Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| 8-K - 8-K PHARMACEUTICALS UPDATE JANUARY 2019 - Viracta Therapeutics, Inc. | snss-8k_20190107.htm |

JPMorgan Conference Update January 2019

Safe Harbor Statement This presentation contains forward-looking statements, including statements related to the continued development of vecabrutinib (SNS-062) and other product candidates, including the timing and preliminary results of Phase 1b/2 trial of vecabrutinib and the therapeutic potential of vecabrutinib, further development and potential of its kinase inhibitor pipeline, and planned development of SNS-510. These forward-looking statements are based upon Sunesis' current expectations. Forward-looking statements involve risks and uncertainties. Sunesis' actual results and the timing of events could differ materially from those anticipated in such forward-looking statements as a result of these risks and uncertainties, which include, without limitation, the risk that Sunesis' development activities for vecabrutinib and other product candidates could be otherwise halted or significantly delayed for various reasons, risks related to Sunesis' need for substantial additional funding to complete the development and commercialization of vecabrutinib and other product candidates, including the risk that Sunesis' clinical studies for vecabrutinib and other product candidates may not demonstrate safety or efficacy or lead to regulatory approval, the risk that data to date and trends may not be predictive of future data or results, risks related to the timing or conduct of Sunesis' clinical trials, and risks related to Sunesis' ability to raise the capital that it believes to be accessible and is required to fully finance the development and commercialization of vecabrutinib and other product candidates. These and other risk factors are discussed under "Risk Factors" and elsewhere in Sunesis’ Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2018 and Sunesis' other filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission. Sunesis expressly disclaims any obligation or undertaking to release publicly any updates or revisions to any forward-looking statements contained herein to reflect any change in Sunesis' expectations with regard thereto or any change in events, conditions or circumstances on which any such statements are based.
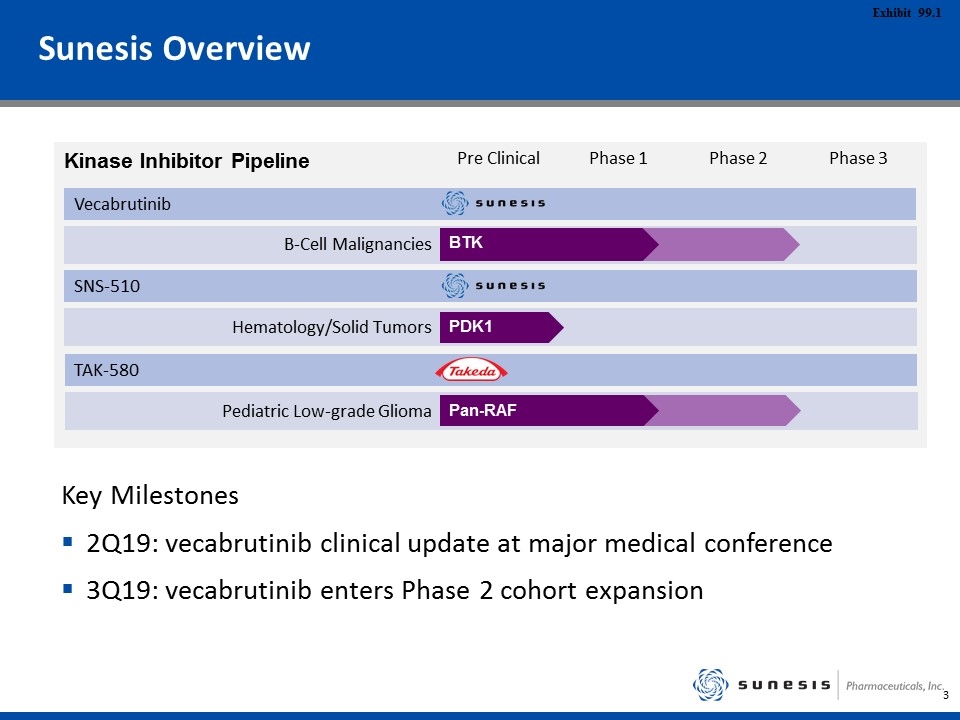
Pre Clinical Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3 B-Cell Malignancies Vecabrutinib BTK Hematology/Solid Tumors SNS-510 PDK1 Sunesis Overview TAK-580 Pediatric Low-grade Glioma Key Milestones 2Q19: vecabrutinib clinical update at major medical conference 3Q19: vecabrutinib enters Phase 2 cohort expansion Kinase Inhibitor Pipeline Pan-RAF
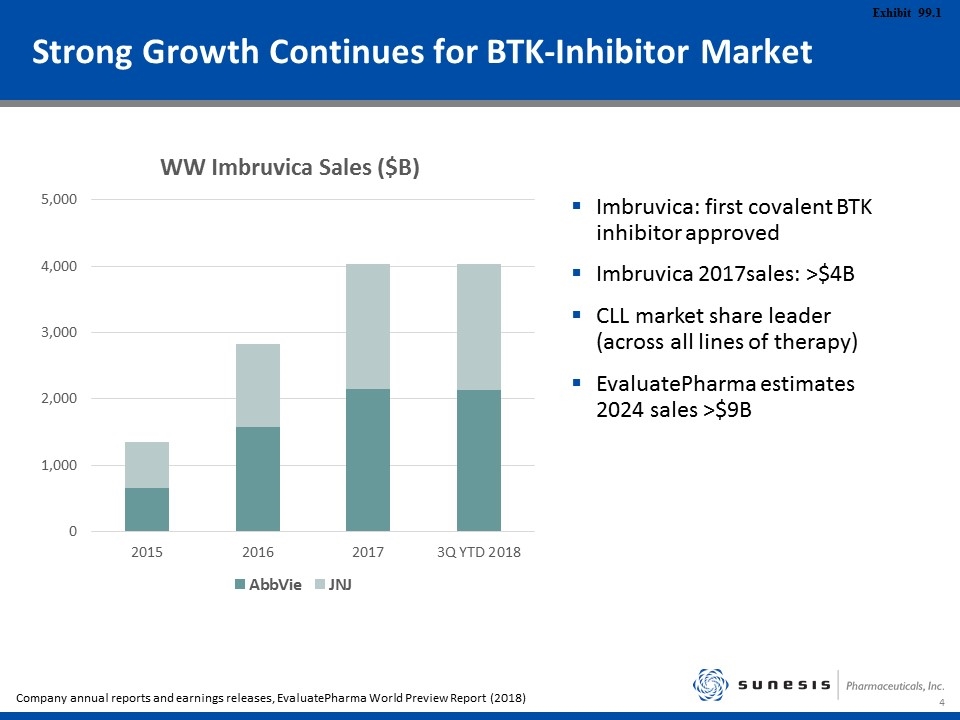
Strong Growth Continues for BTK-Inhibitor Market Imbruvica: first covalent BTK inhibitor approved Imbruvica 2017sales: >$4B CLL market share leader (across all lines of therapy) EvaluatePharma estimates 2024 sales >$9B Company annual reports and earnings releases, EvaluatePharma World Preview Report (2018)
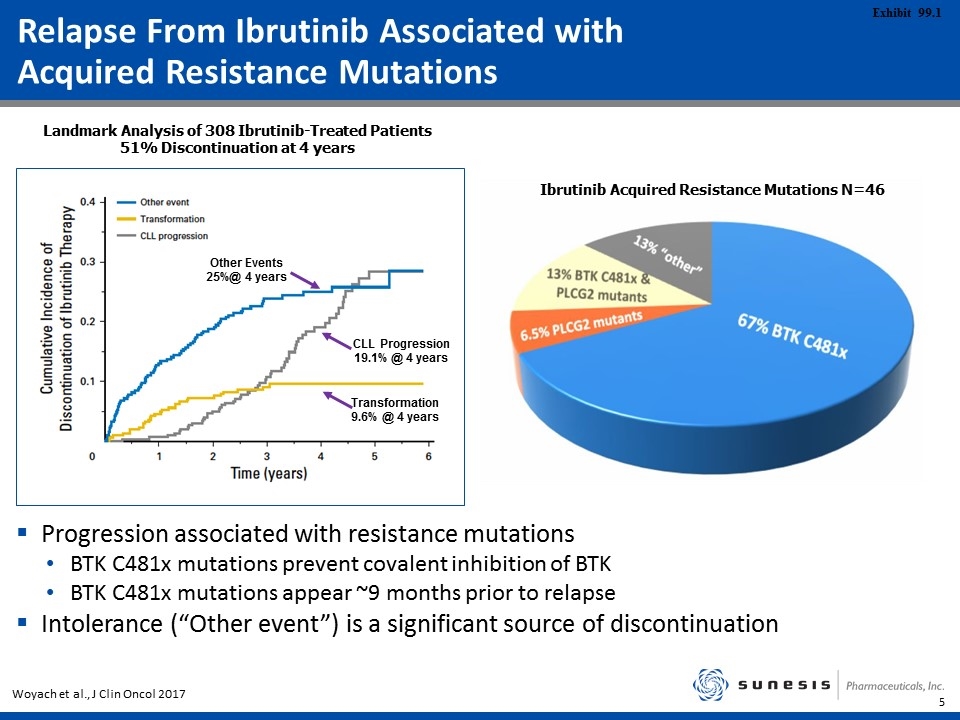
Relapse From Ibrutinib Associated with Acquired Resistance Mutations Other Events 25%@ 4 years CLL Progression 19.1% @ 4 years Transformation 9.6% @ 4 years Woyach et al., J Clin Oncol 2017 Landmark Analysis of 308 Ibrutinib-Treated Patients 51% Discontinuation at 4 years Ibrutinib Acquired Resistance Mutations N=46 Progression associated with resistance mutations BTK C481x mutations prevent covalent inhibition of BTK BTK C481x mutations appear ~9 months prior to relapse Intolerance (“Other event”) is a significant source of discontinuation

Understanding Prevalence of BTK Mutations ERIC (European Research Initiative on CLL) international, retrospective, observational, multicenter study To determine the prevalence of BTK and PLCg2 mutations in CLL patients relapsing or responding to ibrutinib in a real-world setting Presented at EHA 2018 54% of relapsed patients carried a BTK C481 mutation FILO (French Innovative Leukemia Organization) High Prevalence of BTK Mutations on Ibrutinib Therapy after 3 Years of Treatment in a Real-Life Cohort of CLL Patients: A Study from the French Innovative Leukemia Organization (FILO) Group Presented at ASH 2018 88% of relapsed patients sequenced carried a BTK C481 mutation

Vecabrutinib Non-covalent BTK inhibitor
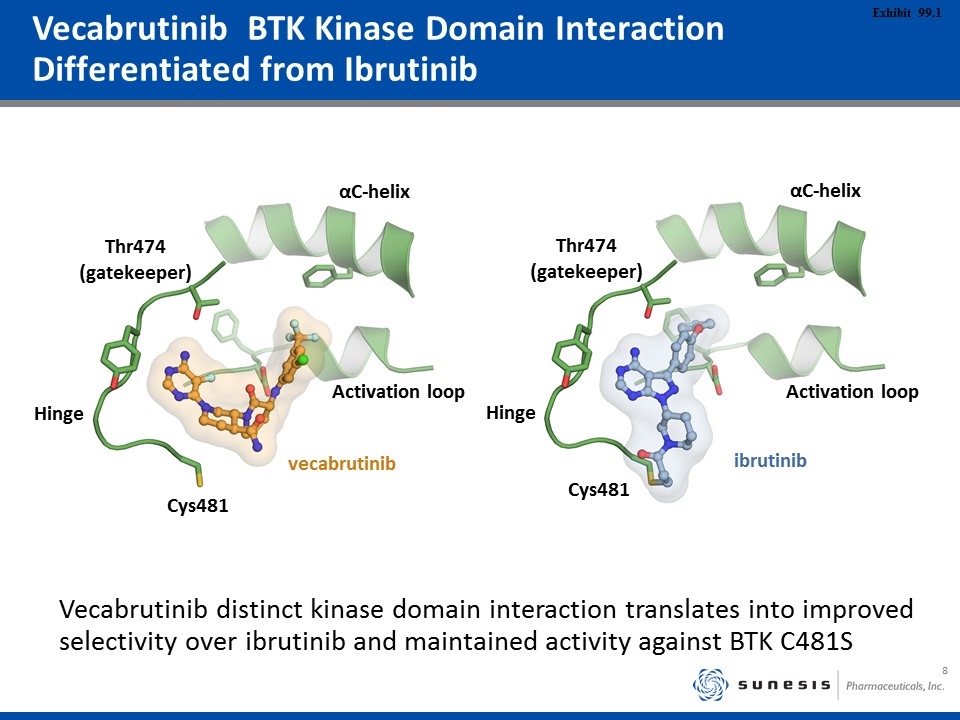
Vecabrutinib BTK Kinase Domain Interaction Differentiated from Ibrutinib Cys481 vecabrutinib ibrutinib Hinge αC-helix Thr474 (gatekeeper) Activation loop Cys481 Hinge αC-helix Thr474 (gatekeeper) Activation loop Vecabrutinib distinct kinase domain interaction translates into improved selectivity over ibrutinib and maintained activity against BTK C481S
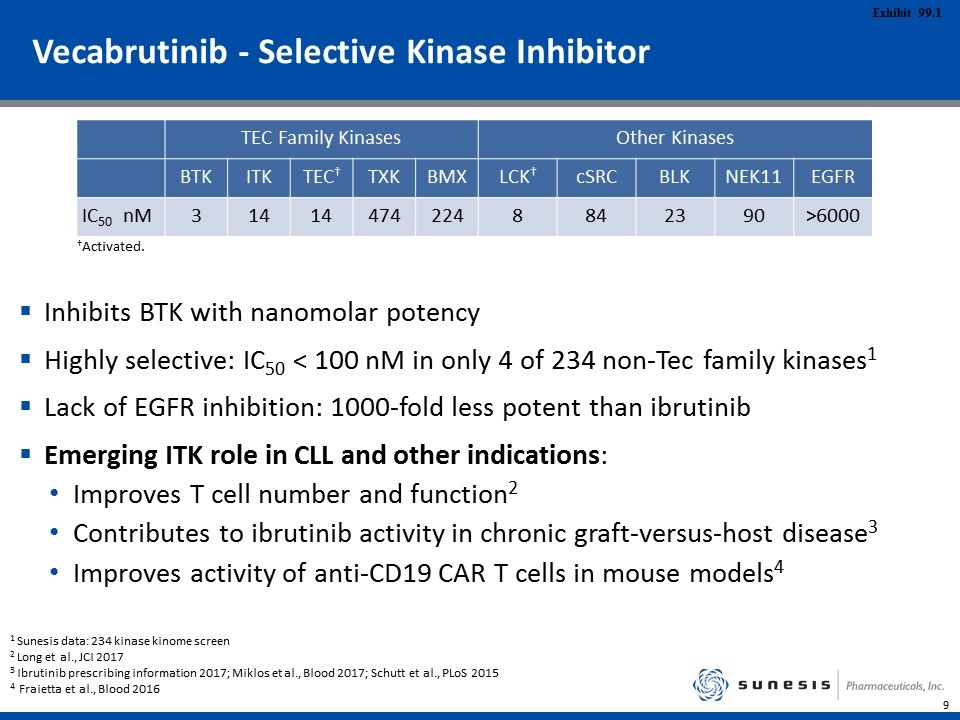
Vecabrutinib - Selective Kinase Inhibitor Inhibits BTK with nanomolar potency Highly selective: IC50 < 100 nM in only 4 of 234 non-Tec family kinases1 Lack of EGFR inhibition: 1000-fold less potent than ibrutinib Emerging ITK role in CLL and other indications: Improves T cell number and function2 Contributes to ibrutinib activity in chronic graft-versus-host disease3 Improves activity of anti-CD19 CAR T cells in mouse models4 TEC Family Kinases Other Kinases BTK ITK TEC† TXK BMX LCK† cSRC BLK NEK11 EGFR IC50 nM 3 14 14 474 224 8 84 23 90 >6000 †Activated. 1 Sunesis data: 234 kinase kinome screen 2 Long et al., JCI 2017 3 Ibrutinib prescribing information 2017; Miklos et al., Blood 2017; Schutt et al., PLoS 2015 4 Fraietta et al., Blood 2016
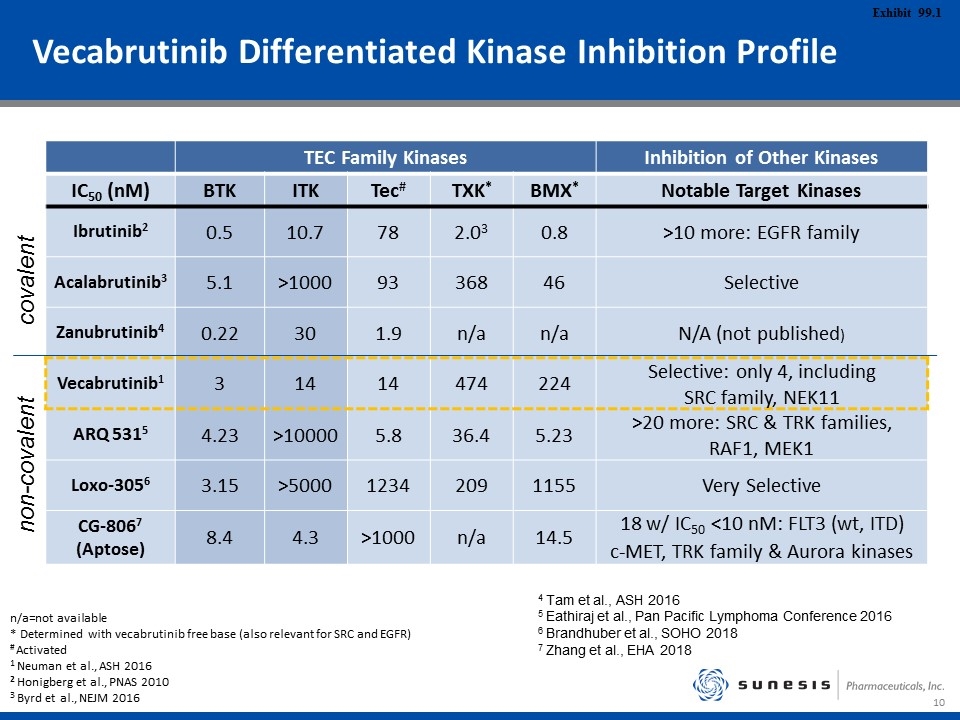
Vecabrutinib Differentiated Kinase Inhibition Profile TEC Family Kinases Inhibition of Other Kinases IC50 (nM) BTK ITK Tec# TXK* BMX* Notable Target Kinases Ibrutinib2 0.5 10.7 78 2.03 0.8 >10 more: EGFR family Acalabrutinib3 5.1 >1000 93 368 46 Selective Zanubrutinib4 0.22 30 1.9 n/a n/a N/A (not published) Vecabrutinib1 3 14 14 474 224 Selective: only 4, including SRC family, NEK11 ARQ 5315 4.23 >10000 5.8 36.4 5.23 >20 more: SRC & TRK families, RAF1, MEK1 Loxo-3056 3.15 >5000 1234 209 1155 Very Selective CG-8067 (Aptose) 8.4 4.3 >1000 n/a 14.5 18 w/ IC50 <10 nM: FLT3 (wt, ITD) c-MET, TRK family & Aurora kinases n/a=not available * Determined with vecabrutinib free base (also relevant for SRC and EGFR) # Activated 1 Neuman et al., ASH 2016 2 Honigberg et al., PNAS 2010 3 Byrd et al., NEJM 2016 covalent non-covalent 4 Tam et al., ASH 2016 5 Eathiraj et al., Pan Pacific Lymphoma Conference 2016 6 Brandhuber et al., SOHO 2018 7 Zhang et al., EHA 2018
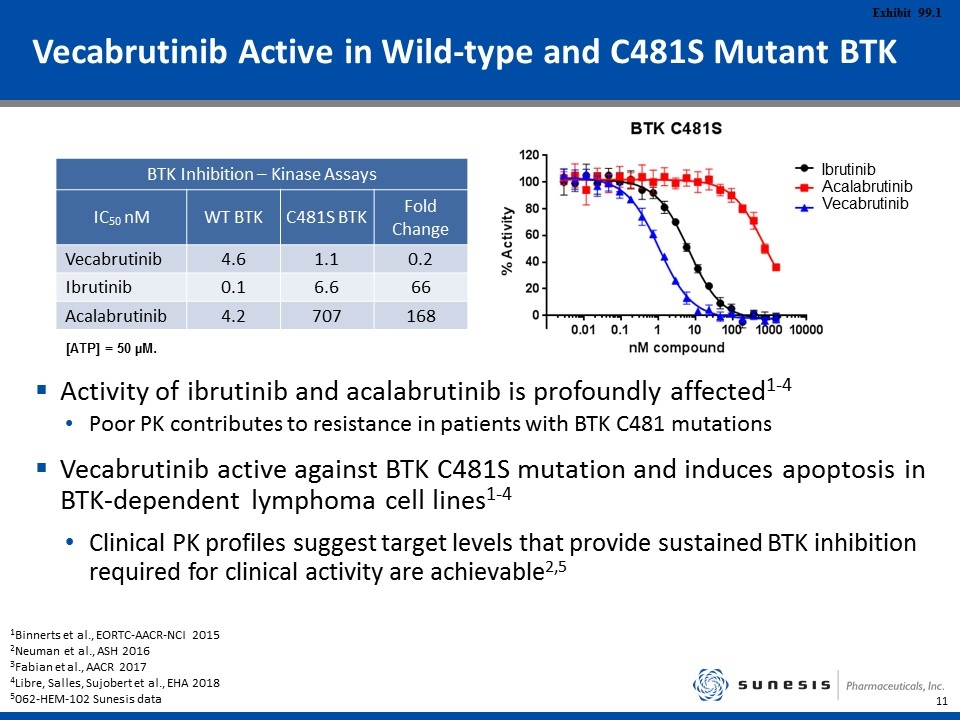
Vecabrutinib Active in Wild-type and C481S Mutant BTK Activity of ibrutinib and acalabrutinib is profoundly affected1-4 Poor PK contributes to resistance in patients with BTK C481 mutations Vecabrutinib active against BTK C481S mutation and induces apoptosis in BTK-dependent lymphoma cell lines1-4 Clinical PK profiles suggest target levels that provide sustained BTK inhibition required for clinical activity are achievable2,5 BTK Inhibition – Kinase Assays IC50 nM WT BTK C481S BTK Fold Change Vecabrutinib 4.6 1.1 0.2 Ibrutinib 0.1 6.6 66 Acalabrutinib 4.2 707 168 [ATP] = 50 µM. 1Binnerts et al., EORTC-AACR-NCI 2015 2Neuman et al., ASH 2016 3Fabian et al., AACR 2017 4Libre, Salles, Sujobert et al., EHA 2018 5062-HEM-102 Sunesis data Ibrutinib Acalabrutinib Vecabrutinib
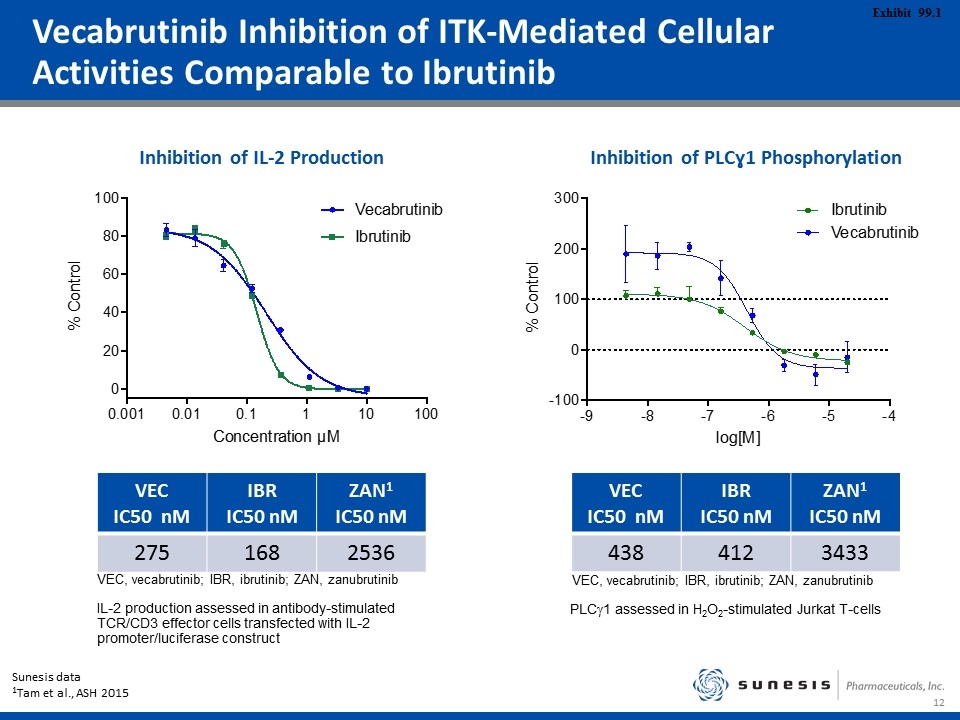
Vecabrutinib Inhibition of ITK-Mediated Cellular Activities Comparable to Ibrutinib Inhibition of IL-2 Production Inhibition of PLCɣ1 Phosphorylation Sunesis data 1Tam et al., ASH 2015 VEC IC50 nM IBR IC50 nM ZAN1 IC50 nM 275 168 2536 VEC IC50 nM IBR IC50 nM ZAN1 IC50 nM 438 412 3433 IL-2 production assessed in antibody-stimulated TCR/CD3 effector cells transfected with IL-2 promoter/luciferase construct VEC, vecabrutinib; IBR, ibrutinib; ZAN, zanubrutinib VEC, vecabrutinib; IBR, ibrutinib; ZAN, zanubrutinib PLCg1 assessed in H2O2-stimulated Jurkat T-cells
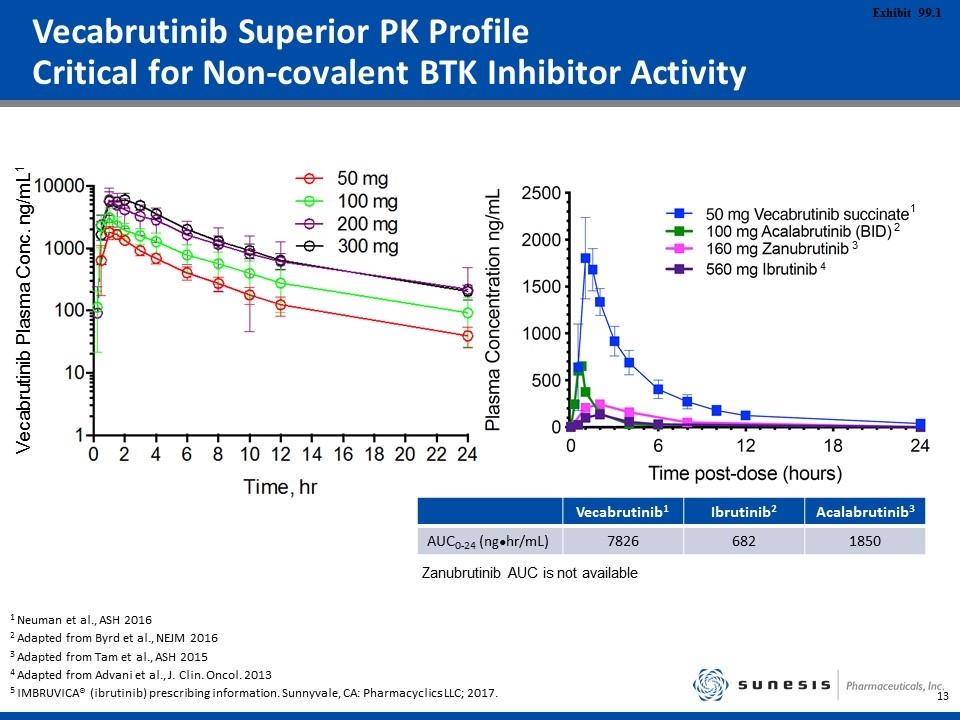
Vecabrutinib Superior PK Profile Critical for Non-covalent BTK Inhibitor Activity 1 Neuman et al., ASH 2016 2 Adapted from Byrd et al., NEJM 2016 3 Adapted from Tam et al., ASH 2015 4 Adapted from Advani et al., J. Clin. Oncol. 2013 5 IMBRUVICA® (ibrutinib) prescribing information. Sunnyvale, CA: Pharmacyclics LLC; 2017. 1 2 3 4 Vecabrutinib1 Ibrutinib2 Acalabrutinib3 AUC0-24 (ng●hr/mL) 7826 682 1850 Vecabrutinib Plasma Conc. ng/mL1 Zanubrutinib AUC is not available
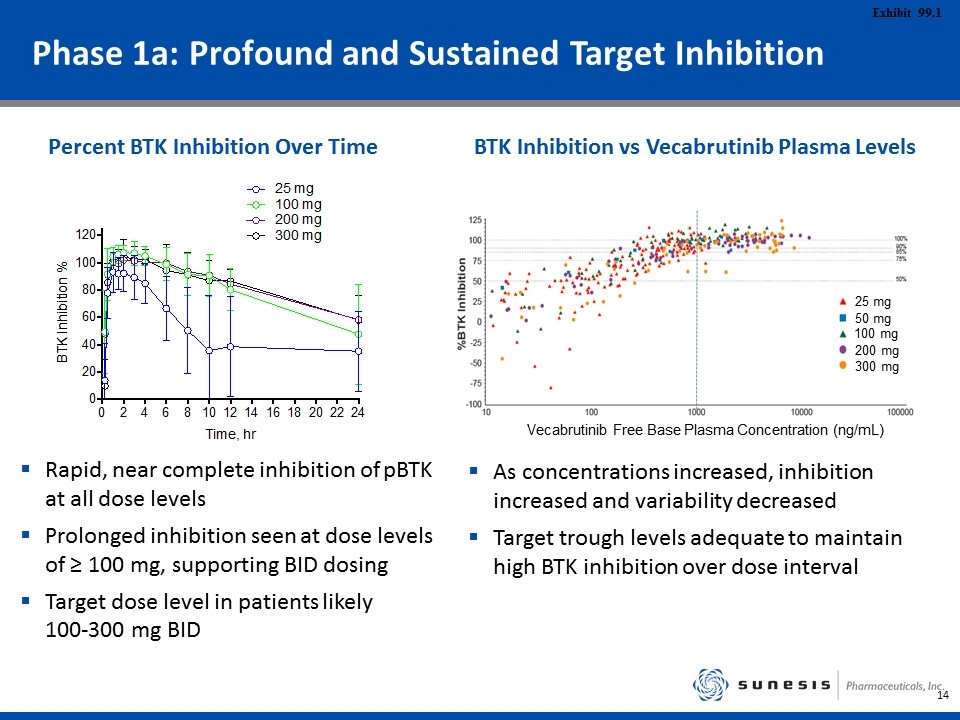
Phase 1a: Profound and Sustained Target Inhibition Rapid, near complete inhibition of pBTK at all dose levels Prolonged inhibition seen at dose levels of ≥ 100 mg, supporting BID dosing Target dose level in patients likely 100-300 mg BID As concentrations increased, inhibition increased and variability decreased Target trough levels adequate to maintain high BTK inhibition over dose interval Percent BTK Inhibition Over Time BTK Inhibition vs Vecabrutinib Plasma Levels 25 mg 50 mg 100 mg 200 mg 300 mg Vecabrutinib Free Base Plasma Concentration (ng/mL)
Vecabrutinib in B-Cell Malignancies Phase 1b/2 Trial Status and Preliminary Data
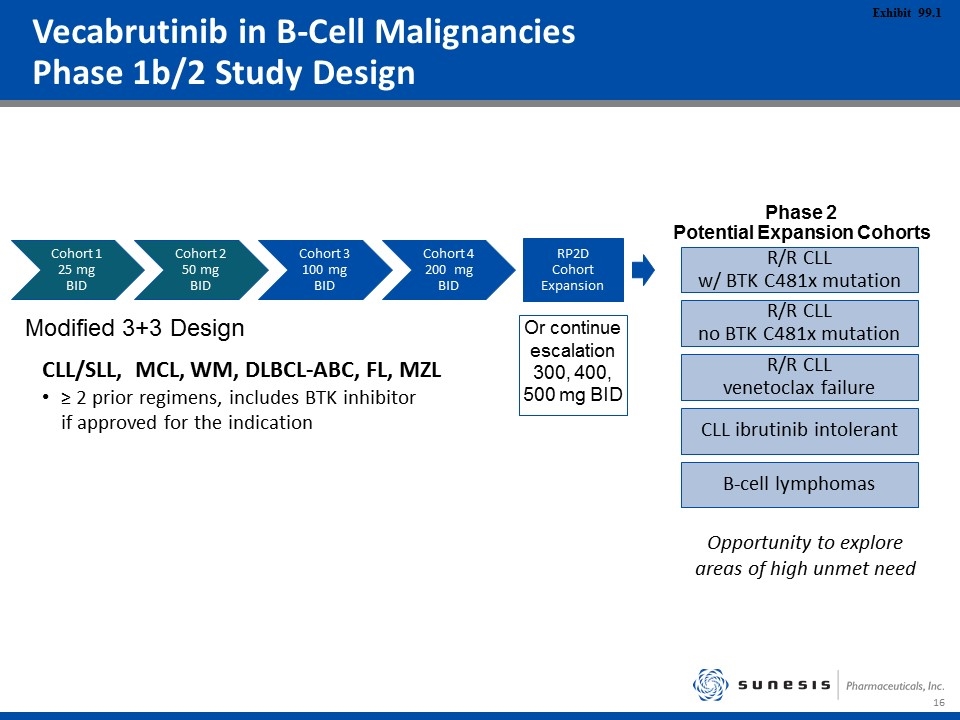
Vecabrutinib in B-Cell Malignancies Phase 1b/2 Study Design Cohort 1 25 mg BID Cohort 2 50 mg BID Cohort 3 100 mg BID Cohort 4 200 mg BID RP2D Cohort Expansion Or continue escalation 300, 400, 500 mg BID CLL/SLL, MCL, WM, DLBCL-ABC, FL, MZL ≥ 2 prior regimens, includes BTK inhibitor if approved for the indication Modified 3+3 Design R/R CLL w/ BTK C481x mutation R/R CLL no BTK C481x mutation R/R CLL venetoclax failure CLL ibrutinib intolerant B-cell lymphomas Phase 2 Potential Expansion Cohorts Opportunity to explore areas of high unmet need
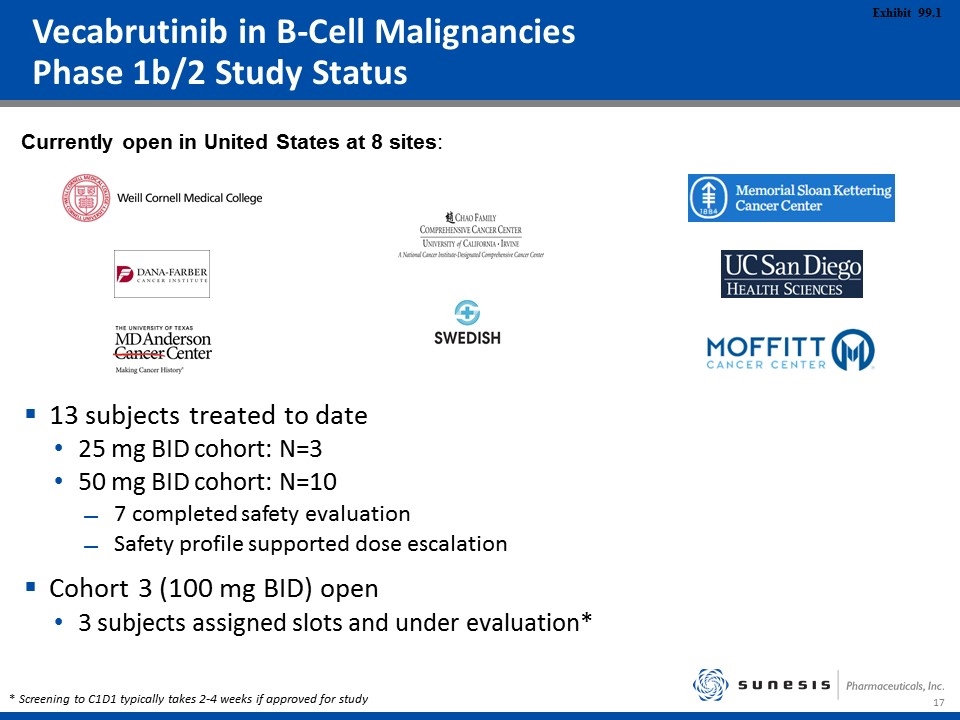
Vecabrutinib in B-Cell Malignancies Phase 1b/2 Study Status Currently open in United States at 8 sites: 13 subjects treated to date 25 mg BID cohort: N=3 50 mg BID cohort: N=10 7 completed safety evaluation Safety profile supported dose escalation Cohort 3 (100 mg BID) open 3 subjects assigned slots and under evaluation* * Screening to C1D1 typically takes 2-4 weeks if approved for study
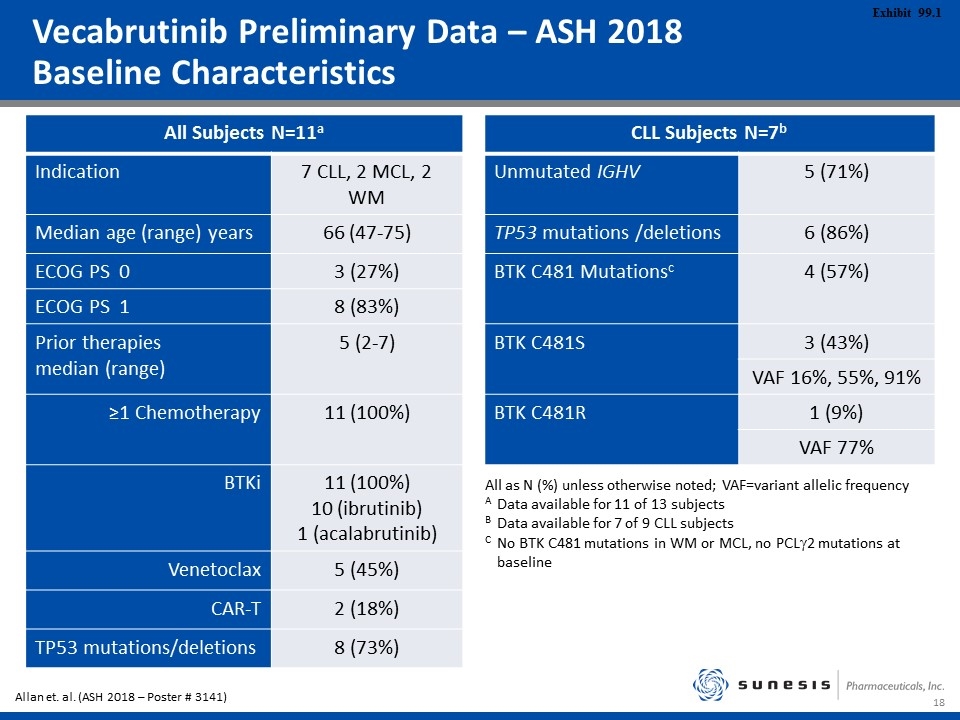
Vecabrutinib Preliminary Data – ASH 2018 Baseline Characteristics All Subjects N=11a CLL Subjects N=7b Indication 7 CLL, 2 MCL, 2 WM Unmutated IGHV 5 (71%) Median age (range) years 66 (47-75) TP53 mutations /deletions 6 (86%) ECOG PS 0 3 (27%) BTK C481 Mutationsc 4 (57%) ECOG PS 1 8 (83%) Prior therapies median (range) 5 (2-7) BTK C481S 3 (43%) VAF 16%, 55%, 91% ≥1 Chemotherapy 11 (100%) BTK C481R 1 (9%) VAF 77% BTKi 11 (100%) 10 (ibrutinib) 1 (acalabrutinib) Venetoclax 5 (45%) CAR-T 2 (18%) TP53 mutations/deletions 8 (73%) All as N (%) unless otherwise noted; VAF=variant allelic frequency AData available for 11 of 13 subjects BData available for 7 of 9 CLL subjects CNo BTK C481 mutations in WM or MCL, no PCLg2 mutations at baseline Allan et. al. (ASH 2018 – Poster # 3141)
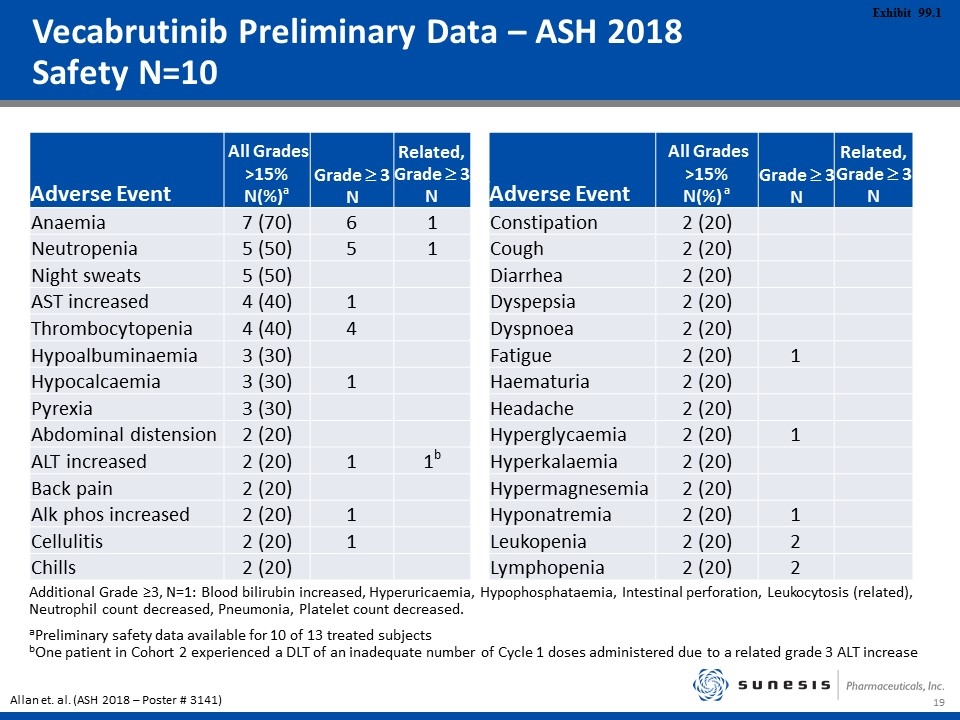
Vecabrutinib Preliminary Data – ASH 2018 Safety N=10 Adverse Event All Grades >15% N(%)a Grade ³ 3 N Related, Grade ³ 3 N Adverse Event All Grades >15% N(%) a Grade ³ 3 N Related, Grade ³ 3 N Anaemia 7 (70) 6 1 Constipation 2 (20) Neutropenia 5 (50) 5 1 Cough 2 (20) Night sweats 5 (50) Diarrhea 2 (20) AST increased 4 (40) 1 Dyspepsia 2 (20) Thrombocytopenia 4 (40) 4 Dyspnoea 2 (20) Hypoalbuminaemia 3 (30) Fatigue 2 (20) 1 Hypocalcaemia 3 (30) 1 Haematuria 2 (20) Pyrexia 3 (30) Headache 2 (20) Abdominal distension 2 (20) Hyperglycaemia 2 (20) 1 ALT increased 2 (20) 1 1b Hyperkalaemia 2 (20) Back pain 2 (20) Hypermagnesemia 2 (20) Alk phos increased 2 (20) 1 Hyponatremia 2 (20) 1 Cellulitis 2 (20) 1 Leukopenia 2 (20) 2 Chills 2 (20) Lymphopenia 2 (20) 2 Additional Grade ≥3, N=1: Blood bilirubin increased, Hyperuricaemia, Hypophosphataemia, Intestinal perforation, Leukocytosis (related), Neutrophil count decreased, Pneumonia, Platelet count decreased. aPreliminary safety data available for 10 of 13 treated subjects bOne patient in Cohort 2 experienced a DLT of an inadequate number of Cycle 1 doses administered due to a related grade 3 ALT increase Allan et. al. (ASH 2018 – Poster # 3141)
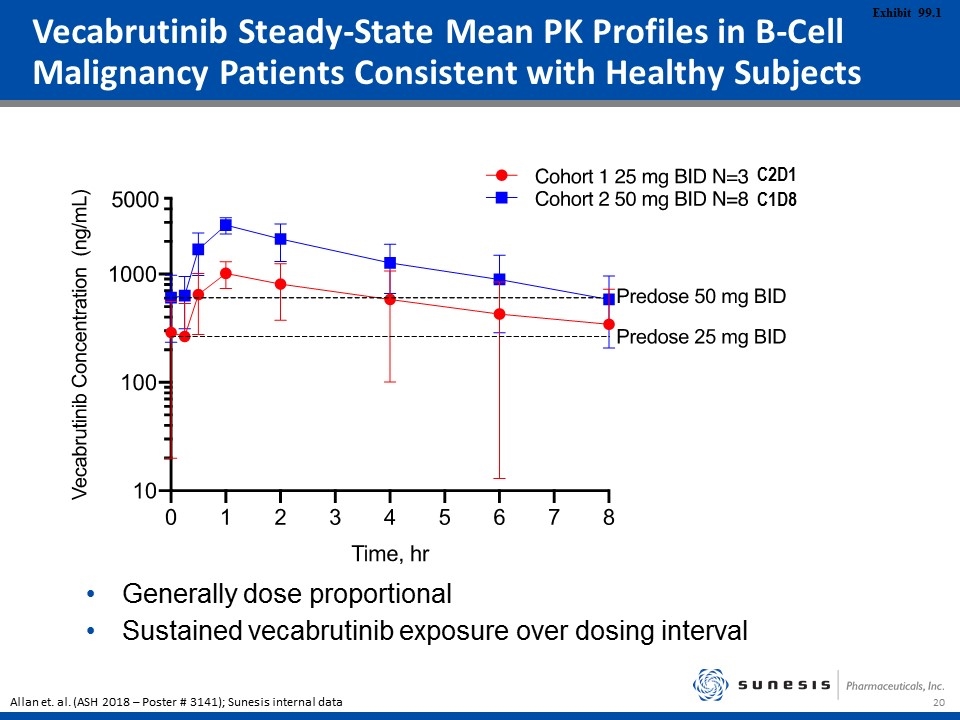
C2D1 C1D8 Generally dose proportional Sustained vecabrutinib exposure over dosing interval Vecabrutinib Steady-State Mean PK Profiles in B-Cell Malignancy Patients Consistent with Healthy Subjects Allan et. al. (ASH 2018 – Poster # 3141); Sunesis internal data
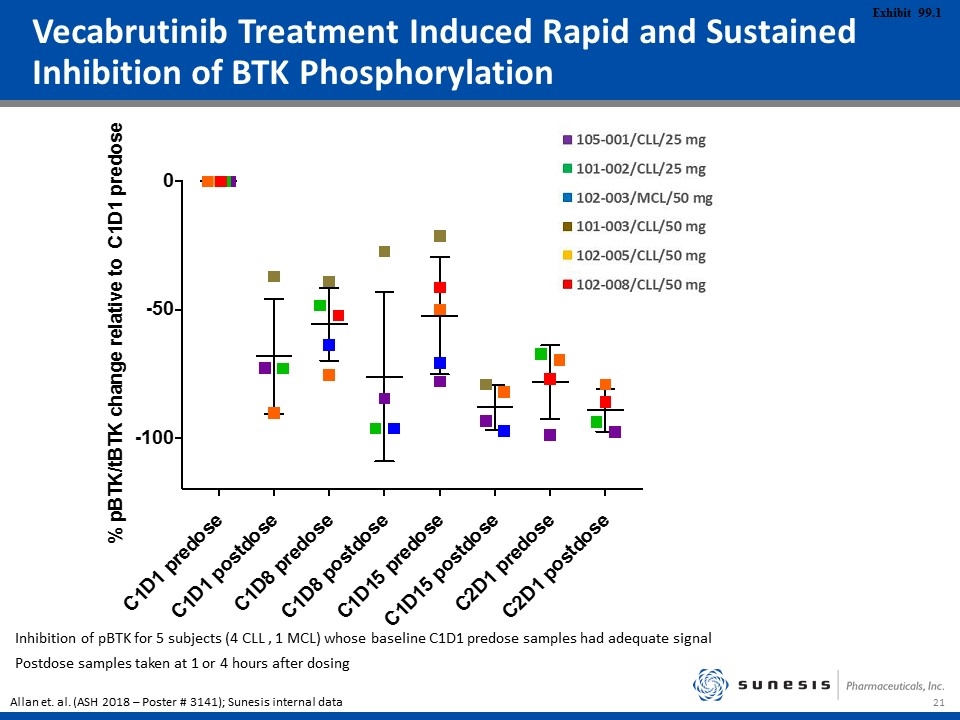
Vecabrutinib Treatment Induced Rapid and Sustained Inhibition of BTK Phosphorylation Inhibition of pBTK for 5 subjects (4 CLL , 1 MCL) whose baseline C1D1 predose samples had adequate signal Postdose samples taken at 1 or 4 hours after dosing Allan et. al. (ASH 2018 – Poster # 3141); Sunesis internal data
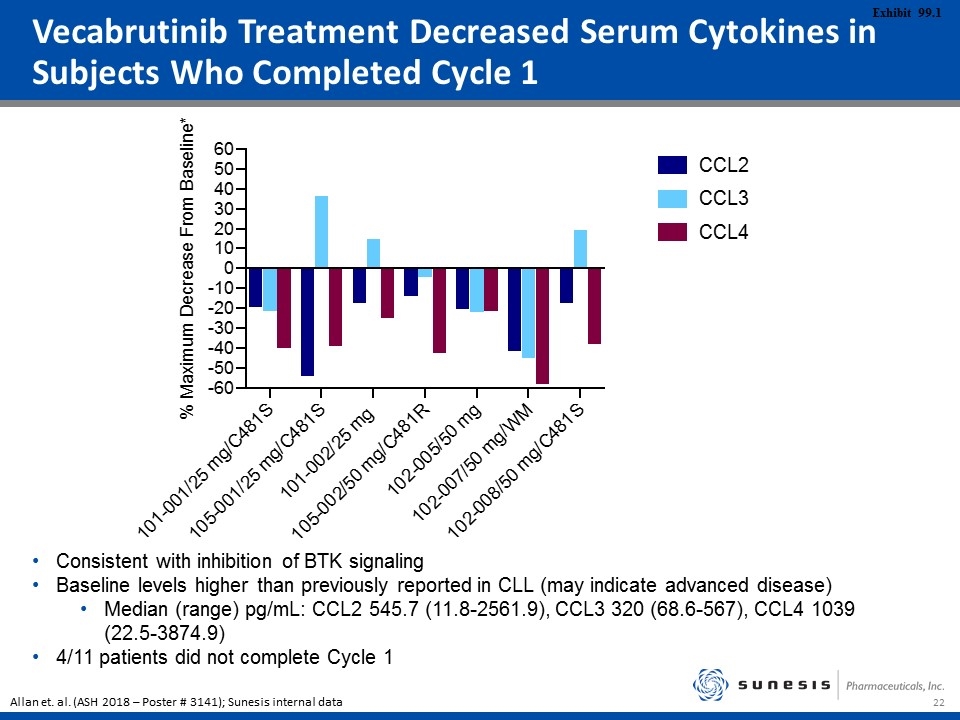
Vecabrutinib Treatment Decreased Serum Cytokines in Subjects Who Completed Cycle 1 Consistent with inhibition of BTK signaling Baseline levels higher than previously reported in CLL (may indicate advanced disease) Median (range) pg/mL: CCL2 545.7 (11.8-2561.9), CCL3 320 (68.6-567), CCL4 1039 (22.5-3874.9) 4/11 patients did not complete Cycle 1 Allan et. al. (ASH 2018 – Poster # 3141); Sunesis internal data
Summary: Preliminary Vecabrutinib Profile & Status Safety – appears well-tolerated in the context of advanced disease Pharmacokinetics – sustained exposure over dosing interval and generally dose proportional Pharmacodynamics – inhibition of BTK phosphorylation & cytokine reduction seen in patients (including BTK C481S subjects) Activity –evidence of clinical benefit in some subjects WM subject improvement in night sweats and fatigue, hemoglobin stabilized CLL subject improvement in fatigue, decreased nodes Dose escalation ongoing 100 mg cohort open, target dose level likely 100 – 300 mg BID 3 subjects assigned slots and under evaluation Clinical update targeted for major medical meeting in 2Q19

Proprietary Pipeline SNS-510, PDK-1 inhibitor
SNS-510 PDK1 Inhibitor: Exciting Preclinical Cancer Program Modality Small-molecule, oral inhibitor of PDK-1 Molecular Hypothesis Major mediator of PI3K signaling and activator of AKT PI3K-independent activator of RSK and S6K kinases Therapeutic Hypothesis Potentially broader activity than PI3K/AKT inhibitors both as a single agent and in combination Potential Target Indications Hematologic tumors including CLL, AML, and BCL Solid tumors including breast, prostate, stomach, lung, colon and pancreatic Program Status Completing pharmacology studies & formulation development
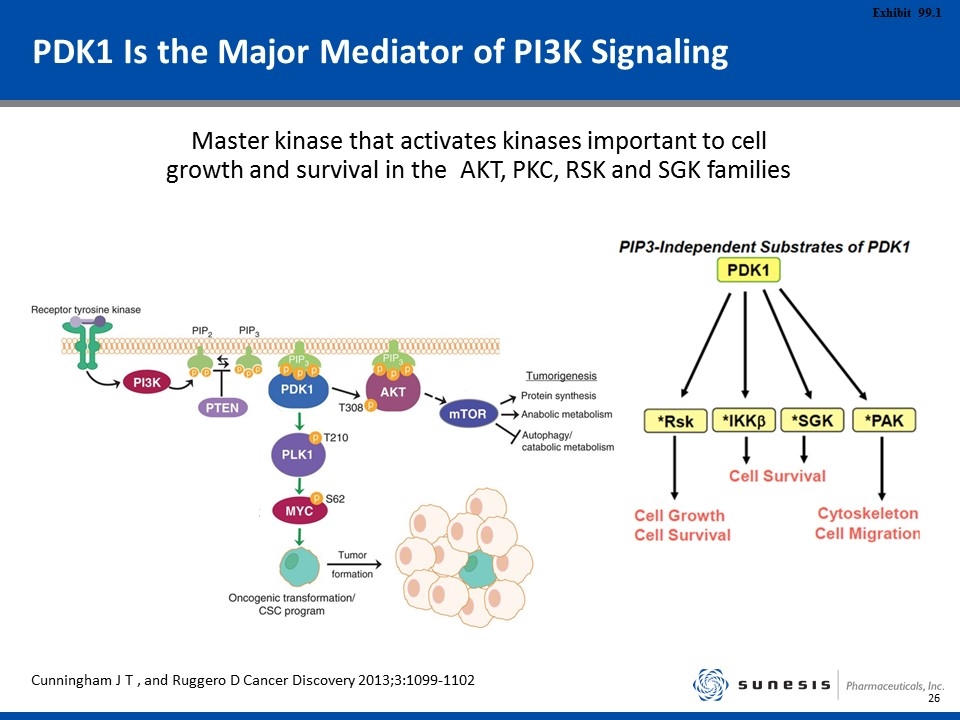
PDK1 Is the Major Mediator of PI3K Signaling Master kinase that activates kinases important to cell growth and survival in the AKT, PKC, RSK and SGK families Cunningham J T , and Ruggero D Cancer Discovery 2013;3:1099-1102

Summary
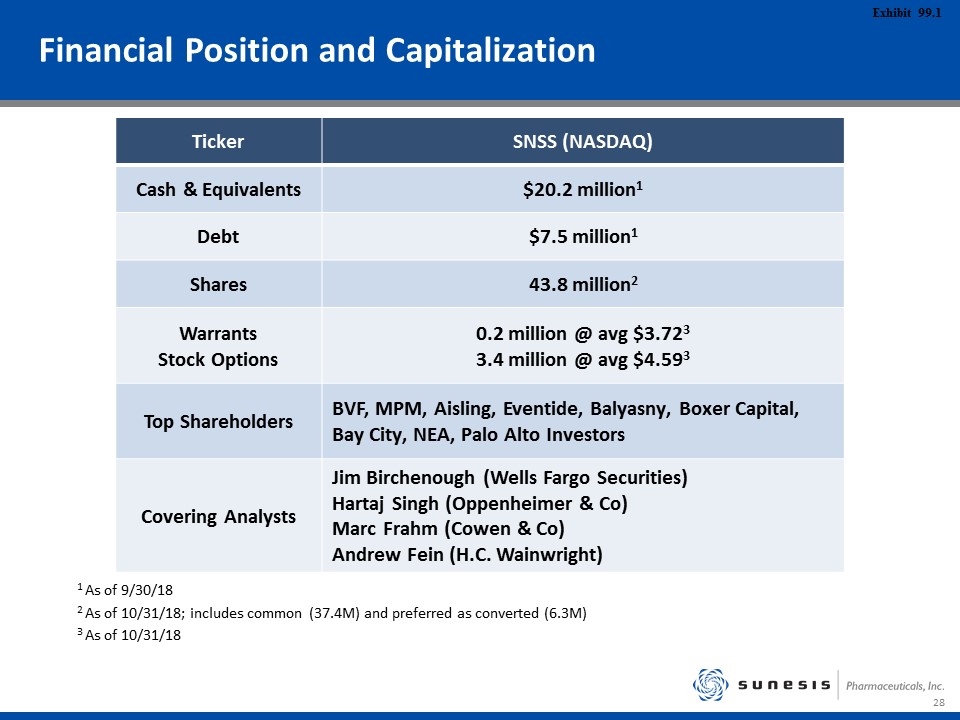
Financial Position and Capitalization 1 As of 9/30/18 2 As of 10/31/18; includes common (37.4M) and preferred as converted (6.3M) 3 As of 10/31/18 Ticker SNSS (NASDAQ) Cash & Equivalents $20.2 million1 Debt $7.5 million1 Shares 43.8 million2 Warrants Stock Options 0.2 million @ avg $3.723 3.4 million @ avg $4.593 Top Shareholders BVF, MPM, Aisling, Eventide, Balyasny, Boxer Capital, Bay City, NEA, Palo Alto Investors Covering Analysts Jim Birchenough (Wells Fargo Securities) Hartaj Singh (Oppenheimer & Co) Marc Frahm (Cowen & Co) Andrew Fein (H.C. Wainwright)

Sunesis Highlights Large and rapidly growing market for BTK inhibitors Validated target, clear mechanism of action Covalent-BTK-inhibitor resistance is a growing problem Near-term milestones expected to create significant value Global rights retained for both BTK and PDK1 programs

Thank You
