Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| 8-K - 8-K - Ardea Biosciences, Inc./DE | a56089e8vk.htm |
Exhibit 99.1

| Company Update May 10, 2010 |

| Safe Harbor Statement Statements contained in this presentation regarding matters that are not historical facts are "forward- looking statements" within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. Because such statements are subject to risks and uncertainties, actual results may differ materially from those expressed or implied by such forward-looking statements. Such statements include, but are not limited to, statements regarding: Ardea's goals, its preclinical and clinical trial plans, timelines and milestones, its expectations about the size of its markets and commercial potential of its compounds, expected results of future clinical trials, expected properties of compounds under development, financial position, cash usage, licensing and partnering opportunities, liquidity and anticipated milestones. Risks that contribute to the uncertain nature of the forward-looking statements include: risks related to the outcomes of preclinical and clinical trials, risks related to regulatory approvals, delays in commencement of preclinical and clinical tests, costs associated with internal development, and the outcome of our business development activities, including collaboration or licensing agreements. These and other risks and uncertainties are described more fully in Ardea's most recently filed SEC documents, including its Annual Report on Form 10-K and Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, under the headings "Risk Factors." All forward-looking statements contained in this presentation speak only as of the date of this presentation, and Ardea undertakes no obligation to update such statements to reflect events that occur or circumstances that exist after the date hereof or otherwise. 2 |

| Status of Development Programs RDEA427 RDEA806 900 Series Discovery Preclinical Phase 0/1 Phase 2 A B Phase 3 NNRTI for HIV NNRTI for HIV MEKI for cancer 3 Gout RDEA594 Next Generation MEKI + sorafenib for cancer RDEA119 Gout RDEA119 3rd Gen NNRTIs |

| Gout/Hyperuricemia 4 - Disease and URAT1 Mechanism |

| Dual-Energy CT Shows Extensive Deposition of Urate Allopurinol, even with optimized dosing, produces very slow clearance of tophi (0.56 mm/month reduction in tophi with 29-month mean time to resolution)1 5 From Nicola Dalbeth 1. Perez-Ruiz F, Arthritis Rheum 2002;47:356-360 |

| Hyperuricemia/Gout - Unmet Medical Need Gout is caused by abnormally elevated levels of uric acid (>6.8 mg/dL) Increasing incidence and severity in US: > 5,000,000 potential patients ~ 90% of patients are "under-excretors" of uric acid RDEA594 increases excretion back to normal levels Allopurinol and febuxostat (Uloric(r), Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited) reduce production, which reduces excretion further The combination of RDEA594 and xanthine oxidase inhibitors will produce greater reduction in uric acid and speed up clearance of tophi and body burden of uric acid Hyperuricemia linked to elevated hypertension in adults1 and children2, increased mortality in Chronic Kidney Disease3 and possibly other cardiovascular risk factors4 including elevated C-Reactive Protein, with potentially more data coming soon 1. Int Urol Nephrol 2007;39:1227-33 ; 2. D Feig, B Soletsky, R Johnson. JAMA. 2008;300(8):924-932; 3. Am J Kidney Dis 2009;53:796-803; 4. JAMA. 2008;300(8):924-932; 6 |
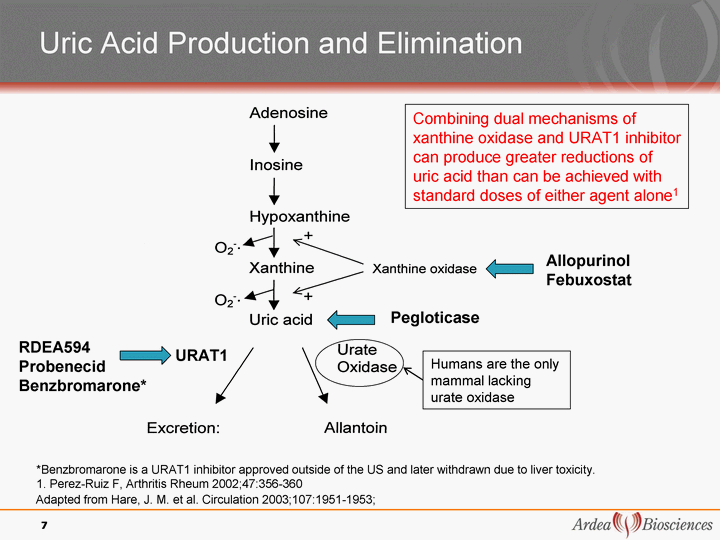
| Adapted from Hare, J. M. et al. Circulation 2003;107:1951-1953; Uric Acid Production and Elimination RDEA594 Probenecid Benzbromarone* 7 *Benzbromarone is a URAT1 inhibitor approved outside of the US and later withdrawn due to liver toxicity. 1. Perez-Ruiz F, Arthritis Rheum 2002;47:356-360 Pegloticase URAT1 Combining dual mechanisms of xanthine oxidase and URAT1 inhibitor can produce greater reductions of uric acid than can be achieved with standard doses of either agent alone1 Allopurinol Febuxostat Humans are the only mammal lacking urate oxidase |

| RDEA594 Normalizes Uric Acid Excretion Gout patients RDEA594 normalizes uric acid excretion in gout patients with inadequate excretion Allopurinol reduces uric acid excretion even further in patients with already low excretion The combination of these two agents reduces production, but also increases excretion to normal levels, resulting in substantial reductions in sUA and increased excretion of UA RDEA594 does not produce hyper-excretion and does not change urinary pH 8 8 |

| Diet & Metabolism <400 mg/day Diet & Metabolism 600-800 mg/day Joint Tophus 10 mg/dL 6 mg/dL serum level Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitor RDEA594 - URAT1 Inhibitor <5 mg/dL RDEA594 is most appropriate mechanism for under- excretors and is additive to allopurinol and febuxostat urine urine 200 mg/day 9 600 mg/day 300 mg/day gout patient |

| 10 Benzbromarone demonstrates benefit of combining URAT1 and xanthane oxidase inhibitors Inhibition of the URAT1 transporter is a well-validated target for gout Benzbromarone (not approved in U.S.; limited approvals in E.U.; sold in Japan with "Black-box" type warning) is a URAT1 inhibitor Over 10 million patient-years of treatment experience, with very few side effects, except liver toxicity due to structural defects of that molecule (not URAT1 effect) Approximately 170 million tablets of benzbromarone are currently sold per year in Japan (where it is still promoted), even with warnings about severe liver toxicity The combination of benzbromarone + allopurinol produces significant reductions in tophi1 1. Perez-Ruiz F, Arthritis Rheum 2002;47:356-360 Velocity of Tophi Reduction |
| Gout/Hyperuricemia 11 - Market Dynamics and Opportunity |

| US Gout Patient Distribution 12 Diagnosed Gout 5.2M ~50% ~90% ~50% ~50% Allopurinol Treated 2.5M Responders (<6mg/dL) 1.25M Severe Chronic Gout 0.1 - 0.3M (3) Allopurinol Non-Responders 1.25M ~10-20% Small % Allopurinol Intollerant Gout Pts on ULT 2.6M Small % Education (DTC) Improved Compliance |
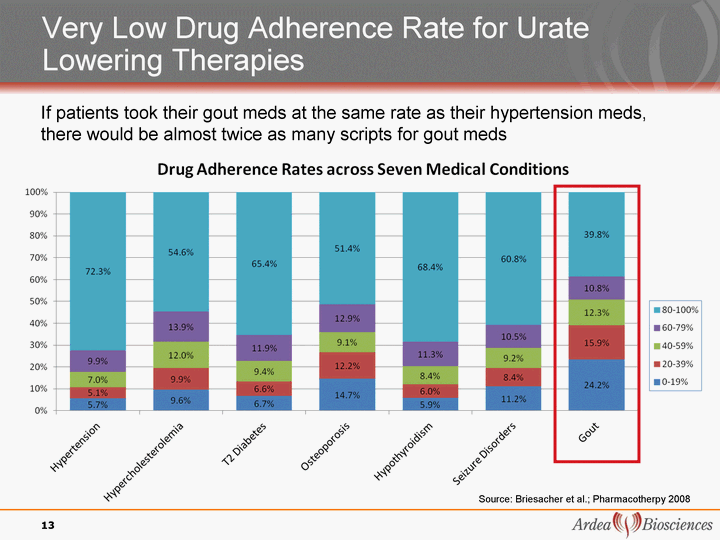
| Very Low Drug Adherence Rate for Urate Lowering Therapies Lowering Therapies Lowering Therapies 13 Source: Briesacher et al.; Pharmacotherpy 2008 If patients took their gout meds at the same rate as their hypertension meds, there would be almost twice as many scripts for gout meds |

| Competitive Landscape - Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitors Allopurinol 40-year old generic xanthine oxidase inhibitor: 36-42% response rate in three large Phase 3 trials (mean ~33% reduction in sUA) 8% SAEs1 and 0.4% incidence of Allopurinol Hypersensitivity Syndrome (AHS), which is 20-25% fatal2 Note: combination with RDEA594 produced ~55% reduction in sUA During first 10 months of treatment, the reduction of sUA causes increased incidence of acute flares and inflammation1 (negative effect on compliance) In the FACT study, at 1 year, the flare rate on allopurinol is approximately the same as it was at initiation of therapy (i.e., no benefit after a year) Under-excretors of uric acid, whose reduced urate clearance causes gout, actually have a further reduction of urate clearance on allopurinol This leads to very slow clearance of urate deposits, such as tophi, and very slow reduction in flare rate 1. Becker et al. N Engl J Med 2005;353:2450-61; 2. Ann Rheum Dis 2008;67(Suppl II):431 14 |

| Competitive Landscape - Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitors Febuxostat (Takeda) Another xanthine oxidase inhibitor approved 2-09 in US; not significantly differentiated from allopurinol The 40 mg starting dose is equivalent to allopurinol; 80 mg has improved efficacy Safety profile similar to allopurinol Approximately half of patients with high starting sUA respond at 6 months to 80 mg febuxostat1 Note: combination of febuxostat 40 mg and RDEA594 400 mg produced >70% sUA reduction in healthy volunteers with baseline sUA > 6 mg/dL Dose of febuxostat not increased as many subjects were already achieving sUA levels below 1 mg/dL; higher doses will be studied next. 1. Becker, et al. CONFIRMS Trial 2008 ACR 15 |

| Competitive Landscape - No Difference in Most Common Adverse Events With Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitors Adverse Event Placebo Febuxostat 40 mg 80 mg Febuxostat 40 mg 80 mg Allopurinol N= 134 757 1279 1277 Liver Function Abnormalities 0.7% 6.6% 4.6% 4.2% Nausea 0.7% 1.1% 1.3% 0.8% Arthralgia 0% 1.1% 0.7% 0.7% Rash 0.7% 0.5% 1.6% 1.6% Uloric US Package Insert 16 |

| Competitive Landscape - Uricosuric Inhibitor of Multiple Renal Transporters Probenecid (Benuryl) Suboptimal dosing frequency: 500 mg BID to 500 mg QID Low to modest efficacy: 23% reduction in sUA with 1 gm/day and 31% reduction with 2 gm/day 1 Side Effects: Headache, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal discomfort, skin rash, flushing, drug fever, rarely anaphylaxis, increased urination, sore gums, dizziness, hemolytic anemia, and aplastic anemia Significant drug-drug interactions: methotrexate, indomethacin, ketorolac, zidovudine, dyphylline, nitrofurantoin, doripenem, zalcitabine, amoxicillin, cefditoren pivoxil, cefpodoxime proxetil, cefprozil, choline salicylate, enprofylline, ertapenem, gatifloxacin, ketorolac, lorazepam, norfloxacin, phenprocoumon, piretanide, tenofovir, zidovudine and zomepirac 17 1. Ogryzlo and Harrison. Ann Rheum Dis 1957;16:425-437 |
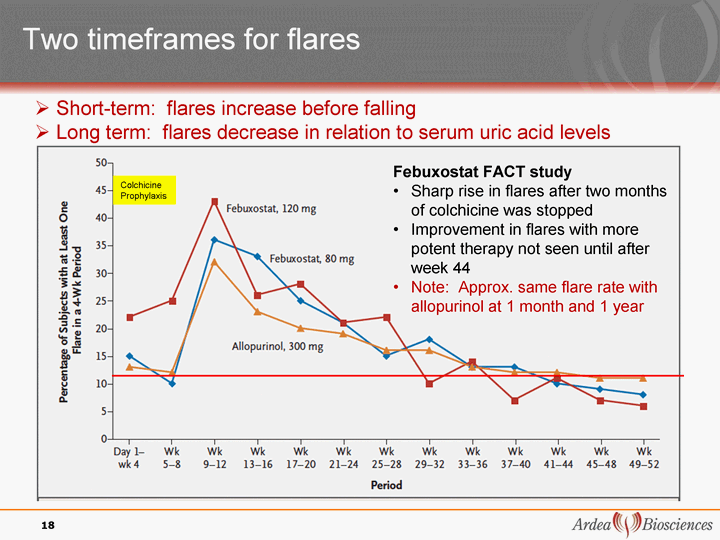
| Two timeframes for flares Two timeframes for flares 18 Colchicine Prophylaxis Febuxostat FACT study Sharp rise in flares after two months of colchicine was stopped Improvement in flares with more potent therapy not seen until after week 44 Note: Approx. same flare rate with allopurinol at 1 month and 1 year Short-term: flares increase before falling Long term: flares decrease in relation to serum uric acid levels |

| Almost Half of Patients Under Treatment are Still Having Flares - Lower sUA Reduces Flares Having Flares - Lower sUA Reduces Flares Having Flares - Lower sUA Reduces Flares 19 Proportion of Subjects (%) Abstract 758: MA Becker, et al. ACR Boston November 2007 *Ardea Market Research Only 2% of patients reach <4 mg/dL with allopurinol and only 20% with febuxostat 80mg Physicians believe that approximately half of the 2.6M treated patients are still having flares* This is consistent with less than half of patients reaching target sUA on allopurinol sUA of non-responders on allopurinol:* |

| RDEA594 Opportunity to Reduce Flares Chronic therapy: The combination of RDEA594 (URAT1 inhibitor) and xanthine oxidase inhibitors will produce greater reductions in sUA than either mechanism alone, with many more patients reaching levels below 6 mg/dL, and even below 5 mg/dL Reduction of sUA from 6-7mg/dL to less than 6 mg/dL reduces the flare rate by approximately one-half Treatment initiation: Faster renal clearance of urate could lead to faster reduction in urate deposits (tophi, crystals, etc.), reducing the risk of flares 20 |

| Gout and Hyperuricemia - Three Key Opportunities Combination Therapy - Potential to Redefine the Standard of Care Approximately 1/2 of treated patients still having flares; consistent with 40% response rate to allopurinol Adding RDEA594 could significantly reduce sUA and the incidence of gout flares over long-term Normalizing urate excretion with RDEA594/allopurinol combination will speed up tophi resolution In POC study, combination of RDEA594 and febuxostat lowered sUA levels >70%; this is an ideal combination for advanced, symptomatic patients with tophaceous gout Monotherapy - Potential Points of Differentiation Superior efficacy profile to allopurinol with much cleaner safety profile Should be good choice for allopurinol intolerant or refractory More appropriate treatment than current standard - treats underlying cause of gout in 90% of patients (under-excretors) Medical Education - Dramatic Opportunity to Grow Market Only half of diagnosed gout patients in U.S. are treated Compliance rates are well below other chronic therapies Potential to add millions more patients with growing body of evidence linking hyperuricemia and cardiovascular disease 21 |
| Gout/Hyperuricemia 22 - Clinical Development |

| 23 RDEA594 - Clinical Summary Phase 2a combination with allopurinol - completed Combination reduced serum uric acid greater than either agent alone POC combination with febuxostat - completed Combination reduced serum acid greater than either agent alone Combination achieved >70% reduction of serum uric acid Phase 2b monotherapy study - completed Observed reduction in serum uric acid appears to be competitive with febuxostat and superior to allopurinol Safety profile similar to placebo Phase 2b RDEA594 and allopurinol combination study - Ongoing |

| Phase 2a: 83% Response in Renally Impaired Patients Observed with RDEA594 All Subjects with Mild to Moderate Renal Insufficiency (Cockcroft-Gault) All Subjects with Mild to Moderate Renal Insufficiency (Cockcroft-Gault) All Subjects with Mild to Moderate Renal Insufficiency (Cockcroft-Gault) All Subjects with Mild to Moderate Renal Insufficiency (Cockcroft-Gault) Response defined as < 6.0 mg/dL Placebo % (n/N) RDEA594 % (n/N) Allopurinol % (n/N) Response Week 1 0 (0/0) 50 (3/6) 100 (1/1) Response Week 2 0 (0/0) 83 (5/6) 100 (1/1) Mean (+-SEM) Change in sUA (%) at nadir - -47.8+-4.2% -56.1 24 |
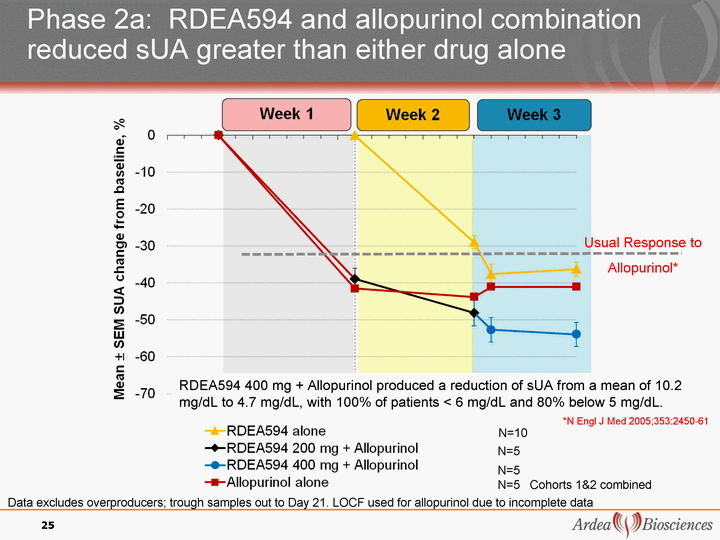
| Phase 2a: RDEA594 and allopurinol combination reduced sUA greater than either drug alone N=5 N=5 N=5 Cohorts 1&2 combined Data excludes overproducers; trough samples out to Day 21. LOCF used for allopurinol due to incomplete data N=10 RDEA594 400 mg + Allopurinol produced a reduction of sUA from a mean of 10.2 mg/dL to 4.7 mg/dL, with 100% of patients < 6 mg/dL and 80% below 5 mg/dL. Usual Response to Allopurinol* 25 *N Engl J Med 2005;353:2450-61 |

| RDEA594 -105: Phase 1 Placebo-Controlled RDEA594 - Febuxostat Drug-Drug Interaction and PD Study Population: 36 normal healthy volunteers with sUA ^ 6 mg/dL; 18 per panel Males and postmenopausal or sterile women 18 - 65 years of age, inclusive 2 panels with escalating doses of RDEA594 or placebo - 200 mg and 400 mg Assessments: pharmacokinetic drug interactions impact on sUA safety and tolerability Design: Each panel is randomized to one of two sequences Sequences for each panel: Febuxostat 40 mg qd RDEA594 or Placebo qd Sequence Days 1-7 Days 8-14 Days 15-21 RDEA594 or Placebo qd Febuxostat 40 mg qd 1 2 26 CONFIDENTIAL |

| Combination of RDEA594 and Febuxostat Produced 70% - 80% Reductions in sUA Mean percent sUA reduction observed with pegloticase* * *Khosravan, et al. Clin Pharmacokinet 2006; 45 (8): 821-841 27 The combination arms are significantly different from febuxostat alone at all points from Days 9-15: p < 0.001 Highest approved dose of febuxostat in healthy subjects* **pegloticase FDA Advisory Committee |

| Overall Summary of Safety for RDEA594 Through Phase 2a Patients exposed to RDEA594 (either administration of RDEA594 or RDEA806): Healthy subjects and HIV pts ~360 for up to 14 days Gout patients ~ 40 for up to 28 days Control subjects ~ 88 28 Arm Discontinuations Due to AEs N (%) Serious Adverse Events N (%) Grade 2 or Greater Laboratory Abnormalities* N (%) RDEA594 1** (0.25%) 1** (0.25%) 6***(1.5%) Control 2 (2.3%) 2 (2.3%) 7 (8%) *Increase in grade from 0 or 1 to grade 2 or greater. **Hemorrhoids considered not likely drug related *** Increases in ALT, lipase and/or amylase were predominately observed with the allopurinol combination; significant laboratory abnormalities were also observed with allopurinol alone 28 |
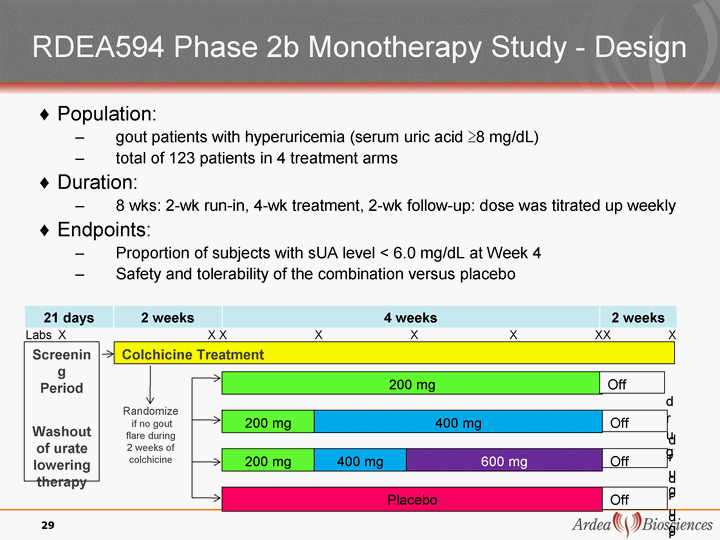
| RDEA594 Phase 2b Monotherapy Study - Design 21 days 2 weeks 4 weeks 2 weeks Population: gout patients with hyperuricemia (serum uric acid ^8 mg/dL) total of 123 patients in 4 treatment arms Duration: 8 wks: 2-wk run-in, 4-wk treatment, 2-wk follow-up: dose was titrated up weekly Endpoints: Proportion of subjects with sUA level < 6.0 mg/dL at Week 4 Safety and tolerability of the combination versus placebo Screenin g Period Washout of urate lowering therapy Colchicine Treatment Randomize if no gout flare during 2 weeks of colchicine 29 200 mg Off d r u g Off d r u g Off d r u g 200 mg Placebo 400 mg 200 mg 400 mg 600 mg Off d r u g Labs X X X X X X XX X |

| RDEA594 Phase 2b Monotherapy Study Full Data to be Presented at 2010 EULAR Preliminary, Top-Line Efficacy Results of Phase 2b Monotherapy Study of RDEA594 in the Treatment of Hyperuricemia in Gout Patients Preliminary, Top-Line Efficacy Results of Phase 2b Monotherapy Study of RDEA594 in the Treatment of Hyperuricemia in Gout Patients Preliminary, Top-Line Efficacy Results of Phase 2b Monotherapy Study of RDEA594 in the Treatment of Hyperuricemia in Gout Patients Preliminary, Top-Line Efficacy Results of Phase 2b Monotherapy Study of RDEA594 in the Treatment of Hyperurice mia in Gout Patients Preliminary, Top-Line Efficacy Results of Phase 2b Monotherapy Study of RDEA594 in the Treatment of Hyperuricemia in Gout Patients Treatment Groups Treatment Groups Treatment Groups Treatment Groups RDEA594 600mg qd RDEA594 400mg qd RDEA594 200mg qd Placebo Response Rate (Primary Endpoint) 45% (n=32) 28% (n=33) 7% (n=31) 0% (n=27) p Value versus Placebo <0.0001 0.0056 NS Response Rate in Pts. with Baseline Serum Urate <10 mg/dL 58% (n=12) 42% (n=14) 11% (n=18) 0% (n=14) p Value versus Placebo 0.0012 0.016 NS 30 |
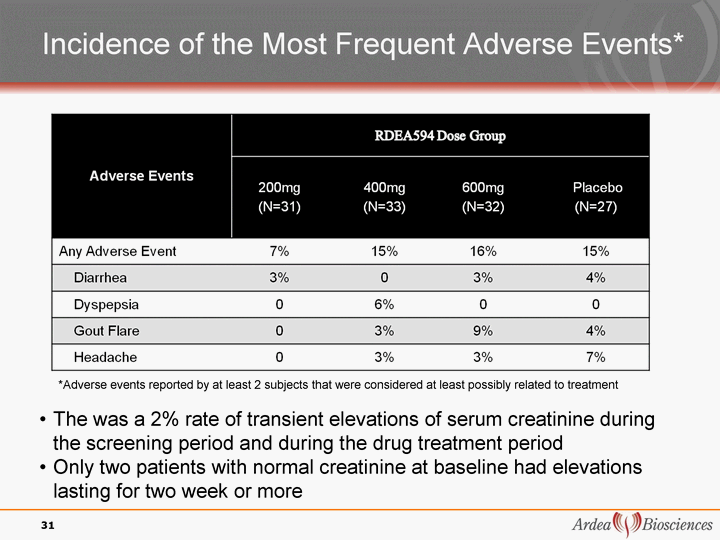
| Incidence of the Most Frequent Adverse Events* 31 *Adverse events reported by at least 2 subjects that were considered at least possibly related to treatment The was a 2% rate of transient elevations of serum creatinine during the screening period and during the drug treatment period Only two patients with normal creatinine at baseline had elevations lasting for two week or more |

| RDEA594 Phase 2b Allopurinol Add-On Combination Safety and Efficacy Study - Enrolling Initial dose selection phase completed: RDEA594 200 mg, 400 mg, 600 mg to be evaluated 72 patients per dose level, including 48 patients randomized to RDEA594 and 24 patients randomized to placebo per cohort and treated for 28 days; expect most patients to go into extension phase Patients must be on stable 300 mg dose of allopurinol with sUA >6 mg/dL. All patients receive colchicine prophylaxis for duration of treatment 32 RDEA594 200 mg or placebo plus allopurinol 300 mg (n=18) RDEA594 200 mg or placebo plus allopurinol 300 mg RDEA594 400 mg or placebo plus allopurinol 300 mg Dosing Decision Completed Higher Dose Group Selected RDEA594 600 mg or placebo plus allopurinol 300 mg Colchicine Prophylaxis Long-Term Extension |

| Cancer 33 MEK program licensed to Bayer HealthCare on April 28, 2009 $35 million upfront license fee Payments could total $407 million, excluding royalties Low double-digit royalties on worldwide sales Ardea responsible for completing two dose-finding studies (expected completion to MTD in 1H10) |
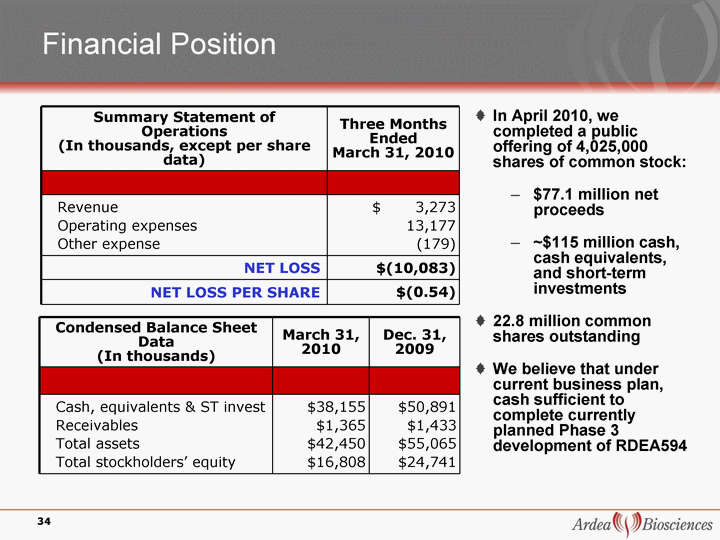
| Financial Position Summary Statement of Operations (In thousands, except per share data) Three Months Ended March 31, 2010 Revenue Operating expenses Other expense $ 3,273 13,177 (179) NET LOSS $(10,083) NET LOSS PER SHARE $(0.54) In April 2010, we completed a public offering of 4,025,000 shares of common stock: $77.1 million net proceeds ~$115 million cash, cash equivalents, and short-term investments 22.8 million common shares outstanding We believe that under current business plan, cash sufficient to complete currently planned Phase 3 development of RDEA594 Condensed Balance Sheet Data (In thousands) March 31, 2010 Dec. 31, 2009 Cash, equivalents & ST invest Receivables Total assets Total stockholders' equity $38,155 $1,365 $42,450 $16,808 $50,891 $1,433 $55,065 $24,741 34 |

| Near-Term Anticipated Milestones Drug Candidate Event Date Date Gout Gout Gout Gout RDEA594 Phase 2a - Cohort 2 Allopurinol Combo Results Phase 2a - Cohort 2 Allopurinol Combo Results ? RDEA594 Febuxostat Combination Study Results Febuxostat Combination Study Results ? RDEA594 Phase 2b Monotherapy Study Results Phase 2b Monotherapy Study Results ? RDEA594 Phase 2b Allopurinol Add-On Study Results Phase 2b Allopurinol Add-On Study Results 3Q10 RDEA594 Renal Impairment Study Results Renal Impairment Study Results 2Q10 Cancer Cancer Cancer Cancer RDEA119 Phase 1 advanced cancer (MTD) Phase 1 advanced cancer (MTD) 1H10 RDEA119 Phase 1/2 sorafenib combination (MTD) Phase 1/2 sorafenib combination (MTD) 1H10 35 |
