Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-10.39 - EX-10.39 - BROADRIDGE FINANCIAL SOLUTIONS, INC. | d758506dex1039.htm |
| EXCEL - IDEA: XBRL DOCUMENT - BROADRIDGE FINANCIAL SOLUTIONS, INC. | Financial_Report.xls |
| EX-32.1 - EX-32.1 - BROADRIDGE FINANCIAL SOLUTIONS, INC. | d758506dex321.htm |
| EX-23.1 - EX-23.1 - BROADRIDGE FINANCIAL SOLUTIONS, INC. | d758506dex231.htm |
| EX-12.1 - EX-12.1 - BROADRIDGE FINANCIAL SOLUTIONS, INC. | d758506dex121.htm |
| EX-31.1 - EX-31.1 - BROADRIDGE FINANCIAL SOLUTIONS, INC. | d758506dex311.htm |
| EX-21.1 - EX-21.1 - BROADRIDGE FINANCIAL SOLUTIONS, INC. | d758506dex211.htm |
| EX-32.2 - EX-32.2 - BROADRIDGE FINANCIAL SOLUTIONS, INC. | d758506dex322.htm |
| EX-31.2 - EX-31.2 - BROADRIDGE FINANCIAL SOLUTIONS, INC. | d758506dex312.htm |
Table of Contents
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
WASHINGTON, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
(Mark One)
| x | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
FOR THE FISCAL YEAR ENDED JUNE 30, 2014
OR
| ¨ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
FOR THE TRANSITION PERIOD FROM TO
COMMISSION FILE NUMBER 001- 33220
BROADRIDGE FINANCIAL SOLUTIONS, INC.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| DELAWARE | 33-1151291 | |
| (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) |
(I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) | |
| 1981 MARCUS AVENUE LAKE SUCCESS, NY |
11042 | |
| (Address of principal executive offices) | (Zip code) |
(516) 472-5400
(Registrant’s telephone number, including area code)
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| Title of Each Class: |
Name of Each Exchange on Which Registered: | |
| Common Stock, par value $0.01 per share | New York Stock Exchange |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act:
None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes x No ¨
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes ¨ No x
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes x No ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (Section 232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes x No ¨
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K (Section 229.405 of this chapter) is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. x
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. (Check one):
Large Accelerated Filer x Accelerated Filer ¨ Non-Accelerated Filer ¨ Smaller Reporting Company ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes ¨ No x
The aggregate market value, as of December 31, 2013, of common stock held by non-affiliates of the registrant was approximately $4,677,450,488.
As of July 31, 2014, there were 119,534,357 shares of the registrant’s common stock outstanding (excluding 34,926,770 shares held in treasury), par value $0.01 per share.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Portions of the registrant’s definitive proxy statement to be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission within
120 days after the fiscal year end of June 30, 2014 are incorporated by reference into Part III.
Table of Contents
2
Table of Contents
Forward-Looking Statements
This Annual Report on Form 10-K may contain “forward-looking statements” within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. Statements that are not historical in nature and which may be identified by the use of words such as “expects,” “assumes,” “projects,” “anticipates,” “estimates,” “we believe,” “could be” and other words of similar meaning, are forward-looking statements. In particular, information appearing under “Business,” “Risk Factors,” and “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” includes forward-looking statements. These statements are based on management’s expectations and assumptions and are subject to risks and uncertainties that may cause actual results to differ materially from those expressed. Factors that could cause actual results to differ materially from those contemplated by the forward-looking statements include:
| • | the success of Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc. (“Broadridge” or the “Company”) in retaining and selling additional services to its existing clients and in obtaining new clients; |
| • | Broadridge’s reliance on a relatively small number of clients, the continued financial health of those clients, and the continued use by such clients of Broadridge’s services with favorable pricing terms; |
| • | changes in laws and regulations affecting Broadridge’s clients or the services provided by Broadridge; |
| • | declines in participation and activity in the securities markets; |
| • | any material breach of Broadridge security affecting its clients’ customer information; |
| • | the failure of our outsourced data center services provider to provide the anticipated levels of service; |
| • | a disaster or other significant slowdown or failure of Broadridge’s systems or error in the performance of Broadridge’s services; |
| • | overall market and economic conditions and their impact on the securities markets; |
| • | Broadridge’s failure to keep pace with changes in technology and demands of its clients; |
| • | the ability to attract and retain key personnel; |
| • | the impact of new acquisitions and divestitures; and |
| • | competitive conditions. |
There may be other factors that may cause our actual results to differ materially from the forward-looking statements. Our actual results, performance or achievements could differ materially from those expressed in, or implied by, the forward-looking statements. We can give no assurances that any of the events anticipated by the forward-looking statements will occur or, if any of them do, what impact they will have on our results of operations and financial condition. You should carefully read the factors described in the “Risk Factors” section of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for a description of certain risks that could, among other things, cause our actual results to differ from these forward-looking statements.
All forward-looking statements speak only as of the date of this Annual Report on Form 10-K and are expressly qualified in their entirety by the cautionary statements included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. We disclaim any obligation to update or revise forward-looking statements that may be made to reflect events or circumstances that arise after the date made or to reflect the occurrence of unanticipated events, other than as required by law.
3
Table of Contents
| ITEM 1. | Business |
Overview
Broadridge is a leading global provider of investor communications and technology-driven solutions to banks, broker-dealers, mutual funds and corporate issuers. Our systems and services include investor communication solutions, and securities processing and business process outsourcing services. In short, we provide the infrastructure that helps the financial services industry operate. With over 50 years of experience, we provide financial services firms with advanced, dependable, scalable and cost-effective integrated systems. Our systems help reduce the need for clients to make significant capital investments in operations infrastructure, thereby allowing them to increase their focus on core business activities.
We deliver a broad range of solutions that help our clients better serve their retail and institutional customers across the entire investment lifecycle, including pre-trade, trade, and post-trade processing. We serve a large and diverse client base across our four businesses: Bank/Broker-Dealer Investor Communication Solutions, Corporate Issuer Solutions, Mutual Fund and Retirement Solutions, and Global Technology and Operations Solutions. Our businesses operate in two business segments: Investor Communication Solutions and Securities Processing Solutions.
Investor Communication Solutions
Our Bank/Broker-Dealer Investor Communication Solutions, Corporate Issuer Solutions, and Mutual Fund and Retirement Solutions businesses operate within this segment. A large portion of our Investor Communication Solutions business involves the processing and distribution of proxy materials to investors in equity securities and mutual funds, as well as the facilitation of related vote processing. ProxyEdge®, our innovative electronic proxy delivery and voting solution for institutional investors and financial advisors, helps ensure the participation of the largest stockholders of many companies. We also provide the distribution of regulatory reports and corporate action/reorganization event information, as well as tax reporting solutions that help our clients meet their regulatory compliance needs. In addition, we provide financial information distribution and transaction reporting services to both financial institutions and securities issuers. These services include the processing and distribution of account statements and trade confirmations, traditional and personalized document fulfillment and content management services, marketing communications, and imaging, archival and workflow solutions that enable and enhance our clients’ communications with investors. All of these communications are delivered through paper or electronic channels. In addition, Broadridge provides corporate issuers with registered proxy services as well as registrar, stock transfer and record-keeping services.
| • | Bank/Broker-Dealer Investor Communication Solutions: Broadridge is a leader in corporate governance activities, processing over 80% of the outstanding shares in the United States (“U.S.”), and over 75% of the shares voted outside the U.S. in the performance of our proxy services. We process over two billion investor communications annually through a combination of physical and electronic channels. |
| • | Corporate Issuer Solutions: Broadridge serves corporate issuers with a variety of their needs including proxy and transfer agency services. |
| • | Mutual Fund and Retirement Solutions: Broadridge is the leading independent provider of retirement fund processing and provides unique data-driven market intelligence, specialized marketing communications and fund governance. |
Securities Processing Solutions
Our Global Technology and Operations Solutions business operates within this segment. We offer a suite of advanced computerized real-time transaction processing services that automate the securities transaction lifecycle, from desktop productivity tools, data aggregation, performance reporting, and portfolio management to order capture and execution, trade confirmation, settlement, and accounting. Our services help financial
4
Table of Contents
institutions efficiently and cost-effectively consolidate their books and records, gather and service assets under management, focus on their core businesses, and manage risk. With multi-currency capabilities, our Global Processing Solution supports real-time global trading of equity, option, mutual fund, and fixed income securities in established and emerging markets. In addition, our business process outsourcing services allow broker-dealers to outsource certain administrative functions relating to clearing and settlement, from order entry to trade matching and settlement, while maintaining their ability to finance and capitalize their businesses.
| • | Global Technology and Operations Solutions: Broadridge is the leading back- and middle-office securities processing platform for North American and global broker-dealers. Provided on an application service provider (“ASP”) basis, Broadridge’s platform is a global market solution, clearing and settling in over 70 countries. Broadridge processes on average over $5 trillion in equity and fixed income trades per day of U.S. and Canadian securities, including approximately 60% of U.S. fixed income trades. |
History and Development of Our Company
We are the former Brokerage Services division of Automatic Data Processing, Inc. (“ADP”). Broadridge was incorporated in Delaware as a wholly-owned subsidiary of ADP on March 29, 2007 in anticipation of our spin-off from ADP. We spun off from ADP and began operating as an independent public company on March 30, 2007. Our company has over 50 years of history in providing innovative solutions to financial services firms and publicly-held companies. In 1962, the Brokerage Services division of ADP opened for business with one client, processing an average of 300 trades per night. In 1979, we expanded our U.S.-based securities processing solutions to process Canadian securities.
We made significant additions to our Securities Processing Solutions business through two key acquisitions in the mid-1990s. In 1995, we acquired a London-based provider of multi-currency clearance and settlement services, to become a global supplier of transaction processing services. In 1996, we acquired a provider of institutional fixed income transaction processing systems.
We began offering our proxy services in 1989. The proxy services business, which started what has become our Investor Communication Solutions business, leveraged the information processing systems and infrastructure of our Securities Processing Solutions business. Our proxy services offering attracted 31 major clients in its first year of operations. In 1992, we acquired The Independent Election Corporation of America which further increased our proxy services capabilities. By 1999, we were handling over 90% of the investor communication distributions for securities held of record by banks and broker-dealers in the U.S.—from proxy statements to annual reports. During the 1990s, we expanded our proxy services business to serve security owners of Canadian and United Kingdom issuers and we began offering a complete outsourced solution for international proxies.
In 1994, we began offering ProxyEdge, our innovative electronic proxy delivery and voting solution for institutional investors that helps ensure the participation of the largest stockholders of many companies. In 1998, having previously provided print and distribution services as an accommodation to our securities processing and proxy clients, we decided to focus on account statement and reporting services. In 2001, we developed and released PostEdge® to meet the need for electronic distribution and archiving of all investor communications. In 2010, we entered the transfer agency business through an acquisition of a provider of registrar, stock transfer and record-keeping services.
In fiscal year 2011, we acquired three businesses in the Investor Communication Solutions segment. In August 2010, we acquired NewRiver, Inc. (“NewRiver”), a leader in mutual fund electronic investor disclosure solutions. In December 2010, we acquired Forefield, Inc. (“Forefield”), a leading provider of real-time sales, education and client communication solutions for financial institutions and their advisors. In January 2011, we acquired Matrix Financial Solutions, Inc. (“Matrix”). Matrix is a provider of mutual fund processing services for third party administrators, financial advisors, banks and wealth management professionals. Matrix’s back-office, trust, custody, trading and mutual fund settlement services are integrated into our product suite thereby strengthening Broadridge’s role as a provider of data processing and distribution channel solutions to the mutual fund industry.
5
Table of Contents
The Company has also acquired businesses in the Securities Processing Solutions segment. In fiscal year 2010, the Company acquired City Networks Ltd, a leading software and services provider of reconciliation, multi-asset process automation and operational risk management solutions to the global financial services industry. In fiscal year 2012, the Company acquired Paladyne Systems, Inc. (“Paladyne”), now known as Broadridge Investment Management, Reference Data and Risk Solutions, a provider of buy-side technology solutions for the global investment management industry.
In fiscal year 2014, we completed the acquisitions of two businesses in the Investor Communication Solutions segment. In July 2013, we acquired Bonaire Software Solutions, LLC (“Bonaire”), a leading provider of fee calculation, billing, and revenue and expense management solutions for asset managers including institutional asset managers, wealth managers, mutual funds, bank trusts, hedge funds and capital markets firms. In February 2014, we acquired Emerald Connect, LLC (“Emerald”), a leading provider of websites and related communications solutions for financial advisors.
The Broadridge Business
Investor Communication Solutions
A majority of publicly-traded shares are not registered in companies’ records in the names of their ultimate beneficial owners. Instead, a substantial majority of all public companies’ shares are held in “street name,” meaning that they are held of record by broker-dealers or banks through their depositories. Most street name shares are registered in the name “Cede & Co.,” the name used by The Depository Trust and Clearing Corporation (“DTCC”), which holds shares on behalf of its participant broker-dealers and banks. These participant broker-dealers and banks (which are known as nominees because they hold securities in name only) in turn hold the shares on behalf of their clients, the individual beneficial owners. Nominees, upon request, are required to provide companies with lists of beneficial owners who do not object to having their names, addresses, and share holdings supplied to companies, so called “non-objecting beneficial owners” (or “NOBOs”). Objecting beneficial owners (or “OBOs”) may be contacted directly only by the broker-dealer or bank.
Because DTCC’s role is only that of custodian, a number of mechanisms have been developed in order to pass the legal rights it holds as the record owner (such as the right to vote) to the beneficial owners. The first step in passing voting rights down the chain is the “omnibus proxy,” which DTCC executes to transfer its voting rights to its participant nominees.
Under applicable rules, nominees must deliver proxy materials to beneficial owners and request voting instructions. Nominees are often prohibited by applicable New York Stock Exchange (“NYSE”), or other self-regulatory organization (“SRO”) rules, or by express agreements with their customers, from voting the securities held in their customers’ accounts on certain types of proposals in the absence of receiving such customers’ voting instructions.
A large number of nominees have contracted out the administrative processes of distributing proxy materials and tabulating voting instructions to us. Nominees accomplish this by transferring to us via powers of attorney the authority to execute a proxy, which authority they receive from DTCC (via omnibus proxy). We then distribute the proxy materials and voting instruction forms (known as “VIFs”) to beneficial owners.
The Securities and Exchange Commission’s (the “SEC”) rules require public companies to reimburse nominees for the expense of distributing stockholder communications to beneficial owners of securities held in street name. The reimbursement rates are set forth in the rules of SROs, including the NYSE. We act as a billing and collection agent for many nominees with respect to this reimbursement. We bill public companies on behalf of the nominees, collect the fee and remit to the nominee any difference between the fee that the nominee is entitled to collect and the amount that the nominee has agreed to pay us for our services. In addition, the NYSE rules establish fees specifically for the services provided by intermediaries in the proxy process such as Broadridge.
6
Table of Contents
In fiscal year 2014, the SEC approved the proxy distribution fee changes proposed by the NYSE in May 2012. The fee changes went into effect for shareholder meetings with record dates on or after January 1, 2014, and we have implemented the approved changes.
We also compile NOBO lists on behalf of nominees in response to requests from issuers. The preparation of NOBO lists is subject to reimbursement by the securities issuers requesting such lists to the broker-dealers. The reimbursement rates are based on the number of NOBOs on the list produced pursuant to NYSE or other SRO rules. Such rules also provide for certain fees to be paid to third party intermediaries who compile such NOBO lists. We function as such an intermediary in the NOBO process.
We also provide proxy distribution, vote tabulation, and various additional investor communication tools and services to institutional investors, corporate issuers, investment companies and financial advisors.
The services we provide in this segment represented approximately 73%, 73%, and 71% of our total Revenues in fiscal years 2014, 2013, and 2012, respectively. These services include the following:
Bank and Brokerage Offerings. We handle the entire proxy materials distribution and voting process for our bank and broker-dealer clients on-line and in real-time, from coordination with third party entities to ordering, inventory maintenance, mailing, tracking and vote tabulation. We offer electronic proxy delivery services for the electronic delivery of proxy materials to investors and collection of consents; maintenance of a database that contains the delivery method preferences of our clients’ customers; posting of documents on the Internet; e-mail notification to investors notifying them that proxy materials are available; and proxy voting over the Internet, mobile devices and tablets. We also have the ability to combine stockholder communications for multiple stockholders residing at the same address which we accomplish by having ascertained the delivery preferences of investors. In addition, we provide a complete outsourced solution for the processing of international proxies. We also provide a complete reorganization communications solution to notify investors of reorganizations or corporate action events such as tender offers, mergers and acquisitions, bankruptcies, and class action lawsuits.
We also offer our bank and brokerage clients financial information distribution and transaction reporting services to help them meet their regulatory compliance requirements and business needs including: prospectus fulfillment services; electronic prospectus services; PostEdge, our electronic document archival and electronic delivery solution for documents including trade confirmations, tax documents and account statements; marketing communications; imaging, archival and workflow solutions; and on-demand digital print services. In addition, we offer our Mailbox products—Advisor Mailbox™ and Investor Mailbox®—which provide a holistic network environment that supports and complements any investor communication strategy. Advisor Mailbox is the latest addition to our Investor Mailbox solution, our service providing the electronic delivery of investor communications to our clients’ websites, creating investor access to regulatory delivery notices, day-to-day account and investment information and convenient response tools. Our Advisor Mailbox is an electronic communications platform for financial advisors that delivers immediate electronic access to the communications and documents sent to such advisors’ customers. Advisor Mailbox streamlines multiple communication paths for all investor-related documents into a single-visit portal that is integrated onto an advisor’s platform.
We also provide tax services to financial services firms that support their various daily workflows, supervisory control and client reporting requirements for information reporting (e.g., Forms 1099 and 1042-S), with a focus on securities and fund processing and clearance operations. Our tax data services provide tax content and data management, including securities tax classifications and reclassifications, calculations of original issue discount and other accrual and cost basis adjusting events. Our tax managed services provide technology and personnel outsourcing, withholding services and client reporting, including print/electronic distribution and archival.
Our fiscal year 2011 acquisition of NewRiver has provided us with important capabilities for the broker-dealer and retirement and annuity markets. Specifically, NewRiver’s proprietary extraction, normalization and
7
Table of Contents
presentment capabilities from the SEC’s EDGAR database have enabled us to enhance our prospectus post-sale fulfillment operations by moving to an on-demand solution. This process provides efficiency for our clients as it reduces their reliance on offset print and fund delivered inventory. Broadridge has also been able to leverage the intellectual property in this business to provide portfolio-specific solutions for the retirement and annuity markets. Through our integration of this functionality into our existing capabilities, we offer a new and efficient fulfillment model for regulatory and compliance mailings.
We also acquired Forefield in fiscal year 2011. Forefield has expanded its services portfolio to leverage its industry leading financial content for use by financial services firms in their social media content libraries. Forefield also provides an advisor website product that can be populated with Forefield’s content or content created by the advisor. Forefield continues to develop new applications that further the goal of creating timely, accurate and meaningful communications for both advisors and their clients. For example, Forefield’s Women’s Resource Center, which contains a broad selection of content for both the advisor and their client, focuses specifically on the requirements and challenges faced by women investors.
In fiscal year 2014, we added to our portfolio of services for financial advisors with the Emerald acquisition. Emerald enables financial institutions and their advisors to advise, educate and communicate with their clients and prospects through a suite of solutions including websites and web optimization services, seminars, newsletters, and print and electronic prospecting campaigns.
Institutional Investor Offerings. We provide a suite of services to manage the entire proxy voting process of institutional investors, including fulfilling their fiduciary obligations and meeting their reporting needs, such as ProxyEdge, our workflow solution that integrates ballots for positions held across multiple custodians and presents them under a single proxy. Voting can be instructed for the entire position, by account vote group or on an individual account basis either manually or automatically based on the recommendations of participating governance research providers. ProxyEdge also provides for client reporting and regulatory reporting. ProxyEdge can be utilized for meetings of U.S. and Canadian companies and for meetings in many non-North American countries based on the holdings of our global custodian clients. ProxyEdge is offered in several languages and there are currently approximately 5,300 ProxyEdge users worldwide.
Corporate Issuer Offerings. We are the largest processor and provider of investor communication solutions to public companies through the performance of beneficial proxy services for our bank and broker-dealer clients. We offer our corporate issuer clients many tools to facilitate their communications with investors such as Internet and telephone proxy voting, electronic delivery of corporate filings, and householding of communications to stockholders at the same address. One of our opportunities for growth in the Investor Communication Solutions segment involves serving corporate issuer clients in providing communications services to registered stockholders—that is, stockholders who do not hold their shares through a broker-dealer in street name. We also offer proxy services to non-North American corporate issuers in connection with their general and special meetings of stockholders. Our corporate issuer services include ShareLink®, which provides complete project management for the beneficial and registered proxy process.
We also provide registrar, stock transfer and record-keeping services. Our strategy in the transfer agency business is to address the needs public companies have expressed for lower cost, more reliable stockholder record maintenance and communication services. We are accomplishing this by leveraging our investor communications and securities processing capabilities to enable us to deliver enhanced transfer agency services to corporate issuers. In addition, we offer issuers and their shareholders the ability to migrate their shareholders’ holdings from registered to beneficial ownership, thereby creating efficiencies for issuers and greater convenience for their shareholders.
Our Shareholder Forum™ solution is an online venue that offers public companies the ability to host structured, controlled communication with their shareholders on a timely and regular basis. Validated shareholders can submit questions, answer surveys in preparation of the annual meeting and year-round, and
8
Table of Contents
communicate in various ways with a corporation. Our Virtual Shareholder Meeting™ service provides corporate issuers with the ability to host their annual meeting electronically on the Internet, either on a stand-alone basis, or in conjunction with their physical annual meeting where permitted by state corporate law. As the provider of beneficial shareholder proxy processing on behalf of many banks and brokerage firms, we provide shareholder validation and voting services to companies that want to hold virtual meetings.
In fiscal year 2014, we introduced Shareholder Data Services, a platform integrating three new capabilities for corporate issuers: an analytics engine for obtaining a comprehensive view of a company’s shareholder base – both registered and beneficial shareholders; custom targeted communications for reaching discrete shareholder segments based on specific criteria; and response reporting for evaluating results of targeted reminder mailings to shareholders. Shareholder Data Services enables companies to better plan and prepare for the proxy process by leveraging information about historical patterns of shareholder participation and behavior in the design of communication strategies with targeted segments of shareholders. Companies can also monitor progress of their proxy voting and easily take action when voting requirements or internal favorable voting thresholds are at risk. Combined with the ability to measure their shareholders’ response to communications, this product suite also enables companies to capture valuable ownership and voting behavior data as a basis for on-going investor communications initiatives.
Mutual Fund Offerings. We provide a full range of tools that enable mutual funds to communicate with large audiences of investors efficiently, reliably, and often with substantial cost savings. Our solutions allow mutual funds to centralize all investor communications through one resource. We also provide printing and mailing of regulatory reports, prospectuses and proxy materials, as well as proxy solicitation services. In addition, we distribute marketing communications and informational materials and create on-demand enrollment materials for mutual fund investors. Our position in the industry enables us to manage the entire communication process with both registered and beneficial stockholders. Our Data Aggregation and Analysis platform, which includes the recently acquired Bonaire services, provides comprehensive data gathering and data management solutions. Our software is delivered as a service and assists mutual funds and investment managers in processing commission and distribution payments, calculating fee revenue, monitoring their compliance with regulatory requirements, and assembling shareholder and intermediary data in a form to better drive their sales strategy and marketing programs.
In addition, we provide mutual fund processing services for third party administrators, financial advisors, banks and wealth management professionals through our subsidiary, Matrix. Our back-office, trust, custody, trading and mutual fund settlement services are integrated into our product suite, thereby strengthening our role as a provider of data processing and distribution channel solutions to the mutual fund industry.
Securities Processing Solutions
Transactions involving securities and other financial market instruments originate with an investor, who places an order with a broker who in turn routes that order to an appropriate market for execution. At that point, the parties to the transaction coordinate payment and settlement of the transaction through a clearinghouse. The records of the parties involved must then be updated to reflect completion of the transaction. Tax, custody, accounting and record-keeping requirements must be complied with in connection with the transaction and the customer’s account information must correctly reflect the transaction. The accurate processing of trading activity and custody activity requires effective automation and information flow across multiple systems and functions within the brokerage firm and across the systems of the various parties that participate in the execution of a transaction.
Our Global Technology and Operations Solutions business provides services that automate the transaction lifecycle of equity, mutual fund, fixed income, and option securities trading operations, from order capture and execution through trade confirmation, settlement, custody and accounting. Our services facilitate the automation of straight-through-processing operations and enable financial institutions to efficiently and cost-effectively
9
Table of Contents
consolidate their books and records, gather and service assets under management, focus on their core businesses, and manage risk. With our multi-currency capabilities, we support trading activities on a global basis.
In September 2011, we acquired Paladyne, now known as Broadridge Investment Management, Reference Data and Risk Solutions, a provider of buy-side technology solutions for the global investment management industry. Broadridge Investment Management, Reference Data and Risk Solutions provides front-, middle-, and back-office solutions such as Order Management, Data Warehousing, Reporting, Risk Management and Portfolio Accounting to hedge funds, investment managers and the providers that service this space (prime brokers, hedge fund administrators and custodians). The client base for these services includes start-up or emerging managers through some of the largest global hedge fund complexes and global administrators. We have integrated our business process outsourcing expertise with this business to offer a set of managed services to the buy-side of the industry. The Broadridge Investment Management, Reference Data and Risk Solutions business has enhanced the asset classes we service and expanded our global footprint and market coverage.
Our securities processing services represented approximately 27%, 27%, and 29% of our total Revenues in fiscal years 2014, 2013, and 2012, respectively. These services include the following:
North American Securities Processing Services. We provide a set of sophisticated, multi-currency systems that support real-time processing of securities transactions in North American equities, options, fixed income securities, and mutual funds. Brokerage Processing Services (“BPS”) is our core multi-currency back-office processing system that supports real-time processing of transactions in the U.S. markets. BPS handles everything from order management to clearance/settlement and custody, and assists our clients in meeting their regulatory reporting and other back-office requirements. BPS is provided on a hosted ASP basis. We also offer a version of BPS for processing Canadian securities. In addition to our BPS offering, we provide specialized transaction processing tools and services for small to mid-market financial firms in Canada. We also provide state-of-the-art fixed income transaction processing capabilities and support for front-, middle-, and back-office functions. Our securities processing services can be integrated with our web-based desktop applications, wealth management tools, enterprise workflow, automated inquiry reporting and record-keeping services.
International Securities Processing Services. We provide advanced multi-currency transaction processing solutions for institutional and retail securities operations, corporate actions, and business process outsourcing services such as data cleansing. Our Global Processing Solution is our integrated delivery of multiple securities processing products and services to create a comprehensive system that is capable of processing transactions in equity, option, mutual fund, and fixed income securities in established and emerging markets, at any time. Its advanced real-time processes automate the securities transaction lifecycle from order capture and execution through confirmation, settlement, and accounting.
In May 2013, we entered a strategic alliance with Accenture plc (“Accenture”) to launch Accenture Post-Trade Processing, combining Accenture’s global business process outsourcing capabilities and global capital markets industry expertise with Broadridge’s leading post-trade securities processing technology. The solution provides post-trade processing and technology services to support settlement, books and records, asset servicing, operational management and control, real-time data access and administrative accounting. It is designed to help banks operating in Europe and the Asia Pacific region reduce post-trade processing costs, adapt to new regulations and technology, and quickly and efficiently launch new products and enter new markets.
Business Process Outsourcing Services. We also provide business process outsourcing services that support the operations of our clients’ businesses including their securities clearing, record-keeping, and custody-related functions. Our clients execute and clear their securities transactions and engage us to perform a number of related administrative back-office functions, such as record-keeping and reconciliations. In this capacity, we are not the broker-dealer of record.
10
Table of Contents
Broadridge’s Integrated Solutions
Our core systems for processing equity, option, and mutual fund transactions in the U.S. markets can also be combined with our specialized systems for processing fixed income and international securities transactions. These specialized securities processing services can be fully integrated with business process outsourcing services. In addition, our clients can integrate our securities processing and business process outsourcing services with our other services including: (i) the processing of trade confirmations and account statements, delivered in paper or electronically; (ii) equity and mutual fund prospectus processing; (iii) automated workflow tools that help our clients streamline their securities processing and operations activities; and (iv) a full suite of wealth management products including data aggregation tools, end-customer websites, broker desktop, financial planning and modeling tools, performance reporting and portfolio accounting.
Clients
We serve a large and diverse client base in the financial services industry including retail and institutional brokerage firms, global banks, mutual funds, annuity companies, institutional investors, specialty trading firms, clearing firms, third party administrators, hedge funds, and financial advisors. We also provide services to corporate issuers.
In fiscal year 2014, we:
| • | processed over 80% of the outstanding shares in the U.S. in the performance of our proxy services; |
| • | processed over two billion investor communications through either paper or electronic channels; |
| • | processed on average over $5 trillion in equity and fixed income trades per day of U.S. and Canadian securities, including approximately 60% of U.S. fixed income trades; and |
| • | provided fixed income trade processing services to 16 of the 22 primary dealers of fixed income securities in the U.S. |
In fiscal year 2014, we derived approximately 25% of our consolidated revenues from five clients. Our largest single client accounted for approximately 5% of our consolidated revenues.
Competition
We operate in a highly competitive industry. Our Investor Communication Solutions business competes with companies that provide investor communication and corporate governance solutions including transfer agents who handle communication services to registered (non-beneficial) securities holders, proxy advisory firms, proxy solicitation firms and other proxy services providers. We also face competition from numerous firms in the compiling and printing of transaction confirmations and account statements. Our Securities Processing Solutions business principally competes with brokerage firms that perform their trade processing in-house, and with numerous other outsourcing vendors. Our back-office support services offered through this segment also compete with very large financial institutions that manage their own back-office record-keeping operations. In many cases, clients engage us only to perform certain functions, such as back-office processing, and do not outsource their other functions such as clearing operations support that we would also perform for them.
Technology
We have several information processing systems which serve as the core foundation of our technology platform. We leverage these systems in order to provide our services. We are committed to maintaining extremely high levels of quality service through our skilled technical employees and the use of our technology within an environment that seeks continual improvement.
Our mission-critical applications are designed to provide high levels of availability, scalability, reliability, and flexibility. They operate on industry standard enterprise architecture platforms that provide high degrees of horizontal and vertical scaling. This scalability and redundancy allows us to provide high degrees of system availability. In March 2010, we entered into an Information Technology Services Agreement (the “IT Services
11
Table of Contents
Agreement”) with International Business Machines Corporation (“IBM”), under which IBM performs a broad range of technology services including supporting our mainframe, midrange, open systems, network and data center operations, as well as providing disaster recovery services. We have the option of incorporating additional services into the agreement over time. The IT Services Agreement expires on June 30, 2022. We have the right to renew the initial term of the IT Services Agreement for up to one additional 12-month term. Our principal data center systems and applications had previously been operated and managed by ADP. The migration of our data center processing from ADP to IBM was completed in August 2012.
In March 2014, the Company and IBM United Kingdom Limited (“IBM UK”) entered into an Information Technology Services Agreement (the “EU IT Services Agreement”), under which IBM UK provides data center services supporting the Company’s technology outsourcing services for certain clients in Europe and Asia. The EU IT Services Agreement expires in October 2023. The Company has the right to renew the initial term of the EU IT Services Agreement for up to one additional 12-month term or one additional 24-month term. We have the right to terminate the agreements with IBM for several reasons including for cause, for convenience, or in the event of a change of ownership control of IBM. However, several of the grounds for termination by Broadridge require us to pay a termination fee to IBM. IBM also has certain termination rights in the event of a material breach of the Company’s obligations under the agreements and its failure to cure.
Most of our systems and applications process in Tier III+ and Tier IV data centers. Tier III+ and Tier IV data centers employ multiple active power and cooling distribution paths, redundant components, and are capable of providing 99.995% availability. Tier III+ and Tier IV data centers provide infrastructure capacity and capability to permit any planned activity without disruption to the critical load, and can sustain at least one worst-case, unplanned failure or event with no critical load impact. Our geographically dispersed processing centers also provide disaster recovery and business continuity processing.
To further demonstrate our commitment to maintaining the highest levels of quality service and client satisfaction within an environment that fosters continual improvement, most of our business units and our core applications and facilities for the provision of many services including our proxy services, U.S. equity and fixed income securities processing services, and IBM’s data centers, are International Organization for Standardization (“ISO”) 27001 certified. This security standard specifies the requirements for establishing, implementing, operating, monitoring, reviewing, maintaining and improving a documented Information Security Management System within the context of the organization’s overall business risks. It specifies the requirements for the implementation of security controls customized to the needs of individual organizations. This standard addresses confidentiality, access control, vulnerability, business continuity, and risk assessment. In addition, our operations facilities are ISO 9001:2000 certified.
Product Development. Our products and services are designed with reliability, availability, scalability, and flexibility so that we can fully meet our clients’ processing needs. These applications are built in a manner which allows us to meet the breadth and depth of requirements of our financial services industry clients in a highly efficient manner. We continually upgrade, enhance, and expand our existing products and services taking into account input from clients, industry-wide initiatives and regulatory changes affecting our clients.
Intellectual Property. We own a portfolio of more than 60 U.S. and non-U.S. patent and patent applications. We also own registered marks for our trade name and own or have applied for trademark registrations for many of our services and products. We regard our products and services as proprietary and utilize internal security practices and confidentiality restrictions in contracts with employees, clients, and others for protection. We believe that we are the owner or in some cases, the licensee, of all intellectual property and other proprietary rights necessary to conduct our business.
Employees
At June 30, 2014, we had approximately 6,700 employees. None of our employees is subject to collective bargaining agreements governing their employment with our company. We believe that our employee relations are good.
12
Table of Contents
Regulation
The securities and financial services industries are subject to extensive regulation in the U.S. and in other jurisdictions. As a matter of public policy, regulatory bodies in the U.S. and the rest of the world are charged with safeguarding the integrity of the securities and other financial markets and with protecting the interests of investors participating in those markets.
In the U.S., the securities and financial services industries are subject to regulation under both federal and state laws. At the federal level, the SEC regulates the securities industry, along with the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority, Inc. (“FINRA”), the various stock exchanges, and other SROs. Our Investor Communication Solutions and Securities Processing Solutions businesses are generally not directly subject to federal, state, or foreign laws and regulations that are specifically applicable to financial institutions. However, as a provider of services to financial institutions and issuers of securities, our services, such as our proxy distribution and processing services, are provided in a manner to assist our clients in complying with the laws and regulations to which they are subject. As a result, the services we provide may change as applicable laws and regulations are adopted or revised. We monitor legislative and rulemaking activity by the SEC, FINRA, the exchanges and other regulatory bodies that may impact our services, and if new laws or regulations are adopted or changes are made to existing laws or regulations applicable to our services, we expect to adapt our business practices and service offerings to continue to assist our clients in fulfilling their obligations under new or modified requirements.
Certain of our securities processing operations are periodically reviewed by the U.S. Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council (“FFIEC”) under its authority to examine financial institutions’ technology service providers. Examinations by the FFIEC generally include areas such as data integrity, disaster recovery, and information security. A sufficiently unfavorable review from the FFIEC could result in our clients not being allowed to use our services.
Our business process outsourcing and mutual fund processing services are performed by a securities broker-dealer, Broadridge Business Process Outsourcing, LLC (“BBPO”). BBPO is registered with the SEC, is a member of FINRA and is required to participate in the Securities Investor Protection Corporation (“SIPC”). Although BBPO’s FINRA membership agreement allows it to engage in clearing, and the retailing of corporate securities in addition to mutual fund retailing on a wire order basis, BBPO does not clear customer transactions, process any retail business or carry customer accounts. BBPO is subject to regulations concerning many aspects of its business, including trade practices, capital requirements, record retention, money laundering prevention, the protection of customer funds and customer securities, and the supervision of the conduct of directors, officers and employees. A failure to comply with any of these laws, rules or regulations could result in censure, fine, the issuance of cease-and-desist orders, or the suspension or revocation of SEC or FINRA authorization granted to allow the operation of its business or disqualification of its directors, officers or employees. Recently, there has been increased regulatory scrutiny of the securities industry including the outsourcing by firms of their operations or functions. This oversight could result in the future enactment of more restrictive laws or rules with respect to business process outsourcing.
In addition, MG Trust Company, LLC (“MG Trust Company”), a subsidiary of Matrix, is a Colorado State non-depository trust company and National Securities Clearing Corporation trust member, whose primary business is to provide cash agent, custodial and directed or non-discretionary trust services to institutional customers. MG Trust Company operates pursuant to the rules and regulations of the Colorado Division of Banking.
Our transfer agency business, Broadridge Corporate Issuer Solutions, is subject to certain rules and regulations promulgated by the SEC, including without limitation, with respect to registration with the SEC, annual reporting, examination, internal controls, proper disposal of shareholder information and obligations relating to its operations. Our transfer agency business has been formally approved by the NYSE to act as a transfer agent or registrar for issuers of NYSE listed securities and is subject to certain NYSE requirements
13
Table of Contents
concerning operational standards. Furthermore, it is also subject to U.S. Internal Revenue Service (the “IRS”) regulations, as well as certain provisions of the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act and the Federal Trade Commission’s regulations with respect to maintenance of information security safeguards.
Privacy and Information Security Regulations
The processing and transfer of sensitive personal information is required to provide our services. Data privacy laws and regulations in the U.S. and foreign countries apply to the collection, transfer, use, storage, and destruction of sensitive personal information. In addition, our clients negotiate information security requirements in our contracts and audit us for compliance with information security industry standards. In the U.S., the federal Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act, which applies to financial institutions, applies to certain aspects of our business process outsourcing services, mutual fund processing and transfer agency businesses and to the services that involve data processing for financial institutions, and applies indirectly to our other businesses through contractual commitments with our clients and through industry standards. In addition, state privacy and information security laws, and consumer protection laws, which apply to businesses that collect or process personal information, also apply directly to our businesses. Privacy laws and regulations may require notification to affected individuals, state officers, and consumer reporting agencies in the event of a security breach that results in unauthorized access to or disclosure of certain non-public personal information. These laws and regulations also impose requirements for safeguarding personal information through internal policies and procedures. Privacy laws outside the U.S. may be more restrictive and may require different compliance requirements than U.S. laws and regulations and may impose additional duties on us in the performance of our services.
There has been increased public attention regarding the use of personal information, accompanied by legislation and regulations intended to strengthen data protection, information security and consumer privacy. The law in these areas continues to develop. While we believe that Broadridge is compliant with its regulatory responsibilities, information security threats continue to evolve resulting in increased risk and exposure. In addition, legislation, regulation, litigation, court rulings, or other events could expose Broadridge to increased costs, liability, and possible damage to our reputation.
Seasonality
Processing and distributing proxy materials and annual reports to investors in equity securities and mutual funds comprises a large portion of our Investor Communication Solutions business. We process and distribute the greatest number of proxy materials and annual reports during our fourth fiscal quarter (the second quarter of the calendar year). The recurring periodic activity of this business is linked to significant filing deadlines imposed by law on public reporting companies and mutual funds. Historically, this has caused our revenues, operating income, net earnings, and cash flows from operating activities to be higher in our fourth fiscal quarter than in any other quarter. The seasonality of our revenues makes it difficult to estimate future operating results based on the results of any specific fiscal quarter and could affect an investor’s ability to compare our financial condition, results of operations, and cash flows on a fiscal quarter-by-quarter basis.
Segment and Geographic Area Financial Information
You can find financial information regarding our operating segments and our geographic areas in Note 19, “Financial Data By Segment” to our Consolidated Financial Statements under Item 8 of Part II of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Available Information
Our headquarters are located at 1981 Marcus Avenue,
Lake Success, New York 11042, and our telephone number is
(516) 472-5400.
We maintain an Investor Relations website on the Internet at www.broadridge-ir.com. We make available free of charge, on or through this website, our annual, quarterly and current reports, and any amendments to those
14
Table of Contents
reports as soon as reasonably practicable following the time they are electronically filed with or furnished to the SEC. To access these reports, just click on the “SEC Filings” link found at the top of our Investor Relations page. You can also access our Investor Relations page through our main website at www.broadridge.com by clicking on the “Investor Relations” link, which is located at the top of our homepage. Information contained on our website is not incorporated by reference into this Annual Report on Form 10-K or any other report filed with or furnished to the SEC.
| ITEM 1A. | Risk Factors |
You should carefully consider each of the following risks and all of the other information set forth in this Annual Report on Form 10-K or incorporated by reference herein. Based on the information currently known to us, we believe that the following information identifies the material risk factors affecting our company. However, additional risks and uncertainties not currently known to us or that we currently believe to be immaterial may also adversely affect our business.
If any of the following risks and uncertainties develop into actual events, they could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, or results of operations.
Consolidation in the financial services industry could adversely affect our revenues by eliminating some of our existing and potential clients and could make us increasingly dependent on a more limited number of clients.
There has been and continues to be merger, acquisition, and consolidation activity in the financial services industry. In recent years, the economic slowdown and in particular, its impact on the financial services industry, resulted in increased mergers or consolidations of our clients. Mergers or consolidations of financial institutions could reduce the number of our clients and potential clients. If our clients merge with or are acquired by other firms that are not our clients, or firms that use fewer of our services, they may discontinue or reduce the use of our services. In addition, it is possible that the larger financial institutions resulting from mergers or consolidations could decide to perform in-house some or all of the services that we currently provide or could provide. Any of these developments could have a material adverse effect on our business and results of operations.
A large percentage of our revenues are derived from a small number of clients in the financial services industry.
In fiscal year 2014, we derived approximately 25% of our consolidated revenues from our five largest clients and approximately 60% of the revenues of our Securities Processing Solutions segment from the 15 largest clients in that segment. Our largest single client accounted for approximately 5% of our consolidated revenues. While these clients generally work with multiple business segments, the loss of business from any of these clients due to merger or consolidation, financial difficulties or bankruptcy, or the termination or non-renewal of contracts would have a material adverse effect on our revenues and results of operations. Also, in the event a client experiences financial difficulties or bankruptcy resulting in a reduction in their demand for our services or loss of the client’s business, in addition to losing the revenue from that client, the Company would be required to write-off any investments made by the Company in connection with that client, including costs incurred to set up or convert a client’s systems to function with our technology. Such costs represented approximately 6% of the Company’s total assets as of June 30, 2014. Under a number of our contracts, our clients have the opportunity to renegotiate their contracts with us and to consider whether to renew their contracts or engage one of our competitors to provide services. If we are not successful in achieving high renewal rates with favorable terms, particularly with these clients, our revenues from such renewals and the associated earnings could be negatively impacted. In addition, the recent economic slowdown and its specific impact on the financial services industry, has resulted in increased pricing pressure, particularly with respect to our Securities Processing Solutions business.
15
Table of Contents
The financial services industry has experienced increasing scrutiny by regulatory authorities in recent years and further changes in legislation or regulations may adversely affect our ability to conduct our business or may reduce our profitability.
Our Investor Communication Solutions and Securities Processing Solutions businesses are generally not directly subject to compliance with laws and regulations that are specifically applicable to financial institutions. However, as a provider of services to financial institutions and issuers of securities, our services are provided in a manner to assist our clients in complying with the laws and regulations to which they are subject. Therefore, our services are particularly sensitive to changes in laws and regulations governing our clients and the securities markets.
The legislative and regulatory environment of the financial services industry has recently undergone significant change and may undergo further change in the future. The SEC, FINRA, various stock exchanges, and other U.S. and foreign governmental or regulatory authorities continuously review legislative and regulatory initiatives and may adopt new or revised laws and regulations. These legislative and regulatory initiatives may adversely affect the way in which we conduct our business and may make our business less profitable. Also, changes in the interpretation or enforcement of existing laws and regulations by those entities may adversely affect our business.
Certain of our securities processing operations are periodically reviewed by the FFIEC under its authority to examine financial institutions’ technology service providers. Examinations by the FFIEC generally include areas such as data integrity, disaster recovery and information security. A sufficiently unfavorable review from the FFIEC could result in our clients not being allowed to use our services.
In addition, our business process outsourcing, mutual fund processing and transfer agency solutions as well as the entities providing those services are subject to regulatory oversight. Our provision of these services must comply with applicable rules and regulations of the SEC, FINRA, and various stock exchanges, state securities commissions, and other regulatory bodies charged with safeguarding the integrity of the securities markets and other financial markets and protecting the interests of investors participating in these markets. If we fail to comply with any applicable regulations in performing those services, we could lose our clients, be subject to suits for breach of contract or to governmental proceedings, censures and fines, our reputation could be harmed and we could be limited in our ability to obtain new clients. Our ability to comply with these regulations depends largely upon the maintenance of an effective compliance system which can be time consuming and costly, as well as our ability to attract and retain qualified compliance personnel.
There has been increased public attention regarding the use of sensitive personal information, accompanied by legislation and regulations intended to strengthen data protection, information security and consumer privacy. The law in these areas continues to develop. While we believe that Broadridge is compliant with its regulatory responsibilities, information security threats continue to evolve resulting in increased risk and exposure. In addition, legislation, regulation, litigation, court rulings or other events could expose Broadridge to increased costs, liability, and possible damage to our reputation.
Our clients in the financial services industry are subject to increasing regulation and oversight by regulators, which could adversely affect our ability to conduct our business or may reduce our profitability.
We provide technology solutions to a large and diverse client base in the financial services industry including retail and institutional brokerage firms, global banks, mutual funds, annuity companies, institutional investors, specialty trading firms, independent broker-dealers, clearing firms, and financial advisors. These clients are generally subject to extensive regulation in the U.S. and in other jurisdictions. The current legislative and regulatory environment may impact our clients in a way that could adversely affect us. For example, new regulations governing our clients could result in significant expenditures that could cause them to reduce their use of our services, seek to renegotiate existing agreements, or cease or curtail their operations, all of which could adversely impact our business. In addition, the financial services industry has experienced increased scrutiny in recent years and penalties and fines sought by regulatory authorities have increased accordingly.
16
Table of Contents
Failure to comply with laws, regulations or policies could result in fines, limitations on business activity or suspension or expulsion from the industry, any of which could have a material adverse effect upon our clients. Adverse regulatory actions that change our clients’ businesses or adversely affect their operating results or financial condition could decrease their ability to purchase, or their demand for, our products and services, thus causing loss of business from these clients. The loss of business from our largest clients could have a material adverse effect on our revenues and results of operations.
Our revenues may decrease due to declines in the levels of participation and activity in the securities markets.
We generate significant revenues from the transaction processing fees we earn from our services. These revenue sources are substantially dependent on the levels of participation and activity in the securities markets. The number of unique securities positions held by investors through our clients and our clients’ customer trading volumes reflect the levels of participation and activity in the markets, which are impacted by market prices, and the liquidity of the securities markets, among other factors. Over the past several years, the U.S. and foreign securities markets have experienced significant volatility. Sudden sharp or gradual but sustained declines in market participation and activity can result in reduced investor communications activity, including reduced proxy and event-driven communications processing such as mutual fund proxy, mergers and acquisitions and other special corporate event communications processing, and reduced trading volumes. The occurrence of any of these events would likely result in reduced revenues and decreased profitability from our business operations.
Security breaches or cybersecurity attacks could adversely affect our ability to operate, could result in sensitive personal information being misappropriated, and may cause us to be held liable or suffer harm to our reputation.
We process and transfer sensitive personal information provided to us by our clients, which include financial institutions, public companies and mutual funds. We also handle sensitive personal information of our employees in connection with their employment. In certain circumstances, vendors such as our data center services provider may have access to sensitive personal information. We maintain systems and procedures including encryption, authentication technology, data loss prevention technology, and transmission of data over private networks to protect against unauthorized access to physical and electronic information, including by cybersecurity attacks, and we require our vendors to have adequate security if they have access to personal information. However, despite those safeguards, it is possible that unauthorized individuals could improperly access our systems or improperly obtain or disclose the personal information that we process or handle. In addition, certain of our services are provided through the Internet which increases our exposure to potential cybersecurity attacks. It is also possible that a vendor could intentionally or inadvertently disclose personal information. Any security breach resulting in the unauthorized use or disclosure of certain personal information could put individuals at risk of identity theft and financial or other harm and result in costs to the Company in investigation, remediation, legal defense and in liability to parties who are financially harmed. A cybersecurity attack could also be directed at our systems and result in interruptions in our operations or delivery of services to our clients. In addition, we may incur significant costs to protect against the threat of information security breaches or to respond to or alleviate problems caused by such breaches. Furthermore, a material security breach could cause us to lose revenues, lose clients or cause damage to our reputation.
We purchase a significant portion of our data center services, including disaster recovery capabilities, from a third party data center services provider, and if our data center services provider fails to adequately perform the data center services in the manner necessary to meet our clients’ requirements, our business, financial condition, and results of operations may be harmed.
IBM provides us with data center services that include supporting our mainframe, midrange, open systems, network and data center operations, as well as disaster recovery services. As a result, we currently purchase a significant portion of our data center services, including disaster recovery capabilities, from IBM. If IBM fails to adequately perform the data center services in the manner necessary to meet our clients’ requirements, our business, financial condition and results of operations may be harmed.
17
Table of Contents
In the event of a disaster, our disaster recovery and business continuity plans may fail, which could result in the loss of client data and adversely interrupt operations.
Our operations are dependent on our ability to protect our infrastructure against damage from catastrophe, natural disaster, or severe weather including events resulting from unauthorized security breach, power loss, telecommunications failure, terrorist attack, or other events that could have a significant disruptive effect on our operations. We have disaster recovery and business continuity plans in place in the event of system failure due to any of these events and we test our plans regularly. In addition, our data center services provider also has disaster recovery plans and procedures in place. However, we cannot be certain that our plans, or those of our data center services provider, will be successful in the event of a disaster. If our disaster recovery or business continuity plans are unsuccessful in a disaster recovery scenario, we could potentially lose client data or experience material adverse interruptions to our operations or delivery of services to our clients, and we could be liable to parties who are financially harmed by those failures. In addition, such failures could cause us to lose revenues, lose clients or damage our reputation.
Any slowdown or failure of our computer or communications systems or those of our data center services provider could impact our ability to provide services to our clients and support our internal operations and could subject us to liability for losses suffered by our clients or their customers.
Our services depend on our ability to store, retrieve, process, and manage significant databases, and to receive and process transactions and investor communications through a variety of electronic systems such as the Internet. Our systems, those of our data center services provider, or any other systems with which ours interact could slow down significantly or fail for a variety of reasons, including:
| • | computer viruses or undetected errors in internal software programs or computer systems; |
| • | direct or indirect hacking or denial of service cybersecurity attacks; |
| • | inability to rapidly monitor all system activity; |
| • | inability to effectively resolve any errors in internal software programs or computer systems once they are detected; |
| • | heavy stress placed on systems during peak times; or |
| • | power or telecommunications failure, fire, flood or any other disaster. |
While we monitor system loads and performance and implement system upgrades to handle predicted increases in trading volume and volatility, we may not be able to predict future volume increases or volatility accurately or that our systems and those of our data center services provider will be able to accommodate these volume increases or volatility without failure or degradation. In addition, we may not be able to prevent cybersecurity attacks on our systems. Moreover, because we have outsourced our data center operations, the operation and performance of the data center involve factors beyond our control. Any significant degradation or failure of our computer systems, communications systems or any other systems in the performance of our services could cause our clients or their customers to suffer delays in their receipt of our services. These delays could cause substantial losses for our clients or their customers, and we could be liable to parties who are financially harmed by those failures. In addition, such failures could cause us to lose revenues, lose clients or damage our reputation.
Operational errors in the performance of our services could lead to liability for claims, client loss and result in reputational damage.
The failure to properly perform our services could result in our clients and/or certain of our subsidiaries being subjected to losses including censures, fines, or other sanctions by applicable regulatory authorities, and we could be liable to parties who are financially harmed by those errors. In addition, such errors could cause us to lose revenues, lose clients or damage our reputation.
18
Table of Contents
General economic and political conditions and broad trends in business and finance that are beyond our control may contribute to reduced levels of activity in the securities markets, which could result in lower revenues from our business operations.
The number of unique securities positions held by investors through our clients, the level of investor communications activity we process on behalf of our clients, trading volumes, market prices, and liquidity of the securities markets are affected by general national and international economic and political conditions, and broad trends in business and finance that result in changes in participation and activity in the securities markets. These factors include:
| • | economic, political and market conditions; |
| • | legislative and regulatory changes; |
| • | the availability of short-term and long-term funding and capital; |
| • | the level and volatility of interest rates; |
| • | currency values and inflation; and |
| • | national, state, and local taxation levels affecting securities transactions. |
These factors are beyond our control and may contribute to reduced levels of participation and activity in the securities markets. Our revenues have historically been largely driven by transaction processing based on levels of participation and activity in the securities markets. Accordingly, any significant reduction in participation and activity in the securities markets would likely result in lower revenues from our business operations.
If the operational systems and infrastructure that we depend on fail to keep pace with our growth, we may experience operating inefficiencies, client dissatisfaction and lost revenue opportunities.
The growth of our business and expansion of our client base may place a strain on our management and operations. We believe that our current and anticipated future growth will require the implementation of new and enhanced communications and information systems, the training of personnel to operate these systems, and the expansion and upgrade of core technologies. While many of our systems are designed to accommodate additional growth without redesign or replacement, we may nevertheless need to make significant investments in additional hardware and software to accommodate growth. In addition, we cannot assure you that we will be able to predict the timing or rate of this growth accurately or expand and upgrade our systems and infrastructure on a timely basis.
Our growth has required and will continue to require increased investments in management personnel and systems, financial systems and controls, and office facilities. We cannot assure you that we will be able to manage or continue to manage our future growth successfully. If we fail to manage our growth, we may experience operating inefficiencies, dissatisfaction among our client base, and lost revenue opportunities.
If we are unable to respond to the demands of our existing and new clients, our ability to reach our revenue goals or maintain our profitability could be diminished.
The global financial services industry is characterized by increasingly complex and integrated infrastructures and products, new and changing business models and rapid technological and regulatory changes. Our clients’ needs and demands for our products and services evolve with these changes. Our future success will depend, in part, on our ability to respond to our clients’ demands for new services, capabilities and technologies on a timely and cost-effective basis, to adapt to technological advancements and changing regulatory standards, and to address our clients’ increasingly sophisticated requirements.
19
Table of Contents
Intense competition could negatively affect our ability to maintain or increase our market share and profitability.
The markets for our products and services continue to evolve and are highly competitive. We compete with a number of firms that provide similar products and services. In addition, our securities processing solutions compete with our clients’ in-house capabilities to perform competitive functions. Our competitors may be able to respond more quickly to new or changing opportunities, technologies, and client requirements and may be able to undertake more extensive promotional activities, offer more attractive terms to clients and adopt more aggressive pricing policies than we will be able to offer or adopt. In addition, we expect that the markets in which we compete will continue to attract new competitors and new technologies, including international providers of similar products and services to ours. There can be no assurances that we will be able to compete effectively with current or future competitors. If we fail to compete effectively, our market share could decrease and our business, financial condition, and results of operations could be materially harmed.
Our business, financial position, and results of operations could be harmed by adverse rating actions by credit rating agencies.
If the credit ratings of our outstanding indebtedness are downgraded, or if rating agencies indicate that a downgrade may occur, our business, financial position, and results of operations could be adversely affected and perceptions of our financial strength could be damaged. A downgrade would have the effect of increasing our borrowing costs, and could decrease the availability of funds we are able to borrow, adversely affecting our business, financial position, and results of operations. In addition, a downgrade could adversely affect our relationships with our clients. For further information with respect to our borrowing costs, see Note 13, “Borrowings” to our Consolidated Financial Statements under Item 8 of Part II of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
We may be unable to attract and retain key personnel.
Our continued success depends on our ability to attract and retain key personnel such as our senior management and other qualified personnel to conduct our business. The market for such experienced senior managers and other qualified personnel is extremely competitive. There can be no assurance that we will be successful in our efforts to recruit and retain the required key personnel. If we are unable to attract and retain qualified individuals or our recruiting and retention costs increase significantly, our operations and financial results could be materially adversely affected.
The inability to identify, obtain and retain important intellectual property rights to technology could harm our business.
Our success depends in part upon the development and acquisition of systems and applications to conduct our business. Our success will increasingly depend in part on our ability to identify, obtain and retain intellectual property rights to technology, both for internal use as well as for use in providing services to our clients, either through internal development, acquisition or licensing from others, or alliances with others. Our inability to identify, obtain and retain rights to certain technology on favorable terms and conditions would make it difficult to conduct business, or to timely introduce new and innovative products and services, which could harm our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
Our products and services, and the products and services provided to us by third parties, may infringe upon intellectual property rights of third parties, and any infringement claims could require us to incur substantial costs, distract our management, or prevent us from conducting our business.
Although we attempt to avoid infringing upon known proprietary rights of third parties, we are subject to the risk of claims alleging infringement of third party proprietary rights. If we infringe upon the rights of third parties, we may be unable to obtain licenses to use those rights on commercially reasonable terms. Additionally,
20
Table of Contents
third parties that provide us with products and services that are integral to the conduct of our business may be subject to similar allegations, which could prevent them from continuing to provide these products and services to us. In either of these events, we would need to undertake substantial reengineering in order to continue offering our services and we may not succeed in doing so. In addition, any claim of infringement could cause us to incur substantial costs defending the claim, even if the claim is invalid, and could distract our management from our business. Furthermore, a party making such a claim could secure a judgment that requires us to pay substantial damages. A judgment could also include an injunction or other court order that could prevent us from conducting our business.
Acquisitions and integrating such acquisitions create certain risks and may affect operating results.
From time to time, we engage in, and expect to continue to engage in, business acquisitions. The acquisition and integration of businesses involve a number of risks. The core risks are in the areas of:
| • | valuation: negotiating a fair price for the business based on inherently limited due diligence reviews; |
| • | integration: managing the complex process of integrating the acquired company’s people, products, technology, and other assets so as to realize the projected value of the acquired company and the synergies projected to be realized in connection with the acquisition; and |
| • | legacy issues: protecting against actions, claims, regulatory investigations, losses, and other liabilities related to the predecessor business. |
Also, the process of integrating these businesses may disrupt our business and divert our resources. These risks may arise for a number of reasons including, for example:
| • | finding suitable businesses to acquire at affordable valuations or on other acceptable terms; |
| • | competition for acquisitions from other potential acquirors; |
| • | incurring unforeseen obligations or liabilities in connection with such acquisitions; |
| • | devoting unanticipated financial and management resources to an acquired business; |
| • | borrowing money from lenders or selling equity or debt securities to the public to finance future acquisitions on terms that may be adverse to us; |
| • | entering markets where we have minimal prior experience; and |
| • | experiencing decreases in earnings as a result of non-cash impairment charges. |
In addition, international acquisitions often involve additional or increased risks including, for example:
| • | geographically separated organizations, systems, and facilities; |
| • | integrating personnel with diverse business backgrounds and organizational cultures; |
| • | complying with foreign regulatory requirements; |
| • | enforcing intellectual property rights in some foreign countries; and |
| • | general economic and political conditions. |
We operate internationally and our operations could be adversely impacted by local legal, economic, political and other conditions.
A portion of our revenue is generated outside the U.S. and in recent years, we have expanded our operations, entered strategic alliances, and acquired businesses outside the U.S. Also, our business is highly dependent on the global financial services industry and exchanges and market centers around the world. Changes in the laws or policies of the countries in which we operate, or inadequate enforcement of laws or policies such as those protecting intellectual property, could affect our business and the company’s overall results of operations. Our operations also could be affected by economic and political changes in those countries, particularly in those with developing economies, and by macroeconomic changes, including recessions, inflation and currency
21
Table of Contents
fluctuations between the U.S. dollar and non-U.S. currencies. In addition, our operations and our ability to deliver our services to our clients could be adversely impacted if there is instability, disruption or destruction in certain geographic regions including as a result of natural or man-made disasters, wars, terrorist activities, or any widespread outbreak of an illness, pandemic or other local or global health issue.
Our mutual fund processing services may be exposed to risk from our counterparties and third parties.
In the normal course of business, our mutual fund processing services involve the settlement of transactions on behalf of our customers and third parties. With these activities, we may be exposed to risk in the event our clients, or other broker-dealers, banks, clearing organizations, or depositories are unable to fulfill contractual obligations and the mutual fund counterparty is unable to cancel the transaction.
Our revenues are subject to seasonal variations because we process and distribute the greatest number of proxy materials and annual reports in our fourth fiscal quarter.
Processing and distributing proxy materials and annual reports to investors in equity securities and mutual funds comprises a large portion of our Investor Communication Solutions business. We process and distribute the greatest number of proxy materials and annual reports during our fourth fiscal quarter. The recurring periodic activity of this business is linked to significant filing deadlines imposed by law on public reporting companies and mutual funds. Historically, this has caused our revenues, operating income, net earnings, and cash flows from operating activities to be higher in our fourth fiscal quarter than in any other fiscal quarter. The seasonality of our revenues makes it difficult to estimate future operating results based on the results of any specific fiscal quarter and could affect an investor’s ability to compare our financial condition, results of operations, and cash flows on a fiscal quarter-by-quarter basis.
| ITEM. 1B. | Unresolved Staff Comments. |
None.
| ITEM 2. | Properties |
We operate our business from 51 facilities. We own a 20,000 square foot facility in Mount Laurel, New Jersey, where we perform certain product development functions. We also own a 36,000 square foot facility in Wheat Ridge, Colorado, where we perform securities processing services. We lease three facilities in Edgewood, New York, with a combined space of 643,065 square feet which are used in connection with our Investor Communication Solutions business. We lease space at 46 additional locations, subject to customary lease arrangements, including a facility in Lake Success, New York, that serves as our corporate headquarters. Our leases expire on a staggered basis. We believe our facilities are currently adequate for their intended purposes and are adequately maintained.
| ITEM 3. | Legal Proceedings. |
In the normal course of business, the Company is subject to claims and litigation. While the outcome of any claim or litigation is inherently unpredictable, the Company believes that the ultimate resolution of these matters will not, individually or in the aggregate, result in a material impact on its financial condition, results of operations, or cash flows.
| ITEM 4. | Mine Safety Disclosures. |
Not applicable.
22
Table of Contents
| ITEM 5. | Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities. |
Our common stock began trading “regular way” on the NYSE under the symbol “BR” on April 2, 2007. There were 13,489 stockholders of record of the Company’s common stock as of July 31, 2014. This figure excludes an estimate of the indeterminate number of beneficial holders whose shares may be held of record by brokerage firms and clearing agencies. The following table presents the high and low closing prices of the Company’s common stock on the NYSE as well as the cash dividends per share of common stock declared during the fiscal quarters indicated:
| Common Stock Market Price |
High | Low | Dividends Declared |
|||||||||
| Fiscal Year 2014 |
||||||||||||
| First Quarter |
$ | 31.75 | $ | 26.93 | $ | 0.21 | ||||||
| Second Quarter |
39.94 | 31.20 | 0.21 | |||||||||
| Third Quarter |
39.60 | 35.28 | 0.21 | |||||||||
| Fourth Quarter |
42.13 | 35.61 | 0.21 | |||||||||
| Fiscal Year 2013 |
||||||||||||
| First Quarter |
$ | 24.22 | $ | 20.41 | $ | 0.18 | ||||||
| Second Quarter |
23.80 | 22.10 | 0.18 | |||||||||
| Third Quarter |
24.84 | 21.98 | 0.18 | |||||||||
| Fourth Quarter |
27.97 | 23.42 | 0.18 | |||||||||
Dividend Policy
We expect to pay cash dividends on our common stock. On August 7, 2014, our Board of Directors increased our quarterly cash dividend by $0.06 per share to $0.27 per share, an increase in our annual dividend amount from $0.84 to $1.08 per share. However, the declaration and payment of future dividends to holders of our common stock will be at the discretion of our Board of Directors, and will depend upon many factors, including our financial condition, earnings, capital requirements of our businesses, legal requirements, regulatory constraints, industry practice, and other factors that the Board of Directors deems relevant.
As a holding company (substantially all our assets being comprised of the capital stock of our subsidiaries), our ability to pay dividends will be dependent on our receiving dividends from our operating subsidiaries. Our subsidiaries through which we provide our business process outsourcing and mutual fund processing services, are regulated and may be subject to restrictions on their ability to pay dividends to us. We do not believe that these restrictions are significant enough to impact the Company’s ability to pay dividends.
23
Table of Contents
Performance Graph
The following graph compares the cumulative total stockholder return on Broadridge common stock from June 30, 2009 to June 30, 2014 with the comparable cumulative return of the (i) S&P 500 Index, (ii) S&P 400 MidCap Index, and (iii) S&P 400 Information Technology Index. The graph assumes $100 was invested on June 30, 2009 in our common stock and in each of the indices and assumes that all cash dividends are reinvested. The table below the graph shows the dollar value of those investments as of the dates in the graph. The comparisons in the graph are required by the SEC and are not intended to forecast or be indicative of future performance of our common stock.
The following performance graph and related information shall not be deemed “soliciting material” or to be “filed” with the SEC, nor shall such information be incorporated by reference into any future filing under the Securities Act of 1933 or the Exchange Act, each as amended, except to the extent that Broadridge specifically incorporates it by reference into such filing.
Comparison of Cumulative Total Return Among Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc., S&P 500 Index, S&P 400 MidCap Index and S&P 400 Information Technology Index (in dollars)
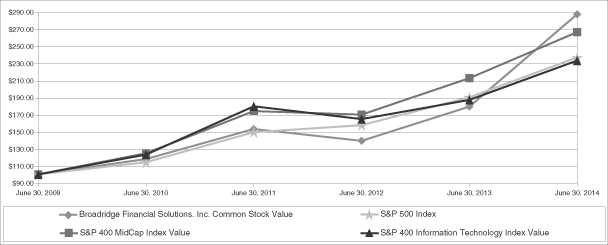
| June 30, 2009 |
June 30, 2010 |
June 30, 2011 |
June 30, 2012 |
June 30, 2013 |
June 30, 2014 |
|||||||||||||||||||
| Broadridge Financial Solutions. Inc. Common Stock Value |
$ | 100.00 | $ | 117.94 | $ | 153.13 | $ | 139.36 | $ | 179.33 | $ | 287.47 | ||||||||||||
| S&P 500 Index |
$ | 100.00 | $ | 114.42 | $ | 149.53 | $ | 157.66 | $ | 190.11 | $ | 236.88 | ||||||||||||
| S&P 400 MidCap Index Value |
$ | 100.00 | $ | 124.90 | $ | 174.09 | $ | 169.99 | $ | 212.66 | $ | 266.26 | ||||||||||||
| S&P 400 Information Technology Index Value |
$ | 100.00 | $ | 123.24 | $ | 179.65 | $ | 164.64 | $ | 187.12 | $ | 233.31 | ||||||||||||
24
Table of Contents
Purchases of Equity Securities by the Issuer and Affiliated Purchasers
The following table contains information about our purchases of our equity securities for each of the three months during our fourth fiscal quarter ended June 30, 2014:
| Period |
Total Number of Shares Purchased |
Average Price Paid per Share |
Total Number of Shares Purchased as Part of Publicly Announced Plans or Programs(2) |
Maximum Number (or Approximate Dollar Value) of Shares (or Units) that May Yet Be Purchased Under the Plans or Programs(2) |
||||||||||||
| April 1, 2014 – April 30, 2014 |
483,754 | (1) | $ | 37.94 | — | — | ||||||||||
| May 1, 2014 – May 31, 2014 |
1,516,695 | 39.93 | 1,516,695 | 4,164,039 | ||||||||||||
| June 1, 2014 – June 30, 2014 |
402,900 | 41.64 | 402,900 | 3,761,139 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total |
2,403,349 | $ | 39.81 | 1,919,595 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| (1) | Represents shares purchased from employees to pay taxes related to the vesting of restricted stock units. |
| (2) | On April 30, 2013, the Board of Directors authorized the repurchase of up to 6,000,000 shares of the Company’s common stock. During the fiscal quarter ended June 30, 2014, the Company repurchased 1,919,595 shares of common stock at an average price per share of $40.29. At June 30, 2014, there were 3,761,139 shares remaining available for repurchase. |
In addition, on August 6, 2014, the Board authorized the repurchase of up to an additional 6,200,000 shares of Broadridge common stock.
The share repurchases will be made in the open market or privately negotiated transactions in compliance with applicable legal requirements and other factors. With this authorization, the Company currently has approximately 10,000,000 shares available for repurchase under its share repurchase program.
25
Table of Contents
| ITEM 6. | Selected Financial Data |
The following tables set forth selected consolidated financial information from our audited Consolidated Financial Statements as of and for the fiscal years ended June 30, 2014, 2013, 2012, 2011, and 2010. The selected financial data presented below should be read in conjunction with our Financial Statements and the accompanying Notes included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K and “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.”
| Years Ended June 30, | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | ||||||||||||||||
| (in millions, except for per share amounts) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Statements of Earnings Data |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Revenues |
$ | 2,558.0 | $ | 2,430.8 | $ | 2,303.5 | $ | 2,166.9 | $ | 2,209.2 | ||||||||||
| Earnings from continuing operations before income taxes |
395.5 | 323.2 | 200.9 | 269.7 | 342.1 | |||||||||||||||
| Net earnings from continuing operations |
263.0 | 212.1 | 125.0 | 171.8 | 225.1 | |||||||||||||||
| Net earnings |
263.0 | 212.1 | 123.6 | 169.6 | 190.0 | |||||||||||||||
| Basic earnings per share from continuing operations(a) |
$ | 2.20 | $ | 1.74 | $ | 1.01 | $ | 1.38 | $ | 1.66 | ||||||||||
| Diluted earnings per share from continuing operations(a) |
$ | 2.12 | $ | 1.69 | $ | 0.98 | $ | 1.34 | $ | 1.62 | ||||||||||
| Basic Weighted-average shares outstanding |
119.6 | 121.9 | 124.1 | 124.8 | 135.9 | |||||||||||||||
| Diluted Weighted-average shares outstanding |
124.1 | 125.4 | 127.5 | 128.3 | 139.1 | |||||||||||||||
| Cash dividends declared per common share |
$ | 0.84 | $ | 0.72 | $ | 0.64 | $ | 0.60 | $ | 0.56 | ||||||||||
| June 30, | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | ||||||||||||||||
| (in millions) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance Sheet Data |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 347.6 | $ | 266.0 | $ | 320.5 | $ | 241.5 | $ | 412.6 | ||||||||||
| Total current assets |
880.6 | 807.0 | 777.4 | 751.4 | 992.4 | |||||||||||||||
| Property, plant and equipment, net |
88.3 | 80.9 | 79.0 | 83.1 | 87.4 | |||||||||||||||
| Total assets |
2,192.1 | 2,018.2 | 1,987.6 | 1,904.0 | 1,794.4 | |||||||||||||||
| Total current liabilities |
484.4 | 469.5 | 410.3 | 782.7 | 486.4 | |||||||||||||||
| Long-term debt |
524.1 | 524.5 | 524.4 | 124.3 | 324.1 | |||||||||||||||
| Total liabilities |
1,230.4 | 1,202.2 | 1,137.1 | 1,106.7 | 987.3 | |||||||||||||||
| Total stockholders’ equity |
961.7 | 816.0 | 850.5 | 797.3 | 807.1 | |||||||||||||||
| (a) | The computation of basic earnings per share from continuing operations is based on the Company’s Net earnings divided by the basic Weighted-average shares outstanding. Diluted earnings per share reflects the potential dilution that could occur if outstanding stock options at the presented date are exercised, shares of restricted stock and restricted stock units have vested. |
26
Table of Contents
| ITEM 7. | Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations |
This discussion summarizes the significant factors affecting the results of operations and financial condition of Broadridge during the fiscal years ended June 30, 2014, 2013, and 2012 and should be read in conjunction with our Consolidated Financial Statements and accompanying Notes thereto included elsewhere herein. Certain information contained in “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” are “forward-looking statements” within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. Statements that are not historical in nature and which may be identified by the use of words such as “expects,” “assumes,” “projects,” “anticipates,” “estimates,” “we believe,” “could be” and other words of similar meaning, are forward-looking statements. These statements are based on management’s expectations and assumptions and are subject to risks and uncertainties that may cause actual results to differ materially from those expressed. Our actual results, performance or achievements may differ materially from the results discussed in this Item 7 because of various factors, including those set forth elsewhere herein. See “Forward-Looking Statements” and “Risk Factors” included in Item 1 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
DESCRIPTION OF THE COMPANY AND BUSINESS SEGMENTS
Broadridge is a leading global provider of investor communications and technology-driven solutions to banks, broker-dealers, mutual funds and corporate issuers. Our systems and services include investor communication solutions, and securities processing and business process outsourcing services. In short, we provide the infrastructure that helps the financial services industry operate. With over 50 years of experience, we provide financial services firms with advanced, dependable, scalable and cost-effective integrated systems. Our systems help reduce the need for clients to make significant capital investments in operations infrastructure, thereby allowing them to increase their focus on core business activities. Our operations are classified into two business segments: Investor Communication Solutions and Securities Processing Solutions.
Investor Communication Solutions
A large portion of our Investor Communication Solutions business involves the processing and distribution of proxy materials to investors in equity securities and mutual funds, as well as the facilitation of related vote processing. ProxyEdge, our innovative electronic proxy delivery and voting solution for institutional investors and financial advisors, helps ensure the participation of the largest stockholders of many companies. We also provide the distribution of regulatory reports and corporate action/reorganization event information, as well as tax reporting solutions that help our clients meet their regulatory compliance needs. In addition, we provide financial information distribution and transaction reporting services to both financial institutions and securities issuers. These services include the processing and distribution of account statements and trade confirmations, traditional and personalized document fulfillment and content management services, marketing communications, and imaging, archival and workflow solutions that enable and enhance our clients’ communications with investors. All of these communications are delivered through paper or electronic channels. In addition, we provide corporate issuers with registered proxy services as well as registrar, stock transfer and record-keeping services.
Securities Processing Solutions
We offer a suite of advanced computerized real-time transaction processing services that automate the securities transaction lifecycle, from desktop productivity tools, data aggregation, performance reporting, and portfolio management to order capture and execution, trade confirmation, settlement, and accounting. Our services help financial institutions efficiently and cost-effectively consolidate their books and records, gather and service assets under management, focus on their core businesses, and manage risk. With multi-currency capabilities, our Global Processing Solution supports real-time global trading of equity, option, mutual fund, and fixed income securities in established and emerging markets. In addition, our business process outsourcing services allow broker-dealers to outsource certain administrative functions relating to clearing and settlement, from order entry to trade matching and settlement, while maintaining their ability to finance and capitalize their business.
27
Table of Contents
ACQUISITIONS
Assets acquired and liabilities assumed in business combinations were recorded on the Company’s Consolidated Balance Sheets as of the respective acquisition dates based upon their estimated fair values at such dates. The results of operations of businesses acquired by the Company were included in the Company’s Consolidated Statements of Earnings since their respective dates of acquisition. The excess of the purchase price over the estimated fair values of the underlying assets acquired and liabilities assumed was allocated to Goodwill.
During the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014, the Company acquired two businesses in the Investor Communication Solutions segment:
Bonaire Software Solutions, LLC
In July 2013, the Company acquired Bonaire Software Solutions, LLC (“Bonaire”), a leading provider of fee calculation, billing, and revenue and expense management solutions for asset managers including institutional asset managers, wealth managers, mutual funds, bank trusts, hedge funds and capital markets firms. The purchase price was $37.6 million, net of cash acquired. Net liabilities assumed in the transaction were $1.5 million. In addition, the Company recorded a $0.5 million liability for the fair value of potential additional cash payments, which are payable over the next three years contingent upon the achievement by the acquired business of certain revenue and earnings targets. During the fourth quarter, the fair value of the contingent consideration was increased by $0.8 million. As a result, as of June 30, 2014, the Company has recorded a $1.3 million liability for the contingent consideration. This acquisition resulted in $29.0 million of Goodwill. Intangible assets acquired, which totaled $10.1 million, consist primarily of acquired software technology and customer relationships, which are being amortized over a seven-year life and ten-year life, respectively. The results of Bonaire’s operations were included in the Company’s Consolidated Financial Statements in this Annual Report on Form 10-K from the date of acquisition. Pro forma supplemental financial information is not provided as the impact of the acquisition on the Company’s operating results, financial position or cash flows was not material.
Emerald Connect, LLC
In February 2014, the Company acquired Emerald Connect LLC (“Emerald”), a leading provider of websites and related communications solutions for financial advisors. The purchase price was $59.8 million, net of cash acquired. Net liabilities assumed in the transaction were $2.1 million. This acquisition resulted in $41.1 million of Goodwill. Intangible assets acquired, which totaled $20.8 million, consist primarily of customer relationships, which are being amortized over a seven-year life. The results of Emerald’s operations were included in the Company’s Consolidated Financial Statements in this Annual Report on Form 10-K from the date of acquisition. Pro forma supplemental financial information is not provided as the impact of the acquisition on the Company’s operating results, financial position or cash flows was not material.
There were no acquisitions in the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013.
During the fiscal year ended June 30, 2012, the Company acquired one business in the Securities Processing Solutions segment:
Paladyne Systems, Inc.
In September 2011, the Company acquired Paladyne Systems, Inc (“Paladyne”), now known as Broadridge Investment Management, Reference Data and Risk Solutions, a provider of buy-side technology solutions for the global investment management industry. The purchase price was $72.4 million, net of cash acquired of $8.3 million. Net liabilities assumed were $15.4 million. This acquisition resulted in $64.0 million of goodwill. Intangible assets acquired, which totaled $23.8 million, consist primarily of acquired software technology and customer relationships, which are being amortized over a seven-year life and ten-year life, respectively. The
28
Table of Contents
results of Paladyne’s operations were included in the Company’s Consolidated Financial Statements in this Annual Report on Form 10-K from the date of acquisition. Pro forma supplemental financial information is not provided as the impact of the acquisition on the Company’s operating results, financial position or cash flows was not material.
DIVESTITURES
In November 2009, the Company and its wholly owned subsidiary Ridge Clearing & Outsourcing Solutions, Inc. (“Ridge”), entered into an asset purchase agreement (the “Asset Purchase Agreement”) with Penson Worldwide, Inc. (“PWI”) and Penson Financial Services, Inc., a wholly owned subsidiary of PWI (“PFSI,” referred to together with PWI as “Penson”), to sell substantially all contracts of the securities clearing clients of Ridge to PFSI.
On June 25, 2010, the Company completed the sale of the contracts of substantially all of the securities clearing clients of Ridge to PFSI for an aggregate purchase price of $35.2 million. The purchase price paid to Broadridge consisted of (i) a five-year subordinated note from PWI (the “Seller Note”) in the principal amount of $20.6 million bearing interest at an annual rate equal to the London Inter-Bank Offer Rate (“LIBOR”) plus 550 basis points, and (ii) 2,455,627 shares of PWI’s common stock (representing 9.5% of PWI’s outstanding common stock as of May 31, 2010), at the June 25, 2010 closing price of PWI’s common stock of $5.95 per share (the “Seller Shares”). As a result of this transaction, we no longer provide securities clearing services for correspondent broker-dealers but continue to provide business process outsourcing services aligned with the Securities Processing Solutions business. See Note 8, “Impairment and Other Charges, Net” to our Consolidated Financial Statements under Item 8 of Part II of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for a discussion on the Seller Note and the Seller Shares.
Concurrent with entering into the Asset Purchase Agreement, the Company entered into a master services agreement with PWI (the “Outsourcing Services Agreement”) for an eleven-year term expiring in December 2022. Under the Outsourcing Services Agreement, Ridge provided securities processing and back-office support services to PFSI, including services for the clients acquired from Ridge and PWI’s existing clients. On June 5, 2012, the Company entered into a ten-year master services agreement (the “Apex MSA”) with Apex Clearing Corporation (“Apex Clearing”) under which Broadridge will perform outsourcing services for Apex Clearing consistent with the securities processing and back-office support services it had previously performed for Penson. The Apex MSA was part of a series of related transactions involving Broadridge, Penson, PEAK6 Investments, L.P. (“PEAK6”) and Apex Clearing Holdings LLC (“Apex Holdings”), an entity created by Penson and PEAK6 to provide clearing and related services to Penson’s U.S. securities correspondents. As part of the series of related transactions, Broadridge transferred ownership of its broker-dealer subsidiary, Ridge, to Apex Holdings and Ridge was renamed Apex Clearing Corporation. Penson’s U.S. broker-dealer subsidiary, PFSI, then sold its U.S. clearing contracts to Apex Clearing.
In addition, on June 5, 2012, Broadridge, Ridge (prior to its transfer to Apex Holdings) and Broadridge Financial Solutions (Canada), Inc. entered into a termination and mutual release agreement with Penson, PFSI and Penson Financial Services Canada, Inc. (“PFSC”) (the “Termination Agreement”), thereby terminating certain schedules including the U.S. schedule (the “U.S. Schedule”) to the Outsourcing Services Agreement.
The Termination Agreement: (i) terminated the schedules under the Outsourcing Services Agreement, including the U.S. Schedule, other than to the extent necessary to provide any transition services that may be required under the Apex MSA and for Broadridge to continue to service Penson’s Canadian subsidiary, PFSC; and (ii) terminated, discharged and released in full Penson’s obligations, including all obligations to make principal and interest payments, under the Seller Note. The Termination Agreement also provided that Penson and Broadridge mutually release all claims arising under the Outsourcing Services Agreement, provided that Broadridge will retain claims of up to $20 million under the Outsourcing Services Agreement against PFSC while Penson retained all of its rights under the Outsourcing Services Agreement to defend any such claims against PFSC.
29
Table of Contents
See Note 7, “Discontinued Operations” to our Consolidated Financial Statements under Item 8 of Part II of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for detailed information on discontinued operations.
BASIS OF PRESENTATION
The Consolidated Financial Statements have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the U.S. (“GAAP”). These financial statements present the consolidated position of the Company. These financial statements include the entities in which the Company directly or indirectly has a controlling financial interest and various entities in which the Company has investments recorded under both the cost and equity methods of accounting. Intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated.
In presenting the Consolidated Financial Statements, management makes estimates and assumptions that affect the amounts reported and related disclosures. Estimates, by their nature, are based on judgment and available information. Accordingly, actual results could differ from those estimates. In management’s opinion, the Consolidated Financial Statements contain all normal recurring adjustments necessary for a fair presentation of results reported. The results of operations reported for the periods presented are not necessarily indicative of the results of operations for subsequent periods.
CRITICAL ACCOUNTING POLICIES
We continually evaluate the accounting policies and estimates used to prepare the Consolidated Financial Statements. The estimates, by their nature, are based on judgment, available information, and historical experience and are believed to be reasonable. However, actual amounts and results could differ from these estimates made by management. Certain accounting policies that require significant management estimates and are deemed critical to our results of operations or financial position are discussed below.
Goodwill. We review the carrying value of all our goodwill in accordance with Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) No. 350, “Intangibles—Goodwill and Other” (“ASC No. 350”), by comparing the carrying value of our reporting units to their fair values. We are required to perform this comparison at least annually or more frequently if circumstances indicate possible impairment. When determining fair value, we utilize a discounted future cash flow approach using various assumptions, including projections of revenues based on assumed long-term growth rates, estimated costs and appropriate discount rates based on the particular business’ weighted-average cost of capital. The principal factors used in the discounted cash flow analysis requiring judgment are the projected future operating cash flows, the weighted-average cost of capital and the terminal value growth rate assumptions. The weighted-average cost of capital takes into account the relative weights of each component of our consolidated capital structure (equity and long-term debt). Our estimates of long-term growth and costs are based on historical data, various internal estimates and a variety of external sources, and are developed as part of our routine, long-range planning process. Changes in economic and operating conditions impacting these assumptions could result in goodwill impairments in future periods. We had $856.1 million of goodwill as of June 30, 2014. Given the significance of our goodwill, an adverse change to the fair value could result in an impairment charge, which could be material to our earnings.
The Company performs a sensitivity analysis under Step 1 of the goodwill impairment test as prescribed in ASC No. 350, assuming hypothetical reductions in the fair values of our reporting units. A 10% change in our estimates of projected future operating cash flows, discount rates, or terminal value growth rates used in our calculations of the fair values of the reporting units would not result in an impairment of our goodwill.
Income Taxes. We account for income taxes in accordance with ASC No. 740, “Income Taxes,” which establishes financial accounting and reporting standards for the effect of income taxes. The objectives of accounting for income taxes are to recognize the amount of taxes payable or refundable for the current year and deferred tax liabilities and assets for the future tax consequences of events that have been recognized in an entity’s financial statements or tax returns. Judgment is required in addressing the future tax consequences of events that have been recognized in our Consolidated Financial Statements or tax returns (e.g., realization of deferred tax assets, changes in tax laws or interpretations thereof). The Company is subject to the continuous
30
Table of Contents
examination of our income tax returns by the IRS, state and foreign tax authorities. A change in the assessment of the outcomes of such matters could materially impact our Consolidated Financial Statements. As of June 30, 2014, we had estimated foreign net operating loss carryforwards of approximately $18.8 million, of which $1.9 million expires in 2017 through 2027, and $16.9 million which has an indefinite utilization period. In addition, the Company has estimated U.S. federal net operating loss carryforwards of approximately $45.5 million, which expire in 2015 through 2030.
Valuation allowances are recognized to reduce deferred tax assets when it is more likely than not that the Company will not be able to utilize the deferred tax assets attributable to net operating and capital loss carryforwards of certain subsidiaries to offset future taxable earnings. The Company has recorded valuation allowances of $10.9 million and $12.5 million at June 30, 2014 and 2013, respectively. The determination as to whether a deferred tax asset will be recognized is made on a jurisdictional basis and is based on the evaluation of historical taxable income or loss, projected future taxable income, carryforward periods, scheduled reversals of deferred tax liabilities and tax planning strategies. Projected future taxable income is based on expected results and assumptions as to the jurisdiction in which the income will be earned. The assumptions used to project future taxable income requires significant judgment and are consistent with the plans and estimates used to manage the underlying businesses.
Share-based Payments. ASC No. 718 “Compensation—Stock Compensation” requires the measurement of stock-based compensation expense based on the fair value of the award on the date of grant. We determine the fair value of stock options issued by using a binomial option-pricing model. The binomial option-pricing model considers a range of assumptions related to volatility, dividend yield, risk-free interest rate and employee exercise behavior. Expected volatilities utilized in the binomial option-pricing model are based on a combination of implied market volatilities, historical volatility of our stock price and other factors. Similarly, the dividend yield is based on historical experience and expected future changes. The risk-free rate is derived from the U.S. Treasury yield curve in effect at the time of grant. The binomial option-pricing model also incorporates exercise and forfeiture assumptions based on an analysis of historical data. The expected life of the stock option grants is derived from the output of the binomial model and represents the period of time that options granted are expected to be outstanding. Determining these assumptions are subjective and complex, and therefore, a change in the assumptions utilized could impact the calculation of the fair value of our stock options. A hypothetical change of five percentage points applied to the volatility assumption used to determine the fair value of the fiscal year 2014 stock option grants would result in approximately a $2.2 million change in total pre-tax stock-based compensation expense for the fiscal year 2014 grants, which would be amortized over the vesting period. A hypothetical change of one year in the expected life assumption used to determine the fair value of the fiscal year 2014 stock option grants would result in approximately a $0.6 million change in the total pre-tax stock-based compensation expense for the fiscal year 2014 grants, which would be amortized over the vesting period. A hypothetical change of one percentage point in the forfeiture rate assumption used for the fiscal year 2014 stock option grants would result in approximately a $0.1 million change in the total pre-tax stock-based compensation expense for the fiscal year 2014 grants, which would be amortized over the vesting period. A hypothetical one-half percentage point change in the dividend yield assumption used to determine the fair value of the fiscal year 2014 stock option grants would result in approximately a $1.1 million change in the total pre-tax stock-based compensation expense for the fiscal year 2014 grants, which would be amortized over the vesting period.
IBM INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY SERVICES AGREEMENTS
In March 2010, the Company and International Business Machines Corporation (“IBM”) entered into an Information Technology Services Agreement (the “IT Services Agreement”), under which IBM provides certain aspects of the Company’s information technology infrastructure that were previously provided by Automatic Data Processing, Inc (“ADP”). Under the IT Services Agreement, IBM provides a broad range of technology services to the Company including supporting its mainframe, midrange, open systems, network and data center operations, as well as providing disaster recovery services. The Company has the option of incorporating additional services into the agreement over time. The IT Services Agreement expires on June 30, 2022. The Company has the right to renew the initial term of the IT Services Agreement for up to one additional 12-month term.
31
Table of Contents
During the course of the migration to IBM, the Company incurred total migration costs of $85.6 million as part of establishing an operable IBM data center. $30.9 million of these costs were expensed, $24.6 million in fiscal year 2012 and $6.3 million in fiscal year 2011. $54.7 million of these costs were capitalized, with $11.3 million amortized through June 30, 2014. For the fiscal years ended June 30, 2014, 2013, and 2012, the Company recorded total expenses of $95.7 million, $96.3 million and $24.6 million, respectively, in the Consolidated Statements of Earnings related to this agreement.
The migration of our data center processing from ADP to IBM was completed in August 2012. The Company realized approximately $15.0 million in cost savings, net of deferred cost amortization, in the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013, and is anticipating that it will realize approximately $25.0 million in average annual cost savings, net of deferred cost amortization, over the term of the IT Services Agreement.
In March 2014, the Company and IBM United Kingdom Limited (“IBM UK”) entered into an Information Technology Services Agreement (the “EU IT Services Agreement”), under which IBM UK provides data center services supporting the Company’s technology outsourcing services for certain clients in Europe and Asia. The EU IT Services Agreement expires in October 2023. The Company has the right to renew the initial term of the EU IT Services Agreement for up to one additional 12-month term or one additional 24-month term.
The Company has begun the build-out of the IBM UK data center associated with the EU IT Services Agreement. For the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014, the Company recorded expenses of $1.5 million in the Consolidated Statements of Earnings and capitalized $1.6 million of costs in Other non-current assets related to this agreement.
RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
The following discussions of Analysis of Consolidated Statements of Earnings from Continuing Operations and Analysis of Reportable Segments refer to the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014 compared to the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013, and the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013 compared to the fiscal year ended June 30, 2012. The following discussions of the Company’s results of continuing operations exclude the results related to the securities clearing business. This business is segregated from continuing operations and included in discontinued operations for fiscal year ended June 30, 2012. The Analysis of Consolidated Statements of Earnings from Continuing Operations should be read in conjunction with the Analysis of Reportable Segments, which provides more detailed discussions concerning certain components of the Consolidated Statements of Earnings from Continuing Operations.
The following references are utilized in the discussions of Analysis of Consolidated Statements of Earnings from Continuing Operations and Analysis of Reportable Segments:
“Acquisition Amortization and Other Costs” represents amortization charges associated with intangible asset values as well as other deal costs associated with the Company’s acquisitions.
“Net New Business” refers to recurring revenue closed sales less revenue from recurring revenue client losses.
“Restructuring Charges” refers to severance costs, facility exit costs, reorganization costs, the impact of system development costs for Apex Clearing Holdings LLC (“Apex Holdings”) and the Canadian subsidiary of Penson Worldwide, Inc., and costs to restructure and outsource certain processing related to our desktop applications.
“Restructuring and Impairment Charges, net” referred to herein represent the Restructuring Charges defined above and the following charges:
| • | “Penson Transition Costs” represent transition costs incurred in fiscal year 2013 related to the June 2012 termination and mutual release agreement with Penson and PFSC terminating the Penson outsourcing services contract, including the transfer of the Ridge entity to Apex Holdings. |
32
Table of Contents
| • | “Penson OTTI charge” refers to the charge that resulted after the Company reviewed its investment in the PWI common stock for impairment. Based on the Company’s review, factoring in the level of decline in the fair value of the PWI common stock, management determined that the market value of the PWI common stock may not equal or exceed the cost basis of our investment within a reasonable period of time. After consideration of the severity and duration of this decline in fair value as well as the reasons for the decline in value, the Company recorded an “other than temporary” impairment charge of $12.5 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2012. |
| • | “Penson Note Receivable impairment charge” refers to the charge the Company recorded as a result of a restructuring support agreement Broadridge and Ridge entered into with PWI and certain of its subsidiaries on March 13, 2012. The restructuring support agreement provided for proposed transactions related to the restructuring of Penson’s outstanding indebtedness, including the note receivable in the principal amount of $20.6 million issued by PWI to Broadridge as part of the consideration in the sale of the Ridge clearing contracts to Penson. As part of PWI’s proposed debt restructuring, Broadridge agreed to cancel this note receivable in exchange for additional shares of PWI’s common stock, and the Company recorded a $21.4 million charge at June 30, 2012, which included $0.8 million of accrued interest on the note receivable. |
| • | “Penson Deferred Costs impairment charge” refers to the charge the Company recorded as a result of the termination of the U.S. Schedule to the Outsourcing Services Agreement on June 5, 2012. Upon termination of this agreement, Broadridge determined that a charge for impairment was appropriate on Broadridge’s deferred client conversion and start-up costs associated with the Outsourcing Services Agreement. The charge taken by the Company on the deferred costs was $47.2 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2012, representing all deferred costs related to the Outsourcing Services Agreement with Penson. |
| • | “Eliminated obligation to pay or credit Penson fees” refers to Broadridge’s obligation to pay or credit to Penson fees in the amount of $15.1 million related to a third party vendor’s services that were replaced by the Outsourcing Services Agreement that was extinguished with the termination of the U.S. Schedule to the Outsourcing Services Agreement on June 5, 2012. |
| • | “Penson Shutdown costs” refers to costs of $8.2 million including severance, legal and other costs associated with the Penson transaction consummated on June 5, 2012 including the transfer of the Ridge entity to Apex Holdings. |
The following definitions describe the Company’s Revenues:
Fee revenues in the Investor Communication Solutions segment are derived from both recurring and event-driven activity. In addition, the level of recurring and event-driven activity we process directly impacts distribution revenues. While event-driven activity is highly repeatable, it may not recur on an annual basis. The types of services we provide that comprise event-driven activity are:
| • | Mutual Fund Proxy: The proxy and related services we provide to mutual funds when certain events occur requiring a shareholder vote including changes in directors, sub-advisors, fee structures, investment restrictions, and mergers of funds. |
| • | Mutual Fund Communications: Mutual fund communications services consist primarily of the distribution on behalf of mutual funds of supplemental information required to be provided to the annual mutual fund prospectus as a result of certain triggering events such as a change in portfolio managers. In addition, mutual fund communications consist of notices and marketing materials such as newsletters. |
| • | Proxy Contests and Specials, Corporate Actions, and Other: The proxy services we provide in connection with shareholder meetings driven by special events such as proxy contests, mergers and acquisitions, and tender/exchange offers. |
33
Table of Contents
Event-driven fee revenues are based on the number of special events and corporate transactions we process. Event-driven activity is impacted by financial market conditions and changes in regulatory compliance requirements, resulting in fluctuations in the timing and levels of event-driven fee revenue. As such, the timing and level of event-driven activity and its potential impact on revenues and earnings is difficult to forecast.
Distribution cost of revenues consists primarily of postage related expenses incurred in connection with our Investor Communication Solutions segment. These costs are reflected in Cost of Revenues.
Generally, mutual fund proxy activity has been subject to a greater level of volatility than the other components of event-driven activity. During fiscal years 2014 and 2013, mutual fund proxy fee revenues were 31% and 54% higher, respectively, than the prior fiscal years while during fiscal year 2012, mutual fund proxy revenues were 28% lower than the prior fiscal year. Although it is difficult to forecast the levels of event-driven activity, we expect that the portion of fee revenues derived from mutual fund proxy activity may continue to experience volatility in the future.
Closed sales represent anticipated revenues for new client contracts that were signed by Broadridge during the periods referenced. A sale is considered closed when the Company has received the signed client contract. For recurring revenue closed sales, the amount of the closed sale is generally a reasonable estimate of annual revenues based on client volumes or activity, excluding pass-through revenues such as distribution revenues. Event-driven revenue closed sales primarily occur in our Investor Communication Solutions segment. The amount of the event-driven revenue closed sale is generally a reasonable estimate of production revenues based on client volumes or activity, excluding pass-through revenues such as distribution revenues. Broadridge’s determination of the amount of a closed sale is based on the client’s estimate of transaction volumes and activity levels, as our fees are largely based on transaction volume and activity levels. The inherent variability of transaction volumes and activity levels can result in some variability of amounts reported as closed sales. Larger recurring revenue closed sales can take up to 12 to 24 months to convert to revenues, particularly for the services provided by our Securities Processing Solutions segment. The majority of event-driven revenue closed sales are usually recognized during the year the contract is signed.
The Company tracks actual revenue achieved during the first year that the client contract is fully implemented and compares this to the amount that was included in the Company’s previously reported closed sales amount. The Company adjusts the current year closed sales amount for any difference between the prior year’s reported closed sales amount and the actual revenue achieved in the first year of the applicable contract. Closed sales were adjusted by $(0.8) million, $(5.9) million and $(3.1) million for the fiscal years ended June 30, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. Recurring revenue closed sales were adjusted by $(1.0) million, $(6.5) million and $(3.1) million for the fiscal years ended June 30, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. Event-driven revenue closed sales were adjusted by $0.2 million and $0.6 million for the fiscal years ended June 30, 2014 and 2013, respectively. Event-driven revenue closed sales were not adjusted for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2012.
34
Table of Contents
ANALYSIS OF CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF EARNINGS FROM CONTINUING OPERATIONS
Fiscal Year 2014 Compared to Fiscal Year 2013
The table below presents Consolidated Statements of Earnings from continuing operations data for the fiscal years ended June 30, 2014 and 2013, and the dollar and percentage changes between periods:
| Years Ended June 30, | ||||||||||||||||
| Change | ||||||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | ($) | (%) | |||||||||||||
| ($ in millions, except for per share amounts) | ||||||||||||||||
| Revenues |
$ | 2,558.0 | $ | 2,430.8 | $ | 127.2 | 5 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Cost of revenues |
1,761.4 | 1,767.8 | (6.4 | ) | — | |||||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative expenses |
376.0 | 323.6 | 52.4 | 16 | ||||||||||||
| Other expenses, net |
25.1 | 16.2 | 8.9 | 55 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total expenses |
2,162.5 | 2,107.6 | 54.9 | 3 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Earnings from continuing operations before income taxes |
395.5 | 323.2 | 72.3 | 22 | ||||||||||||
| Margin |
15.5 | % | 13.3 | % | 2.2 | pts | ||||||||||
| Provision for income taxes |
132.5 | 111.1 | 21.4 | 19 | ||||||||||||
| Effective tax rate |
33.5 | % | 34.4 | % | (0.9 | ) pts | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Net earnings from continuing operations |
$ | 263.0 | $ | 212.1 | $ | 50.9 | 24 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Basic earnings per share from continuing operations |
$ | 2.20 | $ | 1.74 | $ | 0.46 | 26 | |||||||||
| Diluted earnings per share from continuing operations |
$ | 2.12 | $ | 1.69 | $ | 0.43 | 25 | |||||||||
Revenues. Revenues for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014 were $2,558.0 million, an increase of $127.2 million, or 5%, compared to $2,430.8 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013. The $127.2 million increase was driven by higher recurring fee revenues of $131.2 million, higher distribution revenues of $9.7 million and higher event-driven fee revenues of $0.1 million. The positive contribution from recurring fee revenues reflected higher Net New Business, internal growth and acquisitions. Fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates unfavorably impacted revenues by $13.7 million.
Closed sales for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014 were $179.1 million, an increase of $21.6 million, or 14%, compared to $157.5 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013. Recurring revenue closed sales for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014 were $127.0 million, an increase of $6.2 million, or 5%, compared to $120.8 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013. Event-driven closed sales for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014 were $52.1 million, an increase of $15.4 million, or 42%, compared to $36.7 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013.
Total Expenses. Total expenses for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014 were $2,162.5 million, an increase of $54.9 million compared to $2,107.6 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013. The increase reflects higher Selling, general and administrative expenses of $52.4 million, or 16%, higher Other expenses, net of $8.9 million or 55%, partially offset by lower Cost of Revenues of $6.4 million.
Cost of revenues for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014 were $1,761.4 million, a decrease of $6.4 million compared to $1,767.8 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013. The decrease reflects lower Restructuring Charges of $9.6 million, savings related to the migration of the data center to IBM of $6.3 million and lower distribution cost of revenues of $1.2 million, offset by $12.3 million of higher costs related to acquisitions, higher investment spend of $10.9 million and a $5.0 million increase in performance based compensation expense. Fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates decreased cost of fee revenues by $10.3 million. Higher variable expenses were more than offset by savings from operating leverage and improved productivity from strategic initiatives.
35
Table of Contents
Selling, general and administrative expenses for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014 were $376.0 million, an increase of $52.4 million, or 16%, compared to $323.6 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013. The 16% increase was primarily due to higher performance based compensation expense of $23.4 million, higher investment spend of $16.3 million, higher sales and marketing expense of $8.0 million and higher costs related to acquisitions of $6.1 million partially offset by a $3.3 million adjustment due to a decrease in the fair value of our obligations under contingent acquisition consideration arrangements.
Other expenses, net for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014 were $25.1 million, an increase of $8.9 million, compared to $16.2 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013. The increased loss was primarily due to higher interest expenses on our Long-term borrowings of $10.0 million. Fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates decreased Other expenses, net by $0.5 million.
Earnings from continuing operations before income taxes. Earnings from continuing operations before income taxes for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014 were $395.5 million, an increase of $72.3 million, or 22%, compared to $323.2 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013. The increase is mainly due to higher revenues and operating leverage coupled with the positive impact of improved productivity from strategic initiatives. Pre-tax margin increased from 13.3% for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013 to 15.5% for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014.
Provision for income taxes. The Provision for income taxes and the effective tax rates for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014 were $132.5 million and 33.5%, respectively, compared to $111.1 million and 34.4%, for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013, respectively. The decrease in the effective tax rate was primarily attributable to the cumulative tax benefits in fiscal year 2014 exceeding the cumulative tax benefits in fiscal year 2013. The cumulative tax benefits in fiscal year 2014 primarily related to the release of a valuation allowance for a net operating loss carryforward in a foreign tax jurisdiction, and the release of various tax reserves related to certain foreign, U.S. federal and state income taxes due to audit settlements and the expiration of certain audit periods which resulted in a decrease to the effective tax rate of approximately 115 basis points. In addition, the effective tax rate was also positively affected by approximately 30 basis points due to the characterization of a $3.3 million decrease in the fair value of obligations under contingent acquisition consideration arrangements as a deductible permanent tax item. Offsetting these positive benefits were various non-deductible permanent tax items that negatively impacted the tax rate by approximately 60 basis points. The cumulative tax benefits in fiscal year 2013 primarily consisted of the recognition of a previous period’s foreign tax credits. In addition to the higher cumulative tax benefits in fiscal year 2014, the change in the effective tax rate was marginally positively impacted by the geographical mix of income. In general, the Company’s foreign earnings are subject to a lower corporate income tax rate relative to the tax rate applied against U.S. income. In the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014, there was no material change in foreign earnings as a percentage of total Net earnings when compared to the fiscal year ended June 30, 3013. The geographical mix of income may impact the effective tax rate in future periods as the geographical mix of the Company’s business changes.
Net earnings from continuing operations and Basic and Diluted earnings per share from continuing operations. Net earnings from continuing operations for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014 were $263.0 million, an increase of $50.9 million, or 24%, compared to $212.1 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013. The increase in Net earnings from continuing operations reflects higher revenues, increased pre-tax margins from higher margin revenue business and the positive impact of improved productivity from strategic initiatives.
Basic and Diluted earnings per share from continuing operations for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014 were $2.20, an increase of $0.46, or 26%, and $2.12, an increase of $0.43, or 25%, respectively, compared to $1.74 and $1.69 for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013, respectively.
36
Table of Contents
Fiscal Year 2013 Compared to Fiscal Year 2012
The table below presents Consolidated Statements of Earnings from continuing operations data for the fiscal years ended June 30, 2013 and 2012, and the dollar and percentage changes between periods:
| Years Ended June 30, | ||||||||||||||||
| 2013 | 2012 | Change | ||||||||||||||
| ($) | (%) | |||||||||||||||
| ($ in millions, except for per share amounts) | ||||||||||||||||
| Revenues |
$ | 2,430.8 | $ | 2,303.5 | $ | 127.3 | 6 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Cost of revenues |
1,767.8 | 1,715.1 | 52.7 | 3 | ||||||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative expenses |
323.6 | 299.9 | 23.7 | 8 | ||||||||||||
| Impairment and other charges, net |
— | 74.2 | (74.2 | ) | (100 | ) | ||||||||||
| Other expenses, net |
16.2 | 13.4 | 2.8 | 21 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total expenses |
2,107.6 | 2,102.6 | 5.0 | — | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Earnings from continuing operations before income taxes |
323.2 | 200.9 | 122.3 | 61 | ||||||||||||
| Margin |
13.3 | % | 8.7 | % | 4.6 | pts | ||||||||||
| Provision for income taxes |
111.1 | 75.9 | 35.2 | 46 | ||||||||||||
| Effective tax rate |
34.4 | % | 37.8 | % | (3.4 | ) pts | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Net earnings from continuing operations |
$ | 212.1 | $ | 125.0 | $ | 87.1 | 70 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Basic earnings per share from continuing operations |
$ | 1.74 | $ | 1.01 | $ | 0.73 | 72 | |||||||||
| Diluted earnings per share from continuing operations |
$ | 1.69 | $ | 0.98 | $ | 0.71 | 72 | |||||||||
Revenues. Revenues for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013 were $2,430.8 million, an increase of $127.3 million, or 6%, compared to $2,303.5 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2012. The $127.3 million increase was driven by higher recurring fee revenues of $56.9 million, higher distribution revenues of $50.3 million and higher event-driven fee revenues of $23.6 million, mainly due to higher mutual fund proxy and supplemental prospectus activity. The positive contribution from recurring fee revenues reflected higher Net New Business and to a lesser extent, gains from an acquisition partially offset by lower internal growth. Fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates unfavorably impacted revenues by $3.5 million.
Closed sales for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013 were $157.5 million, an increase of $8.8 million, or 6%, compared to $148.7 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2012. Recurring revenue closed sales for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013 were $120.8 million, an increase of $0.6 million compared to $120.2 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2012. Event-driven closed sales for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013 were $36.7 million, an increase of $8.2 million, or 29%, compared to $28.5 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2012.
Total Expenses. Total expenses for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013 were $2,107.6 million, an increase of $5.0 million compared to $2,102.6 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2012. The increase reflects higher Cost of revenues of $52.7 million or 3%, higher Selling, general and administrative expenses of $23.7 million, or 8%, offset by impairment charges, net of $74.2 million in the prior period. Other expenses, net increased $2.8 million or 21%.
Cost of revenues for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013 were $1,767.8 million, an increase of $52.7 million, or 3%, compared to $1,715.1 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2012. The increase reflects higher variable costs of $45.2 million on higher fee revenues, higher cost of distribution revenues of $41.3 million, higher restructuring costs of $18.2 million and costs of $4.5 million related to acquisitions. These costs were partially offset by IBM Migration costs incurred in the prior year of $24.6 million, savings related to the migration of the data center to IBM of $16.2 million and lower investment spend of $8.3 million. Distribution cost of revenues for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013 were $662.3 million, an increase of $41.3 million, or 7%, compared to $621.0 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2012. The increase was due to recurring and event-driven activity increasing by 4% and 3%, respectively. Distribution cost of revenues consists primarily of postage related expenses. Fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates decreased cost of revenues by $5.5 million.
37
Table of Contents
Selling, general and administrative expenses for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013 were $323.6 million, an increase of $23.7 million, or 8%, compared to $299.9 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2012. The 8% increase was mainly due to higher costs related to higher sales and marketing expenses of $13.2 million, strategic initiatives of $4.0 million and the impact of a one-time non-recurring credit in the prior year of $2.4 million.
There were no impairment and other charges, net for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013. Impairment and other charges, net for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2012 were $74.2 million.
Other expenses, net for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013 were $16.2 million, an increase of $2.8 million, compared to $13.4 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2012. The increase is primarily driven by $1.8 million of interest expenses to settle certain income tax adjustments related to tax years 2007 through 2012 as a result of the settlement and execution of an Advance Pricing Agreement (“APA”) with the Internal Revenue Service (“IRS”) and Canadian Revenue Authority (“CRA”), along with higher interest expenses on our Long-term borrowings of $0.5 million. Fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates increased Other expenses, net by $0.5 million.
Earnings from continuing operations before income taxes. Earnings from continuing operations before income taxes for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013 were $323.2 million, an increase of $122.3 million, or 61%, compared to $200.9 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2012. The increase is mainly due to higher Revenues, increased margins driven by the mix of business, impairment charges and IBM Migration costs in the prior period and cost containment. Margin increased from 8.7% for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2012 to 13.3% for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013.
Provision for income taxes. Provision for income taxes and effective tax rates for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013 were $111.1 million and 34.4%, respectively, compared to $75.9 million and 37.8%, for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2012, respectively. The change in the Company’s effective tax rate was primarily attributable to the recognition this fiscal year of certain prior year foreign tax credits, coupled with last year fiscal year’s valuation allowance on capital tax losses and write-off of certain state tax net operating loss carryforwards both of which were related to the PWI transaction resulting in a decrease in the effective tax rate of approximately 500 basis points. Changes in the geographical mix of income partially offset this decrease by approximately 150 basis points, driven by a decrease in foreign earnings as a percentage of total earnings from continuing operations before income taxes in fiscal year 2013. In fiscal year 2012, the PWI transaction negatively impacted U.S. earnings, which increased the influence of the geographical mix of income on the rate change. In general, the Company’s foreign earnings are subject to a lower corporate income tax rate relative to the tax rate applied against U.S. income. Geographical mix of income going forward may impact the effective tax rate as the geographical mix of business changes.
Net earnings from continuing operations and Basic and Diluted earnings per share from continuing operations. Net earnings from continuing operations for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013 were $212.1 million, an increase of $87.1 million, or 70%, compared to $125.0 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2012. The increase in Net earnings from continuing operations reflects higher revenues, increased margins driven by the mix of business, impairment charges and IBM Migration costs recorded in the prior year and cost containment.
Basic and Diluted earnings per share from continuing operations for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013 were $1.74, an increase of $0.73, or 72%, and $1.69, an increase of $0.71, or 72%, respectively, compared to $1.01 and $0.98 for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2012, respectively. Restructuring and Impairment Charges, net decreased Basic and Diluted earnings per share by $0.10 for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013. The IBM Migration costs and Restructuring and Impairment Charges, net decreased diluted earnings per share in the prior year by $0.12 and $0.45, respectively.
ANALYSIS OF REPORTABLE SEGMENTS
Broadridge has two reportable operating business segments: (1) Investor Communication Solutions and (2) Securities Processing Solutions. Ridge’s securities clearing business is reflected in discontinued operations
38
Table of Contents
(see Note 1, “Basis of Presentation” and Note 7, “Discontinued Operations” to our Consolidated Financial Statements under Item 8 of Part II of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for detailed information on discontinued operations).
The primary components of “Other” are IBM Migration costs, Restructuring and Impairment Charges, net, and the elimination of intersegment revenues and profits as well as certain unallocated expenses. Foreign exchange is a reconciling item between the actual foreign exchange rates and budgeted foreign exchange rates.
Certain corporate expenses, as well as certain centrally managed expenses, are allocated based upon budgeted amounts in a reasonable manner. Because the Company compensates the management of its various businesses on, among other factors, segment profit, the Company may elect to record certain segment-related expense items of an unusual or non-recurring nature in consolidation rather than reflect such items in segment profit.
Revenues
| Years Ended June 30, | Change | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2014 vs. 2013 | 2013 vs. 2012 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | $ | % | $ | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ($ in millions) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Investor Communication Solutions |
$ | 1,866.9 | $ | 1,760.2 | $ | 1,634.0 | $ | 106.7 | 6 | $ | 126.2 | 8 | ||||||||||||||||
| Securities Processing Solutions |
694.8 | 660.5 | 655.5 | 34.3 | 5 | 5.0 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Other |
— | 0.1 | 0.5 | (0.1 | ) | (100 | ) | (0.4 | ) | (80 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency exchange |
(3.7 | ) | 10.0 | 13.5 | (13.7 | ) | (137 | ) | (3.5 | ) | (26 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Revenues |
$ | 2,558.0 | $ | 2,430.8 | $ | 2,303.5 | $ | 127.2 | 5 | $ | 127.3 | 6 | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
Earnings (Loss) from Continuing Operations before Income Taxes
| Years Ended June 30, | Change | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2014 vs. 2013 | 2013 vs. 2012 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | $ | % | $ | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ($ in millions) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Investor Communication Solutions |
$ | 336.0 | $ | 302.1 | $ | 242.8 | $ | 33.9 | 11 | $ | 59.3 | 24 | ||||||||||||||||
| Securities Processing Solutions |
119.1 | 85.2 | 91.1 | 33.9 | 40 | (5.9 | ) | (6 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Other |
(75.3 | ) | (80.3 | ) | (146.8 | ) | 5.0 | (6 | ) | 66.5 | (45 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency exchange |
15.7 | 16.2 | 13.8 | (0.5 | ) | (3 | ) | 2.4 | 17 | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Earnings from continuing operations before income taxes |
$ | 395.5 | $ | 323.2 | $ | 200.9 | $ | 72.3 | 22 | $ | 122.3 | 61 | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
Investor Communication Solutions
Revenues
| Years Ended June 30, | Change | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2014 vs. 2013 | 2013 vs. 2012 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | $ | % | $ | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| ($ in millions) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Recurring fee revenues |
$ | 946.9 | $ | 850.0 | $ | 797.7 | $ | 96.9 | 11 | $ | 52.3 | 7 | ||||||||||||||||
| Event-driven revenues |
155.6 | 155.5 | 131.9 | 0.1 | — | 23.6 | 18 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Distribution revenues |
764.4 | 754.7 | 704.4 | 9.7 | 1 | 50.3 | 7 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Revenues |
$ | 1,866.9 | $ | 1,760.2 | $ | 1,634.0 | $ | 106.7 | 6 | $ | 126.2 | 8 | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
39
Table of Contents
Fiscal Year 2014 Compared to Fiscal Year 2013
Revenues. Investor Communication Solutions segment’s Revenues for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014 were $1,866.9 million, an increase of $106.7 million, or 6%, compared to $1,760.2 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013. Recurring fee revenues for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014 were $946.9 million, an increase of $96.9 million, or 11%, compared to $850.0 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013 and event-driven fee revenues for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014 were $155.6 million compared to $155.5 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013. Higher recurring fee revenues were driven by internal growth and Net New Business. Position growth for mutual fund interim communications and annual equity proxy communications were positive 11% and 8%, respectively, for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014 compared to the same period in the prior year. Our internal growth reflects an increase in favorable position growth and fulfillment related market activity. Distribution revenues for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014 were $764.4 million, an increase of $9.7 million, or 1%, compared to $754.7 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013.
Earnings from continuing operations before income taxes. Earnings from continuing operations before income taxes for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014 were $336.0 million, an increase of $33.9 million, or 11%, compared to $302.1 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013, primarily due to higher recurring fee revenues. Margin increased by 80 basis points from 17.2% to 18.0%.
Fiscal Year 2013 Compared to Fiscal Year 2012
Revenues. Investor Communication Solutions segment’s Revenues for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013 were $1,760.2 million, an increase of $126.2 million, or 8%, compared to $1,634.0 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2012. Recurring fee revenues for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013 were $850.0 million, an increase of $52.3 million, or 7%, compared to $797.7 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2012 and event-driven fee revenues for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013 were $155.5 million, an increase of $23.6 million, or 18%, compared to $131.9 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2012. Recurring fee revenues were driven by Net New Business and internal growth. Event-driven revenues were driven by higher mutual fund proxy and supplemental activity. Distribution revenues for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013 were $754.7 million, an increase of $50.3 million, or 7%, compared to $704.4 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2012.
Earnings from continuing operations before income taxes. Earnings from continuing operations before income taxes for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013 were $302.1 million, an increase of $59.3 million, or 24% compared to $242.8 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2012, primarily due to higher recurring fee, event-driven fee and related distribution revenues, as well as improved productivity from strategic initiatives. Margin increased by 230 basis points from 14.9% to 17.2%.
Securities Processing Solutions
Fiscal Year 2014 Compared to Fiscal Year 2013
Revenues. Securities Processing Solutions segment’s Revenues for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014 were $694.8 million, an increase of $34.3 million, or 5%, compared to $660.5 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013. The increase was the result of higher Net New Business.
Earnings from continuing operations before income taxes. Earnings from continuing operations before income taxes for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014 were $119.1 million, an increase of $33.9 million, or 40%, compared to $85.2 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013. Pre-tax margins increased by 420 basis points from 12.9% to 17.1% for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014 as a result of operating leverage and improved productivity from strategic initiatives.
Fiscal Year 2013 Compared to Fiscal Year 2012
Revenues. Securities Processing Solutions segment’s Revenues for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013 were $660.5 million, an increase of $5.0 million, or 1%, compared to $655.5 million for the fiscal year ended June 30,
40
Table of Contents
2012. The increase was driven mainly by positive contributions from Net New Business and the Paladyne acquisition, partially offset by the impact of lower trade volumes and the previously disclosed agreement with Apex Clearing.
Earnings from continuing operations before income taxes. Earnings from continuing operations before income taxes for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013 were $85.2 million, a decrease of $5.9 million, or (6)%, compared to $91.1 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2012. Margin decreased by 100 basis points from 13.9% to 12.9% for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013 mainly due to the impact of lower trade volumes and the previously disclosed agreement with Apex Clearing, partially offset by contributions from Net New Business.
Other
Fiscal Year 2014 Compared to Fiscal Year 2013
Revenues. There were no significant reportable Revenues in our Other segment for the periods presented.
Loss from continuing operations before income taxes. Loss from continuing operations before income taxes was $75.3 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014, a decrease of $5.0 million, compared to a $80.3 million loss from continuing operations before income taxes for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013. The decreased loss was mainly due to a $18.6 million decline in Restructuring Charges and a $3.3 million decrease in the fair value of our obligations under contingent acquisition consideration arrangements, offset by a $8.5 million increase in performance based compensation and benefits and higher interest expense on our Long-term borrowings of $10.0 million.
Fiscal Year 2013 Compared to Fiscal Year 2012
Revenues. There were no significant reportable Revenues in our Other segment for the periods presented.
Loss from continuing operations before income taxes. Loss from continuing operations before income taxes was $80.3 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013, a increase of $66.5 million, compared to a $146.8 million loss from continuing operations before income taxes for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2012. The decreased loss was mainly due to a decline in Restructuring and Impairment Charges, net of $60.7 million and IBM Migration costs of $24.6 million.
Explanation and Reconciliation of the Company’s Use of Non-GAAP Financial Measures
Our results in this Annual Report on Form 10-K are presented in accordance with GAAP; however, in certain circumstances the Company may present results that are not generally accepted accounting principles measures (“Non-GAAP”). We use Non-GAAP financial measures, such as Adjusted net earnings and Free cash flows, for a number of reasons, including:
| • | in communications with our board of directors concerning our consolidated financial performance; |
| • | in communications with analysts and investors as they are commonly reported and widely used enterprise level performance measures; and |
| • | for internal planning purposes, including the preparation of our annual operating budget. |
We provide our Net earnings and Diluted earnings per share information on an adjusted basis to exclude the impact of certain costs, expenses, gains and losses and other specified items that due to their significant nature are evaluated on an individual basis. These items are excluded from our GAAP results because we believe this information helps our investors understand the effect of these significant items on our reported results and, therefore, will provide a better representation of our performance. These Non-GAAP financial measures should be viewed in addition to, and not as a substitute for, our reported results presented in accordance with GAAP.
41
Table of Contents
Our fiscal year 2014 Non-GAAP results exclude the impact of Acquisition Amortization and Other Costs, our fiscal year 2013 Non-GAAP results exclude the impact of Acquisition Amortization and Other Costs and Restructuring Charges, and our fiscal year 2012 Non-GAAP results exclude the impact of Acquisition Amortization and Other Costs, Restructuring and Impairment Charges, net, and IBM Migration costs. The Company incurred $11.1 million in restructuring and reorganization costs during fiscal year 2014 as part of its normal business operations.
Set forth below is a reconciliation of Adjusted net earnings from continuing operations (Non-GAAP) to the comparable GAAP measure:
| Years ended June 30, | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| ($ in millions) | ||||||||||||
| Adjusted net earnings from continuing operations (Non-GAAP) |
$ | 279.0 | $ | 236.0 | $ | 213.4 | ||||||
| Adjustments: |
||||||||||||
| Acquisition Amortization and Other Costs |
(24.7 | ) | (23.8 | ) | (24.8 | ) | ||||||
| Restructuring and Impairment Charges, net |
— | (20.2 | ) | (80.9 | ) | |||||||
| IBM Migration costs |
— | — | (24.6 | ) | ||||||||
| Tax impact of adjustments |
8.7 | 15.7 | 49.3 | |||||||||
| Discrete tax items |
— | 4.4 | (7.4 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net Earnings from continuing operations (GAAP) |
$ | 263.0 | $ | 212.1 | $ | 125.0 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Set forth below is a reconciliation of Adjusted diluted earnings per share from continuing operations (Non-GAAP) to the comparable GAAP measure:
| Years ended June 30, | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| Adjusted diluted earnings per share from continuing operations (Non-GAAP) |
$ | 2.25 | $ | 1.88 | $ | 1.67 | ||||||
| Adjustments: |
||||||||||||
| Acquisition Amortization and Other Costs |
(0.20 | ) | (0.19 | ) | (0.20 | ) | ||||||
| Restructuring and Impairment Charges, net |
— | (0.16 | ) | (0.63 | ) | |||||||
| IBM Migration costs |
— | — | (0.19 | ) | ||||||||
| Tax impact of adjustments |
0.07 | 0.13 | 0.39 | |||||||||
| Discrete tax items |
— | 0.03 | (0.06 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Diluted earnings per share from continuing operations (GAAP) |
$ | 2.12 | $ | 1.69 | $ | 0.98 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
We also provide information on our Free cash flows because we believe this information helps our investors understand the amount of cash available for dividends, share repurchases, acquisitions and other discretionary investments. The Company defines Free cash flows to exclude capital expenditures and software purchases from our GAAP Net operating activity cash flow results.
Set forth below is a reconciliation of Free cash flows (Non-GAAP) to the comparable GAAP measure:
| Years ended June 30, | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| ($ in millions) | ||||||||||||
| Free cash flows (Non-GAAP) |
$ | 334.3 | $ | 220.0 | $ | 243.9 | ||||||
| Adjustment: |
||||||||||||
| Capital expenditures and software purchases |
53.4 | 50.9 | 46.7 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net cash flows provided by operating activities (GAAP) |
$ | 387.7 | $ | 270.9 | $ | 290.6 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
42
Table of Contents
FINANCIAL CONDITION, LIQUIDITY AND CAPITAL RESOURCES
At June 30, 2014 and 2013, Cash and cash equivalents were $347.6 million and $266.0 million, respectively. Total stockholders’ equity was $961.7 million and $816.0 million at June 30, 2014 and 2013, respectively. At June 30, 2014, net working capital was $396.2 million, compared to $337.5 million at June 30, 2013. At the current time, and in future periods, we expect cash generated by our operations, together with existing cash, cash equivalents, marketable securities and borrowings from the capital markets, to be sufficient to cover cash needs for working capital, capital expenditures, strategic acquisitions, dividends and common stock repurchases.
As of June 30, 2014, $151.3 million of the $347.6 million of cash and cash equivalents was held by our foreign subsidiaries. We currently do not intend nor foresee a need to repatriate these funds. We expect existing domestic cash, cash equivalents, short-term investments, and cash flows from operations to continue to be sufficient to fund our domestic operating activities and cash commitments for investing and financing activities, such as regular quarterly dividends, debt repayment schedules, and material capital expenditures, for at least the next 12 months and thereafter for the foreseeable future. In addition, we expect existing foreign cash, cash equivalents, short-term investments, and cash flows from operations to continue to be sufficient to fund our foreign operating activities and cash commitments for investing activities, such as material capital expenditures, for at least the next 12 months and thereafter for the foreseeable future. If these funds are needed for our operations in the U.S., we would be required to accrue and pay U.S. taxes to repatriate these funds. However, our current plans do not demonstrate a need to repatriate them to fund our U.S. operations, as we consider these funds to be permanently reinvested outside the U.S.
On December 28, 2012, Broadridge, the IRS and the CRA entered into an APA relating to tax years 2007 through 2012. Under the APA, a net $50.0 million of cash was transferred from two of the Company’s Canadian subsidiaries to the Broadridge U.S. parent company during the Company’s third fiscal quarter of 2013. All tax effects pertaining to this APA were accrued in the prior fiscal year.
At June 30, 2014, the Company had $524.1 million of outstanding Long-term debt, consisting of senior notes of $124.6 million principal amount due June 2017 and $399.5 million principal amount senior notes due September 2020. These senior notes are senior unsecured obligations of the Company and rank equally with the Company’s other senior indebtedness. Interest on the senior notes due 2017 is payable semiannually on June 1st and December 1st each year based on a fixed per annum rate equal to 6.125%. Interest on the senior notes due 2020 is payable semiannually on March 1st and September 1st each year based on a fixed per annum rate equal to 3.95%.
On September 22, 2011, the Company entered into a $990.0 million senior unsecured credit facility, consisting of a $490.0 million five-year term loan facility (the “Fiscal 2012 Term Loan”) and a $500.0 million five-year revolving credit facility (the “Fiscal 2012 Revolving Credit Facility”) (collectively the “Fiscal 2012 Credit Facilities”). Borrowings under the Fiscal 2012 Credit Facilities bear interest at LIBOR plus 125 basis points. The Fiscal 2012 Revolving Credit Facility also has an annual facility fee equal to 15 basis points, on the unused portion of the facility, which totaled $0.8 million and $0.8 million for the fiscal years ended June 30, 2014 and 2013, respectively. The Company incurred $3.0 million in debt issuance costs to establish the Fiscal 2012 Credit Facilities, of which $0.1 million of these costs were expensed as incurred and $2.9 million of these costs have been capitalized in Other non-current assets in the Consolidated Balance Sheets and are being amortized to Other expenses, net on a straight-line basis, which approximates the effective interest method, over the terms of these facilities. During the quarter ended September 30, 2013, the Company repaid the Fiscal 2012 Term Loan and expensed the remaining issuance costs associated with this debt, which was approximately $0.9 million. As of June 30, 2014 and 2013, $2.3 million and $1.0 million, respectively, had been expensed related to the Fiscal 2012 Credit Facilities, with $0.6 million remaining to be amortized related to the Fiscal 2012 Revolving Credit Facility.
The Fiscal 2012 Term Loan contained a repayment schedule that required the Company to make minimum principal repayments on the loan before the balance of the loan became due in September 2016, with no
43
Table of Contents
prepayment penalty. During the fiscal year ended June 30, 2012, the Company repaid $90.0 million of the $490.0 million of borrowings under the Fiscal 2012 Term Loan and had met the repayment requirements on the Fiscal 2012 Term Loan through September 30, 2014. During the quarter ended September 30, 2013, the Company repaid the remaining $400.0 million outstanding on the Fiscal 2012 Term Loan. During the first quarter of the current fiscal year, the weighted-average interest rate on the Fiscal 2012 Term Loan was 1.44% before being repaid in August 2013. The weighted-average interest rate on the Fiscal 2012 Term Loan was 1.47% and 1.54% for the fiscal years ended June 30, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
The Fiscal 2012 Revolving Credit Facility is subject to covenants, including financial covenants consisting of a leverage ratio and an interest coverage ratio. At June 30, 2014, the Company is not aware of any instances of any non-compliance with the financial covenants of the Fiscal 2012 Revolving Credit Facility.
In May 2007, the Company completed an offering of $250.0 million in aggregate principal amount of senior notes (the “Fiscal 2007 Senior Notes”). The Fiscal 2007 Senior Notes will mature on June 1, 2017 and bear interest at a rate of 6.125% per annum. Interest on the Fiscal 2007 Senior Notes is payable semi-annually in arrears on June 1 and December 1 of each year. The Fiscal 2007 Senior Notes were issued at a price of 99.1% (effective yield to maturity of 6.251%). The indenture governing the Fiscal 2007 Senior Notes contains certain covenants including covenants restricting the Company’s ability to create or incur liens securing indebtedness for borrowed money and to enter into certain sale-leaseback transactions. At June 30, 2014, the Company is not aware of any instances of non-compliance with the covenants of the indenture governing the Fiscal 2007 Senior Notes. The indenture also contains covenants regarding the purchase of the Fiscal 2007 Senior Notes upon a change of control triggering event. The Fiscal 2007 Senior Notes are senior unsecured obligations of the Company and rank equally with the Company’s other senior indebtedness. The Company may redeem the Fiscal 2007 Senior Notes in whole or in part at any time before their maturity. The Company incurred $1.9 million in debt issuance costs to establish the Fiscal 2007 Senior Notes. These costs have been capitalized and are being amortized to interest expense on a straight-line basis, which approximates the effective interest method, over the ten-year term. At June 30, 2014 and June 30, 2013, the accumulated amortization related to the Fiscal 2007 Senior Notes was $1.3 million and $1.1 million, respectively. During the fiscal year ended June 30, 2009, the Company purchased $125.0 million principal amount of the Fiscal 2007 Senior Notes (including $1.0 million unamortized bond discount) pursuant to a cash tender offer for such notes. The fair value of the fixed-rate Fiscal 2007 Senior Notes at June 30, 2014 and June 30, 2013 was $139.1 million and $138.2 million, respectively, based on quoted market prices and has been classified as a Level 1 financial liability (as defined in Note 6, “Fair Value of Financial Instruments”).
In August 2013, the Company completed an offering of $400.0 million in aggregate principal amount of senior notes (the “Fiscal 2014 Senior Notes”). The Fiscal 2014 Senior Notes will mature on September 1, 2020 and bear interest at a rate of 3.95% per annum. Interest on the Fiscal 2014 Senior Notes is payable semi-annually in arrears on March 1 and September 1 of each year. The Fiscal 2014 Senior Notes were issued at a price of 99.871% (effective yield to maturity of 3.971%). The indenture governing the Fiscal 2014 Senior Notes contains certain covenants including covenants restricting the Company’s ability to create or incur liens securing indebtedness for borrowed money and to enter into certain sale-leaseback transactions. At June 30, 2014, the Company is not aware of any instances of non-compliance with the covenants of the indenture governing the Fiscal 2014 Senior Notes. The indenture also contains covenants regarding the purchase of the Fiscal 2014 Senior Notes upon a change of control triggering event. The Fiscal 2014 Senior Notes are senior unsecured obligations of the Company and rank equally with the Company’s other senior indebtedness. The Company may redeem the Fiscal 2014 Senior Notes in whole or in part at any time before their maturity. The Company incurred $4.3 million in debt issuance costs to establish the Fiscal 2014 Senior Notes. These costs have been capitalized and are being amortized to Other expenses, net on a straight-line basis, which approximates the effective interest method, over the seven-year term. At June 30, 2014, the accumulated amortization related to the Fiscal 2014 Senior Notes was $0.6 million. The fair value of the fixed-rate Fiscal 2014 Senior Notes at June 30, 2014 was $426.6 million based on quoted market prices and has been classified as a Level 1 financial liability (as defined in Note 6, “Fair Value of Financial Instruments”).
44
Table of Contents
Please refer to Note 13, “Borrowings” to our Consolidated Financial Statements under Item 8 of Part II of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for a more detailed discussion.
Based upon current and anticipated levels of operation, management believes that the Company’s cash on hand and cash flows from operations, combined with borrowings available under credit facilities, will be sufficient to enable the Company to meet its current and anticipated cash operating requirements, capital expenditures and working capital needs. Please refer to the discussion of net cash flows provided by financing activities in the following section for more detail regarding the Company’s financing activities.
Cash Flows
Fiscal Year 2014 Compared to Fiscal Year 2013
Net cash flows provided by operating activities were $387.7 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014, an increase of $116.8 million, compared to $270.9 million during the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013. The increase in cash provided by operating activities is primarily due to higher net earnings and changes in working capital resulting from the timing of accounts receivable collections and vendor payments.
Free cash flows were $334.3 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014 compared to $220.0 million in Free cash flows during the year ended June 30, 2013. The increase of $114.3 million was driven by an increase in Net cash flows provided by operating activities of $116.8 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014 compared to the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013, partially offset by increased capital expenditures and software purchases of $2.5 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014 compared to the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013.
Net cash flows used in investing activities were $150.3 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014, an increase of $98.3 million, compared to $52.0 million during the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013. The increase reflects higher spending of $96.9 million on acquisitions during the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014, compared to the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013, as well as higher capital expenditures in the current fiscal year as compared to the prior fiscal year.
Net cash flows used in financing activities for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014 were $158.9 million, a decrease of $114.3 million, compared to $273.2 million of net cash flows used in financing activities for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013. The decreased use of cash reflects an decrease in the purchases of common stock of $108.8 million coupled with an increase of $18.2 million in excess tax benefits from the issuance of stock-based compensation awards in the current fiscal year as compared to the prior fiscal year, slightly offset by a $10.9 million increase in dividends paid in the current fiscal year compared to the prior fiscal year.
Fiscal Year 2013 Compared to Fiscal Year 2012
Net cash flows provided by operating activities were $270.9 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013, a decrease of $19.7 million, compared to $290.6 million during the fiscal year ended June 30, 2012. The decrease in cash provided by operating activities is primarily due to changes in working capital resulting from the timing of accounts receivable collections and vendor payments.
Free cash flows were $220.0 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013 compared to $243.9 million in Free cash flows during the year ended June 30, 2012. The decrease was driven by a decrease in Net cash flows provided by operating activities of $19.7 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013 compared to the fiscal year ended June 30, 2012 and increased capital expenditures and software purchases of $4.2 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013 compared to the fiscal year ended June 30, 2012.
Net cash flows used in investing activities for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013 were $52.0 million, a decrease of $58.5 million, compared to $110.5 million of net cash flows used in investing activities for the fiscal
45
Table of Contents
year ended June 30, 2012. The decrease reflects lower spending of $72.4 million on acquisitions during the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013, compared to the fiscal year ended June 30, 2012, slightly offset by higher capital expenditures in the current fiscal year as compared to the prior fiscal year.
Net cash flows used in financing activities for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013 were $273.2 million, an increase of $184.5 million, compared to $88.7 million of net cash flows used in financing activities for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2012. The increased use of cash reflects an increase in the purchases of common stock of $186.9 million coupled with an increase of $7.7 million in dividends paid in the current fiscal year as compared to the prior fiscal year, slightly offset by an $11.7 million increase in proceeds from the exercise of stock options in the current fiscal year compared to the prior fiscal year.
Income Taxes
The Company, headquartered in the U.S., is routinely examined by the IRS and is also routinely examined by the tax authorities in the U.S. states and foreign countries in which it conducts business. The tax years under audit examination vary by tax jurisdiction. The Company regularly considers the likelihood of assessments in each of the jurisdictions resulting from examinations. To the extent the Company determines it has potential tax assessment in particular tax jurisdictions, the Company has established tax reserves which it believes are adequate in relation to the potential assessments. Once established, reserves are adjusted when there is more information available, when an event occurs necessitating a change to the reserves or the statute of limitations for the relevant taxing authority to examine the tax position has expired. The resolution of tax matters should not have a material effect on the financial condition of the Company or on the Company’s Consolidated Statements of Earnings for a particular future period.
Defined Benefit Pension Plans
The Company sponsors a Supplemental Officer Retirement Plan (the “Broadridge SORP”). The Broadridge SORP is a defined benefit plan pursuant to which the Company will pay supplemental pension benefits to certain key officers upon retirement based upon the officers’ years of service and compensation. The amount charged to expense for the Broadridge SORP was $2.9 million, $3.4 million and $2.4 million during the fiscal years ended June 30, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. The Broadridge SORP is currently unfunded, and the benefit obligation under this plan was $21.0 million, $17.0 million and $15.7 million at June 30, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
The Company also sponsors a Supplemental Executive Retirement Plan (the “Broadridge SERP”). The Broadridge SERP is a defined benefit plan pursuant to which the Company will pay supplemental pension benefits to certain key executives upon retirement based upon the executives’ years of service and compensation. The amount charged to expense for the Broadridge SERP was $0.5 million, $0.5 million and $0.3 million during the fiscal years ended June 30, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. The Broadridge SERP is currently unfunded, and the benefit obligation under this plan was $2.3 million, $1.5 million and $1.3 million at June 30, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
Other Post-retirement Benefit Plan
The Company sponsors an Executive Retiree Health Insurance Plan. It is a post-retirement benefit plan pursuant to which the Company helps defray the health care costs of certain eligible key executive retirees and qualifying dependents, based upon the retirees’ age and years of service, until they reach the age of 65. The amount charged to expense under this plan was $0.2 million, $0.2 million and $0.3 million during the fiscal years ended June 30, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. The plan is currently unfunded, and the benefit obligation under this plan was $3.2 million, $3.0 million and $2.8 million at June 30, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
46
Table of Contents
Contractual Obligations
The following table summarizes our contractual obligations to third parties as of June 30, 2014 and the effect such obligations are expected to have on our liquidity and cash flows in future periods:
| Payments Due by Period | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Total | Less than
1 Year |
1-3 Years | 4-5 Years | After 5 Years |
||||||||||||||||
| ($ in millions) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Long-term debt(1) |
$ | 524.1 | $ | — | $ | 124.6 | $ | — | $ | 399.5 | ||||||||||
| Interest on long-term debt(2) |
119.8 | 23.5 | 46.3 | 31.6 | 18.4 | |||||||||||||||
| Facility and equipment operating leases(3) |
135.3 | 31.9 | 50.3 | 26.5 | 26.6 | |||||||||||||||
| Software licensing(4) |
23.9 | 13.7 | 10.2 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
| Purchase obligations(5) |
492.9 | 70.0 | 131.1 | 120.7 | 171.1 | |||||||||||||||
| Uncertain tax positions(6) |
7.0 | — | 7.0 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total |
$ | 1,303.0 | $ | 139.1 | $ | 369.5 | $ | 178.8 | $ | 615.6 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| (1) | These amounts represent the principal repayments of Long-term debt and are included on our Consolidated Balance Sheets. As of June 30, 2014, we had $524.1 million of outstanding debt consisting of senior notes of $124.6 million principal amount due June 2017 and $399.5 million principal amount senior notes due September 2020. See Note 13, “Borrowings” to our Consolidated Financial Statements under Item 8 of Part II of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for additional information about our Borrowings and related matters. |
| (2) | Includes estimated future interest payments on our long-term debt. Interest on the Senior Notes due 2017 is based on a fixed per annum rate equal to 6.125%. Interest on the Senior Notes due 2020 is based on a fixed per annum rate equal to 3.95%. |
| (3) | Included in these amounts are various facilities and equipment leases. We enter into operating leases in the normal course of business relating to facilities and equipment. The majority of our lease agreements have fixed payment terms based on the passage of time. Certain facility and equipment leases require payment of maintenance and real estate taxes and contain escalation provisions based on future adjustments in price indices. Our future operating lease obligations could change if we exit certain contracts and if we enter into additional operating lease agreements. |
| (4) | These amounts represent various software license agreements. We enter into software licenses in the normal course of business. |
| (5) | Purchase obligations relate to payments to IBM related to the IT Services Agreement entered into in March 2010 that expires in June 2022, the EU IT Services Agreement entered into in March 2014 that expires in October 2023, and purchase and maintenance agreements on our software, equipment and other assets. |
| (6) | Due to the uncertainty related to the timing of the reversal of uncertain tax positions, only the uncertain tax benefit related to certain settlements have been provided in the table above. The Company is unable to make reasonably reliable estimates related to the timing of the remaining unrecognized tax benefits expected to be paid. See Note 16, “Income Taxes” to our Consolidated Financial Statements under Item 8 of Part II of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for further detail. |
The Company entered into a data center outsourcing services agreement with ADP before the Company’s spin-off from ADP in March 2007 (the “ADP Agreement”) under which ADP provided the Company with data center services. The ADP Agreement expired on June 30, 2012. The Company entered into a short-term extension of the ADP Agreement which expired in August 2012. At June 30, 2014, the Company had no further obligation to ADP for data center services. For the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014 the Company did not record expenses related to the ADP Agreement. For the fiscal years ended June 30, 2013 and 2012 the Company recorded expenses of $5.8 million and $111.4 million, respectively, in the Consolidated Statements of Earnings related to the ADP Agreement.
47
Table of Contents
In March 2010, the Company and IBM entered into an IT Services Agreement, under which IBM provides certain aspects of the Company’s information technology infrastructure that were previously provided under the ADP Agreement. Under the IT Services Agreement, IBM provides a broad range of technology services to the Company including supporting its mainframe, midrange, open systems, network and data center operations, as well as providing disaster recovery services. The Company has the option of incorporating additional services into the agreement over time. The migration of the data center processing from ADP to IBM was completed in August 2012. The IT Services Agreement expires on June 30, 2022. The Company has the right to renew the initial term of the IT Services Agreement for up to one additional 12-month term. Commitments remaining under this agreement at June 30, 2014 are $442.7 million through fiscal year 2022, the final year of the contract. For the fiscal years ended June 30, 2014, 2013 and 2012, the Company recorded expenses of $95.7 million, $96.3 million and $24.6 million, respectively, in the Consolidated Statements of Earnings related to this agreement. The Company capitalized $54.7 million related to the build-out of the IBM data center in Other non-current assets, with $5.4 million and $5.9 million amortized into expense in the fiscal years ended June 30, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
In March 2014, the Company and IBM UK entered into the EU IT Services Agreement under which IBM UK provides data center services supporting the Company’s technology outsourcing services for certain clients in Europe and Asia. The EU IT Services Agreement expires in October 2023. The Company has the right to renew the initial term of the EU IT Services Agreement for up to one additional 12-month term or one additional 24-month term. Commitments remaining under this agreement at June 30, 2014 are $50.2 million through fiscal year 2024, the final year of the contract. The Company has begun the build-out of the IBM UK data center associated with the EU IT Services Agreement. For the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014, the Company recorded expenses of $1.5 million in the Consolidated Statements of Earnings and capitalized $1.6 million of costs in Other non-current assets related to this agreement.
Other Commercial Commitments
The Company’s Fiscal 2012 Revolving Credit Facility has an available capacity of $500.0 million. This revolving credit facility had zero outstanding at June 30, 2014.
Certain of the Company’s foreign subsidiaries have unsecured, uncommitted lines of credit with banks. There were no outstanding borrowings under these lines of credit at June 30, 2014.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
It is not the Company’s business practice to enter into off-balance sheet arrangements. However, the Company is exposed to market risk from changes in foreign currency exchange rates that could impact its financial position, results of operations, and cash flows. The Company manages its exposure to these market risks through its regular operating and financing activities and, when deemed appropriate, through the use of derivative financial instruments. The Company uses derivative financial instruments as risk management tools and not for trading purposes. The Company was not a party to any derivative financial instruments at June 30, 2014, 2013 and 2012. In the normal course of business, the Company also enters into contracts in which it makes representations and warranties that relate to the performance of the Company’s products and services. The Company does not expect any material losses related to such representations and warranties, or collateral arrangements.
NEW ACCOUNTING PRONOUNCEMENTS
Please refer to Note 2, “Summary of Significant Accounting Policies—Q. New Accounting Pronouncements” to our Consolidated Financial Statements under Item 8 of Part II of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for a discussion on the impact of the adoption of new accounting pronouncements.
48
Table of Contents
| ITEM 7A. | Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk |
As of June 30, 2014, none of our total $524.1 million in debt outstanding is based on floating interest rates. Our revolving credit facility, which had a balance outstanding of zero as of June 30, 2014, bears interest at LIBOR plus 125 basis points.
Our business process outsourcing and mutual fund processing services are performed by a securities broker-dealer, Broadridge Business Process Outsourcing, LLC (“BBPO”). BBPO is registered with the SEC, is a member of FINRA and is required to participate in the Securities Investor Protection Corporation (“SIPC”). Although BBPO’s FINRA membership agreement allows it to engage in clearing, and the retailing of corporate securities in addition to mutual fund retailing on a wire order basis, BBPO does not clear customer transactions, process any retail business or carry customer accounts. BBPO is subject to regulations concerning many aspects of its business, including trade practices, capital requirements, record retention, money laundering prevention, the protection of customer funds and customer securities, and the supervision of the conduct of directors, officers and employees. A failure to comply with any of these laws, rules or regulations could result in censure, fine, the issuance of cease-and-desist orders, or the suspension or revocation of SEC or FINRA authorization granted to allow the operation of its business or disqualification of its directors, officers or employees. Recently, there has been increased regulatory scrutiny of the securities industry including the outsourcing by firms of their operations or functions. This oversight could result in the future enactment of more restrictive laws or rules with respect to business process outsourcing. In addition, MG Trust Company, LLC (“MG Trust Company”), a subsidiary of Matrix, is a Colorado State non-depository trust company and National Securities Clearing Corporation trust member, whose primary business is to provide cash agent, custodial and directed or non-discretionary trust services to institutional customers. MG Trust Company operates pursuant to the rules and regulations of the Colorado Division of Banking.
49
Table of Contents
| ITEM 8. | Financial Statements and Supplementary Data |
INDEX TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULE
| Consolidated Financial Statements |
||||
| 51 | ||||
| Consolidated Statements of Earnings for the Fiscal Years Ended June 30, 2014, 2013, and 2012 |
53 | |||
| 54 | ||||
| 55 | ||||
| Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the Fiscal Years Ended June 30, 2014, 2013, and 2012 |
56 | |||
| 57 | ||||
| 58 | ||||
| Financial Statement Schedule |
||||
| 86 | ||||
50
Table of Contents
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders of
Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc.
1981 Marcus Avenue
Lake Success, NY 11042
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc. and subsidiaries (the “Company”) as of June 30, 2014 and 2013, and the related consolidated statements of earnings, comprehensive income, stockholders’ equity, and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended June 30, 2014. Our audits also included the financial statement schedule listed in the Index at Item 15. We also have audited the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of June 30, 2014, based on criteria established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework (1992) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. The Company’s management is responsible for these financial statements and financial statement schedule, for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting, and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements and financial statement schedule and an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement and whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audits of the financial statements included examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, and evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audits also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinions.
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed by, or under the supervision of, the company’s principal executive and principal financial officers, or persons performing similar functions, and effected by the company’s board of directors, management, and other personnel to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of the inherent limitations of internal control over financial reporting, including the possibility of collusion or improper management override of controls, material misstatements due to error or fraud may not be prevented or detected on a timely basis. Also, projections of any evaluation of the effectiveness of the internal control over financial reporting to future periods are subject to the risk that the controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc. and subsidiaries as of June 30, 2014 and 2013, and
51
Table of Contents
the results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended June 30, 2014, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. Also, in our opinion, such financial statement schedule, when considered in relation to the basic consolidated financial statements taken as a whole, present fairly, in all material respects, the information set forth therein. Also, in our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of June 30, 2014, based on the criteria established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework (1992) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission.
/s/ DELOITTE & TOUCHE LLP
New York, New York
August 7, 2014
52
Table of Contents
Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Earnings
(In millions, except per share amounts)
| Years ended June 30, | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| Revenues |
$ | 2,558.0 | $ | 2,430.8 | $ | 2,303.5 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Cost of revenues |
1,761.4 | 1,767.8 | 1,715.1 | |||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative expenses |
376.0 | 323.6 | 299.9 | |||||||||
| Impairment and other charges, net |
— | — | 74.2 | |||||||||
| Other expenses, net |
25.1 | 16.2 | 13.4 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total expenses |
2,162.5 | 2,107.6 | 2,102.6 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Earnings from continuing operations before income taxes |
395.5 | 323.2 | 200.9 | |||||||||
| Provision for income taxes |
132.5 | 111.1 | 75.9 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net earnings from continuing operations |
263.0 | 212.1 | 125.0 | |||||||||
| Loss from discontinued operations, net of tax benefit |
— | — | (1.4 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net earnings |
$ | 263.0 | $ | 212.1 | $ | 123.6 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Basic earnings per share: |
||||||||||||
| Basic earnings per share from continuing operations |
$ | 2.20 | $ | 1.74 | $ | 1.01 | ||||||
| Basic loss per share from discontinued operations |
— | — | (0.01 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Basic earnings per share |
$ | 2.20 | $ | 1.74 | $ | 1.00 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Diluted earnings per share: |
||||||||||||
| Diluted earnings per share from continuing operations |
$ | 2.12 | $ | 1.69 | $ | 0.98 | ||||||
| Diluted loss per share from discontinued operations |
— | — | (0.01 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Diluted earnings per share |
$ | 2.12 | $ | 1.69 | $ | 0.97 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Weighted-average shares outstanding: |
||||||||||||
| Basic |
119.6 | 121.9 | 124.1 | |||||||||
| Diluted |
124.1 | 125.4 | 127.5 | |||||||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
53
Table of Contents
Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income
(In millions)
| Years ended June 30, | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| Net earnings |
$ | 263.0 | $ | 212.1 | $ | 123.6 | ||||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss), net: |
||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation adjustments |
6.0 | (1.4 | ) | (13.8 | ) | |||||||
| Net unrealized gains (losses) on available-for-sale securities, net of taxes of ($0.5), ($0.6) and $2.6 for the years ended June 30, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively |
0.8 | 0.8 | (4.5 | ) | ||||||||
| Reclassification adjustment for other-than-temporary impairment included in net income, net of taxes of ($4.0) for the year ended June 30, 2012 |
— | — | 6.8 | |||||||||
| Pension and post-retirement liability adjustment, net of taxes of $0.5, ($0.9) and $0.8 for the years ended June 30, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively |
(0.7 | ) | 1.3 | (1.1 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total other comprehensive income (loss), net |
6.1 | 0.7 | (12.6 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Comprehensive income |
$ | 269.1 | $ | 212.8 | $ | 111.0 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
54
Table of Contents
Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc.
(In millions, except per share amounts)
| June 30, 2014 |
June 30, 2013 |
|||||||
| Assets |
||||||||
| Current assets: |
||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 347.6 | $ | 266.0 | ||||
| Accounts receivable, net of allowance for doubtful accounts of $3.3 and $3.7, respectively |
424.8 | 442.4 | ||||||
| Other current assets |
108.2 | 98.6 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total current assets |
880.6 | 807.0 | ||||||
| Property, plant and equipment, net |
88.3 | 80.9 | ||||||
| Goodwill |
856.1 | 778.4 | ||||||
| Intangible assets, net |
130.0 | 120.6 | ||||||
| Other non-current assets |
237.1 | 231.3 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total assets |
$ | 2,192.1 | $ | 2,018.2 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Liabilities and Stockholders’ Equity |
||||||||
| Current liabilities: |
||||||||
| Accounts payable |
$ | 116.3 | $ | 143.1 | ||||
| Accrued expenses and other current liabilities |
306.6 | 277.2 | ||||||
| Deferred revenues |
61.5 | 49.2 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total current liabilities |
484.4 | 469.5 | ||||||
| Long-term debt |
524.1 | 524.5 | ||||||
| Deferred taxes |
62.4 | 71.2 | ||||||
| Deferred revenues |
59.0 | 40.2 | ||||||
| Other non-current liabilities |
100.5 | 96.8 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total liabilities |
1,230.4 | 1,202.2 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Commitments and contingencies (Note 17) |
||||||||
| Stockholders’ equity: |
||||||||
| Preferred stock: Authorized, 25.0 shares; issued and outstanding, none |
— | — | ||||||
| Common stock, $0.01 par value: Authorized, 650.0 shares; issued, 154.5 and 154.5 shares, respectively; outstanding, 119.5 and 119.0 shares, respectively |
1.6 | 1.6 | ||||||
| Additional paid-in capital |
810.7 | 783.0 | ||||||
| Retained earnings |
973.9 | 811.3 | ||||||
| Treasury stock, at cost: 35.0 and 35.5 shares, respectively |
(834.8 | ) | (784.1 | ) | ||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive income |
10.3 | 4.2 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total stockholders’ equity |
961.7 | 816.0 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity |
$ | 2,192.1 | $ | 2,018.2 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
55
Table of Contents
Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
(In millions)
| Years ended June 30, | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| Cash Flows From Operating Activities |
||||||||||||
| Net earnings |
$ | 263.0 | $ | 212.1 | $ | 123.6 | ||||||
| Adjustments to reconcile Net earnings to Net cash flows provided by operating activities: |
||||||||||||
| Loss from discontinued operations, net of tax |
— | — | 1.4 | |||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
46.8 | 47.6 | 51.0 | |||||||||
| Amortization of acquired intangibles |
22.6 | 21.8 | 22.2 | |||||||||
| Amortization of other assets |
28.0 | 24.0 | 18.8 | |||||||||
| Deferred income taxes |
(11.6 | ) | 14.1 | (8.4 | ) | |||||||
| Stock-based compensation expense |
34.6 | 27.1 | 28.3 | |||||||||
| Excess tax benefits from the issuance of stock-based compensation awards |
(22.8 | ) | (4.6 | ) | (3.9 | ) | ||||||
| Impairment of available-for-sale securities and other non-current assets |
— | — | 69.1 | |||||||||
| Other |
2.7 | 11.4 | 3.0 | |||||||||
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities: |
||||||||||||
| Current assets and liabilities: |
||||||||||||
| (Increase) decrease in Accounts receivable, net |
19.1 | (73.2 | ) | 34.7 | ||||||||
| (Increase) decrease in Other current assets |
(2.3 | ) | (15.6 | ) | 23.3 | |||||||
| Increase (decrease) in Accounts payable |
(26.8 | ) | 41.3 | (12.4 | ) | |||||||
| Increase in accrued expenses and other current liabilities |
36.6 | 15.8 | 35.2 | |||||||||
| Increase (decrease) in Deferred revenues |
5.8 | 1.4 | (8.9 | ) | ||||||||
| Non-current assets and liabilities: |
||||||||||||
| Increase in Other non-current assets |
(38.4 | ) | (61.2 | ) | (106.5 | ) | ||||||
| Increase in Other non-current liabilities |
30.4 | 8.9 | 20.1 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net cash flows provided by operating activities of continuing operations |
387.7 | 270.9 | 290.6 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Cash Flows From Investing Activities |
||||||||||||
| Capital expenditures |
(40.3 | ) | (38.2 | ) | (33.8 | ) | ||||||
| Purchases of intangibles |
(13.1 | ) | (12.7 | ) | (12.9 | ) | ||||||
| Sale of available-for-sale securities |
— | — | 2.1 | |||||||||
| Acquisitions, net of cash acquired |
(96.9 | ) | — | (72.4 | ) | |||||||
| Other investing activities |
— | (1.1 | ) | 6.5 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net cash flows used in investing activities of continuing operations |
(150.3 | ) | (52.0 | ) | (110.5 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Cash Flows From Financing Activities |
||||||||||||
| Proceeds from issuance of Long-term debt |
399.5 | — | 490.0 | |||||||||
| Payment on Short-term borrowings |
— | — | (400.0 | ) | ||||||||
| Payment on Long-term debt |
(400.0 | ) | — | (90.0 | ) | |||||||
| Dividends paid |
(96.7 | ) | (85.8 | ) | (78.1 | ) | ||||||
| Proceeds from exercise of stock options |
49.5 | 46.3 | 43.6 | |||||||||
| Purchases of Treasury stock |
(129.7 | ) | (238.5 | ) | (51.6 | ) | ||||||
| Cost related to issuance of Long-term debt |
(4.3 | ) | — | (2.9 | ) | |||||||
| Excess tax benefit from the issuance of stock-based compensation awards |
22.8 | 4.6 | 3.9 | |||||||||
| Other financing transactions |
— | 0.2 | (3.6 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net cash flows used in financing activities of continuing operations |
(158.9 | ) | (273.2 | ) | (88.7 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Cash flows from discontinued operations: |
||||||||||||
| Net cash flows used in operating activities |
— | — | (6.4 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net cash flows used in discontinued operations |
— | — | (6.4 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Effect of exchange rate changes on Cash and cash equivalents |
3.1 | (0.2 | ) | (6.0 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net change in Cash and cash equivalents |
81.6 | (54.5 | ) | 79.0 | ||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents, beginning of fiscal year |
266.0 | 320.5 | 241.5 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents, end of fiscal year |
$ | 347.6 | $ | 266.0 | $ | 320.5 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Supplemental disclosure of cash flow information: |
||||||||||||
| Cash payments made for interest |
$ | 17.1 | $ | 13.5 | $ | 13.8 | ||||||
| Cash payments made for income taxes |
$ | 150.3 | $ | 118.6 | $ | 71.1 | ||||||
| Non-cash investing and financing activities: |
||||||||||||
| Property, plant and equipment included in accrued expenses |
$ | 2.9 | $ | 1.9 | $ | 1.9 | ||||||
| Dividends payable |
$ | 3.7 | $ | 1.1 | $ | 1.6 | ||||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
56
Table of Contents
Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Stockholders’ Equity
(In millions, except per share amounts)
|
Common Stock |
Additional Paid-In Capital |
Retained Earnings |
Treasury Stock |
Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) |
Total Stockholders’ Equity |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares | Amount | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balances, July 1, 2011 |
149.6 | $ | 1.5 | $ | 667.4 | $ | 642.2 | $ | (529.9 | ) | $ | 16.1 | $ | 797.3 | ||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive income (loss) |
— | — | — | 123.6 | — | (12.6 | ) | 111.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock plans and related tax benefits |
3.3 | — | 43.7 | — | — | — | 43.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation |
— | — | 28.3 | — | — | — | 28.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Treasury stock acquired (2.2 shares) |
— | — | — | — | (50.1 | ) | — | (50.1 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Common stock dividends ($0.64 per share) |
— | — | — | (79.7 | ) | — | — | (79.7 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Balances, June 30, 2012 |
152.9 | 1.5 | 739.4 | 686.1 | (580.0 | ) | 3.5 | 850.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive income (loss) |
— | — | — | 212.1 | — | 0.7 | 212.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock plans and related tax benefits |
1.6 | 0.1 | 50.9 | — | — | — | 51.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation |
— | — | 27.1 | — | — | — | 27.1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Treasury stock acquired (9.7 shares) |
— | — | — | — | (238.5 | ) | — | (238.5 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Treasury stock reissued (2.3 shares) |
— | — | (34.4 | ) | — | 34.4 | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Common stock dividends ($0.72 per share) |
— | — | — | (86.9 | ) | — | — | (86.9 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Balances, June 30, 2013 |
154.5 | 1.6 | 783.0 | 811.3 | (784.1 | ) | 4.2 | 816.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive income (loss) |
— | — | — | 263.0 | — | 6.1 | 269.1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock plans and related tax benefits |
— | — | 72.3 | — | — | — | 72.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation |
— | — | 34.4 | — | — | — | 34.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Treasury stock acquired (3.4 shares) |
— | — | — | — | (129.7 | ) | — | (129.7 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Treasury stock reissued (3.9 shares) |
— | — | (79.0 | ) | — | 79.0 | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Common stock dividends ($0.84 per share) |
— | — | — | (100.4 | ) | — | — | (100.4 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Balances, June 30, 2014 |
154.5 | $ | 1.6 | $ | 810.7 | $ | 973.9 | $ | (834.8 | ) | $ | 10.3 | $ | 961.7 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
57
Table of Contents
Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
NOTE 1. BASIS OF PRESENTATION
A. Description of Business. Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc. (“Broadridge” or the “Company”), a Delaware corporation, is a leading global provider of investor communication solutions and securities processing and business process outsourcing services to the financial services industry. The Company classifies its continuing operations into the following two reportable segments:
| • | Investor Communication Solutions—The Bank/Broker-Dealer Investor Communication Solutions, Corporate Issuer Solutions, and Mutual Fund and Retirement Solutions businesses operate within this segment. A large portion of Broadridge’s Investor Communication Solutions business involves the processing and distribution of proxy materials to investors in equity securities and mutual funds, as well as the facilitation of related vote processing. ProxyEdge®, its innovative electronic proxy delivery and voting solution for institutional investors and financial advisors, helps ensure the participation of the largest stockholders of many companies. Broadridge also provides the distribution of regulatory reports and corporate action/reorganization event information, as well as tax reporting solutions that help its clients meet their regulatory compliance needs. In addition, Broadridge provides financial information distribution and transaction reporting services to both financial institutions and securities issuers. These services include the processing and distribution of account statements and trade confirmations, traditional and personalized document fulfillment and content management services, marketing communications, and imaging, archival and workflow solutions that enable and enhance its clients’ communications with investors. All of these communications are delivered through paper or electronic channels. In addition, Broadridge provides corporate issuers with registered proxy services as well as registrar, stock transfer and record-keeping services to corporate issuers. |
In July 2013, Broadridge acquired Bonaire Software Solutions, LLC (“Bonaire”), a leading provider of fee calculation, billing, and revenue and expense management solutions for asset managers including institutional asset managers, wealth managers, mutual funds, bank trusts, hedge funds and capital markets firms.
In February 2014, Broadridge acquired Emerald Connect, LLC (“Emerald”), a leading provider of websites and related communications solutions for financial advisors.
| • | Securities Processing Solutions—Broadridge offers a suite of advanced computerized real-time transaction processing services that automate the securities transaction lifecycle, from desktop productivity tools, data aggregation, performance reporting, and portfolio management to order capture and execution, trade confirmation, settlement, and accounting. Broadridge’s services help financial institutions efficiently and cost-effectively consolidate their books and records, gather and service assets under management, focus on their core businesses, and manage risk. With multi-currency capabilities, its Global Processing Solution supports real-time global trading of equity, option, mutual fund and fixed income securities in established and emerging markets. In addition, its business process outsourcing services allow broker-dealers to outsource certain administrative functions relating to clearing and settlement, from order entry to trade matching and settlement, while maintaining their ability to finance and capitalize their businesses. |
In September 2011, Broadridge acquired Paladyne Systems, Inc. (“Paladyne”), now known as Broadridge Investment Management, Reference Data and Risk Solutions, a provider of buy-side technology solutions for the global investment management industry.
B. Basis of Presentation. The Consolidated Financial Statements have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“U.S.”) (“GAAP”). These financial statements present the consolidated position of the Company. These financial statements include the entities in
58
Table of Contents
which the Company directly or indirectly has a controlling financial interest and various entities in which the Company has investments recorded under both the cost and equity methods of accounting. Intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated.
NOTE 2. SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
A. Use of Estimates. The preparation of these financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the amounts reported in the Consolidated Financial Statements and accompanying notes thereto. The most significant assumptions are employed in estimates used in determining the fair value and potential impairment of goodwill, useful lives and potential impairment of intangible assets, recoverability of deferred tax assets and determination of uncertain tax positions. Actual results may differ from those estimates.
B. Revenue Recognition. The Company’s revenues are primarily generated from fees for providing services. Revenues are recognized for the two reportable segments as follows:
| • | Investor Communication Solutions—Revenues are generated from processing and distributing investor communications as well as vote processing and tabulation. The Company typically enters into agreements with clients to provide services on a fee for service basis. Fees received from the rendering of services are recognized as revenue in the period in which the services have been provided and when collectability is reasonably assured. |
| • | Securities Processing Solutions—Revenues are generated from fees for transaction processing. Client service agreements often include up-front consideration as well as a recurring fee for transaction processing. In accordance with Accounting Standards Codification Topic (“ASC”) No. 605 “Revenue Recognition” up-front implementation fees are deferred and recognized on a straight-line basis over the longer of the respective service term of the contract or the expected customer relationship period which commences after client acceptance when the processing term begins. Fees received from processing and outsourcing services are recognized as revenue in the period in which the services have been rendered and when collectability is reasonably assured. |
C. Cash and Cash Equivalents. Investment securities with an original maturity of 90 days or less are considered cash equivalents. The fair value of the Company’s Cash and cash equivalents approximates carrying value due to their short term nature.
D. Financial Instruments. Substantially all of the financial instruments of the Company other than Long-term debt are carried at fair values, or at carrying amounts that approximate fair values because of the short maturity of the instruments. The carrying value of the Company’s long-term fixed-rate senior notes represent the face value of the long-term fixed-rate senior notes net of the unamortized discount. The fair value of the Company’s long-term fixed-rate senior notes is based on quoted market prices. See Note 13, “Borrowings,” for a further discussion of the Company’s long-term fixed-rate senior notes.
E. Property, Plant and Equipment. Property, plant and equipment is stated at cost and depreciated over the estimated useful lives of the assets using the straight-line method. Leasehold improvements are amortized over the shorter of the term of the lease or the estimated useful lives of the improvements. The estimated useful lives of assets are as follows:
| Equipment |
3 to 5 years | |||
| Buildings |
10 years | |||
| Furniture and fixtures |
3 to 7 years |
F. Available-For-Sale Equity Securities. Available-for-sale equity securities are non-derivatives that are reflected in Other non-current assets in the Consolidated Balance Sheets, unless management intends to dispose of the investment within twelve months of the end of the reporting period, in which case they are reflected in
59
Table of Contents
Other current assets in the Consolidated Balance Sheets. These investments are in entities over which the Company does not have control, joint control, or significant influence. Investments are initially recognized and carried at fair value. Unrealized holding gains and losses, net of tax, on available-for-sale securities are excluded from earnings and are included in Other comprehensive income (loss), net. Realized gains and losses on available-for-sale securities are included in Other expenses, net and, when applicable, are reported as a reclassification adjustment, net of tax, as a component of Other comprehensive income (loss), net.
Declines in the fair value of available-for-sale securities below their cost that are other-than-temporary result in write-downs of the individual securities to their fair value. The related write-downs are included in earnings as realized losses. In estimating other-than-temporary impairment losses, management considers (1) the length of time and the extent to which the fair value has been less than cost, (2) the financial condition and near-term prospects of the issuer, and (3) the intent and ability of the Company to retain its investment in the issuer for a period of time sufficient to allow for any anticipated recovery in fair value.
G. Inventories. Inventories are stated at the lower of cost (determined on a first-in, first-out basis) or market. Inventory balances of $6.7 million and $8.4 million, consisting of forms and envelopes used in the mailing of proxy materials to our customers, are reflected in Other current assets in the Consolidated Balance Sheets at June 30, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
H. Deferred Client Conversion and Start-Up Costs. Direct costs that are incurred to set up or convert a client’s systems to function with the Company’s technology are generally deferred and recognized on a straight-line basis which commences after client acceptance when the processing term begins. To the extent deferred costs exceed related implementation fee revenues, such excess costs are amortized over the service term of the contract. Deferred costs up to the amount of the related implementation fees are recognized and capitalized over the longer of the respective service term of the contract or expected customer relationship period. These deferred costs are reflected in Other non-current assets in the Consolidated Balance Sheets at June 30, 2014 and 2013, respectively. See Note 11, “Other non-current assets”.
I. Deferred Data Center Costs. Data center costs relate to conversion costs associated with our principal data center systems and applications. Costs directly related to the activities necessary to make the data center usable for its intended purpose are deferred and amortized over the life of the contract on a straight-line basis commencing on the date the data center has achieved full functionality. These deferred costs are reflected in Other non-current assets in the Consolidated Balance Sheets at June 30, 2014 and 2013, respectively. See Note 11, “Other non-current assets”.
J. Goodwill. The Company accounts for its goodwill and intangible assets in accordance with ASC No. 350, “Intangibles—Goodwill and Other” (“ASC No. 350”), which states that goodwill and intangible assets with indefinite useful lives should not be amortized, but instead tested for impairment at the reporting unit level at least annually or more frequently if circumstances indicate possible impairment. The Company tests for goodwill impairment annually in the fourth quarter of the fiscal year, using the March 31 financial statement balances. If impairment exists, a write-down to fair value (measured by discounting estimated future cash flows) is recorded.
The Company performs a sensitivity analysis under Step 1 of the goodwill impairment test as prescribed in ASC No. 350, assuming hypothetical reductions in the fair values of the reporting units. A 10% change in our estimates of projected future operating cash flows, discount rates, or terminal value growth rates used in our calculations of the fair values of the reporting units would not result in an impairment of our goodwill.
K. Impairment of Long-Lived Assets. In accordance with ASC No. 360, “Property, Plant and Equipment—Impairment or Disposal of Long-Lived Assets” (“ASC No. 360”), long-lived assets are reviewed for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable. Recoverability of assets to be held and used is measured by a comparison of the carrying amount of an asset to the estimated undiscounted future cash flows expected to be generated by the asset. If the carrying amount of an asset exceeds its expected estimated future cash flows, an impairment charge is recognized for the
60
Table of Contents
amount by which the carrying amount of the asset exceeds the fair value of the asset. Intangible assets with finite lives are amortized primarily on a straight-line basis over their estimated useful lives and are reviewed for impairment in accordance with ASC No. 360.
L. Foreign Currency Translation and Transactions. The assets and liabilities of the Company’s foreign subsidiaries are translated into U.S. dollars based on exchange rates in effect at the end of each period. Revenues and expenses are translated at average exchange rates during the periods. Currency transaction gains or losses are included in Other expenses, net. Gains or losses from balance sheet translation are included in Accumulated other comprehensive income.
M. Distribution Cost of Revenues. Distribution cost of revenues consists primarily of postage related expenses incurred in connection with our Investor Communication Solutions segment. These costs are reflected in Cost of Revenues in the Consolidated Statement of Earnings.
N. Stock-Based Compensation. The Company accounts for stock-based compensation in accordance with ASC No. 718, “Compensation—Stock Compensation,” by recognizing the measurement of stock-based compensation expense in Net earnings based on the fair value of the award on the date of grant. For stock options issued, the fair value of each stock option was estimated on the date of grant using a binomial option pricing model. The binomial model considers a range of assumptions related to volatility, risk-free interest rate, and employee exercise behavior. Expected volatilities utilized in the binomial model are based on a combination of implied market volatilities, historical volatility of the Company’s stock price, and other factors. Similarly, the dividend yield is based on historical experience and expected future changes. The risk-free rate is derived from the U.S. Treasury yield curve in effect at the time of grant. The binomial model also incorporates exercise and forfeiture assumptions based on an analysis of historical data. The expected life of the stock option grants is derived from the output of the binomial model and represents the period of time that options granted are expected to be outstanding.
O. Internal Use Software. Expenditures for major software purchases and software developed or obtained for internal use are capitalized and amortized over a three- to five-year period on a straight-line basis. For software developed or obtained for internal use, the Company capitalizes these costs in accordance with the provisions of ASC No. 350-40, “Internal Use Software.” The Company’s policy provides for the capitalization of external direct costs of materials and services associated with developing or obtaining internal use computer software. In addition, the Company also capitalizes payroll and payroll-related costs for employees who are directly associated with internal use computer software projects. The amount of capitalizable payroll costs with respect to these employees is limited to direct time spent on such projects. Costs associated with preliminary project stage activities, training, maintenance, and all other post-implementation stage activities are expensed as incurred. The Company also expenses internal costs related to minor upgrades and enhancements, as it is impractical to separate these costs from normal maintenance activities.
P. Income Taxes. The Company accounts for income taxes under the liability method, which requires that deferred tax assets and liabilities be determined based on the expected future income tax consequences of events that have been recognized in the Consolidated Financial Statements.
Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized based on temporary differences between the consolidated financial statement carrying amounts and tax bases of assets and liabilities using enacted tax rates in effect in the years in which the temporary differences are expected to reverse.
Q. Advertising Costs. Advertising costs are expensed at the time the advertising takes place. Selling, general and administrative expenses include advertising costs of $2.4 million, $2.4 million and $2.0 million for the fiscal years ended June 30, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
R. New Accounting Pronouncements. In May 2014, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) No. 2014-09, “Revenue from Contracts with Customers” (“ASU
61
Table of Contents
No. 2014-09”), to supersede nearly all existing revenue recognition guidance under U.S. GAAP. The core principle of ASU No. 2014-09 is to recognize revenues when promised goods or services are transferred to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration that is expected to be received for those goods or services. ASU No. 2014-09 defines a five step process to achieve this core principle and, in doing so, it is possible more judgment and estimates may be required within the revenue recognition process than required under existing U.S. GAAP including identifying performance obligations in the contract, estimating the amount of variable consideration to include in the transaction price and allocating the transaction price to each separate performance obligation. ASU No. 2014- 09 is effective for the Company in our first quarter of fiscal 2018 using either of two methods: (i) retrospective to each prior reporting period presented with the option to elect certain practical expedients as defined within ASU No. 2014-09; or (ii) retrospective with the cumulative effect of initially applying ASU No. 2014-09 recognized at the date of initial application and providing certain additional disclosures as defined per ASU No. 2014-09. The Company is currently evaluating the impact of the pending adoption of ASU No. 2014-09 on its consolidated financial statements.
In April 2014, the FASB issued ASU No. 2014-08, “Reporting Discontinued Operations and Disclosures of Disposals of Components of an Entity” (“ASU No. 2014-08”), to change the criteria for determining which disposals can be presented as discontinued operations and enhanced the related disclosure requirements. ASU No. 2014-08 is effective for the Company on a prospective basis in our first quarter of fiscal 2016 with early adoption permitted for disposals (or classifications as held for sale) that have not been reported in financial statements previously issued. The Company is currently evaluating the impact of the pending adoption of ASU No. 2014-08 on its consolidated financial statements.
In July 2013, the FASB issued ASU No. 2013-11, “Presentation of an Unrecognized Tax Benefit When a Net Operating Loss Carryforward, a Similar Tax Loss, or a Tax Credit Carryforward Exists” (“ASU No. 2013-11”) to provide guidance on the presentation of unrecognized tax benefits. ASU No. 2013-11 requires an entity to present an unrecognized tax benefit, or a portion of an unrecognized tax benefit, as a reduction to a deferred tax asset for a net operating loss carryforward, a similar tax loss, or a tax credit carryforward, except as follows: to the extent a net operating loss carryforward, a similar tax loss, or a tax credit carryforward is not available at the reporting date under the tax law of the applicable jurisdiction to settle any additional income taxes that would result from the disallowance of a tax position or the tax law of the applicable jurisdiction does not require the entity to use, and the entity does not intend to use, the deferred tax asset for such purpose, the unrecognized tax benefit should be presented in the financial statements as a liability and should not be combined with deferred tax assets. ASU No. 2013-11 is effective for the Company in our first quarter of fiscal 2015 with earlier adoption permitted. ASU No. 2013-11 should be applied prospectively with retroactive application permitted. The adoption of ASU No. 2013-11 will not impact the Company’s consolidated results of operations, cash flows or financial condition as it only requires a change in the Company’s presentation of unrecognized tax benefits.
In February 2013, the FASB issued ASU No. 2013-02, “Reporting of Amounts Reclassified Out of Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income” (“ASU No. 2013-02”). ASU No. 2013-02 requires entities to provide information about the amounts reclassified out of accumulated other comprehensive income by component. In addition, entities are required to present, either on the face of the statement where net income is presented or in the notes, significant amounts reclassified out of accumulated other comprehensive income by the respective line items of net income but only if the amount reclassified is required to be reclassified to net income in its entirety in the same reporting period. For amounts not required to be reclassified in their entirety to net income, entities are required to cross-reference to other disclosures under GAAP that provide additional detail about those amounts. ASU No. 2013-02 became effective for the Company in the first quarter of fiscal 2014. The adoption of ASU No. 2013-02 did not have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated results of operations, cash flows or financial condition. The disclosures required by this guidance are presented in Note 18, “Changes in Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income by Component.”
In July 2012, the FASB issued ASU No. 2012-02, “Intangibles—Goodwill and Other: Testing indefinite-lived intangible assets for impairment” (“ASU No. 2012-02”). The revised standard is intended to reduce the cost
62
Table of Contents
and complexity of testing indefinite-lived intangible assets other than goodwill for impairment by providing entities with an option to perform a qualitative assessment to determine whether further impairment testing is necessary. The approach is similar to the guidance in ASU No. 2011-08 for goodwill impairment testing. ASU No. 2012-02 became effective for the Company in the first quarter of fiscal 2014. The adoption of ASU No. 2012-02 did not have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated results of operations, cash flows or financial condition.
In September 2011, the FASB issued ASU No. 2011-08, “Intangibles—Goodwill and Other (ASC Topic 350): Testing Goodwill for Impairment” (“ASU No. 2011-08”), which amends guidance for goodwill impairment testing. The amendment allows for entities to first assess qualitative factors in determining whether or not the fair value of a reporting unit exceeds its carrying value. If an entity concludes from this qualitative assessment that it is more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit exceeds its carrying value, then performing a two-step impairment test is unnecessary. ASU No. 2011-08 became effective for the Company in the first quarter of fiscal 2013. The adoption of ASU 2011-08 did not have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated results of operations, cash flows or financial condition.
In June 2011, the FASB issued ASU No. 2011-05, “Comprehensive Income (ASC Topic 220): Presentation of Comprehensive Income” (“ASU No. 2011-05”), which amends current comprehensive income guidance. This accounting update eliminates the option to present the components of other comprehensive income as part of the statement of stockholders’ equity. Instead, the Company must report comprehensive income in either a single continuous statement of comprehensive income which contains two sections, net income and other comprehensive income, or in two separate but consecutive statements. ASU No. 2011-05 became effective for the Company in the first quarter of fiscal 2013. The adoption of ASU 2011-05 did not have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated results of operations, cash flows or financial condition as it only required a change in the format of the Company’s presentation of Comprehensive Income.
S. Subsequent Events. In preparing the accompanying Consolidated Financial Statements, in accordance with ASC No. 855, “Subsequent Events,” the Company has reviewed events that have occurred after June 30, 2014, through the date of issuance of the Consolidated Financial Statements. During this period, the Company did not have any material subsequent events.
NOTE 3. EARNINGS PER SHARE
Basic earnings per share (“EPS”) is calculated by dividing the Company’s Net earnings by the basic Weighted-average shares outstanding for the periods presented.
Diluted EPS reflects the potential dilution that could occur if outstanding stock options at the presented date are exercised and shares of restricted stock units have vested.
As of June 30, 2014, 2013 and 2012, the computation of diluted EPS did not include 2.3 million, 2.8 million and 2.6 million options to purchase Broadridge common stock, respectively, as the effect of their inclusion would have been anti-dilutive.
The following table sets forth the denominators of the basic and diluted EPS computations:
| Years ended June 30, | ||||||||||||
| 2014 |
2013 |
2012 | ||||||||||
| (in millions) | ||||||||||||
| Weighted-average shares outstanding: |
||||||||||||
| Basic |
119.6 | 121.9 | 124.1 | |||||||||
| Common stock equivalents |
4.5 | 3.5 | 3.4 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Diluted |
124.1 | 125.4 | 127.5 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
63
Table of Contents
The following table sets forth the computation of basic EPS utilizing Net earnings from continuing operations and Net earnings for the fiscal year and the Company’s basic Weighted-average shares outstanding:
| Years ended June 30, | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| (in millions, except per share amounts) |
||||||||||||
| Net earnings from continuing operations |
$ | 263.0 | $ | 212.1 | $ | 125.0 | ||||||
| Net earnings |
$ | 263.0 | $ | 212.1 | $ | 123.6 | ||||||
| Basic Weighted-average shares outstanding |
119.6 | 121.9 | 124.1 | |||||||||
| Basic EPS from continuing operations |
$ | 2.20 | $ | 1.74 | $ | 1.01 | ||||||
| Basic EPS |
$ | 2.20 | $ | 1.74 | $ | 1.00 | ||||||
The following table sets forth the computation of diluted EPS utilizing Net earnings from continuing operations and Net earnings for the fiscal year and the Company’s diluted Weighted-average shares outstanding:
| Years ended June 30, | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| (in millions, except per share amounts) |
||||||||||||
| Net earnings from continuing operations |
$ | 263.0 | $ | 212.1 | $ | 125.0 | ||||||
| Net earnings |
$ | 263.0 | $ | 212.1 | $ | 123.6 | ||||||
| Diluted Weighted-average shares outstanding |
124.1 | 125.4 | 127.5 | |||||||||
| Diluted EPS from continuing operations |
$ | 2.12 | $ | 1.69 | $ | 0.98 | ||||||
| Diluted EPS |
$ | 2.12 | $ | 1.69 | $ | 0.97 | ||||||
NOTE 4. OTHER EXPENSES, NET
Other expenses, net consisted of the following:
| Years ended June 30, | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| ($ in millions) | ||||||||||||
| Interest expense on borrowings |
$ | 23.7 | $ | 13.7 | $ | 13.3 | ||||||
| Interest income |
(1.8 | ) | (1.5 | ) | (1.8 | ) | ||||||
| Foreign currency exchange loss |
0.3 | 0.8 | 0.3 | |||||||||
| Other, net |
2.9 | 3.2 | 1.6 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Other expenses, net |
$ | 25.1 | $ | 16.2 | $ | 13.4 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
NOTE 5. ACQUISITIONS
Assets acquired and liabilities assumed in business combinations were recorded on the Company’s Consolidated Balance Sheets as of the respective acquisition dates based upon their estimated fair values at such dates. The results of operations of businesses acquired by the Company were included in the Company’s Consolidated Statements of Earnings since their respective dates of acquisition. The excess of the purchase price over the estimated fair values of the underlying assets acquired and liabilities assumed was allocated to Goodwill.
During the first quarter of the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014, the fair value of contingent consideration associated with one of the Company’s acquisitions was reduced by approximately $3.3 million.
64
Table of Contents
In addition, during the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014, the Company acquired two businesses in the Investor Communication Solutions segment:
Bonaire Software Solutions, LLC
In July 2013, the Company acquired Bonaire, a leading provider of fee calculation, billing, and revenue and expense management solutions for asset managers including institutional asset managers, wealth managers, mutual funds, bank trusts, hedge funds and capital markets firms. The purchase price was $37.6 million, net of cash acquired. Net liabilities assumed in the transaction were $1.5 million. In addition, the Company recorded a $0.5 million liability for the fair value of potential additional cash payments, which are payable over the next three years contingent upon the achievement by the acquired business of certain revenue and earnings targets. During the fourth quarter, the fair value of the contingent consideration was increased by $0.8 million. As a result, as of June 30, 2014, the Company has recorded a $1.3 million liability for the contingent consideration. This acquisition resulted in $29.0 million of Goodwill. Intangible assets acquired, which totaled $10.1 million, consist primarily of acquired software technology and customer relationships, which are being amortized over a seven-year life and ten-year life, respectively. The results of Bonaire’s operations were included in the Company’s Consolidated Financial Statements from the date of acquisition. Pro forma supplemental financial information is not provided as the impact of the acquisition on the Company’s operating results, financial position or cash flows was not material.
Emerald Connect, LLC
In February 2014, the Company acquired Emerald, a leading provider of websites and related communications solutions for financial advisors. The purchase price was $59.8 million, net of cash acquired. Net liabilities assumed in the transaction were $2.1 million. This acquisition resulted in $41.1 million of Goodwill. Intangible assets acquired, which totaled $20.8 million, consist primarily of customer relationships, which are being amortized over a seven-year life. The results of Emerald’s operations were included in the Company’s Consolidated Financial Statements from the date of acquisition. Pro forma supplemental financial information is not provided as the impact of the acquisition on the Company’s operating results, financial position or cash flows was not material.
There were no acquisitions in the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013.
During the fiscal year ended June 30, 2012, the Company acquired one business in the Securities Processing Solutions segment:
Paladyne Systems, Inc.
In September 2011, the Company acquired Paladyne, now known as Broadridge Investment Management, Reference Data and Risk Solutions, a provider of buy-side technology solutions for the global investment management industry. The purchase price was $72.4 million, net of cash acquired of $8.3 million. Net liabilities assumed were $15.4 million. This acquisition resulted in $64.0 million of goodwill. Intangible assets acquired, which totaled $23.8 million, consist primarily of acquired software technology and customer relationships, which are being amortized over a seven-year life and ten-year life, respectively. The results of the acquired company’s operations were included in the accompanying consolidated financial statements from the date of acquisition. Pro forma supplemental financial information is not provided as the impact of the acquisition on the Company’s operating results, financial position or cash flows was not material.
65
Table of Contents
NOTE 6. FAIR VALUE OF FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS
Accounting guidance on fair value measurements for certain financial assets and liabilities requires that assets and liabilities carried at fair value be classified and disclosed in one of the following three categories:
| Level 1 |
Inputs that are based upon unadjusted quoted prices for identical instruments traded in active markets. Level 1 assets for the Company include money market deposit accounts (“MMDA account”). | |
| Level 2 |
Quoted prices in markets that are not considered to be active or financial instruments for which all significant inputs are observable, either directly or indirectly. | |
| Level 3 |
Unobservable inputs that are supported by little or no market activity and that are significant to the fair value of the assets or liabilities. Level 3 assets and liabilities include financial instruments whose value is determined using pricing models, discounted cash flow methodologies, or similar techniques, as well as instruments for which the determination of fair value requires significant management judgment or estimation. | |
In valuing assets and liabilities, the Company is required to maximize the use of quoted market prices and minimize the use of unobservable inputs. The Company calculates the fair value of its Level 1 and Level 2 instruments based on the exchange traded price of similar or identical instruments where available or based on other observable instruments. These calculations take into consideration the credit risk of both the Company and its counterparties. The Company has not changed its valuation techniques in measuring the fair value of any financial assets and liabilities during the period.
In June 2013, the Company purchased certain available-for-sale securities in a non-public entity for which the lowest level of significant inputs was unobservable. On a recurring basis, the Company uses pricing models and similar techniques for which the determination of fair value requires significant judgment by management. Accordingly, the Company classifies the available-for-sale securities as Level 3 in the table below.
The following tables set forth the Company’s financial assets and liabilities at June 30, 2014 and 2013, respectively, that are measured at fair value on a recurring basis during the period, segregated by level within the fair value hierarchy:
| Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total | |||||||||||||
| ($ in millions) | ||||||||||||||||
| Assets |
||||||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents: |
||||||||||||||||
| Money market funds(1) |
$ | 138.9 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 138.9 | ||||||||
| Other current assets: |
||||||||||||||||
| Available-for-sale equity securities |
0.1 | — | — | 0.1 | ||||||||||||
| Other non-current assets: |
||||||||||||||||
| Available-for-sale equity securities |
19.8 | — | 1.1 | 20.9 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total as of June 30, 2014 |
$ | 158.8 | $ | — | $ | 1.1 | $ | 159.9 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total | |||||||||||||
| ($ in millions) | ||||||||||||||||
| Assets |
||||||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents: |
||||||||||||||||
| Money market funds(1) |
$ | 122.1 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 122.1 | ||||||||
| Other current assets: |
||||||||||||||||
| Available-for-sale equity securities |
— | — | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Other non-current assets: |
||||||||||||||||
| Available-for-sale equity securities |
15.8 | — | 1.1 | 16.9 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total as of June 30, 2013 |
$ | 137.9 | $ | — | $ | 1.1 | $ | 139.0 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| (1) | Money market funds include MMDA account balances of $71.6 million and $87.1 million as of June 30, 2014 and 2013, respectively. |
66
Table of Contents
The following table sets forth an analysis of changes during fiscal years 2014 and 2013 in Level 3 financial assets of the Company:
| 2014 | 2013 | |||||||
| ($ in millions) | ||||||||
| Beginning balance |
$ | 1.1 | $ | — | ||||
| Net realized/unrealized gains (losses) |
— | — | ||||||
| Purchases |
— | 1.1 | ||||||
| Transfers in (out) of Level 3 |
— | — | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Ending balance |
$ | 1.1 | $ | 1.1 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
The Company did not incur any Level 3 fair value asset impairments during fiscal years 2014, 2013, and 2012. Changes in economic conditions or model based valuation techniques may require the transfer of financial instruments between levels. The Company’s policy is to record transfers between levels if any, as of the beginning of the fiscal year. For the fiscal years ended June 30, 2014 and 2013, there were no transfers between levels.
NOTE 7. DISCONTINUED OPERATIONS
In November 2009, the Company and its wholly owned subsidiary Ridge Clearing & Outsourcing Solutions, Inc. (“Ridge”) entered into an asset purchase agreement (the “Asset Purchase Agreement”) with Penson Worldwide, Inc. (“PWI”) and Penson Financial Services, Inc., a wholly owned subsidiary of PWI (“PFSI,” referred to together with PWI as “Penson”), to sell substantially all contracts of the securities clearing clients of Ridge to PFSI.
On June 25, 2010, the Company completed the sale of the contracts of substantially all of the securities clearing clients of Ridge to PFSI for an aggregate purchase price of $35.2 million. The purchase price paid to Broadridge consisted of (i) a five-year subordinated note from PWI (the “Seller Note”) in the principal amount of $20.6 million bearing interest at an annual rate equal to the London Inter-Bank Offer Rate (“LIBOR”) plus 550 basis points, and (ii) 2,455,627 shares of PWI’s common stock (representing 9.5% of PWI’s outstanding common stock as of May 31, 2010), at the June 25, 2010 closing price of PWI’s common stock of $5.95 per share (the “Seller Shares”). The Company discontinued its securities clearing services business but continued to provide business process outsourcing services aligned with the Securities Processing Solutions business.
Concurrent with entering into the Asset Purchase Agreement, the Company entered into an Outsourcing Services Agreement with PWI (the “Outsourcing Services Agreement”) for an eleven-year term expiring in December 2022. Under the Outsourcing Services Agreement, Ridge provided securities processing and back-office support services to PFSI, including services for the clients acquired from Ridge and PWI’s existing clients. In January 2012, the Company completed the conversion of PWI’s U.S. and Canadian businesses and at the time projected annual revenues under the original terms of the Outsourcing Services Agreement were approximately $50.0 million. On October 11, 2011, Broadridge entered into an amendment agreement with PWI (the “Amendment Agreement”) to expand the scope of outsourcing support services that Ridge provided to PWI under the Outsourcing Services Agreement. The expanded services were expected to result in additional annual revenues to Broadridge of $8.0 million over the remaining term of the Outsourcing Services Agreement. The Company expected to commence providing the expanded services to PWI at various dates, and expected these services to be completely transitioned by July 1, 2013. Under the Amendment Agreement, in October 2011, Broadridge provided PWI with $7.0 million in consideration of the additional services and other amendments contemplated by the Amendment Agreement, and to defray the costs of PWI associated with the conversion to the Broadridge platform. To the extent that the expanded services provided less than $8.0 million of annualized fees to Broadridge by July 1, 2013, PWI would have been obligated to pay Broadridge an amount equal to the shortfall of such fees below $7.0 million by August 1, 2013. In addition, on October 11, 2011, PWI and
67
Table of Contents
Broadridge entered into an Amended and Restated Seller Note which converted the quarterly interest payment terms under the original Seller Note to the payment of interest on the maturity date of the Seller Note effective July 1, 2011.
On March 13, 2012, Broadridge and Ridge entered into a restructuring support agreement (the “Restructuring Support Agreement”) with Penson and certain holders of Penson’s outstanding indebtedness, which provided for proposed transactions related to the restructuring of Penson’s outstanding indebtedness (the “Restructuring”), including the Seller Note held by Broadridge. The consummation of the Restructuring was subject to the approval and acceptance of Penson’s debt holders, among other parties, and other conditions.
The Restructuring Support Agreement provided that Penson would offer to exchange the Seller Note for newly issued shares of Penson common stock which would have represented, together with Broadridge’s existing holdings in the Seller Shares, 9.9% of the outstanding common stock of Penson upon consummation of the Restructuring Support Agreement.
In addition, in connection with the Restructuring, Broadridge and Penson agreed to enter into an amendment to the Outsourcing Services Agreement, which otherwise remained in place, to clarify or modify, as applicable, certain terms of the Outsourcing Services Agreement. The terms of this amendment were subject to the consummation of the Restructuring and the execution of a definitive amendment to the Outsourcing Services Agreement, and the reasonable acceptance of the terms of such amendment by the holders of a majority in principal amount of Penson’s outstanding indebtedness. On May 17, 2012, the Restructuring Support Agreement terminated automatically pursuant to its terms as PWI did not launch the proposed exchange offer as contemplated under the Restructuring Support Agreement.
On June 5, 2012, the Company entered into a ten-year master services agreement (the “Apex MSA”) with Apex Clearing Corporation (“Apex Clearing”) under which Broadridge will perform outsourcing services for Apex Clearing consistent with the securities processing and back-office support services it had previously performed for Penson. The Apex MSA was part of a series of related transactions involving Broadridge, Penson, PEAK6 Investments, L.P. (“PEAK6”) and Apex Clearing Holdings LLC (“Apex Holdings”), an entity created by Penson and PEAK6 to provide clearing and related services to Penson’s U.S. securities correspondents. As part of the series of related transactions, Broadridge transferred ownership of its broker-dealer subsidiary, Ridge, to Apex Holdings and Ridge was renamed Apex Clearing Corporation. Penson’s U.S. broker-dealer subsidiary, PFSI, then sold its U.S. clearing contracts to Apex Clearing. These related transactions were all consummated on June 5, 2012.
The transfer of Ridge to Apex Holdings was made pursuant to a purchase and sale agreement entered into by Broadridge and its subsidiary, Broadridge Securities Processing Solutions, Inc., on May 31, 2012 (the “Purchase and Sale Agreement”). Under the Purchase and Sale Agreement, Broadridge transferred ownership of Ridge, excluding certain assets and liabilities relating to its ongoing outsourcing business, to Apex Holdings, for a purchase price approximately equal to the amount of regulatory net capital transferred with Ridge, an amount that was not material to Broadridge. As a result of consummation of the transfer, Ridge is a wholly owned subsidiary of Apex Holdings and has been renamed Apex Clearing Corporation.
Broadridge’s fees under the Apex MSA are based on a percentage of Apex Clearing’s revenues, and the Apex MSA provides for a termination fee to be paid to Broadridge in the event it is terminated by Apex Clearing for convenience during its term. In addition, Broadridge has agreed that in the event PFSI becomes incapable of performing transition outsourcing services for Apex Clearing under a transition services agreement between PFSI and Apex Clearing during a transition period not to exceed 24 months, Broadridge will perform those transition outsourcing services.
In addition, on June 5, 2012, Broadridge, Ridge (prior to its transfer to Apex Holdings) and Broadridge Financial Solutions (Canada), Inc. entered into a termination and mutual release agreement with Penson, PFSI and Penson Financial Services Canada, Inc. (“PFSC”) (the “Termination Agreement”), thereby terminating certain schedules including the U.S. schedule (the “U.S. Schedule”) to the Outsourcing Services Agreement.
68
Table of Contents
The Termination Agreement: (i) terminated the schedules under the Outsourcing Services Agreement, including the U.S. Schedule, other than to the extent necessary to provide any transition services that may be required under the Apex MSA and for Broadridge to continue to service Penson’s Canadian subsidiary, PFSC; and (ii) terminated, discharged and released in full Penson’s obligations, including all obligations to make principal and interest payments, under the Seller Note. The Termination Agreement also provided that Penson and Broadridge mutually release all claims arising under the Outsourcing Services Agreement, provided that Broadridge retained claims of up to $20 million under the Outsourcing Services Agreement against PFSC while Penson retained all of its rights under the Outsourcing Services Agreement to defend any such claims against PFSC.
On June 5, 2012, as a result of the termination of the U.S. Schedule to the Outsourcing Services Agreement, Broadridge made the determination to impair the deferred client conversion and start-up costs associated with the Outsourcing Services Agreement (the “Deferred Costs”). The charge taken by the Company on the Deferred Costs was $47.2 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2012 (see Note 8, “Impairment and Other Charges, Net”), representing all deferred costs associated with the Outsourcing Services Agreement with Penson. In addition, as a result of the termination of the U.S. Schedule to the Outsourcing Services Agreement on June 5, 2012, Broadridge’s obligation to pay or credit to Penson fees in the amount of $15.1 million related to a third party vendor’s services that were replaced by the Outsourcing Services Agreement was extinguished (see Note 8, “Impairment and Other Charges, Net”).
For a period of time in fiscal year 2012, the Company continued to generate cash flows and reported income statement activity in Loss from discontinued operations, net of taxes, associated with the securities clearing business. The activities that gave rise to these cash flows and income statement activities were transitional in nature.
During the fiscal year 2012, the Company incurred a loss on disposal of assets of discontinued operations of $1.4 million, net of tax benefit of $1.0 million.
NOTE 8. IMPAIRMENT AND OTHER CHARGES, NET
Fiscal Year 2012
Impairment and other charges, net of $74.2 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2012, included charges resulting from the termination of the U.S. schedule of the Outsourcing Services Agreement with PWI (see Note 7, “Discontinued Operations”). The charges primarily included:
An impairment charge of $47.2 million for the deferred client conversion and start-up costs associated with the U.S. schedule of the Outsourcing Services Agreement, representing all deferred costs associated with PFSI. In reviewing these assets for impairment, management considered: (1) the terms and conditions of the Outsourcing Services Agreement, (2) PWI’s progress toward its stated financial improvement plan and the anticipated improvement to its overall financial condition, (3) the outlook for PWI’s business, and (4) the payment status of the Company’s trade account receivables with Penson. In addition, the Company used its best efforts to calculate the probability of the Company realizing potential weighted undiscounted cash flows related to the Outsourcing Services Agreement based on the occurrence of a number of various scenarios. On June 5, 2012, as a result of the termination of the U.S. Schedule to the Outsourcing Services Agreement, Broadridge determined that a material charge for impairment would be taken on the deferred costs associated with the Outsourcing Services Agreement.
An impairment charge of $12.5 million for marketable securities relating to the Company’s investment in the common stock of PWI. Included in Long-term investments during the fiscal year ended June 30, 2012 was the Company’s investment of 2,455,627 shares in the common stock of PWI (see Note 7, “Discontinued Operations”). In estimating other-than-temporary impairment losses, management’s policy considered, but was not limited to, the following: (1) the length of time and the extent to which the fair value had been less than cost,
69
Table of Contents
(2) the financial condition and near-term prospects of the issuer, and (3) the intent and ability of the Company to retain its investment in the issuer for a period of time sufficient to allow for any anticipated recovery in fair value. Based on the Company’s review, factoring in the level of decline in the fair value of the PWI common stock, management determined that the market value of the PWI common stock would not equal or exceed the cost basis of the Company’s investment within a reasonable period of time. After consideration of the severity and duration of this decline in fair value, as well as the reasons for the decline in value, the Company determined that there was an “other-than-temporary” impairment (“OTTI”) related to the Company’s investment in PWI common stock, for which the Company recorded a $12.5 million charge during the fiscal year ended June 30, 2012 and wrote down the cost basis of this investment to zero.
An impairment charge of $21.4 million of a five-year subordinated note from PWI and $8.2 million of shutdown costs. The five-year subordinated note refers to the Seller Note in the principal amount of $20.6 million issued by PWI to Broadridge as part of the consideration in the sale of the Ridge clearing contracts to Penson (see Note 7, “Discontinued Operations”). On March 13, 2012, Broadridge and Ridge entered into a Restructuring Support Agreement with PWI and certain of its subsidiaries, which provided for proposed transactions related to the restructuring of Penson’s outstanding indebtedness, including the Seller Note. As part of PWI’s debt restructuring, Broadridge agreed to cancel this note receivable in exchange for additional shares of PWI’s common stock, and the Company recorded a $21.4 million charge during the fiscal year ended June 30, 2012, which included $0.8 million of accrued interest on the Seller Note. On May 17, 2012, the Restructuring Support Agreement terminated automatically pursuant to its terms as PWI did not launch the proposed exchange offer as contemplated under the Restructuring Support Agreement.
These charges were partially offset by a $15.1 million benefit associated with the extinguishment of Broadridge’s obligation to pay or credit to PWI fees related to a third party vendor’s services replaced by the Outsourcing Services Agreement. As a result of the termination of the U.S. Schedule to the Outsourcing Services Agreement on June 5, 2012, this $15.1 million obligation was extinguished.
These charges are included in the Other segment (see Note 19, “Financial Data by Segment”).
NOTE 9. PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT, NET
Depreciation and amortization expense for Property, plant and equipment was $35.5 million, $35.2 million, and $36.3 million for the three fiscal years ended June 30, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. Property, plant and equipment at cost and accumulated depreciation at June 30, 2014 and 2013 are as follows:
| June 30, | ||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | |||||||
| ($ in millions) | ||||||||
| Property, plant and equipment: |
||||||||
| Land and buildings |
$ | 4.9 | $ | 4.5 | ||||
| Equipment |
280.9 | 255.5 | ||||||
| Furniture, leaseholds and other |
166.7 | 164.5 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 452.5 | 424.5 | |||||||
| Less: Accumulated depreciation |
(364.2 | ) | (343.6 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Property, plant and equipment, net |
$ | 88.3 | $ | 80.9 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
In fiscal year 2014 and 2013, Property, plant and equipment and Accumulated depreciation were each reduced by $14.0 million and $30.9 million, respectively of asset retirements related to fully depreciated property, plant and equipment.
70
Table of Contents
NOTE 10. GOODWILL AND INTANGIBLE ASSETS, NET
Changes in Goodwill for the fiscal years ended June 30, 2014 and 2013 are as follows:
| Investor Communication Solutions |
Securities Processing Solutions |
Total | ||||||||||
| ($ in millions) | ||||||||||||
| Goodwill, gross, at July 1, 2012 |
$ | 502.4 | $ | 277.6 | $ | 780.0 | ||||||
| Additions |
— | — | — | |||||||||
| Foreign currency translation and other |
— | (1.6 | ) | (1.6 | ) | |||||||
| Accumulated impairment losses |
— | — | — | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Goodwill, net, at June 30, 2013 |
$ | 502.4 | $ | 276.0 | $ | 778.4 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Goodwill, gross, at June 30, 2013 |
$ | 502.4 | $ | 276.0 | $ | 778.4 | ||||||
| Additions |
70.1 | — | 70.1 | |||||||||
| Foreign currency translation and other |
— | 7.6 | 7.6 | |||||||||
| Accumulated impairment losses |
— | — | — | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Goodwill, net, at June 30, 2014 |
$ | 572.5 | $ | 283.6 | $ | 856.1 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Additions for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014 include $41.1 million and $29.0 million for the Emerald and Bonaire acquisitions, respectively (see Note 5, “Acquisitions”).
During fiscal years 2014, 2013 and 2012, the Company performed the required impairment tests of Goodwill under ASC No. 350 and determined that there was no impairment.
Intangible assets at cost and accumulated amortization at June 30, 2014 and 2013 are as follows:
| June 30, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Original Cost |
Accumulated Amortization |
Intangible Assets, net |
Original Cost |
Accumulated Amortization |
Intangible Assets, net |
|||||||||||||||||||
| ($ in millions) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Software licenses |
$ | 79.7 | $ | (58.6 | ) | $ | 21.1 | $ | 70.9 | $ | (49.7 | ) | $ | 21.2 | ||||||||||
| Acquired software technology |
60.1 | (35.6 | ) | 24.5 | 59.8 | (30.0 | ) | 29.8 | ||||||||||||||||
| Customer contracts and lists |
127.6 | (51.8 | ) | 75.8 | 102.2 | (39.8 | ) | 62.4 | ||||||||||||||||
| Other intangibles |
19.8 | (11.2 | ) | 8.6 | 15.1 | (7.9 | ) | 7.2 | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| $ | 287.2 | $ | (157.2 | ) | $ | 130.0 | $ | 248.0 | $ | (127.4 | ) | $ | 120.6 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
In fiscal years 2014 and 2013, intangible assets and accumulated amortization were each reduced by $4.7 million and $4.6 million, respectively of asset retirements related to fully depreciated intangibles.
Other intangibles consist primarily of purchased rights, covenants, patents, and trademarks (acquired directly or through acquisitions). All of the intangible assets have finite lives and, as such, are subject to amortization. The weighted-average remaining useful life of the intangible assets is 5.5 years (5.3 years for software licenses and 3.6 years for acquired software technology, 6.3 years for customer contracts and lists and 3.7 years for other intangibles). Amortization of intangibles totaled $33.9 million, $34.2 million, and $37.0 million for fiscal years 2014, 2013, and 2012, respectively. Estimated remaining amortization expenses of the Company’s existing intangible assets for the next five fiscal years and thereafter are as follows:
| Years Ending June 30, |
($ in millions) | |||
| 2015 |
$ | 32.4 | ||
| 2016 |
27.8 | |||
| 2017 |
22.5 | |||
| 2018 |
17.5 | |||
| 2019 |
6.2 | |||
| Thereafter |
23.6 | |||
71
Table of Contents
NOTE 11. OTHER NON-CURRENT ASSETS
Other non-current assets consisted of the following:
| June 30, | ||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | |||||||
| ($ in millions) | ||||||||
| Deferred client conversion and start-up costs |
$ | 135.5 | $ | 133.3 | ||||
| Deferred data center costs |
44.9 | 48.8 | ||||||
| Long-term investments |
25.3 | 20.9 | ||||||
| Long-term broker fees |
8.7 | 9.2 | ||||||
| Other |
22.7 | 19.1 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total |
$ | 237.1 | $ | 231.3 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
NOTE 12. ACCRUED EXPENSES AND OTHER CURRENT LIABILITIES
Accrued expenses and other current liabilities consist of the following:
| June 30, | ||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | |||||||
| ($ in millions) | ||||||||
| Employee compensation and benefits |
$ | 164.4 | $ | 143.1 | ||||
| Accrued broker fees |
62.0 | 49.2 | ||||||
| Accrued income taxes |
35.0 | 51.8 | ||||||
| Accrued dividend payable |
24.7 | 21.0 | ||||||
| Other |
20.5 | 12.1 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total |
$ | 306.6 | $ | 277.2 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
NOTE 13. BORROWINGS
Fiscal 2012 Credit Facilities: On September 22, 2011, the Company entered into a $990.0 million senior unsecured credit facility, consisting of a $490.0 million five-year term loan facility (the “Fiscal 2012 Term Loan”) and a $500.0 million five-year revolving credit facility (the “Fiscal 2012 Revolving Credit Facility”) (collectively the “Fiscal 2012 Credit Facilities”). Borrowings under the Fiscal 2012 Credit Facilities bear interest at LIBOR plus 125 basis points. The Fiscal 2012 Revolving Credit Facility also has an annual facility fee equal to 15 basis points, on the unused portion of the facility, which totaled $0.8 million and $0.8 million for the fiscal years ended June 30, 2014 and 2013, respectively. The Company incurred $3.0 million in debt issuance costs to establish the Fiscal 2012 Credit Facilities, of which $0.1 million of these costs were expensed as incurred and $2.9 million of these costs were capitalized in Other non-current assets in the Consolidated Balance Sheets and are being amortized to Other expenses, net on a straight-line basis, which approximates the effective interest method, over the terms of these facilities. During the quarter ended September 30, 2013, the Company repaid the Fiscal 2012 Term Loan and expensed the remaining issuance costs associated with this debt, which was approximately $0.9 million. As of June 30, 2014 and 2013, $2.3 million and $1.0 million, respectively, had been expensed related to the Fiscal 2012 Credit Facilities, with $0.6 million remaining to be amortized related to the Fiscal 2012 Revolving Credit Facility.
The Fiscal 2012 Term Loan contained a repayment schedule that required the Company to make minimum principal repayments on the loan before the balance of the loan became due in September 2016, with no prepayment penalty. During the fiscal year ended June 30, 2012, the Company repaid $90.0 million of the $490.0 million of borrowings under the Fiscal 2012 Term Loan and had met the repayment requirements on the Fiscal 2012 Term Loan through September 30, 2014. During the quarter ended September 30, 2013, the Company
72
Table of Contents
repaid the remaining $400.0 million outstanding on the Fiscal 2012 Term Loan. During the first quarter of the current fiscal year, the weighted-average interest rate on the Fiscal 2012 Term Loan was 1.44% before being repaid in August 2013. The weighted-average interest rate on the Fiscal 2012 Term Loan was 1.47% and 1.54% for the fiscal years ended June 30, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
The Fiscal 2012 Revolving Credit Facility is subject to covenants, including financial covenants consisting of a leverage ratio and an interest coverage ratio. At June 30, 2014, the Company is not aware of any instances of any non-compliance with the financial covenants of the Fiscal 2012 Revolving Credit Facility.
Fiscal 2007 Senior Notes: In May 2007, the Company completed an offering of $250.0 million in aggregate principal amount of senior notes (the “Fiscal 2007 Senior Notes”). The Fiscal 2007 Senior Notes will mature on June 1, 2017 and bear interest at a rate of 6.125% per annum. Interest on the Fiscal 2007 Senior Notes is payable semi-annually in arrears on June 1 and December 1 of each year. The Fiscal 2007 Senior Notes were issued at a price of 99.1% (effective yield to maturity of 6.251%). The indenture governing the Fiscal 2007 Senior Notes contains certain covenants including covenants restricting the Company’s ability to create or incur liens securing indebtedness for borrowed money and to enter into certain sale-leaseback transactions. At June 30, 2014, the Company is not aware of any instances of non-compliance with the covenants of the indenture governing the Fiscal 2007 Senior Notes. The indenture also contains covenants regarding the purchase of the Fiscal 2007 Senior Notes upon a change of control triggering event. The Fiscal 2007 Senior Notes are senior unsecured obligations of the Company and rank equally with the Company’s other senior indebtedness. The Company may redeem the Fiscal 2007 Senior Notes in whole or in part at any time before their maturity. The Company incurred $1.9 million in debt issuance costs to establish the Fiscal 2007 Senior Notes. These costs have been capitalized and are being amortized to Other expenses, net on a straight-line basis, which approximates the effective interest method, over the ten year term. At June 30, 2014 and June 30, 2013, the accumulated amortization related to the Fiscal 2007 Senior Notes was $1.3 million and $1.1 million, respectively. During the fiscal year ended June 30, 2009, the Company purchased $125.0 million principal amount of the Fiscal 2007 Senior Notes (including $1.0 million unamortized bond discount) pursuant to a cash tender offer for such notes. The fair value of the fixed-rate Fiscal 2007 Senior Notes at June 30, 2014 and June 30, 2013 was $139.1 million and $138.2 million, respectively, based on quoted market prices and has been classified as a Level 1 financial liability (as defined in Note 6, “Fair Value of Financial Instruments”).
Fiscal 2014 Senior Notes: In August 2013, the Company completed an offering of $400.0 million in aggregate principal amount of senior notes (the “Fiscal 2014 Senior Notes”). The Fiscal 2014 Senior Notes will mature on September 1, 2020 and bear interest at a rate of 3.95% per annum. Interest on the Fiscal 2014 Senior Notes is payable semi-annually in arrears on March 1 and September 1 of each year. The Fiscal 2014 Senior Notes were issued at a price of 99.871% (effective yield to maturity of 3.971%). The indenture governing the Fiscal 2014 Senior Notes contains certain covenants including covenants restricting the Company’s ability to create or incur liens securing indebtedness for borrowed money and to enter into certain sale-leaseback transactions. At June 30, 2014, the Company is not aware of any instances of non-compliance with the covenants of the indenture governing the Fiscal 2014 Senior Notes. The indenture also contains covenants regarding the purchase of the Fiscal 2014 Senior Notes upon a change of control triggering event. The Fiscal 2014 Senior Notes are senior unsecured obligations of the Company and rank equally with the Company’s other senior indebtedness. The Company may redeem the Fiscal 2014 Senior Notes in whole or in part at any time before their maturity. The Company incurred $4.3 million in debt issuance costs to establish the Fiscal 2014 Senior Notes. These costs have been capitalized and are being amortized to Other expenses, net on a straight-line basis, which approximates the effective interest method, over the seven-year term. At June 30, 2014, the accumulated amortization related to the Fiscal 2014 Senior Notes was $0.6 million. The fair value of the fixed-rate Fiscal 2014 Senior Notes at June 30, 2014 was $426.6 million based on quoted market prices and has been classified as a Level 1 financial liability (as defined in Note 6, “Fair Value of Financial Instruments”).
73
Table of Contents
Available Capacity: As of June 30, 2014, outstanding borrowings and available capacity under the Company’s borrowing arrangements were as follows:
| Expiration Date |
Total Capacity |
Outstanding Borrowings |
Unused Available Capacity |
|||||||||||||
| ($ in millions) | ||||||||||||||||
| Long-term debt |
||||||||||||||||
| Fiscal 2012 Revolving Credit Facility |
September 2016 | $ | 500.0 | $ | — | $ | 500.0 | |||||||||
| Fiscal 2007 Senior Notes |
June 2017 | 124.6 | 124.6 | — | ||||||||||||
| Fiscal 2014 Senior Notes |
September 2020 | 399.5 | 399.5 | — | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total |
$ | 1,024.1 | $ | 524.1 | $ | 500.0 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
In addition, the Company and certain subsidiaries established unsecured, uncommitted lines of credit with banks. As of June 30, 2014 and 2013, respectively, there were no amounts outstanding borrowings under these lines of credit.
NOTE 14. STOCK-BASED COMPENSATION
Incentive Equity Awards. The Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc. 2007 Omnibus Award Plan (the “2007 Plan”) provides for the granting of incentive stock options, nonqualified stock options, stock appreciation rights, restricted stock, restricted stock units, phantom stock awards, stock bonuses and performance compensation awards to employees, non-employee directors, and other key individuals who perform services for the Company. The Company accounts for stock-based compensation in accordance with ASC No. 718 which requires the measurement of stock-based compensation expense to be recognized in Net earnings based on the fair value of the award on the date of grant. In accordance with the 2007 Plan, the Company’s stock-based compensation consists of the following:
Stock Options: Stock options are granted to employees at exercise prices equal to the fair market value of the Company’s common stock on the dates of grant. Stock options are generally issued under a graded vesting schedule, meaning that they vest ratably over four years, and have a term of 10 years. A portion of the stock options granted in fiscal year 2014 have a cliff vesting schedule meaning that they vest in four years from the grant date and have a term of 10 years. Compensation expense for stock options under a graded vesting schedule is recognized over the requisite service period for each separately vesting portion of the stock option award. Compensation expense for stock options under a cliff vesting schedule is recognized equally over the four year vesting period with 25 percent of the cost recognized over each 12 month period.
Time-based Restricted Stock Units: The Company has a time-based restricted stock unit (“RSU”) program under which RSUs representing the right to receive one share of the Company’s common stock for each vested RSU are granted. Time-based RSUs typically vest two and one-half years from the date of grant. The Company records stock compensation expense for time-based RSUs on a straight-line basis over the vesting period.
Performance-based Restricted Stock Units: The Company has a performance-based RSU program under which RSUs representing the right to receive one share of the Company’s common stock for each vested RSU are granted. RSUs vest upon the achievement, by the Company, of specific performance metrics. The Company records stock compensation expense for performance-based RSUs on a straight-line basis over the performance period, plus a subsequent vesting period, which typically totals approximately two and one-half years from the date of grant.
Time-based Restricted Stock: The Company has a time-based restricted stock program under which shares of common stock can be issued to certain key employees. These shares are restricted as to transfer and in certain circumstances must be returned to the Company at the original purchase price. The Company records stock compensation expense relating to the issuance of time-based restricted stock over the period during which the
74
Table of Contents
transfer restrictions exist, which is up to five years from the date of grant. The value of the Company’s time-based restricted stock, based on market prices, is recognized as compensation expense over the restriction period on a straight-line basis. There are no shares of time-based restricted stock outstanding at June 30, 2014.
Performance-based Restricted Stock: The Company has performance-based restricted stock programs under which shares of common stock can be issued to certain key employees upon the achievement of specific performance metrics. When it is probable that the performance metrics will be achieved, the Company records stock compensation expense for performance-based restricted stock on a straight-line basis over the performance period, plus a subsequent vesting period, which typically totals approximately two and one-half years from the date of grant. Certain performance-based equity awards granted to non-U.S. employees are to be settled in cash. The Company records a liability for these performance-based equity awards. The liability and the corresponding stock compensation expense are adjusted to reflect the Company’s closing stock price as of the end of each reporting period. There are no shares of performance-based restricted stock outstanding at June 30, 2014.
The activity related to the Company’s incentive equity awards for the fiscal years ended June 30, 2014, 2013 and 2012 consisted of the following:
| Stock Options | Time-based RSUs |
Performance-based RSUs |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of Options |
Weighted Average Exercise Price |
Number of Shares |
Weighted Average Grant-Date Fair Value |
Number of Shares |
Weighted Average Grant-Date Fair Value |
|||||||||||||||||||
| Balances at July 1, 2011 |
13,774,726 | $ | 18.94 | 1,932,003 | $ | 20.19 | 708,724 | $ | 20.18 | |||||||||||||||
| Granted |
1,057,538 | 24.01 | 1,142,616 | 18.37 | 342,628 | 17.61 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Exercised(a) |
(2,151,613 | ) | 18.52 | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
| Vesting of RSUs(b) |
— | — | (887,892 | ) | 18.68 | (279,028 | ) | 18.68 | ||||||||||||||||
| Expired/forfeited |
(299,163 | ) | 20.03 | (161,158 | ) | 19.91 | (69,129 | ) | 18.73 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Balances at June 30, 2012 |
12,381,488 | $ | 19.42 | 2,025,569 | $ | 19.61 | 703,195 | $ | 20.39 | |||||||||||||||
| Granted |
1,497,855 | 22.51 | 1,093,856 | 21.32 | 246,894 | 21.25 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Exercised(a) |
(2,724,439 | ) | 17.23 | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
| Vesting of RSUs(b) |
— | — | (907,922 | ) | 21.62 | (259,431 | ) | 21.70 | ||||||||||||||||
| Expired/forfeited |
(169,422 | ) | 18.82 | (124,669 | ) | 19.38 | (117,835 | ) | 21.42 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Balances at June 30, 2013 |
10,985,482 | $ | 20.39 | 2,086,834 | $ | 19.65 | 572,823 | $ | 19.96 | |||||||||||||||
| Granted |
1,683,875 | 36.88 | 906,061 | 30.46 | 348,997 | 30.93 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Exercised(a) |
(2,686,105 | ) | 18.46 | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
| Vesting of RSUs(b) |
— | — | (961,930 | ) | 17.78 | (237,189 | ) | 17.73 | ||||||||||||||||
| Expired/forfeited |
(135,961 | ) | 20.89 | (164,557 | ) | 21.60 | (22,349 | ) | 27.10 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Balances at June 30, 2014(c) |
9,847,291 | $ | 23.73 | 1,866,408 | $ | 25.69 | 662,282 | $ | 26.30 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| (a) | Stock options exercised during the fiscal years ended June 30, 2014, 2013 and 2012 had intrinsic values of $49.9 million, $19.8 million and $9.7 million, respectively. |
| (b) | Time-based RSUs that vested during the fiscal years ended June 30, 2014, 2013 and 2012 had a total fair value of $36.5 million, $22.1 million and $20.9 million, respectively. Performance-based RSUs that vested during the fiscal years ended June 30, 2014, 2013 and 2012 had a total fair value of $8.9 million, $6.3 million and $6.7 million, respectively. |
| (c) | As of June 30, 2014, the Company’s outstanding “in the money” stock options using the fiscal year-end share price of $41.64 (approximately 6.7 million shares) had an aggregate intrinsic value of $139.6 million. As of June 30, 2014, time-based RSUs and performance-based RSUs expected to vest using the fiscal year-end share price of $41.64 (approximately 1.7 million and 0.6 million shares, respectively) had an aggregate intrinsic value of $70.6 million and $26.2 million, respectively. |
75
Table of Contents
The tables below summarizes information regarding the Company’s outstanding and exercisable stock options as of June 30, 2014:
| Outstanding Options | ||||||||||||
| Range of Exercise Prices |
Options Outstanding |
Weighted Average Remaining Contractual Life |
Weighted Average Exercise Price |
|||||||||
| $0.01 to $16.00 |
495,371 | 4.46 | $ | 14.44 | ||||||||
| $16.01 to $19.00 |
1,980,722 | 2.23 | $ | 18.05 | ||||||||
| $19.01 to $22.00 |
1,918,632 | 4.51 | $ | 21.13 | ||||||||
| $22.01 to $25.00 |
3,322,883 | 6.77 | $ | 23.06 | ||||||||
| $25.01 to $28.00 |
445,808 | 6.02 | $ | 25.73 | ||||||||
| $28.01 to $37.00 |
1,683,875 | 9.60 | $ | 36.88 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| 9,847,291 | 5.75 | $ | 23.73 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Exercisable Options | ||||||||||||
| Range of Exercise Prices |
Options Exercisable |
Weighted Average Remaining Contractual Life |
Weighted Average Exercise Price |
|||||||||
| $0.01 to $16.00 |
495,371 | 4.46 | $ | 14.44 | ||||||||
| $16.01 to $19.00 |
1,980,722 | 2.23 | $ | 18.05 | ||||||||
| $19.01 to $22.00 |
1,847,672 | 4.47 | $ | 21.11 | ||||||||
| $22.01 to $25.00 |
1,883,132 | 6.01 | $ | 23.17 | ||||||||
| $25.01 to $28.00 |
389,999 | 5.61 | $ | 25.69 | ||||||||
| $28.01 to $37.00 |
92,149 | 9.38 | $ | 36.35 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| 6,689,045 | 4.37 | $ | 20.77 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||
Stock-based compensation expense of $34.6 million, $27.1 million, and $28.3 million was recognized in earnings from continuing operations in the Consolidated Statements of Earnings for the fiscal years ended June 30, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively, as well as related tax benefits of $13.0 million, $10.1 million, and $11.3 million, respectively.
As of June 30, 2014, the total remaining unrecognized compensation cost related to non-vested stock options and RSU awards amounted to $13.5 million and $29.2 million, respectively, which will be amortized over the weighted-average remaining requisite service periods of 3.4 years and 1.4 years, respectively.
In April 2013, the Company began reissuing treasury stock to satisfy stock option exercises and issuances under the Company’s RSU awards. From time to time, the Company may repurchase shares of its common stock under its authorized share repurchase programs. The Company repurchased 2.9 million shares in fiscal year 2014 as compared to 9.7 million shares repurchased in fiscal year 2013. The Company considers several factors in determining when to execute share repurchases, including, among other things, actual and potential acquisition activity, cash balances and cash flows, issuances due to employee benefit plan activity, and market conditions.
For stock options issued, the fair value of each stock option was estimated on the date of grant using a binomial option pricing model. The binomial model considers a range of assumptions related to volatility, risk-free interest rate and employee exercise behavior. Expected volatilities utilized in the binomial model are based on a combination of implied market volatilities, historical volatility of the Company’s stock price and other factors. Similarly, the dividend yield is based on historical experience and expected future changes. The risk-free rate is derived from the U.S. Treasury yield curve in effect at the time of grant. The binomial model also
76
Table of Contents
incorporates exercise and forfeiture assumptions based on an analysis of historical data. The expected life of the stock option grants is derived from the output of the binomial model and represents the period of time that options granted are expected to be outstanding.
The following table presents the assumptions used to determine the fair values of the stock option grants using the Binomial options pricing model during the fiscal years ended June 30, 2014, 2013 and 2012:
| Fiscal Year Ended June 30, 2014 |
Fiscal Year Ended June 30, 2013 |
Fiscal Year Ended June 30, 2012 |
||||||||||
| Graded Vesting |
||||||||||||
| Risk-free interest rate |
2.1% | 1.3% | 1.4% | |||||||||
| Dividend yield |
2.3% | 3.2% | 2.6% | |||||||||
| Weighted-average volatility factor |
26.4% | 25.7% | 28.1% | |||||||||
| Weighted-average expected life (in years) |
6.9 | 6.8 | 6.6 | |||||||||
| Weighted-average fair value (in dollars) |
$8.19 | $3.78 | $5.01 | |||||||||
| Cliff Vesting |
||||||||||||
| Risk-free interest rate |
2.3% | — | — | |||||||||
| Dividend yield |
2.3% | — | — | |||||||||
| Weighted-average volatility factor |
26.4% | — | — | |||||||||
| Weighted-average expected life (in years) |
7.7 | — | — | |||||||||
| Weighted-average fair value (in dollars) |
$8.76 | — | — | |||||||||
NOTE 15. EMPLOYEE BENEFIT PLANS
A. Defined Contribution Savings Plan. The Company approved a Broadridge sponsored 401(k) savings plan covering eligible full-time U.S. employees of the Company. This plan provides a base contribution plus Company matching contributions on a portion of employee contributions. The costs recorded by the Company for this plan were $22.1 million, $21.6 million and $20.4 million for the fiscal years ended June 30, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
B. Defined Benefit Pension Plans. The Company sponsors a Supplemental Officer Retirement Plan (the “Broadridge SORP”). The Broadridge SORP is a defined benefit plan pursuant to which the Company will pay supplemental pension benefits to certain key officers upon retirement based upon the officers’ years of service and compensation. The amount charged to expense for the Broadridge SORP was $2.9 million, $3.4 million and $2.4 million during the fiscal years ended June 30, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. The Broadridge SORP is currently unfunded, and the benefit obligation under this plan was $21.0 million, $17.0 million and $15.7 million at June 30, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
The Company also sponsors a Supplemental Executive Retirement Plan (the “Broadridge SERP”). The Broadridge SERP is a defined benefit plan pursuant to which the Company will pay supplemental pension benefits to certain key executives upon retirement based upon the executives’ years of service and compensation. The amount charged to expense for the Broadridge SERP was $0.5 million, $0.5 million and $0.3 million during the fiscal years ended June 30, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. The Broadridge SERP is currently unfunded, and the benefit obligation under this plan was $2.3 million, $1.5 million and $1.3 million at June 30, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
C. Other Post-retirement Benefit Plan. The Company sponsors an Executive Retiree Health Insurance Plan. It is a post-retirement benefit plan pursuant to which the Company helps defray the health care costs of certain eligible key executive retirees and qualifying dependents, based upon the retirees’ age and years of service, until they reach the age of 65. The amount charged to expense under this plan was $0.2 million, $0.2 million and $0.3 million during the fiscal years ended June 30, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. The plan is currently unfunded, and the benefit obligation under this plan was $3.2 million, $3.0 million and $2.8 million at June 30, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
77
Table of Contents
NOTE 16. INCOME TAXES
Earnings from continuing operations before income taxes shown below are based on the geographic location to which such earnings are attributable.
| Years Ended June 30, | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| ($ in millions) | ||||||||||||
| Earnings from continuing operations before income taxes: |
||||||||||||
| U.S. |
$ | 308.1 | $ | 252.3 | $ | 125.5 | ||||||
| Foreign |
87.4 | 70.9 | 75.4 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
$ | 395.5 | $ | 323.2 | $ | 200.9 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
The Provision for income taxes consists of the following components:
| Years Ended June 30, | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| ($ in millions) | ||||||||||||
| Current: |
||||||||||||
| U.S. Domestic |
$ | 114.8 | $ | 73.1 | $ | 53.3 | ||||||
| Foreign |
22.5 | 15.8 | 22.0 | |||||||||
| State |
6.8 | 8.1 | 9.0 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total current |
144.1 | 97.0 | 84.3 | |||||||||
| Deferred: |
||||||||||||
| U.S. Domestic |
(8.7 | ) | 16.0 | (5.2 | ) | |||||||
| Foreign |
(0.4 | ) | — | (1.1 | ) | |||||||
| State |
(2.5 | ) | (1.9 | ) | (2.1 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total deferred |
(11.6 | ) | 14.1 | (8.4 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total Provision for income taxes |
$ | 132.5 | $ | 111.1 | $ | 75.9 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Years Ended June 30, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2014 | % | 2013 | % | 2012 | % | |||||||||||||||||||
| ($ in millions) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Provision for income taxes at U.S. statutory rate |
$ | 138.4 | 35.0 | $ | 113.1 | 35.0 | $ | 70.3 | 35.0 | |||||||||||||||
| Increase (decrease) in Provision for income taxes from: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State taxes, net of federal tax |
4.0 | 1.0 | 4.6 | 1.4 | 4.8 | 2.4 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign taxes |
(7.5 | ) | (1.9 | ) | (4.3 | ) | (1.3 | ) | (5.7 | ) | (2.8 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Valuation allowances |
(0.7 | ) | (0.2 | ) | 1.0 | 0.3 | 3.2 | 1.6 | ||||||||||||||||
| Other |
(1.7 | ) | (0.4 | ) | (3.3 | ) | (1.0 | ) | 3.3 | 1.6 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total Provision for income taxes |
$ | 132.5 | 33.5 | $ | 111.1 | 34.4 | $ | 75.9 | 37.8 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
The Provision for income taxes and the effective tax rates for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014 were $132.5 million and 33.5%, respectively, compared to $111.1 million and 34.4%, for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2013, respectively. The decrease in the effective tax rate was primarily attributable to the cumulative tax benefits in fiscal year 2014 exceeding the cumulative tax benefits in fiscal year 2013. The cumulative tax benefits in fiscal year 2014 primarily related to the release of a valuation allowance for a net operating loss carryforward in a foreign tax jurisdiction, and the release of various tax reserves related to certain foreign, U.S. federal and state income taxes due to audit settlements and the expiration of certain audit periods which resulted in a decrease to the effective tax rate of approximately 115 basis points. In addition, the effective tax rate was also positively affected by approximately 30 basis points due to the characterization of a $3.3 million decrease in the
78
Table of Contents
fair value of obligations under contingent acquisition consideration arrangements as a deductible permanent tax item. Offsetting these positive benefits were various non-deductible permanent tax items that negatively impacted the tax rate by approximately 60 basis points. The cumulative tax benefits in fiscal year 2013 primarily consisted of the recognition of a previous period’s foreign tax credits. In addition to the higher cumulative tax benefits in fiscal year 2014, the change in the effective tax rate was marginally positively impacted by the geographical mix of income. In general, the Company’s foreign earnings are subject to a lower corporate income tax rate relative to the tax rate applied against U.S. income. In the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014 there was no material change in foreign earnings as a percentage of total Net earnings when compared to the fiscal year ended June 30, 3013. The geographical mix of income may impact the effective tax rate in future periods as the geographical mix of the Company’s business changes.
As of June 30, 2014, the Company had approximately $300.6 million of accumulated earnings attributable to foreign subsidiaries. The Company considers such earnings as permanently reinvested outside the U. S. and, therefore, provides no additional taxes that could occur upon repatriation. It is not practicable to determine the amount of income taxes payable in the event all such foreign earnings are repatriated.
Deferred income taxes reflect the net tax effects of temporary differences between the financial reporting and tax bases of assets and liabilities and are measured using the enacted tax rates and laws that will be in effect when such differences are expected to reverse. Significant components of the Company’s deferred tax assets and liabilities at June 30, 2014 and 2013 were as follows:
| June 30, | ||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | |||||||
| ($ in millions) | ||||||||
| Classification: |
||||||||
| Current deferred tax assets (included in Other current assets) |
$ | 18.9 | $ | 16.9 | ||||
| Long-term deferred tax assets (included in Other non-current assets) |
0.9 | 0.4 | ||||||
| Current deferred tax liabilities (included in Accrued expenses and other current liabilities) |
(0.6 | ) | (0.6 | ) | ||||
| Long-term deferred tax liabilities |
(62.4 | ) | (71.2 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net deferred tax liabilities |
$ | (43.2 | ) | $ | (54.5 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Components: |
||||||||
| Deferred tax assets: |
||||||||
| Accrued expenses not currently deductible |
$ | 4.9 | $ | 4.1 | ||||
| Depreciation |
23.9 | 22.2 | ||||||
| Compensation and benefits not currently deductible |
47.5 | 44.9 | ||||||
| Net operating and capital losses |
27.3 | 32.5 | ||||||
| Tax credits |
4.5 | 4.3 | ||||||
| Other |
5.6 | 6.5 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total deferred tax assets |
113.7 | 114.5 | ||||||
| Less: Valuation allowances |
(10.9 | ) | (12.5 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Deferred tax assets, net |
102.8 | 102.0 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Deferred tax liabilities: |
||||||||
| Goodwill and identifiable intangibles |
121.8 | 127.0 | ||||||
| Net deferred expenses |
19.9 | 25.1 | ||||||
| Other |
4.3 | 4.4 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Deferred tax liabilities |
146.0 | 156.5 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net deferred tax liabilities |
$ | (43.2 | ) | $ | (54.5 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
79
Table of Contents
The Company has estimated foreign net operating loss carryforwards of approximately $18.8 million as of June 30, 2014 of which $1.9 million expires in 2017 through 2027 and of which $16.9 million has an indefinite utilization period. In addition, the Company has estimated U.S. federal net operating loss carryforwards of approximately $45.5 million, which expire in 2015 through 2030.
Valuation allowances are recognized to reduce deferred tax assets when it is more likely than not that the Company will not be able to utilize the deferred tax assets attributable to net operating and capital loss carryforwards of certain subsidiaries to offset future taxable earnings. The Company has recorded valuation allowances of $10.9 million and $12.5 million at June 30, 2014 and 2013, respectively. The determination as to whether a deferred tax asset will be recognized is made on a jurisdictional basis and is based on the evaluation of historical taxable income or loss, projected future taxable income, carryforward periods, scheduled reversals of deferred tax liabilities and tax planning strategies. Projected future taxable income is based on expected results and assumptions as to the jurisdiction in which the income will be earned. The assumptions used to project future taxable income require significant judgment and are consistent with the plans and estimates used to manage the underlying businesses.
As of June 30, 2014 and 2013, the Company’s total amounts of unrecognized tax benefits were $26.6 million and $30.0 million, respectively. The change relates to tax positions taken for the current and prior tax year. The amount of the unrecognized tax benefits at June 30, 2014 that, if recognized, would affect the Company’s effective tax rate is approximately $14.5 million.
In the next twelve months, the Company expects to decrease its reserve for unrecognized tax benefits by approximately $2.0 million as a result of statute of limitations expirations and certain potential state settlements.
The following table summarizes the activity related to the Company’s unrecognized tax benefits:
| Fiscal Year
Ended June 30, |
||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| ($ in millions) | ||||||||||||
| Beginning balance |
$ | 30.0 | $ | 62.6 | $ | 47.0 | ||||||
| Gross increase related to prior period tax positions |
0.5 | 1.9 | 9.2 | |||||||||
| Gross increase related to current period tax positions |
2.2 | 2.2 | 6.4 | |||||||||
| Gross decrease related to prior period tax positions |
(6.1 | ) | (36.7 | ) | — | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Ending balance |
$ | 26.6 | $ | 30.0 | $ | 62.6 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
The $6.1 million gross decrease in fiscal year 2014 for prior period tax positions related to the settlement of certain state income tax audits and certain federal and foreign statute of limitation expirations.
The $36.7 million gross decrease in fiscal year 2013 for prior period tax positions related to the settlement and execution of an Advance Pricing Agreement with the Internal Revenue Service and Canadian Revenue Authority and statute of limitation expirations.
The Company’s policy with respect to interest and penalties associated with uncertain tax positions is not to include them in income tax expense but include penalties as a component of other accrued expenses and interest in interest expense. During the fiscal years ended June 30, 2014, 2013 and 2012, the Company recognized approximately $0.9 million, $0.2 million and $1.0 million, respectively, in interest and penalties.
The Company is continuously subject to U.S. Federal, state and foreign income tax exams for the periods beginning March 31, 2007 through June 30, 2014 with no current material examinations.
80
Table of Contents
NOTE 17. CONTRACTUAL COMMITMENTS, CONTINGENCIES, AND OFF-BALANCE SHEET ARRANGEMENTS
In the normal course of business, the Company is subject to various claims and litigation. While the outcome of any claim or litigation is inherently unpredictable, and with the exception of the matter described in the following paragraph, the Company believes that the ultimate resolution of these matters will not, individually or in the aggregate, result in a material impact on its financial condition, results of operations or cash flows.
The Company entered into a data center outsourcing services agreement with Automatic Data Processing, Inc. (“ADP”) before the Company’s spin-off from ADP in March 2007 (the “ADP Agreement”) under which ADP provided the Company with data center services. The ADP Agreement expired on June 30, 2012. The Company entered into a short-term extension of the ADP Agreement which expired in August 2012. At June 30, 2014, the Company had no further obligation to ADP for data center services. For the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014 the Company did not record expenses related to the ADP Agreement. For the fiscal years ended June 30, 2013 and 2012 the Company recorded expenses of $5.8 million and $111.4 million, respectively, in the Consolidated Statements of Earnings related to the ADP Agreement.
In March 2010, the Company and International Business Machines Corporation (“IBM”) entered into an Information Technology Services Agreement (the “IT Services Agreement”), under which IBM provides certain aspects of the Company’s information technology infrastructure that were previously provided under the ADP Agreement. Under the IT Services Agreement, IBM provides a broad range of technology services to the Company including supporting its mainframe, midrange, open systems, network and data center operations, as well as providing disaster recovery services. The Company has the option of incorporating additional services into the agreement over time. The migration of the data center processing from ADP to IBM was completed in August 2012. The IT Services Agreement expires on June 30, 2022. The Company has the right to renew the initial term of the IT Services Agreement for up to one additional 12-month term. Commitments remaining under this agreement at June 30, 2014 are $442.7 million through fiscal year 2022, the final year of the contract. For the fiscal years ended June 30, 2014, 2013 and 2012, the Company recorded expenses of $95.7 million, $96.3 million and $24.6 million, respectively, in the Consolidated Statements of Earnings related to this agreement. The Company capitalized $54.7 million related to the build-out of the IBM data center in Other non-current assets, with $5.4 million and $5.9 million amortized into expense in the fiscal years ended June 30, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
In March 2014, the Company and IBM United Kingdom Limited (“IBM UK”) entered into an Information Technology Services Agreement (the “EU IT Services Agreement”), under which IBM UK provides data center services supporting the Company’s technology outsourcing services for certain clients in Europe and Asia. The EU IT Services Agreement expires in October 2023. The Company has the right to renew the initial term of the EU IT Services Agreement for up to one additional 12-month term or one additional 24-month term. Commitments remaining under this agreement at June 30, 2014 are $50.2 million through fiscal year 2024, the final year of the contract. The Company has begun the build-out of the IBM UK data center associated with the EU IT Services Agreement. For the fiscal year ended June 30, 2014, the Company recorded expenses of $1.5 million in the Consolidated Statements of Earnings and capitalized $1.6 million of costs in Other non-current assets related to this agreement.
The Company has obligations under the IT Services Agreement, the EU IT Services Agreement, and related software maintenance agreements, various facilities and equipment leases, software license agreements, and software/hardware maintenance agreements. The total expenses related to the ADP Agreement, the IT Services Agreement, the EU IT Services Agreement, and related software maintenance agreements were $97.2 million, $102.1 million, and $136.0 million in fiscal years 2014, 2013, and 2012, respectively. Total expenses related to facilities and equipment leases were $39.1 million, $39.5 million, $43.1 million in fiscal years 2014, 2013, and 2012, respectively. Total expenses related to software license agreements were $25.7 million, $20.3 million, and $24.3 million in fiscal years 2014, 2013, and 2012, respectively. Total expenses related to software/hardware maintenance agreements were $52.4 million, $49.6 million, and $40.1 million in fiscal years 2014, 2013, and 2012, respectively.
81
Table of Contents
The minimum commitments under these obligations at June 30, 2014 as follows:
| Years Ending June 30, |
($ in millions) | |||
| 2015 |
$ | 115.6 | ||
| 2016 |
103.8 | |||
| 2017 |
87.8 | |||
| 2018 |
77.9 | |||
| 2019 |
69.3 | |||
| Thereafter |
197.7 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| $ | 652.1 | |||
|
|
|
|||
In addition to fixed rentals, certain leases require payment of maintenance and real estate taxes and contain escalation provisions based on future adjustments in price indices.
As of June 30, 2014, the Company had an outstanding letter of credit for $1.3 million. This letter of credit was issued in May 2007 to guarantee certain claim payments to a third-party insurance company in the event the Company does not pay its portion of the claims. No amounts were drawn on this letter of credit.
In addition, the Company has obligations under various facilities and equipment leases and software license agreements.
It is not the Company’s business practice to enter into off-balance sheet arrangements. However, the Company is exposed to market risk from changes in foreign currency exchange rates that could impact its financial position, results of operations, and cash flows. The Company manages its exposure to these market risks through its regular operating and financing activities and, when deemed appropriate, through the use of derivative financial instruments. The Company may use derivative financial instruments as risk management tools and not for trading purposes. The Company was not a party to any derivative financial instruments as of June 30, 2014 and 2013, respectively. In the normal course of business, the Company also enters into contracts in which it makes representations and warranties that relate to the performance of the Company’s products and services. The Company does not expect any material losses related to such representations and warranties, or collateral arrangements.
Our business process outsourcing and mutual fund processing services are performed by a securities broker-dealer, Broadridge Business Process Outsourcing, LLC (“BBPO”). BBPO is registered with the SEC, is a member of FINRA and is required to participate in the Securities Investor Protection Corporation (“SIPC”). Although BBPO’s FINRA membership agreement allows it to engage in clearing, and the retailing of corporate securities in addition to mutual fund retailing on a wire order basis, BBPO does not clear customer transactions, process any retail business or carry customer accounts. BBPO is subject to regulations concerning many aspects of its business, including trade practices, capital requirements, record retention, money laundering prevention, the protection of customer funds and customer securities, and the supervision of the conduct of directors, officers and employees. A failure to comply with any of these laws, rules or regulations could result in censure, fine, the issuance of cease-and-desist orders, or the suspension or revocation of SEC or FINRA authorization granted to allow the operation of its business or disqualification of its directors, officers or employees. Recently, there has been increased regulatory scrutiny of the securities industry including the outsourcing by firms of their operations or functions. This oversight could result in the future enactment of more restrictive laws or rules with respect to business process outsourcing. In addition, MG Trust Company, LLC (“MG Trust Company”), a subsidiary of Matrix, is a Colorado State non-depository trust company and National Securities Clearing Corporation trust member, whose primary business is to provide cash agent, custodial and directed or non-discretionary trust services to institutional customers. MG Trust Company operates pursuant to the rules and regulations of the Colorado Division of Banking.
82
Table of Contents
NOTE 18. CHANGES IN ACCUMULATED OTHER COMPREHENSIVE INCOME BY COMPONENT
The following tables summarize the changes in the accumulated balances for each component of accumulated other comprehensive income for the fiscal years ended June 30, 2014, 2013, and 2012, respectively:
| Foreign Currency Translation |
Available- for-Sale Securities |
Pension and Post- Retirement Liabilities |
Total | |||||||||||||
| ($ in millions) | ||||||||||||||||
| Balances at July 1, 2011 |
$ | 22.8 | $ | (2.0 | ) | $ | (4.7 | ) | $ | 16.1 | ||||||
| Other comprehensive income before reclassifications |
(13.8 | ) | (4.5 | ) | (1.3 | ) | (19.6 | ) | ||||||||
| Amounts reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive income |
— | 6.8 | 0.2 | 7.0 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Balances at June 30, 2012 |
9.0 | 0.3 | (5.8 | ) | 3.5 | |||||||||||
| Other comprehensive income before reclassifications |
(1.4 | ) | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.2 | |||||||||||
| Amounts reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive income |
— | — | 0.5 | 0.5 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Balances at June 30, 2013 |
7.6 | 1.1 | (4.5 | ) | 4.2 | |||||||||||
| Other comprehensive income before reclassifications |
6.0 | 0.8 | (1.0 | ) | 5.8 | |||||||||||
| Amounts reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive income |
— | — | 0.3 | 0.3 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Balances at June 30, 2014 |
$ | 13.6 | $ | 1.9 | $ | (5.2 | ) | $ | 10.3 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
The following table summarizes the reclassifications out of accumulated other comprehensive income:
| Years Ended June 30, | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| ($ in millions) | ||||||||||||
| Available-for-Sale Securities: |
||||||||||||
| Other-than-temporary impairment reclassified into Impairment and other charges, net |
$ | — | $ | — | $ | 10.8 | ||||||
| Tax (benefit)/expense |
— | — | (4.0 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Amortization of loss/(gain) net of tax |
$ | — | $ | — | $ | 6.8 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Pension and Post-retirement liabilities: |
||||||||||||
| Amortization of loss reclassified into Selling, general and administrative expenses |
$ | 0.5 | $ | 0.8 | $ | 0.3 | ||||||
| Tax (benefit)/expense |
(0.2 | ) | (0.3 | ) | (0.1 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Amortization of loss/(gain) net of tax |
$ | 0.3 | $ | 0.5 | $ | 0.2 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
NOTE 19. FINANCIAL DATA BY SEGMENT
The Company classifies its operations into the following two reportable segments: (1) Investor Communication Solutions and (2) Securities Processing Solutions. See Note 1, “Basis of Presentation” for a further discussion of the Company’s reportable segments. The primary components of “Other” are the elimination of intersegment revenues and profits as well as certain unallocated expenses. Foreign currency exchange is a reconciling item between the actual foreign currency exchange rates and the fiscal year 2014 budgeted foreign currency exchange rates.
Certain corporate expenses, as well as certain centrally managed expenses, are allocated based upon budgeted amounts in a reasonable manner. Because the Company compensates the management of its various
83
Table of Contents
businesses on, among other factors, segment profit, the Company may elect to record certain segment related expense items of an unusual or non-recurring nature in Other rather than reflect such items in segment profit.
| Investor Communication Solutions |
Securities Processing Solutions |
Other | Foreign Currency Exchange |
Total | ||||||||||||||||
| ($ in millions) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Year ended June 30, 2014 |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Revenues |
$ | 1,866.9 | $ | 694.8 | $ | — | $ | (3.7 | ) | $ | 2,558.0 | |||||||||
| Earnings (loss) from continuing operations before income taxes |
336.0 | 119.1 | (75.3 | ) | 15.7 | 395.5 | ||||||||||||||
| Assets |
1,134.8 | 731.6 | 325.7 | — | 2,192.1 | |||||||||||||||
| Capital expenditures |
28.2 | 11.7 | 3.3 | — | 43.2 | |||||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
25.2 | 12.3 | 9.3 | — | 46.8 | |||||||||||||||
| Amortization of acquired intangibles |
17.5 | 5.1 | — | — | 22.6 | |||||||||||||||
| Amortization of other assets |
3.9 | 18.7 | 5.4 | — | 28.0 | |||||||||||||||
| Year ended June 30, 2013 |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Revenues |
$ | 1,760.2 | $ | 660.5 | $ | 0.1 | $ | 10.0 | $ | 2,430.8 | ||||||||||
| Earnings (loss) from continuing operations before income taxes |
302.1 | 85.2 | (80.3 | ) | 16.2 | 323.2 | ||||||||||||||
| Assets |
1,062.3 | 739.4 | 216.5 | — | 2,018.2 | |||||||||||||||
| Capital expenditures |
20.7 | 9.1 | 8.4 | — | 38.2 | |||||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
23.1 | 19.4 | 5.1 | — | 47.6 | |||||||||||||||
| Amortization of acquired intangibles |
15.8 | 6.0 | — | — | 21.8 | |||||||||||||||
| Amortization of other assets |
3.1 | 20.9 | — | — | 24.0 | |||||||||||||||
| Year ended June 30, 2012 |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Revenues |
$ | 1,634.0 | $ | 655.5 | $ | 0.5 | $ | 13.5 | $ | 2,303.5 | ||||||||||
| Earnings (loss) from continuing operations before income taxes |
242.8 | 91.1 | (146.8 | ) | 13.8 | 200.9 | ||||||||||||||
| Assets |
1,018.3 | 718.8 | 250.5 | — | 1,987.6 | |||||||||||||||
| Capital expenditures |
19.9 | 9.2 | 4.7 | — | 33.8 | |||||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
22.8 | 22.2 | 6.0 | — | 51.0 | |||||||||||||||
| Amortization of acquired intangibles |
16.3 | 5.9 | — | — | 22.2 | |||||||||||||||
| Amortization of other assets |
3.1 | 15.7 | — | — | 18.8 | |||||||||||||||
Revenues and assets by geographic area are as follows:
| United States |
Canada | United Kingdom |
Other | Total | ||||||||||||||||
| ($ in millions) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Year ended June 30, 2014 |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Revenues |
$ | 2,208.9 | $ | 244.8 | $ | 65.7 | $ | 38.6 | $ | 2,558.0 | ||||||||||
| Assets |
$ | 1,830.3 | $ | 129.2 | $ | 156.5 | $ | 76.1 | $ | 2,192.1 | ||||||||||
| Year ended June 30, 2013 |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Revenues |
$ | 2,097.9 | $ | 243.2 | $ | 53.4 | $ | 36.3 | $ | 2,430.8 | ||||||||||
| Assets |
$ | 1,739.5 | $ | 86.6 | $ | 123.5 | $ | 68.6 | $ | 2,018.2 | ||||||||||
| Year ended June 30, 2012 |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Revenues |
$ | 1,997.8 | $ | 243.8 | $ | 24.3 | $ | 37.6 | $ | 2,303.5 | ||||||||||
| Assets |
$ | 1,700.0 | $ | 108.8 | $ | 114.0 | $ | 64.8 | $ | 1,987.6 | ||||||||||
84
Table of Contents
NOTE 20. QUARTERLY FINANCIAL RESULTS (UNAUDITED)
Summarized quarterly results of operations for the fiscal years ended June 30, 2014 and 2013 are as follows:
| First Quarter |
Second Quarter |
Third Quarter |
Fourth Quarter |
|||||||||||||
| ($ in millions, except per share amounts) | ||||||||||||||||
| Year ended June 30, 2014 |
||||||||||||||||
| Revenues |
$ | 545.2 | $ | 520.6 | $ | 606.3 | $ | 885.9 | ||||||||
| Gross profit |
147.7 | 135.5 | 178.7 | 334.7 | ||||||||||||
| Earnings before income taxes |
69.3 | 42.7 | 76.9 | 206.6 | ||||||||||||
| Net earnings |
44.4 | 27.6 | 50.8 | 140.2 | ||||||||||||
| Basic EPS |
0.37 | 0.23 | 0.42 | 1.16 | ||||||||||||
| Diluted EPS |
0.36 | 0.22 | 0.41 | 1.13 | ||||||||||||
| Year ended June 30, 2013 |
||||||||||||||||
| Revenues |
$ | 495.8 | $ | 493.2 | $ | 576.7 | $ | 865.1 | ||||||||
| Gross profit |
105.8 | 105.6 | 150.5 | 301.1 | ||||||||||||
| Earnings before income taxes |
28.6 | 24.7 | 67.7 | 202.2 | ||||||||||||
| Net earnings |
18.3 | 15.8 | 43.4 | 134.6 | ||||||||||||
| Basic EPS |
0.15 | 0.13 | 0.36 | 1.12 | ||||||||||||
| Diluted EPS |
0.14 | 0.13 | 0.35 | 1.09 | ||||||||||||
* * * * * * *
85
Table of Contents
Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc.
Schedule II—Valuation and Qualifying Accounts
($ in thousands)
| Column A |
Column B | Column C | Column D | Column E | ||||||||||||
| Balance at beginning of period |
Additions charged to costs and expenses |
Deductions | Balance at end of period |
|||||||||||||
| Fiscal year ended June 30, 2014: |
||||||||||||||||
| Allowance for doubtful accounts |
$ | 3,737 | $ | 995 | $ | (1,456 | ) | $ | 3,276 | |||||||
| Deferred tax valuation allowance |
$ | 12,500 | $ | — | $ | (1,600 | ) | $ | 10,900 | |||||||
| Fiscal year ended June 30, 2013: |
||||||||||||||||
| Allowance for doubtful accounts |
$ | 6,539 | $ | 1,811 | $ | (4,613 | ) | $ | 3,737 | |||||||
| Deferred tax valuation allowance |
$ | 14,700 | $ | 1,000 | $ | (3,200 | ) | $ | 12,500 | |||||||
| Fiscal year ended June 30, 2012: |
||||||||||||||||
| Allowance for doubtful accounts |
$ | 2,010 | $ | 5,076 | $ | (547 | ) | $ | 6,539 | |||||||
| Deferred tax valuation allowance |
$ | 12,100 | $ | 2,600 | $ | — | $ | 14,700 | ||||||||
86
Table of Contents
| ITEM 9. | Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure. |
None.
| ITEM 9A. | Controls and Procedures. |
Management Report
Attached as Exhibits 31.1 and 31.2 to this Form 10-K are certifications of Broadridge’s President and Chief Executive Officer, and Chief Financial Officer, which are required by Rule 13a-14(a) of the Exchange Act, as amended. This “Controls and Procedures” section should be read in conjunction with the Deloitte & Touche LLP audit and attestation of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting that appears in Item 8 “Financial Statements and Supplementary Data” in this Annual Report on Form 10-K and is hereby incorporated herein by reference.
Management’s Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Our management, with the participation of our President and Chief Executive Officer, and Chief Financial Officer as of June 30, 2014, evaluated the effectiveness of our disclosure controls as defined in Rule 13a-15(e) under the Exchange Act. The President and Chief Executive Officer, and Chief Financial Officer concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures as of June 30, 2014 were effective to ensure that the information required to be disclosed by us in reports filed under the Exchange Act is (i) recorded, processed, summarized, and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and forms and (ii) accumulated and communicated to our management, including our President and Chief Executive Officer, and Chief Financial Officer, as appropriate, to allow timely decisions regarding disclosure.
Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
It is the responsibility of Broadridge’s management to establish and maintain effective internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Rule 13a-15(f) under the Exchange Act as defined in Rule 13a-15(f) under the Exchange Act). Internal control over financial reporting is designed to provide reasonable assurance to Broadridge’s management and board of directors regarding the preparation of reliable financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles.
Broadridge’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that: (i) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of Broadridge; (ii) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of Broadridge are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of Broadridge; and (iii) provide reasonable assurance regarding the prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of Broadridge’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements of Broadridge.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Therefore, even those systems determined to be effective can provide only reasonable assurance with respect to financial statement preparation and presentation.
Management has performed an assessment of the effectiveness of Broadridge’s internal control over financial reporting as of June 30, 2014 based upon criteria set forth in Internal Control—Integrated Framework (1992) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. Based on this assessment, management determined that Broadridge’s internal control over financial reporting was effective as of June 30, 2014.
87
Table of Contents
Deloitte & Touche LLP, the Company’s independent registered public accounting firm, has audited the effectiveness of the Company’s internal over financial reporting and has issued an attestation report on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting, which attestation report appears in Item 8 “Financial Statements and Supplementary Data” in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
| /S/ RICHARD J. DALY | ||
| Richard J. Daly | ||
| President and Chief Executive Officer | ||
| /S/ JAMES M. YOUNG | ||
| James M. Young | ||
| Vice President, Chief Financial Officer | ||
Lake Success, New York
August 7, 2014
Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
No change in our internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) under the Exchange Act) occurred during the fiscal quarter ended June 30, 2014 that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
| ITEM 9B. | Other Information. |
None.
88
Table of Contents
| ITEM 10. | Directors. Executive Officers and Corporate Governance. |
We incorporate by reference the information responsive to this Item appearing in our Proxy Statement.
| ITEM 11. | Executive Compensation. |
We incorporate by reference the information responsive to this Item appearing in our Proxy Statement.
| ITEM 12. | Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters. |
We incorporate by reference the information responsive to this Item appearing in our Proxy Statement.
| ITEM 13. | Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence. |
We incorporate by reference the information responsive to this Item appearing in our Proxy Statement.
| ITEM 14. | Principal Accounting Fees and Services. |
We incorporate by reference the information responsive to this Item appearing in our Proxy Statement.
89
Table of Contents
| ITEM 15. | Exhibits, Financial Statement Schedules. |
| (a) | The following documents are filed as part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K: |
| 1. | Financial Statements |
The Consolidated Financial Statements are listed under Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. See Index to Financial Statements and Financial Statement Schedule.
| 2. | Financial Statement Schedule. |
Schedule II—Valuation and Qualifying Accounts is listed under Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. See Index to Financial Statements and Financial Statement Schedule.
| 3. | Exhibits. |
The Exhibits filed as part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K are listed on the Exhibit Index, which Exhibit Index is incorporated in this Annual Report on Form 10-K by reference.
90
Table of Contents
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, the Registrant has duly caused this Annual Report on Form 10-K to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned hereunto duly authorized.
Date: August 7, 2014
| BROADRIDGE FINANCIAL SOLUTIONS, INC. | ||||
| By: | /s/ RICHARD J. DALY |
|||
| Name: | Richard J. Daly | |||
| Title: | President and Chief Executive Officer | |||
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, this Annual Report on Form 10-K has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the Registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| Signature |
Title |
Date | ||
| /S/ RICHARD J. DALY Richard J. Daly |
President and Chief Executive Officer and Director (Principal Executive Officer) | August 7, 2014 | ||
| /S/ JAMES M. YOUNG James M. Young |
Vice President, Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) | August 7, 2014 | ||
| /S/ LESLIE A. BRUN Leslie A. Brun |
Chairman of the Board | August 7, 2014 | ||
| /S/ ROBERT N. DUELKS Robert N. Duelks |
Director | August 7, 2014 | ||
| /S/ RICHARD J. HAVILAND Richard J. Haviland |
Director | August 7, 2014 | ||
|
Sandra S. Jaffee |
Director | |||
| /S/ STUART R. LEVINE Stuart R. Levine |
Director | August 7, 2014 | ||
| /S/ MAURA A. MARKUS Maura A. Markus |
Director | August 7, 2014 | ||
| /S/ THOMAS J. PERNA Thomas J. Perna |
Director | August 7, 2014 | ||
| /S/ ALAN J. WEBER Alan J. Weber |
Director | August 7, 2014 | ||
91
Table of Contents
EXHIBIT INDEX
| Exhibit Number |
Description of Exhibit(1) | |
| 2.1 | Asset Purchase Agreement, dated as of November 2, 2009, by and among Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc., Ridge Clearing & Outsourcing Solutions, Inc., Penson Worldwide, Inc., and Penson Financial Services, Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.1 to Form 10-Q filed on February 4, 2010).(2)(3) | |
| 2.2 | Stock Purchase Agreement, dated as of November 23, 2010, by and among the sellers named therein, Broadridge Investor Communication Solutions, Inc. and Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.1 to Form 8-K/A filed on May 19, 2011).(2)(3) | |
| 2.3 | Escrow Agreement, dated as of January 7, 2011, by and among Capital One, N.A., Broadridge Investor Communication Solutions, Inc., the sellers named therein and Bluff Point Associates Corp. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.2 to Form 8-K/A filed on May 19, 2011).(3) | |
| 3.1 | Certificate of Incorporation of Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to Form 8-K filed on April 2, 2007). | |
| 3.2 | Amended and Restated By-laws of Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.2 to Form 8-K filed on June 7, 2007). | |
| 4.1 | Indenture, dated as of May 29, 2007, by and between Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc. and U.S. Bank National Association, as Trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to Form 8-K filed on May 30, 2007). | |
| 4.2 | First Supplemental Indenture, dated as of May 29, 2007, by and between Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc. and U.S. Bank National Association, as Trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.2 to Form 8-K filed on May 30, 2007). | |
| 4.3 | Form of 6.125% Senior Note due 2017 dated May 29, 2007 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.3 to Form 8-K filed on May 30, 2007). | |
| 4.4 | Second Supplemental Indenture dated as of August 21, 2013, by and between Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc. and U.S. Bank National Association, as Trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.2 to Form 8-K filed on August 21, 2013). | |
| 4.5 | Form of Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc. 3.950% Senior Note due 2020 (included in Exhibit 4.2 to Form 8-K filed on August 21, 2013 and incorporated by reference). | |
| 10.1 | Separation and Distribution Agreement, dated as of March 20, 2007, between Automatic Data Processing, Inc. and Broadridge Financial Solutions, LLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Form 8-K filed on March 21, 2007). | |
| 10.2 | Tax Allocation Agreement, dated as of March 29, 2007, between Automatic Data Processing, Inc. and Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Form 8-K filed on April 2, 2007). | |
| 10.3 | Transition Services Agreement, dated as of March 29, 2007, between Automatic Data Processing, Inc. and Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to Form 8-K filed on April 2, 2007). | |
| 10.4 | Data Center Outsourcing Services Agreement, dated as of March 29, 2007, between Automatic Data Processing, Inc. and Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to Form 8-K filed on April 2, 2007). | |
| 10.5 | Intellectual Property Transfer Agreement, dated as of March 29, 2007, between Automatic Data Processing, Inc. and Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to Form 8-K filed on April 2, 2007). | |
92
Table of Contents
| Exhibit Number |
Description of Exhibit(1) | |
| 10.6 | Employee Matters Agreement, dated as of March 29, 2007, between Automatic Data Processing, Inc. and Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 to Form 8-K filed on April 2, 2007). | |
| 10.7 | Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc. Change in Control Severance Plan for Corporate Officers (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.6 to Form 8-K filed on April 2, 2007). | |
| 10.8 | Amendment No. 1 to the Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc. Change in Control Severance Plan for Corporate Officers (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.26 to Form 10-K/A filed on October 27, 2010). | |
| 10.9 | Amended and Restated Supplemental Officers Retirement Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.27 to Form 10-K/A filed on October 27, 2010). | |
| 10.10 | Change in Control Enhancement Agreement for Richard J. Daly (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.8 to Form 8-K filed on April 2, 2007). | |
| 10.11 | Amendment No. 1 to Change in Control Enhancement Agreement for Richard J. Daly (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.28 to Form 10-K/A filed on October 27, 2010). | |
| 10.12 | Change in Control Enhancement Agreement for John Hogan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.9 to Form 8-K filed on April 2, 2007). | |
| 10.13 | Amendment No. 1 to Change in Control Enhancement Agreement for John Hogan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.29 to Form 10-K/A filed on October 27, 2010). | |
| 10.14 | Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc. 2007 Omnibus Award Plan (Amended and Restated effective August 4, 2008, as amended effective August 4, 2009 and August 3, 2010) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Form 8-K filed on November 19, 2010). | |
| 10.15 | Underwriting Agreement, dated as of May 23, 2007, by and among Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc., Citigroup Global Markets Inc. and J.P. Morgan Securities Inc., as representatives of the underwriters party thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 1.1 to Form 8-K filed on May 30, 2007). | |
| 10.16 | Master Services Agreement, dated as of November 2, 2009, by and between Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc. and Penson Worldwide, Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Form 10-Q/A filed on June 10, 2010).(3) | |
| 10.17 | Information Technology Services Agreement, dated as of March 31, 2010, by and between International Business Machines Corporation and Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to Form 10-Q filed on May 10, 2010).(3) | |
| 10.18 | Amendment Agreement, dated as of June 25, 2010, by and among SAI Holdings, Inc., Penson Financial Services, Inc., Penson Worldwide, Inc., Penson Financial Services Ltd., Penson Financial Services Canada Inc., Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc., Ridge Clearing & Outsourcing Solutions, Inc., Broadridge Financial Solutions (Canada) Inc., and Ridge Clearing & Outsourcing Solutions Limited (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.22 to Form 10-K filed on August 12, 2010).(3) | |
| 10.19 | Amendment, Assignment and Assumption Agreement, dated as of June 25, 2010, by and among SAI Holdings, Inc., Penson Financial Services, Inc., Penson Worldwide, Inc., Penson Financial Services Ltd., Penson Financial Services Canada Inc., Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc., Ridge Clearing & Outsourcing Solutions, Inc., Broadridge Financial Solutions (Canada) Inc., and Ridge Clearing & Outsourcing Solutions Limited (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.23 to Form 10-K filed on August 12, 2010).(2)(3) | |
| 10.20 | Amendment No. 1 to the Information Technology Services Agreement, dated as of June 25, 2010, by and between International Business Machines Corporation and Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.24 to Form 10-K filed on August 12, 2010).(3) | |
93
Table of Contents
| Exhibit Number |
Description of Exhibit(1) | |
| 10.21 | Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc. Director Deferred Compensation Program (Amended and Restated Effective November 17, 2010) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Form 10-Q filed on February 8, 2011). | |
| 10.22 | Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc. Supplemental Executive Retirement Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.31 to Form 10-K/A filed on October 27, 2010). | |
| 10.23 | Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc. Executive Deferred Compensation Plan (Amended and Restated effective June 15, 2011) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.32 to Form 10-K filed on August 12, 2011). | |
| 10.24 | Amendment No. 3 to the Information Technology Services Agreement, dated as of April 15, 2011, by and between International Business Machines Corporation and Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.33 to Form 10-K filed on August 12, 2011). | |
| 10.25 | Amendment No. 5 to the Information Technology Services Agreement, dated as of June 11, 2011, by and between International Business Machines Corporation and Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc.(3) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.34 to Form 10-K filed on August 12, 2011). | |
| 10.26 | Officer Severance Plan dated September 16, 2011 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Form 8-K filed on September 20, 2011). | |
| 10.27 | Credit Agreement dated September 22, 2011, among Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc., as Borrower, the Lenders Party thereto, JPMorgan Chase, N.A., as Administrative Agent, and J.P. Morgan Europe Limited, as London Agent (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Form 8-K filed September 23, 2011). | |
| 10.28 | Amendment Agreement, dated October 11, 2011, by and among SAI Holdings, Inc., Penson Financial Services, Inc., Penson Worldwide, Inc., Penson Financial Services Canada Inc., Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc., Ridge Clearing & Outsourcing Solutions, Inc., Broadridge Solutions (Canada) Inc., and Ridge Clearing & Outsourcing Solutions Limited (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to Form 10-Q filed on November 3, 2011). | |
| 10.29 | Amended and Restated Seller Note, effective as of July 1, 2011, issued by Penson Worldwide, Inc. to Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to Form 10-Q filed November 3, 2011). | |
| 10.30 | Amendment No. 7 to the Information Technology Services Agreement, dated October 10, 2011, by and between International Business Machines Corporation and Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Form 10-Q filed February 7, 2012).(3) | |
| 10.31 | Restructuring Support Agreement, dated as of March 13, 2012, among Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc., Ridge Clearing and Outsourcing Solutions, Inc., Penson Worldwide, Inc. and certain subsidiaries of Penson Worldwide, Inc., and certain Penson Senior Secured Noteholders and Penson Convertible Noteholders (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Form 8-K filed on March 14, 2012). | |
| 10.32 | Purchase and Sale Agreement, dated as of May 31, 2012, by and among Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc., Broadridge Securities Processing Solutions, Inc. and Apex Clearing Holdings LLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.39 to Form 10-K filed on August 9, 2012).(2) | |
| 10.33 | Termination and Mutual Release Agreement entered into on June 5, 2012, by and among Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc., Ridge Clearing & Outsourcing Solutions, Inc., Broadridge Financial Solutions (Canada), Inc., Penson Worldwide, Inc., Penson Financial Services, Inc., and Penson Financial Services Canada, Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.40 to Form 10-K filed on August 9, 2012). | |
94
Table of Contents
| Exhibit Number |
Description of Exhibit(1) | |
| 10.34 | Master Services Agreement entered into on June 5, 2012, between Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc. and Apex Clearing Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.41 to Form 10-K filed on August 9, 2012).(3) | |
| 10.35 | Amendment No. 2, dated September 19, 2013, to the Change in Control Enhancement Agreement, dated as of March 29, 2007 and amended effective December 31, 2008, between Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc. and Richard J. Daly (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Form 8-K filed on September 20, 2013). | |
| 10.36 | Amendment No. 2, dated September 19, 2013, to the Change in Control Enhancement Agreement, dated as of March 29, 2007 and amended effective December 31, 2008, between Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc. and John Hogan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to Form 8-K filed on September 20, 2013). | |
| 10.37 | Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc. 2007 Omnibus Award Plan, Amended and Restated effective November 14, 2013 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to Form 8-K filed on November 15, 2013). | |
| 10.38 | Special Officer Separation Agreement, dated as of February 5, 2014, between Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc. and Dan Sheldon (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Form 8-K filed on February 5, 2014). | |
| 10.39 | Offer Letter, dated May 21, 2014, between Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc. and James M. Young. | |
| 12.1 | Computation of Ratio of Earnings to Fixed Charges. | |
| 14.1 | Code of Ethics for the Company’s Principal Executive Officer and Senior Financial Officers (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 99.1 to Form 8-K filed on August 2, 2007). | |
| 21.1 | Subsidiaries of the Company. | |
| 23.1 | Consent of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm. | |
| 31.1 | Certification of the President and Chief Executive Officer of Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc., pursuant to Rule 13a-14 of the Exchange Act, as adopted pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | |
| 31.2 | Certification of the Chief Financial Officer of Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc., pursuant to Rule 13a-14 of the Exchange Act, as adopted pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | |
| 32.1 | Certification of the President and Chief Executive Officer pursuant to Rule 13a-14(b) of the Exchange Act and 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | |
| 32.2 | Certification of the Chief Financial Officer pursuant to Rule 13a-14(b) of the Exchange Act and 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | |
| 101 | The following financial statements from the Broadridge Financial Solutions, Inc. Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal years ended June 30, 2014, 2013, and 2012, formatted in eXtensible Business Reporting Language (XBRL): (i) consolidated statements of earnings for the fiscal years ended June 30, 2014, 2013 and 2012, (ii) consolidated statements of comprehensive income for the fiscal years ended June 30, 2014, 2013 and 2012, (iii) consolidated balance sheets as of June 30, 2014 and 2013, (iv) consolidated statements of cash flows for the fiscal years ended June 30, 2014, 2013 and 2012, (v) consolidated statements of stockholders’ equity for the fiscal years ended June 30, 2014, 2013 and 2012, and (vi) the notes to the consolidated financial statements. | |
95
Table of Contents
| (1) | The SEC File No. for the Company’s Form 8-K Reports referenced is 001-33220. |
| (2) | Schedules to the Asset Purchase Agreement filed as Exhibit 2.1, as amended by the Amendment, Assignment and Assumption Agreement filed as Exhibit 10.23, and the Stock Purchase Agreement filed as Exhibit 2.2, and the Purchase and Sale Agreement filed as Exhibit 10.38 have been omitted pursuant to Item 601(b)(2) of Regulation S-K. The Registrant hereby undertakes to furnish supplemental copies of any omitted schedules upon request by the Securities and Exchange Commission. |
| (3) | Certain Confidential Information contained in this Exhibit was omitted by means of redacting a portion of the text and replacing it with an asterisk. This Exhibit has been filed separately with the Secretary of the Securities and Exchange Commission without the redaction pursuant to a Confidential Treatment Request under Rule 24b-2 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. |
96
