the Emerging Issues Task Force), or ASU 2016-15, which intends to reduce diversity in practice in how certain cash receipts and payments are classified in the statement of cash flows, including debt prepayment or extinguishment costs, the settlement of contingent liabilities arising from a business combination, proceeds from insurance settlements and distributions from certain equity method investments. ASU 2016-15 is effective for interim and annual periods beginning after December 15, 2017. Early adoption is permitted. The Company is in the process of evaluating the impact that this guidance will have on its consolidated financial statements.
In January 2017, the FASB issued ASU 2017-01, Business Combinations: Clarifying the Definition of a Business, or ASU 2017-01, which clarifies the definition of a business with the objective of adding guidance to assist companies with evaluating whether transactions should be accounted for as acquisitions (or disposals) of assets or businesses. ASU 2017-01 is expected to reduce the number of transactions that need to be further evaluated as businesses. ASU 2017-01 is effective for interim and annual periods beginning after December 15, 2017. Early adoption is permitted for certain types of transactions. The Company is in the process of evaluating the impact that this guidance will have on its consolidated financial statements.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents include cash in banks and highly liquid investments with original maturity dates of three months or less. The Company’s cash and cash equivalents are held principally at one financial institution and at times may exceed insured limits. The Company periodically evaluates the creditworthiness of this institution and has not experienced any losses on such deposits.
Foreign Currency Translations
The accounting records of the Company are maintained in U.S. dollars. All assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies are translated into U.S. dollars based on the foreign exchange rate on the date of valuation. The Company does not isolate that portion of the results of operations resulting from changes in foreign exchange rates on investments from the fluctuations arising from changes in market prices of securities held. Changes in the relationship of foreign currencies to the U.S. dollar can significantly affect the value of these investments and therefore the earnings of the Company.
Short Term Investments
Short term investments include an investment in a U.S. Treasury obligations fund, which seeks to provide current income and daily liquidity by purchasing U.S. Treasury securities and repurchase agreements that are collateralized by such securities. The Company had $70,498 and $18,892 of such investments at December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively, which are included in investments, at fair value on the accompanying consolidated balance sheets and on the consolidated schedules of investments.
Offering, Organizational and Other Pre-Effective Costs
Offering costs include, among other things, legal fees and other costs pertaining to the preparation of the Company’s registration statements in connection with the continuous public offerings of the Company’s shares. Certain offering costs were funded by CIG and its affiliates and there was no liability for these offering costs to the Company until CIG and its affiliates submitted such costs for reimbursement. Upon meeting the minimum offering requirement on December 17, 2012, the Company incurred and capitalized offering costs of $1,000 that were submitted for reimbursement by CIG (see Note 4). These costs were fully amortized over a twelve month period as an adjustment to capital in excess of par value. The remaining offering costs funded by CIG and its affiliates were incurred when CIG and its affiliates submitted such costs for reimbursement during the year ended December 31, 2014.
Organizational costs include, among other things, the cost of organizing the Company as a Maryland corporation, including the cost of legal services and other fees pertaining to the organization of the Company. All organizational costs were funded by CIG and its affiliates and there was no liability for these organizational costs to the Company until CIG and its affiliates submitted such costs for reimbursement. The Company incurred these costs when CIG and its affiliates submitted such costs for reimbursement during the year ended December 31, 2014.
The following table summarizes offering, organizational and other costs incurred by CIG and by the Company from January 31, 2012 (Inception) through December 31, 2016:
84
CĪON Investment Corporation
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
December 31, 2016
(in thousands, except share and per share amounts)
Offering, Organizational and Other Costs Incurred by CIG | ||||||||||||||||
Period | Organizational Costs | Offering Costs | Other Pre-Effective Costs(4) | Total | ||||||||||||
Year Ended | ||||||||||||||||
December 31, 2012(1) | $ | 192 | $ | 1,620 | $ | 200 | $ | 2,012 | ||||||||
December 31, 2013 | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||
December 31, 2014 | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||
December 31, 2015 | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||
December 31, 2016 | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||
Total | 192 | 1,620 | 200 | 2,012 | ||||||||||||
Costs submitted for reimbursement by CIG(2) | (192 | ) | (1,620 | ) | (200 | ) | (2,012 | ) | ||||||||
Total Unreimbursed Costs at December 31, 2016 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||
Offering, Organizational and Other Costs Incurred by the Company(3) | ||||||||||||||||
Period | Organizational Costs | Offering Costs | Other Pre-Effective Costs(4) | Total | ||||||||||||
Year Ended | ||||||||||||||||
December 31, 2012(1) | $ | — | $ | 30 | $ | — | $ | 30 | ||||||||
December 31, 2013 | — | 1,787 | — | 1,787 | ||||||||||||
December 31, 2014 | — | 2,026 | — | 2,026 | ||||||||||||
December 31, 2015 | — | 2,397 | — | 2,397 | ||||||||||||
December 31, 2016 | — | 1,165 | — | 1,165 | ||||||||||||
Total | — | 7,405 | — | 7,405 | ||||||||||||
Costs reimbursed by the Company(2) | 192 | 1,620 | 200 | 2,012 | ||||||||||||
Total Costs Incurred by the Company | $ | 192 | $ | 9,025 | $ | 200 | $ | 9,417 | ||||||||
Costs paid as of December 31, 2016 | $ | 192 | $ | 8,837 | $ | 200 | $ | 9,229 | ||||||||
Costs accrued as of December 31, 2016(5) | — | 188 | — | 188 | ||||||||||||
Total Costs Incurred by the Company | $ | 192 | $ | 9,025 | $ | 200 | $ | 9,417 | ||||||||
(1) | CIG incurred all offering, organizational and other costs prior to the commencement of operations on December 17, 2012. Subsequent to the commencement of operations, the Company incurred all offering and organizational costs and such costs, including reimbursement of costs originally incurred by CIG, will not exceed 1.5% of the actual gross proceeds raised from the offerings. See Note 4 for actual gross proceeds raised from the offerings and the amount of offering and organizational costs that can be paid by the Company. |
(2) | Of this amount, $1,000 of costs charged directly to equity were submitted for reimbursement by CIG on December 17, 2012. Of the remaining amount, $592 and $420 of costs charged directly to operating expense were submitted for reimbursement by CIG during the three months ended March 31, 2014 and December 31, 2014, respectively. |
(3) | Unless otherwise noted, offering costs incurred directly by the Company are included in general and administrative expense on the consolidated statements of operations. |
(4) | Amounts represent general and administrative expenses, consisting primarily of professional fees and insurance expense, incurred by CIG related to the Company prior to December 17, 2012 and are included in offering, organizational and other costs - CIG in the consolidated statements of operations. For Financial Industry Regulatory Authority, Inc., or FINRA, purposes, these costs are treated as offering and organizational costs and are subject to reimbursement by the Company in accordance with the investment advisory agreement. |
(5) | Of this amount, $45 is presented as Due to CIG - offering, organizational and other costs and the remainder is included in accounts payable and accrued expenses on the consolidated balance sheet at December 31, 2016. |
Income Taxes
The Company elected to be treated for federal income tax purposes as a RIC under Subchapter M of the Code. To qualify and maintain qualification as a RIC, the Company must, among other things, meet certain source of income and asset diversification requirements and distribute to shareholders, for each taxable year, at least 90% of the Company’s “investment company taxable income”, which is generally equal to the sum of the
85
CĪON Investment Corporation
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
December 31, 2016
(in thousands, except share and per share amounts)
Company’s net ordinary income plus the excess, if any, of realized net short-term capital gains over realized net long-term capital losses. If the Company continues to qualify as a RIC and continues to satisfy the annual distribution requirement, the Company will not be subject to corporate level federal income taxes on any income that the Company distributes to its shareholders. The Company intends to make distributions in an amount sufficient to maintain RIC status each year and to avoid any federal income taxes on income. The Company will also be subject to nondeductible federal excise taxes if the Company does not distribute at least 98.0% of net ordinary income, 98.2% of capital gains, if any, and any recognized and undistributed income from prior years for which it paid no federal income taxes.
Two of the Company’s wholly-owned consolidated subsidiaries, View ITC, LLC and View Rise, LLC, or collectively the Taxable Subsidiaries, have elected to be treated as taxable entities for U.S. federal income tax purposes. The Taxable Subsidiaries are not consolidated with the Company for income tax purposes and may generate income tax expense or benefit, and the related tax assets and liabilities, as a result of its ownership of certain portfolio investments. The income tax expense, or benefit, if any, and related tax assets and liabilities, where material, are reflected in the Company’s consolidated financial statements. There were no deferred tax assets or liabilities as of December 31, 2016.
Book/tax differences relating to permanent differences are reclassified among the Company’s capital accounts, as appropriate. Additionally, the tax character of distributions is determined in accordance with income tax regulations that may differ from GAAP (see Note 14).
Uncertainty in Income Taxes
The Company evaluates its tax positions to determine if the tax positions taken meet the minimum recognition threshold for the purposes of measuring and recognizing tax liabilities in the consolidated financial statements. Recognition of a tax benefit or liability with respect to an uncertain tax position is required only when the position is “more likely than not” to be sustained assuming examination by the taxing authorities. The Company recognizes interest and penalties, if any, related to unrecognized tax benefits as income tax expense in the consolidated statements of operations. The Company did not have any uncertain tax positions during the periods presented herein.
The Company is subject to examination by U.S. federal, New York State, New York City and Maryland income tax jurisdictions for 2013, 2014 and 2015.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of the consolidated financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires the Company to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities at the date of the consolidated financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results may materially differ from those estimates.
Valuation of Portfolio Investments
The fair value of the Company’s investments is determined quarterly in good faith by the Company’s board of directors pursuant to its consistently applied valuation procedures and valuation process in accordance with Accounting Standards Codification Topic 820, Fair Value Measurements and Disclosure, or ASC 820. ASC 820 defines fair value as the price that would be received from the sale of an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. ASC 820 also establishes a three-tier fair value hierarchy that prioritizes and ranks the level of market price observability of inputs used in measuring investments at fair value. Inputs used to measure these fair values are classified into the following hierarchy:
Level 1 - Quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities, accessible by the Company at the measurement date.
Level 2 - Quoted prices for similar assets or liabilities in active markets, or quoted prices for identical or similar assets or liabilities in markets that are not active, or other observable inputs other than quoted prices.
Level 3 - | Unobservable inputs for the asset or liability. The inputs used in the determination of fair value may require significant management judgment or estimation. Such information may be the result of consensus pricing information or broker quotes that include a disclaimer that the broker would not be held to such a price in an actual transaction. The non-binding nature of consensus pricing and/or quotes accompanied by the disclaimer would result in classification as a Level 3 asset, assuming no additional corroborating evidence. |
Market price observability is affected by a number of factors, including the type of investment and the characteristics specific to the investment. Investments with readily available active quoted prices or for which fair value can be measured from actively quoted prices generally will have a higher degree of market price observability and a lesser degree of judgment used in measuring fair value.
Based on the observability of the inputs used in the valuation techniques, the Company is required to provide disclosures on fair value measurements according to the fair value hierarchy. The level in the fair value hierarchy for each fair value measurement has been determined based on the lowest level of input that is significant to the fair value measurement. Our assessment of the significance of a particular input to the fair value measurement in its entirety requires judgment and considers factors specific to each investment. The level assigned to the investment valuations may not be indicative of the risk or liquidity associated with investing in such investments. Because of the inherent uncertainties of valuation, the values reflected in the financial statements may differ materially from the value that would be received upon an actual sale of such investments. In addition,
86
CĪON Investment Corporation
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
December 31, 2016
(in thousands, except share and per share amounts)
changes in the market environment and other events that may occur over the life of the investments may cause the gains or losses that the Company ultimately realizes on these investments to materially differ from the valuations currently assigned.
The Company’s investments, excluding short term investments, consist primarily of debt securities that are traded on a private over-the-counter market for institutional investments. CIM attempts to obtain market quotations from at least two brokers or dealers for each investment (if available, otherwise from a principal market maker or a primary market dealer or other independent pricing service). CIM utilizes mid-market pricing to determine fair value unless a different point within the range is more representative. Because of the private nature of this marketplace (meaning actual transactions are not publicly reported) and the non-binding nature of consensus pricing and/or quotes, the Company believes that these valuation inputs result in Level 3 classification within the fair value hierarchy.
Notwithstanding the foregoing, if in the reasonable judgment of CIM, the price of any investment held by the Company and determined in the manner described above does not accurately reflect the fair value of such investment, CIM will value such investment at a price that reflects such investment’s fair value and report such change in the valuation to the board of directors or its designee as soon as practicable. Investments that carry certain restrictions on sale will typically be valued at a discount from the public market value of the investment.
Any investments that are not publicly traded or for which a market price is not otherwise readily available are valued at a price that reflects its fair value. With respect to such investments, the investments are reviewed and valued using one or more of the following types of analyses:
i. | Market comparable statistics and public trading multiples discounted for illiquidity, minority ownership and other factors for companies with similar characteristics. |
ii. | Valuations implied by third-party investments in the applicable portfolio companies. |
iii. | Discounted cash flow analysis, including a terminal value or exit multiple. |
Determination of fair value involves subjective judgments and estimates. Accordingly, these notes to the Company’s consolidated financial statements refer to the uncertainty with respect to the possible effect of such valuations, and any change in such valuations, on the Company’s consolidated financial statements. Below is a description of factors that the Company’s board of directors may consider when valuing the Company’s equity and debt investments where a market price is not readily available:
• | the size and scope of a portfolio company and its specific strengths and weaknesses; |
• | prevailing interest rates for like securities; |
• | expected volatility in future interest rates; |
• | leverage; |
• | call features, put features and other relevant terms of the debt; |
• | the borrower’s ability to adequately service its debt; |
• | the fair market value of the portfolio company in relation to the face amount of its outstanding debt; |
• | the quality of collateral securing the Company’s debt investments; |
• | multiples of earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization, or EBITDA, cash flows, net income, revenues or, in some cases, book value or liquidation value; and |
• | other factors deemed applicable. |
All of these factors may be subject to adjustment based upon the particular circumstances of a portfolio company or the Company’s actual investment position. For example, adjustments to EBITDA may take into account compensation to previous owners, or acquisition, recapitalization, and restructuring expenses or other related or non-recurring items. The choice of analyses and the weight assigned to such factors may vary across investments and may change within an investment if events occur that warrant such a change.
The discounted cash flow model deemed appropriate by CIM is prepared for the applicable investments and reviewed by the Company’s valuation committee consisting of senior management. Such models are prepared at least quarterly or on an as needed basis. The model uses the estimated cash flow projections for the underlying investments and an appropriate discount rate is determined based on the latest financial information available for the borrower, prevailing market trends, comparable analysis and other inputs. The model, key assumptions, inputs, and results are reviewed by the Company’s valuation committee with final approval from the board of directors.
Consistent with the Company’s valuation policy, the Company evaluates the source of inputs, including any markets in which the Company’s investments are trading, in determining fair value.
The Company periodically benchmarks the broker quotes from the brokers or dealers against the actual prices at which the Company purchases and sells its investments. Based on the results of the benchmark analysis and the experience of the Company’s management in purchasing and selling these investments, the Company believes that these quotes are reliable indicators of fair value. The Company may also use other methods to determine
87
CĪON Investment Corporation
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
December 31, 2016
(in thousands, except share and per share amounts)
fair value for securities for which it cannot obtain market quotations through brokers or dealers, including the use of an independent valuation firm. The Company’s valuation committee and board of directors review and approve the valuation determinations made with respect to these investments in a manner consistent with the Company’s valuation process.
The value of the total return swap, or TRS, is primarily based on the increase or decrease in the value of the loans underlying the TRS, as determined by the Company. The loans underlying the TRS are valued in the same manner as loans owned by the Company. As in all cases, the level in the fair value hierarchy for each instrument is determined based on the lowest level of inputs that are significant to the fair value measurement. The Company has classified the TRS as Level 3 within the fair value hierarchy based on the lowest level of significant inputs. For additional information on the TRS, see Note 7.
Revenue Recognition
Securities transactions are accounted for on the trade date. The Company records interest and dividend income on an accrual basis beginning on the trade settlement date or the ex-dividend date, respectively, to the extent that the Company expects to collect such amounts. For investments in equity tranches of collateralized loan obligations, the Company records income based on the effective interest rate determined using the amortized cost and estimated cash flows, which is updated periodically. Loan origination fees, original issue discounts, and market discounts/premiums are recorded and such amounts are amortized as adjustments to interest income over the respective term of the loan using the effective interest method. The Company records prepayment premiums on loans and debt securities as interest income when it receives such amounts. In addition, the Company may generate revenue in the form of commitment, structuring or diligence fees, monitoring fees, fees for providing managerial assistance and possibly consulting fees and performance-based fees. Any such fees generated in connection with investments are recognized when earned.
The Company may have investments in its investment portfolio that contain a PIK interest provision. PIK interest is accrued as interest income if the portfolio company valuation indicates that such PIK interest is collectible and recorded as interest receivable up to the interest payment date. On the interest payment dates, the Company will capitalize the accrued interest receivable attributable to PIK as additional principal due from the borrower. Additional PIK securities typically have the same terms, including maturity dates and interest rates, as the original securities. In order to maintain RIC status, substantially all of this income must be paid out to shareholders in the form of distributions, even if the Company has not collected any cash. For additional information on investments that contain a PIK interest provision, see the consolidated schedules of investments as of December 31, 2016 and 2015.
Loans and debt securities, including those that are individually identified as being impaired under Accounting Standards Codification 310, Receivables, or ASC 310, are generally placed on non-accrual status immediately if, in the opinion of management, principal or interest is not likely to be paid in accordance with the terms of the debt agreement, or when principal or interest is past due 90 days or more. Interest accrued but not collected at the date a loan or security is placed on non-accrual status is reversed against interest income. Interest income is recognized on non-accrual loans or debt securities only to the extent received in cash. However, where there is doubt regarding the ultimate collectibility of principal, cash receipts, whether designated as principal or interest, are thereafter applied to reduce the carrying value of the loan or debt security. Loans or securities are restored to accrual status only when interest and principal payments are brought current and future payments are reasonably assured.
Net Realized Gains or Losses and Net Change in Unrealized Appreciation or Depreciation
Gains or losses on the sale of investments are calculated by using the weighted-average method. The Company measures realized gains or losses by the difference between the net proceeds from the repayment or sale and the weighted-average amortized cost of the investment, without regard to unrealized appreciation or depreciation previously recognized, but considering unamortized upfront fees and prepayment penalties. Net change in unrealized appreciation or depreciation reflects the change in portfolio investment values during the reporting period, including any reversal of previously recorded unrealized appreciation or depreciation when gains or losses are realized.
Derivative Instrument
The Company recognizes all derivative instruments as assets or liabilities at fair value in its consolidated financial statements. Derivative contracts entered into by the Company are not designated as hedging instruments, and as a result, the Company presents changes in fair value through current period earnings.
Derivative instruments are measured in terms of the notional contract amount and derive their value based upon one or more underlying instruments. Derivative instruments are subject to various risks similar to non-derivative instruments including market, credit, liquidity and operational risks. For additional information on the Company's derivative instruments, see Note 7.
Capital Gains Incentive Fee
Pursuant to the terms of the investment advisory agreement the Company entered into with CIM, the incentive fee on capital gains earned on liquidated investments of the Company’s investment portfolio during operations is determined and payable in arrears as of the end of each calendar year. Such fee equals 20% of the Company’s incentive fee capital gains (i.e., the Company’s realized capital gains on a cumulative basis from inception, calculated as of the end of each calendar year, computed net of all realized capital losses and unrealized capital depreciation on a cumulative basis), less the aggregate amount of any previously paid capital gains incentive fees. On a cumulative basis and to the extent that all realized capital losses and unrealized capital depreciation exceed realized capital gains as well as the aggregate realized net capital gains for which a fee has previously been paid,
88
CĪON Investment Corporation
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
December 31, 2016
(in thousands, except share and per share amounts)
the Company would not be required to pay CIM a capital gains incentive fee. On a quarterly basis, the Company accrues for the capital gains incentive fee by calculating such fee as if it were due and payable as of the end of such period.
CIM has not taken any incentive fees with respect to the Company’s TRS to date. For purposes of computing the capital gains incentive fee, CIM will become entitled to a capital gains incentive fee only upon the termination or disposition of the TRS, at which point all net gains and losses of the underlying loans constituting the reference assets of the TRS will be realized. Any net unrealized gains on the TRS are reflected in total assets on the Company’s consolidated balance sheets and included in the computation of the base management fee. Any net unrealized losses on the TRS are reflected in total liabilities on the Company’s consolidated balance sheets and excluded in the computation of the base management fee.
While the investment advisory agreement with CIM neither includes nor contemplates the inclusion of unrealized gains in the calculation of the capital gains incentive fee, pursuant to an interpretation of the American Institute for Certified Public Accountants, or AICPA, Technical Practice Aid for investment companies, the Company accrues capital gains incentive fees on unrealized gains. This accrual reflects the incentive fees that would be payable to CIM if the Company’s entire investment portfolio was liquidated at its fair value as of the balance sheet date even though CIM is not entitled to an incentive fee with respect to unrealized gains unless and until such gains are actually realized.
Net Increase (Decrease) in Net Assets per Share
Net increase (decrease) in net assets per share is calculated based upon the daily weighted average number of shares of common stock outstanding during the reporting period.
Distributions
Distributions to shareholders are recorded as of the record date. The amount to be paid as a distribution is determined by the board of directors on a monthly basis. Net realized capital gains, if any, are distributed at least annually.
Note 3. Share Transactions
The Company’s initial continuous public offering commenced on July 2, 2012 and ended on December 31, 2015. The Company’s follow-on continuous public offering commenced on January 25, 2016.
The following table summarizes transactions with respect to shares of the Company’s common stock during the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014:
Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||
Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | |||||||||||||||
Gross shares/proceeds from the offering | 3,575,156 | $ | 34,831 | 47,539,457 | $ | 487,604 | 36,871,074 | $ | 380,483 | |||||||||||
Reinvestment of distributions | 4,413,672 | 39,047 | 3,216,195 | 29,886 | 1,488,917 | 13,997 | ||||||||||||||
Total gross shares/proceeds | 7,988,828 | 73,878 | 50,755,652 | 517,490 | 38,359,991 | 394,480 | ||||||||||||||
Sales commissions and dealer manager fees | — | (2,823 | ) | — | (43,746 | ) | — | (33,965 | ) | |||||||||||
Net shares/proceeds | 7,988,828 | 71,055 | 50,755,652 | 473,744 | 38,359,991 | 360,515 | ||||||||||||||
Share repurchase program | (2,015,632 | ) | (17,832 | ) | (759,920 | ) | (7,097 | ) | (51,540 | ) | (485 | ) | ||||||||
Net shares/proceeds from share transactions | 5,973,196 | $ | 53,223 | 49,995,732 | $ | 466,647 | 38,308,451 | $ | 360,030 | |||||||||||
During the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, the Company sold 7,988,828, 50,755,652 and 38,359,991 shares, respectively, at an average price per share of $9.25, $10.20 and $10.28, respectively.
As of December 31, 2016, the Company sold 109,787,557 shares of common stock for net proceeds of $1,117,566 at an average price per share of $10.18. The net proceeds include gross proceeds received from reinvested shareholder distributions of $84,473, for which the Company issued 9,281,664 shares of common stock, and gross proceeds paid for shares of common stock tendered for repurchase of $25,414, for which the Company repurchased 2,827,092 shares of common stock.
During the period from January 1, 2017 to March 9, 2017, the Company sold 992,095 shares of common stock pursuant to its follow-on continuous public offering for net proceeds of $9,398 at an average price per share of $9.47. The net proceeds include gross proceeds received from reinvested shareholder distributions of $6,881, for which the Company issued 755,158 shares of common stock, and gross proceeds paid for shares of common stock tendered for repurchase of $7,370, for which the Company repurchased 814,223 shares of common stock.
Since commencing its initial continuous public offering on July 2, 2012 and through March 9, 2017, the Company sold 110,720,587 shares of common stock for net proceeds of $1,126,475 at an average price per share of $10.17. The net proceeds include gross proceeds received from reinvested
89
CĪON Investment Corporation
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
December 31, 2016
(in thousands, except share and per share amounts)
shareholder distributions of $91,354, for which the Company issued 10,036,822 shares of common stock, and gross proceeds paid for shares of common stock tendered for repurchase of $32,784, for which the Company repurchased 3,641,315 shares of common stock.
To ensure that the offering price per share, net of sales commissions and dealer manager fees, equaled or exceeded the net asset value per share on each subscription closing date and distribution reinvestment date, certain of the Company’s directors increased the offering price per share of common stock on certain dates. Due to a decline in the Company’s net asset value per share to an amount more than 2.5% below the Company’s then-current net offering price, certain of the Company’s directors decreased the offering price per share of common stock on certain dates.
The changes to our offering price per share since the commencement of our initial continuous public offering and the associated approval and effective dates of such changes were as follows:
Approval Date | Effective Date | New Offering Price Per Share | ||
December 28, 2012 | January 2, 2013 | $10.04 | ||
January 31, 2013 | February 1, 2013 | $10.13 | ||
March 14, 2013 | March 18, 2013 | $10.19 | ||
May 15, 2013 | May 16, 2013 | $10.24 | ||
August 15, 2013 | August 16, 2013 | $10.32 | ||
February 4, 2014 | February 5, 2014 | $10.45 | ||
October 6, 2015 | October 7, 2015 | $10.20 | ||
November 24, 2015 | November 25, 2015 | $10.05 | ||
December 22, 2015 | December 23, 2015 | $9.95 | ||
March 8, 2016 | March 9, 2016 | $9.40 | ||
March 15, 2016 | March 16, 2016 | $9.45 | ||
March 22, 2016 | March 23, 2016 | $9.50 | ||
March 29, 2016 | March 30, 2016 | $9.55 | ||
April 5, 2016 | April 6, 2016 | $9.60 | ||
April 26, 2016 | April 27, 2016 | $9.65 | ||
May 3, 2016 | May 4, 2016 | $9.70 | ||
May 10, 2016 | May 11, 2016 | $9.75 | ||
May 31, 2016 | June 1, 2016 | $9.80 | ||
July 19, 2016 | July 20, 2016 | $9.85 | ||
July 26, 2016 | July 27, 2016 | $9.90 | ||
August 9, 2016 | August 10, 2016 | $9.95 | ||
August 23, 2016 | August 24, 2016 | $10.00 | ||
October 4, 2016 | October 5, 2016 | $10.05 | ||
October 11, 2016 | October 12, 2016 | $10.10 | ||
January 3, 2017 | January 4, 2017 | $9.57(1) | ||
January 24, 2017 | January 25, 2017 | $9.60 | ||
March 7, 2017 | March 8, 2017 | $9.65 | ||
(1) - On December 28, 2016, the Company entered into an amended and restated follow-on dealer manager agreement pursuant to which, among other things, the dealer manager fee was reduced to 2% and selling commissions were reduced to up to 3%. As a result, the Company adjusted its public offering price from $10.10 per share to $9.57 per share in order to maintain its net offering price of $9.09 per share (net of selling commissions and dealer manager fees). | ||||
Share Repurchase Program
Beginning in the first quarter of 2014, the Company began offering, and on a quarterly basis thereafter it intends to continue offering, to repurchase shares on such terms as may be determined by the Company’s board of directors in its complete and absolute discretion unless, in the judgment of the independent directors of the Company’s board of directors, such repurchases would not be in the best interests of the Company’s shareholders or would violate applicable law.
The Company limits the number of shares to be repurchased during any calendar year to the number of shares it can repurchase with the proceeds it receives from the issuance of shares pursuant to its fifth amended and restated distribution reinvestment plan. At the discretion of the Company’s board of directors, it may also use cash on hand, cash available from borrowings and cash from liquidation of investments as of the end of the applicable period to repurchase shares. In addition, the Company limits the number of shares to be repurchased in any calendar year to 15% of the weighted average number of shares outstanding in the prior calendar year, or 3.75% in each quarter, though the actual number of shares that it offers to repurchase may be less in light of the limitations noted above.
90
CĪON Investment Corporation
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
December 31, 2016
(in thousands, except share and per share amounts)
On November 2, 2015, the Company amended the terms of the quarterly share repurchase program, effective as of the Company’s quarterly repurchase offer for the fourth quarter of 2015, which commenced in November 2015 and was completed in January 2016. Under the amended share repurchase program, the Company offered to repurchase shares of common stock at a price per share of $8.96, which was (i) not less than the net asset value per share immediately prior to January 4, 2016 and (ii) not more than 2.5% greater than the net asset value per share as of such date.
On January 22, 2016, the Company further amended the terms of the quarterly share repurchase program, effective as of the Company’s quarterly repurchase offer for the first quarter of 2016, which commenced in February 2016 and was completed in April 2016. Under the further amended share repurchase program, the Company offered to repurchase shares of common stock at a price equal to 90% of the public offering price in effect on each date of repurchase.
On December 8, 2016, the Company further amended the terms of the quarterly share repurchase program, effective as of the Company's quarterly repurchase offer for the fourth quarter of 2016, which commenced in November 2016 and was completed in January 2017. Under the further amended share and repurchase program, the Company will offer to repurchase shares of common stock at a price equal to the estimated net asset value per share determined on each date of repurchase.
Any periodic repurchase offers are subject in part to the Company’s available cash and compliance with the BDC and RIC qualification and diversification rules promulgated under the 1940 Act and the Code, respectively. While the Company conducts quarterly tender offers as described above, it is not required to do so and may suspend or terminate the share repurchase program at any time, upon 30 days’ notice.
The following table summarizes the share repurchases completed during the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015:
Three Months Ended | Repurchase Date | Shares Repurchased | Percentage of Shares Tendered That Were Repurchased | Repurchase Price Per Share | Aggregate Consideration for Repurchased Shares | ||||||||||
2015 | |||||||||||||||
March 31, 2015 | January 7, 2015 | 48,947 | 100% | $ | 9.41 | $ | 460 | ||||||||
June 30, 2015 | April 1, 2015 | 42,288 | 100% | 9.41 | 398 | ||||||||||
September 30, 2015 | July 1, 2015 | 449,538 | 100% | 9.41 | 4,228 | ||||||||||
December 31, 2015 | October 7, 2015 | 219,147 | 100% | 9.18 | 2,011 | ||||||||||
Total share repurchases during the year ended December 31, 2015 | 759,920 | $ | 7,097 | ||||||||||||
2016 | |||||||||||||||
March 31, 2016 | January 4, 2016 | 272,148 | 100% | $ | 8.96 | $ | 2,437 | ||||||||
June 30, 2016 | April 6, 2016 | 674,428 | 100% | 8.64 | 5,827 | ||||||||||
September 30, 2016 | July 6, 2016 | 449,816 | 100% | 8.82 | 3,967 | ||||||||||
December 31, 2016 | October 5, 2016 | 619,240 | 100% | 9.05 | 5,601 | ||||||||||
Total share repurchases during the year ended December 31, 2016 | 2,015,632 | $ | 17,832 | ||||||||||||
Note 4. Transactions with Related Parties
For the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, fees and other expenses incurred by the Company related to CIM and its affiliates were as follows:
Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||
Entity | Capacity | Description | 2016 | 2015 | 2014(3) | |||||||||||
CION Securities, LLC | Dealer manager | Dealer manager fees(1) | $ | 953 | $ | 14,440 | $ | 11,172 | ||||||||
CIM | Investment adviser | Management fees(2) | 20,092 | 14,827 | 6,132 | |||||||||||
CIM | Investment adviser | Incentive fees(2) | — | — | (757 | ) | ||||||||||
ICON Capital, LLC | Administrative services provider | Administrative services expense(2) | 1,834 | 1,900 | 1,792 | |||||||||||
CIG | Sponsor | Reimbursement of offering, organizational and other costs(2) | — | — | 1,012 | |||||||||||
CIG | Sponsor | Recoupment of expense support(2) | 667 | 4,667 | 622 | |||||||||||
$ | 23,546 | $ | 35,834 | $ | 19,973 | |||||||||||
(1) Amounts charged directly to equity.
(2) Amounts charged directly to operations.
91
CĪON Investment Corporation
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
December 31, 2016
(in thousands, except share and per share amounts)
(3) | For the year ended December 31, 2014, CIG provided expense support of $1,880 pursuant to the expense support and conditional reimbursement agreement. Of this amount, $2,106 related to management fees, $1 related to administrative services expense and ($227) related to incentive fees. |
On December 28, 2016, the Company entered into an amended and restated follow-on dealer manager agreement with CIM and CION Securities, LLC, or CION Securities, in connection with the Company's continuous follow-on public offering. Under the amended and restated dealer manager agreement, the dealer manager fee was reduced from 3% to 2% of gross offering proceeds and selling commissions to the selling dealers were reduced from up to 7% to up to 3% of gross offering proceeds. Such costs are charged against capital in excess of par value when incurred. Since commencing its initial continuous public offering on July 2, 2012 and through March 9, 2017, the Company paid or accrued sales commissions of $63,442 to the selling dealers and dealer manager fees of $31,165 to CION Securities.
The Company has entered into an investment advisory agreement with CIM. On November 1, 2016, the board of directors of the Company, including a majority of the board of directors who are not interested persons, approved the renewal of the investment advisory agreement for a period of twelve months commencing December 17, 2016. Pursuant to the investment advisory agreement, CIM is paid an annual base management fee equal to 2.0% of the average value of the Company’s gross assets, less cash and cash equivalents, and an incentive fee based on the Company’s performance, as described below. The base management fee is payable quarterly in arrears and is calculated based on the two most recently completed calendar quarters. The incentive fee consists of two parts. The first part, which is referred to as the subordinated incentive fee on income, is calculated and payable quarterly in arrears based on “pre-incentive fee net investment income” for the immediately preceding quarter and is subject to a hurdle rate, measured quarterly and expressed as a rate of return on adjusted capital, as defined in the investment advisory agreement, equal to 1.875% per quarter, or an annualized rate of 7.5%. The second part of the incentive fee, which is referred to as the incentive fee on capital gains, is described in Note 2. Refer to Note 7 for a discussion of CIM’s entitlement to receive incentive fees and the Company's accrual of the incentive fee on capital gains with respect to the TRS.
The Company accrues the capital gains incentive fee based on net realized gains and net unrealized appreciation; however, under the terms of the investment advisory agreement, the fee payable to CIM is based on net realized gains and unrealized depreciation and no such fee is payable with respect to unrealized appreciation unless and until such appreciation is actually realized. As of and for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, the Company had no liability for and did not record any capital gains incentive fees. For the year ended December 31, 2014, capital gains incentive fees were ($757), of which ($530) related to the change in unrealized depreciation.
With respect to the TRS, CIM will become entitled to receive a capital gains incentive fee only upon the termination or disposition of the TRS, at which point all net gains and losses of the underlying loans constituting the reference assets of the TRS will be realized. See Note 2 and Note 7 for an additional discussion of CIM's entitlement to receive payment of incentive fees and the Company's accrual of the incentive fee on capital gains with respect to the TRS.
The Company entered into an administration agreement with CIM’s affiliate, ICON Capital, LLC, or ICON Capital, pursuant to which ICON Capital furnishes the Company with administrative services including accounting, investor relations and other administrative services necessary to conduct its day-to-day operations. On November 1, 2016, the board of directors of the Company, including a majority of the board of directors who are not interested persons, approved the renewal of the administration agreement for a period of twelve months commencing December 17, 2016. ICON Capital is reimbursed for administrative expenses it incurs on the Company’s behalf in performing its obligations, provided that such reimbursement will be for the lower of ICON Capital’s actual costs or the amount that the Company would be required to pay for comparable administrative services in the same geographic location. Such costs will be reasonably allocated to the Company on the basis of assets, revenues, time records or other reasonable methods. The Company will not reimburse ICON Capital for any services for which it receives a separate fee or for rent, depreciation, utilities, capital equipment or other administrative items allocated to a person with a controlling interest in ICON Capital.
Under the terms of the investment advisory agreement, CIM and certain of its affiliates, which includes CIG, are entitled to receive reimbursement of up to 1.5% of the gross proceeds raised until all offering and organizational costs have been reimbursed. The Company’s payment of offering and organizational costs will not exceed 1.5% of the actual gross proceeds raised from the offerings (without giving effect to any potential expense support from CIG and its affiliates). If the Company sells the maximum number of shares at its latest public offering price of $9.65 per share, the Company estimates that it may incur up to approximately $29,832 of expenses. With respect to any reimbursements for offering and organizational costs, the Company will interpret the 1.5% limit based on actual gross proceeds raised at the time of such reimbursement. In addition, the Company will not issue any of its shares or other securities for services or for property other than cash or securities except as a dividend or distribution to its security holders or in connection with a reorganization.
From inception through December 31, 2012, CIG and its affiliates incurred offering, organizational and other pre-effective costs of $2,012. Of these costs, $1,812 represented offering and organizational costs, all of which have been submitted to the Company for reimbursement. The Company paid $450 in October 2013, $550 in March 2014, $592 in May 2014, and $420 in March 2015. No additional material offering, organizational or other pre-effective costs have been incurred by CIG or its affiliates subsequent to December 31, 2012.
Reinvestment of shareholder distributions and share repurchases are excluded from the gross proceeds from the Company’s offerings for purposes of determining the total amount of offering and organizational costs that can be paid by the Company. As of December 31, 2016, the Company raised gross offering proceeds of $1,058,507, of which it can pay up to $15,878 in offering and organizational costs (which represents 1.5% of the actual gross offering proceeds raised). Through December 31, 2016, the Company paid $9,229 of such costs, leaving an additional $6,649 that can be paid. As of March 9, 2017, the Company raised gross offering proceeds of $1,067,905, of which it can pay up to $16,019 in offering and organizational costs
92
CĪON Investment Corporation
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
December 31, 2016
(in thousands, except share and per share amounts)
(which represents 1.5% of the actual gross offering proceeds raised). Through March 9, 2017, the Company paid $9,464 of such costs, leaving an additional $6,555 that can be paid.
On January 30, 2013, the Company entered into the expense support and conditional reimbursement agreement with CIG, whereby CIG agreed to provide expense support to the Company in an amount that is sufficient to: (1) ensure that no portion of the Company’s distributions to shareholders will be paid from its offering proceeds or borrowings, and/or (2) reduce the Company’s operating expenses until it has achieved economies of scale sufficient to ensure that it bears a reasonable level of expense in relation to its investment income. On December 13, 2013 and January 16, 2015, the Company and CIG amended the expense support and conditional reimbursement agreement to extend the termination date of such agreement from January 30, 2014 to January 30, 2015 and from January 30, 2015 to December 31, 2015, respectively. On December 16, 2015 and December 14, 2016, the Company further amended and restated the expense support and conditional reimbursement agreement for purposes of including AIM as a party to the agreement and extending the termination date from December 31, 2016 to December 31, 2017, respectively. Commencing with the quarter beginning January 1, 2016, CIG and AIM each agrees to provide expense support to the Company for 50% of its expenses as described above.
For the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, the Company did not receive any expense support from CIG or AIM. For the year ended December 31, 2014, the total expense support from CIG, which funded distributions and related to certain operating expenses, was $1,880. See Note 5 for additional information on the sources of the Company’s distributions.
Pursuant to the expense support and conditional reimbursement agreement, the Company will have a conditional obligation to reimburse CIG for any amounts funded by CIG under such agreement (i) if expense support amounts funded by CIG exceed operating expenses incurred during any fiscal quarter, (ii) if the sum of the Company’s net investment income for tax purposes, net capital gains and the amount of any dividends and other distributions paid to the Company on account of investments in portfolio companies (to the extent not included in net investment income or net capital gains for tax purposes) exceeds the distributions paid by the Company to shareholders, and (iii) during any fiscal quarter occurring within three years of the date on which CIG funded such amount. Pursuant to the second amended and restated expense support and conditional reimbursement agreement, the Company will have a conditional obligation to reimburse CIG and AIM for any amounts funded by CIG and AIM under the same circumstances described above. The obligation to reimburse CIG and AIM for any expense support provided by CIG and AIM under such agreement is further conditioned by the following: (i) in the period in which reimbursement is sought, the ratio of operating expenses to average net assets, when considering the reimbursement, cannot exceed the ratio of operating expenses to average net assets, as defined, for the period when the expense support was provided; (ii) in the period when reimbursement is sought, the annualized distribution rate cannot fall below the annualized distribution rate for the period when the expense support was provided; and (iii) the expense support can only be reimbursed within three years from the date the expense support was provided.
Expense support, if any, will be determined as appropriate to meet the objectives of the expense support and conditional reimbursement agreement. During the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, the Company recorded obligations to repay expense support from CIG of $667, $4,667 and $622, respectively. During the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, the Company repaid expense support to CIG of $1,147, $4,187 and $622, respectively. The Company may or may not be requested to reimburse any remaining expense support in the future.
The Company, AIM, or CIG may terminate the expense support and conditional reimbursement agreement at any time. CIG and AIM have indicated that they expect to continue such expense support until they believe that the Company has achieved economies of scale sufficient to ensure that it bears a reasonable level of expenses in relation to its income. If the Company terminates the investment advisory agreement with CIM and/or the investment sub-advisory agreement with AIM, the Company may be required to repay CIG and AIM all unreimbursed expense support funded by CIG and AIM within three years of the date of termination. The specific amount of expense support provided by CIG and AIM, if any, will be determined at the end of each quarter. There can be no assurance that the expense support and conditional reimbursement agreement will remain in effect or that CIG and AIM will support any portion of the Company’s expenses in future quarters.
The table below presents a summary of all expenses supported by CIG for each of the following three month periods in which the Company received expense support from CIG and the associated dates through which such expenses are eligible for reimbursement from the Company.
Three Months Ended | Expense Support from CIG | Recoupment of Expense Support | Unreimbursed Expense Support | Ratio of Operating Expense to Average Net Assets for the Period(1) | Annualized Distribution Rate for the Period(3) | Eligible for Reimbursement through | ||||||||||||||
December 31, 2012 | $ | 117 | $ | 117 | $ | — | 0.93 | % | 0.00%(2) | December 31, 2015 | ||||||||||
March 31, 2013 | 819 | 819 | — | 2.75 | % | 7.00 | % | March 31, 2016 | ||||||||||||
June 30, 2013 | 1,148 | 1,148 | — | 1.43 | % | 7.00 | % | June 30, 2016 | ||||||||||||
September 30, 2013 | 1,297 | 1,297 | — | 0.49 | % | 7.00 | % | September 30, 2016 | ||||||||||||
December 31, 2013 | 695 | 695 | — | 0.31 | % | 7.00 | % | December 31, 2016 | ||||||||||||
March 31, 2014 | 1,049 | 1,049 | — | 0.27 | % | 7.00 | % | March 31, 2017 | ||||||||||||
December 31, 2014 | 831 | 831 | — | 0.15 | % | 7.00 | % | December 31, 2017 | ||||||||||||
Total | $ | 5,956 | $ | 5,956 | $ | — | ||||||||||||||
(1) | Operating expenses include all expenses borne by the Company, except for offering and organizational costs, base management fees, incentive fees, administrative services expenses, other general and administrative expenses owed to CIM and its affiliates and interest expense. |
93
CĪON Investment Corporation
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
December 31, 2016
(in thousands, except share and per share amounts)
(2) | The Company did not declare any distributions during the three months ended December 31, 2012. |
(3) | Annualized Distribution Rate equals the annualized rate of distributions paid to shareholders based on the amount of the regular cash distributions paid immediately prior to the date the expense support payment obligation was incurred by CIG. Annualized Distribution Rate does not include special cash or stock distributions paid to shareholders. Annualized Distribution Rate is calculated based on the maximum historical offering price at each record date. |
As of December 31, 2016 and 2015, the total liability payable to CIM and its affiliates was $6,508 and $5,735, respectively, which primarily related to fees earned by CIM during the three months ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively.
Because CIM’s senior management team is comprised of substantially the same personnel as the senior management team of the Company’s affiliate, ICON Capital, which is the investment manager to certain equipment finance funds, or equipment funds, such members of senior management provide investment advisory and management services to the equipment funds in addition to the Company. In the event that CIM undertakes to provide investment advisory services to other clients in the future, it will strive to allocate investment opportunities in a fair and equitable manner consistent with the Company’s investment objective and strategies so that the Company will not be disadvantaged in relation to any other client of the investment adviser or its senior management team. However, it is currently possible that some investment opportunities will be provided to the equipment funds or other clients of CIM rather than to the Company.
Indemnifications
The investment advisory agreement, the investment sub-advisory agreement, the administration agreement and the dealer manager agreement each provide certain indemnifications from the Company to the other relevant parties to such agreements. The Company’s maximum exposure under these agreements is unknown. However, the Company has not experienced claims or losses pursuant to these agreements and believes the risk of loss related to such indemnifications to be remote.
Note 5. Distributions
On February 1, 2014, the Company changed from semi-monthly closings to weekly closings for the sale of the Company’s shares. As result, the Company’s board of directors authorizes and declares on a monthly basis a weekly distribution amount per share of common stock.
The Company’s board of directors declared distributions for 52, 52 and 49 record dates during the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. Declared distributions are paid monthly.
The following table presents cash distributions per share that were declared during the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014:
Distributions | ||||||||
Three Months Ended | Per Share | Amount | ||||||
2014 | ||||||||
March 31, 2014 (nine record dates) | $ | 0.1679 | $ | 3,315 | ||||
June 30, 2014 (thirteen record dates) | 0.1829 | 5,120 | ||||||
September 30, 2014 (fourteen record dates) | 0.1969 | 7,396 | ||||||
December 31, 2014 (thirteen record dates) | 0.1829 | 8,716 | ||||||
Total distributions for the year ended December 31, 2014 | $ | 0.7306 | $ | 24,547 | ||||
2015 | ||||||||
March 31, 2015 (thirteen record dates) | $ | 0.1829 | $ | 10,767 | ||||
June 30, 2015 (thirteen record dates) | 0.1829 | 13,223 | ||||||
September 30, 2015 (thirteen record dates) | 0.1829 | 15,517 | ||||||
December 31, 2015 (thirteen record dates) | 0.1829 | 17,761 | ||||||
Total distributions for the year ended December 31, 2015 | $ | 0.7316 | $ | 57,268 | ||||
2016 | ||||||||
March 31, 2016 (thirteen record dates) | $ | 0.1829 | $ | 19,004 | ||||
June 30, 2016 (thirteen record dates) | 0.1829 | 19,167 | ||||||
September 30, 2016 (thirteen record dates) | 0.1829 | 19,480 | ||||||
December 31, 2016 (thirteen record dates) | 0.1829 | 19,808 | ||||||
Total distributions for the year ended December 31, 2016 | $ | 0.7316 | $ | 77,459 | ||||
On December 13, 2016, the Company’s board of directors declared five weekly cash distributions of $0.014067 per share, which were paid on February 1, 2017 to shareholders of record on January 3, January 10, January 17, January 24, and January 31, 2017. On January 17, 2017, the
94
CĪON Investment Corporation
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
December 31, 2016
(in thousands, except share and per share amounts)
Company’s board of directors declared four weekly cash distributions of $0.014067 per share, which were paid on March 1, 2017 to shareholders of record on February 7, February 14, February 21, and February 28, 2017. On February 21, 2017, the Company’s board of directors declared four weekly cash distributions of $0.014067 per share, payable on March 29, 2017 to shareholders of record on March 7, March 14, March 21, and March 28, 2017.
The Company has adopted an “opt in” distribution reinvestment plan for shareholders. As a result, if the Company makes a distribution, shareholders will receive distributions in cash unless they specifically “opt in” to the fifth amended and restated distribution reinvestment plan so as to have their cash distributions reinvested in additional shares of the Company’s common stock.
On November 2, 2015, the Company further amended and restated its distribution reinvestment plan pursuant to the third amended and restated distribution reinvestment plan, or the Third Amended DRIP. The Third Amended DRIP was effective as of, and first applied to the reinvestment of cash distributions paid on or after, the closing of the Company’s initial continuous public offering on December 31, 2015. Prior to the Third Amended DRIP, cash distributions to participating shareholders were reinvested in additional shares of common stock at a purchase price equal to 90% of the public offering price per share in effect as of the date of issuance. Under the Third Amended DRIP, cash distributions to participating shareholders were reinvested in additional shares of common stock at a purchase price determined by the Company’s board of directors or a committee thereof, in its sole discretion, that was (i) not less than the net asset value per share determined in good faith by the board of directors or a committee thereof, in their sole discretion, immediately prior to the payment of the distribution, or the NAV Per Share, and (ii) not more than 2.5% greater than the NAV Per Share as of such date.
On January 22, 2016, the Company further amended and restated its distribution reinvestment plan pursuant to the fourth amended and restated distribution reinvestment plan, or the Fourth Amended DRIP. The Fourth Amended DRIP became effective as of, and first applied to the reinvestment of cash distributions paid on, March 30, 2016. Under the Fourth Amended DRIP, cash distributions to participating shareholders were reinvested in additional shares of common stock at a purchase price equal to 90% of the public offering price per share in effect as of the date of issuance.
On December 8, 2016, the Company further amended and restated its distribution reinvestment plan pursuant to the fifth amended and restated distribution reinvestment plan, or the Fifth Amended DRIP. The Fifth Amended DRIP became effective as of, and first applied to the reinvestment of cash distributions paid on, February 1, 2017. Under the Fifth Amended DRIP, cash distributions to participating shareholders will be reinvested in additional shares of common stock at a purchase price equal to the estimated net asset value per share of common stock as of the date of issuance.
The Company may fund its cash distributions to shareholders from any sources of funds available to the Company, including offering proceeds, borrowings, net investment income from operations, capital gains proceeds from the sale of assets, non-capital gains proceeds from the sale of assets, dividends or other distributions paid to it on account of preferred and common equity investments in portfolio companies and expense support from CIG and AIM, which is subject to recoupment. The Company has not established limits on the amount of funds it may use from available sources to make distributions. Through December 31, 2014, a portion of the Company’s distributions resulted from expense support from CIG, and future distributions may result from expense support from CIG and AIM, each of which is subject to repayment by the Company within three years. The purpose of this arrangement is to avoid such distributions being characterized as a return of capital. Shareholders should understand that any such distributions are not based on the Company’s investment performance, and can only be sustained if the Company achieves positive investment performance in future periods and/or CIG and AIM continue to provide such expense support. Shareholders should also understand that the Company’s future repayments of expense support will reduce the distributions that they would otherwise receive. There can be no assurance that the Company will achieve such performance in order to sustain these distributions, or be able to pay distributions at all. CIG and AIM have no obligation to provide expense support to the Company in future periods. For the year ended December 31, 2014, if certain expenses were not supported by CIG, some of the distributions may have been a return of capital as described in Note 14.
The following table reflects the sources of cash distributions on a GAAP basis that the Company has declared on its shares of common stock during the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014:
Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Source of Distribution | Per Share | Amount | Percentage | Per Share | Amount | Percentage | Per Share | Amount | Percentage | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net investment income(1) | $ | 0.4302 | $ | 45,549 | 58.8 | % | $ | 0.3164 | $ | 24,762 | 43.2 | % | $ | 0.1792 | $ | 6,020 | 24.5 | % | |||||||||||||||
Net realized gain on total return swap | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net interest and other income from TRS portfolio | 0.2480 | 26,273 | 33.9 | % | 0.3868 | 30,281 | 52.9 | % | 0.4360 | 14,650 | 59.7 | % | |||||||||||||||||||||
Net gain on TRS loan sales | 0.0277 | 2,916 | 3.8 | % | 0.0060 | 472 | 0.8 | % | 0.0696 | 2,339 | 9.5 | % | |||||||||||||||||||||
Net realized gain on investments | 0.0257 | 2,721 | 3.5 | % | 0.0143 | 1,121 | 2.0 | % | 0.0458 | 1,538 | 6.3 | % | |||||||||||||||||||||
Distributions in excess of net investment income(2) | — | — | — | 0.0081 | 632 | 1.1 | % | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Total distributions | $ | 0.7316 | $ | 77,459 | 100.0 | % | $ | 0.7316 | $ | 57,268 | 100.0 | % | $ | 0.7306 | $ | 24,547 | 100.0 | % | |||||||||||||||
(1) | Distributions from net investment income include expense support from CIG of $1,880 for the year ended December 31, 2014. |
95
CĪON Investment Corporation
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
December 31, 2016
(in thousands, except share and per share amounts)
(2) | Distributions in excess of net investment income represent certain expenses, which are not deductible on a tax-basis. Unearned capital gains incentive fees and certain offering expenses reduce GAAP basis net investment income, but do not reduce tax basis net investment income. These tax-related adjustments represent additional net investment income available for distribution for tax purposes. See Note 14 for the sources of the Company's cash distributions on a tax basis. |
Note 6. Investments
The composition of the Company’s investment portfolio as of December 31, 2016 and 2015 at amortized cost and fair value was as follows:
December 31, 2016 | December 31, 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Cost(1) | Fair Value | Percentage of Investment Portfolio | Cost(1) | Fair Value | Percentage of Investment Portfolio | |||||||||||||||||
Senior secured first lien debt | $ | 489,904 | $ | 489,913 | 48.1 | % | $ | 106,147 | $ | 104,187 | 16.0 | % | ||||||||||
Senior secured second lien debt | 437,240 | 434,347 | 42.6 | % | 468,899 | 453,713 | 69.7 | % | ||||||||||||||
Collateralized securities and structured products - debt | 39,471 | 38,114 | 3.7 | % | 44,361 | 41,663 | 6.4 | % | ||||||||||||||
Collateralized securities and structured products - equity | 37,713 | 34,648 | 3.4 | % | 31,184 | 24,604 | 3.8 | % | ||||||||||||||
Unsecured debt | 17,290 | 16,851 | 1.7 | % | 29,553 | 26,740 | 4.1 | % | ||||||||||||||
Equity | 4,832 | 5,107 | 0.5 | % | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Subtotal/total percentage | 1,026,450 | 1,018,980 | 100.0 | % | 680,144 | 650,907 | 100.0 | % | ||||||||||||||
Short term investments(2) | 70,498 | 70,498 | 18,892 | 18,892 | ||||||||||||||||||
Total investments | $ | 1,096,948 | $ | 1,089,478 | $ | 699,036 | $ | 669,799 | ||||||||||||||
(1) | Cost represents the original cost adjusted for the amortization of premiums and/or accretion of discounts, as applicable, for debt investments, and cost for equity investments. |
(2) | Short term investments represent an investment in a fund that invests in highly liquid investments with average original maturity dates of three months or less. |
Acquisition of Credit Suisse Park View BDC, Inc.
On September 30, 2016, Park South Funding, LLC, or Park South, a newly-formed, wholly-owned consolidated subsidiary of the Company, and Credit Suisse Alternative Capital, LLC, or CSAC, the sole owner of Credit Suisse Park View BDC, Inc., or CS Park View, entered into a Purchase and Sale Agreement to effect and consummate the acquisition of CS Park View by Park South. Pursuant to the Purchase and Sale Agreement, Park South acquired one hundred percent of the issued and outstanding shares of common stock of CS Park View from CSAC for a cash purchase price of $276,852. Substantially all of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed were financial assets (interests in senior secured loans and partnership interests of 26 portfolio companies as well as interest receivable and accrued expenses). The Company funded the cash purchase price partially with cash on hand and proceeds received from the JPM Credit Facility (see Note 8).
The acquisition has been accounted for by the Company under the asset acquisition method of accounting in accordance with ASC 805-50, Business Combinations—Related Issues. Under the asset acquisition method of accounting, net assets are recognized based on their cost to the acquiring entity, which includes transaction costs. The purchase price of the assets acquired is allocated to the individual assets acquired or liabilities assumed based on their determined fair values and does not give rise to goodwill. The Company determined that the fair value of the net assets acquired equaled the purchase price, excluding transaction costs. Accordingly, transaction costs of $498 have been expensed during the three months ended September 30, 2016.
The following tables show the composition of the Company’s investment portfolio by industry classification and geographic dispersion, and the percentage, by fair value, of the total investment portfolio assets in such industries and geographies as of December 31, 2016 and 2015:
96
CĪON Investment Corporation
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
December 31, 2016
(in thousands, except share and per share amounts)
December 31, 2016 | December 31, 2015 | |||||||||||||
Industry Classification | Investments at Fair Value | Percentage of Investment Portfolio | Investments at Fair Value | Percentage of Investment Portfolio | ||||||||||
High Tech Industries | $ | 217,339 | 21.3 | % | $ | 86,848 | 13.3 | % | ||||||
Services: Business | 126,869 | 12.5 | % | 124,412 | 19.1 | % | ||||||||
Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals | 118,337 | 11.6 | % | 54,122 | 8.3 | % | ||||||||
Diversified Financials | 72,762 | 7.1 | % | 66,267 | 10.2 | % | ||||||||
Media: Advertising, Printing & Publishing | 54,354 | 5.3 | % | 24,627 | 3.8 | % | ||||||||
Beverage, Food & Tobacco | 53,658 | 5.3 | % | 62,314 | 9.6 | % | ||||||||
Capital Equipment | 51,155 | 5.0 | % | 2,572 | 0.4 | % | ||||||||
Automotive | 39,192 | 3.9 | % | 19,766 | 3.0 | % | ||||||||
Construction & Building | 39,137 | 3.8 | % | 24,099 | 3.7 | % | ||||||||
Telecommunications | 35,411 | 3.5 | % | 9,148 | 1.4 | % | ||||||||
Hotel, Gaming & Leisure | 28,974 | 2.8 | % | 26,839 | 4.1 | % | ||||||||
Chemicals, Plastics & Rubber | 27,253 | 2.7 | % | 27,161 | 4.2 | % | ||||||||
Media: Diversified & Production | 23,100 | 2.3 | % | 10,153 | 1.6 | % | ||||||||
Aerospace & Defense | 21,780 | 2.1 | % | — | — | |||||||||
Retail | 18,852 | 1.9 | % | 8,623 | 1.4 | % | ||||||||
Banking, Finance, Insurance & Real Estate | 17,636 | 1.7 | % | 32,224 | 5.0 | % | ||||||||
Energy: Electricity | 13,715 | 1.3 | % | 13,677 | 2.1 | % | ||||||||
Energy: Oil & Gas | 12,803 | 1.3 | % | 6,274 | 1.0 | % | ||||||||
Metals & Mining | 11,349 | 1.1 | % | — | — | |||||||||
Media: Broadcasting & Subscription | 9,776 | 1.0 | % | 9,952 | 1.5 | % | ||||||||
Services: Consumer | 9,477 | 0.9 | % | 13,154 | 2.0 | % | ||||||||
Consumer Goods: Non-Durable | 8,611 | 0.8 | % | 13,974 | 2.1 | % | ||||||||
Containers, Packaging & Glass | 3,845 | 0.4 | % | 11,851 | 1.8 | % | ||||||||
Environmental Industries | 2,595 | 0.3 | % | 2,850 | 0.4 | % | ||||||||
Consumer Goods: Durable | 1,000 | 0.1 | % | — | — | |||||||||
Subtotal/total percentage | 1,018,980 | 100.0 | % | 650,907 | 100.0 | % | ||||||||
Short term investments | 70,498 | 18,892 | ||||||||||||
Total investments | $ | 1,089,478 | $ | 669,799 | ||||||||||
December 31, 2016 | December 31, 2015 | |||||||||||||
Geographic Dispersion(1) | Investments at Fair Value | Percentage of Investment Portfolio | Investments at Fair Value | Percentage of Investment Portfolio | ||||||||||
United States | $ | 916,260 | 89.9 | % | $ | 581,756 | 89.4 | % | ||||||
Cayman Islands | 43,234 | 4.2 | % | 32,258 | 5.0 | % | ||||||||
Germany | 24,185 | 2.4 | % | 22,960 | 3.5 | % | ||||||||
Canada | 16,705 | 1.6 | % | 1,963 | 0.3 | % | ||||||||
Netherlands | 10,273 | 1.0 | % | 9,120 | 1.4 | % | ||||||||
Cyprus | 4,728 | 0.5 | % | — | — | |||||||||
United Kingdom | 2,595 | 0.3 | % | 2,850 | 0.4 | % | ||||||||
Bermuda | 1,000 | 0.1 | % | — | — | |||||||||
Subtotal/total percentage | 1,018,980 | 100.0 | % | 650,907 | 100.0 | % | ||||||||
Short term investments | 70,498 | 18,892 | ||||||||||||
Total investments | $ | 1,089,478 | $ | 669,799 | ||||||||||
(1) | The geographic dispersion is determined by the portfolio company's country of domicile. |
97
CĪON Investment Corporation
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
December 31, 2016
(in thousands, except share and per share amounts)
As of December 31, 2016 and 2015, there were no delinquent investments or investments on non-accrual status.
Except for CCSLF, the Company does not “control” and is not an “affiliate” of any of its portfolio companies, each as defined in the 1940 Act. In general, under the 1940 Act, the Company would be presumed to “control” a portfolio company or issuer if the Company owned 25% or more of its voting securities and would be an “affiliate” of a portfolio company or issuer if the Company owned 5% or more of its voting securities.
The Company’s investment portfolio may contain senior secured investments that are in the form of lines of credit, revolving credit facilities, or unfunded commitments, which may require the Company to provide funding when requested in accordance with the terms of the underlying agreements. As of December 31, 2016 and 2015, the Company’s unfunded commitments amounted to $65,096 and $43,404, respectively. As of March 9, 2017, the Company’s unfunded commitments amounted to $85,986. Since these commitments may expire without being drawn upon, unfunded commitments do not necessarily represent future cash requirements or future earning assets for the Company. Refer to Note 11 for further details on the Company’s unfunded commitments.
Note 7. Derivative Instruments
In the normal course of business and subject to the requirements of the 1940 Act, the Company enters into derivative instruments as part of its investment strategy.
Credit Default Swap
A credit default swap contract represents an agreement in which one party, the protection buyer, pays a fixed fee, the premium, in return for a payment by the other party, the protection seller, contingent upon a specified default event relating to the underlying reference asset or pool of assets. The valuation of the swap for the approximate net amount to be received or paid (i.e., the fair value) is marked to market either by using pricing vendor quotations, counterparty prices or model prices, and such valuations are based on the fair value of the underlying security, current credit spreads for the referenced obligation of the underlying issuer relative to the terms of the contract, current interest rates, interest accrual through the valuation date and certain other factors. Entering into swaps involves varying degrees of risk, including the possibility that there is no liquid market for the contracts, the counterparty to the swap may default on its obligation to perform and there may be unfavorable changes in the credit spreads of the underlying financial instruments. Credit default swaps are included in the consolidated balance sheets as derivative assets.
On October 14, 2016, the Company entered into a credit default swap with JPMorgan Chase Bank N.A., which terminates on March 20, 2017, with a base notional amount of €22,000, to purchase protection with respect to Deutsche Bank AG exposure. As of December 31, 2016, the fair value of the credit default swap was $46, which is presented as derivative assets on the consolidated balance sheet. The unrealized depreciation of the credit default swap of $183 is reflected in net change in unrealized appreciation (depreciation) on investments in the consolidated statement of operations.
Total Return Swap
On December 17, 2012, the Company, through its wholly-owned consolidated subsidiary, Flatiron Funding, LLC, or Flatiron, entered into a TRS with Citibank, N.A., or Citibank. Effective December 9, 2013, Flatiron and Citibank amended the TRS to, among other things, increase the maximum aggregate market value of the portfolio of loans subject to the TRS (determined at the time each such loan becomes subject to the TRS) from $150,000 to $225,000, and increase the interest rate payable by Flatiron to Citibank with respect to each loan included in the TRS by increasing the spread over the floating rate index specified for each such loan from 1.25% to 1.35% per year. Flatiron and Citibank further amended the TRS to increase the maximum aggregate market value of the portfolio of loans subject to the TRS to $275,000 effective February 18, 2014, to $325,000 effective April 30, 2014, to $375,000 effective July 30, 2014, to $475,000 effective September 5, 2014, to $600,000 effective January 20, 2015, to $750,000 effective March 4, 2015 and to $800,000 effective March 22, 2016. Effective October 2, 2015, Flatiron and Citibank amended the TRS to extend the termination or call date from December 17, 2015 to March 17, 2016 and to provide that the floating rate index specified for each loan included in the TRS will not be less than zero. On December 22, 2015, Flatiron and Citibank further amended the TRS to reduce the ramp-down period from 90 days to 30 days prior to the termination date, which represents the period when reinvestment is no longer permitted under the terms of the TRS. Effective February 18, 2016, Flatiron and Citibank further amended the TRS to extend the termination or call date from March 17, 2016 to February 18, 2017, and increase the interest rate payable by Flatiron to Citibank with respect to each loan included in the TRS by increasing the spread over the floating rate index specified for each such loan from 1.35% to 1.40% per year. Effective February 18, 2017, Flatiron and Citibank further amended the TRS to extend the termination or call date from February 18, 2017 to April 18, 2017. The agreements between Flatiron and Citibank, which collectively establish the TRS, are referred to herein as the TRS Agreement.
A TRS is a contract in which one party agrees to make periodic payments to another party based on the change in the market value of and interest payments from the assets underlying the TRS in return for periodic payments based on a fixed or variable interest rate. A TRS effectively adds leverage to a portfolio by providing investment exposure to a security or market without owning or taking physical custody of such security or investing directly in such market. Because of the unique structure of a TRS, a TRS typically offers lower financing costs than are offered through more traditional borrowing arrangements.
The TRS with Citibank enables the Company, through its ownership of Flatiron, to obtain the economic benefit of owning the loans subject to the TRS, without actually owning them, in return for an interest-type payment to Citibank. As such, the TRS is analogous to Flatiron borrowing funds to acquire loans and incurring interest expense to a lender. Under the terms of the TRS Agreement, each asset underlying the TRS constitutes a separate total return swap transaction, although all calculations and payments required to be made under the TRS Agreement are calculated and treated on an aggregate basis, based upon all such transactions.
The obligations of Flatiron under the TRS are non-recourse to the Company and the Company’s exposure under the TRS is limited to the value of the Company’s investment in Flatiron, which generally will equal the value of cash collateral provided by Flatiron under the TRS. Pursuant to the terms of the TRS, Flatiron may select loans with a maximum aggregate market value (determined at the time each such loan becomes subject to the TRS) of $800,000. Flatiron is required to initially cash collateralize a specified percentage of each loan (generally 25% of the market value of such loan) included under the TRS in accordance with margin requirements described in the TRS Agreement. Under the terms of the TRS, Flatiron agreed not to draw upon, or post as collateral, such cash collateral in respect of other financings or operating requirements prior to the termination of the TRS. Neither the cash collateral required to be posted with Citibank nor any other assets of Flatiron are available to pay the debts of the Company.
Unless otherwise specified, each individual loan must meet the obligation criteria described in the TRS Agreement, which includes requirements that the loan be rated by Moody’s and S&P, be part of a loan facility of at least $125 million and have at least two bid quotations from a nationally-recognized pricing service. Under the terms of the TRS, Citibank, as calculation agent, determines whether there has been a failure to satisfy the obligation
98
CĪON Investment Corporation
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
December 31, 2016
(in thousands, except share and per share amounts)
criteria for each loan in the TRS. If such failure continues for 30 days following the delivery of notice thereof, then Citibank has the right, but not the obligation, to remove the underlying loan from the TRS either through a sale negotiated by the Company or the price determined by Citibank. Citibank also determines whether there has been a failure to satisfy the portfolio criteria in the TRS, which includes limits on issuer and industry concentration as well as Moody’s and S&P credit metrics. If such failure continues for 30 days following the delivery of notice thereof, then Citibank has the right, but not the obligation, to terminate the TRS. Flatiron receives from Citibank all interest and fees payable in respect of the loans included in the TRS. Flatiron pays to Citibank interest at a rate equal to, in respect of each loan included in the TRS, the floating rate index specified for such loan, which will not be less than zero, plus 1.40% per year. In addition, upon the termination or repayment of any loan subject to the TRS, Flatiron will either receive from Citibank the appreciation in the value of such loan or pay to Citibank any depreciation in the value of such loan.
Under the terms of the TRS, Flatiron may be required to post additional cash collateral, on a dollar-for-dollar basis, in the event of depreciation in the value of the underlying loans after such value decreases below a specified amount. The limit on the additional collateral that Flatiron may be required to post pursuant to the TRS is equal to the difference between the full notional amount of the loans underlying the TRS and the amount of cash collateral already posted by Flatiron. The amount of collateral required to be posted by Flatiron is determined primarily on the basis of the aggregate value of the underlying loans.
The Company has no contractual obligation to post any such additional collateral or to make any interest payments to Citibank on behalf of Flatiron. The Company may, but is not obligated to, increase its investment in Flatiron for the purpose of funding any additional collateral or payment obligations for which Flatiron may become obligated during the term of the TRS. If the Company does not make any such additional investment in Flatiron and Flatiron fails to meet its obligations under the TRS, then Citibank will have the right to terminate the TRS and seize the cash collateral posted by Flatiron under the TRS. In the event of an early termination of the TRS, Flatiron would be required to pay an early termination fee.
Citibank may terminate the TRS on or after April 18, 2017, or the call date. Flatiron may terminate the TRS at any time upon providing no more than 30 days prior notice to Citibank. Any termination prior to the call date will result in payment of an early termination fee to Citibank based on the maximum portfolio amount of the TRS. Under the terms of the TRS, the early termination fee will equal the present value of a stream of monthly payments that would be owed by Flatiron to Citibank for the period from the termination date through and including the call date. Such monthly payments will equal the product of 80% of the maximum portfolio amount, multiplied by the spread over the floating index rate. The Company estimates the early termination fee would have been approximately $1,218 and $1,729 at December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively. Flatiron may also be required to pay a minimum usage fee in connection with the TRS. As of December 31, 2016 and 2015, Flatiron owed Citibank a minimum usage fee of $176 and $4, respectively.
The value of the TRS is based on the increase or decrease in the value of the loans underlying the TRS, as determined by the Company. The loans underlying the TRS are valued in the same manner as loans owned by the Company. As of December 31, 2016 and 2015, the fair value of the TRS was ($15,402) and ($34,900), respectively. The fair value of the TRS is reflected as unrealized depreciation on total return swap on the Company’s consolidated balance sheets. The change in value of the TRS is reflected in the Company’s consolidated statements of operations as net change in unrealized appreciation (depreciation) on total return swap. As of December 31, 2016 and 2015, Flatiron had selected 51 and 90 underlying loans with a total notional amount of $407,847 and $718,025, respectively. For the same periods, Flatiron posted $143,335 and $226,316 in cash collateral held by Citibank (of which only $131,073 and $187,802 was required to be posted), which is reflected in due from counterparty on the Company’s consolidated balance sheets.
Receivable due on the TRS is composed of any amounts due from Citibank that consist of earned but not yet collected net interest and fees and net gains on sales and principal repayments of underlying loans of the TRS. As of December 31, 2016 and 2015, the receivable due on the TRS consisted of the following:
As of December 31, | |||||||
2016 | 2015 | ||||||
Interest and other income from TRS portfolio | $ | 5,620 | $ | 8,882 | |||
Interest and other expense from TRS portfolio | (1,928 | ) | (2,309 | ) | |||
Net gain (loss) on TRS loan sales | 495 | (398 | ) | ||||
Receivable due on total return swap | $ | 4,187 | $ | 6,175 | |||
Realized gains and losses on the TRS are composed of any gains or losses on loans underlying the TRS as well as net interest and fees earned during the period. For the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, the net realized gain on the TRS consisted of the following:
Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
Interest and other income from TRS portfolio | $ | 39,746 | $ | 40,499 | $ | 19,081 | ||||||
Interest and other expense from TRS portfolio | (13,473 | ) | (10,218 | ) | (4,431 | ) | ||||||
Net gain on TRS loan sales | 1,886 | 472 | 2,339 | |||||||||
Net realized gain(1) | $ | 28,159 | $ | 30,753 | $ | 16,989 | ||||||
99
CĪON Investment Corporation
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
December 31, 2016
(in thousands, except share and per share amounts)
(1) Net realized gain is reflected in net realized gain on total return swap on the Company's consolidated statements of operations.
In connection with the TRS, Flatiron is required to comply with various covenants and reporting requirements as defined in the TRS Agreement. As of and for the year ended December 31, 2016, Flatiron was in compliance with all covenants and reporting requirements.
CIM has not taken any incentive fees with respect to the Company’s TRS to date. For purposes of computing the capital gains incentive fee, CIM will become entitled to a capital gains incentive fee only upon the termination or disposition of the TRS, at which point all gains and losses of the underlying loans constituting the reference assets of the TRS will be realized. For purposes of computing the subordinated incentive fee on income, CIM is not entitled to a subordinated incentive fee on income with respect to the TRS. The net unrealized appreciation on the TRS, if any, is reflected in total assets on the Company’s consolidated balance sheets and included in the computation of the base management fee. The base management fee does not include any net unrealized depreciation on the TRS as such amounts are not included in total assets.
While the investment advisory agreement with CIM neither includes nor contemplates the inclusion of unrealized gains in the calculation of the capital gains incentive fee, pursuant to an interpretation of the AICPA Technical Practice Aid for investment companies, the Company accrues capital gains incentive fees on unrealized gains. This accrual reflects the incentive fees that would be payable to CIM if the Company’s entire investment portfolio was liquidated at its fair value as of the balance sheet date even though CIM is not entitled to an incentive fee with respect to unrealized gains unless and until such gains are actually realized.
For purposes of the asset coverage ratio test applicable to the Company as a BDC, the Company treats the outstanding notional amount of the TRS, less the total amount of cash collateral posted by Flatiron under the TRS, as a senior security for the life of that instrument. The Company may, however, accord different treatment to the TRS in the future in accordance with any applicable new rules or interpretations adopted by the staff of the Securities and Exchange Commission, or SEC.
Further, for purposes of Section 55(a) under the 1940 Act, the Company treats each loan underlying the TRS as a qualifying asset if the obligor on such loan is an eligible portfolio company and as a non-qualifying asset if the obligor is not an eligible portfolio company. The Company may, however, accord different treatment to the TRS in the future in accordance with any applicable new rules or interpretations adopted by the staff of the SEC.
The following is a summary of the underlying loans subject to the TRS as of December 31, 2016:
100
CĪON Investment Corporation
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
December 31, 2016
(in thousands, except share and per share amounts)
Underlying Loans(a) | Index Rate(b) | Industry | Notional Amount | Fair Value(c) | Unrealized Appreciation / (Depreciation) | |||||||||||
Senior Secured First Lien Debt | ||||||||||||||||
Academy, Ltd., L+400, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 7/1/2022 | Various | Retail | $ | 14,564 | $ | 13,653 | $ | (911 | ) | |||||||
Access CIG, LLC, L+500, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 10/18/2021 | 3 Month LIBOR | Services: Business | 6,751 | 6,798 | 47 | |||||||||||
ALM Media, LLC, L+450, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 7/31/2020 | 3 Month LIBOR | Media: Advertising, Printing & Publishing | 7,679 | 7,328 | (351 | ) | ||||||||||
Alvogen Pharma US, Inc., L+500, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 4/1/2022 | 3 Month LIBOR | Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals | 9,430 | 9,150 | (280 | ) | ||||||||||
American Dental Partners, Inc., L+475, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 8/29/2021 | 3 Month LIBOR | Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals | 12,158 | 12,219 | 61 | |||||||||||
American Energy - Marcellus, LLC, L+425, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 8/4/2020 | 3 Month LIBOR | Energy: Oil & Gas | 4,254 | 2,370 | (1,884 | ) | ||||||||||
American Residential Services, LLC, L+450, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 6/30/2021 | 3 Month LIBOR | Construction & Building | 14,067 | 14,269 | 202 | |||||||||||
Aquilex, LLC, L+400, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 12/31/2020 | 3 Month LIBOR | Chemicals, Plastics & Rubber | 1,810 | 1,778 | (32 | ) | ||||||||||
Avaya Inc., L+525, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 5/29/2020 | 3 Month LIBOR | Telecommunications | 14,542 | 12,798 | (1,744 | ) | ||||||||||
Azure Midstream Energy, LLC, L+650, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 11/15/2018 | 1 Month LIBOR | Energy: Oil & Gas | 2,375 | 2,200 | (175 | ) | ||||||||||
Caraustar Industries, Inc., L+675, 1.25% LIBOR Floor, 5/1/2019 | 3 Month LIBOR | Forest Products & Paper | 11,954 | 12,521 | 567 | |||||||||||
Central Security Group, Inc., L+563, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 10/6/2020 | 1 Month LIBOR | Services: Consumer | 12,915 | 13,058 | 143 | |||||||||||
Charming Charlie, LLC, L+800, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 12/24/2019 | 3 Month LIBOR | Retail | 7,723 | 4,314 | (3,409 | ) | ||||||||||
CSP Technologies North America, LLC, L+600, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 1/29/2022 | 3 Month LIBOR | Chemicals, Plastics & Rubber | 13,385 | 13,590 | 205 | |||||||||||
CT Technologies Intermediate Holdings, Inc., L+425, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 12/1/2021 | 1 Month LIBOR | Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals | 14,681 | 14,160 | (521 | ) | ||||||||||
David's Bridal, Inc., L+400, 1.25% LIBOR Floor, 10/11/2019 | 3 Month LIBOR | Retail | 3,339 | 3,095 | (244 | ) | ||||||||||
DBRS, Inc., L+525, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 3/4/2022(d) | 3 Month LIBOR | Services: Business | 12,874 | 12,094 | (780 | ) | ||||||||||
EIG Investors Corp., L+548, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 11/9/2019(d) | 3 Month LIBOR | Services: Business | 1,773 | 1,772 | (1 | ) | ||||||||||
Emmis Operating Company, L+600, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 6/10/2021 | 3 Month LIBOR | Media: Broadcasting & Subscription | 7,508 | 7,075 | (433 | ) | ||||||||||
Evergreen Skills Lux S.À.R.L., L+475, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 4/28/2021(d) | 6 Month LIBOR | High Tech Industries | 7,174 | 6,821 | (353 | ) | ||||||||||
Global Cash Access, Inc., L+525, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 12/18/2020 | 2 Month LIBOR | Hotel, Gaming & Leisure | 10,483 | 10,406 | (77 | ) | ||||||||||
Healogics, Inc., L+425, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 7/1/2021 | 3 Month LIBOR | Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals | 4,829 | 4,520 | (309 | ) | ||||||||||
IMG Worldwide Holdings, LLC, L+425, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 5/6/2021 | 3 Month LIBOR | Media: Diversified & Production | 7,111 | 7,277 | 166 | |||||||||||
LTCG Holdings Corp., L+500, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 6/6/2020 | 1 Month LIBOR | Services: Business | 5,882 | 5,409 | (473 | ) | ||||||||||
Murray Energy Corp., L+725, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 4/16/2020 | 3 Month LIBOR | Metals & Mining | 3,588 | 3,528 | (60 | ) | ||||||||||
Navex Global, Inc, L+475, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 11/19/2021 | 6 Month LIBOR | High Tech Industries | 13,597 | 13,617 | 20 | |||||||||||
Nielsen & Bainbridge, LLC, L+500, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 8/15/2020 | 6 Month LIBOR | Consumer Goods: Durable | 15,843 | 15,942 | 99 | |||||||||||
Oasis Outsourcing Holdings, Inc., L+475, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 12/26/2021 | 1 Month LIBOR | Services: Business | 9,319 | 9,472 | 153 | |||||||||||
Onex TSG Holdings II Corp., L+400, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 7/29/2022 | 3 Month LIBOR | Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals | 3,408 | 3,441 | 33 | |||||||||||
Opal Acquisition, Inc., L+400, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 11/27/2020 | 3 Month LIBOR | Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals | 10,236 | 9,802 | (434 | ) | ||||||||||
Pelican Products, Inc., L+425, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 4/10/2020 | 3 Month LIBOR | Chemicals, Plastics & Rubber | 2,493 | 2,503 | 10 | |||||||||||
Photonis Technologies SAS, L+750, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 9/18/2019(d) | 3 Month LIBOR | Aerospace & Defense | 6,337 | 5,564 | (773 | ) | ||||||||||
PSC Industrial Holdings Corp., L+475, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 12/5/2020 | 3 Month LIBOR | Services: Business | 4,851 | 4,741 | (110 | ) | ||||||||||
Scientific Games International, Inc., L+500, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 10/1/2021(d) | Various | Hotel, Gaming & Leisure | 10,400 | 10,665 | 265 | |||||||||||
SESAC Holdco II LLC, L+425, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 2/7/2019 | 1 Month LIBOR | Media: Broadcasting & Subscription | 2,935 | 2,938 | 3 | |||||||||||
SG Acquisition, Inc., L+525, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 8/19/2021 | 3 Month LIBOR | Banking, Finance, Insurance & Real Estate | 11,414 | 11,547 | 133 | |||||||||||
SI Organization, Inc., L+475, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 11/23/2019 | 3 Month LIBOR | Services: Business | 7,746 | 7,866 | 120 | |||||||||||
STG-Fairway Acquisitions, Inc., L+525, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 6/30/2022 | 3 Month LIBOR | Services: Business | 3,845 | 3,840 | (5 | ) | ||||||||||
Survey Sampling International, LLC, L+500, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 12/16/2020 | 3 Month LIBOR | Services: Business | 7,781 | 7,899 | 118 | |||||||||||
TIBCO Software Inc., L+550, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 12/4/2020 | 1 Month LIBOR | High Tech Industries | 16,827 | 17,319 | 492 | |||||||||||
Travel Leaders Group, LLC, L+600, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 12/7/2020 | 1 Month LIBOR | Services: Consumer | 5,169 | 5,176 | 7 | |||||||||||
Vince, LLC, L+500, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 11/27/2019(d) | 3 Month LIBOR | Retail | 1,124 | 1,093 | (31 | ) | ||||||||||
Western Dental Services, Inc., L+650, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 11/1/2018 | 3 Month LIBOR | Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals | 5,573 | 5,566 | (7 | ) | ||||||||||
Total Senior Secured First Lien Debt | 351,747 | 341,194 | (10,553 | ) | ||||||||||||
101
CĪON Investment Corporation
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
December 31, 2016
(in thousands, except share and per share amounts)
Underlying Loans(a) | Index Rate(b) | Industry | Notional Amount | Fair Value(c) | Unrealized Appreciation / (Depreciation) | |||||||||||
Senior Secured Second Lien Debt | ||||||||||||||||
Asurion, LLC, L+750, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 3/3/2021 | 1 Month LIBOR | Services: Consumer | 7,772 | 8,044 | 272 | |||||||||||
Evergreen Skills Lux S.À.R.L., L+825, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 4/28/2022(d) | 6 Month LIBOR | High Tech Industries | 9,798 | 7,594 | (2,204 | ) | ||||||||||
GOBP Holdings, Inc., L+825, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 10/21/2022 | 3 Month LIBOR | Retail | 3,940 | 4,010 | 70 | |||||||||||
Mergermarket USA, Inc., L+650, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 2/4/2022 | 3 Month LIBOR | Services: Business | 6,965 | 6,842 | (123 | ) | ||||||||||
Onex Carestream Finance LP, L+850, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 12/7/2019 | 3 Month LIBOR | Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals | 13,600 | 11,318 | (2,282 | ) | ||||||||||
Pelican Products, Inc., L+825, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 4/11/2021 | 3 Month LIBOR | Chemicals, Plastics & Rubber | 8,050 | 7,830 | (220 | ) | ||||||||||
PFS Holding Corp., L+725, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 1/31/2022 | 1 Month LIBOR | Retail | 4,973 | 4,636 | (337 | ) | ||||||||||
Securus Technologies Holdings, Inc., L+775, 1.25% LIBOR Floor, 4/30/2021 | 3 Month LIBOR | Telecommunications | 1,002 | 977 | (25 | ) | ||||||||||
Total Senior Secured Second Lien Debt | 56,100 | 51,251 | (4,849 | ) | ||||||||||||
Total | $ | 407,847 | $ | 392,445 | $ | (15,402 | ) | |||||||||
(a) | All of the underlying loans subject to the TRS are issued by eligible U.S. portfolio companies, as defined in the 1940 Act, except for investments specifically identified as non-qualifying per note (d) below. The Company does not control and is not an affiliate of any of the companies that are issuers of the underlying loans subject to the TRS. |
(b) | The 1, 2, 3, and 6 month LIBOR rates were 0.77%, 0.82%, 1.00% and 1.32%, respectively, as of December 31, 2016. The actual LIBOR rate for each loan listed may not be the applicable LIBOR rate as of December 31, 2016, as the loan may have been priced or repriced based on a LIBOR rate prior to or subsequent to December 31, 2016. |
(c) | Fair value determined in good faith by the Company’s board of directors (see Note 9). |
(d) | All or a portion of the underlying loan subject to the TRS is not a qualifying asset under the 1940 Act. A business development company may not acquire any asset other than qualifying assets, unless, at the time the acquisition is made, qualifying assets represent at least 70% of the company’s total assets as defined under Section 55 of the 1940 Act. As of December 31, 2016, 90.5% of the Company’s total assets represented qualifying assets. In addition, as described in this Note 7, the Company calculates its compliance with the qualifying asset test on a “look through” basis by treating each loan underlying the TRS as either a qualifying asset or non-qualifying asset based on whether the obligor is an eligible portfolio company. On this basis, 89.1% of the Company’s total assets represented qualifying assets as of December 31, 2016. |
(e) | For the year ended December 31, 2016, the following underlying loans subject to the TRS contain a PIK interest provision whereby the issuer has either the option or the obligation to make interest payments with the issuance of additional securities: |
Interest Rate | Interest Amount | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Issuer of Underlying Loan | Investment Type | Cash | PIK | All-in-Rate | Cash | PIK | All-in-Rate | ||||||||||||||||
Smile Brands Group, Inc.(f) | Senior Secured First Lien Debt | 7.50 | % | 1.50 | % | 9.00 | % | $ | 233 | $ | 41 | $ | 274 | ||||||||||
Southcross Holdings Borrower LP(g) | Senior Secured First Lien Debt | 3.50 | % | 5.50 | % | 9.00 | % | $ | 1 | $ | 1 | $ | 2 | ||||||||||
(f) | Outstanding principal and accrued interest of the underlying loan was fully repaid on August 17, 2016. |
(g) | Prior to December 31, 2016, the underlying loan was assigned to the Company and removed from the TRS. |
102
CĪON Investment Corporation
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
December 31, 2016
(in thousands, except share and per share amounts)
The following is a summary of the underlying loans subject to the TRS as of December 31, 2015:
Underlying Loans(a) | Index Rate(b) | Industry | Notional Amount | Fair Value(c) | Unrealized Appreciation / (Depreciation) | |||||||||||
Senior Secured First Lien Debt | ||||||||||||||||
ABG Intermediate Holdings 2 LLC, L+450, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 5/27/2021 | 3 Month LIBOR | Retail | $ | 6,736 | $ | 6,696 | $ | (40 | ) | |||||||
Academy, Ltd., L+400, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 7/1/2022(d) | 1 Month LIBOR | Retail | 13,254 | 12,954 | (300 | ) | ||||||||||
Access CIG, LLC, L+500, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 10/18/2021 | 3 Month LIBOR | Services: Business | 6,820 | 6,816 | (4 | ) | ||||||||||
Albertson's LLC, L+450, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 12/21/2022(d) | 3 Month LIBOR | Retail | 4,625 | 4,656 | 31 | |||||||||||
ALM Media, LLC, L+450, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 7/31/2020 | 3 Month LIBOR | Media: Advertising, Printing & Publishing | 7,882 | 7,740 | (142 | ) | ||||||||||
Alvogen Pharma US, Inc., L+500, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 4/1/2022 | 3 Month LIBOR | Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals | 15,053 | 14,709 | (344 | ) | ||||||||||
American Dental Partners, Inc., L+475, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 8/29/2021 | 3 Month LIBOR | Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals | 12,282 | 12,359 | 77 | |||||||||||
American Energy - Marcellus, LLC, L+425, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 8/4/2020 | 3 Month LIBOR | Energy: Oil & Gas | 4,253 | 1,160 | (3,093 | ) | ||||||||||
American Residential Services, LLC, L+450, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 6/30/2021 | 3 Month LIBOR | Construction & Building | 14,211 | 14,174 | (37 | ) | ||||||||||
AqGen Ascensus, Inc., L+450, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 12/5/2022 | 3 Month LIBOR | Services: Business | 2,915 | 2,923 | 8 | |||||||||||
Aquilex, LLC, L+400, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 12/31/2020 | 1 Month LIBOR | Chemicals, Plastics & Rubber | 1,933 | 1,850 | (83 | ) | ||||||||||
At Home Holding III Inc., L+400, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 6/3/2022 | 3 Month LIBOR | Retail | 5,560 | 5,420 | (140 | ) | ||||||||||
Avaya Inc., L+525, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 5/29/2020 | 3 Month LIBOR | Telecommunications | 14,718 | 10,462 | (4,256 | ) | ||||||||||
Azure Midstream Energy, LLC, L+650, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 11/15/2018 | 3 Month LIBOR | Energy: Oil & Gas | 2,431 | 1,448 | (983 | ) | ||||||||||
BRG Sports, Inc., L+550, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 4/15/2021(d) | 1 Month LIBOR | Consumer Goods: Durable | 12,798 | 12,690 | (108 | ) | ||||||||||
Builders FirstSource Inc., L+500, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 7/29/2022(e) | 3 Month LIBOR | Forest Products & Paper | 14,242 | 14,129 | (113 | ) | ||||||||||
Caraustar Industries, Inc., L+675, 1.25% LIBOR Floor, 5/1/2019 | 3 Month LIBOR | Forest Products & Paper | 18,131 | 18,568 | 437 | |||||||||||
Cast & Crew Payroll, LLC , L+375, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 8/12/2022 | 3 Month LIBOR | Services: Business | 1,311 | 1,294 | (17 | ) | ||||||||||
CDS U.S. Intermediate Holdings, Inc., L+400, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 7/8/2022 | 3 Month LIBOR | Hotel, Gaming & Leisure | 1,958 | 1,857 | (101 | ) | ||||||||||
Central Security Group, Inc., L+525, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 10/6/2020 | 3 Month LIBOR | Services: Consumer | 13,047 | 12,778 | (269 | ) | ||||||||||
Charming Charlie, LLC, L+800, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 12/24/2019 | 3 Month LIBOR | Retail | 8,647 | 7,223 | (1,424 | ) | ||||||||||
Chemstralia Pty Ltd., L+625, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 2/28/2022(e) | 3 Month LIBOR | Chemicals, Plastics & Rubber | 3,000 | 2,925 | (75 | ) | ||||||||||
CSC Holdings, LLC, L+400, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 10/9/2022(d) | 3 Month LIBOR | Telecommunications | 18,844 | 18,926 | 82 | |||||||||||
CSP Technologies North America, LLC, L+600, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 1/29/2022 | 3 Month LIBOR | Chemicals, Plastics & Rubber | 13,522 | 13,660 | 138 | |||||||||||
CT Technologies Intermediate Holdings, Inc., L+425, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 12/1/2021 | 1 Month LIBOR | Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals | 14,831 | 14,537 | (294 | ) | ||||||||||
DAE Aviation Holdings, Inc., L+425, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 7/7/2022 | 3 Month LIBOR | Aerospace & Defense | 7,591 | 7,579 | (12 | ) | ||||||||||
David's Bridal, Inc., L+400, 1.25% LIBOR Floor, 10/11/2019 | 3 Month LIBOR | Retail | 4,338 | 3,808 | (530 | ) | ||||||||||
DBRS, Inc., L+525, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 3/4/2022(e) | 3 Month LIBOR | Services: Business | 13,005 | 13,087 | 82 | |||||||||||
Deltek, Inc., L+400, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 6/25/2022 | 3 Month LIBOR | Services: Business | 3,068 | 3,053 | (15 | ) | ||||||||||
Diamond Resorts Corp., L+450, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 5/9/2021(e) | 3 Month LIBOR | Consumer Goods: Non-Durable | 3,586 | 3,546 | (40 | ) | ||||||||||
EIG Investors Corp., L+400, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 11/9/2019(e) | 3 Month LIBOR | Services: Business | 1,846 | 1,803 | (43 | ) | ||||||||||
Emmis Operating Company, L+600, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 6/10/2021 | 3 Month LIBOR | Media: Broadcasting & Subscription | 8,739 | 7,790 | (949 | ) | ||||||||||
Evergreen Skills Lux S.À.R.L., L+475, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 4/28/2021(e) | 6 Month LIBOR | High Tech Industries | 7,248 | 5,764 | (1,484 | ) | ||||||||||
Global Cash Access, Inc., L+525, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 12/18/2020 | 2 Month LIBOR | Hotel, Gaming & Leisure | 11,043 | 10,375 | (668 | ) | ||||||||||
GTCR Valor Companies, Inc., L+500, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 5/30/2021 | 3 Month LIBOR | High Tech Industries | 3,898 | 3,918 | 20 | |||||||||||
HC Group Holdings III, Inc., L+500, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 4/7/2022(d) | 3 Month LIBOR | Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals | 10,471 | 10,459 | (12 | ) | ||||||||||
Healogics, Inc., L+425, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 7/1/2021 | 3 Month LIBOR | Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals | 4,879 | 3,993 | (886 | ) | ||||||||||
Hemisphere Media Holdings, LLC, L+400, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 7/30/2020 | 3 Month LIBOR | Media: Broadcasting & Subscription | 4,006 | 3,854 | (152 | ) | ||||||||||
Hilex Poly Co. LLC, L+500, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 12/5/2021 | 3 Month LIBOR | Containers, Packaging & Glass | 8,296 | 8,366 | 70 | |||||||||||
Hyperion Insurance Group Ltd., L+450, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 4/29/2022(e) | 3 Month LIBOR | Banking, Finance, Insurance & Real Estate | 3,039 | 3,024 | (15 | ) | ||||||||||
IMG Worldwide Holdings, LLC, L+425, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 5/6/2021 | 3 Month LIBOR | Media: Diversified & Production | 14,368 | 14,287 | (81 | ) | ||||||||||
Infiltrator Water Technologies, LLC, L+425, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 5/27/2022 | 3 Month LIBOR | Construction & Building | 9,000 | 9,006 | 6 | |||||||||||
inVentiv Health, Inc., L+625, 1.50% LIBOR Floor, 5/15/2018 | 3 Month LIBOR | Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals | 10,000 | 9,890 | (110 | ) | ||||||||||
Lanyon Solutions, Inc., L+450, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 11/13/2020 | 3 Month LIBOR | High Tech Industries | 1,148 | 1,120 | (28 | ) | ||||||||||
LTCG Holdings Corp., L+500, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 6/6/2020 | 3 Month LIBOR | Services: Business | 5,882 | 5,527 | (355 | ) | ||||||||||
Murray Energy Corp., L+600, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 4/17/2017 | 6 Month LIBOR | Metals & Mining | 723 | 752 | 29 | |||||||||||
Murray Energy Corp., L+650, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 4/16/2020 | 6 Month LIBOR | Metals & Mining | 3,472 | 2,286 | (1,186 | ) | ||||||||||
103
CĪON Investment Corporation
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
December 31, 2016
(in thousands, except share and per share amounts)
Underlying Loans(a) | Index Rate(b) | Industry | Notional Amount | Fair Value(c) | Unrealized Appreciation / (Depreciation) | |||||||||||
Navex Global, Inc, L+475, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 11/19/2021 | 6 Month LIBOR | High Tech Industries | 13,736 | 13,444 | (292 | ) | ||||||||||
Nielsen & Bainbridge, LLC, L+500, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 8/15/2020 | 6 Month LIBOR | Consumer Goods: Durable | 16,094 | 16,113 | 19 | |||||||||||
Oasis Outsourcing Holdings, Inc., L+475, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 12/26/2021 | 1 Month LIBOR | Services: Business | 14,392 | 14,428 | 36 | |||||||||||
Onex TSG Holdings II Corp., L+400, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 7/29/2022 | 1 Month LIBOR | Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals | 7,441 | 7,402 | (39 | ) | ||||||||||
Opal Acquisition, Inc., L+400, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 11/27/2020 | 3 Month LIBOR | Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals | 10,361 | 8,724 | (1,637 | ) | ||||||||||
Pelican Products, Inc., L+425, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 4/10/2020 | 3 Month LIBOR | Chemicals, Plastics & Rubber | 5,622 | 5,554 | (68 | ) | ||||||||||
PetroChoice Holdings, Inc., L+500, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 8/19/2022 | 1 Month LIBOR | Chemicals, Plastics & Rubber | 1,645 | 1,664 | 19 | |||||||||||
Photonis Technologies SAS, L+750, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 9/18/2019(e) | 3 Month LIBOR | Aerospace & Defense | 6,564 | 6,396 | (168 | ) | ||||||||||
Pike Corp., L+450, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 12/22/2021 | 1 Month LIBOR | Energy: Electricity | 2,205 | 2,194 | (11 | ) | ||||||||||
Polyconcept Finance B.V., L+475, 1.25% LIBOR Floor, 6/28/2019(e) | 1 Month LIBOR | Consumer Goods: Non-Durable | 6,575 | 6,547 | (28 | ) | ||||||||||
PSC Industrial Holdings Corp., L+475, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 12/5/2020 | 3 Month LIBOR | Services: Business | 4,901 | 4,888 | (13 | ) | ||||||||||
Riverbed Technology, Inc., L+500, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 4/24/2022(d) | 3 Month LIBOR | High Tech Industries | 16,791 | 16,771 | (20 | ) | ||||||||||
RP Crown Parent, LLC, L+500, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 12/21/2018 | 3 Month LIBOR | High Tech Industries | 15,431 | 14,127 | (1,304 | ) | ||||||||||
Scientific Games International, Inc., L+500, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 10/1/2021(e) | Various | Hotel, Gaming & Leisure | 21,430 | 19,847 | (1,583 | ) | ||||||||||
SESAC Holdco II LLC, L+425, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 2/7/2019 | 6 Month LIBOR | Media: Broadcasting & Subscription | 5,049 | 4,998 | (51 | ) | ||||||||||
SG Acquisition, Inc., L+525, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 8/19/2021 | 3 Month LIBOR | Banking, Finance, Insurance & Real Estate | 12,624 | 12,485 | (139 | ) | ||||||||||
SI Organization, Inc., L+475, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 11/23/2019(d) | 3 Month LIBOR | Services: Business | 10,983 | 10,953 | (30 | ) | ||||||||||
Smile Brands Group, Inc., L+775, 1.25% LIBOR Floor, 8/16/2019(f) | 3 Month LIBOR | Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals | 4,657 | 3,297 | (1,360 | ) | ||||||||||
Southcross Holdings Borrower LP, L+500, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 8/4/2021 | 3 Month LIBOR | Energy: Oil & Gas | 1,249 | 678 | (571 | ) | ||||||||||
Steward Health Care System, LLC, L+550, 1.25% LIBOR Floor, 4/10/2020 | 3 Month LIBOR | Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals | 9,817 | 9,760 | (57 | ) | ||||||||||
STG-Fairway Acquisitions, Inc., L+525, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 6/30/2022 | 3 Month LIBOR | Services: Business | 7,690 | 7,690 | — | |||||||||||
Styrolution US Holding LLC, L+550, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 11/7/2019 | 1 Month LIBOR | Chemicals, Plastics & Rubber | 3,933 | 3,997 | 64 | |||||||||||
Surgery Center Holdings, Inc., L+425, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 11/3/2020 | 1 Month LIBOR | Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals | 6,466 | 6,506 | 40 | |||||||||||
Survey Sampling International, LLC, L+500, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 12/16/2020 | 3 Month LIBOR | Services: Business | 7,861 | 7,801 | (60 | ) | ||||||||||
TASC, Inc., L+600, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 5/23/2020(e) | Various | Services: Business | 8,114 | 8,291 | 177 | |||||||||||
TIBCO Software Inc., L+550, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 12/4/2020 | 1 Month LIBOR | High Tech Industries | 16,998 | 15,844 | (1,154 | ) | ||||||||||
TMFS Holdings, LLC, L+450, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 7/30/2021 | 3 Month LIBOR | Banking, Finance, Insurance & Real Estate | 14,657 | 14,746 | 89 | |||||||||||
TOPPS Company, Inc., L+600, 1.25% LIBOR Floor, 10/2/2018 | 3 Month LIBOR | Consumer Goods: Non-Durable | 2,307 | 2,254 | (53 | ) | ||||||||||
Travel Leaders Group, LLC, L+600, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 12/7/2020 | 3 Month LIBOR | Services: Consumer | 5,473 | 5,429 | (44 | ) | ||||||||||
U.S. Farathane, LLC, L+575, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 12/23/2021(d) | 3 Month LIBOR | Automotive | 5,119 | 5,100 | (19 | ) | ||||||||||
U.S. Renal Care, Inc., L+425, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 12/30/2022(d) | 3 Month LIBOR | Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals | 3,233 | 3,245 | 12 | |||||||||||
USS Parent Holdings Corp., L+475, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 8/5/2021 | Prime | Construction & Building | 12,305 | 12,263 | (42 | ) | ||||||||||
Vince, LLC, L+475, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 11/27/2019(e) | 3 Month LIBOR | Retail | 1,124 | 1,031 | (93 | ) | ||||||||||
Western Dental Services, Inc., L+650, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 11/1/2018 | 3 Month LIBOR | Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals | 5,558 | 4,889 | (669 | ) | ||||||||||
Total Senior Secured First Lien Debt | 661,055 | 634,597 | (26,458 | ) | ||||||||||||
Senior Secured Second Lien Debt | ||||||||||||||||
AmWINS Group, LLC, L+850, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 9/4/2020 | 3 Month LIBOR | Banking, Finance, Insurance & Real Estate | 870 | 905 | 35 | |||||||||||
Asurion, LLC, L+750, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 3/3/2021 | 3 Month LIBOR | Services: Consumer | 7,772 | 6,796 | (976 | ) | ||||||||||
Evergreen Skills Lux S.À.R.L., L+825, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 4/28/2022(e) | 6 Month LIBOR | High Tech Industries | 9,798 | 6,675 | (3,123 | ) | ||||||||||
GOBP Holdings, Inc., L+825, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 10/21/2022 | 3 Month LIBOR | Retail | 3,940 | 3,940 | — | |||||||||||
Mergermarket USA, Inc., L+650, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 2/4/2022 | 3 Month LIBOR | Services: Business | 6,965 | 6,370 | (595 | ) | ||||||||||
Onex Carestream Finance LP, L+850, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 12/7/2019 | 3 Month LIBOR | Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals | 13,600 | 12,119 | (1,481 | ) | ||||||||||
Pelican Products, Inc., L+825, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 4/11/2021 | 3 Month LIBOR | Chemicals, Plastics & Rubber | 8,050 | 7,620 | (430 | ) | ||||||||||
PFS Holding Corp., L+725, 1.00% LIBOR Floor, 1/31/2022 | 1 Month LIBOR | Retail | 4,973 | 3,548 | (1,425 | ) | ||||||||||
Securus Technologies Holdings, Inc., L+775, 1.25% LIBOR Floor, 4/30/2021 | 3 Month LIBOR | Telecommunications | 1,002 | 555 | (447 | ) | ||||||||||
Total Senior Secured Second Lien Debt | 56,970 | 48,528 | (8,442 | ) | ||||||||||||
Total | $ | 718,025 | $ | 683,125 | $ | (34,900 | ) | |||||||||
(a) | All of the underlying loans subject to the TRS are issued by eligible U.S. portfolio companies, as defined in the 1940 Act, except for investments specifically identified as non-qualifying per note (e) below. The Company does not control and is not an affiliate of any of the companies that are issuers of the underlying loans subject to the TRS. |
104
CĪON Investment Corporation
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
December 31, 2016
(in thousands, except share and per share amounts)
(b) | The 1, 2, 3, and 6 month LIBOR rates were 0.43%, 0.51%, 0.61% and 0.85%, respectively, as of December 31, 2015. The actual LIBOR rate for each loan listed may not be the applicable LIBOR rate as of December 31, 2015, as the loan may have been priced or repriced based on a LIBOR rate prior to or subsequent to December 31, 2015. The prime rate was 3.50% as of December 31, 2015. |
(c) | Fair value determined in good faith by the Company’s board of directors (see Note 9). |
(d) | Position or a portion thereof unsettled as of December 31, 2015. |
(e) | All or a portion of the underlying loan subject to the TRS is not a qualifying asset under the 1940 Act. A business development company may not acquire any asset other than qualifying assets, unless, at the time the acquisition is made, qualifying assets represent at least 70% of the company’s total assets as defined under Section 55 of the 1940 Act. As of December 31, 2015, 90.0% of the Company’s total assets represented qualifying assets. In addition, as described in this Note 7, the Company calculates its compliance with the qualifying asset test on a “look through” basis by treating each loan underlying the TRS as either a qualifying asset or non-qualifying asset based on whether the obligor is an eligible portfolio company. On this basis, 87.2% of the Company’s total assets represented qualifying assets as of December 31, 2015. |
(f) | For the year ended December 31, 2015, the following underlying loan subject to the TRS contains a PIK interest provision whereby the issuer has either the option or the obligation to make interest payments with the issuance of additional securities: |
Interest Rate | Interest Amount | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Issuer of Underlying Loan | Investment Type | Cash | PIK | All-in-Rate | Cash | PIK | All-in-Rate | ||||||||||||||||
Smile Brands Group, Inc. | Senior Secured First Lien Debt | 7.50 | % | 1.50 | % | 9.00 | % | $ | 362 | $ | 16 | $ | 378 | ||||||||||
Note 8. Credit Facilities
JPM Credit Facility
On August 26, 2016, 34th Street Funding, LLC, or 34th Street, a newly-formed, wholly-owned, consolidated, special purpose financing subsidiary of the Company, entered into a senior secured credit facility with JPMorgan Chase Bank, National Association, or JPM. The senior secured credit facility with JPM, or the JPM Credit Facility, provides for delayed-draw borrowings in an aggregate principal amount of $150,000, of which $25,000 may be funded as a revolving credit facility, each subject to conditions described in the JPM Credit Facility. On August 26, 2016, 34th Street drew down $57,000 of borrowings under the JPM Credit Facility.
On September 30, 2016, 34th Street amended and restated the JPM Credit Facility, or the Amended JPM Credit Facility, with JPM. Under the Amended JPM Credit Facility, the aggregate principal amount available for delayed-draw borrowings was increased from $150,000 to $225,000, of which $25,000 may be funded as a revolving credit facility, each subject to conditions described in the Amended JPM Credit Facility. On September 30, 2016, 34th Street drew down $167,423 of additional borrowings under the Amended JPM Credit Facility, a portion of which was used to purchase the portfolio of loans from CS Park View as discussed in Note 6. No other material terms of the JPM Credit Facility were revised in connection with the Amended JPM Credit Facility.
Advances under the Amended JPM Credit Facility bear interest at a floating rate equal to the three-month LIBOR, plus a spread of 3.50% per year. Interest is payable quarterly in arrears. All advances under the Amended JPM Credit Facility will mature, and all accrued and unpaid interest thereunder will be due and payable, by no later than August 23, 2020. 34th Street may prepay advances pursuant to the terms and conditions of the Amended JPM Credit Facility, subject to a 1% premium in certain circumstances. In addition, 34th Street will be subject to a non-usage fee of 0.5% and 1.0% per year on the amount, if any, of the aggregate principal amount available under the Amended JPM Credit Facility that has not been borrowed during the period from the closing date and ending on, but excluding, May 23, 2017, or the Ramp-Up Period, and from the termination of the Ramp-Up Period and ending on, but excluding, August 23, 2019, respectively. The non-usage fees, if any, are payable quarterly in arrears.
The Company contributed loans and other corporate debt securities to 34th Street in exchange for 100% of the membership interests of 34th Street, and may contribute additional loans and other corporate debt securities to 34th Street in the future. 34th Street’s obligations to JPM under the Amended JPM Credit Facility are secured by a first priority security interest in all of the assets of 34th Street. The obligations of 34th Street under the Amended JPM Credit Facility are non-recourse to the Company, and the Company’s exposure under the Amended JPM Credit Facility is limited to the value of the Company’s investment in 34th Street.
In connection with the Amended JPM Credit Facility, 34th Street has made certain representations and warranties and is required to comply with various covenants, reporting requirements and other customary requirements for similar facilities. As of and from August 26, 2016 to December 31, 2016, 34th Street was in compliance with all covenants and reporting requirements.
The Company incurred debt issuance costs of $3,514 in connection with obtaining and amending the JPM Credit Facility, which were recorded as a direct reduction to the outstanding balance of the Amended JPM Credit Facility, which is included in the Company’s consolidated balance sheet as of December 31, 2016 and will amortize to interest expense over the term of the Amended JPM Credit Facility. At December 31, 2016, the unamortized portion of the debt issuance costs was $3,212.
105
CĪON Investment Corporation
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
December 31, 2016
(in thousands, except share and per share amounts)
For the period from August 26, 2016 through December 31, 2016, the components of interest expense, average borrowings, and weighted average interest rate for the Amended JPM Credit Facility were as follows:
Stated interest expense | $ | 2,753 | ||
Non-usage fee | 45 | |||
Amortization of debt issuance costs | 302 | |||
Total interest expense | $ | 3,100 | ||
Weighted average interest rate(1) | 4.41 | % | ||
Average borrowings | $ | 178,644 | ||
(1) Includes the stated interest expense and non-usage fee on the unused portion of the Amended JPM Credit Facility and is annualized for periods covering less than one year.
East West Bank Credit Facility
On April 30, 2015, the Company entered into a revolving credit facility, or the EWB Credit Facility, with East West Bank, or EWB. The EWB Credit Facility provides for borrowings in an aggregate principal amount of up to $40,000, subject to certain conditions, and the Company is required to maintain $2,000 in a demand deposit account with EWB at all times. As of and for the year ended December 31, 2016, the Company was in compliance with all covenants and reporting requirements under the EWB Credit Facility.
Advances under the EWB Credit Facility bear interest at a floating rate equal to (i) the greater of 3.25% per year or the variable rate of interest per year announced by EWB as its prime rate, which was 3.75% at December 31, 2016, plus (ii) a spread of 0.75%. Interest is payable quarterly in arrears. Each advance under the EWB Credit Facility will be due and payable on the earlier of 90 days from the date such advance was made by EWB, or April 27, 2017. The Company may prepay any advance without penalty or premium. The Company will be subject to a non-usage fee of 0.50% per year on the average amount, if any, of the aggregate principal amount available under the EWB Credit Facility that has not been borrowed, payable at the end of each quarter. The non-usage fee, if any, is payable quarterly in arrears. The Company’s obligations to EWB under the EWB Credit Facility are secured by a first priority security interest in certain eligible investments in which the Company has a beneficial interest, as updated from time to time.
On January 28, 2016 the Company entered into the first amendment to the EWB Credit Facility with EWB. Under the original EWB Credit Facility, the borrowing base was the lesser of (i) the average monthly net proceeds received by the Company from the sale of its equity securities during the trailing three month period ending on the last day of the immediately preceding calendar month; or (ii) 50% of collateral securing the EWB Credit Facility. Under the first amendment, during the period commencing on January 30, 2016 through July 31, 2016, (i) the trailing equity component of the borrowing base was removed; (ii) the borrowing base was decreased to 40% of the collateral securing the EWB Credit Facility; and (iii) the required minimum fair market value of the collateral securing the EWB Credit Facility was increased from two to two and one-half times all outstanding advances under the EWB Credit Facility. Prior to entering into the second amendment to the EWB Credit Facility (as described below), these amended provisions were scheduled to revert back to their original terms on July 31, 2016.
On April 21, 2016, the Company entered into the second amendment to the EWB Credit Facility with EWB. Under the second amendment, the date after which the amended provisions of the first amendment will revert back to their original terms was extended from July 31, 2016 to September 30, 2016 and the maturity date of the EWB Credit Facility was extended from April 29, 2016 to April 27, 2017.
The Company incurred costs of $278 in connection with obtaining the EWB Credit Facility, which the Company initially recorded as prepaid expenses and other assets on the Company’s consolidated balance sheets and amortized to interest expense over the initial life of the EWB Credit Facility. On April 21, 2016, the Company incurred additional costs of $200 in connection with the second amendment to the EWB Credit Facility, which the Company initially recorded as prepaid expenses and other assets on the Company’s consolidated balance sheets and amortizes to interest expense over the life of the EWB Credit Facility pursuant to the second amendment.
For the year ended December 31, 2016 and for the period from April 30, 2015 through December 31, 2015, the components of interest expense, average borrowings, and weighted average interest rate for the EWB Credit Facility were as follows:
106
CĪON Investment Corporation
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
December 31, 2016
(in thousands, except share and per share amounts)
Year Ended December 31, 2016 | Period from April 30, 2015 through December 31, 2015 | |||||||
Amortization of debt issuance costs | $ | 227 | $ | 186 | ||||
Non-usage fee | 198 | 125 | ||||||
Stated interest expense | 44 | 94 | ||||||
Total interest expense | $ | 469 | $ | 405 | ||||
Weighted average interest rate(1) | 23.12 | % | 9.37 | % | ||||
Average borrowings(2) | $ | 1,033 | $ | 3,407 | ||||
(1) Includes the stated interest expense and non-usage fees on the unused portion of the EWB Credit Facility.
(2) During the year ended December 31, 2016 and the period from April 30, 2015 through December 31, 2015, amounts were drawn on the EWB Credit Facility for 21 and 71 days, respectively.
Note 9. Fair Value of Financial Instruments
The following table presents fair value measurements of the Company’s portfolio investments and TRS as of December 31, 2016 and 2015, according to the fair value hierarchy:
December 31, 2016 | December 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Senior secured first lien debt | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 489,913 | $ | 489,913 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 104,187 | $ | 104,187 | |||||||||||||||
Senior secured second lien debt | — | — | 434,347 | 434,347 | — | — | 453,713 | 453,713 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Collateralized securities and structured products - debt | — | — | 38,114 | 38,114 | — | — | 41,663 | 41,663 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Collateralized securities and structured products - equity | — | — | 34,648 | 34,648 | — | — | 24,604 | 24,604 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Unsecured debt | — | — | 16,851 | 16,851 | — | — | 26,740 | 26,740 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Equity | — | — | 5,107 | 5,107 | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Short term investments | 70,498 | — | — | 70,498 | 18,892 | — | — | 18,892 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Total Investments | $ | 70,498 | $ | — | $ | 1,018,980 | $ | 1,089,478 | $ | 18,892 | $ | — | $ | 650,907 | $ | 669,799 | |||||||||||||||
Total return swap | $ | — | $ | — | $ | (15,402 | ) | $ | (15,402 | ) | $ | — | $ | — | $ | (34,900 | ) | $ | (34,900 | ) | |||||||||||
Credit default swap | — | 46 | — | 46 | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Total Derivatives | $ | — | $ | 46 | $ | (15,402 | ) | $ | (15,356 | ) | $ | — | $ | — | $ | (34,900 | ) | $ | (34,900 | ) | |||||||||||
Total Investments and Derivatives | $ | 70,498 | $ | 46 | $ | 1,003,578 | $ | 1,074,122 | $ | 18,892 | $ | — | $ | 616,007 | $ | 634,899 | |||||||||||||||
The following tables provide a reconciliation of the beginning and ending balances for investments that use Level 3 inputs for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015:
107
CĪON Investment Corporation
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
December 31, 2016
(in thousands, except share and per share amounts)
Year Ended December 31, 2016 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Senior Secured First Lien Debt | Senior Secured Second Lien Debt | Collateralized Securities and Structured Products - Debt | Collateralized Securities and Structured Products - Equity | Unsecured Debt | Equity | Total Return Swap | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Beginning balance, December 31, 2015 | $ | 104,187 | $ | 453,713 | $ | 41,663 | $ | 24,604 | $ | 26,740 | $ | — | $ | (34,900 | ) | $ | 616,007 | ||||||||||||||
Investments purchased(2) | 423,262 | 124,281 | — | 10,000 | 6,518 | 5,832 | — | 569,893 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Net realized gain | 528 | 1,384 | — | — | 463 | 350 | 28,159 | 30,884 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Net change in unrealized appreciation | 1,969 | 12,293 | 1,341 | 3,515 | 2,374 | 275 | 19,498 | 41,265 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Accretion of discount | 1,422 | 1,104 | 110 | — | 127 | — | — | 2,763 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Sales and principal repayments | (41,455 | ) | (158,428 | ) | (5,000 | ) | (3,471 | ) | (19,371 | ) | (1,350 | ) | (28,159 | ) | (257,234 | ) | |||||||||||||||
Ending balance, December 31, 2016 | $ | 489,913 | $ | 434,347 | $ | 38,114 | $ | 34,648 | $ | 16,851 | $ | 5,107 | $ | (15,402 | ) | $ | 1,003,578 | ||||||||||||||
Change in net unrealized appreciation on investments still held as of December 31, 2016(1) | $ | 557 | $ | 8,568 | $ | 1,281 | $ | 3,515 | $ | 1,268 | $ | 275 | $ | 15,737 | $ | 31,201 | |||||||||||||||
(1) Included in net change in unrealized appreciation (depreciation) on investments in the consolidated statements of operations except where related to the total return swap, which is included in net change in unrealized appreciation (depreciation) on total return swap.
(2) Includes accrued interest receivable capitalized as additional principal due from the borrower for securities that contain a PIK interest provision.
Year Ended December 31, 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Senior Secured First Lien Debt | Senior Secured Second Lien Debt | Collateralized Securities and Structured Products - Debt | Collateralized Securities and Structured Products - Equity | Unsecured Debt | Total Return Swap | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||
Beginning balance, December 31, 2014 | $ | 69,204 | $ | 245,258 | $ | 27,965 | $ | 9,137 | $ | — | $ | (4,409 | ) | $ | 347,155 | ||||||||||||
Investments purchased | 82,147 | 261,022 | 15,500 | 24,914 | 54,634 | — | 438,217 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Net realized gain | 543 | 27 | — | — | 551 | 30,753 | 31,874 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Net change in unrealized depreciation | (1,925 | ) | (14,550 | ) | (1,911 | ) | (6,388 | ) | (2,813 | ) | (30,491 | ) | (58,078 | ) | |||||||||||||
Accretion of discount | 441 | 390 | 109 | 17 | 68 | — | 1,025 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Sales and principal repayments | (46,223 | ) | (38,434 | ) | — | (3,076 | ) | (25,700 | ) | (30,753 | ) | (144,186 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Ending balance, December 31, 2015 | $ | 104,187 | $ | 453,713 | $ | 41,663 | $ | 24,604 | $ | 26,740 | $ | (34,900 | ) | $ | 616,007 | ||||||||||||
Change in net unrealized depreciation on investments still held as of December 31, 2015(1) | $ | (1,910 | ) | $ | (14,612 | ) | $ | (1,911 | ) | $ | (6,388 | ) | $ | (2,813 | ) | $ | (30,333 | ) | $ | (57,967 | ) | ||||||
(1) | Included in net change in unrealized appreciation (depreciation) on investments in the consolidated statements of operations except where related to the total return swap, which is included in net change in unrealized appreciation (depreciation) on total return swap. |
Significant Unobservable Inputs
The valuation techniques and significant unobservable inputs used in recurring Level 3 fair value measurements of investments as of December 31, 2016 and 2015 were as follows:
108
CĪON Investment Corporation
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
December 31, 2016
(in thousands, except share and per share amounts)
December 31, 2016 | ||||||||||||||||
Fair Value | Valuation Techniques/ Methodologies | Unobservable Inputs | Range | Weighted Average(1) | ||||||||||||
Senior secured first lien debt | $ | 417,736 | Discounted Cash Flow | Discount Rates | 6.0% | - | 21.3% | 16.5% | ||||||||
61,846 | Broker Quotes | Broker Quotes | N/A | N/A | ||||||||||||
10,331 | Market Comparable Approach | EBITDA Multiple | 4.00x | - | 6.00x | 4.78x | ||||||||||
Senior secured second lien debt | 291,189 | Discounted Cash Flow | Discount Rates | 8.5% | - | 20.6% | 10.5% | |||||||||
129,219 | Broker Quotes | Broker Quotes | N/A | N/A | ||||||||||||
13,939 | Market Comparable Approach | EBITDA Multiple | 6.50x | - | 9.50x | 8.09x | ||||||||||
Revenue Multiple | 0.65x | - | 0.90x | 0.65x | ||||||||||||
Collateralized securities and structured products - debt | 38,114 | Discounted Cash Flow | Discount Rates | 7.8% | - | 11.0% | 10.1% | |||||||||
Collateralized securities and structured products - equity | 34,648 | Discounted Cash Flow | Discount Rates | 9.3% | - | 17.0% | 13.8% | |||||||||
Unsecured debt | 16,851 | Broker Quotes | Broker Quotes | N/A | N/A | |||||||||||
Equity | 4,946 | Market Comparable Approach | EBITDA Multiple | 3.75x | - | 10.50x | 7.23x | |||||||||
161 | Options Pricing Model | Expected Volatility | N/A | 36.2% | ||||||||||||
Total return swap | (1,002 | ) | Discounted Cash Flow | Discount Rates | 5.1% | - | 14.6% | 7.3% | ||||||||
(14,400 | ) | Broker Quotes | Broker Quotes | N/A | N/A | |||||||||||
Total | $ | 1,003,578 | ||||||||||||||
(1) | Weighted average amounts are based on the estimated fair values. |
December 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||||||
Fair Value | Valuation Techniques/ Methodologies | Unobservable Inputs | Range | Weighted Average(1) | ||||||||||||
Senior secured first lien debt | $ | 58,715 | Discounted Cash Flow | Discount Rates | 7.3% | — | 13.2% | 8.9% | ||||||||
45,472 | Broker Quotes | Broker Quotes | N/A | N/A | ||||||||||||
Senior secured second lien debt | 233,616 | Discounted Cash Flow | Discount Rates | 9.0% | — | 11.7% | 10.2% | |||||||||
220,097 | Broker Quotes | Broker Quotes | N/A | N/A | ||||||||||||
Collateralized securities and structured products - debt | 41,663 | Discounted Cash Flow | Discount Rates | 9.0% | — | 12.0% | 11.1% | |||||||||
Collateralized securities and structured products - equity | 24,604 | Discounted Cash Flow | Discount Rates | 16.0% | — | 17.0% | 16.5% | |||||||||
Unsecured debt | 26,740 | Broker Quotes | Broker Quotes | N/A | N/A | |||||||||||
Total return swap | (3,991 | ) | Discounted Cash Flow | Discount Rates | 5.6% | — | 28.7% | 7.6% | ||||||||
(30,909 | ) | Broker Quotes | Broker Quotes | N/A | N/A | |||||||||||
Total | $ | 616,007 | ||||||||||||||
(1) | Weighted average amounts are based on the estimated fair values. |
The significant unobservable inputs used in the fair value measurement of the Company’s senior secured first lien debt, senior secured second lien debt, collateralized securities and structured products, unsecured debt, equity, and total return swap are discount rates, EBITDA multiples, revenue multiples, broker quotes and expected volatility. A significant increase or decrease in discount rates would result in a significantly lower or higher fair value measurement, respectively. A significant increase or decrease in the EBITDA multiples, revenue multiples, broker quotes and expected volatility would result in a significantly higher or lower fair value measurement, respectively.
109
Note 10. General and Administrative Expense
General and administrative expense consisted of the following items for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014:
Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
Professional fees | $ | 1,623 | $ | 1,044 | $ | 849 | ||||||
Transfer agent expense | 1,272 | 1,144 | 627 | |||||||||
Dues and subscriptions | 775 | 505 | 230 | |||||||||
Valuation expense | 625 | 310 | 136 | |||||||||
Printing and marketing expense | 553 | 755 | 681 | |||||||||
Due diligence fees | 470 | 1,006 | 967 | |||||||||
Insurance expense | 376 | 297 | 235 | |||||||||
Director fees and expenses | 274 | 296 | 162 | |||||||||
Filing fees | 53 | 478 | 113 | |||||||||
Other expenses | 696 | 413 | 272 | |||||||||
Total general and administrative expense | $ | 6,717 | $ | 6,248 | $ | 4,272 | ||||||
Note 11. Commitments and Contingencies
The Company entered into certain contracts with other parties that contain a variety of indemnifications. The Company’s maximum exposure under these arrangements is unknown. However, the Company has not experienced claims or losses pursuant to these contracts and believes the risk of loss related to such indemnifications to be remote.
As of December 31, 2016 and 2015, the Company’s unfunded commitments were as follows:
Unfunded Commitments | December 31, 2016(1) | December 31, 2015(1) | ||||||
CCSLF(2)(3) | $ | 40,000 | $ | 40,000 | ||||
Tennessee Merger Sub, Inc.(4) | 10,254 | — | ||||||
Ministry Brands, LLC | 5,274 | — | ||||||
Studio Movie Grill Holdings, LLC(3) | 4,127 | 1,069 | ||||||
Elemica Holdings, Inc.(3) | 2,500 | — | ||||||
ABG Intermediate Holdings 2 LLC(3) | 1,119 | 1,128 | ||||||
Ivy Hill Middle Market Credit Fund VIII, Ltd.(3) | 1,111 | — | ||||||
American Media, Inc.(3) | 711 | — | ||||||
ECI Acquisition Holdings, Inc. | — | 1,207 | ||||||
Total | $ | 65,096 | $ | 43,404 | ||||
(1) | Unless otherwise noted, the funding criteria for these unfunded commitments had not been met at the date indicated. |
(2) | On June 24, 2015, the Company entered into a joint venture with Capitala Finance Corp., or Capitala, to create CCSLF. All portfolio and other material decisions regarding CCSLF must be submitted to its board of managers, which is comprised of four members, two of whom were selected by the Company and the other two were selected by Capitala. Further, all portfolio and other material decisions require the affirmative vote of at least one member from the Company and one member from Capitala. |
(3) | As of March 9, 2017, the Company's unfunded commitments were to portfolio companies ABG Intermediate Holdings 2 LLC, American Media, Inc., CF Entertainment Inc., Elemica Holdings, Inc., Ivy Hill Middle Market Credit Fund VIII, Ltd. and Studio Movie Grill Holdings, LLC in the amount of $1,119, $415, $10,000, $2,500, $1,111 and $4,127, respectively, and also included an unfunded commitment of $40,000 to CCSLF. In addition, subsequent to December 31, 2016, the Company entered into unfunded commitments of $5,079, $3,606 and $18,030 with American Axle & Manufacturing, Inc., BWAY Holding Company and CenturyLink, Inc., respectively. |
(4) | As of December 31, 2016, such commitment was subject to the execution of a definitive loan agreement and the consummation of the underlying corporate transaction, and conditional upon receipt of all necessary shareholder, regulatory and other applicable approvals. Prior to March 9, 2017, the unfunded commitment to Tennessee Merger Sub, Inc. was terminated. |
Unfunded commitments to provide funds to companies are not recorded on the Company’s consolidated balance sheets. Since these commitments may expire without being drawn upon, unfunded commitments do not necessarily represent future cash requirements or future earning assets for the Company. The Company intends to use cash on hand, short term investments, proceeds from borrowings, and other liquid assets to fund
110
CĪON Investment Corporation
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
December 31, 2016
(in thousands, except share and per share amounts)
these commitments should the need arise. For information on the companies to which the Company is committed to fund additional amounts as of December 31, 2016 and 2015, refer to the table above and the consolidated schedules of investments.
The Company will fund its unfunded commitments from the same sources it uses to fund its investment commitments that are funded at the time they are made (i.e., advances from its credit facilities and/or cash flows from operations). The Company will not fund its unfunded commitments from future net proceeds generated by securities offerings. The Company follows a process to manage its liquidity and ensure that it has available capital to fund its unfunded commitments. Specifically, the Company prepares detailed analyses of the level of its unfunded commitments relative to its then available liquidity on a daily basis. These analyses are reviewed and discussed on a weekly basis by the Company's executive officers and senior members of CIM (including members of the investment committee) and are updated on a “real time” basis in order to ensure that the Company has adequate liquidity to satisfy its unfunded commitments.
The Company does not include its unfunded capital commitment to CCSLF as a senior security for the asset coverage ratio, as the capital commitments cannot be drawn without an affirmative vote by one of the Company's representatives on CCSLF's board of managers.
Note 12. Fee Income
Fee income consists of commitment fees, amendment fees and administrative agent fees. The following table summarizes the Company’s fee income for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014:
Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
Commitment fees | $ | 417 | $ | 718 | $ | 283 | |||||
Amendment fees | 261 | 97 | 96 | ||||||||
Administrative agent fees | 20 | — | 20 | ||||||||
Total | $ | 698 | $ | 815 | $ | 399 | |||||
Administrative agent fees are recurring income as long as the Company remains the administrative agent for the related investment. Income from all other fees is non-recurring.
111
CĪON Investment Corporation
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
December 31, 2016
(in thousands, except share and per share amounts)
Note 13. Financial Highlights
The following is a schedule of financial highlights for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015, 2014 and 2013 and for the period from January 31, 2012 (Inception) through December 31, 2012:
For the Period from January 31, 2012 (Inception) through December 31, 2012 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||||||||||
Per share data:(1) | ||||||||||||||||||||
Net asset value at beginning of period | $ | 8.71 | $ | 9.22 | $ | 9.32 | $ | 8.97 | $ | — | ||||||||||
Results of operations: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Net investment income (loss)(2) | 0.45 | 0.32 | 0.19 | (0.01 | ) | 0.01 | ||||||||||||||
Net realized gain (loss) and net change in unrealized appreciation (depreciation) on investments and loss on foreign currency(3) | 0.23 | (0.17 | ) | 0.02 | 0.20 | 0.02 | ||||||||||||||
Net realized gain and net change in unrealized appreciation on total return swap | 0.45 | — | 0.33 | 0.91 | 0.02 | |||||||||||||||
Net increase in net assets resulting from operations(3) | 1.13 | 0.15 | 0.54 | 1.10 | 0.05 | |||||||||||||||
Shareholder distributions: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Distributions from net investment income | (0.43 | ) | (0.32 | ) | (0.18 | ) | — | — | ||||||||||||
Distributions from net realized gains | (0.30 | ) | (0.40 | ) | (0.55 | ) | (0.64 | ) | — | |||||||||||
Distributions in excess of net investment income(4) | — | (0.01 | ) | — | (0.08 | ) | — | |||||||||||||
Net decrease in net assets from shareholders' distributions | (0.73 | ) | (0.73 | ) | (0.73 | ) | (0.72 | ) | — | |||||||||||
Capital share transactions: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of common stock above net asset value(5) | — | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.14 | 9.00 | |||||||||||||||
Repurchases of common stock(6) | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Amortization of deferred offering expenses | — | — | — | (0.17 | ) | (0.08 | ) | |||||||||||||
Net increase (decrease) in net assets resulting from capital share transactions | — | 0.07 | 0.09 | (0.03 | ) | 8.92 | ||||||||||||||
Net asset value at end of period | $ | 9.11 | $ | 8.71 | $ | 9.22 | $ | 9.32 | $ | 8.97 | ||||||||||
Shares of common stock outstanding at end of period | 109,787,557 | 103,814,361 | 53,818,629 | 15,510,178 | 500,338 | |||||||||||||||
Total investment return-net asset value(7) | 13.51 | % | 2.13 | % | 6.92 | % | 11.96 | % | (0.35 | )% | ||||||||||
Net assets at beginning of period | $ | 904,326 | $ | 496,389 | $ | 144,571 | $ | 4,487 | $ | 4,503 | ||||||||||
Net assets at end of period | $ | 999,763 | $ | 904,326 | $ | 496,389 | $ | 144,571 | $ | 4,487 | ||||||||||
Average net assets | $ | 936,739 | $ | 719,358 | $ | 313,044 | $ | 51,027 | $ | 4,495 | ||||||||||
Ratio/Supplemental data: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Ratio of net investment income (loss) to average net assets(8) | 5.09 | % | 3.44 | % | 2.08 | % | (0.10 | )% | 0.06 | % | ||||||||||
Ratio of gross operating expenses to average net assets(9) | 3.51 | % | 3.90 | % | 4.18 | % | 11.51 | % | 2.60 | % | ||||||||||
Ratio of expenses (before expense support from CIG and recoupment of expense support) to average net assets(10) | 3.44 | % | 3.25 | % | 3.98 | % | 11.51 | % | 2.60 | % | ||||||||||
Ratio of net expense recoupments (net expense support from CIG) to average net assets(11) | 0.07 | % | 0.65 | % | (0.40 | )% | (7.76 | )% | (2.60 | )% | ||||||||||
Ratio of net operating expenses to average net assets | 3.51 | % | 3.90 | % | 3.58 | % | 3.75 | % | — | |||||||||||
Portfolio turnover rate(12) | 29.78 | % | 20.94 | % | 68.98 | % | 14.97 | % | 0.13 | % | ||||||||||
Asset coverage ratio(13) | 3.04 | 2.84 | 2.52 | 2.34 | 3.02 | |||||||||||||||
(1) | The per share data for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015, 2014 and 2013 was derived by using the weighted average shares of common stock outstanding during each period. The per share data for the period from January 31, 2012 (Inception) through December 31, 2012 was derived by using the weighted average shares of common stock outstanding from the commencement of operations on December 17, 2012 through December 31, 2012. |
(2) | Net investment income (loss) per share includes expense support from CIG of $0.06 and $0.72 per share for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively, and $0.23 per share for the period from January 31, 2012 (Inception) through December 31, 2012. Net investment income (loss) per share also includes expense |
112
CĪON Investment Corporation
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
December 31, 2016
(in thousands, except share and per share amounts)
support recoupments by CIG of $0.01, $0.06 and $0.02 per share for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. There was no expense support from CIG or AIM for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015 and no expense support recoupments by CIG for the year ended December 31, 2013 or for the period from January 31, 2012 (Inception) through December 31, 2012.
(3) | The amount shown for net realized gain (loss) and net change in unrealized appreciation (depreciation) on investments and loss on foreign currency is the balancing figure derived from the other figures in the schedule. The amount shown at this caption for a share outstanding throughout the period may not agree with the change in the aggregate gains and losses in portfolio securities for the period because of the timing of sales and repurchases of the Company’s shares in relation to fluctuating market values for the portfolio. As a result, net increase in net assets resulting from operations in this schedule may vary from the consolidated statements of operations. |
(4) | Distributions in excess of net investment income represent certain expenses, which are not deductible on a tax-basis. Unearned capital gains incentive fees and certain offering expenses reduce GAAP basis net investment income, but do not reduce tax basis net investment income. These tax-related adjustments represent additional net investment income available for distribution for tax purposes. |
(5) | The continuous issuance of shares of common stock may cause an incremental increase in net asset value per share due to the sale of shares at the then prevailing public offering price and the receipt of net proceeds per share by the Company in excess of net asset value per share on each subscription closing date. The per share impact of the continuous issuance of shares of common stock was an increase to net asset value of less than $0.01 per share for the year ended December 31, 2016. |
(6) | Repurchases of common stock may cause an incremental decrease in net asset value per share due to the repurchase of shares at a price in excess of net asset value per share on each repurchase date. The per share impact of repurchases of common stock was a decrease to net asset value of less than $0.01 per share during the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015, 2014 and 2013 and for the period from January 31, 2012 (Inception) through December 31, 2012. |
(7) | Total investment return-net asset value is a measure of the change in total value for shareholders who held the Company’s common stock at the beginning and end of the period, including distributions paid or payable during the period. Total investment return-net asset value is based on (i) the beginning period net asset value per share on the first day of the period, (ii) the net asset value per share on the last day of the period of (A) one share plus (B) any fractional shares issued in connection with the reinvestment of monthly distributions, and (iii) the value of distributions payable, if any, on the last day of the period. The total investment return-net asset value calculation assumes that monthly cash distributions are reinvested in accordance with the Company's distribution reinvestment plan then in effect as described in Note 5. The total investment return-net asset value does not consider the effect of the sales load from the sale of the Company’s common stock. The total investment return-net asset value includes the effect of the issuance of shares at a net offering price that is greater than net asset value per share, which causes an increase in net asset value per share. Total returns covering less than a full year are not annualized. |
(8) | Excluding the impact of expense support from CIG and/or the recoupment of expense support by CIG during the period, the ratio of net investment income (loss) to average net assets would have been 5.16%, 4.09%, 1.68%, (7.86)% and (2.54%) for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015, 2014 and 2013 and for the period from January 31, 2012 (Inception) through December 31, 2012, respectively. |
(9) | Ratio of gross operating expenses to average net assets does not include expense support provided by CIG and/or AIM, if any. |
(10) | The ratio of gross expense recoupment by CIG to average net assets for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014 were 0.07%, 0.65% and 0.20%, respectively. |
(11) | In order to record an obligation to reimburse CIG for expense support provided, the ratio of gross operating expenses to average net assets, when considering the recoupment, in the period in which recoupment is sought, cannot exceeded the ratio of gross operating expenses to average net assets for the period when the expense support was provided. For purposes of this calculation, gross operating expenses include all expenses borne by the Company, except for offering and organizational costs, base management fees, incentive fees, administrative services expenses, other general and administrative expenses owed to CIM and its affiliates and interest expense. For the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015, 2014 and 2013 and for the period from January 31, 2012 (Inception) through December 31, 2012, the ratio of gross operating expenses to average net assets, when considering recoupment of expense support, was 0.59%, 0.63%, 0.80%, 2.45% and 0.93%, respectively. |
(12) | Portfolio turnover rate is calculated using the lesser of year-to-date sales or purchases over the average of the invested assets at fair value, excluding short term investments, and is not annualized. |
(13) | Asset coverage ratio is equal to (i) the sum of (a) net assets at the end of the period and (b) total senior securities outstanding at the end of the period (excluding unfunded commitments), divided by (ii) total senior securities outstanding at the end of the period. For purposes of the asset coverage ratio test applicable to the Company as a BDC, the Company treats the outstanding TRS notional amount at the end of the period, less the total amount of cash collateral posted by Flatiron under the TRS, as well as unfunded commitments (as of December 31, 2014 only), as senior securities. The Company does not include its unfunded capital commitment to CCSLF as a senior security for the asset coverage ratio, as the capital commitments cannot be drawn without an affirmative vote by one of the Company's representatives on CCSLF's board of managers. |
Note 14. Income Taxes
It is the Company's policy to comply with all requirements of the Code applicable to RICs and to distribute substantially all of its taxable income to its shareholders. In addition, by distributing during each calendar year substantially all of its net investment income, net realized capital gains and certain other amounts, if any, the Company intends not to be subject to corporate level federal income tax or federal excise taxes. Accordingly, no federal income tax provision was required for the year ended December 31, 2016.
Income and capital gain distributions are determined in accordance with the Code and federal tax regulations, which may differ from amounts determined in accordance with GAAP. These book/tax differences, which could be material, are primarily due to differing treatments of income and gains on various investments held by the Company. Permanent book/tax differences result in reclassifications to capital in excess of par value, accumulated undistributed net investment income and accumulated undistributed realized gain on investments.
As of December 31, 2016 and 2015, the Company made the following reclassifications of permanent book and tax basis differences:
113
CĪON Investment Corporation
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
December 31, 2016
(in thousands, except share and per share amounts)
Capital Accounts | December 31, 2016 | December 31, 2015 | ||||||
Paid-in-capital in excess of par value | $ | (296 | ) | $ | (632 | ) | ||
Undistributed net investment income | 28,451 | 32,506 | ||||||
Accumulated net realized gains | (28,155 | ) | (31,874 | ) | ||||
These permanent differences are primarily due to the reclassification of foreign currency, the tax treatment of swaps, and nondeductible expenses. These reclassifications had no effect on net assets.
The determination of the tax attributes of the Company’s distributions is made annually as of the end of the Company’s fiscal year based upon the Company’s taxable income for the full year and distributions paid for the full year. The tax characteristics of distributions to shareholders are reported to shareholders annually on Form 1099-DIV and were as follows for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014:
Years Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||||
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||||||||||||
Amount | Percentage | Amount | Percentage | Amount | Percentage | ||||||||||||||||
Ordinary income | |||||||||||||||||||||
Ordinary income (before expense support)(1) | $ | 76,553 | 98.8 | % | $ | 57,268 | 100.0 | % | $ | 22,505 | 91.7 | % | |||||||||
Expense support | — | — | — | — | 1,880 | 7.6 | % | ||||||||||||||
Realized long term capital gains | 906 | 1.2 | % | — | — | 162 | 0.7 | % | |||||||||||||
Total | $ | 77,459 | 100.0 | % | $ | 57,268 | 100.0 | % | $ | 24,547 | 100.0 | % | |||||||||
(1) | Includes net short term capital gains and realized gains on total return swap of $31,007, $31,874 and $18,365 for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. |
See Note 5, Distributions, for further information.
As of December 31, 2016 and 2015, the components of accumulated earnings on a tax basis were as follows:
December 31, 2016 | December 31, 2015 | ||||||
Undistributed ordinary income | $ | 3,847 | $ | — | |||
Undistributed long term capital gains | 924 | — | |||||
Net unrealized depreciation on investments and total return swap | (26,398 | ) | (64,137 | ) | |||
$ | (21,627 | ) | $ | (64,137 | ) | ||
As of December 31, 2016, the aggregate gross unrealized appreciation for all securities in which there was an excess of value over tax cost was $9,389; the aggregate gross unrealized depreciation for all securities in which there was an excess of tax cost over value was $20,202; the net unrealized depreciation was $10,813; and the aggregate cost of securities for Federal income tax purposes was $1,100,291.
As of December 31, 2015, the aggregate gross unrealized appreciation for all securities in which there was an excess of value over tax cost was $3,728; the aggregate gross unrealized depreciation for all securities in which there was an excess of tax cost over value was $67,865; the net unrealized appreciation was $64,137; and the aggregate cost of securities for Federal income tax purposes was $699,036.
114
CĪON Investment Corporation
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
December 31, 2016
(in thousands, except share and per share amounts)
Note 15. Selected Quarterly Financial Data (unaudited)
The following is the selected quarterly financial data as of and for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015. The following information reflects all adjustments, which are of a normal recurring nature, considered necessary for a fair presentation. The operating results for any quarter are not necessarily indicative of results for any future period:
Quarter Ended | March 31, 2016 | June 30, 2016 | September 30, 2016 | December 31, 2016 | ||||||||||||
Investment income | $ | 17,271 | $ | 17,830 | $ | 18,733 | $ | 26,756 | ||||||||
Net investment income | 10,475 | 10,830 | 10,695 | 15,711 | ||||||||||||
Net realized and unrealized (loss) gain on investments, foreign currency and total return swap | (5,859 | ) | 31,107 | 33,042 | 13,672 | |||||||||||
Net increase in net assets resulting from operations | 4,616 | 41,937 | 43,737 | 29,383 | ||||||||||||
Net increase in net assets resulting from operations per share of common stock | 0.04 | 0.40 | 0.41 | 0.27 | ||||||||||||
Net asset value per share of common stock at end of quarter | 8.57 | 8.79 | 9.02 | 9.11 | ||||||||||||
Weighted average shares of common stock outstanding | 103,957,573 | 104,835,705 | 106,581,390 | 108,395,601 | ||||||||||||
Quarter Ended | March 31, 2015 | June 30, 2015 | September 30, 2015 | December 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||
Investment income | $ | 8,914 | $ | 11,918 | $ | 14,833 | $ | 17,144 | ||||||||
Net investment income | 2,131 | 4,506 | 7,912 | 10,213 | ||||||||||||
Net realized and unrealized gain (loss) on investments and total return swap | 14,695 | 6,232 | (11,502 | ) | (35,629 | ) | ||||||||||
Net increase (decrease) in net assets resulting from operations | 16,826 | 10,738 | (3,590 | ) | (25,416 | ) | ||||||||||
Net increase (decrease) in net assets resulting from operations per share of common stock | 0.29 | 0.15 | (0.04 | ) | (0.26 | ) | ||||||||||
Net asset value per share of common stock at end of quarter | 9.35 | 9.33 | 9.13 | 8.71 | ||||||||||||
Weighted average shares of common stock outstanding | 58,939,554 | 72,323,545 | 84,923,397 | 97,313,961 | ||||||||||||
115
Item 9. Changes in and Disagreements With Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure
None.
Item 9A. Controls and Procedures
Evaluation of disclosure controls and procedures
In connection with the preparation of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2016, we carried out an evaluation, under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including our Co-Chief Executive Officers and our Chief Financial Officer, of the effectiveness of the design and operation of our disclosure controls and procedures as of the end of the period covered by this report pursuant to Rule 13a-15(b) and Rule 15d-15(b) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. Based on the foregoing evaluation, the Co-Chief Executive Officers and the Chief Financial Officer concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures were effective.
In designing and evaluating our disclosure controls and procedures, we recognized that disclosure controls and procedures, no matter how well conceived and operated, can provide only reasonable, not absolute, assurance that the objectives of the disclosure controls and procedures are met. Our disclosure controls and procedures have been designed to meet reasonable assurance standards. Disclosure controls and procedures cannot detect or prevent all error and fraud. Some inherent limitations in disclosure controls and procedures include costs of implementation, faulty decision-making, simple error and mistake. Additionally, controls can be circumvented by the individual acts of some persons, by collusion of two or more people, or by management override of the controls. The design of any system of controls is based, in part, upon certain assumptions about the likelihood of future events, and there can be no assurance that any design will succeed in achieving its stated goals under all anticipated and unanticipated future conditions. Over time, controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or the degree of compliance with established policies or procedures.
Management's Annual Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting. As defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f), internal control over financial reporting is a process designed by, or under the supervision of, our principal executive and principal financial officers, or persons performing similar functions, and effected by our board of directors, management and other personnel, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of consolidated financial statements for external purposes in accordance with GAAP.
Our internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that:
1. | Pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect our transactions and our dispositions of assets; |
2. | Provide reasonable assurance that our transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of consolidated financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that our receipts and expenditures are being made only in accordance with authorizations of our management and board of directors; and |
3. | Provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of our assets that could have a material effect on the consolidated financial statements. |
Because of its inherent limitations, a system of internal control over financial reporting can provide only reasonable assurance with respect to financial statement preparation and presentation and may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
In connection with the preparation of our annual consolidated financial statements, our management has conducted an assessment of the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting based on the framework set forth in Internal Control-Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (“COSO”) in 2013. Management's assessment included an evaluation of the design of our internal control over financial reporting and testing of the operational effectiveness of those controls. Based on this evaluation, we have concluded that, as of December 31, 2016, our internal control over financial reporting was effective to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with GAAP.
Pursuant to rules established by the SEC, this annual report does not include an attestation report of our independent registered public accounting firm regarding internal control over financial reporting.
Changes in internal control over financial reporting
There have been no changes in our internal control over financial reporting during the three months ended December 31, 2016 that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
116
Item 9B. Other Information
Not applicable.
117
PART III
We will file a definitive Proxy Statement for our 2017 Annual Meeting of Shareholders with the SEC pursuant to Regulation 14A promulgated under the Exchange Act, not later than 120 days after the end of our fiscal year. Accordingly, certain information required by Part III has been omitted under General Instruction G(3) to Form 10-K. Only those sections of our definitive Proxy Statement that specifically address the items set forth herein are incorporated by reference.
Item 10. Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance
The information required by Item 10 is hereby incorporated by reference from our definitive Proxy Statement relating to our 2017 Annual Meeting of Shareholders, to be filed with the SEC within 120 days following the end of our fiscal year.
Item 11. Executive Compensation
The information required by Item 11 is hereby incorporated by reference from our definitive Proxy Statement relating to our 2017 Annual Meeting of Shareholders, to be filed with the SEC within 120 days following the end of our fiscal year.
Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Shareholder Matters
The information required by Item 12 is hereby incorporated by reference from our definitive Proxy Statement relating to our 2017 Annual Meeting of Shareholders, to be filed with the SEC within 120 days following the end of our fiscal year.
Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence
The information required by Item 13 is hereby incorporated by reference from our definitive Proxy Statement relating to our 2017 Annual Meeting of Shareholders, to be filed with the SEC within 120 days following the end of our fiscal year.
Item 14. Principal Accounting Fees and Services
The information required by Item 14 is hereby incorporated by reference from our definitive Proxy Statement relating to our 2017 Annual Meeting of Shareholders, to be filed with the SEC within 120 days following the end of our fiscal year.
118
PART IV
Item 15. Exhibits, Financial Statement Schedules
(a) 1. Financial Statements
See the index to consolidated financial statements included as Item 8 to this Annual Report on Form 10-K hereof.
2. Financial Statement Schedules
Schedules not listed above have been omitted because they are not applicable or the information required to be set forth therein is included in the consolidated financial statements or notes thereto.
3. Exhibits
Exhibit Number | Description of Document | |
2.1 | Purchase and Sale Agreement, dated as of September 30, 2016, by and between Park South Funding, LLC and Credit Suisse Alternative Capital, LLC (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.1 to Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on October 4, 2016 (File No. 814-00941)). | |
3.1 | Articles of Amendment and Restatement of the Articles of Incorporation of CĪON Investment Corporation (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit (A)(2) to Pre-Effective Amendment No. 4 to Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form N-2 filed with the SEC on June 29, 2012 (File No. 333-178646)). | |
3.2 | Second Articles of Amendment and Restatement of the Articles of Incorporation of CĪON Investment Corporation (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on August 27, 2012 (File No. 814-00941)). | |
3.3 | Bylaws of CĪON Investment Corporation (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit (B) to Pre-Effective Amendment No. 4 to Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form N-2 filed with the SEC on June 29, 2012 (File No. 333-178646)). | |
4.1 | Form of Follow-On Subscription Agreement (Incorporated by reference to Appendix A to Post-Effective Amendment No. 3 to Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form N-2 filed with the SEC on February 24, 2017 (File No. 333-203683)). | |
4.2 | Fifth Amended and Restated Distribution Reinvestment Plan of CĪON Investment Corporation (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on December 8, 2016 (File No. 814-00941)). | |
10.1 | Investment Advisory Agreement by and between CĪON Investment Corporation and CION Investment Management, LLC (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit (G)(1) to Pre-Effective Amendment No. 4 to Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form N-2 filed with the SEC on June 29, 2012 (File No. 333-178646)). | |
10.2 | Investment Sub-Advisory Agreement by and among CĪON Investment Management, LLC, CION Investment Corporation and Apollo Investment Management, L.P. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit (G)(2) to Pre-Effective Amendment No. 4 to Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form N-2 filed with the SEC on June 29, 2012 (File No. 333-178646)). | |
10.3 | Administration Agreement by and between CĪON Investment Corporation and ICON Capital Corp. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit (K)(2) to Pre-Effective Amendment No. 4 to Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form N-2 filed with the SEC on June 29, 2012 (File No. 333-178646)). | |
10.4 | Custody Agreement by and between CĪON Investment Corporation and U.S. Bank National Association (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit (J) to Pre-Effective Amendment No. 4 to Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form N-2 filed with the SEC on June 29, 2012 (File No. 333-178646)). | |
10.5 | Escrow Agreement by and among CĪON Investment Corporation, UMB Bank, N.A., and ICON Securities Corp. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit (K)(1) to Pre-Effective Amendment No. 4 to Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form N-2 filed with the SEC on June 29, 2012 (File No. 333-178646)). | |
10.6 | Dealer Manager Agreement by and among CĪON Investment Corporation, CION Investment Management, LLC and ICON Securities Corp. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit (H)(1) to Pre-Effective Amendment No. 4 to Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form N-2 filed with the SEC on June 29, 2012 (File No. 333-178646)). | |
10.7 | ISDA 2002 Master Agreement, together with the Schedule thereto and Credit Support Annex to such Schedule, each dated as of December 17, 2012, by and between Flatiron Funding, LLC and Citibank, N.A. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on December 19, 2012 (File No. 814-00941)). | |
10.8 | Thirteenth Amended and Restated Confirmation Letter Agreement, dated as of February 18, 2017, by and between Flatiron Funding, LLC and Citibank, N.A. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on February 23, 2017 (File No. 814-00941)). | |
10.9 | Third Amended and Restated Expense Support and Conditional Reimbursement Agreement, dated as of December 14, 2016, by and among CĪON Investment Corporation, Apollo Investment Management, L.P. and CION Investment Group, LLC (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on December 14, 2016 (File No. 814-00941)). | |
10.10 | Amended and Restated Follow-On Dealer Manager Agreement, dated as of December 28, 2016, by and among CĪON Investment Corporation, CION Investment Management, LLC and CION Securities, LLC (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on January 4, 2017 (File No. 814-00941)). | |
119
Exhibit Number | Description of Document | |
10.11 | Form of Follow-On Selected Dealer Agreement (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit (H)(4) to Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form N-2 filed with the SEC on April 28, 2015 (File No. 333-203683)). | |
10.12 | Loan and Security Agreement, dated as of April 30, 2015, by and between CĪON Investment Corporation and East West Bank (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on May 6, 2015 (File No. 814-00941)). | |
10.13 | First Amendment to Loan and Security Agreement, dated as of January 28, 2016, by and between CĪON Investment Corporation and East West Bank (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on February 3, 2016 (File No. 814-00941)). | |
10.14 | Second Amendment to Loan and Security Agreement, dated as of April 21, 2016, by and between CĪON Investment Corporation and East West Bank (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on April 27, 2016 (File No. 814-00941)). | |
10.15 | Custody Control Agreement, dated as of April 30, 2015, by and among CĪON Investment Corporation, East West Bank and U.S. Bank National Association (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on May 6, 2015 (File No. 814-00941)). | |
10.16 | Limited Liability Company Agreement of CION / Capitala Senior Loan Fund I, LLC, dated as of June 24, 2015, by and between CĪON Investment Corporation and Capitala Finance Corp. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on June 26, 2015 (File No. 814-00941)). | |
10.17 | Loan and Security Agreement, dated as of August 26, 2016, by and among 34th Street Funding, LLC, JPMorgan Chase Bank, National Association, U.S. Bank National Association and CION Investment Management, LLC (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on September 1, 2016 (File No. 814-00941)). | |
10.18 | Sale and Contribution Agreement, dated as of August 26, 2016, by and between 34th Street Funding, LLC and CĪON Investment Corporation (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on September 1, 2016 (File No. 814-00941)). | |
10.19 | Master Participation Agreement, dated as of August 26, 2016, by and between 34th Street Funding, LLC and CĪON Investment Corporation (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on September 1, 2016 (File No. 814-00941)). | |
10.20 | Portfolio Management Agreement, dated as of August 26, 2016, by and between 34th Street Funding, LLC and CION Investment Management, LLC (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on September 1, 2016 (File No. 814-00941)). | |
10.21 | Guarantee of CĪON Investment Corporation dated as of August 26, 2016 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 to Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on September 1, 2016 (File No. 814-00941)). | |
10.22 | Amended and Restated Loan and Security Agreement, dated as of September 30, 2016, by and among 34th Street Funding, LLC, JPMorgan Chase Bank, National Association, U.S. Bank National Association and CION Investment Management, LLC (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on October 4, 2016 (File No. 814-00941)). | |
10.23 | Release and Termination Agreement, dated as of September 30, 2016, by and among CĪON Investment Corporation, 34th Street Funding, LLC and JPMorgan Chase Bank, National Association (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on October 4, 2016 (File No. 814-00941)). | |
10.24 | Amended and Restated Portfolio Management Agreement, dated as of September 30, 2016, by and among 34th Street Funding, LLC, CION Investment Management, LLC and JPMorgan Chase Bank, National Association (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on October 4, 2016 (File No. 814-00941)). | |
31.1 | Rule 13a-14(a)/15d-14(a) Certification of Co-Chief Executive Officer. | |
31.2 | Rule 13a-14(a)/15d-14(a) Certification of Co-Chief Executive Officer. | |
31.3 | Rule 13a-14(a)/15d-14(a) Certification of Chief Financial Officer. | |
32.1 | Certification of Co-Chief Executive Officer pursuant to 18 U.S.C. §1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | |
32.2 | Certification of Co-Chief Executive Officer pursuant to 18 U.S.C. §1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | |
32.3 | Certification of Chief Financial Officer pursuant to 18 U.S.C. §1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | |
120
Item 16. Form 10-K Summary
None.
121
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
Date: March 15, 2017
CĪON Investment Corporation
(Registrant)
By: /s/ Michael A. Reisner
Michael A. Reisner
Co-Chief Executive Officer and Co-President
By: /s/ Mark Gatto
Mark Gatto
Co-Chief Executive Officer and Co-President
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
Date: March 15, 2017
CĪON Investment Corporation
(Registrant)
By: /s/ Michael A. Reisner
Michael A. Reisner
Co-Chief Executive Officer, Co-President and Director
(Principal Executive Officer)
By: /s/ Mark Gatto
Mark Gatto
Co-Chief Executive Officer, Co-President and Director
(Principal Executive Officer)
By: /s/ Keith S. Franz
Keith S. Franz
Chief Financial Officer
(Principal Financial and Accounting Officer)
By: /s/ Robert A. Breakstone
Robert A. Breakstone
Director
By: /s/ Peter I. Finlay
Peter I. Finlay
Director
By: /s/ Aron I. Schwartz
Aron I. Schwartz
Director
122
