Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-32 - EXHIBIT 32 - CALIFORNIA FIRST NATIONAL BANCORP | exh_32.htm |
| EX-31.2 - EXHIBIT 31.2 - CALIFORNIA FIRST NATIONAL BANCORP | exh_312.htm |
| EX-31.1 - EXHIBIT 31.1 - CALIFORNIA FIRST NATIONAL BANCORP | exh_311.htm |
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
(Mark One)
| [X] | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15 (d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
| For the fiscal year ended June 30, 2016 |
| [ ] | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15 (d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
| For the transition period from ______________ to ______________ |
Commission File number 0-15641
CALIFORNIA FIRST NATIONAL BANCORP
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| California | 33-0964185 | |
| (State or other jurisdiction of Incorporation or organization) | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) | |
| 28 Executive Park, Irvine, CA 92614 | ||
| (Address of principal executive offices) | ||
| Registrant's telephone number, including area code: | (949) 255-0500 | |
| Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act: | ||
| Title of Each Class | Name of Each Exchange on Which Registered | |
| Common Stock, $.01 par value | The NASDAQ Stock Market LLC | |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant: (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities and Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the Registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of Registrant's knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of “accelerated filer, large accelerated filer and smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. (Check one):
Large accelerated filer ☐ Accelerated filer ☐ Non-accelerated filer ☐ Smaller reporting company ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). Yes ☐ No ☒
The aggregate market value of the Common Stock held by non-affiliates of the Registrant as of December 31, 2015 was $31,235,383. Number of shares outstanding as of September 16, 2016: Common Stock 10,279,807.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Part III incorporates information by reference from Registrant's definitive Proxy Statement to be filed with the Commission within 120 days after the close of the Registrant's fiscal year ended June 30, 2016.
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
TABLE OF CONTENTS
| 1 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
PART I
California First National Bancorp, a California corporation (the “Company”), is a bank holding company headquartered in Orange County, California with a bank subsidiary, California First National Bank (“CalFirst Bank” or the “Bank”) and leasing subsidiary, California First Leasing Corp (“CalFirst Leasing”). The Company is regulated by the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System and the Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco (“FRB”) under the U.S. Bank Holding Company Act of 1956, as amended. CalFirst Bank is regulated by the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency, U.S. Department of the Treasury (“OCC”).
The primary business of the Company is secured financing provided through leasing and financing capital assets, commercial loans acquired through participation in the syndicated commercial loan market, by providing non-recourse loans to third parties secured by leases and equipment, and direct commercial loans. CalFirst Bank, now responsible for substantially all lease and loan origination, gathers deposits through posting rates on the Internet and conducts all banking and other operations from one central location. Over the past few years, the Company has migrated from primarily leasing equipment toward a broader commercial lending program and during the year ended June 30, 2016, commercial loans accounted for 68% of the Company’s bookings, up from 42% in fiscal 2015 and less than 5% five years ago.
At June 30, 2016, the Company had total assets of $888.2 million, up 22% from the prior year, leases and loans of $641.4 million, total deposits of $633.1 million, and a conservative capital profile with stockholders’ equity of $191.0 million producing regulatory capital ratios at June 30, 2016 of 25.1% Tier 1 capital, 26.0% total capital and 21.7% Tier 1 leverage capital, well above required regulatory thresholds.
Leasing Activities
At June 30, 2016, leases accounted for 37% of the Company’s lease and loan portfolio, down from 55% and 72% at June 30, 2015 and 2014, respectively. The Company leases and finances most capital assets used by businesses and organizations, with a focus on high technology systems and other mission critical assets, and has seen an increase in the volume of other assets over the last few years. In addition to computer systems and networks, property leased includes automated warehouse distribution management systems, manufacturing production systems, and telecommunications systems such as wireless networks, voice over Internet protocol (“VoIP”) systems, and satellite tracking systems. Retail point-of-sale and inventory tracking systems often integrate computers, scanners and software. Other electronic equipment leased includes robotic surgical systems, ultrasound and medical imaging systems, computer-based patient monitoring systems, testing equipment, copying and digital printing equipment. In addition, the Company leases a wide variety of non-electronic property, including office equipment, mining equipment, machine tools, school buses, trucks, exercise equipment and office and dormitory furniture. The mixture of property subject to leases booked in any year varies by year. In fiscal 2016, leases involved with computer equipment and software accounted for 35% of the property, up from 15% the prior year but down from 41% in fiscal 2014. A comparison of the mix of property subject to new leases booked in each of the three years ending June 30, 2016 is set forth below (dollars in thousands):
| Year End June 30, | 2016 | % | 2015 | % | 2014 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
| Computer Hardware and Software | $ | 38,372 | 35 | % | $ | 32,857 | 15 | % | $ | 73,922 | 41 | % | ||||||||||||
| Warehouse Management Systems | 24,414 | 22 | % | 33,240 | 15 | % | 1,882 | 1 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Transportation equipment | 14,077 | 13 | % | 16,331 | 7 | % | 15,763 | 9 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Medical Equipment | 10,354 | 9 | % | 16,445 | 8 | % | 13,819 | 8 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Furniture & Fixtures | 10,118 | 9 | % | 27,123 | 12 | % | 21,722 | 12 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Yellow Equipment | 3,426 | 3 | % | 9,179 | 4 | % | 9,095 | 5 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Manufacturing Equipment | 3,174 | 3 | % | 23,554 | 11 | % | 17,170 | 9 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Office Equipment | 1,195 | 1 | % | 10,068 | 5 | % | 2,205 | 1 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Air Transport Equipment | - | 0 | % | 25,000 | 11 | % | 6,750 | 4 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Other | 5,240 | 5 | % | 23,988 | 11 | % | 19,022 | 10 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Cost of Property on Leases Booked | $ | 110,370 | $ | 217,785 | $ | 181,350 | ||||||||||||||||||
The Company provides leasing and financing to customers throughout the United States and across a breadth of industries and disciplines, including commercial, industrial and financial companies, as well as educational, government and non-profit entities. The average size of the lease transactions booked during fiscal 2016 was approximately $751,000, compared with $1.1 million during fiscal 2015 and $935,000 during fiscal 2014. Two customers accounted for 18% and 13% of the property cost subject to leases booked during fiscal 2016, while in fiscal 2015 two customers accounted for 14% and 12% of leases booked and in fiscal 2014 one customer accounted for 13% of leases booked in that year. Leases primarily are originated directly through a centralized marketing program and direct delivery channels, or through other banks or origination sources. During fiscal 2016, 97% of property cost subject to leases booked was originated directly by the Company, compared to 94% originated directly in fiscal 2015 and 89% originated directly in fiscal 2014. The marketing program includes a database of current and potential users of business property, as well as in-house customer relations management systems. The marketing programs have been augmented through the expanded use of web sites and the Internet to identify and communicate with potential customers. Prospect management software is utilized to enhance the productivity of the sales effort. Specific information about potential customers is entered into a confidential database accessible to sales professionals and their managers that allows them to efficiently focus on the most likely purchaser or lessee of capital assets.
| 2 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
Leases generally are for initial terms ranging from two to five years and are structured individually to accommodate a variety of our customers’ objectives. Substantially all leases are non-cancelable "net" leases which contain "hell-or-high-water" provisions under which the lessee must make all lease payments regardless of any defects in the property, and which require the lessee to maintain and service the property, insure the property against casualty loss and pay all property, sales and other taxes. CalFirst Bank or CalFirst Leasing retain ownership of the property on leases they originate, and in the event of default by the lessee, they may declare the lessee in default, accelerate all lease payments due under the lease and pursue other available remedies, including repossession of the property. Upon the expiration of the lease term, the lessee typically has an option, which is dependent upon each lease's defined end of term options, to either purchase the property at a negotiated price, or in the case of a "conditional sales contract," at a predetermined minimum price, or to renew the lease. If the original lessee does not exercise the purchase option, once the leased property is returned, the Company will seek to sell the leased property.
Through its lease purchase operations, the Bank purchases lease receivables on a non-recourse basis from other intermediaries. All banks or lessors from whom the Bank purchases lease receivables are subject to an individual credit review and investigation by the Bank and must be approved by the Bank’s board of directors prior to establishing a discounting relationship. The Bank generally does not assume any obligations as lessor for these transactions, and the original lessor retains ownership of any underlying asset, with the Bank taking a priority first lien position. Periodically, the Bank will purchase a whole lease and assume the role as lessor and take a residual interest in the property subject to such lease. The Bank verifies the completeness of all lease documentation prior to purchase, confirms that the Bank’s position is secure and that liens have been perfected, and legal documentation has been filed as appropriate. Leases purchased from unaffiliated third parties during fiscal 2016 aggregated to $2.9 million, or 3% of total leases booked. In fiscal 2015, purchased leases of $13.5 million represented 6% of total bookings while fiscal 2014 purchased leases of $19.6 million represented 11% of total bookings.
The Company conducts the leasing business in a manner designed to minimize risk, however, we are subject to risks through the investment in lease receivables held in our own portfolios, lease transactions-in-process, and residual investments. We do not purchase leased property until we have received a binding non-cancelable lease from the customer. A portion of lease originations are discounted to banks or finance companies on a non-recourse basis at fixed interest rates that reflect the customers' financial condition. The lender to which a lease has been assigned has no recourse against the Company, unless we are in default under the terms of the agreement by which the lease was assigned. The institution to which a lease has been assigned may take title to the leased property, but only in the event the lessee fails to make lease payments or otherwise defaults under the terms of the lease. If this occurs, the Company may not realize our residual investment, if any, in the leased property.
Lease Portfolio
During the fiscal year ended June 30, 2016, 93.5% of the total dollar amount of new leases completed by the Company were booked by CalFirst Bank, up from 90.4% in fiscal 2015 and 92.7% in fiscal 2014. The only new lease booked by CalFirst Leasing in fiscal 2016 was a participation with CalFirst Bank, as CalFirst Leasing no longer has a direct lease origination effort.
During the fiscal years ended June 30, 2016, 2015 and 2014, 89%, 88% and 97%, respectively, of the total dollar amount of new leases completed by the Company were retained in the Company’s portfolios, with the balance of such leases discounted to unaffiliated financial institutions. The Bank’s strategy is to develop a conservative, diversified portfolio of leases with credit worthy lessees through a portfolio management system that balances risk and reward while also managing exposures to any one credit or industry. The Bank’s credit committee has established underwriting standards and criteria for the lease portfolio and performs an independent credit analysis and due diligence on each lease transaction originated or purchased. The committee applies the same underwriting standards to all leases, regardless of how they are sourced. Through the use of non-recourse financing, the Company avoids risks that do not meet our risk/reward requirements or reduces its exposure to meet internal or regulatory requirements. A small portion of the portfolio, primarily held by CalFirst Leasing, includes leases where the credit profile of the lessee or the underlying leased property is not acceptable to other financial institutions.
| 3 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
The table below presents the discounted minimum lease payments receivable (“Net Lease Receivable") related to leases retained in the Company’s portfolios at June 30, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. Of the Bank’s Net Lease Receivable, approximately 88%, 82% and 74%, respectively, represented leases originated directly by the Bank, with 12%, 16% and 21%, of the Bank’s Net Lease Receivables at June 30, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively, related to leases purchased from unaffiliated parties.
| (dollars in thousands) | As of June 30, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net Lease | Percent of | Net Lease | Percent of | Net Lease | Percent of | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Receivable | Total | Receivable | Total | Receivable | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||
| California First National Bank | $ | 213,355 | 94 | % | $ | 270,657 | 94 | % | $ | 288,331 | 91 | % | |||||||||||||
| California First Leasing | $ | 14,554 | 6 | % | $ | 15,727 | 6 | % | $ | 27,343 | 9 | % | |||||||||||||
The Company often makes payments to purchase leased property prior to the commencement of the lease. The disbursements for such lease transactions-in-process are generally made to facilitate the property implementation schedule of the lessees. The lessee generally is contractually obligated to make rental payments during the period that the transaction is in process, and obligated to reimburse the Company for all disbursements under certain circumstances. Income is not recognized while a transaction is in process and prior to the commencement of the lease. At June 30, 2016, 2015, and 2014, the Company’s total investment in property acquired for transactions-in-process amounted to $30.9 million, $31.3 million and $40.6 million, respectively. Of such amounts, 100%, 91% and 77%, respectively, for each respective year related to CalFirst Bank, with the balance held by CalFirst Leasing.
Commercial Loans
Commercial loans of $403.7 million accounted for 63% of the Company’s net investment in leases and loans at June 30, 2016, an increase from $243.5 million, or 45% of the Company’s investment, at June 30, 2015 and $129.2 million, or 28% of the Company’s investment, at June 30, 2014. During fiscal 2016, the Company boarded $238.1 million of new commercial loans that were offset in part by payoffs and principal reductions of $77.8 million. Fiscal 2016 commercial loan bookings were up 53% from fiscal 2015 bookings of $155.3 million, which were reduced by payoffs and principal reductions of approximately $41.1 million. In January 2015, the OCC removed restrictions that limited the growth in the Bank’s commercial loan portfolio within certain guidelines.
Over 96% of the commercial loan portfolio consists of participations in syndicated transactions led primarily by major money center banks, with approximately 4% of the loan portfolio at June 30, 2016 the result of a direct origination effort. Direct loan origination is directed toward the Company’s existing and targeted customer database as a complementary product leveraging existing resources and extending customer longevity. Commercial loan products offered include commercial mortgages, term loans and lines of credit, and generally will be secured, but unsecured loans will be considered, depending on the nature of the credit. The Bank had four direct commercial loans aggregating to $14.3 million outstanding as of June 30, 2016, all at fixed rates, ranging in size from $1.5 million to $7.6 million, and with remaining terms of 35 months to 15 years. One loan is unsecured with the other three all secured by real estate used in the borrower’s business.
Syndicated bank loans are almost all term loans secured by substantially all of the borrower’s assets, although in some cases term loans have a second lien on working capital assets and less than 100% security interest in certain foreign assets. At June 30, 2016, the Bank had one commitment on a revolving line of credit which was fully drawn at such date. All syndicated loans are priced at floating rates, and generally are made to larger corporations with debt ratings of BB or Ba, or higher, as rated by Standard & Poor’s (“S&P”) or Moody’s Investors Service (“Moody’s), respectively. At June 30, 2016, 24% of the syndicated loan portfolio is rated investment grade (Baa3 or higher by Moody's or BBB- or higher by S&P) by one or more of the rating agencies, compared to 28% of the syndicated loan portfolio at June 30, 2015, while approximately 11.9% of the syndicated loan portfolio at June 30, 2016 relates to companies that are rated lower than Ba, up from 6.3% at June 30, 2015.
Approximately 79% of the loan portfolio at June 30, 2016 is characterized as “leveraged loans” under guidance promulgated by federal bank regulators, compared to 59% under such guidance at June 30, 2015. Credits that the Company characterizes as higher risk leveraged loans accounted for approximately 8% of the syndicated loan portfolio at June 30, 2016, compared to 14% at June 30, 2015 under the same definition. The Bank’s credit policies and administrative processes have been augmented significantly to incorporate guidance issued by federal banking regulators regarding leveraged lending.
The Bank’s syndicated loan portfolio is diversified across industries, with the loans to individual credits ranging in size from $250,000 to $12.4 million. At June 30, 2016, the average principal outstanding on 84 credits was $4.6 million, and the remaining terms ranged from one to seven years. The Bank’s underwriting of commercial loans is consistent with its credit standards for leases, although its policies have been augmented to address credit issues related to the larger average investment in individual loans and regulatory issues governing the participation market. The risks associated with loans in which the Bank participates as part of a syndicate of financial institutions are similar to those of directly originated commercial loans; however, additional risks may arise from the Bank’s limited ability to control actions of the syndicate. Existing staff administer loan operations including documentation, lien perfection, funding, payments and collections. The Bank’s current computer systems are capable of fully processing loans and have the requisite connectivity to the Company’s accounting, customer service and collections processes.
| 4 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
The table below presents the commercial loan balance net of unearned income and discounts and before allowances by loan type in the Company’s portfolios at June 30, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively.
| (dollars in thousands) | As of June 30, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net Loan | Percent of | Net Loan | Percent of | Net Loan | Percent of | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance | Total | Balance | Total | Balance | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial term loans | $ | 398,240 | 97.5 | % | $ | 238,424 | 96.7 | % | $ | 120,803 | 92.1 | % | |||||||||||||
| Revolving lines of credit | $ | 3,389 | 0.8 | % | $ | 562 | 0.2 | % | $ | 2,448 | 1.9 | % | |||||||||||||
| Commercial real estate loans | $ | 6,679 | 1.6 | % | $ | 7,523 | 3.1 | % | $ | 7,907 | 6.0 | % | |||||||||||||
Commercial loan transactions funded during fiscal 2016 of $238.1 million, included two direct real estate loans for $4.7 million and loan participations aggregating to $233.9 million to 55 different credits. This compared to $155.3 million through participations during fiscal 2015. Yields earned on commercial loans tend to be lower than yields earned on lease transactions, but the average life or duration of the investment is expected to be longer and such yields will vary more with changes in market interest rates.
Credit Risk Management
The Company’s strategy for credit risk management includes stringent credit authority centered at the most senior levels of management. The strategy emphasizes diversification on both a geographic and customer level, and spreading risk across a breadth of leases and loans while managing the risk to any one area. The consolidated lease and loan portfolio at June 30, 2016 includes over 598 lease schedules and 87 commercial loans. No customer accounted for more than 4% of the net investment in leases and loans at June 30, 2016 and 3% at June 30, 2015 and June 30, 2014. The ten largest customers accounted for 18% of the lease and loan portfolio at June 30, 2016, compared to 19% of the portfolio at June 30, 2015 and 24% at June 30, 2014.
As a national bank, CalFirst Bank is subject to lending limit rules that restrict the maximum credit that the Bank may extend to any one entity at any one time to 15% of unimpaired capital and surplus. At June 30, 2016, the Bank’s “legal lending” limit was $18.4 million. The Company and CalFirst Leasing are not subject to any regulatory limits. At June 30, 2016, the largest single exposure of CalFirst Bank to one credit was $14.8 million. CalFirst Leasing also has exposure to this same credit, and the combined exposure of $23.4 million represents 3.6% of the Company’s net investment in leases and loans.
The credit policy requires each lease or loan, regardless of whether it is directly originated or acquired through syndication, to have viable repayment sources. The credit process primarily focuses on a customer’s ability to repay the lease or loan through their cash flow, and generally, collateral securing a transaction represents a secondary source of repayment. The credit process includes a policy of classifying all leases and loans in accordance with a risk rating classification system, monitoring changes in the risk ratings of lessees and borrowers, identification of problem leases and loans and special procedures for the collection of problem leases and loans. The lease and loan classification system is consistent with regulatory models under which leases and loans may be rated as “pass”, “special mention”, “substandard”, “doubtful” or “loss”.
An Asset Management (“AM”) group handles the day-to-day management and oversight of the lease and loan portfolios. The AM group monitors the performance of all leases held in the portfolios, transactions-in-process as well as lease transactions assigned to lenders, if the Company retains a residual investment in the leased property subject to the lease. The AM group conducts an ongoing review of all leases 10 or more days delinquent, contacts the lessee directly and generally sends the lessee a notice of non-payment within 15 days after the due date. In the event that payment is not then received, senior management becomes involved. Delinquent leases are coded in the AM tracking system in order to provide management visibility, periodic reporting, and appropriate reserves. Legal recourse is considered and promptly undertaken if alternative resolutions are not obtained. At 90 days past due, leases and loans will be placed on non-accrual status such that interest income no longer accretes into income, unless the Company believes the amounts due are otherwise recoverable.
Allowance for Credit Losses
The allowance for credit losses is an estimate of probable and assessable losses in the Company’s lease and loan portfolios applying the principles of Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) Topic 450, “Contingencies,” and ASC Topic 310-35, “Loan Impairment.” The allowance recorded is based on a quarterly review of all leases and loans outstanding and transactions-in-process. The determination of the appropriate amount of any provision is based on management’s judgment at that time and takes into consideration all known relevant internal and external factors that may affect the lease and loan portfolios. The primary responsibility for setting reserves resides with executive management who report quarterly to the Company’s Audit Committee and Board of Directors regarding overall asset quality, problem leases and loans and the adequacy of valuation allowances. The Bank's classification of its assets and the amount of its valuation allowances are subject to review by regulators who can order the establishment of additional loss allowances.
| 5 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
The Company individually analyzes the net book value of each non-performing or problem lease and loan to determine whether the carrying value is less than or equal to the expected recovery anticipated to be derived from lease or loan payments, additional collateral or residual realization. The amount estimated as unrecoverable is recognized as a reserve specifically identified for the lease or impaired loan. An analysis of the remaining portfolios is conducted, taking into account recent loss experience, known and inherent risks in the portfolio, levels of delinquencies, adverse situations that may affect the customer’s ability to repay, trends in volume and other factors, including regulatory guidance and current and anticipated economic conditions in the market. This portfolio analysis includes a stratification of the lease and loan portfolio by risk classification and segments, and estimation of potential losses based on risk classification or segment. The composition of the portfolio based on risk ratings is monitored, and changes in the overall risk profile of the portfolio also is factored into the evaluation of inherent risks in the portfolios. Regardless of the extent of the Company's analysis of customer performance or portfolio evaluation, certain inherent but undetected losses are probable within the lease and loan portfolios. This is due to several factors including inherent delays in obtaining information regarding a customer’s financial condition or change in business conditions; the judgmental nature of individual credit evaluations and classification, and the interpretation of economic trends; volatility of economic or customer-specific conditions affecting the identification and estimation of losses and the sensitivity of assumptions utilized to establish allowances for losses, among other factors. Therefore, an estimated inherent loss not based directly on the specific problem assets is recorded as an unallocated allowance. The level of such unallocated allowance is determined based on a review of prior years’ loss experience, and may vary depending on general market conditions. The aggregate allowance in any one period is apportioned between allowance for lease and loan losses and allowance for valuation of residual value.
Banking Operations
The Bank is focused on gathering deposits from depositors nationwide for the primary purpose of funding its investment in leases and loans. The Bank’s strategy is to be a low cost producer through marketing its products and services directly to end-users. The Bank believes that its operating costs generally will be lower than those of traditional "bricks and mortar" banks because it does not have the expense of a traditional branch network to generate deposits and conduct operations.
Deposit Products
At June 30, 2016, the Bank had $633.2 million in deposits, of which $82.0 million were demand, savings or money market accounts and $551.2 million, or 87%, were time deposits. The Bank’s deposits have been gathered primarily through the Internet. The Bank offers interest-bearing checking accounts, money market accounts, savings accounts and three (3) month to three (3) year certificates of deposit (“CDs”) to taxable and IRA depositors. CDs are offered with varying maturities in order to achieve a fair approximation or match of the average life of the Bank’s lease and loan portfolio. With leases generally providing for fixed rental rates, a matching fixed rate CD book is intended to allow the Bank to minimize interest rate fluctuation risk. Most of the Bank’s commercial loans are floating rate.
To open a new account, a customer can complete an on-line enrollment form on the Bank’s web site, or can call the Bank’s toll-free customer service number and open an account telephonically. Signature cards and deposits are then mailed to the Bank. Customers can make deposits by wire transfer, via direct deposit programs, or by mail. No teller line is maintained. The Bank’s customers have 24-hour access to account information. Customers can view their banking records and current balances, and transfer funds between accounts through the use of personal computers. They can also pay bills on-line. Customers can receive a free ATM card upon opening a demand deposit or savings account. In order to obtain cash, the Bank’s customers use other banks’ automated teller machines that are affiliated with the Plusä system. The Bank generally will reimburse customers for some portion of any ATM fees charged by other financial institutions. The Bank believes that any inconvenience resulting from the Bank not maintaining automated teller machines or a local branch office will be offset by the Bank’s higher investment yields and lower banking fees.
Operations
The Bank’s operations have been developed by outsourcing certain principal functions to leading bank industry service providers and by sharing established systems utilized by CalFirst Leasing or the Company. Outsourced systems include the Bank’s core processing and electronic banking system, electronic bill payment systems and depository services, including item processing. The Bank believes it benefits from the service provider's expertise and investments in developing technology. A critical element to the Bank’s success is the ability to provide secure transmission of confidential information over the Internet. The Bank’s service providers utilize sophisticated technology to provide maximum security. All banking transactions are encrypted and all transactions are routed from the Internet server through a "firewall" that limits access to the Bank’s and service provider’s systems. Systems are in place to detect attempts by third parties to access other users' accounts and feature a high degree of physical security, secure modem access, service continuity and transaction monitoring. The Bank has implemented the two-factor authentication security to its Internet banking procedures and platform.
| 6 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
Investments
In addition to leases and loans, the Company had total cash and cash equivalents and investment securities of $204.9 million at June 30, 2016 compared to $144.8 million at June 30, 2015 and $69.4 million at June 30, 2014. Cash and cash equivalents of $105.1 million consists of interest-earning deposits with the FRB, other banks and short-term money market securities. The investment portfolio of $99.8 million includes U.S. government agency (“Agency”) mortgage-backed securities (“MBS”), U.S. Treasury Notes, corporate bonds, Federal Reserve Bank and Federal Home Loan Bank stock and other investments. The Company is authorized to invest in high-quality United States agency obligations, mortgage-backed securities, investment grade corporate bonds and municipal securities and selected preferred and equity securities. The investment portfolio may increase or decrease depending upon the comparative returns on investments in relation to leases and loans.
Customers
Leasing and loan customers include major corporations and middle-market companies, subsidiaries and divisions of Fortune 1000 companies, private and state-related educational institutions, municipalities and other not-for-profit organizations and institutions located throughout the United States. The Company does not believe the loss of any one customer would have a material adverse effect on its operations taken as a whole.
The Bank’s deposit customers are primarily individuals from across the nation who place a substantial portion of their savings in safe, government-insured deposits and businesses that spread their liquid investments among a breadth of banks in order to ensure that they are government insured. Such depositors are seeking to maximize their interest income and, therefore, are more inclined to move their investments to a bank that offers the highest yield regardless of the geographic location of the depository.
Competition
The Company competes for the lease and loan financing of capital assets with other banks, commercial finance companies, and other financial institutions, independent leasing companies, credit companies affiliated with equipment manufacturers, and equipment brokers and dealers. Many of the Company's competitors have substantially greater resources, capital, and more extensive and diversified operations than the Company. The Company believes that the principal competitive factors are rate, responsiveness to customer needs, flexibility in structuring lease financing and loans, financial technical proficiency and the offering of a broad range of financing options. The level of competition varies depending upon market and economic conditions, the interest rate environment, and availability of capital.
The Bank competes with other banks and financial institutions to attract deposits. The Bank faces competition from established local and regional banks and savings and loan institutions. Many of them have larger customer bases, greater name recognition and brand awareness, greater financial and other resources, broader product offerings and longer operating histories. The market for Internet banking has seen increased competition over the past several years as large banks and other financial institutions have deployed and aggressively promoted their own on-line banking platforms and aggressively sought deposits over the internet. Additionally, new competitors and competitive factors are likely to emerge with the continued development of Internet banking.
Supervision and Regulation
The Company is a bank holding company within the meaning of the Bank Holding Company Act of 1956, as amended, and is registered with, regulated and examined by the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System (the “FRB”). In addition to the regulation of the Company by the FRB, the Bank is subject to extensive regulation and periodic examination, principally by the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (“OCC”). The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (“FDIC”) insures the Bank’s deposits up to certain prescribed limits. The Bank is a member bank within the San Francisco Federal Reserve district. The Company is also subject to jurisdiction of the Securities and Exchange Commission ("SEC") and to the disclosure and regulatory requirements of the Securities Act of 1933 and the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, and through the listing of the common stock on the NASDAQ Global Select Market is subject to the rules of NASDAQ.
The Bank Holding Company Act, the Federal Reserve Act, and the Federal Deposit Insurance Act subject the Company and the Bank to a number of laws and regulations. In addition, substantial changes to the regulation of banks and bank holding companies have occurred as a result of the enactment in 2010 of the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act (the “Dodd-Frank Act”). The primary concern of banking regulation is “Safety and Soundness” with an emphasis on asset quality and capital adequacy. These laws and regulations also encompass a broad range of other regulatory concerns including insider transactions, the adequacy of the allowance for credit losses, intercompany transactions, regulatory reporting, adequacy of systems of internal controls and limitations on permissible activities. The federal banking agencies possess broad powers to take corrective action as deemed appropriate for an insured depository institution and its holding company. The FRB examines the Company, which exam includes CalFirst Leasing. The OCC, which has primary supervisory authority over the Bank, regularly examines banks in such areas as asset quality, reserves, investments, risk management practices, interest rate exposure, vendor management and other aspects of operations. These examinations are designed for the protection of the Bank’s depositors rather than the Company’s shareholders. The Bank must furnish annual and quarterly reports to the OCC, which has the authority under the Financial Institutions Supervisory Act to prevent a national bank from engaging in an unsafe or unsound practice in conducting its business. The OCC may impose restrictions or new requirements on the Bank, including, but not limited to, growth limitations, dividend restrictions, individual increased regulatory capital requirements, lease and loan loss reserve requirements, increased supervisory assessments, activity limitations or other restrictions that could have an adverse effect on the Bank, the Company or holders of our common stock. Many banking laws and regulations have undergone significant change in recent years and, given the recent financial crisis in the United States, regulators have increased their oversight of financial institutions and taken a more active role in imposing restrictions on bank operations, the classification of assets and determination of the allowance for credit losses. Future changes to these laws and regulations, and other new financial services laws and regulations are likely, and cannot be predicted with certainty.
| 7 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
Under FRB policy, the Company is expected to serve as a source of financial and managerial strength to the Bank and, under appropriate circumstances, to commit resources to support the Bank. Certain loans by the Company to the Bank would be subordinate in right of payment to deposits in, and certain other indebtedness of, the Bank.
Among the regulations that affect the Company and the Bank are provisions of Section 23A of the Federal Reserve Act that places limits on the amount of loans or extensions of credit the Bank may make to affiliates and the amount of assets purchased from affiliates, except for transactions exempted by the FRB. The aggregate of all of the above transactions is limited in amount, as to any one affiliate, to 10% of a bank’s capital and surplus and, as to all affiliates combined, to 20% of a bank's capital and surplus. Regulation W (“Reg. W”) provides a framework under Section 23A by which the Bank does not have to comply with the quantitative limits of Section 23A when making a loan or extension of credit to an affiliate, but also contains certain provisions designed to prohibit the Bank from buying low-quality assets from an affiliate. The Company and the Bank are also subject to the provisions of Section 23B of the Federal Reserve Act which, among other things, prohibits an institution from engaging in transactions with affiliates unless the transactions are on terms substantially the same, or at least as favorable to the institution as those prevailing at the time for comparable transactions with non-affiliated companies. All transactions between the Company or CalFirst Leasing and the Bank are in accordance with these provisions.
In connection with the approval of the Company’s purchase of the stock of the Bank in 2001, the FRB and the OCC required the Company and the Bank to make certain commitments with respect to the operation of the Bank. In September 2006, the OCC approved a change in the Bank’s original operating plan that provided for the Bank to originate commercial loans. In June 2012, the OCC provided a written determination of no objection to a revised business plan to continue development of the commercial loan portfolio, but with certain conditions that required the Bank to maintain a Tier 1 capital ratio of not less than 14% through June 30, 2015 and limit the growth in the commercial loan portfolio within certain guidelines. In January 2015, the OCC terminated the 2001 operating agreement between the OCC and the Bank and eliminated restrictions imposed in 2012. The only continuing commitment after January 2015 is a binding written agreement between the Bank and the Company setting forth the Company’s obligations to provide capital maintenance and liquidity support to the Bank, if and when necessary.
Bank holding companies are subject to risk-based capital guidelines adopted by the FRB. The Company currently is required to maintain (i) Tier 1 capital equal to at least six percent of its risk-weighted assets and (ii) total capital (the sum of Tier 1 and Tier 2 capital) equal to ten percent of risk-weighted assets. The FRB also requires the Company to maintain a minimum Tier 1 "leverage ratio" (measuring Tier 1 capital as a percentage of adjusted total assets) of at least five percent. At June 30, 2016 and 2015, the Company exceeded all these requirements.
The Bank is also subject to risk-based and leverage capital requirements. In July 2013, federal bank regulatory agencies jointly issued final rules that revise the general risk-based capital requirements to incorporate certain revisions by the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision to the Basel capital framework (“Basel III”). Under the final rule, minimum requirements increase both the quantity and quality of capital held by banking organizations. Consistent with Basel III, the rule includes a new minimum ratio of common equity tier 1 capital to risk-weighted assets of 4.5 percent and a common equity tier 1 capital conservation buffer of 2.5 percent of risk-weighted assets. The rule also raises the minimum ratio of tier 1 capital to risk-weighted assets from 4 percent to 6 percent and includes a minimum leverage ratio of 4 percent for all banking organizations. The final rule minimizes the burden on smaller, less complex financial institutions such as the Company and the Bank, with a phase-in period that began in January 2015 while the phase-in period for larger institutions began in January 2014. At June 30, 2016, the Bank had capital in excess of all current minimum risk-based and leverage capital requirements as well as the new guidelines.
Under the Community Reinvestment Act (“CRA”), the Bank has a continuing and affirmative obligation, consistent with safe and sound operation, to help meet the credit needs of its entire communities, including low- and moderate-income neighborhoods. CalFirst Bank is designated as a wholesale institution for CRA purposes. To evaluate the CRA performance of banks with this designation, regulatory agencies use the community development test. This includes an assessment of the level and nature of the Bank’s community development lending, investments and services. The CRA requires the OCC, in connection with its examination of the Bank, to assess and assign one of four ratings to the Bank’s record of meeting the credit needs of its community. The CRA also requires that the Bank publicly disclose its CRA rating. In July 2013, CalFirst Bank was subjected to a CRA examination and received a “satisfactory” rating on the CRA performance evaluation.
| 8 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
The Bank is a member of the Deposit Insurance Fund (“DIF”) maintained by the FDIC. Through the DIF, the FDIC insures the deposits of the Bank up to prescribed limits for each depositor. As a result of the Dodd-Frank Act, the maximum deposit insurance amount has been increased permanently from $100,000 to $250,000. In February 2011, the FDIC adopted a final rule implementing the Dodd-Frank Act provisions which provides for use of a risk scorecard to determine deposit premiums. For FDIC assessment purposes, the bank’s assessment base is its average consolidated total assets minus its average tangible equity. The assessment rate is determined by the FDIC using a risk-based calculation. The Bank's assessment base and assessment rate are calculated and billed each quarter. As of June 30, 2016, the DIF surpassed a target of 1.15 percent to trigger important changes in the FDIC assessments for all banks. The changes take effect for premiums to be billed and paid in December 2016. Banks with less than $10 billion in assets will see their overall schedule decline by two basis points for banks paying the lowest premiums and up to five points for those at the top end of the assessment scale. In addition, a new formula for calculating risk-based assessment rates is now in effect. The FDIC may increase or decrease the assessment rate in the future, and any such increase could have an adverse impact on the earnings of insured institutions, including the Bank.
The Bank also is required to make payments for the servicing of obligations of the Financing Corporation (“FICO”) issued in connection with the resolution of savings and loan associations, so long as such obligations remain outstanding. The FICO annual assessment rate as of June 30, 2016 is $0.56 cents per $100 of deposits compared to $0.58 cents per $100 of deposits as of June 30, 2015.
The FDIC can terminate insurance of the Bank’s deposits upon a finding that the Bank has engaged in unsafe and unsound practices, is in an unsafe or unsound condition to continue operations, or has violated any applicable law, regulation, rule, order, or condition imposed by the OCC. The termination of deposit insurance could have a material adverse effect on the Company’s results of operations, business and financial condition.
The principal source of cash flow to the Company, including cash flow to pay dividends on its common shares, is dividends from its subsidiaries and fees for services rendered to its subsidiaries. Various statutory and regulatory provisions limit the amount of dividends or fees that may be paid to the Company by the Bank. In general, the Bank may not declare or pay a dividend to the Company in excess of 100% of its net retained earnings for the current year combined with its net retained earnings for the preceding two calendar years without prior approval of the OCC. The Company has not received any dividends from the Bank to date, and believes CalFirst Leasing and CalFirst Bank have sufficient resources to meet the Company’s requirements.
There are numerous laws, regulations and policies affecting financial services businesses currently in effect and they are continually under review by Congress and state legislatures and federal and state regulatory agencies. The Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act established requirements for financial institutions to provide privacy protections to consumers and notices to customers about its privacy policies and practices. The Bank Secrecy Act and USA Patriot Act impose obligations to maintain appropriate policies, procedures and controls to detect, prevent and report suspicious activities, money laundering and terrorist financing as well as maintain compliance programs to verify the identity of customers. The Dodd-Frank Act provides for sweeping financial regulatory reform and may have the effect of increasing the cost of doing business, limiting or expanding permissible activities and affect the competitive balance between banks and other financial intermediaries. Under the Dodd-Frank Act, the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (the “CFPB”) has assumed all authority to prescribe rules or issue orders or guidelines pursuant to any federal consumer financial laws. While many of the provisions of the Dodd-Frank Act do not impact the existing business of the Bank, the repeal of prohibitions on the payment of interest on demand deposits, thereby permitting depository institutions to pay interest on business transaction and other accounts, could increase deposit rates to be paid by the Bank in order to retain or grow deposits. In addition, the provisions of the Dodd-Frank Act known as the Volcker Rule prohibit proprietary trading of securities and other financial instruments that do not currently impact the Company but could limit future activities. Changes in the laws, regulations or policies that impact the Company cannot necessarily be predicted, and they may have a material effect on the business and earnings of the Company.
The commercial banking business is also influenced by the monetary and fiscal policies of the federal government and the policies of the FRB. The FRB implements national monetary policies through its management of the discount rate, the money supply, and reserve requirements on bank deposits. Indirectly, such policies and actions may impact the ability of non-bank financial institutions to compete with the Bank. Monetary policies of the FRB have had, and will continue to have, a significant effect on the operating results of financial institutions. The nature and impact of any future changes in monetary or other policies of the FRB cannot be predicted.
Employees
At June 30, 2016, the Company and its subsidiaries had 99 employees, none of whom are represented by a labor union. The Company believes that its relations with its employees are satisfactory.
| 9 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
Available Information
Our Internet address is www.calfirstbancorp.com. There we make available, by link to the SEC, our annual report on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, current reports on Form 8-K and any amendments to those reports, as soon as reasonably practical after we electronically file such material with, or furnish it to, the SEC. Our SEC reports can be accessed through the Investor Relations section of our Internet site. Our Corporate Governance Guidelines and our Code of Ethics for Senior Financial Management are available for viewing and printing under the Corporate Governance section of our Internet site. The information found on our Internet site is not part of this or any other report we file with or furnish to the SEC and is not incorporated herein by reference.
Forward-Looking Statements
This Form 10-K contains forward-looking statements. Forward-looking statements include, among other things, information concerning our possible future consolidated results of operations, business and growth strategies, financing plans, our competitive position and the effects of competition and economic conditions. Forward-looking statements include all statements that are not historical facts and can be identified by forward-looking words such as “anticipate”, “believe”, “could”, “estimate”, “expect”, “intend”, “plan”, “may”, “should”, “will”, “would”, “project” and similar expressions. These forward-looking statements are based on information currently available to us and are subject to inherent risks and uncertainties, and certain factors could cause actual results to differ materially from those anticipated. Some of the risks and uncertainties that may cause our actual results or performance to differ materially from such forward-looking statements are included in “Item 1A. Risk Factors” of this report. All forward-looking statements are qualified in their entirety by this cautionary statement and the Company undertakes no obligation to revise or update any forward-looking statements to reflect events or circumstances arising after the date on which they were made.
There are a number of factors, including those specified below, that may adversely affect the Company’s business, financial results or stock price. Additional risks that the Company currently does not know about or currently views as immaterial may also affect the Company’s business or adversely impact its financial results or stock price.
Industry Risk Factors
The Company’s business and financial results are subject to general business and economic conditions. The economic downturn and slow recovery reduced demand for financing capital assets. Continued or renewed weakness in the economy or in certain sectors could impact the financial performance and condition of customers and negatively affect the repayment of their obligations. In addition, changes in securities markets and monetary fluctuations adversely affect the availability and terms of funding necessary to meet the Company’s liquidity needs.
Changes in the domestic interest rate environment could reduce the Company’s net finance and interest income. The Company’s net finance and interest income, which is the difference between income earned on leases, loans and investments and interest expense paid on deposits, is affected by market rates of interest, which in turn are affected by prevailing economic conditions, by the fiscal and monetary policies of the federal government and by the policies of various regulatory agencies. The Federal Open Market Committee (“FOMC) of the FRB has increased short term interest rates only minimally from the near zero level maintained for several years, and the timing and amount of any further increases is unclear. Increases in interest rates will increase the income earned on the Company’s available cash balances, but will also increase the Bank’s cost of funds over time. If the interest rates on deposits and other borrowings increase at a faster rate than the interest rates received on leases, loans, securities and other interest-earning investments, net interest income and therefore earnings, could be adversely affected.
Uncertain worldwide economic conditions and volatility in the currency and credit markets may negatively impact the Company and its customers. A drop in long term interest rates has resulted in flattening of the yield curve since January 2016. While the decrease in longer term interest rates increases the value of fixed rate securities, the narrowing of the spread between longer and shorter term rates tends to negatively impact net interest margins. Foreign currency fluctuations have hurt the results of many businesses, including certain leveraged loan customers, and may impact their ability to meet their obligations. These circumstances could not only result in increased loan defaults, and charge-offs, but require increases to the allowance for credit losses which may materially and adversely affect our results of operations, business, and financial condition.
Changes in the laws, regulations and policies governing financial services companies could alter the Company’s business environment and adversely affect operations. The Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System regulates the supply of money and credit in the United States. Its fiscal and monetary policies determine in a large part the Company’s cost of funds and the return that can be earned on leases, loans and investments, which affect the Company’s net finance, loan and interest income.
| 10 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
The Company and the Bank are subject to a wide range of complex laws and regulations established by government entities. Most regulation is intended to protect depositors, federal deposit insurance funds and the banking system as a whole. Bank regulators can impose restrictions on the ability of the Company to undertake certain business and growth initiatives. Following the 2008 financial crisis, regulators increased their oversight of banks and taken a more active role in imposing restrictions on bank operations, the classification of assets and determination of the allowance for credit losses. Changes in laws or governmental regulations, or changes in the interpretation of existing laws or regulations by a regulatory authority, could affect the Company in substantial and unpredictable ways. The Company cannot predict whether any additional legislation will be enacted, and if enacted, the effect that it or any regulations would have on the Company’s financial condition or results of operations.
Cyber security and privacy breaches may hurt our business, damage our reputation, increase our costs, and cause losses. Our systems and networks store personal information about our customers and employees. We have security systems and information technology infrastructure in place designed to protect against unauthorized access to such information. However, there is still a risk that the security systems and infrastructure that we maintain may not be successful in protecting against all security breaches, employee error, malfeasance, and cyber-attacks. The techniques used to obtain unauthorized access, disable or degrade service or sabotage systems change frequently and often are not recognized until launched and we may be unable to anticipate these techniques or to implement adequate preventative measures. Third parties, including vendors that provide services for our operations, could also be a source of security risk to us in the event of a failure of their own security systems and infrastructure or outside parties may attempt to fraudulently induce employees or customers to disclose sensitive information in order to gain access to our data or our customers' data. Any significant violations of data privacy could result in a loss of confidence in the security of our products and services, the loss of business, litigation, regulatory investigations, and penalties that could damage our reputation and adversely affect the growth of our business.
The financial services industry is highly competitive, and competitive pressures could intensify and adversely affect the Company’s financial results. The Company operates in a highly competitive industry that could become even more competitive as a result of legislative, regulatory and technological changes. The Company competes with other commercial banks, savings and loan associations, mutual savings banks, finance companies, credit unions and investment companies, many of which have greater resources than the Company.
Acts or threats of terrorism and political or military actions taken by the United States or other governments could adversely affect general economic or industry conditions.
Company Risk Factors
The Company’s allowance for credit losses may not be adequate to cover actual losses. The Company’s subsidiaries retain approximately 90% of lease transactions and all loans in their own portfolios, which expose the Company to credit risk. The Company maintains an allowance for credit losses to provide for probable and estimable losses in the portfolio. The Company’s allowance for credit losses is based on its historical experience as well as industry data, an evaluation of the risks associated with its portfolio, including the size and composition of the lease and loan portfolios, current economic conditions and concentrations within the portfolio. The allowance for credit losses may not be adequate to cover losses resulting from unanticipated adverse changes in the economy or the financial markets. If the credit quality of the customer base materially decreases, or if the reserve for credit losses is not adequate, future provisions for credit losses could materially and adversely affect financial results.
The Company may suffer losses in its lease and loan portfolio despite its underwriting practices. The Company seeks to mitigate the risks inherent in its lease and loan portfolio by adhering to specific credit practices. Although the Company believes that its criteria are appropriate for the various kinds of leases and loans it makes, the Company may incur losses on leases and loans that meet these criteria.
Larger transactions and customer concentration may increase the risk of loss in the event of the deterioration of one of these customers or industries. At June 30, 2016, leases aggregating to $23.3 million to one customer accounted for 3.6% of the Company’s net investment in leases and loans, with the ten largest customers representing 18% of the portfolio. Two industry classifications, hospitals and public and private colleges and universities, each represented just over 5% of the Company’s total investment in leases and loans.
The Bank’s commercial loan initiative may increase the Company’s risk of losses. The commercial loan portfolio increased 66% in fiscal 2016 and contains a number of commercial loans with relatively larger balances than the average lease. About 79% of the portfolio consists of “leveraged loans” as characterized by federal regulatory guidelines, with 8% of the commercial loan portfolio considered to be higher risk leveraged loans by the Company. No loan credit is rated substandard, but the deterioration of one or a few of these loans could cause a significant increase in non-performing loans. An increase in non-performing loans could result in an increase in the provision for credit losses and an increase in charge-offs, all of which could have a material adverse effect on the Company’s results of operations.
| 11 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
The Bank’s lease purchase operations may increase the Company’s risk of losses. CalFirst Bank’s program to grow its lease portfolio through the purchase of lease receivables on a non-recourse basis from other banks and finance companies has accounted for 3% to 21% of leases booked in each of the past five years. The Company seeks to mitigate the risks inherent in this third-party business by adhering to specific underwriting practices, but the Bank could be exposed to risks not inherent with the lease transactions originated directly, including unfamiliar documentation and reliance on sales and funding professionals not subject to the Bank’s policies and practices.
The Company’s diversification into broader investment alternatives may increase the Company’s risk of losses. The Company’s investment portfolio includes U.S. Treasury and Agency Securities, corporate and municipal bonds and closed-end mutual funds, in addition to interest-earning deposits, short-term money market securities and federal funds. These securities subject the Company to increased risk of volatility in the valuation of the investment, as well as greater interest and market risks. The deterioration of one or a few of these investments on a permanent basis could result in an determination that the investment has been permanently impaired and require a write-down of such investment, all of which could have a material adverse effect on the Company’s results of operations.
The Company may be adversely affected by significant changes in the bank deposit market and interest rates. CalFirst Bank represents 96% of the Company’s assets and bank deposits now exceed $633 million, or 331% of stockholders’ equity and up from 129% of equity five years ago. As a result, the Company’s sensitivity to changes in interest rates and demand for bank deposits has increased from historical levels. Time deposits due within one year of June 30, 2016 totaled $440 million. If these maturing deposits do not roll over, CalFirst Bank may be required to seek other sources of funds, including other time deposits and borrowings, or sell assets. Depending on market conditions, rates paid on deposits and borrowings may be higher than currently paid or no longer available. Although the Bank employs a funding strategy designed to correlate the repricing characteristics of assets with liabilities, the impact of interest rate movements and customer demand is not always consistent during different market cycles, and changes in the costs for deposits and yields on assets may not coincide.
The change in residual value of leased assets may have an adverse impact on the Company’s financial results. A portion of the Company’s leases is subject to the risk that the residual value of the property under lease will be less than the Company’s recorded value. Adverse changes in the residual value of leased assets can have a negative impact on the Company’s financial results. The risk of changes in the realized value of the leased assets compared to recorded residual values depends on many factors outside of the Company’s control.
The financial services business involves significant operational risks. Operational risk is the risk of loss resulting from the Company’s operations, including, but not limited to, the risk of fraud by employees or persons outside of the Company, the execution of unauthorized transactions by employees, errors relating to transaction processing and technology, breaches of the internal control system and compliance requirements, and failure of business continuation and disaster recovery plans. This risk of loss also includes the potential legal actions that could arise as a result of an operational deficiency or as a result of noncompliance with applicable regulatory standards, adverse business decisions or their implementation, and customer attrition due to potential negative publicity. In the event of a breakdown in the internal control system, improper operation of systems or improper employee actions, the Company could suffer financial loss, face regulatory action and suffer damage to its reputation.
Bank regulators can impose restrictions on the Company’s ability to execute its strategic plan. The OCC has terminated the operating agreement that imposed restrictions on the Bank’s operations, but the Bank and Company are still subject to periodic examination by the FRB and the OCC and if the Bank were found to be operating in an unsound or unsafe manner, they could impose new restrictions or requirements, including, but not limited to activity or growth limitations, dividend restrictions, increased loan and lease loss reserve requirements, or other restrictions that could have an adverse effect on the Bank or the Company.
Quarterly operating results may fluctuate significantly. Operating results may differ from quarter to quarter due to a variety of factors, including the volume and profitability of leased property being remarketed, the size and credit quality of the lease and loan portfolio, the interest rate environment, the volume of new lease and loan originations, including variations in the property mix and funding of such originations and economic conditions in general. The results of any quarter may not be indicative of results in the future.
Negative publicity could damage the Company’s reputation and adversely impact its business and financial results. Reputation risk, or the risk to the Company’s business from negative publicity, is inherent in the Company’s business. Negative publicity can result from the Company’s actual or alleged conduct in any number of activities, including leasing practices, compliance with bank regulations, corporate governance, and actions taken by government regulators in response to those activities. Negative publicity can adversely affect the Company’s ability to keep and attract customers and deposits and can expose the Company to litigation and regulatory action.
The Company’s reported financial results are subject to certain assumptions and estimates and management’s selection of accounting method. The Company’s management must exercise judgment in selecting and applying many accounting policies and methods so they comply with generally accepted accounting principles and reflect management’s judgment of the most appropriate manner to report the Company’s financial condition and results. In some cases, management may select an accounting policy which might be reasonable under the circumstances yet might result in the Company’s reporting different results than would have been reported under a different alternative.
| 12 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
Certain accounting policies are critical to presenting the Company’s financial condition and results. They require management to make difficult, subjective or complex judgments about matters that are uncertain. Materially different amounts could be reported under different conditions or using different assumptions or estimates. These critical accounting policies include the estimate of residual values, the allowance for credit losses, and income taxes. For more information, refer to “Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates.”
Changes in accounting standards could materially impact the Company’s financial statements. The Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) may change the financial accounting and reporting standards that govern the preparation of the Company’s financial statements. These changes can be hard to predict and can materially impact how the Company records and reports its financial condition and results of operations. Recently, FASB approved new accounting standards related to the accounting for leases and allowance for credit losses that could change the Company’s financial statements when implemented. In some cases, the Company could be required to apply a new or revised standard retroactively, resulting in the Company’s restating prior period financial statements.
Loss of certain key officers would adversely affect the Company’s business. The Company‘s business and operating results are substantially dependent on certain key employees, including the Chief Executive Officer, Chief Operating Officer, Chief Financial Officer and Chief Credit Officer of the Bank and certain key sales managers. The loss of the services of these individuals, particularly the Chief Executive Officer, would have a negative impact on the business because of their expertise and years of industry experience.
The Company’s business could suffer if the Company fails to attract and retain qualified people. The Company’s success depends, in large part, on its ability to attract and retain key people. Competition for personnel in most activities the Company engages in can be intense. The Company may not be able to hire the best people or to keep them.
The Company relies on other companies to provide components of the Company’s business infrastructure. Third party vendors provide certain components of the Company’s business infrastructure, such as the Bank’s core processing and electronic banking systems, item processing, and Internet connections. While the Company has selected these third party vendors carefully, it does not control their actions. Any problems caused by these third parties not providing the Company their services for any reason or their performing their services poorly, could adversely affect the Company’s ability to deliver products and services to the Company’s customers and otherwise to conduct its business. Replacing these third party vendors could also entail significant delay and expense.
A natural disaster could harm the Company’s business. Natural disasters could harm the Company’s operations directly through interference with communications, including the interruption or loss of the Company’s websites, which would prevent the Company from gathering deposits, originating leases and loans and processing and controlling its flow of business, as well as through the destruction of facilities and the Company’s operational, financial and management information systems.
The Company faces systems failure risks as well as security risks, including “hacking” and “identity theft.” The computer systems and network infrastructure the Company and others use could be vulnerable to unforeseen problems. These problems may arise in both our internally developed systems and the systems of our third-party service providers. Our operations are dependent upon our ability to protect computer equipment against damage from fire, power loss or telecommunication failure. Any damage or failure that causes an interruption in our operations could adversely affect our business and financial results. In addition, our computer systems and network infrastructure present security risks, and could be susceptible to hacking or identity theft.
The Company relies on dividends from its subsidiaries for its liquidity needs. The Company is a separate and distinct legal entity from CalFirst Leasing and the Bank. The principal source of funds to pay dividends on the Company’s stock is from distributions from the subsidiaries. Various regulations limit the amount of dividends that the Bank may pay to the Company.
The Company’s stock price can be volatile. The Company’s common stock is not widely held and the limited trading market for the stock can result in fluctuations in prices between trades and make it difficult for stockholders to dispose of their shares. The Company’s stock price can fluctuate widely in response to a variety of factors, including: actual or anticipated variations in the Company’s quarterly operating results and dividend policy; operating and stock price performance of other companies that investors deem comparable to the Company; news reports relating to trends, concerns and other issues in the financial services industry, and changes in government regulations. General market fluctuations, industry factors and general economic and political conditions and events, including terrorist attacks, economic slowdowns or recessions, interest rate changes, credit loss trends or currency fluctuations, could also cause the Company’s stock price to decrease regardless of the Company’s operating results.
| 13 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
The Company is a “controlled company” as defined by NASDAQ, with over 64% of the stock held by the Chief Executive Officer, over 77% held by two senior executives and fewer than 100 shareholders of record. As a result, senior management has the ability to exercise significant influence over the Company’s policies and business, and determine the outcome of corporate actions requiring stockholder approval. These actions may include, for example, the election of directors, the adoption of amendments to corporate documents, the approval of mergers, sales of assets and the continuation of the Company as a registered company with obligations to file periodic reports and other filings with the SEC.
ITEM 1B. UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS
None.
At June 30, 2016 the Company and its subsidiaries occupied approximately 36,000 square feet of office space in Irvine, California leased from an unaffiliated party. The lease provides for monthly rental payments that average $58,850 from July 2016 through August 2018.
The Company is sometimes named as a defendant in litigation relating to its business operations. Management does not expect the outcome of any existing suit to have a material adverse effect on the Company's financial condition or results of operations.
Item 4. Mine Safety Disclosures
Not applicable
PART II
ITEM 5. MARKET FOR COMPANY'S COMMON EQUITY AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES
The common stock of California First National Bancorp trades on the NASDAQ Global Market System under the symbol CFNB. The following high and low closing sale prices for the periods shown reflect inter-dealer prices without retail markup, markdown or commissions and may not necessarily reflect actual transactions.
| For the years ended | |||||||||||||||||
| June 30, 2016 | June 30, 2015 | ||||||||||||||||
| High | Low | High | Low | ||||||||||||||
| First Quarter | $ | 13.60 | $ | 13.06 | $ | 15.25 | $ | 14.26 | |||||||||
| Second Quarter | 13.70 | 13.11 | 15.08 | 14.04 | |||||||||||||
| Third Quarter | 13.97 | 12.85 | 14.70 | 13.61 | |||||||||||||
| Fourth Quarter | $ | 15.00 | $ | 13.45 | $ | 13.85 | $ | 13.27 | |||||||||
The Company had approximately 20 stockholders of record and in excess of 350 beneficial owners as of September 16, 2016.
Beginning in October 2009, the Board of Directors’ dividend policy provided for one annual dividend payment each year. The Company paid an annual dividend in the amount of $0.40 on December 14, 2013, $0.42 on December 13, 2014 and $0.44 on December 15, 2015. The Board of Directors will continue to review the dividend policy on an ongoing basis, taking into consideration a variety of factors including the business, economic and tax environment. No decision to pay dividends in fiscal 2016 and beyond has been made.
In April 2001, the Board of Directors authorized management, at its discretion, to repurchase up to 1,000,000 shares of common stock. This authorization has no termination date, but the Board of Directors reviews the authorization to repurchase common stock from time to time. The Company repurchased 180,117 shares of common stock under this authorization during the year ended June 30, 2016 and no shares purchased during the years ended June 30, 2015 and 2014. As of September 10, 2016, 188,237 shares remain available under this authorization.
| 14 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
Common Stock Performance Graph
The following graph shows a comparison of the five-year cumulative return among the Company, the NASDAQ Composite Index and the Russell 2000. The graph assumes an investment of $100 on June 30, 2011 in our common stock and in each of the indices listed on the graph and reflects the change in the market price of our common stock relative to the changes in the noted indices at June 30, 2012, 2013, 2014, 2015 and 2016. The performance shown below is based on historical data and is not indicative of, nor intended to forecast, future price performance of our common stock. As required by Securities and Exchange Commission rules, total return in each case assumes the reinvestment of dividends paid.
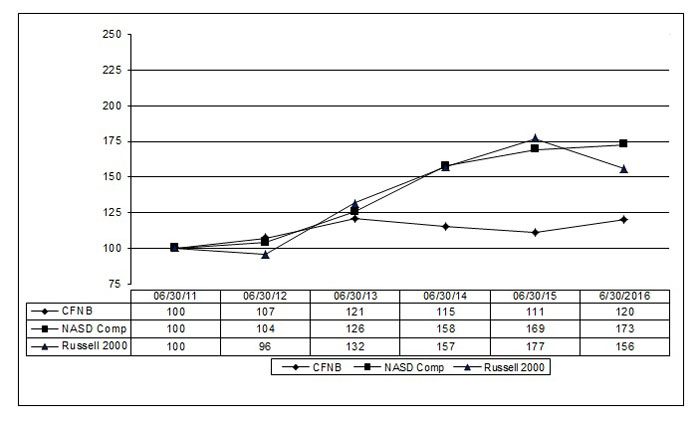
Equity Compensation Plan Information
The following table provides information about shares of the Company’s Common Stock that may be issued upon the exercise of options under our existing equity compensation plans as of June 30, 2016.
| Plan category | Number of shares of common stock to be issued upon exercise of outstanding options | Weighted average exercise price of outstanding options | Number of shares of common stock available for future issuance under equity compensation plans (excluding shares in first column)(1) | |||||||||
| Equity compensation plans approved by shareholders | 10,000 | $ | 16.00 | 2,219,845 | ||||||||
| Equity compensation plans not approved by shareholders | None | N/A | N/A | |||||||||
| Total | 10,000 | $ | 16.00 | 2,219,845 | (1) | |||||||
| (1) | The maximum number of shares that may be issued under the equity
compensation plan increases each year by an amount equal to 1% of the total number of issued and outstanding shares of Common Stock
as of June 30 of the fiscal year immediately preceding such fiscal year. |
| 15 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
ITEM 6. SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA
The following table sets forth selected financial data and operating information of the Company and its subsidiaries. The selected financial data should be read in conjunction with the Financial Statements and notes thereto and Management's Discussion and Analysis of Results of Operations and Financial Condition contained herein.
| INCOME STATEMENT FINANCIAL DATA | YEARS ENDED JUNE 30, | |||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands, except per share amounts) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||||||||
| Finance and loan income | $ | 25,471 | $ | 21,489 | $ | 18,370 | $ | 18,995 | $ | 20,505 | ||||||||||
| Investment and interest income | 2,230 | 1,516 | 1,371 | 2,408 | 3,133 | |||||||||||||||
| Total interest income | 27,701 | 23,005 | 19,741 | 21,403 | 23,638 | |||||||||||||||
| Interest expense on deposits and borrowings | 6,210 | 3,945 | 3,037 | 2,664 | 2,914 | |||||||||||||||
| Net interest income | 21,491 | 19,060 | 16,704 | 18,739 | 20,724 | |||||||||||||||
| Provision for credit losses | 1,475 | 1,175 | 200 | 275 | - | |||||||||||||||
| Net interest income after provision for credit losses | 20,016 | 17,885 | 16,504 | 18,464 | 20,724 | |||||||||||||||
| Operating and sales-type lease income | 1,146 | 305 | 2,152 | 1,711 | 2,755 | |||||||||||||||
| Gain on sale of leases and leased property | 3,497 | 4,791 | 2,980 | 2,278 | 2,478 | |||||||||||||||
| Other income | 220 | 3,132 | 432 | 526 | 569 | |||||||||||||||
| Realized gain on sale of investment securities | 23 | 481 | - | 316 | 56 | |||||||||||||||
| Total non-interest income | 4,886 | 8,709 | 5,564 | 4,831 | 5,858 | |||||||||||||||
| Non-interest expenses | 10,834 | 11,779 | 10,995 | 11,610 | 12,307 | |||||||||||||||
| Earnings before income taxes | 14,068 | 14,815 | 11,073 | 11,685 | 14,275 | |||||||||||||||
| Income taxes | 5,420 | 5,760 | 4,022 | 4,331 | 5,372 | |||||||||||||||
| Net earnings | $ | 8,648 | $ | 9,055 | $ | 7,051 | $ | 7,354 | $ | 8,903 | ||||||||||
| Diluted earnings per share | $ | 0.83 | $ | 0.87 | $ | 0.67 | $ | 0.70 | $ | 0.85 | ||||||||||
| Diluted common shares outstanding | 10,399 | 10,460 | 10,456 | 10,453 | 10,429 | |||||||||||||||
| Cash dividends per share | $ | 0.44 | $ | 0.42 | $ | 0.40 | $ | 2.20 | $ | 1.10 | ||||||||||
| Dividend payout ratio | 53.2 | % | 48.5 | % | 59.3 | % | 312.6 | % | 128.7 | % | ||||||||||
| Net interest margin | 2.78 | % | 3.15 | % | 3.22 | % | 3.77 | % | 4.40 | % | ||||||||||
| Net interest spread | 2.54 | % | 2.88 | % | 2.92 | % | 3.41 | % | 4.00 | % | ||||||||||
| Return on average assets | 1.06 | % | 1.39 | % | 1.30 | % | 1.40 | % | 1.80 | % | ||||||||||
| Return on average equity | 4.59 | % | 4.87 | % | 3.90 | % | 4.00 | % | 4.50 | % | ||||||||||
| BALANCE SHEET DATA | AS OF JUNE 30, | |||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands, except per share amounts) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 105,094 | $ | 60,240 | $ | 40,122 | $ | 75,469 | $ | 56,921 | ||||||||||
| Investment securities | 99,801 | 84,546 | 29,316 | 48,162 | 66,751 | |||||||||||||||
| Net investment in leases and loans | 641,410 | 541,786 | 455,805 | 416,569 | 336,463 | |||||||||||||||
| Total assets | 888,176 | 731,074 | 579,550 | 558,903 | 486,171 | |||||||||||||||
| Deposits | 633,147 | 471,906 | 355,810 | 346,028 | 253,297 | |||||||||||||||
| Borrowings | 40,000 | 42,000 | 6,858 | - | - | |||||||||||||||
| Non-recourse debt | 4,449 | 10,193 | 8,640 | 768 | 3,275 | |||||||||||||||
| Stockholders’ equity | $ | 191,022 | $ | 188,218 | $ | 183,745 | $ | 180,879 | $ | 196,439 | ||||||||||
| Equity to total assets ratio | 21.51 | % | 25.75 | % | 31.70 | % | 32.36 | % | 40.41 | % | ||||||||||
| Book value per common share | $ | 18.58 | $ | 17.99 | $ | 17.57 | $ | 17.31 | $ | 18.83 | ||||||||||
| 16 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
ITEM 7. MANAGEMENT'S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
General
The Company’s results include the operations of CalFirst Bank and CalFirst Leasing. The Company’s finance, loan and interest income includes interest income earned on the Company’s investment in lease receivables and residuals, commercial loans and investment securities. Non-interest income primarily includes gains realized on the sale of leased property, income from sales-type and operating leases, gains realized on the sale of leases, gains or losses recorded on investment securities and other income. Income from sales-type leases relates to the re-lease of off-lease property (“lease extensions”) while operating lease income generally involves lease extensions that do not meet the accounting requirements for sales-type leases.
The Company's operating results are subject to quarterly fluctuations resulting from a variety of factors, including the size and credit quality of the lease and loan portfolios, the interest rate environment, the volume and profitability of leased property being re-marketed through re-lease or sale, the market for investment securities, the volume of new lease or loan originations, including variations in the mix and funding of such originations, and economic conditions in general. The Company’s principal market risk exposure currently is related to interest rates and the differences in the repricing characteristics of interest-earning assets and interest-bearing liabilities. The FRB has maintained historically low market interest rates from 2009 to 2016 that has contributed to lower net interest margins. The Company’s current balance sheet structure is short-term in nature, with over 68% of interest-earning assets and 63% of interest-bearing liabilities that mature or reprice within one year. The Company’s interest margin is susceptible to timing lags related to varying movements in market interest rates. Many of the Company’s leases, loans and liquid investments are tied to U.S. treasury rates and Libor that often do not move in step with bank deposit rates. As a result, this can result in a greater change in net interest income than indicated by the repricing asset and liability comparison.
The Company conducts its business in a manner designed to mitigate risks. However, the assumption of risk is a key source of earnings in the leasing and banking industries and the Company is subject to risks through its investment in leases and loans held in its own portfolio, securities, lease transactions-in-process, and residual investments. The Company takes steps to manage risks through the implementation of strict credit and risk management processes and on-going risk management review procedures.
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
The preparation of the Company’s financial statements requires management to make certain critical accounting estimates that impact the stated amount of assets and liabilities at a financial statement date and the reported amount of income and expenses during a reporting period. These accounting estimates are based on management’s judgment and are considered to be critical because of their significance to the financial statements and the possibility that future events may differ from current judgments, or that the use of different assumptions could result in materially different estimates. The following is a description of the most critical accounting policies management applies, all of which require the use of accounting estimates and management’s judgment, based on the relevant information available at the end of each period.
Allowance for Credit Losses – The allowance for credit losses provides coverage for probable and estimable losses in the Company’s lease and commercial loan portfolios. The allowance recorded is based on a quarterly review of all leases and loans outstanding, loan commitments and transactions-in-process. The determination of the appropriate amount of any provision is highly dependent on management’s judgment at that time and takes into consideration all known relevant internal and external factors that may affect the lease and loan portfolio, including levels of non-performing leases and loans, customers financial condition, leased property values and collateral appraisals as well as general economic conditions and credit quality indicators. The Company’s allowance includes an estimate of reserves needed to cover specifically identified lease and loan losses and certain unidentified but inherent risks in the portfolio.
Fair Value of Investments – Investment securities are characterized as held-to-maturity (Investments) or as available-for-sale (Securities Available-for-Sale) based on management’s ability and intent regarding such investment at acquisition. On an ongoing basis, management must estimate the fair value of its investment securities based on information and assumptions it deems reliable and reasonable, which may be quoted market prices or if quoted market prices are not available, fair values extrapolated from the quoted prices of similar instruments. Based on this information, an assessment must be made as to whether any decline in the fair value of an investment security should be considered an other-than-temporary impairment and recorded in non-interest income as a loss on investments. The determination of such impairment is subject to a variety of factors, including management’s judgment and experience.
| 17 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
Residual Values – For capital leases that qualify as direct financing leases, the aggregate lease payments receivable and estimated residual value, if any, are recorded on the balance sheet, net of unearned income and allowances, as net investment in leases. Of the volume of leases booked during the fiscal years ended June 30, 2016, 2015 and 2014, approximately 6.8%, 15.9% and 25.0%, respectively, were structured such that the Company owns the leased asset at the end of the term and recorded a residual value. The residual value is an estimate for accounting purposes of the fair value of the leased property at lease termination and is determined at the inception of the lease based on the property leased and the terms and conditions of the underlying lease contract. The realizability of any estimated residual value depends on future collateral values, contractual options available to the lessee, the credit of the lessee, market conditions and other subjective and qualitative factors. The estimated residual values established at lease inception are periodically reviewed to determine if values are realizable and any identified losses are recognized at such time.
Initial Direct Costs Deferred – A portion of the Company’s non-interest expenses that management estimates is directly related to originating lease and loan transactions is deferred through a reduction to non-interest expenses recognized in a period. The amount deferred reflects management’s estimate of the expenses applicable to the origination process, taking into account a variety of factors including sales productivity, credit and documentation efficiency and estimates of completion percentages.
Deferred Income Taxes and Valuation Allowance – Deferred tax assets and liabilities result from temporary differences between the time income or expense items are recognized for financial statement purposes and for tax reporting. Such amounts are calculated using the enacted tax rates and laws that are expected to be in effect when the differences are expected to reverse. The determination of current and deferred income taxes is based on complex analyses of many factors including interpretation of federal and state income tax laws, the difference between tax and financial reporting basis of assets and liabilities (temporary differences), estimates of amounts due or owed such as the timing of reversals of temporary differences and current financial accounting standards. A valuation allowance is established if, based upon the relevant facts and circumstances, management believes that some or all of certain tax assets will not be realized. The Company has open tax years that may in the future be subject to examination by federal and state taxing authorities. Management periodically evaluates the adequacy of related valuation allowances, taking into account open tax return positions, tax assessments received and tax law changes. The process of evaluating allowance accounts involves the use of estimates and a high degree of management judgment. Actual results could differ significantly from the estimates and interpretations used in determining the current and deferred income tax liabilities and reserves.
The Company's estimates are reviewed continuously to ensure reasonableness. However, the amounts the Company may ultimately realize could differ from such estimated amounts.
Overview of Results, Trends and Outlook
Net earnings for the year ended June 30, 2016 of $8.65 million decreased $407,000, or 5%, from $9.05 million reported in fiscal 2015. Fiscal 2015 included a $2.7 million pre-tax gain on the settlement of claims filed in an antitrust case. Excluding the settlement claim from the prior year results, fiscal 2016 pre-tax income of $14.1 million was up 16.5%, benefitting from a $2.4 million increase in net interest income and a $945,000 reduction in non-interest expenses.
For the year ended June 30, 2016, total leases and loans booked of $348.5 million were 7% below fiscal 2015 bookings of $373.1 million. Commercial loans boarded of $238.1 million were up 53% from the $155.3 million boarded in fiscal 2015, and offset a 49% decline in new lease bookings to $110.4 million from $217.8 million booked in the prior fiscal year. The Company’s net investment in leases and loans of $641.4 million at June 30, 2016 increased 18% from $541.8 million at June 30, 2015, which included a 65.6% increase in commercial loans that offset a 20.3% decline in the investment in leases.
New lease and loan transactions approved (“lease and loan originations”) of $352.9 million during fiscal 2016 were 3% below the level of the prior year. Fiscal 2016 loan originations of $219.9 million were up $34.7 million or 19% from $185.2 million in fiscal 2015. Lease originations during fiscal 2016 of $133.0 million were down 28% from $184.1 million the prior year, with 99% originated directly in fiscal 2016 and 94% in fiscal 2015. As a result, the estimated backlog of approved lease and loan commitments of $89.4 million at June 30, 2016 is down 28% from $124.8 million at June 30, 2015, with 83% of the backlog related to leases.
Consolidated Statement of Earnings Analysis
Summary – For the fiscal year ended June 30, 2016, net earnings of $8.65 million decreased $407,000 compared to $9.05 million for fiscal 2015. Diluted earnings per share decreased 3.9% to $0.83 in fiscal 2016 from $0.87 fiscal 2015. Diluted earnings per share reflects the impact of the Company’s repurchase of 180,117 shares of common stock in the third quarter of fiscal 2016. Net interest income after provision for credit losses increased $2.1 million and non-interest expenses decreased $945,000 but were offset by a $3.8 million decrease in non-interest income.
Net Interest Income – Net interest income is the difference between interest earned on the investment in leases, loans, securities and other interest earning assets and interest paid on deposits or other borrowings. Net interest income is affected by changes in the volume and mix of interest earning assets and liabilities, the movement of interest rates, and funding and pricing strategies.
| 18 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
The following table presents the components of the increases (decreases) in net interest income by volume and rate:
| 2016 compared to 2015 | 2015 compared to 2014 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Volume | Rate | Total | Volume | Rate | Total | |||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest income | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net investment in leases | $ | (1,786 | ) | $ | 412 | $ | (1,374 | ) | $ | (1,111 | ) | $ | 945 | $ | (166 | ) | ||||||||
| Commercial loans | 5,302 | 54 | 5,356 | 3,650 | (365 | ) | 3,285 | |||||||||||||||||
| Investment securities | 932 | (380 | ) | 552 | 713 | (581 | ) | 132 | ||||||||||||||||
| Interest-earning deposits with banks | 44 | 118 | 162 | (6 | ) | 19 | 13 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total interest income | 4,492 | 204 | 4,696 | 3,246 | 18 | 3,264 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Interest expense | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Demand and savings deposits | 27 | 84 | 111 | (4 | ) | (1 | ) | (5 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Time deposits | 1,427 | 582 | 2,009 | 659 | 193 | 852 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Short-term borrowings | 96 | 49 | 145 | 48 | 13 | 61 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total interest expense | 1,550 | 715 | 2,265 | 703 | 205 | 908 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Net interest income | $ | 2,942 | $ | (511 | ) | $ | 2,431 | $ | 2,543 | $ | (187 | ) | $ | 2,356 | ||||||||||
Net interest income increased 12.8% to $21.5 million for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2016 compared to $19.1 million for fiscal 2015. Total interest income increased 20.4% to $27.7 million compared to $23.0 million in fiscal 2015. This increase was due to a $5.4 million, or 79%, increase in commercial loan income resulting from a 78% increase in average loan balances to $331.8 million from $186.4 million for fiscal 2015, and a 2 basis point increase in average yields earned to 3.66%. The minor increase in loan yields reflects some benefit from an increase in Libor rates, but was offset by narrower pricing spreads. Direct finance income declined 9% for the year to $13.3 million, reflecting a 12% decrease in average investment in leases to $269.4 million which offset a 15 basis point increase in average lease yield to 4.95%. The yield on leases benefitted from the early termination of leases that accelerated interest income recognition. Investment interest income in fiscal 2016 was up 47% to $2.2 million, reflecting a 54% increase in average cash and investment balances to $171.4 million and 6 basis point drop in average yields to 1.30%. While average yields on interest-earning deposits with banks increased 15 basis points, average yields on investment balances declined by 41 basis points as lower yielding treasury and mortgage securities replaced maturing corporate securities. Interest expense on deposits and borrowings increased 57% to $6.2 million, reflecting a 40% increase in average balances to $595.8 million and an 11 basis point increase in average cost to 1.04%. The rise in interest cost for fiscal 2016 includes a 14 basis point increase in average cost of deposits to 1.10% and a $141 million increase in average deposits, tempered by a $30 million increase in average borrowings at an average rate of 0.42%.
The average yield on all interest-earning assets in fiscal 2016 declined 22 basis points to 3.59% while the average rate paid on all interest-bearing liabilities increased by 11 basis points to 1.04% from 0.93% in fiscal 2015. The decline in net interest spread and margin in fiscal 2016 is largely due to the increase in lower yielding commercial loans to 43% of average interest earning assets from 31% in fiscal 2015, and also reflects higher rates paid on deposits.
For the fiscal year ended June 30, 2015, net interest income increased 14.1% to $19.1 million compared to $16.7 million for fiscal 2014. Total interest income increased 16.5% to $23.0 million compared to $19.7 million in fiscal 2014. This increase was due to a $3.3 million, or 94%, increase in commercial loan income resulting from a 104% increase in average loan balances to $186.4 million from $91.3 million for fiscal 2014, which offset a 20 basis point drop in average yields earned to 3.64%. Direct finance income declined 1% for the year to $14.7 million, reflecting a 7% decrease in average investment in leases to $306.7 million, which offset a 31 basis point increase in average lease yield to 4.79%. Combined, the average yield on leases and loans for fiscal 2015 increased by 2 basis points to 4.36% from 4.34% in fiscal 2014. Investment interest income in fiscal 2015 was up 11% to $1.5 million, reflecting a 17% increase in average cash and investment balances to $111.5 million and 8 basis point drop in average yields to 1.36%, driven by a $20 million or 56% increase in average securities balances, albeit at yields averaging 104 basis points less than the prior year. Interest expense on deposits and borrowings increased 30% to $3.9 million, reflecting a 25% increase in average balances to $424.8 million and 4 basis point increase in average cost to 0.93%. The average yield on all interest-earning assets in fiscal 2015 remained flat with the prior year at 3.8%, while the average rate paid on all interest-bearing liabilities increased by 4 basis points to 0.93% from 0.89% in fiscal 2014. As a result, the net interest margin for the year decreased from 3.22% in fiscal 2014 to 3.15% in fiscal 2015.
| 19 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
The following table presents the Company’s average balance sheets, finance and loan income and interest earned or interest paid, the related yields and rates on major categories of the Company’s interest-earning assets and interest-bearing liabilities:
| (dollars in thousands) | Year ended June 30, 2016 | Year ended June 30, 2015 | Year ended June 30, 2014 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average | Yield/ | Average | Yield/ | Average | Yield/ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Assets | Balance | Interest | Rate | Balance | Interest | Rate | Balance | Interest | Rate | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest-earning assets | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest-earning deposits with banks | $ | 78,251 | $ | 269 | 0.34 | % | $ | 55,374 | $ | 107 | 0.19 | % | $ | 59,486 | $ | 94 | 0.16 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
| Investment securities | 93,170 | 1,961 | 2.10 | % | 56,082 | 1,409 | 2.51 | % | 35,986 | 1,277 | 3.55 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial loans | 331,818 | 12,148 | 3.66 | % | 186,357 | 6,792 | 3.64 | % | 91,314 | 3,507 | 3.84 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net investment in leases | 269,419 | 13,323 | 4.95 | % | 306,697 | 14,697 | 4.79 | % | 331,474 | 14,863 | 4.48 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total interest-earning assets | 772,658 | 27,701 | 3.59 | % | 604,510 | 23,005 | 3.81 | % | 518,260 | 19,741 | 3.81 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other assets | 40,402 | 45,625 | 37,849 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| $ | 813,060 | $ | 650,135 | $ | 556,109 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Liabilities and Shareholders' Equity | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest-bearing liabilities | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Demand and savings deposits | $ | 72,829 | 441 | 0.61 | % | $ | 67,338 | 330 | 0.49 | % | $ | 68,150 | 335 | 0.49 | % | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Time deposits | 473,751 | 5,562 | 1.17 | % | 338,080 | 3,553 | 1.05 | % | 271,693 | 2,701 | 0.99 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FHLB borrowings | 49,254 | 207 | 0.42 | % | 19,334 | 62 | 0.32 | % | 549 | 1 | 0.25 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total interest bearing liabilities | 595,834 | 6,210 | 1.04 | % | 424,752 | 3,945 | 0.93 | % | 340,392 | 3,037 | 0.89 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-interest bearing demand deposits | 2,134 | 2,024 | 1,785 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other liabilities | 26,743 | 37,278 | 32,027 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shareholders' equity | 188,349 | 186,081 | 181,905 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| $ | 813,060 | $ | 650,135 | $ | 556,109 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net interest income | $ | 21,491 | $ | 19,060 | $ | 16,704 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net interest spread (2) | 2.55 | % | 2.88 | % | 2.92 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net interest margin (3) | 2.78 | % | 3.15 | % | 3.22 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average interest earning assets over average interest bearing liabilities | 129.7 | % | 142.3 | % | 152.3 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | Average balance is based on month-end balances, includes non-accrual leases, and is presented net of unearned income. |
| (2) | Net interest spread is equal to the difference between the average yield on interest earning assets and the average rate paid on interest-bearing liabilities. |
| (3) | Net interest margin represents net finance and interest income as a percent of average interest earning assets. |
Provision for Credit Losses – The Company recorded a provision for credit losses in fiscal 2016 of $1.48 million, compared to a provision of $1.18 million recorded in fiscal 2015 and a provision of $200,000 in fiscal 2014. The higher provision in fiscal 2016 covered the $1.0 million write-down during the second quarter of a lease in bankruptcy as well as 66% growth in the loan portfolio. The fiscal 2015 provision related to the 88% growth in the commercial loan portfolio and some increased credit risk in the lease portfolio. The provision in fiscal 2014 was made in the fourth quarter of that year and reflected the growth in the portfolios and the emergence of potential problem credits at that time. At June 30, 2016, the allowance for credit losses of $6.9 million, 1.1% of total leases and loans, is considered to be appropriate for the credit profile of the consolidated portfolio.
Total Non-interest Income – Non-interest income of $4.9 million was down 43.9% from $8.7 million in fiscal 2015. Non-interest income for the prior year included the pre-tax recovery of $2,743,920 from the settlement of claims filed in a TFT-LCD (thin-film transistor liquid display) products antitrust case. Excluding that income from the prior year, non-interest income for fiscal 2016 was still down by $1.08 million or 18% due to a $1.3 million decrease in gains from the sale of leases and $458,600 decline in securities gains, offset in part by a $706,000 increase in income from the release of property on leases reaching the end of term during the year.
Total non-interest income for fiscal 2015 of $8.7 million increased $3.1 million or 56.5% from the $5.6 million in fiscal 2014. Excluding pre-tax recovery discussed above, the increase in fiscal 2015 non-interest income included a $788,700 increase in gains from sales of leases and $481,200 in securities gains that offset an $826,200 decline in income from end of term transactions. The residual investments realized in fiscal 2015 were 23% lower than the amount realized in fiscal 2014.
Non-interest Expenses – The Company’s non-interest expenses decreased $945,000, or 8.0%, to $10.8 million recognized for the year ended June 30, 2016. This compared to non-interest expenses in fiscal 2015 of $11.8 million, which had increased by $784,000, or 7.1%, from $11.0 million in fiscal 2014. The decrease in expenses in fiscal 2016 compared to fiscal 2015 was due primarily to a decrease in sales compensation and benefits cost recognized, offset in part by charges taken to write-down the value of a repossessed asset.
Non-interest expenses for the year ended June 30, 2015 of $11.8 million increased $784,000, or 7.1%, compared to non-interest expenses in fiscal 2014 of $11.0 million. The increase in expenses in fiscal 2015 compared to fiscal 2014 was due primarily to a 10% increase in salaries and benefits, primarily related to the sales force.
| 20 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
Income Taxes – Income taxes were accrued at a tax rate of 38.5% for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2016, 38.9% for fiscal year ended June 30, 2015 and 36.3% for fiscal year ended June 30, 2014, representing the Company’s estimated effective tax rate for each respective year. The effective tax rate decreased slightly in fiscal 2016 compared to 2015 due to the decrease in the effective state tax rate. The effective tax rate increased in fiscal 2015 compared to fiscal 2014 due to the increase in the effective state tax rate.
Financial Condition Analysis
Lease and Loan Portfolio
The following table summarizes the Company’s consolidated lease and loan portfolio by category:
| June 30, | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Net investment in leases | $ | 239,964 | $ | 301,733 | $ | 329,935 | $ | 345,753 | $ | 256,686 | |||||||||||
| Commercial loans | 401,629 | 238,978 | 123,238 | 66,541 | 71,478 | ||||||||||||||||
| Commercial real estate loans | 6,679 | 7,531 | 7,920 | 9,411 | 13,504 | ||||||||||||||||
| Total leases and loans | 648,272 | 548,242 | 461,093 | 421,705 | 341,668 | ||||||||||||||||
| Less allowance for credit losses | (6,862 | ) | (6,456 | ) | (5,288 | ) | (5,136 | ) | (5,205 | ) | |||||||||||
| Net leases and loans | $ | 641,410 | $ | 541,786 | $ | 455,805 | $ | 416,569 | $ | 336,463 | |||||||||||
Lease Portfolio
During the fiscal year ended June 30, 2016, 89% of the property value of new leases booked by the Company was held in its own portfolio, compared to 88% during fiscal 2015 and 97% during fiscal 2014. For the fiscal year ended June 30, 2016, the Company’s net investment in lease receivables decreased by $58.5 million and the investment in estimated residual values decreased by $2.2 million. The decrease in the investment in lease receivables reflects the low volume of new lease bookings that didn’t offset payments received and includes the sale or assignment of $26.8 million of lease receivables. The decrease in investment in residual values is due to a lower volume of new leases on which the Company records a residual compared to the volume of residual values recognized during the year.
The Company often makes payments to purchase leased property prior to the commencement of the lease. The disbursements for these lease transactions-in-process are made to facilitate the lessees’ property implementation schedule. The lessee generally is contractually obligated by the lease to make rental payments directly to the Company during the period that the transaction is in process, and obligated to reimburse the Company for all disbursements under certain circumstances. Income is not recognized while a transaction is in process and prior to the commencement of the lease. At June 30, 2016, the Company’s investment in property acquired for transactions-in-process was $30.9 million, down from $31.3 million at June 30, 2015, and $40.6 million at June 30, 2014. Transactions-in-process at June 30, 2015 and 2014 included large amounts related to two large leases that were booked during the subsequent fiscal years.
The Company leases capital assets to businesses and other commercial or non-profit organizations. All leases are secured by the underlying property being leased. The Company’s strategy is to develop lease portfolios with risk/reward profiles that meet its objectives and avoid risks that do not meet these requirements through the use of non-recourse financing. The strategy emphasizes diversification on both a geographic and customer level, and spreading the Company’s risk across a breadth of leases. The average size of lease transactions over the past three years has fluctuated from $751,000 to $1.1 million. During the year ended June 30, 2016, two commercial credits accounted for 18.1% and 13.2% of the property cost of leases booked during the fiscal year, respectively, with the five largest commercial accounts aggregating to 47% of leases booked. During the year ended June 30, 2015, two commercial credits accounted for 14.1% and 12%, respectively, of the property cost of leases booked during the fiscal year, with the five largest commercial accounts aggregating to 41% of leases booked. During the year ended June 30, 2014, one commercial credit accounted for 13.3% of the property cost of leases booked during the fiscal year, with the five largest commercial accounts aggregating to 30.0% of leases booked. At June 30, 2016, one customer accounted for 9.8% of the Company’s net investment in leases, compared to two customers accounting for 4.8% and 4.2% of the Company’s net investment in leases at June 30, 2015 and one customer accounting for 6.1% of the Company’s net investment at June 30, 2014.
Commercial Loan Portfolio
The Company’s commercial loan portfolio was $403.7 million at June 30, 2016, a 65.8% increase from $243.5 million at June 30, 2015. The commercial loan portfolio is comprised primarily of participations in commercial loan syndications where the loans are secured by the borrowers’ and any subsidiary guarantors’ assets. Commercial loan participations represent 96.5% of the commercial loan portfolio with the remainder of the portfolio comprised of three commercial real estate loans and one unsecured loan originated directly. The loan portfolio at June 30, 2016 is distributed among 87 credits with an average balance of $4.6 million and the largest outstanding at $12.4 million. Syndicated loans the Company characterizes as higher risk leveraged loans account for approximately 8.2% of the commercial loan portfolio.
| 21 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
The estimated repayment of principal on the commercial loan portfolio as of June 30, 2016 is as follows:
| Principal Balance Due in | ||||||||||||||||
| Principal | One Year | One to | Due After | |||||||||||||
| Loan Type | Balance | Or less | Five Years | Five Years | ||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||
| Commercial term loans | $ | 399,239 | $ | 9,754 | $ | 322,839 | $ | 66,646 | ||||||||
| Commercial real estate loans | 6,682 | 440 | 3,223 | 3,019 | ||||||||||||
| Revolving lines of credit | 3,405 | - | 3,405 | - | ||||||||||||
| Principal balance outstanding | $ | 409,326 | $ | 10,194 | $ | 329,467 | $ | 69,665 | ||||||||
| Loans with predetermined interest rates | $ | 14,283 | ||||||||||||||
| Loans with floating or adjustable interest rates | $ | 395,043 | ||||||||||||||
The lease and loan portfolio is diversified geographically with the investment spread across all fifty states. The following table shows the geographic distribution of the Company’s net investment in leases and loans (before valuation allowances and initial direct costs) at June 30, 2016 and 2015.
| (dollars in thousands) | Net Investment in Leases & Loans | |||||||||||||||
| June 30, 2016 | June 30, 2015 | |||||||||||||||
| State | Balance | Percent | Balance | Percent | ||||||||||||
| California | $ | 77,868 | 12.0 | % | $ | 86,503 | 15.9 | % | ||||||||
| Texas | 61,040 | 9.4 | % | 40,478 | 7.4 | % | ||||||||||
| Florida | 37,825 | 5.9 | % | 17,874 | 3.3 | % | ||||||||||
| Colorado | 37,012 | 5.7 | % | 19,442 | 3.6 | % | ||||||||||
| New Jersey, New York, Massachusetts, Pennsylvania, Connecticut | 122,333 | 18.9 | % | 83,214 | 15.2 | % | ||||||||||
| Georgia, Virginia, Tennessee, North Carolina | 94,663 | 14.6 | % | 79,476 | 14.6 | % | ||||||||||
| Ohio, Indiana, Wisconsin, Michigan, Minnesota, Illinois | 93,496 | 14.5 | % | 80,362 | 14.7 | % | ||||||||||
| Washington, Utah, Nevada, Oregon, | 54,114 | 8.4 | % | 54,591 | 10.0 | % | ||||||||||
| All other jurisdictions (no jurisdiction greater than 2.0%) | 68,038 | 10.5 | % | 83,738 | 15.3 | % | ||||||||||
| Total all jurisdictions | $ | 646,389 | 100.0 | % | $ | 545,678 | 100.0 | % | ||||||||
The lease and loan portfolio is also distributed across a wide spectrum of industry groups as shown below:
| (dollars in thousands) | Net Investment in Leases & Loans | |||||||||||||||
| June 30, 2016 | June 30, 2015 | |||||||||||||||
| Industry | Balance | Percent | Balance | Percent | ||||||||||||
| Manufacturing - industrial | $ | 82,363 | 12.7 | % | $ | 59,007 | 10.8 | % | ||||||||
| Healthcare and social services | 67,544 | 10.4 | % | 70,932 | 13.0 | % | ||||||||||
| Arts, entertainment and recreation | 64,634 | 10.0 | % | 49,117 | 9.0 | % | ||||||||||
| Manufacturing - chemicals and materials | 63,940 | 9.9 | % | 39,372 | 7.2 | % | ||||||||||
| Retail Trade | 58,350 | 9.0 | % | 38,552 | 7.1 | % | ||||||||||
| Scientific, professional, other business services | 58,038 | 9.0 | % | 52,222 | 9.6 | % | ||||||||||
| Wholesale distribution | 57,710 | 8.9 | % | 23,231 | 4.3 | % | ||||||||||
| Educational services | 40,115 | 6.2 | % | 46,739 | 8.6 | % | ||||||||||
| Agriculture and food products | 34,851 | 5.4 | % | 16,312 | 3.0 | % | ||||||||||
| Commercial airlines and aviation services | 22,705 | 3.5 | % | 24,311 | 4.5 | % | ||||||||||
| Manufacturing - automotive, truck, aerospace | 22,581 | 3.5 | % | 27,742 | 5.1 | % | ||||||||||
| Mining and oil & gas services | 18,264 | 2.8 | % | 28,571 | 5.2 | % | ||||||||||
| Transportation | 17,432 | 2.7 | % | 22,116 | 4.1 | % | ||||||||||
| Utilities | 14,658 | 2.3 | % | 14,856 | 2.7 | % | ||||||||||
| Financial services | 8,931 | 1.4 | % | 13,636 | 2.5 | % | ||||||||||
| Public administration | 8,556 | 1.3 | % | 10,598 | 1.9 | % | ||||||||||
| Building and construction | 5,718 | 0.9 | % | 8,366 | 1.5 | % | ||||||||||
| $ | 646,389 | 100 | % | $ | 545,678 | 100 | % | |||||||||
Most of the industry groups include customers identified by different industry codes and may not be directly comparable or considered a concentration. However, at June 30, 2016 approximately 5.2% of the portfolio is with hospitals and medical centers, down from 6.3% at June 30, 2015. Public and private colleges and universities were 5.3% of the portfolio compared to 7.1% at June 30, 2015. The hospital portfolio involves 17 different credits with over 350 facilities, 27 lease schedules and 2 loans, with the four largest hospital exposures each representing less than 1% of the portfolio. The universities and colleges are located throughout the United States and spread over 220 leases with 75 different institutions and no university representing more than 1% of the portfolio.
| 22 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
Securities Available-for-Sale
The Company maintains a portfolio of securities to generate interest and investment income from the investment of excess funds depending on lease and loan demand and to provide liquidity. Total securities available-for-sale were $95.8 million as of June 30, 2016, compared to $81.2 million at June 30, 2015. The carrying cost and fair value of the Company’s securities portfolio at June 30, 2016 and 2015 is as follows:
| As of June 30, 2016 | As of June 30, 2015 | |||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | Amortized | Fair | Amortized | Fair | ||||||||||||
| Cost | Value | Cost | Value | |||||||||||||
| Available-for-sale | ||||||||||||||||
| U.S. Treasury notes | $ | 47,355 | $ | 48,774 | $ | 47,286 | $ | 47,770 | ||||||||
| Corporate debt securities | 13,291 | 13,385 | 13,165 | 13,152 | ||||||||||||
| Agency MBS | 31,782 | 32,223 | 18,765 | 18,669 | ||||||||||||
| Securities of state and political subdivisions | - | - | 406 | 412 | ||||||||||||
| Mutual fund investments | 1,215 | 1,462 | 1,215 | 1,209 | ||||||||||||
| Total securities available-for-sale | $ | 93,643 | $ | 95,844 | $ | 80,837 | $ | 81,212 | ||||||||
During the fiscal year ended June 30, 2016, the Company’s portfolio of securities available-for-sale increased $14.6 million to $95.8 million. The increase during the year related to the acquisition of $17.2 million in government agency mortgage-backed securities (“Agency MBS”) and a $5 million corporate bond that along with an increase in unrecognized gains in the value of securities of $1.8 million offset maturities and pay downs of $9.4 million. During the twelve months ended June 30, 2016, the Company realized a gain of $23,000 from an early call of a corporate debt security for proceeds of $4.8 million. The net gain is recognized using the specific identification method and is included in non-interest income
Management evaluates investment securities for other-than-temporary impairment on a quarterly basis. Consideration is given to the length of time and the extent to which the fair value has been less than cost, the financial condition and near-term prospects of the issuer, and the intent and ability of the Company to retain its investment in the issuer for a period of time sufficient to allow for any anticipated recovery in fair value. The weighted-average maturity at June 30, 2016 was 5.9 years and the corresponding weighted-average yield was 1.9 percent.
Asset Quality
The Company monitors the performance of all leases and loans held in its own portfolio, transactions-in-process and loan commitments as well as lease transactions assigned to lenders, if the Company retains a residual investment in the leased property subject to those leases. An ongoing review of all leases and loans ten or more days delinquent is conducted. Customers who are delinquent with the Company or an assignee are coded in the Company’s accounting and tracking systems in order to provide management visibility, periodic reporting, and appropriate reserves. The accrual of interest income on leases and loans will be discontinued when the customer becomes ninety days or more past due on its lease or loan payments with the Company, unless the Company believes the investment is otherwise recoverable. Leases and loans may be placed on non-accrual earlier if the Company has significant doubt about the ability of the customer to meet its lease or loan obligations, as evidenced by consistent delinquency, deterioration in the customer’s financial condition or other relevant factors.
The following table summarizes the Company’s non-performing leases and loans.
| June 30, | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-performing Leases and Loans | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-accrual leases and loans | $ | 12 | $ | 41 | $ | 47 | $ | 1,614 | $ | 529 | ||||||||||
| Restructured leases | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||||||||||
| Leases past due 90 days (other than above) | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||||||||||
| Total non-performing leases and loans | $ | 12 | $ | 41 | $ | 47 | $ | 1,614 | $ | 529 | ||||||||||
| Repossessed equipment | 1,300 | - | - | - | - | |||||||||||||||
| Total non-performing assets | $ | 1,312 | $ | 41 | $ | 47 | $ | 1,614 | $ | 529 | ||||||||||
| Non-performing leases as % of net investment in leases and loans before allowances | 0.00 | % | 0.01 | % | 0.01 | % | 0.38 | % | 0.15 | % | ||||||||||
| Non-performing assets as % of total assets | 0.15 | % | 0.01 | % | 0.01 | % | 0.29 | % | 0.11 | % | ||||||||||
Non-performing assets consists of non-performing leases as well as any repossessed assets. In the third quarter of fiscal 2016, the Company transferred $1.7 million of property related to a lease rejected in bankruptcy to repossessed equipment. The $2.7 million lease was placed on non-accrual during the first quarter of fiscal 2016 and written down to $1.7 million during the second quarter. Based on an updated appraisal, the Company wrote the repossessed asset down to a value of $1.3 million at June 30, 2016. The decline in non-accrual leases at June 30, 2016 is due to payments received or write-offs taken with no new leases added. No direct finance income would have been recorded had non-accrual leases at each respective fiscal year end been current in accordance with their original terms during fiscal 2016, 2015 and 2014. There was no direct finance income actually recorded on non-performing leases during fiscal 2016, 2015 and 2014.
| 23 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
In addition to the non-performing leases identified above, there was $4.0 million of investment in leases at June 30, 2016 classified as substandard or with credits that currently are experiencing financial difficulties or that management believes may experience financial difficulties in the future. This amount compared to $5.6 million at June 30, 2015. Although these credits have been identified as potential problems, they may never become non-performing. These potential problem leases are considered in the determination of the allowance for credit losses.
Allowance for Credit Losses
The allowance for credit losses and the residual valuation allowance provide coverage for probable and estimable losses in the Company’s lease and loan portfolios. The allowance recorded is based on a quarterly review of all leases and loans outstanding, loan commitments and transactions-in-process to determine that it is adequate to cover these inherent losses. The evaluation of each element and the overall allowance is based on a continuing assessment of problem credits, recent loss experience and other factors, including regulatory guidance and economic conditions. The Company utilizes similar processes to estimate its liability for unfunded loan commitments, which is included in other liabilities in the Consolidated Balance Sheets. Both the allowance for credit losses and the liability for unfunded loan commitments are included in the Company’s analysis of credit losses. Lease receivables, loans or residuals are charged off when they are deemed completely uncollectible. The determination of the appropriate amount of any provision is based on management’s judgment at that time and takes into consideration all known relevant internal and external factors that may affect the lease and loan portfolio. The following table summarizes the activity in the allowance for loan and lease losses for the five years ended June 30, 2016.
| Years Ended June 30, | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Property acquired for transactions-in-process before allowance | $ | 30,932 | $ | 31,340 | $ | 40,578 | $ | 11,938 | $ | 18,559 | ||||||||||
| Net investment in leases before allowance | 239,964 | 301,733 | 329,935 | 345,753 | 256,686 | |||||||||||||||
| Commercial loans, before allowance | 408,308 | 246,509 | 131,158 | 75,952 | 84,982 | |||||||||||||||
| Leases and loans, before allowances | $ | 679,204 | $ | 579,582 | $ | 501,671 | $ | 433,643 | $ | 360,227 | ||||||||||
| Average leases and loans | $ | 601,237 | $ | 493,054 | $ | 422,788 | $ | 382,343 | $ | 322,992 | ||||||||||
| Allowance for credit losses at beginning of year | 6,456 | 5,299 | 5,147 | 5,216 | 5,060 | |||||||||||||||
| Charge-off of lease receivables and transactions-in-process (1) | (1,120 | ) | (19 | ) | (62 | ) | (350 | ) | (51 | ) | ||||||||||
| Recovery of lease amounts previously written off (1) | 51 | 1 | 14 | 6 | 207 | |||||||||||||||
| Provision for credit losses | 1,475 | 1,175 | 200 | 275 | 0 | |||||||||||||||
| Allowance for credit losses at end of year (“Allowance”) | $ | 6,862 | $ | 6,456 | $ | 5,299 | $ | 5,147 | $ | 5,216 | ||||||||||
| Components of allowance for credit losses: | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Allowance for lease losses | $ | 2,290 | $ | 3,409 | $ | 3,327 | $ | 3,175 | $ | 3,144 | ||||||||||
| Allowance for loan losses | 4,572 | 3,047 | 1,972 | 1,972 | 2,072 | |||||||||||||||
| $ | 6,862 | $ | 6,456 | $ | 5,299 | $ | 5,147 | $ | 5,216 | |||||||||||
| Allowance as percent of leases and loans before allowances | 1.06 | % | 1.18 | % | 1.15 | % | 1.22 | % | 1.53 | % | ||||||||||
| Net (charge-offs) recoveries as percent of average leases and loans | (0.2 | )% | (0.00 | )% | (0.01 | )% | (0.09 | )% | 0.05 | % | ||||||||||
________________________________________________
| (1) | There were no charge-offs or recoveries related to commercial or real estate loans during the five year period ending June 30, 2016. |
The allowance for credit losses increased to $6.86 million (1.06% of net investment in leases and loans) at June 30, 2016 from $6.46 million (1.18% of net investment in leases and loans) at June 30, 2015. The allowance at June 30, 2016 consisted of $48,000 allocated to specific accounts that were identified as problems and $6.8 million that was available to cover losses inherent in the portfolio. This compared to $645,000 allocated to specific accounts at June 30, 2015 and $5.8 million that was available to cover losses inherent in the portfolio at such date. The decrease in the specific allowance at June 30, 2016 primarily relates to a charge-off of over $1.0 million against a lease individually evaluated for impairment offset by new specific problems identified. Based on the above factors, the Company considers the allowance for credit losses of $6.86 million at June 30, 2016 adequate to cover losses specifically identified as well as inherent in the lease and loan portfolios. However, no assurance can be given that the Company will not, in any particular period, sustain lease and loan losses that are sizeable in relation to the amount reserved, or that subsequent evaluations of the lease portfolio, in light of factors then prevailing, including economic conditions and the on-going credit review process, will not require significant increases in the allowance for credit losses. Among other factors, a renewed economic slowdown may have an adverse impact on the adequacy of the allowance for credit losses by increasing credit risk and the risk of potential loss even further. As the Company has retained a significantly greater percentage of leases and loans in its own portfolio, this creates increased exposure to delinquencies, repossessions, foreclosures and losses than the Company has historically experienced.
| 24 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
Based on management’s evaluation of the lease and loan portfolio at each period end, management has allocated the allowance for loan and lease losses for the past five years as shown in the table below:
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| % of | % of | % of | % of | % of | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Allowance | Leases | Allowance | Leases | Allowance | Leases | Allowance | Leases | Allowance | Leases | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Amount | and | Amount | and | Amount | and | Amount | and | Amount | and | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Allocated | Loans | Allocated | Loans | Allocated | Loans | Allocated | Loans | Allocated | Loans | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net Investment in Leases | $ | 2,290 | 37.0 | % | $ | 3,409 | 55.0 | % | $ | 3,327 | 71.6 | % | $ | 3,175 | 82.0 | % | $ | 3,144 | 75.1 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial Loans | 4,511 | 62.0 | % | 2,936 | 43.6 | % | 1,761 | 26.7 | % | 1,561 | 15.8 | % | 1,561 | 20.9 | % | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial Real Estate Loans | 61 | 1.0 | % | 111 | 1.4 | % | 211 | 1.7 | % | 411 | 2.2 | % | 511 | 3.9 | % | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| $ | 6,862 | 100.0 | % | $ | 6,456 | 100.0 | % | $ | 5,299 | 100.0 | % | $ | 5,147 | 100.0 | % | $ | 5,216 | 100.0 | % | |||||||||||||||||||||
While the allowance is allocated by category above, the allowance is general in nature and is available for the portfolio in its entirety.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
The Company funds its operating activities through internally generated funds, bank deposits, borrowings and non-recourse debt. At June 30, 2016 and 2015, the Company’s cash and cash equivalents were $105.1 million and $60.2 million, respectively.
Deposits at CalFirst Bank totaled $633.1 million at June 30, 2016, up 34.2% from $471.9 million at June 30, 2015 and up 77.9% from $355.8 million at June 30, 2014. The Bank generally offers interest rates on deposit accounts that are higher than the national average. Average rates paid by the Bank on deposits over the past three years increased due to market conditions and the Bank’s need to increase deposits to fund the growth in its loan portfolio. The following table presents average balances and average rates paid on deposits for years ended June 30, 2016, 2015 and 2014:
| Years ended June 30, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average | Average | Average | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ending | Average | Rate | Ending | Average | Rate | Ending | Average | Rate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance | Balance | Paid | Balance | Balance | Paid | Balance | Balance | Paid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-interest bearing demand deposits | $ | 2,181 | $ | 2,134 | n/a | $ | 2,193 | $ | 2,024 | n/a | $ | 1,060 | $ | 1,785 | n/a | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest-bearing demand deposits | 1,298 | 2,125 | 0.20 | % | 2,715 | 2,023 | 0.20 | % | 1,167 | 1,607 | 0.20 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Savings deposits | 78,510 | 70,704 | 0.62 | % | 65,539 | 65,315 | 0.50 | % | 63,356 | 66,543 | 0.50 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Time deposits less than $100,000 | 98,604 | 83,191 | 1.17 | % | 69,226 | 60,176 | 1.05 | % | 52,647 | 51,426 | 1.00 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Time deposits, $100,000 or more | $ | 452,554 | 390,560 | 1.17 | % | $ | 332,233 | $ | 277,904 | 1.05 | % | $ | 237,580 | $ | 220,267 | 0.99 | % | |||||||||||||||||||
The following table shows the maturities of certificates of deposits at the dates indicated:
| June 30, 2016 | |||||||||
| $250,000 Or less | More than $250,000 |
||||||||
| (in thousands) | |||||||||
| Under 3 months | $ | 72,824 | $ | 23,774 | |||||
| 3 – 6 months | 83,144 | 25,105 | |||||||
| 7 – 12 months | 184,238 | 51,551 | |||||||
| 13 – 24 months | 67,580 | 21,941 | |||||||
| 25 – 36 months | 15,367 | 5,634 | |||||||
| $ | 423,153 | $ | 128,005 | ||||||
The Bank has borrowing agreements with the Federal Home Loan Bank of San Francisco (“FHLB”) and as such, can take advantage of FHLB programs for overnight and term advances at published daily rates. The Bank has short-term borrowings outstanding of $40.0 million at June 30, 2016 at an average rate of 0.42%, down from $42.0 million outstanding at June 30, 2015. Under terms of the blanket collateral agreement, advances from the FHLB are collateralized by qualifying securities and real estate loans, with $40.8 million available under the agreement as of June 30, 2016. The Bank also has the authority to borrow from the Federal Reserve Bank (“FRB”) discount window amounts secured by certain lease receivables with unused borrowing availability at June 30, 2016 of approximately $107.2 million.
An additional source of liquidity for financing and managing the lease portfolio comes from selling, participating or assigning certain lease term payments to banks or other financial institutions. If the transaction is characterized as a sale of the financial asset or meets the parameters of a participating interest, the lease is removed from the balance sheet and a resulting gain or loss recognized. If the Company retains a controlling interest in the lease, the assignment is considered a secured borrowing with the associated financing characterized as non-recourse debt. The assigned lease payments are discounted at fixed rates such that the lease payments are sufficient to fully amortize the aggregate outstanding debt. During fiscal 2016, the Company sold or assigned net lease receivables aggregating to $26.8 million, all of which were characterized as sales by the Bank. This compared to leases sold or assigned of $73.8 million and $33.5 million for fiscal 2015 and 2014, respectively. At June 30, 2016, the Company had outstanding non-recourse debt aggregating $4.4 million relating to property under leases assigned to unaffiliated parties. In the past, the Company has been able to obtain adequate non-recourse funding commitments, and the Company believes it will be able to do so in the future.
| 25 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
The following table presents capital and capital ratio information for the Company and CalFirst Bank as of June 30, 2016 and June 30, 2015 and reflects the transition to the Basel III capital standard from previous regulatory capital adequacy guidelines under the Basel I framework. The Basel III capital standard phases in through 2019 and revises the definition of capital, increases minimum capital ratios, introduces regulatory capital buffers above those minimums, introduces a common equity Tier 1 capital ratio and revises the rules for calculating risk-weighted assets. Under Basel III, the Bank made a one-time election to opt out of the requirement to include components of accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) in common equity Tier 1 capital. The adoption of the new capital standard had an immaterial impact on capital levels and related ratios and the Company and Bank continue to exceed regulatory capital requirements and are considered “well-capitalized” under guidelines established by the FRB and OCC.
| June 30, | |||||||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||
| California First National Bancorp | Amount | Ratio | Amount | Ratio | |||||||||||||
| Common equity Tier 1 capital | $ | 189,677 | 25.12 | % | $ | 187,987 | 29.17 | % | |||||||||
| Tier 1 risk-based capital | $ | 189,677 | 25.12 | % | $ | 187,987 | 29.17 | % | |||||||||
| Total risk-based capital | $ | 196,589 | 26.04 | % | $ | 194,493 | 30.18 | % | |||||||||
| Tier 1 leverage capital | $ | 189,677 | 21.67 | % | $ | 187,987 | 26.79 | % | |||||||||
| California First National Bank | |||||||||||||||||
| Common equity Tier 1 capital | $ | 116,379 | 15.88 | % | $ | 109,147 | 17.65 | % | |||||||||
| Tier 1 risk-based capital | $ | 116,379 | 15.88 | % | $ | 109,147 | 17.65 | % | |||||||||
| Total risk-based capital | $ | 123,091 | 16.79 | % | $ | 115,306 | 18.65 | % | |||||||||
| Tier 1 leverage capital | $ | 116,379 | 13.94 | % | $ | 109,147 | 17.10 | % | |||||||||
Contractual Obligations and Commitments
The following table summarizes various contractual obligations at June 30, 2016. Commitments to purchase property for unfunded leases are binding but generally have fixed expiration dates and other termination clauses. Commercial loan commitments are agreements to purchase participation or lend to a customer provided there is no violation of any condition in the contract. Since the Company expects some of the commitments to expire without being funded, the total commitment amounts do not necessarily represent the Company’s future liquidity requirements.
| Due by Period | |||||||||||||||||
| Less Than | After | ||||||||||||||||
| Contractual Obligations | Total | 1 Year | 1-5 Years | 5 Years | |||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||
| Lease property purchases (1) | $ | 41,315 | $ | 41,315 | $ | - | $ | - | |||||||||
| Commercial loan and lease purchase commitments | 15,300 | 15,300 | - | - | |||||||||||||
| FHLB Borrowings | 40,000 | 40,000 | - | - | |||||||||||||
| Operating lease rental payments | 1,530 | 689 | 841 | - | |||||||||||||
| Total contractual commitments | $ | 98,145 | $ | 97,304 | $ | 841 | $ | - | |||||||||
________________________________________________
| (1) | Disbursements to purchase property on approved lease or loan commitments are estimated to be completed within one year, but it is likely that some portion could be deferred or never funded. |
The need for cash for operating activities will increase as the Company expands. The Company believes that existing cash balances, cash flow from operations, cash flows from its financing and investing activities, and assignments (on a non-recourse basis) of lease payments will be sufficient to meet its foreseeable financing needs.
Inflation has not had a significant impact upon the operations of the Company.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
See Note 1, “Summary of Significant Accounting Policies,” of the Company’s consolidated financial statements for disclosure of recent accounting pronouncements.
| 26 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
ITEM 7A. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK
Market risk is the risk of loss in a financial instrument arising from changes in market indices such as interest rates and equity prices. The Company’s principal market risk exposure is interest rate risk, which is the exposure due to differences in the repricing characteristics of interest-earning assets and interest-bearing liabilities. Market risk also arises from the impact that fluctuations in interest rates may have on security prices that may result in changes in the values of financial instruments, such as available-for-sale securities that are accounted for at fair value. As the banking operations of the Company have grown and securities and deposits represent a greater portion of the Company’s assets and liabilities, the Company is subject to increased market risk. The Bank has an Asset/Liability Management Committee and policies established to manage its interest rate and market risk.
At June 30, 2016, the Company had $106.6 million of cash or invested in securities of very short duration. The Company’s gross investment in lease payments receivable and loan principal of $668.7 million consists of leases with fixed rates and loans with fixed and variable rates, however, $499.4 million of such investment is due or will reprice within one year of June 30, 2016. This compares to the Company’s interest bearing deposit and borrowing liabilities of $671.0 million, of which 83.5%, or $560.4 million, mature within one year. Non-recourse debt does not represent an interest rate risk to the Company because it is fully amortized through direct payments from lessees to the purchaser of the lease receivable. Based on the foregoing, at June 30, 2016 the Company had assets of $605.9 million subject to changes in interest rates over the next twelve months, compared to repricing liabilities of $560.4 million.
The consolidated gap analysis below sets forth the maturity and repricing characteristics of interest-earning assets and interest-bearing liabilities for selected time bands. The mismatch between repricings or maturities within a time band is commonly referred to as the “gap” for that period. A positive gap (asset sensitive) where interest rate sensitive assets exceed interest rate sensitive liabilities generally will result in the net interest margin increasing in a rising rate environment and decreasing in a falling rate environment. A negative gap (liability sensitive) will generally have the opposite result on the net interest margin. However, the traditional gap analysis does not assess the relative sensitivity of assets and liabilities to changes in interest rates and other factors that could have an impact on interest rate sensitivity or net interest income. Sudden and substantial increase or decrease in interest rates may adversely impact our income to the extent that the interest rates associated with the assets and liabilities do not change at the same speed, to the same extent, or on the same basis.
Consolidated Interest Rate Sensitivity
| Over 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 Months | Over 3 to | Through | Over | Non-rate | |||||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | or Less | 12 Months | 5 years | 5 years | Sensitive | Total | |||||||||||||||||||
| Rate Sensitive Assets (RSA): | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash due from banks | $ | 105,094 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 105,094 | |||||||||||||
| Investment securities | 1,463 | - | 62,158 | 36,180 | - | 99,801 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Net investment in leases | 29,094 | 73,616 | 146,586 | 10,102 | (21,724 | ) | 237,674 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial loans | 395,446 | 1,211 | 9,343 | 3,326 | (5,590 | ) | 403,736 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Non-interest earning assets | - | - | - | - | 41,871 | 41,871 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Totals | 531,097 | 74,827 | 218,087 | 49,608 | 14,557 | $ | 888,176 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Cumulative total for RSA | $ | 531,097 | $ | 605,924 | $ | 824,011 | $ | 873,619 | |||||||||||||||||
| Rate Sensitive Liabilities (RSL): | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Demand and savings deposits | $ | 79,808 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 2,181 | $ | 81,989 | |||||||||||||
| Time deposits | 96,599 | 344,037 | 110,522 | - | - | 551,158 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Borrowings | 40,000 | - | - | - | - | 40,000 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Non-interest bearing liabilities | - | - | - | - | 24,007 | 24,007 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Stockholders' equity | - | - | - | - | 191,022 | 191,022 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Totals | $ | 216,407 | $ | 344,037 | $ | 110,522 | $ | - | $ | 217,210 | $ | 888,176 | |||||||||||||
| Cumulative total for RSL | $ | 216,407 | $ | 560,444 | $ | 670,966 | $ | 670,966 | |||||||||||||||||
| Interest rate sensitivity gap | $ | 314,690 | $ | (269,210 | ) | $ | 107,565 | $ | 49,608 | ||||||||||||||||
| Cumulative GAP | $ | 314,690 | $ | 45,480 | $ | 153,045 | $ | 202,653 | |||||||||||||||||
| RSA divided by RSL (cumulative) | 245.42 | % | 108.11 | % | 122.81 | % | 130.20 | % | |||||||||||||||||
| Cumulative GAP / total assets | 35.43 | % | 5.12 | % | 17.23 | % | 22.82 | % | |||||||||||||||||
In addition to the consolidated gap analysis,
the Bank measures its asset/liability position through duration measures and sensitivity analysis, and calculates the potential
effect on earnings using maturity gap analysis. The interest rate sensitivity modeling includes the creation of prospective twelve
month "baseline" and "rate shocked" net interest income simulations. After a "baseline" net interest
income is determined, using assumptions that the Bank deems reasonable, market interest rates are raised or lowered by 100 to 300
basis points instantaneously, parallel across the entire yield curve, and a "rate shocked" simulation is run. Interest
rate sensitivity is then measured as the difference between calculated "baseline" and "rate shocked" net interest
income.
| 27 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
ITEM 8. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
The following financial statements and supplementary financial information are included herein at the pages indicated below:
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders of California First National Bancorp
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries as of June 30, 2016 and 2015 and the related consolidated statements of earnings, comprehensive income, stockholders' equity, and cash flows for each of the years in the three year period ended June 30, 2016. These consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of the Company's management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these consolidated financial statements based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the consolidated financial statements are free of material misstatement. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. Our audits included consideration of internal control over financial reporting as a basis for designing audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the consolidated financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries as of June 30, 2016 and 2015, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the years in the three year period ended June 30, 2016, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
Laguna Hills, California
September 26, 2016
| 28 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
(in thousands, except share amounts)
| June 30, | |||||||||
| ASSETS | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Cash and due from banks | $ | 105,094 | $ | 60,240 | |||||
| Securities available-for-sale | 95,844 | 81,212 | |||||||
| Investments | 3,957 | 3,334 | |||||||
| Receivables | 1,333 | 1,174 | |||||||
| Property acquired for transactions-in-process | 30,932 | 31,340 | |||||||
| Leases and loans: | |||||||||
| Net investment in leases | 239,964 | 301,733 | |||||||
| Commercial loans | 408,308 | 246,509 | |||||||
| Allowance for credit losses | (6,862 | ) | (6,456 | ) | |||||
| Net investment in leases and loans | 641,410 | 541,786 | |||||||
| Property on operating leases, less accumulated depreciation of $378 (2016) and $562 (2015) | 2,928 | 773 | |||||||
| Income tax receivable | 121 | 231 | |||||||
| Other assets | 2,108 | 791 | |||||||
| Discounted lease rentals assigned to lenders | 4,449 | 10,193 | |||||||
| $ | 888,176 | $ | 731,074 | ||||||
| LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | |||||||||
| Liabilities: | |||||||||
| Demand and savings deposits | $ | 81,989 | $ | 70,447 | |||||
| Time certificates of deposit | 551,158 | 401,459 | |||||||
| Short-term borrowings | 40,000 | 42,000 | |||||||
| Accounts payable | 1,697 | 2,635 | |||||||
| Accrued liabilities | 3,622 | 2,278 | |||||||
| Lease deposits | 1,565 | 1,900 | |||||||
| Non-recourse debt | 4,449 | 10,193 | |||||||
| Deferred income taxes, net | 12,674 | 11,944 | |||||||
| 697,154 | 542,856 | ||||||||
| Commitments and contingencies | |||||||||
| Stockholders' equity: | |||||||||
| Preferred stock; 2,500,000 shares authorized; none issued | - | - | |||||||
| Common stock; $.01 par value; 20,000,000 shares authorized; 10,279,807 (2016) and 10,459,924 (2015) issued and outstanding | 103 | 105 | |||||||
| Additional paid in capital | 2,240 | 3,376 | |||||||
| Retained earnings | 187,334 | 184,506 | |||||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive income, net of tax | 1,345 | 231 | |||||||
| 191,022 | 188,218 | ||||||||
| $ | 888,176 | $ | 731,074 | ||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
| 29 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF EARNINGS
(in thousands, except share and per share amounts)
| Years ended June 30, | |||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||||
| Finance and loan income | $ | 25,471 | $ | 21,489 | $ | 18,370 | |||||||
| Investment interest income | 2,230 | 1,516 | 1,371 | ||||||||||
| Total interest income | 27,701 | 23,005 | 19,741 | ||||||||||
| Interest expense | |||||||||||||
| Deposits | 6,003 | 3,883 | 3,036 | ||||||||||
| Borrowings | 207 | 62 | 1 | ||||||||||
| Net interest income | 21,491 | 19,060 | 16,704 | ||||||||||
| Provision for credit losses | 1,475 | 1,175 | 200 | ||||||||||
| Net interest income after provision for credit losses | 20,016 | 17,885 | 16,504 | ||||||||||
| Non-interest income | |||||||||||||
| Operating and sales-type lease income | 1,146 | 305 | 2,152 | ||||||||||
| Gain on sale of leases, loans and leased property | 3,497 | 4,791 | 2,980 | ||||||||||
| Realized gain on sale of investment securities | 23 | 481 | - | ||||||||||
| Recovery realized on TFT-LCD settlement | - | 2,744 | - | ||||||||||
| Other fee income | 220 | 388 | 432 | ||||||||||
| Total non-interest income | 4,886 | 8,709 | 5,564 | ||||||||||
| Non-interest expenses | |||||||||||||
| Compensation and employee benefits | 7,254 | 8,582 | 7,796 | ||||||||||
| Occupancy | 685 | 634 | 682 | ||||||||||
| Professional services | 771 | 664 | 590 | ||||||||||
| Repossessed assets | 397 | - | - | ||||||||||
| Other general and administrative | 1,727 | 1,899 | 1,927 | ||||||||||
| Total non-interest expenses | 10,834 | 11,779 | 10,995 | ||||||||||
| Earnings before income taxes | 14,068 | 14,815 | 11,073 | ||||||||||
| Income taxes | 5,420 | 5,760 | 4,022 | ||||||||||
| Net earnings | $ | 8,648 | $ | 9,055 | $ | 7,051 | |||||||
| Basic earnings per common share | $ | 0.83 | $ | 0.87 | $ | 0.67 | |||||||
| Diluted earnings per common share | $ | 0.83 | $ | 0.87 | $ | 0.67 | |||||||
| Dividends declared per common share outstanding | $ | 0.44 | $ | 0.42 | $ | 0.40 | |||||||
| Average common shares outstanding – basic | 10,399,393 | 10,459,924 | 10,453,107 | ||||||||||
| Average common shares outstanding – diluted | 10,399,393 | 10,459,924 | 10,456,359 | ||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
| 30 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
(in thousands)
| Years ended June 30, | |||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||||
| Net earnings | $ | 8,648 | $ | 9,055 | $ | 7,051 | |||||||
| Other comprehensive income/(loss): | |||||||||||||
| Unrealized gain/(loss) on securities available-for-sale | 1,845 | 166 | (266 | ) | |||||||||
| Other-than-temporary impairment loss on securities available-for-sale | - | 91 | - | ||||||||||
| Reclassification adjustment of realized gain included in net income on securities available-for-sale | (23 | ) | (572 | ) | - | ||||||||
| 1,822 | (315 | ) | (266 | ) | |||||||||
| Tax effect | (708 | ) | 122 | 100 | |||||||||
| Total other comprehensive income/(loss) | 1,114 | (193 | ) | (166 | ) | ||||||||
| Total comprehensive income | $ | 9,762 | $ | 8,862 | $ | 6,885 | |||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
| 31 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY
(in thousands, except for share amounts)
| Additional | Accumulated | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Stock | Paid in | Retained | Comprehensive | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares | Amount | Capital | Earnings | Income | Total | |||||||||||||||||||
| Balance, June 30, 2013 | 10,447,227 | 104 | 3,213 | 176,972 | 590 | 180,879 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings | - | - | - | 7,051 | - | 7,051 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive loss | - | - | - | - | (166 | ) | (166 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Shares issued - Stock options exercised | 12,697 | 1 | 155 | - | - | 156 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Stock based compensation expense | - | - | 4 | - | - | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Dividends paid | - | - | - | (4,179 | ) | - | (4,179 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Balance, June 30, 2014 | 10,459,924 | 105 | 3,372 | 179,844 | 424 | 183,745 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings | - | - | - | 9,055 | - | 9,055 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive loss | - | - | - | - | (193 | ) | (193 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Stock based compensation expense | - | - | 4 | - | - | 4 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Dividends paid | - | - | - | (4,393 | ) | - | (4,393 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Balance, June 30, 2015 | 10,459,924 | $ | 105 | $ | 3,376 | $ | 184,506 | $ | 231 | $ | 188,218 | |||||||||||||
| Net earnings | - | - | - | 8,648 | - | 8,648 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive loss | - | - | - | - | 1,114 | 1,114 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Stock based compensation expense | - | - | 5 | - | - | 5 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Stock repurchased | (180,117 | ) | (2 | ) | (1,141 | ) | (1,217 | ) | - | (2,360 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Dividends paid | - | - | - | (4,603 | ) | - | (4,603 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Balance, June 30, 2016 | 10,279,807 | $ | 103 | $ | 2,240 | $ | 187,334 | $ | 1,345 | $ | 191,022 | |||||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
| 32 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(in thousands)
| Years Ended June 30, | ||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
| CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES: | ||||||||||||
| Net Earnings | $ | 8,648 | $ | 9,055 | $ | 7,051 | ||||||
| Adjustments to reconcile net earnings to cash flows provided by (used for) operating activities: | ||||||||||||
| Provision for credit losses | 1,475 | 1,175 | 200 | |||||||||
| Depreciation and net amortization (accretion) | (129 | ) | (496 | ) | 76 | |||||||
| Write-down of repossessed assets | 397 | - | - | |||||||||
| Gain on sale of leased property and sales-type lease income | (1,834 | ) | (2,033 | ) | (396 | ) | ||||||
| Net gain recognized on investment securities | (23 | ) | (481 | ) | 0 | |||||||
| Deferred income taxes, including income taxes payable | 17 | (3,240 | ) | (3,178 | ) | |||||||
| Decrease in income taxes receivable | 110 | 1,427 | 1,643 | |||||||||
| Net increase (decrease) in accounts payable and accrued liabilities | 1,344 | (275 | ) | 397 | ||||||||
| Other, net | (320 | ) | 37 | 673 | ||||||||
| Net cash provided by operating activities | 9,685 | 5,169 | 6,466 | |||||||||
| CASH FLOWS FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES: | ||||||||||||
| Investment in leases, loans and transactions in process | (349,231 | ) | (381,763 | ) | (283,904 | ) | ||||||
| Payments received on lease receivables and loans | 214,331 | 224,830 | 170,147 | |||||||||
| Proceeds from sales of leased property and sales-type leases | 5,395 | 4,457 | 5,796 | |||||||||
| Proceeds from sales and assignments of leases | 27,817 | 75,926 | 35,573 | |||||||||
| Purchase of investment securities | (22,798 | ) | (68,294 | ) | (8,229 | ) | ||||||
| Pay down on investment securities | 4,414 | 12,067 | 26,188 | |||||||||
| Proceeds from sale of investment securities | 4,769 | 994 | - | |||||||||
| Net increase in other assets | (1,806 | ) | (113 | ) | (1 | ) | ||||||
| Net cash used for investing activities | (117,109 | ) | (131,896 | ) | (54,430 | ) | ||||||
| CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES: | ||||||||||||
| Net increase in time certificates of deposit | 149,699 | 111,232 | 16,145 | |||||||||
| Net increase (decrease) in demand and savings deposits | 11,542 | 4,864 | (6,363 | ) | ||||||||
| Net (decrease) increase in short-term borrowings | (2,000 | ) | 35,142 | 6,858 | ||||||||
| Payments to repurchase common stock | (2,360 | ) | - | - | ||||||||
| Dividends to stockholders | (4,603 | ) | (4,393 | ) | (4,179 | ) | ||||||
| Proceeds from exercise of stock options | - | - | 156 | |||||||||
| Net cash provided by financing activities | 152,278 | 146,845 | 12,617 | |||||||||
| NET CHANGE IN CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS | 44,854 | 20,118 | (35,347 | ) | ||||||||
| CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS AT BEGINNING OF PERIOD | 60,240 | 40,122 | 75,469 | |||||||||
| CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS AT END OF PERIOD | $ | 105,094 | $ | 60,240 | $ | 40,122 | ||||||
| SUPPLEMENTAL SCHEDULE OF NONCASH INVESTING AND FINANCING ACTIVITIES | ||||||||||||
| (Decrease) increase in lease rentals assigned to lenders and related non-recourse debt | $ | (5,744 | ) | $ | 1,553 | $ | 7,872 | |||||
| Estimated residual values recorded on leases | $ | (579 | ) | $ | (2,565 | ) | $ | (3,556 | ) | |||
| SUPPLEMENTAL DISCLOSURES OF CASH FLOW INFORMATION | ||||||||||||
| Net cash paid during the year for: | ||||||||||||
| Interest | $ | 6,124 | $ | 3,875 | $ | 3,045 | ||||||
| Income Taxes | $ | 5,293 | $ | 7,573 | $ | 5,557 | ||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
| 33 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 1 - Summary of Significant Accounting Policies:
Nature of Operations
California First National Bancorp, a California corporation (the “Company”) is a bank holding company with two subsidiaries, California First National Bank (“CalFirst Bank” or the “Bank”) and California First Leasing Corp. (“CalFirst Leasing”). The primary business of the Company is secured financing provided through leasing and financing capital assets, commercial loans acquired through participation in the syndicated commercial loan market, by providing non-recourse loans to third parties secured by leases and equipment, and direct commercial loans. The Company’s business has migrated from predominately leasing toward over 50% commercial loans, with a lease and loan portfolio diversified geographically and across industries. CalFirst Bank is an Internet bank that gathers deposits from a centralized location primarily through posting rates on the Internet with all banking and other operations conducted from one central location.
The Company is regulated by the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System (the “FRB”) while CalFirst Bank is subject to regulation and examination by the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (“OCC”), its primary regulator. The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (“FDIC”) insures the Bank’s deposit accounts up to the maximum allowable amount.
Basis of Presentation
The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of California First National Bancorp and its wholly owned subsidiaries, CalFirst Bank and CalFirst Leasing. All intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Critical accounting estimates particularly susceptible to change include the allowance for credit losses, residual values and taxes. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents include cash in banks, cash in demand deposit accounts, and money market accounts, all of which have initial maturities of less than ninety days. The Company had cash in interest-bearing accounts of $102.0 million and $56.6 at June 30, 2016 and 2015, respectively. Included in cash and cash equivalents at June 30, 2016 and 2015 was $92.0 million and $35.5 million, respectively, that was held by the Bank. At June 30, 2016, CalFirst Leasing and California First National Bancorp had $13.1 million held in money market accounts not subject to FDIC insurance.
Securities
Securities are designated at the time of acquisition as available for sale or held to maturity. Securities that the Company will hold for indefinite periods of time and that might be sold in the future as part of efforts to manage interest rate risk, or in response to changes in interest rates, changes in prepayment rates, changes in market conditions or changes in economic factors are classified as available for sale and carried at fair values. Net aggregate unrealized gains or losses are reported, net of taxes, as a component of comprehensive income. Securities that the Company has the intent and ability to hold until maturity are classified as Investments “held-to-maturity” and are stated at cost adjusted for amortization of premium or accretion of discount. The Company does not have any securities classified as trading.
The Company conducts a regular assessment of its securities portfolio to determine whether any are other-than-temporarily impaired. In estimating other-than-temporary impairment losses, management considers, among other factors, the length of time and extent to which the fair value has been less than cost, the financial condition and near term prospects of the issuer, and the intent and ability of the Company to retain its investment for a period of time sufficient to allow for any anticipated recovery. The term “other-than-temporary” is not intended to indicate that the decline is permanent, but indicates that the prospects for a near-term recovery of value is not necessarily favorable, or that there is a lack of evidence to support a realizable value equal to or greater than the carrying value of the investment. Once a decline in value for a debt security is determined to be other-than-temporary, the other-than-temporary impairment is separated into (a) the amount of the total other-than-temporary impairment related to a decrease in cash flows expected to be collected from the debt security (the credit loss) and (b) the amount of the total other-than-temporary impairment related to all other factors. The amount of the total other-than-temporary impairment related to the credit loss is recognized in other income. The amount of the total other-than-temporary impairment related to all other factors is recognized in other comprehensive income. For equity securities, the full amount of the other-than-temporary impairment is recorded in non-interest income as an impairment loss on investment securities.
| 34 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
Leases
Capital Leases
New lease transactions are generally structured as direct financing leases. The re-lease of property that has come off lease may be accounted for as a sales-type lease or as an operating lease, depending on the terms of the re-lease. Leased property that comes off lease and is re-marketed through a sale to the lessee or a third party is accounted for as sale of leased property.
For leases that qualify as direct financing leases, the aggregate lease payments receivable and estimated residual value, if any, are recorded net of unearned income as net investment in leases. The unearned income is recognized as direct finance income on an internal rate of return method calculated to achieve a level yield on the Company’s investment over the lease term. There are no costs or expenses related to direct financing leases since lease income is recorded on a net basis.
For leases that qualify as sales-type leases, the Company recognizes profit or loss at lease inception to the extent the fair value of the property leased differs from the Company's carrying value. The difference between the discounted value of the aggregate lease payments receivable and the property cost, less the discounted value of the residual, if any, and any initial direct costs is recorded as sales-type lease income. For balance sheet purposes, the aggregate lease payments receivable and estimated residual value, if any, are recorded net of unearned income as net investment in leases. Unearned income is recognized as direct finance income over the lease term on an internal rate of return method.
The residual value is an estimate for accounting purposes of the fair value of the lease property at lease termination. The estimates are reviewed periodically to ensure reasonableness, however, the amounts the Company may ultimately realize could differ from the estimated amounts.
In some instances, the Company assigns on a nonrecourse basis or participates out the lease payments receivable related to direct financing leases to unaffiliated financial institutions at fixed interest rates. The accounting for the participation or sale of lease receivables is governed by Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) 860 Transfer and Servicing, which establishes a framework for determining which transactions should be treated as a sale of the financial asset by the Company or a secured borrowing through retention of the lease as an asset and reporting of non-recourse debt. For lease receivables accounted for as a sale, the Company derecognizes the lease receivable and the unearned income related to the lease is recognized as a gain from the sale of lease receivable in the period in which the lease receivable has been sold. For lease receivables accounted for as a secured borrowing, the minimum lease payments receivable is re-categorized on the balance sheet as discounted lease rentals assigned to lenders. The related obligations resulting from the discounting of the leases are recorded as non-recourse debt. The unearned income related to the lease is reduced by the interest expense from the non-recourse debt. In the event of default by a lessee, the participant or lender has a first lien against the underlying leased property with no further recourse against the Company. If this occurs, the Company may not realize its residual investment in the leased property.
A portion of the Company's non-interest expenses directly related to originating lease transactions is deferred through a reduction to non-interest expenses recognized in the period, with the deferred costs amortized over the lease term as a reduction to direct finance income utilizing the effective interest method.
Operating Leases
Lease contracts which do not meet the criteria of capital leases are accounted for as operating leases. Property on operating leases is recorded at the lower of cost or fair value and depreciated on a straight-line basis over the lease term to the estimated residual value at the termination of the lease. Most operating leases involve the re-lease of off-lease property and the associated cost is the Company’s estimated residual. Rental income is recorded on a straight-line basis over the lease term.
Loans
Loans are reported at their principal amount outstanding, net of unearned discounts and unamortized nonrefundable fees and direct costs associated with their origination or acquisition. Interest earned on loans without discounts is credited to income based on loan principal amounts outstanding at appropriate interest rates. Material origination and other nonrefundable fees net of direct costs and discounts on loans are credited to income over the terms of the loans using a method that approximates an effective yield.
Allowance for Credit Losses
The allowance for credit losses is an estimate based on management’s judgment applying the principles of ASC Topic 450, “Contingencies,” and ASC Topic 310-35, “Loan Impairment.” The determination of the adequacy of the allowance is based on an assessment of the inherent loss potential in the lease and loan portfolios given the conditions at the time and are continuously reviewed for adequacy considering levels of past due payments and non-performing assets, customers’ financial condition, leased property values as well as general economic conditions and credit quality indicators. The need for reserves is subject to future events, which by their nature are uncertain. Therefore, changes in economic conditions or other events affecting specific customers or industries may necessitate additions or deductions to the allowance for credit losses or the residual valuation allowance. The allowance is maintained at a level believed to be adequate to absorb probable losses inherent in the portfolios.
| 35 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
The allowance for credit losses includes specific and general reserves. Specific reserves relate to leases and loans that are individually classified as problems or impaired. Leases are individually evaluated for impairment under ASC Topic 450, while loans are evaluated under ASC 310-35, which does not apply to leases. A lease or loan is impaired when, based on current information and events, it is probable that the Company will be unable to collect amounts due according to the contractual terms. Factors considered in determining impairment include payment status, collateral value and the probability of collecting all amounts when due. The net book value of each non-performing or problem lease is evaluated to determine whether the carrying value is less than or equal to the expected recovery anticipated to be derived from lease payments, additional collateral or residual realization. Measurement of impairment of a loan is based on expected future cash flows of the impaired loan, which are to be discounted at the loan’s effective interest rate, or measured by reference to an observable market value, if one exists, or the fair value of the collateral for a collateral-dependent loan. The Company selects the measurement method on a loan-by-loan basis. The amount estimated as unrecoverable is recognized as a reserve individually identified for the lease or impaired loan.
General reserves are an estimate of probable or inherent losses related to the remaining portfolio. An ongoing review of all leases and loans is conducted, taking into account recent loss experience, known and inherent risks in the portfolio, levels of delinquencies, adverse situations that may affect customers’ ability to repay, trends in volume and other factors, including regulatory guidance and current and anticipated economic conditions. This portfolio analysis includes a stratification of the portfolio by the risk classifications and segments and estimation of potential losses based on risk classification or segment. The composition of the portfolio based on risk ratings is monitored, and changes in the overall risk profile of the portfolio are also factored into the evaluation of inherent risks in the portfolio. Based on the foregoing, an estimated inherent loss not based directly on specific problem assets is recorded as a collective allowance. The Company utilizes similar processes to estimate its liability for unfunded loan commitments, which is included in other liabilities and not in the allowance for credit losses. Lease receivables and loans are charged off when they are deemed completely uncollectible. Subsequent recoveries, if any, are credited to the allowance.
Property Acquired for Transactions-in-process
Property acquired for transactions-in-process represents partial deliveries of property which the lessee has accepted on in-process lease transactions. Such amounts are stated at cost, net of any lessee payments related to the property. Income is not recognized while a transaction is in process and prior to the commencement of the lease. At lease commencement, any pre-commencement payments are included in minimum lease payments receivable and the unearned income is recognized as direct finance income over the lease term.
Comprehensive Income
Accumulated other comprehensive income consists of unrealized gains and losses on available-for-sale securities.
Earnings Per Share
Basic net income per share is computed by dividing income available to common stockholders by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding. Diluted net income per share includes the effect of the potential shares outstanding, including dilutive stock options, using the treasury stock method.
The following table reconciles the components of the basic net income per share calculation to diluted net income per share:
| Years ended June 30, | ||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
| (in thousands, except share and per amounts) | ||||||||||||
| Net earnings | $ | 8,648 | $ | 9,055 | $ | 7,051 | ||||||
| Weighted average number of common shares outstanding assuming no exercise of outstanding options | 10,399,393 | 10,459,924 | 10,453,107 | |||||||||
| Dilutive stock options using the treasury stock method | - | - | 3,252 | |||||||||
| Dilutive common shares outstanding | 10,399,393 | 10,459,924 | 10,456,359 | |||||||||
| Basic earnings per common share | $ | 0.83 | $ | 0.87 | $ | 0.67 | ||||||
| Diluted earnings per common share | $ | 0.83 | $ | 0.87 | $ | 0.67 | ||||||
The Company had 10,000 antidilutive stock options in its calculation of diluted earnings per share for the year ended June 30, 2016, 2015 and 2014.
| 36 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
In June 2016, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) No. 2016-13, Financial Instruments - Credit Losses (Topic 326): Measurement of Credit Losses on Financial Instruments. ASU 2016-13 requires the measurement of all expected credit losses for financial assets held at the reporting date based on historical experience, current conditions, and reasonable and supportable forecasts and requires enhanced disclosures related to the significant estimates and judgments used in estimating credit losses, as well as the credit quality and underwriting standards of an organization’s portfolio. In addition, ASU 2016-13 amends the accounting for credit losses on available-for-sale debt securities and purchased financial assets with credit deterioration. ASU 2016-13 will be effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2019, including interim periods within those fiscal years. The Company is currently evaluating the potential impact of ASU 2016-13 on its financial statements.
In February 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-02, Leases (Topic 842). ASU 2016 will require that all leases be recognized on the balance sheet as lease assets and lease liabilities and disclosing key information about leasing arrangements. The guidance is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2018, including interim periods within those fiscal years. The Company is currently evaluating the potential impact of ASU 2016-02 on its financial statements and disclosures.
In January 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-01, Financial Instruments – Overall: Recognition and Measurement of Financial Assets and Financial Liabilities. Changes made to the current measurement model primarily affect the accounting for equity securities with readily determinable fair values, where changes in fair value will impact earnings instead of other comprehensive income. The accounting for other financial instruments, such as loans, investments in debt securities, and financial liabilities is largely unchanged. ASU 2016-01 also changes the presentation and disclosure requirements for financial instruments including a requirement that public business entities use exit price when measuring the fair value of financial instruments measured at amortized cost for disclosure purposes. ASU 2016-01 is generally effective for public business entities in fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, including interim periods within those fiscal years. The Company is currently evaluating the potential impact of ASU 2016-01 on its financial statements and disclosures.
Reclassifications
Certain reclassifications have been made to the fiscal 2015 and 2014 financial statements to conform to the presentation of the fiscal 2016 financial statements.
Note 2 – Investments
Investments are carried at cost and consist of the following:
| June 30, 2016 | June 30, 2015 | ||||||||||||||||
| Carrying Cost | Fair Value | Carrying Cost | Fair Value | ||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||
| Federal Reserve Bank Stock | $ | 1,955 | $ | 1,955 | $ | 1,955 | $ | 1,955 | |||||||||
| Federal Home Loan Bank Stock | 1,886 | 1,886 | 1,260 | 1,260 | |||||||||||||
| Mortgage-backed investment | 116 | 131 | 119 | 134 | |||||||||||||
| $ | 3,957 | $ | 3,972 | $ | 3,334 | $ | 3,349 | ||||||||||
The investment in Federal Home Loan Bank of San Francisco (“FHLB”) stock is a required investment related to CalFirst Bank’s borrowing relationship with the FHLB. The FHLB obtains its funding primarily through issuance of consolidated obligations of the Federal Home Loan Bank system. The U.S. Government does not guarantee these obligations, and each of the twelve FHLB’s are generally jointly and severally liable for repayment of each other’s debt. Therefore, the Company’s investment could be adversely impacted by the financial operations of the FHLB and actions by the Federal Housing Finance Agency. These investments have no stated maturity.
CalFirst Bank is required to hold Federal Reserve Bank stock equal to 6% of its capital surplus, which is defined as additional paid-in capital stock, less any gains (losses) on available for sale securities as of the current period end.
The mortgage-backed investment consists of one U.S. agency issued security. The Company has determined that it has the ability to hold this investment until maturity and, given the Company’s intent to do so, anticipates that it will realize the full carrying value of its investment and carries the security at amortized cost.
| 37 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
Note 3 - Securities Available for Sale:
Securities available-for-sale include U.S. Treasury securities, corporate and municipal bonds, U.S. government agency (“Agency”) mortgaged-backed securities (“MBS”), mutual fund and equity investments. The amortized cost, fair value, and carrying value of available-for-sale-securities were as follows:
| at June 30, 2016 | |||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | Amortized | Gross Unrealized | Fair | ||||||||||||||
| Cost | Gains | Losses | Value | ||||||||||||||
| U.S. Treasury notes | $ | 47,355 | $ | 1,419 | $ | - | $ | 48,774 | |||||||||
| Corporate debt securities | 13,291 | 97 | (3 | ) | 13,385 | ||||||||||||
| Agency MBS | 31,782 | 441 | - | 32,223 | |||||||||||||
| Mutual fund investments | 1,215 | 247 | - | 1,462 | |||||||||||||
| Total securities available-for-sale | $ | 93,643 | $ | 2,204 | $ | (3 | ) | $ | 95,844 | ||||||||
| at June 30, 2015 | |||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | Amortized | Gross Unrealized | Fair | ||||||||||||||
| Cost | Gains | Losses | Value | ||||||||||||||
| U.S. Treasury notes | $ | 47,286 | $ | 484 | $ | - | $ | 47,770 | |||||||||
| Corporate debt securities | 13,165 | 18 | (31 | ) | 13,152 | ||||||||||||
| Agency MBS | 18,765 | 53 | (149 | ) | 18,669 | ||||||||||||
| Securities of state and political subdivisions | 406 | 6 | - | 412 | |||||||||||||
| Mutual fund investments | 1,215 | - | (6 | ) | 1,209 | ||||||||||||
| Total securities available-for-sale | $ | 80,837 | $ | 561 | $ | (186 | ) | $ | 81,212 | ||||||||
The following table presents the fair value and associated gross unrealized loss on available-for-sale securities with a gross unrealized loss at June 30, 2016 and 2015.
| Less than 12 Months | 12 Months or More | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unrealized | Estimated | Unrealized | Estimated | Unrealized | Estimated | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Loss | Fair Value | Loss | Fair Value | Loss | Fair Value | ||||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| At June 30, 2016 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Corporate debt securities | $ | (3 | ) | $ | 3,266 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | (3 | ) | $ | 3,266 | |||||||||||
| Total | $ | (3 | ) | $ | 3,266 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | (3 | ) | $ | 3,266 | |||||||||||
| At June 30, 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Corporate debt securities | $ | (31 | ) | $ | 8,388 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | (31 | ) | $ | 8,388 | |||||||||||
| Agency MBS | (149 | ) | 14,170 | - | - | (149 | ) | 14,170 | |||||||||||||||||
| Mutual fund investments | (6 | ) | 1,209 | - | - | (6 | ) | 1,209 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total | $ | (186 | ) | $ | 23,767 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | (186 | ) | $ | 23,767 | |||||||||||
The Company conducts a regular assessment of its investment portfolios to determine whether any securities are other-than-temporarily impaired. In estimating other-than-temporary impairment losses, management considers, among other factors, length of time and extent to which the fair value has been less than cost, the financial condition and near term prospects of the issuer, and the intent and ability of the Company to retain its investment in the issuer for a period of time sufficient to allow for any recovery. The $3,000 unrealized loss at June 30, 2016 relates to fluctuations in interest rates and financial markets and not credit quality. Because the Company has the intent to hold this security and more likely than not will not need to sell it, the Company does not consider this investment to be other-than-temporarily impaired at June 30, 2016.
The $186,000 in unrealized losses at June 30, 2015 related to fluctuations in interest rates and financial markets and not credit quality. Because the Company has the intent to hold these securities and more likely than not will not need to sell them, the Company does not consider these investments to be other-than-temporarily impaired at June 30, 2015. In September 2014, the Company recorded a pre-tax impairment charge of $91,000 related to the mutual fund investment. While the Company had the ability and intent to retain this investment, given that the fund lowered its dividend by 11% in May 2014 and had traded below its recorded cost for over twelve months, the Company determined that an other than temporary impairment had occurred.
| 38 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
The amortized cost and estimated fair value of available-for-sale securities at June 30, 2016, by contractual maturity, are shown below. Expected maturities may differ from contractual maturities because borrowers may have the right to call or prepay obligations with or without call or prepayment penalties.
| Amortized Cost | Fair Value | ||||||||
| (in thousands) | |||||||||
| Due in three months or less | $ | - | $ | - | |||||
| Due after three months to one year | - | - | |||||||
| Due after one year to five years | 60,646 | 62,159 | |||||||
| Due after five years | 31,782 | 32,223 | |||||||
| No stated maturity | 1,215 | 1,462 | |||||||
| Total securities available-for-sale | $ | 93,643 | $ | 95,844 | |||||
The following table presents the Company’s gross realized gains and gross realized losses on available-for-sale securities. These gains and losses were recognized using the specific identification method and were included in non-interest income.
| (in thousands) | Available-for-sale | ||||||||||||
| For the years ended June 30, | |||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||||
| Gross realized gains | $ | 23 | $ | 572 | $ | - | |||||||
| Gross realized losses | - | - | - | ||||||||||
| Other than temporary impairment | - | (91 | ) | - | |||||||||
| Total | $ | 23 | $ | 481 | $ | - | |||||||
During the twelve months ended June 30, 2016, the Company realized a gain of $23,000 from an early call of a corporate debt security for proceeds of $4.8 million. The net gain is recognized using the specific identification method and is included in non-interest income. During the twelve months ended June 30, 2015, the Company realized a gain of $572,000 from the sale of equity investments for proceeds of $994,000. The net gain is recognized using the specific identification method and is included in non-interest income. In September 2014, the Company recorded a pre-tax impairment charge of $91,000 related to the mutual fund investment discussed above.
At June 30, 2016, U.S. Treasury notes and Agency MBS with an amortized cost of $79.1 million are pledged to secure borrowings from the FHLB (see Note 9). At June 30, 2015, U.S. Treasury notes and Agency MBS with an amortized cost of $66.1 million are pledged to secure borrowings from the FHLB.
Note 4 - Receivables:
The Company's receivables consist of the following:
| June 30, | |||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||
| (in thousands) | |||||||||
| Other lessee receivables | $ | 214 | $ | 440 | |||||
| Accrued interest and dividends | 1,119 | 734 | |||||||
| $ | 1,333 | $ | 1,174 | ||||||
Note 5 – Net Investment in Leases:
The Company's net investment in leases consists of the following:
| June 30, | |||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||
| (in thousands) | |||||||||
| Minimum lease payments receivable | $ | 248,527 | $ | 310,960 | |||||
| Estimated residual value | 10,871 | 13,819 | |||||||
| Less unearned income | (19,434 | ) | (23,046 | ) | |||||
| Net investment in leases before allowances | 239,964 | 301,733 | |||||||
| Less allowance for lease losses | (2,228 | ) | (3,339 | ) | |||||
| Less valuation allowance for estimated residual value | (62 | ) | (70 | ) | |||||
| Net investment in leases | $ | 237,674 | $ | 298,324 | |||||
The minimum lease payments receivable and estimated residual value are discounted using the internal rate of return method related to each specific lease. Unearned income and discounts include the offset of initial direct costs of $2.6 million and $2.4 million at June 30, 2016 and 2015, respectively.
| 39 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
At June 30, 2016, a summary of the installments due on minimum lease payments receivable, and the expected maturity of the Company's estimated residual value are as follows:
| Lease | Estimated | ||||||||||||
| Years ending June 30, | Receivable | Residual Value | Total | ||||||||||
| (in thousands) | |||||||||||||
| 2017 | $ | 98,920 | $ | 3,790 | $ | 102,710 | |||||||
| 2018 | 68,795 | 4,197 | 72,992 | ||||||||||
| 2019 | 42,701 | 1,646 | 44,347 | ||||||||||
| 2020 | 20,194 | 123 | 20,317 | ||||||||||
| 2021 | 8,469 | 461 | 8,930 | ||||||||||
| Thereafter | 9,448 | 654 | 10,102 | ||||||||||
| 248,527 | 10,871 | 259,398 | |||||||||||
| Less unearned income | (18,390 | ) | (1,044 | ) | (19,434 | ) | |||||||
| Less allowances | (2,228 | ) | (62 | ) | (2,290 | ) | |||||||
| $ | 227,909 | $ | 9,765 | $ | 237,674 | ||||||||
Non-recourse debt, which relates to the discounting of lease receivables, bears interest at rates ranging from 2.11% to 4.75%. Maturities of such obligations at June 30, 2016 are as follows:
| Non-recourse | |||||
| Years ending June 30, | Debt | ||||
| (in thousands) | |||||
| 2017 | $ | 4,115 | |||
| 2018 | 276 | ||||
| Total non-recourse debt | 4,391 | ||||
| Deferred interest expense | 58 | ||||
| Discounted lease rentals assigned to lenders | $ | 4,449 | |||
Deferred interest expense of $58,000 at June 30, 2016 will be amortized against direct finance income related to the Company's discounted lease rentals assigned to lenders of $4.4 million using the effective yield method over the applicable lease term.
Note 6 – Commercial Loans:
The Company’s investment in commercial loans consists of the following:
| June 30, | |||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||
| (in thousands) | |||||||||
| Commercial term loans | $ | 399,239 | $ | 238,973 | |||||
| Commercial real estate loans | 6,682 | 7,531 | |||||||
| Revolving lines of credit | 3,405 | 585 | |||||||
| Total commercial loans | 409,326 | 247,089 | |||||||
| Less unearned income and discounts | (1,018 | ) | (580 | ) | |||||
| Less allowance for loan losses | (4,572 | ) | (3,047 | ) | |||||
| Net commercial loans | $ | 403,736 | $ | 243,462 | |||||
In addition to the amount outstanding on revolving lines of credit set forth above, the Company had additional unused commitments on revolving lines of credit in the amount of $524,000 at June 30, 2016 and $7.4 million at June 30, 2015.
| 40 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
Note 7 – Allowance for Credit Losses:
The allowance for credit losses includes amounts to cover losses related to the net investment in leases, commercial loans, and transactions-in-process (“risk assets”). A summary of the allocation of the allowance for credit losses and selected statistics is as follows:
| June 30, | |||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | |||||||||
| Allowance for credit losses at beginning of year | $ | 6,456 | $ | 5,299 | |||||
| Charge-off of leases | (1,120 | ) | (19 | ) | |||||
| Recovery of lease amounts previously written off | 51 | 1 | |||||||
| Provision for credit losses | 1,475 | 1,175 | |||||||
| Allowance for credit losses at end of year | $ | 6,862 | $ | 6,456 | |||||
| Components of allowance for credit losses: | |||||||||
| Allowance for lease losses | $ | 2,290 | $ | 3,409 | |||||
| Allowance for loan losses | 4,572 | 3,047 | |||||||
| $ | 6,862 | $ | 6,456 | ||||||
| Allowance for credit losses as percent of net investment in leases and loans before allowances | 1.06 | % | 1.18 | % | |||||
| Net recoveries (charge-offs) as percent of average leases and loans | (0.2 | %) | 0.00 | % | |||||
In addition to the allowance for credit losses, the Company has recorded a liability for unfunded loan commitments of $50,000 at June 30, 2016 and 2015.
Note 8 – Credit Quality of Financing Receivables:
The following tables provide information on the credit profile of the components of the portfolio and allowance for credit losses related to “financing receivables” as defined under Topic 310, Receivables. This disclosure on “financing receivables” covers the Company’s direct finance and sales-type leases and all commercial loans, but does not include operating leases and transactions in process. The portfolio is disaggregated into segments and classifications appropriate for assessing and monitoring the portfolios’ risk and performance. This disclosure does not encompass all risk assets or the entire allowance for credit losses.
Portfolio segments identified by the Company include leases and loans. These segments have been disaggregated into four classes: 1) commercial leases, 2) education, government and non-profit leases, 3) commercial and industrial loans and 4) commercial real estate loans. Relevant risk characteristics for establishing these portfolio classes generally include the nature of the borrower, structure of the transaction and collateral type. The Company’s credit process includes a policy of classifying all leases and loans in accordance with a risk rating classification system consistent with regulatory models under which leases and loans may be rated as “pass”, “special mention”, “substandard”, or “doubtful”. These risk categories reflect an assessment of the ability of the borrowers to service their obligation based on current financial position, historical payment experience, and collateral adequacy, among other factors. The Company uses the following definitions for risk ratings:
| Pass – Includes credits of the highest quality as well as credits with positive primary repayment source but one or more characteristics that are of higher than average risk. |
| Special Mention – Have a potential weakness that if left uncorrected may result in deterioration of the repayment prospects for the lease or loan or of the Company’s credit position at some future date. |
| Substandard – Are inadequately protected by the paying capacity of the obligor or of the collateral, if any. Substandard credits have a well-defined weakness that jeopardize the liquidation of the debt or indicate the distinct possibility that the Company will sustain some loss if the deficiencies are not corrected. |
Doubtful – Based on current information and events, collection of all amounts due according to the contractual terms of the lease or loan agreement is considered highly questionable and improbable.
| 41 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
The risk classification of financing receivables by portfolio class is as follows:
| Education | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Government | Commercial | Commercial | Total | |||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | Commercial | Non-profit | & Industrial | Real Estate | Financing | |||||||||||||||
| Leases | Leases | Loans | Loans | Receivable | ||||||||||||||||
| As of June 30, 2016: | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Pass | $ | 174,679 | $ | 58,344 | $ | 397,910 | $ | 6,679 | $ | 637,612 | ||||||||||
| Special Mention | 6,308 | 380 | 3,719 | - | 10,407 | |||||||||||||||
| Substandard | 241 | - | - | - | 241 | |||||||||||||||
| Doubtful | 10 | 2 | - | - | 12 | |||||||||||||||
| $ | 181,238 | $ | 58,726 | $ | 401,629 | $ | 6,679 | $ | 648,272 | |||||||||||
| Non-accrual | $ | 10 | $ | 2 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 12 | ||||||||||
| As of June 30, 2015: | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Pass | $ | 219,791 | $ | 69,865 | $ | 234,076 | $ | 7,523 | $ | 531,255 | ||||||||||
| Special Mention | 6,080 | 304 | 4,910 | - | 11,294 | |||||||||||||||
| Substandard | 5,435 | 217 | - | - | 5,652 | |||||||||||||||
| Doubtful | 37 | 4 | - | - | 41 | |||||||||||||||
| $ | 231,343 | $ | 70,390 | $ | 238,986 | $ | 7,523 | $ | 548,242 | |||||||||||
| Non-accrual | $ | 37 | $ | 4 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 41 | ||||||||||
The accrual of interest income on leases and loans will be discontinued when the customer becomes ninety days or more past due on its lease or loan payments with the Company, unless the Company believes the investment is otherwise recoverable. Leases and loans may be placed on non-accrual earlier if the Company has significant doubt about the ability of the customer to meet its lease or loan obligations, as evidenced by consistent delinquency, deterioration in the customer’s financial condition or other relevant factors. Payments received while on non-accrual are applied to reduce the Company’s recorded value.
The following table presents the aging of the financing receivables by portfolio class:
| Greater | Total | Over 90 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 31-89 | Than | Total | Financing | Days & | ||||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | Days | 90 Days | Past Due | Current | Receivable | Accruing | ||||||||||||||||||
| As of June 30, 2016: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial Leases | $ | - | $ | 10 | $ | 10 | $ | 181,228 | $ | 181,238 | $ | - | ||||||||||||
| Education, Government, Non-profit Leases | - | 2 | 2 | 58,724 | 58,726 | - | ||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial and Industrial Loans | - | - | - | 401,629 | 401,629 | - | ||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial Real Estate Loans | - | - | - | 6,679 | 6,679 | - | ||||||||||||||||||
| $ | - | $ | 12 | $ | 12 | $ | 648,260 | $ | 648,272 | $ | - | |||||||||||||
| As of June 30, 2015: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial Leases | $ | 2,733 | $ | 37 | $ | 2,770 | $ | 228,573 | $ | 231,343 | $ | - | ||||||||||||
| Education, Government, Non-profit Leases | 8 | 4 | 12 | 70,378 | 70,390 | - | ||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial and Industrial Loans | - | - | - | 238,986 | 238,986 | - | ||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial Real Estate Loans | - | - | - | 7,523 | 7,523 | - | ||||||||||||||||||
| $ | 2,741 | $ | 41 | $ | 2,782 | $ | 545,460 | $ | 548,242 | $ | - | |||||||||||||
| 42 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
The following table presents the allowance balances and activity in the allowance related to financing receivables, along with the recorded investment and allowance determined based on impairment method as of June 30, 2016 and 2015:
| Education | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Government | Commercial | Commercial | Total | |||||||||||||||||
| Commercial | Non-profit | & Industrial | Real Estate | Financing | ||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | Leases | Leases | Loans | Loans | Receivable | |||||||||||||||
| As of June 30, 2016: | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Allowance for lease and loan losses | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance beginning of period | $ | 2,592 | $ | 817 | $ | 2,936 | $ | 111 | $ | 6,456 | ||||||||||
| Charge-offs | (1,118 | ) | (2 | ) | - | - | (1,120 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Recoveries | 1 | 50 | - | - | 51 | |||||||||||||||
| Provision | 350 | (400 | ) | 1,575 | (50 | ) | 1,475 | |||||||||||||
| Balance end of period | $ | 1,825 | $ | 465 | $ | 4,511 | $ | 61 | $ | 6,862 | ||||||||||
| Individually evaluated for impairment | $ | 37 | $ | 2 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 39 | ||||||||||
| Collectively evaluated for impairment | 1,788 | 463 | 4,511 | 61 | 6,823 | |||||||||||||||
| Total ending allowance balance | $ | 1,825 | $ | 465 | $ | 4,511 | $ | 61 | $ | 6,862 | ||||||||||
| Finance receivables | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Individually evaluated for impairment | $ | 242 | $ | 2 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 244 | ||||||||||
| Collectively evaluated for impairment | 180,996 | 58,724 | 401,629 | 6,679 | 648,028 | |||||||||||||||
| Total ending finance receivable balance | $ | 181,238 | $ | 58,726 | $ | 401,629 | $ | 6,679 | $ | 648,272 | ||||||||||
| As of June 30, 2015: | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Allowance for lease and loan losses | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance beginning of period | $ | 2,510 | $ | 817 | $ | 1,761 | $ | 211 | $ | 5,299 | ||||||||||
| Charge-offs | (19 | ) | - | - | - | (19 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Recoveries | 1 | - | - | - | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| Provision | 100 | - | 1,175 | (100 | ) | 1,175 | ||||||||||||||
| Balance end of period | $ | 2,592 | $ | 817 | $ | 2,936 | $ | 111 | $ | 6,456 | ||||||||||
| Individually evaluated for impairment | $ | 563 | $ | 58 | $ | $ | $ | 621 | ||||||||||||
| Collectively evaluated for impairment | 2,029 | 759 | 2,936 | 111 | 5,835 | |||||||||||||||
| Total ending allowance balance | $ | 2,592 | $ | 817 | $ | 2,936 | $ | 111 | $ | 6,456 | ||||||||||
| Finance receivables | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Individually evaluated for impairment | $ | 5,449 | $ | 221 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 5,670 | ||||||||||
| Collectively evaluated for impairment | 225,894 | 70,169 | 238,986 | 7,523 | 542,572 | |||||||||||||||
| Total ending finance receivable balance | $ | 231,343 | $ | 70,390 | $ | 238,986 | $ | 7,523 | $ | 548,242 | ||||||||||
Note 9 – Borrowings:
CalFirst Bank is a member of the Federal Home Loan Bank of San Francisco and can take advantage of FHLB programs for overnight and term advances at published daily rates. Under terms of a blanket collateral agreement, advances from the FHLB are collateralized by qualifying real estate loans and investment securities. The Bank also has authority to borrow from the Federal Reserve Bank (“FRB”) discount window amounts secured by certain lease receivables. Borrowing capacity from the FHLB or FRB may fluctuate based upon the acceptability and risk rating of securities, loan and lease collateral and both the FRB and FHLB could adjust advance rates applied to such collateral at their discretion.
Short-term borrowings consist of funds with remaining maturities of one year or less and long-term debt consists of borrowings with remaining maturities greater than one year. The Company had no long-term borrowings at June 30, 2016 and 2015. The borrowings from the FHLB and weighted average interest rates at June 30, 2016 and 2015 were as follows:
| June 30, 2016 | June 30, 2015 | ||||||||||||||||
| Weighted | Weighted | ||||||||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | Amount | Average Rate | Amount | Average Rate | |||||||||||||
| Short-term borrowings | |||||||||||||||||
| FHLB advances | $ | 40,000 | 0.42 | % | $ | 42,000 | 0.32 | % | |||||||||
| 43 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
At June 30, 2016, there was estimated available borrowing capacity from the FHLB of $40.8 million related to qualifying real estate loans of $3.5 million and securities with a carrying value of $79.1 million. There were no borrowings from the FRB, leaving availability of approximately $107.2 million secured by $140.4 million of lease receivables.
Note 10 – Deposits:
The composition of deposits is as follows:
| June 30, 2016 | June 30, 2015 | ||||||||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||
| Non-interest bearing deposits | |||||||||||||||||
| Demand deposits | $ | 2,181 | 0.34 | % | $ | 2,193 | 0.5 | % | |||||||||
| Interest-bearing deposits | |||||||||||||||||
| Demand | 1,298 | 0.21 | % | 2,715 | 0.6 | % | |||||||||||
| Savings and money market | 78,510 | 12.40 | % | 65,539 | 13.9 | % | |||||||||||
| Time certificates of deposits | 551,158 | 87.05 | % | 401,459 | 85.0 | % | |||||||||||
| Total Deposits | $ | 633,147 | 100.00 | % | $ | 471,906 | 100.0 | % | |||||||||
Included in savings and money market deposits at June 30, 2016 is a deposit in the amount of $20.2 million from an affiliate, as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, of the Company. The terms of such account are the same terms offered on similar accounts to non-affiliated depositors.
Time certificates of deposits with balances of more than $250,000 were $128.0 million and $82.2 million at June 30, 2016 and 2015, respectively.
At June 30, 2016, the scheduled maturities of time certificates of deposit are as follows:
| Years Ending: | (in thousands) | ||||
| 2017 | $ | 440,636 | |||
| 2018 | 89,521 | ||||
| 2019 | 21,001 | ||||
| Total time certificates of deposit | $ | 551,158 | |||
Note 11 – Fair Value Measurement:
ASC Topic 820: “Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures” defines fair value as the price that would be received for an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants in the principal or most advantageous market for the asset or liability. ASC Topic 820 establishes a three-tiered value hierarchy that prioritizes inputs based on the extent to which inputs used are observable in the market and requires the Company to maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs. If a value is based on inputs that fall in different levels of the hierarchy, the instrument will be categorized based upon the lowest level of input that is significant to the fair value calculation. The three levels of inputs are defined as follows:
| • | Level 1 - Valuation is based upon unadjusted quoted prices for identical instruments traded in active markets; |
| • | Level 2 - Valuation is based upon quoted prices for similar instruments in active markets, quoted prices for identical or similar instruments in markets that are not active and model-based valuation techniques for which all significant assumptions are observable in the market; |
| • | Level 3 - Valuation is generated from model-based techniques that use inputs not observable in the market and based on the entity’s own judgment. Level 3 valuation techniques could include the use of option pricing models, discounted cash flow models and similar techniques, and rely on assumptions that market participants would use in pricing the asset or liability. |
ASC 820 applies whenever other accounting pronouncements require presentation of fair value measurements, but does not change existing guidance as to whether or not an instrument is carried at fair value. As such, ASC 820 does not apply to the Company’s investment in leases. The Company’s financial assets measured at fair value on a recurring basis include primarily securities available-for-sale and at June 30, 2016, there were no liabilities subject to ASC 820.
| 44 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
The Company classifies financial assets and liabilities within the fair value hierarchy based on the availability of observable market information. Securities available-for-sale include U.S. Treasury securities, corporate and municipal bonds, U.S. government agency (“Agency”) mortgage-backed securities (“MBS”), mutual fund and equity investments and generally are reported at fair value utilizing Level 1 and Level 2 inputs. The fair value of corporate and municipal bonds and the MBS are obtained from independent quotation bureaus that use computerized valuation formulas to calculate current values based on observable transactions, but not a quoted bid, or are valued using prices obtained from the custodian, who uses third party data service providers (Level 2 input). U.S. Treasury securities, mutual funds and equity investments are valued by reference to the market closing or last trade price (Level 1 inputs). In the unlikely event that no trade occurred on the applicable date, an indicative bid or the last trade most proximate to the applicable date would be used (Level 2 input). Changes in markets, economic conditions or the Company valuation model may require the transfer of financial instruments from one level to another. Such transfer, if any, would be recorded at the fair value as of the beginning of the period in which the transfer occurred. The Company has had no transfers in fiscal 2016 and 2015.
The following table summarizes the Company’s assets, which are measured at fair value on a recurring basis as of June 30, 2016 and 2015:
| Quoted Price in | Significant | ||||||||||||||||
| Active Markets for | Significant Other | Unobservable | |||||||||||||||
| Total | Identical Assets | Observable Inputs | Inputs | ||||||||||||||
| Description of Assets / Liabilities | Fair Value | (Level 1) | (Level 2) | (Level 3) | |||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||
| As of June 30, 2016 | |||||||||||||||||
| U.S. Treasury Notes | $ | 48,774 | $ | 48,774 | $ | - | $ | - | |||||||||
| Corporate debt securities | 13,385 | - | 13,385 | - | |||||||||||||
| Agency MBS | 32,223 | - | 32,223 | - | |||||||||||||
| Mutual fund investments | 1,462 | 1,462 | - | - | |||||||||||||
| $ | 95,844 | $ | 50,236 | $ | 45,608 | $ | - | ||||||||||
| As of June 30, 2015 | |||||||||||||||||
| U.S. Treasury notes | $ | 47,770 | $ | 47,770 | $ | - | $ | - | |||||||||
| Corporate debt securities | 13,152 | - | 13,152 | - | |||||||||||||
| Agency MBS | 18,669 | - | 18,669 | - | |||||||||||||
| Securities of state and political subdivisions | 412 | - | 412 | - | |||||||||||||
| Mutual fund investment | 1,209 | 1,209 | - | - | |||||||||||||
| $ | 81,212 | $ | 48,979 | $ | 32,233 | $ | - | ||||||||||
Certain financial assets, such as collateral dependent impaired loans and repossessed or returned assets are measured at fair value on a nonrecurring basis; that is, the assets are not measured at fair value on an ongoing basis but are subject to fair value adjustments only in certain circumstances. During the year ended June 30, 2016, the equipment subject to a lease rejected in bankruptcy was transferred from lease receivables and recorded as repossessed equipment in other assets.
The fair value of repossessed equipment is based on available market information, including sales results and appraisal, less estimated selling costs. The equipment repossessed was initially recorded at the estimated fair value less estimated selling costs at the time of transfer to repossessed assets and subsequently written down based on an updated appraisal.
The following table summarizes the Company’s assets which are measured at fair value on a non-recurring basis as of June 30, 2016. The Company had no such assets or liabilities at June 30, 2015.
| Quoted Price in | Significant | ||||||||||||||||
| Active Markets for | Significant Other | Unobservable | |||||||||||||||
| Total | Identical Assets | Observable Inputs | Inputs | ||||||||||||||
| Description of Assets / Liabilities | Fair Value | (Level 1) | (Level 2) | (Level 3) | |||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||
| As of June 30, 2016 | |||||||||||||||||
| Repossessed asset | $ | 1,300 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 1,300 | |||||||||
Note 12 – Fair Value of Financial Instruments:
In accordance with ASC 825-50, the following table summarizes the estimated fair value of financial instruments as of June 30, 2016, and June 30, 2015, and includes financial instruments that are not accounted for or carried at fair value. In accordance with disclosure guidance, certain financial instruments, including all lease related assets and liabilities and all non-financial instruments are excluded from fair value of financial instrument disclosure requirements. Accordingly, the aggregate of the fair values presented does not represent the total underlying value of the Company. These fair value estimates are based on relevant market information and data, however, given there is no active market or observable market transactions for certain financial instruments, the Company has made estimates of fair values which are subjective in nature, involve uncertainties and matters of significant judgment and therefore cannot be determined with precision. Changes in assumptions could significantly affect the estimated values.
| 45 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
For cash and cash equivalents and demand and savings deposits, because of their short-term nature, the carrying amounts approximate the fair value and are classified as Level 1 in the fair value hierarchy. Values for investments and available-for-sale securities are determined as set forth in Note 2 and 11. The fair values of loan participations that trade regularly in the secondary market are based upon current bid prices in such market at the measurement date and are classified as Level 2 in the fair value hierarchy. For other loans, the estimated fair value is calculated based on discounted cash flow analyses, using interest rates currently being offered for loans with similar terms to borrowers of similar credit quality and are classified as Level 3 in the fair value hierarchy. These calculations have been adjusted for credit risk based on the Company’s historical credit loss experience. The fair value of certificates of deposit and short-term borrowings are estimated based on discounted cash flows using current offered market rates or interest rates for borrowings of similar maturity and are classified as Level 3 in the fair value hierarchy.
The estimated fair values of financial instruments were as follows:
| June 30, 2016 | June 30, 2015 | ||||||||||||||||
| Carrying | Estimated | Carrying | Estimated | ||||||||||||||
| Amount | Fair Value | Amount | Fair Value | ||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||
| Financial Assets: | |||||||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 105,094 | $ | 105,094 | $ | 60,240 | $ | 60,240 | |||||||||
| Investments | 3,957 | 3,972 | 3,334 | 3,349 | |||||||||||||
| Securities available-for-sale | 95,844 | 95,844 | 81,212 | 81,212 | |||||||||||||
| Commercial loan participations | 389,511 | 388,781 | 227,238 | 226,627 | |||||||||||||
| Other loans | 14,225 | 14,512 | 16,224 | 16,381 | |||||||||||||
| Financial Liabilities: | |||||||||||||||||
| Demand and savings deposits | 81,989 | 81,989 | 70,447 | 70,447 | |||||||||||||
| Time certificate of deposits | 551,158 | 551,508 | 401,459 | 401,211 | |||||||||||||
| Short-term borrowings | $ | 40,000 | $ | 40,001 | $ | 42,000 | $ | 42,004 | |||||||||
Note 13 – Income Taxes:
The Company accounts for its income taxes under ASC 740, “Income Taxes.” Among other provisions, this standard requires deferred tax balances to be determined using the enacted income tax rate for the years in which taxes will be paid or refunds received. The Company is subject to U.S. Federal income tax jurisdiction, as well as multiple state and local jurisdictions as a result of doing business in most states. The Company’s Federal tax returns remain subject to examination from 2014 forward, while state income tax returns are generally open from 2012 forward, and vary by individual state statute of limitation. The Company believes that its accrual for income taxes is adequate for adjustments, if any, which may result from these examinations.
The provision for income taxes is summarized as follows:
| Years ended June 30, | |||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||||
| (in thousands) | |||||||||||||
| Current tax (benefit) expense: | |||||||||||||
| Federal | $ | 9,801 | $ | 8,652 | $ | 6,299 | |||||||
| State | 1,240 | 1,067 | 912 | ||||||||||
| 11,041 | 9,719 | 7,211 | |||||||||||
| Deferred tax (benefit) expense: | |||||||||||||
| Federal | (5,064 | ) | (3,678 | ) | (2,792 | ) | |||||||
| State | (557 | ) | (281 | ) | (397 | ) | |||||||
| (5,621 | ) | (3,959 | ) | (3,189 | ) | ||||||||
| $ | 5,420 | $ | 5,760 | $ | 4,022 | ||||||||
At June 30, 2016 and 2015, the Company had an income taxes receivable balance of $121,000 and $231,000 respectively.
| 46 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
Deferred taxes result principally from the method of recording lease income on capital leases and depreciation methods for tax reporting, which differ from financial statement reporting. Deferred income tax liabilities (assets) are comprised of the following:
| June 30, | |||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||
| (in thousands) | |||||||||
| Deferred income tax liabilities: | |||||||||
| Tax operating leases | $ | 13,799 | $ | 14,003 | |||||
| Deferred selling expenses | 1,072 | 965 | |||||||
| Depreciation | 632 | 77 | |||||||
| Other investments | 673 | 19 | |||||||
| Total liabilities | 16,176 | 15,064 | |||||||
| Deferred income tax assets: | |||||||||
| Allowances and reserves | (3,061 | ) | (2,741 | ) | |||||
| State income taxes | (434 | ) | (374 | ) | |||||
| Stock-based compensation | (7 | ) | (5 | ) | |||||
| Total assets | (3,502 | ) | (3,120 | ) | |||||
| Net deferred income tax liabilities | $ | 12,674 | $ | 11,944 | |||||
The differences between the federal statutory income tax rate and the Company's effective tax rate are as follows:
| Years ended June 30, | |||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||||
| Federal statutory rate | 35.00 | % | 35.00 | % | 35.00 | % | |||||||
| State tax, net of Federal benefit | 4.86 | 5.31 | 4.65 | ||||||||||
| Other, mainly tax exempt leases | (1.36 | ) | (1.41 | ) | (2.25 | ) | |||||||
| Derecognition of uncertain tax positions | - | - | (1.10 | ) | |||||||||
| Effective rate | 38.50 | % | 38.90 | % | 36.30 | % | |||||||
As of June 30, 2016, there was $188,000 of unrecognized tax benefits, all of which, if recognized, would affect the effective tax rate. The Company’s policy is to include interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits in income tax expense. As of June 30, 2016, accrued penalties and interest on unrecognized tax benefits are estimated to be $34,000.
The following table sets forth the change in unrecognized tax benefits:
| Years ended June 30, | |||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||
| (in thousands) | |||||||||
| Balance, beginning of period | $ | 188 | $ | 188 | |||||
| Increase for tax positions in current year | 47 | 47 | |||||||
| Increase (decrease) for tax positions taken in prior years | (48 | ) | (48 | ) | |||||
| Increase (decrease) for interest and penalties | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| Balance, end of period | $ | 188 | $ | 188 | |||||
At June 30, 2016, there were no material changes to the liability for uncertain tax positions and unrecognized tax benefits. The amount of unrecognized tax benefits may increase or decrease in the future for various reasons; including additions related to current year tax provisions, the expiration of the statute of limitations on open tax years, the status of examinations and changes in management judgment.
| 47 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
Note 14 – Capital Structure and Stock-based Compensation:
At June 30, 2016, the Company has 20,000,000 authorized shares of common stock and is authorized to issue 2,500,000 shares of preferred stock, from time to time, in one or more series and to fix the voting powers, designations, preferences and the relative participating, optional or other rights, if any, of any wholly unissued series of preferred stock.
In November 1995, the Company’s stockholders approved the 1995 Equity Participation Plan (the “1995 Plan”). The 1995 Plan provides for the granting of options, restricted stock and stock appreciation rights (“SARs”) to key employees, directors and consultants of the Company. Under the 1995 Plan, the maximum number of shares of common stock that can be issued upon the exercise of options or SARs, or upon the vesting of restricted stock awards, was initially 1,000,000, but the maximum number of available shares of common stock could increase by an amount equal to 1% of the total number of issued and outstanding shares of common stock as of June 30 of the fiscal year immediately preceding such fiscal year. Each grant or issuance under the 1995 Plan is set forth in a separate agreement and indicates, as determined by the stock option committee, the type, terms, vesting period and conditions of the award.
On July 1, 2005, the Company implemented ASC Topic 718, “Compensation – Stock Compensation (“ASC 718”). ASC 718 addresses accounting for equity-based compensation arrangements, including employee stock options. The Company adopted the “modified prospective method” where stock-based compensation expense is recorded beginning on the adoption date. Under this method, compensation expense is recognized using the fair-value based method for all new awards granted after July 1, 2005. The fair value of each grant is estimated using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model. There were no option grants in fiscal years 2016, 2015 and 2014. The Company has not awarded any new grants since fiscal 2013.
The Company recognized stock-based compensation expense for the years ended June 30, 2016 and 2015 and 2014 of $4,500, $4,400 and $4,400, respectively. As of June 30, 2016, the Company had $4,800 of unrecognized stock-based compensation expense to be recognized over the next 13 months.
The following table summarizes activity related to stock options for the periods indicated:
| June 30, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Weighted | Weighted | Weighted | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average | Average | Average | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares | Exercise Price | Shares | Exercise Price | Shares | Exercise Price | |||||||||||||||||||
| Options outstanding at beginning of period | 10,000 | $ | 16.00 | 10,000 | $ | 16.00 | 22,697 | $ | 13.91 | |||||||||||||||
| Exercised | - | - | - | - | (12,697 | ) | 12.26 | |||||||||||||||||
| Granted | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||
| Options outstanding at end of period | 10,000 | $ | 16.00 | 10,000 | $ | 16.00 | 10,000 | $ | 16.00 | |||||||||||||||
| Options exercisable at end of period | 6,000 | 4,000 | 2,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares available for issuance | 2,219,845 | 2,115,246 | 2,010,647 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| As of June 30, 2016 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Options Outstanding | Options Exercisable | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Weighted Average | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Range of | Number | Remaining Contractual | Weighted Average | Number | Weighted Average | |||||||||||||||||
| Exercise prices | Outstanding | Life (in years) | Exercise Price | Exercisable | Exercise Price | |||||||||||||||||
| $16.00 | - | $16.00 | 10,000 | 6.08 | $ | 16.00 | 6,000 | $ | 16.00 | |||||||||||||
At June 30, 2016, the aggregate intrinsic value of options outstanding and options exercisable was $0. There were no options exercised during the year ended June 30, 2016. The total intrinsic value of options exercised during the year ended June 30, 2015 and 2014 was $0 and $35,496, respectively.
| 48 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
Note 15 – Regulatory Capital Requirements:
The Company and CalFirst Bank are subject to regulatory capital adequacy guidelines administered by federal banking agencies. Failure to meet minimum capital requirements can result in the initiation of certain actions by the federal agencies that, if undertaken, could have a material effect on the Company’s financial statements. The Basel III capital standard became effective January 2, 2015 and phases in through 2019. It revises the definition of capital, increases minimum capital ratios, introduces regulatory capital buffers above those minimums, introduces a common equity Tier 1 capital ratio and revises the rules for calculating risk-weighted assets. Effective January 2, 2015 Basel III capital standards require the Company and Bank to maintain minimum ratios of core capital to adjusted average assets of 4.0%, common equity tier 1 capital to risk-weighted assets of 4.5%, tier 1 capital to risk-weighted assets of 6.0% and total risk-based capital to risk-weighted assets of 8.0%.
The following table presents capital and capital ratio information for the Company and CalFirst Bank as of June 30, 2016 and June 30, 2015, with information for June 30, 2015 reflecting the transition to the Basel III capital standard from previous regulatory capital adequacy guidelines under the Basel I framework. Under Basel III, the Bank could make a one-time election to opt out of the requirement to include components of accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) in common equity Tier 1 capital. The Bank has elected to opt-out of the accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) requirement. The adoption of the new capital standard had an immaterial impact on capital levels and related ratios and the Company and Bank continue to exceed regulatory capital requirements and are considered “well-capitalized” under guidelines established by federal regulators.
| June 30, | |||||||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||
| California First National Bancorp | Amount | Ratio | Amount | Ratio | |||||||||||||
| Common equity Tier 1 capital | $ | 189,677 | 25.12% | $ | 187,987 | 29.17% | |||||||||||
| Tier 1 risk-based capital | $ | 189,677 | 25.12% | $ | 187,987 | 29.17% | |||||||||||
| Total risk-based capital | $ | 196,589 | 26.04% | $ | 194,493 | 30.18% | |||||||||||
| Tier 1 leverage capital | $ | 189,677 | 21.67% | $ | 187,987 | 26.79% | |||||||||||
| California First National Bank | |||||||||||||||||
| Common equity Tier 1 capital | $ | 116,379 | 15.88% | $ | 109,147 | 17.65% | |||||||||||
| Tier 1 risk-based capital | $ | 116,379 | 15.88% | $ | 109,147 | 17.65% | |||||||||||
| Total risk-based capital | $ | 123,091 | 16.79% | $ | 115,306 | 18.65% | |||||||||||
| Tier 1 leverage capital | $ | 116,379 | 13.94% | $ | 109,147 | 17.10% | |||||||||||
Note 16 – Commitments and Contingencies:
The Company has commitments to extend credit provided there is no violation of any condition in the terms of the approval or agreement. At June 30, 2016 and 2015, the Company had approved lease and loan commitments of $57.0 million and $88.4 million, respectively. These lease and loan commitments are approved transactions, but it is likely that some portion of these commitments will not fund or be completed. The Company does not issue standby letters of credit.
Leases
The Company leases its corporate offices under an operating lease that expires in fiscal 2019. Rent expense was $684,100 (2016), $634,000 (2015) and $680,000 (2014).
| Future minimum | |||||||
| Years ending | lease payments | ||||||
| June 30, | (in thousands) | ||||||
| 2017 | $ | 689 | |||||
| 2018 | 720 | ||||||
| 2019 | 121 | ||||||
| $ | 1,530 | ||||||
| 49 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
Litigation
From time to time, the Company is party to legal actions and administrative proceedings and subject to various claims arising out of the Company’s normal business activities. Management does not expect the outcome of any of these matters, individually and in the aggregate, to have a material adverse effect on the financial condition and results of operations of the Company.
401(k) Plan
Employees of the Company may participate in a voluntary defined contribution plan (the "401K Plan") qualified under Section 401(k) of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986. Under the 401K Plan, employees who have met certain age and service requirements may contribute up to a certain percentage of their compensation. The Company has made contributions of $94,287 (2016), $97,607 (2015) and $121,889 (2014).
Note 17 – Segment Reporting:
The Company’s banking subsidiary, CalFirst Bank, and leasing subsidiary, CalFirst Leasing, are considered to be two different business segments. The accounting policies of each segment are the same as those described in “Summary of Significant Accounting Policies” (see Note 1). Below is a summary of each segment’s financial results for fiscal years 2016, 2015 and 2014:
| Bancorp and | |||||||||||||||||
| CalFirst | CalFirst | Eliminating | |||||||||||||||
| Bank | Leasing | Entries | Consolidated | ||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||
| Year end June 30, 2016: | |||||||||||||||||
| Total interest income | $ | 26,334 | $ | 1,358 | $ | 9 | $ | 27,701 | |||||||||
| Net interest income after provision for credit losses | 18,331 | 1,676 | 9 | 20,016 | |||||||||||||
| Non-interest income | 2,300 | 2,586 | - | 4,886 | |||||||||||||
| Net earnings | 7,232 | 2,376 | (960 | ) | 8,648 | ||||||||||||
| Total assets | $ | 852,056 | $ | 78,183 | $ | (42,063 | ) | $ | 888,176 | ||||||||
| Year end June 30, 2015: | |||||||||||||||||
| Total interest income | $ | 21,092 | $ | 1,912 | $ | 1 | $ | 23,005 | |||||||||
| Net interest income after provision for credit losses | 15,730 | 2,154 | 1 | 17,885 | |||||||||||||
| Non-interest income | 3,947 | 4,762 | - | 8,709 | |||||||||||||
| Net earnings | 6,367 | 3,577 | (889 | ) | 9,055 | ||||||||||||
| Total assets | $ | 671,785 | $ | 90,337 | $ | (31,048 | ) | $ | 731,074 | ||||||||
| Year end June 30, 2014: | |||||||||||||||||
| Total interest income | $ | 17,062 | $ | 2,678 | $ | 1 | $ | 19,741 | |||||||||
| Net interest income after provision for credit losses | 13,783 | 2,720 | 1 | 16,504 | |||||||||||||
| Non-interest income | 2,520 | 3,044 | - | 5,564 | |||||||||||||
| Net earnings | 5,081 | 2,817 | (847 | ) | 7,051 | ||||||||||||
| Total assets | $ | 518,940 | $ | 92,787 | $ | (32,177 | ) | $ | 579,550 | ||||||||
| 50 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
Note 18 – California First National Bancorp (Parent Only) Financial Information:
The condensed financial statements of California First National Bancorp as of June 30, 2016 and 2015 and for the years ended June 30, 2016, 2015 and 2014 are presented as follows:
| Condensed Balance Sheets | June 30, | ||||||||
| (in thousands, except per share amounts) | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| ASSETS | |||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 3,910 | $ | 3,091 | |||||
| Investments and marketable securities | - | - | |||||||
| Intercompany receivable | 3 | 69 | |||||||
| Investment in banking subsidiary | 117,573 | 109,382 | |||||||
| Investment in nonbanking subsidiaries | 70,237 | 75,706 | |||||||
| Intercompany note receivable | - | - | |||||||
| Other assets | 169 | 664 | |||||||
| Premises and other fixed assets | 124 | 197 | |||||||
| $ | 192,016 | $ | 189,109 | ||||||
| LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY | |||||||||
| Liabilities | |||||||||
| Accrued liabilities | $ | 470 | $ | 492 | |||||
| Intercompany payable | 123 | 120 | |||||||
| Income taxes payable- deferred | 401 | 279 | |||||||
| 994 | 891 | ||||||||
| Stockholders' equity | |||||||||
| Preferred stock; 2,500,000 shares authorized; none issued | - | - | |||||||
| Common stock, $.01 par value; 20,000,000 shares authorized: 10,279,807 (2016) and 10,459,924 (2015) issued and outstanding | 103 | 105 | |||||||
| Additional paid in capital | 2,240 | 3,376 | |||||||
| Retained earnings | 187,334 | 184,506 | |||||||
| Other comprehensive income, net of tax | 1,345 | 231 | |||||||
| 191,022 | 188,218 | ||||||||
| $ | 192,016 | $ | 189,109 | ||||||
| Condensed Statements of Earnings | Years Ended June 30, | ||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
| Income: | |||||||||||||
| Dividends from non-bank subsidiary | $ | 8,000 | $ | 5,000 | $ | - | |||||||
| Management fee income bank subsidiary | 968 | 676 | 569 | ||||||||||
| Management fee income non-bank subsidiaries | 59 | 151 | 151 | ||||||||||
| Interest income non-bank subsidiaries | - | - | 22 | ||||||||||
| Other interest income | 9 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| Gain (loss) on investment securities | - | - | - | ||||||||||
| 9,036 | 5,828 | 743 | |||||||||||
| Non-interest Expenses: | |||||||||||||
| Salaries & benefits | 1,508 | 1,209 | 1,186 | ||||||||||
| Occupancy | 146 | 95 | 140 | ||||||||||
| Professional services | 243 | 244 | 274 | ||||||||||
| Other general & administrative | 198 | 322 | 488 | ||||||||||
| 2,095 | 1,870 | 2,088 | |||||||||||
| Income (Loss) before taxes and equity in undistributed earnings of subsidiaries | 6,941 | 3,958 | (1,345 | ) | |||||||||
| Income tax expense | (99 | ) | (154 | ) | (498 | ) | |||||||
| Equity in undistributed earnings of subsidiaries | 1,608 | 4,943 | 7,898 | ||||||||||
| Net Income | $ | 8,648 | $ | 9,055 | $ | 7,051 | |||||||
| 51 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
| Condensed Statements of Cash Flows | Years Ended June 30, | ||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
| CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES: | |||||||||||||
| Net income | $ | 8,648 | $ | 9,055 | $ | 7,051 | |||||||
| Adjustments to reconcile net earnings to cash flows: | |||||||||||||
| Deferred income taxes | 122 | 49 | (706 | ) | |||||||||
| Equity in undistributed earnings of subsidiaries | (1,608 | ) | (4,943 | ) | (7,898 | ) | |||||||
| Net change in other liabilities | (22 | ) | (3 | ) | 74 | ||||||||
| Net change in other assets | 500 | 510 | 37 | ||||||||||
| Other, net | 73 | 64 | (68 | ) | |||||||||
| Net cash provided by (used) for operating activities | 7,713 | 4,732 | (1,510 | ) | |||||||||
| CASH FLOWS FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES: | |||||||||||||
| Payments for investments in and (advances to) subsidiaries | 69 | (44 | ) | 3,745 | |||||||||
| Net cash provided by (used for) investing activities | 69 | (44 | ) | 3,745 | |||||||||
| CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES: | |||||||||||||
| Proceeds from issuance of common stock | - | - | 156 | ||||||||||
| Payments to repurchase common stock | (2,360 | ) | - | - | |||||||||
| Dividends paid | (4,603 | ) | (4,393 | ) | (4,179 | ) | |||||||
| Net cash used for financing activities | (6,963 | ) | (4,393 | ) | (4,023 | ) | |||||||
| NET CHANGE IN CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS | 819 | 295 | (1,788 | ) | |||||||||
| CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS AT BEGINNING OF PERIOD | 3,091 | 2,796 | 4,584 | ||||||||||
| CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS AT END OF PERIOD | $ | 3,910 | $ | 3,091 | $ | 2,796 | |||||||
Note 19 – Selected Quarterly Financial Data (Unaudited):
Summarized quarterly financial data for the fiscal years ended June 30, 2016 and 2015 is as follows:
| Three Months Ended | |||||||||||||||||
| September 30, | December 31, | March 31, | June 30, | ||||||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands, except per share amounts) | |||||||||||||||||
| 2016 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total interest income | $ | 6,250 | $ | 6,570 | $ | 6,837 | $ | 8,044 | |||||||||
| Net interest income after provision for credit losses | 4,457 | 4,556 | 5,022 | 5,981 | |||||||||||||
| Non-interest income | 896 | 708 | 497 | 2,785 | |||||||||||||
| Net earnings | $ | 1,724 | $ | 1,558 | $ | 1,611 | $ | 3,755 | |||||||||
| Basic earnings per common share | $ | 0.16 | $ | 0.15 | $ | 0.15 | $ | 0.37 | |||||||||
| Diluted earnings per common share | $ | 0.16 | $ | 0.15 | $ | 0.15 | $ | 0.37 | |||||||||
| Dividends declared per common share | $ | - | $ | 0.44 | $ | - | $ | - | |||||||||
| 2015 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total finance and loan income | $ | 5,257 | $ | 5,714 | $ | 5,787 | $ | 6,247 | |||||||||
| Net interest income after provision for credit losses | 4,124 | 4,403 | 4,674 | 4,684 | |||||||||||||
| Non-interest income | 2,547 | 4,665 | 967 | 530 | |||||||||||||
| Net earnings | $ | 2,459 | $ | 3,557 | $ | 1,678 | $ | 1,360 | |||||||||
| Basic earnings per common share | $ | 0.24 | $ | 0.34 | $ | 0.16 | $ | 0.13 | |||||||||
| Diluted earnings per common share | $ | 0.24 | $ | 0.34 | $ | 0.16 | $ | 0.13 | |||||||||
| Dividends declared per common share | $ | - | $ | 0.42 | $ | - | $ | - | |||||||||
| 52 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
ITEM 9. CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE
None.
ITEM 9A. CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES
Conclusion Regarding the Effectiveness of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
The Company maintains disclosure controls and procedures designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed in the reports that it files or submits under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 is recorded, processed, summarized and reported, within the time periods specified in the Securities and Exchange Commission’s rules and forms. As of the end of the period covered by this report, the Company's management, including its principal executive officer and its principal financial officer, evaluated the effectiveness of the Company's disclosure controls and procedures, as such term is defined in Rule 13a-15(e) promulgated under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended and have concluded that the Company's disclosure controls and procedures are adequate and effective for the purposes set forth in the definition in Exchange Act rules.
Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
The management of California First National Bancorp is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting. Internal control over financial reporting is a process designed by, or under the supervision of, the Company’s principal executive and principal financial officers and effected by the Company’s board of directors, management and other personnel to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles and includes those policies and procedures that:
| • | Pertain to the maintenance of records that in reasonable detail accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the Company; |
| • | Provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the Company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the Company; and |
| • | Provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of the Company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements. |
Because of inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risks that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Management assessed the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of June 30, 2016. In making its assessment, management used the criteria set forth in the Internal Control-Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (“COSO”). The assessment included the documentation and understanding of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Management evaluated the design effectiveness and tested the operating effectiveness of internal controls over financial reporting to form its conclusion.
Based on this evaluation, management concluded that, as of June 30, 2016, the Company’s internal control over financial reporting is effective to provide reasonable assurance that the Company’s financial statements are fairly presented in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles.
Vavrinek, Trine, Day and Co., LLP, independent registered public accounting firm, is not required to nor has it reported on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of June 30, 2016.
Changes in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
There were no significant changes made during the most recent fiscal year to the Company's internal controls or other factors that could significantly affect the Company's internal control over financial reporting.
None.
| 53 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
PART III
ITEM 10. DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
The information required by this item is incorporated herein by reference to the Company's definitive proxy statement to be filed not later than October 28, 2016 with the Securities and Exchange Commission pursuant to Regulation 14A under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended.
We have a Code of Business Conduct and Ethics within the meaning of Item 406 of Regulation S-K adopted by the SEC under the Exchange Act that applies to our principal executive officer, principal financial and accounting officer. Our Code of Business Conduct and Ethics is available on the Company’s website (www.calfirstbancorp.com), and we intend to satisfy the disclosure requirement under Item 5.05 of Form 8-K regarding any amendment to, or waiver from, a provision of our code of ethics by posting such information on our website. The information contained on the Company’s website is not part of this or any other report we file with or furnish to the SEC and is not incorporated by reference herein.
ITEM 11. EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION
The information required by this item is incorporated herein by reference to the Company's definitive proxy statement to be filed not later than October 28, 2016 with the Securities and Exchange Commission pursuant to Regulation 14A under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended.
ITEM 12. SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS
The information required by this item is incorporated herein by reference to the Company's definitive proxy statement to be filed not later than October 28, 2016 with the Securities and Exchange Commission pursuant to Regulation 14A under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended.
ITEM 13. CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS
The information required by this item is incorporated herein by reference to the Company's definitive proxy statement to be filed not later than October 28, 2015 with the Securities and Exchange Commission pursuant to Regulation 14A under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended.
ITEM 14. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTANT FEES AND SERVICES
The information required by this item is incorporated herein by reference to the Company's definitive proxy statement to be filed not later than October 28, 2016 with the Securities and Exchange Commission pursuant to Regulation 14A under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended.
| 54 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
PART IV
ITEM 15. EXHIBITS AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES
| (a) | Financial Statements and Schedules |
| All financial statements are set forth under Item 8 of this annual report on Form 10-K. Financial statement schedules have been omitted since they are either not required, not applicable, or the information is otherwise included. |
| (b) | Exhibits: |
| Exhibit # | Description of Exhibit | Page No. | ||
| 2.1 | Agreement of Merger dated as of May 22, 2001 among Amplicon, Inc., California First National Bancorp and CFNB Merger Sub (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.1 to Registrant's Statement on Form 8-K dated May 25, 2001) | |||
| 3.1 | Articles of Incorporation of California First National Bancorp (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to Registrant's Statement on Form 8-K dated May 25, 2001) | |||
| 3.2 | Bylaws of California First National Bancorp (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.2 to Registrant's Statement on Form 8-K dated May 25, 2001) | |||
| 10.1 | 1995 Equity Participation Plan, as amended to date (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Registrant’s Statement on Form S-8 File No. 333-15683) | |||
| 10.2 | Capital Assurances and Liquidity Maintenance Agreement between California First National Bancorp and California First National Bank, effective as of May 23, 2001 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Registrant's Statement on Form 8-K dated May 25, 2001) | |||
| 10.3 | Agreement by and between California First National Bank and the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency dated as of May 23, 2001 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to Registrant's Statement on Form 8-K dated May 25, 2001) | |||
| 10.4 | Business Loan Agreement between California First Leasing Corporation and Bank of America dated as of March 25, 2010 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.6 to Registrant's Statement on Form 8-K dated April 20, 2010) | |||
| 10.5 | Second Amendment to the Business Loan Agreement between California First Leasing Corporation and Bank of America dated as of April 26, 2011 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.11 to Registrant's March 31, 2011 10-Q) | |||
| 10.6 | Third Amendment to the Business Loan Agreement between California First Leasing Corporation and Bank of America dated as of April 20, 2012 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.12 to Registrant's March 31, 2012 10-Q) | |||
| 31.1 | Rule 13a-14(a)/15d-14(a) Certifications of Principal Executive Officer | 57 | ||
| 31.2 | Rule 13a-14(a)/15d-14(a) Certifications of Principal Financial Officer | 58 | ||
| 32.0 | Section 1350 Certifications by Principal Executive Officer and Principal Financial Officer | 59 |
| 55 |
| California First National Bancorp and Subsidiaries |
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15 (d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the Registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
CALIFORNIA FIRST NATIONAL BANCORP
| By: | /s/ S. Leslie Jewett | Date: | September 26, 2016 | |
|
S. Leslie Jewett Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) |
POWER OF ATTORNEY
Each person whose signature appears below hereby authorizes each of Patrick E. Paddon, S. Leslie Jewett and Glen T. Tsuma as attorney-in-fact to sign on his behalf, individually in each capacity stated below, and to file all amendments and/or supplements to this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the Registrant in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| Signature | Title | Date | ||
| /s/ Patrick E. Paddon | President, Chief Executive | September 26, 2016 | ||
| Patrick E. Paddon | Officer and Director | |||
| /s/ Glen T. Tsuma | Vice President, Chief Operating | September 26, 2016 | ||
| Glen T. Tsuma | Officer and Director | |||
| /s/ S. Leslie Jewett | Chief Financial Officer | September 26, 2016 | ||
| S. Leslie Jewett | (Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) | |||
| /s/ Michael H. Lowry | Director | September 26, 2016 | ||
| Michael H. Lowry | ||||
| /s/ Harris Ravine | Director | September 26, 2016 | ||
| Harris Ravine | ||||
| /s/ Danilo Cacciamatta | Director | September 26, 2016 | ||
| Danilo Cacciamatta |
56
