Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-99.1 - EX-99.1 - BeiGene, Ltd. | a18-3293_1ex99d1.htm |
| EX-99.2 - EX-99.2 - BeiGene, Ltd. | a18-3293_1ex99d2.htm |
| 8-K - 8-K - BeiGene, Ltd. | a18-3293_18k.htm |
2 Disclosures Certain statements contained in this presentation and in the accompanying oral presentation, other than statements of fact that are independently verifiable at the date hereof, may constitute forward-looking statements. Examples of such forward-looking statements include those regarding investigational drug candidates and clinical trials and the status and related results thereto, as well as those regarding continuing and further development and commercialization efforts and transactions with third parties. Such statements, based as they are on the current analysis and expectations of management, inherently involve numerous risks and uncertainties, known and unknown, many of which are beyond BeiGene’s control. Such risks include but are not limited to: the impact of general economic conditions, general conditions in the pharmaceutical industries, changes in the global and regional regulatory environments in the jurisdictions in which BeiGene does business, market volatility, fluctuations in costs and changes to the competitive environment. Consequently, actual future results may differ materially from the anticipated results expressed in the forward-looking statements. In the case of forward-looking statements regarding investigational drug candidates and continuing further development efforts, specific risks which could cause actual results to differ materially from BeiGene’s current analysis and expectations include: failure to demonstrate the safety, tolerability and efficacy of our drug candidates, final and quality controlled verification of data and the related analyses, the expense and uncertainty of obtaining regulatory approval, including from the FDA, CFDA and EMA, the possibility of having to conduct additional clinical trials and BeiGene’s reliance on third parties to conduct drug development, manufacturing and other services. Further, even if regulatory approval is obtained, pharmaceutical products are generally subject to stringent on-going governmental regulation, challenges in gaining market acceptance and competition. These statements are also subject to a number of material risks and uncertainties that are described in BeiGene’s filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). The reader should not place undue reliance on any forward-looking statements included in this presentation or in the accompanying oral presentation. These statements speak only as of the date made, and BeiGene is under no obligation and disavows any obligation to update or revise such statements as a result of any event, circumstances or otherwise, unless required by applicable legislation or regulation. Clinical data in this presentation relating to BeiGene’s investigational drug candidates is from early phase, single-arm trials. When such data are presented in relation to other investigational or marketed drug products, the presentation and discussion are not based on head-to-head trials between BeiGene’s investigational drug candidates and other products. BeiGene is still conducting clinical trials and, as additional patients are enrolled and evaluated, data on BeiGene’s investigational drug candidates may change. This presentation and the accompanying oral presentation contains data and information obtained from third-party studies and internal company analysis of such data and information. BeiGene has not independently verified the data and information obtained from these sources. Forward-looking information obtained from these sources is subject to the same qualifications noted above.

BeiGene Company Overview Founded in 2010 in Beijing as an R&D organization focused on developing best-in-class oncology therapeutics Three proprietary programs: zanubrutinib (BTK inhibitor), tislelizumab (PD-1 antibody) and pamiparib (PARP inhibitor) have initially come from these efforts In the past few years, BeiGene has evolved into fully-integrated biopharmaceutical company Global team with over 850 employees and a deep presence in both US and China Full capabilities from R&D to manufacturing, with a commercial presence in China Poised to realize two significant, program-based opportunities Globally commercialize zanubrutinib, a potentially best-in-class BTK inhibitor Data to date supportive of BIC activity, supporting broad registrational program, including head-to-head comparisons with ibrutinib ongoing or planned in WM and CLL Global development team with deep expertise in lymphoid malignancies Develop and successfully commercialize tislelizumab, a PD-1 inhibitor, in a rapidly and favorably evolving China market Experienced and dedicated China-based development team Established commercial team (via Celgene deal) Only China-developed PD-1 undertaking broad global development and likely to have global label Large-scale biologics manufacturing capabilities under construction Significant regulatory reforms in China provide access to over twice the cancer patients accessible for global development in EU and US Few multinational pharmaceutical companies have the ability to operate effectively in China We believe BeiGene is well-positioned to take advantage of the opportunity Celgene collaboration on tislelizumab leverages this China opportunity and BeiGene’s strong China presence by integrating global and China development Nine global Phase 3 studies planned (including US and China), with additional studies ongoing Potential NDA filing in China in 2018 Collaboration provides commercial infrastructure and marketed product portfolio in China, positioning BeiGene well for planned launches of internally developed product candidates and potential future commercialization of additional in-licensed compounds 3

Over 40 clinical trials ongoing or planned for initiation with over 2,000 patients dosed (including 650+ in China) Global clinical team (300+): US (150+), China (140+), AU (10+) Strong relationships with leading KOLs in China and globally Single clinical trials designed for both global and China registration Broad Capabilities in China and Globally 4 Proprietary cancer biology platform World-renowned scientific advisory board Working relationships with key Chinese cancer centers Experienced leadership team driving R&D innovation engine 150+ research team Commercial-scale small molecule and pilot-scale biologics manufacturing facility in Suzhou Building 24,000L state of the art commercial-scale biologics manufacturing facility in Guangzhou Bring a potentially best-in-class BTK inhibitor to the global market Develop and successfully commercialize a PD-1 inhibitor in a rapidly and favorably evolving China market Drive continued development and commercialization of novel cancer therapeutics for the global market 850+ person global biotech company poised in the near-term to potentially: Integration of Celgene’s China commercial organization that markets ABRAXANE®, REVLIMID®, and VIDAZA® Growing team to bolster commercial infrastructure Commercial organization supports potential launch of pipeline products in China Research Development Manufacturing Commercial
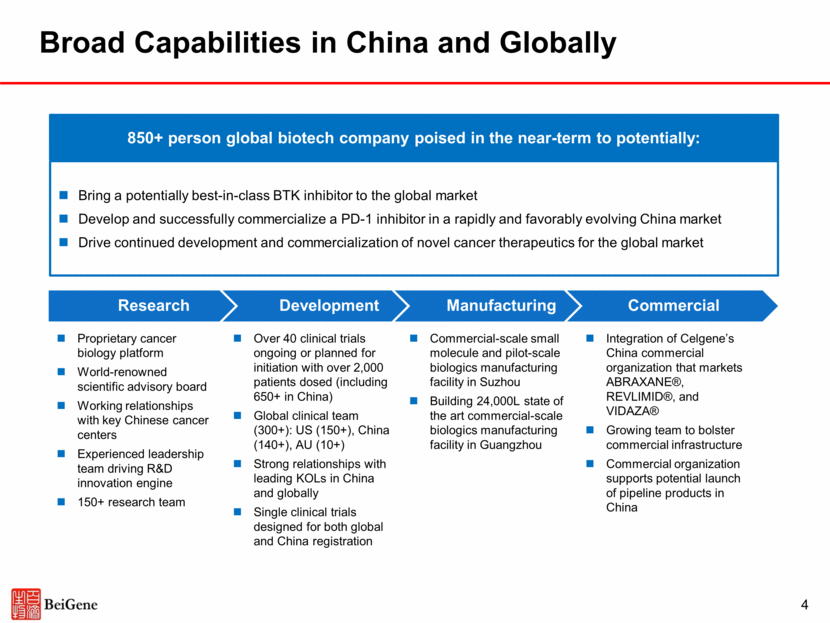
5 Experienced Leadership Team John V. Oyler Founder, CEO, and Chairman Howard Liang, Ph.D. CFO and Chief Strategy Officer Ji Li, Ph.D. EVP, Global Head of Business Development Eric Hedrick, M.D. Chief Advisor Amy Peterson, M.D. Chief Medical Officer, Immuno-oncology Jane Huang, M.D. Chief Medical Officer, Hematology Xiaodong Wang,Ph.D Founder & Chairman SAB Lai Wang, Ph.D. SVP, Head of China Development Founder & CEO Co-CEO Co-CEO Founder & President Management Consultant Managing Director and Head of Biotechnology Equity Research Senior Scientist Chief Medical Officer VP of Oncology Development Vice President of Clinical Development General Manager, Celgene China VP, Bio-medicines Business Unit Lilly China Executive Licensing Director, External R&D Vice President of Business Development and Licensing Joyant Pharmaceuticals Director of Research Founding Director & Architect Professor in Biomedical Sciences Investigator Member Instructor Associate Group Medical Director Group Medical Director June Yan SVP & GM of Commercial Operations, China Vice President and Head of Clinical Development Group Medical Director, Product Development-oncology Adjunct Clinical Faculty Wendy Yan SVP, Global Head Of Regulatory Director, Head of Regulatory Affairs, Global Regulatory Strategist Director, Head of Regulatory Affairs Senior Regulatory Affairs Manager
CFDA Reforms Expected to Make China Integral to Global Oncology Development and Commercialization Source: CFDA; press research 6 CFDA reforms expand China’s role in global development Reforms expand clinical patient access by removing delays CFDA joined ICH in June 2017 and set international quality standards for China trials China agreed to recognize ex-China data Ability to effectively operate in China can significantly enhance global development With patient access being a key limiting factor in development, adding China (more patients than EU and US combined) significantly accelerates enrollment of global clinical trials Local KOL relationships critical Few companies have capabilities to leverage this opportunity May substantially reduce overall cost China’s commitment to national reimbursement makes China an increasingly critical market for leading oncology assets Fundamental shift, due to reimbursement, from a niche, high-priced market to a volume market Change implies a need for large-scale, truly national distribution with medical expertise We believe BeiGene’s combination of a world-class clinical development team and an experienced commercial team in China is unique and differentiates us Over 300 person team supporting clinical trial design to regulatory approval in China and globally, with strong KOL relationships Over 170 commercial person team (and growing) supporting China sales Emphasis on quality has been focus for BeiGene from founding BeiGene is an early mover in this new paradigm, as it has initiated or plans to initiate in collaboration with Celgene nine dual purpose trials designed for both China and global approvals

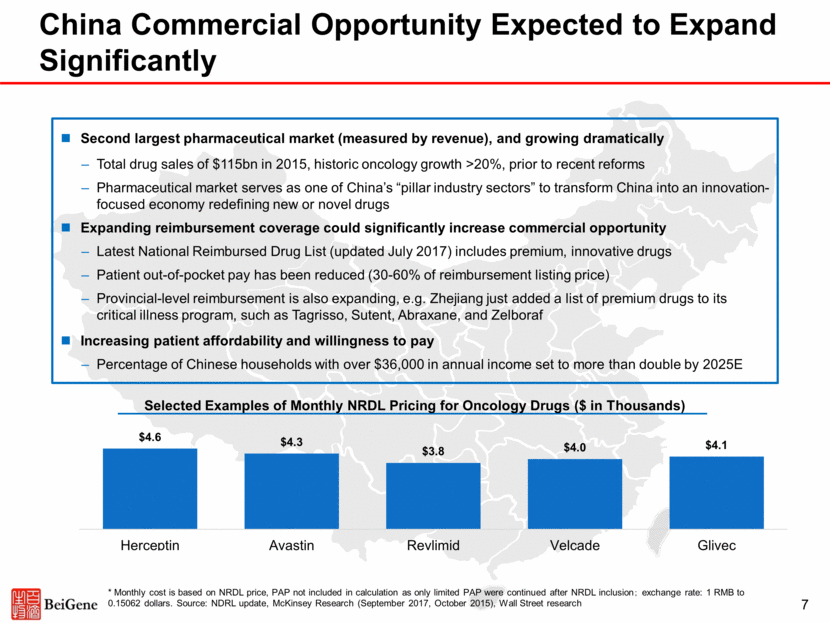
China Commercial Opportunity Expected to Expand Significantly * Monthly cost is based on NRDL price, PAP not included in calculation as only limited PAP were continued after NRDL inclusion; exchange rate: 1 RMB to 0.15062 dollars. Source: NDRL update, McKinsey Research (September 2017, October 2015), Wall Street research 7 Second largest pharmaceutical market (measured by revenue), and growing dramatically Total drug sales of $115bn in 2015, historic oncology growth >20%, prior to recent reforms Pharmaceutical market serves as one of China’s “pillar industry sectors” to transform China into an innovation-focused economy redefining new or novel drugs Expanding reimbursement coverage could significantly increase commercial opportunity Latest National Reimbursed Drug List (updated July 2017) includes premium, innovative drugs Patient out-of-pocket pay has been reduced (30-60% of reimbursement listing price) Provincial-level reimbursement is also expanding, e.g. Zhejiang just added a list of premium drugs to its critical illness program, such as Tagrisso, Sutent, Abraxane, and Zelboraf Increasing patient affordability and willingness to pay Percentage of Chinese households with over $36,000 in annual income set to more than double by 2025E Selected Examples of Monthly NRDL Pricing for Oncology Drugs ($ in Thousands)
Near-Term Opportunities Through Collaborations Celgene Broad development strategy leverages BeiGene’s China capabilities, while addressing the market opportunity for PD-1, both in China and globally Nine pivotal, global clinical trials planned to run in conjunction with Celgene Focus on four highest incidence solid tumors in Asia (NSCLC, Gastric, Esophageal, HCC) Two in-progress: 1L HCC (vs. sorafenib) and 2L NSCLC (vs. docetaxel) Potential for first NDA filing for tislelizumab in China in 2018 BeiGene is leading six of the nine global trials, Celgene is funding some and can opt-in to others Upon an opt-in, BeiGene will be reimbursed for agreed-upon development costs based on an attractive multiple that varies according to stage of development These six trials are first wave of dual purpose (China and Global) designed trials to be initiated Strong economic and strategic synergy that makes this broad of a program highly attractive BeiGene has begun marketing in-licensed products in China already, and is preparing for potential additional China product launches to form a commercial organization with critical mass to succeed Sales in China of in-licensed products in 2017 and expectation of additional sales in 2018 (ABRAXANE®, REVLIMID®, and VIDAZA®) Integration of Celgene’s China commercial team, combined with additional hires to form an expanding commercial organization Mirati In-licensed Mirati’s investigational tyrosine kinase inhibitor sitravatinib for $upfront, up to $123M milestone payments, and revenue royalty in Asia (ex-JP), Australia, and New Zealand10M Complements BeiGene’s portfolio, combination with tislelizumab may have significant opportunity in NSCLC Leverage China capabilities to expand the evaluation of sitravatinib to patients with tumor types beyond NSCLC who are checkpoint inhibitor naïve or experienced 8

Overview of Zanubrutinib (BGB-3111) Potentially Best-in-Class BTK Inhibitor 9 Overview Development Plan Clinical Data Key Expected Catalysts in 2018 Potential pharmacologic advantages of zanubrutinib could allow for complete, sustained, and selective BTK inhibition in all tissue compartments Development hypothesis: may translate into higher quality responses and tolerability advantages over ibrutinib Broad global registrational program in multiple indications, including CLL, WM, and FL (potential for global first in class approval) Accelerated approval trials in China for CLL, MCL, and WM Head-to-head Phase 3 trial versus ibrutinib in WM ongoing, head-to-head Phase 3 trial in relapsed/refractory CLL planned Clinical experience to date supports best-in-class hypothesis Strong suggestion of deeper responses in WM Favorable response rate, depth and durability in CLL Potentially differentiated activity in combination with CD20 antibodies – high overall and complete response rates in FL with obinutuzumab combination Paucity of treatment discontinuations for adverse events or progression Present updated Phase I monotherapy or combination data at a medical conference Present China pivotal trial data Initiate head-to-head Phase 3 trial versus ibrutinib in R/R CLL NDA submission in China Completion of global WM registrational trial enrollment (Q3)
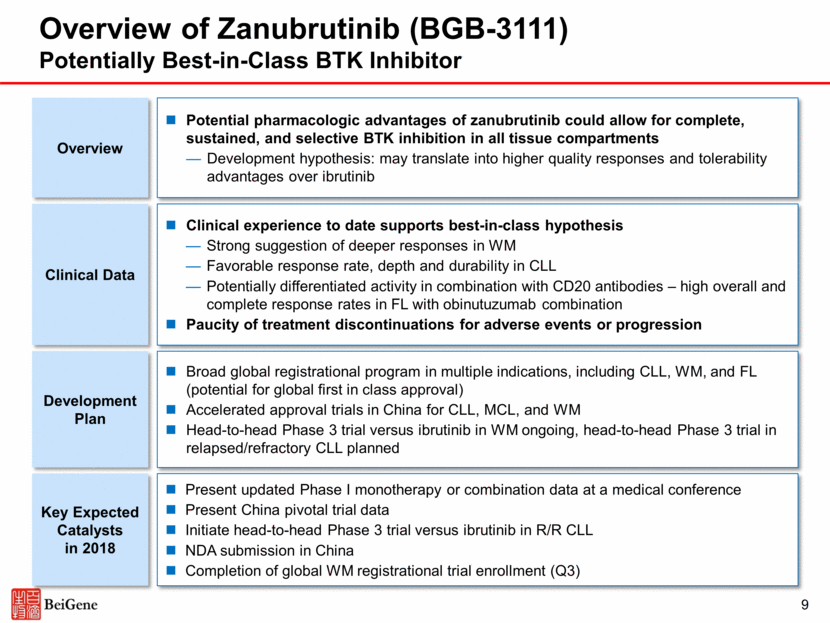
Program (Target) Commercial Rights Preclinical Dose Escalation Dose Expansion* Pivotal** Phase 1a Phase 1b Phase 2 Phase 2 Phase 3 Zanubrutinib (BGB-3111) (BTK) Worldwide Zanubrutinib + Gazyva® (BTK + CD20) Worldwide Relapsed / Refractory (R/R) CLL *Some indications will not require a non-pivotal Phase 2 clinical trial prior to beginning pivotal Phase 2 or 3 clinical trials. **Confirmatory clinical trials post approval are required for accelerated approvals. ¹As of December 1, 2017. Over 800 patients and healthy adults¹ enrolled across zanubrutinib program, including combination trials Zanubrutinib Clinical Program Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia (WM) R/R mantle cell lymphoma Treatment-naïve chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) WM R/R diffuse large B-cell lymphoma 10 R/R follicular lymphoma B-cell malignancies China Global (ex-China) B-cell malignancies
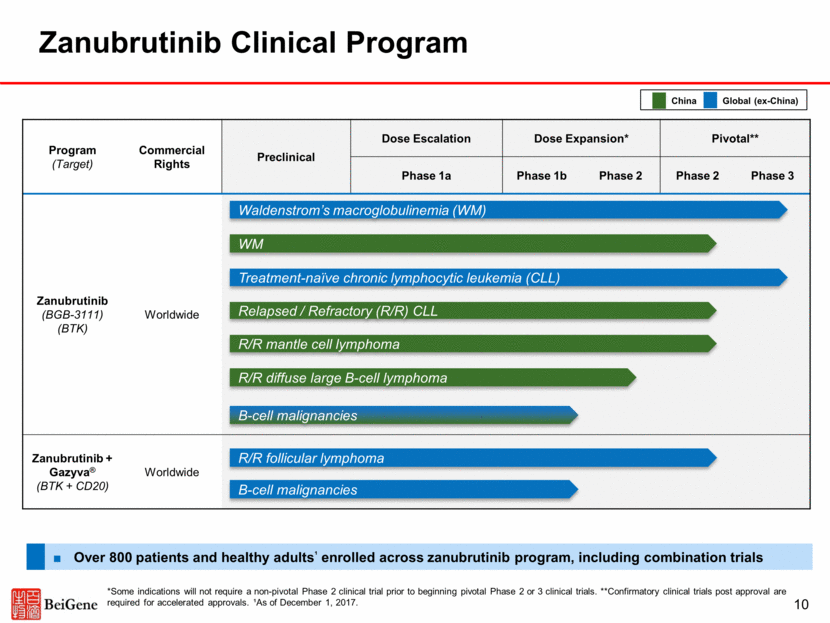
Adapted from Advani et al., JCO, 2013 Zanubrutinib Pharmacokinetics Profile Cmax and AUC of zanubrutinib at 80mg QD appear to be similar to those of ibrutinib at 560mg Free drug exposure of zanubrutinib at 40mg QD appears to be comparable to that of ibrutinib at 560mg Distinct profile compared to acalabrutinib which has a short half-life (1 hour)2 and lower in vitro BTK inhibition IC50¹-4 In vitro BTK inhibition IC50 relative to ibrutinib: 1.1¹ (zanubrutinib) and 3.4²–7.2³ (acalabrutinib) Zanubrutinib Ibrutinib Acalabrutinib Adapted from Byrd et al., NEJM, 2016 ^Cross-trial comparison Source: 1Tam et al., ASH, 2015; 2Byrd et al., NEJM, 2016; 3Lannutti et al., AACR, 2015, 4BeiGene data Phase 3 Dose: 160mg BID Phase 3 Dose: 100mg BID Approved Doses: 420mg QD for CLL/WM 560mg QD for MCL/MZL 11 Data from separate Phase 1/2 trials^ 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 0 6 12 18 24 Time post - dose (hours) 560mg QD 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 0 6 12 18 24 Time post - dose (hours) 100mg QD 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 0 6 12 18 24 Plasma Concentration (ng/mL) Time post - dose (hours) 40mg QD 80mg QD 160mg QD 320mg QD
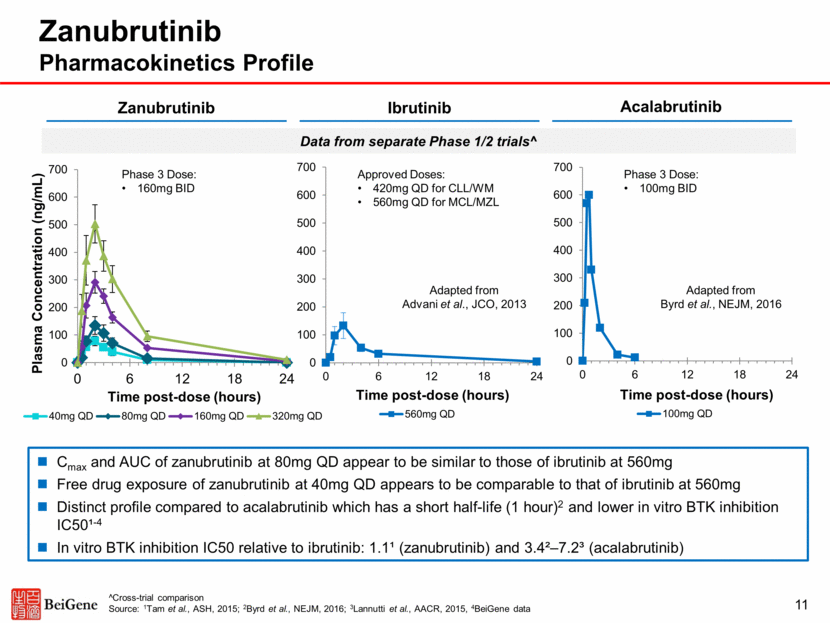
BTK Occupancy Is Not Sustained With Ibrutinib Potentially better bioavailability and higher exposure of zanubrutinib may allow deeper target suppression in disease-relevant tissues *Animal studies Note: PBMC = Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell; Source: BeiGene data and Byrd et al, NEJM, 2013 Ibrutinib Clinical Data in Blood PBMC Spleen Bone Marrow Lymph Node Byrd et al., NEJM, 2013 Approved Ibrutinib Doses: 420mg for CLL and WM; 560mg for MCL Preclinical models* show significant recovery of target occupancy in disease relevant tissues for ibrutinib Clinical data show borderline target inhibition by ibrutinib in the blood at approved dose Sub-Optimal Inhibition 12 100 9 9 37 68 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 Vehicle 4 hrs 8 hrs 12 hrs 24 hrs Unoccupied BTK (%) 100 0 1 19 27 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 Vehicle 4 hrs 8 hrs 12 hrs 24 hrs Unoccupied BTK (%) 100 0 1 16 62 Vehicle 4 hrs 8 hrs 12 hrs 24 hrs 100 2 9 24 66 Vehicle 4 hrs 8 hrs 12 hrs 24 hrs
Zanubrutinib Complete and Sustained BTK Occupancy to Date in Blood and Lymph Nodes 13 PBMC* Lymph Node Complete BTK inhibition in PBMCs at the starting dose (40mg) Paired lymph node biopsies were collected during screening or pre-dose on day 3 Median trough occupancy: 100% (160mg BID) vs 94% (320mg QD), p=0.002 Proportion >90% trough occupancy: 94% (160mg BID) vs 58% (320mg QD), p=0.027 * Data from 20 patients Note: PBMC = Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cell; Source: Tam et al. ASH 2016 (abstracts 642 and 1216)
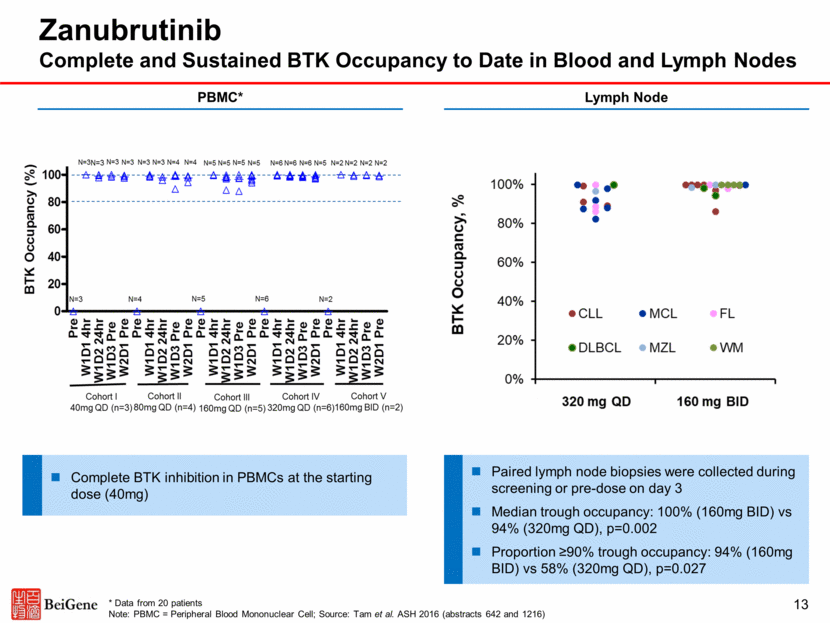
Zanubrutinib Responses in WM Favorable Response to Date in Depth and Durability 14 Source: Trotman et al. 14-ICML (abstract 059) Probability of Progression-free Survival (%) No. of Subjects at Risk Month 42 42 39 31 24 20 18 13 9 4 4 Zanubrutinib PFS in WM 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 0 3 6 9 12 15 18 21 24 27 30 Zanubrutinib WM n 42 Median time-on-treatment 12.3 months Best Response CR VGPR PR MR SD/PD 0 18 (43%) 14 (33%) 6 (14%) 4 (10%) IgM reduction (median, %) 32.7 g/L to 6.1 g/L (81%) Hemoglobin change (median) 104.5 g/L to 142 g/L Zanubrutinib Responses in WM
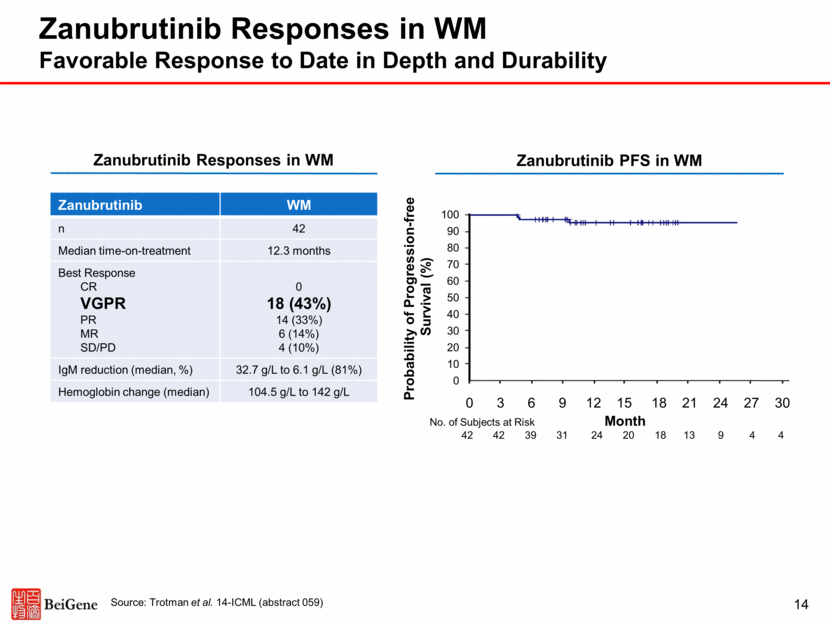
Ibrutinib Responses in WM 15 Source: Treon et al., NEJM, 2015 Ibrutinib WM n 63 Median time-on-treatment 19.1 months Best Response CR VGPR PR MR SD/PD 0 10 (16%) 36 (57%) 11 (17%) 6 (10%) IgM reduction (median, %) 35.2 g/L to 8.8 g/L (75%) Hemoglobin change (median) 105 g/L to 138 g/L Probability of Progression-free Survival (%) Ibrutinib PFS in WM 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 No. of Subjects at Risk Month 63 62 59 55 50 50 45 37 24 17 8 0 3 6 9 12 15 18 21 24 27 30 Ibrutinib Responses in WM
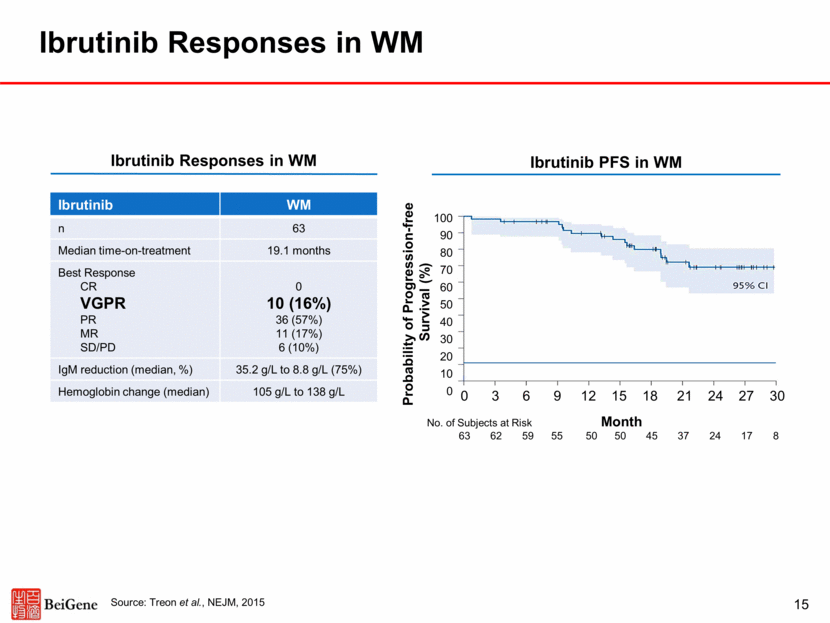
Zanubrutinib Responses in CLL Highly Active With Encouraging Response Durability 16 Source: Seymour et al. 14-ICML 2017 (abstract 237) poster Zanubrutinib TN CLL R/R CLL Total CLL n 16 50 66 Median follow-up (mo) 7.6 14.0 10.5 Best Response ORR CR PR PR-L SD Non-evaluable* 16 (100%) 1 (6%) 13 (81%) 2 (13%) 0 0 46 (92%) 1 (2%) 41 (82%) 4 (8%) 3 (6%) 1 (2%) 62 (94%) 2 (3%) 54 (82%) 6 (9%) 3 (5%) 1 (2%) Probability of Progression-free Survival (%) No. of Subjects at Risk Month 66 66 62 53 45 37 27 25 19 11 9 6 4 * D/C prior to first assessment Zanubrutinib Responses in CLL Zanubrutinib PFS in CLL
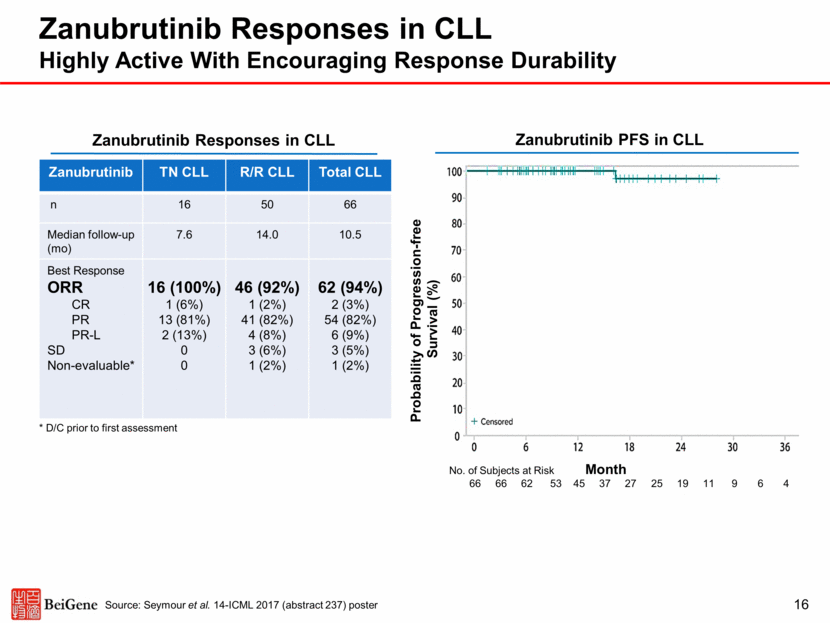
Ibrutinib Responses in CLL 17 Source: For TN, Burger, et al New Engl J Med 2015. For R/R, Byrd, et al New Engl J Med 2013 Ibrutinib Responses in R/R CLL Ibrutinib TN TN CLL n 136 Median FU (mo) 18.4 Best Response ORR CR PR PR-L SD PD 117 (86%) 5 (4%) 107 (79%) 5 (4%) NR NR Ibrutinib R/R CLL n 85 Median FU (mo) 20.9 Best Response ORR CR PR PR-L SD PD 75 (88%) 2 (2%) 58 (68%) 15 (18%) NR NR Ibrutinib PFS in R/R CLL Data from separate trials^ Ibrutinib Responses in TN CLL Ibrutinib PFS in TN CLL
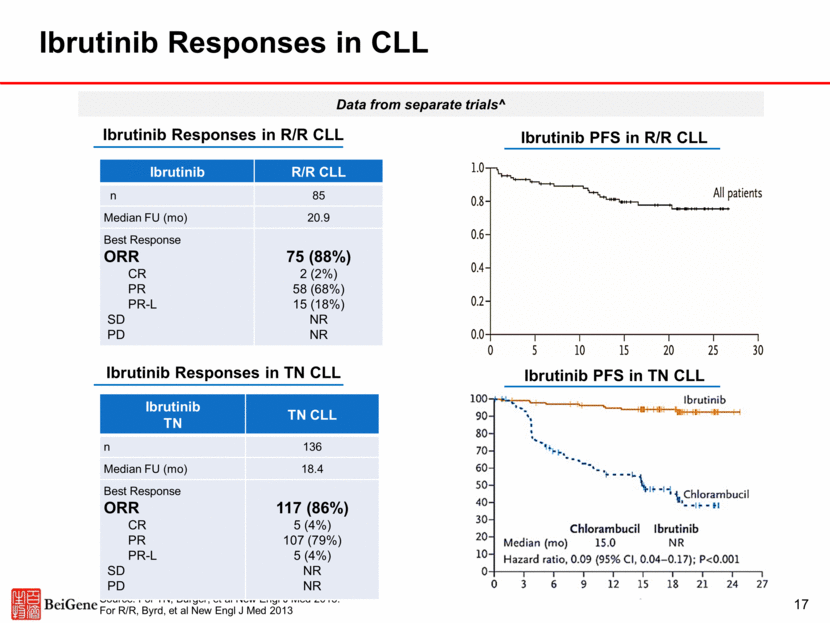
Ibrutinib Discontinuation for Toxicity or Progression in CLL 18 Treatment-Naïve (n=80) Relapsed/ Refractory (n=536) Median Follow up 14.5 months Total Treatment D/C 19 (24%) 231 (43%) Toxicity/ Tolerability 12 (15%) 117 (22%) CLL Progression 3 (4%) 49 (9%) Transformation (RT or HD) 0 (0%) 10 (2%) Death Unrelated to Treatment 1 (1%) 28 (5%) Physician or Patient Decision 2 (2%) 15 (3%) Transplant 0 (0%) 8 (1.5%) Financial Concerns 0 (0%) 1 (0.2%) Secondary Malignancy 1 (1%) 2 (0.5%) Source: Mato ASH 2016 Note: At med f/u 24.5 mos, 22% discontinuation rate with acalabrutinib in R/R CLL; 9% AE-related, 8% PD-related. Byrd ASH 2017.
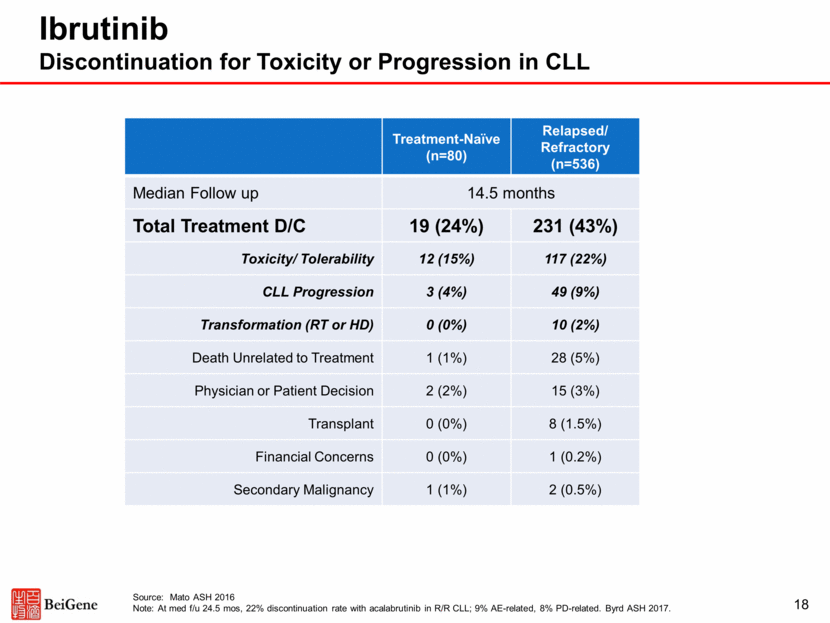
Zanubrutinib Discontinuation for Toxicity or Progression in CLL Is Uncommon 19 Treatment-Naïve (n=18) Relapsed/ Refractory (n=51) Median Follow up 10.3 months Total Treatment D/C 0 (0%) 2 (4%) Toxicity/ Tolerability 0 (0%) 1 (2%) CLL Progression 0 (0%) 0 (0%) Transformation (RT or HD) 0 (0%) 1 (2%) Source: Seymour, ICML 2017
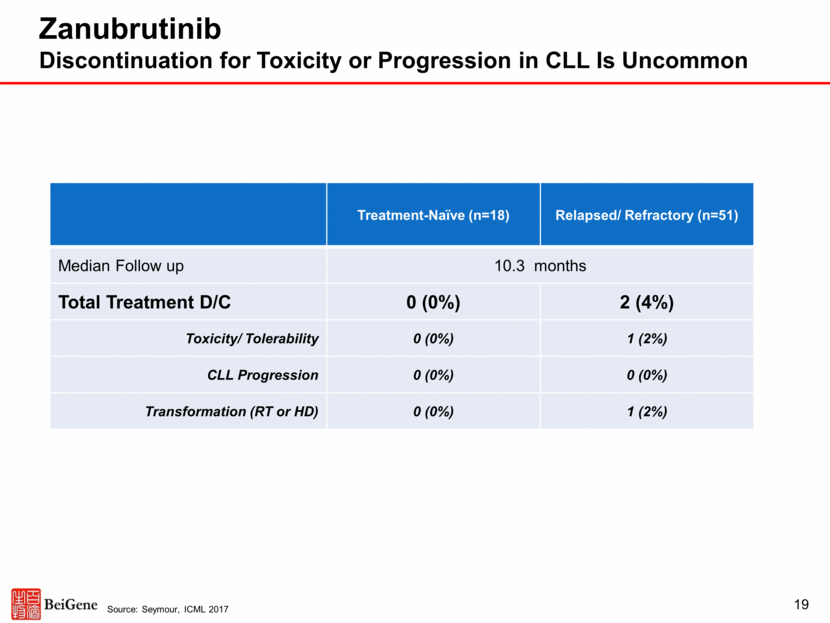
Zanubrutinib Tolerability in Over 600 Patients to Date AE of Interest (All Causes) Zanubrutinib (Including Patients Enrolled in Combo Studies) Patient Number N = 641 Mean Exposure Time 7.7 mo Atrial Fibrillation 1.7% Serious Hemorrhage 1.9% AE of Interest (All Causes) Zanubrutinib (Single Agent Only) Patient Number N = 424 Mean Exposure Time 8.1 mo Diarrhea (All Gr) 14.2% Diarrhea (Gr 3-5) 0.7% 20 No new safety or tolerability signals observed, such as headache and hypertension Concomitant use of vitamin K antagonists was allowed in these zanubrutinib trials Paucity of treatment discontinuations for adverse events Source: pooled safety analysis of ongoing zanubrutinib clinical trials, data cut-off September 2017, n=641; Seymour, ICML 2017 Adverse Events of Interest for BTK Inhibitors in Patients Treated with Zanubrutinib
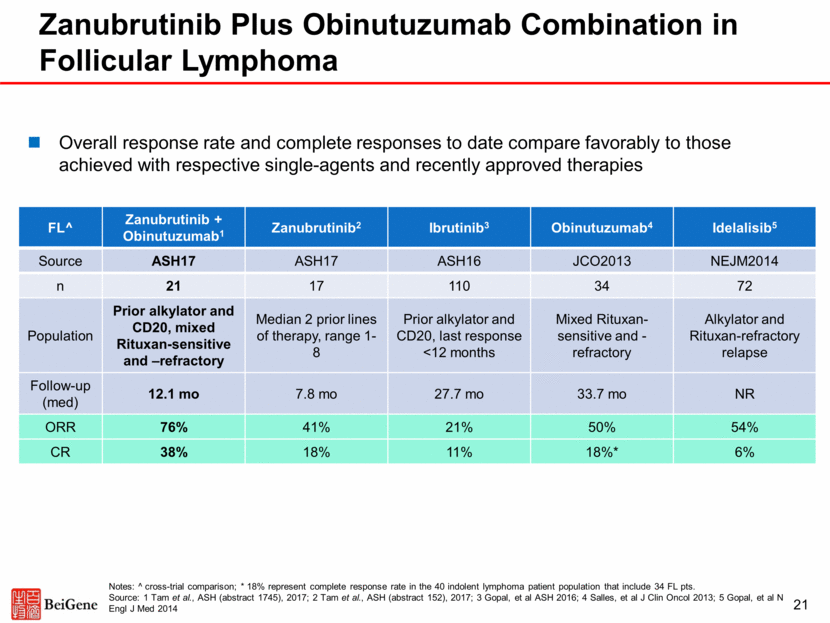
Zanubrutinib Plus Obinutuzumab Combination in Follicular Lymphoma 21 Overall response rate and complete responses to date compare favorably to those achieved with respective single-agents and recently approved therapies FL^ Zanubrutinib + Obinutuzumab1 Zanubrutinib2 Ibrutinib3 Obinutuzumab4 Idelalisib5 Source ASH17 ASH17 ASH16 JCO2013 NEJM2014 n 21 17 110 34 72 Population Prior alkylator and CD20, mixed Rituxan-sensitive and –refractory Median 2 prior lines of therapy, range 1-8 Prior alkylator and CD20, last response <12 months Mixed Rituxan-sensitive and -refractory Alkylator and Rituxan-refractory relapse Follow-up (med) 12.1 mo 7.8 mo 27.7 mo 33.7 mo NR ORR 76% 41% 21% 50% 54% CR 38% 18% 11% 18%* 6% Notes: ^ cross-trial comparison; * 18% represent complete response rate in the 40 indolent lymphoma patient population that include 34 FL pts. Source: 1 Tam et al., ASH (abstract 1745), 2017; 2 Tam et al., ASH (abstract 152), 2017; 3 Gopal, et al ASH 2016; 4 Salles, et al J Clin Oncol 2013; 5 Gopal, et al N Engl J Med 2014
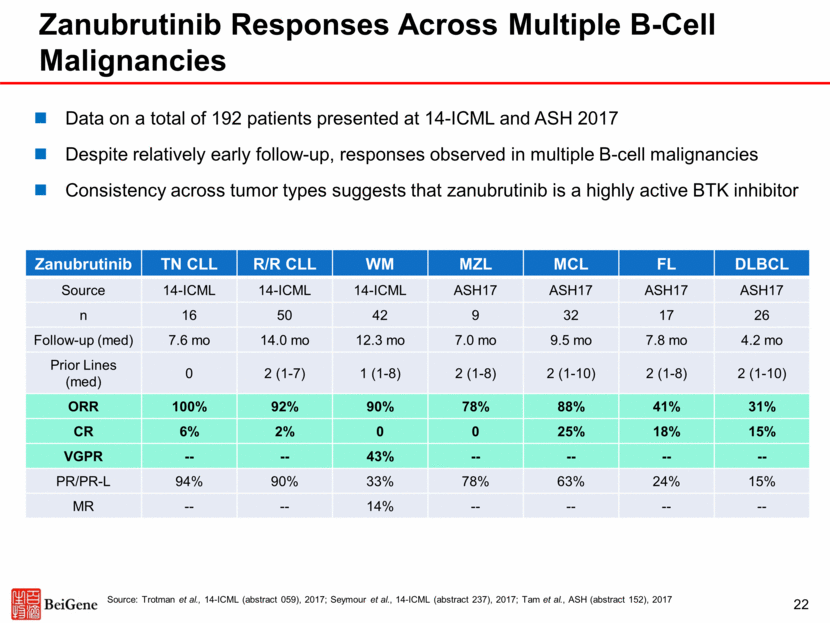
22 Zanubrutinib Responses Across Multiple B-Cell Malignancies Zanubrutinib TN CLL R/R CLL WM MZL MCL FL DLBCL Source 14-ICML 14-ICML 14-ICML ASH17 ASH17 ASH17 ASH17 n 16 50 42 9 32 17 26 Follow-up (med) 7.6 mo 14.0 mo 12.3 mo 7.0 mo 9.5 mo 7.8 mo 4.2 mo Prior Lines (med) 0 2 (1-7) 1 (1-8) 2 (1-8) 2 (1-10) 2 (1-8) 2 (1-10) ORR 100% 92% 90% 78% 88% 41% 31% CR 6% 2% 0 0 25% 18% 15% VGPR -- -- 43% -- -- -- -- PR/PR-L 94% 90% 33% 78% 63% 24% 15% MR -- -- 14% -- -- -- -- Data on a total of 192 patients presented at 14-ICML and ASH 2017 Despite relatively early follow-up, responses observed in multiple B-cell malignancies Consistency across tumor types suggests that zanubrutinib is a highly active BTK inhibitor Source: Trotman et al., 14-ICML (abstract 059), 2017; Seymour et al., 14-ICML (abstract 237), 2017; Tam et al., ASH (abstract 152), 2017
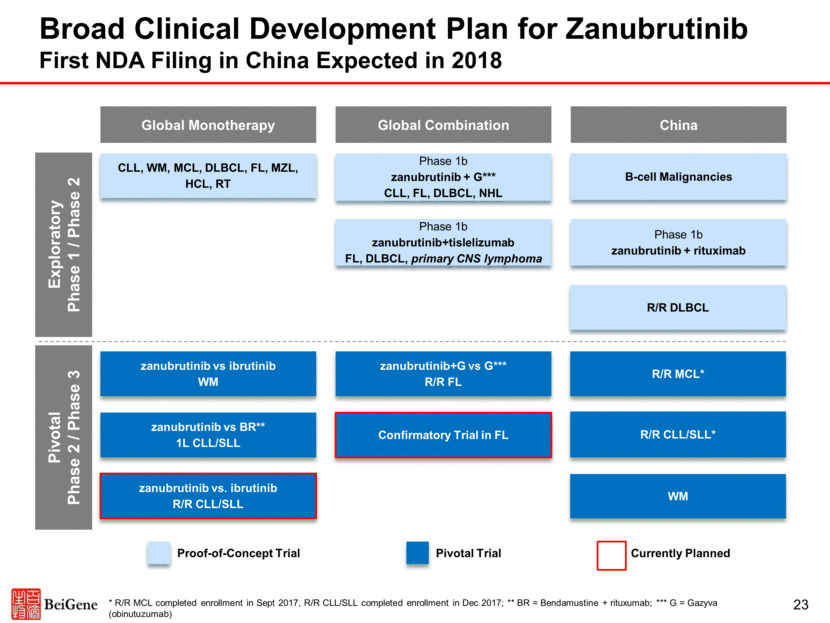
Broad Clinical Development Plan for Zanubrutinib First NDA Filing in China Expected in 2018 Global Monotherapy China Global Combination CLL, WM, MCL, DLBCL, FL, MZL, HCL, RT B-cell Malignancies Phase 1b zanubrutinib + G*** CLL, FL, DLBCL, NHL Phase 1b zanubrutinib+tislelizumab FL, DLBCL, primary CNS lymphoma R/R MCL* R/R CLL/SLL* zanubrutinib vs ibrutinib WM WM zanubrutinib vs BR** 1L CLL/SLL zanubrutinib+G vs G*** R/R FL Phase 1b zanubrutinib + rituximab Confirmatory Trial in FL * R/R MCL completed enrollment in Sept 2017, R/R CLL/SLL completed enrollment in Dec 2017; ** BR = Bendamustine + rituxumab; *** G = Gazyva (obinutuzumab) 23 zanubrutinib vs. ibrutinib R/R CLL/SLL Exploratory Phase 1 / Phase 2 Proof-of-Concept Trial Pivotal Trial Currently Planned Pivotal Phase 2 / Phase 3 R/R DLBCL
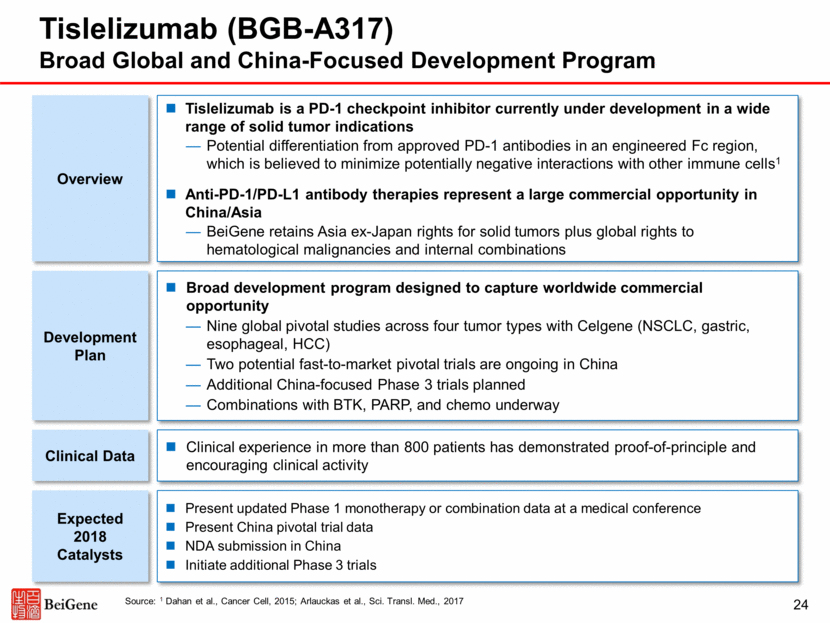
Tislelizumab (BGB-A317) Broad Global and China-Focused Development Program 24 Overview Development Plan Clinical Data Expected 2018 Catalysts Tislelizumab is a PD-1 checkpoint inhibitor currently under development in a wide range of solid tumor indications Potential differentiation from approved PD-1 antibodies in an engineered Fc region, which is believed to minimize potentially negative interactions with other immune cells1 Anti-PD-1/PD-L1 antibody therapies represent a large commercial opportunity in China/Asia BeiGene retains Asia ex-Japan rights for solid tumors plus global rights to hematological malignancies and internal combinations Broad development program designed to capture worldwide commercial opportunity Nine global pivotal studies across four tumor types with Celgene (NSCLC, gastric, esophageal, HCC) Two potential fast-to-market pivotal trials are ongoing in China Additional China-focused Phase 3 trials planned Combinations with BTK, PARP, and chemo underway Clinical experience in more than 800 patients has demonstrated proof-of-principle and encouraging clinical activity Present updated Phase 1 monotherapy or combination data at a medical conference Present China pivotal trial data NDA submission in China Initiate additional Phase 3 trials Source: 1 Dahan et al., Cancer Cell, 2015; Arlauckas et al., Sci. Transl. Med., 2017
Program (Target) Commercial Rights Preclinical Dose Escalation Dose Expansion* Pivotal** Phase 1a Phase 1b Phase 2 Phase 2 Phase 3 Tislelizumab (BGB-A317) (PD-1) Worldwide (Heme Malignancies); Asia ex-Japan (Solid Tumors)1 Tislelizumab + Pamiparib (PD-1 + PARP) Worldwide Tislelizumab + Zanubrutinib (PD-1 + BTK) Worldwide *Some indications will not require a non-pivotal Phase 2 clinical trial prior to beginning pivotal Phase 2 or 3 clinical trials. **Confirmatory clinical trials post approval are required for accelerated approvals. 1 Celgene has the right to develop and commercialize tislelizumab in solid tumors in the United States, European Union, Japan and the rest-of-world outside of Asia. 2 As of December 1, 2017. Tislelizumab Clinical Program 25 R/R Hodgkin’s lymphoma 2L+ urothelial carcinoma Solid tumors Hematological tumors China Global (ex-China) Over 800 patients2 enrolled across tislelizumab program, including combination trials 2L non-small cell lung cancer 1L hepatocellular carcinoma Solid tumors
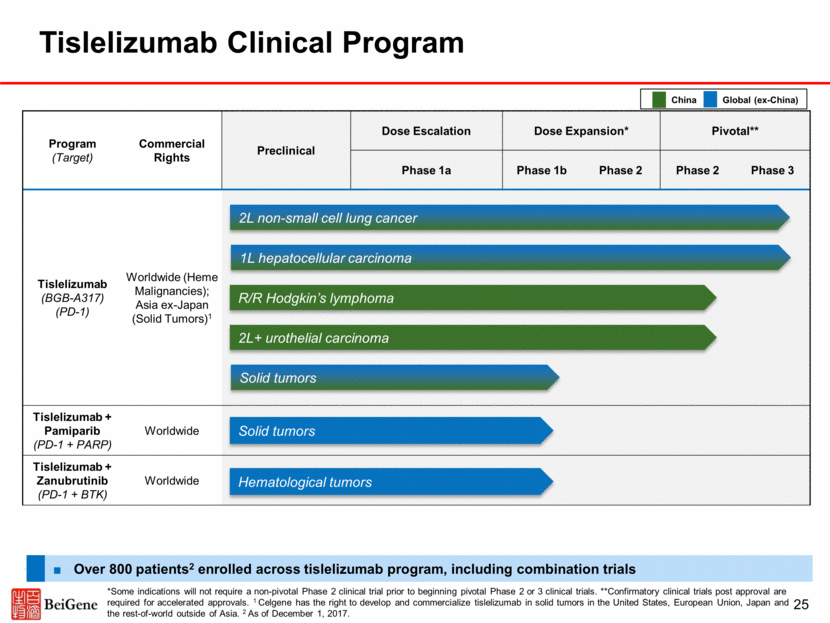
Anti-PD-1 Antibody Therapies Represent a Large Market Opportunity, Particularly in China Source: LEK Analysis, Data from World Health Organization (2012); Chen et al., CA Cancer J Clin, 2016; SEER.cancer.gov ¹ China data is from 2015, U.S. data is from 2017, EU5 data is from 2012, Japan data is from ganjoho.jp in 2013 Projected Sales in China’s Top-4 Cancer Types of PD-1/ PD-L1 Antibodies 26 2015 incidence of top four PD-1 responsive solid tumor types was 2.4m Additional upside when other PD-1 responsive tumor types included ’20-’26 CAGR ~51% 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 2025 2026 $ in billions NSCLC Gastric Esophageal HCC $2 $5 $8 $10 $11 $12 1 st MNC Launch 1 st Batch Domestic Launch $1 Incidence of Top-10 PD-1 Responsive Solid Tumors, by Region¹ China has a higher proportion of PD-1 responsive tumors Inclusive of PD-L1 and MSI-h selected tumors, China incidence could be as high as ~3.5m Total Solid Tumor Incidence, by Region¹ 1.7m 1.7m 4.3m 3.0m 0.9m 0.8m 0.5m 0.9m China Japan US EU5
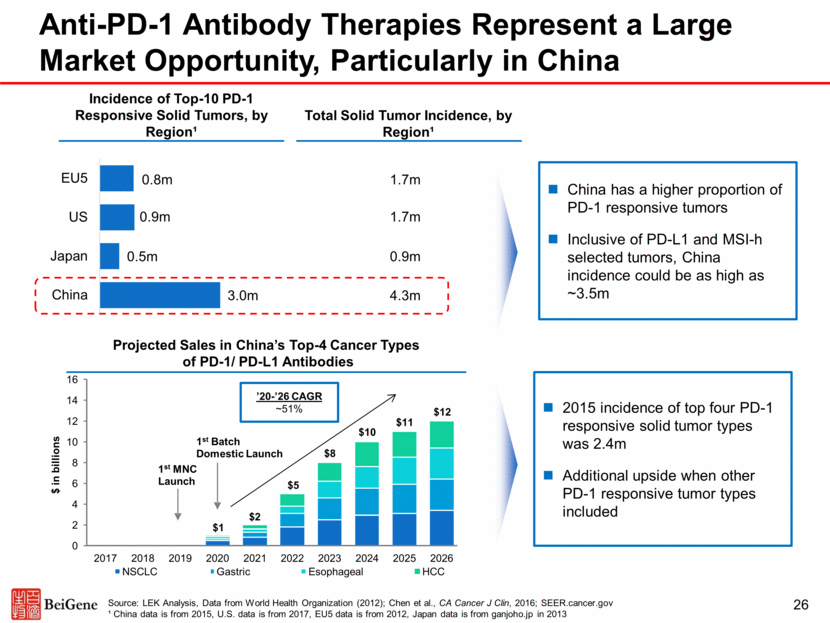
27 Tislelizumab Phase 1 Data Demonstrated Proof of Principle and Clinical Activity Note: 93 pts included in the chart, the remaining 6 pts were not evaluable for target lesion response based on imaging assessment at the cutoff time Source: 1 Phase 1 data as of September 30, 2016, presented at the Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer (SITC) Annual Meeting, 2016 (Desai et al) 2 Phase 1 data as of April 28, 2017, presented at the ESMO World Congress on Gastrointestinal Cancer (WCGI), 2017 (Yen et al) 3Phase 1 data as of June 16, 2017 presented at the Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology (CSCO) Annual Meeting, 2017 (Shen et al) Best Response (%) in Target Lesions Phase 1 Data at SITC 20161 The dose escalation data presented at SITC1 represented a mixed population with 27 tumor types which excluded melanoma, NSCLC or head and neck cancer; nearly 15% of the enrolled patients had RCC or urothelial carcinoma (UC) In the SITC1 analysis, 99 patients were evaluable for efficacy as of September 30, 2016, and 15 patients achieved confirmed PRs including 3/9 RCC, 3/6 urothelial carcinoma, 2/4 gastric cancer, 2/2 Merkel cell carcinoma, 1/4 NPC, 1/1 penis squamous cell carcinoma, 1/1 duodenal carcinoma, 1/1 evaluable MSI-h CRC, and 1/1 MSI-h pancreatic cancer patients In early data presented at ESMO WCGI 20172 from hepatocellular carcinoma patients enrolled in dose-escalation and dose-expansion portions of the Phase I trial, there were 3 PRs (1 confirmed, 2 unconfirmed) and 9 cases of SD in 27 efficacy-evaluable patients In early data presented from the China Phase 1 trial at CSCO 20173, the PK profile in Chinese patients was consistent with global trials. In 12 evaluable patients, there were 2 PRs (1 confirmed, 1 unconfirmed) and 3 cases of SD.
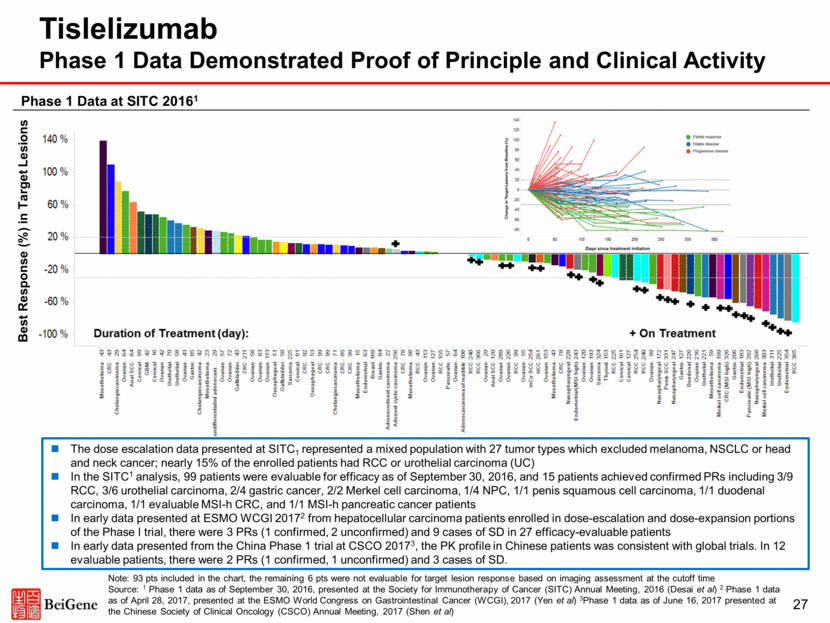
28 Tumor Type Gastric Cancer Esophageal Cancer Head & Neck SCC Ovarian Cancer Hepatocellular Carcinoma Median Treatment Duration 45 days (4-457) 50 days (1-246) 104 days (30-339) 71 days (29-540) 64 days (1-471) Evaluable Patients N=34 N=31 N=17 N=50 N=27 PR Confirmed Unconfirmed 4 -- 2 3 3 -- 2 -- 1 2 SD 3 6 6 20 9 Pts Remaining on Treatment* 18 9 3 6 24 Source ESMO 20171 ESMO 20171 ESMO 20172 ESMO 20173 WCGI 20174 *At the time of the data cutoff. Sources:1Phase 1 data as of June 8, 2017, presented at the ESMO 2017 Congress (Desai et al, Abstract 387P) 2Phase 1 data as of June 8, 2017, presented at the ESMO 2017 Congress (Horvath et al, Abstract 389P) 3Phase 1 data as of June 8, 2017, presented at the ESMO 2017 Congress (Meniawy et al, Abstract 388P) 4Phase 1 data as of April 28, 2017, presented at the ESMO World Congress on Gastrointestinal Cancer (WCGI), 2017 (Yen et al). Note: For additional safety and efficacy data, see the BeiGene press releases issued June 29, 2017 and September 11, 2017 Data on a total of 159 patients presented at ESMO 2017 and ESMO WCGI 2017 Objective responses observed with limited follow-up in multiple disease-specific Phase 1 expansion cohorts Tislelizumab Response Data
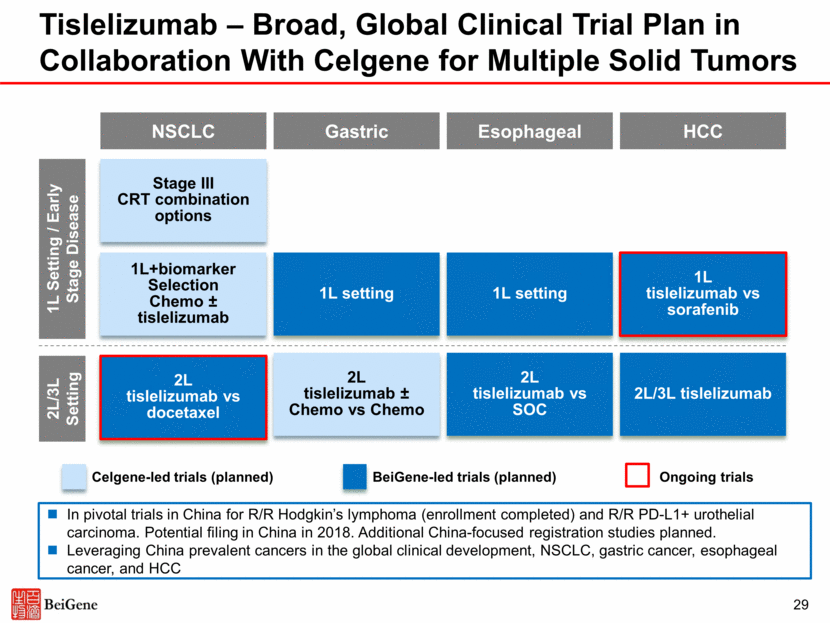
Tislelizumab – Broad, Global Clinical Trial Plan in Collaboration With Celgene for Multiple Solid Tumors 29 NSCLC Esophageal Gastric 1L Setting / Early Stage Disease Celgene-led trials (planned) BeiGene-led trials (planned) Ongoing trials 2L/3L Setting HCC Stage III CRT combination options 2L tislelizumab vs docetaxel 1L+biomarker Selection Chemo ± tislelizumab 2L tislelizumab ± Chemo vs Chemo 1L setting 2L tislelizumab vs SOC 1L setting 1L tislelizumab vs sorafenib 2L/3L tislelizumab In pivotal trials in China for R/R Hodgkin’s lymphoma (enrollment completed) and R/R PD-L1+ urothelial carcinoma. Potential filing in China in 2018. Additional China-focused registration studies planned. Leveraging China prevalent cancers in the global clinical development, NSCLC, gastric cancer, esophageal cancer, and HCC
Pamiparib (BGB-290) Selective Inhibitor of PARP1 and PARP2 30 Overview Development Plan Clinical Data Expected 2018 Catalysts Highly selective PARP1 and PARP2 inhibitor with significant brain penetration and strong PARP trapping activity in preclinical studies Two ongoing global Phase 1b/2 trials with chemotherapy: combination with radiation therapy and temozolomide (TMZ) in glioblastoma or combination with TMZ in advanced solid tumors Initiated China pivotal Phase 2 trial in patients with gBRCA+ ovarian cancer Expect to enter late-stage development globally Internal combination with tislelizumab: Preliminary anti-tumor activity observed in multiple solid tumors Phase 1/2 data demonstrated pamiparib was generally well-tolerated and showed promising anti-tumor activity in ovarian cancer Low incidence of hematological toxicities (e.g. thrombocytopenia), no liver toxicity Present additional monotherapy and combination data Initiate global pivotal trial (1H) Source: Phase 1/2 data as of June 1, 2017, presented at the ESMO 2017 meeting (Lickliter et al)
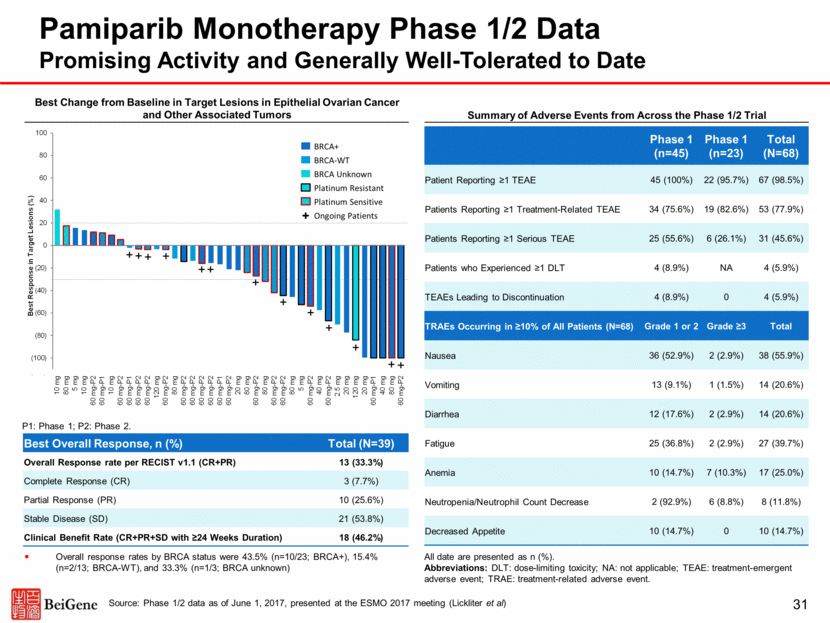
31 Pamiparib Monotherapy Phase 1/2 Data Promising Activity and Generally Well-Tolerated to Date Source: Phase 1/2 data as of June 1, 2017, presented at the ESMO 2017 meeting (Lickliter et al) Best Change from Baseline in Target Lesions in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer and Other Associated Tumors Summary of Adverse Events from Across the Phase 1/2 Trial Phase 1 (n=45) Phase 1 (n=23) Total (N=68) Patient Reporting >1 TEAE 45 (100%) 22 (95.7%) 67 (98.5%) Patients Reporting >1 Treatment-Related TEAE 34 (75.6%) 19 (82.6%) 53 (77.9%) Patients Reporting >1 Serious TEAE 25 (55.6%) 6 (26.1%) 31 (45.6%) Patients who Experienced >1 DLT 4 (8.9%) NA 4 (5.9%) TEAEs Leading to Discontinuation 4 (8.9%) 0 4 (5.9%) TRAEs Occurring in >10% of All Patients (N=68) Grade 1 or 2 Grade >3 Total Nausea 36 (52.9%) 2 (2.9%) 38 (55.9%) Vomiting 13 (9.1%) 1 (1.5%) 14 (20.6%) Diarrhea 12 (17.6%) 2 (2.9%) 14 (20.6%) Fatigue 25 (36.8%) 2 (2.9%) 27 (39.7%) Anemia 10 (14.7%) 7 (10.3%) 17 (25.0%) Neutropenia/Neutrophil Count Decrease 2 (92.9%) 6 (8.8%) 8 (11.8%) Decreased Appetite 10 (14.7%) 0 10 (14.7%) All date are presented as n (%). Abbreviations: DLT: dose-limiting toxicity; NA: not applicable; TEAE: treatment-emergent adverse event; TRAE: treatment-related adverse event. Best Overall Response, n (%) Total (N=39) Overall Response rate per RECIST v1.1 (CR+PR) 13 (33.3%) Complete Response (CR) 3 (7.7%) Partial Response (PR) 10 (25.6%) Stable Disease (SD) 21 (53.8%) Clinical Benefit Rate (CR+PR+SD with >24 Weeks Duration) 18 (46.2%) Overall response rates by BRCA status were 43.5% (n=10/23; BRCA+), 15.4% (n=2/13; BRCA-WT), and 33.3% (n=1/3; BRCA unknown) P1: Phase 1; P2: Phase 2. + BRCA+ BRCA-WT BRCA Unknown Platinum Resistant Platinum Sensitive Ongoing Patients
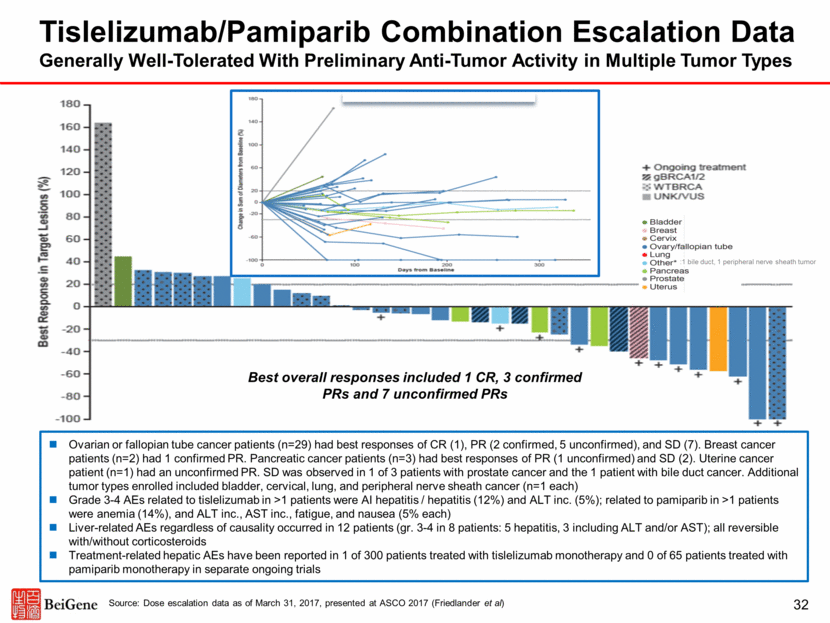
A. Change in Tumor Volume by Baseline Tumor Type Tislelizumab/Pamiparib Combination Escalation Data Generally Well-Tolerated With Preliminary Anti-Tumor Activity in Multiple Tumor Types :1 bile duct, 1 peripheral nerve sheath tumor Best overall responses included 1 CR, 3 confirmed PRs and 7 unconfirmed PRs Ovarian or fallopian tube cancer patients (n=29) had best responses of CR (1), PR (2 confirmed, 5 unconfirmed), and SD (7). Breast cancer patients (n=2) had 1 confirmed PR. Pancreatic cancer patients (n=3) had best responses of PR (1 unconfirmed) and SD (2). Uterine cancer patient (n=1) had an unconfirmed PR. SD was observed in 1 of 3 patients with prostate cancer and the 1 patient with bile duct cancer. Additional tumor types enrolled included bladder, cervical, lung, and peripheral nerve sheath cancer (n=1 each) Grade 3-4 AEs related to tislelizumab in >1 patients were AI hepatitis / hepatitis (12%) and ALT inc. (5%); related to pamiparib in >1 patients were anemia (14%), and ALT inc., AST inc., fatigue, and nausea (5% each) Liver-related AEs regardless of causality occurred in 12 patients (gr. 3-4 in 8 patients: 5 hepatitis, 3 including ALT and/or AST); all reversible with/without corticosteroids Treatment-related hepatic AEs have been reported in 1 of 300 patients treated with tislelizumab monotherapy and 0 of 65 patients treated with pamiparib monotherapy in separate ongoing trials 32 Source: Dose escalation data as of March 31, 2017, presented at ASCO 2017 (Friedlander et al)
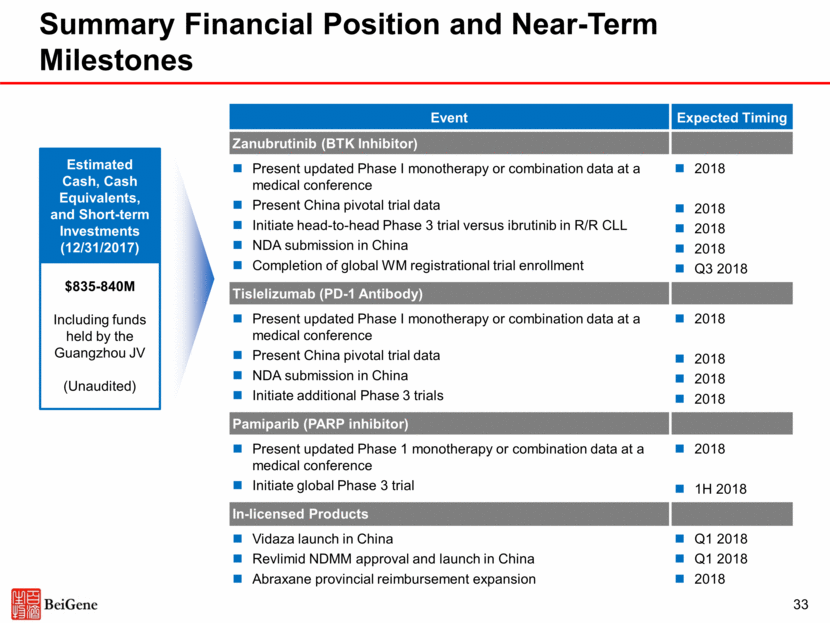
33 Event Expected Timing Zanubrutinib (BTK Inhibitor) Present updated Phase I monotherapy or combination data at a medical conference Present China pivotal trial data Initiate head-to-head Phase 3 trial versus ibrutinib in R/R CLL NDA submission in China Completion of global WM registrational trial enrollment 2018 2018 2018 2018 Q3 2018 Tislelizumab (PD-1 Antibody) Present updated Phase I monotherapy or combination data at a medical conference Present China pivotal trial data NDA submission in China Initiate additional Phase 3 trials 2018 2018 2018 2018 Pamiparib (PARP inhibitor) Present updated Phase 1 monotherapy or combination data at a medical conference Initiate global Phase 3 trial 2018 1H 2018 In-licensed Products Vidaza launch in China Revlimid NDMM approval and launch in China Abraxane provincial reimbursement expansion Q1 2018 Q1 2018 2018 Summary Financial Position and Near-Term Milestones Estimated Cash, Cash Equivalents, and Short-term Investments (12/31/2017) $835-840M Including funds held by the Guangzhou JV (Unaudited)
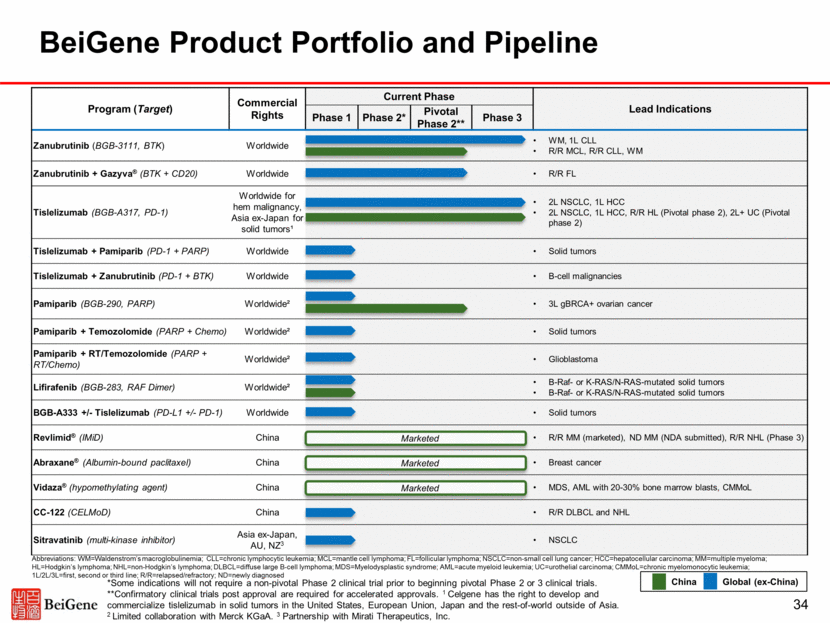
Program (Target) Commercial Rights Current Phase Lead Indications Phase 1 Phase 2* Pivotal Phase 2** Phase 3 Zanubrutinib (BGB-3111, BTK) Worldwide WM, 1L CLL R/R MCL, R/R CLL, WM Zanubrutinib + Gazyva® (BTK + CD20) Worldwide R/R FL Tislelizumab (BGB-A317, PD-1) Worldwide for hem malignancy, Asia ex-Japan for solid tumors¹ 2L NSCLC, 1L HCC 2L NSCLC, 1L HCC, R/R HL (Pivotal phase 2), 2L+ UC (Pivotal phase 2) Tislelizumab + Pamiparib (PD-1 + PARP) Worldwide Solid tumors Tislelizumab + Zanubrutinib (PD-1 + BTK) Worldwide B-cell malignancies Pamiparib (BGB-290, PARP) Worldwide² 3L gBRCA+ ovarian cancer Pamiparib + Temozolomide (PARP + Chemo) Worldwide² Solid tumors Pamiparib + RT/Temozolomide (PARP + RT/Chemo) Worldwide² Glioblastoma Lifirafenib (BGB-283, RAF Dimer) Worldwide² B-Raf- or K-RAS/N-RAS-mutated solid tumors B-Raf- or K-RAS/N-RAS-mutated solid tumors BGB-A333 +/- Tislelizumab (PD-L1 +/- PD-1) Worldwide Solid tumors Revlimid® (IMiD) China R/R MM (marketed), ND MM (NDA submitted), R/R NHL (Phase 3) Abraxane® (Albumin-bound paclitaxel) China Breast cancer Vidaza® (hypomethylating agent) China MDS, AML with 20-30% bone marrow blasts, CMMoL CC-122 (CELMoD) China R/R DLBCL and NHL Sitravatinib (multi-kinase inhibitor) Asia ex-Japan, AU, NZ3 NSCLC BeiGene Product Portfolio and Pipeline Marketed Marketed *Some indications will not require a non-pivotal Phase 2 clinical trial prior to beginning pivotal Phase 2 or 3 clinical trials. **Confirmatory clinical trials post approval are required for accelerated approvals. 1 Celgene has the right to develop and commercialize tislelizumab in solid tumors in the United States, European Union, Japan and the rest-of-world outside of Asia. 2 Limited collaboration with Merck KGaA. 3 Partnership with Mirati Therapeutics, Inc. China Global (ex-China) Marketed Abbreviations: WM=Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia; CLL=chronic lymphocytic leukemia; MCL=mantle cell lymphoma; FL=follicular lymphoma; NSCLC=non-small cell lung cancer; HCC=hepatocellular carcinoma; MM=multiple myeloma; HL=Hodgkin’s lymphoma; NHL=non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma; DLBCL=diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; MDS=Myelodysplastic syndrome; AML=acute myeloid leukemia; UC=urothelial carcinoma; CMMoL=chronic myelomonocytic leukemia; 1L/2L/3L=first, second or third line; R/R=relapsed/refractory; ND=newly diagnosed 34
Conclusion – BeiGene Company Highlights 850+ person, global biotech company rooted in China with research, development, manufacturing, and commercial capabilities Ability to leverage regulatory changes in China as the country becomes an integral component of novel drug development and the oncology drug market continues to grow Plans to globally market potentially best-in-class BTK inhibitor zanubrutinib, with an expectation to file for marketing approval in China in 2018 Collaborating with Celgene in the development and potential commercialization of PD-1 inhibitor tislelizumab globally and in China Continued development of proprietary pipeline assets Potential to further expand internal portfolio through future strategic relationships (as evidenced by the Celgene and Mirati collaborations) 35