Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| 8-K - 8-K - Neoleukin Therapeutics, Inc. | d31660d8k.htm |

Corporate Presentation January 2021 Exhibit 99.1

Forward Looking Statements Certain of the statements made in these slides and the accompanying oral presentation are forward looking, including those relating to Neoleukin’s business, strategy, future operations, advancement of its product candidates and product pipeline, clinical development of its product candidates, including expectations regarding timing of regulatory submissions and initiation of clinical trials, regulatory requirements for initiation of clinical trials and registration of product candidates, properties of its product candidates, the use and sufficiency of its cash resources and other statements containing the words “anticipate,” “believe,” “expect,” “may,” “plan,” “project,” “potential,” “will,” “would,” “could,” “continue,” and similar expressions. These statements are subject to risks and uncertainties that could cause actual results and events to differ materially from those anticipated, including, but not limited to, risks and uncertainties related to: whether results of early clinical trials or preclinical studies will be indicative of the results of future trials, the adequacy of any clinical models, uncertainties associated with regulatory review of clinical trials; our ability to identify or acquire additional clinical candidates, our ability to obtain and maintain regulatory approval for any product candidates and the potential safety, efficacy or clinical utility of or any product candidates; further impacts of COVID-19 on our operations; and other factors discussed in the “Risk Factors” section of the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2020 as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission. Actual results or developments may differ materially from those projected or implied in these forward-looking statements. More information about the risks and uncertainties faced by the Company is contained in its Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2020, Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2019, and subsequent reports, filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission. The Company disclaims any intention or obligation to update or revise any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise.
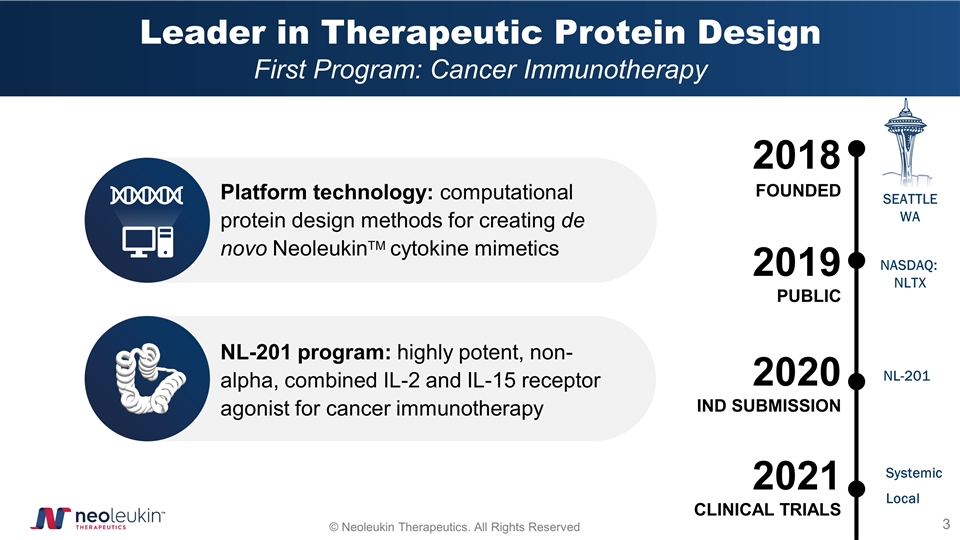
Leader in Therapeutic Protein Design First Program: Cancer Immunotherapy 2018 FOUNDED 2019 PUBLIC NL-201 program: highly potent, non-alpha, combined IL-2 and IL-15 receptor agonist for cancer immunotherapy Platform technology: computational protein design methods for creating de novo NeoleukinTM cytokine mimetics NASDAQ: NLTX 2020 IND SUBMISSION SEATTLE WA NL-201 2021 CLINICAL TRIALS Systemic Local

Carl Walkey, Ph.D. VP, Corporate Development Previous: Postdoctoral Fellow, UW-IPD Daniel-Adriano Silva, Ph.D. VP, Head of Research Previous: Translational Investigator, UW-IPD Umut Ulge, M.D., Ph.D. VP, Clinical Development Previous: Postdoctoral Fellow, UW-IPD Jonathan Drachman, M.D. Chief Executive Officer Previous: CMO, EVP R&D, Seattle Genetics Robert Ho Chief Financial Officer Previous: Morgan Stanley & Co., DaVita Samantha Willing VP, People Previous: Seattle Genetics, Microsoft Holly Vance, J.D., Pharm.D. General Counsel Previous: Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation Leadership Team
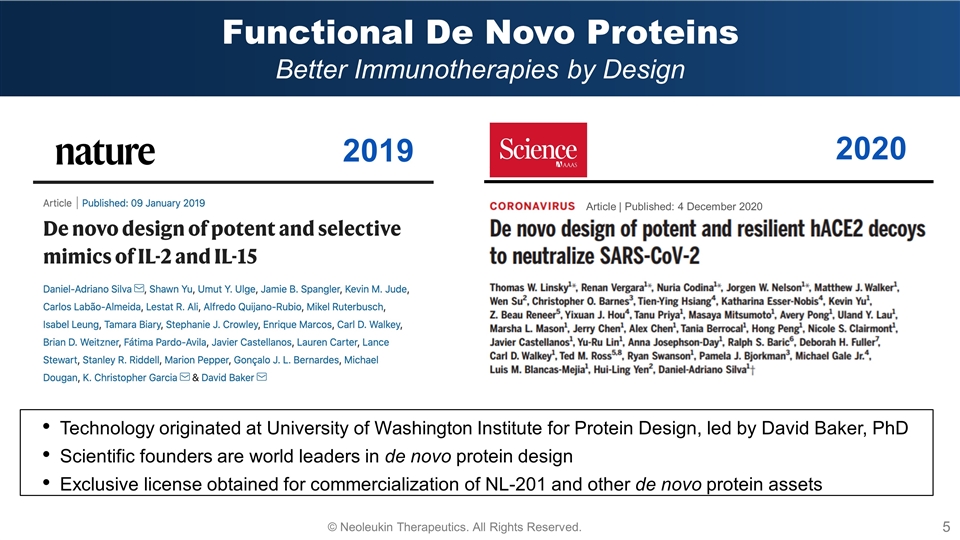
Functional De Novo Proteins Better Immunotherapies by Design Technology originated at University of Washington Institute for Protein Design, led by David Baker, PhD Scientific founders are world leaders in de novo protein design Exclusive license obtained for commercialization of NL-201 and other de novo protein assets 2019 2020 Article | Published: 4 December 2020 © Neoleukin Therapeutics. All Rights Reserved.
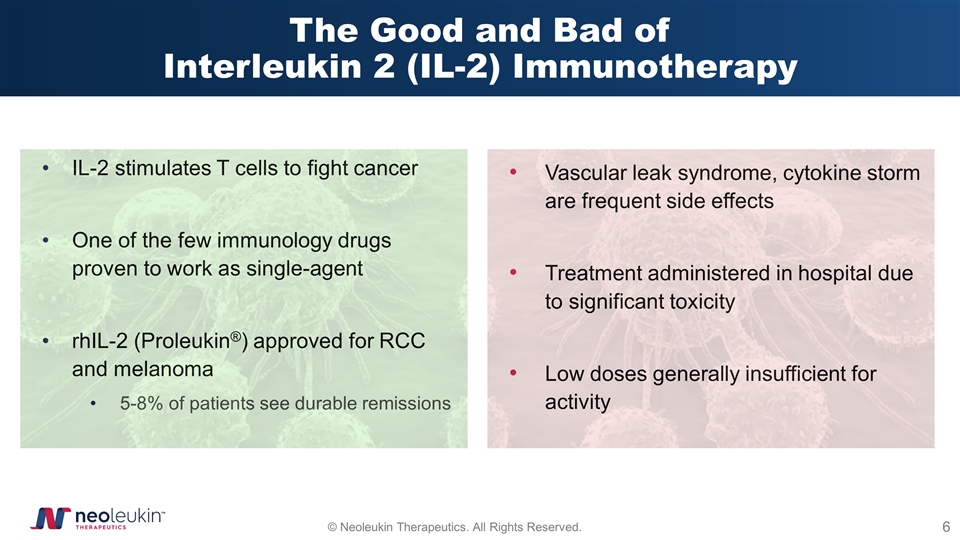
The Good and Bad of Interleukin 2 (IL-2) Immunotherapy IL-2 stimulates T cells to fight cancer One of the few immunology drugs proven to work as single-agent rhIL-2 (Proleukin®) approved for RCC and melanoma 5-8% of patients see durable remissions Vascular leak syndrome, cytokine storm are frequent side effects Treatment administered in hospital due to significant toxicity Low doses generally insufficient for activity
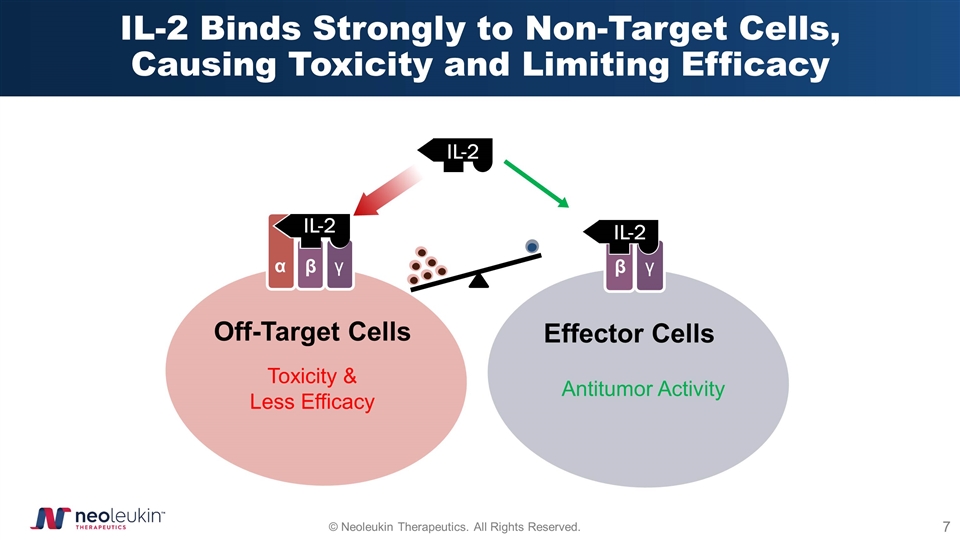
IL-2 Binds Strongly to Non-Target Cells, Causing Toxicity and Limiting Efficacy α β γ β γ IL-2 Off-Target Cells Effector Cells Toxicity & Less Efficacy Antitumor Activity IL-2 IL-2
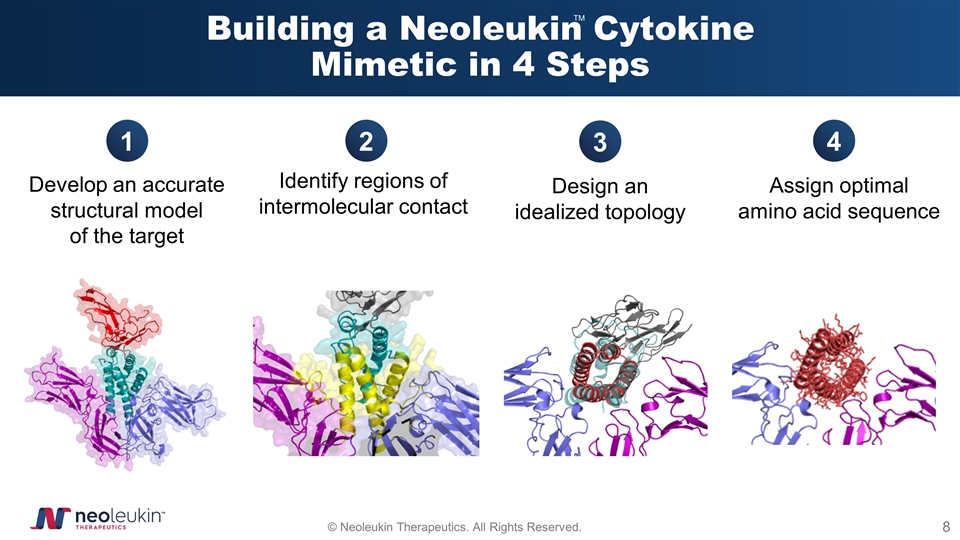
Building a Neoleukin Cytokine Mimetic in 4 Steps Develop an accurate structural model of the target Identify regions of intermolecular contact Design an idealized topology Assign optimal amino acid sequence 1 2 3 4 TM
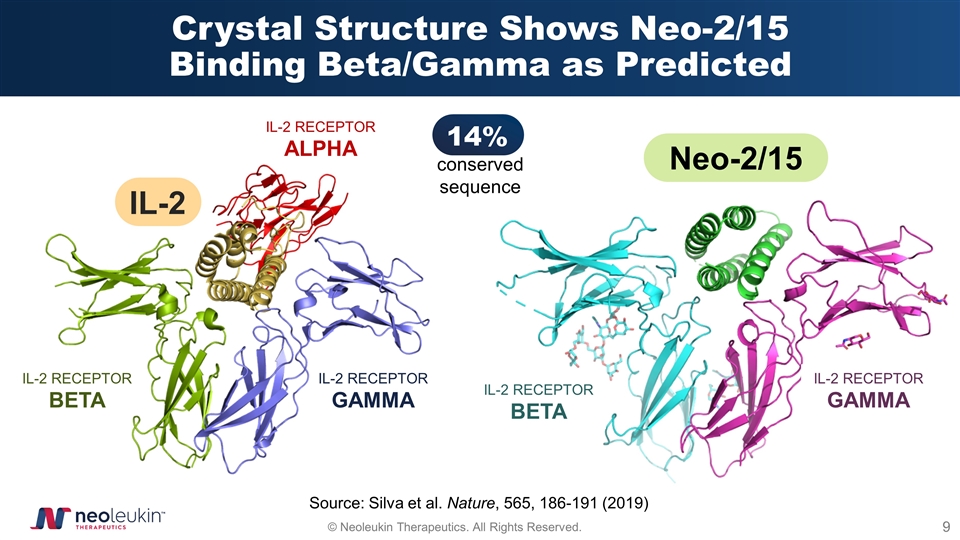
Crystal Structure Shows Neo-2/15 Binding Beta/Gamma as Predicted IL-2 RECEPTOR ALPHA IL-2 RECEPTOR BETA IL-2 RECEPTOR GAMMA IL-2 Neo-2/15 IL-2 RECEPTOR BETA IL-2 RECEPTOR GAMMA 14% conserved sequence Source: Silva et al. Nature, 565, 186-191 (2019)
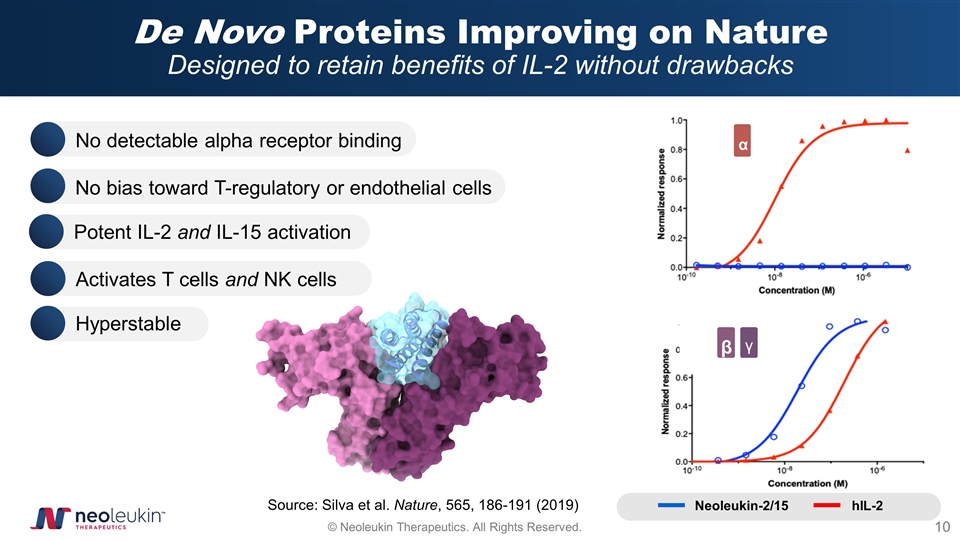
De Novo Proteins Improving on Nature Designed to retain benefits of IL-2 without drawbacks Source: Silva et al. Nature, 565, 186-191 (2019) α β γ hIL-2 Neoleukin-2/15 No bias toward T-regulatory or endothelial cells Hyperstable Potent IL-2 and IL-15 activation Activates T cells and NK cells No detectable alpha receptor binding
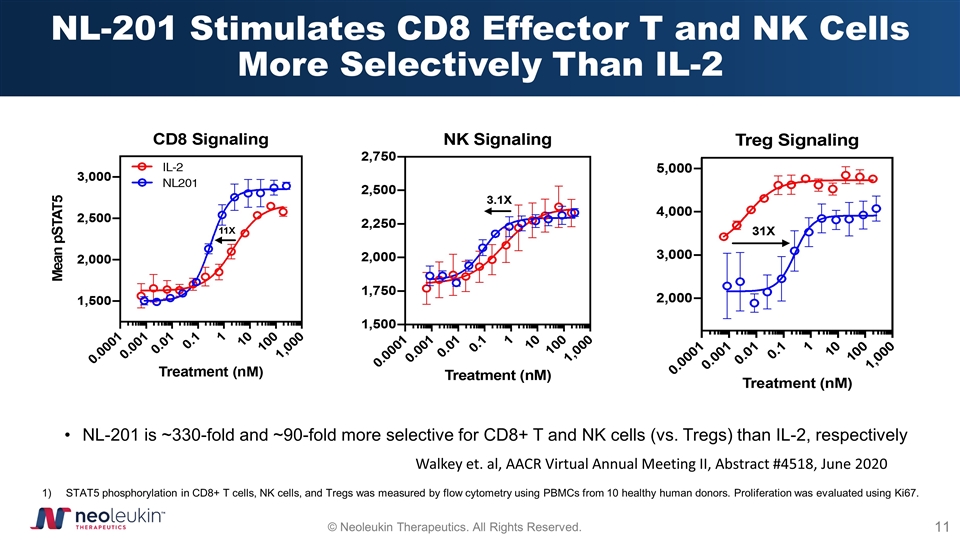
NL-201 Stimulates CD8 Effector T and NK Cells More Selectively Than IL-2 NL-201 is ~330-fold and ~90-fold more selective for CD8+ T and NK cells (vs. Tregs) than IL-2, respectively STAT5 phosphorylation in CD8+ T cells, NK cells, and Tregs was measured by flow cytometry using PBMCs from 10 healthy human donors. Proliferation was evaluated using Ki67. Walkey et. al, AACR Virtual Annual Meeting II, Abstract #4518, June 2020
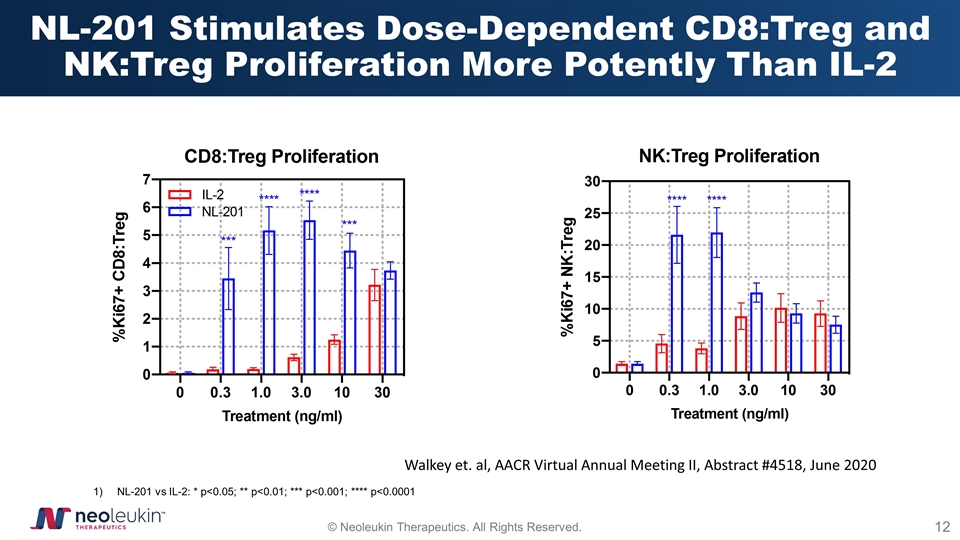
NL-201 Stimulates Dose-Dependent CD8:Treg and NK:Treg Proliferation More Potently Than IL-2 NL-201 vs IL-2: * p<0.05; ** p<0.01; *** p<0.001; **** p<0.0001 Walkey et. al, AACR Virtual Annual Meeting II, Abstract #4518, June 2020
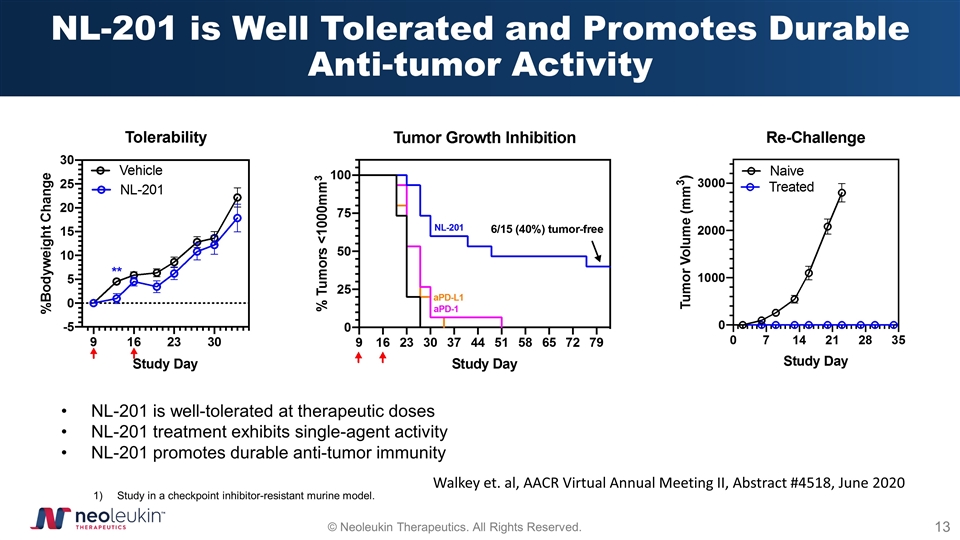
NL-201 is Well Tolerated and Promotes Durable Anti-tumor Activity NL-201 is well-tolerated at therapeutic doses NL-201 treatment exhibits single-agent activity NL-201 promotes durable anti-tumor immunity Study in a checkpoint inhibitor-resistant murine model. Walkey et. al, AACR Virtual Annual Meeting II, Abstract #4518, June 2020
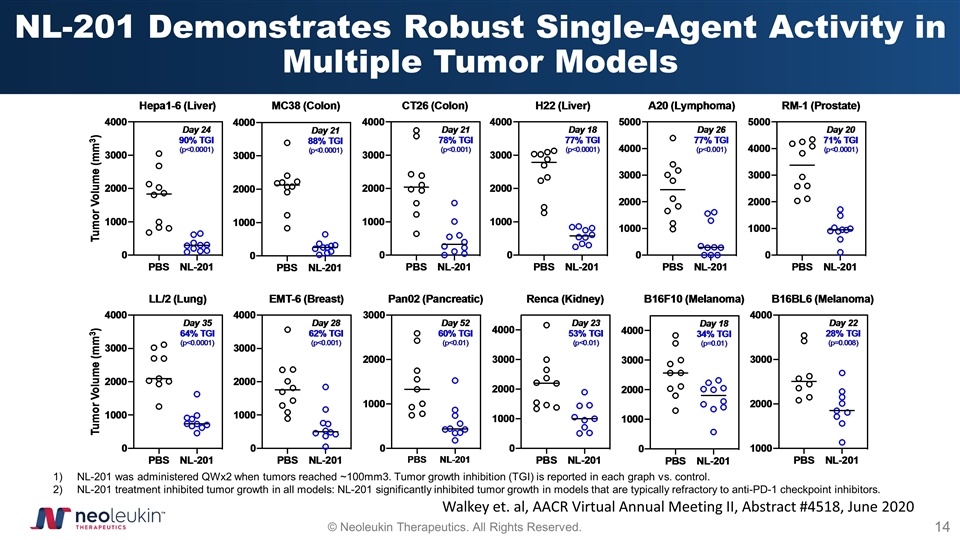
NL-201 Demonstrates Robust Single-Agent Activity in Multiple Tumor Models NL-201 was administered QWx2 when tumors reached ~100mm3. Tumor growth inhibition (TGI) is reported in each graph vs. control. NL-201 treatment inhibited tumor growth in all models: NL-201 significantly inhibited tumor growth in models that are typically refractory to anti-PD-1 checkpoint inhibitors. Walkey et. al, AACR Virtual Annual Meeting II, Abstract #4518, June 2020
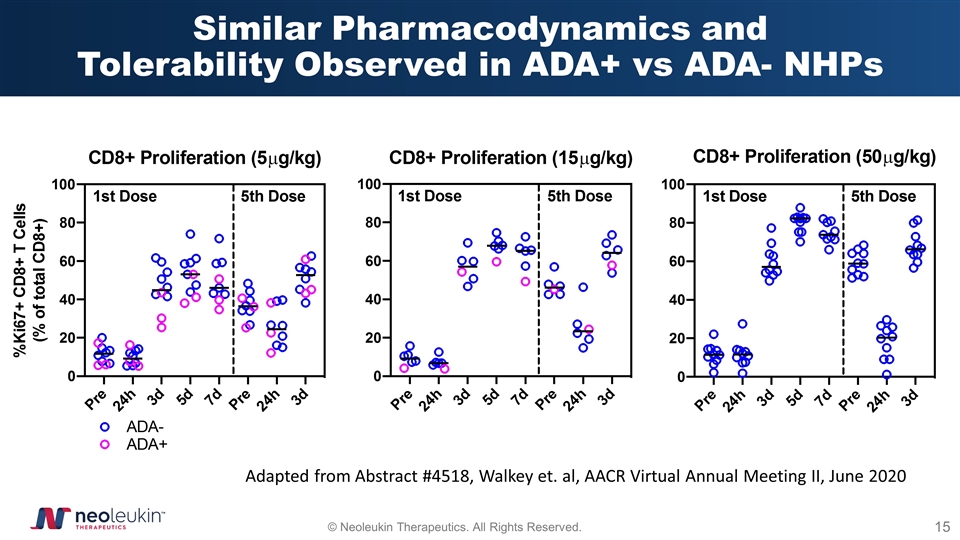
Similar Pharmacodynamics and Tolerability Observed in ADA+ vs ADA- NHPs Adapted from Abstract #4518, Walkey et. al, AACR Virtual Annual Meeting II, June 2020
NL-201 Phase 1 Clinical Trials Systemic administration: CTN submitted in Australia IND submitted in U.S. – working to address FDA requests related to CMC assay development IV, monotherapy in patients with advanced solid tumors Evaluate multiple schedules and dose levels to assess safety, PK, PD, and antitumor activity Indication-specific expansion cohorts, including renal cell carcinoma and melanoma Local administration: Designed to achieve higher NL-201 concentrations in tumor microenvironment Targeted to begin in 2021
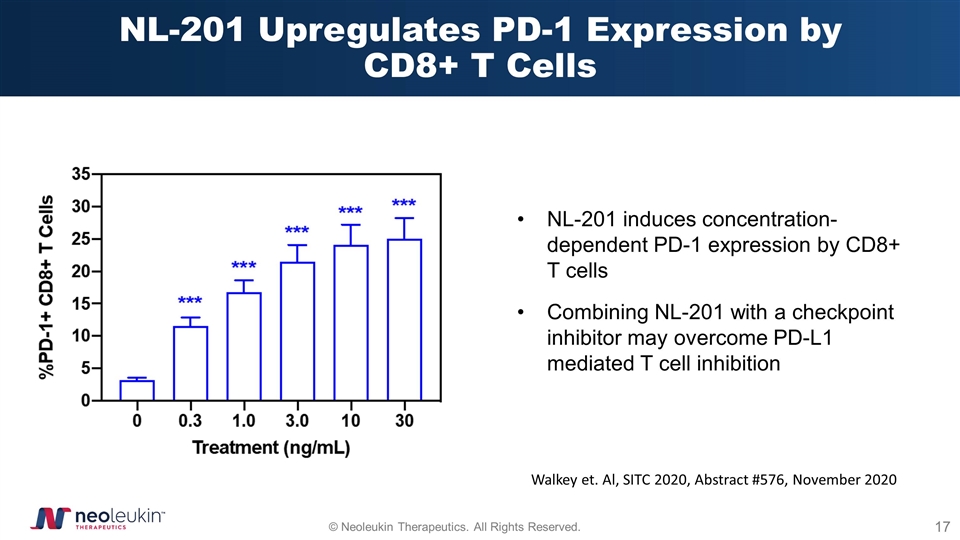
NL-201 Upregulates PD-1 Expression by CD8+ T Cells Walkey et. Al, SITC 2020, Abstract #576, November 2020 NL-201 induces concentration-dependent PD-1 expression by CD8+ T cells Combining NL-201 with a checkpoint inhibitor may overcome PD-L1 mediated T cell inhibition
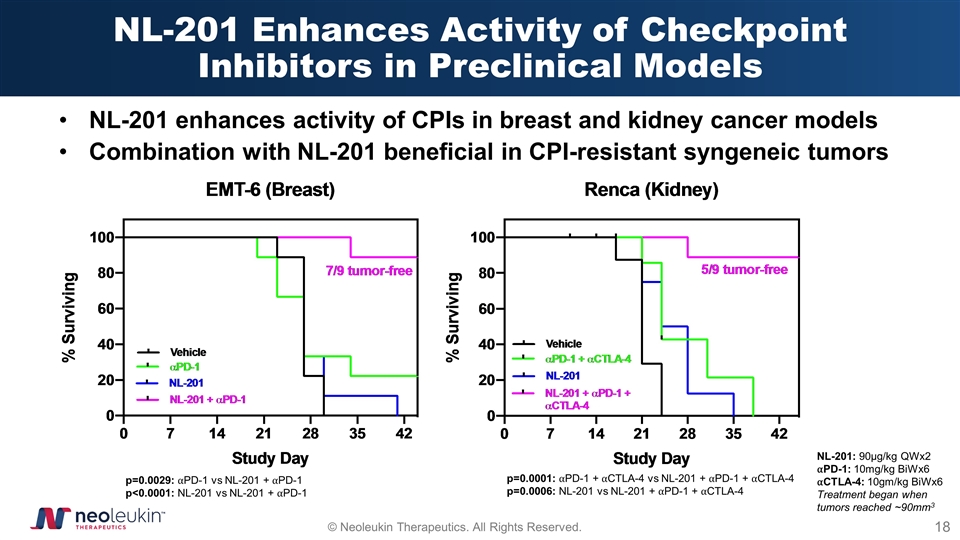
NL-201 Enhances Activity of Checkpoint Inhibitors in Preclinical Models NL-201 enhances activity of CPIs in breast and kidney cancer models Combination with NL-201 beneficial in CPI-resistant syngeneic tumors p=0.0001: ⍺PD-1 + ⍺CTLA-4 vs NL-201 + ⍺PD-1 + ⍺CTLA-4 p=0.0006: NL-201 vs NL-201 + ⍺PD-1 + ⍺CTLA-4 p=0.0029: ⍺PD-1 vs NL-201 + ⍺PD-1 p<0.0001: NL-201 vs NL-201 + ⍺PD-1 NL-201: 90µg/kg QWx2 ⍺PD-1: 10mg/kg BiWx6 ⍺CTLA-4: 10gm/kg BiWx6 Treatment began when tumors reached ~90mm3
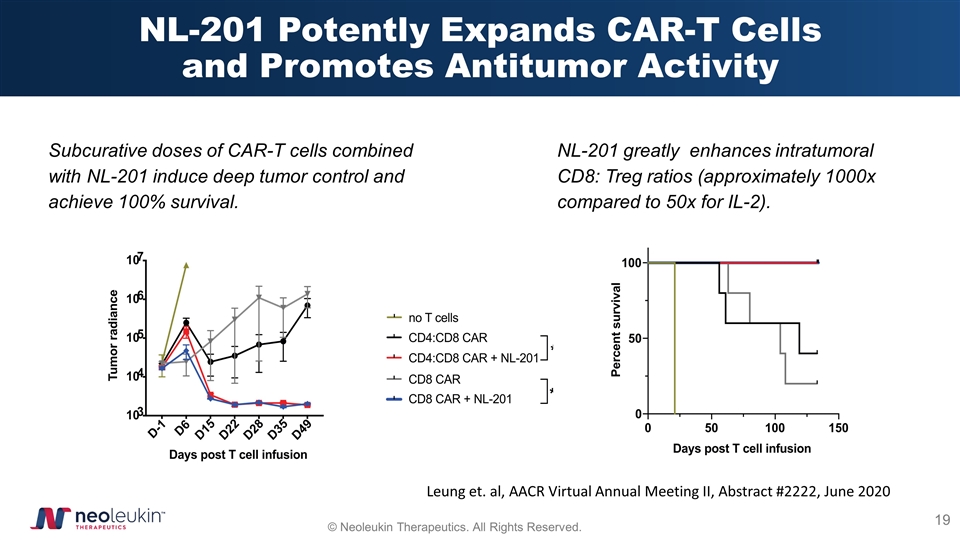
NL-201 Potently Expands CAR-T Cells and Promotes Antitumor Activity Subcurative doses of CAR-T cells combined with NL-201 induce deep tumor control and achieve 100% survival. NL-201 greatly enhances intratumoral CD8: Treg ratios (approximately 1000x compared to 50x for IL-2). Leung et. al, AACR Virtual Annual Meeting II, Abstract #2222, June 2020
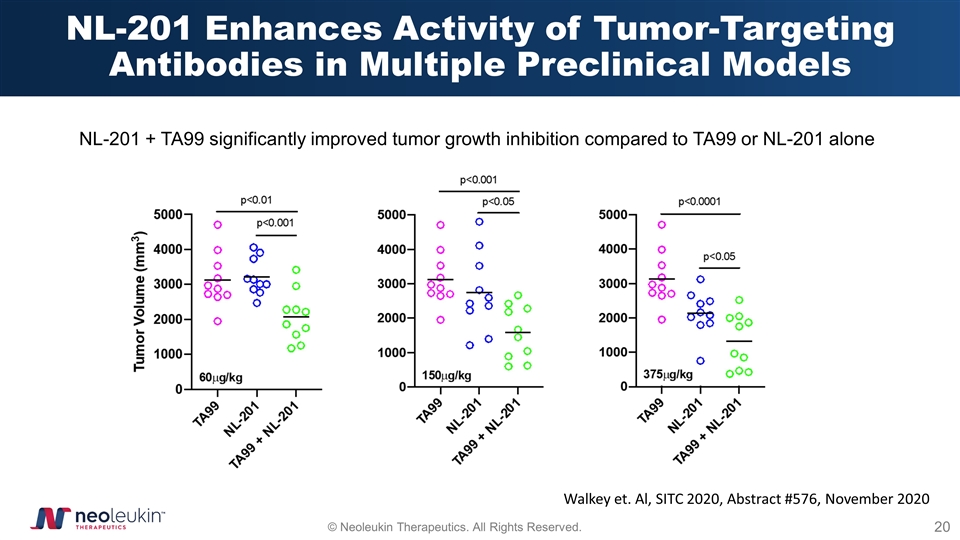
NL-201 Enhances Activity of Tumor-Targeting Antibodies in Multiple Preclinical Models Walkey et. Al, SITC 2020, Abstract #576, November 2020 NL-201 + TA99 significantly improved tumor growth inhibition compared to TA99 or NL-201 alone
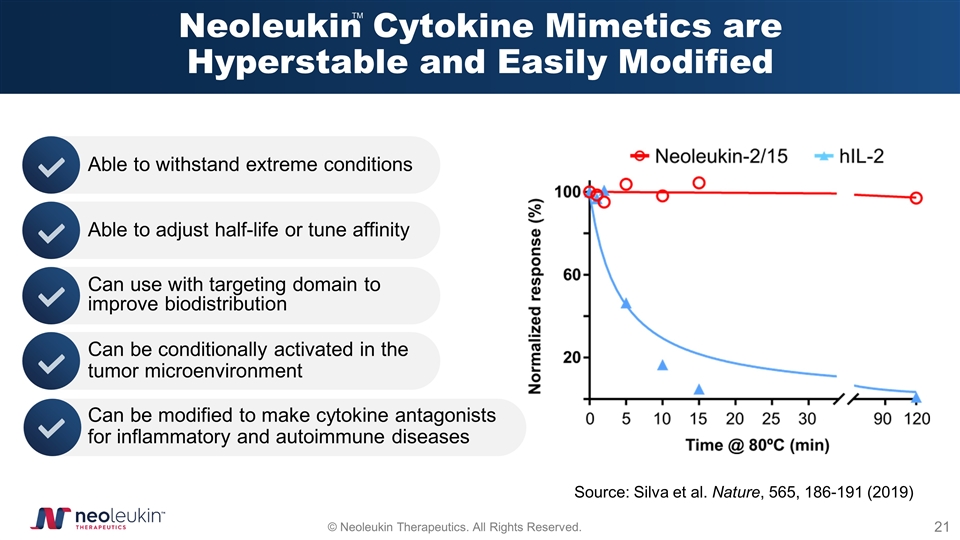
Neoleukin Cytokine Mimetics are Hyperstable and Easily Modified Able to withstand extreme conditions Able to adjust half-life or tune affinity Can be conditionally activated in the tumor microenvironment Can be modified to make cytokine antagonists for inflammatory and autoimmune diseases Can use with targeting domain to improve biodistribution Source: Silva et al. Nature, 565, 186-191 (2019) TM
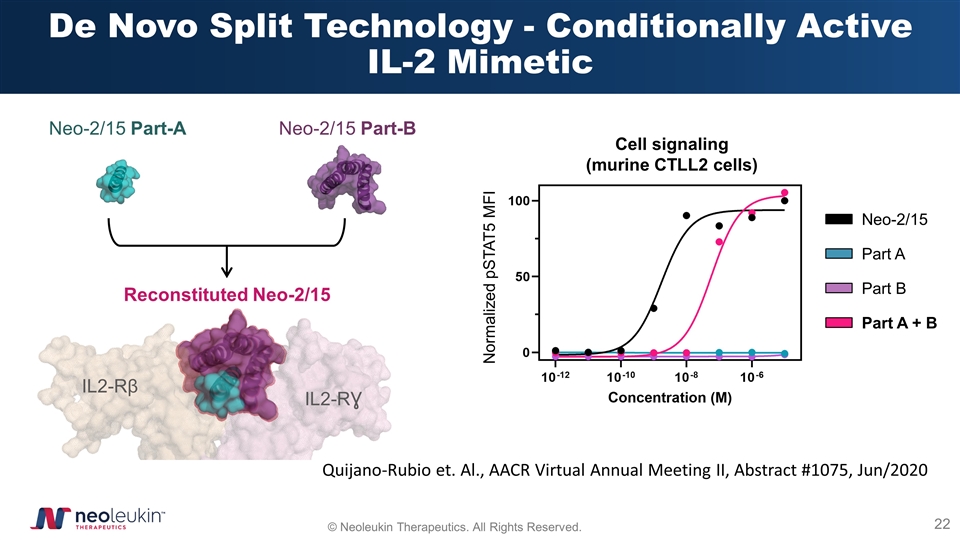
De Novo Split Technology - Conditionally Active IL-2 Mimetic Cell signaling (murine CTLL2 cells) Normalized pSTAT5 MFI Neo-2/15 Part A Part B Part A + B Quijano-Rubio et. Al., AACR Virtual Annual Meeting II, Abstract #1075, Jun/2020 Neo-2/15 Part-A Neo-2/15 Part-B Reconstituted Neo-2/15 IL2-Rβ IL2-RƔ
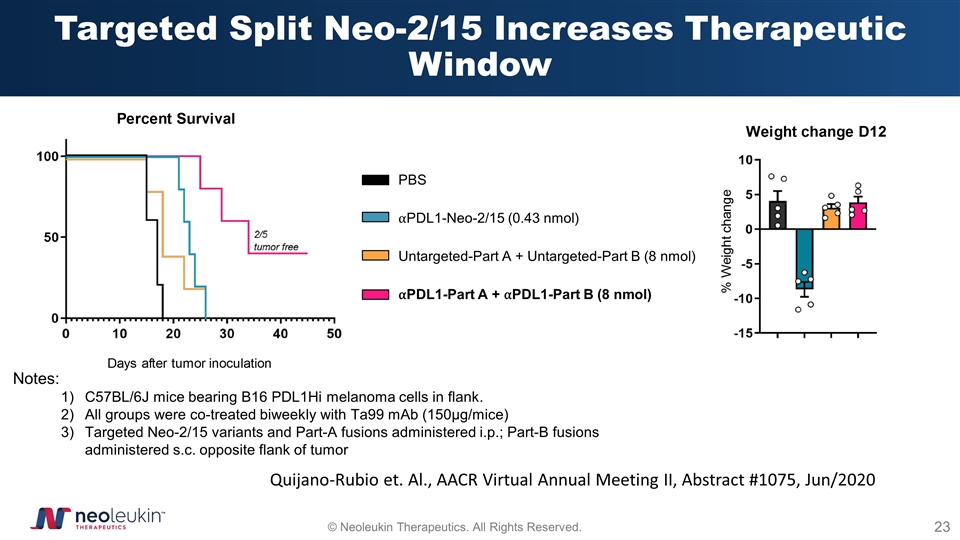
Targeted Split Neo-2/15 Increases Therapeutic Window Notes: C57BL/6J mice bearing B16 PDL1Hi melanoma cells in flank. All groups were co-treated biweekly with Ta99 mAb (150µg/mice) Targeted Neo-2/15 variants and Part-A fusions administered i.p.; Part-B fusions administered s.c. opposite flank of tumor PBS ⍺PDL1-Neo-2/15 (0.43 nmol) Untargeted-Part A + Untargeted-Part B (8 nmol) ⍺PDL1-Part A + ⍺PDL1-Part B (8 nmol) Quijano-Rubio et. Al., AACR Virtual Annual Meeting II, Abstract #1075, Jun/2020
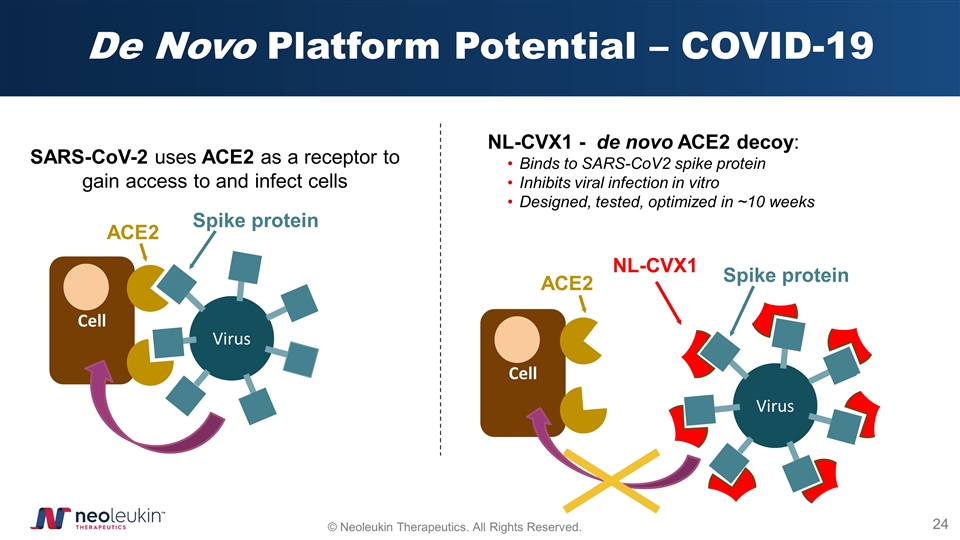
De Novo Platform Potential – COVID-19 ACE2 NL-CVX1 - de novo ACE2 decoy: Binds to SARS-CoV2 spike protein Inhibits viral infection in vitro Designed, tested, optimized in ~10 weeks Cell Virus Spike protein Cell Virus ACE2 Spike protein ACE2 SARS-CoV-2 uses ACE2 as a receptor to gain access to and infect cells NL-CVX1
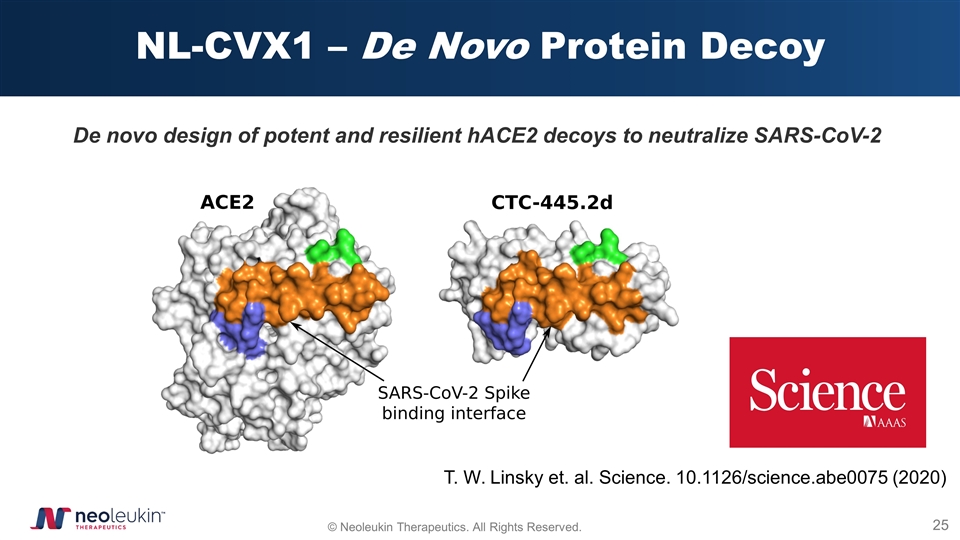
NL-CVX1 – De Novo Protein Decoy De novo design of potent and resilient hACE2 decoys to neutralize SARS-CoV-2 T. W. Linsky et. al. Science. 10.1126/science.abe0075 (2020)
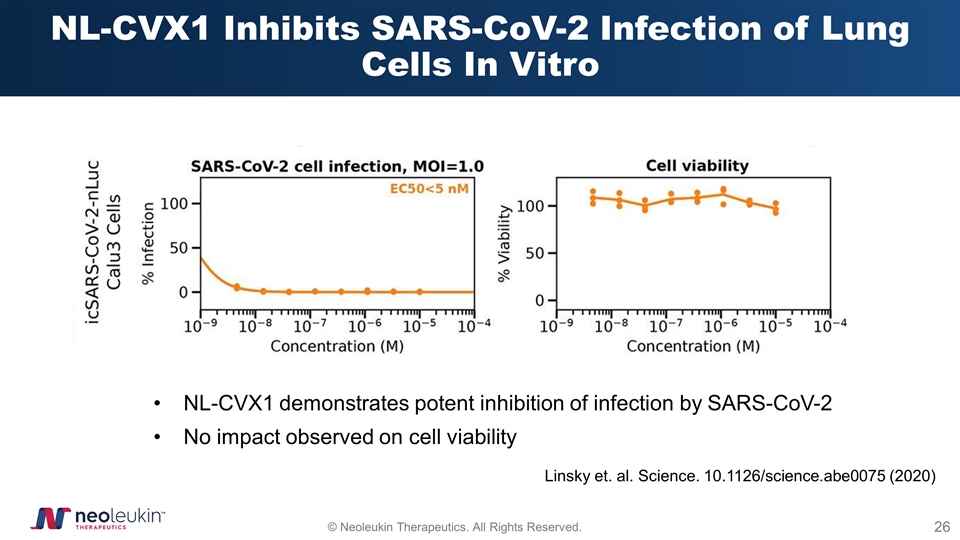
NL-CVX1 Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Infection of Lung Cells In Vitro Linsky et. al. Science. 10.1126/science.abe0075 (2020) NL-CVX1 demonstrates potent inhibition of infection by SARS-CoV-2 No impact observed on cell viability
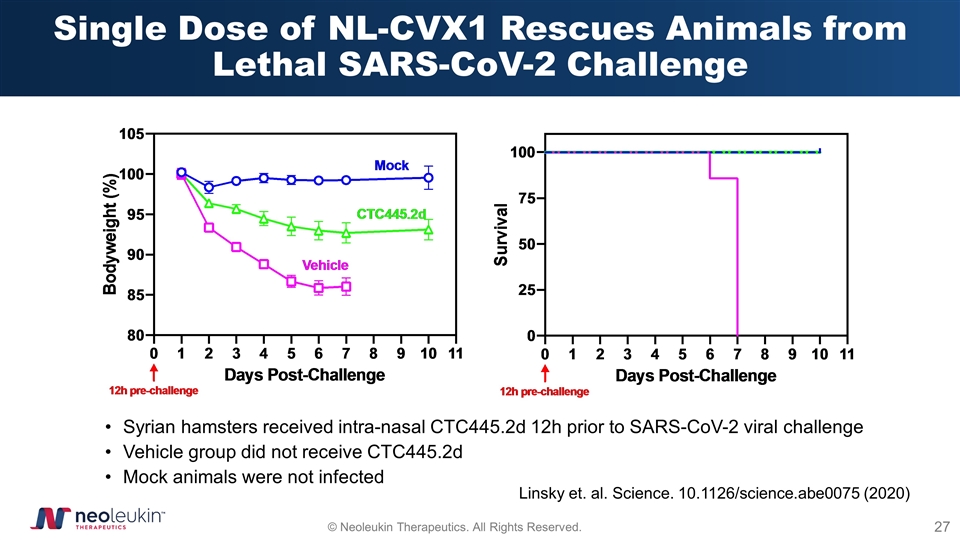
Single Dose of NL-CVX1 Rescues Animals from Lethal SARS-CoV-2 Challenge Syrian hamsters received intra-nasal CTC445.2d 12h prior to SARS-CoV-2 viral challenge Vehicle group did not receive CTC445.2d Mock animals were not infected Linsky et. al. Science. 10.1126/science.abe0075 (2020)

Anticipated Milestones Event Timeline Initiation of NL-201 systemic administration trial 1H2021 Planning NL-CVX1 first-in-human trial 1H2021 Initiation of NL-201 local administration trial 2H2021 Disclose next de novo cytokine mimetic program 2H2021

Financial Highlights $201.2 million cash & cash equivalents as of September 30, 2020 Cash and cash equivalents expected to fund operations into 2023 41.9M common shares outstanding and 12.7M pre-funded warrants1 Click to edit footnotes Click to edit footnotes Click to edit footnotes Click to edit footnotes 1Warrants to purchase common shares 1:1 with an exercise price of $0.000001

Improving on nature. Designing for life.
