Attached files
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
x ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2009
Commission File Number 0-23272
NPS PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.

(Exact Name of Registrant as Specified in its Charter)
|
|
|
|
|
|
550 Hills Drive, 3rd Floor Bedminster, New Jersey 07921
(Address of Principal Executive Offices including Zip Code)
(908) 450-5300
(Registrant's Telephone Number, Including Area Code)
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
|
Title Of Each Class |
|
Name Of Each Exchange On Which Registered |
|
Common Stock, $.001 Par Value Per Share |
|
The NASDAQ Stock Market LLC |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the Registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. YES
o NO xIndicate by check mark if the Registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act. YES
o NO xIndicate by check mark whether the Registrant: (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the Registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for at least the past 90 days. YES
x NO oIndicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). YES
o NO oIndicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of Registrant's knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K.
oIndicate by check mark whether the Registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, or a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of "large accelerated filer," and large "accelerated filer" and "smaller reporting company" in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
|
Large accelerated filer ¨ |
Accelerated filer x |
Non-accelerated filer ¨
|
Smaller reporting company ¨ |
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). YES
o NO xThe aggregate market value of the common stock held by non-affiliates of the Registrant was $223,945,965 as of June 30, 2009, based upon the closing price for the shares of common stock reported on The NASDAQ Global Market on such date.
As of March 4, 2010, there were 48,447,880 shares of common stock, par value $0.001 per share, outstanding.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE:
Portions of the Registrant's definitive Proxy Statement for its 2010 Annual Meeting of Stockholders are incorporated by reference into Part II - "Securities Authorized For Issuance Under Equity Compensation Plans" and Part III of this Form 10-K.
PDF provided as courtesy
TABLE OF CONTENTS Item Page PART I 1. 3 1A. 20 1B. 32 2. 32 3. 32 4. 33 PART II 5. 34 6. 36 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations 37 7A. 50 8. 52 9. Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure 88 9A. 88 9B. 89 PART III 10. 89 11. 89 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder
Matters 89 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence 89 14. 89 PART IV 15. 90 2
PART I Unless the context requires otherwise, references in this report to "NPS", the
"Company", "we", "us", "our" and similar terms mean NPS Pharmaceuticals, Inc. and its
subsidiaries. This Annual Report on Form 10-K and the documents incorporated by reference into this report contain certain forward-looking
statements within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. These statements are based on our current
expectations and are subject to uncertainty and changes in circumstances. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of such statements, and
you should be aware that results and events could differ materially from those contained in such statements. You should consider
carefully the statements set forth in Item 1A of this report entitled "Risk Factors" and Item 7 of
this report entitled "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations".
Overview NPS is a clinical-stage biopharmaceutical company focused on the development of
new treatment options for patients with rare gastrointestinal and endocrine disorders and serious unmet medical needs. Our
lead clinical programs involve two proprietary therapeutic peptides to restore or replace biological function: teduglutide and NPSP558.
Teduglutide, our analog of GLP-2, a protein involved in the regeneration and repair of the intestinal lining, is in Phase 3 clinical
development as GATTEX® (planned brand name) for parenteral nutrition (PN) dependent short bowel syndrome
(SBS). SBS is a highly disabling condition that results from surgical resection, congenital defect or disease-associated loss of
absorption in the bowel in which patients are subsequently unable to maintain fluid, electrolyte, and nutrient balances on a conventional
diet. Despite an adaptation that occurs generally in the two years after resection, a certain proportion of SBS patients require the
chronic use of parenteral nutrition (PN) or intravenous feeding to supplement and stabilize their nutritional needs. The cost of PN can exceed $100,000 annually per patient. In addition, PN use is
associated with potentially life-threatening complications including sepsis and liver damage, and reduced quality-of-life due to the time
required for and consequences of frequent access to an intravenous pump. Our Phase 3 registration study
of GATTEX is known as STEPS. NPSP558 is our recombinant full-length human parathyroid hormone
(rhPTH (1-84)) that is in Phase 3 clinical development as a hormone replacement therapy for hypoparathyroidism, a rare hormone
deficiency disorder in which patients are physiologically unable to regulate the levels of calcium and phosphates in their blood due to
insufficient levels of endogenous parathyroid hormone (PTH). Endogenous PTH is the body's principal regulator of serum
calcium and phosphate levels. Hypoparathyroidsim is associated with hypocalcemia, hypercalciuria (excessive urinary calcium
excretion), and increased bone mineral density. It typically results from permanent injury to the parathyroid gland(s) during thyroid or
parathyroid surgery or other surgical procedures in the neck, radiation to the neck region, autoimmune destruction of the parathyroid
glands, or their congenital absence. Although rare, hypoparathyroidism can also result from genetic mutations. Current therapy
is limited to calcium supplementation and parenteral or metabolic forms of vitamin D. These palliative therapies are sometimes
suboptimal and can also contribute to long-term health risks including kidney failure. Hypoparathyroidism is one of the few
hormonal deficiency syndromes with no approved replacement therapy using the native hormone. If approved, NPSP558 could
be the first treatment targeting the underlying cause of hypoparathyroidism by replacing the native hormone. Our
Phase 3 registration study of NPSP558 is known as REPLACE. We believe positive results from STEPS and REPLACE will enable us to seek U.S. marketing approval of GATTEX for SBS and
NPSP558 for hypoparathyroidism. While SBS and hypoparathyroidism are relatively rare disorders, we believe these
indications represent substantial commercial opportunities to us due to the significant unmet need and lack of effective therapies, as
well as the serious complications and chronic nature of both disorders. We have collaborations or royalty agreements with a number of pharmaceutical companies. In 2009, we reported $79.3
million of royalty revenue that was driven by (i) Amgen's sales of Sensipar® (cinacalcet HCl), (ii)
Nycomed's sales of Preotact®, which is our rhPTH (1-84) compound that is approved for the treatment of
osteoporosis in postmenopausal women at high risk of fractures under a centralized procedure in the European Union, (iii) Kyowa
Kirin's sales of REGPARA® (cinacalcet HCl) in Japan and (iv) Ortho-McNeil Pharmaceuticals' (Ortho-McNeil) sales
of Nucynta™ (tapentadol) in the U.S. As described further herein, we have partially monetized our royalty rights related
to Sensipar under our agreement with Amgen through the issuance of non-recourse debt and we have sold
3
certain of our rights to
receive royalty payments arising from sales of Preotact and REGPARA under our agreements with Nycomed and Kyowa Kirin. In
2007, we granted Nycomed the rights to develop and market teduglutide outside of North America that may provide future milestone
payments and royalties and the two companies are collaborating and sharing certain external development costs for the SBS indication.
Business Model Our business model balances rewards, risks and resources through the following three key elements: Focus on indications with few, if any, therapeutic options and limited competition. Our investment in non-clinical and clinical
development is singularly focused on advancing our pipeline for rare disorders with serious unmet medical needs. We believe this
strategy will help us create a product portfolio that can be successfully commercialized through a focused and specialized sales team
as patients with rare disorders are typically treated by physician specialists. Utilize outsourcing partners to optimize resources and limit financial exposure. We believe that combining traditional
outsourcing with collaborations that enhance our organization's internal capabilities offer an efficient and cost-effective approach. We
are applying this model to all areas of our business. Rather than investing substantial resources in building and maintaining
infrastructure, we have a core internal team of seasoned industry professionals and we complement this internal knowledge base
through collaborations with outside contractors. By blending internal and external innovation, we expect to optimize each stage of our
clinical development and effectively manage our resources, risk, and time-to-market for our key clinical programs. Collaborate or license to manage risk and accelerate the development and commercialization of product candidates. We
believe that collaborating with pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies with relevant expertise in areas outside of our proprietary
therapeutic or geographic focus will accelerate the development and commercialization of our products in these non-core focus areas.
This strategy allows us to allocate our resources and support our core programs that we believe have an appropriate probability of
development and commercial success in rare diseases with serious unmet medical needs. We also selectively pursue new product
development opportunities in indications that are complementary to our proprietary programs. 4
Proprietary Product Candidates and Royalty-Based Agreements The table below summarizes our proprietary product pipeline and certain royalty-based agreements. Product/Product Candidate Indication Status Market Rights Proprietary Product Candidates Teduglutide (GATTEX® planned brand) SBS Phase 3 N. America Proprietary NPSP558 (parathyroid hormone 1-84 ) Hypoparathyroidism Phase 3 N. America3 Proprietary PREOS® (parathyroid hormone 1-84) Osteoporosis Phase 3 N. America Proprietary Teduglutide Crohn's disease Phase 2 N. America Proprietary Glycine reuptake inhibitors CNS Phase 1 Worldwide Proprietary Teduglutide Pediatric indications Preclinical N. America Proprietary Teduglutide Chemotherapy-induced GI mucositis Preclinical N. America Proprietary NPSP156 CNS Preclinical Worldwide Proprietary Royalty-Based Agreements: Sensipar®/Mimpara® (cinacalcet
HCl) Secondary hyperparathyroidism Market Worldwide Ex-Asia Amgen Sensipar® (cinacalcet HCl) Hypercalcemia in parathyroid cancer Market Worldwide Ex-Asia Amgen REGPARA® (cinacalcet HCl) Secondary hyperparathyroidism Market Asia Kyowa Kirin Preotact® (parathyroid hormone 1-84) Osteoporosis Market Worldwide Ex-U.S., Ex-Israel, Ex-Japan Nycomed NUCYNTA™ (tapentadol) Moderate to severe acute pain Market U.S. Ortho-McNeil Teduglutide SBS Phase 3 Worldwide Ex-N. America Nycomed Cinacalcet HCl Primary hyperparathyroidism Phase 2 Worldwide Ex-Asia Amgen 1 This indication is outside of our core focus and has been designated it as an out-licensing or partnering
opportunity. 2 We currently do not receive cash payments related to our Sensipar, REGPARA and Preotact royalties as these
payments service non-recourse debt. 3 If we receive U.S. approval for NPSP558, Nycomed's license in Canada and Mexico reverts to us or a
licensee. Proprietary Product Candidates Teduglutide Teduglutide is our proprietary analog of naturally occurring human glucagon-like peptide 2 (GLP-2), a peptide secreted primarily in
the distal intestine and involved in the regeneration and repair of the intestinal epithelium.
We are developing teduglutide for commercialization in North America and we have licensed to Nycomed the right to develop and commercialize it in all other regions. We discuss the license agreement in further detail below under the captions "Royalty-Based Products and Product Candidates."
5
Our most advanced program for teduglutide is in Phase 3 development as GATTEX® (planned brand name) for patients with short bowel syndrome (SBS) who are dependent on PN. We are also conducting preclinical studies for teduglutide in other intestinal failure-related conditions, namely complications associated with preterm births, such as PN-dependent pediatric SBS or feeding intolerance, and chemotherapy-induced gastrointestinal mucositis. In addition, we believe there may be additional potential for teduglutide in indications that are outside of our proprietary therapeutic focus, such as Crohn's disease, which we would only pursue on a partnered basis.
SBS Market Opportunity
SBS is a highly disabling condition that can impair a patient's quality-of-life and lead to serious life-threatening complications. SBS typically arises after extensive resection of the bowel due to Crohn's disease, cancer or other conditions. As a consequence, SBS patients often suffer from malnutrition, severe diarrhea, dehydration, fatigue, osteopenia, and weight loss due to a loss in the ability to absorb adequate amounts of nutrients and water. The goals of current treatment are to maintain fluid electrolyte, and nutrient balances through dietary management, including the use of PN. The use of PN is associated with potential life-threatening complications, including sepsis and liver damage and the risks increase the longer patients are on PN.
Scientific journal articles and our own market studies indicate there are 10,000 to 15,000 SBS patients in North America who are PN-dependent, the direct cost of which can exceed $100,000 annually per patient. Currently, only somatropin (rDNA origin) for injection (human growth hormone) in patients receiving specialized nutrition support, and glutamine when used in conjunction with a recombinant human growth hormone are FDA approved treatments for SBS, and therapy is limited to only four weeks. We believe the SBS market is attractive because of the lack of effective drug therapies in this rare indication, the high cost of PN, the serious complications and morbidities associated with PN, and the clinical benefits and improvements in the quality-of-life that we believe patients will experience with teduglutide therapy.
We have received orphan drug designation for teduglutide from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for SBS, which provides
a seven-year period of exclusive marketing after approval, subject to several restrictions. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) has also designated teduglutide as an orphan medicinal product for the treatment of SBS offering a ten-year period of exclusive marketing rights.Teduglutide for SBS
Preclinical and clinical studies have demonstrated that teduglutide promotes the repair and regeneration of cells lining the small intestine, expanding the available surface area for absorption of nutrients. In our completed Phase 3 clinical study, teduglutide demonstrated a favorable safety profile and significant reductions in weekly PN requirements were observed. In animal models of small bowel resections, the administration of teduglutide resulted in increased mucosal and total weight, crypt-villus height, and D-xylose absorption while restoring the adaptive capacity post-resection. Additionally, in PN-induced atrophy animal studies, the administration of teduglutide prevented PN-induced atrophy when administered prior to or with PN and restored the intestinal integrity.
In the first Phase 3 study of GATTEX, completed in 2007, 83 patients with SBS were randomized 2:2:1 to a low dose of GATTEX (0.05 mg/kg/day), a higher dose (0.10 mg/kg/day) or placebo. The clinical efficacy endpoint of the study was a reduction in PN of at least 20 percent comparing baseline to weeks 20 to 24, measured as a graded response to capture reductions up to 100 percent. In an intent-to-treat analysis, forty-six percent (46%) of patients receiving the lower dose of GATTEX (n=35) responded and achieved a significant reduction in PN compared to placebo (p=0.007). Twenty-five percent (25%) of patients who received the higher dose of GATTEX (n=32) responded and showed a trend in the difference between the treatment group and placebo, but this did not reach statistical significance (p=0.161). Two low-dose patients gained independence from and discontinued PN by week 16 and a high-dose patient discontinued PN at the end of treatment. The study's criteria for conducting the statistical analysis of the primary endpoint required that the results for the high-dose group show statistical significance before the results of the low-dose group could be considered. Top line results were first reported in October 2007 with full results subsequently presented at the 2008 annual Digestive Disease Week (DDW) Congress.
Sixty-five of the 71 patients (91%) who completed the pivotal Phase 3 study elected to enroll in a Phase 3-extension study. In the extension phase, patients already on GATTEX continued to receive the dose they were already receiving for an additional 28 weeks, for a total of 52 weeks of treatment, and patients who were on placebo were randomized to one of the two GATTEX doses (0.05 mg/kg/day or 0.10 mg/kg/day). The objective of the extension
6
study was to evaluate the long-term safety and efficacy of daily dosing of GATTEX. The results demonstrated that GATTEX was well tolerated out to one year and provided the ability to safely reduce PN dependence.
Twelve of the 16 patients (75%) who responded to low-dose GATTEX during the initial 24-week phase maintained their response during the 28-week extension phase, with 10 of the 12 (83%) achieving further reductions in PN volumes during the extension phase. Six of the eight (75%) patients who responded to high-dose GATTEX during the initial 24-week phase maintained their response during the 28-week extension phase, with two of the six (33%) achieving further reductions in PN volumes during the extension phase. The three patients who gained independence from PN during the first 24 weeks of therapy remained off PN at week 52 and one additional patient was weaned from PN during the 28-week extension phase. Six out of six patients (100%) who had previously received placebo in the initial 24-week phase and were randomized to low-dose and two out of seven (29 percent) patients who had previously received placebo in the Phase 3 study and were randomized to high-dose GATTEX therapy achieved a 20 percent or greater reduction in PN after 28 weeks of therapy in the extension study. To assess the crypt-villus architecture, investigators reviewed endoscopic biopsies obtained at weeks zero and 24 of small intestine (placebo (n=9), low-dose (n=17), and high-dose (n=20) or large intestine (placebo (n=9), low-dose (n=20), and high-dose (n=22). The data indicate that GATTEX induced the expansion of the mucosal epithelium of adult patients with SBS and may therefore enhance their capacity to digest and absorb orally consumed nutrients. Importantly, the DNA, RNA, and protein composition of the GATTEX remodeled mucosa did not differ from placebo. The foregoing data and results were presented at the 2008 American College of Gastroenterology Annual Scientific Meeting.
In a Phase 2 proof-of-concept study, 16 patients with SBS received subcutaneous injection of GATTEX for 21 days. Three patients received 0.03 mg/kg/day, ten patients received 0.10 mg/kg/day, and three patients received 0.15 mg/kg/day. Results of the Phase 2 study indicated that GATTEX was safe and well tolerated, resulted in intestinal epithelial regeneration and significantly increased intestinal absorption and body weight in PN-dependent SBS patients. These results were published in the international peer- reviewed journal Gut (Jeppesen et al. Gut 2005; 54:1223-1231).
We have also completed a single-center, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled ascending-dose study. Separate cohorts of healthy subjects were administered multiple doses of teduglutide or placebo in order to investigate the tolerability and pharmacokinetics of teduglutide. Following completion of eight days of treatment in a cohort and prior to the initiation of the next scheduled cohort(s), safety and tolerability were reviewed and assessed by an independent safety review panel. The study involved 95 subjects and the results indicated that subcutaneous injections of 10 mg to 80 mg of teduglutide were safe and well tolerated.
Analysis and a final report of a two-year rat carcinogenicity study for teduglutide have been completed and will be included as part of our new drug application or NDA. All of the findings were considered to be either sporadic (not of statistical or biological significance), benign, or expected due to the pharmacological properties of the test material. Non-neoplastic changes were observed at all doses tested. No teduglutide -related malignant tumors were observed following treatment with teduglutide.
A study was conducted to assess the pharmacokinetics of a single fixed subcutaneous 20 mg dose of GATTEX in patients with moderate hepatic impairment compared to healthy subjects. This open-label single center study enrolled 24 patients. Administration of GATTEX 20 mg appeared to be safe and well tolerated by the subjects with normal liver function and moderate liver impairment in this study.
In December 2008, investigators began enrolling patients in STEPS, a second Phase 3 registration study to confirm previously reported data that demonstrated GATTEX was well tolerated and reduced PN dependence in SBS patients. STEPS is an international, double-blind, placebo-controlled safety and efficacy study. We believe that positive results would enable us to seek U.S. marketing approval for GATTEX for patients with PN dependent SBS.
STEPS will randomize 86 PN-dependent SBS patients in North America and Europe. The trial includes an initial four to 16 week PN optimization and stabilization period, after which patients are randomized 1:1 to compare daily subcutaneous dosing of 0.05 mg/kg of GATTEX to placebo over a 24-week treatment period. The primary efficacy endpoint is the percentage of patients who achieve a 20 percent or greater reduction in weekly PN volume at week 20 and maintain that response at week 24, when compared to baseline. The study's secondary objectives will evaluate safety and efficacy variables based on reductions in PN volume or the direct effects of improved intestinal absorption of fluid. These variables include: duration of response (total number of weeks at greater than or equal to 20 percent reduction from baseline); the proportion of patients with a 20 percent or greater reduction or a two liter or greater reduction from baseline in weekly PN at week 20 and maintained through week 24; the number of patients who discontinue PN, including the time of discontinuation; and the absolute and percentage change in PN.
7
In September 2009, we began enrolling patients in STEPS 2, an open-label follow-on study of STEPS. Patients have the option of entering STEPS 2 to receive teduglutide for up to two years. We believe STEPS 2 will provide important long-term safety and efficacy data in SBS.
We are advancing STEPS and STEPS 2 with the support of our partner Nycomed and they are sharing 50% of the external costs for the study with us.
Teduglutide for Other Indications
Given the mechanism of action of teduglutide in promoting gastrointestinal rehabilitation, we believe it may have potential in treating other intestinal failure-related conditions, like chemotherapy-induced gastrointestinal mucositis, PN-dependent pediatric SBS, and pediatric feeding intolerance. We continue to advance preclinical studies that may support the filing of an investigational new drug application (IND) for these indications.
Pediatric SBS is often caused by necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC). NEC is a gastrointestinal or GI disease that primarily affects premature infants. NEC involves infection and inflammation that causes destruction of the bowel or intestine or part of the bowel. The incidence of NEC has been estimated at 0.7 to 3.0 per 1,000 live births, and approximately one-third of these infants with NEC are expected to undergo intestinal surgery, including resection, frequently resulting in SBS. The etiology of NEC is unknown, but NEC has become a more common clinical problem as improvements in neonatal intensive care allow the survival of increasing numbers of premature and low-birth-weight infants.
Pediatric feeding intolerance is a morbidity associated with preterm infants, especially in the very low birth weight segment (less than 1500 grams). The condition is due to an immature gut and may require PN to prevent severe malnutrition. Teduglutide may accelerate intestinal maturation in infants with PN-dependent feeding intolerance and thus allow a decrease in PN-dependence or an earlier independence from PN in these infants.
Chemotherapy-induced gastrointestinal mucositis or CIGIM is a side effect associated with certain cancer treatments. Some chemotherapies and radiotherapy, individually or in combination, damage rapidly dividing normal cells of the GI tract, which can result in mucositis. Mucositis can occur anywhere along the GI tract and can become a dose-limiting side effect of cancer treatment. Mucositis is one of the major side effects that severely limit chemotherapy treatment along with nausea and vomiting, neutropenia, and anemia. In late 2009, we completed a pre-investigational new drug application or pre-IND meeting with the FDA to review the path forward for this indication.
NPSP558 (parathyroid hormone 1-84 [rDNA origin] injection)
NPSP558 is our proprietary recombinant, full-length (1-84), human parathyroid hormone (PTH 1-84) that we are developing in the U.S. as a potential treatment for hypoparathyroidism.
Hypoparathyroidism is a rare endocrine disorder in which the body produces insufficient levels of parathyroid hormone. Parathyroid hormone is an 84-amino acid polypeptide that regulates the amount of calcium and phosphorus in bone and blood. A lack of parathyroid hormone leads to decreased blood levels of calcium (hypocalcemia) and increased levels of blood phosphorus (hyperphosphatemia). Patients with hypoparathyroidism are unable to regulate serum calcium and phosphate handling physiologically. Calcium plays a central role in the activity of many physiological systems, including the health and functioning of the skeletal, muscular, nervous, urinary, and cardiovascular systems. Hypoparathyroidism can affect all aspects of calcium metabolism with consequences that include abnormal calcium and phosphate handling by the kidneys, altered absorption of calcium, decreased activation of vitamin D, and abnormal bone quality.
Hypocalcemia is the characteristic clinical feature of hypoparathyroidism. The duration, severity, and rate of development of hypocalcemia determine the nature of the symptoms associated with the condition. Hypocalcemia can present dramatically as tetany, seizures, altered mental status, refractory congestive heart failure or stridor. Generally, neuromuscular symptoms are the most prominent and include muscle cramping; twitching; numbness and paresthesias of the mouth and/or extremities; laryngeal chord or bronchial spasms; and even seizures. Other complications include damage to soft tissues, including the kidneys, the brain, and the lenses of the eye due to calcification from the abnormal calcium-phosphate levels associated with hypoparathyroidism and exacerbated by existing therapies.
8
Hypoparathyroidism Market Opportunity
Epidemiological data on hypoparathyroidism are limited given the rarity of hypoparathyroidism, as well as the variability in the severity of the symptoms associated with this disorder. Based on our preliminary market research, we believe there may be as many as 65,000 patients with hypoparathyroidism in the U.S. The most common cause of hypoparathyroidism is injury to or removal of the parathyroid glands during neck surgery. The definition of permanent post-surgical hypoparathyroidism is generally accepted to be insufficient parathyroid hormone to maintain normal calcium levels six months after surgery. Hypoparathyroidism can also be associated with autoimmune or other disorders or it can be idiopathic in nature.
Hypoparathyroidism is one of the few hormonal deficiency syndromes in which replacement therapy using the native hormone is not clinically available. Treatment of hypoparathyroidism is further complicated by the lack of national or international consensus management guidelines.
Presently, the only available treatments for hypoparathyroidism sanctioned by regulatory oversight are oral supplementation of calcium and active vitamin D metabolites or analogs. These supplements are often taken for life. The goal of current therapies is to reduce the severity of symptoms; however, these therapies do not return calcium metabolism to a normal or physiological state and present specific challenges for adequate clinical care. Under-treatment or missed doses may result in persistent symptoms; whereas, treatment with high doses of oral calcium can contribute to soft tissue calcification and organ damage, with the kidneys being especially vulnerable to hypercalciuria, hypercalcemia, nephrolithiasis, nephrocalcinosis, and renal failure, a common and severe adverse outcome in hypoparathyroidism patients.
Because NPSP558 is identical in structure to the 84-amino acid single-chain polypeptide human parathyroid hormone and mimics the action of natural parathyroid hormone, we believe it has the ideal mechanism of action to fulfill the unmet need of this chronic condition and offer a more physiological treatment outcome than is possible with existing treatments.
In 2007, the FDA granted orphan drug status for NPSP558 for the treatment of hypoparathyroidism.
NPSP558 for Hypoparathyroidism
Our previous clinical studies of our rhPTH (1-84) compound for the treatment of osteoporosis demonstrated that daily subcutaneous dosing causes parathyroid hormone levels to rise rapidly and then return to normal levels over a period of hours. Results from an investigator-initiated Phase 2 open-label proof-of-concept study demonstrated that rhPTH (1-84) potentially can be used as a therapeutic agent in hypoparathyroidism effectively and safely. Thirty subjects with documented hypoparathyroidism participated in the study, which was conducted at Columbia University's College of Physicians and Surgeons. Subjects were treated with rhPTH (1-84) at a dose of 100 mcg every-other-day by subcutaneous injection for 24 months, with monitoring of calcium and vitamin D supplementation requirements, serum and 24 hour urinary calcium excretion, and bone mineral density. The study showed that rhPTH (1-84) treatment in hypoparathyroidism significantly reduces supplemental calcium and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D requirements while maintaining serum calcium levels. These data were published online on January 22, 2010 in the international peer-reviewed journal Osteoporosis International. Based on these data, we believe NPSP558 has the potential to be the first hormone replacement therapy for chronic hypoparathyroidism.
In December 2008, we initiated a Phase 3 registration study, known as REPLACE, a randomized, double-blind, dose escalating, placebo-controlled study to investigate the use of NPSP558 for the treatment of adults with hypoparathyroidism.
REPLACE will randomize approximately 110 patients at over 25 sites in the U.S., Canada, and Europe. The study will consist of an average 10-week screening and stabilization period followed by a 24-week treatment period marked by randomization (2:1) to NPSP558 50mcg (with the potential for titration up to 75mcg and 100mcg) or placebo. Following randomization, patients will undergo staged reductions in calcium and vitamin D supplementation.
The primary efficacy endpoint is to demonstrate by week 24 at least a 50% reduction from baseline of oral calcium supplementation and active vitamin D metabolite/analog therapy and a total serum calcium concentration that is normalized or maintained compared to baseline (≥7.5 mg/dL). Other objectives of the study will look at safety, calcium homeostasis, urinary calcium excretion, bone effects and quality-of-life. We believe that positive results from REPLACE would enable us to seek U.S. marketing approval of NPSP558 as a new standard of care for the treatment of hypoparathyroidism.
9
Royalty-Based Products and Product Candidates
We complement our proprietary clinical programs with collaborative research, development or commercial agreements with Amgen, Ortho-McNeil, GlaxoSmithKline, Kyowa Kirin, and Nycomed. Generally, these agreements provide for payments to us for the achievement of specified milestones, and royalties on sales of products developed under the terms of the particular agreement. In return for these financial benefits, we grant the particular company a license to the technology that is the subject of the collaboration or to intellectual property that we own or control. We believe that collaborating with pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies with relevant expertise in areas that are outside of our proprietary therapeutic or geographic focus will accelerate the development and commercialization of our products.
Amgen and Kyowa Kirin (Cinacalcet HCl)
Cinacalcet HCl is a small molecule compound used in treating hyperparathyroidism in patients with chronic kidney disease on dialysis and hypercalcemia in patients with parathyroid cancer. Hyperparathyroidism is a medical condition in which excessive amounts of parathyroid hormone circulate in the blood. It is typically characterized as being either primary or secondary hyperparathyroidism. Cinacalcet HCl is a calcimimetic compound that interacts with the calcium receptor on parathyroid cells and thereby decreases the production of parathyroid hormone in such cells.
In 1995, we licensed cinacalcet HCl to Kyowa Kirin Pharma, a wholly-owned subsidiary of Kyowa Kirin Holdings, for the drug's development and commercial sale in China, Japan, North and South Korea, and Taiwan. In 1996, we licensed worldwide rights (with the exception of the previously licensed Asian territories) to Amgen, Inc. to develop and commercialize cinacalcet HCl for the treatment of hyperparathyroidism.
In March 2004, Amgen received FDA approval for cinacalcet HCl for the treatment of secondary hyperparathyroidism in chronic kidney disease patients on dialysis, often referred to as "Stage V" chronic kidney disease patients, and for the treatment of hypercalcemia, or excess serum calcium levels, in patients with parathyroid carcinoma. In October 2004, Amgen received approval from the European Medicines Agency or EMA for cinacalcet HCl for the treatment of secondary hyperparathyroidism in Stage V chronic kidney disease patients and for treatment of hypercalcemia in patients with parathyroid carcinoma. Amgen markets cinacalcet HCl as Sensipar® in the U.S. and as Mimpara® in the EU.
Following review by the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA), Japan's Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare (MHLW) approved the drug for the treatment of patients with secondary hyperparathyroidism during dialysis therapy. Kyowa Kirin began selling cinacalcet HCl in Japan as REGPARA® during the first quarter of 2008.
Cinacalcet HCl for Secondary Hyperparathyroidism
Parathyroid hormone is produced by the four parathyroid glands located in the neck. Serum levels of parathyroid hormone directly influence serum levels of calcium. The parathyroid glands regulate the amount of parathyroid hormone in the body by releasing more parathyroid hormone as the body needs additional calcium and less when there is excess serum calcium.
Secondary hyperparathyroidism most commonly results from chronic renal disease, which can develop in hemodialysis patients. Chronic hypocalcemia and secondary hyperparathyroidism can also be products of pseudohypoparathyroidism, vitamin D deficiency, and intestinal malabsorption syndromes that are characterized by inadequate vitamin D and calcium absorption. Parathyroid hormone acts in the kidneys and bones to elevate levels of calcium in the blood. Normal functioning healthy kidneys convert the parent vitamin D into the active form of vitamin D. Vitamin D helps in intestinal absorption of dietary calcium. Chronic kidney disease generally results in (i) reduced intestinal absorption of calcium due to reduced vitamin D levels, and (ii) reduced removal of phosphorus from the blood, elevating serum phosphate, which then combines with serum calcium to further reduce serum calcium levels. This in turn leads to the chronic overproduction of parathyroid hormone as the body tries to raise serum calcium levels. Symptoms of secondary hyperparathyroidism include excessive bone loss, bone pain and chronic, severe itching. Current treatments for secondary hyperparathyroidism, in addition to cinacalcet HCl, include phosphate binders and vitamin D supplements.
10
In October 2003, the National Kidney Foundation released Clinical Practice Guidelines for Bone Metabolism and Disease in Chronic Kidney Disease. These guidelines set goals for the four key measures involved in managing secondary hyperparathyroidism: the serum level of parathyroid hormone; the serum level of calcium; the serum level of phosphorus; and the product of the serum level of calcium multiplied by the serum level of phosphorus ("Ca x P"). Traditional therapies such as phosphate binders and vitamin D supplements lower parathyroid hormone levels only by increasing one or more of the other measures, particularly calcium and/or Ca x P levels. Thus, under traditional therapies, patients and their physicians have typically had to choose between elevated parathyroid hormone or elevated calcium and/or Ca x P levels. Elevated parathyroid hormone levels cause excessive bone loss, bone pain and chronic, severe itching, while elevated calcium and/or Ca x P levels can lead to calcification of the heart and blood vessels and increases the risk of kidney stones.
Cinacalcet HCl is the only FDA-approved medication that simultaneously lowers all four of the key measures. By directly suppressing production of parathyroid hormone, cinacalcet HCl also causes serum levels of calcium, phosphorus and Ca x P to decline, providing patients and their physicians an effective treatment to avoid elevated parathyroid hormone, calcium and Ca x P.
The EVOLVE™ (EValuation Of cinacalcet HCl therapy to Lower cardioVascular Events) trial, initiated in 2006, is a large (3,800) patient, multi-center, international, randomized, double-blind study to assess the effects of Sensipar on mortality and cardiovascular morbidity in patients with chronic kidney disease undergoing maintenance dialysis. The EVOLVE study completed enrollment in January 2008.
Payments from Amgen for Cinacalcet HC1
Cumulatively through December 31, 2009, Amgen has paid us $38.5 million, which consists of license fees, research support payments, milestone payments (including the milestone payment for the filing of an NDA) and equity purchases of our common stock. Amgen will pay us up to an additional $7.0 million if it achieves other development and regulatory milestones. In addition to these milestones, we earn royalties on Amgen's sales of cinacalcet HCl in its licensed territories.
We have partially monetized our royalty revenue and future milestone payments from Amgen through the issuance of non-recourse debt that is both serviced and secured by our Sensipar royalty revenue and future milestone payments. In December 2004, we completed a private placement of $175.0 million in Secured 8.0% Notes due March 30, 2017, or Class A Notes and in August 2007, we completed a private placement of $100.0 million in Secured 15.5% Class B Notes due 2017, or Class B Notes. The Class A Notes and Class B Notes are non-recourse to us and are secured by our royalty and milestone payment rights under our agreement with Amgen. Until the Class A Notes and Class B Notes are repaid, all payments from Amgen will be used for the payment of interest and principal on the notes. We pay the interest due on the Class B Notes through the issuance of additional Class B Notes in lieu of cash, and as a result, the aggregate principal amount of our outstanding Class B Notes will continue to increase until the Class A Notes are paid in full. As of December 31, 2009, we had approximately $238.7 million in aggregate principal amounts of Class A and Class B Notes outstanding, including $44.0 million in Class B Notes that had been issued to cover interest payments on the Class B Notes. Under our agreements for the Class A Notes and Class B Notes, we would potentially be liable for our breaches or defaults, if any.
Payments from Kyowa Kirin for Cinacalcet HC1
Cumulatively through December 31, 2009, Kyowa Kirin has paid us $25.0 million in license fees, research and development support payments and milestone payments, which include a $2.0 million milestone payment we received in October 2007 after the approval of cinacalcet HCl in Japan. Under the terms of our agreement, Kyowa Kirin is required to pay royalties on any sales of cinacalcet HCl in its territories.
On February 26, 2010, we sold our royalty rights from sales of REGPARA® (cinacalcet HCl) to an affiliate of DRI Capital, Inc or DRI for $38.4 million. Royalties will revert to us once DRI receives cumulative royalties of $96 million or 2.5 times the amount paid to us. Under the agreement, DRI is entitled to receive royalty payments related to net sales of REGPARA occurring on or after July 1, 2009. NPS has received approximately $3.5 million in cumulative royalty revenue on net sales of REGPARA prior to July 1, 2009. We have $2.1 million recorded as Accounts Receivable from Kyowa Kirin at December 31, 2009, which will be paid to DRI in March 2010. In connection with this agreement, we granted DRI a security interest in our license agreement with Kyowa Kirin and certain of our patents related to REGPARA and other intellectual property underlying that agreement. In the event of a default by NPS under
11
the agreement with DRI, DRI would be entitled to enforce its security interest against us and the property described above.
Nycomed (Preotact
® (parathyroid hormone 1-84 [rDNA origin] injection))In April 2004, we signed a distribution and license agreement with Nycomed (the "2004 Agreement"), in which we granted Nycomed the exclusive right to develop and market Preotact in Europe. Preotact is the brand name that Nycomed uses to market parathyroid hormone 1-84 [rDNA origin] injection. Nycomed also made an equity investment in our business of $40.0 million through the purchase of 1.3 million shares of our common stock in a private placement, which closed in July 2004. The 2004 Agreement required Nycomed to pay us up to €20.8 million in milestone payments upon the receipt of specified regulatory approvals and the achievement of certain sales targets, to purchase drug product and devices from us, and to pay us royalties on product sales. In July 2007, we entered into a new license agreement with Nycomed ("2007 Agreement"), as described below, which superseded the 2004 Agreement.
Under the 2007 Agreement, we granted to Nycomed an exclusive license to sell, market and commercialize Preotact in all non-U.S. territories, excluding Japan and Israel. We also granted Nycomed a non-exclusive license to manufacture and develop Preotact. If parathyroid hormone 1-84 [rDNA origin] injection is approved in the U.S., Nycomed's licensed rights in Canada and Mexico will revert to us or to a third-party whom we select. We also granted Nycomed a right to negotiate for any new product we offer via a competitive process. Nycomed is required to commercialize Preotact in most countries in Europe. If Nycomed unreasonably delays the launch of Preotact in any country, then we have the right to ensure the launch of Preotact in that country. Nycomed also assumed primary responsibility for manufacturing Preotact and for its further development and improvement. As part of Nycomed's assumption of manufacturing responsibility for Preotact, Nycomed paid us $11.0 million during 2007 for a significant portion of our existing bulk drug inventory.
The 2007 Agreement requires Nycomed to make milestone payments similar to those in the 2004 Agreement upon the receipt of certain approvals in Europe and the achievement of certain sales targets for Preotact. Nycomed is also required to pay us a royalty on a quarterly basis based upon sales of Preotact in the European Union, European countries outside the European Union, the Commonwealth of Independent States and Turkey. Nycomed is also responsible to maintain our patents in its territories under the 2007 Agreement. If Nycomed reasonably determines that it has no prospects for making a reasonable profit under the 2007 Agreement, and it is unable to agree to terms on a renegotiated agreement with us within eight weeks, Nycomed may terminate the agreement by providing us with six months prior written notice; provided, however, that, upon any such termination the ownership of all rights to Preotact technology, products, regulatory filings and know-how will revert to us. Cumulatively through December 31, 2009, we have received €7.1 million in milestone payments from Nycomed under the 2004 and 2007 Agreements.
In July 2007, we entered into an agreement with DRI Capital Inc., or DRI (formerly Drug Royalty L.P.3) under which we sold to DRI our right to receive future royalty payments arising from sales of Preotact under the 2007 Agreement. Under the agreement, DRI paid us an up-front purchase price of $50.0 million for the royalty rights. The agreement provides that if DRI receives royalties representing two and a half times the $50.0 million paid to us, the agreement will terminate and the remainder of the royalties paid by Nycomed under the 2007 Agreement, if any, will revert to us. In connection with our agreement with DRI, we granted DRI a security interest in the 2007 Agreement and certain of our patents related to Preotact and other intellectual property underlying that agreement. In the event of a default by NPS under the agreement with DRI, DRI would be entitled to enforce its security interest against us and the property described above.
Nycomed (Teduglutide, ex-North American Development)
In September 2007, we signed a license agreement with Nycomed in which we granted Nycomed the right to develop and commercialize teduglutide outside of North America. We received $35.0 million in up-front fees shortly after executing the agreement. Under the terms of the agreement, we have the potential to earn more than $180.0 million in development and sales milestone payments. Additionally, the agreement provides for royalties on sales in the licensed territories and provides an option for development cost sharing equally for indications that we elect to pursue jointly. Pursuant to a previously existing licensing agreement with a third party, we paid $6.6 million to the licensor in 2007 and will be required to make future payments based on future GATTEX royalties and milestones earned.
Under the terms of the license agreement with Nycomed, we were responsible for completing the first Phase 3 GATTEX clinical trial in SBS. Nycomed is responsible for conducting Phase 4 studies in its licensed territory at its expense. We also may work with Nycomed to jointly develop, commercialize and investigate further indications for GATTEX in the licensed territories; we would share joint development costs equally for such work. We are advancing
12
the STEPS and STEPS 2 studies on a collaborative basis and we are sharing certain external development costs for the SBS indication with Nycomed. Nycomed may terminate on 180-day written notice prior to the first commercial sale under the agreement. Following the first commercial sale, Nycomed must provide 365-day written notice in order to terminate. After we have received such a termination notice, we may terminate the agreement at anytime prior to the expiration of Nycomed's requisite notice period.
Ronacaleret (751689)
Ronacaleret (751689) is a calcilytic compound developed under a November 1993 collaborative research and worldwide exclusive license agreement with GlaxoSmithKline or GSK for the research, development and commercialization of calcium receptor active compounds for the treatment of osteoporosis and other bone metabolism disorders, excluding hyperparathyroidism. Calcilytic compounds are small molecule antagonists of the calcium receptor that temporarily increase the secretion of the body's own parathyroid hormone, which may result in the formation of new bone. In animal studies, we demonstrated that intermittent increases in circulating levels of parathyroid hormone could be obtained using calcilytics. In these studies, increased levels of parathyroid hormone were achieved by this mechanism and were equivalent to those achieved by an injection of parathyroid hormone sufficient to cause bone growth.
We received an initial upfront license fee payment from GSK of $4.0 million, a subsequent payment of $2.0 million by January 1, 1995, and we later began receiving payments from GSK in support of our research efforts under the initial research term of the agreement. GSK also has a first right to negotiate for an exclusive license under our patents to make, use or sell items for indications within the field of bone metabolism disorders, and an exclusive right to negotiate for a license to compounds covered under the agreement not selected for development to treat bone metabolism disorders for indications outside that field, which rights expire upon termination of this agreement.
GSK has the authority and responsibility to conduct and fund all product development, including clinical trials and regulatory submissions, and manufacturing for any compounds selected for development. We have the right to co-promote, in the U.S., products resulting from the collaboration to certain targeted physician specialties. Cumulatively through December 31, 2009, GSK has paid us a total of $26.1 million for license fees, research support, milestone payments and equity purchases as part of our collaboration. We will receive additional payments of up to an aggregate of $32.0 million, which includes additional milestones under the December 2006 amendment noted below, if certain clinical milestones are achieved. Our agreement also provides for royalties on any sales by GSK of commercialized products based on compounds identified in this collaboration. In addition to the milestone and royalty payments, we have a limited right to co-promote any products that are developed through our collaboration and we will receive co-promotion revenue if we elect to exercise these rights. Upon termination, the rights and licenses we granted GSK revert to us. In December 2006, we entered into an amendment to our agreement with GSK under which we provided GSK rights to additional compounds discovered by us. In connection with such amendment GSK paid a one-time licensing fee of $3.0 million and agreed to pay additional milestone payments for the achievement of certain clinical milestones with such compounds as well as royalties on sales of such compounds should GSK commercialize any such compounds.
GSK may terminate the agreement on 30-day written notice on a country-by-country basis if it reasonably determines that any compound developed under the agreement is not worth continued development. Upon termination, the rights and licenses we granted GSK revert to us.
In September 2008, we were notified by GSK that it has decided to terminate a Phase 2 dose-range finding study of ronacaleret in post-menopausal women with osteoporosis earlier than expected due to an observed lack of efficacy based on lumbar spine and hip bone mineral density. We are not required to return to GSK any of the payments we received to date. GSK has not yet notified us of the ongoing development program of ronacaleret and other calcilytics under this agreement.
Other Royalty Agreements
Ortho-McNeil Pharmaceuticals
In December 2006, we entered into an agreement with Ortho-McNeil Pharmaceuticals, Inc. ("Ortho-McNeil"), a wholly-owned subsidiary of Johnson & Johnson, pertaining to certain of our patents. Under this agreement, Ortho-McNeil is required to pay us royalties on any product sales of tapentadol hydrochloride and other related compounds in all countries in which we have patents whose claims cover such sales. We also received an up-front licensing fee. Ortho-McNeil pays us its royalty on a quarterly basis. We are responsible for patent prosecution and maintenance of
13
the related patents. In November 2008, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved tapentadol immediate-release tablets for the relief of moderate to severe acute pain in adults 18 years of age or older. In December 2009, Johnson & Johnson Pharmaceutical Research & Development, L.L.C. announced that it submitted a New Drug Application (NDA) to the FDA for tapentadol extended release (ER) tablets as a line extension of their initial approval. Both the immediate and extended release products will be indicated for the management of moderate to severe chronic pain in patients 18 years of age or older. Tapentadol is a centrally acting oral analgesic.
Hoffman-La Roche Inc. and F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
In December 2008, we entered into an agreement with Hoffman-La Roche Inc. and F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. ("Roche"), under which we granted Roche a non-exclusive license (with the right to grant sublicenses) to develop, make, import, use for sale or sell products covered by patents relating to the modulation of NMDA receptor activity using glycine uptake antagonists. In return, Roche paid us an upfront licensing fee of $2.0 million and agreed to pay us for the achievement of certain regulatory milestones. Further, Roche agreed to pay a royalty on any future sales of licensed products on a quarterly basis.
Out-licensing Opportunities
In 2007, we restructured our operations and implemented a new business strategy to focus our resources on developing GATTEX and NPSP558 for rare disorders with serious unmet medical needs. Previously, our strategic priority was to obtain U.S. regulatory approval of PREOS® (parathyroid hormone 1-84 [rDNA origin] injection) for the treatment of osteoporosis. We have studied PREOS in a number of clinical settings to document its safety and effects on bone. In 2006, we received an approvable letter and guidance from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to support a U.S. marketing application for PREOS. While we continue to believe that the U.S. osteoporosis market remains a viable commercial opportunity for this compound, we elected to focus our resources on specialty opportunities within our pipeline and pursue osteoporosis only on a partnered, rather than a proprietary, basis.
Supporting our strategic focus, we are seeking opportunities to out-license a number of proprietary compounds for areas that are outside of our proprietary therapeutic and/or geographic focus. In addition to PREOS, these include teduglutide for Crohn's disease and glycine reuptake inhibitors and NPSP156 for central nervous system disorders.
PREOS for Osteoporosis
We have studied PREOS in a number of clinical settings to document its safety and effects on bone. The pivotal Phase 3 study, known as TOP (Treatment of Osteoporosis with PTH), was a multi-center, randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled trial designed to evaluate the potential of rhPTH (1-84) to reduce the risk of first and subsequent vertebral fractures in post-menopausal women. In the TOP study, PREOS demonstrated a statistically significant reduction in the risk of new vertebral fractures in women with and without pre-existing osteoporosis-related fractures.
In May 2005, we filed an NDA with the FDA seeking approval to market PREOS in the U.S. In March 2006, we received notification from the FDA that the PREOS NDA is approvable. In the approvable letter, the FDA indicated that our pivotal Phase 3 study with PREOS demonstrated significant fracture risk reductions in post-menopausal women with osteoporosis, but noted the higher incidence of hypercalcemia with PREOS compared to placebo. The FDA expressed concern regarding hypercalcemia associated with the proposed daily dose of PREOS and requested additional clinical information. The FDA also requested additional information regarding the reliability and use of the injection device for delivery of PREOS.
We have had further communications with the FDA since receiving the approvable letter from the FDA. The FDA proposed that we generate additional clinical data through a new clinical trial to address the hypercalcemia issue raised in the approvable letter. Since receiving the approvable letter, we have been carefully evaluating the appropriate regulatory path forward for PREOS. We submitted a new clinical trial protocol for PREOS to the FDA to support U.S. registration, and believe the protocol design is now finalized following communications with the FDA. Under this protocol, the clinical study will be a 12-month bone-mineral density bridging trial designed to evaluate the relative efficacy and safety of three dosing regimens of PREOS (100 mcg once daily, 100 mcg every-other-day, and 75 mcg once daily) compared to placebo in women with post-menopausal osteoporosis. As noted above, we would only continue our efforts to develop and commercialize PREOS for osteoporosis in the U.S. market if we were to secure a partner who would be willing to assume part of the cost and risk of such development.
Teduglutide for Crohn's Disease
We have completed a Phase 2a proof-of-concept clinical study with teduglutide in patients with Crohn's disease. While we believe the data support further evaluation of teduglutide for the treatment of Crohn's disease, given our
14
strategy to focus on indications with few, if any, therapeutic options and limited competition, we would only pursue the development of teduglutide for Crohn's disease on a partnered basis.
The four-arm, eight-week clinical trial compared three doses of teduglutide delivered by daily subcutaneous injection to a placebo. The study was designed to evaluate the safety and potential efficacy of teduglutide in the treatment of Crohn's disease. The study results showed a positive and consistent trend toward efficacy and a dose response favoring the highest dose group, with 36.8% of patients receiving the highest dose of teduglutide reaching clinical remission, at week two versus 16.7% of the placebo group, while 55.6% of patients in the highest dose group reached clinical remission by week eight compared to 33.3% of the placebo group. Clinical remission was defined as a Crohn's Disease Activity Index score, or CDAI score, of less than 150 points. Teduglutide was well tolerated with no serious adverse events related to the drug. The most common treatment-related adverse event in the trial was redness at the injection site. While this study was not powered to demonstrate statistical significance and thus the primary endpoint was not met due to the relatively small number of study subjects and a high placebo response, we believe clinical remission rates seen in patients receiving the highest dose of teduglutide support further evaluation of teduglutide for the treatment of Crohn's disease.
Glycine Reuptake Inhibitors
We collaborated with Janssen on glycine reuptake inhibitors to identify prospective drug candidates for schizophrenia and dementia. After the research phase of the collaboration ended, Janssen assumed full responsibility for the development of product candidates identified. In August 2008, Janssen notified us that the clinical data did not meet their criteria to pursue further development and subsequently terminated the agreement. This termination by Janssen returns the rights to any compounds or products from the collaboration to us. We are not actively engaged in the further development of these proprietary compounds and we are seeking opportunities to out-license them.
NPSP156 (D-serine)
NPSP156 is our proprietary D-serine analog of a naturally occurring neurotransmitter and endogenous ligand at the glycine site of the NMDA receptor. We believe NPSP156 may have therapeutic potential in the treatment of epilepsy, neuropathic pain, and other central nervous system (CNS) disorders. While there are many clinical-stage and commercialized products for epilepsy and neuropathic pain, we believe that the unique mechanism of action of NPSP156 could favorably position this compound in this market segment and we are seeking opportunities to out-license them.
In-licensing Agreements
We have entered into certain research and license agreements that require us to make research support payments to academic or research institutions when the research is performed. Additional payments may be required upon the accomplishment of research milestones by the institutions or as license fees or royalties to maintain the licenses.
In February 1993, we entered into a patent license agreement with The Brigham and Women's Hospital, an affiliate of Harvard University Medical School. The patent license agreement grants us an exclusive license to certain calcium receptor and inorganic ion receptor technology covered by patents we jointly own with the hospital. Under the patent license agreement, we are responsible for all costs relating to obtaining regulatory approval from the FDA or any other federal, state or local government agency and carrying out any clinical studies, relating to the technology. The Brigham and Women's Hospital is also entitled to a royalty on any sales of certain products under the patent license agreement, and we have committed to promote sales of any licensed products for hyperparathyroidism for which we receive regulatory approval. Brigham and Women's Hospital may terminate the patent agreement if we breach the terms of the patent agreement and do not cure the breach within 60 days of receiving notice of the breach. Certain violations of terms of the patent agreement, if pursued by Brigham and Women's Hospital, might result in the exclusive, royalty-free license of the technology to Brigham and Women's Hospital or other adverse consequences.
We have also entered into a license agreement with Daniel J. Drucker, MD, and his Canadian corporation 1149336 Ontario Inc. The license agreement grants to us an exclusive license under Dr. Drucker's patent portfolio for glucagon-like peptide-2, or GLP-2, and its therapeutic uses. Under the license agreement, we have agreed to ensure that reasonable commercial efforts are used to develop and commercialize any product covered by the licensed patents. The
15
agreement requires us to pay annual non-refundable license maintenance fees, royalties on sales and licensing fees, and milestone payments. If we default on any of the material obligations under the agreement Dr. Drucker may terminate the license agreement and all rights granted under the agreement will revert to Dr. Drucker.
New Drug Development and Approval Process
Regulation by governmental authorities in the U.S. and other countries is a significant factor in the manufacture and marketing of pharmaceuticals and in our ongoing research and development activities. All of our product candidates will require regulatory approval by governmental agencies prior to commercialization. In particular, all of our drug candidates are subject to rigorous preclinical testing, clinical trials, and other pre-marketing approval requirements by the FDA and regulatory authorities in other countries. In the U.S., various federal, and in some cases state statutes and regulations also govern or affect the manufacturing, safety, labeling, storage, record keeping and marketing of such products. The lengthy process of seeking required approvals and the continuing need for compliance with applicable statutes and regulations require the expenditure of substantial resources. Regulatory approval, when and if obtained, may significantly limit the indicated uses for which our products may be marketed. Further, approved drugs, as well as their manufacturers, are subject to ongoing review and discovery of previously unknown problems with such products may result in restrictions on their manufacture, sale or use or in their withdrawal from the market.
The steps required by the FDA before our drug candidates may be marketed in the U.S. include, among other things:
|
|
• |
|
The performance of preclinical laboratory and animal tests and formulation studies; |
|
|
• |
|
The submission to the FDA of an Investigational New Drug application, or IND, which must become effective before human clinical trials may commence; |
|
|
• |
|
The completion of adequate and well-controlled human clinical trials to establish the safety and efficacy of the drug; and |
|
|
• |
|
The submission and FDA approval of a new drug application or NDA. |
The testing and approval process requires substantial time, effort and financial resources and we cannot be certain that any approvals for any of our proposed products will be granted on a timely basis, if at all.
Prior to commencing a clinical trial, we must submit an IND to the FDA. The IND becomes effective 30 days after receipt by the FDA, unless within the 30-day period, the FDA raises concerns or questions with respect to the conduct of the trial. In such a case, the IND sponsor and the FDA must resolve any outstanding concerns before the study can begin. As a result, the submission of an IND may not necessarily result in FDA authorization to commence a clinical trial. Further, an independent institutional review board at the medical center or centers proposing to conduct the trial must review and approve the plan for any clinical trial before it commences.
Human clinical trials are typically conducted in three sequential phases that may overlap:
|
|
• |
|
Phase 1: the drug is initially introduced into healthy human subjects or patients and tested for safety, dosage tolerance, absorption, metabolism, distribution and excretion. |
|
|
• |
|
Phase 2: involves studies in a limited patient population to identify possible adverse effects and safety risks, to determine the efficacy of the product for specific targeted diseases and to determine optimal dosage. |
|
|
• |
|
Phase 3: when Phase 2 evaluations demonstrate that a dosage range of the product is effective and has an acceptable safety profile, Phase 3 trials are undertaken to further evaluate dosage and clinical efficacy and to further test for safety in an expanded patient population at geographically dispersed clinical study sites. |
We cannot be certain that we, or any of our collaborative partners, will successfully complete Phase 1, Phase 2 or Phase 3 testing of any compound within any specific period, if at all. Furthermore, the FDA or the study sponsor may suspend clinical trials at any time on various grounds, including a finding that the subjects or patients are being exposed to an unacceptable health risk.
The results of product development, preclinical studies and clinical trials are submitted to the FDA as part of an NDA. The FDA may withhold approval for an NDA if the applicable regulatory criteria are not satisfied or may require additional data. Even if such data are submitted, the FDA may ultimately decide that the NDA does not satisfy the risk-to-benefit criteria for approval. If approved, the FDA may withdraw product approval if compliance with regulatory standards is not maintained or if problems occur after the product reaches the market. In addition, the FDA may require testing and surveillance programs to monitor approved products even after they have been commercialized, and the
16
FDA has the power to prevent or limit further marketing of a product based on the results of these post-marketing programs.
The FDA's fast track program is intended to facilitate the development and expedite the review of drugs intended for the treatment of serious or life-threatening diseases and that demonstrate the potential to address unmet medical needs for such conditions. Under this program, the FDA can, for example, review portions of an NDA for a fast track product before the entire application is complete, thus potentially beginning the review process at an earlier time. We cannot guarantee that the FDA will grant any requests that we may make for fast track designation, that any fast track designation would affect the time of review, or that the FDA will approve the NDA submitted for any of our drug candidates, whether or not fast track designation is granted. Additionally, the FDA's approval of a fast track product can include restrictions on the product's use or distribution, such as permitting use only for specified medical procedures or limiting distribution to physicians or facilities with special training or experience. Approval of fast track products can be conditional with a requirement for additional clinical studies after approval.
Satisfaction of the above FDA requirements or similar requirements of state, local and foreign regulatory agencies typically takes several years and the actual time required may vary substantially, based upon the type, complexity and novelty of a product or indication.
Government regulation may delay or prevent marketing of potential products for a considerable period and impose costly procedures upon our or our partner's activities. The FDA or any other regulatory agency may not grant any approvals on a timely basis, if at all. Success in early-stage clinical trials does not assure success in later-stage clinical trials. Data obtained from clinical activities are not always conclusive and may be susceptible to varying interpretations, which could delay, limit or prevent regulatory approval. Even if a product receives regulatory approval, the approval may be significantly limited to specific indications and dosages. Further, even if regulatory approval is obtained, later discovery of previously unknown problems with a product may result in restrictions on the product or even complete withdrawal of the product from the market. Delays in obtaining, or failures to obtain regulatory approvals may have a material adverse effect on our business. In addition, we cannot predict what adverse governmental regulations may arise from future U.S. or foreign governmental action.
Any products manufactured or distributed by us or our partners pursuant to Health Authority approvals are subject to pervasive and continuing regulation by that Health Authority, including record-keeping requirements and reporting of adverse experiences with the drug. In the US, drug manufacturers are required to register their establishments with the FDA and certain state agencies, and are subject to periodic unannounced inspections by the FDA for compliance with current Good Manufacturing Practice, or cGMP, regulations, which impose certain procedural and documentation requirements. We cannot be certain that we, or our present or future suppliers, will be able to comply with the cGMP regulations and other FDA regulatory requirements.
Under the Orphan Drug Act, the FDA may grant orphan drug designation to drugs intended to treat a rare disease or condition, which is a disease or condition that affects fewer than 200,000 individuals in the U.S. Orphan drug designation must be requested before submitting an NDA. After the FDA grants orphan drug designation, the non-proprietary identity of the therapeutic agent and its potential orphan use are disclosed publicly by the FDA. Orphan drug designation does not convey any advantage in or shorten the duration of the regulatory review and approval process. If a product that has orphan drug designation subsequently receives FDA approval for the disease for which it has such designation, the product is entitled to orphan drug market exclusivity. For example, the FDA may not approve any other applications to market the same drug for the same disease, except in very limited circumstances, for seven years. We intend to file for orphan drug designation for those diseases that meet the criteria for orphan exclusivity. Although obtaining FDA approval to market a product with orphan drug exclusivity can be advantageous, there can be no assurance that it would provide us with a material commercial advantage.
Steps similar to those in the U.S. must be undertaken in virtually every other country comprising the market for our product candidates before any such product can be commercialized in those countries. The approval procedure and the time required for approval vary from country to country and may involve additional testing. There can be no assurance that approvals will be granted on a timely basis, or at all. In addition, regulated approval of prices is required in most countries other than the U.S. There can be no assurance that the resulting prices would be sufficient to generate an acceptable return to us.
17
Patents and Other Proprietary Technology
Our intellectual property portfolio includes patents, patent applications, trade secrets, know-how and trademarks. Our success will depend in part on our ability to obtain additional patents, maintain trade secrets and operate without infringing the proprietary rights of others, both in the U.S. and in other countries. We periodically file patent applications to protect the technology, inventions and improvements that may be important to the development of our business. We rely on trade secrets, know-how, continuing technological innovations and licensing opportunities to develop and maintain our competitive position.
We file patent applications on our own behalf as assignee and, when appropriate, have filed and expect to continue to file, applications jointly with our collaborators. These patent applications cover compositions of matter, methods of treatment, methods of discovery, use of novel compounds and novel modes of action, as well as recombinantly expressed receptors and gene sequences that are important in our research and development activities. Some of our principal intellectual property rights related to processes, compounds, uses and techniques related to calcium receptor science are protected by issued U.S. patents. We intend to file additional patent applications relating to our technology and to specific products, as we think appropriate.
We hold patents directed to potential therapeutic products such as new chemical entities, pharmaceutical compositions and methods of treating diseases. We hold patents directed also to nucleic acid and amino acid sequences of novel cellular receptors and methods of screening for compounds active at such cellular receptors. We continue actively to seek patent protection for these and related technologies in the U.S. and in foreign countries.
We have been issued approximately 191 patents in the U.S. Seven issued U.S. patents cover technology related to parathyroid hormone. These patents have expiration dates (not including any patent term extensions) ranging from 2011 to 2018. Seven issued U.S. patents cover technology related to calcilytic compounds. These patents have expiration dates (not including any patent term extensions) ranging from 2016 to 2019. Fifteen issued U.S. patents cover calcimimetics (including cinacalcet HCl) and calcium receptor technology. These patents have expiration dates (not including any patent term extensions) ranging from 2013 to 2017. Seventeen issued U.S. patents cover technology related to GATTEX and GLP-2, certain of which are licensed from 1149336 Ontario Inc. These patents have expiration dates (not including any patent term extensions) ranging from 2015 to 2026. Thirteen issued U.S. patents, certain of which are licensed from Glytech, Inc., cover technology related to glycine reuptake inhibitors. These patents have expiration dates (not including any patent term extensions) ranging from 2015 to 2022. Our intellectual property portfolio also includes patents in countries outside the U.S., which also cover the technology referenced above.
In connection with our research and development activities, we have sponsored research at various university and government laboratories. For example, we have executed license and research agreements regarding research in the area of calcium and other ion receptors with The Brigham and Women's Hospital. We have also sponsored work at other government and academic laboratories for various evaluations, assays, screenings and other tests. Generally, under these agreements, we fund the work of investigators in exchange for the results of the specified work and the right or option to a license to any patentable inventions that may result in certain designated areas. If the sponsored work produces patentable subject matter, we generally have the first right to negotiate for license rights related to that subject matter. Any resulting license would be expected to require us to pay royalties on net sales of licensed products.
Competition
Competition in the pharmaceutical industry is intense and is expected to continue to increase. Many competitors, including biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies, are actively engaged in research and development in areas that we, or our partners, are also developing or commercializing products, including the fields of gastrointestinal disorders, hyperparathyroidism, osteoporosis, and central nervous system disorders.
Competition for GATTEX will depend on the applicable indication. We have focused our internal research and development on niche indications of significant unmet medical need where we believe a company of our size can successfully compete. For example, we have been granted orphan drug designation in SBS, where very few competitors exist. Current therapies for SBS include parenteral nutrition, or PN, and somatropin (rDNA origin) for injection, a human growth hormone marketed by Serono and glutamine in combination with somatropin (rDNA origin) for injection. PN is a costly option as studies show that PN costs can exceed $100,000 annually per patient. In addition, there can be a negative impact on patient quality-of-life as well as morbidities associated with PN. Treatment with somatropin (rDNA origin) for injection is limited to 28 days and requires a specialized diet. If approved by the FDA for SBS, GATTEX would compete directly with somatropin (rDNA origin) for injection. PN-dependent pediatric SBS,
18
pediatric feeding intolerance, and gastrointestinal mucositis or GIM are other specialty indications where few competitors exist. We are aware of two GLP-2 peptide analogs under development by Zealand Pharma, specifically ZP1846, which was licensed to Helsinn Healthcare, is in Phase 1 clinical development for chemotherapy-induced diarrhea and ZP1848 is in Phase 1 clinical development for inflammatory bowel diseases.
We have been granted orphan drug status for NPSP558 for the treatment of hypoparathyroidism. Presently, the only available treatments for hypoparathyroidism include high-dose supplementation of calcium and Vitamin D and treatment is typically life-long. Severe hypocalcemia can be life threatening and is treated with intravenous calcium. We believe, with its mechanism of action, NPSP558 has the potential to be the first hormone replacement therapy for hypoparathyroidism and meet the unmet need of this chronic condition.
Many of our competitors have substantially greater financial, technical, marketing and personnel resources. In addition, some of them have considerable experience in preclinical testing, human clinical trials and other regulatory approval procedures. Moreover, certain academic institutions, governmental agencies and other research organizations are conducting research in the same areas in which we are working. These institutions are becoming increasingly aware of the commercial value of their findings and are more actively seeking patent protection and licensing arrangements to collect royalties for the technology that they have developed. These institutions may also market competitive commercial products on their own or through joint ventures and will compete with us in recruiting highly qualified personnel. Our ability to compete successfully will depend, in part, on our ability to:
|
|
• |
|
outsource activities critical to the advancement of our product candidates and manage those companies to whom such activities are outsourced; |
|
|
• |
|
outsource manufacturing capabilities for our proprietary products; |
|
|
• |
|
leverage our established collaborations and enter into new collaborations for the development of our products; |
|
|
• |
|
identify new product candidates; |
|
|
• |
|
develop products that reach the market first; |
|
|
• |
|
develop products that are superior to other products in the market; |
|
|
• |
|
develop products that are cost-effective and competitively priced; and |
|
|
• |
|
obtain and enforce patents covering our technology. |
Manufacturing
We rely on corporate collaborators and contract manufacturing organizations to supply drug product for our clinical trials and potential future commercial supply chain. We have established substantially all of our commercial supply chain for teduglutide and NPSP558. We have agreements in place for the production of bulk supplies of the active pharmaceutical ingredients in teduglutide and NPSP558 for our clinical and future commercial requirements. In addition, we have manufacturing agreements in place for the production of our fill and finish clinical and commercial supplies of both teduglutide and NPSP558. We have also established agreements with other third parties to perform additional steps in the manufacturing process, including testing and storage of our product candidates.
If we secure regulatory approval for NPSP558 in hypoparathyroidism, we will need to develop an injection device to successfully commercialize this product. We have developed a prototype of this device and we have a manufacturing agreement in place.
We believe that our existing supplies of drug product, our contract manufacturing relationships, and potential contract manufacturers, who we are in discussions with, will be sufficient to accommodate our clinical trials and our commercial supply chain for teduglutide and NPSP558.
We are dependent on third parties for the manufacture of our product candidates and injection devices and in most instances we are sole sourced to these manufacturers. If we are unable to contract for a sufficient supply of our product candidates or injection devices on acceptable terms, or encounter delays or difficulties in the manufacturing or supply process, we may not have sufficient product or injection devices to conduct or complete our clinical trials or support preparations for the commercial launch of our product candidates, if approved. Based on the highly-specialized and proprietary nature of the products provided to us by certain of our manufacturing partners, we could be subject to significant added costs and delays if we are required to replace our existing agreements or arrangements with those partners for any reason. For a more complete discussion of the various risks and uncertainties related to our
19
manufacturing and supply relationships, see the discussion in Item 1A of this Annual Report under the heading "Risk Factors."
Employees
As of March 4, 2010, we had approximately 53 employees. None of our employees is covered by a collective bargaining agreement and we believe that our relationship with our employees is good.
Trademarks
"NPS", "NPS Pharmaceuticals", "GATTEX", and "PREOS" are our trademarks. In addition, "Preotact" is our registered trademark in the E.U. All other trademarks, trade names or service marks appearing in this Annual Report on Form 10-K are the property of their respective owners.
Available Information
Our Internet address is www.npsp.com. We make available free of charge on or through our Internet website our Annual Reports on Form 10-K, Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, Current Reports on Form 8-K, and amendments to those reports filed or furnished pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act as soon as reasonably practicable after we electronically file such material with, or furnish it to, the SEC.
|
Risk Factors. |
The following information sets forth risk factors that could cause our actual results to differ materially from those contained in forward-looking statements we have made in this Annual Report on Form 10-K and those we may make from time to time. If any of the following risks actually occur, our business, results of operation, prospects or financial condition could be harmed. These are not the only risks we face. Additional risks not presently known to us, or that we currently deem immaterial, may also affect our business operations.
Risks Related to Our Business
We have a history of operating losses. We expect to incur net losses and we may never achieve or maintain profitability.
With the exception of 1996, we have not been profitable since our inception in 1986. As of December 31, 2009, we had an accumulated deficit of approximately $922.7 million. To date, our revenue from product sales has been in the form of royalty payments from Amgen on sales of Sensipar (cinacalcet HCl), royalty payments from Nycomed on sales of Preotact, royalty payments from Kyowa Kirin on sales of REGPARA, milestone revenue from our collaborative agreements with Nycomed, product sales to Nycomed and beginning in 2009, royalty payments on sales of Nucynta by Ortho-McNeil. In July 2007, we entered into an agreement with Nycomed whereby they assumed sole responsibility for manufacturing Preotact. As described further herein, we have non-recourse debt that is secured by our royalty rights related to sales of Sensipar under our agreement with Amgen. In addition, we have sold to DRI and an affiliate of DRI our rights to receive royalty payments under our agreements with Nycomed and Kyowa Kirin for Preotact and REGPARA, respectively. The right to royalties on Amgen's Sensipar sales will only be returned to us if those royalties are sufficient to repay our non-recourse Class A Notes and Class B Notes on a timely basis. The right to royalties on Nycomed's Preotact sales and Kyowa Kirin's REGPARA sales will only be returned to us if the amount of royalties received by the purchasers exceed two and a half times the amount paid to us.
We are entirely dependent on Amgen, Nycomed and Kyowa Kirin for sales of Sensipar, Preotact and REGPARA, respectively, and we cannot assure that they will pay royalties in amounts sufficient to cause the royalty rights to be returned to us. Other than the royalty payments we receive from Ortho-McNeil, we are not currently receiving any cash inflows, including from royalty payments or product sales, and it is possible that we will never have sufficient product sales revenue to achieve profitability. We expect to continue to incur losses for at least the next several years as we and our collaborators and licensees pursue clinical trials and research and development efforts. To become profitable, we, alone or with our collaborators and licensees, must successfully develop, manufacture and market our current product candidates and continue to identify, develop, manufacture and market new product candidates. It is possible that we will never have significant product sales revenue or receive significant royalties on our licensed product candidates to achieve profitability.
20
Pursuant to the Company's license agreement with Amgen, so long as a patent infringement proceeding by a third party against Amgen continues for the manufacture, use or sale of a compound under the agreement in any country, Amgen may reserve up to 50% of the royalties otherwise payable by Amgen with respect to the affected compound in the country in question until the proceedings are concluded. If the third party's patent is finally determined to be uninfringed, unenforceable or invalid, Amgen is required to promptly pay the reserved royalties to the Company. If the third party's patent is held to be valid and infringed or if Amgen enters into a settlement of such infringement claim, then Amgen may deduct any damages or settlement amount with respect to such claim from the reserved royalties prior to payment of any remaining amount. In the event any damages and/or settlement amounts exceed the amount of reserved royalties, Amgen could withhold such excess from its future royalty obligations in that country. If Amgen reserves or reduces the royalties paid on Sensipar sales as a result of a third party claim, our ability to repay the non-recourse Class A and Class B Notes on a timely basis could be adversely affected. In addition, if any such claim is successful or if Amgen settles the claim, the right to receive future royalty payments on the sales of Sensipar may never be returned to us.
For example, on May 20, 2009, Teva Pharmaceuticals USA, Inc. and Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd which we refer to collectively as Teva filed a lawsuit in federal court in the Eastern District of Pennsylvania against Amgen alleging that certain processes used by Amgen to manufacture Sensipar (cinacalcet HCl) infringe Teva's U.S. Patent No. 7,449,603. Teva is seeking declaratory relief and damages in an unspecified amount. As described above, so long as a patent infringement proceeding by a third party against Amgen continues for the manufacture, use or sale of cinacalcet HCl in any country, Amgen may reserve up to fifty percent of the royalties otherwise payable to the Company with respect to cinacalcet HCl sales in the country in question until the proceeding is concluded. To date, Amgen has elected to not reserve any such royalties. If Teva's patent is determined to be uninfringed, unenforceable or invalid, Amgen is required to promptly pay any reserved royalties to the Company. If Teva's patent is held to be valid and infringed, or if Amgen enters into a settlement of Teva's infringement claim, then Amgen may deduct any damages or settlement amount with respect to such claim from the reserved royalties prior to payment of any remaining amount. In the event any damages and/or settlement amounts exceed the amount of reserved royalties, Amgen could withhold such excess from its future royalty obligations in that country. Amgen filed a motion to dismiss the complaint, in part, based on Amgen's claim that the Court lacks subject matter jurisdiction over Teva U.S. On July 22, 2009, an amended complaint was filed by Teva Israel against Amgen. Teva U.S. is not named as a plaintiff in the amended complaint.
We may require additional funds.
Currently, we are not a self-sustaining business and certain economic, operational and strategic factors may require us to secure additional funds. If we are unable to obtain sufficient funding at any time in the future, we may not be able to develop or commercialize our products, take advantage of business opportunities or respond to competitive pressures.
Our current and anticipated operations require substantial capital. We expect that our existing cash, cash equivalents, and short-term investments will sufficiently fund our current and planned operations through at least 2010. However, our future capital needs will depend on many factors, including the extent to which we enter into collaboration agreements with respect to any of our proprietary product candidates, receive royalty and milestone payments from our collaborators and make progress in our development and commercialization activities. Our capital requirements will also depend on the magnitude and scope of these activities, our ability to maintain existing and establish new collaborations, the terms of those collaborations, the success of our collaborators in developing and marketing products under their respective collaborations with us, our ability to effectively out-source our clinical development, regulatory, data management, research, quality control and assurance, and other activities, the success of our contract manufacturers in producing clinical and commercial supplies of our product candidates and drug delivery devices on a timely basis and in sufficient quantities to meet our requirements, competing technological and market developments, the time and cost of obtaining regulatory approvals, the cost of preparing, filing, prosecuting, maintaining and enforcing patent and other rights and our success in acquiring and integrating complementary products, technologies or companies. We do not have committed external sources of funding, and we cannot assure you that we will be able to obtain additional funds on acceptable terms, if at all. If adequate funds are not available, we may be required to:
- engage in equity financings that would be dilutive to current stockholders;
- delay, reduce the scope of or eliminate one or more of our development programs;
- obtain funds through arrangements with collaborators or others that may require us to relinquish rights to technologies, product candidates or products that we would otherwise seek to develop or commercialize ourselves; or
21
- license rights to technologies, product candidates or products on terms that are less favorable to us than might otherwise be available.
In addition, the capital and credit markets have been experiencing extreme volatility and disruption which, particularly during the latter part of 2008 through 2009, has led to uncertainty and liquidity issues for both borrowers and investors. In the future, we may not be able to obtain capital market financing on favorable terms, or at all, which could have a material adverse effect on our business and results of operations.
If we do not receive regulatory approval to market our product candidates in a timely manner, or at all, or if we obtain regulatory approval to market those product candidates but the approved label is not competitive with then existing competitive products, our business will be materially harmed and our stock price may be adversely affected.
We are developing teduglutide and NPSP558 as a potential treatment for SBS and hypoparathyroidism, respectively. We are currently advancing Phase 3 registration quality studies for both product candidates. For more information, see "Item 1 - Business - Proprietary Product Candidates."
While we presently believe that we have the financial resources to fund the continued development of these product candidates in the U.S., all clinical trials are long, expensive and uncertain processes and there can be no assurance that data collected from these studies will be sufficient to support a new drug application, or NDA, or obtain FDA approval once the studies are completed. Our ability to generate revenues to sustain our operations will be substantially impaired and our business will be materially harmed if our Phase 3 study for either of our product candidates fails to produce the required safety and efficacy data to support an NDA for that product candidate or obtain regulatory approval by the FDA.
If we are ultimately unable to obtain regulatory approval to commercialize any one of our product candidates in a timely manner, or at all, or if the FDA approved indication, side effect and adverse events profile, and product distribution requirements are not competitive with existing competitor products:
- Our ability to generate revenues to sustain our operations will be substantially impaired, which would increase the likelihood that we would need to obtain additional financing for our other development efforts;
- Our reputation among investors might be harmed, which might make it more difficult for us to obtain equity capital on attractive terms or at all; and
- Our profitability would be delayed, our business will be materially harmed and our stock price may be adversely affected.
Biotechnology stock prices, including our stock price, have declined significantly in certain instances where companies have failed to meet expectations with respect to FDA approval or the timing for FDA approval.
We may never develop any more commercial drugs or other products that generate revenues.
Sensipar (Mimpara in Europe), REGPARA in Japan, Preotact and Nucynta are our only sources, to date, of commercial revenues. Our remaining product candidates will require significant additional development, clinical trials, regulatory approvals and additional investment before their commercialization. Our product development efforts may not lead to commercial drugs for a number of reasons, including our inability to demonstrate that our product candidates are safe and effective in clinical trials or a lack of financial or other resources to pursue the programs through the clinical trial process. Even if we are able to commercialize one or more of our product candidates, we cannot assure you that such product candidates will find acceptance in the medical community.
Our dependence on contract research organizations could result in delays in and additional costs for our drug development efforts.
We rely almost entirely on contract research organizations, or CROs, to perform preclinical testing and clinical trials for drug candidates that we choose to develop without a collaborator. If the CROs that we hire to perform our preclinical testing and clinical trials or our collaborators or licensees do not meet deadlines, do not follow proper procedures, or a conflict arises between us and our CROs, our preclinical testing and clinical trials may take longer than expected, may be delayed or may be terminated. If we were forced to find a replacement CRO to perform any of our preclinical testing or clinical trials, we may not be able to find a suitable replacement on favorable terms, if at all. Even if we were able to find another CRO to perform a preclinical test or clinical trial, any material delay in a test or clinical
22
trial may result in significant additional expenditures that could adversely affect our operating results. Events such as these may also delay regulatory approval for our drug candidates or our ability to commercialize our products.
In addition, we may enter into agreements with collaborators or licensees to advance certain of our drug candidates through the later-stage, more expensive clinical trials, rather than invest our own resources to conduct these clinical trials. Depending on the terms of our agreements with these collaborators or licensees, we may have little or no control over the manner in which these clinical trials are conducted, and would be subject to other risks that are similar to those associated with our reliance on CROs, as described above.
We depend exclusively on third parties, including a number of sole suppliers, for the manufacture, supply, and storage of our product candidates and drug delivery devices; if these third parties fail to supply us with sufficient quantities of products and devices on a timely basis, or if the products and devices they provide do not meet our specifications, our clinical trials and product introductions may be delayed or suspended
We do not have the internal manufacturing capabilities to produce the supplies of teduglutide and NPSP558 that are needed to support clinical trials or the commercial launch of these products, if they are approved. We also do not have internal manufacturing capabilities to produce supplies of the injection devices used to administer teduglutide and NPSP558. We are dependent on third parties for the manufacture, supply, and storage of our product candidates and injection devices. If we are unable to contract for a sufficient supply of our product candidates or injection devices on acceptable terms, or if we encounter delays or difficulties in the manufacturing or supply process we may not have sufficient product or injection devices to conduct or complete our clinical trials or to support the commercial launch of our product candidates, if approved.
We depend on a number of contract manufacturers to supply key components of teduglutide and NPSP558. For a description of our agreements with these manufacturers, see "Item 1. - Business - Manufacturing." Although we anticipate that our contract manufacturers will be able to produce the raw materials and finished products that we require, the process for manufacturing biological products is complex and no assurances can be provided that our manufacturers will be able to produce the required quantities in a timely manner or at all.
We have experienced certain instances where our contract manufacturers have produced product and injection devices that have not met our required specifications and could not be used in clinical trials or for commercialization. Any extended disruption or termination of our relationship with any of our contract manufacturers could materially harm our business and financial condition and adversely affect our stock price.
Dependence on contract manufacturers for commercial production involves a number of additional risks, many of which are outside our control. These additional risks include:
|
|
• |
|
there may be delays as manufacturers scale-up to quantities needed for clinical trials and the commercial launch of our product candidates; manufacturers may be unable to manufacture such quantities to our specifications, or to deliver such quantities on the dates we require; |
|
|
• |
|
our current and future manufacturers are subject to ongoing, periodic, unannounced inspection by the FDA and corresponding state and international regulatory authorities for compliance with strictly enforced cGMP regulations and similar foreign standards, and we are unable to ensure their compliance with these regulations and standards; |
|
|
• |
|
our current and future manufacturers may not be able to comply with applicable regulatory requirements, which would prohibit them from manufacturing products or drug delivery devices for us; |
|
|
• |
|
if we need to change to other commercial manufacturing contractors, the FDA and comparable foreign regulators must first approve these contractors, which would require new testing and compliance inspections, and the new manufacturers would have to be educated in, or themselves develop substantially equivalent processes necessary for, the production of our products and drug delivery devices; |
|
|
• |
|
our manufacturers might not be able to fulfill our commercial needs, which would require us to seek new manufacturing arrangements that could result in substantial delays and higher costs; and |
|
|
• |
|
we may not have intellectual property rights, or may have to share intellectual property rights, to any improvements in the manufacturing processes or new manufacturing processes for our products or drug delivery devices. |
23
Any of these factors could cause us to delay or suspend clinical trials, regulatory submission, required approvals or
commercialization of our products under development, entail higher costs and result in our inability to commercialize our products
effectively. In addition, if we receive regulatory approval for NPSP558 for hypoparathyroidism, in order to successfully commercialize our
product, we will need to develop an injection device for this indication. There is no guarantee that we will be able to develop an
injection device and find a supplier to adequately supply our potential commercial needs. We are subject to extensive government regulations that may cause us to cancel or delay the introduction of our products to
market. Our business is subject to extensive regulation by governmental authorities in the U.S. and other countries. Prior to marketing in
the United States, a drug must undergo rigorous testing and an extensive regulatory approval process implemented by the FDA under
federal law, including the Federal Food, Drug and Cosmetic Act. To receive approval, our collaborators or we must demonstrate,
among other things, with substantial evidence from well-controlled clinical trials that the product is both safe and effective for each
indication where approval is sought. Depending upon the type, complexity and novelty of the product and the nature of the disease or
disorder to be treated, the approval process can take several years and require substantial expenditures. Data obtained from testing
are susceptible to varying interpretations that could delay, limit or prevent regulatory approvals of our products. Drug testing is subject
to complex FDA rules and regulations, including the requirement to conduct human testing on a large number of test subjects. Our
collaborators, the FDA or we may suspend human trials at any time if a party believes that the test subjects are exposed to
unacceptable health risks. We cannot assure you that any of our product candidates will be safe for human use. Other countries also
have extensive requirements regarding clinical trials, market authorization and pricing. These regulatory requirements vary widely from
country to country, but, in general, are subject to all of the risks associated with U.S. approvals. If any of our products receive regulatory approval, the approval will be limited to those disease states and conditions for which the
product is safe and effective, as demonstrated through clinical trials. In addition, results of preclinical studies and clinical trials with
respect to our products could subject us to adverse product labeling requirements that could harm the sale of such products. Even if
regulatory approval is obtained, later discovery of previously unknown problems may result in restrictions of the product, including
withdrawal of the product from the market. Further, governmental approval may subject us to ongoing requirements for post-marketing
studies. Even if we obtain governmental approval, a marketed product, its respective manufacturer and its manufacturing facilities are
subject to unannounced inspections by the FDA and must comply with the FDA's cGMP and other regulations. These regulations
govern all areas of production, record keeping, personnel and quality control. If a manufacturer fails to comply with any of the
manufacturing regulations, it may be subject to, among other things, product seizures, recalls, fines, injunctions, suspensions or
revocations of marketing licenses, operating restrictions and criminal prosecution. Other countries also impose similar manufacturing
requirements. Our promotional materials and sales activities are governed by FDA regulation. The FDA may require us to withdraw
promotional material, to issue corrected material, or to cease promotion resulting in loss of credibility with our customers, reduced sales
revenue or increased costs. Steps similar to those in the U.S. must be undertaken in virtually every other country comprising the market for our product
candidates before any such product can be commercialized in those countries. The approval procedure and the time required for
approval vary from country to country and may involve additional testing. There can be no assurance that approvals will be granted on
a timely basis, or at all. Clinical trials are long, expensive and uncertain processes; if the data collected from preclinical and clinical trials of our product
candidates are not sufficient to support approval by the FDA, our profitability and stock price could be adversely affected. Before we receive regulatory approval for the commercial sale of our product candidates, our product candidates are subject to
extensive preclinical testing and clinical trials to demonstrate their safety and efficacy. Clinical trials are long, expensive and uncertain
processes. Clinical trials may not be commenced or completed on schedule, and the FDA may not ultimately approve our product
candidates for commercial sale. Further, even if the results of our preclinical studies or clinical trials are initially positive, it is possible that we will obtain different
results in the later stages of drug development or that results seen in clinical trials will not continue with longer-term treatment. Drugs in
late stages of clinical development may fail to show the desired safety and efficacy traits despite having progressed through initial
clinical testing. For example, positive results in early Phase 1 or Phase 2 clinical trials may not be repeated in larger Phase 2 or Phase
3 clinical trials. All of our potential drug
24
candidates are prone to the risks of failure inherent in drug development. The clinical trials of
any of our drug candidates, including teduglutide and NPSP558, could be unsuccessful, which would prevent us from commercializing
the drug. Our failure to develop safe, commercially viable drugs would substantially impair our ability to generate revenues and sustain
our operations and would materially harm our business and adversely affect our stock price. If we fail to maintain our existing or establish new collaborative relationships, or if our existing collaborations fail, or if our
collaborators do not devote adequate resources to the development and commercialization of our licensed drug candidates, we may
have to reduce our rate of product development and may not see products brought to market or be able to achieve profitability. Our strategy for developing, manufacturing and commercializing our products includes entering into various
relationships with other pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies to advance many of our programs. We have granted
development, commercialization and marketing rights to a number of our collaborators for some of our key product development
programs, including cinacalcet HCl, Preotact, teduglutide and calcilytics. Our collaborators typically have full control over those efforts
in their territories and the resources they commit to the programs. Accordingly, the success of the development and commercialization
of product candidates in those programs depends on the efforts of our collaborators and is beyond our control. For us to receive any
significant milestone or royalty payments from our collaborators, they must advance drugs through clinical trials, establish the safety
and efficacy of our drug candidates, obtain regulatory approvals and achieve market acceptance of those products. As a result, if a
collaborator elects to terminate its agreement with us with respect to a research program, our ability to advance the program may be
significantly impaired or we may elect to discontinue funding the program altogether. For example, in early 2002, Abbott terminated its
agreement with respect to isovaleramide, and Forest Laboratories terminated its agreement with us with respect to ALX-0646. As a
result, these programs were discontinued. As an additional example, in September 2008, we were notified by GSK that it has
decided to terminate a Phase 2 dose-range finding study of ronacaleret in post-menopausal women with osteoporosis earlier than
expected due to an observed lack of efficacy based on lumbar spine and hip bone mineral density. The counterparties to certain
of our collaborative research, development or commercial agreements have the right to terminate those agreements
prior to their expiration after providing us with the requisite notice. See the description of these agreements under "Item 1 -
Business - Royalty-Based Products and Product Candidates." As part of our product development and commercialization strategy, we evaluate whether to seek collaborators for our product
candidates. If we elect to collaborate, we may not be able to negotiate collaborative arrangements for our product candidates on
acceptable terms, if at all. If we are unable to establish collaborative arrangements, we will either need to increase our expenditures
and undertake the development and commercialization activities at our own expense or delay further development of the affected
product candidate. Collaborative agreements, including our existing collaborative agreements, pose the following risks:
|
|
• |
|
our contracts with collaborators may be terminated and we may not be able to replace our collaborators; |
|
|
• |
|
the terms of our contracts with our collaborators may not be favorable to us in the future; |
|
|
• |
|
our collaborators may not pursue further development and commercialization of compounds resulting from their collaborations with us or may pursue the same on a different regulatory pathway from us; |
|
|
• |
|
a collaborator with marketing and distribution rights to one or more of our product candidates may not commit enough resources to the marketing and distribution of such candidates; |
|
|
• |
|
disputes with our collaborators may arise, leading to delays in or termination of the research, development or commercialization of our product candidates, or resulting in significant litigation or arbitration; |
|
|
• |
|
contracts with our collaborators may fail to provide significant protection if one or more of them fail to perform; |
|
|
• |
|
in some circumstances, if a collaborator terminates an agreement, or if we are found to be in breach of our obligations, we may be unable to secure all of the necessary intellectual property rights and regulatory approval to continue developing the same compound or product; |
|
|
• |
|
our collaborators could independently develop, or develop with third parties, drugs that compete with our products; and |
|
|
• |
|
we may be unable to meet our financial or other obligations under our collaborative agreements. |
We cannot assure you that our current or future collaborative efforts will be successful. If our collaborative efforts fail, our business and financial condition would be materially harmed.
25
We have limited marketing and sales experience and have never distributed a product and may need to rely on third parties to successfully market and sell our products and generate revenues.
We do not have commercial sales and related field operations. As a result, if and when we receive regulatory approval to market and sell one or more of our product candidates we will have to either build a commercial organization or enter into agreements with contract sales organizations to provide sales, marketing, market research and product planning services. Our ability to gain market acceptance and generate revenues will be substantially dependent upon our ability to build a commercial organization and/or enter into such agreements on favorable terms and to manage the efforts of those service providers successfully. We may also benefit from establishing a relationship with one or more companies with existing distribution systems and direct sales forces to market any or all of our product candidates; however, we cannot assure you that we will be able to enter into or maintain agreements with these companies on acceptable terms, if at all.
Because of the uncertainty of pharmaceutical pricing, reimbursement and healthcare reform measures, we or our licensees may be unable to sell our products profitably.
The availability of reimbursement by governmental and other third-party payers affects the market for any pharmaceutical product. These third-party payers continually attempt to contain or reduce the costs of healthcare. There have been a number of legislative and regulatory proposals to change the healthcare system and further proposals are likely. Medicare's policies may decrease the market for our products that are designed to treat patients with age-related disorders, such as hyperparathyroidism. Significant uncertainty exists with respect to the reimbursement status of newly approved healthcare products.
In addition, third-party payers are increasingly challenging the price and cost-effectiveness of medical products and services. We might not be able to sell our products profitably or recoup the value of our investment in product development if reimbursement is unavailable or limited in scope, particularly for product candidates addressing small patient populations, such as teduglutide for the treatment of short bowel syndrome and NPSP558 for hypoparathyroidism.
In addition, in some foreign countries, the proposed pricing for a drug must be approved before it may be lawfully marketed. The requirements governing drug pricing vary widely from country to country. We expect that there will continue to be a number of U.S. federal and state proposals to implement governmental pricing controls. While we cannot predict whether such legislative or regulatory proposals will be adopted, the adoption of such proposals could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and profitability.
On July 15, 2008, the Medicare Improvements for Patients and Providers Act of 2008 became law with a number of Medicare and Medicaid reforms to establish a bundled Medicare payment rate that includes services and drug/labs that are currently separately billed. The bundled reimbursement rate will be phased in over a four year period in equal increments starting in 2011. It is possible that some providers could elect to move to a full Medicare bundled payment in 2011. Additionally, one proposal on healthcare reform being considered by Congress calls for the inclusion of certain oral drugs such as Sensipar® (cinacalcet HCl) as part of the end stage renal disease Program of Medicare bundled payment beginning in 2011. Bundling initiatives that have been implemented in other healthcare settings have occasionally resulted in lower utilization of services that had not previously been a part of the bundled payment. We cannot speculate on the sales impact to Sensipar based on the proposed rule and at this time cannot predict whether a final bill on healthcare reform would include Sensipar in the bundled payment.
Because of intense competition and technological change in the pharmaceutical industry, the marketplace may not accept our products, and we may not be able to compete successfully against other companies in our industry and achieve profitability.
The pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries are intensely competitive, with many companies in our industry having substantially greater financial and management resources, superior intellectual property positions and greater manufacturing, marketing and sales capabilities, areas in which we have limited or no experience. In addition, many companies have significantly greater experience than we do in undertaking preclinical testing and clinical trials of new or improved pharmaceutical products and obtaining required regulatory approvals. Consequently, potential future competitors may obtain FDA and other regulatory approvals for product candidates sooner and may be more successful in manufacturing and marketing their products than we or our collaborators, which could render our product candidates obsolete and non-competitive.
26
Existing and future products, therapies and technological approaches may compete directly with the products we seek to develop. Prospective competing products may provide greater therapeutic benefits for a specific problem, may offer easier delivery or may offer comparable performance at a lower cost. Any product candidate that we develop and that obtains regulatory approval must then compete for market acceptance and market share. Our product candidates may not gain market acceptance among physicians, patients, healthcare payers and the medical community. Further, any products we develop may become obsolete before we recover any expenses we incurred in connection with the development of these products. As a result, we may never achieve profitability.
We may be unable to obtain patents to protect our technologies from other companies with competitive products, our patents may be challenged or circumvented by third parties, and patents of other companies could prevent us from manufacturing, developing or marketing our products.
The patent positions of pharmaceutical and biotechnology firms are uncertain and involve complex legal and factual questions. The U.S. Patent and Trademark Office has not established a consistent policy regarding the breadth of claims that it will allow in biotechnology patents. If it allows broad claims, the number and cost of patent interference proceedings in the U.S. and the risk of infringement litigation may increase. If it allows narrow claims, the risk of infringement may decrease, but the value of our rights under our patents, licenses and patent applications may also decrease. In addition, the scope of the claims in a patent application can be significantly modified during prosecution before the patent is issued. Consequently, we cannot know whether our pending applications will result in the issuance of patents or, if any patents are issued, whether they will provide us with significant proprietary protection or will be circumvented, invalidated, or found to be unenforceable. Until recently, patent applications in the U.S. were maintained in secrecy until the patents were issued, and publication of discoveries in scientific or patent literature often lags behind discoveries. Patent applications filed in the U.S. after November 2000 generally will be published 18 months after the filing date unless the applicant certifies that the invention will not be the subject of a foreign patent application. We cannot assure you that, even if published, we will be aware of all such literature. Accordingly, we cannot be certain that the named inventors of our products and processes were the first to invent that product or process or that we were the first to pursue patent coverage for our inventions.
Our commercial success depends in part on our ability to maintain and enforce our proprietary rights. If third parties engage in activities that infringe our proprietary rights we may incur significant costs in asserting our rights. We may not be successful in asserting our proprietary rights, which could result in our patents being held invalid or a court holding that the third party is not infringing, either of which would harm our competitive position. In addition, we cannot assure you that others will not design around our patented technology.
Moreover, we may have to participate in interference proceedings declared by the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office or other analogous proceedings in other parts of the world to determine priority of invention and the validity of patent rights granted or applied for, which could result in substantial cost and delay, even if the eventual outcome is favorable to us. We cannot assure you that our pending patent applications, if issued, would be held valid or enforceable. Additionally, many of our foreign patent applications have been published as part of the patent prosecution process in such countries. Protection of the rights revealed in published patent applications can be complex, costly and uncertain.
Additionally, under the Hatch-Waxman Act, a generic pharmaceutical manufacturer may file an Abbreviated New Drug Application, or ANDA, seeking permission to market a generic version of one of our products prior to the expiration of our relevant patents. For example, on June 15, 2008, we reported the receipt of Paragraph IV certification notification letters related to ANDA's submitted to the FDA by Barr Laboratories and Teva Pharmaceuticals USA, Inc. requesting approval to market and sell generic versions of cinacalcet HCl. Such a filing is an act of patent infringement and resulted in our filing patent infringement litigation to enforce our proprietary rights.
In order to protect goodwill associated with our company and product names, we rely on trademark protection for our marks. We have registered the "PREOS" and "GATTEX" trademarks with the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office. A third party may assert a claim that one of those marks is confusingly similar to its mark, and such claims or the failure to timely register a mark or objections by the FDA could force us to select a new name for our product candidates, which could cause us to incur additional expense or delay the introduction of a product candidate to market.
We also rely on trade secrets, know-how and confidentiality provisions in our agreements with our collaborators, employees and consultants to protect our intellectual property. However, these and other parties may not comply with the terms of their agreements with us, and we might be unable to adequately enforce our rights against these people or
27
obtain adequate compensation for the damages caused by their unauthorized disclosure or use. Our trade secrets or those of our collaborators may also become known or may be independently discovered by others.
We granted security interests in our intellectual property in connection with the agreements to monetize Preotact and REGPARA, and these security interests could be enforced against us if we default on these agreements.
In connection with our July 2007 agreement with DRI Capital, or DRI (formerly Drug Royalty L.P.3) to monetize Preotact, we granted DRI a security interest in the our license agreement with Nycomed for Preotact and certain of our patents related to Preotact and other intellectual property underlying that agreement. In the event of a default by NPS under the agreement with DRI, DRI would be entitled to enforce its security interest against us and the property described above. If DRI validly enforced its security interest, we could potentially lose rights to our Preotact intellectual property.
In addition, in connection with our February 2010 agreement with an affiliate of DRI or DRI, we granted DRI a security interest in our license agreement with Kyowa Kirin and certain of our patents related to REGPARA and other intellectual property underlying that agreement. In the event of a default by NPS under the agreement with DRI, DRI would be entitled to enforce its security interest against us and the property described above. If DRI validly enforced its security interest, we could potentially lose rights to our REGPARA intellectual property.
If the market opportunities for our product candidates are smaller than we believe they are, then our revenues may be adversely affected and our business may suffer.
Each of the diseases that our product candidates are being developed to address is relatively rare. Our projections of both the number of people who have these diseases, as well as the subset of people with these diseases who have the potential to benefit from treatment with our product candidates, are based on estimates.
Currently, most reported estimates of the prevalence of these diseases are based on studies based on small numbers or small subsets of the population of specific geographic areas, which are then extrapolated to estimate the prevalence of the diseases in the broader world population. If our estimates of the prevalence of short bowel syndrome or hypoparathyroidism, or of the number of patients who may benefit from treatment with our product candidates prove to be incorrect, the market opportunities for our product candidates may be smaller than we believe they are and our prospects for generating revenue may be adversely affected and our business may suffer.
Our products and product candidates may infringe the intellectual property rights of others, which could increase our costs and negatively affect our profitability.
Our success also depends on avoiding infringement of the proprietary technologies of others. In particular, there may be certain issued patents and patent applications claiming subject matter that our collaborators or we may be required to license in order to research, develop or commercialize at least some of our product candidates, including teduglutide, NPSP558 and PREOS. In addition, third parties may assert infringement or other intellectual property claims against us based on our patents or other intellectual property rights. An adverse outcome in these proceedings could subject us to significant liabilities to third parties, require disputed rights to be licensed from third parties or require us to cease or modify our use of the technology. If we are required to license such technology, we cannot assure you that a license under such patents and patent applications will be available on acceptable terms or at all. Further, we may incur substantial costs defending ourselves in lawsuits against charges of patent infringement or other unlawful use of another's proprietary technology.
Because of reductions in our workforce related to our prior restructuring activities, we have reallocated certain employment responsibilities and have increased our dependence on third parties to perform certain corporate functions.
We restructured our operations, which included reductions in our workforce as well as a transition to an outsourcing business strategy. The reductions resulted in the loss of numerous long-term employees, the loss of institutional knowledge and expertise and the reallocation of certain employment responsibilities, all of which could adversely affect operational efficiencies, employee performance and retention. In addition, because of these reductions, we are outsourcing certain corporate functions, which makes us more dependent on third parties for the performance of these functions in connection with our business and product candidates. To the extent that we are unable to effectively reallocate employee responsibilities, retain key employees, establish and maintain agreements with competent third-party contractors on terms that are acceptable to us, or effectively manage the work performed by any retained third-
28
party contractors, our ability to advance our business or product candidates may be significantly impaired and our stock price may be adversely affected.
If we fail to attract and retain key executives and employees, the development and commercialization of our products may be adversely affected.
We depend heavily on our executive, managerial and clinical personnel. To the extent that we lose any of these key personnel, our ability to develop products and become profitable may suffer. The risk of being unable to retain key personnel may be increased by the fact that, other than with respect to our CEO, we have not entered into long-term employment contracts with our executives or employees. Our future success will also depend in large part on our ability to attract and retain qualified executives and employees in the future. We face competition for personnel from other companies, academic institutions, government entities and other organizations. In particular, we are highly dependent on members of our executive team to manage our business. In connection with our transition to an outsourcing business strategy, certain members of our executive team are no longer with the company and new executive team members have been hired. Our transition in expertise, as with any company, will take time and resources and may result in unexpected expense and delay to our business programs. Each member of our executive team is highly qualified, important to our business and would be difficult to replace. We are also dependent on several key employees who would also be difficult to replace. If we are unable to retain our executives and key employees, our ability to operate under the outsourcing business model and compete in our industry may be hindered and our business may suffer. Each of our executives and key employees is an employee at will and, despite our retention efforts; we cannot assure you that they will remain with the company.
If product liability claims are brought against us or we are unable to obtain or maintain product liability insurance, we may incur substantial liabilities that could reduce our financial resources.
The clinical testing and commercial use of pharmaceutical products involves significant exposure to product liability claims. We have obtained limited product liability insurance coverage for our clinical trial in humans; however, our insurance coverage may be insufficient to protect us against all product liability damages. Further, liability insurance coverage is becoming increasingly expensive and we might not be able to obtain or maintain product liability insurance in the future on acceptable terms or in sufficient amounts to protect us against product liability damages. Regardless of merit or eventual outcome, liability claims may result in decreased demand for a future product, injury to our reputation, withdrawal of clinical trial volunteers, loss of revenue, costs of litigation, distraction of management and substantial monetary awards to plaintiffs. Additionally, if we are required to pay a product liability claim, we may not have sufficient financial resources to complete development or commercialization of any of our product candidates and our business and results of operations will be adversely affected.
Research and development involves hazardous materials and we must comply with environmental laws and regulations, which can be expensive and restrict how we do business.
Research and development activities involve the controlled use of hazardous materials, radioactive compounds and other potentially dangerous chemicals and biological agents. Although we believe our contractors' safety procedures for these materials comply with governmental standards, we cannot eliminate the risk of accidental contamination or injury from these materials. We currently have insurance, in amounts and on terms typical for companies in businesses that are similarly situated, that could cover all or a portion of a damage claim arising from our use of hazardous and other materials. However, if an accident or environmental discharge occurs, and we are held liable for any resulting damages, the associated liability could exceed our insurance coverage and our financial resources.
29
Risks Related to Our Common Stock and Notes Payable
Our stock price has been and likely will continue to be volatile and an investment in our common stock could suffer a decline in value.
You should consider an investment in our common stock as risky and invest only if you can withstand a significant loss and wide fluctuations in the market value of your investment. We receive only limited attention by securities analysts and frequently experience an imbalance between supply and demand for our common stock. The market price of our common stock has been highly volatile and is likely to continue to be volatile. Factors affecting our common stock price include:
|
|
• |
|
fluctuations in our operating results; |
|
|
• |
|
announcements of technological innovations or new commercial products by us, our collaborators or our competitors; |
|
|
• |
|
published reports by securities analysts; |
|
|
• |
|
the progress of our and our collaborators' clinical trials, including our and our collaborators' ability to produce clinical supplies of our product candidates on a timely basis and in sufficient quantities to meet our clinical trial requirements; |
|
|
• |
|
governmental regulation and changes in medical and pharmaceutical product reimbursement policies; |
|
|
• |
|
developments in patent or other intellectual property rights; |
|
|
• |
|
publicity concerning the discovery and development activities by our licensees; |
|
|
• |
|
public concern as to the safety and efficacy of drugs that we and our competitors develop; |
|
|
• |
|
our ability to meet market expectations with respect to FDA approval or the timing for FDA approval for our product candidates; and. |
|
|
• |
|
general market conditions. |
Anti-takeover provisions in our Certificate of Incorporation, Bylaws, stockholder rights plan and under Delaware law may discourage or prevent a change of control.
Provisions of our Certificate of Incorporation and Bylaws and Section 203 of the Delaware General Corporation Law could delay or prevent a change of control of us. For example, our Board of Directors, without further stockholder approval, may issue preferred stock that could delay or prevent a change of control as well as reduce the voting power of the holders of common stock, even to the extent of losing control to others. In addition, our Board of Directors has adopted a stockholder rights plan, commonly known as a "poison pill," that may delay or prevent a change of control.
Substantial future sales of our common stock by us or by our existing stockholders could cause our stock price to fall.
Additional equity financings or other share issuances by us could adversely affect the market price of our common stock. From time to time we may issue our previously authorized and unissued securities, including shares of our common stock or securities convertible into or exchangeable for our common stock, resulting in the dilution of the ownership interests of our existing stockholders. We have an effective shelf registration statement from which additional shares of our common stock and other securities can be issued at any time. We may also issue additional shares of our common stock or securities convertible into or exchangeable for our common stock in connection with future strategic alliances or acquisitions, future private placements of our securities for capital raising purposes or for other business purposes. In addition, existing shareholders could sell a large number of our shares into the public market. Future issuances or sales of our common stock, or the perception that such issuances or sales could occur, could cause a decline in the price of our common stock.
Royalty revenues received from Amgen on sales of cinacalcet HCl may not be sufficient to cover the interest and principal payments on our Class A Notes and Class B Notes; we would have to either voluntarily make such payments out of available cash resources or risk forfeiture of certain royalty rights under the Amgen agreement.
Our outstanding Class A Notes and Class B Notes are non-recourse to us and are secured by our royalty and milestone payment rights under our agreement with Amgen. Until the Class A Notes and Class B Notes are repaid, all payments from Amgen will go to the payment of interest and principal on the notes If the revenues received from
30
Amgen are insufficient to cover the interest and other payments due under the notes, we would have to forfeit our rights to future royalties and other rights under the Amgen agreement, unless we make the payments due out of our available cash resources. If we make the payments, our cash resources would be significantly reduced and we may not have sufficient cash resources to fund our programs and operations. The principal amount of the Class B Notes will increase through the issuance of additional notes in lieu of payment of cash interest until the Class A Notes are paid in full.
Our liquidity and future cash flow may not be sufficient to cover interest payments on our 5.75% Convertible Notes due 2014 or to repay the notes at maturity.
Our ability to make interest payments on and to repay at maturity or refinance our 5.75% convertible notes due 2014 or the Convertible Notes, will depend on our ability to maintain sufficient cash and generate future cash flow. Other than in 2007, we have never generated positive annual cash flow from our operating activities, and we may not generate or sustain positive cash flows from operations in the future. Our ability to generate sufficient cash flow will depend on our ability to commercialize our proprietary product candidates in the U.S. and the ability of our partners to commercialize and successfully market our partnered products throughout the world. We cannot assure you that we, or our partners, will be successful in developing, commercializing and marketing our product candidates. Various factors such as general economic, financial, competitive, legislative and regulatory conditions may affect our and our partners' ability to successfully commercialize our product candidates and thereby limit our ability to generate future cash flow to repay our Convertible Notes.
Additionally, the Convertible Notes provide for certain events of default, including payment defaults, breaches of covenants and certain events of bankruptcy, insolvency and reorganization. If any event of default occurs and is continuing, the principal amount of the notes, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, may be declared immediately due and payable. The notes also provide that if a fundamental change occurs to our business, as defined in the note, at any time prior to the maturity of the note, then the holder shall have the right to require us to redeem the notes, or any portion thereof plus accrued interest and liquidated damages. There can be no assurance that, if any of the foregoing events were to occur, we would have the ability repay the principal amount and interest accrued under the notes and/or any additional monies owed in connection with the acceleration of the notes.
Conversion of the Convertible Notes will dilute the ownership interest of our existing stockholders, including holders who had previously converted their notes.
The conversion of some or all of our outstanding Convertible Notes will dilute the ownership interests of existing stockholders. Any sales in the public market of the common stock issuable upon such conversion could adversely affect prevailing market prices of our common stock. In addition, the existence of the notes may encourage short selling by market participants.
Changes in interest rates can affect the fair value of our investment portfolio and the debt we have issued and its interest earnings.
Our interest rate risk exposure results from our investment portfolio and our secured notes. Our primary objectives in managing our investment portfolio are to preserve principal, maintain proper liquidity to meet operating needs and maximize yields. The securities we hold in our investment portfolio are subject to interest rate risk. At any time, sharp changes in interest rates can affect the fair value of the investment portfolio and its interest earnings. Currently, we do not hedge these interest rate exposures. We have established policies and procedures to manage exposure to fluctuations in interest rates. We place our investments with high quality issuers, limit the amount of credit exposure to any one issuer, and do not use derivative financial instruments in our investment portfolio.
The fair value of the Convertible Notes is affected by changes in the interest rates and by changes in the price of our common stock. The fair values of our Class A and Class B Notes are affected by changes in the interest rates and by historical and future rates of royalty revenues from cinacalcet HCl sales. The fair value of our DRI debt is affected by changes in the interest rates and by historical and future rates of royalty revenues from Preotact sales.
If securities or industry analysts do not publish research or reports or publish unfavorable research about our business, the price of our common stock and trading volume could decline.
The trading market for our common stock will depend in part on the research and reports that securities or industry analysts publish about us or our business. If securities or industry analysts do not continue coverage of us the trading price for our common stock would be negatively affected. In the event we obtain securities or industry analyst coverage, if one or more of the analysts who covers us downgrades our common stock, the price of our common stock
31
would likely decline. If one or more of these analysts ceases to cover us or fails to publish regular reports on us, interest in the purchase of our common stock could decrease, which could cause the price of our common stock or trading volume to decline.
|
Unresolved Staff Comments. |
None.
|
Properties. |
During 2007, we consolidated our business operations into one facility in Bedminster, New Jersey. In Bedminster, we lease approximately 33,500 square feet of administrative space. The Bedminster lease will expire in April 2013.
|
Legal Proceedings. |
Information with respect to this item is set forth in Note 16, Legal Proceedings, in "Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements" in Part II of this annual report on Form 10-K, which information is incorporated into this item by reference.
Executive Officers of the Registrant
Listed below is information on our executive officers as of March 4, 2010. Executive officers are elected by the Board of Directors for an initial term, which continues until the first Board meeting following the next annual meeting of stockholders and thereafter are re-elected each year for a one-year term or until their successors have been elected. All executive officers serve at the pleasure of the Board of Directors.
Francois Nader, MD, MBA
President and Chief Executive Officer
Age: 53
Francois Nader has been President and Chief Executive Officer of NPS since March 2008. Dr. Nader joined NPS in June 2006 and served as Executive Vice President and Chief Operating Officer until March 2008. In that capacity, he was responsible for managing the Company's worldwide research and development, commercial operations, manufacturing and regulatory affairs. Before joining NPS, Dr. Nader was a venture partner at Care Capital, LLC from July 2005 to June 2006, during which time he served as Chief Medical Officer of its Clinical Development Capital unit. From 2000 to July 2005, Dr. Nader was with Aventis Pharmaceuticals where he served as Senior Vice President, Integrated Healthcare Markets and Senior Vice President, North America Medical and Regulatory Affairs. He was also Vice President, North America Medical and Regulatory Affairs and Vice President, U.S. Medical Affairs and Global Health Economics at Hoechst Marion Roussel from 1990 to 1999. Dr. Nader also served as Head of Global Commercial Operations at the Pasteur Vaccines division of Rhone-Poulenc from 1985 to 1990. Dr. Nader received a French State Doctorate in Medicine from St. Joseph University and a Physician Executive M.B.A. from the University of Tennessee.
Luke M. Beshar, CPA
Sr. Vice President and Chief Financial Officer
Age: 51
Luke Beshar joined NPS in November 2007. He is a former Chief Financial Officer of various public and private companies and has more than 25 years of general and financial management experience. Most recently, he served as Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer of Cambrex Corporation from December 2002 to November 2007, a global life sciences company, and Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer at Dendrite International from January 2002 to December 2002, a leading provider of services to the life sciences industry. Mr. Beshar began his career with Arthur Andersen & Co. in 1980 and is a Certified Public Accountant. Mr. Beshar obtained his B.S. degree in Accounting and Finance from Michigan State University and is a graduate of The Executive Program at the Darden Graduate School of Business at the University of Virginia.
32
Sandra C. Cottrell, PhD
Vice President, Regulatory Affairs & Drug Safety
Age: 61
Sandra Cottrell, MA, PhD joined NPS in April 2009. Prior to joining NPS, she had served as hemostasis franchise and therapeutic area head in regulatory affairs at Novo Nordisk Inc. Previously she served as vice president at B&H Consulting Services, Inc. and as global vice president of regulatory affairs for INO Therapeutics LLC. Dr. Cottrell has over 25 years experience within Johnson & Johnson's pharmaceutical sector. With over 30 years experience working in the pharmaceutical industry across multiple therapeutic areas, she has an in-depth knowledge of the drug development process. Dr. Cottrell is an adjunct professor at Temple University, as well as being a lecturer for Medicademy in Denmark. She received her Bachelor and Master degrees in Chemistry and Doctorate degree in Pharmaceutics with an emphasis on Regulatory Affairs from Temple University.
Roger J. Garceau, MD, FAAP
Sr. Vice President and Chief Medical Officer
Age: 56
Roger Garceau, MD, joined NPS in December 2008 and brings over 20 years of broad pharmaceutical industry experience to his position. From 2002 to December 2008, Dr. Garceau served in a number of senior leadership positions at Sanofi-aventis and most recently was vice president of the new products group. Previously, Dr. Garceau held various positions, including vice president of clinical operations, interim head of North American medical and regulatory affairs, and head of U.S. medical research, where he lead a team of over 200 professionals and oversaw the design and execution of over 50 sponsored clinical trials in five different therapeutic areas. Prior to his tenure at Sanofi-aventis, Dr. Garceau spent 16 years with Pharmacia Corporation in global development and medical affairs where he successfully contributed to a number of marketing applications. Dr. Garceau is a board-certified pediatrician. He received a bachelor of science in biology from Fairfield University in Fairfield, Connecticut and his doctorate of medicine from the University of Massachusetts Medical School. He is a Fellow of the American Academy of Pediatrics.
Edward H. Stratemeier, JD, MBA
Sr. Vice President and General Counsel
Age: 61
Edward Stratemeier joined NPS in October 2009. He has more than 25 years of experience in pharmaceutical and biotechnology law including relationship management, litigation and alternative dispute resolution. Prior to joining NPS, Mr. Stratemeier served as general counsel and global senior vice president for Aventis Pharmaceuticals North America and was a member of the North American leadership team. In private practice, he counseled pharmaceutical and biotech companies on product life cycle management; patent, regulatory and litigation strategies; and product licensing. Mr. Stratemeier received a J.D. from the University of Missouri at Kansas City.
|
Reserved |
33
PART II
|
Market for Registrant's Common Equity and Related Stockholder Matters |
Market Information
Since May 26, 1994, our common stock has been quoted on the Nasdaq National Market under the symbol "NPSP." In connection with NASDAQ's transition to a national securities exchange in October 2006, our common stock is now quoted on the NASDAQ Global Market under the same symbol. The following table sets forth, for the periods indicated, the high and low closing sales prices for our common stock, as reported on the NASDAQ Global Market.
|
High
|
Low
|
|||||
| 2008 | ||||||
| First Quarter | $ | 4.20 | $ | 3.56 | ||
| Second Quarter | 4.52 | 3.54 | ||||
| Third Quarter | 8.81 | 4.44 | ||||
| Fourth Quarter | 7.38 | 5.22 | ||||
| 2009 | ||||||
| First Quarter | $ | 6.66 | $ | 3.50 | ||
| Second Quarter | 4.83 | 2.95 | ||||
| Third Quarter | 5.05 | 3.89 | ||||
| Fourth Quarter | 3.89 | 2.87 | ||||
Holders
As of March 4, 2010, there were approximately 166 holders of record of our common stock.
Dividends
We have never declared or paid cash dividends on capital stock. We intend to retain any future earnings to finance growth and development and therefore do not anticipate paying cash dividends in the foreseeable future.
34
Stock Performance Graph
The graph below matches the cumulative 5-year total return of holders of NPS Pharmaceuticals, Inc.'s common stock with the cumulative total returns of the NASDAQ Composite index, the RDG MicroCap Biotechnology index, the NASDAQ Pharmaceutical index, and the NASDAQ Biotechnology index. The graph assumes that the value of the investment in the company's common stock, and in each index (including reinvestment of dividends) was $100 on 12/31/2004 and tracks it through 12/31/2009.
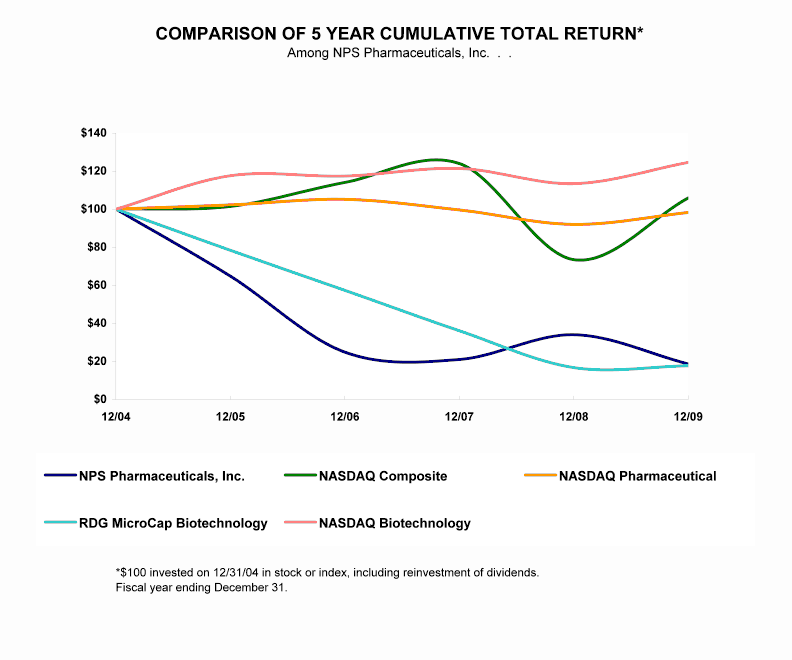
|
|
|
12/04 |
12/05 |
12/06 |
12/07 |
12/08 |
12/09 |
|
NPS Pharmaceuticals, Inc. |
100.00 |
64.77 |
24.78 |
20.95 |
33.97 |
18.60 |
|
|
NASDAQ Composite |
100.00 |
101.41 |
114.05 |
123.94 |
73.43 |
105.89 |
|
|
NASDAQ Pharmaceutical |
100.00 |
102.23 |
105.16 |
99.56 |
91.99 |
98.21 |
|
|
RDG MicroCap Biotechnology |
100.00 |
78.32 |
57.31 |
36.04 |
16.68 |
17.65 |
|
|
NASDAQ Biotechnology |
100.00 |
117.54 |
117.37 |
121.37 |
113.41 |
124.58 |
The stock price performance included in this graph is not necessarily indicative of future stock price performance.
Certain of the information required by this item will be contained in our definitive Proxy Statement with respect to our 2010 Annual Meeting of Stockholders under the caption "Equity Compensation Plan Information," and is incorporated into this section by reference.
35
|
Selected Financial Data. |
The selected consolidated financial data presented below are for each fiscal year in the five-year period ended December 31, 2009. This data is derived from, and qualified by reference to, our audited consolidated financial statements and notes thereto appearing elsewhere in this Form 10-K.
Consolidated Statements of Operations Data:
|
Years Ended December 31,
|
|||||||||||||||
|
2009
|
2008
|
2007
|
2006 (1)
|
2005
|
|||||||||||
| (in thousands, except per share amounts) | |||||||||||||||
| Revenues: | |||||||||||||||
| Royalties | $ | 79,339 | $ | 70,217 | $ | 49,626 | $ | 32,078 | $ | 12,533 | |||||
| Product sales | 66 | 4,544 | 20,310 | 2,662 | - | ||||||||||
| Milestones and license fees |
4,742
|
27,518
|
16,312
|
13,762
|
292
|
||||||||||
| Total revenues |
84,147
|
102,279
|
86,248
|
48,502
|
12,825
|
||||||||||
| Operating expenses: | |||||||||||||||
| Cost of royalties | 500 | 5,831 | 4,659 | 2,980 | 1,144 | ||||||||||
| Cost of goods sold | - | 1,350 | 6,180 | 1,413 | - | ||||||||||
| Cost of license fees | 481 | 5,665 | 1,547 | - | - | ||||||||||
| Research and development | 35,339 | 18,965 | 36,195 | 62,470 | 112,769 | ||||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative | 20,101 | 22,563 | 29,526 | 58,118 | 53,311 | ||||||||||
| Restructuring (credits) charges |
26
|
(272)
|
13,386
|
8,179
|
-
|
||||||||||
| Total operating expenses |
56,447
|
54,102
|
91,493
|
133,160
|
167,224
|
||||||||||
| Other operating (gains) losses: | |||||||||||||||
| Gain on sale of assets held for sale | - | - | (1,826) | - | - | ||||||||||
| Gain on sale of fixed assets | - | (186) | (6,384) | - | - | ||||||||||
| Gain on sale of assets (2) | - | - | (30,000) | - | - | ||||||||||
| Write-down of long-lived assets |
-
|
-
|
-
|
8,297
|
-
|
||||||||||
| Total other operating (gains) losses |
-
|
(186)
|
(38,210)
|
8,297
|
-
|
||||||||||
| Operating income (loss) |
27,700
|
48,363
|
32,965
|
(92,955)
|
(154,399)
|
||||||||||
| Other income (expense): | |||||||||||||||
| Interest income | 1,708 | 4,778 | 9,518 | 9,120 | 8,639 | ||||||||||
| Interest expense | (52,627) | (65,373) | (41,397) | (28,970) | (25,119) | ||||||||||
| Loss on impairment of marketable | |||||||||||||||
| investment securities | (2,206) | (20,898) | (4,162) | - | - | ||||||||||
| Gain on sale of subsidiary | 4,875 | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||
| Other |
944
|
1,225
|
(426)
|
137
|
1,101
|
||||||||||
| Total other expense, net |
(47,306)
|
(80,268)
|
(36,467)
|
(19,713)
|
(15,379)
|
||||||||||
| Loss before income tax expense (benefit) | (19,606) | (31,905) | (3,502) | (112,668) | (169,778) | ||||||||||
| Income tax expense (benefit) |
(1,744)
|
(179)
|
780
|
-
|
(55)
|
||||||||||
| Net loss | $ |
(17,862)
|
$ |
(31,726)
|
$ |
(4,282)
|
$ |
(112,668)
|
$ |
(169,723)
|
|||||
| Basic and diluted net loss per share (3) | $ |
(0.37)
|
$ |
(0.67)
|
$ |
(0.09)
|
$ |
(2.43)
|
$ |
(4.14)
|
|||||
| Basic and diluted weighted | |||||||||||||||
| average shares outstanding (3) | 48,271 | 47,699 | 46,804 | 46,374 | 41,036 | ||||||||||
___________
|
(1) |
We adopted the fair value recognition provisions of the Financial Accounting Standards Board's Accounting Standards Codification ("ASC") 718, "Compensation - Stock Compensation" (ASC 718), using the modified prospective method. The adoption of ASC 718 increased our operating loss, loss before income tax expense (benefit) and net loss for 2006 by $13.4 million and basic and diluted net loss per share by $0.29. |
|
(2) |
Amount relates to the sale of our mGluRs program to AstraZeneca. See note 2 to the consolidated financial statements for information concerning the AstraZeneca agreement. |
|
(3) |
See note 1 to the consolidated financial statements for information concerning the computation of net loss per share. |
36
Consolidated Balance Sheets Data:
|
Years Ended December 31,
|
|||||||||||||||
|
2009
|
2008
|
2007
|
2006
|
2005
|
|||||||||||
| (in thousands) | |||||||||||||||
| Cash, cash equivalents, and current | |||||||||||||||
| marketable investment securities | $ | 74,928 | $ | 97,380 | $ | 133,331 | $ | 146,152 | $ | 258,967 | |||||
| Working capital | 71,280 | 96,607 | 102,921 | 145,222 | 233,907 | ||||||||||
| Total assets | 159,592 | 203,606 | 231,853 | 224,740 | 331,052 | ||||||||||
| Long-term portion of lease financing, | |||||||||||||||
| convertible notes payable, non-recourse | |||||||||||||||
| debt and other long-term liabilities | 308,419 | 336,803 | 341,345 | 373,517 | 390,117 | ||||||||||
| Accumulated deficit | (922,742) | (904,880) | (873,154) | (868,872) | (756,204) | ||||||||||
| Stockholders' deficit | (222,799) | (215,086) | (191,656) | (193,244) | (97,524) | ||||||||||
|
Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations. |
SPECIAL NOTE REGARDING FORWARD LOOKING STATEMENTS
The following discussion should be read in conjunction with our consolidated financial statements and related notes appearing elsewhere in this Annual Report.
This Annual Report on Form 10-K contains forward-looking statements made pursuant to the safe harbor provisions of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. Forward-looking statements represent our management's judgment regarding future events. In many cases, you can identify forward-looking statements by terminology such as "may," "will," "should," "plan," "expect," "anticipate," "estimate," "predict," "intend," "potential" or "continue" or the negative of these terms or other words of similar import, although some forward-looking statements are expressed differently. All statements other than statements of historical fact included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K regarding our financial position, business strategy and plans or objectives for future operations are forward-looking statements. Without limiting the broader description of forward-looking statements above, we specifically note that statements regarding potential drug candidates, their potential therapeutic effect, the possibility of obtaining regulatory approval, our ability or the ability of our collaborators to manufacture and sell any products, market acceptance, or our ability to earn a profit from sales or licenses of any drug candidate are all forward-looking in nature. We cannot guarantee the accuracy of the forward-looking statements, and you should be aware that results and events could differ materially from those described in the forward-looking statements due to a number of factors, including those described in Item 1A of this Annual Report under the heading "Risk Factors" which addresses factors that could cause results or events to differ materially from those set forth in the forward-looking statements. In addition, new risks emerge from time to time and it is not possible for management to predict all such risks or to assess the impact of such risks on our business. Given these risks and uncertainties, you should not place undue reliance on these forward-looking statements. We undertake no obligation to update or revise these forward-looking statements to reflect subsequent events or circumstances.
Overview
We are a biopharmaceutical company focused on the development of new treatment options for patients with rare gastrointestinal and endocrine disorders and serious unmet medical needs. Our lead clinical programs involve two proprietary therapeutic proteins to restore or replace biological function: teduglutide and NPSP558 (recombinant parathyroid hormone (rhPTH (1-84))). Teduglutide is our analog of GLP-2, a peptide involved in the regeneration and repair of the intestinal lining, and is in Phase 3 clinical development for short bowel syndrome (SBS). SBS is a highly disabling condition that results from surgical resection, congenital defect or disease-associated loss of absorption and the subsequent inability to maintain fluid, electrolyte, and nutrient balances on a conventional diet. NPSP558 is our recombinant full-length human parathyroid hormone (rhPTH (1-84)) that is in Phase 3 clinical development for hypoparathyroidism, a rare condition in which the body does not maintain normal calcium levels in the blood due to insufficient levels of parathyroid hormone.
We are currently advancing registration studies for teduglutide and NPSP558. Our study of teduglutide is known as STEPS and our study of NPSP558 is known as REPLACE. We believe that positive results from STEPS and
37
REPLACE would enable us to seek U.S. marketing approval of teduglutide for SBS and NPSP558 for hypoparathyroidism. While SBS and hypoparathyoridism are relatively rare disorders, we believe they represent a substantial commercial opportunity to us due to the significant unmet need and lack of effective therapies, as well as the serious complications involved with and the chronic nature of these diseases.
We have incurred cumulative losses from inception through December 31, 2009 of approximately $922.7 million. We expect to continue to incur significant operating losses over at least the next several years as we continue our current and anticipated development projects. Activities that will increase our future operating losses include current and future clinical trials with teduglutide and NPSP558; activities to obtain FDA approval to market teduglutide and NPSP558 in the U.S.; and manufacturing and commercial-readiness costs for teduglutide and NPSP558 in the U.S.
During the years ended December 31, 2009, 2008 and 2007, we incurred expenses of $15.5 million, $7.0 million and $19.6 million, respectively, in the research and development of teduglutide, including costs associated with the manufacture of clinical supplies of teduglutide. We have incurred expenses of approximately $153.0 million since we assumed development obligations of this product candidate upon our acquisition of Allelix Biopharmaceuticals Inc. in December 1999. During the years ended December 31, 2009, 2008 and 2007 we incurred expenses of $11.3 million, $4.9 million and $5.4 million, respectively, in the research and development of NPSP558, including costs associated with the manufacture of clinical and commercial supplies of NPSP558. We have incurred expenses of approximately $363.3 million since we assumed development obligations for NPSP558 upon our acquisition of Allelix Biopharmaceuticals Inc. in December 1999. Our development administration overhead costs are included in total research and development expense for each period, but are not allocated among our various projects. See "Item 1 - Business - Proprietary Product Candidates." Our ability to complete our research and development efforts and commercialize our product candidates is subject to various risks and uncertainties. See "Item 1A - Risk Factors."
Although we are pursuing NPSP558 only for hypoparathyroidism at this time, previous development efforts focused on developing this compound for osteoporosis using the brand name PREOS®. The expenditures described as part of our results of operations and financial condition through 2007 relate primarily to expense incurred for the osteoporosis indication. After refocusing our proprietary clinical development on rare gastrointestinal and endocrine disorders of serious unmet medical need, we have determined that we would pursue the development for PREOS for osteoporosis only on a partnered basis.
38
Results of Operations
The following table summarizes selected operating statement data for the years ended December 31, 2009, 2008 and 2007 (dollars in thousands):
|
2009
|
2008
|
2007
|
||||||||
| Revenues: | ||||||||||
| Royalties | $ | 79,339 | $ | 70,217 | $ | 49,626 | ||||
| Product sales | 66 | 4,544 | 20,310 | |||||||
| Milestones and license fees |
4,742
|
27,518
|
16,312
|
|||||||
| Total Revenues | $ | 84,147 | $ | 102,279 | $ | 86,248 | ||||
| Operating expenses: | ||||||||||
| Cost of royalties | $ | 500 | $ | 5,831 | $ | 4,659 | ||||
| % of royalties | 1 | % | 8 | % | 9 | % | ||||
| Cost of goods sold | $ | - | $ | 1,350 | $ | 6,180 | ||||
| % of product sales | - | % | 30 | % | 30 | % | ||||
| Cost of license fees | $ | 481 | $ | 5,665 | $ | 1,547 | ||||
| % of milestones and license fees | 10 | % | 21 | % | 9 | % | ||||
| Research and development | $ | 35,339 | $ | 18,965 | $ | 36,195 | ||||
| % of revenues | 42 | % | 19 | % | 42 | % | ||||
| Selling, general and administrative | $ | 20,101 | $ | 22,563 | $ | 29,526 | ||||
| % of revenues | 24 | % | 22 | % | 34 | % | ||||
| Restructuring charges (credits) | $ | 26 | $ | (272) | $ | 13,386 | ||||
| Gain on sale of assets held for sale | $ | - | $ | - | $ | (1,826) | ||||
| Gain on sale of fixed assets | $ | - | $ | (186) | $ | (6,384) | ||||
| Gain on sale of assets | $ | - | $ | - | $ | (30,000) |
Years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008
Revenues. Substantially all our revenues relate to license fees, milestone payments, product sales and royalty payments from our licensees and collaborators. These revenues fluctuate from year to year. Our revenues were $84.1 million in 2009 compared to $102.3 million in 2008. We recognized revenue under our research and license agreements as follows (amounts in thousands):
|
2009
|
2008
|
|||||
| Royalties: | ||||||
| Sensipar and Mimpara (cinacalcet HC1) | $ | 64,566 | $ | 59,644 | ||
| Preotact (parathyroid hormone (PTH 1-84)) | 10,541 | 8,658 | ||||
| Regpara (cinacalcet HCl) | 3,753 | 1,915 | ||||
| Nucynta (tapentadol) | 477 | - | ||||
| Other |
2
|
-
|
||||
| Total royalties | 79,339 | 70,217 | ||||
| Product sales: | ||||||
| Preotact | 35 | 2,055 | ||||
| Teduglutide |
31
|
2,489
|
||||
| Total product sales | 66 | 4,544 | ||||
| Milestones and license fees: | ||||||
| Teduglutide | 2,494 | 25,167 | ||||
| Preotact | 2,203 | 302 | ||||
| Other |
45
|
2,049
|
||||
| Total milestones and license fees | 4,742 | 27,518 | ||||
| Total revenues | $ |
84,147
|
$ |
102,279
|
39
The increase in royalty revenue earned from Amgen is due to the sales growth of Sensipar. Amgen pays Sensipar royalties directly to a wholly owned subsidiary of NPS and the royalties secure non-recourse debt that we issued in August 2007 and December 2004, therefore we do not receive any such royalty payments.
For the year ended December 31, 2009, our revenues related to our agreement with Nycomed for Preotact were comprised of $10.5 million in royalty revenue, $2.2 million in milestone revenue related to Preotact achieving a certain cumulative sales threshold during the year and $35,000 in sales of Preotact clinical material. For the year ended December 31, 2008, our revenues related to our agreement with Nycomed for Preotact were comprised of (i) $8.7 million in royalty revenue; (ii) $2.1 million in sales of finished inventory and clinical material; and (iii) $302,000 in milestone revenue. In April 2006, the European Medicines Agency or EMA approved Preotact for the treatment of postmenopausal women with osteoporosis at high risk for fractures. In July 2007, we sold our right to receive certain future royalty payments from Nycomed's sale of Preotact in Europe to DRI Capital (previously Drug Royalty L.P.3), therefore, all royalty payments due in 2009, 2008 and the second half of 2007 were paid to DRI. Under our agreement with Nycomed for Preotact, Nycomed has assumed the responsibility for manufacturing Preotact in the first quarter of 2008. Therefore, we will no longer recognize product sale revenue in the future under this arrangement.
For the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008, our revenues related to our agreement with Nycomed for teduglutide were $2.5 million and $25.2 million, respectively. In September 2007, we entered into an agreement with Nycomed for the rights to develop and commercialize teduglutide in territories outside of North America for gastrointestinal disorders. In connection with this agreement, we received a $35.0 million up-front license fee in 2007 under the Nycomed agreement and recognized $2.5 million and $25.2 million in revenue during the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008, respectively. Due to our continued involvement under the agreement we recognized revenue over the estimated performance period and at December 31, 2009 we have fully recognized the deferred revenue. We also entered into a one-time agreement to sell bulk teduglutide to Nycomed for $2.5 million during the year ended December 31, 2008.
For the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008, we recognized $3.8 million and $1.9 million, respectively, in royalty revenue under our agreement with Kyowa Kirin (formerly Kirin Pharma) for sales of REGPARA. The Japanese Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency's approved REGPARA in 2007. In February 2010, we sold our rights to receive certain future royalty payments from Kyowa Kirin's sale of REGPARA® subsequent to July 1, 2009 to an affiliate of DRI Capital, Inc. or DRI for $38.4 million. We have $2.1 million recorded as Accounts Receivable from Kyowa Kirin at December 31, 2009, which will be paid to DRI in March 2010.
For the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008, we recognized royalty revenue of $477,000 and $0, respectively, from Ortho-McNeil for sales of Nucynta, which was launched in the second quarter of 2009.
We recognized an up-front license fee from Roche of $2.0 million during the year ended December 31, 2008, for a non-exclusive patent license.
See "Liquidity and Capital Resources" below for further discussion of payments that we may earn in the future under these agreements.
Cost of Royalties. Our cost of royalties consists of royalties owed under our agreement with a third party based on reaching certain cumulative sales milestones of Preotact and our agreement with the Brigham and Women's Hospital on sales of cinacalcet HCl. We recorded cost of royalties of $500,000 and $5.8 million, respectively, during the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008. The decrease in cost of royalties is due to meeting the lifetime contractual obligations under the agreement with the Brigham and Women's Hospital during the fourth quarter of 2008 offset by achieving a threshold for cumulative sales of Preotact which resulted in us owing a $500,000 milestone during the year ended December 31, 2009. Under our agreement with the Brigham and Women's Hospital, our lifetime royalty expense obligation was met when cumulative royalty expense reaches $15.0 million, which we reached during the year ended December 31, 2008.
Cost of Goods Sold. Our cost of goods sold consists of the cost of inventory. We recorded cost of goods sold of $0 and $1.4 million, respectively, during the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008. Nycomed assumed the responsibility for manufacturing Preotact during the first quarter of 2008, which resulted in no subsequent material Preotact product sales or cost of goods sold.
Cost of License Fees. Our cost of license fees relate to fees and royalties owed to a third party upon the licensing of teduglutide to Nycomed in September 2007. We recorded cost of license fees of $481,000 and $5.7 million
40
during the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008, respectively. Under a third party licensing agreement we made cash payments of approximately $6.6 million, and we incurred additional costs of $591,000 related to the Nycomed teduglutide agreement, both in 2007. These costs were amortized over the same period and in the same manner as the related deferred revenue. All of the deferred costs of license fees have been recognized as expense as of December 31, 2009 in conjunction with full recognition of the related deferred revenue.
Research and Development. Our research and development expenses are primarily comprised of the fees paid and costs reimbursed to outside professionals to conduct research, preclinical and clinical trials, and to manufacture drug compounds and related supplies prior to FDA approval, as well as personnel-related costs for our employees who are dedicated to development activities. Historically, our research and development expenses included costs for our employees who performed research activities; however, in 2007 we restructured our business and eliminated substantially all of our internal research functions. For the year ended December 31, 2009, our research and development expenses increased to $35.3 million from $19.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2008. The increase in research and development expenses primarily related to a $14.9 million increase in outside services principally due to higher levels of activity in our ongoing clinical studies and commercial supply chain management and a $1.4 million increase in personnel and related costs primarily due to the advancement of our registration programs for teduglutide and NPSP558.
Selling, General and Administrative. Our selling, general and administrative expenses consist primarily of professional fees, the costs of our management and administrative staff and administrative expenses. Our selling, general and administrative expenses decreased to $20.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2009 from $22.6 million in 2008. The reduction in general and administrative expenses primarily related to a $1.8 million decrease in personnel costs (we recognized approximately $3.3 million of expenses during the year ended December 31, 2008, associated with the departure of the former CEO, which included a cash payment and non-cash charges related to the acceleration of previously issued equity awards), and a $600,000 decrease in general outside costs for the year ended December 31, 2009.
Interest Income. Interest income decreased to $1.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2009 from $4.8 million from the comparative period in 2008, primarily due to lower interest rates on our investments and lower average cash, cash equivalent and marketable investment securities balances in 2009 compared with 2008.
Interest Expense. Our interest expense decreased to $52.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2009 from $65.4 million for the comparable period in 2008. Our long-term royalty forecasts for Sensipar and Preotact are used in conjunction with the calculation of interest expense related to our non-recourse debt. The decrease in interest expense is due primarily to a lower effective interest rate related to the Class A Notes resulting from a decrease in the forecast of Sensipar royalties ($13.0 million decrease) and a $35.3 million principal payment in April 2009 ($2.6 million decrease) partially offset by increased interest expense on the Class B notes ($3.0 million increase) due to an increased balance on the notes due to the issuance of paid-in-kind notes for interest accrued.
Loss on Impairment of Marketable Investment Securities. We recorded impairment charges in earnings of $2.2 million and $20.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2009 and 2008, respectively, related to other-than-temporary declines in fair value of our ARS.
Gain on Sale of Subsidiary. We recorded a gain of $4.9 million related to the sale of a majority interest in our subsidiary, NPS Allelix Corp. ("Allelix") in 2009. We received $5.6 million in connection with the transaction and may receive an additional Cnd. $4.8 million depending on the outcome of certain administrative proceedings in Canada related to the former subsidiary (see note 17 to the consolidated financial statements).
Income Taxes. We reported an income tax benefit of $1.7 million and $179,000 in 2009 and 2008, respectively. The income tax benefit in 2009 primarily relates to the recognition of tax credits from the Canadian province of Quebec for research and development activities for which the statute of limitations expired and the federal alternative minimum taxable loss carryback claim pursuant to a tax law which passed in November 2009. The income tax benefit in 2008 relates to the recognition of tax credits from the Canadian province of Quebec for research and development activities which were claimed during the year.
As of December 31, 2009, we had a United States federal and New Jersey state income tax net operating loss carryforward of approximately $600.7 million and $527.7 million, respectively, federal and New Jersey capital loss carryforward of approximately $197.7 million and a United States federal research credit carryforward of approximately $17.9 million. Our ability to utilize the United States operating loss and credit carryforwards against future taxable
41
income may be subject to annual limitations in future periods pursuant to the "change in ownership rules" under Section 382 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986.
Years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007
Revenues. Our revenues were $102.3 million in 2008 compared to $86.2 million in 2007. We recognized revenue under our research and license agreements as follows (in thousands):
|
2008
|
2007
|
|||||
| Royalties: | ||||||
| Sensipar and Mimpara (cinacalcet HC1) | $ | 59,644 | $ | 46,390 | ||
| Preotact (parathyroid hormone (PTH 1-84)) | 8,658 | 3,236 | ||||
| Regpara (cinacalcet HCl) |
1,915
|
-
|
||||
| Total royalties | 70,217 | 49,626 | ||||
| Product sales: | ||||||
| Preotact | 2,055 | 20,310 | ||||
| Teduglutide |
2,489
|
-
|
||||
| Total product sales | 4,544 | 20,310 | ||||
| Milestones and license fees: | ||||||
| Teduglutide | 25,167 | 7,338 | ||||
| Preotact | 302 | 6,528 | ||||
| Regpara | - | 2,000 | ||||
| Other |
2,049
|
446
|
||||
| Total milestones and license fees | 27,518 | 16,312 | ||||
| Total revenues | $ |
102,279
|
$ |
86,248
|
The increase in royalty revenue earned from Amgen is due to sales growth of Sensipar. Amgen pays Sensipar royalties directly to a wholly owned subsidiary of NPS and the royalties secure non-recourse debt that we issued in August 2007 and December 2004.
For the year ended December 31, 2008, our revenues related to our agreement with Nycomed for Preotact were comprised of (i) $8.7 million in royalty revenue; (ii) $2.1 million in sales of finished inventory and clinical material; and (iii) $302,000 in milestone revenue. For the year ended December 31, 2007, our revenues related to our agreement with Nycomed for Preotact were comprised of (i) $20.3 million in sales of bulk product and finished inventory; (ii) $6.5 million in milestone revenue; and (iii) $3.2 million in royalty revenue. In April 2006, the European Medicines Agency or EMA approved Preotact for the treatment of postmenopausal women with osteoporosis at high risk for fractures. In July 2007, we sold our right to receive certain future royalty payments from Nycomed's sale of Preotact in Europe to DRI Capital (previously Drug Royalty L.P.3).
For the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007, our revenues related to our agreement with Nycomed for teduglutide were $25.2 million and $7.3 million, respectively. In September 2007, we entered into an agreement with Nycomed for the rights to develop and commercialize teduglutide in territories outside of North America for gastrointestinal disorders. In connection with this agreement, we received a $35.0 million up-front license fee in 2007 under the Nycomed agreement and recognized $25.2 million and $7.3 million in revenue during the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007, respectively. Due to our continued involvement under the agreement we recognized revenue over the estimated performance period. We also entered into a one-time agreement to sell bulk teduglutide to Nycomed for $2.5 million during the year ended December 31, 2008.
For the year ended December 31, 2008, we recognized $1.9 million in royalty revenue under our agreement with Kyowa Kirin for sales of REGPARA. During the year ended December 31, 2007 we recognized milestone revenue of $2.0 million from Kyowa Kirin. The Japanese Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency's approval of REGPARA in 2007 triggered the milestone payment.
We recognized an up-front license fee from Roche of $2.0 million during the year ended December 31, 2008, for a non-exclusive patent license.
42
Cost of Royalties. We recorded cost of royalties of $5.8 million and $4.7 million, respectively, during the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007. The increase in cost of royalties is due to increased sales of cinacalcet HCl by Amgen. Under our agreement with the Brigham and Women's Hospital, our lifetime royalty obligation was fulfilled when cumulative royalty expense reaches $15.0 million, which we reached during the year ended December 31, 2008.
Cost of Goods Sold. We recorded cost of goods sold of $1.4 million and $6.2 million, respectively, during the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007. The decrease in cost of goods sold is due to decreased sales to Nycomed offset partially by the utilization of zero-costed inventory layers in 2007. Nycomed assumed the responsibility for manufacturing Preotact during the first quarter of 2008, which resulted in no subsequent Preotact product sales or cost of goods sold.
Cost of License Fees. We recorded cost of license fees of $5.7 million and $1.5 million during the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007 respectively. Under a third-party licensing agreement we made cash payments of $6.6 million, and we incurred additional costs of $591,000 related to the Nycomed teduglutide agreement in 2007. These costs are being amortized over the same period and in the same manner as the related deferred revenue.
Research and Development. Our research and development expenses are primarily comprised of personnel-related costs for our employees who are dedicated to development activities, and from the fees paid and costs reimbursed to outside professionals to conduct research, preclinical and clinical trials, and to manufacture drug compounds and related supplies prior to FDA approval. Historically, our research and development expenses included costs for our employees who performed research activities; however, our 2007 restructuring initiatives eliminated substantially all of our internal research functions. During 2007, we restructured our business to focus our clinical development on rare gastrointestinal and endocrine disorders of serious unmet medical need. For the year ended December 31, 2008 our research and development expenses decreased to $19.0 million from $36.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2007. The decrease was primarily related to (i) a $10.1 million decrease in third-party costs, consisting primarily of outside services and consulting fees, investigator grants, site management and monitoring services related to the completion of a Phase 3 study for teduglutide in short bowel syndrome during 2007 and the corresponding decline in costs associated with that study, as well as the discontinuation of certain research and development activities due to the restructuring; (ii) a $5.6 million decrease in personnel-related costs primarily due to the 2007 and 2006 restructurings, and (iii) a $1.4 million decline in depreciation expense that related to research and development.
Selling, General and Administrative. Our selling, general and administrative expenses consist primarily of the costs of our management and administrative staff, business insurance, property taxes, professional fees, legal fees and product planning activities. Our selling, general and administrative expenses decreased to $22.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2008 from $29.5 million in 2007. The reduction in selling, general and administrative expenses was primarily due to (i) a $1.6 million decrease in personnel-related costs primarily due to our 2007 and 2006 restructurings; (ii) a $4.0 million net decrease in legal fees, which includes a $2.7 million insurance reimbursements from our insurance carrier related to the consolidated shareholders' securities class action lawsuit; and (iii) $1.8 million decrease in administrative costs, including information technology, insurance, taxes and utilities.
Restructuring Charges. Our restructuring charges relate to our initiatives to restructure operations as announced in March 2007 and June 2006. In connection with our restructuring initiatives, we reduced our worldwide workforce, including employees and contractors; eliminated all commercial sales and related field-based activities; terminated certain collaboration agreements; and closed and sold facilities located outside of New Jersey. The reductions in workforce involved all functional disciplines within the company. Restructuring credits or charges for the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007 were a credit of $272,000 and a charge of $13.4 million, respectively. The credit during the year ended December 31, 2008 relates primarily to the reversal of previously accrued severance for certain employees who had previously been expected to be terminated and had earned their severance and had no further service obligations, but who we later retained. These costs were partially offset by employee termination benefits. Restructuring charges during the year ended December 31, 2007 were primarily comprised of employee termination benefits.
Gain on Sale of Assets Held for Sale. Our gain on sale of assets held for sale during the year ended December 31, 2008 and 2007 was $0 and $1.8 million, respectively. The gain recorded during the year ended December 31, 2007 relates to the sale of our laboratory and administrative office building, including equipment, located in Mississauga, Ontario, Canada in June 2007.
Gain on Sale of Fixed Assets. We reported a gain on sale of fixed assets for the year ended December 31, 2008 and 2007 of $186,000 and $6.4 million, respectively. The gain in 2007 was primarily due to the sale of our laboratory
43
and administrative office building, including equipment, located in Salt Lake City, Utah in July 2007, and the sale of our leasehold improvements and equipment at a laboratory facility in Toronto, Canada in August 2007.
Gain on Sale of Assets. Our gain on sale of assets during the year ended 2007 was $30.0 million. This gain was related the sale of our interests in our metabotropic glutamate receptors or mGluRs, program to AstraZeneca, or AZ, which we sold in connection with our 2007 restructuring initiatives.
Interest Income. Interest income decreased to $4.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2008 from the comparative period in 2007, primarily due to lower interest rates on our investments and lower average cash, cash equivalent and marketable investment securities balances in 2008 compared with 2007.
Interest Expense. Our interest expense increased to $65.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2008 from $41.4 million for the comparable period in 2007. Our long-term royalty forecasts for Sensipar and Preotact are used in conjunction with the calculation of interest expense related to our non-recourse debt. The increase in interest expense is due primarily to an $18.2 million increase in interest expense on debt agreements entered into in 2007, which included (i) the Class B Notes ($11.5 million increase), (ii) the 5.75% Convertible Notes ($1.8 million increase) and (iii) DRI Capital's purchase of rights to our Preotact royalties which we account for as debt, ($4.9 million). The increase was also attributable to a $14.0 million increase in interest expense, under the effective interest method, on the Class A Notes due to an increased forecast of sales of Sensipar which increased our redemption premium. The increase in interest expense was partially offset by (i) a reduction in interest expense from our repayment of substantially all of our 3% convertible notes during the fourth quarter of 2007 ($5.5 million decrease); (ii) a reduction in interest expense on the Class A notes due to a $24.5 million principal payment in March 2008 ($1.9 million decrease); and (iii) a reduction in interest expense on the lease financing obligation, which related to the Salt Lake City building that we sold in 2007 ($808,000 decrease).
Loss on Impairment of Marketable Investment Securities. We recorded impairment charges in earnings of $20.9 million and $4.2 million for the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007, respectively, related to other-than-temporary declines in fair value of our ARS.
Other Income (Expense). Other income increased to $1.2 million in the year ended December 31, 2008 from an expense of $426,000 in 2007 primarily from recording a gain of $1.3 million on the extinguishment of our 3% convertible notes which occurred during 2007 partially offset by a $970,000 loss on the extinguishment of lease financing obligations related to the Salt Lake City building in 2007.
Income Taxes. We reported an income tax benefit of $179,000 in 2008 and income tax expense of $780,000 in 2007 related to the United States Federal alternative minimum tax.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
The following table summarizes selected financial data (amounts in the thousands):
|
December 31, 2009
|
December 31, 2008
|
|||||
| Cash, cash equivalents, | ||||||
| and current marketable investment securities | $ | 74,928 | $ | 97,380 | ||
| Total assets | 159,592 | 203,606 | ||||
| Current debt | 48,514 | 35,498 | ||||
| Non-current debt | 290,194 | 318,291 | ||||
| Stockholders' deficit | $ | (222,799) | $ | (215,086) |
Currently, we are not a self-sustaining business and certain economic, operational and strategic factors may require us to secure additional funds. If we are unable to obtain sufficient funding at any time in the future, we may not be able to develop or commercialize our products, take advantage of business opportunities or respond to competitive pressures. Our current and anticipated operations require substantial capital. We expect that our existing capital resources including interest earned thereon and the proceeds from the monetization of our royalties on REGPARA (see below and note 1 to the consolidated financial statements), will be sufficient to fund our current and planned operations through at least January 1, 2011. However, our actual needs will depend on numerous factors, including the progress and scope of our internally funded development and commercialization activities; our ability to comply with the terms
44
of our research funding agreements; our ability to maintain existing collaborations; our decision to seek additional collaborators; the success of our collaborators in developing and marketing products under their respective collaborations with us; our success in producing clinical and commercial supplies of our product candidates on a timely basis sufficient to meet the needs of our clinical trials and commercial launch; the costs we incur in obtaining and enforcing patent and other proprietary rights or gaining the freedom to operate under the patents of others; and our success in acquiring and integrating complementary products, technologies or businesses. Our clinical trials may be modified or terminated for several reasons including the risk that our product candidates will demonstrate safety concerns; the risk that regulatory authorities may not approve our product candidates for further development or may require additional or expanded clinical trials to be performed; and the risk that our manufacturers may not be able to supply sufficient quantities of our drug candidates to support our clinical trials or commercial launch, which could lead to a disruption or cessation of the clinical trials or commercial activities. We may also be required to conduct unanticipated preclinical or clinical trials to obtain regulatory approval of our product candidates, teduglutide and NPSP558. If any of the events that pose these risks comes to fruition, our actual capital needs may substantially exceed our anticipated capital needs and we may have to substantially modify or terminate current and planned clinical trials or postpone conducting future clinical trials. As a result, our business may be materially harmed, our stock price may be adversely affected, and our ability to raise additional capital may be impaired.
We will need to raise additional funds to support our long-term research, product development, and commercialization programs. We regularly consider various fund raising alternatives, including, for example, partnering of existing programs, monetizing of potential revenue streams, debt or equity financing and merger and acquisition alternatives. We may also seek additional funding through strategic alliances, collaborations, or license agreements and other financing mechanisms. There can be no assurance that additional financing will be available on acceptable terms, if at all. If adequate funds are not available, we may be required to delay, reduce the scope of, or eliminate one or more of our research and development programs, or to obtain funds through arrangements with licensees or others that may require us to relinquish rights to certain of our technologies or product candidates that we may otherwise seek to develop or commercialize on our own.
We require cash to fund our operating expenses, to make capital expenditures, acquisitions and investments and to service our debt. We have financed operations since inception primarily through payments received under collaborative research and license agreements, the private and public issuance and sale of equity securities, and the issuance and sale of secured debt, convertible debt and lease financing. Through December 31, 2009, we have recognized $433.8 million of cumulative revenues from payments for research support, license fees, product sales, milestone and royalty payments, $567.6 million from the sale of equity securities for cash and $555.2 million from the sale of secured debt and convertible debt for cash.
Our principal sources of liquidity are cash, cash equivalents, and marketable investment securities, which totaled $74.9 million at December 31, 2009. The primary objectives for our marketable investment security portfolio are liquidity and safety of principal. Investments are intended to achieve the highest rate of return to us, consistent with these two objectives. Our investment policy limits investments to certain types of instruments issued by institutions with investment grade credit ratings and places restrictions on maturities and concentration by type and issuer.
Our investment portfolio includes investments in certain ARS. ARS are variable interest rate securities tied to short-term interest rates with nominal long-term maturities. ARS have interest rate resets through a modified Dutch auction, at predetermined short-term intervals, usually every 7, 28, 35, or 49 days. With the liquidity issues experienced in global credit and capital markets, our ARS portfolio continued to experience multiple unsuccessful auctions as the amount of securities submitted for sale has exceeded the amount of purchase orders.
In October 2008, we entered into a settlement agreement to sell certain of our ARS back to our investment advisor no later than June 2010 at par of $1.8 million. During November 2009, one of these ARS was called and we received par value of $350,000 during the year ended December 31, 2009. The par and fair values of the remaining ARS subject to this settlement agreement are $1.4 million and $1.2 million at December 31, 2009, respectively.
In February 2010, we sold all our remaining ARS, except those subject to the settlement, to a third party and therefore, we have classified all ARS as current assets as of December 31, 2009. These ARS, which had a cost basis of $4.6 million at December 31, 2009, were sold for $8.2 million in total.
On February 26, 2010, we sold our royalty rights from sales of REGPARA® (cinacalcet HCl) by Kyowa Kirin to DRI for $38.4 million. Royalties will revert to us once DRI receives cumulative royalties of $96 million or 2.5 times the amount paid to us. Under the agreement, DRI is entitled to receive royalty payments related to net sales of
45
REGPARA occurring on or after July 1, 2009, including the $2.1 million receivable from Kyowa Kirin we have recorded at December 31, 2009, which will be paid to DRI in March 2010.
On August 5, 2009, we entered into an equity line of credit arrangement (the "Agreement") with Azimuth Opportunity Ltd. ("Azimuth"), which provides that, upon the terms and subject to the conditions set forth therein, Azimuth is committed to purchase up to $40,000,000 of our common stock, or the number of shares which is one share less than twenty percent (20%) of the issued and outstanding shares of our common stock as of August 5, 2009 (subject to automatic reduction in certain circumstances), at varying price discounts of up to 5% as defined, over the 18-month term of the Purchase Agreement. We are not obligated to utilize this facility but if we elect to make a draw under this facility, the timing, dollar amount, and floor price per share are at the sole discretion of NPS, subject to certain limits as to the price per share and the draw down amounts. Azimuth is permitted to terminate this agreement under certain circumstances. On September 29, 2009, Azimuth purchased 842,511 shares of our common stock under the Agreement at an aggregate purchase price of $3.5 million.
The following table summarizes our cash flow activity for the years ended December 31, 2009, 2008 and 2007 (amounts in thousands):
|
2009
|
2008
|
2007
|
|||||||
| Net cash (used in) provided by operating activities | $ | (1,427) | $ | (1,655) | $ | 27,602 | |||
| Net cash provided by (used in) investing activities | 5,242 | (3,437) | 62,632 | ||||||
| Net cash used in financing activities | $ | (36,414) | $ | (36,768) | $ | (35,484) |
Net cash used in operating activities was $1.4 million and $1.6 million in 2009 and 2008, respectively, compared to cash provided by operating activities of $27.6 million in 2007. Net cash used in operating activities were approximately the same for the year ended December 31, 2009 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2008. The swing to net cash used in operating activities in 2008 compared to the cash provided by operating activities in 2007 resulted primarily from $35.0 million received related to the agreement in 2007 with Nycomed for teduglutide and $30.0 million received on the sale of assets to AstraZeneca in 2007, offset by a reduction in spending as a result of the restructuring activities undertaken during 2007. The majority of our royalty revenue is pledged to service the principal and interest on our secured notes and is not available to fund operations.
Net cash provided by investing activities was $5.2 million in 2009 and $62.6 million in 2007 compared to cash used in investing activities of $3.4 million in 2008. Net cash provided by investing activities during 2009 was primarily the result of selling our majority interest in our subsidiary Allelix. Net cash used in investing activities during 2008 was primarily the result of investing excess cash not currently required to fund operations. Net cash provided by investing activities during 2007 was primarily the result of selling marketable investment securities to fund current operations. Additionally, during 2007, we received proceeds from the sales of our assets held for sale and our fixed assets of $4.4 million and $24.7 million, respectively. Additionally, capital expenditures for 2009, 2008 and 2007 were $248,000, $128,000 and $160,000, respectively.
Net cash used in financing activities was $36.4 million in 2009 compared to $36.8 million in 2008 and $35.5 million in 2007. Cash used in financing activities in 2009 primarily relates to principal payments of $35.3 on our Class A Notes and a $4.8 million increase in our restricted cash balances related to our Class A Notes. Cash used in financing activities in 2008 primarily relates to principal payments of $24.5 and $598,000 on our Class A Notes and 3% convertible notes, respectively and a $12.5 million increase in our restricted cash balances related to our Class A Notes. Cash used in financing activities in 2007 primarily related to the repurchase and retirement of substantially all of our 3% convertible notes for $189.3 million, principal payments of $19.3 million on our Class A Notes, the purchase of our Salt Lake City administrative and office building and related retirement of our lease financing obligations for $20.0 million in May 2007, the payment of $4.7 million in debt issuance costs, and the $2.6 million increase in our restricted cash balances related to our Class A Notes. Cash used in financing activities was partially offset by cash received from the issuance of $100.0 million Class B notes, the $50.0 million issuance in 5.75% convertible notes, and the $50.0 million sale of Preotact royalties to DRI. Additionally, we received cash from the sale of common stock to Azimuth of $3.5 million during the year ended December 31, 2009 and the exercise of employee stock options and proceeds from the sale of stock by us pursuant to the employee stock purchase plan. Employee stock option exercises and proceeds from the sale of stock by us pursuant to the employee stock purchase plan provided approximately $314,000, $790,000, and $448,000, respectively, of cash during 2009, 2008 and 2007. Proceeds from the exercise of employee stock options vary from period to period based upon, among other factors, fluctuations in the market price of our common stock relative to the exercise price of such options and the availability of stock under the employee stock purchase plan.
46
We could receive future milestone payments from all our agreements of up to $221.8 million in the aggregate if each of our current licensees accomplishes the specified research and/or development milestones provided in the respective agreements. In addition, all of the agreements require the licensees to make royalty payments to us if they sell products covered by the terms of our license agreements. However, we do not control the subject matter, timing or resources applied by our licensees to their development programs. Thus, potential receipt of milestone and royalty payments from these licensees is largely beyond our control. Further, each of these agreements may be terminated before its scheduled expiration date by the respective licensee either for any reason or under certain conditions.
We have entered into certain research and license agreements that require us to make research support payments to academic or research institutions when the research is performed. Additional payments may be required upon the accomplishment of research milestones by the institutions or as license fees or royalties to maintain the licenses. As of December 31, 2009, we have a total commitment of up to $178,000 for future research support and milestone payments. Further, depending on the commercial success of certain of our products, we may be required to pay license fees or royalties. For example, we are required to make royalty payments to certain licensors on teduglutide net sales and cinacalcet HCl royalty revenues. We may enter into additional sponsored research and license agreements in the future.
We have entered into long-term agreements with certain manufacturers and suppliers that require us to make contractual payment to these organizations. We expect to enter into additional collaborative research, contract research, manufacturing, and supplier agreements in the future, which may require up-front payments and long-term commitments of cash.
The following represents our contractual obligations as of December 31, 2009 (in millions):
| Less than | More than | ||||||||||||||
|
Contractual Obligations
|
Total
|
1 year
|
2-3 years
|
4-5 years
|
5 years
|
||||||||||
| Operating leases | $ | 2.3 | $ | 0.4 | $ | 1.6 | $ | 0.3 | $ | - | |||||
| Purchase commitments (1) | 48.2 | 39.8 | 8.3 | 0.1 | - | ||||||||||
| Convertible notes payable | 50.0 | - | - | 50.0 | - | ||||||||||
| Interest on convertible notes payable | 12.5 | 2.2 | 5.7 | 4.6 | - | ||||||||||
| Non-recourse debt (2) | 288.7 | 48.5 | 190.6 | 26.8 | 22.8 | ||||||||||
| Interest on non-recourse debt (2) | 142.6 | 26.6 | 96.4 | 15.1 | 4.5 | ||||||||||
| Royalty payment obligation | 9.6 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 4.6 |
___________
|
(1) |
Purchase obligations primarily represent commitments for services ($26.4 million), manufacturing agreements ($19.2 million) and other research and purchase commitments ($2.6 million). Commitments for services primarily represent agreements with external Contract Research Organizations (CROs), under which we will continue to incur expenses relating to clinical trials of teduglutide, NPSP558 and other clinical candidates. These agreements are cancellable on notice of up to six months. |
|
(2) |
Amounts shown as contractual commitments under our non-recourse debt represent our estimate of expected principal repayment based on anticipated cinacalcet HCl and Preotact royalty income. Amounts shown in interest on non-recourse debt include our expected premium redemption payment and estimated interest payments based on cinacalcet HCl and Preotact royalty income levels. |
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
Our discussion and analysis of our consolidated financial condition and results of operations are based upon our consolidated financial statements, which have been prepared in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles. The preparation of these financial statements requires us to make estimates and judgments that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses, and related disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities. On an ongoing basis, we evaluate our estimates, including those related to revenue and research and development costs. We base our estimates on historical experience and on various other assumptions that are believed to be reasonable under the circumstances, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about carrying values of assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other sources. Actual results may differ from these estimates under different assumptions or conditions.
47
We believe the following critical accounting policies affect the significant judgments and estimates used in the preparation of our consolidated financial statements:
- revenue recognition;
- accrual of research and development expenses;
- share based payments;
- valuation of marketable investment securities;
- accrued redemption premium and effective interest computation and;
- valuation of long-lived and intangible assets and goodwill.
Revenue Recognition.
We earn our revenue from product sales, license fees, milestone payments, research and development support payments and royalty payments. As described below, significant management judgment and estimates must be made and used in connection with the revenue recognized in any accounting period. Material differences may result in the amount and timing of our revenue for any period if our management made different judgments or utilized different estimates.We recognize revenue from product sales when persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists, title to product and associated risk of loss has passed to the customer, the price is fixed or determinable, collection from the customer is reasonably assured and we have no further performance obligations. All revenues from product sales are recorded net of the applicable provision for returns in the same period the related sales are recorded. We recognize revenue from milestone payments as agreed upon events representing the achievement of substantive steps in the development process are achieved and where the amount of the milestone payment approximates the fair value of achieving the milestone. We defer and recognize revenue from up-front nonrefundable license fees on a straight-line basis over the period we have continuing involvement in the research and development project, unless another pattern is apparent. Royalties from licensees are based on third-party sales of licensed products and are recorded in accordance with the contract terms when third-party results are reliably measurable and collectability is reasonably assured.
We analyze our arrangements entered into to determine whether the elements can be separated and accounted for individually or as a single unit of accounting. Allocation of revenue to individual elements which qualify for separate accounting is based on the estimated fair value of the respective elements.
Accrual of Research and Development Expenses. Research and development costs are expensed as incurred and include salaries and benefits; costs paid to third-party contractors to perform research, conduct clinical trials, develop and manufacture drug materials and delivery devices; and associated overhead expenses and facilities costs. Clinical trial costs are a significant component of research and development expenses and include costs associated with third-party contractors. Invoicing from third-party contractors for services performed can lag several months. We accrue the costs of services rendered in connection with third-party contractor activities based on our estimate of management fees, site management and monitoring costs and data management costs. Differences between actual clinical trial costs from estimated clinical trial costs have not been material and are adjusted for in the period in which they become known.
Share-Based Payments. We grant options to purchase our common stock to our employees and directors under our stock option plans. For options awards with market conditions we use the Monte Carlo simulation to value the awards. We estimate the fair value of stock option awards which vest based on passage of time, on the date of grant using a Black-Scholes pricing model (Black-Scholes model). The determination of the fair value of share-based payment awards on the date of grant using the Black- Scholes model is affected by our stock price as well as assumptions regarding a number of complex and subjective variables. These variables include, but are not limited to, our expected stock price volatility over the expected term of the awards, actual and projected employee stock option exercise behaviors, risk-free interest rate and expected dividends. If factors change and we employ different assumptions in future periods, the compensation expense that we record may differ significantly from what we have recorded in the current period.
Estimates of share-based compensation expenses are significant to our financial statements, but these expenses are based on option valuation models and will never result in the payment of cash by us.
48
There are significant differences among valuation models, and there is a possibility that we will adopt different valuation models in the future. This may result in a lack of consistency in future periods and materially affect the fair value estimate of share-based payments. It may also result in a lack of comparability with other companies that use different models, methods and assumptions.
For purposes of estimating the fair value of stock options granted during 2009 using the Black-Scholes model, we have made an estimate regarding our stock price volatility. We consider the historical volatility and the implied volatility of market-traded options in our stock for the expected volatility assumption input to the Black-Scholes model. The risk-free interest rate is based on the yield curve of U.S. Treasury strip securities for a period consistent with the expected term of the option in effect at the time of grant. The dividend yield assumption is based on our history and expectation of dividend payouts. The expected term is estimated considering historical option information.
Valuation of Marketable Investment Securities. We classify our marketable investment securities as available for sale or trading securities. Available for sale securities are recorded at fair value. Unrealized holding gains and losses, net of the related tax effect, are excluded from earnings and are reported as a separate component of stockholders' deficit until realized. A decline in the market value below cost that is deemed other than temporary is charged to results of operations, resulting in the establishment of a new cost basis for the security. Trading securities are also recorded at fair value, however, holding gains and losses are charged to results of operations when incurred. Our marketable securities consist primarily U.S. dollar denominated corporate or government debt securities. Debt securities generally are long-term securities with coupons that may or may not reset periodically against a benchmark interest rate.
We conduct periodic reviews to identify and evaluate each investment that has an unrealized loss. An unrealized loss exists when the current fair value of an individual security is less than its amortized cost basis. Unrealized losses on available-for-sale securities that are determined to be temporary, and not related to credit loss, are recorded, net of tax, in accumulated other comprehensive income.
For available-for-sale debt securities with unrealized losses, management performs an analysis to assess whether we intend to sell or whether it would more likely than not be required to sell the security before the expected recovery of the amortized cost basis. Where we intend to sell a security, or where it may be more likely than not be required to sell the security before the expected recovery of the amortized cost basis, the security's decline in fair value is deemed to be other-than-temporary and the full amount of the unrealized loss is recorded within earnings as an impairment loss.
Regardless of our intent to sell a security, we perform additional analysis on all securities with unrealized losses to evaluate losses associated with the creditworthiness of the security. Credit losses are identified where we do not expect to receive cash flows sufficient to recover the amortized cost basis of a security.
Accrued Redemption Premium and Effective Interest Computation. We accrue for estimated redemption premiums on our Class A Notes as provided for in our December 2004 note agreement. The Class A Notes accrue interest at an annual rate of 8.0%. Additionally, in the event we receive royalty and milestone payments under our agreement with Amgen above certain specified amounts, a redemption premium on principal payments is owed. The redemption premium ranges from 0% to 41.5% of principal payments, depending on the annual net sales of Sensipar by Amgen. We estimate future net sales of Sensipar by Amgen, compare our estimate to specified amounts in the Class A Note agreement to determine estimated redemption premiums over the life of the Class A Notes, and then calculate the effective interest rate on the Class A Notes by including the forecasted redemption premiums. As a result, the effective interest rate is comprised of the stated interest rate of 8.0% on Class A Notes plus the estimated redemption premiums on the Class A Notes. Changes to the future Sensipar net sales forecast may have a material impact on interest expense. Management evaluates its future Sensipar net sales estimates on a quarterly basis and adjusts the effective interest rate and corresponding accrued redemption premium when information indicates that the estimate is materially above or below the prior estimate.
In July 2007, we entered into an agreement with DRI Capital, or DRI, in which we sold to DRI our right to receive future royalty payments arising from sales of Preotact under our licensing agreement with Nycomed. We received an up-front purchase price of $50.0 million in 2007. If and when DRI receives two and a half times the payment we received, the agreement will terminate and the remainder of the royalties, if any, will revert back to us. We have determined that we should classify the initial up-front purchase price as debt and amortize this using the effective interest rate method over the estimated period to recover two and a half times the initial principal advanced. We estimate future net sales of Preotact by Nycomed and then calculate the effective interest rate on the DRI debt. Changes to the future Preotact net sales forecast may have a material impact on interest expense. Management evaluates its
49
future Preotact net sales estimates on a quarterly basis and adjusts the effective interest rate when information indicates that the estimate is materially above or below the prior estimate.
Valuation of Long-lived and Intangible Assets and Goodwill. We assess the impairment of long-lived assets and goodwill whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying value may not be recoverable. Factors we consider important which could trigger an impairment review include the following:
|
|
• |
|
significant underperformance relative to expected historical or projected future operating results; |
|
|
• |
|
significant changes in the manner of our use of the acquired assets or the strategy for our overall business; |
|
|
• |
|
significant negative industry or economic trends; |
|
|
• |
|
significant decline in our stock price for a sustained period; and |
|
|
• |
|
our market capitalization relative to net book value. |
When we determine that the carrying value of long-lived assets may not be recoverable based upon the existence of one or more of the above indicators of impairment, we measure any impairment based on a probability weighted projected discounted cash flow method using a discount rate determined to be commensurate with the risk inherent in our current business model.
Goodwill represents the excess of costs over fair value of net assets of businesses acquired. Goodwill and intangible assets acquired in a purchase business combination and determined to have an indefinite useful life are not amortized, but instead tested for impairment at least annually, or sooner if circumstances indicate that an impairment might have occurred.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
See note 14 to the consolidated financial statements for a full description of recent accounting pronouncements including the respective expected dates of adoption and expected effects on results of operations and financial condition.
|
Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk. |
Interest Rate Risk. Our interest rate risk exposure results from our investment portfolio, our convertible notes, and our secured notes. Our primary objectives in managing our investment portfolio are to preserve principal, maintain proper liquidity to meet operating needs and maximize yields. The securities we hold in our investment portfolio are subject to interest rate risk. At any time, sharp changes in interest rates can affect the fair value of the investment portfolio and its interest earnings. For certain securities, such as ARS, there are limits on the interest rate these securities can pay contractually. Increases in interest rates in excess of these contractual limits could cause the value of our investments to decline. After a review of our marketable investment securities, we believe that in the event of a hypothetical ten percent increase in interest rates, the resulting decrease in fair value of our marketable investment securities would be insignificant to the consolidated financial statements. Currently, we do not hedge these interest rate exposures. We have established policies and procedures to manage exposure to fluctuations in interest rates. We place our investments with high quality issuers and limit the amount of credit exposure to any one issuer and do not use derivative financial instruments in our investment portfolio. We invest in highly liquid, investment-grade securities and money market funds of various issues, types and maturities. These securities are classified as available for sale and, consequently, are recorded on the balance sheet at fair value with unrealized gains or losses reported as accumulated other comprehensive income as a separate component in stockholders' deficit unless a loss is deemed other than temporary, in which case the loss is recognized in earnings. Our 5.75% Convertible Notes due 2014, our 8.0% Class A Notes due 2017, and our 15.5% Class B Notes due 2017, each have a fixed interest rate. As of December 31, 2009, our Convertible Notes, Class A Notes, and Class B Notes had $50.0 million, $94.7 million and $144.0 million, respectively, in aggregate principal amount outstanding. The fair value of the Convertible Notes is affected by changes in the interest rates and by changes in the price of our common stock. The fair value of the Class A Notes and Class B Notes are affected by changes in the interest rates and by historical rates of royalty revenues from cinacalcet HCl sales.
Foreign Currency Risk. We have significant clinical and commercial manufacturing agreements which are denominated in Euros and Canadian Dollars. As a result, our financial results could be affected by factors such as a change in the foreign currency exchange rate between the U.S. dollar and the Canadian dollar or Euro, or by weak economic conditions in Canada or Europe. When the U.S. dollar strengthens against the Canadian dollar or Euros, the cost of expenses in Canada or Europe decreases. When the U.S. dollar weakens against the Canadian dollar or Euro, the cost of expenses in Canada or Europe increases. The monetary assets and liabilities in our foreign subsidiary which are
50
impacted by the foreign currency fluctuations are cash, accounts payable, and certain accrued liabilities. A hypothetical ten percent increase or decrease in the exchange rate between the U.S. dollar and the Canadian dollar or Euro from the December 31, 2009 rate would cause the fair value of such monetary assets and liabilities in our foreign subsidiary to change by an insignificant amount. We are not currently engaged in any foreign currency hedging activities.
51
|
Financial Statements and Supplementary Data. |
NPS PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Table of Contents
|
|
|
Page |
|
|
53 |
|
|
|
55 |
|
|
|
56 |
|
|
Consolidated Statements of Stockholders' Deficit and Comprehensive Loss |
|
57 |
|
|
59 |
|
|
|
60 |
|
52
The Board of Directors and Stockholders
NPS Pharmaceuticals, Inc.:
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of NPS Pharmaceuticals, Inc. and subsidiaries as of December 31, 2009 and 2008, and the related consolidated statements of operations, stockholders' deficit and comprehensive loss, and cash flows for each of the years in the three-year period ended December 31, 2009. These consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of the Company's management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these consolidated financial statements based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of NPS Pharmaceuticals, Inc. and subsidiaries as of December 31, 2009 and 2008, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the years in the three-year period ended December 31, 2009, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
As discussed in Note 4 to the consolidated financial statements, the Company changed its method of accounting for fair value due to the adoption of a new accounting standard issued by the Financial Accounting Standards Board, as of January 1, 2008.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), NPS Pharmaceuticals, Inc.'s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2009, based on criteria established in Internal Control-Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO), and our report dated March 11, 2010, expressed an unqualified opinion on the effectiveness of the Company's internal control over financial reporting.
/s/ KPMG LLP
Princeton, New Jersey
March 11, 2010
53
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
The Board of Directors and Stockholders
NPS Pharmaceuticals, Inc.:
We have audited NPS Pharmaceuticals, Inc.'s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2009, based on criteria established in Internal Control-Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). NPS Pharmaceuticals, Inc.'s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Management's Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting appearing under Item 9A(b). Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company's internal control over financial reporting based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audit also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
A company's internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company's internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company's assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
In our opinion, NPS Pharmaceuticals, Inc. maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2009, based on criteria established in Internal Control-Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission . We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the consolidated balance sheets of NPS Pharmaceuticals, Inc. as of December 31, 2009 and 2008, and the related consolidated statements of operations, stockholders' deficit and comprehensive loss, and cash flows for each of the years in the three-year period ended December 31, 2009, and our report dated March 11, 2010 expressed an unqualified opinion on these consolidated financial statements.
/s/ KPMG LLP
Princeton, New Jersey
March 11, 2010
54
NPS PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES Consolidated Balance Sheets
December 31, 2009 and 2008
(In thousands, except share data)
|
2009
|
2008
|
|||||
| Assets | ||||||
| Current assets: | ||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 18,276 | $ | 50,834 | ||
| Marketable investment securities | 56,652 | 46,546 | ||||
| Restricted cash and cash equivalents | 41,821 | 37,016 | ||||
| Accounts receivable | 23,965 | 25,406 | ||||
| Prepaid expenses | 2,458 | 1,144 | ||||
| Litigation settlement receivable | - | 16,000 | ||||
| Other current assets |
2,080
|
1,550
|
||||
| Total current assets | 145,252 | 178,496 | ||||
| Equipment, net | 399 | 285 | ||||
| Goodwill | 9,429 | 9,429 | ||||
| Marketable investment securities | - | 8,752 | ||||
| Debt issuance costs, net of accumulated amortization | ||||||
| of $7,449 and $5,744, respectively | 3,454 | 5,158 | ||||
| Other assets |
1,058
|
1,486
|
||||
| Total assets | $ |
159,592
|
$ |
203,606
|
||
| Liabilities and Stockholders' Deficit | ||||||
| Current liabilities: | ||||||
| Accounts payable | $ | 1,761 | $ | 830 | ||
| Accrued expenses and other current liabilities | 3,791 | 4,241 | ||||
| Accrued research and development expenses | 7,569 | 3,754 | ||||
| Accrued interest expense | 12,337 | 19,072 | ||||
| Litigation settlement payable | - | 16,000 | ||||
| Deferred revenue | - | 2,494 | ||||
| Current portion of non-recourse debt and capital lease obligation |
48,514
|
35,498
|
||||
| Total current liabilities | 73,972 | 81,889 | ||||
| Non-recourse debt, less current portion | 240,194 | 268,277 | ||||
| Convertible notes payable and capital lease, less current portion | 50,000 | 50,014 | ||||
| Accrued interest expense, less current portion | 9,363 | 7,627 | ||||
| Other liabilities |
8,862
|
10,885
|
||||
| Total liabilities |
382,391
|
418,692
|
||||
| Commitments and contingencies (notes 7, 8, 9, 15, 16 and 17) | ||||||
| Stockholders' deficit: | ||||||
| Preferred stock, $0.001 par value. Authorized 5,000,000 shares; | ||||||
| issued and outstanding no shares | - | - | ||||
| Common stock, $0.001 par value. Authorized 105,000,000 shares; issued and | ||||||
| outstanding 48,427,880 shares and 47,467,164 shares, respectively | 48 | 47 | ||||
| Additional paid-in capital | 697,002 | 689,947 | ||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) | 2,893 | (200) | ||||
| Accumulated deficit |
(922,742)
|
(904,880)
|
||||
| Total stockholders' deficit |
(222,799)
|
(215,086)
|
||||
| Total liabilities and stockholders' deficit | $ |
159,592
|
$ |
203,606
|
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
55
NPS PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Consolidated Statements of Operations
Years ended December 31, 2009, 2008, and 2007
(In thousands, except per share data)
|
2009
|
2008
|
2007
|
|||||||
| Revenues: | |||||||||
| Royalties | $ | 79,339 | $ | 70,217 | $ | 49,626 | |||
| Product sales | 66 | 4,544 | 20,310 | ||||||
| Milestones and license fees |
4,742
|
27,518
|
16,312
|
||||||
| Total revenues |
84,147
|
102,279
|
86,248
|
||||||
| Operating expenses: | |||||||||
| Cost of royalties | 500 | 5,831 | 4,659 | ||||||
| Cost of goods sold | - | 1,350 | 6,180 | ||||||
| Cost of license fees | 481 | 5,665 | 1,547 | ||||||
| Research and development | 35,339 | 18,965 | 36,195 | ||||||
| Selling, general and administrative | 20,101 | 22,563 | 29,526 | ||||||
| Restructuring charges (credits) |
26
|
(272)
|
13,386
|
||||||
| Total operating expenses |
56,447
|
54,102
|
91,493
|
||||||
| Other operating (gains) losses: | |||||||||
| Gain on sale of assets held for sale | - | - | (1,826) | ||||||
| Gain on sale of fixed assets | - | (186) | (6,384) | ||||||
| Gain on sale of assets |
-
|
-
|
(30,000)
|
||||||
| Total other operating (gains) losses |
-
|
(186)
|
(38,210)
|
||||||
| Operating income |
27,700
|
48,363
|
32,965
|
||||||
| Other income (expense): | |||||||||
| Interest income | 1,708 | 4,778 | 9,518 | ||||||
| Interest expense | (52,627) | (65,373) | (41,397) | ||||||
| Loss on impairment of marketable investment securities | (2,206) | (20,898) | (4,162) | ||||||
| Gain (loss) on sale of marketable investment securities | 1,326 | (52) | 49 | ||||||
| Gain on sale of subsidiary | 4,875 | - | - | ||||||
| Gain on extinguishment of debt | - | - | 1,315 | ||||||
| Loss on extinguishment of lease financing obilgation | - | - | (970) | ||||||
| Foreign currency transaction (loss) gain | (246) | 504 | (815) | ||||||
| Other |
(136)
|
773
|
(5)
|
||||||
| Total other expense, net |
(47,306)
|
(80,268)
|
(36,467)
|
||||||
| Loss before income tax expense (benefit) | (19,606) | (31,905) | (3,502) | ||||||
| Income tax expense (benefit) |
(1,744)
|
(179)
|
780
|
||||||
| Net loss | $ |
(17,862)
|
$ |
(31,726)
|
$ |
(4,282)
|
|||
| Basic and diluted net loss per common and potential common share | $ |
(0.37)
|
$ |
(0.67)
|
$ |
(0.09)
|
|||
| Weighted average common and potential common | |||||||||
| shares outstanding — basic and diluted |
48,271
|
47,699
|
46,804
|
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
56
NPS PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Consolidated Statements of Stockholders' Deficit and Comprehensive Loss
Years ended December 31, 2009, 2008 and 2007
(In thousands, except share data)
| Accumulated | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Additional | other | Total | |||||||||||||||||||
| Preferred | Common | paid-in | Comprehensive | comprehensive | Accumulated | stockholders' | |||||||||||||||
|
stock
|
stock
|
capital
|
loss
|
(loss) income
|
deficit
|
deficit
|
|||||||||||||||
| Balances, December 31, 2006 | $ | - | $ | 46 | $ | 677,474 | $ | (1,892) | $ | (868,872) | $ | (193,244) | |||||||||
| Issuance of 10,386 shares of common | |||||||||||||||||||||
| stock for exercise of stock options | - | - | 52 | - | - | 52 | |||||||||||||||
| Issuance of 247,347 shares of common | |||||||||||||||||||||
| stock for deferred and restricted | |||||||||||||||||||||
| stock units | - | 1 | - | - | - | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| Issuance of 229,733 shares of common | |||||||||||||||||||||
| stock for services rendered | - | - | 942 | - | - | 942 | |||||||||||||||
| Issuance of 123,101 shares of common | |||||||||||||||||||||
| stock for cash under employee | |||||||||||||||||||||
| purchase plan | - | - | 395 | - | - | 395 | |||||||||||||||
| Compensation expense on restricted | |||||||||||||||||||||
| stock, deferred stock units and | |||||||||||||||||||||
| restricted stock units | - | - | 1,509 | - | - | 1,509 | |||||||||||||||
| Compensation expense on stock | |||||||||||||||||||||
| options and stock appreciation rights | |||||||||||||||||||||
| and employee stock purchase plan | - | - | 3,583 | - | - | 3,583 | |||||||||||||||
| Gross unrealized loss on | |||||||||||||||||||||
| marketable securities | $ | (2,118) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Reclassification for realized losses | |||||||||||||||||||||
| on marketable investment securities |
49
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Net unrealized losses on marketable | |||||||||||||||||||||
| investment securities | - | - | - | (2,069) | (2,069) | - | (2,069) | ||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation gain | - | - | - | 1,457 | 1,457 | - | 1,457 | ||||||||||||||
| Net loss | - | - | - |
(4,282)
|
- | (4,282) | (4,282) | ||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive loss |
-
|
-
|
-
|
$ |
(4,894)
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Balances, December 31, 2007 | - | 47 | 683,955 | (2,504) | (873,154) | (191,656) | |||||||||||||||
| Issuance of 173,629 shares of common | |||||||||||||||||||||
| stock for exercise of stock options | - | - | 790 | - | - | 790 | |||||||||||||||
| Issuance of 459,319 shares of common | |||||||||||||||||||||
| stock for services rendered | - | - | 894 | 894 | |||||||||||||||||
| Compensation expense on restricted | |||||||||||||||||||||
| stock | - | - | 119 | - | - | 119 | |||||||||||||||
| Compensation expense on stock | |||||||||||||||||||||
| options and stock appreciation rights | - | - | 4,189 | - | - | 4,189 | |||||||||||||||
| Gross unrealized gain on | |||||||||||||||||||||
| marketable investment securities | $ | 2,813 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Reclassification for realized losses | |||||||||||||||||||||
| on marketable investment securities |
52
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Net unrealized gains on marketable | |||||||||||||||||||||
| investment securities | - | - | - | 2,865 | 2,865 | - | 2,865 | ||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation loss | - | - | - | (561) | (561) | - | (561) | ||||||||||||||
| Net loss | - | - | - |
(31,726)
|
- | (31,726) | (31,726) | ||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive loss |
-
|
-
|
-
|
$ |
(29,422)
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Balances, December 31, 2008 | $ |
-
|
$ |
47
|
$ |
689,947
|
$ |
(200)
|
$ |
(904,880)
|
$ |
(215,086)
|
57
NPS PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES Consolidated Statements of Stockholders' Deficit and Comprehensive Loss-(Continued)
Years ended December 31, 2009, 2008 and 2007
(In thousands, except share data)
| Accumulated | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Additional | other | Total | |||||||||||||||||||
| Preferred | Common | paid-in | Comprehensive | comprehensive | Accumulated | stockholders' | |||||||||||||||
|
stock
|
stock
|
capital
|
loss
|
(loss) income
|
deficit
|
deficit
|
|||||||||||||||
| Balances, December 31, 2008 | $ | - | $ | 47 | $ | 689,947 | $ | (200) | $ | (904,880) | $ | (215,086) | |||||||||
| Issuance of 80,006 shares of common | |||||||||||||||||||||
| stock for exercise of stock options | - | - | 314 | - | - | 314 | |||||||||||||||
| Issuance of 38,199 shares of common | |||||||||||||||||||||
| stock for services rendered | - | - | 118 | - | - | 118 | |||||||||||||||
| Compensation expense on | |||||||||||||||||||||
| share-based awards | - | - | 3,150 | - | - | 3,150 | |||||||||||||||
| Proceeds from sale of 842,511 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| common shares | - | 1 | 3,473 | - | - | 3,474 | |||||||||||||||
| Gross unrealized gain on | |||||||||||||||||||||
| marketable investment securities | $ | 2,746 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Reclassification for realized gains | |||||||||||||||||||||
| on marketable investment securities |
(370)
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Net unrealized gains on marketable | |||||||||||||||||||||
| investment securities | - | - | - | 2,376 | 2,376 | - | 2,376 | ||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation gain | - | - | - | 42 | 42 | - | 42 | ||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation loss | |||||||||||||||||||||
| recognized on sale of subsidiary | 675 | 675 | - | 675 | |||||||||||||||||
| Net loss | - | - | - |
(17,862)
|
- | (17,862) | (17,862) | ||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive loss |
-
|
-
|
-
|
$ |
(14,769)
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Balances, December 31, 2009 | $ |
-
|
$ |
48
|
$ |
697,002
|
$ |
2,893
|
$ |
(922,742)
|
$ |
(222,799)
|
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
58
NPS PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
Years ended December 31, 2009, 2008 and 2007
(In thousands)
|
2009
|
2008
|
2007
|
|||||||
| Cash flows from operating activities: | |||||||||
| Net loss | $ | (17,862) | $ | (31,726) | $ | (4,282) | |||
| Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash | |||||||||
| provided by (used in) operating activities: | |||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 154 | 144 | 1,501 | ||||||
| Accretion of premium (discount) on marketable | |||||||||
| investment securities | 203 | (67) | (41) | ||||||
| Realized gain on disposition of assets held for sale | - | - | (1,826) | ||||||
| Loss (gain) on sale or disposal of fixed assets | - | 10 | (6,384) | ||||||
| Gain on sale of subsidiary | (4,875) | - | - | ||||||
| Non-cash interest expense | 31,215 | 28,357 | 12,911 | ||||||
| Non-cash reduction in interest accrual/change | |||||||||
| in royalty receivable | (10,538) | (8,661) | (2,931) | ||||||
| Realized (gain) loss on marketable investment securities | (1,326) | 52 | (49) | ||||||
| Realized gain on extinguishment of debt and | |||||||||
| lease financing obligation | - | - | (345) | ||||||
| Recognized loss on impairment of marketable | |||||||||
| investment securities | 2,206 | 20,898 | 4,162 | ||||||
| Compensation expense on share based awards | 3,268 | 4,308 | 6,035 | ||||||
| Decrease (increase) in operating assets: | |||||||||
| Accounts receivable | 2,500 | (4,680) | (2,131) | ||||||
| Prepaid expenses, other current assets and other assets | 14,584 | (12,507) | (3,786) | ||||||
| Inventory | - | - | 396 | ||||||
| Increase (decrease) in operating liabilities: | |||||||||
| Accounts payable and accrued expenses | (17,641) | 22,755 | (204) | ||||||
| Deferred revenue | (2,494) | (26,526) | 22,581 | ||||||
| Other liabilities |
(821)
|
5,988
|
1,995
|
||||||
| Net cash (used in) provided by operating activities |
(1,427)
|
(1,655)
|
27,602
|
||||||
| Cash flows from investing activities: | |||||||||
| Sales of marketable investment securities | 4,082 | 33,405 | 373,738 | ||||||
| Maturities of marketable investment securities | 63,395 | 17,345 | 49,996 | ||||||
| Purchases of marketable investment securities | (67,537) | (54,059) | (389,975) | ||||||
| Acquisitions of equipment | (248) | (128) | (160) | ||||||
| Proceeds from sale of subsidiary | 5,550 | - | - | ||||||
| Proceeds from sale of assets held for sale | - | - | 4,371 | ||||||
| Proceeds from sale of fixed assets |
-
|
-
|
24,662
|
||||||
| Net cash provided by (used in) investing activities |
5,242
|
(3,437)
|
62,632
|
||||||
| Cash flows from financing activities: | |||||||||
| Proceeds from issuance of notes payable | - | - | 200,000 | ||||||
| Principal payments on debt, capital lease obligation | |||||||||
| and lease financing obligation | (35,397) | (25,102) | (228,546) | ||||||
| Payment of debt issuance costs | - | - | (4,747) | ||||||
| Proceeds from the sale of common stock and exercise | |||||||||
| of stock options | 3,788 | 790 | 448 | ||||||
| Increase in restricted cash and cash equivalents |
(4,805)
|
(12,456)
|
(2,639)
|
||||||
| Net cash used in financing activities |
(36,414)
|
(36,768)
|
(35,484)
|
||||||
| Effect of exchange rate changes on cash |
41
|
1,012
|
688
|
||||||
| Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | (32,558) | (40,848) | 55,438 | ||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of year |
50,834
|
91,682
|
36,244
|
||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of year | $ |
18,276
|
$ |
50,834
|
$ |
91,682
|
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
59
NPS PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
December 31, 2009, 2008, and 2007
(1) Organization and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
The consolidated financial statements are comprised of the financial statements of NPS Pharmaceuticals, Inc. and its subsidiaries (NPS), collectively referred to as the Company or NPS. NPS is a biopharmaceutical company focused on the development of new treatment options for patients with rare gastrointestinal and endocrine disorders and serious unmet medical needs. The Company's lead clinical programs involve two proprietary therapeutic proteins to restore or replace biological function: teduglutide and NPSP558 (recombinant parathyroid hormone (rhPTH (1-84))). Teduglutide is an analog of GLP-2, a peptide involved in the regeneration and repair of the intestinal lining, and is in Phase 3 clinical development for short bowel syndrome (SBS). SBS is a highly disabling condition that results from surgical resection, congenital defect or disease-associated loss of absorption and the subsequent inability to maintain fluid, electrolyte, and nutrient balances on a conventional diet. NPSP558 is a recombinant full-length human parathyroid hormone (rhPTH (1-84)) that is in Phase 3 clinical development for hypoparathyroidism, a rare condition in which the body does not maintain normal calcium levels in the blood due to insufficient levels of parathyroid hormone.
In addition to the Company's proprietary clinical portfolio, it has a number of royalty-based clinical and commercial stage programs.
On December 7, 2009, the Company sold a majority interest in its subsidiary, NPS Allelix Corp. ("Allelix"), to a group of investors. NPS received $5.6 million in connection with the transactions (see note 17).
In 2007, the Company restructured operations and implemented a new business strategy to focus resources on developing teduglutide and NPSP558 for specialty indications with serious unmet medical needs. In connection with the implementation of its new plan, during 2007 the Company suspended or monetized programs within its product portfolio that were no longer deemed strategic and discontinued investment in discovery and early stage research. Since inception, the Company's principal activities have been performing research and development, raising capital and establishing research and license agreements. All monetary amounts are reported in U.S. dollars unless specified otherwise.
Liquidity
The Company has a history of losses and has been incurring negative cash flow from operations, and has expended, and expects to continue to expend substantial funds to implement its planned product development efforts and commercialization programs. The Company believes its existing capital resources at December 31, 2009, along with the receipt of $38.4 million from the sale of its REGPARA royalty stream (see below in this note 1), should be sufficient to fund our current and planned operations through at least January 1, 2011. If available liquidity is not sufficient to meet the Company's current and planned operations through at least January 1, 2011, management's plans include pursuing additional financing arrangements or reducing expenditures as necessary to meet the Company's cash requirements throughout 2010. However, there is no assurance that, if required, the Company will be able to raise additional capital or reduce spending, including modifying or terminating current clinical trials, to provide the required liquidity. The Company will need to raise additional funds to support its long-term research, product development, and commercialization programs.
New Accounting Pronouncements
In June 2009, the Financial Accounting Standards Board ("FASB") issued the FASB Accounting Standards Codification ("ASC"). The Codification became the single source for all authoritative generally accepted accounting principles, or GAAP, recognized by the FASB and is required to be applied to financial statements issued for interim and annual periods ending after September 15, 2009. The Codification did not change GAAP and did not impact the Company's financial position or results of operations.
60
Subsequent Events
The Company has evaluated all events and transactions since December 31, 2009. The Company did not have any material recognized subsequent events; however, the Company did have the following non-recognized subsequent events as summarized below:
- In February 2010, the Company sold its royalty rights from sales of REGPARA® subsequent to July 1, 2009 to an affiliate of DRI Capital, Inc. or DRI for $38.4 million. Royalties will revert to the Company once DRI receives cumulative royalties of $96 million or 2.5 times the amount paid to the Company. The Company has earned approximately $3.5 million in cumulative royalty revenue on net sales of REGPARA prior to July 1, 2009. The Company has $2.1 million recorded as Accounts Receivable from Kyowa Kirin at December 31, 2009, which will be paid to DRI in March 2010.
- In February 2010, the Company sold its remaining ARS securities, except those subject to a settlement, with the principal value of $23.5 million and a cost basis of $4.6 million for $8.2 million (see note 4).
The following significant accounting policies are followed by the Company in preparing its consolidated financial statements:
(a) Cash Equivalents
The Company considers all highly liquid investments with maturities at the date of purchase of three months or less to be cash equivalents. Cash equivalents at December 31, 2009 and 2008 consist of commercial paper, money market funds, debt securities and other highly liquid instruments of approximately $16.9 million and $49.0 million, respectively. At December 31, 2009 and 2008, the book value of cash equivalents approximates fair value.
Total restricted cash and cash equivalent balances at December 31, 2009 and 2008 were $41.8 million and $37.0 million, respectively. The restricted amount at December 31, 2009 and 2008 consists of amounts for estimated redemption premiums, interest and principal on the Class A Notes (see note 9), and is classified as current.
(b) Marketable Investment Securities
The Company classifies its marketable investment securities as available-for-sale or as trading securities. Available-for-sale and trading securities are recorded at fair value. Unrealized holding gains and losses on available-for-sale securities, net of the related tax effect, are excluded from earnings and are reported as a separate component of stockholders' deficit until realized. A decline in the fair value below cost of available-for-sale securities that is deemed other than temporary is charged to results of operations, resulting in the establishment of a new cost basis for the security. Premiums and discounts are amortized or accreted into the cost basis over the life of the related security as adjustments to the yield using the effective-interest method. Unrealized holding gains and losses on trading securities are included in earnings in each period. Interest income is recognized when earned. Realized gains and losses from the sale of marketable investment securities are based on the specific identification method and are included in results of operations and are determined on the specific-identification basis.
In April 2009, the Company implemented newly issued accounting standards that provide guidance for the recognition, measurement and presentation of other-than-temporary impairments. These newly issued standards amended the other-than-temporary impairment model for debt securities and requires additional disclosures regarding the calculation of credit losses and the factors considered in reaching a conclusion that an investment is not other-than-temporarily impaired, described below. The impairment model for equity securities was not affected. The adoption of this guidance did not have a material impact on the Company's financial position or results of operations.
The Company conducts periodic reviews to identify and evaluate each investment that has an unrealized loss. An unrealized loss exists when the current fair value of an individual security is less than its amortized cost basis. Unrealized losses on available-for-sale securities that are determined to be temporary, and not related to credit loss, are recorded, net of tax, in accumulated other comprehensive income.
For available-for-sale debt securities with unrealized losses, management performs an analysis to assess whether the Company intends to sell or whether it would more likely than not be required to sell the security before the expected recovery of the amortized cost basis. Where the Company intends to sell a security, or where it may be more likely than not be required to sell the security before the expected recovery of the amortized cost basis, the security's decline in fair
61
value is deemed to be other-than-temporary and the full amount of the unrealized loss is recorded within earnings as an impairment loss.
Regardless of the Company's intent to sell a security, the Company performs additional analysis on all securities with unrealized losses to evaluate losses associated with the creditworthiness of the security. Credit losses are identified where the Company does not expect to receive cash flows sufficient to recover the amortized cost basis of a security.
(c) Trade Accounts Receivable
Trade accounts receivable are recorded for research and development support performed, for license fees, milestone payments and royalty income earned, and for product sales, and do not bear interest. The Company determines an allowance for doubtful accounts based on assessed customers' ability to pay, historical write-off experience, and economic trends. Such allowance for doubtful accounts is the Company's best estimate of the amount of probable credit losses in the Company's existing accounts receivable. The Company reviews its allowance for doubtful accounts monthly. The Company did not record any bad debt expense for the years ended December 31, 2009 2008 and 2007. At December 31, 2009 and 2008 the allowance for bad debts was zero.
(d) Equipment
Equipment are stated at cost. Depreciation and amortization of equipment are calculated on the straight-line method over estimated useful lives of 3 to 5 years. Leasehold improvements are amortized using the straight-line method over the shorter of the life of the asset or remainder of the lease term.
(e) Goodwill
Goodwill represents the excess of costs over fair value of assets of businesses acquired. Goodwill and intangible assets acquired in a purchase business combination and determined to have an indefinite useful life are not amortized, but instead tested for impairment at least annually, or sooner if circumstances indicate that impairment might have occurred. As a result of the annual impairment test performed by management at year-end, it was noted that fair value significantly exceeded the carrying value of the reporting unit.
(f) Income Taxes
The Company accounts for income taxes using the asset and liability method. Under the asset and liability method, deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the future tax consequences attributable to differences between the financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax bases, operating loss, and tax credit carryforwards. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized in income in the period that includes the enactment date.
The Company evaluates the need for a valuation allowance based on historical and projected income and whether the realizability of a deferred tax asset is deemed to be more likely than not.(g) Revenue Recognition
The Company analyzes its revenue arrangements to determine whether the elements should be separated and accounted for individually or as a single unit of accounting. Allocation of revenue to individual elements which qualify for separate accounting is based on the estimated fair value of the respective elements.
The Company earns revenue from license fees, milestone payments, royalty payments, research and development support payments and product sales. The Company defers and recognizes revenue from up-front nonrefundable license fees on a straight-line basis over the period wherein the Company has continuing involvement in the research and development project unless another pattern is apparent. The Company recognizes revenue from up-front nonrefundable license fees upon receipt when there is no continuing involvement in the research and development project. The Company recognizes revenue from its milestone payments as agreed-upon events representing the achievement of substantive steps in the development process are achieved and where the amount of the milestone payment approximates the fair value of achieving the milestone. Royalties from licensees are based on third-party sales of licensed products and are recorded in accordance with contract terms when sales results are reliably measurable and collectability is reasonably assured. The Company recognizes revenue from product sales when persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists, title to product and associated risk of loss has passed to the customer, the price is fixed or determinable, collection from the customer is reasonably assured and the Company has no further performance
62
obligations. All revenues from product sales are recorded net of the applicable provision for returns in the same period the related sales are recorded.
(h) Research and development expenses
Research and development expenses, are expensed as incurred and are primarily comprised of the following types of costs incurred in performing research and development activities: clinical trial and related clinical manufacturing costs, contract services, outside costs, salaries and benefits, overhead and occupancy costs.
The Company analyzes how to characterize payments under collaborative agreements based on the relevant facts and circumstances related to each agreement.
(i) Income (Loss) per Common Share
Basic income (loss) per common share is the amount of income (loss) for the period divided by the sum of the weighted average shares of common stock outstanding during the reporting period. Diluted income (loss) per common share is the amount of income (loss) for the period plus interest expense on convertible debt divided by the sum of weighted average shares of common stock outstanding during the reporting period and weighted average share that would have been outstanding assuming the issuance of common shares for all dilutive potential common shares.
(j) Share-Based Compensation
The Company accounts for share-based compensation in accordance with Financial Accounting Standards Board's Accounting Standards Codification ("ASC") 718, "Compensation - Stock Compensation" (ASC 718). Compensation cost includes the portion of the award vesting during the period for (1) all share-based payments granted prior to, but not vested as of December 31, 2005, and (2) all share-based payments granted subsequent to December 31, 2005, based on the grant date fair value estimated using the Black-Scholes option-pricing for awards which vest based on a service condition or the Monte Carlo simulation model for awards with market conditions. The Company recognizes compensation cost for awards on a straight-line basis over the requisite service period for the entire award.
(k) Use of Estimates
Management of the Company has made estimates and assumptions relating to reporting of assets and liabilities and the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities to prepare these consolidated financial statements in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (U.S. GAAP). Actual results could differ from those estimates.
(l) Principles of Consolidation
The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company, all subsidiaries in which it owns a majority voting interest including a variable interest entity in which the Company is the primary beneficiary. The Company eliminates all intercompany accounts and transactions in consolidation.
(m) Accounting for Impairment of Long-Lived Assets
As described in (f), goodwill is tested for impairment at least annually. The Company reviews all other long-lived assets for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable. Recoverability of assets held and used is measured by a comparison of the carrying amount of an asset to future net cash flows (undiscounted) expected to be generated by the asset. If such assets are considered to be impaired, the impairment to be recognized is measured as the amount by which the carrying amount of the assets exceeds the fair value of the assets. Assets held for sale are reported at the lower of the carrying amount, or fair value, less costs to sell.
(n) Foreign Currency Translation
Assets and liabilities of foreign operations with non-U.S. dollar functional currencies are translated into U.S. dollars at the period end exchange rates. Income, expenses and cash flows are translated at the average exchange rates prevailing during the period. Adjustments resulting from translation are reported as a separate component of accumulated other comprehensive loss in stockholders' deficit. Certain transactions are denominated in currencies other than the functional currency. Transaction gains and losses are included in other income (expense) for the period in which the transaction occurs.
63
(o) Comprehensive Income (Loss)
Comprehensive income (loss) consists of net income (loss) and other gains and losses affecting stockholders' equity (deficit) that, under U.S. GAAP, are excluded from net income (loss). For the Company, these consist of net unrealized gains or losses on marketable investment securities and foreign currency translation gains and losses. Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) as of December 31, 2009 and 2008 consists of accumulated net unrealized gains on marketable investment securities of $2.8 million and $470,000, respectively, and foreign currency translation gains of $47,000 and losses of $670,000, respectively.
(p) Concentration of Suppliers
The Company has entered into agreements with contract manufacturers to manufacture clinical and commercial supplies of its product candidates. In some instances, the Company is dependent upon a single supplier. The loss of one of these suppliers could have a material adverse effect upon the Company's operations.
(q) Leases
The Company leases its facility under terms of a lease agreement which provides for rent holidays and escalating payments. Rent under operating leases is recognized on a straight-line basis beginning with lease commencement through the end of the lease term. The Company records deferred lease payments in other long-term liabilities.
(r) Deferred Financing Costs
Costs incurred in issuing the 5.75% convertible notes are amortized using the straight-line method over the shorter of the term of the related instrument or the initial date on which the holders can require repurchase of the notes. The amortization of deferred financing costs is included in Interest expense in the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Costs incurred in connection with the issuance of the Class A and B Notes and under the agreement with DRI, in which the Company sold to DRI its right to receive future royalty payments arising from sales of Preotact under its license agreement with Nycomed, are amortized using the effective-interest method over the same period and in the same manner as the related debt. The amortization of deferred financing costs is included in Interest expense in the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
(s) Deferred License Fees
Cost of license fees are deferred if they are a direct cost of a revenue generating activity and that revenue is being deferred. These deferred costs are amortized over the same period and in the same manner as the related deferred revenue. The amortization of deferred license fees is included in Cost of license fees in the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
(t) Reclassifications
Certain prior year amounts have been reclassified to conform with the current year presentation.
(2) Collaborative and License Agreements
The Company is pursuing product development both on an independent basis and in collaboration with others. Because the Company has granted exclusive development, commercialization, and marketing rights under certain of the below-described collaborative research, development, and license agreements, the success of each program is dependent upon the efforts of the licensees. Each of the respective agreements may be terminated early. If any of the licensees terminates an agreement, such termination may have a material adverse effect on the Company's operations.
Effective January 1, 2009, the Company adopted a newly issued accounting standard for the accounting and disclosure of an entity's collaborative arrangements. This newly issued standard prescribes that certain transactions between collaborators be recorded in the income statement on either a gross or net basis, depending on the characteristics of the collaboration relationship, and provides for enhanced disclosure of collaborative relationships. In accordance with this guidance, the Company evaluated its collaborative agreements for proper income statement classification based on the nature of the underlying activity. If payments to and from the Company's collaborative
64
partners are not within the scope of other authoritative accounting literature, the income statement classification for the payments is based on a reasonable, rational analogy to authoritative accounting literature that is applied in a consistent manner. Amounts due from the Company's collaborative partners related to development activities are generally reflected as a reduction of research and development expense because the performance of contract development services is not central to the Company's operations. For collaborations with commercialized products, if the Company is the principal the Company records revenue and the corresponding operating costs in their respective line items within the Company's consolidated statements of operations, if the Company is not the principal, the Company records the corresponding operating costs as a reduction of revenue. The principal is the party who has certain characteristics including being responsible for delivering the product or service to the customer, having latitude with establishing price, and having the risks and rewards of providing product or service to the customer, including inventory and credit risk. The adoption of this new accounting standard did not affect the Company's financial position or results of operations, however it resulted in enhanced disclosures for the Company's collaboration activities.
Following is a description of significant current collaborations and license agreements:
(a) Amgen Inc.
The Company has a development and license agreement with Amgen to develop and commercialize compounds for the treatment of hyperparathyroidism and indications other than osteoporosis. Amgen also acquired an equity investment in the Company in 1995. Amgen paid the Company a $10.0 million nonrefundable license fee and agreed to pay up to $400,000 per year through 2000 in development support, potential additional development milestone payments totaling $26.0 million, and royalties on any future product sales. Through December 31, 2009, Amgen has paid the Company $19.0 million in milestone payments. Amgen is incurring all costs of developing and commercializing these products. Amgen received exclusive worldwide rights excluding Japan, China, Korea, and Taiwan. The Company recognized royalties from product sales of $64.6 million, $59.6 million and $46.4 million in 2009, 2008 and 2007, respectively, under the contract.
(b) AstraZeneca AB
In 2001, the Company entered into a collaborative effort with AstraZeneca AB (AstraZeneca) to discover, develop, and market new small molecule therapies for the treatment of various disorders of the central nervous system. Under the terms of the agreement, the Company licensed to AstraZeneca its proprietary technology related to protein structures known as metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs). Additionally, the Company granted AstraZeneca exclusive rights to commercialize mGluRs subtype-selective compounds. The Company was required to co-direct the research and pay for an equal share of the preclinical research costs, including capital and a minimum number of personnel, through March 2009 unless terminated earlier by AstraZeneca or the Company upon six months advance written notice. During 2009, 2008 and 2007, the Company incurred $0, $0 and $2.3 million, respectively in research and development expenses under the agreement while all other collaboration costs were borne by AstraZeneca.
On October 9, 2007, the Company entered into an Asset Purchase Agreement with AstraZeneca in which the Company agreed to sell its rights, including intellectual property, in drugs targeting mGluRs to AstraZeneca for $30.0 million. As the net assets sold had no book basis, the Company recorded a gain of $30.0 million. Additionally, the Company and AstraZeneca agreed to terminate the collaborative research and development agreement related to drugs targeting mGluRs that was entered into in 2001. As a result of this termination, the Company is no longer required to provide research FTE support or pay for an equal share of external discovery costs, including patent related costs.
(c) GlaxoSmithKline
In 1993, the Company entered into an agreement with GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) to collaborate on the research, development and commercialization of calcium receptor active compounds to treat osteoporosis and other bone metabolism disorders, excluding hyperparathyroidism. GSK also acquired an equity investment in the Company in 1993. Under the terms of the agreement, the Company may receive milestone payments and royalties from any product sales under the license and a share of the profits from co-promoted products. To date, GSK has paid the Company $12.0 million in milestone payments. A total of $5.0 million in milestone payments may still be earned under the agreement. The Company granted GSK the exclusive license to develop and market worldwide compounds described under the GSK agreement, subject to the Company's right to co-promote in the United States. Once compounds have been selected for development, GSK has agreed to conduct and fund all development of such products, including all human clinical trials and regulatory submissions. In December 2006, the Company entered into an amendment to the agreement with GSK that permits GSK to develop additional compounds. In consideration for this amendment, the Company received a $3.0 million fee and GSK agreed to pay up to an additional $27.0 million upon achievement of
65
certain development and regulatory milestones for these compounds. The Company recognized no revenue in 2009, 2008 or 2007.
In September 2008, the Company was notified by GSK that they have decided to terminate a Phase 2 dose-range finding study with Ronacaleret (SB-751689) in post-menopausal women with osteoporosis (study "CR9108963") earlier than expected due to an observed lack of efficacy based on lumbar spine and hip bone mineral density. Ronacaleret (751689) is a calcilytic compound developed under the November 1993 collaborative research and worldwide exclusive license agreement.
(d) Kyowa Kirin
In 1995, the Company entered into an agreement with the pharmaceutical division of Kyowa Kirin, formerly Kirin Pharma, to develop and commercialize compounds for the treatment of hyperparathyroidism in Japan, China, Korea, and Taiwan. Kyowa Kirin paid the Company a $5.0 million license fee and agreed to pay up to $7.0 million in research support, potential additional milestone payments totaling $13.0 million and royalties on product sales. Kyowa Kirin is incurring all costs of developing and commercializing products. Any payments subsequent to June 2000 represent milestone and royalty payments. To date, Kyowa Kirin has paid the Company $13.0 million in milestone payments. In October 2007, Kyowa Kirin received approval from the Japanese Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency to market cinacalcet HCl in Japan for the treatment of patients with secondary hyperparathyroidism during maintenance dialysis which triggered a milestone payment. The parties participate in a collaborative research program utilizing the Company's parathyroid calcium receptor technology. The Company recognized milestone and license fee revenue of $0, $0 and $2.0 million in 2009, 2008 and 2007, respectively. The Company recognized royalty revenue of $3.8 million in 2009, $1.9 million in 2008 and $0 in 2007 under the agreement.
(e) Nycomed
Teduglutide
In September 2007 the Company entered into a license agreement with Nycomed Danmark ApS (Nycomed) in which the Company granted Nycomed the right to develop and commercialize teduglutide, outside the United States, Canada and Mexico for the treatment of gastrointestinal disorders. Teduglutide, a proprietary analog of GLP-2, is being evaluated as GATTEX® in a Phase 3 registration study known as STEPS for intestinal failure associated with short bowel syndrome and in preclinical development for chemotherapy-induced gastrointestinal mucositis and other pediatric indications. The Company received $35.0 million in up-front fees under the agreement. Nycomed paid the Company $10.0 million upon signing the license agreement and paid the Company an additional $25.0 million in up-front license fees in the fourth quarter of 2007. Under the terms of the agreement, the Company has the potential to earn up to $180.0 million in development and sales milestone payments plus royalties on product sales. Under the terms of the agreement, the Company was responsible to complete the first Phase 3 clinical trial in SBS and Nycomed may elect to share equally the future development costs with NPS to advance and broaden the indications for teduglutide. Additionally, under a previously existing licensing agreement with a third party, the Company paid $6.6 million in 2007 to the licensor and will be required to make future payments based on teduglutide royalties and milestone payments earned. Due to the Company's continuing involvement, the Company recognized revenue associated with the upfront fees over the estimated performance period and for the years ended December 31, 2009, 2008 and 2007, the Company has recognized $2.5 million, $25.2 and $7.3 million in license fee revenue, respectively. The up-front license fee has been fully recognized as revenue as of December 31, 2009.
In December 2008, Nycomed and the Company agreed to share equally in certain external clinical costs incurred by both companies, including those related to a second Phase 3 study of teduglutide in SBS. Reimbursements from Nycomed for their portion of the research and development activities are characterized as a reduction of the Company's research and development costs because performing contract research and development services is not central to the Company's operations.
66
Preotact® (parathyroid hormone 1-84)
In 2004, the Company signed a distribution and license agreement with Nycomed in which the Company granted Nycomed the right to develop and market Preotact® (parathyroid hormone 1-84) in Europe. Nycomed also acquired an equity investment in the Company of $40.0 million through the purchase of 1.33 million shares of the Company's common stock. The agreement requires Nycomed to pay the Company up to 20.8 million Euros in milestone payments upon regulatory approvals and achievement of certain sales targets and pay the Company royalties on product sales. In July 2007, the Company entered into a new license agreement with Nycomed, pursuant to which the Company granted to Nycomed the right to commercialize Preotact in all non-U.S. territories, excluding Japan and Israel; however, Nycomed's licensed rights in Canada and Mexico, revert back to the Company if the Company receives regulatory approval for the compound in the U.S. The 2007 license agreement contains milestone and royalty payment obligations which are similar to those under the 2004 distribution and license agreement. Nycomed is required to pay the Company royalties on sales of Preotact only in the European Union, the Commonwealth of Independent States and Turkey. The 2007 license agreement provides for the assumption by Nycomed of NPS' manufacturing and supply obligations and patent prosecution and maintenance obligations under the 2004 license agreement, which occurred in 2008. As part of the manufacturing and supply transfer, Nycomed paid the Company $11.0 million during 2007, for a significant portion of the Company's existing bulk drug inventory. Cumulatively through December 31, 2009, the Company has received 7.1 million Euros in milestone payments from Nycomed under the 2004 and 2007 agreements, all of which have been recognized as revenue.
Revenues from Nycomed related to the Preotact agreement, for the years ended December 31, are as follows (in thousands):
|
2009
|
2008
|
2007
|
|||||||
| Royalties | $ | 10,541 | $ | 8,658 | $ | 3,236 | |||
| Product sales | 35 | 2,055 | 20,310 | ||||||
| Milestone and license fees |
2,203
|
302
|
6,528
|
||||||
| Total revenues | $ |
12,779
|
$ |
11,015
|
$ |
30,074
|
(f) Ortho-McNeil Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
In December 2006, the Company entered into an agreement with Ortho-McNeil Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (Ortho-McNeil), a wholly owed subsidiary of Johnson & Johnson, pertaining to certain NPS patents. Ortho-McNeil paid the Company an $8.0 million fee and agreed to pay royalties on product sales. NPS will not incur any development or commercialization costs for these products. The Company is responsible for patent prosecution and maintenance of the related patents. The Company may terminate the agreement if Ortho-McNeil fails to make a payment and does not cure that default within 30 days, or if it does not cure any other default within sixty days of notice. Ortho-McNeil may terminate the agreement on 60 days written notice for material breach if NPS has not cured the breach by that time or on 60 days written notice. Termination does not affect any previously-matured payment obligations. In November 2008, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Nucynta (tapentadol) hydrochloride immediate release (IR) tablets for the relief of moderate to severe acute pain. This compound is covered under our agreement and Ortho-McNeil is required to pay us a royalty on the product's sales. Nucynta is a novel investigational, centrally acting oral analgesic, which was launched in the second quarter of 2009. The Company recognized revenue of $477,000 in 2009. The Company did not recognize any revenue in 2008 and 2007.
(g) Hoffman-La Roche Inc. and F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
In December 2008, the Company entered into an agreement with Hoffman-La Roche Inc. and F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. (Roche), under which the Company granted the Roche entities a non-exclusive license (with the right to grant sublicenses) to develop, make, import, use of for sale or sell products covered by patents relating to modulation of NMDA receptor activity using glycine uptake antagonists. In return Roche paid the Company an upfront licensing fee of $2.0 million, and agreed to make additional payments for the achievement of certain regulatory milestones. Further, Roche agreed to pay royalties on sales of licensed products, if any. Either party may terminate the agreement on 30 days written notice due to a material breach by the other, or in the case of the other party's insolvency. Amounts due prior to termination will remain due thereafter. NPS will not incur any development or commercialization costs for these products. The Company recognized revenue of $2.0 million in 2008 as the Company had no continuing involvement in the arrangement. The Company did not recognize any revenue in 2009 and 2007.
67
(h) In-License and Purchase Agreements
The Company has entered into certain sponsored research, license, and purchase agreements that require the Company to make research support and milestone payments to academic or commercial research institutions. During 2009, 2008, and 2007, the Company paid to these institutions $983,000, $551,000, and $239,000, respectively, in sponsored research payments and license fees. As of December 31, 2009, the Company had a total commitment of up to $178,000 for future research support. Depending on the commercial success of certain products, the Company may be required to pay license fees or royalties. Additionally, the Company is required to pay royalties on sales of cinacalcet HCl up to a cumulative maximum of $15.0 million. To date, $15.0 million has been accrued for related royalties payable on sales of cinacalcet HC1, of which, $5.4 million has been paid. Annual payments due are limited to a maximum of $1.0 million. Accruals of $8.6 million and $1.0 million at December 31, 2009 are recorded in other liabilities and accrued expenses and other current liabilities, respectively.
(3) Income (loss) Per Common Share
Basic income (loss) per common share is the amount of income (loss) for the period divided by the weighted average shares of common stock outstanding during the reporting period. Diluted income (loss) per common share is the amount of income (loss) for the period plus interest expense on convertible debt divided by the sum of weighted average shares of common stock outstanding during the reporting period and weighted average shares that would have been outstanding assuming the issuance of common shares for all dilutive potential common shares.
Potential common shares of approximately 14.3 million, 13.4 million and 13.1 million during the years ended December 31, 2009, 2008, and 2007, respectively, that could potentially dilute basic income (loss) per common share in the future were not included in the computation of diluted income (loss) per share because to do so would have been anti-dilutive for the periods presented. Potential dilutive common shares for the years ended December 31, 2009, 2008 and 2007 include approximately 9.2 million, 9.2 million and 7.8 million, common shares related to convertible debentures, respectively, and 5.1 million, 4.2 million, and 5.3 million shares, respectively, related to stock options, restricted stock, and restricted stock units.
(4) Fair Value Measurement
Summary of Assets Recorded at Fair Value
The Company's financial assets and liabilities are measured using inputs from the three levels of the fair value hierarchy. The three levels are as follows:
Level 1- Inputs are unadjusted quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities that the Company has the ability to access at the measurement date.
Level 2- Inputs are other than quoted prices included within Level 1 that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly. Level 2 inputs include quoted prices for similar assets and liabilities in active markets, quoted prices for identical or similar assets or liabilities in markets that are not active, inputs other than quoted prices that are observable for the asset or liability (i.e., interest rates, yield curves, etc.), and inputs that are derived principally from or corroborated by observable market data by correlation or other means (market corroborated inputs).
Level 3- Inputs are unobservable and reflect the Company's assumptions that market participants would use in pricing the asset or liability. The Company develops these inputs based on the best information available.
68
In accordance with the fair value hierarchy described above, the following table shows the fair value of the Company's financial assets (all marketable investment securities) that are required to be measured at fair value as of December 31, 2009 and December 31, 2008 (in thousands):
| December 31, | ||||||||||||
|
Level 1
|
Level 2
|
Level 3
|
2009
|
|||||||||
| Marketable investment securities | $ |
36,070
|
$ |
11,996
|
$ |
8,586
|
$ |
56,652
|
||||
| Total assets at fair value at December 31, 2009 | $ |
36,070
|
$ |
11,996
|
$ |
8,586
|
$ |
56,652
|
| December 31, | ||||||||||||
|
Level 1
|
Level 2
|
Level 3
|
2008
|
|||||||||
| Marketable investment securities | $ | 46,546 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 46,546 | ||||
| Marketable investment securities, non-current |
-
|
-
|
8,752
|
8,752
|
||||||||
| Total assets at fair value at December 31, 2008 | $ |
46,546
|
$ |
-
|
$ |
8,752
|
$ |
55,298
|
The following table summarizes the changes in fair value of the Company's Level 3 assets (in thousands):
| For the Years Ended | ||||||||
|
December 31,
|
||||||||
|
2009
|
2008
|
|||||||
| Beginning balance | $ | 8,752 | $ | 53,286 | ||||
| Total gains (losses) (realized or unrealized) | ||||||||
| Included in earnings | (880) | (20,898) | ||||||
| Included in other comprehensive income | 2,780 | 650 | ||||||
| Transfers in (out) of Level 3 | - | 1,750 | ||||||
| Sales |
(2,066)
|
(26,036)
|
||||||
| Ending balance | $ |
8,586
|
$ |
8,752
|
||||
| Losses included in earnings attributable to change | ||||||||
| in unrealized gains or losses (including other- | ||||||||
| than-temporary impairments) relating to | ||||||||
| assets still held at the reporting date | $ | 1,748 | $ | 20,898 | ||||
The carrying amounts reflected in the consolidated balance sheets for certain short-term financial instruments including cash and cash equivalents, restricted cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable, accounts payable, accrued expenses, and other liabilities approximate fair value due to their short-term nature except that the estimated fair value and carrying value of the Brigham and Women's Hospital royalty liability using a discounted cash flow model is approximately $5.4 million and $9.6 million, respectively, at December 31, 2009.
69
Summary of Liabilities Recorded at Carrying Value
The fair and carrying value of our debt instruments are detailed as follows (in thousands):
|
As of December 31, 2009
|
As of December 31, 2008
|
||||||||||||
| Fair | Carrying | Fair | Carrying | ||||||||||
|
Value
|
Value
|
Value
|
Value
|
||||||||||
| 5.75% Convertible Notes | $ | 47,599 | $ | 50,000 | $ | 50,380 | $ | 50,000 | |||||
| 8.0% Secured Notes - Class A | 100,363 | 94,682 | 140,402 | 130,002 | |||||||||
| 15.0% Secured Notes - Class B |
122,410
|
144,012
|
92,771
|
123,695
|
|||||||||
| Total | $ |
270,372
|
$ |
288,694
|
$ |
283,553
|
$ |
303,697
|
|||||
The fair values of the Company's convertible notes were estimated using the (i) terms of the convertible notes; (ii) rights, preferences, privileges, and restrictions of the underlying security; (iii) time until any restriction(s) are released; (iv) fundamental financial and other characteristics of the Company; (v) trading characteristics of the underlying security (exchange, volume, price, and volatility); and (vi) precedent sale transactions. The fair values of the Company's secured notes were estimated using market observable inputs, including quoted prices and market indices. Within the hierarchy of fair value measurements, these are Level 2 fair values.
(5) Financial Instruments
Financial instruments that potentially subject the Company to concentrations of credit risk are accounts receivable and marketable investment securities. The majority of the Company's accounts receivable are payable by large pharmaceutical companies and collateral is generally not required from these large customers. Substantially all of the Company's revenues for the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008 were from five licensees of the Company. At December 31, 2009 and December 31, 2008, substantially all of the Company's accounts receivable balances were from four licensees. The Company monitors the financial performance and credit worthiness of its large customers so that it can properly assess and respond to changes in their credit profile. The Company's portfolio of marketable investment securities is subject to concentration limits set within the Company's investment policy that help to mitigate its credit exposure.
The Company's investment portfolio includes investments in certain auction-rate securities (ARS). ARS are variable interest rate securities tied to short-term interest rates with nominal long-term maturities. ARS have interest rate resets through a modified Dutch auction, at predetermined short-term intervals, usually every 7, 28, 35, or 49 days. With the liquidity issues experienced in global credit and capital markets, the Company's ARS portfolio continues to experience unsuccessful auctions as the amount of securities submitted for sale has exceeded the amount of purchase orders. Given the unsuccessful auctions, the Company's ARS are illiquid and will be until there is a successful auction for them or the Company can sell them to a third party.
In March 2008, the Company sold certain of its ARS, or the Sold ARS, to one of the Company's investment advisors for $26.0 million. The fair value and the principal value of the Sold ARS as of December 31, 2007 were $24.9 million and $30.1 million, respectively. During the fourth quarter 2007, the Company recognized an other-than-temporary loss of $4.1 million on the Sold ARS in the Statement of Operations. $1.1 million was recorded as an unrealized loss on the Sold ARS in Accumulated Other Comprehensive Loss at December 31, 2007. Excluding the Sold ARS, the Company believed that the decrease in market value on its ARS was temporary in nature due to the underlying assets securing the ARS, the AAA ratings by Standard & Poors as of December 31, 2007 and February 29, 2008, the Company's belief that historical liquidity would return to the global credit and capital markets, and the Company's intent and ability to hold to recovery. None of the ARS are backed by sub-prime mortgages. Accordingly, a $1.3 million unrealized loss was recorded at December 31, 2007 in Accumulated Other Comprehensive Loss section of the Balance Sheet related to the ARS, excluding the Sold ARS.
In October 2008, the Company entered into a settlement agreement to sell certain of its ARS back to its investment advisor no later than June 2010 at par of $1.8 million, and the Company transferred these ARS from the available for sale category to the trading category. During November 2009, one of these ARS was called at par of $350,000 and the Company recognized a gain of $82,000 during the year ended December 31, 2009. The fair values of the ARS are $1.2 million and $1.3 million at December 31, 2009 and 2008, respectively, which has been recorded as current at December 31, 2009 and as long-term at December 31, 2008. The Company has recognized $222,000 and $351,000 as a put option in other current assets at December 31, 2009 and other long-term assets at December 31, 2008,
70
respectively and losses of $129,000 in other income for the year ended December 31, 2009 and a gain of $351,000 in other income for the year ended December 31, 2008. The Company elected the fair value measurement option for its ARS put option. The fair value election was made to minimize the net volatility of earnings in future periods as the change in fair value of the put option will approximate the opposite change in fair value of the related ARS. In estimating the fair value of this put option, the Company has used the fair values which were determined based on valuations performed by Pluris Valuation Advisors LLC. The fair values were determined using proprietary valuation models.
In November 2009, the Company sold certain ARS securities to a third party with the principal value of $4.4 million and cost basis of $567,000 for $1.7 million, excluding the ARS discussed above that were called at par in November 2009 which were subject to the settlement agreement. The Company recognized a gain of $1.1 million during the year ended December 31, 2009 related to the sale of these ARS. The estimated fair value of the Company's remaining ARS holdings was $8.6 million and $8.8 million at December 31, 2009 and December 31, 2008, respectively, which were $16.3 million and $20.9 million, respectively, less than the principal value of $24.9 and $29.7 million, respectively. In estimating the fair value of the Company's ARS, the Company has used the fair values which were determined based on valuations performed by Pluris Valuation Advisors LLC. The fair values were determined with proprietary valuation models using the quality of the underlying securities or assets securing the ARS investments, the fair values of comparable securities, the quality of credit enhancement (if any) applicable to the specific security, estimated time to maturity or unwinding of the arrangement, an analysis of the terms of the indentures and other factors depending on the individual ARS. In February 2010, the Company sold the remaining ARS securities, except those subject to the settlement, with the principal value of $23.5 million and a cost basis of $4.6 million for $8.2 million. The Company has classified all ARS as current assets as of December 31, 2009 and as non-current assets as of December 31, 2008.
The following is a summary of the Company's cash, cash equivalents and marketable investment securities (in thousands):
| Gross | Gross | |||||||||||
| unrealized | unrealized | |||||||||||
| Amortized | holding | holding | Fair | |||||||||
| As of December 31, 2009: |
cost
|
gains
|
losses
|
value
|
||||||||
| Cash and Cash Equivalents | $ |
18,281
|
$ |
-
|
$ |
(5)
|
$ |
18,276
|
||||
| Marketable Investment Securities: | ||||||||||||
| Available for Sale: | ||||||||||||
| Debt securities: | ||||||||||||
| Corporate | $ | 17,346 | $ | 59 | $ | (6) | $ | 17,399 | ||||
| Auction rate securities | 4,632 | 2,780 | - | 7,412 | ||||||||
| Government agency |
30,649
|
31
|
(13)
|
30,667
|
||||||||
| Total marketable investment securites-current | $ |
52,627
|
$ |
2,870
|
$ |
(19)
|
$ |
55,478
|
||||
| Trading: | ||||||||||||
| Debt securities: | ||||||||||||
| Auction rate securities |
1,292
|
-
|
(118)
|
1,174
|
||||||||
| Total marketable investment securites-current | $ |
1,292
|
$ |
-
|
$ |
(118)
|
$ |
1,174
|
71
| Gross | Gross | |||||||||||
| unrealized | unrealized | |||||||||||
| Amortized | holding | holding | Fair | |||||||||
| As of December 31, 2008: |
cost
|
gains
|
losses
|
value
|
||||||||
| Cash and Cash Equivalents | $ |
50,825
|
$ |
9
|
$ |
-
|
$ |
50,834
|
||||
| Marketable Investment Securities: | ||||||||||||
| Available for Sale: | ||||||||||||
| Debt securities: | ||||||||||||
| Corporate | $ | 2,992 | $ | 51 | $ | - | $ | 3,043 | ||||
| Government agency |
43,093
|
412
|
(2)
|
43,503
|
||||||||
| Total marketable investment securites-current | $ |
46,085
|
$ |
463
|
$ |
(2)
|
$ |
46,546
|
||||
| Debt securities: | ||||||||||||
| Auction rate securities |
7,404
|
-
|
-
|
7,404
|
||||||||
| Total marketable investment securites-noncurrent | $ |
7,404
|
$ |
-
|
$ |
-
|
$ |
7,404
|
||||
| Trading: | ||||||||||||
| Debt securities: | ||||||||||||
| Auction rate securities |
1,561
|
-
|
(213)
|
1,348
|
||||||||
| Total marketable investment securites-current | $ |
1,561
|
$ |
-
|
$ |
(213)
|
$ |
1,348
|
Marketable investment securities available for sale in an unrealized loss position as of December 31, 2009 and 2008 are summarized as follows (in thousands):
|
Held for less than 12 months
|
Held for more than 12 months
|
Total
|
||||||||||||||||
| Unrealized | Unrealized | Unrealized | ||||||||||||||||
|
Fair value
|
losses
|
Fair value
|
losses
|
Fair value
|
losses
|
|||||||||||||
| December 31, 2009 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Available for Sale: | ||||||||||||||||||
| Debt securities: | ||||||||||||||||||
| Corporate | $ | 6,603 | $ | 6 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 6,603 | $ | 6 | ||||||
| Government agency |
22,750
|
13
|
-
|
-
|
22,750
|
13
|
||||||||||||
| $ |
29,353
|
$ |
19
|
$ |
-
|
$ |
-
|
$ |
29,353
|
$ |
19
|
|||||||
| December 31, 2008 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Available for Sale: | ||||||||||||||||||
| Debt securities: | ||||||||||||||||||
| Government agency | $ |
2,998
|
$ |
2
|
$ |
-
|
$ |
-
|
$ |
2,998
|
$ |
2
|
||||||
| $ |
2,998
|
$ |
2
|
$ |
-
|
$ |
-
|
$ |
2,998
|
$ |
2
|
|||||||
Summary of Contractual Maturities
Maturities of marketable investment securities are as follows at December 31, 2009 and December 31, 2008 (in thousands):
|
As of December 31, 2009
|
As of December 31, 2008
|
||||||||||||
| Amortized | Amortized | ||||||||||||
|
cost
|
Fair value
|
cost
|
Fair value
|
||||||||||
| Due within one year | $ | 49,169 | $ | 49,240 | $ | 39,482 | $ | 39,820 | |||||
| Due after one year through five years | - | - | 7,951 | 8,074 | |||||||||
| Due after five years through ten years | - | - | - | - | |||||||||
| Due after ten years |
4,632
|
7,412
|
7,404
|
7,404
|
|||||||||
| Total debt securities | $ |
53,801
|
$ |
56,652
|
$ |
54,837
|
$ |
55,298
|
|||||
72
Impairments
Due to the severity of the decline in fair value, as well as the duration of time for which these securities have been in a loss position, the Company concluded that its ARS held during the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008, except those subject to the settlement, have experienced other-than-temporary declines in fair value. Accordingly, the Company has recorded impairment charges of $2.2 million and $20.9 million during the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008, respectively.
Proceeds from Marketable Investment Securities
The proceeds from maturities and sales of marketable investment securities and resulting realized gains and losses, were as follows (in thousands):
| For the Years | |||||||
|
Ended December 31,
|
|||||||
|
2009
|
2008
|
||||||
| Proceeds from sales and maturities | $ | 67,477 | $ | 50,750 | |||
| Realized gains | 1,326 | - | |||||
| Realized losses | - | 52 | |||||
The realized gains and losses for the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008 primarily relate to sale of corporate debt securities.
Equipment is recorded at cost and consists of the following (in thousands):
|
December 31,
|
|||||||||
|
2009
|
2008
|
||||||||
| Equipment | $ | 914 | $ | 646 | |||||
| Less accumulated depreciation |
(515)
|
(361)
|
|||||||
| Total equipment, net | $ |
399
|
$ |
285
|
|||||
In July 2007, the Company entered into a Lease Termination Agreement with the MaRS Discovery District, or MaRS, under which the Company's operating lease for the office and laboratory space in Toronto, Canada was terminated. Pursuant to the Lease Termination Agreement, the Company sold its leasehold tenant improvements to a third party for $2.4 million. In August 2007, the Company auctioned off the remaining Toronto facility equipment for $1.1 million. The Company recognized a gain on sale of fixed assets during the year ended December 31, 2007 of $3.2 million on these transactions.
The termination of the Company's operating lease and sale of its leasehold tenant improvements was part of the Company's restructuring initiatives, which included a plan to close its Mississauga and Toronto facilities and discontinue all operations in Canada.In May 2007, the Company closed an Agreement of Purchase and Sale to repurchase its 93,000 square foot laboratory and office building located in Salt Lake City, Utah, for $20.0 million. Under the terms of the agreement, the Company's 15-year lease obligation was extinguished. The repurchase of the laboratory and office building is considered an early extinguishment of debt. The amount paid to repurchase the laboratory and office building was in excess of the carrying value of the lease financing obligation. Accordingly, the Company recorded a loss of $1.0 million during the year ended December 31, 2007 on such extinguishment.
In July 2007, the Company sold its 93,000 square foot laboratory and office building, including certain laboratory and office equipment and furnishings, located in Salt Lake City, Utah for $21.0 million. As part of the sale, the University of Utah agreed to release the Company from all obligations under a 40 year ground lease for land upon which the building is located. The Company recognized a gain on sale of fixed assets during the year ended December 31, 2007 of $3.3 million on this transaction. The sale of this facility was part of the Company's restructuring initiative which included a plan to close its Salt Lake City facility and to discontinue all Salt Lake City operations.
73
In June 2007, the Company sold its land and 85,795 square foot laboratory and office building, including certain equipment and furnishings, located in Mississauga, Ontario, Canada for $4.4 million. The Company recognized a gain on sale of assets held for sale during the year ended December 31, 2007 of $1.8 million on this transaction.
(7) Leases
The Company has a non-cancelable operating sub-lease for its office space in Bedminster, New Jersey that expires in 2010. In 2009, the Company entered into a new non-cancelable operating lease for its office space in Bedminster, New Jersey that will begin after the existing sub-lease expires and will continue until 2013. The Company also has non-cancelable operating leases for certain equipment that expire between 2010 and 2011. Rent-free periods and other incentives granted under the leases and scheduled rent increases are charged to rent expense on a straight-line basis over the related terms of the lease. Rental expense for operating leases was approximately $405,000, $443,000, and $2.4 million for 2009, 2008, and 2007, respectively. The future lease payments under non-cancelable operating leases as of December 31, 2009 are as follows (in thousands):
| Operating | |||||||
|
leases
|
|||||||
| Year ending December 31: | |||||||
| 2010 | $ | 399 | |||||
| 2011 | 795 | ||||||
| 2012 | 808 | ||||||
| 2013 | 271 | ||||||
| 2014 |
-
|
||||||
| Total minimum lease payments | $ |
2,273
|
(8) Restructuring Charges
In March 2007, the Company announced an initiative to restructure operations and to reduce its work force from 196 employees to approximately 35 employees by the end of 2007 (the 2007 Restructuring Plan). Under the 2007 Restructuring Plan, the Company closed its operations in Toronto, Canada and Salt Lake City, Utah. These steps are part of the Company's strategy to transition to an organization that will rely primarily on outsourcing research, development activities and manufacturing operations, as well as other functions critical to its business.
The charge related to the 2007 Restructuring Plan during the years ended December 31, 2009, 2008 and 2007 were a charge of $26,000, a credit of $272,000 and a charge of $12.9 million, respectively. The charge during the year ended December 31, 2009 related primarily to employee termination benefits. The credit during the year ended December 31, 2008 relates primarily to a reversal of previously accrued severance for employees the Company has retained who had previously been expected to be terminated and had earned their severance and had no further service obligations. These credits were partially offset by employee termination benefits. The charge during the year ended December 31, 2007 was comprised of $8.7 million in severance related cash expenses, $1.0 million for accelerated vesting of options under existing employee severance agreements and retirement plan, $2.7 million for accelerated vesting of restricted stock units under employee retention plans and $485,000 for stock awards under employee severance enhancement agreements. Associated severance payments were substantially paid by February 28, 2008 for severed U.S. employees and are anticipated to be paid by December 31, 2011 for severed Canadian employees. During 2008, $771,000 of the 2007 accrued restructuring charges were satisfied through the issuance of common stock. The cumulative restructuring charges through December 31, 2009 related to the 2007 Restructuring Plan were $12.6 million. Total anticipated restructuring charges as a result of the 2007 Restructuring Plan are estimated to be approximately $12.7 million.
74
A summary of accrued restructuring costs is as follows (in thousands):
| December 31, | December 31, | ||||||||||||||
|
2007
|
Charges
|
Cash
|
Non-Cash
|
2008
|
|||||||||||
| 2007 Restructuring Plan: | |||||||||||||||
| Severance | $ |
2,330
|
$ |
(272)
|
$ |
(1,070)
|
$ |
(771)
|
$ |
217
|
| December 31, | December 31, | ||||||||||||||
|
2008
|
Charges
|
Cash
|
Non-Cash
|
2009
|
|||||||||||
| 2007 Restructuring Plan: | |||||||||||||||
| Severance | $ |
217
|
$ |
26
|
$ |
(132)
|
$ |
-
|
$ |
111
|
(9) Long-term Debt
The following table reflects the carrying value of our long-term debt under various financing arrangements as of December 31, 2009 and 2008 (in thousands):
|
December 31,
|
||||||
|
2009
|
2008
|
|||||
| Convertible notes payable | $ | 50,000 | $ | 50,000 | ||
| Non-recourse debt | 288,694 | 303,697 | ||||
| Capital lease obligation |
14
|
92
|
||||
| Total debt | 338,708 | 353,789 | ||||
| Less current portion |
48,514
|
35,498
|
||||
| Total long-term debt | $ |
290,194
|
$ |
318,291
|
||
(a) Convertible Notes Payable
In August 2007, the Company completed a private placement of $50.0 million in 5.75% Convertible Notes due August 7, 2014 (5.75% Convertible Notes). The Company received net proceeds from the 5.75% Convertible Notes of approximately $49.4 million, after deducting costs associated with the offering. The 5.75% Convertible Notes accrue interest at an annual rate of 5.75% payable quarterly in arrears on the first day of the succeeding calendar quarter commencing January 1, 2008. Accrued interest on the 5.75% Convertible Notes was approximately $0 and $725,000 as of December 31, 2009 and 2008, respectively. The holders may convert all or a portion of the 5.75% Convertible Notes into common stock at any time, subject to certain milestones, on or before August 7, 2014. The 5.75% Convertible Notes are convertible into common stock at a conversion price of $5.44 per share, subject to adjustments in certain events. The 5.75% Convertible Notes are unsecured debt obligations and rank equally in right of payment with all existing and future unsecured senior indebtedness. On or after August 7, 2012, the Company may redeem any or all of the 5.75% Convertible Notes at a redemption price of 100% of their principal amount, plus accrued and unpaid interest to the day preceding the redemption date. The 5.75% Convertible Notes provide for certain events of default, including payment defaults, breaches of covenants and certain events of bankruptcy, insolvency and reorganization. The 5.75 % Convertible Notes also provide that if there shall occur a fundamental change, as defined, at any time prior to the maturity of the Note, then the holder shall have the right, at the Holder's option, to require the Company to redeem the notes, or any portion thereof plus accrued interest and liquidated damages, if any. If a change of control, as defined, occurs and if the holder converts notes in connection with any such transaction, the Company will pay a make whole premium by increasing the conversion rate applicable to the notes. If any event of default occurs and is continuing, the principal amount of the 5.75% Convertible Notes, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, may be declared immediately due and payable. The Company has filed a registration statement with the SEC, which has been declared effective, covering the common stock issuable upon conversion of the 5.75% Convertible Notes. The Company incurred debt issuance costs of approximately $600,000, which have been deferred and which are being amortized over a seven-year period. The effective interest rate on the 5.75% Convertible Notes, including debt issuance costs, is 5.9%.
Pursuant to the Registration Rights Agreement, the Company has filed a shelf registration statement with the SEC, covering resales of the common stock issuable upon conversion of the 5.75% Convertible Notes. The registration statement has been declared effective. The Company agreed to use its reasonable best efforts to keep the registration statement effective until the earlier of (i) the date as of which holders may sell all of the securities covered by the
75
registration statement without restriction pursuant to Rule 144(k) promulgated under the Securities Act of 1933 or (ii) the date on which holders shall have sold all of the securities covered by the registration statement. If the Company fails to comply with these covenants or suspends use of the registration statement for periods of time that exceed what is permitted under the Registration Rights Agreement, the Company is required to pay liquidated damages in an amount equivalent to 1% per annum of (a) the principal amount of the notes outstanding, or (b) the conversion price of each underlying share of common stock that has been issued upon conversion of a note, in each case, until the Company is in compliance with these covenants. The Company believes the likelihood of such an event occurring is remote and, as such, the Company has not recorded a liability as of December 31, 2009.
In July 2003, the Company completed a private placement of $192.0 million in 3.0% Convertible Notes due June 15, 2008 (3% Convertible Notes). The Company received net proceeds from the 3% Convertible Notes of approximately $185.9 million, after deducting costs associated with the offering. The Company incurred debt issuance costs of $6.1 million, which were deferred and were being amortized over a five-year period.
In August 2007, the Company repurchased $20.2 million par value of outstanding 3% Convertible Notes in the open market at a price of $19.5 million plus accrued interest. Additionally, in October 2007, the Company closed a tender offer in which $171.2 million of the 3.0% Convertible Notes were tendered to the Company for $169.1 million plus accrued interest. These 3% Convertible Notes were subsequently retired during the year ended December 31, 2007. The repurchase and subsequent retirement of the 3% Convertible Notes is considered an early extinguishment of debt. The amount paid to repurchase the 3% Convertible Notes was less than the carrying value of the 3% Convertible Notes. Accordingly, the Company recorded a gain of $1.3 million, which is net of the write-off of $823,000 of deferred financing costs, during the year ended December 31, 2007 on such extinguishment. The Company had $598,000 of the 3% Convertible Notes outstanding as of December 31, 2007. In accordance with the terms of the notes, the remaining outstanding balance was paid during the second quarter of 2008.
(b) Non-recourse Debt
Sensipar-secured Non-recourse Debt
In December 2004, the Company completed a private placement of $175.0 million in Class A Notes. The Company received net proceeds from the issuance of the Class A Notes of approximately $169.3 million, after deducting costs associated with the offering. The Class A Notes accrue interest at an annual rate of 8.0% payable quarterly in arrears on March 30, June 30, September 30 and December 30 of each year (Payment Date). The Class A Notes are secured by certain royalty and related rights of the Company under its agreement with Amgen, Inc., for Sensipar® (cinacalcet HC1). Additionally, the only source for interest payments and principal repayment of the Class A Notes is limited to royalty and milestone payments received from Amgen. The Class A Notes are non-recourse to NPS Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Payments of principal will be made on March 30 of each year commencing March 30, 2006, to the extent there is sufficient cash available for such principal payment. As of December 31, 2009 and 2008, the outstanding principal balance on the Class A Notes was $94.7 million and $130.0 million, respectively. In the event the Company receives royalty and milestone payments under its agreement with Amgen above certain specified amounts for a given year, an annual redemption premium on principal repayment will be owed. The redemption premium ranges from 0% to 41.5% of principal payments, depending on the annual net sales of cinacalcet HC1 by Amgen. As of December 31, 2009 and 2008, the Company classified $48.5 million and $35.4 million, respectively, of the Class A Notes as current based on royalty payments accrued during the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008, respectively, plus other available balances in the restricted cash reserve account less estimated redemption premiums. The Company may repurchase, in whole but not in part, the Class A Notes on any Payment Date at a premium ranging from 0% to 41.5% of outstanding principal, depending on the preceding four quarters' sales of cinacalcet HC1 by Amgen. The Company is accruing the estimated redemption premiums over the estimated life of the debt using the effective interest method; full repayment of the Class A Notes is estimated to occur in 2011. The estimated life is based on projections of royalties to be earned from cinacalcet HC1 sales. Accrued interest on the Class A Notes was approximately $17.9 million and $21.9 million as of December 31, 2009 and 2008, respectively, which includes the Company's estimate of the redemption premium. The Company incurred debt issuance costs of $5.7 million, which are also being amortized using the effective interest method. The current effective interest rate on the Class A Notes, including debt issuance costs and estimated redemption premiums, is approximately 15.7%.
In August 2007, the Company completed a private placement of $100.0 million in Secured 15.5% Notes due March 30, 2017 (Class B Notes). The Company received net proceeds from the issuance of the Class B Notes of approximately $97.0 million, after deducting costs associated with the offering. The Class B Notes accrue interest at an annual rate of 15.5% payable quarterly in arrears on March 30, June 30, September 30 and December 30 of each year. The Class B Notes are secured by certain royalty and related rights of the Company under its agreement with Amgen.
76
Additionally, the only source for interest payments and principal repayment of the Class B Notes is limited to royalty and milestone payments received from Amgen and only after the Class A Notes are paid in full. Prior to repayment in full of the Class A Notes, interest on the Class B Notes will be paid in kind through the issuance of notes (the PIK Notes) which will be part of the same class and have the same terms and rights as the Class B Notes, except that interest on the PIK Notes will begin to accrue from the date that such PIK Notes are issued. The aggregate principal amount of the outstanding Class B Notes will continue to increase until the Class A Notes are paid in full. The Class B Notes are non-recourse to NPS Pharmaceuticals, Inc. The Company may repurchase, in whole but not in part, the Class B Notes at a calculated Redemption Price based on the timing of repurchase and the source of proceeds for the repurchase. The Redemption Price varies between 100.0% and 107.75% depending on these variables. The outstanding principal balance on the Class B Notes, including PIK Notes of $44.0 million and $23.7 million, were $144.0 million and $123.7 million, as of December 31, 2009 and 2008, respectively. The Company incurred debt issuance costs of $3.6 million, which are being amortized using the effective interest method. The effective interest rate on the Class B Notes, including debt issuance costs, is approximately 16.0%.
Under the Company's agreements for the Class A Notes and Class B Notes, the Company would potentially be liable for its breaches or defaults, if any.
Preotact-secured Non-recourse Debt
In July 2007, the Company entered into an agreement with DRI Capital, or DRI, formerly Drug Royalty L.P.3, in which the Company sold to DRI its right to receive future royalty payments arising from sales of Preotact under its license agreement with Nycomed. Under the agreement, DRI paid the Company an up-front purchase price of $50.0 million. If and when DRI receives two and a half times the amount paid to the Company, the agreement will terminate and the remainder of the royalties, if any, will revert back to the Company. In connection with the Company's July 2007 agreement with DRI, the Company granted DRI a security interest in its license agreement with Nycomed for Preotact and certain of its patents and other intellectual property underlying that agreement. In the event of a default by NPS under the agreement with DRI, DRI would be entitled to enforce its security interest against NPS and the property described above. The Company has determined that it should classify the initial up-front purchase price as debt which should be amortized using the effective interest method over the estimated life of 9 years. The liability recorded related to the DRI transaction was $50.0 million as of December 31, 2009 and 2008, and accrued interest under the DRI agreement was $3.8 million and $4.1 million as of December 31, 2009 and 2008, respectively. As of December 31, 2009, $18.6 million has been paid to DRI. The repayment of the $50.0 million is secured solely by future royalty payments arising from sales of Preotact by Nycomed. The effective interest rate under the agreement, including issuance costs, is approximately 22.4%.
(c) Lease Financing Obligations
In December 2005, the Company completed a sale-leaseback transaction with BioMed Realty, in which the Company sold its 93,000 square foot laboratory and office building located in Salt Lake City, Utah for $19.0 million and leased back the property under a 15-year lease. Net proceeds from the sale were $19.0 million. Because the lease agreement in the sale-leaseback transaction contained a purchase option by the Company, the Company accounted for the transaction as a financing arrangement where the gain on the sale of $4.3 million was deferred.
In May 2007, the Company closed an Agreement of Purchase and Sale to repurchase from BioMed Realty its 93,000 square foot laboratory and office building for $20.0 million. Under the terms of the agreement, the Company's 15-year lease obligation was extinguished. The repurchase of the laboratory and office building is considered an early extinguishment of debt. The amount paid to repurchase the laboratory and office building was in excess of the carrying value of the lease financing obligation. Accordingly, the Company recorded a loss of $1.0 million during the year ended December 31, 2007 on such extinguishment. See note 6.
77
(d) Contractual maturities of long-term debt
The aggregate contractual maturities of long-term debt, including estimated maturities of the Non-recourse Debt, due subsequent to December 31, 2009 are as follows (in thousands):
| Year ending December 31: | ||||||
| 2010 | $ | 48,514 | ||||
| 2011 | 86,746 | |||||
| 2012 | 103,845 | |||||
| 2013 | 15,777 | |||||
| 2014 | 61,040 | |||||
| Thereafter |
22,786
|
|||||
| Total long-term debt | $ |
338,708
|
(10) Capital Stock
Stockholder Rights Plan
In December 1996, the board of directors approved the adoption of a Stockholder Rights Plan (the Rights Plan). The Rights Plan was subsequently amended on December 31, 2001 to increase the purchase price of a share of Series A Junior Participating Preferred Stock and to extend the expiration date of the Rights Plan. The Rights Plan provides for the distribution of a preferred stock purchase right (Right) as a dividend for each outstanding share of the Company's common stock. This Right entitles stockholders to acquire stock in the Company or in an acquirer of the Company at a discounted price in the event that a person or group acquires 20% or more of the Company's outstanding voting stock or announces a tender or exchange offer that would result in ownership of 20% or more of the Company's stock. Each right entitles the registered holder to purchase from the Company 1/100th of a share of Series A Junior Participating Preferred Stock, par value $0.001 per share at a price of $300 per 1/100th of a preferred share, subject to adjustment. The Rights may only be exercised on the occurrence of certain events related to a hostile takeover of the Company as described above. In any event, the Rights will expire on December 31, 2011. The Rights may be redeemed by the Company at $0.01 per right at any time prior to expiration or the occurrence of an event triggering exercise. At December 31, 2009, the Rights were not exercisable.
Equity Financing
On August 5, 2009, the Company entered into an equity line of credit arrangement (the "Agreement") with Azimuth Opportunity Ltd. ("Azimuth"), which provides that, upon the terms and subject to the conditions set forth therein, Azimuth is committed to purchase up to $40,000,000 of the Company's common stock, or the number of shares which is one share less than twenty percent (20%) of the issued and outstanding shares of the Company's common stock as of August 5, 2009 (subject to automatic reduction in certain circumstances), at varying price discounts of up to 5% as defined, over the 18-month term of the Purchase Agreement. The Company is not obligated to utilize this facility but if it elects to make a draw under this facility, the timing, dollar amount, and floor price per share are at the sole discretion of the Company, subject to certain limits as to the price per share and the draw down amounts. Azimuth is permitted to terminate this agreement under certain circumstances. NPS did not pay a commitment fee or issue any warrants to secure this facility. On September 29, 2009, Azimuth purchased 842,511 shares of the Company's common stock under the Agreement at an aggregate purchase price of $3.5 million.
Convertible Debt
As of December 31, 2009, the Company had outstanding $50 million in aggregate principal amount of its 5.75% Convertible Notes. The holders of the 5.75% Convertible Notes may convert all or a portion of their notes into common stock at any time, subject to certain milestones, on or before August 7, 2014 at a conversion price equal to approximately $5.44 per share, subject to adjustment in certain events. The Company has reserved 9,191,176 share of its common stock for issuance upon conversion of the 5.75% Convertible Notes.
(11) Share-Based Compensation Plans
As of December 31, 2009, the Company has five equity incentive plans: the 1987 Stock Option Plan (the 1987 Plan), the 1994 Equity Incentive Plan (the 1994 Plan), the 1994 Nonemployee Directors' Stock Option Plan (the
78
Directors' Plan), the 1998 Stock Option Plan (the 1998 Plan), and the 2005 Omnibus Incentive Plan (the 2005 Plan). These plans provide that in the event of certain change in control transactions, including a merger or consolidation in which the Company is not the surviving corporation or a reorganization in which more than fifty-percent (50%) of the shares of the Company's common stock entitled to vote are exchanged, all outstanding, unvested equity awards under these plans will vest, and in the case of stock options, will become immediately exercisable.
As of December 31, 2009, there are no shares reserved for future grant under the 1987 Plan, the 1994 Plan and the Directors' Plan. As of December 31, 2009, there are 1,724,131 and 1,369,705 shares reserved for future grant under the 2005 Plan and 1998 Plan, respectively. The Company's 2005 Plan provides for the grant of nonqualified stock options, incentive stock options, stock appreciation rights, restricted stock, restricted stock units, deferred stock units, performance shares, cash-based awards and other stock-based awards. Under the Company's 2005 Plan, the exercise price of stock options, the grant price of stock appreciation rights and the initial value of performance awards, must be equal to at least 100% of the fair market value of the Company's common stock on the date of grant. Stock options generally vest 28% after year one and 2% per month thereafter or 25% after year one and 6.25% every three months thereafter. During 2009, 2008 and 2007, directors of the Company were granted 110,760, 151,038 and 197,357, respectively, in deferred stock units for services that were recorded at fair value. Under the Company's 1998 Plan, the exercise price of options is generally not less than the fair market value of the Company's common stock on the date of grant. The number of shares, terms, and exercise period are determined by the board of directors on a grant-by-grant basis, and the exercise period does not extend beyond ten years from the date of the grant. Stock options generally vest 28% after one year and 2% or 3% per month thereafter.
During the year ended December 31, 2009, the Company's Board of Directors awarded a total of 378,000 options to certain of the Company's executive officers. Vesting of these options is subject to the Company achieving certain performance criteria established at the beginning of each of the two and three year performance periods, beginning January 20, 2009. Vesting percentages are calculated based on the Total Shareholder Return (TSR) of the Company's common stock as compared to the TSR of the NASDAQ Biotechnology Index. The vesting schedule, as seen below, can produce vesting percentages of 0%, 50%, 115% and 125% of the options granted, half of which relate to each performance period. TSR is determined as the change in stock prices from January 20, 2009 to the end of each performance period using a 20 day average of the adjusted closing price.
|
Vesting Schedule
|
||
| Vesting | ||
| Performance of Company | (% of Target | |
| Stock Price Relative to the NASDAQ | Award for | |
|
Biotechnology Index
|
Performance Period)
|
|
| Top Quartile | 125% | |
| Second Quartile | 115% | |
| Third Quartile | 50% | |
| Bottom Quartile | 0% | |
The Company utilized a Monte Carlo simulation to determine the grant date fair value of the awards. Compensation expense is recognized over the performance period of each tranche. For the year ended December 31, 2009, the Company recorded $458,000 of share-based compensation expense related to these options. The assumptions used in this model were as follows for the year ended December 31, 2009.
|
2009
|
||
| Fair value of the Company's common stock | $ 5.71 | |
| Expected volatility | 70.0% | |
| Risk-free interest rate | 1.1% | |
| Dividend yield | 0% |
For the year ended December 31, 2009, the Monte Carlo simulation model also assumed correlations of returns of the stock prices of the Company's common stock and the common stock of a peer group of companies and historical stock price volatilities of the peer group of companies. The valuation model also used terms based on the length of the performance period and compound annual growth rate goals for total stockholder return based on the provisions of the award.
79
The Company also had an Employee Stock Purchase Plan (the Purchase Plan) whereby qualified employees were allowed to purchase limited amounts of the Company's common stock at the lesser of 85% of the market price at the beginning or end of the offering period or purchase period. The Company authorized 685,000 shares for purchase by employees. Employees purchased zero, zero and 123,101 shares under the Purchase Plan in the years ended December 31, 2009, 2008, and 2007, respectively, and 13 shares remain available for future purchase. The Purchase Plan has been discontinued until additional shares are made available.
The Company estimates expected volatility considering implied volatility based on market-traded options on the Company's common stock and historical volatility of the Company's common stock over the expected life of the options. In estimating volatility for the years ended December 31, 2009, 2008 and 2007 the Company weighted implied volatility at zero percent and historical volatility at 100%. The Company recognizes compensation cost for awards on a straight-line basis over the requisite service period for the entire award. Additionally, the Company's policy is to issue new shares of common stock to satisfy stock option exercises or grants of restricted shares or deferred stock units.
The compensation expense related to stock options restricted shares and deferred stock units are recorded in expense categories based on where other compensation cost is recorded for employees receiving the awards.
The following table summarizes the effect of compensation cost arising from share-based payment arrangements on the Company's Statements of Operations for the years ended December 31, 2009, 2008 and 2007 for the Company's stock option plans, the employee stock purchase plan and other share-based awards: (in thousands)
|
Years ended December 31,
|
|||||||||
|
2009
|
2008
|
2007
|
|||||||
| Research and development | $ | 720 | $ | 504 | $ | 1,000 | |||
| Selling, general and administrative | 2,548 | 3,804 | 4,005 | ||||||
| Restructuring charges |
-
|
-
|
1,030
|
||||||
| Total cost of share-based compensation | 3,268 | 4,308 | 6,035 | ||||||
| Amount capitalized in inventory during the year | - | - | - | ||||||
| Amount recognized in income for amount | |||||||||
| previously capitalized in inventory |
-
|
-
|
(18)
|
||||||
| Amounts charged against income, before | |||||||||
| income tax expense (benefit) | $ |
3,268
|
$ |
4,308
|
$ |
6,017
|
|||
Excluding the 378,000 options awarded in 2009 discussed above, the fair value of each option award is estimated, on the date of grant using the Black-Scholes option-pricing valuation model, which incorporates ranges of assumptions for inputs as shown in the following table. The assumptions are as follows:
|
|
• |
|
The expected volatility is a blend of implied volatility based on market-traded options on the Company's common stock and historical volatility of the Company's stock over the expected term of the options. |
|
|
• |
|
The Company uses historical data to estimate the expected term of the option; separate groups of employees that have similar historical exercise behavior are considered separately for valuation purposes. The expected term of options granted represents the period of time the options are expected to be outstanding. |
|
|
• |
|
The risk-free interest rate is based on the U.S. Treasury yield curve in effect at the time of grant for periods within the expected term of the option. |
|
|
• |
|
The expected dividend yield is based on the Company's current dividend yield as the best estimate of projected dividend yield for periods within the expected term of the option. |
|
Years ended December 31,
|
|||||||||
|
2009
|
2008
|
2007
|
|||||||
| Dividend yield | — | — | — | ||||||
| Expected volatility | 60.6% — 64.6% | 59.9% — 66.7% | 58.5% — 62.4% | ||||||
| Risk-free interest rate | 1.3% — 3.1% | 2.6% — 3.4% | 4.3% — 5.0% | ||||||
| Expected term (in years) | 5.4 — 6.2 | 5.4 — 6.2 | 3.2 — 4.1 | ||||||
80
A summary of activity related to aggregate stock options under all plans is indicated in the following table (in thousands, except per share amounts):
|
Year ended December 31, 2009
|
||||||||||||
| Weighted | Weighted | |||||||||||
| Number | average | average remaining | Aggregate | |||||||||
| of | exercise | contractual | intrinsic | |||||||||
|
options
|
price
|
term
|
value
|
|||||||||
| (in thousands) | (in years) | (in thousands) | ||||||||||
| Options outstanding at beginning | ||||||||||||
| of year | 4,488 | $ | 10.79 | |||||||||
| Options granted | 1,748 | 5.13 | ||||||||||
| Options exercised | 80 | 3.92 | ||||||||||
| Options forfeited/expired |
991
|
13.39 | ||||||||||
| Options outstanding at end of year |
5,165
|
8.48 | 6.23 | $ | 5 | |||||||
| Vested and expected to vest |
4,743
|
8.79 | 6.00 | $ | 3 | |||||||
| Options exercisable at end of year |
2,766
|
$ | 11.49 | 4.05 | $ | - | ||||||
The weighted-average grant-date fair value of options granted during the years ended December 31, 2009, 2008 and 2007 was $2.93, $2.64 and $2.05, respectively. The intrinsic value for stock options is defined as the difference between the current market value and the grant price. The total intrinsic value of stock options exercised during the years ended December 31, 2009, 2008 and 2007 was $91,000, $408,000 and $9,000, respectively.
Restricted stock, restricted stock units and deferred stock unit grants consist of the Company's common stock. The fair value of each restricted stock grant, restricted stock unit and deferred stock unit is equal to the market price of the Company's stock at the date of grant. Restricted stock and restricted stock unit grants are time vested. During the years ended December 31, 2009, 2008 and 2007, the Company granted 110,760, 151,038 and 197,357 deferred stock units, respectively, which did not contain any vesting restrictions. A summary of activity related to aggregate restricted stock and restricted stock units as of December 31, 2009, is indicated in the following table (shares in thousands):
| Number of | Weighted-average | ||||
|
shares
|
grant date fair value
|
||||
| Nonvested at beginning of year | 72 | $ | 4.12 | ||
| Granted | 130 | 4.44 | |||
| Vested | (149) | 4.26 | |||
| Forfeited |
-
|
- | |||
| Nonvested at December 31, 2009 |
53
|
$ | 4.51 |
As of December 31, 2009, there was $5.4 million of total unrecognized compensation cost related to all unvested share-based compensation arrangements that is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of 1.92 years.
(12) Income Taxes
The Company has recorded income tax expense (benefit) for the years ended December 31, 2009, 2008 and 2007 of ($1.7 million), ($179,000) and $780,000, respectively.
81
Income tax differed from the amounts computed by applying the U.S. federal income tax rate of 34% to loss before income tax expense (benefit) as a result of the following (in thousands):
|
Years ended December 31,
|
|||||||||
|
2009
|
2008
|
2007
|
|||||||
| Computed "expected" tax benefit | $ | (6,666) | $ | (10,848) | $ | (1,191) | |||
| Expiration of tax attributes | 317 | - | 6,025 | ||||||
| Foreign tax rate differential | - | (837) | (812) | ||||||
| Change in the valuation allowance for deferred tax assets | |||||||||
| attributable to operations and other adjustments | 12,385 | 27,040 | (48,407) | ||||||
| Adjustment to deferred tax assets for changes in foreign taxes, | |||||||||
| laws and rates | - | (11,353) | 38,478 | ||||||
| U.S. and foreign credits | (6,440) | (334) | - | ||||||
| State income taxes, net of federal tax effect | 1 | 2 | 2,083 | ||||||
| Equity based compensation expense | 401 | 726 | 58 | ||||||
| Quebec income tax credits | (1,043) | (179) | - | ||||||
| Other |
(699)
|
(4,396)
|
4,546
|
||||||
| $ |
(1,744)
|
$ |
(179)
|
$ |
780
|
||||
The Company recorded income tax benefits of $1.7 million and $179,000 during the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008, respectively. For 2009, this benefit related to the Company's recognition of income tax credits from the Canadian province of Quebec relating to research and development activities for which the statute of limitations expired in 2009 and the federal alternative minimum taxable loss carryback claim pursuant to a tax law which passed in November 2009. For 2008, this benefit related to the Company's recognition of income tax credits from the Canadian province of Quebec relating to research and development activities and changes in estimates in the calculation of U.S. alternative minimum tax for 2007. The Company recorded income tax expense of $780,000 during the year ended December 31, 2007 for U.S. alternative minimum tax.
Domestic and foreign components of income (loss) before taxes are as follows (in thousands):
|
Years ended December 31,
|
|||||||||
|
2009
|
2008
|
2007
|
|||||||
| Domestic | $ | (506,468) | $ | (199,307) | $ | 34,806 | |||
| Foreign |
486,862
|
167,402
|
(38,308)
|
||||||
| Total loss before taxes | $ |
(19,606)
|
$ |
(31,905)
|
$ |
(3,502)
|
|||
82
The tax effects of temporary differences that give rise to significant portions of the deferred tax assets at December 31, 2009 and 2008 are presented below (in thousands):
|
2009
|
2008
|
|||||||||||
|
Domestic
|
Foreign
|
Domestic
|
Foreign
|
|||||||||
| Deferred tax assets: | ||||||||||||
| Stock compensation expense | $ | 5,633 | $ | - | $ | 4,770 | $ | - | ||||
| Accrued compensation | 437 | - | 81 | - | ||||||||
| Capital loss carryforward | 79,429 | - | - | - | ||||||||
| Research and development pool carryforward | - | - | - | 44,591 | ||||||||
| Net operating loss carryforward | 232,176 | - | 108,190 | 130,106 | ||||||||
| Research credit carryforward | 17,891 | - | 6,686 | - | ||||||||
| Investment tax credit carryforward | - | - | - | 13,124 | ||||||||
| Unrealized loss marketable investment securities | 9,204 | - | 9,850 | - | ||||||||
| Acquired intellectal property | 45,963 | - | 49,206 | - | ||||||||
| Other |
(24)
|
-
|
679
|
7,514
|
||||||||
| Total gross deferred tax assets | 390,709 | - | 179,462 | 195,335 | ||||||||
| Less valuation allowance |
(390,709)
|
-
|
(179,462)
|
(195,335)
|
||||||||
| Deferred tax assets | - | - | - | - | ||||||||
| Deferred tax liabilities |
-
|
-
|
-
|
-
|
||||||||
| Net deferred tax asset (liability) | $ |
-
|
$ |
-
|
$ |
-
|
$ |
-
|
||||
The Company has a cumulative loss for the previous three years and projects losses into the future. Accordingly, as of December 31, 2009, the Company believes that it is not more likely than not that results of future operations will generate insufficient income to realize any of our gross deferred tax assets and has recorded a 100%
valuation allowance. The net change in the Company's total valuation allowance for the years ended December 31, 2009, 2008, and 2007 was an increase of $15.9 million, a decrease of $15.5 million and an increase of $4.8 million, respectively. The valuation allowance includes the benefit for stock option exercises which increased the domestic net operating loss carryforwards. Future reductions to the domestic valuation allowance will be allocated $380.8 million to operations and $9.9 million to paid-in capital.On December 7, 2009, the Company sold a majority interest in its foreign subsidiary, Allelix, to a group of investors. As a result, NPS has deconsolidated Allelix, which resulted in a reduction of $195.3 million of gross deferred tax assets and $195.3 million of valuation allowance. See note 17 for further information on the transaction.
At December 31, 2009, the Company had U.S. federal net operating losses of $600.7 million which begin to expire in 2018 available to offset future income for tax purposes. The Company also had U.S. federal capital loss carryforwards of $197.7 million which begins to expire in 2012. At December 31, 2009, the Company also had U.S. federal research credit carryforwards of $17.9 million which begin to expire in 2010 (approximately $166,000 in 2010) available to offset future income for tax purposes.
The Company also has New Jersey state net operating loss and capital loss carryforwards of approximately $527.7 million and $197.7 million, respectively, and other domestic state net operating loss carryforwards and tax credit carryforwards in varying amounts depending on the different state laws. The Company's domestic tax loss carryforwards for alternative minimum tax purposes is approximately the same as the Company's regular tax loss carryforwards.
As measured under the rules of the Tax Reform Act of 1986, the Company has undergone one or more greater than 50% changes of ownership since 1986. Consequently, use of the Company's domestic net operating loss carryforward and research credit carryforward against future taxable income in any one year may be limited. The maximum amount of carryforwards available in a given year is limited to the product of the Company's fair market value on the date of ownership change and the federal long-term tax-exempt rate, plus any limited carryforward not utilized in prior years.
The Company applies the provisions of ASC 740, "Income Taxes", which prescribe a comprehensive model for how a company should recognize, measure, present, and disclose in its consolidated financial statements uncertain tax positions that the Company has taken or expects to take on a tax return. The Company regularly evaluates, assesses and adjusts the related assets and liabilities in light of changing facts and circumstances.
83
A reconciliation of the unrecognized tax benefits for the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008 is as follows (in thousands):
| Unrecognized | ||||||
|
Tax Benefits
|
||||||
| Balance as of January 1, 2008 | $ | 4,868 | ||||
| Additions for current year tax positions | 923 | |||||
| Reductions for prior year tax positions |
(55)
|
|||||
| Balance as of December 31, 2008 | 5,736 | |||||
| Additions for current year tax positions | - | |||||
| Reductions for prior year tax positions |
(1,122)
|
|||||
| Balance as of December 31, 2009 | $ |
4,614
|
Unrecognized tax benefits amounted to $4.6 million at December 31, 2009, and did not include any accrued potential penalties or interest. The total amount of unrecognized tax benefits relating to the Company's tax positions is subject to change based on future events including, but not limited to, the settlements of ongoing audits and/or the expiration of applicable statutes of limitations. Although the outcomes and timing of such events are highly uncertain, it is reasonably possible that the balance of gross unrecognized tax benefits will not change during the next 12 months. However, changes in the occurrence, expected outcomes and timing of those events could cause the Company's current estimate to change materially in the future.
The Company accounts for penalties or interest related to uncertain tax positions as part of its provision for income taxes. Due to the Company's net operating loss carryforwards, any adjustment related to a liability would not be expected to result in a cash tax liability. Accordingly, the Company has not accrued for penalties or interest for the U.S. (both Federal and State) as of December 31, 2009 and 2008. Assuming the continued existence of a full valuation allowance on the Company's net deferred tax assets, future recognition of any of the Company's unrecognized tax benefits would not impact the effective tax rate.
The Company files income tax returns in various jurisdictions with varying statutes of limitations. The statute of limitations for income tax audits in the U.S. remains open for the tax years ended on or after December 31, 2004.
(13) Employee Benefit Plans
The Company maintains a tax-qualified employee savings and retirement plan (401(k) Plan) covering all of the Company's employees in the United States. Pursuant to the 401(k) Plan, employees may elect to reduce their current compensation up to the maximum percent allowable, not to exceed the limits of code section 401(k), 403(b), 404 and 415, of eligible compensation or the prescribed IRS annual limit and have the amount of such reduction contributed to the 401(k) Plan. The 401(k) Plan permits, but does not require, additional matching contributions to the 401(k) Plan by the Company on behalf of all participants. During the years ended December 31, 2009, 2008 and 2007, the Company matched 100% of employee contributions up to 3% of employee pre-tax contributions and 50% of employee contribution on the next 3% of employee pre-tax contributions. The Company recorded an expense associated with these matching contributions for the years ended December 31, 2009, 2008, and 2007 of $294,000, $249,000 and $602,000, respectively.
Additionally, the Company maintains a tax-qualified defined contribution pension plan for its Canadian employees. Employees may elect to reduce their current compensation by 2% or 4% of eligible compensation up to a maximum of Cnd. $11,000 per year in 2009, and have the amount of such reduction contributed to the pension plan. The Company matches 100% of such contributions. The Company recorded an expense associated with these matching contributions for the years ended December 31, 2009, 2008, and 2007 of $29,000, $43,000, and $128,000, respectively.
(14) Recent Accounting Pronouncements
From time to time, new accounting pronouncements are issued by the FASB or other standard setting bodies that are adopted by the Company as of the specified effective date. Unless otherwise discussed, the Company believes that the impact of recently issued standards that are not yet effective will not have a material impact on its financial position or results of operations upon adoption.
84
In October 2009, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update ("ASU") No. 2009-13, Multiple-Deliverable Revenue Arrangements, ("ASU 2009-13"). ASU 2009-13, amends existing revenue recognition accounting pronouncements that are currently within the scope of ASC Subtopic 605-25 (previously included within EITF Issue No. 00-21, Revenue Arrangements with Multiple Deliverables, ("EITF 00-21"). ASU No. 2009-13 provides accounting principles and application guidance on how the arrangement should be separated, and the consideration allocated. This guidance eliminates the requirement to establish the fair value of undelivered products and services and instead provides for separate revenue recognition based upon management's estimate of the selling price for an undelivered item when there is no other means to determine the fair value of that undelivered item. This new guidance is effective prospectively for revenue arrangements entered into or materially modified in fiscal years beginning on or after June 15, 2010. The Company is currently evaluating the potential impact of this standard on its financial position and results of operations.
In September 2009, the FASB issued ASU No. 2009-06, "Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures (Topic 820): Improving Disclosures about Fair Value Measurements." ASU 2009-06 amends certain disclosure requirements of Subtopic 820-10. This ASU provides additional disclosures for transfers in and out of Levels I and II and for activity in Level III. This ASU also clarifies certain other existing disclosure requirements including level of desegregation and disclosures around inputs and valuation techniques. The final amendments to the Accounting Standards Codification will be effective for annual or interim reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2009, except for the requirement to provide the Level III activity disclosures for purchases, sales, issuances, and settlements on a gross basis. That requirement will be effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2010, and for interim periods within those fiscal years. The Company is assessing the potential impact of adoption of this standard.
In June 2009, the FASB issued ASU No. 2009-17, Improvements to Financial Reporting by Enterprises Involved with Variable Interest Entities (ASU No. 2009-17). ASU No. 2009-17 amends previously issued accounting guidance for the consolidation of variable interest entities to require an enterprise to determine whether its variable interest or interests give it a controlling financial interest in a variable interest entity. The primary beneficiary of a variable interest entity is the enterprise that has both (1) the power to direct the activities of a variable interest entity that most significantly impact the entity's economic performance and (2) the obligation to absorb losses of the entity that could potentially be significant to the variable interest entity or the right to receive benefits from the entity that could potentially be significant to the variable interest entity. The new standard also amends existing literature to require ongoing reassessments of whether an enterprise is the primary beneficiary of a variable interest entity. ASU No. 2009-17 is effective for all variable interest entities and relationships with variable interest entities existing as of January 1, 2010. The Company does not expect that the adoption of ASU No. 2009-17 will have a material impact on its financial position or results of operations.
(15) Commitments and Contingencies
The Company has agreed to indemnify, under certain circumstances, certain manufacturers and service providers from and against any and all losses, claims, damages or liabilities arising from services provided by such manufacturers and service providers or from any use, including clinical trials, or sale by the Company or any Company agent of any product supplied by the manufacturers.
The Company has contractual commitments of $15.3 million with external contract research organizations, relating to clinical trials of teduglutide, NPSP558 and other clinical candidates. These agreements are cancellable on notice of up to six months. The Company also has approximately $13.7 million in contractual commitments for other service agreements with varying terms and conditions.
The Company has entered into long-term agreements with various third-party contract manufacturers for the production and packaging of drug product and vials. Under the terms of these various contracts, the Company is required to purchase certain minimum quantities of drug product each year.
The Company has contractual commitments of $19.2 million for drug product as of December 31, 2009 for the manufacture of clinical supplies of teduglutide and PTH 1-84. Amounts owed to third-party contract manufacturers are based on firm commitments for the purchase of drug product. Amounts purchased under contractual inventory commitments from third-party contract manufacturers for the years ended December 31, 2009, 2008 and 2007 were $4.2 million, $4.0 million and $11.4 million, respectively.
85
(16) Legal Proceedings
Securities Class Action and Derivatives Actions
A final settlement and dismissal of a consolidated shareholders' securities class action lawsuit that was filed against the Company and certain of its present and former officers and directors in the U.S. District Court for the District of Utah, Central Division, as Case No. 2:06cv00570 DAK was approved by the court on June 18, 2009. The Company's directors' and officers' liability insurers paid $15.0 million in resolution of the matter and all claims asserted against the Company, and the other named defendants were dismissed with prejudice with no admission or finding of wrongdoing on the part of any defendant.
A final settlement and dismissal of the consolidated shareholder derivative action against certain of the Company's present and former officers and directors that was filed in the U.S. District Court for the District of Utah, titled In re NPS Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Derivative Litigation, No. 2:07-cv-0611-DAK was approved by the federal court on May 13, 2009. A final settlement and dismissal of the shareholder derivative action against certain of the Company's present and former officers and directors that was filed in the Third Judicial District Court of Salt Lake County, State of Utah, as Deane v. Tombros, et al., Case No. 060913838 was approved by the Utah state court on June 25, 2009. For both the federal and state shareholder derivative actions, the Company's directors' and officers' liability insurers paid $1.0 million toward plaintiffs' legal fees in resolution of the matter and all claims asserted against the defendants, were dismissed with prejudice with no admission or finding of wrongdoing on the part of any defendant. As a term of the settlement, the Company will implement or reaffirm certain corporate governance measures.
All settlement amounts were paid by the Company's directors' and officers' liability insurers in the second quarter of 2009. The Company's balance sheet reflected a $0 and $16.0 million litigation receivable and a $0 and $16.0 million litigation settlement payable as of December 31, 2009 and 2008, respectively.
Sensipar® (cinacalcet HCl) Patent Infringement Litigation
On June 16, 2008, the Company reported the receipt of Paragraph IV Certification Notice Letters ("Notice Letters") related to Abbreviated New Drug Applications (ANDA) submitted to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration ("FDA") by Barr Laboratories Inc. ("Barr") and Teva Pharmaceuticals USA, Inc. ("Teva U.S.") requesting approval to market and sell generic versions of Sensipar (cinacalcet HCl). The Notice Letters alleged that the U.S. Patent Numbers 6,011,068 ("the `068 patent"), 6,031,003 ("the `003 patent"), 6,313,146 ("the `146 patent"), and 6,211,244 ("the `244 patent") covering Sensipar are invalid, unenforceable and/or will not be infringed by the manufacture, use or sale of the product described in the ANDAs.
Under the Company's licensing agreement with Amgen, Amgen is responsible for all development and commercial activities involving Sensipar, as well as enforcing applicable patent rights, in the licensed territories. The `068 patent, the `003 patent and the `146 patent are co-owned by the Company and The Brigham and Women's Hospital, which licensed its rights to the Company. The Company has licensed rights to these patents and the `244 patent to Amgen. On July 25, 2008, The Brigham and Women's Hospital, Amgen and the Company ("the Plaintiffs") filed a patent infringement action in United States District Court, District of Delaware, No. 1:08cv00464 HB, against Barr, Teva U.S. and Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd ("Teva Israel" and collectively with Teva U.S., "Teva") relating to each of the patents referenced above. On August 18, 2008, Barr and Teva filed answers, defenses, and counterclaims alleging that the `068, `003, `146, and `244 are invalid and/or not infringed. On September 10, 2008, the Company, The Brigham and Women's Hospital and Amgen filed answers to Barr's and Teva's counterclaims. On April 3, 2009, Barr and Teva filed motions to amend their answers, defenses, and counterclaims to include allegations that the Sensipar patents are unenforceable for inequitable conduct. Teva also sought to add a counterclaim asserting that Amgen infringed Teva's U.S. Patent No. 7,449,603. On May 15, 2009, the Court denied the motion to add the counterclaim against Amgen but granted motions by Teva and Barr to add counterclaims of unenforceability for inequitable conduct. On September 24, 2009, the Court granted a motion brought by Teva and Barr to proceed on representative claims. The trial in the first instance shall be on the representative claims selected by the Plaintiffs (no more than 12) without prejudice to a trial at a later point if Plaintiffs request on any remaining claims. The parties are currently engaged in active fact discovery and the case is scheduled to be placed in the trial pool on September 1, 2010. By statute, since plaintiffs initiated a patent infringement lawsuit against Barr and Teva within 45 days of receipt of the Notice Letters, the FDA is automatically precluded from approving the ANDAs until the earlier of September 8, 2011 or a district court decision finding the patents invalid, unenforceable or not infringed. The Company is confident of the validity and enforceability of these patents and in conjunction with The Brigham and Women's Hospital and Amgen is vigorously prosecuting these actions to protect these patents from infringement.
86
On May 20, 2009, Teva filed a lawsuit in federal court in the Eastern District of Pennsylvania against Amgen alleging that certain processes used by Amgen to manufacture Sensipar (cinacalcet HCl) infringe Teva's U.S. Patent No. 7,449,603. Teva is seeking declaratory relief and damages in an unspecified amount. Pursuant to the Company's license agreement with Amgen, so long as a patent infringement proceeding by a third party against Amgen continues for the manufacture, use or sale of cinacalcet HCl in any country, Amgen may reserve up to fifty percent of the royalties otherwise payable to the Company with respect to cinacalcet HCl sales in the country in question until the proceeding is concluded. If Teva's patent is determined to be uninfringed, unenforceable or invalid, Amgen is required to promptly pay any reserved royalties to the Company. If Teva's patent is held to be valid and infringed, or if Amgen enters into a settlement of Teva's infringement claim, then Amgen may deduct any damages or settlement amount with respect to such claim from the reserved royalties prior to payment of any remaining amount. In the event any damages and/or settlement amounts exceed the amount of reserved royalties, Amgen could withhold such excess from its future royalty obligations in that country. On February 10, 2010, Amgen notified the Company that it is not reserving any of the 2009 fourth quarter's cinacalcet HCl royalties payable to the Company and has not previously reserved any cinacalcet HC1 royalties payable to the Company. The Company received the $17.1 million in February 2010 representing the full amount of royalties earned during the fourth quarter of 2009. Amgen filed a motion to dismiss the complaint, in part, based on Amgen's claim that the Court lacks subject matter jurisdiction over Teva U.S. On July 22, 2009, an amended complaint was filed by Teva Israel against Amgen. Teva U.S. is not named as a plaintiff in the amended complaint.
(17) Sale of Subsidiary
In December 2009, the Company sold a majority interest in its subsidiary, Allelix, to a group of investors ("Investors"). NPS received $5.6 million in connection with the transactions. NPS is entitled to receive an additional Cnd. $4.8 million, which would only be paid upon further investment in Allelix by the Investors, which would be expected to occur upon the successful completion of certain Canadian court proceedings. Allelix has not had active operations for approximately two years. NPS has recorded a gain of $4.9 million in its consolidated statement of operations for the year ended December 31, 2009 on this sale. In connection with the transaction, the Company has indemnified the Investors for various items including product liabilities arising from the past operations of Allelix and has guaranteed that certain tax attributes exist as of the closing date. The maximum potential future payments related to these indemnifications or guarantees shall not exceed the amounts the Company has received in connection with the transaction ($5.6 million at December 31, 2009).
(18) Supplemental Cash Flow Information and Non-cash Investing and Financing Activities:
(in thousands)
|
Year Ended December 31,
|
|||||||||
|
2009
|
2008
|
2007
|
|||||||
| Cash Paid for: | |||||||||
| Interest | $ | 26,123 | $ | 24,349 | $ | 31,442 | |||
| Income taxes | - | 900 | - | ||||||
| Noncash Investing and Financing Activities: | |||||||||
| Unrealized gains (losses) on marketable investment securities | $ | 2,376 | $ | 2,865 | $ | (2,069) | |||
| Accrued acquisition of equipment, leasehold improvements and | |||||||||
| construction-in-progress | 76 | 67 | - | ||||||
| Debt issued in lieu of interest | 20,316 | 17,450 | 6,246 | ||||||
87
(19) Selected Quarterly Financial Data (Unaudited)
The following is a summary of the quarterly results of operations for the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008 (in thousands, except for per share amounts):
|
Quarters Ended
|
|||||||||||||||
|
March 31
|
June 30
|
September 30
|
December 31
|
||||||||||||
| (in thousands, except per share amounts) | |||||||||||||||
| 2009 | |||||||||||||||
| Revenues | $ | 16,329 | $ | 25,649 | $ | 20,119 | $ | 22,050 | |||||||
| Operating income | 5,586 | 14,118 | 3,964 | 4,032 | |||||||||||
| Net income (loss) | (10,736) | 2,617 | (7,766) | (1,977) | |||||||||||
| Basic income (loss) per common share | $ | (0.22) | $ | 0.05 | $ | (0.16) | $ | (0.04) | |||||||
| Diluted income (loss) per common | |||||||||||||||
| and potential common share | $ | (0.22) | $ | 0.05 | $ | (0.16) | $ | (0.04) | |||||||
| 2008 | |||||||||||||||
| Revenues | $ | 25,180 | $ | 26,959 | $ | 26,075 | $ | 24,065 | |||||||
| Operating income | 5,088 | 16,334 | 14,545 | 12,396 | |||||||||||
| Net income (loss) | (13,093) | 1,203 | (11,359) | (8,477) | |||||||||||
| Basic income (loss) per common share | $ | (0.28) | $ | 0.03 | $ | (0.24) | $ | (0.18) | |||||||
| Diluted income (loss) per common | |||||||||||||||
| and potential common share | $ | (0.28) | $ | 0.03 | $ | (0.24) | $ | (0.18) | |||||||
|
ITEM 9. |
Changes in and Disagreements With Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure. |
Not applicable
|
Controls and Procedures. |
a) Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
We maintain "disclosure controls and procedures" within the meaning of Rule 13a-15(e) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, or the Exchange Act. Our disclosure controls and procedures, or Disclosure Controls, are designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed by us in the reports we file or submit under the Exchange Act, such as this Annual Report on Form 10-K, is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission's rules and forms. Our Disclosure Controls include, without limitation, controls and procedures designed to ensure that such information is accumulated and communicated to our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
As of the end of the period covered by this Annual Report on Form 10-K, we evaluated the effectiveness of the design and operation of our disclosure controls and procedures, which was done under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and our Chief Financial Officer. Based on the controls evaluation, our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer have concluded that, as of the date of their evaluation, our disclosure controls and procedures were effective as of December 31, 2009.
(b) Management's Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting.
Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting. Our internal control system was designed to provide our management and board of directors reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with GAAP. Internal control over financial reporting has inherent limitations. Internal control over financial reporting is a process that involves human diligence and compliance and is subject to lapses in judgment and breakdowns resulting from human failures. Internal control over financial reporting also can be circumvented by collusion or improper management override. Because of such limitations, there is a risk that material misstatements will not be prevented or detected on a timely basis by internal control over financial reporting. However, these inherent
88
limitations are known features of the financial reporting process. Therefore, it is possible to design into the process safeguards to reduce, though not eliminate, this risk.
Our management has assessed the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2009. In making this assessment, we used the criteria set forth by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO) in Internal Control-Integrated Framework. Based on our assessment we believe that, as of December 31, 2009, our internal control over financial reporting is effective based on those criteria.
KPMG LLP, our independent registered public accounting firm that audited the financial statements included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K has issued an audit report on our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2009. This report appears on page 54 of this report.
(c) Change in Internal Control over Financial Reporting.
There have been no changes in our internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the most recent fiscal quarter that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
|
Other Information. |
None.
PART III
ITEM 10. Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance.
Certain of the information required by this item will be contained in our definitive Proxy Statement with respect to our 2010 Annual Meeting of Stockholders, under the captions "Election of Directors," and "Compliance with Section 16(a) of the Exchange Act." Such information is incorporated into this item by reference. For information regarding our executive officers see Part I of this Form 10-K under the caption "Executive Officers of the Registrant."
ITEM 11. Executive Compensation.
The information required by this item will be contained in our definitive Proxy Statement with respect to our 2010 Annual Meeting of Stockholders, under the captions "Executive Compensation," "Compensation Committee Interlocks and Insider Participation ," and "Compensation Committee Report" and is incorporated into this item by reference.
The information required by this item will be contained in our definitive Proxy Statement with respect to our 2010 Annual Meeting of Stockholders, under the captions "Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management" and "Equity Compensation Plan Information" and is incorporated into this item by reference.
ITEM 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence.
The information required by this item will be contained in our definitive Proxy Statement with respect to our 2010 Annual Meeting of Stockholders under the captions "Certain Relationships and Related Transactions" and "Independence of the Board" and is incorporated into this item by reference.
ITEM 14. Principal Accountant Fees and Services.
The information required by this item will be contained in our definitive Proxy Statement with respect to our 2010 Annual Meeting of Stockholders, under the caption "Principal Accountant Fees and Services" and is incorporated into this item by reference.
89
PART IV
ITEM 15. Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules.
(a) The following documents are filed as part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
1. Financial Statements. The financial statements listed on the accompanying Index to Consolidated Financial Statements are filed as part of this report.
2. Financial statement schedules. There are no financial statements schedules included because they are either not applicable or the required information is shown in the consolidated financial statements or the notes thereto.
3. Exhibits. The following exhibits are filed or incorporated by reference as part of this Form 10-K.
|
Exhibit |
|
|
|
3.1A |
|
Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation of the Registrant (1) |
|
3.1B |
|
Certificate of Amendment of the Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation of the Registrant, dated December 16, 1999 (2) |
|
3.1C |
|
Certificate of Designation of Series A Junior Participating Preferred Stock of the Registrant, dated December 18, 1996 (3) |
|
3.1D |
|
Amendment to Certificate of Designation of Series A Junior Participating Preferred Stock of the Registrant, dated September 5, 2000 (2) |
|
3.1E |
|
Certificate of Amendment of the Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation of the Registrant, dated September 30, 2003 (12) |
|
3.2A |
|
Amended and Restated Bylaws of the Registrant (27) |
|
3.2B |
|
Certificate of Adoption of Amendments to the Amended and Restated Bylaws of the Registrant, dated February 19, 2003 (9) |
|
4.1 |
|
Specimen Common Stock Certificate (1) |
|
4.2A |
|
Rights Agreement, dated as of December 4, 1996, between the Registrant and American Stock Transfer & Trust, Inc., with Exhibit A, Form of Certificate of Designation of Series A Junior Participating Preferred Stock of the Registrant; Exhibit B, Form of Right Certificate; and Exhibit C, Summary of Rights to Purchase Shares of Preferred Stock of the Registrant (3) |
|
4.2B |
|
First Amendment to the Rights Agreement and Certificate of Compliance with Section 27 thereof, dated December 31, 2001 (4) |
|
4.2C |
|
Second Amendment to the Rights Agreement and Certificate of Compliance with Section 27 thereof, dated February 19, 2003 (5) |
|
4.3 |
|
Indenture, dated as of June 17, 2003, between Registrant and U.S. Bank National Association, as Trustee, including the form of 3% Convertible Subordinated Notes due 2008 attached as Exhibit A thereto (11) |
|
4.4A |
|
Composite Indenture, dated as of December 22, 2004, by and between Cinacalcet Royalty Sub LLC, a wholly-owned subsidiary of Registrant, and U.S. National Bank Association, incorporating the amendments provided for in the Supplemental Indenture dated as of February 2, 2005, between the same parties (the "Indenture") (14) |
|
4.4B |
Second Supplemental Indenture dated October 20, 2006 to the Indenture (18) |
|
|
4.4C |
Third Supplemental Indenture dated July 9, 2007 to the Indenture (18) |
|
|
4.4D |
Fourth Supplemental Indenture dated August 1, 2007 to the Indenture (18) |
|
|
4.4E |
Fifth Supplemental Indenture dated August 7, 2007 to the Indenture (18) |
|
|
10.1A |
|
1998 Stock Option Plan (23) |
90
|
10.1B |
|
1998 Stock Option Plan, as amended December 2002 (9) |
|
10.1C |
|
1998 Stock Option Plan, as amended June 2003 (12) |
|
10.1D |
|
1998 Stock Option Plan (reflects all amendments by the Board of Directors through May 2008) (26) |
|
10.1E |
|
Form of Performance-Based Stock Option Agreement under the NPS Pharmaceutical, Inc. 1998 Stock Option Plan (28) |
|
10.2 |
|
Form of Indemnity Agreement entered into between the Registrant and each of its officers and directors (1) |
|
10.3A |
|
Change in Control Severance Pay Plan, as amended (28) |
|
10.3B |
|
Form of Agreement Providing Specified Benefits Following Termination of Employment Incident to a Merger, Acquisition or Other Change of Control or to Some Other Strategic Corporate Event, between the Registrant and each of its executive officers (12) |
|
10.4A |
|
Collaborative Research and License Agreement between the Registrant and SmithKline Beecham Corporation (now GlaxoSmithKline), dated November 1, 1993 (1) |
|
10.4B |
|
Amendment Agreement to Collaborative Research and License Agreement between GlaxoSmithKline, effective June 29, 1995 (6) |
|
10.4C |
|
Amendment Agreement between the Registrant and GlaxoSmithKline, dated October 28, 1996 (3) |
|
10.4D |
|
Amendment Agreement between the Registrant and GlaxoSmithKline, dated October 27, 1997 (7) |
|
10.4E |
|
Amendment to Collaborative Research and License Agreement between the Registrant and GlaxoSmithKline, dated November 26, 1997 (7) |
|
10.4F |
|
Letter, dated January 24, 2000, from SmithKline Beecham to NPS Re: Amendment Agreement to Amend the November 26, 1997 Amendment Agreement (9) |
|
10.4G |
|
Letter, dated May 15, 2000, from SmithKline Beecham to NPS Re: Amendment Agreement (9) |
|
10.4H |
|
Letter, dated August 1, 2001, from GlaxoSmithKline to NPS Re: Amendment Agreement to Amend the January 24, 2000 Amendment Agreement (9) |
|
10.4I |
|
Amendment Agreement dated December 14, 2006 between the Registrant and SmithKline Beecham Corporation, dba GlaxoSmithKline (19) |
|
10.5A |
|
Patent Agreement between the Registrant and The Brigham and Women's Hospital, Inc., dated February 19, 1993 (1) |
|
10.5B |
|
Letter dated March 15, 1993 from the Registrant to The Brigham and Women's Hospital, Inc. regarding Patent Agreement between the Registrant and The Brigham and Women's Hospital, Inc. (9) |
|
10.5C |
|
Amendment to Patent Agreement between the Registrant and The Brigham and Women's Hospital, Inc., effective February 7, 1996 (8) |
|
10.5D |
|
1999 Patent Agreement Amendment between the Registrant and The Brigham and Women's Hospital, Inc., effective February 18, 1999 (9) |
|
10.6 |
|
Collaborative Research and License Agreement between the Registrant and Kirin Brewery Company, Ltd. dated June 29, 1995 (8) |
|
10.7 |
|
Development and License Agreement between the Registrant and Amgen Inc. effective as of December 27, 1995 (6) |
|
10.8 |
|
Manufacturing Agreement between NPS Allelix Corp. and SynCo Bio Partners B.V., effective as of June 21, 2001 (10) |
|
10.9 |
|
Addendum to Manufacturing Agreement between NPS Allelix Corp. and SynCo Bio Partners B.V., effective as of October 26, 2001 (10) |
|
10.10 |
|
Lease Agreement between MaRS Discovery District and Registrant, dated April 12, 2004 (13) |
91
|
10.11A* |
|
Distribution and License Agreement between Registrant and Nycomed Danmark ApS, dated April 26, 2004 (13) |
||
|
10.11B* |
|
First Amendment to Distribution and License Agreement between the Registrant and Nycomed Danmark ApS, dated July 1, 2004 (13) |
||
|
10.11C* |
License Agreement, dated July 2, 2007, between NPS Allelix Corp. and Nycomed Danmark ApS (22) |
|||
|
10.12A |
|
2005 Omnibus Incentive Plan, as amended (24) |
||
|
10.12B |
|
Form of Stock Option Grant Agreement under the 2005 Omnibus Incentive Plan (16) |
||
|
10.13A |
|
Non-Employee Director Deferred Compensation Program (15) |
||
|
10.13B |
|
Form of Deferred Stock Unit Award Agreement (15) |
||
|
10.14A |
|
Agreement of Purchase and sale between Registrant and Biomed Realty, L.P. dated December 20, 2005 (17) |
||
|
10.14B |
|
Lease Agreement between Registrant and BMR-383 Colorow Drive, LLC dated December 22, 2005 (17) |
||
|
10.14C |
Agreement of Purchase and Sale, dated May 9, 2007, between NPS Pharmaceuticals, Inc. and BMR-383 Colorow Drive LLC (20) |
|||
|
10.15 |
Agreement of Purchase and Sale, dated May 9, 2007, between NPS Allelix Corp. and Transglobe Property Management Services Ltd. in Trust (20) |
|||
|
10.16 |
Sublease Agreement, dated June 19, 2007, between NPS Pharmaceuticals, Inc. and Celanese Americas Corporation (21) |
|||
|
10.17 |
Purchase and Sale Agreement, dated June 29, 2007, by and between NPS Pharmaceuticals, Inc. and the University of Utah (21) |
|||
|
10.18A |
Securities Purchase Agreement dated as of August 7, 2007 among NPS Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (the "Issuer") and Visium Balanced Fund, LP, Visium Balanced Offshore Fund, Ltd., Visium Long Bias Fund, LP, Visium Long Bias Offshore Fund, Ltd. and Atlas Master Fund (collectively, the "Investors") (18) |
|||
|
10.18B |
Form of Note issued pursuant to the Securities Purchase Agreement referred to in Exhibit 10.22A above (18) |
|||
|
10.18C |
Registration Rights Agreement dated as of August 7, 2007 among the Issuer and the Investors (18) |
|||
|
10.19* |
Agreement for Sale and Assignment of Rights, dated July 16, 2007, among NPS Pharmaceuticals, Inc., NPS Allelix Corp. and DRI (22) |
|||
|
10.20* |
Distribution and License Agreement, dated September 24, 2007, among NPS Pharmaceuticals, Inc., NPS Allelix Corp. and Nycomed GmbH (22) |
|||
|
10.21* |
Amendment Agreement to the Distribution and License Agreement, dated October 29, 2007, among NPS Pharmaceuticals, Inc., NPS Allelix Corp. and Nycomed GmbH (22) |
|||
|
10.22* |
License Agreement, dated September 28, 1995, between 1149336 Ontario Inc., Daniel J. Drucker, and Allelix Biopharmaceuticals Inc. (22) |
|||
|
10.23 |
Asset Purchase Agreement, dated October 9, 2007, between AstraZeneca AB and NPS Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (24) |
|||
|
10.24A* |
Commercial Manufacturing Agreement, dated October 18, 2002, by and between NPS Allelix Corp. and Boehringer Ingelheim Austria GmbH (24) |
|||
|
10.24B* |
Amending Agreement, dated March 15, 2004, by and between NPS Allelix Corp. and Boehringer Ingelheim Austria GmbH (24) |
|||
|
10.24C* |
Amendment Number One to Amending Agreement, dated December 22, 2005, by and between NPS Allelix Corp. and Boehringer Ingelheim Austria GmbH (24) |
|||
|
10.25 |
Employment Agreement with Francois Nader (25) |
|||
|
10.26 |
First Amendment to Restrictive Covenant Agreement with Francois Nader (25) |
|||
92
___________
|
+ |
Filed herewith. |
|
* |
Confidential information was omitted from this exhibit pursuant to a request for confidential treatment and filed separately with the Securities and Exchange Commission. |
|
(1) |
Incorporated herein by reference to the Registrant's Registration Statement on Form S-1 filed on January 21, 1994 (SEC File No. 333-74318). |
|
(2) |
Incorporated herein by reference to the Registrant's Registration Statement on Form S-3 filed on September 6, 2000 (SEC File No. 333-45274, Film No. 717603). |
|
(3) |
Incorporated herein by reference to the Registrant's Current Report on Form 8-K dated December 19, 1996 (SEC File No. 000-23272, Film No. 96683282). |
|
(4) |
Incorporated herein by reference to the Registrant's Registration Statement on Form 8-A12G/A (SEC File No. 000-23272, Film No. 1826478, filing date December 31, 2001). |
|
(5) |
Incorporated herein by reference to the Registrant's Registration Statement on Form 8-A12G/A (SEC File No. 000-23272, Film No. 03575669, filing date February 21, 2003). |
|
(6) |
Incorporated herein by reference to Amendment No. 1 to the Registrant's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 1995, filed on March 29, 1996. |
|
(7) |
Incorporated herein by reference to the Registrant's Current Report on Form 8-K dated January 27, 1998 (SEC File No. 000-23272, Film No. 98513828). |
|
(8) |
Incorporated herein by reference to the Registrant's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 1995. |
|
(9) |
Incorporated herein by reference to the Registrant's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2002 (SEC File No. 000-23272, Film No. 03612691, filing date March 21, 2003). |
|
(10) |
Incorporated herein by reference to the Registrant's Annual Report on Form 10-K/A for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2002 (SEC File No. 000-23272, Film No. 03739737, filing date June 11, 2003). |
|
(11) |
Incorporated herein by reference to the Registrant's Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended June 30, 2003 (SEC File No. 000-23272, Film No. 03838243, filing date August 12, 2003). |
|
(12) |
Incorporated herein by reference to the Registrant's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2003 (SEC File No. 000-23272, Film No. 04582125, filing date February 10, 2004). |
|
(13) |
Incorporated herein by reference to the Registrant's Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended June 30, 2004 (SEC File No. 000-23272, Film No. 04962020, filing date August 9, 2004). |
|
(14) |
Incorporated herein by reference to the Registrant's Current Report on Form 8-K dated February 2, 2005 (SEC File No. 000-23272, Film No. 05578512, filing date February 7, 2005). |
|
(15) |
Incorporated herein by reference to the Registrant's Current Report on Form 8-K dated July 1, 2005 (SEC File No. 000-23272, Film No. 05933233, filing date July 1, 2005). |
|
(16) |
Incorporated herein by reference to the Registrant's Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended June 30, 2005 (SEC File No. 000-23272, Film No. 05974685, filing date July 26, 2005). |
|
(17) |
Incorporated herein by reference to the Registrant's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2005 (SEC File No. 000-23272, Film No. 06663187, filing date March 3, 2006). |
|
(18) |
Incorporated herein by reference to the Registrant's Current Report on Form 8-K dated August 31, 2007 (SEC File No. 000-23272, Film No. 071094546, filing date August 31, 2007). |
|
(19) |
Incorporated herein by reference to the Registrant's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2006 (SEC File No. 000-23272, Film No. 07693379, filing date March 14, 2007). |
|
(20) |
Incorporated herein by reference to the Registrant's Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended March 31, 2007 (SEC File No. 000-23272, Film No. 07833270, filing date May 9, 2007). |
|
(21) |
Incorporated herein by reference to the Registrant's Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended June 30, 2007 (SEC File No. 000-23272, Film No. 071032512, filing date August 7, 2007). |
|
(22) |
Incorporated herein by reference to the Registrant's Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended September 30, 2007 (SEC File No. 000-23272, Film No. 071231813, filing date November 9, 2007). |
|
(23) |
Incorporated herein by reference to the Registrant's Definitive Proxy Statement (SEC File No. 000-23272, Film No. 98590984, filing date April 9, 1998). |
|
(24) |
Incorporated herein by reference to the Registrant's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2007 (SEC File No. 000-23272, Film No. 08691123, filing date March 17, 2008). |
|
(25) |
Incorporated herein by reference to the Registrant's Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarterly period ended March 31, 2008 (SEC File No. 000-23272, Film No. 08845693, filing date May 19, 2008). |
|
(26) |
Incorporated herein by reference to the Registrant's Current Report on Form 8-K dated May 22, 2008 (SEC File No. 000-23272, Film No. 08864183, filing date May 28, 2008). |
|
(27) |
Incorporated herein by reference to the Registrant's Current Report on Form 8-K dated August 14, 2008 (SEC File No. 000-23272, Film No. 081030212, filing date August 20, 2008). |
|
(28) |
Incorporated herein by reference to the Registrant's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2008 (SEC File No. 000-23272, Film No. 09685262, filing date March 16, 2009). |
|
(29) |
Incorporated herein by reference to the Registrant's Current Report on Form 8-K dated August 5, 2009 (SEC File No. 000-23272, Film No. 09990146, filing date August 6, 2009). |
94
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NPS PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. |
||
|
Date: March 11, 2010 |
|
By: |
|
/s/ F RANCOIS NADERFrancois Nader President and Chief Executive Officer (Principal Executive Officer) |
|
Date: March 11, 2010 |
|
By: |
|
/s/ L UKE M. BESHARLuke M. Beshar Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the date indicated.
|
Signature |
Title |
Date |
||
|
|
||||
|
/s/ FRANCOIS NADER Francois Nader |
President and Chief Executive Officer (principal executive officer) and Director |
March 11, 2010 |
||
|
|
||||
|
/s/ LUKE M. BESHAR Luke M. Beshar |
Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer (principal financial and accounting officer) |
March 11, 2010 |
||
|
|
||||
|
/s/ MICHAEL W. BONNEY Michael W. Bonney |
Director |
March 11, 2010 |
||
|
|
||||
|
/s/ COLIN BROOM Colin Broom |
Director |
March 11, 2010 |
||
|
|
||||
|
/s/ JAMES G. GRONINGER James G. Groninger |
Director |
March 11, 2010 |
||
|
|
||||
|
/s/ DONALD E. KUHLA Donald E. Kuhla |
Director |
March 11, 2010 |
||
|
|
||||
|
/s/ RACHEL R. SELISKER Rachel R. Selisker |
Director |
March 11, 2010 |
||
|
|
||||
|
/s/ PETER G. TOMBROS Peter G. Tombros |
Chairman of the Board of Directors |
March 11, 2010 |
||
