Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-32.2 - EXHIBIT 32.2 - TINGO, INC. | tv487849_ex32-2.htm |
| EX-32.1 - EXHIBIT 32.1 - TINGO, INC. | tv487849_ex32-1.htm |
| EX-31.2 - EXHIBIT 31.2 - TINGO, INC. | tv487849_ex31-2.htm |
| EX-31.1 - EXHIBIT 31.1 - TINGO, INC. | tv487849_ex31-1.htm |
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
WASHINGTON, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
(Mark One)
x ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2017
OR
¨ ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
FOR THE ANNUAL PERIOD FROM TO
Commission file number: 333-205835
IWEB, INC.
(Exact name of Registrant as specified in its charter)
| Nevada | 47-3149295 | |
|
(State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) |
(I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
121/34, RS Tower, 8th Floor
Ratchadaphisek Road, Din Daeng Sub-district, din Daeng District,
Bangkok, Thailand
(Address of principal executive offices, including zip code)
+662-248-2436
(Registrant’s telephone number, including area code)
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
None
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act:
None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ¨ No x
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes ¨ No x
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes x No ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes x No ¨
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company,” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| Large accelerated filer ¨ | Accelerated filer ¨ |
| Non-accelerated filer ¨ (Do not check if a smaller reporting company) | Smaller reporting company x |
| Emerging growth company ¨ |
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). Yes ¨ No x
The Company cannot determine the aggregate market value of common equity held by non-affiliates as of June 30, 2017, because there were no trades of the Company’s common stock on or around such date. As of March 18, 2018 the registrant had outstanding 37,697,750* shares of common stock.
*The Company effected 1-for-2 reverse stock split on March 13, 2018.
IWEB, INC.
Table of Contents
NOTE ABOUT FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This report contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, or the Securities Act, and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, or the Exchange Act, regarding our company that include, but are not limited to, any projections of earnings, revenue or other financial items; any statements of the plans, strategies and objectives of management for future operations; any statements concerning proposed new products, services or developments; any statements regarding future economic conditions or performance; any statements of belief; and any statements of assumptions underlying any of the foregoing. These forward-looking statements are based on our current expectations, estimates and projections about our industry, management’s beliefs and certain assumptions made by us. Words such as “anticipates,” “expects,” “intends,” “plans,” “predicts,” “potential,” “believes,” “seeks,” “hopes,” “estimates,” “should,” “may,” “will,” “with a view to” and variations of these words or similar expressions are intended to identify forward-looking statements. These statements are not guarantees of future performance and are subject to risks, uncertainties and assumptions that are difficult to predict.
| 2 |
These forward-looking statements involve various risks and uncertainties. Although we believe our expectations expressed in these forward-looking statements are reasonable, our expectations may later be found to be incorrect. Our actual results could be materially different from our expectations. Important risks and factors that could cause our actual results to be materially different from our expectations are generally set forth in “Risk Factors,” “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations,” “Our Business” and other sections in this report. You should read this report and the documents we refer to thoroughly with the understanding that our actual future results may be materially different from and worse than what we expect. Other sections of this report include additional factors which could adversely impact our business and financial performance.
This report contains statistical data we obtained from various publicly available government publications and industry-specific third party reports. Statistical data in these publications also include projections based on a number of assumptions. The markets for our products may not grow at the rate projected by market data, or at all. The failure of these markets to grow at the projected rates may have a material adverse effect on our business and the market price of our securities. In addition, the rapidly changing nature of our customers’ industries results in significant uncertainties in any projections or estimates relating to the growth prospects or future condition of our markets. Furthermore, if any one or more of the assumptions underlying the market data is later found to be incorrect, actual results may differ from the projections based on these assumptions. You should not place undue reliance on these forward-looking statements.
Unless otherwise indicated, information in this report concerning economic conditions and our industry is based on information from independent industry analysts and publications, as well as our estimates. Except where otherwise noted, our estimates are derived from publicly available information released by third party sources, as well as data from our internal research, and are based on such data and our knowledge of our industry, which we believe to be reasonable. None of the independent industry publication market data cited in this report was prepared on our or our affiliates’ behalf.
The forward-looking statements made in this report relate only to events or information as of the date on which the statements are made in this report. Except as required by law, we undertake no obligation to update or revise publicly any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise, after the date on which the statements are made or to reflect the occurrence of unanticipated events. You should read this report and the documents we refer to in this report and have filed as exhibits to this report completely and with the understanding that our actual future results may be materially different from what we expect.
| 3 |
IWEB, Inc. (the “Company”) was incorporated under the laws of the State of Nevada on February 17, 2015.
The Company’s original business plan was to actively engage in providing high impact internet marketing strategies to internet based businesses and people seeking to create websites, but this business was not successful. On December 12, 2016, 49,995,000 shares of the common stock of the Company, representing 97.08% of the Company’s issued and outstanding shares of common stock at that time, were sold by Dmitriy Kolyvayko in a private transaction to Mr. Wai Hok Fung (the “Transaction”) for an aggregate purchase price of $380,000. In connection with the Transaction, Mr. Kolyvayko released the Company from certain liabilities and obligations arising out of his service as a director and officer of the Company.
On January 5, 2017, the Company’s Board of Directors approved an amendment to the Company’s Bylaws to change the Company’s fiscal year end from June 30 to December 31, effective as of December 31, 2016.
On May 15, 2017, the Company entered into a share exchange agreement (the “Share Exchange Agreement”) with Enigma Technology International Corporation (“Enigma BVI”), and all the shareholders of Enigma BVI, namely, Mr. Ratanaphon Wongnapachant, Ms. Chanikarn Lertchawalitanon and S-Mark Co. Ltd. (collectively the “Shareholders”), to acquire all the issued and outstanding capital stock of Enigma BVI in exchange for the issuance to the Shareholders of an aggregate of 63,000,000 restricted shares of IWEB, Inc.’s common stock (the “Reverse Merger”). The Reverse Merger closed on May 15, 2017. As a result of the Reverse Merger, Enigma BVI is now a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Company.
Enigma BVI was incorporated on February 22, 2017 in the British Virgin Islands.
Digiwork (Thailand) Co., Ltd. (“Digiwork”) was established and incorporated in Thailand on November 24, 2016. The authorized capital of the Digiwork is THB5,000,000 (approximately $153,604), divided into 500,000 common shares with a par value of THB10 per share, which has been fully paid up as of December 31, 2016.
On May 15, 2017, Enigma BVI, Digiwork and the shareholders of Digiwork entered into the following commercial arrangements, or collectively, “VIE Agreements,” pursuant to which Enigma BVI has contractual rights to control and operate the businesses of Digiwork.
Pursuant to an Exclusive Technology Consulting and Service Agreement, Enigma BVI agreed to act as the exclusive consultant of Digiwork and provide technology consulting and services to Digiwork. In exchange, Digiwork agreed to pay Enigma BVI a technology consulting and service fee, the amount of which is decided by Enigma BVI on the basis of the work performed and commercial value of the services and the fee amount to be equivalent to the amount of net profit before tax of Digiwork on a quarterly basis; provided that the minimum amount of which is no less than THB30,000 (approximately $9,224) per quarter. Without the prior written consent of Enigma BVI, Digiwork may not accept the same or similar technology consulting and services provided by any third party during the term of the agreement. All the benefits and interests generated from the agreement, including but not limited to intellectual property rights, know-how and trade secrets, will be Enigma BVI’s sole and exclusive property. The term of this agreement will expire on May 15, 2027 and may be extended unilaterally by Enigma BVI with Enigma BVI's written confirmation prior to the expiration date. Digiwork cannot terminate the agreement early unless Enigma BVI commits fraud, gross negligence or illegal acts, or becomes bankrupt or winds up;
| 4 |
Pursuant to an Exclusive Purchase Option Agreement, the shareholders of Digiwork granted to Enigma BVI and any party designated by Enigma BVI the exclusive right to purchase at any time during the term of this agreement all or part of the equity interests in Digiwork, or the “Equity Interests,” at a purchase price equal to the registered capital paid by the shareholders of Digiwork for the Equity Interests, or, in the event that applicable law requires an appraisal of the Equity Interests, the lowest price permitted under applicable law; Pursuant to powers of attorney executed by each of the shareholders of Digiwork, such shareholders irrevocably authorized any person appointed by Enigma BVI to exercise all shareholder rights, including but not limited to voting on their behalf on all matters requiring approval of Digiwork’s shareholders, disposing of all or part of the shareholder's equity interest in Digiwork, and electing, appointing or removing directors and executive officers. The person designated by Enigma BVI is entitled to dispose of dividends and profits on the equity interest without reliance of any oral or written instructions of the shareholder. Each power of attorney will remain in force for so long as the shareholder remains a shareholder of Digiwork. Each shareholder has waived all the rights which have been authorized to Enigma BVI’s designated person under each power of attorney;
Pursuant to equity pledge agreements, each of the shareholders of Digiwork pledged all of the Equity Interests to Enigma BVI to secure the full and complete performance of the obligations and liabilities on the part of Digiwork and each of its shareholders under this and the above contractual arrangements. If Digiwork or the shareholders of Digiwork breach their contractual obligations under these agreements, then Enigma BVI, as pledgee, will have the right to dispose of the pledged equity interests. The shareholders of Digiwork agree that, during the term of the equity pledge agreements, they will not dispose of the pledged equity interests or create or allow any encumbrance on the pledged equity interests, and they also agree that Enigma BVI’s rights relating to the equity pledge should not be prejudiced by the legal actions of the shareholders, their successors or their designees. During the term of the equity pledge, Enigma BVI has the right to receive all of the dividends and profits distributed on the pledged equity. The equity pledge agreements will terminate on the second anniversary of the date when Digiwork and the shareholders of Digiwork have completed all their obligations under the contractual agreements described above.
As a result of the above contractual arrangements, Enigma BVI has substantial control over Digiwork’s daily operations and financial affairs, election of its senior executives and all matters requiring shareholder approval. Furthermore, as the primary beneficiary of Digiwork, the Company, via Enigma BVI, is entitled to consolidate the financial results of Digiwork in its own consolidated financial statements under Financial Accounting Standards Board Accounting Standard Codification (ASC) Topic 810 and related subtopics related to the consolidation of variable interest entities, or ASC Topic 810.
Digiwork was set up pursuant to a joint business agreement among its shareholders on August 4, 2016 and as amended and restated on March 31, 2017 (“JBA”). Pursuant to the JBA, Digiwork is obligated to pay a total of $10,000,000 to a shareholder of Digiwork, Digiwork Co., Ltd. (“Digiwork Korea”). As consideration for such payments, Digiwork Korea agreed to provide research and development services to Digiwork for a period of five years commencing from March 31, 2017. As of December 31, 2017 and 2016, an initial payment of $100,000 was paid to Digiwork Korea.
On July 10, 2017, the parties to the JBA entered into an amendment to the Amended and Restated Joint Business Agreement which amended the total payment from $10,000,000 to $1,100,000. The final payment of $1,000,000 is due on August 31, 2017. As of the date of this annual report, the amount remains unpaid. Mr. Ratanaphon Wongnapachant, the CEO, a director and major shareholder of the Company, has agreed to make loans to Digiwork to make the payment due to Digiwork Korea, if necessary.
Digiwork Korea also agreed to grant Digiwork full and exclusive licenses of any new launches, developments, improvements and any other intellectual property rights of coding technology so developed by Digiwork Korea. The territories for such licenses are in Thailand, Vietnam, Myanmar, Laos, Cambodia, United Arab Emirates and Qatar.
Digiwork was authorized by Digiwork Korea to be an official licensee and distributor of its technology exclusively in Thailand, Vietnam, Myanmar, Laos, Cambodia, United Arab Emirates and Qatar, and the authorization covers all four of Digiwork Korea’s coding technology: image, audio, web and security coding. This technology enables governments and enterprises around the world to give digital identities to media and objects that computers can sense and recognize, and to which they can react.
Digiwork is a technology development and services provider specializing in coding services in various industries and markets.
In the first quarter of 2017, Digiwork signed two service contracts with two unrelated entities for coding services. Both service contracts were completed as of December 31, 2017.
| 5 |
Organization and reorganization
Enigma BVI was incorporated on February 22, 2017 in the British Virgin Islands with limited liability as an investment holding company. Upon incorporation, Enigma BVI issued 50,000 shares at $1 each. Prior to the reorganization, Enigma BVI was owned 57.5% by Mr. Ratanaphon Wongnapachant, 2.5% by Ms. Chanikarn Lertchawalitanon, and 40% by S-Mark Co. Ltd., a KOSDAQ-listed corporation and 100% shareholder of Digiwork Korea.
Digiwork (Thailand) Co. Ltd was incorporated in Thailand with limited liability on November 24, 2016. Digiwork was also owned 57.5% by Mr. Ratanaphon Wongnapachant, 2.5% by Ms. Chanikarn Lertchawalitanon, and 40% by S-Mark Co. Ltd.
On May 15, 2017, Enigma BVI, Digiwork and the shareholders of Digiwork entered into the abovementioned VIE Agreements, pursuant to which Enigma BVI has contractual rights to control and operate the businesses of Digiwork. The change in control of and the acquisition of Digiwork by Enigma BVI have been accounted for as common control transaction in a manner similar to a pooling of interests and there was no recognition of any goodwill or excess of the acquirers’ interest in the net fair value of the acquirees’ identifiable assets, liabilities and contingent liabilities over cost at the time of the common control combinations. Therefore, this transaction was recorded at historical cost with a reclassification of equity from retained profits to additional paid in capital to reflect the deemed value of consideration given in the local jurisdiction and the capital structure of Enigma BVI.
On May 15, 2017, the Company entered into a share exchange agreement (the “Share Exchange Agreement”) with Enigma Technology International Corporation (“Enigma BVI”), and all the shareholders of Enigma BVI, namely, Mr. Ratanaphon Wongnapachant, Ms. Chanikarn Lertchawalitanon and S-Mark Co. Ltd. (collectively the “Shareholders”), to acquire all the issued and outstanding capital stock of Enigma BVI in exchange for the issuance to the Shareholders of an aggregate of 63,000,000 restricted shares of IWEB, Inc.’s common stock (the “Reverse Merger”). The Reverse Merger closed on May 15, 2017. As a result of the Reverse Merger, Enigma BVI is now a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Company.
On May 15, 2017, the Company filed a Current Report on Form 8-K with the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) announcing the completion of the business combination between the Company and Enigma BVI in accordance with the terms of the Share Exchange Agreement. As a result of the transaction, Enigma BVI is now a wholly owned subsidiary of the Company, and the former shareholders of Enigma BVI became the holders of approximately 84% of the Company’s issued and outstanding capital stock on a fully-diluted basis. The acquisition was accounted for as a recapitalization effected by a share exchange, wherein Enigma BVI is considered the acquirer for accounting and financial reporting purposes. The assets and liabilities of the acquired entity have been brought forward at their book value and no goodwill has been recognized.
The financial statements of the Company include all of the accounts of the Company, its subsidiary, Enigma BVI and its VIE entity, Digiwork.
All references above to share and per share data of IWEB, Inc. have not been adjusted to give effect of the reverse stock split (see below).
On March 7, 2018, the Company filed a Certificate of Change with the State of Nevada (the “Certificate”) to effect a 1-for-2 reverse stock split of the Company’s authorized shares of common stock, par value $0.0001 (the “Common Stock”), accompanied by a corresponding decrease in the Company’s issued and outstanding shares of Common Stock (the “Reverse Stock Split”) such that, following the consummation of the Reverse Stock Split, the number of authorized shares of Common Stock shall be reduced from 150,000,000 to 75,000,000. The Reverse Stock Split became effective on March 13, 2018.
Our Business Strategy
Digiwork was set up pursuant to a joint business agreement among its shareholders (“JBA”) on August 4, 2016, as amended and restated on March 31, 2017. Pursuant to the JBA, Digiwork was originally obligated to pay a total of $10,000,000 to S-Mark Co., Ltd. or Digiwork Co., Ltd. (“Digiwork Korea”, a 100% wholly owned subsidiary of S-Mark Co., Ltd., which is a shareholder of Digiwork and a 33.6% shareholder of the Company). On July 10, 2017, parties to the JBA entered into an amendment to the Amended and Restated Joint Business Agreement which amended the total payment from $10,000,000 to $1,100,000. As the consideration for such payments, Digiwork Korea agreed to provide research and development services to Digiwork for a period of five years commencing from March 31, 2017. Digiwork currently has 8 full time employees, all of which are administrative staff members. The technical services are currently provided by contracted technicians from Digiwork Korea.
Digiwork Korea also agreed to grant to Digiwork full and exclusive licenses of any new launches, developments, improvements and any other intellectual property rights of coding technology so developed by Digiwork Korea. The territories for such licenses are Thailand, Vietnam, Myanmar, Laos, Cambodia, United Arab Emirates and Qatar.
| 6 |
Digiwork was authorized by Digiwork Korea to be an official licensee and distributor of its technology exclusively in Thailand, Vietnam, Myanmar, Laos, Cambodia, United Arab Emirates and Qatar, and the authorization covers all four categories of Digiwork Korea’s coding technology: image, audio, web and security coding. This technology enables governments and enterprises around the world to give digital identities to media and objects that computers can sense and recognize, and to which they can react.
Digiwork is a technology development and services provider specializing in coding services in various industries and markets. Digiwork’s technology enables enterprises to imbed or imprint invisible digital identities to media and objects that various computer devices can sense and recognize and to which they can react. Our coding technology provides the means to infuse persistent digital information, perceptible only to computers and digital devices, into all forms of media content. Our coding technology permits computers and digital devices including smartphones, tablets, industrial scanners and other computer interfaces to quickly identify relevant data from vast amounts of media content. We focus on four coding technologies:
| · | Image coding technology, |
| · | Audio coding technology, |
| · | Web coding technology, and |
| · | Security coding technology |
There are currently no competing technologies existing in our authorized territories, however, older technologies like QR code remains as our primary competitor. We need to convince customers that our technology is more advanced and will replace QR code and similar identification technologies in the near future.
We provide tailor-made coding technological solutions to various commercial entities in different markets. Our technologies enable companies to give digital identity or information through various media like music, movies, television broadcasts, images and printed materials. The wide range application of the above four technologies can provide improved media rights, asset management, reduce piracy and counterfeiting losses, improve marketing programs, permit more efficient and effective distribution of valuable media content and enhance consumer experiences.
Our technologies and products are as follows:
Completed portion of the pattern
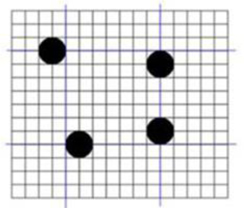
The above basic pattern will be generated through our pattern generator with constantly varied variables and spread over the product surface as below. The patterns are generated before usage and kept in the server to be issued when needed. All patterns will be unique due to its varied coordinates, and the usage of each code can be tracked individually.
| 7 |
The coordinate dot patterns are processed through 7 steps:
| 1. | Recognition of pattern through device |
| A. | Software will limit amount data captured through camera |
| B. | Frameware configurations will enhance recognition |
| 2. | Captured data will be filtered for better recognition of location |
| A. | Visually unleveled patterns will be corrected in 3D within software to level the grid |
| B. | Software will filter in dots only |
| 3. | Captured data will be segmented to a predefined amount of bits |
| A. | Dots will be segmented into predefined spacing and values and identified |
| 4. | Dots will go through decoding |
| A. | Decoded values will turn into keys |
| 5. | Value of the segmented portion will go through a dot finder which is in the server library |
| A. | Dot coordinates will be stored in a library with exact offsets prior to production |
| 6. | Software analyzes offsets of each dot within segmented area |
| A. | Offset values give each dot a unique position by calculating other dots beside it |
| 7. | Connected to application or content |

Some of our products and technologies are currently still in development stage and distinguishes with those products that are currently available on the market
As the market is currently using RFID, QR, Barcodes and other similar marking methods, we are developing key solutions to create innovative ways to preserve and protect the original identity of the product through:
| 8 |
| · | Color adaptation (Scheduled to be in final stage for production within 1-2 months) |
| o | Color value configuration to create minimum disruption to the naked eye and create maximum differentiation for the data captured and processed in the software stage and firmware stage, |
| o | Ink development, |
| § | Inks with different reactions to light and material to prevent copying and minimize disruption of color to the naked eye. |
| · | Printing methods (Scheduled to be in final stage for production within 3-4 months) |
| o | Development of printing processes for different printing methods for offset, digital, pad printing and etc. to cut down on time due to addition of pattern prints. |
| · | Application Platform (Scheduled to be in final stage for production within 2-3 months) |
| o | Develop services to retrieve user usage data and data analysis for the admin. |
| o | Real-time marketing information database of the consumer for the client. |
All in-development solutions are correlated through the resulting final product where multiple mobile phones and platforms will be tested for successful.
Employees
Digiwork currently has 8 full time employees, all of which are administrative staff members. The technical services are currently provided by contracted technicians from Digiwork Korea.
Research and Development
Research and development costs are paid to Digiwork Korea, which is providing research and development services to Digiwork for a period of five years commencing from March 31, 2017. Research and development costs are recognized in general and administrative expenses and expensed as incurred. Research and development expense was $163,159 and nil for years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively.
Available Information
Our common stock is listed on the OTCQB Marketplace and trades under the symbol “IWBB.” Our principal executive offices are located at RS Tower Building, 8th Floor, Address No. 121/34, Ratchadaphisek Road, Din Daeng Sub-District, Din Daeng District, Bangkok, Thailand, and our telephone number is +662-248-2436. The internet address of our corporate website is http://www.digiwork.co.th/.
We file annual reports, quarterly reports, current reports, proxy statements and other information with the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. You can inspect and obtain a copy of our reports, proxy statements and other information filed with the SEC at the offices of the SEC’s Public Reference Room at 100 F Street N.E., Washington, D.C. 20549, on official business days during the hours of 10 a.m. to 3 p.m. EST. Please call the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330 for further information on the Public Reference Room. The SEC maintains an internet website at http://www.sec.gov where you can access copies of most of our SEC filings.
We make our annual reports on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, current reports on Form 8-K, and amendments to those reports, available free of charge on our corporate website. The contents of our corporate website are not incorporated into, or otherwise to be regarded as part of, this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
The Company operates in an environment that involves a number of risks and uncertainties. The risks and uncertainties described in this Annual Report on Form 10-K are not the only risks and uncertainties that we face. Additional risks and uncertainties that presently are not considered material or are not known to us, and therefore are not mentioned herein, may impair our business operations. If any of the risks described in this Annual Report on Form 10-K actually occur, our business, operating results and financial position could be adversely affected.
| 9 |
Risks Related to Our Business
We have a history of losses and we may not achieve or sustain profitability, particularly if we were to lose large contracts.
Digiwork was formed on November 24, 2016. As of December 31, 2017, revenue of $126,456 was generated from the operation and the company is still in developing stage. In 2017, Digiwork signed and completed two service contracts with two unrelated entities for coding services. Digiwork has incurred net losses from inception. Digiwork's accumulated deficit was $597,849 as of December 31, 2017. Although we anticipate that Digiwork will be a profitable company, in order to achieve sustained profitability we will need to generate more revenue from coding technologies. Achieving sustained profitability will depend upon a variety of factors, including the extent to which we may be required to increase the size of our workforce in order to execute our business strategy and capitalize on new opportunities. In addition, we will evaluate our strategy and market opportunities on an ongoing basis and will adjust our approach to market conditions from time to time. Finally, various adverse developments, including the loss of contracts or cost overruns on our existing contracts, could have a negative effect on our revenue or our margins. Accordingly, increases in our expenses may not be offset by revenue generated and as a result we may not be able to achieve or sustain profitability.
Our independent registered auditors have expressed substantial doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern.
Our audited financial statements included in this report include an explanatory paragraph that indicates that they were prepared assuming that we would continue as a going concern. As discussed in Note 3 to the financial statements included with this report, we suffered recurring losses from operations and had a net capital deficiency accumulated deficit as of December 31, 2017. These conditions raise substantial doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern. The ability to continue as a going concern is dependent upon generating profitable operations in the future and/or obtaining the necessary financing to meet our obligations and repay our liabilities arising from normal business operations when they become due. There can be no assurance that we will be successful in our plans described above or in attracting equity or alternative financing on acceptable terms, or if at all. These consolidated financial statements do not include any adjustments to the recoverability and classification of recorded asset amounts and classification of liabilities that might be necessary should we be unable to continue as a going concern.
The majority of our revenue is subject to commercial contracts and development of new markets that may involve unpredictable delays and other unexpected changes, which might limit our actual revenue in any given quarter or year.
We will derive substantial portions of our revenue from commercial contracts tied to development schedules or development of new markets, which could shift for months, quarters or years as the needs of our customers and the markets in which they participate change. Commercial customers also face budget pressures that introduce added uncertainty. Any shift in development schedules, the markets in which we participate, or customer procurement processes, which are outside our control and may not be predictable, could result in delays in bookings forecasted for any particular period, could affect the predictability of our quarterly and annual results, and might limit our actual revenue in any given quarter or year, resulting in reduced and less predictable revenue and adversely affecting profitability.
| 10 |
The market for our products is highly competitive and alternative technologies or larger companies may undermine, limit or eliminate the market for our products' technologies, which would decrease our revenue and profits.
The markets in which we compete for business are intensely competitive and rapidly evolving. We expect competition to continue from both existing competitors and new market entrants. We face competition from other companies and from alternative technologies. Because the market solutions based on our technologies are still in an early stage of development, we also may face competition from unexpected sources.
Alternative technologies that may directly or indirectly compete with particular applications of our watermarking technologies include:
• Encryption—securing data during distribution using a secret code so it cannot be accessed except by authorized users;
• Containers—inserting a media object in an encrypted wrapper, which prevents the media object from being duplicated and is used for content distribution and transaction management;
• DataGlyphs®—a slightly visible modification of the characteristics of an image or document that is machine-readable;
• Scrambled Indicia®—an optical refraction-based data-hiding technique that is inserted into an image and can be read with a lens;
• Traditional anti-counterfeiting technologies—a number of solutions used by many enterprises (and that compete for budgetary outlays) designed to deter counterfeiting, including traditional barcode, QR code, laser printing etc;
• Radio frequency tags—embedding a chip that emits a signal when in close proximity with a receiver, which is being used in photo identification credentials, labels and tags;
• Internet technologies—numerous existing and potential Internet access and search methods are competitive with Digiwork (Thailand);
• Digital fingerprints and signatures—a metric, or metrics, computed solely from a source image or audio or video track, that can be used to identify an image or track, or authenticate the image or track;
• Smart cards—badges and cards including a semiconductor memory and /or processor used for authentication and related purposes; and
• Bar codes or QR codes—data-carrying codes, typically visible in nature (but may be invisible if printed in ultraviolet- or infrared responsive inks).
In the competitive environment in which we operate, product generation, development and marketing processes relating to technology are uncertain and complex, requiring accurate prediction of demand as well as successful management of various development risks inherent in technology development. In light of these dependencies, it is possible that failure to successfully accommodate future changes in technologies related to our technologies could have a long-term effect on our growth and results of operations.
New developments are expected to continue, and we do not assure you that discoveries by others, including current and potential competitors, will not render our services and products noncompetitive. Moreover, because of rapid technological changes, we may be required to expend greater amounts of time and money than anticipated to develop new products and services, which in turn may require greater revenue streams from these products and services to cover developmental costs. Many of the companies that compete with us for some of our business, as well as other companies with whom we may compete in the future, are larger and may have greater technical, financial, marketing, and political resources than we do. These resources could enable these companies to initiate severe price cuts or take other measures in an effort to gain market share or otherwise impede our progress. We do not assure you that we will be able to compete successfully against current or future participants in our market or against alternative technologies, or that the competitive pressures we face will not decrease our revenue and profits in the future.
We depend on our management and key employees for our future success. If we are not able to retain, hire or integrate these employees, we may not be able to meet our commitments.
Our success depends to a significant extent on the performance and continued service of our management and our intellectual property team. The loss of the services of any of these employees could limit our growth or undermine customer relationships.
| 11 |
Due to the high level of technical expertise that our industry requires, our ability to successfully develop, market, sell, license and support our products, services, and intellectual property depends to a significant degree upon the continued contributions of our key personnel in engineering, sales, marketing, operations, legal and licensing, many of whom would be difficult to replace. We believe our future success will depend in large part upon our ability to retain our current key employees and our ability to attract, integrate and retain these personnel in the future. It may not be practical for us to match the compensation some of our employees could garner at other employment. In addition, we may encounter difficulties in hiring and retaining employees because of concerns related to our financial performance. These circumstances may have a negative effect on the market price of our common stock, and employees and prospective employees may factor in the uncertainties relating to our stability and the value of any equity-based incentives in their decisions regarding employment opportunities and decide to leave our employ. Moreover, our business is based in large part on patented technology, which is unique and not generally known. New employees require substantial training, involving significant resources and management attention. Competition for experienced personnel in our business can be intense. If we do not succeed in attracting new, qualified personnel or in integrating, retaining and motivating our current personnel, our growth and ability to deliver products and services that our customers require may be hampered. Although our employees generally have executed agreements containing non-competition clauses, we do not assure you that a court would enforce all of the terms of these clauses or the clauses generally. If these clauses were not fully enforced, our employees could be able to freely join our competitors. Although we generally attempt to control access to and distribution of our proprietary information by our employees, we do not assure you that the confidential nature of our proprietary information will be maintained in the course of such future employment. Any of these events could have a material adverse effect on our financial and business prospects.
If leading companies in our industry or standard-setting bodies or institutions downplay, minimize, or reject the use of our technologies, deployment may be slowed and we may be unable to achieve revenue growth, particularly in the media and entertainment sectors.
Many of our business endeavors, such as our development of intellectual property in support of audio and video copy-control applications, can be impeded or frustrated by larger, more influential companies or by standard-setting bodies or institutions downplaying, minimizing or rejecting the value or use of our other technologies. A negative position by these companies, bodies or institutions, if taken, may result in obstacles for us that we would be incapable of overcoming and may block or impede the adoption of digital coding, particularly in the media and entertainment market. In addition, potential customers in the media and entertainment industry may delay or reject initiatives that relate to deployment of our technologies. Such a development would make the achievement of our business objectives in this market difficult or impossible.
If we are unable to respond to regulatory or industry standards effectively, or if we are unable to develop and integrate new technologies effectively, our growth and the development of our products and services could be delayed or limited.
Our future success will depend in part on our ability to enhance and improve the responsiveness, functionality and features of our products and services, and those of our business partners, in accordance with regulatory or industry standards. Our ability to remain competitive will depend in part on our ability to influence and respond to emerging industry and governmental standards in a timely and cost-effective manner. If we are unable to influence these or other standards or respond to such standards effectively, our growth and the development of certain products and services could be delayed or limited.
Our market is characterized by new and evolving technologies. The success of our business will depend on our ability to develop and integrate new technologies effectively and address the increasingly sophisticated technological needs of our customers in a timely and cost effective manner. Our ability to remain competitive will depend in part on our ability to:
| · | enhance and improve the responsiveness, functionality and other features of the products and services we offer or plan to offer; |
| · | continue to develop our technical expertise; and |
| · | develop and introduce new services, applications and technologies to meet changing customer needs and preferences and to integrate new technologies. |
| 12 |
We cannot assure you that we will be successful in responding to these technological and industry challenges in a timely and cost-effective manner. If we are unable to develop or integrate new technologies effectively or respond to these changing needs, our margins could decrease, and our release of new products and services and the deployment of our coding technology could be adversely affected.
We may need to retain additional employees or contract labor in the future in order to take advantage of new business opportunities arising from increased demand, which could impede our ability to achieve or sustain profitability.
We have staffed our company with the intent of achieving and sustaining profitability. Our current staffing levels could affect our ability to respond to increased demand for our services. In addition, to meet any increased demand and take advantage of new business opportunities in the future, we may need to increase our workforce through additional employees or contract labor, which would increase our costs. If we experience such an increase in costs, we may not succeed in achieving or sustaining profitability.
We are dependent on the licenses granted by our Korean business partner and their R&D efforts, and our future growth will depend to some extent on our successful implementation of our technology in solutions provided by our Korean joint venture party, S-Mark Co Ltd.
Our business and strategy rely substantially on deployment of our technologies licensed and research and development provided by our Korean shareholder and business partner, S-Mark Co Ltd because the coding technologies are owned by Digiwork Korea, a 100% owned subsidiary of S-Mark Co Ltd. Although Digiwork Korea agrees to provide existing coding technologies to Digiwork pursuant to the executed Amended and Restated Joint Business Agreement, S-Mark Co Ltd. and Digiwork Korea may not provide or even may not be able to develop any new or updated coding technologies to Digiwork, which could harm our business and competitive position and make us lost in competition environment.
Any delay or failure to pay R&D fees to Digiwork Korea could adversely affect our profitability and slow our growth.
Pursuant to the Joint Business Agreement, we are obligated to pay a total of $10,000,000 to Digiwork Korea on or before December 31, 2017. On July 10, 2017, parties to the JBA entered into an amendment to the Amended and Restated Joint Business Agreement which amended the total payment from $10,000,000 to $1,100,000. As the consideration for such payments, Digiwork Korea agrees to provide research and development services to Digiwork for a period of five years commencing from March 31, 2017. As of December 31, 2017, we had a cash balance of less than $100,000. The final payment of $1,000,000 is due on August 31, 2017. As of the date of this annual report, the amount remains unpaid. Our ability to pay Digiwork Korea is dependent on improving our profitability, additional debt financing, loans from existing directors and shareholders and private placements of capital stock for additional funding. However, we cannot assure you that we will be able to obtain short-term financing, or that sources of such financing, if any, will continue to be available, and if available, that they will be on terms favorable to us. Any delay or failure to pay Digiwork Korea may adversely affect our R&D efforts which in turn affect our profitability and slow our growth.
The loss of international customers or the failure to find new international customers could adversely affect our profitability and slow our growth.
We believe that revenue from sales of products and services to commercial customers outside the Thailand could represent a growing percentage of our total revenue in the future. Pursuant to the Amended and Restated Joint Business Agreement, Digiwork may launch the coding technologies services in seven countries, Thailand, Vietnam, Myanmar, Laos, Cambodia, United Arab Emirates and Qatar. International sales and services are subject to a number of risks that can adversely affect our sales of products and services to customers outside of Thailand, including the following:
• changes in foreign government regulations and security requirements;
• export license requirements, tariffs and taxes;
• trade barriers;
• difficulty in protecting intellectual property;
• difficulty in collecting accounts receivable;
• currency fluctuations;
• longer payment cycles than those for customers in Thailand;
• difficulty in managing foreign operations; and
• political and economic instability.
| 13 |
We do not have an extensive operational infrastructure for international business. We generally depend on local or international business partners and subcontractors for performance of substantial portions of our business. These factors may result in greater risk of performance problems or of reduced profitability with respect to our international programs in these markets. In addition, if foreign customers terminate or delay the implementation of our products and services, it may be difficult for us to recover our potential losses.
We are exposed to currency exchange fluctuations and do not engage in foreign currency hedging transactions. We may in the future choose to limit our exposure by the purchase of forward foreign exchange contracts, collared options, currency swap agreements or through similar hedging strategies. No currency hedging strategy, however, can fully protect against exchange-related losses.
We are planning to establish local technology supporting team in different countries for promoting the coding services in domestic market and also provide technical support there. However, such local teams in different countries may significantly increase our operating costs and may have negative impact on our profits.
The terms and conditions of our contracts could subject us to damages, losses and other expenses if we fail to meet delivery and other performance requirements.
Our service contracts typically include provisions imposing (i) development, delivery and installation schedules and milestones, (ii) customer acceptance and testing requirements and (iii) other performance requirements. To the extent these provisions involve performance over extended periods of time, risks of noncompliance may increase. Companies operating in these industries often experience delays in system implementation, timely acceptance of programs, concerns regarding program performance and other contractual disputes. Any failure to meet contractual milestones or other performance requirements as promised, or to successfully resolve customer disputes, could result in us incurring liability for damages, as well as increased costs, lower margins, or compensatory obligations in addition to other losses, such as harm to our reputation. Any unexpected increases in costs to meet our contractual obligations or any other requirements necessary to address claims and damages with regard to our customer contracts could have a material adverse effect on our business and financial results.
Our products could have unknown defects or errors, which may give rise to claims against us, divert application of our resources from other purposes or increase our project implementation and support costs.
Products and services as complex as those we offer or develop may contain undetected defects or errors. Furthermore, we anticipate providing complex implementation, integration, customization, consulting and other technical services in connection with the implementation and ongoing maintenance of our products and services. Despite testing, defects or errors in our products and services may occur, which could result in delays in the development and implementation of products and systems, inability to meet customer requirements or expectations in a timely manner, loss of revenue or market share, increased implementation and support costs, failure to achieve market acceptance, diversion of development resources, injury to our reputation, increased insurance costs, increased service and warranty costs and warranty or breach of contract claims. Although we attempt to reduce the risk of losses resulting from warranty or breach of contract claims through warranty disclaimers and liability limitation clauses in our sales agreements when we can, these contractual provisions are sometimes not included and may not be enforceable in every instance. If a court refuses to enforce the liability-limiting provisions of our contracts for any reason, or if liabilities arose that were not contractually limited or adequately covered by insurance, the expense associated with defending these actions or paying the resultant claims could be significant.
| 14 |
The security systems used in our product and service offerings may be circumvented or sabotaged by third parties, which could result in the disclosure of sensitive information or private personal information or cause other business interruptions that could damage our reputation and disrupt our business.
Our business relies on computers and other information technologies, both internal and at customer locations. The protective measures that we use may not prevent security breaches, and failure to prevent security breaches may disrupt our business, damage our reputation, and expose us to litigation and liability. A party who is able to circumvent security measures could misappropriate sensitive or proprietary information or materials or cause interruptions or otherwise damage our products, services and reputation, and the property of our customers. If unintended parties obtain sensitive data and information, or create bugs or viruses or otherwise sabotage the functionality of our systems, we may receive negative publicity, incur liability to our customers or lose the confidence of our customers, any of which may cause the termination or modification of our contracts. Further, our insurance coverage may be insufficient to cover losses and liabilities that may result from these events.
In addition, we may be required to expend significant capital and other resources to protect ourselves against the threat of security breaches or to alleviate problems caused by these breaches. Any protection or remedial measures may not be available at a reasonable price or at all, or may not be entirely effective if commenced.
We are subject to risks encountered by companies developing and relying upon new technologies, products and services for substantial amounts of their growth or revenue.
Our business and prospects must be considered in light of the risks and uncertainties to which companies with new and rapidly evolving technologies, products and services are exposed. These risks include the following:
• we may be unable to develop sources of new revenue or sustainable growth in revenue because our current and anticipated technologies, products and services may be inadequate or may be unable to attract or retain customers;
• the intense competition and rapid technological change in our industry could adversely affect the market's acceptance of our existing and new products and services; and
• we may be unable to develop and maintain new technologies upon which our existing and new products and services are dependent in order for our products and services to be sustainable and competitive and in order for us to expand our revenue and business.
Some of our key technologies and solutions are in the development stage. Consequently, products incorporating these technologies and solutions are undergoing technological change and are in the early stage of introduction in the marketplace. Delays in the adoption of these products or adverse competitive developments may result in delays in the development of new revenue sources or the growth in our revenue. In addition, we may be required to incur unanticipated expenditures if product changes or improvements are required. Additionally, new industry standards might redefine the products that we are able to sell, especially if these products are only in the prototype stage of development. If product changes or improvements are required, success in marketing these products by us and achieving profitability from these products could be delayed or halted. We also may be required to fund any changes or improvements out of operating income, which could adversely affect our profitability.
We may not be able to protect adequately our intellectual property, and we may be subject to infringement claims and other litigation, which could adversely affect our business.
Our success depends in part on our licensed technologies. To protect our intellectual property portfolio, we rely on a combination of trademark and trade secret rights, confidentiality procedures and licensing arrangements. Unlicensed copying and use of our intellectual property or infringement of our intellectual property rights result in the loss of revenue to us.
We face risks associated with our intellectual property rights, including the potential need from time to time to engage in significant legal proceedings to enforce our intellectual property rights, the possibility that the validity or enforceability of our intellectual property rights may be denied, and the possibility that third parties will be able to compete against us without infringing our intellectual property rights. Budgetary concerns may cause us not to file, or continue, litigation against known infringers of our intellectual property rights, or may cause us not to file for, or pursue, intellectual property protection for all of our inventive technologies in jurisdictions where they may have value. Some governmental entities that might infringe our intellectual property rights may enjoy sovereign immunity from such claims. If we fail to protect our intellectual property rights and proprietary technologies adequately, if there are changes in applicable laws that are adverse to our interests, or if we become involved in litigation relating to our intellectual property rights and proprietary technologies or relating to the intellectual property rights of others, our business could be seriously harmed because the value ascribed to our intellectual property could diminish and result in a lower stock price or we may incur significant costs in bringing legal proceedings against third parties who are infringing our intellectual property rights.
| 15 |
Effective protection of intellectual property rights may be unavailable or limited. Intellectual property protection throughout the world is generally established on a country-by-country basis. We do not assure you that the protection of our proprietary rights will be adequate or that our competitors will not independently develop similar technologies, duplicate our services or design around any of our patents or other intellectual property rights.
As more companies engage in business activities relating to digital coding, and develop corresponding intellectual property rights, it is increasingly likely that claims may arise which assert that some of our products or services infringe upon other parties' intellectual property rights. These claims could subject us to costly litigation, divert management resources and result in the invalidation of our intellectual property rights. These claims may require us to pay significant damages, cease production of infringing products, terminate our use of infringing technologies or develop non-infringing technologies. In these circumstances, continued use of our technologies may require that we acquire licenses to the additional intellectual property that is the subject of the alleged infringement, and we might not be able to obtain these licenses on commercially reasonable terms or at all. Our use of protected technologies may result in liability that threatens our continuing operation.
Some of our contracts include provisions regarding our non-infringement of third-party intellectual property rights. As deployment of our technology increases, and more companies enter our markets, the likelihood of a third party lawsuit resulting from these provisions increases. If an infringement arose in a context governed by such a contract, we may have to refund to our customer amounts already paid to us or pay significant damages, or we may be sued by the party allegedly infringed upon. Compliance with any such contract provisions may require that we pursue litigation where our costs exceed our likely recovery.
As part of our confidentiality procedures, we generally enter into non-disclosure agreements with our employees, directors, consultants and corporate partners, and attempt to control access to and distribution of our technologies, solutions, documentation and other proprietary information. Despite these procedures, third parties could copy or otherwise obtain and make unauthorized use of our technologies, solutions or other proprietary information or independently develop similar technologies, solutions or information. The steps that we have taken to prevent misappropriation of our solutions, technologies or other proprietary information may not prevent their misappropriation, particularly outside Thailand where laws or law enforcement practices may not protect our proprietary rights as fully as in Thailand.
We have identified material weaknesses in our internal control over financial reporting. If we fail to remediate the material weaknesses or maintain an effective system of internal control over financial reporting, we may be unable to accurately report our financial results or prevent fraud, and investor confidence and the market price of our shares may be adversely affected.
To implement Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, or SOX 404, the SEC adopted rules requiring public companies to include a report of management on the company’s internal control over financial reporting in their annual reports on Form 10-K. Under current law, we are subject to the requirement that we maintain internal controls and that management perform periodic evaluation of the effectiveness of the internal controls, assuming our filing status remains as a smaller reporting company. A report of our management is included under Item 9A of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Our management has identified the following material weaknesses in our internal control over financial reporting: we did not have an Audit Committee, we did not maintain appropriate cash controls, we did not implement appropriate information technology controls, and we currently lack sufficient accounting personnel with the appropriate level of knowledge, experience and training in U.S. GAAP and SEC reporting requirements. A "material weakness" is a deficiency, or a combination of deficiencies, in internal control over financial reporting, such that there is a reasonable possibility that a material misstatement of the company's annual or interim financial statements will not be prevented or detected on a timely basis. We plan to take measures to remedy these material weaknesses. Our Board of Directors plans, if possible, to recommend the addition of an audit committee or a financial expert on our Board of Directors in fiscal 2018. We plan, as funding permits, to appoint additional personnel to assist with the preparation of the Company’s periodic financial reporting. However, the implementation of these measures may not fully address the material weakness in our internal control over financial reporting. Our failure to address any control deficiency could result in inaccuracies in our financial statements and could also impair our ability to comply with applicable financial reporting requirements and related regulatory filings on a timely basis. Moreover, effective internal control over financial reporting is important to prevent fraud. As a result, our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects, as well as the trading price of our shares, may be materially and adversely affected.
| 16 |
If our revenue models and pricing structures relating to products and services that are under development do not gain market acceptance, the products and services may fail to attract or retain customers and we may not be able to generate new or sustain existing revenue.
Some of our business involves embedding digital watermarks in traditional and digital media, including identification documents, secure documents, audio, video and imagery. Our revenue stream is based primarily on a combination of development, consulting, subscription and license fees from copyright protection, counterfeit deterrence and advertisement applications. We have not fully developed revenue models for some of our future digital coding applications. Because some of our products and services are not yet well-established in the marketplace, and because some of these products and services will not directly displace existing solutions, we cannot be certain that the pricing structure for these products and services will gain market acceptance or be sustainable over time or that the marketing for these products and services will be effective.
While we currently have no claims, litigation or regulatory actions filed or pending by or against us, future claims, litigation or enforcement actions could arise, and any obligation to pay a judgment or damages could materially harm our business or financial condition.
From time to time, Digiwork may be engaged in litigation and incurred significant costs relating to these matters. The inherent uncertainties of litigation, and the ultimate cost and outcome of litigation cannot be predicted. We currently do not carry director and officer liability insurance and other insurance policies that provide protection against various liabilities relating to claims against us and our executive officers and directors. Any expenses and liabilities relating to future lawsuits will materially harm our financial condition. In addition, we are unable to obtain this insurance coverage due to cost or other reasons. It could make it more difficult for us to retain and attract officers and directors and could expose us to potentially self-funding certain future liabilities ordinarily mitigated by director and officer liability insurance.
Risks Relating to our VIE Structure
If the Thailand government deems that the contractual arrangements in relation to our VIE do not comply with Thailand regulatory restrictions on foreign investment in the relevant industries, or if these regulations or the interpretation of existing regulations change in the future, we could be subject to severe penalties or be forced to relinquish our interests in those operations.
Foreign ownership in Thailand is subject to restrictions under current Thai laws and regulations. For example, foreign investors are generally not allowed to own more than 50% of the equity interests in a Thai company.
We are a U.S. company. To comply with Thai laws and regulations, we conduct such business activities through Digiwork, a Thai VIE of ours. Digiwork is 57.5 % owned by Mr. Ratanaphon Wongnapachant, our chairman and chief executive officer, 2.5% owned by Ms. Chanikarn Lertchawalitanon, and 40% owned by S-Mark Co. Ltd. Mr. Ratanaphon Wongnapachant and Ms. Chanikarn Lertchawalitanon are Thai citizens. We entered into a series of contractual arrangements with of our VIE and its respective shareholders, which enable us to:
| · | exercise effective control over our VIE; |
| · | receive substantially all of the economic benefits of our VIE; and |
| 17 |
| · | have an exclusive option to purchase all or part of the equity interests and assets in our VIE when and to the extent permitted by Thai law. |
Because of these contractual arrangements, we are the primary beneficiary of our VIE and hence consolidate their financial results as our VIE under U.S. GAAP. For a detailed discussion of these contractual arrangements, see “Section 2. Contractual Arrangements with Digiwork (Thailand) Co., Ltd.
In the opinion of MVP International Law Office & Associates Co., Ltd, our Thai legal counsel, (i) the ownership structure of our VIE in Thailand does not result in any violation of Thai laws and regulations currently in effect; and (ii) the contractual arrangements between our subsidiary and VIE and their respective shareholders governed by Thai law will not result in any violation of Thai laws or regulations currently in effect. However, we have been advised by our Thai legal counsel that there are substantial uncertainties regarding the interpretation and application of current and future Thai laws, regulations and rules; accordingly, the Thai regulatory authorities may take a view that is contrary to or otherwise different from the opinion of our Thai legal counsel. If our ownership structure, contractual arrangements and businesses of our VIE are found to be in violation of any existing or future Thai laws or regulations, or we fail to obtain the foresaid market entry clearance, or our VIE fail to obtain or maintain any of the required permits or approvals, the relevant Thai regulatory authorities would have broad discretion to take action in dealing with such violations or failures, including:
| · | revoking the business licenses and/or operating licenses of such entities; |
| · | shutting down our services or blocking our website, or discontinuing or placing restrictions or onerous conditions on our operation through any transactions between our subsidiary and VIE; |
| · | imposing fines, confiscating the income from VIE, or imposing other requirements with which we or our VIE may not be able to comply; |
| · | requiring us to restructure our ownership structure or operations, including terminating the contractual arrangements with our VIE and deregistering the equity pledges of our VIE, which in turn would affect our ability to consolidate, derive economic interests from, or exert effective control over our VIE; or |
| · | restricting or prohibiting our use of the proceeds of our offshore offerings to finance our business and operations in Thai. |
Any of these actions could cause significant disruption to our business operations and severely damage our reputation, which would in turn materially and adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations. If any of these occurrences results in our inability to direct the activities of our VIE that most significantly impact its economic performance, and/or our failure to receive the economic benefits from our VIE, we may not be able to consolidate such entities in our consolidated financial statements in accordance with U.S. GAAP.
We rely on contractual arrangements with our VIE and its respective shareholders for a portion of our business operations, which may not be as effective as direct ownership in providing operational control.
We have relied and expect to continue to rely on contractual arrangements with our VIE and their respective shareholders to hold our business license in Thailand. For a description of these contractual arrangements, see “Section 2. Contractual Arrangements with Digiwork (Thailand) Co., Ltd.” These contractual arrangements may not be as effective as direct ownership in providing us with control over our VIE. For example, our VIE and its respective shareholders could breach their contractual arrangements with us by, among other things, failing to conduct their operations, including maintaining our website and using the domain names and trademarks, in an acceptable manner or taking other actions that are detrimental to our interests.
| 18 |
If we had direct ownership of our VIE, we would be able to exercise our rights as a shareholder to effect changes in the board of directors of our VIE, which in turn could implement changes, subject to any applicable fiduciary obligations, at the management and operational level. However, under the current contractual arrangements, we rely on the performance by our VIE and its respective shareholders of their obligations under the contracts to exercise control over our VIE. The shareholders of our consolidated VIE may not act in the best interests of our company or may not perform their obligations under these contracts. Such risks exist throughout the period in which we intend to operate our business through the contractual arrangements with our VIE. If any dispute relating to these contracts remains unresolved, we will have to enforce our rights under these contracts through the operations of Thai law and arbitration, litigation and other legal proceedings and therefore will be subject to uncertainties in the Thai legal system. Therefore, our contractual arrangements with our VIE may not be as effective in ensuring our control over the relevant portion of our business operations as direct ownership would be.
Any failure by our VIE or their shareholders to perform their obligations under our contractual arrangements with them would have a material and adverse effect on our business.
If our VIE or their shareholders fail to perform their respective obligations under the contractual arrangements, we may have to incur substantial costs and expend additional resources to enforce such arrangements. We may also have to rely on legal remedies under Thai law, including seeking specific performance or injunctive relief, and claiming damages, which we cannot assure you will be effective under Thai law. For example, if the respective shareholders of our VIE were to refuse to transfer their equity interest in the VIE to us or our designee if we exercise the purchase option pursuant to these contractual arrangements, or if they were otherwise to act in bad faith toward us, then we may have to take legal actions to compel them to perform their contractual obligations.
All the agreements under our contractual arrangements are governed by Thai law and provide for the resolution of disputes through arbitration in Thailand. Accordingly, these contracts would be interpreted in accordance with Thai law and any disputes would be resolved in accordance with Thai legal procedures. The legal system in the Thailand is not as developed as in some other jurisdictions, such as the United States. As a result, uncertainties in the Thai legal system could limit our ability to enforce these contractual arrangements. Meanwhile, there are very few precedents and little formal guidance as to how contractual arrangements in the context of a variable interest entity should be interpreted or enforced under Thai law. There remain significant uncertainties regarding the ultimate outcome of such arbitration should legal action become necessary. In addition, under Thai law, rulings by arbitrators are final, parties cannot appeal the arbitration results in courts, and if the losing parties fail to carry out the arbitration awards within a prescribed time limit, the prevailing parties may only enforce the arbitration awards in Thai courts through arbitration award recognition proceedings, which would require additional expenses and delay. In the event we are unable to enforce these contractual arrangements, or if we suffer significant delay or other obstacles in the process of enforcing these contractual arrangements, we may not be able to exert effective control over our VIE, and our ability to conduct our business may be negatively affected
The shareholders of our VIE may have potential conflicts of interest with us, which may materially and adversely affect our business and financial condition.
Mr. Ratanaphon Wongnapachant, Ms. Chanikarn Lertchawalitanon and S-Mark Co., Ltd, are the shareholders of Digiwork, owning 57.5%, 2.5% and 40% equity interest, respectively, in Digiwork. Mr. Ratanaphon Wongnapachant is our chairman of board of directors and chief executive officer. The shareholders of our VIE may have potential conflicts of interest with us. These shareholders may breach, or cause our VIE to breach, or refuse to renew, the existing contractual arrangements we have with them and our VIE, which would have a material and adverse effect on our ability to effectively control our VIE and receive economic benefits from them. For example, the shareholders may be able to cause our agreements with our VIE to be performed in a manner adverse to us by, among other things, failing to remit payments due under the contractual arrangements to us on a timely basis. We cannot assure you that when conflicts of interest arise, any or all of these shareholders will act in the best interests of our company or such conflicts will be resolved in our favor.
Currently, we do not have any arrangements to address potential conflicts of interest between the respective shareholders of our VIE and our company. Mr. Ratanaphon Wongnapachant is also a director of our company. We rely on Mr. Ratanaphon Wongnapachant to abide by the laws of the U.S. and Thai, which provide that directors owe a fiduciary duty to the company that requires them to act in good faith and in what they believe to be the best interests of the company and not to use their position for personal gains. There is currently no specific and clear guidance under Thai laws that address any conflict between Thai laws and laws of U.S. in respect of any conflict relating to corporate governance. If we cannot resolve any conflict of interest or dispute between us and the shareholders of our VIE, we would have to rely on legal proceedings, which could result in disruption of our business and subject us to substantial uncertainty as to the outcome of any such legal proceedings.
| 19 |
Contractual arrangements in relation to our VIE may be subject to scrutiny by the Thai tax authorities and they may determine that we or our Thai VIE owe additional taxes, which could negatively affect our financial condition and the value of your investment.
Under applicable Thai laws and regulations, arrangements and transactions among related parties may be subject to audit or challenge by the Thai tax authorities within ten years after the taxable year when the transactions are conducted. We could face material and adverse tax consequences if the Thai tax authorities determine that the contractual arrangements between our wholly-owned subsidiary in BVI, our VIE in Thailand, and their respective shareholders were not entered into on an arm’s length basis in such a way as to result in an impermissible reduction in taxes under applicable Thai laws, rules and regulations, and adjust our VIE income in the form of a transfer pricing adjustment. A transfer pricing adjustment could, among other things, result in a reduction of expense deductions recorded by our VIE for Thai tax purposes, which could in turn increase their tax liabilities without reducing our subsidiaries’ tax expenses. In addition, the Thai tax authorities may impose late payment fees and other penalties on our VIE for the adjusted but unpaid taxes according to the applicable regulations. Our financial position could be materially and adversely affected if our VIE’ tax liabilities increase or if they are required to pay late payment fees and other penalties.
We may lose the ability to use and enjoy assets held by our VIE that are material to the operation of our business if the entities go bankrupt or become subject to dissolution or liquidation proceedings.
As part of our contractual arrangements with our VIE, our VIE holds certain assets that are material to the operation of our business. If our VIE goes bankrupt and all or part of its assets become subject to liens or rights of third-party creditors, we may be unable to continue some or all of our business activities, which could materially and adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations. Under the contractual arrangements, our VIE may not, in any manner, sell, transfer, mortgage or dispose of their assets or legal or beneficial interests in the business without our prior consent. If our VIE undergoes a voluntary or involuntary liquidation proceeding, the independent third-party creditors may claim rights to some or all of these assets, thereby hindering our ability to operate our business, which could materially and adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Risks Relating to Doing Business in Thailand
Our business operation is headquartered in Thailand. Accordingly, our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects may be influenced to a significant degree by political, economic and social conditions in Thailand generally and by continued economic growth in Thailand as a whole.
Thai economy differs from the economies of most developed countries in many respects, including the amount of government involvement, level of development, growth rate, control of foreign investment and allocation of resources. Thai government has implemented various measures to encourage economic growth and guide the allocation of resources. Some of these measures may benefit the overall Thai economy, but may have a negative effect on us. For example, our financial condition and results of operations may be adversely affected by government control over capital investments or changes in tax regulations.
Uncertainties in the interpretation and enforcement of Thai laws and regulations could limit the legal protections available to you and us. We may be adversely affected by the complexity, uncertainties and changes in Thai regulations of IT businesses and companies.
Fund Reservation in Thailand
The reform government of Thailand may issue laws or regulations without the approval by parliament that might have a material adverse impact on our financial and business prospects. For example, in 2014, the reform government issued new laws and regulations pursuant to section 44 exemption of the Constitution which allowed the government to issue new laws without approval of the parliament. The new law required all businesses in Thailand to have a reservation fund that equals to 30% of the entity’s annual net profits. The change of law affected the whole business sector in terms of dividend contributions and discouraged foreign investments in Thailand. Due to sharp criticism from the foreigner investors, the reform government withdrew the respective new laws and regulations and removed such reservation fund requirement.
| 20 |
Tax collection in Thailand
In 2016, the reform government issued the amnesty for tax law violations. However, the policy was subsequently changed in 180 degree and the government issued stricter tax collection policies covering all companies and their accounts in order to collect more revenues from the business sectors. The new policies impose punishment not only on accountants and auditors as before but also extended to company directors. The uncertain tax regulation and enforcement increases our compliance cost and poses risks of potential violation of tax laws in Thailand.
IT Laws in Thailand
The current IT laws in Thailand have been outdated and might not be able to effectively protect our IT related intellectual properties and licenses, and thus make them vulnerable to imitation and infringements. Although the reform government is now considering new laws and regulations that better protect intellectual properties in Thailand, it might take time for such rules and regulations to be implemented. Any possible infringement of our intellectual properties could have a material adverse effect on our business and financial results.
Natural disasters, epidemics, acts of terrorism and other destabilizing developments could harm our business, financial condition, and operating results.
Natural disasters, such as the October to November 2011 flooding in Thailand, could severely disrupt our operations. These events, over which we have little or no control, could cause a decrease in demand for our services, make it difficult or impossible for us to deliver products and services or require large expenditures to repair or replace our facilities. Potential outbreaks of infectious diseases in the countries in which we operate, including Thailand, such as the H1N1 influenza virus, severe acute respiratory syndrome (“SARS”) or bird flu could disrupt our operations and reduce demand for our products and services. In addition, increased international political instability, evidenced by the threat or occurrence of terrorist attacks, enhanced national security measures, conflicts in the Middle East and Asia, strained international relations arising from these conflicts and the related decline in consumer confidence and economic weakness, may hinder our ability to do business. Any escalation in these events or similar future events may disrupt our operations and the operations of our customers. These events have had, and may continue to have, an adverse impact on the Thailand and world economy in general, and customer confidence and spending in particular, which in turn could adversely affect our total revenues and operating results.
Risks Related to Our Common Stock
The market price for our common stock is highly volatile and subject to wide fluctuations in response to factors including the following:
| · | actual or anticipated fluctuations in our quarterly operating results, | |
| · | announcements of new services by us or our competitors, | |
| · | changes in financial estimates by securities analysts, | |
| · | conditions in the information technology services market, | |
| · | changes in the economic performance or market valuations of other companies involved in the same industry, | |
| · | announcements by our competitors of significant acquisitions, strategic partnerships, joint ventures or capital commitments, | |
| · | additions or departures of key personnel, | |
| · | potential litigation, or | |
| · | conditions in the market. |
| 21 |
In addition, the securities markets from time to time experience significant price and volume fluctuations that are not related to the operating performance of particular companies. These market fluctuations may also materially and adversely affect the market price of our common stock.
Shareholders could experience substantial dilution.
We may issue additional shares of our capital stock to raise additional cash for working capital. If we issue additional shares of our capital stock, our shareholders will experience dilution in their respective percentage ownership in the company.
A large portion of our common stock is controlled by a small number of shareholders.
A large portion of our common stock is held by a small number of shareholders. As a result, these shareholders are able to influence the outcome of shareholder votes on various matters, including the election of directors and extraordinary corporate transactions including business combinations. In addition, the occurrence of sales of a large number of shares of our common stock, or the perception that these sales could occur, may affect our stock price and could impair our ability to obtain capital through an offering of equity securities. Furthermore, the current ratios of ownership of our common stock reduce the public float and liquidity of our common stock which can in turn affect the market price of our common stock.
We may be subject to “penny stock” regulations.
The Securities and Exchange Commission, or SEC, has adopted rules that regulate broker-dealer practices in connection with transactions in “penny stocks.” Penny stocks generally are equity securities with a price of less than $5.00 (other than securities registered on certain national securities exchanges, provided that current price and volume information with respect to transactions in such securities is provided by the exchange or system). Penny stock rules require a broker-dealer, prior to a transaction in a penny stock not otherwise exempt from those rules, to deliver a standardized risk disclosure document prepared by the SEC, which specifies information about penny stocks and the nature and significance of risks of the penny stock market. A broker-dealer must also provide the customer with bid and offer quotations for the penny stock, the compensation of the broker-dealer, and our sales person in the transaction, and monthly account statements indicating the market value of each penny stock held in the customer’s account. In addition, the penny stock rules require that, prior to a transaction in a penny stock not otherwise exempt from those rules, the broker-dealer must make a special written determination that the penny stock is a suitable investment for the purchaser and receive the purchaser’s written agreement to the transaction. These disclosure requirements may have the effect of reducing the trading activity in the secondary market for stock that becomes subject to those penny stock rules. These additional sales practice and disclosure requirements could impede the sale of our securities. Whenever any of our securities become subject to the penny stock rules, holders of those securities may have difficulty in selling those securities.
We do not intend to pay dividends on our common stock in the foreseeable future.
For the foreseeable future, we intend to retain any earnings to finance the development of our business, and we do not anticipate paying any cash dividends on our common stock. Any future determination to pay dividends will be at the discretion of our board of directors and will be dependent upon then-existing conditions, including our operating results and financial condition, capital requirements, contractual restrictions, business prospects and other factors that our board of directors considers relevant. Accordingly, investors must rely on sales of their common stock after price appreciation, which may never occur, as the only way to realize a return on their investment.
Item 1B. Unresolved Staff Comments
Not applicable.
| 22 |
Our executive offices and our consolidated entity are located at RS Tower Building, 8th Floor, Address No. 121/34, with approximate area of 363.20 square meters, located on Ratchadaphisek Road, Din Daeng Sub-District, Din Daeng District, Bangkok, Thailand. We lease our facilities pursuant to a lease agreement that will expire on February 20, 2020. We believe that all our properties have been adequately maintained, are generally in good condition, and are suitable and adequate for our business.
Rent expense amounted to $40,604 and $22,539 for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively.
From time to time, we may be subject to legal proceedings and claims in the ordinary course of business. We are not currently a party to any material legal proceedings, and to our knowledge none is threatened. There can be no assurance that future legal proceedings arising in the ordinary course of business or otherwise will not have a material adverse effect on our financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
Item 4. Mine Safety Disclosures
Not applicable.
Item 5. Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
Market Information
Our common stock has cleared for quotation on the OTCQB marketplace using the symbol “IWBB” since March 1, 2016.
Our shares of common stock are subject to Section 15(g) and Rule 15g-9 of the Securities and Exchange Act, commonly referred to as the “penny stock” rule. The rule defines penny stock to be any equity security that has a market price less than $5.00 per share, subject to certain exceptions. These rules may restrict the ability of broker-dealers to trade or maintain a market in our common stock and may affect the ability of stockholders to sell their shares. Broker-dealers who sell penny stocks to persons other than established customers and accredited investors must make a special suitability determination for the purchase of the security. Accredited investors, in general, include individuals with assets in excess of $1,000,000 or annual income exceeding $200,000 or $300,000 together with their spouse, and certain institutional investors. The rules require the broker-dealer to receive the purchaser’s written consent to the transaction prior to the purchase and require the broker-dealer to deliver a risk disclosure document relating to the penny stock prior to the first transaction. A broker-dealer also must disclose the commissions payable to both the broker-dealer and the registered representative, and current quotations for the security. Finally, monthly statements must be sent to customers disclosing recent price information for the penny stocks.
| 23 |
Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
| Period | (a) Total Number of Shares Purchased (1)(2) |
(b) Average Price Paid per Share |
(c) Total Number of Shares Purchased as Part of Publicly Announced Plans or Programs |
(d) Approximate Dollar Value of Shares that May Yet Be Purchased Under the Plans or Programs |
||||||||||||
| May 1 – May 31 | 39,495,000 | * | - | - | ||||||||||||
| Total | 39,495,000 | * | - | - | ||||||||||||
(1) In connection with the Share Exchange Agreement, Wai Hok Fung entered into a Repurchase Agreement, dated May 14, 2017, pursuant to which the Company repurchased 39,495,000 shares of its common stock at a per share purchase price equal to approximately $0.000000002532.
*$0.000000002532
(2) prior to 1-for-2 reverse stock split effected by the Company on March 13, 2018.
Holders of Record
We have 335 stockholders of record as of March 18, 2018.
Dividend
The holders of our common stock are entitled to receive pro rata such dividends as our Board, from time to time, may declare out of funds legally available therefor. The current policy of the Board is to retain earnings, if any, for operations and growth.
Dividend Policy
The Company has never declared or paid a cash dividend. Any future decisions regarding dividends will be made by our Board, which has complete discretion on whether to pay dividends. We currently intend to retain and use any future earnings for the development and expansion of our business and do not anticipate paying any cash dividends in the foreseeable future. Even if our Board decides to pay dividends, the form, frequency and amount will depend upon our future operations and earnings, capital requirements and surplus, general financial condition, contractual restrictions and other factors that the Board may deem relevant.
Item 6. Selected Financial Data
Not applicable.
Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
The following management’s discussion and analysis should be read in conjunction with our financial statements and the notes thereto and the other financial information appearing elsewhere in this report. Our financial statements are prepared in U.S. dollars and in accordance with U.S. GAAP.
Special Note Regarding Forward Looking Statements
In addition to historical information, this report contains forward-looking statements. We use words such as “believe,” “expect,” “anticipate,” “project,” “target,” “plan,” “optimistic,” “intend,” “aim,” “will” or similar expressions which are intended to identify forward-looking statements. Such statements include, among others, those concerning market and industry segment growth; any projections of earnings, revenue, margins or other financial items; any statements of the plans, strategies and objectives of management for future operations; any statements regarding future economic conditions or performance; as well as all assumptions, expectations, predictions, intentions or beliefs about future events. You are cautioned that any such forward-looking statements are not guarantees of future performance and involve risks and uncertainties, including without limitation, those listed in the “Risk Factors” section, as well as assumptions, which, if they were to ever materialize or prove incorrect, could cause our results to differ materially from those expressed or implied by such forward-looking statements.
Readers are urged to carefully review and consider the various disclosures made by us in this report and our other filings with the SEC. These reports attempt to advise interested parties of the risks and factors that may affect our business, financial condition and results of operations and prospects. The forward-looking statements made in this report speak only as of the date hereof and we disclaim any obligation, except as required by law, to provide updates, revisions or amendments to any forward-looking statements to reflect changes in our expectations or future events.
| 24 |
Overview
IWEB Inc. is a corporation in a stage of early development that was formed in the State of Nevada on February 17, 2015. Our initial strategy was to design web sites for clients, manage advertising campaigns and to develop and become a company that provides better search engine optimization (“SEO”) software and techniques to smaller clients.
On May 15, 2017, we entered into a share exchange agreement (the “Share Exchange Agreement”) with Enigma Technology International Corporation, a British Virgin Islands company, (“Enigma BVI”), and all the shareholders of Enigma BVI, namely, Ratanaphon Wongnapachant, Chanikarn Lertchawalitanon, and S-Mark Co. Ltd. (each a “Shareholder” and collectively the “Shareholders”), to acquire all the issued and outstanding capital stock of Enigma BVI in exchange for the issuance to the Shareholders of an aggregate of 63,000,000 restricted shares of our common stock (the “Reverse Merger”). As a result of the Reverse Merger, Enigma BVI is now our wholly-owned subsidiary. For accounting purposes, the transaction with Enigma BVI was treated as a reverse acquisition, with Enigma BVI as the acquirer and the Company as the acquired party. Unless the context suggests otherwise, when we refer in this report to business and financial information for periods prior to the consummation of the reverse acquisition, we are referring to the business and financial information of Enigma BVI and its consolidated subsidiary.
As result of the Reverse Merger, Enigma BVI became our wholly-owned subsidiary and its business became our business. Enigma BVI is a holding company incorporated under the laws of British Virgin Islands on February 22, 2017. Enigma BVI conducts its business through its variable interest entity, Digiwork (Thailand) Co., Ltd. (“Digiwork” or “VIE”), a company incorporated in Thailand on November 24, 2016 with registered capital of Thai Baht (“THB”) 5,000,000 (approximately $153,604). Digiwork is an operating vehicle that is a joint venture company by two Thai shareholders (Ratanaphon Wongnapachant, Chanikarn Lertchawalitanon) and one Korean shareholder, S-Mark Co., Ltd., which is a publicly listed company in Korea. Digiwork Korea is a 100% wholly-owned subsidiary of S-Mark Co., Ltd., and provides licenses of various coding technologies to Digiwork for the operation in seven countries: Thailand, Vietnam, Myanmar, Laos, Cambodia, United Arab Emirates and Qatar.
All references above to share and per share data of IWEB, Inc. have not been adjusted to give effect of the 1-for-2 reverse stock split by the Company effective on March 13, 2018.
Our Business Strategy
Digiwork was set up pursuant to a joint business agreement among its shareholders (“JBA”) on August 4, 2016, as amended and restated on March 31, 2017. Pursuant to the JBA, Digiwork was originally obligated to pay a total of $10,000,000 to S-Mark Co., Ltd., a shareholder of Digiwork or Digiwork Co., Ltd. (“Digiwork Korea”, a 100% wholly owned subsidiary of S-Mark Co., Ltd., a 33.6% shareholder of the Company). On July 10, 2017, parties to the JBA entered into an amendment to the Amended and Restated Joint Business Agreement which amended the total payment from $10,000,000 to $1,100,000. As the consideration for such payments, Digiwork Korea agreed to provide research and development services to Digiwork for a period of five years commencing from March 31, 2017. Digiwork currently has 8 full time employees, all of which are administrative staff members. The technical services are currently provided by contracted technicians from Digiwork Korea.
Digiwork Korea also agreed to grant to Digiwork full and exclusive licenses of any new launches, developments, improvements and any other intellectual property rights so developed by Digiwork Korea. The territories for such licenses are Thailand, Vietnam, Myanmar, Laos, Cambodia, United Arab Emirates and Qatar.
Digiwork was authorized by Digiwork Korea to be an official licensee and distributor of its technology exclusively in Thailand, Vietnam, Myanmar, Laos, Cambodia, United Arab Emirates and Qatar, and the authorization covers all four categories of Digiwork Korea’s coding technology: image, audio, web and security coding. This technology enables governments and enterprises around the world to give digital identities to media and objects that computers can sense and recognize, and to which they can react.
| 25 |
Digiwork is a technology development and services provider specializing in coding services in various industries and markets. Digiwork’s technology enables enterprises to imbed or imprint invisible digital identities to media and objects that various computer devices can sense and recognize and to which they can react. Our coding technology provides the means to infuse persistent digital information, perceptible only to computers and digital devices, into all forms of media content. Our coding technology permits computers and digital devices including smartphones, tablets, industrial scanners and other computer interfaces to quickly identify relevant data from vast amounts of media content. We focus on four coding technologies:
| · | Image coding technology, |
| · | Audio coding technology, |
| · | Web coding technology, and |
| · | Security coding technology |
There are currently no competing technologies existing in our authorized territories, however, older technologies like QR code remains as our primary competitor. We need to convince customers that our technology is more advanced and will replace QR code and similar identification technologies in the near future.
We provide tailor-made coding technological solutions to various commercial entities in different markets. Our technologies enable companies to give digital identity or information through various media like music, movies, television broadcasts, images and printed materials. The wide range application of the above four technologies can provide improved media rights, asset management, reduce piracy and counterfeiting losses, improve marketing programs, permit more efficient and effective distribution of valuable media content and enhance consumer experiences.
Results of Operations
The following table sets forth key components of our results of operations for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016:
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Revenue | $ | 126,456 | $ | - | ||||
| Cost of revenue | (19,119 | ) | - | |||||
| General and administrative expenses | (564,384 | ) | (112,405 | ) | ||||
| Other income (expense) | 5,120 | - | ||||||
| Loss before income tax | (451,927 | ) | (112,405 | ) | ||||
| Income tax expense | - | - | ||||||
| Net loss | $ | (451,927 | ) | $ | (112,405 | ) | ||
Revenues and cost of revenue. Revenue is principally comprised of image coding services revenue, and represents the fair value of the consideration received or receivable for the provision of services in the ordinary course of our activities and is recorded net of value-added tax ("VAT"). Enigma BVI has not earned any revenue since its inception. Digiwork’s revenues for the year ended December 31, 2017 of $126,456 were derived from two customers, which individually accounted for 65% and 35% of the Company’s revenues.
Two unrelated individuals were hired by Digiwork in relation to its two projects and incurred costs totaled $19,119 for the year ended December 31, 2017.
We did not recognize any revenue or associated cost of revenues for the year ended December 31, 2016.
General and administrative expenses. Our general and administrative expenses for the year ended December 31, 2017 was $564,384, $74,463 of which were costs associated with our personnel in Thailand, $163,159 of which were R&D expenses and $171,351 of which were professional fees. Our general and administrative expenses for the year ended December 31, 2016 were $112,405, $75,931 of which was staff costs of our personnel in Thailand. We began to incur R&D expenses on the R&D services provided by Digiwork Korea commencing from March 31, 2017. We expect our general and administrative expenses to increase when we expand our operations in Thailand.
| 26 |
Net loss. As a result of the above, we recorded a net loss of $451,927 and $112,405 for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Working Capital
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 60,716 | $ | 586 | ||||
| Total current assets | 1,069,854 | 100,586 | ||||||
| Total assets | 1,082,631 | 100,586 | ||||||
| Total liabilities | 1,390,021 | 69,299 | ||||||
| Accumulated deficit | (564,332 | ) | (112,405 | ) | ||||
| Total stockholders’ (deficit) equity | (307,390 | ) | 31,287 | |||||
Going Concern Uncertainties
From our inception to December 31, 2017, we have primarily relied upon the capital contributed by our shareholders and the advances from our directors to fund our operations. At December 31, 2017 and 2016, we had an accumulated deficit of $564,332 and $112,405, respectively, and net working capital deficit of $320,167 at December 31, 2017. We anticipate requiring additional financing to fund our short-term cash needs. Our ability to continue as a going concern is dependent upon improving our profitability, and we may have to rely on additional debt financing, loans from existing directors and shareholders and private placements of capital stock for additional funding. However, we cannot assure you that we will be able to obtain short-term financing, or that sources of such financing, if any, will continue to be available, and if available, that they will be on terms favorable to us.
The following table provides detailed information about our net cash flow for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016:
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Net cash used in operating activities | $ | (313,191 | ) | $ | (212,405 | ) | ||
| Net cash used in investing activities | (13,734 | ) | - | |||||
| Net cash provided by financing activities | 386,891 | 210,662 | ||||||
| Effect of exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents | 164 | 2,329 | ||||||
| Net increase in cash and cash equivalents | $ | 60,130 | $ | 586 | ||||
Operating Activities
Net cash used in operating activities was $313,191 for the year ended December 31, 2017, which was mainly due to our net loss of $451,927 and increase in prepayments and deposits of $838,538, and partially offset by cash inflow of $957,489 increase in payable to a related company and $44,671 increase in accruals. Net cash used in operating activities was $212,405 for the year ended December 31, 2016.
Investing Activities
We used cash of $13,734 and nil for purchases of property, plant and equipment for the year ended December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively.
Financing Activities
Net cash provided by financing for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016 were $386,891 and $210,662. In 2017, we received advances of $286,891 from our directors, and repaid $147,750 to directors. We also received proceeds of $197,750 from issue of our shares and capital contribution of $50,000 from shareholders of VIE. In 2016, we received advances of $69,299 from a director, and capital contribution of $141,363 from shareholders of VIE.
Contractual Obligations and Commercial Commitments
We had the following contractual obligations and commercial commitments as of December 31, 2017:
| 27 |
| Contractual Obligations | Total | Less than 1 year | 1-3 years | 3-5 years | More than 5 years | |||||||||||||||
| Amounts due to directors | $ | 345,099 | $ | 345,099 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||||
| Lease | 101,751 | 47,078 | 54,673 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
| Amount due to a related company - R&D | 1,000,000 | 1,000,000 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
| TOTAL | $ | 1,446,850 | $ | 1,392,177 | $ | 54,673 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||||
Digiwork was set up pursuant to a joint business agreement among its shareholders (“JBA”) on August 4, 2016, which was amended and restated on March 31, 2017. Pursuant to the JBA, Digiwork was originally obligated to pay a total of $10,000,000 to S-Mark Co., Ltd., a shareholder of Digiwork, or Digiwork Co., Ltd. (Digiwork Korea, a 100% wholly owned subsidiary of S-Mark Co., Ltd., a 33.6% shareholder of the Company). On July 10, 2017, parties to the JBA entered into an amendment to the Amended and Restated Joint Business Agreement which amended the total payment from $10,000,000 to $1,100,000. As the consideration for such payments, Digiwork Korea agreed to provide research and development services to Digiwork for a period of five years commencing from March 31, 2017. $0.1 million is payable before December 31, 2016 and $1 million is payable on or before August 31, 2017. As of December 31, 2017, an amount of $100,000 had been paid to Digiwork Korea, and the remaining of $1 million remained unpaid.
Mr. Ratanaphon Wongnapachant, a major shareholder, Chairman of the Board and Chief Executive Officer of the Company, has agreed to make loans to Digiwork to make such payment due, if necessary.
We entered into a lease for office space located in Din Daeng Sub-District, Din Daeng District, Bangkok, Thailand for the period from February 21, 2017 to February 20, 2020, at THB127,120 ($3,905) per month.
Off-Balance Sheet Transactions
We do not have any off balance sheet arrangements that have or are reasonably likely to have a current or future effect on our financial condition, changes in financial condition, revenues or expenses, results of operations, liquidity or capital expenditures or capital resources that is material to an investor in our securities.
Critical Accounting Policies
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States requires our management to make assumptions, estimates and judgments that affect the amounts reported, including the notes thereto, and related disclosures of commitments and contingencies, if any. We have identified certain accounting policies that are significant to the preparation of our financial statements. These accounting policies are important for an understanding of our financial condition and results of operation. Critical accounting policies are those that are most important to the portrayal of our financial condition and results of operations and require management’s difficult, subjective, or complex judgment, often as a result of the need to make estimates about the effect of matters that are inherently uncertain and may change in subsequent periods. Certain accounting estimates are particularly sensitive because of their significance to financial statements and because of the possibility that future events affecting the estimate may differ significantly from management’s current judgments. We believe the following critical accounting policies involve the most significant estimates and judgments used in the preparation of our financial statements:
Basis of Presentation
The financial statements have been prepared in accordance with United States of America generally accepted accounting principles (“U.S. GAAP”).
| 28 |
Use of Estimates
The preparation of the accompanying financial statements requires management to make estimates and judgments that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues, costs and expenses, and related disclosures. On an on-going basis, we evaluate our estimates based on historical experience and on various other assumptions that are believed to be reasonable under the circumstances, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying values of assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other sources. Actual results may differ from these estimates under different assumptions or conditions.
VIE Consolidation
Digiwork (Thailand) Co., Ltd. is wholly owned by Mr. Ratanaphon Wongnapachant, Ms. Chanikarn Lertchawalitanon and S-Mark Co. Ltd. (a KOSDAQ-listed corporation) as nominee shareholders. For the consolidated VIE, management made evaluations of the relationships between Enigma BVI and the VIE and the economic benefit flow of contractual arrangements with the VIE. In connection with such evaluation, management also took into account the fact that, as a result of such contractual arrangements, Enigma BVI controls the shareholders’ voting interests in the VIE. As a result of such evaluation, management concluded that Enigma BVI is the primary beneficiary of its VIE.
Owing primarily to the Thailand legal restrictions on foreign ownership, we currently conduct the coding business in Thailand through Digiwork, which we effectively control through a series of contractual arrangements. We consolidate in our financial statements the VIE of which we are the primary beneficiary.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
In May 2014, the FASB issued ASU No. 2014-09, ‘‘Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606).’’ This guidance supersedes current guidance on revenue recognition in Topic 605, ‘‘Revenue Recognition.” In addition, there are disclosure requirements related to the nature, amount, timing, and uncertainty of revenue recognition. In August 2015, the FASB issued ASU No.2015-14 to defer the effective date of ASU No. 2014-09 for all entities by one year. For public business entities that follow U.S. GAAP, the deferral results in the new revenue standard are being effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those fiscal years, beginning after December 15, 2017, with early adoption permitted for interim and annual periods beginning after December 15, 2016. We will apply the new revenue standard beginning January 1, 2018. Based on management’s assessment of the application of this guidance, we do not expect a material impact on amounts reported and disclosures made in our consolidated financial statements.
On January 5, 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-01 (“ASU 2016-01”), Recognition and Measurement of Financial Assets and Financial Liabilities, which amends certain aspects of recognition, measurement, presentation and disclosure of financial instruments. This amendment requires all equity investments to be measured at fair value, with changes in the fair value recognized through net income (other than those accounted for under equity method of accounting or those that result in consolidation of the investee). This standard will be effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, including interim periods within those fiscal years. We do not expect this standard to have a material impact on our consolidated financial statements.
On February 25, 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-02 (“ASU 2016-02”), Leases. ASU 2016-02 specifies the accounting for leases. For operating leases, ASU 2016-02 requires a lessee to recognize a right-of-use asset and a lease liability, initially measured at the present value of the lease payments, in its balance sheet. The standard also requires a lessee to recognize a single lease cost, calculated so that the cost of the lease is allocated over the lease term, on a generally straight-line basis. In addition, this standard requires both lessees and lessors to disclose certain key information about lease transactions. ASU 2016-02 is effective for public companies for annual reporting periods, and interim periods within those years, beginning after December 15, 2018. Early adoption is permitted. Management is currently assessing the potential impact of adopting this standard on our consolidated financial statements.
In June 2016, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) 2016-13, Financial Instruments-Credit Losses (Topic 326), which requires entities to measure all expected credit losses for financial assets held at the reporting date based on historical experience, current conditions, and reasonable and supportable forecasts. This replaces the existing incurred loss model and is applicable to the measurement of credit losses on financial assets measured at amortized cost. This guidance is effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those fiscal years, beginning after December 15, 2019. Early application will be permitted for all entities for fiscal years, and interim periods within those fiscal years, beginning after December 15, 2018. We do not expect this standard to have a material impact on our consolidated financial statements.
| 29 |
In August 2016, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) 2016-15, Statement of Cash Flows — Classification of Certain Cash Receipts and Cash Payments, which clarifies the presentation and classification of certain cash receipts and cash payments in the statement of cash flows. This guidance is effective for financial statements issued for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, and interim periods within those fiscal years. Early adoption is permitted. We do not expect this standard to have a material impact on our consolidated financial statements.
In November 2016, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) No. 2016-18, Statement of Cash Flows (Topic 230): Restricted Cash. The guidance requires that a statement of cash flows explain the change during the period in the total of cash, cash equivalents, and amounts generally described as restricted cash or restricted cash equivalents. Therefore, amounts generally described as restricted cash and restricted cash equivalents should be included with cash and cash equivalents when reconciling the beginning-of-period and end-of-period total amounts shown on the statement of cash flows. The standard is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, and interim period within those fiscal years. Early adoption is permitted, including adoption in an interim period. The standard should be applied using a retrospective transition method to each period presented. We do not expect this standard to have a material impact on our consolidated financial statements.
In January 2017, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) No. 2017-01, Business Combinations (Topic 805): Clarifying the Definition of a Business, which clarifies the definition of a business with the objective of adding guidance to assist entities with evaluating whether transactions should be accounted for as acquisitions or disposals of assets or businesses. The standard is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, including interim periods within those fiscal years. Early adoption is permitted. The standard should be applied prospectively on or after the effective date. We do not expect this standard to have a material impact on our consolidated financial statements.
In January 2017, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) 2017-04, “Simplifying the Test for Goodwill Impairment.” The guidance removes Step 2 of the goodwill impairment test, which requires a hypothetical purchase price allocation. A goodwill impairment will now be the amount by which a reporting unit’s carrying value exceeds its fair value, not to exceed the carrying amount of goodwill. The guidance should be adopted on a prospective basis for the annual or any interim goodwill impairment tests beginning after December 15, 2019. Early adoption is permitted for interim or annual goodwill impairment tests performed on testing dates after January 1, 2017. We do not expect this standard to have a material impact on our consolidated financial statements.
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk
Not Applicable.
Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data
| 30 |
TABLE OF CONTENTS
| F-1 |
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Stockholders and the Board of Directors of IWEB, Inc.
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of IWEB, Inc. and subsidiaries (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, and the related consolidated statements of comprehensive loss, stockholders’ equity (deficit) and cash flows for each of the two years in the period ended December 31, 2017, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the “financial statements”). In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company at December 31, 2017 and 2016, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the two years in the period ended December 31, 2017, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared assuming that the Company will continue as a going concern. As discussed in Note 3 to the financial statements, the Company has suffered recurring losses from operations and has a net capital deficiency that raise substantial doubt about its ability to continue as a going concern. Management's plans in regard to these matters are also described in Note 3. The consolidated financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of this uncertainty.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company's management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company's consolidated financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) ("PCAOB") and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. As part of our audits we are required to obtain an understanding of internal control over financial reporting but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion.
Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
| /s/ Centurion ZD CPA Limited | |
| Centurion ZD CPA Limited | |
| We have served as the Company's auditor since 2017. | |
| Hong Kong, China | |
| March 20, 2018 |
| F-2 |
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
AS OF DECEMBER 31, 2017 AND 2016
(In U.S. dollars)
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| ASSETS | ||||||||
| CURRENT ASSETS | ||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 60,716 | $ | 586 | ||||
| Prepayments and deposits | 982,523 | 100,000 | ||||||
| Other receivables | 5,365 | - | ||||||
| Amounts due from shareholders | 21,250 | - | ||||||
| Total current assets | 1,069,854 | 100,586 | ||||||
| NON-CURRENT ASSETS | ||||||||
| Property, plant and equipment, net | 12,777 | - | ||||||
| TOTAL ASSETS | $ | 1,082,631 | $ | 100,586 | ||||
| LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ DEFICIT | ||||||||
| CURRENT LIABILITIES | ||||||||
| Accruals | $ | 44,922 | $ | - | ||||
| Amounts due to directors | 345,099 | 69,299 | ||||||
| Amount due to a related company | 1,000,000 | - | ||||||
| Total current liabilities | 1,390,021 | 69,299 | ||||||
| TOTAL LIABILITIES | 1,390,021 | 69,299 | ||||||
| COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES | ||||||||
| STOCKHOLDERS' (DEFICIT) EQUITY | ||||||||
| Preferred stock: $0.0001 par value, 25,000,000 shares authorized, none issued and outstanding | - | - | ||||||
| Common stock, par value $0.0001 per share; 75,000,000 (December 31, 2016: 37,500,000) shares authorized, 37,697,750 (December 31, 2016: 25,747,500) shares issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2017* | 7,540 | 5,149 | ||||||
| Additional paid-in capital | 256,937 | 136,214 | ||||||
| Accumulated deficit | (564,332 | ) | (112,405 | ) | ||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive (loss) income | (7,535 | ) | 2,329 | |||||
| Total stockholders' (deficit) equity | (307,390 | ) | 31,287 | |||||
| TOTAL LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS' (DEFICIT) EQUITY | $ | 1,082,631 | $ | 100,586 | ||||
*Post a 1-for-2 reverse stock split effective on March 13, 2018.
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
| F-3 |
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE LOSS
FOR THE YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2017 AND 2016
(In U.S. dollars)
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Revenue | $ | 126,456 | $ | - | ||||
| Cost of revenue | (19,119 | ) | $ | - | ||||
| Gross profit | 107,337 | $ | - | |||||
| General and administrative expenses | (564,384 | ) | (112,405 | ) | ||||
| Loss from operations | (457,047 | ) | (112,405 | ) | ||||
| Other (expense) income, net | 5,120 | - | ||||||
| Loss before income tax | (451,927 | ) | (112,405 | ) | ||||
| Income tax expense | - | - | ||||||
| Net loss | $ | (451,927 | ) | $ | (112,405 | ) | ||
| Other comprehensive (loss) income | ||||||||
| Foreign currency translation adjustment | (9,864 | ) | 2,329 | |||||
| Total comprehensive loss | $ | (461,791 | ) | $ | (110,076 | ) | ||
| Loss per share - Basic and diluted* | $ | (0.01 | ) | $ | - | |||
| Weighted average number of common shares outstanding Basic and diluted* | 33,210,306 | 25,747,500 | ||||||
*Post a 1-for-2 reverse stock split effective on March 13, 2018.
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
| F-4 |
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS
FOR THE YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2017 AND 2016
(In U.S. dollars)
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Cash flows from operating activities | ||||||||
| Net loss | $ | (451,927 | ) | $ | (112,405 | ) | ||
| Adjustments to reconcile net loss to cash used in operating activities: | ||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 1,500 | - | ||||||
| Changes in assets and liabilities | ||||||||
| Prepayments and deposits | (838,538 | ) | (100,000 | ) | ||||
| Amounts due from shareholders | (21,250 | ) | - | |||||
| Other receivables | (5,136 | ) | - | |||||
| Amount due to a related company | 957,489 | - | ||||||
| Accruals | 44,671 | - | ||||||
| Net cash used in operating activities | (313,191 | ) | (212,405 | ) | ||||
| Cash flows from investing activities | ||||||||
| Purchase of property, plant and equipment | (13,734 | ) | - | |||||
| Net cash used in investing activities | (13,734 | ) | - | |||||
| Cash flows from financing activities | ||||||||
| Capital contribution from shareholders of VIE | 50,000 | 141,363 | ||||||
| Advance from directors | 286,891 | 69,299 | ||||||
| Repayment to director | (147,750 | ) | - | |||||
| Proceed from issue of shares | 197,750 | - | ||||||
| Net cash provided by financing activities | 386,891 | 210,662 | ||||||
| Effect of exchange rates on cash | 164 | 2,329 | ||||||
| Net increase in cash and cash equivalents | 60,130 | 586 | ||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of year | 586 | - | ||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of year | $ | 60,716 | $ | 586 | ||||
| Supplemental of cash flow information | ||||||||
| Cash paid during the year for: | ||||||||
| Interest | $ | - | $ | - | ||||
| Income taxes | $ | - | $ | - | ||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
| F-5 |
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY (DEFICIT)
FOR THE YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2017 AND 2016
| Common Stock | Treasury Shares | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of Shares | Amount | Additional Paid-In Capital | Number of Shares | Amount | Accumulated Deficit | Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) | Total Stockholders’ Equity (Deficit) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance as of January 1, 2016 | 51,495,000 | 5,149 | $ | 136,214 | - | $ | - | - | $ | - | $ | 141,363 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss | - | - | - | - | (112,405 | ) | - | (112,405 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation adjustment | - | - | 2,329 | 2,329 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance as of December 31, 2016 | 51,495,000 | $ | 5,149 | $ | 136,214 | - | $ | - | $ | (112,405 | ) | $ | 2,329 | $ | 31,287 | |||||||||||||||||
| Capital contribution from shareholders of VIE | - | - | 50,000 | - | - | - | - | 50,000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares repurchased as treasury shares (Note 6) | - | - | (39,495,000 | ) | (1 | ) | - | - | (1 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares issued due to recapitalization (Note 1) | 23,505,000 | 2,351 | (126,987 | ) | 39,495,000 | 1 | - | - | (124,635 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares issued | 395,500 | 40 | 197,710 | - | - | - | - | 197,750 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss | - | - | - | - | - | (451,927 | ) | - | (451,927 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation adjustment | - | - | - | - | - | - | (9,864 | ) | (9,864 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance as of December 31, 2017 | 75,395,500 | $ | 7,540 | $ | 256,937 | - | $ | - | $ | (564,332 | ) | $ | (7,535 | ) | $ | (307,390 | ) | |||||||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
| F-6 |
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FOR THE YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2017 AND 2016
(Unaudited)
NOTE 1 - ORGANIZATION AND BUSINESS
IWEB, Inc. (the “Company”) was incorporated under the laws of the State of Nevada on February 17, 2015.
The Company’s original business plan was to actively engage in providing high impact internet marketing strategies to internet based businesses and people seeking to create websites, but this business was not successful. On December 12, 2016, 49,995,000 shares of the common stock of the Company, representing 97.08% of the Company’s issued and outstanding shares of common stock at that time, were sold by Dmitriy Kolyvayko in a private transaction to Mr. Wai Hok Fung (the “Transaction”) for an aggregate purchase price of $380,000. In connection with the Transaction, Mr. Kolyvayko released the Company from certain liabilities and obligations arising out of his service as a director and officer of the Company.
On January 5, 2017, the Company’s Board of Directors approved an amendment to the Company’s Bylaws to change the Company’s fiscal year end from June 30 to December 31, effective as of December 31, 2016.
On May 15, 2017, the Company entered into a share exchange agreement (the “Share Exchange Agreement”) with Enigma Technology International Corporation (“Enigma BVI”), and all the shareholders of Enigma BVI, namely, Mr. Ratanaphon Wongnapachant, Ms. Chanikarn Lertchawalitanon and S-Mark Co. Ltd. (collectively the “Shareholders”), to acquire all the issued and outstanding capital stock of Enigma BVI in exchange for the issuance to the Shareholders of an aggregate of 63,000,000 restricted shares of IWEB, Inc.’s common stock (the “Reverse Merger”). The Reverse Merger closed on May 15, 2017. As a result of the Reverse Merger, Enigma BVI is now a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Company.
Enigma BVI was incorporated on February 22, 2017 in the British Virgin Islands.
Digiwork (Thailand) Co., Ltd. (“Digiwork”) was established and incorporated in Thailand on November 24, 2016. The authorized capital of the Digiwork is THB5,000,000 (approximately $147,390), divided into 500,000 common shares with a par value of THB10 per share, which has been fully paid up as of December 31, 2016.
On May 15, 2017, Enigma BVI, Digiwork and the shareholders of Digiwork entered into the following commercial arrangements, or collectively, “VIE Agreements,” pursuant to which Enigma BVI has contractual rights to control and operate the businesses of Digiwork.
Pursuant to an Exclusive Technology Consulting and Service Agreement, Enigma BVI agreed to act as the exclusive consultant of Digiwork and provide technology consulting and services to Digiwork. In exchange, Digiwork agreed to pay Enigma BVI a technology consulting and service fee, the amount of which is decided by Enigma BVI on the basis of the work performed and commercial value of the services and the fee amount to be equivalent to the amount of net profit before tax of Digiwork on a quarterly basis; provided that the minimum amount of which is no less than THB30,000 (approximately $874) per quarter. Without the prior written consent of Enigma BVI, Digiwork may not accept the same or similar technology consulting and services provided by any third party during the term of the agreement. All the benefits and interests generated from the agreement, including but not limited to intellectual property rights, know-how and trade secrets, will be Enigma BVI’s sole and exclusive property. The term of this agreement will expire on May 15, 2027 and may be extended unilaterally by Enigma BVI with Enigma BVI's written confirmation prior to the expiration date. Digiwork cannot terminate the agreement early unless Enigma BVI commits fraud, gross negligence or illegal acts, or becomes bankrupt or winds up;
| F-7 |
Pursuant to an Exclusive Purchase Option Agreement, the shareholders of Digiwork granted to Enigma BVI and any party designated by Enigma BVI the exclusive right to purchase at any time during the term of this agreement all or part of the equity interests in Digiwork, or the “Equity Interests,” at a purchase price equal to the registered capital paid by the shareholders of Digiwork for the Equity Interests, or, in the event that applicable law requires an appraisal of the Equity Interests, the lowest price permitted under applicable law; Pursuant to powers of attorney executed by each of the shareholders of Digiwork, such shareholders irrevocably authorized any person appointed by Enigma BVI to exercise all shareholder rights, including but not limited to voting on their behalf on all matters requiring approval of Digiwork’s shareholders, disposing of all or part of the shareholder's equity interest in Digiwork, and electing, appointing or removing directors and executive officers. The person designated by Enigma BVI is entitled to dispose of dividends and profits on the equity interest without reliance of any oral or written instructions of the shareholder. Each power of attorney will remain in force for so long as the shareholder remains a shareholder of Digiwork. Each shareholder has waived all the rights which have been authorized to Enigma BVI’s designated person under each power of attorney;
Pursuant to equity pledge agreements, each of the shareholders of Digiwork pledged all of the Equity Interests to Enigma BVI to secure the full and complete performance of the obligations and liabilities on the part of Digiwork and each of its shareholders under this and the above contractual arrangements. If Digiwork or the shareholders of Digiwork breach their contractual obligations under these agreements, then Enigma BVI, as pledgee, will have the right to dispose of the pledged equity interests. The shareholders of Digiwork agree that, during the term of the equity pledge agreements, they will not dispose of the pledged equity interests or create or allow any encumbrance on the pledged equity interests, and they also agree that Enigma BVI’s rights relating to the equity pledge should not be prejudiced by the legal actions of the shareholders, their successors or their designees. During the term of the equity pledge, Enigma BVI has the right to receive all of the dividends and profits distributed on the pledged equity. The equity pledge agreements will terminate on the second anniversary of the date when Digiwork and the shareholders of Digiwork have completed all their obligations under the contractual agreements described above.
As a result of the above contractual arrangements, Enigma BVI has substantial control over Digiwork’s daily operations and financial affairs, election of its senior executives and all matters requiring shareholder approval. Furthermore, as the primary beneficiary of Digiwork, the Company, via Enigma BVI, is entitled to consolidate the financial results of Digiwork in its own consolidated financial statements under Financial Accounting Standards Board Accounting Standard Codification (ASC) Topic 810 and related subtopics related to the consolidation of variable interest entities, or ASC Topic 810.
Digiwork was set up pursuant to a joint business agreement among its shareholders on August 4, 2016 and as amended and restated on March 31, 2017 (“JBA”). Pursuant to the JBA, Digiwork is obligated to pay a total of $10,000,000 to a shareholder of Digiwork, Digiwork Co., Ltd. (“Digiwork Korea”). As consideration for such payments, Digiwork Korea agreed to provide research and development services to Digiwork for a period of five years commencing from March 31, 2017. On December 31, 2016, an initial payment of $100,000 was paid to Digiwork Korea.
On July 10, 2017, the parties to the JBA entered into an amendment to the Amended and Restated Joint Business Agreement which amended the total payment from $10,000,000 to $1,100,000. The final payment of $1,000,000 is due on August 31, 2017. As of the date of this annual report, the amount remains unpaid. Mr. Ratanaphon Wongnapachant, the CEO, a director and major shareholder of the Company, has agreed to make loans to Digiwork to make the payment due to Digiwork Korea, if necessary.
Digiwork Korea also agrees to grant Digiwork full and exclusive licenses of any new launches, developments, improvements and any other intellectual property rights of coding technology so developed by Digiwork Korea. The territories for such licenses are in Thailand, Vietnam, Myanmar, Laos, Cambodia, United Arab Emirates and Qatar.
Digiwork was authorized by Digiwork Korea to be an official licensee and distributor of its technology exclusively in Thailand, Vietnam, Myanmar, Laos, Cambodia, United Arab Emirates and Qatar, and the authorization covers all four of Digiwork Korea’s coding technology: image, audio, web and security coding. This technology enables governments and enterprises around the world to give digital identities to media and objects that computers can sense and recognize, and to which they can react.
Digiwork is a technology development and services provider specializing in coding services in various industries and markets.
| F-8 |
Organization and reorganization
Enigma BVI was incorporated on February 22, 2017 in the British Virgin Islands with limited liability as an investment holding company. Upon incorporation, Enigma BVI issued 50,000 shares at $1 each. Prior to the reorganization, Enigma BVI was owned 57.5% by Mr. Ratanaphon Wongnapachant, 2.5% by Ms. Chanikarn Lertchawalitanon, and 40% by S-Mark Co. Ltd., a KOSDAQ-listed corporation and 100% shareholder of Digiwork Korea.
Digiwork (Thailand) Co. Ltd was incorporated in Thailand with limited liability on November 24, 2016. Digiwork was also owned 57.5% by Mr. Ratanaphon Wongnapachant, 2.5% by Ms. Chanikarn Lertchawalitanon, and 40% by S-Mark Co. Ltd.
On May 15, 2017, Enigma BVI, Digiwork and the shareholders of Digiwork entered into the abovementioned VIE Agreements, pursuant to which Enigma BVI has contractual rights to control and operate the businesses of Digiwork. The change in control of and the acquisition of Digiwork by Enigma BVI have been accounted for as common control transaction in a manner similar to a pooling of interests and there was no recognition of any goodwill or excess of the acquirers’ interest in the net fair value of the acquirees’ identifiable assets, liabilities and contingent liabilities over cost at the time of the common control combinations. Therefore, this transaction was recorded at historical cost with a reclassification of equity from retained profits to additional paid in capital to reflect the deemed value of consideration given in the local jurisdiction and the capital structure of Enigma BVI.
On May 15, 2017, the Company entered into a share exchange agreement (the “Share Exchange Agreement”) with Enigma Technology International Corporation (“Enigma BVI”), and all the shareholders of Enigma BVI, namely, Mr. Ratanaphon Wongnapachant, Ms. Chanikarn Lertchawalitanon and S-Mark Co. Ltd. (collectively the “Shareholders”), to acquire all the issued and outstanding capital stock of Enigma BVI in exchange for the issuance to the Shareholders of an aggregate of 63,000,000 restricted shares of IWEB, Inc.’s common stock (the “Reverse Merger”). The Reverse Merger closed on May 15, 2017. As a result of the Reverse Merger, Enigma BVI is now a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Company.
All references above to share and per share data of IWEB, Inc. have not been adjusted to give effect of the reverse stock split effective on March 13, 2018 (see Note 12).
On May 15, 2017, the Company filed a Current Report on Form 8-K with the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) announcing the completion of the business combination between the Company and Enigma BVI in accordance with the terms of the Share Exchange Agreement. As a result of the transaction, Enigma BVI is now a wholly owned subsidiary of the Company, and the former shareholders of Enigma BVI became the holders of approximately 84% of the Company’s issued and outstanding capital stock on a fully-diluted basis. The acquisition was accounted for as a recapitalization effected by a share exchange, wherein Enigma BVI is considered the acquirer for accounting and financial reporting purposes. The assets and liabilities of the acquired entity have been brought forward at their book value and no goodwill has been recognized.
NOTE 2 – SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Basis of Presentation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with United States of America generally accepted accounting principles (“U.S. GAAP”).
Use of Estimates
The preparation of these financial statements in conformity with U.S. GAAP requires management of the Company to make estimates and judgments that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues, costs and expenses, and related disclosures. On an on-going basis, the Company evaluates its estimates based on historical experience and on various other assumptions that are believed to be reasonable under the circumstances, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying values of assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other sources. Actual results may differ from these estimates under different assumptions or conditions. Identified below are the accounting policies that reflect the Company’s most significant estimates and judgments, and those that the Company believes are the most critical to fully understanding and evaluating its consolidated financial statements.
| F-9 |
Basis of Consolidation
The consolidated financial statements include the financial statements of the Company, its subsidiary and VIE entity. All significant inter-company balances and transactions within the Company have been eliminated upon consolidation.
A subsidiary is an entity in which (i) the Company directly or indirectly controls more than 50% of the voting power; or (ii) the Company has the power to appoint or remove the majority of the members of the board of directors or to cast a majority of votes at the meeting of the board of directors or to govern the financial and operating policies of the investee pursuant to a statute or under an agreement among the shareholders or equity holders.
VIE Consolidation
The Company’s VIE is owned as to 57.5% by Mr. Ratanaphon Wongnapachant, 2.5% by Ms. Chanikarn Lertchawalitanon, and 40% by S-Mark Co. Ltd., a KOSDAQ-listed corporation. For the consolidated VIE, management made evaluations of the relationships between the Company and the VIE and the economic benefit flow of contractual arrangements with the VIE. In connection with such evaluation, management also took into account the fact that, as a result of such contractual arrangements, the Company controls the shareholders’ voting interests in these VIE. As a result of such evaluation, management concluded that Enigma BVI is the primary beneficiary of its consolidated VIE.
Owing predominantly to the Thailand legal restrictions on foreign ownership, Enigma BVI currently conducts the coding business in Thailand through Digiwork, which it effectively controls through a series of contractual arrangements. The Company consolidates in its consolidated financial statements of the VIE of which the Company is the primary beneficiary.
The following financial information of the Company’s consolidated VIE is included in the accompanying consolidated financial statements:
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| ASSETS | ||||||||
| Cash at bank and on hand | $ | 60,295 | $ | 586 | ||||
| Prepayments and deposits | 982,523 | 100,000 | ||||||
| Other receivables | 5,365 | - | ||||||
| Amounts due from shareholders | 21,250 | - | ||||||
| Property, plant and equipment, net | 12,777 | - | ||||||
| TOTAL ASSETS | $ | 1,082,210 | $ | 100,586 | ||||
| LIABILITIES | ||||||||
| Accruals | $ | 5,898 | $ | - | ||||
| Amount due to a director | 266,029 | 69,299 | ||||||
| Amount due to a related company | 1,000,000 | - | ||||||
| TOTAL LIABILITIES | $ | 1,271,927 | $ | 69,299 | ||||
| F-10 |
| Year ended December 31, 2017 |
Period from November 24, 2016 (inception of VIE) through December 31, 2016 |
|||||||
| Revenues | $ | 126,456 | $ | - | ||||
| Net loss | $ | 226,199 | $ | 112,405 | ||||
| Year ended December 31, 2017 | Period from November 24, 2016 (inception of VIE) through December 31, 2016 | |||||||
| Net cash used in operating activities | $ | (105,237 | ) | $ | (212,405 | ) | ||
| Net cash used in investing activities | (13,734 | ) | - | |||||
| Net cash provided by financing activities | 127,549 | 210,662 | ||||||
Property, plant and equipment
Property, plant and equipment are recorded at cost less accumulated depreciation and accumulated impairment. Depreciation is computed using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the assets.
| Estimated useful lives (years) | ||||
| Office and computer equipment | 5 | |||
| Software | 5 | |||
Expenditure for maintenance and repairs is expensed as incurred.
The gain or loss on the disposal of property, plant and equipment is the difference between the net sales proceeds and the lower of the carrying value or fair value less cost to sell the relevant assets and is recognized in general and administrative expenses in the consolidated statements of comprehensive loss.
Impairment of Long-lived Assets
In accordance with ASC 360-10-35, the Company reviews the carrying values of long-lived assets for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying value of an asset may not be recoverable. Based on the existence of one or more indicators of impairment, the Company measures any impairment of long-lived assets using the projected discounted cash flow method at the asset group level. The estimation of future cash flows requires significant management judgment based on the Company’s historical results and anticipated results and is subject to many factors. The discount rate that is commensurate with the risk inherent in the Company’s business model is determined by its management. An impairment loss would be recorded if the Company determined that the carrying value of long-lived assets may not be recoverable. The impairment to be recognized is measured by the amount by which the carrying values of the assets exceed the fair value of the assets. No impairment has been recorded by the Company as of December 31, 2017 and 2016.
Revenue Recognition
Revenue is principally comprised of image coding services revenue, and represents the fair value of the consideration received or receivable for the provision of services in the ordinary course of the Company's activities and is recorded net of value-added tax ("VAT"). Consistent with the criteria of ASC 605 "Revenue Recognition" ("ASC 605"), the Company recognizes revenue when persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists, the price is fixed or determinable, collection is reasonably assured and delivery of products has occurred or services have been rendered. Customer payments received prior to the recognition of revenue are recorded as advance from customers.
| F-11 |
Revenue is recognized at the time when the services are provided or ratably over the term of the service contracts as appropriate.
The Company and Enigma BVI have not earned any revenue since its inception. Digiwork did not earn any revenue in fiscal 2016. Digiwork’s revenues for the year ended December 31, 2017 of $126,456 were derived from two customers, which individually accounted for 65% and 35% of the Company’s revenues.
Two unrelated individuals were hired by Digiwork in relation to its two projects and incurred costs totaled $19,119 for the year ended December 31, 2017.
Foreign Currency and Foreign Currency Translation
The functional currency of the Company and Enigma BVI is US$. The Company's VIE with operations in Thailand uses its respective local currency, Thai Baht (“THB”), as its functional currency. An entity’s functional currency is the currency of the primary economic environment in which it operates, normally that is the currency of the environment in which the entity primarily generates and expends cash. Management’s judgment is essential to determine the functional currency by assessing various indicators, such as cash flows, sales price and market, expenses, financing and inter-company transactions and arrangements.
Foreign currency transactions denominated in currencies other than the functional currency are translated into the functional currency using the exchange rates prevailing at the dates of the transactions. Monetary assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies at the balance sheet date are re-measured at the applicable rates of exchange in effect at that date. Gains and losses resulting from foreign currency re-measurement are included in the statements of comprehensive loss.
The financial statements are presented in U.S. dollars. Assets and liabilities are translated into U.S. dollars at the current exchange rate in effect at the balance sheet date, and revenues and expenses are translated at the average of the exchange rates in effect during the reporting period. Stockholders’ equity accounts are translated using the historical exchange rates at the date the entry to stockholders’ equity was recorded, except for the change in retained earnings during the period, which is translated using the historical exchange rates used to translate each period’s income statement. Differences resulting from translating functional currencies to the reporting currency are recorded in accumulated other comprehensive income in the balance sheets.
Translation of amounts from THB into U.S. dollars has been made at the following exchange rates:
| Balance sheet items, except for equity accounts | |||
| December 31, 2017 | THB32.5512 to $1 | ||
| December 31, 2016 | THB35.6666 to $1 | ||
| Income statement and cash flows items | |||
| For the year ended December 31, 2017 | THB33.9964 to $1 | ||
|
For the period from November 24, 2016 (inception of VIE) through December 31, 2016 |
THB35.3699 to $1 |
Research and Development
Research and development costs are paid to Digiwork Korea, which is providing research and development services to Digiwork for a period of five years commencing from March 31, 2017. Research and development costs are recognized in general and administrative expenses and expensed as incurred. Research and development expense was $163,159 and nil for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively.
| F-12 |
Income Taxes
Income taxes are accounted for using an asset and liability approach which requires the recognition of income taxes payable or refundable for the current year and deferred tax liabilities and assets for the future tax consequences of events that have been recognized in the Company’s financial statements or tax returns. Deferred income taxes are determined based on the differences between the accounting basis and the tax basis of assets and liabilities and are measured using the currently enacted tax rates and laws. Deferred tax assets are reduced by a valuation allowance, if based on available evidence, it is considered that it is more likely than not that some portion of or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized. In making such determination, the Company considers factors including future reversals of existing taxable temporary differences, future profitability, and tax planning strategies. If events were to occur in the future that would allow the Company to realize more of its deferred tax assets than the presently recorded net amount, an adjustment would be made to the deferred tax assets that would increase income for the period when those events occurred. If events were to occur in the future that would require the Company to realize less of its deferred tax assets than the presently recorded net amount, an adjustment would be made to the valuation allowance against deferred tax assets that would decrease income for the period when those events occurred. Significant management judgment is required in determining income tax expense and deferred tax assets and liabilities.
Thailand Withholding Tax on Dividends
Dividends payable by a foreign invested enterprise in Thailand to its foreign investors are subject to a 10% withholding tax, unless any foreign investor’s jurisdiction of incorporation has a tax treaty with Thailand that provides for a different withholding arrangement.
Uncertain Tax Positions
Management reviews regularly the adequacy of the provisions for taxes as they relate to the Company’s income and transactions. In order to assess uncertain tax positions, the Company applies a more likely than not threshold and a two-step approach for tax position measurement and financial statement recognition. For the two-step approach, the first step is to evaluate the tax position for recognition by determining if the weight of available evidence indicates that it is more likely than not that the position will be sustained, including resolution of related appeals or litigation processes, if any. The second step is to measure the tax benefit as the largest amount that is more than 50% likely to be realized upon settlement.
Net loss per share of common stock
The Company has adopted ASC Topic 260, “Earnings per Share,” (“EPS”) which requires presentation of basic EPS on the face of the income statement for all entities with complex capital structures and requires a reconciliation of the numerator and denominator of the basic EPS computation. In the accompanying financial statements, basic earnings (loss) per share is computed by dividing net loss by the weighted average number of shares of common stock outstanding during the period.
| Years ended December 31, | ||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Net loss | $ | (451,927 | ) | $ | (112,405 | ) | ||
| Weighted average number of common shares outstanding – basic and diluted | 33,210,306 | 25,747,500 | ||||||
| Basic and diluted loss per share | $ | (0.01 | ) | $ | - | * | ||
* Less than $0.01 per share
The calculation of basic net loss per share of common stock is based on the net loss for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016 and the weighted average number of ordinary shares of 33,210,306 outstanding post-split and 66,420,612 outstanding pre-split during the year ended December 31, 2017 (2016: 25,747,500 shares post-split and 51,495,000 pre-split). The numbers of outstanding shares represent retroactive effect to the Company’s 1-for-2 reverse stock split effected on March 13, 2018. The Company completed a reverse stock split on March 13, 2018, pursuant to which every two shares of the Company’s common stock were combined into one share of common stock. Except for net loss per share data and authorized and outstanding share information presented in the balance sheets, all share information and amounts included in the consolidated financial statements have not been retroactively adjusted to effect for this stock split. Retroactive adjustment will be made in the Company’s fiscal 2018 consolidated financial statements.
The Company has no potentially dilutive securities, such as options or warrants, currently issued and outstanding.
Segments
The Company evaluates a reporting unit by first identifying its operating segments, and then evaluates each operating segment to determine if it includes one or more components that constitute a business. If there are components within an operating segment that meets the definition of a business, the Company evaluates those components to determine if they must be aggregated into one or more reporting units. If applicable, when determining if it is appropriate to aggregate different operating segments, the Company determines if the segments are economically similar and, if so, the operating segments are aggregated. The Company has one reportable segment in the periods presented (see note 8).
| F-13 |
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
U.S. GAAP establishes a three-tier hierarchy to prioritize the inputs used in the valuation methodologies in measuring the fair value of financial instruments. This hierarchy also requires an entity to maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs when measuring fair value. The three-tier fair value hierarchy is:
Level 1 – observable inputs that reflect quoted prices (unadjusted) for identical assets or liabilities in active markets.
Level 2 – include other inputs that are directly or indirectly observable in the market place.
Level 3 – unobservable inputs which are supported by little or no market activity.
The carrying value of the Company’s financial instruments, including cash at banks and on hand and balances with related parties approximate their fair value due to their short maturities.
Comprehensive Income
Comprehensive income is defined as the change in equity of a company during a period from transactions and other events and circumstances excluding transactions resulting from investments from owners and distributions to owners. Accumulated other comprehensive income includes cumulative foreign currency translation adjustment.
Recently issued accounting pronouncements
In May 2014, the FASB issued ASU No. 2014-09, ‘‘Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606).’’ This guidance supersedes current guidance on revenue recognition in Topic 605, ‘‘Revenue Recognition.” In addition, there are disclosure requirements related to the nature, amount, timing, and uncertainty of revenue recognition. In August 2015, the FASB issued ASU No.2015-14 to defer the effective date of ASU No. 2014-09 for all entities by one year. For public business entities that follow U.S. GAAP, the deferral results in the new revenue standard are being effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those fiscal years, beginning after December 15, 2017, with early adoption permitted for interim and annual periods beginning after December 15, 2016. The Company will apply the new revenue standard beginning January 1, 2018. Based on management’s assessment of the application of this guidance, the Company does not expect a material impact on amounts reported and disclosures made in the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
On January 5, 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-01 (“ASU 2016-01”), Recognition and Measurement of Financial Assets and Financial Liabilities, which amends certain aspects of recognition, measurement, presentation and disclosure of financial instruments. This amendment requires all equity investments to be measured at fair value, with changes in the fair value recognized through net income (other than those accounted for under equity method of accounting or those that result in consolidation of the investee). This standard will be effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, including interim periods within those fiscal years. The Company does not expect this standard to have a material impact on its consolidated financial statements.
On February 25, 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-02 (“ASU 2016-02”), Leases. ASU 2016-02 specifies the accounting for leases. For operating leases, ASU 2016-02 requires a lessee to recognize a right-of-use asset and a lease liability, initially measured at the present value of the lease payments, in its balance sheet. The standard also requires a lessee to recognize a single lease cost, calculated so that the cost of the lease is allocated over the lease term, on a generally straight-line basis. In addition, this standard requires both lessees and lessors to disclose certain key information about lease transactions. ASU 2016-02 is effective for public companies for annual reporting periods, and interim periods within those years, beginning after December 15, 2018. Early adoption is permitted. Management is currently assessing the potential impact of adopting this standard on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
| F-14 |
In June 2016, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) 2016-13, Financial Instruments-Credit Losses (Topic 326), which requires entities to measure all expected credit losses for financial assets held at the reporting date based on historical experience, current conditions, and reasonable and supportable forecasts. This replaces the existing incurred loss model and is applicable to the measurement of credit losses on financial assets measured at amortized cost. This guidance is effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those fiscal years, beginning after December 15, 2019. Early application will be permitted for all entities for fiscal years, and interim periods within those fiscal years, beginning after December 15, 2018. The Company does not expect this standard to have a material impact on its consolidated financial statements.
In August 2016, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) 2016-15, Statement of Cash Flows – Classification of Certain Cash Receipts and Cash Payments, which clarifies the presentation and classification of certain cash receipts and cash payments in the statement of cash flows. This guidance is effective for financial statements issued for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, and interim periods within those fiscal years. Early adoption is permitted. The Company does not expect this standard to have a material impact on its consolidated financial statements.
In November 2016, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) No. 2016-18, Statement of Cash Flows (Topic 230): Restricted Cash. The guidance requires that a statement of cash flows explain the change during the period in the total of cash, cash equivalents, and amounts generally described as restricted cash or restricted cash equivalents. Therefore, amounts generally described as restricted cash and restricted cash equivalents should be included with cash and cash equivalents when reconciling the beginning-of-period and end-of-period total amounts shown on the statement of cash flows. The standard is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, and interim period within those fiscal years. Early adoption is permitted, including adoption in an interim period. The standard should be applied using a retrospective transition method to each period presented. The Company does not expect this standard to have a material impact on its consolidated financial statements.
In January 2017, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) No. 2017-01, Business Combinations (Topic 805): Clarifying the Definition of a Business, which clarifies the definition of a business with the objective of adding guidance to assist entities with evaluating whether transactions should be accounted for as acquisitions or disposals of assets or businesses. The standard is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, including interim periods within those fiscal years. Early adoption is permitted. The standard should be applied prospectively on or after the effective date. The Company does not expect this standard to have a material impact on its consolidated financial statements.
In January 2017, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) 2017-04, “Simplifying the Test for Goodwill Impairment.” The guidance removes Step 2 of the goodwill impairment test, which requires a hypothetical purchase price allocation. A goodwill impairment will now be the amount by which a reporting unit’s carrying value exceeds its fair value, not to exceed the carrying amount of goodwill. The guidance should be adopted on a prospective basis for the annual or any interim goodwill impairment tests beginning after December 15, 2019. Early adoption is permitted for interim or annual goodwill impairment tests performed on testing dates after January 1, 2017. The Company does not expect this standard to have a material impact on its consolidated financial statements.
NOTE 3 - GOING CONCERN
The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared assuming the Company will continue as a going concern. The Company has incurred recurring losses from operations resulting in an accumulated deficit of $564,332 as of December 31, 2017, and had net working capital deficiency of $320,167 as of that date. These conditions raise substantial doubt about the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern. The ability to continue as a going concern is dependent upon the Company generating profitable operations in the future and/or obtaining the necessary financing to meet its obligations and repay its liabilities arising from normal business operations when they become due. We may have to rely on additional debt financing, loans from existing directors and shareholders and private placements of capital stock for additional funding. There can be no assurance that the Company will be successful in its plans described above or in attracting equity or alternative financing on acceptable terms, if at all.
| F-15 |
These consolidated financial statements do not include any adjustments to the recoverability and classification of recorded asset amounts and classification of liabilities that might be necessary should the Company be unable to continue as a going concern.
NOTE 4 - BALANCES WITH RELATED PARTIES
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Due from shareholders | $ | 21,250 | $ | - | ||||
| Due to directors | ||||||||
| Mr Ratanaphon Wongnapachant | $ | 266,029 | $ | 69,299 | ||||
| Mr. Wai Hok Fung | 79,070 | - | ||||||
| $ | 345,099 | $ | 69,299 | |||||
| Due to a related company – Digiwork Korea (Note 1) | $ | 1,000,000 | $ | - | ||||
The balances with shareholders and directors detailed above as of December 31, 2017 and 2016 are unsecured, non-interest bearing and repayable on demand.
NOTE 5 - PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT, NET
Property, plant and equipment, net consist of the following:
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Office and computer equipment | $ | 12,912 | $ | - | ||||
| Software | 1,432 | - | ||||||
| Less: Accumulated depreciation | (1,567 | ) | - | |||||
| $ | 12,777 | $ | - | |||||
Depreciation expenses charged to the statements of comprehensive loss for the year ended December 31, 2017 and 2016 were $1,500 and nil, respectively.
NOTE 6 - COMMON STOCK
On May 15, 2017, the Company entered into a share exchange agreement (the “Share Exchange Agreement”) with Enigma BVI, and all the shareholders of Enigma BVI, namely, Mr. Ratanaphon Wongnapachant, Ms. Chanikarn Lertchawalitanon, and S-Mark Co. Ltd. (each a “Shareholder” and collectively the “Shareholders”), to acquire all the issued and outstanding capital stock of Enigma BVI in exchange for the issuance to the Shareholders of an aggregate of 63,000,000 (the “Reverse Merger”) restricted shares of our common stock. Immediately after the closing of the Reverse Merger, we had a total of 75,000,000 issued and outstanding shares of common stock, 63,000,000 of which were held by the Shareholders.
In connection with the transactions contemplated by the Share Exchange Agreement, the Company and Mr. Wai entered into a Repurchase Agreement, dated May 14, 2017, pursuant to which the Company purchased 39,495,000 shares of the Company’s common stock (the “Repurchase Shares”) from Mr. Wai for a total purchase price of $1.00, effective immediately prior to the consummation of the Share Exchange Agreement. The Repurchase Shares were held as treasury shares and issued to the Shareholders pursuant to the Share Exchange Agreement.
| F-16 |
Effective June 28, 2017, the Company’s Board of Directors and holders of a majority of the Company’s outstanding shares of common stock approved and adopted an amendment to the Company’s Articles of Incorporation to (i) increase the Company’s authorized shares of common stock, par value $0.0001 per share, from 75,000,000 to 150,000,000 shares and (ii) authorize the issuance of up to 25,000,000 shares of blank check preferred stock, par value $0.0001 per share (the “Amendment”). The Company filed the Amendment with the Secretary of State for the State of Nevada to effect the changes on August 17, 2017.
On November 16, 2017, the Company entered into a Securities Purchase Agreement (the “Purchase Agreement”) with certain investors (collectively, the “Purchasers”), pursuant to which the Company sold to the Purchasers in a private placement an aggregate of 395,500 shares (the “Shares”) of the Company’s common stock, par value $0.0001 per share, at a purchase price of $1.00 per Share for an aggregate offering price of $197,750 (the “Private Placement”). The Private Placement was completed pursuant to the exemption from registration provided by Regulation S promulgated under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended.
NOTE 7 - INCOME TAXES
| (a) | The local (United States) and foreign components of loss before income taxes were comprised of the following: |
| Years ended December 31, | ||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Tax jurisdictions from: | ||||||||
| - Local | $ | (140,786 | ) | $ | - | |||
| - Foreign, representing: | ||||||||
| BVI | (84,942 | ) | - | |||||
| Thailand | (226,199 | ) | (112,405 | ) | ||||
| Loss before income taxes | $ | (451,927 | ) | $ | (112,405 | ) | ||
United States of America
The Company is incorporated in the State of Nevada and is subject to the U.S. federal tax and state statutory tax rates of up to 34% and 0%, respectively. No provision for income taxes in the United States has been made as the Company had no taxable income for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016.
British Virgin Islands
Under the current laws of the British Virgin Islands, entities incorporated in British Virgin Islands are not subject to tax on their income or capital gains.
Thailand
The statutory corporate income tax rate in Thailand (“CIT”) is 20%.
Digiwork, assuming a paid-in capital not exceeding 5 million Thai baht (THB)($153,604) at the end of any accounting period and income from the sale of goods and/or the provision of services not exceeding THB 30 million ($921,625) in any accounting period, is subject to CIT in Thailand at the following reduced rates:
For accounting periods beginning on or after January 1, 2017:
| Net profit | ||||
| Nil – THB300,000 ($9,216) | 0 | % | ||
| THB300,000 – THB3,000,000 ($92,162) | 15 | % | ||
| Over THB3,000,000 ($92,162) | 20 | % | ||
A reconciliation of loss before income taxes to the effective tax rate as follows:
| F-17 |
| Years ended December 31, | ||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Loss before income taxes | $ | (451,927 | ) | $ | (112,405 | ) | ||
| Statutory income tax rate | 34 | % | 34 | % | ||||
| Income tax credit computed at statutory income tax rate | (153,655 | ) | (38,218 | ) | ||||
| Reconciling items: | ||||||||
| Non-deductible expenses | 20,141 | 21,278 | ||||||
| Tax effect of tax exempt entity | 28,880 | - | ||||||
| Rate differential in different tax jurisdictions | 31,668 | 15,737 | ||||||
| Provisional re-measurement of deferred taxes – TCJ Act | (43,026 | ) | ||||||
| Valuation allowance on deferred tax assets | 115,992 | 1,203 | ||||||
| Total tax expenses | $ | - | $ | - | ||||
| (b) | The tax effects of temporary differences that give rise to significant portions of the deferred tax assets and liabilities as of December 31, 2017 and 2016 are presented below |
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Deferred tax assets: | ||||||||
| Net operating loss carryforwards: | ||||||||
| - United States of America | $ | 60,154 | $ | - | ||||
| - Thailand | 27,520 | 1,193 | ||||||
| 87,674 | 1,193 | |||||||
| Less: Valuation allowance | (87,674 | ) | (1,193 | ) | ||||
| $ | - | $ | - | |||||
Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (“TCJ Act”)
During the fourth quarter of 2017, the TCJ Act was enacted in the United States. Among its many provisions, the TCJ Act imposed a mandatory one-time transition tax on undistributed international earnings and reduced the U.S. corporate income tax rate to 21%, effective January 1, 2018. The Company is required to re-measure its deferred tax assets and liabilities to the new, lower U.S. corporate income tax rate, effective January 1, 2018. The effect of the remeasurement was recorded in the fourth quarter of 2017, consistent with the enactment date of the TCJ Act, and reflected in the provision for income taxes. The Company has accumulated net operating loss carryovers of approximately $286,446 as of December 31, 2017, which are available to reduce future taxable income. Due to the change in ownership provisions of the Tax Reform Act of 1986, net operating loss carry forwards of $145,660 for federal income tax reporting purposes may be subject to annual limitations. A change in ownership may limit the utilization of the net operating loss carry forwards in future years. The tax losses begin to expire in 2035. The fiscal years 2016 and 2017 remain open to examination by federal tax authorities and other tax jurisdictions.
As of December 31, 2017 and 2016, Digiwork had net operating loss carry forwards of $137,598 and $5,966, respectively, which will expire in various years through 2022. Its tax years 2016 and 2017 remain open to examination by the local authorities.
Management believes that it is more likely than not that the Company will not realize these potential tax benefits as these operations will not generate any operating profits in the foreseeable future. As a result, a valuation allowance was provided against the full amount of the potential tax benefits.
| F-18 |
NOTE 8 - SEGMENT INFORMATION
The Company, via its relationship with Digiwork, is a technology development and services provider specializing in coding services in various industries and markets.
The Company’s chief operating decision maker (“CODM”) has been identified as the CEO who reviews the financial information of separate operating segments when making decisions about allocating resources and assessing performance of the Company. Based on management’s assessment, the Company has determined that it has one operating segment, being technology development and provision of coding services in various industries and markets.
The Company primarily operates in Thailand. Substantially all the Company’s long-lived assets are located in Thailand.
NOTE 9 - COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
Capital Commitments
Digiwork engaged a related party to provide research and development services for a period of five years commencing from March 31, 2017, with a total contract amount of $10,000,000, which was subsequently lowered to $1,100,000 (see note 1). The final payment of $1,000,000 is due on August 31, 2017. As of the date of this annual report, the amount remained unpaid.
Lease Commitments
Rental expense of the Company was $40,604 and $22,539 for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively
The Company has entered into a lease for office space located in Din Daeng Sub-district, din Daeng District, Bangkok, Thailand for the period from February 21, 2017 to February 20, 2020, at THB127,120 ($3,905) per month.
The total future minimum lease payments under the non-cancellable operating lease with respect to the office premises as of December 31, 2017 are payable as follows:
| 12 months ending December 31, | ||||
| 2018 | $ | 47,078 | ||
| 2019 | 46,863 | |||
| 2020 | 7,810 | |||
| Total | $ | 101,751 | ||
NOTE 10 - THAILAND CONTRIBUTION PLAN
In accordance with the rules and regulations of Thailand, the employees of the VIE established in Thailand are required to participate in a defined contribution retirement plan organized by local government. Contributions to this plan are expensed as incurred and other than these monthly contributions, the VIE has no further obligation for the payment of retirement benefits to its employees. For the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016, the VIE contributed a total of $1,554 and minimal, respectively, to this plan.
NOTE 11 - CERTAIN RISKS AND CONCENTRATIONS
Credit risk
At December 31, 2017 and 2016, the Company’s cash and cash equivalents included bank deposits in accounts maintained in Thailand. The Company does not experience any losses in such accounts and believes it is not exposed to any significant risks on its cash in bank accounts.
Major customers
The Company did not earn any revenue in fiscal 2016. Its revenues for the year ended December 31, 2017 of $126,456 were derived from two customers, which individually accounted for 65% and 35% of the Company’s revenues.
Two unrelated individuals were hired in relation to its two projects and incurred costs totaled $19,119 for the year ended December 31, 2017.
Foreign currency risk
As a result of the operations in Thailand, the Company is exposed to foreign exchange risk arising from the currency exposures primarily with respect to THB. The Company's VIE with operations in Thailand uses its respective local currency, THB, as its functional currency. Although a majority of its total revenues, its payroll and other operating expenses are incurred and paid in Thai baht, its payment of R&D services provided by Digiwork Korea is required to be made in the U.S. dollar. As of December 31, 2017 and 2016, the Company owed Digiwork Korea $1,000,000 for such R&D services.
NOTE 12 - SUBSEQUENT EVENT
The Company has analyzed its operations subsequent to December 31, 2017, and has determined that it does not have any material subsequent events to disclose in these financial statements, except for the following:
On March 7, 2018, the Company filed a Certificate of Change with the State of Nevada (the “Certificate”) to effect a 1-for-2 reverse stock split of the Company’s authorized shares of common stock, par value $0.0001 (the “Common Stock”), accompanied by a corresponding decrease in the Company’s issued and outstanding shares of Common Stock (the “Reverse Stock Split”) such that, following the consummation of the Reverse Stock Split, the number of authorized shares of Common Stock shall be reduced from 150,000,000 to 75,000,000. The Reverse Stock Split became effective on March 13, 2018.
Except for net loss per share data and authorized and outstanding share information presented in the balance sheets, all share information and amounts included in the consolidated financial statements have not been retroactively adjusted to effect for this stock split. Retroactive adjustment will be made in the Company’s fiscal 2018 consolidated financial statements.
| F-19 |
Item 9. Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure
The disclosure required under this section was previously reported as such term is defined in Rule 12b-2 under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, on a Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on April 28, 2017.
Item 9A. Controls and Procedures
Disclosure Controls and Procedures
We maintain disclosure controls and procedures, as defined in Rule 13a-15(e) promulgated under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 (the "Exchange Act"), that are designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed by us in the reports that we file or submit under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the Securities and Exchange Commission's rules and forms and that such information is accumulated and communicated to our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
We carried out an evaluation, under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, of the effectiveness of the design and operation of our disclosure controls and procedures as of December 31, 2017. Based on the evaluation of these disclosure controls and procedures, and in light of the material weaknesses found in our internal controls over financial reporting, our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures were not effective.
Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting, as defined in Exchange Act Rule 13a-15(f). The Company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Under the supervision and with the participation of management, including the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, the Company conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017, using the criteria established in “Internal Control - Integrated Framework” issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission ("COSO") (2013 framework).
A material weakness is a deficiency, or combination of deficiencies, in internal control over financial reporting, such that there is a reasonable possibility that a material misstatement of the Company’s annual or interim financial statements will not be prevented or detected on a timely basis. In its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017, the Company determined that there were control deficiencies that constituted material weaknesses, as described below.
| 1. | We do not have an Audit Committee – While not being legally obligated to have an audit committee, it is the management’s view that such a committee, including a financial expert member, is of the utmost importance for entity-level control over the Company’s financial statement. Currently, the Board of Directors acts in the capacity of the Audit Committee. |
| 2. | We did not maintain appropriate cash controls – As of December 31, 2017, the Company had not maintained sufficient internal controls over financial reporting for the cash process, including failure to segregate cash handling and accounting functions, and did not require dual signature on the Company’s bank accounts. However, the effects of poor cash controls were mitigated in part by the fact that the Company had limited transactions in their bank accounts. |
| 3. | We did not implement appropriate information technology controls – As of December 31, 2017, the Company was retaining copies of all financial data and material agreements; however there is no formal procedure or evidence of normal backup of the Company’s data or off-site storage of the data in the event of theft, misplacement, or loss due to unmitigated factors. |
| 31 |
| 4. | We currently lack sufficient accounting personnel with the appropriate level of knowledge, experience and training in U.S. GAAP and SEC reporting requirements. |
Accordingly, the Company concluded that these control deficiencies resulted in a reasonable possibility that a material misstatement of the annual or interim financial statements will not be prevented or detected on a timely basis by the company’s internal controls.
As a result of the material weaknesses described above, management has concluded that the Company did not maintain effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017 based on criteria established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework issued by COSO (2013 framework).
Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
There has been no change in our internal control over financial reporting identified in connection with our evaluation we conducted of the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017, that occurred during our fourth fiscal quarter that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
This Annual Report does not include an attestation report of the Company’s registered public accounting firm regarding internal control over financial reporting. Management’s report was not subject to attestation by the Company’s registered public accounting firm pursuant to the rules of the SEC that permit the Company to provide only management’s report in this annual report.
Continuing Remediation Efforts to address deficiencies in Company’s Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Once the Company has sufficient personnel available, then our Board of Directors, in particular and in connection with the aforementioned deficiencies, will establish the following remediation measures:
| 1. | Our Board of Directors plans, if possible, to recommend the addition of an audit committee or a financial expert on our Board of Directors in fiscal 2018. |
| 2. | We plan, as funding permits, to appoint additional personnel to assist with the preparation of the Company’s monthly financial reporting. |
None.
Item 10. Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance
Directors and Executive Officers
Our directors and executive officers and their respective ages, positions, term of office and biographical information are set forth below. Our directors to serve for a term of one year or until they are replaced by a qualified director. Our executive officers are chosen by our board of directors and serve at its discretion. There are no existing family relationships between or among any of our executive officers or directors.
| 32 |
| Name | Age | Position | Served From | |||
| Ratanaphon Wongnapachant | 37 | Chief Executive Officer, Chairman and Director | May, 2017 | |||
| Wai Hok Fung | 42 | President and Director | December, 2016 | |||
| Bodin Kasemset | 43 | Director | May, 2017 | |||
| Cheng Kim Sing | 43 | Chief Financial Officer, Treasurer and Secretary | December, 2016 |
Director and Executive Officer Qualification
Ratanaphon Wongnapachant was appointed on May 15, 2017 as a director and the Chairman of the Board, and as the Company’s Chief Executive Officer. Mr. Wongnapachant has served as the chief executive officer of Digiwork (Thailand) Co., Ltd. since 2016, and as the managing director of SWA. Capital Co. Ltd. since 2014. He was previously the executive director of PAE (Thailand) PLC, an engineering and construction company, from 2010 to 2011, and as its managing director from 2011 to 2014. Mr. Wongnapachant received his bachelor’s degree in marketing research from Seattle University in 2005 and his Executive MBA from the SASIN Graduate Institute of Business Administration of Chulalongkorn University in Bangkok, Thailand, in 2016. The Board believes that Mr. Wongnapachant’s experience leading Digiwork (Thailand) Co., Ltd. and other enterprises as a performance executive will benefit the Company and make him a valuable member of the Board and the Company’s management team.
Wai Hok Fung has served as a director of the Company since December, 2016. Mr. Wai also currently serves as a director of SGOCO Group Ltd. (NASDAQ: SGOC), focusing on display and computer products and energy saving products and services. Mr. Wai has also served as a director of Wahfong Industrial Development Co., Ltd., a manufacturing company located in the PRC producing women’s clothing, since 2002, and as a director of Hebort International Limited, an exporter and wholesaler of wine, cigarettes and other products, since 2006. Mr. Wai provides consulting services from time to time to companies exploring mining and energy projects internationally. Mr. Wai received his high school certificate from the Jockey Club TI-I College in Hong Kong in 1996, his Diploma of Account and Finance from the Sydney Institute of Business and Technology in 1998, and his Bachelor of Account and Finance from Macquarie University in Sydney, Australia, in 2002.
Dr. Bodin Kasemset was appointed on May 15, 2017, as a director of the Board and has served as an innovation director with NXP Manufacturing Thailand Co. Ltd., since August 2011. He received his bachelor’s degree in engineering from Chulalongkorn University in Bangkok, Thailand, in 1997, his Master of Sciences degree from Technische Universitaet Hamburg-Harburg, in 2001, his Doktor-Ingenieur (Microsystems Technology) degree from Technische Universitaet Hamburg-Harburg, in 2009, and his Executive MBA from the SASIN Graduate Institute of Business Administration of Chulalongkorn University, in Bangkok, Thailand, in 2016. The Board believes that Dr. Kasemset’s extensive technical expertise and knowledge will benefit the Company’s develop and operations and make him a valuable member of the Board.
Cheng Kim Sing has served as the Company’s Chief Financial Officer, Treasurer and Secretary since December, 2016, and previously served as a director on the Board. Mr. Cheng previously served as the Finance Manager of Good View Fruits Co. Ltd., a fruit manufacturer, distributor and retailer based predominantly in Hong Kong, from December, 2008 to July, 2016. He served as the Assistant Manager of Wofoo Plastics Ltd., a plastic manufacturing company located in Hong Kong, from April, 2007 to September, 2008. Mr. Cheng has received and holds a number of degrees and certifications, including but not limited to his Master of Professional Accounting degree from Hong Kong Polytechnic University in 2003, his Master of Accountancy degree from Jinan University in China in 2004, his Master of Business Administration degree from Hong Kong Baptist University in 2006 and his Master of Laws degree from Renmin University of China in 2010. Mr. Cheng is also a certified public accountant in the PRC and Hong Kong, a certified information systems auditor, a certified internal auditor and a certified fraud examiner in the USA.
Code of Ethics
Because the Company has a small number of persons serving as directors and executive officers, we have not adopted a code of ethics for our principal executive and financial officers. Our Board will revisit this issue in the future to determine if, and when, adoption of a code of ethics is appropriate. In the meantime, our management intends to promote honest and ethical conduct, full and fair disclosure in our reports to the SEC, and comply with applicable governmental laws and regulations.
| 33 |
Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance
The Company’s officers and directors are not subject to Section 16(a).
Item 11. Executive Compensation
Executive Officer Compensation
| Name and Principal Position (1) | Year | Salary | Stock Awards | All Other Compensation | Total | |||||||||||||||
| Ratanaphon Wongnapachant, | 2017 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | |||||||||||
| Chief Executive Officer, Chairman and Director | 2016 | 56,545 | - | - | 56,545 | |||||||||||||||
| Wai Hok Fung, | 2017 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | |||||||||||
| President and Director | 2016 | - | - | - | - | |||||||||||||||
| Cheng Kim Sing, Chief Financial | 2017 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | |||||||||||
| Officer, Treasurer and Secretary | 2016 | - | - | - | - | |||||||||||||||
| (1) | On May 15, 2017, we acquired Enigma BVI in a reverse acquisition transaction that was structured as a share exchange. The annual, long term and other compensation shown in this table include the amounts that these officers received from Enigma BVI and/or its VIE prior to the consummation of the reverse acquisition. |
Compensation of Directors
Since our inception, no compensation has been paid to our directors.
Employment Contracts
As of the date of this Annual Report, we have no employment agreements with our directors or executive officers.
Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters
The following table sets forth information regarding beneficial ownership of our common stock as of March 12, 2018, the most recent practicable date for computing beneficial ownership, by:
| ● | each of our named executive officers; | |
|
|
● | each of our directors; |
| ● | each person, or group of affiliated persons, known by us to beneficially own more than 5% of our common stock; and | |
| ● | all of our directors and executive officers as a group. |
| 34 |
We have determined beneficial ownership in accordance with the rules of the SEC. These rules generally attribute beneficial ownership of securities to persons who possess sole or shared voting or investment power with respect to those securities. Unless otherwise indicated, the persons or entities identified in this table have sole voting and investment power with respect to all shares shown as beneficially owned by them, subject to applicable community property laws.
Applicable percentage ownership is based on 75,395,500 shares of our common stock issued and outstanding as of March 12, 2018. The number of shares of common stock used to calculate the percentage ownership of each listed person includes the shares of common stock underlying options and warrants held by such persons that are currently exercisable or convertible, or will be exercisable or convertible within 60 days of March 12, 2018. We did not deem these shares outstanding, however, for the purpose of computing the percentage ownership of any other person. Except as otherwise indicated, the address of each of the shareholders listed below is: c/o IWeb, Inc., at 121/34, RS Tower, 8th Floor, Ratchadaphisek Road, Din Daeng Sub-district, Din Daeng District, Bangkok, Thailand.
| Name of beneficial owner |
Number of shares beneficially owned |
(1) | Percent of class |
|||||
| Wai Hok Fung, President and Director | 10,500,000 | 13.9 | % | |||||
| Ratanaphon Wongnapachant, Chief Executive Officer and Director | 35,910,000 | 47.3 | % | |||||
| Cheng Kim Sing, Chief Financial Officer, Secretary, Treasurer | - | - | ||||||
| Directors and executive officers as a group (3 people) | 46,410,000 | 61.2 | % | |||||
| S-Mark Co. Ltd. | 25,200,000 | 33.4 | % | |||||
| (1) | prior to 1-for-2 reverse stock split effected by the Company on March 13, 2018. |
Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence
Certain Relationships and Related Transactions
Mr. Wai Hok Fung, our President, former Chief Executive Officer, director and shareholder, has loaned to the Company an aggregate amount of $79,070 as of December 31, 2017, which is interest free, unsecured and payable on demand.
Mr. Ratanaphon Wongnapachant, our chairman and chief executive officer, has loaned to Enigma Technology International Corporation (“Enigma BVI”) and its VIE an aggregate amount of $266,029 and $69,299 as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively, which are interest free, unsecured and payable on demand.
As of December 31, 2017, S-Mark and Ms. Lertchawalitanon owed $20,000 and $1,250 to Enigma BVI, respectively, in relation to their shares of capital contribution to Enigma BVI. These amounts are interest free, unsecured and payable on demand.
Digiwork (Thailand) Co., Ltd. (“Digiwork”) was set up pursuant to a joint business agreement among its shareholders (“JBA”) on August 4, 2016, as amended and restated on March 31, 2017. Pursuant to the JBA, Digiwork was originally obligated to pay a total of $10,000,000 to S-Mark Co., Ltd. or Digiwork Co., Ltd. (“Digiwork Korea”, a 100% wholly owned subsidiary of S-Mark Co., Ltd., which is a shareholder of Digiwork and a 33.6% shareholder of the Company). On July 10, 2017, parties to the JBA entered into an amendment to the Amended and Restated Joint Business Agreement which amended the total payment from $10,000,000 to $1,100,000. As the consideration for such payments, Digiwork Korea agreed to provide research and development services to Digiwork for a period of five years commencing from March 31, 2017. Digiwork currently has 8 full time employees, all of which are administrative staff members. The technical services are currently provided by contracted technicians from Digiwork Korea. Digiwork Korea also agreed to grant to Digiwork full and exclusive licenses of any new launches, developments, improvements and any other intellectual property rights of coding technology so developed by Digiwork Korea. The territories for such licenses are Thailand, Vietnam, Myanmar, Laos, Cambodia, United Arab Emirates and Qatar.
Board Independence
As of the date of this Annual Report, Mr. Bodin Kasemset is the only director of the Company who is independent under the independence requirements of Rule 10A-3 promulgated under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. This rule defines persons as “independent” who are neither officers nor employees of the company and have no relationships that, in the opinion of the Board, would interfere with the exercise of independent judgment in carrying out their responsibilities as directors.
Item 14. Principal Accounting Fees and Services
The following table sets forth the aggregate fees by categories specified below in connection with certain professional services rendered by Centurion ZD CPA Limited, our independent registered public accounting firm.
| 35 |
| Years ended December 31, | ||||||||
| 2017 | 2016 | |||||||
| Audit fees | $ | 107,000 | $ | - | ||||
| Audit-related fees | - | - | ||||||
| Tax fees | - | - | ||||||
| All other services | - | - | ||||||
| Total | 107,000 | $ | - | |||||
AUDIT FEES
Audit fees represent the aggregate fees billed for the audit of our annual financial statements, review of our quarterly financial statements, review of registration statements or services that are normally provided in connection with statutory and regulatory filings or engagements for those fiscal years. The 2017 fees include the Company’s 2016 annual audit.
AUDIT-RELATED FEES
There were no fees were billed or incurred for assurance or related services by our auditors that were reasonably related to the audit or review of financial statements reported above.
TAX FEES
There were no tax preparation fees billed for the Annual Period.
ALL OTHER FEES
There were no other fees were billed or incurred for services by our auditors other than the fees noted above. Our board, acting as an audit committee, deemed the fees charged to be compatible with maintenance of the independence of our auditors.
THE BOARD OF DIRECTORS PRE-APPROVAL POLICIES
As of December 31, 2017, the Company did not have a formal documented pre-approval policy for the fees of the principal accountant. The Company does not have an audit committee. The percentage of hours expended on the principal accountant's engagement to audit our financial statements for the most recent fiscal year that were attributed to work performed by persons other than the principal accountant's full-time, permanent employees was 0%.
The board approved all fees described above.
Item 15. Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules
Financial statement schedules have been omitted because they are not applicable or the required information is shown in the financial statements or notes thereto.
Item 16. Form 10-K Summary
Not applicable.
| 36 |
Exhibits
The following exhibits are filed herewith and this list is intended to constitute the exhibit index.
| 37 |
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| IWEB, Inc. | ||
| Date: March 20, 2018 | By: | /s/ Ratanaphon Wongnapachant |
| Ratanaphon Wongnapachant | ||
| Chief Executive Officer and Director |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, this Annual Report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| Signature | Title | Date | ||
| /s/ Ratanaphon Wongnapachant | Chief Executive Officer and Director | March 20, 2018 | ||
| Ratanaphon Wongnapachant | (Principal Executive Officer) | |||
| /s/ Wai Hok Fung | President and Director | March 20, 2018 | ||
| Wai Hok Fung | (Principal Executive Officer) | |||
| /s/ Cheng Kim Sing | Secretary, Treasurer, Chief Financial Officer | March 20, 2018 | ||
| Cheng Kim Sing | (Principal Financial Officer) | |||
| /s/ Bodin Kasemset | Director | March 20, 2018 | ||
| Bodin Kasemset |
| 38 |
