Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| 8-K - 8-K - FASTENAL CO | fast1231138k.htm |
EXHIBIT 99.1
Fastenal Company Reports 2013 Fourth Quarter and Annual Earnings
WINONA, Minn., January 15, 2014 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- Fastenal Company of Winona, MN (Nasdaq:FAST) reported the results of the quarter and year ended December 31, 2013. Except for per share information, or as otherwise noted below, dollar amounts are stated in thousands.
Net sales (and the related daily sales), pre-tax earnings, net earnings, and net earnings per share were as follows for the periods ended December 31:
Twelve-month Period | Three-month Period | ||||||||||||||||
2013 | 2012 | Change | 2013 | 2012 | Change | ||||||||||||
Net sales | $ | 3,326,106 | 3,133,577 | 6.1% | $ | 813,760 | 757,235 | 7.5% | |||||||||
Business days | 254 | 254 | 63 | 63 | |||||||||||||
Daily sales | 13,095 | 12,337 | 6.1% | 12,917 | 12,020 | 7.5% | |||||||||||
Pre-tax earnings | $ | 713,468 | 674,155 | 5.8% | $ | 157,274 | 158,151 | -0.6% | |||||||||
% of sales | 21.5 | % | 21.5 | % | 19.3 | % | 20.9 | % | |||||||||
Net earnings | $ | 448,636 | 420,536 | 6.7% | $ | 99,229 | 98,716 | 0.5% | |||||||||
Net earnings per share (basic) | $ | 1.51 | 1.42 | 6.3% | $ | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.0% | |||||||||
Set forth below is certain information as of December 31: | |||||||
2013 | 2012 | Change | |||||
Number of stores | 2,687 | 2,652 | 1.3% | ||||
FAST Solutions® (industrial vending) machines (equivalent basis - defined later in document) | 33,920 | 21,095 | 60.8% | ||||
Employee count | 17,277 | 15,145 | 14.1% | ||||
FOURTH QUARTER
In December 2013 we issued a press release intended to provide an update on the fourth quarter of 2013. This is only the second time, in our 26 years of being a public company, we have taken this step. Our goal is to keep this type of communication very rare. We took this step because our December sales trends were weak, but, more importantly, because our gross margin trends were deteriorating. In the days following our release, our sales and gross margin trends continued to weaken. This weakening was worse than we expected and this created additional drain on our ability to grow earnings. We did grow our net earnings in the fourth quarter of 2013, but we are disappointed our net earnings per share did not grow.
Regarding gross margin, we slid outside our expected 51% to 53% range in the fourth quarter. As previously disclosed in our December release, this is largely due to: (1) lower utilization of our trucking network which is expected to naturally correct in the new year as seasonality lifts our utilization; (2) supplier incentives, which are typically aligned with the calendar year and reset for 2014; (3) product mix (fasteners carry a higher gross margin), and (4) a very competitive marketplace. The last two factors require external and internal improvements. We are actively working on the internal component and are positioning our business to take advantage of improvements in the industrial economy, but the timing is uncertain. Despite this, we continue to believe the 51% to 53% range is appropriate for our business given our end market and product mix.
BUSINESS DISCUSSION
Similar to previous quarters, we have included comments regarding several aspects of our business:
1. | Monthly sales changes, sequential trends, and end market performance – a recap of our recent sales trends and some insight into the activities with different end markets. |
2. | Growth drivers of our business – a recap of how we grow our business. |
3. | Profit drivers of our business – a recap of how we increase our profits. |
4. | Statement of earnings information – a recap of the components of our income statement. |
5. | Operational working capital, balance sheet, and cash flow – a recap of the operational working capital utilized in our business, and the related cash flow. |
1
While reading these items, it is helpful to appreciate several aspects of our marketplace: (1) it's big, the North American marketplace for industrial supplies is estimated to be in excess of $160 billion per year (and we have expanded beyond North America), (2) no company has a significant portion of this market, (3) many of the products we sell are individually inexpensive, (4) when our customer needs something quickly or unexpectedly our local store is a quick source, (5) the cost and time to manage and procure these products is meaningful, and (6) the cost to move these products, many of which are bulky, can be significant.
Our motto is Growth through Customer Service®. This is important given the points noted above. We believe in efficient markets – to us, this means we can grow our market share if we provide the greatest value to the customer. We believe our ability to grow is amplified if we can service our customer at the closest economic point of contact. For us, this 'closest economic point of contact' is the local store; therefore, our focus centers on understanding our customers' day, their opportunities, and their obstacles.
The concept of growth is simple, find more customers every day and increase your activity with them. However, execution is hard work. First, we recruit service minded individuals to support our customers and their business. Second, we operate in a decentralized fashion to help identify the greatest value for our customers. Third, we build a great machine behind the store to operate efficiently and to help identify new business solutions. Fourth, we do these things every day. Finally, we strive to generate strong profits; these profits produce the cash flow necessary to fund the growth and to support the needs of our customers.
SALES GROWTH:
Net sales and growth rates in net sales were as follows:
Twelve-month Period | Three-month Period | ||||||||||||||
2013 | 2012 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||||
Net sales | $ | 3,326,106 | $ | 3,133,577 | $ | 813,760 | $ | 757,235 | |||||||
Percentage change | 6.1 | % | 13.3 | % | 7.5 | % | 8.5 | % | |||||||
The increase in net sales in 2013 and 2012 (and also in the latest three-month periods) came primarily from higher unit sales. Our growth in net sales was impacted by slight inflationary price changes in our non-fastener products and some price deflation in our fastener products, with the net impact being a slight drag on growth. Our growth in net sales was not meaningfully impacted by the introduction of new products or services, with one exception. Over the last several years, our FAST Solutions® (industrial vending) initiative has stimulated faster growth with a subset of our customers (discussed later in this document). The higher unit sales resulted primarily from increases in sales at older store locations (discussed below and again later in this document) and to a lesser degree the opening of new store locations in the last several years. The growth in net sales at the older store locations was due to the growth drivers of our business (discussed later in this document), and, in the case of 2012, the moderating impacts of the recessionary environment. The change in currencies in foreign countries (primarily Canada) relative to the United States dollar lowered our daily sales growth rate by 0.2% and 0.1% in 2013 and 2012, respectively, lowered it by 0.4% in the three-month period of 2013, and lifted it by 0.2% in the last three months of 2012.
MONTHLY SALES CHANGES, SEQUENTIAL TRENDS, AND END MARKET PERFORMANCE
Note – Daily sales are defined as the net sales for the period divided by the number of business days (in the United States) in the period.
This section focuses on three distinct views of our business – monthly sales changes, sequential trends, and end market performance. The first discussion regarding monthly sales changes provides a good mechanical view of our business based on the age of our stores. The second discussion provides a framework for understanding the sequential trends (that is, comparing a month to the immediately preceding month) in our business. Finally, we believe the third discussion regarding end market performance provides insight into activities with our various types of customers.
MONTHLY SALES CHANGES:
All company sales – During the months in 2013, 2012, and 2011, all of our selling locations, when combined, had daily sales growth rates of (compared to the comparable month in the preceding year):
Jan. | Feb. | Mar. | Apr. | May | June | July | Aug. | Sept. | Oct. | Nov. | Dec. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
2013 | 6.7 | % | 8.2 | % | 5.1 | % | 4.8 | % | 5.3 | % | 6.0 | % | 2.9 | % | 7.2 | % | 5.7 | % | 7.7 | % | 8.2 | % | 6.7 | % | |||||||||||
2012 | 21.3 | % | 20.0 | % | 19.3 | % | 17.3 | % | 13.1 | % | 14.0 | % | 12.1 | % | 12.0 | % | 12.9 | % | 6.8 | % | 8.2 | % | 9.7 | % | |||||||||||
2011 | 18.8 | % | 21.5 | % | 22.8 | % | 23.2 | % | 22.6 | % | 22.5 | % | 22.4 | % | 20.0 | % | 18.8 | % | 21.4 | % | 22.2 | % | 21.2 | % | |||||||||||
2
Stores opened greater than two years – Our stores opened greater than two years (store sites opened as follows: 2013 group – opened 2011 and earlier, 2012 group – opened 2010 and earlier, and 2011 group – opened 2009 and earlier) represent a consistent 'same-store' view of our business. During the months in 2013, 2012, and 2011, the stores opened greater than two years had daily sales growth rates of (compared to the comparable month in the preceding year):
Jan. | Feb. | Mar. | Apr. | May | June | July | Aug. | Sept. | Oct. | Nov. | Dec. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
2013 | 5.0 | % | 6.5 | % | 3.4 | % | 3.1 | % | 3.5 | % | 4.3 | % | 1.4 | % | 5.5 | % | 4.2 | % | 6.1 | % | 6.2 | % | 4.9 | % | |||||||||||
2012 | 18.8 | % | 17.1 | % | 16.8 | % | 14.5 | % | 10.1 | % | 11.1 | % | 9.1 | % | 8.6 | % | 9.8 | % | 3.8 | % | 5.1 | % | 6.6 | % | |||||||||||
2011 | 16.0 | % | 18.4 | % | 19.4 | % | 19.6 | % | 19.2 | % | 19.1 | % | 18.7 | % | 16.5 | % | 15.2 | % | 18.0 | % | 18.5 | % | 17.5 | % | |||||||||||
Stores opened greater than five years – The impact of the economy, over time, is best reflected in the growth performance of our stores opened greater than five years (store sites opened as follows: 2013 group – opened 2008 and earlier, 2012 group – opened 2007 and earlier, and 2011 group – opened 2006 and earlier). This group, which represented about 88% of our total sales in 2013, is more cyclical due to the increased market share they enjoy in their local markets. During the months in 2013, 2012, and 2011, the stores opened greater than five years had daily sales growth rates of (compared to the comparable month in the preceding year):
Jan. | Feb. | Mar. | Apr. | May | June | July | Aug. | Sept. | Oct. | Nov. | Dec. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
2013 | 3.2 | % | 5.6 | % | 2.3 | % | 2.0 | % | 2.7 | % | 3.4 | % | 0.6 | % | 4.7 | % | 3.2 | % | 5.3 | % | 6.1 | % | 4.8 | % | |||||||||||
2012 | 17.4 | % | 15.8 | % | 15.7 | % | 13.7 | % | 9.0 | % | 10.2 | % | 8.3 | % | 7.9 | % | 8.5 | % | 2.6 | % | 4.6 | % | 5.6 | % | |||||||||||
2011 | 15.3 | % | 17.9 | % | 19.2 | % | 19.1 | % | 17.9 | % | 18.2 | % | 17.3 | % | 15.2 | % | 14.5 | % | 17.0 | % | 17.4 | % | 16.9 | % | |||||||||||
There are three distinct influences to our growth: (1) execution, (2) currency fluctuations, and (3) economic fluctuations. This discussion centers on (2) and (3).
Summarizing comments – The change in currencies in foreign countries (primarily Canada) relative to the United States dollar impacted our growth over the last several years. During 2011 it lifted our growth by 0.7%, in 2012 it lowered our growth by 0.1%, and in 2013 it lowered our growth by 0.2%.
Regarding economic fluctuations, in 2011 we enjoyed strong growth. This reflected the strengthening economic environment being experienced by our customers. While the strength did not apply to all customers and to all geographies we serve, it was strong enough to produce acceptable results. During 2012, the growth in the first three and a half months generally continued the relative strength we saw in 2011. Then we began to experience several distinct economic slowdowns. The first occurred in the late April/May time frame, and then moderated until September 2012. The second occurred in the October/November time frame. This was exaggerated by the impact of Hurricane Sandy and an unusual business day comparison in October (23 days in 2012 versus 21 days in 2011 - the maintenance portion of our business is often linked to monthly spend patterns of our customers, which are not as business day dependent, this can dilute the daily growth picture given the change in business day divisor). The third occurred in the spring of 2013. This involved our fastener product line and our construction business (primarily non-residential construction). This third slowdown, similar to the first two listed, mirrored or slightly led some softening in the PMI index (discussed later in this document). The fastener piece was heavily impacted by our OEM (original equipment manufacturing) customers. These customers utilize our fasteners in the manufacture/assembly of their finished products. The end markets with the most pronounced weakening included heavy machinery manufacturers with exposure to: mining, military, agriculture, and construction. The construction piece in 2013 was also hampered by poor weather during the winter and spring time frame throughout many areas in North America. The fourth and fifth occurred in July 2013 and December 2013. The daily sales growth in July 2013 and December 2013 were negatively impacted by the timing of the July 4th holiday (Thursday in 2013, Wednesday in 2012, Monday in 2011) and the Christmas/New Year holiday (Wednesday in 2013, Tuesday in 2012, and Sunday in 2011). This resulted in a 'lone' business day on Friday, July 5th in which many of our customers were closed, and three distinct one to two day work periods in the last two weeks of December. The December impact was amplified due to poor weather conditions.
Our daily sales growth trends have improved since September 2013. This was largely related to changing comparisons to 2012. Our sales to customers engaged in light and medium duty manufacturing (largely related to consumer products) are improving; this makes sense given the trends in the PMI index. However, our sales to customers engaged in heavy machinery manufacturing (primarily serving the mining, military, agricultural, and construction end markets), which represents approximately one fifth of our business, continued to experience weak performance in the fourth quarter of 2013.
SEQUENTIAL TRENDS:
We find it helpful to think about the monthly sequential changes in our business using the analogy of climbing a stairway – This stairway has several predictable landings where there is a pause in the sequential gain (i.e. April, July, and
3
October to December), but generally speaking, climbs from January to October. The October landing then establishes the benchmark for the start of the next year.
History has identified these landings in our business cycle. They generally relate to months with impaired business days (certain holidays). The first landing centers on Easter, which alternates between March and April (Easter occurred in March in 2013, and in April in 2012 and 2011), the second landing centers on July 4th, and the third landing centers on the approach of winter with its seasonal impact on primarily our construction business and with the Christmas/New Year holidays. The holidays we noted impact the trends because they either move from month-to-month or because they move around during the week (the July 4th and Christmas/New Year holiday impacts noted earlier in this document are examples).
The table below shows the pattern to the sequential change in our daily sales. The line labeled 'Old Benchmark' is an historical average of our sequential daily sales change for the period 1998 to 2003. We chose this time frame because it had similar characteristics, a weaker industrial economy in North America, and could serve as a benchmark for current performance. The '2013', '2012', and '2011' lines represent our actual sequential daily sales changes. The '13Delta', '12Delta', and '11Delta' lines indicate the difference between the 'Old Benchmark' and the actual results in the respective year.
Beginning in 2014, we intend to utilize a new benchmark. The new benchmark, labeled 'New Benchmark' in the table below, is an historical average of our sequential daily sales change for the period 1998 to 2013, excluding 2008 and 2009. Similar to the 'Old Benchmark' we believe this updated benchmark will serve to show the historical pattern. We excluded the 2008 to 2009 time frame because it contains an extreme economic event and we don't believe it is comparable.
Jan.(1) | Feb. | Mar. | Apr. | May | June | July | Aug. | Sept. | Oct. | Cumulative Change from Jan. to Oct. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Old Benchmark | 0.9 | % | 3.3 | % | 2.9 | % | -0.3 | % | 3.4 | % | 2.8 | % | -2.3 | % | 2.6 | % | 2.6 | % | -0.7 | % | 15.1 | % | ||||||||||
2013 | -0.4 | % | 2.0 | % | 3.4 | % | -1.1 | % | 1.0 | % | 3.2 | % | -5.5 | % | 5.5 | % | 2.9 | % | -2.9 | % | 8.2 | % | ||||||||||
13Delta | -1.3 | % | -1.3 | % | 0.5 | % | -0.8 | % | -2.4 | % | 0.4 | % | -3.2 | % | 2.9 | % | 0.3 | % | -2.2 | % | -6.9 | % | ||||||||||
2012 | -0.3 | % | 0.5 | % | 6.4 | % | -0.8 | % | 0.5 | % | 2.5 | % | -2.7 | % | 1.3 | % | 4.3 | % | -4.8 | % | 7.1 | % | ||||||||||
12Delta | -1.2 | % | -2.8 | % | 3.5 | % | -0.5 | % | -2.9 | % | -0.3 | % | -0.4 | % | -1.3 | % | 1.7 | % | -4.1 | % | -8.0 | % | ||||||||||
2011 | -0.2 | % | 1.6 | % | 7.0 | % | 0.9 | % | 4.3 | % | 1.7 | % | -1.0 | % | 1.4 | % | 3.4 | % | 0.7 | % | 21.7 | % | ||||||||||
11Delta | -1.1 | % | -1.7 | % | 4.1 | % | 1.2 | % | 0.9 | % | -1.1 | % | 1.3 | % | -1.2 | % | 0.8 | % | 1.4 | % | 6.6 | % | ||||||||||
New Benchmark | 0.8 | % | 2.2 | % | 3.8 | % | 0.4 | % | 3.1 | % | 2.7 | % | -2.1 | % | 2.5 | % | 3.7 | % | -1.2 | % | 15.9 | % | ||||||||||
(1) | The January figures represent the percentage change from the previous October, whereas the remaining figures represent the percentage change from the previous month. |
A graph of the sequential daily sales change pattern discussed above, starting with a base of '100' in the previous October and ending with the next October, would be as follows: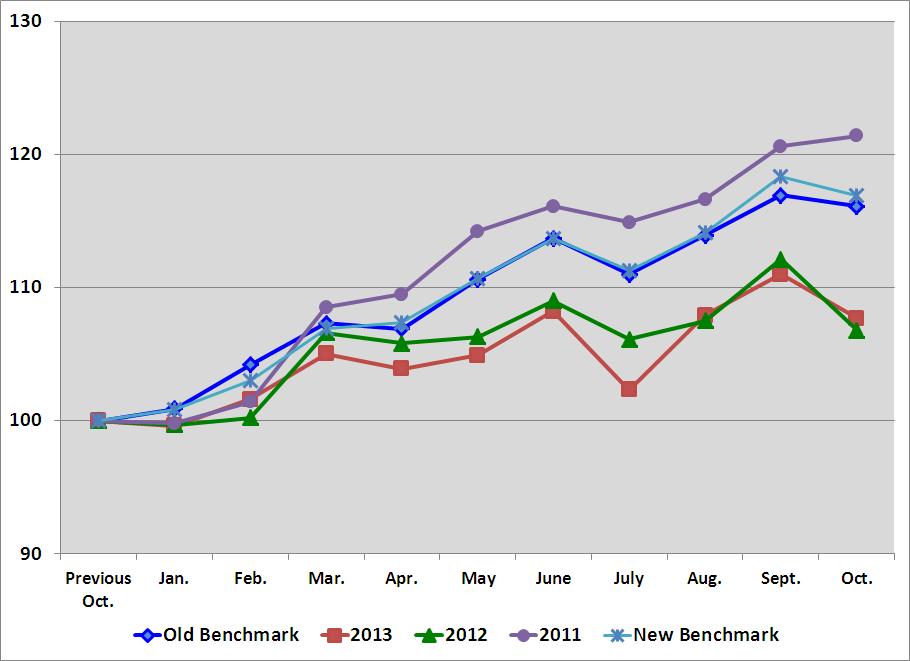

4
END MARKET PERFORMANCE:
Fluctuations in end market business – The sequential trends noted above were directly linked to fluctuations in our end markets. To place this in perspective – approximately 50% of our business has historically been with customers engaged in some type of manufacturing. The daily sales to these customers grew, when compared to the same period in the prior year, as follows:
Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Annual | ||||||||||
2013 | 7.0 | % | 5.9 | % | 4.7 | % | 7.2 | % | 6.3 | % | ||||
2012 | 20.3 | % | 15.8 | % | 14.0 | % | 9.7 | % | 14.9 | % | ||||
2011 | 15.5 | % | 18.5 | % | 18.3 | % | 21.0 | % | 20.0 | % | ||||
Our manufacturing business consists of two subsets: the industrial production business (this is business where we supply products that become part of the finished goods produced by our customers) and the maintenance portion (this is business where we supply products that maintain the facility or the equipment of our customers engaged in manufacturing). The industrial business is more fastener centered, while the maintenance portion is represented by all product categories.
The best way to understand the change in our industrial production business is to examine the results in our fastener product line. From a company perspective, sales of fasteners grew, when compared to the same period in the prior year, as follows (note: this information includes all end markets):
Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Annual | ||||||||||
2013 | 1.7 | % | 1.9 | % | 1.0 | % | 1.9 | % | 1.6 | % | ||||
2012 | 15.4 | % | 8.0 | % | 6.0 | % | 2.6 | % | 7.8 | % | ||||
2011 | 15.4 | % | 18.1 | % | 13.6 | % | 15.9 | % | 15.7 | % | ||||
By contrast, the best way to understand the change in the maintenance portion of the manufacturing business is to examine the results in our non-fastener product lines. From a company perspective, sales of non-fasteners grew, when compared to the same period in the prior year, as follows (note: this information includes all end markets):
Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Annual | ||||||||||
2013 | 10.8 | % | 8.5 | % | 8.9 | % | 12.0 | % | 10.1 | % | ||||
2012 | 25.1 | % | 21.1 | % | 18.0 | % | 13.6 | % | 19.2 | % | ||||
2011 | 26.5 | % | 27.3 | % | 26.9 | % | 27.4 | % | 27.0 | % | ||||
The non-fastener business has demonstrated greater relative resilience when compared to our fastener business and to the distribution industry in general, due to our strong FAST Solutions® (industrial vending) program; this is discussed in greater detail later in this document. However, this business has not been immune to the impact of a weak industrial environment.
The patterns related to the industrial production business, as noted above, are influenced by the movements noted in the Purchasing Manufacturers Index ('PMI') published by the Institute for Supply Management (http://www.ism.ws/), which is a composite index of economic activity in the United States manufacturing sector. The PMI in 2013, 2012, and 2011 was as follows:
Jan. | Feb. | Mar. | Apr. | May | June | July | Aug. | Sept. | Oct. | Nov. | Dec. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
2013 | 53.1 | 54.2 | 51.3 | 50.7 | 49.0 | 50.9 | 55.4 | 55.7 | 56.2 | 56.4 | 57.3 | 57.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
2012 | 53.7 | 51.9 | 53.3 | 54.1 | 52.5 | 50.2 | 50.5 | 50.7 | 51.6 | 51.7 | 49.9 | 50.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
2011 | 59.2 | 59.6 | 59.3 | 59.4 | 53.5 | 55.8 | 52.3 | 53.2 | 53.2 | 51.5 | 52.3 | 52.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
5
For background to readers not familiar with the PMI index, it is a monthly indicator of the economic health of the manufacturing sector in the United States. Five major indicators that influence the PMI index are new orders, inventory levels, production, supplier deliveries, and the employment environment. When a PMI of 50 or higher is reported, this indicates expansion in the manufacturing industry compared to the previous month. If the PMI is below 50, this represents a contraction in the manufacturing sector. (Note - the Institute for Supply Management made annual adjustments to reflect seasonal factors to the PMI index effective with the January 2013 report. This table represents the updated PMI index.)
Our non-residential construction customers have historically represented 20% to 25% of our business. The daily sales to these customers grew when compared to the same period in the prior year, as follows:
Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Annual | ||||||||||
2013 | 2.9 | % | 0.7 | % | 3.9 | % | 2.8 | % | 2.5 | % | ||||
2012 | 17.1 | % | 12.7 | % | 8.2 | % | 4.2 | % | 10.3 | % | ||||
2011 | 17.7 | % | 15.8 | % | 15.8 | % | 17.4 | % | 17.1 | % | ||||
We believe the weakness in the economy in the fourth quarter of 2012 and throughout 2013, particularly in the non-residential construction market, was amplified by global economic uncertainty combined with economic policy uncertainty in the United States and poor weather conditions.
A graph of the sequential daily sales trends to these two end markets in 2013, 2012, and 2011, starting with a base of '100' in the previous October and ending with the next October, would be as follows:
Manufacturing

6
Non-Residential Construction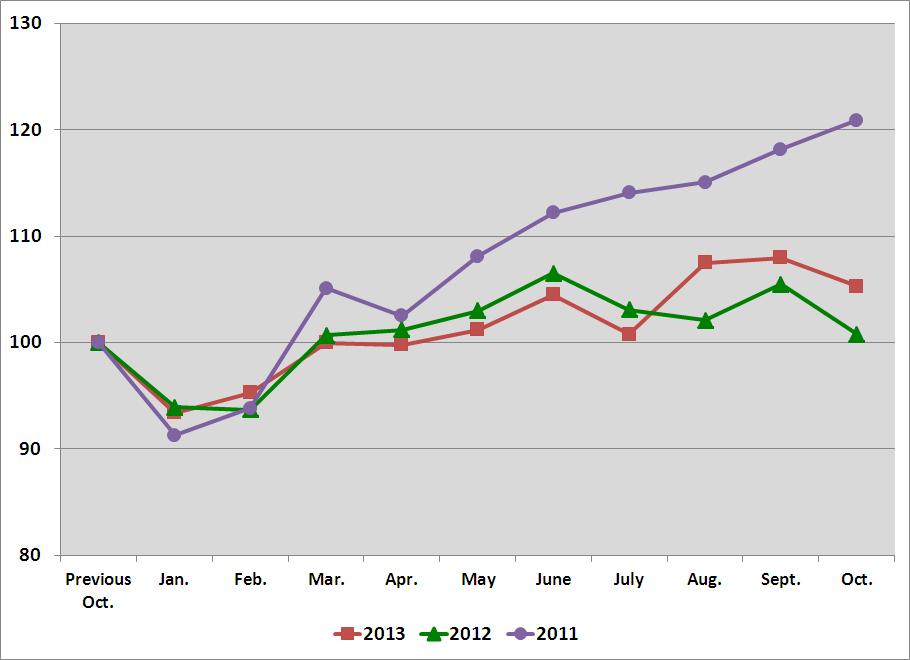

GROWTH DRIVERS OF OUR BUSINESS
We grow by continuously adding customers and by increasing the activity with each customer. We believe this growth is enhanced by our close proximity to our customers, which allows us to provide a range of services and product availability that our competitors can't easily match. Historically, we expanded our reach by opening stores at a very fast pace. These openings were initially in the United States, but expanded beyond the United States beginning in the mid 1990's.
For a little perspective, we began our business in 1967 with an idea to sell nuts and bolts (fasteners) through vending machines. We soon learned the technology of the 1960's wasn't ready, and also learned a lot of products didn't fit, so we went to 'Plan B'; sell to business users with a direct sales force. It took us a number of years to 'work out the bugs', but ten years later we began to pick up the pace of store openings. After another ten years of expansion we had approximately 50 stores and sales of about $20 million. Our need for cash was growing, as was our desire to allow employee ownership. This led us to a public offering in 1987.
In our first ten years of being public (1987 to 1997), we opened stores at an annual rate approaching 30% per year. In the next ten years (1997 to 2007), we opened stores at an annual rate of approximately 10% to 15% and, since 2007, at an annual rate of approximately 2% to 8% (we opened 53 stores in 2013, or an annual rate of approximately 2.0%, and currently expect to open approximately 50 to 70 stores, or an annual rate of approximately 1.9% to 2.6%, in 2014).
As we gained proximity to more customers, we continued to diversify our growth drivers. This was done to provide existing store personnel with more tools to grow their business organically, and the results of this are reflected in our earlier discussion on sales growth at stores opened greater than five years. In the early 1990's, we began to expand our product lines, and we added new product knowledge to our bench (the non-fastener products now represent over 50% of our sales). This was our first big effort to diversify our growth drivers. The next step began in the mid to late 1990's when we began to add sales personnel with certain specialties or focus. This began with our National Accounts group in 1995, and, over time, has expanded to include individuals dedicated to: (1) sales related to our internal manufacturing division, (2) government sales, (3) internet sales, (4) specific products (most recently metalworking), and (5) FAST Solutions® (industrial vending). Another step occurred at our sales locations (this includes Fastenal stores as well as strategic account stores and in-plant locations) and at our distribution centers, and began with a targeted merchandising and inventory placement strategy that included our 'Customer Service Project' approximately ten years ago and our 'Master Stocking Hub' initiative approximately five years ago. These strategies allowed us to better target where to stock certain products (local store, regional distribution center, master stocking hub, or supplier) and allowed us to improve our fulfillment, lower our freight costs, and improve our ability to serve a broader range of customers. During 2013, we expanded our store based inventory offering around select industries (with an emphasis on fasteners, construction products, and safety products) and in the latter half of 2013 we expanded two key employee groups: (1) the number of employees working in our stores and (2) the number of district and regional leaders supporting our stores. The theme that shines through in all these changes, particularly the last several, is a simple one – invest into and support our sales machine – the local store.
7
Our FAST Solutions® (industrial vending) operation is a rapidly expanding component of our business. We believe industrial vending will be an important chapter in the Fastenal story; we also believe it has the potential to be transformative to industrial distribution, and that we have a 'first mover' advantage. We are investing aggressively to maximize this advantage. At our investor day in May 2011, we discussed our progress with industrial vending. In addition to our discussion regarding progress, we discussed our goals with the rollout of the industrial vending machines. One of the goals we identified related to our rate of 'machine signings' (the first category below) – our goal was simple, sign 2,500+ machines per quarter (or an annualized run rate of 10,000 machines). In 2012, we crushed this goal, and surpassed the 10,000 signings benchmark in July; our 2012 momentum continued as we finished the year with more than 20,000 machine signings. In 2013, we signed more than 19,000 machines. We consciously slowed the pace in the second quarter of 2013 to promote a 'quality of install' mentality into our rapid approach. We think this was a good decision, and will continue our aggressive push with FAST Solutions® (industrial vending). In July 2013, we began the process of 'optimizing' our installed vending machines. This optimization centered on two aspects: (1) the product mix in each machine to maximize customer savings by promoting frequently consumed items and (2) the brand mix in each machine to streamline replenishment. The latter centers on our vending catalog.
The following table includes some statistics regarding our industrial vending business:
Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Annual | |||||||||||
Number of vending machines in | 2013 | 5,728 | 5,357 | 4,372 | 3,848 | 19,305 | |||||||||
contracts signed during the period1 | 2012 | 4,568 | 4,669 | 5,334 | 5,591 | 20,162 | |||||||||
2011 | 1,405 | 2,107 | 2,246 | 2,084 | 7,842 | ||||||||||
Cumulative machines installed2 | 2013 | 25,447 | 29,549 | 32,248 | 33,920 | ||||||||||
2012 | 9,798 | 13,036 | 17,013 | 21,095 | |||||||||||
2011 | 2,659 | 3,867 | 5,642 | 7,453 | |||||||||||
Percent of installed machines that are a FAST 5000 | 2013 | 54.3 | % | 52.2 | % | 51.1 | % | 50.4 | % | ||||||
(our most common helix vending machine)3 | 2012 | 70.1 | % | 66.2 | % | 60.2 | % | 57.2 | % | ||||||
2011 | 78.6 | % | 76.0 | % | 74.7 | % | 72.8 | % | |||||||
Percent of total net sales to | 2013 | 27.5 | % | 30.0 | % | 33.3 | % | 36.6 | % | ||||||
customers with vending machines4 | 2012 | 17.8 | % | 20.8 | % | 23.2 | % | 25.8 | % | ||||||
2011 | 8.9 | % | 10.5 | % | 13.1 | % | 15.7 | % | |||||||
Daily sales growth to customers | 2013 | 23.9 | % | 18.9 | % | 15.2 | % | 18.7 | % | ||||||
with vending machines5 | 2012 | 33.9 | % | 34.3 | % | 32.9 | % | 28.6 | % | ||||||
2011 | 50.6 | % | 43.9 | % | 42.5 | % | 40.7 | % | |||||||
1 | This represents the gross number of machines signed during the quarter, not the number of contracts. |
2 | This represents the number of machines installed and dispensing product on the last day of the quarter. |
3 | This information is intended to highlight the mix change in the machines deployed as our business expands beyond the flagship FAST 5000 machine. |
4 | The percentage of total sales (vended and traditional) to customers currently using a vending solution. |
5 | The growth in total sales (vended and traditional) to customers currently using a vending solution compared to the same period in the preceding year. |
Note - The 'fleet' of machines we utilize to vend product has expanded over the last several years, and currently includes helix vending machines, lockers, and other formats. The helix machine and lockers (three door, twelve door, and eighteen door) represent the majority of our installed machines. Our total installed machine count was 40,775 at the end of fourth quarter; however, given the lower revenue potential of the three and twelve door locker machines, we report an 'equivalent' machine count where each of these locker machines is counted as a half of a machine (for example, the 33,920 noted in the table above, and the goals indicated earlier in this document). We intend to refine the reporting of all machine equivalencies as we move through 2014 to better reflect the varying revenue potential to our installed vending machines.
8
PROFIT DRIVERS OF OUR BUSINESS
As we state several times in this document, profit is important to us. For a distribution business it is linked to cash flow, and cash flow funds our growth and creates value for our customers, our employees, our suppliers, and our shareholders. We grow our profits by continuously working to grow sales and to improve our relative profitability. We also grow our profits by allowing our inherent profitability to shine through – we refer to this as the 'pathway to profit'. The distinction is important.
We achieve improvements in our relative profitability by increasing our gross margin, by structurally lowering our operating expenses, or both. We advance on the 'pathway to profit' by increasing the average store size (measured in terms of monthly sales), and by allowing the changing store mix to improve our profits. This is best explained by comparing the varying profitability of our 'traditional' stores in the table below. The average store size for the group, and the average age, number of stores, and pre-tax earnings data by store size for the fourth quarter of 2013, 2012, and 2011, respectively, were as follows:
Sales per Month | Average Age (Years) | Number of Stores | Percentage of Stores | Pre-Tax Earnings Percentage | ||||||||
Three months ended December 31, 2013 | Average store sales = $87,798 | |||||||||||
$0 to $30,000 | 5.6 | 258 | 9.6 | % | -14.2 | % | ||||||
$30,001 to $60,000 | 8.0 | 776 | 28.9 | % | 9.9 | % | ||||||
$60,001 to $100,000 | 10.9 | 789 | 29.4 | % | 18.8 | % | ||||||
$100,001 to $150,000 | 12.8 | 414 | 15.4 | % | 23.4 | % | ||||||
Over $150,000 | 15.6 | 317 | 11.8 | % | 26.1 | % | ||||||
Strategic Account/Overseas Store | 133 | 4.9 | % | |||||||||
Company Total | 2,687 | 100.0 | % | 19.3 | % | |||||||
Three months ended December 31, 2012 | Average store sales = $83,098 | |||||||||||
$0 to $30,000 | 4.7 | 304 | 11.5 | % | -14.4 | % | ||||||
$30,001 to $60,000 | 7.6 | 830 | 31.3 | % | 12.2 | % | ||||||
$60,001 to $100,000 | 10.0 | 759 | 28.6 | % | 21.3 | % | ||||||
$100,001 to $150,000 | 12.9 | 375 | 14.1 | % | 26.0 | % | ||||||
Over $150,000 | 14.9 | 272 | 10.3 | % | 28.8 | % | ||||||
Strategic Account/Overseas Store | 112 | 4.2 | % | |||||||||
Company Total | 2,652 | 100.0 | % | 20.9 | % | |||||||
Three months ended December 31, 2011 | Average store sales = $78,781 | |||||||||||
$0 to $30,000 | 3.8 | 353 | 13.7 | % | -13.7 | % | ||||||
$30,001 to $60,000 | 7.2 | 882 | 34.1 | % | 11.7 | % | ||||||
$60,001 to $100,000 | 9.4 | 680 | 26.3 | % | 21.3 | % | ||||||
$100,001 to $150,000 | 12.0 | 352 | 13.6 | % | 25.9 | % | ||||||
Over $150,000 | 15.1 | 227 | 8.8 | % | 27.4 | % | ||||||
Strategic Account/Overseas Store | 91 | 3.5 | % | |||||||||
Company Total | 2,585 | 100.0 | % | 20.2 | % | |||||||
Note – Amounts may not foot due to rounding difference.
When we originally announced the 'pathway to profit' strategy in 2007, our goal was to increase our pre-tax earnings, as a percentage of sales, from 18% to 23%. This goal was to be accomplished by slowly moving the mix from the first three categories ($0 to $30,000, $30,001 to $60,000, and $60,001 to $100,000, these groups represented 76.5% of our store base in the first three months of 2007, the last quarter before we announced the 'pathway to profit') to the last three categories ($60,001 to $100,000, $100,001 to $150,000, and over $150,000, these groups represented 56.6% of our store base in the fourth quarter of 2013) and by increasing the average store sales from $71,600 (in the first three months of 2007) to approximately $125,000 per month. The weak economic environment in 2009 caused our average store size to decrease, and consequently lowered our level of profitability; however, we never lost sight of the simple 'economic math' of our business, and our ability to grow the level of profitability long-term. In the aftermath of 2009, we grew the average store size, we improved our gross margin, and we structurally lowered our operating expenses. The improvement in the latter two allowed us to amplify the 'pathway to profit' and effectively lowered the average store size required to hit our 23% goal. Today we believe we can accomplish our 'pathway to profit' goal with average store sales of approximately $100,000 to $110,000 per month.
Note – Dollar amounts in this section are presented in whole dollars, not thousands.
9
Store Count and Full-Time Equivalent (FTE) Headcount – The table that follows highlights certain impacts on our business of the 'pathway to profit' since its introduction in 2007. Under the 'pathway to profit' we increased both our store count and our store FTE headcount during 2007 and 2008. However, the rate of increase in store locations slowed and our FTE headcount for all types of personnel was reduced when the economy weakened late in 2008. In the table that follows, we refer to our 'store' net sales, locations, and personnel. When we discuss 'store' net sales, locations, and personnel, we are referring to (1) 'Fastenal' stores and (2) strategic account stores. 'Fastenal' stores are either a 'traditional' store, the typical format in the United States or Canada, or an 'overseas' store, which is the typical format outside the United States and Canada. This is discussed in greater detail in our 2012 annual report on Form 10-K. Strategic account stores are stores that are focused on selling to a group of large customers in a limited geographic market. The sales, outside of our 'store' group, relate to either (1) our in-plant locations, (2) the portion of our internally manufactured product that is sold directly to a customer and not through a store (including our Holo-Krome® business acquired in December 2009), or (3) our direct import business.
The breakdown of our sales, the average monthly sales per store, the number of stores at quarter end, the average headcount at our stores during a quarter, the average FTE headcount during a quarter, and the percentage change were as follows for the first quarter of 2007 (the last completed quarter before we began the 'pathway to profit'), for the third quarter of 2008 (our peak quarter before the economy weakened), and for each of the last five quarters:
Q1 2007 | Q3 2008 | Q4 2012 | Q1 2013 | Q2 2013 | Q3 2013 | Q4 2013 | ||||||||||||||
Total net sales reported | $489,157 | $625,037 | $757,235 | $806,326 | $847,596 | $858,424 | $813,760 | |||||||||||||
Less: non-store sales (approximate) | 40,891 | 57,267 | 95,951 | 101,624 | 109,300 | 108,427 | 105,499 | |||||||||||||
Store net sales (approximate) | $448,266 | $567,770 | $661,284 | $704,702 | $738,296 | $749,997 | $708,261 | |||||||||||||
% change since Q1 2007 | 26.7 | % | 47.5 | % | 57.2 | % | 64.7 | % | 67.3 | % | 58.0 | % | ||||||||
% change (twelve months) | 17.5 | % | 8.2 | % | 4.2 | % | 4.6 | % | 6.8 | % | 7.1 | % | ||||||||
Percentage of sales through a store | 92 | % | 91 | % | 87 | % | 87 | % | 87 | % | 87 | % | 87 | % | ||||||
Average monthly sales per store | $72 | $82 | $83 | $88 | $92 | $93 | $88 | |||||||||||||
(using ending store count) | ||||||||||||||||||||
% change since Q1 2007 | 13.9 | % | 15.3 | % | 22.2 | % | 27.8 | % | 29.2 | % | 22.2 | % | ||||||||
% change (twelve months) | 9.3 | % | 5.1 | % | 2.3 | % | 3.4 | % | 5.7 | % | 6.0 | % | ||||||||
Company pre-tax earnings | 18.1% | 18.8% | 20.9% | 21.7% | 22.7% | 22.0% | 19.3% | |||||||||||||
10
Q1 2007 | Q3 2008 | Q4 2012 | Q1 2013 | Q2 2013 | Q3 2013 | Q4 2013 | ||||||||||||||
Store locations - quarter end count | 2,073 | 2,300 | 2,652 | 2,660 | 2,677 | 2,686 | 2,687 | |||||||||||||
% change since Q1 2007 | 11.0 | % | 27.9 | % | 28.3 | % | 29.1 | % | 29.6 | % | 29.6 | % | ||||||||
% change (twelve months) | 7.2 | % | 2.6 | % | 1.9 | % | 1.6 | % | 1.4 | % | 1.3 | % | ||||||||
Store personnel - absolute headcount | 6,849 | 9,123 | 10,347 | 10,108 | 10,160 | 10,607 | 11,261 | |||||||||||||
% change since Q1 2007 | 33.2 | % | 51.1 | % | 47.6 | % | 48.3 | % | 54.9 | % | 64.4 | % | ||||||||
% change (twelve months) | 17.9 | % | 0.2 | % | -3.6 | % | -4.5 | % | 0.0 | % | 8.8 | % | ||||||||
Store personnel - FTE | 6,383 | 8,280 | 9,035 | 8,875 | 8,943 | 9,350 | 9,771 | |||||||||||||
Non-store selling personnel - FTE | 616 | 599 | 1,070 | 1,121 | 1,174 | 1,190 | 1,214 | |||||||||||||
Sub-total of all sales personnel - FTE | 6,999 | 8,879 | 10,105 | 9,996 | 10,117 | 10,540 | 10,985 | |||||||||||||
Distribution personnel-FTE | 1,646 | 1,904 | 1,872 | 1,819 | 1,867 | 1,986 | 2,040 | |||||||||||||
Manufacturing personnel - FTE 1 | 316 | 340 | 544 | 565 | 572 | 570 | 581 | |||||||||||||
Administrative personnel-FTE | 767 | 805 | 811 | 832 | 857 | 867 | 876 | |||||||||||||
Sub-total of non-sales personnel - FTE | 2,729 | 3,049 | 3,227 | 3,216 | 3,296 | 3,423 | 3,497 | |||||||||||||
Total - average FTE headcount | 9,728 | 11,928 | 13,332 | 13,212 | 13,413 | 13,963 | 14,482 | |||||||||||||
% change since Q1 2007 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Store personnel - FTE | 29.7 | % | 41.5 | % | 39.0 | % | 40.1 | % | 46.5 | % | 53.1 | % | ||||||||
Non-store selling personnel - FTE | -2.8 | % | 73.7 | % | 82.0 | % | 90.6 | % | 93.2 | % | 97.1 | % | ||||||||
Sub-total of all sales personnel - FTE | 26.9 | % | 44.4 | % | 42.8 | % | 44.5 | % | 50.6 | % | 57.0 | % | ||||||||
Distribution personnel-FTE | 15.7 | % | 13.7 | % | 10.5 | % | 13.4 | % | 20.7 | % | 23.9 | % | ||||||||
Manufacturing personnel-FTE 1 | 7.6 | % | 72.2 | % | 78.8 | % | 81.0 | % | 80.4 | % | 83.9 | % | ||||||||
Administrative personnel-FTE | 5.0 | % | 5.7 | % | 8.5 | % | 11.7 | % | 13.0 | % | 14.2 | % | ||||||||
Sub-total of non-sales personnel - FTE | 11.7 | % | 18.2 | % | 17.8 | % | 20.8 | % | 25.4 | % | 28.1 | % | ||||||||
Total - average FTE headcount | 22.6 | % | 37.0 | % | 35.8 | % | 37.9 | % | 43.5 | % | 48.9 | % | ||||||||
% change (twelve months) | ||||||||||||||||||||
Store personnel - FTE | 15.2 | % | 4.0 | % | -0.3 | % | -0.2 | % | 1.1 | % | 8.1 | % | ||||||||
Non-store selling personnel - FTE | -2.4 | % | 12.3 | % | 12.3 | % | 11.4 | % | 11.6 | % | 13.5 | % | ||||||||
Sub-total of all sales personnel - FTE | 13.8 | % | 4.9 | % | 1.0 | % | -0.6 | % | 2.2 | % | 8.7 | % | ||||||||
Distribution personnel-FTE | 6.0 | % | 2.9 | % | 0.2 | % | -0.7 | % | 5.2 | % | 9.0 | % | ||||||||
Manufacturing personnel - FTE 1 | 1.8 | % | 5.4 | % | 7.2 | % | 5.0 | % | 4.8 | % | 6.8 | % | ||||||||
Administrative personnel - FTE | 7.9 | % | 1.9 | % | 4.5 | % | 7.9 | % | 7.3 | % | 8.0 | % | ||||||||
Sub-total of non-sales personnel - FTE | 6.0 | % | 3.0 | % | 2.5 | % | 2.4 | % | 5.7 | % | 8.4 | % | ||||||||
Total - average FTE headcount | 11.7 | % | 4.4 | % | 1.4 | % | 0.1 | % | 3.1 | % | 8.6 | % | ||||||||
1 | The manufacturing headcount was impacted by the addition of 92 employees with the acquisition of Holo-Krome® in December 2009. |
11
STATEMENT OF EARNINGS INFORMATION (percentage of net sales) for the periods ended December 31: | |||||||||
Twelve-month Period | |||||||||
2013 | 2012 | 2011 | |||||||
Net sales | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | |||
Gross profit | 51.7 | % | 51.5 | % | 51.8 | % | |||
Operating and administrative expenses | 30.3 | % | 30.0 | % | 31.1 | % | |||
(Gain) loss on sale of property and equipment | 0.0 | % | 0.0 | % | 0.0 | % | |||
Operating income | 21.4 | % | 21.5 | % | 20.8 | % | |||
Net interest income | 0.0 | % | 0.0 | % | 0.0 | % | |||
Earnings before income taxes | 21.5 | % | 21.5 | % | 20.8 | % | |||
Note – Amounts may not foot due to rounding difference. | |||||||||
Gross profit – percentage for 2013 increased from 2012.
The gross profit percentage in the first, second, third, and fourth quarters was as follows:
Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | |||||||||
2013 | 52.3 | % | 52.2 | % | 51.7 | % | 50.6 | % | ||||
2012 | 51.3 | % | 51.6 | % | 51.6 | % | 51.6 | % | ||||
2011 | 52.0 | % | 52.2 | % | 51.9 | % | 51.2 | % | ||||
The fluctuations in our gross profit percentages are typically driven by changes in: (1) transactional gross profit, (2) organizational gross profit, and (3) vendor incentive gross profit. The transactional gross profit represents the gross profit realized from the day-to-day fluctuations in customer pricing relative to product and freight costs. The organizational gross profit represents the component of gross profit we attribute to buying scale and efficiency gains. The third component relates to vendor volume allowances. In the short-term, periods of inflation or deflation can influence the first two categories, while sudden changes in business volume can influence the third.
We believe a normal gross profit percentage range for our business is 51% to 53%. This is based on our current mix of products, geographies, end markets, and end market uses (such as industrial production business versus maintenance business). The following narrative may be more detail than you want; however, we believe it is an important recap to understanding the dynamics surrounding our gross margin patterns. Our business operated below our expected gross profit range at the end of 2009, and expanded into the low end of this range during 2010. In the second quarter of 2010, we moved into the middle of the range as the three components of gross profit improved, the contribution being split fairly evenly between the three components. We remained in the middle of the range until the fourth quarter of 2011. In the fourth quarter of 2011, our gross margin felt pressure and dropped to the lower end of the range. This drop was primarily due to changes in our transactional margin (primarily due to changes in product and customer mix), lower vendor incentive gross profit, and lower freight utilization. The latter two items created half of the gross margin drop and are more of a seasonal issue. In the first quarter of 2012, our gross margin improved nominally over the previous quarter. This was primarily caused by the seasonal improvement of vendor volume allowances as rising fuel prices offset our improvements in freight utilization. In the second, third, and fourth quarters of 2012, our gross margin improved when compared to the first quarter. Most of this improvement related to improvements in our transactional gross margin. The improvement was partially offset by the weakening of our selling prices in certain foreign markets due to changes in the exchange rate. One item of note, in the fourth quarter of 2012 we experienced a drop off in the freight component of our gross margin due to lower freight utilization, a typical pattern due to the seasonal drop off in business; this gross margin decline was offset by an improvement in the remaining portion of our transactional gross margin that centers on product transactional cost and customer pricing.
The first two quarters of 2013 experienced a strong improvement in gross margin. A piece of this related to the seasonal impact of improving freight utilization, but this improvement was constrained due to the weak sales growth. The real driver of improvement related to our store personnel, armed with our newly implemented price guidance system, exercising great judgment about pricing their product. During the third quarter of 2013, we experienced a sequential (second to third quarter) decline in our gross margin. Most of this decline was in the transaction margin (about 85% of the change); with the balance in the supplier incentive gross profit. The decline in our supplier incentive gross profit was due to our continued pattern of weak sales growth. Within the transaction component, product mix stood out as the most identifiable portion (this was about 40% of the total drop, and reflects the continued weakness in our fastener growth and the strength in the growth in safety products - fasteners carry a higher gross margin, safety products don't). The remaining portion of the transactional decline was split across a number of causes, the result of a very competitive landscape and our competitive nature. Beginning in the third quarter, we
12
had placed a greater emphasis on expanding the headcount at our store locations, putting more emphasis on shorter cycle sales efforts, and moving the needle on top line growth. This impacted our gross margin in the short term; however, we think this approach is the correct long-term move as it reinforces our trust in our store personnel and our desire to grow our business long-term, but it does make for a bumpier ride. In the fourth quarter of 2013, we experienced another sequential (third to fourth quarter) decline in gross margin. Similar to prior years, we lost some gross margin due to a seasonal drop in freight utilization and in supplier incentive gross profit. This represented about 30% of the drop and is expected to recover in the new year as volume increases (seasonality) and incentive programs reset (typically calendar based). The remaining drop relates to factors noted in the third quarter. We believe our expected gross margin range (51% to 53%) is still reasonable for 2014.
Operating and administrative expenses - as a percentage of sales were essentially unchanged from 2012 to 2013.
Historically, our two largest components of operating and administrative expenses have consisted of employee related expenses (approximately 65% to 70%) and occupancy related expenses (approximately 15% to 20%). The remaining expenses cover a variety of items with selling transportation typically being the largest.
The three largest components of operating and administrative expenses grew as follows for the periods ended December 31 (compared to the comparable periods in the preceding year):
Twelve-month Period | |||||||||
2013 | 2012 | 2011 | |||||||
Employee related expenses | 4.6 | % | 10.1 | % | 19.7 | % | |||
Occupancy related expenses | 11.2 | % | 4.8 | % | 7.4 | % | |||
Selling transportation costs | 0.8 | % | 10.1 | % | 26.5 | % | |||
Employee related expenses include: (1) payroll (which includes cash compensation, stock option expense, and profit sharing), (2) health care, (3) personnel development, and (4) social taxes. Performance bonuses (other than those related to our vending business) were down in 2013; however, this decrease was offset by increases related to the following factors: (1) average employee headcount, measured on a full-time equivalent basis compared to the fourth quarter of 2012, grew 8.6% in 2013, (2) sales commissions grew in 2013 due to the static gross profit combined with sales growth, (3) our industrial vending bonuses grew in the first quarter and the twelve month period, although they contracted in the second, third and fourth quarters due to changes in the pace of the vending rollout, (4) our profit sharing contribution grew, and (5) our health care costs grew. The increase in 2012 was driven by the following factors: (1) average employee headcount, measured on a full-time equivalent basis compared to the fourth quarter of 2011, grew 4.4%, (2) sales commissions grew, (3) bonus amounts related to our growth drivers grew (this includes items such as industrial vending bonuses and manager minimum pay adjustments), and (4) our profit sharing contribution grew.
Occupancy related expenses include: (1) building rent and depreciation, (2) building utility costs, (3) equipment related to our stores and distribution locations, and (4) FAST Solutions® (industrial vending) equipment (we consider the vending equipment to be a logical extension of our store operation and classify the expense as occupancy). The increase in 2013 was driven by (1) a dramatic increase in the amount of FAST Solutions® (industrial vending) equipment as discussed earlier in this document, (2) an increase in building utility cost, (3) a nominal increase in the number of store locations, and (4) an increased investment in our distribution infrastructure over the last several years. In 2013, the industrial vending component represented approximately 60% of the increase, with the balance related to our distribution automation/expansion and changes to utilities and external rent. Almost all of our occupancy increase in 2012 related to the increase in the amount of FAST Solutions® (industrial vending) equipment, as our energy savings offset most of the increase relating to items (3) and (4). The energy savings were driven by our efforts to lower energy consumption, a mild winter, and a drop in natural gas prices during the heating season.
Our selling transportation costs consist primarily of our store fleet as most of the distribution fleet costs are included in the cost of sales. Selling transportation costs included in operating and administrative expenses were essentially flat in 2013, when compared to 2012. This was helped by stronger sales patterns related to our used store truck fleet, which lowered our vehicle ownership costs. The increase in 2012 was primarily related to the increase in per gallon fuel costs discussed below and the expansion of our fleet related to additions to our non-store sales personnel, particularly FAST Solutions® (industrial vending) vehicles.
13
The last several years have seen meaningful swings in the cost of diesel fuel and gasoline – During the first, second, third, and fourth quarters of 2013, our total vehicle fuel costs were approximately $10.6, $10.6, $11.2, and $9.6 million, respectively. During the first, second, third, and fourth quarters of 2012, our total vehicle fuel costs were approximately $10.6, $10.8, $10.8, and $10.3 million, respectively. The changes resulted from variations in fuel costs, variations in the service levels provided to our stores from our distribution centers, changes in the number of vehicles at our store locations, and changes in the number of other sales centered vehicles as a result of store openings and the expansion of our non-store sales force. These fuel costs include the fuel utilized in our distribution vehicles (semi-tractors, straight trucks, and sprinter trucks) which is recorded in cost of sales and the fuel utilized in our store delivery and other sales centered vehicles which is included in operating and administrative expenses (the split in the last several years has been approximately 50:50 between distribution and store and other sales centered use).
The average per gallon fuel costs (in actual dollars) and the percentage change (on a year-over-year basis) for the last three years was as follows:
Per Gallon Average Price | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Annual Average1 | |||||||||||
2013 price | ||||||||||||||||
Diesel fuel | $ | 4.02 | 3.90 | 3.90 | 3.88 | 3.93 | ||||||||||
Gasoline | $ | 3.51 | 3.60 | 3.56 | 3.30 | 3.49 | ||||||||||
2012 price | ||||||||||||||||
Diesel fuel | $ | 3.92 | 3.98 | 3.88 | 4.05 | 3.96 | ||||||||||
Gasoline | $ | 3.53 | 3.73 | 3.61 | 3.53 | 3.60 | ||||||||||
2011 price | ||||||||||||||||
Diesel fuel | $ | 3.60 | 4.04 | 3.90 | 3.87 | 3.85 | ||||||||||
Gasoline | $ | 3.22 | 3.78 | 3.62 | 3.37 | 3.50 | ||||||||||
Per Gallon Price Change | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | Annual1 | |||||||||||
2013 change | ||||||||||||||||
Diesel fuel | 2.6 | % | -2.0 | % | 0.5 | % | -4.2 | % | -0.8 | % | ||||||
Gasoline | -0.6 | % | -3.5 | % | -1.4 | % | -6.5 | % | -3.1 | % | ||||||
2012 change | ||||||||||||||||
Diesel fuel | 8.9 | % | -1.5 | % | -0.5 | % | 4.7 | % | 2.9 | % | ||||||
Gasoline | 9.6 | % | -1.3 | % | -0.3 | % | 4.7 | % | 2.9 | % | ||||||
1 | Average of the four quarterly figures contained in the table. |
Income taxes – Incomes taxes, as a percentage of earnings before income taxes, were approximately 37.1% and 37.6% for 2013 and 2012, respectively. As our international business and profits grow over time, the lower income tax rates in those jurisdictions, relative to the United States, have begun to lower our effective tax rate.
14
OPERATIONAL WORKING CAPITAL:
The year-over-year comparison and the related dollar and percentage changes related to accounts receivable and inventories were as follows:
Balance at December 31: | Twelve Month Dollar Change | Twelve Month Percentage Change | ||||||||||||||||||||
2013 | 2012 | 2011 | 2013 | 2012 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||||||||
Accounts receivable, net | $ | 414,331 | 372,159 | 338,594 | 42,172 | 33,565 | 11.3 | % | 9.9 | % | ||||||||||||
Inventories | $ | 784,068 | 715,383 | 646,152 | 68,685 | 69,231 | 9.6 | % | 10.7 | % | ||||||||||||
Operational working capital1 | $ | 1,198,399 | 1,087,542 | 984,746 | 110,857 | 102,796 | 10.2 | % | 10.4 | % | ||||||||||||
Sales in last two months | $ | 502,868 | 468,696 | 451,069 | 34,172 | 17,627 | 7.3 | % | 3.9 | % | ||||||||||||
1 For purposes of this discussion, we are defining operational working capital as accounts receivable, net and inventories.
The growth in accounts receivable noted above was driven by our sales growth in the final two months of the period. The strong growth in recent years with our international business and of our large customer accounts has created some difficulty with managing the growth of accounts receivable relative to the growth in sales.
Our growth in inventory balances over time does not have as direct a relationship to our monthly sales patterns as does our growth in accounts receivable. This is impacted by other aspects of our business. For example, the dramatic economic slowdown in late 2008 and early 2009 caused our inventory to spike. This occurred because the lead time for inventory procurement is typically longer than the visibility we have into future monthly sales patterns. Over the last decade, we increased our relative inventory levels due to the following: (1) new store openings, (2) expanded stocking breadth at our distributions centers (for example, our master stocking hub in Indianapolis expanded its product breadth over six fold from 2005 to 2011), (3) expanded direct sourcing, (4) expanded exclusive brands (private label), (5) expanded industrial vending solutions, (6) national accounts growth, (7) international growth, and (8) expanded stocking breadth at individual stores. Items (1) through (7) created most of our inventory growth in both 2013 and 2012, while item (8), related to our inventory growth in 2012.
BALANCE SHEET AND CASH FLOW:
Our balance sheet continues to be very strong and our operations have good cash generating characteristics. During the fourth quarter of 2013, we generated $100,847 (or 101.6% of net earnings) of operating cash flow. During all of 2013, we generated $416,120 (or 92.8% of net earnings) of operating cash flow. Our first quarter typically has stronger cash flow characteristics due to the timing of tax payments; this benefit reverses itself in the second, third, and fourth quarters as income tax payments go out in April, June, September, and December. The remaining amounts of cash flow from operating activities are largely linked to the pure dynamics of a distribution business and its strong correlation to working capital as discussed above. During December 2012 and periodically during 2013, we incurred some short-term debt to fund capital expenditures and dividends. This was expected in 2013 and is expected in 2014 and possibly 2015.
Our dividends (per share basis) were as follows in 2013 and 2012:
2013 | 2012 | |||||
First quarter | $ | 0.10 | 0.17 | |||
Second quarter | 0.20 | 0.17 | ||||
Third quarter | 0.25 | 0.19 | ||||
Fourth quarter | 0.25 | 0.21 | ||||
Supplemental* | — | 0.50 | ||||
Total | $ | 0.80 | 1.24 | |||
*Due to income tax rate uncertainties, we paid a supplemental dividend in December 2012.
15
STOCK REPURCHASE:
During the third quarter of 2013, we repurchased 200,000 shares of our common stock at an average price of approximately $45.40 per share. We currently have remaining authority to purchase up to 1,600,000 shares of our common stock.
CONFERENCE CALL TO DISCUSS QUARTERLY EARNINGS:
As we previously disclosed, we will host a conference call today to review the quarterly results, as well as current operations. This conference call will be broadcast live over the Internet at 9:00 a.m., central time. To access the webcast, please go to the Fastenal Company Investor Relations Website at http://investor.fastenal.com/events.cfm.
Fastenal Company publishes on the "Investor Relations" page of its website at www.fastenal.com, both its monthly and consolidated net sales figures and certain quarterly supplemental sales information. Fastenal expects to publish the consolidated net sales figures for each month, other than the third month of a quarter, at 6:00 a.m. (central time) on the third business day of the following month. Fastenal expects to publish the consolidated net sales figures for the third month of each quarter and the supplemental sales information for each quarter at 6:00 a.m. (central time) on the date the company's earnings announcement for such quarter is publicly released.
Fastenal Company anticipates its 2013 Annual Report on Form 10-K will be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission in February 2014.
Fastenal Company anticipates its Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q will be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission within 30 days after the end of the quarter.
The Fastenal Company logo is available at http://www.globenewswire.com/newsroom/prs/?pkgid=6432.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION:
Except for the historical information contained herein, the matters set forth in this release are forward-looking statements that represent our expectations, beliefs, intentions or strategies concerning future events. These forward-looking statements are subject to certain risks and uncertainties that could cause actual results to differ materially from our historical experience or our present expectations, including, but not limited to, such factors as downturns or continued weakness in the economy or in the manufacturing or commercial construction industries, competitive pressure on selling prices, changes in our current mix of products, customers or geographic locations, changes in our purchasing patterns, difficulties in modifying our sales process, changes in fuel or commodity prices, inclement weather, changes in foreign currency exchange rates, weak acceptance or adoption of vending technology or increased competition in vending, difficulty in hiring, relocating, training or retaining qualified personnel, failure to accurately predict the number of North American markets able to support stores or to meet store opening goals, difficulty in controlling operating expenses, potential liability and reputational damage that can arise if our products are defective, and other risks and uncertainties detailed in our annual and quarterly reports. Each forward-looking statement speaks only as of the date on which such statement is made, and we undertake no obligation to update any such statement to reflect events or circumstances arising after such date. FAST-E
16
FASTENAL COMPANY AND SUBSIDIARIES | |||||||
Consolidated Balance Sheets | |||||||
(Amounts in thousands except share information) | |||||||
December 31, 2013 | December 31, 2012 | ||||||
Assets | (Unaudited) | ||||||
Current assets: | |||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 58,506 | 79,611 | ||||
Marketable securities | 451 | 354 | |||||
Trade accounts receivable, net of allowance for doubtful accounts of $9,248 and $6,728, respectively | 414,331 | 372,159 | |||||
Inventories | 784,068 | 715,383 | |||||
Deferred income tax assets | 18,248 | 14,420 | |||||
Prepaid income taxes | 24,869 | 7,368 | |||||
Other current assets | 107,988 | 97,361 | |||||
Total current assets | 1,408,461 | 1,286,656 | |||||
Property and equipment, less accumulated depreciation | 654,850 | 516,427 | |||||
Other assets, net | 12,473 | 12,749 | |||||
Total assets | $ | 2,075,784 | 1,815,832 | ||||
Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity | |||||||
Current liabilities: | |||||||
Accounts payable | $ | 91,253 | 78,019 | ||||
Accrued expenses | 148,579 | 126,155 | |||||
Total current liabilities | 239,832 | 204,174 | |||||
Deferred income tax liabilities | 63,255 | 51,298 | |||||
Stockholders' equity: | |||||||
Preferred stock, 5,000,000 shares authorized | — | — | |||||
Common stock, 400,000,000 shares authorized, 296,753,544 and 296,564,382 shares issued and outstanding, respectively | 2,968 | 2,966 | |||||
Additional paid-in capital | 69,847 | 61,436 | |||||
Retained earnings | 1,688,781 | 1,477,601 | |||||
Accumulated other comprehensive income | 11,101 | 18,357 | |||||
Total stockholders' equity | 1,772,697 | 1,560,360 | |||||
Total liabilities and stockholders' equity | $ | 2,075,784 | 1,815,832 | ||||
17
FASTENAL COMPANY AND SUBSIDIARIES | |||||||||||||
Consolidated Statements of Earnings | |||||||||||||
(Amounts in thousands except earnings per share) | |||||||||||||
Year Ended December 31, | Three Months Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
2013 | 2012 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
(Unaudited) | (Unaudited) | (Unaudited) | |||||||||||
Net sales | $ | 3,326,106 | 3,133,577 | 813,760 | 757,235 | ||||||||
Cost of sales | 1,606,661 | 1,519,053 | 402,311 | 366,414 | |||||||||
Gross profit | 1,719,445 | 1,614,524 | 411,449 | 390,821 | |||||||||
Operating and administrative expenses | 1,007,431 | 941,236 | 254,390 | 232,913 | |||||||||
Gain on sale of property and equipment | (643 | ) | (403 | ) | (75 | ) | (136 | ) | |||||
Operating income | 712,657 | 673,691 | 157,134 | 158,044 | |||||||||
Interest income | 924 | 464 | 191 | 107 | |||||||||
Interest expense | (113 | ) | — | (51 | ) | — | |||||||
Earnings before income taxes | 713,468 | 674,155 | 157,274 | 158,151 | |||||||||
Income tax expense | 264,832 | 253,619 | 58,045 | 59,435 | |||||||||
Net earnings | $ | 448,636 | 420,536 | 99,229 | 98,716 | ||||||||
Basic net earnings per share | $ | 1.51 | 1.42 | 0.33 | 0.33 | ||||||||
Diluted net earnings per share | $ | 1.51 | 1.42 | 0.33 | 0.33 | ||||||||
Basic weighted average shares outstanding | 296,754 | 296,089 | 296,749 | 296,457 | |||||||||
Diluted weighted average shares outstanding | 297,684 | 297,151 | 297,627 | 297,339 | |||||||||
18
FASTENAL COMPANY AND SUBSIDIARIES | |||||||
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows | |||||||
(Amounts in thousands) | |||||||
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||
2013 | 2012 | ||||||
(Unaudited) | |||||||
Cash flows from operating activities: | |||||||
Net earnings | $ | 448,636 | 420,536 | ||||
Adjustments to reconcile net earnings to net cash provided by operating activities: | |||||||
Depreciation of property and equipment | 63,770 | 53,459 | |||||
Gain on sale of property and equipment | (643 | ) | (403 | ) | |||
Bad debt expense | 9,421 | 9,726 | |||||
Deferred income taxes | 8,129 | 15,442 | |||||
Stock based compensation | 5,400 | 4,800 | |||||
Excess tax benefits from stock based compensation | (2,787 | ) | (10,149 | ) | |||
Amortization of non-compete agreements | 421 | 593 | |||||
Changes in operating assets and liabilities: | |||||||
Trade accounts receivable | (51,593 | ) | (43,291 | ) | |||
Inventories | (68,685 | ) | (69,231 | ) | |||
Other current assets | (10,627 | ) | (7,528 | ) | |||
Accounts payable | 13,234 | 4,240 | |||||
Accrued expenses | 22,424 | 14,193 | |||||
Income taxes | (14,714 | ) | 704 | ||||
Other | (6,266 | ) | 3,201 | ||||
Net cash provided by operating activities | 416,120 | 396,292 | |||||
Cash flows from investing activities: | |||||||
Purchase of property and equipment | (206,540 | ) | (138,406 | ) | |||
Proceeds from sale of property and equipment | 4,990 | 4,524 | |||||
Net (increase) decrease in marketable securities | (97 | ) | 26,811 | ||||
Increase in other assets | (145 | ) | (133 | ) | |||
Net cash used in investing activities | (201,792 | ) | (107,204 | ) | |||
Cash flows from financing activities: | |||||||
Borrowings under line of credit | 260,000 | — | |||||
Payments against line of credit | (260,000 | ) | — | ||||
Proceeds from exercise of stock options | 9,306 | 29,644 | |||||
Excess tax benefits from stock based compensation | 2,787 | 10,149 | |||||
Purchase of common stock | (9,080 | ) | — | ||||
Payment of dividends | (237,456 | ) | (367,306 | ) | |||
Net cash used in financing activities | (234,443 | ) | (327,513 | ) | |||
Effect of exchange rate changes on cash | (990 | ) | 360 | ||||
Net decrease in cash and cash equivalents | (21,105 | ) | (38,065 | ) | |||
Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of year | 79,611 | 117,676 | |||||
Cash and cash equivalents at end of year | $ | 58,506 | 79,611 | ||||
Supplemental disclosure of cash flow information: | |||||||
Cash paid during each year for interest | $ | 112 | — | ||||
Cash paid during each year for income taxes | $ | 270,615 | 268,357 | ||||
19
CONTACT: | Ellen Trester |
Financial Reporting & Regulatory Compliance Manager | |
507-313-7282 | |
20
