Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-32.2 - EXHIBIT 32.2 - Panbela Therapeutics, Inc. | ex_108272.htm |
| EX-32.1 - EXHIBIT 32.1 - Panbela Therapeutics, Inc. | ex_108271.htm |
| EX-31.2 - EXHIBIT 31.2 - Panbela Therapeutics, Inc. | ex_108270.htm |
| EX-31.1 - EXHIBIT 31.1 - Panbela Therapeutics, Inc. | ex_108269.htm |
| EX-24.1 - EXHIBIT 24.1 - Panbela Therapeutics, Inc. | ex_108063.htm |
| EX-23.1 - EXHIBIT 23.1 - Panbela Therapeutics, Inc. | ex_108062.htm |
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
|
☒ |
|
ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
|
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2017 |
||
|
OR |
||
|
☐ |
|
TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
|
For the transition period from to
Commission file number: 000-55242
|
||
SUN BIOPHARMA, INC.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
|
Delaware |
|
87-0543922 |
|
712 Vista Blvd, #305 |
||
|
Waconia, Minnesota |
55387 |
|
|
(Address of principal executive offices) |
(Zip Code) |
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code: (952) 479-1196
Securities Registered Pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act: None.
Securities Registered Pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: Common Stock, $0.001 par value
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K (§229.405) is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company, or emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company,” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. (Check one):
|
Large accelerated filer ☐ |
|
Accelerated filer ☐ |
|
Non-accelerated filer ☐ |
|
Smaller reporting company ☒ |
|
Emerging growth company ☒ |
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes ☐ No ☒
The aggregate market value of the registrant’s common stock, excluding shares beneficially owned by affiliates, computed by reference to price at which the registrant’s common stock was last sold as of June 30, 2017 (the last trading day of the registrant’s second fiscal quarter) was $27,415,181.
As of March 19, 2018, there were 4,093,852 shares of the registrant’s common stock outstanding.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Portions of our proxy statement for the annual meeting of stockholders to be held in 2018 are incorporated by reference into Part III of this report.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
|
|
Page | |
|
Cautionary Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements |
ii | |
|
Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act Disclosure |
iii | |
|
PART I |
||
|
Item 1. |
Business |
4 |
|
Item 1A. |
Risk Factors |
25 |
|
Item 1B. |
Unresolved Staff Comments |
38 |
|
Item 2. |
Properties |
38 |
|
Item 3. |
Legal Proceedings |
38 |
|
Item 4. |
Mine Safety Disclosures |
38 |
|
PART II |
||
|
Item 5. |
Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities |
39 |
|
Item 6. |
Selected Financial Data |
39 |
|
Item 7. |
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations |
40 |
|
Item 7A. |
Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk |
50 |
|
Item 8. |
Financial Statements and Supplementary Data |
50 |
|
Item 9. |
Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure |
50 |
|
Item 9A. |
Controls and Procedures |
50 |
|
Item 9B. |
Other Information |
51 |
|
PART III |
||
|
Item 10. |
Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance |
52 |
|
Item 11. |
Executive Compensation |
53 |
|
Item 12. |
Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters |
53 |
|
Item 13. |
Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence |
53 |
|
Item 14. |
Principal Accounting Fees and Services |
53 |
|
PART IV |
||
|
Item 15. |
Exhibits, Financial Statements Schedules |
54 |
|
Item 16. |
Form 10-K Summary |
56 |
|
Financial Statements |
F-1 | |
Cautionary Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements
This annual report on Form 10-K contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. In some cases, you can identify forward-looking statements by the following words: “anticipate,” “believe,” “continue,” “could,” “estimate,” “expect,” “intend,” “may,” “ongoing,” “plan,” “potential,” “predict,” “project,” “should,” “will,” “would,” or the negative of these terms or other comparable terminology, although not all forward-looking statements contain these words. Forward-looking statements are not a guarantee of future performance or results, and will not necessarily be accurate indications of the times at, or by, which such performance or results will be achieved. Forward-looking statements are based on information available at the time the statements are made and involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors that may cause our results, levels of activity, performance or achievements to be materially different from the information expressed or implied by the forward-looking statements in this report. These factors include:
|
● |
the fact that we are a company with limited operating history for you to evaluate our business; |
|
● |
our lack of diversification and the corresponding risk of an investment in our Company; |
|
● |
potential deterioration of our financial condition and results due to failure to diversify; |
|
● |
our ability to obtain additional capital, on acceptable terms or at all, required to implement our business plan; and |
|
● |
other risk factors included under the caption “Risk Factors” starting on page of this report. |
You should read the matters described in “Risk Factors” and the other cautionary statements made in this report as being applicable to all related forward-looking statements wherever they appear in this report. We cannot assure you that the forward-looking statements in this report will prove to be accurate and therefore you are encouraged not to place undue reliance on forward-looking statements. You should read this report completely. Other than as required by law, we undertake no obligation to update or revise these forward-looking statements, even though our situation may change in the future.
We caution readers not to place undue reliance on any forward-looking statement that speaks only as of the date made and to recognize that forward-looking statements are predictions of future results, which may not occur as anticipated. Actual results could differ materially from those anticipated in the forward-looking statements and from historical results, due to the risks and uncertainties described in Part I, Item 1A, of this annual report, as well as others that we may consider immaterial or do not anticipate at this time. Although we believe that the expectations reflected in our forward-looking statements are reasonable, we do not know whether our expectations will prove correct. Our expectations reflected in our forward-looking statements can be affected by inaccurate assumptions that we might make or by known or unknown risks and uncertainties, including those described in Part I, Item 1A, of this annual report. The risks and uncertainties described in Part I, Item 1A, of this annual report are not exclusive and further information concerning us and our business, including factors that potentially could materially affect our financial results or condition, may emerge from time to time. We assume no obligation to update forward-looking statements to reflect actual results or changes in factors or assumptions affecting such forward-looking statements. We advise stockholders and investors to consult any further disclosures we may make on related subjects in our subsequent annual reports on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q and current reports on Form 8-K that we file with or furnish to the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”).
Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act Disclosure
Our company qualifies as an “emerging growth company,” as defined in Section 2(a)(19) of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”), as further amended by the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act (the “JOBS Act”). An issuer qualifies as an “emerging growth company” if it has total annual gross revenues of less than $1.0 billion during its most recently completed fiscal year, and will continue to be deemed an emerging growth company until the earliest of:
|
● |
the last day of the fiscal year of the issuer during which it had total annual gross revenues of $1.0 billion or more; |
|
● |
the last day of the fiscal year of the issuer following the fifth anniversary of the date of the first sale of common equity securities of the issuer pursuant to an effective registration statement; |
|
● |
the date on which the issuer has, during the previous three-year period, issued more than $1.0 billion in non-convertible debt; or |
|
● |
the date on which the issuer is deemed to be a “large accelerated filer,” as defined in Section 240.12b-2 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 (the “Exchange Act”). |
As an emerging growth company, we are exempt from various reporting requirements. Specifically, the Company is exempt from the following provisions:
|
● |
Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, which requires evaluations and reporting related to an issuer’s internal controls; |
|
● |
Section 14A(a) of the Exchange Act, which requires an issuer to seek stockholder approval of the compensation of its executives not less frequently than once every three years; and |
|
● |
Section 14A(b) of the Exchange Act, which requires an issuer to seek stockholder approval of its so-called “golden parachute” compensation, or compensation upon termination of an employee’s employment. |
Under the JOBS Act, emerging growth companies may delay adopting new or revised accounting standards that have different effective dates for public and private companies until such time as those standards apply to private companies. We have elected to not use the extended transition period for complying with these new or revised accounting standards and such election is irrevocable pursuant to Section 107 of the JOBS Act.
PART I
|
Item 1. |
Business |
As used in this report, unless specifically indicated, the terms “Sun BioPharma,” the “Company,” “we,” “us,” “our” and similar references refer to Sun BioPharma, Inc. and its wholly-owned subsidiary, Sun BioPharma Australia Pty Ltd. (“SBA”). The term “common stock” refers to our common stock, par value $0.001 per share.
Overview
We are a clinical stage drug development company founded with technology licensed from The University of Florida Research Foundation (“UFRF”). The polyamine analogue compound we have licensed from UFRF, which we refer to as “SBP-101,” exhibits extraordinary specificity for the exocrine pancreas, with therapeutic potential for both pancreatic cancer and pancreatitis indications. Xenograft studies of human pancreatic cancer cells transplanted into mice indicate that the unique specificity of SBP-101 for the exocrine pancreas facilitates suppression of both primary and metastatic pancreatic cancer which is known to originate in the exocrine pancreas. To facilitate and accelerate the development of this compound in the pancreatic cancer indication, we have also acquired data and materials related to this technology from other researchers. Studies in dogs revealed ablation, or “chemical resection,” of the exocrine pancreatic architecture, while leaving the islet cells functionally unchanged. We may refer to this effect as: “pharmaceutical pancreatectomy with islet auto-transplant” (“PP-IAT”). We believe that SBP-101, if successfully developed, may represent a novel approach that effectively treats pancreatic cancer and pancreatitis, and could become a dominant product in these markets. Only three first-line treatment and one second-line drug have been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (“FDA”) for pancreatic cancer in the last 20 years, and no drugs have been approved for the specific treatment of patients with pancreatitis, other than supportive care.
On August 22, 2017, we filed with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) a definitive consent solicitation statement on Schedule 14A seeking stockholder approval of a proposal to amend our Certificate of Incorporation of the Company to effect a reverse stock split of the Company’s common stock at a ratio of one-for-ten (1:10) and reduce the shares authorized for issuance by 50%, with such reverse stock split and reduction in authorized shares to be effective at such date and time, if at all, as determined by our Board of Directors in its sole discretion. As of September 11, 2017, we received sufficient written consents to approve the proposal and on November 7, 2017, we implemented the 1-for-10 reverse split of our common stock. No fractional shares were issued in connection with the reverse stock split. Stockholders received a proportionate cash payment for any fractional shares based upon the closing price of our common stock on this date. The reverse stock split did not affect the par value of our common stock, however, concurrent with the reverse stock split, the number of shares of common and preferred stock authorized for issuance by the Company was reduced by 50% to 100,000,000 and 10,000,000, respectively. Proportional adjustments were also made to the Company’s 2016 Omnibus Incentive Plan, outstanding stock options, warrants and outstanding convertible notes payable. All references to share and per share amounts included in annual report have been retroactively restated to reflect the reverse split. The primary purpose of the reverse stock split was to enable us to meet the minimum bid price standard required to list our common stock on a national securities exchange. Our common stock is currently traded on the over-the-counter markets through the OTCQB marketplace.
In August 2015, the FDA accepted our Investigational New Drug (“IND”) application for our SBP-101 product candidate. We have completed an initial clinical trial of SBP-101 in patients with previously treated locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic cancer. This was a Phase 1, first-in-human, dose-escalation, safety study. From January 2016 through September 2017, we enrolled twenty-nine patients into six cohorts, or groups, in the dose-escalation phase of our current Phase 1 trial. Twenty-four of the patients received at least two prior chemotherapy regimens. No drug-related serious adverse events occurred during the first four cohorts. In cohort five, serious adverse events (klebsiella sepsis with metabolic acidosis in one patient, and renal and hepatic toxicity in one patient) were observed in two of the ten patients, both of whom exhibited progressive disease at the end of their first cycle of treatment, and were determined by the Data Safety Monitoring Board (“DSMB”) to be dose-limiting toxicities (“DLTs”). Consistent with the study protocol, the DSMB recommended continuation of the study by expansion of cohort 4. Four patients were enrolled in this expansion cohort.
In addition to being evaluated for safety, twenty-four of the twenty-nine patients were evaluable for preliminary signals of efficacy prior to or at the eight-week conclusion of their first cycle of treatment using the Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (“RECIST”), the current standard for evaluating changes in the size of tumors. Eight of the twenty-four patients (33%) had Stable Disease (“SD”) and sixteen of twenty-four (67%) had Progressive Disease (“PD”). It should be noted that of the sixteen patients with PD, six came from cohorts one and two and are considered to have received less than potentially therapeutic doses of SBP-101. We also noted that twenty-eight of the twenty-nine patients had follow-up blood tests measuring the Tumor Marker CA 19-9 associated with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Eleven of these patients (39%) had reductions in the CA 19-9 levels, as measured at least once after the baseline assessment. Seven of the remaining seventeen patients showed no reduction in CA 19-9 came from cohorts one and two.
The best response outcomes and survival were observed in the group of thirteen patients who received total cumulative doses between 2.5 mg/kg and 8.0 mg/kg. Twelve of the thirteen patients in this group were evaluable for preliminary signs of efficacy at eight weeks by RECIST. Five patients (42%) showed SD at week eight. Five of the thirteen patients (38%) had reductions in the CA19-9 levels, as measured at least once after the baseline assessment. Median survival in this group was 3.8 months as of October 2017. To date, nine patients (69%) have exceeded 3 months of overall survival (“OS”), four have exceeded four months of OS and two patients have exceeded 10 months of OS, with some patients continuing to be followed for survival.
In January 2018, we announced the initiation of a first-line dose-escalation study of SBP-101 in combination with gemcitabine and nab-paclitaxel in previously untreated patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer. We anticipate that the first patient will be enrolled in early Q2 2018. Clinical sites participating in the study are expected to include the University of Florida, Gainesville, Florida, the Ashford Cancer Centre in Adelaide, the Olivia Newton-John Cancer and Wellness Centre in Melbourne and the Blacktown Cancer and Haematology Centre in Sydney, Australia. The Company further notes that it will require additional capital to complete this study.
Additional clinical trials will be required for FDA approval of SBP-101 in pancreatic cancer and pancreatitis. We estimate that the additional time and cost to obtain FDA and European Medicines Agency (“EMA”) approval and to bring SBP-101 to market in these two indications will be six to seven years and cost at least $200 million, however, such time and cost estimates are subject to significant variability and subject to change depending on the results of current and future clinical trials.
With the approximately $17.0 million raised through December 31, 2017, we have:
|
● |
organized the Company; |
|
● |
evaluated and secured the intellectual property for our core technology; |
|
● |
completed required pre-clinical steps in the development plan for SBP-101 for pancreatic cancer; |
|
● |
secured an orphan drug designation from the FDA; |
|
● |
submitted an IND application to the FDA (May 18, 2015); |
|
● |
received an acceptance of an IND application from the FDA (August 21, 2015); |
|
● |
received acceptance of a Clinical Trial Notification by the Australian Therapeutic Goods Administration (September 23, 2015); |
|
● |
substantially completed a phase 1a safety study of SBP-101in the treatment of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; and |
|
● |
commenced further pre-clinical studies for the use of SBP-101 to treat pancreatitis. |
Introduction
An effective treatment for pancreatic cancer remains a major unmet medical need. Adenocarcinoma of the pancreas, which accounts for approximately 95% of all cases of pancreatic cancer, has a median overall survival of 8 to 11 months in clinical studies of patients with favorable prognostic signs and optimal chemotherapy. Adenocarcinoma of the pancreas afflicts approximately 83,000 people in the European Union (Eurostat 2014), over 53,000 people in the United States annually (https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/pancreas.html), and 337,000 people worldwide (World Health Organization 2014, NIH/NCI). Pancreatic cancer is now the third most common cause of cancer death in the United States (SEER Cancer Statistics Factsheets 2016). A recent report from the Pancreatic Cancer Action Network states that pancreatic cancer deaths in the United States have surpassed those from breast cancer and will soon surpass deaths from colorectal cancer to rank number two in deaths, behind only lung cancer in 2020. The five-year survival rate remains less than 3% for patients diagnosed with metastatic pancreatic cancer and approximately 7.7% across all pancreatic stages, and there has been little significant improvement in survival since gemcitabine was approved in the United States in 1996.
Pancreatic cancer is generally not diagnosed early because the initial clinical signs and symptoms are vague and non-specific. By the time of diagnosis, the cancer is most often locally advanced or metastatic, having spread to regional lymph nodes, liver, lung and/or peritoneum, and is seldom amenable to surgical resection, or removal, with curative intent. Currently, surgical resection offers the only potentially curative therapy, although only 15-20% of patients are candidates for surgical resection at the time of the diagnosis. Patients who undergo radical surgery still have a limited survival rate, averaging 23 months (Macarulla T, et al Clin Transl Oncol 2017).
The prognosis for patients diagnosed with pancreatic cancer is poor and most die from complications related to progression of the disease. The primary treatment for metastatic disease is chemotherapy. Current first-line chemotherapy treatment regimens vary from single agent gemcitabine and various gemcitabine combinations to the multi-chemotherapy drug combination, FOLFIRINOX, comprised of leucovorin, fluorouracil, irinotecan, and oxaliplatin (Conroy NEJM 2011), frequently supplemented with white blood cell (“WBC”) growth factors. These combination therapies deliver median survival benefits ranging from 7 weeks (Von Hoff NEJM 2013) to 4 months (Conroy NEJM 2011) for selected patients with good performance status, meaning that they are in relatively good physical condition at the time of diagnosis, when compared with gemcitabine alone. In 2015, the FDA approved Onivyde® (irinotecan liposome injection), in combination with fluorouracil and leucovorin, to treat patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer who have been previously treated with a gemcitabine-based chemotherapy. Because most patients with good performance status receive variations of the FOLFIRINOX (generic), regimen second-line, Onivyde is not widely prescribed as indicated.
University laboratory studies have demonstrated that SBP-101 induces programmed cell death, or “apoptosis,” in the acinar and ductal cells of the pancreas by activation of caspase 3 and poly(adenosine diphosphate-ribose) polymerase (“PARP”) cleavage. In animal models at two independent laboratories, SBP-101, alone or in combination, has demonstrated nearly complete suppression of transplanted human pancreatic cancer, including metastases. SBP-101 has demonstrated both superior and additive efficacy to gemcitabine and nab-paclitaxel in laboratory models of pancreatic cancer. We intend to develop SBP-101 as a unique and novel targeted approach to treating patients with pancreatic cancer. We intend to develop SBP-101 in combination with existing standard chemotherapy agents. With adequate funding, we also expect to continue evaluation of the potential value of SBP-101 in the treatment of patients with recurrent acute or chronic pancreatitis.
Pancreatic Cancer
Adenocarcinoma of the pancreas afflicts approximately 83,000 people in the European Union (Eurostat 2014), over 53,000 people in the United States annually (https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/pancreas.html), and 337,000 people worldwide (World Health Organization 2014, NIH/NCI). It is the seventh leading cause of death from cancer in Europe (GLOBOCAN 2012) and the third leading cause of death from cancer in the United States (SEER Cancer Statistics Factsheets 2016). PDA represents approximately 95% of all pancreatic cancers. Considering that the median overall survival for previously untreated patients with good performance status is between 8.5 months (Von Hoff 2013) and 11.1 months (Conroy 2011) with the best available treatment regimens, effective treatment for PDA remains a major unmet medical need.
Pancreatic cancer is generally not diagnosed early because the initial clinical signs and symptoms are vague and non-specific. The most common presenting symptoms include weight loss, epigastric (upper central region of the abdomen) and/or back pain, and jaundice. The back pain is typically dull, constant, and of visceral origin radiating to the back, in contrast to the epigastric pain which is vague and intermittent. Less common symptoms include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, anorexia, and new onset diabetes or glucose intolerance (Hidalgo 2010).
Surgery remains the only treatment option with curative intent, although only 15-20% of patients are candidates for surgical resection at the time of the diagnosis. Patients who undergo radical surgery still have a limited survival rate, averaging 23 months (Macarulla T, et al Clin Transl Oncol 2017).
For the minority of patients who present with resectable disease, surgery is the treatment of choice. Depending on the location of the tumor the operative procedures may involve cephalic pancreatoduodenectomy, referred to as a “Whipple procedure”, distal pancreatectomy or total pancreatectomy. Pancreatic enzyme deficiency and diabetes are frequent complications of these procedures. Up to 70% of patients with pancreatic cancer present with biliary obstruction that can be relieved by percutaneous or endoscopic stent placement. However, even if the tumor is fully resected, the outcome in patients with pancreatic cancer is disappointing (Hidalgo 2010, Seufferlein 2012). Post-operative administration of chemotherapy improved progression-free and overall survival in three large, randomized clinical trials (Hidalgo 2010), but median post-surgical survival in patients treated in all three trials was similar: only 20-22 months.
For the majority of patients who present with unresectable locally advanced or metastatic disease, management options range from chemotherapy alone to combined forms of treatment with radiation therapy and chemotherapy. However, due to the increased toxicity of combined treatment, randomized trials of such combined regimens have had low enrollment, precluding a firm conclusion as to any advantage of adding radiation to chemotherapy (Hidalgo 2010).
Gemcitabine was the first chemotherapeutic agent approved for the treatment of patients with PDA, providing a median survival duration of 5.65 months (Burris 1997). Gemcitabine monotherapy was the standard of care for patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer until combination therapy with gemcitabine plus erlotinib (Tarceva®) was shown to increase median survival by 2 weeks. This modest benefit was tempered by a significant side effect profile and high cost, limiting its adoption as a standard treatment regimen. More recently, the multidrug chemotherapy combination FOLFIRINOX, was shown to provide a median survival benefit of 4.3 months (OS = 11.1 months) over gemcitabine alone (6.8 months), but its significant side effect profile limits the regimen to select patients with a good performance status and often requires supplementation with WBC growth factor therapy. Nab-paclitaxel (Abraxane®) received marketing authorization for use in combination with gemcitabine after showing an increase in overall survival of 7 weeks compared to gemcitabine alone (Von Hoff 2013). Thus, combination therapies have demonstrated a modest survival benefit compared to gemcitabine alone as summarized in the table below (Thota 2014).
Current First-Line Treatment Approaches: Survival & Toxicity Profiles Across Three Major Positive Clinical Trials
|
Gemcitabine vs. Gemcitabine/Erlotinib Phase 3 trial |
ACCORD 11 Trial |
Metastatic Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Clinical Trial (MPACT) |
||||
|
Gemcitabine |
Gemcitabine/ Erlotinib |
Gemcitabine |
FOLFIRINOX(1) |
Gemcitabine |
Gemcitabine/ Nab-Paclitaxel |
|
|
One-Year Survival |
17% |
23% |
20.6% |
48.4% |
22% |
35% |
|
Median Overall Survival (months) |
5.91 |
6.24 |
6.8 |
11.1 |
6.7 |
8.5 |
|
Median Progression-Free Survival (months) |
3.55 |
3.75 |
3.3 |
6.4 |
3.7 |
5.5 |
|
Overall Response Rate |
8% |
8.6% |
9.4% |
31.6% |
7% |
23% |
|
Toxicity |
||||||
|
Neutropenia |
– |
– |
21% |
45.7% |
27% |
38% |
|
Febrile neutropenia |
– |
– |
1.2% |
5.4% |
1% |
3% |
|
Thrombocytopenia |
– |
– |
3.6% |
9.1% |
9% |
13% |
|
Diarrhea |
2% |
6% |
1.8% |
12.7% |
1% |
6% |
|
Sensory neuropathy |
– |
– |
0% |
9% |
1% |
17% |
|
Fatigue |
15% |
15% |
17.8% |
23.6% |
7% |
17% |
|
Rash |
6% |
1% |
– |
– |
– |
– |
|
Stomatitis |
<1% |
0% |
– |
– |
– |
– |
|
Infection |
17% |
16% |
– |
– |
– |
– |
Source: Thota R et al., Oncology 2014; Jan 28(1):70–74
1 FOLFIRINOX represents leucovorin (folic acid), fluorouracil, irinotecan, and oxaliplatin.
Other drugs are currently under investigation, but none have received marketing authorization as a first-line treatment of PDA since the approval of Abraxane. Most notably, Jameson et al presented preliminary results of a Phase 1b/2 pilot study of a combination of gemcitabine, nab-paclitaxel and cisplatin in patients with stage 4 pancreatic cancer. Although adverse events were frequent and severe, the response rate was encouraging (Jameson ASCO GI 2017).
Pancreatitis
Additional potential indications for SBP-101 are the treatment of patients with the serious and potentially life-threatening conditions of acute/recurrent acute and chronic pancreatitis, which has a mortality rate of between two and five percent. In the United States, acute pancreatitis occurs in approximately 300,000 patients per year, with approximately 50% of those cases considered to be recurrent acute pancreatitis. Approximately 30,000 patients progress to chronic pancreatitis each year.
Patients with chronic pancreatitis endure repeated episodes of abdominal pain, often with progression to narcotic dependency and to pancreatic enzyme deficiency, as well as insulin dependent diabetes mellitus as a consequence of the ultimate destruction of pancreatic function. Once a patient has suffered from repeated painful bouts of chronic pancreatitis they may be offered a total pancreatectomy. A total pancreatectomy is a surgical procedure resulting in the resection, or removal, of the pancreas (guaranteeing both pancreatic enzyme deficiency as well as insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus), and often includes the spleen, gall bladder and appendix. The operation is both extensive, requiring 8+ hours in the operating room, and expensive. While the goal of a total pancreatectomy in patients with chronic pancreatitis is pain relief, as many as 60% remain narcotic dependent, and even with the isolation and reintroduction of any of the patient’s remaining functional insulin producing islet cells, or islet auto-transplant, over 70% of patients remain insulin dependent. The combination of a total pancreatectomy and islet auto transplant (“TP & IAT”) represents a small subset of the current surgical approaches to patients with chronic pancreatitis. Thus, a patient with chronic pancreatitis may face months of abdominal pain, narcotic dependence, the onset of diabetes mellitus, the requirement for both insulin and pancreatic enzyme replacement, and finally, an extensive and expensive surgical procedure which may not materially improve any of their symptoms.
Patients with acute pancreatitis experience abdominal pain, which can be severe and even life threatening. Acute pancreatitis occurs most often in adults aged 30-40 years, and is associated in some cases with increased consumption of alcohol and tobacco, and in other cases, with the presence of stones in the bile or pancreatic duct system. In a small minority of cases the disease may be hereditary, but many affected patients have no clear precipitating cause. There are no specific agents approved for treatment of acute or chronic pancreatitis, as such, current treatment is limited to supportive care with intravenous fluids, narcotics and the avoidance of oral intake.
SBP-101, which has demonstrated the specificity to target the acinar and ductal cells of the pancreas, and if successfully developed, may represent an opportunity for up to 30,000 US patients presenting annually with chronic pancreatitis to receive an early, non-surgical intervention into the natural history of their disease, with the potential to avoid narcotic dependency, insulin dependency, surgery and months or years of chronic pain. Patients would still require pancreatic enzyme replacement. We believe that our consultations with pancreatitis experts at Harvard University, the Ohio State University, the University of Minnesota, Cedars Sinai Medical Center, the University of Miami, the University of Florida and the National Institute of Health (“NIH”) have resulted in enthusiastic endorsement of the study of SBP-101 in the treatment of patients with pancreatitis.
Clinical development of SBP-101 for the treatment of patients with pancreatitis is expected to proceed following the pancreatic cancer indication, with FDA consultation in a pre-IND meeting, completion of a series of IND-enabling nonclinical toxicology and pharmacology studies, and submission of an IND package to the FDA. Clinical development of SBP-101 for pancreatitis is also contingent upon raising additional funds.
Proprietary Technology
Function and Characteristics of Polyamines
Polyamines are metabolically distinct entities within human cells that bind to and facilitate DNA replication, RNA transcription and processing, and protein (such as pancreatic enzymes) synthesis. Human cells contain three essential and naturally occurring polyamines - putrescine, spermidine, and spermine - that, in contrast to cell building blocks such as amino acids and sugars, remain as metabolically distinct entities inside the cell. Polyamines perform many functions necessary for cellular proliferation and protein synthesis. The critical balance of polyamines within cells is maintained by several enzymes such as ornithine decarboxylase (“ODC”) and spermidine/spermine N1 acetyl transferase (“SSAT”). All of these homeostatic enzymes are short-lived, rapidly inducible intracellular proteins that serve to tightly and continuously regulate native polyamine pools. These enzymes constantly maintain polyamines within a very narrow range of concentration inside the cell.
Polyamine Analogue
Polyamine analogues such as SBP-101 are structurally similar to naturally occurring polyamines and are recognized by the cell’s polyamine uptake system, allowing these compounds to gain rapid entrance to the cell. We believe that pancreatic acinar cells, because of their extraordinary protein synthesis capacity, exhibit enhanced uptake of polyamines and polyamine analogues such as SBP-101. Because of preferential uptake by pancreatic acinar cells, polyamine analogies such as SBP-101 disrupt the cell’s polyamine balance and biosynthetic network, and induce programmed cell death, or apoptosis, via caspase 3 activation and PARP cleavage. Proof of concept has been demonstrated in multiple human pancreatic cancer models, both in vivo and in vitro, that pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma exhibits sensitivity to SBP-101. Many tumors, including pancreatic cancer, display an increased uptake rate of polyamines and polyamine analogues.
SBP-101
SBP-101 is a proprietary polyamine analogue, which we believe accumulates in the acinar cells due to unique chemical structure alterations. SBP-101 was discovered and extensively studied by Professor Raymond J. Bergeron at the University of Florida College of Pharmacy. In a key, independent, pre-clinical study we observed the accumulation of SBP-101 in the acinar cells of the beagle pancreas causing a complete pharmaceutical resection of the exocrine tissues of the pancreas and notably, without producing an inflammatory response. We believe that SBP-101,when administered in a sufficiently high pharmacologic dosage, disrupts the normal metabolic process of acinar cells and pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells, which exhibit similar responses, including programmed cell death, or apoptosis. Importantly, pancreatic islet cells, which secrete insulin, are structurally and functionally dissimilar to acinar cells and are not impacted by SBP-101.
The primary mechanism of action for SBP-101 has been demonstrated to include the enhanced uptake of the compound in the exocrine pancreas. This effect leads to corresponding depressed levels of native polyamines, with caspase 3 activation, PARP cleavage and apoptotic destruction (programmed cell death) of the exocrine pancreatic acinar and ductal cells without an inflammatory response. In animal models at two independent laboratories, SBP-101 has demonstrated significant suppression of transplanted human pancreatic cancer cells, including metastatic pancreatic cancer growth. See “Proof of Principle” below.
We believe that SBP-101 will have a distinct advantage over current pancreatic cancer therapies in that it specifically targets the exocrine pancreas and may cause ablation, or pharmaceutical resection, of the acinar and ductal cells, as well as the primary and metastatic pancreatic cancer, while leaving the insulin-producing islet cells and most non-pancreatic tissue unharmed. Most current cancer therapies, including chemotherapy, radiation and surgery, are associated with significant side effects that further reduce the patient’s quality of life. However, we believe that the adverse effects of SBP-101 will not overlap with or exacerbate those seen with typical chemotherapy options. It is expected that SBP-101 may produce exocrine pancreatic insufficiency and, potentially, other gastro intestinal (“GI”) adverse events, many of which are generally expected to occur as common complications of advanced pancreatic cancer and part of the natural history/progression of the disease. The dose-limiting toxicities observed in cohort five of our Phase 1a study, as noted above, were not observed at lower doses. Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency is a common complication of pancreatic cancer and is treatable with currently marketed digestive enzyme replacement capsules, such as Creon® (AbbVie). As the endocrine pancreas is expected to be unaffected by SBP-101, no new requirement for insulin is expected.
Proof of Principle
SBP-101 has been tested and found effective in reducing pancreatic tumor growth in multiple separate in vivo models of human pancreatic cancer. SBP-101 was used to treat mice subcutaneously implanted with human pancreatic cancer cell line PANC-1 tumor fragments. A dose-response for efficacy was demonstrated with a 26 mg/kg daily injection resulting in near complete suppression of the transplanted tumor, as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1. Impact of SBP-101 on PANC-1 Tumor Burden in a Murine Xenograft Model
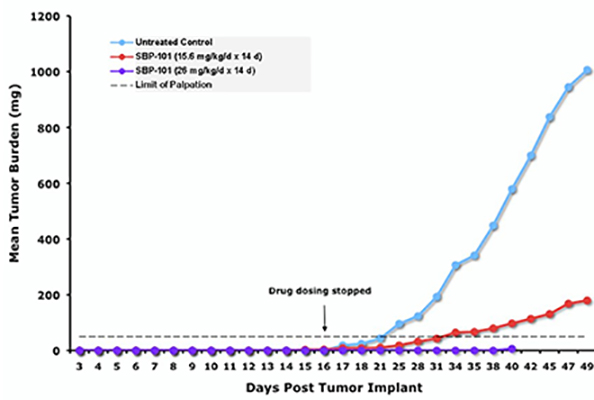 |
Source: Study BERG20100R1a(MIR1581)
A separate orthotopic xenograft study (direct implant of human tumor cells into the pancreas of the mouse) employed a particularly aggressive human pancreatic cancer cell line, L3.6pl, that is known to metastasize from the pancreas to the liver and the peritoneum in mice. Mice implanted with L3.6pl were treated with SBP-101 and the results were compared with saline-treated control mice, with mice treated with gemcitabine alone (Gemzar®, the then current “gold standard” treatment), and the combination of both drugs. Both gemcitabine and SBP-101 significantly reduced tumor volume compared to the control group, but the combination of SBP-101 and gemcitabine was significantly better than gemcitabine alone as shown in Figure 2.
|
Figure 2. |
L3.6pl Orthotopic Xenograft Study - Mean (+SD) Tumor Volume after Treatment with SBP-101, Gemcitabine (Gemzar®) or Both |
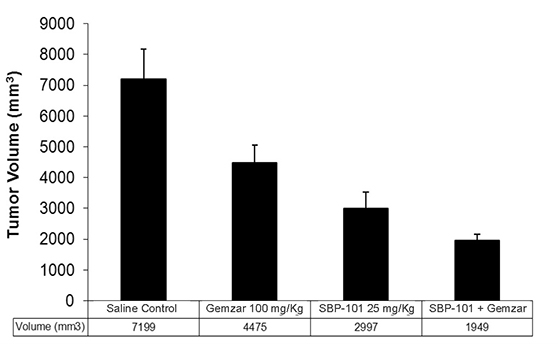 |
Source: Study101-Biol-101-001
The potential for SBP-101 as an effective therapy for pancreatic cancer has therefore been demonstrated in vivo by separate investigators, in different human pancreatic cancer cell lines and in two different animal models, using SBP-101 synthesized by two different routes, confirming nearly equal, and remarkably effective, doses of 25 and 26 mg/kg, respectively.
Additionally, when compared in vitro to existing therapies, SBP-101 produced superior results in suppressing growth of pancreatic cancer cells.
Development Plan for SBP-101
Development of SBP-101 for the pancreatic cancer indication includes a pre-clinical and a clinical phase. The pre-clinical phase, which was substantially completed during 2015, consists of four primary components: chemistry, manufacturing and controls (“CMC”), preclinical (laboratory and animal) pharmacology studies, preclinical toxicology studies, and regulatory submissions in Australia and the United States. In Australia, a Human Research Ethics Committee (“HREC”) application was submitted with subsequent Clinical Trial Notification (“CTN”) to the Therapeutic Goods Administration (“TGA”). Complementing the Australian initiative, a similar, but considerably more extensive, preclinical package has been submitted to the FDA in support of an IND application. Our initial clinical trial in previously treated patients with locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic cancer was a Phase 1, first-in-human, dose-escalation, safety study conducted at clinical sites in both Australia and the United States. We engaged expert clinicians who treat pancreatic cancer at major cancer treatment centers in Melbourne and Adelaide, Australia as well as the Mayo Clinic Scottsdale and HonorHealth in Scottsdale, Arizona. These Key Opinion Leaders (“KOLs”), with proven performance in pancreatic cancer studies, enthusiastically agreed to participate as investigators for our Phase 1 First-in-Human study.
Enrollment in our initial Phase 1 safety trial of SBP-101 in previously treated pancreatic cancer patients commenced in January 2016 and was completed in September 2017. This study was a dose-escalation study with 8-week treatment/observation cycles at each dose level. Preliminary results from this trial are discussed in Clinical Development – Pancreatic Cancer below.
We anticipate initiation of patient enrollment in our next clinical trial in the second quarter of 2018. Our second clinical trial will be a Phase 1a/1b study of the safety and efficacy of SBP-101 administered in combination with two standard-of-care chemotherapy agents, gemcitabine and nab-paclitaxel, and we plan to conduct the trial at four study sites (three in Australia and one in the United States). In the Phase 1a portion of this trial, we expect to enroll three cohorts of 3-6 patients with increased dosage levels of SBP-101 administered in the second and third cohorts. Demonstration of adequate safety in the Phase 1a portion of the trial is expected to lead to the Phase 1b exploration of efficacy, in which we plan to enroll ten patients using the recommended dosage level determined in the Phase 1a portion of the trial. We believe that meeting the primary endpoint in Phase 1b would predict a successful randomized Phase 3 trial. Early results from the Phase 1a portion are expected to be available in late 2018. Early results from the Phase 1b expansion could become available as soon as the second half of 2019.
With additional funding SBP-101 may also be explored for use as a treatment for recurrent acute and chronic pancreatitis and maintenance therapy in patients responding to first line treatment and/or for adjuvant treatment after surgery in appropriate patients. There is also preclinical data to suggest that SBP-101 may have potential therapeutic uses outside of the pancreas, but due to the current focus on pancreatic cancer and pancreatitis, none have been formally explored.
Preclinical Development
To enable IND and HREC/CTN submission and as part of our pharmacology work, we conducted plasma and urine assay development and validation in animals, in vitro metabolism studies in liver microsomes and hepatocytes, in vitro interaction studies with hepatic and renal transporters, a protein binding study, animal pharmacokinetic and metabolism/mass balance studies, and human plasma and urine assay development and validation. As a part of the pharmacology evaluation, we conducted an in vitro pharmacology screen profiling assay, a study in six human pancreatic cell lines, and studies in tumor xenograft models in mice using human pancreatic cancer PANC-1 tumor fragments, human pancreatic cancer BxPC-3 tumor fragments and human pancreatic cancer cells (L3.6pl) injected orthotopically in the tail of the pancreas of nude mice.
To meet regulatory requirements and to establish the safety profile of SBP-101, we conducted, in rodents and non-rodents, toxicology dose-ranging studies, IND-enabling general toxicology studies, and genetic toxicology studies, including an Ames test. Exploratory studies in mice and rats and a Good Laboratory Practice (“GLP”)-compliant dog toxicology study have also been completed. The relationship between dose and exposure (pharmacokinetics) has been described for three animal species. We have also completed a preclinical hERG assay to detect any electrocardiographic QTc interval effects (IKr potassium ion channel testing).
In anticipation of the potential for using SBP-101 in combination therapy with gemcitabine and/or nab-paclitaxel (Abraxane®), we also conducted appropriate nonclinical studies which confirmed the potential value of such combinations, including assessing the comparative efficacy of SBP-101, gemcitabine and nab-paclitaxel in various combinations as shown in Figure 3.
|
Figure 3. |
Evaluation of SBP-101 alone and in combination with gemcitabine and nab-paclitaxel in 6 human pancreatic cancer cell lines |
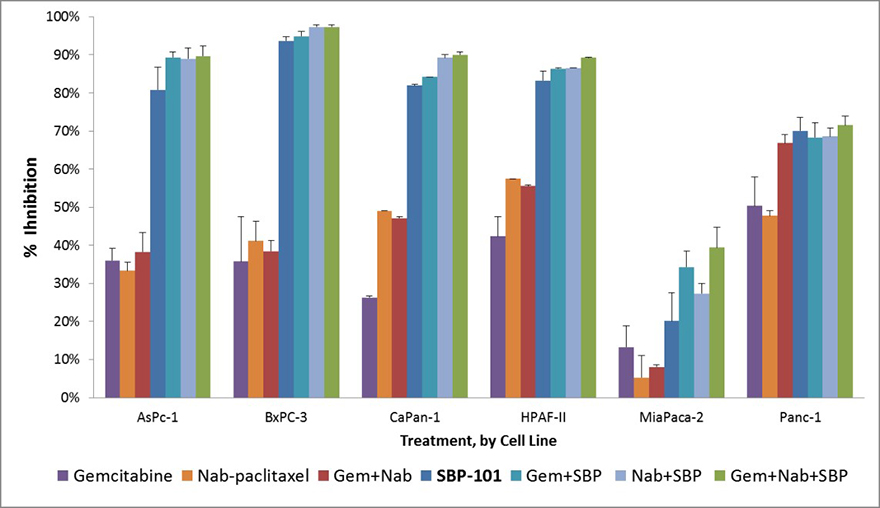
Source: Baker CB et al Pancreas 2015;44(8) 1350
Note that maximum percent growth inhibition (mean ± SE) at 96 hours was observed with 10 µM SBP-101 alone and in combination with gemcitabine and/or nab-paclitaxel in 6 human pancreatic cancer cell lines.
We have met FDA-mandated Chemistry, Manufacturing and Control (“CMC”) requirements with a combination of in-house expertise and contractual arrangements. To date, preparation of anticipated metabolites and an internal standard, as a prerequisite for analytical studies, have been completed through a Sponsored Research Agreement with the University of Florida and a contract manufacturer. We have Service Agreements with Syngene International Ltd. (“Syngene”) for the manufacture and supply of specific quantities of Good Manufacturing Practice (“GMP”)-compliant SBP-101 active pharmaceutical ingredient (“API”) and for the development of synthetic process improvements. Investigational product (IP or clinical trial supply) has been made and tested at Albany Molecular Research Inc. (“AMRI”) in Burlington, MA. Initial lots of GMP-compliant API were prepared by Syngene and released for conversion into supply dosage form. Two clinical trial supply lots have been successfully prepared and released by AMRI. In addition, efforts continue to refine both the synthetic process at Syngene and to prepare improved formulations of the clinical supply.
Pancreatic Cancer Investigational New Drug (“IND”)
The preclinical work to support the IND submission has been completed. Our IND application package contained the following:
|
● |
Investigator’s Brochure; |
|
● |
Statement of general investigative plans; |
|
● |
Proposed Phase 1 pancreatic cancer study protocol; |
|
● |
Data management and statistical plan; |
|
● |
CMC data; and |
|
● |
Pharmacology, absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion (or “ADME”), and toxicology data. |
Preparation of the SBP-101 IND for pancreatic cancer required collaboration by our manufacturing, preclinical toxicology, pharmacokinetic and metabolism experts, our regulatory affairs project management, and our in-house clinical expertise. In August 2015, the FDA accepted our application and in January 2016 we commenced patient enrollment in our Phase 1 clinical trial, which was a safety and tolerability study in patients with previously treated metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. This is further discussed in “Clinical Development” below.
Clinical Development – Pancreatic Cancer
Phase 1 Clinical Trial Design
Our initial Phase 1 study in patients with pancreatic cancer commenced the enrollment of patients in January 2016 and enrollment was completed in September 2017. This study was a dose-escalation study with 8-week cycles of treatment/observation at each dose level.
The absence of adverse events, which could potentially overlap with adverse events typically observed in the use of conventional chemotherapeutic agents, supports the case for combination of SBP-101 with conventional chemotherapeutic agents, such as gemcitabine, nab-paclitaxel, or even FOLFIRINOX.
A favorable characteristic of the pancreatic action of SBP-101 is the lack of an effect on the normal insulin-producing islet cells. Preservation of islet cell function implies the likely absence of diabetes as a complication of SBP-101 therapy. It is important to note that diabetes is a common co-morbidity in patients with pancreatic cancer, but it is not expected to be an adverse effect of treatment with SBP-101. The potential adverse effect of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency is mitigated by the observation that many patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma require pancreatic enzyme replacement as a feature of their underlying disease, a complication so common that pancreatic enzyme replacement with one of several commercially available products is typically covered by United States and Australian health care plans. Patients with cystic fibrosis, chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer are the populations most often treated with pancreatic enzyme replacement.
Patients in our Phase 1 trial underwent regular pancreatic and hepatic enzyme evaluation, and obtained periodic chest and abdominal CT follow-up. Patients were also carefully monitored for clinical signs of GI adverse events.
In August 2015, the FDA accepted our IND application for our SBP-101 product candidate. We have completed enrollment in a clinical trial of SBP-101 in patients with previously treated locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic cancer. This is a Phase 1, first-in-human, dose-escalation, safety study. From January 2016 through September 2017, we enrolled twenty-nine patients into six cohorts, or groups, in the dose-escalation phase of our current Phase 1 trial. Twenty-four of the patients received at least two prior chemotherapy regimens. No drug-related serious adverse events occurred during the first four cohorts. In cohort five, serious adverse events (klebsiella sepsis with metabolic acidosis in one patient, and renal and hepatic toxicity in one patient) were observed in two of the ten patients, both of whom exhibited progressive disease at the end of their first cycle of treatment, and were determined by the DSMB to be DLTs. Consistent with the study protocol, the DSMB recommended continuation of the study by expansion of cohort 4. Four patients were enrolled in this expansion cohort.
In addition to being evaluated for safety, twenty-four of the twenty-nine patients were evaluable for preliminary signals of efficacy prior to or at the eight-week conclusion of their first cycle of treatment using RECIST, the current standard for evaluating changes in the size of tumors. Eight of the twenty-four patients (33%) had SD and sixteen of twenty-four (67%) had PD. It should be noted that of the sixteen patients with PD, six came from cohorts one and two and are considered to have received less than potentially therapeutic doses of SBP-101. We also noted that twenty-eight of the twenty-nine patients had follow-up blood tests measuring the Tumor Marker CA 19-9 associated with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Eleven of these patients (39%) had reductions in the CA 19-9 levels, as measured at least once after the baseline assessment. Seven of the remaining seventeen patients showed no reduction in CA 19-9 came from cohorts one and two.
The best response outcomes and survival were observed in the group of thirteen patients who received total cumulative doses between 2.5 mg/kg and 8.0 mg/kg. Twelve of the thirteen patients in this group were evaluable for preliminary signs of efficacy at eight weeks by RECIST. Five patients (42%) showed SD at week eight. Five of the thirteen patients (38%) had reductions in the CA19-9 levels, as measured at least once after the baseline assessment. Median survival in this group was 3.8 months as of October 2017. To date, nine patients (69%) have exceeded 3 months of overall survival OS, four have exceeded four months of OS and two patients have exceeded 10 months of OS, with some patients continuing to be followed for survival.
Given the life-threatening nature of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, the limited efficacy of current treatment options, and the long history of failures in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma developmental therapeutics, we will attempt to evaluate SBP-101 expeditiously as noted below.
We anticipate initiation of patient enrollment in our next clinical trial in the second quarter of 2018. Our second clinical trial will be a Phase 1a/1b study of the safety and efficacy of SBP-101 administered in combination with two standard-of-care chemotherapy agents, gemcitabine and nab-paclitaxel, and we plan to conduct the trial at four study sites (three in Australia and one in the United States). In the Phase 1a portion of this trial, we expect to enroll three cohorts of 3-6 patients with increased dosage levels of SBP-101 administered in the second and third cohorts. Demonstration of adequate safety in the Phase 1a portion of the trial is expected to lead to the Phase 1b exploration of efficacy, in which we plan to enroll ten patients using the recommended dosage level determined in the Phase 1a portion of the trial. We believe that meeting the primary endpoint in Phase 1b would predict a successful randomized Phase 3 trial. Early results from the Phase 1a portion are expected to be available in late 2018. Early results from the Phase 1b expansion could become available as soon as the second half of 2019.
Phase 2 Pivotal Clinical Trial
A Phase 2 study of SBP-101 in combination with two standard chemotherapy agents, gemcitabine and nab-paclitaxel, is expected to directly extend from the Phase 1 safety study with an exploration of efficacy and may result in an expedited development pathway, leading toward a randomized pivotal trial.
If the results of our planned Phase 2 combination clinical trial demonstrate safety and sufficiently successful efficacy results, we intend to meet with the FDA to obtain advice on potential breakthrough therapy designation, fast track designation (to both provide guidance to facilitate development and expedite review) and an accelerated approval strategy.
If we are able to successfully complete FDA recommended clinical studies, we intend to seek marketing authorization from the FDA, the EMA (European Union), Ministry of Health and Welfare (Japan) and TGA (Australia). The submission fees may be waived when SBP-101 has been designated an orphan drug in each geographic region, as described under “Orphan Drug Status.”
Total Development Costs
The development of SBP-101 involves a preclinical and a clinical development phase. We believe that we have completed our preclinical development work for pancreatic cancer and are concluding our initial clinical trial in pancreatic cancer. We have accomplished this using the approximately $17.0 million of capital raised through December 31, 2017. Additional clinical trials will be required. We estimate the total time and cost to obtain FDA and EU approval and bring SBP-101 to market is 6 to 7 years and up to two hundred million dollars ($200 million), however, such time and cost estimates are subject to significant variability and subject to change depending on the results of current and future clinical trials. Also note that this process could be accelerated and less funds may be needed if SBP-101 qualifies for Breakthrough Status, however, we can provide no assurance that SBP-101 will qualify for Breakthrough Status. A breakthrough therapy designation conveys fast track program features, more intensive FDA guidance on an efficient drug development program, an organizational commitment involving senior managers at the FDA and eligibility for rolling review and priority review of an NDA submission.
Orphan Drug Status
The Orphan Drug Act (“ODA”) provides special status to drugs which are intended for the safe and effective treatment, diagnosis or prevention of rare diseases that affect fewer than 200,000 people in the United States, or that affect more than 200,000 persons but for which a manufacturer is not expected to recover the costs of developing and marketing such a drug. Orphan drug designation has the advantage of reducing drug development costs by: (i) streamlining the FDA’s approval process, (ii) providing tax breaks for expenses related to the drug development, (iii) allowing the orphan drug manufacturer to receive assistance from the FDA in funding the clinical testing necessary for approval of an orphan drug, and (iv) facilitating drug development efforts. More significantly, the orphan drug manufacturer’s ability to recover its investment in developing the drug is also greatly enhanced by the FDA granting the manufacturer seven years of exclusive US marketing rights upon approval. Designation of a drug candidate as an orphan drug therefore provides its sponsor with the opportunity to adopt a faster and less expensive pathway to commercializing its product. We obtained US Orphan Drug Status in 2014 and we intend to submit an application for Orphan Drug Status in Europe, Japan and Australia when we have further clinical data. Depending on certain factors, including the timing and progression of our second clinical trial, we expect to obtain Orphan Drug status in Europe during the fourth quarter of 2018.
Intellectual Property
Intellectual property licensed by us from the University of Florida includes U.S. Patent No. 6,160,022 covering the methods of using SBP-101 for the chemical reaction of the exocrine portion of the pancreas, which expires in 2019.
In addition, we have filed International Application No. PCT/US2016/055888 in September 2016, which takes priority from US Provisional Patent Application No. 62/238,916, which was filed in October 2015. This application covers the use of SBP-101 to treat patients suffering from pancreatitis.
Development Project Managers
Project managers have been hired or contracted to coordinate all the functions identified in our Development Plan for SBP-101. The personnel responsible for overseeing critical functions of the Development Plan are as follows:
Our CMC program is under the direction of Dr. Thomas Neenan, Ph.D., a highly experienced pharmaceutical industry synthetic chemist, who is a founding member of Sun BioPharma, Inc. and our Chief Scientific Officer. Dr. Neenan has commissioned Contract Manufacturing Organizations (“CMOs”), which have improved the process for synthesis of SBP-101, and have produced high-quality compound, chemically identical to that synthesized by Dr. Bergeron at the University of Florida. Dr. Neenan’s completed work includes development, confirmation and documentation of the synthetic chemistry process, analytical purity, reproducibility, stability (shelf-life), degradation products and pharmaceutical formulation and packaging. This work has culminated in a supply of drug to support preclinical work and human clinical trials. Dr. Neenan also leads our preclinical group.
Dr. Ajit Shah, Ph.D., is a long-term consultant with and, during 2016 and 2017, was an employee of the Company. Dr. Shah has extensive prior experience with numerous compounds at both large and mid-size sponsoring companies, including Pfizer and MGI Pharma. His completed work includes development of analytical methods to quantify levels of drug and characterization of metabolites in plasma, urine and tissues, plus distribution of the compound in living tissues, metabolic pathways and products, anticipated drug blood levels, half-life in the organism, and excretion pathways. Dr. Shah’s work has enabled informed dose and schedule planning for human clinical trials. Dr. Shah manages pharmacokinetic analyses in support of our clinical studies.
Dr. Anthony Kiorpes, Ph.D., D.V.M., is a long-term consultant with the Company. Dr. Kiorpes has responsibility for our toxicology program, a role he has assumed previously for many preclinical projects at other companies. His studies have determined single- and multiple-dose safety profiles in rodent and non-rodent species, enabling improved safety monitoring in the design of clinical trials for SBP-101. Dr. Kiorpes’ results have helped management to predict and prevent potential side effects in humans.
Dr. Michael Cullen, M.D., M.B.A, is our founder and Executive Chairman. Dr. Cullen is an experienced drug development specialist with 10 prior NDA approvals and has led our overall Clinical, Regulatory Affairs and Project Management effort, including timeline and budget management, critical path timeline synchronization, IND/HREC/CTN package submissions, management of industry partner collaborative efforts, initial EU Regulatory Affairs planning, and collaboration on oversight of outsourced CMC efforts. Dr. Cullen has recruited additional experienced and talented staff in the positions of statistical analyses, manufacturing operations, clinical operations, clinical research and non-clinical studies.
Dr. Suzanne Gagnon, M.D., is our Chief Medical Officer and a member of our Board of Directors. Dr. Gagnon is an experienced CMO, having served in that capacity for several private and public companies, including BioPharm/IBAH/Omnicare, ICON, Idis, NuPathe, Luitpold (Daiichi-Sankyo), and Rhone-Poulenc and Rorer (Sanofi) where she helped develop docetaxel, still an important chemotherapy agent. Dr. Gagnon assumed the lead in the design and implementation of our clinical trials, recruiting investigators, monitoring the safety of the patients and reporting the findings to the FDA, EMA and TGA, and in medical literature.
We have engaged Courante Oncology, an experienced clinical Contract Research Organization (“CRO”), to manage clinical operations in the United States, and have engaged Novotech Pty Ltd, another experienced CRO for our Australian operations. These two CROs will provide regulatory documentation for HREC/CTN and Investigational Review Board (“IRB”) submissions, FDA 1571 regulation compliance, and informed consents, as well as clinical study site qualification, contracting and payment, study conduct monitoring, data collection, analysis and reporting.
Competition
The development and commercialization of new products to treat cancer is intensely competitive and subject to rapid and significant technological change. While we believe that our knowledge, experience and scientific resources provide us with competitive advantages, we face substantial competition from major pharmaceutical companies, specialty pharmaceutical companies, and biotechnology companies worldwide. Many of our competitors have significantly greater financial, technical, and human resources. Smaller and early-stage companies may also prove to be significant competitors, particularly through collaborative arrangements with large and established companies. As a result, our competitors may discover, develop, license or commercialize products before or more successfully than we do.
We face competition with respect to our current product candidates, and will face competition with respect to future product candidates, from segments of the pharmaceutical, biotechnology and other related markets that pursue approaches to targeting molecular alterations and signaling pathways associated with cancer. Our competitors may obtain regulatory approval of their products more rapidly than we do or may obtain patent protection or other intellectual property rights that limit our ability to develop or commercialize our product candidates. Our competitors may also develop drugs that are more effective, more convenient, less costly, or possessing better safety profiles than our products, and these competitors may be more successful than us in manufacturing and marketing their products.
In addition, we may need to develop our product candidates in collaboration with diagnostic companies, and we will face competition from other companies in establishing these collaborations. Our competitors will also compete with us in recruiting and retaining qualified scientific, management and commercial personnel, establishing clinical trial sites and patient registration for clinical trials, as well as in acquiring technologies complementary to, or necessary for, our programs.
Furthermore, we also face competition more broadly across the market for cost-effective and reimbursable cancer treatments. The most common methods of treating patients with cancer are surgery, radiation and drug therapy, including chemotherapy, hormone therapy and targeted drug therapy or a combination of such methods. There are a variety of available drug therapies marketed for cancer. In many cases, these drugs are administered in combination to enhance efficacy. While our product candidates, if any are approved, may compete with these existing drug and other therapies, to the extent they are ultimately used in combination with or as an adjunct to these therapies, our product candidates may be approved as companion treatments and not be competitive with current therapies. Some of these drugs are branded and subject to patent protection, and others are available on a generic basis. Insurers and other third-party payors may also encourage the use of generic products or specific branded products. We expect that if our product candidates are approved, they will be priced at a premium over competitive generic, including branded generic, products. As a result, obtaining market acceptance of, and gaining significant share of the market for, any of our product candidates that we successfully introduce to the market will pose challenges. In addition, many companies are developing new therapeutics and we cannot predict what the standard of care will be as our product candidate progresses through clinical development.
SBP-101
Commercialization
We have not established a sales, marketing or product distribution infrastructure nor have we devoted significant management resources to planning such an infrastructure because our lead product candidate is still in early clinical development. We currently anticipate that we will partner with a larger pharmaceutical organization having the expertise and capacity to perform these functions.
Manufacturing and Suppliers
We do not own or operate, and currently have no plans to establish, any manufacturing facilities. We currently rely, and expect to continue to rely, on third parties for the manufacture of our product candidates for preclinical and clinical testing as well as for commercial manufacture of any products that we may commercialize. If needed, we intend to engage, by entering into a supply agreement or through another arrangement, third party manufacturers to provide us with additional SBP-101 clinical supply. We identified and qualified manufacturers to provide the active pharmaceutical ingredient and fill-and-finish services for our initial product candidate prior to our submission of an NDA to the FDA and expect to continue utilizing this approach for any future product candidates.
Employees
As of March 19, 2018, we had six employees, five of whom were full-time employees and one of whom was a part-time employee. We may hire additional employees to support the growth of our businesses. We believe that operational responsibilities can be handled by our current employees and independent consultants. We have historically used, and expect to continue to use, the services of independent consultants and contractors to perform various professional services. We believe that this use of third-party service providers enhances our ability to minimize general and administrative expenses. None of our employees is represented by a labor union, and we consider our relationship with our employees to be good.
Material Agreements
The Standard Exclusive License Agreement dated December 22, 2011, between us and UFRF grants us an exclusive license to the proprietary technology covered by issued United States Patents Nos. US 5,962,533, which expired in February 2016, and US 6,160,022 which expires in July 2019, with reservations by UFRF for academic or government uses. Under this agreement, we agree to pay various royalties, expenses and milestone payments to UFRF. Additionally, pursuant to this agreement, we initially issued to UFRF 80,000 shares of common stock. Anti-dilution protection for UFRF pursuant to this agreement required us to issue additional shares in order for UFRF to maintain its ownership stake at ten percent (10%) of the total number of issued and outstanding shares of our common stock, calculated on a fully diluted basis, until such time as we had received a total of two million dollars ($2,000,000) in exchange for our issuance of equity securities. This requirement was met in 2012, and UFRF is therefore afforded no further anti-dilution protection. Pursuant to this anti-dilution provision, we issued an additional 34,423 shares of common stock to UFRF increasing the total shares of common stock issued to UFRF to 114,423 shares.
Under the License Agreement, we have a number of performance related milestones we must meet in order to retain our rights to the technology. Included in such milestones is the commitment to have our first commercial sale of a product incorporating the technology by the end of 2020. Also, in the event that we are not actively pursuing commercialization of the technology in any country or territory other than the United States and certain other countries by the end of 2014, UFRF may terminate the license as to that country or territory under certain circumstances. UFRF may also terminate this license for standard and similar causes such as material breach of the agreement, bankruptcy, failure to pay royalties and other customary conditions.
The foregoing description of the material terms of the License Agreement is qualified by the full text of the License Agreement, a copy of which was filed as Exhibit 10.5 to our current report on Form 8-K filed on September 11, 2015 and is incorporated herein by reference.
Government Regulation
FDA Approval Process
In the United States, pharmaceutical products are subject to extensive regulation by the FDA. The Federal Food, Drug and Cosmetic Act and other federal and state statutes and regulations govern, among other things, the research, development, testing, manufacture, storage, recordkeeping, approval, labeling, promotion and marketing, distribution, post-approval monitoring and reporting, sampling and import and export of pharmaceutical products. Failure to comply with applicable US requirements may subject a company to a variety of administrative or judicial sanctions, such as FDA refusal to approve pending NDAs, warning or untitled letters, product recalls, product seizures, total or partial suspension of production or distribution, injunctions, fines, civil penalties and criminal prosecution.
Pharmaceutical product development for a new product or certain changes to an approved product in the United States typically involves preclinical laboratory and animal tests, the submission to the FDA of an IND which must become effective before clinical testing may commence, and adequate and well-controlled clinical trials to establish the safety and effectiveness of the drug for each indication for which FDA approval is sought. Satisfaction of FDA pre-market approval requirements typically takes many years and the actual time required may vary substantially based upon the type, complexity and novelty of the product or disease.
Preclinical tests include laboratory evaluation of product chemistry, formulation and toxicity, as well as animal trials to assess the characteristics and potential safety and efficacy of the product. The conduct of the preclinical tests must comply with federal regulations and requirements, including good laboratory practices. The results of preclinical testing are submitted to the FDA as part of an IND along with other information, including information about product chemistry, manufacturing and controls, and a proposed clinical trial protocol. Long-term preclinical tests, such as animal tests of reproductive toxicity and carcinogenicity, may continue after the IND is submitted.
A 30-day waiting period after the submission of each IND is required prior to the commencement of clinical testing in humans. If the FDA has neither commented on nor questioned the IND within this 30-day period, the clinical trial proposed in the IND may begin.
Clinical trials involve the administration of the investigational new drug to healthy volunteers or patients under the supervision of a qualified investigator. Clinical trials must be conducted: (i) in compliance with federal regulations; (ii) in compliance with good clinical practice (“GCP”), an international standard meant to protect the rights and health of patients and to define the roles of clinical trial sponsors, administrators and monitors; as well as (iii) under protocols detailing the objectives of the trial, the parameters to be used in monitoring safety and the effectiveness criteria to be evaluated. Each protocol involving testing on US patients and subsequent protocol amendments must be submitted to the FDA as part of the IND.
The FDA may order the temporary, or permanent, discontinuation of a clinical trial at any time, or impose other sanctions, if it believes that the clinical trial either is not being conducted in accordance with FDA requirements or presents an unacceptable risk to the clinical trial patients. The study protocol and informed consent information for patients in clinical trials must also be submitted to an institutional review board (“IRB”) for approval. An IRB may also require the clinical trial at the site to be halted, either temporarily or permanently, for failure to comply with the IRB’s requirements, or may impose other conditions.
Clinical trials to support NDAs for marketing approval are typically conducted in three sequential phases, but the phases may overlap. In Phase 1, the initial introduction of the drug into healthy human subjects/patients, the drug is tested to assess metabolism, pharmacokinetics, pharmacological actions, side effects associated with increasing doses, and, if possible, early evidence of effectiveness. Phase 2 usually involves trials in a limited patient population to determine the effectiveness of the drug for a particular indication, dosage tolerance and optimum dosage, and to identify common adverse effects and safety risks. If a compound demonstrates evidence of effectiveness and an acceptable safety profile in Phase 2 evaluations, Phase 3 trials are undertaken to obtain the additional information about clinical efficacy and safety in a larger number of patients, typically at geographically dispersed clinical trial sites, to permit the FDA to evaluate the overall benefit-risk relationship of the drug and to provide adequate information for the labeling of the drug. In many cases the FDA requires two adequate and well-controlled Phase 3 clinical trials to demonstrate the efficacy of the drug. A single Phase 3 trial with other confirmatory evidence may be sufficient in instances where the study is a large multicenter trial demonstrating internal consistency and a statistically very persuasive finding of a clinically meaningful effect on mortality, irreversible morbidity or prevention of a disease with a potentially serious outcome and confirmation of the result in a second trial would be practically or ethically impossible.
After completion of the required clinical testing, an NDA is prepared and submitted to the FDA. FDA approval of the NDA is required before marketing of the product may begin in the United States. The NDA must include the results of all preclinical, clinical and other testing and a compilation of data relating to the product’s pharmacology, chemistry, manufacture and controls. The cost of preparing and submitting an NDA is substantial, and the fees are typically increased annually.
The FDA has 60 days from its receipt of an NDA to determine whether the application will be accepted for filing based on the agency’s threshold determination that it is sufficiently complete to permit substantive review. Once the submission is accepted for filing, the FDA begins an in-depth review. The FDA has agreed to certain performance goals in the review of new drug applications to encourage timeliness. Most applications for standard review drug products are reviewed within twelve months from submission; most applications for priority review drugs are reviewed within eight months from submission. Priority review can be applied to drugs that the FDA determines offer major advances in treatment, or provide a treatment where no adequate therapy exists. The review process for both standard and priority review may be extended by the FDA for three additional months to consider certain late-submitted information, or information intended to clarify information already provided in the submission.
The FDA may also refer applications for novel drug products, or drug products that present difficult questions of safety or efficacy, to an outside advisory committee—typically a panel that includes clinicians and other experts—for review, evaluation and a recommendation as to whether the application should be approved. The FDA is not bound by the recommendation of an advisory committee, but it generally follows such recommendations.
Before approving an NDA, the FDA will typically inspect one or more clinical sites to assure compliance with GCP. Additionally, the FDA will inspect the facility or the facilities at which the drug is manufactured. The FDA will not approve the product unless compliance with current good manufacturing practice (“cGMP”), a quality system regulating manufacturing, is satisfactory and the NDA contains data that provide substantial evidence that the drug is safe and effective in the indication studied.
After the FDA evaluates the NDA and the manufacturing facilities, it issues either an approval letter or a complete response letter. A complete response letter generally outlines the deficiencies in the submission and may require substantial additional testing, or information, in order for the FDA to reconsider the application. If, or when, those deficiencies have been addressed to the FDA’s satisfaction in a resubmission of the NDA, the FDA will issue an approval letter. The FDA has committed to reviewing such resubmissions in two or six months depending on the type of information included.
An approval letter authorizes commercial marketing of the drug with specific prescribing information for specific indications. As a condition of NDA approval, the FDA may require a risk evaluation and mitigation strategy (“REMS”) to help ensure that the benefits of the drug outweigh the potential risks. REMS can include medication guides, communication plans for healthcare professionals, and elements to assure safe use (“ETASU”). ETASU can include, but are not limited to, special training or certification for prescribing or dispensing, dispensing only under certain circumstances, special monitoring and the use of patient registries. The requirement for a REMS can materially affect the potential market and profitability of the drug. Moreover, product approval may require substantial post-approval testing and surveillance to monitor the drug’s safety or efficacy. Once granted, product approvals may be withdrawn if compliance with regulatory standards is not maintained or problems are identified following initial marketing.
Changes to some of the conditions established in an approved application, including changes in indications, labeling, or manufacturing processes or facilities, require submission and FDA approval of a new NDA or NDA supplement before the change can be implemented. An NDA supplement for a new indication typically requires clinical data similar to that in the original application, and the FDA uses the same procedures and actions in reviewing NDA supplements as it does in reviewing NDAs.
Fast Track Designation and Accelerated Approval
The FDA is required to facilitate the development, and expedite the review, of drugs that are intended for the treatment of a serious or life-threatening disease or condition for which there is no effective treatment and which demonstrate the potential to address unmet medical needs for the condition. Under the Fast Track program, the sponsor of a new product candidate may request that the FDA designate the product candidate for a specific indication as a Fast Track drug concurrent with, or after, the filing of the IND for the product candidate. The FDA must determine if the product candidate qualifies for Fast Track Designation within 60 days of receipt of the sponsor’s request.
Under the Fast Track program and FDA’s accelerated approval regulations, the FDA may approve a drug for a serious or life-threatening illness that provides meaningful therapeutic benefit to patients over existing treatments based upon a surrogate endpoint that is reasonably likely to predict clinical benefit, or on a clinical endpoint that can be measured earlier than irreversible morbidity or mortality, that is reasonably likely to predict an effect on irreversible morbidity or mortality or other clinical benefit, taking into account the severity, rarity, or prevalence of the condition and the availability or lack of alternative treatments.
In clinical trials, a surrogate endpoint is a measurement of laboratory or clinical signs of a disease or condition that substitutes for a direct measurement of how a patient feels, functions, or survives. Surrogate endpoints can often be measured more easily or more rapidly than clinical endpoints. A product candidate approved on this basis is subject to rigorous post-marketing compliance requirements, including the completion of Phase 4 or post-approval clinical trials to confirm the effect on the clinical endpoint. Failure to conduct required post-approval studies, or confirm a clinical benefit during post-marketing studies, will allow FDA to withdraw the drug from the market on an expedited basis. All promotional materials for product candidates approved under accelerated regulations are subject to priority review by FDA.
If a submission is granted Fast Track Designation, the sponsor may engage in more frequent interactions with the FDA, and the FDA may review sections of the NDA before the application is complete. This rolling review is available if the applicant provides, and the FDA approves, a schedule for the submission of the remaining information and the applicant pays applicable user fees. However, the FDA’s time period goal for reviewing an application does not begin until the last section of the NDA is submitted. Additionally, Fast Track Designation may be withdrawn by the FDA if the FDA believes that the designation is no longer supported by data emerging in the clinical trial process.
Breakthrough Therapy Designation
The FDA is also required to expedite the development and review of the application for approval of drugs that are intended to treat a serious or life-threatening disease or condition where preliminary clinical evidence indicates that the drug may demonstrate substantial improvement over existing therapies on one or more clinically significant endpoints. Under the Breakthrough Therapy program, the sponsor of a new product candidate may request that the FDA designate the product candidate for a specific indication as a breakthrough therapy. The FDA must determine if the product candidate qualifies for Breakthrough Therapy designation within 60 days of receipt of the sponsor’s request.
Orphan Drug Designation and Exclusivity
The Orphan Drug Act provides incentives for the development of products intended to treat rare diseases or conditions. Under the Orphan Drug Act, the FDA may grant orphan designation to a drug intended to treat a rare disease or condition, which is generally a disease or condition that affects fewer than 200,000 individuals in the United States, or more than 200,000 individuals in the United States and for which there is no reasonable expectation that the cost of developing and making a drug available in the United States for this type of disease or condition will be recovered from sales of the product. If a sponsor demonstrates that a drug is intended to treat a rare disease or condition, the FDA will grant orphan designation for that product for the orphan disease indication, assuming that the same drug has not already been approved for the indication for which the sponsor is seeking orphan designation. If the same drug has already been approved for the indication for which the sponsor is seeking orphan designation, the sponsor must present a plausible hypothesis of clinical superiority in order to obtain orphan designation. Orphan designation must be requested before submitting an NDA. After the FDA grants orphan designation, the FDA discloses the identity of the therapeutic agent and its potential orphan use.
Orphan designation may provide manufacturers with benefits such as research grants, tax credits, PDUFA application fee waivers and eligibility for orphan drug exclusivity. If a product that has orphan designation subsequently receives the first FDA approval of the active moiety for that disease or condition for which it has such designation, the product is entitled to orphan drug exclusivity, which for seven years prohibits the FDA from approving another product with the same active ingredient for the same indication, except in limited circumstances. Orphan drug exclusivity will not bar approval of another product under certain circumstances, including if a subsequent product with the same active ingredient for the same indication is shown to be clinically superior to the approved product on the basis of greater efficacy or safety, or providing a major contribution to patient care, or if the company with orphan drug exclusivity is not able to meet market demand. Further, the FDA may approve more than one product for the same orphan indication or disease as long as the products contain different active ingredients. Moreover, competitors may receive approval of different products for the indication for which the orphan drug has exclusivity or obtain approval for the same product but for a different indication for which the orphan drug has exclusivity.
In the European Union, orphan drug designation also entitles a party to financial incentives such as reduction of fees or fee waivers and 10 years of market exclusivity is granted following drug or biological product approval. This period may be reduced to 6 years if the orphan drug designation criteria are no longer met, including where it is shown that the product is sufficiently profitable not to justify maintenance of market exclusivity.
Orphan drug designation must be requested before submitting an application for marketing approval. Orphan drug designation does not convey any advantage in, or shorten the duration of, the regulatory review and approval process.
Post-Approval Requirements
Once an NDA is approved, a product will be subject to certain post-approval requirements. For instance, the FDA closely regulates the post-approval marketing and promotion of drugs, including standards and regulations for direct-to-consumer advertising, off-label promotion, industry-sponsored scientific and educational activities and promotional activities involving the internet. Drugs may be marketed only for the approved indications and in accordance with the provisions of the approved labeling.
Adverse event reporting and submission of periodic reports are required following FDA approval of an NDA. The FDA also may require post-marketing testing, known as Phase 4 testing, risk evaluation and mitigation strategies, or REMS, and surveillance to monitor the effects of an approved product, or FDA may place conditions on an approval that could restrict the distribution or use of the product. In addition, quality control, drug manufacture, packaging and labeling procedures must continue to conform to current good manufacturing practices, or cGMPs, after approval. Drug manufacturers and certain of their subcontractors are required to register their establishments with the FDA and certain state agencies. Registration with FDA subjects entities to periodic unannounced inspections by the FDA, during which the Agency inspects manufacturing facilities to assess compliance with cGMPs. Accordingly, manufacturers must continue to expend time, money and effort in the areas of production and quality-control to maintain compliance with cGMPs. Regulatory authorities may withdraw product approvals or request product recalls if a company fails to comply with regulatory standards, if it encounters problems following initial marketing, or if previously unrecognized problems are subsequently discovered.
Additional Regulations and Environmental Matters
In addition to FDA restrictions on marketing of pharmaceutical products, we are subject to additional healthcare regulation and enforcement by the federal government and by authorities in the states and foreign jurisdictions in which we conduct our business. These laws, which generally will not be applicable to us or our product candidates unless and until we obtain FDA marketing approval for any of our product candidates, include transparency laws, anti-kickback statutes, false claims statutes and regulation regarding providing drug samples, among others.
The federal Anti-Kickback Statute prohibits, among other things, individuals and entities from knowingly and willfully offering, paying, soliciting or receiving remuneration to induce or in return for purchasing, leasing, ordering or arranging for the purchase, lease or order of any healthcare item or service reimbursable under Medicare, Medicaid or other federally financed healthcare programs. Violations of the federal Anti-Kickback Statute are punishable by imprisonment, criminal fines, civil monetary penalties and exclusion from participation in federal healthcare programs.
Federal false claims laws and civil monetary penalties, including the False Claims Act, prohibit, among other things, any person or entity from knowingly presenting, or causing to be presented, a false claim for payment to the federal government, or knowingly making, or causing to be made, a false statement to have a false claim paid. Recently, several pharmaceutical companies have been prosecuted under these laws for allegedly inflating drug prices they report to pricing services, which in turn were used by the government to set Medicare and Medicaid reimbursement rates, and for allegedly providing free product to customers with the expectation that the customers would bill federal programs for the product. In addition, certain marketing practices, including off-label promotion, may also violate false claims laws.
HIPAA imposes criminal and civil liability for, among other things, executing a scheme to defraud any healthcare benefit program or making false statements relating to healthcare matters.
HIPAA, as amended by the HITECH Act and its implementing regulations, also imposes obligations, including mandatory contractual terms, with respect to safeguarding the privacy, security and transmission of individually identifiable health information. Many states and foreign jurisdictions also have laws and regulations that govern the privacy and security of individually identifiable health information and such laws often vary from one another and from HIPAA.
The federal Physician Payment Sunshine Act requires certain manufacturers of drugs, devices, biologics and medical supplies for which payment is available under Medicare, Medicaid or the Children’s Health Insurance Program, with specific exceptions, to report annually to CMS, information related to payments or other transfers of value made to physicians and teaching hospitals, and ownership and investment interests held by the physicians and their immediate family members.
The majority of states also have statutes or regulations similar to the federal Anti-Kickback Law and false claims laws, which apply to items and services reimbursed under Medicaid and other state programs, or, in several states, apply regardless of the payor. Our activities may also be subject to certain state laws regarding the privacy and security of health information that may not be preempted by HIPAA, as well as additional tracking and reporting obligations regarding payments to healthcare providers and marketing expenditures.
In addition to regulatory schemes that apply, or may in the future apply, to our business, we are or may become subject to various environmental, health and safety laws and regulations governing, among other things, laboratory procedures and any use and disposal by us of hazardous or potentially hazardous substances in connection with our research and development activities. We do not presently expect such environmental, health and safety laws or regulations to materially impact our present or planned future activities.
Coverage and Reimbursement
Sales of any of our product candidates that may be approved will depend, in part, on the extent to which the cost of the product will be covered by third party payors. Third party payors may limit coverage to an approved list of products, or formulary, which might not include all drug products approved by the FDA for an indication. A payor’s decision to provide coverage for a drug product does not imply that an adequate reimbursement rate will be approved. Further, one payor’s determination to provide coverage for a drug product does not assure that other payors will also provide coverage for the drug product. Adequate third-party reimbursement may not be available to enable us to maintain price levels sufficient to realize an appropriate return on our investment in product development.
Any product candidates for which we obtain marketing approval may not be considered medically necessary or cost-effective by third party payors and we may need to conduct expensive pharmacoeconomic studies in the future to demonstrate the medical necessity and/or cost effectiveness of any such product. Nonetheless, our product candidates may not be considered medically necessary or cost effective. The U.S. government, state legislatures and foreign governments have shown increased interest in implementing cost containment programs to limit government-paid health care costs, including price controls, restrictions on reimbursement and requirements for substitution of generic products. Continued interest in and adoption of such controls and measures, and tightening of restrictive policies in jurisdictions with existing controls and measures, could limit payments for pharmaceuticals such as the product candidates we are developing.
Health Reform
The United States and some foreign jurisdictions are considering or have enacted a number of legislative and regulatory proposals to change the healthcare system in ways that could affect our ability to sell our products profitably. Among policy makers and payors in the United States and elsewhere, there is significant interest in promoting changes in healthcare systems with the stated goals of containing healthcare costs, improving quality and expanding access. In the United States, the pharmaceutical industry has been a particular focus of these efforts and has been significantly affected by major legislative initiatives. By way of example, in March 2010, the ACA was signed into law, which intended to broaden access to health insurance, reduce or constrain the growth of healthcare spending, enhance remedies against fraud and abuse, add transparency requirements for the healthcare and health insurance industries, impose taxes and fees on the health industry and impose additional health policy reforms. With regard to pharmaceutical products, among other things, the ACA expanded and increased industry rebates for drugs covered under Medicaid programs and made changes to the coverage requirements under the Medicare prescription drug benefit. We continue to evaluate the effect that the ACA has on our business.
In addition, other legislative changes have been proposed and adopted since the ACA was enacted. These changes included aggregate reductions to Medicare payments to providers of up to 2% per fiscal year effective April 1, 2013 and, due to subsequent legislative amendments to the statute, will stay in effect through 2024 unless additional Congressional action is taken. In January 2013, President Obama signed into law the American Taxpayer Relief Act of 2012, which, among other things, reduced Medicare payments to several providers, and increased the statute of limitations period for the government to recover overpayments to providers from three to five years. These new laws may result in additional reductions in Medicare and other healthcare funding, which could have a material adverse effect on customers for our drugs, if approved, and, accordingly, our financial operations.
In the coming years, additional legislative and regulatory changes could be made to governmental health programs that could significantly impact pharmaceutical companies and the success of our product candidates.
Available Information
Our website is located at www.SunBioPharma.com. The information contained on or connected to our website is not a part of this report. We have included our website address as a factual reference and do not intend it to be an active link to our website.
We make available, free of charge, through our website materials we file or furnish to the SEC pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Exchange Act, including our annual report on Form 10-K, our quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, our current reports on Form 8-K and amendments to those reports. These materials are posted to our website as soon as reasonably practicable after we electronically file them with or furnish them to the SEC.
Members of the public may read and copy any materials we file with the SEC at its Public Reference Room at 450 Fifth Street, NW, Washington, DC 20549. Information on the operation of the Public Reference Room is available by calling the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330. The SEC maintains a website that contains reports, proxy and information statements and other information about us and other issuers that file electronically at http://www.sec.gov.
|
Item 1A. |
Risk Factors |
You should carefully consider the following information about risks, together with the other information contained in this report before making an investment in our common stock. If any of the circumstances or events described below actually arises or occurs, our business, results of operations, cash flows and financial condition could be harmed.
Risks Related to Our Business
We are a company with limited revenue history for you to evaluate our business.
We have a limited operating history for you to consider in evaluating our business and prospects. As such, it is difficult for potential investors to evaluate our business.
We have experienced negative cash flows for our operating activities since inception, primarily due to the investments required to commercialize our primary drug candidate, SBP-101. Our financing cash flows historically have been positive due to proceeds from the sale of equity securities and promissory notes issuances. Our net cash used in operating activities was $3.4 million and $2.4 million for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively, and we had negative working capital of $3.4 million and $4.6 million as of the same dates, respectively.
Our operations are subject to all of the risks, difficulties, complications and delays frequently encountered in connection with the formation of any new business, as well as those risks that are specific to the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries in which we compete. Investors should evaluate us in light of the delays, expenses, problems and uncertainties frequently encountered by companies developing markets for new products, services and technologies. We may never overcome these obstacles.
As a result of our current lack of financial liquidity, we and our auditors have expressed substantial doubt regarding our ability to continue as a “going concern.”
As a result of our current lack of financial liquidity, our auditors’ report for our 2017 financial statements, which are included as part of this report, contains a statement concerning our ability to continue as a “going concern.” Our lack of sufficient liquidity could make it more difficult for us to secure additional financing or enter into strategic relationships on terms acceptable to us, if at all, and may materially and adversely affect the terms of any financing that we may obtain and our public stock price generally.
Our continuation as a “going concern” is dependent upon, among other things, achieving positive cash flow from operations and, if necessary, augmenting such cash flow using external resources to satisfy our cash needs. Our plans to achieve positive cash flow primarily include engaging in offerings of securities. Additional potential sources of funds include negotiating up-front and milestone payments on our current and potential future product candidates or royalties from sales of our products that secure regulatory approval and any milestone payments associated with such approved products. These cash sources could, potentially, be supplemented by financing or other strategic agreements. However, we may be unable to achieve these goals or obtain required funding on commercially reasonable terms, or at all, and therefore may be unable to continue as a going concern.
Our lack of diversification increases the risk of an investment in our Company and our financial condition and results of operations may deteriorate if we fail to diversify.
Our Board of Directors has centered our attention on our drug development activities, which are currently focused on our initial product candidate SBP-101, the polyamine analogue compound we licensed from the UFRF. Our ability to diversify our investments will depend on our access to additional capital and financing sources and the availability and identification of suitable opportunities.
Larger companies have the ability to manage their risk by diversification. However, we lack and expect to continue to lack diversification, in terms of both the nature and geographic scope of our business. As a result, we will likely be impacted more acutely by factors affecting pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries in which we compete than we would if our business were more diversified, enhancing our risk profile. If we cannot diversify our operations, our financial condition and results of operations could deteriorate.
We may be unable to obtain the additional capital that is required to execute our business plan, which could restrict our ability to grow.
Our current capital and our other existing resources will be sufficient only to provide a limited amount of working capital and will not be sufficient to fund our expected continuing opportunities. We will require additional capital to continue to operate our business.
Future acquisitions, research and development and capital expenditures, as well as our administrative requirements, such as clinical trial costs, salaries, insurance expenses and general overhead expenses, as well as legal compliance costs and accounting expenses, will require a substantial amount of additional capital and cash flow. There is no guarantee that we will be able to raise additional capital required to fund our ongoing business on commercially reasonable terms or at all.
We intend to pursue sources of additional capital through various financing transactions or arrangements, including collaboration arrangements, debt financing, equity financing or other means. We may not be successful in locating suitable financing transactions on commercially reasonable terms, in the time period required or at all, and we may not obtain the capital we require by other means. If we do not succeed in raising additional capital, our resources will not be sufficient to fund our operations going forward.
Any additional capital raised through the sale of equity may dilute the ownership percentage of our stockholders. This could also result in a decrease in the fair market value of our equity securities because our assets would be owned by a larger pool of outstanding equity. The terms of securities we issue in future capital transactions may be more favorable to our new investors, and may include preferences, superior voting rights and the issuance of warrants or other derivative securities which may have a further dilutive effect.
Our ability to obtain needed financing may be impaired by such factors as the capital markets, both generally and in the pharmaceutical and other drug development industries in particular, our status as a new enterprise without a significant demonstrated operating history, the limited diversity of our activities and/or the loss of key personnel. If the amount of capital we are able to raise from financing activities is not sufficient to satisfy our capital needs, even to the extent that we reduce our operations, we may be required to cease our operations.
We may incur substantial costs in pursuing future capital financing, including investment banking fees, legal fees, accounting fees, securities law compliance fees, printing and distribution expenses and other costs, which may adversely impact our financial condition.
U.S. federal income tax reform could adversely affect our Company and its stockholders.
On December 22, 2017, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 became law (the “Tax Act”). The Tax Act enacts a broad range of changes to the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended (the “IRC”). The Tax Act, among other things, includes changes to U.S. federal tax rates, imposes significant additional limitations on the deductibility of interest and net operating losses, allows for the expensing of capital expenditures and puts into effect the migration from a “worldwide” system of taxation to a territorial system. We do not expect tax reform to have a material impact to our financial statements as our net deferred tax assets and liabilities are fully reserved. We continue to examine the impact this tax reform legislation may have on our business. The impact of the Tax Act on holders of our common shares is uncertain and could be adverse. This annual report does not discuss any such tax legislation or the manner in which it might affect purchasers of our common stock. We urge our stockholders to consult with their legal and tax advisors with respect to any such legislation and the potential tax consequences of investing in our common stock.
We may not be able to effectively manage our growth, which may harm our profitability.
Our strategy envisions expanding our business. If we fail to effectively manage our growth, our financial results could be adversely affected. Growth may place a strain on our management systems and resources. We must continue to refine and expand our business development capabilities, our systems and processes and our access to financing sources. As we grow, we must continue to hire, train, supervise and manage new employees. We cannot assure you that we will be able to:
|
● |
expand our systems effectively or efficiently or in a timely manner; |
|
● |
allocate our human resources optimally; |
|
● |
identify and hire qualified employees or retain valued employees; or |
|
● |
incorporate effectively the components of any business that we may acquire in our effort to achieve growth. |
If we are unable to manage our growth, our operations and our financial results could be adversely affected by inefficiency, which could diminish our profitability.
Our business may suffer if we do not attract and retain talented personnel.
Our success will depend in large measure on the abilities, expertise, judgment, discretion, integrity and good faith of our management and other personnel in conducting our business. We have a small management team, and the loss of a key individual or inability to attract suitably qualified staff could materially adversely impact our business.
Our success depends on the ability of our management, employees, consultants and joint venture partners, if any, to interpret market data correctly and to interpret and respond to economic market and other conditions in order to locate and adopt appropriate investment opportunities, monitor such investments, and ultimately, if required, to successfully divest such investments. Further, no assurance can be given that our key personnel will continue their association or employment with us or that replacement personnel with comparable skills can be found. We will seek to ensure that management and any key employees are appropriately compensated; however, their services cannot be guaranteed. If we are unable to attract and retain key personnel, our business may be adversely affected.
The market for our product candidate is highly competitive and is subject to rapid scientific change, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
The pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries in which we compete are highly competitive and characterized by rapid and significant technological change. We face intense competition from organizations such as pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies, as well as academic and research institutions and government agencies. Some of these organizations are pursuing products based on technologies similar to our technology. Other of these organizations have developed and are marketing products, or are pursuing other technological approaches designed to produce products that are competitive with our product candidates in the therapeutic effect these competitive products have on the disease targeted by our product candidate. Our competitors may discover, develop or commercialize products or other novel technologies that are more effective, safer or less costly than any that we may develop. Our competitors may also obtain FDA or other regulatory approval for their products more rapidly than we may obtain approval for our product candidate.
Many of our competitors are substantially larger than we are and have greater capital resources, research and development staffs and facilities than we have. In addition, many of our competitors are more experienced in drug discovery, development and commercialization, obtaining regulatory approvals and drug manufacturing and marketing.
We anticipate that the competition with our product candidate and technology will be based on a number of factors including product efficacy, safety, availability and price. The timing of market introduction of our planned future product candidates and competitive products will also affect competition among products. We expect the relative speed with which we can develop our product candidate, complete the required clinical trials, establish a strategic partner and supply appropriate quantities of the product candidate for late stage trials, if required, to be important competitive factors. Our competitive position will also depend upon our ability to attract and retain qualified personnel, to obtain patent protection in non-U.S. markets, which we currently do not have, or otherwise develop proprietary products or processes and to secure sufficient capital resources for the period between technological conception and commercial sales or out-license to a pharmaceutical partner. If we fail to develop and deploy our proposed product candidate in a successful and timely manner, we will in all likelihood not be competitive.
We face significant risks in our product candidate development efforts.
Our business depends on the successful development and commercialization of our product candidates. We are currently focused on developing our initial product candidate, SBP-101, for the treatment of Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (“PDA”) and are not permitted to market it in the United States until we receive approval of a NDA from the FDA, or in any foreign jurisdiction until we receive the requisite approvals from such jurisdiction. The process of developing new drugs and/or therapeutic products is inherently complex, unpredictable, time-consuming, expensive and uncertain. We must make long-term investments and commit significant resources before knowing whether our development programs will result in drugs that will receive regulatory approval and achieve market acceptance. A product candidate that appears to be promising at all stages of development may not reach the market for a number of reasons that may not be predictable based on results and data from the clinical program. A product candidate may be found ineffective or may cause harmful side effects during clinical trials, may take longer to progress through clinical trials than had been anticipated, may not be able to achieve the pre-defined clinical endpoints even though clinical benefit may have been achieved, may fail to receive necessary regulatory approvals, may prove impracticable to manufacture in commercial quantities at reasonable cost and with acceptable quality, or may fail to achieve market acceptance.
We cannot predict whether or when we will obtain regulatory approval to commercialize our initial product candidate and we cannot, therefore, predict the timing of any future revenues from this or other product candidates, if any. The FDA has substantial discretion in the drug approval process, including the ability to delay, limit or deny approval of a product candidate for many reasons. For example, the FDA:
|
● |
could determine that the information provided by us was inadequate, contained clinical deficiencies or otherwise failed to demonstrate the safety and effectiveness of any of our product candidates for any indication; |
|
● |
may not find the data from clinical trials sufficient to support the submission of an NDA or to obtain marketing approval in the United States, including any findings that the clinical and other benefits of our product candidates outweigh their safety risks; |
|
● |
may disagree with our trial design or our interpretation of data from preclinical studies or clinical trials, or may change the requirements for approval even after it has reviewed and commented on the design for our trials; |
|
● |
may identify deficiencies in the manufacturing processes or facilities of third-party manufacturers with which we enter into agreements for the manufacturing of our product candidates; |
|
● |
may approve our product candidates for fewer or more limited indications than we request, or may grant approval contingent on the performance of costly post-approval clinical trials; |
|
● |
may change its approval policies or adopt new regulations; or |
|
● |
may not approve the labeling claims that we believe are necessary or desirable for the successful commercialization of our product candidates. |
Any failure to obtain regulatory approval of our initial product candidate or future product candidates we develop, if any, would significantly limit our ability to generate revenues, and any failure to obtain such approval for all of the indications and labeling claims we deem desirable could reduce our potential revenues.
Our product candidate is based on new formulation of an existing technology which has never been approved for the treatment of any cancer and, consequently, is inherently risky. Concerns about the safety and efficacy of our product candidate could limit our future success.
We are subject to the risks of failure inherent in the development of product candidates based on new technologies. These risks include the possibility that any product candidates we create will not be effective, that our current product candidate will be unsafe, ineffective or otherwise fail to receive the necessary regulatory approvals or that our product candidate will be hard to manufacture on a large scale or will be uneconomical to market.
Many pharmaceutical products cause multiple potential complications and side effects, not all of which can be predicted with accuracy and many of which may vary from patient to patient. Long term follow-up data may reveal additional complications associated with our product candidate. The responses of potential physicians and others to information about complications could materially affect the market acceptance of our product candidate, which in turn would materially harm our business.
Clinical trials required for our product candidate are expensive and time-consuming, and their outcome is highly uncertain. If any of our drug trials are delayed or yield unfavorable results, we will have to delay or may be unable to obtain regulatory approval for our product candidate.
We must conduct extensive testing of our product candidate before we can obtain regulatory approval to market and sell it. We need to conduct both preclinical animal testing and human clinical trials. Conducting these trials is a lengthy, time-consuming and expensive process. These tests and trials may not achieve favorable results for many reasons, including, among others, failure of the product candidate to demonstrate safety or efficacy, the development of serious or life-threatening adverse events, or side effects, caused by or connected with exposure to the product candidate, difficulty in enrolling and maintaining subjects in the clinical trial, lack of sufficient supplies of the product candidate or comparator drug, and the failure of clinical investigators, trial monitors, contractors, consultants, or trial subjects to comply with the trial protocol. A clinical trial may fail because it did not include a sufficient number of patients to detect the endpoint being measured or reach statistical significance. A clinical trial may also fail because the dose(s) of the investigational drug included in the trial were either too low or too high to determine the optimal effect of the investigational drug in the disease setting. Many clinical trials are conducted under the oversight of Independent Data Monitoring Committees (“IDMCs”). These independent oversight bodies are made up of external experts who review the progress of ongoing clinical trials, including available safety and efficacy data, and make recommendations concerning a trial’s continuation, modification, or termination based on interim, unblinded data. Any of our ongoing clinical trials may be discontinued or amended in response to recommendations made by responsible IDMCs based on their review of such interim trial results.
We will need to reevaluate our product candidate if it does not test favorably and either conduct new trials, which are expensive and time consuming, or abandon our drug development program. Even if we obtain positive results from preclinical or clinical trials, we may not achieve the same success in future trials. Many companies in the biopharmaceutical industry have suffered significant setbacks in clinical trials, even after promising results have been obtained in earlier trials. The failure of clinical trials to demonstrate safety and effectiveness for the desired indication could harm the development of our product candidate and our business, financial condition and results of operations may be materially harmed.
The results of pre-clinical studies and completed clinical trials are not necessarily predictive of future results, and our current product candidates may not have favorable results in later studies or trials.
Pre-clinical studies and Phase 1 and Phase 2 clinical trials are not primarily designed to test the efficacy of a product candidate in the general population, but rather to test initial safety, to study pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics, to study limited efficacy in a small number of study patients in a selected disease population, and to identify and attempt to understand the product candidate’s side effects at various doses and dosing schedules. Success in pre-clinical studies or completed clinical trials does not ensure that later studies or trials, including continuing pre-clinical studies and large-scale clinical trials, will be successful nor does it necessarily predict future results. Favorable results in early studies or trials may not be repeated in later studies or trials, and product candidates in later stage trials may fail to show acceptable safety and efficacy despite having progressed through earlier trials.
Due to our reliance on third-parties to conduct our clinical trials, we are unable to directly control the timing, conduct, expense and quality of our clinical trials, which could adversely affect our clinical data and results and related regulatory approvals.
We extensively outsource our clinical trial activities and expect to directly perform only a small portion of the preparatory stages for planned trials. We rely on independent third-party contract research organizations (“CROs”) to perform most of our clinical trials, including document preparation, site identification, screening and preparation, pre-study visits, training, program management and bio-analytical analysis. Many important aspects of the services performed for us by the CROs are out of our direct control. If there is any dispute or disruption in our relationship with our CROs, our clinical trials may be delayed. Moreover, in our regulatory submissions, we rely on the quality and validity of the clinical work performed by third-party CROs. If a CRO’s processes, methodologies or results are determined to be invalid or inadequate, our own clinical data and results and related regulatory approvals could be adversely affected or invalidated.
Regulatory and legal uncertainties could result in significant costs or otherwise harm our business.
In order to manufacture and sell our product candidate, we must comply with extensive international and domestic regulations. In order to sell our product candidate in the United States, approval from the FDA is required. The FDA approval process is expensive and time-consuming. We cannot predict whether our product candidate will be approved by the FDA. Even if our product candidate is approved, we cannot predict the time frame for such approval. Foreign regulatory requirements differ from jurisdiction to jurisdiction and may, in some cases, be more stringent or difficult to obtain than FDA approval. As with the FDA, we cannot predict if or when we may obtain these regulatory approvals. If we cannot demonstrate that our product candidate can be used safely and successfully in a broad enough segment of the indicated patient population for a satisfactory length of time, our product candidate would likely be denied approval by the FDA and the regulatory agencies of foreign governments.
We may be unable to formulate or manufacture our product candidate in a way that is suitable for clinical or commercial use.
Changes in product formulations and manufacturing processes may be required as our product candidate progresses in clinical development and is ultimately commercialized. If we are unable to develop suitable product formulations or manufacturing processes to support large scale clinical testing of our product candidate, we may be unable to supply necessary materials for our clinical trials, which would delay the development of our product candidate. Similarly, if we are unable to supply sufficient quantities of our product candidate or develop product formulations suitable for commercial use, we will not be able to successfully commercialize our product candidate.
We lack sales, marketing and distribution capabilities and currently expect to rely on third parties to market and distribute our product candidate, which may harm or delay our commercialization efforts.
We currently have no sales, marketing, or distribution capabilities and do not currently intend to develop such capabilities in the foreseeable future. If we are unable to partner with a larger pharmaceutical organization having the expertise and capacity to perform these functions, then we may be unable to sell any product that we develop. We may not be able to enter into any necessary arrangements, including marketing or distribution agreements, on acceptable terms, if at all. Should our strategic partners, if any, be unable to effectively sell our products, then our ability to generate revenues will be significantly harmed.
We may be required to defend lawsuits or pay damages for product liability claims.
Product liability is a major risk in testing and marketing biotechnology and pharmaceutical products. We may face substantial product liability exposure in human clinical trials and in the sale of products after regulatory approval. Product liability claims, regardless of their merits, could exceed policy limits, divert management’s attention and adversely affect our reputation and the demand for our product. In any such event, your investment in our securities could be materially and adversely affected.
Risks Related to the Regulation of our Business
Federal and state pharmaceutical marketing compliance and reporting requirements may expose us to regulatory and legal action by state governments or other government authorities.
The Food and Drug Administration Modernization Act (the “FDMA”), established a public registry of open clinical trials involving drugs intended to treat serious or life-threatening diseases or conditions in order to promote public awareness of and access to these clinical trials. Under the FDMA, pharmaceutical manufacturers and other trial sponsors are required to post the general purpose of these trials, as well as the eligibility criteria, location and contact information of the trials. Failure to comply with any clinical trial posting requirements could expose us to negative publicity, fines and other penalties, all of which could materially harm our business.
In recent years, several states, including California, Vermont, Maine, Minnesota, New Mexico and West Virginia have enacted legislation requiring pharmaceutical companies to establish marketing compliance programs and file periodic reports on sales, marketing, pricing and other activities. Similar legislation is being considered in other states. Many of these requirements are new and uncertain, and available guidance is limited. Unless we are in full compliance with these laws, we could face enforcement actions and fines and other penalties and could receive adverse publicity, all of which could harm our business.
If the product candidate we develop becomes subject to unfavorable pricing regulations, third party reimbursement practices or healthcare reform initiatives, our ability to successfully commercialize our product candidate may be impaired.
Our future revenues, profitability and access to capital will be affected by the continuing efforts of governmental and private third party payors to contain or reduce the costs of health care through various means. We expect a number of federal, state and foreign proposals to control the cost of drugs through government regulation. We are unsure of the impact recent health care reform legislation may have on our business or what actions federal, state, foreign and private payors may take in response to the recent reforms. Therefore, it is difficult to predict the effect of any implemented reform on our business. Our ability to commercialize our product candidate successfully will depend, in part, on the extent to which reimbursement for the cost of such product candidate and related treatments will be available from government health administration authorities, such as Medicare and Medicaid in the United States, private health insurers and other organizations. Significant uncertainty exists as to the reimbursement status of newly approved health care products, particularly for indications for which there is no current effective treatment or for which medical care typically is not sought. Adequate third party coverage may not be available to enable us to maintain price levels sufficient to realize an appropriate return on our investment in product research and development. If adequate coverage and reimbursement levels are not provided by government and third party payors for use of our product candidates, our product candidates may fail to achieve market acceptance and our results of operations will be harmed.
Healthcare legislative reform measures may have a material adverse effect on our business and results of operations.
In the United States, there have been and continue to be a number of legislative initiatives to contain healthcare costs. For example, in March 2010, the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, as amended by the Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act (“PPACA”), was passed, which substantially changed the way health care is financed by both governmental and private insurers, and has significantly impacted the U.S. pharmaceutical industry. PPACA, among other things, subjects biologic products to potential competition by lower-cost biosimilars, addresses a new methodology by which rebates owed by manufacturers under the Medicaid Drug Rebate Program are calculated for drugs that are inhaled, infused, instilled, implanted or injected, increases the minimum Medicaid rebates owed by manufacturers under the Medicaid Drug Rebate Program and extends the rebate program to individuals enrolled in Medicaid managed care organizations, establishes annual fees and taxes on manufacturers of certain branded prescription drugs and subjects additional drugs to lower pricing under the 340B Drug Discount Program by adding new entities to the program.
Risks Related to Our Intellectual Property
UFRF, our sole licensor, may under certain circumstances terminate our license agreement, which may be required for us to conduct our proposed business.
Our license agreement with UFRF provides it with the right to terminate our agreement upon written notice to us if we do not meet all of our requirements under the license agreement that requires us to file an IND application with the FDA, have a commercial sale of a licensed product within an agreed upon period of time and raise certain amounts of capital. If the license or any other agreement we enter into with UFRF is terminated for any reason, our business may be materially adversely affected and may cause our business to fail.
If we are unable to obtain, maintain and enforce our proprietary rights, we may not be able to compete effectively or operate profitably.
We have entered into a license agreement with UFRF. The patent underlying the licensed intellectual property and those of other biopharmaceutical companies, are generally uncertain and involve complex legal, scientific and factual questions.
Our ability to develop and commercialize drugs depends in significant part on our ability to: (i) obtain and/or develop broad, protectable intellectual property; (ii) obtain additional licenses, if required, to the proprietary rights of others on commercially reasonable terms; (iii) operate without infringing upon the proprietary rights of others; (iv) prevent others from infringing on our proprietary rights; and (v) protect our corporate know-how and trade secrets.
Patents that we may acquire and those that might be issued in the future, may be challenged, invalidated or circumvented, and the rights granted thereunder may not provide us with proprietary protection or competitive advantages against competitors with similar technology. Furthermore, our competitors may independently develop similar technologies or duplicate any technology we develop. Because of the extensive time required for development, testing and regulatory review of a potential product candidates, it is possible that, before any of our product candidates can be commercialized, any related patent may expire or remain in force for only a short period following commercialization, thus reducing any advantage of the patent.
Because patent applications in the U.S. and many foreign jurisdictions are typically not published until at least 12 months after filing, or in some cases not at all, and because publications of discoveries in the scientific literature often lag behind actual discoveries, neither we nor our licensors can be certain that either we or our licensors were the first to make the inventions claimed in issued patents or pending patent applications, or that we were the first to file for protection of the inventions set forth in these patent applications.
Additionally, UFRF previously elected to seek protection for certain elements of the licensed technology only in the United States, and the time to file for international patent protection has expired. This limits the strength of the Company’s intellectual property position in certain markets and could affect the overall value of the Company to a potential corporate partner.
We may be exposed to infringement or misappropriation claims by third parties, which, if determined adversely to us, could cause us to pay significant damage awards.
There has been substantial litigation and other proceedings regarding patent and other intellectual property rights in the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries. We may become a party to various types of patent litigation or other proceedings regarding intellectual property rights from time to time even under circumstances where we are not using and do not intend to use any of the intellectual property involved in the proceedings.
The cost of any patent litigation or other proceeding, even if resolved in our favor, could be substantial. Some of our competitors may be able to sustain the cost of such litigation or proceedings more effectively than we will be able to because our competitors may have substantially greater financial resources. If any patent litigation or other proceeding is resolved against us, we or our collaborators may be enjoined from developing, manufacturing, selling or importing our drugs without a license from the other party and we may be held liable for significant damages. We may not be able to obtain any required license(s) on commercially acceptable terms or at all.
Uncertainties resulting from the initiation and continuation of patent litigation or other proceedings could have a material adverse effect on our ability to compete in the marketplace. Patent litigation and other proceedings may also absorb significant management time.
Obtaining and maintaining our patent protection depends upon compliance with various procedural, document submission, fee payment and other requirements imposed by governmental patent agencies, and our patent protection could be reduced or eliminated for non-compliance with these requirements.
The United States Patent and Trademark Office and various foreign governmental patent agencies require compliance with a number of procedural, documentary, fee payment and other provisions during the patent process. There are situations in which noncompliance can result in abandonment or lapse of a patent or patent application, resulting in partial or complete loss of patent rights in the relevant jurisdiction. In such an event, competitors might be able to enter the market earlier than would otherwise have been the case.
Confidentiality agreements with employees and others may not adequately prevent disclosure of our know-how, trade secrets and other proprietary information and may not adequately protect our intellectual property, which could impede our ability to compete.
Because we operate in the highly technical field of medical technology development, we rely in part on trade secret protection in order to protect our proprietary trade secrets and unpatented know-how. However, trade secrets are difficult to protect, and we cannot be certain that others will not develop the same or similar technologies on their own. We have taken steps, including entering into confidentiality agreements with all of our employees, consultants and corporate partners to protect our trade secrets and unpatented know-how. These agreements generally require that the other party keep confidential and not disclose to third parties any confidential information developed by the party or made known to the party by us during the course of the party’s relationship with us. We also typically obtain agreements from these parties which provide that inventions conceived by the party in the course of rendering services to us will be our exclusive property. However, these agreements may not be honored and may not effectively assign intellectual property rights to us. Enforcing a claim that a party illegally obtained and is using our trade secrets or know-how is difficult, expensive and time consuming, and the outcome is unpredictable. In addition, courts outside the United States may be less willing to protect trade secrets or know-how. The failure to obtain or maintain trade secret protection could adversely affect our competitive position.
We may be subject to claims that our employees have wrongfully used or disclosed alleged trade secrets of their former employers.
As is common in the biotechnology industry, we employ individuals who were previously employed at other biotechnology companies, including our competitors or potential competitors. Although no claims against us are currently pending, we may be subject to claims that these employees or we have inadvertently or otherwise used or disclosed trade secrets or other proprietary information of their former employers. Litigation may be necessary to defend against these claims. Even if we are successful in defending against these claims, litigation could result in substantial costs and be a distraction to management.
Risks Associated With Our Common Stock
Our directors, executive officers and significant stockholders have substantial control over us and could limit stockholders’ ability to influence the outcome of key transactions, including changes of control.
As of December 31, 2017 our directors and executive officers beneficially owned 29.3% of our outstanding common stock and together are able to influence significantly all matters requiring approval by our stockholders. In addition, three holders of greater than five percent of our outstanding common stock beneficially owned 26.9% and, acting together, would be able to influence significantly all matters requiring approval by our stockholders, including the election of directors and the approval of mergers or other significant corporate transactions. These stockholders may have interests that differ from other stockholders, and they may vote in a way with which other stockholders disagree and that may be adverse to the interests of other stockholders. The concentration of ownership of our common stock may have the effect of delaying, preventing or deterring a change of control of our company, could deprive our stockholders of an opportunity to receive a premium for their common stock as part of a sale of our company, and may affect the market price of our common stock. This concentration of ownership of our common stock may also have the effect of influencing the completion of a change in control that may not necessarily be in the best interests of all of our stockholders.
Our common stock is eligible for quotation on the over-the-counter-market but not listed on any national securities exchange.
Our shares of common stock are eligible for quotation on the OTCQB tier of the over-the-counter markets under the symbol “SNBP.” Despite eligibility for quotation, no assurance can be given that any market for our common stock will develop or, if one develops, that it will be maintained for any period of time. Quotation on the over-the-counter markets is generally understood to be a less active, and therefore less liquid, trading market than other types of markets such as a national securities exchange. In comparison to a listing on a national securities exchange, quotation on the over-the-counter markets is expected to have an adverse effect on the liquidity of shares of our common stock, both in terms of the number of shares that can be bought and sold at a given price, but also through delays in the timing of transactions and reduction in analyst and media coverage. This may result in lower prices for our common stock than might otherwise be obtained and could also result in a larger spread between the bid and ask prices for our common stock.
Our common stock is a “penny stock,” which may make it difficult to sell shares of our common stock.
Our common stock is currently categorized as a “penny stock” as defined in Rule 3a51-1 of the Exchange Act and is subject to the requirements of Rule 15g-9 of the Exchange Act. Under this rule, broker-dealers who sell penny stocks must, among other things, provide purchasers of these stocks with a standardized risk-disclosure document prepared by the SEC. Under applicable regulations, unless it becomes listed on a national securities exchange, our common stock will generally remain a “penny stock” until such time as its per-share price is $5.00 or more (as determined in accordance with SEC regulations), or until we meet certain net asset or revenue thresholds. These thresholds include the possession of net tangible assets (i.e., total assets less intangible assets and liabilities) in excess of $2 million or average revenues equal to at least $6 million for each of the last three years.
The penny-stock rules significantly limit the liquidity of securities in the secondary market, and many brokers choose not to participate in penny-stock transactions. As a result, there is generally less trading in penny stocks. If you become a holder of our common stock, you may not always be able to resell shares of our common stock in a public broker’s transaction, if at all, at the times and prices that you feel are fair or appropriate.
Trading in our stock has been minimal and investors may not be able to sell as much stock as they want at prevailing prices.
As of March 19, 2018, the 30-day average daily trading volume in our common stock was less than 500 shares as reported by OTC Markets Group Inc. If trading in our stock continues at that level, it may be difficult for investors to sell or buy substantial quantities of shares in the public market at any given time at prevailing prices as significant price movement can be caused trading a relatively small number of shares. Accordingly, the market price for shares of our common stock may be made more volatile because of the relatively low volume of trading in our common stock. We cannot guarantee that a more liquid market for our common stock will develop.
Offers or availability for sale of a substantial number of shares of our common stock may cause the price of our common stock to decline and cause investors to lose part or all of their investment.
If our stockholders sell substantial amounts of our common stock in the public market or upon the expiration of any statutory holding period under Rule 144, or upon expiration of lock-up periods applicable to outstanding shares, or issued upon the exercise of outstanding options or warrants, it could create a circumstance commonly referred to as an “overhang” and in anticipation of which the market price of our common stock could fall. The existence of an overhang, whether or not sales have occurred or are occurring, also could make our ability to raise additional financing through the sale of equity or equity-related securities in the future at a time and price that we deem reasonable or appropriate more difficult. As of December 31, 2017, we had outstanding stock options to purchase 733,960 shares of our common stock at a weighted-average exercise price of $9.79 per share, outstanding warrants to purchase 151,500 shares of common stock at a weighted-average exercise price of $11.28 per share and outstanding convertible notes payable, including accrued interest, convertible into an estimated 319,193 shares at a weighted-average conversion price of $10.10.
Securities analysts may not initiate coverage or continue to cover our common stock, and this may have a negative impact on the market price of our common stock.
Common stock prices are often significantly influenced by the research and reports that securities analysts publish about companies and their business. We do not have any control over these analysts. There is no guarantee that securities analysts will cover our common stock. If securities analysts do not cover our common stock, the lack of research coverage may adversely affect the market price of our common stock. If our common stock is covered by securities analysts and our stock is downgraded, our stock price will likely decline. If one or more of these analysts ceases to cover us or fails to publish regular reports on us, we can lose visibility in the financial markets, which can cause our stock price or trading volume to decline.
Raising additional capital may cause dilution to our stockholders or restrict our operations.
To the extent that we raise additional capital through the sale of equity or convertible debt securities, stockholders’ ownership interest will be diluted, and the terms may include liquidation or other preferences that adversely affect their rights as stockholders. Debt financing, if available, may involve agreements that include covenants limiting or restricting our ability to take specific actions such as incurring additional debt, making capital expenditures or declaring dividends. Any of these events could adversely affect our ability to achieve our product development and commercialization goals and harm our business. We do not anticipate any adverse effects stemming from the lack of available credit facilities at this time.
Our charter documents and Delaware law may inhibit a takeover that stockholders consider favorable.
Provisions of our certificate of incorporation and bylaws and applicable provisions of Delaware law may make it more difficult for or prevent a third party from acquiring control of us without the approval of our board of directors. These provisions:
|
● |
set limitations on the removal of directors; |
|
● |
limit who may call a special meeting of stockholders; |
|
● |
establish advance notice requirements for nominations for election to our board of directors or for proposing matters that can be acted upon at stockholder meetings; |
|
● |
do not permit cumulative voting in the election of our directors, which would otherwise permit less than a majority of stockholders to elect directors; |
|
● |
establish a classified board of directors limiting the number of directors that are elected each year; and |
|
● |
provide our board of directors the ability to designate the terms of and issue preferred stock without stockholder approval. |
In addition, Section 203 of the Delaware General Corporation Law generally limits our ability to engage in any business combination with certain persons who own 15% or more of our outstanding voting stock or any of our associates or affiliates who at any time in the past three years have owned 15% or more of our outstanding voting stock unless our board of directors has pre-approved the acquisitions that lead to such ownership. These provisions may have the effect of entrenching our management team and may deprive stockholders of the opportunity to sell their shares to potential acquirers at a premium over prevailing prices. This potential inability to obtain a control premium could reduce the price of our common stock.
If we issue preferred stock, the rights of holders of our common stock and the value of such common stock could be adversely affected.
Our Board of Directors is authorized to issue classes or series of preferred stock, without any action on the part of the stockholders. The Board of Directors also has the power, without stockholder approval, to set the terms of any such classes or series of preferred stock, including voting rights, dividend rights and preferences over the common stock with respect to dividends or upon the liquidation, dissolution or winding-up of our business and other terms. If we issue preferred stock in the future that has a preference over the common stock with respect to the payment of dividends or upon liquidation, dissolution or winding-up, or if we issue preferred stock with voting rights that dilute the voting power of the common stock, the rights of holders of the common stock or the value of the common stock would be adversely affected.
The protection provided by the federal securities laws relating to forward-looking statements does not apply to us. The lack of this protection could harm us in the event of an adverse outcome in a legal proceeding relating to forward-looking statements made by us.
Although federal securities laws provide a safe harbor for forward-looking statements made by a public company that files reports under the federal securities laws, this safe harbor is not available to certain issuers, including penny stock issuers. We believe we are not currently eligible for the statutory safe harbor included in the Exchange Act of 1934. As a result, we will not have the benefit of this statutory safe harbor protection in the event of certain legal actions based upon forward-looking statements. The lack of this protection in a contested proceeding could harm our financial condition and, ultimately, the value of our common stock.
We are an emerging growth company and we cannot be certain if reduced disclosure requirements applicable to emerging growth companies will make our common stock less attractive to investors.
We are an emerging growth company under the JOBS Act. For as long as we continue to be an emerging growth company, we intend to take advantage of certain exemptions from various reporting requirements that are applicable to other public companies including, but not limited to, reduced disclosure obligations regarding executive compensation in our periodic reports and proxy statements, exemptions from the requirements of holding a nonbinding advisory stockholder vote on executive compensation and any golden parachute payments not previously approved, exemption from the requirement of auditor attestation in the assessment of our internal control over financial reporting and exemption from any requirement that may be adopted by the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board. If we do, the information that we provide stockholders may be different than what is available with respect to other public companies. We cannot predict if investors will find our common stock less attractive because we will rely on these exemptions. If some investors find our common stock less attractive as a result, there may be a less active trading market for our common stock and our stock price may be more volatile.
We have identified a significant deficiency in internal control over financial reporting, if we fail to maintain effective internal controls over financial reporting, the price of our common stock may be adversely affected.
We are required to establish and maintain appropriate internal controls over financial reporting. Failure to establish those controls, or any failure of those controls once established, could adversely impact our public disclosures regarding our business, financial condition or results of operations. Any failure of these controls could also prevent us from maintaining accurate accounting records and discovering accounting errors and financial fraud.
In the course of completing its assessment of internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017, management did not identify any material weaknesses but did identify a significant deficiency in the number of personnel available to serve the Company’s accounting function, specifically management believes that we may not be able to adequately segregate responsibility over financial transaction processing and reporting. A significant deficiency is a deficiency, or a combination of deficiencies, in internal control over financial reporting, that is less severe than a material weakness yet important enough to merit attention by those responsible for oversight of the Company’s financial reporting. Although we are unable to remediate the significant deficiency with current personnel, we are mitigating its potential impact, primarily through greater involvement of senior management in the review and monitoring of financial transaction processing and reporting.
In addition, management’s assessment of internal controls over financial reporting may identify additional weaknesses and conditions that need to be addressed or other potential matters that may raise concerns for investors. Any actual or perceived weaknesses and conditions that need to be addressed in our internal control over financial reporting or disclosure of management’s assessment of our internal controls over financial reporting may have an adverse impact on the price of our common stock.
|
Item 1B. |
Unresolved Staff Comments |
As a smaller reporting company, we are not required to provide disclosure pursuant to this item.
|
Item 2. |
Properties |
Our primary business functions are conducted by our employees and independent contractors on a distributed basis. Accordingly, we do not lease or own any real property and all employees currently work from their homes. We maintain our principal mailing address at Suite 305 at 712 Vista Boulevard in Waconia, Minnesota.
|
Item 3. |
Legal Proceedings |
We are not currently party to any material legal proceedings. From time to time, we may be named as a defendant in legal actions arising from our normal business activities. We believe that we have obtained adequate insurance coverage or rights to indemnification in connection with potential legal proceedings that may arise.
|
Item 4. |
Mine Safety Disclosures |
None.
PART II
|
Item 5. |
Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities |
Market Information
There is no “established trading market” for our shares of common stock. Our common stock was quoted on the OTCPink tier of the over-the-counter markets administered by OTC Markets Group, Inc. under the symbol “SNBP.” On September 28, 2016, our stock became quoted on the OTCQB tier under the same symbol and we secured DTC Eligibility from the Depository Trust Company for our shares to trade electronically.
Despite eligibility for quotation, no assurance can be given that any market for our common stock will develop or be maintained. If an “established trading market” ever develops in the future, the sale of shares of our common stock that are deemed to be “restricted securities” pursuant to Rule 144 of the SEC by members of management or others may have a substantial adverse impact on any such market.
Set forth below are the high and low bid prices for our common stock for each quarter of 2017 and 2016 for which data is available. These bid prices were obtained from OTC Markets Group Inc. All prices listed herein reflect inter-dealer prices, without retail mark-up, mark-down or commissions and may not represent actual transactions.
|
Fiscal 2017: |
High |
Low |
||||||
|
Fourth Quarter |
$ | 18.00 | $ | 7.01 | ||||
|
Third Quarter |
$ | 14.50 | $ | 5.70 | ||||
|
Second Quarter |
$ | 29.00 | $ | 12.50 | ||||
|
First Quarter |
$ | 40.00 | $ | 7.80 | ||||
|
Fiscal 2016: |
High |
Low |
||||||
|
Fourth Quarter |
$ | 35.00 | $ | 5.60 | ||||
|
Third Quarter |
$ | 30.00 | $ | 20.10 | ||||
|
Second Quarter |
$ | 35.00 | $ | 25.00 | ||||
|
First Quarter |
$ | 60.10 | $ | 25.00 | ||||
As of March 19, 2018, there were 182 holders of record of our common stock.
Dividends
We have never paid cash dividends on any of our securities. We currently intend to retain any earnings for use in operations and do not anticipate paying cash dividends in the foreseeable future.
Recent Sales of Unregistered Equity Securities
None.
Purchases of Equity Securities by the Company
None.
|
Item 6. |
Selected Financial Data |
As a smaller reporting company, we are not required to provide disclosure pursuant to this item.
|
Item 7. |
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations |
The following discussion of our financial condition and results of operations should be read in conjunction with our financial statements and the notes to those financial statements included elsewhere in this annual report. This discussion contains forward-looking statements, which are based on our assumptions about the future of our business. Our actual results will likely differ materially from those contained in the forward-looking statements. Please read “Cautionary Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements” included at the beginning of this annual report for additional information.
Overview
We exist for the primary purpose of advancing the commercial development of our proprietary polyamine analogue for pancreatic cancer and for a second indication in pancreatitis. We have exclusively licensed the worldwide rights to this compound, which has been designated as SBP-101, from the University of Florida Research Foundation, Inc. (“UFRF”).
In August 2015, the FDA accepted our IND application for our SBP-101 product candidate. We have completed an initial clinical trial of SBP-101 in patients with previously treated locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic cancer. This was a Phase 1, first-in-human, dose-escalation, safety study. From January 2016 through September 2017, we enrolled twenty-nine patients into six cohorts, or groups, in the dose-escalation phase of our current Phase 1 trial. Twenty-four of the patients received at least two prior chemotherapy regimens. No drug-related serious adverse events occurred during the first four cohorts. In cohort five, serious adverse events (klebsiella sepsis with metabolic acidosis in one patient, and renal and hepatic toxicity in one patient) were observed in two of the ten patients, both of whom exhibited progressive disease at the end of their first cycle of treatment, and were determined by the DSMB to be DLTs. Consistent with the study protocol, the DSMB recommended continuation of the study by expansion of cohort 4. Four patients were enrolled in this expansion cohort.
In addition to being evaluated for safety, twenty-four of the twenty-nine patients were evaluable for preliminary signals of efficacy prior to or at the eight-week conclusion of their first cycle of treatment using RECIST, the current standard for evaluating changes in the size of tumors. Eight of the twenty-four patients (33%) had SD and sixteen of twenty-four (67%) had PD. It should be noted that of the sixteen patients with PD, six came from cohorts one and two and are considered to have received less than potentially therapeutic doses of SBP-101. We also noted that twenty-eight of the twenty-nine patients had follow-up blood tests measuring the Tumor Marker CA 19-9 associated with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Eleven of these patients (39%) had reductions in the CA 19-9 levels, as measured at least once after the baseline assessment. Seven of the remaining seventeen patients showed no reduction in CA 19-9 came from cohorts one and two.
The best response outcomes and survival were observed in the group of thirteen patients who received total cumulative doses between 2.5 mg/kg and 8.0 mg/kg. Twelve of the thirteen patients in this group were evaluable for preliminary signs of efficacy at eight weeks by RECIST. Five patients (42%) showed SD at week eight. Five of the thirteen patients (38%) had reductions in the CA19-9 levels, as measured at least once after the baseline assessment. Median survival in this group was 3.8 months as of October 2017. To date, nine patients (69%) have exceeded 3 months of overall survival OS, four have exceeded four months of OS and two patients have exceeded 10 months of OS, with some patients continuing to be followed for survival.
This study was conducted at clinical sites in both Australia and the United States including The Mayo Clinic Scottsdale and HonorHealth in Scottsdale, AZ, the Austin Health Olivia Newton-John Cancer Wellness & Research Centre in Melbourne, Australia and the Ashford Cancer Centre in Adelaide, Australia.
Additional clinical trials will be required for FDA or other similar approvals if the results of the first clinical trial of our SBP-101 product candidate justify continued development. We estimate that the additional time and cost to obtain FDA and European Medicines Agency (“EMA”) approval and to bring our SBP-101 product candidate to market as a treatment for pancreatic cancer could be 6 to 7 years and cost up to $200 million, however, such time and cost estimates are subject to significant variability and subject to change depending on the results of current and future clinical trials.
Financial Overview
We have incurred losses of $29.2 million since our inception in 2011. For the year ended December 31, 2017, we incurred a net loss of $10.4 million, which includes a non-cash charge of $3.7 million related to the induced conversions of $2.9 million of convertible promissory notes, including accrued but unpaid interest, originally issued in 2013 and 2014, and $250,000 aggregate principal amount of demand notes originally issued in September 2015. We also incurred negative cash flows from operating activities of $3.4 million for this period. We expect to incur substantial losses, which will continue to generate negative net cash flows from operating activities, as we continue to pursue research and development activities and commercialize our SBP-101 product candidate.
During February and March 2017, we issued convertible promissory notes raising gross proceeds of approximately $3.1 million which are convertible into our common stock or other securities upon the completion of a qualified financing of at least $2.0 million on or before the maturity of the notes. In addition, we negotiated the conversion of approximately $3.1 million of previously outstanding debt and accrued interest into 418,332 shares of our common stock. See Note 6 titled “Indebtedness” in the Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements elsewhere in this report.
On July 3, 2017, we received a research and development tax incentive payment from the government of Australia related to the research activities of our Australian subsidiary during 2016. The incentive payment received was approximately $460,000.
As of December 31, 2017, we had cash of $152,000, negative working capital of $3.4 million and stockholders’ deficit of $3.7 million.
On March 1, 2016 we instituted substantial salary deferrals for all senior employees in order to conserve cash. Effective October 1, 2017, we entered into second amendments to the previously disclosed employment agreements, as amended, with our Executive Chairman, Michael T. Cullen, M.D., M.B.A., our President and Chief Executive Officer, David B. Kaysen, our Chief Financial Officer, Scott Kellen and our Chief Medical Officer, Suzanne Gagnon, M.D. (the “Employees”). The Amendments discontinued further salary deferrals and, For Dr. Cullen, Mr. Kaysen and Dr. Gagnon, established new annual base salaries representing a 25% reduction from prior levels. Mr. Kellen’s annual base salary remained unchanged.
We will need additional funds to continue our operations and execute our business plan, including completing our current Phase 1 clinical trial, planning for required future trials and pursuing regulatory approvals in the United States, the European Union and other international markets. We historically have financed our operations principally from the sale of convertible debt and equity securities. While we have been successful in the past in obtaining the necessary capital to support our operations and we are likely to seek additional financing through similar means, there is no assurance that we will be able to obtain additional financing under commercially reasonable terms and conditions, or at all. This risk would increase if our clinical data is not positive or if economic or market conditions deteriorate.
On each of February 17, March 3, March 10 and March 17, 2017, we entered into Note Purchase Agreements (the “Note Agreements”) with a number of accredited purchasers in private transactions. Pursuant to these Note Agreements we sold convertible promissory notes payable (the “2017 Convertible Notes”) raising gross proceeds of $3.1 million. See Note 6 titled “Indebtedness” in the Consolidated Financial Statements in Item 8 below for more information.
Subsequent to the end of 2017, on February 20, 2018 and March 16, 2018 we entered into Securities Purchase Agreements (the “2018 Purchase Agreements”) with a number of accredited purchasers. Pursuant to these 2018 Purchase Agreements, we issued 252,200 shares of common stock and warrants to purchase up to an aggregate of 252,200 additional shares, resulting in gross proceeds of $1.3 million.
If we are unable to obtain additional financing when needed, we would need to scale back our operations taking actions which may include, among other things, reducing use of outside professional service providers, reducing staff or staff compensation, significantly modify or delay the development of our SBP-101 product candidate, license to third parties the rights to commercialize our SBP-101 product candidate for pancreatic cancer, pancreatitis or other applications that we would otherwise seek to pursue, or cease operations.
Key Components of Our Results of Operations
General and Administrative Expenses
Our selling, general and administrative expenses consist primarily of salaries, benefits and other costs, including stock-based compensation, for our executive and administrative personnel; legal and other professional fees; travel, insurance and other corporate costs.
Research and Development Expenses
Since our inception, we have focused our activities on the development of SBP-101, our initial product candidate, for the treatment of pancreatic cancer. We expense both internal and external research and development costs as incurred. Research and development costs include expenses incurred in the conduct of our Phase 1 human clinical trial, for third-party service providers performing various testing and accumulating data related to our preclinical studies; sponsored research agreements; developing and scaling the manufacturing process necessary to produce sufficient amounts of the SBP-101 compound for use in our pre-clinical studies and human clinical trials; consulting resources with specialized expertise related to execution of our development plan for our SBP-101 product candidate; personnel costs, including salaries, benefits and stock-based compensation; and costs to license and maintain our licensed intellectual property. During 2016 and 2017, research and development expenditures were focused primarily on costs related to the execution of our Phase 1 human clinical trial.
We cannot determine with certainty the timing of initiation, the duration or the completion costs of current or future preclinical studies and clinical trials of our product candidates. At this time, due to the inherently unpredictable nature of preclinical and clinical development, we are unable to estimate with any certainty the costs we will incur and the timelines we will require in the continued development of our initial product candidate for pancreatic cancer and our other potential pipeline programs. Clinical and preclinical development timelines, the probability of success and development costs can differ materially from expectations. Our future research and development expenses will depend on the preclinical and clinical success of each product candidate that we develop, as well as ongoing assessments of the commercial potential of such product candidates. In addition, we cannot forecast whether our current or future product candidates may be subject to future collaborations, when such arrangements will be secured, if at all, and to what degree such arrangements would affect our development plans and capital requirements.
Completion of clinical trials may take several years or more, and the length of time generally varies according to the type, complexity, novelty and intended use of a product candidate. The cost of clinical trials may vary significantly over the life of a project as a result of differences arising during clinical development, including, among others:
|
● |
per patient trial costs; |
|
● |
the number of trials required for approval; |
|
● |
the number of sites included in the trials; |
|
● |
the length of time required to enroll suitable patients; |
|
● |
the number of doses that patients receive; |
|
● |
the number of patients that participate in the trials; |
|
● |
the drop-out or discontinuation rates of patients; |
|
● |
the duration of patient follow-up; |
|
● |
potential additional safety monitoring or other studies requested by regulatory agencies; |
|
● |
the number and complexity of analyses and tests performed during the trial; |
|
● |
the phase of development of the product candidate; and |
|
● |
the efficacy and safety profile of the product candidate. |
Our expenses related to clinical trials are based on estimates of the services received and efforts expended pursuant to contracts with multiple clinical trial sites and, for certain trials, contract research organizations, (“CRO”), which administer clinical trials on our behalf. The financial terms of these agreements are subject to negotiation and vary from contract to contract and may result in uneven payment flows. Generally, these agreements set forth the scope of work to be performed at a fixed fee or unit price. Payments under the contracts depend on factors such as the successful enrollment of patients and the completion of clinical trial milestones. Expenses related to clinical trials generally are accrued based on contracted amounts and the achievement of milestones, such as number of patients enrolled. If timelines or contracts are modified based upon changes to the clinical trial design or scope of work to be performed, we modify our estimates of accrued expenses accordingly.
We expense costs associated with obtaining licenses for patented technologies when it is determined there is no alternative future use of the intellectual property subject to the license.
Other Income (Expense)
Interest income consists of interest income, cash and non-cash interest expense and transaction gains and losses resulting from transactions denominated in other than our functional currency.
Grant Income
Grant income is derived from a one-time grant awarded to the Company by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases of the National Institutes of Health (the “Grant Agreement”). The total grant awarded under the Grant Agreement was $225,000 and is intended to fund studies of SBP-101 as a potential treatment for pancreatitis. Grant income is recognized as a non-operating income when the related research and development expenses are incurred, terms of the grant have been complied with and the Company is eligible for reimbursement under the Grant Agreement.
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
Our management’s discussion and analysis of financial condition and results of operations is based on our financial statements, which have been prepared in accordance with GAAP. The preparation of these financial statements requires us to make estimates and judgments that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities and expenses. On an ongoing basis, we evaluate these estimates and judgments, including those described below. We base our estimates on our historical experience and on various other assumptions that we believe to be reasonable under the circumstances. These estimates and assumptions form the basis for making judgments about the carrying values of assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other sources. Actual results and experiences may differ materially from these estimates.
While our significant accounting policies are more fully described in Note 4 to our Consolidated Financial Statements starting on page F-1, we believe that the following accounting policies are the most critical to aid you in fully understanding and evaluating our reported financial results and affect the more significant judgments and estimates that we use in the preparation of our financial statements.
Stock-based Compensation
In accounting for share-based incentive awards we measure and recognize the cost of employee and non-employee services received in exchange for awards of equity instruments based on the grant date fair value of those awards. Calculating share-based compensation expense requires the input of highly subjective assumptions, which represent our best estimates and involve inherent uncertainties and the application of management’s judgment. Compensation cost is recognized ratably using the straight-line attribution method over the vesting period, which is considered to be the requisite service period. The performance date for non-employee awards is generally not met until the individual award vests. Accordingly we re-measure the current fair value each quarter until the award vests. Compensation expense for performance-based stock option awards is recognized when “performance” has occurred or is probable of occurring.
The fair values of share-based awards are estimated at the date of grant using the Black-Scholes option pricing model. The determination of the fair value of share-based awards is affected by our stock price, as well as assumptions regarding a number of complex and subjective variables. Risk free interest rates are based upon U.S. Treasury rates appropriate for the expected term of each award. Expected volatility rates are based primarily on the volatility rates of a set of guideline companies, which consist of public and recently public biotechnology companies. The assumed dividend yield is zero, as we do not expect to declare any dividends in the foreseeable future. The expected term of options granted is determined using the “simplified” method. Under this approach, the expected term is presumed to be the mid-point between the average vesting date and the end of the contractual term.
We grant options to employees and non-employees, including our directors. Option grants to employees generally vest quarterly over two years from the date of grant. Options granted to our non-employee directors generally vest over one-year from the date of grant. Options granted to other non-employees generally vest over two years with 50% of the total shares underlying the option vesting on the first and second anniversaries of the date of grant. Options issued to employees and non-employee directors generally have a maximum term of ten years and options issued to non-employees generally have a maximum term of five years.
Option grants to non-employees have been made in conjunction with their service as advisors to us. Certain of these advisors have also purchased shares of stock in our private placement offerings, but none beneficially own 5% or more of our outstanding common stock. The fair value of options granted to non-employees is measured at each reporting date until the option, or respective portion of the option, vests and the expense recorded by us is updated accordingly. See Note 9 to the Consolidated Financial Statements in Item 8 below for additional information.
Research and Development Costs
We charge research and development costs, including clinical trial costs, to expense when incurred. Our human clinical trials are, and will be, performed at clinical trial sites and are administered jointly by us with assistance from contract research organizations (“CROs”). Costs of setting up clinical trial sites are accrued upon execution of the study agreement. Expenses related to the performance of clinical trials generally are accrued based on contracted amounts and the achievement of agreed upon milestones, such as patient enrollment, patient follow-up, etc. We monitor levels of performance under each significant contract, including the extent of patient enrollment and other activities through communications with the clinical trial sites and CROs, and adjust the estimates, if required, on a quarterly basis so that clinical expenses reflect the actual effort expended at each clinical trial site and by each CRO.
Results of Operations
Comparison of the Year Ended December 31, 2017 to the Year Ended December 31, 2016
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||||
|
2017 |
2016 |
Percent Change | ||||||||||
|
Operating expenses: |
||||||||||||
|
General and administrative |
$ | 3,423 | $ | 2,664 | 28.5 | % | ||||||
|
Research and development |
2,593 | 2,504 | 3.6 | |||||||||
|
Total operating expenses |
6,016 | 5,168 | 16.4 | |||||||||
|
Other expense, net |
(4,894 | ) | (285 | ) | nm | |||||||
|
Income tax benefit |
536 | 341 | 57.2 | |||||||||
|
Net loss |
$ | (10,374 | ) | $ | (5,112 | ) | 102.9 | % | ||||
General and administrative and research and development expenses include non-cash stock-based compensation expense as a result of our issuance of stock options. The terms and vesting schedules for stock-based awards vary by type of grant and the employment status of the grantee. The awards granted through December 31, 2017 vest based upon time-based and performance conditions. We expect to record additional non-cash compensation expense in the future, which may be significant. The following table summarizes the stock-based compensation expense in our statement of Consolidated Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Loss for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016 (in thousands):
|
Year Ended December 31, |
||||||||
|
2017 |
2016 |
|||||||
|
General and administrative |
$ | 1,430 | $ | 810 | ||||
|
Research and development |
303 | 92 | ||||||
|
Total stock-based compensation |
$ | 1,733 | $ | 902 | ||||
General and administrative expense
Our general and administrative (“G&A”) expenses increased 28.5% to $3.4 million in 2017, up from $2.7 million in 2016. This increase was primarily due to an increase in stock-based compensation and costs incurred in connection with efforts to complete a public offering in the fourth quarter of 2017, partially offset by decreased license fees due to the University of Florida.
Research and product development expense
Our research and development (“R&D”) expenses increased 3.6% to $2.6 million in 2017, up from $2.5 million in 2016. The increase in R&D expenses resulted from an increase in stock-based compensation and contract research costs incurred under an NIH sponsored pancreatitis study partially offset by decreased clinical trial and related costs for our Phase 1 clinical trial.
Other expense, net
Other expense, net, increased to $4.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2017, up from $285,000 in the same period of the prior year. The increase was due primarily to charges recorded related to the induced conversion of debt and increased interest expense resulting from the amortization of the discount on the 2017 convertible notes payable. These expenses were partially offset by a foreign currency transaction gains recognized by our Australian subsidiary and grant income earned during the current year period.
Income tax benefit
Income tax benefit increased to $536,000 in 2017, up from $341,000 in 2016. Our income tax benefit is derived primarily from refundable tax credits associated with our R&D activities conducted in Australia. The current year increase reflects an increase in the costs eligible for the Australian R&D tax credit.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
The following table summarizes our liquidity and capital resources as of December 31, 2017 and 2016 and for each of fiscal years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016, and is intended to supplement the more detailed discussion that follows (in thousands):
|
Liquidity and Capital Resources |
December 31, |
|||||||
|
2017 |
2016 |
|||||||
|
Cash |
$ | 152 | $ | 438 | ||||
|
Working capital |
$ | (3,403 | ) | $ | (4,642 | ) | ||
|
Year Ended December 31, |
||||||||
|
Cash Flow Data |
2017 |
2016 |
||||||
|
Cash provided by (used in): |
||||||||
|
Operating activities |
$ | (3,402 |
) |
$ | (2,398 |
) |
||
|
Investment activities |
— | — | ||||||
|
Financing activities |
3,106 | 1,915 | ||||||
|
Effect of exchange rate changes on cash |
10 | (4 |
) |
|||||
|
Net decrease in cash |
$ | (286 |
) |
$ | (487 |
) |
||
Working Capital
Our total cash resources were $152,000 as of December 31, 2017, compared to $438,000 as of December 31, 2016. As of December 31, 2017, we had $4.2 million in current liabilities and negative net working capital of $3.4 million. As of December 31, 2016, we had $5.5 million in current liabilities and $4.6 million in net working capital.
Subsequent to the end of 2017, on February 20, 2018 and March 16, 2018 we entered into the 2018 Purchase Agreements with a number of accredited purchasers. Pursuant to these closings under the 2018 Purchase Agreements, we issued 252,200 shares of common stock and warrants to purchase up to an aggregate of 252,200 additional shares, resulting in gross proceeds of $1.3 million.
Cash Flows
Net Cash Used in Operating Activities
Net cash used in operating activities was $3.4 million during 2017, compared to $2.4 million during 2016. The net cash used in each of these periods primarily reflects the net loss for these periods, and is partially offset by the effects of changes in operating assets and liabilities. In the year ended December 31, 2017, the net loss is also offset by a non-cash charge of $3.7 million related to the induced conversions of $2.9 million of convertible promissory notes, including accrued but unpaid interest, and $250,000 aggregate principal amount of demand notes and a non-cash charge of $1.4 million related to the amortization of the discount on the 2017 convertible notes payable.
Net Cash Provided by Financing Activities
Net cash provided by financing activities was $3.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2017, which was comprised primarily of net proceeds from the sale of convertible promissory notes. During the year ended December 31, 2016, net cash provided by financing activities was $1.9 million which resulted from net proceeds received in the sale of common stock and warrants.
Capital Requirements
As we continue to pursue our operations and execute our business plan, including the completion of our current Phase 1 clinical trial for our initial product candidate, SBP-101, in pancreatic cancer, planning for required future trials and pursuing regulatory approvals in the United States, the European Union and other international markets, we expect to continue to incur substantial and increasing losses, which will continue to generate negative net cash flows from operating activities.
Our future capital uses and requirements depend on numerous current and future factors. These factors include, but are not limited to, the following:
|
● |
the progress of clinical trials required to support our applications for regulatory approvals, including our Phase 1 clinical trial, a human clinical trial in Australia and the United States; |
|
● |
our ability to demonstrate the safety and effectiveness of our SBP-101 product candidate; |
|
● |
our ability to obtain regulatory approval of our SBP-101 product candidate in the United States, the European Union or other international markets; |
|
● |
the cost and delays in product development that may result from changes in regulatory oversight applicable to our SBP-101 product candidate; |
|
● |
the market acceptance and level of future sales of our SBP-101 product candidate; |
|
● |
the rate of progress in establishing reimbursement arrangements with third-party payors; |
|
● |
the effect of competing technological and market developments; and |
|
● |
the costs involved in filing and prosecuting patent applications and enforcing or defending patent claims. |
As of December 31, 2017, we did not have any existing credit facilities under which we could borrow funds. We historically have financed our operations principally from the sale of convertible debt and equity securities. While we have been successful in the past in obtaining the necessary capital to support our operations and we are likely to seek additional financing through similar means, there is no assurance that we will be able to obtain additional financing under commercially reasonable terms and conditions, or at all.
Issuance of Convertible Promissory Notes During 2017
On each of February 17, March 3, March 10 and March 17, 2017, we entered into Note Purchase Agreements (the “Note Agreements”) with a number of accredited investors in private transactions. Pursuant to these Note Agreements, we sold convertible promissory notes (the “2017 Notes”) raising gross proceeds of approximately $3.1 million. The 2017 Notes are scheduled to mature on December 1, 2018 and bear interest at a rate of 5.0% per year. Principal and interest on the 2017 Notes are payable at maturity. The Company may prepay the 2017 Notes in whole or in part at any time without penalty or premium. The 2017 Notes are convertible into shares of common stock or other securities of the Company upon the occurrence of a Qualified Financing, including the sale of equity securities or a strategic partnership, raising gross proceeds of at least $2.0 million on or before the maturity of the 2017 Notes or upon the request of a holder of any 2017 Note at a fixed conversion rate of $10.10 per share. Upon issuance, the 2017 Notes were convertible into our common stock at a conversion rate of $10.10 per share. The fair market value of our stock on the dates of issuance ranged from $15.00 to $39.00 per share. Therefore the 2017 Notes contained a beneficial conversion feature with an aggregate intrinsic value of approximately $3.0 million, which was recorded as a debt discount and is presented as a direct deduction from the carrying value of the 2017 Notes. The discount will be amortized through interest expense over the life of the 2017 Notes. Upon the occurrence of certain events of default, the 2017 Notes require the Company to repay the unpaid principal amount of the Notes and any unpaid accrued interest. The Company has used the net proceeds from the sales of the Notes to further the clinical development of SBP-101 and for working capital and general corporate purposes. One of our stockholders, who beneficially owns more than 10% of our common stock, purchased $200,000 of the 2017 Notes.
On March 27, 2017, we entered into a Participation Agreement (collectively, the “Participation Agreements”) with each holder of the 2017 Notes (the “Participants”), pursuant to which the Participants have a right to purchase his, her, or its pro rata portion of any future equity issuances in the Company (based on the Company equity securities shares held by the Participant immediately prior to the subject issuance), subject to certain exceptions described therein. Prior to any proposed issuance or sale of new equity securities, we will give the Participants written notice thereof pursuant to the terms and conditions of the Participation Agreement.
Under the Participation Agreements, we are obligated to give each participant notice of the proposed issuances pursuant to this offering as promptly as is reasonably practical and prudent in light of the timing and nature of the offering and to use commercially reasonable efforts to cause the underwriters to allow (but not obligate) each participant to participate in the offering in an amount up to their respective pro rata portion on the same terms, conditions and price to be provided to the public. Our obligations remain subject to each participant’s compliance with any timing, indication, eligibility and documentation requirements imposed by the underwriters.
Settlement of 2013 Convertible Notes with Common Stock
In March 2017, we offered to all holders of outstanding convertible notes payable, originally issued in the fourth quarter of 2013 (the “2013 Convertible Notes”) and to all holders of the demand notes payable (collectively the “Notes”), who were accredited investors an opportunity to convert all outstanding principal and accrued interest through March 31, 2017 into shares of our common stock at a rate of $0.75 per share. The offered conversion rate represents a $0.375, or 33.3%, discount from the rate stated in the terms of the 2013 Convertible Notes, which at the time was $1.125 per share. The eligible holders had until March 27, 2017 to accept the offer and holders of $3,000,000 aggregate principle amount of the Notes accepted the offer. Accordingly, on March 31, 2017 we issued 4,183,333 shares of common stock in exchange for the surrender of the Notes representing $3,000,000 of principal amount and $137,500 of accrued but previously unpaid interest. See Note 6 titled “Indebtedness” to the Consolidated Financial Statements in Item 8 below for more information.
Recent Issuance of Common Stock and Warrants
Subsequent to the end of 2017, on February 20, 2018 and March 16, 2018 we entered into the 2018 Purchase Agreements with a number of accredited purchasers. Pursuant to these closings under the 2018 Purchase Agreements we issued 252,200 shares of common stock and warrants to purchase up to an aggregate of 252,200 additional shares, resulting in gross proceeds of $1.3 million. See Note 11 titled “Subsequent Events” to the Consolidated Financial Statements appearing in Part II, Item 8, for further details.
We will need additional funds to continue our operations and execute our business plan, including completing our current Phase 1 clinical trial, planning for required future trials and pursuing regulatory approvals in the United States, the European Union and other international markets. We historically have financed our operations principally from the sale of convertible debt and equity securities. While we have been successful in the past in obtaining the necessary capital to support our operations and we are likely to seek additional financing through similar means, there is no assurance that we will be able to obtain additional financing under commercially reasonable terms and conditions, or at all. We believe that our existing cash, combined with the proceeds from the sale of the 2017 Notes and the 2018 Purchase Agreement, will be sufficient to fund our operating expenses through the third quarter of 2018.
If we are unable to obtain additional financing when needed, we would need to scale back our operations taking actions which may include, among other things, reducing use of outside professional service providers, reducing staff or staff compensation, significantly modify or delay the development of our SBP-101 product candidate, license to third parties the rights to commercialize our SBP-101 product candidate for pancreatic cancer, pancreatitis or other applications that we would otherwise seek to pursue, or cease operations.
To the extent that we raise additional capital through the sale of equity or convertible debt securities, the interests of our current stockholders would be diluted, and the terms may include liquidation or other preferences that adversely affect the rights of our current stockholders. If we issue preferred stock, it could affect the rights of our stockholders or reduce the value of our common stock. In particular, specific rights granted to future holders of preferred stock may include voting rights, preferences as to dividends and liquidation, conversion and redemption rights, sinking fund provisions, and restrictions on our ability to merge with or sell our assets to a third party. Debt financing, if available, may involve agreements that include covenants limiting or restricting our ability to take specific actions, such as incurring additional debt, making capital expenditures or declaring dividends. Any of these events could adversely affect our ability to achieve our regulatory approvals and commercialization goals and harm our business.
Our future success is dependent upon our ability to obtain additional financing, the success of our current Phase 1 clinical trial and required future trials, our ability to obtain marketing approval for our SBP-101 product candidate in the United States, the European Union and other international markets. If we are unable to obtain additional financing when needed, if our Phase 1 clinical trial is not successful, if we do not receive regulatory approval required future trials or if once these studies are concluded, we do not receive marketing approval for our SBP-101 product candidate, we would not be able to continue as a going concern and would be forced to cease operations. The financial statements included in this report have been prepared assuming that we will continue as a going concern and do not include any adjustments relating to the recoverability or classification of assets or the amounts of liabilities that might result from the outcome of these uncertainties.
Indebtedness
As of December 31, 2017, we had $3.1 million aggregate principal amount of convertible promissory notes outstanding. Of this amount, $3,076,000 aggregate principal amount was outstanding under the 2017 Notes, which accrue interest at 5.0% per year and are convertible into common stock or other securities upon the completion of a qualified financing of at least $2.0 million on or before the maturity of the 2017 Notes, or upon the request of a holder at a fixed conversion rate of $10.10 per share. The 2017 Notes mature in December 2018 at which time all principal and interest are payable. One 2013 Note remains outstanding in a principal amount of $25,000, which accrues interest of 5% per year, payable quarterly, and is convertible into common stock at $11.25 per share. The 2013 Note matures in December 2018. We also had $300,000 outstanding in an unsecured loan that accrues annual interest of 4.125%. The terms of this loan were amended in October 2017 to extend the maturity date to May 1, 2019 with monthly payments of $10,000 commencing on May 1, 2018.
License Agreement
On December 22, 2011, we entered into an exclusive license agreement with the University of Florida Research Foundation (“UFRF”), which was acquired in exchange for $15,000 in cash and the issuance of 10% of our common stock. Upon executing the license agreement, 80,000 shares of common stock were issued to UFRF which was determined to have a fair value of $20,000 based upon an estimated fair value of our common stock of $0.25 per share. The license agreement also contained an anti-dilution provision which required the Company to issue additional shares to UFRF sufficient for UFRF to maintain its 10% ownership interest in the Company until we secured an addition $2.0 million external investment. This investment was received during 2012.
The license agreement requires the Company to pay royalties to UFRF ranging from 2.5% to 5% of net sales of licensed products developed from the licensed technology. Minimum annual royalties are required after the initial occurrence of a commercial sale of a marketed product. Royalties are payable for the longer of (i) the last to expire of the claims in the licensed patents or (ii) ten (10) years from the first commercial sale of a licensed product in each country in which licensed product is sold. The minimum annual royalties are as follows:
|
● |
$50,000 is due 270 days after occurrence of first commercial sale; |
|
● |
$100,000 is due on the first anniversary date of the first payment; |
|
● |
$100,000 is due on the second anniversary date of the first payment; and |
|
● |
$300,000 is due on the third anniversary date of the first payment and subsequent anniversary dates thereafter, continuing for the life of the license agreement. |
The Company is subject to six different milestone payments under the license agreement.
|
● |
$50,000 is due upon enrollment of the first subject in a Phase I clinical trial; |
|
● |
$300,000 is due upon enrollment of the first subject in a Phase II clinical trial; |
|
● |
$3,000,000 is due upon approval of a New Drug Application; |
|
● |
$2,000,000 is due upon approval to manufacture and market in either the European Union or Japan (one time only); |
|
● |
$1,000,000 is due upon the first time annual net sales of licensed product or licensed process by the Company reaches $100,000,000; and |
|
● |
$3,000,000 is due upon the first time annual net sales of licensed product or licensed process by the Company reaches $500,000,000. |
On January 4, 2016, we enrolled the first patient in our Phase 1 clinical trial of SBP-101 in patients with previously treated pancreatic cancer. Accordingly, we recorded a milestone obligation of $50,000 as a license expense as of this date. As of December 31, 2017, no royalty or milestone payments were due. The Company is also committed to pay an annual license maintenance fee of $10,000.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
We have no off-balance sheet arrangements.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
See Note 4 to the Consolidated Financial Statements contained in Item 8 below for a discussion of recent accounting pronouncements.
|
Item 7A. |
Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk |
As a smaller reporting company, we are not required to provide disclosure pursuant to this item.
|
Item 8. |
Financial Statements and Supplementary Data |
The financial statements and notes thereto required pursuant to this Item begin on page F-1 of this annual report on Form 10-K.
|
Item 9. |
Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure |
None.
|
Item 9A. |
Controls and Procedures |
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Our management, with the participation of our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, has evaluated our disclosure controls and procedures. Based on such evaluation, and after considering the controls implemented to mitigate the significant deficiency related to insufficient accounting personnel discussed below, our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer have concluded that, as of December 31, 2017, our disclosure controls and procedures were effective in ensuring that information relating to the Company required to be disclosed in the reports that we file or submit under the Exchange Act, is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and forms, including ensuring that such information is accumulated and communicated to our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
Changes to Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
We have not identified any change in our internal control over financial reporting during our most recently completed fiscal quarter that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting, as such term is defined in Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) under the Exchange. Internal control over financial reporting refers to the processes designed by, or under the supervision of, our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, and effected by our Board of Directors, management and other personnel, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and includes those policies and procedures that:
|
(1) |
Pertain to the maintenance of records that in reasonable detail accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of our assets; |
|
(2) |
Provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that our receipts and expenditures are being made only in accordance with authorization of our management and directors; and |
|
(3) |
Provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of our assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements. |
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting cannot provide absolute assurance of preventing and detecting misstatements on a timely basis. It is possible to design into the process safeguards to reduce, though not eliminate, the risk that misstatements are not prevented or detected on a timely basis.
In the course of completing its assessment of internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017, management did not identify any material weaknesses but did identify a significant deficiency in the number of personnel available to serve the Company’s accounting function, specifically management believes that we may not be able to adequately segregate responsibility over financial transaction processing and reporting. A significant deficiency is a deficiency, or a combination of deficiencies, in internal control over financial reporting, that is less severe than a material weakness yet important enough to merit attention by those responsible for oversight of the Company’s financial reporting. Although we are unable to remediate the significant deficiency with current personnel, we are mitigating its potential impact, primarily through greater involvement of senior management in the review and monitoring of financial transaction processing and financial reporting.
Our management conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting based on the framework set forth in the report entitled Internal Control—Integrated Framework published by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission, known as COSO (2013 Framework). Based on this assessment, management has concluded that, as of December 31, 2017, our internal control over financial reporting was effective.
This report does not include an attestation report of our independent registered public accounting firm regarding internal control over financial reporting. Management’s report was not subject to attestation by our independent registered public accounting firm pursuant to Section 989G of the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, which exempts smaller reporting companies from the auditor attestation requirement.
|
Item 9B. |
Other Information |
None.
PART III
Certain information required by Part III will be incorporated by reference from our definitive proxy statement for the annual meeting of stockholders to be held in 2018 (the “Proxy Statement”), which we expect to file with the SEC pursuant to Regulation 14A within 120 days after December 31, 2017. Except for those portions specifically incorporated in this annual report on Form 10-K by reference to the Proxy Statement, no other portions of the Proxy Statement are deemed to be filed as part of this annual report on Form 10-K.
|
Item 10. |
Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance |
The information appearing under the headings “Proposal No. 1 – Election of Directors” and “Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance” in the Proxy Statement is incorporated into this Item by reference.
Executive Officers
The name, age and position of each of our executive officers are as follows:
| Name | Age | Position | ||||
|
Michael T. Cullen |
|
71 |
|
Executive Chairman of the Board and Director |
||
|
David B. Kaysen |
|
68 |
|
President, Chief Executive Officer and Director |
||
|
Scott Kellen |
52 |
Chief Financial Officer and Vice President of Finance |
||||
Michael T. Cullen, M.D., M.B.A., has served as Executive Chairman of the board and as a director of our Company since the effective time of the Merger. Dr. Cullen brings 30 years of pharmaceutical experience to our Company, including expertise in working with development-stage companies in planning, designing and advancing drug candidates from preclinical through clinical development. Dr. Cullen co-founded the Company in November 2011 and had continuously served as Chairman its board of directors since that date. He previously served as our Chief Executive Officer and President from November 2011 to June 2015. Dr. Cullen provided due diligence consulting to the pharmaceutical industry from 2009 to 2011, after one year in transition consulting to Eisai Pharmaceuticals. He developed several oncology drugs as Chief Medical Officer for MGI Pharma Inc. from 2000 to 2008, and previously at G.D. Searle, SunPharm Corporation, and as Vice President for Clinical Consulting at IBAH Inc., the world’s fifth largest contract research organization, where he provided consulting services on business strategy, creating development plans, regulatory matters and designing clinical trials for several development stage companies in the pharmaceutical industry. Dr. Cullen was also a co-founder and Chief Executive Officer of IDD Medical, a pharmaceutical start-up company. Dr. Cullen joined 3M Pharmaceuticals in 1988 and contributed to the development of cardiovascular, pulmonary, rheumatology and immune-response modification drugs. Over the course of his career Dr. Cullen has been instrumental in obtaining the approval of ten drugs, including three (3) since 2004: Aloxi®, Dacogen® and Lusedra®. Board-certified in Internal Medicine, Dr. Cullen practiced from 1977 to 1988 at Owatonna Clinic, Owatonna, MN, where he served as president. Dr. Cullen earned his MD and BS degrees from the University of Minnesota and his MBA from the University of St. Thomas and completed his residency and Board certification in Internal Medicine through the University of North Carolina in Chapel Hill and Wilmington, NC.
David B. Kaysen has served as our President and Chief Executive Officer and as a director of our Company since July 2015. Prior to joining the Company, Mr. Kaysen was a self-employed medical technology consultant since April 2013. Mr. Kaysen previously was the President, Chief Executive Officer and a board member of Uroplasty, Inc. from May 2006 through April 2013.
Scott Kellen has served as our Vice President and Chief Financial Officer since October 1, 2015. Prior to joining Sun BioPharma, Inc., Mr. Kellen was the Chief Financial Officer of Kips Bay Medical, Inc. from 2010 through 2015 originally joining to help lead them through their initial public offering and multiple follow-on offerings. In March 2012, Scott also became the Chief Operating Officer. From 2007 to 2009, Scott served as Director of Finance for Transoma Medical, Inc., during which time Transoma prepared for its proposed initial public offering, which was withdrawn in February 2008 due to deteriorated market conditions. From 2005 to 2007, Scott served as the Corporate Controller for ev3 Inc. during that company’s initial public offering and during additional follow-on offerings. From 2003 to 2005, Scott served as Senior Audit Manager of Deloitte & Touche, LLP (now Deloitte LLP), providing auditing and consulting services to mid-size public companies adjusting to the requirements of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. Altogether, Scott has spent more than 20 years in the medical device industry, serving early stage and growth companies that produced Class II and III medical devices. Scott has a Bachelor of Science degree in Business Administration from the University of South Dakota and is a Certified Public Accountant (inactive).
Code of Ethics and Business Conduct
We have adopted a code of ethics and business conduct (the “Code”) that applies to our principal executive officer, principal financial officer, principal accounting officer or controller or persons performing similar functions, as well as other employees and our directors. The Code is posted to the Investor Relations-Corporate Governance section of our website at www.SunBioPharma.com. We intend to include on our website, with the time period required by Form 8-K, an amendment to, or waiver from, a provision of our Code that applies to our principal executive officer, principal financial officer, principal accounting officer, controller, or persons performing similar functions, and that relates to any element of the Code of Ethics definition enumerated in Item 406(b) of SEC Regulation S-K.
|
Item 11. |
Executive Compensation |
The information appearing under the headings “Director Compensation” and “Executive Compensation” in the Proxy Statement is incorporated into this Item by reference.
|
Item 12. |
Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters |
The information appearing under the headings “Security Ownership of Principal Stockholders and Management” and “Equity Compensation Plan Information” in the Proxy Statement is incorporated into this Item by reference.
|
Item 13. |
Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence |
The information regarding director independence appearing under the heading “Proposal No. 1 – Election of Directors” and the information regarding related person transactions under the heading “Corporate Governance” in the Proxy Statement is incorporated into this Item by reference.
|
Item 14. |
Principal Accounting Fees and Services |
The information regarding principal accounting fees and services appearing under the heading “Proposal No. 2 – Ratification of Appointment of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm” in the Proxy Statement is incorporated into this Item by reference.
PART IV
|
Item 15. |
Exhibits, Financial Statements Schedules |
|
(a) |
Financial Statements, Financial Statement Schedules, and Exhibits. |
|
(1) |
Financial Statements |
| The following financial statements are filed as part of this report: | ||||
| Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm | F-1 | |||
| Consolidated Balance Sheets | F-2 | |||
| Consolidated Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Loss | F-3 | |||
| Consolidated Statements of Stockholders’ Deficit | F-4 | |||
| Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows | F-5 | |||
| Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements | F-6 |
|
(2) |
Financial Statement Schedules |
Schedules not listed above have been omitted because they are not applicable or not required or the information required to be set forth therein is included in the Consolidated Financial Statements and notes thereto identified above.
|
(3) |
Exhibits |
Unless otherwise indicated, all documents incorporated into this annual report on Form 10-K by reference to a document filed with the SEC pursuant to the Exchange Act are located under SEC file number 000-55242.
|
Exhibit No. |
Description |
||
|
3.1 |
|||
|
3.2 |
|||
|
4.1 |
|||
|
4.2 |
|||
|
4.3 |
|||
|
4.4 |
|||
|
10.1* |
|||
|
10.2* |
|||
|
10.3* |
|||
|
10.4* |
|||
|
Exhibit No. |
Description | ||
|
10.5* |
|||
|
10.6* |
|||
|
10.7* |
|||
|
10.8* |
|||
|
10.9** |
|||
|
10.10* |
|||
|
10.11* |
|||
|
10.12* |
|||
|
10.13* |
|||
|
10.14* |
|||
|
10.15* |
|||
|
10.16* |
|||
|
10.17* |
|||
|
10.18* |
|||
|
10.19* |
|||
|
10.20* |
|||
|
10.21* |
|||
|
10.22* |
|||
|
10.23* |
|||
|
10.24* |
|||
|
10.25* |
|||
|
Exhibit No. |
Description | ||
|
10.26* |
|||
|
10.27 |
|||
|
10.28 |
|||
|
10.29 |
|||
|
10.30 |
|||
|
21.1 |
|||
|
23.1+ |
|||
|
24.1+ |
|||
|
31.1+ |
|||
|
31.2+ |
|||
|
32.1++ |
|||
|
32.2++ |
|||
|
101+ |
Financial statements from the annual report on Form 10-K of the Company for the year ended December 31, 2017, formatted in XBRL: (i) the Consolidated Balance Sheets, (ii) Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Loss, (iii) the Consolidated Statements of Stockholders’ Deficit, (iv) the Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows, and (v) the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements |
||
|
+ |
Filed herewith |
|
++ |
Furnished herewith |
|
* |
Management compensatory plan or arrangement required to be filed as an exhibit to this report. |
|
** |
Portions of exhibit omitted pursuant to order granting confidential treatment issued by the Securities and Exchange Commission. |
|
Item 16. |
Form 10-K Summary |
None.
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized on March 21, 2018.
|
|
SUN BIOPHARMA, INC. |
|
|
|
By: |
/s/ DAVID B. KAYSEN |
|
David B. Kaysen |
||
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities indicated on March 21, 2018.
|
/s/ DAVID B. KAYSEN |
/s/ SCOTT KELLEN |
|
|
David B. Kaysen, (Principal Executive Officer) and Director |
Scott Kellen, (Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) |
|
|
* |
* |
|
|
Michael T. Cullen, |
J. Robert Paulson, Jr., Director |
|
|
* |
* |
|
|
Suzanne Gagnon, Director |
Paul W. Schaffer, Director |
|
|
* |
* |
|
|
Dalvir Gill, Director |
D. Robert Schemel, Director |
|
|
* |
||
|
Jeffrey S. Mathiesen, Director |
|
* |
David B. Kaysen, by signing his name hereto, does hereby sign this document on behalf of each of the above-named directors of the Registrant pursuant to powers of attorney duly executed by such persons. |
|
By: |
/s/ David B. Kaysen |
|
|
David B. Kaysen, |
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders of
Sun BioPharma, Inc.
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Sun Biopharma, Inc. and Subsidiary (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, and the related consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive loss, stockholders’ deficit, and cash flows for each of the years then ended, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the “financial statements”). In our opinion, the financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the years then ended in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
Substantial Doubt about the Company's Ability to Continue as a Going Concern
The accompanying financial statements have been prepared assuming that the Company will continue as a going concern. As discussed in Note 2 to the financial statements, the Company has recurring losses and negative cash flows from operations that raise substantial doubt about its ability to continue as a going concern. Management’s evaluations of the events and conditions and management’s plans regarding those matters are also described in Note 3. The financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of this uncertainty.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board of the United States of America (“PCAOB”) and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. As part of our audits, we are required to obtain an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion.
Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
/s/ Cherry Bekaert
We have served as the Company’s auditors since 2014.
Tampa, Florida
March 21, 2018
Sun BioPharma, Inc.
Consolidated Balance Sheets
(In thousands, except share amounts)
|
December 31, |
||||||||
|
2017 |
2016 |
|||||||
|
ASSETS |
||||||||
|
Current assets: |
||||||||
|
Cash |
$ | 152 | $ | 438 | ||||
|
Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
195 | 118 | ||||||
|
Income tax receivable |
420 | 321 | ||||||
|
Total current assets |
767 | 877 | ||||||
|
Total assets |
$ | 767 | $ | 877 | ||||
|
LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ DEFICIT |
||||||||
|
Current liabilities: |
||||||||
|
Accounts payable |
$ | 1,196 | $ | 1,245 | ||||
|
Accrued expenses |
1,254 | 842 | ||||||
|
Convertible notes payable, net |
1,525 | 2,733 | ||||||
|
Term debt, current portion |
14 | 294 | ||||||
|
Demand notes payable |
— | 250 | ||||||
|
Accrued interest |
181 | 155 | ||||||
|
Total current liabilities |
4,170 | 5,519 | ||||||
|
Long-term liabilities: |
||||||||
|
Term debt, noncurrent portion |
286 | — | ||||||
|
Total long-term liabilities |
286 | — | ||||||
|
Commitments and contingencies (Note 7) |
||||||||
|
Stockholders’ deficit: |
||||||||
|
Preferred stock, $0.001 par value; 10,000,000 authorized; no shares issued or outstanding as of December 31, 2017 and 2016 |
— | — | ||||||
|
Common stock, $0.001 par value; 100,000,000 authorized; 3,841,652 and 3,220,100 shares issued and outstanding, as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively |
4 | 3 | ||||||
|
Additional paid-in capital |
25,625 | 14,058 | ||||||
|
Accumulated deficit |
(29,153 | ) | (18,779 | ) | ||||
|
Accumulated other comprehensive gain (loss), net |
(165 | ) | 76 | |||||
|
Total stockholders’ deficit |
(3,689 | ) | (4,642 | ) | ||||
|
Total liabilities and stockholders’ deficit |
$ | 767 | $ | 877 | ||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
Sun BioPharma, Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Loss
(In thousands, except share and per share amounts)
|
Year Ended December 31, |
||||||||
|
2017 |
2016 |
|||||||
|
Operating expenses: |
||||||||
|
General and administrative |
$ | 3,423 | $ | 2,664 | ||||
|
Research and development |
2,593 | 2,504 | ||||||
|
Operating loss |
(6,016 | ) | (5,168 | ) | ||||
|
Other income (expense): |
||||||||
|
Interest income |
1 | 2 | ||||||
|
Grant income |
163 | — | ||||||
|
Interest expense |
(1,617 | ) | (180 | ) | ||||
|
Loss on induced debt conversions |
(3,696 | ) | — | |||||
|
Other income (expense) |
255 | (107 | ) | |||||
|
Total other expense |
(4,894 | ) | (285 | ) | ||||
|
Loss before income tax benefit |
(10,910 | ) | (5,453 | ) | ||||
|
Income tax benefit |
536 | 341 | ||||||
|
Net loss |
(10,374 | ) | (5,112 | ) | ||||
|
Foreign currency translation adjustment gain (loss) |
(241 | ) | 63 | |||||
|
Comprehensive loss |
$ | (10,615 | ) | $ | (5,049 | ) | ||
|
Basic and diluted net loss per share |
$ | (2.91 | ) | $ | (1.65 | ) | ||
|
Weighted average shares outstanding – basic and diluted |
3,566,098 | 3,106,846 | ||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
Sun BioPharma, Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Stockholders’ Deficit
(In thousands except share and per share amounts)
|
Accumulated |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Additional |
Other |
Total |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Common Stock |
Paid-In |
Accumulated |
Comprehensive |
Stockholders’ |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Shares |
Amount |
Capital |
Deficit |
Gain (Loss) |
Deficit |
|||||||||||||||||||
|
Balances at December 31, 2015 |
2,989,250 | $ | 3 | $ | 10,970 | $ | (13,667 | ) | $ | 13 | $ | (2,681 | ) | |||||||||||
|
Issuance of common stock and warrants, net of offering costs of $152 |
222,100 | — | 2,069 | — | — | 2,069 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
Issuance of common stock for services |
3,750 | — | 75 | — | — | 75 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
Exercise of stock warrants |
5,000 | — | 42 | — | — | 42 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
Stock-based compensation expense |
— | — | 902 | — | — | 902 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
Net loss |
— | — | — | (5,112 | ) | — | (5,112 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
|
Foreign currency translation adjustment, net of taxes of $0 |
— | — | — | — | 63 | 63 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
Balances at December 31, 2016 |
3,220,100 | $ | 3 | $ | 14,058 | $ | (18,779 | ) | $ | 76 | $ | (4,642 | ) | |||||||||||
|
Conversion of convertible notes payable and accrued interest into common stock |
385,000 | 1 | 5,840 | — | — | 5,841 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
Conversion of demand notes into common stock |
33,332 | — | 993 | — | — | 993 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
Charge for fair market value of beneficial conversion feature |
— | — | 2,954 | — | — | 2,954 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
Exercise of common stock options |
22,000 | — | 28 | — | — | 28 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
Exercise of stock purchase warrants |
181,220 | — | 19 | — | — | 19 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
Stock-based compensation expense |
— | — | 1,733 | — | — | 1,733 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
Net loss |
— | — | — | (10,374 | ) | — | (10,374 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
|
Foreign currency translation adjustment, net of taxes of $0 |
— | — | — | — | (241 | ) | (241 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
|
Balances at December 31, 2017 |
3,841,652 | $ | 4 | $ | 25,625 | $ | (29,153 | ) | $ | (165 | ) | $ | (3,689 | ) | ||||||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
Sun BioPharma, Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
(In thousands)
|
Year Ended December 31, |
||||||||
|
2017 |
2016 |
|||||||
|
Cash flows from operating activities: |
||||||||
|
Net loss |
$ | (10,374 | ) | $ | (5,112 | ) | ||
|
Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash used in operating activities: |
||||||||
|
Loss on induced debt conversions |
3,696 | — | ||||||
|
Stock-based compensation |
1,733 | 902 | ||||||
|
Amortization of debt discount |
1,387 | — | ||||||
|
Non-cash interest expense |
162 | 12 | ||||||
|
Amortization of debt issuance costs |
56 | 28 | ||||||
|
Changes in operating assets and liabilities: |
||||||||
|
Income and other tax receivables |
(70 | ) | 426 | |||||
|
Prepaid expenses and other assets |
(75 | ) | 19 | |||||
|
Accounts payable |
(319 | ) | 726 | |||||
|
Accrued liabilities |
402 | 601 | ||||||
|
Net cash used in operating activities |
(3,402 | ) | (2,398 | ) | ||||
|
Cash flows from financing activities: |
||||||||
|
Proceeds from the sale of convertible promissory notes, net of offering costs of $16 |
3,059 | — | ||||||
|
Proceeds from issuance of common stock and warrants, net of offering costs of $152 |
— | 1,873 | ||||||
|
Proceeds from the exercise of stock options |
28 | — | ||||||
|
Proceeds from the exercise of stock purchase warrants |
19 | 42 | ||||||
|
Net cash provided by financing activities |
3,106 | 1,915 | ||||||
|
Effect of exchange rate changes on cash |
10 | (4 | ) | |||||
|
Net decrease in cash |
(286 | ) | (487 | ) | ||||
|
Cash at beginning of year |
438 | 925 | ||||||
|
Cash at end of year |
$ | 152 | $ | 438 | ||||
|
Supplemental disclosure of cash flow information: |
||||||||
|
Cash paid during year for interest |
$ | 11 | $ | 57 | ||||
|
Supplemental disclosure of non-cash transactions: |
||||||||
|
Conversion of promissory notes and accrued interest into common stock |
2,888 | — | ||||||
|
Charge for fair market value of beneficial conversion feature |
2,954 | — | ||||||
|
Conversion of demand notes into common stock |
250 | — | ||||||
|
Deferred compensation exchanged for common stock and warrants |
$ | — | $ | 196 | ||||
|
Issuance of common stock for services |
$ | — | $ | 75 | ||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
Sun BioPharma, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
|
1. |
Business |
Sun BioPharma, Inc. and its wholly-owned subsidiary Sun BioPharma Australia Pty Ltd. (collectively “we,” “us,” “our,” and the “Company”) exist for the primary purpose of advancing the commercial development of a proprietary polyamine analogue for pancreatic cancer and for a second indication in chronic pancreatitis. We have exclusively licensed the worldwide rights to this compound, which has been designated as SBP-101, from the University of Florida Research Foundation, Inc. (“UFRF”). Sun BioPharma, Inc. was incorporated under the laws of the State of Delaware on September 21, 2011. Sun BioPharma Australia Pty Ltd was established on May 24, 2013, and incorporated under the laws of Australian Securities and Investments Commission.
Effective November 7, 2017, we implemented a 1-for-10 reverse split of our common stock. The reverse stock split was approved by our stockholders as of September 12, 2017, and was intended to increase the market price per share of our common stock to a level that qualifies for listing on the Nasdaq Capital Market. Concurrent with the reverse stock split, there was a 50% reduction in the number of shares authorized for issuance by the Company. All references to share and per share amounts included in these Consolidated Financial Statements have been retroactively restated to reflect the reverse split. Our common stock is currently traded on the over-the-counter markets through the OTCQB marketplace.
|
2. |
Risks and Uncertainties |
The Company operates in a highly regulated and competitive environment. The development, manufacturing and marketing of pharmaceutical products require approval from, and are subject to ongoing oversight by, the Food and Drug Administration (“FDA”) in the United States, the Therapeutic Goods Administration (“TGA”) in Australia, the European Medicines Agency (“EMA”) in the European Union, and comparable agencies in other countries. Obtaining approval for a new pharmaceutical product is never certain, may take many years, and is normally expected to involve substantial expenditures.
We have incurred losses of $29.2 million since our inception in 2011. For the year ended December 31, 2017, we incurred a net loss and negative cash flows from operating activities of $10.4 million and $3.4 million, respectively. We expect to incur substantial losses for the foreseeable future, which will continue to generate negative net cash flows from operating activities, as we continue to pursue research and development activities and the clinical development of our primary product candidate, SBP-101. As of December 31, 2017, we had cash of $152,000, negative working capital of $3.4 million and stockholders’ deficit of $3.7 million. The Company’s principal sources of cash have included the issuance of convertible debt and equity securities.
The accompanying Consolidated Financial Statements have been prepared assuming that we will continue as a going concern which contemplates the realization of assets and liquidation of liabilities in the normal course of business and do not include any adjustments relating to the recoverability or classification of assets or the amounts of liabilities that might result from the outcome of these uncertainties. Our ability to continue as a going concern, realize the carrying value of our assets and discharge our liabilities in the ordinary course of business is dependent upon a number of factors, including our ability to obtain additional financing, the success of our development efforts, our ability to obtain marketing approval for our initial product candidate, SBP-101, in the United States, Australia, the European Union or other markets and ultimately our ability to market and sell our initial product candidate. These factors, among others, raise substantial doubt about our ability to continue operations as a going concern. See Note 3 entitled “Liquidity and Management’s Plans.”
|
3. |
Liquidity and Management Plans |
We will need to seek additional sources of funds to support our current business plans. We may seek to raise additional funds through various sources, such as equity and debt financings, or through strategic collaborations and license agreements. We can give no assurances that we will be able to secure additional sources of funds to support our operations, or if such funds are available to us, that such additional financing will be sufficient to meet our needs or on terms acceptable to us. This risk would increase if our clinical data is not positive or economic and market conditions deteriorate.
If we are unable to obtain additional financing when needed, we would need to scale back our operations taking actions that may include, among other things, reducing use of outside professional service providers, reducing staff or staff compensation, significantly modify or delay the development of our SBP-101 product candidate, license to third parties the rights to commercialize our SBP-101 product candidate for pancreatic cancer, pancreatitis or other applications that we would otherwise seek to pursue, or cease operations.
On March 1, 2016 we instituted substantial salary deferrals for all senior employees in order to conserve cash. Effective October 1, 2017, we entered into second amendments to the previously disclosed employment agreements, as amended, with our Executive Chairman, Michael T. Cullen, M.D., M.B.A., our President and Chief Executive Officer, David B. Kaysen, our Chief Financial Officer, Scott Kellen and our Chief Medical Officer, Suzanne Gagnon, M.D. (the “Employees”). For Dr. Cullen, Mr. Kaysen and Dr. Gagnon, the Amendments established new annual base salaries representing a 25% reduction from prior levels. Mr. Kellen’s annual base salary remained unchanged. The Amendments also discontinued further salary deferrals. As of December 31, 2017, the total accrued wages for these officers was $1.1 million. On February 27, 2018, these officers agreed to waive their rights to receive the accrued wages in exchange for non-qualified stock option grants. See Note 11 entitled “Subsequent Events.”
Subsequent to the end of 2017, on February 20, 2018 and March 16, 2018 we entered into the 2018 Purchase Agreements with a number of accredited purchasers. Pursuant to these closings under the 2018 Purchase Agreements, we issued 252,200 shares of common stock and warrants to purchase up to an aggregate of 252,200 additional shares, resulting in gross proceeds of $1.3 million. See Note 11 titled “Subsequent Events” for further details.
Our future success is dependent upon our ability to obtain additional financing, the success of our development efforts, our ability to demonstrate clinical progress for our SBP-101 product candidate in the United States or other markets and ultimately our ability to market and sell our SBP-101 product candidate. If we are unable to obtain additional financing when needed, if our clinical trials are not successful, if we are unable to obtain marketing approval, we would not be able to continue as a going concern and would be forced to cease operations and liquidate our company.
There can be no assurances that we will be able to obtain additional financing on commercially reasonable terms, or at all. The sale of additional convertible debt or equity securities would likely result in dilution to our current stockholders.
|
4. |
Summary of Significant Accounting Policies |
Basis of presentation
We have prepared the accompanying Consolidated Financial Statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“GAAP”). Our fiscal year ends on December 31.
Principles of consolidation
The accompanying Consolidated Financial Statements include the assets, liabilities and expenses of Sun BioPharma, Inc. and our wholly-owned subsidiary. All significant intercompany transactions and balances have been eliminated in consolidation.
Use of estimates
The preparation of Consolidated Financial Statements requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the Consolidated Financial Statements and the reported amount of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Concentration of credit risk
Financial instruments that potentially subject the company to significant concentrations of credit risk consist primarily of cash. Cash is deposited in demand accounts at commercial banks. At times, such deposits may be in excess of insured limits. The Company has not experienced any losses on its deposits of cash.
Beneficial conversion feature
For convertible debt where the rate of conversion is below fair market value for our common stock, the Company records a charge for the beneficial conversion feature (“BCF”) and related debt discount which is presented as a direct deduction from the carrying amount of the related debt. The discount is amortized to interest expense over the life of the debt.
Debt issuance costs
Costs associated with the issuance of debt instruments are capitalized. These costs are amortized on a straight-line basis, which approximates the effective interest method, over the term of the debt agreements and are included in interest expense. The unamortized balance of debt issuance costs is presented as a direct reduction of the carrying amount of the related debt.
Research and development costs
Research and development costs include expenses incurred in the conduct of our Phase 1 human clinical trial, for third-party service providers performing various testing and accumulating data related to our preclinical studies; sponsored research agreements; developing and scaling the manufacturing process necessary to produce sufficient amounts of the SBP-101 compound for use in our pre-clinical studies and human clinical trials; consulting resources with specialized expertise related to execution of our development plan for our SBP-101 product candidate; personnel costs, including salaries, benefits and share-based compensation; and costs to license and maintain our licensed intellectual property.
We charge research and development costs, including clinical trial costs, to expense when incurred. Our human clinical trials are performed at clinical trial sites and are administered jointly by us with assistance from contract research organizations (“CROs”). Costs of setting up clinical trial sites are accrued upon execution of the study agreement. Expenses related to the performance of clinical trials generally are accrued based on contracted amounts and the achievement of agreed upon milestones, such as patient enrollment, patient follow-up, etc. We monitor levels of performance under each significant contract, including the extent of patient enrollment and other activities through communications with the clinical trial sites and CROs, and adjust the estimates, if required, on a quarterly basis so that clinical expenses reflect the actual effort expended at each clinical trial site and by each CRO.
We expense costs associated with obtaining licenses for patented technologies when it is determined there is no alternative future use of the intellectual property subject to the license.
Stock-based compensation
In accounting for stock-based incentive awards we measure and recognize the cost of employee and non-employee services received in exchange for awards of equity instruments based on the grant date fair value of those awards. Compensation cost is recognized ratably using the straight-line attribution method over the vesting period, which is considered to be the requisite service period. We record forfeitures in the periods in which they occur. Compensation expense for performance-based stock option awards is recognized when “performance” has occurred or is probable of occurring.
The fair value of stock-based awards is estimated at the date of grant using the Black-Scholes option pricing model. The determination of the fair value of stock-based awards is affected by our stock price, as well as assumptions regarding a number of complex and subjective variables. Risk free interest rates are based upon U.S. Treasury rates appropriate for the expected term of each award. Expected volatility rates are based primarily on the volatility rates of a set of guideline companies, which consist of public and recently public biotechnology companies. The assumed dividend yield is zero, as we do not expect to declare any dividends in the foreseeable future. The expected term of options granted is determined using the “simplified” method. Under this approach, the expected term is presumed to be the mid-point between the average vesting date and the end of the contractual term.
Income taxes
Income taxes are accounted for under the asset and liability method. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the estimated future tax consequences attributable to differences between the Consolidated Financial Statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax bases and operating loss and tax credit carry-forwards. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted rates, for each of the jurisdictions in which the Company operates, expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized in operations in the period that includes the enactment date. Valuation allowances are established when necessary to reduce deferred tax assets to the amount that is more likely than not to be realized. The Company has provided a full valuation allowance against the gross deferred tax assets as of December 31, 2017 and 2016. See Note 10 for additional information. The Company’s policy is to classify interest and penalties related to income taxes as income tax expense in the Consolidated Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Loss.
Foreign currency translation
The functional currency of Sun BioPharma Australia Pty Ltd is the Australian Dollar (“AUD”). Accordingly, assets and liabilities, and equity transactions of Sun BioPharma Australia Pty Ltd are translated into U.S. dollars at period-end exchange rates. Expenses are translated at the average exchange rate in effect for the period. The resulting translation gains and losses are recorded as a component of accumulated comprehensive gain (loss) in the Consolidated Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Loss. During the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016, any reclassification adjustments from accumulated other comprehensive gain to operations were inconsequential.
Grant Income
Grant income is derived from a one-time grant awarded to the Company by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases of the National Institutes of Health (the “Grant Agreement”). The total grant awarded under the Grant Agreement was $225,000 and is intended to fund studies of SBP-101 as a potential treatment for pancreatitis. Grant income is recognized as a non-operating income when the related research and development expenses are incurred, terms of the grant have been complied with and the Company is eligible for reimbursement under the Grant Agreement.
Comprehensive loss
Comprehensive loss consists of our net loss and the effects of foreign currency translation.
Net loss per share
We compute net loss per share by dividing our net loss (the numerator) by the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding (the denominator) during the period. Shares issued during the period and shares reacquired during the period, if any, are weighted for the portion of the period that they were outstanding. The computation of diluted earnings per share, or EPS, is similar to the computation of basic EPS except that the denominator is increased to include the number of additional common shares that would have been outstanding if the dilutive potential common shares had been issued. Our diluted EPS is the same as basic EPS due to common equivalent shares being excluded from the calculation, as their effect is anti-dilutive.
The following table summarizes our calculation of net loss per common share for the periods (in thousands, except share and per share data):
|
December 31, |
||||||||
|
2017 |
2016 |
|||||||
|
Net loss |
$ | (10,374 | ) | $ | (5,112 | ) | ||
|
Weighted average shares outstanding—basic and diluted |
3,566,098 | 3,106,846 | ||||||
|
Basic and diluted net loss per share |
$ | (2.91 | ) | $ | (1.65 | ) | ||
The following outstanding potential common shares were not included in the diluted net loss per share calculations as their effects were not dilutive:
|
Year Ended December 31, |
||||||||
|
2017 |
2016 |
|||||||
|
Employee and non-employee stock options |
733,960 | 701,960 | ||||||
|
Estimated common shares issuable upon conversion of notes payable and accrued interest |
319,193 | 246,666 | ||||||
|
Common shares issuable under common stock purchase warrants |
151,500 | 361,500 | ||||||
| 1,204,653 | 1,310,126 | |||||||
Recently adopted accounting pronouncement
In March 2016, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued ASU No. 2016-09, Improvements to Employee Share-Based Payment Accounting. The guidance in ASU 2016-09 is intended to simplify aspects of the accounting for employee share-based payments, including the accounting for income taxes, forfeitures, statutory withholding requirements, and classification on the statement of cash flows. The standard is effective for interim and annual periods beginning after December 15, 2016, with early adoption permitted. The adoption of ASU 2016-09 during the year ended December 31, 2017, did not have any impact on the Consolidated Financial Statements and related disclosures.
In July 2017, the FASB issued ASU 2017-11, Earnings Per Share (Topic 260), Distinguishing Liabilities from Equity (Topic 480) and Derivatives and Hedging (Topic 815): I. Accounting for Certain Financial Instruments with Down Round Features; and II. Replacement of the Indefinite Deferral for Mandatorily Redeemable Financial Instruments of Certain Nonpublic Entities and Certain Mandatorily Redeemable Non-controlling Interests with a Scope Exception. Part I of this update addresses the complexity of accounting for certain financial instruments with down round features. Down round features are features of certain equity-linked instruments (or embedded features) that result in the strike price being reduced on the basis of the pricing of future equity offerings. Current accounting guidance creates cost and complexity for entities that issue financial instruments (such as warrants and convertible instruments) with down round features that require fair value measurement of the entire instrument or conversion option. Part II of this update addresses the difficulty of navigating Topic 480, Distinguishing Liabilities from Equity, because of the existence of extensive pending content in the FASB Accounting Standards Codification. This pending content is the result of the indefinite deferral of accounting requirements about mandatorily redeemable financial instruments of certain nonpublic entities and certain mandatorily redeemable non-controlling interests. The amendments in Part II of this update do not have an accounting effect. This ASU is effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those years, beginning after December 15, 2018, with early adoption permitted. The adoption of ASU 2017-11, during the year ended December 31, 2017, did not have any impact on the Consolidated Financial Statements and related disclosures.
In February 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-02, Leases. The guidance in ASU 2016-02 supersedes the lease recognition requirements in the Accounting Standards Codification Topic 840, Leases. ASU 2016-02 requires an entity to recognize assets and liabilities arising from a lease for both financing and operating leases, along with additional qualitative and quantitative disclosures. The new standard requires the immediate recognition of all excess tax benefits and deficiencies in the income statement, and requires classification of excess tax benefits as an operating activity as opposed to a financing activity in the statements of cash flows. ASU 2016-02 is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2018, with early adoption permitted. The adoption of ASU 2016-02 during the year ended December 31, 2017, did not have any impact on the Consolidated Financial Statements and related disclosures.
5. Accrued liabilities
Accrued liabilities consisted of the following (in thousands):
|
December 31, 2017 |
December 31, 2016 |
|||||||
|
Deferred payroll and related expenses |
$ | 1,094 | $ | 637 | ||||
|
Clinical trial related expense |
95 | 97 | ||||||
|
Professional services |
61 | 70 | ||||||
|
Product and process development expenses |
— | 29 | ||||||
|
Other |
470 | 970 | ||||||
|
Total accrued liabilities |
$ | 1,254 | $ | 842 | ||||
6. Indebtedness
2017 Convertible notes payable
On each of February 17, March 3, March 10 and March 17, 2017, we entered into Note Purchase Agreements (the “Note Agreements”) with a number of accredited investors in private transactions. Pursuant to these Note Agreements, we sold convertible promissory notes (the “2017 Notes”) raising gross proceeds of approximately $3.1 million. The 2017 Notes are scheduled to mature on December 1, 2018 and bear interest at a rate of 5.0% per year. Principal and accrued interest on the 2017 Notes are payable at maturity. The Company may prepay the 2017 Notes in whole or in part at any time without penalty or premium. The 2017 Notes are convertible into shares of common stock or other securities of the Company upon the occurrence of a Qualified Financing, including the sale of equity securities or a strategic partnership, raising gross proceeds of at least $2.0 million on or before the maturity of the 2017 Notes or upon the request of a holder of any 2017 Note at a fixed conversion rate of $10.10 per share. Upon issuance, the 2017 Notes were convertible into our common stock at a conversion rate of $10.10 per share. The fair market value of our stock on the dates of issuance ranged from $15.00 to $39.00 per share. Therefore the 2017 Notes contained a beneficial conversion feature with an aggregate intrinsic value of approximately $3.0 million, which was recorded as a debt discount and is presented as a direct deduction from the carrying value of the 2017 Notes. The discount will be amortized through interest expense over the life of the 2017 Notes. Upon the occurrence of certain events of default, the 2017 Notes require the Company to repay the unpaid principal amount of the Notes and any unpaid accrued interest. The Company has used the net proceeds from the sales of the Notes to further the clinical development of SBP-101 and for working capital and general corporate purposes.. One of our stockholders, who beneficially owns more than 10% of our common stock, purchased $200,000 of the 2017 Notes.
2013 Convertible notes payable
In 2013, we initiated an offering of convertible promissory notes (the “2013 Notes”). In total, gross proceeds raised were $3.1 million. The 2013 Notes accrue interest at 5% per year, payable quarterly, are convertible into shares of common stock at $11.25 per share at the option of the holder and mature in December 2018.
In March 2017, we offered to all holders of outstanding 2013 Notes, who were accredited investors, an opportunity to convert all outstanding principal and accrued interest through March 31, 2017 into shares of our common stock at a rate of $7.50 per share. The offered conversion rate represented a $3.75, or 33.3%, discount from the rate stated in the terms of the 2013 Notes, which at the time was $11.25 per share. Holders of $2,750,000 aggregate principal amount of the 2013 Notes accepted the offer to convert and on March 31, 2017 we issued 385,000 shares of common stock in exchange for the surrender of the 2013 Notes which included $138,000 of accrued but unpaid interest. The fair market value of the shares issued was $11.5 million, compared to $8.5 million under the original conversion terms, resulting in a loss on the induced debt conversion of approximately $3.0 million. One of our stockholders, who beneficially owns more than 10% of our common stock, converted $700,000 aggregate principal amount of 2013 Notes, along with $35,000 of accrued but unpaid interest, into 98,000 shares of our common stock. The shares were issued in reliance on the exemption from registration set forth in Section 3(a)(9) of the Securities Act as securities exchanged by an issuer with existing security holders where no commission or other remuneration is paid or given directly or indirectly by the issuer for soliciting such exchange.
Demand notes payable
In September 2015, we assumed $250,000 of unsecured demand notes in conjunction with our merger with Cimarron Medical, Inc. that were previously issued by Cimarron (the “Demand Notes”). We included the holders of Demand Notes in our offer to convert all outstanding principal into shares of our common stock at a rate of $7.50 per share. The Demand Notes had no conversion feature. The holders of all $250,000 aggregate principal amount of the Demand Notes accepted the offer to convert and on March 31, 2017 we issued 33,332 shares of common stock in exchange for the surrender of all Demand Notes. The fair market value of the shares issued was $1.0 million resulting in a loss on induced debt conversion of $700,000. The shares were issued in reliance on the exemption from registration set forth in Section 3(a)(9) of the Securities Act as securities exchanged by an issuer with existing security holders where no commission or other remuneration is paid or given directly or indirectly by the issuer for soliciting such exchange.
The following table sets forth the changes in convertible and demand notes payable during the year ended December 31, 2017 (in thousands):
|
Convertible Notes Payable |
||||||||||||
|
Principal |
Accrued Interest |
Demand Notes |
||||||||||
|
Principal value at December 31, 2016 |
$ | 2,775 | $ | 105 | $ | 250 | ||||||
|
Accrued interest |
— | 159 | — | |||||||||
|
Aggregate principal value of 2017 Notes sold |
3,076 | — | — | |||||||||
|
Aggregate principal value of 2013 Notes and accrued interest converted into common stock |
(2,750 | ) | (138 | ) | — | |||||||
|
Aggregate principal value of Demand Notes converted into common stock |
— | — | (250 | ) | ||||||||
| Principal value at December 31, 2017 | $ | 3,101 | $ | 126 | $ | — | ||||||
Term debt
On October 26, 2012, we entered into an unsecured loan agreement (the “Agreement”) with the Institute for Commercialization of Public Research, Inc. (the “Institute”). Under the terms of the agreement, we borrowed $300,000 at a fixed interest rate of 4.125%. No principal or interest payments were due until the maturity date, October 26, 2017, unless a mandatory repayment event occurred. Effective October 26, 2017, we entered into an amendment to our unsecured loan agreement with the Institute. Under the terms of the amendment the maturity date of the note was extended to May 1, 2019 with monthly payments of $10,000 to begin on May 1, 2018 with the remaining balance due in full on May 1, 2019. The monthly payments will apply first to accrued and unpaid interest.
Debt issuance costs
The following table summarizes the deferred financing costs which are presented as a direct reduction of the carrying amount of their related debt liabilities (in thousands):
|
December 31, 2017 |
December 31, 2016 |
|||||||||||||||
|
Convertible Notes Payable |
Term Debt |
Convertible Notes Payable |
Long-Term Debt |
|||||||||||||
|
Loan principal amount |
$ | 3,101 | $ | 300 | $ | 2,775 | $ | 300 | ||||||||
|
Deferred financing costs |
16 | 37 | 105 | 37 | ||||||||||||
|
Accumulated amortization |
(7 | ) | (37 | ) | (63 | ) | (31 | ) | ||||||||
|
Unamortized balance |
9 | — | 42 | 6 | ||||||||||||
|
Discount on debt |
2,954 | |||||||||||||||
|
Accumulated amortization |
(1,387 | ) | ||||||||||||||
|
Unamortized balance |
1,567 | |||||||||||||||
|
Loan carrying amounts, net |
$ | 1,525 | $ | 300 | $ | 2,733 | $ | 294 | ||||||||
We recorded amortization of debt issuance costs of $56,000 and $28,000 for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively, which is included in interest expense in the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Operations and comprehensive loss.
7. Commitments and Contingencies
License agreement
On December 22, 2011, we entered into an exclusive license agreement with the University of Florida research Foundation (“UFRF”). The license agreement requires the company to pay royalties to UFRF ranging from 2.5% to 5% of net sales of licensed products developed from the licensed technology. Minimum annual royalties are required after the initial occurrence of a commercial sale of a marketed product. Royalties are payable for the longer of (i) the last to expire of the claims in the licensed patents or (ii) ten (10) years from the first commercial sale of a licensed product in each country in which licensed product is sold. The minimum annual royalties are as follows:
|
● |
$50,000 is due 270 days after occurrence of first commercial sale; |
|
● |
$100,000 is due on the first anniversary date of the first payment; |
|
● |
$100,000 is due on the second anniversary date of the first payment; and |
|
● |
$300,000 is due on the third anniversary date of the first payment and subsequent anniversary dates thereafter, continuing for the life of the license agreement. |
In addition, the company is subject to five remaining milestone payments under the license agreement.
|
● |
$300,000 is due upon enrollment of the first subject in a Phase ii clinical trial; |
|
● |
$3,000,000 is due upon approval of a new drug application; |
|
● |
$2,000,000 is due upon approval to manufacture and market in either the European Union or Japan (one time only); |
|
● |
$1,000,000 is due upon the first time annual net sales of licensed product or licensed process by the Company reaches $100,000,000; and |
|
● |
$3,000,000 is due upon the first time annual net sales of licensed product or licensed process by the Company reaches $500,000,000. |
The license agreement is subject to customary and usual termination provisions. The Company must also pay an annual license maintenance fee of $10,000. Accordingly, we recorded $10,000 as a license expense in the accompanying 2017 and 2016 Consolidated Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Loss.
On January 4, 2016, we enrolled the first patient in our Phase 1 clinical trial of SBP-101 in patients with previously treated pancreatic cancer. Accordingly, we recorded a milestone obligation of $50,000 as a license expense as of this date which is included in general and administrative expenses in the accompanying 2016 Consolidated Statement of Operations and Comprehensive Loss.
Clinical trials
We have recently concluded a Phase 1 study in patients with previously treated pancreatic cancer. Patient enrollment began in January 2016 and was completed in September 2017. In total, 29 patients were enrolled at four study sites in the United States and Australia. This study was a performed to evaluate the safety profile of SBP-101 as a monotherapy. Final collection and processing study data and production of the final study report are expected to be completed by the middle of 2018.
Based upon the results of our first study we have initiated a Phase 1a/1b first-line dose-escalation study of SBP-101 in combination with gemcitabine and nab-paclitaxel in newly diagnosed patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer. It is anticipated that the first patient will be enrolled in early Q2 2018. Additional clinical trials will be subsequently required if the results of the Phase 1a/1b pancreatic cancer trial are positive. We estimate the total time and cost to obtain FDA and EU approval and bring SBP-101 to market is 5 to 6 years and up to two-hundred million dollars ($200 million), however, such time and cost estimates are subject to significant variability and subject to change depending on the results of current and future clinical trials. Clinical trial costs are expensed as incurred.
Indemnification of directors and officers
The Company, as permitted under Delaware law and in accordance with its bylaws, will indemnify and advance expenses to its directors and officers to the fullest extent permitted by law or, if applicable, pursuant to indemnification agreements. They further provide that we may choose to indemnify other employees or agents of our Company from time to time. The Company has secured insurance on behalf of any officer, director, employee or other agent for any liability arising out of his or her actions in connection with their services to the Company. As of December 31, 2017, there was no pending litigation or proceeding involving any director or officer of the Company as to which indemnification is required or permitted, and we are not aware of any threatened litigation or proceeding that may result in a claim for indemnification. Insofar as indemnification for liabilities arising under the Securities Act may be permitted to directors, officers and controlling persons of the Company, the Company has been advised that, in the opinion of the SEC, such indemnification is against public policy as expressed in the Securities Act and is therefore unenforceable.
The Company believes the fair value of these indemnification agreements is minimal. Accordingly, the Company had not recorded any liabilities for these obligations as of December 31, 2017 or 2016.
|
8. |
Stockholders’ Deficit |
Private placement, resale registration
On each of June 10, June 24, August 11 and September 2, 2016, we entered into Securities Purchase Agreements (the “Purchase Agreements”) with the purchasers named therein, pursuant to which we sold an aggregate of 222,100 shares of common stock (the “Purchased Shares”) and warrants (the “Warrants”) to purchase an aggregate of 111,050 shares of common stock (the “Warrant Shares”). The purchase price for each unit, consisting of one share of common stock and a warrant to purchase one-half share of common stock, was $10.00. The Warrants are exercisable for a period of five years from their respective date of issuance at an exercise price of $15.00 per share. The Company received aggregate gross proceeds of $1.9 million from the Purchase Agreements closings under these private placement transactions and an additional $196,000 was invested by management through the conversion of previously deferred compensation. As of December 31, 2017, 108,550 of the Warrants remained outstanding.
Pursuant to the Purchase Agreements, we filed a registration statement on Form S-1 with the SEC covering the resale of the Purchased Shares and Warrant Shares. On October 3, 2016, the SEC declared the registration statement effective. We have also agreed, among other things, to indemnify the selling stockholders under the registration statements from certain liabilities and to pay all fees and expenses (excluding underwriting discounts and selling commissions and legal fees) incident to our obligations under the Purchase Agreements.
Authorized capital stock
Effective November 7, 2017, we implemented a 1-for-10 reverse split of our common stock. No fractional shares were issued in connection with the reverse stock split. Stockholders received a proportionate cash payment for any fractional shares based upon the closing price of our common stock on the effective date of the reverse stock split. The reverse stock split did not affect the par value of our common stock, however, concurrent with the reverse stock split, the number of shares of common and preferred stock authorized for issuance by the Company was reduced by 50% to 100,000,000 and 10,000,000, respectively. Proportional adjustments were also made to the Company’s 2016 Omnibus Incentive Plan, outstanding stock options, warrants and outstanding convertible notes payable. All references to share and per share amounts included in these Consolidated Financial Statements have been retroactively restated to reflect the reverse split.
Shares reserved
Shares of common stock reserved for future issuance are as follows:
|
December 31, 2017 |
||||
|
Stock options outstanding |
733,960 | |||
|
Shares available for grant under the 2016 Omnibus Equity Incentive Plan |
1,060,400 | |||
|
Estimated common shares issuable upon conversion of notes payable and accrued interest |
319,193 | |||
|
Common shares issuable under common stock purchase warrants |
151,500 | |||
|
Total |
2,265,053 | |||
|
9. |
Stock-Based Compensation |
2016 Omnibus Incentive Plan
The Sun BioPharma, Inc. 2016 Omnibus Incentive Plan (the “2016 Plan”) was adopted by our Board of Directors in March 2016 and approved by our stockholders at our annual meeting of stockholders on May 17, 2016. The 2016 Plan permits the granting of incentive and non-statutory stock options, restricted stock, stock appreciation rights, performance units, performance shares and other stock awards to eligible employees, directors and consultants. We grant options to purchase shares of common stock under the 2016 Plan at no less than the fair market value of the underlying common stock as of the date of grant. Options granted under the Plan have a maximum term of ten years. Under the Plan, a total of 1,500,000 shares of common stock are reserved for issuance. As of December 31, 2017, options to purchase 439,600 shares of common stock were outstanding under the 2016 Plan.
2011 Stock Option Plan
The Sun BioPharma, Inc. 2011 Stock Option Plan (the “2011 Plan”) was adopted by our Board of Directors in September 2011 and approved by our stockholders in January 2012. In conjunction with stockholder approval of the 2016 Plan, the Board terminated the 2011 Plan, although awards outstanding under the 2011 Plan will remain outstanding in accordance with and pursuant to the terms thereof. Options granted under the 2011 Plan have a maximum term of ten years and generally vest over zero to two years for employees. As of December 31, 2017, options to purchase 294,360 shares of common stock remained outstanding under the 2011 Plan.
We recognize stock-based compensation based on the fair value of each award as estimated using the Black-Scholes option valuation model. Ultimately, the actual expense recognized over the vesting period will only be for those shares that actually vest.
A summary of option activity is as follows:
|
Shares Available for Grant |
Shares Underlying Options |
Weighted Average Exercise Price Per Share |
Aggregate Intrinsic Value |
|||||||||||||
|
Balances at December 31, 2015 |
610,226 | 346,360 | $ | 2.70 | $ | 23,300,785 | ||||||||||
|
Shares Reserved |
889,774 | — | — | |||||||||||||
|
Granted |
(385,600 | ) | 385,600 | 15.10 | ||||||||||||
|
Exercised |
— | — | — | |||||||||||||
|
Cancelled |
— | (30,000 | ) | 3.18 | ||||||||||||
|
Balances at December 31, 2016 |
1,114,400 | 701,960 | $ | 9.50 | $ | 3,896,235 | ||||||||||
|
Granted |
(54,000 | ) | 54,000 | 10.00 | ||||||||||||
|
Exercised |
— | (22,000 | ) | 1.25 | ||||||||||||
|
Cancelled |
— | — | — | |||||||||||||
|
Balances at December 31, 2017 |
1,060,400 | 733,960 | $ | 9.79 | $ | 2,121,985 | ||||||||||
A summary of the status of our unvested shares during the year ended and as of December 31, 2017 is as follows:
|
Shares Under Option |
Weighted Average Grant-Date Fair Value |
|||||||
|
Unvested at December 31, 2016 |
298,400 | $ | 9.47 | |||||
|
Granted |
54,000 | 9.48 | ||||||
|
Vested |
(217,200 | ) | 8.79 | |||||
|
Forfeitures |
— | — | ||||||
|
Unvested at December 31, 2017 |
135,200 | $ | 9.31 | |||||
Information about stock options outstanding, vested and expected to vest as of December 31, 2017, is as follows:
|
Outstanding, Vested and Expected to Vest |
Options Vested and Exercisable |
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
Weighted Average |
Weighted Average |
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
Remaining |
Weighted |
Remaining |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Per Share |
Contractual |
Average |
Options |
Contractual |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Exercise Price |
Shares |
Life (Years) |
Exercise Price |
Exercisable |
Life (Years) |
|||||||||||||||||
| $ | 0.88 | – | 1.10 | 38,360 | 4.83 | $ | 1.00 | 38,360 | 4.83 | |||||||||||||
| 2.28 | – | 2.50 | 42,000 | 6.11 | 2.47 | 42,000 | 6.11 | |||||||||||||||
| 3.18 | 214,000 | 7.17 | 3.18 | 214,000 | 7.17 | |||||||||||||||||
| 10.00 | – | 10.10 | 54,000 | 9.55 | 10.00 | 50,000 | 9.99 | |||||||||||||||
| 15.10 | 385,600 | 8.51 | 15.10 | 254,400 | 8.64 | |||||||||||||||||
| 733,960 | 7.87 | $ | 9.79 | 598,760 | 7.81 | |||||||||||||||||
The cumulative grant date fair value of options vested during the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016 was $1.9 million and $336,000, respectively. Total proceeds received for options exercised during the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016 were $28,000 and $0, respectively.
As of December 31, 2017 and 2016, total compensation expense related to unvested employee stock options not yet recognized was $1.0 million and $1.9 million, respectively, which is expected to be allocated to expenses over a weighted-average period of 0.95 and 1.95 years, respectively.
The assumptions used in calculating the fair value under the Black-Scholes option valuation model are set forth in the following table for options issued by the Company for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016:
|
2017 |
2016 |
|||||||||
|
Common stock fair value |
$10.00 | – | $29.80 | $15.10 | ||||||
|
Risk-free interest rate |
1.43 | - | 2.23% | 1.56 | - | 2.04% | ||||
|
Expected dividend yield |
0% | 0% | ||||||||
|
Expected option life (years) |
2.25 | - | 5.5 | 3.5 | - | 5.75 | ||||
|
Expected stock price volatility |
75.0 | – | 78.0% | 75.0% | ||||||
Nonemployee stock-based compensation
We account for stock options granted to nonemployees in accordance with FASB ASC 505. In connection with stock options granted to nonemployees, we recorded $495,000 and $557,000 for nonemployee stock-based compensation during the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively. These amounts were based upon the fair values of the vested portion of the grants. Amounts expensed during the remaining vesting period will be determined based on the fair value at the time of vesting.
Stock-based payments
In the first quarter of 2016, our Board of Directors authorized the issuance of 3,750 shares of our common stock to two vendors who agreed to provide services to the Company upon terms that provided for a portion of their consideration to be paid in shares of our common stock. The fair value of each share of common stock was determined by our Board of Directors, and accordingly, we recorded a charge of $75,000.
10. Income Taxes
We have incurred net operating losses since inception. We have not reflected the benefit of net operating loss carryforwards in the accompanying financial statements and have established a full valuation allowance against our deferred tax assets.
Changes in tax laws and rates may affect recorded deferred tax assets and liabilities and our effective tax rate in the future. On December 22, 2017 the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 (the “Tax Act”) became law. The Tax Act enacted significant tax law changes, largely effective for tax years beginning after December 31, 2017. The Tax Act reduces the corporate tax rate to 21%, effective January 1, 2018, for all corporations. GAAP requires the effect of a change in tax laws or rates to be recognized as of the date of enactment, therefore we have revalued our deferred tax assets and liabilities as of December 22, 2017. As a result of the revaluation of our deferred tax assets and liabilities, we have reduced the value of our deferred tax asset and the related valuation allowance as of December 31, 2017, by $1.8 million.
At December 31, 2017 and 2016, the Company had an income tax receivable of $420,000 and $321,000, respectively, comprised of refundable tax incentives related to research and development activities of our subsidiary Sun BioPharma Australia Pty Ltd.
Deferred income taxes reflect the net tax effects of temporary differences between the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities for financial reporting purposes and the amounts used for income tax purposes as well as operating losses and tax credit carryforwards.
The significant components of our deferred tax assets and liabilities are as follows (in thousands):
|
December 31, |
||||||||
|
2017 |
2016 |
|||||||
|
Deferred tax assets (liabilities): |
||||||||
|
Net operating loss carryforwards |
$ | 3,440 | $ | 3,550 | ||||
|
Research credit carryforwards |
235 | 235 | ||||||
|
Stock-based compensation |
530 | 420 | ||||||
|
Accrued expenses |
236 | 188 | ||||||
|
Beneficial conversion feature, net |
(338 | ) | — | |||||
|
Other |
(24 | ) | 79 | |||||
|
Total deferred tax asset, net |
4,079 | 4,472 | ||||||
|
Valuation allowance |
(4,079 | ) | (4,472 | ) | ||||
|
Net deferred tax asset |
$ | — | $ | — | ||||
Realization of the future tax benefits is dependent on our ability to generate sufficient taxable income within the carry-forward period. Because of our history of operating losses, management believes that the deferred tax assets arising from the above-mentioned future tax benefits are currently not likely to be realized and, accordingly, we have provided a full valuation allowance.
A reconciliation of the statutory tax rates and the effective tax rates is as follows:
|
Year Ended December 31, |
||||||||
|
2017 |
2016 |
|||||||
|
Statutory rate |
34.0 | % | 34.0 | % | ||||
|
Permanent differences |
(13.5 | ) | (4.0 | ) | ||||
|
Change in effective tax rates |
(17.2 | ) | — | |||||
|
Valuation allowance |
(6.6 | ) | (30.7 | ) | ||||
|
Foreign research incentives |
3.8 | — | ||||||
|
Deferred true-up |
3.0 | — | ||||||
|
State tax rate true-up |
— | 0.6 | ||||||
|
Other |
0.3 | (0.1 | ) | |||||
|
Effective rate |
3.8 | % | 0.0 | % | ||||
Net operating losses and tax credit carryforwards as of December 31, 2017, are as follows:
|
Amount (In thousands) |
Expiration Years |
||||
|
Net operating losses—federal |
$ | 12,958 |
Beginning 2031 |
||
|
Tax credits—federal |
235 |
Beginning 2041 |
|||
Utilization of the net operating loss carryforwards and credits may be subject to a substantial annual limitation due to the ownership change limitations provided by the IRC, and similar state provisions. We have not performed a detailed analysis to determine whether an ownership change under Section 382 of the IRC has occurred. The effect of an ownership change would be the imposition of an annual limitation on the use of net operating loss carryforwards attributable to periods before the change.
The Company is subject to taxation in the United States and Australia. Tax returns, since the inception of Sun BioPharma, Inc. in 2011 and thereafter, are subject to examinations by federal and state tax authorities and may change upon examination. Tax returns of Sun BioPharma Australia Pty Ltd. for the year ended December 31, 2013 and thereafter are subject to examination by the Australian tax authorities.
11. Subsequent Events
Sale of common stock and stock purchase Warrants
On February 20, 2018 and March 16, 2016, we entered into the 2018 Purchase Agreements with certain accredited investors and completed closings on those dates. Pursuant to these closings, we sold units, each consisting of a share of common stock and a warrant to purchase one share of common stock. A total of 252,200 units were issued in these closings consisting of an aggregate of 252,200 shares of our common stock and warrants to purchase up to an aggregate of 252,200 additional shares of common stock. The purchase price for each unit was $5.00 and the Warrants will be exercisable for a period of three years from the date of issuance at an exercise price of $5.00. We received aggregate gross proceeds of $1.3 million in these private placement transactions, of which $95,000 was received from directors and officers of our Company or its subsidiary. Pursuant to the 2018 Purchase Agreements, we may be required to file a registration statement with the SEC covering the resale of the shares issued and/or warrant shares issuable thereunder.
Employment agreement amendments and waiver of rights to accrued compensation
Effective February 27, 2018, Sun BioPharma, Inc. (the “Company”) entered into waivers and third amendments (collectively, the “Amendments”) to the previously disclosed employment agreements, as amended (the “Agreements”), with our Executive Chairman, Michael T. Cullen, M.D., M.B.A., our President and Chief Executive Officer, David B. Kaysen, and our Chief Financial Officer, Scott Kellen, each of whom is an executive officer of the Company (collectively, the “Executives”), and our Chief Medical Officer, Suzanne Gagnon, M.D. (together with the Executives, the “Employees”). Dr. Cullen, Mr. Kaysen and Dr. Gagnon are also current members of the Company’s Board of Directors.
For each of the Employees, the Amendments waive the contingent payment of previously accrued wages and/or equity that had been established by the amendments to the Agreements dated October 1, 2017, each of which could have become due on or before June 30, 2018, upon a change of control or the Company’s completion of an underwritten public offering of its common stock. The total accrued wages waived by the Employees was $1.1 million as of December 31, 2017. The Amendments also entitled Dr. Cullen, Mr. Kaysen, Mr. Kellen and Dr. Gagnon to grants of new non-qualified stock options to purchase up to 100,000 shares, 50,000 shares, 25,000 shares and 95,000 shares of Company common stock, respectively, at an exercise price equal to fair market value as of the date of grant. These options vested upon grant and have option terms of 10 years. The options were granted under the Company’s 2016 Omnibus Incentive Plan effective as of February 27, 2018.
F-19
