Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-99.1 - EX-99.1 - Gossamer Bio, Inc. | goss-ex991_6.htm |
| 8-K - 8-K - Gossamer Bio, Inc. | goss-8k_20201013.htm |

GB001 Phase 2 Clinical Trial Topline Results October 13, 2020 Exhibit 99.2

This presentation contains forward-looking statements. All statements other than statements of historical facts contained in this presentation, including statements regarding the potential for the LEDA Study results to allow for the design of a well-powered Phase 3 program for GB001 and our plans to discuss such results with global regulatory authorities to inform potential partnerships or strategic alternatives; potential plans to advance GB001; the potential of GB001 to serve asthma patients; and expected cash runway, our future results of operations and financial position, business strategy, prospective products, product approvals, research and development costs, timing and likelihood of success, plans and objectives of management for future operations, and future results of current and anticipated products, are forward-looking statements. In some cases, you can identify forward-looking statements by terms such as “may,” “will,” “should,” “expect,” “plan,” “anticipate,” “could,” “intend,” “target,” “project,” “contemplates,” “believes,” “estimates,” “predicts,” “potential” or “continue” or the negative of these terms or other similar expressions. These statements involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other important factors that may cause our actual results, performance or achievements to be materially different from any future results, performance or achievements expressed or implied by the forward-looking statements. These known risks and uncertainties include: the potential for the LEDA Study results to allow for the design of a well-powered Phase 3 program for GB001 and our plans to discuss such results with global regulatory authorities to inform potential partnerships or strategic alternatives; topline results Gossamer reports are based on preliminary analysis of key efficacy and safety data, and such data may change following a more comprehensive review of the data related to the clinical trial and such topline data may not accurately reflect the complete results of the clinical trial, and the FDA and other regulatory authorities may not agree with Gossamer's interpretation of such results; disruption to our operations from the recent global outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic, including clinical trial and regulatory meeting delays; the Company's dependence on third parties in connection with product manufacturing, research and preclinical and clinical testing; potential delays in the commencement, enrollment and completion of any future clinical trials of GB001 and the success of any such trials, including any Phase 3 trials; Gossamer may not be successful in establishing strategic partnership or collaborations and may not realize the benefits of such arrangements; regulatory developments in the United States and foreign countries; unexpected adverse side effects or inadequate efficacy of our product candidates that may limit their development, regulatory approval and/or commercialization, or may result in recalls or product liability claims; Gossamer may use its capital resources sooner than it expects; and other risks described in the Company's prior press releases and the Company's filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), including under the heading “Risk Factors” in the Company's annual report on Form 10-K and any subsequent filings with the SEC. Because forward-looking statements are inherently subject to risks and uncertainties, some of which cannot be predicted or quantified and some of which are beyond our control, you should not rely on these forward looking statements as predictions of future events. The events and circumstances reflected in our forward-looking statements may not be achieved or occur and actual results could differ materially from those projected in the forward-looking statements. Except as required by applicable law, we do not plan to publicly update or revise any forward-looking statements contained herein, whether as a result of any new information, future events, changed circumstances or otherwise. All forward-looking statements are qualified in their entirety by this cautionary statement, which is made under the safe harbor provisions of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995 and we undertake no obligation to revise or update this presentation to reflect events or circumstances after the date hereof. This presentation also contains estimates and other statistical data made by independent parties and by us relating to market size and growth and other data about our industry. This data involves a number of assumptions and limitations, and you are cautioned not to give undue weight to such estimates. In addition, projections, assumptions, and estimates of our future performance and the future performance of the markets in which we operate are necessarily subject to a high degree of uncertainty and risk. Forward Looking Statements
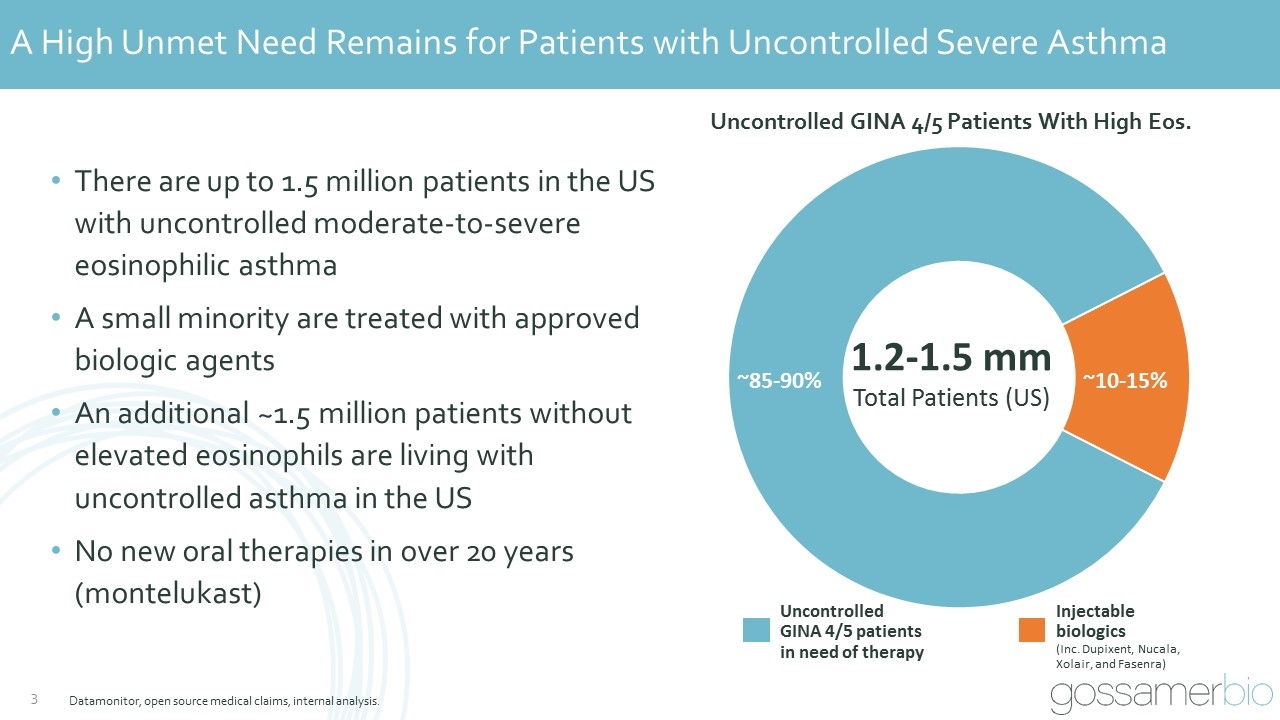
Datamonitor, open source medical claims, internal analysis. A High Unmet Need Remains for Patients with Uncontrolled Severe Asthma 1.2-1.5 mm Total Patients (US) ~85-90% ~10-15% Uncontrolled GINA 4/5 Patients With High Eos. Injectable biologics (Inc. Dupixent, Nucala, Xolair, and Fasenra) Uncontrolled GINA 4/5 patients in need of therapy There are up to 1.5 million patients in the US with uncontrolled moderate-to-severe eosinophilic asthma A small minority are treated with approved biologic agents An additional ~1.5 million patients without elevated eosinophils are living with uncontrolled asthma in the US No new oral therapies in over 20 years (montelukast)

GB001 is a potent, insurmountable antagonist of the DP2 receptor DP2 antagonism has shown the potential to inhibit recruitment of airway eosinophils and reduce airway inflammation GB001 exhibits prolonged receptor residence time and extended pharmacodynamic effects Previously demonstrated clinical effects on asthma worsening in steroid withdrawal setting Topline results of LEDA and TITAN Phase 2 studies announced today GB001: Oral DP2 Antagonist for the Treatment of Severe Asthma
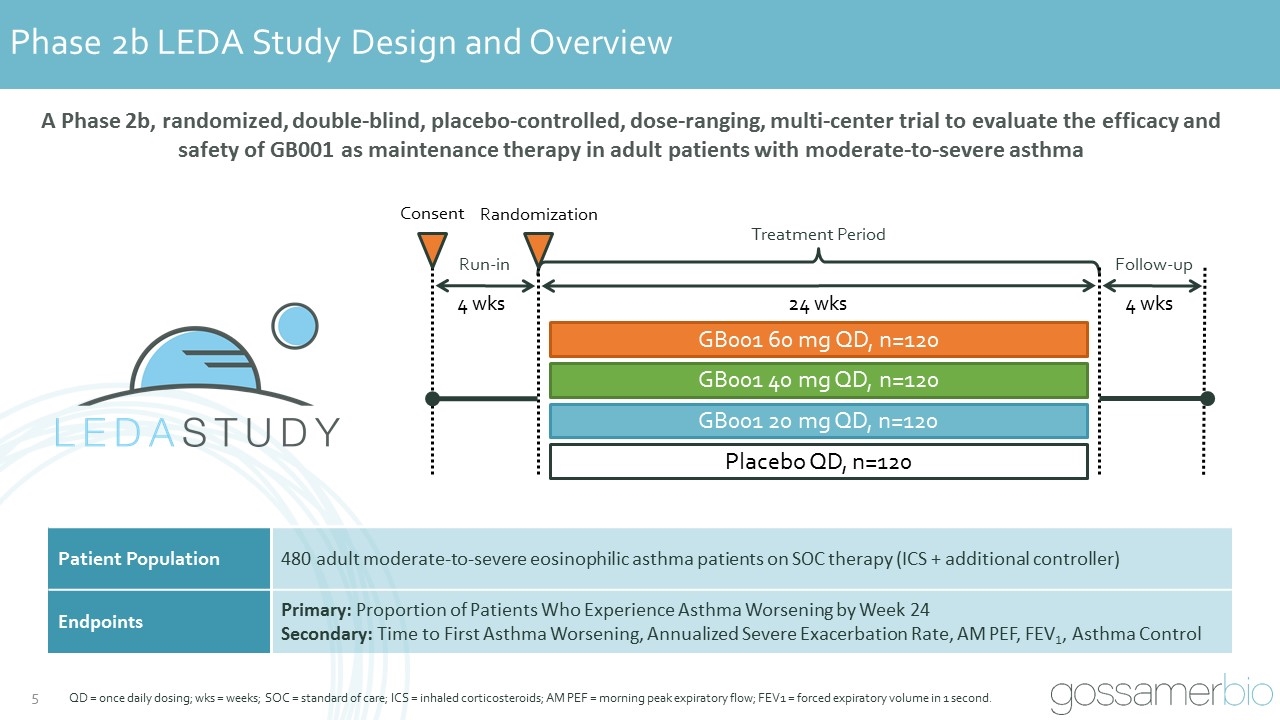
Phase 2b LEDA Study Design and Overview QD = once daily dosing; wks = weeks; SOC = standard of care; ICS = inhaled corticosteroids; AM PEF = morning peak expiratory flow; FEV1 = forced expiratory volume in 1 second. Run-in Treatment Period Follow-up 4 wks 24 wks Consent Randomization 4 wks Placebo QD, n=120 GB001 20 mg QD, n=120 GB001 40 mg QD, n=120 GB001 60 mg QD, n=120 A Phase 2b, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging, multi-center trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of GB001 as maintenance therapy in adult patients with moderate-to-severe asthma Patient Population 480 adult moderate-to-severe eosinophilic asthma patients on SOC therapy (ICS + additional controller) Endpoints Primary: Proportion of Patients Who Experience Asthma Worsening by Week 24 Secondary: Time to First Asthma Worsening, Annualized Severe Exacerbation Rate, AM PEF, FEV1, Asthma Control

Evaluate whether once-daily, oral GB001 has a clinically meaningful impact on efficacy outcomes relevant to anti-inflammatory mechanism (asthma worsening and severe exacerbation) to inform effects and statistical powering on potential registrational Phase 3 endpoints Dose-range to understand effect of efficacy and safety outcomes to determine dose selection for future trials Identify the optimal Phase 3 patient population Goals for LEDA Study
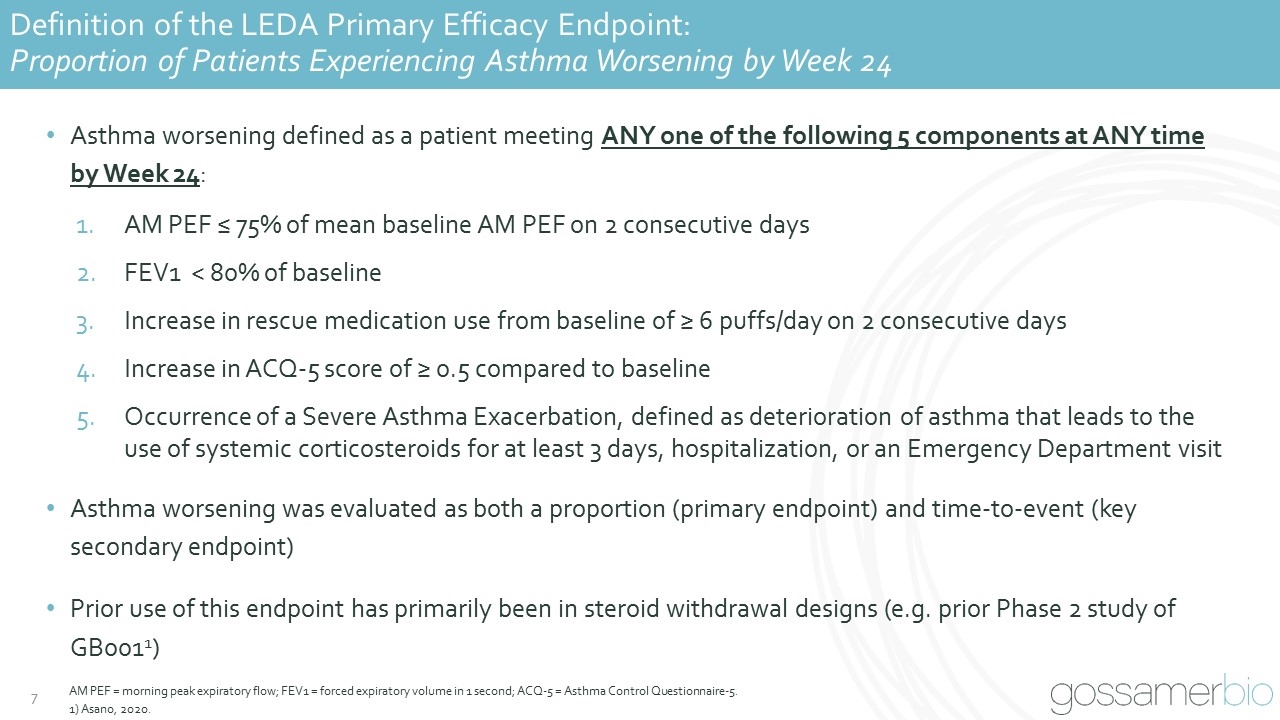
Definition of the LEDA Primary Efficacy Endpoint: Proportion of Patients Experiencing Asthma Worsening by Week 24 Asthma worsening defined as a patient meeting ANY one of the following 5 components at ANY time by Week 24: AM PEF ≤ 75% of mean baseline AM PEF on 2 consecutive days FEV1 < 80% of baseline Increase in rescue medication use from baseline of ≥ 6 puffs/day on 2 consecutive days Increase in ACQ-5 score of ≥ 0.5 compared to baseline Occurrence of a Severe Asthma Exacerbation, defined as deterioration of asthma that leads to the use of systemic corticosteroids for at least 3 days, hospitalization, or an Emergency Department visit Asthma worsening was evaluated as both a proportion (primary endpoint) and time-to-event (key secondary endpoint) Prior use of this endpoint has primarily been in steroid withdrawal designs (e.g. prior Phase 2 study of GB0011) AM PEF = morning peak expiratory flow; FEV1 = forced expiratory volume in 1 second; ACQ-5 = Asthma Control Questionnaire-5. 1) Asano, 2020.
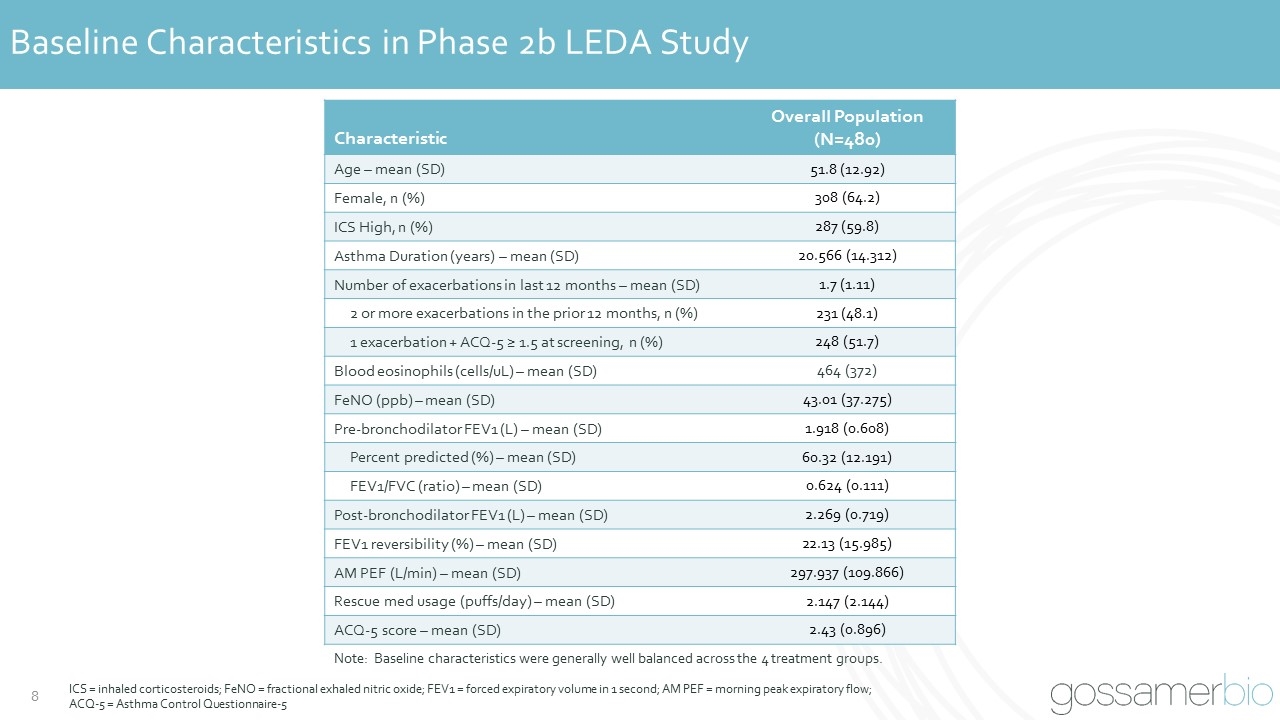
Baseline Characteristics in Phase 2b LEDA Study Characteristic Overall Population (N=480) Age – mean (SD) 51.8 (12.92) Female, n (%) 308 (64.2) ICS High, n (%) 287 (59.8) Asthma Duration (years) – mean (SD) 20.566 (14.312) Number of exacerbations in last 12 months – mean (SD) 1.7 (1.11) 2 or more exacerbations in the prior 12 months, n (%) 231 (48.1) 1 exacerbation + ACQ-5 ≥ 1.5 at screening, n (%) 248 (51.7) Blood eosinophils (cells/uL) – mean (SD) 464 (372) FeNO (ppb) – mean (SD) 43.01 (37.275) Pre-bronchodilator FEV1 (L) – mean (SD) 1.918 (0.608) Percent predicted (%) – mean (SD) 60.32 (12.191) FEV1/FVC (ratio) – mean (SD) 0.624 (0.111) Post-bronchodilator FEV1 (L) – mean (SD) 2.269 (0.719) FEV1 reversibility (%) – mean (SD) 22.13 (15.985) AM PEF (L/min) – mean (SD) 297.937 (109.866) Rescue med usage (puffs/day) – mean (SD) 2.147 (2.144) ACQ-5 score – mean (SD) 2.43 (0.896) Note: Baseline characteristics were generally well balanced across the 4 treatment groups. ICS = inhaled corticosteroids; FeNO = fractional exhaled nitric oxide; FEV1 = forced expiratory volume in 1 second; AM PEF = morning peak expiratory flow; ACQ-5 = Asthma Control Questionnaire-5
Summary of Phase 2b LEDA Primary and Secondary Endpoints GB001 groups did not meet the primary endpoint of proportion of patients who experience asthma worsening by week 24 However, consistent numeric reductions in the odds of asthma worsening of 32% to 35% observed (p-values: 0.1086 to 0.1482) across GB001 groups GB001 20 mg and 60 mg groups significantly improved time to first asthma worsening (20 mg, 28% risk reduction, p=0.0466; 60 mg, 30% risk reduction, p=0.0304), with GB001 40 mg also demonstrating a numeric effect (23%, p=0.1222) Numeric improvements in annualized severe exacerbation rate, lung function (morning peak flow and FEV1), and asthma control (ACQ-5) observed Consistent treatment effect in all GB001 groups across clinical endpoints suggests all doses met the biological threshold for clinical response Preliminary identification of patient subgroup with potential to enrich patient selection and enhance treatment response FEV1 = forced expiratory volume in 1 second; ACQ-5 = Asthma Control Questionnaire-5.
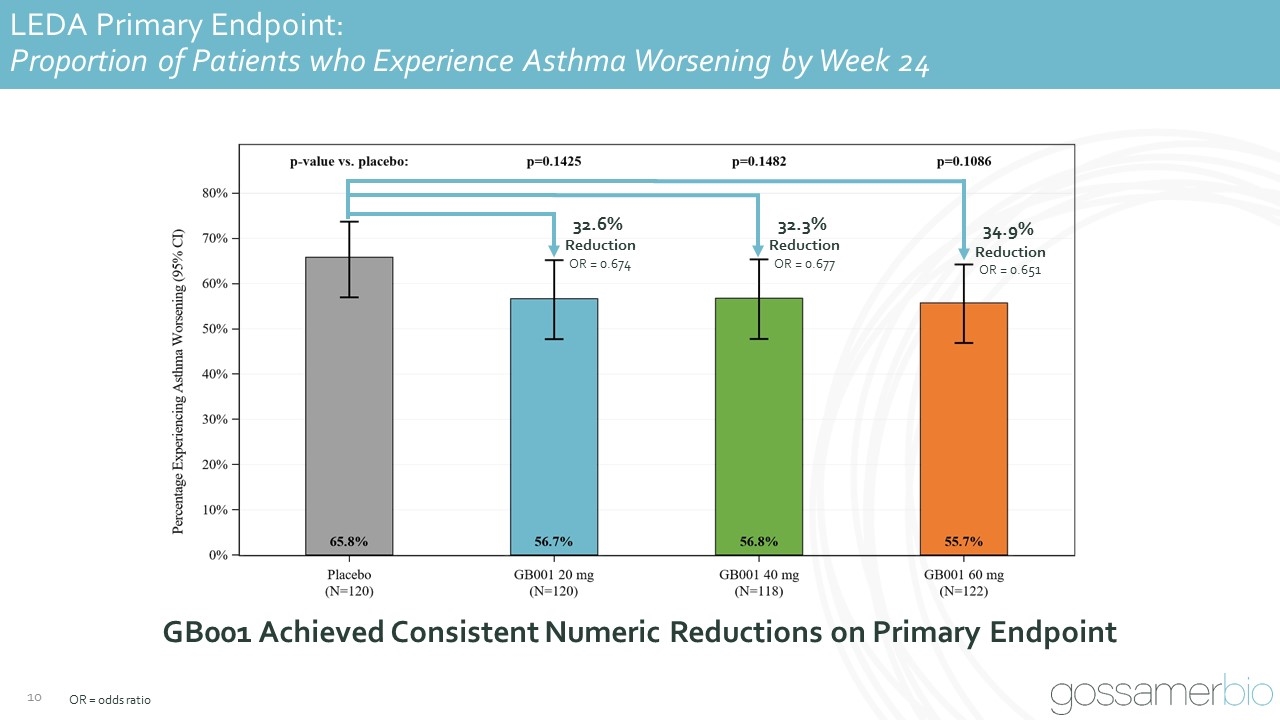
LEDA Primary Endpoint: Proportion of Patients who Experience Asthma Worsening by Week 24 GB001 Achieved Consistent Numeric Reductions on Primary Endpoint OR = odds ratio 32.6% Reduction OR = 0.674 32.3% Reduction OR = 0.677 34.9% Reduction OR = 0.651
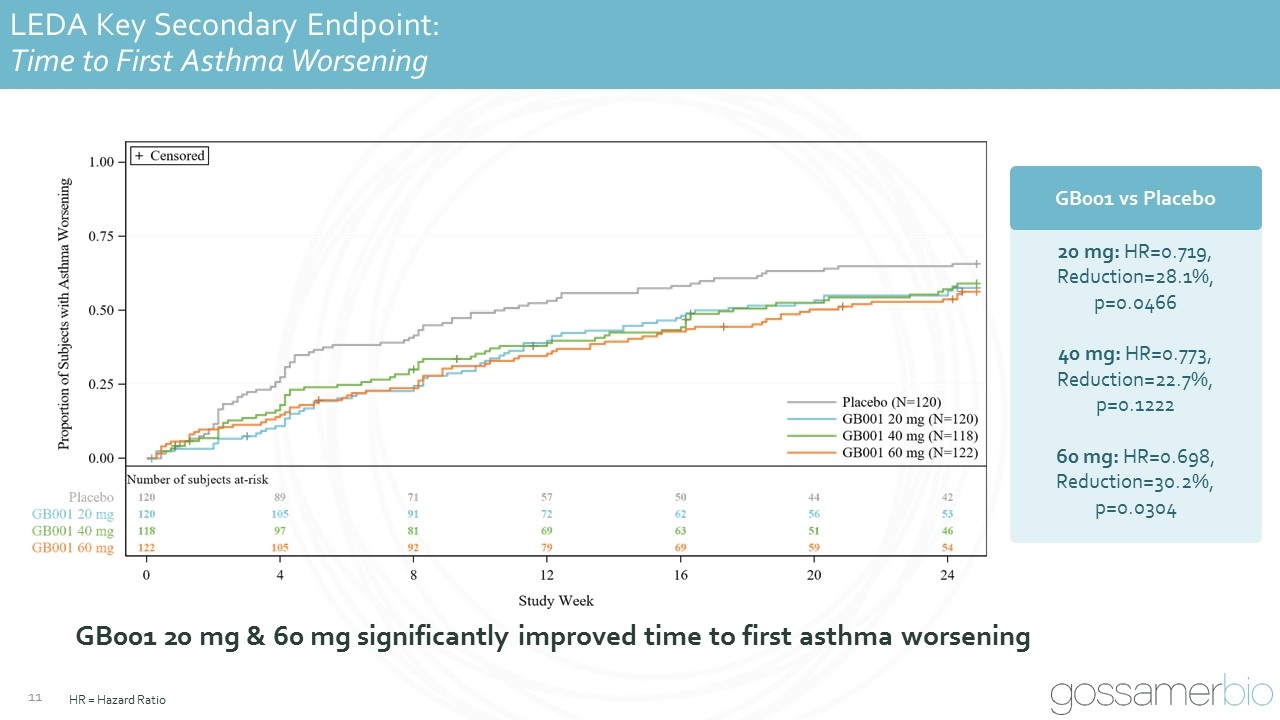
LEDA Key Secondary Endpoint: Time to First Asthma Worsening GB001 20 mg & 60 mg significantly improved time to first asthma worsening HR = Hazard Ratio 20 mg: HR=0.719, Reduction=28.1%, p=0.0466 40 mg: HR=0.773, Reduction=22.7%, p=0.1222 60 mg: HR=0.698, Reduction=30.2%, p=0.0304 GB001 vs Placebo
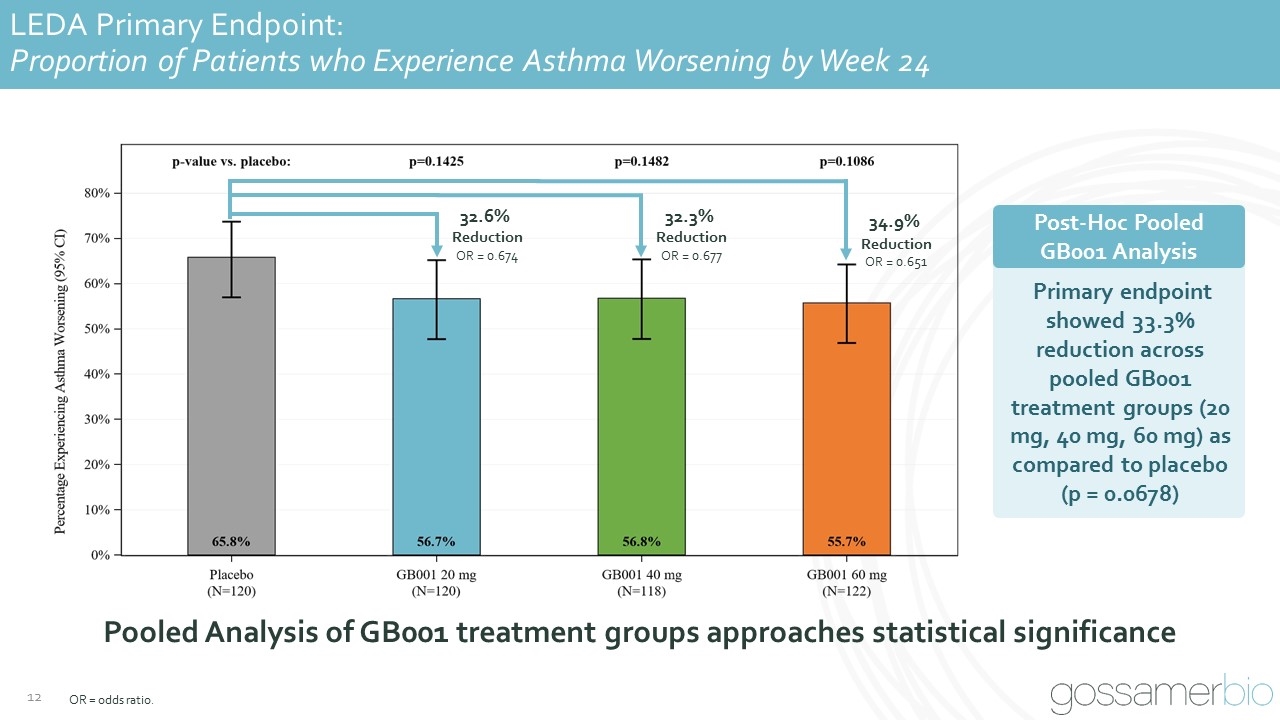
LEDA Primary Endpoint: Proportion of Patients who Experience Asthma Worsening by Week 24 OR = odds ratio. 32.6% Reduction OR = 0.674 32.3% Reduction OR = 0.677 34.9% Reduction OR = 0.651 Pooled Analysis of GB001 treatment groups approaches statistical significance Post-Hoc Pooled GB001 Analysis Primary endpoint showed 33.3% reduction across pooled GB001 treatment groups (20 mg, 40 mg, 60 mg) as compared to placebo (p = 0.0678)
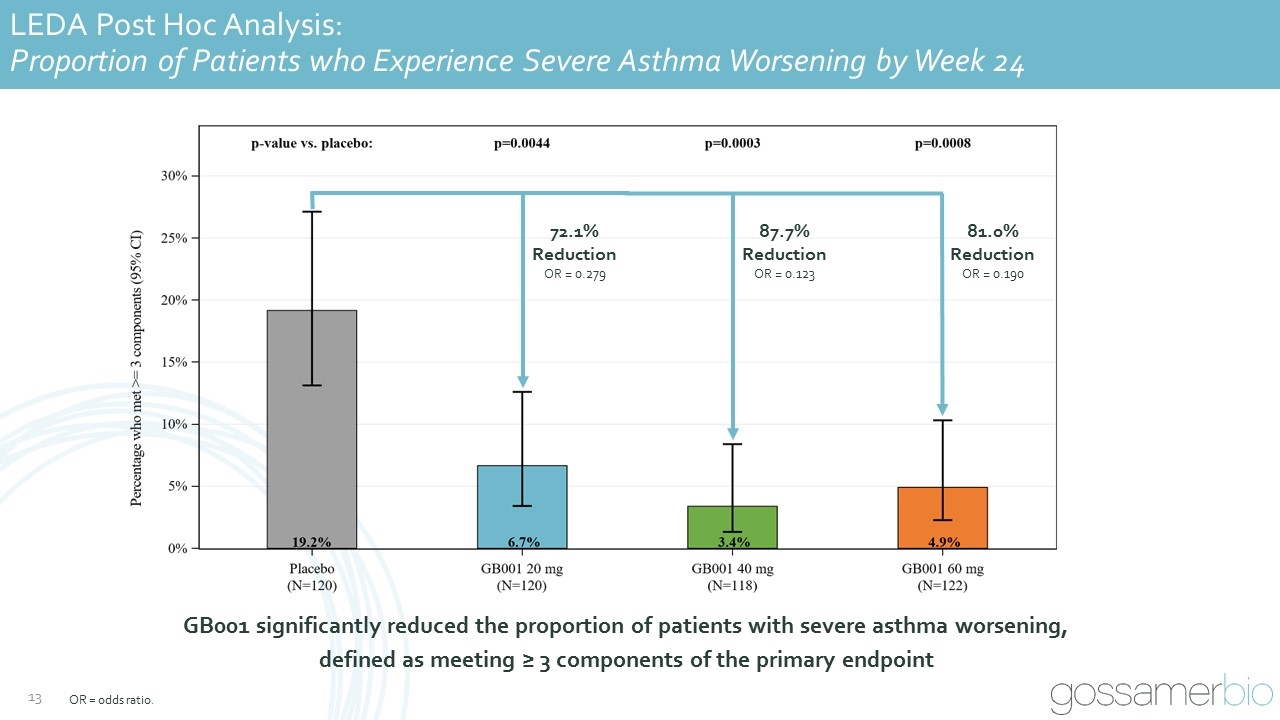
GB001 significantly reduced the proportion of patients with severe asthma worsening, defined as meeting ≥ 3 components of the primary endpoint LEDA Post Hoc Analysis: Proportion of Patients who Experience Severe Asthma Worsening by Week 24 72.1% Reduction OR = 0.279 87.7% Reduction OR = 0.123 81.0% Reduction OR = 0.190 OR = odds ratio.
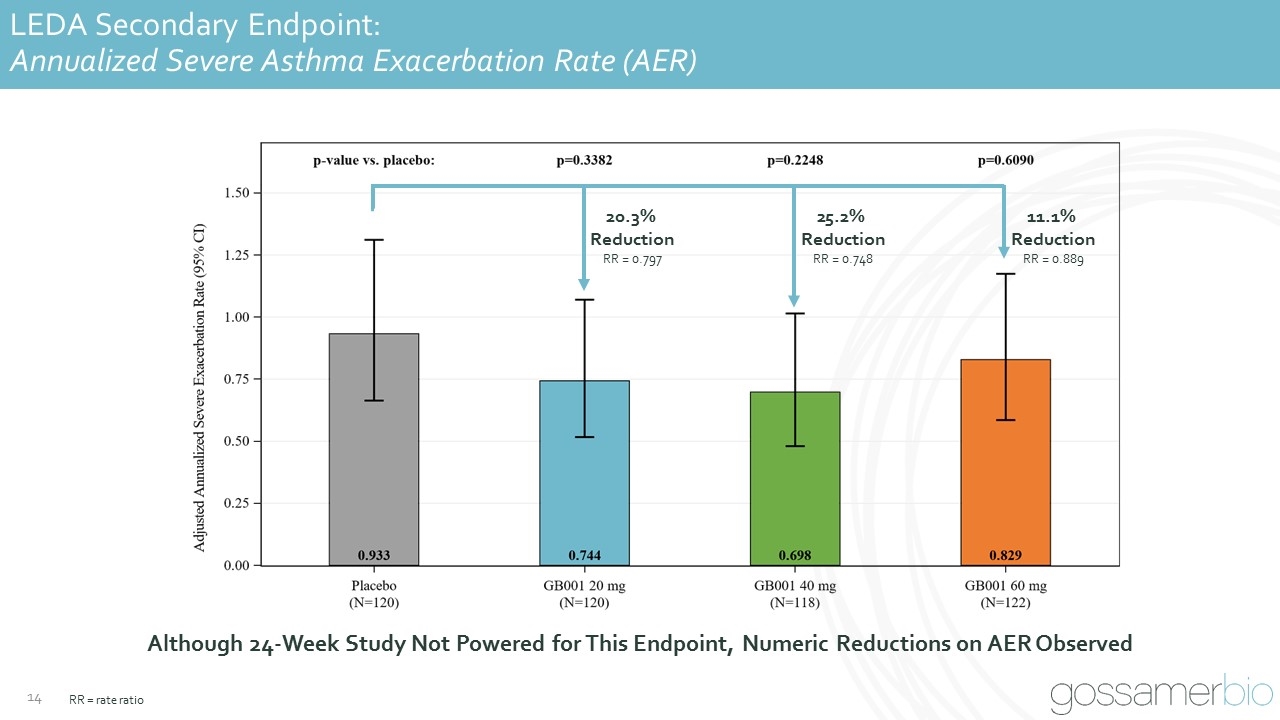
LEDA Secondary Endpoint: Annualized Severe Asthma Exacerbation Rate (AER) 20.3% Reduction RR = 0.797 25.2% Reduction RR = 0.748 11.1% Reduction RR = 0.889 Although 24-Week Study Not Powered for This Endpoint, Numeric Reductions on AER Observed RR = rate ratio
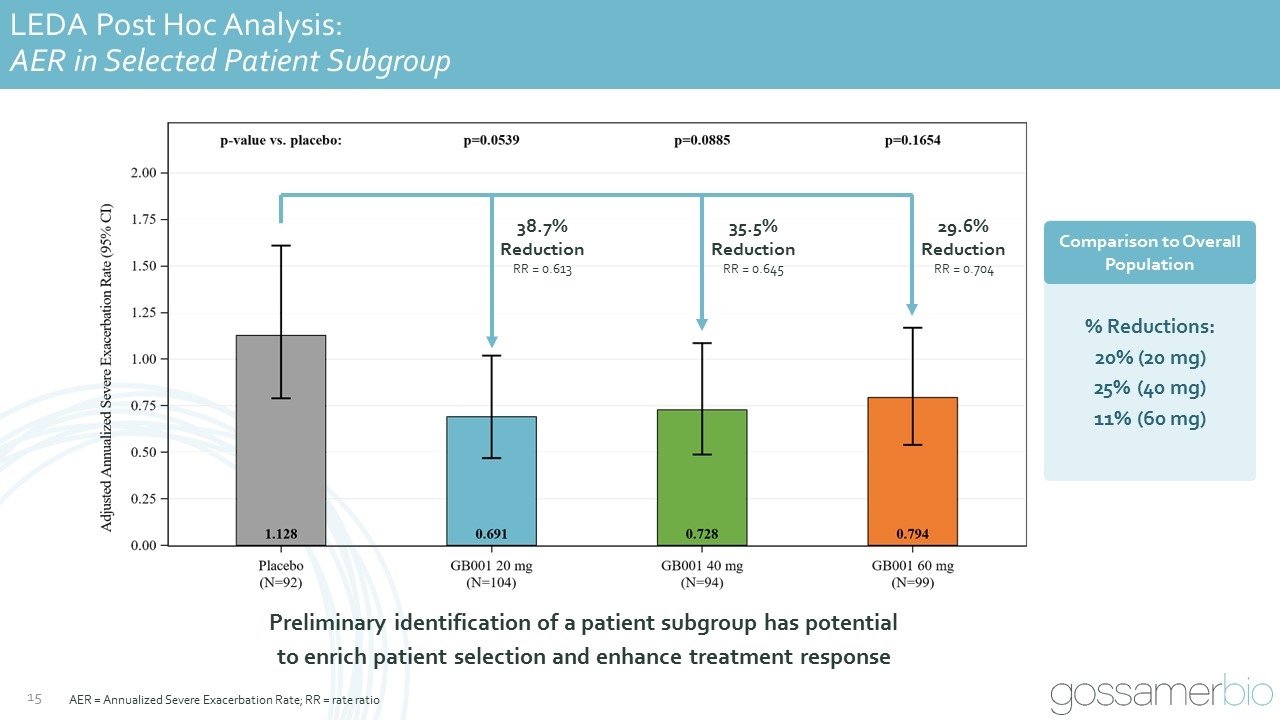
LEDA Post Hoc Analysis: AER in Selected Patient Subgroup 38.7% Reduction RR = 0.613 35.5% Reduction RR = 0.645 29.6% Reduction RR = 0.704 Preliminary identification of a patient subgroup has potential to enrich patient selection and enhance treatment response Comparison to Overall Population % Reductions: 20% (20 mg) 25% (40 mg) 11% (60 mg) AER = Annualized Severe Exacerbation Rate; RR = rate ratio
Incidence of adverse events was generally comparable across treatment groups: 65.8% Placebo, 65.8% GB001 20 mg, 69.5% GB001 40 mg, 68.0% GB001 60 mg Adverse events of interest (liver chemistry elevations leading to study drug discontinuation) occurred more frequently in GB001 60 mg (4.1%, n=5) than placebo (0.8%, n=1), GB001 20 mg (0.8%, n=1), or GB001 40 mg (1.7%, n=2) One adverse event of interest was an SAE of liver chemistry elevations meeting Hy’s Law criteria in GB001 60 mg. The patient was asymptomatic during the event, which was reversible and resolved without sequelae Summary of LEDA Safety Profile SAE = serious adverse event
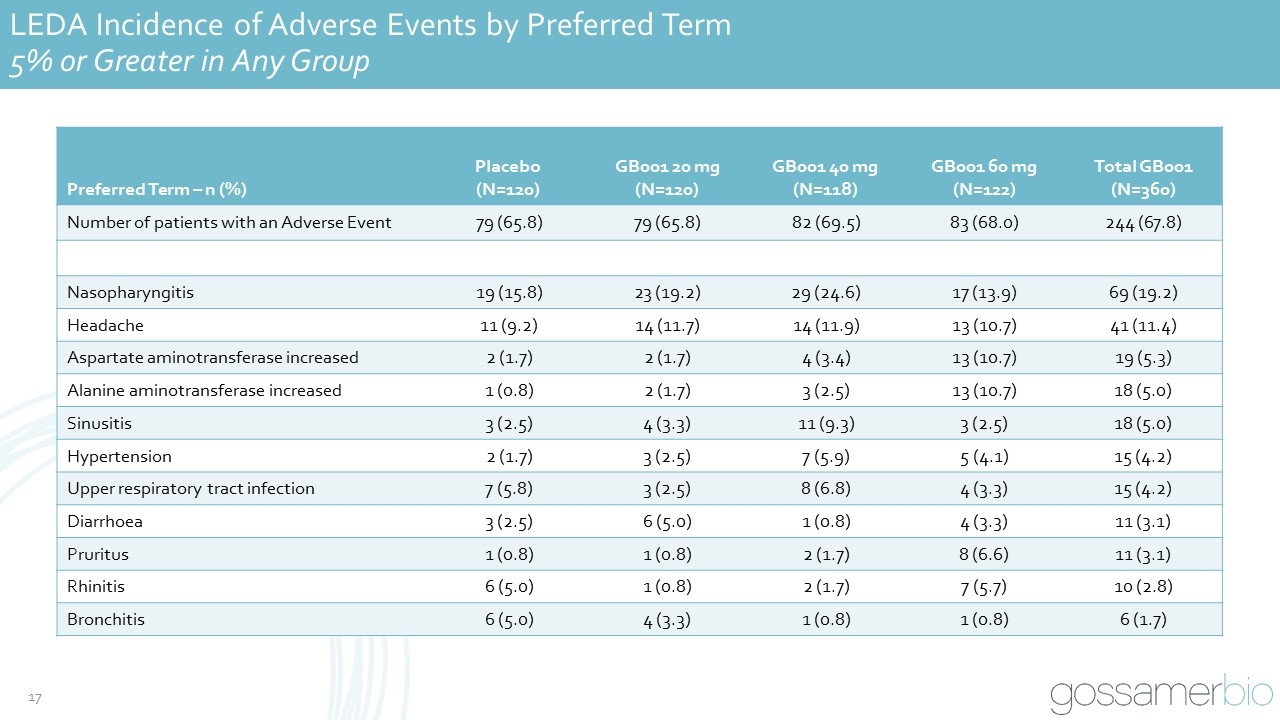
LEDA Incidence of Adverse Events by Preferred Term 5% or Greater in Any Group Preferred Term – n (%) Placebo (N=120) GB001 20 mg (N=120) GB001 40 mg (N=118) GB001 60 mg (N=122) Total GB001 (N=360) Number of patients with an Adverse Event 79 (65.8) 79 (65.8) 82 (69.5) 83 (68.0) 244 (67.8) Nasopharyngitis 19 (15.8) 23 (19.2) 29 (24.6) 17 (13.9) 69 (19.2) Headache 11 (9.2) 14 (11.7) 14 (11.9) 13 (10.7) 41 (11.4) Aspartate aminotransferase increased 2 (1.7) 2 (1.7) 4 (3.4) 13 (10.7) 19 (5.3) Alanine aminotransferase increased 1 (0.8) 2 (1.7) 3 (2.5) 13 (10.7) 18 (5.0) Sinusitis 3 (2.5) 4 (3.3) 11 (9.3) 3 (2.5) 18 (5.0) Hypertension 2 (1.7) 3 (2.5) 7 (5.9) 5 (4.1) 15 (4.2) Upper respiratory tract infection 7 (5.8) 3 (2.5) 8 (6.8) 4 (3.3) 15 (4.2) Diarrhoea 3 (2.5) 6 (5.0) 1 (0.8) 4 (3.3) 11 (3.1) Pruritus 1 (0.8) 1 (0.8) 2 (1.7) 8 (6.6) 11 (3.1) Rhinitis 6 (5.0) 1 (0.8) 2 (1.7) 7 (5.7) 10 (2.8) Bronchitis 6 (5.0) 4 (3.3) 1 (0.8) 1 (0.8) 6 (1.7)

Summary of Phase 2b LEDA Results GB001 groups did not meet the primary endpoint of proportion of patients who experience asthma worsening by week 24 However, consistent numeric reductions in the odds of asthma worsening of 32% to 35% observed (p-values: 0.1086 to 0.1482) across GB001 groups GB001 20 mg and 60 mg groups significantly improved time to first asthma worsening (20 mg, 28% risk reduction, p=0.0466; 60 mg, 30% risk reduction, p=0.0304), with GB001 40 mg also demonstrating a numeric effect (23%, p=0.1222) Consistent treatment effect in all GB001 groups across clinical endpoints suggests all doses met the biological threshold for clinical response Incidence of adverse events was generally comparable across treatment groups; liver enzyme elevations were observed more frequently in 60 mg dose group

Market Research Suggests GB001’s Target Profile is Compelling for an Oral Therapy Exacerbation Data Was Viewed at the Most Important Measure of Efficacy in Moderate-to-Severe Asthma Clinical Trials1 Efficacy Threshold for Surveyed Physicians to Find an Oral Asthma Therapeutic to be Compelling2 20-30% Reduction in AER Reduction in AER Ranked as #1 Most Important Measure of Efficacy 1 (N=200) Survey of allergists and pulmonologists; 2019 2 (N=37) Interviews of asthma KOLs, Specialists, and PCP’s; 2019 AER = annualized severe exacerbation rate

TITAN Phase 2 Study in Chronic Rhinosinusitis – Topline Results TITAN: 16-week, Phase 2 study in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS), both with and without polyps, randomized 97 patients to GB001 40 mg or placebo Study failed to meet primary endpoint of change from baseline in SNOT-22 score and secondary endpoints GB001 40 mg was generally well tolerated with a similar safety profile as LEDA

Next Steps LEDA Phase 2b suggests potential of oral DP2 pathway inhibition for the treatment of patients with uncontrolled severe asthma Gossamer will discuss these results and next steps for clinical development with global regulatory authorities and continue partnering discussions Full results from LEDA will be presented at future medical conference
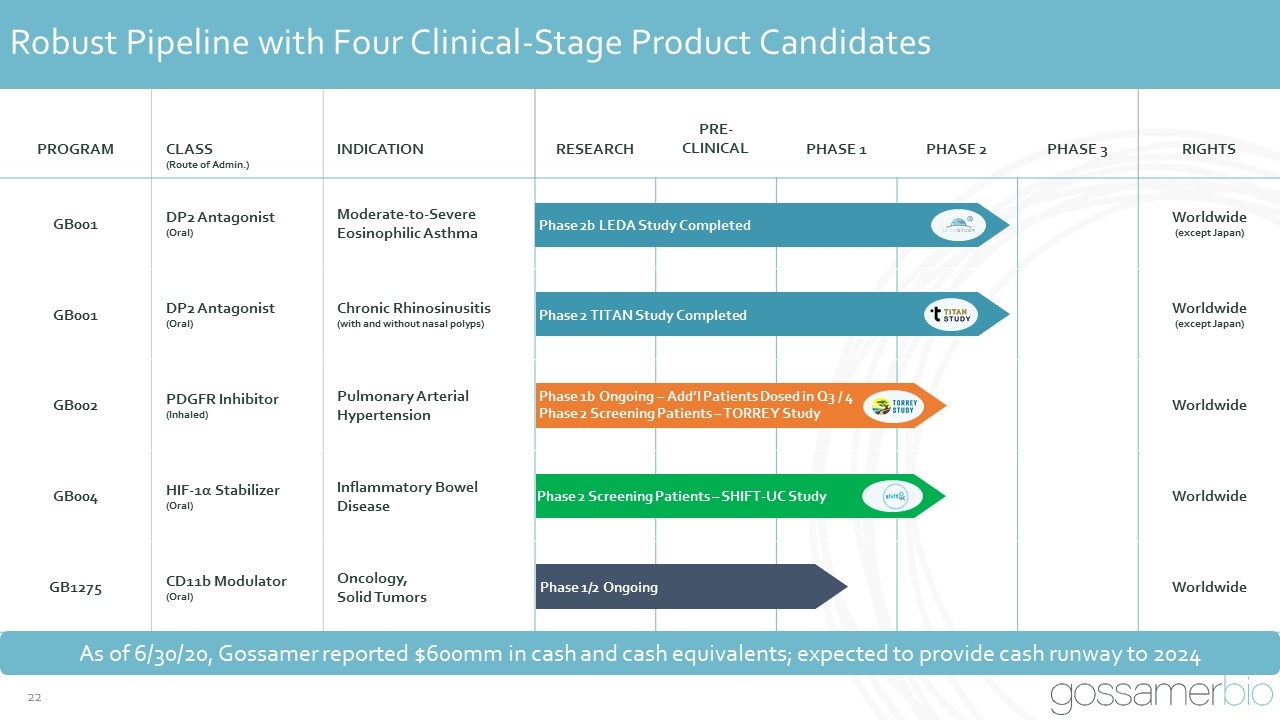
Robust Pipeline with Four Clinical-Stage Product Candidates PROGRAM CLASS (Route of Admin.) INDICATION RESEARCH PRE-CLINICAL PHASE 1 PHASE 2 PHASE 3 RIGHTS GB001 DP2 Antagonist (Oral) Moderate-to-Severe Eosinophilic Asthma Worldwide (except Japan) GB001 DP2 Antagonist (Oral) Chronic Rhinosinusitis (with and without nasal polyps) Worldwide (except Japan) GB002 PDGFR Inhibitor (Inhaled) Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Worldwide GB004 HIF-1α Stabilizer (Oral) Inflammatory Bowel Disease Worldwide GB1275 CD11b Modulator (Oral) Oncology, Solid Tumors Worldwide Phase 2b LEDA Study Completed Phase 2 TITAN Study Completed Phase 1/2 Ongoing Phase 2 Screening Patients – SHIFT-UC Study Phase 1b Ongoing – Add’l Patients Dosed in Q3 / 4 Phase 2 Screening Patients – TORREY Study As of 6/30/20, Gossamer reported $600mm in cash and cash equivalents; expected to provide cash runway to 2024

Thank you to all patients, caregivers, investigators, and Gossamer employees who participated in and contributed to these studies!
