Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| 8-K - CURRENT REPORT - XpresSpa Group, Inc. | v328284_8k.htm |

0 Communication Flow in GSM Architecture Communication Flow in GSM Architecture www.vringo.com

1 Communication Flow in GSM Architecture This presentation includes forward - looking statements, which may be identified by words such as "believes," "expects," "anticipates," "estimates," "projects," "intends," "should," "seeks," "future," "continue," or the negative of such terms, or other comparable terminology . Forward - looking statements are statements that are not historical facts . Such forward - looking statements are subject to risks and uncertainties, which could cause actual results to differ materially from the forward - looking statements contained herein . Factors that could cause actual results to differ materially include, but are not limited to : the inability to realize the potential value created by the merger with Innovate/Protect for our stockholders ; our inability to raise additional capital to fund our combined operations and business plan ; our inability to monetize and recoup our investment with respect to patent assets that we acquire ; our inability to maintain the listing of our securities on the NYSE MKT ; the potential lack of market acceptance of our products ; our inability to protect our intellectual property rights ; potential competition from other providers and products ; our inability to license and monetize the patents owned by Innovate/Protect, including the outcome of the litigation against online search firms and other companies ; our inability to monetize and recoup our investment with respect to patent assets that we acquire ; and other risks and uncertainties and other factors discussed from time to time in our filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission ("SEC"), including our quarterly report on Form 10 - Q filed with the SEC on August 14 , 2012 . Vringo expressly disclaims any obligation to publicly update any forward - looking statements contained herein, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise, except as required by law .
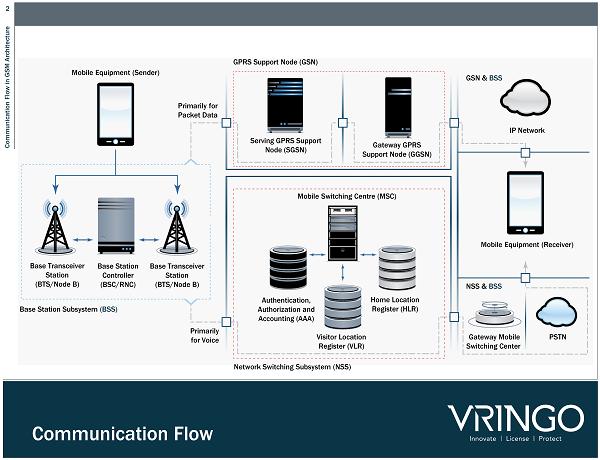
2 Communication Flow in GSM Architecture Communication Flow Mobile Equipment (Sender) Base Transceiver Station (BTS/Node B) Base Station Controller (BSC/ RNC ) Base Transceiver Station (BTS/Node B) Mobile Equipment (Receiver) Base Station Subsystem (BSS) Primarily for Voice Authentication, Authorization and Accounting (AAA) Home Location Register ( HLR ) Visitor Location Register ( VLR ) Mobile Switching Centre (MSC) Network Switching Subsystem ( NSS ) GPRS Support Node ( GSN ) Serving GPRS Support Node ( SGSN ) Gateway GPRS Support Node ( GGSN ) GSN & BSS Primarily for Packet Data IP Network Gateway Mobile Switching Center PSTN NSS & BSS

3 Communication Flow in GSM Architecture Communication Flow Details Category - Level Zero Explanation Using the Diagram Communication Management The category comprises patents involving messaging and supplementary services like call waiting, conferencing etc. These patents describe communication from the mobile device to BTS or BTS to BSC or BSC to MSC etc. Data & Signal Transmission These patents describes transmission of data & signal. Patents describing data transmission describe communication from mobile device to BTS , BSC to MSC, MSC to PSTN OR BSC to SGSN , SGSN to GGSN , GGSN to IP Network. Mobility Management These describe tracking subscribers when they move from one location to another, allowing calls, SMS and other mobile phone services to be delivered to them. These patents primarily involves communication amongst MSC, HLR and VLR . Radio Resources Management These patents describe communication between network elements like routers, switches, gateways etc. These patents primarily describe communication between BSC and MSC or BSC and SGSN . Services The patents in this category cover various remote transactions like billing, ticketing, e - services , notifications etc. These patents describe communication from the mobile device to BTS, BTS to BSC, BSC to MSC, MSC to PSTN etc. or the alternative path using IP network.
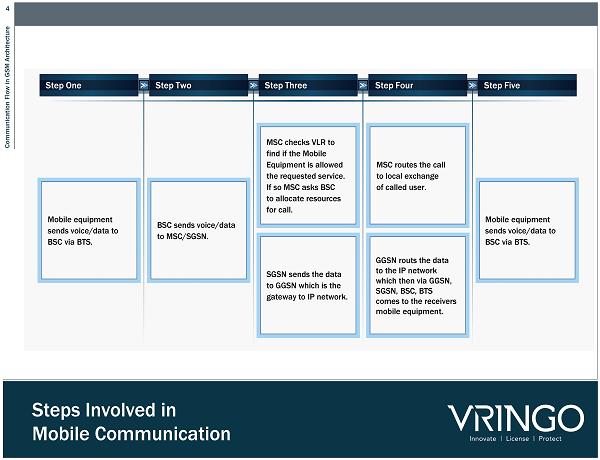
4 Communication Flow in GSM Architecture Steps Involved in Mobile Communication Step One Step Two Step Three Step Four Step Five Mobile equipment sends voice/data to BSC via BTS. BSC sends voice/data to MSC/SGSN. MSC checks VLR to find if the Mobile Equipment is allowed the requested service. If so MSC asks BSC to allocate resources for call. MSC routes the call to local exchange of called user. Mobile equipment sends voice/data to BSC via BTS. SGSN sends the data to GGSN which is the gateway to IP network. GGSN routs the data to the IP network which then via GGSN , SGSN , BSC, BTS comes to the receivers mobile equipment.
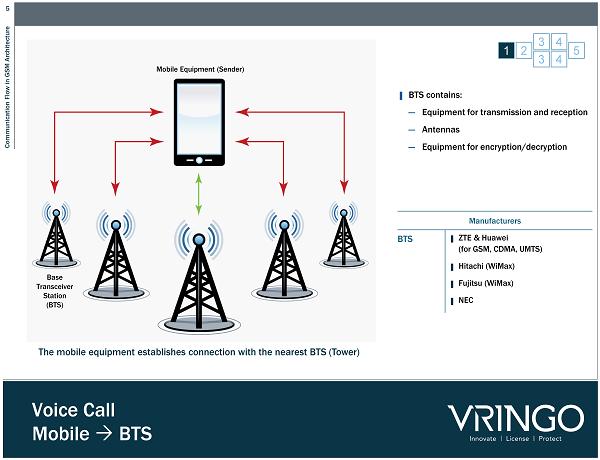
5 Communication Flow in GSM Architecture Voice Call Mobile BTS ▌ BTS contains: ― Equipment for transmission and reception ― Antennas ― Equipment for encryption/decryption 1 2 3 4 5 3 4 Base Transceiver Station (BTS) Mobile Equipment (Sender) The mobile equipment establishes connection with the nearest BTS (Tower) Manufacturers BTS ▌ ZTE & Huawei (for GSM, CDMA, UMTS) ▌ Hitachi ( WiMax ) ▌ Fujitsu ( WiMax ) ▌ NEC

6 Communication Flow in GSM Architecture BSC controls a group of BTS’s and manages all radio - related functions, e.g.: ▌ Allocation of channels ▌ Handover between BTS’s ▌ Monitoring power level, etc. Voice Call BTS BSC 1 2 3 4 5 3 4 Base Transceiver Station (BTS) Mobile Equipment (Sender) Router Switch Base Station Controller (BSC) Manufacturers BSC ▌ ZTE & Huawei (for GSM, CDMA, UMTS) ▌ Alcatel - Lucent ▌ Motorola Solutions ▌ Ericsson ▌ Hitachi ( WiMax ) ▌ Fujitsu ( WiMax ) ▌ Cisco, Juniper, Tellabs & Ciena (Routers & Switches)

7 Communication Flow in GSM Architecture Voice Call BSC MSC 1 2 3 4 5 3 4 Router Switch Mobile Switching Centre (MSC) Visitor Location Register (VLR) Home Location Register (HLR) Authentication, Authorization and Accounting (AAA) Base Transceiver Station (BTS) Base Station Controller (BSC) Base Transceiver Station (BTS) ▌ MSC is responsible for routing of traffic, keeping track of mobile subscribers, etc. ▌ HLR stores current location of subscriber and all services to which they have access to. ▌ VLR contains both subscriber information and information related to MSC service area in which subscriber is currently located. ▌ AAA authenticates subscribers attempting to access the network. It is for security purpose. Manufacturers BSC ▌ Alcatel - Lucent ▌ ZTE ▌ Huawei ▌ Cisco & Juniper (Routers & Switches) ▌ Siemens ▌ TE Connectivity ▌ Motorola ▌ Ericsson
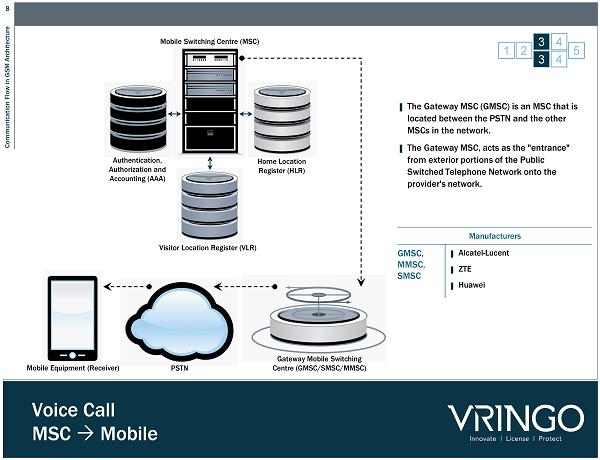
8 Communication Flow in GSM Architecture Voice Call MSC Mobile 1 2 3 4 5 3 4 Mobile Equipment (Receiver) PSTN Gateway Mobile Switching Centre (GMSC/SMSC/MMSC) Mobile Switching Centre (MSC) Visitor Location Register (VLR) Home Location Register (HLR) Authentication, Authorization and Accounting (AAA) ▌ The Gateway MSC (GMSC) is an MSC that is located between the PSTN and the other MSCs in the network. ▌ The Gateway MSC, acts as the "entrance" from exterior portions of the Public Switched Telephone Network onto the provider's network. Manufacturers GMSC, MMSC, SMSC ▌ Alcatel - Lucent ▌ ZTE ▌ Huawei
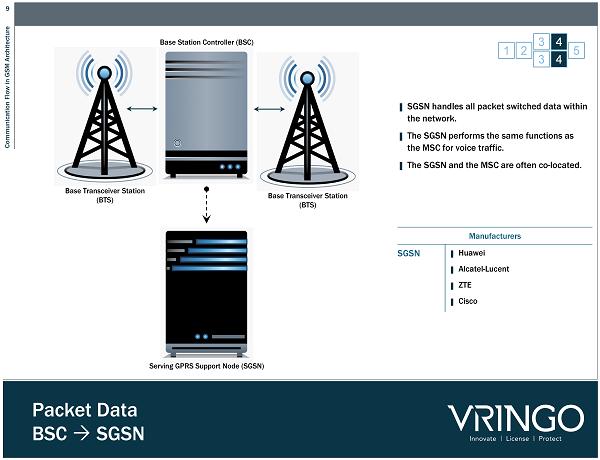
9 Communication Flow in GSM Architecture Packet Data BSC SGSN 1 2 3 4 5 3 4 Base Transceiver Station (BTS) Base Station Controller (BSC) Base Transceiver Station (BTS) Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN) ▌ SGSN handles all packet switched data within the network. ▌ The SGSN performs the same functions as the MSC for voice traffic. ▌ The SGSN and the MSC are often co - located. Manufacturers SGSN ▌ Huawei ▌ Alcatel - Lucent ▌ ZTE ▌ Cisco
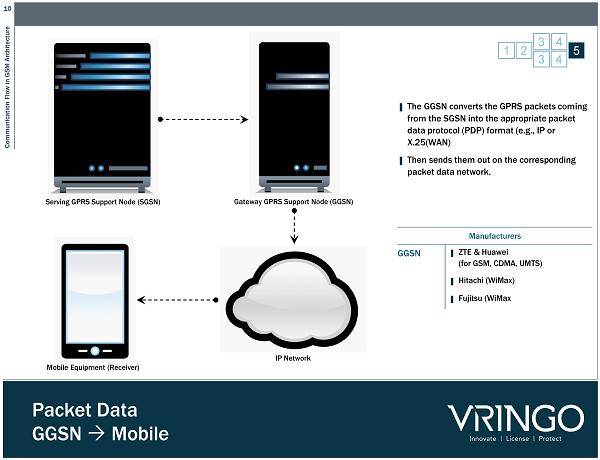
10 Communication Flow in GSM Architecture Packet Data GGSN Mobile 1 2 3 4 5 3 4 Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN) Mobile Equipment (Receiver) Gateway GPRS Support Node (GGSN) IP Network ▌ The GGSN converts the GPRS packets coming from the SGSN into the appropriate packet data protocol (PDP) format (e.g., IP or X.25(WAN) ▌ Then sends them out on the corresponding packet data network. Manufacturers GGSN ▌ ZTE & Huawei (for GSM, CDMA, UMTS) ▌ Hitachi ( WiMax ) ▌ Fujitsu ( WiMax

11 Communication Flow in GSM Architecture 524 Infrastructure Patents and Applications 138 42 7 13 23 23 39 35 15 26 1 3 444 Patents 401 Nationally Enforceable Patents 80 Patent Applications 124 Patent Families 10
12 Communication Flow in GSM Architecture Appendix: Patents The patents identified have been determined, following a preliminary analysis, to be relevant to the architectures and systems described. Certain Vringo patents have been declared in relation to ETSI, 3GPP and other standards . Vringo has not verified the essentiality of those patents at this time.
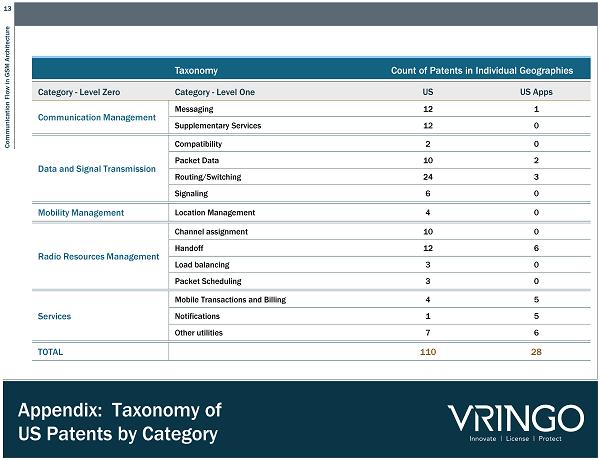
13 Communication Flow in GSM Architecture Appendix: Taxonomy of US Patents by Category Taxonomy Count of Patents in Individual Geographies Category - Level Zero Category - Level One US US Apps Communication Management Messaging 12 1 Supplementary Services 12 0 Data and Signal Transmission Compatibility 2 0 Packet Data 10 2 Routing/Switching 24 3 Signaling 6 0 Mobility Management Location Management 4 0 Radio Resources Management Channel assignment 10 0 Handoff 12 6 Load balancing 3 0 Packet Scheduling 3 0 Services Mobile Transactions and Billing 4 5 Notifications 1 5 Other utilities 7 6 TOTAL 110 28
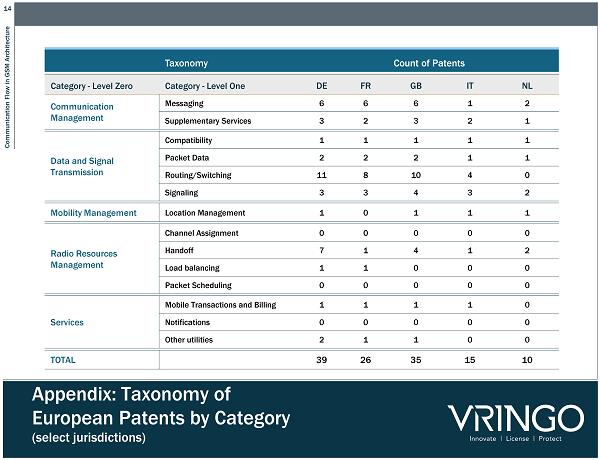
14 Communication Flow in GSM Architecture Appendix: Taxonomy of European Patents by Category (select jurisdictions) Taxonomy Count of Patents Category - Level Zero Category - Level One DE FR GB IT NL Communication Management Messaging 6 6 6 1 2 Supplementary Services 3 2 3 2 1 Data and Signal Transmission Compatibility 1 1 1 1 1 Packet Data 2 2 2 1 1 Routing/Switching 11 8 10 4 0 Signaling 3 3 4 3 2 Mobility Management Location Management 1 0 1 1 1 Radio Resources Management Channel Assignment 0 0 0 0 0 Handoff 7 1 4 1 2 Load balancing 1 1 0 0 0 Packet Scheduling 0 0 0 0 0 Services Mobile Transactions and Billing 1 1 1 1 0 Notifications 0 0 0 0 0 Other utilities 2 1 1 0 0 TOTAL 39 26 35 15 10
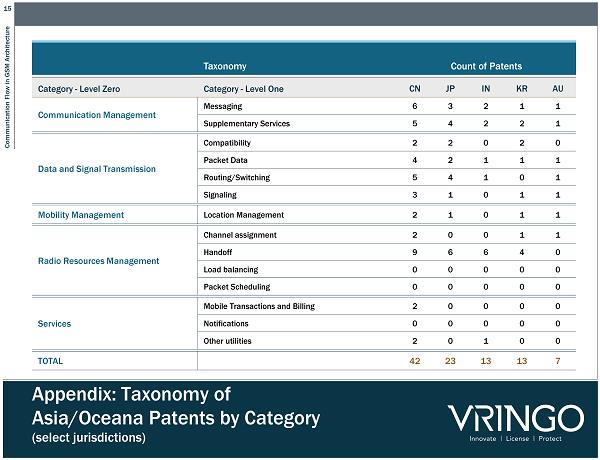
15 Communication Flow in GSM Architecture Appendix: Taxonomy of Asia/Oceana Patents by Category (select jurisdictions) Taxonomy Count of Patents Category - Level Zero Category - Level One CN JP IN KR AU Communication Management Messaging 6 3 2 1 1 Supplementary Services 5 4 2 2 1 Data and Signal Transmission Compatibility 2 2 0 2 0 Packet Data 4 2 1 1 1 Routing/Switching 5 4 1 0 1 Signaling 3 1 0 1 1 Mobility Management Location Management 2 1 0 1 1 Radio Resources Management Channel assignment 2 0 0 1 1 Handoff 9 6 6 4 0 Load balancing 0 0 0 0 0 Packet Scheduling 0 0 0 0 0 Services Mobile Transactions and Billing 2 0 0 0 0 Notifications 0 0 0 0 0 Other utilities 2 0 1 0 0 TOTAL 42 23 13 13 7

16 Communication Flow in GSM Architecture Appendix: Communication Management How Messages/Supplementary Services are Handled by Equipment Messaging Describes patents involving managing short message service and multimedia messaging service. Supplementary Services These patents include additional features provided during a call like Call Transfer, Call Waiting, Clear Call Waiting, Conference Calls, Caller I.D., etc.

17 Communication Flow in GSM Architecture Appendix: Data and Signal Transmission How Data Handling and Signaling is Performed in a Network Packet Data The patents describes splitting data into various packets, processing the packets and transmitting through the network. Routing/Switching The patents describe methods of selecting paths, channels or links in a network along which to transmit network traffic. Signaling The patents describe use of signals and protocols for controlling communications in a specific manner. Compatibility The patents describe use of signals and protocols for controlling communications in a specific manner.
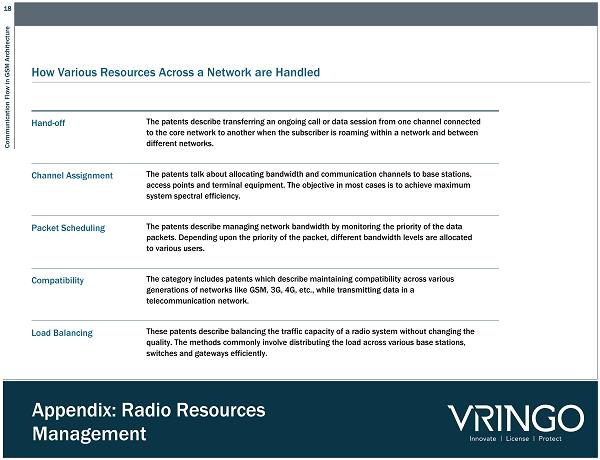
18 Communication Flow in GSM Architecture Appendix: Radio Resources Management How Various Resources Across a Network are Handled Hand - off The patents describe transferring an ongoing call or data session from one channel connected to the core network to another when the subscriber is roaming within a network and between different networks. Channel Assignment The patents talk about allocating bandwidth and communication channels to base stations, access points and terminal equipment. The objective in most cases is to achieve maximum system spectral efficiency. Packet Scheduling The patents describe managing network bandwidth by monitoring the priority of the data packets. Depending upon the priority of the packet, different bandwidth levels are allocated to various users. Compatibility The category includes patents which describe maintaining compatibility across various generations of networks like GSM , 3G, 4G, etc., while transmitting data in a telecommunication network. Load Balancing These patents describe balancing the traffic capacity of a radio system without changing the quality. The methods commonly involve distributing the load across various base stations, switches and gateways efficiently.

19 Communication Flow in GSM Architecture Appendix Mobility Management and Services How Services are Provided to Subscribers on the Move Location Management The patents in this category describe tracking subscribers when they move from one location to another, allowing calls, SMS and other mobile phone services to be delivered to them. How Various Operations other than Making Calls, Sending Messages are Performed Mobile Transactions and Billing The patents in this category cover various remote transactions like billing, ticketing, e - services, etc. possible though a mobile device and a cellular/IP network. Notifications The patents involve receiving and processing updates on software, firmware from a remote system through the network. For E.g. Over the Air programming for distributing new software updates or configuration settings to devices like cellular phones and set - top boxes.

20 Communication Flow in GSM Architecture Appendix: Interfaces and Protocols Used in GSM Communicating Components Interface Protocols Used Mobile equipment - BTS Um interface (air interface) For signaling, a modified version of the ISDN LAPD, known as LAPDm is used BTS - BTS No direct communication BTS - BSC A - bis interface LAPD, BTSM, RR, MM, CC, SMS, GCC, BCC BSC - MSC A – interface MTP2, MTP3, SCCP, BSSMAP, MM, CC, SMS, GCC, BCC, DTAP MSC - MSC E - interface MAP HLR,VLR, MSC,AAA B,C,D - interface SCCP, TCAP, GSM MAP BSC - SGSN Gs, Gb MTP2, MTP3, SCCP, BSSAP+
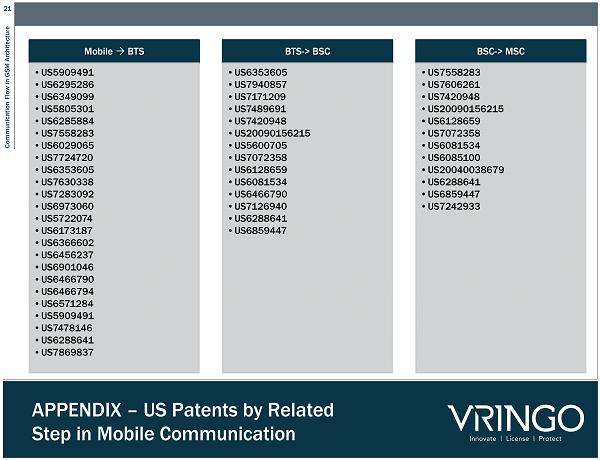
21 Communication Flow in GSM Architecture APPENDIX – US Patents by Related Step in Mobile Communication Mobile BTS • US5909491 • US6295286 • US6349099 • US5805301 • US6285884 • US7558283 • US6029065 • US7724720 • US6353605 • US7630338 • US7283092 • US6973060 • US5722074 • US6173187 • US6366602 • US6456237 • US6901046 • US6466790 • US6466794 • US6571284 • US5909491 • US7478146 • US6288641 • US7869837 BTS - > BSC • US6353605 • US7940857 • US7171209 • US7489691 • US7420948 • US20090156215 • US5600705 • US7072358 • US6128659 • US6081534 • US6466790 • US7126940 • US6288641 • US6859447 BSC - > MSC • US7558283 • US7606261 • US7420948 • US20090156215 • US6128659 • US7072358 • US6081534 • US6085100 • US20040038679 • US6288641 • US6859447 • US7242933
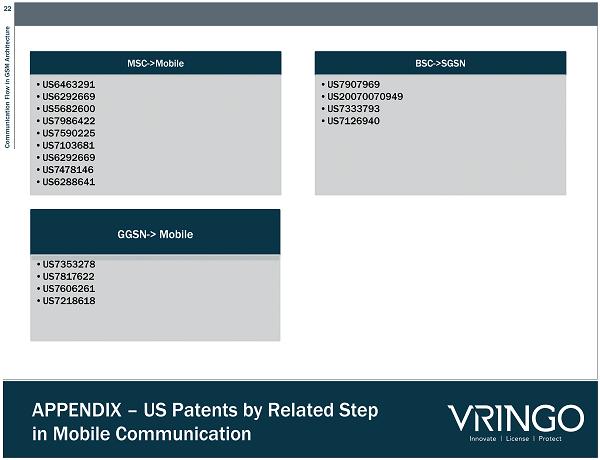
22 Communication Flow in GSM Architecture APPENDIX – US Patents by R elated Step in Mobile Communication MSC - >Mobile • US6463291 • US6292669 • US5682600 • US7986422 • US7590225 • US7103681 • US6292669 • US7478146 • US6288641 BSC - >SGSN • US7907969 • US20070070949 • US7333793 • US7126940 GGSN - > Mobile • US7353278 • US7817622 • US7606261 • US7218618
