Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| 8-K - 8-K - Viracta Therapeutics, Inc. | d24964d8k.htm |

Exhibit 99.1 VIRACTA CORPORATE OVERVIEW NASDAQ: VIRX I WWW.VIRACTA.COM

Forward Looking Statements This communication contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995, which are based on current expectations, estimates and projections based on information currently available to management, including, without limitation, statements regarding: effects of the recent merger resulting in the combined company Viracta Therapeutics, Inc. (“Viracta” or the “Company”) ta’s ; cliV nical irac development pipeline, including expected timing of the registration trial for EBV-associated lymphomas and the Phase 1b/2 trial in EBV-associated solid tumors; Viracta’s expected cash forecast and runway into 2024; the expected ability of Viracta to undertake certain activities and accomplish certain goals with respect to its clinical program in EBV+ lymphoma or other virus-associated malignancies, the projected timeline of clinical development and other regulatory activities related to Viracta’s clinical program in EBV+ lymphoma or other -virus associated malignancies, and expectations regarding future therapeutic and commercial potential with respect to Viracta’s clinical program in EBV+ lymphoma or other -asso virus ciated malignancies; anticipated market opportunity and patient populations; the potential for multiple approvals in EBV+ lymphomas; the potential of Viracta’s synthetic lethality approach; and other ents stat tha em t are not historical facts. Risks and uncertainties related to Viracta that may cause actual results to differ materially from those expressed or implied in any forward-looking statement include, but are not limited to: the ability of Viracta to timely and successfully achieve the anticipated benefits of the recent merger and concurrent financing, including Viracta’s ability to successfully operate as a public company; Viracta’s ability to successfully enroll pa an tien d complet ts in e its ongoing and planned clinical trials; Viracta's plans to develop and commercialize its product candidates, including all oral combinations of nanatinostat and valganciclovir; the timing of initiation of Viracta's planned clinical trials; the timing of the availability of data from Viracta's clinical trials; the possibility that previous preclinical and clinical results may not be predictive of future clinical results; the timing of any planned investigational new drug application or new drug application; Viracta's plans to research, develop and commercialize its current and future product candidates; the clinical utility, potential benefits and market acceptance of Viracta's product candidates; Viracta's ability to identify additional products or product candidates with significant commercial potential; developments and projections relating to Viracta's competitors and its industry; the impact of government laws and regulations; Viracta's ability to protect its intellectual property position; and Viracta's estimates regarding future expenses, capital requirements and need for additional financing. These risks and uncertainties may be amplified by the COVID-19 pandemic, which has caused significant economic uncertainty. If any of these risks materialize or underlying assumptions prove incorrect, actual results could differ materially from the results implied by these forward-looking statements. Additional risks and uncertainties that could cause actual outcomes and results to differ materially from those contemplated by the forward-looking statements are included under the caption “Risk Factors” and elsewhere in Viracta’s most recent filings with the SEC and any subsequent repo rm rts 10-on K, Form Fo 10-Q or Form 8-K filed with the SEC from time to time and available at www.sec.gov. The forward-looking statements included in this communication are made only as of the date hereof. Viracta assumes no obligation and does not intend to update these forward-looking statements, except as required by law or applicable regulation. 2

Viracta Therapeutics: Introduction Viracta is a precision oncology company focused on the treatment of virus-associated malignancies Novel “kick and kill” oral therapy with a combination of nanatinostat (Nstat) and valganciclovir (VGCV) selectively + targets EBV cancer cells EBV associated with >265,000 cases/year in lymphoma, nasopharyngeal and gastric cancer (globally) + Lead program in relapsed/refractory (R/R) EBV lymphoma completed enrollment of phase 2 clinical trial, demonstrating promising efficacy and safety; updated data in H2 2021 Preliminary ORR/CR of 80%/40% in T/NK-NHL (n=10) & 60%/33% in DLBCL (n=6) + NAVAL-1, a late-stage global pivotal clinical trial for R/R EBV lymphomas, is expected to begin in H1 2021 + Unique single arm basket study with an adaptive design intended to support potential approvals across multiple EBV lymphoma subtypes + Upcoming expansion of clinical pipeline into EBV solid tumors Phase 1b/2 trial expected to begin in H2 2021 Strong balance sheet ~$120 million in cash as of February 24, 2021, with projected runway into 2024 3 EBV: Epstein-Barr virus; R/R: Relapsed/refractory
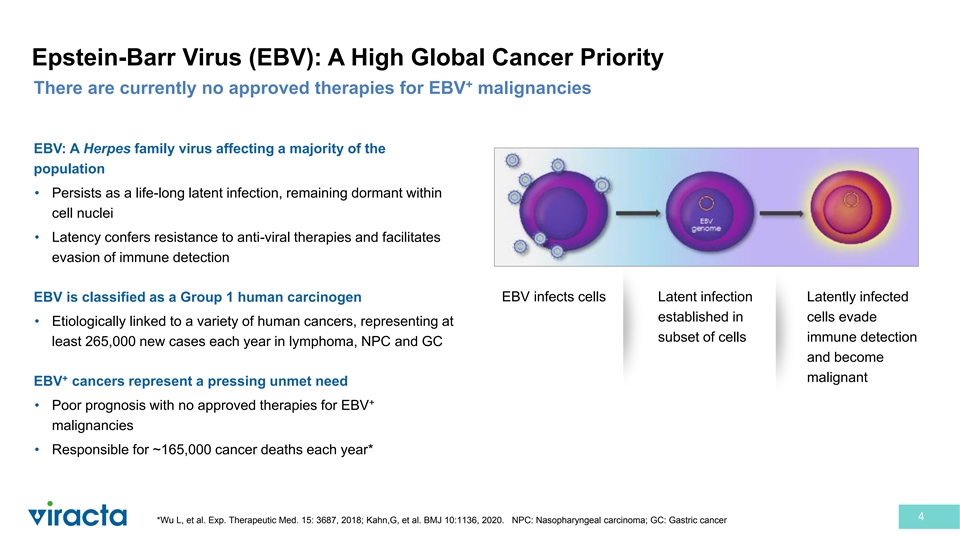
Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV): A High Global Cancer Priority + There are currently no approved therapies for EBV malignancies EBV: A Herpes family virus affecting a majority of the population • Persists as a life-long latent infection, remaining dormant within cell nuclei • Latency confers resistance to anti-viral therapies and facilitates evasion of immune detection EBV infects cells Latent infection Latently infected EBV is classified as a Group 1 human carcinogen established in cells evade • Etiologically linked to a variety of human cancers, representing at subset of cells immune detection least 265,000 new cases each year in lymphoma, NPC and GC and become + malignant EBV cancers represent a pressing unmet need + • Poor prognosis with no approved therapies for EBV malignancies • Responsible for ~165,000 cancer deaths each year* 4 *Wu L, et al. Exp. Therapeutic Med. 15: 3687, 2018; Kahn,G, et al. BMJ 10:1136, 2020. NPC: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma; GC: Gastric cancer
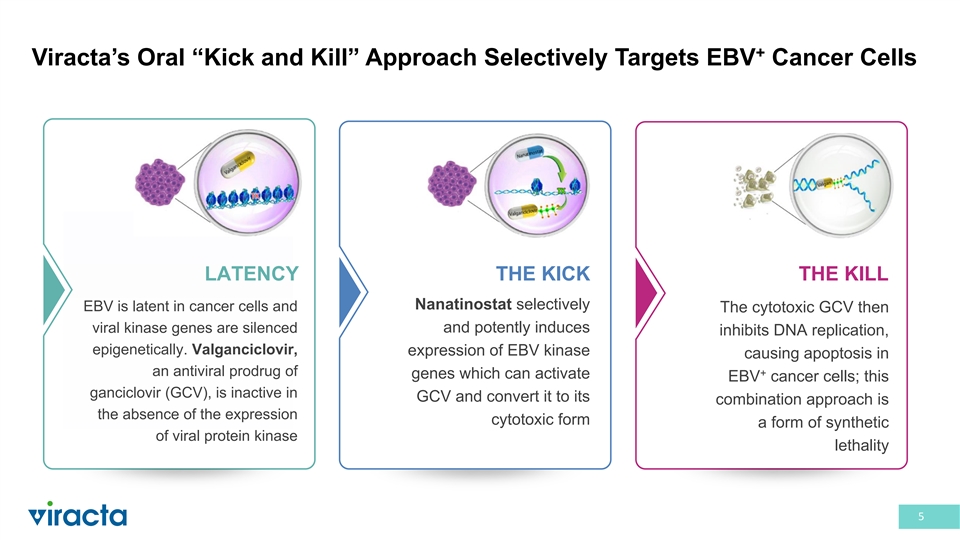
+ Viracta’s Oral “Kick and Kill” Approach Selectively Targets EBV Cancer Cells LATENCY THE KICK THE KILL Nanatinostat selectively EBV is latent in cancer cells and The cytotoxic GCV then viral kinase genes are silenced and potently induces inhibits DNA replication, epigenetically. Valganciclovir, expression of EBV kinase causing apoptosis in an antiviral prodrug of + genes which can activate EBV cancer cells; this ganciclovir (GCV), is inactive in GCV and convert it to its combination approach is the absence of the expression cytotoxic form a form of synthetic of viral protein kinase lethality 5
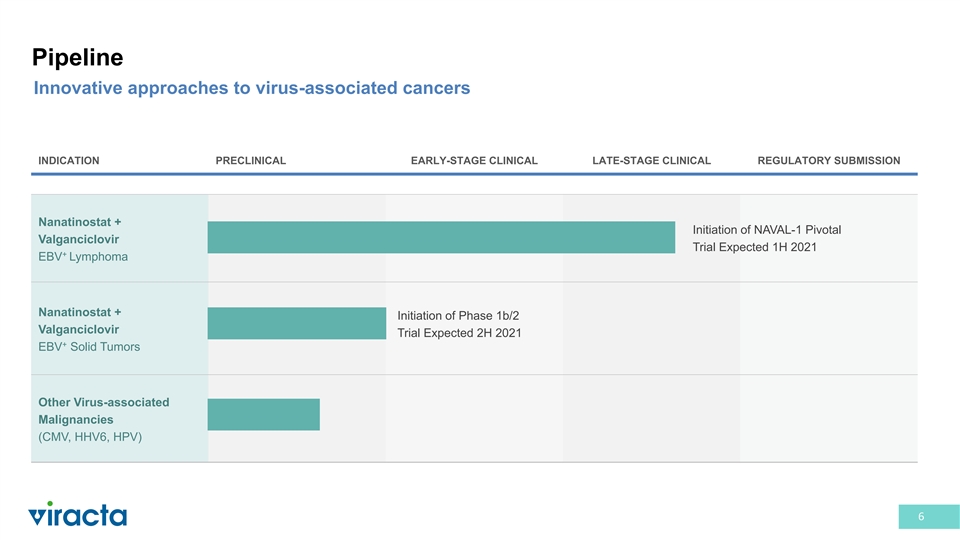
Pipeline Innovative approaches to virus-associated cancers INDICATION PRECLINICAL EARLY-STAGE CLINICAL LATE-STAGE CLINICAL REGULATORY SUBMISSION Nanatinostat + Initiation of NAVAL-1 Pivotal Valganciclovir Trial Expected 1H 2021 + EBV Lymphoma Nanatinostat + Initiation of Phase 1b/2 Valganciclovir Trial Expected 2H 2021 + EBV Solid Tumors Other Virus-associated Malignancies (CMV, HHV6, HPV) 6

+ EBV Lymphoma Program
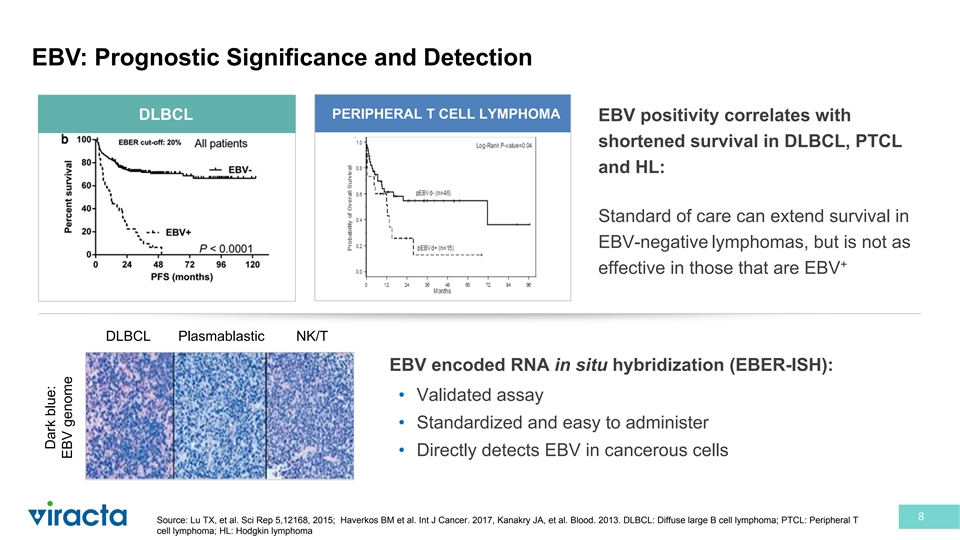
EBV: Prognostic Significance and Detection PERIPHERAL T CELL LYMPHOMA DLBCL EBV positivity correlates with shortened survival in DLBCL, PTCL and HL: Standard of care can extend survival in EBV-negative lymphomas, but is not as + effective in those that are EBV DLBCL Plasmablastic NK/T EBV encoded RNA in situ hybridization (EBER-ISH): • Validated assay • Standardized and easy to administer • Directly detects EBV in cancerous cells 8 Source: Lu TX, et al. Sci Rep 5,12168, 2015; Haverkos BM et al. Int J Cancer. 2017, Kanakry JA, et al. Blood. 2013. DLBCL: Diffuse large B cell lymphoma; PTCL: Peripheral T cell lymphoma; HL: Hodgkin lymphoma Dark blue: EBV genome
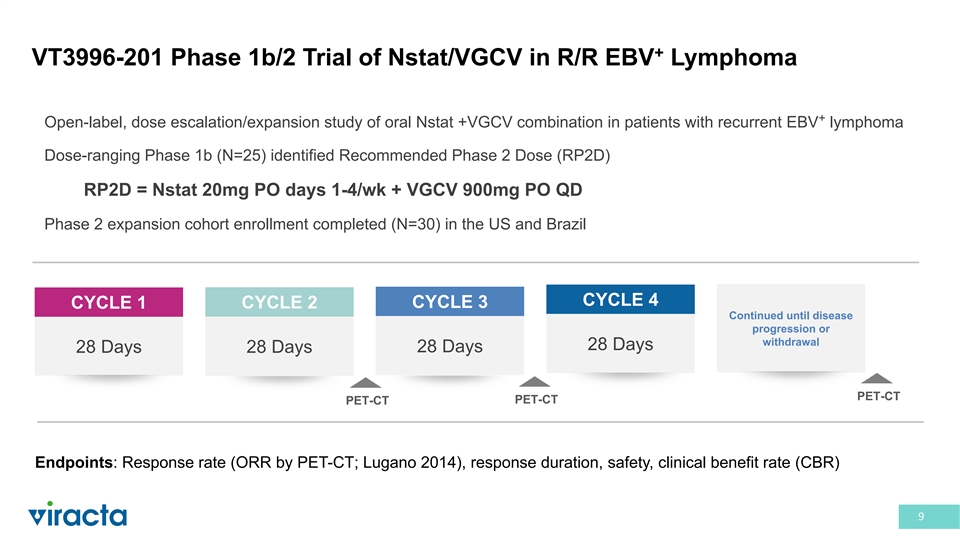
+ VT3996-201 Phase 1b/2 Trial of Nstat/VGCV in R/R EBV Lymphoma + Open-label, dose escalation/expansion study of oral Nstat +VGCV combination in patients with recurrent EBV lymphoma Dose-ranging Phase 1b (N=25) identified Recommended Phase 2 Dose (RP2D) RP2D = Nstat 20mg PO days 1-4/wk + VGCV 900mg PO QD Phase 2 expansion cohort enrollment completed (N=30) in the US and Brazil CYCLE 4 CYCLE 3 CYCLE 1 CYCLE 2 Continued until disease progression or withdrawal 28 Days 28 Days 28 Days 28 Days PET-CT PET-CT PET-CT Endpoints: Response rate (ORR by PET-CT; Lugano 2014), response duration, safety, clinical benefit rate (CBR) 9
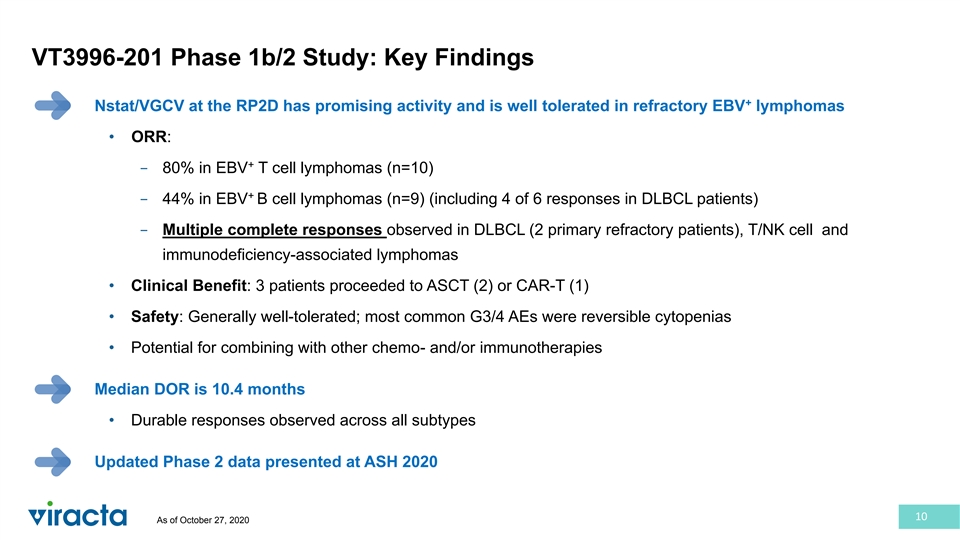
VT3996-201 Phase 1b/2 Study: Key Findings + Nstat/VGCV at the RP2D has promising activity and is well tolerated in refractory EBV lymphomas • ORR: + − 80% in EBV T cell lymphomas (n=10) + − 44% in EBV B cell lymphomas (n=9) (including 4 of 6 responses in DLBCL patients) − Multiple complete responses observed in DLBCL (2 primary refractory patients), T/NK cell and immunodeficiency-associated lymphomas • Clinical Benefit: 3 patients proceeded to ASCT (2) or CAR-T (1) • Safety: Generally well-tolerated; most common G3/4 AEs were reversible cytopenias • Potential for combining with other chemo- and/or immunotherapies Median DOR is 10.4 months • Durable responses observed across all subtypes Updated Phase 2 data presented at ASH 2020 10 As of October 27, 2020
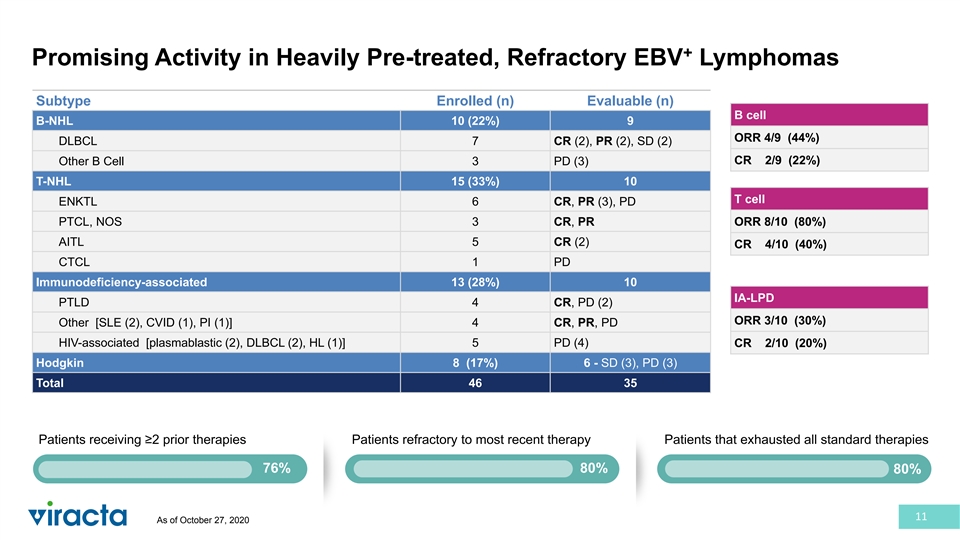
+ Promising Activity in Heavily Pre-treated, Refractory EBV Lymphomas Subtype Enrolled (n) Evaluable (n) B cell B-NHL 10 (22%) 9 ORR 4/9 (44%) DLBCL 7 CR (2), PR (2), SD (2) CR 2/9 (22%) Other B Cell 3 PD (3) T-NHL 15 (33%) 10 T cell ENKTL 6 CR, PR (3), PD PTCL, NOS 3 CR, PR ORR 8/10 (80%) AITL 5 CR (2) CR 4/10 (40%) CTCL 1 PD Immunodeficiency-associated 13 (28%) 10 IA-LPD PTLD 4 CR, PD (2) ORR 3/10 (30%) Other [SLE (2), CVID (1), PI (1)] 4 CR, PR, PD HIV-associated [plasmablastic (2), DLBCL (2), HL (1)] 5 PD (4) CR 2/10 (20%) Hodgkin 8 (17%) 6 - SD (3), PD (3) Total 46 35 Patients receiving ≥2 prior therapies Patients refractory to most recent therapy Patients that exhausted all standard therapies 76% 80% 80% 11 As of October 27, 2020
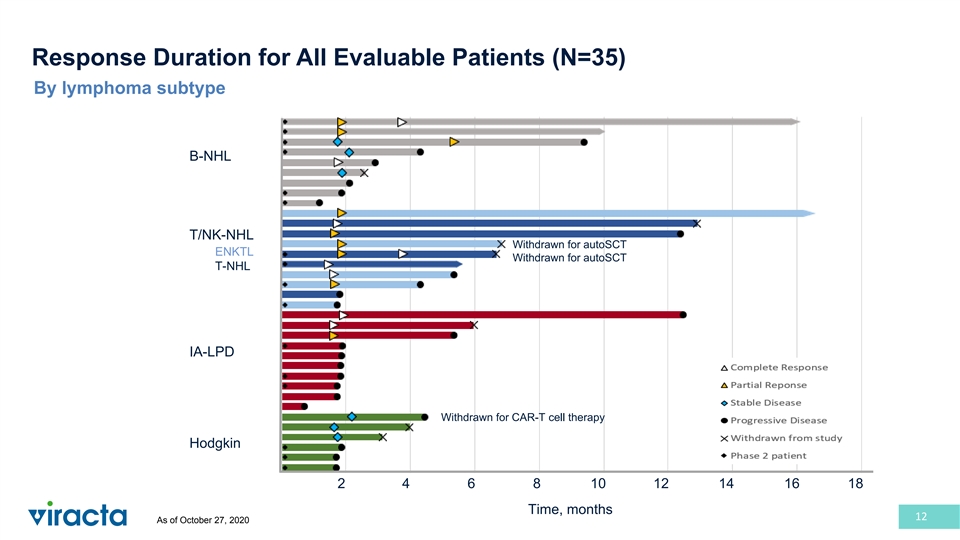
Response Duration for All Evaluable Patients (N=35) By lymphoma subtype B-NHL T/NK-NHL Withdrawn for autoSCT ENKTL Withdrawn for autoSCT T-NHL IA-LPD Withdrawn for CAR-T cell therapy Hodgkin 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 Time, months 12 As of October 27, 2020
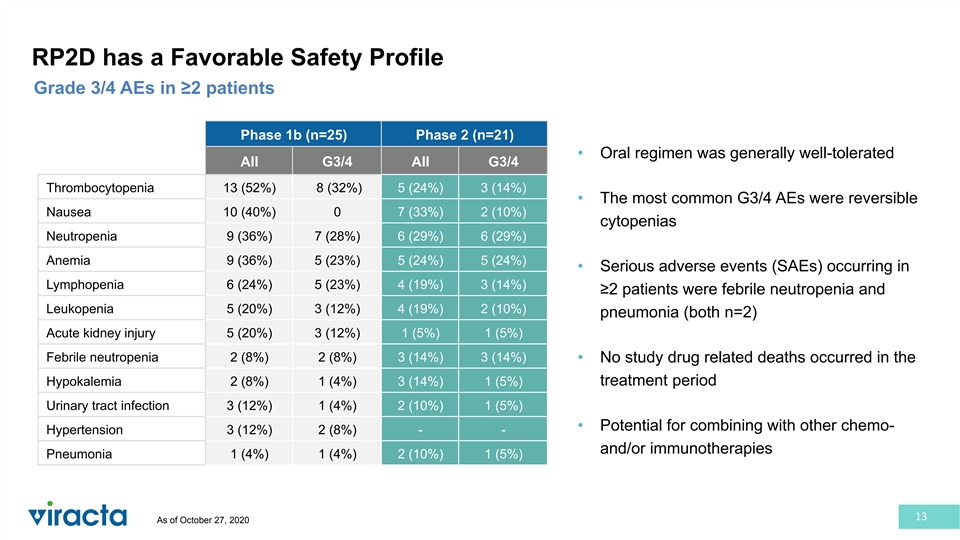
RP2D has a Favorable Safety Profile Grade 3/4 AEs in ≥2 patients Phase 1b (n=25) Phase 2 (n=21) • Oral regimen was generally well-tolerated All G3/4 All G3/4 Thrombocytopenia 13 (52%) 8 (32%) 5 (24%) 3 (14%) • The most common G3/4 AEs were reversible Nausea 10 (40%) 0 7 (33%) 2 (10%) cytopenias Neutropenia 9 (36%) 7 (28%) 6 (29%) 6 (29%) Anemia 9 (36%) 5 (23%) 5 (24%) 5 (24%) • Serious adverse events (SAEs) occurring in Lymphopenia 6 (24%) 5 (23%) 4 (19%) 3 (14%) ≥2 patients were febrile neutropenia and Leukopenia 5 (20%) 3 (12%) 4 (19%) 2 (10%) pneumonia (both n=2) Acute kidney injury 5 (20%) 3 (12%) 1 (5%) 1 (5%) Febrile neutropenia 2 (8%) 2 (8%) 3 (14%) 3 (14%) • No study drug related deaths occurred in the Hypokalemia 2 (8%) 1 (4%) 3 (14%) 1 (5%) treatment period Urinary tract infection 3 (12%) 1 (4%) 2 (10%) 1 (5%) • Potential for combining with other chemo- Hypertension 3 (12%) 2 (8%) - - and/or immunotherapies Pneumonia 1 (4%) 1 (4%) 2 (10%) 1 (5%) 13 As of October 27, 2020
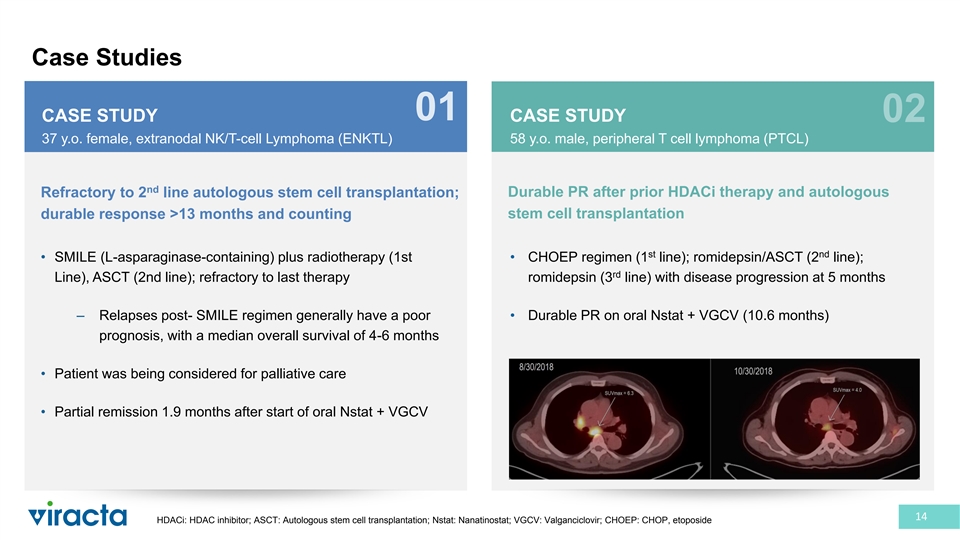
Case Studies 01 CASE STUDY CASE STUDY 02 37 y.o. female, extranodal NK/T-cell Lymphoma (ENKTL) 58 y.o. male, peripheral T cell lymphoma (PTCL) nd Refractory to 2 line autologous stem cell transplantation; Durable PR after prior HDACi therapy and autologous stem cell transplantation durable response >13 months and counting st nd • SMILE (L-asparaginase-containing) plus radiotherapy (1st • CHOEP regimen (1 line); romidepsin/ASCT (2 line); rd Line), ASCT (2nd line); refractory to last therapy romidepsin (3 line) with disease progression at 5 months – Relapses post- SMILE regimen generally have a poor • Durable PR on oral Nstat + VGCV (10.6 months) prognosis, with a median overall survival of 4-6 months • Patient was being considered for palliative care • Partial remission 1.9 months after start of oral Nstat + VGCV 14 HDACi: HDAC inhibitor; ASCT: Autologous stem cell transplantation; Nstat: Nanatinostat; VGCV: Valganciclovir; CHOEP: CHOP, etoposide

Key FDA Regulatory Milestones Achieved Orphan Drug Designations End of Phase 2 Meeting Fast Track Designation granted for Nstat/VGCV for (November 2020) (November 2019) treatment of: Obtained alignment on the For the treatment of + design of Viracta’s Phase 2 relapsed/refractory EBV • T-cell lymphoma - 2020 pivotal study; a single arm lymphoid malignancies • Post-transplant basket study with an adaptive lymphoproliferative disorder design in patients with relapsed (PTLD) - 2019 + or refractory EBV lymphomas • Plasmablastic lymphoma - 2019 15

ORR/DoR from Single Arm Studies in R/R Lymphoma Receiving Accelerated Approval Nstat/VGCV comparison to lymphoma drugs receiving accelerated approval + 25 ORR and DoR for Nstat/VGCV in EBV lymphoma tafasitamab/lenalidomide compare favorably with other accelerated zanubrutinib approvals in various R/R lymphomas 20 ibrutinib Nstat/VGCV + EBV B cell Bubbles represent ORR/DoR for single-arm Nstat/VGCV romidepsin + accelerated approvals: EBV T cell 15 copanlisib tazemetostat (WT) Teal T cell lymphomas pralatrexate 10 axicabtagene Red DLBCL (Kymriah® ORR 50%; mDoR NR) bendamustine belinostat bortezomib vorinostat 5 Brentuximab vedotin Other lymphomas duvelisib Blue selinexor Preliminary response data for Orange 0 Nstat/VGCV in T cell and B cell NHL 0 20 40 60 80 100 Objective Response Rate 16 Nstat: Nanatinostat; VGCV: Valganciclovir; ORR: Objective response rate; DoR; Duration of response; mDoR: Median DoR; NHL: Non-Hodgkin lymphoma; R/R Relapsed/refractory; NR: Not reached Median Duration of Response (months)
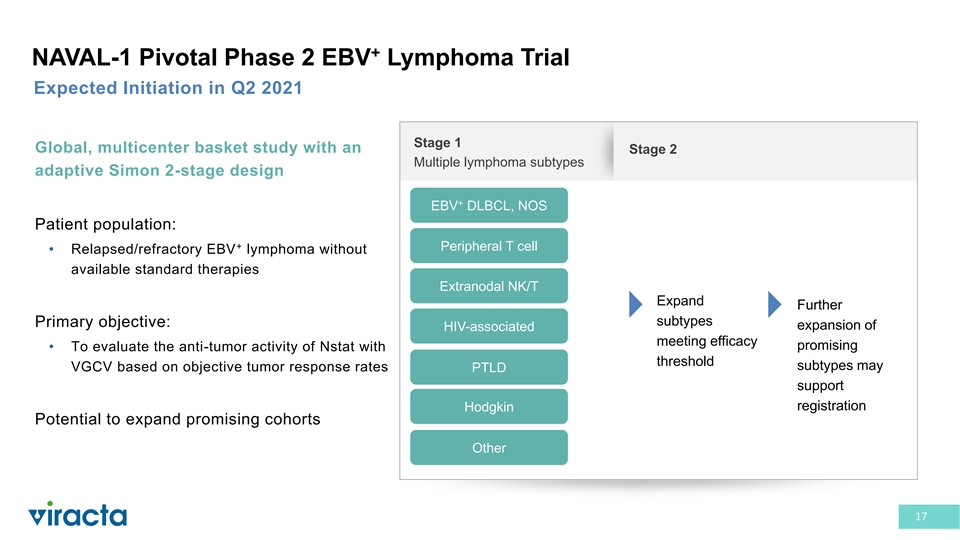
+ NAVAL-1 Pivotal Phase 2 EBV Lymphoma Trial Expected Initiation in Q2 2021 Stage 1 Global, multicenter basket study with an Stage 2 Multiple lymphoma subtypes adaptive Simon 2-stage design + EBV DLBCL, NOS Patient population: + Peripheral T cell • Relapsed/refractory EBV lymphoma without available standard therapies Extranodal NK/T Expand Further subtypes Primary objective: expansion of HIV-associated meeting efficacy promising • To evaluate the anti-tumor activity of Nstat with threshold subtypes may VGCV based on objective tumor response rates PTLD support registration Hodgkin Potential to expand promising cohorts Other 17
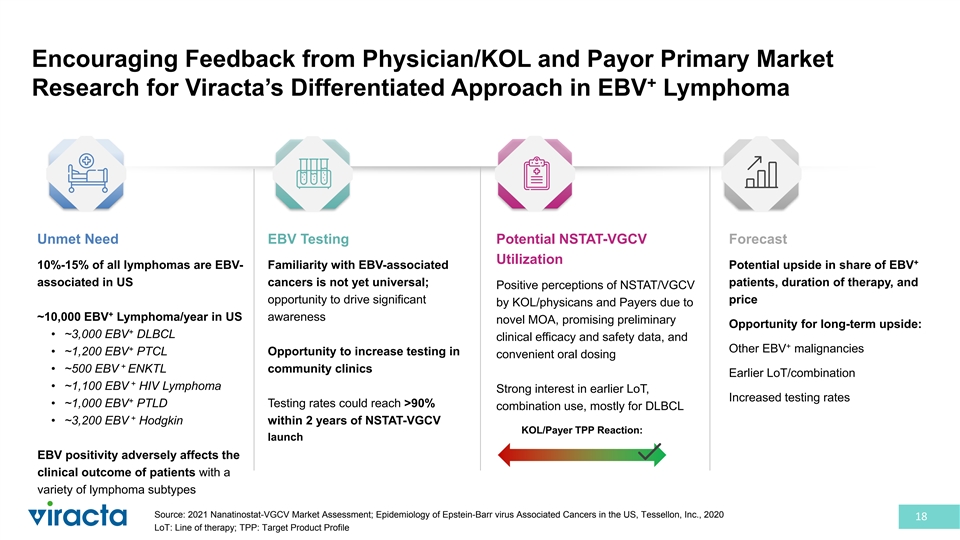
Encouraging Feedback from Physician/KOL and Payor Primary Market + Research for Viracta’s Differentiated Approach in EBV Lymphoma Unmet Need EBV Testing Potential NSTAT-VGCV Forecast Utilization + 10%-15% of all lymphomas are EBV- Familiarity with EBV-associated Potential upside in share of EBV associated in US cancers is not yet universal; patients, duration of therapy, and Positive perceptions of NSTAT/VGCV opportunity to drive significant price by KOL/physicans and Payers due to + ~10,000 EBV Lymphoma/year in US awareness novel MOA, promising preliminary Opportunity for long-term upside: + • ~3,000 EBV DLBCL clinical efficacy and safety data, and + + Other EBV malignancies • ~1,200 EBV PTCL Opportunity to increase testing in convenient oral dosing + • ~500 EBV ENKTL community clinics Earlier LoT/combination + • ~1,100 EBV HIV Lymphoma Strong interest in earlier LoT, Increased testing rates + • ~1,000 EBV PTLD Testing rates could reach >90% combination use, mostly for DLBCL + • ~3,200 EBV Hodgkin within 2 years of NSTAT-VGCV KOL/Payer TPP Reaction: launch EBV positivity adversely affects the clinical outcome of patients with a variety of lymphoma subtypes Source: 2021 Nanatinostat-VGCV Market Assessment; Epidemiology of Epstein-Barr virus Associated Cancers in the US, Tessellon, Inc., 2020 18 LoT: Line of therapy; TPP: Target Product Profile

+ EBV Solid Tumor Program
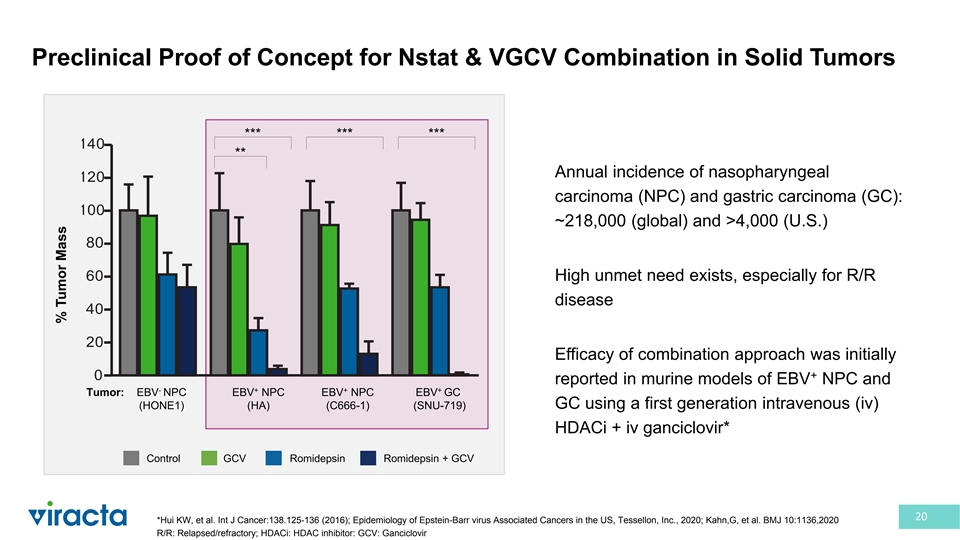
Preclinical Proof of Concept for Nstat & VGCV Combination in Solid Tumors *** *** *** ** Annual incidence of nasopharyngeal 2 carcinoma (NPC) and gastric carcinoma (GC): ~218,000 (global) and >4,000 (U.S.) High unmet need exists, especially for R/R disease 2 Efficacy of combination approach was initially + reported in murine models of EBV NPC and - + + + Tumor: EBV NPC EBV NPC EBV NPC EBV GC (HONE1) (HA) (C666-1) (SNU-719) GC using a first generation intravenous (iv) HDACi + iv ganciclovir* Control GCV Romidepsin Romidepsin + GCV 20 *Hui KW, et al. Int J Cancer:138.125-136 (2016); Epidemiology of Epstein-Barr virus Associated Cancers in the US, Tessellon, Inc., 2020; Kahn,G, et al. BMJ 10:1136,2020 R/R: Relapsed/refractory; HDACi: HDAC inhibitor: GCV: Ganciclovir % Tumor Mass
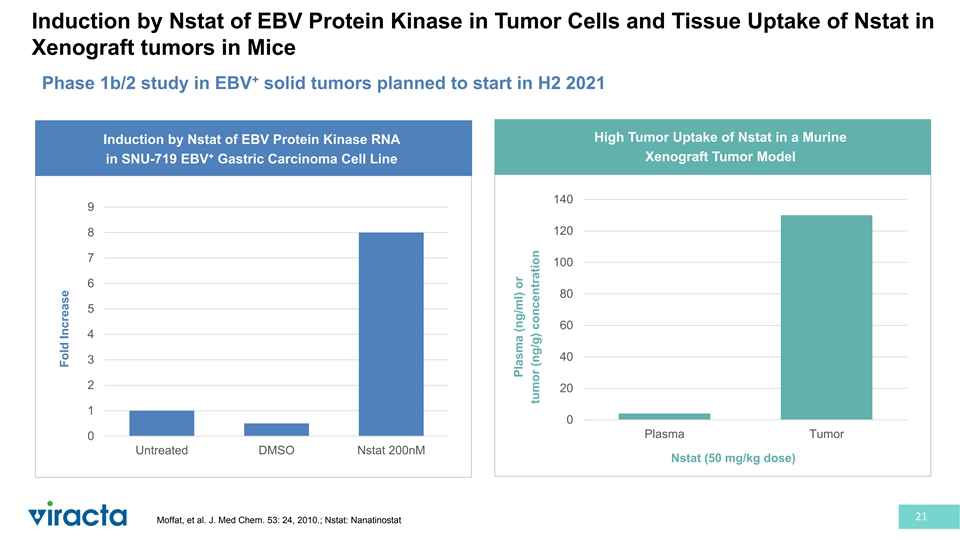
Induction by Nstat of EBV Protein Kinase in Tumor Cells and Tissue Uptake of Nstat in Xenograft tumors in Mice + Phase 1b/2 study in EBV solid tumors planned to start in H2 2021 High Tumor Uptake of Nstat in a Murine Induction by Nstat of EBV Protein Kinase RNA + Xenograft Tumor Model in SNU-719 EBV Gastric Carcinoma Cell Line 140 9 120 8 7 100 6 80 5 60 4 40 3 2 20 1 0 Plasma Tumor 0 Untreated DMSO Nstat 200nM Nstat (50 mg/kg dose) 21 Moffat, et al. J. Med Chem. 53: 24, 2010.; Nstat: Nanatinostat Fold Increase Plasma (ng/ml) or tumor (ng/g) concentration
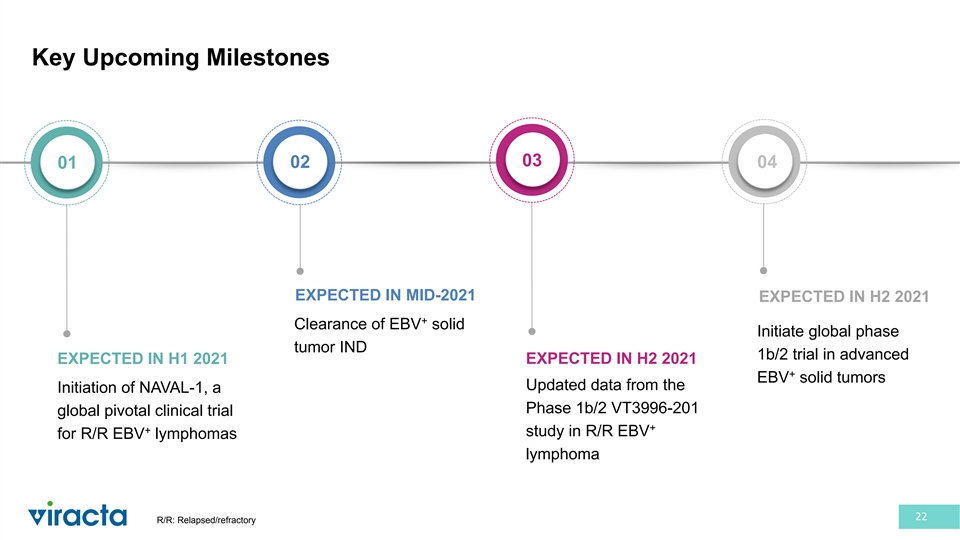
Key Upcoming Milestones 03 02 04 01 EXPECTED IN MID-2021 EXPECTED IN H2 2021 + Clearance of EBV solid Initiate global phase tumor IND 1b/2 trial in advanced EXPECTED IN H1 2021 EXPECTED IN H2 2021 + EBV solid tumors Updated data from the Initiation of NAVAL-1, a Phase 1b/2 VT3996-201 global pivotal clinical trial + + study in R/R EBV for R/R EBV lymphomas lymphoma 22 R/R: Relapsed/refractory

Leadership Team Ivor Royston, MD Daniel Chevallard, CPA Lisa Rojkjaer, MD President and Chief Executive Officer Chief Operating Officer & Chief Financial Officer Chief Medical Officer Hybritech Robert McRae Douglas Faller, MD, PhD Cheryl Madsen VP, Operations & Strategic Alliances Senior VP, Regulatory Affairs Chief Scientific Officer Michael Mueller Shelly Vandertie Mark McCamish, MD, PhD VP, Legal Affairs & General Counsel VP, Finance Strategic Advisor 23
Viracta Therapeutics: Investment Thesis Focused on unmet medical need with novel targeted therapeutic approach representing a new MOA for the + Expansion into EBV solid tumors with global phase treatment EBV-associated cancers 1b/2 clinical trial EBV associated with >265,000 cases/year in lymphoma, Total Addressable Market in US (NPC+GC) = >4,000/year NPC and GC (globally) Promising efficacy and safety from early clinical trials Strong balance sheet with projected runway + in advanced EBV lymphomas with poor prognosis into 2024 Total Addressable Market in US = 10,000/year Initiating global pivotal study to for the treatment of + Solid IP estate with protection to 2040 EBV lymphoma to support potential accelerated approval for patients with relapsed/refractory disease Contact Us: info@viracta.com 24 Epidemiology of Epstein-Barr virus Associated Cancers in the US, Tessellon, Inc., 2020
