Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| 8-K - FORM 8-K - Passage BIO, Inc. | tm2030435-1_8k.htm |
Exhibit 99.1

Corporate Presentation SEPTEMBER 2020

Forward - Looking Statements This presentation includes “forward - looking statements” within the meaning of, and made pursuant to the safe harbor provisions of, the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995 , including, but not limited to : our expectation about timing and execution of anticipated milestones, including our planned IND submissions and initiation of clinical trials ; our expectations about our collaborators’ and partners’ ability to execute key initiatives ; estimates regarding our cash forecasts ; the expected impact of the COVID - 19 pandemic on our operations ; and the ability of our lead product candidates to treat the underlying causes of their respective target monogenic CNS disorders . These forward - looking statements may be accompanied by such words as “aim,” “anticipate,” “believe,” “could,” “estimate,” “expect,” “forecast,” “goal,” “intend,” “may,” “might,” “plan,” “potential,” “possible,” “will,” “would,” and other words and terms of similar meaning . These statements involve risks and uncertainties that could cause actual results to differ materially from those reflected in such statements, including : our ability to develop, obtain regulatory approval for and commercialize PBGM 01 , PBFT 02 , PBKR 03 and future product candidates ; the timing and results of preclinical studies and clinical trials ; the risk that positive results in a preclinical study or clinical trial may not be replicated in subsequent trials or success in early stage clinical trials may not be predictive of results in later stage clinical trials ; risks associated with clinical trials, including our ability to adequately manage clinical activities, unexpected concerns that may arise from additional data or analysis obtained during clinical trials, regulatory authorities may require additional information or further studies, or may fail to approve or may delay approval of our drug candidates ; the occurrence of adverse safety events ; failure to protect and enforce our intellectual property, and other proprietary rights ; failure to successfully execute or realize the anticipated benefits of our strategic and growth initiatives ; risks relating to technology failures or breaches ; our dependence on collaborators and other third parties for the development of product candidates and other aspects of our business, which are outside of our full control ; risks associated with current and potential delays, work stoppages, or supply chain disruptions caused by the coronavirus pandemic ; risks associated with current and potential future healthcare reforms ; risks relating to attracting and retaining key personnel ; failure to comply with legal and regulatory requirements ; risks relating to access to capital and credit markets ; and the other risks and uncertainties that are described in the Risk Factors section of our most recent filings with the U . S . Securities and Exchange Commission . These statements are based on our current beliefs and expectations and speak only as of the date of this presentation . We do not undertake any obligation to publicly update any forward - looking statements except as required by law . By attending or receiving this presentation you acknowledge that you are cautioned not to place undue reliance on these forward - looking statements, which speak only as of the date such statements are made ; you will be solely responsible for your own assessment of the market and our market position ; and that you will conduct your own analysis and be solely responsible for forming your own view of the potential future performance of Passage Bio . 2

Passage Bio Company Overview 3 Establishing dedicated manufacturing capabilities Deep pipeline of potentially transformative genetic medicines Collaboration with UPenn’s Gene Therapy Program and Orphan Disease Center Multiple potential value creating clinical catalysts Cash runway into 2023 Differentiated approach to achieve a higher probability of technical & regulatory success Our vision is to become the premier genetic medicines company by developing and commercializing transformative therapies that positively impact the lives of patients suffering from life - threatening rare monogenic CNS disorders

4 BOARD OF DIRECTORS Tachi Yamada, M.D. (Chair) Frazier Patrick Heron Frazier Stephen Squinto , Ph.D. OrbiMed Tom Woiwode , Ph.D. Versant Sandip Kapadia Intercept Saqib Islam, J.D. SpringWorks Liam Ratcliffe , M.D., Ph.D. Access Industries Athena Countouriotis , M.D. Turning Point Bruce Goldsmith, Ph.D. Passage Bio LEADERSHIP TEAM Jill Quigley Chief Operating Officer Rich Morris Chief Financial Officer Gary Romano, M.D., Ph.D. Chief Medical Officer Alex Fotopoulos Chief Technology Officer Chip Cale General Counsel Bruce Goldsmith, Ph.D. Chief Executive Officer Stephen Squinto, Ph.D. Acting Head of R&D Demonstrated Leadership Deep experience in rare disease, CNS disorders and gene therapy

The Passage Bio Approach Differentiated to achieve a higher probability of technical and regulatory success 5 M itigation of early developmental risk of programs prior to IND submission M itigation of clinical development risk through our relationships with the Orphan Disease Center (ODC) at Penn Strategic relationship with Penn’s GTP led by our co - founder and Chief Scientific Advisor, Dr. James Wilson Collaboration with GTP allows us to choose clinical indications that have been validated through extensive testing in preclinical disease models by an institution with deep expertise with IND filings Exclusive rights and licenses to technologies arising from discovery research for products developed with GTP, such as novel capsids, toxicity reduction technologies and delivery and formulation improvements We believe ODC’s close ties to leading clinical centers for rare, monogenic CNS disorders will improve our ability to identify potential patients for trial enrollment, improve patient retention and data quality The ODC is currently performing a natural history study for GM1 sponsored by Passage Bio Rigorous process for selecting product candidates Identify optimal route of administration Select the capsid, transgene and promoter Leverage mechanisms such as the cross - correction effect Determine measurable, predictive biomarkers

Program Indication Gene Discovery Candidate selection IND - enabling Phase 1/2 Pivotal Milestones Global commercial rights PB GM01 1 GM1 GLB1 • Initiate Phase 1/2 clinical trial in 4q 2020 1q 2021 PB FT02 FTD GRN • Initiate Phase 1/2 clinical trial in 1h 2021 PB KR03 Krabbe GALC • Initiate Phase 1/2 clinical trial in 1h 2021 PBML04 MLD ARSA PBAL05 ALS C9orf72 PBCM06 CMT2A MFN2 11 additional programs CNS Monogenic • License from GTP Deep Portfolio of Candidates in Rare Monogenic CNS Multiple potential value creating catalysts in 2020 and 2021 6 1 Program includes ongoing natural history study of infantile and juvenile GM1 gangliosidosis patients

Our Programs

GM1: Infantile GM1 Gangliosidosis PBGM01 a potential transformative therapy for a rare, underserved disorder 8 Source: NIH, CHOP, American Journal of Neuroradiology Severe lysosomal storage disease • Spectrum of disease caused by GLB1 gene mutations • Symptoms include reduced muscle tone, progressive CNS dysfunction leading to deafness, blindness, rigidity and skeletal dysplasia • Infantile form of disease shows rapid progression with life expectancy from 2 - 4 years Rare and underserved • Estimated worldwide incidence of Infantile GM1 is 0.5 1:100,000 live births • No approved disease - modifying therapies PBGM01 Our solution • Next - generation, proprietary AAVhu68 capsid delivers a functional GLB1 gene encoding β - gal to the brain and peripheral tissues • Meaningful transduction of both central nervous system & critical peripheral organs in preclinical models • Received Orphan Drug and Rare Pediatric Disease designations by FDA for treatment in GM1 • Initiate Phase 1/2 trial in late 4Q20 or early 1Q21 • Report initial 30 - day safety and biomarker data in late 1H21 GM1 Gangliosidosis PBGM01 for Infantile GM1

PBGM01: Knock Out Mouse Model Clear, supportive preclinical biomarker and pathophysiology data Increased Biomarker Activity • Stable, dose - dependent increases in β - gal expression in the brain and peripheral organs • Increased β - gal enzyme activity in serum, brain, cerebrospinal fluid and critical peripheral tissues Histological Confirmation • LAMP1 positive cells (i.e., cells exhibiting lysosomal distention) were quantified Reduction of brain lysosomal storage lesions in a dose - dependent manner observed p<0.05, p<0.01, NS=not significant. GLB1 +/ - + PBS GLB1 - / - + PBS GLB1 - / - + AAV 10,000 10 1 10.1 CSF 100 1,000 ß - gal activity ( nmol /mL/h) GLB1 +/ - + PBS GLB1 - / - + PBS GLB1 - / - + AAV GLB1 +/ - + PBS GLB1 - / - + PBS GLB1 - / - + AAV 10,000 1,000 100 10 NS Liver GLB1 +/ - + PBS GLB1 - / - + PBS GLB1 - / - + AAV NS GLB1 +/ - + vehicle GLB1 - / - + vehicle GLB1 - / - + PBGM01 9

PBGM01: Knock Out Mouse Model Clear, supportive preclinical functional data Preservation of Neurological Function Dose related improvements in neurological function demonstrated Top two doses similar to GLB +/ - vehicle 0 5 10 15 20 Total score ( + SEM) Days 240 180 120 60 0 Neurological Examinations GLB1 / (KO) GLB1 +/ (HET) Dose 4 (highest) Dose 3 Dose 2 Dose 1 (lowest) Vehicle Vehicle PBGM01 Dose - Related Effect on Survival GLB1 - / - (KO) GLB1 +/ - (HET) Dose 4 (highest) Dose 3 Dose 2 Dose 1 (lowest) Vehicle Vehicle Percent Survival 0 Day 100 200 300 0 50 100 Increased Survival Treated mice demonstrated increased survival at all doses tested Top 2 doses achieved 100% survival to study endpoint Lowest two doses also show significantly improved survival over KO mice 10

PBGM01: Phase 1/2 Clinical Trial Update 11 Submitted IND to FDA for proposed Phase 1/2 dose - escalating trial in June 2020 Received FDA clinical hold letter confirming that IND has been placed on clinical hold due solely to the biocompatibility of the proposed ICM delivery device Discussions ongoing with FDA on plan to address issues Expect to clear FDA’s biocompatibility requirements and receive FDA notification of a safe - to - proceed to support initiation of our clinical trial in line with guidance Aligned with FDA on revised clinical trial design Enroll 4 cohorts of 2 patients each Two dose - escalation cohorts for late onset infantile GM1 Two dose - escalation cohorts for early onset infantile GM1 Expected trial m ilestones Initiate Phase 1/2 trial late in the fourth quarter of 2020 or early in the first quarter of 2021 Report initial 30 - day safety and biomarker data late in the first half of 2021
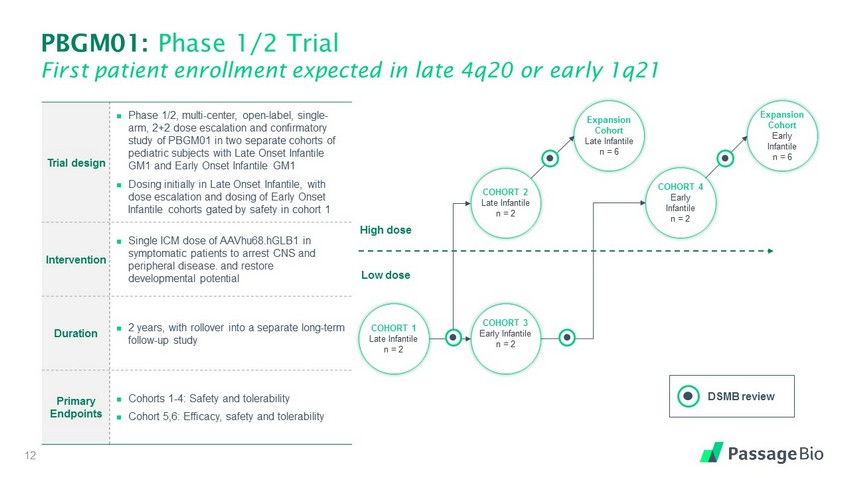
PBGM01: Phase 1/2 Trial First patient enrollment expected in late 4q20 or early 1q21 12 Trial design Phase 1/2, multi - center, open - label, single - arm, 2+2 dose escalation and confirmatory study of PBGM01 in two separate cohorts of pediatric subjects with Late Onset Infantile GM1 and Early Onset Infantile GM1 Dosing initially in Late Onset Infantile, with dose escalation and dosing of Early Onset Infantile cohorts gated by safety in cohort 1 Intervention Single ICM dose of AAVhu68.hGLB1 in symptomatic patients to arrest CNS and peripheral disease. and restore developmental potential Duration 2 years, with rollover into a separate long - term follow - up study Primary Endpoints Cohorts 1 - 4: Safety and tolerability Cohort 5,6: Efficacy, safety and tolerability COHORT 4 Early Infantile n = 2 H igh d ose L ow d o s e Expansion Cohort Early Infantile n = 6 Expansion Cohort Late Infantile n = 6 COHORT 2 Late Infantile n = 2 COHORT 3 Early Infantile n = 2 COHORT 1 Late Infantile n = 2 DSMB review

FTD - GRN: Frontotemporal Dementia Caused by a Progranulin Deficiency A potential transformative therapy for a rare, underserved disorder 13 Devasting form of dementia FTD is one of the more common causes of early - onset dementia Approximately 5 - 10% of FTD is caused by a GRN gene mutation, causing progranulin (PGRN) deficiency Progresses to immobility and severe behavioral changes and loss of speech and expression Rapid progression, with average survival of 8 years, after onset of symptoms Rare and underserved Estimated prevalence of FTD - GRN in the United States is ~ 3,000 to 6,000 patients Currently no approved disease - modifying therapies PBGM01 Our solution Proprietary AAV1 capsid - based product candidate Designed to deliver to the brain a functional GRN gene encoding PGRN Meaningful transduction in NHP studies showing high transduction of ependymal cells that line brain ventricles Increases in CSF PGRN concentrations in NHP studies to more than 50 - fold normal human CSF PGRN concentrations Clinical trial initiation 1h21 FTD - PGRN PBFT02
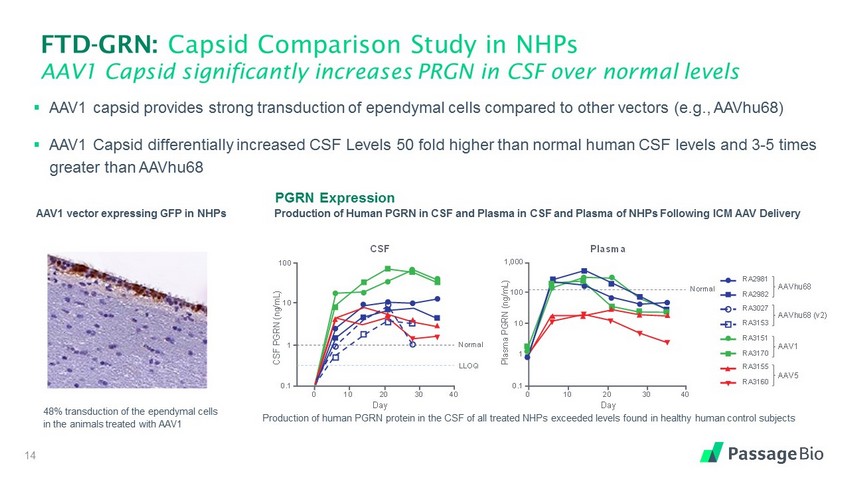
FTD - GRN: Capsid Comparison Study in NHPs AAV1 Capsid significantly increases PRGN in CSF over normal levels 14 ▪ AAV1 capsid provides strong transduction of ependymal cells compared to other vectors (e.g., AAVhu68) ▪ AAV1 Capsid differentially increased CSF Levels 50 fold higher than normal human CSF levels and 3 - 5 times greater than AAVhu68 PGRN Expression Production of Human PGRN in CSF and Plasma in CSF and Plasma of NHPs Following ICM AAV Delivery Production of human PGRN protein in the CSF of all treated NHPs exceeded levels found in healthy human control subjects RA2981 RA2982 RA3027 RA3153 RA3151 RA3170 RA3155 RA3160 AAVhu68 AAVhu68 (v2) AAV1 AAV5 CSF PGRN (ng/mL) 0 10 2 0 30 4 0 CSF 0.1 1 10 100 LLOQ Normal Day Plasma Plasma PGRN (ng/mL) 0 10 2 0 30 4 0 0.1 1 10 100 Normal Day 1,000 AAVhu68 AAV1 Ependyma 1 2% transduction 48% transduction AAV1 vector expressing GFP in NHPs 48% transduction of the ependymal cells in the animals treated with AAV1

Hippocampus Thalamus 0 200 400 600 800 WT KO+PBS KO+AAV Lipofuscin Count Cortex 0 20 40 60 80 100 WT KO+PBS KO+AAV Lipofuscin Count p<0.05, p<0.001, p<0.0001 FTD - GRN: Knock out Mouse Model Comparing Lipofuscin Deposits Preclinical data supporting underlying pathophysiology of FTD - GRN 0 20 40 60 WT KO+PBS KO+AAV Lipofuscin Count ▪ Pathological accumulation of lipofuscin, an electron dense material in lysosomes, is implicated in various neurodegenerative conditions, including FTD ▪ Histological analysis confirmed that treatment reduced lipofuscin deposits in mice broadly throughout the brain ▪ AAV - treated GRN - / - mice exhibited fewer lipofuscin deposits in all brain regions compared to those of vehicle - treated GRN - / - mice ▪ Demonstrative of the potential to treat the underlying pathophysiology of FTD - GRN 15

PBFT02: Clinical Development Trial initiation expected in 1h21 16 TRIAL DESIGN A Phase 1/2, Multi - Center, Open Label, Single - arm, Dose Escalation Study to Assess the Safety and Tolerability of a Single Dose of PBFT02 Delivered into the Cisterna Magna (ICM) of Adult Subjects with Frontotemporal Dementia and Heterozygous Mutations in the Granulin Precursor GRN Gene INTERVENTION Single ICM dose of AAVh1.hPGRN in all symptomatic patients to prevent clinical progression of FTD DURATION 5 years; 12 / 24 months endpoints for safety, 1, 6 months CSF PGRN levels PRIMARY ENDPOINTS Primary: Safety and tolerability Secondary: CSF progranulin levels; serum and Nfl ; disease progression biomarkers; clinical outcome measure; and others COHORT 3 n = 3 (simultaneous enrollment ) D S M B re v iew after the four w eek follo w - up is co m plete for the third subject enrolled COHORT 2 n = 3 (4 weeks between subject enrollment ) COHORT 1 n = 3 (4 weeks between subject enrollment ) H IGH D OSE L OW D O S E

Krabbe : Lysosomal Storage Disease PBKR03 a potential transformative therapy for a rare, underserved disorder 17 Source: NIH, CHOP, American Journal of Neuroradiology Severe Form of Disease Infantile Krabbe disease is the most severe form, accounting for 60% to 70% of diagnoses Disease progression is highly predictable and includes loss of acquired milestones, staring episodes, apnea, peripheral neuropathy, severe weakness, unresponsiveness to stimuli, seizures, blindness and deafness Rapid progression with mortality by ~2 years Rare and underserved Estimated worldwide incidence of Krabbe is 2.6:100,000 births There are currently no approved disease - modifying therapies PBKR03 Our solution PBKR03 utilizes a next - generation, proprietary AAVhu68 capsid to deliver to the brain and peripheral tissues a functional gene encoding the enzyme galactosylceramidase (GALC) In preclinical models, observed meaningful transduction of both CNS & peripheral nerve Preliminary results show that dogs treated with PBKR03 exhibit correction of central and peripheral hypomyelination, reduced neuroinflammation and increased survival rates with full phenotypic recovery Clinical trial initiation in 1h21 Infantile Krabbe PBKR03
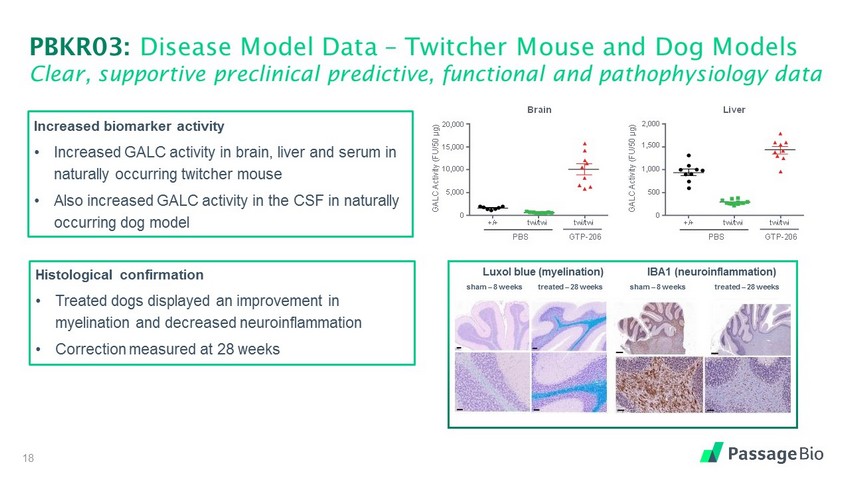
PBKR03: Disease Model Data Twitcher Mouse and Dog Models Clear, supportive preclinical predictive, functional and pathophysiology data Increased biomarker activity Increased GALC activity in brain, liver and serum in naturally occurring twitcher mouse Also increased GALC activity in the CSF in naturally occurring dog model Histological confirmation Treated dogs displayed an improvement in myelination and decreased neuroinflammation Correction measured at 28 weeks GALC Activity (FU/50 µg) 2, 000 1,500 0 500 +/+ t wi / twi t wi / twi PBS GTP - 206 1,000 Liver GALC Activity (FU/50 µg) 2 0,000 15,000 10,000 0 5,000 +/+ t wi / twi t wi / twi PBS GTP - 206 Brain Luxol blue (myelination) treated 28 weeks treated 28 weeks IBA1 (neuroinflammation) sham 8 weeks sham 8 weeks 18

PBKR03: Naturally Occurring Dog Model Clear, supportive preclinical data 19 Naturally occurring Krabbe Dog model study Treatment Animals treated using ICM at 3 weeks, which approximates treatment timing in humans 2 sham treated animals; 4 PBKR03 - treated animals; 1 sham treated wildtype control Untreated animals were sacrificed at 8 - 10 weeks for ethical reasons due to disease progression PBKR03 - treated animal exhibited full phenotypic recovery after ICM administration Body weight and nerve conduction velocity comparable to wild - type dog Scheduled necropsy of 2 treated dogs at 28 weeks; showed normal phenotype and improvement in peripheral and central myelination One treated dog sacrificed after a seizure at 39 weeks; prior to seizure animal exhibited normal phenotype; necropsy showed positive treatment effects on brain pathology Remaining treated dog had normal phenotype at 70+ weeks but was recently euthanized due to weight loss and decreased oral intake

PBKR03: Clinical Development Trial initiation expected in 1h21 20 TRIAL DESIGN Phase 1/2, FIH, multi - center , open - label, single - arm, dose escalation study of PBKR03 administered by a single ICM injection in pediatric subjects with infantile Krabbe disease INTERVENTION Single ICM dose of AAVhu68.hGALC in patients to restore normal development DURATION 5 years total; 12 / 24 months endpoints for safety, 1, 6 months CSF GALC levels PRIMARY ENDPOINTS Safety and tolerability Efficacy (prevention of further developmental regression and restoration of developmental trajectories, safety and tolerability) COHORT 3 n = 12 (simultaneous enrollment ) COHORT 2 n = 3 (4 weeks between subject enrollment ) COHORT 1 n = 3 (4 weeks between subject enrollment ) H IGH D OSE L OW D O S E D S M B re v iew after the four w eek follo w - up is co m plete for the third subject enrolled

Financial Summary 21 ▪ Strong cash balance of $353M at June 30, 2020 ▪ Cash on hand to fund operations into 2023 ▪ Runway to potentially deliver multiple meaningful catalysts over multiple programs

Anticipated Upcoming Milestones 22 ▪ Initiate Phase 1/2 trial for PBGM01 in patients with infantile GM1 late in 4q20 or early 1q21 ▪ Initiate Phase 1/2 trials for PBFT02 in FTD and PBKR03 in Krabbe disease in 1h21 ▪ Advance PBML04, PBLA05 and PBCM06 toward IND - enabling studies ▪ Continue to evaluate robust pipeline of preclinical research to identify new product candidates

Appendix

Strategic Manufacturing Collaboration Established Programs will utilize a Passage Bio dedicated cGMP facility 24 Manufacturing Technology Mammalian cells rAAV platform Transient transfection Single - use fixed - bed iCellis ® manufacturing platform First - in - human (FIH) process and analytical development capabilities by UPenn’s GTP Established Dedicated GMP Production Capacity GMP manufacturing for three candidates to support INDs and FIH clinical trials Capable of meeting production requirements for our current lead product candidates through early commercialization Clinical Supply Chain & Current Investments Establishing end - to - end rare disease supply chain Collaborating with strategic vendors to enable global clinical trials for all our product candidates Long - Term Supply Chain Planning Investments in internalizing manufacturing will be based on production experience, redundancy capabilities and commercial needs

GM1

Preclinical Data Showed an Increase in β - gal Activity in GLB1 Knockout Mice Treated with PBGM01 26 We believe PBGM01 has the potential to increase levels of β - gal activity in the brain, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and critical peripheral tissues GLB1 +/ - + PBS GLB1 - / - + PBS GLB1 - / - + AAV 10,000 10 1 10.1 CSF 100 1,000 ß - gal activity ( nmol /mL/h) GLB1 +/ - + PBS GLB1 - / - + PBS GLB1 - / - + AAV 1,000 10 1 Brain 100 ß - gal activity ( nmol /mg/h) NS Serum β - gal Activity Treatment with PBGM01 increased β - gal Activity in the Brain and CSF in a Knockout Mouse Model Treatment with PBGM01 increased β - gal Activity in Peripheral Organs in a Knockout Mouse Model p<0.05, p<0.01, NS=not significant. p<0.01, NS=not significant 10 100 1,000 10,000 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 ß - gal activity ( nmol /Ml/H) Days GLB1 +/ - + PBS GLB1 - / - + PBS GLB1 - / - + AAV GLB1 +/ - + PBS GLB1 - / - + PBS GLB1 - / - + AAV 100 10 1 0.1 ß - gal activity ( nmol /mg/h) Lung GLB1 +/ - + PBS GLB1 - / - + PBS GLB1 - / - + AAV 10,000 1,000 100 10 NS Liver GLB1 +/ - + PBS GLB1 - / - + PBS GLB1 - / - + AAV 100 10 1 0.1 ß - gal activity ( nmol /mg/h) Heart GLB1 +/ - + PBS GLB1 - / - + PBS GLB1 - / - + AAV 10,000 1,000 100 10 NS Spleen GLB1 +/ - + PBS GLB1 - / - + PBS GLB1 - / - + AAV GLB1 +/ - + PBS GLB1 - / - + PBS GLB1 - / - + AAV GLB1 +/ - + PBS GLB1 - / - + PBS GLB1 - / - + AAV GLB1 +/ - + PBS GLB1 - / - + PBS GLB1 - / - + AAV GLB1 +/ - + PBS GLB1 - / - + PBS GLB1 - / - + AAV GLB1 +/ - + PBS GLB1 - / - + PBS GLB1 - / - + AAV NS NS NS
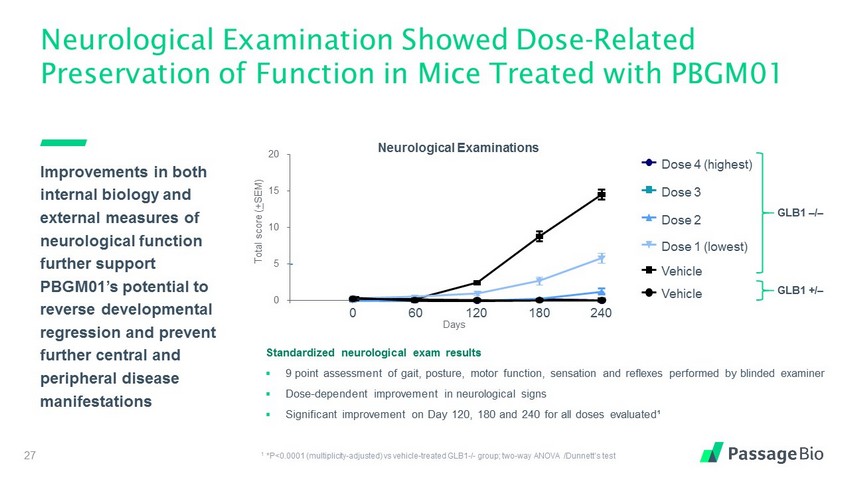
Neurological Examination Showed Dose - Related Preservation of Function in Mice Treated with PBGM01 27 Improvements in both internal biology and external measures of neurological function further support PBGM01’s potential to reverse developmental regression and prevent further central and peripheral disease manifestations 0 5 10 15 20 Total score ( + SEM) Days 240 180 120 60 0 Neurological Examinations Standardized neurological exam results ▪ 9 point assessment of gait, posture, motor function, sensation and reflexes performed by blinded examiner ▪ Dose - dependent improvement in neurological signs ▪ Significant improvement on Day 120, 180 and 240 for all doses evaluated¹ 1 *P<0.0001 (multiplicity - adjusted) vs vehicle - treated GLB1 - / - group; two - way ANOVA / Dunnett’s test GLB1 / GLB1 +/ Dose 4 (highest) Dose 3 Dose 2 Dose 1 (lowest) Vehicle Vehicle

Histological Analysis Demonstrated a Dose - Related Reduction in Brain Storage Lesions Automated quantification of LAMP1+ cells in entire cortex of one coronal brain section. One - way ANOVA of log - transformed data followed by Dunnett’s test GLB1 +/ - + vehicle GLB1 - / - + vehicle GLB1 - / - + PBGM01 PBGM01 administered ICV to one - month old mice. Animals were sacrificed 150 days after vector administration. Cerebral cortex representative 10x images. LAMP1 (red) DAPI (blue). Brightness + 20% p <0.0001 p = 0.66 p = 0.027 p <0.0001 p <0.0001 0 20 40 60 % LAMP1+ Cells PBGM01 - treated mice displayed histology supportive of PBGM01’s potential to treat the underlying pathophysiology of GM1
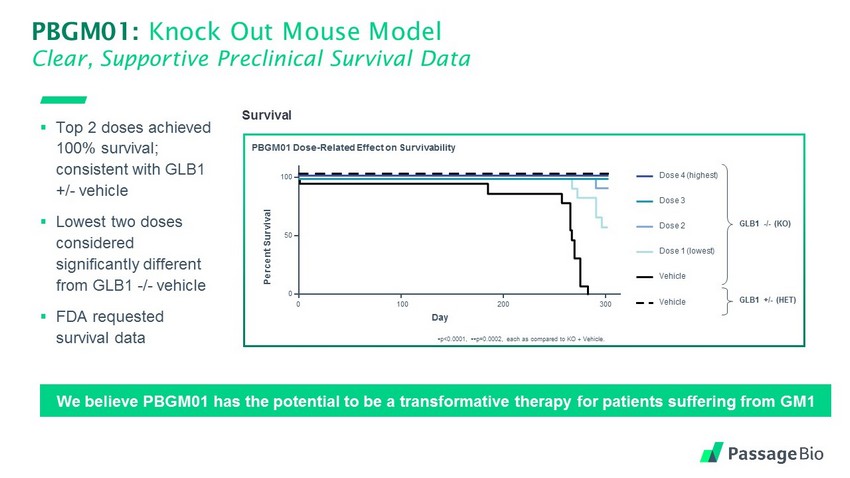
PBGM01: Knock Out Mouse Model Clear, Supportive Preclinical Survival Data Survival PBGM01 Dose - Related Effect on Survivability p<0.0001, p=0.0002, each as compared to KO + Vehicle. GLB1 - / - (KO) GLB1 +/ - (HET) Dose 4 (highest) Dose 3 Dose 2 Dose 1 (lowest) Vehicle Vehicle Percent Survival 0 Day 100 200 300 0 50 100 ▪ Top 2 doses achieved 100% survival; consistent with GLB1 +/ - vehicle ▪ Lowest two doses considered significantly different from GLB1 - / - vehicle ▪ FDA requested survival data We believe PBGM01 has the potential to be a transformative therapy for patients suffering from GM1

FTD

Histology Comparison of Lipofuscin Deposits in the Brain AAV - treated GRN - / - mice exhibited fewer lipofuscin deposits in all brain regions compared to those of vehicle - treated GRN - / - mice Hippocampus Thalamus 0 200 400 600 800 WT KO+PBS KO+AAV Lipofuscin Count Cortex 0 20 40 60 80 100 WT KO+PBS KO+AAV Lipofuscin Count p<0.05, p<0.001, p<0.0001 Histological Analysis Showed a Reduction in Lipofuscin* Deposits in AAV - GRN Treated Knockout Mice 0 20 40 60 WT KO+PBS KO+AAV Lipofuscin Count WT KO+PBS KO+AAV Hippocampus Thalamus Cortex ▪ Histological analysis confirmed that treatment reduced lipofuscin deposits in mice ▪ Demonstrative of the potential to treat the underlying pathophysiology of FTD - GRN * Pathological accumulation of lipofuscin, an electron dense material, in lysosomes is implicated in various neurodegenerative conditions, including FTD

Capsid Comparison Study in NHPs Demonstrated That Using an AAV1 Capsid Differentially Increased CSF Levels of Progranulin Without Further Elevating Plasma Levels 32 We believe PBFT02 has the potential to increase PGRN levels in the brain sufficiently to overcome the intracellular deficiency of progranulin in GRN mutation carriers PGRN Expression Production of Human PGRN in CSF and Plasma in CSF and Plasma of NHPs Following ICM AAV Delivery Production of human PGRN protein in the CSF of all treated NHPs exceeded levels found in healthy human control subjects RA2981 RA2982 RA3027 RA3153 RA3151 RA3170 RA3155 RA3160 AAVhu68 AAVhu68 (v2) AAV1 AAV5 CSF PGRN (ng/mL) 0 10 2 0 30 4 0 CSF 0.1 1 10 100 LLOQ Normal Day Plasma Plasma PGRN (ng/mL) 0 10 2 0 30 4 0 0.1 1 10 100 Normal Day 1,000

PBFT02 Utilizes an AAV1 Capsid Which Provides Strong Transduction of Ependymal Cells 33 We believe PBFT02 has the potential to be a transformative therapy for patients suffering from FTD - GRN given its superior transduction of ependymal cells in the brain which differentially increases CSF progranulin without further increases in plasma progranulin levels AAVhu68 AAV1 Ependyma 1 2% transduction 48% transduction AAVhu68 AAV1 Ependyma 1 2% transduction 48% transduction Ependymal cell transduction following ICM delivery of AAV1 and AAVhu68 vectors expressing GFP in NHPs AAVhu68 AAV1 Ependyma 1 2% transduction 48% transduction Transduction of the ependymal cells (as shown by density of darkened ependymal cells) was substantially higher in the animals treated with AAV1 (48%) as compared to the animals treated with AAVhu68 (1 - 2%)

Proactive Exploration of AAV - Related DRG Toxicity DRG toxicity was previously identified as potential AAV platform risk DRG toxicity has been seen across capsids, transgenes and delivery methods NHP studies where minimal to mild dose - dependent DRG toxicity was observed without clinical manifestations NHP studies examining DRG toxicity revealed no increase in severity, along with no clinical manifestations at 4 6 months or up to 4 years after administration. ( Hordeaux , et al., Hum Gen Ther , 2019) Preliminary findings in completed Passage Bio toxicology studies Noted minimal/mild trigeminal ganglia and dorsal root ganglia degeneration and axonopathy Reduction in median nerve sensory action potential amplitudes by Day 28 observed in some animals No clinical manifestations noted; not clearly dose dependent or progressive Findings support clinical nerve conduction studies for clinical safety monitoring Proactive monitoring in clinical programs will be implemented Sensory NCS testing readily detects subclinical DRG toxicity 34

Krabbe

PBKR03 Treatment Showed an Increase in Brain and Peripheral Organ GALC Activity in Naturally Occurring Twitcher Mouse Disease Model and Dog Disease Model 36 We believe PBKR03 has the potential to increase levels of GALC activity in the brain, CSF and critical peripheral tissues CSF GALC activity in treated dogs 0 200 400 600 800 D0 D28 D35 D70 D100 D120 D180 Fluo units +/+ t wi / twi t wi / twi PBS GTP - 206 GALC Activity (FU/10 µL) 15, 000 10,000 5,000 0 Serum GALC Activity (FU/50 µg) 2, 000 1,500 0 500 +/+ t wi / twi t wi / twi PBS GTP - 206 1,000 Liver GALC Activity (FU/50 µg) 2 0,000 15,000 10,000 0 5,000 +/+ t wi / twi t wi / twi PBS GTP - 206 Brain K933-Krabbe K937-Krabbe K938-Krabbe K939-Krabbe

Further Studies in a Dog Model Showed a Normalization in Body Weight and Nerve Conduction Velocity 37 Treated dogs responded well to the therapy, showed similar growth and NCVs as wild - type dogs 0 20 40 60 80 6 weeks 12 weeks 20 weeks 28 weeks 42 weeks m/s K933-Krabbe AAV K937-Krabbe AAV K938-Krabbe AAV K939-Krabbe AAV K930-Krabbe sham K948-Krabbe sham K928-WT sham 0 20 40 60 80 6 weeks 12 weeks 20 weeks 28 weeks 42 weeks m/s Tibial motor NCV Radial sensory NCV Nerve conduction velocities in tibial motor and radial sensory nerves of PBKR03 - treated dogs 0 5 10 15 20 25 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 Body weight (Kg) Age (weeks) WT sham Krabbe sham Krabbe treated Body weight curve (Treated 28 weeks)

Histological Analysis Showed an Improvement in Myelination in Brain and Decrease in Neuroinflammation Histology: Myelination and Neuroinflammation Correction at 28 Weeks A Luxol blue (myelination) treated 28 weeks treated 28 weeks B IBA1 (neuroinflammation) sham 8 weeks sham 8 weeks ▪ Treated dogs displayed an improvement in myelination and decreased neuroinflammation ▪ Supportive of the ability to treat the underlying pathopysiology of Krabbe

Corporate Presentation SEPTEMBER 2020
