Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| 8-K - FORM 8-K - Lipocine Inc. | tm2012454d1_8k.htm |
| EX-99.1 - EXHIBIT 99.1 - Lipocine Inc. | tm2012454d1_ex99-1.htm |

Enabling Oral Drug Delivery to Improve Patient Compliance March 2020 Corporate Presentation Exhibit 99.2

Forward - Looking Statements This presentation contains forward - looking statements about Lipocine Inc. (the “Company”). These forward - looking statements are made pursuant to the safe harbor provisions of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. These forward - looking statement s relate to the Company’s product candidates, FDA review process related to our resubmitted NDA for TLANDO™, the expected timing of Phase 3 t ria ls for TLANDO XR and LPCN 1107 and Phase 2 studies for LPCN 1144 and LPCN 1148, clinical and regulatory processes and objectives, po ten tial benefits of the Company’s product candidates, intellectual property and related matters, all of which involve known and unkno wn risks and uncertainties. Actual results may differ materially from the forward - looking statements discussed in this presentation . Accordingly, the Company cautions investors not to place undue reliance on the forward - looking statements contained in, or made in connection with, this presentation . Several factors may affect the initiation and completion of clinical trials and studies, the potential advantages of the Company’s product candidates and the Company’s capital needs. The forward - looking statements contained in this presentation are qualified by the detailed discussion of risks and uncertainties set forth in the Company’s annual report on For m 10 - K and other periodic reports filed by the Company with the Securities and Exchange Commission, all of which can be obtained on the Com pany’s website at www.lipocine.com or on the SEC website at www.sec.gov . The forward - looking statements contained in this document represent the Company’s estimates and assumptions only as of the date of this presentation and the Company undertakes no duty or obligation to update or revise publicly any forward - looking statements contained in this presentation as a result of new information, future events or changes in the Company’s expectations. 2
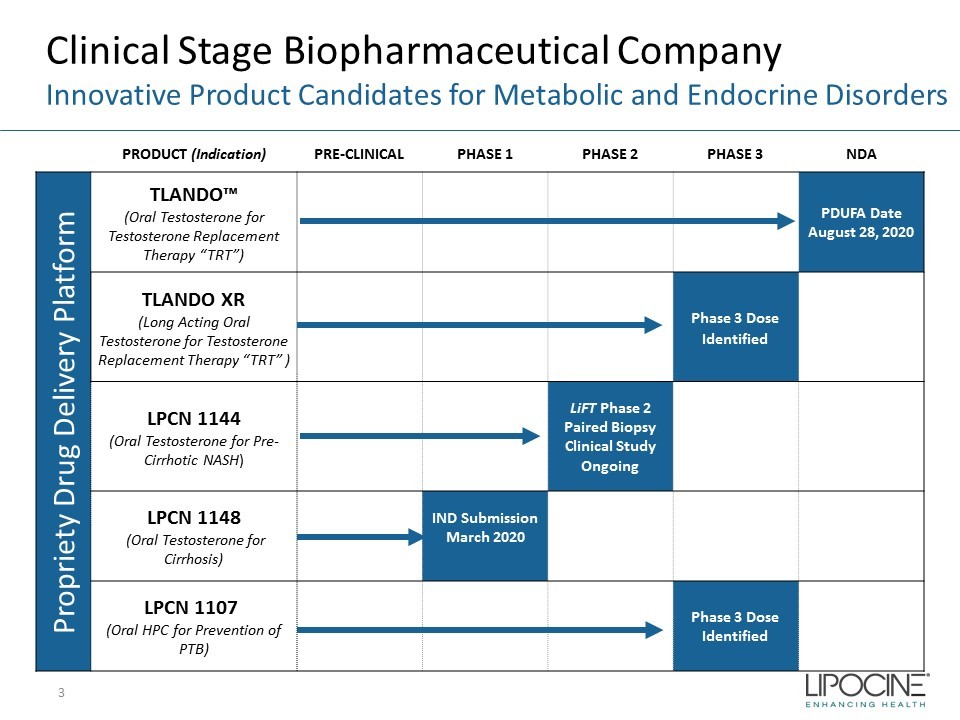
Clinical Stage Biopharmaceutical Company Innovative Product Candidates for Metabolic and Endocrine Disorders 3 PRODUCT (Indication) PRE - CLINICAL PHASE 1 PHASE 2 PHASE 3 NDA Propriety Drug Delivery Platform TLANDO ™ (Oral Testosterone for Testosterone Replacement Therapy “TRT”) PDUFA Date August 28, 2020 TLANDO XR (Long Acting Oral Testosterone for Testosterone Replacement Therapy “ TRT” ) Phase 3 Dose Identified LPCN 1144 (Oral Testosterone for Pre - Cirrhotic NASH ) LiFT Phase 2 Paired Biopsy Clinical Study Ongoing LPCN 1148 (Oral Testosterone for Cirrhosis) IND Submission March 2020 LPCN 1107 (Oral HPC for Prevention of PTB) Phase 3 Dose Identified

4 Fixed Dose Oral TRT
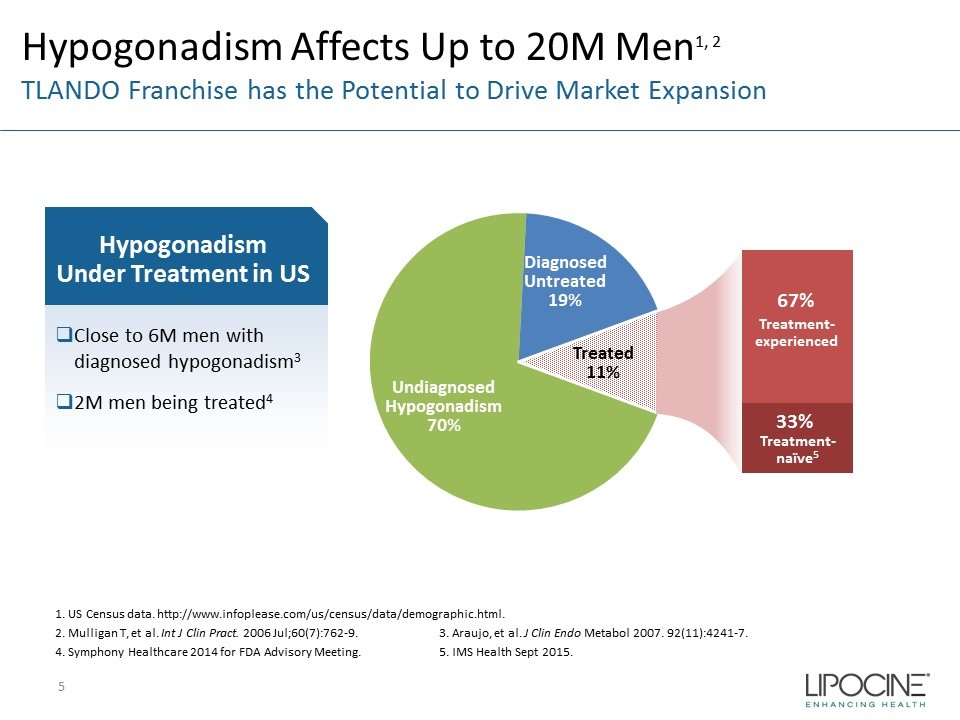
Confidential □ Close to 6M men with diagnosed hypogonadism 3 □ 2M men being treated 4 1. US Census data. http://www.infoplease.com/us/census/data/demographic.html. 2. Mulligan T, et al. Int J Clin Pract. 2006 Jul;60(7):762 - 9. 3. Araujo, et al. J Clin Endo Metabol 2007. 92(11):4241 - 7. 4. Symphony Healthcare 2014 for FDA Advisory Meeting. 5. IMS Health Sept 2015. Hypogonadism Affects Up to 20M Men 1, 2 TLANDO Franchise has the Potential to Drive Market Expansion reated 1,2 Hypogonadism Under Treatment in US Undiagnosed Hypogonadism 70% Diagnosed Untreated 19% 67% 33% Treated 11% Treatment - naïve 5 Treatment - experienced 5
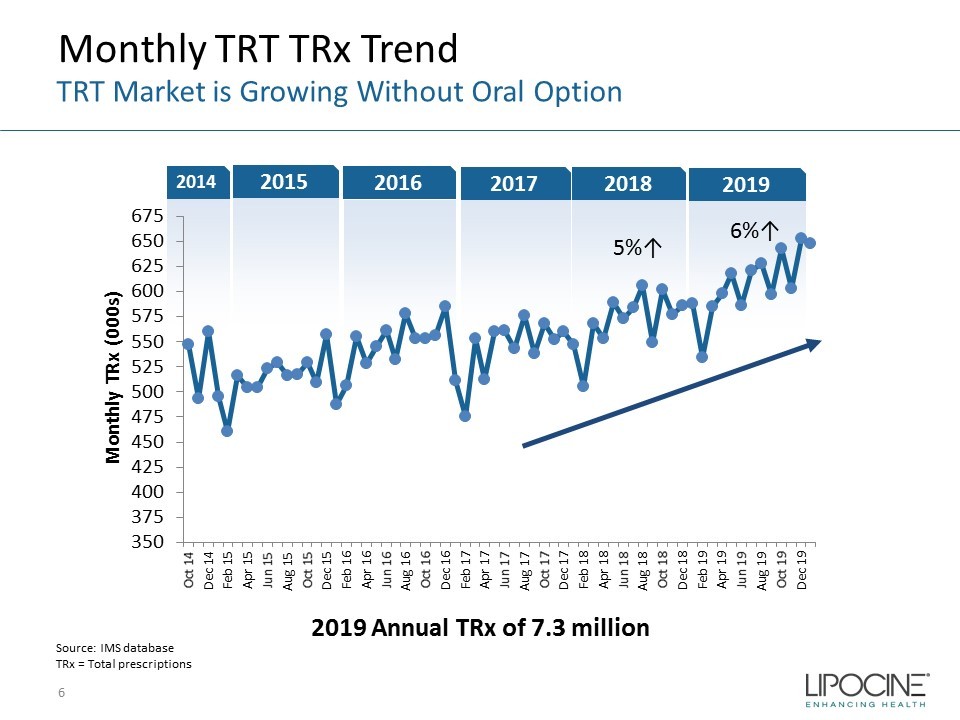
2019 2018 2017 2016 2014 2015 350 375 400 425 450 475 500 525 550 575 600 625 650 675 Oct 14 Dec 14 Feb 15 Apr 15 Jun 15 Aug 15 Oct 15 Dec 15 Feb 16 Apr 16 Jun 16 Aug 16 Oct 16 Dec 16 Feb 17 Apr 17 Jun 17 Aug 17 Oct 17 Dec 17 Feb 18 Apr 18 Jun 18 Aug 18 Oct 18 Dec 18 Feb 19 Apr 19 Jun 19 Aug 19 Oct 19 Dec 19 Monthly TRx (000s) Monthly TRT TRx Trend 6 TRT Market is Growing Without Oral Option 2019 Annual TRx of 7.3 million Source: IMS database TRx = Total prescriptions 6%↑ 5%↑
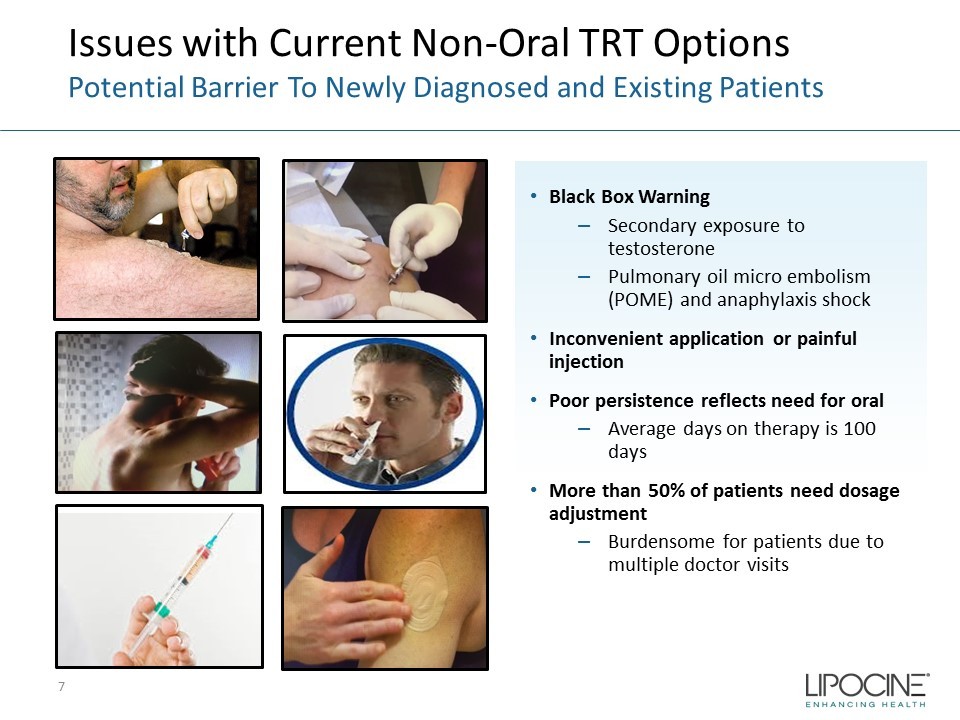
Issues with Current Non - Oral TRT Options Potential Barrier To Newly Diagnosed and Existing Patients • Black Box Warning – Secondary exposure to testosterone – Pulmonary oil micro embolism (POME) and anaphylaxis shock • Inconvenient application or painful injection • Poor persistence reflects need for oral – Average days on therapy is 100 days • More than 50% of patients need dosage adjustment – Burdensome for patients due to multiple doctor visits 7
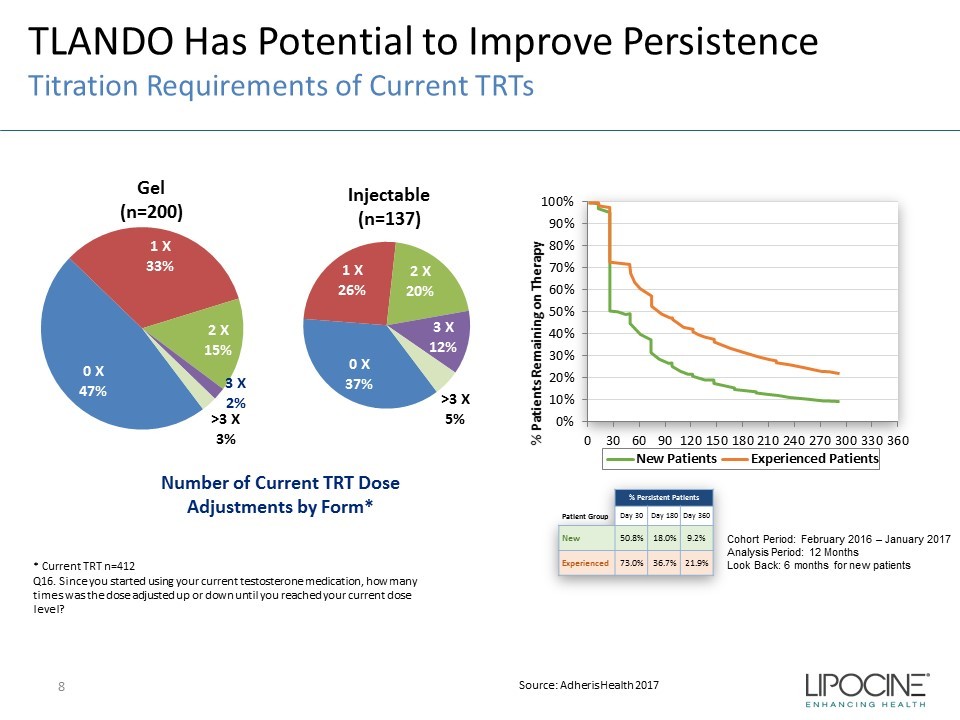
Source: Adheris Health 2017 TLANDO Has Potential to Improve Persistence Titration Requirements of Current TRTs Cohort Period: February 2016 – January 2017 Analysis Period: 12 Months Look Back: 6 months for new patients Patient Group % Persistent Patients Day 30 Day 180 Day 360 New 50.8% 18.0% 9.2% Experienced 73.0% 36.7% 21.9% 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% 90% 100% 0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 270 300 330 360 % Patients Remaining on Therapy Days to Discontinuation New Patients Experienced Patients CONFIDENTIAL * Current TRT n=412 Q16. Since you started using your current testosterone medication, how many times was the dose adjusted up or down until you reached your current dose level? 0 X 47% 1 X 33% 2 X 15% 3 X 2% >3 X 3% 0 X 37% 1 X 26% 2 X 20% 3 X 12% >3 X 5% Number of Current TRT Dose Adjustments by Form* Gel (n=200) Injectable (n=137) 8
TLANDO ™ Attributes Fixed Dose Oral TRT Option Convenient Oral Route • Patient and Physician preferred Easy to Prescribe Fixed Dosing Regimen • No additional dose adjustment visits • Less prone to drop out after first Rx • The “right” dose from the start of therapy with TLANDO ™ for all patients • Not prone to titration decision errors Differentiated Hypertension (“HTN”) and Hematocrit Profile • ~ 1% new anti - HTN starts or increase in anti - HTN dose • Low incidence of hematocrit increase (erythrocytosis) Consistent Inter - Day Restoration of T Levels Demonstrated Paradigm Shifting Liver Benefits 9

TLANDO Regulatory Update Near Term PDUFA Date 10 PDUFA Date August 28, 2020 NDA Filed February 28, 2020 The NDA incorporates the reanalysis of existing data to address the deficiency discussed in the Post Action Meeting with the FDA Post Action Meeting January 16, 2020 The FDA indicated approach to addressing the deficiency through reanalysis in accordance with FDA feedback appears to be a reasonable path forward CRL received November 9, 2019 One deficiency: Did not meet the three secondary endpoints for maximal testosterone concentrations ( Cmax )

Enabling Oral Drug Delivery to Improve Patient Compliance LPCN 1144 for Pre - Cirrhotic NASH
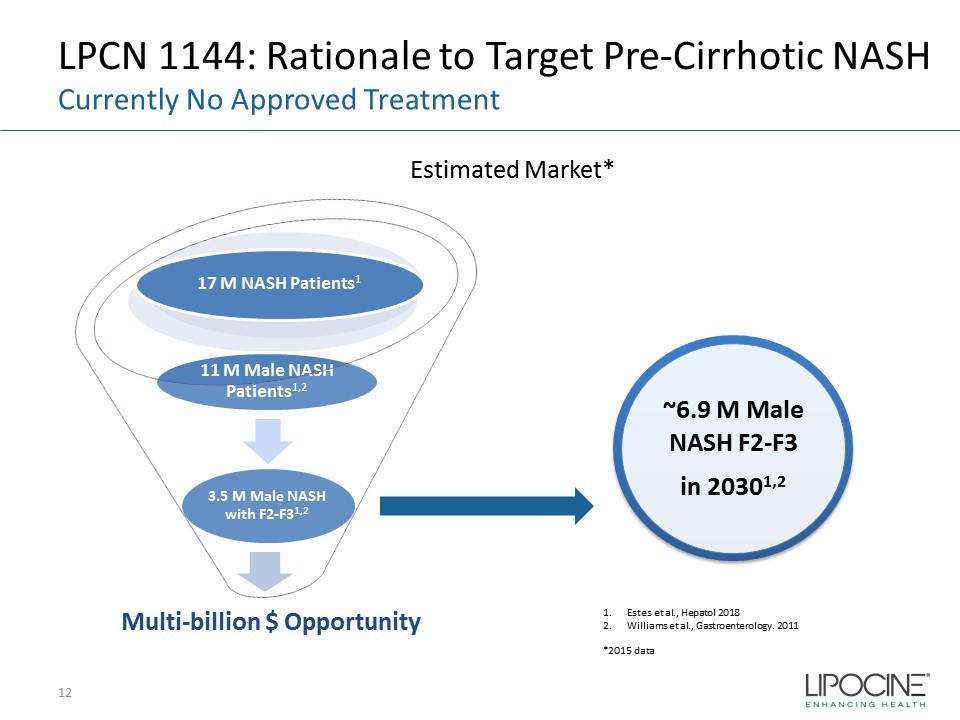
LPCN 1144: Rationale to Target Pre - Cirrhotic NASH 12 1. Estes et al., Hepatol 2018 2. Williams et al., Gastroenterology. 2011 *2015 data ~6.9 M Male NASH F2 - F3 in 2030 1,2 Estimated Market* Currently No Approved Treatment Multi - billion $ Opportunity 3.5 M Male NASH with F2 - F3 1,2 11 M Male NASH Patients 1,2 17 M NASH Patients 1

LPCN 1144: Oral Testosterone Therapy Differentiated NASH Treatment Candidate Targets Unmet Need Mechanistic Evidence Clinical Experience • NASH resolution and/or fibrosis improvement • Acceptable tolerability for chronic use • Improvement of sarcopenia • Improvement of sexual dysfunction • Improvement of mental health • Anti - steatosis • Anti - inflammatory • Anti - oxidative • Cell regenerative • Meaningfully reduced liver fat in POC study • Well tolerated in 700+ subjects with up to 52 - week exposure • Improved sexual and mood dysfunction 13
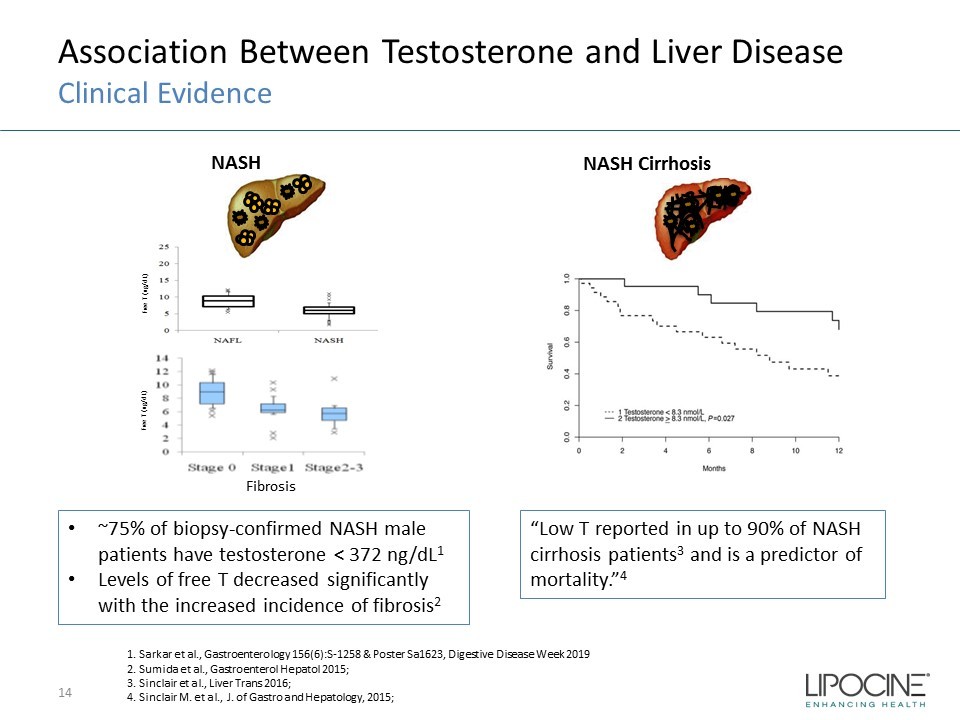
14 1. Sarkar et al., Gastroenterology 156(6):S - 1258 & Poster Sa1623, Digestive Disease Week 2019 2. Sumida et al., Gastroenterol Hepatol 2015; 3. Sinclair et al., Liver Trans 2016; 4. Sinclair M. et al., J. of Gastro and Hepatology, 2015; “Low T reported in up to 90% of NASH cirrhosis patients 3 and is a predictor of mortality.” 4 NASH Cirrhosis • ~75% of biopsy - confirmed NASH male patients have testosterone < 372 ng/dL 1 • Levels of free T decreased significantly with the increased incidence of fibrosis 2 NASH Free T (ng/dL) Free T (ng/dL) Fibrosis Association Between Testosterone and Liver Disease Clinical Evidence
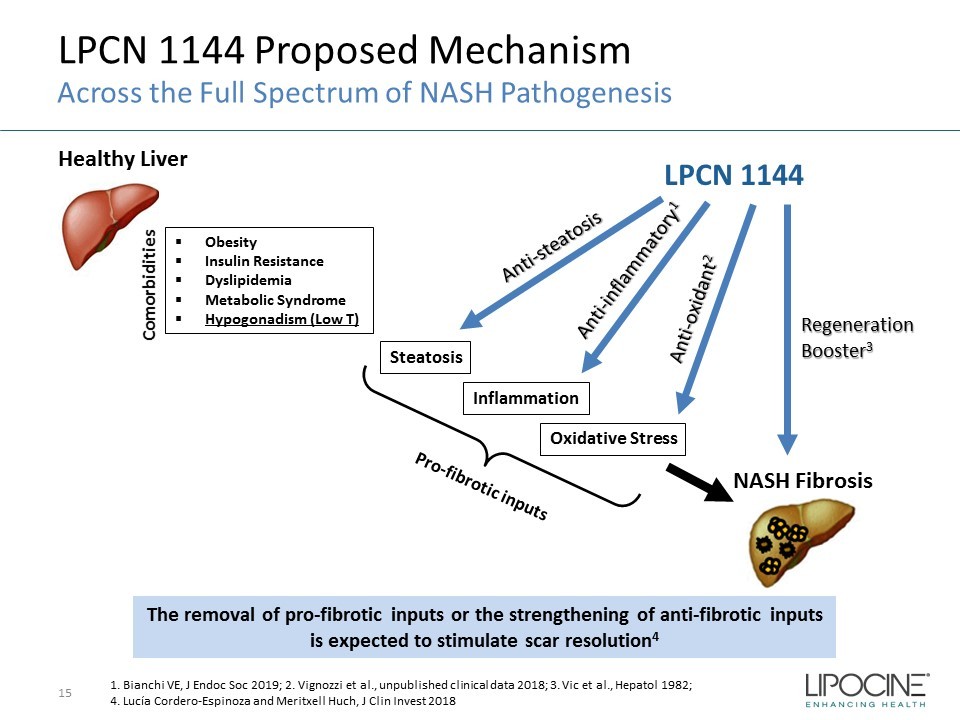
LPCN 1144 Proposed Mechanism 15 Across the Full Spectrum of NASH Pathogenesis Healthy Liver Steatosis Inflammation NASH Fibrosis LPCN 1144 Regeneration Booster 3 ▪ Obesity ▪ Insulin Resistance ▪ Dyslipidemia ▪ Metabolic Syndrome ▪ Hypogonadism (Low T) The removal of pro - fibrotic inputs or the strengthening of anti - fibrotic inputs is expected to stimulate scar resolution 4 Oxidative Stress 1. Bianchi VE, J Endoc Soc 2019; 2. Vignozzi et al., unpublished clinical data 2018; 3. Vic et al., Hepatol 1982; 4. Lucía Cordero - Espinoza and Meritxell Huch , J Clin Invest 2018 Comorbidities
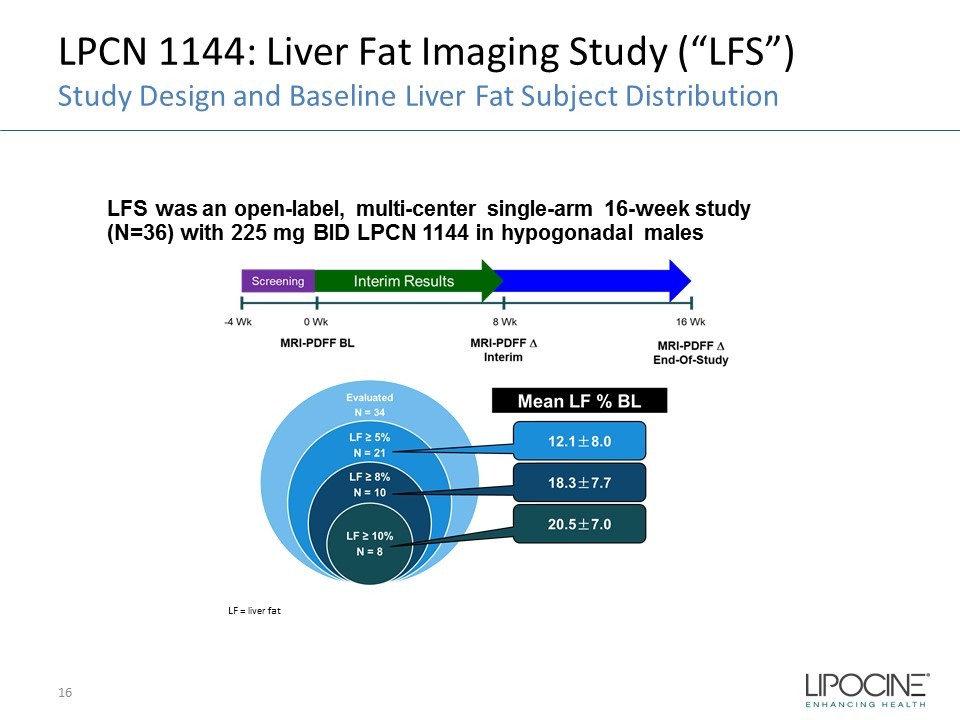
LPCN 1144: Liver Fat Imaging Study (“LFS”) Study Design and Baseline Liver Fat Subject Distribution 16 LFS was an open - label, multi - center single - arm 16 - week study (N=36) with 225 mg BID LPCN 1144 in hypogonadal males LF = liver fat
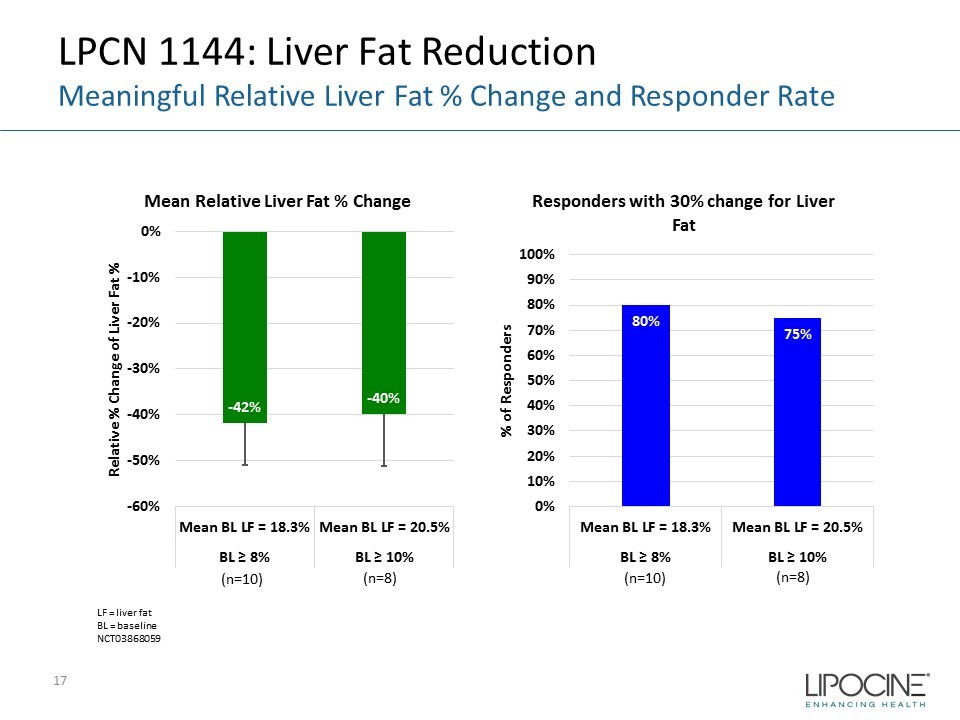
LPCN 1144: Liver Fat Reduction Meaningful Relative Liver Fat % Change and Responder Rate 17 LF = liver fat BL = baseline NCT03868059 - 42% - 40% -60% -50% -40% -30% -20% -10% 0% Mean BL LF = 18.3% Mean BL LF = 20.5% BL ≥ 8% BL ≥ 10% Relative % Change of Liver Fat % Mean Relative Liver Fat % Change (n=10) (n=8) 80% 75% 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% 90% 100% Mean BL LF = 18.3% Mean BL LF = 20.5% BL ≥ 8% BL ≥ 10% % of Responders Responders with 30% change for Liver Fat (n=10) (n=8)
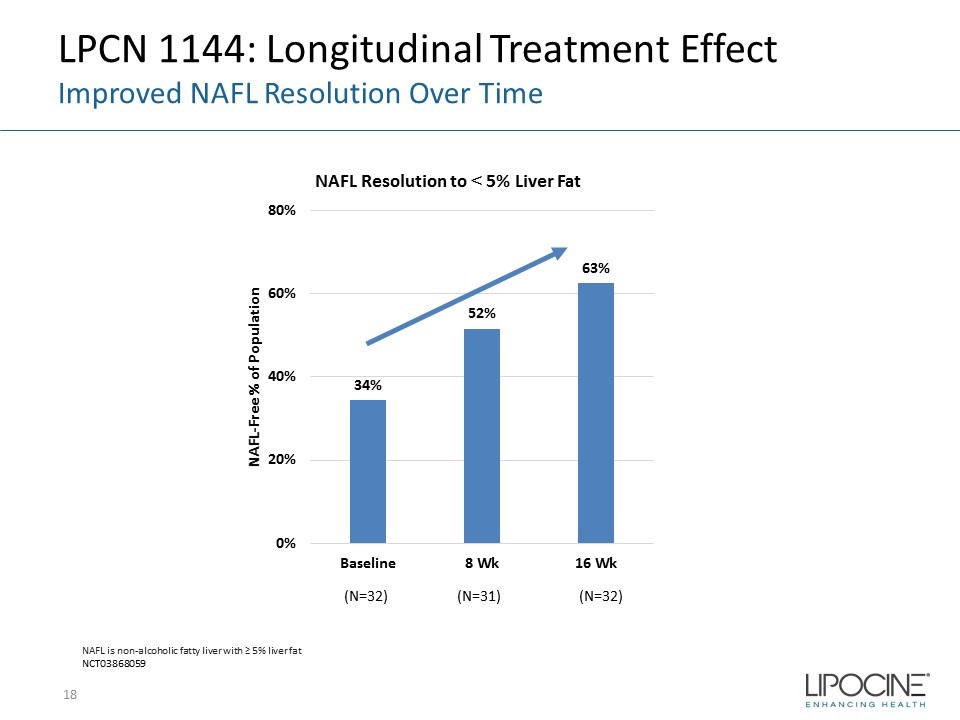
18 LPCN 1144: Longitudinal Treatment Effect Improved NAFL Resolution Over Time 34% 52% 63% 0% 20% 40% 60% 80% Baseline 8 Wk 16 Wk NAFL - Free % of Population NAFL Resolution to < 5% Liver Fat (N=31) (N=32) (N=32) NAFL is non - alcoholic fatty liver with ≥ 5% liver fat NCT03868059
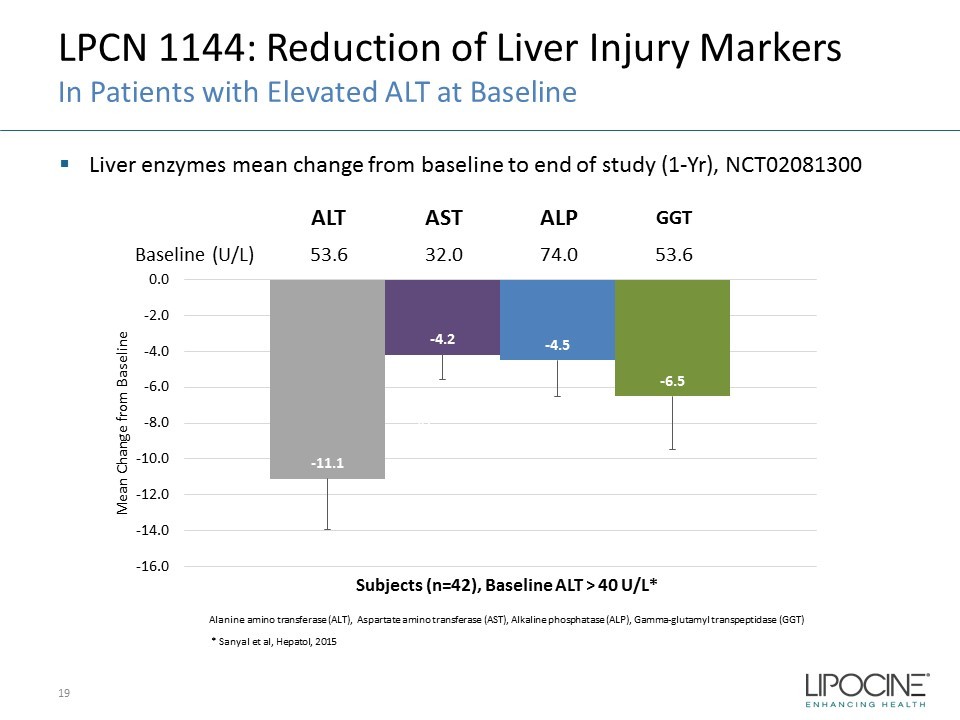
- 11.1 - 4.2 - 4.5 - 6.5 -16.0 -14.0 -12.0 -10.0 -8.0 -6.0 -4.0 -2.0 0.0 2.0 Mean Change from Baseline ALT, U/L AST, U/L ALP, U/L GGT, U/L LPCN 1144: Reduction of Liver Injury Markers In Patients with Elevated ALT at Baseline ▪ Liver enzymes mean change from baseline to end of study (1 - Yr), NCT02081300 19 * Sanyal et al, Hepatol , 2015 x2 x2 x5 Alanine amino transferase (ALT), Aspartate amino transferase (AST), Alkaline phosphatase (ALP), Gamma - glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT) Subjects (n=42), Baseline ALT > 40 U/L* ALT AST ALP GGT Baseline (U/L) 53.6 32.0 74.0 53.6
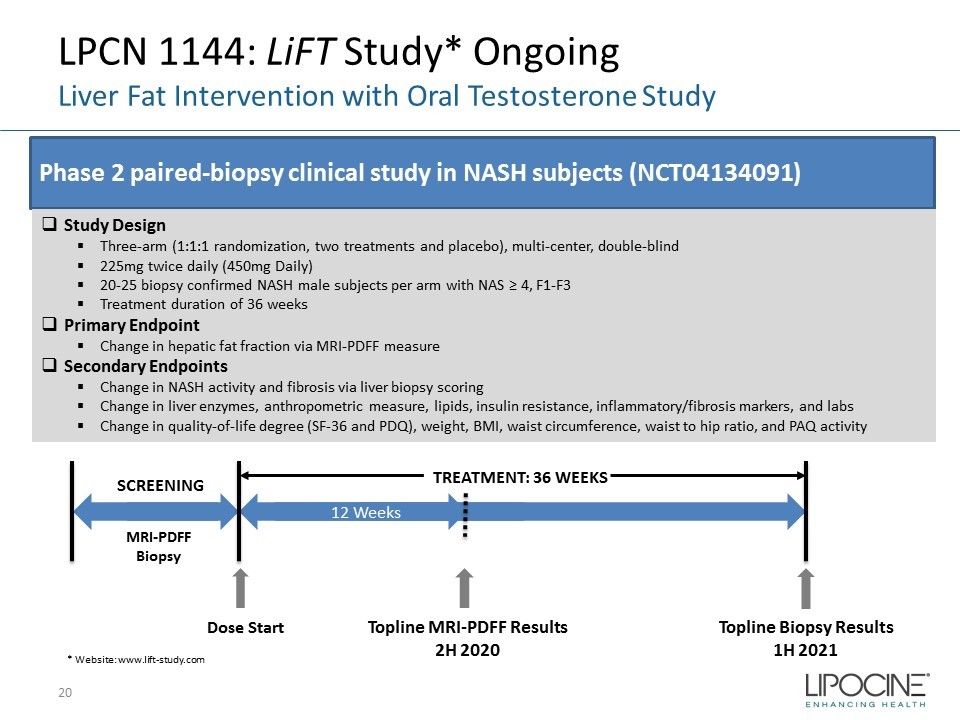
LPCN 1144: LiFT Study* Ongoing Liver Fat Intervention with Oral Testosterone Study 20 Phase 2 paired - biopsy clinical study in NASH subjects (NCT04134091) □ Study Design ▪ Three - arm (1:1:1 randomization, two treatments and placebo), multi - center, double - blind ▪ 225mg twice daily (450mg Daily) ▪ 20 - 25 biopsy confirmed NASH male subjects per arm with NAS ≥ 4, F1 - F3 ▪ Treatment duration of 36 weeks □ Primary Endpoint ▪ Change in hepatic fat fraction via MRI - PDFF measure □ Secondary Endpoints ▪ Change in NASH activity and fibrosis via liver biopsy scoring ▪ Change in liver enzymes, anthropometric measure, lipids, insulin resistance, inflammatory/fibrosis markers, and labs ▪ Change in quality - of - life degree (SF - 36 and PDQ), weight, BMI, waist circumference, waist to hip ratio, and PAQ activity * Website: www.lift - study.com 12 Weeks SCREENING TREATMENT: 36 WEEKS Topline MRI - PDFF Results 2H 2020 Dose Start Topline Biopsy Results 1H 2021 MRI - PDFF Biopsy
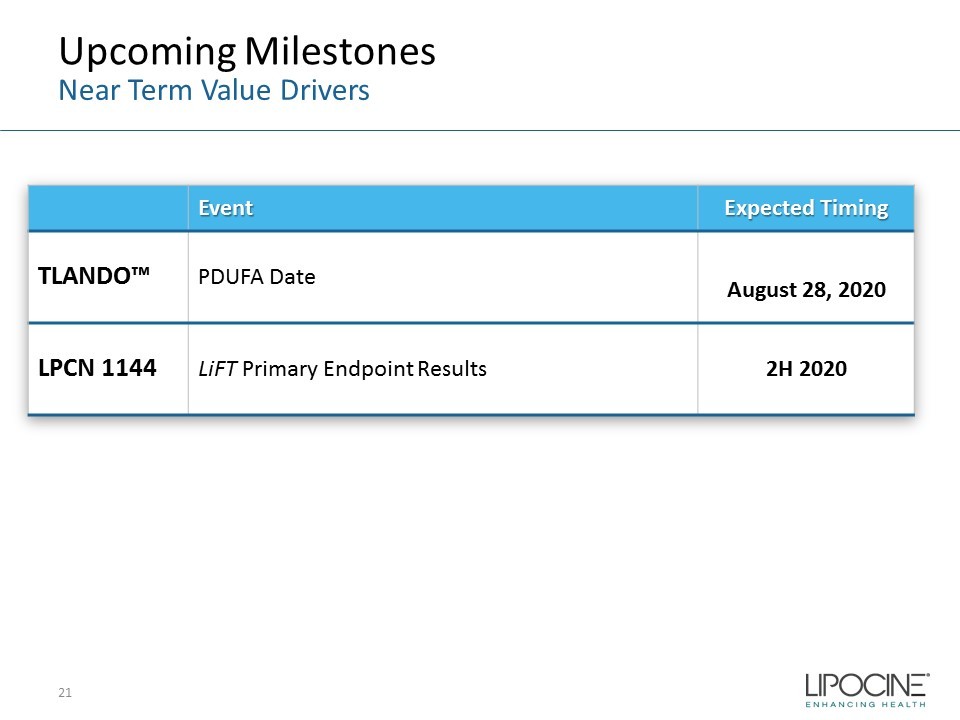
Upcoming Milestones 21 Near Term Value Drivers Event Expected Timing TLANDO™ PDUFA Date August 28, 2020 LPCN 1144 LiFT Primary Endpoint Results 2H 2020
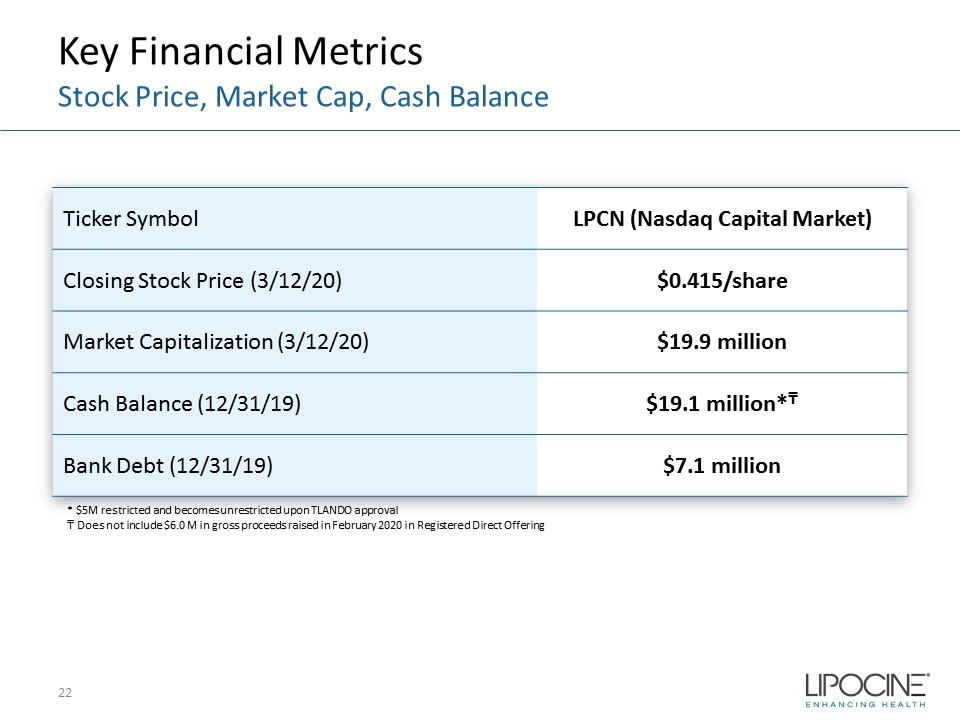
Key Financial Metrics 22 Stock Price, Market Cap, Cash Balance Ticker Symbol LPCN (Nasdaq Capital Market) Closing Stock Price (3/12/20) $0.415/share Market Capitalization (3/12/20) $19.9 million Cash Balance (12/31/19) $19.1 million* ₸ Bank Debt (12/31/19) $7.1 million * $5M restricted and becomes unrestricted upon TLANDO approval ₸ Does not include $6.0 M in gross proceeds raised in February 2020 in Registered Direct Offering
Lipocine Investment Highlights Near Term TLANDO PDUFA with a Promising Pipeline • TLANDO™: Differentiated product profile with potential for market expansion • TLANDO XR: Unique long acting oral with potential to maintain leadership • ~$2B+ opportunity in an established and growing market with favorable market dynamics Potential to be a TRT Market Leader • LPCN 1144: A differentiated modality with potential for mono/combo pre - cirrhotic NASH therapy • LPCN 1148: Targeting cirrhosis • Unmet need with no approved drug • Meaningfully reduced liver fat in POC study • Well tolerated in 700+ subjects with up to 52 - week exposure Oral Testosterone Targeted for Pre - Cirrhotic NASH/Cirrhosis • LPCN 1107 : Superior Cavg to standard of care (Makena®) Orphan Designated Oral Candidate for the Prevention of Preterm Birth 23

24

Current Market Dynamics in TRT Space Prime Opportunity for TLANDO™ • 85% of physicians have strong interest in oral • 95% of TRT patients likely to ask their doctor about TLANDO ™ Patient and physicians preferred 1 • Able to have high share of voice with far less competitive promotion than in the past Current promotional spend all time low in this detail sensitive category 2 • Decile 7 - 10 prescribers (~ 10,000) write 40% of the Scripts Concentrated call points 3 • Novel convenient oral option Detail sensitive category • Encouraging TRx trend in 2019 • ~47% of TRx from new patient starts Recent injectable TRT launch data 4 1. Lipocine Market Research; 2. iVH Research & Insights; 3. Prescriber Profiler 2019;.4. Antares Pharma presentation March 2020 26

Once Daily Oral Testosterone Replacement Therapy
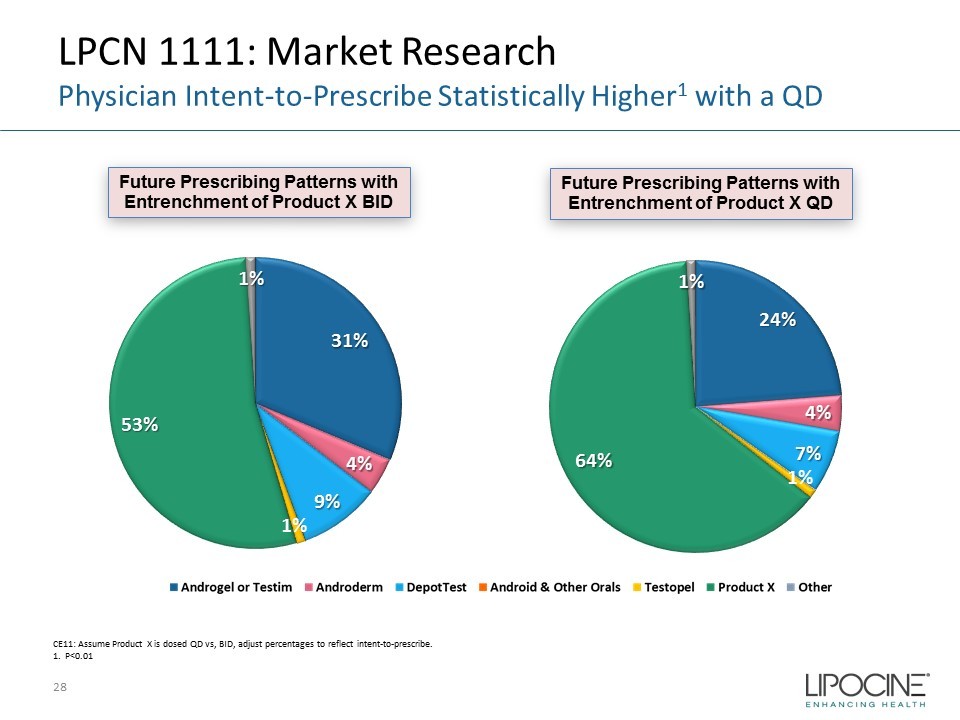
Future Prescribing Patterns with Entrenchment of Product X BID Future Prescribing Patterns with Entrenchment of Product X QD CE11: Assume Product X is dosed QD vs, BID, adjust percentages to reflect intent - to - prescribe. 1. P<0.01 31% 4% 9% 1% 53% 1% 24% 4% 7% 1% 64% 1% 28 LPCN 1111: Market Research Physician Intent - to - Prescribe Statistically Higher 1 with a QD

Phase 2b Study: Result Summary Met Primary and Secondary Endpoints • Once daily dose for 14 days in an open label, multiple dose PK study in hypogonadal men (n=36 subjects) x Phase 3 dose identified x No Drug related SAEs x Drug Related AEs are Mild to Moderate ▪ Next step: Pivotal study protocol submission to FDA Confidential 29 29

Enabling Oral Drug Delivery to Improve Patient Compliance LPCN 1144 for Pre - Cirrhotic NASH
Unmet Needs in Pre - Cirrhotic NASH 31 Currently No Approved Treatment 1. Bhanji et al, Hepatol 2017 2. Koo et al, J Hepatol 2017 3. Petta et al, Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2017 4. Hawksworth et al., Sex Med Rev 2019 5. Duman et al., J Sex Med. 2016 6. Ali et al., Psychosomatics 2011 7. Assimakopoulos et al., J Psychosom Res 2018 NASH Resolution and/or Fibrosis Improvement Safety & Tolerability for Chronic Use Improvement of Sarcopenia 1 (35% - 67% sarcopenia in NASH 2,3 ) Improvement of Sexual Dysfunction 4 (68% experienced erectile dysfunction 5 ) Improvement of Mental Health/QOL 5,6 (27% of NAFLD has depression 6 ) Comorbidities
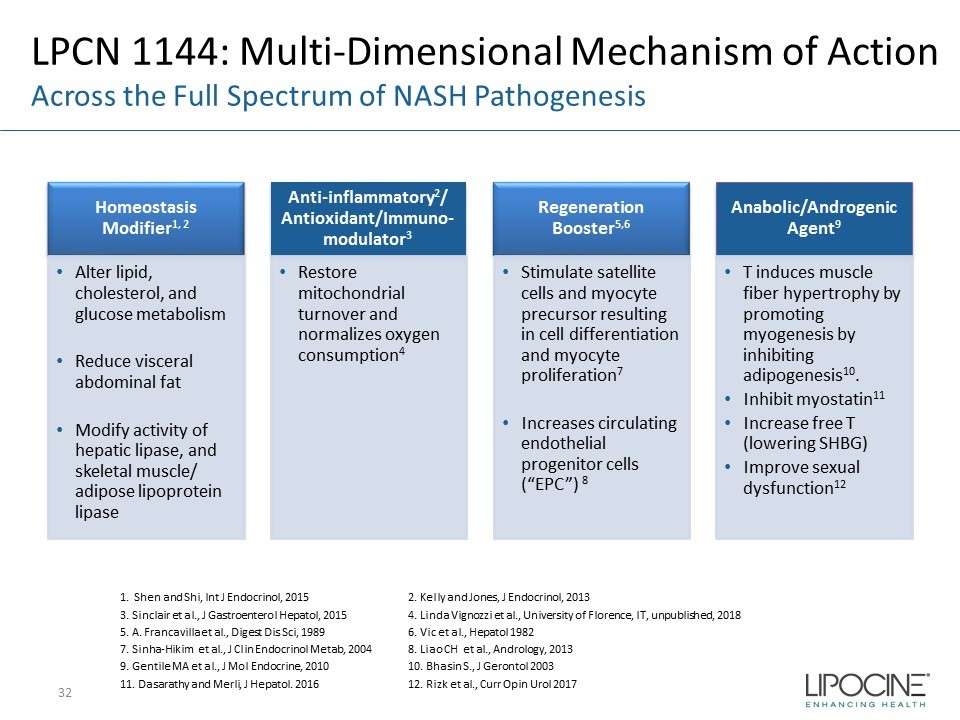
LPCN 1144: Multi - Dimensional Mechanism of Action Across the Full Spectrum of NASH Pathogenesis 32 Homeostasis Modifier 1, 2 • Alter lipid, cholesterol, and glucose metabolism • Reduce visceral abdominal fat • Modify activity of hepatic lipase, and skeletal muscle/ adipose lipoprotein lipase Anti - inflammatory 2 / Antioxidant/Immuno - modulator 3 • Restore mitochondrial turnover and normalizes oxygen consumption 4 Regeneration Booster 5,6 • Stimulate satellite cells and myocyte precursor resulting in cell differentiation and myocyte proliferation 7 • Increases circulating endothelial progenitor cells (“EPC”) 8 Anabolic/Androgenic Agent 9 • T induces muscle fiber hypertrophy by promoting myogenesis by inhibiting adipogenesis 10 . • Inhibit myostatin 11 • Increase free T (lowering SHBG) • Improve sexual dysfunction 12 1. Shen and Shi, Int J Endocrinol, 2015 2. Kelly and Jones, J Endocrinol, 2013 3. Sinclair et al., J Gastroenterol Hepatol , 2015 4. Linda Vignozzi et al., University of Florence, IT, unpublished, 2018 5. A. Francavilla et al., Digest Dis Sci, 1989 6. Vic et al., Hepatol 1982 7. Sinha - Hikim et al., J Clin Endocrinol Metab , 2004 8. Liao CH et al., Andrology, 2013 9. Gentile MA et al., J Mol Endocrine, 2010 10. Bhasin S., J Gerontol 2003 11. Dasarathy and Merli , J Hepatol . 2016 12. Rizk et al., Curr Opin Urol 2017
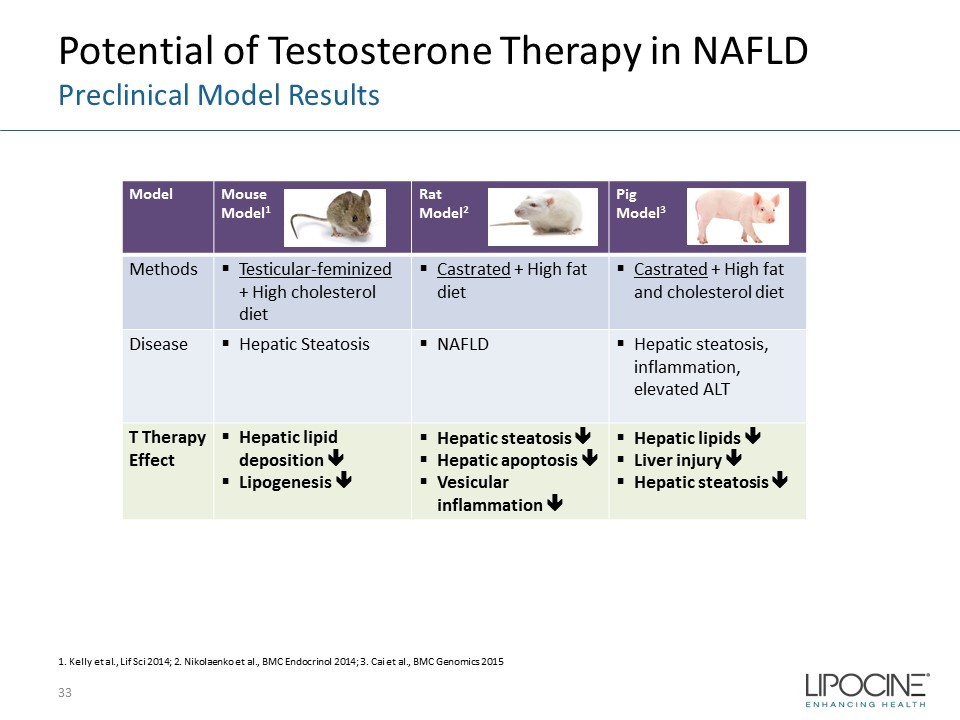
Potential of Testosterone Therapy in NAFLD Preclinical Model Results 33 1. Kelly et al., Lif Sci 2014; 2. Nikolaenko et al., BMC Endocrinol 2014; 3. Cai et al., BMC Genomics 2015 Model Mouse Model 1 Rat Model 2 Pig Model 3 Methods ▪ Testicular - feminized + High cholesterol diet ▪ Castrated + High fat diet ▪ Castrated + High fat and cholesterol diet Disease ▪ Hepatic Steatosis ▪ NAFLD ▪ Hepatic steatosis, inflammation, elevated ALT T Therapy Effect ▪ Hepatic lipid deposition ▪ Lipogenesis ▪ Hepatic steatosis ▪ Hepatic apoptosis ▪ Vesicular inflammation ▪ Hepatic lipids ▪ Liver injury ▪ Hepatic steatosis
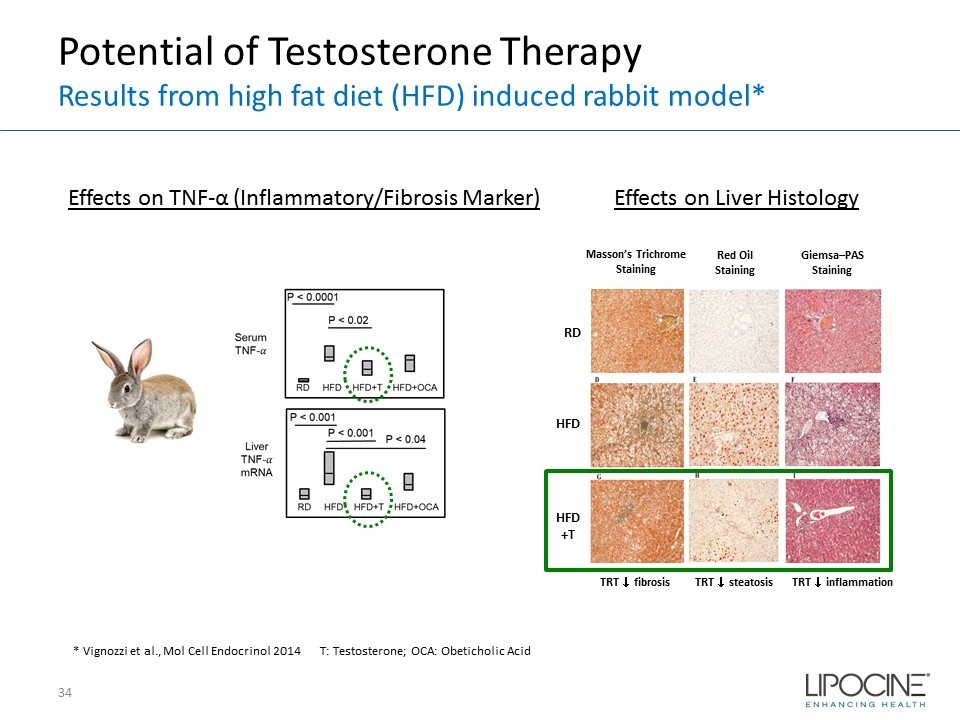
Potential of Testosterone Therapy Results from high fat diet (HFD) induced rabbit model* Giemsa – PAS Staining Red Oil Staining Masson’s Trichrome Staining TRT ↓ fibrosis TRT ↓ steatosis TRT ↓ inflammation RD HFD HFD +T * Vignozzi et al., Mol Cell Endocrinol 2014 34 T: Testosterone; OCA: Obeticholic Acid Effects on Liver Histology Effects on TNF - α (Inflammatory/Fibrosis Marker)
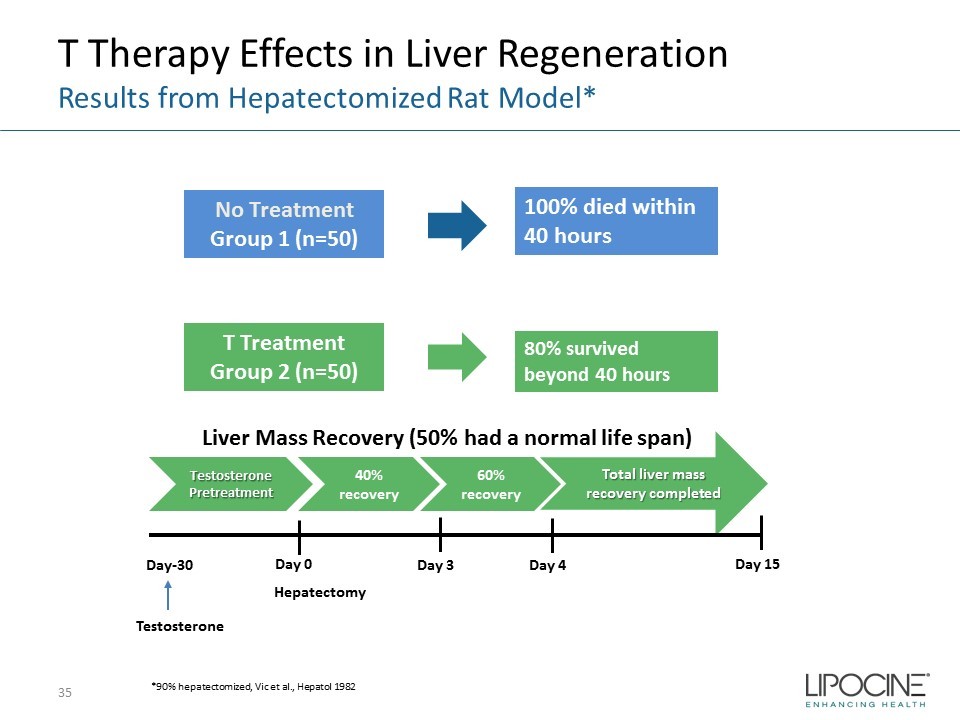
T Therapy Effects in Liver Regeneration Results from Hepatectomized Rat Model* 35 *90% hepatectomized, Vic et al., Hepatol 1982 40% recovery 60% recovery Total liver mass recovery completed Day 3 Day 4 Day 15 Testosterone Pretreatment Day 0 Day - 30 Testosterone Hepatectomy No Treatment Group 1 (n=50) T Treatment Group 2 (n=50) 100% died within 40 hours 80% survived beyond 40 hours Liver Mass Recovery (50% had a normal life span)
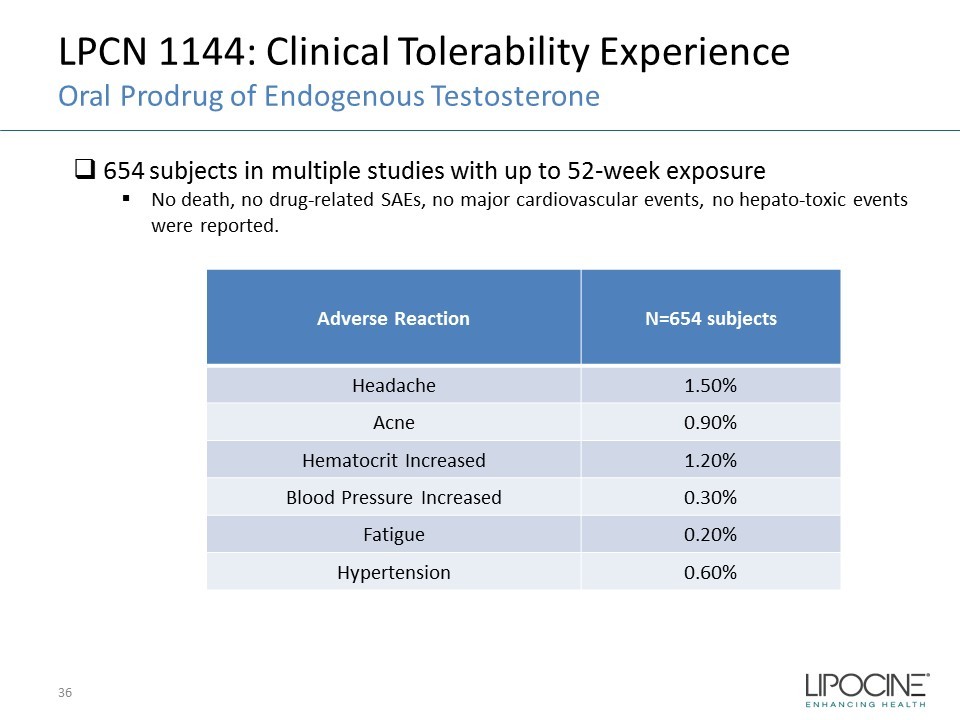
LPCN 1144: Clinical Tolerability Experience Oral Prodrug of Endogenous Testosterone 36 Adverse Reaction N=654 subjects Headache 1.50% Acne 0.90% Hematocrit Increased 1.20% Blood Pressure Increased 0.30% Fatigue 0.20% Hypertension 0.60% □ 654 subjects in multiple studies with up to 52 - week exposure ▪ No death, no drug - related SAEs, no major cardiovascular events, no hepato - toxic events were reported.
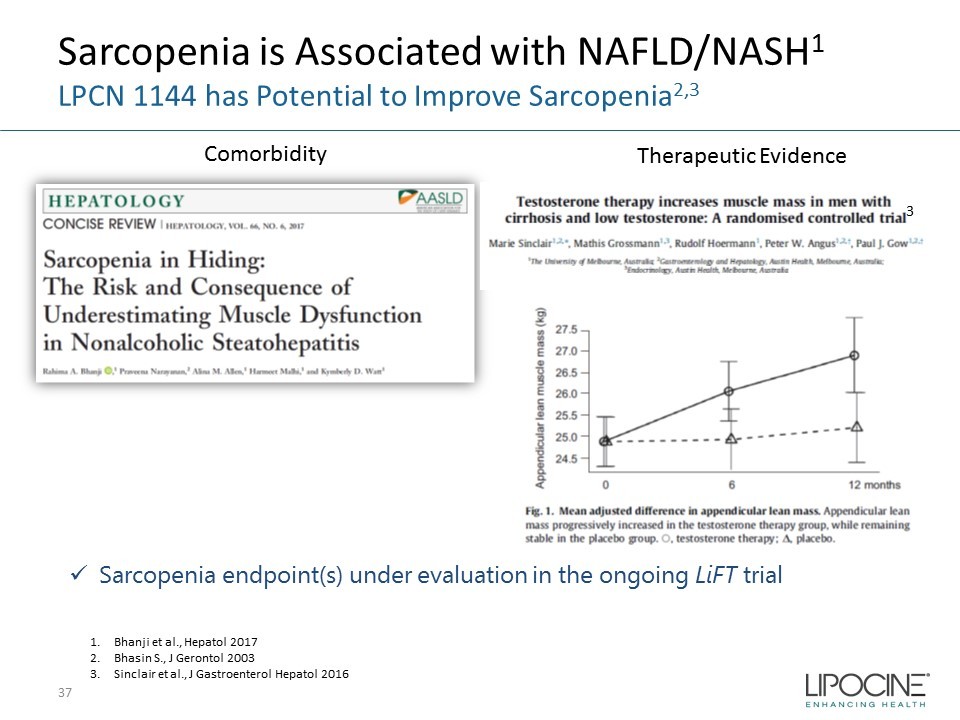
Sarcopenia is Associated with NAFLD/NASH 1 LPCN 1144 has Potential to Improve Sarcopenia 2,3 37 1. Bhanji et al., Hepatol 2017 2. Bhasin S., J Gerontol 2003 3. Sinclair et al., J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2016 x Sarcopenia endpoint(s) under evaluation in the ongoing LiFT trial 3 Comorbidity Therapeutic Evidence
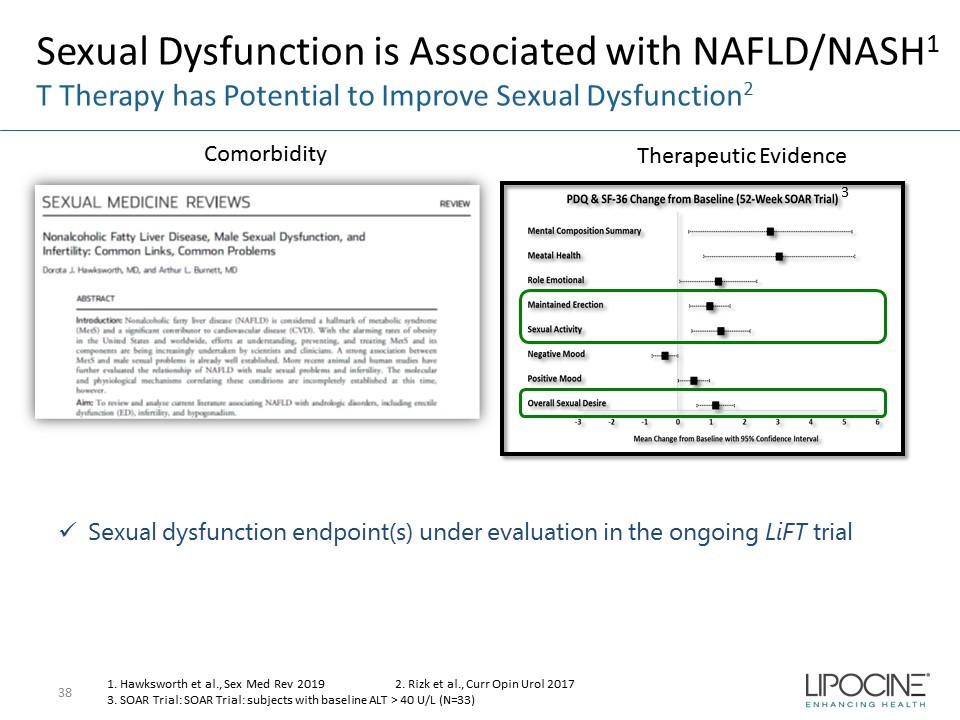
Sexual Dysfunction is Associated with NAFLD/NASH 1 T Therapy has Potential to Improve Sexual Dysfunction 2 38 1. Hawksworth et al., Sex Med Rev 2019 2. Rizk et al., Curr Opin Urol 2017 3. SOAR Trial: SOAR Trial: subjects with baseline ALT > 40 U/L (N=33) 3 x Sexual dysfunction endpoint(s) under evaluation in the ongoing LiFT trial Comorbidity Therapeutic Evidence
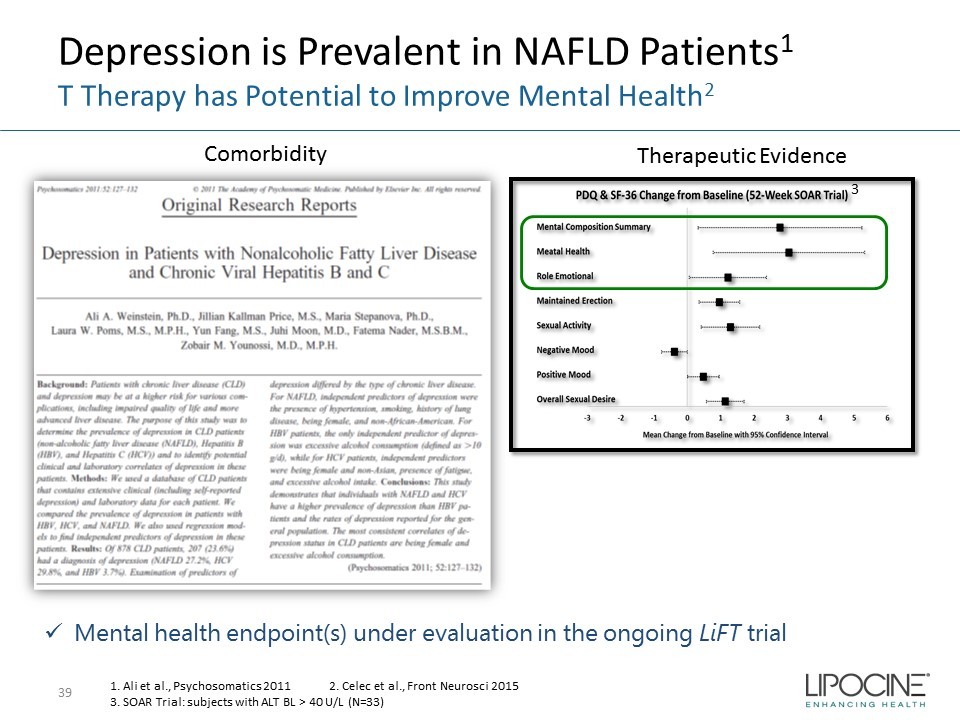
Depression is Prevalent in NAFLD Patients 1 T Therapy has Potential to Improve Mental Health 2 39 3 1. Ali et al., Psychosomatics 2011 2. Celec et al., Front Neurosci 2015 3. SOAR Trial: subjects with ALT BL > 40 U/L (N=33) x Mental health endpoint(s) under evaluation in the ongoing LiFT trial Comorbidity Therapeutic Evidence

Enabling Oral Drug Delivery to Improve Patient Compliance
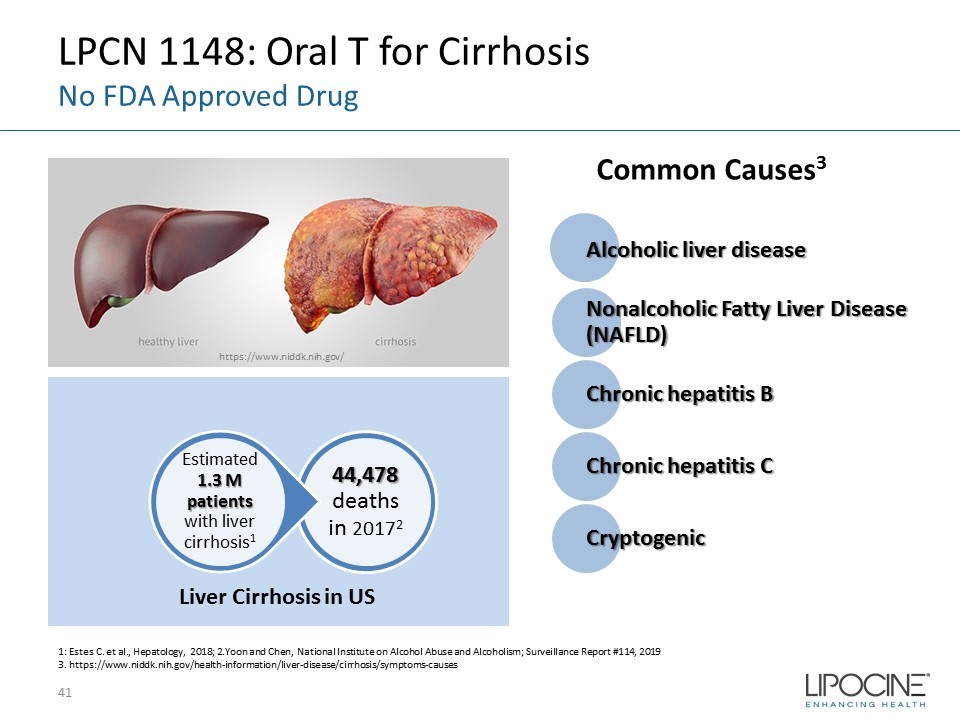
LPCN 1148: Oral T for Cirrhosis No FDA Approved Drug 41 Alcoholic liver disease Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Chronic hepatitis B Chronic hepatitis C Cryptogenic 44,478 deaths in 2017 2 Estimated 1.3 M patients with liver cirrhosis 1 Liver Cirrhosis in US 1: Estes C. et al., Hepatology, 2018; 2.Yoon and Chen, National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism; Surveillance Rep ort #114, 2019 3. https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health - information/liver - disease/cirrhosis/symptoms - causes Common Causes 3 https://www.niddk.nih.gov/
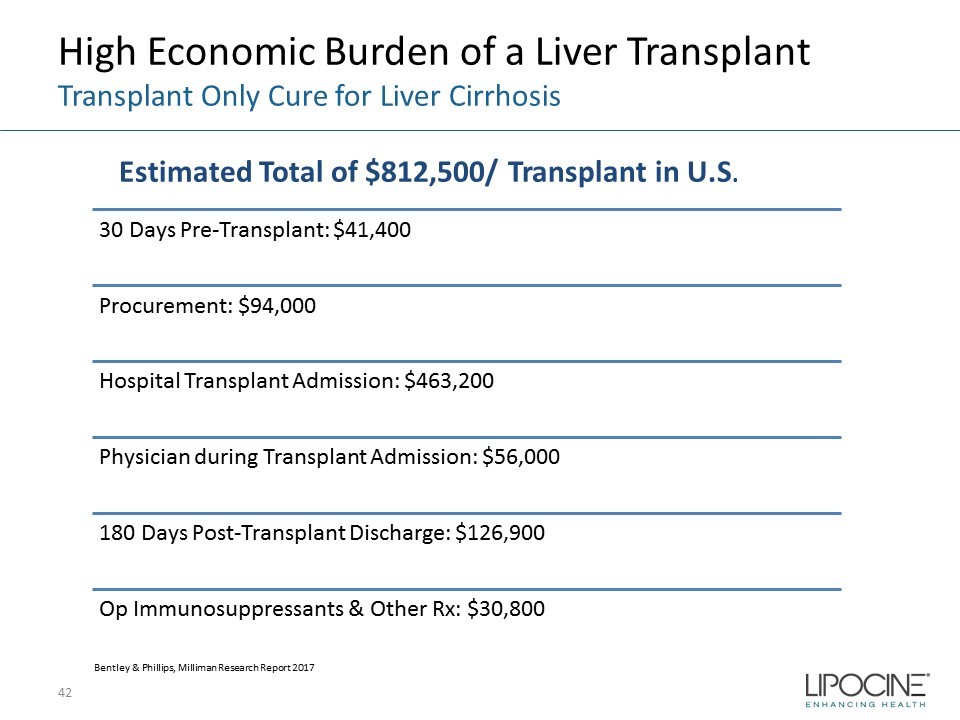
High Economic Burden of a Liver Transplant Transplant Only Cure for Liver Cirrhosis 42 30 Days Pre - Transplant: $41,400 Procurement: $94,000 Hospital Transplant Admission: $463,200 Physician during Transplant Admission: $56,000 180 Days Post - Transplant Discharge: $126,900 Op Immunosuppressants & Other Rx: $30,800 Bentley & Phillips, Milliman Research Report 2017 Estimated Total of $812,500/ Transplant in U.S .
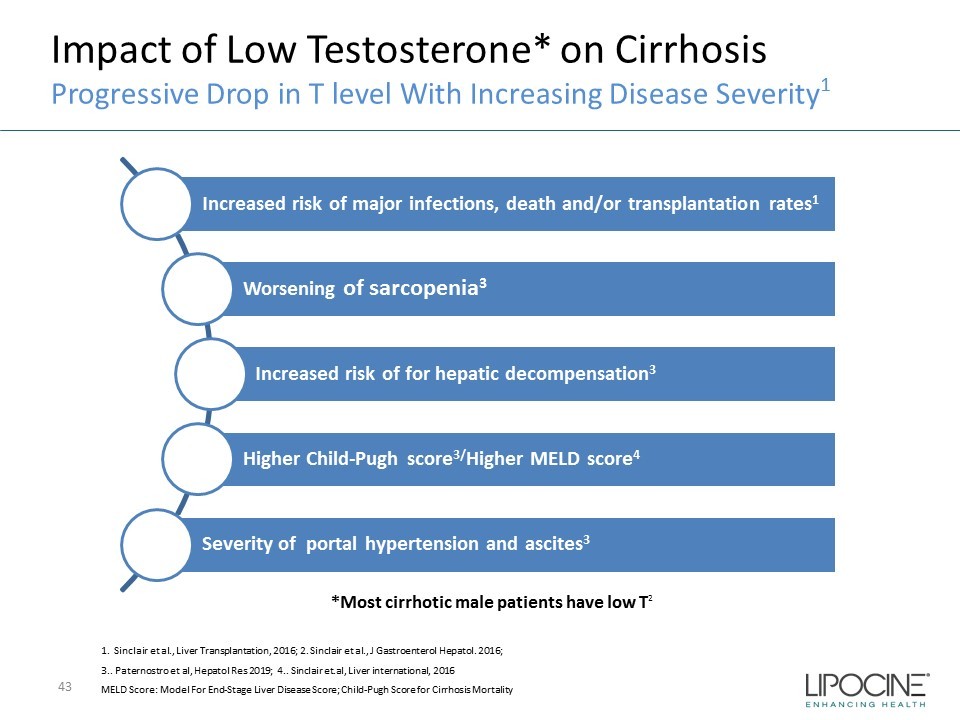
Impact of Low Testosterone* on Cirrhosis Progressive Drop in T level With Increasing Disease Severity 1 Increased risk of major infections, death and/or transplantation rates 1 Worsening of sarcopenia 3 Increased risk of for hepatic decompensation 3 Higher Child - Pugh score 3/ Higher MELD score 4 Severity of portal hypertension and ascites 3 1. Sinclair et al., Liver Transplantation, 2016; 2. Sinclair et al., J Gastroenterol Hepatol . 2016; 3.. Paternostro et al, Hepatol Res 2019; 4.. Sinclair et.al, Liver international, 2016 MELD Score: Model For End - Stage Liver Disease Score; Child - Pugh Score for Cirrhosis Mortality *Most cirrhotic male patients have low T 2 43

LPCN 1107 Prevention of Preterm Birth Enabling Oral Drug Delivery to Improve Patient Compliance 44

• A leading cause of neonatal mortality • ≥ $26 billion economic impact 2 • 10% of all US pregnancies 3 – PTB in singleton pregnancies: 8.1% • Medical costs for PTB infants are ~10x higher than for full term infants 4 1. Pediatric Research (2006) 60, 775 – 776 2. Institute of Medicine of the National Academies. Jul.200 3. National Vital Statistics Reports, Vol 67, No. 8, Nov 7, 2018: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2017) 4. J. Maternal - Fetal and Neonatal Medicine, Dec. 2006, 19(12), 773 – 782 Unmet Medical Need One Preterm Birth (PTB) Every Minute 1 45

LPCN 1107 Opportunity Market Potential: ~$1 Billion Potential to be the First Oral HPC for Prevention of Recurrent PTB • Preferred route - of - administration is oral • ~140,000 annually pregnancy with history of at least one singleton spontaneous PTB* Potential for Clinical Success • Superior Cavg to Makena® • Targeting high - risk population (similar to MEIS trial) Strong Pharmaco - Economic Justification • Fewer PTB babies with significant healthcare cost savings • Minimize travel related cost/time and healthcare provider cost/time • Premium pricing potential to generic IM injections Strong Exclusivity Position • Orphan Drug Designation • Technology/IP protection *Deutsche Bank Markets Research, 11 June 2015 46
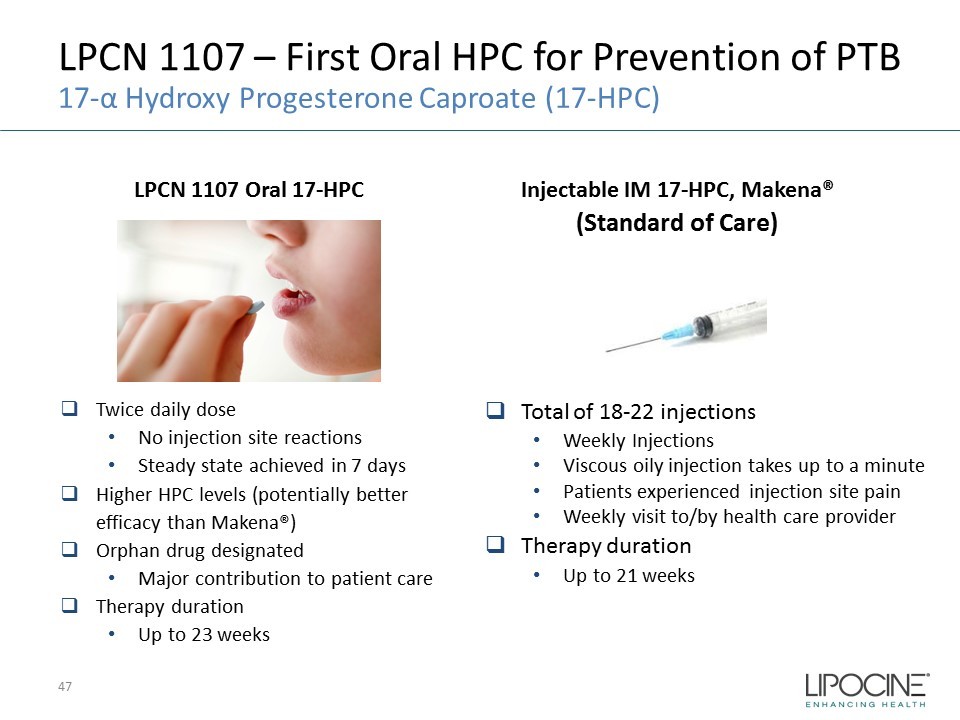
LPCN 1107 – First Oral HPC for Prevention of PTB Injectable IM 17 - HPC, Makena® (Standard of Care) LPCN 1107 Oral 17 - HPC □ Twice daily dose • No injection site reactions • Steady state achieved in 7 days □ Higher HPC levels (potentially better efficacy than Makena®) □ Orphan drug designated • Major contribution to patient care □ Therapy duration • Up to 23 weeks □ Total of 18 - 22 injections • Weekly Injections • Viscous oily injection takes up to a minute • Patients experienced injection site pain • Weekly visit to/by health care provider □ Therapy duration • Up to 21 weeks 17 - α Hydroxy Progesterone Caproate (17 - HPC) 47
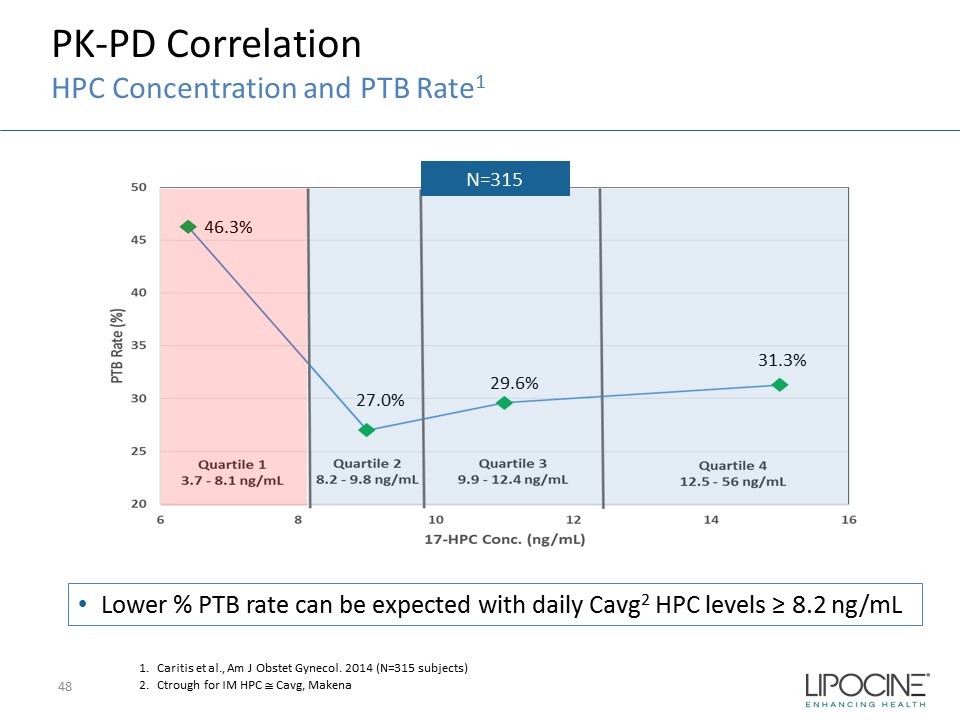
• Lower % PTB rate can be expected with daily Cavg 2 HPC levels ≥ 8.2 ng/mL 1. Caritis et al., Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2014 (N=315 subjects) 2. Ctrough for IM HPC Cavg , Makena PK - PD Correlation HPC Concentration and PTB Rate 1 46.3% 27.0% 29.6% 31.3% N=315 48
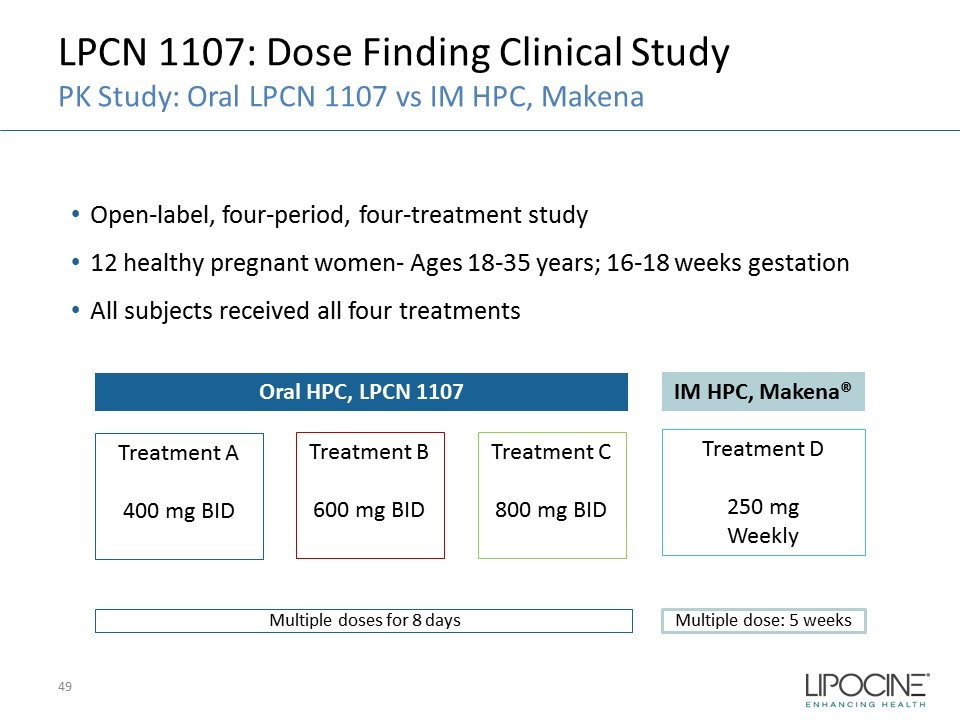
LPCN 1107: Dose Finding Clinical Study PK Study: Oral LPCN 1107 vs IM HPC, Makena • Open - label, four - period, four - treatment study • 12 healthy pregnant women - Ages 18 - 35 years; 16 - 18 weeks gestation • All subjects received all four treatments Treatment A 400 mg BID Treatment B 600 mg BID Treatment C 800 mg BID Treatment D 250 mg Weekly Oral HPC, LPCN 1107 IM HPC, Makena® Multiple doses for 8 days Multiple dose: 5 weeks 49
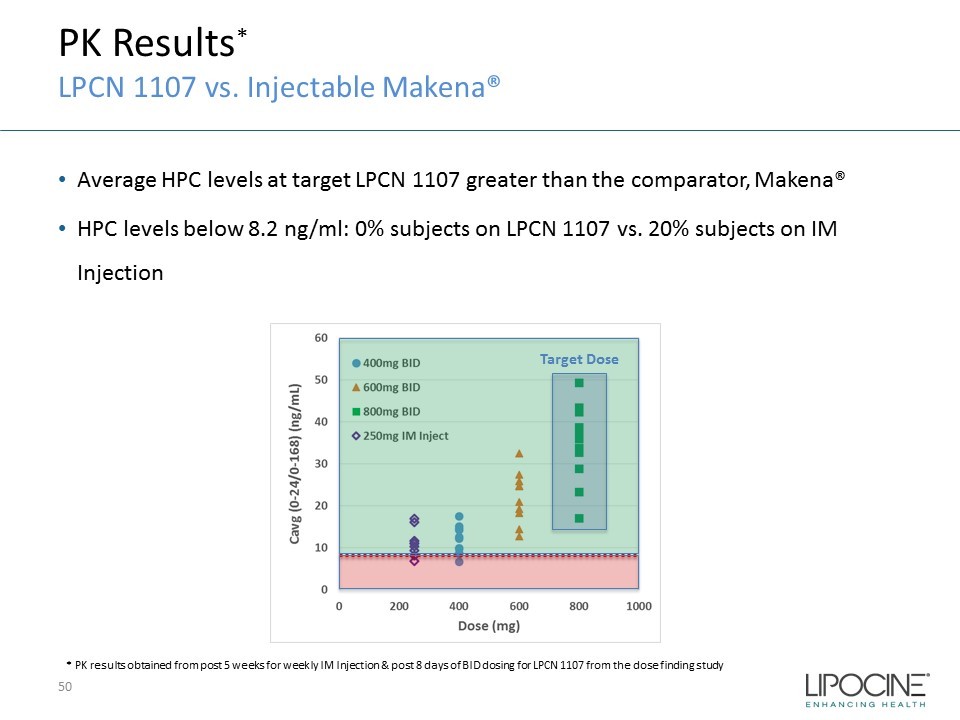
PK Results * LPCN 1107 vs. Injectable Makena® • Average HPC levels at target LPCN 1107 greater than the comparator, Makena® • HPC levels below 8.2 ng/ml: 0% subjects on LPCN 1107 vs. 20% subjects on IM Injection * PK results obtained from post 5 weeks for weekly IM Injection & post 8 days of BID dosing for LPCN 1107 from the dose finding s tudy Target Dose 50
