Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-32.2 - ASIA EQUITY EXCHANGE GROUP, INC. | ex32-2.htm |
| EX-32.1 - ASIA EQUITY EXCHANGE GROUP, INC. | ex32-1.htm |
| EX-31.2 - ASIA EQUITY EXCHANGE GROUP, INC. | ex31-2.htm |
| EX-31.1 - ASIA EQUITY EXCHANGE GROUP, INC. | ex31-1.htm |
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
(Mark One)
[X] ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the fiscal year ended: December 31, 2017
[ ] TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the transition period from ____________ to _____________
Commission File No. 333-192272
ASIA EQUITY EXCHANGE GROUP, INC.
(EXACT NAME OF REGISTRANT AS SPECIFIED IN ITS CHARTER)
| Nevada | 46-3366428 | |
| (State
or Other Jurisdiction of Incorporation or Organization) |
(I.R.S.
Employer Identification No.) |
Suite 2501A, 25/F, Skyline Tower,
39 Wang Kwong Road, Kowloon Bay, Hong Kong
(Address of Principal Executive Offices)
+852-2818 2998
(Registrant’s telephone number, including area code)
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act: None
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Exchange Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act.
Yes [ ] No [X]
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act.
Yes [ ] No [X]
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days.
Yes [X] No [ ]
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files).
Yes [X] No [ ]
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. [ ]
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| Large Accelerated Filer [ ] | Accelerated Filer [ ] | |
Non-Accelerated Filer [ ] |
(Do not check if a smaller reporting company) | Smaller reporting company [X] |
| Emerging Growth Company [X] |
Indicate by check mark whether registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act) Yes [ ] No [X]
Indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any
new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. [ ]
As of June 26, 2017 (the last business day of the registrant’s most recently completed second fiscal quarter), the aggregate market value of the shares of the registrant’s common stock held by non-affiliates (based upon the closing sale price of $12.3 per share as reported on The OTC Market) was approximately $740 million. Shares of the registrant’s common stock held by each executive officer and director and by each person who owns 10% or more of the outstanding common stock have been excluded from the calculation in that such persons may be deemed to be affiliates of the registrant. This determination of affiliate status is not necessarily a conclusive determination for other purposes.
There were a total of 118,900,016 shares of the registrant’s common stock outstanding as of April 9, 2018.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
None.
ASIA EQUITY EXCHANGE GROUP, INC.
Annual Report on Form 10-K
TABLE OF CONTENTS
| 2 |
INTRODUCTORY NOTE
Use of Terms
Except as otherwise indicated by the context and for the purposes of this report only, references in this report to:
| ● | “Company”, “we”, “us” and “our” are to the combined business of Asia Equity Exchange Group, Inc., a Nevada corporation, and its consolidated subsidiaries; | |
| ● | “AEEGCL” are to our Samoa subsidiary, Asian Equity Exchange Group Co., Ltd.; | |
| ● | “AEEX HK” are to AEEX (HK) International Financial Services Limited (formerly known as Yinfu International Enterprise Limited), a company formed in Hong Kong; | |
| ● | “AACCL” are to Asia America Consultants (Shenzhen) Co., Ltd., (formerly known as Yinfu Guotai Investment Consultant (Shenzhen) Co., Ltd.),our PRC subsidiary ; | |
| ● | “China” and “PRC” are to the People’s Republic of China; | |
| ● | “RMB” are to Renminbi, the legal currency of China; | |
| ● | “U.S. dollar”, “$” and “US$” are to the legal currency of the United States; | |
| ● | “SEC” are to the United States Securities and Exchange Commission; | |
| ● | “Securities Act” are to the Securities Act of 1933, as amended; and | |
| ● | “Exchange Act” are to the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. |
Special Note Regarding Forward Looking Statements
Statements contained in this report include “forward-looking statements” that involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors which could cause actual financial or operating results, performances or achievements expressed or implied by such forward-looking statements not to occur or be realized. Forward-looking statements made in this report generally are based on our best estimates of future results, performances or achievements, predicated upon current conditions and the most recent results of the companies involved and their respective industries. Forward-looking statements may be identified by the use of forward-looking terminology such as “may,” “will,” “could,” “should,” “project,” “expect,” “believe,” “estimate,” “anticipate,” “intend,” “continue,” “potential,” “opportunity” or similar terms, variations of those terms or the negative of those terms or other variations of those terms or comparable words or expressions. Potential risks and uncertainties include, among other things, such factors as:
| ● | our future business development, results of operations and financial condition; | |
| ● | our ability to maintain or increase our market share in the competitive markets in which we do business; | |
| ● | our ability to diversify our product offerings and capture new market opportunities; | |
| ● | uncertainties with respect to the PRC legal and regulatory environment; | |
| ● | other risks identified in this report and in our other reports filed with the SEC, including those identified in “Item 1A. Risk Factors” below. |
Readers are urged to carefully review and consider the various disclosures made by us in this report and our other filings with the SEC. These reports attempt to advise interested parties of the risks and factors that may affect our business, financial condition and results of operations and prospects. The forward-looking statements made in this report speak only as of the date hereof and we disclaim any obligation to provide updates, revisions or amendments to any forward-looking statements to reflect changes in our expectations or future events.
| 3 |
| ITEM 1. | BUSINESS. |
Overview of Our Business
We were incorporated in the State of Nevada on July 15, 2013, under the name “I In The Sky, Inc.” On July 22, 2015, we changed the company name to Asia Equity Exchange Group, Inc.. Our original business plan was to manufacture and market low cost GPS tracking devices and software to businesses and families. However this business was not successful and we had no revenues generated from our business until April 12, 2016 when we completed our reverse acquisition of AEEGCL.
AEEGCL is a company incorporated under the laws of Samoa on May 29, 2015. Effective November 30, 2015, we executed a Sale and Purchase Agreement (the “Purchase Agreement”) to acquire 100% of the shares and assets of AEEGCL, in exchange for one billion (1,000,000,000) shares of common stock of the Company that were issued to the owners of AEEGCL. The transactions contemplated by the Purchase Agreement were closed on April 12, 2016. As a result, our previous business plan was terminated and we are currently engaged in the business of AEEGCL.
The acquisition of AEEGCL and its subsidiaries by us was accounted for as a reverse merger because there was a change of control, and on a post-merger basis, the former shareholders of AEEGCL held a majority of our outstanding common stock on a fully-diluted basis. As a result, AEEGCL is deemed to be the acquirer for accounting purposes. Accordingly, the consolidated financial statement data presented are those of AEEGCL, recorded at the historical basis of AEEGCL, for all periods prior to our acquisition of AEEGCL on April 12, 2016, and the financial statements of the historical operations of the consolidated companies from the effective date of the closing of the reverse merger.
AEEGCL offers an international equity assistance and information service platform designed to provide member registration services, equity investment financing information to enterprises in Asia, mainly in China. Currently 59 companies are registered with us, and additional 31 companies are in the process of preparing the necessary documents for registration with us. All companies currently registered with us are located in China, as are the additional companies in the process.
Our member registration services refer to companies seeking to join our equity investment and financing information platform. All medium and small-sized enterprises in Asia can apply to register with us. They can distribute their basic information, project status, financial status and equity structure information through our platform to attract individual investors and investment institutions all over the world. Our current focus is on helping companies in China which seek financing while we plan to offer our services in other Asian countries where we can assist with a company’s public and investor awareness and investor relationship needs and financing needs. Where we can, we will assist companies by finding appropriate legal as well as accounting services.
AEEGCL owns 100% of AEEX HK, a Hong Kong corporation incorporated on December 22, 2014. AEEX HK owns 100% of Asian & American Consultant (Shenzhen) Co., Ltd. (“AACCL”), a corporation incorporated in the PRC on April 15, 2015. Both AEEX HK and AACCL are engaged in the provision of investment and corporate management consultancy services.
We generated revenues of $2,889,222 and $565,413 for the fiscal years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively. We had a net profit of $1,411,060 in 2017 and a net loss of $469,716 in 2016. As of December 31, 2017, we had a retained earnings of $756,192 and net assets of $16,035,787.
| 4 |
Recent Developments
Reverse Stock Split
On July 21, 2017, the Board of Directors of Asia Equity Exchange Group, Inc. approved a reverse stock split of the Company’s common stock, par value $0.001 per share (the “Common Stock”), at a ratio of 1-for-10 (the “Reverse Stock Split”) as of July 31, 2017 (the “Effective Date”).
Before the Effective Date, the Company was authorized to issue 3,000,000,000 shares of Common Stock and had 1,146,000,000 shares of Common Stock issued and outstanding. Simultaneously with the Reverse Stock Split, the Company decreased its authorized Common Stock to 300,000,000 shares. As a result of the Reverse Stock Split, the Company currently has 114,600,000 shares of Common Stock issued and outstanding (subject to adjustment due to the effect of rounding fractional shares into whole shares).
The Reverse Stock Split does not have any effect on the stated par value of the Common Stock and the Company’s authorized preferred stock of 1,000,000 shares which will remain unchanged. Immediately after the Reverse Stock Split, each stockholder’s percentage ownership interest in the Company and proportional voting power remain virtually unchanged except for minor changes and adjustments resulting from rounding fractional shares into whole shares. The rights and privileges of the holders of shares of Common Stock are substantially unaffected by the Reverse Stock Split.
| 5 |
Entry into a Material Definitive Agreement
On November 21, 2017, we entered into a Subscription Agreement (the “Agreement”) with Yanru Zhou (the “Investor”). Pursuant to the Agreement, the Investor purchased 4,300,000 shares (the “Shares”) of the common stock of the Company, par value $0.001 per share (the “Common Stock”), at the price of $3.5 per share (the “Purchase Price Per Share”) and for an aggregate price of $15,050,000 in a private sale transaction (the “Private Sale”). The Private Sale contemplated in the Agreement closed on the same day.
Pursuant to the Agreement, the Company will apply to be listed on the NASDAQ Capital Market or such other national securities exchange as is reasonably acceptable to the Purchaser (the “National Exchanges”), so that the Company’s Common Stock will commence trading on one of the National Exchanges (the “Uplisting”) no later than December 31, 2018 (the “Uplisting Deadline”).
If the Company does not complete Uplisting on or before the Uplisting Deadline (the “Eligible Uplisting”), the Investor will, within 30 days following the Uplisting Deadline, have the right to request the Company to buy back any number of the Shares, at the same price of the Purchase Price Per Share, subject to the terms and conditions of the Subscription Agreement.
| 6 |
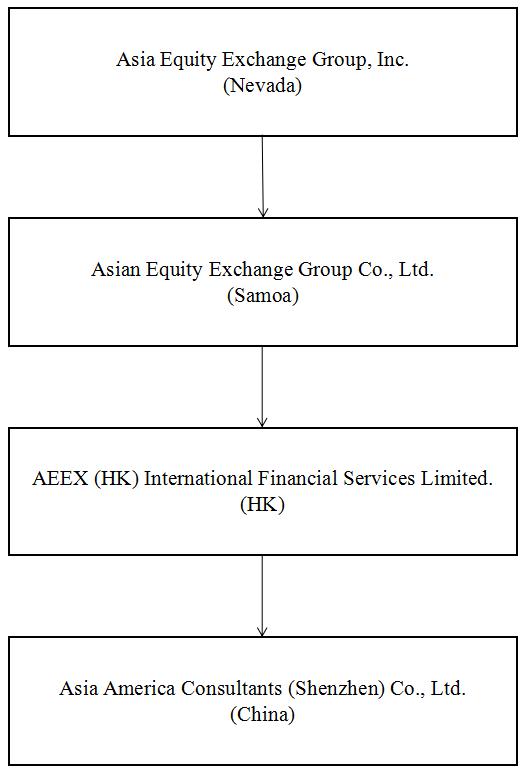
Our Corporate Structure
All of our business operations are conducted primarily through our operating subsidiaries. The chart below presents our current corporate structure:
Our Business
Many small and medium-sized enterprises throughout Asia seek to take potential advantages of becoming a publicly traded company since greater public awareness and the increased ability to access to international financing can accelerate the company’s growth.
However, many enterprises may not be familiar with public company listing requirements and overseas financing methods. The complicated listing rules and regulations together with high listing cost are also barriers for these enterprises to realize their full potential.
In addition, foreign languages and different securities laws and legal requirements of the listing jurisdictions will also deter the management desire to overseas listing. To assist these enterprises, we have a team of qualified and experienced local personnel with legal, regulatory and language expertise in those jurisdictions.
The multi-task service platform of AEEX serves as a means to assist these enterprises to secure a public listing and achieve overseas financing. Meanwhile, we also help overseas individual and institutional investors seek quality equity investment in our platform in which we provide registration, supervision and management services.
To accomplish these goals on behalf of our clients, our services include:
Listing services:
We provide listing services to companies seeking to join our equity investment and financing information dissemination platform. Medium and small-sized enterprises in Asia can apply to list with us, but our current focus is on helping companies in China, which seek financing and increased public awareness. Our services for companies that list with us relate primarily to markets and regulatory structures in China, but we plan to offer our services in other Asian countries where we can assist with a company’s public and investor awareness and investor relationship needs and with their financing needs. Where we can, we will assist the companies by finding appropriate legal and accounting services. We believe there are numerous U.S.-based law firms and American consulting services that are better equipped to deal with those services.
We conduct a strict due diligence review of any potential client’s business, history and management. Potential clients must disclose their audited financial statements and legal opinions in accordance with international standards issued by third party professional firms. They are also required to conform to strict standards for disclosure for information update after the listing, which helps to facilitate their connections to international capital markets.
| 7 |
To be a qualified applicant for listing with us, a potential client must:
| ● | Be duly established and in good standing pursuant to relevant laws and regulations in a country or region in Asia; | |
| ● | Demonstrate that they have a good business reputation and operating performance, and comply with professional ethics; | |
| ● | Have experienced, qualified and stable management team and sound operation; | |
| ● | Have a sustainable operating project with the expectation of a good return on investment; | |
| ● | Have not breached any law or regulation in a material respect, or have received any administrative penalty from a regulatory body or other department in the past twenty four months; | |
| ● | Acknowledge and comply with our relevant listing rules and is willing to pay fees relating to our client enterprise listing services; | |
| ● | Pass a professional due diligence conducted by us. |
It is important to note that we are not in fact nor do we intend to be a trading market or provide quotations services for our clients. We merely provide a platform designed solely for distributing equity investment information and financing information, which facilitates connections and negotiations between investors and project management. We assist investors seeking investment opportunities and companies seeking international investment.
Since August 2015, we have carried out a number of roadshows in various cities such as Shenyang, Dalian, Shanghai, Hangzhou, Xiamen and Shenzhen, which have extended our influence and enhanced our brand recognition. We plan to continue our all-round roadshows at regional, national and international levels to further increase awareness of our brand and advance our business development.
Listing Planning and Evaluation:
| ● | We conduct comprehensive evaluation of any prospective client, including its assets and liabilities, financial position, management, development prospect and business model; | |
| ● | We offer assistance in reorganizing and standardizing the client’s business, work to optimize its business model and procedures, and help the client integrate its resources to highlight the value of the client; | |
| ● | We help reorganize the corporate structure and assist the client to build a management team for going public based on the actual conditions of the client; and | |
| ● | We assess and recommend qualified lawyers, auditors, investment banks and other institutions which can provide the client with pre-listing services. |
We also ensure that we are in regular and efficient communication with all our clients who are planning to become a public company, or have already become public, and make certain that they have received the consulting services they need.
Where necessary, we will meet with clients on critical issues in public listing, or help them become familiar with important regulations in the securities markets and assist them in meeting the standards for going public. We also make sure that clients are updated with regulatory and legal changes.
Listing Solutions: We provide clients planning for a public listing with consulting services, which include models for reference and examples of successful cases. We also use our resources and experience to help clients connect directly with the corresponding securities regulatory commission.
Assistance with Negotiation and Implementation: With our advantages in resources and information, we assist clients with key negotiations with different parties and help them deal with various issues and problems before and after their public listing.
| 8 |
Funding Initiation: We use our resources to help clients who plan to go public, but face funding shortages to connect with venture capital, banks or other financial institutions that can provide potential assistance in their financing needs.
Client Equity Securitization Reform: We help to confirm the equity position of companies planning for going public, and provide assistance for them in working with qualified accounting and law firms to determine the share capital structure, stock par value and holding percentages of shareholders, and, where necessary, help clients to build a new equity structure in accordance with requirements of the relevant securities regulatory commission with whom the client is dealing.
Restructuring Consultancy: We work with qualified lawyers and auditing firms to help reorganize the client’s business model, procedures and organizational structure in order to maximize the client’s value and ensure that its public listing needs and requirements are met.
Route Design: We plan and design the proper procedures and methods for going public on behalf of our clients based on their assets, financial position, operations and other conditions.
Team Establishment: In accordance with the conditions of the clients and requirements by the relevant securities regulatory commission, we assist the clients to establish an organizational structure and a management team best suited for going public.
“Headhunting” Services: We work with headhunting companies, i.e. companies that provide employment or recruiting services to find the most qualified managers and professionals to meet the specific needs of our clients.
Follow-up Service: We provide clients with continuous consultancy and following-up services throughout the entire public listing process, from planning and preparation to success in becoming a public company.
Merger, Acquisition and Initial Public Offerings (“IPO”) Planning: A major feature of our service is overall merger, acquisition and IPO planning and assistance with listing on international main boards of various countries, assistance with the preparation and execution of overseas initial public offering efforts and main board listing through public shell companies by means of reverse merger.
One useful tool in the transition from private to public company is the reverse merger or reverse takeover.
In a reverse merger, the shareholders of a private company acquire a majority of the shares of a “shell company”. The shell company is a public company that does not have an active business operation or significant assets. The shell company is then merged with the private company. This makes the public company registration process less time consuming and potentially less expensive. To finalize the reverse merger, the private company trades shares with the public shell in exchange for the shell company’s stock, and the private enterprise becomes a public company because there is a change of control.
With numerous jurisdictions with which to deal, these mergers can be difficult. For small private companies, extra-jurisdictional government regulations and laws governing mergers are often difficult to understand, and without careful planning, there is a high failure rate with companies conducting mergers and acquisitions. Careful planning and pre-merger research is vital. Many companies starting out do not have the experience or resources to do the research necessary to complete a successful merger and to see a successful entity emerge from the process.
Among other requirements for a successful merger is detailed advance evaluation of the merger target, and the evaluation of the merger organization and its business plan. Clients will also need experienced assistance to develop strategies as they move beyond the merger process. Assistance with post-merger or post-acquisition organization, negotiations and planning are also important elements in determining the client’s success or failure. We have designed a program specifically tailored to address those issues for companies seeking to go public by means of a merger.
| 9 |
Assistance with Public Company Corporate Management: Among the services provided by us on behalf of our clients are those corporate services that are fundamental to a company’s survival and success. These include:
| ● | Assistance with and the preparation of all internal corporate documents, including corporate resolutions, minutes, changes and amendments to corporate documents as required; | |
| ● | Assistance with and the preparation of required legal and regulatory documents, including, but not limited to disclosure statements and agreements, subscription agreements, federal, state and regulatory filings, such registration statement(s), as required; | |
| ● | Assistance with the preparation of all required responses resulting from the filing of any of the aforesaid documents, and the preparation or assistance with the preparation of any and all required amendments to the aforesaid documents; | |
| ● | Guidance for the proper maintenance of all required legal and regulatory filings related to the foregoing documents; | |
| ● | Direct and continuous liaison with corporate attorneys, accountants and auditors on behalf of the enterprise; | |
| ● | Assisting the client with the proper maintenance of all company files. |
Resource Matching: As we move forward in our business and increase our client base, we are working to establish long-term cooperation with a number of qualified accounting firms, law firms, investment banks, venture capital and other relevant institutions.
Developing Public Awareness: We are working to develop public awareness for clients through an in-house publication, by creating and producing road-shows for clients and by developing publicity materials as part of an ongoing commitment to help our client to achieve success.
Markets
Our market includes small and medium-sized enterprises (“SME”) in Asia, enterprises with financial requirements, enterprises seeking to increase public awareness and enterprises planning to expand their business internationally.
Competition
There is a similar equity financing platform in China, the ‘National Equities Exchange and Quotations’ (NEEQ, www.neeq.cc). It is managed by the Chinese Government and has considerable support from the government itself. NEEQ has been in operation since September 2012, and currently services more than 5,000 listed companies. While its services are limited to mainland China, there is no assurance that other countries or groups will not initiate similar services to compete directly with us. NEEQ is a financial service platform which deals with both equity information services as well as equity trading. While we offer information services for clients, we are not involved with equity trading and we are not an equity trading market and it is important to note that we are not now nor does it intend to be a trading market or provide quotations services for its clients. It is a platform designed solely for equity investment information and financing information services. It facilitates connections and negotiations between investors and project management. We assist investors seeking investment opportunities and companies seeking international investment.
Additionally, the online equity information industry we are entering into is intensely competitive. Large companies may preempt the field if they view opportunities that have sufficient financial rewards to enter the market. We are a relatively late entry into a mature market for most online information services. There can be no assurance that we will be able to develop a profitable niche in this market. While we intend to find niche products and services relying on previously unexploited services, there can be no assurance that we will be successful in this endeavor.
Intellectual Property
We are in the process of registering our trademark in China, Hong Kong and the United States.
| 10 |
Employees
We had a total of 39 employees as of December 31, 2017. The following table sets forth the number of our employees by function.
| Function | Number | |||
| Finance | 4 | |||
| Technological | 3 | |||
| Listing Service | 23 | |||
| General and administrative | 9 | |||
| Total | 39 | |||
Our employees are not represented by a labor organization or covered by a collective bargaining agreement. We have not experienced any work stoppages. We believe we maintain good relations with our employees.
Government Regulations
Through AEEGCL and its Chinese subsidiaries, we are providing consulting services to our clients. Our platform is designed to provide information of equity investment and financing to medium and small-sized enterprises in Asia. Upon becoming member clients, we assist these enterprises to distribute information about themselves, their project status, financial status and equity structure information and use our platform to attract individual investors and investment institutions worldwide. Our business goal is to develop business partners not only in China but throughout Asia. However, at present we have only 26 business partners all of which are located in China. These partners include legal consulting and accounting firms which are also responsible for seeking out and identifying suitable business enterprise clients and to help these potential clients to understand what we offer and to assist these clients to register as members of our platform. As we move forward we will seek business partners and clients throughout Asia.
Our business is mainly conducted by our China-based subsidiary, AACCL. AACCL provides training courses for our business partners to help them understand our platform and provides management and business consultancy for our Chinese business clients. Such services are within the scope of AACCL’s business license and is permitted by Chinese laws. We established AACCL due to our expectation that most of the business will originate in China and, as such, we are required to have a Chinese entity to conduct business in China.
The business scope of AACCL registered and recorded with the Chinese government as required during incorporation of AACCL includes: engaging in enterprise management consulting, economic information consulting, corporate image planning and the research and development, import and export service of electronic products, computer software and hardware products. As a foreign-invested company in China, AACCL is subject to government regulations on foreign investment and business operation. Specifically, according to Article 14 of Law of the People’s Republic on Foreign-capital Enterprises, all foreign-invested enterprises should establish account books, conduct independent accounting, submit accounting reports and statements as required and accept supervision by the financial and tax authorities. If an enterprise with foreign capital refuses to maintain account books in China, the financial and tax authorities may impose a fine on it, and the industry and commerce administration authorities may order it to suspend operations or may revoke its business license. In addition, China adopted a new Labor Contract Law, effective on January 1, 2008, and issued its implementation rules, effective on September 18, 2008. The Labor Contract Law and related rules and regulations impose more stringent requirements on our Chinese subsidiaries with regard to, among others, minimum wages, severance payment and non-fixed-term employment contracts, time limits for probation periods, as well as the duration and the times that an employee can be placed on a fixed-term employment contract. Furthermore, pursuant to company law of China, our Chinese subsidiaries are required to allocate at least 10% of their annual after-tax profits determined in accordance with accounting standards and regulations of China to a statutory general reserve fund until the amounts in said fund reaches 50% of their registered capital.
Other than the required adherence to general business laws and regulatory disclosure as described above, our services do not appear to be affected by any specific Chinese government regulations. However, this does not preclude the possibility that China will institute regulations that will make it difficult or impossible for us to operate successfully, if at all, in China, and we would have to focus our business on companies located outside China.
However, it should also be noted that our business is operated by AEEGCL, a company incorporated in Samoa. No special license is required for its operations in Samoa. Though most of its business currently comes from China, its Samoan operations are not subject to regulations by the Chinese government.
| ITEM 1A. | RISK FACTORS. |
This item is not applicable to a small reporting company such as us.
| ITEM 1B. | UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS. |
Not applicable.
| 11 |
| ITEM 2. | PROPERTIES. |
Our principal place of business and corporate offices are located at Suite 2501A, 25/F, Skyline Tower, 39 Wang Kwong Road, Kowloon Bay, Hong Kong comprising an aggregate of approximately 4,134 square feet, under a 2-year lease that expires in December 2018 and provides for monthly lease payments of $14,590 (fiscal year 2017 exchange rate).
Our subsidiary company AACCL leased a place of 890 square meter in China as office facilities to house their administrative, marketing, and engineering and professional services which cost $28,782 (fiscal year 2017 exchange rate) per month. We believe our facilities and equipment to be in good condition and reasonably suited and adequate for our current needs.
| ITEM 3. | LEGAL PROCEEDINGS. |
From time to time, we may become involved in various lawsuits and legal proceedings, which arise, in the ordinary course of business. However, litigation is subject to inherent uncertainties, and an adverse result in these, or other matters, may arise from time to time that may harm our business. We are currently not aware of any such legal proceedings or claims that we believe will have, individually or in the aggregate, a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition or operating results.
| ITEM 4. | MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES. |
Not applicable.
| 12 |
| ITEM 5. | MARKET FOR REGISTRANT’S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES. |
Market Information
Our common stock is quoted on OTC Market under the symbol “AEEX”.
The following table sets forth the quarterly high and low sales prices of a share of our common stock as reported by on Yahoo.com for the periods indicated. These prices do not include retail markup, markdown or commission and may not represent actual transactions.
| Closing Prices(1) | ||||||||
| High | Low | |||||||
| Year Ended December 31, 2017 | ||||||||
| First Quarter | $ | 13.00 | $ | 8.00 | ||||
| Second Quarter | $ | 15.60 | $ | 7.50 | ||||
| Third Quarter | $ | 14.90 | $ | 6.57 | ||||
| Fourth Quarter | $ | 7.87 | $ | 5.23 | ||||
| Year Ended December 31, 2016 | ||||||||
| First Quarter | $ | 62.00 | $ | 50.00 | ||||
| Second Quarter | $ | 58.00 | $ | 5.00 | ||||
| Third Quarter | $ | 18.90 | $ | 4.99 | ||||
| Fourth Quarter | $ | 20.40 | $ | 7.50 | ||||
(1) The above table sets forth the range of high and low closing prices per share of our common stock as reported by OTC Markets for the periods indicated, giving retrospective effect of the 1 for 10 reverse stock split effected on July 21, 2017.
Reverse Stock Split
On July 21, 2017, the Board of Directors of Asia Equity Exchange Group, Inc. approved a reverse stock split of the Company’s common stock, par value $0.001 per share (the “Common Stock”), at a ratio of 1-for-10 (the “Reverse Stock Split”) as of July 31, 2017 (the “Effective Date”).
Before the Effective Date, the Company was authorized to issue 3,000,000,000 shares of Common Stock and had 1,146,000,000 shares of Common Stock issued and outstanding. Simultaneously with the Reverse Stock Split, the Company decreased its authorized Common Stock to 300,000,000 shares. As a result of the Reverse Stock Split, the Company currently has 114,600,000 shares of Common Stock issued and outstanding (subject to adjustment due to the effect of rounding fractional shares into whole shares).
The Reverse Stock Split does not have any effect on the stated par value of the Common Stock. The Reverse Stock Split does not affect the Company’s authorized preferred stock. There are no outstanding shares of the Company’s preferred stock. After the Reverse Stock Split, the Company’s authorized preferred Stock of 1,000,000 shares will remain unchanged. Immediately after the Reverse Stock Split, each stockholder’s percentage ownership interest in the Company and proportional voting power remains virtually unchanged except for minor changes and adjustments resulting from rounding fractional shares into whole shares. The rights and privileges of the holders of shares of Common Stock are substantially unaffected by the Reverse Stock Split.
| 13 |
Approximate Number of Holders of Our Common Stock
As of March 27, 2018, there were 148 holders of record of our common stock, which does not include the number of stockholders holding shares of our common stock in “street name”.
Dividend Policy
We have never declared or paid any cash dividends on our common stock. We anticipate that we will retain any earnings to support operations and to finance the growth and development of our business. Therefore, we do not expect to pay cash dividends in the foreseeable future. Any future determination relating to our dividend policy will be made at the discretion of our Board of Directors and will depend on a number of factors, including future earnings, capital requirements, financial conditions and future prospects and other factors the Board of Directors may deem relevant. Payments of dividends by Asia America Consultants (Shenzhen) Co., Ltd. (“AACCL”) to our company are subject to restrictions including primarily the restriction that foreign invested enterprises may only buy, sell and/or remit foreign currencies at those banks authorized to conduct foreign exchange business after providing valid commercial documents.
Securities Authorized for Issuance Under Equity Compensation Plans
See Item 12, “Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters — Securities Authorized for Issuance Under Equity Compensation Plans.”
Recent Sales of Unregistered Securities
On November 21, 2017, pursuant to a subscription agreement between the Company and an investor, the Company sold 4,300,000 shares of common stock, for a price of $3.50 per share, for an aggregate purchase price of $15,050,000.
The above issuances were made pursuant to the exemption from registration contained in Regulation S promulgated under the Securities Act.
| ITEM 6. | SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA. |
Not applicable.
| ITEM 7. | MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS. |
The following management’s discussion and analysis should be read in conjunction with our financial statements and the notes thereto and the other financial information appearing elsewhere in this report. In addition to historical information, the following discussion contains certain forward-looking information. See “Special Note Regarding Forward Looking Statements” above for certain information concerning those forward looking statements. Our financial statements are prepared in U.S. dollars and in accordance with U.S. GAAP.
Overview
We derived our revenue from offering various consulting services to our customers through our international equity assistance and information service platform designed to provide member registration services, equity investment financing information to enterprises in Asia, mainly in China. Currently 59 companies are registered with us, and additional 31 companies are in the process of registration with us. All companies currently registered with us are located in China, as are the additional companies in the process.
| 14 |
Results of Operations
The following table sets forth key components of our results of operations for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016:
| For the Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | Variances | % of variance | |||||||||||||
| Revenue | $ | 2,889,222 | $ | 565,413 | $ | 2,323,809 | 411 | % | ||||||||
| Operating expenses | - | |||||||||||||||
| Selling expenses | 412,014 | 439,664 | (27,650 | ) | -6 | % | ||||||||||
| General and administrative expenses | 1,026,905 | 592,982 | 433,923 | 73 | % | |||||||||||
| Total Operating Expenses | 1,438,919 | 1,032,646 | 406,273 | 39 | % | |||||||||||
| Income (loss) from operations | 1,450,303 | (467,233 | ) | 1,917,536 | -410 | % | ||||||||||
| Other income (expense) | ||||||||||||||||
| Interest income | 86,357 | 73 | 86,284 | 118197 | % | |||||||||||
| Foreign exchange gain (loss) | 247,976 | (560 | ) | 248,535 | -44381 | % | ||||||||||
| Other expense | (13,566 | ) | (1,996 | ) | (11,570 | ) | 580 | % | ||||||||
| Total other income (expense), net | 320,767 | (2,483 | ) | 323,249 | -13019 | % | ||||||||||
| Income (loss) before income taxes | 1,771,070 | (469,716 | ) | 2,240,786 | -477 | % | ||||||||||
| Provision for income taxes | 360,010 | - | 360,010 | 100 | % | |||||||||||
| Net income (loss) | $ | 1,411,060 | $ | (469,716 | ) | $ | 1,880,776 | -400 | % | |||||||
Revenues. Our revenue increased by $2,323,809 or 411% from $565,413 for the year ended December 31, 2016 to $2,889,222 for the year ended December 31, 2017, primarily due to increased public-listing related consulting services provided to customers during 2017. In 2016, we only provided such consulting services to one customer for pre-listing knowledge education and tutoring, due diligence, market information analysis and business plan draft. In contrast, we provided more extended consulting services to three customers in 2017, including but not limited to due diligence, market information collection and analysis, business plan, pre-listing education and tutoring, legal structure re-organization advisory services, shell company identification and recommendation, auditing and legal firm recommendation, investor referral and pre-listing financing coordination as well as many follow-up services. Through such comprehensive consulting services provided to customers, we enhanced public awareness of our service platform and developed more members and potential customers in 2017. Our revenue increased accordingly as we completed the services.
Selling expenses. Our selling expense slightly decreased by $27,650 or 6% from $439,664 in 2016 to $412,014 in 2017. The decrease in our selling expense was primarily because we reduced outsourcing some of the services to our business partners when we hired more qualified competent employees in 2017, which enabled us to bring certain service rendering in house. . During 2017, in response to our rapid market and customer development, we hired more employees and internally established four excellent service teams including the commerce, media, technology and legal department. Number of employees in these departments increased from 2 employees in 2016 to 26 employees in 2017. As a result, some previously outsourced services can be performed in-house in 2017 to help us lower down related costs.
| 15 |
General and administrative expenses. General and administrative expenses increased by $433,923 or 73%, from $592,982 in 2016 to $1,026,905 in 2017. The increase in our general and administrative expense in 2017 was largely due to increased audit and accounting fees by $198,645 when we switched the small auditing firm to a larger U.S based accounting firm, increased in salary expense by $67,907 due to increased administrative staff, and increased office lease expense by $235,638 due to larger office space leased to meet our business expansion demand.
Interest income: Our interest income increased by $86,284 from only $73 in 2016 to $86,357 in 2017. In November 2017, we purchased a wealth management product from China Construction Bank. The investment bears an interest of 4.8% per annum. The related interest income of $78,987 has been accrued in 2017. In addition, from September to December 2017, we advanced one year short-term loans of $2,295,000 (RMB 15 million) to a former customer Shenzhen Shangyuan Electronic Business Development Co., Ltd. (“Shangyuan”) for working capital. Among the RMB 15 million loan, RMB 5 million is non-interest bearing and the remaining RMB 10 million are interest-bearing loans with interest rate of 5% per annum. Related interest income of $6,350 has been accrued in 2017. These factors led to our increased interest income for 2017.
Foreign exchange gain (loss): Foreign currency exchange gain increased by $248,535 when comparing 2017 to 2016. We have operations in the Samoa, Hong Kong and the PRC, and our receipts and payments are mostly in currencies other than our reporting currency of U.S. Dollars. Our financial income (expenses) for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016 primarily reflects the foreign currency transaction income or loss expressed in U.S. Dollars. We provide various consulting services to customers and received the customer payment in currencies other than USD. The foreign currency exchange gain was mainly the result of the favorable USD against RMB in fiscal 2017.
Provision for income taxes. Our income tax expense increased by $360,010 when comparing 2017 to 2016, primarily due to increased revenue and taxable income in 2017.
Net income (loss). As a result of the foregoing, we reported a net income of $1,411,060 for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2017, compared to a net loss of $469,716 for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2016.
Plan of Operation
Consistent with prior years, we plan to enroll more qualified businesses in mainland China as well as other Asian countries to be listed in our website www.asiaotcmarkets.com for equity financing. This is achieved by cooperating with authorized institutions in commercial roadshows and seeking support and assistance from local governments at all levels. Our ultimate aim in 2018 is to achieve a double-digit growth in the business.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
As of December 31, 2017, we had $512,729 cash and cash equivalents compared to $55,371 as of December 31, 2016. We also had $994,500 accounts receivable from one customer who has completed its reverse merger transaction with our help. We believe we can collect this balance in the short term. In addition, in November 2017, we completed a private placement transaction and sold 4.3 million shares of our common stock to an investor for cash of $15.3 million. We used the issuance proceeds received from the private placement to purchase a wealth management investment product with China Construction Bank. Once it matures on May 20, 2018, it will be released from the investment account and become available for use in our operation as working capital if necessary. As of December 31, 2017, we also have deferred revenue of $2.3 million derived from customer deposits for our membership and consulting services. Such amount will be recognized as revenue as our consulting services are gradually provided, which will increase our operating cash flows in the near future.
Based on our current business development and expansion plan, we are expecting to generate additional cash flows in the near future from attracting more new customers and expanding our revenue through our service platform.
| 16 |
As of December 31, 2017, we had positive working capital of $15.9 million. We have historically funded our working capital needs from operations, advance payments from customers, related-party loans and equity financing. Our working capital requirements are influenced by the level of our operations, the numerical volume and dollar value of our sales contracts, the progress of execution on our customer contracts, and the timing of accounts receivable collections. We believe that our current cash and cash flow from operations will be sufficient to meet our anticipated cash needs, including our cash needs for working capital for the next 12 months. We may, however, require additional cash resources due to changing business conditions or other future developments, including any investments or acquisitions we may decide to pursue. Our ability to maintain sufficient liquidity depends partially on our ability to achieve anticipated levels of revenue, while continuing to control costs. We continue to seek favorable additional financing to meet our capital requirements to fund our operations and growth plans in the ordinary course of business.
The following table sets forth a summary of our cash flows for the periods indicated:
For the years ended December 31, | ||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities | $ | 2,811,028 | $ | (271,784 | ) | |||
| Net cash provided by (used in) investing activities | $ | (17,324,729 | ) | $ | (28,078 | ) | ||
| Net cash provided by financing activities | $ | 15,209,536 | $ | 352,158 | ||||
| Net increase in cash and cash equivalents | $ | 457,358 | $ | 33,013 | ||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at the beginning of year | $ | 55,371 | $ | 22,358 | ||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at the end of year | $ | 512,729 | $ | 55,371 | ||||
Operating Activities
Net cash provided by operating activities amounted to $2,811,028 for the year ended December 31, 2017, including net income of $1,411,060 generated from provided member registration and various public-listing related consulting services to our customers. In addition, our accounts receivable increased by $962,650 representing a balance due from one of our customers which we believe we can collect in full in the near future. Our deferred revenue also increased by $2,242,678 because we received cash deposits from customers for our member registration and listing consulting services that have not been rendered completely as of the balance sheet date. Our taxes payable also increased by $459,454 due to our increased taxable income in 2017. The overall increase in our cash flow from operating activities reflected the above combined factors.
Net cash used in operating activities amounted to $271,784 for the year ended December 31, 2016, including our net operating loss of $469,716 adjusted by an increase in other payable and accrued expense by $176,163.
Investing Activities
Net cash used in investing activities amounted to $17,324,729 for the year ended December 31, 2017, including purchases of property and equipment of $59,638 as we leased larger office space and hired more employees to meet our business expansion, an increase in loans receivable of $2,221,500 because we advanced RMB 15 million loans to a third-party to generate interest income at an interest rate of 5%, and an increase in short-term investment of $15,050,000 million because we used cash of RMB 100 million to purchase a wealth management product from China Construction Bank for 180 days in order to earn interest income at 4.8% interest rate per annum.
Net cash used in investing activities amounted to $28,078 for the year ended December 31, 2016 which primarily includes purchases of property and equipment in the same amount in 2016.
Financing Activities
Net cash provided by financing activities amounted to $15,209,536 for the year ended December 31, 2017, primarily include an increase in borrowing from a related party of $159,536 and proceeds from a stock issuance under a private placement of $15,050,000 during 2017.
Net cash provided by financing activities amounted to $352,158 for the year ended December 31, 2016 primarily due to increased borrowing from a related party in the same amount as working capital.
| 17 |
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
We do not have any off-balance sheet arrangements.
Inflation
Inflation does not materially affect our business or the results of our operations.
Seasonality
The nature of our business does not appear to be affected by seasonal variations
Critical Accounting Policies and Management Estimates
We prepare our consolidated financial statements in accordance with U.S. GAAP. These accounting principles require us to make judgments, estimates and assumptions on the reported amounts of assets and liabilities at the end of each fiscal period, and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during each fiscal period. We continually evaluate these judgments and estimates based on our own historical experience, knowledge and assessment of current business and other conditions, our expectations regarding the future based on available information and assumptions that we believe to be reasonable.
The selection of critical accounting policies, the judgments and other uncertainties affecting application of those policies and the sensitivity of reported results to changes in conditions and assumptions are factors that should be considered when reviewing our financial statements. We believe the following accounting policies involve the most significant judgments and estimates used in the preparation of our consolidated financial statements.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with U.S. GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Significant estimates required to be made by management, include, but are not limited to, the valuation of accounts and loans receivable, useful lives of property and equipment, the recoverability of long-lived assets, realization of deferred income tax assets, revenue recognition and provision necessary for contingent liabilities. Actual results could differ from these estimates.
Accounts Receivable, net
Accounts receivable are recognized and carried at original invoiced amount less an estimated allowance for uncollectible amounts. The Company generally receives a cash payment before delivery of the services, but may extend unsecured credit to its customers in the ordinary course of business. The Company mitigates the associated risks by performing credit checks and actively pursuing past due accounts. An allowance for doubtful accounts is established and recorded based on management’s assessment of the credit history of the customers and current relationships with them.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
The Company follows the provision of Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) 820, “Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures,” which defines fair value as the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. A three-level fair value hierarchy prioritizes the inputs used to measure fair value. The hierarchy requires entities to maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs. The three levels of inputs used to measure fair value are as follows:
| 18 |
Level 1- Observable inputs such as unadjusted quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities available at the measurement date.
Level 2- Observable inputs (other than Level 1 quoted prices) such as quoted prices active markets for similar assets or liabilities, quoted prices in markets that are not active for identical or similar as or liabilities, or other inputs that are observable or can be corroborated by observable market data.
Level 3- Inputs are unobservable inputs which reflect management’s assumptions based on the best available information.
The Company considers the recorded value of its financial assets and liabilities, which consist primarily of cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable, loans receivable, prepaid expenses and other current assets, short-term investment, deferred revenue, accrued and other liabilities, taxes payable and due to related party to approximate the fair value of the respective assets and liabilities at December 31, 2017 and 2016 based upon the short-term nature of the assets and liabilities.
Revenue Recognition
The Company’s revenue is recognized when persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists, service has occurred and all obligations have been performed pursuant to the terms of the agreement, the sales price is fixed or determinable, and collectability is reasonably assured.
The Company currently generates its revenue from the following main sources:
● Revenue from membership fee
The Company develops and attracts corporate enterprises to become members and join in the Company’s service platform www.aeexotcmarkets.com. To become a member, customer needs to pay a one-time non-refundable registration fee first. The Company recognizes revenue from membership fee when it posts member’s information and profiles on its platform www.aeexotcmarkets.com, which enables the member’s corporate information and specific needs exposed to the public.
● Revenue from consulting services
The Company also provides various consulting services to its members, especially to those who have the intention to be publicly listed in the stock exchanges in the United States and other countries. The Company categorizes its consulting services into three Phases:
Phase I consulting services primarily include due diligence review, market research and feasibility study, business plan drafting, accounting record review, and business analysis and recommendations etc. Management estimates that Phase I normally takes around three months to complete based on its past experiences.
Phase II consulting services primarily include reorganization, pre-listing education and tutoring, talent search, legal and audit firm recommendation and coordination, VIE contracts and other public-listing related documents review, merger and acquisition planning, investor referral and pre-listing equity financing source identification and recommendation, independent directors and audit committee candidates recommendation etc. Management estimates that Phase II normally takes about eight months to complete based its past experiences.
Phase III consulting services primarily include shell company identification and recommendation for customers expecting to become publicly listed through reverse merger transaction; assistance in preparation of customers’ registration statement under IPO transactions or Form 8-K under reverse merger transactions; assistance in answering comments and questions received from regulatory agencies etc. Management believes it is very difficult to estimate the timing of this phase of service as the completion of Phase III services is not within the Company’s control.
Each phase of consulting services are standalone and fees associated with each phase are clearly identified in service agreements. Revenue from providing Phase I and Phase II consulting services to customers is recognized ratably over the estimated completion period of each phase. Revenue from providing Phase III consulting services to customers is recognized upon completion of reverse merger transaction or IPO transaction, which is evidenced by filing of 8-K for reverse merger transaction or receipt of effective notice from regulatory agencies for IPO transaction. Revenue that has been billed and not yet recognized is reflected as deferred revenue on the balance sheet.
| 19 |
Depending on the complexity of the underlying service arrangement and related terms and conditions, significant judgments, assumptions and estimates may be required to determine when substantial delivery of contract elements has occurred, whether any significant ongoing obligations exist subsequent to contract execution, whether amounts due are collectible and the appropriate period or periods in which, or during which, the completion of the earnings process occurs. Depending on the magnitude of specific revenue arrangements, adjustment may be made to the judgments, assumptions and estimates regarding contracts executed in any specific period.
Income Tax
The Company accounts for income taxes under ASC 740. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the future tax consequences attributable to differences between the consolidated financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax bases. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized in income in the period including the enactment date. Valuation allowances are established, when necessary, to reduce deferred tax assets to the amount expected to be realized.
The provisions of ASC 740-10-25, “Accounting for Uncertainty in Income Taxes,” prescribe a more-likely-than-not threshold for consolidated financial statement recognition and measurement of a tax position taken (or expected to be taken) in a tax return. This interpretation also provides guidance on the recognition of income tax assets and liabilities, classification of current and deferred income tax assets and liabilities, accounting for interest and penalties associated with tax positions, and related disclosures. Management does not believe that there was any uncertain tax position at December 31, 2017 and 2016.
To the extent applicable, the Company records interest and penalties as a general and administrative expense. The Company’s subsidiaries in China and Hong Kong are subject to the income tax laws of the PRC and Hong Kong. The statute of limitations for the Company’s U.S. federal income tax returns and certain state income tax returns remains open for tax years 2013 and after. As of December 31, 2017, the tax years ended December 31, 2015 through December 31, 2017 for the Company’s PRC subsidiary remain open for statutory examination by PRC tax authorities.
On December 22, 2017, the “Tax Cuts and Jobs Act” (“The Act”) was enacted. Under the provisions of The Act, the U.S. corporate tax rate decreased from 35% to 21%. Additionally, the Tax Act imposes a one-time transition tax on deemed repatriation of historical earnings of foreign subsidiaries, and future foreign earnings are subject to U.S. taxation. The change in rate has caused the Company to re-measure all U.S. deferred income tax assets and liabilities for temporary differences. Net operating loss (“NOL”) carryforwards are limited to 80% of taxable income and can be carried forward indefinitely.
| ITEM 7A. | QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK. |
Not applicable.
| 20 |
| ITEM 8. | FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA. |
INDEX TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| 21 |
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the shareholders and the board of directors of Asia Equity Exchange Group, Inc.
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Asia Equity Exchange Group, Inc. and its subsidiaries (collectively, the “Company”) as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, and the related consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive income (loss), changes in stockholders’ equity, and cash flows for each of the two years in the period ended December 31, 2017, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the “consolidated financial statements”). In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the two years in the period ended December 31, 2017, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
Basis for Opinion
These consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s consolidated financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (“PCAOB”) and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the consolidated financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. As part of our audits we are required to obtain an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion.
Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the consolidated financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the consolidated financial statement. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
/s/ Friedman LLP
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2018.
New York, New York
April 13, 2018
| F-1 |
Asia Equity Exchange Group, Inc.
| As of December 31, | ||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| ASSETS | ||||||||
| Current Assets | ||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 512,729 | $ | 55,371 | ||||
| Accounts receivable | 994,500 | - | ||||||
| Loans receivable | 2,295,000 | - | ||||||
| Short-term investment | 15,300,000 | - | ||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | 432,262 | 40,999 | ||||||
| Total current assets | 19,534,491 | 96,370 | ||||||
| Property and equipment, net | 76,040 | 40,230 | ||||||
| Deferred tax assets | 93,349 | - | ||||||
| Total assets | $ | 19,703,880 | $ | 136,600 | ||||
| LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | ||||||||
| Current Liabilities | ||||||||
| Deferred revenue | $ | 2,315,123 | $ | - | ||||
| Accrued expense and other current liabilities | 297,405 | 175,389 | ||||||
| Taxes payable | 396,221 | 1,105 | ||||||
| Due to related party | 583,787 | 423,570 | ||||||
| Total current liabilities | $ | 3,592,536 | $ | 600,064 | ||||
| Income tax payable – noncurrent portion | 75,557 | - | ||||||
| Total liabilities | 3,668,093 | 600,064 | ||||||
| Commitments and contingencies | ||||||||
| Equity | ||||||||
| Preferred stock, 1,000,000 shares authorized; par value $0.001, none issued and outstanding | - | - | ||||||
| Common stock, 300 million shares authorized; par value $0.001, 118,900,016 shares and 114,600,000 shares issued and outstanding, respectively * | 118,900 | 114,600 | ||||||
| Additional paid in capital | 15,045,700 | - | ||||||
| Statutory reserve | 63,950 | - | ||||||
| Retained earnings (accumulated deficit) | 756,192 | (590,918 | ) | |||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) | 51,045 | 12,854 | ||||||
| Total equity | 16,035,787 | (463,464 | ) | |||||
| TOTAL LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | $ | 19,703,880 | $ | 136,600 | ||||
* Giving retrospective effect of reverse merger transaction consummated on April 12, 2016 and the 1 for 10 reverse stock split effected on July 21, 2017
The accompanying notes are an integral parts to the consolidated financial statements
| F-2 |
Asia Equity Exchange Group, Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Income (loss)
| For the Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Revenue | $ | 2,889,222 | $ | 565,413 | ||||
| Operating expenses | ||||||||
| Selling expenses | 412,014 | 439,664 | ||||||
| General and administrative expenses | 1,026,905 | 592,982 | ||||||
| Total Operating Expenses | 1,438,919 | 1,032,646 | ||||||
| Income (loss) from operations | 1,450,303 | (467,233 | ) | |||||
| Other income (expense) | ||||||||
| Interest income | 86,357 | 73 | ||||||
| Foreign currency transaction gain (loss) | 247,976 | (560 | ) | |||||
| Other expense | (13,566 | ) | (1,996 | ) | ||||
| Total other income (expense), net | 320,767 | (2,483 | ) | |||||
| Income (loss) before income tax | 1,771,070 | (469,716 | ) | |||||
| Provision for income taxes | 360,010 | - | ||||||
| Net income (loss) | 1,411,060 | (469,716 | ) | |||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss) | ||||||||
| Net income (loss) | 1,411,060 | (469,716 | ) | |||||
| Foreign currency translation gain | 38,191 | 13,867 | ||||||
| Comprehensive income (loss) | $ | 1,449,251 | $ | (455,849 | ) | |||
| Earnings (loss) per share Basic and diluted | $ | 0.00 | $ | (0.00 | ) | |||
| Weighted average number of shares Basic and diluted * | 115,071,233 | 114,600,000 | ||||||
* Giving retrospective effect of reverse merger transaction consummated on April 12, 2016 and the 1 for 10 reverse stock split effected on July 21, 2017
The accompanying notes are an integral parts to the consolidated financial statements
| F-3 |
Asia Equity Exchange Group, Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Changes in Stockholders’ Equity
For the Years Ended December 31, 2017 and 2016
| Preferred stock | Common Stock | Additional | Retained earnings | Other income | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares | Amount | Number of Shares * | Amount | Paid in Capital | Statutory Reserve | (accumulated deficit) | Comprehensive (loss) | Stockholders’ Equity | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2015 | - | $ | - | 114,600,016 | $ | 114,600 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | (121,202 | ) | $ | (1,013 | ) | $ | (7,615 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
| Net loss | - | - | - | - | - | - | (469,716 | ) | - | (469,716 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation gain | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 13,867 | 13,867 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2016 | - | 114,600,016 | $ | 114,600 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | (590,918 | ) | $ | 12,854 | $ | (463,464 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Common stock issued under private placement | - | - | 4,300,000 | 4,300 | 15,045,700 | - | - | - | 15,050,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appropriation to statutory surplus reserve | - | - | - | - | - | 63,950 | (63,950 | ) | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1,411,060 | - | 1,411,060 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation gain | - | - | - | - | - | - | 38,191 | 38,191 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2017 | - | $ | - | 118,900,016 | $ | 118,900 | $ | 15,045,700 | $ | 63,950 | $ | 756,192 | $ | 51,045 | $ | 16,035,787 | ||||||||||||||||||||
* Giving retrospective effect of reverse merger transaction consummated on April 12, 2016 and the 1 for 10 reverse stock split effected on July 21, 2017
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements
| F-4 |
Asia Equity Exchange Group, Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
| For the years ended December 31, | ||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES | ||||||||
| Net income (loss) | $ | 1,411,060 | $ | (469,716 | ) | |||
| Adjusted to reconcile net income (loss) to cash provided by (used in) operating activities: | ||||||||
| Depreciation | 9,313 | 11,858 | ||||||
| Loss from disposal of fixed assets | 11,655 | |||||||
| Deferred tax benefit | (90,360 | ) | - | |||||
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities: | ||||||||
| Accounts receivable | (962,650 | ) | 9,475 | |||||
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | (380,237 | ) | 3,286 | |||||
| Deferred revenue | 2,242,678 | - | ||||||
| Other payables and accrued expenses | 110,115 | 176,163 | ||||||
| Income taxes payable | 459,454 | (2,850 | ) | |||||
| Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities | 2,811,028 | (271,784 | ) | |||||
| CASH FLOWS FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES | ||||||||
| Purchases of property and equipment | (59,638 | ) | (28,078 | ) | ||||
| Proceeds from disposal of fixed assets | 6,409 | - | ||||||
| Loans to a third party | (2,221,500 | ) | - | |||||
| Short-term investment | (15,050,000 | ) | - | |||||
| Net cash used in investing activities | (17,324,729 | ) | (28,078 | ) | ||||
| CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES | ||||||||
| Proceeds received from related party | 159,536 | 352,158 | ||||||
| Proceeds from stock issuance under a private placement | 15,050,000 | - | ||||||
| Net cash provided by financing activities | 15,209,536 | 352,158 | ||||||
| EFFECT OF EXCHANGE RATES ON CASH | (238,477 | ) | (19,283 | ) | ||||
| NET INCREASE IN CASH | 457,358 | 33,013 | ||||||
| CASH, BEGINNING OF YEAR | 55,371 | 22,358 | ||||||
| CASH, END OF YEAR | $ | 512,729 | $ | 55,371 | ||||
| SUPPLEMENTAL DISCLOSURE OF CASH FLOW INFORMATION | ||||||||
| Cash paid for interest expense | $ | - | $ | - | ||||
| Cash paid for income tax | $ | 7,226 | $ | 2,977 | ||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements
| F-5 |
NOTE 1 -ORGANIZATION AND DESCRIPTION OF BUSINESS
Asia Equity Exchange Group, Inc. (“the Company” or “AEEX”) is a Nevada corporation incorporated on July 15, 2013, under the name “I In The Sky, Inc.” (“SYYF”). The Company filed a name change to AEEX with the state of Nevada on July 22, 2015.
The Company’s original business plan was to manufacture and market low cost GPS tracking devices and software to businesses and families. However, this business was not successful and the Company had no revenues generated from its business from its inception until April 12, 2016 when it completed the reverse acquisition of Asian Equity Exchange Group Company Limited (“AEEGCL”).
On November 30, 2015, the Company executed a Sale and Purchase Agreement (the “Purchase Agreement”) to acquire 100% of the shares and assets of AEEGCL (the “Acquisition”). Pursuant to the Purchase Agreement, the Company issued one billion (1,000,000,000) shares of common stock to the former owners of AEEGCL. The Acquisition was consummated on April 12, 2016. As a result, AEEGCL became a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Company. The Company had a total of 146,000,000 shares of common stock outstanding immediately prior to the closing of the Acquisition. Upon completion of the Acquisition, the Company had a total of 1,146,000,000 shares of common stock outstanding, with the former owners of AEEGCL controlled 87.3% of the total issued and outstanding shares of the Company’s common stock.
The acquisition of AEEGCL and its subsidiaries by us was accounted for as a reverse merger because there was a change of control, and on a post-merger basis, the former shareholders of AEEGCL held a majority of our outstanding common stock on a fully-diluted basis. As a result, AEEGCL is deemed to be the acquirer for accounting purposes. Accordingly, the consolidated financial statement data presented are those of AEEGCL, recorded at the historical basis of AEEGCL, for all periods prior to our acquisition of AEEGCL on April 12, 2016, and the financial statements of the historical operations of the consolidated companies from the effective date of the closing of the reverse merger.
AEEGCL was incorporated under the laws of Samoa on May 29, 2015. It offers an international equity assistance and information service platform designed to provide listing assistance services, equity investment financing information and public relationship services to enterprises in Asia, mainly in China. AEEGCL owns 100% of AEEX (HK) International Financial Service Limited (formerly known as Yinfu International Enterprise Limited, “AEEX HK”), a, entity incorporated in Hong Kong on December 22, 2014. AEEX HK owns 100% of Asia America Consultants (Shenzhen) Co., Ltd. (formerly known as Yinfu Guotai Investment Consultant (Shenzhen) Co., Ltd., “AACCL”), a wholly-owned foreign enterprise organized under the laws of the People’s Republic of China (the “PRC”) on April 15, 2015.
The Company, through its subsidiaries AEEX HK and AACCL, engages in providing investment and corporate management consulting services to customers.
| F-6 |
NOTE 2 - SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Basis of Presentation and Principles of Consolidation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“U.S. GAAP”). The consolidated financial statements of the Company reflect the principal activities of the following entities. All intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated upon consolidation.

Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with U.S. GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Significant estimates required to be made by management, include, but are not limited to, the valuation of accounts and loans receivable, useful lives of property and equipment, the recoverability of long-lived assets, realization of deferred income tax assets, revenue recognition and provision necessary for contingent liabilities. Actual results could differ from these estimates.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
Cash includes cash on hand and demand deposits in accounts maintained with commercial banks. The Company considers all highly liquid investments with original maturities of three months or less when purchased to be cash equivalents. The Company maintained most of the bank accounts in the PRC. Cash balances in bank accounts in PRC are not insured by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation or other programs.
Accounts Receivable, net
Accounts receivable are recognized and carried at original invoiced amount less an estimated allowance for uncollectible amounts. The Company generally receives a cash payment before delivery of the services, but may extend unsecured credit to its customers in the ordinary course of business. The Company mitigates the associated risks by performing credit checks and actively pursuing past due accounts. An allowance for doubtful accounts is established and recorded based on management’s assessment of the credit history of the customers and current relationships with them. At December 31, 2017 and 2016, there was no allowance recorded as the Company considers all of the accounts receivable fully collectible.
Property, Plant and Equipment
Property, plant and equipment are recorded at cost. The straight-line depreciation method is used to compute depreciation over the estimated useful lives of the assets, as follows:
| Useful life | ||
| Electronic equipment | 3 years | |
| Office furniture | 5 years | |
| Transportation vehicles | 4 years | |
| Computer software | 5 years |
Expenditures for maintenance and repairs, which do not materially extend the useful lives of the assets, are charged to expense as incurred. Expenditures which substantially increase the useful lives of the related assets are capitalized. Expenditures for major renewals and betterments which substantially extend the useful life of assets are capitalized. The cost and related accumulated depreciation of assets retired or sold are removed from the respective accounts, and any gain or loss is recognized in the consolidated statements of operations and other comprehensive income (loss) in other income or expenses.
Impairment of Long-lived Assets
The Company reviews long-lived assets, including definitive-lived intangible assets, for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable. If the estimated cash flows from the use of the asset and its eventual disposition are below the asset’s carrying value, then the asset is deemed to be impaired and written down to its fair value. There were no events or changes in circumstances that triggered a review of impairments of long-lived assets as of December 31, 2017 and 2016.
Reclassification
Certain prior year amounts have been reclassified to conform to the current year presentation.
| F-7 |
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
The Company follows the provision of Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) 820, “Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures,” which defines fair value as the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. A three-level fair value hierarchy prioritizes the inputs used to measure fair value. The hierarchy requires entities to maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs. The three levels of inputs used to measure fair value are as follows:
Level 1- Observable inputs such as unadjusted quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities available at the measurement date.
Level 2- Observable inputs (other than Level 1 quoted prices) such as quoted prices active markets for similar assets or liabilities, quoted prices in markets that are not active for identical or similar as or liabilities, or other inputs that are observable or can be corroborated by observable market data.
Level 3- Inputs are unobservable inputs which reflect management’s assumptions based on the best available information.
The Company considers the recorded value of its financial assets and liabilities, which consist primarily of cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable, loans receivable, prepaid expenses and other current assets, short-term investment, deferred revenue, accrued and other liabilities, taxes payable and due to related party to approximate the fair value of the respective assets and liabilities at December 31, 2017 and 2016 based upon the short-term nature of the assets and liabilities.
Revenue recognition
The Company’s revenue is recognized when persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists, service has occurred and all obligations have been performed pursuant to the terms of the agreement, the sales price is fixed or determinable, and collectability is reasonably assured.
The Company currently generates its revenue from the following main sources:
● Revenue from membership fee
The Company develops and attracts corporate enterprises to become members and join in the Company’s service platform www.aeexotcmarkets.com. To become a member, customer needs to pay a one-time non-refundable registration fee first. The Company recognizes revenue from membership fee when it posts member’s information and profiles on its platform www.aeexotcmarkets.com, which enables the member’s corporate information and specific needs exposed to the public.
● Revenue from consulting services
The Company also provides various consulting services to its members, especially to those who have the intention to be publicly listed in the stock exchanges in the United States and other countries. The Company categorizes its consulting services into three Phases:
Phase I consulting services primarily include due diligence review, market research and feasibility study, business plan drafting, accounting record review, and business analysis and recommendations etc. Management estimates that Phase I normally takes around three months to complete based on its past experiences.
Phase II consulting services primarily include reorganization, pre-listing education and tutoring, talent search, legal and audit firm recommendation and coordination, VIE contracts and other public-listing related documents review, merger and acquisition planning, investor referral and pre-listing equity financing source identification and recommendation, independent directors and audit committee candidates recommendation etc. Management estimates that Phase II normally takes about eight months to complete based its past experiences.
Phase III consulting services primarily include shell company identification and recommendation for customers expecting to become publicly listed through reverse merger transaction; assistance in preparation of customers’ registration statement under IPO transactions or Form 8-K under reverse merger transactions; assistance in answering comments and questions received from regulatory agencies etc. Management believes it is very difficult to estimate the timing of this phase of service as the completion of Phase III services is not within the Company’s control.
| F-8 |
Each phase of consulting services are standalone and fees associated with each phase are clearly identified in service agreements. Revenue from providing Phase I and Phase II consulting services to customers is recognized ratably over the estimated completion period of each phase. Revenue from providing Phase III consulting services to customers is recognized upon completion of reverse merger transaction or IPO transaction, which is evidenced by filing of 8-K for reverse merger transaction or receipt of effective notice from regulatory agencies for IPO transaction. Revenue that has been billed and not yet recognized is reflected as deferred revenue on the balance sheet.
Depending on the complexity of the underlying service arrangement and related terms and conditions, significant judgments, assumptions and estimates may be required to determine when substantial delivery of contract elements has occurred, whether any significant ongoing obligations exist subsequent to contract execution, whether amounts due are collectible and the appropriate period or periods in which, or during which, the completion of the earnings process occurs. Depending on the magnitude of specific revenue arrangements, adjustment may be made to the judgments, assumptions and estimates regarding contracts executed in any specific period.
Income Tax
The Company accounts for income taxes under ASC 740. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the future tax consequences attributable to differences between the consolidated financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax bases. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized in income in the period including the enactment date. Valuation allowances are established, when necessary, to reduce deferred tax assets to the amount expected to be realized.
The provisions of ASC 740-10-25, “Accounting for Uncertainty in Income Taxes,” prescribe a more-likely-than-not threshold for consolidated financial statement recognition and measurement of a tax position taken (or expected to be taken) in a tax return. This interpretation also provides guidance on the recognition of income tax assets and liabilities, classification of current and deferred income tax assets and liabilities, accounting for interest and penalties associated with tax positions, and related disclosures. The Company does not believe that there was any uncertain tax position at December 31, 2017 and 2016.
To the extent applicable, the Company records interest and penalties as a general and administrative expense. The Company’s subsidiaries in China and Hong Kong are subject to the income tax laws of the PRC and Hong Kong. The statute of limitations for the Company’s U.S. federal income tax returns and certain state income tax returns remains open for tax years 2013 and after. As of December 31, 2017, the tax years ended December 31, 2015 through December 31, 2017 for the Company’s PRC subsidiary remain open for statutory examination by PRC tax authorities.
On December 22, 2017, the “Tax Cuts and Jobs Act” (“The Act”) was enacted. Under the provisions of The Act, the U.S. corporate tax rate decreased from 35% to 21%. Additionally, the Tax Act imposes a one-time transition tax on deemed repatriation of historical earnings of foreign subsidiaries, and future foreign earnings are subject to U.S. taxation. The change in rate has caused the Company to re-measure all U.S. deferred income tax assets and liabilities for temporary differences. Net operating loss (“NOL”) carryforwards are limited to 80% of taxable income and can be carried forward indefinitely.
Earnings (Loss) Per Share
Basic earnings (loss) per share are computed by dividing income (loss) available to ordinary shareholders of the Company by the weighted average ordinary shares outstanding during the period. Diluted earnings per share takes into account the potential dilution that could occur if securities or other contracts to issue ordinary shares were exercised and converted into ordinary shares. As of December 31, 2017 and 2016, there were no dilutive shares.
| F-9 |
Foreign Currency Translation
The accounts of the Company and its subsidiaries are measured using the currency of the primary economic environment in which the entity operates (the “functional currency”). The Company’s functional currency is the U.S. dollar (“USD”) while its subsidiary in Hong Kong reports its financial positions and results of operations in Hong Kong Dollar and the Company’s subsidiary in China reports its financial position sand results of operations in Renminbi (“RMB”). The accompanying consolidated financial statements are presented in United States Dollar (USD). The results of operations and the consolidated statements of cash flows denominated in foreign currency are translated at the average rate of exchange during the reporting period. Assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies at the balance sheet date are translated at the applicable rates of exchange in effect at that date. The equity denominated in the functional currency is translated at the historical rate of exchange at the time of capital contribution. Because cash flows are translated based on the average translation rate, amounts related to assets and liabilities reported on the consolidated statements of cash flows will not necessarily agree with changes in the corresponding balances on the consolidated balance sheets. Translation adjustments arising from the use of different exchange rates from period to period are included as a separate component of accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) included in consolidated statements of changes in equity. Gains and losses from foreign currency transactions are included in the results of operations.
The following table outlines the currency exchange rates that were used in creating the consolidated financial statements in this report:
| December 31, | ||||||||||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency | Balance Sheet | Profits/Loss | Balance Sheet | Profits/Loss | ||||||||||||
| RMB:1USD | 0.1530 | 0.1481 | 0.1442 | 0.1504 | ||||||||||||
| HKD:1USD | 0.1279 | 0.1283 | 0.1289 | 0.1288 | ||||||||||||
Risks and Uncertainty
The Company’s major operations are conducted in the PRC. Accordingly, the political, economic, and legal environments in the PRC, as well as the general state of the PRC’s economy may influence the Company’s business, financial condition, and results of operations.
The Company’s major operations in the PRC are subject to special considerations and significant risks not typically associated with companies in North America and Western Europe. These include risks associated with, among others, the political, economic, and legal environment. The Company’s results may be adversely affected by changes in governmental policies with respect to laws and regulations, anti-inflationary measures, and rates and methods of taxation, among other things. Although the Company has not experienced losses from these situations and believes that it is in compliance with existing laws and regulations including its organization and structure disclosed in Note 1, this may not be indicative of future results.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
In May 2014, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued ASU No. 2014-09, “Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606)” (“ASU 2014-09”). ASU 2014-09 requires an entity to recognize the amount of revenue to which it expects to be entitled for the transfer of promised goods or services to customers. ASU 2014-09 will replace most existing revenue recognition guidance in U.S. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles when it becomes effective and permits the use of either the retrospective or cumulative effect transition method. The guidance also requires additional disclosure about the nature, amount, timing and uncertainty of revenue and cash flows arising from customer contracts. The guidance in ASU 2014-09 will be effective for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2017 (including interim reporting periods within those periods), which means it will be effective for the Company’s fiscal year beginning January 1, 2018. In March 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-08, “Principal versus Agent Considerations (Reporting Revenue versus Net)” (“ASU 2016-08”), which clarifies the implementation guidance on principal versus agent considerations in the new revenue recognition standard. In April 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-10, “Identifying Performance Obligations and Licensing” (“ASU 2016-10”), which reduces the complexity when applying the guidance for identifying performance obligations and improves the operability and understandability of the license implementation guidance. In May 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-12 “Narrow-Scope Improvements and Practical Expedients” (“ASU 2016-12”), which amends the guidance on transition, collectability, noncash consideration and the presentation of sales and other similar taxes. In December 2016, the FASB further issued ASU 2016-20, “Technical Corrections and Improvements to Topic 606, Revenue from Contracts with Customers” (“ASU 2016-20”), which makes minor corrections or minor improvements to the Codification that are not expected to have a significant effect on current accounting practice or create a significant administrative cost to most entities. The amendments are intended to address implementation and provide additional practical expedients to reduce the cost and complexity of applying the new revenue standard. These amendments have the same effective date as the new revenue standard. The Company’s current revenue recognition policies are generally consistent with the new revenue recognition standards set forth in ASU 2014-09. Potential adjustments to input measures are not expected to be pervasive to the majority of the Company’s contracts.
| F-10 |
In January 2017, the FASB issued ASU No. 2017-01, “Business Combinations (Topic 805): Clarifying the Definition of a Business”. The amendments in this ASU clarify the definition of a business with the objective of adding guidance to assist entities with evaluating whether transactions should be accounted for as acquisitions (or disposals) of assets or businesses. Basically these amendments provide a screen to determine when a set is not a business. If the screen is not met, the amendments in this ASU first, require that to be considered a business, a set must include, at a minimum, an input and a substantive process that together significantly contribute to the ability to create output and second, remove the evaluation of whether a market participant could replace missing elements. These amendments take effect for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017 and interim periods within those periods. The adoption of this guidance will not have a material impact on its consolidated financial statements.
In February 2017, the FASB issued ASU No. 2017-05 (“ASU 2017-05”) to provide guidance for recognizing gains and losses from the transfer of nonfinancial assets and in-substance nonfinancial assets in contracts with non-customers, unless other specific guidance applies. The standard requires a company to derecognize nonfinancial assets once it transfers control of a distinct nonfinancial asset or distinct in substance nonfinancial asset. Additionally, when a company transfers its controlling interest in a nonfinancial asset, but retains a noncontrolling ownership interest, the company is required to measure any noncontrolling interest it receives or retains at fair value. The guidance requires companies to recognize a full gain or loss on the transaction. As a result of the new guidance, the guidance specific to real estate sales in ASC 360-20 will be eliminated. ASU 2017-05 is effective for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2017, including interim periods within that reporting period. The effective date of this guidance coincides with revenue recognition guidance. The adoption of this guidance will not have a material impact on its consolidated financial statements.
In September 2017, the FASB has issued ASU No. 2017-13, “Revenue Recognition (Topic 605), Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606), Leases (Topic 840), and Leases (Topic 842): Amendments to SEC Paragraphs Pursuant to the Staff Announcement at the July 20, 2017 EITF Meeting and Rescission of Prior SEC Staff Announcements and Observer Comments.” The amendments in ASU No. 2017-13 amends the early adoption date option for certain companies related to the adoption of ASU No. 2014-09 and ASU No. 2016-02. The effective date is the same as the effective date and transition requirements for the amendments for ASU 2014-09 and ASU 2016-02. The adoption of this guidance will not have a material impact on its consolidated financial statements.
In November 2017, the FASB issued ASU 2017-14, Income Statement-Reporting Comprehensive Income (Topic 220), Revenue Recognition (Topic 605), and Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606). This Accounting Standards Update supersedes various SEC paragraphs and amends an SEC paragraphs pursuant to the issuance of Staff Accounting Bulletin No. 116 and SEC Release No.33-10403. Management plans to adopt this ASU during the year ending December 2019. The Company does not believe the adoption of this ASU would have a material effect on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
In February 2018, the FASB has issued Accounting Standards Update (ASU) No. 2018-02, “Reclassification of Certain Tax Effects From Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income.” The ASU amends ASC 220, Income Statement — Reporting Comprehensive Income, to “allow a reclassification from accumulated other comprehensive income to retained earnings for stranded tax effects resulting from the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act.” In addition, under the ASU, an entity will be required to provide certain disclosures regarding stranded tax effects. The ASU is effective for all entities for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2018, and interim periods within those fiscal years. The adoption of this guidance will not have a material impact on its consolidated financial statements.
In March 2018, the FASB issued ASU 2018-05 — Income Taxes (Topic 740): Amendments to SEC Paragraphs Pursuant to SEC Staff Accounting Bulletin No. 118 (“ASU 2018-05”), which amends the FASB Accounting Standards Codification and XBRL Taxonomy based on the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (the “Act”) that was signed into law on December 22, 2017 and Staff Accounting Bulletin No. 118 (“SAB 118”) that was released by the Securities and Exchange Commission. The Act changes numerous provisions that impact U.S. corporate tax rates, business-related exclusions, and deductions and credits and may additionally have international tax consequences for many companies that operate internationally. The Company has evaluated the impact of the Act as well as the guidance of SAB 118 and incorporated the changes into the determination of a reasonable estimate of its deferred tax liability and appropriate disclosures in the notes to its consolidated financial statements (See Note 9). The Company will continue to evaluate the impact this tax reform legislation may have on its results of operations, financial position, cash flows and related disclosures.
| F-11 |
NOTE 3 - ACCOUNTS RECEIVABLE, NET
The Company’s net accounts receivable is as follows:
| December 31, 2017 | December 31, 2016 | |||||||
| Accounts receivable | $ | 994,500 | $ | - | ||||
| Less: allowances for doubtful accounts | - | - | ||||||
| Accounts receivables, net | $ | 994,500 | $ | - | ||||
Accounts receivable of $994,500 resulted from balance due from providing public listing related consulting services to customer Guangdong Donggao High-tech Materials Co,, Ltd., who successfully filed the Form 8-K with SEC on November 27, 2017 to consummate the reverse merger transaction. This is the first customer that the Company completed the comprehensive consulting services and accordingly the Company extended the credit term to this customer for additional six months. The Company subsequently collected approximately $236,593 (RMB 1.5 million) of this outstanding account receivable from this customer and expects to fully collect the remaining balance before June 30, 2018.
NOTE 4 - LOANS RECEIVABLE
From September to December 2017, the Company advanced a total of $2,295,000 (RMB 15 million) one year short-term loans to a former customer, Shenzhen Shangyuan Electronic Business Development Co., Ltd. (“Shangyuan”) as working capital. Among the RMB 15 million loan, RMB 5 million is non-interest bearing and RMB 10 million are interest-bearing loans with interest rate of 5% per annum. Interest income of $6,350 was accrued for the year ended December 31, 2017. The Company subsequently collected RMB 5 million (approximately $781,250) non-interest bearing portion of the loan from Shangyuan in the first quarter of 2018.
NOTE 5 - SHORT-TERM INVESTMENT
On November 21, 2017, the Company entered into an investment agreement with China Construction Bank (“the Bank”). The agreement allows the Company to invest RMB 100 million ($15.3 million) with the Bank for a six-month term maturing on May 20, 2018. The Bank invests the Company’s fund in certain financial instruments including money market funds, bonds or mutual funds. The rates of return on these instruments was guaranteed as 4.8% per annum. The Company’s investment is not subject to market fluctuation and therefore, the Company did not experience gain or loss on its investment. However, the Company’s funds deposited with the Bank is not insured. Interest income of $78,987 was accrued and reflected in the consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive income (loss) for the years ended December 31, 2017.
NOTE 6. PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT, NET
As of December 31, 2017 and 2016, property and equipment was as follows:
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Office equipment | $ | 33,114 | $ | 5,379 | ||||
| Furniture | 47,226 | 14,488 | ||||||
| Computer software | 8,369 | 7,023 | ||||||
| Automobiles | 930 | 27,036 | ||||||
| Total | 89,639 | 53,926 | ||||||
| Less: accumulated depreciation | (13,599 | ) | (13,696 | ) | ||||
| Property and equipment, net | $ | 76,040 | $ | 40,230 | ||||
Depreciation expense for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016 was $9,313 and $11,858, respectively.
| F-12 |
NOTE 7 – DEFERRED REVENUE
Deferred revenue consists of amounts received from customers for membership and public listing related consulting services not yet completed as of the balance sheets date. The details of customer deposits are as follows:
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Customer deposit for membership | $ | 53,077 | $ | - | ||||
| Customer deposits for consulting services | 2,262,046 | - | ||||||
| Total deferred revenue | $ | 2,315,123 | $ | - | ||||
NOTE 8 - RELATED PARTY TRANSACTION
As of December 31, 2017 and 2016, the balances due to a major stockholder are comprised of non-interest bearing advances used for working capital.
NOTE 9 – TAXES
The Company is subject to income taxes on an entity basis on income arising in or derived from the tax jurisdiction in which each entity is domiciled.
AEEX is incorporated in the United States and has incurred net operating loss for income tax purposes for 2017 and 2016. The Company has loss carry forwards of approximately $166,000 for U.S. income tax purposes available for offsetting against future taxable U.S. income, expiring in 2037. Management believes that the realization of the benefits from these losses is uncertain due to its history of continuing losses in the United States. Accordingly, a full deferred tax asset valuation allowance has been provided and no deferred tax asset benefit has been recorded. The valuation allowance as of December 31, 2017 and 2016 was approximately $45,000 and $29,000, respectively. The changes in the valuation allowance for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016 was approximately $16,300 and $16,000, respectively.
AEEGCL was incorporated under the International Companies Act 1988 of Samoa as a non-resident company. Under current laws of Samoa, income earned is not subject to income tax.
AEEX HK is subject to Hong Kong profits tax at a rate of 16.5%, and did not have any assessable profits arising in or derived from Hong Kong for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2017 and 2016, and accordingly no provision for Hong Kong profits tax made in these periods.
AACCL is incorporated in the PRC and is subject to PRC income tax, which is computed according to the relevant laws and regulations in the PRC. The applicable tax rate is 25% for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016. The Company recorded $93,349 and $Nil deferred income tax assets as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively.
On December 22, 2017, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 (the “Act”) was signed into law making significant changes to the Internal Revenue Code. Changes include, but are not limited to, a U.S. corporate tax rate decrease from 35% to 21% effective for tax years beginning after December 31, 2017, the transition of U.S international taxation from a worldwide tax system to a territorial system, and a one-time transition tax on the mandatory deemed repatriation of cumulative foreign earnings as of December 31, 2017.
On December 22, 2017, Staff Accounting Bulletin No. 118 (“SAB 118”) was issued to address the application of US GAAP in situations when a registrant does not have the necessary information available, prepared, or analyzed (including computations) in reasonable detail to complete the accounting for certain income tax effects of the Act. In accordance with SAB 118, the Company has recorded a provisional amount for its one-time transition tax for all of its foreign subsidiaries, resulting in an increase in income tax expense of $82,127 for the year ended December 31, 2017. The one-time transition tax was calculated using the Company’s total post-1986 overseas net earnings and profits which amounted to approximately $0.92 million. The one-time transition tax is taxed at the rate of 15.5% for the Company’s cash and cash equivalents and 8% for the other assets to be paid over 8 years. Additional work is necessary to conduct a more detailed analysis of the Act as well as potential correlative adjustments. Any subsequent adjustment to these amounts will be recorded to current tax expense in fiscal 2018 when the analysis is complete.
| F-13 |
The Company’s income tax expense (benefit) for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016 are as follows:
| For
the years ended December 31, | ||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Current income tax (benefit) | ||||||||
| USA | $ | 82,127 | $ | - | ||||
| Samoa | - | - | ||||||
| Hong Kong | - | - | ||||||
| China | 368,243 | - | ||||||
| 450,370 | - | |||||||
| Deferred income tax (benefit) | ||||||||
| China | (90,360 | ) | - | |||||
| (90,360 | ) | |||||||
| Total income tax expense | $ | 360,010 | $ | - | ||||
The Company’s deferred tax assets are comprised of the following:
| For
the years ended December 31, | ||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Net operating loss | 148,074 | 119,993 | ||||||
| Total deferred tax assets | 148,074 | 119,993 | ||||||
| Valuation allowance | (54,725 | ) | (119,993 | ) | ||||
| Deferred tax assets, long-term | $ | 93,349 | $ | - | ||||
The Company’s taxes payable consists of the following:
| December 31, 2017 | December 31, 2016 | |||||||
| VAT tax payable | $ | 14,470 | $ | 839 | ||||
| Corporate income tax payable | 455,017 | - | ||||||
| Others | 2,291 | 266 | ||||||
| Total tax payable | 471,778 | 1,105 | ||||||
| Less: noncurrent portion | (75,557 | ) | - | |||||
| Total tax payable- current portion | $ | 396,221 | $ | 1,105 | ||||
NOTE 10 - EQUITY
Preferred Stock
The Company has authorized 1,000,000 preferred shares with par value of $0.001 per share. None issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2017 and 2016. The following mentioned reverse stock split has no impact on the Company’s authorized preferred stock.
| F-14 |
Common Stock
On November 30, 2015, the Company executed a Sale and Purchase Agreement (the “Purchase Agreement”) to acquire 100% of the shares and assets of AEEGCL (the “Acquisition”). Pursuant to the Purchase Agreement, the Company issued one billion (1,000,000,000) shares of common stock to the former owners of AEEGCL. The Acquisition was consummated on April 12, 2016. As a result, AEEGCL became a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Company and the business of AEEGCL became current business of the Company. The Company had a total of 146,000,000 shares of common stock outstanding immediately prior to the closing of the Acquisition. After the closing of the Acquisition, the Company had a total of 1,146,000,000 shares of common stock outstanding.
On July 21, 2017, the Company’s Board of Directors approved a reverse stock split of the Company’s common stock at a ratio of 1-for-10. Total 1,031,399,984 shares of the Company’s common stock has been cancelled accordingly. As a result of this stock reverse split, the Company’s equity statement has been retroactively restated so that the ending outstanding share balance as of the stock split date is equal to the number of post stock shares.
On November 21, 2017, the Company entered into a Subscription Agreement with an investor, pursuant to which the investor purchased 4.3 million shares of the Company’s common stock at $3.5 per share for an aggregate purchase price of $15,050,000.
Statutory reserve
In accordance with the Regulations on Enterprises with Foreign Investment of China and their articles of association, a foreign invested enterprise established in the PRC is required to provide certain statutory reserves, namely general reserve fund, the enterprise expansion fund and staff welfare and bonus fund which are appropriated from net profit as reported in the enterprise’s PRC statutory accounts. A wholly-owned foreign invested enterprise is required to allocate at least 10% of its annual after-tax profit to the general reserve until such reserve has reached 50% of its respective registered capital based on the enterprise’s PRC statutory accounts. Appropriations to the enterprise expansion fund and staff welfare and bonus fund are at the discretion of the board of directors for all foreign invested enterprises. These reserves can only be used for specific purposes and are not distributable as cash dividends. The Company’s subsidiary AACCL was established as a wholly-owned foreign invested enterprise and therefore is subject to the above mandated restrictions on distributable profits.
Additionally, in accordance with the Company Law of the PRC, a domestic enterprise is required to provide statutory common reserve at least 10% of its annual after-tax profit until such reserve has reached 50% of its respective registered capital based on the enterprise’s PRC statutory accounts. A domestic enterprise is also required to provide for discretionary surplus reserve, at the discretion of the board of directors, from the profits determined in accordance with the enterprise’s PRC statutory accounts. These reserves can only be used for specific purposes and are not distributable as cash dividends.
As a result of these PRC laws and regulations that require annual appropriations of 10% of after-tax income to be set aside prior to payment of dividends as general reserve fund, the Company’s PRC subsidiary is restricted in its ability to transfer a portion of their net assets to the Company. The restricted amounts include paid-in capital and statutory reserve funds of the Company’s PRC subsidiary as determined pursuant to PRC generally accepted accounting principles, totaling $63,950 and $Nil at December 31, 2017 and 2016,respectively.
NOTE 11 – CONCENTRATIONS AND RISKS
The Company maintains certain bank accounts in the PRC and Hong Kong, which are not insured by Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (“FDIC”) insurance or other insurance. As of December 31, 2017 and 2016, cash balances of $512,324 and $55,059, respectively, were maintained at financial institutions in the PRC and Hong Kong, which were not insured by any of the authorities.
For the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016, substantial of the Company’s assets were located in the PRC and substantial of the Company’s revenues were derived from its subsidiaries located in the PRC.
For the year ended December 31, 2017, three customers accounted for approximately 10.5%, 18.4% and 62.1% of the Company’s total revenue. For the year ended December 31, 2016, one customer accounted for approximately 88.8% of the Company’s total revenue.
For the year ended December 31, 2017, one customer accounted for 100% of the Company’s outstanding accounts receivable.
NOTE 12 – COMMITMENTS
Lease Obligation
The Company leases office spaces under operating leases. Operating lease expense amounted to $445,117 and $209,479 for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively.
| F-15 |
Future minimum lease payments under non-cancelable operating leases are as follows as of December 31, 2017:
| Year ending December 31, | ||||
| 2018 | $ | 563,943 | ||
| 2019 | 340,147 | |||
| Thereafter | - | |||
| Total | $ | 904,090 | ||
Up-listing Commitment
November 21, 2017, the Company entered into a Subscription Agreement with an investor, pursuant to which the investor purchased 4.3 million shares of the Company’s common stock at $3.5 per share for an aggregate purchase price of $15,050,000(see Note 10).
Pursuant to the Subscription Agreement, the Company will apply to be listed on the NASDAQ Capital Market or similar national securities exchange as is reasonably acceptable to the Purchaser, so that the Company’s Common Stock will commence trading on one of the National Exchanges (the “Uplisting”) no later than December 31, 2018 (the “Uplisting Deadline”). If the Company does not complete Uplisting on or before the Uplisting Deadline, the Investor, within 30 days following the Uplisting Deadline, has the right to request the Company to buy back any number of the Shares, at the same price of the Purchase Price Per Share, subject to the terms and conditions of the Subscription Agreement.
| F-16 |
| ITEM 9 | CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE. |
| Changes in Registrant’s Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm |
The Company decided to change its independent registered public accounting firm for the annual report of the fiscal years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016 and the remainder of the fiscal year ending December 31, 2018. On February 8, 2018, the Board approved the appointment of Friedman as the Company’s independent registered public accounting firm for the Company’s fiscal years ended December 31, 2017 and ending December 31, 2018 and the dismissal of Yongtuo from that role, each effective as of February 8, 2018.
| (a) | Dismissal of independent registered public accounting firm |
The Board approved the dismissal of Yongtuo as the Company’s independent registered public accounting firm, effective as of February 8, 2018.
Yongtuo’s audit reports on the Company’s consolidated financial statements as of and for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2016, as amended on November 17, 2017 did not contain an adverse opinion or a disclaimer of opinion and were not qualified or modified as to uncertainty, audit scope or accounting principles.
During the fiscal years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016, and the subsequent interim period through February 8, 2018, there were (i) no “disagreements” (as that term is described in Item 304(a)(1)(iv) of Regulation S-K and the related instructions) between the Company and Yongtuo on any matter of accounting principles or practices, financial statement disclosure, or auditing scope or procedure, which, if not resolved to Yongtuo’s satisfaction, would have caused Yongtuo to make reference thereto in their reports, and (ii) no “reportable events” (as that term is described in Item 304(a)(1)(v) of Regulation S-K).
The Company provided Yongtuo with a copy of the disclosures made within this Current Report on Form 8-K and requested that Yongtuo furnish a letter addressed to the Securities and Exchange Commission stating whether or not it agrees with such disclosures. A copy of Yongtuo letter dated February 12, 2018 is filed as Exhibit 16.1 hereto.
| (b) | Appointment of new independent registered public accounting firm |
During the fiscal years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016, and the subsequent interim period through February 8, 2018, neither the Company nor anyone on its behalf consulted with Friedman regarding (i) the application of accounting principles to a specified transaction, (ii) the type of audit opinion that might be rendered on the Company’s financial statements by Friedman, in either case where written or oral advice provided by Friedman would be an important factor considered by the Company in reaching a decision as to any accounting, auditing or financial reporting issues or (iii) any other matter that was the subject of a disagreement between us and our former auditor, Yongtuo or was a reportable event (as described in Items 304(a)(1)(iv) or Item 304(a)(1)(v) of Regulation S-K, respectively).
| 22 |
| ITEM 9A | CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES. |
| (a) | Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures |
As required by Rule 13a-15 under the Exchange Act, our management has carried out an evaluation, with the participation and under the supervision of our chief executive officer and chief financial officer, of the effectiveness of the design and operation of our disclosure controls and procedures as of December 31, 2017. Disclosure controls and procedures refer to controls and other procedures designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed in the reports we file or submit under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the rules and forms of the SEC and that such information is accumulated and communicated to our management, including our chief executive officer and chief financial officer, as appropriate, to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure. In designing and evaluating our disclosure controls and procedures, management recognizes that any controls and procedures, no matter how well designed and operated, can provide only reasonable assurance of achieving the desired control objectives, and management is required to apply its judgment in evaluating and implementing possible controls and procedures.
Management conducted its evaluation of disclosure controls and procedures under the supervision of our chief executive officer and our chief financial officer. Based upon, and as of the date of this evaluation, our Chief Executive Officer and Interim Chief Financial Officer concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures were ineffective as of December 31, 2017 because of the material weaknesses set forth below that our management identified in our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017.
| (b) | Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting |
Management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting for the Company. Internal control over financial reporting refers to the process designed by, or under the supervision of, our chief executive officer and chief financial officer, and effected by our board of directors, management and other personnel, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of our financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with U.S. GAAP, and includes those policies and procedures that:
| ● | pertain to the maintenance of records that in reasonable detail accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of our assets; |
| ● | provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with U.S. GAAP, and that our receipts and expenditures are being made only in accordance with the authorization of our management and directors; and |
| ● | provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of our assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements. |
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Management assessed the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017. In making this assessment, management used the framework set forth in the report entitled Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission, or COSO. The COSO framework summarizes each of the components of a company’s internal control system, including (i) the control environment, (ii) risk assessment, (iii) control activities, (iv) information and communication, and (v) monitoring.
Based on this evaluation and as a result of the material weakness discussed below, our chief executive officer and interim chief financial officer concluded that the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures as of December 31, 2017 were not effective because of the following material weakness in our internal control over financial reporting has been identified:
| 23 |
| 1. | The Company has insufficient accounting and financial reporting policies and procedures, which lead to inadequate financial statement closing process. | |
| 2. | Material audit adjustments were proposed by the auditors and recorded by the Company for fiscal years 2017 and 2016; | |
| 3. | Lack of full-time qualified U.S. GAAP personnel in the accounting department with sufficient knowledge of US GAAP and SEC reporting standards; |
Management is committed to improving its internal controls and will (1) plan to use third party specialists to address shortfalls in staffing and to assist us with accounting and finance responsibilities, (2) increase the frequency of independent reconciliations of significant accounts which will mitigate the lack of segregation of duties until there are sufficient personnel and (3) prepare and implement sufficient written policies and checklists for financial reporting and closing processes.
We intend to complete the remediation of the material weaknesses discussed above as soon as practicable but we can give no assurance that we will be able to do so. Designing and implementing an effective disclosure controls and procedures is a continuous effort that requires us to anticipate and react to changes in our business and the economic and regulatory environments and to devote significant resources to maintain a financial reporting system that adequately satisfies our reporting obligations. The remedial measures that we have taken and intend to take may not fully address the material weakness that we have identified, and material weaknesses in our disclosure controls and procedures may be identified in the future. Should we discover such conditions, we intend to remediate them as soon as practicable. We are committed to taking appropriate steps for remediation, as needed.
| 24 |
( c ) Changes in internal control over financial reporting
The management is committed to improving the internal controls over financial reporting and will undertake the consistent improvements or enhancements on an ongoing basis. Except for the matters described above, there were no changes in our internal controls over financial reporting during our most recent fiscal quarter that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
| ITEM 9B. | OTHER INFORMATION. |
None.
| ITEM 10. | DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE. |
Directors and Executive Officers
The following sets forth the name and position of each of our current executive officers and directors.
| NAME | AGE | POSITION | ||
| Xiangyu Wang | 45 | Chairman of the Board, President and Chief Executive Officer | ||
| Zaixian Yu | 37 | Director and Secretary | ||
| Yau Chit Man Samuel | 57 | Director and Chief Financial Officer |
Mr. Xiangyu Wang has served as the Chairman of Board, President and Chief Executive Officer since September 8, 2017 and has served as the vice president of the Company since February 2017. From October 2015 to February 2017, he served as the general manager and founding partner of Shenzhen Qianhai Ruixin Capital Management Co., Limited. From April 2015 to October 2015, he served as the vice president of Moxian, Inc., a NASDAQ listed company engaging in the business of providing social marketing and promotion platforms that are designed to help merchants to advertise through social media to accelerate business growth. From June 2013 to February 2015, he served as the founding partner and chief consultant in Shanghai Chenshi Management Consulting Co., Ltd. From May 2009 to May 2013, he served as the executive vice president in Shanghai Shipeng Laboratory (Science and Technology) Group. Mr. Wang obtained a bachelor’s degree in science in Business Administration and Information Sciences and a master’s degree in Computer Science from Northwestern Polytechnic University in the U.S in 2000 and 2001, respectively. He obtained a doctor’s degree in Business Administration from Shanghai Jiaotong University in 2010.
Zaixian Yu has served as our director since December 26, 2016 and our Secretary since July 1, 2016. Ms. Yu served as a training manager assistant and training manager at ZTE Corporation, one of global IT Top 100 Enterprises and Top 10 Public Companies in China, from 2003 to 2006. From 2007 to 2011, she was an international sales manager in charge of sales, order follow-up and customer relationship at Shenzhen Sunidea Technology Co., Ltd. Prior to joining the Company as the secretary of the Board in 2015, Ms. Yu served as the vice president for customer relationship and market development at Shangyuan Electronic Commence Co., Ltd. from 2012 to 2014. Ms. Yu holds a Bachelor’s degree in English literature from Xi’an International Studies University.
Yau Chit Man Samuel has served as our director and Chief Financial Officer since October 30, 2017. Mr. Yau had served as the financial controller of Hontrade Engineering Limited from May 2010 to March 2017. Mr. Yau is a licensed CPA in Hong Kong and the United States. Mr. Yau obtained a bachelor’s degree in Business Administration and Accounting & Management Information Systems and a master’s degree in Accounting, both from University of Hawaii at Manoa in 1985 and 1987, respectively.
Directors are elected until their successors are duly elected and qualified.
Family Relationships
No family relationships exist among our directors, executive officers, or persons nominated or chosen by us to become directors or executive officers.
| 25 |
All directors hold office until the next annual stockholders’ meeting or until their death, resignation, retirement, removal, disqualification, or until their successors have been elected and are qualified. Our officers serve at the will of the Board of Directors.
Involvement in Certain Legal Proceedings
To the best of our knowledge, none of our directors or executive officers has, during the past ten years:
| ● | been convicted in a criminal proceeding or been subject to a pending criminal proceeding (excluding traffic violations and other minor offences); | |
| ● | had any bankruptcy petition filed by or against the business or property of the person, or of any partnership, corporation or business association of which he was a general partner or executive officer, either at the time of the bankruptcy filing or within two years prior to that time; | |
| ● | been subject to any order, judgment, or decree, not subsequently reversed, suspended or vacated, of any court of competent jurisdiction or federal or state authority, permanently or temporarily enjoining, barring, suspending or otherwise limiting, his involvement in any type of business, securities, futures, commodities, investment, banking, savings and loan, or insurance activities, or to be associated with persons engaged in any such activity; | |
| ● | been found by a court of competent jurisdiction in a civil action or by the Securities and Exchange Commission or the Commodity Futures Trading Commission to have violated a federal or state securities or commodities law, and the judgment has not been reversed, suspended, or vacated; | |
| ● | been the subject of, or a party to, any federal or state judicial or administrative order, judgment, decree, or finding, not subsequently reversed, suspended or vacated (not including any settlement of a civil proceeding among private litigants), relating to an alleged violation of any federal or state securities or commodities law or regulation, any law or regulation respecting financial institutions or insurance companies including, but not limited to, a temporary or permanent injunction, order of disgorgement or restitution, civil money penalty or temporary or permanent cease-and-desist order, or removal or prohibition order, or any law or regulation prohibiting mail or wire fraud or fraud in connection with any business entity; or | |
| ● | been the subject of, or a party to, any sanction or order, not subsequently reversed, suspended or vacated, of any self- regulatory organization (as defined in Section 3(a)(26) of the Exchange Act (15 U.S.C. 78c(a)(26))), any registered entity (as defined in Section 1(a)(29) of the Commodity Exchange Act (7 U.S.C. 1(a)(29))), or any equivalent exchange, association, entity or organization that has disciplinary authority over its members or persons associated with a member. |
Board Composition
The board of directors is currently composed of three members, Mr. Xiangyu Wang, Mr. Yau Chit Man Samuel and Ms. Zaixian Yu. All board action requires the approval of a majority of the directors in attendance at a meeting at which a quorum is present.
We currently do not have standing audit, nominating or compensation committees. Our entire board of directors handles the functions that would otherwise be handled by each of the committees. We intend, however, to establish an audit committee, a nominating committee and a compensation committee of the board of directors as soon as practicable. We envision that the audit committee will be primarily responsible for reviewing the services performed by our independent auditors, evaluating our accounting policies and our system of internal controls. The nominating committee would be primarily responsible for nominating directors and setting policies and procedures for the nomination of directors. The nominating committee would also be responsible for overseeing the creation and implementation of our corporate governance policies and procedures. The compensation committee will be primarily responsible for reviewing and approving our salary and benefit policies (including stock options), including compensation of executive officers.
None of our directors is an audit committee financial expert. Upon the establishment of an audit committee, the board will determine whether any of the directors qualify as an audit committee financial expert.
| 26 |
Code of Business Ethics and Conduct
We have adopted a Code of Business Conduct and Ethics relating to the conduct of our business by our employees, officers and directors. We intend to maintain the highest standards of ethical business practices and compliance with all laws and regulations applicable to our business, including those relating to doing business outside the United States. During the fiscal year ended December 31, 2017, there were no amendments to or waivers of our Code of Business Ethics and Conduct. If we effect an amendment to, or waiver from, a provision of our Code of Business Ethics and Conduct, we intend to satisfy our disclosure requirements by posting a description of such amendment or waiver via a current report on Form 8-K.
Our Code of Business Conduct and Ethics has been filed as Exhibit 14.2 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K for fiscal year ended September 30, 2015. We will provide a copy of the Code of Business Conduct and Ethics to any person without charge, upon request. Requests can be sent to: Asia Equity Exchange Group, Inc., Suite 2501A, 25/F, Skyline Tower, 39 Wang Kwong Road, Kowloon Bay, Hong Kong.
Section 16(A) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance
Not applicable.
| ITEM 11. | EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION. |
Summary Compensation Table
The following table sets forth information concerning all cash and non-cash compensation awarded to, earned by or paid to the named person for services rendered in all capacities during the fiscal years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016. No other executive officer received total annual salary and bonus compensation in excess of $100,000.
| Stock | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Awards | Option | |||||||||||||||||||
| Name and Principal Position | Year | Salary ($)(1) | ($) | Awards ($) | Total ($) | |||||||||||||||
| Xiangyu Wang, President, Chief Executive Officer (2) | 2017 | 28,531 | - | - | 28,531 | |||||||||||||||
| 2016 | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||||||||
| Jun Liu, former President and Chief Executive Officer (2) | 2017 | 19,994 | - | - | 19,994 | |||||||||||||||
| 2016 | 9,042 | (3) | - | - | 9,042 | |||||||||||||||
(1) The amounts reported in this table have been converted from RMB to U.S. dollars based on the average conversion rate between the U.S. dollar and RMB for the applicable fiscal year, or RMB 1 to $0.1481 (fiscal year 2017 exchange rate), RMB 1 to $0.1504 (2016 exchange rate).
(2) Mr. Wang was appointed as President and Chief Executive Officer on September 8, 2017 upon Mr. Liu’s resignation on the same date. Mr. Wang received $28,531 for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2017.
(3) Mr. Liu received $19,994 for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2017 compared with $9,042.
Summary of Employment Agreements
Asian Equity Exchange Group Co., Ltd. and Jun Liu entered into a three year employment agreement effective August 1, 2017. Under the agreement Mr. Liu is entitled to receive an annual salary of RMB240, 000 or $35,544 (fiscal year 2017 exchange rate).
| 27 |
Outstanding Equity Awards at Fiscal Year-End 2017
There was no unexercised option, stock that has not vested or equity incentive plan award for any named executive officer as of December 31, 2017.
Compensation of Directors
There have been no fees earned or paid in cash for services to our directors. No stock or stock options or other equity incentives were awarded to our directors for their services as directors during the fiscal year ended December 31, 2017. In the future, we may adopt a policy of paying independent directors a fee for their attendance at board and committee meetings. However, we do reimburse each director for reasonable travel expenses related to such director’s attendance at board of directors and committee meetings.
| ITEM 12. | SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS. |
Securities Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management
The following table sets forth information known to us with respect to the beneficial ownership of our Common Stock as of the close of business on March [ ], 2018 (the “Reference Date”) for: (i) each person known by us to beneficially own more than 5% of our voting securities, (ii) each named executive officer, (iii) each of our directors and nominees, and (iv) all of our executive officers and directors as a group:
| Names of Management and Names | Amount and Nature of | |||||||
| of Certain Beneficial Owners (1) | Beneficial Ownership (1) | |||||||
| Number (2) | Percent (3) | |||||||
| Jun Liu Hao, Rong Chao Da Xia, Block B Room 609 Bao’an Zhong Xin Qu Shenzhen City 2021-1 China, 518101 | 4,466,000 | 3.76 | % | |||||
| Xiang yu Wang, Director and CEO | - | * | ||||||
| Yau Chit Man Samuel, Director and CFO
| - | * | ||||||
Zaixian Yu, Director and Secretary Room 402, 7th Building, Yu Kang Hua Yuan, 14 XueFu Road, NanShan District, Shenzhen, Guangdong, China, 518000 | - | * | ||||||
| All executive officers and directors as a group (4 persons) | 4,446,000 | 3.76 | % | |||||
| 5% Security Holders | ||||||||
| Blue Tech Holding Limited
(4) Room 1504, No.11, Sheng Shi Hua Cheng, Yinzhou District, Ningbo Zhejiang, China | 50,000,000 | 42.05 | % | |||||
Great State Investments Limited(5) Portcullis Chambers P.O.Box 1225 Apia, Samoa | 20,000,000 | 16.82 | % | |||||
| Qi Jian Unit B, 5/F, CKK Commercial Centre 289 Hennessy Road Wanchai, Hong Kong | 6,000,000 | 5.05 | % | |||||
| 28 |
| * | Denotes less than 1% of the outstanding shares of Common Stock. |
| (1) | The number of shares beneficially owned is determined under Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) rules, and the information is not necessarily indicative of beneficial ownership for any other purpose. Under those rules, beneficial ownership includes any shares as to which the individual has sole or shared voting power or investment power, and also any shares which the individual has the right to acquire within 60 days of the Reference Date, through the exercise or conversion of any stock option, convertible security, warrant or other right (a “Presently Exercisable” security). Including those shares in the table does not, however, constitute an admission that the named stockholder is a direct or indirect beneficial owner of those shares. |
| (2) | Unless otherwise indicated, each person or entity named in the table has sole voting power and investment power (or shares that power with that person’s spouse) with respect to all shares of Common Stock listed as owned by that person or entity. |
| (3) | A total of 148 shares of Common Stock are considered to be outstanding on March 27, 2018. For each beneficial owner above, any Presently Exercisable securities of such beneficial owner have been included in the denominator, pursuant to Rule 13d-3(d)(1) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, or the Exchange Act. |
| (4) | Ma Ning has controlling interests and exercises voting and investment power over the shares owned by Blue Tech Holding Limited. Liu Jun is the beneficial owner of Blue Tech Holding Limited in accordance with a declaration of trust dated November 10, 2015 entered into between Ma Ning and Liu Jun. |
| (5) | Liu Haiyun has controlling interests and exercises voting and investment power over the shares owned by Great State Investments Limited. |
Changes in Control
There are no arrangements known to us, including any pledge by any person of our securities, the operation of which may at a subsequent date result in a change in control of the Company.
Securities Authorized for Issuance Under Equity Compensation Plans
None.
| ITEM 13. | CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE. |
Transactions with Related Persons
Mr. Jun Liu is the founder, former Chief Executive Officer (“CEO”) and current major shareholder of the Company. Mr. Liu periodically provides non-interest bearing working capital loan to support the Company’s operations when needed. As of December 31, 2017 and 2016, the balances due to Mr. Liu amounted to $583,787 and $423,570, respectively.
Promoters and Certain Control Persons
We did not have any promoters at any time during the past five fiscal years.
Director Independence
Our Board of Directors has determined that it does not have a member that is “independent” as the term is used in Item 7(d) (3) (iv) of Schedule 14A under the Exchange Act.
| 29 |
| ITEM 14. | PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING FEES AND SERVICES. |
Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm’s Fees and Services
Changes in Registrant’s Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
The Company decided to change its independent registered public accounting firm for the annual report of the fiscal years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016 and the remainder of the fiscal year ending December 31, 2018. On February 8, 2018, the Board of Director of the Company (the “Board”) approved the appointment of Friedman LLP (“Friedman”) as the Company’s independent registered public accounting firm and the dismissal of Yongtuo from that role, effective as of February 8, 2018.
On March 24, 2017, the Company dismissed Centurion ZD CPA Limited and engaged Beijing Yongtuo CPAs (Special general partner) (Shenzhen Branch) (“BY”) as the independent registered public accounting firm of the Company with the approval of its Board of Directors, effective immediately.
The aggregate audit fee and other fees paid and payable to Friedman, BY and Centurion ZD CPA for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016 are as follows:
| Fiscal Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Audit Fees (1) | $ | 198,645 | $ | 3,225 | ||||
| Audit Related Fees (2) | - | 4,495 | ||||||
| Tax Fees (3) | 500 | 900 | ||||||
| All Other Fees (4) | - | 108 | ||||||
| Total Fees | $ | 199,145 | $ | 8,728 | ||||
| (1) | Audit fees consist of fees incurred for professional services rendered for the audit of our financial statements, for reviews of our interim financial statements included in our quarterly reports on Form 10-Q and for services that are normally provided in connection with statutory or regulatory filings or engagements. |
| (2) | Audit-related fees consist of fees billed for professional services that are reasonably related to the performance of the audit or review of our financial statements, but are not reported under “Audit fees.” |
| (3) | Tax fees consist of fees billed for professional services relating to tax compliance, tax planning, and tax advice. |
| (4) | All other fees consist of fees billed for all other services. |
Pre-Approval Policies and Procedures
All auditing services and permitted non-audit services (including the fees and terms thereof) to be performed for the Company by our independent auditor must be approved by the Board of Directors in advance, except non-audit services (other than review and attestation services) if such services fall within exceptions established by the SEC. The Board of Directors will pre-approve any permissible non-audit services to be provided by the Company’s independent auditors on behalf of the Company that do not fall within any exception to the pre-approval requirements established by the SEC. The Board of Directors may delegate to one or more members the authority to pre-approve permissible non-audit services, but any such delegate or delegates must present their pre-approval decisions to the Board of Directors at its next meeting. All of our accountants’ services described above were pre-approved by the Board of Directors or by one or more members under the delegate authority described above.
| 30 |
| ITEM 15. | EXHIBITS, FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES. |
Financial Statements and Schedules
The financial statements are set forth under Item 8 of this annual report on Form 10-K. Financial statement schedules have been omitted since they are either not required, not applicable, or the information is otherwise included.
Exhibit List
The list of exhibits in the Exhibit Index to this Report is incorporated herein by reference.
EXHIBIT INDEX
* Filed herewith
| 31 |
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
Date: April 13, 2018
| ASIA EQUITY EXCHANGE GROUP, INC. | ||
| By: | /s/ Xiangyu Wang | |
| Xiangyu Wang | ||
| Chief Executive Officer | ||
| By: | /s/ Yau Chit Man Samuel | |
| Yau Chit Man Samuel | ||
| Chief Financial Officer | ||
In accordance with the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the Registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| Signature | Title | Date | ||
| /s/ Xiangyu Wang | Chairman and Chief Executive Officer | April 13 , 2018 | ||
| Xiangyu Wang | (Principal Executive Officer) | |||
| /s/ Yau Chit Man Samuel | Director and Chief Financial Officer | April 13, 2018 | ||
| Yau Chit Man Samuel | (Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) | |||
| /s/ Zaixian Yu | Director and Secretary | April 13, 2018 | ||
| Zaixian Yu |
| 32 |
