Attached files
Table of Contents
As filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on October 9, 2020.
Registration No. 333-249077
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
Amendment No. 1
to
FORM S-1
REGISTRATION STATEMENT
Under
The Securities Act of 1933
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| Delaware (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) |
2836 (Primary Standard Industrial Classification Code Number) |
82-4724808 (I.R.S. Employer Identification Number) |
One Corporate Dr., 2nd Floor
South San Francisco, CA 94080
(800) 466-6059
(Address, including zip code, and telephone number, including area code, of Registrant’s principal executive offices)
Lawrence M. Blatt, Ph.D.
Chief Executive Officer
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
One Corporate Dr., 2nd Floor
South San Francisco, CA 94080
(800) 466-6059
(Name, address, including zip code, and telephone number, including area code, of agent for service)
Copies to:
| Mark V. Roeder John C. Williams Latham & Watkins LLP 140 Scott Drive Menlo Park, California 94025 (650) 328-4600 |
Lucinda Quan, J.D. Executive Vice President, Chief Business Officer and General Counsel Aligos Therapeutics, Inc. One Corporate Dr., 2nd Floor South San Francisco, CA 94080 (800) 466-6059 |
Alan F. Denenberg Emily Roberts Davis Polk & Wardwell LLP 1600 El Camino Real Menlo Park, California 94025 (650) 752-2000 |
Approximate date of commencement of proposed sale to the public: As soon as practicable after the effective date of this registration statement.
If any of the securities being registered on this Form are to be offered on a delayed or continuous basis pursuant to Rule 415 under the Securities Act of 1933, check the following box. ☐
If this Form is filed to register additional securities for an offering pursuant to Rule 462(b) under the Securities Act, please check the following box and list the Securities Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering. ☐
If this Form is a post-effective amendment filed pursuant to Rule 462(c) under the Securities Act, check the following box and list the Securities Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering. ☐
If this Form is a post-effective amendment filed pursuant to Rule 462(d) under the Securities Act, check the following box and list the Securities Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| Large accelerated filer | ☐ | Accelerated filer | ☐ | |||
| Non-accelerated filer | ☒ | Smaller reporting company | ☒ | |||
| Emerging growth company | ☒ | |||||
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided to Section 7(a)(2)(B) of the Securities Act. ☐
CALCULATION OF REGISTRATION FEE
|
| ||||||||
| Title of each class of securities to be registered | Amount to be registered(1) |
Proposed maximum aggregate offering price per share |
Proposed maximum aggregate offering price(2) |
Amount of registration fee(3) | ||||
| Common Stock, $0.0001 par value per share |
11,500,000 |
$16.00 | $184,000,000 | $20,074.40 | ||||
|
| ||||||||
|
| ||||||||
| (1) | Includes 1,500,000 shares of common stock that the underwriters have the option to purchase. |
| (2) | Estimated solely for the purpose of calculating the amount of the registration fee in accordance with Rule 457(a) under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended. |
| (3) | The Registrant previously paid a total of $12,980 in connection with the previous filing of the Registration Statement. In accordance with Rule 457(a), an additional registration fee of $7,094.40 is being paid with this amendment to the Registration Statement. |
The Registrant hereby amends this Registration Statement on such date or dates as may be necessary to delay its effective date until the Registrant shall file a further amendment which specifically states that this Registration Statement shall thereafter become effective in accordance with Section 8(a) of the Securities Act of 1933 or until the Registration Statement shall become effective on such date as the Commission, acting pursuant to said Section 8(a), may determine.
Table of Contents
The information in this preliminary prospectus is not complete and may be changed. We may not sell these securities until the registration statement filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission is effective. This preliminary prospectus is not an offer to sell these securities and is not soliciting an offer to buy these securities in any jurisdiction where such offer or sale is not permitted.
Subject to completion, dated October 9, 2020
Preliminary prospectus
10,000,000 shares

Common stock
This is the initial public offering of shares of common stock of Aligos Therapeutics, Inc. We are selling 10,000,000 shares of our common stock. The estimated initial public offering price is between $14.00 and $16.00 per share.
Prior to this offering, there has been no public market for our common stock.
We have applied to list our common stock on the Nasdaq Global Market under the symbol “ALGS.”
We are an “emerging growth company” as defined under the federal securities laws and, as such, have elected to comply with certain reduced public company reporting requirements for this prospectus and may elect to do so in future filings.
| Per share | Total | |||||||
| Initial public offering price |
$ | $ | ||||||
| Underwriting discounts and commissions(1) |
$ | $ | ||||||
| Proceeds, before expenses, to us |
$ | $ | ||||||
| (1) | See the section titled “Underwriting” beginning on page 204 for additional information regarding compensation payable to the underwriters. |
We have granted the underwriters an option to purchase up to an additional 1,500,000 shares from us at the initial public offering price less the underwriting discounts and commissions. The underwriters may exercise this right at any time within 30 days after the date of this prospectus.
We have and will have following this offering two classes of common stock: the voting common stock offered hereby and non-voting common stock. For a description of the rights of the voting common stock and non-voting common stock, please see “Description of capital stock” beginning on page 191 of this prospectus. We are offering voting common stock in this offering, and unless otherwise noted, all references in this prospectus to our “common stock,” “common shares” or “shares” refers to our voting common stock.
Investing in our common stock involves a high degree of risk. See the section titled “Risk factors” beginning on page 13 to read about factors you should consider before buying shares of our common stock.
Neither the Securities and Exchange Commission nor any other state securities commission has approved or disapproved of these securities, or passed upon the adequacy or accuracy of this prospectus. Any representation to the contrary is a criminal offense.
The underwriters expect to deliver the shares against payment in New York, New York on , 2020.
| J.P. Morgan | Jefferies | Piper Sandler | ||
| Cantor | ||||
Prospectus dated , 2020
Table of Contents
| Page | ||||
| 1 | ||||
| 13 | ||||
| 82 | ||||
| 84 | ||||
| 85 | ||||
| 87 | ||||
| 88 | ||||
| 91 | ||||
| 94 | ||||
| Management’s discussion and analysis of financial condition and results of operations |
96 | |||
| 113 | ||||
| 158 | ||||
| 168 | ||||
| 181 | ||||
| 187 | ||||
| 191 | ||||
| 197 | ||||
| Material U.S. federal income tax consequences to non-U.S. holders |
200 | |||
| 204 | ||||
| 217 | ||||
| 217 | ||||
| 217 | ||||
| F-1 | ||||
Neither we nor the underwriters have authorized anyone to provide you with information that is different from that, or to make any representations other than those, contained in this prospectus or in any free writing prospectus we may authorize to be delivered or made available to you. We and the underwriters take no responsibility for, and can provide no assurance as to the reliability of, any other information that others may give you. We and the underwriters are offering to sell shares of common stock and seeking offers to buy shares of common stock only in jurisdictions where offers and sales are permitted. The information contained in this prospectus or in any applicable free writing prospectus is accurate only as of the date on the front of this prospectus or any such free writing prospectus, as applicable, or other earlier date stated in this prospectus or such free writing prospectus, regardless of the time of delivery of this prospectus or such free writing prospectus or any sale of shares of our common stock. Our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects may have changed since that date.
No action is being taken in any jurisdiction outside the United States to permit a public offering of our common stock or possession or distribution of this prospectus in that jurisdiction. Persons who come into possession of this prospectus in jurisdictions outside the United States are required to inform themselves about and to observe any restrictions as to this offering and the distribution of this prospectus applicable to that jurisdiction.
Table of Contents
Aligos® and our logo are some of our trademarks used in this prospectus. This prospectus also includes trademarks, tradenames and service marks that are the property of other organizations. Solely for convenience, our trademarks, service marks and tradenames referred to in this prospectus may appear without the ® and ™ symbol, but those references are not intended to indicate, in any way, that we will not assert, to the fullest extent under applicable law, our rights, or the right of the applicable licensor to these trademarks, service marks and tradenames.
Through and including , 2020 (the 25th day after the date of this prospectus), all dealers effecting transactions in these securities, whether or not participating in this offering, may be required to deliver a prospectus. This delivery requirement is in addition to the obligation of dealers to deliver a prospectus when acting as underwriters and with respect to their unsold allotments or subscriptions.
Table of Contents
This summary highlights information contained elsewhere in this prospectus. This summary does not contain all of the information you should consider before investing in our common stock. You should read this entire prospectus carefully, especially the section titled “Risk factors” and our consolidated financial statements and the related notes thereto included at the end of this prospectus, before making an investment decision. As used in this prospectus, unless the context otherwise requires, references to “we,” “us,” “our,” “our company,” “the Company”, “Aligos” and “Aligos Therapeutics” refer to Aligos Therapeutics, Inc. and its subsidiaries, taken as a whole.
Overview
We are a clinical-stage biopharmaceutical company currently focused on developing novel therapeutics to address unmet medical needs in viral and liver diseases. We utilize our proprietary oligonucleotide and small molecule platforms to develop pharmacologically optimized drug candidates for use in combination regimens designed to achieve improved treatment outcomes. Our lead effort is to develop a functional cure for Chronic Hepatitis B (“CHB”), which often results in other life-threatening conditions such as cirrhosis, end-stage liver disease (“ESLD”) and the most common form of liver cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma (“HCC”). The most widely used treatment for CHB, nucleos(t)ide analogs, suppresses viral replication but only achieves low rates of functional cure and often requires long-term administration. To address this issue, we have developed a portfolio of differentiated drug candidates for CHB, including an S-antigen Transport-inhibiting Oligonucleotide Polymers (“STOPS”) molecule, a small molecule Capsid Assembly Modulator (“CAM”), and oligonucleotides (ASO and siRNA), each of which is designed against clinically validated targets in the Hepatitis B Virus (“HBV”) life cycle. We believe that combination regimens utilizing our portfolio of CHB drug candidates may lead to higher rates of functional cure. A Phase 1 proof of concept trial for our STOPS molecule is ongoing in New Zealand and we expect to initiate a Phase 1 clinical trial with our CAM in the second half of 2020. Our second area of focus is in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (“NASH”), a complex, chronic liver disease where combination regimens may likewise prove beneficial. Our most advanced drug candidate for NASH is ALG-055009, a small molecule THR-b agonist currently in nonclinical studies to enable a first-in-human clinical trial. We believe ALG-055009 has the potential to become an integral component of future combination regimens for NASH. Our third area of focus is to develop drug candidates with pan-coronavirus activity, including Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome coronavirus 2 (“SARS-CoV-2”), the virus responsible for COVID-19.
Our oligonucleotide and small molecule platforms allow us to discover drug candidates that can be used to develop potentially best-in-class combination regimens. Oligonucleotide approaches enable specific inhibition of the translation of viral or host genes to affect a desired outcome that would be challenging to achieve with traditional small molecules. We believe the diversity of chemical matter we can generate with these complementary modalities broadens the range of therapeutic targets we can address with our platforms, and provides us with a differentiated set of in-house capabilities to use in developing novel, optimized combination regimens across all of our current areas of focus.
Our approach of combining multiple mechanisms from these distinct modalities is based on the observation that most chronic diseases, whether extrinsic (e.g., HIV and Hepatitis C) or intrinsic (e.g., metabolic syndrome conditions such as hypertension and diabetes), often require combination therapy to achieve optimal outcomes. Combination approaches have the advantage of simultaneously targeting multiple pathways and can act broadly and potentially synergistically. Particularly in the case of viral diseases, the simultaneous use of multiple drugs in combination can increase the barrier to viral resistance. As part of our drug candidate screening paradigm, we perform in vitro combination studies to ensure that none of the combinations we plan to evaluate clinically demonstrate antagonistic interactions.
1
Table of Contents
Our approach to developing best-in-class regimens for our therapeutic areas of interest leverages the most promising modalities from our oligonucleotide and small molecule platforms to advance rapidly from monotherapy Phase 1 trials into Phase 2 combination trials. As a first step, we evaluate the safety and activity of each drug candidate in healthy volunteers and patients with the disease of interest. We intend to then efficiently evaluate drug candidates shown to have activity in Phase 1 in various combinations in Phase 2 platform protocols to enable us to identify optimized combination regimens that will then be evaluated in Phase 3 pivotal trials. The combinations we evaluate may include additional drug candidates or current standard of care. Throughout all phases of clinical development, pre-specified adaptive study rules allow real-time adjustment of trial conduct based on emerging clinical trial data. These practices allow us to gain a rapid understanding of the risk/benefit profile for our individual drug candidates and combination regimens, and iteratively refine our strategy based on emerging data.
Our management team consists of a group of highly collaborative, culturally diverse executives with decades of drug discovery and development experience and a proven track record of success in the areas of viral infections and liver diseases. Most members of our management team have worked together across multiple companies, many for over a decade, and have been collectively involved in the discovery and/or development of a number of drugs that have been successfully commercialized, including Ganovo, Olysio, Sovaldi, Hepsera, Infergen, Valtrex, Sirturo, Neupogen, Andexxa and Esbriet, among others. In support of our management team, we also have assembled an industry-leading board of directors and a world-class group of scientific advisors with significant experience in drug development for viral and liver diseases. Finally, we have top-tier investors, including Boxer Capital of Tavistock Group, Cormorant Asset Management, Janus Henderson Investors, Logos Capital, Novo Holdings, Pivotal bioVenture Partners, Roche Venture Fund, Versant Ventures, Vivo Capital and Wellington Management Company.
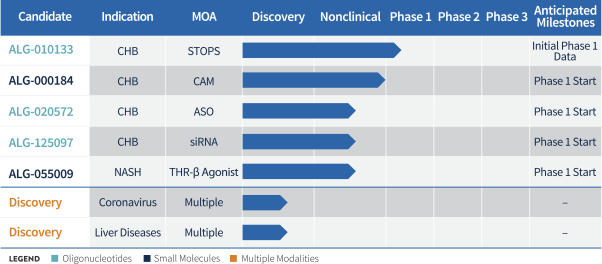
Our pipeline
Our pipeline is focused on viral and liver diseases for which there is a significant unmet medical need. We hold worldwide development and commercialization rights, including through exclusive licenses, to all of our drug candidates, which allows us to strategically maximize value from our product portfolio over time. Our drug candidates are summarized below:
2
Table of Contents
Our most advanced drug candidates are for the treatment of CHB, a disease that affects more than 290 million people worldwide with approximately 30 million people becoming newly infected every year, despite the availability of an efficacious prophylactic vaccine. Approximately 900,000 people worldwide died from complications of CHB in 2015, according to the World Health Organization, and CHB is the primary cause of liver cancer worldwide. Currently approved therapies for CHB include pegylated forms of interferon-alfa (“peg-IFNa”) and nucleos(t)ide analogs, which are designed to boost the body’s immune response to the virus or inhibit viral replication, respectively. While these therapies have improved treatment outcomes for some patients with CHB, they have not been able to achieve meaningful rates of functional cure, which is the consensus goal of treatment and defined as a sustained loss of HBsAg with or without hepatitis B surface antibody seroconversion. Functional cure has been shown to greatly reduce the risk of developing certain other more serious downstream liver conditions, such as cirrhosis and ESLD.
Our clinical development strategy involves evaluating both Hepatitis B E-antigen (“HBeAg”) positive and HBeAg negative CHB patient populations. HBeAg is typically present in earlier stages of the disease and is associated with higher rates of viral replication. During the natural course of the disease, HBeAg can be cleared and antibodies develop, resulting in an HBeAg negative state where viral replication is often lower. Patients with HBeAg negative CHB are typically older and have more progressive disease-related complications (e.g., fibrosis of the liver). In addition, their immune system is likely to be more exhausted by chronic exposure to HBsAg, which makes viral clearance more difficult. Although we plan to ultimately study both populations, due to the greater availability of patients with HBeAg negative CHB at investigational sites, we intend to study this population first.
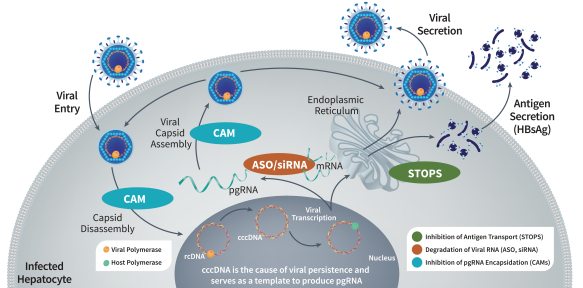
Multiple steps in the HBV life cycle, including those involving capsid assembly and production and secretion of HBsAg, are known to be essential to sustain HBV infection. We have built a portfolio of CHB drug candidates directed against clinically validated targets at several critical stages of the HBV life cycle. Our CHB portfolio includes:
| • | STOPS are protein-binding oligonucleotides that share structural similarity with nucleic acid polymers (“NAPs”), which have been reported in clinical trials to significantly reduce circulating HBsAg and result in high rates of functional cure when used in combination with nucleos(t)ide analogs and peg-IFNa. Our most |
3
Table of Contents
| advanced STOPS molecule is ALG-010133, which is currently being evaluated in a Phase 1 clinical trial. In nonclinical studies, ALG-010133 has demonstrated higher inhibitory activity than a reference NAP compound that is currently in clinical development. |
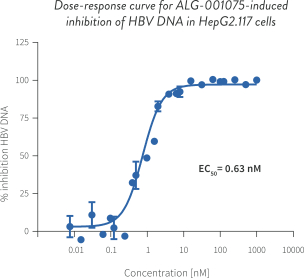
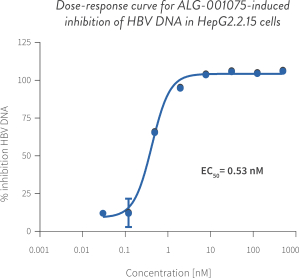
| • | CAMs are small molecule antiviral agents that accelerate HBV capsid assembly and inhibit pregenomic RNA (“pgRNA”) encapsidation, which reduces production of new virions capable of infecting other cells. CAMs may also inhibit the de novo establishment of covalently closed circular DNA (“cccDNA”), a major factor for the persistence of HBV infection, when introduced at the onset of infection. In clinical trials, other CAM drug candidates have demonstrated significant reductions in HBV DNA and pgRNA. However, it is likely that CAMs will need to be combined with other modalities that affect HBsAg in order to achieve functional cure. Our most advanced CAM drug candidate is ALG-000184, a prodrug of ALG-001075 which we plan to advance into a Phase 1 clinical trial in the second half of 2020. In nonclinical studies, we have shown that ALG-001075 has significantly enhanced potency compared to other CAMs in clinical development of which we are aware. |
| • | ASOs are single-stranded DNA or RNA molecules that interfere with viral replication by binding to complementary messenger RNA (“mRNA”), allowing the combined ASO and mRNA to be degraded by the enzyme RNase H. Using our oligonucleotide discovery capabilities, we identified ALG-020572, an ASO that targets HBV mRNA and can reduce HBsAg production, which we plan to advance into clinical trials in the second half of 2021. In third-party clinical trials, ASOs targeting HBV mRNA have demonstrated significant reductions in HBsAg. Our ASO approach utilizes state of the art bioinformatics, proprietary stabilization chemistry and liver targeting technology that we believe provides a number of potential benefits compared to other ASO candidates of which we are aware, including increased potency, a higher barrier to resistance and broad genotype coverage. |
| • | siRNAs are a class of double-stranded, non-coding RNA that interferes with viral replication by silencing gene expression. Multiple siRNAs have demonstrated significant reductions in HBsAg levels in clinical trials. Our oligonucleotide discovery capabilities resulted in the identification of ALG-125097, an siRNA drug candidate directed at HBV mRNA, which utilizes our proprietary liver targeting technology. |
We believe that a combination of drugs capable of inhibiting HBV DNA replication and RNA packaging (e.g., using CAMs) while simultaneously suppressing HBsAg production (e.g., using STOPS molecules, ASO, and/or siRNA) has the potential to act additively or synergistically and may lead to a higher rate of functional cure. Our clinical development strategy is designed to evaluate safety and antiviral activity as monotherapy prior to evaluating multiple combinations of our CHB assets, with or without other currently available treatment modalities such as nucleos(t)ide analogs or peg-IFNa, to identify optimized combination regimens.
Our second development effort is focused on the treatment of NASH. An estimated 1.5% to 6.5% of the global population, or up to about 450 million people, was believed to have NASH as of 2015 and this is expected to increase significantly in the coming decade due to the adoption of Western dietary habits. In the absence of lifestyle modifications, the inflammation inherent in NASH persists and results in progressive fibrosis of the liver, which may lead to cirrhosis, ESLD, HCC, the need for liver transplant, and death. We believe one of the most promising pharmacologic approaches in development for NASH is a selective agonist of the beta subtype of the thyroid hormone receptor (“THR-b”), which, in clinical trials conducted by third parties, has demonstrated significant reduction in liver fat and inflammation, as well as the reduction in lipid levels in the serum, which may have important advantages in the NASH patient population that is at a high risk of cardiovascular co-morbidities. Utilizing our expertise in small molecule drug discovery, we identified ALG-055009, a once-daily oral THR-b agonist. In nonclinical studies, ALG-055009 has been shown to be substantially more potent compared to other THR-b agonists currently in development of which we are aware
4
Table of Contents
and may avoid some of their potential safety liabilities while having the potential to achieve equal or better efficacy. As a result, we believe ALG-055009 has the potential to become an integral component of combination regimens to treat NASH. We intend to advance ALG-055009 into clinical development in the second half of 2021.
Our third area of focus is to develop pan-coronavirus treatment regimens. SARS-CoV-2 is responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic, which has been identified as a cause of more than 750,000 deaths worldwide as of August 2020. After MERS and SARS (SARS-CoV-1), SARS-CoV-2 is the third known coronavirus to have crossed over from animal species to humans in the past 20 years and cause significant morbidity and mortality. While multiple vaccines are likely to become available in the future, it is unlikely that a vaccine will be fully efficacious and widely adopted, indicating that the need for effective therapeutic treatments will remain. Currently, repurposed drugs which have not been optimized for the treatment of coronavirus infections are being studied to treat SARS-CoV-2, and there is a need for purpose-built drugs which are suitable across a broad range of coronaviruses, patient populations and clinical settings, including prophylactic and post-exposure settings. We believe that, similar to CHB, a combination of antiviral and/or immunomodulatory drugs which target multiple points in the viral replication cycle offers the best chance of success. To address this urgent, unmet medical need, we are in early stages of development for multiple drug candidates including nucleos(t)ide, siRNA/ASO and protease inhibitors that are specifically designed to interact with targets that are highly conserved across multiple coronaviruses. Each of these drug candidates is intended to have pan-coronavirus activity and to be used in combination regimens to maximize their antiviral activity.
Our strategy
Our strategy is to develop pharmacologically optimized drug candidates for use in combination regimens designed to achieve improved treatment outcomes. Our initial areas of focus are viral and liver diseases where our team can leverage their in-depth knowledge and expertise to develop potentially best-in-class combination regimens addressing large areas of unmet medical need. The core elements of our business strategy include:
| • | Developing improved drug candidates against clinically validated targets; |
| • | Creating combination regimens to achieve better outcomes; |
| • | Developing a functional cure for CHB; |
| • | Expanding our development capabilities and pipeline; and |
| • | Maximizing the value of our drug candidates. |
Risks related to our business
Our ability to execute our business strategy is subject to numerous risks, including those described in the section titled “Risk factors” immediately following this prospectus summary. These risks include the following, among others:
| • | We are a clinical-stage biopharmaceutical company with a limited operating history and no products approved for commercial sale. We have incurred significant losses since inception. We expect to incur losses for at least the next several years and may never achieve or maintain profitability, which, together with our limited operating history, makes it difficult to assess our future viability. |
| • | We have never generated revenue from product sales and may never be profitable. |
| • | Even if this offering is successful, we will require substantial additional financing to achieve our goals, which may not be available on acceptable terms, or at all. A failure to obtain this necessary capital when needed could force us to delay, limit, reduce or terminate our product development or commercialization efforts. |
5
Table of Contents
| • | We are early in our development efforts, and our business is dependent on the successful development of our current and future drug candidates. If we are unable to advance our current or future drug candidates through clinical trials, obtain marketing approval and ultimately commercialize any drug candidates we develop, or experience significant delays in doing so, our business will be materially harmed. |
| • | Our current or future drug candidates may cause undesirable side effects or have other properties when used alone or in combination with other approved products or investigational new drugs that could delay or halt their clinical development, prevent their marketing approval, limit their commercial potential or result in significant negative consequences. |
| • | We depend on collaborations with third parties for the development of certain of our potential drug candidates, and we may depend on additional collaborations in the future for the development and commercialization of these or other potential candidates. If our collaborations are not successful, we may not be able to capitalize on the market potential of these drug candidates. |
| • | We intend to develop our current drug candidates, and expect to develop other future drug candidates, in combination with other therapies, which exposes us to additional risks. |
| • | We face significant competition, and if our competitors develop and market products that are more effective, safer or less expensive than the drug candidates we develop, our commercial opportunities will be negatively impacted. |
| • | If we and our collaborators are unable to obtain, maintain, protect and enforce sufficient patent and other intellectual property protection for our drug candidates and technology, our competitors could develop and commercialize products and technology similar or identical to ours, and we may not be able to compete effectively in our market or successfully commercialize any drug candidates we may develop. |
| • | Third parties may initiate legal proceedings alleging that we are infringing, misappropriating or otherwise violating their intellectual property rights, the outcome of which would be uncertain and could negatively impact the success of our business. |
| • | We have entered into licensing agreements with third parties. If we fail to comply with our obligations in the agreements under which we license intellectual property rights to or from third parties, or these agreements are terminated, or we otherwise experience disruptions to our business relationships with our licensors or licensees, our competitive position, business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects could be harmed. |
| • | We are highly dependent on our key personnel, and if we are not successful in attracting, motivating and retaining highly qualified personnel, we may not be able to successfully implement our business strategy. |
Corporate information
We were founded in February 2018 as a Delaware corporation. Our principal executive offices are located at One Corporate Dr., 2nd Floor, South San Francisco, California 94080, and our telephone number is (800) 466-6059.
Our website address is www.aligos.com. The information on, or that can be accessed through, our website is not part of this prospectus and is not incorporated by reference herein. We have included our website address as an inactive textual reference only.
6
Table of Contents
Implications of being an emerging growth company
We are an emerging growth company as defined in the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act of 2012 (the “JOBS Act”). We will remain an emerging growth company until the earliest of: (1) the last day of the fiscal year following the fifth anniversary of the consummation of this offering, (2) the last day of the fiscal year in which we have total annual gross revenue of at least $1.07 billion, (3) the last day of the fiscal year in which we are deemed to be a “large accelerated filer” as defined in Rule 12b-2 under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”), which would occur if the market value of our common stock held by non-affiliates exceeded $700.0 million as of the last business day of the second fiscal quarter of such year or (4) the date on which we have issued more than $1.0 billion in non-convertible debt securities during the prior three-year period. An emerging growth company may take advantage of specified reduced reporting requirements and is relieved of certain other significant requirements that are otherwise generally applicable to public companies. As an emerging growth company:
| • | we will present in this prospectus only two years of audited annual financial statements, plus any required unaudited financial statements, and related management’s discussion and analysis of financial condition and results of operations; |
| • | we will avail ourselves of the exemption from the requirement to obtain an attestation and report from our independent registered public accounting firm on the assessment of our internal control over financial reporting pursuant to the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002; |
| • | we will provide less extensive disclosure about our executive compensation arrangements; and |
| • | we will not require stockholder non-binding advisory votes on executive compensation or golden parachute arrangements. |
In addition, the JOBS Act provides that an emerging growth company can take advantage of an extended transition period for complying with new or revised accounting standards. This provision allows an emerging growth company to delay the adoption of some accounting standards until those standards would otherwise apply to private companies. We have elected to use the extended transition period for any other new or revised accounting standards during the period in which we remain an emerging growth company; however, we may adopt certain new or revised accounting standards early.
7
Table of Contents
The offering
| Common stock offered by us |
10,000,000 shares. |
| Underwriters’ option to purchase additional shares from us |
We have granted the underwriters a 30-day option to purchase up to 1,500,000 additional shares at the initial public offering price, less underwriting discounts and commissions. |
| Common stock to be oustanding immediately after this offering |
33,797,848 shares (or 35,297,848 shares if the underwriters exercise in full their option to purchase additional shares). |
| Non-voting common stock to be outstanding immediately after this offering |
3,092,338 shares. |
| Total common stock and non-voting common stock to be outstanding immediately after this offering |
36,890,186 shares (or 38,390,186 shares if the underwriters exercise in full their option to purchase additional shares). |
| Use of proceeds |
We estimate that the net proceeds from this offering will be approximately $135.4 million, or approximately $156.3 million if the underwriters exercise their option to purchase additional shares in full, at an assumed initial public offering price of $15.00 per share, the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover of this prospectus, after deducting the underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us. |
| We currently expect to use the net proceeds from this offering to fund the advancement, including clinical development and manufacturing activities, of our STOPS candidate, ALG-010133, our CAM candidate, ALG-000184, our ASO candidate, ALG-020572, our siRNA candidate, ALG-125097 and our NASH THR-b candidate, ALG-055009, and to fund discovery and research to broaden our pipeline of drug and backup candidates, as well as for other general corporate purposes, which may include the hiring of additional personnel, capital expenditures and the costs of operating as a public company. See the section titled “Use of proceeds” on page 85 for a more complete description of the intended use of proceeds from this offering. |
| Risk factors |
See the section titled “Risk factors” beginning on page 13 and other information included in this prospectus for a discussion of factors that you should consider carefully before deciding to invest in our common stock. |
8
Table of Contents
| Proposed Nasdaq Global Market symbol |
“ALGS ” |
The total number of shares of common stock and non-voting common stock to be outstanding after this offering is based on 23,237,407 shares of common stock outstanding as of June 30, 2020, plus 3,569,630 shares of common stock issuable pursuant to the conversion of our Series B-2 convertible preferred stock issued on October 6, 2020, and excludes the following:
| • | 2,246,633 shares of common stock issuable upon the exercise of outstanding stock options as of June 30, 2020 having a weighted-average exercise price of $3.16 per share; |
| • | 4,426,822 shares of common stock reserved for issuance pursuant to future awards under our 2020 Incentive Award Plan, which will become effective on the day prior to the first public trading date of our common stock, of which options to purchase 159,118 shares of common stock at an exercise price equal to the initial public offering price set forth on the cover of this prospectus will be granted coincident with this offering, as well as any automatic increases in the number of shares of our common stock reserved for future issuance under this plan; and |
| • | 368,901 shares of common stock reserved for issuance under our 2020 Employee Stock Purchase Plan, which will become effective on the day prior to the first public trading date of our common stock, as well as any automatic increases in the number of shares of our common stock reserved for future issuance under this plan. |
In addition, unless we specifically state otherwise, all information in this prospectus reflects and assumes the following:
| • | a 1-for-9.3197 reverse stock split of our common stock and preferred stock effected on October 9, 2020, pursuant to which (i) every 9.3197 shares of our outstanding capital stock were combined into one share of the same class and series of capital stock, (ii) the number of shares of our capital stock for which each outstanding option or warrant is exercisable was proportionally decreased on a 1-for-9.3197 basis and (iii) the exercise price of each outstanding option or warrant was proportionately increased on a 1-for-9.3197 basis; and all share numbers, share prices, exercise prices and per share amounts have been adjusted in this prospectus on a retroactive basis to reflect this reverse stock split for all periods presented; |
| • | the conversion of all 19,201,429 shares of our outstanding preferred stock as of June 30, 2020 into 16,392,640 shares of common stock and 2,808,789 shares of non-voting common stock immediately prior to the closing of this offering; |
| • | the issuance of 3,569,630 shares of our Series B-2 convertible preferred stock on October 6, 2020, and the conversion of such shares into 3,286,081 shares of common stock and 283,549 shares of non-voting common stock immediately prior to the completion of this offering; |
| • | the issuance of 83,149 shares of our common stock upon the exercise of all Series A Warrants outstanding as of June 30, 2020 (which will be exercised prior to the closing of this offering at an exercise price of $9.32 per share), as a result of the conversion of 83,149 shares of our Series A convertible preferred stock issuable upon the exercise of our Series A Warrants and the automatic conversion of such shares of Series A convertible preferred stock into an equivalent number of shares of common stock immediately prior to the closing of this offering; |
9
Table of Contents
| • | the filing and effectiveness of our amended and restated certificate of incorporation in Delaware and the adoption of our amended and restated bylaws, each of which will occur immediately prior to the closing of this offering; |
| • | no exercise of outstanding stock options subsequent to June 30, 2020; and |
| • | no exercise of the underwriters’ option to purchase additional shares of common stock. |
Unless otherwise specified and unless the context otherwise requires, in this prospectus, we refer to our Series A redeemable convertible preferred stock as our Series A convertible preferred stock, our Series B-1 redeemable convertible preferred stock as our Series B-1 convertible preferred stock and our Series B-2 redeemable convertible preferred stock as our Series B-2 convertible preferred stock, and collectively our Series A convertible preferred stock, Series B-1 convertible preferred stock and Series B-2 convertible preferred stock as our “preferred stock” (other than for financial reporting purposes and in the financial tables included in this prospectus). In this prospectus, we refer to our outstanding warrants to purchase shares of our Series A convertible preferred stock issued in April 2018 and June 2018 as our Series A Warrants.
10
Table of Contents
Summary consolidated financial data
The following tables present our summary consolidated financial data. You should read this data together with our consolidated financial statements and related notes appearing elsewhere in this prospectus and the information under the sections titled “Selected consolidated financial data” and “Management’s discussion and analysis of financial condition and results of operations.” We refer to the year ended December 31, 2019 as “Fiscal 2019” and the period from February 5, 2018 to December 31, 2018 as “Fiscal 2018.”
We have derived the consolidated summary statements of operations and comprehensive loss data for the years ended December 31, 2018 and 2019 (except for the pro forma net loss per share and the pro forma share information) from our audited consolidated financial statements and related notes included in this prospectus. The consolidated summary statements of operations and comprehensive loss data for the six months ended June 30, 2019 and 2020 and the balance sheet data as of June 30, 2020 have been derived from our unaudited consolidated financial statements included in this prospectus and have been prepared on the same basis as the audited consolidated financial statements. Results for historical periods may not be indicative of results expected for future periods, and results for the six months ended June 30, 2020 may not be indicative of results expected for the full year or any other period.
| Fiscal | Six Months Ended June 30, | |||||||||||||||
| 2018 | 2019 | 2019 | 2020 | |||||||||||||
| (in thousands, except share and per share data) | ||||||||||||||||
| Consolidated Statements of Operations Data |
||||||||||||||||
| Operating expenses: |
||||||||||||||||
| Research and development |
$ | 10,456 | $ | 44,038 | $ | 17,336 | $ | 34,478 | ||||||||
| General and administrative |
3,205 | 10,005 | 3,767 | 7,514 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Total operating expenses |
13,661 | 54,043 | 21,103 | 41,992 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Loss from operations |
(13,661 | ) | (54,043 | ) | (21,103 | ) | (41,992 | ) | ||||||||
| Interest and other income (expense), net |
(272 | ) | 1,864 | 1,073 | 1,108 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Loss before income tax expense |
(13,933 | ) | (52,179 | ) | (20,030 | ) | (40,884 | ) | ||||||||
| Income tax expense |
— | (85 | ) | — | 58 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Net loss |
(13,933 | ) | (52,264 | ) | (20,030 | ) | (40,826 | ) | ||||||||
| Other comprehensive (loss) income: |
||||||||||||||||
| Unrealized gain (loss) on pension plans |
3 | (118 | ) | (46 | ) | 27 | ||||||||||
| Unrealized gain on available-for-sale investments |
— | — | — | 238 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive loss |
$ | (13,930 | ) | $ | (52,382 | ) | $ | (20,076 | ) | $ | (40,561 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Net loss per share, basic and diluted(1)(3) |
$ | (11.69 | ) | $ | (26.04 | ) | $ | (11.54 | ) | $ | (14.96 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Weighted average shares of common stock, basic and diluted(3) |
1,191,787 | 2,007,173 | 1,735,358 | 2,729,827 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Pro forma net loss per share, basic and diluted (unaudited)(2)(3) |
$ | (2.47 | ) | $ | (1.86 | ) | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Pro forma weighted average shares of common stock, basic and diluted (unaudited)(3) |
21,171,050 | 21,931,256 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
| (1) | See Note 16 to our audited consolidated financial statements and Note 13 to our unaudited consolidated financial statements appearing elsewhere in this prospectus for details on the calculation of basic and diluted net loss per share. |
| (2) | See Note 17 to our audited consolidated financial statements and Note 14 to our unaudited consolidated financial statements appearing elsewhere in this prospectus for details on the calculation of basic and diluted pro forma net loss per share. |
| (3) | All share and per share amounts set forth in the table above have been adjusted to give retrospective effect to the 1-for-9.3197 reverse stock split effected on October 9, 2020. |
11
Table of Contents
| As of June 30, 2020 | ||||||||||||
| Actual | Pro forma | Pro forma as adjusted(1) |
||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||
| Consolidated Balance Sheet Data: |
||||||||||||
| Cash, cash equivalents and investments |
$ | 88,122 | $ | 128,897 | 264,317 | |||||||
| Working capital(2) |
76,090 | 116,865 | 252,285 | |||||||||
| Total assets |
107,901 | 148,676 | 284,096 | |||||||||
| Current liabilities |
15,364 | 15,364 | 15,364 | |||||||||
| Derivative liabilities |
380 | — | — | |||||||||
| Redeemable convertible preferred stock liabilities |
2,810 | — | — | |||||||||
| Operating lease liabilities, net of current portion |
11,106 | 11,106 | 11,106 | |||||||||
| Redeemable convertible preferred stock |
182,566 | — | — | |||||||||
| Accumulated deficit |
(107,023 | ) | (107,023 | ) | (107,023 | ) | ||||||
| Total stockholders’ (deficit) equity |
(104,573 | ) | 121,958 | 257,378 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| (1) | Each $1.00 increase (decrease) in the assumed initial public offering price of $15.00 per share (the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover of this prospectus), would increase (decrease) the amount of each of cash, cash equivalents and investments, working capital, total assets and total stockholders’ (deficit) equity by $9.3 million, assuming the number of shares offered by us, as set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, remains the same and after deducting the underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us. We may also increase (decrease) the number of shares we are offering. Each increase (decrease) of 1,000,000 in the number of shares we are offering would increase (decrease) the amount of each of cash, cash equivalents and investments, working capital, total assets and total stockholders’ (deficit) equity by $14.0 million, assuming the assumed initial public offering price of $15.00 per share (the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover of this prospectus), remains the same and after deducting the underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us. The pro forma as adjusted information is illustrative only and we will adjust this information based on the actual initial public offering price and other terms of this offering determined at pricing. |
| (2) | We define working capital as current assets less current liabilities. |
The preceding table presents our consolidated balance sheet data as of June 30, 2020:
| • | on an actual basis, giving effect to the filing of our amended and restated certificate of incorporation on October 9, 2020, including the 1-for-9.3197 reverse stock split; |
| • | on a pro forma basis to give further effect to: (i) the conversion of all 19,201,429 shares of our preferred stock outstanding as of June 30, 2020 into 16,392,640 shares of our common stock and 2,808,789 shares of our non-voting common stock, which will be effective immediately prior to the closing of this offering; (ii) the issuance of 3,569,630 shares of our Series B-2 convertible preferred stock on October 6, 2020, and the subsequent conversion of such shares into 3,286,081 shares of common stock and 283,549 shares of non-voting common stock immediately prior to the closing of this offering; (iii) the issuance of 83,149 shares of our common stock upon the exercise of all Series A Warrants outstanding as of June 30, 2020 (which will be exercised prior to the closing of this offering at an exercise price of $9.32 per share), as a result of the conversion of 83,149 shares of our Series A convertible preferred stock issuable upon the exercise of our Series A Warrants and the automatic conversion of such shares of Series A convertible preferred stock into an equivalent number of shares of common stock immediately prior to the closing of this offering; and (iv) the filing and effectiveness of our further amended and restated certificate of incorporation, which will occur immediately prior to the closing of this offering; and |
| • | on a pro forma as adjusted basis to give further effect to the sale of 10,000,000 shares of common stock in this offering at an assumed initial public offering price of $15.00 per share, the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover of this prospectus, after deducting the underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us. |
12
Table of Contents
Investing in our common stock involves a high degree of risk. You should carefully consider the risks described below, as well as the other information in this prospectus, including our consolidated financial statements and the related notes and “Management’s discussion and analysis of financial condition and results of operations,” before deciding whether to invest in our common stock. Many of the following risks and uncertainties are, and will be, exacerbated by the coronavirus pandemic (“COVID-19”) and any worsening of the global business and economic environment as a result. The occurrence of any of the events or developments described below could harm our business, financial condition, results of operations and growth prospects. In such an event, the market price of our common stock could decline, and you may lose all or part of your investment. Additional risks and uncertainties not presently known to us or that we currently deem immaterial may also impair our business operations.
Risks related to our limited operating history, financial position and need for additional capital
We are a clinical-stage biopharmaceutical company with a limited operating history and no products approved for commercial sale. We have incurred significant losses since inception. We expect to incur losses for at least the next several years and may never achieve or maintain profitability, which, together with our limited operating history, makes it difficult to assess our future viability.
Biopharmaceutical product development is a highly speculative undertaking and involves a substantial degree of risk. We are a clinical-stage biopharmaceutical company, and we have only a limited operating history upon which you can evaluate our business and prospects. We currently have no products approved for commercial sale, have not generated any revenue from sales of products and have incurred losses in each year since our inception in February 2018. In addition, we have limited experience as a company and have not yet demonstrated an ability to successfully overcome many of the risks and uncertainties frequently encountered by companies in new and rapidly evolving fields, particularly in the biopharmaceutical industry. Only one of our drug candidates, ALG-010133, is currently in clinical development.
Since inception, we have incurred significant net losses. Our net losses were $13.9 million for the period from February 5, 2018 (date of inception) to December 31, 2018, $52.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 and $40.8 million for the six months ended June 30, 2020. As of June 30, 2020, we had a total stockholders’ deficit of $104.6 million. We have funded our operations to date primarily with proceeds from the sale of preferred stock and convertible notes. To date, we have devoted substantially all of our resources to organizing and staffing our company, business planning, raising capital, acquiring and discovering development programs, securing intellectual property rights and conducting discovery, research and development activities for our programs. We have not yet demonstrated our ability to successfully complete any clinical trials, including pivotal clinical trials, obtain marketing approvals, manufacture a commercial-scale product or arrange for a third party to do so on our behalf, or conduct sales and marketing activities necessary for successful product commercialization. Our drug candidates will require substantial additional development time and resources before we will be able to apply for or receive regulatory approvals and, if approved, begin generating revenue from product sales. We expect to continue to incur significant expenses and operating losses for the foreseeable future.
We have never generated revenue from product sales and may never be profitable.
Our ability to generate revenue from product sales and achieve profitability depends on our ability, alone or with our collaboration partners, to successfully complete the development of, and obtain the regulatory approvals necessary to commercialize, our drug candidates. We do not anticipate generating revenue from
13
Table of Contents
product sales for the next several years, if ever. Our ability to generate revenue from product sales depends heavily on our and our current and potential future collaborators’ success in:
| • | completing clinical and nonclinical development of drug candidates and programs and identifying and developing new drug candidates; |
| • | seeking and obtaining marketing approvals for any drug candidates that we develop; |
| • | launching and commercializing drug candidates for which we obtain marketing approval by establishing a sales force, marketing, medical affairs and distribution infrastructure or, alternatively, collaborating with a commercialization partner; |
| • | achieving adequate coverage and reimbursement by third-party payors for drug candidates that we develop; |
| • | establishing and maintaining supply and manufacturing relationships with third parties that can provide adequate, in both amount and quality, products and services to support clinical development and the market demand for drug candidates that we develop, if approved; |
| • | obtaining market acceptance of drug candidates that we develop as viable treatment options; |
| • | addressing any competing technological and market developments; |
| • | negotiating favorable terms in any collaboration, licensing or other arrangements into which we may enter and performing our obligations in such collaborations; |
| • | maintaining, protecting, enforcing and expanding our portfolio of intellectual property rights, including patents, trade secrets and know-how; |
| • | defending against third-party interference, infringement or other intellectual property-related claims, if any; and |
| • | attracting, hiring and retaining qualified personnel. |
Even if one or more of the drug candidates that we develop is approved for commercial sale, we anticipate incurring significant costs associated with commercializing any approved drug candidate. Our expenses could increase beyond expectations if we are required by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (the “FDA”), the European Medicines Agency (the “EMA”), or other regulatory agencies to perform clinical trials or studies in addition to those that we currently anticipate. Even if we are able to generate revenue from the sale of any approved products, we may not become profitable and may need to obtain additional funding to continue operations.
Even if this offering is successful, we will require substantial additional financing to achieve our goals, which may not be available on acceptable terms, or at all. A failure to obtain this necessary capital when needed could force us to delay, limit, reduce or terminate our product development or commercialization efforts.
Our operations have consumed substantial amounts of cash since our inception. Since our inception, we have invested a significant portion of our efforts and financial resources in research and development activities for our initial nonclinical and clinical drug candidates. Nonclinical studies and clinical trials and additional research and development activities will require substantial funds to complete. As of June 30, 2020, we had cash, cash equivalents and investments of $88.1 million. We expect to continue to spend substantial amounts to continue the nonclinical and clinical development of our current and future programs. If we are able to gain marketing approval for drug candidates that we develop, we will require significant additional amounts of cash in order to launch and commercialize such drug candidates. In addition, other unanticipated costs may arise.
14
Table of Contents
Because the design and outcome of our planned and anticipated clinical trials is highly uncertain, we cannot reasonably estimate the actual amounts necessary to successfully complete the development and commercialization of any drug candidate we develop.
Our future capital requirements depend on many factors, including:
| • | the scope, progress, results and costs of researching and developing our drug candidates and programs, and of conducting nonclinical studies and clinical trials; |
| • | the timing of, and the costs involved in, obtaining marketing approvals for drug candidates we develop if clinical trials are successful; |
| • | the cost of commercialization activities for our current drug candidates, and any future drug candidates we develop, whether alone or in collaboration, including marketing, sales and distribution costs if our current drug candidates or any future drug candidate we develop is approved for sale; |
| • | the cost of manufacturing our current and future drug candidates for clinical trials in preparation for marketing approval and commercialization; |
| • | our ability to establish and maintain strategic licenses or other arrangements and the financial terms of such agreements; |
| • | the costs involved in preparing, filing, prosecuting, maintaining, expanding, defending and enforcing patent claims, including litigation costs and the outcome of such litigation; |
| • | the timing, receipt and amount of sales of, or profit share or royalties on, our future products, if any; |
| • | the emergence of competing therapies for hepatological indications and viral diseases and other adverse market developments; and |
| • | any acquisitions or in-licensing of other programs or technologies. |
We expect to finance our cash needs through a combination of public or private equity offerings, debt financings, collaborations, strategic alliances, licensing arrangements and other marketing or distribution arrangements. In addition, we may seek additional capital to take advantage of favorable market conditions or strategic opportunities even if we believe we have sufficient funds for our current or future operating plans. Based on our research and development plans, we expect that our existing cash, cash equivalents and investments will enable us to fund our operations for at least 12 months following the date of this offering. However, our operating plan may change as a result of many factors currently unknown to us, and we may need to seek additional funds sooner than planned. Moreover, it is particularly difficult to estimate with certainty our future expenses given the dynamic nature of our business, the COVID-19 pandemic and the macro-economic environment generally.
Our ability to raise additional funds will depend on financial, economic and other factors, many of which are beyond our control. In particular, the COVID-19 pandemic continues to rapidly evolve and has already resulted in a significant disruption of global financial markets. If the disruption persists or deepens, we could be unable to access additional capital, which could negatively affect our ability to consummate certain corporate development transactions or other important, beneficial or opportunistic investments. If additional funds are not available to us when we need them, on terms that are acceptable to us, or at all, we may be required to:
| • | delay, limit, reduce or terminate nonclinical studies, clinical trials or other research and development activities or eliminate one or more of our development programs altogether; or |
15
Table of Contents
| • | delay, limit, reduce or terminate our efforts to establish manufacturing and sales and marketing capabilities or other activities that may be necessary to commercialize any future approved products, or reduce our flexibility in developing or maintaining our sales and marketing strategy. |
Raising additional capital may cause dilution to our stockholders, restrict our operations or require us to relinquish rights to our technologies.
To date, we have primarily financed our operations through the sale of preferred stock and convertible notes. We will be required to seek additional funding in the future and may to do so through public or private equity offerings or debt financings, credit or loan facilities, collaborations or a combination of one or more of these funding sources. If we raise additional funds by issuing equity securities, our stockholders may suffer dilution and the terms of any equity financing may adversely affect the rights of our stockholders. In addition, as a condition to providing additional funds to us, future investors may demand, and may be granted, rights superior to those of existing stockholders. Debt financing, if available, is likely to involve restrictive covenants limiting our flexibility in conducting future business activities, and, in the event of insolvency, debt holders would be repaid before holders of our equity securities received any distribution of our corporate assets. If we raise additional capital through marketing and distribution arrangements or other collaborations, strategic alliances or licensing arrangements with third parties, we may have to relinquish certain valuable rights to our drug candidates, technologies, future revenue streams or research programs or grant licenses on terms that may not be favorable to us. Attempting to secure additional financing may also divert our management’s attention from our day-to-day activities, which may adversely affect our ability to develop our drug candidates.
Our operating results may fluctuate significantly, which will make our future results difficult to predict and could cause our results to fall below expectations.
Our quarterly and annual operating results may fluctuate significantly, which will make it difficult for us to predict our future results. These fluctuations may occur due to a variety of factors, many of which are outside of our control and may be difficult to predict, including:
| • | the timing and cost of, and level of investment in, research, development and commercialization activities, which may change from time to time; |
| • | the timing and status of enrollment for our clinical trials; |
| • | the timing of regulatory approvals, if any, in the United States and internationally; |
| • | the timing of expanding our operational, financial and management systems and personnel, including personnel to support our clinical development, quality control, manufacturing and commercialization efforts and our operations as a public company; |
| • | the cost of manufacturing, as well as building out our supply chain, which may vary depending on the quantity produced, and the terms of any agreements we enter into with third-party suppliers; |
| • | the timing and amount of any milestone, royalty or other payments due under any current or future collaboration or license agreement, including our existing license agreements with Emory University (“Emory”) and Luxna Biotech Co., Ltd. (“Luxna”); |
| • | coverage and reimbursement policies with respect to any future approved products, and potential future drugs that compete with our products; |
| • | the timing and cost to establish a sales, marketing, medical affairs and distribution infrastructure to commercialize any products for which we may obtain marketing approval and intend to commercialize on our own or jointly with current or future collaborators; |
16
Table of Contents
| • | expenditures that we may incur to acquire, develop or commercialize additional products and technologies; |
| • | the level of demand for any future approved products, which may vary significantly over time; |
| • | future accounting pronouncements or changes in accounting principles or our accounting policies; and |
| • | the timing and success or failure of nonclinical studies and clinical trials for our drug candidates or competing drug candidates, or any other change in the competitive landscape of our industry, including consolidation among our competitors or collaboration partners. |
The cumulative effects of these factors could result in large fluctuations and unpredictability in our quarterly and annual operating results. As a result, comparing our operating results on a period-to-period basis may not be meaningful. Investors should not rely on our past results as an indication of our future performance.
This variability and unpredictability could also result in our failing to meet the expectations of industry or financial analysts or investors for any period. If our revenue or operating results fall below the expectations of analysts or investors or below any forecasts we may provide to the market, or if the forecasts we provide to the market are below the expectations of analysts or investors, the price of our common stock could decline substantially. Such a stock price decline could occur even if we have met any previously publicly stated revenue or earnings guidance we may provide.
Our business could be materially adversely affected by the effects of health pandemics or epidemics, including the current outbreak of COVID-19 and future coronavirus outbreaks, and in particular in regions where we or third parties on which we rely have significant manufacturing facilities, concentrations of clinical trial sites or other business operations, including the San Francisco Bay Area where our headquarters are located.
Our business could be materially adversely affected by the effects of health pandemics or epidemics, including the current outbreak of COVID-19, which the World Health Organization declared a global pandemic and which has prompted severe lifestyle and commercial restrictions aimed at reducing the spread of the disease. In March 2020, the San Francisco Bay Area counties issued a joint shelter-in-place order, which was subsequently followed by a California state-wide shelter order, and other state and local governments implemented similar orders which, among other things, directed individuals to shelter at their places of residence, directed businesses and governmental agencies to cease non-essential operations at physical locations, prohibited certain non-essential gatherings, and ordered cessation of non-essential travel. As a result of these developments, we implemented work-from-home policies for most of our employees. The California state-wide order has no current expiration date. The state-wide shelter order, the local shelter-in-place orders implemented by San Mateo County and any other San Francisco Bay Area counties, government-imposed quarantines and our work-from-home policies may negatively impact productivity, disrupt our business and delay our clinical programs and timelines, the magnitude of which will depend, in part, on the length and severity of the restrictions, the potential impact of changing government orders in response to upticks in COVID-19 cases and other limitations on our ability to conduct our business in the ordinary course. Although we do not anticipate any impacts to our clinical programs, these and similar, and perhaps more severe, disruptions in our operations could negatively impact our business, operating results and financial condition in the future.
Quarantines, shutdowns and shelter-in-place and similar government orders related to COVID-19 or other infectious diseases, or the perception that such events, orders or other restrictions on the conduct of business operations could occur, could impact personnel at third-party manufacturing facilities in the United States and other countries, or the availability or cost of materials, which would disrupt our supply chain. Although we do not anticipate any clinical supply issues or concerns for our planned clinical trials, restrictions resulting from the COVID-19 outbreak may disrupt our supply chain in the future and delay or limit our ability to obtain sufficient materials for our drug candidates.
17
Table of Contents
In addition, our current clinical trial and planned clinical trials may be affected by the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. Site initiation and patient enrollment may be delayed due to prioritization of hospital resources toward the COVID-19 pandemic, and potential patients may not be able or willing to comply with clinical trial protocols, whether due to quarantines impeding patient movement or interrupting healthcare services, or due to potential patient concerns regarding interactions with medical facilities or staff. Similarly, our ability to recruit and retain principal investigators and site staff who, as healthcare providers, may have heightened exposure to COVID-19, may be delayed or disrupted, which may adversely impact our clinical trial operations.
In addition, the global COVID-19 pandemic has adversely affected, and any future significant outbreak of contagious diseases in the human population could similarly adversely affect, the economies and financial markets of many countries, including the United States, resulting in an economic downturn that could suppress demand for our future products. Any of these events could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations or cash flows.
In addition, while the duration and severity of the effects of COVID-19 may be difficult to assess or predict, a continuing widespread pandemic could result in significant disruption of global financial markets, reducing our ability to access capital, which could negatively affect our liquidity and ability to progress our operations. In addition, a recession, down-turn or market correction resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic could materially adversely affect the value of our common stock.
Unfavorable global economic conditions could adversely affect our business, financial condition, stock price and results of operations.
Our results of operations could be adversely affected by general conditions in the global economy and in the global financial markets. For example, the 2008 global financial crisis caused extreme volatility and disruptions in the capital and credit markets. A severe or prolonged economic downturn, such as the 2008 global financial crisis, could result in a variety of risks to our business, including, weakened demand for any drug candidates we may develop and our ability to raise additional capital when needed on acceptable terms, if at all. A weak or declining economy could also strain our suppliers, possibly resulting in supply disruption. If the current equity and credit markets deteriorate, it may make any necessary debt or equity financing more difficult, more costly, and more dilutive. Failure to secure any necessary financing in a timely manner and on favorable terms could have a material adverse effect on our growth strategy, financial performance and stock price and could require us to delay or abandon clinical development plans. In addition, there is a risk that one or more of our current service providers, manufacturers or other partners may not survive such difficult economic times, which could directly affect our ability to attain our operating goals on schedule and on budget. Any of the foregoing could harm our business and we cannot anticipate all of the ways in which the current economic climate and financial market conditions could adversely impact our business. Furthermore, our stock price may decline due in part to the volatility of the stock market and any general economic downturn.
Risks related to product development and regulatory process
We are early in our development efforts, and our business is dependent on the successful development of our current and future drug candidates. If we are unable to advance our current or future drug candidates through clinical trials, obtain marketing approval and ultimately commercialize any drug candidates we develop, or experience significant delays in doing so, our business will be materially harmed.
Our clinical development efforts across our drug candidates are in an early stage. In August 2020, we initiated a clinical trial for our most advanced drug candidate, ALG-010133, in New Zealand. In addition, our clinical trial application for our CAM candidate (ALG-000184) was approved in New Zealand in September 2020 and we expect to commence a Phase 1 clinical trial to evaluate ALG-000184 in the fourth quarter of 2020. Our other
18
Table of Contents
programs are in the discovery or nonclinical development stage. We have invested substantially all of our efforts and financial resources in the identification of targets and nonclinical development of therapeutics to address hepatological indications and viral diseases. However, the biology of these indications and diseases is complex and not completely understood, and our current and future drug candidates may never achieve expected or functional levels of efficacy or achieve an acceptable safety profile. Our use of clinically validated targets to pursue treatments of these indications and diseases does not guarantee efficacy or safety or necessarily reduce the risk that our current or future drug candidates will not achieve expected or functional levels of efficacy or achieve an acceptable safety profile.
The success of our business, including our ability to finance our company and generate revenue from products in the future, which we do not expect will occur for several years, if ever, will depend heavily on the successful development and eventual commercialization of the drug candidates we develop, which may never occur. Our current drug candidates, and any future drug candidates we develop, will require additional nonclinical and clinical development, management of clinical, nonclinical and manufacturing activities, marketing approval in the United States and other markets, demonstrating effectiveness to pricing and reimbursement authorities, obtaining sufficient manufacturing supply for both clinical development and commercial production, building of a commercial organization, and substantial investment and significant marketing efforts before we generate any revenues from product sales.
As an organization, we have not yet completed any clinical trials for any of our drug candidates. Our lead drug candidate, ALG-010133, is currently being evaluated in a Phase 1 clinical trial in New Zealand. In addition, our clinical trial application for our CAM candidate (ALG-000184) was approved in September 2020 and we expect to commence a Phase 1 clinical trial to evaluate ALG-000184 in the fourth quarter of 2020. As a company, we have limited experience in preparing, submitting and prosecuting regulatory filings. Specifically, we have not previously submitted a new drug application (“NDA”) to the FDA or similar approval filings to a comparable foreign regulatory authority for any drug candidate. An NDA or other relevant regulatory filing must include extensive nonclinical and clinical data and supporting information to establish that the drug candidate is safe and effective for each desired indication. The NDA or other comparable regulatory filing must also include significant information regarding the chemistry, manufacturing and controls for the product. We have had limited interactions with the FDA and cannot be certain how many clinical trials of any of our drug candidates will be required or whether the FDA will agree with the design or implementation of our clinical trials. In addition, we cannot be certain that our current or future drug candidates will be successful in clinical trials such that the information contained in an NDA or comparable regulatory filing would support approval, and thus we cannot guarantee that any of our drug candidates will receive regulatory approval. Further, even if our current or future drug candidates are successful in clinical trials, such candidates may not receive regulatory approval. If we do not receive regulatory approvals for current or future drug candidates, we may not be able to continue our operations. Even if we successfully obtain regulatory approval to market a drug candidate, our revenue will depend, in part, upon the size of the markets in the territories for which we gain regulatory approval and have commercial rights, as well as the availability of competitive products, third-party reimbursement and adoption by physicians.
We plan to seek regulatory approval to commercialize our drug candidates both in the United States and in select foreign countries. While the scope of regulatory approval in other countries is generally similar to that in the United States, in order to obtain separate regulatory approval in other countries we must comply with numerous and varying regulatory requirements of such countries regarding safety and efficacy. Other countries also have their own regulations governing, among other things, clinical trials and commercial sales, as well as pricing and distribution of drugs, and we may be required to expend significant resources to obtain regulatory approval and to comply with ongoing regulations in these jurisdictions.
19
Table of Contents
The success of our current and future drug candidates will depend on many factors, which may include the following:
| • | sufficiency of our financial and other resources to complete the necessary nonclinical studies and clinical trials, and our ability to raise any additional required capital on acceptable terms, or at all; |
| • | our ability to develop and successfully utilize our drug discovery platforms; |
| • | the timely and successful completion of our nonclinical studies and clinical trials, which may be significantly slower or cost more than we currently anticipate and will depend substantially upon the performance of third-party contractors; |
| • | acceptance of investigational new drug applications (“INDs”), CTAs and/or similar applications in other jurisdictions for our planned and future clinical trials; |
| • | whether we are required by the FDA or a comparable foreign regulatory agency to conduct additional clinical trials or other studies beyond those planned to support approval of our drug candidates; |
| • | successful enrollment and completion of clinical trials; |
| • | successful data from our clinical program that supports an acceptable risk-benefit profile of our drug candidates in the intended populations; |
| • | receipt and maintenance of marketing approvals from applicable regulatory authorities; |
| • | establishing agreements with third-party manufacturers for clinical supply for our clinical trials and commercial manufacturing, if our drug candidates are approved; |
| • | our ability, and the ability of any third parties with whom we contract, to remain in good standing with regulatory agencies and develop, validate and maintain commercially viable manufacturing processes that are compliant with current good manufacturing practices (“cGMPs”); |
| • | entry into collaborations to further the development of our drug candidates in select indications or geographies; |
| • | obtaining, maintaining and expanding our portfolio of intellectual property rights, including patents, trade secrets and know-how; |
| • | enforcing and defending our intellectual property rights and having and successfully executing an intellectual property life cycle management strategy that supports long-term product development and commercialization goals; |
| • | obtaining and maintaining regulatory exclusivity for our drug candidates; |
| • | successfully launching commercial sales of our drug candidates, if approved; |
| • | acceptance of the drug candidate’s benefits and uses, if approved, by patients, the medical community and third-party payors; |
| • | the prevalence, duration and severity of potential side effects or other safety issues experienced with our drug candidates following approval; |
| • | effectively competing with other therapies; and |
| • | obtaining and maintaining healthcare coverage and adequate reimbursement from third-party payors. |
20
Table of Contents
If we are not successful with respect to one or more of these factors in a timely manner or at all, we could experience significant delays or an inability to successfully obtain approval of or commercialize the drug candidates we develop, which would materially harm our business. If we do not receive marketing approvals for our current or future drug candidates, we may not be able to continue our operations. Even if regulatory approvals are obtained, we may never be able to successfully commercialize any products. Accordingly, we cannot provide assurances that we will be able to generate sufficient revenue through the sale of products to continue our business.
Nonclinical development is uncertain. Our nonclinical programs may experience delays or may never advance to clinical trials, which would adversely affect our ability to obtain regulatory approvals or commercialize our drug candidates on a timely basis or at all, which would have an adverse effect on our business.
In order to obtain approval from the FDA and other major regulatory agencies in non-U.S. countries to market a new drug candidate, we must demonstrate proof of safety and efficacy in humans. To meet these requirements, we will have to conduct adequate and well-controlled clinical trials. Before we can commence clinical trials for a drug candidate, we must complete extensive nonclinical studies that support our planned INDs or CTAs in the United States and other countries. At this time, we have one drug candidate being evaluated in a clinical trial in New Zealand, ALG-010133. In addition, our clinical trial application for our CAM candidate (ALG-000184) was approved in September 2020 and we expect to commence a Phase 1 clinical trial to evaluate ALG-000184 in the fourth quarter of 2020. The rest of our programs are in nonclinical research or earlier stages of development, including our other chronic hepatitis B (“CHB”) drug candidates, our nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (“NASH”) drug candidate and our coronavirus drug candidates. We cannot be certain of the timely completion or outcome of our nonclinical studies and cannot predict if the FDA or other regulatory authorities will accept our proposed clinical programs or if the outcome of our nonclinical studies will ultimately support further development of our programs. In addition, the FDA may decline to accept the data we obtain from foreign clinical studies in support of an IND or NDA in the United States, which may require us to repeat or conduct additional nonclinical studies or clinical trials that we did not anticipate in the United States. As a result, we cannot be sure that we will be able to submit INDs in the United States, or CTAs or similar applications in other jurisdictions, on the timelines we expect, if at all, and we cannot be sure that submission of INDs, CTAs or similar applications will result in the FDA or other regulatory authorities allowing additional clinical trials to begin.
Conducting nonclinical testing is a complex, lengthy, time-consuming and expensive process. The length of time may vary substantially according to the type, complexity and novelty of the program, and often can take several years or more per program. Delays associated with programs for which we are directly conducting nonclinical studies may cause us to incur additional operating expenses. Moreover, we may be affected by delays associated with the studies of certain programs that are the responsibility of potential future partners, if any, over which we have no control. The commencement and rate of completion of nonclinical studies and clinical trials for a drug candidate may be delayed by many factors, including:
| • | inability or failure by us or third parties to comply with regulatory requirements, including the requirements of good laboratory practice (“GLP”); |
| • | inability to generate sufficient nonclinical or other in vivo or in vitro data to support the initiation of clinical studies; |
| • | delays in reaching a consensus with regulatory agencies on study design and obtaining regulatory authorization to commence clinical trials; |
| • | obtaining sufficient quantities of our drug candidates for use in nonclinical studies and clinical trials from third-party suppliers on a timely basis; |
21
Table of Contents
| • | delays due to the COVID-19 pandemic, including due to reduced workforce productivity as a result of our implementation of a temporary work-from-home policy or illness among personnel, or due to delays at our third-party contract research organizations throughout the world for similar reasons or due to restrictions imposed by applicable governmental authorities; and |
| • | delays due to other global-scale potentially catastrophic events, including other pandemics, terrorism, war, and climate changes. |
Moreover, even if candidates from our drug programs advance into clinical trials, our development efforts may not be successful, and clinical trials that we conduct or that third parties conduct on our behalf may not demonstrate sufficient safety or efficacy to obtain the requisite regulatory approvals for any drug candidates we develop. Even if we obtain positive results from nonclinical studies or initial clinical trials, we may not achieve the same success in future trials.
The regulatory approval processes of the FDA, the EMA and comparable foreign authorities are lengthy, time-consuming, complex and inherently unpredictable, and if we are ultimately unable to obtain regulatory approval for our drug candidates, our business will be substantially harmed.
The time required to obtain approval by the FDA, the EMA and comparable foreign authorities is unpredictable but typically takes many years following the commencement of clinical trials and depends upon numerous factors, including the substantial discretion of the regulatory authorities. In addition, approval policies, regulations, or the type and amount of clinical data necessary to gain approval may change during the course of a drug candidate’s clinical development and may vary across jurisdictions. We have not obtained regulatory approval for any drug candidate and it is possible that none of our current or future drug candidates will ever obtain regulatory approval.
Our current and future drug candidates could fail to receive regulatory approval for many reasons, including the following:
| • | the FDA, the EMA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities may disagree with the design or implementation of our clinical trials; |
| • | we may be unable to demonstrate to the satisfaction of the FDA, the EMA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities that a drug candidate is safe or effective for its proposed indication; |
| • | the results of clinical trials may not meet the level of statistical significance required by the FDA, the EMA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities for approval; |
| • | we may be unable to demonstrate that a drug candidate’s clinical and other benefits outweigh its safety risks; |
| • | the FDA, the EMA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities may disagree with our interpretation of data from clinical trials or nonclinical studies; |
| • | the data collected from clinical trials of our drug candidates may not be sufficient to support the submission of an NDA to the FDA or other submission or to obtain regulatory approval in the United States, the European Union or elsewhere; |
| • | the FDA, the EMA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities may find deficiencies with or fail to approve the manufacturing processes or facilities of third-party manufacturers with which we contract for clinical and commercial supplies; and |
| • | the approval policies or regulations of the FDA, the EMA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities may significantly change in a manner rendering our clinical data insufficient for approval. |
22
Table of Contents
This lengthy approval process as well as the unpredictability of clinical trial results may result in our failing to obtain regulatory approval to market any drug candidate we develop, which would significantly harm our business, results of operations and prospects. The FDA, the EMA and other comparable foreign authorities have substantial discretion in the approval process, and in determining when or whether regulatory approval will be obtained for any drug candidate that we develop. Even if we believe the data collected from future clinical trials of our drug candidates are promising, such data may not be sufficient to support approval by the FDA, the EMA or any other regulatory authority.
In addition, even if we were to obtain approval, regulatory authorities may approve any of our drug candidates for fewer or more limited indications than we request, may not approve the price we intend to charge for our products, may grant approval contingent on the performance of costly post-marketing clinical trials, or may approve a drug candidate with a label that does not include the labeling claims that we believe are necessary or desirable for the successful commercialization of that drug candidate. Any of the foregoing scenarios could materially harm the commercial prospects for our drug candidates.
We cannot be certain that any of our programs will be successful in clinical trials or receive regulatory approval. Further, drug candidates we develop may not receive regulatory approval even if they are successful in clinical trials. If we do not receive regulatory approvals for our drug candidates, we may not be able to continue our operations.
Clinical product development involves a lengthy and expensive process, with uncertain outcomes. We may experience delays in completing, or ultimately be unable to complete, the development and commercialization of our current and future drug candidates, which could result in increased costs to us, delay or limit our ability to generate revenue and adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
To obtain the requisite regulatory approvals to commercialize any of our drug candidates, we must demonstrate through extensive nonclinical studies and clinical trials that our products are safe and effective in humans. Clinical trials are expensive and can take many years to complete, and their outcomes are inherently uncertain. Failure can occur at any time during the clinical trial process and our future clinical trial results may not be successful.
We may experience delays in completing our clinical trials and initiating or completing additional clinical trials. We may also experience numerous unforeseen events prior to, during, or as a result of our nonclinical studies or clinical trials that could delay or prevent our ability to receive marketing approval or commercialize the drug candidates we develop, including:
| • | regulators, Institutional Review Boards (“IRBs”) or ethics committees may not authorize us or our investigators to commence a clinical trial or conduct a clinical trial at a prospective trial site; |
| • | we may experience delays in reaching, or fail to reach, agreement on acceptable terms with prospective trial sites and prospective contract research organizations (“CROs”); |
| • | the number of patients required for clinical trials may be larger than we anticipate; |
| • | it may be difficult to enroll a sufficient number of suitable patients, or enrollment in these clinical trials may be slower than we anticipate or participants may drop out of these clinical trials or fail to return for post-treatment follow-up at a higher rate than we anticipate; |
| • | our third-party contractors may fail to comply with regulatory requirements or meet their contractual obligations to us in a timely manner, or at all, or may deviate from the clinical trial protocol or drop out of the trial, which may require us to add new clinical trial sites or investigators; |
23
Table of Contents
| • | the supply or quality of materials for drug candidates we develop or other materials necessary to conduct clinical trials may be insufficient or inadequate; and |
| • | we may experience disruptions by man-made or natural disasters or public health pandemics or epidemics or other business interruptions, including the current COVID-19 pandemic and future outbreaks of the disease. |
We could encounter delays if a clinical trial is suspended or terminated by us, by the IRBs or ethics committees of the institutions in which such trials are being conducted, by a Data Safety Monitoring Board for such trial or by the FDA or other regulatory authorities. Such authorities may impose such a suspension or termination due to a number of factors, including failure to conduct the clinical trial in accordance with regulatory requirements or our clinical protocols, inspection of the clinical trial operations or trial site by the FDA or other regulatory authorities resulting in the imposition of a clinical hold, unforeseen safety issues or adverse side effects, failure to demonstrate a benefit from using a product, changes in governmental regulations or administrative actions or lack of adequate funding to continue the clinical trial. Many of the factors that cause, or lead to, a delay in the commencement or completion of clinical trials may also ultimately lead to the denial of marketing approval of our drug candidates.
Further, we are currently conducting a clinical trial for ALG-010133 in New Zealand and may in the future conduct clinical trials for ALG-010133 and other drug candidates in other countries and territories, including South Korea, Hong Kong, Moldova, the United Kingdom, and China, which presents additional risks that may delay completion of our clinical trials. These risks include the possibility that we could be required to conduct additional nonclinical studies before initiating any clinical trials, may be unable to enroll and retain patients as a result of differences in healthcare services, research guidelines or cultural customs, or may face additional administrative burdens associated with comparable foreign regulatory schemes, as well as political and economic risks relevant to such foreign countries.
If we experience termination or delays in the completion of any clinical trial of our drug candidates, the commercial prospects of our drug candidates will be harmed, and our ability to generate product revenues from any of these drug candidates will be delayed. In addition, any delays in completing our clinical trials will increase our costs, slow down our drug candidate development and approval process and jeopardize our ability to commence product sales and generate revenues. Significant clinical trial delays could also allow our competitors to bring products to market before we do, shorten any periods during which we may have the exclusive right to commercialize our drug candidates, impair our ability to commercialize our drug candidates and harm our business and results of operations.
Specifically, the clinical trial sites for our current and future planned drug trials, including for ALG-010133 and ALG-000184, may be affected by the COVID-19 outbreak due to prioritization of hospital resources toward COVID-19 efforts, travel or quarantine restrictions imposed by national, federal, state or local governments, and the inability to access sites for initiation and patient monitoring and enrollment. As a result, patient screening, new patient enrollment, monitoring and data collection may be affected or delayed. Some of our third-party manufacturers we use for the supply of materials for drug candidates or other materials necessary to manufacture product to conduct clinical trials are located in countries affected by COVID-19, and, should they experience disruptions such as temporary closures or suspension of services, we would likely experience delays in advancing these trials.
Separately, principal investigators for our clinical trials serve as scientific advisors or consultants to us from time to time and may receive cash or equity compensation in connection with such services. If these relationships and any related compensation result in perceived or actual conflicts of interest, or a regulatory authority concludes that the financial relationship may have affected the interpretation of the clinical trial, the integrity of the data generated at the applicable clinical trial site may be questioned and the utility of the
24
Table of Contents
clinical trial itself may be jeopardized, which could result in the delay or rejection of any applications we submit. Any such delay or rejection could prevent or delay us from commercializing our current or future drug candidates.
Any of these occurrences may harm our business, financial condition and prospects significantly. In addition, many of the factors that cause, or could lead to, a delay in the commencement or completion of clinical trials may also ultimately lead to the denial of regulatory approval of our drug candidates or result in the development of our drug candidates being terminated.
Our pursuit of potential treatments for NASH is at an early stage and we may be unable to produce a therapy that successfully treats NASH. Even if successful, we may be unable to obtain regulatory approval for and successfully commercialize our drug candidates.
We have invested, and will continue to invest, a significant portion of our time and financial resources in the pursuit of a treatment for NASH. If we cannot successfully develop, obtain regulatory approval for and commercialize our drug candidates for the treatment of NASH, our business may be harmed. The mechanism of action of our NASH drug candidates is complex, and we do not know the degree to which it will translate into a therapeutic benefit, if any, in NASH or any other indication, and we do not know the degree to which the complex mechanism of action may contribute to long-term safety issues or adverse events when our drug candidates are taken for prolonged periods, as is inherent in the treatment of NASH.
In addition, the standards implemented by clinical or regulatory agencies may change at any time and we cannot be certain what efficacy endpoints the FDA or foreign clinical or regulatory agencies may require at the time we plan to conduct clinical trials with respect to NASH or any other applicable indication. Also, if we are able to obtain accelerated approval of our drug candidates based on a liver biopsy endpoint, we may be required to conduct a post-approval clinical outcomes trial to confirm the clinical benefit of the drug candidate; if any such post-approval trial is not successful, we would not be able to continue marketing the product.
If we are successful and any of our drug candidates are approved for the treatment of NASH, our drug candidates will likely compete with products that may be approved for the treatment of NASH prior to our drug candidates and/or that have greater efficacy than our drug candidates, either alone or in combination. Behavioral modifications, such as diet and exercise, can also decrease or eliminate the demand for our potential NASH treatments.
Our pursuit of potential therapies for COVID-19 is at an early stage.
In response to the recent outbreak of COVID-19, the disease caused by the virus SARS-CoV-2, we are pursuing various potential therapies to address the disease, including protease inhibitors and oligonucleotides. Our identification and development of these potential therapies is at an early stage, and we may be unable to produce in a timely manner a therapy that successfully treats the virus or that has broad clinical applicability, if at all.
For example, in June 2020, we entered into a Research, Licensing and Commercialization Agreement (the “KU Leuven Agreement”) with Katholieke Universiteit Leuven (“KU Leuven”) under which we are collaborating with KU Leuven’s Rega Institute for Medical Research, as well as its Centre for Drug Design and Discovery, to research, develop, manufacture and commercialize potential protease inhibitors for the treatment of coronaviruses, including SARS-CoV-2. We are in the earliest stages of our collaboration under the KU Leuven Agreement. The KU Leuven Agreement may not result in a therapy that successfully treats SARS-CoV-2. Further, if the KU Leuven Agreement does result in such a therapy, the therapy may not be developed and commercialized in a timely manner.
25
Table of Contents
We are also committing significant financial resources and personnel to the development of potential therapies for COVID-19, which may cause delays in or otherwise negatively impact our other development programs, despite uncertainties surrounding the longevity and extent of COVID-19 as a global health concern. COVID-19 may be substantially eradicated prior to our development of a successful therapy or a vaccine may be developed that is highly efficacious and widely adopted, reducing or eliminating the need for therapies to treat the disease. Further, while we hope to develop potential therapies that are effective against other or future coronaviruses, in addition to SARS-CoV-2, we cannot be certain this will be the case. If our potential therapies are not effective against other or future coronaviruses, the value and/or sales potential of our therapies will be reduced or eliminated. Our business could be negatively impacted by our allocation of significant resources to a global health threat that is unpredictable and could rapidly dissipate or against which our potential therapies, if developed, may not be partially or fully effective, and may ultimately prove unsuccessful or unprofitable. Furthermore, there are no assurances that our therapy will be approved for inclusion in government stockpile programs, which may be material to the commercial success of any approved coronavirus-related drug candidate, either in the United States or abroad.
We will also need to enter into manufacturing arrangements in the future in order to create a supply chain for our COVID-19 drug candidates that can adequately support demand. Even if we are successful in developing and manufacturing an effective treatment for COVID-19, the SARS-CoV-2 virus could develop resistance to our treatment, which could affect any long-term demand or sales potential for our potential therapies.
In addition, another party may be successful in producing a more efficacious therapy for COVID-19 or a therapy with a more convenient or preferred route of administration or in producing a therapy in a more timely manner, which may lead to the diversion of funding away from us and toward other companies or lead to decreased demand for our potential therapies. Further, other therapies that are more affordable than our potential therapies may be used to treat COVID-19, including existing generic drugs, which could also hurt the funding of and demand for our potential therapies. There are efforts by several public and private entities to develop a therapy or vaccine for COVID-19, including Alexion Pharmaceuticals Inc., Incyte Corporation, Sanofi S.A., Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Amgen Inc. (together with Adaptive Biotechnologies Corporation), Abcellera Biologics, Inc. (together with Eli Lilly and Company), Vir Biotechnology, Inc. (together with GSK, Biogen Inc. and WuXi Biologics Ltd.), Altimmune, Inc., AstraZeneca PLC (together with Oxford University), BioNTech SE (together with Pfizer Inc.), GlaxoSmithKline (“GSK”) (together with Sanofi), Heat Biologics, Inc., Inovio Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Johnson & Johnson, Moderna, Inc., Novavax, Inc., and Vaxart, Inc., many of which are further along in the development process than we are. These other entities may be more successful at developing, manufacturing or commercializing a therapy for COVID-19, especially given that several of these other organizations are much larger than we are and have access to larger pools of capital, including U.S. government funding, and broader manufacturing infrastructure. The success or failure of other entities, or perceived success or failure, may adversely impact our ability to obtain any future funding for our development and manufacturing efforts or to ultimately commercialize a therapy for COVID-19, if approved.
The regulatory pathways for our drug candidates targeting SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, are continually evolving, and may result in unexpected or unforeseen challenges.
Our drug candidates targeting SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, are in the early discovery stages. The speed at which companies and institutions are acting to create and test many therapeutics and vaccines for COVID-19 is unusually rapid, and evolving or changing plans or priorities within the FDA, including changes based on new knowledge of COVID-19 and how the disease affects the human body, may significantly affect the regulatory timelines for our COVID-19 drug candidates. Results from our continued development and planned clinical trials may raise new questions and require us to redesign proposed nonclinical studies and clinical trials, including revising proposed endpoints or adding new clinical trial sites or cohorts of subjects, with minimal lead time.
26
Table of Contents
The FDA has the authority to grant an Emergency Use Authorization (“EUA”) to allow unapproved medical products to be used in an emergency to diagnose, treat, or prevent serious or life-threatening diseases or conditions when, based on the totality of scientific evidence, there is evidence of effectiveness of the medical product, and there are no adequate, approved, and available alternatives. Depending on the outcomes of our planned nonclinical and initial clinical testing for our proposed COVID-19 therapies, we may seek an EUA for one or more of our drug candidates for use in the ongoing public health emergency, which would permit us to commercialize a drug candidate prior to FDA approval of an NDA. However, commercialization under an EUA is permitted only during the underlying public health emergency (as declared by the Secretary of the Department of Health and Human Services), meaning that once the emergency declaration is terminated, we would be required to obtain NDA approval to continue marketing the product. Furthermore, the FDA may revoke an EUA based on a determination that the product no longer satisfies the criteria for issuance of an EUA—for example, if there is no longer evidence of effectiveness of the product or there are other adequate, approved alternatives. Accordingly, we cannot predict how long, if at all, an EUA for any of our drug candidates may remain in place. Any termination or revocation of an EUA (if any) for one of our drug candidates could adversely impact our business in a variety of ways, including if one of our COVID-19 drug candidates is not yet approved by the FDA and if we and our manufacturing partners have invested in the supply chain to provide one of our COVID-19 drug candidates under an EUA.
The results of nonclinical studies and early-stage clinical trials may not be predictive of future results.
The results of nonclinical studies may not be predictive of the results of clinical trials, and the results of any early-stage clinical trials we commence may not be predictive of the results of the later-stage clinical trials. Drug candidates in later stages of clinical trials may fail to show the desired safety and efficacy despite having progressed through nonclinical studies and initial clinical trials. There is a high failure rate for drugs proceeding through clinical trials, and a number of companies in the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries have suffered significant setbacks in clinical development even after achieving promising results in earlier studies. There can be no assurance that any of our current or future clinical trials will ultimately be successful or support further clinical development of any of our drug candidates. Even if our clinical trials are completed, the results may not be sufficient to obtain regulatory approval of any products. Any such setbacks in our clinical development could have a material adverse effect on our business and operating results.
Interim, “topline” and preliminary data from our clinical trials may differ materially from the final data.
From time to time, we may disclose interim data from our clinical trials. Interim data from clinical trials are subject to the risk that one or more of the clinical outcomes may materially change as patient enrollment continues and more data on existing patients become available. Adverse differences between interim data and final data could significantly harm our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects. From time to time, we may also publicly disclose preliminary or “topline” data from our clinical trials, which are based on a preliminary analysis of then-available data, and the results and related findings and conclusions are subject to change following a more comprehensive review of the data related to the particular study or trial. We also make assumptions, estimations, calculations and conclusions as part of our analyses of data, and we may not have received or had the opportunity to fully and carefully evaluate all data. As a result, the topline results that we report may differ from future results of the same clinical trials, or different conclusions or considerations may qualify such topline results, once additional data have been received and fully evaluated. Topline data also remain subject to audit and verification procedures that may result in the final data being materially different from the preliminary data we previously published. As a result, topline data should be viewed with caution until the final data are available.
Further, others, including regulatory agencies, may not accept or agree with our assumptions, estimates, calculations, conclusions or analyses or may interpret or weigh the importance of data differently, which could
27
Table of Contents
impact the value of the particular program, the approvability or commercialization of the particular drug candidate or product and the value of our company in general. In addition, the information we choose to publicly disclose regarding a particular study or clinical trial is typically a summary of extensive information, and you or others may not agree with what we determine is the material or otherwise appropriate information to include in our disclosure, and any information we determine not to disclose may ultimately be deemed significant with respect to future decisions, conclusions, views, activities or otherwise regarding a particular product, drug candidate or our business. If the topline data that we report differ from actual results, or if others, including regulatory authorities, disagree with the conclusions reached, our ability to obtain approval for, and commercialize, our drug candidates may be harmed, which could harm our business, financial condition, operating results and prospects.
If we encounter difficulties enrolling patients in our clinical trials, our clinical development activities could be delayed or otherwise adversely affected.
The timely completion of clinical trials in accordance with their protocols depends, among other things, on our ability to enroll a sufficient number of patients who remain in the trial until its conclusion. We may experience difficulties in patient enrollment in our clinical trials for a variety of reasons. The enrollment of patients depends on many factors, including:
| • | the patient eligibility criteria defined in the protocol; |
| • | the size of the patient population required for analysis of the trial’s primary endpoints; |
| • | the proximity of patients to study sites; |
| • | the design of the trial; |
| • | our ability to recruit clinical trial investigators with the appropriate competencies and experience; |
| • | clinicians’ and patients’ perceptions as to the potential advantages of the drug candidate being studied in relation to other available therapies, including any new products that may be approved for the indications we are investigating; |
| • | our ability to obtain and maintain patient consents for participation in our clinical trials and, where appropriate, biopsies for future patient enrichment efforts; |
| • | the risk that patients enrolled in clinical trials will not remain in the trial through the completion of evaluation; and |
| • | disruption by man-made or natural disasters, or public health pandemics or epidemics or other business interruptions, including the current COVID-19 pandemic and future outbreaks of the virus. |
In addition, our clinical trials will compete with other clinical trials for drug candidates that are in the same therapeutic areas as our current and potential future drug candidates. This competition will reduce the number and types of patients available to us, because some patients who might have enrolled in our trials may instead opt to enroll in a trial conducted by one of our competitors. Since the number of qualified clinical investigators is limited, we may conduct some of our clinical trials at the same clinical trial sites that some of our competitors use, which would reduce the number of patients who are available for our clinical trials at such sites. Moreover, because our current and potential future drug candidates may represent a departure from more commonly used methods for treatment, potential patients and their doctors may be inclined to use conventional therapies rather than enroll patients in our clinical trials.
28
Table of Contents
Delays in patient enrollment may result in increased costs or may affect the timing or outcome of clinical trials, which could prevent completion of these trials and adversely affect our ability to advance the development of our drug candidates.
Changes in methods of drug candidate manufacturing or formulation may result in additional costs or delay.
As drug candidates proceed from nonclinical studies to late-stage clinical trials towards potential approval and commercialization, it is common that various aspects of the development program, such as manufacturing methods and formulation, are altered to optimize results. However, any change could entails additional cost and risks potential delay if the reformulated or otherwise altered drug candidate performs different than expected or intended, which could require modification to the nonclinical or clinical program. Such changes may also require additional testing, including bridging or comparability testing to demonstrate the validity of clinical data obtained in clinical trials following manufacturing changes, FDA notification or FDA approval.
Moreover, we have not yet manufactured or processed on a commercial scale any of our drug candidates. We may make changes as we work to optimize our manufacturing processes, but we cannot be sure that even minor changes in our processes will result in therapies that are safe and effective or that will be approved for commercial sale.
Our current or future drug candidates may cause undesirable side effects or have other properties when used alone or in combination with other approved products or investigational new drugs that could delay or halt their clinical development, prevent their marketing approval, limit their commercial potential or result in significant negative consequences.
Undesirable or clinically unmanageable side effects from one or more of our drug candidates or potential future products could occur and cause us or regulatory authorities to interrupt, delay or terminate clinical trials, could result in a more restrictive label or could cause the delay or denial of marketing approval by the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities. Further, results of our planned clinical trials could reveal unacceptably severe and prevalent side effects or unexpected characteristics.
If unacceptable toxicities or other undesirable side effects arise in the development of any of our current or future drug candidates, we could suspend or terminate our trials, or the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities could order us to cease clinical trials or deny approval of the drug candidate for any or all targeted indications. Treatment-related side effects could also affect patient recruitment or the ability of enrolled subjects to complete the trial, or result in potential product liability claims. In addition, these side effects may not be appropriately recognized or managed by the treating medical staff. Inadequately recognizing or managing the potential side effects of our drug candidates could result in patient injury or death. Any of these occurrences may prevent us from achieving or maintaining market acceptance of the affected drug candidate and may harm our business, financial condition and prospects significantly.
Although our current and future drug candidates will undergo safety testing to the extent possible and, where applicable, under such conditions discussed with regulatory authorities, not all adverse effects of drugs can be predicted or anticipated. Unforeseen side effects could arise either during clinical development or, if such side effects are more rare, after our products have been approved by regulatory authorities and the approved product has been marketed, resulting in the exposure of additional patients. To date, we have not demonstrated that any of our drug candidates are safe in humans, and we cannot predict if ongoing or future clinical trials will do so.
Furthermore, we plan to evaluate our drug candidates in combination with approved and/or experimental therapies. These combinations may have additional or more severe side effects than caused by our drug candidates as monotherapies or may cause side effects at lower doses. The uncertainty resulting from the use
29
Table of Contents
of our drug candidates in combination with other therapies may make it difficult to accurately predict side effects in potential future clinical trials.
If any of our drug candidates receives marketing approval and we or others later identify undesirable side effects caused by such products, a number of potentially significant negative consequences could occur, including:
| • | regulatory authorities may withdraw their approval of the product; |
| • | we may be required to recall a product or change the way such product is administered to patients; |
| • | additional restrictions may be imposed on the marketing of the particular product or the manufacturing processes for the product or any component thereof; |
| • | regulatory authorities may require the addition of labeling statements, such as a “black box” warning or a contraindication; |
| • | we may be required to implement a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (“REMS”) or create a Medication Guide outlining the risks of such side effects for distribution to patients; |
| • | we could be sued and held liable for harm caused to patients; |
| • | the product may become less competitive; and |
| • | our reputation may suffer. |
Any of the foregoing events could prevent us from achieving or maintaining market acceptance of the particular drug candidate, if approved, and result in the loss of significant revenue to us, which would adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects. In addition, if one or more of our drug candidates prove to be unsafe, our entire technology platform and pipeline could be affected, which would have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
Even if we complete the necessary nonclinical studies and clinical trials, the marketing approval process is expensive, time-consuming and uncertain and may prevent us or any of our future collaboration partners from obtaining approvals for the commercialization of our current drug candidates and any other drug candidate we develop.
Any current or future drug candidates we may develop and the activities associated with their development and commercialization, including their design, testing, manufacture, safety, efficacy, recordkeeping, labeling, storage, approval, advertising, promotion, sale, and distribution, are subject to comprehensive regulation by the FDA and other regulatory authorities in the United States and by comparable authorities in other countries. Failure to obtain marketing approval for a drug candidate will prevent us from commercializing the drug candidate in a given jurisdiction. We have not received approval to market any drug candidates from regulatory authorities in any jurisdiction and it is possible that none of our current or future drug candidates will ever obtain regulatory approval. As an organization, we have no experience in filing and supporting the applications necessary to gain marketing approvals and expect to rely on third-party CROs or regulatory consultants to assist us in this process. Securing regulatory approval requires the submission of extensive nonclinical and clinical data and supporting information to the various regulatory authorities for each therapeutic indication to establish the drug candidate’s safety and efficacy. Securing regulatory approval also requires the submission of information about the product manufacturing process to, and inspection of manufacturing facilities by, the relevant regulatory authority. Any drug candidates we develop may not be effective, may be only moderately effective, or may prove to have undesirable or unintended side effects, toxicities or other characteristics that may preclude our obtaining marketing approval or prevent or limit commercial use.
30
Table of Contents
The process of obtaining marketing approvals, both in the United States and abroad, is expensive, may take many years if additional clinical trials are required, if approval is obtained at all, and can vary substantially based upon a variety of factors, including the type, complexity, and novelty of the drug candidates involved. Changes in marketing approval policies during the development period, changes in or the enactment of additional statutes or regulations, or changes in regulatory review for each submitted product application, may cause delays in the approval or rejection of an application. The FDA and comparable authorities in other countries have substantial discretion in the approval process and may refuse to accept any application or may decide that our data are insufficient for approval and require additional nonclinical, clinical or other studies. In addition, varying interpretations of the data obtained from nonclinical and clinical testing could delay, limit, or prevent marketing approval of a drug candidate. Any marketing approval we ultimately obtain may be limited or subject to restrictions or post-approval commitments that render the approved product not commercially viable.
If we experience delays in obtaining marketing approval or if we fail to obtain marketing approval of any current or future drug candidates we may develop, the commercial prospects for those drug candidates may be harmed, and our ability to generate revenues will be materially impaired.
Even if a current or future drug candidate receives marketing approval, it may fail to achieve the degree of market acceptance by physicians, patients, third-party payors and others in the medical community necessary for commercial success.
If any current or future drug candidate we develop receives marketing approval, whether as a single agent or in combination with other therapies, it may nonetheless fail to gain sufficient market acceptance by physicians, patients, third-party payors, and others in the medical community, or such participants may prefer existing treatment options such as nucleos(t)ide analogs including tenofovir and entecavir. If the drug candidates we develop do not achieve an adequate level of acceptance, we may not generate significant product revenues and we may not become profitable. The degree of market acceptance of any drug candidate, if approved for commercial sale, will depend on a number of factors, including:
| • | efficacy and potential advantages compared to alternative treatments; |
| • | the ability to offer our products, if approved, for sale at competitive prices; |
| • | convenience and ease of administration compared to alternative treatments; |
| • | the willingness of the target patient population to try new therapies and of physicians to prescribe these therapies; |
| • | the strength of marketing and distribution support; |
| • | the ability to obtain sufficient third-party coverage and adequate reimbursement, including with respect to the use of the approved product as a combination therapy; |
| • | adoption of a companion diagnostic and/or complementary diagnostic (if any); and |
| • | the prevalence and severity of any side effects. |
Adverse events in our therapeutic areas of focus, including hepatological indications and viral diseases, could damage public perception of our current or future drug candidates and negatively affect our business.
The commercial success of our products will depend in part on public acceptance of our therapeutic areas of focus. Adverse events in clinical trials of our drug candidates, or post-marketing activities, or in clinical trials of others developing similar products or targeting similar indications and the resulting publicity, as well as any
31
Table of Contents
other adverse events in our therapeutic areas of focus, including hepatological indications and viral diseases, could result in decreased demand for any product that we may develop. If public perception is influenced by claims that the use of therapies in our therapeutic areas of focus are unsafe, whether related to our therapies or those of our competitors, our products may not be accepted by the general public or the medical community.
Future adverse events in our therapeutic areas of focus or the biopharmaceutical industry could also result in greater governmental regulation, stricter labeling requirements and potential regulatory delays in the testing or approvals of our products. Any increased scrutiny could delay or increase the costs of obtaining marketing approval for the drug candidates we have developed, are developing and may in the future develop.
Negative developments and negative public opinion of technologies on which we rely may damage public perception of our drug candidates or adversely affect our ability to conduct our business or obtain regulatory approvals for our drug candidates.
The clinical and commercial success of our drug candidates will depend in part on public acceptance of the use of technologies for the prevention or treatment of human diseases. Adverse public attitudes may adversely impact our ability to enroll clinical trials. Moreover, our success will depend upon physicians specializing in our targeted diseases prescribing, and their patients being willing to receive, our drug candidates as treatments in lieu of, or in addition to, existing, more familiar, treatments for which greater clinical data may be available. Any increase in negative perceptions of the technologies that we rely on may result in fewer physicians prescribing our products (if approved) or may reduce the willingness of patients to utilize our products or participate in clinical trials for our drug candidates.
Increased negative public opinion or more restrictive government regulations in response thereto, would have a negative effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations or prospects and may delay or impair the development and commercialization of our drug candidates or demand for such drug candidates. Adverse events in our nonclinical studies or clinical trials or those of our competitors or of academic researchers utilizing similar technologies, even if not ultimately attributable to drug candidates we may discover and develop, and the resulting publicity could result in increased governmental regulation, unfavorable public perception, potential regulatory delays in the testing or approval of potential drug candidates we may identify and develop, stricter labeling requirements for those drug candidates that are approved, a decrease in demand for any such drug candidates and a suspension or withdrawal of approval by regulatory authorities of our drug candidates.
Even if we receive marketing approval of a drug candidate, we will be subject to ongoing regulatory obligations and continued regulatory review, which may result in significant additional expense, and we may be subject to penalties if we fail to comply with regulatory requirements or experience unanticipated problems with our products, if approved.
Any marketing approvals that we receive for any current or future drug candidate may be subject to limitations on the approved indicated uses for which the product may be marketed, or contain requirements for potentially costly post-market testing and surveillance to monitor the safety and efficacy of the drug candidate. The FDA may also require a REMS as a condition of approval of any drug candidate, which could include requirements for a Medication Guide, physician communication plans or additional elements to ensure safe use, such as restricted distribution methods, patient registries and other risk-minimization tools. In addition, if the FDA or a comparable foreign regulatory authority approves a drug candidate, the manufacturing processes, labeling, packaging, distribution, adverse event reporting, storage, advertising, promotion, import and export and record keeping for the product will be subject to extensive and ongoing regulatory requirements. These requirements include submissions of safety and other post-marketing information and reports, establishment registration, as well as continued compliance with current Good Manufacturing Practice, or cGMP, and Good Clinical Practice, or
32
Table of Contents
GCP, for any clinical trials that we conduct post-approval. Later discovery of previously unknown problems with any approved candidate, including adverse events of unanticipated severity or frequency, or with our third-party manufacturers or manufacturing processes, or failure to comply with regulatory requirements, may result in, among other things:
| • | restrictions on the marketing or manufacturing of the product, withdrawal of the product from the market, or product recalls; |
| • | fines, untitled and warning letters, or holds on clinical trials; |
| • | refusal by the FDA or other regulatory authorities to approve pending applications or supplements to approved applications we filed or suspension or revocation of license approvals; |
| • | product seizure or detention, or refusal to permit the import or export of the product; and |
| • | injunctions or the imposition of civil or criminal penalties. |
The FDA’s and other regulatory authorities’ policies may change and additional government regulations may be enacted that could prevent, limit or delay marketing approval of a product. We cannot predict the likelihood, nature or extent of government regulation that may arise from future legislation or administrative action, either in the United States or abroad. If we are slow or unable to adapt to changes in existing requirements or the adoption of new requirements or policies, or if we are not able to maintain regulatory compliance, we may lose any marketing approval that we may have obtained, and we may not achieve profitability.
Even if we obtain and maintain approval for our drug candidates from the FDA, we may never obtain approval outside the United States, which would limit our market opportunities.
Approval of a drug candidate in the United States by the FDA does not ensure approval of such drug candidate by regulatory authorities in other countries or jurisdictions, and approval by one foreign regulatory authority does not ensure approval by regulatory authorities in other foreign countries. Sales of our drug candidates outside the United States will be subject to foreign regulatory requirements governing clinical trials and marketing approval. Even if the FDA grants marketing approval for a drug candidate, comparable foreign regulatory authorities also must approve the manufacturing and marketing of the drug candidate in those countries. Approval procedures vary among jurisdictions and can involve requirements and administrative review periods different from, and more onerous than, those in the United States, including additional nonclinical studies or clinical trials. In many countries outside the United States, a drug candidate must be approved for reimbursement before it can be approved for sale in that country. In some cases, the price that we intend to charge for any drug candidates, if approved, is also subject to approval. Obtaining approval for our drug candidates in the European Union (the “EU”) from the European Commission following the opinion of the EMA, if we choose to submit a marketing authorization application there, would be a lengthy and expensive process. Even if a drug candidate is approved, the EMA may limit the indications for which the product may be marketed, require extensive warnings on the product labeling or require expensive and time-consuming additional clinical trials or reporting as conditions of approval. Approval of certain drug candidates outside of the United States, particularly those that target diseases that are more prevalent outside of the United States, will be particularly important to the commercial success of such drug candidates. Obtaining foreign regulatory approvals and compliance with foreign regulatory requirements could result in significant delays, difficulties and costs for us and could delay or prevent the introduction of our drug candidates in certain countries.
Further, clinical trials conducted in one country may not be accepted by regulatory authorities in other countries. For example, we plan to conduct our initial clinical trials for ALG-010133 and ALG-000184 in New Zealand and several other countries and territories within the Asia Pacific and/or Europe, including South
33
Table of Contents
Korea, Hong Kong, Moldova, the United Kingdom, and China, and our conduct of the trial must satisfy specific requirements in order for the FDA to accept the data in support of an IND or NDA in the United States. Further, any regulatory approval for our drug candidates may be withdrawn. If we fail to comply with the applicable regulatory requirements, our target market will be reduced and our ability to realize the full market potential of our drug candidates will be harmed and our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects could be harmed.
Risks associated with our international operations, including seeking and obtaining approval to commercialize our drug candidates in foreign jurisdictions, could harm our business.
We engage in international operations with offices in the United States and Belgium and intend to seek approval to market our drug candidates outside of the United States. We may also do so for future drug candidates. We expect that we are or will be subject to additional risks related to these international business markets and relationships, including:
| • | different regulatory requirements for approval of drug candidates in foreign countries, including challenging processes for marketing biopharmaceutical products; |
| • | reduced protection for and enforcement of intellectual property rights; |
| • | heightened or different data privacy and information security laws, regulations and policies; |
| • | unexpected changes in tariffs, trade barriers and regulatory requirements; |
| • | economic weakness, including inflation or political instability in particular foreign economies and markets; |
| • | compliance with tax, employment, immigration and labor laws for employees living or traveling abroad; |
| • | foreign currency fluctuations, which could result in increased operating expenses and reduced revenue, and other obligations incident to doing business in another country; |
| • | foreign reimbursement, pricing and insurance regimes; |
| • | workforce uncertainty in countries where labor unrest is more common than in the United States; |
| • | production shortages resulting from any events affecting raw material supply or manufacturing capabilities; |
| • | business interruptions resulting from geopolitical actions, including war and terrorism, or natural disasters including earthquakes, typhoons, floods and fires; and |
| • | disruptions resulting from the impact of public health pandemics or epidemics (including, for example, the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic). |
In addition, there are complex regulatory, tax, labor and other legal requirements imposed by many of the individual countries in which we may operate, with which we will need to comply.
Disruptions at the FDA and other government agencies caused by funding shortages or global health concerns could hinder their ability to hire, retain or deploy key leadership and other personnel, or could otherwise prevent new or modified products from being developed, approved or commercialized in a timely manner or at all, which could negatively impact our business.
The ability of the FDA to review and approve new products can be affected by a variety of factors, including government budget and funding levels, statutory, regulatory, and policy changes, the FDA’s ability to hire and retain key personnel and accept the payment of user fees, and other events that may otherwise affect the FDA’s ability to perform routine functions. Average review times at the agency have fluctuated in recent years as a
34
Table of Contents
result. Disruptions at the FDA and other agencies may also slow the time necessary for new products to be reviewed and/or approved by necessary government agencies, which would adversely affect our business. For example, over the last several years, including for 35 days beginning on December 22, 2018, the U.S. government has shut down several times and certain regulatory agencies, such as the FDA, have had to furlough critical FDA employees and stop critical activities.
Relatedly, in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, on March 10, 2020 the FDA announced its intention to postpone most inspections of foreign manufacturing facilities, and on March 18, 2020, the FDA temporarily postponed routine surveillance inspections of domestic manufacturing facilities. Subsequently, on July 10, 2020 the FDA announced its intention to resume certain on-site inspections of domestic manufacturing facilities subject to a risk-based prioritization system. The FDA intends to use this risk-based assessment system to identify the categories of regulatory activity that can occur within a given geographic area, ranging from mission-critical inspections to resumption of all regulatory activities. The resumption of prioritized domestic inspections is dependent on the current COVID-19 data in a given state or county and the rules and guidelines established by state and local government. Regulatory authorities outside the United States may adopt similar restrictions or other policy measures in response to events such as the COVID-19 pandemic. If a prolonged government shutdown occurs, or if global health concerns continue to prevent the FDA or other regulatory authorities from conducting their regular inspections, reviews, or other regulatory activities, it could significantly impair the ability of the FDA or other regulatory authorities to timely review and process our regulatory submissions, which could have a material adverse effect on our business.
If the market opportunities for our drug candidates are smaller than we believe or any approval we obtain is based on a narrower definition of the patient population, our business may suffer.
We currently focus our product development on novel therapeutics to address unmet needs in hepatological indications and viral diseases. Our eligible patient population, pricing estimates and available coverage and reimbursement may differ significantly from the actual market addressable by our drug candidates. Our estimates of both the number of people who have these diseases, as well as the subset of people with these diseases who have the potential to benefit from treatment with our drug candidates, are based on our beliefs and analyses based on a variety of sources, including scientific literature, patient foundations or market research, and may prove to be incorrect. Further, new studies may change the estimated incidence or prevalence of the diseases we are targeting. The number of patients may turn out to be lower than expected, and the potentially addressable patient population for each of our drug candidates may be limited or may not be receptive to treatment with our drug candidates, and new patients may become increasingly difficult to identify or access. Certain potential patients may have or develop a resistance to our potential therapies or otherwise be unable to be treated with our potential therapies for COVID-19, HBV or other viral diseases as a result of their genetic makeup. In addition, the route of administration for our potential therapies could be inconvenient and/or not commercially viable, which could also limit the potential market for our therapies. If the market opportunities for our drug candidates are smaller than we estimate, it could have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
For example, we believe NASH to be one of the most prevalent chronic liver diseases worldwide, however, our projections of the number of people who have NASH, as well as the subset of people with the disease who have the potential to benefit from treatment with our drug candidates, are based on our beliefs and estimates. The effort to identify patients with NASH is in early stages, and we cannot accurately predict the number of patients for whom treatment might be possible. NASH is often undiagnosed and may be left undiagnosed for a long time, partly because a definitive diagnosis of NASH is currently based on a histological assessment of a liver biopsy, which impairs the ability to easily identify patients. If improved diagnostic techniques for identifying NASH patients who will benefit from treatment are not developed, our market opportunity may be smaller than we currently anticipate. Further, if government authorities and third-party payors choose to limit coverage and
35
Table of Contents
reimbursement of our NASH drug candidate, such as limiting the number of patients’ treatment that would be covered and reimbursable, this could result in a smaller market opportunity for our NASH drug candidate than we anticipate.
In addition, the number of people who have HBV, as well as the subset of people with the disease who have the potential to benefit from treatment with our drug candidates, may be reduced due to factors including the genotype or variant of HBV, more widespread use of vaccines or alternative therapies, political roadblocks to approval and/or treatment in certain countries and the virus’s development of resistance to our potential treatments after long-term and persistent exposure to antiviral therapy.
We intend to develop our current drug candidates, and expect to develop other future drug candidates, in combination with other therapies, which exposes us to additional risks.
We intend to develop our current drug candidates, and expect to develop other future drug candidates, in combination with one or more therapies, including therapies that we develop and those developed externally. Even if a drug candidate we develop were to receive marketing approval or be commercialized for use in combination with other therapies, we would face the risk that the FDA or similar regulatory authority outside of the United States could revoke approval of the therapy used in combination with our drug candidate or that safety, efficacy, manufacturing or supply issues could arise with these other therapies. Combination therapies are commonly used for the treatment of viral diseases and it is generally believed they will be required for NASH, and we would be subject to similar risks if we develop any of our drug candidates for use in combination with other drugs. This could result in our own products, if approved, being removed from the market or suffering commercially. In addition, we may evaluate our current drug candidates and other future drug candidates in combination with one or more other therapies that may have not yet been approved for marketing by the FDA or similar regulatory authorities outside of the United States. We will not be able to market and sell any drug candidate we develop in combination with any such unapproved therapies that do not ultimately obtain marketing approval.
If the FDA or similar regulatory authorities outside of the United States do not approve these other drugs or revoke their approval of, or if safety, efficacy, manufacturing, or supply issues arise with, the drugs we choose to evaluate in combination with or any of our drug candidate, we may be unable to obtain approval of or market any of our combination treatments.
We face significant competition, and if our competitors develop and market products that are more effective, safer or less expensive than the drug candidates we develop, our commercial opportunities will be negatively impacted.
The life sciences industry is highly competitive. We are currently developing therapies that will compete, if approved, with other products and therapies that currently exist or are being developed. Products we may develop in the future are also likely to face competition from other products and therapies, some of which we may not currently be aware of. We have competitors both in the United States and internationally, including major multinational pharmaceutical companies, established biotechnology companies, specialty pharmaceutical companies, universities and other research institutions. Many of our competitors have significantly greater financial, manufacturing, marketing, product development, technical and human resources than we do. Large pharmaceutical companies, in particular, have extensive experience in clinical testing, obtaining marketing approvals, recruiting patients and manufacturing pharmaceutical products. These companies also have significantly greater research and marketing capabilities than we do and may also have products that have been approved or are in late stages of development, and collaborative arrangements in our target markets with leading companies and research institutions. Established pharmaceutical companies may also invest heavily to accelerate discovery and development of novel compounds or to in-license novel
36
Table of Contents
compounds that could make the drug candidates that we develop obsolete. Further, mergers and acquisitions in the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries may result in even more resources being concentrated among a smaller number of our competitors. As a result of all of these factors, our competitors may succeed in obtaining patent protection and/or marketing approval or discovering, developing and commercializing products in our field before we do.
There are a number of companies developing or marketing treatments for CHB, including Roche Holding AG (“Roche”), Gilead, Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, Arbutus Biopharma Corporation, Dicerna Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (together with Roche), Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (together with GSK), Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (together with Janssen Pharmaceuticals Company (“Janssen”)), Vir Biotechnology, Inc. (together with Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, Inc.), Johnson & Johnson, Assembly Biosciences Inc., Enanta Pharmaceuticals, Altimmune, Inc., GSK, Janssen, Transgene SA, Dynavax Technologies, Inc., Merck & Co. and Replicor, Inc.
There are also companies developing or marketing treatments or vaccines for COVID-19, including Alexion Pharmaceuticals Inc., Incyte Corporation, Sanofi S.A., Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Amgen Inc. (together with Adaptive Biotechnologies Corporation), Abcellera Biologics, Inc. (together with Eli Lilly and Company), Vir Biotechnology, Inc. (together with GSK, Biogen Inc. and WuXi Biologics Ltd.), Altimmune, Inc., AstraZeneca PLC (together with Oxford University), BioNTech SE (together with Pfizer Inc.), GlaxoSmithKline plc (“GSK”) (together with Sanofi), Heat Biologics, Inc., Inovio Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Johnson & Johnson, Moderna, Inc., Novavax, Inc., and Vaxart, Inc.
Furthermore, there are companies developing or marketing treatments for NASH, including AbbVie, Inc., AstraZeneca PLC/MedImmune LLC, Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, Eli Lilly and Company, Janssen, Merck & Co., Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation (together with Pfizer, Inc.), Novo Nordisk A/S, Pfizer Inc., Roche, Sanofi, Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited (together with HemoShear Therapeutics, LLC), 89bio, Inc., Akero Therapeutics, Inc., Blade Therapeutics, Inc., Cirius Therapeutics, Inc., Enanta Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Galectin Therapeutics Inc., Galmed Pharmaceuticals Ltd., Genfit SA, Gilead, Intercept Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Inventiva Pharma SA, Madrigal Pharmaceuticals, Inc., MediciNova, Inc., NGM Biopharmaceuticals, Inc., Pliant Therapeutics, Inc. (together with Novartis), Terns Pharmaceuticals, Inc. and Viking Therapeutics, Inc.
Our commercial opportunity could be reduced or eliminated if our competitors develop and commercialize products that are safer, more effective, have fewer or less severe effects, are more convenient, have a broader label, are marketed more effectively, including gaining exclusivity for their competing products on formularies thereby excluding our products from such formularies, are reimbursed or are less expensive than any products that we may develop. Our competitors also may obtain FDA, EMA or other marketing approval for their products more rapidly than we may obtain approval for ours (if at all), which could result in our competitors establishing a strong market position before we are able to enter the market (if ever). Even if the drug candidates we develop achieve marketing approval, they may be priced at a significant premium over competitive products, resulting in reduced competitiveness of our products.
Smaller and other early stage companies may also prove to be significant competitors. In addition, academic research departments and public and private research institutions may be conducting research on compounds that could prove to be competitive.
These third parties compete with us not only in drug candidate development, but also in recruiting and retaining qualified scientific and management personnel, establishing clinical trial sites and patient registration for clinical trials, as well as in acquiring and/or licensing technologies complementary to, or necessary for, our programs.
In addition, the biopharmaceutical industry is characterized by rapid technological change. If we fail to keep pace with technological change, we may be unable to compete effectively. Technological advances or products
37
Table of Contents
developed by our competitors may render our drug candidates obsolete, less competitive or not economical, thereby adversely affecting our business, financial condition and results of operations.
If any of our current or future drug candidates obtain regulatory approval, additional competitors could enter the market with generic versions of such products, which may result in a material decline in sales of our competing products.
Under the Drug Price Competition and Patent Term Restoration Act of 1984, or the Hatch-Waxman Amendments to the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (the “FDCA”), a pharmaceutical manufacturer may file an abbreviated new drug application (an “ANDA”) seeking approval of a generic version of an approved innovator product. Under the Hatch-Waxman Amendments, a manufacturer may also submit an NDA under section 505(b)(2) of the FDCA that references the FDA’s prior approval of the innovator product. A 505(b)(2) NDA product may be for a new or improved version of the original innovator product. The Hatch-Waxman Amendments also provide for certain periods of regulatory exclusivity, which preclude FDA approval (or in some circumstances, FDA filing and review) of an ANDA or 505(b)(2) NDA. In addition to the benefits of regulatory exclusivity, an innovator NDA holder may have patents claiming the active ingredient, product formulation or an approved use of the drug, which would be listed with the product in the FDA publication “Approved Drug Products with Therapeutic Equivalence Evaluations,” known as the Orange Book. If there are patents listed in the Orange Book for a product, a generic or 505(b)(2) applicant that seeks to market its product before expiration of the patents must include in their applications what is known as a “Paragraph IV” certification, challenging the validity or enforceability, or claiming non-infringement, of the listed patent or patents. Notice of the certification must be given to the patent owner and NDA holder and if, within 45 days of receiving notice, either the patent owner or NDA holder sues for patent infringement, approval of the ANDA or 505(b)(2) NDA is stayed for up to 30 months.
Accordingly, if any of our future drug candidates are approved, competitors could file ANDAs for generic versions of these products or 505(b)(2) NDAs that reference our products. If there are patents listed for such drug products in the Orange Book, those ANDAs and 505(b)(2) NDAs would be required to include a certification as to each listed patent indicating whether the ANDA applicant does or does not intend to challenge the patent. We cannot predict which, if any, patents in our current portfolio or patents we may obtain in the future will be eligible for listing in the Orange Book, how any generic competitor would address such patents, whether we would sue on any such patents or the outcome of any such suit.
We may not be successful in securing or maintaining proprietary patent protection for products and technologies we develop or license, despite expending a significant amount of resources that could have been focused on other areas of our business. Moreover, if any of our owned or in-licensed patents that are listed in the Orange Book are successfully challenged by way of a Paragraph IV certification and subsequent litigation, the affected product could immediately face generic competition and its sales would likely decline rapidly and materially.
Even if we are able to commercialize any drug candidates, such products may become subject to unfavorable pricing regulations or third-party coverage and reimbursement policies, which would harm our business.
The regulations that govern marketing approvals, pricing and reimbursement for new products vary widely from country to country. Some countries require approval of the sale price of a product before it can be marketed. In many countries, the pricing review period begins after marketing approval is granted. In some foreign markets, prescription pharmaceutical pricing remains subject to continuing governmental control even after initial approval is granted. As a result, we might obtain marketing approval for a drug candidate in a particular country, but then be subject to price regulations that delay our commercial launch of the drug candidate, possibly for lengthy time periods, and negatively impact the revenues we are able to generate from
38
Table of Contents
the sale of the drug candidate in that country, potentially to the point of unviability. Adverse pricing limitations may hinder our ability to recoup our investment in one or more drug candidates, even if our drug candidates obtain marketing approval.
Our ability to successfully commercialize any drug candidates, whether as a single agent or in combination, will also depend in part on the extent to which coverage and reimbursement for these drug candidates and related treatments is available from government authorities, private health insurers and other organizations. Government authorities and third-party payors, such as private health insurers and health maintenance organizations, decide which medications they will pay for and establish reimbursement levels. It is difficult to predict at this time what government authorities and third-party payors may decide with respect to coverage and reimbursement for our programs (if approved).
A primary trend in the U.S. healthcare industry and elsewhere is cost containment. Government authorities, particularly in the European Union, and third-party payors have attempted to control costs by limiting coverage and the amount of reimbursement for particular products and requiring substitutions of generic products and/or biosimilars. Increasingly, third-party payors are scrutinizing the prices charged for drugs. We cannot be sure that coverage will be available for any drug candidate that we commercialize and, if coverage is available, the level of reimbursement. These government authorities and third-party payors are also examining the cost-effectiveness of drugs, in addition to their safety and efficacy. For example, in some countries, we, or any future collaborators, may be required to conduct a clinical trial that compares the cost-effectiveness of our drug to other therapies to obtain reimbursement or pricing approval. Reimbursement may impact the demand for, or the price of, any drug candidate for which we obtain marketing approval. If reimbursement is not available or is available only to limited levels, we may not be able to successfully commercialize any drug candidate for which we obtain marketing approval.
Further, there may be significant delays in obtaining coverage and reimbursement for newly approved drugs, as the process is time-consuming and costly, and coverage may be more limited than the purposes for which the drug is approved by the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities. Additionally, no uniform policy requirement for coverage and reimbursement for drug products exists among third-party payors in the United States, which may result in coverage and reimbursement for drug products that differ significantly from payor to payor. Moreover, eligibility for reimbursement does not imply that any drug will be paid for in all cases or at a rate that covers our costs, including research, development, manufacture, sale and distribution. Interim reimbursement levels for new drugs, if applicable, may not be sufficient to cover our costs and may not be permanent. Reimbursement rates may vary according to the use of the drug and the clinical setting in which it is used, may be based on reimbursement levels already set for lower-cost drugs and may be incorporated into existing payments for other services. Net prices for drugs may be reduced by mandatory discounts or rebates required by government healthcare programs or private payors and by any future relaxation of laws that presently restrict imports of drugs from countries where they may be sold at lower prices than in the United States. Our inability to promptly obtain coverage and profitable payment rates from both government-funded and private payors for any approved drugs that we develop could have a material adverse effect on our operating results, our ability to raise capital needed to commercialize drugs and our overall financial condition.
We may not be successful in our efforts to identify or discover other drug candidates and may fail to capitalize on programs or drug candidates that may present a greater commercial opportunity or for which there is a greater likelihood of success.
The success of our business depends upon our ability to identify, develop and commercialize drug candidates. If we do not successfully develop and eventually commercialize products, we will face difficulty in obtaining product revenue in future periods, resulting in significant harm to our financial position and adversely affecting
39
Table of Contents
our share price. Research programs to identify new drug candidates require substantial technical, financial and human resources, and we may fail to identify potential drug candidates for numerous reasons.
Additionally, because we have limited resources, we may forego or delay pursuit of opportunities with certain programs or drug candidates or for indications that later prove to have greater commercial potential. For example, we are currently focused on the development of our current drug candidates for hepatological indications. In addition, we are pursuing other drug candidates for viral diseases. However, the advancement of these drug candidates may ultimately prove to be unsuccessful or less successful than another program in our pipeline that we might have chosen to pursue on a less aggressive basis. However, due to the significant resources required for the development of our drug candidates, we must focus on specific diseases and disease pathways and decide which drug candidates to pursue and the amount of resources to allocate to each. Our near-term objective is to demonstrate favorable risk/benefit profiles through Phase 1 clinical trials of our drug candidates, ALG-010133 and ALG-000184. Our estimates regarding the potential market for our drug candidates could be inaccurate and our decisions concerning the allocation of research, development, collaboration, management and financial resources toward particular drug candidates or therapeutic areas may not lead to the development of any viable commercial product and may divert resources away from better opportunities. Similarly, any potential decision to delay or terminate development of a drug candidate or program may subsequently also prove to be suboptimal and could cause us to miss valuable opportunities. Further, if we do not accurately evaluate the commercial potential for a particular drug candidate, we may relinquish valuable rights to that drug candidate through collaboration, licensing or other arrangements in cases in which it would have been more advantageous for us to retain sole development and commercialization rights to such drug candidate. Alternatively, we may allocate internal resources to a drug candidate in a therapeutic area in which it would have been more advantageous to enter into a partnering arrangement.
If any of these events occur, we may be forced to abandon or delay our development efforts with respect to a particular drug candidate or we may fail to develop a potentially successful drug candidate or capitalize on profitable market opportunities, all of which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
We may seek and fail to obtain fast track or breakthrough therapy designations from the FDA for our current or future drug candidates or priority review designation for any NDA we may submit to the FDA. Even if we are successful, these programs may not lead to a faster development or regulatory review process, and they do not guarantee we will receive approval for any drug candidate. We may also seek to obtain accelerated approval for one or more of our drug candidates but the FDA may disagree that we have met the requirements for such approval.
If a product is intended for the treatment of a serious or life-threatening condition and nonclinical or clinical data demonstrate the potential to address an unmet medical need for this condition, the product sponsor may apply for fast track designation. The FDA has broad discretion whether or not to grant this designation, so even if we believe a particular drug candidate is eligible for this designation, we cannot assure you that the FDA would decide to grant it. Even if we do receive fast track designation, we may not experience a faster development process, review or approval compared to conventional FDA procedures. The FDA may rescind the fast track designation if it believes that the designation is no longer supported by data from our clinical development program.
We may also seek breakthrough therapy designation for any drug candidate that we develop. A breakthrough therapy is defined as a drug that is intended, alone or in combination with one or more other drugs, to treat a serious or life-threatening disease or condition, and preliminary clinical evidence indicates that the drug may demonstrate substantial improvement over currently approved therapies on one or more clinically significant endpoints, such as substantial treatment effects observed early in clinical development. Like fast track
40
Table of Contents
designation, breakthrough therapy designation is within the discretion of the FDA. Accordingly, even if we believe a drug candidate we develop meets the criteria for designation as a breakthrough therapy, the FDA may disagree and instead determine not to make such designation. In any event, the receipt of breakthrough therapy designation for a drug candidate may not result in a faster development process, review or approval compared to drugs considered for approval under conventional FDA procedures and does not assure ultimate approval by the FDA. In addition, even if a drug candidate we develop qualifies as a breakthrough therapy, the FDA may later decide that the drug no longer meets the conditions for qualification and rescind the designation.
Drugs designated as fast track products or breakthrough therapies by the FDA are also eligible for priority review of any NDA submitted for such drug candidates, which could result in FDA action on the NDA in a shorter timeframe than under standard review. In order to grant priority review designation, the FDA must find that the product, if approved, would provide a significant improvement in the safety or effectiveness of the treatment, diagnosis or prevention of a serious disease or condition. However, priority review does not guarantee approval of the NDA and may not result in a shorter overall review timeline if the FDA has significant questions or additional requests as part of the NDA review.
In addition, the FDA may grant accelerated approval to a product if the FDA determines that it has an effect on a surrogate endpoint that is reasonably likely to predict clinical benefit, or on a clinical endpoint that can be measured earlier than irreversible morbidity or mortality, that is reasonably likely to predict an effect on irreversible morbidity or mortality or other clinical benefit, taking into account the severity, rarity, or prevalence of the condition and the availability or lack of alternative treatments. For example, this is currently the case with drugs for the treatment of NASH. As a condition of accelerated approval, the FDA will generally require the sponsor to perform adequate and well-controlled post-marketing clinical studies to verify and describe the anticipated effect on irreversible morbidity or mortality or other clinical benefit. In addition, the FDA requires pre-approval of promotional materials for accelerated approval products, once approved. We cannot guarantee that the FDA will conclude that any of our drug candidates has met the criteria to receive accelerated approval, which would require us to conduct additional clinical testing prior to seeking FDA approval. Even if any of our drug candidates received approval through this pathway, the product may fail required post-approval confirmatory clinical trials, and we may be required to remove the product from the market or amend the product label in a way that adversely impacts its marketing.
We may seek Orphan Drug Designation for drug candidates we develop, and we may be unsuccessful or may be unable to maintain the benefits associated with Orphan Drug Designation, including the potential for market exclusivity.
As part of our business strategy, we may seek Orphan Drug Designation for any drug candidates we develop, and we may be unsuccessful in obtaining such designation. Regulatory authorities in some jurisdictions, including the United States and the EU, may designate drugs for relatively small patient populations as orphan drugs. Under the Orphan Drug Act, the FDA may designate a drug as an orphan drug if it is a drug intended to treat a rare disease or condition, which is generally defined as a patient population of fewer than 200,000 individuals annually in the United States, or a patient population greater than 200,000 in the United States where there is no reasonable expectation that the cost of developing the drug will be recovered from sales in the United States. In the United States, Orphan Drug Designation entitles a party to financial incentives such as opportunities for grant funding towards clinical trial costs, tax advantages and user-fee waivers.
Similarly, in the EU, the European Commission grants Orphan Drug Designation after receiving the opinion of the EMA Committee for Orphan Medicinal Products on an Orphan Drug Designation application. Orphan Drug Designation is intended to promote the development of drugs that are intended for the diagnosis, prevention or treatment of life-threatening or chronically debilitating conditions affecting not more than 5 in 10,000 persons in Europe and for which no satisfactory method of diagnosis, prevention, or treatment has been authorized (or
41
Table of Contents
the product would be a significant benefit to those affected). Additionally, designation is granted for drugs intended for the diagnosis, prevention, or treatment of a life-threatening, seriously debilitating or serious and chronic condition and when, without incentives, it is unlikely that sales of the drug in Europe would be sufficient to justify the necessary investment in developing the drug. In Europe, Orphan Drug Designation entitles a party to a number of incentives, such as protocol assistance and scientific advice specifically for designated orphan medicines, and potential fee reductions depending on the status of the sponsor.
Generally, if a drug with an Orphan Drug Designation subsequently receives the first marketing approval for the indication for which it has such designation, the drug is entitled to a period of marketing exclusivity, which precludes the EMA or the FDA from approving another marketing application for the same drug and indication for that time period, except in limited circumstances. The applicable period is seven years in the United States and ten years in the EU. The EU exclusivity period can be reduced to six years if a drug no longer meets the criteria for Orphan Drug Designation or if the drug is sufficiently profitable such that market exclusivity is no longer justified.
Even if we obtain orphan drug exclusivity for a drug candidate, that exclusivity may not effectively protect the drug candidate from competition because different therapies can be approved for the same condition. Even after an orphan drug is approved, the FDA can subsequently approve the same drug for the same condition if the FDA concludes that the later drug is clinically superior in that it is shown to be safer, more effective or makes a major contribution to patient care. In addition, a designated orphan drug may not receive orphan drug exclusivity if it is approved for a use that is broader than the indication for which it received orphan designation. Moreover, orphan drug exclusive marketing rights in the United States may be lost if the FDA later determines that the request for designation was materially defective or if the manufacturer is unable to assure sufficient quantity of the drug to meet the needs of patients with the rare disease or condition. Orphan Drug Designation neither shortens the development time or regulatory review time of a drug candidate nor gives the drug candidate any advantage in the regulatory review or approval process. While we may seek Orphan Drug Designation for applicable indications for our current and any future drug candidates, we may never receive such designations. Even if we do receive such designations, there is no guarantee that we will enjoy the benefits of those designations.
We may be required to make significant payments under our license agreements with Emory University and Luxna Biotech Co., Ltd.
We entered into a License Agreement with Emory in June 2018 (the “Emory License Agreement”), and a License Agreement with Luxna in December 2018 and an amendment in April 2020 (as amended, the “Luxna Agreement”). Under the Emory License Agreement and Luxna Agreement, we are subject to significant obligations, including milestone payments, royalty payments, and certain other agreed-to costs. For more information regarding our license agreements, please see “Business—License agreements.” If these payments become due under the terms of either the Emory University License Agreement or Luxna Agreement, we may not have sufficient funds available to meet our obligations and our development efforts may be materially harmed. Furthermore, if we are forced to raise additional funds, we may be required to delay, limit, reduce or terminate our product development or future commercialization efforts, or grant rights to develop and market drug candidates that we would otherwise develop and market ourselves.
If product liability lawsuits are brought against us, we may incur substantial liabilities and may be required to limit commercialization of any approved products.
We face an inherent risk of product liability as a result of the clinical testing of drug candidates and will face an even greater risk if we commercialize any products. For example, we may be sued if any drug candidate we develop causes or is perceived to cause illness or is found to be otherwise unsuitable during clinical testing,
42
Table of Contents
manufacturing, marketing or sale. Any such product liability claims may include allegations of defects in manufacturing, defects in design, a failure to warn of dangers inherent in the product, negligence, strict liability or a breach of warranties. Claims could also be asserted under state consumer protection acts. If we cannot successfully defend ourselves against product liability claims, we may incur substantial liabilities or be required to limit commercialization of any approved products. Even successful defense would require significant financial and management resources. Regardless of the merits or eventual outcome, liability claims may result in:
| • | decreased demand for any approved product; |
| • | injury to our reputation; |
| • | withdrawal of clinical trial participants; |
| • | initiation of investigations by regulators; |
| • | costs to defend the related litigation; |
| • | a diversion of management’s time and our resources; |
| • | substantial monetary payments to trial participants or patients; |
| • | product recalls, withdrawals or labeling, marketing or promotional restrictions; |
| • | loss of revenue; |
| • | exhaustion of any available insurance and our capital resources; |
| • | adverse effects to our results of operations and business; |
| • | the inability to commercialize any drug candidate; and |
| • | a decline in our share price. |
Our inability to obtain sufficient product liability insurance at an acceptable cost or at all to protect against potential product liability claims could prevent or inhibit the commercialization of products we develop, alone or with collaboration partners.
Insurance coverage is increasingly expensive. We may not be able to maintain insurance, including product liability insurance at a reasonable cost or in an amount adequate to satisfy any liability that may arise, if at all. Our product liability insurance policy contains various exclusions, and we may be subject to a product liability claim for which we have no coverage. We may have to pay any amounts awarded by a court or negotiated in a settlement that exceed our coverage limitations or that are not covered by our insurance, and we may not have, or be able to obtain, sufficient capital to pay such amounts. Even if our agreements with current or future collaborators entitle us to indemnification against losses, such indemnification may not be available or adequate should any claim arise.
Our insurance policies are expensive and protect us only from some business risks, which leaves us exposed to significant uninsured liabilities.
We do not carry insurance for all categories of risk that our business may encounter. Some of the policies we currently maintain include general liability, property, umbrella, clinical trials and directors’ and officers’ insurance. Any additional insurance coverage we acquire in the future may not be sufficient to reimburse us for any expenses or losses we may suffer. Moreover, insurance coverage is becoming increasingly expensive and in the future we may not be able to maintain insurance coverage at a reasonable cost or in sufficient amounts to protect us against losses due to liability. Any significant uninsured liability may require us to pay substantial amounts, which would adversely affect our cash position and results of operations.
We also expect that operating as a public company will make it more difficult and more expensive for us to obtain directors’ and officers’ liability insurance, and we may be required to accept reduced policy limits and coverage or incur substantially higher costs to obtain the same or similar coverage. As a result, it may be more difficult for us to attract and retain qualified people to serve on our board of directors, our board committees or as executive officers.
43
Table of Contents
Healthcare legislative reform measures may have a material adverse effect on our business and results of operations.
In the United States, there have been and continue to be a number of legislative initiatives to contain healthcare costs. For example, in March 2010, the Affordable Care Act (the “ACA”) was passed, which substantially changed the way healthcare is financed by both governmental and private insurers, and significantly impacted the U.S. pharmaceutical industry. The ACA, among other things, increased the minimum Medicaid rebates owed by manufacturers under the Medicaid Drug Rebate Program and extended the rebate program to individuals enrolled in Medicaid managed care organizations, established annual fees and taxes on manufacturers of certain branded prescription drugs, and created a new Medicare Part D coverage gap discount program, in which manufacturers must agree to offer 70% point-of-sale discounts off negotiated prices of applicable brand drugs to eligible beneficiaries during their coverage gap period, as a condition for the manufacturer’s outpatient drugs being covered under Medicare Part D.
Since its enactment, there have been judicial and Congressional challenges to the ACA, as well as efforts by the Trump administration to repeal or replace certain aspects of the ACA. By way of example, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 (the “TCJA”) was signed into law, which included a provision repealing, effective January 1, 2019, the tax-based shared responsibility payment imposed by the ACA on certain individuals who fail to maintain qualifying health coverage for all or part of a year, commonly referred to as the individual mandate. On December 14, 2018, a Texas U.S. District Court Judge ruled that the ACA is unconstitutional in its entirety because the “individual mandate” was repealed by Congress as part of the TCJA. Additionally, on December 18, 2019, the U.S. Court of Appeals for the 5th Circuit ruled that that the individual mandate was unconstitutional and remanded the case back to the District Court to determine whether the remaining provisions of the ACA are invalid as well. On March 2, 2020, the United States Supreme Court granted the petitions for writs of certiorari to review this case, although it is unclear when or how the Supreme Court will rule. It is also unclear how other efforts to challenge, repeal or replace the ACA will impact the ACA or our business.
Other legislative changes have been proposed and adopted in the United States since the ACA was enacted. On August 2, 2011, the Budget Control Act of 2011, among other things, included aggregate reductions of Medicare payments to providers of 2% per fiscal year. These reductions went into effect on April 1, 2013 and, due to subsequent legislative amendments to the statute, will remain in effect through 2030, with the exception of a temporary suspension from May 1, 2020 through December 31, 2020, unless additional Congressional action is taken. In addition, on January 2, 2013, the American Taxpayer Relief Act of 2012 was signed into law, which, among other things, further reduced Medicare payments to several types of providers.
Moreover, payment methodologies may be subject to changes in healthcare legislation and regulatory initiatives. We expect that additional state and federal healthcare reform measures will be adopted in the future, any of which could limit the amounts that federal and state governments will pay for healthcare products and services, which could result in additional pricing pressure or reduced demand for any drug candidate we develop or complementary or companion diagnostics. For example, it is possible that additional governmental action will be taken to address the COVID-19 pandemic, which could impact our business in an as-yet unknown manner.
Additionally, there has been increasing legislative and enforcement interest in the United States with respect to specialty drug pricing practices. Specifically, there have been several recent U.S. Congressional inquiries and proposed and enacted federal and state legislation and regulation designed to, among other things, bring more transparency to drug pricing, reduce the cost of prescription drugs under Medicare, review the relationship between pricing and manufacturer patient programs, and reform government program reimbursement methodologies for drugs.
44
Table of Contents
Legal, political and economic uncertainty surrounding the exit of the United Kingdom from the European Union may be a source of instability in international markets, create significant currency fluctuations and pose additional risks to our business.
Following the result of a referendum in 2016, the United Kingdom left the European Union on January 31, 2020, commonly referred to as “Brexit.” Pursuant to the formal withdrawal arrangements agreed to between the United Kingdom and the EU, the United Kingdom will be subject to a transition period until December 31, 2020 (the “Transition Period”), during which EU rules will continue to apply. Negotiations between the United Kingdom and the EU are expected to continue in relation to the customs and trading relationship between the United Kingdom and the EU following the expiry of the Transition Period.
The uncertainty concerning the United Kingdom’s legal, political and economic relationship with the EU after the Transition Period may be a source of instability in the international markets, create significant currency fluctuations, and/or otherwise adversely affect trading agreements or similar cross-border co-operation arrangements (whether economic, tax, fiscal, legal, regulatory or otherwise). These developments, or the perception that any of them could occur, have had, and may continue to have, a significant adverse effect on global economic conditions and the stability of global financial markets, and could significantly reduce global market liquidity and limit the ability of key market participants to operate in certain financial markets. In particular, it could also lead to a period of considerable uncertainty in relation to the U.K. financial and banking markets, as well as on the regulatory process in the EU. Asset valuations, currency exchange rates and credit ratings may also be subject to increased market volatility.
Such a withdrawal from the EU is unprecedented, and it is unclear how the United Kingdom’s access to the European single market for goods, capital, services and labor, and the wider commercial, legal and regulatory environment, will impact our business, and in particular our business in Belgium and planned operations in the EU, non-EU European nations and the United Kingdom.
We are subject to certain U.S. and foreign anti-corruption, anti-money laundering, export control, sanctions, and other trade laws and regulations, violations of which can have serious negative consequences for our business.
U.S. and foreign anti-corruption, anti-money laundering, export control, sanctions, and other trade laws and regulations (collectively, “Trade Laws”), prohibit, among other matters, companies and their employees, agents, clinical research organizations, legal counsel, accountants, consultants, contractors, and other partners from authorizing, promising, offering, providing, soliciting, or receiving directly or indirectly, corrupt or improper payments or anything else of value to or from recipients in the public or private sector. Violations of Trade Laws can result in substantial criminal fines and civil penalties, imprisonment, the loss of trade privileges, debarment, tax reassessments, breach of contract and fraud litigation, and reputational harm, among other consequences. We routinely have direct or indirect interactions with officials and employees of government agencies or government-affiliated hospitals, universities, and other organizations, and we expect our non-U.S. activities to increase in time. We plan to engage third parties for clinical trials and/or obtain necessary permits, licenses, patent registrations, and other regulatory approvals from such officials, employees and government agencies and affiliates and we may be held liable for any corrupt or other illegal activities of our personnel, agents, or partners, even if we do not explicitly authorize or have prior knowledge of such activities.
45
Table of Contents
Failure to comply with current or future federal, state and foreign laws and regulations and industry standards relating to privacy and data protection laws could lead to government enforcement actions, which could include civil or criminal penalties, private litigation, and/or adverse publicity and could negatively affect our operating results and business.
We and our partners may be subject to federal, state and foreign data privacy and security laws and regulations. Failure by us or our third-party vendors, collaborators, contractors and consultants to comply with any of these laws and regulations could result in notification obligations or enforcement actions against us, which could result in, among other things, fines, claims for damages by affected individuals, damage to our reputation and loss of goodwill, any of which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations or prospects. These laws, rules and regulations evolve frequently and their scope may continually change, through new legislation, amendments to existing legislation and changes in enforcement, and may be inconsistent from one jurisdiction to another. The interpretation and application of consumer, health-related and data protection laws in the United States, the EU and elsewhere, are often uncertain, contradictory and in flux. As a result, implementation standards and enforcement practices are likely to remain uncertain for the foreseeable future. As our operations and business grow, we may become subject to or affected by new or additional data protection laws and regulations and face increased scrutiny or attention from regulatory authorities.
In the United States, numerous federal and state laws and regulations, including federal health information privacy laws, state data breach notification laws, state health information privacy laws and federal and state consumer protection laws (e.g., Section 5 of the Federal Trade Commission Act), which govern the collection, use, disclosure and protection of health-related and other personal information could apply to our operations or the operations of our collaborators. In addition, we may obtain health information from third parties (including research institutions from which we obtain clinical trial data) that are subject to privacy and security requirements under the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (“HIPAA”), as amended by the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act. Depending on the facts and circumstances, we could be subject to criminal penalties if we knowingly obtain, use, or disclose individually identifiable health information maintained by a HIPAA-covered entity in a manner that is not authorized or permitted by HIPAA.
Many states have also adopted comparable privacy and security laws and regulations, some of which may be more stringent than HIPAA. Such laws and regulations will be subject to interpretation by various courts and other governmental authorities, thus creating potentially complex compliance issues for us and our future customers and strategic partners. In addition, California recently enacted the CCPA, which became effective on January 1, 2020. The CCPA, among other things, requires new disclosures to California consumers and affords such consumers new abilities to access and delete their personal information, opt-out of certain sales of personal information and receive detailed information about how their personal information is used. The CCPA provides for civil penalties for violations, as well as a private right of action for data breaches that is expected to increase the frequency of data breach litigation. In the event that we are subject to or affected by HIPAA, the CCPA or other domestic privacy and data protection laws, any liability from failure to comply with the requirements of these laws could adversely affect our financial condition.
We currently operate in countries outside of the United States, including Belgium and Australia, where laws may in some cases be more stringent than the requirements in the United States. For example, in Europe, the European Union General Data Protection Regulation (the “GDPR”) went into effect in May 2018 and imposes strict requirements for the collection, storage, use, disclosure, transfer and other processing of the personal data of individuals within the European Economic Area (the “EEA”). The GDPR applies extra-territorially under certain circumstances and imposes stringent requirements on controllers and processors of personal data, including, for example, requirements to obtain consent or other legal bases from individuals to process their
46
Table of Contents
personal data, provide robust disclosures to individuals, accommodate a set of individual data rights, provide data security breach notifications within 72 hours after discovering the breach, limit retention of personal information and apply enhanced protections to health data and other special categories of personal data. The GDPR also applies to pseudonymized data, which is defined as “the processing of personal data in such a way that the data can no longer be attributed to a specific data subject without the use of additional information,” and imposes additional obligations when we contract with third-party processors in connection with the processing of any personal data. The GDPR provides that EU and EEA member states may make their own further laws and regulations limiting the processing of personal data, including genetic, biometric or health data, which could limit our ability to use and share personal data, could cause our costs to increase and could harm our financial condition. Failure to comply with the requirements of the GDPR and the applicable national data protection laws of the EU and EEA member states may result in fines of up to €20 million or up to 4% of the total worldwide annual turnover of our preceding fiscal year, whichever is higher, and other administrative penalties. Further, following the United Kingdom’s withdrawal from the EU and the EEA and the end of the transition period on December 31, 2020, we will have to comply with the GDPR and the GDPR as incorporated into United Kingdom national law, the latter regime having the ability to separately fine up to the greater of £17.5 million or 4% of global turnover. Failure to comply with the GDPR and other countries’ privacy or data security-related laws, rules or regulations could result in material penalties imposed by regulators, affect our compliance with contracts entered into with our collaborators and other third-party payors, and have an adverse effect on our business and financial condition.
The GDPR further prohibits, without an appropriate legal basis, the transfer of personal data to countries outside of the EEA, such as the United States, which are not considered by the European Commission to provide an adequate level of data protection. Recent legal developments in Europe have created complexity and uncertainty regarding transfers of personal data from the EEA to the United States. For example, on July 16, 2020, the Court of Justice of the European Union (“CJEU”) invalidated the EU-US Privacy Shield Framework (the “Privacy Shield”) under which personal data could be transferred from the EEA to United States entities that had self-certified under the Privacy Shield scheme. While the CJEU upheld the adequacy, subject to certain conditions, of the standard contractual clauses (a standard form of contract approved by the European Commission as an adequate personal data transfer mechanism), future regulatory guidance could result in changes to the use of standard contractual clauses.
Compliance with U.S. and foreign privacy and security laws, rules and regulations could require us to take on more onerous obligations in our contracts, require us to engage in costly compliance exercises, restrict our ability to collect, use and disclose data, or in some cases, impact our or our partners’ ability to operate in certain jurisdictions. Each of these evolving laws can be subject to varying interpretations. Failure to comply with U.S. and foreign data protection laws and regulations could result in government investigations and enforcement actions (which could include civil or criminal penalties), fines, private litigation, and/or adverse publicity and could negatively affect our operating results and business.
Our internal computer systems, or those used by our CROs or other contractors or consultants, may fail or suffer security breaches.
Despite the implementation of security measures, our internal computer systems and those of our CROs and other contractors and consultants are vulnerable to damage from cyber-attacks, computer hacks, theft, viruses, malicious software, phishing, employee error, denial-of-service attacks, unauthorized access and other security breaches that could jeopardize the performance of our software and computer systems, and could expose us to financial and reputational harm. While we have not to our knowledge experienced any such material system failure or security breach to date, if such an event were to occur and cause interruptions in our operations, it could result in a material disruption of our development programs and our business operations. For example, the loss of clinical trial data from completed or future clinical trials could result in delays in our marketing
47
Table of Contents
approval efforts and significantly increase our costs to recover or reproduce the data. Likewise, we rely on third parties for the manufacture of our drug candidates and to conduct clinical trials, and similar events relating to their computer systems could also have a material adverse effect on our business. To the extent that any disruption or security breach were to result in a loss of, or damage to, our data or applications, or inappropriate disclosure of confidential or proprietary information, we could incur liability and the development and commercialization of our future drug candidates could be delayed.
Risks related to reliance on third parties
We depend on collaborations with third parties for the development of certain of our potential drug candidates, and we may depend on additional collaborations in the future for the development and commercialization of these or other potential candidates. If our collaborations are not successful, we may not be able to capitalize on the market potential of these drug candidates.
We are currently collaborating with third parties to develop certain of our potential drug candidates. For example, we are collaborating with the Rega Institute and Centre for Drug Design and Discovery at KU Leuven with respect to potential protease inhibitors for the treatment of coronaviruses, including SARS-CoV-2, and with Emory University with respect to certain aspects of our small molecule CHB program. In the future, we may form or seek strategic alliances, joint ventures, or collaborations, or enter into additional licensing arrangements with third parties that we believe will complement or augment our development and commercialization efforts with respect to drug candidates we develop.
Collaborations involving our current and future drug candidates may pose the following risks to us:
| • | collaborators have significant discretion in determining the efforts and resources that they will apply to these collaborations; |
| • | collaborators may delay clinical trials, provide insufficient funding for a clinical trial program, stop a clinical trial, abandon a drug candidate, repeat or conduct new clinical trials or require a new formulation of a drug candidate for clinical testing; |
| • | collaborators could independently develop, or develop with third parties, products that compete directly or indirectly with our products (if any) or drug candidates; |
| • | a collaborator with marketing, manufacturing and distribution rights to one or more products may not commit sufficient resources to or may otherwise not perform satisfactorily in carrying out these activities; |
| • | collaborators may not properly prosecute, maintain, enforce or defend our intellectual property rights or may use our proprietary information in a way that gives rise to actual or threatened litigation that could jeopardize or invalidate our intellectual property or proprietary information or expose us to potential litigation, or other intellectual property proceedings; |
| • | collaborators may own or co-own intellectual property covering products that result from our collaboration with them, and in such cases, we may not have the exclusive right to develop, license or commercialize such intellectual property; |
| • | disputes may arise with respect to ownership of any intellectual property developed pursuant to our collaborations; |
| • | disputes may arise between a collaborator or strategic partner and us that cause the delay or termination of the research, development or commercialization of the drug candidate, or that result in costly litigation or arbitration that diverts management attention and resources; and |
48
Table of Contents
| • | if a current or future collaborator of ours were to be involved in a business combination, the continued pursuit and emphasis on our product development or commercialization program under such collaboration could be delayed, diminished or terminated. |
As a result, if we enter into additional collaboration agreements and strategic partnerships or license our intellectual property, products or businesses, we may not be able to realize the benefit of such transactions if we are unable to successfully integrate them with our existing operations, which could delay our timelines or otherwise adversely affect our business. We also cannot be certain that, following a strategic transaction or license, we will achieve the revenue or specific net income that justifies such transaction. Any delays in entering into new collaborations or strategic partnership agreements related to any drug candidate we develop could delay the development and commercialization of our drug candidates, which would harm our business prospects, financial condition, and results of operations.
We may seek to establish additional collaborations, and, if we are not able to establish them on commercially reasonable terms, we may have to alter our development and commercialization plans.
The advancement of our drug candidates and development programs and the potential commercialization of our current and future drug candidates will require substantial additional cash to fund expenses. For some of our programs, we may decide to collaborate with other pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies with respect to development and potential commercialization. Any of these relationships may require us to incur non-recurring and other charges, increase our near- and long-term expenditures, issue securities that dilute our existing stockholders, divert our management’s attention and disrupt our business.
We face significant competition in seeking appropriate strategic partners and the negotiation process is time-consuming and complex. Whether we reach a definitive agreement for any other collaborations will depend, among other things, upon our assessment of the collaborator’s resources and expertise, the terms and conditions of the proposed collaboration and the proposed collaborator’s evaluation of a number of factors. Those factors may include the design or results of clinical trials, the progress of our clinical trials, the likelihood of approval by the FDA or similar regulatory authorities outside the United States, the potential market for the subject drug candidate, the costs and complexities of manufacturing and delivering such drug candidate to patients, the potential of competing products, the existence of uncertainty with respect to our ownership of technology, which can exist if there is a challenge to such ownership without regard to the merits of the challenge and industry and market conditions generally. The collaborator may also consider alternative drug candidates or technologies for similar indications that may be available to collaborate on and whether such a collaboration could be more attractive than the one with us for our drug candidate. Further, we may not be successful in our efforts to establish a strategic partnership or other alternative arrangements for future drug candidates because they may be deemed to be at too early of a stage of development for collaborative efforts and third parties may not view them as having the requisite potential to demonstrate safety and efficacy.
We may also be restricted under future collaboration agreements from entering into additional agreements on certain terms with potential collaborators.
In addition, there have been a significant number of recent business combinations among large pharmaceutical companies that have resulted in a reduced number of potential future collaborators.
We may not be able to negotiate collaborations on a timely basis, on acceptable terms, or at all. If we are unable to do so, we may have to curtail the development of the drug candidate for which we are seeking to collaborate, reduce or delay its development program or one or more of our other development programs, delay its potential commercialization or reduce the scope of any sales or marketing activities, or increase our expenditures and undertake development or commercialization activities at our own expense. If we elect to increase our expenditures to fund development or commercialization activities on our own, we may need to
49
Table of Contents
obtain additional capital, which may not be available to us on acceptable terms or at all. If we do not have sufficient funds, we may not be able to further develop our drug candidates or bring them to market and generate product revenue.
If conflicts arise between us and our collaborators or strategic partners, these parties may act in a manner adverse to us and could limit our ability to implement our strategies.
If conflicts arise between our academic collaborators or strategic partners and us, the other party may act in a manner adverse to us and could limit our ability to implement our strategies. Current or future collaborators or strategic partners may develop, either alone or with others, products in related fields that are competitive with the products or potential products that are the subject of these collaborations.
Our current or future collaborators or strategic partners may preclude us from entering into collaborations with their competitors, fail to obtain timely regulatory approvals, terminate their agreements with us prematurely, or fail to devote sufficient resources to the development and commercialization of products. Furthermore, competing products, either developed by our current or future collaborators or strategic partners or to which our collaborators or strategic partners may have rights, may result in the withdrawal of partner support for our drug candidates. Any of these developments could harm our product development efforts.
We rely on third parties to conduct our ongoing and planned clinical trials and certain of our nonclinical studies for drug candidates we develop. If these third parties do not successfully carry out their contractual duties, comply with regulatory requirements or meet expected deadlines, we may not be able to obtain marketing approval for or commercialize the drug candidates we are developing and our business could be substantially harmed.
We do not have the ability to independently conduct certain nonclinical studies and clinical trials. We rely on medical institutions, clinical investigators, contract laboratories, and other third parties, such as CROs, to conduct or otherwise support certain nonclinical studies and clinical trials for our drug candidates, including ALG-010133 and ALG-000184, and we control only certain aspects of their activities. Nevertheless, we are responsible for ensuring that each of our nonclinical studies and clinical trials is conducted in accordance with the applicable protocol, legal and regulatory requirements and scientific standards, and our reliance on CROs will not relieve us of our regulatory responsibilities. For any violations of laws and regulations during the conduct of our nonclinical studies or clinical trials, we could be subject to untitled and warning letters or enforcement action that may include civil penalties up to and including criminal prosecution.
We and our CROs are required to comply with regulations and requirements, including GLP and GCP, for conducting, monitoring, recording and reporting the results of nonclinical studies and clinical trials, respectively, to ensure that the data and results are scientifically credible and accurate, and that the trial patients are adequately informed of the potential risks of participating in clinical trials and their rights are protected. These regulations are enforced by the FDA, the Competent Authorities of the Member States of the EEA and comparable foreign regulatory authorities for any drugs in clinical development. The FDA enforces GLP and GCP requirements through periodic inspections of laboratories conducting studies, clinical trial sponsors, principal investigators and trial sites. If we or our CROs fail to comply with applicable GLP or GCP, the data generated in our nonclinical studies or clinical trials may be deemed unreliable and the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities may require us to perform additional nonclinical studies before allowing us to proceed with clinical trials or additional clinical trials before approving our marketing applications. We cannot assure you that, upon inspection, the FDA will determine that any of our future nonclinical studies or clinical trials will comply with GLP or GCP, as applicable. In addition, our nonclinical studies and clinical trials must be conducted with drug candidates produced under cGMP regulations. Our failure or the failure of our CROs to comply with these regulations may require us to delay or repeat nonclinical studies or clinical trials, which
50
Table of Contents
would delay the marketing approval process and could also subject us to enforcement action. We also are required to register certain ongoing clinical trials and provide certain information, including information relating to the trial’s protocol, on a government-sponsored database, ClinicalTrials.gov, within specific timeframes. Failure to do so can result in fines, adverse publicity and civil and criminal sanctions.
Although we intend to design the nonclinical studies and clinical trials for our drug candidates, CROs conduct all of the clinical trials and certain nonclinical studies. As a result, many important aspects of our nonclinical and clinical development, including their conduct and timing, will be outside of our direct control. Our reliance on third parties to conduct future nonclinical studies and clinical trials will also result in less direct control over the management of data developed through nonclinical studies or clinical trials than would be the case if we were relying entirely upon our own staff. Communicating with outside parties can also be challenging, potentially leading to mistakes as well as difficulties in coordinating activities. Outside parties may:
| • | have staffing difficulties; |
| • | fail to comply with contractual obligations; |
| • | experience regulatory compliance issues; |
| • | undergo changes in priorities; |
| • | become financially distressed; or |
| • | form relationships with other entities, some of which may be our competitors. |
These factors may materially adversely affect the willingness or ability of third parties to conduct our nonclinical studies or clinical trials and may subject us to unexpected cost increases and/or delays that are beyond our control. If the CROs do not perform nonclinical studies or clinical trials in a satisfactory manner, breach their obligations to us or fail to comply with regulatory requirements, the development, marketing approval and commercialization of our drug candidates may be delayed, we may not be able to obtain marketing approval and commercialize our drug candidates, or our development program may be materially and irreversibly harmed. If we are unable to rely on nonclinical or clinical data collected by our CROs, we could be required to repeat, extend the duration of, or increase the size of any nonclinical studies or clinical trials we conduct and this could significantly delay commercialization and require significantly greater expenditures.
If any of our relationships with these third-party CROs terminate, we may not be able to enter into arrangements with alternative CROs on commercially reasonable terms, or at all. If CROs do not successfully carry out their contractual duties or obligations or meet expected deadlines, if they need to be replaced, if the quality or accuracy of the nonclinical or clinical data they obtain are compromised due to the failure to adhere to our protocols, regulatory requirements or for other reasons, or if they are negatively impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic, any nonclinical studies or clinical trials such CROs are associated with may be extended, delayed or terminated, and we may not be able to obtain marketing approval for or successfully commercialize our drug candidates. As a result, we believe that our financial results and the commercial prospects for our drug candidates in the subject indication would be harmed, our costs would increase and our ability to generate revenue would be delayed.
We rely on third parties to manufacture nonclinical and clinical drug supplies, and we intend to rely on third parties to produce commercial supplies of any approved product which increases the risk that we will not have sufficient quantities of such drug candidates or products or such quantities at an acceptable cost, which could delay, prevent or impair our development or commercialization efforts.
We do not own or operate manufacturing facilities for the production of nonclinical, clinical or commercial supplies of the drug candidates that we are developing or evaluating in our development programs. We have limited personnel with experience in drug manufacturing and lack the resources and the capabilities to manufacture any of our drug candidates on a nonclinical, clinical or commercial scale. We rely on third parties
51
Table of Contents
for supply of our nonclinical and clinical drug supplies (including key starting and intermediate materials), and our strategy is to outsource all manufacturing of our drug candidates and products to third parties.
In order to conduct clinical trials of drug candidates, we will need to have them manufactured in potentially large quantities. Our third-party manufacturers may be unable to successfully increase the manufacturing capacity for any of our clinical drug supplies (including key starting and intermediate materials) in a timely or cost-effective manner, or at all. In addition, quality issues may arise during scale-up activities and at any other time. For example, ongoing data on the stability of our drug candidates may shorten the expiry of our drug candidates and lead to clinical trial material supply shortages, and potentially clinical trial delays. If these third-party manufacturers are unable to successfully scale up the manufacture of our drug candidates in sufficient quality and quantity, the development, testing and clinical trials of that drug candidate may be delayed or infeasible, and regulatory approval or commercial launch of that drug candidate may be delayed or not obtained, which could significantly harm our business.
Our use of new third-party manufacturers increases the risk of delays in production or insufficient supplies of our drug candidates (and the key starting and intermediate materials for such drug candidates) as we transfer our manufacturing technology to these manufacturers and as they gain experience manufacturing our drug candidates (and the key starting and intermediate materials for such drug candidates).
Even after a third-party manufacturer has gained significant experience in manufacturing our drug candidates (or the key starting and intermediate materials for such drug candidates) or even if we believe we have succeeded in optimizing the manufacturing process, there can be no assurance that such manufacturer will produce sufficient quantities of our drug candidates (or the key starting and intermediate materials for such drug candidates) in a timely manner or continuously over time, or at all.
We may be delayed if we need to change the manufacturing process used by a third party. Further, if we change an approved manufacturing process, then we may be delayed if the FDA or a comparable foreign authority needs to review the new manufacturing process before it may be used.
We do not currently have any agreements with third-party manufacturers for long-term commercial supply. In the future, we may be unable to enter into agreements with third-party manufacturers for commercial supplies of any drug candidate that we develop, or may be unable to do so on acceptable terms. Even if we are able to establish and maintain arrangements with third-party manufacturers, reliance on third-party manufacturers entails risks, including:
| • | reliance on the third party for regulatory compliance and quality assurance; |
| • | the possible breach of the manufacturing agreement by the third party; |
| • | the possible misappropriation of our proprietary information, including our trade secrets and know-how; and |
| • | the possible termination or non-renewal of the agreement by the third party at a time that is costly or inconvenient for us. |
Third-party manufacturers may not be able to comply with cGMP requirements or similar regulatory requirements outside the United States. Our failure, or the failure of our third-party manufacturers, to comply with applicable requirements could result in sanctions being imposed on us, including fines, injunctions, civil penalties, delays, suspension or withdrawal of approvals, license revocation, seizures or recalls of drug candidates or products, operating restrictions and/or criminal prosecutions, any of which could significantly and adversely affect supplies of our drug candidates.
52
Table of Contents
Our future drug candidates and any products that we may develop may compete with other drug candidates and products for access to manufacturing facilities. There are a limited number of manufacturers that operate under cGMP requirements and that might be capable of manufacturing for us.
If the third parties that we engage to supply any materials or manufacture product for our nonclinical studies and clinical trials should cease to continue to do so for any reason, we likely would experience delays in advancing these studies and trials while we identify and qualify replacement suppliers or manufacturers and we may be unable to obtain replacement supplies on terms that are favorable to us or at all. In addition, if we are not able to obtain adequate supplies of our drug candidates or the substances used to manufacture them, it will be more difficult for us to develop our drug candidates and compete effectively.
Some of our third-party manufacturers which we use for the supply of materials for drug candidates or other materials necessary to manufacture product to conduct clinical trials are located in countries affected by COVID-19, and should they experience disruptions, such as temporary closures or suspension of services, we would likely experience delays in advancing our clinical development.
Our current and anticipated future dependence upon others for the manufacture of our drug candidates (or the key starting and intermediate materials for such drug candidates) may adversely affect our future profit margins and our ability to develop drug candidates and commercialize any products that receive marketing approval on a timely and competitive basis.
Our future relationships with customers and third-party payors in the United States and elsewhere may be subject, directly or indirectly, to applicable anti-kickback, fraud and abuse, false claims, transparency, health information privacy and security and other healthcare laws and regulations, which could expose us to criminal sanctions, civil penalties, contractual damages, reputational harm, administrative burdens and diminished profits and future earnings.
Healthcare providers, physicians and third-party payors in the United States and elsewhere will play a primary role in the recommendation and prescription of any drug candidates for which we obtain marketing approval. Our future arrangements with third-party payors and customers may expose us to broadly applicable fraud and abuse and other healthcare laws and regulations, including, without limitation, the federal Anti-Kickback Statute and the federal False Claims Act (the “FCA”), which may constrain the business or financial arrangements and relationships through which we sell, market and distribute any products for which we obtain marketing approval. In addition, we may be subject to transparency laws and patient privacy regulation by the U.S. federal and state governments and by governments in foreign jurisdictions in which we conduct our business. The applicable federal, state and foreign healthcare laws and regulations that may affect our ability to operate include:
| • | the federal Anti-Kickback Statute, which prohibits, among other things, knowingly and willfully soliciting, receiving, offering or paying any remuneration (including any kickback, bribe, or rebate), directly or indirectly, overtly or covertly, in cash or in kind, to induce, or in return for, either the referral of an individual, or the purchase, lease, order or recommendation of any good, facility, item or service for which payment may be made, in whole or in part, under the Medicare and Medicaid programs or other federal healthcare programs. A person or entity can be found guilty of violating the statute without actual knowledge of the statute or specific intent to violate it. The Anti-Kickback Statute has been interpreted to apply to arrangements between pharmaceutical manufacturers on the one hand and prescribers, purchasers, and formulary managers on the other; |
| • | the federal civil and criminal false claims laws, including the FCA, which prohibit any person or entity from, among other things, knowingly presenting, or causing to be presented, a false, fictitious or fraudulent claim for payment to, or approval by, the federal government or knowingly making, using or causing to be made or |
53
Table of Contents
| used a false record or statement material to a false or fraudulent claim to the federal government. In addition, the government may assert that a claim including items or services resulting from a violation of the federal Anti-Kickback Statute constitutes a false or fraudulent claim for purposes of the FCA; |
| • | HIPAA, which created federal criminal statutes that prohibit knowingly and willfully executing, or attempting to execute, a scheme to defraud any healthcare benefit program or obtain, by means of false or fraudulent pretenses, representations, or promises, any of the money or property owned by, or under the custody or control of, any healthcare benefit program, regardless of the payor (e.g., public or private) and knowingly and willfully falsifying, concealing or covering up by any trick or device a material fact or making any materially false statements in connection with the delivery of, or payment for, healthcare benefits, items or services relating to healthcare matters. Similar to the federal Anti-Kickback Statute, a person or entity can be found guilty of violating HIPAA without actual knowledge of the statutes or specific intent to violate them; |
| • | the Physician Payments Sunshine Act, created under the ACA, and its implementing regulations, which requires manufacturers of drugs, devices, biologics and medical supplies for which payment is available under Medicare, Medicaid or the Children’s Health Insurance Program (with certain exceptions) to report annually to CMS information related to payments or other transfers of value made to physicians (defined to include doctors, dentists, optometrists, podiatrists and chiropractors) and teaching hospitals, as well as ownership and investment interests held by physicians and their immediate family members. Beginning in 2022, such obligations will include payments and other transfers of value provided in the previous year to certain other healthcare professionals, including physician assistants, nurse practitioners, clinical nurse specialists, certified nurse anesthetists, and certified nurse-midwives; |
| • | federal consumer protection and unfair competition laws, which broadly regulate marketplace activities and activities that potentially harm consumers; and |
| • | analogous state laws and regulations, such as state anti-kickback and false claims laws, which may apply to sales or marketing arrangements and healthcare items or services reimbursed by non-governmental third-party payors, including private insurers; state laws that require pharmaceutical companies to comply with the pharmaceutical industry’s voluntary compliance guidelines and the relevant compliance guidance promulgated by the federal government or otherwise restrict payments that may be made to healthcare providers; state laws that require drug manufacturers to report information related to payments and other transfers of value to physicians and other healthcare providers or marketing expenditures; and healthcare laws in the EU and other jurisdictions, including reporting requirements detailing interactions with and payments to healthcare providers. |
Because of the breadth of these laws and the narrowness of the statutory exceptions and regulatory safe harbors available under such laws, it is possible that some of our business activities could be subject to challenge under one or more of such laws. The scope and enforcement of each of these laws is uncertain and subject to rapid change in the current environment of healthcare reform, especially in light of the lack of applicable precedent and regulations. Federal and state enforcement bodies have recently increased their scrutiny of interactions between healthcare companies and healthcare providers, which has led to a number of investigations, prosecutions, convictions and settlements in the healthcare industry. Ensuring that our business arrangements with third parties comply with applicable healthcare laws, as well as responding to investigations by government authorities, can be time- and resource-consuming and can divert management’s attention from the business.
If our operations are found to be in violation of any of the laws described above or any other government regulations that apply to us, we may be subject to penalties, including civil, criminal and administrative penalties, damages, fines, disgorgement, individual imprisonment, possible exclusion from participation in
54
Table of Contents
federal- and state-funded healthcare programs, contractual damages and the curtailment or restricting of our operations, as well as additional reporting obligations and oversight if we become subject to a corporate integrity agreement or other agreement to resolve allegations of non-compliance with these laws, any of which could harm our ability to operate our business and our financial results. Further, if the physicians or other providers or entities with whom we expect to do business are found not to be in compliance with applicable laws, they may be subject to criminal, civil or administrative sanctions, including exclusions from government funded healthcare programs. In addition, the approval and commercialization of any drug candidate we develop outside the United States will also likely subject us to foreign equivalents of the healthcare laws mentioned above, among other foreign laws.
Risks related to intellectual property
If we and our collaborators are unable to obtain and maintain sufficient patent and other intellectual property protection for our drug candidates and technology, our competitors could develop and commercialize products and technology similar or identical to ours, and we may not be able to compete effectively in our market or successfully commercialize any drug candidates we may develop.
Our success depends in significant part on our ability and the ability of our current or future collaborators and licensors to obtain, maintain, enforce and defend patents and other intellectual property rights with respect to our drug candidates and technology and to operate our business without infringing, misappropriating, or otherwise violating the intellectual property rights of others. If we and our current or future collaborators and licensors are unable to obtain and maintain sufficient intellectual property protection for our drug candidates or other drug candidates that we may identify, or if the scope of the intellectual property protection obtained is not sufficiently broad, our competitors and other third parties could develop and commercialize drug candidates similar or identical to ours, and our ability to successfully commercialize our drug candidates and other drug candidates that we may pursue may be impaired. We do not own any issued patents with respect to our programs, including our CHB and NASH programs, and we do not own or in-license any issued patents with claims that specifically recite our ALG-010133, ALG-000184, ALG-020572, ALG-125097 and ALG-055009 drug candidates, and we can provide no assurance that any of our current or future patent applications will result in issued patents or that any issued patents will provide us with any competitive advantage. We cannot be certain that there is no invalidating prior art of which we and the patent examiner are unaware or that our interpretation of the relevance of prior art is correct. For example, there are certain patents and patent applications (and there may be other patents and patent applications) that are owned by third parties, including our competitors, that have (or may have) an earlier filing date, and could be determined to have an earlier priority date, than our patent applications relating to our STOPS candidate, ALG-010133. If a patent or patent application is determined to have an earlier priority date, it may prevent our patent applications from issuing at all or issuing in a form that provides any competitive advantage for our product candidates. Failure to obtain issued patents could have a material adverse effect on our ability to develop and commercialize our drug candidates. Even if our patent applications do issue as patents, third parties may be able to challenge the validity and enforceability of our patents on a variety of grounds, including that such third party’s patents and patent applications have an earlier priority date, and if such challenges are successful we may be required to obtain one or more licenses from such third parties, or be prohibited from commercializing our product candidates. We may not be able to obtain these licenses on acceptable or commercially reasonable terms, if at all, or these licenses may be non-exclusive, which could result in our competitors using the same intellectual property.
We seek to protect our proprietary positions by, among other things, filing patent applications in the United States and abroad related to our current drug candidates and other drug candidates that we may identify. Obtaining, maintaining, defending and enforcing pharmaceutical patents is costly, time consuming and complex, and we may not be able to file and prosecute all necessary or desirable patent applications, or
55
Table of Contents
maintain, enforce and license any patents that may issue from such patent applications, at a reasonable cost or in a timely manner. It is also possible that we will fail to identify patentable aspects of our research and development output before it is too late to obtain patent protection. Moreover, under certain of our license or collaboration agreements, we may not have the right to control the preparation, filing, prosecution and maintenance of patent applications, or to maintain the rights to patents licensed to or from third parties.
We currently are the assignee of a number of U.S. provisional patent applications. U.S. provisional patent applications are not eligible to become issued patents until, among other things, we file a non-provisional patent application within 12 months of filing of one or more of our related provisional patent applications. With regard to such U.S. provisional patent applications, if we do not timely file any non-provisional patent applications, we may lose our priority dates with respect to our provisional patent applications and any patent protection on the inventions disclosed in our provisional patent applications. Further, in the event that we do timely file non-provisional patent applications relating to our provisional patent applications, we cannot predict whether any such patent applications will result in the issuance of patents or if such issued patents will provide us with any competitive advantage.
Although we enter into confidentiality agreements with parties who have access to confidential or patentable aspects of our research and development output, such as our employees, collaborators, CROs, contract manufacturers, consultants, advisors and other third parties, any of these parties may breach these agreements and disclose such output before a patent application is filed, thereby jeopardizing our ability to seek patent protection. Further, we may not be aware of all third-party intellectual property rights potentially relating to our drug candidates. Publications of discoveries in the scientific literature often lag behind the actual discoveries, and patent applications in the United States and other jurisdictions are typically not published until 18 months after filing or, in some cases, not at all. Therefore, we cannot know with certainty whether we were the first to make the inventions claimed in our patents or pending patent applications, or that we were the first to file for patent protection of such inventions.
The patent position of pharmaceutical companies generally is highly uncertain, involves complex legal, technological and factual questions and has, in recent years, been the subject of much debate and litigation throughout the world. In addition, the laws of foreign countries may not protect our rights to the same extent as the laws of the United States, or vice versa. As a result, the issuance, scope, validity, enforceability, and commercial value of our patent rights are highly uncertain. The subject matter claimed in a patent application can be significantly reduced or eliminated before the patent issues, if at all, and its scope can be reinterpreted or narrowed after issuance. Therefore, our pending and future patent applications may not result in patents being issued in relevant jurisdictions that protect our drug candidates, in whole or in part, or that effectively prevent others from commercializing competitive drug candidates, and even if our patent applications issue as patents in relevant jurisdictions, they may not issue in a form that will provide us with any meaningful protection for our drug candidates or technology, prevent competitors from competing with us or otherwise provide us with any competitive advantage. Additionally, our competitors may be able to circumvent our patents by challenging their validity or by developing similar or alternative drug candidates or technologies in a non-infringing manner.
The issuance of a patent is not conclusive as to its inventorship, scope, validity or enforceability, and our patents may be challenged in the courts or patent offices in the United States and abroad. We may be subject to a third-party preissuance submission of prior art to the United States Patent and Trademark Office (the “USPTO”), or become involved in opposition, derivation, revocation, reexamination, inter partes review, post-grant review or interference proceedings challenging our patent rights or the patent rights of others, or other proceedings in the USPTO or applicable foreign offices that challenge priority of invention or other features of patentability. An adverse determination in any such submission, proceeding or litigation could result in loss of exclusivity or ability to sell our products free from infringing the patents of third parties, patent claims being narrowed, invalidated or held unenforceable, in whole or in part, and limitation of the scope or duration
56
Table of Contents
of the patents directed to our drug candidates, all of which could limit our ability to stop others from using or commercializing similar or identical drug candidates or technology to compete directly with us, without payment to us, or result in our inability to manufacture or commercialize drug candidates or approved products (if any) without infringing third-party patent rights. In addition, if the breadth or strength of the claims of our patents and patent applications is threatened, regardless of the outcome, it could dissuade companies from collaborating with us to license, develop or commercialize current or future drug candidates, or could have a material adverse effect on our ability to raise funds necessary to continue our research programs or clinical trials. Such proceedings also may result in substantial cost and require significant time from our scientists and management, even if the eventual outcome is favorable to us.
In addition, given the amount of time required for the development, testing and regulatory review of new drug candidates, patents protecting such candidates might expire before or shortly after such candidates are commercialized. As a result, our patent portfolio may not provide us with sufficient rights to exclude others from commercializing products or technology similar or identical to ours for a meaningful amount of time, or at all. Moreover, some of our licensed patents and owned or licensed patent applications may in the future be co-owned with third parties. If we are unable to obtain exclusive licenses to any such co-owners’ interest in such patents or patent applications, such co-owners may be able to license their rights to other third parties, including our competitors, and our competitors could market competing products and technology. In addition, we may need the cooperation of any such co-owners in order to enforce such patents against third parties, and such cooperation may not be provided to us. Any of the foregoing could harm our competitive position, business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
We have entered into licensing agreements with third parties. If we fail to comply with our obligations in the agreements under which we license intellectual property rights to or from third parties, or these agreements are terminated, or we otherwise experience disruptions to our business relationships with our licensors or licensees, our competitive position, business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects could be harmed.
In addition to patent and other intellectual property rights we own or co-own, we have licensed, and may in the future license, patent and other intellectual property rights to and from other parties. In particular, we have in-licensed significant intellectual property rights from Emory and Luxna. Licenses may not provide us with exclusive rights to use the applicable intellectual property and technology in all relevant fields of use and in all territories in which we may wish to develop or commercialize our drug candidates, products (if approved) and technology in the future. As a result, we may not be able to prevent competitors from developing and commercializing competitive products or technologies.
In addition, in some circumstances, we may not have the right to control the preparation, filing and prosecution of patent applications or to maintain, defend and enforce the patents that we license to or from third parties, and we may have to rely on our partners to fulfill these responsibilities. For example, under the Luxna Agreement, we obtained a license from Luxna under patents relevant to certain aspects of our HBV programs as well as to various potential therapies, which we are pursuing to address SARS-CoV-2. Although we have review and comment rights regarding prosecution of patents that we license under the Luxna Agreement, Luxna retains ultimate decision-making control with respect to the prosecution of these patents. Additionally, under the Emory License Agreement, we obtained a license from Emory University under patents relevant to certain aspects of our small molecule CHB program. Although we direct prosecution of patents licensed under the Emory License Agreement, we are obligated to consult with Emory University with respect to prosecution of these patents and Emory and its counsel are responsible for making all filings related to such prosecution. Similarly, although we will control the prosecution of jointly developed patents resulting from our collaboration with the Rega Institute for Medical Research and the Centre for Drug Design and Discovery under the KU Leuven Agreement, we are obligated to consult with such parties with respect to prosecution of these patents.
57
Table of Contents
Consequently, any such licensed patents and applications may not be prepared, filed, prosecuted, maintained, enforced, and defended in a manner consistent with the best interests of our business. If our current or future licensors, licensees or collaborators fail to prepare, file, prosecute, maintain, enforce, and defend licensed patents and other intellectual property rights, such rights may be reduced or eliminated, and our right to develop and commercialize any of our drug candidates or technology that are the subject of such licensed rights could be adversely affected. In addition, our licensors may own or control intellectual property that has not been licensed to us and, as a result, we may be subject to claims, regardless of their merit, that we are infringing or otherwise violating the licensor’s rights.
If we fail to comply with our obligations, including the obligation to make various milestone payments and royalty payments, under any of the agreements under which we license intellectual property rights from third parties, such as the Emory License Agreement or Luxna Agreement, the licensor may have the right to terminate the license. Under some of our in-license agreements, as a sublicensee, we may be obligated to comply with applicable requirements, limitations or obligations of our sublicensors to other third parties. For example, the Luxna Agreement includes rights that Luxna in-licensed from Osaka University (“Osaka”), which are in turn sublicensed to us. Prior to granting such rights to Luxna, Osaka granted certain rights to third parties and therefore the rights we in-license from Luxna are subject to such third-party rights. Although we understand that these rights granted to such third parties are for uses outside the scope of our business, license agreements are complex, subject to multiple interpretations and disputes may arise regarding scope of such licensed rights. Further, under the Luxna Agreement and other in-licenses under which we sublicense certain rights, we rely on Luxna and our other sublicensors to comply with their obligations under their upstream license agreements, where we may have no relationship with the original licensor of such rights. If our sublicensors fail to comply with their obligations under their upstream license agreements, and the upstream license agreements are consequently terminated, such termination may result in the termination of our sublicenses.
If any of our license agreements are terminated, the underlying licensed patents fail to provide the intended exclusivity or we otherwise experience disruptions to our business relationships with our licensors, we could lose intellectual property rights that are important to our business or be prevented from developing and commercializing our drug candidates, and competitors could have the freedom to seek regulatory approval of, and to market, products identical to ours. Termination of these agreements or reduction or elimination of our rights under these agreements may also result in our having to negotiate new or reinstated agreements with less favorable terms, cause us to lose our rights under these agreements, including our rights to important intellectual property or technology, or impede, delay or prohibit the further development or commercialization of one or more drug candidates that rely on such agreements. It is possible that we may be unable to obtain any additional licenses at a reasonable cost or on reasonable terms, if at all. In that event, we may be required to expend significant time and resources to redesign our drug candidates or the methods for manufacturing them or to develop or license replacement technology, all of which may not be feasible on a technical or commercial basis.
In addition, the research resulting in certain of our owned and in-licensed patent rights and technology may have been funded in part by the U.S. federal or state governments. As a result, the government may have certain rights, including march-in rights, to such patent rights and technology. When new technologies are developed with government funding, the government generally obtains certain rights in any resulting patents, including a non-exclusive license authorizing the government to use the invention for noncommercial purposes. These rights may permit the government to disclose our confidential information to third parties or allow third parties to use our licensed technology. The government can exercise its march-in rights if it determines that action is necessary because we fail to achieve practical application of the government-funded technology, or because action is necessary to alleviate health or safety needs, to meet requirements of federal regulations, or to give preference to U.S. industry. In addition, our rights in such inventions may be subject to certain
58
Table of Contents
requirements to manufacture products embodying such inventions in the United States. Any of the foregoing could harm our competitive position, business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
Licensing of intellectual property is of critical importance to our business and involves complex legal, business and scientific issues and certain provisions in intellectual property license agreements may be susceptible to multiple interpretations. Disputes may arise between us and our licensing partners regarding intellectual property subject to a license agreement, including:
| • | the scope of rights granted under the license agreement and other interpretation-related issues; |
| • | whether and the extent to which technology and processes of one party infringe intellectual property of the other party that are not subject to the licensing agreement; |
| • | rights to sublicense patent and other rights to third parties; |
| • | any diligence obligations with respect to the use of the licensed technology in relation to development and commercialization of our drug candidates, and what activities satisfy those diligence obligations; |
| • | the ownership of inventions and know-how resulting from the joint creation or use of intellectual property; |
| • | rights to transfer or assign the license; and |
| • | the effects of termination. |
The resolution of any contract interpretation disagreement that may arise could narrow what we believe to be the scope of our rights to the relevant intellectual property or technology, or increase what we believe to be our financial or other obligations under the relevant agreement, either of which could harm our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects. If disputes over intellectual property that we have licensed prevent or impair our ability to maintain our current licensing arrangements on acceptable terms or at all, we may be unable to successfully develop and commercialize the affected drug candidates. Moreover, any dispute or disagreement with our licensing partners may result in the delay or termination of the research, development or commercialization of our drug candidates or any future drug candidates, and may result in costly litigation or arbitration that diverts management attention and resources away from our day-to-day activities, which may adversely affect our business, financial conditions, results of operations and prospectus.
Furthermore, current and future collaborators or strategic partners may develop, either alone or with others, products in related fields that are competitive with the products or potential products that are the subject of these collaborations. Competing products, either developed by our collaborators or strategic partners or to which the collaborators or strategic partners have rights, may result in the withdrawal of partner support for our drug candidates. Any of these developments could harm our product development efforts.
In addition, if our licensors fail to abide by the terms of the license, if the licensors fail to prevent infringement by third parties or if the licensed patents or other rights are found to be invalid or unenforceable, our business, competitive position, financial condition, results of operations and prospects could be materially harmed. For more information regarding our license agreements, see “Business—License agreements.”
If we are unable to obtain licenses from third parties on commercially reasonable terms or at all, our business could be harmed.
It may be necessary for us to use the patented or proprietary technology of third parties to commercialize our products (if approved), in which case we would be required to obtain a license from these third parties. The licensing of third-party intellectual property rights is a competitive area, and more established companies may pursue strategies to license or acquire third-party intellectual property rights that we may consider attractive or necessary. More established companies may have a competitive advantage over us due to their size, capital resources and greater clinical development and commercialization capabilities. In addition, companies that
59
Table of Contents
perceive us to be a competitor may be unwilling to assign or license rights to us. We also may be unable to license or acquire third party intellectual property rights on terms that would allow us to make an appropriate return on our investment or at all. If we are unable to license such technology, or if we are forced to license such technology on unfavorable terms, our business could be materially harmed. If we are unable to obtain a necessary license, we may be unable to develop or commercialize the affected drug candidates, which could materially harm our business, and the third parties owning such intellectual property rights could seek either an injunction prohibiting our sales, or, with respect to our sales, an obligation on our part to pay royalties and/or other forms of compensation. Even if we are able to obtain a license, it may be or become non-exclusive, thereby giving our competitors access to the same technologies licensed to us. For example, under the Emory License Agreement we currently have an exclusive license with respect to certain patents and a non-exclusive license with respect to certain of Emory’s specified know-how. Beginning in June 2022, the license to such patents will become non-exclusive with respect to all fields except for the treatment and prevention of HBV. For more information regarding our license agreements, see the section titled “Business—License agreements.” Any of the foregoing could harm our competitive position, business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
We may not identify relevant third-party patents or may incorrectly interpret the relevance, scope or expiration of a third-party patent, which might subject us to infringement claims or adversely affect our ability to develop and market our drug candidates.
We cannot guarantee that any of our or our licensors’ patent searches or analyses, including the identification of relevant patents, the scope of patent claims or the expiration of relevant patents, are complete or thorough, nor can we be certain that we have identified each and every third-party patent and pending patent application in the United States and abroad that is relevant to or necessary for the commercialization of our drug candidates in any jurisdiction. For example, U.S. patent applications filed before November 29, 2000 and certain U.S. patent applications filed after that date that will not be filed outside the United States remain confidential until patents issue. As mentioned above, patent applications in the United States and elsewhere are published approximately 18 months after the earliest filing for which priority is claimed, with such earliest filing date being commonly referred to as the priority date. Therefore, patent applications covering our drug candidates could have been filed by third parties without our knowledge. Additionally, pending patent applications that have been published can, subject to certain limitations, be later amended in a manner that could cover our drug candidates or the use of our drug candidates. The scope of a patent claim is determined by an interpretation of the law, the written disclosure in a patent and the patent’s prosecution history. Our interpretation of the relevance or the scope of a patent or a pending application may be incorrect, which may negatively impact our ability to market our drug candidates. We may incorrectly determine that our drug candidates are not covered by a third-party patent or may incorrectly predict whether a third party’s pending application will issue with claims of relevant scope. Our determination of the expiration date of any patent in the United States or abroad that we consider relevant may be incorrect, which may negatively impact our ability to develop and market our drug candidates. Our failure to identify and correctly interpret relevant patents may negatively impact our ability to develop and market our drug candidates.
We are aware of certain third-party issued patents and pending patent applications, including those of our competitors, that, if issued with their current claim scope, may be construed to cover our drug candidates, including ALG-055009, ALG-125097 and ALG-010133. In the event that any of these patents were asserted against us, we believe that we would have defenses against any such action, including that such patents are not valid. However, if any such patents were to be asserted against us and our defenses to such assertion were unsuccessful and alternative technology was not available or technologically or commercially practical, unless we obtain a license to such patents, we could be liable for damages, which could be significant and include treble damages and attorneys’ fees if we are found to willfully infringe such patents, and we could be precluded from commercializing any drug candidates that were ultimately held to infringe such patents.
60
Table of Contents
In addition, if we fail to identify and correctly interpret relevant patents, we may be subject to infringement claims. We cannot guarantee that we will be able to successfully settle or otherwise resolve such infringement claims. If we fail in any such dispute, in addition to being forced to pay damages, which may be significant, we may be temporarily or permanently prohibited from commercializing any of our drug candidates that are held to be infringing. We might, if possible, also be forced to redesign drug candidates so that they no longer infringe the third-party intellectual property rights. Any of these events, even if we were ultimately to prevail, could require us to divert substantial financial and management resources that we would otherwise be able to devote to our business and could adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
Patent terms may be inadequate to establish our competitive position on our drug candidates for an adequate amount of time.
Patents have a limited lifespan. In the United States, if all maintenance fees are timely paid, the natural expiration of a patent is generally 20 years from its earliest U.S. non-provisional filing date. Various extensions may be available, but the life of a patent, and the protection it affords, is limited. Even if patents covering our drug candidates are obtained, once the patent life has expired for a drug candidate, we may be open to competition from competitive medications, including generic versions. Given the amount of time required for the development, testing and regulatory review of new drug candidates, patents directed towards such drug candidates might expire before or shortly after such drug candidates are commercialized. As a result, our owned and licensed patent portfolio may not provide us with sufficient rights to exclude others from commercializing drug candidates similar or identical to ours for a meaningful amount of time, or at all.
Depending upon the timing, duration and conditions of any FDA marketing approval of our drug candidates, one or more of our owned or licensed U.S. patents may be eligible for limited patent term extension under the Hatch-Waxman Act, and similar legislation in the EU and certain other countries. The Hatch-Waxman Act permits a patent term extension of up to five years for a patent covering an approved product as compensation for effective patent term lost during product development and the FDA regulatory review process. However, we may not receive an extension if we fail to exercise due diligence during the testing phase or regulatory review process, fail to apply within applicable deadlines, fail to apply prior to expiration of relevant patents or otherwise fail to satisfy applicable requirements. Moreover, the length of the extension could be less than we request. Only one patent per approved product can be extended, the extension cannot extend the total patent term beyond 14 years from approval and only those claims for the approved drug, a method for using it or a method for manufacturing it may be extended. If we are unable to obtain patent term extension or the term of any such extension is less than we request, the period during which we can enforce our patent rights for the applicable drug candidate will be shortened and our competitors may obtain approval to market competing products sooner. As a result, our revenue from applicable products could be reduced. Further, if this occurs, our competitors may take advantage of our investment in development and trials by referencing our clinical and nonclinical data and launch their product earlier than might otherwise be the case, and our competitive position, business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects could be materially harmed.
Further, there are detailed rules and requirements regarding the patents that may be submitted to the FDA for listing in the Orange Book. We may be unable to obtain patents covering our drug candidates that contain one or more claims that satisfy the requirements for listing in the Orange Book. Even if we submit a patent for listing in the Orange Book, the FDA may decline to list the patent, or a manufacturer of generic drugs may challenge the listing. If one of our drug candidates is approved and a patent covering that drug candidate is not listed in the Orange Book, a manufacturer of generic drugs would not have to provide advance notice to us of any abbreviated new drug application filed with the FDA to obtain permission to sell a generic version of such drug candidate. Any of the foregoing could harm our competitive position, business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
61
Table of Contents
We may not be able to protect our intellectual property rights throughout the world.
Filing, prosecuting, maintaining, defending and enforcing patents on our drug candidates in all countries throughout the world would be prohibitively expensive, and consequently our intellectual property rights in some countries outside the United States may be less extensive than those in the United States. In addition, the laws of some foreign countries do not protect intellectual property rights to the same extent as federal and state laws in the United States. Consequently, we may not be able to prevent third parties from practicing our inventions in all countries outside the United States, or from selling or importing products made using our inventions in and into the United States or other jurisdictions. Competitors may use our technologies in jurisdictions where we have not obtained patents to develop their own products and may export otherwise infringing products to territories where we have patents, but enforcement rights are not as strong as those in the United States. These products may compete with our drug candidates and our patents or other intellectual property rights may not be effective or sufficient to prevent them from competing.
Many companies have encountered significant problems in protecting and defending intellectual property rights in foreign jurisdictions. The legal systems of some countries do not favor the enforcement or protection of patents, trade secrets and other intellectual property, which could make it difficult for us to stop the infringement of our patents or marketing of competing products in violation of our intellectual property and proprietary rights generally. Proceedings to enforce our intellectual property rights in foreign jurisdictions could result in substantial costs and divert our efforts and attention from other aspects of our business, could put our patents at risk of being invalidated or interpreted narrowly and our patent applications at risk of not issuing and could provoke third parties to assert claims against us. We may not prevail in any lawsuits that we initiate, and the damages or other remedies awarded, if any, may not be commercially meaningful.
Many foreign countries, including some EU countries, India, Japan and China, have compulsory licensing laws under which a patent owner may be compelled under specified circumstances to grant licenses to third parties. In addition, many countries limit the enforceability of patents against government agencies or government contractors. In those countries, we may have limited remedies if patents are infringed or if we are compelled to grant a license to a third party, which could materially diminish the value of the applicable patents and limit our potential revenue opportunities. Accordingly, our efforts to enforce our intellectual property rights around the world may be inadequate to obtain a significant commercial advantage from the intellectual property that we develop or license, which could adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
Changes in patent law could diminish the value of patents in general, thereby impairing our ability to protect our drug candidates.
Obtaining and enforcing patents in the pharmaceutical industry is inherently uncertain, due in part to ongoing changes in the patent laws. For example, in the United States, depending on decisions by Congress, the federal courts, and the USPTO, the laws and regulations governing patents, and interpretation thereof, could change in unpredictable ways that could weaken our and our collaborators’ or licensors’ ability to obtain new patents or to enforce existing or future patents. For example, the U.S. Supreme Court has ruled on several patent cases in recent years, either narrowing the scope of patent protection available in certain circumstances or weakening the rights of patent owners in certain situations. Therefore, there is increased uncertainty with regard to our and our collaborators’ or licensors’ ability to obtain patents in the future, as well as uncertainty with respect to the value of patents once obtained.
Patent reform legislation could increase the uncertainties and costs surrounding the prosecution of our and our collaborators’ or licensors’ patent applications and the enforcement or defense of our or our collaborators’ or licensors’ issued patents. For example, assuming that other requirements for patentability are met, prior to
62
Table of Contents
March 2013, in the United States, the first to invent the claimed invention was entitled to the patent, while outside the United States, the first to file a patent application was entitled to the patent. After March 2013, under the Leahy-Smith America Invents Act (the “Leahy-Smith Act”), enacted in September 2011, the United States transitioned to a first inventor to file system in which, assuming that other requirements for patentability are met, the first inventor to file a patent application will be entitled to the patent on an invention regardless of whether a third party was the first to invent the claimed invention. The Leahy-Smith Act also includes a number of significant changes that affect the way patent applications are prosecuted and may also affect patent litigation. These include allowing third-party submission of prior art to the USPTO during patent prosecution and additional procedures to challenge the validity of a patent by USPTO-administered post-grant proceedings, including post-grant review, inter partes review and derivation proceedings. The USPTO has developed new regulations and procedures to govern administration of the Leahy-Smith Act, and many of the substantive changes to patent law associated with the Leahy-Smith Act, particularly the first inventor-to-file provisions. Accordingly, it is not clear what, if any, impact the Leahy-Smith Act will have on the operation of our business. However, the Leahy-Smith Act and its implementation could increase the uncertainties and costs surrounding the prosecution of our or our licensors’ patent applications and the enforcement or defense of our or our licensors’ issued patents. Similarly, statutory or judicial changes to the patent laws of other countries may increase the uncertainties and costs surrounding the prosecution of patent applications and the enforcement or defense of issued patents. All of the foregoing could harm our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
Obtaining and maintaining our patent protection depends on compliance with various procedural, document submission, fee payment and other requirements imposed by governmental patent agencies, and our patent rights, if any, could be reduced or eliminated if we fail to comply with these requirements.
Periodic maintenance fees, renewal fees, annuity fees, and various other fees are required to be paid to the USPTO and foreign patent agencies in several stages over the lifetime of a patent. In certain circumstances, we rely on our collaborators or licensors to pay these fees. The USPTO and various foreign patent agencies also require compliance with a number of procedural, documentary, fee payment and other similar requirements during the patent application and prosecution process. Non-compliance events that could result in abandonment or lapse of a patent or patent application include failure to respond to official communications within prescribed time limits, non-payment of fees and failure to properly legalize and submit formal documents. While an inadvertent lapse can in some cases be cured by payment of a late fee or by other means in accordance with the applicable rules, there are situations in which non-compliance can result in irrevocable abandonment or lapse of the patent or patent application, resulting in partial or complete loss of patent rights in the relevant jurisdiction. If we or our licensors fail to maintain the patents and patent applications covering our drug candidates, our competitors might be able to enter the market with similar or identical products or technology, which would harm our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
We may become involved in lawsuits to protect or enforce our patents or other intellectual property, which could be expensive, time-consuming and unsuccessful, and issued patents directed towards our technology and drug candidates could be found invalid or unenforceable if challenged.
Competitors and other third parties may infringe or otherwise violate our issued patents or other intellectual property or the patents or other intellectual property of our licensors and collaborators. In addition, our patents or the patents of our licensors and collaborators may become involved in inventorship or priority disputes. To counter infringement or other unauthorized use, we may be required to file infringement claims, which can be expensive and time-consuming. Significantly, our pending patent applications cannot be enforced against third parties practicing the technology claimed in such applications unless and until a patent issues from such applications. Our ability to enforce patent rights also depends on our ability to detect infringement. It may be difficult to detect infringers who do not advertise the components or methods that are used in
63
Table of Contents
connection with their products and services. Moreover, it may be difficult or impossible to obtain evidence of infringement in a competitor’s or potential competitor’s product or service. Any claims we assert against perceived infringers could provoke these parties to assert counterclaims against us alleging that we infringe their patents or that our patents are invalid or unenforceable. In a patent infringement proceeding, a court may decide that a patent of ours is invalid or unenforceable, in whole or in part, construe the patent’s claims narrowly or refuse to stop the other party from using the technology at issue on the grounds that our patents do not cover the technology. An adverse result in any litigation proceeding could put one or more of our owned or licensed patents at risk of being invalidated, held unenforceable or interpreted narrowly. We may find it impractical or undesirable to enforce our intellectual property against some third parties.
If we were to initiate legal proceedings against a third party to enforce a patent directed to our drug candidates, or one of our future drug candidates, the defendant could counterclaim that our patent is invalid or unenforceable. In patent litigation in the United States, defendant counterclaims alleging invalidity or unenforceability are commonplace. Grounds for a validity challenge could be an alleged failure to meet any of several statutory requirements, including lack of novelty, obviousness, non-enablement or insufficient written description. Grounds for an unenforceability assertion could be an allegation that someone connected with prosecution of the patent withheld relevant information from the USPTO or made a misleading statement during prosecution. Third parties may also raise similar claims before the USPTO or an equivalent foreign body, even outside the context of litigation. Potential proceedings include reexamination, post-grant review, inter partes review, interference proceedings, derivation proceedings and equivalent proceedings in foreign jurisdictions (e.g., opposition proceedings). Such proceedings could result in the revocation of, cancellation of, or amendment to our patents in such a way that they no longer cover our technology or any drug candidates that we may develop. The outcome following legal assertions of invalidity and unenforceability is unpredictable. With respect to the validity question, for example, we cannot be certain that there is no invalidating prior art of which we and the patent examiner were unaware during prosecution. If a defendant were to prevail on a legal assertion of invalidity or unenforceability, we would lose at least part, and perhaps all, of the patent rights directed towards the applicable drug candidates or technology related to the patent rendered invalid or unenforceable. Such a loss of patent rights would materially harm our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
Interference proceedings provoked by third parties or brought by us or declared by the USPTO may be necessary to determine the priority of inventions with respect to our patents or patent applications. An unfavorable outcome could require us to cease using the related technology or to attempt to license rights to it from the prevailing party. Our business could be materially harmed if the prevailing party does not offer us a license on commercially reasonable terms.
Furthermore, because of the substantial amount of discovery required in connection with intellectual property litigation, there is a risk that some of our confidential information could be compromised by disclosure during this type of litigation.
Some of our competitors are larger than we are and have substantially greater resources. They are, therefore, likely to be able to sustain the costs of complex patent litigation or proceedings more effectively than we can because of their greater financial resources and more mature and developed intellectual property portfolios. Accordingly, despite our efforts, we may not be able to prevent third parties from infringing, misappropriating or otherwise violating our intellectual property. Even if resolved in our favor, litigation or other legal proceedings relating to intellectual property claims could result in substantial costs and diversion of management resources, which could harm our business. In addition, the uncertainties associated with litigation could compromise our ability to raise the funds necessary to continue our clinical trials, continue our internal research programs, or in-license needed technology or other drug candidates. There could also be public announcements of the results of the hearing, motions, or other interim proceedings or developments. If
64
Table of Contents
securities analysts or investors perceive those results to be negative, it could cause the price of shares of our common stock to decline. Any of the foregoing events could harm our business, financial condition, results of operation and prospects.
Third parties may initiate legal proceedings alleging that we are infringing, misappropriating or otherwise violating their intellectual property rights, the outcome of which would be uncertain and could negatively impact the success of our business.
Our commercial success depends upon our ability to develop, manufacture, market and sell our drug candidates and use our proprietary technologies without infringing, misappropriating or otherwise violating the intellectual property and other proprietary rights of third parties. There is considerable intellectual property litigation in the pharmaceutical industry. We may become party to, or threatened with, future adversarial proceedings or litigation regarding intellectual property rights with respect to our drug candidates and their manufacture and our other technology, including reexamination, interference, post-grant review, inter partes review or derivation proceedings before the USPTO or an equivalent foreign body. Numerous U.S.- and foreign-issued patents and pending patent applications owned by third parties exist in the fields in which we are developing our drug candidates. Third parties may assert infringement claims against us based on existing patents or patents that may be granted in the future, regardless of their merit.
Even if we believe third-party intellectual property claims are without merit, there is no assurance that a court would find in our favor on questions of claim scope, infringement, validity, enforceability or priority. A court of competent jurisdiction could hold that third-party patents asserted against us are valid, enforceable and infringed, which could materially and adversely affect our ability to commercialize any drug candidates we may develop and any other drug candidates or technologies covered by the asserted third-party patents. In order to successfully challenge the validity of any such U.S. patent in federal court, we would need to overcome a presumption of validity. As this burden is a high one requiring us to present clear and convincing evidence as to the invalidity of any such U.S. patent claim, there is no assurance that a court of competent jurisdiction would invalidate the claims of any such U.S. patent. If we are found to infringe, misappropriate or otherwise violate a third party’s intellectual property rights, and we are unsuccessful in demonstrating that such rights are invalid or unenforceable, we could be required to obtain a license from such a third party in order to continue developing and marketing our products and technology. However, we may not be able to obtain any required license on commercially reasonable terms or at all. Even if we were able to obtain a license, it could be or may become non-exclusive, thereby giving our competitors access to the same technologies licensed to us. We could be forced, including by court order, to cease commercializing the infringing technology or product. A finding of infringement could prevent us from commercializing our drug candidates or force us to cease some of our business operations. In the event of a successful claim of infringement against us, we may have to pay substantial damages, including treble damages and attorneys’ fees for willful infringement, pay royalties and other fees, redesign our infringing drug candidate or obtain one or more licenses from third parties, which may be impossible or require substantial time and monetary expenditure. Claims that we have misappropriated the confidential information or trade secrets of third parties could have a similar negative impact on our business. Any of the foregoing events would harm our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
We may be subject to claims by third parties asserting that we or our employees have infringed, misappropriated or otherwise violated their intellectual property rights, or claiming ownership of what we regard as our own intellectual property.
Many of our employees were previously employed at other biotechnology or pharmaceutical companies. Although we try to ensure that our employees, consultants and advisors do not use the proprietary information or know-how of others in their work for us, we may be subject to claims that we or these individuals have used or disclosed intellectual property, including trade secrets or other proprietary information, of any such
65
Table of Contents
individual’s former employer. We may also be subject to claims that patents and applications we have filed to protect inventions made on our behalf by our employees, consultants and advisors, even those related to one or more of our drug candidates, are rightfully owned by their former or concurrent employer. Litigation may be necessary to defend against these claims.
If we fail in prosecuting or defending any such claims, in addition to paying monetary damages, we may lose valuable intellectual property rights or personnel. Even if we are successful in prosecuting or defending against such claims, litigation could result in substantial costs, delay development of our drug candidates and be a distraction to management. Any of the foregoing events would harm our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
We may be subject to claims challenging the inventorship of our patents and other intellectual property.
We or our licensors may be subject to claims that former employees, collaborators or other third parties have an interest in our owned or in-licensed patents, trade secrets, or other intellectual property as an inventor or co-inventor. For example, we or our licensors or collaborators may have inventorship disputes arising from conflicting obligations of employees, consultants or others who are involved in developing our drug candidates. While it is our policy to require our employees and contractors who may be involved in the development of intellectual property to execute agreements assigning such intellectual property to us, we may be unsuccessful in executing such an agreement with each party who in fact develops intellectual property that we regard as our own. Our and their assignment agreements may not be self-executing or may be breached, and litigation may be necessary to defend against these and other claims challenging inventorship or our or our licensors’ or collaborators’ ownership of our owned or in-licensed patents, trade secrets or other intellectual property. If we or our licensors or collaborators fail in defending any such claims, in addition to paying monetary damages, we may lose valuable intellectual property rights, such as exclusive ownership of, or right to use, intellectual property that is important to our drug candidates. Even if we are successful in defending against such claims, litigation could result in substantial costs and be a distraction to management and other employees. Any of the foregoing could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
Intellectual property litigation could cause us to spend substantial resources and distract our personnel from their normal responsibilities.
Even if resolved in our favor, litigation or other legal proceedings relating to intellectual property claims may cause us to incur significant expenses, and could distract our technical and management personnel from their normal responsibilities. In addition, there could be public announcements of the results of hearings, motions or other interim proceedings or developments, and if securities analysts or investors perceive these results to be negative, it could have a substantial adverse effect on the price of our common stock. Such litigation or proceedings could substantially increase our operating losses and reduce the resources available for development activities or any future sales, marketing or distribution activities. We may not have sufficient financial or other resources to conduct such litigation or proceedings adequately. As noted above, some of our competitors may be able to sustain the costs of such litigation or proceedings more effectively than we can because of their greater financial resources. Uncertainties resulting from the initiation and continuation of patent litigation or other proceedings could compromise our ability to compete in the marketplace, including compromising our ability to raise the funds necessary to continue our clinical trials, continue our research programs, license necessary technology from third parties, or enter into development collaborations that would help us commercialize our drug candidates, if approved. Any of the foregoing events would harm our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
66
Table of Contents
If we are unable to protect the confidentiality of our trade secrets, our business and competitive position would be harmed.
We rely on confidential methodologies and processes and confidentiality agreements to protect our unpatented know-how, technology and other proprietary information and to maintain our competitive position. Trade secrets and know-how can be difficult to protect. We seek to protect these trade secrets and other proprietary technology, in part, by entering into non-disclosure and confidentiality agreements with parties who have access to them, such as our employees, licensors, collaborators, CROs, contract manufacturers, consultants, advisors and other third parties. We also enter into confidentiality and invention or patent assignment agreements with our employees and consultants. We cannot guarantee that we have entered into such agreements with each party that may have or has had access to our trade secrets or proprietary technology and processes. Despite these efforts, any of these parties may breach the agreements and disclose our proprietary information, including our trade secrets, and we may not be able to obtain adequate remedies for such breaches. Unauthorized parties may also attempt to copy or reverse engineer certain aspects of our drug candidates that we consider proprietary. Monitoring unauthorized uses and disclosures is difficult, and we do not know whether the steps we have taken to protect our proprietary information will be effective.
We also seek to preserve the integrity and confidentiality of our confidential proprietary information by maintaining physical security of our premises and physical and electronic security of our information technology systems, but it is possible that these security measures could be breached. Enforcing a claim that a party illegally disclosed or misappropriated a trade secret is difficult, expensive and time-consuming, and the outcome is unpredictable. In addition, some courts inside and outside the United States are less willing or unwilling to protect trade secrets. If any of our trade secrets were to be lawfully obtained or independently developed by a competitor or other third party, we would have no right to prevent them from using that technology or information to compete with us. If any of our trade secrets were to be disclosed to or independently developed by a competitor or other third party, our competitive position would be materially and adversely harmed.
If our trademarks and trade names are not adequately protected, then we may not be able to build name recognition in our markets of interest and our business may be adversely affected.
Our registered or unregistered trademarks or trade names may be challenged, infringed, circumvented or declared generic or determined to be infringing other marks. We may not be able to protect our rights to these trademarks and trade names, which we need to build name recognition among potential collaborators or customers in our markets of interest. At times, competitors may adopt trade names or trademarks similar to ours, thereby impeding our ability to build brand identity and possibly leading to market confusion. In addition, there could be potential trade name or trademark infringement claims brought by owners of other trademarks or trademarks that incorporate variations of our registered or unregistered trademarks or trade names. Over the long term, if we are unable to establish name recognition based on our trademarks and trade names, then we may not be able to compete effectively and our business may be adversely affected. Further, we may license our trademarks and trade names to third parties, such as distributors. Though these license agreements may provide guidelines for how our trademarks and trade names may be used, a breach of these agreements or misuse of our trademarks and tradenames by our licensees may jeopardize our rights in or diminish the goodwill associated with our trademarks and trade names. Our efforts to enforce or protect our proprietary rights related to trademarks, trade names, trade secrets, domain names, copyrights or other intellectual property may be ineffective and could result in substantial costs and diversion of resources and could adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
67
Table of Contents
Intellectual property rights do not necessarily address all potential threats.
The degree of future protection, if any, afforded by our intellectual property rights is uncertain because intellectual property rights have limitations and may not adequately protect our business or permit us to maintain our competitive advantage. For example:
| • | others may be able to make products that are similar to any drug candidates we may develop or utilize similar technology but that are not covered by the claims of the patents that we license or may own in the future; |
| • | we, or our current or future licensors or collaborators might not have been the first to make the inventions covered by the issued patent or pending patent application that we license or may own in the future; |
| • | we, or our current or future licensors or collaborators might not have been the first to file patent applications covering certain of our or their inventions; |
| • | others may independently develop similar or alternative technologies or duplicate any of our technologies without infringing our owned or licensed intellectual property rights; |
| • | it is possible that our pending owned or licensed patent applications or those that we may own or license in the future will not lead to issued patents; |
| • | issued patents that we hold rights to may be held invalid or unenforceable, including as a result of legal challenges by our competitors; |
| • | our competitors might conduct research and development activities in countries where we do not have patent rights and then use the information learned from such activities to develop competitive products for sale in our major commercial markets; |
| • | we may not develop additional proprietary technologies that are patentable; |
| • | the intellectual property rights of others may harm our business; and |
| • | we may choose not to file a patent in order to maintain certain trade secrets or know-how, and a third party may subsequently file a patent directed to such intellectual property. |
Should any of these events occur, they could harm our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
Risks related to employee matters, managing our growth and other risks related to our business
We are highly dependent on our key personnel, and if we are not successful in attracting, motivating and retaining highly qualified personnel, we may not be able to successfully implement our business strategy.
We are highly dependent on our management, scientific and medical personnel, including our Chief Executive Officer, Dr. Blatt, and our President, Dr. Beigelman. The loss of the services of any of them may adversely impact the achievement of our objectives. Any of our executive officers could leave our employment at any time, as all of our employees are “at-will” employees. We currently do not have “key person” insurance on any of our employees.
Recruiting and retaining qualified employees, consultants and advisors for our business, including scientific and technical personnel, also will be critical to our success. Competition for skilled personnel is intense and the turnover rate can be high. We may not be able to attract and retain personnel on acceptable terms given the
68
Table of Contents
competition among numerous pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies and academic institutions for skilled individuals. In addition, failure to succeed in nonclinical studies, clinical trials or applications for marketing approval may make it more challenging to recruit and retain qualified personnel. The inability to recruit, or the loss of services of certain executives, significant employees, consultants or advisors, may impede the progress of our research, development and commercialization objectives and have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
We currently have no sales organization. If we are unable to establish sales capabilities on our own or through third parties, we may not be able to market and sell any products effectively, if approved, or generate product revenue.
We currently do not have a marketing or sales organization. In order to commercialize any product, if approved, in the United States and foreign jurisdictions, we must build our marketing, sales, distribution, managerial and other non-technical capabilities or make arrangements with third parties to perform these services, and we may not be successful in doing so. In advance of any of our drug candidates receiving regulatory approval, we expect to establish a sales organization with technical expertise and supporting distribution capabilities to commercialize each such drug candidate, which will be expensive and time-consuming. We have no prior experience in the marketing, sale and distribution of pharmaceutical products, and there are significant risks involved in building and managing a sales organization, including our ability to hire, retain, and incentivize qualified individuals, generate sufficient sales leads, provide adequate training to sales and marketing personnel, and effectively manage a geographically dispersed sales and marketing team. Any failure or delay in the development of our internal sales, marketing and distribution capabilities would adversely impact the commercialization of our drug candidates. We may choose to collaborate with third parties that have direct sales forces and established distribution systems, either to augment our own sales force and distribution systems or in lieu of our own sales force and distribution systems. If we are unable to enter into such arrangements on acceptable terms or at all, we may not be able to successfully commercialize our drug candidates. If we are not successful in commercializing products, either on our own or through arrangements with one or more third parties, we may not be able to generate any future product revenue and we would incur significant additional losses.
We will need to grow the size of our organization, and we may experience difficulties in managing this growth.
As of June 30, 2020, we had 67 full-time employees, including 55 employees engaged in research and development. As our development and commercialization plans and strategies develop, and as we transition into operating as a public company, we expect to need additional managerial, operational, sales, marketing, financial and other personnel. Future growth would impose significant added responsibilities on members of management, including:
| • | identifying, recruiting, integrating, maintaining and motivating additional employees; |
| • | managing our internal development efforts effectively, including the clinical and FDA review process for our current drug candidates and any other drug candidate we develop, while complying with our contractual obligations to contractors and other third parties; and |
| • | expanding and enhancing our operational, financial and management controls, reporting systems and procedures. |
Our future financial performance and our ability to advance development of and, if approved, commercialize our current drug candidates and any other drug candidate we develop will depend, in part, on our ability to effectively manage any future growth, and our management may also have to divert a disproportionate amount of its attention away from day-to-day activities in order to devote a substantial amount of time to managing these growth activities.
69
Table of Contents
We currently rely, and for the foreseeable future will continue to rely, in substantial part on certain independent organizations, advisors and consultants to provide certain services, including substantially all aspects of marketing, clinical management, and manufacturing. We cannot assure you that the services of independent organizations, advisors and consultants will continue to be available to us on a timely basis when needed or at a reasonable cost, or that we can find qualified replacements. In addition, if we are unable to effectively manage our outsourced activities or if the quality or accuracy of the services provided by consultants is compromised for any reason, our nonclinical studies and clinical trials may be extended, delayed or terminated, and we may not be able to obtain marketing approval of any current or future drug candidates or otherwise advance our business. We cannot assure you that we will be able to manage our existing consultants or find other competent outside contractors and consultants on economically reasonable terms, or at all.
If we are not able to effectively expand our organization by hiring new employees and expanding our groups of consultants and contractors, we may experience delays or may not be able to successfully implement the tasks necessary to further develop and commercialize our current drug candidates and any future drug candidates we develop and, accordingly, may not achieve our research, development and commercialization goals.
We may in the future engage in strategic transactions; such transactions could affect our liquidity, dilute our existing stockholders, increase our expenses and present significant challenges in focus and energy to our management or prove not to be successful.
From time to time, we may consider strategic transactions, such as acquisitions of companies, asset purchases and out-licensing or in-licensing of intellectual property, products or technologies.
Such potential transactions that we may consider in the future include a variety of business arrangements, including spin-offs, strategic partnerships, joint ventures, restructurings, divestitures, business combinations, investments and licensings. Any future transactions could result in potentially dilutive issuances of our equity securities, including our common stock, or the incurrence of debt, contingent liabilities, amortization expenses or acquired in-process research and development expenses, any of which could affect our financial condition, liquidity and results of operations. Future acquisitions may also require us to obtain additional financing, which may not be available on favorable terms or at all. These transactions may never be successful and may require significant time and attention of management. In addition, the integration of any business that we may acquire in the future may disrupt our existing business and may be a complex, risky and costly endeavor for which we may never realize the full benefits of the acquisition.
If we fail to comply with environmental, health and safety laws and regulations, we could become subject to fines or penalties or incur costs that could have a material adverse effect on the success of our business.
We are subject to numerous environmental, health and safety laws and regulations, including those governing laboratory procedures and the handling, use, storage, treatment and disposal of hazardous materials and wastes. Our operations involve the use of hazardous and flammable materials, including chemicals and biological and radioactive materials. Our operations also produce hazardous waste products. We cannot eliminate the risk of contamination or injury from these materials, and we generally contract with third parties for the disposal of these materials and wastes. In the event of contamination or injury resulting from our use or third-party disposal of hazardous materials, we could be held liable for any resulting damages, and any liability could exceed our resources. We also could incur significant costs associated with civil or criminal fines and penalties.
Although we maintain workers’ compensation insurance to cover us for costs and expenses we may incur due to injuries to our employees resulting from the use of hazardous materials, this insurance may not provide adequate coverage against potential liabilities. We do not maintain insurance for environmental liability or toxic tort claims that may be asserted against us in connection with our storage or disposal of biological, hazardous
70
Table of Contents
or radioactive materials, and as such we would have to pay the full amount of any resultant liability out of pocket, which could significantly impair our financial condition.
We or the third parties upon whom we depend may be adversely affected by earthquakes or other natural disasters and our business continuity and disaster recovery plans may not adequately protect us from a serious disaster.
Our corporate headquarters and other facilities are located in the San Francisco Bay Area, which in the past has experienced both severe earthquakes and wildfires. We are also conducting our initial clinical trials for ALG-010133 in New Zealand, an area also known for earthquakes. We do not carry earthquake insurance, and as such we would have to pay the full amount of any resultant liability out of pocket, which could significantly impair our financial condition. In addition, earthquakes, wildfires or other natural disasters could severely disrupt our operations. If a natural disaster, power outage or other event occurred that prevented us from using all or a significant portion of our headquarters, that damaged critical infrastructure, such as our enterprise financial systems or manufacturing resource planning and enterprise quality systems, that delayed our clinical trials, or that otherwise disrupted operations, it may be difficult or, in certain cases, impossible, for us to continue our business for a substantial period of time. The disaster recovery and business continuity plans we have in place currently are limited and are unlikely to prove adequate in the event of a serious disaster or similar event. We may incur substantial expenses as a result of the limited nature of our disaster recovery and business continuity plans, which, particularly when taken together with our lack of earthquake insurance, could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and prospects. Furthermore, integral parties in our supply chain are similarly vulnerable to natural disasters or other sudden, unforeseen and severe adverse events. If such an event were to affect our supply chain, it could have a material adverse effect on our business.
Public health pandemics or epidemics, political instability, terrorist attacks, other acts of violence or war, or other unexpected events could materially and adversely impact us.
Public health pandemics or epidemics, political instability, terrorist attacks, other acts of violence or war or other unexpected events could materially interrupt our business operations (or those of the third parties upon whom we depend), cause consumer confidence and spending to decrease or result in increased volatility in the United States and worldwide financial markets and economy. They also could result in or prolong an economic recession in the United States. Any of these occurrences could materially and adversely affect us.
Our employees, independent contractors, vendors, principal investigators, CROs and consultants may engage in misconduct or other improper activities, including non-compliance with regulatory standards and requirements and insider trading.
We are exposed to the risk that our employees, independent contractors, vendors, principal investigators, CROs and consultants may engage in fraudulent conduct or other illegal activity. Misconduct by these parties could include intentional, reckless and/or negligent conduct or disclosure of unauthorized activities to us that violate the regulations of the FDA and comparable foreign regulatory authorities, including those laws requiring the reporting of true, complete and accurate information to such authorities; healthcare fraud and abuse laws and regulations in the United States and abroad; or laws that require the reporting of financial information or data accurately. In particular, sales, marketing and business arrangements in the healthcare industry are subject to extensive laws and regulations intended to prevent fraud, misconduct, kickbacks, self-dealing and other abusive practices. These laws and regulations may restrict or prohibit a wide range of pricing, discounting, marketing and promotion, sales commission, customer incentive programs and other business arrangements. Activities subject to these laws also involve the improper use of information obtained in the course of clinical trials or creating fraudulent data in our nonclinical studies or clinical trials, which could result in regulatory sanctions
71
Table of Contents
and cause serious harm to our reputation. It is not always possible to identify and deter misconduct by employees and other third parties, and the precautions we take to detect and prevent this activity may not be effective in controlling unknown or unmanaged risks or losses or in protecting us from governmental investigations or other actions or lawsuits stemming from a failure to comply with these laws or regulations. Additionally, we are subject to the risk that a person could allege such fraud or other misconduct, even if none occurred. If any such actions are instituted against us, and we are not successful in defending ourselves or asserting our rights, those actions could have a significant impact on our business, including the imposition of civil, criminal and administrative penalties, damages, monetary fines, possible exclusion from participation in Medicare, Medicaid and other federal healthcare programs, contractual damages, reputational harm, diminished profits and future earnings, and curtailment of our operations, any of which could adversely affect our ability to operate our business and our results of operations.
Current or future litigation or administrative proceedings could have a material adverse effect on our business, our financial condition and our results of operations.
We may be involved in legal proceedings, administrative proceedings, claims, and other litigation that arise in the ordinary course of business. Unfavorable outcomes or developments relating to proceedings to which we are a party or transactions involving our current or future drug candidates, such as judgments for monetary damages, injunctions, or denial or revocation of permits, could have a material adverse effect on our business, our financial condition, and our results of operations. In addition, settlement of claims could adversely affect our financial condition and our results of operations.
Risks related to our common stock and this offering
If you purchase our common stock in this offering, you will incur immediate and substantial dilution in the book value of your shares.
The initial public offering price of our common stock will be substantially higher than the pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value per share of our common stock. Therefore, if you purchase our common stock in this offering, you will pay a price per share that substantially exceeds the pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value per share after the completion of this offering. Based on an assumed initial public offering price of $15.00 per share, which is the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, you will experience immediate dilution of $8.02 per share. As a result of this dilution, investors purchasing stock in this offering may receive significantly less than the full purchase price that they paid for the shares purchased in this offering in the event of a liquidation. In addition, investors purchasing common stock in this offering will contribute 39.7% of the total amount invested by stockholders since inception, but will own only 27.1% of our common stock outstanding after this offering. In the past, we issued options and other securities to acquire common stock at prices significantly below the initial public offering price. To the extent these outstanding securities are ultimately exercised, investors purchasing common stock in this offering will incur further dilution. See “Dilution” for a more detailed description of the dilution to new investors in the offering.
72
Table of Contents
The price of our common stock may be volatile and fluctuate substantially, which could result in substantial losses for purchasers of our common stock in this offering.
Our stock price is likely to be volatile. The stock market in general and the market for biopharmaceutical companies in particular have experienced extreme volatility that has often been unrelated to the operating performance of particular companies. The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, for example, has negatively affected the stock market and investor sentiment and has resulted in significant volatility. As a result of this volatility, you may not be able to sell your common stock at or above the initial public offering price. The market price for our common stock may be influenced by many factors, including:
| • | the success of our and competitive products or technologies; |
| • | results of clinical trials and nonclinical studies or those of our competitors; |
| • | regulatory or legal developments in the United States and other countries; |
| • | developments or disputes concerning patent applications, issued patents or other proprietary rights; |
| • | the recruitment or departure of key personnel; |
| • | the level of expenses related to our drug candidates or clinical development programs; |
| • | the results of our efforts to discover, develop, acquire or in-license drug candidates; |
| • | actual or anticipated changes in estimates as to financial results, development timelines or recommendations by securities analysts; |
| • | variations in our financial results or those of companies that are perceived to be similar to us; |
| • | changes in the structure of healthcare payment systems; |
| • | market conditions in the pharmaceutical and biotechnology sectors; |
| • | general economic, political, and market conditions and overall fluctuations in the financial markets in the United States and abroad; |
| • | the COVID-19 pandemic; and |
| • | investors’ general perception of us and our business. |
These and other market and industry factors may cause the market price and demand for our common stock to fluctuate substantially, regardless of our actual operating performance, which may limit or prevent investors from selling their shares at or above the price paid for the shares and may otherwise negatively affect the liquidity of our common stock.
Some companies that have experienced volatility in the trading price of their shares have been the subject of securities class action litigation. Any lawsuit to which we are a party, with or without merit, may result in an unfavorable judgment. We also may decide to settle lawsuits on unfavorable terms. Any such negative outcome could result in payments of substantial damages or fines, damage to our reputation or adverse changes to our business practices. Defending against litigation is costly and time-consuming, and could divert our management’s attention and our resources. Furthermore, during the course of litigation, there could be negative public announcements of the results of hearings, motions or other interim proceedings or developments, which could have a further negative effect on the market price of our common stock.
73
Table of Contents
An active trading market for our common stock may not develop, and you may not be able to resell your shares at or above the initial public offering price.
Prior to this offering, there has been no public market for shares of our common stock and an active trading market for our shares may never develop or be sustained following this offering. The initial public offering price of our common stock will be determined through negotiations between us and the underwriters. This initial public offering price may not be indicative of the market price of our common stock after this offering. In the absence of an active trading market for our common stock, investors may not be able to sell their common stock at or above the initial public offering price or at the time that they would like to sell.
We do not intend to pay dividends on our common stock so any returns will be limited to the value of our stock.
We do not currently intend to pay any cash dividends on our common stock for the foreseeable future. We currently intend to invest our future earnings, if any, to fund our growth. Therefore, you are not likely to receive any dividends on your common stock for the foreseeable future. Since we do not intend to pay dividends, your ability to receive a return on your investment will depend on any future appreciation in the market value of our common stock. There is no guarantee that our common stock will appreciate or even maintain the price at which you purchase it.
We are an emerging growth company and a smaller reporting company, and we cannot be certain if the reduced reporting requirements applicable to emerging growth companies and smaller reporting companies will make our common stock less attractive to investors.
We are an emerging growth company, as defined in the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act of 2012 (the “JOBS Act”). For as long as we continue to be an emerging growth company, we may take advantage of exemptions from various reporting requirements that are applicable to other public companies that are not emerging growth companies, including the auditor attestation requirements of Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, certain disclosure obligations regarding executive compensation in this prospectus and our periodic reports and proxy statements and the requirements of holding nonbinding advisory votes on executive compensation and stockholder approval of any golden parachute payments not previously approved. We could be an emerging growth company for up to five years following the year in which we complete this offering, although circumstances could cause us to lose that status earlier. We will remain an emerging growth company until the earlier of (1) the last day of the fiscal year (a) following the fifth anniversary of the completion of this offering, (b) in which we have total annual gross revenue of at least $1.07 billion or (c) in which we are deemed to be a large accelerated filer, which requires the market value of our common stock that is held by non-affiliates to exceed $700.0 million as of the prior June 30th, and (2) the date on which we have issued more than $1.0 billion in non-convertible debt during the prior three-year period.
Under the JOBS Act, emerging growth companies can also delay adopting new or revised accounting standards until such time as those standards apply to private companies. We have elected to use the extended transition period for any other new or revised accounting standards during the period in which we remain an emerging growth company; however, we may adopt certain new or revised accounting standards early. As a result, changes in rules of U.S. generally accepted accounting principles or their interpretation, the adoption of new guidance or the application of existing guidance to changes in our business could significantly affect our financial position and results of operations.
Even after we no longer qualify as an emerging growth company, we may continue to qualify as a smaller reporting company, which would allow us to rely on certain reduced disclosure requirements, such as an exemption from providing selected financial data and executive compensation information. We are also exempt from the requirement to obtain an external audit on the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting provided in Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act. These exemptions and reduced disclosures in
74
Table of Contents
this prospectus and our periodic reports and proxy statements due to our status as a smaller reporting company mean that our auditors do not review our internal controls over financial reporting and may make it harder for investors to analyze our results of operations and financial prospects.
We cannot predict if investors will find our common stock less attractive because we may rely on these exemptions as an emerging growth company and a smaller reporting company. If some investors find our common stock less attractive as a result, there may be a less active trading market for our common stock and our stock price may be more volatile.
Our executive officers, directors and their affiliates will continue to exercise significant influence over our company after this offering, which will limit your ability to influence corporate matters and could delay or prevent a change in corporate control.
Based upon the number of shares of common stock, on an as-converted basis, outstanding as of October 6, 2020, immediately following the completion of this offering, our executive officers, directors and their affiliates will beneficially own, in the aggregate, approximately 45.4% of our outstanding common stock (assuming all shares of non-voting common stock are converted into voting common stock in accordance with the terms of our amended and restated certificate of incorporation), assuming the sale by us of 10,000,000 shares of common stock in this offering, based on an assumed initial public offering price of $15.00 per share, which is the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover page of this prospectus. As a result, these stockholders, if they act together, will be able to influence our management and affairs and the outcome of matters submitted to our stockholders for approval, including the election of directors and any sale, merger, consolidation or sale of all or substantially all of our assets. These stockholders acquired their shares of common stock for substantially less than the price of the shares of common stock sold in this offering, and these stockholders may have interests, with respect to their common stock, that are different from those of investors purchasing shares of our common stock in this offering, and the concentration of voting power among these stockholders may have an adverse effect on the price of our common stock. In addition, this concentration of ownership might adversely affect the market price of our common stock by:
| • | delaying, deferring or preventing a change of control of us; |
| • | impeding a merger, consolidation, takeover or other business combination involving us; or |
| • | discouraging a potential acquirer from making a tender offer or otherwise attempting to obtain control of us. |
See “Principal stockholders” in this prospectus for more information regarding the ownership of our outstanding common stock by our executive officers, directors and their affiliates.
We have broad discretion in how we use the proceeds of this offering and may not use these proceeds effectively, which could affect our results of operations and cause our stock price to decline.
We will have considerable discretion in the application of the net proceeds from this offering. As a result, investors will be relying upon management’s judgment with only limited information about our specific intentions for the use of the net proceeds from this offering. We may use the net proceeds from this offering for purposes that do not yield a significant return or any return at all for our stockholders. In addition, pending their use, we may invest the net proceeds from this offering in a manner that does not produce income or that loses value.
We will incur significantly increased costs as a result of operating as a public company, and our management will be required to devote substantial time to new compliance initiatives and corporate governance practices.
As a public company, and particularly after we are no longer an emerging growth company or a smaller reporting company, we will incur significant legal, accounting and other expenses that we did not incur as a
75
Table of Contents
private company. We will be subject to the reporting requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”), which will require, among other things, that we file with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”), annual, quarterly and current reports with respect to our business and financial condition. In addition, the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, as well as rules subsequently adopted by the SEC and Nasdaq to implement provisions of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, impose significant requirements on public companies, including requiring establishment and maintenance of effective disclosure and financial controls and changes in corporate governance practices. Further, in July 2010, the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act (the “Dodd-Frank Act”) was enacted. There are significant corporate governance and executive compensation-related provisions in the Dodd-Frank Act that require the SEC to adopt additional rules and regulations in these areas, such as “say on pay” and proxy access. Recent legislation permits emerging growth companies to implement many of these requirements over a longer period and up to five years from the pricing of this offering. We intend to take advantage of this legislation, but cannot guarantee that we will not be required to implement these requirements sooner than budgeted or planned and thereby incur unexpected expenses. Stockholder activism, the current political environment and the current high level of government intervention and regulatory reform may lead to substantial new regulations and disclosure obligations, which may lead to additional compliance costs and impact the manner in which we operate our business in ways we cannot currently anticipate.
We expect the rules and regulations applicable to public companies to substantially increase our legal and financial compliance costs and to make some activities more time-consuming and costly. If these requirements divert the attention of our management and personnel from other business concerns, they could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects. The increased costs will decrease our net income or increase our net loss, and may require us to reduce costs in other areas of our business or increase the prices of our products or services (if approved). For example, we expect these rules and regulations to make it more difficult and more expensive for us to obtain director and officer liability insurance and we may be required to incur substantial costs to maintain the same or similar coverage. We cannot predict or estimate the amount or timing of additional costs we may incur to respond to these requirements. The impact of these requirements could also make it more difficult for us to attract and retain qualified persons to serve on our board of directors, our board committees or as executive officers.
The dual class structure of our common stock may limit your ability to influence corporate matters and may limit your visibility with respect to certain transactions.
The dual class structure of our common stock may limit your ability to influence corporate matters. Holders of our common stock are entitled to one vote per share, while holders of our non-voting common stock are not entitled to any votes. Nonetheless, each share of our non-voting common stock may be converted at any time into one share of our common stock at the option of its holder by providing written notice to us, subject to the limitations provided for in our amended and restated certificate of incorporation to become effective upon the completion of this offering. Immediately following this offering, entities affiliated with or managed by Baker Brothers Life Sciences, L.P. will hold an aggregate of 3,092,338 shares of our non-voting common stock. At any time following completion of this offering, upon written notice, these entities could convert a portion of these shares of non-voting common stock into up to an aggregate of 4.99% of our shares of common stock. Upon 61 days’ prior written notice, these entities could convert all of their respective shares of non-voting common stock into shares of common stock, which would result in such entities holding approximately 8.4% of the voting power of our outstanding common stock following the completion of this offering (excluding any shares acquired by such entities in this offering). See “Description of capital stock—Common stock and non-voting common stock.” Consequently, the exercise by holders of our non-voting common stock following this offering of their option to make this conversion will have the effect of increasing the relative voting power of such holders, and correspondingly decreasing the voting power of the holders of our common stock, which may limit
76
Table of Contents
your ability to influence corporate matters. Additionally, stockholders who hold, in the aggregate, more than 10% of our common stock and non-voting common stock, but 10% or less of our common stock, and are not otherwise a company insider, may not be required to report changes in their ownership due to transactions in our non-voting common stock pursuant to Section 16(a) of the Exchange Act, and may not be subject to the short-swing profit provisions of Section 16(b) of the Exchange Act.
Sales of a substantial number of shares of our common stock in the public market could cause our stock price to fall.
If our existing stockholders sell, or indicate an intention to sell, or if the market perceives that such existing stockholders might sell, substantial amounts of our common stock in the public market after the lock-up and other legal restrictions on resale discussed in this prospectus lapse, the market price of our common stock could decline. Based upon the number of shares of common stock, on an as-converted basis, outstanding as of October 6, 2020, upon the completion of this offering, we will have outstanding 36,857,845 shares of total common stock and non-voting common stock (of which 3,092,338 shares will be non-voting common shares), assuming no exercise of the underwriters’ option to purchase an additional 1,500,000 shares and no exercise of outstanding options after October 6, 2020. Of these shares, as of the date of this prospectus, approximately 10,000,000 shares of our common stock, or 27.1% of shares of our common stock, plus any shares sold upon exercise of the underwriters’ option to purchase additional shares, will be freely tradable, without restriction, in the public market immediately following this offering, assuming that current stockholders and affiliates do not purchase shares in this offering.
The lock-up agreements with the underwriters pertaining to this offering will expire 180 days from the date of this prospectus. J.P. Morgan Securities LLC, Jefferies LLC and Piper Sandler & Co., in their sole discretion, may permit our equityholders who are subject to these lock-up agreements to sell shares prior to the expiration of the lock-up agreements. After the lock-up agreements expire, based upon the number of shares of common stock, on an as-converted basis, outstanding as of October 6, 2020, up to an additional 26,857,845 shares of common stock will be eligible for sale in the public market (including 3,092,338 shares of common stock issuable upon the conversion of 3,092,338 shares of non-voting common stock). Approximately 13.9% of these additional shares are owned by directors, executive officers and other affiliates and will be subject to certain limitations of Rule 144 under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”).
Upon completion of this offering, 7,042,356 shares of common stock that are either subject to outstanding options or reserved for future issuance under our equity incentive plans will become eligible for sale in the public market to the extent permitted by the provisions of various vesting schedules, the lock-up agreements and Rule 144 and Rule 701 under the Securities Act. If these additional shares of common stock are sold, or if it is perceived that they will be sold, in the public market, the market price of our common stock could decline.
After this offering, the holders of approximately 23.2 million of our total common stock and non-voting common stock (including 3,092,338 shares of non-voting common stock), including those issuable upon the conversion of our preferred stock, will be entitled to rights with respect to the registration of their shares under the Securities Act, subject to the lock-up agreements described above. Registration of these shares under the Securities Act would result in the shares becoming freely tradable without restriction under the Securities Act, except for shares purchased by affiliates. Any sales of securities by these stockholders could have a material adverse effect on the market price of our common stock.
Our ability to utilize our net operating loss carryforwards and certain other tax attributes may have been limited by “ownership changes” and may be further limited.
Under Sections 382 and 383 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended (the “Code”), and corresponding provisions of state law, if a corporation undergoes an “ownership change” (generally defined as a greater than
77
Table of Contents
50 percentage point change (by value) in its equity ownership over a rolling three-year period), the corporation’s ability to use its pre-change net operating loss carryforwards and other pre-change tax attributes to offset its post-change income may be limited. We may have experienced, and we may in the future experience, ownership changes, either as a result of this offering or other changes in our stock ownership (some of which are not in our control). For these reasons, our ability to utilize our NOL carryforwards and other tax attributes to reduce future tax liabilities may be limited.
We may experience fluctuations in our tax obligations and effective tax rate, which could materially and adversely affect our results of operations.
We are subject to U.S. federal and state income taxes and taxes in certain other non-U.S. jurisdictions. Tax laws, regulations and administrative practices in various jurisdictions may be subject to significant change, with or without advance notice, due to economic, political and other conditions, and significant judgment is required in evaluating and estimating our provision and accruals for these taxes. There are many transactions that occur during the ordinary course of business for which the ultimate tax determination is uncertain. Our effective tax rates could be affected by numerous factors, such as changes in tax, accounting and other laws, regulations, administrative practices, principles and interpretations, the mix and level of earnings in a given taxing jurisdiction or our ownership or capital structures.
If we sell shares of our common stock in future financings, stockholders may experience immediate dilution and, as a result, our stock price may decline.
We may from time to time issue additional shares of common stock at a discount from the current trading price of our common stock. As a result, our stockholders would experience immediate dilution upon the purchase of any shares of our common stock sold at such discount. In addition, as opportunities present themselves, we may enter into financing or similar arrangements in the future, including the issuance of debt securities, preferred stock or common stock. If we issue common stock or securities convertible into common stock, our common stockholders would experience additional dilution and, as a result, our stock price may decline.
If securities analysts do not publish research or reports about our business or if they publish negative evaluations of our stock, the price of our stock could decline.
The trading market for our common stock will rely, in part, on the research and reports that industry or financial analysts publish about us or our business. We may never obtain research coverage by industry or financial analysts. If no or few analysts commence coverage of us, the trading price of our stock would likely decrease. Even if we do obtain analyst coverage, if one or more of the analysts covering our business downgrade their evaluations of our stock, the price of our stock could decline. If one or more of these analysts cease to cover our stock, we could lose visibility in the market for our stock, which, in turn, could cause our stock price to decline.
If we fail to implement and maintain proper and effective internal control over financial reporting, our ability to produce accurate and timely financial statements could be impaired, investors may lose confidence in our financial reporting and the trading price of our common stock may decline.
Pursuant to Section 404 of Sarbanes-Oxley, our management will be required to report upon the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting beginning with the annual report for our fiscal year ending December 31, 2021. When we lose our status as an “emerging growth company,” our independent registered public accounting firm will be required to attest to the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting. The rules governing the standards that must be met for management to assess our internal control over financial reporting are complex and require significant documentation, testing and possible remediation. To comply with the requirements of being a reporting company under the Exchange Act, we will need to
78
Table of Contents
implement additional financial and management controls, reporting systems and procedures and hire additional accounting and finance staff, all of which will entail additional expense.
We cannot assure you that there will not be material weaknesses in our internal control over financial reporting in the future. Any failure to implement and maintain internal control over financial reporting could severely inhibit our ability to accurately report our financial condition, results of operations or cash flows. If we are unable to conclude that our internal control over financial reporting is effective, or if our independent registered public accounting firm determines we have a material weakness in our internal control over financial reporting, investors may lose confidence in the accuracy and completeness of our financial reports, the market price of our common stock could decline, and we could be subject to sanctions or investigations by Nasdaq, the SEC or other regulatory authorities. Failure to remedy any material weakness in our internal control over financial reporting, or to implement or maintain other effective control systems required of public companies, could also restrict our future access to the capital markets.
If our estimates or judgments relating to our critical accounting policies are based on assumptions that change or prove to be incorrect, our operating results could fall below our publicly announced guidance or the expectations of securities analysts and investors, resulting in a decline in the market price of our common stock.
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the amounts reported in our consolidated financial statements and accompanying notes. We base our estimates on historical experience and on various other assumptions that we believe to be reasonable under the circumstances, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying values of assets, liabilities, equity, revenue and expenses that are not readily apparent from other sources. If our assumptions change or if actual circumstances differ from our assumptions, our operating results may be adversely affected and could fall below our publicly announced guidance or the expectations of securities analysts and investors, resulting in a decline in the market price of our common stock.
Provisions in our charter documents and under Delaware law could discourage a takeover that stockholders may consider favorable and may lead to entrenchment of management.
Our amended and restated certificate of incorporation and amended and restated bylaws that will be in effect upon the consummation of this offering will contain provisions that could delay or prevent changes in control or changes in our management without the consent of our board of directors. These provisions will include the following:
| • | a classified board of directors with three-year staggered terms, which may delay the ability of stockholders to change the membership of a majority of our board of directors; |
| • | no cumulative voting in the election of directors, which limits the ability of minority stockholders to elect director candidates; |
| • | the exclusive right of our board of directors to elect a director to fill a vacancy created by the expansion of the board of directors or the resignation, death or removal of a director, which prevents stockholders from being able to fill vacancies on our board of directors; |
| • | the ability of our board of directors to authorize the issuance of shares of preferred stock and to determine the price and other terms of those shares, including preferences and voting rights, without stockholder approval, which could be used to significantly dilute the ownership of a hostile acquiror; |
| • | the ability of our board of directors to alter our amended and restated bylaws without obtaining stockholder approval; |
79
Table of Contents
| • | the required approval of at least 66 2/3% of the shares entitled to vote at an election of directors to adopt, amend or repeal our amended and restated bylaws or repeal the provisions of our amended and restated certificate of incorporation regarding the election and removal of directors; |
| • | a prohibition on stockholder action by written consent, which forces stockholder action to be taken at an annual or special meeting of our stockholders; |
| • | the requirement that a special meeting of stockholders may be called only by our chief executive officer or, in the absence of a chief executive officer, president or by the board of directors, which may delay the ability of our stockholders to force consideration of a proposal or to take action, including the removal of directors; and |
| • | advance notice procedures that stockholders must comply with in order to nominate candidates to our board of directors or to propose matters to be acted upon at a stockholders’ meeting, which may discourage or deter a potential acquiror from conducting a solicitation of proxies to elect the acquiror’s own slate of directors or otherwise attempting to obtain control of us. |
We are also subject to the anti-takeover provisions contained in Section 203 of the Delaware General Corporation Law. Under Section 203, a corporation may not, in general, engage in a business combination with any holder of 15% or more of its capital stock unless the holder has held the stock for three years or, among other exceptions, the board of directors has approved the transaction. For a description of our capital stock, see the section titled “Description of capital stock.”
Claims for indemnification by our directors and officers may reduce our available funds to satisfy successful third-party claims against us and may reduce the amount of money available to us.
Our amended and restated certificate of incorporation and amended and restated bylaws will provide that we will indemnify our directors and officers, in each case to the fullest extent permitted by Delaware law.
In addition, as permitted by Section 145 of the Delaware General Corporation Law, our amended and restated bylaws to be effective upon the completion of this offering and our indemnification agreements that we have entered into with our directors and officers will provide that:
| • | we will indemnify our directors and officers for serving us in those capacities or for serving other business enterprises at our request, to the fullest extent permitted by Delaware law. Delaware law provides that a corporation may indemnify such person if such person acted in good faith and in a manner such person reasonably believed to be in or not opposed to the best interests of the registrant and, with respect to any criminal proceeding, had no reasonable cause to believe such person’s conduct was unlawful; |
| • | we may, in our discretion, indemnify employees and agents in those circumstances where indemnification is permitted by applicable law; |
| • | we are required to advance expenses, as incurred, to our directors and officers in connection with defending a proceeding, except that such directors or officers shall undertake to repay such advances if it is ultimately determined that such person is not entitled to indemnification; |
| • | we will not be obligated pursuant to our amended and restated bylaws to indemnify a person with respect to proceedings initiated by that person against us or our other indemnitees, except with respect to proceedings authorized by our board of directors; |
| • | the rights conferred in our amended and restated bylaws are not exclusive, and we are authorized to enter and have entered into indemnification agreements with our directors, officers, employees and agents and to obtain insurance to indemnify such persons; and |
80
Table of Contents
| • | we may not retroactively amend our amended and restated bylaw provisions to reduce our indemnification obligations to directors, officers, employees and agents. |
Our amended and restated certificate of incorporation will provide that the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware will be the exclusive forum for certain disputes between us and our stockholders, which could limit our stockholders’ ability to obtain a favorable judicial forum for disputes with us or our directors, officers or employees.
Our amended and restated certificate of incorporation that will become effective upon the closing of this offering specifies that, unless we consent in writing to the selection of an alternative forum, the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware will be the sole and exclusive forum for any derivative action or proceeding brought on our behalf; any action asserting a breach of fiduciary duty; any action asserting a claim against us arising pursuant to the Delaware General Corporation Law, our amended and restated certificate of incorporation, our amended and restated bylaws or any action as to which the Delaware General Corporation Law confers jurisdiction to the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware; or any action asserting a claim against us that is governed by the internal affairs doctrine. Our amended and restated certificate of incorporation will also provide that the federal district courts of the United States of America will be the exclusive forum for the resolution of any complaint asserting a cause of action against us or any of our directors, officers, employees or agents and arising under the Securities Act. We believe these provisions may benefit us by providing increased consistency in the application of Delaware law and federal securities laws by chancellors and judges, as applicable, particularly experienced in resolving corporate disputes, efficient administration of cases on a more expedited schedule relative to other forums and protection against the burdens of multi-forum litigation. However, these provisions may have the effect of discouraging lawsuits against our directors and officers. The choice of forum provision requiring that the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware or the federal district courts of the United States of America be the exclusive forum for certain actions would not apply to suits brought to enforce any liability or duty created by the Exchange Act. Our exclusive forum provision will not relieve us of our duties to comply with the federal securities laws and the rules and regulations thereunder, and our stockholders will not be deemed to have waived our compliance with these laws, rules and regulations. Although our amended and restated certificate of incorporation will contain the choice of forum provisions described above, it is possible that a court could find that such a provision is inapplicable for a particular claim or action or that such provision is unenforceable.
81
Table of Contents
Special note regarding forward-looking statements
This prospectus contains forward-looking statements concerning our business, operations and financial performance and condition, as well as our plans, objectives and expectations for our business, operations and financial performance and condition. Any statements contained herein that are not statements of historical facts may be deemed to be forward-looking statements. In some cases, you can identify forward-looking statements by terminology such as “aim,” “anticipate,” “assume,” “believe,” “contemplate,” “continue,” “could,” “due,” “estimate,” “expect,” “goal,” “intend,” “may,” “objective,” “plan,” “predict,” “potential,” “positioned,” “seek,” “should,” “target,” “will,” “would,” and other similar expressions that are predictions of or indicate future events and future trends, or the negative of these terms or other comparable terminology. These forward-looking statements include, but are not limited to, statements about:
| • | the scope, progress, results and costs of developing our drug candidates or any other future drug candidates, and conducting nonclinical studies and clinical trials, including our ALG-010133 and ALG-000184 Phase 1 clinical trials; |
| • | the scope, progress, results and costs related to the research and development of our pipeline; |
| • | the timing of and costs involved in obtaining and maintaining regulatory approval for any of our current or future drug candidates, and any related restrictions or limitations; |
| • | the impact of COVID-19 on our business and operations, including clinical trials, manufacturing suppliers, collaborators, use of contract research organizations and employees; |
| • | our expectations regarding the potential market size and size of the potential patient populations for ALG-010133 and ALG-000184, our other drug candidates and any future drug candidates, if approved for commercial use; |
| • | our ability to maintain existing, and establish new, collaborations, licensing or other arrangements and the financial terms of any such agreements; |
| • | our commercialization, marketing and manufacturing capabilities and expectations; |
| • | the rate and degree of market acceptance of our drug candidates, as well as the pricing and reimbursement of our drug candidates, if approved; |
| • | the implementation of our business model and strategic plans for our business, drug candidates and technology, including additional indications for which we may pursue; |
| • | the scope of protection we are able to establish and maintain for intellectual property rights covering our drug candidates, including the projected term of patent protection; |
| • | estimates of our expenses, future revenue, capital requirements, our needs for additional financing and our ability to obtain additional capital; |
| • | developments and projections relating to our competitors and our industry, including competing therapies and procedures; |
| • | regulatory and legal developments in the United States and foreign countries; |
| • | the performance of our third-party suppliers and manufacturers; |
| • | our ability to attract and retain key management, scientific and medical personnel; |
82
Table of Contents
| • | our expectations regarding the period during which we will qualify as an emerging growth company under the JOBS Act; |
| • | our expectations regarding our ability to obtain, maintain, enforce and defend our intellectual property protection for our drug candidates; |
| • | our use of proceeds from this offering; and |
| • | other risks and uncertainties, including those listed under the caption “Risk factors.” |
These forward-looking statements are based on management’s current expectations, estimates, forecasts and projections about our business and the industry in which we operate and management’s beliefs and assumptions and are not guarantees of future performance or development and involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors that are in some cases beyond our control. As a result, any or all of our forward-looking statements in this prospectus may turn out to be inaccurate. Factors that may cause actual results to differ materially from current expectations include, among other things, those listed under the section titled “Risk factors” and elsewhere in this prospectus. Potential investors are urged to consider these factors carefully in evaluating the forward-looking statements. These forward-looking statements speak only as of the date of this prospectus. Except as required by law, we assume no obligation to update or revise these forward-looking statements for any reason, even if new information becomes available in the future. You should, however, review the factors and risks we describe in the reports we will file from time to time with the SEC after the date of this prospectus. See the section titled “Where you can find more information.”
83
Table of Contents
This prospectus contains estimates, projections and other information concerning our industry and business, as well as data regarding market research, estimates and forecasts prepared by our management. Information that is based on estimates, forecasts, projections, market research or similar methodologies is inherently subject to uncertainties and actual events or circumstances may differ materially from events and circumstances that are assumed in this information. Unless otherwise expressly stated, we obtained this industry, business, market and other data from reports, research surveys, studies and similar data prepared by market research firms and other third parties, industry, medical and general publications, government data and similar sources. In some cases, we do not expressly refer to the sources from which this data is derived. In that regard, when we refer to one or more sources of this type of data in any paragraph, you should assume that other data of this type appearing in the same paragraph is derived from the same sources, unless otherwise expressly stated or the context otherwise requires.
This industry, business, market and other information involves a number of assumptions and limitations, and you are cautioned not to give undue weight to such estimates. We have not independently verified any third-party information and cannot assure you of its accuracy or completeness. Although we are responsible for all of the disclosure contained in this prospectus and we believe the market position, market opportunity, market size and other information included in this prospectus is reliable, such information is inherently imprecise. In addition, projections, assumptions and estimates of our future performance and the future performance of the industry in which we operate is necessarily subject to a high degree of uncertainty and risk due to a variety of factors, including those described in the section titled “Risk factors” and elsewhere in this prospectus. These and other factors could cause results to differ materially from those expressed in the estimates made by the independent parties and by us.
84
Table of Contents
We estimate that the net proceeds to us from the sale of 10,000,000 shares of our common stock in this offering will be approximately $135.4 million at an assumed initial public offering price of $15.00 per share (the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover of this prospectus), after deducting the underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us. If the underwriters exercise their option to purchase additional shares in full, we estimate that the net proceeds will be approximately $156.3 million at an assumed initial public offering price of $15.00 per share (the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover of this prospectus), after deducting the underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us.
Each $1.00 increase (decrease) in the assumed initial public offering price of $15.00 per share (the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover of this prospectus) would increase (decrease) the net proceeds to us from this offering, after deducting the underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us, by $9.3 million, assuming that the number of shares offered by us, as set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, remains the same. We may also increase or decrease the number of shares we are offering. Each increase (decrease) of 1,000,000 in the number of shares we are offering would increase (decrease) the net proceeds to us from this offering, after deducting the underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us, by $14.0 million, assuming the assumed initial public offering price stays the same. We do not expect that a change in the offering price or the number of shares by these amounts would have a material effect on our intended uses of the net proceeds from this offering, although it may impact the amount of time prior to which we may need to seek additional capital.
The principal purposes of this offering are to obtain additional capital to support our operations, create a public market for our common stock and facilitate our future access to the public markets. We currently intend to use the net proceeds from this offering, together with our existing cash and cash equivalents, as follows:
| • | approximately $40.0 million to $43.0 million to advance our STOPS candidate, ALG-010133, including to fund the Phase 1 clinical trial and drug product manufacturing activities; |
| • | approximately $35.0 million to $38.0 million to advance our CAM candidate, ALG-000184, including to fund the Phase 1 clinical trial and drug product manufacturing activities; |
| • | approximately $12.0 million to $15.0 million to advance our ASO candidate, ALG-020572; |
| • | approximately $20.0 million to $25.0 million to advance our siRNA candidate, ALG-125097; |
| • | approximately $12.0 million to $14.0 million to advance our NASH THR-b candidate, ALG-055009; and |
| • | the remainder (if any) to fund discovery and research to broaden our pipeline of drug and backup candidates, including other discovery candidates for viral and liver diseases, development of our technology platform, and any potential future combination or other clinical trials and nonclinical studies. In addition, the remainder of the net proceeds, if any, may be used for working capital and other general corporate purposes, which may include the hiring of additional personnel, capital expenditures and the costs of operating as a public company. |
Due to the uncertainties inherent in the clinical development and regulatory approval process, it is difficult to estimate with certainty the exact amounts of the net proceeds from this offering that may be used for the above purposes. As such, our management will retain broad discretion over the use of the net proceeds from this offering. The amounts and timing of our expenditures may depend upon numerous factors, including: (i) the time and cost necessary to advance our drug candidates through nonclinical studies and clinical trials; (ii) the
85
Table of Contents
time and cost associated with our research and development activities for our pipeline; (iii) the time and cost associated with the manufacture and supply of drug candidates for clinical development; (iv) our ability to obtain regulatory approval for and subsequently commercialize our drug candidates; and (v) potential payments under our licensing agreements.
We believe that our existing cash, cash equivalents and investments will enable us to fund our operations for at least 12 months following the date of this offering. After this offering, we will require substantial capital in order to advance our current and future drug candidates through clinical trials, regulatory approval and, if approved, commercialization. For additional information regarding our potential capital requirements, see the section titled “Risk factors—Even if this offering is successful, we will require substantial additional financing to achieve our goals, which may not be available on acceptable terms, or at all. A failure to obtain this necessary capital when needed could force us to delay, limit, reduce or terminate our product development or commercialization efforts.”
Pending the use of the proceeds from this offering, we intend to invest the net proceeds in interest-bearing, investment-grade securities, certificates of deposit or government securities.
86
Table of Contents
We have never declared or paid cash dividends on our capital stock. We intend to retain all available funds and future earnings, if any, to fund the development and expansion of our business, and we do not anticipate paying any cash dividends in the foreseeable future. Any future determination related to dividend policy will be made at the discretion of our board of directors and will depend upon, among other factors, our results of operations, financial condition, capital requirements, contractual restrictions, business prospects and other factors our board of directors might deem relevant.
87
Table of Contents
The following table sets forth our cash, cash equivalents and investments and capitalization as of June 30, 2020:
| • | on an actual basis, giving effect to the filing of our amended and restated certificate of incorporation on October 9, 2020, including the 1-for-9.3197 reverse stock split; |
| • | on a pro forma basis to give further effect to: (i) the conversion of all 19,201,429 shares of our preferred stock outstanding as of June 30, 2020 into 16,392,640 shares of our common stock and 2,808,789 shares of our non-voting common stock, which will be effective immediately prior to the closing of this offering; (ii) the issuance of 3,569,630 shares of our Series B-2 convertible preferred stock on October 6, 2020 and the subsequent conversion of such shares into 3,286,081 shares of common stock and 283,549 shares of non-voting common stock immediately prior to the closing of this offering, (iii) the issuance of 83,149 shares of our common stock upon the exercise of all Series A Warrants outstanding as of June 30, 2020 (which will be exercised prior to the closing of this offering at an exercise price of $9.32 per share), as a result of the conversion of 83,149 shares of our Series A convertible preferred stock issuable upon the exercise of our Series A Warrants and the automatic conversion of such shares of Series A convertible preferred stock into an equivalent number of shares of common stock immediately prior to the closing of this offering; and (iv) the filing and effectiveness of our further amended and restated certificate of incorporation, which will occur immediately prior to the closing of this offering; and |
| • | on a pro forma as adjusted basis to give further effect to the sale of 10,000,000 shares of common stock in this offering at an assumed initial public offering price of $15.00 per share (the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover of this prospectus), after deducting the underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us. |
You should read this information together with our consolidated financial statements and related notes appearing elsewhere in this prospectus and the information set forth in the sections titled “Selected consolidated financial data” and “Management’s discussion and analysis of financial condition and results of operations.”
88
Table of Contents
| As of June 30, 2020 | ||||||||||||
| Actual | Pro forma | Pro forma as adjusted(1) |
||||||||||
| (in thousands, except share and per share amounts) | ||||||||||||
| Cash, cash equivalents and investments |
$ | 88,122 | $ | 128,897 | $ | 264,317 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Derivative liabilities |
380 | — | — | |||||||||
| Redeemable convertible preferred stock liabilities |
2,810 | — | — | |||||||||
| Series A redeemable convertible preferred stock, $0.0001 par value per share; 101,962,864 shares authorized, 10,857,395 shares issued and outstanding, actual; no shares authorized, issued and outstanding, pro forma and pro forma as adjusted |
101,182 | — | — | |||||||||
| Series B-1 redeemable convertible preferred stock, $0.0001 par value per share; 77,764,055 shares authorized, 8,344,034 shares issued and outstanding, actual; no shares authorized, issued and outstanding, pro forma and pro forma as adjusted |
81,384 | — | — | |||||||||
| Series B-2 redeemable convertible preferred stock, $0.0001 par value per share; 33,268,045 shares authorized, no shares issued and outstanding, actual; no shares authorized, issued and outstanding, pro forma and pro forma as adjusted |
— | — | — | |||||||||
| Stockholders’ (deficit) equity: |
||||||||||||
| Preferred stock, $0.0001 par value per share; no shares authorized, issued and outstanding, actual; 10,000,000 shares authorized, and no shares issued and outstanding, pro forma and pro forma as adjusted |
— | — | — | |||||||||
| Common stock, $0.0001 par value per share; 278,000,000 shares authorized, 4,035,978 shares issued and outstanding, actual; 278,000,000 shares authorized, 23,797,848 shares issued and outstanding, pro forma; 300,000,000 shares authorized, 33,797,848 shares issued and outstanding, pro forma as adjusted |
— | 2 | 3 | |||||||||
| Non-voting Common Stock, $0.0001 par value per share; no shares authorized, issued or outstanding, actual; 20,000,000 shares authorized, 3,092,338 shares issued and outstanding, pro forma and pro forma as adjusted |
— | — | — | |||||||||
| Additional paid-in capital |
2,300 | 228,829 | 364,248 | |||||||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive income |
150 | 150 | 150 | |||||||||
| Accumulated deficit |
(107,023 | ) | (107,023 | ) | (107,023 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total stockholders’ (deficit) equity |
(104,573 | ) | 121,958 | 257,378 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total capitalization |
$ | 81,183 | $ | 121,958 | $ | 257,378 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| (1) | Each $1.00 increase (decrease) in the assumed initial public offering price of $15.00 per share (the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover of this prospectus) would increase (decrease) the amount of each of cash, cash equivalents and investments, additional paid-in capital, total stockholders’ (deficit) equity and total capitalization by $9.3 million, assuming the number of shares offered by us, as set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, remains the same and after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us. We may also increase or decrease the number of shares we are offering. Each increase (decrease) of 1,000,000 shares in the number of shares offered by us would increase (decrease) each of cash, cash equivalents and investments, additional paid-in capital, total stockholders’ (deficit) equity and total capitalization by $14.0 million, assuming the assumed initial public offering price of $15.00 per share (the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover of this prospectus) remains the same, and after deducting underwriting discounts and |
89
Table of Contents
| commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us. The pro forma as adjusted information discussed above is illustrative only and will be adjusted based on the actual public offering price and other terms of this offering determined at pricing. |
The outstanding share information in the table above excludes the following:
| • | 2,246,633 shares of common stock issuable upon the exercise of outstanding stock options as of June 30, 2020 having a weighted-average exercise price of $3.16 per share; |
| • | 4,426,822 shares of common stock reserved for issuance pursuant to future awards under our 2020 Incentive Award Plan, which will become effective on the day prior to the first public trading date of our common stock, of which options to purchase 159,118 shares of common stock at an exercise price equal to the initial public offering price set forth on the cover of this prospectus will be granted coincident with this offering, as well as any automatic increases in the number of shares of our common stock reserved for future issuance under this plan; and |
| • | 368,901 shares of common stock reserved for issuance under our 2020 Employee Stock Purchase Plan, which will become effective on the day prior to the first public trading date of our common stock, as well as any automatic increases in the number of shares of our common stock reserved for future issuance under this plan. |
90
Table of Contents
If you invest in our common stock in this offering, your ownership interest will be immediately diluted to the extent of the difference between the initial public offering price per share of our common stock and the pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value per share of our common stock immediately after this offering.
As of June 30, 2020, we had a historical net tangible book value of $(104.6) million, or $(25.91) per share of common stock. Our historical net tangible book value represents total tangible assets less total liabilities and redeemable convertible preferred stock, all divided by 4,035,978 shares of common stock outstanding on June 30, 2020. Our pro forma net tangible book value as of June 30, 2020, before giving effect to this offering, was $122.0 million, or $4.54 per share of our common stock. Pro forma net tangible book value, before the issuance and sale of shares in this offering, gives effect to:
| • | the conversion of all 19,201,429 outstanding shares of our preferred stock as of June 30, 2020 into 16,392,640 shares of common stock and 2,808,789 shares of non-voting common stock immediately prior to the closing of this offering; |
| • | the issuance of 3,569,630 shares of our Series B-2 convertible preferred stock on October 6, 2020, and the subsequent conversion of such shares into 3,286,081 shares of common stock and 283,549 shares of non-voting common stock immediately prior to the closing of this offering; |
| • | the issuance of 83,149 shares of our common stock upon the exercise of all Series A Warrants outstanding as of June 30, 2020 (which will be exercised prior to the closing of this offering at an exercise price of $9.32 per share), as a result of the conversion of 83,149 shares of our Series A convertible preferred stock issuable upon the exercise of our Series A Warrants and the automatic conversion of such shares of Series A convertible preferred stock into an equivalent number of shares of common stock immediately prior to the closing of this offering; and |
| • | the filing and effectiveness of our amended and restated certificate of incorporation on October 9, 2020 and the filing and effectiveness of our further amended and restated certificate of incorporation immediately prior to the closing of this offering. |
After giving effect to the sale of 10,000,000 shares of common stock in this offering at an assumed initial public offering price of $15.00 per share (the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover of this prospectus) and after deducting the underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us, our pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value as of June 30, 2020 would have been $257.4 million, or $6.98 per share. This represents an immediate increase in pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value of $2.44 per share to existing stockholders and an immediate dilution in pro forma net tangible book value of $8.02 per share to new investors. The following table illustrates this per share dilution:
| Assumed initial public offering price per share |
$ | 15.00 | ||||||
| Historical net tangible book value per share as of June 30, 2020 |
$ | (25.91 | ) | |||||
| Pro forma change in historical net tangible book value per share attributable to the pro forma transactions described in the preceding paragraphs |
30.45 | |||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Pro forma net tangible book value per share as of June 30, 2020 |
4.54 | |||||||
| Increase in pro forma net tangible book value per share attributable to new investors purchasing shares in this offering |
2.44 | |||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value per share after this offering |
6.98 | |||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Dilution per share to new investors purchasing shares in this offering |
$ | 8.02 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||
91
Table of Contents
Each $1.00 increase (decrease) in the assumed initial public offering price of $15.00 per share (the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover of this prospectus) would increase (decrease) our pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value as of June 30, 2020 after this offering by $9.3 million, or $0.25 per share, and would decrease (increase) dilution to investors in this offering by $0.25 per share, assuming that the number of shares offered by us, as set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, remains the same, after deducting the underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us. We may also increase or decrease the number of shares we are offering. Assuming the assumed initial public price of $15.00 per share (the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover of this prospectus) remains the same, after deducting the underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us, each increase of 1,000,000 in the number of shares we are offering would increase our pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value as of June 30, 2020 after this offering by $14.0 million, or $0.38 per share, and would decrease dilution to investors in this offering by $0.38 per share, and a decrease of 1,000,000 in the number of shares we are offering would decrease our pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value as of June 30, 2020 after this offering by $14.0 million, or $0.38 per share, and would increase dilution to investors in this offering by $0.38 per share. The pro forma as adjusted information is illustrative only, and we will adjust this information based on the actual initial public offering price and other terms of this offering determined at pricing.
If the underwriters fully exercise their option to purchase additional shares, the pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value after this offering would be $278.3 million, the increase in pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value per share to existing stockholders would be $2.71 per share, and there would be an immediate dilution of $7.75 per share to new investors, in each case assuming an initial offering price of $15.00 per share (the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover of this prospectus).
To the extent that outstanding options with an exercise price per share that is less than the pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value per share are exercised, new investors will experience further dilution. In addition, we may choose to raise additional capital due to market conditions or strategic considerations even if we believe we have sufficient funds for our current or future operating plans. To the extent that we raise additional capital through the sale of equity or convertible debt securities, the issuance of these securities could result in further dilution to our stockholders.
The following table shows, as of June 30, 2020, on a pro forma as adjusted basis, the number of shares of common stock purchased from us, the total consideration paid or to be paid to us and the average price paid per share by existing stockholders for shares issued prior to this offering and the price to be paid by new investors purchasing common stock in this offering at an assumed initial public offering price of $15.00 per share (the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover of this prospectus), before deducting the underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us:
| Shares purchased | Total consideration | Average price per share |
||||||||||||||||||
| Number | Percent | Amount | Percent | |||||||||||||||||
| Existing stockholders |
26,890,186 | 72.9% | $ | 227,688,682 | 60.3% | $ | 8.47 | |||||||||||||
| New investors |
10,000,000 | 27.1% | $ | 150,000,000 | 39.7% | $ | 15.00 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Total |
36,890,186 | 100.0% | $ | 377,688,682 | 100.0% | |||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
92
Table of Contents
The total number of shares of common stock and non-voting common stock to be outstanding after this offering is based on 23,237,407 shares of common stock outstanding as of June 30, 2020, plus 3,569,630 shares of common stock issuable pursuant to the conversion of our Series B-2 convertible preferred stock issued on October 6, 2020, and excludes the following:
| • | 2,246,633 shares of common stock issuable upon the exercise of outstanding stock options as of June 30, 2020 having a weighted-average exercise price of $3.16 per share; |
| • | 4,426,822 shares of common stock reserved for issuance pursuant to future awards under our 2020 Incentive Award Plan, which will become effective on the day prior to the first public trading date of our common stock, of which options to purchase 159,118 shares of common stock at an exercise price equal to the initial public offering price set forth on the cover of this prospectus will be granted coincident with this offering, as well as any automatic increases in the number of shares of our common stock reserved for future issuance under this plan; and |
| • | 368,901 shares of common stock reserved for issuance under our 2020 Employee Stock Purchase Plan, which will become effective on the day prior to the first public trading date of our common stock, as well as any automatic increases in the number of shares of our common stock reserved for future issuance under this plan. |
93
Table of Contents
Selected consolidated financial data
The following tables summarize our selected consolidated financial data. You should read this data together with our consolidated financial statements and related notes included in this prospectus and the information under the section titled “Management’s discussion and analysis of financial condition and results of operations.” The selected consolidated financial data in this section are not intended to replace the financial statements and are qualified in their entirety by the consolidated financial statements and related notes included elsewhere in this prospectus. Our historical results are not necessarily indicative of results that should be expected in any future period, and our results for the six months ended June 30, 2020 are not necessarily indicative of results that should be expected for the full year or any other period.
We have derived the following selected consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive loss data for Fiscal 2018 and Fiscal 2019 (except for the pro forma net loss per share and the pro forma share information) and the balance sheet data as of December 31, 2018 and 2019 from our audited consolidated financial statements and related notes included in this prospectus . The consolidated summary statements of operations and comprehensive loss data for the six months ended June 30, 2019 and 2020 and the balance sheet data as of June 30, 2020 have been derived from our unaudited consolidated financial statements included in this prospectus and have been prepared on the same basis as the audited consolidated financial statements. Our historical results and unaudited interim results are not necessarily indicative of the results that may be expected in the future.
| Six Months Ended June 30, | ||||||||||||||||
| Fiscal 2018 | Fiscal 2019 | 2019 | 2020 | |||||||||||||
| (in thousands, except share and per share data) | ||||||||||||||||
| Consolidated Statements of Operations Data: |
||||||||||||||||
| Operating expenses:(1) |
||||||||||||||||
| Research and development |
$ | 10,456 | $ | 44,038 | $ | 17,336 | $ | 34,478 | ||||||||
| General and administrative |
3,205 | 10,005 | 3,767 | 7,514 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total operating expenses |
13,661 | 54,043 | 21,103 | 41,992 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Loss from operations |
(13,661 | ) | (54,043 | ) | (21,103 | ) | (41,992 | ) | ||||||||
| Interest and other (income) expense, net |
(272 | ) | 1,864 | 1,073 | 1,108 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Loss before provision for income taxes |
(13,933 | ) | (52,179 | ) | (20,030 | ) | (40,884 | ) | ||||||||
| Income tax (expense) benefit |
— | (85 | ) | — | 58 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Net loss |
$ | (13,933 | ) | $ | (52,264 | ) | $ | (20,030 | ) | $ | (40,826 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Net loss per share:(2)(3) |
||||||||||||||||
| Basic and diluted |
$ | (11.69 | ) | $ | (26.04 | ) | $ | (11.54 | ) | $ | (14.96 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Weighted-average number of shares used in computing net loss per share:(2)(3) |
||||||||||||||||
| Basic and diluted |
1,191,787 | 2,007,173 | 1,735,358 | 2,729,827 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Unaudited pro forma net loss per share:(2)(3) |
||||||||||||||||
| Basic and diluted |
$ | (2.47 | ) | $ | (1.86 | ) | ||||||||||
| Unaudited weighted-average shares used in computing pro forma net loss per share:(2)(3) |
||||||||||||||||
| Basic and diluted |
21,171,050 | 21,931,256 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
94
Table of Contents
| (1) | Includes stock-based compensation expense as follows (in thousands): |
| Six Months Ended June 30, | ||||||||||||||||
| Fiscal 2018 | Fiscal 2019 | 2019 | 2020 | |||||||||||||
| Research and development |
$ | 130 | $ | 462 | $ | 272 | $ | 350 | ||||||||
| General and administrative |
49 | 290 | 181 | 308 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total |
$ | 179 | $ | 752 | $ | 453 | $ | 658 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
| (2) | See Notes 16 and 17 to our audited consolidated financial statements and Notes 13 and 14 to our unaudited consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this prospectus for an explanation of the calculations of our basic and diluted net loss per share and our pro forma net loss per share, respectively. |
| (3) | All share and per share amounts set forth in the table above have been adjusted to give retrospective effect to the 1-for-9.3197 reverse stock split effected on October 9, 2020. |
| Fiscal 2018 | Fiscal 2019 | As of June 30, 2020 |
||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||
| Consolidated Balance Sheet Data: |
||||||||||||
| Cash, cash equivalents and investments |
$ | 90,852 | $ | 127,682 | $ | 88,122 | ||||||
| Working capital |
84,880 | 106,408 | 76,090 | |||||||||
| Total assets |
107,731 | 146,520 | 107,901 | |||||||||
| Current liabilities |
7,489 | 13,818 | 15,364 | |||||||||
| Derivative liabilities |
861 | 461 | 380 | |||||||||
| Convertible preferred stock liabilities |
— | 3,174 | 2,810 | |||||||||
| Operating lease liabilities, net of current portion |
12,584 | 11,701 | 11,106 | |||||||||
| Redeemable convertible preferred stock |
100,519 | 182,079 | 182,566 | |||||||||
| Accumulated deficit |
(13,933 | ) | (66,197 | ) | (107,023 | ) | ||||||
| Total stockholders’ (deficit) |
(13,748 | ) | (64,891 | ) | (104,573 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
95
Table of Contents
Management’s discussion and analysis of financial condition and results of operations
You should read the following discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations in conjunction with the consolidated financial statements and the related notes and other financial information included elsewhere in this prospectus. In addition to historical financial information, this discussion contains forward-looking statements based upon current expectations that involve risks and uncertainties. Our actual results could differ materially from those anticipated in these forward-looking statements as a result of various factors, including those set forth under “Special note regarding forward-looking statements” and “Risk factors” and elsewhere in this prospectus. Our fiscal year ends on December 31 each year.
Overview
We are a clinical-stage biopharmaceutical company currently focused on developing novel therapeutics to address unmet medical needs in viral and liver diseases. We utilize our proprietary oligonucleotide and small molecule platforms to develop pharmacologically optimized drug candidates for use in combination regimens designed to achieve improved treatment outcomes. Our lead effort is to develop a functional cure for Chronic Hepatitis B (“CHB”), which often results in other life-threatening conditions such as cirrhosis, end-stage liver disease (“ESLD”) and the most common form of liver cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma (“HCC”). The most widely used treatment for CHB, nucleos(t)ide analogs, suppresses viral replication but only achieves low rates of functional cure and often requires long-term administration. To address this issue, we have developed a portfolio of differentiated drug candidates for CHB, including an S-antigen Transport-inhibiting Oligonucleotide Polymers (“STOPS”) molecule, a small molecule Capsid Assembly Modulator (“CAM”), and oligonucleotides (ASO and siRNA), each of which is designed against clinically validated targets in the Hepatitis B Virus (“HBV”) life cycle. We believe that combination regimens utilizing our portfolio of CHB drug candidates may lead to higher rates of functional cure. A Phase 1 proof of concept trial for our STOPS molecule is ongoing and in New Zealand we expect to initiate a Phase 1 clinical trial with our CAM in the second half of 2020. Our second area of focus is in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (“NASH”), a complex, chronic liver disease where combination regimens may prove beneficial. Our most advanced drug candidate for NASH is ALG-055009, a small molecule THR-b agonist currently in nonclinical studies to enable a first-in-human clinical trial. We believe ALG-055009 has the potential to become an integral component of future combination regimens for NASH. Our third area of focus is to develop drug candidates with pan-coronavirus activity, including SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for COVID-19.
We have incurred net losses and negative cash flows from operations in each year since our inception in February 2018. Our net losses were $13.9 million and $52.3 million for the period from February 5, 2018, to December 31, 2018 and for the year ended December 31, 2019, respectively, and were $20.0 million and $40.8 million for the six months ended June 30, 2019 and 2020, respectively. We have had no revenue from product sales. As of June 30, 2020, we had an accumulated deficit of $107.0 million. Substantially all of our net losses have resulted from costs incurred in connection with our research and development programs and from general and administrative costs associated with our operations. We expect to continue to incur significant expenses and increasing operating losses over at least the next several years. Our net operating losses may fluctuate from quarter to quarter and year to year depending primarily on the timing of our clinical trials and nonclinical studies and our other research and development expenses. We have no internal manufacturing capabilities or salesforce and outsource a substantial portion of our clinical trial work to third parties.
96
Table of Contents
Components of our results of operations
Operating expenses
Our operating expenses since inception have consisted solely of research and development costs and general and administrative costs.
Research and development expenses
We rely substantially on third parties to conduct our discovery activities, nonclinical studies, clinical trials and manufacturing. We estimate research and development expenses based on estimates of services performed, and rely on third party contractors and vendors to provide us with timely and accurate estimates of expenses of services performed to assist us in these estimates. Research and development costs consist primarily of costs incurred for the identification and development of our drug candidates through our technology platforms, which include:
| • | salaries, benefits and other employee-related costs, including stock-based compensation expense, for personnel engaged in research and development functions; |
| • | costs of outside consultants, including their fees, and related travel expenses; |
| • | costs associated with in-process research and development, including license fees and milestones paid to third-party collaborators for technologies with no alternative use; |
| • | costs related to production of clinical materials, including fees paid to contract manufacturers; |
| • | expenses incurred under agreements with collaborators that perform nonclinical activities; |
| • | costs related to compliance with regulatory requirements; and |
| • | facility costs, depreciation, and other expenses, which include direct and allocated expenses for rent and maintenance of facilities, insurance, and other supplies. |
We expense research and development costs as the services are performed or the goods are received. Non-refundable payments for goods or services that will be used for future research and development activities are deferred and capitalized. Such amounts are recognized as an expense as the goods are delivered or the related services are performed until it is no longer expected that the goods will be delivered or the services will be rendered.
We expect our research and development costs to increase in future periods as we continue to invest in research and development activities and advance our nonclinical and clinical programs through clinical development. The process of conducting nonclinical studies and, eventually, clinical trials necessary to obtain regulatory approval is costly and time consuming, and the successful development of our drug candidates is highly uncertain. As a result, we are unable to determine the duration and completion costs of our research and development projects or clinical trials or if and to what extent we will generate revenue from the commercialization and sale of any of our drug candidates.
General and administrative expenses
General and administrative expenses consist primarily of salaries and other related costs, including stock-based compensation, for personnel in our executive, finance, corporate and business development and administrative functions. General and administrative expenses also include legal fees relating to patent and corporate matters; professional fees for accounting, auditing, tax and consulting services; insurance costs; travel expenses; and facility-related expenses, which include direct depreciation costs and allocated expenses for rent and maintenance of facilities and other operating costs not otherwise classified as research and development costs.
97
Table of Contents
We expect that our general and administrative expenses will increase in the future as we increase our general and administrative personnel headcount to support personnel in research and development and to support our operations generally as we increase our research and development activities and activities related to the potential commercialization of our drug candidates. We also expect to incur increased expenses associated with operating as a public company, including costs of accounting, audit, legal, regulatory and tax-related services associated with maintaining compliance with exchange listing rules and requirements of the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”), director and officer insurance costs, and investor and public relations costs.
Interest and other income (expense), net
Interest and other income (expense), net comprises interest income (expense), net and other income (expense), net. Interest income (expense), net primarily consists of interest earned on our cash, cash equivalents, and short-term investments and interest expense related to our convertible note instruments. Other income (expense), net consists primarily of the change in fair value of our derivative liabilities.
We classify our warrants and the commitment to sell redeemable convertible preferred stock as liabilities on our consolidated balance sheets and record changes in fair value at each balance sheet date with the corresponding change recorded as other income (expense). We will continue to record adjustments to the fair value of the warrants and the redeemable convertible preferred stock liability at each balance sheet date until they are exercised, automatically converted into common stock or expire. Immediately prior to the completion of this offering, any then outstanding warrants will automatically be exercised, on net share basis, for the issuance of shares of common stock and, upon that exercise, such warrants will no longer be outstanding.
We anticipate other income (expense) to fluctuate in the future based on subsequent revaluations at each balance sheet date of the redeemable convertible preferred stock liability through the date on which such shares are converted into shares of common in connection with the consummation of this offering, if not earlier converted.
Provision for income taxes
Since our inception in 2018, we have not recorded any U.S. federal or state income tax benefits for the net losses we have incurred in any year or for our earned research and development tax credits, due to our uncertainty of realizing a benefit from those items. As of December 31, 2019, we had federal net operating loss (“NOL”) carryforwards of $57.6 million available to reduce taxable income and these NOLs can be carried forward indefinitely. We have state NOL carryforwards of $60.5 million as of December 31, 2019, available to reduce future state taxable income, which expire at various dates beginning in 2038. As of December 31, 2019, we also had federal and state research and development tax credit carryforwards of $1.4 million and $1.1 million, respectively. The federal development tax credit carryforwards begin to expire in 2029, while the state development tax credit carryforwards can be carried forward indefinitely. In addition, we may in the future experience ownership changes, either as a result of this offering or other changes in our stock ownership (some of which are not in our control). For these reasons, our ability to utilize our NOL carryforwards and other tax attributes to reduce future tax liabilities may be limited.
98
Table of Contents
Comparison of six months ended June 30, 2019 and 2020
Operating expenses
The following table summarizes our operating expenses for the six months ended June 30, 2019 and 2020:
| Six Months Ended June 30, |
Change | |||||||||||||||
| 2019 | 2020 | ($) | % | |||||||||||||
| (in thousands, except percentages) | ||||||||||||||||
| Operating expenses: |
||||||||||||||||
| Research and development |
$ | 17,336 | $ | 34,478 | $ | 17,142 | 99% | |||||||||
| General and administrative |
3,767 | 7,514 | 3,747 | 99% | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Total operating expenses |
$ | 21,103 | $ | 41,992 | $ | 20,889 | ||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
Research and development expenses
| Six Months Ended June 30, |
Change | |||||||||||||||
| 2019 | 2020 | ($) | % | |||||||||||||
| (in thousands, except percentages) | ||||||||||||||||
| Third party expenses |
$ | 9,365 | $ | 22,242 | $ | 12,877 | 138% | |||||||||
| Employee related expenses |
5,276 | 8,533 | 3,257 | 62% | ||||||||||||
| Laboratory supplies and other costs |
1,238 | 2,223 | 985 | 80% | ||||||||||||
| Facilities and other allocated expenses |
1,178 | 861 | (317) | (27)% | ||||||||||||
| Depreciation and other expenses |
279 | 619 | 340 | 122% | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Total research and development expenses |
$ | 17,336 | $ | 34,478 | $ | 17,142 | ||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
Research and development expenses were $17.3 million for the six months ended June 30, 2019, compared to $34.5 million for the six months ended June 30, 2020, an increase of $17.1 million. The increase was primarily due to an increase of $12.9 million in third-party expenses for our preclinical programs and the continued increase in expenditures related to research and development activities associated with our STOPs molecule and CAM candidates, as well as activities related to our NASH program. The increase also includes $3.3 million of additional employee-related costs, including a $0.1 million increase in stock-based compensation, and $1.0 million of increased laboratory supplies primarily due to higher headcount. Additional increases include $0.3 million in depreciation and other expenses. These increases were partially offset by a decrease of $0.3 million in allocable facilities costs as a result of less overall rent expense from the amortization of leasehold improvements paid by the landlord at our new corporate headquarters.
General and administrative expenses
General and administrative expenses were $3.8 million for the six months ended June 30, 2019, compared to $7.5 million for the six months ended June 30, 2020, an increase of $3.7 million. The increase was primarily due to $3.0 million in increased personnel-related costs, including an increase of $0.1 million of additional stock-based compensation expense, primarily due to increased general and administrative headcount to support the growth of our research and development organization, and $0.7 million in increased facilities and other expenses related to the continued expansion of our new corporate headquarters and subsidiary facilities.
99
Table of Contents
Interest and other income (expense), net
| Six Months Ended June 30, |
Change | |||||||||||||||
| 2019 | 2020 | ($) | % | |||||||||||||
| (in thousands, except percentages) | ||||||||||||||||
| Interest income, net |
$ | 960 | $ | 748 | $ | (212 | ) | (22)% | ||||||||
| Other income, net |
113 | 360 | 247 | (219)% | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Total interest and other income, net |
$ | 1,073 | $ | 1,108 | $ | 35 | ||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
Interest income, net decreased from $1.0 million for the six months ended June 30, 2019 to $0.8 million for the six months ended June 30, 2020, a decrease in $0.2 million, primarily due to the change in our portfolio of cash equivalents, short-term investments and long-term investments.
Other income, net increased from $0.1 million for the six months ended June 30, 2019 to $0.4 million for the six months ended June 30, 2020, a increase of $0.2 million, primarily due to the gain recognized on the net decrease in fair value of both our redeemable convertible preferred stock liability and warrant liabilities.
Comparison of Fiscal 2018 and 2019
Operating expenses
The following table summarizes our operating expenses for Fiscal 2018 and 2019:
| Change | ||||||||||||||||
| Fiscal 2018 | Fiscal 2019 | ($) | % | |||||||||||||
| (in thousands, except percentages) | ||||||||||||||||
| Operating expenses: |
||||||||||||||||
| Research and development |
$ | 10,456 | $ | 44,038 | $ | 33,582 | 321% | |||||||||
| General and administrative |
3,205 | 10,005 | 6,800 | 212% | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Total operating expenses |
$ | 13,661 | $ | 54,043 | $ | 40,382 | ||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
Research and development expenses
| Change | ||||||||||||||||
| Fiscal 2018 | Fiscal 2019 | ($) | % | |||||||||||||
| (in thousands, except percentages) | ||||||||||||||||
| Third party expenses |
$ | 4,141 | $ | 26,416 | $ | 22,275 | 538% | |||||||||
| Employee related expenses |
4,977 | 11,694 | 6,717 | 135% | ||||||||||||
| Laboratory supplies and other costs |
834 | 3,157 | 2,323 | 279% | ||||||||||||
| Facilities and other allocated expenses |
438 | 2,087 | 1,649 | 376% | ||||||||||||
| Depreciation and other expenses |
66 | 684 | 618 | 936% | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Total research and development expenses |
$ | 10,456 | $ | 44,038 | $ | 33,582 | ||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
Research and development expenses were $10.5 million in Fiscal 2018, compared to $44.0 million in Fiscal 2019, an increase of $33.5 million. The increase was primarily due to an increase of $22.3 million in third party expenses for our pre-clinical programs and the continued increase in expenditures related to research and development activities associated with ongoing development activities associated with STOPs and CAM as well as activities related to our NASH program. The increase also includes $6.7 million of additional
100
Table of Contents
employee-related costs, including $2.3 million of increased laboratory supplies and a $0.3 million increase in stock-based compensation primarily due to higher headcount. Additional increases related to $1.6 million in increased allocable facilities costs, which is allocated based on personnel headcount within research and development, from the expansion to our new corporate headquarters (including laboratory space) in late 2018, and an increase of $0.6 million in depreciation and other expenses.
General and administrative expenses
General and administrative expenses were $3.2 million for Fiscal 2018, compared to $10.0 million for Fiscal 2019, an increase of $6.8 million. The increase was primarily due to $5.2 million in increased personnel-related costs, including an increase of $0.1 million of stock-based compensation expense, primarily due to increased general and administrative headcount to support the growth of our organization, and $1.6 million in increased facilities and other expenses related to the expansion to our new corporate headquarters in late 2018.
Interest and other income (expense), net
| Change | ||||||||||||||||
| Fiscal 2018 | Fiscal 2019 | ($) | % | |||||||||||||
| (in thousands, except percentages) | ||||||||||||||||
| Interest income, net |
$ | 163 | $ | 1,562 | $ | 1,399 | 858% | |||||||||
| Other (expense) income, net |
(435 | ) | 302 | 737 | 169% | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Total interest and other income (expense), net |
$ | (272 | ) | $ | 1,864 | $ | 2,136 | |||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
Interest income, net increased from $0.2 million for Fiscal 2018 to $1.6 million for Fiscal 2019, primarily due to an increase in cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments. This also coincided with a decrease in interest expense in Fiscal 2019 as compared to Fiscal 2018 as a result of certain conversions of convertible notes into Series A convertible preferred stock during Fiscal 2018.
Other income (expense), net increased from a $0.4 million expense for Fiscal 2018 to $0.3 million of income for Fiscal 2019. In Fiscal 2018, other expense was primarily due to the $0.4 million charge associated with the conversion of the convertible notes into Series A convertible preferred stock. In Fiscal 2019, $0.3 million in income was recognized, related to the net change in fair value of our warrant liabilities during the year.
Liquidity and capital resources
Since our inception, we have not generated any revenue from product sales or any other sources, and have incurred significant operating losses. We have not yet commercialized any products and we do not expect to generate revenue from sales of any drug candidates for at least several years, if ever. To date, we have financed our operations through private placements of preferred stock, issuances of common stock and convertible debt. Through June 30, 2020, we had received gross proceeds of $186.9 million from sales of our preferred stock, issuances of common stock and our issuance of convertible debt. As of June 30, 2020, we had cash, cash equivalents and investments of $88.1 million.
Funding requirements
We have incurred net losses since inception. Our primary use of cash is to fund operating expenses, which consist primarily of research and development costs related to our drug candidates and our discovery programs, and to a lesser extent, general and administrative expenditures. We expect our expenses to increase substantially in connection with our ongoing clinical development activities related to our most advanced drug
101
Table of Contents
candidates, ALG-010133 and ALG-000184, which are still in the early stages of development, as well as our research and development of our other drug candidates within our CHB, NASH and coronavirus programs.
In addition, commencing upon the closing of this offering, we expect to incur additional costs associated with operating as a public company. We expect that our expenses will increase substantially to the extent we:
| • | conduct our current and future clinical trials, and additional nonclinical studies; |
| • | initiate and continue research and nonclinical and clinical development of other drug candidates; |
| • | seek to identify additional drug candidates; |
| • | pursue marketing approvals for any of our drug candidates that successfully complete clinical trials, if any; |
| • | establish a sales, marketing and distribution infrastructure to commercialize any products for which we may obtain marketing approval; |
| • | require the manufacture of larger quantities of our drug candidates for clinical development and potentially commercialization; |
| • | obtain, maintain, expand, protect and enforce our intellectual property portfolio; |
| • | acquire or in-license other drug candidates and technologies; |
| • | hire and retain additional clinical, quality control and scientific personnel; |
| • | achieve milestones triggering payments by us under our current and potential future licensing and/or collaboration agreements; |
| • | build out or expand existing facilities to support our ongoing development activity; and |
| • | add operational, financial and management information systems and personnel, including personnel to support our drug development, any future commercialization efforts and our transition to becoming a public company. |
As of June 30, 2020, we had cash, cash equivalents and investments of $88.1 million. We believe that our existing cash, cash equivalents and investments will enable us to fund our planned operating expenses and capital expenditure requirements through at least the next twelve months. We have based this estimate on assumptions that may prove to be wrong, and we could exhaust our available capital resources sooner than we expect. Furthermore, we may elect to raise additional capital on an opportunistic basis to fund operations.
Because of the numerous risks and uncertainties associated with our research and development programs and because the extent to which we may enter into collaborations with third parties for development of our drug candidates is unknown, we are unable to estimate the timing and amounts of increased capital outlays and operating expenses associated with completing the research and development of our drug candidates. Our future capital requirements will depend on many factors, including:
| • | the scope, progress, results and costs of researching and developing our drug candidates and programs, and of conducting nonclinical studies and clinical trials; |
| • | the timing of, and the costs involved in, obtaining marketing approvals for drug candidates we develop if clinical trials are successful; |
| • | the cost of commercialization activities for our current drug candidates, and any future drug candidates we develop, whether alone or in collaboration, including marketing, sales and distribution costs if our current drug candidates or any future drug candidate we develop is approved for sale; |
102
Table of Contents
| • | the cost of manufacturing our current and future drug candidates for clinical trials in preparation for marketing approval and commercialization; |
| • | our ability to establish and maintain strategic licenses or other arrangements and the financial terms of such agreements, including milestone payments to our licensors; |
| • | the costs involved in preparing, filing, prosecuting, maintaining, expanding, defending and enforcing patent claims, including litigation costs and the outcome of such litigation; |
| • | the timing, receipt and amount of sales of, or profit share or royalties on, our future products, if any; |
| • | the emergence of competing therapies and other adverse market developments; and |
| • | any acquisitions or in-licensing of other programs or technologies. |
Developing pharmaceutical products, including conducting nonclinical studies and clinical trials, is a time-consuming, expensive and uncertain process that takes years to complete, and we may never generate the necessary data or results required to obtain marketing approval for any drug candidates or generate revenue from the sale of any drug candidate for which we may obtain marketing approval. In addition, our drug candidates, if approved, may not achieve commercial success. Our commercial revenues, if any, will be derived from sales of drugs that we do not expect to be commercially available for many years, if ever. Accordingly, we will need to obtain substantial additional funds to achieve our business objectives.
Adequate additional funds may not be available to us on acceptable terms, or at all. We do not currently have any committed external source of funds. To the extent that we raise additional capital through the sale of equity or convertible debt securities, your ownership interest may be diluted, and the terms of these securities may include liquidation or other preferences and anti-dilution protections that could adversely affect your rights as a common stockholder. Additional debt or preferred equity financing, if available, may involve agreements that include restrictive covenants that may limit our ability to take specific actions, such as incurring debt, making capital expenditures or declaring dividends, which could adversely constrain our ability to conduct our business, and may require the issuance of warrants, which could potentially dilute your ownership interest.
If we raise additional funds through collaborations, strategic alliances or licensing arrangements with third parties, we may have to relinquish valuable rights to our technology, future revenue streams, research programs, or drug candidates or grant licenses on terms that may not be favorable to us. If we are unable to raise additional funds through equity or debt financings or collaborations, strategic alliances or licensing arrangements with third parties when needed, we may be required to delay, limit, reduce and/or terminate our product development programs or any future commercialization efforts or grant rights to develop and market drug candidates that we would otherwise prefer to develop and market ourselves.
Cash flows
The following table summarizes our sources and uses of cash for each of the periods presented:
| Fiscal |
Six Months Ended June 30, | |||||||||||||||
| 2018 | 2019 | 2019 | 2020 | |||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||
| Net cash (used in) operating activities |
$ | (6,049 | ) | $ | (46,767 | ) | $ | (18,335 | ) | $ | (38,013 | ) | ||||
| Net cash (used in) provided by investing activities |
(69,289 | ) | 6,791 | 21,694 | (8,838 | ) | ||||||||||
| Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities |
99,885 | 85,532 | (17 | ) | (21 | ) | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Net increase (decrease) in cash, cash equivalents, and restricted cash |
$ | 24,547 | $ | 45,556 | $ | 3,342 | $ | (46,872 | ) | |||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
103
Table of Contents
Operating activities
During the six months ended June 30, 2020, operating activities used $38.0 million of cash, primarily resulting from our net loss of $40.8 million, partially offset by non-cash charges of $2.0 million and cash provided by changes in our operating assets and liabilities of $0.8 million. Net cash provided by changes in our operating assets and liabilities of $0.8 million consisted of an increase of $2.0 million in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, partially offset by a decrease of $0.6 million in operating lease liability and an increase of $0.6 million in other current assets. The increase in accounts payable and accrued liabilities was largely due to an increase in external research and development costs. The decrease in the operating lease liability was a result of payments made on outstanding lease obligations. The increase in other assets was largely due to an increase in prepayments for services.
During the six months ended June 30, 2019, operating activities used $18.3 million of cash, primarily resulting from our net loss of $20.0 million, partially offset by non-cash charges of $0.7 million and cash provided by changes in our operating assets and liabilities of $1.0 million. Net cash provided by changes in our operating assets and liabilities of $1.0 million consisted of an increase of $0.3 million in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, an increase of $0.3 million in operating lease liability, a decrease of $0.1 million in right of use assets, and a decrease of $0.3 million in other current assets. The increase in accounts payable and accrued liabilities was largely due to an increase in external research and development costs. The decrease in other assets was largely due to receipt of tax credits associated with income taxes paid by us on behalf of employees due to the exercise of restricted stock purchase rights.
During Fiscal 2019, operating activities used $46.8 million of cash, primarily resulting from our net loss of $52.3 million, partially offset by non-cash charges of $1.8 million and cash provided by changes in our operating assets and liabilities of $3.7 million. Net cash provided by changes in our operating assets and liabilities of $3.7 million consisted of an increase of $4.6 million in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, a decrease of $0.3 million in other receivables, and a decrease of $0.1 million in right of use assets, partially offset by an increase of $1.3 million in other current assets. The increase in accounts payable and accrued liabilities was largely due to an increase in external research and development costs. The increase in other assets was largely due to an increase in prepayments for services. The decrease in other receivables was due to receipt of tax credits associated with income taxes paid by us on behalf of employees due to the exercise of restricted stock purchase rights.
During Fiscal 2018, operating activities used $6.1 million of cash, primarily resulting from our net loss of $13.9 million, partially offset by non-cash charges of $3.0 million and cash provided by changes in our operating assets and liabilities of $4.8 million. Net cash provided by changes in operating assets and liabilities of $4.8 million consisted of an increase of $6.2 million in accounts payable and accrued liabilities, partially offset by an increases of $0.7 million in other assets, $0.4 million in other receivables, and $0.1 million in right of use assets. The increase in accounts payable and accrued liabilities was largely due to an increase in external research and development costs. The increase in other assets was largely due to an increase in prepayments for services. The increase in other receivables related to income taxes paid by us on behalf of employees due to the exercise of restricted stock purchase rights and tax credit receivables.
Investing activities
During the six months ended June 30, 2020, investing activities used $8.8 million of cash, consisting primarily of $45.3 million of short-term and long-term investment purchases and $1.6 million of purchases of property and equipment, offset by $38.1 million of short-term investment maturities.
104
Table of Contents
During the six months ended June 30, 2019, investing activities provided $21.7 million of cash, consisting primarily of $49.5 million of short-term investment maturities, offset by $26.4 million of short-term investment purchases and $1.4 million of purchases of property and equipment.
During Fiscal 2019, investing activities provided $6.8 million of cash, consisting primarily of $80.0 million of short-term investment maturities, offset by $70.4 million of short-term and long-term investment purchases and $2.8 million of purchases of property and equipment.
During Fiscal 2018, investing activities used $69.3 million of cash, consisting primarily of $66.8 million of short-term investment purchases and $2.5 million for the purchase of property and equipment.
Financing activities
During the six months ended June 30, 2020, net cash used in financing activities was a de minimis amount, consisting primarily of a $0.4 million payment of Series B-1 convertible preferred stock issuance costs, partially offset by the proceeds from the exercise of warrants to purchase shares of Series A convertible preferred stock of $0.4 million and proceeds from the exercise of stock options of $0.1 million.
During the six months ended June 30, 2019, net cash used in financing activities was a de minimis amount, consisting solely of payments of finance leases.
During Fiscal 2019, net cash provided by financing activities was $85.5 million, consisting primarily of net proceeds of $85.0 million from our sales of shares of our Series B-1 convertible preferred stock, proceeds from the exercise of stock options of $0.5 million, and proceeds from the exercise of warrants to purchase shares of Series A convertible preferred stock of $0.1 million, partially offset by the payment of finance leases of $0.1 million.
During Fiscal 2018, net cash provided by financing activities was $99.9 million, consisting of net proceeds of $94.8 million from our sales of shares of Series A convertible preferred stock, proceeds from the issuance of convertible notes and warrants of $5.0 million, and proceeds from the exercise of stock options and sale of common stock of $0.1 million.
Contractual obligations and commitments
The following table summarizes our commitments and contractual obligations as of December 31, 2019:
| Payments Due by Period | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Total | Less Than 1 Year |
1-3 Years |
3-5 Years |
More Than 5 Years |
||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating lease commitments |
$ | 19,588 | $ | 2,507 | $ | 5,292 | $ | 5,375 | $ | 6,414 | ||||||||||
| Finance lease commitments |
264 | 75 | 149 | 40 | — | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total |
$ | 19,852 | $ | 2,582 | $ | 5,441 | $ | 5,415 | $ | 6,414 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
The operating lease commitments noted in the table above represent operating lease obligations related to our currently occupied premises in South San Francisco, California and Belgium. The finance lease commitments represent obligations related to vehicle leases for employees in Belgium. We do not have any material purchase commitments for contracts with fixed or minimum service requirements. We also enter into contracts in the normal course of business with various vendors that generally provide for contract termination following a certain notice period. These contracts do not contain any minimum purchase commitments, and as a result, are not included in the table of contractual obligations above. Payments due upon cancelation consist only of
105
Table of Contents
payments for services provided, expenses incurred up to the date of cancelation and de minimis termination penalties. Accordingly, we believe that our non-cancelable obligations under such agreements are not material and therefore have excluded these from the table above.
This table also does not include any milestone or royalty payments to third parties as the amounts, timing and likelihood of such payments are not known at this time. For a summary of certain milestone and royalty payment obligations under our agreements with Emory and Luxna, see the section titled “Business—License agreements”.
Off-balance sheet arrangements
We did not have during the periods presented, and we do not currently have, any off-balance sheet arrangements, as defined in the rules and regulations of the SEC.
Indemnification agreements
We enter into standard indemnification arrangements in the ordinary course of business. Pursuant to these arrangements, we indemnify, hold harmless and agree to reimburse the indemnified parties for losses suffered or incurred by the indemnified party, in connection with any trade secret, copyright, patent or other intellectual property infringement claim by any third party with respect to its technology. The term of these indemnification agreements is generally perpetual any time after the execution of the agreement. The maximum potential amount of future payments we could be required to make under these arrangements is not determinable. We have never incurred costs to defend lawsuits or settle claims related to these indemnification agreements. As a result, we believe the fair value of these agreements is minimal.
Quantitative and qualitative disclosures about market risk
Interest rate risk
We are exposed to market risk related to changes in interest rates applicable to our investment portfolio of cash equivalents and short-term and long-term investments. As of June 30, 2020, our cash equivalents consisted of money market funds. As of June 30, 2020, our short-term and long-term investments consisted of U.S. Treasury securities. Our primary exposure to market risk is interest income sensitivity, which is affected by changes in the general level of U.S. interest rates. Should U.S. interest rates decline, interest income would be reduced in future periods for short- and long-term investments which mature and the proceeds of which are reinvested in similar instruments at lower interest rates. Additionally, the fair value of our short-term and long-term investments is subject to change as a result of potential changes in market interest rates, including changes resulting from the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. The potential change in fair value from interest-rate-sensitive instruments has been assessed on a hypothetical 100 basis point adverse movement across all maturities. As of June 30, 2020, we estimate that a hypothetical 100 basis point adverse movement would not result in a material impact on our financial position or results of operations or cash flows. As of June 30, 2020, we had no debt outstanding, besides short-term payables arising in the normal course of business, and are therefore not exposed to interest rate risk with respect to debt.
Foreign currency exchange risk
We have employees and operations, including contracts with third-party vendors, in Europe through our subsidiary Aligos Belgium BVBA. We have similar, but more limited, operations in Australia. Though the functional currency in these locations is the U.S. dollar, we remeasure transactions initially recorded in local
106
Table of Contents
currencies in these locations, the Euro and Australian dollar, respectively, to the U.S. dollars periodically. As such, we are exposed to foreign currency exchange risk as the underlying contracts to pay employees or vendors in these locations are generally denominated in the local currencies. A decline in the value of the U.S. dollar relative to these currencies would increase our cost of doing business in these locations. We are subject to foreign currency transaction gains or losses on our contracts denominated in foreign currencies. To date, foreign currency transaction gains and losses have not been material to our financial statements, and we have not had a formal hedging program with respect to foreign currency. A 10% increase or decrease in current exchange rates would not have a material effect on our financial position or results of operations or cash flows.
Critical accounting policies and use of estimates
Our management’s discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations is based on our consolidated financial statements, which have been prepared in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”). The preparation of these consolidated financial statements requires us to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts and the disclosure of assets and liabilities at the date of the consolidated financial statements, as well as the reported expenses incurred during the reporting periods. Our estimates are based on relevant assumptions that we believe are reasonable under the circumstances, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying value of assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other sources. Actual results may differ from these estimates under different assumptions or conditions.
While our significant accounting policies are described in the notes to our consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this prospectus, we believe that the following critical accounting policies are most important to understanding and evaluating our reported financial results and future performance, as these policies relate to the more significant areas involving management’s judgments and estimates.
Accrued research and development costs
We record accrued expenses for estimated costs of our research and development activities conducted by third-party service providers, which include the conduct of clinical trials and nonclinical studies. We record the estimated costs of research and development activities based upon the estimated amount of services provided but not yet invoiced and include these costs in accrued liabilities in the consolidated balance sheets and within research and development expense in the consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive loss. These expenses are a significant component of our research and development costs. We record accrued expenses for these costs based on factors such as estimates of the work completed and in accordance with agreements established with these third-party service providers. Any payments made in advance of services provided are recorded as prepaid expenses and other assets, which are expensed as the contracted services are performed.
We estimate the amount of work completed through discussions with internal personnel and external service providers as to the progress or stage of completion of the services and the agreed-upon fee to be paid for such services. We make significant judgments and estimates in determining the accrued balance in each reporting period. As actual costs become known, we adjust our accrued estimates. Although we do not expect our estimates to be materially different from amounts actually incurred, our understanding of the status and timing of services performed could vary from actuals and result in us reporting amounts that are too high or too low in any particular period. Our accrued expenses are dependent, in part, upon the receipt of timely and accurate reporting from clinical research organizations and other third-party service providers. For the periods presented, we have experienced no material differences between our accrued expenses and actual expenses.
107
Table of Contents
Research and development expenses
We expense research and development costs as incurred. Acquired intangible assets are expensed as research and development if, at the time of payment, the technology is under development; is not approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration or other regulatory agencies for marketing; has not reached technical feasibility; or otherwise has no foreseeable alternative future use.
Research and development expenses also include costs incurred for internal and sponsored and collaborative research and development activities. Research and development expenses consist of salaries and benefits, including associated stock-based compensation, and laboratory supplies and facility costs, as well as fees paid to other entities that conduct certain research and development activities on our behalf. Costs associated with co-development activities performed under the various license and collaboration agreements are included in research and development expense as incurred.
Stock-based compensation
We measure stock options and other stock-based awards granted to employees, directors and other service providers based on their fair value on the date of grant and recognize compensation expense of those awards over the requisite service period, which is generally the vesting period of the respective award. We recognize the impact of forfeitures on stock-based compensation expense as forfeitures occur. We apply the straight-line method of expense recognition to all awards with only service-based vesting conditions. During the period from inception through December 31, 2018 and the year ended December 31, 2019, we did not grant any stock-based awards with performance-based vesting conditions. During the six months ended June 30, 2020, we granted stock-based awards with performance-based vesting conditions. We recognize compensation expense related to these awards when it is determined that satisfying the performance conditions is probable using the accelerated attribution method over the requisite service period.
We estimate the fair value of each stock option grant on the date of grant using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model, which requires the use of highly subjective assumptions including:
| • | Expected term—We have opted to use the “simplified method” for estimating the expected term of plain-vanilla options, whereby the expected term equals the arithmetic average of the vesting term and the original contractual term of the option (generally 10 years). We estimated the expected term of performance-based vesting options based on the expected life of the options to remain outstanding, which is estimated to be materially consistent with time-vesting options. |
| • | Risk-free interest rate—The risk-free rate assumption is based on the U.S. Treasury instruments with maturities similar to the expected term of our stock options. |
| • | Expected dividend—We have not issued any dividends and do not anticipate to issue dividends on our common stock. As a result, we have estimated the dividend yield to be zero. |
| • | Expected volatility—Due to our limited operating history and a lack of company-specific historical and implied volatility data, we have based our estimate of expected volatility on the historical volatility of a group of similar companies that are publicly traded. The historical volatility data was computed using the daily closing prices for the selected companies’ shares during the equivalent period of the calculated expected term of the stock-based awards. |
Determination of fair value of common stock
As there has been no public market for our common stock to date, the estimated fair value of our common stock has been determined by our board of directors, or compensation committee thereof, as of the date of
108
Table of Contents
each option grant, with input from management, considering our most recently available third-party valuations of common stock and our board of directors’ assessment of additional objective and subjective factors that it believed were relevant and which may have changed from the date of the most recent valuation through the date of the grant. Historically, these independent third-party valuations of our equity instruments were performed contemporaneously with identified value inflection points, including recent preferred stock financings.
These third-party valuations were performed in accordance with the guidance outlined in the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants’ Accounting and Valuation Guide, Valuation of Privately-Held-Company Equity Securities Issued as Compensation (the “Practice Aid”). The Practice Aid identifies various available methods for allocating the enterprise value across classes of capital stock in determining the fair value of our common stock at each valuation date.
In accordance with the Practice Aid, the probability-weighed expected return method (“PWERM”) and the Option Pricing Method (“OPM”) were the most appropriate methods for determining the fair value of our common stock based on our stage of development and other relevant factors. Our valuation as of June 2020 contemplated the PWERM, which considers probability weighted future events outcomes for us. Our valuation as of December 2019 contemplated the Hybrid Method, which is a combination of the PWERM and the OPM to allocate the value to the securities, based on the terms of our then-concurrent Series B financing. Our valuation in October 2018 employed an OPM model, and was based on our Series A financing that occurred in September 2018, and included certain adjustments for changes in market conditions and drug failure data sets.
In addition to considering the results of these third-party valuations, our board of directors considered various objective and subjective factors to determine the fair value of our common stock as of each grant date, including:
| • | the rights, preferences, and privileges or our preferred securities as compared to those of our common stock, including liquidation preferences of our preferred stock; |
| • | the progress of our research and development programs, including the status and results of nonclinical studies and clinical trials for our drug candidates: |
| • | our stage of development and outlook for potential commercialization of our drug candidates and our business strategy; |
| • | external market conditions affecting the biopharmaceutical industry and trends within the biopharmaceutical industry, including a review of the performance and metrics of guideline public companies; |
| • | our financial position, including cash on hand, and our historical and forecasted performance and operating results; |
| • | the lack of an active public market for our common stock and our preferred stock; |
| • | the likelihood of achieving a liquidity event, such as an initial public offering (“IPO”) or sale of our company in light of prevailing market conditions; and |
| • | an analysis of IPOs and the market performance of similar companies in the biopharmaceutical industry. |
Our valuations were performed using the OPM, PWERM or the Hybrid Method. The method selected was based on the availability and the quality of information to develop the assumptions for the methodology, based on the facts and circumstances applicable to each valuation date.
OPM - The OPM treats common stock and preferred stock as call options on the total equity value of a company, with exercise prices based on the value thresholds at which the allocation among the various holders of a
109
Table of Contents
company’s securities changes. The common stock is modeled as a call option on the underlying equity value at a predetermined exercise price. In the model, the exercise price is based on a comparison with the total equity value rather than, as in the case of a regular option, a comparison with a per share stock price. Thus, common stock is considered to be a call option with a claim on the enterprise at an exercise price equal to the remaining value immediately after the preferred stock liquidation preference is paid. The OPM uses the Black-Scholes option pricing model to price the call options. This model defines the fair value of securities as functions of the current fair value of the subject company and uses assumptions such as the anticipated timing of a potential liquidity event and the estimated volatility of the equity securities. The OPM method was used for our October 2018 and December 2019 valuations. The OPM might be used to determine the enterprise value of an entity by using a “backsolve method.” By considering the sale price of shares in a recent arms-length financing, the aggregate equity value (and, by implication, enterprise value) can be “back-solved” using an option pricing theory-based model that gives consideration to the subject company’s capitalization structure and rights of the holders of preferred stock and common stock. This methodology is most applicable when a valuation is conducted close to the date of a financing transaction, which was the case for our October 2018 and December 2019 valuations.
PWERN - Under the PWERM methodology, the fair value of the common stock is estimated based upon an analysis of future values for the company, assuming various scenario outcomes. The common stock value is based on the probability weighted present value of expected future investment returns considering each of the possible outcomes available, as well as the rights of each class of stock under each scenario. The future value of the common stock under each outcome is discounted back to the valuation date at an appropriate risk-adjusted discount rate and probability to arrive at an indication of value for the common stock. Subsequent to our decision to pursue a public offering of our shares, it was determined that the PWERM was the appropriate methodology to employ for our June 2020 valuation analysis.
The relative probability of each type of future-event scenario was determined based on management’s best estimate as of the date of valuation, including then-current expectations as to the timing and likely prospects of the future event scenarios.
Hybrid Method - The Hybrid Method is a PWERM where the equity value in one or more of the scenarios is calculated using an OPM. This method was employed in our December 2019 valuation analysis. In considering valuation approaches for the Company, the third-party valuation specialist applied the Hybrid Method in our December 2019 valuation to determine the implied equity value of the Company in various scenarios, based on the latest round of financing - Series B convertible preferred stock. However, the purchase agreement for this financing round also provided for a second closing if we meet certain milestones before March 31, 2021 (the “Series B Milestones”). The milestones in the agreement are described as follows:
| • | receipt of permission to proceed under an Investigational New Drug application submitted to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration or approval of the clinical trial application by a comparable foreign regulatory agency having jurisdiction (the “CTA Approval”) with respect to our HBV STOPs program; and |
| • | the CTA Approval with respect to our HBV CAM program. |
The relative probability of each type of future-event scenario was determined based on management’s best estimate as of the date of valuation, including then-current expectations as to the timing and likely prospects of the future event scenarios.
Our valuation in October 2018 employed an OPM model and was based on our Series A convertible preferred stock financing that occurred in September 2018, and included certain adjustments for changes in market conditions and drug failure data sets. The valuation specialist performed a backsolve analysis based on the Series A convertible preferred stock financing to determine the implied enterprise value. This value was then
110
Table of Contents
adjusted based on a change in market conditions that occurred between the financing date and the valuation date. In addition, certain failure rate data sets were reviewed and incorporated into the adjusted invested capital value. An OPM model was then used to estimate the value of the common stock as of October 2018.
The assumptions underlying these valuations represented management’s best estimates, which involved inherent uncertainties and the application of management’s judgment. As a result, if we had used significantly different assumptions or estimates, the fair value of our common stock and our stock-based compensation expense could have been materially different.
Once a public trading market for our common stock has been established in connection with the closing of this offering, it will no longer be necessary for our board of directors to estimate the fair value of our common stock in connection with our accounting for granted stock options and other such awards we may grant, as the fair value of our common stock will be determined based on the quoted market price of shares of our common stock.
Redeemable convertible preferred stock liability
The freestanding instruments related to the commitments by holders of shares of Series B-1 convertible preferred stock to purchase and by us to sell our shares of Series B-2 convertible preferred stock in a subsequent closing, contingent upon the achievement of certain developmental milestones or an election by investors to waive such contingencies, at a fixed price per share, are considered a liability measured at fair value as the shares underlying the rights contain liquidation preferences upon certain “deemed liquidation events” that are not solely within our control. The instruments are subject to revaluation at each balance sheet date until settlement, with revaluations recognized as a component of interest and other income (expense) net in the consolidated statement of operations and comprehensive loss.
The fair value of the commitment is estimated using a probability weighted multi-scenario Black Scholes hybrid valuation method, which is most sensitive to the probability of each possible outcome and the estimated value for the shares of Series B-2 convertible preferred stock at the end of the term with respect to the achievement of the milestones and issuance of shares of Series B-2 convertible preferred stock. The probability of each scenario is estimated by management based on available information at the end of each reporting period.
Warrants liability
We account for the warrants issued in connection with our 2018 convertible financing as a liability at its fair value and adjust the instrument to fair value at each reporting period as the warrants are exercisable into our Series A convertible preferred stock. This liability is subject to re-measurement at each balance sheet date until exercised or terminated, and any change in fair value is recognized as a component of interest and other income (expense), net on our consolidated statement of operations and comprehensive loss. The fair value of warrants has been estimated using a probability weighted multi-scenario Black Scholes hybrid valuation model. The model accounts for the probability of a liquidity event as best estimated by management, which could significantly impact the valuation of the warrants.
Emerging growth company status
In April 2012, the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act of 2012 (the “JOBS Act”), was enacted. Section 107 of the JOBS Act provides that an “emerging growth company” (an “EGC”) can take advantage of the extended transition period provided in Section 7(a)(2)(B) of the Securities Act for complying with new or revised accounting standards. Thus, an EGC can delay the adoption of certain accounting standards until those standards would otherwise apply to private companies. We have elected to use the extended transition period
111
Table of Contents
for any new or revised accounting standards during the period in which we remain an EGC; however, we may adopt certain new or revised accounting standards early.
We will remain an EGC until the earliest to occur of: (1) the last day of the fiscal year in which we have more than $1.07 billion in annual revenue; (2) the date we qualify as a “large accelerated filer,” with at least $700.0 million of equity securities held by non-affiliates; (3) the date on which we have issued more than $1.0 billion in non-convertible debt securities during the prior three-year period; and (4) the last day of the fiscal year ending after the fifth anniversary of our initial public offering.
In addition, we intend to rely on the other exemptions and reduced reporting requirements provided to EGCs by the JOBS Act. Subject to certain conditions set forth in the JOBS Act, as an EGC, we are not required to, among other things, (i) provide an auditor’s attestation report on our system of internal controls over financial reporting pursuant to Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, (ii) provide all of the compensation disclosure that may be required of non-emerging growth public companies under the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, (iii) comply with any requirement that may be adopted by the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board regarding mandatory audit firm rotation or a supplement to the auditor’s report providing additional information about the audit and the financial statements (auditor discussion and analysis) or (iv) disclose certain executive compensation-related items such as the correlation between executive compensation and performance and comparisons of the Chief Executive Officer’s compensation to median employee compensation.
Recently issued and adopted accounting pronouncements
A description of recently issued accounting pronouncements that may potentially impact our financial position and results of operations is disclosed in Note 2 to our consolidated financial statements and Note 2 to our unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements appearing at the end of this prospectus.
112
Table of Contents
Overview
We are a clinical-stage biopharmaceutical company currently focused on developing novel therapeutics to address unmet medical needs in viral and liver diseases. We utilize our proprietary oligonucleotide and small molecule platforms to develop pharmacologically optimized drug candidates for use in combination regimens designed to achieve improved treatment outcomes. Our lead effort is to develop a functional cure for Chronic Hepatitis B (“CHB”), which often results in other life-threatening conditions such as cirrhosis, end-stage liver disease (“ESLD”) and the most common form of liver cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma (“HCC”). The most widely used treatment for CHB, nucleos(t)ide analogs, suppresses viral replication but only achieves low rates of functional cure and often requires long-term administration. To address this issue, we have developed a portfolio of differentiated drug candidates for CHB, including an S-antigen Transport-inhibiting Oligonucleotide Polymers (“STOPS”) molecule, a small molecule Capsid Assembly Modulator (“CAM”), and oligonucleotides (ASO and siRNA), each of which is designed against clinically validated targets in the Hepatitis B Virus (“HBV”) life cycle. We believe that combination regimens utilizing our portfolio of CHB drug candidates may lead to higher rates of functional cure. A Phase 1 proof of concept trial for our STOPS molecule is ongoing in New Zealand and we expect to initiate a Phase 1 clinical trial with our CAM in the second half of 2020. Our second area of focus is in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (“NASH”), a complex, chronic liver disease where combination regimens may likewise prove beneficial. Our most advanced drug candidate for NASH is ALG-055009, a small molecule THR-ß agonist currently in nonclinical studies to enable a first-in-human clinical trial. We believe ALG-055009 has the potential to become an integral component of future combination regimens for NASH. Our third area of focus is to develop drug candidates with pan-coronavirus activity, including Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome coronavirus 2 (“SARS-CoV-2”), the virus responsible for COVID-19.
Our team’s collective experience and success in discovering and developing drugs targeting viruses and liver diseases, combined with our in-house expertise in oligonucleotide and small molecule drug discovery, gives us a differentiated set of capabilities, which has enabled us to rapidly establish a robust pipeline of multiple novel drug candidates, as summarized in the pipeline chart below.

Our most advanced drug candidates are for the treatment of CHB, a disease that affects more than 290 million people worldwide with approximately 30 million people becoming newly infected every year, despite the availability of an efficacious prophylactic vaccine. Approximately 900,000 people worldwide died from
113
Table of Contents
complications of CHB in 2015, according to the World Health Organization, and CHB is the primary cause of liver cancer worldwide. Currently approved therapies for CHB include pegylated forms of interferon-alfa (“peg-IFNa”) and nucleos(t)ide analogs, which are designed to boost the body’s immune response to the virus or inhibit viral replication, respectively. While these therapies have improved treatment outcomes for some patients with CHB, they have not been able to achieve meaningful rates of functional cure, which is the consensus goal of treatment and defined as a sustained loss of HBsAg with or without hepatitis B surface antibody seroconversion. Functional cure has been shown to greatly reduce the risk of developing certain other more serious downstream liver conditions, such as cirrhosis and ESLD.
Our clinical development strategy involves evaluating both Hepatitis B E-antigen (“HBeAg”) positive and HBeAg negative CHB patient populations. HBeAg is typically present in earlier stages of the disease and is associated with higher rates of viral replication. During the natural course of the disease, HBeAg can be cleared and antibodies develop, resulting in an HBeAg negative state where viral replication is often lower. Patients with HBeAg negative CHB are typically older and have more progressive disease-related complications (e.g., fibrosis of the liver). In addition, their immune system is likely to be more exhausted by chronic exposure to HBsAg, which makes viral clearance more difficult. Although we plan to ultimately study both populations, due to the greater availability of patients with HBeAg negative CHB at investigational sites, we intend to study this population first.
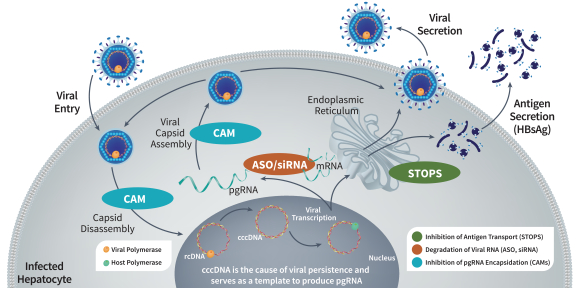
Multiple steps in the HBV life cycle, including those involving capsid assembly and production and secretion of HBsAg, are known to be essential to sustain HBV infection. We have built a portfolio of CHB drug candidates directed against clinically validated targets at several critical stages of the HBV life cycle. Our CHB portfolio includes:
| • | STOPS are protein-binding oligonucleotides that share structural similarity with nucleic acid polymers (“NAPs”), which have been reported in clinical trials to significantly reduce circulating HBsAg and result in high rates of functional cure when used in combination with nucleos(t)ide analogs and peg-IFNa. Our most advanced STOPS molecule is ALG-010133, which is currently being evaluated in a Phase 1 clinical trial. In nonclinical studies, ALG-010133 has demonstrated higher inhibitory activity than a reference NAP compound that is currently in clinical development. |
| • | CAMs are small molecule antiviral agents that accelerate HBV capsid assembly and inhibit pregenomic RNA (“pgRNA”) encapsidation, which reduces production of new virions capable of infecting other cells. CAMs may |
114
Table of Contents
| also inhibit the de novo establishment of covalently closed circular DNA (“cccDNA”), a major factor for the persistence of HBV infection, when introduced at the onset of infection. In clinical trials, other CAM drug candidates have demonstrated significant reductions in HBV DNA and pgRNA. However, it is likely that CAMs will need to be combined with other modalities that affect HBsAg in order to achieve functional cure. Our most advanced CAM drug candidate is ALG-000184, a prodrug of ALG-001075, which we plan to advance into a Phase 1 clinical trial in the second half of 2020. In nonclinical studies, we have shown that ALG-001075 has significantly enhanced potency compared to other CAMs in clinical development of which we are aware. |
| • | ASOs are single-stranded DNA or RNA molecules that interfere with viral replication by binding to complementary messenger RNA (“mRNA”), allowing the combined ASO and mRNA to be degraded by the enzyme RNase H. Using our oligonucleotide discovery capabilities, we identified ALG-020572, an ASO that targets HBV mRNA and can reduce HBsAg production, which we plan to advance into clinical trials in the second half of 2021. In third-party clinical trials, ASOs targeting HBV mRNA have demonstrated significant reductions in HBsAg. Our ASO approach utilizes state of the art bioinformatics, proprietary stabilization chemistry and liver targeting technology that we believe provides a number of potential benefits compared to other ASO candidates of which we are aware, including increased potency, a higher barrier to resistance and broad genotype coverage. |
| • | siRNAs are a class of double-stranded, non-coding RNA that interferes with viral replication by silencing gene expression. Multiple siRNAs have demonstrated significant reductions in HBsAg levels in clinical trials. Our oligonucleotide discovery capabilities resulted in the identification of ALG-125097, an siRNA drug candidate directed at HBV mRNA, which utilizes our proprietary liver targeting technology. |
We believe that a combination of drugs capable of inhibiting HBV DNA replication and RNA packaging (e.g., using CAMs) while simultaneously suppressing HBsAg production (e.g., using our STOPS molecule, ASO, and/or siRNA) has the potential to act additively or synergistically and may lead to a higher rate of functional cure. Our clinical development strategy is designed to evaluate safety and antiviral activity as monotherapy prior to evaluating multiple combinations of our CHB assets, with or without other currently available treatment modalities such as nucleos(t)ide analogs or peg-IFNa, to identify optimized combination regimens.
Our second development effort is focused on the treatment of NASH. An estimated 1.5% to 6.5% of the global population, or up to about 450 million people, was believed to have NASH as of 2015 and this is expected to increase significantly in the coming decade due to the adoption of Western dietary habits. In the absence of lifestyle modifications, the inflammation inherent in NASH persists and results in progressive fibrosis of the liver, which may lead to cirrhosis, ESLD, HCC, the need for liver transplant, and death. We believe one of the most promising pharmacologic approaches in development for NASH is a selective agonist of the beta subtype of the thyroid hormone receptor (“THR-ß”), which, in clinical trials conducted by third parties, has demonstrated significant reduction in liver fat and inflammation, as well as the reduction in lipid levels in the serum, which may have important advantages in the NASH patient population that is at a high risk of cardiovascular co-morbidities. Utilizing our expertise in small molecule drug discovery, we identified ALG-055009, a once-daily oral THR-ß agonist. In nonclinical studies, ALG-055009 has been shown to be substantially more potent compared to other THR-ß agonists currently in development of which we are aware and may avoid some of their potential safety liabilities while having the potential to achieve equal or better efficacy. As a result, we believe ALG-055009 has the potential to become an integral component of combination regimens to treat NASH. We intend to advance ALG-055009 into clinical development in the second half of 2021.
Our third area of focus is to develop pan-coronavirus treatment regimens. SARS-CoV-2 is responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic, which has been identified as a cause of more than 750,000 deaths worldwide as of August 2020. After MERS and SARS (SARS-CoV-1), SARS-CoV-2 is the third known coronavirus to have crossed over from animal species to humans in the past 20 years and cause significant morbidity and mortality. While
115
Table of Contents
multiple vaccines are likely to become available in the future, it is unlikely that a vaccine will be fully efficacious and widely adopted, indicating that the need for effective therapeutic treatments will remain. Currently, repurposed drugs which have not been optimized for the treatment of coronavirus infections are being studied to treat SARS-CoV-2, and there is a need for purpose-built drugs which are suitable across a broad range of coronaviruses, patient populations and clinical settings, including prophylactic and post-exposure settings. We believe that, similar to CHB, a combination of antiviral and/or immunomodulatory drugs which target multiple points in the viral replication cycle offers the best chance of success. To address this urgent, unmet medical need, we are in early stages of development for multiple drug candidates including nucleos(t)ide, siRNA/ASO and protease inhibitors that are specifically designed to interact with targets that are highly conserved across multiple coronaviruses. Each of these drug candidates is intended to have pan-coronavirus activity and to be used in combination regimens to maximize their antiviral activity.
Our management team consists of a group of highly collaborative, culturally diverse executives with decades of drug discovery and development experience and a proven track record of success in the areas of viral infections and liver diseases. Most members of our management team have worked together across multiple companies, many for over a decade, and have been collectively involved in the discovery and/or development of a number of drugs that have been successfully commercialized, including Ganovo, Olysio, Sovaldi, Hepsera, Infergen, Valtrex, Sirturo, Neupogen, Andexxa and Esbriet, among others. In support of our management team, we also have assembled an industry-leading board of directors and a world-class group of scientific advisors with significant experience in drug development for viral and liver diseases. Finally, we have top-tier investors, including Boxer Capital of Tavistock Group, Cormorant Asset Management, Janus Henderson Investors, Logos Capital, Novo Holdings, Pivotal bioVenture Partners, Roche Venture Fund, Versant Ventures, Vivo Capital and Wellington Management Company.
Our strategy
Our strategy is to develop pharmacologically optimized drug candidates for use in combination regimens designed to achieve improved treatment outcomes. Our initial areas of focus are viral and liver diseases where our team can leverage their in-depth knowledge and expertise to develop potentially best-in-class combination regimens addressing large areas of unmet medical need. The core elements of our business strategy include:
| • | Developing improved drug candidates against clinically validated targets. We leverage our oligonucleotide and small molecule platforms to identify drug candidates with pharmacologically optimized characteristics compared to other drug candidates, including the potential for improved efficacy, safety and/or route of administration. By initially focusing on clinically validated targets, we increase the likelihood of demonstrating clinical efficacy and delivering optimized combination regimens. |
| • | Creating combination regimens to achieve better outcomes. We believe that most chronic and viral diseases require combination therapies for optimal treatment outcomes, and that combining individual drugs which can act additively or synergistically provides the greatest potential for enhanced efficacy. For each of our drug candidates, our strategy in Phase 1 is to rapidly evaluate safety and demonstrate proof of activity for each individual drug. Subsequently, we plan to combine multiple drug candidates in Phase 2 trials to identify optimized combination regimens to be advanced into pivotal trials. |
| • | Developing a functional cure for CHB. We have a portfolio of differentiated drug candidates for CHB, including a STOPS molecule, a small molecule CAM, and oligonucleotides (ASO and siRNA) each of which is designed to inhibit clinically validated, distinct and critical points in the HBV life cycle. Our two lead drug candidates for CHB, ALG-010133, a STOPS molecule, and ALG-000184, a CAM, are currently in, or advancing in the second half of 2020, into Phase 1 trials, respectively. Based on nonclinical studies, we believe that each of these drug candidates has demonstrated strong potential relative to other drugs in development. In |
116
Table of Contents
| combination, we expect our drug candidates to provide greater viral suppression, potentially leading to higher rates of functional cure. |
| • | Expanding our development capabilities and pipeline. We are utilizing our in-house discovery expertise to continually improve upon our existing drug candidates by identifying promising backup candidates and exploring novel and emerging drug targets in viral and liver diseases. We are also evaluating novel mechanisms of action with the potential to complement our current pipeline. To further supplement our internal discovery and development efforts, we actively evaluate external technology platforms and assets for future development candidates for liver and viral diseases. To date, we have secured licenses for technology from Emory, Luxna and AM Chemicals, LLC (“AM Chemicals”), and have entered into a collaboration with KU Leuven’s Rega Institute for Medical Research, as well as its Centre for Drug Design and Discovery. |
| • | Maximizing the value of our drug candidates. We currently hold worldwide development and commercialization rights, including through exclusive licenses, to all of our drug candidates. We intend to pursue independent development and commercialization in select indications and markets that we can address with a specialty sales and marketing organization. We may opportunistically explore licensing agreements, collaborations or partnerships to develop our drug candidates in larger market indications where we could accelerate development utilizing the resources of larger biopharmaceutical companies, or to commercialize them in specific geographies. |
Our approach to research and development
Our oligonucleotide and small molecule platforms allow us to discover drug candidates that can be used to develop potentially best-in-class combination regimens. Oligonucleotide approaches enable specific inhibition of the translation of viral or host genes to affect a desired outcome that would be challenging to achieve with traditional small molecules. We believe the diversity of chemical matter we can generate with these complementary modalities broadens the range of therapeutic targets we can address with our platforms, and provides us with a differentiated set of in-house capabilities to use in developing novel, optimized combination regimens across all of our current areas of focus.
Our approach of combining multiple mechanisms from these distinct modalities is based on the observation that most chronic diseases, whether extrinsic (e.g., HIV and Hepatitis C) or intrinsic (e.g., metabolic syndrome conditions such as hypertension and diabetes), often require combination therapy to achieve optimal outcomes. Combination approaches have the advantage of simultaneously targeting multiple pathways and can act broadly and potentially synergistically. Particularly in the case of viral diseases, the simultaneous use of multiple drugs in combination can increase the barrier to viral resistance. As part of our drug candidate screening paradigm, we perform in vitro combination studies to ensure that none of the combinations we plan to evaluate clinically demonstrate antagonistic interactions.
Our team has extensive end-to-end drug discovery and development experience across multiple therapeutic areas and disciplines. Our clinical development strategy leverages past experience to rapidly advance drug candidates towards optimized combination regimens. We have strengthened our platforms by in-licensing select intellectual property, which, together with our in-house expertise, allows us to develop novel and proprietary drug candidates.
Oligonucleotide platform
We have multiple distinct modalities within our oligonucleotide platform, including STOPS molecules, ASOs, and siRNAs. We have developed a portfolio of oligonucleotide drug candidates for the treatment of CHB, including: ALG-010133, a STOPS molecule drug candidate; ALG-020572, an ASO drug candidate; and ALG-125097, an siRNA
117
Table of Contents
drug candidate. In addition, we are leveraging our oligonucleotide platform to develop drug candidates for coronaviruses and other diseases.
We have exclusively licensed proprietary technologies that enhance our oligonucleotide platform. These technologies include third generation bridged nucleic acid (“BNA”) and N-acetylgalactosamine (“GalNAc”) chemistries, which can improve liver targeting, increase potency and enhance pharmacokinetic properties.
S-antigen Transport-inhibiting Oligonucleotide Polymers (“STOPS”) molecules
STOPS molecules are oligonucleotides which in vitro reduce the levels of key HBV viral markers, including HBsAg. They share structural similarity with NAPs such as IV-administered REP 2139 and REP 2165, which, when used in combination with nucleos(t)ides analogs and peg-IFNa in clinical trials conducted by others, have demonstrated significant declines in key HBV viral markers and increased functional cure rates over current standard of care. Our STOPS molecules, such as our lead drug candidate ALG-010133, have been highly optimized and contain several novel chemical features, leading to enhanced in vitro potency and allowing for subcutaneous dosing.
Antisense oligonucleotides (“ASOs”)
ASOs are single-stranded DNA or RNA molecules that interfere with viral replication by binding to and down-regulating mRNA expression, preventing subsequent protein translation. This technology has been validated across multiple indications, including CHB, where significant reductions in viral markers have been observed. We have discovered potent, liver-targeted ASOs, including ALG-020572, which has demonstrated a promising profile in nonclinical CHB models.
Small interfering RNAs (“siRNAs”)
siRNAs are a class of double-stranded RNA that interfere with viral replication by silencing gene expression and subsequent protein translation. siRNAs have shown efficacy across multiple indications, including CHB, where significant reductions in viral markers have been observed. Our novel and proprietary siRNA technology has resulted in the identification of molecules, including ALG-125097, that have demonstrated high potency and long-lasting durability in nonclinical CHB models.
Small molecule platform
Our team has the capability and experience to rapidly identify and optimize small molecules, including traditional small molecules, peptidomimetics and prodrugs. Our team has a strong track record of developing and commercializing small molecule drug candidates. We use state-of-the-art computational chemistry and crystallography to enable structure-guided drug design. We have applied this approach to the multidimensional optimization of potential drug candidates in multiple therapeutic areas, including for viral and liver diseases.
Traditional small molecules
To date, traditional small molecules represent the vast majority of approved drugs and are the primary chemistry approach used for drug discovery. CAMs are small molecules that have been shown to significantly reduce viral markers in CHB patients in clinical studies. Applying our small molecule platform, we have identified ALG-001075 which has demonstrated improved in vitro potency and increased efficacy in nonclinical animal models, as compared to other CAM candidates that have advanced into the clinic. ALG-001075 is currently being advanced as the prodrug ALG-000184.
118
Table of Contents
THR-ß agonists are small molecules that have been shown to significantly reduce circulating lipid levels and improve liver histology in patients with NASH. We have discovered ALG-055009, a THR-ß agonist that has demonstrated improved potency in vitro and increased efficacy in nonclinical animal models relative to other THR-ß agonists in Phase 2 or later stages of development.
Peptidomimetics
Peptidomimetics are small molecules derived from short polypeptides that can be used as drug candidates against multiple targets. The peptidomimetic approach has been successfully used in the antiviral field to develop protease inhibitor drugs against Hepatitis C virus (“HCV”) and human immunodeficiency virus (“HIV”). Our team has discovered multiple potential nanomolar potency drug candidates targeting the 3C-Like protease of coronaviruses. These projects are moving towards the identification of a lead drug candidate with potentially broad spectrum activity against COVID-19, SARS, MERS, and possibly other emergent coronaviruses.
Small molecule prodrugs
A prodrug is a compound that, after administration, is metabolized into the pharmacologically active parent drug. We use small molecule prodrug chemistry to optimize the drug-like properties of drug candidates to improve their solubility and pharmacokinetics. We have successfully applied this approach to ALG-001075 to create ALG-000184, which is our lead CAM drug candidate that we are advancing towards the clinic for the treatment of CHB.
We are engaged in multiple other small molecule discovery efforts to identify additional potentially best-in-class drug candidates for the treatment of CHB, NASH and coronaviruses.
119
Table of Contents
Our approach to developing best-in-class therapeutic combinations
Our approach to developing best-in-class regimens for our therapeutic areas of interest leverages the most promising modalities from our oligonucleotide and small molecule platforms to advance rapidly from monotherapy Phase 1 trials into Phase 2 combination trials. As a first step, we evaluate the safety and activity of each drug candidate in healthy volunteers and patients with the disease of interest. We intend to then efficiently evaluate drug candidates shown to have activity in Phase 1 in various combinations in Phase 2 platform protocols to enable us to identify optimized combination regimens that will then be evaluated in Phase 3 pivotal trials. The combinations we evaluate may include additional drug candidates or current standard of care. Throughout all phases of clinical development, pre-specified adaptive study rules allow real-time adjustment of trial conduct based on emerging clinical trial data. These practices allow us to gain a rapid understanding of the risk/benefit profile for our individual drug candidates and combination regimens, and iteratively refine our strategy based on emerging data. This approach is summarized in the figure below.
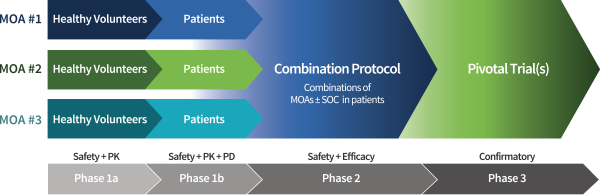
120
Table of Contents
Our pipeline
We are focused on viral and liver diseases, areas in which our employees have expertise and decades of experience. Our most advanced drug candidates are designed for use in CHB to achieve higher rates of functional cure, which we believe will require the use of a combination of drugs with complementary mechanisms of action (“MOA”). Each of our CHB modalities plays an important role in disrupting the HBV life cycle and, in nonclinical studies, certain combinations have been shown to act additively or synergistically. We are also advancing a THR-ß agonist for NASH and purpose-built drug candidates for coronaviruses. As with CHB, we believe combination therapy will be critical for improved patient outcomes in these disease settings and intend to combine our drug candidates with others that have potentially complementary MOAs.

Functional cure for CHB
CHB is the most common viral infection in the world and an area of substantial unmet medical need. There were over 290 million chronic carriers worldwide as of July 2020 and approximately 30 million individuals become newly infected every year despite the availability of a prophylactic vaccine. In 2015, there were more than 90 million cases of CHB in China alone, while the EU, United States and Japan accounted for nearly 8 million cases. Complications from CHB include cirrhosis, end-stage liver disease, and hepatocellular carcinoma, which collectively resulted in approximately 900,000 deaths in 2015, according to the World Health Organization. CHB is the primary cause of liver cancer worldwide, and the mortality associated with HBV-related liver cancer continues to increase.
Current therapy for CHB may entail life-long treatment and does not eliminate the virus in a meaningful number of patients. In the case of nucleos(t)ide analogs, long-term treatment can lower the amount of HBV DNA in circulation, resulting in improvements in long-term disease outcomes, but virological relapse is common after treatment cessation. Our goal is to achieve meaningful rates of functional cure, which is defined as a sustained loss of HBsAg with or without hepatitis B surface antibody seroconversion. Our team’s years of experience in antiviral drug development suggest that only by developing a combination regimen targeting multiple mechanisms can meaningful functional cure rates for CHB be achieved.
121
Table of Contents
HBV viral lifecycle and targets
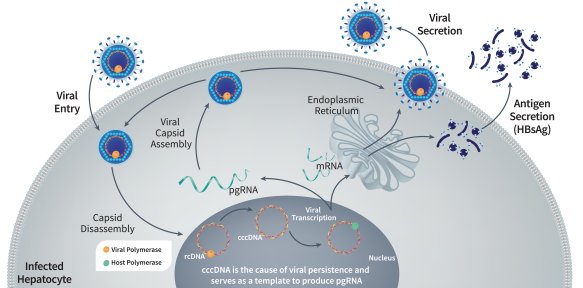
HBV is a small DNA virus consisting of a nucleocapsid in which the viral DNA is packaged together with the HBV polymerase by the hepatitis B core protein and a membranous envelope containing HBsAg. After infection of liver cells, HBV DNA is transformed in the nucleus into a stable viral mini-chromosome, which is composed of a cccDNA molecule, from which mRNAs encoding viral proteins are transcribed, and pgRNA, the template for the formation of new viral DNA genomes by reverse transcription. Parts of the viral genome can integrate into the host genome, which is thought to contribute to the production of HBsAg in chronically infected patients and play an important role in liver carcinogenesis, but the integrated viral genome does not produce infectious virus. HBsAg is known to prevent immune-mediated clearance of infected liver cells. HBsAg seroclearance correlates with significant decreases in cccDNA levels and implies immune control of HBV, indicating the need to reduce HBsAg to achieve functional cure.
We have developed a portfolio of differentiated drug candidates for CHB, including a STOPS molecule, a small molecule CAM, and oligonucleotides (ASO and siRNA), each of which are designed to interfere with multiple clinically validated targets in the HBV life cycle and may lead to higher rates of functional cure when used in combination.
ALG-010133 (STOPS molecule) for CHB
STOPS molecules share structural similarity with NAPs but contain several novel chemical features, providing enhanced potency in several HBV-infected cell lines. NAPs such as REP 2139 and REP 2165 have been reported to significantly reduce circulating HBsAg in patients with CHB when administered either as a monotherapy or as a combination therapy, resulting in multiple log10 IU/mL reductions in HBsAg levels. The Replicor 401 study, a study of NAPs in combination with tenofovir and pegylated interferon, reported a 39% functional cure rate. A major drawback of NAP drug candidates is the requirement for weekly IV infusions given over two hours for 48 weeks. However, by exploring the chemistry around the STOPS structure, we have optimized STOPS molecules for activity, dose frequency and subcutaneous delivery, potentially negating the need for lengthy IV infusions. Use of our STOPS molecules given via subcutaneous injections and in combination with other convenient drug regimens may improve treatment adherence and functional cure rates. Enrollment in the Phase 1 proof of concept trial of our lead STOPS molecule, ALG-010133, is currently ongoing and we anticipate study completion in the second half 2022.
122
Table of Contents
ALG-010133 is a synthetic oligonucleotide discovered by our team that we are developing for the treatment of CHB. We originally optimized existing compounds to generate ALG-010133 by using nucleotide stabilization chemistry. Varying the length of the STOPS molecule revealed a length dependency on antiviral activity; potency was maintained at lengths of more than 34 nucleotides, and dramatically reduced at lengths of less than 30 nucleotides. Nucleotide sequence variations in STOPS molecules also had effects on activity. In addition to length and sequence, backbone and sugar chemistry were modified; activity was improved with site-specific incorporation of backbone chemistries. Collectively, these structural elements provided a framework for STOPS molecule design and were important for the progression of ALG-010133 into clinical development.
As shown in the figure and table below, transfection of STOPS molecules into multiple HBV-infected cell lines, including primary human hepatocytes, resulted in the inhibition of HBsAg release into the supernatant in a dose-dependent manner. In addition, transfection of close analogs of ALG-010133 were shown to decrease intracellular levels of HBsAg, indicating that this inhibition occurs inside the cell. This suggests that the inhibition of HBsAg release is not the result of only an inhibition of protein secretion, which would result in HBsAg accumulation within the cell, but instead could be the result of inhibition of synthesis and intracellular transport of HBsAg. The data below shows the comparison of ALG-010133 to a NAP reference compound, ALG-010004, which has an identical oligonucleotide sequence to REP 2139.
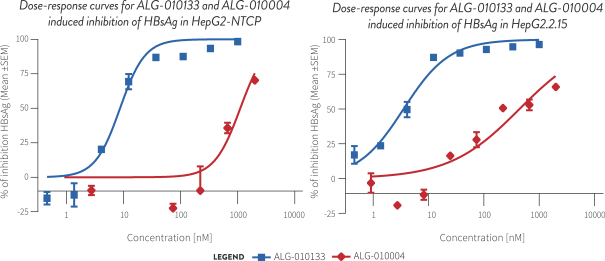
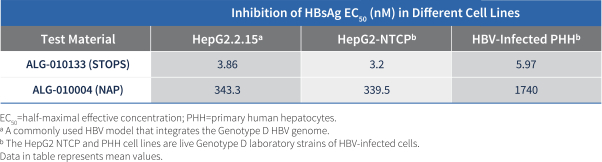
The HepG2.2.15 cell line is a commonly used in vitro HBV cell model. The cells contain two copies of the Genotype D HBV genome that produce infectious HBV and other subviral particles. The HepG2-NTCP (Na+-taurocholate co-transporting polypeptide) cell line over-expresses the NTCP receptor and has been shown
123
Table of Contents
to be a robust cell culture system supporting the complete life cycle of HBV. HepG2-NTCP cells were infected with a Genotype D HBV laboratory strain. In this cell line, HBsAg and other HBV viral proteins are produced from RNA transcripts derived from HBV cccDNA. ALG-010133 and ALG-010004 were evaluated in the HepG2.2.15 cell line to assess HBsAg release in the supernatant and cell viability.
In addition, ALG-010133 demonstrated potent activity in the inhibition of HBsAg release from a variety of infected cell types with half-maximal effective concentration (EC50) values £22.5 nM when tested against cells infected with all major HBV genotypes (A, B, C, and D), indicating that ALG-010133 may have pan-genotypic activity in CHB patients. Further, in patients with CHB, HBsAg can also be derived from an integrated HBV genome. The PLC/PRF/5 cell line, which contains an integrated partial HBV genome and produces HBsAg but not infectious virions, was used as a cell model of this condition. ALG-010133 demonstrated activity in the inhibition of HBsAg secretion from the PLC/PRF/5 cell line with an EC50 of 23.7 nM with a 50% cellular cytotoxic concentration (“CC50”) of more than 1000 nM.
To assess the capability for immune activation, ALG-010133 was assayed in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells from three independent donors for cytokine induction. The results of these experiments demonstrated that no direct immune activation is mediated by ALG-010133. Nonclinical PK studies following subcutaneous dosing indicate long liver residence time that supports weekly or less frequent dosing for patients.
Our ongoing three-part Phase 1 first-in-human clinical trial comprises single and multiple ascending dose (SAD/MAD) evaluations in healthy volunteers followed by a multiple dose evaluation in patients with HBeAg negative CHB. ALG-010133 is being administered subcutaneously once (SAD) or once weekly for three doses (MAD) in up to 104 healthy volunteers, or once weekly for twelve doses in up to 60 patients with virologically suppressed HBeAg negative CHB.
ALG-000184 (CAM) for CHB
CAMs are a class of small molecule antiviral agents that accelerate HBV capsid assembly and inhibit pgRNA encapsidation, resulting in lower circulating HBV pgRNA and DNA levels. CAMs are also believed to regulate formation and transcription of cccDNA at the onset of infection, a major factor for the persistence of HBV infection. In clinical trials, CAMs have been shown to provide greater HBV DNA and RNA reduction when combined with nucleos(t)ide analogs than can be achieved with the current standard of care, nucleos(t)ide analogs alone.
In 2018, we in-licensed a lead drug candidate (GLP-26) and the associated IP for a CAM from the laboratory of Professor Raymond Schinazi at Emory. Our scientists optimized this lead drug candidate to discover the potent CAM ALG-001075, which was further optimized to the prodrug ALG-000184. ALG-000184 is on track to enter clinical development in the second half of 2020.
124
Table of Contents
Molecular characteristics and nonclinical data
In biochemical assays, ALG-001075 was shown to induce the rapid assembly of core proteins into small, spherical capsids. Capsids assembled in the presence of ALG-001075 were highly stable with a compound residence time of more than 16 hours. In assays using genotype D HBV infected HepG2.2.15 cells, ALG-001075 demonstrated enhanced potency with an EC50 value of 0.53 nM compared to several CAM reference compounds. This finding was repeated in HepG2.117 cells where ALG-001075 had an EC50 value of 0.63 nM. This level of potency exceeds that of all other known CAMs that have entered clinical development.
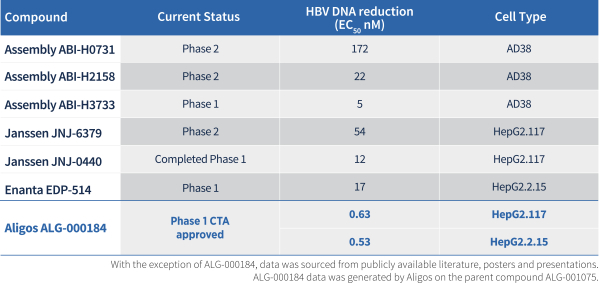
|
|
|
ALG-001075 was further tested in a transient HBV assay against a broad panel of HBV screens from genotypes A through J and was shown to maintain good activity against all genotypes tested except for certain genotypes with known CAM-resistant mutations.
125
Table of Contents
In the adeno-associated virus (AAV)-HBV mouse efficacy model, ALG-001075 demonstrated a dose-dependent inhibition of viral replication with >5 log10 reduction in HBV DNA IU/mL at a dose of 15 mg/kg/dose given twice daily at 12-hour intervals (BID) as compared to a vehicle group.
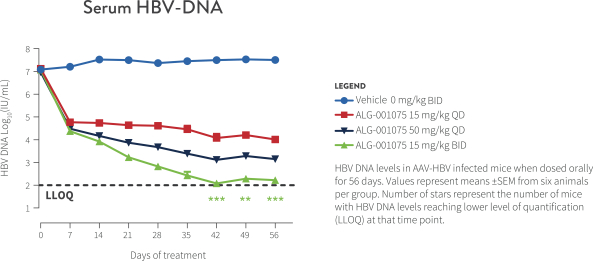
We developed a highly soluble prodrug of ALG-001075, ALG-000184, to address the bioavailability limitations of ALG-001075. ALG-000184 has improved aqueous solubility, significantly better permeability and a reduced efflux ratio compared with ALG-001075. Consequently, ALG-000184 has significantly improved oral bioavailability compared to ALG-001075. When administered in vivo, as shown in the figure below, ALG-000184 was rapidly absorbed and efficiently converted to ALG-001075 in nonclinical animal models.
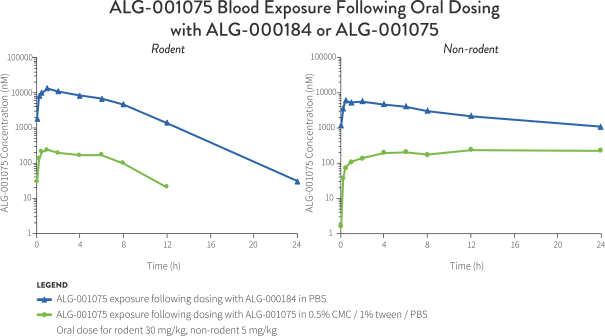
Our planned three-part Phase 1 first-in-human clinical trial comprises single and multiple ascending dose (SAD/MAD) evaluations in healthy volunteers followed by a multiple dose evaluation in patients with CHB.
126
Table of Contents
ALG-000184 will be orally administered once (SAD) or once-daily for 7 days (MAD) in up to 96 healthy volunteers, or once-daily for 28 days in up to 60 patients with CHB who are not currently receiving treatment. We plan to initiate dosing in this Phase 1 study in the second half of 2020.
ALG-020572 (ASO) for HBV
ASOs are single-stranded DNA or RNA molecules that are complementary to a selected target sequence. ASO structures are typically composed of three sections, known as the wings and the gap. The wings are on each end of the oligonucleotide strand with the gap section bridging the wing sections. Wings are generally made up of BNAs, while the gap sections are typically made up of DNA or modified DNA nucleotides. ASOs interfere with viral replication by binding to complementary mRNA, a process known as hybridization. If binding occurs, this hybrid can be degraded by the enzyme RNase H resulting in significant down-regulation of mRNA expression, and, in the case of our CHB ASOs, preventing subsequent HBsAg translation and secretion. This process is shown in the figure below. ASOs have been validated across multiple indications, including CHB, where rapid and significant reductions in HBsAg have been observed.
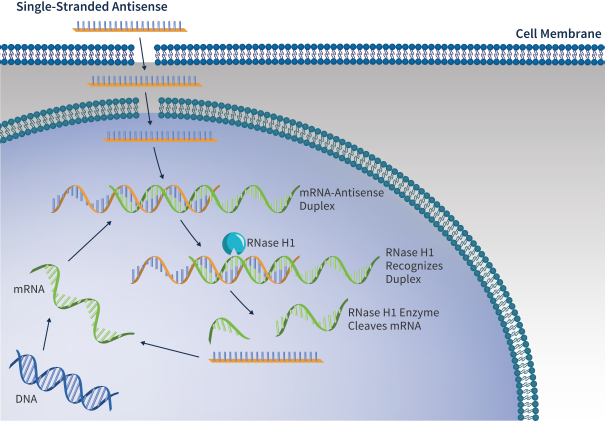
We have exclusively licensed Luxna’s intellectual property for use of next-generation nucleotide monomers in our current focus areas, including CHB and SARS-CoV-2. This chemistry forms the basis of our ASO platform and has enabled us to design highly potent, stable ASOs that have an improved toxicology profile, including a reduction of hepatotoxicity, as compared to ASOs using earlier nucleotide monomer technology. The application of this technology, combined with our proprietary liver-targeting GalNAc conjugation, has led to our discovery of ALG-020572, a potentially best-in-class HBV ASO targeting the open reading frame of HBsAg.
127
Table of Contents
Molecular characteristics and nonclinical data
We explored the structure activity relationship of BNA wing and nucleobase gap modifications across a set of diverse locked nucleic acid ASOs. When conjugated to our proprietary GalNAc moiety and subcutaneously administered 5 times at a 10 mg/kg dose to mice previously infected with an AAV-HBV construct, ALG-020572 demonstrated a 1.17 log10 IU/mL mean reduction in serum HBsAg. Vehicle-treated animals did not exhibit any significant changes in their serum HBsAg. Importantly, this intensive dosing regimen was not associated with any changes in alanine aminotransferase (“ALT”) levels, a marker of liver cell damage.
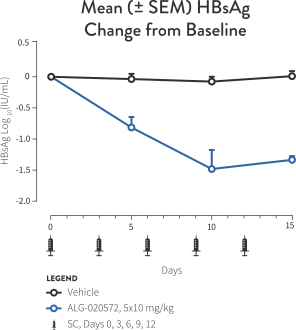
|
|
We have discovered potent, liver-targeted ASOs, including ALG-020572, which has demonstrated a promising profile in nonclinical CHB models. These ASO drug candidates may also be combined with other drug candidates against CHB.
siRNA
Small interfering RNA (“siRNA”), also known as short interfering RNA or silencing RNA (“RNAi”), are a class of double-stranded, non-coding RNA, typically 20-27 base pairs in length. siRNA interferes with viral replication by silencing gene expression and subsequent protein (e.g., HBsAg) translation and secretion. siRNAs have shown efficacy across multiple indications, including CHB, where significant, gradual and durable reductions in HBsAg have been observed in clinical trials.
128
Table of Contents
siRNA-induced gene silencing is initiated with the assembly of the RNA-induced silencing complex (“RISC”). One of the two siRNA strands, the guide strand or anti-sense strand, is loaded into the RISC while the other strand, the passenger strand or sense strand, is degraded. Dicer enzymes are responsible for loading the guide strand into RISC. The cleavage of the mRNA molecule is thought to be catalyzed by the Argonaute proteins of the RISC. The mRNA molecule is then cut by cleaving the phosphodiester bond between the target nucleotides which are paired to siRNA residues. This cleavage results in mRNA fragments that are further degraded by cellular exonucleases. The process of siRNA-mediated RNA degradation is shown in the figure below.
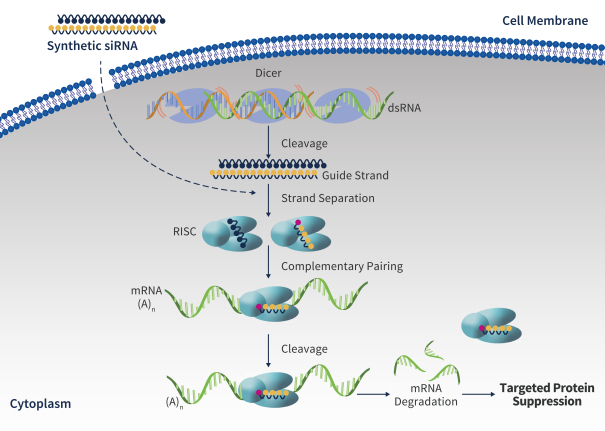
We started with our bioinformatics approach to identify regions of the HBV genome for targeting, and used our proprietary technology to maximize potency and minimize the number of 2’-F nucleotides in our sequences. We applied this approach to our screening paradigm to identify our lead siRNA candidate, ALG-125097.
129
Table of Contents
Molecular characteristics and nonclinical data
In cell-based assays measuring reduction in HBsAg in infected cells, our lead siRNA drug candidate, ALG-125097, as well as additional backup compounds ALG-125755 and ALG-125819, demonstrated potent inhibition of HBsAg release from HBV-infected cells. When dosed in vivo in the AAV-HBV mouse model of CHB infection, a single 5 mg/kg subcutaneous injection resulted in a sustained reduction of serum HBsAg of approximately 1-1.5 log10 IU/mL through the last measurement at 28 days. The results from these experiments are shown in the figure below.
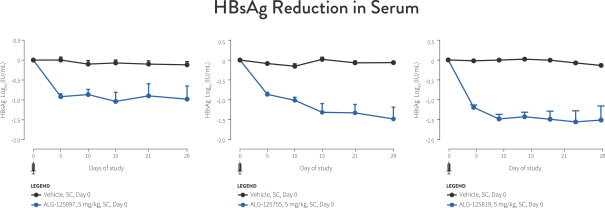
Currently, we are conducting additional studies using these siRNA drug candidates in the AAV-HBV mouse model to establish the effect of doses and dosing regimens on the extent and duration of HBsAg reduction.
In conclusion, our proprietary siRNA technology is based on modifying chemistries and has resulted in the identification of drug candidates, including ALG-125097, that have promising profiles with long lasting durability in nonclinical CHB models.
Nonclinical combination data
We performed in vitro studies in HepG2.2.15 cells to assess the potential for drug-drug interactions on HBsAg or HBV DNA reductions when combining our drug candidates, and the degree of synergy was quantified using MacSynergy II software. Combinations of our STOPS molecule, ALG-010133, our CAM drug candidate, ALG-001075, or our ASO drug candidate, ALG-020572, with other inhibitors of HBV replication generally demonstrated either additive or synergistic interactions. We also studied in vivo combinations in the AAV-HBV mouse model with ALG-020572. These studies indicate that our drug candidates could become part of an effective combination regimen for CHB.
130
Table of Contents
Clinical development plan for CHB
Our approach for developing a best-in-class CHB combination regimen is to discover and develop drug candidates initially targeting clinically validated MOAs, which are evaluated as monotherapy in Phase 1 and subsequently studied in Phase 2 and Phase 3 combination trials. This approach maximizes the chance of achieving higher rates of functional cure compared to current standard of care. Our CHB development strategy is depicted in the figure below.
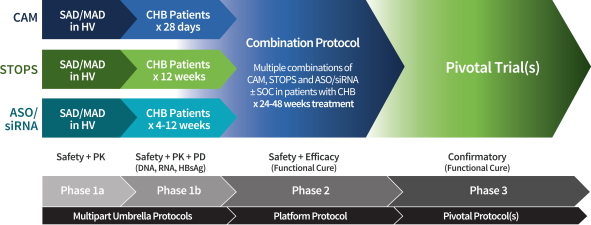
Our STOPS molecule (ALG-010133) trial is ongoing and our clinical trial application for our CAM candidate (ALG-000184) was approved in September 2020 and we expect to commence a Phase 1 clinical trial to evaluate ALG-000184 in the fouth quarter of 2020.
The figure below illustrates our planned general approach to Phase 1 trial design for each of our CHB drug candidates.
131
Table of Contents
Although we expect the basic Phase 1 trial design to be the same across all of our CHB drug candidates, we anticipate there will be important differences, which include routes of administration, dose and dosing frequency, patient population, and key viral markers. A summary table of the key Phase 1 design elements and how we expect them to differ across our drug candidates can be found in the table below.
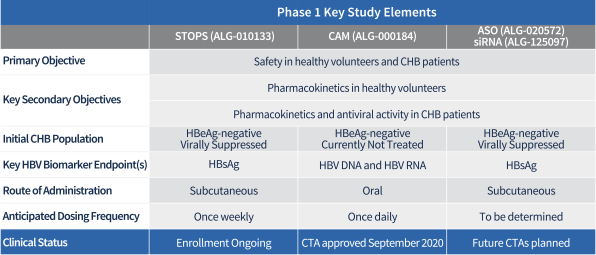
Drug candidates that show favorable risk/benefit profiles as monotherapy in Phase 1 will be evaluated in combination in our Phase 2 platform trials. This platform approach allows us to evaluate many combinations of our drug candidates along with approved drugs and/or other drug candidates in development, as needed. This strategy allows us to identify combination regimens that could achieve a higher rate of functional cure compared to current standard of care. The optimized regimen(s) identified in Phase 2 will then be evaluated in Phase 3 registrational trials.
NASH
One of the effects of improper diet and insufficient exercise is the accumulation of fatty deposits in the liver, referred to as nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (“NAFLD”), which was estimated to occur in approximately 25% of the worldwide population as of 2015. At that time, an estimated 1.5% to 6.5% of the global population was estimated to have an ongoing inflammatory response to these excess fat deposits, which is referred to as NASH. Over the past several years, the prevalence of NASH has continued to rise. In the United States alone, the prevalence of NASH is projected to increase from approximately 16.5 million in 2015 to 27.0 million in 2030. In the absence of changes in diet and exercise, the inflammation inherent in NASH persists and may result in progressive fibrosis of the liver, which may result in cirrhosis. These fibrotic changes are associated with numerous morbidities including recurrent hospitalization for complications of cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma, need for liver transplant, and death.
The only widely accepted treatment for NASH is weight loss through behavioral modifications such as diet and exercise, which is difficult to achieve at the broad population level. As there are currently no approved drugs to treat NASH, many development programs are underway to identify drugs to address this epidemic. One of the promising MOAs in the NASH space appears to be drugs which preferentially target the beta subtype of the THR receptor.
132
Table of Contents
THR-ß background
The thyroid hormone triiodothyronine (“T3”) has many physiological effects throughout the body, ranging from increasing metabolism, including fat metabolism, to stimulating growth and development. T3 exerts its effects by binding to the thyroid hormone receptor (THR), which has two subtypes: alpha (THR-a) and beta (THR-ß). The distribution of the two THR subtypes varies by organ, with THR-ß predominantly expressed in the liver and THR-a predominantly expressed in other tissues (e.g., heart, skeletal muscles and bone). Drug candidates like resmetirom, which preferentially binds the THR-ß subtype, have been shown in clinical trials to lower lipid levels in serum and the liver, while avoiding the unwanted effects associated with THR-a stimulation. In addition to the intended effect of lowering liver lipid levels in NASH patients, lowering serum lipid levels via THR-ß agonism may have favorable consequences in this population, which has a high rate of underlying cardiovascular disease.
There are multiple other mechanisms being explored for the treatment of NASH, but none have yet to demonstrate a favorable risk/benefit profile and many have important limitations. In some cases, mechanisms such as Farnesoid X Receptor (“FXR”) agonists, Fibroblast Growth Factor-19 analogs, and Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase inhibitors have been shown to increase serum lipid profiles, which may require additional pharmacologic therapy or put patients at additional risk of cardiovascular disease. In other cases, mechanisms such as FXR agonists and drugs targeting various subtypes of the Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptors are associated with dose limiting toxicities such as pruritus and edema, respectively, that might limit widespread uptake even if approved. Other mechanisms in development, such as FGF19/FGF21 analogs, require subcutaneous administration, which may similarly limit widespread adoption even if approved.
The most advanced THR-ß agonists in clinical development are VK-2809 in Phase 2b and resmetirom in Phase 3. Both of these drugs have demonstrated significant reductions in lipid levels in the liver and serum and, to date, have an acceptable risk-benefit profile. In addition, resmetirom has demonstrated histologic evidence of NASH resolution in Phase 2 trials, which is one of two FDA approvable endpoints. Our lead THR-ß drug candidate ALG-055009 may have important advantages over these compounds. Side-by-side biochemical and cell-based experiments in HEK293T cells indicate that ALG-055009 is 5- to 47-fold more potent and 3- to 2-fold more selective for the ß receptor compared to VK-2809 and resmetirom, respectively, which may optimize the risk-benefit profile for ALG-055009. When studied in a diet induced obesity (DIO) mouse model, these potency advantages were shown to result in greater serum lipid reductions compared to what has been previously reported for VK-2809 and resmetirom at exposures being evaluated in the clinic. Specifically, ALG-055009 achieved a 34% reduction in serum total cholesterol levels with an acceptable safety profile (e.g., no clinically relevant changes in thyroid hormone levels) in mice, as shown in the figure below. An ALG-055009 dose-related decrease in serum LDL-C was also noted in mice. Further, nonclinical pharmacokinetic studies of ALG-055009 predict low, once-daily dosing in humans with a low risk of drug-drug interactions.
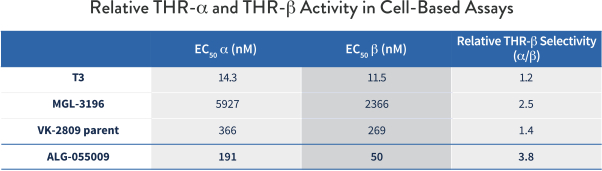
133
Table of Contents
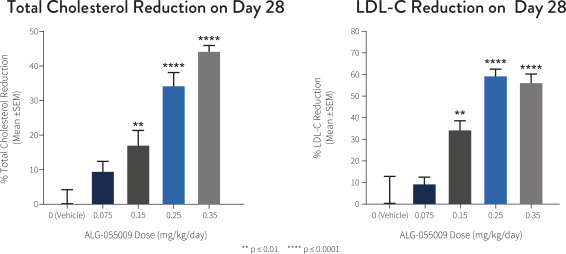
ALG-055009 development plans
We plan to initiate toxicology studies in 2021 to support first-in-human trials. In keeping with our general clinical development strategy, the first planned human trial of ALG-055009 is expected to be a Phase 1a/1b umbrella study assessing orally administered single ascending doses in healthy volunteers followed by multiple ascending doses administered orally once-daily (QD) in subjects with mild hyperlipidemia. We expect this study to commence in the second half of 2021 (with data readouts expected to begin in the first half of 2022) and the study to be complete by the second half of 2022. The data from this study will establish proof of activity and help identify doses that may be evaluated in larger studies involving patients with NASH. With this proof of activity in hand, we plan to partner ALG-055009 with a third-party that has a NASH candidate with a complementary MOA. We believe this may be an ideal time to seek a partnership for ALG-055009, as we expect enthusiasm for the THR-b MOA to be high after the expected Phase 3 resmetirom and Phase 2b VK-2809 readouts, which are expected in late 2021 and early 2022.
Coronaviruses
SARS-CoV-2 is responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic, which has infected more than 21 million individuals and is responsible for the death of more than 750,000 individuals worldwide. After MERS and SARS (SARS-CoV-1), SARS-CoV-2 is the third known coronavirus to cross over from animal species to humans and cause significant morbidity and mortality in the past 20 years. Due to the ongoing SARS-CoV-2 pandemic and the risk of additional novel coronaviruses emerging in the future, there is a need to develop novel therapeutics with pan-coronavirus activity that have a high barrier to resistance. While multiple vaccines are likely to become available in the next several years, it is unlikely that a vaccine will be fully efficacious and adopted, indicating that a need for effective treatments will remain.
Currently, repurposed drugs which have not been optimized for the treatment of coronavirus infections are being used against SARS-CoV-2, with efficacy only in certain patient populations. Therefore, there is a need for new efficacious, purpose-built drugs which target a broad range of coronaviruses that would be suitable for use across a wide range of patient populations and clinical settings, including in pre-exposure prophylaxis and post-exposure treatment. We believe that a combination of antiviral drugs targeting multiple steps of the viral replication cycle poses the best chance of success. This approach maximizes the odds of covering a broad range of coronavirus strains and protecting against the emergence of resistance. To address this urgent unmet medical need, we are developing pan-coronavirus drug candidates including oligonucleotide and small molecule approaches that may be used in combination regimens.
134
Table of Contents
Disease overview and biology
The life cycle of SARS-CoV-2 is illustrated in the figure below. The spike (S) protein binds to the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 cellular receptor, leading to a fusion of the viral envelope with the cell membrane through the endosomal pathway. SARS-CoV-2 RNA is then released into the host cell and is subsequently translated into viral replicase polyproteins pp1a and 1ab, which are then cleaved into small products by viral protease to form the RNA replicase–transcriptase complex. The polymerase produces a series of subgenomic mRNAs by transcription, which are eventually translated into relevant viral proteins. Viral proteins and genome RNA are subsequently assembled into virions in the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi and then transported via vesicles and released out of the infected cells through exocytosis.
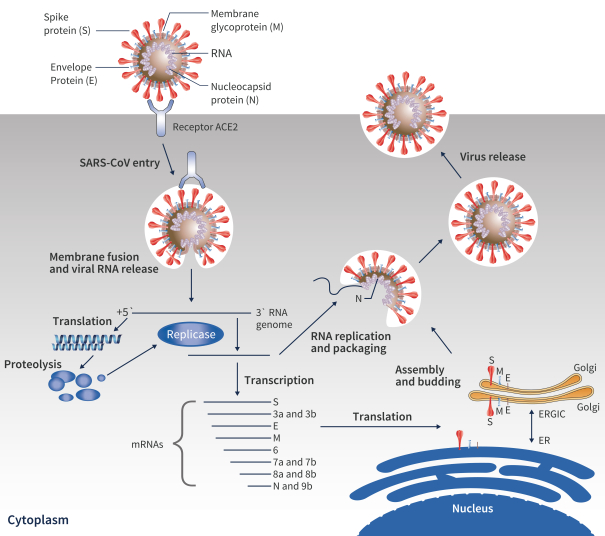
Therapeutic approaches to coronaviruses
Therapeutic options for coronaviruses are currently limited and have significant drawbacks. Remdesivir, a drug originally advanced for HCV and Respiratory Syncytial Virus, but repurposed for Ebola and, now, SARS-CoV-2, is currently limited to IV administration in hospitalized patients and has been commonly associated with a high risk of ALT elevation. Dexamethasone, a corticosteroid, has been shown to lower mortality in severe
135
Table of Contents
SARS-CoV-2 infections, but has important safety liabilities, including immunosuppression, impaired wound healing and, rarely, anaphylaxis.
We are leveraging our expertise in virology and utilizing both our oligonucleotide and small molecule platforms to develop purpose-built pan-coronavirus drug candidates targeting key steps of the viral life cycle, which we intend to evaluate in combination. Building on the success of HIV and HCV protease inhibitors, which are integral components of existing therapies, we are exploring small molecule peptidomimetics that inhibit the 3C-like protease (“3CLPro”). 3CLPro is the essential enzyme that is responsible for cleaving well-defined regions of the viral polyprotein and is highly conserved across major coronaviruses including MERS, SARS-CoV-1 and SARS-CoV-2. Drug candidates inhibiting the 3CLPro have the potential to be active against a wide range of coronavirus strains and become a foundational component of future combination regimens. We have identified multiple distinct proprietary lead series with potent nanomolar activity in a SARS-CoV-2 3CLPro protease assay and in multiple coronavirus cell-based assays. Our work in this area is being performed in collaboration with KU Leuven’s Rega Institute for Medical Research, as well as its Centre for Drug Design and Discovery.
We are also leveraging our oligonucleotide platform to develop broadly active coronavirus drug candidates. Using our bioinformatics capabilities, we have identified over 350 highly conserved regions across coronavirus genomes. We are currently evaluating oligonucleotides with the goal of identifying a suitable lead sequence for further optimization into a drug candidate.
Drawing on our small molecule and oligonucleotide approaches, we plan to develop a combination drug regimen that can serve in both treatment and prophylactic settings.
Clinical development plan
We plan to advance our coronavirus drug candidates individually in Phase 1 studies designed to evaluate the safety and pharmacokinetics of single and multiple ascending doses in healthy volunteers. Following this, we plan to conduct dose range finding Phase 2 studies in subjects infected with COVID-19 to evaluate proof of activity and identify a dosing regimen(s) to advance into larger confirmatory studies that could support drug registration. Following the initial Phase 2 study, we may evaluate combinations of our drug candidates, with or without the then-prevailing standard of care. We intend to assess a range of patient populations, including community and hospital-based subjects, as well as various degrees of disease severity, following the establishment of proof of activity. In addition to evaluating our drug candidates as treatment options after infection, we may also evaluate them as potential prophylactic or post-exposure therapies.
Early stage discovery efforts
For all of our drug candidates, we are pursuing backup candidates in order to create a robust portfolio of assets which we can draw upon to create an optimized combination regimen for treatment in all of our disease areas of interest. We are also targeting additional novel viral and host targets with our oligonucleotide and small molecule platforms.
Sales and marketing
All of our assets are currently pre-commercial, and as such we have not yet established a sales and marketing organization or distribution capabilities. We intend to pursue independent development and commercialization in select indications and markets, and plan to build a commercial infrastructure to support a specialty sales and marketing organization, as well as distribution capabilities. Similar to our research, clinical and manufacturing operations, we expect to manage sales, marketing and distribution through dedicated staff and third-party contractors and consultants. We may opportunistically explore licensing agreements, collaborations or partnerships with one or more pharmaceutical companies to enhance our commercial capabilities.
136
Table of Contents
Manufacturing
We are currently developing drug candidates in two primary modalities: oligonucleotides and small molecules. We have internal oligonucleotide and small molecule chemistry teams that are able to produce drug candidates at sufficient scale to support discovery activities. In addition, we have a dedicated internal chemistry, manufacturing and control (“CMC”) team that works with contract development and manufacturing organizations to produce drug candidates in larger quantities, including to support nonclinical and clinical studies. We have built the teams and infrastructure needed to conduct and manage process development, analytical development, quality, manufacturing and supply chain activities.
Oligonucleotides
Oligonucleotide manufacturing technology has matured significantly over the last several decades, with advanced oligonucleotide synthesizers commercially available to support smaller-scale synthesis, and a network of oligonucleotide contract manufacturers available to support larger-scale syntheses. Our internal CMC team supports our contract manufacturers with process development and optimization, or, where needed, we may collaborate with external consultants and contractors to optimize synthesis and scale-up.
Small molecules
Small molecule manufacturing is a mature industry and is well supported by an extensive network of contract manufacturers. Like our approach for oligonucleotides, our internal CMC team conducts process development and optimization, and supports our contract manufacturers with technology transfer.
Competition
The biotechnology industry is intensely competitive and subject to rapid and significant technological change. Our competitors include multinational pharmaceutical companies, specialized biotechnology companies, universities and other research institutions. Many of our competitors have substantially greater financial, technical, human and other resources than we do and may be better equipped to develop, manufacture and market technologically superior products. In addition, many of these competitors may have significantly greater experience than we have in undertaking nonclinical studies and human clinical trials of new pharmaceutical drug candidates and in obtaining regulatory approvals of human therapeutic candidates. Accordingly, our competitors may develop superior drug candidates and may succeed in obtaining FDA approval for such candidates. Many of our competitors have established distribution channels for the commercialization of their products, whereas we have no such channel or capabilities. In addition, many competitors have greater name recognition and more extensive collaborative relationships.
Any drug candidates that we successfully develop and commercialize may compete with existing therapies and/or new therapies that may become available in the future. Our competitors may obtain regulatory approval of their candidates more rapidly than we do or may obtain patent protection or other intellectual property rights that limit our ability to develop or commercialize our drug candidates or any future drug candidates. Our competitors may also develop drugs that are more effective, more convenient, more widely used and less costly or that have a better safety profile than our drugs (if any) and these competitors may also be more successful than we are in manufacturing and marketing their products. If we are unable to compete effectively against our competitors, we may not be able to commercialize our drug candidates or any future drug candidates or achieve a competitive position in the market. This would adversely affect our ability to generate revenue. It is likely that our competitors, either working alone or in collaboration with others, will have significantly greater financial resources, an established presence in target markets, expertise in research and development,
137
Table of Contents
manufacturing, nonclinical and clinical testing, and experience obtaining regulatory approvals and reimbursement and marketing approved products than we do. We are also in competition for the limited qualified scientific, sales, marketing and management personnel, space at clinical trial sites, for patient registration for clinical trials and technologies complementary to, or necessary for, our programs. New competitors may emerge, smaller or early-stage companies may grow, either on their own or through collaborative arrangements with large and established companies and competitors may concentrate through mergers and acquisitions.
Chronic Hepatitis B (CHB)
Current FDA-approved treatments for chronic HBV infection include peg-IFNa, marketed by Roche Holding AG (“Roche”), and oral antiviral agents such as nucleoside analogs, marketed by Gilead Sciences, Inc. (“Gilead”) and Bristol-Myers Squibb Company. These treatments do not lead to either a functional or a complete cure in the vast majority of patients, and in the case of nucleoside analogs, may require life-long treatment. Several large and small pharmaceutical companies are developing programs with various mechanisms of action, to be used alone or in combination, with the goal of achieving higher rates of functional or complete cure in patients with CHB. Companies with oligonucleotide agents in clinical development include Arbutus Biopharma Corporation, Dicerna Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (together with Roche), Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (together with GlaxoSmithKline plc (“GSK”)), Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (together with Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (“Janssen”)), and Vir Biotechnology, Inc. (together with Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, Inc.). Several companies are developing CAMs, including Johnson & Johnson, Assembly Biosciences Inc., Arbutus Biopharma Corporation, Roche and Enanta Pharmaceuticals. Several companies, including Altimmune, Inc., GSK, Janssen and Transgene SA, are developing therapeutic vaccines for HBV, and several others have approved HBV vaccines, including Dynavax Technologies, Inc., GSK, Johnson & Johnson, and Merck & Co. Replicor, Inc. is developing NAPs for use in CHB patients.
Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH)
There currently are no FDA-approved treatments for NASH. A number of pharmaceutical companies, including AbbVie, Inc., AstraZeneca PLC/MedImmune LLC, Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, Eli Lilly and Company, Janssen, Merck & Co., Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation (together with Pfizer, Inc.), Novo Nordisk A/S, Pfizer Inc., Roche, Sanofi S.A. and Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited (together with HemoShear Therapeutics, LLC), as well as large and small biotechnology companies such as 89bio, Inc., Akero Therapeutics, Inc., Blade Therapeutics, Inc., Cirius Therapeutics, Inc., Enanta Pharmaceuticals, Inc., FronThera US Pharmaceuticals LLC, Galectin Therapeutics Inc., Galmed Pharmaceuticals Ltd., Genfit SA, Gilead, Intercept Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Inventiva Pharma SA, Madrigal Pharmaceuticals, Inc., MediciNova, Inc., NGM Biopharmaceuticals, Inc., Pliant Therapeutics, Inc. (together with Novartis), Terns Pharmaceuticals, Inc. and Viking Therapeutics, Inc. are pursuing the development or marketing of pharmaceuticals that target NASH. It is also probable that the number of companies seeking to develop products and therapies for the treatment of serious metabolic diseases, such as NASH, will increase.
Coronaviruses
Other than Remdesivir, which is FDA-approved via an emergency use authorization, there are currently no approved treatments for SARS-CoV-2. Several drugs are likely being used off-label for treatment, such as dexamethasone. Several approved drugs are being studied for their utility in reducing the severity of SARS-CoV-2 infections, including Soliris by Alexion Pharmaceuticals Inc., Jakafi by Incyte Corporation, and Kevzara by Sanofi S.A./Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. There are significant efforts globally to develop both
138
Table of Contents
therapeutic and prophylactic drug candidates. Several companies are focused on antibody treatments, including Amgen Inc. (together with Adaptive Biotechnologies Corporation), Abcellera Biologics, Inc. (with Eli Lilly and Company), Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. and Vir Biotechnology, Inc. (together with GSK, Biogen Inc. and WuXi Biologics Ltd.). Numerous efforts are underway to develop vaccines against SARS-CoV-2, including by Altimmune, Inc., AstraZeneca PLC (together with Oxford University), BioNTech SE (together with Pfizer Inc.), GSK (together with Sanofi S.A.), Heat Biologics, Inc., Inovio Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Johnson & Johnson, Moderna, Inc., Novavax, Inc., and Vaxart, Inc. If a vaccine is developed that is highly efficacious and widely adopted it would reduce or eliminate the market for therapies to treat COVID-19.
License agreements
License agreement with Emory University
In June 2018, we entered into the Emory License Agreement. In June 2020, we amended the Emory License Agreement (the “Emory Amendment”). Under the Emory License Agreement, Emory granted us a worldwide, sublicenseable license under certain of its intellectual property rights to make, have made, develop, use, offer to sell, sell, import and export products containing certain compounds relating to Emory’s hepatitis B virus capsid assembly modulator technology, for all therapeutic and prophylactic uses. Such license is initially exclusive with respect to specified licensed patents owned by Emory and non-exclusive with respect to certain of Emory’s specified know-how. Beginning in June 2022, the license to such patents will become non-exclusive with respect to all fields except for the treatment and prevention of HBV; however, we may select up to six compounds which will maintain exclusivity with respect to all therapeutic and prophylactic uses. With respect to all other compounds that are enabled by the licensed patents, those which are jointly invented by Aligos and Emory or inventors in the Schinazi laboratory, or which are disclosed in a specified licensed patent, are licensed to us exclusively including as to Emory, whereas all other such compounds are licensed to us non-exclusively. We have the right to sublicense rights licensed under the Emory License Agreement, provided that the sublicense agreement must be in compliance and consistent with the terms of the Emory License Agreement.
Emory reserves the right for itself to practice, and have practiced by other entities solely for purposes of collaborative research with Emory, under the licensed patents for educational purposes, Emory’s internal purposes, and for non-commercial research, patient care and treatment. Emory can further grant licenses to not-for-profit and governmental institutions for their internal non-commercial research and scholarly use.
Ownership of any new inventions arising out of our activities under the Emory License Agreement follows the inventorship laws of the United States. With respect to the licensed patents owned by Emory, we are required to prepare documents and filings for the prosecution and maintenance of such licensed patents, while Emory retains the option to provide final edits and approval of such documents and is responsible for the actual filing of such documents. We are responsible for the cost of the prosecution and maintenance of the licensed patents, and we have the first right, but not the obligation, to enforce such patents. We are solely responsible for the costs of any lawsuits we elect to initiate to enforce the licensed patents and cannot enter into a settlement in respect of such lawsuits without the prior written consent of Emory. Any sums recovered in such lawsuits will be shared equally between us and Emory after reimbursement of our costs for such litigation, except that for any award based on lost profits, Emory shall recover the greater of fifty percent of the award or the royalty Emory would have received had the infringing sales been made by us.
The technology claimed by the licensed patents under the Emory License Agreement may have been developed using U.S. government funding and the licenses therefore may be subject to a non-exclusive license held by the U.S. government, certain requirements that licensed products be manufactured substantially in the United States and U.S. government march-in rights. For more information on risks related to technology developed using government funding see the section titled “Risk Factors—Risks related to intellectual property.”
139
Table of Contents
Under the terms of the Emory License Agreement, we are obligated to use commercially reasonable efforts to bring licensed products to market in accordance with a mutually agreed upon development plan.
Pursuant to the Emory License Agreement, we paid an upfront fee of $290,000 to Emory, reimbursed Emory for past patent expenses, and issued a convertible promissory note with a principal amount of $600,000 to Emory. In August 2018, the convertible promissory note was cancelled and converted into 605,600 shares of Series A convertible preferred stock. We paid Emory an additional $150,000 in connection with the Emory Amendment. Additionally, we agreed to pay Emory up to an aggregate of $125 million upon the achievement of specified development, regulatory, and commercial milestones, and all ongoing patent costs. We also agreed to pay Emory tiered single-digit royalties on worldwide annual net sales of licensed products, on a quarterly basis and calculated on a product-by-product basis. With respect to licensed products containing any of a specified subset of the licensed compounds, such royalties range from a mid-single digit to a high-single digit percentage rate. With respect to licensed products which do not contain such compounds, the royalties span a range of percentage rates within the mid-single digits if a Phase 1 clinical trial is initiated for the product within three years of the effective date of the Emory License Agreement, and range from a low-single digit to a mid-single digit rate if a Phase 1 clinical trial is initiated more than three years after the effective date. Our obligation to pay royalties expires on a product-by-product and country-by-country basis upon the later of ten years after the date of first commercial sale of such product in such country and the expiration of the last-to-expire licensed patent right covering such product in such country. Lastly, if we sublicense any of the licensed patent rights, we are required to pay Emory a percentage of any license issuance or upfront fees we might receive, with the percent decreasing if we sublicense after the first anniversary and third anniversary of the effective date of the Emory License Agreement from a mid-double digit to a mid-single digit percentage rate. To date we have not granted any sublicense.
The Emory License Agreement will expire upon expiration of the last-to-expire patent licensed to us thereunder. We may terminate the Emory License Agreement at any time in its entirety or with respect to specific patents for convenience by providing Emory with 90 days’ written notice, and are required to terminate the Emory License Agreement if we make a final decision to cease research, development or commercialization of any licensed products. Either party may terminate the Emory License Agreement if the other party materially breaches such agreement and fails to timely cure such breach. Emory may terminate the Emory License Agreement if we fail to reach a milestone at an agreed date and fail to timely provide commercially reasonable evidence of a reasonable, good-faith business or technical justification for such failure. Upon termination of the Emory License Agreement for our material breach, we will, upon Emory’s request, grant to Emory a non-exclusive, royalty-free license to all of our rights in patents owned by, licensed or controlled by us to the extent they relate to our exercise of the licensed rights under the Emory License Agreement and include claims covering the manufacture, use or sale of any licensed products containing the licensed compounds. The Emory License Agreement will automatically terminate if we become bankrupt or insolvent or if we challenge the validity or enforceability of any patent licensed to us under the Emory License Agreement.
We have agreed to indemnify Emory and certain others under the Emory License Agreement for losses they may suffer arising out of the rights licensed thereunder or the manufacturing, testing, design, use, sale or labeling of any product containing a licensed compound, unless caused by such potential indemnitee’s negligence.
License agreement with Luxna Biotech Co., Ltd.
In December 2018, we entered into the Luxna Agreement. Under the Luxna Agreement, Luxna granted us an exclusive, worldwide, sublicenseable license under certain of Luxna’s intellectual property rights to research, develop, make, have made, and commercialize for all therapeutic and prophylactic uses, (i) products containing oligonucleotides targeting the hepatitis B virus genome, (ii) products containing certain oligonucleotides
140
Table of Contents
targeting up to three genes which contribute to NASH, which we may select at any time during the first eight years of the term, to the extent not licensed to a third party, and (iii) products containing oligonucleotides targeting up to three genes which contribute to HCC, which we may select at any time during the first three years of the term. During the first three years of the term, Luxna will not grant rights to any third parties under the licensed patents to research or develop any compounds or products targeting an HCC gene target. As of June 30, 2020, we have identified two HCC gene targets and two NASH gene targets for the exclusive license. In addition, we have a right of first refusal for any additional xeno-nucleic acid (“XNA”) and/or gapmer modifications that are not claimed by the licensed patents that Luxna controls. If we exercise this right, we and Luxna will use good faith, diligent efforts to negotiate additional commercially reasonable financial terms for such additional modifications. We are obligated to use commercially reasonable efforts to pursue the research, development and commercialization of the licensed products throughout the term. We have the right to sublicense our licensed rights provided that the sublicense agreement must be in compliance and consistent with the terms of the Luxna Agreement.
Additionally, pursuant to an April 2020 amendment to the Luxna Agreement (the “Luxna Amendment”), we obtained an exclusive, worldwide license under the licensed patents to research, develop, make, have made, and commercialize products containing oligonucleotides targeting three families of viruses: orthomyxoviridae, paramyxoviridae, and coronaviridae (a family which includes SARS-CoV-2).
Pursuant to the Luxna Agreement, we paid Luxna an upfront fee of $600,000 and pursuant to the Luxna Amendment, we paid Luxna an additional $200,000. Additionally, we agreed to pay Luxna up to an aggregate of $55.5 million upon achievement of specified development, regulatory, and commercial milestones. We also agreed to pay Luxna tiered royalties on worldwide annual net sales of licensed products, on a product-by-product basis, spanning a range of rates within low-single digit percentages, on a quarterly basis. With respect to each licensed product, our obligation to pay royalties will continue until the expiration of the last-to-expire licensed patent covering such licensed product in any country.
Luxna’s rights to the intellectual property subject to the Luxna Agreement stem from an exclusive license (the “Luxna-Osaka Agreement”) from Osaka University (“Osaka”) for certain rights pertaining to modifications of XNA and other gapmer technologies covered by the licensed patents. Separately, Osaka granted rights to certain third parties in connection with the licensed patents, such as rights to amido-bridged nucleic acid (“AmNA”) for specific indications including NASH, rights to manufacture reagents containing the modifications of AmNA and rights to use specified genes. Such rights are not included in the scope of rights granted to us under the Luxna Agreement and the Luxna Agreement does not prevent Osaka from using any of the licensed rights under the Luxna Agreement for its non-commercial research purposes relating to the modifications of XNA.
Ownership of any new inventions arising out of our activities under the Luxna Agreement will follow the inventorship laws of the United States. Luxna retains the responsibility for the prosecution and maintenance of the licensed patents, provided that Luxna consider our comments and suggestions in connection therewith. We retain step-in rights should Luxna decide to no longer prosecute or maintain any licensed patents under the Luxna Agreement. We have the first right, but not the obligation, at our sole expense to enforce the licensed patents. In connection with any infringement suit, neither party can enter into a settlement without the prior written consent of the other.
The Luxna Agreement will expire upon expiration of the last-to-expire patent licensed to us under the agreement. We may terminate the Luxna Agreement at any time for convenience by providing Luxna with 90 days’ written notice. In addition, we have agreed to terminate the Luxna Agreement if we make a final decision to cease research, development or commercialization of the licensed products. Either party may terminate the Luxna Agreement if the other party materially breaches the Luxna Agreement and fails to timely cure such breach. The Luxna Agreement will automatically terminate if we become bankrupt or insolvent.
141
Table of Contents
We have agreed to indemnify Luxna and certain others under the Luxna Agreement for losses they may suffer arising out of the rights licensed thereunder or the manufacturing, testing, design, use, sale or labeling of any product containing a licensed product, unless caused by such potential indemnitee’s negligence.
Intellectual property
One key to our success is our ability to establish and maintain protection for our drug candidates, platform technology and know-how, in order to enforce and defend our intellectual property rights. To protect our drug candidates and technologies, we file U.S., Patent Cooperation Treaty (“PCT”) and foreign patent applications related to our inventions, improvements, manufacturing and analytical processes and technology. We also rely on our know-how, confidential methodologies and processes and continuing technological innovation as well as our active third-party intellectual property in-licensing program to develop and maintain our proprietary positions, in addition to trademarks, copyrights and trade secret laws, and employee disclosure and invention assignment agreements. Although we take steps to protect our proprietary information and trade secrets, including through contractual means with our employees, advisors and consultants, these agreements may be breached and we may not have adequate remedies for any breach. In addition, third parties may independently develop substantially equivalent proprietary information and techniques or otherwise gain access to our trade secrets or disclose our technology. As a result, we may not be able to meaningfully protect our trade secrets. It is our policy to require our employees, consultants, outside scientific collaborators, sponsored researchers and other advisors to execute confidentiality agreements upon the commencement of employment or consulting relationships with us. These agreements provide that all confidential information concerning our business or financial affairs developed or made known to the individual or entity during the course of the party’s relationship with us is to be kept confidential and not disclosed to third parties except in specific circumstances. In the case of employees, the agreements provide that all inventions conceived of by the individual during the course of employment, and which relate to or are reasonably capable or being used in our current or planned business or research and development, are our exclusive property. In addition, we take other appropriate precautions, such as physical and technological security measures, to guard against misappropriation of our proprietary technology by third parties. However, such agreements and policies may be breached and we may not have adequate remedies for such breaches. For more information regarding the risks related to our intellectual property, see the section titled “Risk factors—Risks related to intellectual property.”
We have licensed patents and patent applications from various entities, including Emory, Luxna and AM Chemicals, which are further described below. As of September 23, 2020, we own 11 U.S. non-provisional patent applications, 23 U.S. provisional patent applications (excluding any non-expired U.S. provisional applications to which priority has already been claimed), 11 PCT applications and 11 foreign patent applications, including pending applications in Argentina and Taiwan. The projected expiration date of any patent that issues from our non-provisional U.S. and foreign applications is between 2039 to 2040, excluding any additional term from a potential patent term extension and/or patent term adjustment.
For our drug candidates, although we have filed and licensed certain patent applications and we generally intend to pursue patent protection covering compositions of matter, methods of making, and methods of use, as of September 23, 2020, we do not own or license any issued patents directed to our ALG-010133, ALG-000184, ALG-020572, ALG-125097 and ALG-055009 drug candidates.
Licensed intellectual property
Emory University
We have licensed the exclusive rights to a patent estate from Emory in the CAM chemical space, consisting of one issued U.S. patent, one pending nonprovisional U.S. patent application as well as 22 foreign patent
142
Table of Contents
applications. The issued U.S. patent has an expected expiration of March 2037, excluding any potential patent term extension or adjustment.
Luxna
We have licensed the right to a patent estate from Luxna in the oligonucleotide chemical space, consisting of 3 issued U.S. patents, 2 nonprovisional U.S. patent applications and 14 issued foreign patents and 6 foreign patent applications. We have exclusive rights to use this technology in the development of drug candidates for CHB, as well as rights to certain named targets in NASH and respiratory diseases, including coronaviruses. These U.S. patents have an expected expiration between October 2030 and February 2035, excluding any potential patent term extension or adjustment.
AM Chemicals
We have licensed the exclusive right to the use of specific constructs encompassed by the patent estate from AM Chemicals, including 1 issued U.S. patent, 1 U.S. non-provisional patent application and 2 foreign patent applications. The issued U.S. patent has an expected expiration of July 2037. Any patent issuing from such non-provisional applications in this patent estate is projected to expire in July 2037, excluding any potential patent term extension or patent term adjustment.
Drug candidate intellectual property
Hepatitis B—ALG-010133 and additional potential drug candidates
We own a patent family that includes 5 applications pending across multiple jurisdictions (including the United States) and have claims directed to composition of matter, including ALG-010133 (our lead STOPS molecule), pharmaceutical composition and method of use. This patent family also includes claims directed to combination treatment with our lead molecule with other modes of action drugs and drug candidates directed against CHB. The U.S. application, if issued, is projected to expire in November 2039, excluding any potential patent term extension or adjustment.
Hepatitis B—ALG-000184 and additional potential drug candidates
We own a patent family that includes 3 applications pending across multiple jurisdictions (including the United States), and have claims directed to composition of matter, including ALG-000184 (our lead CAM molecule), pharmaceutical composition and method of use claims. This patent family also includes claims directed to combination treatment with our lead molecule with other modes of action drugs and drug candidates directed against CHB. The U.S. application, if issued, is projected to expire in April 2040, excluding any potential patent term extension or adjustment.
Hepatitis B—ALG-020572 and additional potential drug candidates
We own a patent family that includes 3 patent applications pending across multiple jurisdictions (including the United States), and have claims to compositions of matter, including ALG-020572, our lead ASO candidate, and methods of use. This patent family also discloses combination therapies with our lead molecule. Any patent that issues from such non-provisional applications in this patent family is projected to expire in May 2040, excluding any potential patent term extension or patent term adjustment.
143
Table of Contents
Hepatitis B—ALG-125097 and additional potential drug candidates
We own a patent family that includes 1 U.S. provisional application, and have claims to compositions of matter, including ALG-125097, our lead siRNA candidate, and methods of use. This patent family will also disclose combination therapies with our lead molecule. Any patent that issues from such non-provisional applications in this patent family is projected to expire in March 2040, excluding additional term from a potential patent term extension and/or patent term adjustment.
NASH—ALG-055009 and additional potential drug candidates
We own a patent family that includes 3 applications across multiple jurisdictions, and have claims to compositions of matter, including ALG-055009, our lead drug candidate for the treatment of NASH, and methods of use. This patent family also discloses combination therapies with our lead molecule. Any patent that issues from such non-provisional applications in this patent family is projected to expire in May 2040, excluding any potential patent term extension or patent term adjustment.
Discovery pipeline intellectual property
Hepatitis B
We own multiple families of applications that include claims to compositions of matter, pharmaceutical compositions and methods of use for the treatment of CHB with our additional drug candidates. This includes 5 U.S. non-provisional patent applications, 2 U.S. provisional patent applications, 5 PCT patent applications and 5 foreign patent applications in the small molecule space and more than 5 U.S. provisional applications in the oligonucleotide space. These patent families also disclose combination therapies with our drug candidates and other compounds for treating CHB. Any patent that issues from a non-provisional application in one of these patent families is projected to expire in 2039 to 2041, excluding any potential patent term extension or patent term adjustment.
NASH
We have filed a U.S. provisional application that includes claims to compositions of matter and methods of use with our additional drug candidates for the treatment of NASH. This U.S. provisional application also discloses combination therapies with our drug candidates and other compounds for treating NASH. Any patent that issues from a non-provisional application claiming priority to this U.S. provisional application is projected to expire in July 2041, excluding any potential patent term extension or patent term adjustment.
Coronaviruses
We have filed 10 provisional U.S. patent applications that include claims to compositions of matter, pharmaceutical compositions and methods of use for treating coronaviruses. This includes multiple applications covering both small molecule and oligonucleotide approaches. These patent families also include disclosure relating to combination therapy strategies for treating coronaviruses. Any patent that issues from a non-provisional patent application claiming priority to one or more of these U.S. provisional applications is projected to expire in April 2041, excluding any potential patent term extension or patent term adjustment.
With respect to both our licensed and our owned intellectual property, we cannot be sure that patents will be granted with respect to any of our pending patent applications or with respect to any patent applications filed by us in the future, nor can we be sure that any current patents or any patents that may be granted to us in the future will be commercially useful in protecting our platforms and drug candidates and the methods used to
144
Table of Contents
manufacture them. Moreover, the time required for development, testing and regulatory review of our candidate drug candidates may shorten the length of effective patent protection following commercialization. If we do obtain any patents for our drug candidates, the term of such patents depends upon the legal term of the patents in the countries in which they are obtained. In most countries in which we file, the patent term is 20 years from the earliest date of filing of a non-provisional patent application. In the United States, the patent term of a patent that covers an FDA approved drug or biologic may also be eligible for patent term extension, which permits patent term restoration as compensation for the patent term lost during FDA regulatory review process. The Hatch-Waxman Act permits a patent term extension of up to five years beyond the expiration of the patent. The length of the patent term extension is related to the length of time that the drug or biologic is under regulatory review. Patent term extension cannot extend the remaining term of a patent beyond a total of 14 years from the date of product approval and only one patent applicable to an approved drug or biologic may be extended. Similar provisions are available in the EU and other foreign jurisdictions to extend the term of a patent that covers an approved drug or biologic. In the future, if our drug candidates receive FDA approval and if our patent applications relating to such drug candidates issue as patents, we expect to apply for patent term extensions where applicable on patents covering those drugs. We plan to seek patent term extensions to any of our future issued patents in any jurisdiction where these are available, however there is no guarantee that the applicable authorities, including FDA in the United States, will agree with our assessment of whether these extensions should be granted, and if granted, the length of these extensions. For this and other risks related to our proprietary technology, inventions, improvements, platforms and product candidates, see the section titled “Risk factors—Risks related to intellectual property.”
Trademarks
Our trademark portfolio contains several trademark applications and registrations, including U.S. and foreign, as of September 23, 2020. The trademark portfolio includes the marks ALIGOS and STOPS. The mark STOPS is registered in Australia, and is pending in the United States, the EU and Japan. The mark ALIGOS is registered in the United States, Australia, EU and Japan.
Government regulation and product approval
Government regulation
The FDA and other regulatory authorities at the federal, state, and local level, as well as in foreign countries, extensively regulate, among other things, the research, development, testing, manufacture, storage, recordkeeping, approval, labeling, marketing and promotion, distribution, post-approval monitoring and reporting, sampling, and import and export of pharmaceutical products, such as those we are developing. The process of obtaining regulatory approvals and the subsequent compliance with appropriate federal, state, local and foreign statutes and regulations require the expenditure of substantial time and financial resources.
U.S. drug regulation
In the United States, the FDA regulates drugs under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (the “FDCA”), and its implementing regulations. FDA approval is required before any new unapproved drug can be marketed in the United States. Drugs are also subject to other federal, state and local statutes and regulations. Failure to comply with applicable FDA or other requirements may subject a company to a variety of administrative or judicial sanctions, such as FDA clinical holds, refusal to approve pending applications, withdrawal of an approval, warning or untitled letters, product recalls, product seizures, total or partial suspension of production or distribution, injunctions, fines, civil penalties and criminal prosecution.
145
Table of Contents
The process required by the FDA before drug candidates may be marketed in the United States generally involves the following:
| • | completion of nonclinical laboratory tests and animal studies, where all supporting safety and toxicity studies are performed in accordance with the FDA’s Good Laboratory Practice (“GLP”) regulations; |
| • | submission to the FDA of an investigational new drug application (“IND”), which must become effective before human clinical trials may begin and must be updated annually or when significant changes are made; |
| • | approval by an independent institutional review board (“IRB”), representing each clinical site before a clinical trial may be initiated; |
| • | performance of adequate and well-controlled human clinical trials in accordance with good clinical practice (“GCP”) regulations to establish the safety and efficacy of the product candidate for each proposed indication; |
| • | preparation of and submission to the FDA of a new drug application (“NDA”); |
| • | a determination by the FDA within 60 days of its receipt of an NDA to file the application for review; |
| • | satisfactory completion of an FDA advisory committee review, if applicable; |
| • | satisfactory completion of an FDA pre-approval inspection of the manufacturing facility(ies) where the product is manufactured to assess compliance with current good manufacturing practice (“cGMP”) regulations, and of selected clinical investigation sites to assess compliance with GCP; and |
| • | FDA review and approval of an NDA to permit commercial marketing of the product for its particular labeled uses in the United States. |
Nonclinical and clinical studies
The nonclinical and clinical testing process can take many years and the actual time required to obtain approval, if any, may vary substantially based upon the type, complexity and novelty of the drug or condition being treated.
Nonclinical tests include laboratory (in vitro) evaluation of drug chemistry, formulation and toxicity, as well as animal (in vivo) studies to assess the characteristics and potential safety and efficacy of the drug candidate. The conduct of nonclinical studies that provide safety and toxicological information must comply with federal regulations and requirements, including GLPs. The results of nonclinical studies are submitted to the FDA as part of an IND along with other information, including information about drug CMC and any available human data or literature to support use of the drug in humans. Long-term nonclinical tests, such as animal tests of reproductive toxicity and carcinogenicity, may continue after the IND is submitted.
The central focus of an IND submission is on the general investigational plan and the protocol(s) for human studies. An IND must become effective before human clinical trials may begin. An IND will automatically become effective 30 days after receipt by the FDA unless, before that time, the FDA raises concerns or questions related to the proposed clinical trials. In such a case, the IND may be placed on clinical hold and the IND sponsor and the FDA must resolve any outstanding concerns or questions before clinical trials can begin.
For each successive clinical trial conducted with the investigational drug, a separate, new protocol submission to an existing IND must be made, along with any subsequent changes to the investigational plan. Sponsors are also subject to ongoing reporting requirements, including submission of IND safety reports for any serious adverse experiences associated with use of the investigational drug or findings from nonclinical studies suggesting a significant risk for human subjects, as well as IND annual reports on the progress of the investigations conducted under the IND.
146
Table of Contents
Clinical trials involve the administration of the investigational drug to human subjects under the supervision of qualified investigators in accordance with GCPs, which include the requirement that all research subjects provide their informed consent for participation in each clinical trial. Clinical trials are conducted under protocols detailing, among other things, the objectives of the trial, the parameters to be used in monitoring safety and the efficacy criteria to be evaluated. A protocol for each clinical trial and any subsequent protocol amendments must be submitted to the FDA as part of the IND. Additionally, approval must also be obtained from each clinical trial site’s IRB before a trial may be initiated at the site, and the IRB must monitor the trial until completed. Sponsors of clinical trials generally must register and report ongoing clinical trials and clinical trial results to public registries, including the website maintained by the U.S. National Institutes of Health, ClinicalTrials.gov.
For purposes of NDA approval, human clinical trials are typically divided into three or four phases. Although the phases are usually conducted sequentially, they may overlap or be combined.
| • | Phase 1. The drug is initially introduced into healthy human subjects or into patients with the target disease or condition. These studies are designed to evaluate the safety, dosage tolerance, metabolism and pharmacologic actions of the drug in humans, the side effects associated with increasing doses, and if possible, to gain early evidence of effectiveness. |
| • | Phase 2. The drug is administered to a limited patient population to evaluate tolerance and optimal dose, identify possible adverse side effects and safety risks, and preliminarily evaluate efficacy. Multiple Phase 2 trials may be conducted to obtain additional data prior to beginning Phase 3 trials. |
| • | Phase 3. The drug is administered to an expanded patient population, generally at geographically dispersed clinical trial sites to generate enough data to statistically evaluate dosage, clinical effectiveness and safety, to establish the overall benefit-risk relationship of the investigational drug and to provide an adequate basis for drug approval. |
| • | Phase 4. In some cases, the FDA may condition approval of an NDA for a drug candidate on the sponsor’s agreement to conduct additional clinical trials after approval. In other cases, a sponsor may voluntarily conduct additional clinical trials after approval to gain more information about the drug. Such post-approval trials are typically referred to as Phase 4 clinical trials. |
The FDA, the IRB or the clinical trial sponsor may suspend or terminate a clinical trial at any time on various grounds, including a finding that the research subjects are being exposed to an unacceptable health risk. The sponsor may also suspend or terminate a clinical trial based on evolving business objectives and/or competitive climate.
Concurrent with clinical trials, companies may complete additional in vivo studies and develop additional information about the characteristics of the drug candidate. Companies must also finalize a process for manufacturing the drug in commercially applicable quantities in accordance with cGMP requirements. The manufacturing process must be capable of consistently producing quality batches of the drug and, among other things, must use validated methods for testing the drug against specifications to confirm its identity, strength, quality and purity. Additionally, appropriate packaging must be selected and tested and stability studies must be conducted to demonstrate that the drug does not undergo unacceptable deterioration over its shelf life.
Submission of an NDA to the FDA
Assuming successful completion of all required testing in accordance with all applicable regulatory requirements, the results of product development and testing are submitted to the FDA in the form of an NDA requesting approval to market the drug for one or more indications. The submission of an NDA requires payment of a substantial application user fee to the FDA, unless a waiver or exemption applies.
147
Table of Contents
An NDA must include all relevant data available from pertinent nonclinical studies and clinical trials, including negative or ambiguous results as well as positive findings, together with detailed information relating to the drug’s chemistry, manufacturing, controls and proposed labeling, among other things. Data can come from company-sponsored clinical trials intended to test the safety and effectiveness of the drug for a specific use, or from a number of alternative sources, including studies initiated by investigators. To support marketing approval, the data submitted must be sufficient in quality and quantity to establish the safety and effectiveness of the drug to the satisfaction of the FDA.
The FDA has 60 days from its receipt of an NDA to determine whether the application will be accepted for filing based on the agency’s threshold determination that it is sufficiently complete to permit substantive review. The FDA may request additional information rather than accept an application for filing. In this event, the application must be resubmitted with the additional information and is subject to payment of additional user fees. The resubmitted application is also subject to review before the FDA accepts it for filing. Once the submission is accepted for filing, the FDA begins an in-depth substantive review. Under applicable Prescription Drug User Fee Act (“PDUFA”) performance goals, the FDA endeavors to review NDAs for drugs containing new molecular entities within ten months of the 60-day filing date under standard review or within six months of the 60-day filing date under priority review.
The FDA may refer applications for novel drug products or drug products which present difficult questions of safety or efficacy to an advisory committee for review, evaluation and recommendation as to whether the application should be approved and under what conditions.
Before approving an NDA, the FDA typically will inspect the facility or facilities where the drug is manufactured. The FDA will not approve an application unless it determines that the manufacturing processes and facilities are in compliance with cGMP requirements and are adequate to assure consistent production of the drug within required specifications. Additionally, the FDA will typically inspect one or more clinical sites to assure that relevant trial data was obtained in compliance with GCP requirements.
After the FDA evaluates the NDA and conducts inspections of manufacturing facilities, it may issue an approval letter or a complete response letter. A complete response letter indicates that the review cycle of the application is complete and the application is not ready for approval. A complete response letter generally outlines the deficiencies in the submission and may require substantial additional testing or information in order for the FDA to reconsider the application. Even with submission of this additional information, the FDA may ultimately decide that an application does not satisfy the regulatory criteria for approval. If, or when, the deficiencies have been addressed to the FDA’s satisfaction in a resubmission of the application, the FDA will issue an approval letter. An approval letter authorizes commercial marketing of the drug with specific prescribing information for specific indications.
As a condition of NDA approval, the FDA may require a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (“REMS”) program to help ensure that the benefits of the drug outweigh its risks. If the FDA determines a REMS program is necessary, the drug sponsor must develop and submit a REMS as part of its NDA prior to approval. A REMS program may be required to include various elements, such as a medication guide or patient package insert, a communication plan to educate healthcare providers of the drug’s risks, or other elements to assure safe use, such as limitations on who may prescribe or dispense the drug, dispensing only under certain circumstances, special monitoring and the use of patient registries. In addition, all REMS programs must include a timetable to periodically assess the strategy following implementation.
Further, the FDA may require substantial post-approval testing and surveillance as a condition of NDA approval to monitor the drug’s safety and efficacy, and the FDA has the authority to prevent or limit further marketing of a product based on the results of these post-marketing programs. Once granted, product approvals may be
148
Table of Contents
withdrawn if compliance with regulatory requirements is not maintained or problems are identified following initial marketing. Moreover, changes to the conditions established in an approved application, including changes in indications, labeling or manufacturing processes or facilities may require submission and FDA approval of a new NDA or NDA supplement before the changes can be implemented. An NDA supplement for a new indication typically requires clinical data similar to that supporting the original approval, and the FDA uses similar procedures in reviewing supplements as it does in reviewing original applications.
Expedited development and review programs
The FDA offers a number of expedited development and review programs for qualifying drugs, one or more of which may be available for our current or future drug candidates.
New drug candidates are eligible for fast track designation if they are intended to treat a serious or life-threatening disease or condition and demonstrate the potential to address unmet medical needs for the disease or condition. Fast track designation applies to the combination of the drug and the specific indication for which it is being studied. The sponsor of a fast track drug candidate has opportunities for frequent interactions with the review team during drug development and, once an NDA is submitted, the drug candidate may be eligible for priority review. A fast track drug candidate may also be eligible for rolling review, where the FDA may consider for review sections of the NDA on a rolling basis before the complete application is submitted, if the sponsor provides a schedule for the submission of the sections of the NDA, the FDA agrees to accept sections of the NDA and determines that the schedule is acceptable, and the sponsor pays any required user fees upon submission of the first section of the NDA.
A drug candidate intended to treat a serious or life-threatening disease or condition may also be eligible for breakthrough therapy designation to expedite its development and review. A drug candidate can receive breakthrough therapy designation if preliminary clinical evidence indicates that the drug candidate may demonstrate substantial improvement over existing therapies on one or more clinically significant endpoints, such as substantial treatment effects observed early in clinical development. The designation includes all of the fast track program features, as well as more intensive FDA interaction and guidance beginning as early as Phase 1 and an organizational commitment to expedite the development and review of the drug candidate, including involvement of senior managers.
After an NDA is submitted for a drug candidate, including a drug candidate with a fast track designation and/or breakthrough therapy designation, the NDA may be eligible for priority review. An NDA is eligible for priority review if it has the potential to provide a significant improvement in the treatment, diagnosis or prevention of a serious disease or condition compared to marketed products. Depending on whether a drug candidate contains a new molecular entity, priority review designation means the FDA’s goal is to take an action on the marketing application within six to eight months of the 60-day filing date, compared with ten to twelve months under standard review.
Additionally, drug candidates studied for their safety and effectiveness in treating serious or life-threatening diseases or conditions may receive accelerated approval upon a determination that the drug candidate has an effect on a surrogate endpoint that is reasonably likely to predict clinical benefit, or on a clinical endpoint that can be measured earlier than irreversible morbidity or mortality, that is reasonably likely to predict an effect on irreversible morbidity or mortality or other clinical benefit, taking into account the severity, rarity, or prevalence of the condition and the availability or lack of alternative treatments. As a condition of accelerated approval, the FDA will generally require the sponsor to perform adequate and well-controlled post-marketing clinical trials to verify and describe the anticipated effect on irreversible morbidity or mortality or other clinical benefit. In addition, the FDA currently requires, as a condition for accelerated approval, pre-approval of promotional materials, which could adversely impact the timing of the commercial launch of the drug.
149
Table of Contents
Orphan drug designation
We may pursue orphan drug designation for one or more of our current or future drug candidates, as appropriate, with the potential to obtain orphan drug exclusivity for our products, if approved.
Under the Orphan Drug Act, the FDA may grant orphan designation to a drug intended to treat a rare disease or condition, which is a disease or condition that affects fewer than 200,000 individuals in the United States, or more than 200,000 individuals in the United States for which there is no reasonable expectation that the cost of developing and making available in the United States a drug for this type of disease or condition will be recovered from sales in the United States for that drug. Orphan drug designation must be requested before submitting an NDA. After the FDA grants orphan drug designation, the generic identity of the therapeutic agent and its potential orphan use are disclosed publicly by the FDA. The orphan drug designation does not convey any advantage in, or shorten the duration of, the regulatory review or approval process.
If a drug that has orphan drug designation subsequently receives the first FDA approval for the disease for which it has such designation, the drug is entitled to orphan drug exclusive approval (or exclusivity), which means that the FDA may not approve any other applications, including a full NDA, to market the same drug for the same indication for seven years, except in limited circumstances, such as a showing of clinical superiority to the drug with orphan drug exclusivity. Orphan drug exclusivity does not prevent the FDA from approving a different drug for the same disease or condition, or the same drug for a different disease or condition. Among the other benefits of orphan drug designation are tax credits for certain research and a waiver of the application user fee.
A designated orphan drug may not receive orphan drug exclusivity if it is approved for a use that is broader than the indication for which it received orphan designation. In addition, exclusive marketing rights in the United States may be lost if the FDA later determines that the request for designation was materially defective or if the manufacturer is unable to assure sufficient quantities of the drug to meet the needs of patients with the rare disease or condition.
Under the Pediatric Research Equity Act, certain NDAs and certain supplements to an NDA must contain data to assess the safety and efficacy of the drug for the claimed indications in all relevant pediatric subpopulations and to support dosing and administration for each pediatric subpopulation for which the product is safe and effective. The FDA may grant deferrals for submission of pediatric data or full or partial waivers. The Food and Drug Administration Safety and Innovation Act amended the FDCA to require that a sponsor who is planning to submit an NDA for a drug that includes a new active ingredient, new indication, new dosage form, new dosing regimen or new route of administration submit an initial Pediatric Study Plan (“iPSP”), within 60 days of an end-of-Phase 2 meeting or, if there is no such meeting, as early as practicable before the initiation of a Phase 3 or Phase 2/3 study. The iPSP must include an outline of the pediatric study or studies that the sponsor plans to conduct, including study objectives and design, age groups, relevant endpoints and statistical approach, or a justification for not including such detailed information, and any request for a deferral of pediatric assessments or a full or partial waiver of the requirement to provide data from pediatric studies along with supporting information. The FDA and the sponsor must reach an agreement on the iPSP. A sponsor can submit amendments to an agreed-upon iPSP at any time if changes to the pediatric plan need to be considered based on data collected from nonclinical studies, early phase clinical trials and/or other clinical development programs.
A drug product can also obtain pediatric market exclusivity in the United States. Pediatric exclusivity, if granted, adds six months to existing exclusivity periods and patent terms. This six-month exclusivity, which runs from the end of other exclusivity protection or patent term, may be granted based on the voluntary completion of a pediatric study in accordance with an FDA-issued “Written Request” for such a study.
150
Table of Contents
Post-approval requirements
Once an NDA is approved, a drug will be subject to pervasive and continuing regulation by the FDA, including, among other things, requirements relating to drug listing and registration, recordkeeping, periodic reporting, product sampling and distribution, adverse event reporting and advertising, marketing and promotion. Drugs may be marketed only for the approved indications and in accordance with the provisions of the approved labeling. While physicians may prescribe for off-label uses, manufacturers may only promote for the approved indications and in accordance with the provisions of the approved label. However, companies may share truthful and not misleading information that is otherwise consistent with a product’s FDA approved labeling. The FDA and other agencies actively enforce the laws and regulations prohibiting the promotion of off-label uses, and a company that is found to have improperly promoted off-label uses may be subject to significant liability.
After approval, most changes to the approved drug, such as adding new indications or other labeling claims, are subject to prior FDA review and approval. There also are continuing user fee requirements, under which FDA assesses an annual program fee for each drug identified in an approved NDA. In addition, quality-control, drug manufacture, packaging and labeling procedures must continue to conform to cGMPs after approval. Drug manufacturers and certain of their subcontractors are required to register their establishments with the FDA and certain state agencies. Registration with the FDA subjects entities to periodic unannounced and announced inspections by the FDA and these state agencies, during which the agency inspects manufacturing facilities to assess compliance with cGMPs. FDA regulations also require investigation and correction of any deviations from cGMP and impose reporting requirements upon manufacturers and their subcontractors, if applicable. Accordingly, manufacturers must continue to expend time, money and effort in the area of production and quality control to maintain compliance with cGMP and other aspects of regulatory compliance.
The FDA may withdraw approval of a drug if compliance with regulatory requirements is not maintained or if problems occur after the drug reaches the market. Later discovery of previously unknown problems with a drug, including adverse events of unanticipated severity or frequency, or with manufacturing processes, or failure to comply with regulatory requirements, may result in revisions to the approved labeling to add new safety information; imposition of post-market studies or clinical trials to assess new safety risks; or imposition of distribution restrictions or other restrictions under a REMS program. Other potential consequences include, among other things:
| • | restrictions on the marketing or manufacturing of a drug, complete withdrawal of the drug from the market or drug recalls; |
| • | fines, warning or untitled letters or holds on post-approval clinical studies; |
| • | refusal of the FDA to approve pending applications or supplements to approved applications, or suspension or revocation of existing drug approvals; |
| • | drug seizure or detention, or refusal of the FDA to permit the import or export of drugs; or |
| • | injunctions or the imposition of civil or criminal penalties. |
The FDA may also require post-approval studies and clinical trials if the FDA finds that scientific data, including information regarding related drugs, deem it appropriate. The purpose of such studies would be to assess a known serious risk or signals of serious risk related to the drug or to identify an unexpected serious risk when available data indicate the potential for a serious risk. The FDA may also require a labeling change if it becomes aware of new safety information that it believes should be included in the labeling of a drug.
151
Table of Contents
International regulation
In addition to regulations in the United States, we are subject to certain and could become subject to a variety of additional foreign regulations regarding development, approval, commercial sales and distribution of our drugs if we seek to market our drugs (if approved) in other jurisdictions. Whether or not we obtain FDA approval for a drug candidate, we must obtain the necessary approvals by the comparable regulatory authorities of foreign countries before we can commence clinical trials or marketing of the drug in those countries. The approval process varies from country to country and can involve additional drug testing and additional review periods, and the time may be longer or shorter than that required to obtain FDA approval. The requirements governing, among other things, the conduct of clinical trials, drug licensing, pricing and reimbursement vary greatly from country to country. Regulatory approval in one country does not ensure regulatory approval in another, but a failure or delay in obtaining regulatory approval in one country may negatively impact the regulatory process in others. If we fail to comply with applicable foreign regulatory requirements, we may be subject to fines, suspension or withdrawal of regulatory approvals, drug recalls, seizure of drugs, operating restrictions and criminal prosecution.
Other U.S. healthcare laws and compliance requirements
Pharmaceutical companies are subject to additional healthcare regulation and enforcement by the federal government and by authorities in the states and foreign jurisdictions in which they conduct their business. In the United States, such laws include, without limitation, state and federal anti-kickback, fraud and abuse, false claims, price reporting, and physician payment sunshine laws and regulations. Violation of any of such laws or any other governmental regulations that apply may result in significant penalties, including, without limitation, administrative civil and criminal penalties, damages, disgorgement fines, additional reporting requirements and oversight obligations, contractual damages, the curtailment or restructuring of operations, exclusion from participation in governmental healthcare programs and imprisonment.
Pharmaceutical coverage, pricing and reimbursement
Significant uncertainty exists as to the coverage and reimbursement status of any drug candidates for which we or our collaborators obtain regulatory approval. In the United States and markets in other countries, sales of any drugs for which we or our collaborators receive regulatory approval for commercial sale will depend, in part, on the extent to which third-party payors provide coverage, and establish adequate reimbursement levels for such drug products.
In the United States, third-party payors include federal and state healthcare programs, government authorities, private managed care providers, private health insurers, and other organizations. Third-party payors are increasingly challenging the price, examining the medical necessity and reviewing the cost-effectiveness of medical drug products and medical services, in addition to questioning their safety and efficacy. Such payors may limit coverage to specific drug products on an approved list, also known as a formulary, which might not include all of the FDA-approved drugs for a particular indication. We or our collaborators may need to conduct expensive pharmacoeconomic studies in order to demonstrate the medical necessity and cost-effectiveness of our drugs, in addition to the costs required to obtain the FDA approvals. Nonetheless, our drug candidates may not be considered medically necessary or cost-effective. A payor’s decision to provide coverage for a drug product does not imply that an adequate reimbursement rate will be approved. Further, one payor’s determination to provide coverage for a drug product does not assure that other payors will also provide coverage for the drug product.
Moreover, the process for determining whether a third-party payor will provide coverage for a drug product may be separate from the process for setting the price of a drug product or for establishing the reimbursement
152
Table of Contents
rate that such a payor will pay for the drug product. For drugs administered under the supervision of a physician, obtaining coverage and adequate reimbursement may be particularly difficult because of the higher prices often associated with such drugs. Additionally, separate reimbursement for the drug itself or the treatment for which the drug is used may not be available, which may impact physician utilization. Adequate third-party reimbursement may not be available to enable us to maintain price levels sufficient to realize an appropriate return on our investment in drug development.
Different pricing and reimbursement schemes exist in other countries. In Europe, governments influence the price of pharmaceutical products through their pricing and reimbursement rules and control of national health care systems that fund a large part of the cost of those products to consumers. Some jurisdictions operate positive and negative list systems under which drugs may only be marketed once a reimbursement price has been agreed. To obtain reimbursement or pricing approval, some of these countries may require the completion of clinical trials that compare the cost-effectiveness of a particular drug candidate to currently available therapies. Other member states allow companies to fix their own prices for medicines, but monitor and control company profits. The downward pressure on health care costs in general, particularly prescription drugs, has become very intense. As a result, increasingly high barriers are being erected to the entry of new drugs. In addition, in some countries, cross-border imports from low-priced markets exert a commercial pressure on pricing within a country.
The marketability of any drug candidates for which we or our collaborators receive regulatory approval for commercial sale may suffer if the government and third-party payors fail to provide adequate coverage and reimbursement. In addition, emphasis on managed care in the United States has increased and we expect will continue to increase the pressure on pharmaceutical pricing. Coverage policies and third-party reimbursement rates may change at any time. Even if favorable coverage and reimbursement status is attained for one or more drug candidates for which we or our collaborators receive regulatory approval, less favorable coverage policies and reimbursement rates may be implemented in the future.
Healthcare reform
A primary trend in the U.S. healthcare industry and elsewhere is cost containment. Government authorities and other third-party payors have attempted to control costs by limiting coverage and the amount of reimbursement for particular medical products and services, implementing reductions in Medicare and other healthcare funding and applying new payment methodologies. For example, in March 2010, the Affordable Care Act was enacted, which affected existing government healthcare programs and resulted in the development of new programs.
Among the Affordable Care Act’s provisions of importance to the pharmaceutical industry, in addition to those otherwise described above, are the following:
| • | an annual, nondeductible fee on any entity that manufactures or imports certain specified branded prescription drugs and biologic agents apportioned among these entities according to their market share in some government healthcare programs; |
| • | an increase in the statutory minimum rebates a manufacturer must pay under the Medicaid Drug Rebate Program to 23.1% and 13% of the average manufacturer price for most branded and generic drugs, respectively, and a cap on the total rebate amount for innovator drugs at 100% of the Average Manufacturer Price (“AMP”); |
| • | a new Medicare Part D coverage gap discount program, in which manufacturers must agree to offer 70% point-of-sale discounts off negotiated prices of applicable brand drugs to eligible beneficiaries during their |
153
Table of Contents
| coverage gap period, as a condition for the manufacturers’ outpatient drugs to be covered under Medicare Part D; |
| • | extension of manufacturers’ Medicaid rebate liability to covered drugs dispensed to individuals who are enrolled in Medicaid managed care organizations; |
| • | expansion of eligibility criteria for Medicaid programs by, among other things, allowing states to offer Medicaid coverage to additional individuals, including individuals with income at or below 133% of the federal poverty level, thereby potentially increasing manufacturers’ Medicaid rebate liability; |
| • | expansion of the entities eligible for discounts under the Public Health Service pharmaceutical pricing program; and |
| • | a new Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute to oversee, identify priorities in, and conduct comparative clinical effectiveness research, along with funding for such research. |
Since its enactment, there have been judicial and Congressional challenges to certain aspects of the Affordable Care Act, as well as recent efforts by the Trump administration to repeal or replace certain aspects of the Affordable Care Act. For example, the TCJA was enacted, which includes a provision repealing, effective January 1, 2019, the tax-based shared responsibility payment imposed by the Affordable Care Act on certain individuals who fail to maintain qualifying health coverage for all or part of a year that is commonly referred to as the “individual mandate.” On December 14, 2018, a U.S. District Court Judge in the Northern District of Texas ruled that the individual mandate is a critical and inseverable feature of the Affordable Care Act, and therefore, because it was repealed as part of the TCJA, the remaining provisions of the Affordable Care Act are invalid as well. Additionally, on December 18, 2019, the U.S. Court of Appeals for the 5th Circuit ruled that that the individual mandate was unconstitutional and remanded the case back to the District Court to determine whether the remaining provisions of the Affordable Care Act are invalid as well. On March 2, 2020, the U.S. Supreme Court granted the petitions for writs of certiorari to review this case, although it is unclear when or how the Supreme Court will rule. It is also unclear how other efforts to challenge, repeal or replace the Affordable Care Act will impact the law.
Other legislative changes have been proposed and adopted in the United States since the Affordable Care Act was enacted. On August 2, 2011, the Budget Control Act of 2011, among other things, included aggregate reductions to Medicare payments to providers of 2% per fiscal year, which went into effect on April 1, 2013, and will remain in effect through 2030, with the exception of a temporary suspension from May 1, 2020 through December 31, 2020, unless additional Congressional action is taken. In addition, in January 2013, the American Taxpayer Relief Act of 2012 was signed into law, which, among other things, further reduced Medicare payments to several providers, including hospitals, imaging centers and cancer treatment centers, and increased the statute of limitations period for the government to recover overpayments to providers from three to five years.
There has also been heightened governmental scrutiny recently over the manner in which pharmaceutical companies set prices for their marketed products, which has resulted in several Congressional inquiries and proposed federal legislation, as well as state efforts, designed to, among other things, bring more transparency to drug pricing, reduce the cost of prescription drugs under Medicare, review the relationship between pricing and manufacturer patient programs, and reform government program reimbursement methodologies for drug products. Congress and the Trump administration have each indicated that it will continue to seek new legislative and/or administrative measures to control drug costs.
We anticipate that these new laws will result in additional downward pressure on coverage and the price that we receive for any approved drug, and could seriously harm our business. Any reduction in reimbursement
154
Table of Contents
from Medicare and other government programs may result in a similar reduction in payments from private payors. The implementation of cost containment measures or other healthcare reforms may prevent us from being able to generate revenue, attain profitability, or commercialize our drugs (if approved). In addition, it is possible that there will be further legislation or regulation that could harm our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
Data privacy and security
We may also be subject to federal, state and foreign data privacy and security laws and regulations. In the United States, numerous federal and state laws and regulations, including state data breach notification laws, state health information privacy laws, and federal and state consumer protection laws and regulations (e.g., Section 5 of the FTC Act), govern the collection, use, disclosure, and protection of health-related and other personal information could apply to our operations or the operations of our partners. HIPAA, as amended by HITECH, and its implementing regulations, impose requirements relating to the privacy, security and transmission of individually identifiable health information on certain health care providers, health plans and health care clearinghouses, known as covered entities, as well as their business associates that perform certain services that involve creating, receiving, maintaining or transmitting individually identifiable health information for or on behalf of such covered entities. Entities that are found to be in violation of HIPAA as the result of a breach of unsecured protected health information, a complaint about privacy practices or an audit by HHS, may be subject to significant civil, criminal and administrative fines and penalties and/or additional reporting and oversight obligations if required to enter into a resolution agreement and corrective action plan with HHS to settle allegations of HIPAA non-compliance. Further, entities that knowingly obtain, use, or disclose individually identifiable health information maintained by a HIPAA covered entity in a manner that is not authorized or permitted by HIPAA may be subject to criminal penalties.
Even when HIPAA does not apply, according to the FTC, violating consumers’ privacy rights or failing to take appropriate steps to keep consumers’ personal information secure may constitute unfair acts or practices in or affecting commerce in violation of Section 5 of the FTC Act. The FTC expects a company’s data security measures to be reasonable and appropriate in light of the sensitivity and volume of consumer information it holds, the size and complexity of its business, and the cost of available tools to improve security and reduce vulnerabilities. Individually identifiable health information is considered sensitive data that merits stronger safeguards.
In addition, state laws govern the privacy and security of health information in specified circumstances, many of which differ from each other in significant ways and may not have the same effect, thus complicating compliance efforts. By way of example, California recently enacted the CCPA, which creates new individual privacy rights for California consumers (as defined in the law) and places increased privacy and security obligations on entities handling certain personal data of consumers or households. The CCPA requires covered companies to provide new disclosure to consumers about such companies’ data collection, use and sharing practices, provide such consumers new ways to opt-out of certain sales or transfers of personal information, and provide consumers with additional causes of action. The CCPA became effective on January 1, 2020, and the California Attorney General may bring enforcement actions for violations beginning July 1, 2020. The CCPA has been amended from time to time, and it remains unclear what, if any, further modifications will be made to this legislation or how it will be interpreted. As currently written, the CCPA may impact our business activities and exemplifies the vulnerability of our business to the evolving regulatory environment related to personal data and protected health information.
We also are or will become subject to privacy laws in the jurisdictions in which we sell or market our products or run clinical trials. For example, in the EU we are subject to the GDPR in relation to our collection, control,
155
Table of Contents
processing, and other use of personal data (i.e. data relating to an identifiable living individual). We process personal data in relation to participants in our clinical trials in the EEA, including the health and medical information of these participants. The GDPR is directly applicable in each EU and EEA Member State, however, it provides that EU and EEA Member States may introduce further conditions, including limitations which could limit our ability to collect, use and share personal data (including health and medical information), or could cause our compliance costs to increase, ultimately having an adverse impact on our business. The GDPR imposes onerous accountability obligations requiring data controllers and processors to maintain a record of their data processing and implement policies as part of its mandated privacy governance framework. It also requires data controllers to be transparent and disclose to data subjects (in a concise, intelligible and easily accessible form) how their personal information is to be used, imposes limitations on retention of personal data; defines pseudonymized (i.e., key-coded) data; introduces mandatory data breach notification requirements; and sets higher standards for data controllers to demonstrate that they have obtained valid consent for certain data processing activities. We are also subject to EEA rules with respect to cross-border transfers of personal data out of the EEA. Recent legal developments in the EU have created complexity and uncertainty regarding transfers of personal data from the EEA to the United States. On July 16, 2020, the Court of Justice of the European Union (“CJEU”) invalidated the EU-US Privacy Shield Framework (the “Privacy Shield”) under which personal data could be transferred from the EEA to US entities who had self-certified under the Privacy Shield scheme. While the CJEU upheld the adequacy, subject to certain conditions, of the standard contractual clauses (a standard form of contract approved by the European Commission as an adequate personal data transfer mechanism), future regulatory guidance could result in changes to the use of standard contractual clauses. As supervisory authorities issue further guidance on personal data export mechanisms, including circumstances where the standard contractual clauses cannot be used, and/or start taking enforcement action, we could suffer additional costs, complaints and/or regulatory investigations or fines, and/or if we are otherwise unable to transfer personal data between and among countries and regions in which we operate, it could affect the manner in which we operate and the geographical location or segregation of our relevant systems and operations, and could adversely affect our financial results.
We are subject to the supervision of local data protection authorities in those EU jurisdictions where we are subject to the GDPR, and we maintain an office in Belgium, which has its own set of stringent privacy and data protection laws and regulations. Fines for certain breaches of the GDPR are significant: up to the greater of €20 million or 4% of total global annual turnover. Further, following the withdrawal of the UK from the EU on January 31, 2020, pursuant to the transitional arrangements agreed between the UK and the EU, we will have to comply with the GDPR and separately the GDPR as implemented in the UK, each regime having the ability to fine up to the greater of €20 million/ £17 million or 4% of global turnover. The relationship between the UK and the EU in relation to certain aspects of data protection law remains unclear, including how data transfers between EU member states and the UK will be treated. These changes may lead to additional compliance costs and could increase our overall risk. In addition to the foregoing, a breach of the GDPR or other applicable privacy and data protection laws and regulations could result in regulatory investigations, reputational damage, orders to cease / change our use of data, enforcement notices, or potential civil claims including class action type litigation.
Legal proceedings
From time to time, we may become involved in litigation or other legal proceedings. We are not currently a party to any litigation or legal proceedings that, in the opinion of our management, are likely to have a material adverse effect on our business. Regardless of outcome, litigation can have an adverse impact on our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects because of defense and settlement costs, diversion of management resources and other factors.
156
Table of Contents
Facilities
Our corporate headquarters is located in South San Francisco, California, where we lease and occupy approximately 39,000 square feet of office and laboratory space. The current term of our South San Francisco lease expires in March 2027, with an option to extend the term through March 2035.
We also have an office in Leuven, Belgium, where we lease and occupy approximately 5,400 square feet of office and laboratory space. The current term of our Leuven, Belgium lease expires in August 2023, with an option to extend the term through August 2028.
We believe our existing facilities are sufficient for our needs for the foreseeable future. To meet the future needs of our business, we may lease additional or alternate space, and we believe suitable additional or alternative space will be available in the future on commercially reasonable terms.
Employees
As of June 30, 2020, we had 67 full-time employees, including 55 employees engaged in research and development. None of our employees are represented by labor unions or covered by collective bargaining agreements. We consider our relationship with our employees to be good.
157
Table of Contents
Executive officers, significant employees and directors
The following table sets forth information regarding our executive officers and directors as of June 30, 2020:
| Name | Age | Position(s) | ||||
| Executive Officers and Employee Directors |
||||||
| Lawrence M. Blatt, Ph.D. | 58 | Chief Executive Officer and Director | ||||
| Leonid Beigelman, Ph.D. |
62 | President and Director | ||||
| Lesley Ann Calhoun |
54 | Executive Vice President, Chief Financial Officer | ||||
| Lucinda Y. Quan, J.D. |
48 | Executive Vice President, Chief Business Officer and General Counsel | ||||
| Julian A. Symons, D.Phil. |
59 | Executive Vice President, Chief Scientific Officer | ||||
| Significant Employees |
||||||
| John Fry |
57 | Executive Vice President, Clinical Development | ||||
| Matthew W. McClure, M.D. |
49 | Executive Vice President, Chief Medical Officer | ||||
| Sushmita M. Chanda, Ph.D., DABT |
54 | Executive Vice President, Translational Safety Sciences | ||||
| Non-Employee Directors |
||||||
| Jack B. Nielsen(1)(2)(3) |
56 | Chair and Director | ||||
| K. Peter Hirth, Ph.D.(2) |
69 | Director | ||||
| Carole Nuechterlein(2)(3) |
59 | Director | ||||
| Peter Moldt, Ph.D.(1) |
61 | Director | ||||
| Thomas Woiwode, Ph.D.(2)(3) |
48 | Director | ||||
| Kathleen Sereda Glaub(1) |
67 | Director | ||||
|
| ||||||
| (1) | Member of the audit committee. |
| (2) | Member of the compensation committee. |
| (3) | Member of the nominating and corporate governance committee. |
Executive officers and employee directors
Lawrence M. Blatt, Ph.D., has served as our Chief Executive Officer and a member of our board of directors since February 2018. Prior to co-founding the Company, Dr. Blatt served as the Global Head of Infectious Diseases and Vaccines at Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies of Johnson & Johnson, a pharmaceutical company, from November 2014 to February 2018. Dr. Blatt co-founded Alios BioPharma, Inc., a biotechnology company, and served as its Chief Executive Officer, President and Director from January 2009 until its acquisition by Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies of Johnson & Johnson in November 2014. Prior to Alios, he served as Chief Scientific Officer at InterMune, Inc., a biotechnology company, from 2002 to 2008. Dr. Blatt currently serves on
158
Table of Contents
the board of directors of ReViral Ltd. and previously served on the boards of directors of Alveo Technologies, Inc., which he co-founded in 2014, and Meissa Vaccines, Inc. Dr. Blatt received a B.S. in Microbiology from Indiana University Bloomington, an M.B.A. from California State University, Northridge, and a Ph.D. in Public Health Administration from the University of La Verne. We believe that Dr. Blatt’s extensive experience as an executive of several companies in the biopharmaceutical and biotechnology industries, his extensive knowledge of our company and his educational background provides him with the qualifications and skills necessary to serve as a member of our board of directors.
Leonid Beigelman, Ph.D., has served as President and a member of our board of directors since March 2018. Dr. Beigelman has over 30 years of experience in medicinal chemistry and drug discovery of small molecules and oligonucleotides. Prior to co-founding the Company, he was Vice President of Medicinal Chemistry and Global Head of Discovery of Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies of Johnson & Johnson, a pharmaceutical company, from September 2014 to March 2018, where he established the Center of Excellence in Nucleic Acids. Prior to that, Dr. Beigelman co-founded Alios BioPharma, Inc. and served as its Chief Scientific Officer before it was acquired by Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies of Johnson & Johnson in November 2014. From 2005 to 2009, Dr. Beigelman served as Vice President, Technical Operations at InterMune, Inc. leading teams in hepatitis C virus (“HCV”) drug discovery. From 2002 to 2005, Dr. Beigelman worked at Transgenomic, Inc., a biotechnology company, as Vice President of Nucleic Acids Chemistry. While at Ribozyme Pharmaceuticals Inc., a biotechnology company, from 1992 to 2002 (which became SiRNA Pharmaceuticals, Inc.), Dr. Beigelman assumed positions including Senior Director of Chemistry and Biochemistry. Dr. Beigelman received his Ph.D. in Bioorganic Chemistry from The Institute of Molecular Biology (USSR Academy of Sciences) and completed his post-doctoral training at the Department of Pharmacology, Yale University Medical school. We believe that Dr. Beigelman’s extensive experience as an executive of several companies in the biopharmaceutical and biotechnology industries, his extensive knowledge of our company and his educational background provides him with the qualifications and skills necessary to serve as a member of our board of directors.
Lesley Ann Calhoun has served as our Executive Vice President, Chief Financial Officer since June 2020. From August 2016 to June 2020, Ms. Calhoun served in various roles at Global Blood Therapeutics, Inc., a drug discovery, development and commercial-stage biopharmaceutical company, including most recently as Senior Vice President, Finance & Administration and Chief Accounting Officer. Prior to these roles, Ms. Calhoun served as Vice President of Finance at Hyperion Therapeutics, Inc., a commercial stage biopharmaceutical company, from January 2013 to September 2015, continuing in her role after it was acquired by Horizon Pharma plc, a pharmaceutical company, in May 2015. Ms. Calhoun also previously served as Senior Director of Finance, Corporate Controller at Innoviva, Inc. (formerly Theravance, Inc.), a biopharmaceutical company, from August 2005 to January 2013. Earlier in her career, Ms. Calhoun was a member of the audit practice of Deloitte & Touche LLP from 1989 to 2001. Ms. Calhoun received her B.S. in Business Administration with a concentration in Accounting from San Francisco State University, College of Business and is a Certified Public Accountant (inactive).
Lucinda Y. Quan, J.D., has served as our Executive Vice President, Chief Business Officer & General Counsel since March 2018. Prior to joining the Company, Ms. Quan served as the Executive Director of Transactions, Business Development & Licensing at the West Coast Innovations Hub of Merck & Co., a multinational pharmaceutical company, from January 2016 to April 2018. From November 2013 to January 2016, Ms. Quan served as Vice President, Head of Legal Affairs at Alios BioPharma, Inc., which was acquired by Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies of Johnson & Johnson, a pharmaceutical company, in November 2014. She also served as Vice President, Legal Affairs & Associate General Counsel at InterMune, Inc. (acquired by Roche in September 2014) from September 2004 to November 2013. Prior to InterMune, Inc., Ms. Quan spent seven years in private practice at various law firms, including Clifford Chance LLP, before transitioning to in-house. Ms. Quan received both her B.A. in Business Economics and J.D. from the University of California, Los Angeles.
159
Table of Contents
Julian A. Symons, D.Phil., has served as our Executive Vice President, Chief Scientific Officer since May 2018. Prior to joining the Company, from January 2010 to March 2015, Dr. Symons served in various roles at Alios BioPharma, Inc., which was acquired by Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies of Johnson & Johnson, a pharmaceutical company, in November 2014, including Senior Director, Product Development from January 2013 to March 2015, and Vice President, Disease Area Research & Development Leader, Respiratory Infections from March 2015 to April 2018. Prior to his time with Alios BioPharma, Inc., Dr. Symons held positions with the Pharmaceutical Division of F. Hoffman-La Roche Ltd and the Departments of Medicine at the University of Edinburgh (1986 – 1990), University of Sheffield (1990 – 1994) and the Sir William Dunn School of Pathology, University of Oxford (1994 – 1999). Dr. Symons received a B.Sc. (Hons) I in Biochemistry and Physiology from the University of Central Lancashire, UK and a D.Phil. in Immunology and Autoimmunity from the University of York, UK.
Significant employees
John Fry has served as our Executive Vice President, Clinical Development since September 2018. Prior to joining the Company, Mr. Fry joined Alios Biopharma, Inc. in March 2011, serving in various roles including Vice President, Clinical Development, from February 2012 until its acquisition by Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies of Johnson & Johnson, a pharmaceutical company, in November 2014, and Vice President, Head of Early Development, Infectious Diseases from November 2014 to August 2018. Mr. Fry received an R.N. from Medway School of Nursing (now part of Canterbury Christ Church University) and a BSc (hons) from the School of Biology, Sussex University, UK.
Matthew W. McClure, M.D., has served as our Executive Vice President and Chief Medical Officer since August 2019. Prior to joining the Company, Dr. McClure served as Chief Medical Officer at Second Genome, Inc., a biotechnology company, from March 2018 to June 2019. From November 2012 to March 2018, Dr. McClure served as Senior Director at Alios BioPharma, Inc., which was acquired by Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies of Johnson & Johnson, a pharmaceutical company, in November 2014. Prior to his tenure at Alios BioPharma, Inc., Dr. McClure held positions with Portola Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Dr. McClure received a B.S. in Biochemistry and Cell Biology from the University of California, San Diego, and an M.D. from Duke University School of Medicine.
Sushmita M. Chanda, Ph.D., has served as our Executive Vice President, Translational Safety Sciences, since August 2018. Prior to joining the Company, from February 2010 to July 2018, Dr. Chanda served as Vice President, Preclinical Development at Alios BioPharma, Inc., which was acquired by Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies of Johnson & Johnson, a pharmaceutical company. Prior to Alios BioPharma, Dr. Chanda served as the Senior Director and Head of Nonclinical Safety at F. Hoffman-La Roche Ltd, a multinational healthcare company, from 2000 to 2010. Prior to Roche, she was a toxicologist at Sugen Inc., a pharmaceutical company (bought by Pfizer), from May 1998 to January 2000. Dr. Chanda is a Diplomate of American Board of Toxicology (DABT). Dr. Chanda received her B.S. and M.S. from Birla Institute of Technology, Mesra, India and a Ph.D. in Toxicology and Pharmacology from the University of Louisiana at Monroe. She completed her post-doctoral fellowship in Toxicology at USEPA through the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
Non-employee directors
Kathleen Sereda Glaub has served as a member of our board of directors since October 2019. Ms. Glaub is co-founder and executive chair of CuraSen Therapeutics, Inc., a biotechnology company, a position she has held since October 2018. She also serves as a director on the boards of Escient Pharmaceuticals, Inc., a biotechnology company, and IO Biotech ApS, a Danish biotechnology company. She previously served on the boards of Codexis, Inc., a publicly traded protein engineering company, from September 2014 to September
160
Table of Contents
2019 and Afferent Pharmaceuticals, Inc., a biotechnology company, from November 2013 to October 2016. Ms. Glaub also served as the Chief Executive Officer of Afferent Pharmaceuticals from August 2014 to October 2016. Ms. Glaub also served as president of Plexxicon Inc. for 12 years. Previously, she held positions as senior vice president and chief financial officer of Cell Genesys, Inc., a biotechnology company, treasurer of Genentech, Inc., a biotechnology company, and various finance and treasury roles with Intel Corporation, a technology company. Ms. Glaub received a B.A. from the University of California, Berkeley, and an M.B.A. from Northwestern University Kellogg School of Management. We believe that Ms. Glaub’s extensive experience in strategy, business development, strategic transactions, financing and operations in both private and public biotechnology companies provides her with the qualifications and skills necessary to serve as a member of our board of directors.
K. Peter Hirth, Ph.D., has served as a member of our board of directors since August 2018. In 2001, Dr. Hirth co-founded Plexxikon, Inc., a pharmaceutical company, and served as its Chief Executive Officer until April 2013. Dr. Hirth currently serves on the boards of directors of Vaxcyte, Inc., a publicly traded biotechnology company, and several private companies. Dr. Hirth holds a M.Sc. and Ph.D. in Molecular Genetics from Heidelberg University, Germany and completed his post-doctoral work at the University of California, San Diego. We believe that Dr. Hirth’s extensive experience in the biopharmaceutical and biotechnology industries and his educational background provides him with the qualifications and skills necessary to serve as a member of our board of directors.
Peter Moldt, Ph.D., has served as a member of our board of directors since August 2018. Since May 2012, Dr. Moldt has been employed as a Senior Partner with Novo Ventures (US) Inc., which provides certain consultancy services to Novo Holdings A/S, a Danish limited liability company that manages investments and financial assets. From 2009 to May 2012, Dr. Moldt was employed as a Partner with Novo Holdings A/S. Dr. Moldt founded and served as Chief Executive Officer of Curalogic A/S, a publicly listed Danish pharmaceutical company, from 2004 through its liquidation in 2009. From 2000 to 2004, Dr. Moldt was Chief Operating Officer of 7TM Pharma A/S, a private biotechnology company, which he also co-founded. For the prior 11 years, Dr. Moldt held various positions with NeuroSearch A/S, a publicly listed Danish biotechnology company, including Director of Drug Development where he was responsible for all aspects of preclinical and clinical drug development. Dr. Moldt currently serves on the board of directors of several private biotechnology and biopharmaceutical companies and previously served on the board of directors of Corvus Pharmaceuticals, Inc., a publicly traded company, from 2015 to January 2019. He received an M.Sc. and a Ph.D. in Pharmacy and Medicinal Chemistry from the Royal Danish School of Pharmacy. He also completed his post-doctoral training at Yale University in the Department of Organic Chemistry. We believe that Dr. Moldt’s extensive experience in the biopharmaceutical and biotechnology industries, including as a venture capital investor in, and director of, several biotechnology companies, and his educational background provides him with the qualifications and skills necessary to serve as a member of our board of directors.
Jack B. Nielsen has served as a member our board of directors since August 2018. Since August 2017, Mr. Nielsen has also served as a Managing Director at Vivo Capital LLC, a healthcare focused investment firm. Prior to March, 2017, Mr. Nielsen worked within the Novo Holdings A/S organization and its venture activities since 2001 in several roles, most recently being employed as a Senior Partner based in Copenhagen, Denmark. From 2006 to 2012, Mr. Nielsen was employed as a Partner at Novo Ventures (US) Inc. in San Francisco, where he established the office which provides certain consultancy services to Novo Holdings A/S. Mr. Nielsen is currently a member of the board of directors of Reata Pharmaceuticals, Inc. and ALX Oncology Holdings Inc., both of which are publicly traded companies, and a number of private companies. Mr. Nielsen, in the past, has served on the boards of directors of Akebia Therapeutics, Inc., Crinetics Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Merus, N.V. and Apollo Endosurgery, Inc., each of which is publicly traded. Mr. Nielsen received a M.Sc. in Chemical Engineering from the Technical University of Denmark and a Masters in Management of Technology and Economics from the
161
Table of Contents
Center for Technology, Economics and Management, Technical University of Denmark. We believe that Mr. Nielsen’s experience as a venture capital investor in and director of life sciences companies provides him with the qualifications and skills necessary to serve as a member of our board of directors.
Carole Nuechterlein, J.D., has served as a member of our board of directors since August 2018. Ms. Nuechterlein joined F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. in 2001 and currently serves as a Deputy Director and Head of the Roche Venture Fund. She currently serves as a member of the boards of directors of Millendo Therapeutics, Inc., a publicly traded biopharmaceutical company, BCTG Acquisition Corp., a publicly traded special purpose acquisition company, and a number of private companies, including Entrada Therapeutics, Inc., MacuLogix, Inc., Vivet Therapeutics, CiVi Biopharma, Inc., Mission Therapeutics Ltd., Arch Oncology, Inc., Second Genome, Inc., and Lysosomal Therapeutics Inc. Ms. Nuechterlein previously served as a member of the board of directors of the publicly traded gene therapy company AveXis, Inc., from October 2014 to May 2017, prior to its acquisition by Novartis International AG. She received a B.A. in English and Humanities from Valparaiso University and a J.D. from the University of Michigan. We believe that Ms. Nuechterlein’s extensive experience as a venture capital investor in, and director of, several biotechnology companies, provides her with the qualifications and skills necessary to serve as a member of our board of directors.
Thomas Woiwode, Ph.D., has served as a member of our board of directors since August 2018. Dr. Woiwode has served in various roles at Versant Venture Management, LLC, a healthcare investment firm, since 2002, including serving as a Managing Director since July 2014. He also served as the Chief Operating Officer of Okairos AG, a biopharmaceutical company developing genetic vaccines for major infectious diseases, from April 2011 until May 2013 when it was acquired by GlaxoSmithKline plc. Prior to Okairos, Dr. Woiwode co-founded EuroVentures, a wholly owned biotechnology incubator within Versant Ventures, and in this role, served as the founding Chief Business Officer for three biotechnology companies created within Versant Ventures. Before joining Versant Ventures, Dr. Woiwode served as a Research Scientist at XenoPort, Inc., a biopharmaceutical company. He currently serves on the boards of directors of Gritstone Oncology, Inc., a publicly traded immuno-oncology company, Passage Bio, Inc., a publicly traded genetic medicines company, and Adverum Biotechnologies, Inc., a publicly traded gene therapy company, as well as several private companies. He previously served on the board of directors of Audentes Therapeutics, Inc., a publicly traded AAV-based genetic medicines company, from July 2013 to July 2017 and CRISPR Therapeutics AG, a publicly traded biopharmaceutical company, from April 2014 to June 2019. Dr. Woiwode holds a B.A. in English and a B.S. in Chemistry from the University of California, Berkeley and a Ph.D. in Chemistry from Stanford University. We believe that Dr. Woiwode’s experience in the biopharmaceutical and biotechnology industries, his educational background and his experience as a venture capital investor in life sciences companies provides him with the qualifications and skills necessary to serve as a member of our board of directors.
Board composition
Director independence
Our board of directors currently consists of nine members. Our board of directors has determined that all of our directors, other than Dr. Blatt and Dr. Beigelman, qualify as “independent” directors in accordance with the Nasdaq Global Market listing requirements. Dr. Blatt and Dr. Beigelman are not considered independent because they are employees of Aligos Therapeutics, Inc. The Nasdaq Global Market’s independence definition includes a series of objective tests, such as that the director is not, and has not been for at least three years, one of our employees and that neither the director nor any of his or her family members has engaged in various types of business dealings with us. In addition, as required by the Nasdaq Global Market rules, our board of directors has made a subjective determination as to each independent director that no relationship exists that, in the opinion of our board of directors, would interfere with the exercise of independent judgment in carrying
162
Table of Contents
out the responsibilities of a director. In making these determinations, our board of directors reviewed and discussed information provided by the directors and us with regard to each director’s business and personal activities and relationships as they may relate to us and our management. There are no family relationships among any of our directors or executive officers.
Classified board of directors
In accordance with our amended and restated certificate of incorporation to be in effect immediately prior to the closing of this offering, our board of directors will be divided into three classes with staggered, three-year terms. At each annual meeting of stockholders, the successors to directors whose terms then expire will be elected to serve from the time of election and qualification until the third annual meeting following election.
Effective upon the closing of this offering, we expect that our directors will be divided among the three classes as follows:
| • | the Class I directors will be Lawrence M. Blatt, Ph.D., Kathleen Sereda Glaub and Peter Moldt, Ph.D., and their terms will expire at the annual meeting of stockholders to be held in 2021; |
| • | the Class II directors will be Thomas Woiwode, Ph.D., Leonid Beigelman, Ph.D. and K. Peter Hirth, Ph.D., and their terms will expire at the annual meeting of stockholders to be held in 2022; and |
| • | the Class III directors will be Jack B. Nielsen and Carole Nuechterlein, and their terms will expire at the annual meeting of stockholders to be held in 2023. |
Our amended and restated certificate of incorporation will provide that the authorized number of directors may be changed only by resolution of the board of directors. Any additional directorships resulting from an increase in the number of directors will be distributed among the three classes so that, as nearly as possible, each class will consist of one-third of the directors. The division of our board of directors into three classes with staggered three-year terms may delay or prevent a change of our management or a change in control of our company.
Voting arrangements
In December 2019, we entered into an Amended and Restated Voting Agreement (the “Voting Agreement”), with certain holders of our capital stock, including certain members of, and affiliates of, our board of directors and certain of our executive officers.
Pursuant to the Voting Agreement, each of Vivo Capital Fund VIII, L.P. or Vivo Capital Surplus Fund VIII, L.P., Versant Venture Capital VI, L.P., Roche Finance Ltd, Novo Holdings A/S and an additional stockholder has the right to designate one member to be elected to our board of directors, subject to maintaining certain ownership minimums. The Voting Agreement will terminate by its terms in connection with the closing of this offering and none of our stockholders will have any continuing rights regarding the election or designation of members of our board of directors following this offering.
Leadership structure of the board
Our amended and restated bylaws and corporate governance guidelines that will be in effect upon the closing of this offering will provide our board of directors with flexibility to combine or separate the positions of Chairman of the board of directors and Chief Executive Officer.
Our board of directors has concluded that our current leadership structure is appropriate at this time. However, our board of directors will continue to periodically review our leadership structure and may make such changes in the future as it deems appropriate.
163
Table of Contents
Role of board in risk oversight process
Risk assessment and oversight are an integral part of our governance and management processes. Our board of directors encourages management to promote a culture that incorporates risk management into our corporate strategy and day-to-day business operations. Management discusses strategic and operational risks at regular management meetings, and conducts specific strategic planning and review sessions during the year that include a focused discussion and analysis of the risks facing us. Throughout the year, senior management reviews these risks with the board of directors at regular board meetings as part of management presentations that focus on particular business functions, operations or strategies, and presents the steps taken by management to mitigate or eliminate such risks.
Our board of directors does not have a standing risk management committee, but rather administers this oversight function directly through our board of directors as a whole, as well as through various standing committees of our board of directors that address risks inherent in their respective areas of oversight. While our board of directors is responsible for monitoring and assessing strategic risk exposure, our audit committee is responsible for overseeing our major financial risk exposures and the steps our management has taken to monitor and control these exposures. The audit committee also monitors compliance with legal and regulatory requirements and considers and approves or disapproves any related person transactions. Our nominating and corporate governance committee monitors the effectiveness of our corporate governance guidelines. Our compensation committee assesses and monitors whether any of our compensation policies and programs has the potential to encourage excessive risk-taking.
Board committees
Audit committee
Our audit committee oversees our corporate accounting and financial reporting process. Among other matters, the audit committee:
| • | appoints our independent registered public accounting firm; |
| • | evaluates the independent registered public accounting firm’s qualifications, independence and performance; |
| • | determines the terms of engagement of the independent registered public accounting firm; |
| • | reviews and approves the scope of the annual audit and the audit fee; |
| • | discusses with management and the independent registered public accounting firm the results of the annual audit and the review of our quarterly financial statements; |
| • | approves the retention of the independent registered public accounting firm to perform any proposed permissible non-audit services; |
| • | is responsible for reviewing our audited consolidated financial statements and our management’s discussion and analysis of financial condition and results of operations to be included in our annual and quarterly reports to be filed with the SEC; |
| • | reviews our critical accounting policies and estimates; |
| • | establishes procedures for the receipt, retention and treatment of complaints received by us regarding accounting, internal controls or auditing matters; |
164
Table of Contents
| • | discusses on a periodic basis, or as appropriate, with management, our policies and procedures with respect to risk assessment; and |
| • | reviews the audit committee charter at least annually and the committee’s performance periodically. |
The current members of our audit committee are Kathleen Sereda Glaub, Peter Moldt, Ph.D. and Jack B. Nielsen. Kathleen Sereda Glaub serves as the chairperson of the committee. All members of our audit committee meet the requirements for financial literacy under the applicable rules and regulations of the SEC and the Nasdaq Global Market. Our board of directors has determined that Kathleen Sereda Glaub is an audit committee financial expert as defined under the applicable rules of the SEC and has the requisite financial sophistication as defined under the applicable rules and regulations of the Nasdaq Global Market. Under the rules of the SEC, members of the audit committee must also meet heightened independence standards. Our board of directors has determined that each of the members of our audit committee are independent under the applicable rules of the SEC and the Nasdaq Global Market. The audit committee operates under a written charter that satisfies the applicable standards of the SEC and the Nasdaq Global Market.
Compensation committee
Our compensation committee oversees policies relating to compensation and benefits of our officers and employees. Among other things, the compensation committee:
| • | reviews and approves or recommends corporate goals and objectives relevant to compensation of our executive officers, other than our Chief Executive Officer; |
| • | evaluates the performance of our executive officers in light of those goals and objectives and approves the compensation of these officers based on such evaluations; |
| • | reviews and approves or makes recommendations to our board of directors regarding the issuance of stock options and other awards under our stock plans to our executive officers, other than our Chief Executive Officer; |
| • | reviews the performance of our Chief Executive Officer and makes recommendations with respect to his compensation to our board of directors, which retains the authority to make compensation decisions relative to our Chief Executive Officer; |
| • | evaluates compliance with applicable compensation rules, regulations, guidelines and other laws, as applicable; and |
| • | reviews the compensation committee charter at least annually and the performance of the compensation committee and its members, including compliance by the compensation committee, periodically. |
The current members of our compensation committee are Carole Nuechterlein, K. Peter Hirth, Ph.D., Jack B. Nielsen and Thomas Woiwode, Ph.D. Carole Nuechterlein serves as the chair of the committee. Each of the members of our compensation committee is independent under the applicable rules and regulations of the Nasdaq Global Market and is a “non-employee director” as defined in Rule 16b-3 promulgated under the Exchange Act. The compensation committee operates under a written charter that satisfies the applicable standards of the SEC and the Nasdaq Global Market.
Nominating and corporate governance committee
The nominating and corporate governance committee is responsible for making recommendations to our board of directors regarding candidates for directorships and the size and composition of our board of directors. In
165
Table of Contents
addition, the nominating and corporate governance committee is responsible for overseeing our corporate governance policies and reporting and making recommendations to our board of directors concerning governance matters. The current members of our nominating and corporate governance committee are Jack B. Nielsen, Carole Nuechterlein and Thomas Woiwode, Ph.D. Jack Nielsen serves as the chair of the committee. Each of the members of our nominating and corporate governance committee is an independent director under the applicable rules and regulations of the Nasdaq Global Market relating to nominating and corporate governance committee independence. The nominating and corporate governance committee operates under a written charter that satisfies the applicable standards of the SEC and the Nasdaq Global Market.
Compensation committee interlocks and insider participation
During the year ended December 31, 2019, our compensation committee consisted of Ms. Nuechterlein, Mr. Nielsen, Dr. Hirth and Dr. Woiwode. None of the members of our compensation committee during 2019 nor any of the current members of our compensation committee has at any time been one of our officers or employees. None of our executive officers currently serves, or in the past fiscal year has served, as a member of the board of directors or compensation committee of any entity that has one or more executive officers on our board of directors or compensation committee. For a description of transactions between us and members of our compensation committee and affiliates of such members, please see the section titled “Certain relationships and related party transactions.”
Board diversity
Upon consummation of this offering, our nominating and corporate governance committee will be responsible for reviewing with the board of directors, on a periodic basis, the appropriate characteristics, skills and experience required for the board of directors as a whole and its individual members. In evaluating the suitability of individual candidates (both new candidates and current members), the nominating and corporate governance committee, in recommending candidates for election, and the board of directors, in approving (and, in the case of vacancies, appointing) such candidates, may take into account many factors, including but not limited to the following:
| • | personal and professional integrity; |
| • | ethics and values; |
| • | experience in corporate management, such as serving as an officer or former officer of a publicly held company; |
| • | experience as a board member of another publicly held company; |
| • | experience in the life sciences industry; |
| • | diversity of expertise and experience in substantive matters pertaining to our business relative to other board members; |
| • | conflicts of interest; and |
| • | business judgment. |
Currently, our board of directors evaluates, and following the consummation of this offering will evaluate, each individual in the context of the board of directors as a whole, with the objective of assembling a group that can best exercise oversight of management and the business and effectively represent stockholder interests through the exercise of sound business judgment using its diversity and depth of experience in these various areas.
166
Table of Contents
Code of business conduct and ethics
Our board of directors has adopted a code of business conduct and ethics that will apply to all of our employees, officers and directors, including those officers responsible for financial reporting. Following the consummation of this offering, the code of business conduct and ethics will be available on our website. We expect that any amendments to the code, or any waivers of its requirements, will be disclosed on our website or in public filings.
Limitation of liability and indemnification matters
Our amended and restated certificate of incorporation, which will become effective immediately prior to the closing of this offering, will contain provisions that limit the liability of our directors for monetary damages to the fullest extent permitted by Delaware law. Consequently, our directors will not be personally liable to us or our stockholders for monetary damages for any breach of fiduciary duties as directors, except liability for:
| • | any breach of the director’s duty of loyalty to us or our stockholders; |
| • | any act or omission not in good faith or that involves intentional misconduct or a knowing violation of law; |
| • | unlawful payments of dividends or unlawful stock repurchases or redemptions as provided in Section 174 of the Delaware General Corporation Law; or |
| • | any transaction from which the director derived an improper personal benefit. |
Each of our amended and restated certificate of incorporation and amended and restated bylaws, which will become effective immediately prior to the closing of this offering, will provide that we are required to indemnify our directors and officers, in each case to the fullest extent permitted by Delaware law. Our amended and restated bylaws will also obligate us to advance expenses incurred by a director or officer in advance of the final disposition of any action or proceeding, and permit us to secure insurance on behalf of any officer, director, employee or other agent for any liability arising out of his or her actions in that capacity regardless of whether we would otherwise be permitted to indemnify him or her under Delaware law. We have entered and expect to continue to enter into agreements to indemnify our directors, executive officers and other employees as determined by our board of directors. With specified exceptions, these agreements provide for indemnification for related expenses including, among other things, attorneys’ fees, judgments, fines and settlement amounts incurred by any of these individuals in any action or proceeding. We believe that these bylaw provisions and indemnification agreements are necessary to attract and retain qualified persons as directors and officers. We also maintain directors’ and officers’ liability insurance.
The limitation of liability and indemnification provisions that will be included in our amended and restated certificate of incorporation and amended and restated bylaws may discourage stockholders from bringing a lawsuit against our directors and officers for breach of their fiduciary duty. They may also reduce the likelihood of derivative litigation against our directors and officers, even though an action, if successful, might benefit us and our stockholders. Further, a stockholder’s investment may be adversely affected to the extent that we pay the costs of settlement and damage.
167
Table of Contents
Director and executive compensation
Director compensation
Historically, we have not had a formalized non-employee director compensation program. However, Dr. Hirth and Ms. Glaub earned $30,000 and $5,000, respectively, for their board service in 2019. In addition, we reimburse our non-employee directors for travel and other necessary business expenses incurred in the performance of their services for us.
The following table sets forth information concerning the compensation earned by our non-employee directors during the year ended December 31, 2019.
| Name | Fees earned or paid in cash ($) |
Stock (1) ($) |
Option awards (1) ($) |
All other compensation ($) |
Total ($) |
|||||||||||||||
| K. Peter Hirth, Ph.D.(1) |
30,000 | — | — | — | 30,000 | |||||||||||||||
| Kathleen Sereda Glaub |
5,000 | — | — | — | 5,000 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | As of December 31, 2019, Dr. Hirth held 25,036 restricted shares of our common stock acquired upon exercise of an option prior to vesting. Upon a termination of Dr. Hirth’s service, we have the right to repurchase any unvested shares at the original purchase price, which was $1.30 per share. The restricted shares vest, and our right of repurchase lapses, in equal monthly installments through August 16, 2022, subject to Dr. Hirth continuing to provide services to the Company through the applicable vesting date. |
We have adopted and are implementing a compensation program for our non-employee directors (the “Director Compensation Program”), to be effective in connection with the consummation of this offering, which will supersede the current arrangements with our non-employee, non-investor directors and apply broadly to all of our non-employee directors. Pursuant to the Director Compensation Program, our non-employee directors will receive cash compensation as follows:
| • | Each non-employee director will receive an annual cash retainer in the amount of $35,000 per year. |
| • | A non-executive chair of the Board will receive an additional annual cash retainer in the amount of $30,000 per year. |
| • | The chairperson of the audit committee will receive additional annual cash compensation in the amount of $20,000 per year for such chairperson’s service on the audit committee. Each non-chairperson member of the audit committee will receive additional annual cash compensation in the amount of $7,500 per year for such member’s service on the audit committee. |
| • | The chairperson of the compensation committee will receive additional annual cash compensation in the amount of $10,000 per year for such chairperson’s service on the compensation committee. Each non-chairperson member of the compensation committee will receive additional annual cash compensation in the amount of $5,000 per year for such member’s service on the compensation committee. |
| • | The chairperson of the nominating and corporate governance committee will receive additional annual cash compensation in the amount of $8,000 per year for such chairperson’s service on the nominating and corporate governance committee. Each non-chairperson member of the nominating and corporate governance committee will receive additional annual cash compensation in the amount of $4,000 per year for such member’s service on the nominating and corporate governance committee. |
Under the Director Compensation Program, each non-employee director will automatically be granted an option to purchase 30,000 shares of our common stock upon such director’s initial appointment or election to our Board (the “Initial Grant”), and each non-employee director who has been serving on the board for at least
168
Table of Contents
four months will automatically be granted an option to purchase 15,000 shares of our common stock on the date of each annual stockholder’s meeting following the completion of this offering (the “Annual Grant”). The Initial Grant will vest in substantially equal monthly installments for three years from the date of grant, subject to continued service through each applicable vesting date. The Annual Grant will vest on the earlier of the first anniversary of the date of grant or the date of the next annual stockholder’s meeting, subject to continued service through the vesting date.
Executive compensation
The following is a discussion and analysis of compensation arrangements of our named executive officers (“NEOs”). This discussion contains forward looking statements that are based on our current plans, considerations, expectations and determinations regarding future compensation programs. Actual compensation programs that we adopt may differ materially from currently planned programs as summarized in this discussion. As an “emerging growth company” as defined in the JOBS Act, we are not required to include a Compensation Discussion and Analysis section and have elected to comply with the scaled disclosure requirements applicable to emerging growth companies.
We seek to ensure that the total compensation paid to our executive officers is reasonable and competitive. Compensation of our executives is structured around the achievement of individual performance and near-term corporate targets as well as long-term business objectives.
Our NEOs for fiscal year 2019 were as follows: Lawrence M. Blatt, Chief Executive Officer, Leonid Beigelman, President and Lucinda Y. Quan, Executive Vice President, Chief Business Officer and General Counsel.
2019 summary compensation table
The following table sets forth total compensation paid to our named executive officers for the fiscal year ended on December 31, 2019.
| Name and principal position | Year | Salary ($) |
Non-equity incentive plan compensation ($)(1) |
All other compensation ($)(2) |
Total ($) |
|||||||||||||||
| Lawrence M. Blatt Ph.D., Chief Executive Officer |
2019 | 475,000 | 180,500 | 18,866 | 674,366 | |||||||||||||||
| Leonid Beigelman, Ph.D., President |
2019 | 400,000 | 152,000 | 2,957 | 554,957 | |||||||||||||||
| Lucinda Y. Quan, J.D., Executive Vice President, Chief Business Officer and General Counsel |
2019 | 325,000 | 108,063 | 11,200 | 444,263 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | Amounts shown represent the annual performance-based cash bonuses earned by our NEOs based on the achievement of certain performance objectives during 2019. These amounts were paid to the NEOs in early 2020. Please see the descriptions of the annual performance bonuses paid to our named executive officers under the section titled “2019 bonuses” below. |
| (2) | Amounts shown for Dr. Blatt and Ms. Quan include matching contributions of $11,200 under our 401(k) plan and amounts shown for Drs. Blatt and Beigelman include $7,666 and $2,957, respectively, paid by us in lieu of the employee portion of premiums for health and welfare benefits, including medical, dental and vision benefits, which is a benefit not available to all salaried employees. |
169
Table of Contents
Narrative to summary compensation table
2019 salaries
Our NEOs each receive a base salary to compensate the NEO for services rendered to our company. The base salary payable to each NEO is intended to provide a fixed component of compensation reflecting the executive’s skill set, experience, role and responsibilities.
For fiscal year 2019, Drs. Blatt and Beigelman and Ms. Quan had an annual base salary of $475,000, $400,000 and $325,000, respectively.
Our board of directors and compensation committee may adjust base salaries from time to time in their discretion.
2019 bonuses
We maintain an annual performance-based cash bonus program in which each of our NEOs participated in 2019. Each NEO’s target bonus is expressed as a percentage of his or her annual base salary which can be achieved by meeting company and individual goals at target level. The 2019 annual bonuses for Drs. Blatt and Beigelman were targeted at 40% and for Ms. Quan at 35% of their respective base salaries.
For determining performance bonus amounts, our board of directors set certain corporate performance goals applicable to each of our NEOs. For our Chief Executive Officer, our board of directors also set certain individual performance goals after receiving input from our Chief Executive Officer. Our Chief Executive Officer set individual performance goals for each other executive after receiving input from the executive. Following its review and determinations of corporate performance for 2019, our board of directors determined an achievement level of 95% and approved a bonus pool to be allocated among all the employees, including each NEO. The board then determined a 2019 individual performance achievement level of 100% for our Chief Executive Officer, and our Chief Executive Officer determined that each other executive had achieved his or her 2019 individual performance goals at a level of 100%. The actual amount of the 2019 annual bonus paid to each NEO for 2019 performance are set forth above in the 2019 Summary compensation table in the column titled “Non-equity incentive plan compensation.”
Equity-based compensation
We intend to adopt a 2020 Incentive Award Plan (the “Award Plan”), in order to facilitate the grant of cash and equity incentives to directors, employees (including our NEOs) and consultants of our company and certain of its affiliates and to enable us to obtain and retain services of these individuals, which is essential to our long-term success. We expect that the Award Plan will be effective on the date on which it is adopted by our board of directors, subject to approval of such plan by our stockholders. For additional information about the Award Plan, please see the section titled “Equity compensation plans” below.
Other elements of compensation
Retirement savings and health and welfare benefits
We currently maintain a 401(k) retirement savings plan for our employees, including our NEOs, who satisfy certain eligibility requirements. Our NEOs are eligible to participate in the 401(k) plan on the same terms as other full-time employees. We match 100% of a participant’s annual eligible contribution to the 401(k) plan, up to 4% of their annual base salary or up to the IRS limit, whichever is lower. We believe that providing a vehicle for tax-deferred retirement savings though our 401(k) plan adds to the overall desirability of our executive compensation package and further incentivizes our employees, including our NEOs, in accordance with our compensation policies.
170
Table of Contents
All of our full-time employees, including our named executive officers, are eligible to participate in our health and welfare plans, including medical, dental and vision benefits; short-term and long-term disability insurance; and life and AD&D insurance.
Perquisites and other personal benefits
We determine perquisites on a case-by-case basis and will provide a perquisite to an NEO when we believe it is necessary to attract or retain the NEO. In 2019, except for amounts paid on behalf of Drs. Blatt and Beigelman for the employee portion of health and welfare plan premiums, we did not provide any perquisites or personal benefits to our NEOs not otherwise made available to our other employees.
Outstanding equity awards at 2019 fiscal year end
The following table lists all outstanding equity awards held by our NEOs as of December 31, 2019.
| Option awards | Stock awards | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name | Vesting commencement date |
Number of securities underlying unexercised options (#) exercisable |
Number of securities underlying unexercised options (#) unexercisable |
Option exercise price ($) |
Option expiration date |
Number of shares that have not vested (#) |
Market value of shares or units of shares that have not vested as ($)(4) |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Lawrence M. Blatt, Ph.D. |
3/2/2018 | (1) | — | — | — | — | 271,602 | 936,563 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Leonid Beigelman, Ph.D. |
4/15/2018 | (1) | — | — | — | — | 281,661 | 971,250 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Lucinda Y. Quan, J.D. |
03/15/2018 | (2) | — | — | — | — | 98,078 | 210,234 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 03/19/2018 | (3) | — | — | — | — | 80,603 | 277,945 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 03/19/2018 | (3) | — | — | — | — | 3,224 | 11,118 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | The shares of restricted stock vest and are no longer subject to a risk of forfeiture in substantially equal monthly installments through the fourth anniversary of the vesting commencement date, subject to the holder’s continuing to provide services to us through the applicable vesting date. In the event of a change in control the vesting of the shares will be fully accelerated. |
| (2) | Constitute shares of restricted stock acquired by Ms. Quan upon exercise of a stock option prior to vesting. Unvested shares of restricted stock may be repurchased by us at the original exercise price of $1.30 per share upon a termination of Ms. Quan’s services to us. The unvested shares vest in substantially equal monthly installments through the fourth anniversary of the vesting commencement date, subject to Ms. Quan’s continued service to us through the applicable vesting date. In the event that Ms. Quan is terminated without cause or resigns for good reason, then the vesting of the shares that would have vested within the six-month period following her termination of employment will be accelerated, or in the event such resignation or termination occurs during the twelve month period commencing on a change in control, then the vesting of the shares will be fully accelerated. |
| (3) | The shares of restricted stock vest and become no longer subject to a risk of forfeiture in substantially equal monthly installments through the third anniversary of the vesting commencement date, subject to the Ms. Quan continuing to provide services to us through the applicable vesting date. In the event that, within the period of time 60 days prior to and ending one year following a change in control, Ms. Quan is terminated without cause or resigns for good reason, then the vesting of the shares will be fully accelerated. |
| (4) | The market value of shares that have not vested is calculated by subtracting any repurchase price from the fair market value of our common stock as of December 31, 2019 which our board of directors determined to be $3.45 per share. |
Narrative to 2019 summary compensation table and outstanding equity awards at 2019 fiscal year end
Executive compensation arrangements
Employment agreements
On August 16, 2018, we entered into employment agreements with Drs. Blatt and Beigelman setting forth the terms and conditions of their employment. The employment agreements provide for an annual base salary of
171
Table of Contents
$475,000 for Dr. Blatt and $400,000 for Dr. Beigelman per year. The employment agreements provided for the grant of 482,848 shares of restricted stock and that upon a change in control (as defined in the employment agreement) all shares of restricted stock will immediately vest in full and any risk of forfeiture will lapse. The employment agreements entitle Drs. Blatt and Beigelman to an annual performance bonus targeted at 40% of their annual base salary as determined by our board of directors and/or compensation committee.
In the event Dr. Blatt or Beigelman resigns for good reason or we terminate Dr. Blatt’s or Beigelman’s employment without cause (in each case as defined in the employment agreement), in addition to any accrued obligations, he is entitled to amount equal to two times the sum of (i) his annual base salary (as of the date of termination) and (ii) the bonus earned for the calendar year preceding termination of employment, as well as continued healthcare coverage under our medical plan paid or reimbursed by us for up to two years. The severance amount will be paid in substantially equal installments over a 24-month period. Payment of severance is contingent on providing us a general release of claims.
In the event Dr. Blatt or Beigelman resigns for good reason or we terminate Dr. Blatt’s or Beigelman’s employment without cause, in each case, within the twelve month period commencing on a change in control, in addition to any accrued obligations, he is entitled to receive as severance an amount equal to the present value of his average annual compensation for the five-year period, or such lesser period during which he has then been employed by us, ending with the calendar year immediately preceding the year in which the change in control occurs, as well as continued healthcare coverage under our medical plan paid or reimbursed by us for up to three years. The severance amount will be paid in substantially equal installments over a 12-month period. Payment of severance is contingent on providing us a general release of claims.
On May 14, 2019, we entered into an offer letter with Ms. Quan to confirm the terms and conditions of her employment. The offer letter provides for an annual base salary of $325,000 per year and entitles Ms. Quan to an annual performance bonus targeted at 35% of her annual base salary as determined at our sole discretion. Ms. Quan has also executed our standard confidential information and invention assignment agreement.
In the event Ms. Quan resigns for good reason or we terminate Ms. Quan’s employment without cause (in each case as defined in the offer letter), Ms. Quan is entitled to the following: (i) six months of base salary continuation, (ii) continued healthcare coverage under our medical plan for up to six months, (iii) accelerated vesting of any equity award that would have vested within the six-month period following her termination of employment or, if such resignation or termination occurs during the 12 month period commencing on a change in control, accelerated vesting of all equity awards and (iv) all vested options as of her termination date, after giving effect to any accelerated vesting of options will remain exercisable until the earlier of the three-year anniversary of her termination of employment, or the original expiration date of the applicable option. The severance amount will be payable in substantially equal installments for a six-month period. Payment of severance is contingent on providing us a general release of claims. Ms. Quan also has certain accelerated vesting for her restricted stock grants from March 2018 and July 2018, as described in the “Outstanding equity awards at 2019 fiscal year end” table above.
For purposes of the employment agreements, “cause” means (i) material breach of any of the executive’s representations or obligations contained in the employment agreement, including a willful failure or refusal to perform the job duties and responsibilities assigned to him by us, which if such material breach is reasonably susceptible of cure is not cured after 30 days have elapsed following the date on which we give written notice of such breach; (ii) conviction of, or plea of guilty or nolo contendere to, any felony or any crime involving moral turpitude; (iii) participation in a fraud, act of dishonesty or misappropriation or similar conduct against us; (iv) conduct that is materially injurious to us or our affiliates or subsidiaries, monetarily or otherwise; (v) improper use or disclosure of our confidential or proprietary information; or (vi) obtaining a direct or indirect personal benefit from the transfer or use of our trade secrets or intellectual property other than on our behalf.
172
Table of Contents
For purposes of the employment agreements, “good reason” means, subject to notice and cure, the continuance of any of the following events without the executive’s written consent: (i) any material breach of the terms of the employment agreement by us; (ii) any material restriction or diminution in the executive’s responsibilities; (iii) introduction of a requirement that Dr. Blatt report to an officer or employee instead of directly to the board or that Dr. Biegelman report to anyone other than the Chief Executive Officer; (iv) any change in the location of the executive’s principal place of employment that increases the executive’s one-way commute in excess of 50 miles from the executive’s principal place of employment prior to such change; and (v) any material failure by us to pay the executive’s annual base salary, earned bonuses, or benefits that the executive is entitled to receive under the employment agreement, or any material reduction by us of the executive’s annual base salary under the employment agreement, provided, however, that if we institute a company-wide reduction in salaries, bonuses and benefits for other executive management team members, such reduction will not be deemed material.
For purposes of Ms. Quan’s offer letter, “cause” means (i) material breach of any of Ms. Quan’s representations or obligations contained in the offer letter, including Ms. Quan’s willful failure or refusal to perform the job duties and responsibilities assigned to her by us, which if such material breach is reasonably susceptible of cure is not cured after 30 days have elapsed following the date on which we give written notice of such breach; (ii) conviction of, or plea of guilty or nolo contendere to, any felony or any crime involving moral turpitude; (iii) participation in a fraud, act of dishonesty or misappropriation or similar conduct against us; (iv) conduct that is materially injurious to us or our affiliates or subsidiaries, monetarily or otherwise; (v) improper use or disclosure of our confidential or proprietary information; or (vi) obtaining a direct or indirect personal benefit from the transfer or use of our trade secrets or intellectual property other than on our behalf.
For purposes of Ms. Quan’s offer letter, “good reason” means, subject to notice and cure, the continuance of any of the following events without Ms. Quan’s written consent: (i) any material breach of the terms of the offer letter by us; (ii) any material restriction or diminution in Ms. Quan’s responsibilities; (iii) any change in the location of Ms. Quan’s principal place of employment that increases Ms. Quan’s one-way commute in excess of fifty miles from Ms. Quan’s principal place of employment prior to such change; and (iv) any material failure by us to pay Ms. Quan’s annual base salary, bonuses that Ms. Quan has earned, or benefits that Ms. Quan is entitled to receive under the offer letter or any material reduction by us of Ms. Quan’s annual base salary under the offer letter, provided, however, that if we institute a company-wide reduction in salaries, bonuses and benefits for other executive management team members, such reduction will not be deemed material.
For purposes of Drs. Blatt and Beigelman’s employment agreements and Ms. Quan’s offer letter, “change in control” means the consummation of any of the following (x) sale of all or substantially all of our assets, (y) a sale of all of the shares held by our stockholders or (z) any merger, consolidation, sale of a majority of our capital stock (other than in a transaction described in clause (y)) or other similar transaction involving us and as a result of which the holders of our capital stock immediately prior to the transaction will own less than 50% of the voting power of the our capital stock following the transaction.
Equity compensation plans
The following summarizes the material terms of the 2020 Incentive Award Plan (the “Award Plan”) we intend to adopt in connection with this offering as the long-term incentive compensation plan in which our NEOs will be eligible to participate following the consummation of this offering, our 2018 Equity Incentive Plan (the “2018 Plan”), under which we have previously made periodic grants of equity and equity-based awards to our named executive officers and other employees, and the 2020 Employee Stock Purchase Plan (the “ESPP”) we intend to adopt in connection with this offering to provide our employees an opportunity to purchase our common stock at a discount to fair market value.
173
Table of Contents
2020 Incentive award plan
We intend to adopt the Award Plan, which will be effective on the pricing of this offering. The principal purpose of the Award Plan is to attract, retain and motivate selected employees, consultants and directors through the granting of stock-based compensation awards and cash-based performance bonus awards. The material terms of the Award Plan are summarized below.
Share Reserve. Under the Award Plan, 4,426,822 shares of our common stock will be initially reserved for issuance pursuant to a variety of stock-based compensation awards, including stock options, stock appreciation rights (“SARs”), restricted stock awards, restricted stock unit awards and other stock-based awards. The number of shares initially reserved for issuance or transfer pursuant to awards under the Award Plan will be increased by an annual increase on the first day of each fiscal year beginning in 2021 and ending in 2030, equal to the lesser of (A) 5% of the shares of stock outstanding (on an as converted basis) on the last day of the immediately preceding fiscal year and (B) such smaller number of shares of stock as determined by our board of directors; provided, however, that no more than 32,672,731 shares of stock may be issued upon the exercise of incentive stock options.
The following counting provisions will be in effect for the share reserve under the Award Plan:
| • | to the extent that an award terminates, expires or lapses for any reason or an award is settled in cash without the delivery of shares, any shares subject to the award at such time will be available for future grants under the 2020 Plan; |
| • | to the extent shares are tendered or withheld to satisfy the grant, exercise price or tax withholding obligation with respect to any award under the Award Plan, such tendered or withheld shares will be available for future grants under the Award Plan; |
| • | to the extent shares subject to stock appreciation rights are not issued in connection with the stock settlement of stock appreciation rights on exercise thereof, such shares will be available for future grants under the Award Plan; |
| • | to the extent that shares of our common stock are repurchased by us prior to vesting so that shares are returned to us, such shares will be available for future grants under the Award Plan; |
| • | the payment of dividend equivalents in cash in conjunction with any outstanding awards will not be counted against the shares available for issuance under the Award Plan; and |
| • | to the extent permitted by applicable law or any exchange rule, shares issued in assumption of, or in substitution for, any outstanding awards of any entity acquired in any form of combination by us or any of our subsidiaries will not be counted against the shares available for issuance under the Award Plan. |
Administration. The compensation committee of our board of directors is expected to administer the Award Plan unless our board of directors assumes authority for administration. The compensation committee must consist of at least three members of our board of directors, each of whom is intended to qualify as a “non-employee director” for purposes of Rule 16b-3 under the Exchange Act and an “independent director” within the meaning of the rules of the Nasdaq Global Market, or other principal securities market on which shares of our common stock are traded. The Award Plan provides that our board of directors or compensation committee may delegate its authority to grant awards to employees other than executive officers and certain senior executives of the company to a committee consisting of one or more members of our board of directors or one or more of our officers, other than awards made to our non-employee directors, which must be approved by our full board of directors.
174
Table of Contents
Subject to the terms and conditions of the Award Plan, the administrator has the authority to select the persons to whom awards are to be made, to determine the number of shares to be subject to awards and the terms and conditions of awards, and to make all other determinations and to take all other actions necessary or advisable for the administration of the Award Plan. The administrator is also authorized to adopt, amend or rescind rules relating to administration of the Award Plan. Our board of directors may at any time remove the compensation committee as the administrator and revest in itself the authority to administer the Award Plan. The full board of directors will administer the Award Plan with respect to awards to non-employee directors.
Eligibility. Options, SARs, restricted stock, restricted stock units and all other stock-based and cash-based awards under the Award Plan may be granted to individuals who are then our officers, employees or consultants or are the officers, employees or consultants of certain of our subsidiaries. Such awards also may be granted to our directors. Only employees of our company or certain of our subsidiaries may be granted incentive stock options (“ISOs”).
Awards. The Award Plan provides that the administrator may grant or issue stock options, SARs, restricted stock, restricted stock units, other stock- or cash-based awards and dividend equivalents, or any combination thereof. Each award will be set forth in a separate agreement with the person receiving the award and will indicate the type, terms and conditions of the award.
| • | Nonstatutory Stock Options (“NSOs”) will provide the right to purchase shares of our common stock at a specified price which may not be less than fair market value on the date of grant, and usually will become exercisable (at the discretion of the administrator) in one or more installments after the grant date, subject to the participant’s continued employment or service with us and/or subject to the satisfaction of corporate performance targets and individual performance targets established by the administrator. NSOs may be granted for any term specified by the administrator that does not exceed ten years. |
| • | Incentive Stock Options will be designed in a manner intended to comply with the provisions of Section 422 of the Code and will be subject to specified restrictions contained in the Code. Among such restrictions, ISOs must have an exercise price of not less than the fair market value of a share of common stock on the date of grant, may only be granted to employees, and must not be exercisable after a period of ten years measured from the date of grant. In the case of an ISO granted to an individual who owns (or is deemed to own) at least 10% of the total combined voting power of all classes of our capital stock, the Award Plan provides that the exercise price must be at least 110% of the fair market value of a share of common stock on the date of grant and the ISO must not be exercisable after a period of five years measured from the date of grant. |
| • | Restricted Stock may be granted to any eligible individual and made subject to such restrictions as may be determined by the administrator. Restricted stock, typically, may be forfeited for no consideration or repurchased by us at the original purchase price if the conditions or restrictions on vesting are not met. In general, restricted stock may not be sold or otherwise transferred until restrictions are removed or expire. Purchasers of restricted stock, unlike recipients of options, will have voting rights and will have the right to receive dividends, if any, prior to the time when the restrictions lapse, however, extraordinary dividends will generally be placed in escrow, and will not be released until restrictions are removed or expire. |
| • | Restricted Stock Units may be awarded to any eligible individual, typically without payment of consideration, but subject to vesting conditions based on continued employment or service or on performance criteria established by the administrator. Like restricted stock, restricted stock units may not be sold, or otherwise transferred or hypothecated, until vesting conditions are removed or expire. Unlike restricted stock, stock underlying restricted stock units will not be issued until the restricted stock units have vested, and recipients of restricted stock units generally will have no voting or dividend rights prior to the time when vesting conditions are satisfied. |
175
Table of Contents
| • | Stock Appreciation Rights may be granted in connection with stock options or other awards, or separately. SARs granted in connection with stock options or other awards typically will provide for payments to the holder based upon increases in the price of our common stock over a set exercise price. The exercise price of any SAR granted under the Award Plan must be at least 100% of the fair market value of a share of our common stock on the date of grant. SARs under the Award Plan will be settled in cash or shares of our common stock, or in a combination of both, at the election of the administrator. |
| • | Other Stock or Cash Based Awards are awards of cash, fully vested shares of our common stock and other awards valued wholly or partially by referring to, or otherwise based on, shares of our common stock. Other stock or cash based awards may be granted to participants and may also be available as a payment form in the settlement of other awards, as standalone payments and as payment in lieu of base salary, bonus, fees or other cash compensation otherwise payable to any individual who is eligible to receive awards. The plan administrator will determine the terms and conditions of other stock or cash based awards, which may include vesting conditions based on continued service, performance and/or other conditions. |
| • | Dividend Equivalents represent the right to receive the equivalent value of dividends paid on shares of our common stock and may be granted alone or in tandem with awards other than stock options or SARs. Dividend equivalents are credited as of dividend payments dates during the period between a specified date and the date such award terminates or expires, as determined by the plan administrator. In addition, dividend equivalents with respect to shares covered by a performance award will only be paid to the participant at the same time or times and to the same extent that the vesting conditions, if any, are subsequently satisfied and the performance award vests with respect to such shares. |
Any award may be granted as a performance award, meaning that the award will be subject to vesting and/or payment based on the attainment of specified performance goals.
Change in Control. In the event of a change in control, unless the plan administrator elects to terminate an award in exchange for cash, rights or other property, or cause an award to accelerate in full prior to the change in control, such award will continue in effect or be assumed or substituted by the acquirer, provided that any performance-based portion of the award will be subject to the terms and conditions of the applicable award agreement. In the event the acquirer refuses to assume or replace awards granted, prior to the consummation of such transaction, awards issued under the Award Plan will be subject to accelerated vesting such that 100% of such awards will become vested and exercisable or payable, as applicable. The administrator may also make appropriate adjustments to awards under the Award Plan and is authorized to provide for the acceleration, cash-out, termination, assumption, substitution or conversion of such awards in the event of a change in control or certain other unusual or nonrecurring events or transactions.
Adjustments of Awards. In the event of any stock dividend or other distribution, stock split, reverse stock split, reorganization, combination or exchange of shares, merger, consolidation, split-up, spin-off, recapitalization, repurchase or any other corporate event affecting the number of outstanding shares of our common stock or the share price of our common stock that would require adjustments to the Award Plan or any awards under the Award Plan in order to prevent the dilution or enlargement of the potential benefits intended to be made available thereunder, the administrator will make appropriate, proportionate adjustments to: (i) the aggregate number and type of shares subject to the Award Plan; (ii) the number and kind of shares subject to outstanding awards and terms and conditions of outstanding awards (including, without limitation, any applicable performance targets or criteria with respect to such awards); and (iii) the grant or exercise price per share of any outstanding awards under the Award Plan.
Amendment and Termination. The administrator may terminate, amend or modify the Award Plan at any time and from time to time. However, we must generally obtain stockholder approval to the extent required by
176
Table of Contents
applicable law, rule or regulation (including any applicable stock exchange rule). Notwithstanding the foregoing, an option may be amended to reduce the per share exercise price below the per share exercise price of such option on the grant date and options may be granted in exchange for, or in connection with, the cancellation or surrender of options having a higher per share exercise price without receiving additional stockholder approval.
No incentive stock options may be granted pursuant to the Award Plan after the tenth anniversary of the effective date of the Award Plan, and no additional annual share increases to the Award Plan’s aggregate share limit will occur from and after such anniversary. Any award that is outstanding on the termination date of the Award Plan will remain in force according to the terms of the Award Plan and the applicable award agreement.
2018 Equity incentive plan
Our board of directors adopted the 2018 Plan on August 15, 2018, which was amended on December 23, 2019. Following this offering, and in connection with the effectiveness of our Award Plan, no further awards will be granted under the 2018 Plan. However, all outstanding awards under the 2018 Plan will continue to be governed by their existing terms under the 2018 Plan. Upon the circumstances set forth under the description of our Award Plan, shares subject to outstanding awards under the 2018 Plan will be added to the share reserve of the Award Plan. The purpose of the 2018 Plan is to attract, retain and motivate eligible persons whose present and potential contributions are important to our success by offering eligible persons an opportunity to participate in the 2018 Plan.
Share Reserve. Under the 2018 Plan, we have previously reserved 4,913,665 shares of common stock. Upon the effectiveness of the Award Plan, no additional stock awards may be granted under the 2018 Plan. Any equity awards granted under the 2018 Plan will remain subject to the terms of the 2018 Plan and applicable award agreement, until such outstanding awards that are stock options are exercised, terminate or expire by their terms, and until any restricted stock awards become vested, terminate or are forfeited.
Administration. Our board of directors or a committee appointed by our board of directors acts as the administrator of the 2018 Plan. The 2018 Plan provides that the board may delegate its authority to grant to a committee consisting of one or more members of our board of directors or one or more of our executive officers so long as such officer is a member of the board. Subject to the terms and conditions of the 2018 Plan, the administrator has the authority to select the persons to whom awards are to be made, to determine the number of shares to be subject to awards and the terms and conditions of awards, and to make all other determinations and to take all other actions necessary or advisable for the administration of the 2018 Plan. The administrator has the full power to implement and carry out the 2018 Plan.
Eligibility. Options, restricted stock, restricted stock units and other stock-based awards under the 2018 Plan may be granted to officers, employees, directors and consultants of the Company and its affiliates. Only employees of our company or certain of our subsidiaries may be granted ISOs.
Awards. The 2018 Plan provides for the grant or issue of stock options (both ISOs and NSOs), restricted stock, restricted stock units, other stock- or cash-based awards and dividend equivalents, or any combination thereof. Each award is set forth in a separate agreement with the person receiving the award which indicates the type, terms and conditions of the award.
Adjustments of Awards. In the event that the administrator determines that any dividend or other distribution, reorganization, merger, consolidation, combination, repurchase, recapitalization, liquidation, dissolution, or sale, transfer, exchange or other disposition of all or substantially all of the assets of our company, or sale or exchange of common stock or other securities, issuance of warrants or other rights to purchase common stock or other
177
Table of Contents
securities, or other similar corporate transaction or event, affects our common stock, as determined by the administrator, then the administrator may adjust as it may deem equitable, (a) the number of shares of common stock reserved for issuance under the 2018 Plan, (b) the number and kind of shares of common stock subject to outstanding awards, (c) the grant or exercise prices with respect to any award and (d) the terms and conditions of any awards, including any applicable financial or performance targets specified in an award agreement.
Change in Control. If a Change in Control (as defined in the 2018 Plan) occurs and awards are not continued, converted, assumed, or replaced with a substantially similar award by (i) the Company, or (ii) a successor entity or its parent or subsidiary (an “Assumption”), and the participant continues to provide service to the Company, then immediately prior to the Change in Control such awards shall become fully vested, exercisable and/or payable, as applicable, and all forfeiture, repurchase and other restrictions on such awards shall lapse, in which case, such awards shall be canceled upon the consummation of the Change in Control in exchange for the right to receive the Change in Control consideration payable to other holders of Common Stock (A) which may be on such terms and conditions as apply generally to holders of Common Stock under the Change in Control documents (including, without limitation, any escrow, earn-out or other deferred consideration provisions) or such other terms and conditions as the administrator may provide, and (B) determined by reference to the number of shares subject to such awards and net of any applicable exercise price; provided that if the amount to which a participant would be entitled upon the settlement or exercise of such award at the time of the Change in Control is equal to or less than zero, then such award may be terminated without payment. The administrator shall determine whether an Assumption of an award has occurred in connection with a Change in Control.
Amendment and Termination. The administrator may terminate or amend the 2018 Plan at any time and from time to time, provided that no amendment shall materially or adversely affect any award outstanding at the time of the amendment without the consent of the affected participant. However, we must generally obtain stockholder approval to the extent required by applicable law.
2020 Employee stock purchase plan
We intend to adopt and ask our stockholders to approve the ESPP, which will be effective upon the pricing of the offering to which this prospectus relates. The ESPP is designed to allow our eligible employees to purchase shares of our common stock, at semi-annual intervals, with their accumulated payroll deductions. The ESPP is intended to qualify under Section 423 of the Code. The material terms of the ESPP, as it is currently contemplated, are summarized below.
Administration. Subject to the terms and conditions of the ESPP, our compensation committee will administer the ESPP. Our compensation committee can delegate administrative tasks under the ESPP to the services of an agent and/or employees to assist in the administration of the ESPP. The administrator will have the discretionary authority to administer and interpret the ESPP. Interpretations and constructions of the administrator of any provision of the ESPP or of any rights thereunder will be conclusive and binding on all persons. We will bear all expenses and liabilities incurred by the ESPP administrator.
Share Reserve. The maximum number of shares of our common stock which will be authorized for sale under the ESPP is equal to the sum of (a) 368,901 shares of common stock and (b) an annual increase on the first day of each year beginning in 2021 and ending in 2030, equal to the lesser of (i) 1% of the shares of common stock outstanding (on an as converted basis) on the last day of the immediately preceding fiscal year and (ii) such number of shares of common stock as determined by our board of directors; provided, however, that no more than 6,534,546 shares of our common stock may be issued under the ESPP. The shares reserved for issuance under the ESPP may be authorized but unissued shares or reacquired shares.
178
Table of Contents
Eligibility. Employees eligible to participate in the ESPP for a given offering period generally include employees who are employed by us or one of our subsidiaries on the first day of the offering period, or the enrollment date. Our employees (and, if applicable, any employees of our subsidiaries) who customarily work less than five months in a calendar year or are customarily scheduled to work less than 20 hours per week will not be eligible to participate in the ESPP. Finally, an employee who owns (or is deemed to own through attribution) 5% or more of the combined voting power or value of all our classes of stock or of one of our subsidiaries will not be allowed to participate in the ESPP.
Participation. Employees will enroll under the ESPP by completing a payroll deduction form permitting the deduction from their compensation of at least 1% of their compensation but not more than the lesser of 15% of their compensation or $50,000. Such payroll deductions may be expressed as either a whole number percentage or a fixed dollar amount, and the accumulated deductions will be applied to the purchase of shares on each purchase date. However, a participant may not subscribe for more than $25,000 in fair market value of shares of our common stock (determined at the time the option is granted) during any calendar year. The ESPP administrator has the authority to change these limitations for any subsequent offering period.
Offering. Under the ESPP, participants are offered the option to purchase shares of our common stock at a discount during a series of successive offering periods, the duration and timing of which will be determined by the ESPP administrator. However, in no event may an offering period be longer than 27 months in length.
The option purchase price will be the lower of 85% of the closing trading price per share of our common stock on the first trading date of an offering period in which a participant is enrolled or 85% of the closing trading price per share on the purchase date, which will occur on the last trading day of each offering period.
Unless a participant has previously canceled his or her participation in the ESPP before the purchase date, the participant will be deemed to have exercised his or her option in full as of each purchase date. Upon exercise, the participant will purchase the number of whole shares that his or her accumulated payroll deductions will buy at the option purchase price, subject to the participation limitations listed above.
A participant may cancel his or her payroll deduction authorization at any time prior to the end of the offering period. Upon cancellation, the participant will have the option to either (i) receive a refund of the participant’s account balance in cash without interest or (ii) exercise the participant’s option for the current offering period for the maximum number of shares of common stock on the applicable purchase date, with the remaining account balance refunded in cash without interest. Following at least one payroll deduction, a participant may also decrease (but not increase) his or her payroll deduction authorization once during any offering period. If a participant wants to increase or decrease the rate of payroll withholding, he or she may do so effective for the next offering period by submitting a new form before the offering period for which such change is to be effective.
A participant may not assign, transfer, pledge or otherwise dispose of (other than by will or the laws of descent and distribution) payroll deductions credited to a participant’s account or any rights to exercise an option or to receive shares of our common stock under the ESPP, and during a participant’s lifetime, options in the ESPP shall be exercisable only by such participant. Any such attempt at assignment, transfer, pledge or other disposition will not be given effect.
Adjustments upon Changes in Recapitalization, Dissolution, Liquidation, Merger or Asset Sale. In the event of any increase or decrease in the number of issued shares of our common stock resulting from a stock split, reverse stock split, stock dividend, combination or reclassification of the common stock, or any other increase or decrease in the number of shares of common stock effected without receipt of consideration by us, we will proportionately adjust the aggregate number of shares of our common stock offered under the ESPP, the
179
Table of Contents
number and price of shares which any participant has elected to purchase under the ESPP and the maximum number of shares which a participant may elect to purchase in any single offering period. If there is a proposal to dissolve or liquidate us, then the ESPP will terminate immediately prior to the consummation of such proposed dissolution or liquidation, and any offering period then in progress will be shortened by setting a new purchase date to take place before the date of our dissolution or liquidation. We will notify each participant of such change in writing at least ten business days prior to the new exercise date. If we undergo a merger with or into another corporation or sell all or substantially all of our assets, each outstanding option will be assumed or an equivalent option substituted by the successor corporation or the parent or subsidiary of the successor corporation. If the successor corporation refuses to assume the outstanding options or substitute equivalent options, then any offering period then in progress will be shortened by setting a new purchase date to take place before the date of our proposed sale or merger. We will notify each participant of such change in writing at least ten business days prior to the new exercise date.
Amendment and Termination. Our board of directors may amend, suspend or terminate the ESPP at any time. However, the board of directors may not amend the ESPP without obtaining stockholder approval before or after such amendment to the extent required by applicable laws.
180
Table of Contents
Certain relationships and related party transactions
In addition to the compensation arrangements, including employment, termination of employment, severance and change in control arrangements, with our directors and executive officers, including those discussed in the sections titled “Management” and “Director and executive compensation,” the following is a description of each transaction since February 5, 2018 in which:
| • | we have been or are to be a participant; |
| • | the amounts involved exceeded or will exceed $120,000; and |
| • | any of our directors, executive officers or holders of more than 5% of our capital stock, or an affiliate or immediate family member thereof, had or will have a direct or indirect material interest. |
Sales and purchases of securities
Series seed convertible note and warrant financing
In March 2018, we entered into a note and warrant purchase agreement pursuant to which we issued in April and June 2018 (i) convertible promissory notes (the “Seed Notes”), in an aggregate principal amount of $5.0 million and (ii) warrants to purchase shares of capital stock. The Seed Notes provided for an annual interest rate of 8%. Under the terms of the Seed Notes, under certain circumstances, the unpaid principal of the Seed Notes, including any accrued but unpaid interest thereon, would convert into preferred stock upon the closing of a future preferred stock financing that met specified criteria at the per share price of the preferred stock sold in the financing. In August 2018, as part of the issuance of Series A convertible preferred stock described below, the outstanding principal of $5.0 million under the Seed Notes, plus $0.1 million of accrued interest, converted into 547,995 shares of Series A convertible preferred stock at a rate of $9.32 per share in full payment for the note and accrued interest. In addition, each investor who purchased Seed Notes received a warrant to purchase, depending on the occurrence of certain events, a number of shares of either common stock or a future series of preferred stock equal 25% of the principal amount of Seed Notes purchased by an investor divided by the price per share of the common stock or future series of preferred stock issued, which resulted in the issuance of warrants to purchase an aggregate of 134,112 shares of our Series A convertible preferred stock. The table below sets forth the principal amount of convertible promissory notes and the number of warrants to purchase shares of Series A convertible preferred stock sold to our directors, executive officers or owners of more than 5% of our capital stock, or an affiliate or immediate family member thereof:
| Name | Principal amount of Seed Notes |
Number of shares of Series A convertible preferred stock underlying warrants issued in connection with the Seed Notes |
||||||
| Trusts affiliated with Lawrence M. Blatt, Ph.D.(1) |
$ | 1,400,000 | 37,552 | |||||
| Trusts affiliated with Leonid Beigelman, Ph.D.(2) |
$ | 1,400,000 | 37,552 | |||||
| Julian Symons, D.Phil.(3) |
$ | 100,000 | 2,682 | |||||
| Trust affiliated with Lucinda Quan, J.D.(4) |
$ | 50,000 | 1,341 | |||||
|
|
||||||||
| (1) | The purchasers are trusts affiliated with Lawrence M. Blatt, Ph.D, a member of our board of directors and one of our executive officers, and his immediate family members. |
| (2) | The purchasers are trusts affiliated with Leonid Beigelman, Ph.D., a member of our board of directors and one of our executive officers, and his immediate family members. |
| (3) | Julian Symons, D.Phil. is one of our executive officers. |
| (4) | The purchaser is a trust affiliated with Lucinda Quan, J.D., one of our executive officers. |
181
Table of Contents
Series A convertible preferred stock financing
In August and September 2018, we issued an aggregate of 10,806,432 shares of our Series A convertible preferred stock at a price per share of $9.32 for aggregate proceeds to us of $100.7 million (including the cancellation of indebtedness and accrued interest thereon in exchange for which we issued certain of these shares) The table below sets forth the number of shares of Series A convertible preferred stock sold to our directors, executive officers or owners of more than 5% of our capital stock, or an affiliate or immediate family member thereof:
| Name | Number of shares of Series A convertible preferred Stock |
Purchase price ($) |
||||||
| Entities affiliated with Vivo Capital Fund(1) |
2,145,991 | 20,000,000 | ||||||
| Versant Venture Capital VI, L.P.(2) |
2,145,991 | 20,000,000 | ||||||
| Roche Finance Ltd(3) |
2,145,991 | 20,000,000 | ||||||
| Entities affiliated with Baker Brothers(4) |
2,145,991 | 20,000,000 | ||||||
| Novo Holdings A/S(5) |
1,609,493 | 15,000,000 | ||||||
| Trusts affiliated with Lawrence M. Blatt, Ph.D.(6) |
153,407 | 1,429,732 | ||||||
| Trusts affiliated with Leonid Beigelman, Ph.D.(7) |
153,408 | 1,429,731 | ||||||
| Julian Symons, D.Phil.(8) |
10,989 | 102,422 | ||||||
| Trust affiliated with Lucinda Quan, J.D.(9) |
5,494 | 51,211 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||
| (1) | (i) Vivo Capital Fund VIII, L.P. purchased 1,885,611 shares for a total purchase price of $17,573,333 and (ii) Vivo Capital Surplus Fund VIII, L.P. purchased 260,380 shares for a total purchase price of $2,426,667. Entities affiliated with Vivo Capital Fund became beneficial owners of (in the aggregate) more than 5% of our capital stock upon the initial closing of the transaction. Jack B. Nielsen, who is a member of our board of directors, is an affiliate of Vivo Capital Fund. |
| (2) | Versant Venture Capital VI, L.P. became a beneficial owner of more than 5% of our capital stock upon the initial closing of the transaction. Thomas Woiwode, who is a member of our board of directors, is an affiliate of Versant Venture Capital VI, L.P. |
| (3) | Roche Finance Ltd became a beneficial owner of more than 5% of our capital stock upon the initial closing of the transaction. Carole Nuechterlein, who is a member of our board of directors, is an affiliate of Roche Finance Ltd. |
| (4) | (i) Baker Brothers Life Sciences, L.P. purchased 1,931,371 shares for a total purchase price of $17,999,800 and (ii) 667, L.P. purchased 214,620 shares for a total purchase price of $2,000,200. Entities affiliated with Baker Brothers became beneficial owners of (in the aggregate) more than 5% of our capital stock upon a subsequent closing of the transaction. |
| (5) | Novo Holdings A/S became the beneficial owner of more than 5% of our capital stock upon the initial closing of the transaction. Peter Moldt, who is a member of our board of directors, is employed as a senior partner at Novo Ventures (US), Inc., which provides certain consultancy services to Novo Holdings A/S. Dr. Moldt is not deemed to hold any beneficiary ownership or reportable pecuniary interest in the shares held by Novo Holdings A/S. |
| (6) | The purchasers are trusts affiliated with Lawrence M. Blatt, Ph.D., a member of our board of directors and one of our executive officers, and his immediate family members. |
| (7) | The purchasers are trusts affiliated with Leonid Beigelman, Ph.D., a member of our board of directors and one of our executive officers, and his immediate family members. |
| (8) | Julian Symons, D.Phil. is one of our executive officers. |
| (9) | The purchaser is a trust affiliated with Lucinda Quan, J.D., one of our executive officers. |
182
Table of Contents
Series B convertible preferred stock financing
In December 2019, we issued an aggregate of 8,344,034 shares of our Series B-1 convertible preferred stock in the first tranche of our Series B convertible preferred stock financing at a price per share of $10.1869 for aggregate proceeds to us of $85 million. The table below sets forth the number of shares of Series B-1 convertible preferred stock sold to our directors, executive officers or owners of more than 5% of our capital stock, or an affiliate or immediate family member thereof:
| Name | Number of shares of Series B-1 convertible preferred stock |
Total purchase price ($) |
||||||
| Wellington Biomedical Innovation Master Investors (Cayman) I L.P.(1) |
1,335,048 | 13,600,001 | ||||||
| ATI Holdings LLC(2) |
1,335,048 | 13,600,001 | ||||||
| Entities affiliated with Versant Venture Capital(3) |
662,798 | 6,751,868 | ||||||
| Roche Finance Ltd(4) |
662,799 | 6,751,868 | ||||||
| Entities affiliated with Baker Brothers(5) |
662,798 | 6,751,868 | ||||||
| Entities affiliated with Vivo Capital Fund(6) |
596,046 | 6,071,868 | ||||||
| Novo Holdings A/S(7) |
563,851 | 5,743,901 | ||||||
| Trusts affiliated Leonid Beigelman, Ph.D.(8) |
57,499 | 585,757 | ||||||
| Trusts affiliated Lawrence M. Blatt, Ph.D.(9) |
57,500 | 585,756 | ||||||
| Julian Symons, D.Phil.(10) |
3,394 | 34,576 | ||||||
| Trust affiliated with Lucinda Quan, J.D.(11) |
1,697 | 17,288 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||
| (1) | Wellington Biomedical Innovation Master Investors (Cayman) I L.P. became a beneficial owner of more than 5% of our capital stock upon the initial closing of the transaction. |
| (2) | ATI Holdings LLC became a beneficial owner of more than 5% of our capital stock upon the initial closing of the transaction. |
| (3) | (i) Versant Venture Capital VI, L.P. purchased 198,839 shares of Series B-1 convertible preferred stock for a total purchase price of $2,025,560 and (ii) Versant Vantage I, L.P. purchased 463,959 shares of Series B-1 convertible preferred stock for a total purchase price of $4,726,307. Entities affiliated with Versant were beneficial owners of more than 5% of our capital stock at the time of the initial closing of the transaction. Thomas Woiwode, who is a member of our board of directors, is an affiliate of Versant Venture Capital VI, L.P. |
| (4) | Roche Finance Ltd was a beneficial owner of more than 5% of our capital stock at the time of the initial closing of the transaction. Carole Nuechterlein, who is a member of our board of directors, is an affiliate of Roche Finance Ltd. |
| (5) | (i) Baker Brothers Life Sciences, L.P. purchased 607,847 shares of Series B-1 convertible preferred stock for a total purchase price of $6,192,082 and (ii) 667, L.P. purchased 54,951 shares of Series B-1 convertible preferred stock for a total purchase price of $559,785. Entities affiliated with Baker Brothers were beneficial owners of (in the aggregate) more than 5% of our capital stock at the time of initial closing of the transaction. |
| (6) | (i) Vivo Capital Fund VIII, L.P. purchased 523,726 shares of Series B-1 convertible preferred stock for a total purchase price of $5,335,149 and (ii) Vivo Capital Surplus Fund VIII, L.P. purchased 73,320 shares of Series B-1 convertible preferred stock for a total purchase price of $736,720. Entities affiliated with Vivo Capital Fund were beneficial owners of (in the aggregate) more than 5% of our capital stock at the time of the initial closing of the transaction. Jack B. Nielsen, who is a member of our board of directors, is an affiliate of Vivo Capital Fund. |
| (7) | Novo Holdings A/S was the beneficial owner of more than 5% of our capital stock at the time of the initial closing of the transaction. Peter Moldt, who is a member of our board of directors, is employed as Senior Partner at Novo Ventures (US), Inc., which provides consulting services to Novo Holdings A/S. Dr. Moldt is not deemed to hold any beneficial ownership or pecuniary interest in the shares held by Novo Holdings A/S. |
| (8) | The purchasers are trusts affiliated with Leonid Beigelman, Ph.D., a member of our board of directors and one of our executive officers, and his immediate family members. |
| (9) | The purchasers are trusts affiliated with Lawrence M. Blatt, Ph.D., a member of our board of directors and one of our executive officers, and his immediate family members. |
| (10) | Julian Symons, D.Phil. is one of our executive officers. |
| (11) | The purchaser is a trust affiliated with Lucinda Quan, J.D., one of our executive officers. |
Series B-2 convertible preferred stock financing
In October 2020, we issued an aggregate of 3,569,630 shares of our Series B-2 convertible preferred stock in the second tranche of our Series B convertible preferred stock financing at a price per share of $11.20563 for
183
Table of Contents
aggregate proceeds to us of $40 million. The table below sets forth the number of shares of Series B-2 convertible preferred stock sold to our directors, executive officers or owners of more than 5% of our capital stock, or an affiliate or immediate family member thereof:
| Name | Number of shares of Series B-2 convertible |
Total price ($) |
||||||
| Wellington Biomedical Innovation Master Investors (Cayman) I L.P.(1) |
571,143 | 6,400,026 | ||||||
| Entities affiliated with Vivo Capital Fund(2) |
254,993 | 2,857,362 | ||||||
| Entities affiliated with Versant Venture Capital(3) |
283,550 | 3,177,364 | ||||||
| Roche Finance Ltd.(4) |
283,550 | 3,177,363 | ||||||
| Entities affiliated with Baker Brothers(5) |
283,549 | 3,177,363 | ||||||
| Novo Holdings A/S(6) |
241,219 | 2,703,023 | ||||||
| Trusts affiliated Leonid Beigelman, Ph.D.(7) |
24,598 | 275,652 | ||||||
| Trusts affiliated Lawrence M. Blatt, Ph.D.(8) |
24,599 | 275,652 | ||||||
| Julian Symons, D.Phil.(9) |
1,452 | 16,272 | ||||||
| Trust affiliated with Lucinda Quan, J.D.(10) |
726 | 8,136 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||
| (1) | Wellington Biomedical Innovation Master Investors (Cayman) I L.P. was a beneficial owner of more than 5% of our capital stock at the time of the initial closing of the transaction. |
| (2) | (i) Vivo Capital Fund VIII, L.P. purchased 224,054 shares of Series B-2 convertible preferred stock for a total purchase price of $2,510,668 and (ii) Vivo Capital Surplus Fund VIII, L.P. purchased 30,939 shares of Series B-2 convertible preferred stock for a total purchase price of $346,693. Entities affiliated with Vivo Capital Fund were beneficial owners of more than 5% of our capital stock at the time of the initial closing of the transaction. Jack B. Nielsen, who is a member of our board of directors, is an affiliate of Vivo Capital Fund. |
| (3) | (i) Versant Venture Capital VI, L.P. purchased 85,065 shares of Series B-2 convertible preferred stock for a total purchase price of $953,209 and (ii) Versant Vantage I, L.P. purchased 198,485 shares of Series B-2 convertible preferred stock for a total purchase price of $2,224,154. Entities affiliated with Versant were beneficial owners of more than 5% of our capital stock at the time of the initial closing of the transaction. Thomas Woiwode, who is a member of our board of directors, is an affiliate of Versant Venture Capital VI, L.P. |
| (4) | Roche Finance Ltd. was a beneficial owner of more than 5% of our capital stock at the time of the initial closing of the transaction. Carole Nuechterlein, who is a member of our board of directors, is an affiliate of Roche Finance Ltd. |
| (5) | (i) Baker Brothers Life Sciences, L.P. purchased 260,041 shares of Series B-2 convertible preferred stock for a total purchase price of $2,913,933 and (ii) 667, L.P. purchased 23,508 shares of Series B-2 convertible preferred stock for a total purchase price of $263,430. Entities affiliated with Baker Brothers were beneficial owners of more than 5% of our capital stock at the time of initial closing of the transaction. |
| (6) | Novo Holdings A/S was the beneficial owner of more than 5% of our capital stock at the time of the initial closing of the transaction. Peter Moldt, who is a member of our board of directors, is an affiliate of Novo Holdings A/S. |
| (7) | The purchasers are trusts affiliated with Leonid Beigelman, Ph.D., a member of our board of directors and one of our executive officers, and his immediate family members. |
| (8) | The purchasers are trusts affiliated with Lawrence M. Blatt, Ph.D., a member of our board of directors and one of our executive officers, and his immediate family members. |
| (9) | Julian Symons, D.Phil. is one of our executive officers. |
| (10) | The purchaser is a trust affiliated with Lucinda Quan, J.D., one of our executive officers. |
Director and executive officer compensation
Please see the section titled “Director and executive compensation” for information regarding the compensation of our directors and executive officers.
Employment agreements
We have entered into employment agreements with our executive officers. For more information regarding these agreements, see the section titled “Director and executive compensation—Narrative to the summary
184
Table of Contents
compensation table” and “Director and executive compensation—Outstanding equity awards at 2019 fiscal year end.”
Indemnification agreements and directors’ and officers’ liability insurance
We have entered into or intend to enter into indemnification agreements with each of our directors and executive officers. These agreements will require us to, among other things, indemnify each director and executive officer to the fullest extent permitted by Delaware law, including indemnification of expenses such as attorneys’ fees, judgments, penalties, fines and settlement amounts incurred by the director or executive officer in any action or proceeding, including any action or proceeding by or in right of us, arising out of the person’s services as a director or executive officer. We have obtained an insurance policy that insures our directors and officers against certain liabilities, including liabilities arising under applicable securities laws. For additional information see the section titled “Management—Limitation of liability and indemnification matters.”
Investors’ rights agreement
We entered into an amended and restated investors’ rights agreement with the purchasers of our outstanding preferred stock, including entities with which certain of our directors are affiliated. Following the consummation of this offering, the holders of approximately 23.2 million shares of our common stock, including the shares of common stock issuable upon the conversion of our preferred stock, will be entitled to rights with respect to the registration of their shares under the Securities Act. For a more detailed description of these registration rights, see the section titled “Description of capital stock—Registration rights.” The amended and restated investors’ rights agreement also provides for a right of first offer in favor of certain holders of preferred stock with regard to certain issuances of our capital stock. The rights of first offer will not apply to, and will terminate immediately before the closing of, this offering.
Voting agreement
We entered into an amended and restated voting agreement with certain holders of our common stock and preferred stock. Upon the closing of this offering, the amended and restated voting agreement will terminate. For a description of the amended and restated voting agreement, see the section titled “Management—Board composition—Voting arrangements.”
Right of first refusal and co-sale agreement
We entered into an amended and restated right of first refusal and co-sale agreement with certain holders of our common stock and preferred stock. This agreement provides for rights of first refusal (which are secondary to our right of first refusal) and co-sale relating to the shares of our common stock held by certain of our stockholders who are parties to the agreement. The amended and restated right of first refusal and co-sale agreement will terminate immediately prior to the closing of this offering.
Public offering participation rights
We entered into letter agreements in December 2019 with Baker Bros. Advisors LP and ATI Holdings LLC pursuant to which we granted Baker Bros. Advisors LP and ATI Holdings LLC participation rights to purchase a specified percentage of shares of our common stock in this offering at the public offering price, subject to compliance with applicable securities laws. The letter agreements terminate upon the closing of this offering.
185
Table of Contents
Policies and procedures for related party transactions
Our board of directors has adopted a written related person transaction policy setting forth the policies and procedures for the review and approval or ratification of related person transactions. This policy covers, with certain exceptions set forth in Item 404 of Regulation S-K under the Securities Act, any transaction, arrangement or relationship, or any series of similar transactions, arrangements or relationships, in which we were or are to be a participant where the amount involved exceeds $120,000 and a related person had or will have a direct or indirect material interest, including without limitation purchases of goods or services by or from the related person or entities in which the related person has a material interest, indebtedness, guarantees of indebtedness and employment by us of a related person. In reviewing and approving any such transactions, our audit committee is tasked to consider all relevant facts and circumstances, including but not limited to whether the transaction is on terms comparable to those that could be obtained in an arm’s length transaction with an unrelated third party and the extent of the related person’s interest in the transaction. All of the transactions described in this section occurred prior to the adoption of this policy.
186
Table of Contents
The following table sets forth information relating to the beneficial ownership of our common stock as of October 6, 2020, by:
| • | each person, or group of affiliated persons, known by us to beneficially own more than 5% of our outstanding shares of common stock; |
| • | each of our current directors; |
| • | each of our named executive officers; and |
| • | all current directors and executive officers as a group. |
The number of shares beneficially owned by each entity, person, director or executive officer is determined in accordance with the rules of the SEC, and the information is not necessarily indicative of beneficial ownership for any other purpose. Under such rules, beneficial ownership includes any shares over which the individual has sole or shared voting power or investment power as well as any shares that the individual has the right to acquire within 60 days of October 6, 2020 through the exercise of any stock option, warrants or other rights. The table below excludes any purchases that may be made pursuant to the exercise of participation rights held by certain of our stockholders described in the section titled “Certain relationships and related party transactions—Public offering participation rights” or otherwise in this offering. Except as otherwise indicated, and subject to applicable community property laws, the persons named in the table have sole voting and investment power with respect to all shares of common stock held by that person.
187
Table of Contents
The percentage of shares beneficially owned is computed on the basis of 26,857,845 shares of our common stock outstanding as of October 6, 2020, which reflects the assumed conversion of all of our outstanding shares of preferred stock into an aggregate of 22,771,059 shares of common stock (including 3,092,338 shares of our non-voting common stock) and gives effect to the filing of our amended and restated certificate of incorporation on October 9, 2020, including the 1-for-9.3197 reverse stock split. Shares of our common stock that a person has the right to acquire within 60 days of October 6, 2020 are deemed outstanding for purposes of computing the percentage ownership of the person holding such rights, but are not deemed outstanding for purposes of computing the percentage ownership of any other person, except with respect to the percentage ownership of all directors and executive officers as a group. The percentage ownership information under the column titled “Beneficial ownership after this offering” is based on the sale of shares of common stock in this offering, (including 3,092,338 shares of our non-voting common stock) assuming no exercise of the underwriters’ option to purchase additional shares. Unless otherwise indicated below, the address for each beneficial owner listed is c/o Aligos Therapeutics, Inc., One Corporate Dr., 2nd Floor, South San Francisco, California 94080.
| Beneficial ownership prior to this offering | Beneficial ownership after this offering |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name of beneficial owner | Number of outstanding voting shares beneficially owned |
Number of outstanding non-voting shares beneficially owned |
Number of shares exercisable within 60 days |
Number of shares beneficially owned |
Percentage of beneficial ownership |
Number of voting shares beneficially owned |
Number
of |
Percentage of beneficial |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5% and greater stockholders: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Roche Finance Ltd(1) |
3,092,340 | — | — | 3,092,340 | 11.5% | 3,092,340 | — | 8.4% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Entities affiliated with Versant Ventures(2) |
3,092,339 | — | — | 3,092,339 | 11.5% | 3,092,339 | — | 8.4% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Entities affiliated with Baker Bros. Advisors LP(3) |
3,092,338 | — | — | 3,092,338 | 11.5% | — | 3,092,338 | 8.4% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Entities affiliated with Vivo Capital(4) |
2,997,030 | — | — | 2,997,030 | 11.2% | 2,997,030 | — | 8.1% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Novo Holdings A/S(5) |
2,414,563 | — | — | 2,414,563 | 9.0% | 2,414,563 | — | 6.6% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Entities affiliated with Wellington Management(6) |
1,906,191 | — | — | 1,906,191 | 7.1% | 1,906,191 | — | 5.2% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Directors and Named Executive Officers: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lawrence M. Blatt, Ph.D.(7) |
1,486,215 | — | 858,396 | 2,344,611 | 8.5% | 2,344,611 | — | 6.2% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Leonid Beigelman, Ph.D.(8) |
1,510,352 | — | 268,248 | 1,778,600 | 6.6% | 1,778,600 | — | 4.8% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lucinda Quan, J.D.(9) |
383,464 | — | 38,860 | 422,324 | 1.6% | 214,413 | — | 1.1% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Jack B. Nielsen |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| K. Peter Hirth(10) |
59,549 | — | — | 59,549 | * | 59,549 | — | * | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Carole Nuechterlein |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Peter Moldt |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thomas Woiwode, Ph.D.(11) |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kathleen Sereda Glaub(12) |
59,550 | — | — | 59,550 | * | 59,550 | — | * | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| All current directors and executive officers as a group (11 persons) (13) |
3,890,512 | — | 1,439,028 | 5,329,540 | 18.8% | 5,329,540 | — | 13.9% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| * | Represents beneficial ownership of less than one percent. |
| (1) | Consists of (i) 2,145,991 shares of common stock issuable upon the conversion of the Series A convertible preferred stock directly held by Roche Finance Ltd (“Roche Finance”), (ii) 662,799 shares of common stock issuable upon the conversion of the Series B-1 convertible preferred |
Table of Contents
| stock directly held by Roche Finance and (iii) 283,550 shares of common stock issuable upon the conversion of the Series B-2 convertible preferred stock directly held by Roche Finance. Roche Finance is a wholly owned subsidiary of Roche Holding Ltd (“Roche Holding”), a publicly held Swiss corporation, traded on the SIX Swiss Exchange. Carole Nuechterlein, a member of our board of directors, is an employee of F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, a subsidiary of Roche Finance. The address of Roche Finance is Grenzacherstrasse 122, Basel, 4058 Switzerland and the address of Roche Holding is Grenzacherstrasse 124, Basel, 4058 Switzerland. |
| (2) | Consists of (i) 2,145,991 shares of common stock issuable upon the conversion of the Series A convertible preferred stock directly held by Versant Venture Capital VI, L.P. (“Versant VI”), (ii) 463,959 shares of common stock issuable upon the conversion of the Series B-1 convertible preferred stock directly held by Versant Vantage I, L.P. (“Versant Vantage”, and together with Versant VI, the “Versant Funds”), (iii) 198,839 shares of common stock issuable upon the conversion of the Series B-1 convertible preferred stock directly held by Versant VI, (iv) 198,485 shares of common stock issuable upon the conversion of the Series B-2 convertible preferred stock directly held by Versant Vantage and (v) 85,065 shares of common stock issuable upon the conversion of the Series B-2 convertible preferred stock directly held by Versant VI. Versant Ventures VI GP, L.P. is the general partner of Versant VI and Versant Ventures VI GP-GP, LLC is the general partner of Versant Ventures VI GP, L.P. and has voting and dispositive control over the shares held by Versant VI. Each of Bradley J. Bolzon, Jerel C. Davis, Kirk G. Nielsen, Clare Ozawa, Robin L. Praeger and Thomas Woiwode Ph.D., the managing directors of Versant Ventures VI GP-GP, LLC, may be deemed to possess voting and dispositive control over the shares held by Versant VI and may be deemed to have indirect beneficial ownership of the shares held by Versant VI. Versant Vantage I GP, L.P. is the general partner of Versant Vantage and Versant Vantage I GP-GP, LLC is the general partner of Versant Vantage I GP, L.P. and has voting and dispositive control over the shares held by Versant Vantage. Each of Bradley J. Bolzon, Jerel C. Davis, Clare Ozawa, Robin L. Praeger and Thomas Woiwode Ph.D., the managing directors of Versant Vantage I GP-GP, LLC, may be deemed to possess voting and dispositive control over the shares held by Versant Vantage and may be deemed to have indirect beneficial ownership of the shares held by Versant Vantage. Dr. Woiwode is a member of our board of directors. The address for the Versant Funds is One Sansome Street, Suite 3630, San Francisco, CA 94104. |
| (3) | Consists of (i) 214,620 shares of non-voting common stock issuable upon the conversion of the Series A convertible preferred stock directly held by 667, L.P. (“667”), (ii) 1,931,371 shares of non-voting common stock issuable upon the conversion of the Series A convertible preferred stock directly held by Baker Brothers Life Sciences, L.P. (“Life Sciences”, and together with 667, the (“BBA Funds”)), (iii) 54,951 shares of nonvoting common stock issuable upon the conversion of the Series B-1 convertible preferred stock directly held by 667, (iv) 607,847 shares of non-voting common stock issuable upon the conversion of the Series B-1 convertible preferred stock directly held by Life Sciences, (v) 23,508 shares of nonvoting common stock issuable upon the conversion of the Series B-2 convertible preferred stock directly held by 667, (vi) 260,041 shares of non-voting common stock issuable upon the conversion of the Series B-2 convertible preferred stock directly held by Life Sciences. Baker Bros. Advisors LP (“BBA”) is the investment advisor to the BBA Funds and has the sole voting and investment power with respect to the shares held by the BBA Funds. Baker Bros. Advisors (GP) LLC (“BBA-GP”) is the sole general partner of BBA. The managing members of BBA-GP are Julian C. Baker and Felix J. Baker and may be deemed to share voting and dispositive power over the shares held by the BBA Funds. The address of the BBA Funds is 860 Washington Street, 3rd Floor, New York, NY 10014. |
| (4) | Consists of (i) 1,885,611 shares of common stock issuable upon the conversion of the Series A convertible preferred stock directly held by Vivo Capital Fund VIII, L.P. (“Vivo VIII”), (ii) 260,380 shares of common stock issuable upon the conversion of the Series A convertible preferred stock directly held by Vivo Capital Surplus Fund VIII, L.P. (“Vivo Surplus VIII”, and together with Vivo VIII, the “Vivo Funds”), (iii) 523,726 shares of common stock issuable upon the conversion of the Series B-1 convertible preferred stock directly held by Vivo VIII, (iv) 72,320 shares of common stock issuable upon the conversion of the Series B-1 convertible preferred stock directly held by Vivo Surplus VIII, (v) 224,054 shares of common stock issuable upon the conversion of the Series B-2 convertible preferred stock directly held by Vivo VIII and (vi) 30,939 shares of common stock issuable upon the conversion of the Series B-2 convertible preferred stock directly held by Vivo Surplus VIII. Vivo Capital VIII, LLC (“Vivo LLC”) is the general partner of Vivo VIII and Vivo Surplus VIII and may be deemed the beneficial owner of the securities. The voting members of Vivo LLC are Frank Kung, Edgar Engleman and Shan Fu, who may be deemed to share voting and dispositive power over the shares held by the Vivo Funds. Mr. Nielsen, a member of our board of directors, is an affiliate of Vivo LLC. The address for the Vivo Funds is 192 Lytton Avenue, Palo Alto, CA 94301. |
| (5) | Consists of (i) 1,609,493 shares of common stock issuable upon the conversion of the Series A convertible preferred stock directly held by Novo Holdings A/S (“Novo”), (ii) 563,851 shares of common stock issuable upon the conversion of the Series B-1 convertible preferred stock directly held by Novo and (iii) 241,219 shares of common stock issuable upon the conversion of the Series B-2 convertible preferred stock directly held by Novo. The board of directors of Novo has shared voting and investment power with respect to the shares held by Novo and may exercise such control only with the support of a majority of the members of the Novo board of directors. As such, no individual member of the Novo board of directors is deemed to hold any beneficial ownership or reportable pecuniary interest in the shares held by Novo. Dr. Moldt, a member of our board of directors, is employed as a Senior Partner at Novo Ventures (US), Inc., which provides certain consultancy services to Novo, and Dr. Moldt is not deemed to have beneficial ownership of the shares held by Novo. The address for Novo is Tuborg Havnevej 19, DK-2900 Hellerup, Denmark. |
| (6) | Consists of (i) 1,335,048 shares of common stock issuable upon the conversion of the Series B-1 convertible preferred stock directly held by Wellington Biomedical Innovation Master Investors (Cayman) I L.P. (“Wellington”) and (ii) 571,143 shares of common stock issuable upon the conversion of the Series B-2 convertible preferred stock directly held by Wellington. Wellington Management Company LLP is the investment advisor to Wellington and has investment and voting power over the shares held by Wellington. The address for Wellington is 280 Congress Street, Boston, MA 02210. |
| (7) | Consists of (i) 1,237,298 shares of common stock directly held by Lawrence M. Blatt, 1,086,401 of which shares will be vested within 60 days of October 6, 2020 and 150,897 of which shares will be unvested within 60 days of October 6, 2020, (ii) 41,016 shares of common stock issuable upon the conversion of the Series A convertible preferred stock directly held by the Lawrence M. Blatt Living Trust dated 8/27/14 (“Living Trust”), (iii) 98,460 shares of common stock issuable upon the conversion of the Series A convertible preferred stock directly held by PENSCO Trust Company LLC FBO Dr. Lawrence Blatt IRA (“Blatt IRA”), (iv) 13,671 shares of common stock issuable upon the conversion of the Series A convertible preferred stock directly held by the Zachary David Blatt Irrevocable Trust dated 8/24/14 (“Zachary Blatt Trust”); (v) 13,671 shares of common stock issuable upon the conversion of the Series A convertible preferred stock directly held by Zoe Anne Blatt Irrevocable Trust 8/24/14 (“Zoe Blatt Trust”), (vi) 50,712 shares of common stock issuable upon the conversion of the Series B-1 convertible preferred stock directly held by the Living Trust, (vii) 3,394 shares of common stock issuable upon the conversion of the Series B-1 convertible preferred stock directly held by the Zachary Blatt Trust; (viii) 3,394 shares of common stock issuable upon the conversion of the Series B-1 convertible |
189
Table of Contents
| preferred stock directly held by the Zoe Blatt Trust, (ix) 21,695 shares of common stock issuable upon the conversion of the Series B-2 convertible preferred stock directly held by the Living Trust, (x) 1,452 shares of common stock issuable upon the conversion of the Series B-2 convertible preferred stock directly held by the Zachary Blatt Trust, (xi) 1,452 shares of common stock issuable upon the conversion of the Series B-2 convertible preferred stock directly held by the Zoe Blatt Trust, (xii) warrants directly held by the Blatt IRA to purchase 24,141 shares of common stock issuable upon the conversion of Series A convertible preferred stock and (xiii) 858,396 shares of common stock that may be acquired pursuant to the exercise of stock options within 60 days of October 6, 2020. |
| (8) | Consists of (i) 1,026,991 shares of common stock directly held by Leonid Beigelman, 855,976 of which shares will be vested within 60 days of October 6, 2020 and 171,015 of which shares will be unvested within 60 days of October 6, 2020, (ii) 163,842 shares of common stock issuable upon the conversion of the Series A preferred stock directly held by the Beigelman and Lozovsky Living Trust (“Living Trust”), (iii) 13,559 shares of common stock issuable upon the conversion of the Series A convertible preferred stock directly held by Dina Beigelman Irrevocable Trust (“Dina Trust”), (iv) 13,559 shares of common stock issuable upon the conversion of the Series A convertible preferred stock directly held by the Victor Beigelman Irrevocable Trust (“Victor Trust”), (v) 50,781 shares of common stock issuable upon the conversion of the Series B-1 convertible preferred stock directly held by the Living Trust, (vi) 3,359 shares of common stock issuable upon the conversion of the Series B-1 convertible preferred stock directly held by the Dina Trust, (vii) 3,359 shares of common stock issuable upon the conversion of the Series B-1 convertible preferred stock directly held by the Victor Trust, (viii) 21,724 shares of common stock issuable upon the conversion of the Series B-2 convertible preferred stock directly held by the Living Trust, (ix) 1,437 shares of common stock issuable upon the conversion of the Series B-2 convertible preferred stock directly held by the Dina Trust, (x) 1,437 shares of common stock issuable upon the conversion of the Series B-2 convertible preferred stock directly held by the Victor Trust, (xi) 69,744 shares of common stock held by the Beigelman 2020 Grantor Retained Annuity Trust dated June 25, 2020, (xii) 35,408 shares of common stock held by the Dina Beigelman 2020 Irrevocable Trust, dated July 02, 2020, (xiii) 35,408 shares of common stock held by the Victor Beigelman 2020 Irrevocable Trust, dated July 02, 2020, (xiv) 69,744 shares of common stock held by the Lozovsky 2020 Grantor Retained Annuity Trust dated June 25, 2020 and (xv) 268,248 shares of common stock that may be acquired pursuant to the exercise of stock options within 60 days of October 6, 2020. |
| (9) | Consists of (i) 375,547 shares of common stock directly held by Lucinda Quan, 295,036 of which shares will be vested within 60 days of October 6, 2020 and 80,511 of which shares will be unvested within 60 days of October 6, 2020, (ii) 5,494 shares of common stock issuable upon the conversion of the Series A convertible preferred stock directly held by the LYQ Trust, dated August 22, 2010 (“LYQ Trust”), (iii) 1,697 shares of common stock issuable upon the conversion of the Series B-1 convertible preferred stock directly held by the LYQ Trust, (iv) 726 shares of common stock issuable upon the conversion of the Series B-2 convertible preferred stock directly held by the LYQ Trust, (v) warrants directly held by the LYQ Trust to purchase 1,341 shares of common stock issuable upon the conversion of Series A convertible preferred stock and (vi) 38,860 shares of common stock that may be acquired pursuant to the exercise of stock options within 60 days of October 6, 2020. |
| (10) | Consists of 59,549 shares of common stock directly held by K. Peter Hirth, 30,308 of which shares will be vested within 60 days of October 6, 2020 and 29,241 of which shares will continue to be subject to our repurchase right. |
| (11) | Consists of the shares described in footnote (2) above. |
| (12) | Consists of 59,550 shares of common stock directly held by Kathleen Sereda Glaub, 26,786 of which shares will be vested within 60 days of October 6, 2020 and 32,764 of which shares will continue to be subject to our repurchase right. |
| (13) | Consists of (i) 3,344,786 shares of common stock, 2,585,725 of which shares will be vested within 60 days of October 6, 2020, and 564,608 of which shares will continue to be subject to our repurchase right, (ii) 1,439,028 shares of common stock that may be acquired pursuant to the exercise of stock options within 60 days of October 6, 2020, (iii) 545,726 shares of common stock issuable upon conversion of preferred stock and (iv) warrants to purchase 28,164 shares of common stock issuable upon the conversion of Series A convertible preferred stock. |
190
Table of Contents
The following summary describes our capital stock and certain provisions of our amended and restated certificate of incorporation and our amended and restated bylaws, which will become effective immediately prior to the closing of this offering, the amended and restated investors’ rights agreement to which we and certain of our stockholders are parties and of the Delaware General Corporation Law. Because the following is only a summary, it does not contain all of the information that may be important to you. For a complete description, you should refer to our amended and restated certificate of incorporation, amended and restated bylaws and amended and restated investors’ rights agreement, copies of which have been filed as exhibits to the registration statement of which this prospectus is part.
General
Immediately prior to the closing of this offering, we will file our amended and restated certificate of incorporation that authorizes 300,000,000 shares of common stock, $0.0001 par value per share, 20,000,000 shares of non-voting common stock, $0.0001 par value per share, and 10,000,000 shares of preferred stock, $0.0001 par value per share. As of June 30, 2020, there were outstanding:
| • | 23,237,407 shares of our common stock, on an as-converted basis, held by approximately 77 stockholders of record; and |
| • | 2,246,633 shares of our common stock issuable upon exercise of outstanding stock options. |
On October 9, 2020, we consummated a 1-for-9.3197 reverse stock split of our common stock and preferred stock.
Common stock and non-voting common stock
The holders of our common stock and non-voting common stock have identical rights, provided that, (i) except as otherwise expressly provided in our amended and restated certificate of incorporation or as required by applicable law, on any matter that is submitted to a vote by our stockholders, holders of our common stock are entitled to one vote per share of common stock, and holders of our non-voting common stock are not entitled to any votes per share of non-voting common stock, including for the election of directors, and (ii) holders of our common stock have no conversion rights, while holders of our non-voting common stock shall have the right to convert each share of non-voting common stock into one share of common stock at such holder’s election, provided that as a result of such conversion, such holder, together with its affiliates and any members of a Schedule 13(d) group with such holder, would not beneficially own in excess of 4.99% of our common stock immediately prior to and following such conversion, unless otherwise expressly provided for in our amended and restated certificate of incorporation. However, this ownership limitation may be increased to any other percentage designated by such holder of non-voting common stock upon 61 days’ notice to us or decreased at any time upon notice to us.
Each holder of our common stock is entitled to one vote for each share on all matters submitted to a vote of the stockholders, including the election of directors. Our stockholders do not have cumulative voting rights in the election of directors. Accordingly, holders of a majority of the voting shares are able to elect all of the directors. In addition, the affirmative vote of holders of 66-2/3% of the voting power of all of the then outstanding voting stock will be required to take certain actions, including amending certain provisions of our amended and restated certificate of incorporation, such as the provisions relating to amending our amended and restated bylaws, our classified board and director liability.
191
Table of Contents
Subject to preferences that may be applicable to any then outstanding preferred stock, holders of our common stock and non-voting common stock are entitled to receive dividends, if any, as may be declared from time to time by our board of directors out of legally available funds.
In the event of our liquidation, dissolution or winding up, holders of our common stock and non-voting common stock will be entitled to share ratably in the net assets legally available for distribution to stockholders after the payment of all of our debts and other liabilities and the satisfaction of any liquidation preference granted to the holders of any then outstanding shares of preferred stock.
Holders of our common stock and non-voting common stock have no preemptive, conversion, subscription or other rights, and there are no redemption or sinking fund provisions applicable to our common stock or non-voting common stock. The rights, preferences and privileges of the holders of our common stock and non-voting common stock are subject to and may be adversely affected by the rights of the holders of shares of any series of our preferred stock that we may designate in the future.
All of our outstanding shares of common stock and non-voting common stock are, and the shares of common stock to be issued in this offering will be, fully paid and nonassessable.
Preferred stock
As of June 30, 2020, there were 19,201,429 shares of preferred stock outstanding, held of record by 48 stockholders. Immediately upon the closing of this offering, all 19,201,429 outstanding shares of our preferred stock as of June 30, 2020 will be converted into 16,392,640 shares of our common stock and 2,808,789 shares of our non-voting common stock. See Note 8 to our consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this prospectus for a description of our currently outstanding preferred stock. Immediately prior to the closing of this offering, our amended and restated certificate of incorporation will be amended and restated to delete all references to such shares of preferred stock. From and after the consummation of this offering, our board of directors will have the authority, without further action by our stockholders, to issue up to 10,000,000 shares of preferred stock in one or more series and to fix the rights, preferences, privileges and restrictions thereof. These rights, preferences and privileges could include dividend rights, conversion rights, voting rights, terms of redemption, liquidation preferences, sinking fund terms and the number of shares constituting, or the designation of, such series, any or all of which may be greater than the rights of common stock. The issuance of our preferred stock could adversely affect the voting power of holders of common stock and the likelihood that such holders will receive dividend payments and payments upon our liquidation. In addition, the issuance of preferred stock could have the effect of delaying, deferring or preventing a change in control of our company or other corporate action. Immediately after consummation of this offering, no shares of preferred stock will be outstanding, and we have no present plan to issue any shares of preferred stock.
Options
As of June 30, 2020, we had outstanding options to purchase 2,246,633 shares of our common stock, with a per share weighted-average exercise price of $3.16, under our 2018 Equity Incentive Plan.
Warrants
As of June 30, 2020, 83,149 shares of preferred stock were issuable upon exercise of our Series A Warrants, which will be exercised for a total cash payment of $0.8 million prior to the closing of this offering. Immediately upon the consummation of this offering, all outstanding shares of our preferred stock will be converted into equivalent number of shares of our common stock, at an exercise price of $9.32 per share, and no warrants will remain outstanding.
192
Table of Contents
Registration rights
Under our amended and restated investors’ rights agreement following the closing of this offering, the holders of approximately 23.2 million shares of common stock and non-voting common stock, or their transferees, will have the right to require us to register their shares under the Securities Act so that those shares may be publicly resold, and the holders of approximately 23.2 million shares of common stock and non-voting common stock, or their transferees, will have the right to include their shares in any registration statement we file, in each case as described below.
Form S-1 demand registration rights
After the closing of this offering, the holders of approximately 23.2 million shares of our common stock and non-voting common stock, or their transferees, will be entitled to certain Form S-1 demand registration rights. Beginning six months following the effectiveness of the registration statement of which this prospectus is a part, the holders of at least 30% of these shares can request that we register all or a portion of their shares (including the shares of common stock into which any shares of non-voting common stock held by such investors may be converted), so long as such holders request that we register at least 20% of the shares entitled to these demand registration rights and the aggregate proceeds, net of underwriting discounts and commissions, would exceed $20 million if the first offering or $5 million after the first offering. These stockholders may make up to two requests for registration on Form S-1.
Form S-3 demand registration rights
After the closing of this offering, the holders of approximately 23.2 million shares of our common stock and non-voting stock, or their transferees, will be entitled to certain Form S-3 demand registration rights. If we are eligible to use a Form S-3 registration statement, the holders of these shares can request that we register all or a portion of their shares on a Form S-3 registration statement if the anticipated aggregate offering price is at least $2 million, net of underwriting discounts and commissions and certain other expenses related to the sale of the shares. These stockholders may make unlimited requests for registration on Form S-3, provided that we are not obligated to effect, or take any action to effect, a registration on Form S-3 if we have effected two registrations on Form S-3 pursuant to requests by these stockholders within the twelve month period immediately preceding such request.
Piggyback registration rights
After the closing of this offering, in the event that we determine to register any of our common stock under the Securities Act (subject to certain exceptions), either for our own account or for the account of other security holders, the holders of approximately 23.2 million shares of our common stock and non-voting common stock or their transferees will be entitled to certain “piggyback” registration rights allowing the holders to include their shares in such registration, subject to certain marketing and other limitations and the conversion of non-voting common stock into shares of common stock prior to registration thereof. As a result, whenever we propose to file a registration statement under the Securities Act, other than with respect to certain registrations, including related to the sale of securities to employees pursuant to employee benefit plans, the offer and sale of convertible debt securities, an SEC Rule 145 transaction, or a registration on any form that does not include substantially the same information as would be required to be included in a registration statement covering the sale of the registerable shares, the holders of these shares are entitled to notice of the registration and have the right to include their shares of common stock in the registration. In an underwritten offering, the underwriters have the right, subject to specified conditions, to limit the number of shares such holders may include.
193
Table of Contents
Expenses of registration
We will pay the registration expenses, excluding underwriting discounts and commissions and certain other expenses, of the holders of the shares registered pursuant to the Form S-1 demand, Form S-3 demand and piggyback registration rights described above, including the reasonable expenses of one counsel for the selling holders not to exceed $50,000.
Expiration of registration rights
The Form S-1 demand, Form S-3 demand and piggyback registration rights described above will terminate, with respect to any particular stockholder, upon the earlier of (i) three years after the consummation of this offering, (ii) following this offering, the date that Rule 144 or another similar exemption under the Securities Act is available to such stockholder for the sale of all of such stockholder’s shares without limitation during a three-month period, or (iii) upon the consummation of a merger or consolidation.
Anti-takeover effects of provisions of our amended and restated certificate of incorporation, our amended and restated bylaws and Delaware law
Some provisions of Delaware law and our amended and restated certificate of incorporation and our amended and restated bylaws that will become effective immediately prior to the consummation of this offering contain provisions that could make the following transactions more difficult: acquisition of us by means of a tender offer; acquisition of us by means of a proxy contest or otherwise; or removal of our incumbent officers and directors. It is possible that these provisions could make it more difficult to accomplish or could deter transactions that stockholders may otherwise consider to be in their best interest or in our best interests, including transactions that might result in a premium over the market price for our shares.
These provisions, summarized below, are expected to discourage coercive takeover practices and inadequate takeover bids. These provisions are also designed to encourage persons seeking to acquire control of us to first negotiate with our board of directors. We believe that the benefits of increased protection of our potential ability to negotiate with the proponent of an unfriendly or unsolicited proposal to acquire or restructure us outweigh the disadvantages of discouraging these proposals because negotiation of these proposals could result in an improvement of their terms.
Delaware anti-takeover statute
We are subject to Section 203 of the Delaware General Corporation Law, which prohibits persons deemed “interested stockholders” from engaging in a “business combination” with a publicly-held Delaware corporation for three years following the date these persons become interested stockholders unless the business combination is, or the transaction in which the person became an interested stockholder was, approved in a prescribed manner or another prescribed exception applies. Generally, an “interested stockholder” is a person who, together with affiliates and associates, beneficially owns, or within three years prior to the determination of interested stockholder status did own, 15% or more of a corporation’s voting stock. Generally, a “business combination” includes a merger, asset or stock sale, or other transaction resulting in a financial benefit to the interested stockholder. The existence of this provision may have an anti-takeover effect with respect to transactions not approved in advance by the board of directors, such as discouraging takeover attempts that might result in a premium over the market price of our common stock.
Undesignated preferred stock
The ability to authorize undesignated preferred stock makes it possible for our board of directors to issue preferred stock with voting or other rights or preferences that could impede the success of any attempt to
194
Table of Contents
institute a change of control of our company. These and other provisions may have the effect of deterring hostile takeovers or delaying changes in control or management of our company.
Special stockholder meetings
Our amended and restated bylaws that will be in effect immediately prior to the closing of this offering will provide that a special meeting of stockholders may only be called by our board of directors, Chief Executive Officer or, in the absence of a chief executive officer, our President.
Requirements for advance notification of stockholder nominations and proposals
Our amended and restated bylaws that will be in effect immediately prior to the closing of this offering will establish advance notice procedures with respect to stockholder proposals and the nomination of candidates for election as directors, other than nominations made by or at the direction of the board of directors or a committee of the board of directors.
Elimination of stockholder action by written consent
Our amended and restated certificate of incorporation and our amended and restated bylaws that will be in effect immediately prior to the closing of this offering will eliminate the right of stockholders to act by written consent without a meeting.
Classified board; election and removal of directors; filling vacancies
Our board of directors is divided into three classes. The directors in each class will serve for a three-year term, one class being elected each year by our stockholders. Only one class of directors will be elected at each annual meeting of our stockholders, with the other classes continuing for the remainder of their respective three-year terms. Because our stockholders do not have cumulative voting rights, our stockholders holding a majority of the shares of common stock outstanding will be able to elect all of our directors. Our amended and restated certificate of incorporation that will be in effect immediately prior to the closing of this offering will provide for the removal of any of our directors only for cause and will require a stockholder vote by the holders of at least a 66-2/3% of the voting power of the then outstanding voting stock. For more information on the classified board, see the section titled “Management—Board composition.” Furthermore, any vacancy on our board of directors, however occurring, including a vacancy resulting from an increase in the size of the board, may only be filled by a resolution of the board of directors unless the board of directors determines that such vacancies shall be filled by the stockholders. This system of electing and removing directors and filling vacancies may tend to discourage a third party from making a tender offer or otherwise attempting to obtain control of us, because it generally makes it more difficult for stockholders to replace a majority of our directors.
Choice of forum
Our amended and restated certificate of incorporation will provide that, unless we consent in writing to the selection of an alternative forum, the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware will be the sole and exclusive forum for any derivative action or proceeding brought on our behalf; any action asserting a breach of fiduciary duty; any action asserting a claim against us arising pursuant to the Delaware General Corporation Law, our amended and restated certificate of incorporation, our amended and restated bylaws or as to which the Delaware General Corporation Law confers jurisdiction to the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware; or any action asserting a claim against us that is governed by the internal affairs doctrine. Our amended and restated certificate of incorporation will also provide that the federal district courts of the United States of America will be the exclusive forum for the resolution of any complaint asserting a cause of action against us or any of our directors, officers, employees or agents and arising under the Securities Act.
195
Table of Contents
We believe these provisions may benefit us by providing increased consistency in the application of Delaware law and federal securities laws by chancellors and judges, as applicable, particularly experienced in resolving corporate disputes, efficient administration of cases on a more expedited schedule relative to other forums and protection against the burdens of multi-forum litigation. However, these provisions may have the effect of discouraging lawsuits against our directors and officers. The choice of forum provision requiring that the Court of Chancery of the State of Delaware or the federal district courts of the United States of America be the exclusive forum for certain actions would not apply to suits brought to enforce any liability or duty created by the Exchange Act.
Our exclusive forum provision will not relieve us of our duties to comply with the federal securities laws and the rules and regulations thereunder, and our stockholders will not be deemed to have waived our compliance with these laws, rules and regulations.
Although our amended and restated certificate of incorporation will contain the choice of forum provisions described above, it is possible that a court could find that such a provision is inapplicable for a particular claim or action or that such provision is unenforceable.
Amendment of certificate of incorporation provisions
The amendment of any of the above provisions, except for the provision making it possible for our board of directors to issue undesignated preferred stock, would require approval by a stockholder vote by the holders of at least a 66-2/3% of the voting power of the then outstanding voting stock.
The provisions of the Delaware General Corporation Law, our amended and restated certificate of incorporation and our amended and restated bylaws could have the effect of discouraging others from attempting hostile takeovers and, as a consequence, they may also inhibit temporary fluctuations in the market price of our common stock that often result from actual or rumored hostile takeover attempts. These provisions may also have the effect of preventing changes in our management. It is possible that these provisions could make it more difficult to accomplish transactions that stockholders may otherwise deem to be in their best interests.
Limitation of liability and indemnification matters
For a discussion of liability and indemnification, see the section titled “Management—Limitation of liability and indemnification matters.”
Nasdaq Global Market listing
We have applied to have our common stock approved for listing on the Nasdaq Global Market under the symbol “ALGS.”
Transfer agent and registrar
The transfer agent and registrar for our common stock is Continental Stock Transfer & Trust Co. The transfer agent and registrar’s address is 1 State Street, 30th Floor, New York, NY 10004.
196
Table of Contents
Shares eligible for future sale
Prior to this offering, there has been no public market for our common stock, and we cannot assure investors that an active trading market for our common stock will develop or be sustained after this offering. Future sales of our common stock, including shares issued upon the exercise of outstanding options, in the public market after this offering, or the perception that those sales may occur, could cause the prevailing market price for our common stock to fall or impair our ability to raise equity capital in the future. As described below, only a limited number of shares of our common stock will be available for sale in the public market for a period of several months after consummation of this offering due to contractual and legal restrictions on resale described below.
Future sales of our common stock in the public market either before (to the extent permitted) or after such restrictions lapse, or the perception that those sales may occur, could adversely affect the prevailing market price of our common stock at such time and our ability to raise equity capital at a time and price we deem appropriate.
Sale of restricted shares
Based on the number of shares of our common stock outstanding as of June 30, 2020 and assuming an initial public offering price of $15.00 per share (the midpoint of the price range set forth on the cover of this prospectus), upon the consummation of this offering and assuming (1) the conversion of all 19,201,429 shares of our outstanding preferred stock as of June 30, 2020 into 16,392,640 shares of common stock and 2,808,789 shares of non-voting common stock, (2) the issuance of 3,569,630 shares of our Series B-2 convertible preferred stock on October 6, 2020, and the conversion of such shares into 3,286,081 shares of common stock and 283,549 shares of non-voting common stock, (3) the issuance of 83,149 shares of our common stock upon the exercise of our Series A Warrants outstanding as of June 30, 2020 for Series A convertible preferred stock and the conversion thereof, (4) no exercise of the underwriters’ option to purchase additional shares of common stock, (5) no exercise of any outstanding options after June 30, 2020 and (6) the filing of our amended and restated certificate of incorporation on October 9, 2020, including a 1-for-9.3179 reverse stock split, we will have outstanding an aggregate of approximately 33,797,848 shares of common stock and 3,092,338 shares of non-voting common stock.
All of the shares of common stock to be sold in this offering, and any shares sold upon exercise of the underwriters’ option to purchase additional shares, will be freely tradable in the public market without restriction or further registration under the Securities Act, unless the shares are held by any of our “affiliates” as such term is defined in Rule 144 of the Securities Act. All remaining shares of common stock held by existing stockholders immediately prior to the consummation of this offering will be “restricted securities” as such term is defined in Rule 144. These restricted securities were issued and sold by us, or will be issued and sold by us, in private transactions and are eligible for public sale only if registered under the Securities Act or if they qualify for an exemption from registration under the Securities Act, including the exemptions provided by Rule 144 or Rule 701, which rules are summarized below.
197
Table of Contents
As a result of the lock-up agreements referred to below and the provisions of Rule 144 and Rule 701 under the Securities Act, based on the number of shares of our common stock outstanding as of June 30, 2020 and assumptions (1)-(6) described above, the shares of our common stock (excluding the shares sold in this offering and assuming the conversion of all non-voting common stock into shares of common stock) that will be available for sale in the public market are as follows:
| Approximate number of shares | First date available for sale into public market | |
| 26,890,186 shares |
180 days after the date of this prospectus upon expiration of the lock-up agreements referred to below, subject in some cases to applicable volume limitations under Rule 144 | |
|
| ||
Lock-up agreements
In connection with this offering, we, our directors, our executive officers and substantially all of our stockholders and other equityholders have agreed, subject to certain exceptions, with the underwriters not to offer, pledge, sell, contract to sell, sell any option or contract to purchase, purchase any option or contract to sell, grant any option, right or warrant to purchase, lend or otherwise transfer or dispose of (directly or indirectly), enter into any hedging, swap or other agreement or transaction that transfers, in whole or in part, any of the economic consequences of, or make any demand for, or exercise any right with respect to, the registration of, any shares of our common stock or any securities convertible into or exercisable or exchangeable for our common stock during the period from the date of the applicable lock-up agreement continuing through the date 180 days after the date of this prospectus, except with the prior written consent of J.P. Morgan Securities LLC, Jefferies LLC and Piper Sandler & Co. See the section titled “Underwriting” for additional information.
Subject to certain limitations, certain of our employees, including our executive officers, and/or directors, may enter into written trading plans that are intended to comply with Rule 10b5-1 under the Exchange Act. Sales under these trading plans would not be permitted until the expiration of the lock-up agreements described above.
Following the lock-up periods set forth in the agreements described above, and assuming that J.P. Morgan Securities LLC, Jefferies LLC and Piper Sandler & Co. on behalf of the underwriters do not release any parties from these agreements, all of the shares of our common stock that are restricted securities or are held by our affiliates as of the date of this prospectus will be eligible for sale in the public market in compliance with Rule 144 under the Securities Act.
Rule 144
In general, under Rule 144, as currently in effect, once we have been subject to the public company reporting requirements of the Exchange Act for at least 90 days, a person (or persons whose shares are required to be aggregated) who is not deemed to have been one of our “affiliates” for purposes of Rule 144 at any time during the three months preceding a sale, and who has beneficially owned restricted securities within the meaning of Rule 144 for at least six months, including the holding period of any prior owner other than one of our “affiliates,” is entitled to sell those shares in the public market (subject to the lock-up agreement referred to above, if applicable) without complying with the manner of sale, volume limitations or notice provisions of Rule 144, but subject to compliance with the public information requirements of Rule 144. If such a person has beneficially owned the shares proposed to be sold for at least one year, including the holding period of any prior owner other than “affiliates,” then such person is entitled to sell such shares in the public market without complying with any of the requirements of Rule 144 (subject to the lock-up agreement referred to above, if applicable). In general, under Rule 144, as currently in effect, once we have been subject to the public company reporting requirements of the Exchange Act for at least 90 days, our “affiliates,” as defined in Rule 144, who
198
Table of Contents
have beneficially owned the shares proposed to be sold for at least six months are entitled to sell in the public market, upon expiration of any applicable lock-up agreements and within any three-month period, a number of those shares of our common stock that does not exceed the greater of:
| • | 1% of the number of shares of common stock and non-voting common stock then outstanding, which will equal approximately 268,902 shares of common stock immediately after this offering (calculated as of June 30, 2020 on the basis of the assumptions (1)-(6) described above); or |
| • | the average weekly trading volume of our common stock on the Nasdaq Global Market during the four calendar weeks preceding the filing of a notice on Form 144 with respect to such sale. |
Such sales under Rule 144 by our “affiliates” or persons selling shares on behalf of our “affiliates” are also subject to certain manner of sale provisions, notice requirements and to the availability of current public information about us. Notwithstanding the availability of Rule 144, the holders of substantially all of our restricted securities have entered into lock-up agreements as referenced above and their restricted securities will become eligible for sale (subject to the above limitations under Rule 144) upon the expiration of the restrictions set forth in those agreements.
Rule 701
In general, under Rule 701 as currently in effect, any of our employees, directors, officers, consultants or advisors who acquired common stock from us in connection with a written compensatory stock or option plan or other written agreement in compliance with Rule 701 under the Securities Act before the effective date of the registration statement of which this prospectus is a part (to the extent such common stock is not subject to a lock-up agreement) is entitled to rely on Rule 701 to resell such shares beginning 90 days after we become subject to the public company reporting requirements of the Exchange Act in reliance on Rule 144, but without compliance with the holding period requirements contained in Rule 144.
Accordingly, subject to any applicable lock-up agreements, beginning 90 days after we become subject to the public company reporting requirements of the Exchange Act, under Rule 701 persons who are not our “affiliates,” as defined in Rule 144 may resell those shares without complying with the minimum holding period or public information requirements of Rule 144, and persons who are our “affiliates” may resell those shares without complying with Rule 144’s minimum holding period requirements (subject to the terms of the lock-up agreement referred to above).
Registration rights
After the consummation of this offering, the holders of approximately 23.2 million shares of our common stock and non-voting common stock, or their transferees, will, subject to the lock-up agreements referred to above, be entitled to certain rights with respect to the registration of the offer and sale of those shares under the Securities Act. For a description of these registration rights, see the section titled “Description of capital stock—Registration rights.” If the offer and sale of these shares are registered, they will be freely tradable without restriction under the Securities Act.
Stock plans
We intend to file with the SEC a registration statement under the Securities Act covering the shares of common stock reserved for issuance under our 2018 Equity Incentive Plan, our 2020 Incentive Award Plan and our 2020 Employee Stock Purchase Plan. Such registration statement is expected to be filed and become effective as soon as practicable after the consummation of this offering. Accordingly, shares registered under such registration statement will be available for sale in the open market following its effective date, subject to Rule 144 volume limitations and the lock-up agreements described above, if applicable.
199
Table of Contents
Material U.S. federal income tax consequences to non-U.S. holders
The following discussion is a summary of the material U.S. federal income tax consequences to Non-U.S. Holders (as defined below) of the purchase, ownership and disposition of our common stock issued pursuant to this offering, but does not purport to be a complete analysis of all potential tax effects. The effects of other U.S. federal tax laws, such as estate and gift tax laws, and any applicable state, local or non-U.S. tax laws are not discussed. This discussion is based on the U.S. Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended (the “Code”), Treasury Regulations promulgated thereunder, judicial decisions, and published rulings and administrative pronouncements of the U.S. Internal Revenue Service (the “IRS”), in each case in effect as of the date hereof.
These authorities may change or be subject to differing interpretations. Any such change or differing interpretation may be applied retroactively in a manner that could adversely affect a Non-U.S. Holder. We have not sought and will not seek any rulings from the IRS regarding the matters discussed below. There can be no assurance the IRS or a court will not take a contrary position to that discussed below regarding the tax consequences of the purchase, ownership and disposition of our common stock.
This discussion is limited to Non-U.S. Holders that hold our common stock as a “capital asset” within the meaning of Section 1221 of the Code (generally, property held for investment). This discussion does not address all U.S. federal income tax consequences relevant to a Non-U.S. Holder’s particular circumstances, including the impact of the Medicare contribution tax on net investment income or the alternative minimum tax. In addition, it does not address consequences relevant to Non-U.S. Holders subject to special rules, including, without limitation:
| • | U.S. expatriates and former citizens or long-term residents of the United States; |
| • | persons holding our common stock as part of a straddle or other risk reduction strategy or as part of a conversion transaction; |
| • | banks, insurance companies and other financial institutions; |
| • | brokers, dealers or traders in securities; |
| • | “controlled foreign corporations,” “passive foreign investment companies” and corporations that accumulate earnings to avoid U.S. federal income tax; |
| • | partnerships or other entities or arrangements treated as partnerships for U.S. federal income tax purposes (and investors therein); |
| • | tax-exempt organizations or governmental organizations; |
| • | persons deemed to sell our common stock under the constructive sale provisions of the Code; |
| • | tax-qualified retirement plans; and |
| • | “qualified foreign pension funds” as defined in Section 897(l)(2) of the Code and entities all of the interests of which are held by qualified foreign pension funds. |
If an entity treated as a partnership for U.S. federal income tax purposes holds our common stock, the tax treatment of a partner in the partnership will depend on the status of the partner, the activities of the partnership and certain determinations made at the partner level. Accordingly, partnerships holding our common stock and the partners in such partnerships should consult their tax advisors regarding the U.S. federal income tax consequences to them.
200
Table of Contents
THIS DISCUSSION IS NOT TAX ADVICE. INVESTORS SHOULD CONSULT THEIR TAX ADVISORS WITH RESPECT TO THE APPLICATION OF THE U.S. FEDERAL INCOME TAX LAWS TO THEIR PARTICULAR SITUATIONS AS WELL AS ANY TAX CONSEQUENCES OF THE PURCHASE, OWNERSHIP AND DISPOSITION OF OUR COMMON STOCK ARISING UNDER THE U.S. FEDERAL ESTATE OR GIFT TAX LAWS OR UNDER THE LAWS OF ANY STATE, LOCAL OR NON-U.S. TAXING JURISDICTION OR UNDER ANY APPLICABLE INCOME TAX TREATY.
Definition of non-U.S. holder
For purposes of this discussion, a “Non-U.S. Holder” is any beneficial owner of our common stock that is neither a “U.S. person” nor an entity treated as a partnership for U.S. federal income tax purposes. A U.S. person is any person that, for U.S. federal income tax purposes, is or is treated as any of the following:
| • | an individual who is a citizen or resident of the United States; |
| • | a corporation created or organized under the laws of the United States, any state thereof or the District of Columbia; |
| • | an estate, the income of which is subject to U.S. federal income tax regardless of its source; or |
| • | a trust that (1) is subject to the primary supervision of a U.S. court and all substantial decisions of which are subject to the control of one or more “United States persons” (within the meaning of Section 7701(a)(30) of the Code), or (2) has a valid election in effect to be treated as a United States person for U.S. federal income tax purposes. |
Distributions
As described in the section titled “Dividend policy,” we have never declared or paid cash dividends on our capital stock, and we do not anticipate paying any cash dividends in the foreseeable future. However, if we do make distributions of cash or property on our common stock, such distributions will constitute dividends for U.S. federal income tax purposes to the extent paid from our current or accumulated earnings and profits, as determined under U.S. federal income tax principles. Amounts not treated as dividends for U.S. federal income tax purposes will constitute returns of capital and first be applied against and reduce a Non-U.S. Holder’s adjusted tax basis in its common stock, but not below zero. Any excess will be treated as capital gain and will be treated as described below under “—Sale or other taxable disposition.”
Subject to the discussion below regarding effectively connected income, dividends paid to a Non-U.S. Holder will be subject to U.S. federal withholding tax at a rate of 30% of the gross amount of the dividends (or such lower rate specified by an applicable income tax treaty, provided the Non-U.S. Holder furnishes a valid IRS Form W-8BEN or IRS Form W-8BEN-E (or other applicable documentation) certifying qualification for the lower treaty rate). A Non-U.S. Holder that does not timely furnish the required documentation, but that qualifies for a reduced treaty rate, may obtain a refund of any excess amounts withheld by timely filing an appropriate claim for refund with the IRS. Non-U.S. Holders should consult their tax advisors regarding their entitlement to benefits under any applicable tax treaties.
If dividends paid to a Non-U.S. Holder are effectively connected with the Non-U.S. Holder’s conduct of a trade or business within the United States (and, if required by an applicable income tax treaty, the Non-U.S. Holder maintains a permanent establishment in the United States to which such dividends are attributable), the Non-U.S. Holder will be exempt from the U.S. federal withholding tax described above. To claim the exemption, the Non-U.S. Holder must furnish to the applicable withholding agent a valid IRS Form W-8ECI, certifying that the dividends are effectively connected with the Non-U.S. Holder’s conduct of a trade or business within the United States. Any such effectively connected dividends will be subject to U.S. federal income tax on a net
201
Table of Contents
income basis at the regular rates. A Non-U.S. Holder that is a corporation also may be subject to a branch profits tax at a rate of 30% (or such lower rate specified by an applicable income tax treaty) on such effectively connected dividends, as adjusted for certain items. Non-U.S. Holders should consult their tax advisors regarding any applicable tax treaties that may provide for different rules.
Sale or other taxable disposition
Subject to the discussion below regarding backup withholding, a Non-U.S. Holder will not be subject to U.S. federal income tax on any gain realized upon the sale or other taxable disposition of our common stock unless:
| • | the gain is effectively connected with the Non-U.S. Holder’s conduct of a trade or business within the United States (and, if required by an applicable income tax treaty, the Non-U.S. Holder maintains a permanent establishment in the United States to which such gain is attributable); |
| • | the Non-U.S. Holder is a nonresident alien individual present in the United States for 183 days or more during the taxable year of the disposition and certain other requirements are met; or |
| • | our common stock constitutes a U.S. real property interest (“USRPI”), by reason of our status as a U.S. real property holding corporation (“USRPHC”), for U.S. federal income tax purposes. |
Gain described in the first bullet point above generally will be subject to U.S. federal income tax on a net income basis at the regular rates. A Non-U.S. Holder that is a corporation also may be subject to a branch profits tax at a rate of 30% (or such lower rate specified by an applicable income tax treaty) on such effectively connected gain, as adjusted for certain items.
Gain described in the second bullet point above will be subject to U.S. federal income tax at a rate of 30% (or such lower rate specified by an applicable income tax treaty), which may be offset by certain U.S.-source capital losses of the Non-U.S. Holder (even though the individual is not considered a resident of the United States), provided the Non-U.S. Holder has timely filed U.S. federal income tax returns with respect to such losses.
With respect to the third bullet point above, we believe we currently are not, and do not anticipate becoming, a USRPHC. Because the determination of whether we are a USRPHC depends, however, on the fair market value of our USRPIs relative to the fair market value of our non-U.S. real property interests and our other business assets, there can be no assurance that we currently are not a USRPHC or will not become one in the future. Even if we are or were to become a USRPHC, gain arising from the sale or other taxable disposition by a Non-U.S. Holder will not be subject to U.S. federal income tax if our common stock is “regularly traded,” as defined by applicable Treasury Regulations, on an established securities market, and such Non-U.S. Holder owned, actually and constructively, 5% or less of our common stock throughout the shorter of the five-year period ending on the date of the sale or other taxable disposition or the Non-U.S. Holder’s holding period.
Non-U.S. Holders should consult their tax advisors regarding any applicable tax treaties that may provide for different rules.
Information reporting and backup withholding
Payments of dividends on our common stock will not be subject to backup withholding, provided the Non-U.S. Holder certifies its non-U.S. status, such as by furnishing a valid IRS Form W-8BEN, W-8BEN-E or W-8ECI, or otherwise establishes an exemption. However, information returns are required to be filed with the IRS in connection with any distributions on our common stock paid to the Non-U.S. Holder, regardless of whether any tax was actually withheld. In addition, proceeds of the sale or other taxable disposition of our common stock within the United States or conducted through certain U.S.-related brokers generally will not be subject to
202
Table of Contents
backup withholding or information reporting if the applicable withholding agent receives the certification described above or the Non-U.S. Holder otherwise establishes an exemption. Proceeds of a disposition of our common stock conducted through a non-U.S. office of a non-U.S. broker that does not have certain enumerated relationships with the United States generally will not be subject to backup withholding or information reporting.
Copies of information returns that are filed with the IRS may also be made available under the provisions of an applicable treaty or agreement to the tax authorities of the country in which the Non-U.S. Holder resides or is established.
Backup withholding is not an additional tax. Any amounts withheld under the backup withholding rules may be allowed as a refund or a credit against a Non-U.S. Holder’s U.S. federal income tax liability, provided the required information is timely furnished to the IRS.
Additional withholding tax on payments made to foreign accounts
Withholding taxes may be imposed under Sections 1471 to 1474 of the Code (such Sections commonly referred to as the Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act (“FATCA”)) on certain types of payments made to non-U.S. financial institutions and certain other non-U.S. entities. Specifically, a 30% withholding tax may be imposed on dividends on, or (subject to the proposed Treasury Regulations discussed below) gross proceeds from the sale or other disposition of, our common stock paid to a “foreign financial institution” or a “non-financial foreign entity” (each as defined in the Code), unless (1) the foreign financial institution undertakes certain diligence and reporting obligations, (2) the non-financial foreign entity either certifies it does not have any “substantial United States owners” (as defined in the Code) or furnishes identifying information regarding each substantial United States owner, or (3) the foreign financial institution or non-financial foreign entity otherwise qualifies for an exemption from these rules. If the payee is a foreign financial institution and is subject to the diligence and reporting requirements in (1) above, it must enter into an agreement with the U.S. Department of the Treasury requiring, among other things, that it undertakes to identify accounts held by certain “specified United States persons” or “United States owned foreign entities” (each as defined in the Code), annually reports certain information about such accounts, and withholds 30% on certain payments to non-compliant foreign financial institutions and certain other account holders. Foreign financial institutions located in jurisdictions that have an intergovernmental agreement with the United States governing FATCA may be subject to different rules.
Under the applicable Treasury Regulations and administrative guidance, withholding under FATCA generally applies to payments of dividends on our common stock. While, beginning on January 1, 2019, withholding under FATCA would have applied also to payments of gross proceeds from the sale or other disposition of our common stock, proposed Treasury Regulations eliminate FATCA withholding on payments of gross proceeds entirely. Taxpayers generally may rely on these proposed Treasury Regulations until final Treasury Regulations are issued.
Prospective investors should consult their tax advisors regarding the potential application of withholding under FATCA to their investment in our common stock.
203
Table of Contents
We are offering the shares of common stock described in this prospectus through a number of underwriters. J.P. Morgan Securities LLC, Jefferies LLC and Piper Sandler & Co. are acting as joint book-running managers of the offering and as representatives of the underwriters. We have entered into an underwriting agreement with the underwriters. Subject to the terms and conditions of the underwriting agreement, we have agreed to sell to the underwriters, and each underwriter has severally agreed to purchase, at the public offering price less the underwriting discounts and commissions set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, the number of shares of common stock listed next to its name in the following table:
| Name | Number of shares |
|||
| J.P. Morgan Securities LLC |
||||
| Jefferies LLC |
||||
| Piper Sandler & Co. |
||||
| Cantor Fitzgerald & Co. |
||||
|
|
|
|||
| Total |
10,000,000 | |||
|
|
||||
The underwriters are committed to purchase all the shares of common stock offered by us if they purchase any shares. The underwriting agreement also provides that if an underwriter defaults, the purchase commitments of non-defaulting underwriters may also be increased or the offering may be terminated.
The underwriters propose to offer the shares of common stock directly to the public at the initial public offering price set forth on the cover page of this prospectus and to certain dealers at that price less a concession not in excess of $ per share. Any such dealers may resell shares to certain other brokers or dealers at a discount of up to $ per share from the initial public offering price. After the initial offering of the shares to the public, if all of the shares of common stock are not sold at the initial public offering price, the underwriters may change the offering price and the other selling terms. Sales of any shares made outside of the United States may be made by affiliates of the underwriters.
The underwriters have an option to buy up to 1,500,000 additional shares of common stock from us to cover sales of shares by the underwriters which exceed the number of shares specified in the table above. The underwriters have 30 days from the date of this prospectus to exercise this option to purchase additional shares. If any shares are purchased with this option to purchase additional shares, the underwriters will purchase shares in approximately the same proportion as shown in the table above. If any additional shares of common stock are purchased, the underwriters will offer the additional shares on the same terms as those on which the shares are being offered.
The underwriters do not expect to sell more than 5% of the shares of common stock in the aggregate to accounts over which they exercise discretionary authority.
204
Table of Contents
The underwriting fee is equal to the public offering price per share of common stock less the amount paid by the underwriters to us per share of common stock. The underwriting fee is $ per share. The following table shows the per share and total underwriting discounts and commissions to be paid to the underwriters assuming both no exercise and full exercise of the underwriters’ option to purchase additional shares.
| Without option to purchase additional shares exercise |
With full option to purchase additional shares exercise |
|||||||
| Per Share |
$ | $ | ||||||
| Total |
$ | $ | ||||||
We estimate that the total expenses of this offering, including registration, filing and listing fees, printing fees and legal and accounting expenses, but excluding the underwriting discounts and commissions, will be approximately $4.1 million. We have agreed to reimburse the underwriters for expenses of up to $40,000 relating to the clearance of this offering with the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority.
A prospectus in electronic format may be made available on the websites maintained by one or more underwriters, or selling group members, if any, participating in the offering. The underwriters may agree to allocate a number of shares to underwriters and selling group members for sale to their online brokerage account holders. Internet distributions will be allocated by the representatives to underwriters and selling group members that may make Internet distributions on the same basis as other allocations.
We have agreed that we will not (i) offer, pledge, sell, contract to sell, sell any option or contract to purchase, purchase any option or contract to sell, grant any option, right or warrant to purchase, lend or otherwise transfer or dispose of, directly or indirectly, or submit to, or file with, the SEC a registration statement under the Securities Act relating to, any shares of our common stock or securities convertible into or exercisable or exchangeable for any shares of our common stock, or publicly disclose the intention to make any offer, sale, pledge, loan, disposition or filing, or (ii) enter into any swap or other arrangement that transfers all or a portion of the economic consequences associated with the ownership of any shares of common stock or any such other securities (regardless of whether any of the transactions described in clause (i) or (ii) are to be settled by the delivery of shares of common stock or such other securities, in cash or otherwise), in each case without the prior written consent of J.P. Morgan Securities LLC, Jefferies LLC and Piper Sandler & Co. for a period of 180 days after the date of the final prospectus, other than the shares of our common stock to be sold in this offering.
The restrictions on our actions, as described above, do not apply to certain transactions, including (i) the issuance of shares of our common stock or securities convertible into or exercisable for shares of our common stock pursuant to the conversion or exchange of convertible or exchangeable securities or the exercise of warrants or options (including net exercise) or the settlement of RSUs (including net settlement), in each case outstanding on the date of the underwriting agreement and described in this prospectus; (ii) grants of stock options, stock awards, restricted stock, RSUs, or other equity awards and the issuance of shares of our common stock or securities convertible into or exercisable or exchangeable for shares of our common stock (whether upon the exercise of stock options or otherwise) to our employees, officers, directors, advisors, or consultants pursuant to the terms of an equity compensation plan in effect as of the closing of this offering and described in this prospectus; or (iii) in connection with the issuance of up to 10% of the shares of common stock outstanding immediately following the closing of this offering in acquisitions or other strategic transactions, provided that, in each case, such recipients enter into a lock-up agreement with the underwriters.
Our directors and executive officers, and substantially all of our stockholders and other equityholders (such persons, the “lock-up parties”) have entered into lock-up agreements with the underwriters prior to the
205
Table of Contents
commencement of this offering pursuant to which each lock-up party, with limited exceptions, for a period of 180 days after the date of the final prospectus (such period, the “restricted period”), may not (and may not cause any of their direct or indirect affiliates to), without the prior written consent of J.P. Morgan Securities LLC, Jefferies LLC and Piper Sandler & Co., (1) offer, pledge, sell, contract to sell, sell any option or contract to purchase, purchase any option or contract to sell, grant any option, right or warrant to purchase, lend or otherwise transfer or dispose of, directly or indirectly, any shares of our common stock or any securities convertible into or exercisable or exchangeable for our common stock (including, without limitation, common stock or such other securities which may be deemed to be beneficially owned by such lock-up parties in accordance with the rules and regulations of the SEC and securities which may be issued upon exercise of a stock option or warrant (collectively with the common stock, the “lock-up securities”)), (2) enter into any hedging, swap or other agreement or transaction that transfers, in whole or in part, any of the economic consequences of ownership of the lock-up securities, whether any such transaction described in clause (1) or (2) above is to be settled by delivery of lock-up securities, in cash or otherwise, (3) make any demand for, or exercise any right with respect to, the registration of any lock-up securities, or (4) publicly disclose the intention to do any of the foregoing. Such persons or entities have further acknowledged that these undertakings preclude them from engaging in any hedging or other transactions or arrangements (including, without limitation, any short sale or the purchase or sale of, or entry into, any put or call option, or combination thereof, forward, swap or any other derivative transaction or instrument, however described or defined) designed or intended, or which could reasonably be expected to lead to or result in, a sale or disposition or transfer (by any person or entity, whether or not a signatory to such agreement) of any economic consequences of ownership, in whole or in part, directly or indirectly, of any lock-up securities, whether any such transaction or arrangement (or instrument provided for thereunder) would be settled by delivery of lock-up securities, in cash or otherwise.
The restrictions described in the immediately preceding paragraph and contained in the lock-up agreements between the underwriters and the lock-up parties do not apply, subject in certain cases to various conditions, to certain transactions, including (a) transfers of lock-up securities: (i) as bona fide gifts, or for bona fide estate planning purposes, (ii) by will, other testamentary document or intestacy, (iii) to any trust for the direct or indirect benefit of the lock-up party or any immediate family member, (iv) to a corporation, partnership, limited liability company or other entity of which the lock-up party and/or its immediate family members are, directly or indirectly, the legal and beneficial owner of all of the outstanding equity securities or similar interests, (v) to a nominee or custodian of a person or entity to whom a disposition or transfer would be permissible under clauses (i) through (iv), (vi) in the case of a corporation, partnership, limited liability company, trust or other business entity, (A) to another corporation, partnership, limited liability company, trust or other business entity that is an affiliate of the lock-up party, or to any investment fund or other entity controlling, controlled by, managing or managed by or under common control with the lock-up party or its affiliates or (B) as part of a distribution to affiliates, direct or indirect members, partners, stockholders or other equityholders of the lock-up party; (vii) by operation of law, (viii) to us from an employee or service provider upon death, disability or termination of employment of such employee or service provider, (ix) as part of a sale of lock-up securities acquired in open market transactions after the closing of this offering or from the underwriters in this offering, (x) to us in connection with the vesting, settlement or exercise of restricted stock units, options, warrants or other rights to purchase shares of our common stock (including “net” or “cashless” exercise), including for the payment of exercise price and tax and remittance payments, or (xi) pursuant to a bona fide third-party tender offer, merger, consolidation or other similar transaction approved by our board of directors and made to all stockholders involving a change in control, provided that if such transaction is not completed, all such lock-up securities would remain subject to the restrictions in the immediately preceding paragraph; (b) the exercise of options, the settlement of RSUs or other equity awards, or the exercise of warrants granted pursuant to plans described in in this prospectus, provided that any lock-up securities received upon such exercise, vesting or
206
Table of Contents
settlement would be subject to restrictions similar to those in the immediately preceding paragraph; (c) the conversion of outstanding preferred stock, warrants to acquire preferred stock, or convertible securities into shares of our common stock or warrants to acquire shares of our common stock, provided that any common stock or warrant received upon such conversion would be subject to restrictions similar to those in the immediately preceding paragraph; and (d) the establishment by lock-up parties of trading plans under Rule 10b5-1 under the Exchange Act, provided that any such plan does not provide for the transfer of lock-up securities during the restricted period.
J.P. Morgan Securities LLC, Jefferies LLC and Piper Sandler & Co., in their sole discretion, may release the securities subject to any of the lock-up agreements with the underwriters described above, in whole or in part at any time.
We have agreed to indemnify the underwriters against certain liabilities, including liabilities under the Securities Act of 1933.
We have applied to have our common stock approved for listing/quotation on Nasdaq Global Market under the symbol “ALGS”.
In connection with this offering, the underwriters may engage in stabilizing transactions, which involves making bids for, purchasing and selling shares of common stock in the open market for the purpose of preventing or retarding a decline in the market price of the common stock while this offering is in progress. These stabilizing transactions may include making short sales of common stock, which involves the sale by the underwriters of a greater number of shares of common stock than they are required to purchase in this offering, and purchasing shares of common stock on the open market to cover positions created by short sales. Short sales may be “covered” shorts, which are short positions in an amount not greater than the underwriters’ option to purchase additional shares referred to above, or may be “naked” shorts, which are short positions in excess of that amount. The underwriters may close out any covered short position either by exercising their option to purchase additional shares, in whole or in part, or by purchasing shares in the open market. In making this determination, the underwriters will consider, among other things, the price of shares available for purchase in the open market compared to the price at which the underwriters may purchase shares through the option to purchase additional shares. A naked short position is more likely to be created if the underwriters are concerned that there may be downward pressure on the price of the common stock in the open market that could adversely affect investors who purchase in this offering. To the extent that the underwriters create a naked short position, they will purchase shares in the open market to cover the position.
The underwriters have advised us that, pursuant to Regulation M of the Securities Act of 1933, they may also engage in other activities that stabilize, maintain or otherwise affect the price of the common stock, including the imposition of penalty bids. This means that if the representatives of the underwriters purchase common stock in the open market in stabilizing transactions or to cover short sales, the representatives can require the underwriters that sold those shares as part of this offering to repay the underwriting discount received by them.
These activities may have the effect of raising or maintaining the market price of the common stock or preventing or retarding a decline in the market price of the common stock, and, as a result, the price of the common stock may be higher than the price that otherwise might exist in the open market. If the underwriters commence these activities, they may discontinue them at any time. The underwriters may carry out these transactions on the Nasdaq Global Market, in the over-the-counter market or otherwise.
Prior to this offering, there has been no public market for our common stock. The initial public offering price will be determined by negotiations between us and the representatives of the underwriters. In determining the
207
Table of Contents
initial public offering price, we and the representatives of the underwriters expect to consider a number of factors including:
| • | the information set forth in this prospectus and otherwise available to the representatives; |
| • | our prospects and the history and prospects for the industry in which we compete; |
| • | an assessment of our management; |
| • | our prospects for future earnings; |
| • | the general condition of the securities markets at the time of this offering; |
| • | the recent market prices of, and demand for, publicly traded common stock of generally comparable companies; and |
| • | other factors deemed relevant by the underwriters and us. |
Neither we nor the underwriters can assure investors that an active trading market will develop for our common stock, or that the shares will trade in the public market at or above the initial public offering price.
Other relationships
Certain of the underwriters and their affiliates have provided in the past to us and our affiliates and may provide from time to time in the future certain commercial banking, financial advisory, investment banking and other services for us and such affiliates in the ordinary course of their business, for which they have received and may continue to receive customary fees and commissions. In addition, from time to time, certain of the underwriters and their affiliates may effect transactions for their own account or the account of customers, and hold on behalf of themselves or their customers, long or short positions in our debt or equity securities or loans, and may do so in the future.
Selling restrictions
Other than in the United States, no action has been taken by us or the underwriters that would permit a public offering of the securities offered by this prospectus in any jurisdiction where action for that purpose is required. The securities offered by this prospectus may not be offered or sold, directly or indirectly, nor may this prospectus or any other offering material or advertisements in connection with the offer and sale of any such securities be distributed or published in any jurisdiction, except under circumstances that will result in compliance with the applicable rules and regulations of that jurisdiction. Persons into whose possession this prospectus comes are advised to inform themselves about and to observe any restrictions relating to the offering and the distribution of this prospectus. This prospectus does not constitute an offer to sell or a solicitation of an offer to buy any securities offered by this prospectus in any jurisdiction in which such an offer or a solicitation is unlawful.
Notice to prospective investors in the European Economic Area and the United Kingdom
In relation to each Member State of the European Economic Area and the United Kingdom (each a “Relevant State”), no shares have been offered or will be offered pursuant to the offering to the public in that Relevant State prior to the publication of a prospectus in relation to the shares which has been approved by the competent authority in that Relevant State or, where appropriate, approved in another Relevant State and notified to the competent authority in that Relevant State, all in accordance with the Prospectus Regulation,
208
Table of Contents
except that offers of shares may be made to the public in that Relevant State at any time under the following exemptions under the Prospectus Regulation:
| (a) | to any legal entity which is a qualified investor as defined under the Prospectus Regulation; |
| (b) | to fewer than 150 natural or legal persons (other than qualified investors as defined under the Prospectus Regulation), subject to obtaining the prior consent of the underwriters; or |
| (c) | in any other circumstances falling within Article 1(4) of the Prospectus Regulation, |
provided that no such offer of shares shall require us or any underwriter to publish a prospectus pursuant to Article 3 of the Prospectus Regulation or supplement a prospectus pursuant to Article 23 of the Prospectus Regulation and each person who initially acquires any shares or to whom any offer is made will be deemed to have represented, acknowledged and agreed to and with each of the underwriters and us that it is a “qualified investor” within the meaning of Article 2(e) of the Prospectus Regulation. In the case of any shares being offered to a financial intermediary as that term is used in the Prospectus Regulation, each such financial intermediary will be deemed to have represented, acknowledged and agreed that the shares acquired by it in the offer have not been acquired on a non-discretionary basis on behalf of, nor have they been acquired with a view to their offer or resale to, persons in circumstances which may give rise to an offer of any shares to the public other than their offer or resale in a Relevant State to qualified investors as so defined or in circumstances in which the prior consent of the underwriters have been obtained to each such proposed offer or resale.
For the purposes of this provision, the expression an “offer to the public” in relation to shares in any Relevant State means the communication in any form and by any means of sufficient information on the terms of the offer and any shares to be offered so as to enable an investor to decide to purchase or subscribe for any shares, and the expression “Prospectus Regulation” means Regulation (EU) 2017/1129.
Notice to prospective investors in the United Kingdom
In addition, in the United Kingdom, this document is being distributed only to, and is directed only at, and any offer subsequently made may only be directed at persons who are “qualified investors” (as defined in the Prospectus Regulation) (i) who have professional experience in matters relating to investments falling within Article 19(5) of the Financial Services and Markets Act 2000 (Financial Promotion) Order 2005, as amended (the “Order”) and/or (ii) who are high net worth companies (or persons to whom it may otherwise be lawfully communicated) falling within Article 49(2)(a) to (d) of the Order (all such persons together being referred to as “relevant persons”) or otherwise in circumstances which have not resulted and will not result in an offer to the public of the shares in the United Kingdom within the meaning of the Financial Services and Markets Act 2000.
Any person in the United Kingdom that is not a relevant person should not act or rely on the information included in this document or use it as basis for taking any action. In the United Kingdom, any investment or investment activity that this document relates to may be made or taken exclusively by relevant persons.
Notice to prospective investors in Switzerland
The shares may not be publicly offered in Switzerland and will not be listed on the SIX Swiss Exchange (the “SIX”) or on any other stock exchange or regulated trading facility in Switzerland. This document does not constitute a prospectus within the meaning of, and has been prepared without regard to the disclosure standards for issuance prospectuses under art. 652a or art. 1156 of the Swiss Code of Obligations or the disclosure standards for listing prospectuses under art. 27 ff. of the SIX Listing Rules or the listing rules of any other stock exchange or regulated trading facility in Switzerland. Neither this document nor any other offering
209
Table of Contents
or marketing material relating to the shares or the offering may be publicly distributed or otherwise made publicly available in Switzerland.
Neither this document nor any other offering or marketing material relating to the offering, the Company, the shares have been or will be filed with or approved by any Swiss regulatory authority. In particular, this document will not be filed with, and the offer of shares will not be supervised by, the Swiss Financial Market Supervisory Authority FINMA (the “FINMA”), and the offer of shares has not been and will not be authorized under the Swiss Federal Act on Collective Investment Schemes (the “CISA”). The investor protection afforded to acquirers of interests in collective investment schemes under the CISA does not extend to acquirers of shares.
Notice to prospective investors in France
This prospectus (including any amendment, supplement or replacement thereto) is not being distributed in the context of a public offering in France within the meaning of Article L. 411-1 of the French Monetary and Financial Code (Code monétaire et financier). This prospectus has not been and will not be submitted to the French Autorité des marchés financiers (the “AMF”) for approval in France and accordingly may not and will not be distributed to the public in France.
Pursuant to Article 211-3 of the AMF General Regulation, French residents are hereby informed that:
| 1. | the transaction does not require a prospectus to be submitted for approval to the AMF; |
| 2. | persons or entities referred to in Point 2°, Section II of Article L. 411-2 of the Monetary and Financial Code may take part in the transaction solely for their own account, as provided in Articles D. 411-1, D. 734-1, D. 744-1, D. 754-1 and D. 764-1 of the Monetary and Financial Code; and |
| 3. | the financial instruments thus acquired cannot be distributed directly or indirectly to the public otherwise than in accordance with Articles L. 411-1, L. 411-2, L. 412-1 and L. 621-8 to L. 621-8-3 of the Monetary and Financial Code. |
This prospectus is not to be further distributed or reproduced (in whole or in part) in France by the recipients of this prospectus. This prospectus has been distributed on the understanding that such recipients will only participate in the issue or sale of our common stock for their own account and undertake not to transfer, directly or indirectly, our common stock to the public in France, other than in compliance with all applicable laws and regulations and in particular with Articles L. 411-1 and L. 411-2 of the French Monetary and Financial Code.
Notice to Prospective Investors in Germany
Each person who is in possession of this prospectus is aware of the fact that no German securities prospectus (wertpapierprospekt) within the meaning of the German Securities Prospectus Act (Wertpapierprospektgesetz, or the Act) of the Federal Republic of Germany has been or will be published with respect to the shares of our common stock. In particular, each underwriter has represented that it has not engaged and has agreed that it will not engage in a public offering in the Federal Republic of Germany within the meaning of the Act with respect to any of the shares of our common stock otherwise than in accordance with the Act and all other applicable legal and regulatory requirements
Notice to Prospective Investors in Canada
The shares may be sold only to purchasers purchasing, or deemed to be purchasing, as principal that are accredited investors, as defined in National Instrument 45-106 Prospectus Exemptions or subsection 73.3(1) of
210
Table of Contents
the Securities Act (Ontario), and are permitted clients, as defined in National Instrument 31-103 Registration Requirements, Exemptions and Ongoing Registrant Obligations. Any resale of the shares must be made in accordance with an exemption from, or in a transaction not subject to, the prospectus requirements of applicable securities laws.
Securities legislation in certain provinces or territories of Canada may provide a purchaser with remedies for rescission or damages if this prospectus (including any amendment thereto) contains a misrepresentation, provided that the remedies for rescission or damages are exercised by the purchaser within the time limit prescribed by the securities legislation of the purchaser’s province or territory. The purchaser should refer to any applicable provisions of the securities legislation of the purchaser’s province or territory for particulars of these rights or consult with a legal advisor.
Pursuant to section 3A.3 of National Instrument 33-105 Underwriting Conflicts (NI 33-105), the underwriters are not required to comply with the disclosure requirements of NI 33-105 regarding underwriter conflicts of interest in connection with this offering.
Notice to Prospective Investors in Australia
This prospectus:
• does not constitute a disclosure document or a prospectus under Chapter 6D.2 of the Corporations Act 2001 (Cth) (the “Corporations Act”);
• has not been, and will not be, lodged with the Australian Securities and Investments Commission (“ASIC”), as a disclosure document for the purposes of the Corporations Act and does not purport to include the information required of a disclosure document for the purposes of the Corporations Act; and
• may only be provided in Australia to select investors who are able to demonstrate that they fall within one or more of the categories of investors, available under section 708 of the Corporations Act (“Exempt Investors”).
The shares may not be directly or indirectly offered for subscription or purchased or sold, and no invitations to subscribe for or buy the shares may be issued, and no draft or definitive offering memorandum, advertisement or other offering material relating to any shares may be distributed in Australia, except where disclosure to investors is not required under Chapter 6D of the Corporations Act or is otherwise in compliance with all applicable Australian laws and regulations. By submitting an application for the shares, you represent and warrant to us that you are an Exempt Investor.
As any offer of shares under this document will be made without disclosure in Australia under Chapter 6D.2 of the Corporations Act, the offer of those securities for resale in Australia within 12 months may, under section 707 of the Corporations Act, require disclosure to investors under Chapter 6D.2 if none of the exemptions in section 708 applies to that resale. By applying for the shares you undertake to us that you will not, for a period of 12 months from the date of issue of the shares, offer, transfer, assign or otherwise alienate those shares to investors in Australia except in circumstances where disclosure to investors is not required under Chapter 6D.2 of the Corporations Act or where a compliant disclosure document is prepared and lodged with ASIC.
Notice to Prospective Investors in New Zealand
This prospectus has not been registered, filed with or approved by any New Zealand regulatory authority under the Financial Markets Conduct Act 2013 (the “FMC Act”). The securities may only be offered or sold in New Zealand (or allotted with a view to being offered for sale in New Zealand) to a person who:
| • | is an investment business within the meaning of clause 37 of Schedule 1 of the FMC Act; |
211
Table of Contents
| • | meets the investment activity criteria specified in clause 38 of Schedule 1 of the FMC Act; |
| • | is large within the meaning of clause 39 of Schedule 1 of the FMC Act; |
| • | is a government agency within the meaning of clause 40 of Schedule 1 of the FMC Act; or |
| • | is an eligible investor within the meaning of clause 41 of Schedule 1 of the FMC Act. |
Notice to Prospective Investors in Japan
The shares have not been and will not be registered pursuant to Article 4, Paragraph 1 of the Financial Instruments and Exchange Act. Accordingly, none of the shares nor any interest therein may be offered or sold, directly or indirectly, in Japan or to, or for the benefit of, any “resident” of Japan (which term as used herein means any person resident in Japan, including any corporation or other entity organized under the laws of Japan), or to others for re-offering or resale, directly or indirectly, in Japan or to or for the benefit of a resident of Japan, except pursuant to an exemption from the registration requirements of, and otherwise in compliance with, the Financial Instruments and Exchange Act and any other applicable laws, regulations and ministerial guidelines of Japan in effect at the relevant time.
Notice to Prospective Investors in Hong Kong
The shares have not been offered or sold and will not be offered or sold in Hong Kong, by means of any document, other than (a) to “professional investors” as defined in the Securities and Futures Ordinance (Cap. 571 of the Laws of Hong Kong) (the “SFO”) of Hong Kong and any rules made thereunder; or (b) in other circumstances which do not result in the document being a “prospectus” as defined in the Companies (Winding Up and Miscellaneous Provisions) Ordinance (Cap. 32) of Hong Kong) (the “CO”) or which do not constitute an offer to the public within the meaning of the CO. No advertisement, invitation or document relating to the shares has been or may be issued or has been or may be in the possession of any person for the purposes of issue, whether in Hong Kong or elsewhere, which is directed at, or the contents of which are likely to be accessed or read by, the public of Hong Kong (except if permitted to do so under the securities laws of Hong Kong) other than with respect to shares which are or are intended to be disposed of only to persons outside Hong Kong or only to “professional investors” as defined in the SFO and any rules made thereunder.
Notice to Prospective Investors in Singapore
Singapore SFA Product Classification — In connection with Section 309B of the SFA and the CMP Regulations 2018, unless otherwise specified before an offer of Notes, we have determined, and hereby notifies all relevant persons (as defined in Section 309A(1) of the SFA), that the Notes are ‘‘prescribed capital markets products’’ (as defined in the CMP Regulations 2018) and Excluded Investment Products (as defined in MAS Notice SFA 04-N12: Notice on the Sale of Investment Products and MAS Notice FAA-N16: Notice on Recommendations on Investment Products).
Each representative has acknowledged that this prospectus has not been registered as a prospectus with the Monetary Authority of Singapore. Accordingly, each representative has represented and agreed that it has not offered or sold any shares or caused the shares to be made the subject of an invitation for subscription or purchase and will not offer or sell any shares or cause the shares to be made the subject of an invitation for subscription or purchase, and has not circulated or distributed, nor will it circulate or distribute, this prospectus or any other document or material in connection with the offer or sale, or invitation for subscription or purchase, of the shares, whether directly or indirectly, to any person in Singapore other than:
(a) to an institutional investor (as defined in Section 4A of the Securities and Futures Act (Chapter 289) of Singapore, as modified or amended from time to time (the “SFA”)) pursuant to Section 274 of the SFA;
212
Table of Contents
(b) to a relevant person (as defined in Section 275(2) of the SFA) pursuant to Section 275(1) of the SFA, or any person pursuant to Section 275(1A) of the SFA, and in accordance with the conditions specified in Section 275 of the SFA; or
(c) otherwise pursuant to, and in accordance with the conditions of, any other applicable provision of the SFA.
Where the shares are subscribed or purchased under Section 275 of the SFA by a relevant person which is:
(a) a corporation (which is not an accredited investor (as defined in Section 4A of the SFA)) the sole business of which is to hold investments and the entire share capital of which is owned by one or more individuals, each of whom is an accredited investor; or
(b) a trust (where the trustee is not an accredited investor) whose sole purpose is to hold investments and each beneficiary of the trust is an individual who is an accredited investor, securities or securities-based derivatives contracts (each term as defined in Section 2(1) of the SFA) of that corporation or the beneficiaries’ rights and interest (howsoever described) in that trust shall not be transferred within six months after that corporation or that trust has acquired the shares pursuant to an offer made under Section 275 of the SFA except:
i. to an institutional investor or to a relevant person, or to any person arising from an offer referred to in Section 275(1A) or Section 276(4)(i)(B) of the SFA;
ii. where no consideration is or will be given for the transfer;
iii. where the transfer is by operation of law;
iv. as specified in Section 276(7) of the SFA; or
v. as specified in Regulation 37A of the Securities and Futures (Offers of Investments) (Securities and Securities-based Derivatives Contracts) Regulations 2018.
Notice to Prospective Investors in China
This prospectus will not be circulated or distributed in the PRC and the shares will not be offered or sold, and will not be offered or sold to any person for re-offering or resale directly or indirectly to any residents of the PRC except pursuant to any applicable laws and regulations of the PRC. Neither this prospectus nor any advertisement or other offering material may be distributed or published in the PRC, except under circumstances that will result in compliance with applicable laws and regulations.
Notice to Prospective Investors in Korea
The shares have not been and will not be registered under the Financial Investments Services and Capital Markets Act of Korea and the decrees and regulations thereunder (the “FSCMA”), and the shares have been and will be offered in Korea as a private placement under the FSCMA. None of the shares may be offered, sold or delivered directly or indirectly, or offered or sold to any person for re-offering or resale, directly or indirectly, in Korea or to any resident of Korea except pursuant to the applicable laws and regulations of Korea, including the FSCMA and the Foreign Exchange Transaction Law of Korea and the decrees and regulations thereunder (the “FETL”). The shares have not been listed on any of securities exchanges in the world including, without limitation, the Korea Exchange in Korea.
Furthermore, the purchaser of the shares shall comply with all applicable regulatory requirements (including but not limited to requirements under the FETL) in connection with the purchase of the shares. By the purchase
213
Table of Contents
of the shares, the relevant holder thereof will be deemed to represent and warrant that if it is in Korea or is a resident of Korea, it purchased the shares pursuant to the applicable laws and regulations of Korea.
Notice to Prospective Investors in Taiwan
The shares have not been and will not be registered with the Financial Supervisory Commission of Taiwan pursuant to relevant securities laws and regulations and may not be sold, issued or offered within Taiwan through a public offering or in circumstances which constitutes an offer within the meaning of the Securities and Exchange Act of Taiwan that requires a registration or approval of the Financial Supervisory Commission of Taiwan. No person or entity in Taiwan has been authorized to offer, sell, give advice regarding or otherwise intermediate the offering and sale of the shares in Taiwan.
Notice to prospective investors in Saudi Arabia
This document may not be distributed in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia except to such persons as are permitted under the Offers of Securities Regulations as issued by the board of the Saudi Arabian Capital Market Authority (the “CMA”) pursuant to resolution number 2-11-2004 dated 4 October 2004 as amended by resolution number 1-28-2008, as amended (the “CMA Regulations”). The CMA does not make any representation as to the accuracy or completeness of this document and expressly disclaims any liability whatsoever for any loss arising from, or incurred in reliance upon, any part of this document. Prospective purchasers of the securities offered hereby should conduct their own due diligence on the accuracy of the information relating to the securities. If you do not understand the contents of this document, you should consult an authorized financial adviser.
Notice to prospective investors in the Dubai International Financial Centre (“DIFC”)
This document relates to an Exempt Offer in accordance with the Markets Rules 2012 of the Dubai Financial Services Authority (the “DFSA”). This document is intended for distribution only to persons of a type specified in the Markets Rules 2012 of the DFSA. It must not be delivered to, or relied on by, any other person. The DFSA has no responsibility for reviewing or verifying any documents in connection with Exempt Offers. The DFSA has not approved this prospectus supplement nor taken steps to verify the information set forth herein and has no responsibility for this document. The securities to which this document relates may be illiquid and/or subject to restrictions on their resale. Prospective purchasers of the securities offered should conduct their own due diligence on the securities. If you do not understand the contents of this document you should consult an authorized financial advisor.
In relation to its use in the DIFC, this document is strictly private and confidential and is being distributed to a limited number of investors and must not be provided to any person other than the original recipient, and may not be reproduced or used for any other purpose. The interests in the securities may not be offered or sold directly or indirectly to the public in the DIFC.
Notice to prospective investors in the United Arab Emirates
The shares have not been, and are not being, publicly offered, sold, promoted or advertised in the United Arab Emirates (including the Dubai International Financial Centre) other than in compliance with the laws of the United Arab Emirates (and the Dubai International Financial Centre) governing the issue, offering and sale of securities. Further, this prospectus does not constitute a public offer of securities in the United Arab Emirates (including the Dubai International Financial Centre) and is not intended to be a public offer. This prospectus has not been approved by or filed with the Central Bank of the United Arab Emirates, the Securities and Commodities Authority or the Dubai Financial Services Authority.
214
Table of Contents
Notice to prospective investors in Bermuda
Shares may be offered or sold in Bermuda only in compliance with the provisions of the Investment Business Act of 2003 of Bermuda which regulates the sale of securities in Bermuda. Additionally, non-Bermudian persons (including companies) may not carry on or engage in any trade or business in Bermuda unless such persons are permitted to do so under applicable Bermuda legislation.
Notice to prospective investors in the British Virgin Islands
The shares are not being, and may not be offered to the public or to any person in the British Virgin Islands for purchase or subscription by or on behalf of us. The shares may be offered to companies incorporated under the BVI Business Companies Act, 2004 (British Virgin Islands),“BVI Companies”), but only where the offer will be made to, and received by, the relevant BVI Company entirely outside of the British Virgin Islands.
Notice to prospective investors in South Africa
Due to restrictions under the securities laws of South Africa, no “offer to the public” (as such term is defined in the South African Companies Act, No. 71 of 2008 (as amended or re-enacted) (the “South African Companies Act”)) is being made in connection with the issue of the shares in South Africa. Accordingly, this document does not, nor is it intended to, constitute a “registered prospectus” (as that term is defined in the South African Companies Act) prepared and registered under the South African Companies Act and has not been approved by, and/or filed with, the South African Companies and Intellectual Property Commission or any other regulatory authority in South Africa. The shares are not offered, and the offer shall not be transferred, sold, renounced or delivered, in South Africa or to a person with an address in South Africa, unless one or other of the following exemptions stipulated in section 96 (1) applies:
| Section 96 (1) (a) |
the offer, transfer, sale, renunciation or delivery is to: i. persons whose ordinary business, or part of whose ordinary business, is to deal in securities, as principal or agent; ii. the South African Public Investment Corporation; iii. persons or entities regulated by the Reserve Bank of South Africa; iv. authorised financial service providers under South African law; v. financial institutions recognised as such under South African law; vi. a wholly-owned subsidiary of any person or entity contemplated in (c), (d) or (e), acting as agent in the capacity of an authorised portfolio manager for a pension fund, or as manager for a collective investment scheme (in each case duly registered as such under South African law); or vii. any combination of the person in (i) to (vi); or | |
| Section 96 (1) (b) |
the total contemplated acquisition cost of the securities, for any single addressee acting as principal is equal to or greater than ZAR1,000,000 or such higher amount as may be promulgated by notice in the Government Gazette of South Africa pursuant to section 96(2)(a) of the South African Companies Act. | |
Information made available in this prospectus should not be considered as “advice” as defined in the South African Financial Advisory and Intermediary Services Act, 2002.
215
Table of Contents
Notice to prospective investors in Israel
This document does not constitute a prospectus under the Israeli Securities Law, 5728-1968, and has not been filed with or approved by the Israel Securities Authority. In Israel, this prospectus is being distributed only to, and is directed only at, qualified investors listed in the first addendum, or the Addendum, to the Israeli Securities Law. Qualified investors may be required to submit written confirmation that they fall within the scope of the Addendum.
216
Table of Contents
The validity of the issuance of our common stock offered in this prospectus will be passed upon for us by Latham & Watkins LLP, Menlo Park, California. Davis Polk & Wardwell LLP, Menlo Park, California is acting as counsel for the underwriters in connection with this offering. Certain attorneys at Latham & Watkins LLP own shares of our preferred stock which will be converted into an aggregate of 14,294 shares of common stock immediately upon the closing of this offering.
The consolidated financial statements of Aligos Therapeutics, Inc. at December 31, 2018 and 2019, and for the period from February 5, 2018 (inception date) to December 31, 2018 and for the year ended December 31, 2019, appearing in this Prospectus and Registration Statement have been audited by Ernst & Young LLP, independent registered public accounting firm, as set forth in their report thereon appearing elsewhere herein, and are included in reliance upon such report given on the authority of such firm as experts in accounting and auditing.
Where you can find more information
We have filed with the SEC a registration statement on Form S-1 under the Securities Act with respect to the shares of common stock offered hereby. This prospectus, which constitutes a part of the registration statement, does not contain all of the information set forth in the registration statement or the exhibits and schedules filed therewith. For further information with respect to Aligos Therapeutics, Inc. and the common stock offered hereby, reference is made to the registration statement and the exhibits and schedules filed therewith. Statements contained in this prospectus regarding the contents of any contract or any other document that is filed as an exhibit to the registration statement are not necessarily complete, and each such statement is qualified in all respects by reference to the full text of such contract or other document filed as an exhibit to the registration statement. The SEC also maintains a website that contains reports, proxy and information statements and other information regarding registrants that file electronically with the SEC. The address is www.sec.gov.
Upon consummation of this offering, we will become subject to the information and periodic reporting requirements of the Exchange Act and, in accordance therewith, will file periodic reports, proxy statements and other information with the SEC. Such periodic reports, proxy statements and other information will be available for inspection at the website of the SEC referred to above. We maintain a website at www.aligos.com. Upon consummation of this offering, you may access our annual reports on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, current reports on Form 8-K, and amendments to those reports filed or furnished pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Exchange Act with the SEC free of charge at our website as soon as reasonably practicable after such material is electronically filed with, or furnished to, the SEC. The reference to our website address does not constitute incorporation by reference of the information contained on our website, and you should not consider the contents of our website in making an investment decision with respect to our common stock.
217
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Index to consolidated financial statements
| Page | ||||
| F-2 | ||||
| Consolidated financial statements |
||||
| F-3 | ||||
| Consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive loss |
F-4 | |||
| F-5 | ||||
| F-6 | ||||
| F-8 | ||||
Index to unaudited interim condensed consolidated financial statements
| Unaudited interim condensed consolidated financial statements |
||||
| Condensed consolidated balance sheets as of December 31, 2019 and June 30, 2020 |
F-51 | |||
| F-52 | ||||
| F-53 | ||||
| Condensed consolidated statements of cash flows for the six months ended June 30, 2019 and 2020 |
F-54 | |||
| Notes to unaudited interim condensed consolidated financial statements |
F-56 | |||
F-1
Table of Contents
Report of independent registered public accounting firm
To the Stockholders and the Board of Directors of Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Opinion on the financial statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Aligos Therapeutics, Inc. (the Company) as of December 31, 2018 and 2019, the related consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive loss, changes in redeemable convertible preferred stock and stockholders’ deficit and cash flows for the period from February 5, 2018 (inception date) to December 31, 2018 and for the year ended December 31, 2019, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the “consolidated financial statements”). In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company at December 31, 2018 and 2019, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for the period from February 5, 2018 (inception date) to December 31, 2018 and for the year ended December 31, 2019 in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
Basis for opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB) and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. As part of our audits we are required to obtain an understanding of internal control over financial reporting but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion.
Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
/s/ Ernst & Young LLP
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2019.
Redwood City, California
August 25, 2020, except for the effects of the reverse stock split described in Note 1, as to which the date is October 9, 2020.
F-2
Table of Contents
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
| December 31, 2018 |
December 31, 2019 |
|||||||
| ASSETS | ||||||||
| Current assets: |
||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 24,035 | $ | 69,565 | ||||
| Restricted cash |
512 | 538 | ||||||
| Short-term investments |
66,817 | 48,098 | ||||||
| Other current assets |
1,005 | 2,025 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total current assets |
92,369 | 120,226 | ||||||
| Operating lease right-of-use assets |
12,306 | 7,570 | ||||||
| Property and equipment, net |
2,878 | 8,517 | ||||||
| Other assets |
178 | 188 | ||||||
| Long-term investments |
— | 10,019 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total assets |
$ | 107,731 | $ | 146,520 | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| LIABILITIES, REDEEMABLE CONVERTIBLE PREFERRED STOCK, AND STOCKHOLDERS’ DEFICIT | ||||||||
| Current liabilities: |
||||||||
| Accounts payable |
$ | 2,977 | $ | 3,767 | ||||
| Accrued liabilities |
3,258 | 7,599 | ||||||
| Operating lease liabilities, current |
1,244 | 2,378 | ||||||
| Finance lease liabilities, current |
10 | 74 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total current liabilities |
7,489 | 13,818 | ||||||
| Derivative liabilities |
861 | 461 | ||||||
| Redeemable convertible preferred stock liabilities |
— | 3,174 | ||||||
| Operating lease liabilities, net of current portion |
12,584 | 11,701 | ||||||
| Finance lease liabilities, net of current portion |
26 | 178 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total liabilities |
20,960 | 29,332 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Commitments and contingencies (Note 14) |
||||||||
| Series A Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock, $0.0001 par value; 102,500,000 and 101,962,864 shares authorized as of December 31, 2018 and 2019, respectively; 10,806,432 and 10,819,843 shares issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2018 and 2019, respectively; aggregate minimum liquidation preference of $100,838 at December 31, 2019 |
100,519 | 100,695 | ||||||
| Series B-1 Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock, $0.0001 par value; no shares and 77,764,055 shares authorized as of December 31, 2018 and 2019, respectively; no shares and 8,344,034 issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2018 and 2019, respectively; aggregate minimum liquidation preference of $85,005 at December 31, 2019 |
— | 81,384 | ||||||
| Stockholders’ deficit: |
||||||||
| Common stock, $0.0001 par value; 149,000,000 and 278,000,000 shares authorized as of December 31, 2018 and 2019, respectively; 3,036,574 and 3,927,803 shares issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2018 and 2019, respectively |
|
— |
|
|
— |
| ||
| Additional paid-in capital |
182 | 1,421 | ||||||
| Accumulated deficit |
(13,933 | ) | (66,197 | ) | ||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) |
3 | (115 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total stockholders’ deficit |
(13,748 | ) | (64,891 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total liabilities, redeemable convertible preferred stock, and stockholders’ deficit |
$ | 107,731 | $ | 146,520 | ||||
|
|
||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-3
Table of Contents
Consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive loss
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
| Period from February 5, 2018 (inception date) through December 31, 2018 |
Year ended December 31, 2019 |
|||||||
| Operating expenses: |
||||||||
| Research and development |
$ | 10,456 | $ | 44,038 | ||||
| General and administrative |
3,205 | 10,005 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total operating expenses |
13,661 | 54,043 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Loss from operations |
(13,661 | ) | (54,043 | ) | ||||
| Interest and other (expense) income, net |
(272 | ) | 1,864 | |||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Loss before income tax expense |
(13,933 | ) | (52,179 | ) | ||||
| Income tax expense |
— | (85 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net loss |
(13,933 | ) | (52,264 | ) | ||||
| Other comprehensive (loss) income: |
||||||||
| (Loss) gain on pension plans |
3 | (118 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Comprehensive loss |
$ | (13,930 | ) | $ | (52,382 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net loss per share, basic and diluted |
$ | (11.69 | ) | $ | (26.04 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Weighted average shares of common stock, basic and diluted |
1,191,787 | 2,007,173 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Pro forma net loss per share, basic and diluted (unaudited) |
$ | (2.47 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Pro forma weighted average shares of common stock, basic and diluted (unaudited) |
21,171,050 | |||||||
|
|
||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-4
Table of Contents
Consolidated statements of changes in redeemable convertible preferred stock and stockholders’ deficit
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
| Series A redeemable convertible preferred stock |
Series B-1 redeemable convertible preferred stock |
Common stock | Additional paid-in capital |
Accumulated deficit |
Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) |
Total stockholders’ deficit |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance as of February 5, 2018 (inception date) |
— | $ | — | — | $ | — | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock |
— | — | — | — | 1,508,900 | — | 2 | — | — | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock for services and cash subject to repurchase |
— | — | — | — | 1,527,674 | — | 1 | — | — | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of Series A redeemable convertible preferred stock, net of $194 issuance costs |
10,193,457 | 94,806 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Conversion of convertible notes to Series A redeemable convertible preferred stock |
612,975 | 5,713 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 179 | — | — | 179 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive income |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 3 | 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | (13,933 | ) | — | (13,933 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance as of December 31, 2018 |
10,806,432 | 100,519 | — | — | 3,036,574 | — | 182 | (13,933 | ) | 3 | (13,748 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock upon exercise of stock options |
— | — | — | — | 891,229 | — | 461 | — | — | 461 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vesting of early exercised common stock |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 26 | — | — | 26 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of Series B-1 redeemable convertible preferred stock, net of $442 issuance costs and $3,174 of convertible preferred stock liabilities |
— | — | 8,344,034 | 81,384 | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of Series A redeemable convertible preferred stock upon exercise of warrants |
13,411 | 176 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 752 | — | — | 752 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive loss |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (118 | ) | (118 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | (52,264 | ) | — | (52,264 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance as of December 31, 2019 |
10,819,843 | $ | 100,695 | 8,344,034 | $ | 81,384 | 3,927,803 | $ | — | $ | 1,421 | $ | (66,197 | ) | $ | (115 | ) | $ | (64,891 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-5
Table of Contents
Consolidated statements of cash flows
(In thousands)
| Period
from February 5, 2018 (inception date) through December 31, 2018 |
Year ended December 31, 2019 |
|||||||
| Cash flows from operating activities: |
||||||||
| Net loss |
$ | (13,933 | ) | $ | (52,264 | ) | ||
| Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash used in operating activities: |
||||||||
| Accretion of debt discount |
493 | — | ||||||
| Loss on conversion of debt |
433 | — | ||||||
| Accretion of discount on short term investments |
(44 | ) | (877 | ) | ||||
| Amortization of right of use assets |
1,179 | 903 | ||||||
| Depreciation expense |
112 | 1,396 | ||||||
| Stock-based compensation |
179 | 752 | ||||||
| Interest expense on convertible note |
113 | — | ||||||
| Change in fair value of derivative liability |
(66 | ) | (348 | ) | ||||
| In process research and development |
600 | — | ||||||
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities: |
||||||||
| Other assets |
(1,183 | ) | (1,030 | ) | ||||
| Right of use assets |
(95 | ) | 95 | |||||
| Accounts payable |
2,977 | 385 | ||||||
| Accrued liabilities |
3,186 | 4,222 | ||||||
| Operating lease liabilities |
— | (1 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net cash and cash equivalents used in operating activities |
(6,049 | ) | (46,767 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Cash flows from investing activities: |
||||||||
| Purchases of short-term investments |
(66,773 | ) | (60,404 | ) | ||||
| Purchases of long-term investments |
— | (10,019 | ) | |||||
| Maturities of short-term investments |
— | 80,000 | ||||||
| Purchases of property and equipment |
(2,516 | ) | (2,786 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net cash and cash equivalents (used in) provided by investing activities |
(69,289 | ) | 6,791 | |||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Cash flows from financing activities: |
||||||||
| Proceeds from issuance of convertible notes and warrants |
5,001 | — | ||||||
| Proceeds from exercise of stock options |
77 | 487 | ||||||
| Proceeds from issuance of series A redeemable convertible preferred stock, net of $194 issuance costs |
94,806 | — | ||||||
| Proceeds from issuance of series B-1 redeemable convertible preferred stock, net of $37 issuance costs paid |
— | 84,963 | ||||||
| Proceeds from exercise of warrants for series A redeemable convertible preferred stock |
— | 125 | ||||||
| Payments on finance lease |
(1 | ) | (43 | ) | ||||
| Proceeds from issuance of common stock |
2 | — | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net cash and cash equivalents provided by financing activities |
99,885 | 85,532 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net increase in cash, cash equivalents, and restricted cash |
24,547 | 45,556 | ||||||
| Cash, cash equivalents, and restricted cash, beginning of period |
— | 24,547 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Cash, cash equivalents, and restricted cash, end of period |
$ | 24,547 | $ | 70,103 | ||||
|
|
||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-6
Table of Contents
Consolidated statements of cash flows
(In thousands)
| Period
from February 5, 2018 (inception date) through December 31, 2018 |
Year ended December 31, 2019 |
|||||||
| Reconciliation to amounts on the consolidated balance sheet: |
||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 24,035 | $ | 69,565 | ||||
| Restricted cash |
512 | 538 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total cash, cash equivalents, and restricted cash |
$ | 24,547 | $ | 70,103 | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Supplemental disclosures of cash flow information: |
||||||||
| Interest paid |
$ | — | $ | 6 | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Income taxes paid |
$ | — | $ | 1 | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Supplemental disclosures of noncash financing and investing activities: |
||||||||
| Leasehold improvement directly paid by landlord |
$ | 438 | $ | 3,990 | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Liability in connection to the issuance of series B-1 redeemable convertible preferred stock |
$ | — | $ | 3,174 | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Unpaid issuance cost in connection to the issuance of series B-1 redeemable convertible preferred stock |
$ | — | $ | 405 | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Equipment acquired through finance lease |
$ | 37 | $ | 259 | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Acquisition of right-of-use asset through operating lease obligation |
$ | 13,828 | $ | 252 | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Change in fair value of derivative liability upon exercise of warrants |
$ | — | $ | 52 | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Discount on convertible note from derivative liability |
$ | 927 | $ | — | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Conversion of convertible notes and accrued interest to series A redeemable convertible preferred stock |
$ | 5,713 | $ | — | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Issuance of convertible note for in process research and development |
$ | 600 | $ | — | ||||
|
|
||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-7
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
Unless otherwise indicated, financial information except share and per share data, including dollar values stated in the text of the notes to financial statements, is expressed in thousands.
1. Organization
Description of business
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc. (“Aligos-US”) was incorporated in the state of Delaware on February 5, 2018 (“inception”). On September 10, 2018, the Company formed Aligos Belgium BVBA (the “Subsidiary” or “Aligos-Belgium” and together with Aligos-US, the “Company” or “Aligos”) a limited liability company organized under the laws of Belgium.
Aligos is a clinical-stage biopharmaceutical company developing novel therapeutics to address unmet medical needs in viral and liver diseases, including chronic hepatitis B and coronaviruses and therapeutics for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (“NASH”).
The Company is devoting substantially all of its efforts to the research and development of its drug candidates. The Company has not generated any product revenue to date. The Company is also subject to a number of risks similar to other companies in the biotechnology industry, including the uncertainty of success of its preclinical studies and clinical trials, regulatory approval of drug candidates, uncertainty of market acceptance of products, competition from substitute products and larger companies, the need to obtain additional financing, compliance with government regulations, protection of proprietary technology, dependence on third-parties, product liability, and dependence on key individuals.
Reverse stock split
On October 8, 2020, the Company’s board of directors approved a 1-for-9.3197 reverse stock split (the “Reverse Stock Split”) of the Company’s common stock and redeemable convertible preferred stock to be consummated prior to the effectiveness of the Company’s planned initial public offering (“IPO”). The par value and authorized shares of the common stock and redeemable convertible preferred stock were not adjusted as a result of the reverse stock split. All issued and outstanding common stock, options to purchase common stock and per share amounts contained in the financial statements have been retroactively adjusted to give effect to the reverse stock split for all periods presented. The Company filed an amended and restated certificate of incorporation in Delaware on October 9, 2020 that automatically effectuated the Reverse Stock Split without any further action required.
Liquidity and going concern assessment
The Company has incurred losses and negative cash flows from operations since its inception. As of December 31, 2018 and 2019, the Company has an accumulated deficit of approximately $13,933 and $66,197, respectively. Since inception through December 31, 2019, the Company has funded operations primarily with the net proceeds from the issuance of redeemable convertible preferred stock and convertible notes. Management expects to continue to incur additional substantial losses in the foreseeable future as a result of expanded research and development activities.
F-8
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
1. Organization, continued
Liquidity and going concern assessment, continued
As of December 31, 2019, the Company has unrestricted cash, cash equivalent and short-term investments of approximately $117,663, which is available to fund future operations. The Company expects to continue to spend substantial amounts to continue the nonclinical and clinical development of its current and future programs. If the Company is able to gain marketing approval for drug candidates that are being developed, it will require significant additional amounts of cash in order to launch and commercialize such drug candidates. In addition, other unanticipated costs may arise. Because the design and outcome of the Company’s planned and anticipated clinical trials is highly uncertain, the Company cannot reasonably estimate the actual amounts necessary to successfully complete the development and commercialization of any drug candidate the Company may develop.
The Company is seeking to complete an IPO of its Common Stock. Upon the closing of a qualified public offering, the Company’s outstanding redeemable convertible preferred stock will automatically convert into shares of Common Stock (Note 9).
2. Summary of significant accounting policies
The Company expects to finance its cash needs through a combination of public or private equity offerings, debt financings, collaborations, strategic alliances, licensing arrangements and other marketing or distribution arrangements. In addition, the Company may seek additional capital to take advantage of favorable market conditions or strategic opportunities even if the Company believes it has sufficient funds for its current or future operating plans. Based on the Company’s research and development plans, it is expected that the net proceeds from this offering, together with the Company’s existing cash, cash equivalents and investments, will enable the Company to fund its operations for at least 12 months following the date the consolidated financial statements are issued. However, the Company’s operating plan may change as a result of many factors currently unknown, and the Company may need to seek additional funds sooner than planned. Moreover, it is particularly difficult to estimate with certainty the Company’s future expenses given the dynamic nature of its business, the COVID-19 pandemic and the macro-economic environment generally.
The Company’s ability to raise additional funds will depend on financial, economic and other factors, many of which are beyond its control. In particular, the COVID-19 pandemic continues to rapidly evolve and has already resulted in a significant disruption of global financial markets. If the disruption persists or deepens, the Company could be unable to access additional capital, which could negatively affect its ability to consummate certain corporate development transactions or other important, beneficial or opportunistic investments. If additional funds are not available to the Company when needed, on terms that are acceptable to the Company, or at all, the Company may be required to: delay, limit, reduce or terminate nonclinical studies, clinical trials or other research and development activities or eliminate one or more of its development programs altogether; or delay, limit, reduce or terminate its efforts to establish manufacturing and sales and marketing capabilities or other activities that may be necessary to commercialize any future approved products, or reduce the Company’s flexibility in developing or maintaining its sales and marketing strategy.
F-9
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
2. Summary of significant accounting policies, continued
The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared on a basis that assumes the Company will continue as a going concern and contemplates the continuity of operations, realization of assets and the satisfaction of liabilities and commitments in the normal course of business.
Basis of presentation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”) and include all adjustments necessary for the fair presentation of the Company’s financial position for the periods presented. Any reference in these notes to applicable accounting guidance is meant to refer to the authoritative U.S. GAAP included in the Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”), and Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) issued by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”).
Principles of consolidation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements include Aligos-US and its wholly owned subsidiary Aligos-Belgium. All intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated.
Use of estimates
The preparation of the consolidated financial statements in conformity with GAAP generally requires management to make certain estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts in the consolidated financial statements and accompanying notes. The Company regularly evaluates estimates and assumptions related to assets and liabilities, and disclosures of contingent assets and liabilities at the dates of the consolidated financial statements and the reported amounts of expenses during the reporting period. Areas where management uses subjective judgments include, but are not limited to, right-of-use assets, lease obligations, impairment of long-lived assets, stock-based compensation, accrued research and development costs, pension liabilities, derivative liabilities and redeemable convertible preferred stock liability in the accompanying consolidated financial statements. Management bases its estimates on historical experience and on various other assumptions that are believed to be reasonable under the circumstances, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying values of assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other sources. Actual results may differ materially from these estimates under different assumptions or conditions.
Foreign currency
The Company’s foreign subsidiary uses the U.S. dollar as its functional currency, and it initially measures the foreign currency denominated assets and liabilities at the transaction date. Monetary assets and liabilities are then re-measured at exchange rates in effect at the end of each period, and non-monetary assets and liabilities are converted at historical rates. Re-measurement losses incurred during the period from inception through December 31, 2018 and the year ended December 31, 2019 were $18 and $47, respectively, and are reflected within interest and other income (expense), net on the consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive loss.
F-10
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
2. Summary of significant accounting policies, continued
Unaudited pro forma information
The Company has presented the unaudited pro forma basic and diluted net loss per share attributable to common stockholders for the year ended December 31, 2019, which shows the assumed effect of an initial public offering, including the conversion of all redeemable convertible preferred stock into shares of Common Stock as if the conversion had occurred as of the later of the beginning of the period or the original date of issuance. The pro forma net loss per share attributable to common stockholders does not include proceeds to be received from nor does it include shares expected to be sold in the assumed IPO.
Segment information
The Company has determined that the Chief Executive Officer is its Chief Operating Decision Maker. The Company’s Chief Executive Officer reviews financial information presented on a consolidated basis for the purposes of assessing the performance and making decisions on how to allocate resources. Accordingly, the Company has determined that it operates in a single reportable segment. No revenue has been generated since inception.
Cash equivalents
The Company considers all highly liquid investments purchased with original maturities of 90 days or less at acquisition to be cash equivalents.
Restricted cash
As of December 31, 2018 and 2019, the restricted cash balance was $512 and $538, respectively, and was used to secure the letters of credit in relation to the Company’s operating leases and deposits on rental assets (Note 6).
Investments
The Company determines the appropriate classification of debt securities at the time of purchase and re-evaluates such designation as of each balance sheet date. Debt securities are classified as held-to-maturity when the Company has the positive intent and ability to hold the securities to maturity. Held-to-maturity securities are carried at amortized cost.
Investments are considered to be impaired when a decline in fair value is judged to be other-than-temporary. On an annual basis, the Company considers available quantitative and qualitative evidence in evaluating potential impairment of its investments. If the cost of an investment exceeds its fair value, the Company evaluates, among other factors, general market conditions, the duration and extent to which the fair value is less than cost, and its intent and ability to hold the investment to maturity. Once a decline in fair value is determined to be other-than-temporary, an impairment charge is recorded in earnings and a new cost basis in the investment is established. No impairment charges were recorded during the period from inception through December 31, 2018 or the year ended December 31, 2019.
F-11
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
2. Summary of significant accounting policies, continued
Investments, continued
As of December 31, 2018 and 2019, short-term investments consisted of U.S. Treasury securities with original maturities of less than one year. As of December 31, 2019, long-term investments consisted of U.S. Treasury securities with original maturities of more than one year while there were no long-term investments as of December 31, 2018.
Deferred offering costs
The Company capitalizes certain legal, professional accounting and other third-party fees that are directly associated with in-process equity financings as deferred offering costs until such financings are consummated. After consummation of the financing, these costs are recorded as a reduction of the proceeds received from the equity financing. If a planned equity financing is abandoned, the deferred offering costs are expensed immediately as a charge to operating expenses in the consolidated statement of operations and comprehensive loss. There were no deferred offering costs on the Company’s consolidated balance sheets at December 31, 2018 and 2019.
Concentrations of credit risk and significant suppliers
The Company has no significant off-balance sheet risk, such as foreign exchange contracts, option contracts, or other foreign hedging arrangements. Financial instruments that potentially expose the Company to concentrations of credit risk consist primarily of cash, restricted cash and investments. Periodically, the Company maintains deposits in accredited financial institutions in excess of federally insured limits. The Company deposits its cash in financial institutions that it believes have high credit quality and has not experienced any losses on such accounts and does not believe it is exposed to any unusual credit risk beyond the normal credit risk associated with commercial banking relationships. The Company generally invests its excess capital in money market funds, U.S. treasury bonds and U.S. treasury bills that are subject to minimal credit and market risks.
The Company is dependent on various third parties to manufacture compounds for the Company to conduct research and studies for its programs. These programs would be adversely delayed by a significant interruption in the supply of active pharmaceutical ingredients.
Leases
The Company determines if an arrangement is a lease at the inception of the lease. Operating leases are included in operating lease right-of-use (“ROU”) assets and operating lease liabilities in the consolidated balance sheet. Finance leases are included in property and equipment and finance lease liabilities in the consolidated balance sheet.
ROU assets represent the right to use an underlying asset for the lease term and lease liabilities represent the obligation to make lease payments arising from the lease. Operating lease ROU assets and liabilities are recognized at the lease commencement date based on the present value of lease payments over the lease term.
F-12
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
2. Summary of significant accounting policies, continued
Leases, continued
When the Company’s leases do not provide an implicit rate, an incremental borrowing rate is used based on the information available at the commencement dates in determining the present value of lease payments. The Company uses the implicit rate when readily determinable. The operating lease ROU assets also include any lease payments made and excludes lease incentives when paid by the Company or on the Company’s behalf. The Company’s lease terms may include the period covered by options to extend or terminate the lease when it is reasonably certain that the Company will exercise that option. Lease expense for operating leases is recognized on a straight-line basis over the lease term.
The Company has lease agreements with lease and non-lease components. The Company elected to not separate lease and non-lease components for all of its building leases. For vehicle leases, lease and non-lease components are accounted for separately. The Company also made an accounting policy election to recognize lease expense for leases with a term of 12 months or less on a straight-line basis over the lease term and not recognize ROU assets or lease liabilities for such leases.
Property and equipment
Property and equipment is stated at cost less accumulated depreciation, and is depreciated using the straight-line method over the estimated useful life of the asset, which are as follows:
| Lab equipment |
3 years | |
| Computer equipment |
3 years | |
| Furniture and office equipment |
3-8 years | |
| Vehicles |
4 years | |
| Leasehold improvements |
Shorter of the useful life or remaining lease term | |
|
| ||
Expenditures for repairs and maintenance of assets are charged to expense as incurred. Upon retirement or sale, the cost and related accumulated depreciation of assets disposed of are removed from the accounts and any resulting gain or loss is included in loss from operations.
Impairment of long-lived assets
The Company regularly reviews the carrying amount of its property, equipment and intangible assets to determine whether indicators of impairment may exist which warrant adjustments to carrying values or estimated useful lives. If indications of impairment exist, projected future undiscounted cash flows associated with the asset are compared to the carrying amount to determine whether the asset’s value is recoverable. If the carrying value of the asset exceeds such projected undiscounted cash flows, the asset will be written down to its estimated fair value. No impairment charges were recorded during the period from inception through December 31, 2018 or the year ended December 31, 2019.
F-13
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
2. Summary of significant accounting policies, continued
Research and development expenses
Research and development costs are expensed as incurred. Research and development expenses consist of costs incurred in performing research and development activities, including salaries, stock-based compensation and benefits, facilities costs, depreciation, and third-party license fees. Non-refundable prepayments for goods or services that will be used or rendered for future research and development activities are deferred and capitalized. Such amounts are recognized as an expense as the goods are delivered or the related services are performed or until it is no longer expected that the goods will be delivered or the services will be rendered.
In-process research and development
In-process research and development (“IPR&D”) expense represents the costs to acquire technologies to be used in research and development that have not reached technological feasibility or have no alternative future uses and thus are expensed as incurred. IPR&D expense also includes upfront license fees and milestones paid to collaborators for technologies with no alternative use.
Collaborative arrangements
The Company and its future collaborative partners would be active participants in a collaborative arrangement and all parties would be exposed to significant risks and rewards depending on the technical and commercial success of the activities. Contractual payments to the other party in collaboration agreements and costs incurred by the Company when the Company is deemed to be the principal participant for a given transaction are recognized on a gross basis in research and development expenses. Royalties and license payments are recorded as due. During the period from inception through December 31, 2018 and the year ended December 31, 2019, no milestones were met and no royalties were due; therefore, the Company did not pay or expense any milestone or royalties.
Derivative liabilities
The Company accounts for certain warrants and conversion features as liabilities at fair value and adjusts the instruments to fair value at each reporting period. The Company determined that its outstanding warrants are freestanding derivative instruments. The conversion features qualify as derivatives as they continuously reset as the underlying stock price increases or decreases so as to provide a fixed value of equity to the holders at any conversion date. Both the warrants and conversion features are subject to re-measurement at each balance sheet date until exercised, and any change in fair value is recognized as a component of interest and other income (expense), net in the consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive loss. The fair value of the warrants issued by the Company has been estimated using a probability weighted multi-scenario Black-Scholes option-pricing model. The fair value of the conversion feature has been estimated using a Monte Carlo simulation (Note 11).
F-14
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
2. Summary of significant accounting policies, continued
Redeemable convertible preferred stock liability
The freestanding instrument related to the commitment by certain preferred stockholders to purchase and the commitment by the Company to sell its convertible preferred stock in a subsequent closing, contingent upon the achievement of certain developmental milestones or an election by preferred stockholders to waive such milestones, at a fixed price per share, is considered a derivative liability (“Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock Liability”). The Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock Liability is measured at fair value as the underlying shares contain liquidation preferences upon certain “deemed liquidation events” that are not solely within the Company’s control and which are considered in-substance contingent redemption features (refer to Note 9 for further discussion on the redemption rights of the convertible preferred stock). The Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock Liability is subject to revaluation at each balance sheet date until settlement or extinguishment, with revaluations recognized as a component of interest and other income (expense), net in the consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive loss. The fair value of the Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock Liability in subsequent closings has been estimated using a probability-weighted multi-scenario Black Scholes hybrid valuation method (Note 11).
Redeemable convertible preferred stock
The Company’s shares of preferred stock are assessed at issuance for classification and redemption features requiring bifurcation. The Company presents as temporary equity any stock which (i) the Company undertakes to redeem at a fixed or determinable price on the fixed or determinable date or dates; (ii) is redeemable at the option of the holders, or (iii) has conditions for redemption which are not solely within the control of the Company. The Company’s preferred stock is redeemable upon a deemed liquidation event which the Company determined is not solely within its control and thus has classified shares of preferred stock as temporary equity until such time as the conditions are removed or lapse. Because the occurrence of a deemed liquidation event is not currently probable, the carrying values of the shares of convertible preferred stock are not being accreted to their redemption values. Subsequent adjustments to the carrying values of the shares of convertible preferred stock would be made only when a deemed liquidation event becomes probable.
Fair value measurements
Certain assets and liabilities of the Company are carried at fair value under GAAP. Fair value is defined as the exchange price that would be received for an asset or paid to transfer a liability (an exit price) in the principal or most advantageous market for the asset or liability in an orderly transaction between market participants on the measurement date. Valuation techniques used to measure fair value must maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs. Financial assets and liabilities carried at fair value are to be classified and disclosed in one of the following three levels of the fair value hierarchy, of which the first two are considered observable and the last is considered unobservable:
Level 1—Quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities.
Level 2—Observable inputs (other than Level 1 quoted prices), such as quoted prices in active markets for similar assets or liabilities, quoted prices in markets that are not active for identical or similar assets or liabilities, or other inputs that are observable or can be corroborated by observable market data.
F-15
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
2. Summary of significant accounting policies, continued
Fair value measurements, continued
Level 3—Unobservable inputs that are supported by little or no market activity that are significant to determining the fair value of the assets or liabilities, including pricing models, discounted cash flow methodologies and similar techniques.
Stock-based compensation
The Company’s stock-based awards consist of restricted stock awards and stock options. For stock-based awards issued to employees and nonemployees, the Company measures the estimated fair value of the stock-based awards on the date of grant and recognizes compensation expense for those awards over the requisite service period, which is generally the vesting period of the respective awards. The Company records expense for awards with service-based vesting using the straight-line method. The Company accounts for forfeitures as they occur.
The Company classifies stock-based compensation expense in its consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive loss in the same manner in which the award recipient’s cash compensation costs are classified.
The fair value of each restricted stock award is determined based on the number of shares granted and the value of the Company’s common stock on the date of grant. The fair value of each stock option award is estimated on the date of grant using the Black-Scholes option pricing model. The Black-Scholes option-pricing model requires the use of a number of complex assumptions including the fair value of the common stock, expected volatility, risk-free interest rate, expected dividends, and expected term of the option. The Company has been a private company and lacks company-specific historical and implied fair value information. Therefore, the Board of Directors (the “Board”) of the Company considers numerous objective and subjective factors to determine the fair value of the Company’s common stock options at each meeting in which awards are approved. The factors considered include, but are not limited to (i) the results of contemporaneous independent third-party valuations of the Company’s common stock and the prices, rights, preferences and privileges of the Company’s preferred stock relative to those of its common stock; (ii) the lack of marketability of the Company’s common stock; (iii) actual operating and financial results; (iv) current business conditions and projections; (v) the likelihood of achieving a liquidity event, such as an initial public offering or sale of the Company, given prevailing market conditions, and (vi) precedent transactions involving the Company’s shares.
The Company determined the expected stock volatility using a weighted-average of the historical volatility of a group of guideline companies that issued options with substantially similar terms, and expects to continue to do so until such time as the Company has adequate historical data regarding the volatility of its own traded stock price. The expected term of the Company’s stock options has been determined utilizing the simplified method for awards that qualify as “plain-vanilla” options. The risk-free interest rate is determined by reference to the U.S. Treasury yield curve in effect at the time of grant of the award for time periods approximately equal to the expected term of the award. The Company has not paid, and does not anticipate paying, cash dividends on its common stock; therefore, the expected dividend yield is assumed to be zero.
See Note 10 for the assumptions used by the Company in determining the grant date fair value of stock-based awards granted, as well as a summary of the stock-based award activity under the Company’s stock-based
F-16
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
2. Summary of significant accounting policies, continued
Stock-based compensation, continued
compensation plan for the period from inception through December 31, 2018 and the year ended December 31, 2019.
Income taxes
Deferred tax assets and liabilities are determined on the basis of the differences between the consolidated financial statements and tax basis of assets and liabilities using enacted tax rates in effect for the year in which the differences are expected to reverse. Changes in deferred tax assets and liabilities are recorded in the provision for income taxes. The Company assesses the likelihood that its deferred tax assets will be recovered from future taxable income and, to the extent it believes, based upon the weight of available evidence, that it is more likely than not that all or a portion of the deferred tax assets will not be realized, a valuation allowance is established.
The Company accounts for uncertain tax positions recognized in the consolidated financial statements by prescribing a more-likely-than-not threshold for financial statement recognition and measurement of a tax position taken or expected to be taken in a tax return. The provision for income taxes includes the effects of any resulting tax reserves, or unrecognized tax benefits, that are considered appropriate as well as the related interest and penalties.
Net loss per share
Basic net loss per share attributable to common stockholders is calculated by dividing the net loss attributable to common stockholders by the weighted-average number of shares of common stock outstanding during the period, without consideration for potentially dilutive securities.
Diluted net loss per share attributable to common stockholders is computed by dividing the net loss attributable to common stockholders by the weighted-average number of common stock and potentially dilutive securities outstanding for the period. For purposes of the diluted net loss per share calculation, redeemable convertible preferred stock, stock options, common stock subject to repurchase related to early exercise of stock options, unvested restricted stock subject to repurchase, warrants and convertible notes are considered to be potentially dilutive securities.
The Company applies the two-class method to calculate its basic and diluted net loss per share as the Company has issued shares that meet the definition of participating securities. The two-class method is an earnings allocation formula that treats a participating security as having rights to earnings that otherwise would have been available to common stockholders. The Company’s participating securities contractually entitle the holders of such shares to participate in dividends, but do not contractually require the holders of such shares to participate in losses of the Company. Accordingly, in periods in which the Company reports a net loss, such losses are not allocated to such participating securities.
Accordingly, in periods in which the Company reports a net loss, diluted net loss per share is the same as basic net loss per share, since dilutive common shares are not assumed to have been issued if their effect is anti-dilutive.
F-17
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
2. Summary of significant accounting policies, continued
Recently adopted accounting pronouncements
In June 2018, the FASB issued ASU No. 2018-07, Compensation-Stock Compensation (Topic 718): Improvements to Nonemployee Share-Based Payment Accounting (“ASU 2018-07”). ASU 2018-07 amends the FASB ASC to expand the scope of FASB ASC Topic 718, Compensation-Stock Compensation, to include accounting for share-based payment transactions for acquiring goods and services from non-employees. The amendments in ASU 2018-07 are effective for all entities for annual periods, and interim periods within those annual periods, beginning after December 15, 2018. Early adoption was permitted. The Company early adopted this guidance at inception.
In May 2014, the FASB issued ASU No. 2014-09, Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606) (“ASU 2014-09”), which supersedes existing revenue recognition guidance under GAAP. The standard’s core principle is that a company will recognize revenue when it transfers promised goods or services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration to which the Company expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods or services. The standard defines a five-step process to achieve this principle and requires companies to use more judgment and make more estimates than under the current guidance. These judgments and estimates include identifying performance obligations in the customer contract, estimating the amount of variable consideration to include in the transaction price and allocating the transaction price to each separate performance obligation. ASU 2014-09 also requires additional disclosure about the nature, amount, timing and uncertainty of revenue and cash flows arising from customer contracts. The Company early adopted ASU 2014-09 at inception. The adoption of ASU 2014-09 did not have an impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements as the Company does not currently have any revenue-generating arrangements.
In November 2018, the FASB issued ASU No. 2018-18, Collaborative Arrangements (Topic 808)—Clarifying the Interaction between Topic 808 and Topic 606 (“ASU 2018-18”). The amendments in ASU 2018-18 clarify that certain transactions between collaborative arrangement participants should be accounted for as revenue under ASC 606 when the collaborative arrangement participant is a customer in the context of a unit of account. The amendments under ASU 2018-18 are effective for interim and annual fiscal periods beginning after December 15, 2019, with early adoption permitted. The amendments in ASU 2018-18 should be applied retrospectively to the date of initial application of ASC 606. The Company early adopted ASU 2018-18 at inception.
In January 2017, the FASB issued ASU No. 2017-01, Business Combinations (Topic 805): Clarifying the Definition of a Business (“ASU 2017-01”). ASU 2017-01 provides guidance to evaluate whether transactions should be accounted for as acquisitions (or disposals) of assets or businesses. If substantially all of the fair value of the gross assets acquired (or disposed of) is concentrated in a single asset or a group of similar assets, the assets acquired (or disposed of) are not considered a business. The Company adopted this standard at inception.
In February 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-02, Leases (Topic 842) (“ASU 2016-02”), which sets out the principles for the recognition, measurement, presentation and disclosure of leases for both parties to a contract (i.e., lessees and lessors). The new standard requires lessees to apply a dual approach, classifying leases as either finance or operating leases based on the principle of whether or not the lease is effectively a financed purchase by the lessee. This classification determines whether lease expense is recognized based on an effective interest method or on a straight-line basis over the term of the lease. A lessee is also required to
F-18
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
2. Summary of significant accounting policies, continued
Recently adopted accounting pronouncements, continued
record a right-of-use asset and a lease liability for all leases with a term of greater than 12 months regardless of their classification. Leases with a term of 12 months or less may be accounted for similar to existing guidance for operating leases. The standard is effective for all entities for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2019. Early adoption is permitted. The Company adopted this standard at inception.
In November 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-18, Statement of Cash Flows (Topic 230) Restricted Cash (“ASU 2016-18”), which requires that a statement of cash flows explain the change during the period in the total of cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash. Therefore, amounts described as restricted cash should be included with cash and cash equivalents when reconciling the beginning of period and end of period amounts shown on the statement of cash flows. The standard is effective for all entities for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2018. The Company early adopted this guidance at inception. The cash, cash equivalent and restricted cash balances as of December 31, 2018 and 2019 are presented in the Company’s consolidated statements of cash flows.
In March 2017, the FASB issued ASU No. 2017-07, Compensation-Retirement Benefits (ASC Topic 715) (“ASU 2017-07”), which requires employers to disaggregate the service cost component from other components of net periodic benefit costs and to disclose the amounts of net periodic benefit costs that are included in each income statement line item. The standard requires employers to report the service cost component in the same line item as other compensation costs and to report the other components of net periodic benefit costs separately and outside a subtotal of operating income. The Company adopted this standard at inception and has recognized its net periodic benefit costs, excluding service costs, in interest and other income (expense), net on its consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive loss.
In August 2018, the FASB issued ASU No. 2018-14, Compensation—Retirement Benefits—Defined Benefit Plans—General (Subtopic 715-20) (“ASU 2018-14”). The guidance eliminates requirements for certain disclosures that are no longer considered cost beneficial and requires new ones that the FASB considers pertinent. The standard is effective for fiscal years ending after December 15, 2021 for all entities. Early adoption is permitted. The Company adopted this standard at inception.
Recently issued accounting standards
In August 2018, the FASB issued ASU No. 2018-13, Fair Value Measurement (Topic 820): Disclosure Framework— Changes to the Disclosure Requirements for Fair Value Measurement (“ASU 2018-13”). The amendments eliminate, add, and modify certain disclosure requirements for fair value measurements. The amendments are effective for interim and annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2019, with early adoption permitted for either the entire ASU or only the provisions that eliminate or modify requirements. The amendments with respect to changes in unrealized gains and losses, the range and weighted-average of significant unobservable inputs used to develop Level 3 fair value measurements, and the narrative description of measurement uncertainty are to be applied prospectively. All other amendments are to be applied retrospectively to all periods presented. The Company does not expect the adoption of ASU 2018-13 to have a material impact on its disclosures.
F-19
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
2. Summary of significant accounting policies, continued
Recently issued accounting standards, continued
In June 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-13. Financial Instruments—Credit Losses (Topic 326): Measurement of Credit Losses on Financial Instruments (“ASU 2016-13”), which requires that financial assets measured at amortized cost be presented at the net amount expected to be collected. Currently, U.S. GAAP delays recognition of the full amount of credit losses until the loss is probable of occurring. Under this ASU, the income statement will reflect an entity’s current estimate of all expected credit losses. The measurement of expected credit losses will be based upon historical experience, current conditions, and reasonable and supportable forecasts that affect the collectability of the reported amount. In November 2018, the FASB issued ASU No. 2018-19, Codification Improvements to Topic 326, Financial Instruments—Credit Losses (“ASU 2018-19”), which clarifies that receivables from operating leases are accounted for using the lease guidance and not as financial instruments. In April 2019, the FASB issued ASU No. 2019-04, Codification Improvements to Topic 326, Financial Instruments—Credit Losses (“ASU 2019-04”), which clarifies the new expected credit loss methodology for loans, receivables and other financial assets, including recoveries and accrued interest on receivables. In November 2019, the FASB issued ASU No. 2019-11, Codification Improvements to Topic 326, Financial Instruments—Credit Losses (“ASU 2019-11”), which clarifies guidance around how to report expected recoveries. The standard is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2022, including interim periods within those fiscal years. Early adoption is permitted. The Company is evaluating the potential impact of this standard on its consolidated financial statements.
In December 2019, the FASB issued ASU No. 2019-12, Income Taxes (Topic 740): Simplifying the Accounting for Income Taxes (“ASU 2019-12”). The guidance removes specific exceptions to the general principles in ASC 740, improves application of income tax-related guidance and reduces complexity related to the accounting for income taxes. The standard is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2021, and interim periods with fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2022. Early adoption is permitted. The Company is evaluating the potential impact of this standard on its consolidated financial statements.
From time to time, new accounting pronouncements are issued by FASB that the Company adopts as of the specified effective date. The Company qualifies as an “emerging growth company” as defined in the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act of 2012 and has the option to not “opt out” of the extended transition related to complying with new or revised accounting standards. This means that when a standard is issued or revised and it has different application dates for public and nonpublic companies, the Company has the option to adopt the new or revised standard at the time nonpublic companies adopt the new or revised standard and can do so until such time that the Company either (i) irrevocably elects to “opt out” of such extended transition period or (ii) no longer qualifies as an emerging growth company.
F-20
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
3. Property and equipment
The components of property and equipment were as follows as of December 31, 2018 and 2019:
| 2018 | 2019 | |||||||
| Leasehold improvements |
$ | 270 | $ | 5,100 | ||||
| Lab equipment |
1,936 | 3,204 | ||||||
| Computer equipment |
238 | 890 | ||||||
| Furniture and office equipment |
124 | 425 | ||||||
| Vehicles |
37 | 296 | ||||||
| Asset under construction |
385 | 110 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total, at cost |
2,990 | 10,025 | ||||||
| Accumulated depreciation |
(112 | ) | (1,508 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total, net |
$ | 2,878 | $ | 8,517 | ||||
|
|
||||||||
During the period from inception through December 31, 2018 and the year ended December 31, 2019, depreciation expense was $112 and $1,396, respectively. Finance leases are also included in property and equipment as vehicles on the consolidated balance sheets (Note 6).
4. Investments
As of December 31, 2018 and 2019, amortized cost, gross unrealized gains and losses, and estimated fair values of total fixed-maturity securities were as follows:
| 2018 | ||||||||||||||||
| Amortized cost |
Gross unrealized gain |
Gross unrealized loss |
Estimated fair value |
|||||||||||||
| Held-to-maturity securities: |
||||||||||||||||
| U.S. Treasury bonds |
$ | 66,817 | $ | 1 | $ | (9 | ) | $ | 66,809 | |||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
| 2019 | ||||||||||||||||
| Amortized cost |
Gross unrealized gain |
Gross unrealized loss |
Estimated fair value |
|||||||||||||
| Held-to-maturity securities: |
||||||||||||||||
| U.S. Treasury bonds |
$ | 58,117 | $ | 31 | $ | (1 | ) | $ | 58,147 | |||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
Changes in fair value are related to changes in market interest rates. The Company expects to collect all contractual principal and interest payments.
F-21
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
4. Investments, continued
Amortized cost and estimated fair value of fixed-maturity securities at December 31, 2019 by contractual maturity were as follows:
| 2019 | ||||||||
| Amortized cost |
Estimated fair value |
|||||||
| Amounts maturing in: |
||||||||
| One year or less |
$ | 48,098 | $ | 48,127 | ||||
| More than one year |
10,019 | 10,020 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total investments |
$ | 58,117 | $ | 58,147 | ||||
|
|
||||||||
The Company recorded interest income of $769 and $1,568, respectively, during the period from inception through December 31, 2018 and the year ended December 31, 2019, as a component of interest and other income (expense), net on the Company’s consolidated statement of operations and comprehensive loss.
5. Accrued liabilities
Accrued liabilities consisted of the following as of December 31:
| 2018 | 2019 | |||||||
| Accrued compensation |
$ | 2,986 | $ | 3,211 | ||||
| Accrued payables |
159 | 3,113 | ||||||
| Liability with early exercised stock options |
77 | 753 | ||||||
| Other |
36 | 522 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
$ | 3,258 | $ | 7,599 | ||||
|
|
||||||||
6. Leases
The Company has operating and finance leases for corporate offices, research and development facilities, and certain vehicles. These leases have remaining lease terms of four to eight and a half years, some of which include options to extend the leases for five to eight years. The Company has determined that it is not reasonably certain to exercise the options under any leases. The lease of research and development facilities includes costs for utilities and common area maintenance which have been included in the calculation of lease payments. Differences between lease payments as measured at lease inception and variations in monthly payments will be recognized as operating expenses in the period in which the obligation is incurred.
Leases with an initial term of 12 months or less are not recorded on the balance sheet, and the Company recognizes lease expense for these leases on a straight-line basis over the lease terms. Leases with terms greater than 12 months are included in operating lease ROU assets and operating lease liabilities in the Company’s consolidated balance sheets as of December 31, 2018 and 2019. Lease expense for lease payments is recognized on a straight-line basis over the lease term.
F-22
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
6. Leases, continued
Maturities of lease liabilities as of December 31, 2019, were as follows:
| Operating lease |
Finance lease |
|||||||
| Year ending December 31: |
||||||||
| 2020 |
$ | 2,507 | $ | 75 | ||||
| 2021 |
2,604 | 75 | ||||||
| 2022 |
2,688 | 74 | ||||||
| 2023 |
2,697 | 39 | ||||||
| 2024 |
2,678 | 1 | ||||||
| Thereafter |
6,414 | — | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| 19,588 | 264 | |||||||
| Less: imputed interest |
(5,509 | ) | (12 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Present value of lease liabilities |
14,079 | 252 | ||||||
| Less: current portion |
(2,378 | ) | (74 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Lease liabilities net of current portion |
$ | 11,701 | $ | 178 | ||||
|
|
||||||||
The components of lease expense were as follows for the period from inception through December 31, 2018 and the year ended December 31, 2019:
| 2018 | 2019 | |||||||
| Operating lease cost |
$ | 1,187 | $ | 2,228 | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Finance lease cost: |
||||||||
| Amortization of right-of-use assets |
$ | 1 | $ | 46 | ||||
| Interest on lease liabilities |
— | 6 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total finance lease cost |
$ | 1 | $ | 52 | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Short-term lease cost |
$ | 13 | $ | 11 | ||||
|
|
||||||||
The Company made payments of $95 and $1,231 during the period from inception through December 31, 2018 and the year ended December 31, 2019, respectively, which are included as cash flow from operations on the consolidated statements of cash flows.
As of December 31, 2018 and 2019, $37 and $296 of finance lease ROU assets, respectively, were presented as part of property and equipment on the consolidated balance sheet with accumulated amortization of $1 and $47, respectively.
F-23
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
6. Leases, continued
Additional information related to the Company’s leases was as follows as of December 31:
| 2019 | 2018 | |||||||
| Operating Lease: |
||||||||
| Weighted-average remaining lease term (years) |
7.10 | 8.15 | ||||||
| Weighted-average discount rate |
9.34% | 9.30% | ||||||
| Finance Lease: |
||||||||
| Weighted-average remaining lease term (years) |
3.66 | 3.92 | ||||||
| Weighted-average discount rate |
3.18% | 6.00% | ||||||
|
|
||||||||
7. Convertible notes
The Company entered into a Note and Warrant Purchase Agreement (the “Note Agreement”) on March 26, 2018 with several lenders (the “Lenders”). The Lenders provided in the aggregate approximately $5,000 in cash consideration to the Company. The Company provided for the sale and issuance of $5,000 in convertible notes (the “Notes”), along with detachable warrants (the “Warrants”) (Note 8). The Notes accrued interest at 8% per annum, which was payable in cash or was capitalized with the note balance. The Notes provided for maturity upon the six-month anniversary of the initial closing, which was October 20, 2018.
The Notes were issued in two separate closings. The first closing occurred on April 20, 2018 and provided for the sale and purchase of Notes for approximately $3,675 in cash consideration. The second closing occurred on June 6, 2018 for sale and purchase of Notes for approximately $1,325 in cash consideration.
Pursuant to the Note Agreement, the outstanding principal balance and unpaid accrued interest was to be converted as follows (“Conversion Feature”): automatic conversion into equity shares issued in the next equity financing round of at least $10,000 (“Next Equity Financing”) calculated as the unpaid principal and unpaid interest divided by the price per share for equity securities in the Next Equity Financing; upon maturity date if the Next Equity Financing has not occurred, the holder had the option to receive cash consideration or shares of Common Stock, calculated as the outstanding unpaid principal and unpaid interest divided by the fair value of the Common Stock on the conversion date; or into Common Stock in the event of a change of control or IPO, as defined in the Note Agreement, calculated as the outstanding unpaid principal and unpaid interest divided by the fair value of the Common Stock immediately prior to the closing of the change of control or IPO.
The Warrants and Conversion Feature are accounted for as liabilities. The fair value of the Warrants (Note 8) and Conversion Feature as of the issuance date of the Notes was $905 and $22, respectively, and the debt was assigned the remaining value of the total proceeds.
On June 26, 2018, the Company executed an agreement with Emory University to purchase an exclusive license to proprietary know-how and patents related to hepatitis B virus (“HBV”) for $290 in cash and a $600 convertible note (the “Emory Convertible Note”). These notes were not issued with warrants. The outstanding principal balance and unpaid accrued interest of the Emory Convertible Note provided for conversion under the Conversion Feature described above.
F-24
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
7. Convertible notes, continued
The Company issued Series A Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock (“Series A”) for $9.32 per share on August 16, 2018 for proceeds of $75,000 and an additional $20,000 on September 19, 2018, which qualified as the Next Equity Financing (Note 9). The Notes and Emory Convertible Note and unpaid accrued interest of $113 were cancelled and converted into shares of Series A at a conversion price of $9.32 per share. For the period from the issuance of the Notes and Emory Convertible Note through conversion on August 16, 2018, the Company recorded $493 of amortization of the debt discount and $113 of interest, resulting in $5,279 of unamortized value of the Notes and Emory Convertible Note prior to conversion and $606 of interest expense recorded as a component of interest and other income (expense), net on the consolidated statement of operations and comprehensive loss. The Company issued 612,975 shares of Series A valued at $5,713, resulting in a loss on debt conversion of $433, which is recorded as a component of interest and other income (expense), net on the consolidated statement of operations and comprehensive loss.
8. Derivative liabilities and redeemable convertible preferred stock liability
Warrants
In connection with the issuance of the Notes, Lenders were issued Warrants to purchase 134,112 shares of the Company’s capital stock. The Warrants have a coverage percentage of 25% of the principal amount of the Notes and have a ten-year expiration date from the applicable closing date of April 20, 2018 or June 6, 2018.
The underlying shares issuable upon the exercise of the Warrants were eligible to be converted into the next round of equity financing. The Warrants became exercisable into shares of Series A for an exercise price of $9.32 per share. There were warrants to purchase 134,112 shares of Series A outstanding as of December 31, 2018.
The Company recorded the Warrants initially at fair value (Note 7 and Note 11) as derivative liabilities on the consolidated balance sheet with the remaining value being allocated to the Notes as a debt discount. The fair value of the Warrants upon issuance on April 20, 2018 and June 6, 2018, was $667 and $238, respectively. The fair value of the Warrants was $861 and $461 as of December 31, 2018 and 2019, respectively.
In December 2019, Warrants were exercised into 13,411 shares of Series A. As a result, there were Warrants to purchase 120,701 shares of Series A outstanding as of December 31, 2019. Following completion of an IPO or change of control, any then outstanding warrants will automatically be exercised, on net share basis, for the issuance of shares of Common Stock and, upon that exercise, such warrants will no longer be outstanding. As Series A contains a conditional obligation for the Company to repurchase the shares for cash consideration, the Warrants remain outstanding as derivative liabilities with changes in fair value being recorded on the consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive loss. For the period from inception through December 31, 2018 and the year ended December 31, 2019, the Company recorded a change in fair value of derivative liabilities of $44 and $348, respectively.
Conversion feature
The Company evaluated whether the Notes and the Emory Convertible Note contain embedded conversion features, which meet the definition of derivatives under ASC Topic 815, Derivatives and Hedging (“ASC 815”) and
F-25
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
8. Derivative liabilities and redeemable convertible preferred stock liability, continued
Conversion feature, continued
related interpretations. The Company determined that the terms of the Notes and the Emory Convertible Note (Note 7) include a variable conversion price based on the price of the underlying equity, which cause the embedded conversion options to be bifurcated and accounted for as derivative liabilities. Thus, the Company recorded the bifurcated conversion feature initially at fair value determined using the Monte Carlo simulation as derivative liabilities on the consolidated balance sheet with the residual value being allocated to the Notes and the Emory Convertible Note as a debt discount. The fair value of the conversion feature upon issuance on April 20, 2018 and June 6, 2018 were $16 and $6, respectively. The fair value of the conversion feature on the conversion date of August 16, 2018 was $0 and the Company recorded a change in fair value of derivative liabilities of $22 in interest and other income (expense), net on the consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive loss.
Redeemable convertible preferred stock liability
In connection with the issuance of Series B-1 Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock (the “Series B-1”) (Note 9), the Series B-1 preferred stockholders committed to purchase and the Company committed to sell 3,569,630 shares of Series B-2 Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock (the “Series B-2”) at a price of $11.20563 per share in a subsequent closing, contingent upon the achievement of certain developmental milestones or a receipt of a waiver of achievement of the milestones. The Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock Liability is considered a freestanding instrument that qualifies as a liability under ASC Topic 480, Distinguishing Liabilities from Equity (“ASC 480”) as the Company is committed to issue an instrument that ultimately may require a transfer of assets. The liability is accounted for at fair value and re-measured at each reporting date (Note 11). On the date of the initial closing, the Company recorded the Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock Liability at a fair value of $3,174. As of December 31, 2019, none of the Series B-2 shares were issued and the fair value of the liability related to this freestanding instrument remained unchanged.
9. Capital stock
Common stock
On February 5, 2018, the date of incorporation, the Company was authorized to issue 20,000,000 shares of common stock with a par value of $0.0001 per share (the “Common Stock”).
On March 19, 2018, the Company granted two founders the right to purchase 1,508,900 shares of the Company’s Common Stock at a purchase price of $0.001 per share upon the terms and subject to the conditions set forth in a restricted stock purchase agreement. The shares were purchased for $2 on the grant date and the shares vested immediately upon grant.
On March 19, 2018, the Company granted two founders and one employee the right to purchase 425,585 shares of the Company’s Common Stock at a purchase price of $0.001 per share upon the terms and subject to the conditions set forth in a restricted stock purchase agreement. The shares were purchased for a de-minimis amount on the grant date and the shares vest monthly over a three-year period after a one-year cliff. If the purchasers no longer provide services to the Company, any portion of the shares that have not vested pursuant
F-26
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
9. Capital stock, continued
Common stock, continued
to the vesting schedule shall, on the date that is 61 days following such termination of service, automatically be forfeited by purchaser without any additional consideration therefore and without any further action by the Company and such shares shall immediately be canceled by the Company and shall no longer be outstanding.
On July 23, 2018, the certificate of incorporation was amended to increase the number of shares authorized for issuance to 25,000,000 shares of Common Stock. On that same date, the Company issued for purchase by employees and founders an additional 77,379 shares for a de-minimis amount subject to the same terms and conditions as the shares issued on March 19, 2018.
The Common Stock issuances with vesting conditions were issued outside of the equity incentive plan and are described in more detail in Note 10—Stock-Based Compensation.
On August 15, 2018, the certificate of incorporation was amended to increase the total shares of Common Stock authorized for issuance to 149,000,000 and additionally 102,500,000 shares of preferred stock with a par value of $0.0001 per share. Effective immediately on filing date, the Company converted all shares of Common Stock into 0.90144231 shares of Common Stock (the “Reverse Stock Split”). All share and data shown in the accompanying consolidated financial statements and related notes have been retroactively revised to reflect the Reverse Stock Split. Shares of Common Stock underlying outstanding stock options and other equity instruments were proportionately reduced and the respective exercise prices, if applicable, were proportionately increased in accordance with the terms of the agreements governing such securities.
On December 23, 2019, the certificate of incorporation was amended to increase the total shares of Common Stock authorized for issuance to 278,000,000 and the total shares of preferred stock authorized for issuance to 212,994,964 with a par value of $0.0001 per share. The total shares of preferred stock authorized comprised 101,962,864 shares of Series A, 77,764,055 shares of Series B-1, and 33,268,045 shares of Series B-2.
The holders of shares of Common Stock are entitled to one vote for each share of Common Stock at all meetings of stockholders.
Redeemable convertible preferred stock
On August 16, 2018, the Company entered into the Series A Preferred Stock Purchase Agreement for the purchase and sale of Series A preferred stock for $9.32 per share. The Company received $75,000 in cash proceeds from the initial purchasers. On September 19, 2018, the Company received an additional $20,000 in cash proceeds from subsequent purchasers. Additionally, on the initial closing date, $5,600 in convertible notes plus accrued interest converted into shares of Series A and the notes were subsequently cancelled. The Warrants associated with the convertible notes became exercisable into Series A. Each share of Series A is convertible into Common Stock on a one-for-one basis. In connection with the issuance of Series A, the Company incurred $194 in issuance costs which have offset amounts reported as temporary equity as of December 31, 2018 and 2019.
On December 23, 2019, the Company entered into the Series B-1 and Series B-2 Preferred Stock Purchase Agreement, pursuant to which the investors committed to invest an aggregate amount of up to $125,000 for the
F-27
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
9. Capital stock, continued
Redeemable convertible preferred stock, continued
issuance and sale of shares of Series B-1 and Series B-2 (collectively, the “Series B”), at a price of $10.18690 and $11.20563 per share, respectively. The Company issued 8,344,034 shares of Series B-1 for cash proceeds of $85,000 at the initial closing on December 23, 2019. The investors also committed to purchase and the Company committed to sell 3,569,630 shares of Series B-2 in a subsequent closing (the “Second Closing”), contingent upon achievement by the Company of certain development milestones or a receipt of a waiver of achievement of the milestones. No shares of Series B-2 were issued as of December 31, 2019. In connection with the issuance of Series B-1, the Company incurred $442 in issuance costs which have offset amounts reported as temporary equity as of December 31, 2019.
The holders of the Company’s Series A and Series B (collectively, the “Preferred Stock”) have the following rights, preferences, and privileges:
(a) Dividends
The holders of shares of Preferred Stock, in preference to the holders of Common Stock, shall be entitled to receive, on a pari passu basis, when, as and if declared by the board of directors (“Board”) out of funds legally available, noncumulative cash dividends at the rate of eight percent (8%) of the original issue price per annum on each outstanding share of Preferred Stock. So long as any shares of Preferred Stock are outstanding, the Company shall not pay or declare any dividend, or make any other distribution on the Common Stock, or purchase, redeem or otherwise acquire for value any shares of Common Stock until all dividends on the Preferred Stock shall have been paid or declared and set apart, except for: acquisitions of Common Stock by the Company pursuant to agreements which permit the Company to repurchase such shares upon termination of services to the Company or acquisitions of Common Stock in exercise of the Company’s right of first refusal to repurchase such shares as approved by the Board. After the dividends on the Preferred Stock have been paid, then the Company may declare and distribute in such year dividends among the holders of Preferred Stock and the holders of Common Stock pro rata based on the number of shares of Common Stock held by each, determined on an as-if-converted to Common Stock basis (assuming full conversion of all such Preferred Stock) as of the record date with respect to the declaration of such dividends.
(b) Liquidation preference and redemption
In the event of any voluntary or involuntary liquidation, dissolution or winding up of the Company, the holders of shares of Preferred Stock then outstanding shall be entitled to be paid out of the assets of the Company available for distribution to its stockholders or, in the case of a Deemed Liquidation Event (as defined below), out of the consideration payable to stockholders in such Deemed Liquidation Event or the Available Proceeds (as defined below), before any payment shall be made to the holders of Common Stock by reason of their ownership thereof, an amount per share equal to one (1) times the applicable Original Issue Price of such series of Preferred Stock, plus any dividends declared but unpaid thereon. If upon any such liquidation, dissolution or winding up of the Company or Deemed Liquidation Event, the assets of the Company available for distribution to its stockholders shall be insufficient to pay the holders of shares of
F-28
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
9. Capital stock, continued
Redeemable convertible preferred stock, continued
Preferred Stock the full amount to which they shall be entitled, the assets or consideration will be distributed ratably among such holders.
After the payment in full of all liquidation amounts required to be paid to the holders of shares of Preferred Stock, the remaining assets of the Company available for distribution to its stockholders or, in the case of a Deemed Liquidation Event, the consideration not payable to the holders of shares of Preferred Stock or the remaining Available Proceeds, as the case may be, shall be distributed among the holders of the shares of Preferred Stock and Common Stock, pro rata based on the number of shares held by each such holder, treating for this purpose all such securities as if they had been converted to Common Stock immediately prior to such liquidation, dissolution or winding up of the Company; provided, however, that if the aggregate amount which the holders of shares of Preferred Stock are entitled to receive shall exceed one and one-half (1.5) times the applicable Original Issue Price of such series of Preferred Stock per share, plus any dividends declared, but unpaid thereon (such amount, with respect to a series of Preferred Stock, the “Maximum Participation Amount”), each holder of shares of a series of Preferred Stock shall be entitled to receive upon such liquidation, dissolution or winding up of the Company the greater of (i) the Maximum Participation Amount applicable to such series or (ii) the amount such holder would have received if all shares of such series of Preferred Stock had been converted into Common Stock immediately prior to such liquidation, dissolution or winding up of the Company.
Each of the following events shall be considered a “Deemed Liquidation Event” unless the holders of at least 67% of the outstanding shares of Preferred Stock (voting as a single class on an as-converted to Common Stock basis) which must include certain non-strategic holders of Series B-1 or Series B-2 holding at least 33% of outstanding shares of Series B-1 and Series B-2 elect otherwise by written notice sent to the Company prior to the effective date of any such event:
| (a) | a merger or consolidation in which the Company is a constituent party or a subsidiary of the Company is a constituent party and the Company issues shares of its capital stock pursuant to such merger or consolidation, except (1) any such merger or consolidation involving the Company or a subsidiary in which the shares of capital stock of the Company outstanding immediately prior to such merger or consolidation continue to represent, or are converted into or exchanged for shares of capital stock that represent, immediately following such merger or consolidation, a majority, by voting power, of the capital stock of (a) the surviving or resulting corporation; or (b) if the surviving or resulting corporation is a wholly owned subsidiary of another corporation immediately following such merger or consolidation, the parent corporation of such surviving or resulting corporation; or (2) a merger effected exclusively to change the domicile of the Company; |
| (b) | the closing of the sale, in a single transaction or series of related transactions, of equity securities of the Company other than (a) bona fide equity financing, and (b) any transaction in which, the stockholders of the Company prior to such transaction continue to hold at least fifty percent (50%) of the outstanding shares of the surviving corporation; or |
| (c) | (1) the sale, lease, transfer, exclusive license or other disposition, in a single transaction or series of related transactions, by the Company or any subsidiary of the Company of all or substantially all the |
F-29
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
9. Capital stock, continued
Redeemable convertible preferred stock, continued
| assets of the Company and its subsidiaries taken as a whole, or (2) the sale or disposition (whether by merger, consolidation or otherwise, and whether in a single transaction or a series of related transactions) of one or more subsidiaries of the Company if substantially all of the assets of the Company and its subsidiaries taken as a whole are held by such subsidiary or subsidiaries, except where such sale, lease, transfer, exclusive license or other disposition is to a wholly owned subsidiary of the Company. |
(c) Conversion
Each share of Preferred Stock is convertible into fully paid and non-assessable shares of Common Stock at any time at the option of the holder, and is subject to mandatory conversion upon the written consent of certain holders or upon the closing of a firm commitment underwritten public offering (i) approved by a majority of the then-outstanding shares of Series B-1 or Series B-2 held by certain non-strategic Series B-1 and Series B-2 holders or (ii) after the earlier of (A) September 30, 2021 and (B) the occurrence of a developmental milestone, in the case of clause (ii) which firm commitment underwritten public offering involves a price per share dependent upon whether it is prior to the Second Closing or on or after the Second Closing and gross proceeds to the Company of at least $75,000. The conversion ratio at December 31, 2018 and 2019 was one for one, and is subject to certain anti-dilutive adjustments.
(d) Voting
The holders of Preferred Stock have voting rights equivalent to the number of shares of Common Stock into which their shares of Preferred Stock convert. Except as provided by law or by the other provisions of the amended and restated certificate of incorporation, holders of shares of Preferred Stock shall vote together with the holders of shares of Common Stock as a single class and on an as-converted to Common Stock basis.
The holders of record of shares of Series A, exclusively and as a separate class, shall be entitled to elect four (4) directors of the Company, the holders of record of shares of Series B-1 and Series B-2, exclusively and as a separate class on an as-converted basis, shall be entitled to elect one (1) director of the Company and the holders of record of shares of Common Stock, exclusively and as a separate class, shall be entitled to elect two (2) directors of the Company.
10. Stock-based compensation
2018 Equity incentive plan
The Company’s 2018 Equity Incentive Plan (the “Plan”) allows the Company to issue restricted stock awards and restricted stock units, and to grant incentive stock options or non-qualified stock options. Incentive stock options may be granted only to the Company’s employees including officers and members of the Board who are also employees. Restricted stock awards, restricted stock units and non-qualified stock options may be granted to employees, members of the Board, outside advisors, and consultants of the Company (the “Participants”). The Company is authorized to issue awards for 4,913,665 shares of Common Stock under the Plan. The
F-30
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
10. Stock-based compensation, continued
2018 Equity incentive plan, continued
Company has granted 2,262,793 shares subject to awards as of December 31, 2019 with 2,650,872 remaining available for future grant.
Stock options
The exercise price for incentive stock options is at least 100% of the fair market value on the date of grant for stockholders owning less than 10% of the voting power of all classes of stock, or at least 110% of the fair market value for stockholders owning more than 10% of the voting power of all classes of stock. Options generally expire in 10 years and vest over periods determined by the Board, generally 48 months. Certain stock options referred to as “early exercise stock options” permit the holders to exercise the option in whole or in part prior to the full vesting of the option in exchange for unvested shares of Restricted Stock with respect to any unvested portion of the option so exercised.
During the period from inception through December 31, 2018 and the year ended December 31, 2019, the Company’s stock option compensation expense was approximately $45 and $261, respectively, and there was no recognized tax benefit in either year. As of December 31, 2019, unamortized expense balance was $612, to be amortized over a weighted-average period of 2.74 years.
The assumptions that the Company used to determine the grant-date fair value of stock options granted to Participants were as follows, presented on a weighted-average basis:
| 2018 | 2019 | |||||||
| Expected term (in years) |
5.90 | 6.06 | ||||||
| Risk-free interest rate |
2.98% | 1.94% | ||||||
| Dividend yield |
— | — | ||||||
| Volatility |
58.98% | 60.24% | ||||||
|
|
||||||||
F-31
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
10. Stock-based compensation, continued
Stock options, continued
Stock option activity during the period from inception through December 31, 2018 and the year ended December 31, 2019 was as follows:
| Shares subject to options |
Weighted- average exercise price |
Weighted- average remaining contractual term (years) |
Aggregate intrinsic value |
|||||||||||||
| Outstanding as of February 5, 2018 |
— | $ | — | |||||||||||||
| Granted |
1,062,457 | $ | 1.30 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Outstanding as of December 31, 2018 |
1,062,457 | $ | 1.30 | 9.88 | $ | — | ||||||||||
| Granted |
178,863 | $ | 1.30 | |||||||||||||
| Exercised |
(891,229 | ) | $ | 1.30 | 37 | |||||||||||
| Forfeited |
(3,219 | ) | $ | 1.30 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Outstanding as of December 31, 2019 |
346,872 | $ | 1.30 | 9.01 | 744 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Options vested and expected to vest as of December 31, 2019 |
884,623 | $ | 1.30 | 9.01 | 1,896 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Options vested and exercisable as of December 31, 2019 |
31,330 | $ | 1.30 | 8.88 | 67 | |||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
The weighted-average grant date fair value of stock options granted was $0.08 per share both during the period from inception through December 31, 2018 and the year ended December 31, 2019.
During the period from inception through December 31, 2018 and the year ended December 31, 2019, the Company issued 59,014 and 537,781 shares of Common Stock, respectively, upon exercise of unvested stock options or purchases for unvested restricted stock awards. As of December 31, 2018 and 2019, there were 59,014 and 577,124 shares of Common Stock, respectively, held by employees subject to repurchase at an aggregate price of $77 and $753, respectively. A corresponding liability was recorded and included in accrued expenses on the consolidated balance sheet as of December 31, 2018 and 2019.
Restricted stock awards
The Company may grant restricted stock purchase awards to the Participants to purchase restricted stock under the Company’s Plan, which are subject to vesting conditions. The purchase prices of the restricted stock are determined by the Board. The Company has a right to repurchase the shares if the Participant’s service period is not fulfilled or upon termination of service at the original per share issuance price. The right of repurchase lapses over a service period which is typically four years with 25% vesting on the first anniversary of the vesting commencement date and 1/48 each month thereafter.
Before the adoption of the Company’s Plan, the Company granted 502,964 restricted stock awards to employees and founders. These restricted stock awards have similar characteristics to the restricted stock awards granted under the Company’s Plan, other than the right of repurchase, which typically lapses over three
F-32
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
10. Stock-based compensation, continued
Restricted stock awards, continued
years with 33% vesting on the first anniversary of the vesting commencement date and 1/36 each month thereafter.
During the period from inception through December 31, 2018 and the year ended December 31, 2019, the Company recorded a total stock-based compensation expense of $134 and $492, respectively, related to the restricted stock awards. As of December 31, 2019, unrecognized stock-based compensation costs related to outstanding unvested restricted stock awards that are expected to vest were approximately $813, expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of 2.04 years.
The following table summarizes the Company’s restricted common stock activity for the period from inception through December 31, 2018 and the year ended December 31, 2019:
| Shares subject to awards |
Weighted- average grant date fair value |
Aggregate fair value |
||||||||||
| Issued and unvested as of February 5, 2018 |
— | $ | — | $ | — | |||||||
| Restricted stock awards granted |
1,527,674 | $ | 0.94 | 1,438 | ||||||||
| Restricted stock awards vested |
(6,287 | ) | 1.30 | (8 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Issued and unvested as of December 31, 2018 |
1,521,387 | $ | 0.94 | 1,430 | ||||||||
| Restricted stock awards granted |
— | — | — | |||||||||
| Restricted stock awards vested |
(694,200 | ) | $ | 0.86 | (596 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Issued and unvested as of December 31, 2019 |
827,187 | $ | 1.01 | $ | 834 | |||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
Stock-based compensation expense was allocated as follows for the period from inception through December 31, 2018 and the year ended December 31, 2019:
| 2018 | 2019 | |||||||
| Research and development |
$ | 130 | $ | 462 | ||||
| General and administrative |
49 | 290 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
$ | 179 | $ | 752 | ||||
|
|
||||||||
F-33
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
11. Fair value
The following tables present the fair value of the Company’s financial instruments that are measured or disclosed at fair value on a recurring basis:
| Fair value measurements as of December 31, 2018 |
||||||||||||
| Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | ||||||||||
| Assets: |
||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 24,035 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||
| U.S. Treasury bonds |
66,810 | — | — | |||||||||
| Liabilities: |
||||||||||||
| Derivative liabilities |
— | — | (861 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| $ | 90,845 | $ | — | $ | (861 | ) | ||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| Fair value measurements as of December 31, 2019 |
||||||||||||
| Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | ||||||||||
| Assets: |
||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 69,565 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||
| U.S. Treasury bonds |
58,146 | — | — | |||||||||
| Liabilities: |
||||||||||||
| Derivative liabilities |
— | — | (461 | ) | ||||||||
| Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock Liability |
— | — | (3,174 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| $ | 127,711 | $ | — | $ | (3,635 | ) | ||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
The derivative liability in the table above is composed of the fair value of Warrants and Conversion Features issued in connection with the Notes, which were subsequently converted into shares of Series A. The fair values of the Warrants and Conversion Features were determined based on significant inputs not observable in the market, which represents a Level 3 measurement within the fair value hierarchy.
In order to determine the fair value of the Warrants, the Company utilized a probability-weighted multi-scenario Black-Scholes option-pricing model to determine the fair value of the Warrants by accounting for the probability of multiple possible outcomes, including deemed liquidation events, as best estimated by management. Estimates and assumptions impacting the fair value measurement including the fair value of the underlying shares of Series A, the remaining contractual or expected term of the Warrants, risk-free interest rate, expected dividend yield and expected volatility of the price of the underlying preferred stock on an as converted basis. The Company considered the probability of a deemed liquidation event in determining the remaining expected term of the Warrants, which was used as an input to the probability-weighted multi-scenario Black-Scholes option-pricing model adopted in 2019. The Company lacks company-specific historical and implied volatility information of its stock since there is currently no market. Therefore, it estimated its expected stock volatility based on the historical volatility of publicly traded guideline companies for a term equal to the remaining contractual or expected term of the Warrants. The risk-free interest rate was determined by reference to the U.S. Treasury yield curve for time periods approximately equal to the remaining
F-34
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
11. Fair value, continued
contractual or expected term of the Warrants. The Company estimated no expected dividend yield based on the fact that the Company has never paid or declared dividends and does not intend to do so in the foreseeable future.
The Warrants were measured at fair value under the following assumptions as of December 31:
| 2018 | 2019 | |||||||
| Exercise price |
$ | 9.32 | $ | 9.32 | ||||
| Term (in years) |
9.30 - 9.43 | 2.00 - 3.00 | ||||||
| Risk-free interest rate |
2.69% | 1.63% | ||||||
| Dividend yield |
— | — | ||||||
| Volatility |
60.56% | 75.00% | ||||||
|
|
||||||||
The significant unobservable inputs used in the fair value measurement of the Warrants are the remaining expected term, which considers the timing of a liquidation event that would net settle the awards before their contractual term expires, and the equity volatility, which is a statistical measure of the dispersion of returns for a given security. Significant increases (decreases) in the term would result in significantly higher (lower) fair value measurements. Significant increases (decreases) in the volatility would result in significantly higher (lower) fair value measurements.
The fair value of the bifurcated conversion feature was immaterial at inception and is included in the initial fair value of the derivative liabilities. As of December 31, 2018 and 2019, the fair value of the bifurcated conversion feature was $0 as the Notes are converted into shares of Series A preferred stock in August 2018 (Note 7).
The following table sets forth a summary of changes in fair value of the Company’s derivative liability for which fair value was determined by Level 3 inputs:
| Derivative liabilities |
||||
| Balance as of February 5, 2018 |
$ | — | ||
| Initial fair value of derivative |
927 | |||
| Change in fair value |
(66 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|||
| Balance as of December 31, 2018 |
861 | |||
| Exercise of warrants |
(52 | ) | ||
| Change in fair value |
(348 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|||
| Balance as of December 31, 2019 |
$ | 461 | ||
|
|
||||
F-35
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
11. Fair value, continued
In order to determine the fair value of the Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock Liability, the Company used a probability weighted multi-scenario Black Scholes hybrid valuation method that accounts for the probability of achieving milestones as estimated by the management. The Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock Liability has a fair value of $3,174 at inception, which remained unchanged as of December 31, 2019. The Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock Liability was measured at fair value under the following assumption as of December 31, 2019:
| 2019 | ||||
| Exercise price |
$ | 11.21 | ||
| Term (in years) |
1.27 | |||
| Risk-free interest rate |
1.55% | |||
| Dividend yield |
— | |||
| Volatility |
60.00% | |||
|
|
||||
The significant unobservable inputs used in the fair value measurement of the Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock Liability include the probability of milestone achievement and/or milestone achievement waiver, the Series B-2 current or future value estimate under each scenario, the term, and the equity volatility, which is a statistical measure of the dispersion of returns for a given security. Significant increases (decreases) in the milestone achievement and/or milestone waiver would result in a significantly higher (lower) fair value measurement. Significant decreases (increases) in assumed current or future Series B-2 value would result in a significantly lower (higher) fair value measurement. Significant increases (decreases) in the term would result in a significantly higher (lower) fair value measurement. Significant increases (decreases) in the volatility would result in significantly higher (lower) fair value measurements.
12. License and collaboration agreements
Agreement with Emory University (“Emory”)
In June 2018, the Company entered into a license agreement with Emory (the “Emory License Agreement”), pursuant to which Emory granted the Company a worldwide, sublicenseable license under certain of its intellectual property rights to make, have made, develop, use, offer to sell, sell, import and export products containing certain compounds relating to Emory’s hepatitis B virus capsid assembly modulator technology, for all therapeutic and prophylactic uses. Such license is initially exclusive with respect to specified licensed patents owned by Emory and non-exclusive with respect to certain of Emory’s specified know-how. Beginning in June 2022, the license to such patents will become non-exclusive with respect to all fields except for the treatment and prevention of HBV; however, the Company may select up to six compounds which will maintain exclusivity with respect to all therapeutic and prophylactic uses. With respect to all other compounds that are enabled by the licensed patents, those which are jointly invented by the Company and Emory or inventors in the Schinazi laboratory, or which are disclosed in a specified licensed patent, are licensed to the Company exclusively including as to Emory; whereas all other such compounds are licensed to the Company non-exclusively. Under the terms of the Emory License Agreement, the Company is obligated to use commercially reasonable efforts to bring licensed products to market in accordance with a mutually agreed upon development plan. Unless terminated earlier by either party in accordance with the provisions thereof,
F-36
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
12. License and collaboration agreements, continued
Agreement with Emory University (“Emory”), continued
the Emory License Agreement shall continue until the expiration of the last–to-expire of the patents licensed to the Company thereunder.
As consideration for the Emory License Agreement, the Company paid an upfront license fee of $290 and issued the Emory Convertible Note of $600 (Note 7). Both the upfront cash payment of $290 and the value of the Emory Convertible Note of $600 were recorded as research and development expense during the period from inception through December 31, 2018. As discussed in Note 7, upon issuance of the Series A in August 2018, the Emory Convertible Note and unpaid accrued interest was cancelled and converted into shares of Series A at a conversion price of $9.32 per share.
The Company has agreed to pay Emory up to an aggregate of $125,000 upon the achievement of specified development, regulatory, and commercial milestones, and all ongoing patent costs. During the period from inception through December 31, 2018 and the year ended December 31, 2019, the Company had no expenses related to milestone payments. The Company also agreed to pay Emory tiered single-digit royalties on worldwide annual net sales of licensed products, on a quarterly basis and calculated on a product-by-product basis. With respect to licensed products containing any of a specified subset of the licensed compounds, such royalties range from a mid-single digit to a high-single digit percentage rate. With respect to licensed products which do not contain such compounds, the royalties span a range of percentage rates within the mid-single digits if a Phase 1 clinical trial is initiated for the product within three years of the effective date of the Emory License Agreement, and range from a low-single digit to a mid-single digit rate if a Phase 1 clinical trial is initiated more than three years after the effective date. During the period from inception through December 31, 2018 and the year ended December 31, 2019, the Company made no payments associated with royalties. See Note 18 for further discussion of the Emory License Agreement.
Agreement with Luxna Biotech Co., Ltd. (“Luxna”)
On December 19, 2018, the Company entered into a license agreement with Luxna, pursuant to which Luxna granted the Company an exclusive, worldwide, sublicenseable license under certain of Luxna’s intellectual property rights to research, develop, make, have made, and commercialize for all therapeutic and prophylactic uses, (i) products containing oligonucleotides targeting the hepatitis B virus genome, (ii) products containing certain oligonucleotides targeting up to three genes which contribute to NASH, which the Company may select at any time during the first eight years of the term, to the extent not licensed to a third party, and (iii) products containing oligonucleotides targeting up to three genes which contribute to hepatocellular carcinoma, which the Company may select at any time during the first three years of the term. Unless terminated earlier by either party in accordance with provisions in the agreement, the agreement shall continue until the expiration of the last-to-expire of the patents licensed thereunder.
As consideration for this agreement, the Company paid an upfront license fee of $600, which was recorded as research and development expense during the period from inception through December 31, 2018 and the year ended December 31, 2019.
F-37
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
12. License and collaboration agreements, continued
Agreement with Luxna Biotech Co., Ltd. (“Luxna”), continued
The Company is obligated to make payments to Luxna, in aggregate, totaling up to but no more than $55,500 upon the achievement of specified development, regulatory, and commercial milestones. During the period from inception through December 31, 2018 and the year ended December 31, 2019, the Company recognized no expenses related to milestone payments. The Company is also required to pay Luxna a low-single digit royalty percentage on net sale of applicable products, if any. During the period from inception through December 31, 2018 and the year ended December 31, 2019, the Company made no payments associated with royalties. See Note 18 for further discussion of the agreement with Luxna.
13. Income taxes
The components of the current provision for income taxes were as follows for the period from inception through December 31, 2018 and the year ended December 31, 2019:
| 2018 | 2019 | |||||||
| Current: |
||||||||
| State |
$ | — | $ | 1 | ||||
| Foreign |
— | 84 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total provision for income taxes |
$ | — | $ | 85 | ||||
|
|
||||||||
The Company did not have any deferred provision for income taxes for the period from inception through December 31, 2018 and the year ended December 31, 2019.
A reconciliation of the expected income tax (benefit) computed using the federal statutory income tax rate to the Company’s effective income tax rate is as follows for the period from inception through December 31, 2018 and the year ended December 31, 2019:
| 2018 | 2019 | |||||||
| Income tax computed at federal statutory rate |
21.00% | 21.00% | ||||||
| State taxes, net of federal benefit |
7.52% | 8.18% | ||||||
| R&D credit carryovers |
0.35% | 1.87% | ||||||
| Change in valuation allowance |
-26.71% | -29.71% | ||||||
| Permanent differences |
-2.16% | -1.32% | ||||||
| Other |
— | -0.18% | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| 0.00% | -0.16% | |||||||
|
|
||||||||
F-38
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
13. Income taxes, continued
The components of the deferred tax assets and liabilities were as follows at December 31:
| 2018 | 2019 | |||||||
| Deferred tax assets: |
||||||||
| Federal net operating loss carryforward |
$ | 2,153 | $ | 12,106 | ||||
| State net operating loss carryforward |
747 | 4,227 | ||||||
| Operating lease liabilities |
3,761 | 3,776 | ||||||
| Tax credits |
194 | 1,865 | ||||||
| Other accruals and reserves |
573 | 675 | ||||||
| Other |
31 | 7 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| 7,459 | 22,656 | |||||||
| Valuation allowance |
(3,755 | ) | (19,362 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net deferred tax assets |
3,704 | 3,294 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Deferred tax liabilities: |
||||||||
| Right of use assets |
(3,390 | ) | (2,067 | ) | ||||
| Stock-based compensation |
(292 | ) | (115 | ) | ||||
| Property and equipment |
(22 | ) | (1,112 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total deferred tax liabilities |
(3,704 | ) | (3,294 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total deferred income taxes |
$ | — | $ | — | ||||
|
|
||||||||
Management believes that, based on a number of factors, including the Company’s historical operating performance and accumulated deficit, it is more likely than not that the deferred tax assets will not be utilized, such that full valuation allowance has been recorded against the Company’s deferred tax assets. In assessing the reliability of deferred tax assets, management considers whether it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized on a jurisdiction by jurisdiction basis. The ultimate realization of deferred tax assets is dependent upon the generation of future taxable income during the periods in which those temporary differences become deductible. The valuation allowance increased by $15,607 during the year ended December 31, 2019.
As of December 31, 2019, the Company had $57,648 of federal and $60,527 of state net operating loss (“NOL”) carryforwards available to offset future taxable income. The Company’s federal NOL carryforwards can be carried forward indefinitely while state NOL carryforwards, if not utilized, will begin expiring in 2038. As of December 31, 2019, the Company had research and development credit carryforwards of $1,377 and $1,125 available to reduce future taxable income, if any, for federal and state income tax purposes, respectively. If not utilized, the federal credit carryforwards will begin expiring in 2029. Internal Revenue Code Section 382 (“Section 382”) limits the use of NOL and tax credit carryforwards in certain situations where changes occur in the stock ownership of a company. In the event that the Company had a change of ownership, utilization of the NOL and tax credit carryforwards may be limited under Section 382.
The Company adopted the provisions of FASB Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC 740-10”), Accounting for Uncertainty in Income Taxes, upon the date of incorporation. ASC 740-10 prescribes a comprehensive model for
F-39
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
13. Income taxes, continued
the recognition, measurement, presentation and disclosure in financial statements of any uncertain tax positions that have been taken or expected to be taken on a tax return. It is the Company’s policy to include penalties and interest expense related to income taxes as a component of other expense and interest expense, respectively, as necessary. During the period from inception though December 31, 2018 and the year ended December 31, 2019, the Company had not recognized any tax-related penalties or interest. At December 31, 2019, the gross unrecognized tax benefit relating to research and development credit was $637, none of which if recognized would reduce the effective tax rate in a future period, due to the Company’s full valuation allowance on U.S. net deferred tax assets. The Company does not expect that its uncertain tax positions will materially change in the next twelve months. The following table summarizes the changes to the Company’s unrecognized tax benefits:
| 2018 | 2019 | |||||||
| Balance, beginning of the period |
$ | — | $ | 79 | ||||
| Increase related to prior year positions |
— | — | ||||||
| Increase related to current year positions |
79 | 558 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Balance, ending of the period |
$ | 79 | $ | 637 | ||||
|
|
||||||||
The Company files income tax returns in the United States and California. The Company is not currently under examination by income tax authorities in federal, state or other jurisdictions. All tax returns will remain open for examination by the federal and state authorities for three and four years, respectively, from the date of utilization of any NOLs or credits.
In January 2018, the FASB released guidance on the accounting for tax on the global intangible low-taxed income (“GILTI”) provisions of the Tax Reform Act. The GILTI provisions impose a tax on foreign income in excess of a deemed return on tangible assets of foreign corporations. The guidance allows companies to make an accounting policy election to either (i) account for GILTI as a component of tax expense in the period in which they are subject to the rules (the period cost method), or (ii) account for GILTI in the Company’s measurement of deferred taxes (the deferred method). After completing the analysis of the GILTI provisions, the Company elected to account for GILTI using the period cost method.
14. Commitments and contingencies
From time to time, the Company may have certain contingent liabilities, including legal matters that arise in the ordinary course of its business activities. The Company accrues a liability for such matters when it is probable that future expenditures will be made and such expenditures can be reasonably estimated. The Company had no contingent liabilities requiring accrual as of December 31, 2018 and 2019.
15. Benefit plans
Defined contribution plans
The Company established a defined contribution savings plan under Section 401(k) of the Internal Revenue Code. This plan covers substantially all employees who meet minimum age and service requirements and allows
F-40
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
15. Benefit plans, continued
Defined contribution plans, continued
participants to defer a portion of their annual compensation on a pre-tax basis. The Company made matching contributions of $48 and $274 to the plan during the period from inception through December 31, 2018 and the year ended December 31, 2019, respectively.
Defined benefit plans—regular pension plan
ASC Topic 715, Compensation—Retirement Benefits, requires an employer to: (a) recognize in its statement of financial position an asset for a plan’s overfunded status or a liability for a plan’s under-funded status; (b) measure a plan’s assets and its obligations that determine its funded status as of the end of the employer’s fiscal year; and (c) recognize changes in the funded status of a defined benefit post retirement plan in the year in which the changes occur. Accordingly, the Company is required to report changes in its funded status on its consolidated statement of stockholders’ deficit and consolidated statement of operations and comprehensive loss.
Aligos-Belgium offers its employees a regular pension plan in the form of a defined contribution plan (the “Regular Pension Plan”), which contains a 1.75% legally required minimum rate of return for the participants. The Regular Pension Plan does not meet all the requirements that are needed for recognition of the plans as a defined contribution plan. The Company therefore recognizes the Regular Pension Plan as a defined benefit plan.
Net periodic benefit costs and other amounts recognized in other comprehensive loss for the Regular Pension Plan include the following components for the period from inception through December 31, 2018 and the year ended December 31, 2019:
| 2018 | 2019 | |||||||
| Service cost |
$ | 36 | $ | 94 | ||||
| Expected return on plan assets |
— | (2 | ) | |||||
| Interest costs |
— | 6 | ||||||
| Other costs |
29 | 29 | ||||||
| Prior service costs |
284 | 58 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| 349 | 185 | |||||||
| Net actuarial loss (gain) in plan asset and projected benefit obligation recognized in other comprehensive loss |
(3 | ) | 86 | |||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total recognized |
$ | 346 | $ | 271 | ||||
|
|
||||||||
The net periodic benefit costs, excluding service costs, are included in interest and other income (expense), net on the Company’s consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive loss.
F-41
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
15. Benefit plans, continued
Defined benefit plans—regular pension plan, continued
The activities under the Regular Pension Plan are as follow:
| 2018 | 2019 | |||||||
| Change in benefit obligation: |
||||||||
| Benefit obligation, beginning of year |
$ | — | $ | 317 | ||||
| Service cost |
36 | 94 | ||||||
| Interest cost |
— | 6 | ||||||
| Prior service cost |
284 | 58 | ||||||
| Actuarial loss (gain) |
(3 | ) | 85 | |||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Benefit obligation, end of year |
317 | 560 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Change in plan assets: |
||||||||
| Fair value of plan assets, beginning of year |
— | 317 | ||||||
| Company contributions |
346 | 182 | ||||||
| Expected net return on plan assets |
— | 2 | ||||||
| Other costs |
(29 | ) | (30 | ) | ||||
| Actuarial loss |
— | (1 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Fair value of plan assets, end of year |
317 | 470 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Funded status |
$ | — | $ | (90 | ) | |||
|
|
||||||||
The underfunded amount of $0 and $90 is recognized in accrued liabilities on the consolidated balance sheet as of December 31, 2018 and 2019, respectively. In addition, $3 of actuarial gain and $86 of actuarial loss is recognized in accumulated other comprehensive (loss) income for the period from inception through December 31, 2018 and the year ended December 31, 2019, respectively.
The accumulated benefit obligation for the defined benefit plan was $317 and $561 as of December 31, 2018 and 2019, respectively.
The weighted-average rates used to determine the net periodic benefit costs and projected benefit obligations were as follows:
| 2018 | 2019 | |||||||
| Discount rate |
1.90% | 0.90% | ||||||
| Rate of increased salary levels |
1.80% | 1.80% | ||||||
| Expected long-term rate of return on assets |
0.65% | 0.65% | ||||||
|
|
||||||||
The discount rate used in 2018 and 2019 is based on a yield curve constructed from a portfolio of high-quality, Euro-denominated fixed income investments with various maturities up to 12 years. Each year’s expected future benefit payments are discounted to their present value at the appropriate yield curve rate, thereby generating the overall discount rate for the projected benefit obligation.
F-42
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
15. Benefit plans, continued
Defined benefit plans—regular pension plan, continued
The expected long-term rate of return on plan assets is deemed to equal 0.75%, as guaranteed by the insurance company that holds the fund investments, less 0.1% of asset management fee, resulting in 0.65%.
The fair values of the Regular Pension Plan assets as of December 31, 2018 and 2019 are as follows:
| Significant unobservable inputs (Level 3) |
||||
| 2018: |
||||
| Sundry liabilities |
$ | (20 | ) | |
| Insurance policies |
337 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| $ | 317 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| 2019: |
||||
| Current account with insurer |
$ | (15 | ) | |
| Insurance policies |
485 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| $ | 470 | |||
|
|
||||
The following table sets forth a summary of changes in fair value of the Regular Pension Plan assets for which fair value was determined by Level 3 inputs:
| 2018 | 2019 | |||||||
| Unobservable inputs—beginning |
$ | — | $ | 317 | ||||
| Actual return on plan assets |
— | 1 | ||||||
| Net purchases, sales and settlements |
346 | 182 | ||||||
| Transfers out of Level 3 assets |
(29 | ) | (30 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Unobservable inputs—ending |
$ | 317 | $ | 470 | ||||
|
|
||||||||
The Company anticipates making $200 funding contributions to the Regular Pension Plan in 2020.
Estimated future benefit payments are as follows:
| Fiscal year: |
||||
| 2020 |
$ | 4 | ||
| 2021 |
3 | |||
| 2022 |
2 | |||
| 2023 |
2 | |||
| 2024 |
2 | |||
| 2025—2028 |
9 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| $ | 22 | |||
|
|
||||
F-43
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
15. Benefit plans, continued
Defined benefit plans—Top Hat Plan
In Aligos-Belgium, the Company established a pension bonus complementary plan (the “Top Hat Plan”), where the bonus payments to each participant are added to the Top Hat Plan. The annual contributions to this plan are based on performance and determined on a discretionary basis by the Company. The Top Hat Plan contains a legal yield guarantee of 1.75%. The Top Hat Plan became effective as of January 1, 2019.
In 2018, the Company accounted for the Top Hat Plan in accordance with ASC 710—Compensation, and recognized approximately $286 as research and development expenses in the consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive loss. The Top Hat Plan was underfunded and the Company recorded a corresponding liability of approximately $286 in accrued liabilities on the consolidated balance sheets as of December 31, 2018.
In 2019, the Company accounted for the Top Hat Plan in accordance with ASC 715—Compensation—Retirement Benefits, once it became effective. The Top Hat Plan does not meet all the requirements that are needed for recognition as a defined contribution plan. The Company therefore recognizes the Top Hat Plan as a defined benefit plan.
Net periodic benefit costs and other amounts recognized in other comprehensive loss for the Top Hat Plan included the following components for the year ended December 31, 2019:
| Prior service costs |
$ | 348 | ||
| Interest costs |
5 | |||
| Other costs |
27 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| 380 | ||||
| Net actuarial loss in plan asset and projected benefit obligation recognized in other comprehensive loss |
32 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Total recognized |
$ | 412 | ||
|
|
||||
The net periodic benefit costs, excluding prior service costs, are included in other expenses on the Company’s consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive loss.
F-44
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
15. Benefit plans, continued
Defined benefit plans—Top Hat Plan, continued
The activities under the Top Hat Plan were as follow for the year ended December 31, 2019:
| Change in benefit obligation: |
||||
| Benefit obligation, beginning of year |
$ | 261 | ||
| Prior service cost |
348 | |||
| Interest expense |
5 | |||
| Actuarial loss |
35 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Benefit obligation, end of year |
649 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Change in plan assets: |
||||
| Fair value of plan assets, beginning of year |
(20 | ) | ||
| Company contributions |
281 | |||
| Other costs |
(27 | ) | ||
| Actuarial gain |
3 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Fair value of plan assets, end of year |
237 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Funded status |
$ | (412 | ) | |
|
|
||||
The underfunded amount of $412 is recognized in accrued liabilities on the consolidated balance sheet as of December 31, 2019. In addition, $32 of actuarial loss is recognized in accumulated other comprehensive (loss) income for the year ended December 31, 2019.
The accumulated benefit obligation for the Top Hat Plan was $649 as of December 31, 2019.
The weighted-average rates used to determine the net periodic benefit costs and projected benefit obligations were as follows:
| Discount rate |
1.90% | |||
| Rate of increased salary levels |
1.80% | |||
| Expected long-term rate of return on assets |
0.00% | |||
|
|
||||
The discount rate used in 2019 is based on a yield curve constructed from a portfolio of high-quality, Euro-denominated fixed income investments with various maturities up to 12 years. Each year’s expected future benefit payments are discounted to their present value at the appropriate yield curve rate, thereby generating the overall discount rate for the projected benefit obligation.
The expected long-term rate of return on plan assets is deemed to equal 0.00%, as there is no guarantee of return from the insurance company holding the investments.
F-45
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
15. Benefit plans, continued
Defined benefit plans—Top Hat Plan, continued
The fair values of the Top Hat Plan assets as of December 31, 2019 were as follows:
| Significant unobservable inputs (Level 3) |
||||
| Sundry liabilities |
$ | (27 | ) | |
| Insurance policies |
264 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| $ | 237 | |||
|
|
||||
The following table sets forth a summary of changes in fair value of the Top Hat Plan assets in 2019 for which fair value was determined by Level 3 inputs:
| Unobservable inputs—beginning |
$ | (20 | ) | |
| Actual return on plan assets |
3 | |||
| Net purchases, sales and settlements |
281 | |||
| Transfers out of Level 3 assets |
(27 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|||
| Unobservable inputs—ending |
$ | 237 | ||
|
|
||||
The Company anticipates making $337 in funding contributions to the Top Hat Plan in 2020.
Estimated future benefit payments are as follows:
| Fiscal year: |
||||
| 2020 |
$ | 2 | ||
| 2021 |
2 | |||
| 2022 |
2 | |||
| 2023 |
2 | |||
| 2024 |
2 | |||
| 2025—2029 |
10 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| $ | 20 | |||
|
|
||||
F-46
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
16. Net loss per share
The following table summarizes the computation of basic and diluted net loss per share of the Company:
| Year ended December 31, | ||||||||
| 2018 | 2019 | |||||||
| WASO, basic and diluted |
1,191,787 | 2,007,173 | ||||||
| Net loss per share—basic and diluted |
$ | (11.69 | ) | $ | (26.04 | ) | ||
| Net loss |
$ | (13,933 | ) | $ | (52,264 | ) | ||
| Weighted average common stock outstanding, basic and diluted |
11,107,095 | 18,833,136 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net loss per share—basic and diluted |
$ | (1.25 | ) | $ | (2.78 | ) | ||
|
|
||||||||
The Company’s potentially dilutive securities, which include redeemable convertible preferred stock, forward contracts to issue Preferred Stock, options to purchase common stock and unvested restricted stock, have been excluded from the computation of diluted net loss per share as the effect would be to reduce the net loss per share. Therefore, the weighted-average number of shares of Common Stock outstanding used to calculate both basic and diluted net loss per share is the same. The Company excluded the following potential shares of Common Stock, presented based on amounts outstanding at each period end, from the computation of diluted net loss per share for the periods indicated because including them would have had an anti-dilutive effect:
| Year ended December 31, | ||||||||
| 2018 | 2019 | |||||||
| Redeemable convertible preferred stock |
10,806,432 | 19,163,877 | ||||||
| Forward contract to issue redeemable convertible preferred stock |
— | 3,569,630 | ||||||
| Options to purchase common stock |
1,062,457 | 884,623 | ||||||
| Unvested restricted stock |
1,521,387 | 827,187 | ||||||
| Warrants |
134,112 | 120,701 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| 13,524,388 | 24,566,018 | |||||||
|
|
||||||||
F-47
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
17. Pro forma net loss per share (unaudited)
The unaudited pro forma basic and diluted loss per share for the year ended December 31, 2019, as set forth in the table below gives effect to the conversion of all shares of redeemable convertible preferred stock upon the closing of the planned IPO by treating all shares of redeemable convertible preferred stock as if they had been converted to Common Stock at the beginning of the earliest period presented or the date of the original issuance, if later. Shares to be sold in the planned IPO are excluded from the unaudited pro forma basic and diluted net loss per share calculation. Pro forma net loss per common share, basic and diluted, for the year ended December 31, 2019 is calculated as follows:
| Year ended 2019 |
||||
| Numerator: |
||||
| Net loss |
$ | (52,264 | ) | |
|
|
|
|||
| Denominator: |
||||
| Weighted average common shares outstanding—basic and diluted |
2,007,173 | |||
| Add: Pro forma adjustment |
19,163,877 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Pro forma weighted average common shares outstanding |
21,171,050 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Pro forma net loss per common share—basic and diluted |
$ | (2.47 | ) | |
|
|
||||
18. Subsequent events
The Company has evaluated all events occurring through August 25, 2020, the date on which the consolidated financial statements were issued, during which time, nothing has occurred outside the normal course of business operations that would require disclosure other than the events disclosed below.
License and collaboration agreements
In April 2020, the Company amended the license agreement with Luxna. Pursuant to the amended license agreement, Luxna granted the Company an exclusive, worldwide license under the licensed patents to research, develop, make, have made, and commercialize products containing oligonucleotides targeting three families of viruses: orthomyxoviridae, paramyxoviridae, and coronaviridae (a family which includes SARS-CoV-2). As consideration for the amended license agreement, the Company paid Luxna a one-time non-refundable fee of $200.
In June 2020, the Company amended the license agreement with Emory. Pursuant to the amended license agreement, Emory granted the Company additional patent rights to certain compounds targeting the treatment or prevention of HBV. As consideration for the additional rights, the Company made a one-time, non-refundable payment to Emory in the amount of $150, with an additional obligation to pay up to a maximum of $35. On the same date, the Company entered into a collaboration agreement with Emory, with the initial research plan pertaining to the synthesis and evaluation of the compounds licensed through the additional patent rights granted in the amended license agreement. The research plan terminates one year from the effective date, with
F-48
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
18. Subsequent events, continued
License and collaboration agreements, continued
the Company having an option to extend for a second year. In connection with the research plan, the Company will provide Emory funding up to $270 per year.
On June 25, 2020, the Company entered into a Research, Licensing and Commercialization Agreement (“KU Leuven Agreement”) with Katholieke Universiteit Leuven (“KU Leuven”), under which the Company is collaborating with KU Leuven’s Rega Institute for Medical Research, as well as its Centre for Drug Design and Discovery, to research and develop potential protease inhibitors for the treatment, diagnosis or prevention of coronaviruses, including of SARS-CoV-2. Unless terminated earlier by either party in accordance with provisions in the agreement, the collaboration period will terminate at the earlier of completion of all collaboration activities or 2.5 years. In connection with this agreement, KU Leuven and the Company granted each other exclusive cross-licenses to use certain know-how and existing patents of the other party as well as certain joint know-how and joint patents to carry out research and development collaboration activities during the collaboration period. KU Leuven granted to the Company an exclusive (including as to KU Leuven), worldwide license under certain of KU Leuven’s know-how and existing patents, and certain joint patents and joint know-how, to manufacture and commercialize the licensed products for the treatment, diagnosis or detection of viral infections in humans. KU Leuven reserved the right to use all KU Leuven knowhow, existing KU Leuven patents, joint patents and joint know-how for academic and non-commercial research and teaching purposes. As consideration for this license, the Company is obligated to make payments to KU Leuven, in aggregate, totaling up to but no more than $30,000 upon the achievement of certain commercial sales milestones. For each licensed product developed through KU Leuven and the Company’s collaborative effort, the Company is obligated to make payments to KU Leuven, in aggregate, totaling up to $32,000 upon the achievement of certain development and regulatory milestones. The Company is also required to pay KU Leuven a low-to-mid-single digit royalty percentage, subject to certain adjustments, on net sales of applicable products, if any. Unless terminated earlier by either party, the agreement shall continue until the expiration of the last to expire royalty term, which is the later of the expiration or termination of the last valid patent claim covering the manufacture, use, sale or importation of the licensed product in a particular country or 10 years after the first commercial sale of a licensed product.
Stock options
During the period from February through June 2020, the Board of Directors granted options to purchase a total of 2,007,936 shares of Common Stock to management and certain employees at an exercise price of $3.45 per share. Of the options granted, options to purchase 454,994 shares of Common Stock were granted with performance-based vesting conditions. These performance-based conditions are met upon the completion of a subsequent closing pursuant to the Series B preferred stock purchase agreement or waiver from the Board of the requirement.
Coronavirus aid, relief and economic security act (“CARES Act”)
In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, the CARES Act was signed into law in March 2020. The CARES Act lifts certain deduction limitations originally imposed by the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 (the “2017 Tax Act”).
F-49
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
18. Subsequent events, continued
Coronavirus aid, relief and economic security act (“CARES Act”), continued
Corporate taxpayers may carryback NOLs originating during 2018 through 2020 for up to five years, which was not previously allowed under the 2017 Tax Act. The CARES Act also eliminates the 80% of taxable income limitations by allowing corporate entities to fully utilize NOL carryforwards to offset taxable income in 2018, 2019 or 2020. Taxpayers may generally deduct interest up to the sum of 50% of adjusted taxable income plus business interest income (30% limit under the 2017 Tax Act) for tax years beginning January 1, 2019 and 2020. The CARES Act allows taxpayers with alternative minimum tax credits to claim a refund in 2020 for the entire amount of the credits instead of recovering the credits through refunds over a period of years, as originally enacted by the 2017 Tax Act. The Company does not anticipate any adverse impacts as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Incorporation of wholly owned subsidiary
On March 30, 2020, Aligos Australia Pty LTD (“Aligos Australia”) was incorporated as a wholly owned subsidiary of the Company. Aligos Australia is primarily focused on conducting clinical trials.
F-50
Table of Contents
Condensed consolidated balance sheets
(Unaudited)
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
| December 31, 2019 |
June 30, 2020 |
Pro forma June 30, 2020 |
||||||||||
| ASSETS | ||||||||||||
| Current assets: |
||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 69,565 | $ | 22,678 | $ | 63,453 | ||||||
| Restricted cash |
538 | 553 | 553 | |||||||||
| Investments in available-for-sale securities, at fair value |
— | 40,415 | 40,415 | |||||||||
| Investments in held-to-maturity securities |
48,098 | 25,029 | 25,029 | |||||||||
| Other current assets |
2,025 | 2,779 | 2,779 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total current assets |
120,226 | 91,454 | 132,229 | |||||||||
| Operating lease right-of-use assets |
7,570 | 7,225 | 7,225 | |||||||||
| Property and equipment, net |
8,517 | 8,987 | 8,987 | |||||||||
| Other assets |
188 | 235 | 235 | |||||||||
| Long-term investments in held-to-maturity securities |
10,019 | — | — | |||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total assets |
$ | 146,520 | $ | 107,901 | $ | 148,676 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| LIABILITIES, REDEEMABLE CONVERTIBLE PREFERRED STOCK, AND STOCKHOLDERS’ DEFICIT | ||||||||||||
| Current liabilities: |
||||||||||||
| Accounts payable |
$ | 3,767 | 3,296 | 3,296 | ||||||||
| Accrued liabilities |
7,599 | 9,612 | 9,612 | |||||||||
| Operating lease liabilities, current |
2,378 | 2,381 | 2,381 | |||||||||
| Finance lease liabilities, current |
74 | 75 | 75 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total current liabilities |
13,818 | 15,364 | 15,364 | |||||||||
| Derivative liabilities |
461 | 380 | — | |||||||||
| Redeemable convertible preferred stock liabilities |
3,174 | 2,810 | — | |||||||||
| Operating lease liabilities, net of current portion |
11,701 | 11,106 | 11,106 | |||||||||
| Finance lease liabilities, net of current portion |
178 | 149 | 149 | |||||||||
| Other liabilities |
— | 99 | 99 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total liabilities |
29,332 | 29,908 | 26,718 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Commitments and contingencies (Note 12) |
||||||||||||
| Series A Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock, $0.0001 par value; 101,962,864 shares authorized as of December 31, 2019 and June 30, 2020 (unaudited); 10,819,843, 10,857,395 and no shares issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2019, June 30, 2020 actual and pro forma (unaudited), respectively; aggregate minimum liquidation preference of $101,188 at June 30, 2020 |
100,695 | 101,182 | — | |||||||||
| Series B-1 Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock, $0.0001 par value; 77,764,055 shares authorized as of December 31, 2019 and June 30, 2020 (unaudited); 8,344,034, 8,344,034 and no shares issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2019, June 30, 2020 actual and pro forma (unaudited); aggregate minimum liquidation preference of $85,005 at June 30, 2020 |
81,384 | 81,384 | — | |||||||||
| Stockholders’ deficit: |
||||||||||||
| Common stock, $0.0001 par value per share; 278,000,000 shares authorized as of December 31, 2019 and June 30, 2020 (unaudited); 3,927,803, 4,035,978 and 23,797,848 shares issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2019, June 30, 2020 actual and pro forma (unaudited), respectively |
— | — | 2 | |||||||||
| Non-voting common stock, $0.0001 par value per share; no shares issued or outstanding as of December 31, 2019 and June 30, 2020, respectively; 3,092,338 issued and outstanding, pro forma (unaudited); |
|
— |
|
— | — | |||||||
| Additional paid-in capital |
1,421 | 2,300 | 228,829 | |||||||||
| Accumulated deficit |
(66,197 | ) | (107,023 | ) | (107,023 | ) | ||||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive (loss) income |
(115 | ) | 150 | 150 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total stockholders’ deficit |
(64,891 | ) | (104,573 | ) | 121,958 | |||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total liabilities, redeemable convertible preferred stock, and stockholders’ deficit |
$ | 146,520 | $ | 107,901 | $ | 148,676 | ||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-51
Table of Contents
Condensed consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive loss
(Unaudited)
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
| Six months ended June 30, | ||||||||
| 2019 | 2020 | |||||||
| Operating expenses: |
||||||||
| Research and development |
$ | 17,336 | $ | 34,478 | ||||
| General and administrative |
3,767 | 7,514 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total operating expenses |
21,103 | 41,992 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Loss from operations |
(21,103 | ) | (41,992 | ) | ||||
| Interest and other income, net |
1,073 | 1,108 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Loss before income tax expense |
(20,030 | ) | (40,884 | ) | ||||
| Income tax benefits |
— | 58 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net loss |
(20,030 | ) | (40,826 | ) | ||||
| Other comprehensive gain (loss): |
||||||||
| Unrealized gain on available-for-sale securities |
— | 238 | ||||||
| Unrealized (loss) gain on pension plans |
(47 | ) | 27 | |||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Other comprehensive (loss) income |
(47 | ) | 265 | |||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Comprehensive loss |
$ | (20,077 | ) | $ | (40,561 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net loss per share, basic and diluted |
$ | (11.54 | ) | $ | (14.96 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Weighted average shares of common stock, basic and diluted |
1,735,358 | 2,729,827 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Pro forma net loss per share, basic and diluted (unaudited) |
$ | (1.86 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Pro forma weighted average shares of common stock, basic and diluted (unaudited) |
21,931,256 | |||||||
|
|
||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-52
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Condensed consolidated statements of changes in redeemable convertible preferred stock and stockholders’ deficit
(Unaudited)
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
| Series A redeemable convertible preferred stock |
Series B-1 redeemable convertible preferred stock |
Common stock | Additional paid-in capital |
Accumulated deficit |
Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) |
Total stockholders’ deficit |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance as of December 31, 2018 |
10,806,432 | 100,519 | — | — | 3,036,574 | — | 182 | (13,933 | ) | 3 | (13,748 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 453 | — | — | 453 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive loss |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (47 | ) | (47 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | (20,030 | ) | — | (20,030 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance as of June 30, 2019 |
10,806,432 | $ | 100,519 | — | $ | — | 3,036,574 | $ | 0 | $ | 635 | $ | (33,963 | ) | $ | (44 | ) | $ | (33,372 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Series A redeemable convertible preferred stock |
Series B-1 redeemable convertible preferred stock |
Common stock | Additional paid-in capital |
Accumulated deficit |
Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) |
Total stockholders’ deficit |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance as of December 31, 2019 |
10,819,843 | 100,695 | 8,344,034 | 81,384 | 3,927,803 | — | 1,421 | (66,197 | ) | (115 | ) | (64,891 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of Series A redeemable convertible preferred stock upon exercise of warrants |
37,552 | 487 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock upon exercise of stock options |
— | — | — | — | 108,175 | — | 94 | — | — | 94 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 658 | — | — | 658 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vesting of early exercised common stock options |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 127 | — | — | 127 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive income |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 265 | 265 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | (40,826 | ) | — | (40,826 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance as of June 30, 2020 |
10,857,395 | $ | 101,182 | 8,344,034 | $ | 81,384 | 4,035,978 | $ | 0 | $ | 2,300 | $ | (107,023 | ) | $ | 150 | $ | (104,573 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-53
Table of Contents
Condensed consolidated statements of cash flows
(Unaudited)
(In thousands)
| Six months ended June 30, |
||||||||
| 2019 | 2020 | |||||||
| Cash flows from operating activities: |
||||||||
| Net loss |
$ | (20,030 | ) | $ | (40,826 | ) | ||
| Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash used in operating activities: |
||||||||
| Accretion of discount on investments |
(666 | ) | 90 | |||||
| Amortization of right of use assets |
548 | 267 | ||||||
| Depreciation expense |
481 | 1,290 | ||||||
| Stock-based compensation |
453 | 658 | ||||||
| Change in fair value of derivative liability |
(140 | ) | 56 | |||||
| Change in fair value of redeemable convertible preferrable stock liabilities |
— | (364 | ) | |||||
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities: |
||||||||
| Other current assets |
284 | (564 | ) | |||||
| Right of use assets |
95 | — | ||||||
| Accounts payable |
732 | (89 | ) | |||||
| Accrued liabilities |
(412 | ) | 2,061 | |||||
| Operating lease liabilities |
320 | (592 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net cash and cash equivalents used in operating activities |
(18,335 | ) | (38,013 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Cash flows from investing activities: |
||||||||
| Activities in available-for-sale investments: |
||||||||
| Maturities of investments |
— | 5,000 | ||||||
| Purchase of investments |
— | (45,279 | ) | |||||
| Activities in held-to-maturity investments: |
||||||||
| Maturities of investments |
49,500 | 33,100 | ||||||
| Purchase of investments |
(26,378 | ) | — | |||||
| Purchases of property and equipment |
(1,428 | ) | (1,659 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net cash and cash equivalents provided by (used in) investing activities |
21,694 | (8,838 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Cash flows from financing activities: |
||||||||
| Proceeds from exercise of warrants for series A convertible preferred stock |
— | 350 | ||||||
| Payment of Series B-1 redeemable convertible preferred stock issuance cost |
— | (405 | ) | |||||
| Payments on finance lease |
(17 | ) | (28 | ) | ||||
| Proceeds from the exercise of common stock option |
— | 62 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net cash and cash equivalents used in financing activities |
(17 | ) | (21 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net increase (decrease) in cash, cash equivalents, and restricted cash |
3,342 | (46,872 | ) | |||||
| Cash, cash equivalents, and restricted cash, beginning of period |
24,547 | 70,103 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Cash, cash equivalents, and restricted cash, end of period |
$ | 27,889 | $ | 23,231 | ||||
|
|
||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-54
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Condensed consolidated statements of cash flows
(Unaudited)
(In thousands)
| Six months ended June 30, |
||||||||
| 2019 | 2020 | |||||||
| Reconciliation to amounts on the consolidated balance sheet: |
||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 27,350 | $ | 22,678 | ||||
| Restricted cash |
539 | 553 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total cash, cash equivalents, and restricted cash |
$ | 27,889 | $ | 23,231 | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Supplemental disclosures of cash flow information: |
||||||||
| Interest paid |
$ | 3 | $ | 4 | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Income taxes paid |
$ | — | $ | — | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Supplemental disclosures of noncash financing and investing activities: |
||||||||
| Leasehold improvement directly paid by landlord |
$ | 3,208 | $ | 79 | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Equipment acquired through finance lease |
$ | 133 | $ | — | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Mark to market adjustment for available-for-sale investments |
$ | — | $ | 237 | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Acquisition of right of use asset through operating lease obligation |
$ | 252 | $ | — | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Change in fair value of derivative liability upon exercise of warrants |
$ | — | $ | 137 | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Vesting of early exercised options |
$ | — | $ | 127 | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Receivable from exercise of common stock options |
$ | — | $ | 237 | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Property and equipment purchases in accounts payable |
$ | 213 | $ | 22 | ||||
|
|
||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-55
Table of Contents
Notes to unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
1. Organization
Description of business
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc. (“Aligos-US”) was incorporated in the state of Delaware on February 5, 2018 (“inception”). On September 10, 2018, the Company formed Aligos Belgium BVBA (“Aligos-Belgium”), a limited liability company organized under the laws of Belgium. On March 30, 2020, the Company formed as a wholly owned subsidiary, Aligos Australia Pty LTD, a proprietary limited company, (“Aligos-Australia,” and together with Aligos-US and Aligos-Belgium, the “Company” or “Aligos”).
Aligos is a clinical-stage biopharmaceutical company developing novel therapeutics to address unmet medical needs in viral and liver diseases, including chronic hepatitis B and coronaviruses therapeutics for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (“NASH”).
The Company is devoting substantially all of its efforts to the research and development of its drug candidates. The Company has not generated any product revenue to date. The Company is also subject to a number of risks similar to other companies in the biotechnology industry, including the uncertainty of success of its nonclinical studies and clinical trials, regulatory approval of drug candidates, uncertainty of market acceptance of products, competition from substitute products and larger companies, the need to obtain additional financing, compliance with government regulations, protection of proprietary technology, dependence on third-parties, product liability, and dependence on key individuals.
Reverse stock split
On October 8, 2020, the Company’s board of directors approved a 1-for-9.3197 reverse stock split (the “Reverse Stock Split”) of the Company’s common stock and redeemable convertible preferred stock to be consummated prior to the effectiveness of the Company’s planned initial public offering (“IPO”). The par value and authorized shares of the common stock and redeemable convertible preferred stock were not adjusted as a result of the reverse stock split. All issued and outstanding common stock, options to purchase common stock and per share amounts contained in the financial statements have been retroactively adjusted to give effect to the reverse stock split for all periods presented. The Company filed an amended and restated certificate of incorporation in Delaware on October 9, 2020 that automatically effectuated the Reverse Stock Split without any further action required.
2. Summary of significant accounting policies
Liquidity
The Company has incurred losses and negative cash flows from operations since its inception. As of December 31, 2019 and June 30, 2020, the Company has an accumulated deficit of approximately $66,197 and $107,023, respectively. Since inception through June 30, 2020, the Company has funded operations primarily with the net proceeds from the issuance of redeemable convertible preferred stock and convertible notes. Management expects to continue to incur additional substantial losses in the foreseeable future as a result of expanded research and development activities.
As of June 30, 2020, the Company has unrestricted cash, cash equivalent and investments of approximately $88,122, which is available to fund future operations. The Company expects to continue to spend substantial
F-56
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
2. Summary of significant accounting policies, continued
Liquidity, continued
amounts to continue the nonclinical and clinical development of its current and future programs. If the Company is able to gain marketing approval for drug candidates that are being developed, it will require significant additional amounts of cash in order to launch and commercialize such drug candidates. In addition, other unanticipated costs may arise. Because the design and outcome of the Company’s planned and anticipated clinical trials is highly uncertain, the Company cannot reasonably estimate the actual amounts necessary to successfully complete the development and commercialization of any drug candidate the Company may develop.
The Company is seeking to complete an IPO of its Common Stock. Upon the closing of a qualified public offering, the Company’s outstanding redeemable convertible preferred stock will automatically convert into shares of Common Stock (Note 8).
The Company expects to finance its cash needs through a combination of public or private equity offerings, debt financings, collaborations, strategic alliances, licensing arrangements and other marketing or distribution arrangements. In addition, the Company may seek additional capital to take advantage of favorable market conditions or strategic opportunities even if the Company believes it has sufficient funds for its current or future operating plans. Based on the Company’s research and development plans, it is expected that the Company’s existing cash, cash equivalents and investments, will enable the Company to fund its operations for at least 12 months following the date the condensed consolidated financial statements are issued. However, the Company’s operating plan may change as a result of many factors currently unknown.
The accompanying condensed consolidated financial statements have been prepared on a basis that assumes the Company will continue as a going concern and contemplates the continuity of operations, realization of assets and the satisfaction of liabilities and commitments in the normal course of business.
Risks and uncertainties
The Company is subject to risks common to companies in the biotechnology industry including, but not limited to, new technological innovations, protection of proprietary technology, dependence on key personnel, compliance with government regulations and the need to obtain additional financing. As a result, the Company is unable to predict the timing or amount of increased expenses or when or if the Company will be able to achieve or maintain profitability. Drug candidates currently under development will require significant additional research and development efforts, including extensive nonclinical and clinical testing.
Moreover, it is particularly difficult to estimate with certainty the Company’s future expenses given the dynamic nature of its business, the COVID-19 pandemic and the macro-economic environment generally.
The Company’s ability to raise additional funds will depend on financial, economic and other factors, many of which are beyond its control. In particular, the COVID-19 pandemic continues to rapidly evolve and has already resulted in a significant disruption of global financial markets. If the disruption persists or deepens, the Company could be unable to access additional capital, which could negatively affect its ability to consummate certain corporate development transactions or other important, beneficial or opportunistic investments. If
F-57
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
2. Summary of significant accounting policies, continued
Liquidity, continued
additional funds are not available to the Company when needed, on terms that are acceptable to the Company, or at all, the Company may choose to reduce spending by delaying, limiting, reducing or terminating nonclinical studies, clinical trials or other research and development activities or eliminate one or more of its development programs altogether; or delaying, limiting, reducing or terminating its efforts to establish manufacturing and sales and marketing capabilities or other activities that may be necessary to commercialize any future approved products, or reduce the Company’s flexibility in developing or maintaining its sales and marketing strategy.
Basis of presentation
The accompanying unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”) and applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) regarding interim financial reporting. Accordingly, they do not include all of the information and footnotes required by U.S. GAAP for complete financial statements. Any reference in these notes to applicable accounting guidance is meant to refer to the authoritative U.S. GAAP included in the Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”), and Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) issued by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”). The unaudited interim condensed consolidated financial statements have been prepared on a basis consistent with the audited financial statements and in the opinion of management, all adjustments, consisting of normal recurring adjustments, considered necessary for a fair presentation of the financial statements have been included.
The accompanying unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements should be read in conjunction with the audited consolidated financial statements and notes thereto for the year ended December 31, 2019. The unaudited condensed balance sheet as of December 31, 2019 included herein was derived from the audited financial statements as of that date. The results of operations for the six months ended June 30, 2020 are not necessarily indicative of the results for the fiscal year ending December, 31, 2020 or any future interim period.
Principles of consolidation
The accompanying condensed consolidated financial statements include Aligos-US and its wholly owned subsidiaries Aligos-Belgium and Aligos-Australia. All intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated.
Use of estimates
The preparation of the condensed consolidated financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make certain estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts in the condensed consolidated financial statements and accompanying notes. The Company regularly evaluates estimates and assumptions related to assets and liabilities, and disclosures of contingent assets and liabilities at the dates of the condensed consolidated financial statements and the reported amounts of expenses during the reporting period. Areas where management uses subjective judgments include, but are not limited to right-of-use assets, lease obligations, impairment of long-lived assets, stock-based compensation, accrued research and
F-58
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
2. Summary of significant accounting policies, continued
Use of estimates, continued
development costs, pension liabilities, derivative liabilities and redeemable convertible preferred stock liability in the accompanying condensed consolidated financial statements. Management bases its estimates on historical experience and on various other assumptions that are believed to be reasonable under the circumstances, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying values of assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other sources. Actual results may differ materially from these estimates under different assumptions or conditions.
Unaudited pro forma information
Immediately prior to the completion of this offering, all outstanding shares of redeemable convertible preferred stock will automatically convert into common stock. In addition, the convertible preferred stock warrants will be exercised into shares of convertible preferred stock which will automatically convert into shares of common stock and the related warrant liability will be reclassified to additional paid-in capital in stockholders’ equity. Unaudited pro forma balance sheet information as of June 30, 2020 assumes the net exercise of the preferred stock warrants and the conversion of all outstanding convertible preferred stock into shares of common stock. The shares of common stock issuable and the proceeds expected to be received in the initial public offering are excluded from such pro forma financial information. The Company has presented the unaudited pro forma basic and diluted net loss per share attributable to common stockholders for the six months ended June 30, 2020, which shows the assumed effect of an initial public offering, including the conversion of all redeemable convertible preferred stock into shares of Common Stock as if the conversion had occurred as of the later of the beginning of the period or the original date of issuance. The pro forma net loss per share attributable to common stockholders does not include proceeds to be received from nor does it include shares expected to be sold in the assumed IPO.
Investments
The Company determines the appropriate classification of debt securities at the time of purchase and re-evaluates such designation as of each balance sheet date. Debt securities are classified as held-to-maturity when the Company has the positive intent and ability to hold the securities to maturity, otherwise debt securities are classified as available-for sale. Held-to-maturity securities are carried at amortized cost. Available-for-sale debt securities are measured and reported at fair value using quoted prices in active markets for similar securities. Unrealized gains and losses on available-for-sale debt securities are reported as a separate component of stockholders’ deficit. Premiums or discounts from par value are amortized to investment income over the life of the underlying investment. The cost of securities sold is determined on a specific identification basis, and realized gains and losses are included in other income (expense), net within the condensed consolidated statement of operations and comprehensive loss.
For both held-to-maturity and available-for-sale investments, the Company periodically reviews each individual security position that has an unrealized loss, or impairment, to determine if that impairment is other-than-temporary. If the Company believes an impairment of a security position is other-than-temporary, based on available quantitative and qualitative information as of the report date, the loss will be recognized as other
F-59
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
2. Summary of significant accounting policies, continued
Investments, continued
income (expense), net in the Company’s condensed consolidated statements of operations and a new cost basis in the investment is established. No impairment charges were recorded during the six months ended June 30, 2019 and 2020.
As of December 31, 2019 and June 30, 2020, short-term investments consisted of U.S. Treasury securities with original maturities of less than one year. As of December 31, 2019 and June 30, 2020, long-term investments consisted of U.S. Treasury securities with original maturities of more than one year.
Deferred offering costs
The Company capitalizes certain legal, professional accounting and other third-party fees that are directly associated with in-process equity financings, including the planned IPO, as deferred offering costs until such financings are consummated. After consummation of the financing, these costs are recorded as a reduction of the proceeds received from the equity financing. If a planned equity financing is abandoned, the deferred offering costs are expensed immediately as a charge to operating expenses in the condensed consolidated statement of operations and comprehensive loss. There were $0 and $47 deferred offering costs on the Company’s condensed consolidated balance sheets at December 31, 2019 and June 30, 2020.
Leases
The Company determines if an arrangement is a lease at the inception of the lease. Operating leases are included in operating lease right-of-use (“ROU”) assets and operating lease liabilities in the condensed consolidated balance sheet. Finance leases are included in property and equipment and finance lease liabilities in the condensed consolidated balance sheet.
ROU assets represent the right to use an underlying asset for the lease term and lease liabilities represent the obligation to make lease payments arising from the lease. Operating lease ROU assets and liabilities are recognized at the lease commencement date based on the present value of lease payments over the lease term. When the Company’s leases do not provide an implicit rate, an incremental borrowing rate is used based on the information available at the commencement dates in determining the present value of lease payments. The operating lease ROU assets also include any lease payments made and excludes lease incentives when paid by the Company or on the Company’s behalf. The Company’s lease terms may include the period covered by options to extend or terminate the lease when it is reasonably certain that the Company will exercise that option. Lease expense for operating leases is recognized on a straight-line basis over the lease term.
The Company has lease agreements with lease and non-lease components. The Company elected to not separate lease and non-lease components for all of its building leases. For vehicle leases, lease and non-lease components are accounted for separately. The Company also made an accounting policy election to recognize lease expense for leases with a term of 12 months or less on a straight-line basis over the lease term and not recognize ROU assets or lease liabilities for such leases.
F-60
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
2. Summary of significant accounting policies, continued
Property and equipment
Property and equipment is stated at cost less accumulated depreciation, and is depreciated using the straight-line method over the estimated useful life of the asset, which are as follows:
| Lab equipment |
3 years | |
| Computer equipment |
3 years | |
| Furniture and office equipment |
3-8 years | |
| Vehicles |
4 years | |
| Leasehold improvements |
Shorter of the useful life or remaining lease term | |
|
| ||
Expenditures for repairs and maintenance of assets are charged to expense as incurred. Upon retirement or sale, the cost and related accumulated depreciation of assets disposed of are removed from the accounts and any resulting gain or loss is included in loss from operations.
Impairment of long-lived assets
The Company regularly reviews the carrying amount of its property, equipment and intangible assets to determine whether indicators of impairment may exist which warrant adjustments to carrying values or estimated useful lives. If indications of impairment exist, projected future undiscounted cash flows associated with the asset are compared to the carrying amount to determine whether the asset’s value is recoverable. If the carrying value of the asset exceeds such projected undiscounted cash flows, the asset will be written down to its estimated fair value. No impairment charges were recorded during the six months ended June 30, 2019 and 2020.
Research and development expenses
Research and development costs are expensed as incurred. Research and development expenses consist of costs incurred in performing research and development activities, including salaries, stock-based compensation and benefits, facilities costs, depreciation, and third-party license fees. Non-refundable prepayments for goods or services that will be used or rendered for future research and development activities are deferred and capitalized. Such amounts are recognized as an expense as the goods are delivered or the related services are performed or until it is no longer expected that the goods will be delivered or the services will be rendered.
Derivative liabilities
The Company accounts for certain warrants as liabilities at fair value and adjusts the instruments to fair value at each reporting period. The Company determined that its outstanding warrants are freestanding derivative instruments. The warrants are subject to re-measurement at each balance sheet date until exercised, and any change in fair value is recognized as a component of interest and other income (expense), net in the condensed consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive loss. The fair value of the warrants issued by the Company has been estimated using a probability-weighted multi-scenario Black-Scholes option-pricing model. (Note 10).
F-61
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
2. Summary of significant accounting policies, continued
Redeemable convertible preferred stock liability
The freestanding instrument related to the commitment by certain preferred stockholders to purchase and the commitment by the Company to sell its convertible preferred stock in a subsequent closing, contingent upon the achievement of certain developmental milestones or an election by preferred stockholders to waive such milestones, at a fixed price per share, is considered a derivative liability (“Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock Liability”). The Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock Liability is measured at fair value as the underlying shares contain liquidation preferences upon certain “deemed liquidation events” that are not solely within the Company’s control and which are considered in-substance contingent redemption features (refer to Note 8 for further discussion on the redemption rights of the convertible preferred stock). The Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock Liability is subject to revaluation at each balance sheet date until settlement or extinguishment, with revaluations recognized as a component of interest and other income (expense), net in the condensed consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive loss. The fair value of the Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock Liability in subsequent closings has been estimated using a probability-weighted multi-scenario Black Scholes hybrid valuation method (Note 10).
Redeemable convertible preferred stock
The Company’s shares of preferred stock are assessed at issuance for classification and redemption features requiring bifurcation. The Company presents as temporary equity any stock which (i) the Company undertakes to redeem at a fixed or determinable price on the fixed or determinable date or dates; (ii) is redeemable at the option of the holders, or (iii) has conditions for redemption which are not solely within the control of the Company. The Company’s preferred stock is redeemable upon a deemed liquidation event which the Company determined is not solely within its control and thus has classified shares of preferred stock as temporary equity until such time as the conditions are removed or lapse. Because the occurrence of a deemed liquidation event is not currently probable, the carrying values of the shares of convertible preferred stock are not being accreted to their redemption values. Subsequent adjustments to the carrying values of the shares of convertible preferred stock would be made only when a deemed liquidation event becomes probable.
Fair value measurements
Certain assets and liabilities of the Company are carried at fair value under GAAP. Fair value is defined as the exchange price that would be received for an asset or paid to transfer a liability (an exit price) in the principal or most advantageous market for the asset or liability in an orderly transaction between market participants on the measurement date. Valuation techniques used to measure fair value must maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs. Financial assets and liabilities carried at fair value are to be classified and disclosed in one of the following three levels of the fair value hierarchy, of which the first two are considered observable and the last is considered unobservable:
Level 1—Quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities.
Level 2—Observable inputs (other than Level 1 quoted prices), such as quoted prices in active markets for similar assets or liabilities, quoted prices in markets that are not active for identical or similar assets or liabilities, or other inputs that are observable or can be corroborated by observable market data.
F-62
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
2. Summary of significant accounting policies, continued
Fair value measurements, continued
Level 3—Unobservable inputs that are supported by little or no market activity that are significant to determining the fair value of the assets or liabilities, including pricing models, discounted cash flow methodologies and similar techniques.
Stock-based compensation
The Company’s stock-based awards consist of restricted stock awards and stock options. For stock-based awards issued to employees and nonemployees with service-based vesting, the Company measures the estimated fair value of the stock-based awards on the date of grant and recognizes compensation expense for those awards over the requisite service period, which is generally the vesting period of the respective award. The Company has granted certain options with performance-based vesting for which expense is recognized over the explicit service period when achievement of the performance-based milestones is deemed probable. The Company uses judgement to determine whether and, if so, how many awards are deemed probable of vesting at each reporting period. The fair value of stock-based awards with non-market performance conditions is estimated on the grant date. The Company records expense for awards with service-based vesting using the straight-line method and for awards with performance conditions utilizing an accelerated attribution method. The Company accounts for forfeitures as they occur.
The Company classifies stock-based compensation expense in its condensed consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive loss in the same manner in which the award recipient’s cash compensation costs are classified.
The fair value of each restricted stock award is determined based on the number of shares granted and the value of the Company’s common stock on the date of grant. The fair value of each stock option award is estimated on the date of grant using the Black-Scholes option pricing model. The Black-Scholes option-pricing model requires the use of a number of complex assumptions including the fair value of the common stock, expected volatility, risk-free interest rate, expected dividends, and expected term of the option. The Company has been a private company and lacks company-specific historical and implied fair value information. Therefore, the Board of Directors (the “Board”) of the Company considers numerous objective and subjective factors to determine the fair value of the Company’s common stock options at each meeting in which awards are approved. The factors considered include, but are not limited to (i) the results of contemporaneous independent third-party valuations of the Company’s common stock and the prices, rights, preferences and privileges of the Company’s preferred stock relative to those of its common stock; (ii) the lack of marketability of the Company’s common stock; (iii) actual operating and financial results; (iv) current business conditions and projections; (v) the likelihood of achieving a liquidity event, such as an initial public offering or sale of the Company, given prevailing market conditions, and (vi) precedent transactions involving the Company’s shares.
The Company determined the expected stock volatility using a weighted-average of the historical volatility of a group of guideline companies that issued options with substantially similar terms, and expects to continue to do so until such time as the Company has adequate historical data regarding the volatility of its own traded stock price. The expected term of the Company’s stock options has been determined utilizing the simplified method for awards that qualify as plain-vanilla options. The risk-free interest rate is determined by reference to the U.S.
F-63
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
2. Summary of significant accounting policies, continued
Stock-based compensation, continued
Treasury yield curve in effect at the time of grant of the award for time periods approximately equal to the expected term of the award. The Company has not paid, and does not anticipate paying, cash dividends on its common stock; therefore, the expected dividend yield is assumed to be zero.
See Note 9 for the assumptions used by the Company in determining the grant date fair value of stock-based awards granted, as well as a summary of the stock-based award activity under the Company’s stock-based compensation plan for the six months ended June 30, 2019 and 2020.
Income taxes
Deferred tax assets and liabilities are determined on the basis of the differences between the condensed consolidated financial statements and tax basis of assets and liabilities using enacted tax rates in effect for the year in which the differences are expected to reverse. Changes in deferred tax assets and liabilities are recorded in the provision for income taxes. The Company assesses the likelihood that its deferred tax assets will be recovered from future taxable income and, to the extent it believes, based upon the weight of available evidence, that it is more likely than not that all or a portion of the deferred tax assets will not be realized, a valuation allowance is established.
The Company accounts for uncertain tax positions recognized in the condensed consolidated financial statements by prescribing a more-likely-than-not threshold for financial statement recognition and measurement of a tax position taken or expected to be taken in a tax return. The provision for income taxes includes the effects of any resulting tax reserves, or unrecognized tax benefits, that are considered appropriate as well as the related net interest and penalties.
Net loss per share
Basic net loss per share attributable to common stockholders is calculated by dividing the net loss attributable to common stockholders by the weighted-average number of shares of common stock outstanding during the period, without consideration for potentially dilutive securities.
Diluted net loss per share attributable to common stockholders is computed by dividing the net loss attributable to common stockholders by the weighted-average number of common stock and potentially dilutive securities outstanding for the period. For purposes of the diluted net loss per share calculation, redeemable convertible preferred stock, stock options, common stock subject to repurchase related to early exercise of stock options, unvested restricted stock subject to repurchase, warrants and convertible notes are considered to be potentially dilutive securities.
The Company applies the two-class method to calculate its basic and diluted net loss per share as the Company has issued shares that meet the definition of participating securities. The two-class method is an earnings allocation formula that treats a participating security as having rights to earnings that otherwise would have been available to common stockholders. The Company’s participating securities contractually entitle the holders of such shares to participate in dividends; but do not contractually require the holders of such shares to
F-64
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
2. Summary of significant accounting policies, continued
Net loss per share, continued
participate in losses of the Company. Accordingly, in periods in which the Company reports a net loss, such losses are not allocated to such participating securities.
Accordingly, in periods in which the Company reports a net loss, diluted net loss per share is the same as basic net loss per share, since dilutive common shares are not assumed to have been issued if their effect is anti-dilutive.
Recently adopted accounting pronouncements
In August 2018, the FASB issued ASU No. 2018-13, Fair Value Measurement (Topic 820): Disclosure Framework— Changes to the Disclosure Requirements for Fair Value Measurement (“ASU 2018-13”). The amendments eliminate, add, and modify certain disclosure requirements for fair value measurements. The amendments are effective for interim and annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2019, with early adoption permitted for either the entire ASU or only the provisions that eliminate or modify requirements. The amendments with respect to changes in unrealized gains and losses, the range and weighted-average of significant unobservable inputs used to develop Level 3 fair value measurements, and the narrative description of measurement uncertainty are to be applied prospectively. All other amendments are to be applied retrospectively to all periods presented. The Company adopted ASU 2018-13 on January 1, 2020. This guidance did not have a significant impact on the Company’s condensed consolidated financial statements and related disclosures.
In June 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-13. Financial Instruments—Credit Losses (Topic 326): Measurement of Credit Losses on Financial Instruments (“ASU 2016-13”), which requires that financial assets measured at amortized cost be presented at the net amount expected to be collected. Currently, U.S. GAAP delays recognition of the full amount of credit losses until the loss is probable of occurring. Under this ASU, the income statement will reflect an entity’s current estimate of all expected credit losses. The measurement of expected credit losses will be based upon historical experience, current conditions, and reasonable and supportable forecasts that affect the collectability of the reported amount. In November 2018, the FASB issued ASU No. 2018-19, Codification Improvements to Topic 326, Financial Instruments—Credit Losses (“ASU 2018-19”), which clarifies that receivables from operating leases are accounted for using the lease guidance and not as financial instruments. In April 2019, the FASB issued ASU No. 2019-04, Codification Improvements to Topic 326, Financial Instruments—Credit Losses (“ASU 2019-04”), which clarifies the new expected credit loss methodology for loans, receivables and other financial assets, including recoveries and accrued interest on receivables. In November 2019, the FASB issued ASU No. 2019-11, Codification Improvements to Topic 326, Financial Instruments—Credit Losses (“ASU 2019-11”), which clarifies guidance around how to report expected recoveries. In March 2020, the FASB issued ASU No. 2020-03, Codification Improvements to Financial Instruments (“ASU 2020-03”), which makes narrow-scope improvements to various aspects of the financial instruments guidance, including the current expected credit losses standard issued in 2016. In March 2020, the FASB issued ASU No. 2020-02, Financial Instruments—Credit Losses (Topic 326) and Leases (Topic 842): Amendments to SEC Paragraphs Pursuant to SEC Staff Accounting Bulletin No. 119 and Update to SEC Section on Effective Date Related to Accounting Standards Update No. 2016-02, Leases (Topic 842) (“ASU 2020-02”), which adds an SEC paragraph
F-65
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
2. Summary of significant accounting policies, continued
Recently adopted accounting pronouncements, continued
pursuant to the issuance of SEC Staff Accounting Bulletin No. 119 on loan losses to the FASB Codification Topic 326 and also updates the SEC section of the Codification for the change in the effective date of Topic 842. The standard is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2022, including interim periods within those fiscal years. Early adoption is permitted. The Company adopted the standard on January 1, 2020, on a prospective basis. This guidance did not have a significant impact on the Company’s condensed consolidated financial statements and related disclosures.
Recently issued accounting standards
In December 2019, the FASB issued ASU No. 2019-12, Income Taxes (Topic 740): Simplifying the Accounting for Income Taxes (“ASU 2019-12”). The guidance removes specific exceptions to the general principles in ASC 740, improves application of income tax-related guidance and reduces complexity related to the accounting for income taxes. The standard is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2021, and interim periods with fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2022. Early adoption is permitted. The Company is evaluating the potential impact of this standard on its condensed consolidated financial statements.
In January 2020, the FASB issued ASU No. 2020-01, Investments—Equity Securities (Topic 321), Investments—Equity Method and Joint Ventures (Topic 323), and Derivatives and Hedging (Topic 815)—clarifying the interactions between Topic 321, Topic 323 and Topic 815 (a consensus of the emerging issues task force) (“ASU 2020-01”). The amendments in this ASU clarify the interaction between the accounting for investments in equity securities, investment in equity method and certain derivatives instruments. ASU 2020-01 states any equity security transitioning from the alternative method of accounting under Topic 321 to the equity method, or vice versa, due to an observable transaction will be remeasured immediately before the transition. In addition, the ASU clarifies the accounting for certain non-derivative forward contracts or purchased call options to acquire equity securities, stating such instruments will be measured using the fair value principles of Topic 321 before settlement or exercise. The pronouncement is effective for fiscal years, and for interim periods within those fiscal years, beginning after December 15, 2021. Early adoption is permitted. The Company is currently in evaluating the effects of this pronouncement on its condensed consolidated financial statements.
In March 2020, the FASB issued ASU No. 2020-04, Reference Rate Reform (Topic 848): Facilitation of the Effects of Reference Rate Reform on Financial Reporting (“ASU 2020-04”), which provide optional expedients and exceptions for applying generally accepted accounting principles to contracts, hedging relationships, and other transactions that reference the London Interbank Offered Rate (“LIBOR”) or another reference rate expected to be discontinued because of reference rate reform if contract modifications are made on or before December 31, 2022. The amendments in this update are effective for all entities as of March 12, 2020 and does not apply to contract modifications made, and hedging relationships entered into or evaluated, after December 31, 2022. The Company is currently evaluating the adoption of ASU 2020-04 and does not expect it to have a material impact to the condensed consolidated financial statements.
In August 2020, the FASB issued ASU No. 2020-06, Debt—Debt with Conversion and Other Options (Subtopic 470-20) and Derivatives and Hedging—Contracts in Entity’s Own Equity (Subtopic 815-40): Accounting for
F-66
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
2. Summary of significant accounting policies, continued
Recently issued accounting standards, continued
Convertible Instruments and Contracts in an Entity’s Own Equity (ASU “2020-06”). This ASU amends the guidance on convertible instruments and the derivatives scope exception for contracts in an entity’s own equity and improves and amends the related earnings per share (“EPS”) guidance for both Subtopics. The ASU will be effective for annual reporting periods after December 15, 2023 and interim periods within those annual periods and early adoption is permitted in annual reporting periods ending after December 15, 2020. The Company is assessing the impact of ASU 2020-06 on the condensed consolidated financial statements and does not expect it to have a material impact on its condensed consolidated financial statements.
From time to time, new accounting pronouncements are issued by FASB that the Company adopts as of the specified effective date. The Company qualifies as an “emerging growth company” as defined in the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act of 2012 and has the option to not “opt out” of the extended transition related to complying with new or revised accounting standards. This means that when a standard is issued or revised and it has different application dates for public and nonpublic companies, the Company has the option to adopt the new or revised standard at the time nonpublic companies adopt the new or revised standard and can do so until such time that the Company either (i) irrevocably elects to “opt out” of such extended transition period or (ii) no longer qualifies as an emerging growth company.
3. Property and equipment
The components of property and equipment were as follows as of December 31, 2019 and June 30, 2020:
| December 31, 2019 |
June 30, 2020 |
|||||||
| Leasehold improvements |
$ | 5,100 | $ | 5,540 | ||||
| Lab equipment |
3,204 | 4,558 | ||||||
| Computer equipment |
890 | 913 | ||||||
| Furniture and office equipment |
425 | 460 | ||||||
| Vehicles |
296 | 296 | ||||||
| Asset under construction |
110 | 18 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total, at cost |
10,025 | 11,785 | ||||||
| Accumulated depreciation |
(1,508 | ) | (2,798 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total, net |
$ | 8,517 | $ | 8,987 | ||||
|
|
||||||||
During the six months ended June 30, 2019 and 2020, depreciation expense was $481 and $1,290, respectively. Finance leases are also included in property and equipment as vehicles on the condensed consolidated balance sheets (Note 6).
F-67
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
4. Investments
As of December 31, 2019 and June 30, 2020, amortized cost, gross unrealized gains and losses, and estimated fair values of total fixed-maturity securities were as follows:
| December 31, 2019 | ||||||||||||||||
| Amortized cost |
Gross unrealized gain |
Gross unrealized loss |
Estimated value |
|||||||||||||
| Held-to-maturity securities: |
||||||||||||||||
| U.S. Treasury bonds |
$ | 58,117 | $ | 31 | $ | (1 | ) | $ | 58,147 | |||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
| June 30, 2020 | ||||||||||||||||
| Amortized cost |
Gross unrealized gain |
Gross unrealized loss |
Estimated value |
|||||||||||||
| Held-to-maturity securities: |
||||||||||||||||
| U.S. Treasury bonds |
25,029 | 133 | — | 25,162 | ||||||||||||
| Available-for-sale securities |
||||||||||||||||
| U.S. Treasury bonds |
40,177 | 238 | — | 40,415 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| $ | 65,206 | $ | 371 | $ | — | $ | 65,577 | |||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
Changes in fair value are related to changes in market interest rates. The Company expects to collect all contractual principal and interest payments.
The following is a summary of maturities of securities held-to-maturity and available-for-sale as of June 30, 2020:
| Held-to-maturity | Available-for-sale | |||||||||||||||
| Amortized cost |
Estimated value |
Amortized cost |
Estimated value |
|||||||||||||
| Amounts maturing in: |
||||||||||||||||
| One year or less |
$ | 25,029 | $ | 25,162 | $ | 40,177 | $ | 40,415 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Total investments |
$ | 25,029 | $ | 25,162 | $ | 40,177 | $ | 40,415 | ||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||
The Company recorded interest income of $963 and $752, respectively, during the six months ended June 30, 2019 and 2020, respectively, as a component of interest and other income (expense), net on the Company’s condensed consolidated statement of operations and comprehensive loss.
F-68
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
5. Accrued liabilities
Accrued liabilities consisted of the following as of:
| December 31, 2019 |
June 30, 2020 |
|||||||
| Accrued payables |
$ | 3,113 | $ | 5,307 | ||||
| Accrued compensation |
3,211 | 3,473 | ||||||
| Liability with early exercised stock options |
753 | 806 | ||||||
| Other |
522 | 26 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
$ | 7,599 | $ | 9,612 | ||||
|
|
||||||||
6. Leases
The Company has operating and finance leases for corporate offices, research and development facilities, and certain vehicles. These leases have remaining lease terms of four to eight and a half years, some of which include options to extend the leases for five to eight years. The Company has determined that it is not reasonably certain to exercise the options under any leases. The lease of research and development facilities includes costs for utilities and common area maintenance, which have been included in the calculation of lease payments. Differences between lease payments as measured at lease inception and variations in monthly payments will be recognized as operating expenses in the period in which the obligation is incurred.
Leases with an initial term of 12 months or less are not recorded on the balance sheet, and the Company recognizes lease expense for these leases on a straight-line basis over the lease terms. Leases with terms greater than 12 months are included in operating lease ROU assets and operating lease liabilities in the Company’s condensed consolidated balance sheets as of December 31, 2019 and June 30, 2020. Lease expense for lease payments is recognized on a straight-line basis over the lease term.
Maturities of lease liabilities as of June 30, 2020 and are as follows:
| Operating lease |
Finance lease |
|||||||
| Year ending December 31: |
||||||||
| 2020 (excluding the six months ended June 30, 2020) |
$ | 1,271 | $ | 38 | ||||
| 2021 |
2,604 | 75 | ||||||
| 2022 |
2,688 | 74 | ||||||
| 2023 |
2,690 | 46 | ||||||
| 2024 |
2,678 | 1 | ||||||
| Thereafter |
6,431 | — | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| 18,362 | 234 | |||||||
| Less: imputed interest |
(4,875 | ) | (10 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Present value of lease liabilities |
13,487 | 224 | ||||||
| Less: current portion |
(2,381 | ) | (75 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Lease liabilities net of current portion |
$ | 11,106 | 149 | |||||
|
|
||||||||
F-69
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
6. Leases, continued
The components of lease expense were as follows for the six months ended June 30, 2019 and 2020:
| Six months ended June 30, |
||||||||
| 2019 | 2020 | |||||||
| Operating lease cost |
$ | 1,205 | $ | 934 | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Finance lease cost: |
||||||||
| Amortization of right-of-use assets |
$ | 18 | $ | 29 | ||||
| Interest on lease liabilities |
3 | 4 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total finance lease cost |
$ | 21 | $ | 33 | ||||
|
|
||||||||
The Company made payments of $237 and $1,243 during the six months ended June 30, 2019 and 2020, respectively, which are included as cash flow from operations on the condensed consolidated statements of cash flows.
As of December 31, 2019 and June 30, 2020, $296 of finance lease ROU assets were presented as part of property and equipment on the condensed consolidated balance sheet with accumulated amortization of $47 and $76, respectively.
Additional information related to the Company’s leases was as follows as of December 31, 2019 and June 30, 2020:
| December 31, 2019 |
June 30, 2020 |
|||||||
| Operating Lease: |
||||||||
| Weighted-average remaining lease term (years) |
7.10 | 6.60 | ||||||
| Weighted-average discount rate |
9.34% | 9.35% | ||||||
| Finance Lease: |
||||||||
| Weighted-average remaining lease term (years) |
3.66 | 3.16 | ||||||
| Weighted-average discount rate |
3.18% | 3.17% | ||||||
|
|
||||||||
7. Derivative liabilities and convertible preferred stock liability
Warrants
In connection with the issuance of certain notes, lenders were issued warrants to purchase 134,112 shares of the Company’s capital stock. The warrants have a coverage percentage of 25% of the principal amount of the notes and have a ten-year expiration date from the applicable closing date of April 20, 2018 or June 6, 2018.
The underlying shares issuable upon the exercise of the warrants were eligible to be exercised into the next round of equity financing. The warrants became exercisable into shares of Series A for an exercise price of $9.32 per share. There were warrants to purchase 120,701 and 83,149 shares of Series A preferred stock outstanding as of December 31, 2019 and June 30, 2020, respectively.
F-70
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
7. Derivative liabilities and convertible preferred stock liability, continued
Warrants, continued
The Company recorded the warrants initially at fair value (Note 10) as derivative liabilities on the condensed consolidated balance sheet with the value being allocated to the notes as a debt discount. The fair value of the warrants upon issuance on April 20, 2018 and June 6, 2018, was $667 and $238, respectively. The fair value of the warrants was $461 and $380 as of December 31, 2019 and June 30, 2020, respectively.
During the six months ended June 30, 2019, no warrants were exercised and 37,552 warrants were exercised during the six months ended June 30, 2020. As Series A contains a conditional obligation for the Company to repurchase the shares for cash consideration, the warrants remain outstanding as derivative liabilities with changes in fair value being recorded on the condensed consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive loss. For the six months ended June 30, 2019 and 2020, the Company recorded a change in fair value of derivative liabilities of $140 and $56, respectively.
Convertible preferred stock liability
In connection with the issuance of Series B-1 Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock (the “Series B-1”) (Note 8), the Series B-1 preferred stockholders committed to purchase and the Company committed to sell 3,569,630 shares of Series B-2 Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock (the “Series B-2”) at a price of $11.20563 per share in a subsequent closing, contingent upon the achievement of certain developmental milestones or a receipt of a waiver of achievement of the milestones. The Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock Liability is considered a freestanding instrument that qualifies as a liability under ASC Topic 480, Distinguishing Liabilities from Equity (“ASC 480”) as the Company is committed to issue an instrument that ultimately may require a transfer of assets. The liability is accounted for at fair value and re-measured at each reporting date (Note 10). On the date of the initial closing, the Company recorded the Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock Liability at a fair value of $3,174. As of June 30, 2020, none of the Series B-2 shares were issued and the fair value of the liability related to this freestanding instrument decreased by $364 during the six months ended June 30, 2020 compared to the six months ended June 30, 2019.
8. Capital stock
Common stock
On December 23, 2019, pursuant to the Second Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation, the total shares of common stock authorized was set to 278,000,000 and the total shares of preferred stock was set to 212,994,964 with a par value of $0.0001 per share. The total shares of preferred stock authorized comprised 101,962,864 shares of Series A preferred stock, 77,764,055 shares of Series B-1 preferred stock, and 33,268,045 shares of Series B-2 preferred stock.
The holders of shares of Common Stock are entitled to one vote for each share of Common Stock at all meetings of stockholders.
F-71
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
8. Capital stock, continued
Redeemable convertible preferred stock
On August 16, 2018, the Company entered into the Series A Preferred Stock Purchase Agreement for the purchase and sale of Series A preferred stock for $9.32 per share. The Company received $75,000 in cash proceeds from the initial purchasers. On September 19, 2018, the Company received an additional $20,000 in cash proceeds from subsequent purchasers. Additionally, on the initial closing date, $5,600 in convertible notes plus accrued interest converted into shares of Series A and the notes were subsequently cancelled. The Warrants associated with the convertible notes became exercisable into Series A. Each share of Series A is convertible into Common Stock on a one-for-one basis. In connection with the issuance of Series A, the Company incurred $194 in issuance costs which have offset amounts reported as temporary equity as of June 30, 2020.
On December 23, 2019, the Company entered into the Series B-1 and Series B-2 Preferred Stock Purchase Agreement, pursuant to which the investors committed to invest an aggregate amount of up to $125,000 for the issuance and sale of shares of Series B-1 and Series B-2 (collectively, the “Series B”), at a price of $10.1869 and $11.20563 per share, respectively. The Company issued 8,344,034 shares of Series B-1 for cash proceeds of $85,000 at the initial closing. The investors also committed to purchase and the Company committed to sell 3,569,630 shares of Series B-2 in a subsequent closing (the “Second Closing”), contingent upon achievement by the Company of certain development milestones or a receipt of a waiver of achievement of the milestones. No shares of Series B-2 were issued as of June 30, 2020. In connection with the issuance of Series B-1, the Company incurred $442 in issuance costs which have offset amounts reported as temporary equity as of June 30, 2020.
The holders of the Company’s Series A and Series B (collectively, the “Preferred Stock”) have the following rights, preferences, and privileges:
(a) Dividends
The holders of shares of Preferred Stock, in preference to the holders of Common Stock, shall be entitled to receive, on a pari passu basis, when, as and if declared by the board of directors (“Board”) out of funds legally available, noncumulative cash dividends at the rate of eight percent (8%) of the original issue price per annum on each outstanding share of Preferred Stock. So long as any shares of Preferred Stock are outstanding, the Company shall not pay or declare any dividend, or make any other distribution on the Common Stock, or purchase, redeem or otherwise acquire for value any shares of Common Stock until all dividends on the Preferred Stock shall have been paid or declared and set apart, except for: acquisitions of Common Stock by the Company pursuant to agreements which permit the Company to repurchase such shares upon termination of services to the Company; or acquisitions of Common Stock in exercise of the Company’s right of first refusal to repurchase such shares as approved by the Board. After the dividends on the Preferred Stock have been paid, then the Company may declare and distribute in such year dividends among the holders of Preferred Stock and the holders of Common Stock pro rata based on the number of shares of Common Stock held by each, determined on an as-if-converted to Common Stock basis (assuming full conversion of all such Preferred Stock) as of the record date with respect to the declaration of such dividends.
F-72
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
8. Capital stock, continued
Redeemable convertible preferred stock, continued
(b) Liquidation preference and redemption
In the event of any voluntary or involuntary liquidation, dissolution or winding up of the Company, the holders of shares of Preferred Stock then outstanding shall be entitled to be paid out of the assets of the Company available for distribution to its stockholders or, in the case of a Deemed Liquidation Event (as defined below), out of the consideration payable to stockholders in such Deemed Liquidation Event or the Available Proceeds (as defined below), before any payment shall be made to the holders of Common Stock by reason of their ownership thereof, an amount per share equal to one (1) times the applicable Original Issue Price of such series of Preferred Stock, plus any dividends declared but unpaid thereon. If upon any such liquidation, dissolution or winding up of the Company or Deemed Liquidation Event, the assets of the Company available for distribution to its stockholders shall be insufficient to pay the holders of shares of Preferred Stock the full amount to which they shall be entitled, the assets or consideration will be distributed ratably among such holders.
After the payment in full of all liquidation amounts required to be paid to the holders of shares of Preferred Stock the remaining assets of the Company available for distribution to its stockholders or, in the case of a Deemed Liquidation Event, the consideration not payable to the holders of shares of Preferred Stock or the remaining Available Proceeds, as the case may be, shall be distributed among the holders of the shares of Preferred Stock and Common Stock, pro rata based on the number of shares held by each such holder, treating for this purpose all such securities as if they had been converted to Common Stock immediately prior to such liquidation, dissolution or winding up of the Company; provided, however, that if the aggregate amount which the holders of shares of Preferred Stock are entitled to receive shall exceed one and one-half (1.5) times the applicable Original Issue Price of such series of Preferred Stock per share, plus any dividends declared, but unpaid thereon (such amount, with respect to a series of Preferred Stock, the “Maximum Participation Amount”), each holder of shares of a series of Preferred Stock shall be entitled to receive upon such liquidation, dissolution or winding up of the Company the greater of (i) the Maximum Participation Amount applicable to such series or (ii) the amount such holder would have received if all shares of such series of Preferred Stock had been converted into Common Stock immediately prior to such liquidation, dissolution or winding up of the Company.
Each of the following events shall be considered a “Deemed Liquidation Event” unless the holders of at least 67% of the outstanding shares of Preferred Stock (voting as a single class on an as-converted to Common Stock basis) which must include certain non-strategic holders of Series B-1 or Series B-2 holding at least 33% of outstanding shares of Series B-1 and Series B-2 elect otherwise by written notice sent to the Company prior to the effective date of any such event:
| (a) | a merger or consolidation in which the Company is a constituent party or a subsidiary of the Company is a constituent party and the Company issues shares of its capital stock pursuant to such merger or consolidation, except (1) any such merger or consolidation involving the Company or a subsidiary in which the shares of capital stock of the Company outstanding immediately prior to such merger or consolidation continue to represent, or are converted into or exchanged for shares of capital stock that represent, immediately following such merger or consolidation, a majority, by voting power, of |
F-73
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
8. Capital stock, continued
Redeemable convertible preferred stock, continued
| the capital stock of (a) the surviving or resulting corporation; or (b) if the surviving or resulting corporation is a wholly owned subsidiary of another corporation immediately following such merger or consolidation, the parent corporation of such surviving or resulting corporation; or (2) a merger effected exclusively to change the domicile of the Company; |
| (b) | the closing of the sale, in a single transaction or series of related transactions, of equity securities of the Company other than (a) bona fide equity financing, and (b) any transaction in which, the stockholders of the Company prior to such transaction continue to hold at least fifty percent (50%) of the outstanding shares of the surviving corporation; or |
| (c) | (1) the sale, lease, transfer, exclusive license or other disposition, in a single transaction or series of related transactions, by the Company or any subsidiary of the Company of all or substantially all the assets of the Company and its subsidiaries taken as a whole, or (2) the sale or disposition (whether by merger, consolidation or otherwise, and whether in a single transaction or a series of related transactions) of one or more subsidiaries of the Company if substantially all of the assets of the Company and its subsidiaries taken as a whole are held by such subsidiary or subsidiaries, except where such sale, lease, transfer, exclusive license or other disposition is to a wholly owned subsidiary of the Company. |
(c) Conversion
Each share of Preferred Stock is convertible into fully paid and non-assessable shares of Common Stock at any time at the option of the holder, and is subject to mandatory conversion upon the written consent of certain holders or upon the closing of a firm commitment underwritten public offering (i) approved by a majority of the then-outstanding shares of Series B-1 or Series B-2 held by certain non-strategic Series B-1 and Series B-2 holders or (ii) after the earlier of (A) September 30, 2021 and (B) the occurrence of a developmental milestone, in the case of clause (ii) which firm commitment underwritten public offering involves a price per share dependent upon whether it is prior to the Second Closing or on or after the Second Closing, and gross proceeds to the Company of at least $75,000. The conversion ratio at December 31, 2019 and June 30, 2020, was one for one, and is subject to certain anti-dilutive adjustments.
(d) Voting
The holders of Preferred Stock have voting rights equivalent to the number of shares of Common Stock into which their shares of Preferred Stock convert. Except as provided by law or by the other provisions of the amended and restated certificate of incorporation, holders of shares of Preferred Stock shall vote together with the holders of shares of Common Stock as a single class and on an as-converted to Common Stock basis.
The holders of record of shares of Series A, exclusively and as a separate class, shall be entitled to elect four (4) directors of the Company, the holders of record of shares of Series B-1 and Series B-2, exclusively and as a separate class on an as-converted basis, shall be entitled to elect one (1) director of the Company and the holders of record of shares of Common Stock, exclusively and as a separate class, shall be entitled to elect two (2) directors of the Company.
F-74
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
9. Stock-based compensation
2018 Equity incentive plan
The Company’s 2018 Equity Incentive Plan (the “Plan”) allows the Company to issue restricted stock awards and restricted stock units, and to grant incentive stock options or non-qualified stock options. Incentive stock options may be granted only to the Company’s employees including officers and members of the Board who are also employees. Restricted stock awards, restricted stock units and non-qualified stock options may be granted to employees, members of the Board, outside advisors, and consultants of the Company (the “Participants”). The Company is authorized to issue awards for 4,913,665 shares of Common Stock under the Plan. The Company had 4,270,748 awards granted as of June 30, 2020 with 642,917 available for future issuances.
Stock options
The exercise price for incentive stock options is at least 100% of the fair market value on the date of grant for stockholders owning less than 10% of the voting power of all classes of stock, or at least 110% of the fair market value for stockholders owning more than 10% of the voting power of all classes of stock. Options generally expire in 10 years. Options may vest over periods determined by the Board, generally 48 months (“Time-Vesting Options”), or vest upon the achievement of a certain performance condition (“Performance-Vesting Options”). Certain stock options referred to as “early exercise stock options” permit the holders to exercise the option in whole or in part prior to the full vesting of the option in exchange for unvested shares of Restricted Stock with respect to any unvested portion of the option so exercised.
Of the option awards outstanding as of June 30, 2020, 1,806,257 were Time-Vesting Options, with an unamortized expense balance of $3,587, to be amortized over a weighted average period of 3.10 years.
Of the option awards outstanding as of June 30, 2020, 440,376 were Performance-Vesting Options. As of June 30, 2020, the Company determined that the vesting condition associated with the Performance-Vesting Options was not probable of being achieved, and therefore did not recognized any expense. The Company will continue to evaluate the probability of such vesting condition being achieved at each subsequent reporting period. Once the Performance-Vesting Awards are deemed probable of vesting, the Company will record compensation expense for the vested portion equal to the grant date fair value. The total unrecognized expense for Performance-Vesting options was $1,021 as of June 30, 2020, with remaining contractual term of 9.68 years.
During the six months ended June 30, 2019 and 2020, the Company’s stock option compensation expense was approximately $143 and $478, respectively, and there was no recognized tax benefit in either of the periods.
F-75
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
9. Stock-based compensation, continued
Stock options, continued
The assumptions that the Company used to determine the grant-date fair value of both Time-Vesting Options and Performance-Vesting Options granted to Participants were as follows, presented on a weighted-average basis:
| December 31, 2019 |
June 30, 2020 |
|||||||
| Expected term (in years) |
6.06 | 5.92 | ||||||
| Risk-free interest rate |
1.94% | 1.24% | ||||||
| Dividend yield |
— | — | ||||||
| Volatility |
60.24% | 63.62% | ||||||
|
|
||||||||
Stock option activity during the six months ended June 30, 2020 was as follows:
| Time-vesting options | Performance- vesting options |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares subject to options |
Weighted- average |
Shares subject to options |
Weighted- average |
Weighted- average |
Aggregate intrinsic value |
|||||||||||||||||||
| Outstanding as of January 1, 2020 |
346,872 | $ | 1.30 | — | $ | — | 9.01 | $ | 744 | |||||||||||||||
| Granted |
1,552,942 | 3.45 | 454,994 | $ | 3.45 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Exercised |
(93,557 | ) | 2.38 | (14,618 | ) | $ | 3.45 | 382 | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Outstanding as of June 30, 2020 |
1,806,257 | $ | 3.09 | 440,376 | $ | 3.45 | 9.52 | $ | 6,506 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Options vested and expected to vest as of June 30, 2020 |
2,291,540 | $ | 2.75 | 454,994 | $ | 3.45 | 9.37 | $ | 8,771 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Options vested and exercisable as of June 30, 2020 |
1,375,156 | $ | 3.31 | 5,399 | $ | 3.45 | 9.61 | $ | 3,795 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
The weighted-average grant date fair value of both Time-Vesting Options and Performance-Vesting Options granted was $0.24 per share during the six months ended June 30, 2020.
Restricted stock awards
The Company may grant restricted stock purchase awards to the Participants to purchase restricted stock under the Company’s Plan, which are subject to vesting conditions. The purchase prices of the restricted stock are determined by the Board. The Company has a right to repurchase the shares if the Participant’s service period is not fulfilled or upon termination of service at the original per share issuance price. The right of repurchase lapses over a service period which is typically four years with 25% vesting on the first anniversary of the vesting commencement date and 1/48 each month thereafter.
Before the adoption of the Company’s Plan, the Company granted 502,964 restricted stock awards to employees and founders. These restricted stock awards have similar characteristics to the restricted stock
F-76
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
9. Stock-based compensation, continued
Restricted stock awards, continued
awards granted under the Company’s Plan, other than the right of repurchase, which typically lapses over three years with 33% vesting on the first anniversary of the vesting commencement date and 1/36 each month thereafter.
During the six months ended June 30, 2019 and 2020, the Company recorded a total stock-based compensation expense of $310 and $180, respectively, related to the restricted stock awards. As of June 30, 2020 unrecognized stock-based compensation costs related to outstanding unvested restricted stock awards that are expected to vest were approximately $633, expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of 1.58 years.
The following table summarizes the Company’s restricted common stock activity for the six months ended June 30, 2020:
| Number of awards |
Weighted- average grant date fair value |
Aggregate fair value |
||||||||||
| Issued and unvested as of January 1, 2020 |
827,187 | $ | 1.01 | $ | 834 | |||||||
| Restricted stock awards granted |
— | — | ||||||||||
| Restricted stock awards vested |
(209,397 | ) | 0.86 | (181 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Issued and unvested as of June 30, 2020 |
617,790 | $ | 1.06 | $ | 653 | |||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
Stock-based compensation expense was allocated as follows for the six months ended June 30, 2019 and 2020:
| June 30, 2019 | June 30, 2020 | |||||||
| Research and development |
$ | 272 | $ | 350 | ||||
| General and administrative |
181 | 308 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
$ | 453 | $ | 658 | ||||
|
|
||||||||
During the six months ended June 30, 2020, the Company issued 52,062 shares of Common Stock upon the exercise of unvested stock options or purchases for unvested restricted stock awards. As of December 31, 2019 and June 30, 2020, there were 577,124 and 531,946 shares of Common Stock held by employees subject to repurchase at an aggregate price of $753 and $806, respectively. A corresponding liability was recorded and included in accrued expenses on the condensed consolidated balance sheet as of December 31, 2019 and June 30, 2020, respectively.
F-77
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
10. Fair value
The following tables present the fair value of the Company’s financial instruments that are measured or disclosed at fair value on a recurring basis:
| Fair value measurements as of December 31, 2019 |
||||||||||||
| Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | ||||||||||
| Assets: |
||||||||||||
| Cash equivalents: |
||||||||||||
| Money market funds |
$ | 68,608 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||
| Held-to-maturity securities: |
||||||||||||
| U.S. Treasury bonds |
58,147 | — | — | |||||||||
| Liabilities: |
||||||||||||
| Derivative liabilities |
— | — | (461 | ) | ||||||||
| Redeemable convertible preferred stock liability |
— | — | (3,174 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| $ | 126,755 | $ | — | $ | (3,635 | ) | ||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
| Fair value measurements as of June 30, 2020 |
||||||||||||
| Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | ||||||||||
| Assets: |
||||||||||||
| Cash equivalents: |
||||||||||||
| Money market funds |
$ | 21,285 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||
| Held-to-maturity securities: |
||||||||||||
| U.S. Treasury bonds |
25,162 | — | — | |||||||||
| Available-for-sale securities: |
||||||||||||
| U.S. Treasury bonds |
40,415 | — | — | |||||||||
| Liabilities: |
||||||||||||
| Derivative liabilities |
— | — | (380 | ) | ||||||||
| Redeemable convertible preferred stock liability |
— | — | (2,810 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| $ | 86,862 | $ | — | $ | (3,190 | ) | ||||||
|
|
||||||||||||
The derivative liability in the table above refers to the fair value of warrants. The fair values of the warrants were determined based on significant inputs not observable in the market, which represents a Level 3 measurement within the fair value hierarchy.
In order to determine the fair value of the warrants, the Company utilized a probability-weighted multi-scenario Black-Scholes option-pricing model to determine the fair value of the warrants by accounting for the probability of multiple possible outcomes, including deemed liquidation events, as best estimated by management. Estimates and assumptions impacting the fair value measurement including the fair value of the underlying shares of Series A, the remaining contractual or expected term of the warrants, risk-free interest rate, expected dividend yield and expected volatility of the price of the underlying preferred stock on an as converted basis.
F-78
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
10. Fair value, continued
The Company considered the probability of a deemed liquidation event in determining the remaining expected term of the warrants, which was used as an input to the probability-weighted multi-scenario Black-Scholes option-pricing model adopted in 2019. The Company lacks company-specific historical and implied volatility information of its stock since there is currently no market. Therefore, it estimated its expected stock volatility based on the historical volatility of publicly traded guideline companies for a term equal to the remaining contractual or expected term of the warrants. The risk-free interest rate was determined by reference to the U.S. Treasury yield curve for time periods approximately equal to the remaining contractual or expected term of the warrants. The Company estimated no expected dividend yield based on the fact that the Company has never paid or declared dividends and does not intend to do so in the foreseeable future.
The warrants were measured at fair value under the following assumptions:
| December 31, 2019 |
June 30, 2020 |
|||||||
| Exercise price |
$ | 9.32 | $ | 9.32 | ||||
| Term (in years) |
2.00 - 3.00 | 0.74 | ||||||
| Risk-free interest rate |
1.63% | 0.17% | ||||||
| Dividend yield |
— | — | ||||||
| Volatility |
75.00% | 120.00% | ||||||
|
|
||||||||
The significant unobservable inputs used in the fair value measurement of the warrants are the remaining expected term, which considers the timing of a liquidation event that would net settle the awards before their contractual term expires, and the equity volatility, which is a statistical measure of the dispersion of returns for a given security. Significant increases (decreases) in the term would result in significantly higher (lower) fair value measurements. Significant increases (decreases) in the volatility would result in significantly higher (lower) fair value measurements.
The following table sets forth a summary of changes in fair value of the Company’s derivative liability and Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock Liability for which fair value was determined by Level 3 inputs:
| Derivative liabilities |
Redeemable convertible preferred stock liability |
|||||||
| Balance as of December 31, 2019 |
$ | 461 | $ | 3,174 | ||||
| Exercise of warrants |
(137 | ) | — | |||||
| Change in fair value |
56 | (364 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Balance as of June 30, 2020 |
$ | 380 | $ | 2,810 | ||||
|
|
||||||||
F-79
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
10. Fair value, continued
In order to determine the fair value of the Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock Liability, the Company used a probability-weighted multi-scenario Black Scholes hybrid valuation method that accounts for the probability of achieving milestones as estimated by the management. The Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock Liability has a fair value of $2,810 as of June 30, 2020. The Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock Liability was measured at fair value under the following assumption as of June 30, 2020:
| December 31, 2019 |
June 30, 2020 |
|||||||
| Exercise price |
$ | 11.21 | $ | 11.21 | ||||
| Term (in years) |
1.27 | 0.42 - 1.00 | ||||||
| Risk-free interest rate |
1.55% | 0.17% | ||||||
| Dividend yield |
— | — | ||||||
| Volatility |
60.00% | 82.10% | ||||||
|
|
||||||||
The significant unobservable inputs used in the fair value measurement of the Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock Liability include the probability of milestone achievement and/or milestone achievement waiver, the Series B-2 current or future value estimate under each scenario, the term, and the equity volatility, which is a statistical measure of the dispersion of returns for a given security. Significant increases (decreases) in the probability of milestone achievement and/or milestone waiver would result in a significantly higher (lower) fair value measurement. Significant decreases (increases) in assumed current or future Series B-2 value would result in a significantly lower (higher) fair value measurement. Significant increases (decreases) in the term would result in a significantly higher (lower) fair value measurement. Significant increases (decreases) in the volatility would result in significantly higher (lower) fair value measurements.
11. License and collaboration agreements
Agreement with Emory University (“Emory”)
In June 2018, the Company entered into a license agreement with Emory (the “Emory License Agreement”), pursuant to which Emory granted the Company a worldwide, sublicensable license under certain of its intellectual property rights to make, have made, develop, use, offer to sell, sell, import and export products containing certain compounds relating to Emory’s hepatitis B virus capsid assembly modulator technology, for all therapeutic and prophylactic uses.
In June 2020, the Company amended the license agreement with Emory. Pursuant to the amended license agreement, Emory granted the Company additional patent rights to certain compounds targeting the treatment or prevention of HBV. As consideration for the additional rights, the Company made a one-time, non-refundable payment to Emory in the amount of $150, with an additional obligation to pay up to a maximum of $35. On the same date, the Company entered into a collaboration agreement with Emory, with the initial research plan pertaining to the synthesis and evaluation of the compounds licensed through the additional patent rights granted in the amended license agreement. The research plan terminates one year from the effective date, with the Company having an option to extend for a second year. In connection with the research plan, the Company will provide Emory funding up to $270 per year.
F-80
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
11. License and collaboration agreements, continued
Agreement with Luxna Biotech Co., Ltd. (“Luxna”)
On December 19, 2018, the Company entered into a license agreement with Luxna, pursuant to which Luxna granted the Company an exclusive, worldwide, sublicensable license under certain of Luxna’s intellectual property rights to research, develop make, have made and commercialize for all therapeutic and prophylactic uses, (i) products containing oligonucleotides targeting the hepatitis B virus genome, (ii) products containing certain oligonucleotides targeting up to three genes which contribute to NASH, which the Company may select at any time during the first eight years of the term, to the extent not licensed to a third party, and (iii) products containing oligonucleotides targeting up to three genes which contribute to hepatocellular carcinoma, which the Company may select at any time during the first three years of the term.
In April 2020, the Company amended the license agreement with Luxna. Pursuant to the amended license agreement, Luxna granted the Company an exclusive, worldwide license under the licensed patents to research, develop, make, have made and commercialize products containing oligonucleotides targeting three families of viruses: orthomyxoviridae, paramyxoviridae, and coronaviridae (a family which includes SARS-CoV-2). As consideration for the amended license agreement, the Company paid Luxna a one-time non-refundable fee of $200.
Agreement with Katholieke Universiteit Leuven (“KU Leuven”)
On June 25, 2020, the Company entered into a Research, Licensing and Commercialization Agreement (“KU Leuven Agreement”) with KU Leuven, under which the Company is collaborating with KU Leuven’s Rega Institute for Medical Research, as well as its Centre for Drug Design and Discovery, to research and develop potential protease inhibitors for the treatment, diagnosis, prediction, detection or prevention of coronaviruses, including SARS-CoV-2. Unless terminated earlier by either party in accordance with provisions in the agreement, the collaboration period will terminate at the earlier of completion of all collaboration activities or 2.5 years. In connection with the KU Leuven Agreement, KU Leuven and the Company granted each other exclusive cross-licenses to use certain know-how and existing patents of the other party as well as certain joint know-how and joint patents to carry out research and development collaboration activities during the collaboration period. KU Leuven granted to the Company an exclusive (including as to KU Leuven), worldwide license under certain of KU Leuven’s know-how and existing patents, and certain joint patents and joint know-how, to manufacture and commercialize the licensed products for the treatment, diagnosis, prediction, detection or prevention of viral infections in humans or animals. KU Leuven reserved the right to use all KU Leuven know-how, existing KU Leuven patents, joint patents and joint know-how for academic and non-commercial research and teaching purposes. As consideration for this license, the Company is obligated to make payments to KU Leuven, in aggregate, totaling up to but no more than $30,000 upon the achievement of certain commercial sales milestones. For each licensed product developed through KU Leuven and the Company’s collaborative effort, the Company is obligated to make payments to KU Leuven, in aggregate, totaling up to $32,000 upon the achievement of certain development and regulatory milestones. The Company is also required to pay KU Leuven a low-to-mid-single digit royalty percentage, subject to certain adjustments, on net sales of applicable products, if any. The royalty term for each licensed product will extend until the later of 10 years after the first commercial sale of the licensed product and the expiration or termination of the last valid patent claim covering the manufacture, use, sale or importation of the licensed product in a particular
F-81
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
11. License and collaboration agreements, continued
Agreement with Katholieke Universiteit Leuven (“KU Leuven”), continued
country. Unless terminated earlier by either party, the agreement shall continue until the expiration of the last to expire royalty term.
12. Commitments and contingencies
From time to time, the Company may have certain contingent liabilities, including legal matters that arise in the ordinary course of its business activities. The Company accrues a liability for such matters when it is probable that future expenditures will be made and such expenditures can be reasonably estimated. The Company had no contingent liabilities requiring accrual as of December 31, 2019 and June 30, 2020.
13. Net loss per share
The following table summarizes the computation of basic and diluted net loss per share of the Company:
| Six months ended June 30, | ||||||||
| 2019 | 2020 | |||||||
| Net loss |
$ | (20,030 | ) | $ | (40,826 | ) | ||
| WASO, basic and diluted |
1,735,358 | 2,729,827 | ||||||
| Net loss per share—basic and diluted |
$ | (11.54 | ) | $ | (14.96 | ) | ||
|
|
||||||||
The Company’s potentially dilutive securities, which include convertible preferred stock, a forward contract to issue preferred stock, options to purchase common stock and unvested restricted stock, have been excluded from the computation of diluted net loss per share as the effect would be to reduce the net loss per share. Therefore, the weighted-average number of shares of Common Stock outstanding used to calculate both basic and diluted net loss per share is the same. The Company excluded the following potential shares of Common Stock, presented based on amounts outstanding at each period end, from the computation of diluted net loss per share for the periods indicated because including them would have had an anti-dilutive effect:
| Six months ended June 30, | ||||||||
| 2019 | 2020 | |||||||
| Convertible Preferred share |
10,806,432 | 19,201,429 | ||||||
| Forward contract to issue redeemable convertible preferred stock |
— | 3,569,630 | ||||||
| Options to purchase common stock |
1,129,195 | 2,298,695 | ||||||
| Unvested restricted stock |
1,048,882 | 617,790 | ||||||
| Warrants |
134,112 | 83,149 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| 13,118,621 | 25,770,693 | |||||||
|
|
||||||||
14. Pro forma net loss per share (unaudited)
The unaudited pro forma basic and diluted net loss per share set forth in the table below gives effect to the conversion of all shares of convertible preferred stock upon the closing of the planned IPO by treating all shares
F-82
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
14. Pro forma net loss per share (unaudited), continued
of convertible preferred stock as if they had been converted to Common Stock at the beginning of the earliest period presented or the date of the original issuance, if later. Shares to be sold in the planned IPO are excluded from the unaudited pro forma basic and diluted net loss per share calculation. Unaudited pro forma net loss per common share, basic and diluted, for the six months ended June 30, 2020 is calculated as follows:
| Six months ended June 30, 2020 |
||||
| Numerator: |
||||
| Net loss |
$ | (40,826 | ) | |
|
|
|
|||
| Denominator: |
||||
| Weighted average common shares outstanding—basic and diluted |
2,729,827 | |||
| Add: Conversion of convertible preferred stock |
19,201,429 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Pro forma weighted average common shares outstanding |
21,931,256 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Pro forma net loss per common share—basic and diluted |
$ | (1.86 | ) | |
|
|
||||
15. Subsequent events
The Company has evaluated all events occurring through October 9, 2020, the date on which the condensed consolidated financial statements were issued, during which time nothing has occurred outside the normal course of business operations that would require disclosure other than the event disclosed below.
In connection with the issuance of shares of Series B-1 (Note 8), the investors party to the Series B-1 and Series B-2 Preferred Stock Purchase Agreement, dated December 23, 2019, committed to purchase and the Company committed to sell 3,569,630 shares of Series B-2 at a price of $11.20563 per share in a subsequent closing, contingent upon the achievement of the certain milestones (the “Series B Milestones”). The Series B Milestones in the agreement are described as follows:
| • | receipt of permission to proceed under an Investigational New Drug application submitted to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration or approval of the clinical trial application by a comparable foreign regulatory agency having jurisdiction (the “CTA Approval”) with respect to the Company’s HBV STOPs program; and |
| • | the CTA Approval with respect to the Company’s HBV CAM program. |
On September 25, 2020, the Company achieved the Series B Milestones. On October 6, 2020, the Company issued 3,569,630 shares of Series B-2 at a price of $11.20563 per share for proceeds of $40,000 at the Second Closing.
F-83
Table of Contents
Aligos Therapeutics, Inc.
Notes to unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
15. Subsequent events, continued
Non-voting common stock election
In October 2020, certain holders of the Company’s Convertible Preferred Stock elected to have such shares convert into 3,092,338 shares of non-voting Common Stock upon the closing of the Company’s planned IPO. The non-voting shares of Common Stock shall have the same rights and preferences as the Common Stock, but shall be non-voting.
F-84
Table of Contents
10,000,000 shares

Common stock
| J.P. Morgan | Jefferies | Piper Sandler | ||
| Cantor | ||||
Prospectus dated , 2020
Table of Contents
Part II
Information not required in prospectus
Item 13. Other expenses of issuance and distribution.
The following table sets forth the costs and expenses, other than the underwriting discounts and commissions, payable by the registrant in connection with the sale of common stock being registered. All amounts are estimates except for the SEC registration fee, the FINRA filing fee and the Nasdaq Global Market listing fee.
| Item | Amount paid or to be paid |
|||
| SEC registration fee |
$ | 20,074 | ||
| FINRA filing fee |
28,100 | |||
| Nasdaq Global Market Listing fee |
170,000 | |||
| Printing and engraving expenses |
400,000 | |||
| Legal fees and expenses |
1,700,000 | |||
| Accounting fees and expenses |
1,700,000 | |||
| Transfer Agent fees and expenses |
10,000 | |||
| Miscellaneous expenses |
51,826 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Total |
$ | 4,080,000 | ||
|
|
||||
Item 14. Indemnification of directors and officers.
As permitted by Section 102 of the Delaware General Corporation Law, provisions in our amended and restated certificate of incorporation and bylaws that will be in effect immediately prior to the closing of the offering will limit or eliminate the personal liability of our directors for a breach of their fiduciary duty of care as a director. The duty of care generally requires that, when acting on behalf of the corporation, directors exercise an informed business judgment based on all material information reasonably available to them. Consequently, a director will not be personally liable to us or our stockholders for monetary damages for breach of fiduciary duty as a director, except for liability for:
| • | any breach of the director’s duty of loyalty to us or our stockholders; |
| • | any act or omission not in good faith or that involves intentional misconduct or a knowing violation of law; |
| • | any act related to unlawful stock repurchases, redemptions or other distributions or payment of dividends; or |
| • | any transaction from which the director derived an improper personal benefit. |
These limitations of liability do not affect the availability of equitable remedies such as injunctive relief or rescission. Our amended and restated certificate of incorporation will also authorize us to indemnify our officers, directors and other agents to the fullest extent permitted under Delaware law.
As permitted by Section 145 of the Delaware General Corporation Law, our amended and restated bylaws will provide that:
| • | we shall indemnify our directors and officers, and may indemnify our employees and agents, to the fullest extent permitted by the Delaware General Corporation Law, subject to limited exceptions; |
| • | we shall advance expenses to our directors and officers and may advance expenses to our employees and agents in connection with a legal proceeding to the fullest extent permitted by the Delaware General Corporation Law, subject to limited exceptions; and |
| • | the rights provided in our amended and restated bylaws are not exclusive. |
II-1
Table of Contents
Our amended and restated certificate of incorporation, attached as Exhibit 3.3 hereto, and our amended and restated bylaws, attached as Exhibit 3.5 hereto, will provide for the indemnification provisions described above and elsewhere herein. We intend to enter into separate indemnification agreements with our directors and officers which may be broader than the specific indemnification provisions contained in the Delaware General Corporation Law. These indemnification agreements will generally require us, among other things, to indemnify our officers and directors against liabilities that may arise by reason of their status or service as directors or officers, other than liabilities arising from willful misconduct. These indemnification agreements also generally require us to advance any expenses incurred by the directors or officers as a result of any proceeding against them as to which they could be indemnified. In addition, we will purchase prior to the closing of this offering a policy of directors’ and officers’ liability insurance that insures our directors and officers against the cost of defense, settlement or payment of a judgment in some circumstances. These indemnification provisions and the indemnification agreements may be sufficiently broad to permit indemnification of our officers and directors for liabilities, including reimbursement of expenses incurred, arising under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”).
The form of Underwriting Agreement, attached as Exhibit 1.1 hereto, provides for indemnification by the underwriters of us and our officers who sign this Registration Statement and directors for specified liabilities, including matters arising under the Securities Act.
Item 15. Recent sales of unregistered securities.
The following list sets forth information as to all securities we have sold since February 5, 2018, which were not registered under the Securities Act.
1. In March and July 2018, we issued an aggregate of 2,011,864 shares of restricted common stock pursuant to restricted stock purchase agreements to our founders, early employees and academic collaborators at a price of $0.001033865384 per share.
2. In April and June 2018, we issued convertible promissory notes in an aggregate principal amount of $5 million and warrants to purchase shares of capital stock to 19 accredited investors.
3. In June 2018, we issued a convertible promissory note in a principal amount of $600,000 to one accredited investor.
4. In August and September 2018, we issued an aggregate of 10,806,432 shares of Series A convertible preferred stock to 27 accredited investors at a price per share of either (i) $9.32 in cash or (ii) with respect 612,975 shares of Series A preferred stock issued upon conversion of convertible promissory notes issued by us, $5.7 million in cancellation of indebtedness, for a total amount raised (including the cancellation of indebtedness and accrued interest thereon) of $100.7 million.
5. In December 2019, we issued an aggregate of 8,344,034 shares of Series B-1 convertible preferred stock to 38 accredited investors at a price per share of $10.1869 for aggregate proceeds to us of $85 million.
6. In October 2020, we issued an aggregate of 3,569,630 shares of Series B-2 convertible preferred stock to 38 accredited investors at a price per share of $11.20563 for aggregate proceeds to us of $40 million.
7. We have granted stock options and stock awards to employees, directors and consultants covering an aggregate of 3,254,084 shares of common stock, at a weighted-average exercise price of $2.63 per share. Of these, options covering an aggregate of 40,012 shares were cancelled or forfeited without being exercised.
8. We have sold an aggregate of 1,050,265 shares of common stock to employees, directors and consultants for cash consideration in the aggregate amount of $1.5 million pursuant to stock options and restricted stock awards.
II-2
Table of Contents
We claimed exemption from registration under the Securities Act for the sale and issuance of securities in the transactions described in paragraphs (1) through (6) by virtue of Section 4(a)(2) of the Securities Act and/or Regulation D promulgated thereunder as transactions not involving any public offering. All of the purchasers of unregistered securities for which we relied on Section 4(a)(2) and/or Regulation D represented that they were accredited investors as defined under the Securities Act. We claimed such exemption on the basis that (a) the purchasers in each case represented that they intended to acquire the securities for investment only and not with a view to the distribution thereof and that they either received adequate information about the registrant or had access, through employment or other relationships, to such information and (b) appropriate legends were affixed to the stock certificates issued in such transactions.
We claimed exemption from registration under the Securities Act for the sales and issuances of securities in the transactions described in paragraphs (7) and (8) above under Section 4(a)(2) of the Securities Act in that such sales and issuances did not involve a public offering or under Rule 701 promulgated under the Securities Act, in that they were offered and sold either pursuant to written compensatory plans or pursuant to a written contract relating to compensation, as provided by Rule 701.
Item 16. Exhibits and financial statement schedules.
(a) Exhibits.
II-3
Table of Contents
II-4
Table of Contents
| Incorporated by reference | Filed herewith |
|||||||||||||||||
| Exhibit number |
Exhibit description | Form | Date | Number | ||||||||||||||
| 23.1 | Consent of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm. | X | ||||||||||||||||
| 23.4 | Consent of Latham & Watkins LLP (included in Exhibit 5.1). | X | ||||||||||||||||
| 24.1 | Power of Attorney. Reference is made to the signature page to the Registration Statement. | S-1 | 9/25/2020 | 24.1 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
| † | Portions of the exhibit, marked by brackets, have been omitted because the omitted information (i) is not material and (ii) would likely cause competitive harm if publicly disclosed. |
| # | Indicates management contract or compensatory plan. |
(b) Financial Statement Schedules. Schedules not listed above have been omitted because the information required to be set forth therein is not applicable or is shown in the financial statements or notes thereto.
Item 17. Undertakings.
Insofar as indemnification for liabilities arising under the Securities Act may be permitted to directors, officers and controlling persons of the Registrant pursuant to the foregoing provisions, or otherwise, the Registrant has been advised that in the opinion of the SEC such indemnification is against public policy as expressed in the Securities Act, and is, therefore, unenforceable. In the event that a claim for indemnification against such liabilities (other than the payment by the Registrant of expenses incurred or paid by a director, officer, or controlling person of the Registrant in the successful defense of any action, suit or proceeding) is asserted by such director, officer or controlling person in connection with the securities being registered, the Registrant will, unless in the opinion of its counsel the matter has been settled by controlling precedent, submit to a court of appropriate jurisdiction the question of whether such indemnification by it is against public policy as expressed in the Securities Act and will be governed by the final adjudication of such issue.
The undersigned Registrant hereby undertakes that:
| 1. | For purposes of determining any liability under the Securities Act, the information omitted from the form of prospectus filed as part of this Registration Statement in reliance upon Rule 430A and contained in a form of prospectus filed by the Registrant pursuant to Rule 424(b)(1) or (4) or 497(h) under the Securities Act shall be deemed to be part of this Registration Statement as of the time it was declared effective. |
| 2. | For the purpose of determining any liability under the Securities Act, each post-effective amendment that contains a form of prospectus shall be deemed to be a new registration statement relating to the securities offered therein, and the offering of such securities at that time shall be deemed to be the initial bona fide offering thereof. |
II-5
Table of Contents
Signatures
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, the Registrant has duly caused this Registration Statement on Form S-1 to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized, in South San Francisco, California on October 9, 2020.
| Aligos Therapeutics, Inc. | ||
| By: | /s/ Lawrence M. Blatt | |
| Lawrence M. Blatt, Ph.D. Chief Executive Officer | ||
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Act, this Registration Statement has been signed by the following persons in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| Signature | Title | Date | ||
| /s/ Lawrence M. Blatt Lawrence M. Blatt, Ph.D. |
Chief Executive Officer and Director (Principal Executive Officer) |
October 9, 2020 | ||
| /s/ Lesley Ann Calhoun Lesley Ann Calhoun |
Executive Vice President, Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) |
October 9, 2020 | ||
| * Leonid Beigelman, Ph.D. |
Director | October 9, 2020 | ||
| * K. Peter Hirth, Ph.D. |
Director | October 9, 2020 | ||
| * Jack B. Nielsen |
Director | October 9, 2020 | ||
| * Peter Moldt, Ph.D. |
Director | October 9, 2020 | ||
| * Carole Nuechterlein |
Director | October 9, 2020 | ||
| * Thomas Woiwode, Ph.D. |
Director | October 9, 2020 | ||
| * Kathleen Sereda Glaub |
Director | October 9, 2020 | ||
| *By: |
/s/ Lawrence M. Blatt |
October 9, 2020 | ||||
| Lawrence M. Blatt, Ph.D. Attorney-in-Fact |
||||||
II-6