Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-99.2 - EX-99.2 - Aclaris Therapeutics, Inc. | tmb-20200617xex99d2.htm |
| 8-K - 8-K - Aclaris Therapeutics, Inc. | tmb-20200617x8k.htm |
Exhibit 99.1
| © Copyright 2020 Aclaris Therapeutics, Inc. All rights reserved (PP--US-0484 06/20) ATI-450: A Potential Treatment for Patients with COVID-19 ATI-450, an investigational oral MK2 inhibitor June 17, 2020 EMPOWERING PATIENTS THROUGH KINOME INNOVATION |
| © Copyright 2020 Aclaris Therapeutics, Inc. All rights reserved (PP--US-0484 06/20) Any statements contained in this presentation that do not describe historical facts may constitute forward-looking statements as that term is defined in the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. These statements may be identified by words such as "believe,” "expect," "may,“ "plan," "potential," "will," and similar expressions, and are based on Aclaris' current beliefs and expectations. These forward-looking statements include expectations regarding ATI-450 as a potential treatment for patients with COVID-19 and the clinical development of ATI-450. These statements involve risks and uncertainties that could cause actual results to differ materially from those reflected in such statements. Risks and uncertainties that may cause actual results to differ materially include uncertainties inherent in the conduct of clinical trials, Aclaris' reliance on third parties over which it may not always have full control, the uncertainty regarding the COVID-19 pandemic including its impact on the timing of Aclaris’ regulatory and research and development activities, and other risks and uncertainties that are described in the Risk Factors section of Aclaris’ Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2019, Aclaris’ Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 2020 and other filings Aclaris makes with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission from time to time. These documents are available under the “SEC filings" section of the Investors page of Aclaris' website at http://www.aclaristx.com. Any forward-looking statements speak only as of the date of this presentation and are based on information available to Aclaris as of the date of this presentation, and Aclaris assumes no obligation to, and does not intend to, update any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise This presentation also contains estimates and other statistical data made by independent parties and by us relating to market size and other data about our industry. This data involves a number of assumptions and limitations, and you are cautioned not to give undue weight to such estimates. In addition, projections, assumptions and estimates of our future performance and the future performance of the markets in which we operate are necessarily subject to a high degree of uncertainty and risk. Cautionary Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements 2 |
| © Copyright 2020 Aclaris Therapeutics, Inc. All rights reserved (PP--US-0484 06/20) • Mortality in COVID-19 disease is driven, in large part, by cytokine release syndrome (CRS), resulting in acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)1,2 • CRS is characterized by elevated levels of cytokines and chemokines such as: IFNg, IL-1Ra, IL-1b, IL-2, IL-6, IL-10, IL-18, MCP-1, MCP-3, M-CSF, G- CSF, GM-CSF, IL-8, TNFa, MIP1a, and IP-101 • Biologics targeting IL-6 have demonstrated signs of efficacy in treating COVID-19.3 Biologics that target individual cytokines such as GM-CSF, IL- 1, IL-6 and IL-8 are currently in clinical studies4,5,6,7 • ATI-450 blocks multiple relevant cytokines such as TNFa, IL-1b, IL-2, IL-6, IFNg, GM-CSF, IL-8 and MIP1a* ATI-450: Potential Treatment for COVID-19-Induced Cytokine Storm Inhibition of Multiple Pro-inflammatory Cytokines 3 * Data on file |
| © Copyright 2020 Aclaris Therapeutics, Inc. All rights reserved (PP--US-0484 06/20) MK2 Pathway Regulates Key Cytokines Involved in COVID-19-Induced Cytokine Release Syndrome 4 |
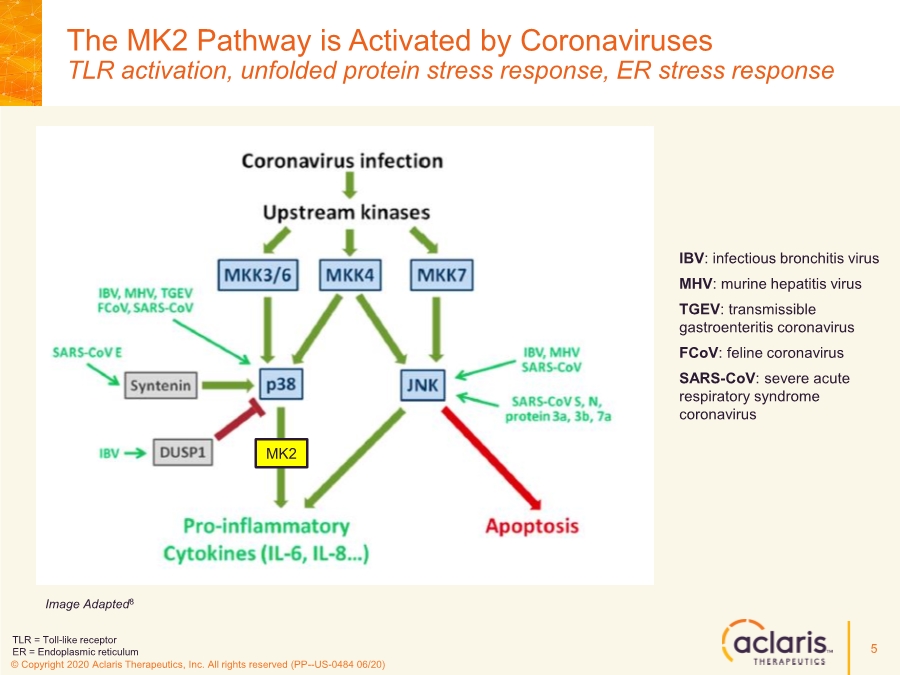
| © Copyright 2020 Aclaris Therapeutics, Inc. All rights reserved (PP--US-0484 06/20) The MK2 Pathway is Activated by Coronaviruses TLR activation, unfolded protein stress response, ER stress response 5 IBV: infectious bronchitis virus MHV: murine hepatitis virus TGEV: transmissible gastroenteritis coronavirus FCoV: feline coronavirus SARS-CoV: severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus MK2 Image Adapted8 TLR = Toll-like receptor ER = Endoplasmic reticulum |
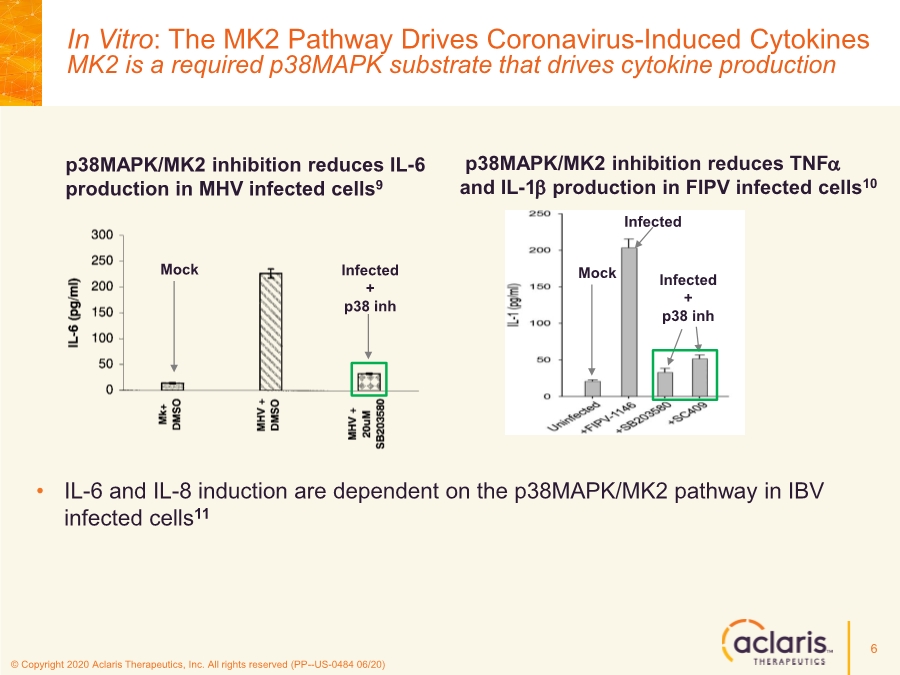
| © Copyright 2020 Aclaris Therapeutics, Inc. All rights reserved (PP--US-0484 06/20) 6 p38MAPK/MK2 inhibition reduces IL-6 production in MHV infected cells9 p38MAPK/MK2 inhibition reduces TNFa and IL-1b production in FIPV infected cells10 • IL-6 and IL-8 induction are dependent on the p38MAPK/MK2 pathway in IBV infected cells11 Mock Infected Infected + p38 inh Mock Infected + p38 inh In Vitro: The MK2 Pathway Drives Coronavirus-Induced Cytokines MK2 is a required p38MAPK substrate that drives cytokine production |
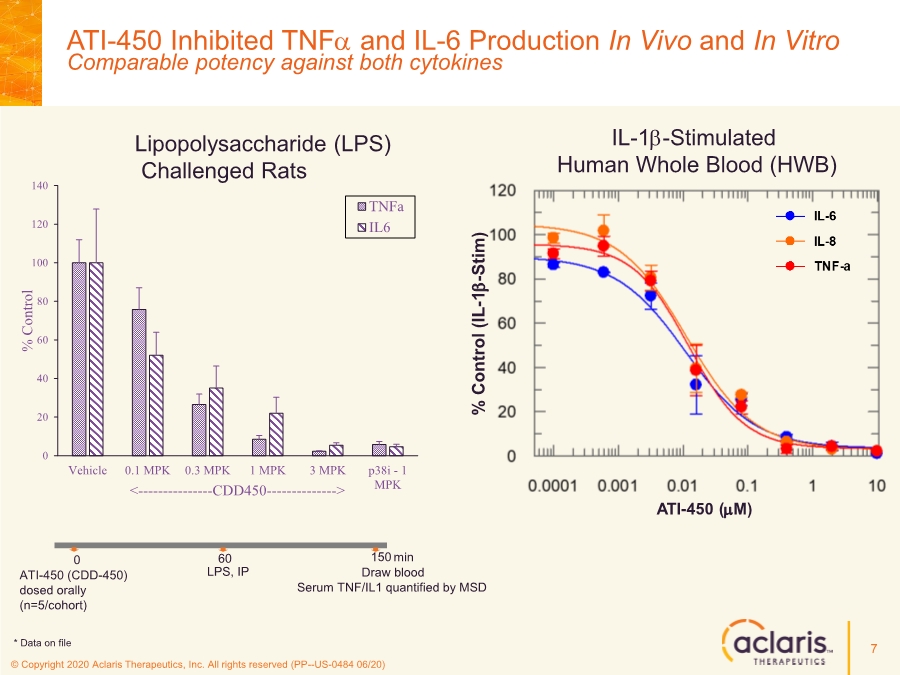
| © Copyright 2020 Aclaris Therapeutics, Inc. All rights reserved (PP--US-0484 06/20) 7 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 Vehicle 0.1 MPK 0.3 MPK 1 MPK 3 MPK p38i - 1 MPK % Control <---------------CDD450--------------> TNFa IL6 LPS, IP ATI-450 (CDD-450) dosed orally (n=5/cohort) min 0 60 150 Draw blood Serum TNF/IL1 quantified by MSD IL-1b-Stimulated Human Whole Blood (HWB) Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) Challenged Rats ATI-450 (mM) % Control (IL - 1 b - Stim) * Data on file ATI-450 Inhibited TNFa and IL-6 Production In Vivo and In Vitro Comparable potency against both cytokines |
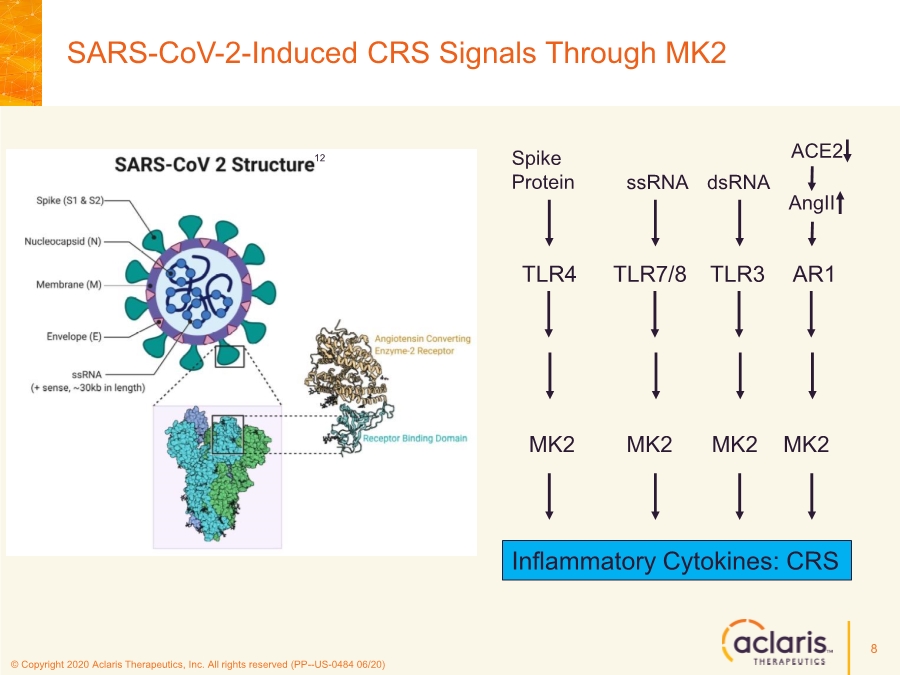
| © Copyright 2020 Aclaris Therapeutics, Inc. All rights reserved (PP--US-0484 06/20) SARS-CoV-2-Induced CRS Signals Through MK2 8 Spike Protein ssRNA dsRNA AngII MK2 MK2 MK2 MK2 TLR4 TLR7/8 TLR3 AR1 Inflammatory Cytokines: CRS ACE2 12 |
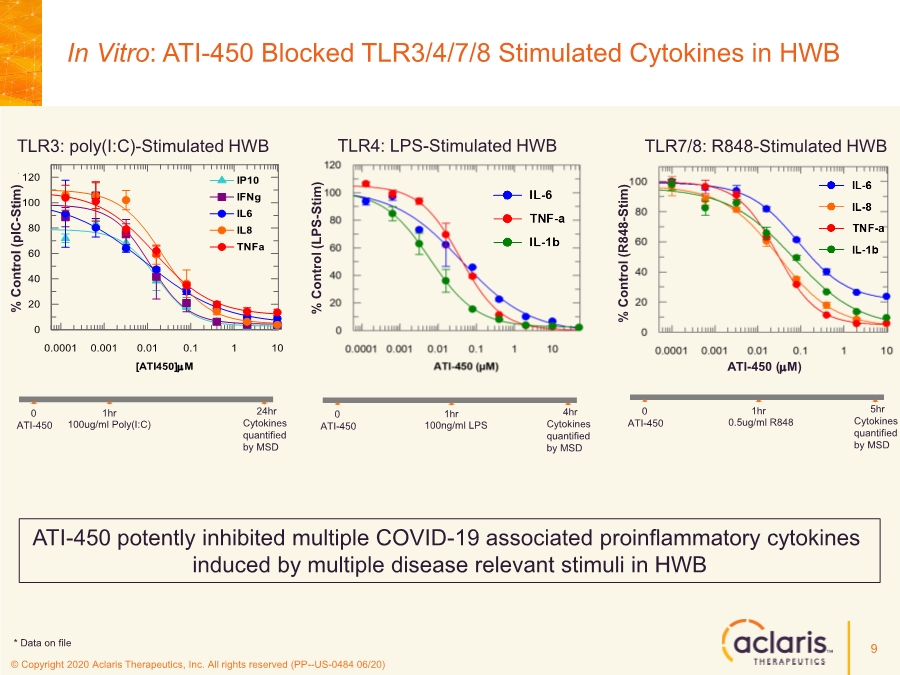
| © Copyright 2020 Aclaris Therapeutics, Inc. All rights reserved (PP--US-0484 06/20) 9 TLR4: LPS-Stimulated HWB % Control (LPS - Stim) TLR7/8: R848-Stimulated HWB % Control (R848 - Stim) ATI-450 (mM) 100ng/ml LPS ATI-450 0 1hr 4hr Cytokines quantified by MSD TLR3: poly(I:C)-Stimulated HWB 0.5ug/ml R848 ATI-450 0 1hr 5hr Cytokines quantified by MSD 100ug/ml Poly(I:C) ATI-450 0 1hr 24hr Cytokines quantified by MSD ATI-450 potently inhibited multiple COVID-19 associated proinflammatory cytokines induced by multiple disease relevant stimuli in HWB [ATI450]mM 0.0001 0.001 0.01 0.1 1 10 % Control (pIC, 24hr - Stim) 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 IP10 IFNg IL6 IL8 TNFa % Control ( pIC - Stim) * Data on file In Vitro: ATI-450 Blocked TLR3/4/7/8 Stimulated Cytokines in HWB |
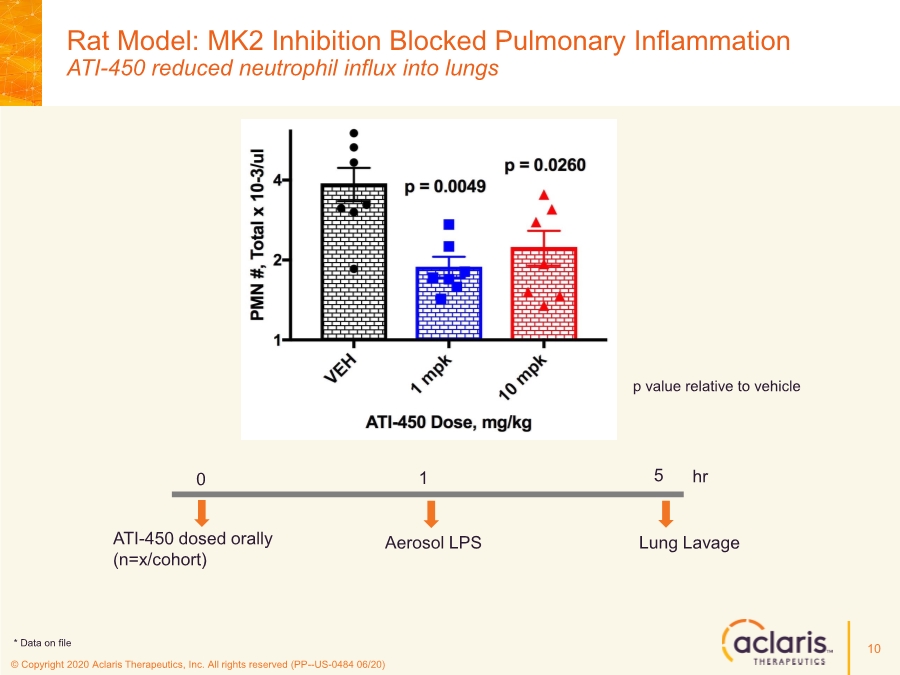
| © Copyright 2020 Aclaris Therapeutics, Inc. All rights reserved (PP--US-0484 06/20) Rat Model: MK2 Inhibition Blocked Pulmonary Inflammation ATI-450 reduced neutrophil influx into lungs 10 p value relative to vehicle * * Aerosol LPS ATI-450 dosed orally (n=x/cohort) hr 0 1 5 Lung Lavage * Data on file |
| © Copyright 2020 Aclaris Therapeutics, Inc. All rights reserved (PP--US-0484 06/20) 11 • LPS (TLR4) stimulated cytokine and chemokine production – Blood samples from the ATI-450-PKPD-101 Trial – Cytokines and chemokines elevated in patients with COVID-19 were analyzed including: IL1-b, IL-2, IL-6, IL-8, GM-CSF, IFNγ, MIP1a and TNFa o TNFa, IL-1b, IL-6 and IL-8 analyzed pre-dose and 4hr/12hr post- dose in the Day 7 MAD cohorts o Follow up analysis of IL-2, GM-CSF, IFNγ and MIP1a from SAD 100mg cohort (1hr post-dose) and MAD 4hr post-dose Day 7 cohorts ATI-450 Impact on Human Blood Cytokines & Chemokines: Ex Vivo LPS-Stimulated HWB Phase 1 SAD/MAD Trial * Data on file |
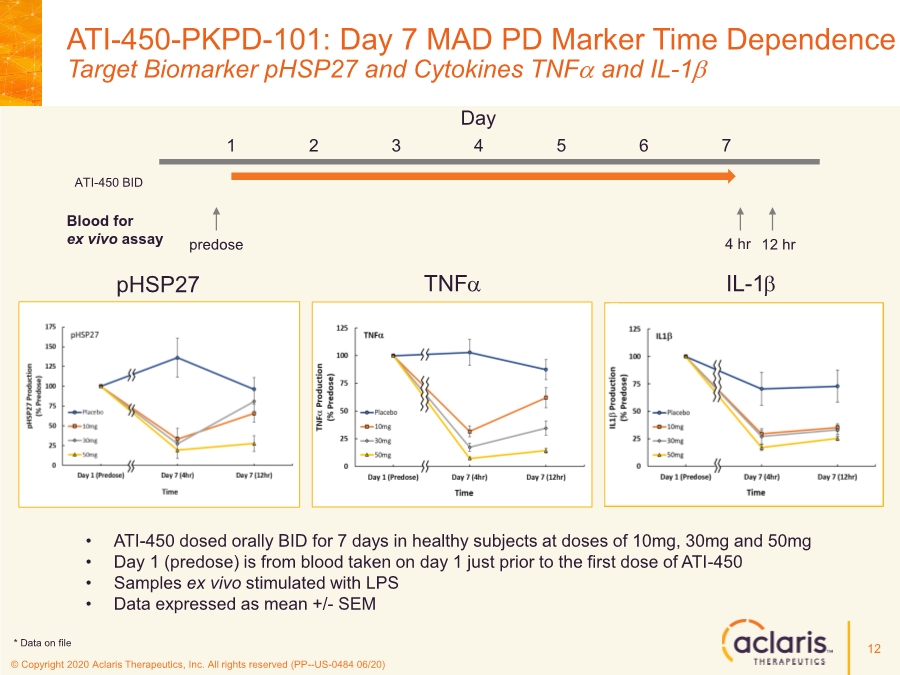
| © Copyright 2020 Aclaris Therapeutics, Inc. All rights reserved (PP--US-0484 06/20) ATI-450-PKPD-101: Day 7 MAD PD Marker Time Dependence Target Biomarker pHSP27 and Cytokines TNFa and IL-1b • ATI-450 dosed orally BID for 7 days in healthy subjects at doses of 10mg, 30mg and 50mg • Day 1 (predose) is from blood taken on day 1 just prior to the first dose of ATI-450 • Samples ex vivo stimulated with LPS • Data expressed as mean +/- SEM TNFa IL-1b pHSP27 Day 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 ATI-450 BID Blood for ex vivo assay predose 4 hr 12 hr 12 * Data on file |
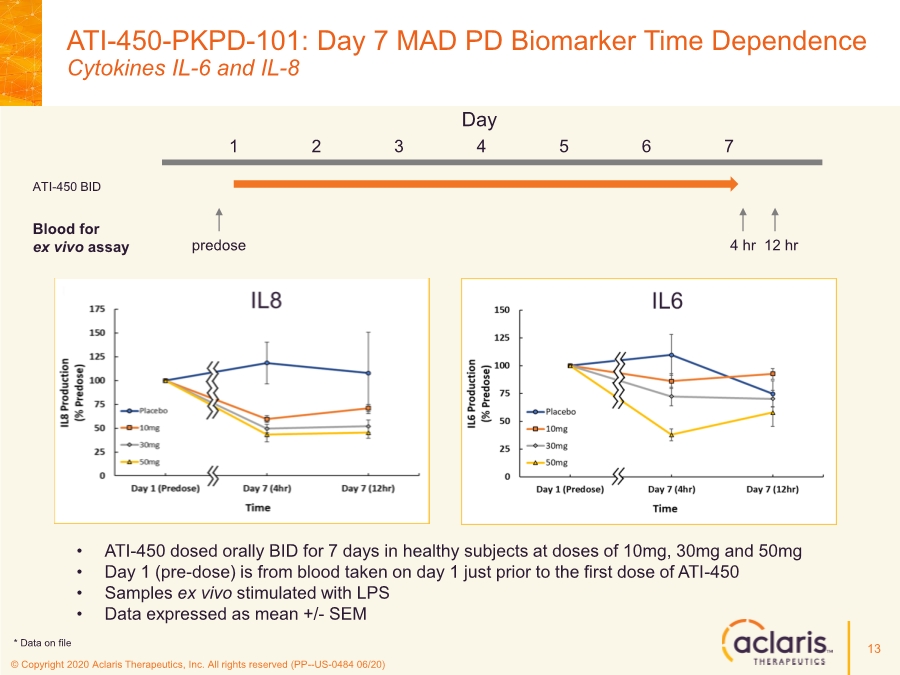
| © Copyright 2020 Aclaris Therapeutics, Inc. All rights reserved (PP--US-0484 06/20) • ATI-450 dosed orally BID for 7 days in healthy subjects at doses of 10mg, 30mg and 50mg • Day 1 (pre-dose) is from blood taken on day 1 just prior to the first dose of ATI-450 • Samples ex vivo stimulated with LPS • Data expressed as mean +/- SEM Day 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 predose 4 hr 12 hr ATI-450 BID Blood for ex vivo assay 13 * Data on file ATI-450-PKPD-101: Day 7 MAD PD Biomarker Time Dependence Cytokines IL-6 and IL-8 |
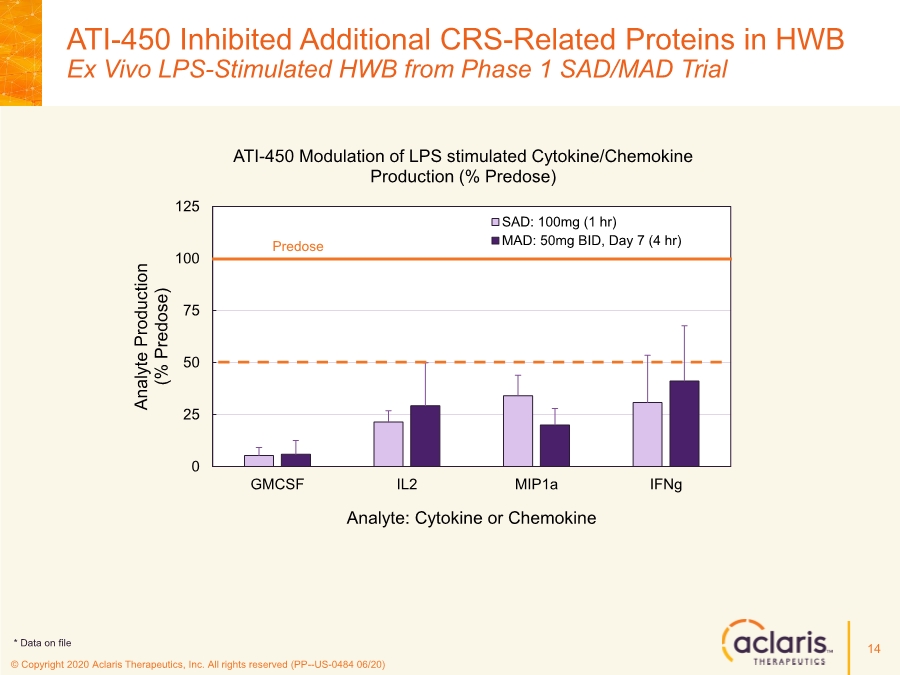
| © Copyright 2020 Aclaris Therapeutics, Inc. All rights reserved (PP--US-0484 06/20) ATI-450 Inhibited Additional CRS-Related Proteins in HWB Ex Vivo LPS-Stimulated HWB from Phase 1 SAD/MAD Trial 14 0 25 50 75 100 125 GMCSF IL2 MIP1a IFNg Analyte Production (% Predose) Analyte: Cytokine or Chemokine ATI-450 Modulation of LPS stimulated Cytokine/Chemokine Production (% Predose) SAD: 100mg (1 hr) MAD: 50mg BID, Day 7 (4 hr) Predose * Data on file |
| © Copyright 2020 Aclaris Therapeutics, Inc. All rights reserved (PP--US-0484 06/20) The MK2 Pathway Regulates Coronavirus Replication/Pathology 15 |
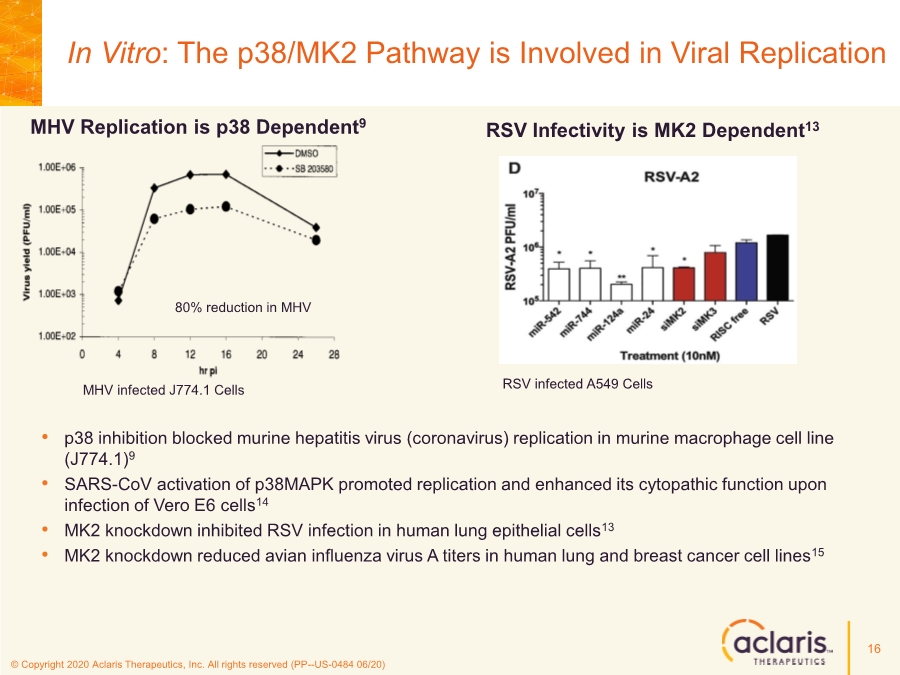
| © Copyright 2020 Aclaris Therapeutics, Inc. All rights reserved (PP--US-0484 06/20) 16 MHV Replication is p38 Dependent9 MHV infected J774.1 Cells RSV Infectivity is MK2 Dependent13 RSV infected A549 Cells • p38 inhibition blocked murine hepatitis virus (coronavirus) replication in murine macrophage cell line (J774.1)9 • SARS-CoV activation of p38MAPK promoted replication and enhanced its cytopathic function upon infection of Vero E6 cells14 • MK2 knockdown inhibited RSV infection in human lung epithelial cells13 • MK2 knockdown reduced avian influenza virus A titers in human lung and breast cancer cell lines15 In Vitro: The p38/MK2 Pathway is Involved in Viral Replication 80% reduction in MHV |
| © Copyright 2020 Aclaris Therapeutics, Inc. All rights reserved (PP--US-0484 06/20) Mouse Model: p38MAPK/MK2 Inhibition Increased Survival of SARS-CoV Infected Mice 17 • Mice infected with SARS-CoV intranasal • p38MAPKi dosed 8mpk ip BID for 8 days • Mortality measured daily p38MAPK/MK2 Inhibition Improves Survival16 Infected Infected + p38i Mock |
| © Copyright 2020 Aclaris Therapeutics, Inc. All rights reserved (PP--US-0484 06/20) MK2 Inhibition Prevents Pulmonary Fibrosis 18 |
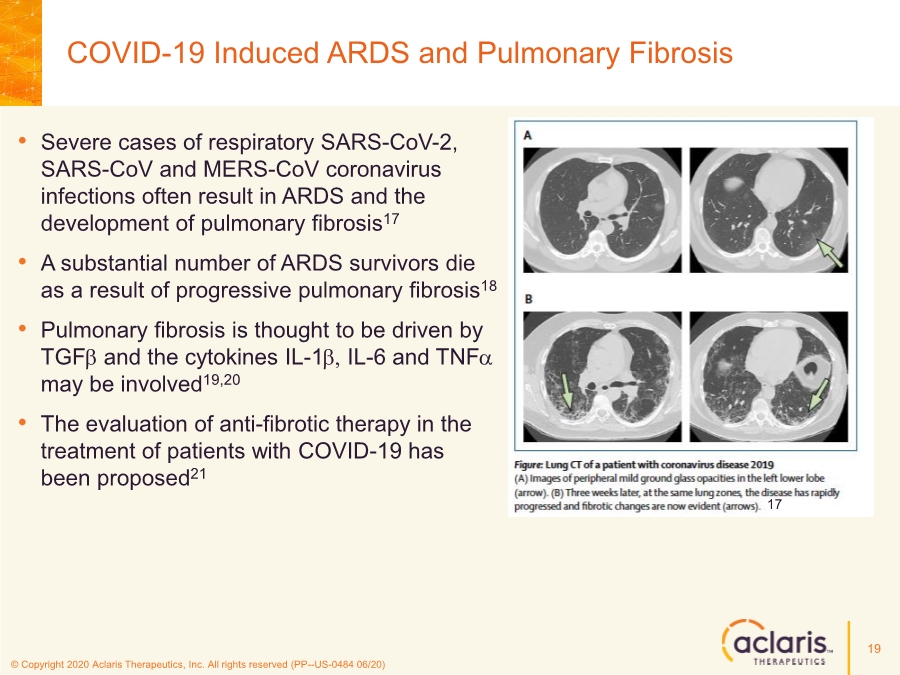
| © Copyright 2020 Aclaris Therapeutics, Inc. All rights reserved (PP--US-0484 06/20) • Severe cases of respiratory SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV coronavirus infections often result in ARDS and the development of pulmonary fibrosis17 • A substantial number of ARDS survivors die as a result of progressive pulmonary fibrosis18 • Pulmonary fibrosis is thought to be driven by TGFb and the cytokines IL-1b, IL-6 and TNFa may be involved19,20 • The evaluation of anti-fibrotic therapy in the treatment of patients with COVID-19 has been proposed21 COVID-19 Induced ARDS and Pulmonary Fibrosis 19 17 |
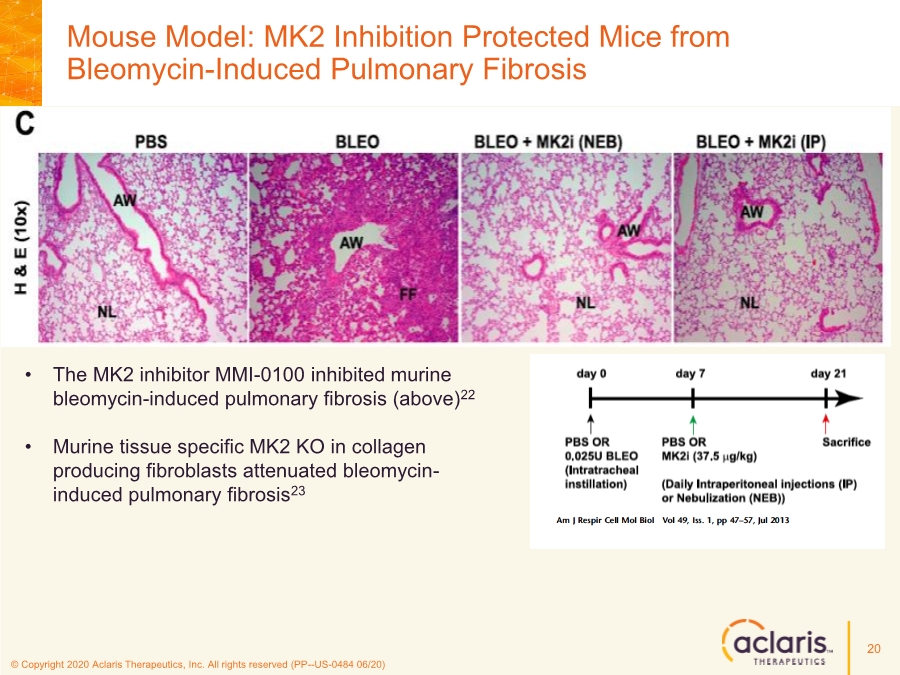
| © Copyright 2020 Aclaris Therapeutics, Inc. All rights reserved (PP--US-0484 06/20) Mouse Model: MK2 Inhibition Protected Mice from Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis 20 • The MK2 inhibitor MMI-0100 inhibited murine bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis (above)22 • Murine tissue specific MK2 KO in collagen producing fibroblasts attenuated bleomycin- induced pulmonary fibrosis23 |
| © Copyright 2020 Aclaris Therapeutics, Inc. All rights reserved (PP--US-0484 06/20) • ATI-450 has the potential to: – Inhibit multiple key inflammatory cytokines associated with CRS in patients with COVID-19; – Inhibit coronavirus replication and infectivity; and – Block COVID-19-induced pulmonary fibrosis. • Next step: Investigator-Initiated Trial (IIT)-2020-ATI-450- COVID-19 will evaluate if ATI-450’s inhibition of multiple key inflammatory cytokines provides benefits for CRS in patients with COVID-19 21 ATI-450 as a Potential Treatment for COVID-19 Summary |
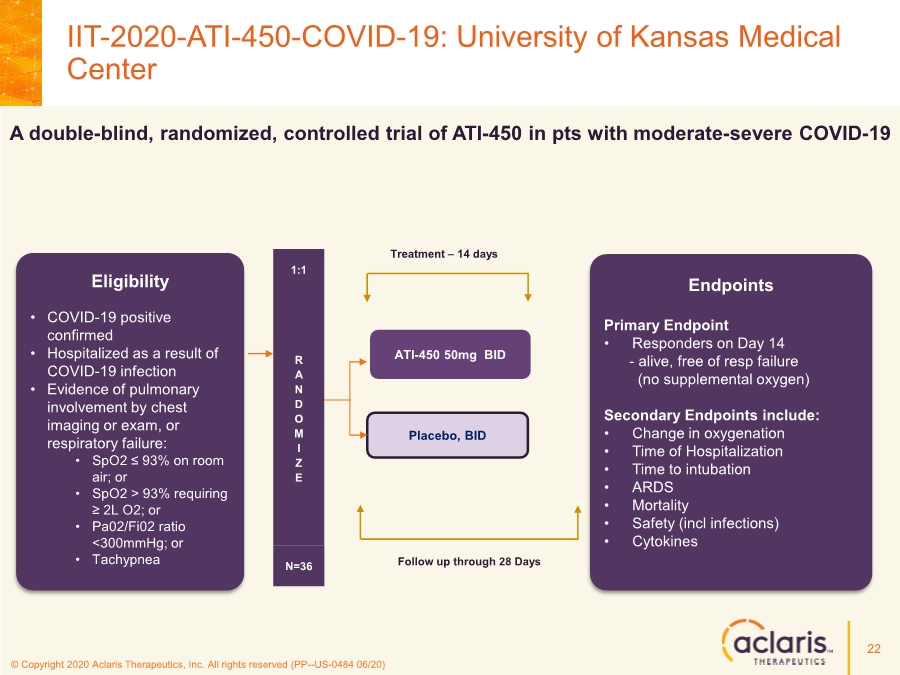
| © Copyright 2020 Aclaris Therapeutics, Inc. All rights reserved (PP--US-0484 06/20) Eligibility • COVID-19 positive confirmed • Hospitalized as a result of COVID-19 infection • Evidence of pulmonary involvement by chest imaging or exam, or respiratory failure: • SpO2 ≤ 93% on room air; or • SpO2 > 93% requiring ≥ 2L O2; or • Pa02/Fi02 ratio <300mmHg; or • Tachypnea R A N D O M I Z E 1:1 N=36 ATI-450 50mg BID Placebo, BID Endpoints Primary Endpoint • Responders on Day 14 - alive, free of resp failure (no supplemental oxygen) Secondary Endpoints include: • Change in oxygenation • Time of Hospitalization • Time to intubation • ARDS • Mortality • Safety (incl infections) • Cytokines Treatment – 14 days Follow up through 28 Days A double-blind, randomized, controlled trial of ATI-450 in pts with moderate-severe COVID-19 IIT-2020-ATI-450-COVID-19: University of Kansas Medical Center 22 |
| © Copyright 2020 Aclaris Therapeutics, Inc. All rights reserved (PP--US-0484 06/20) References 23 1. Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. 2020;395:497-506. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5 2. Zhou F, Yu T, Du R, et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet. 2020;395:1054-1062. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3 3. Xu X, Han M, Li T, et al. Effective treatment of severe COVID-19 patients with tocilizumab. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020;117(20):10970-10975. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2005615117 4. Investigating Otilimab in Patients With Severe Pulmonary COVID-19 Related Disease (OSCAR). ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT04376684. Accessed June 15, 2020. https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04376684 5. Study of Efficacy and Safety of Canakinumab Treatment for CRS in Participants With COVID-19-induced Pneumonia (CAN-COVID). ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT04362813. Accessed June 15, 2020. https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04362813 6. Safety and Efficacy of Tocilizumab in Moderate to Severe COVID-19 With Inflammatory Markers (TOCIBRAS). ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT04403685. Accessed June 16, 2020. https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04403685 7. Anti-Interleukin-8 (Anti-IL-8) for Patients With COVID-19. ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT04347226. Accessed June 15, 2020. https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04347226 8. Fung TS, Liao Y, Liu DX. Regulation of Stress Responses and Translational Control by Coronavirus. Viruses. 2016;8(7):184. doi: 10.3390/v8070184 9. Banerjee S, Narayanan K, Mizutani T, Makino S. Murine Coronavirus Replication-Induced p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Activation Promotes Interleukin-6 Production and Virus Replication in Cultured Cells. J Virol. 2002;76(12):5937-5948. doi:10.1128/JVI.76.12.5937–5948.2002 10. Regan, AD, Cohen RD, Whittaker GR. Activation of p38 MAPK by feline infectious peritonitis virus regulates pro-inflammatory cytokine production in primary blood-derived feline mononuclear cells. J Virol. 2009;384(1):135-143. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2008.11.006 11. Liao Y, Wang X, Huang M, Tam JP, Liu DX. Regulation of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and dual-specificity phosphatase 1 feedback loop modulates the induction of interleukin 6 and 8 in cells infected with coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus. J Virol. 2011;420(2):106-116. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2011.09.003 12. Cascella M, Rajnik M, Cuomo A, Dulebohn S. Features, Evaluation and Treatment Coronavirus (COVID-19). StatPearls. Updated May 18, 2020. Accessed June 16, 2020. https://www.statpearls.com/kb/viewarticle/52171 13. McCaskill JL, Ressel S, Alber A, et al. Broad-Spectrum Inhibition of Respiratory Virus Infection by MicroRNA Mimics Targeting p38 MAPK Signaling. Mol Therapy: Nuc Acids. 2017;7:256- 266. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2017.03.008 14. Yoshino S, Mizutani N. Intranasal exposure to monoclonal antibody Fab fragments to Japanese cedar pollen Cry j1 suppresses Japanese cedar pollen‐induced allergic rhinitis. Br J Pharmacol. 2016;173(10):1629–1638. doi: 10.1111/bph.13463 15. Luig C, Köther K, Dudek SE, et al. MAP kinase-activated protein kinases 2 and 3 are required for influenza A virus propagation and act via inhibition of PKR. FASEB J. 2010; 24:4068- 4077. doi: 10.1096/fj.10-158766 16. Jimenez-Guardeño JM, Nieto-Torres JL, DeDiego ML, et al. The PDZ-Binding Motif of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Envelope Protein Is a Determinant of Viral Pathogenesis. PLoS Pathog. 2014;10(8):1-20. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004320 17. Spagnolo P, Balestro E, Aliberti S, et al. Pulmonary fibrosis secondary to COVID-19: a call to arms? Lancet Respir Med. Published online May 15, 2020. doi: 10.1016/ S2213- 2600(20)30222-8 18. Herridge MS, Tansey CM, Matté A, et al. Functional Disability 5 Years after Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2011;364(14):1293-1304. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1011802 19. Borthwick LA. The IL-1 Cytokine Family and Its Role in Inflammation and Fibrosis in the Lung. Semin Immunopathol. 2016;38(4):517-34. doi: 10.1007/s00281-016-0559-z 20. Meduri GU, Headley S, Kohler G, Stentz F, Tolley E, Umberger R, Leeper K. Persistent Elevation of Inflammatory Cytokines Predicts a Poor Outcome in ARDS. Plasma IL-1 Beta and IL-6 Levels Are Consistent and Efficient Predictors of Outcome Over Time. Chest. 1995;107(4):1062-1073. doi: 10.1378/chest.107.4.1062 21. Fang L, Karakiulakis G, Roth M. Are patients with hypertension and diabetes mellitus at increased risk for COVID-19 infection? Lancet Respir Med. 2020;8(4):e21. doi: 10.1016/S2213- 2600(20)30116-8 22. Vittal R, Fisher A, Gu H, et al. Peptide-Mediated Inhibition of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase–Activated Protein Kinase–2 Ameliorates Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2013;49(1):47–57. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2012-0389OC 23. Liang J, Liu N, Liu X, et al. Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase–activated Protein Kinase 2 Inhibition Attenuates Fibroblast Invasion and Severe Lung Fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2019;60(1):41–48. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2018-0033OC |