Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| 8-K - 8-K - Enumeral Biomedical Holdings, Inc. | s102104_8k.htm |
Exhibit 99.1

Enumeral PD - 1 Program Update: Differentiated Anti - PD - 1 Antibody Elicits Higher T Cell Activation in Ex Vivo Human Assays than a Currently Marketed Anti - PD - 1 Antibody November 3, 2015
Background • Enumeral uses a unique single cell technology platform and approach to identify functionally differentiated antibody candidates – Enumeral has identified two distinct classes of anti - PD - 1 antibodies with distinct modes of binding to PD - 1 – Both classes demonstrate enhancement of T cell activation via reversal of PD - 1 - dependent immunosuppression 2

Enumeral’s Approach to Developing Differentiated Antibodies Starts with Diversity • Enumeral antibody discovery results in exceptional diversity* • Potential for strong IP position • Breadth of diversity: keys to unlocking the target physiology • Multiple potential program opportunities OPDIVO® KEYTRUDA® Pidilizumab 392C5 246A10 413D2 413E1 244C8 388D4 *Based on ENUM evaluation of published literature Cladogram representing heavy chain AA sequences N= 159 sequences shown 28 families of antibodies 3
Enumeral PD - 1 Program • Enumeral has identified a novel potentially allosteric anti - PD1 antagonist (ENUM 244C8) displaying the following properties: – Reversal of PD - L1 - dependent immunosuppression – Binding to PD - 1 via a novel epitope – Increased levels of T cell activation in cell - based assays – Binding to PD - 1 independent of PD - L1 • ENUM 244C8 antibody and a currently - marketed anti - PD1 antibody were tested for their ability to reverse tumor infiltrating lymphocyte (TIL) exhaustion using lymphocytes derived from human lung biopsy – ENUM 244C8 observed restoring T cell function to a higher level than the positive control nivolumab 4

ENUM 244C8 Binding to PD - 1 Does Not Displace PD - L1 Positive control EH12.2H7 Negative control mIgG1K 388D4 244C8 ENUM 388D4, but not ENUM 244C8, blocks the binding of soluble PD - L1 to cells expressing PD1 . HEK293 cells expressing PD1 were incubated with 10ug/mL of isotype, EH12.2H7, 388D4 or 244C8 antibodies. Cells were washed and then stained with soluble PD - L1 - I g protein labeled with Alexa488. Cells were washed and analyzed for PD - L1 binding by FACS analysis. Antibody 244C8 behaves like the isotype negative control, and inhibition of PD - L1 binding to cells expressing PD1 is not observed. Antibody ENUM 388D4 is a ‘conventional’ binder to PD1 with anti - PD - 1 antagonist immune activation properties. 5
Ex Vivo Reversal of TIL Exhaustion: Methods • NSCLC samples from staging surgeries were analyzed within 24 hours of collection • Flow cytometry analyzed extent of T cell infiltration and co - expression of immunomodulatory receptors • Cells were incubated with anti - CD3/anti - CD28 antibodies for 24 hours and either negative control (isotype), nivolumab , or ENUM 244C8 • Interferon gamma production was measured (ELISA) and data is expressed as fold increase normalized to isotype control 6
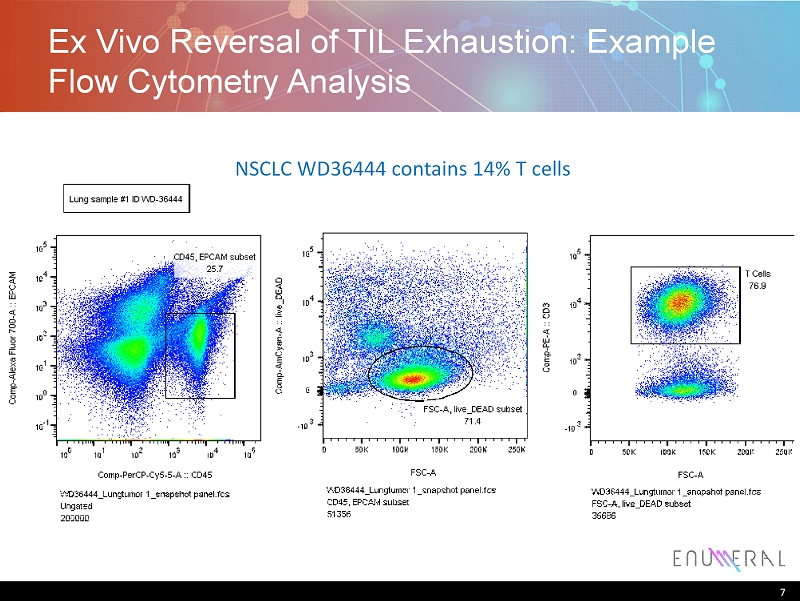
Ex Vivo Reversal of TIL Exhaustion: Example Flow Cytometry Analysis 7 NSCLC WD36444 contains 14% T cells

Ex Vivo Reversal of TIL Exhaustion: Co - expression of Immunomodulatory Receptors • WD36444 CD4+ and CD8+ TILs express exhaustion markers (IMRs) • PD - 1 expressed on 55% of CD4 cells and 75% of CD8 cells • ‘IMR X’ expressed 5.5% of CD4 cells and 13% of CD8 cells 8 CD4 cells CD8 cells PD - 1 Immunomodulatory Receptor (IMR) X

Ex Vivo Reversal of TIL Exhaustion: Variability Across Patients 9 Tumor Identifier % EpCAM - CD45+ %CD3+ %CD4 + PD1 + %CD8 + PD1 + WD - 36444* 25.7 14 55 75 WD - 36571 10.3 6.3 47 64 WD - 36686* 21.6 17 55 84 WD - 36790* 16.8 10.4 38 68 WD - 36904 12.8 7 63 72 M115801A2 3.4 2.9 79 84 WD - 36923 1.6 0.9 53 51 WD - 36988 8.9 7 58 93 M4150952 5.4 3 78 79 • Data from flow cytometry analysis – Lymphocyte infiltration ranged from 1.6% - 25.7 % – T cell infiltration ranged from 0.9% - 17% NSCLC tumor biopsies demonstrate varying degrees of lymphocyte infiltration and PD - 1 expression on T cells *Data on functional reversal of exhaustion reported on following slides

Ex Vivo Reversal of TIL Exhaustion: Experimental Questions • Tumor biopsy from n=9 patients found to harbor TILs that express exhaustion markers including PD - 1. 1. What is the activity of the T cells following activation? 2. Is cellular activity modified by the addition of an anti - PD1 antibody? 3. Do n ivolumab and ENUM antibodies behave differently in this experiment? 10
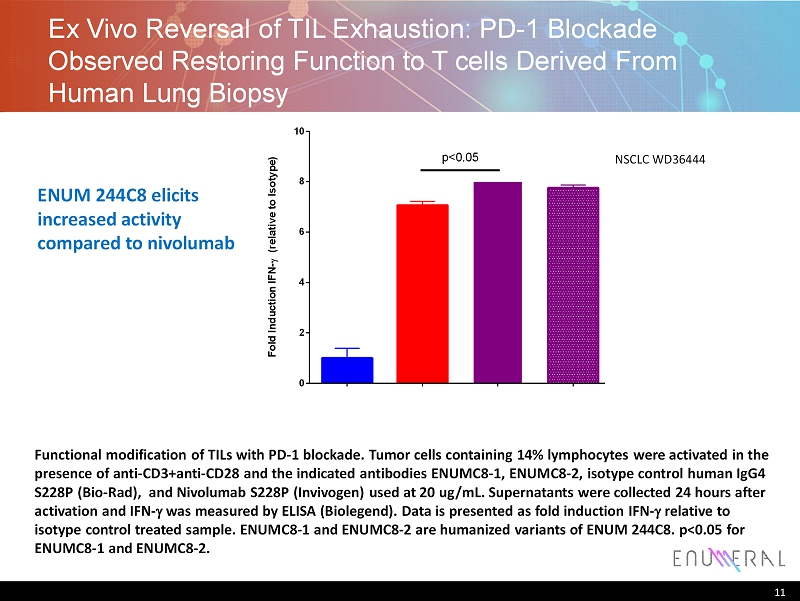
Ex Vivo Reversal of TIL Exhaustion: PD - 1 B lockade Observed Restoring F unction to T cells Derived F rom H uman L ung B iopsy Functional modification of TILs with PD - 1 blockade. Tumor cells containing 14% lymphocytes were activated in the presence of anti - CD3+anti - CD28 and the indicated antibodies ENUMC8 - 1, ENUMC8 - 2, isotype control human IgG4 S228P (Bio - Rad), and Nivolumab S228P ( Invivogen ) used at 20 ug / mL. Supernatants were collected 24 hours after activation and IFN - g was measured by ELISA ( Biolegend ). Data is presented as fold induction IFN - g relative to i sotype control treated sample. ENUMC8 - 1 and ENUMC8 - 2 are humanized variants of ENUM 244C8. p<0.05 for ENUMC8 - 1 and ENUMC8 - 2. 11 NSCLC WD36444 I s o t y p e C o n t r o l N i v o l u m a b E N U M C 8 - 1 E N U M C 8 - 2 E N U M C 8 - 3 0 2 4 6 8 10 F o l d I n d u c t i o n I F N - ( r e l a t i v e t o I s o t y p e ) p<0.05 ENUM 244C8 elicits increased activity compared to nivolumab
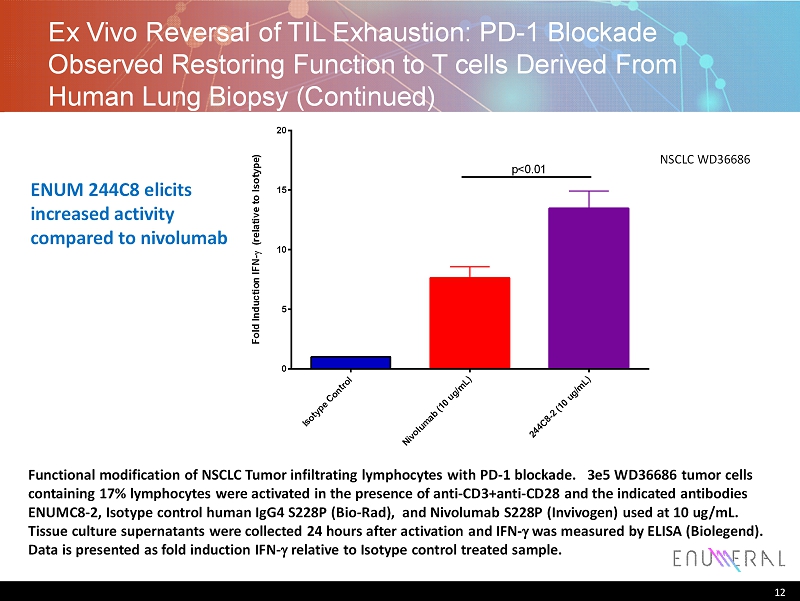
Ex Vivo Reversal of TIL Exhaustion: PD - 1 Blockade Observed Restoring Function to T cells Derived From Human Lung Biopsy ( C ontinued) 12 I s o t y p e C o n t r o l N i v o l u m a b ( 1 0 u g / m L ) 2 4 4 C 8 - 2 ( 1 0 u g / m L ) 0 5 10 15 20 F o l d I n d u c t i o n I F N - ( r e l a t i v e t o I s o t y p e ) p<0.01 Functional modification of NSCLC Tumor infiltrating lymphocytes with PD - 1 blockade. 3e5 WD36686 tumor cells containing 17% lymphocytes were activated in the presence of anti - CD3+anti - CD28 and the indicated antibodies ENUMC8 - 2, Isotype control human IgG4 S228P (Bio - Rad), and Nivolumab S228P ( Invivogen ) used at 10 ug / mL. Tissue culture supernatants were collected 24 hours after activation and IFN - g was measured by ELISA ( Biolegend ). Data is presented as fold induction IFN - g relative to Isotype control treated sample. NSCLC WD36686 ENUM 244C8 elicits increased activity compared to nivolumab
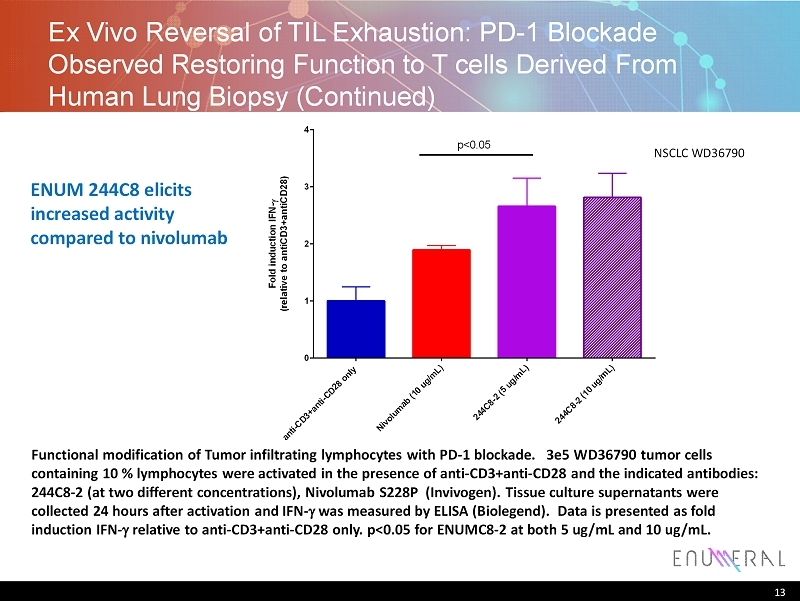
13 Functional modification of Tumor infiltrating lymphocytes with PD - 1 blockade. 3e5 WD36790 tumor cells containing 10 % lymphocytes were activated in the presence of anti - CD3+anti - CD28 and the indicated antibodies: 244C8 - 2 (at two different concentrations), Nivolumab S228P ( Invivogen ). Tissue culture supernatants were collected 24 hours after activation and IFN - g was measured by ELISA ( Biolegend ). Data is presented as fold induction IFN - g relative to anti - CD3+anti - CD28 only . p<0.05 for ENUMC8 - 2 at both 5 ug /mL and 10 ug / mL. a n t i - C D 3 + a n t i - C D 2 8 o n l y N i v o l u m a b ( 1 0 u g / m L ) 2 4 4 C 8 - 2 ( 5 u g / m L ) 2 4 4 C 8 - 2 ( 1 0 u g / m L ) 0 1 2 3 4 F o l d i n d u c t i o n I F N - ( r e l a t i v e t o a n t i C D 3 + a n t i C D 2 8 ) p<0.05 NSCLC WD36790 Ex Vivo Reversal of TIL Exhaustion: PD - 1 Blockade Observed Restoring Function to T cells Derived From Human Lung Biopsy (Continued) ENUM 244C8 elicits increased activity compared to nivolumab

Conclusions • ENUM 244C8 is a humanized anti - PD - 1 antibody that binds PD - 1 but does not compete with PD - L1 and thus represents a pharmacologically novel class of anti - PD - 1 therapeutic. • Following incubation with anti - CD3/anti - CD28 antibodies activation of NSCLC tumor - derived T cells was limited and addition of anti - PD - 1 antibodies was required to enhance IFN - g secretion. • ENUM 244C8 can augment ex vivo IFN - g secretion by PD - 1 + TILs to a greater level than n ivolumab . • Enumeral’s platform enables generation of broad antibody diversity that can translate into functionally distinct and potentially improved therapeutic candidates. 14

THE POWER of HUMAN™
