Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| 8-K - FORM 8-K - Lipocine Inc. | tm2113019d2_8k.htm |
| EX-99.5 - EXHIBIT 99.5 - Lipocine Inc. | tm2113019d2_ex99-5.htm |
| EX-99.4 - EXHIBIT 99.4 - Lipocine Inc. | tm2113019d2_ex99-4.htm |
| EX-99.2 - EXHIBIT 99.2 - Lipocine Inc. | tm2113019d2_ex99-2.htm |
| EX-99.1 - EXHIBIT 99.1 - Lipocine Inc. | tm2113019d2_ex99-1.htm |

EASL 2021 Jun 23 – 26, 2021 Oral LPCN 1144 treatment significantly reduced liver fat and key liver injury markers in biopsy confirmed NASH subjects: a Phase 2 randomized controlled study Presenter: Kilyoung Kim, PhD Exhibit 99.3
Background & Aim • Non - alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is a common cause of liver disease and is on a trajectory to become the most common indication for liver transplantation in Western Europe and the United States. • In large multi - ethnic cross - sectional studies, low testosterone (T) levels are independently predictive of fatty liver. (1,2) • Hepatic steatosis (measured by MRI - PDFF), together with serum transaminase levels, specifically alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), are predictive of liver pathology and histology in NASH subjects. • LPCN 1144 is an oral prodrug of endogenous Testosterone (T) under development for treatment of noncirrhotic NASH. – Therapy with vitamin E has previously been shown to improve biochemical (ALT) and histological features of NASH albeit in a non - diabetic population. (3,4) • Currently, LPCN 1144 is being investigated for safety and efficacy in a 36 - week randomized, double - blind, paired biopsy, placebo - controlled phase 2 LiFT ("Liver Fat intervention with oral Testosterone") study (NCT04134091). • Here, we present the topline liver fat and key liver injury marker results post 12 weeks of treatment. 2 1 Kim et al. A low level of serum total testosterone is independently associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. BMC Gastroenterol 2012, 12:69 2 Albhaisi et al. LPCN 1144 resolves NAFLD in hypogonadal males. Hepatol Commun 2020, 4(10):1430 - 1440 3 Sanyal et al. Pioglitazone, vitamin E, or placebo for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. N Engl J Med 2010, 362(18):1675 - 85 4 Hoofnagle et al. Vitamin E and changes in serum alanine aminotransferase levels in patients with non - alcoholic steatohepatitis . Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2013, 38(2):134 - 143
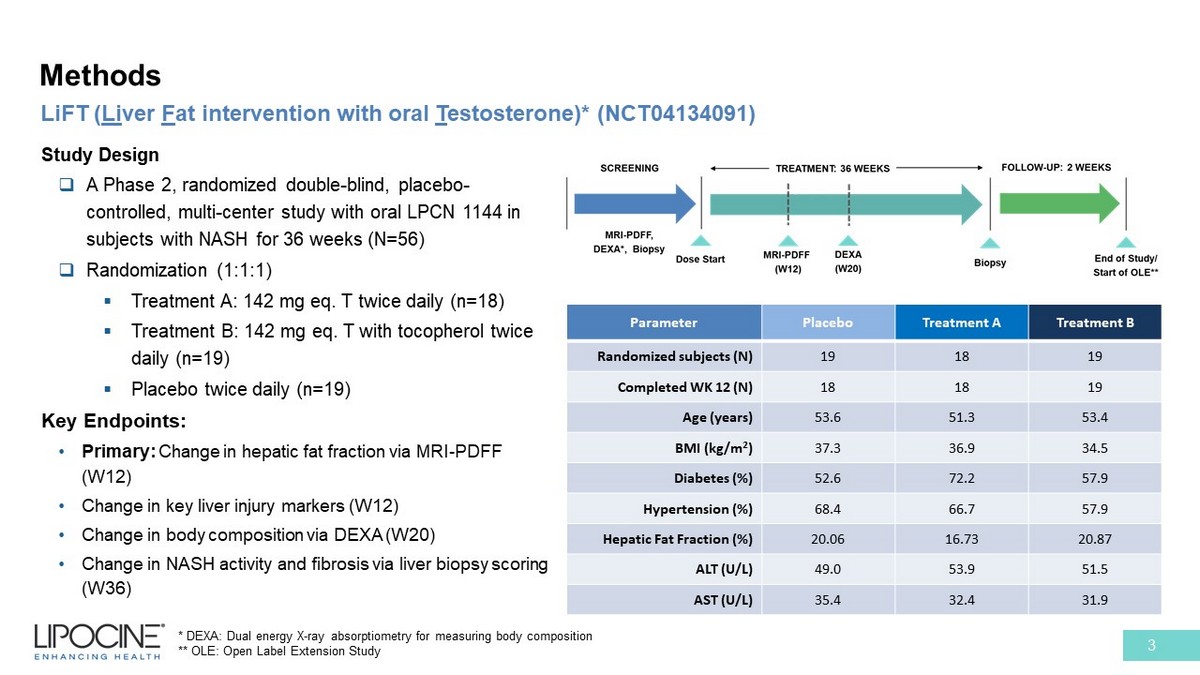
Methods 3 LiFT ( Li ver F at intervention with oral T estosterone)* (NCT04134091) * DEXA: Dual energy X - ray absorptiometry for measuring body composition ** OLE: Open Label Extension Study Study Design □ A Phase 2, randomized double - blind, placebo - controlled, multi - center study with oral LPCN 1144 in subjects with NASH for 36 weeks (N=56) □ Randomization (1:1:1) ▪ Treatment A: 142 mg eq. T twice daily (n=18) ▪ Treatment B: 142 mg eq. T with tocopherol twice daily (n=19) ▪ Placebo twice daily (n=19) Key Endpoints: • Primary: Change in hepatic fat fraction via MRI - PDFF (W12) • Change in key liver injury markers (W12) • Change in body composition via DEXA (W20) • Change in NASH activity and fibrosis via liver biopsy scoring (W36) Parameter Placebo Treatment A Treatment B Randomized subjects (N) 19 18 19 Completed WK 12 (N) 18 18 19 Age (years) 53.6 51.3 53.4 BMI (kg/m 2 ) 37.3 36.9 34.5 Diabetes (%) 52.6 72.2 57.9 Hypertension (%) 68.4 66.7 57.9 Hepatic Fat Fraction (%) 20.06 16.73 20.87 ALT (U/L) 49.0 53.9 51.5 AST (U/L) 35.4 32.4 31.9

Results: Changes in Liver Fat and Key Liver Injury Markers at Week 12 from Baseline 4 Both LPCN 1144 treatment a rms reduced liver fat, ALT, and AST with statistical s ignificance † Two missing data at week 12 (one in placebo and one in treatment A) were multiple - imputed ‡ Among subjects with baseline liver fat ≥ 5% * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 vs placebo; † p < 0.05, †† p < 0.01, ns = not significant between treatment A and B < Changes in Liver Fat > < Changes in Key Liver Injury Markers >

Conclusions 5 LPCN 1144 treatment significantly improved the key non - invasive markers of liver health in male patients with biopsy confirmed NASH with fibrosis. Leveraging the largest, multi - modal proprietary clinical database of its kind to expand a robust pipeline of predictive algorithms with regulatory grade evidence. Developing novel transformative algorithms to transform healthcare. Commercially validated across 3 business models Experienced team Statistically significant reduction in liver fat was observed compared to placebo independent of hypogonadal status Statistically significant reduction in markers of liver injury were observed compared to placebo independent of hypogonadal status 68% on Treatment B had concurrent reductions of liver fat, ALT, and AST Adverse events in both the treatment arms were comparable to the placebo arm 01 02 03 04
