Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| 8-K - FORM 8-K - RHYTHM PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. | tm213890d4_8k.htm |
Exhibit 99.1

© Rhythm® Pharmaceuticals, Inc. All rights reserved. ® February 2021 Rhythm Pharmaceuticals Targeting MC4R pathway and transforming the care of patients with rare genetic diseases of obesity

® 2 This presentation contains certain statements that are forward - looking within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, and that involve risks and uncertainties, including without limitations statements regarding the potential, safety, efficacy, and regulatory and clinical progress of setmelanotide, anticipated timing for enrollment and release of our clinical trial results, the timing for filing of NDA, MAA or other similar filings, our goal of changing the paradigm for the treatment of rare genetic disorders of obesity, the application of genetic testing and related growth potential, expectations surrounding the potential market opportunity for our product candidates, and strategy, prospects and plans, including regarding the commercialization of setmelanotide. Statements using words such as "expect", "anticipate", "believe", "may", "will" and similar terms are also forward - looking statements. Such statements are subject to numerous risks and uncertainties, including but not limited to, our ability to enroll patients in clinical trials, the outcome of clinical trials, the impact of competition, the impact of management departures and transitions, the ability to achieve or obtain necessary regulatory approvals, risks associated with data analysis and reporting, our expenses, the impact of the COVID - 19 pandemic on our business operations, including our preclinical studies, clinical trials and commercialization prospects, and general economic conditions, and other risks as may be detailed from time to time in our Annual Reports on Form 10 - K and Quarterly Reports on Form 10 - Q and other reports we file with the Securities and Exchange Commission. Except as required by law, we undertake no obligations to make any revisions to the forward - looking statements contained in this presentation or to update them to reflect events or circumstances occurring after the date of this presentation, whether as a result of new information, future developments or otherwise. Forward Looking Statements

® 3 Living with Early - onset, Severe Obesity and Hyperphagia Adalissa and Solomon with their siblings (unaffected) “They are constantly, all day long saying they are hungry and asking what’s for the next meal and what are we eating the next day. We keep a menu planned and if we deviate from that menu it’s a disaster.” “We have had to put locks on our cupboards and fridge and freezer to protect them from themselves!” – Olivia, Mother of Adalissa and Solomon, siblings diagnosed with BBS Katy, at 23 years old, 450 pounds “It causes extreme unrelenting hunger and excessive eating. As a child…the fridge and food was controlled massively…but nobody could understand that I was desperately hungry and just wanted to stop that feeling.” - Katy, diagnosed with POMC heterozygous deficiency obesity Hallmark Symptoms of Rare Genetic Diseases of Obesity

® 4 Change the Paradigm for the Treatment of Rare Genetic Diseases of Obesity Our mission:

® 5 Classic Rare Disease Challenges Apply to Genetic Obesities Lost in the system No treatment Little awareness Little knowledge No tools or testing Worst case: An irritation. It’s your fault. Eat less, exercise more.

® 6 MC4R Pathway Biology is Clear and Strong: Regulates Hunger, Caloric Intake, and Energy Expenditure, and, Consequently, Body Weight DOWNSTREAM ACTIVATION MC4R - EXPRESSING NEURON Appetite Weight Energy expenditure POMC NEURON UPSTREAM LEPR Leptin Satiety Signals (e.g. Leptin) MSH MC4R POMC SRC1 SH2B1 PCSK1 ALMS1 BBSx RAI1 Setmelanotide Setmelanotide can redress MC4R pathway impairment contributing to early - onset, severe obesity

® 7 Disease Phase 2 Phase 3 Regulatory Submission Approved Obesity due to POMC, PCSK1 or LEPR deficiency* Bardet - Biedl and Alström syndromes Weekly formulation Phase 3 MC4R Pathway Study: HETs, SRC1, SH2B1 Phase 2 Basket Study: HETs, SRC1, SH2B1, MC4R - rescuable, Smith - Magenis syndrome Phase 2 Exploratory Pathway Basket Study: Variants in 31 genes Pediatric Study Hypothalamic obesity U.S. EU Setmelanotide MC4R Pathway Studies Initiate 2H21 Initiate 2H21 Initiate 2H21 New data 1H21 Initiate 2H21 Initiate 1H21 Rhythm Pipeline Focused on MC4R Pathway Diseases * Indicated for chronic weight management in adult and pediatric patients 6 years of age and older with obesity due to POMC , P CSK1 or LEPR deficiency confirmed by genetic testing demonstrating variants in POMC, PCSK1, or LEPR genes that are interpreted as pathogenic, likely pathogenic , o r of uncertain significance.

® 8 Rare Genetic Diseases of Obesity Associated with the MC4R Pathway Represent a Significant Opportunity LEPR, leptin receptor, POMC, pro - opiomelanocortin; MC4R, melanocortin - 4 receptor. * Estimated prevalence of U.S. patients based on company estimates; ** Estimated prevalence of U.S. patients with addressabl e v ariants of the MC4R; *** RYTM believes a portion of these patients may be setmelanotide responsive; Estimated prevalence of craniopharyngioma in the United States is 3400 - 6800 (Garnet et al, 2007), and approximately 50 - 55% these patients develop severe obesity post tumor resection and experience rapid weight gain in first 6 - 12 months. (Zacharia, 2012) Bardet - Biedl syndrome Alström syndrome MC4R - rescuable deficiency obesity Hypothalamic obesity >20,000 * >23,000 * ~500 - 1,000 * ~1,500 - 2,500 * ~10,000 ** 1,700 - 3,400 *** ~1,500 - 2,500 * Obesity due to POMC, PCSK1 or LEPR deficiency ~600 – 2,500 * HETs (POMC, PCSK1 or LEPR) heterozygous deficiency obesity HETs SRC1 or SH2B1 deficiency obesity 100,000 – 200,000 * MC4R Pathway (31 additional genes) TBD People in the U.S. have early - onset severe obesity ~5M *

® 9 Total Potential Addressable Market for Five Genes in U.S. Exceeds 100K * 1.7% of the US population (328M; 2019 US census) presents with severe early onset obesity (Hales et al 2018 Ɨ ); ~95% of individuals with severe early onset obesity remain obese into adulthood (Ward et al 2017) People in the U.S. have early - onset severe obesity ~5M * Pathogenic, likely pathogenic and VOUS yield for HETs, SRC1 and SH2B1; and N221D 10 - 15% 100K – 200K Estimated patients who may benefit based on current estimated responder rates Planned Phase 3 MC4R Pathway Trial

® 10 Now Approved in the United States; Initial Commercialization in 1Q21 Obesity due to LEPR deficiency Obesity due to POMC, PCSK1 deficiency ~100 - 500 * ~500 - 2,000 * Approved by the U.S. FDA for chronic weight management in people with obesity due to proopiomelanocortin (POMC), proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 1 (PCSK1) or leptin receptor (LEPR) deficiency confirmed by genetic testing demonstrating variants in POMC , PCSK1 , or LEPR genes that are interpreted as: • Pathogenic ; • L ikely pathogenic ; • Variant of uncertain significance (VOUS) * Estimated prevalence of U.S. patients based on company estimates.

® 11 Bardet - Biedl Syndrome Phase 3 Update

® 12 Working to Change the Paradigm for the Treatment of Rare Genetic Diseases of Obesity Drive COMMUNITY BUILDING and GENETIC SEQUENCING Established proof - of - concept in new indications in Phase 2 Basket Study Growth Potential Positive topline results in Bardet - Biedl syndrome Meaningful Opportunity Validation FDA approved for chronic weight management for obesity due to POMC, PCSK1 or LEPR deficiency
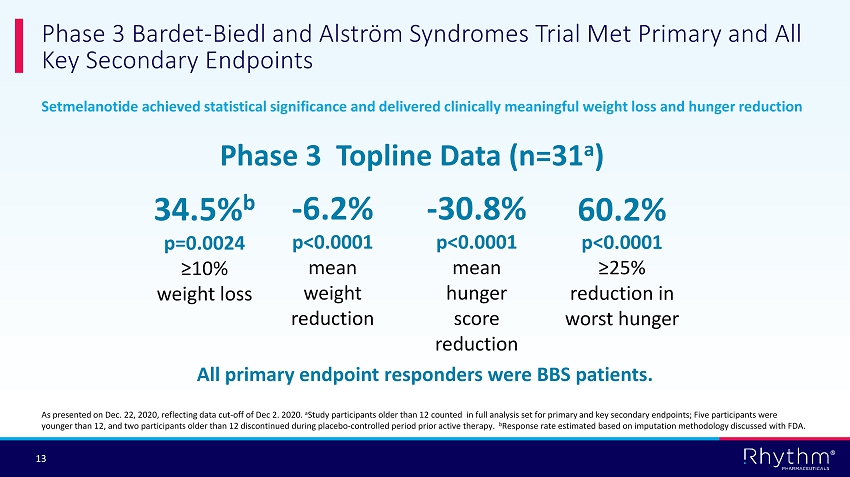
® 13 Setmelanotide achieved statistical significance and delivered clinically meaningful weight loss and hunger reduction Phase 3 Bardet - Biedl and Alström Syndromes Trial Met Primary and All Key Secondary Endpoints Phase 3 Topline Data (n=31 a ) 34.5% b p=0.0024 ≥10% weight loss - 6.2% p<0.0001 mean weight reduction - 30.8% p<0.0001 mean hunger score reduction 60.2% p<0.0001 ≥25% reduction in worst hunger All primary endpoint responders were BBS patients. As presented on Dec. 22, 2020, reflecting data cut - off of Dec 2. 2020. a Study participants older than 12 counted in full analysis set for primary and key secondary endpoints; Five participants were younger than 12, and t wo participants older than 12 discontinued during placebo - controlled period prior active therapy. b Response rate estimated based on imputation methodology discussed with FDA.
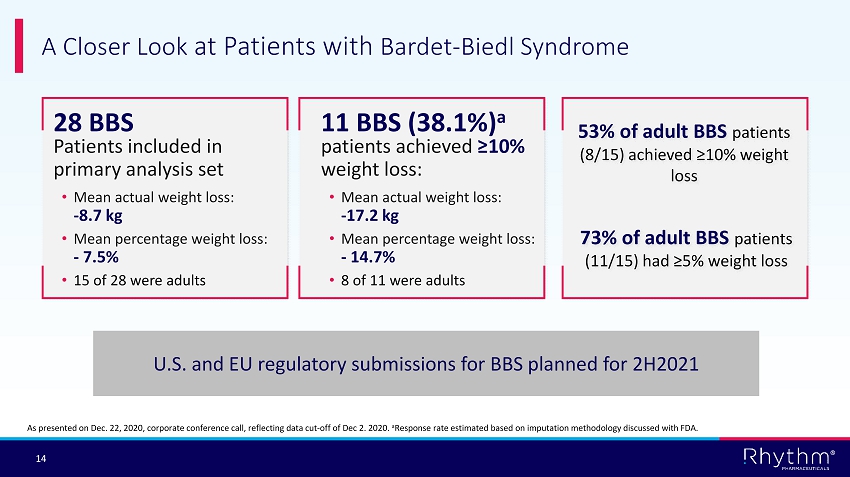
® 14 A Closer Look at Patients with Bardet - Biedl Syndrome patients achieved ≥10% weight loss: • Mean actual weight loss: - 17.2 kg • Mean percentage weight loss: - 14.7% • 8 of 11 were adults 11 BBS (38.1%) a 28 BBS Patients included in primary analysis set • Mean actual weight loss: - 8.7 kg • Mean percentage weight loss: - 7.5% • 15 of 28 were adults As presented on Dec. 22, 2020, corporate conference call, reflecting data cut - off of Dec 2. 2020. a Response rate estimated based on imputation methodology discussed with FDA. 73% of adult BBS patients (11/15) had ≥5% weight loss 53% of adult BBS patients (8/15) achieved ≥10% weight loss U.S. and EU regulatory submissions for BBS planned for 2H2021

® 15 BMI - Z score, or BMI standard deviation score, represents the number of standard deviations from median BMI by child age and sex. Setmelanotide achieved statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvements in BMI - Z scores in pediatric patients with obesity due to POMC, PCSK1 or LEPR deficiency. Setmelanotide achieved statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvements in BMI - Z scores in pediatric patients with BBS (predefined exploratory endpoint). Setmelanotide and BMI - Z Scores for Pediatric BBS Patients in Phase 3 Trial

® 16 Chart adapted from Kleinendorst et al 2017 Data on file. Image used with permission. At 2 years of age, the patient’s BMI was 38.7 kg/m 2 BMI - Z Score or BMI standard deviation score: Number of Standard Deviations from Median BMI by Child Age and Sex

® 17 Setmelanotide was Associated with Reductions in BMI - Z Score in Participants with BBS (<18 Years Old) Over ~1 Year at Therapeutic Dose BMI, body mass index. Error bars are the standard error of the mean, which was calculated by dividing the standard deviation by the square root of n. 3.74 2.98 0 1 2 3 4 5 Baseline ~1 year at therapeutic dose Average BMI Z - score Mean change from baseline: - 0.76 Mean % change from baseline: - 24.48%; (P=0.0006) Participants aged <18 years (n=16)

® 18 Phase 2 Basket Study Results

® 19 2021 Highlights : Delivered on Proof of Concept in Basket Indications with Significant Market Opportunity Rhythm’s largest data readout from five genetic cohorts with 65 patients Proof of concept achieved in five MC4R pathway genes U.S. target patient population across these five genes expanded to 100K - 200K Largest known genetic obesity database of approximately 37,500 individuals Support of our approach for gene selection and variant classification Two new trials planned for MC4R pathway diseases in a total of 36 genes
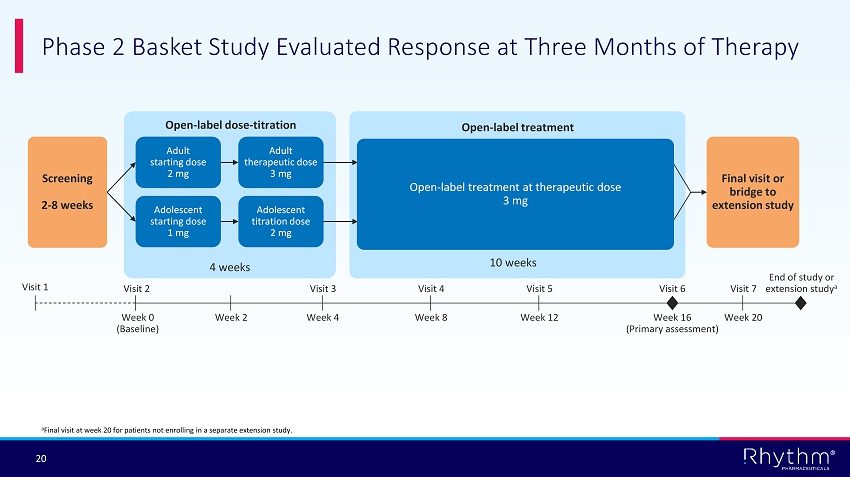
® 20 Phase 2 Basket Study Evaluated Response at Three Months of Therapy Adult starting dose 2 mg Adolescent starting dose 1 mg Adult therapeutic dose 3 mg Adolescent titration dose 2 mg Open - label dose - titration 4 weeks Final visit or bridge to extension study Screening 2 - 8 weeks 10 weeks Open - label treatment at therapeutic dose 3 mg Open - label treatment Week 2 End of study or extension study a Visit 6 Week 16 (Primary assessment) a Final visit at week 20 for patients not enrolling in a separate extension study. Week 0 (Baseline) Visit 2 Visit 1 Week 4 Visit 3 Week 8 Visit 4 Week 12 Visit 5 Week 20 Visit 7

® 21 HETs Patient Demographics – Full Analysis Set Baseline Characteristics HETs patients (N=35) Mean age (years) at enrollment (SD) Range 39 (18) 15, 68 Female Male 68.6% 31.4% Mean weight lbs (SD) Range lbs 315.9 (65.7) 210, 459 Mean weight kg (SD) Range kg 143.3 (29.8) 95, 208 BMI Mean kg/m 2 (SD) Range 50, (9) 35, 79 Failed bariatric surgery 5 Hets , POMC/PCSK1/LEPR heterozygous deficiency obesity; SD, standard deviation.
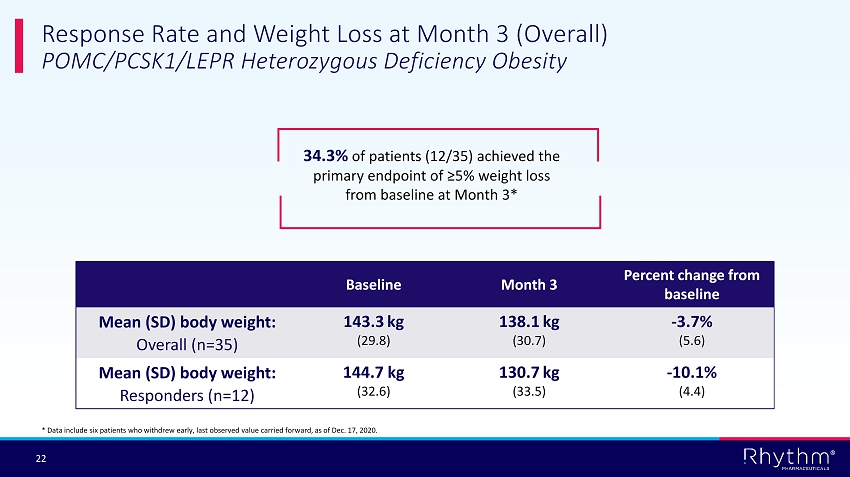
® 22 Response Rate and Weight Loss at Month 3 (Overall) POMC/PCSK1/LEPR Heterozygous Deficiency Obesity 34.3% of patients (12/35) achieved the primary endpoint of ≥5% weight loss from baseline at Month 3* Baseline Month 3 Percent change from baseline Mean (SD) body weight: Overall (n=35) 143.3 kg (29.8) 138.1 kg (30.7) - 3.7% (5.6) Mean (SD) body weight: Responders (n=12) 144.7 kg (32.6) 130.7 kg (33.5) - 10.1% (4.4) * Data include six patients who withdrew early, last observed value carried forward, as of Dec. 17, 2020.

® 23 -16 -12 -8 -4 0 4 Responders (n=12) Non-responders (n=23) Response Rate and Weight Loss at Month 3 (Responder/ Nonresponder ) POMC/PCSK1/LEPR Heterozygous Deficiency Obesity Mean Weight change, % Responders (n=12) Nonresponders (n=23) Data as of Dec. 17, 2020; Error bars represent the 90% confidence interval. - 10.1% (90% CI, - 12.4 to - 7.9) - 0.4% (90% CI, - 1.2 to 0.5)

® 24 Percent Weight Loss Over Time POMC/PCSK1/LEPR Heterozygous Deficiency Obesity -16 -12 -8 -4 0 4 2 3 4 5 6 Mean weight change, % Visit Data as of Dec. 17, 2020; Error bars represent the 90% confidence interval. Responders Nonresponders
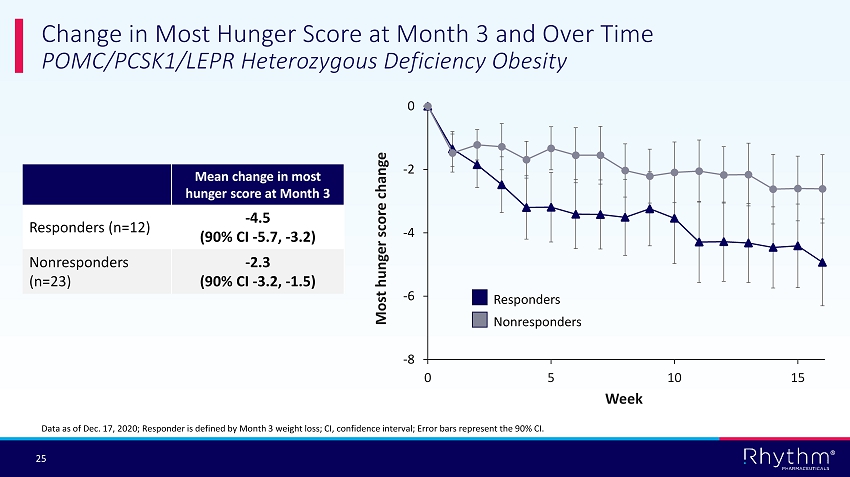
® 25 Change in Most Hunger Score at Month 3 and Over Time POMC/PCSK1/LEPR Heterozygous Deficiency Obesity Data as of Dec. 17, 2020; Responder is defined by Month 3 weight loss; CI, confidence interval; Error bars represent the 90% CI. Mean change in most hunger score at Month 3 Responders (n=12) - 4.5 (90% CI - 5.7, - 3.2) Nonresponders (n=23) - 2.3 (90% CI - 3.2, - 1.5) -8 -6 -4 -2 0 0 5 10 15 Responders Nonresponders Most hunger score change Week
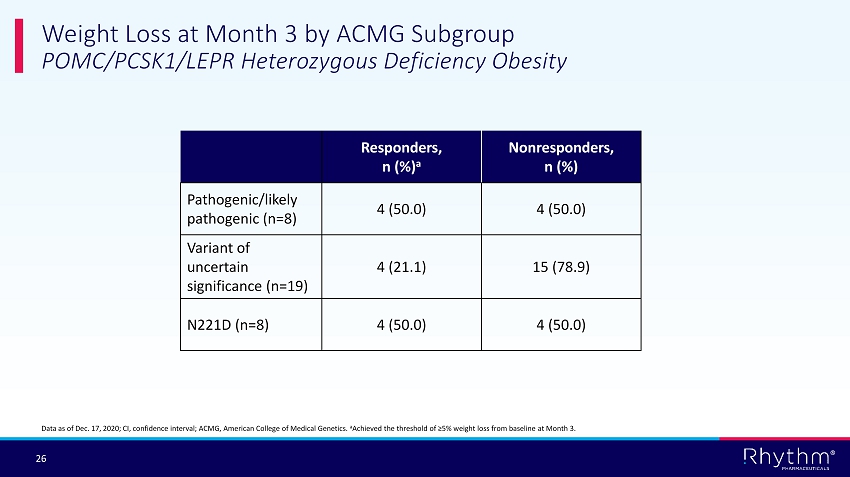
® 26 Weight Loss at Month 3 by ACMG Subgroup POMC/PCSK1/LEPR Heterozygous Deficiency Obesity Responders, n (%) a Nonresponders , n (%) Pathogenic/likely pathogenic (n=8) 4 (50.0) 4 (50.0) Variant of uncertain significance (n=19) 4 (21.1) 15 (78.9) N221D (n=8) 4 (50.0) 4 (50.0) Data as of Dec. 17, 2020; CI, confidence interval; ACMG, American College of Medical Genetics. a Achieved the threshold of ≥5% weight loss from baseline at Month 3.

® 27 SRC1 and SH2B1 Patient Demographics – Completers Set Baseline Characteristics SRC1 (N=13) SH2B1 (N=17) Mean age (years) at enrollment (SD) Range 32 (18) 12, 66 30 (15) 12, 60 Female Male 77% 23% 58% 41% Mean weight lbs (SD) Range lbs 258 (44) 168, 313 272 (60) 161, 357 Mean weight kg (SD) Range kg 117 (20) 76, 142 123 (27) 73, 162 BMI Mean kg/m 2 (SD) Range 44 (6) 34, 55 44 (9) 32, 68 Failed bariatric surgery 4 5 Data cutoff date of Dec. 17, 2020. Completers Set excludes 15 patients who withdrew early due to COVID - related issues, AEs, or lost to follow - up; and 12 ongoing patients who had not reached 12 weeks of therapy. A majority of patients who withdrew early experienced weight loss.

® 28 Response Rate and Weight Loss at Month 3 (Overall) SRC1 Deficiency Obesity – Completers Set 30.8% of patients (4/13) achieved the primary endpoint of ≥5% weight loss from baseline at Month 3 Baseline Month 3 Percent change from baseline Mean (SD) body weight: Overall (n= 13) 117.1 kg (20.3) 112.6 kg (18.5) - 3.7% (4.0) Mean (SD) body weight: Responders (n=4) 116.6 kg (29.1) 106.4 kg (24.6) - 8.4% (2.5) Interim data as of Dec. 17, 2020.

® 29 Response Rate and Weight Loss at Month 3 (Responder/ Nonresponder ) SRC1 Deficiency Obesity – Completers Set Data as of Dec. 17, 2020; Error bars represent the 90% confidence interval. -14 -12 -10 -8 -6 -4 -2 0 Responders (n=4) Non-responders (n=9) Responders (n=4) Nonresponders (n=9) - 8.4 (90% CI, - 11.4 to - 5.5) - 1.5 (90% CI, - 2.9 to - 0.2) Mean weight change, %

® 30 Response Rate and Weight Loss at Month 3 (Overall) SH2B1 Deficiency Obesity – Completers Set 52.9% of patients (9/17) achieved the primary endpoint of ≥5% weight loss from baseline at Month 3 Baseline Month 3 Percent change from baseline Mean (SD) body weight: Overall (n=17) 123.4 kg (27.4) 118.6 kg (27.3) - 3.9% (4.2) Mean (SD) body weight: Responders (n=9) 123.6 kg (28.1) 114.8 kg (26.4) - 7.1% ( 2.1) Interim data as of Dec. 17, 2020.

® 31 Response Rate and Weight Loss at Month 3 (Responder/ Nonresponder ) SH2B1 Deficiency Obesity – C ompleters Set Data as of Dec. 17, 2020; Error bars represent the 90% confidence interval. -10 -8 -6 -4 -2 0 2 4 Responders (n=9) Non-responders (n=8) Responders (n=9) Nonresponders (n=8) - 7.1 (90% CI, - 8.4 to - 5.8) - 0.3 (90% CI, - 2.2 to 1.6) Mean weight change, %

® 32 Setmelanotide has been evaluated in 590 patients with obesity, with some individual patient treatment duration now exceeding five years Setmelanotide has been generally well - tolerated Most AEs are mild: • Mild injection site reactions • Hyperpigmentation and skin lesions, mediated by the closely related MC1 receptor • Nausea/vomiting: mild and early in treatment Discontinuations are rare; no increase in CV parameters • In POMC and LEPR pivotal trials, setmelanotide was not associated with significant changes to blood pressure or heart rate Setmelanotide Generally Well - tolerated Across Development Program Patient experience with setmelanotide* * Estimates as of November 2020, inclusive of patients likely randomized to treatment in certain double - blinded clinical studies; does not include subjects in studies evaluating once - weekly formulation. Duration on therapy # of patients < 1 year 515 > 1 year 75 > 2 years 29 > 3 years 10 > 4 years 2 > 5 years 1

® 33 Safety: Hyperpigmentation, Nausea and Vomiting Events Occurred Early in Treatment Number of Events 342 100 35 27 12 8 2 3 4 3 7 2 0 40 80 120 160 200 240 280 320 360 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Hyperpigmentation 175 22 11 13 1 3 6 1 0 0 3 2 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Nausea and vomiting 58 20 8 11 2 0 3 0 0 2 0 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Vomiting Months Safety data as of Nov. 10, 2020; Months defined as 30 - day periods.
® 34 Setmelanotide Achieves Proof of Concept in HETs, SRC1 and SH2B1 Overall: Approximately 35% of patients responded with > 5% weight loss at 12 weeks Strong separation between responders and non - responders validates three - step approach Responders mean weight loss of 10% for HETs, 8% for SRC1 and 7% SH2B1 Enhanced responder rate seen within cohorts stratified by ACMG variant classification N221D represents potential expansion opportunity Setmelanotide is generally well tolerated in these populations

® 35 Future Clinical Plans

® 36 STEP 1 STEP 2 STEP 3 Targeted but Simple Approach to Treating Obesity Phenotype Genotype Setmelanotide response • Early - onset, severe obesity • Adults: BMI>40 • Children: <18 yrs weight >97th percentile • Genetic variants in the MC4R pathway • ACMG variant classifications • 5% weight loss in adults • BMI - Z scores in children

® 37 Phase 3 Basket Study Designed to Evaluate Response Compared to Placebo After 24 Weeks of Treatment Setmelanotide QD Dose titration to 3 mg a Placebo QD Randomized, double - blind, placebo - controlled period (24 weeks) Final visit or bridge to extension study Randomization 1:1 Week 2 Visit 8 Week 24 (Primary assessment) a For patients ≥12 years old, initial dose of 2 mg for 14 days, followed by 3 mg for the remainder of the study. For patients 6 to <12 years old, initial dose of 1 mg for 7 days, followed by 2 mg for 7 days, followed by 3 mg for the remainder of the study. b A patient may be eligible for open - label setmelanotide treatment if experiencing body weight increase ≥5% from baseline, or by i nvestigator decision based on best medical interest of the patient. c Virtual study visit. d Final visit at Week 28 for patients not enrolling in a separate extension study. QD, once daily. Week 0 (Baseline) Visit 1 Visit 0 Week 28 End of study or extension study d Visit 9 Screening 2 – 8 weeks Week 4 Week 6 Week 8 Week 10 Week 12 Week 14 Week 16 Week 18 Week 20 Week 22 Visit 2 c Visit 3 c Visit 5 c Visit 6 c Visit 4 Visit 7 Potential eligibility for open - label rescue treatment b
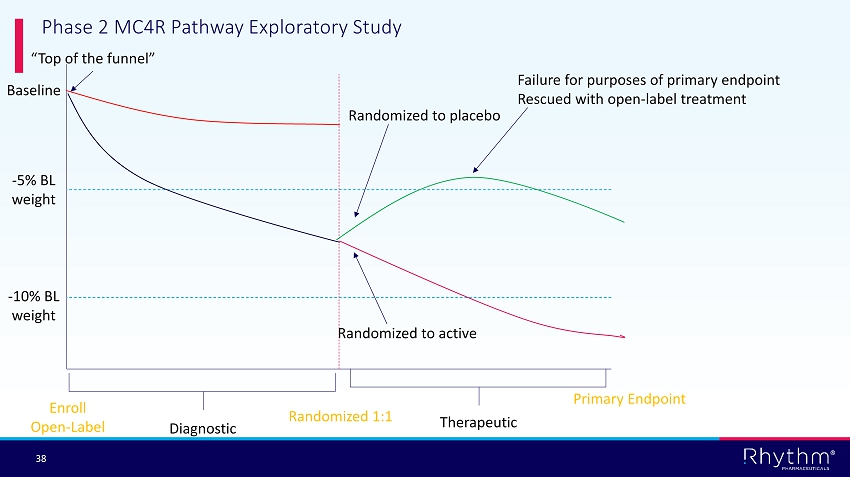
® 38 Baseline - 5% BL weight - 10% BL weight Randomized to active Failure for purposes of primary endpoint Rescued with open - label treatment Randomized to placebo Enroll Open - Label Primary Endpoint Diagnostic Therapeutic Randomized 1:1 “Top of the funnel” Phase 2 MC4R Pathway Exploratory Study

® 39 Transformational Progress Expected in 2021 1H 2021 ض Proof - of - concept data in HET patients, SRC1 and SH2B1 deficiency obesities ض Update on genetic sequencing and epidemiology data IMCIVREE commercially available in U.S. for POMC, PCSK1 and LEPR deficiency obesities Initiate Phase 2 trial in hypothalamic obesity Initial data from Phase 2 Basket study in MC4R - rescuable patients Full data analyses from pivotal Phase 3 trial in BBS and Alstr ö m syndrome 2H 2021 EU decision on POMC, PCSK1 and LEPR MAA U.S. and EU regulatory submissions for BBS Initiate trial in pediatric patients aged 2 - 6 years old Initiate pivotal MC4R Pathway trial in HET patients, SRC1 and SH2B1 deficiency obesities Initiate exploratory MC4R Pathway Basket Study in 31 additional genes Initiate registrational trial for weekly formulation

® 40 David Meeker, MD Chair, President and Chief Executive Officer Hunter Smith Chief Financial Officer Yann Mazabraud Executive Vice President, Head of International Jennifer Chien Executive Vice President, Head of North America Murray Stewart, MD Chief Medical Officer Simon Kelner Chief Human Resources Officer Financial leadership for Otezla ® ; 20 - plus years in finance, M&A, capital markets 20 years leading global commercial strategy in rare diseases More than 20 years leading global commercial strategy in rare diseases 20 - plus marketed products and NDAs 10 - plus INDs 25 - plus years global HR leadership experience in biopharma Rhythm Leadership – Strong Team with Broad Biopharma Experience 25 - plus years; focus on rare genetic disease treatments, including Aldurazyme ®, Fabrazyme® and Myozyme ®

®
