Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| 8-K - SCHOLAR ROCK HOLDING CORPORATION 8-K - Scholar Rock Holding Corp | a52262995.htm |
| EX-99.1 - EXHIBIT 99.1 - Scholar Rock Holding Corp | a52262995ex99_1.htm |
Exhibit 99.2

2Q20 Financial Results and Business Progress August 7, 2020

Disclaimers Various statements in this presentation concerning Scholar Rock’s future expectations, plans
and prospects, including without limitation, Scholar Rock’s expectations regarding its strategy, its product candidate selection and development timing, including timing for the initiation of and reporting results from its clinical trials for
its product candidates, its disease indication selection and timing for such selection, the ability of SRK-015 to affect the treatment of patients suffering from Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA) either as a monotherapy or in conjunction with the
current standard of care, and the ability of SRK-181 to affect the treatment of cancer patients in a manner consistent with preclinical data constitute forward-looking statements for the purposes of the safe harbor provisions under The Private
Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. The use of words such as “may,” “might,” “will,” “should,” “expect,” “plan,” “anticipate,” “believe,” “estimate,” “target,” “project,” “intend,” “future,” “potential,” or “continue,” and other similar
expressions are intended to identify such forward-looking statements. Actual results may differ materially from those indicated by these forward-looking statements as a result of various important factors, including, without limitation, Scholar
Rock’s ability to provide the financial support and resources necessary to identify and develop multiple product candidates on the expected timeline, competition from others developing products for similar uses, the preliminary nature of
interim clinical data, Scholar Rock’s ability to obtain, maintain and protect its intellectual property, Scholar Rock’s dependence on third parties for development and manufacture of product candidates including to supply any clinical trials,
and Scholar Rock’s ability to manage expenses and to obtain additional funding when needed to support its business activities and establish and maintain strategic business alliances and new business initiatives as well as those risks more fully
discussed in the section entitled "Risk Factors" in the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2020, which is on file with the Securities and Exchange Commission, as well as discussions of potential risks, uncertainties,
and other important factors in Scholar Rock’s subsequent filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission. Any forward-looking statements represent Scholar Rock’s views only as of today and should not be relied upon as representing its views
as of any subsequent date. Scholar Rock explicitly disclaims any obligation to update any forward-looking statements unless required by law. © Scholar Rock, Inc. All rights reserved. August 2020.

Newest Members of Highly Experienced Leadership Team 3 TONY KINGSLEY, MBAPresident & CEO TED
MYLES, MBACFO & Head of Business Operations Joined Scholar Rock’s Board of Directors in May 2020President & CEO of Taris Bio President & COO of The Medicines CompanyEVP at Biogen, led global commercial operations Strategic,
operational, and commercial leader Financial and operational executive Served on Scholar Rock’s Board of Directors for nearly 2 yearsCFO & COO of AMAG Pharmaceuticals, Inc.CFO & COO of Ocata TherapeuticsCFO & Vice President of
Operations at PrimeraDx, Inc.

Proprietary platform has produced multiple programs with significant therapeutic potential Two most
advanced programs, SRK-015 and SRK-181, are advancing quickly and address markets that are well developed and growing Multiple programs and multiple anticipated milestones offer near- and long-term value inflection points and strategic
optionality 4
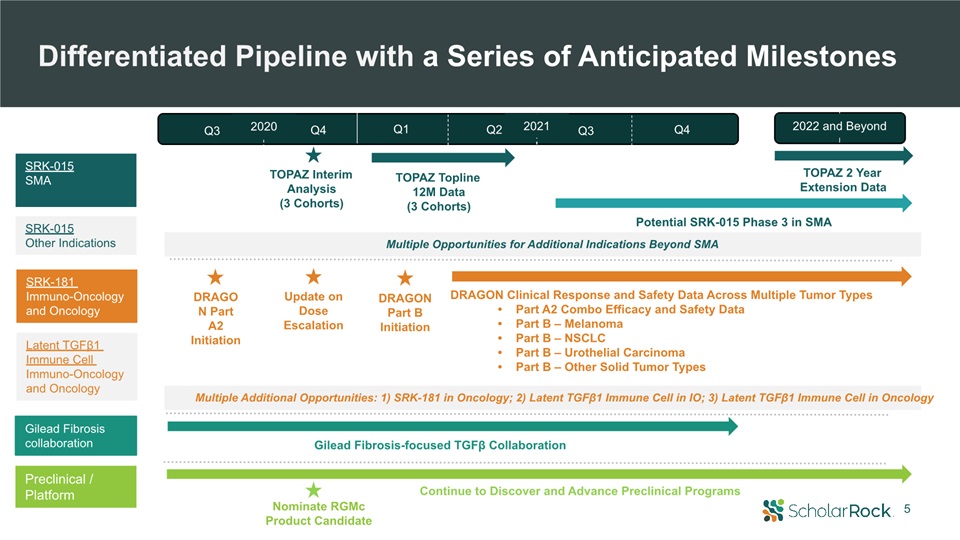
5 DRAGON Part A2 Initiation DRAGON Part B Initiation Nominate RGMcProduct Candidate Gilead
Fibrosis-focused TGFβ Collaboration DRAGON Clinical Response and Safety Data Across Multiple Tumor TypesPart A2 Combo Efficacy and Safety DataPart B – MelanomaPart B – NSCLCPart B – Urothelial CarcinomaPart B – Other Solid Tumor
Types SRK-015SMA SRK-181 Immuno-Oncology and Oncology Preclinical / Platform TOPAZ Topline12M Data(3 Cohorts) Potential SRK-015 Phase 3 in SMA TOPAZ Interim Analysis(3 Cohorts) Differentiated Pipeline with a Series of Anticipated
Milestones TOPAZ 2 Year Extension Data Continue to Discover and Advance Preclinical Programs Update on Dose Escalation Multiple Opportunities for Additional Indications Beyond SMA Multiple Additional Opportunities: 1) SRK-181 in
Oncology; 2) Latent TGFβ1 Immune Cell in IO; 3) Latent TGFβ1 Immune Cell in Oncology SRK-015Other Indications Gilead Fibrosis collaboration 2022 and Beyond 2021 Q3 Q4 Q3 Q4 Q1 Q2 2020 Latent TGFβ1 Immune Cell Immuno-Oncology and
Oncology

Review of Clinical Programs: SRK-015 and SRK-181 6 Yung Chyung, MDChief Medical Officer
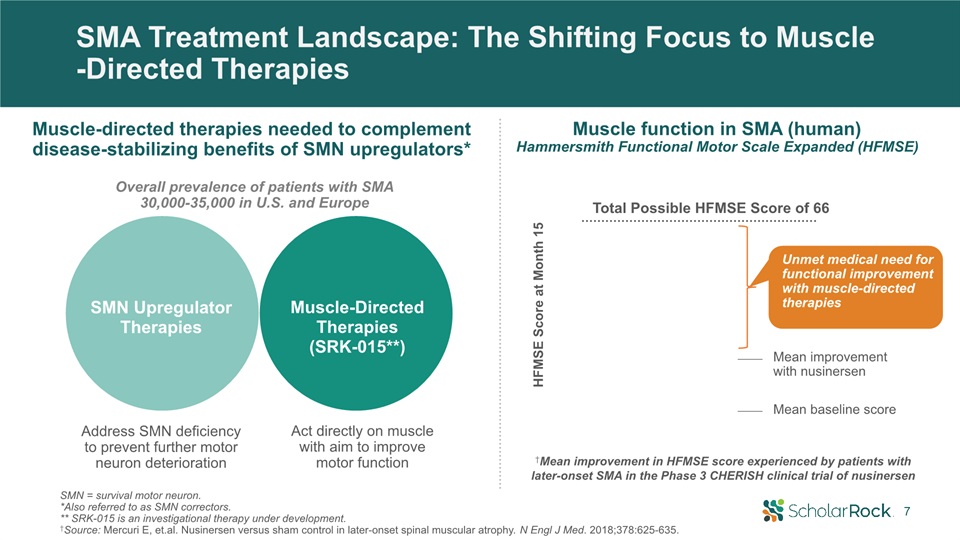
SMA Treatment Landscape: The Shifting Focus to Muscle-Directed Therapies †Mean improvement in HFMSE
score experienced by patients withlater-onset SMA in the Phase 3 CHERISH clinical trial of nusinersen HFMSE Score at Month 15 Mean baseline score Mean improvement with nusinersen Unmet medical need for functional improvement with
muscle-directed therapies Total Possible HFMSE Score of 66 Muscle function in SMA (human)Hammersmith Functional Motor Scale Expanded (HFMSE) Address SMN deficiency to prevent further motor neuron deterioration Act directly on muscle
with aim to improve motor function SMN Upregulator Therapies Muscle-Directed Therapies (SRK-015**) SMN = survival motor neuron. *Also referred to as SMN correctors. ** SRK-015 is an investigational therapy under development.†Source: Mercuri
E, et.al. Nusinersen versus sham control in later-onset spinal muscular atrophy. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:625-635. Muscle-directed therapies needed to complement disease-stabilizing benefits of SMN upregulators* Overall prevalence of patients
with SMA 30,000-35,000 in U.S. and Europe 7

†Source: Mercuri E, et.al. Nusinersen versus sham control in later-onset spinal muscular atrophy. N Engl
J Med. 2018;378:625-635.† †Efficacy and safety of risdiplam (RG7916) in patients with Type 2 or non-ambulant Type 3 spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) Roche/PTC Therapeutics Nusinersen CHERISH Trial in Later-Onset SMA† In patients with later-onset
SMA who were age >5 at screening…Primary benefit of nusinersen - stabilization of motor functionAttainment of >3-point increase - rare (<15% of patients) even with nusinersen treatment Later-Onset SMA: High Unmet Need for
Muscle-Directed Therapy to Complement SMN Upregulator Therapy 8 Risdiplam SUNFISH Trial in Later-Onset SMA†† Low percentage of patients over the age of 5 achieved ≥3-point increase on MFM32 scale, even with risdiplam treatmentHFMSE secondary
endpoint showed a mean 0.58-point improvement over placebo (not statistically significant) % of patients with >3 change in MFM32 total at Month 12 2-5 years 6-11 years 12-17 years 18-25 years Change in MFM32 total score Risdiplam
Placebo 100806040200

Progress on Path Towards Investigating SRK-015’s Therapeutic Potential in SMA Phase 2 TOPAZ interim
analysis to evaluate efficacy and safety in SMA Results anticipated 4Q20 Strong translational rationale for investigating myostatin blockade in SMA Therapeutic effects in SMA preclinical mouse model Phase 1 trial in adult healthy
volunteers demonstrated: Initial safetyPK profile supporting every 4-week dosing regimenPD data confirming robust target engagement Phase 2 TOPAZ trial showed: Preliminary PD analysis demonstrates target engagement in patients with
SMA 9 Sources: Poster presentations at various scientific congresses: Cure SMA Annual Conference (June 2020), MDA Clinical and Scientific Conference (March 2020), World Muscle Society Congress (October 2019).
https://scholarrock.com/platform/publications/.

SRK-015 Phase 2 Trial Design Cohort 1 Cohort 3 Design Patients N= 23*; ages
5-21Open-label, single-arm20 mg/kg SRK-015 IV Q4W12-month treatment period Ambulatory Type 3 SMAReceiving treatment with approved SMN upregulator or as monotherapy Cohort 2 N= 15; ages 5-21 Open-label, single-arm20 mg/kg SRK-015 IV
Q4W12-month treatment period Type 2 or non-ambulatory Type 3 SMAReceiving treatment with approved SMN upregulator N= 20; ages ≥2Double-blind, randomized (1:1) to 2 mg/kg or 20 mg/kg SRK-015 IV Q4W12-month treatment period Type 2 SMA
Initiated treatment with approved SMN upregulator before age 5 Primary Objectives SafetyMean change from baseline in RHS SafetyMean change from baseline in HFMSE SafetyMean change from baseline in HFMSE HFMSE=Hammersmith Functional Motor
Scale Expanded; RHS=Revised Hammersmith Scale.*Baseline demographics presented as part of AAN virtual platform (May 2020). https://scholarrock.com/platform/publications/. We believe SRK-015 has the potential to be backbone therapy to all SMN
upregulators Interim Efficacy and Safety Results Expected 4Q20; Top-line 12-Month Data 1H21 10

Each Cohort Represents Important POC Opportunity With Significant Potential Cohort 3 Efficacy –
Therapeutic Goals Safety Goals Efficacy signal enables investigation of SRK-015’s broader potential Cohort 1 RHS: Absolute increase in mean change from baseline RHS: Substantial % of patients attain >3-point increase Additional
outcomes: timed motor tests No significant safety signals Broader age rangeAny SMN upregulatorMonotherapy in some settingsAdditional neuromuscular indications Cohort 2 HFMSE: Absolute increase in mean change from baseline HFMSE:
Substantial % of patients attain >3-point increase Additional outcomes: RULM, WHO motor developmental milestones No significant safety signals Broader age rangeAny SMN upregulatorAdditional neuromuscular indications Cohort 3 HFMSE:
Substantial improvement in mean change from baseline Explore potential differentiation (e.g. timing to onset of therapeutic effect) between high dose and low dose arms Additional outcomes: RULM, WHO motor developmental milestones No
significant safety signals Any SMN upregulatorAdditional early intervention settings (Type 1 and pre-symptomatic)Additional neuromuscular indications 11

SRK-181 Has Potential to Increase Response and Be Backbone Therapy to All Checkpoint Inhibitors
*Source: Company information, Wall Street research, Evaluate Pharma.†Source: Carretero-Gonzalez A, et al. Oncotarget. 2018;9:8706-8715. Meta-analysis of 12 randomized trials with control arm or adequate safety profile (includes nivolumab,
pembrolizumab, and atezolizumab), Significant Unmet Potential to Increase Response to Checkpoint Inhibitors (CPIs) Current Checkpoint Inhibitor Market: $25B+*~20% of patients respond to checkpoint inhibitors† 12

Significant Interest in Potential Role of TGFβ Inhibition in Immuno-Oncology Nature (online), Feb. 14,
2018. AuthorsWilly Hugo, Jesse M. Zaretsky, Lu Sun, Douglas B. Johnson, Antoni Ribas, Roger S. Lo Volume 165, Issue 1, 24 March 2016, Pages 35-44 July 24, 2020: https://doi.org/10.1038/ s41571-020-0403-1 February 2019: “GSK and Merck
KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany announce global alliance to jointly develop and commercialise M7824, a novel immunotherapy with potential in multiple difficult-to-treat cancers”€300 million upfront and up to €3.7 billion total June 2019: “Merck to
Acquire Tilos Therapeutics: Merck Gains Portfolio of Investigational Antibodies Modulating TGFβ”$773 million total potential deal value 13

Cancer Genome Atlas RNAseq analysis of >10,000 samples spanning 33 tumor types* *Source: National
Cancer Institute - Cancer Genome Atlas Program.†Priti H, et al. Top 10 challenges in cancer immunotherapy. Immunity. 2020 Jan 14:52(1):17-35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2019.12.011. Substantial proportion of solid tumors exhibit immune
exclusion† Broad Potential for TGFβ Blockade Across Many Solid Tumors Human Tumor Analyses Reveal TGFβ1 as Most Likely Driver of TGFβ Pathway Signaling in Cancers 14

SRK-181: Unique TGFβ1-Selective Approach to Overcoming Checkpoint Inhibitor Resistance 15 SRK-181Latent
TGFβ1 Inhibitor Inhibits TGFβ1 pathway - implicated in CPI resistance Highly selective targeting - avoids binding to latent TGFβ2 and TGFβ3 isoforms Aimed at increasing therapeutic window – potentially avoids toxicities associated with
non-selective TGFβ inhibition Therapeutic flexibility - pair with any CPI and optimize dosing of each component of combination therapy

SRK-181: Therapeutic Rationale Continues to Strengthen EVIDENCE TO DATE Increasing evidence implicating
TGFβ1’s pivotal role in CPI resistance TGFβ1 implicated in immune excluded tumor phenotype; poor CPI responsesTGFβ1 expression and immune exclusion broadly observed across solid tumorsMerck KGaA/GSK’s bintrasfusp alfa (M7824) showed
encouraging long-term survival potential in NSCLC* SRK-181 evaluated in 3 preclinical syngeneic tumor models aimed at emulating primary resistance to CPI in humansTreatment with SRK-181 combined with CPI led to significant impact on anti-tumor
responses and survival rates in preclinical models† Nonselective TGFβ inhibition associated with significant tox; constrains dosingSRK-181: highly selective inhibitor of latent TGFβ1 activation with minimal or no binding to latent TGFβ2/3
isoforms SRK-181 did not lead to cardiac or other toxicities in 4-week GLP nonclinical toxicology studies SRK-181: potential for robust blockade of TGFβ1 pathway Significant anti-tumor efficacy in preclinical tumor models *Presented at ASCO
2020. Bintrasfusp alfa (M7824) is a bifunctional protein comprised of anti-PD-L1 and TGFβ trap † Preclinical data published in Science Translational Medicine. Martin CJ, et al. Sci Transl Med. 2020 Mar 25;12(536):eaay8456.
https://scholarrock.com/platform/publications. 16

DRAGON Phase 1 POC Trial to Evaluate SRK-181’s Ability to Overcome Primary Resistance to Checkpoint
Inhibitors Open-label, dose escalation, and dose expansion clinical trialEvaluate the efficacy, safety/tolerability, and PK/PD of SRK-181 in combination with approved anti-PD-(L)1 therapyPatients with locally advanced or metastatic solid
tumors that exhibit primary resistance to anti-PD(L)1 therapyLack of response characterized as stable or progressive disease following ≥3 cycles of anti-PD-(L)1 therapy either alone or in combination with chemotherapy NCT04291079 on
www.clinicaltrials.gov. Update on dose escalation expected in 4Q20; clinical response and safety data expected in 2021 SRK-181:selective inhibitor of TGFβ1 activation Part A Part A1:SRK-181 as a single agent Modified 3+3 dose
escalationAssess SRK-181 dose range of 80-2400 mg (avg weight 80kg)Part A2:SRK-181 with approved anti-PD-(L)13+3 dose escalation Treat with same anti-PD-(L)1 as previously given with no response Part B SRK-181 in combo with approved
anti-PD-(L)1 therapy4 parallel cohorts – each will enroll up to 40 patientsTarget indications expected to include NSCLC, urothelial carcinoma, melanoma, amongst other solid tumor typesTreat with same anti-PD-(L)1 as previously given with no
response 17
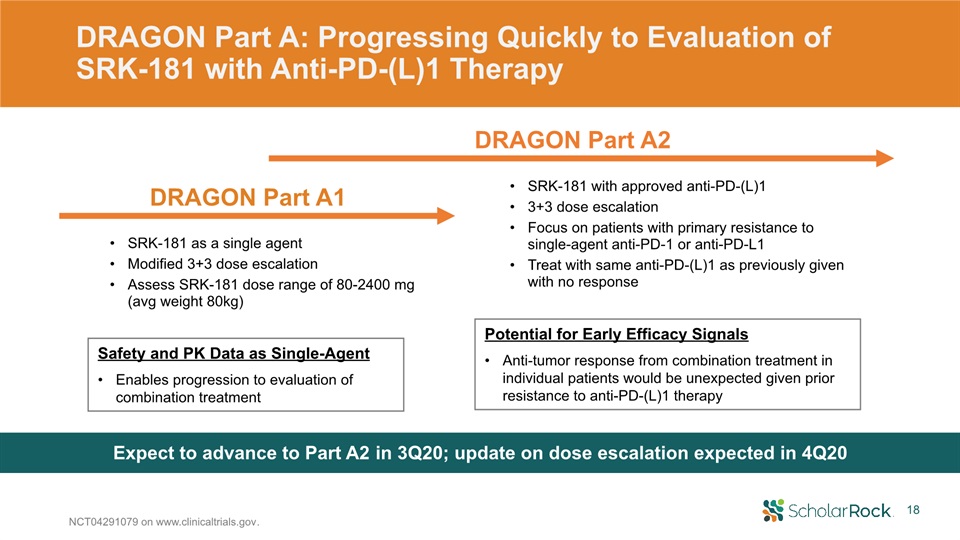
DRAGON Part A: Progressing Quickly to Evaluation of SRK-181 with Anti-PD-(L)1 Therapy NCT04291079 on
www.clinicaltrials.gov. SRK-181 with approved anti-PD-(L)13+3 dose escalation Focus on patients with primary resistance to single-agent anti-PD-1 or anti-PD-L1 Treat with same anti-PD-(L)1 as previously given with no response Expect to
advance to Part A2 in 3Q20; update on dose escalation expected in 4Q20 SRK-181 as a single agent Modified 3+3 dose escalationAssess SRK-181 dose range of 80-2400 mg (avg weight 80kg) Safety and PK Data as Single-AgentEnables progression to
evaluation of combination treatment Potential for Early Efficacy SignalsAnti-tumor response from combination treatment in individual patients would be unexpected given prior resistance to anti-PD-(L)1 therapy DRAGON Part A1 DRAGON Part
A2 18

DRAGON Part B: Multiple Opportunities for Efficacy Signals * Planning to open eligibility to patients
with history of primary resistance to either pembrolizumab or nivolumabNCT04291079 on www.clinicaltrials.gov. Study population focused on patients already shown to have primary resistance to single-agent CPI4 parallel cohorts; each to enroll
up to 40 patientsNSCLC: SRK-181 + pembrolizumabUrothelial carcinoma: SRK-181 + pembrolizumabMelanoma: SRK-181 + pembrolizumab*Additional tumor types: SRK-181 + anti-PD-(L)1 therapy for which patient experienced primary resistance DRAGON Part B
initiation planned 1Q21; anti-tumor and safety data expected starting in 2021 Potential for Rapid Path to Proof-of-ConceptAnti-tumor response and safety with combination treatmentResponse in individual patients would be unexpected given prior
resistance to anti-PD-(L)1 therapyEvaluation of patients with stable or progressive diseaseAbility to evaluate response across multiple tumor typesPatient population with high unmet medical needStrong proof-of-concept signal could support
efficient registrational path DRAGON Part B 19

20 2Q20 Financial ResultsTed MylesCFO & Head of Business Operations

21 2Q20 Financial Update (GAAP) Revenues Operating Expenses Net Loss Ended June 30, 2020 with $141M
in cash, cash equivalents, and marketable securities Revenues of $3.9 millionRelated to the Gilead fibrosis-focused collaboration R&D expense of $17.0 millionY/Y increase due to acceptance of Specifica, Inc. antibody display library,
SRK-015 TOPAZ Phase 2 trial, personnel-related costs G&A expense of $6.4 millionY/Y increase due to personnel-related costs and professional services $19.3 million or $0.65 per share
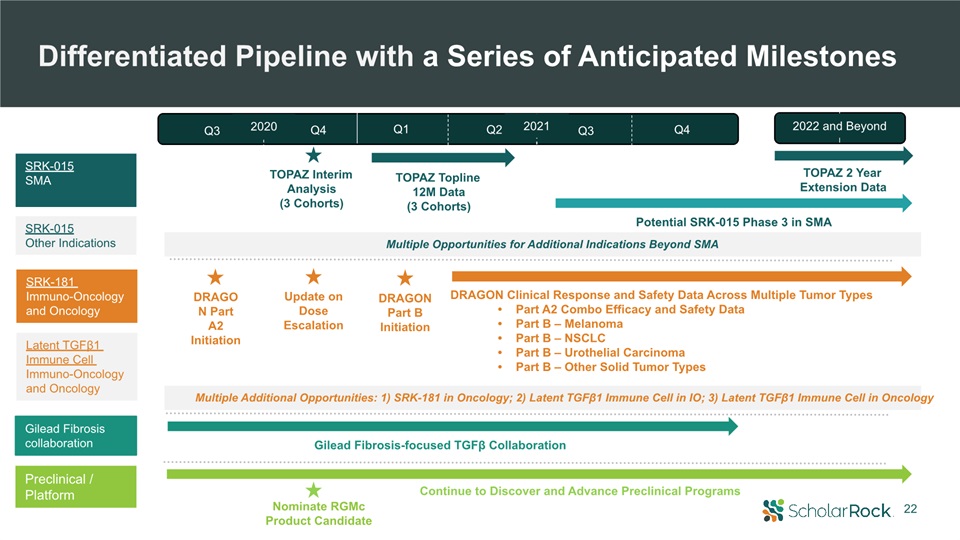
22 DRAGON Part A2 Initiation DRAGON Part B Initiation Nominate RGMcProduct Candidate Gilead
Fibrosis-focused TGFβ Collaboration DRAGON Clinical Response and Safety Data Across Multiple Tumor TypesPart A2 Combo Efficacy and Safety DataPart B – MelanomaPart B – NSCLCPart B – Urothelial CarcinomaPart B – Other Solid Tumor
Types SRK-015SMA SRK-181 Immuno-Oncology and Oncology Preclinical / Platform TOPAZ Topline12M Data(3 Cohorts) Potential SRK-015 Phase 3 in SMA TOPAZ Interim Analysis(3 Cohorts) Differentiated Pipeline with a Series of Anticipated
Milestones TOPAZ 2 Year Extension Data Continue to Discover and Advance Preclinical Programs Update on Dose Escalation Multiple Opportunities for Additional Indications Beyond SMA Multiple Additional Opportunities: 1) SRK-181 in
Oncology; 2) Latent TGFβ1 Immune Cell in IO; 3) Latent TGFβ1 Immune Cell in Oncology SRK-015Other Indications Gilead Fibrosis collaboration 2022 and Beyond 2021 Q3 Q4 Q3 Q4 Q1 Q2 2020 Latent TGFβ1 Immune Cell Immuno-Oncology and
Oncology

Appendix

24 Robust Target Engagement Observed~100-fold increases in serum latent myostatin levels following
single 20 mg/kg dose in all cohorts of TOPAZConfirms presence of latent myostatin in patients with SMAWell-Behaved, Linear PK Profile Minimal variability across TOPAZ cohortsDose proportional increase in serum drug exposure between low (2
mg/kg) and high (20 mg/kg) doses Preliminary TOPAZ Biomarker Data Provide First Demonstration of Target Engagement in Patients with SMA Preliminary PK/PD results include data from 29 patients (12 in Cohort 1, 8 in Cohort 2, and 9 in Cohort
3).Source: Poster presentation at the MDA Clinical and Scientific Conference (March 2020). https://scholarrock.com/platform/publications/. Latent Myostatin Change Over Baseline in SRK-015 TOPAZ Trial Latent Myostatin Change Over Baseline in
Phase 1 HV Trial Preliminary TOPAZ Phase 2 Pharmacokinetic (PK) Data

25 TGFβ1 Blockade with SRK-181-mIgG1 Rendered Preclinical Tumor Models Susceptible to Anti-PD1
Therapy Preclinical data published in Science Translational Medicine. Martin CJ, et al. Sci Transl Med. 2020 Mar 25;12(536):eaay8456. https://scholarrock.com/platform/publications. Melanoma (Cloudman S91) model: Combination treatment led to
tumor regression and survival benefitSimilar results in bladder (MBT2) and breast (EMT6) preclinical tumor models Anti-PD1/SRK-181-mIgG1 (10 mg/kg QW) Anti-PD1/SRK-181-mIgG1 (30 mg/kg QW) 4/9 8/11 SRK-181-mIgG1 (30 mg/kg
QW) 3/12 0/12 Anti-PD1 (10 mg/kg BIW) *P<0.01. †P<0.05 Log-rank (Mantel-Cox test) vs anti-PD1. **† Tumor Regression: Monotherapy Tumor Regression: Combination Therapy Days after treatment initiation Days after treatment
initiation Days after treatment initiation Survival Benefit Anti-PD1/ SRK-181-mIgG1 led to influx of CD8+ cells in preclinical bladder tumor model Anti-PD1 Overcoming immune exclusion

TGFβ1 Isoform Specificity of SRK-181 Improved Preclinical Toxicity Profile Preclinical data published
in Science Translational Medicine. Martin CJ, et al. Sci Transl Med 2020 Mar 25;12(536): eaay8456. *Source: Anderton MJ, et al. Induction of heart valve lesions by small-molecule ALK5 inhibitors. Toxicol Pathol. 2011;39: 916-924.; and Stauber
AJ, et al. Nonclinical safety evaluation of a transforming growth factor β Receptor I kinase inhibitor in Fischer 344 rats and beagle dogs. J Clin Pract. 2014: 4:3. Selectivity of SRK-181 offers potential to overcome toxicity and dose-limiting
challenges of non-selective TGFβ pathway approaches Microscopic observations in heart Valvulopathy Atrium—Mixed cell infiltrate Myocardium—Degeneration/necrosis Myocardium—Hemorrhage Myocardium—Miced cell infiltrate, base Coronary
artery—Necrosis with inflammation Cardiomyocyte—Necrosis/inflammatory cell infiltrate Control Vehicle iv, qwk x 4 LY2109761 300
mg/kg po, qd x 8 PanTGFβAb 30 mg/kg po, qd x 8 10
mg/kg iv, qwk x 4 30 mg/kg iv, qwk x 4 100 mg/kg iv, qwk x
4 SRK-181 LEGEND UnremarkableMinimalSlightModerate Repeat dose pilot toxicology study in adult female Sprague Dawley rats:Cardiac findings were exhibited
in animals dosed with a pan-TGFβ antibody or LY2109761 (inhibitor of ALK5, common TGFβ receptor kinase) as expected based on published data†No cardiotoxicities (valvulopathy) were noted with SRK-181 NOAEL for SRK-181 was the highest dose
evaluated of 100 mg/kg QW 4-week GLP toxicology studies: Rats: NOAEL for SRK-181 was up to highest evaluated dose of 200 mg/kg QWNon-human primates: NOAEL for SRK-181 was up to highest evaluated dose of 300 mg/kg QW 26
