Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| 8-K - FORM 8-K - Ignyta, Inc. | d933944d8k.htm |
| EX-99.2 - EXHIBIT 99.2 - Ignyta, Inc. | d933944dex992.htm |
| EX-99.3 - EXHIBIT 99.3 - Ignyta, Inc. | d933944dex993.htm |
| EX-99.1 - EXHIBIT 99.1 - Ignyta, Inc. | d933944dex991.htm |
 Catalyzing
Precision Medicine with Integrated Rx/Dx in Oncology ASCO 2015
May 31
st
, 2015
Exhibit
99.4 |
 Safe Harbor
Statement 2
This document contains forward-looking statements, as that term is defined in Section 27A of the
Securities Act of 1933 and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, about Ignyta,
Inc. (“us” or the “Company”). Statements that are not purely historical are
forward-looking statements. These include statements regarding, among other things: the clinical
and/or non-clinical data or plans underlying entrectinib or any of our other development programs;
our ability to design and conduct development activities for entrectinib and our other
development programs; our ability to develop or access companion diagnostics for our product
candidates; our ability to obtain and maintain intellectual property protection for our product
candidates; our ability to adequately fund our development programs; the Teva transaction serving as a
transformative event for us and the development and market potential of our pipeline; our ability to
obtain regulatory approvals in order to market any of our product candidates; and our ability
to successfully commercialize any approved products. Forward-looking statements
involve known and unknown risks that relate to future events or the Company’s future
financial performance, some of which may be beyond our control, and the actual results could differ
materially from those discussed in this document. Accordingly, the Company cautions
investors not to place undue reliance on the forward- looking statements contained in, or
made in connection with, this document.
Important factors that could cause actual results to differ materially from those indicated by such
forward-looking statements, include, among others, the potential for results of past or
ongoing clinical or non-clinical studies to differ from expectations or previous results;
the interpretation of data from our clinical and non-clinical studies; our ability to initiate
and complete clinical trials and non-clinical studies; regulatory developments; the potential
advantages of our product candidates; the markets any approved products are intended to serve;
and our capital needs; as well as those set forth under the headings “Special Note
Regarding Forward-Looking Statements,” “Risk Factors” and “Management’s
Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” contained in the
Company’s Form 10-K filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission
(“SEC”) on March 12, 2015, and similar disclosures made in the Company’s Form
10-Q filings and other SEC filings and press releases.
The forward-looking statements contained in this document represent our estimates and assumptions
only as of the date of this document, and we undertake no duty or obligation to update or
revise publicly any forward-looking statements contained in this document as a result of
new information, future events or changes in our expectations.
Third-party information included herein has been obtained from sources believed to be reliable,
but the accuracy or completeness of such information is not guaranteed by, and should not be
construed as a representation by, the Company.
|
 Contents
Ignyta overview
Entrectinib preclinical data
ASCO clinical program update
Entrectinib future plans
Vision and milestones
3 |
 Company
History and Financial Highlights San Diego based biotechnology company (NASDAQ: RXDX),
incorporated in 2011 ~75 employees: more than half with M.D.’s, Ph.D.’s or
other graduate degrees Robust Rx Pipeline:
-
In-licensed from Nerviano Medical Sciences exclusive worldwide rights to entrectinib in
Oct. 2013 and RXDX-103 in Aug. 2014
-
Acquired oncology R&D pipeline of 4 clinical and preclinical assets from Teva in Mar.
2015 -
Lead
program
entrectinib
granted
FDA
orphan
drug
designation
for
NSCLC,
CRC
and
neuroblastoma, and rare pediatric disease designation for neuroblastoma
In-house Dx: CLIA certified, QSR compliant diagnostic lab with multi-modality assay
capabilities
Cash, cash equivalents & marketable securities of ~$108mm at end
of 1Q 2015
4
Ignyta’s vision is to catalyze precision medicine for the benefit of cancer
patients everywhere, with an integrated approach to "Rx/Dx" in
oncology |
 Jonathan Lim,
M.D., Chairman, CEO, and Co-Founder. Former Chair, CEO of Eclipse; CEO at
Halozyme; McKinsey; NIH post-doc at Harvard; Surgical resident at NYH-Cornell.
Jacob Chacko, M.D., Chief Financial Officer. Marshall Scholar at
Oxford University; UCLA Med; Harvard Business School. Zachary Hornby, Chief Operating
Officer. Former Senior Director of Business Development at Fate
Therapeutics; Director of BD at Halozyme; L.E.K. Consulting; Harvard Business School.
Pratik Multani, M.D., Chief Medical Officer.
Former CMO at Fate; VP, Clinical Development at
Kalypsys; CMO at Kanisa; VP, Clinical Development at Salmedix (sold to Cephalon); Sr. Director
of Medical Research at Biogen Idec; MD, MS at Harvard; Residency, MGH; Oncology, Dana
Farber. Robert Wild, Ph.D., Chief Scientific Officer.
Former CSO, Oncology Research/Drug Discovery at Eli
Lilly; Sr. Dir., Oncology Research at OSI Pharma; BMS; SUGEN. Has contributed to multiple
discovery/preclinical/translational
programs,
including
Tarceva,
Erbitux,
Sprycel
and
Sutent.
Matt Onaitis, General Counsel and Secretary.
Former GC at Trius and Somaxon; Associate GC at
Biogen Idec; Director of Legal Affairs at Elan; Stanford Law School.
Senior Management Team
5
Former
Vice
President
at
TPG
Capital;
McKinsey; |
 Ignyta’s
Strategic Approach to Generating Value from Novel Targets and Optimally Positioned
Assets 6
External Targets
Identify attractive
targets: If target of
interest is being
developed externally,
engage in discussion for
potential in-licensing
Internal Targets
Identify attractive
targets: If target of
interest is not being
developed externally,
then initiate internal
discovery program
Oncology Assets
Identify oncology assets to
optimally position, using Rx/Dx
expertise; i.e.: (a) developed
without a biomarker strategy;
(b) failed due to lack of
sufficient efficacy; or (c) were
deprioritized for strategic
reasons
Examples
•
Spark discovery
programs
•
Acquisition of RXDX-
105/106/107/108 assets
from Teva
•
In-licensing of
entrectinib and
RXDX-103 from
Nerviano
Approach |
 Ignyta’s
Pipeline 7
1
In-licensed from Nerviano Medical Sciences (NMS); ²Acquired from Teva Pharmaceutical Industries |
 8
Central
Lab
Clinical Sites
Specimens
•
QSRs
•
CLIA
Platforms
Output
FFPE
Fresh Tissue
FISH
IHC
PCR
NGS
Oncolome®
Trial Enrollment
CDx
Ignyta’s Dx Capabilities Enable Leadership
in Precision Medicine
•
SNPs
•
Splice variants
•
InDels
•
Amplifications
•
Overexpression
•
Rearrangements |
 Contents
Ignyta overview
Entrectinib preclinical data
ASCO clinical program update
Entrectinib future plans
Vision and milestones
9 |
 Entrectinib:
A Potent Inhibitor of Trk A/B/C, ROS1 and ALK
Entrectinib is a potent, selective, orally available ATP-competitive inhibitor
of 5 oncogenic drivers
In vitro,
entrectinib demonstrates inhibition of targets as well as
downstream effectors in the MAPK and PI3K/AKT pathways
In vivo,
entrectinib demonstrates tumor eradication and tumor growth
inhibition in multiple models
Composition of matter patent issued in the US and allowed in Europe, with
commercial protection out to 2029 (excluding patent term extension)
Target
TrkA
TrkB
TrkC
ROS1
ALK
IC50* (nM)
1.7
0.1
0.1
0.2
1.6
10
* Biochemical kinase assay |
 TrkA/B/C
Signaling Pathways 11 |
 Identified
NTRK Rearrangements in Human Malignancy PTC: papillary thyroid cancer
DIPG: diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma
NBS-HGG: non-brainstem high-grade glioma
12
CD74-NTRK1
TPM3-NTRK1
TPR-NTRK1
TP53-NTRK1
TM
Kinase Domain
NTRK1 (wild-type)
Signal Peptide/Extracellular Domain
MPRIP-NTRK1
NSCLC
NSCLC, GBM
RFWD2-NTRK1
NSCLC
CRC, PTC, AML, DIPG, NBS-HGG
LMNA-NTRK1
CRC, Spitzoid melanoma, Spitz tumors
Spitzoid melanoma, Spitz tumors
TFG-NTRK1
PTC, NSCLC
PTC
NFASC-NTRK1
GBM
QKI-NTRK2
Pilocytic astrocytoma
Pilocytic astrocytoma
NACC2-NTRK2
VCL-NTRK2
AGBL4-NTRK2
DIPG, NBS-HGG
DIPG, NBS-HGG
ETV6-NTRK3
Salivary gland tumor, Secretory BC, AML,
Sarcoma, Nephroma, DIPG, NBS-HGG
BTBD1-NTRK3
DIPG, NBS-HGG |
 Entrectinib
Demonstrates Robust in vitro and in vivo Activity against
NTRK1-Rearranged Colorectal Cancer Cell Line (KM-12) KM-12 is a human CRC
line driven by a constitutively active TrkA fusion, TPM3-NTRK1 Entrectinib potently
inhibits TrkA phosphorylation and downstream signaling Entrectinib induces in vivo
tumor regression and durable tumor stabilization In vitro
13
Continuous dosing treatments started at
Day 9, bid; 21 treatments completed
In vivo xenograft
entrectinib
TPM3
(partial) TM TrkA
Kinase domain |
 Patient-derived xenograft (PDX) model
established from tumor biopsy obtained prior to
entrectinib treatment from patient #20 in ALKA
trial. This patient showed partial response (PR) to
entrectinib (see clinical data section).
Entrectinib Demonstrates Potent in vivo
Efficacy in a Patient-
Derived Xenograft model (Patient with NTRK1-Rearranged CRC)
Tumor harbors an
activating NTRK1
fusion: LMNA-TrkA
High level of p-TrkA
detected in un-treated
tumor by Western blot
(preliminary data),
indicating constitutive
activation of the fusion
protein.
4 days on, 3 days off
per 7 day cycle, similar to
clinical regimen
Source: Siena, Niguarda; Bardelli, IRCC
P<0.001 vs vehicle
entrectinib
entrectinib
14
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
500
1000
1500
2000
2500
3000
3500
weeks
Vehicle
60mg/Kg
15mg/Kg |
 Entrectinib
Pre-Clinical Summary Rearrangements of NTRK, ROS1 and ALK are known to be oncogenic
drivers in multiple tumor types
TrkA/B/C overexpression has been reported across a large array of tumor types,
suggesting that these tumors may rely on Trk pathway signaling
In vitro,
entrectinib effectively inhibits the proliferation of cells expressing
rearranged (fusion) and over-expressed wild-type Trks
In vivo,
entrectinib potently inhibits tumor growth in multiple preclinical tumor
models driven by NTRK, ROS1 or ALK molecular alterations
Our data support clinical exploration of entrectinib in cancers with NTRK, ROS1
and ALK rearrangements and other activating alterations
15 |
 Contents
Ignyta overview
Entrectinib preclinical data
ASCO clinical program update
Entrectinib future plans
Vision and milestones
16 |
 Entrectinib
Clinical Development Overview 17
STARTRK-1
Global Phase 1/2 study in U.S., EU
and Asia
* “RP2D”
= Recommended Phase 2 Dose
ALKA-372-001
Phase 1 dose escalation study of
intermittent dosing schedule in
Italy: patients with ALK,
ROS1 or TrkA alterations
•
First-in-human study initiated
by Nerviano in Oct. 2012
•
Ignyta assumed control in
Nov. 2013
•
Phase 1 initiated in the U.S. in
Jul. 2014
Dose escalation of daily continuous
dosing schedule in patients with
Trk, ROS1 or ALK molecular
alterations
“Basket trial”
expansion cohorts in
100 patients with TrkA, TrkB, TrkC,
ROS1 or ALK molecular alterations,
treated at the RP2D* |
 ALKA and
STARTRK-1: Regimens and Doses 18
* Exploration of a fixed daily dosing regimen is ongoing
“RP2D”
= recommended phase 2 dose
Dose
Break
1
2
3
4
Week
Schedule A: PO, QD (4 on, 3 off) x 3 weeks, fasting
Dose
Break
1
2
3
4
Week
Schedule C: PO, QD (4 on, 3 off) x 4 weeks, fed
Dose
1
2
3
4
Week
Schedule B: PO, QD, fed
ALKA Study
STARTRK-1 Study
Dose
1
2
3
4
Week
Schedule: PO, QD, fed
Dose Cohorts
(mg/m²):
100->200->400->
800->1200->1600
(no longer enrolling)
200->400->…
(ongoing)
400->800
(no longer enrolling)
100->200->400->800*
(fixed)…
(ongoing)
RP2D |
 Demographics
of ALKA and STARTRK-1 (n=67) ALKA-372-001 (n=38)
STARTRK-1 (n=29)
Age, years, median (range)
52 (22-75)
55 (28-76)
Sex, male/female (%)
45/55
34/66
ECOG performance status, n (%)
0
19 (50)
8 (28)
1
18 (47)
18 (62)
2
1 (3)
3 (10)
Tumor type, n (%)
NSCLC
25 (66)
13 (45)
Neoplasms of the CNS
6 (16)
1 (3)
Gastrointestinal tract (CRC)
3 (8)
5 (17)
Gastrointestinal tract (non-CRC)
2 (5)
2 (7)
Head and neck
1 (3)
1 (3)
Sarcomas
1 (3)
0
Breast
0
2 (7)
Other
0
5 (17)
19
Note: Data as of May 1, 2015 |
 Dose and
Safety Assessment of Entrectinib As of May 1, 2015
67 subjects have been treated with entrectinib in two Phase 1 trials
-
ALKA-372-001 and STARTRK-1
Doses explored were from 100 mg/m
2
to 1600 mg/m
2
-
ALKA Sch A (4 days on/3 days off x 3 weeks; 28-day cycle): 19 pts
-
ALKA Sch B and STARTRK-1 (both QD continuous): 42 pts
-
ALKA Sch C (4 days on/3 days off continuous): 6 pts
-
Majority of subjects (n=48, 72% total pts) have received doses
400 mg/m
2
No treatment-related serious adverse events (AEs)
Treatment-related AEs have been mostly Grade 1 or 2, and reversible
No evidence of cumulative AEs
No evidence of hepatic or renal toxicity
No evidence of QTc prolongation
20 |
 Treatment-Related Adverse Events for ALKA and STARTRK-1
Adverse event term
ALKA-372-001 n(%)
STARTRK-1 n(%)
Paresthesia
16 (42)
6 (22)
Nausea
14 (37)
6 (22)
Myalgia
13 (34)
-
Asthenia
10 (27)
3 (11)
Fatigue
-
9 (33)
Dysgeusia
10 (27)
7 (26)
Constipation
-
6 (22)
Vomiting
8 (21)
4 (15)
Arthralgia
7 (19)
3 (11)
Diarrhea
7 (19)
3 (11)
Cognitive disorder
-
4 (15)
Pain in extremity
5 (13)
-
Attention disturbance
4 (11)
3 (11)
Peripheral neuropathy
-
3 (11)
Musculoskeletal pain
4 (11)
-
Rash
4 (11)
-
Dizziness
4 (11)
5 (19)
21
Note: Data as of May 1, 2015; all grades as per NCI CTCAE v4.03
|
 Safety and
RP2D Determination ALKA-372-001
-
Two treatment-related Grade 3 AEs were observed:
Asthenia and Muscular Weakness; both resolved with dose reduction
-
No DLTs were observed in this study
STARTRK-1
-
Three treatment-related Grade 3 AEs were observed:
Neutropenia; resolved with dose reduction
2 DLTs at fixed daily dose of 800 mg:
Cognitive Impairment and Fatigue; both resolved upon study drug interruption
Based upon these two DLT events, the MTD was exceeded at 800 mg fixed
dose and 400 mg/m
2
per day was selected as the BSA-based RP2D
Further exploration of a fixed daily dose regimen and new formulation is
ongoing
22
Note: Data as of May 1, 2015 |
 ALKA and
STARTRK-1: Pharmacokinetics •
With continuous daily dosing, exposure increased in a dose proportional manner
•
Plasma half-life is ~ 20-24 hours
compatible with QD dosing
•
At the RP2D (400 mg/m²
QD), the plasma protein binding corrected mean C
trough
is ~ 2.5X to 3X
that of Target Concentrations correlating with complete tumor growth inhibition in preclinical
xenograft models
23 |
 Entrectinib
Responses in STARTRK-1 and ALKA-372-001 Studies 24
17 patients were ALK/ROS1 TKI-naïve with NTRK1/2/3, ROS1, or ALK
fusions Note: Data as of May 1, 2015; responses per RECIST v1.1 and based
upon local assessment |
 Entrectinib
Responses in STARTRK-1 and ALKA-372-001 Studies 25
91% response rate (10 out of 11) in Phase 2-Eligible Patient Population*
Phase 2-Eligible Patient Population*
Highlights
Note: Data as of May 1, 2015; one ALK responder was ALKi intolerant
*
NTRK1/2/3,
ROS1
or
ALK
fusion;
ALK/ROS1
TKI-naïve;
dosed
at
RP2D (400mg/m
2
)
•
•
•
•
•
3 of 3 responses in NTRK1/2/3+
NSCLC, CRC and acinic cell
cancer
5 of 6 responses, including 1 CR,
in ROS1+ NSCLC
2 of 2 responses in ALK+ NSCLC
and other solid tumor
9 patients remain on study
treatment
Durable responses of up to 16
treatment cycles |
 STARTRK-1
Subject with NTRK3 Fusion 42F
with
acinic
cell
CA
of
the
parotid,
first
diagnosed
in
March
2006
-
Prior therapies: surgery/EBRT, vinorelbine, carboplatin/paclitaxel,
additional surgery, doxorubicin, crizotinib
-
ECOG performance status of 1
-
Identified to have tumor harboring ETV6-NTRK3 fusion
-
Enrolled in STARTRK-1 at MSKCC in December 2014 with baseline
staging showing multiple paraspinal and pleural masses
26 |
 STARTRK-1
Subject with NTRK3 Fusion 27
•
Restaging during Cycle 2 (~8 wks) showed evidence for partial response
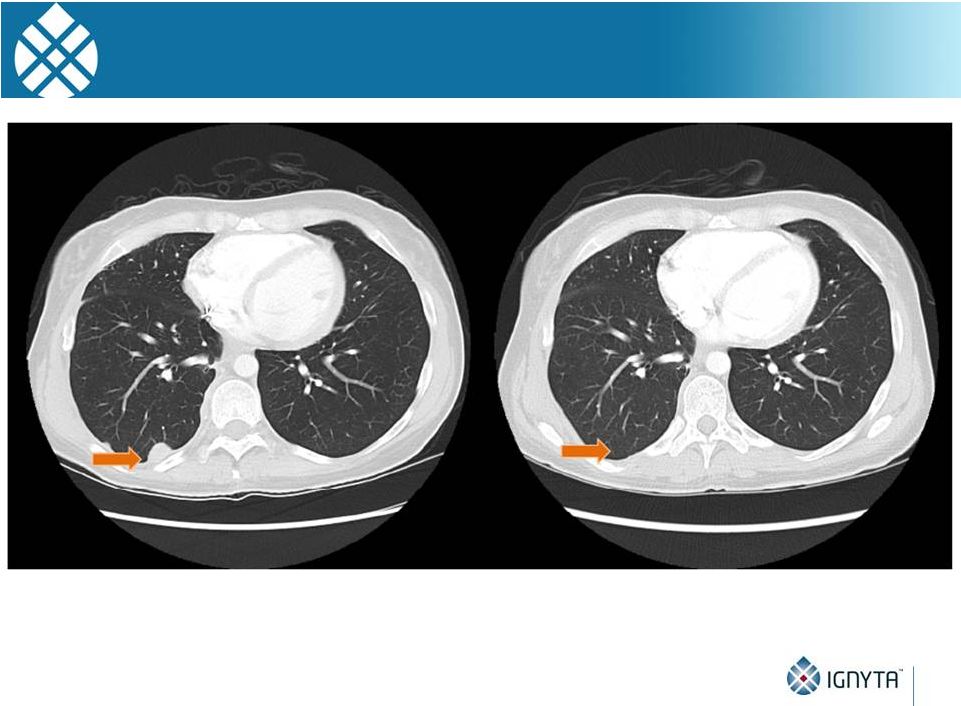
Images courtesy of A. Drilon, MD (MSKCC) |
 STARTRK-1
Subject with NTRK3 Fusion 28
Images courtesy of A. Drilon, MD (MSKCC) |
 STARTRK-1
Subject with NTRK3 Fusion 29
Images courtesy of A. Drilon, MD (MSKCC) |
 STARTRK-1
Subject with NTRK1 Fusion 46M with metastatic NSCLC, first diagnosed in November
2013 -
30 pack-year smoking history
-
Prior therapies: carboplatin/pemetrexed, pembrolizumab, docetaxel,
vinorelbine
-
ECOG performance status of 2
-
Required supplemental O
2
-
Significant pain and dyspnea due to widely metastatic disease
-
Staging head CT also revealed numerous (15 to 20) asymptomatic
brain metastases measuring up to 1.7 cm that had not been previously
treated
-
In hospice
-
Identified to have tumor harboring SQSTM1-NTRK1 fusion
-
Enrolled in STARTRK-1 at MGH in March 2015
30 |
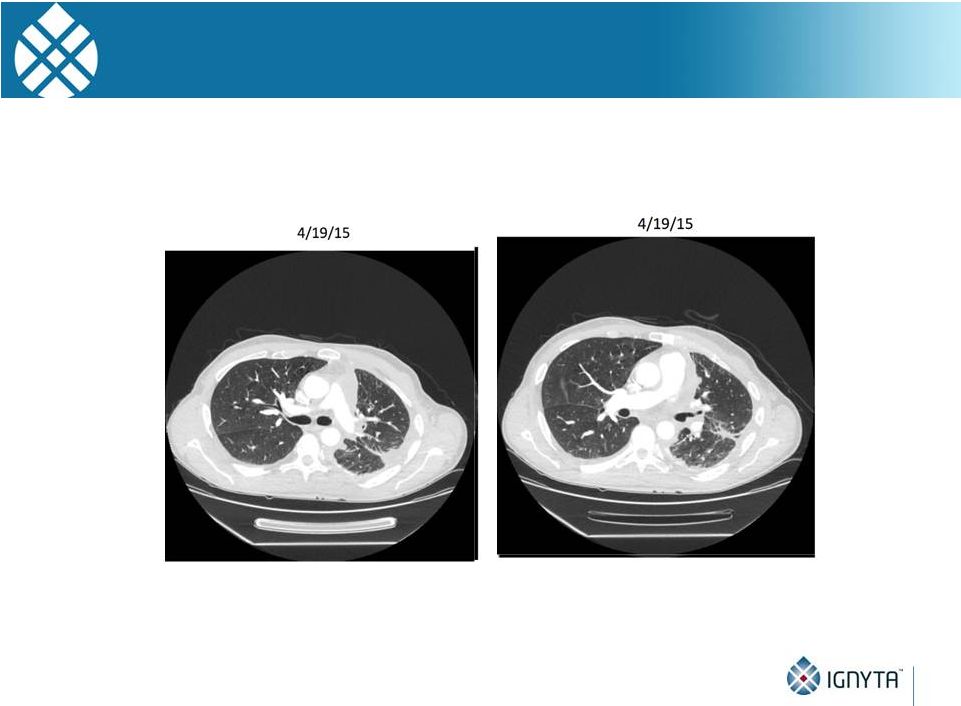
 STARTRK-1
Subject with NTRK1 Fusion Images courtesy of A. Shaw, MD, PhD and A. Farago, MD, PhD
(MGH) •
Baseline scan showing extensive lung lesions and pleural effusions
31 |
 STARTRK-1
Subject with NTRK1 Fusion Images courtesy of A. Shaw, MD, PhD and A. Farago, MD, PhD
(MGH) 32
•
Restaging during Cycle 1 (~4 wks) showed evidence for partial response
(and resolution of pleural effusions) |
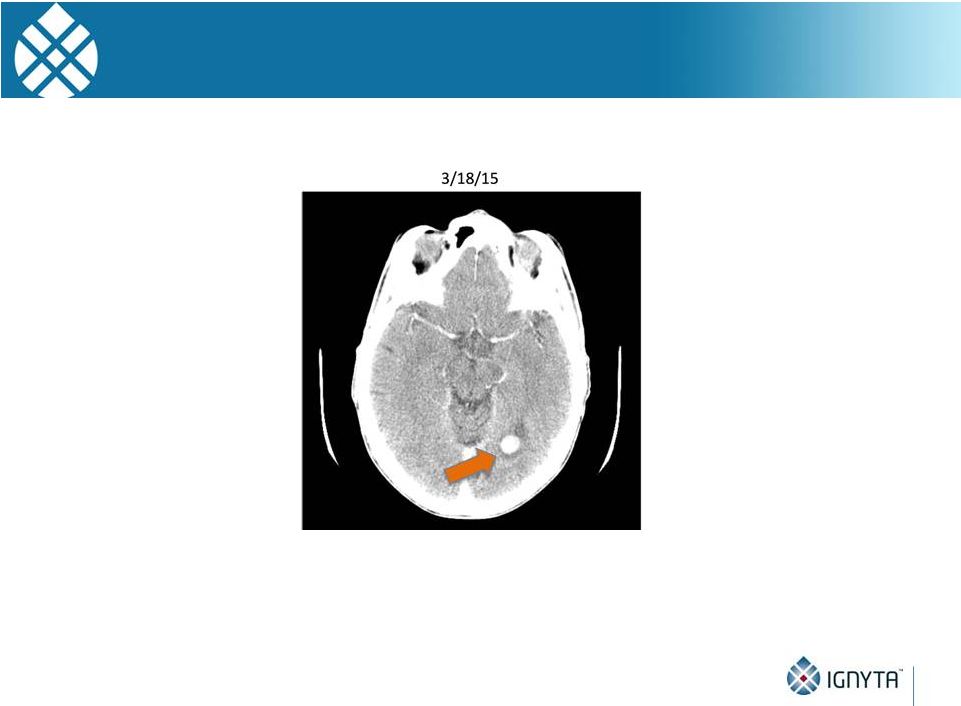 STARTRK-1
Subject with NTRK1 Fusion 33
•
Baseline scan showing brain metastases
Images courtesy of A. Shaw, MD, PhD and A. Farago, MD, PhD (MGH)
|
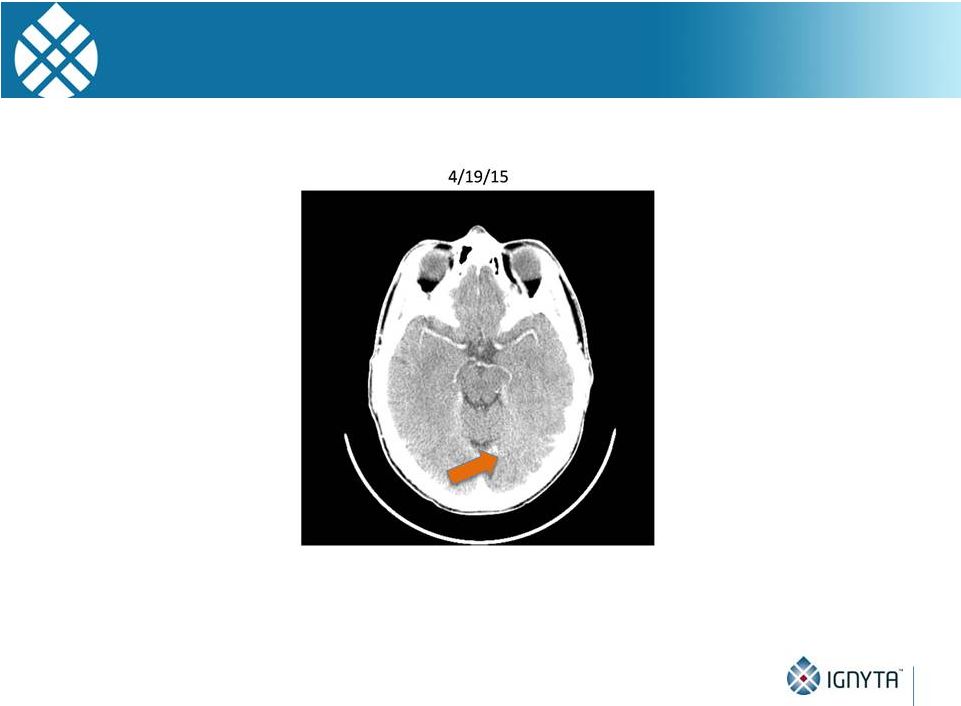 STARTRK-1
Subject with NTRK1 Fusion Images courtesy of A. Shaw, MD, PhD and A. Farago, MD, PhD
(MGH) 34
•
Evidence for tumor response in the CNS |
 ALKA and
STARTRK-1: NTRK Rearrangements 35
•
Compelling clinical activity in 3 patients with NTRK rearrangements (100% response rate)
-
3 different tumor types: NSCLC, CRC, acinic cell cancer
-
2 different Trk targets (TrkA, TrkC) with 3 different fusion partners
•
Compelling CNS activity in the only patient with an NTRK rearrangement and brain
metastases treated to date
•
All responded (3 PRs) within 1-2 cycles; 2 responses ongoing
Note: Data as of May 1, 2015 |
 ALKA and
STARTRK-1: ROS1 Rearrangements 36
•
10 patients with no prior ROS1i therapy
-
9 with NSCLC; 1 with neuroblastoma
-
3 treated below RP2D doses and one with nonevaluable disease
-
Remaining 5/6 responded (4 PRs, 1 CR) within 2 cycles; all responses ongoing
Note: Data as of May 1, 2015 |
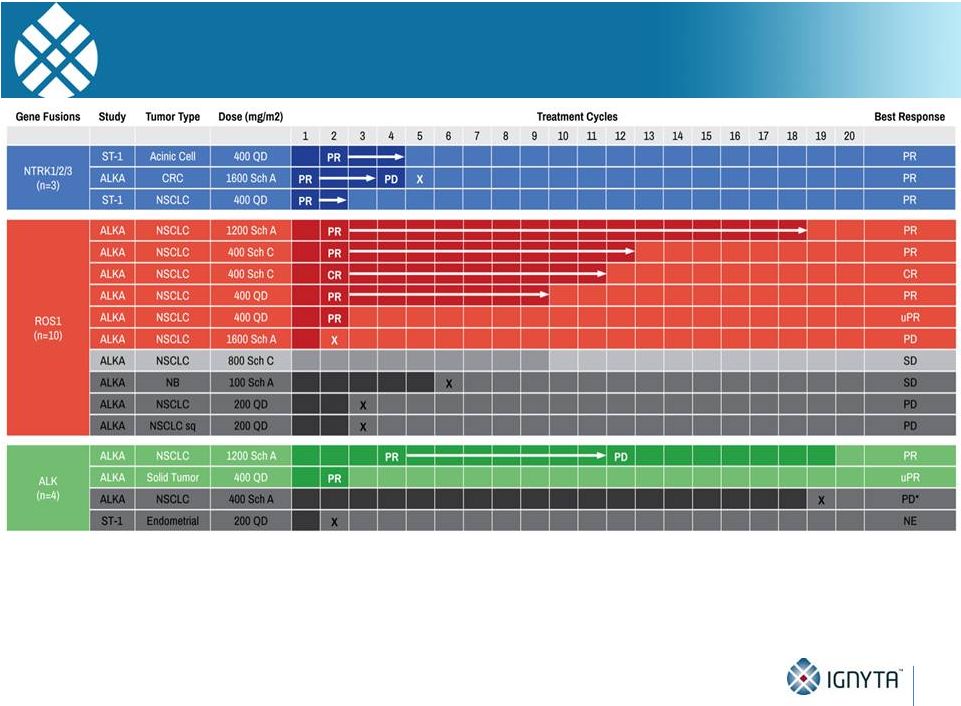 ALKA and
STARTRK-1: ALK Rearrangements 37
•
4 patients with no prior ALKi therapy
-
2 with NSCLC; 2 with other solid tumors
-
2 treated below RP2D doses
-
Remaining 2/2 responded (1 PR, 1 uPR) within 4 cycles; 1 response ongoing
Note: Data as of May 1, 2015 |
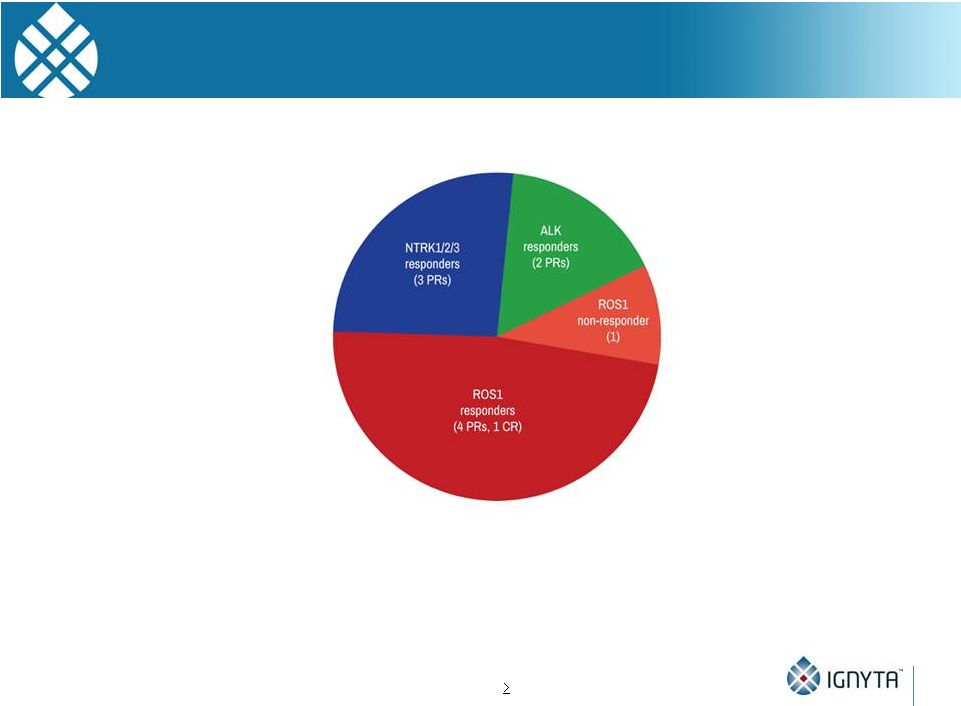 Entrectinib
Responses in Phase 2 Population •
11 patients across both studies
•
NTRK: 3 of 3 responses, including in NSCLC, CRC and acinic cell cancer;
•
ROS1: 5 of 6 responses, including one complete response, in NSCLC;
•
ALK: 2 of 2 responses in NSCLC and another solid tumor;
•
9 patients remain on study treatment; and
•
Durable responses of up to 16 treatment cycles
38
Note: Data as of May 1, 2015; one ALK responder was ALKi intolerant
91% response rate (10 out of 11) in Phase 2-Eligible Patient Population*
•
NTRK1/2/3,
ROS1
or
ALK
fusion;
ALK/ROS1
TKI-naïve;
dosed
at
RP2D (400mg/m²) |
 ALKA and
STARTRK-1: Other Alterations/Treatment History Among the remaining 50 patients,
most either had non-fusion alterations or were ALKi-
or ROS1i-resistant:
-
Non-fusion alterations (n=26)
NTRK1/2/3 SNPs, IHC+, amplifications: n=15 (6 ongoing)
ROS1 amplifications, deletions: n=4
ALK SNPs, amplifications, deletions: n=7
(2 ongoing : 1 patient with neuroblastoma had a PR for 9 cycles and remains on
study)
-
Resistant (n=20)
ROS1 fusions, ROS1i-resistant: n=3 (1 ongoing); all 3 pts had one prior TKI
ALK fusions, ALKi-resistant: n=17 (4 ongoing); 3 pts had 3 prior TKIs, 9 pts had 2
prior TKIs, and 5 pts had 1 prior TKI
-
Other (n=4):
False positives (n=2)
No alterations (n=2)
-
13 patients (26%) remain on study
39 |
 Entrectinib
Clinical Summary Status: Two Phase 1 clinical studies of entrectinib are ongoing
Safety: Entrectinib has been well tolerated, including with daily dosing, with
no treatment-related SAEs and two reversible DLTs
RP2D:
The
BSA-based
RP2D
is
400
mg/m
2
daily with ongoing exploration of
fixed dose regimen
Preliminary efficacy:
-
Phase 2 studies will focus on rearrangements of NTRK1/2/3, ROS1 and ALK;
rearrangements are known to be oncogenic drivers in multiple tumor types
-
10 responses (1 CR, 7 PRs, 2 uPRs) have been demonstrated—across multiple
different tumor types and gene fusions—out of 11 Phase 2 eligible
patients (91% response rate)
-
1 additional response in a neuroblastoma patient with an activating ALK SNP
40
Note: Data as of May 1, 2015 |
 Contents
Ignyta overview
Entrectinib preclinical data
ASCO clinical program update
Entrectinib future plans
Vision and milestones
41 |
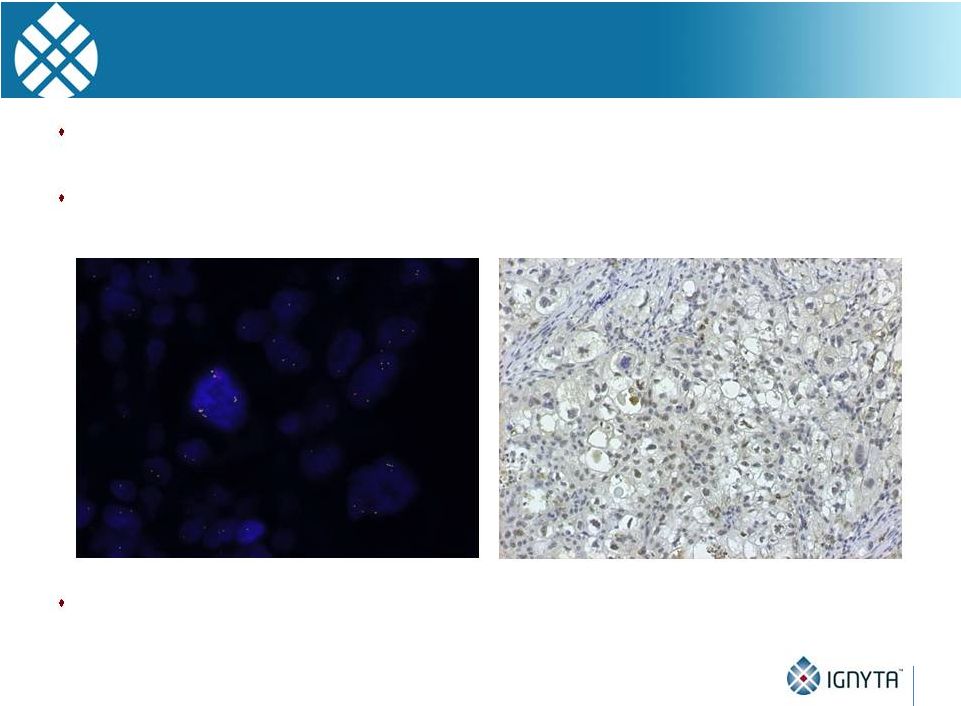 Why
“Rx/Dx” Matters
42
Unlike ALK, which has one predominant fusion partner (EML4), NTRKs have at
least 17 fusion partners, each with different break points
Thus, a sophisticated diagnostic screening methodology is required
Ignyta’s NGS-based assay has been specifically optimized for the detection of
activating
NTRK1, NTRK2 and NTRK3 alterations, in addition to ROS1 and ALK
-
Multiplex NGS assay scalable to add future genes of interest
ALK gene fusion positive by FISH…
But no active protein expressed (IHC) |
 Ignyta’s
Internal CDx Approach Is a Differentiator in the Competition to Identify and Recruit
Patients 43
Another difference from ALK, which predominantly occurs in one tumor type
(NSCLC), NTRK fusions are found in at least 13 different tumor types
Thus, a sophisticated trial design and clinical development strategy is required to
collect data across multiple tumor types, using the CDx as the common feature…
TrkA IHC+
NTRK1 FISH+
Ignyta NGS:
TPM3-NTRK1 |
 Studies
Targeting Alterations Responsive to Targeted Receptor Kinase inhibition Patients with
Solid Tumors (any line of therapy) Tumor sample submission for CDx analysis at
Ignyta’s central lab Separate by molecular alteration and solid tumor type
NTRK1/2/3
fusions
STARTRK-2 Basket Study initiated at clinical sites globally
SIMON 2-STAGE RULES:
1
st
stage: 6 pts (
1 response)
2
nd
stage: + 8 pts (
5 responses)
Open new “basket” STARTRK-2: Entrectinib Global Phase 2 Basket
Study Combines Previously Described STARTRK-1 Ph 2a and STARTRK-2 Designs
ROS1
fusions
NTRK1/2/3
fusions
Separate analyses by Cohort (basket)
Primary endpoint = ORR
Key secondary endpoint = DOR
ROS1
fusions
NTRK1/2/3
fusions
ROS1
fusions
ALK fusions
ALK fusions
NTRK1/2/3,
ROS1, and ALK
non-fusion
alterations
Pancreatic Ca
NTRK1/2/3
overexpression
e.g.,
NSCLC
Possible chemotherapy per MD
44
Note: ORR = objective response rate; DOR = duration of response
CRC
All other non-NSCLC, non-CRC solid tumors
All solid tumors |
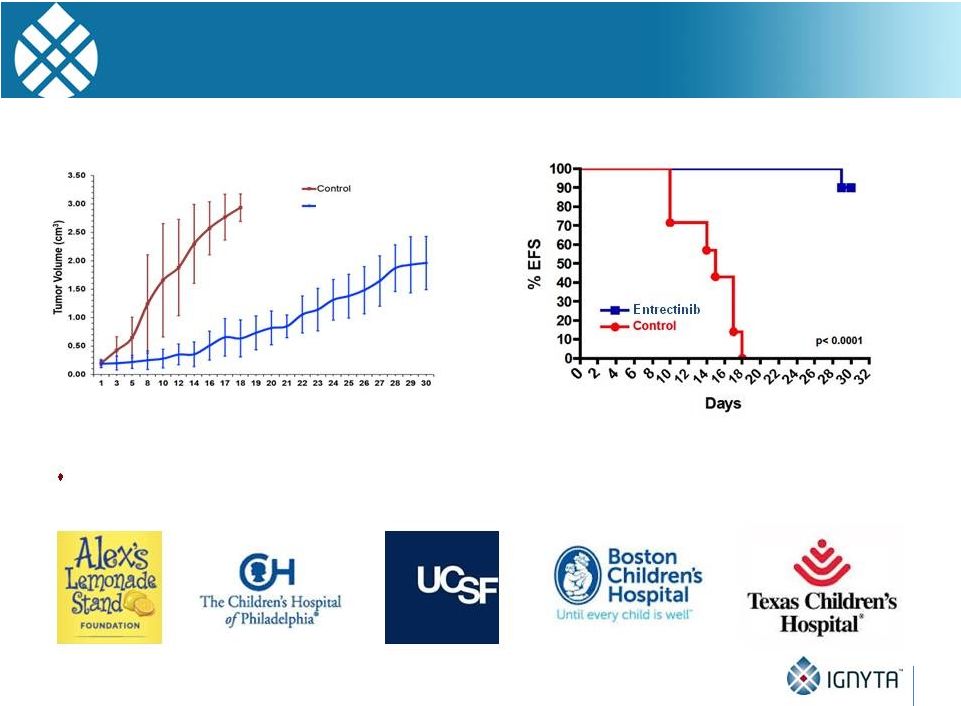 45
Indication Expansion Beyond Fusions
Pediatric Neuroblastoma
SY5Y-TrkB Neuroblastoma Xenograft Model
Ph 1/1b pediatric CNS tumor (including neuroblastoma) study planned for Q4:15
Days post treatment start
Entrectinib (60 mg/kg, BID) |
 Contents
Ignyta overview
Entrectinib preclinical data
ASCO clinical program update
Entrectinib future plans
Vision and milestones
46 |
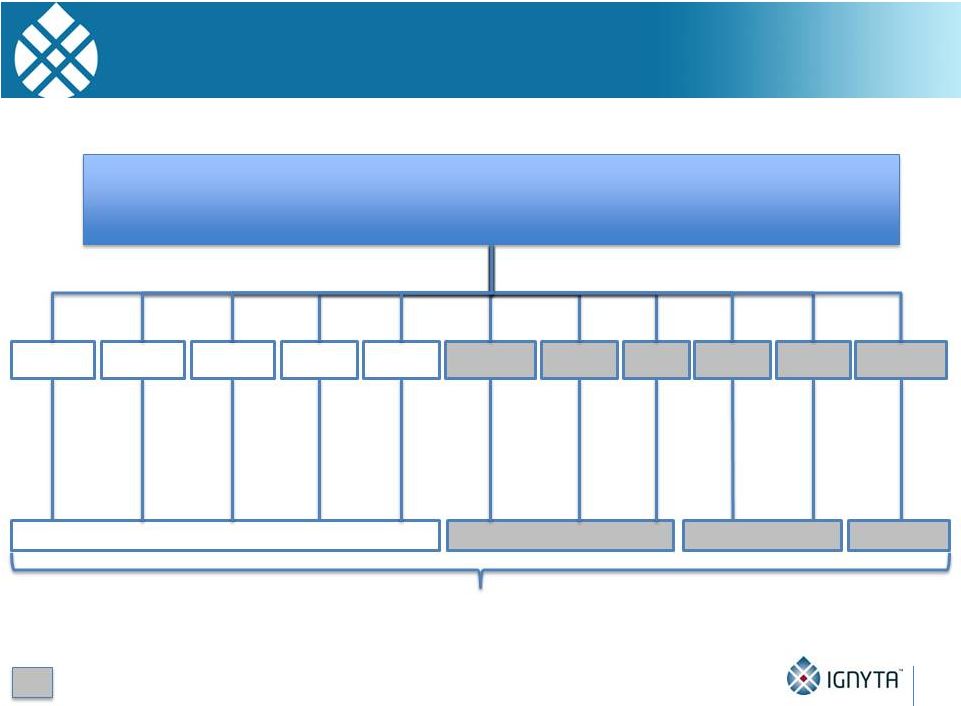 Ignyta’s
Precision Oncology Vision: A CRx for Each Oncogene Driver Identified by Our CDx
47
Ignyta’s Trailblaze™
Companion Diagnostic (CDx):
Multiplex assay(s) for identifying actionable oncogenes in various solid tumors
that can then be targeted with Ignyta’s pipeline of companion therapeutics (CRx)
NTRK1+
Entrectinib
ROS1+
mBRAF
RET+
cMET+
mKRAS
EGFR+
RXDX-105
RXDX-108
NTRK2+
NTRK3+
AXL+
RXDX-106
ALK+
Recently expanded oncogene targets and programs
Ignyta’s first-in-class and best-in-class CRx’s
|
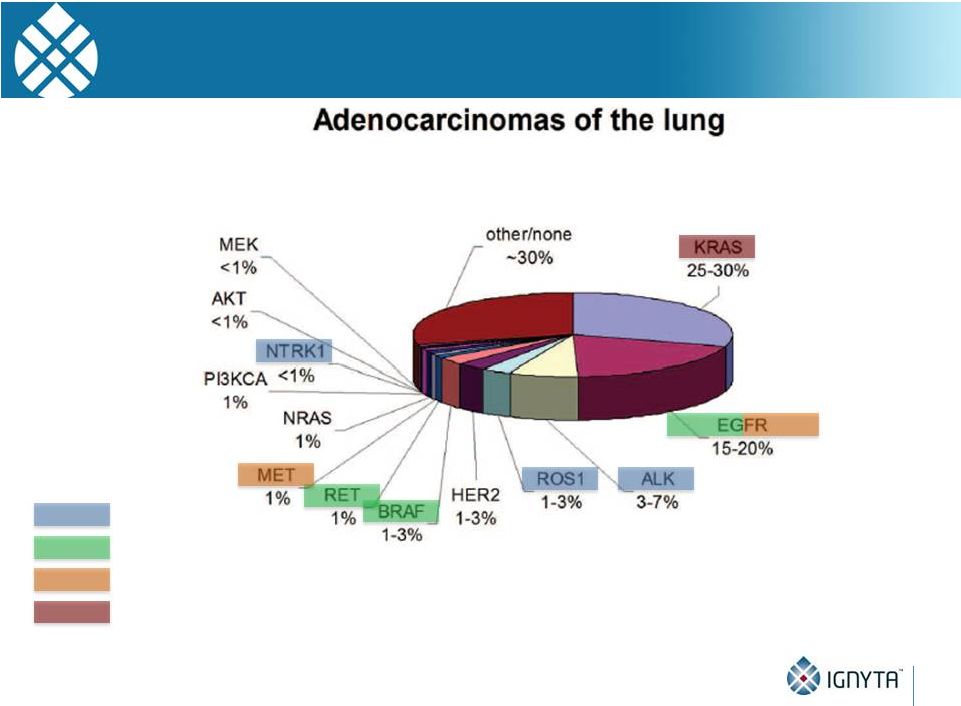 Ignyta
Pipeline Now Has Potential to Address More than 80% of Known Oncogenic Drivers in
NSCLC 48
entrectinib
RXDX-105
RXDX-106
RXDX-108
Gerber et al., 2014 ASCO Educational Book. |
 Driver
Oncogenes in Just 2 Solid Tumor Indications Represent Substantial Market Opportunities
for Two Lead Programs >30,000 NSCLC or CRC patients
in the US each year have a newly detected known
oncogenic fusion kinase or activating mutation that may be targeted by entrectinib
or RXDX-105
49
NTRK1
fusions
NTRK2
fusions
NTRK3
fusions
ROS1
fusions
ALK
fusions
RET
fusions
BRAF
fusions
BRAF
mutations
Total
Patients
NSCLC
~1%
<1%
<1%
1-2%
4-7%
2%
<1%
1-3%
12,400
Colorectal
~1%
<1%
<1%
~1%
~1%
~1%
5-10%
18,000
Total
2,300
500
1,500
2,100
6,400
3,200
1,900
12,500
30,400
entrectinib:
12.8k pts
RXDX-105:
17.6k pts
Source: NCI; NHS; Shaw et al., Nature Reviews Cancer 2013; Gerber et al., 2014 ASCO
Educational Book; Stransky et al., Nature Communications
2014;
Wiesner
et
al.,
Nature
Communications
2014;
Lipson
et
al.,
Nature
Medicine
2012;
unpublished
communications
with
study
authors
Note: Estimates above based on US incidence only; assumed midpoint of incidence ranges
multiplied by published incidence data for each indication. Indication | Alteration
|
 Driver
Oncogenes in Just 2 Solid Tumor Indications Represent Substantial Market Opportunities
for Two Lead Programs 50
NTRK1
fusions
NTRK2
fusions
NTRK3
fusions
ROS1
fusions
ALK
fusions
RET
fusions
BRAF
fusions
BRAF
mutations
Total
Patients
NSCLC
~1%
<1%
<1%
1-2%
4-7%
2%
<1%
1-3%
4,200
Colorectal
~1%
<1%
<1%
~1%
~1%
~1%
5-10%
7,300
Total
2,300
500
1,500
700
1,400
3,200
1,900
-
11,500
entrectinib:
6.4k pts
RXDX-105:
5.1k pts
We estimate over 11,000 patients
in
Source: NCI; NHS; Shaw et al., Nature Reviews Cancer 2013; Gerber et al., 2014 ASCO
Educational Book; Stransky et al., Nature Communications
2014;
Wiesner
et
al.,
Nature
Communications
2014;
Lipson
et
al.,
Nature
Medicine
2012;
unpublished
communications
with
study
authors
Note: Estimates above based on US incidence only; assumed midpoint of incidence ranges
multiplied by published incidence data for each indication. FIC opportunity
Indication | Alteration
represent potential FIC opportunities for entrectinib or RXDX-105
11 biomarker positive cohorts of
NSCLC and CRC |
 Driver
Oncogenes in Just 2 Solid Tumor Indications Represent Substantial Market Opportunities
for Two Lead Programs 51
FIC opportunity
BIC upside opportunity
BIC BRAF-mutant metastatic CRC doubles the addressable market with upside
of >10,000 patients
for RXDX-105, or >22,000
patients
for entrectinib and
RXDX-105
NTRK1
fusions
NTRK2
fusions
NTRK3
fusions
ROS1
fusions
ALK
fusions
RET
fusions
BRAF
fusions
BRAF
mutations
Total
Patients
NSCLC
~1%
<1%
<1%
1-2%
4-7%
2%
<1%
1-3%
4,200
Colorectal
~1%
<1%
<1%
~1%
~1%
~1%
5-10%
18,000
Total
2,300
500
1,500
700
1,400
3,200
1,900
10,700
22,200
entrectinib:
6.4k pts
RXDX-105:
15.8k pts
Source: NCI; NHS; Shaw et al., Nature Reviews Cancer 2013; Gerber et al., 2014 ASCO
Educational Book; Stransky et al., Nature Communications
2014;
Wiesner
et
al.,
Nature
Communications
2014;
Lipson
et
al.,
Nature
Medicine
2012;
unpublished
communications
with
study
authors
Note: Estimates above based on US incidence only; assumed midpoint of incidence ranges
multiplied by published incidence data for each indication. Indication | Alteration
|
 2015
– 2016 Corporate Milestones & Clinical Updates
52
2030 Vision
2015 -
2016 Milestones
Obtain US orphan drug designation for at least one indication
Identify RP2D, preferred dosing schedule for entrectinib, mid-2015
Initiate STARTRK-2 Ph 2, including internally developed CDx, 3Q15
Identify RP2D for RXDX-105, 2H15; initiate Study 1105 Ph 1b RET+ and BRAF+ solid tumors,
4Q15 File IND for RXDX-106 and/or RXDX-107, 2H15
Clinical data from ALKA-372-001 and STARTRK-1 at ASCO, 2Q15
Clinical data for entrectinib and RXDX-105 at ESMO or ENA, 2H15
Clinical study update from STARTRK-2 Ph 2 and Study 1105 Ph 1b at AACR/ASCO, 2Q16
Clinical update or data for entrectinib, RXDX-105, -106, -107 at ESMO/ENA,
2H16 2015 -
2016 Clinical Updates
2011 –
2015
Advance clinical
pipeline
2016 –
2020
Commercialize
RXDX lead
2021 –
2025
Scale pipeline
revenue
2026 –
2030
Drive sustainable
profitability
Leading precision
medicine
company |
 Company
Highlights 53
Precision oncology company with integrated approach to Rx/Dx development
Experienced management team, excellent track record in oncology
Pipeline
with
of targeted first-in-class and
best-in-class product candidates under clinical
development in oncology Multiple potential registration-enabling studies initiating
in 2015 Comprehensive diagnostic capabilities and biomarker strategies for patient
screening and confirmation
Composition of matter IP for pipeline of development candidates
Strong financial position
20-year vision to be the leading precision oncology company
critical mass |
