Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-32.1 - EX-32.1 - Ra Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | a2234137zex-32_1.htm |
| EX-31.2 - EX-31.2 - Ra Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | a2234137zex-31_2.htm |
| EX-31.1 - EX-31.1 - Ra Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | a2234137zex-31_1.htm |
| EX-23.1 - EX-23.1 - Ra Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | a2234137zex-23_1.htm |
Use these links to rapidly review the document
TABLE OF CONTENTS
INDEX TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
WASHINGTON, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
(Mark One) |
||
ý |
ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
|
For the Fiscal Year Ended December 31, 2017 |
||
Or |
||
o |
TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
|
For the transition period
from to
|
||
Commission File Number: 001-37926

RA PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
Delaware |
2834 (Primary Standard Industrial Classification Code Number) |
26-2908274 (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
87 Cambridge Park Drive
Cambridge, Massachusetts 02140
(Address of Principal Executive Offices) (Zip Code)
(Registrant's Telephone Number, Including Area Code): (617) 401-4060
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| Title of Each Class | Name of Each Exchange on which Registered | |
|---|---|---|
Common Stock, par value $0.001 per share |
The Nasdaq Global Market |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes o No ý
Indicate by check mark if the Registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes o No ý
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the Registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ý No o
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Website, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§ 232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the Registrant was required to submit and post such files.) Yes ý No o
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of the Registrant's knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. ý
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of "large accelerated filer," "accelerated filer," "smaller reporting company" and "emerging growth company" in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
Large accelerated filer o |
Accelerated filer ý | Non-accelerated filer o (Do not check if smaller reporting company) |
Smaller reporting company o | Emerging growth company ý |
If an emerging growth company, indicate by a check mark if the Registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ý
Indicate by a check mark whether the Registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes o No ý
The aggregate market value of the common stock held by non-affiliates of the Registrant was approximately $264.7 million based upon the closing price of the common stock as reported on the Nasdaq Global Select Market on June 30, 2017, the last business day of the Registrant's most recently completed second fiscal quarter. As of March 2, 2018, there were 32,286,684 shares of the Registrant's common stock outstanding, $0.001 par value.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Part III of this Annual Report on Form 10 K incorporates information by reference to portions of the definitive proxy statement for the Company's Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be held in 2018.
Ra Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Annual Report on Form 10-K for the Fiscal Year Ended December 31, 2017
2
NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This Annual Report on Form 10-K contains "forward-looking statements" within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the "Securities Act"), and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the "Exchange Act"). We have based these forward-looking statements largely on our current expectations and projections about future events and financial trends affecting the financial condition of our business. Forward-looking statements should not be read as a guarantee of future performance or results, and will not necessarily be accurate indications of the times at, or by, which such performance or results will be achieved. Forward-looking statements are based on information available at the time those statements are made and/or management's good faith belief as of that time with respect to future events, and are subject to risks and uncertainties that could cause actual performance or results to differ materially from those expressed in or suggested by the forward-looking statements.
Forward-looking statements include all statements that are not historical facts. In some cases, you can identify forward-looking statements by terms such as "may," "might," "will," "objective," "intend," "should," "could," "can," "would," "expect," "believe," "anticipate," "project," "target," "design," "estimate," "predict," "potential," "plan" or the negative of these terms, and similar expressions intended to identify forward-looking statements, and similar expressions and comparable terminology intended to identify forward -looking statements. These statements reflect our current views with respect to future events and are based on assumptions and subject to risks and uncertainties, including those set forth below in Item 1A, "Risk Factors" and elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Forward-looking statements include, but are not limited to, statements about:
- •
- the initiation, timing, progress and results of our research and development programs and future preclinical and clinical studies;
- •
- the risk that topline data from our Phase 2 clinical program in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria ("PNH") may not be indicative of
final study results or results from future trials;
- •
- our ability to advance any product candidates into, and successfully complete, clinical studies and obtain regulatory approval for them;
- •
- our ability to identify additional product candidates using our Extreme DiversityTM platform;
- •
- the timing or likelihood of regulatory filings and approvals;
- •
- the commercialization, marketing and manufacturing of our product candidates, if approved;
- •
- the pricing and reimbursement of our product candidates, if approved;
- •
- the rate and degree of market acceptance and clinical utility of any products for which we receive marketing approval;
- •
- the implementation of our strategic plans for our business, product candidates and technology;
- •
- the scope of protection we are able to establish and maintain for intellectual property rights covering our product candidates and technology;
- •
- our expectations related to the use of proceeds from our previous financing activities, and estimates of our expenses, future revenues, capital
requirements and our needs for additional financing;
- •
- our ability to maintain and establish collaborations;
- •
- our financial performance;
- •
- developments relating to our competitors and our industry, including the impact of government regulation; and
3
- •
- other risks and uncertainties, including those listed under the caption "Risk Factors."
Given these uncertainties, you should not place undue reliance on these forward-looking statements. These forward-looking statements represent our estimates and assumptions only as of the date of this Annual Report on Form 10-K and, except as required by law, we undertake no obligation to update or revise publicly any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise after the date of this Annual Report on Form 10 -K. We qualify all of our forward-looking statements by these cautionary statements.
All brand names or trademarks appearing in this report are the property of their respective holders. Unless the context requires otherwise, references in this report to the "Company," "we," "us," and "our" refer to Ra Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
4
Overview
We are a clinical-stage biopharmaceutical company using our proprietary peptide chemistry platform to develop novel therapeutics for the treatment of serious diseases that are caused by excessive or uncontrolled activation of the complement system, a critical component of the immune system. Inappropriate activation of the complement system can quickly turn it from a beneficial defense system to an aggressor that plays a major role in immune and inflammatory diseases. The complement system, which consists of approximately 30 interacting proteins, offers a target-rich opportunity for us to leverage our proprietary peptide chemistry platform, which was pioneered by Nobel Laureate Dr. Jack Szostak and allows us to inhibit certain uncontrolled complement pathway factors involved in complement-mediated diseases. Known as our Extreme Diversity platform, this proprietary macrocyclic peptide chemistry technology allows us to produce synthetic macrocyclic peptides that combine the diversity and specificity of antibodies with the pharmacological properties of small molecules. We believe this technology will allow us to pursue challenging targets for which only monoclonal antibodies have been developed.
We are developing our lead product candidate, RA101495 SC, a convenient self-administered subcutaneous ("SC") injection, which is an injection into the tissue under the skin, for the treatment of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria ("PNH"). PNH is a rare, chronic, life-threatening, blood disorder where red blood cells are mistakenly attacked and destroyed by the complement system and has an estimated worldwide population of 16,000 and treated population of 4,000 to 5,000. RA101495 SC is a potent synthetic macrocyclic peptide inhibitor of complement component 5 ("C5"). C5 plays a key role in the rupture and destruction of red blood cells, or hemolysis, associated with PNH. Inhibition of C5 is a clinically validated target for the control and suppression of complement-induced hemolysis in patients with PNH. In February 2018, we announced the completion of dosing and topline data for our global Phase 2 clinical program in PNH. In November 2016 and July 2017, the European Commission and the Food and Drug Administration ("FDA"), respectively, granted orphan drug designation to RA101495 SC for the treatment of PNH.
We are also developing RA101495 SC, to treat other debilitating complement-mediated diseases such as generalized myasthenia gravis ("gMG") with an estimated worldwide patient population and treated population of 94,000 and 47,000, respectively, atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome ("aHUS") with an estimated worldwide patient population and treated population of 5,500 and 2,000 to 3,000, respectively, and lupus nephritis ("LN"). We initiated a Phase 2 clinical trial with RA101495 SC for gMG in the fourth quarter of 2017 and a Phase 1b clinical trial supporting development in aHUS and LN in the first quarter of 2018.
Additionally, we are developing a portfolio of drug candidates designed to treat a variety of complement-mediated diseases, including rare blood, neurologic, ocular, renal and inflammatory diseases. We have discovery and preclinical programs targeting selective inhibition of certain complement factors, including Factor D for ocular and renal diseases, and an oral, small molecule C5 inhibitor and inhibitors of other complement factors for certain ocular, autoimmune and central nervous system ("CNS") diseases. In addition to our focus on developing novel therapeutics to treat complement-mediated diseases, we have validated our Extreme Diversity platform by successfully identifying and delivering orally-available cyclic peptides for a non-complement cardiovascular target with a large market opportunity in a collaboration with Merck & Co., Inc. ("Merck").
We were founded by Dr. Douglas A. Treco, an experienced rare disease drug developer and our chief executive officer and president, and by Dr. Jack Szostak, a pioneer in the field of mRNA display from the Massachusetts General Hospital, an affiliate of Harvard University, and Howard Hughes
5
Medical Institute. Dr. Szostak currently serves as the chairman of our scientific advisory board and a consultant to us. Our management team consists of drug discovery, development and commercialization experts with experience in translating scientific discoveries into innovative approved products for rare diseases, including Replagal for Fabry disease, Elaprase for Hunter syndrome, and Vpriv for Gaucher's disease, as well as Dynepo for chronic kidney disease, and immunology products, including Rituxan and Actemra.
Our Pipeline
The following table summarizes key information about our lead program and other pipeline programs. We hold worldwide commercialization rights to all of our product candidates, except for our non-complement cardiovascular target with a large market opportunity, which is subject to our collaboration with Merck.
Program
|
Indication(1) | Description | Status | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
RA101495 SC for C5 Inhibition |
PNH | Potential first-line therapy for eculizumab-naïve patients, and convenient alternative for transfusion-free patients switched from eculizumab and eculizumab inadequate responders | Completed Phase 2 first quarter of 2018; end-of-phase 2 meeting first half 2018; commence Phase 3 program second half of 2018 | |||
|
gMG | Phase 2 with gMG patients | Commenced Phase 2 fourth quarter of 2017(2) | |||
|
Renal: aHUS/LN | Phase 1b PK study supporting development in aHUS and LN patients | Commenced Phase 1b first quarter of 2018(2) | |||
Factor D Inhibition |
Orphan renal diseases DDD and C3GN | Preclinical program | Preclinical activities in process | |||
Oral C5 Inhibitor |
PNH, gMG, aHUS, LN and CNS Diseases | Preclinical program | Preclinical activities in process | |||
Other Complement Inhibitors |
Autoimmune/CNS Diseases | Preclinical program | Discovery activities in process | |||
Merck Collaboration(3) |
Non-complement cardiovascular target with large market opportunity | Collaboration agreement | Lead oral peptide class selected June 2016; Merck's preclinical activities in process |
- (1)
- In
the table above, we refer to various indications as follows: PNH: paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria; gMG: generalized myasthenia gravis; aHUS: atypical
hemolytic uremic syndrome; LN: lupus nephritis; DDD: dense deposit disease; C3GN: C3 glomerulonephritis; and CNS: central nervous system.
- (2)
- We intend to leverage our work in PNH, including the chemistry, manufacturing and controls ("CMC") and preclinical data packages, to advance our programs for RA101495 SC for gMG, aHUS and LN.
6
- (3)
- For additional information about our collaboration with Merck, see the section titled "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Conditions and Results of Operations—Financial Overview."
Our Strategy
Our goal is to become a leading biopharmaceutical company that transforms the lives of patients with serious complement-mediated diseases by combining our expertise in complement with our leadership in macrocyclic peptide technology. To achieve this goal, we are executing on the following strategy:
- •
- Advance our lead program, RA101495 SC, through clinical development for the treatment of PNH. Based on the topline results from our recently completed Phase 2 studies, which provided evidence supporting the dose required for near-complete complement inhibition in both eculizumab naïve and eculizumab switch patients who were transfusion-independent on eculizumab, we plan to hold end-of-Phase 2 meetings with regulators in the first half of 2018 and start our Phase 3 program for PNH in the second half of 2018. Our goal is to seek rapid approval of RA101495 SC for PNH and, if approved, leverage competitive pricing for RA101495 SC and patient convenience to expand patient access around the world.
- •
- Efficiently advance clinical development of RA101495 SC for other serious complement-mediated diseases,
such as gMG, aHUS and LN. We intend to leverage our work in PNH, including the CMC and preclinical data packages, to advance RA101495 SC for
other complement-mediated diseases, initially including gMG, aHUS and LN. There is strong mechanistic and clinical evidence for a beneficial effect of C5 inhibition in patients with gMG, an autoimmune
disease characterized by muscle weakness, and in aHUS and LN, autoimmune diseases characterized by kidney inflammation and failure. We have established relationships with key opinion leaders in these
fields and initiated a Phase 2 clinical trial with RA101495 SC for gMG in the fourth quarter of 2017 and a Phase 1b PK clinical trial in renally-impaired patients, supporting development
in aHUS and LN, in the first quarter of 2018.
- •
- If approved, commercialize RA101495 SC globally either independently or by collaborating selectively in
certain geographies. We have worldwide development and commercialization rights to RA101495 SC. We intend to independently pursue the approval
and commercialization of RA101495 SC in PNH patients in the United States ("U.S.") and Europe. Outside of the U.S. and Europe, we may pursue the approval and commercialization of RA101495 SC for PNH
patients either independently or in collaboration with others. We intend to develop and commercialize RA101495 SC for other indications independently or through collaborations with third parties.
- •
- Pursue clinical development of our pipeline programs targeting additional serious complement-mediated diseases with limited treatment options. In addition to developing RA101495 SC for PNH, gMG, aHUS and LN, we are also leveraging our structural knowledge of C5 to develop traditional, oral C5 inhibitors for follow on, next generation products to RA101495 SC and a
If developed and approved, we believe, due to its convenient product profile and our anticipated pricing flexibility, RA101495 SC has the potential to serve as the natural first-line therapy for newly diagnosed naïve patients with PNH, which we estimate to constitute approximately 10% of the patient population, as well as an attractive and convenient alternative for transfusion-free patients switching from eculizumab, which we estimate to constitute approximately 72% of the patient population. In sum, we believe we can address over 80% of the current PNH market. In developing its commercial presentation, we intend to leverage key properties of RA101495 SC, including its stability at room temperature, small volume, as well as its low viscosity, resistance to shear forces, and compatibility with fine-gauge needles.
7
- •
- Enhance our leadership position in the field of macrocyclic peptide technology through continued development of our Extreme Diversity platform. We have validated our Extreme Diversity platform by successfully identifying and delivering orally-available cyclic peptides for a non-complement cardiovascular target with a large market opportunity in a collaboration with Merck. We intend to enhance our proprietary drug discovery capabilities by expanding the chemical diversity of our peptide libraries to identify molecules with more favorable drug-like properties. We are also using our novel macrocyclic peptides to guide the development of next-generation, orally-available small molecule drugs that bind to and inhibit targets in similar ways as the original peptides.
broader spectrum of diseases of complement dysfunction such as diabetes, autoimmune diseases and neurodegeneration. Other programs in our complement pipeline include Factor D administered SC for orphan renal diseases, DDD and C3GN, and other complement inhibitors for certain autoimmune and CNS diseases.
The Complement System
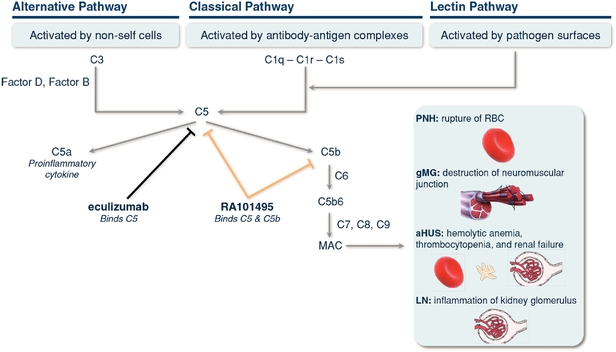
The complement system is a critical component of the immune system. The immune system protects the body by recognizing and removing bacteria, viruses and other infectious agents, collectively referred to as pathogens. The complement system consists of approximately 30 interacting proteins that are produced primarily by the liver and circulate in the blood and through the body's tissues. Activation of the complement system leads to a series of enzyme reactions that produce factors that both directly kill pathogens and recruit immune cells to sites of infection. The complement system is activated in three distinct pathways, referred to as the classical pathway, the lectin pathway and the alternative pathway. Each pathway is activated by different triggers associated with the presence of an abnormal cell or pathogen. Irrespective of the activation event, these pathways converge on C5, triggering a series of enzyme reactions that leads to the formation of a pore in the target cell, which is known as the membrane attack complex ("MAC"). In its physiological role, this is an extremely potent agent causing the rupture and destruction of bacterial cell walls.
Normally the complement system is tightly regulated to restrict activation to the site of infection and avoid injury to host tissues, or "self" cell surfaces. Under conditions of excessive or uncontrolled activation, the complement system plays a key role in a range of debilitating autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. In these conditions, the complement system causes damage:
- •
- directly through the inappropriate formation of the MAC and destruction of healthy tissue or by the activation of detrimental pathways within
cells;
- •
- indirectly by signaling other elements of the immune system to attack healthy tissues; or
- •
- passively through deposition of complement factors in tissues.
The following Figure 1 depicts the key elements, proteins and factors within the complement system cascade. Many of these proteins are abbreviated with a "C" followed by a number. For example, C5 denotes complement component 5. Others are called "Factor" followed by a letter, such as Factor B. As depicted in Figure 1 below, irrespective of the activation event, these pathways converge on C5, triggering a series of enzyme reactions that lead to the cleavage of C5 into C5a and C5b. C5b then binds to C6, C7, C8 and C9 to form a MAC.
8
Figure 1. Schematic Diagram of the Complement System Cascade.
Our Approach
There are numerous potential therapeutic targets in the complement cascade, and inhibiting the cascade at different points may be beneficial to treat different conditions depending on the disease biology. Inhibition of C5 cleavage effectively blocks generation of C5a and MAC regardless of the specific pathway involved in complement activation. This approach of inhibiting C5 cleavage is most relevant to diseases with significant MAC deposition resulting in tissue injury, as is the case for PNH, gMG, aHUS and LN. In other conditions, the tissue injury is related to activation of a specific pathway of complement, such as kidney diseases like C3 glomerulopathies, in which tissue injury may be mediated by deposition of complement component C3 following uncontrolled activation of the alternative pathway. In this case, selective inhibition of the alternative pathway by targeting a key enzyme in the alternative pathway, Factor D, may block C3 deposition while preserving the capacity of the classical and lectin pathways of complement to continue to fight infection. The classical pathway is activated when an antibody binds to the surface of a pathogen, and recruits a complex of C1q, C1r, and C1s, and we believe that inhibition of C1 may be efficacious for treatment of certain autoimmune and CNS diseases.
Our pipeline of product candidates was discovered using our Extreme Diversity platform, a proprietary macrocyclic peptide chemistry technology pioneered by Nobel Laureate Dr. Jack Szostak. Our platform allows us to produce synthetic macrocyclic peptides that combine the diversity and specificity of antibodies with the pharmacological properties of small molecules. This platform allows us to generate highly specific and stable cyclic peptides that are much smaller than monoclonal antibodies and other biologics. Traditional peptides have been difficult to develop into drugs due to their susceptibility to degradation, limiting their circulating half-life, and lack of structural rigidity, limiting their potency and specificity. We have developed our Extreme Diversity platform to efficiently discover synthetic macrocyclic peptides that have greater structural rigidity and are less prone to degradation. We believe our synthetic macrocyclic peptides will be deliverable through more convenient routes of administration than monoclonal antibodies due to much greater bioavailability.
9
The complement system offers a number of particularly attractive targets where we can apply our platform technology to disrupt protein-protein interactions or produce highly specific enzyme inhibitors. We are initially developing a portfolio of drug candidates to treat a variety of complement-mediated diseases, including rare blood, neurologic, ocular, renal and inflammatory diseases.
Our Programs
Our lead product candidate, RA101495 SC, is a potent synthetic macrocyclic peptide inhibitor of C5 formulated for daily SC administration that we are initially developing for the treatment of PNH. We initiated our Phase 2 clinical program for RA101495 SC in PNH patients in the second quarter of 2017, completed dosing and announced our topline data in February 2018 and expect to have our end-of-Phase 2 meeting with various regulators in the first half of 2018.In addition to developing RA101495 SC for PNH, we are also developing RA101495 SC to treat other serious complement-mediated diseases such as gMG, aHUS and LN. We initiated a Phase 2 clinical trial with RA101495 SC for gMG in the fourth quarter of 2017 and a Phase 1b clinical trial in patients with renal impairment, supporting development in aHUS and LN, in the first quarter of 2018. We expect topline data from our gMG trial in the first half of 2019 and data from our renal impairment study in the second half of 2018. In addition to RA101495 SC and our collaboration with Merck, we have discovery and preclinical programs targeting selective inhibition of other complement factors, including Factor D administered SC for DDD and C3GN, an oral, small molecule C5 inhibitor, and other complement inhibitors for certain autoimmune and CNS diseases.
RA101495 SC for Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria
Background
PNH is a rare, chronic, debilitating, acquired blood disorder that is most frequently diagnosed in early adulthood and usually continues throughout the life of the patient. Some of the prominent symptoms of PNH include severe anemia, a condition that results from having too few healthy red blood cells, severe abdominal pain, severe headaches, back pain, excessive weakness and fatigue. If not treated, PNH results in the death of approximately 35% of affected individuals within five years of diagnosis, and 50% of affected individuals within 10 years of diagnosis, primarily due to the formation of life-threatening blood clots inside the blood vessels, or thrombosis. We estimate that there are approximately 16,000 PNH patients worldwide. Eculizumab, the only drug currently approved to treat PNH, had reported worldwide sales of approximately $3.1 billion in 2017 for its two approved indications. A third-party study estimated that, as of 2015, the cost per year for treatment with eculizumab was approximately $543,000 in adults.
Certain PNH patients acquire a genetic mutation that prevents the normal attachment of complement regulatory proteins to the membranes of blood cells. On normal cells, these proteins are critical inhibitors of complement activity and provide one means of distinguishing host cells from invading pathogens. The absence of these proteins results in the accumulation of a complement protein called C3b, which leads to cleavage of C5 and the deposition of the MAC on essentially all blood cells, including red blood cells and platelets. Red blood cells are particularly susceptible to lysis by MAC, resulting in their destruction and release of hemoglobin, leading to anemia. Uncontrolled activation of complement on platelets can promote thrombosis which is the most common cause of death in PNH patients. Other serious and potentially life-threatening complications of PNH include high blood pressure in the lungs and damage to the kidneys.
Current Therapies and Their Limitations
The only approved disease-modifying therapy is eculizumab, marketed under the name Soliris by Alexion Pharmaceuticals. Eculizumab is a monoclonal antibody that binds C5 and prevents its cleavage
10
to C5a and C5b, thus blocking a key step in the complement activation pathway. Eculizumab prevents hemolysis, reduces the risk of thrombosis, and reduces the overall mortality rate in PNH patients to less than 3% over three years. Eculizumab is administered intravenously by healthcare professionals at biweekly intervals. Treatment duration is indefinite as the management of PNH requires ongoing chronic treatment. While eculizumab has demonstrated that inhibition of C5 cleavage results in improved clinical outcomes, breakthrough hemolysis has been observed to occur in a subset of patients in the last few days of each bi-monthly eculizumab treatment period. Such breakthrough hemolysis episodes are associated with worsening anemia and other symptoms of PNH. Furthermore, the recommended dosing regimen of eculizumab for PNH is 600 mg weekly for four weeks, followed by 900 mg on week five and 900 mg every two weeks thereafter. However, to address breakthrough hemolysis, a proportion of patients require higher off-label doses or more frequent dosing, leading to higher costs or further inconvenience.
Potential Benefits of Our Approach
RA101495 SC is a potent synthetic macrocyclic peptide inhibitor of C5, which is a clinically validated target for patients with PNH. We are developing RA101495 SC as a convenient, self-administered product that can be administered in a small daily, or less frequent, such as weekly, dose. We believe this approach will facilitate sustained hemolysis suppression, greatly reducing the possibility of breakthrough hemolysis in eculizumab naïve and eculizumab switch patients who were transfusion-independent on eculizumab. In addition, we believe self-administration will alleviate the significant time and cost burden associated with regular intravenous infusions by healthcare professionals, as well as reduce complications associated with IV infusions, including infections, thrombosis, and loss of venous access.
RA101495 SC is designed to bind C5 and block generation of C5a, C5b and MAC, potentially reducing hemolysis in humans to similar levels as eculizumab and allowing physicians to treat PNH with the same therapeutic rationale as the approved monoclonal antibody. Also, RA101495 SC binds to a site on C5 that is distinct from that of eculizumab, potentially conferring additional benefits, including the treatment of patients with R885H/C mutations, a population of PNH patients that does not respond to eculizumab. Importantly, RA101495 SC also blocks interaction of C5b with C6 and the formation of the MAC. For more information, see the figure in the section titled "The Complement System." We believe this feature of directly blocking MAC assembly would be a differentiating property of RA101495 SC that may be beneficial to patients in hypercoagulative and inflammatory states, such as infection, sepsis and trauma.
In addition, RA101495 SC is a synthetic product, and we expect that it can be produced at commercial scale at lower cost than biologics and monoclonal antibodies. As a synthetic, non-biologic product, RA101495 SC has essentially no risk for contamination by viruses and animal cell products.
Clinical Development
We have completed a Phase 1 clinical trial of RA101495 SC in healthy volunteers in Australia. We initiated our Phase 2 clinical program in PNH patients in the second quarter of 2017, completed dosing and announced our topline data in February 2018 and expect to have our end-of-Phase 2 meeting with various regulators in the first half of 2018.
Phase 2 Clinical Program
The global Phase 2 program was designed to evaluate the safety, tolerability, efficacy, PK, and PD of RA101495 SC in patients with PNH. The program consisted of two open-label Phase 2 trials, one
11
conducted in the U.S., and one conducted outside the U.S. In these trials, we enrolled three distinct populations of PNH patients based on their treatment history:
- •
- eculizumab naïve patients, meaning patients who have never received eculizumab (Ex-U.S. Protocol).
- •
- eculizumab switch patients, meaning patients who are currently treated with eculizumab (Ex-U.S. Protocol).
- •
- eculizumab inadequate responders, meaning patients who are currently treated with eculizumab but have inadequate response.
All patients enrolled in the Phase 2 studies received a single, 0.3 mg/kg SC loading dose of RA101495 SC, followed by 0.1 mg/kg SC daily thereafter. Following two weeks of treatment and based on a review of safety and efficacy data, patients continued with 0.1 mg/kg daily or, if needed, the dose was increased to 0.3 mg/kg daily to achieve adequate control of hemolysis. Patients in all three cohorts were eligible for a long-term extension study following the completion of the initial 12-week studies. The primary efficacy endpoint is change in lactate dehydrogenase ("LDH") from baseline.
On February 12, 2018, we announced the completion of dosing and topline data for our global Phase 2 clinical program in PNH.
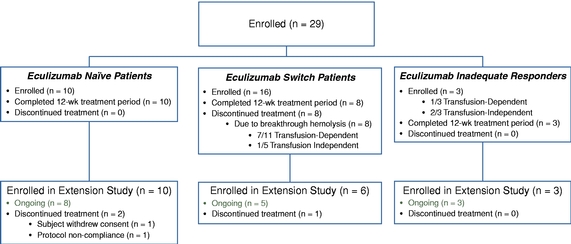
We enrolled a total of 29 patients across three cohorts in the Phase 2 clinical program in PNH. The first cohort enrolled 10 patients who had not previously been treated with eculizumab. We refer to these patients as eculizumab naïve patients. The second cohort enrolled 16 patients, who, prior to the trial were treated with an eculizumab regimen and, in connection with the trial, were switched over to treatment with RA101495 SC. We refer to these patients as eculizumab switch patients. The third cohort enrolled three patients. These patients are U.S.-based and were inadequate responders to eculizumab and who were also switching over to RA101495 SC. We refer to these patients as eculizumab inadequate responders.
The primary efficacy endpoint was the change in LDH levels, from baseline to the mean level from week 6 to week 12 of the trial. Patients in all three cohorts were eligible to enter a long-term extension study following the completion of the initial 12-week dosing period.
The Figure 2 below summarizes, with respect to all three cohorts in our global Phase 2 clinical program in PNH, the patient enrollment, disposition, and continuation in the long-term extension study following the completion of the initial 12-week dosing period.
Figure 2. Phase 2 Patient Disposition
12
A total of 21 patients across all three cohorts completed the initial 12-week dosing period of whom 16 (or 76%) continue to receive treatment with RA101495 SC in our long-term extension study: 8 eculizumab naïve patients, 5 eculizumab switch patients, and all 3 eculizumab inadequate responders.
The data cut-off date for the December 4, 2017 interim results was November 30, 2017 and the data cut-off date for the topline data published on February 12, 2018 was February 7, 2018.
Eculizumab Naïve Cohort
On December 4, 2017, we announced that all 10 patients enrolled in the eculizumab naïve cohort had completed dosing and that RA101495 SC met the primary endpoint in these eculizumab naïve patients (n=10). As previously noted, we observed a rapid, robust, and sustained reduction in LDH levels compared to baseline (p=0.002) and near complete suppression of complement activity, as depicted in the right panel in Figure 3 below. The study population enrolled in this cohort is typical of patients referred for initiation of C5 inhibitor therapy in real-world clinical practice. The mean baseline LDH level was greater than 1000 U/L, with a range up to 2435 U/L, and the median granulocyte clone size was 87.7%, indicative of severe disease. As shown in the left panel of Figure 3 below, RA101496 SC administration resulted in a rapid, sustained, and near-complete inhibition of hemolysis activity in patients' sera.
Figure 3. Complement Inhibition (left) and LDH Reduction (right).
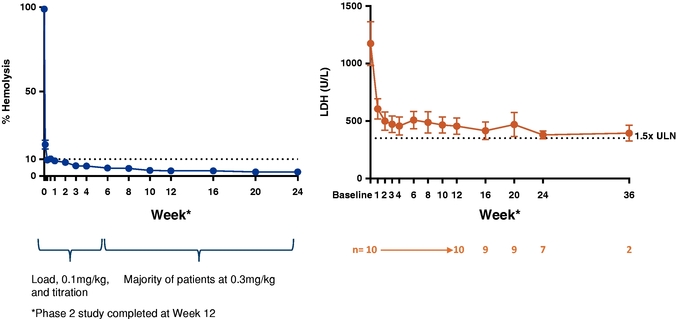
Data presented based on data cut-off of February 7, 2018
Of note, six out of the ten eculizumab naïve patients were transfusion dependent prior to initiation of RA101495 SC. As depicted in Figure 4 below, 50% (3/6) of eculizumab naïve patients who required a blood transfusion during the six months prior to enrollment, who we refer to as transfusion-dependent patients remained transfusion-free while on study.
13
Figure 4. Transfusion Dependence on RA101495 SC.
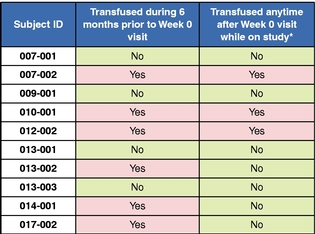
Data presented based on data cut-off of February 7, 2018
Based on topline data, meaningful improvements in standard measures of quality of life, as shown by the Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy ("FACIT") fatigue score, were observed, as well as a high level of patient satisfaction with SC self-administration based on patient surveys. By the end of the 12-week treatment period with RA101495 SC, the mean FACIT score increased by 5.9 points, consistent in both direction and magnitude with the eculizumab experience from TRIUMPH study, and which we believe is illustrative of how similar improvements in hemolytic markers such as LDH may translate to clinical benefits in quality of life.
Additionally, at the end of the 12-week treatment period with RA101495 SC, we conducted a brief survey to evaluate patients' degree of treatment satisfaction with once daily SC self-administration on a simple 5-point scale. The mean treatment satisfaction score for the cohort was 4.3 points, falling between the responses of "satisfied" and "very satisfied."
On December 4, 2017, we summarized two case studies from the treatment naïve cohort, which we believe further illustrate the pharmacologic activity of RA101495 SC. In case study one (as depicted in the left Figure 5 below), with data available through the cutoff date of February 7, 2018, RA101495 SC controlled LDH in the patient with the very highest baseline LDH levels in the study (2435U/L), a level consistent with that seen in patients enrolled in the TRIUMPH trial of eculizumab. Treatment with RA101495 SC in this patient resulted in an 88% reduction in LDH from baseline to week 12, and continued through the extension study to week 24. We believe these results support that RA101495 SC has the potential to control LDH even in PNH patients with the highest levels of hemolytic activity, and indicate that the LDH level achieved on treatment is not governed by the baseline LDH, but by the adequacy of complement inhibition achieved.
In case study two (as depicted in the right Figure 5 below), the long-term follow-up is provided for one of the two patients presented in our initial data release from June 2017 (and December 2017). This patient had a transient breakthrough hemolysis event at week six that was attributed to an inter-current viral infection. Treatment with RA101495 SC was continued at the same dose, and LDH levels normalized rapidly at that time. With continued long-term treatment, LDH has remained well-controlled, and there have been no further recurrences of breakthrough hemolysis during the following 7.5 months of treatment.
14
Figure 5. Case Studies from Eculizumab Naïve Cohort
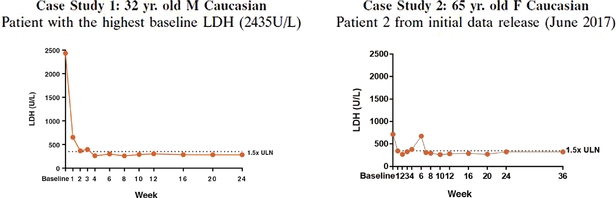
Data presented based on data cut-off of February 7, 2018
As of February 7, 2018, eight of 10 eculizumab naïve patients continue on the long-term extension study, with the two initial eculizumab naïve patients dosing out to 36 weeks with sustained LDH control with no significant safety or tolerability issues observed.
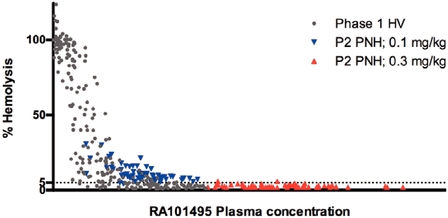
The Phase 2 study provided evidence supporting the dose required for near-complete complement inhibition. Whereas the 0.1 mg/kg dose of RA101495 SC administered in the Phase 2 study in PNH resulted in sub-maximal inhibition of hemolysis (<95% at trough), the 0.3 mg/kg dose of RA101495 SC resulted in near-complete inhibition of hemolysis (³ 95% at trough at all timepoints). We believe these data supports the selection of 0.3 mg/kg RA101495 SC daily as the recommended dose for our planned Phase 3 studies in PNH.
Figure 6. PK/PD Relationship for RA101495 SC Based on Phase 1 (HV) and Phase 2 (PNH, Naïve) Data.
Eculizumab Switch Cohort
In the eculizumab switch cohort, which enrolled 16 patients, 5 patients were transfusion-independent at baseline (before switching to RA101495 SC) and 11 were transfusion-dependent at baseline. Topline results from the completed switch cohort provide initial evidence of near complete, sustained, and uninterrupted inhibition of complement activity during and after eculizumab washout. As depicted in Figure 7 below, the LDH response observed to date in switch patients was bimodal based on prior transfusion requirements on eculizumab. In transfusion-independent patients from this cohort (n=5), a population segment representing the majority of patients currently treated with eculizumab
15
(approximately 80% of patients on long-term eculizumab therapy), switching to RA101495 SC has resulted in overall stable mean LDH levels with only one patient (1/5) withdrawing early due to breakthrough hemolysis and reverting to eculizumab without complications. Among patients who were transfusion-dependent at baseline (n=11), breakthrough hemolysis occurred after switching in seven patients (7/11), who all reverted to eculizumab treatment without complications. Of note, our Phase 2 clinical trial of RA101495 SC enrolled a disproportionately larger percentage of transfusion-dependent PNH patients compared to estimates of the percentage of transfusion-dependent PNH patients on long-term eculizumab therapy in the real world. Persistent transfusion-dependence, which occurs in up to 20 percent of the eculizumab-treated population, is most commonly attributable to extravascular hemolysis driven by intense C3 deposition on erythrocytes. This condition, a unique complication of long-term eculizumab therapy in certain PNH patients, may not be adequately addressed by inhibition at the level of C5, and published data suggest that targeting complement upstream of C5 (e.g. Factor D or C3) may have greater utility in this small subset of PNH patients.
Figure 7. Mean LDH Values in Switch Cohort.
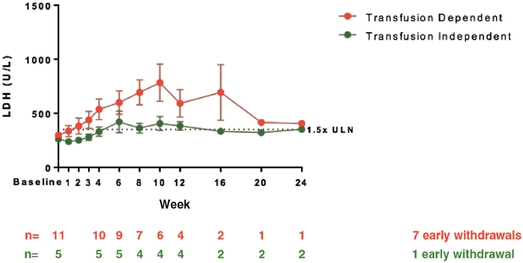
Data presented based on data cut-off of February 7, 2018
On December 4, 2017 (as depicted in Figure 8 below), we summarized a case study of a 28-year old male who had been on eculizumab for seven years and was transfusion-independent at the time of enrollment. His last dose of eculizumab was two weeks prior to the baseline visit. After switching to RA101495 SC, LDH has remained well-controlled through 24 weeks of administration, and the patient continues to receive study drug in the long-term extension.
16
Figure 8. Case Study: Successful Switching from Eculizumab to RA101495 SC.
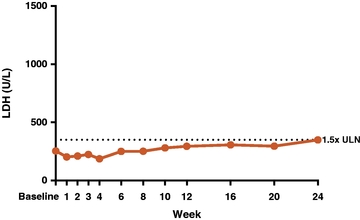
Data presented based on data cut-off of February 7, 2018
As of February 7, 2018, five of the eight patients in the eculizumab switch cohort who completed dosing are continuing on the long-term extension study with sustained LDH control, and no major safety or tolerability issues observed.
Eculizumab Inadequate Responder Cohort
In the U.S.-based cohort of inadequate responders to eculizumab who have a history of elevated LDH, three patients were enrolled, consisting of two patients that were transfusion-independent at baseline and one patient that was transfusion-dependent at baseline. As of February 7, 2018, all three patients have completed 12 weeks of dosing and all three inadequate responders to eculizumab continue on the long-term extension study with sustained LDH control with no major safety or tolerability issues observed.
Topline results from the first patient in this cohort show LDH stabilization and relief of side effects associated with eculizumab intolerance, as depicted in Figure 9 below. The patient is a 53-year old male with modestly elevated LDH and documented intolerance to eculizumab characterized by fatigue and whole-body pain after each infusion. As a result of eculizumab-intolerance he was only able to receive 450 mg of eculizumab every two weeks, lower than the standard dose of 900 mg. As depicted in Figure 9 below, following switching from eculizumab to RA101495 SC, LDH improved and remained consistently below 1.5xULN, while at the same time the symptoms related to eculizumab-intolerance have resolved and the patient has been able to down-titrate pain medications.
17
Figure 9. Case Study: First Inadequate Responder (U.S.).
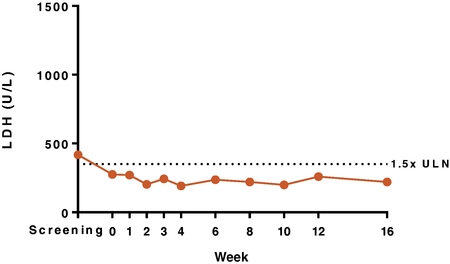
Data presented based on data cut-off of February 7, 2018
As depicted in Figure 10 below, across transfusion-independent patients switching from eculizumab to RA101495 SC (n=7), pooled from both the switch cohort and the U.S.-based inadequate responder cohort, mean LDH and hemoglobin levels have remained stable from baseline through the cut-off date of February 7, 2018 for those patients remaining on study. One patient out of these seven withdrew from the study early and reverted to eculizumab due to breakthrough hemolysis.
Figure 10. Stabilization of LDH and Hemoglobin in Transfusion-Independent Patients after Switching from Eculizumab to RA101495 SC in Switch and Inadequate Responder Cohorts—Pooled Data.
SC
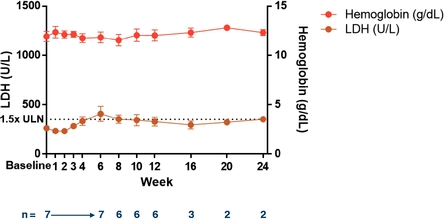
Data presented based on data cut-off of February 7, 2018
Across all cohorts, no major safety or tolerability concerns have been identified as of February 7, 2018 after more than 500 patient weeks of cumulative exposure. The majority of adverse events were deemed unrelated to the study drug and the most frequent study drug-related adverse event to date was headache. No meningococcal infections or thromboembolic events have been observed. Out of more than 3,500 doses administered to date, only nine mild (grade 1) injection site reactions have occurred in five patients. As of February 7, 2018, full compliance with once daily SC self-administration of RA101495 SC has been observed.
18
Based on the topline results of the Phase 2 studies, we are planning to conduct a Phase 3 program to support the approval of RA101495 SC in PNH. Both treatment naïve and switch patients who were transfusion-independent on eculizumab were generally well-controlled on RA101495 SC, and both of these populations are planned for inclusion in our Phase 3 program.
Our goal is to seek rapid approval of RA101495 SC for PNH and, if approved, leverage convenience and competitive pricing for RA101495 SC to expand patient access around the world and establish RA101495 SC as first-line therapy in PNH. We plan to hold end-of-Phase 2 meetings with regulators in the first half of 2018 and start our Phase 3 program for PNH in the second half of 2018. If developed and approved, we believe, due to its convenient product profile and our anticipated pricing flexibility, RA101495 SC has the potential to serve as the natural first-line therapy for newly diagnosed naïve patients with PNH, which we estimate to constitute approximately 10% of the patient population, as well as an attractive and convenient alternative for transfusion-free patients switching from eculizumab, which we estimate to constitute approximately 72% of the patient population. In sum, we believe we can address over 80% of the current PNH market. We believe the majority of patients with PNH have yet to initiate treatment. In developing its commercial presentation, we intend to leverage key properties of RA101495 SC, including its stability at room temperature, small volume, as well as low viscosity, resistance to shear forces and compatibility with fine-gauge needles.
Phase 1 Clinical Trial in Healthy Volunteers
In the second quarter of 2016, we completed a Phase 1 randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled clinical trial of RA101495 SC in healthy volunteers. The Phase 1 study was designed to assess the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics ("PK") (the activity of a drug after it enters the body of the patient), and pharmacodynamics ("PD") (the effect of a drug on the target of interest and the patient), of RA101495 SC following single- and multiple-dose SC administration. In the Phase 1 trial, PK assessment focused on the concentration of drug in the plasma, and PD assessment focused on the suppression of hemolysis and complement activity. The results from this trial were presented at the European Hematology Association meeting on June 10, 2016.
Results from the Phase 1 Trial
In healthy volunteers, we observed the following in subjects treated with RA101495 SC, as compared to placebo:
- •
- highly predictable, dose dependent PK after single and multiple dose SC injections;
- •
- maintenance of robust ex vivo hemolysis suppression and complement inhibition with daily SC dosing;
- •
- near-complete suppression of ex vivo hemolysis and complement activity after a single SC dose; and
- •
- an acceptable safety and tolerability profile with no serious adverse events reported.
Preclinical Studies
We have completed numerous preclinical studies with RA101495 SC in laboratory animals and in vitro experiments. RA101495 SC is designed to be a potent inhibitor of primate complement and a poor inhibitor in most other species, therefore in vivo evaluation of PK and PD was conducted in cynomolgus monkeys. Preclinical data demonstrate the strong correlation between plasma levels of drug and inhibition of complement activity in cynomolgus monkeys. These data show that plasma concentrations greater than or equal to 2.5 µg/ml are sufficient to inhibit greater than 90% of complement activity in cynomolgus monkey.
19
Preclinical data are representative of multiple studies conducted in cynomolgus monkeys and show plasma levels of RA101495 SC and complement activity as measured by hemolysis of antibody sensitized sheep red blood cells following seven daily SC doses of 0.21 mg/kg and for 11 days following the last dose.
We have evaluated the effects of RA101495 SC in a combination of efficacy and standard in vitro and in vivo toxicology assays to identify what we believe to be the appropriate first-in-human dose and dose-limiting toxicity for RA101495 SC.
RA101495 SC for Generalized Myasthenia Gravis
Background
Myasthenia gravis ("MG") is a chronic, autoimmune, neuromuscular disease characterized by weakness and fatigue of voluntary muscles.
Patients with MG present with muscle weakness that becomes increasingly severe with repeated use and recovers with rest. Weakness can be localized to specific muscles, such as those responsible for eye movements, but often progresses to affect a broader range, including head, limb, and respiratory muscles. This progression is often described as the generalized, or severe, form of the disease. gMG is estimated to affect over 80,000 individuals worldwide.
gMG symptoms may become life-threatening when muscle weakness involves the diaphragm and intercostal muscles in the chest wall that are responsible for breathing. The most severe complication of gMG, known as myasthenic crisis, requires hospitalization, intubation, and mechanical ventilation.
MG is characterized by the production of autoantibodies that interfere with the normal transmission of electrical signals from nerves to muscles. The most common target of autoantibodies in MG is the acetylcholine receptor ("AChR"), which is located at the site at which a motor neuron transmits signals to a skeletal muscle fiber, known as the neuromuscular junction. Binding of anti-AChR autoantibodies to the AChR results in activation of the classical complement cascade and assembly of the membrane attack complex ("MAC"). Influx of calcium through the MAC causes local damage to the postsynaptic membrane, local inflammation, diminished response to acetylcholine, and reduced responsiveness of the muscle.
Inhibition of terminal complement activity at the level of C5 or C6 has been demonstrated to prevent development of disease pathology in experimental animal models of MG. RA101495 SC potently inhibits C5. Furthermore, eculizumab, a humanized monoclonal inhibitor of C5, was recently approved to treat MG patients.
Current Therapies and Their Limitations
Current therapies focus on either boosting the AchR signal or suppressing the immune response, and none of these treatments targets the injury to the post-synaptic muscle endplate caused by complement attack. First-line therapy for mild symptomatic rMG is with inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase, the enzyme that breaks down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, such as pyridostigmine bromide, marketed as Mestinon by Valeant Pharmaceuticals. If remission is not achieved with acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, a course of systemic immunosuppressive therapy may be initiated. These agents have inconsistent evidence of efficacy, and all have long-term toxicities. They include corticosteroids, azathioprine, mycophenylate mofetil, and rituximab. Surgical removal of the thymus is sometimes performed in patients with moderate to severe rMG to try to switch off the production of autoantibodies. Intravenous immunoglobulin and plasma exchange may be needed in patients with myasthenic crisis.
20
MG is currently treated with cholinesterase inhibitors and non-specific immunosuppressive agents, including azathioprine, cyclophosphamide, cyclosporine, intravenous immunoglobulin ("IVIG") mycophenolate, prednisone, and tacrolimus. Alexion Pharmaceuticals recently announced approval of eculizumab for the treatment of refractory MG in Europe and gMG in the U.S.
Potential Benefits of Our Approach
We believe that inhibiting terminal complement activity with our C5 inhibitor RA101495 SC may block complement-mediated damage to the motor endplate thereby preserving responsiveness to signaling and potentially preventing muscle weakness. Following promising clinical data collected to date from which we observed the favorable PK and PD profile for RA101495 SC, we believe the convenience of once-daily, SC, self-administration of RA101495 SC may enable treatment of a broad population of gMG patients.
Clinical Development Plan
We plan to leverage our work in PNH to efficiently advance clinical development of RA101495 SC for gMG. In December 2017, we initiated dosing in our Phase 2, dose-finding, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, which is designed to evaluate the safety, tolerability, and preliminary efficacy of RA101495 SC in patients with gMG. The trial is expected to enroll approximately 36 patients. At the outset of the 12-week treatment period, patients will be randomized in a 1:1:1 ratio to receive daily SC doses of 0.1 mg/kg of RA101495 SC, 0.3 mg/kg of RA101495 SC, or matching placebo. The primary efficacy endpoint is change in Quantitative Myasthenia Gravis ("QMG") score from baseline to week 12. All patients will have the opportunity to receive RA101495 SC in a long-term extension study. We expect topline data from this trial in the first half of 2019.
RA101495 SC for Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome
Background
aHUS is a rare disease driven by uncontrolled activity of the alternative pathway of complement characterized by blood clot formation in small vessels, destruction of red blood cells (hemolysis) leading to anemia, and acute kidney injury. The atypical form of HUS occurs in the absence of infection with Shiga toxin producing strains of E. Coli or Streptococcus pneumoniae, which are common in cases of "typical" HUS. aHUS comprises <10% of cases of hemolytic uremic syndrome. The prognosis of aHUS is poor with ~50% of patients progressing to end stage renal disease within 5 years of diagnosis. Approximately 40% of aHUS can be linked to mutations in genes encoding complement proteins such as Factor H, Factor I, CD46, C3 and Factor B. These mutations cause dysregulation of the alternative pathway of complement and generation of C5a and MAC deposition on endothelial cells, leading to cell injury. The estimated annual incidence of aHUS is approximately 2 per million.
Current Treatments and Limitations
Eculizumab (Soliris, Alexion), a monoclonal antibody targeting C5, is currently the only FDA-approved therapy for aHUS. Eculizumab therapy is administered via intravenous infusion by a healthcare professional every other week. Eculizumab binds circulating C5 and prevents cleavage by C5 convertases, thereby blocking formation of C5a and assembly of MAC. Patients on eculizumab therapy experience substantial reduction in thrombosis and improved kidney function, providing clinical validation for inhibition of C5 in this disease, although the response was more pronounced in patients with shorter duration of disease prior to initiation of eculizumab treatment.
21
Potential Benefits of Our Approach
We believe that because RA101495 SC binds C5 and inhibits generation of C5a and MAC, it will be effective in preventing clot formation, anemia, and kidney disease in aHUS. Finally, we believe that daily SC administration of RA101495 SC may provide improved disease control and improved patient quality of life over biweekly intravenous infusion.
Clinical Development Plan
In January 2018, we initiated dosing in our Phase 1b clinical trial in patients with renal impairment, supporting development of RA101495 SC in complement-mediated renal diseases, such as aHUS and LN. Our Phase 1b, multi-center, open-label trial is designed to evaluate the PK profile of RA101495 SC in these patients. The trial is planned to enroll approximately 16 subjects, including eight patients with severe renal impairment matched with eight healthy control subjects with normal renal function. Each patient will receive a single SC dose of 0.3 mg/kg of RA101495 SC. The trial will compare the PK profile in patients with renal impairment with subjects with normal renal function. We expect topline data in our renal impairment study in mid-2018, enabling the initiation of a follow-on study in aHUS in the second half of 2018.
RA101495 SC for Lupus Nephritis
Background
Systemic lupus erythematosus ("SLE") is a serious, potentially lethal autoimmune disorder characterized by multi-organ involvement and a chronic relapsing clinical course. LN refers to the specific involvement of the kidney that is seen in approximately 20% of SLE patients. It is estimated that approximately 63,000 individuals in the U.S. have LN. Although LN is a chronic disease, its course is characterized by intermittent periods of acute kidney inflammation and high disease activity, which are known as nephritic flares. The cumulative impact of these flares over time can cause irreversible damage to the kidneys. Although immunosuppressive therapy has improved prognosis for patients with LN, approximately 10% to 15% of these patients will develop end-stage renal disease, requiring a kidney transplant or initiation of dialysis. As such, LN is associated with an approximately six-fold increase in the rate of mortality compared with the general population.
The pathophysiology of LN involves the inappropriate production of autoantibodies which recognize self or "host" antigens, such as double-stranded DNA. The deposition of autoantibody-antigen complexes in the kidney activates the classical pathway of complement, resulting in generation of C5a, deposition of MAC, and subsequent tissue injury. Levels of the circulating complement components C3 and C4 are depleted in patients during LN flares, due to accelerated consumption of classical complement pathway proteins. Deposition of MAC has been observed in kidney biopsy samples from patients with LN. In a recent case report, MAC deposition, as measured by the presence of C9 in kidney tissue, was significantly reduced following treatment with eculizumab, and was accompanied by corresponding improvement in kidney function and clinical status. There have been several other case reports of improved kidney function in LN patients treated with eculizumab, suggesting that inhibition of C5 may be disease modifying. Additionally, inhibition of C5a activity has been shown to improve renal function and histopathological features associated with LN in animal models of the disease.
Current Treatments and Limitations
Treatment of LN flares varies according to disease severity and the type of lesions seen on kidney biopsy. Generally, inhibitors of angiotensin converting enzyme are used to reduce proteinuria and hypertension, while corticosteroids, cyclophosphamide, mycophenolate mofetil, or azathioprine are used
22
to suppress the immune system. These immunosuppressive treatments have significant toxicities associated with long-term use, and do not address complement-mediated tissue injury.
Potential Benefits of Our Approach
We believe that RA101495 SC, by binding C5 and inhibiting generation of both C5a and MAC, may prevent progression of kidney disease in LN by blocking complement-mediated damage to kidney cells. By inhibiting renal injury, we believe that RA101495 SC may reduce dependence on steroids and other immunosuppresive agents, thereby potentially improving the long-term outcome for patients.
Clinical Development Plan
In January 2018, we initiated dosing in our Phase 1b clinical trial in patients with renal impairment, supporting development of RA101495 SC in complement-mediated renal diseases, such as aHUS and LN. Our Phase 1b, multi-center, open-label trial is designed to evaluate the PK profile of RA101495 SC in these patients. The trial is planned to enroll approximately 16 subjects, including eight patients with severe renal impairment matched with eight healthy control subjects with normal renal function. Each patient will receive a single SC dose of 0.3 mg/kg of RA101495 SC. The trial will compare the PK profile in patients with renal impairment with subjects with normal renal function. We expect topline data in our renal impairment study in mid-2018, enabling the initiation of a follow-on study in LN in 2019.
Our Discovery Programs
Factor D—C3 Glomerulonephritis/Dense Deposit Disease
We are developing specific inhibitors of Factor D, a critical component of the alternative pathway of complement, as targeted drug candidates for C3GN. By blocking the alternative pathway upstream of C3, we believe that this mechanism may prevent C3 deposition and subsequent renal injury.
C3GN and DDD are closely-related but distinct alternative pathway complement-mediated diseases characterized by C3 deposition in the kidney, with absent or minimal immunoglobulin deposition. The two diseases can be distinguished from each other by electron microscopy, based on the precise location and pattern of C3 deposits within the kidney. The combined prevalence of C3GN and DDD is 1-3 per million individuals, with an estimate of approximately 1,000 patients in the U.S. The clinical features of C3GN and DDD include compromised renal function and high blood pressure. The pathophysiology of C3GN and DDD involves both genetic factors and acquired triggers. Patients typically present in adolescence or early adulthood, following an infectious episode which, in susceptible individuals results in uncontrolled activation of C3. Susceptibility to C3GN and DDD may be inherited on the basis of mutations in proteins that regulate the alternative pathway of complement activation.
There are no approved therapies for C3GN or DDD. Patients are usually treated with angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers to modulate proteinuria, and with nonspecific immunosuppressants, including corticosteroids, when kidney inflammation is present.
Oral C5 Inhibitor
We are actively pursuing the identification of orally-bioavailable inhibitors of C5 that bind to and inhibit targets in similar ways as our peptides but are traditional small molecules with the benefit of oral bioavailability. Leveraging our structural knowledge of C5 we have identified two series of molecules. Both series have demonstrated oral bioavailability in rat DMPK and low nanomolar potency has been observed in vitro in a red blood cell hemolysis assay. Furthermore, one of these series bind to a previously unrecognized site on C5, inhibiting cleavage and activation of C5.
23
These series are being further optimized by structural understanding of crystals obtained with full length C5 in stabilized tertiary co-complex. It is expected that this could yield a pipeline of orally available products for a broader set of systemic indications including metabolic diseases (e.g., diabetes). We have also identified early evidence of CNS penetration in one series, offering the possibility of treating complement dysfunction in complex CNS disorders such as neuroinflammatory (e.g., stroke, multiple sclerosis) and neurodegenerative disease (e.g., Huntington's disease, Alzheimer's disease).
In addition to the programs described above, we also have discovery and preclinial programs targeting selective inhibition of various complement factors for other indications. For example, we are also developing a Factor D inhibitor program designed to reduce C3 fragment coating on PNH red blood cells and subsequent spleen phagocytosis, which could potentially increase the risk of infection and limit investigator interest, but which we also believe has the potential to serve as an efficacious treatment method.
Our Extreme Diversity Platform
Known as our Extreme Diversity platform, our proprietary macrocyclic peptide chemistry technology allows us to produce synthetic macrocyclic peptides that combine the diversity and specificity of antibodies with the pharmacological properties of small molecules.
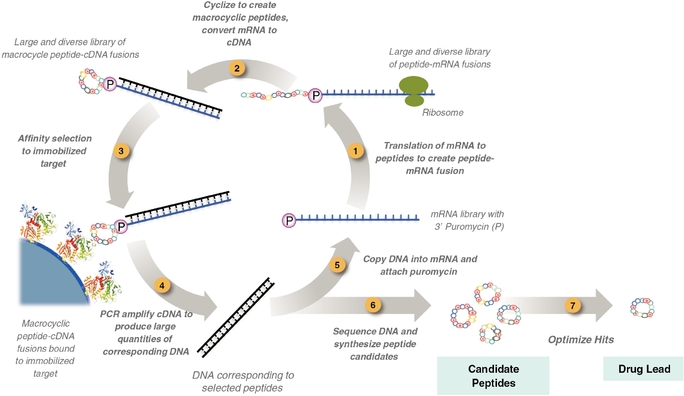
We utilize a process called "mRNA display" to produce extremely large and diverse libraries of peptides from which to screen for potential product candidates. Figure 11 illustrates the step-by-step process of mRNA display.
- •
- Step 1, creation of peptide-mRNA fusion
libraries. mRNA is translated into peptides by ribosomes using both naturally occurring amino acids and non-natural amino acids. The antibiotic
puromycin is linked to each mRNA to create peptide-mRNA fusions. As a result, the translation of a relatively small amount of mRNA results in a large and diverse library of up to 100 trillion
peptide-mRNA fusions.
- •
- Step 2, creating rigid macrocycle peptides. The
peptide-mRNA display libraries are then modified chemically to link two specific amino acids together and cyclize the peptide into rigid macrocycle peptides. In addition, the mRNA components of the
fusions are converted to cDNA (a hybrid of mRNA and DNA) at this step.
- •
- Step 3, selecting target peptides. Once a cyclic
peptide mRNA display library is prepared we select peptides that bind to the desired target protein immobilized on the surface of a small, solid bead.
- •
- Step 4, DNA amplification. After an initial set of
peptides that bind to the target protein are selected, we leverage the mRNA to then amplify the peptides' corresponding DNA via a DNA amplifying technique called Polymerase Chain Reaction ("PCR").
- •
- Steps 5, 6 and 7, repeat process to select lead candidate. The cycle can be repeated to enrich for candidate peptides (Step 5), and the DNA's sequence is ultimately determined, and desired peptide candidates are synthesized based on the information in its corresponding DNA (Step 6), and candidate peptides are then further screened and optimized for desired target binding affinity to select a lead candidate (Step 7).
24
Figure 11. A Diagram Illustrating Our Extreme Diversity Platform.
RA101495 SC and our pipeline of peptide product candidates were discovered using our Extreme Diversity platform, our proprietary technology that allows us to rapidly and efficiently discover cyclic peptides comprised of natural and non-natural amino acids, with the advantages set forth below.
- •
- High affinity and potency. Our peptides are cyclic,
and therefore are conformationally rigid, thereby "locking" the molecule in the conformation in which it binds optimally to its target and leading to affinity and potency similar to antibodies.
- •
- High specificity. Our peptides are larger than most
drugs taken in pill form, allowing them to have more contact points when bound to their targets, thus affording similar specificity as antibodies.
- •
- Novel mechanisms of
interaction. The use of non-natural amino acids with new chemical functionalities expands the manner in which peptides can interact with target
proteins, potentially enabling new mechanisms to modulate protein function in the body.
- •
- High stability. The backbone
modification and relatively rigid, cyclic structure of our peptides are designed to reduce degradation. As a result, we believe our peptides will have higher stability in the body than natural
peptides. Further, they will not denature or unfold over time, and have higher stability than antibodies and biologics, potentially allowing for room temperature storage over the entire distribution
chain.
- •
- Improved bioavailability. The
relatively small size of our peptides allows them to enter the circulation readily when administered by a variety of potential routes, including SC injection or oral administration, an advantage over
many monoclonal antibody and biologic therapies which require intravenous infusion.
- •
- Half-life modification. As synthetic products, we can readily modify our cyclic peptides with chemical groups that modify the circulating half-life in the body, including lipids, carbohydrates,
25
- •
- Reduced safety risks. Unlike
antibodies and biologics, our peptides are completely synthetic, eliminating the potential for viral and cellular protein contamination, risks to therapeutics produced in mammalian cells, and
potentially allowing for administration to patients with hypersensitivity to products produced using mammalian cells.
- •
- Favorable manufacturing processes and costs. As synthetic products, our peptides do not need complex fermentation facilities, allowing their production to be easily sourced from multiple vendors at lower costs than mammalian cell products.
and polymers such as polyethylene glycol, providing the potential to optimize dosing by fine-tuning the pharmacokinetic properties and improve patient outcomes.
We are driving the development of the next generation of orally available drugs. Certain of our cyclic peptides are being developed into orally available drugs, as exemplified by our high value target developed in our collaboration with Merck. We can also use our platform to develop novel macrocycle peptides to guide the development of orally-available, traditional small molecule drugs such as our oral C5 inhibitors.
We protect our intellectual property rights related to the Extreme Diversity program through a combination of licensed patents, trade secrets and know-how. For more information, see the section titled "Intellectual Property."
Our Merck Collaboration and License Agreement
In April 2013, we entered into a multi-target collaboration and license agreement with Merck to use our proprietary drug discovery technology platform to identify orally available cyclic peptides for non-complement program targets nominated by Merck and provide specific research and development services. Under the agreement, we granted Merck licenses under certain of our intellectual property rights to manufacture, develop and commercialize compounds and products directed to selected program targets. The agreement consists of a research phase, where we and Merck collaborated on identifying and pre-clinically developing orally available cyclic peptides suitable for further development by Merck, and a development and commercialization phase pursuant to which Merck has sole discretion and responsibility, including financial responsibility, for further development and commercialization of these peptides, on a program-by-program basis, from the collaboration. In April 2015, the agreement was amended to extend the research term of the collaboration to April 2016.
At the signing of the agreement, Merck made an upfront non-refundable, technology license fee of $4.5 million to us. In addition, during the research term, which ended in April 2016, the agreement provided for reimbursement of research and development services provided by us in accordance with pre-specified limits for the number of our full-time equivalent employees working under the agreement. At the conclusion of the research term, Merck elected to continue the development of a non-complement cardiovascular target with a large market opportunity, for which we had received $3.5 million in preclinical milestone payments as of December 2017.
We are entitled to receive future aggregate milestone payments of up to $61.5 million for the non-complement cardiovascular target selected, consisting of remaining preclinical and clinical milestones of $16.5 million, regulatory milestones of $19.0 million and commercial milestones of $26.0 million, and low-to-mid single digit percentage royalties on future sales, if any. Royalties will be payable from the first commercial sale in a country until the later of the last to expire valid claim in such country and a specified number of years from the date of such first commercial sale. The agreement expires on a country-by-country basis upon expiration of Merck's royalty obligations. Merck may terminate the agreement in its entirety upon prior written notice to us. Either party may terminate the agreement in the event of bankruptcy of the other party or uncured material breach. We may terminate the agreement if Merck challenges any of our patent rights covered by the agreement.
26
Intellectual Property
Overview
We strive to protect and enhance the proprietary technology, inventions, and improvements that are commercially important to the development of our business, including our Extreme Diversity platform. This includes seeking, maintaining, and defending patent rights, whether developed internally or licensed from third parties. We also rely on trade secrets and know-how that may be important for the development of our business. This includes aspects of our proprietary technology platform, our continuing technological innovation; and on in-licensing opportunities used to develop, maintain, and strengthen our position in the field of peptide, peptidomimetic, and small molecule-based therapeutics. We additionally may rely on regulatory protection afforded through data exclusivity, market exclusivity and patent term extensions where available.
Our commercial success may depend in part on our ability to obtain and maintain patent and other proprietary protection for our product candidates, technology and know-how, defend and enforce our patents, prevent others from practicing our technology by enforcing our proprietary rights, preserve the confidentiality of our trade secrets, and operate without infringing the proprietary rights of others.
Our ability to stop third parties from making, having made, using, selling, offering to sell or importing our products depends in large part on the extent to which we have rights under valid and enforceable licenses, patents or trade secrets that cover these activities. In some cases, these rights may need to be enforced by third-party licensors. With respect to both licensed and company-owned intellectual property, we cannot be sure that patents will be granted with respect to any of our pending patent applications or with respect to any patent applications filed by us in the future, nor can we be sure that any of our existing patents, or any patents that may be granted to us in the future, will be commercially useful in protecting our commercial products and methods of manufacturing the same. For more information, please see "Risk Factors—Risks Related to Our Intellectual Property."
We seek to protect our proprietary position in a variety of ways, including by pursuing patent protection in certain jurisdictions where it is available. For example, we file U.S. and selected foreign patent applications related to our proprietary technology, inventions and improvements that are important to the development of our business. We also intend to seek patent protection, or rely upon trade secret rights, to protect other technologies that may be used to discover and validate targets and that may be used to identify and develop novel products or improvements thereof. We seek protection, in part, through confidentiality and proprietary information agreements. We are a party to various other license agreements that give us rights to use specific technologies in our research and development.
The term of individual patents depends upon the legal term of the patents in the countries in which they are obtained. In most countries in which we file, the patent term is 20 years from the earliest date of filing a non-provisional application which matures into a granted patent. A U.S. patent also may be accorded a patent term adjustment, or PTA, under certain circumstances to compensate for delays in obtaining the patent caused by the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office. In some instances, such a PTA may result in a U.S. patent term extending beyond 20 years from the earliest date of filing a non-provisional patent application. In addition, in the U.S., the term of a U.S. patent that covers an FDA-approved drug may also be eligible for patent term extension, which permits patent term restoration as compensation for the patent term lost during the FDA regulatory review process. The Hatch-Waxman Act permits a patent term extension of up to five years beyond the expiration of the patent. The length of the patent term extension is related to the length of time the drug is under regulatory review. Patent term extension cannot extend the remaining term of a patent beyond a total of 14 years from the date of product approval and only one patent applicable to an approved drug may be extended. Similar provisions are available in Europe and other foreign jurisdictions to extend the term of a patent that covers an approved drug. In the future, if and when our products receive FDA
27
approval, we expect to apply for patent term extensions on patents covering those products. We plan to seek patent term extensions to any of our issued patents in any jurisdiction where these are available; however, there is no guarantee that the applicable authorities, including the FDA in the U.S., will agree with our assessment of whether such extensions should be granted, and if granted, the length of such extensions.
Company-Owned Intellectual Property
Our lead C5 inhibitor portfolio includes six families of U.S. patent applications directed to our lead C5 inhibitor and related methods of formulation and use in addition to clinical studies outcomes, and to date have received a notice of allowance for one set of claims in this series. Any patents that may grant from these patent applications are generally expected to expire between 2035 and 2038, subject to possible patent term extensions.
We also own two U.S. patents, and have received a notice of allowance in a third application in the same family. Along with this family we are prosecuting various patent applications directed to other technologies. The U.S. patents are expected to expire in 2034, and any patents granted on the pending applications are expected to expire between 2034 and 2038, subject to possible patent term extensions.
Licensed Intellectual Property
We have exclusively licensed one patent family directed to an in vitro translation system for incorporating unnatural amino acids from Dr. A. C. Forster. This family, which covers certain rights related to our Extreme Diversity platform, includes five granted patents, including one in the U.S. and four in foreign jurisdictions including Australia, Canada, Europe and Japan. Patents in this family are generally expected to expire in 2022, subject to possible patent term extensions. This license may be terminated if we fail to make payments thereunder, if we commit a material breach of our obligations thereunder, or if we make an assignment for benefit of creditors or have a petition in bankruptcy filed; also, we may terminate the license for any reason upon 30 days' prior written notice. As of the date of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, we have paid an aggregate amount of approximately $265,000 under this license. In connection with the execution of this license, we paid an issue fee of approximately $175,000, and annual maintenance fees are approximately $15,000. In addition, we issued equity in the amount of approximately 8,500 shares of common stock in connection with this license. The license provides for running royalties equal to 0.25% of net sales of licensed products thereunder, payable on a country-by-country and licensed product-by-licensed product basis until the expiration of the last valid claim covering such product in such country.
We also have a fully paid-up, non-exclusive license to more than 20 U.S. and more than 50 foreign granted patents directed to various display library technologies as a result of our acquisition of Cosmix, which covers other rights related to our Extreme Diversity platform. These include patents that have been granted in the U.S., Canada, China, Europe, India, Israel, Japan, Korea, New Zealand, Russia, South Africa, and Taiwan. These patents are generally expected to expire between 2018 and 2022, subject to possible patent term extensions. We paid an aggregate amount of approximately $1.4 million and approximately 123,456 shares of common stock in connection with the Cosmix acquisition that includes this fully paid-up license, though no breakdown of amounts specifically attributable to this license is available.
Trademark Protection
We have filed for protection and our marks are allowed in the U.S. for the RA PHARMACEUTICALS mark for goods and services, the RA PHARMA word mark for goods, and the RA PHARMA logo mark for goods. We have filed for protection for goods and services in foreign jurisdictions, including Europe, Australia and Canada for the RA PHARMACEUTICALS word mark,
28
the RA PHARMA word mark, and the RA PHARMA logo mark. We have received a Notice of Opposition for the RA PHARMA word mark (Application No. 015611726).
We have filed for and obtained trademark protection in the U.S. for the RA PHARMA service word mark for "pharmaceutical research and development in the field of peptides and/or peptidomimetics; the foregoing services not related to rheumatoid arthritis." The mark is listed on the Principal Register, Registration No. 5022228.
We have filed for and obtained trademark protection in the U.S. for the RA PHARMA service mark logo for "pharmaceutical research and development in the field of peptides and/or peptidomimetics; the foregoing services not related to rheumatoid arthritis." The mark is listed on the Principal Register, Registration No. 5026109.
We have filed for and obtained trademark protection in Europe for the RA PHARMA logo mark for goods and services. The mark registered as Registration No. 015611775.
While we have not filed for federal protection for our mark, EXTREME DIVERSITY, we do use the mark and rely on common law protections for such use.
Trade Secret Protection
Finally, we may rely, in some circumstances, on trade secrets to protect our technology. In particular, with the earlier patents expiring by 2022, we anticipate relying in part on trade secrets to protect the know-how behind our proprietary peptide chemistry platform. However, trade secrets can be difficult to protect. We seek to protect our proprietary technology and processes, in part, by entering into confidentiality agreements with our employees, consultants, scientific advisors and contractors. We also seek to preserve the integrity and confidentiality of our data and trade secrets by maintaining physical security of our premises and physical and electronic security of our information technology systems. While we have confidence in these individuals, organizations and systems, agreements or security measures may be breached, and we may not have adequate remedies for any breach. In addition, our trade secrets may otherwise become known or be independently discovered by competitors. To the extent that our consultants, contractors or collaborators use intellectual property owned by others in their work for us, disputes may arise as to the rights in related or resulting know-how and inventions. For further information, please see "Risk Factors—Risks Related to Our Intellectual Property."
Competition
The biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries are characterized by rapidly advancing technologies, intense competition and a strong emphasis on proprietary products. While we believe that our technologies, knowledge, experience and scientific resources provide us with competitive advantages, we face potential competition from many different sources, including major pharmaceutical, specialty pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies, academic institutions and governmental agencies and public and private research institutions. Any product candidates that we successfully develop and commercialize will compete with existing therapies and new therapies that may become available in the future.
There are a number of currently marketed products and product candidates in preclinical research and clinical development by third parties to treat the various diseases that we are targeting. In general, these products and product candidates can be categorized based on their proposed mechanisms of action. The mechanisms of action for these product candidates include inflammation suppression by agents such as complement inhibitors and corticosteroids, as well as immune modulators, visual cycle modulators, anti-amyloid agents, antioxidants, neuroprotectants, cell and gene therapies and vascular and interstitial tissue remodeling agents.
29
If our lead product candidates are approved for the indications for which we are currently undertaking clinical trials, they will compete with the products and product candidates discussed below.
PNH. The principal competitor for our program in PNH is eculizumab, a C5 inhibitor, which is marketed as Soliris by Alexion Pharmaceuticals and is the only drug approved for the treatment of PNH. Alexion Pharmaceuticals is also developing a next-generation C5 inhibitor named ALXN 1210 that has a less frequent intravenous dosing schedule. In addition, we are aware that there are a number of other companies that are actively developing product candidates for the treatment of PNH, including the following:
- •
- product candidates directed at C5 inhibition such as Coversin, a small protein inhibitor of C5 being developed by Akari Pharmaceuticals that is
in early clinical trials, LFG316, a monoclonal antibody inhibitor of C5 being developed by Novartis Pharma, ABP595, a biosimilar product candidate being developed by Amgen that is currently in
clinical trials, and RO7112689, a monoclonal antibody inhibitor of C5 being developed by F. Hoffmann-La Roche;
- •
- a product candidate directed at C3 inhibition that is currently in preclinical development by Amyndas Pharmaceuticals;
- •
- a product candidate directed at C3 inhibition such as APL-2 that is currently in clinical development by Apellis Pharmaceuticals; and
- •
- other product candidates directed at other mechanisms of complement inhibition such as TNT009, an antibody against C1s, being developed by Bioverativ in early clinical trials, and ACH-4471, orally available small molecule inhibitors of complement Factor D, that are currently in preclinical and clinical development by Achillion Pharmaceuticals.
Certain of our competitors are developing product candidates intended to be administered SC, IV or orally, with dosing frequencies ranging from twice daily to monthly, and with varying dose strengths and half-lives. We believe that the combination of SC administration, dose frequency, and dose strength will allow RA101495 SC to provide improved control of hemolysis and suppression of breakthrough hemolysis.
gMG. gMG is currently treated with cholinesterase inhibitors and non-specific immunosuppressive agents, including azathioprine, cyclophosphamide, cyclosporine, IVIG, mycophenolate, prednisone, and tacrolimus. Alexion Pharmaceuticals recently announced approval of eculizumab for the treatment of refractory MG in Europe and gMG in the U.S. Both rituximab, marketed by F. Hoffmann-La Roche, and belimumab, marketed by GlaxoSmithKline, which target B cell activity, and are in clinical development for gMG. Anti-CD40, in development as CFZ533 by Novartis Pharma, bortezomib, and the FcRN agonist ARGX-113 developed by Argen-X, are being tested in clinical trials in gMG. A therapeutic vaccine targeting B and T-cell receptors (CV-MG-01) is in early clinical testing for gMG.
aHUS. Eculizumab (Soliris, Alexion), a monoclonal antibody targeting C5, is currently the only FDA-approved therapy for aHUS. Eculizumab therapy is administered via intravenous infusion by a healthcare professional every other week. Eculizumab binds circulating C5 and prevents cleavage by C5 convertases, thereby blocking formation of C5a and assembly of MAC. Patients on eculizumab therapy experience substantial reduction in thrombosis and improved kidney function, providing clinical validation for inhibition of C5 in this disease, although the response was more pronounced in patients with shorter duration of disease prior to initiation of eculizumab treatment. Other compounds in development include ALXN 1210 (Alexion, Phase 3), Cemdisiran (Alnylam, Phase 2), OMS721 (Omeros, Phase 3).
LN. There are no specific therapies for LN. Although approved for patients with active, autoantibody-positive, systemic lupus erythematosus who are receiving standard therapy, belimumab, which is marketed under the name Benlysta by GlaxoSmithKline, has not been evaluated in patients
30
with LN. There are numerous Phase 2 and later stage clinical studies on non-specific immunosuppressive agents, including agents currently used as standard of care in LN, with tacrolimus, mycophenolate, bortezomib, cyclophosphamide, azothioprim, voclosporin, laquinimod, and ACTHAR Gel being tested. In addition, a number of agents are being tested as targeted monoclonal antibody therapies, such as anti-CD40, anti-IL6, rituximab (anti-CD20), anti-TWEAK (an antibody directed against the TNF-like weak inducer of apoptosis), and belimumab (anti BLys), as well as B7 antagonists such as CTLA4-Ig. The only complement pathway inhibitors proposed as targeted, disease-modifying agents in LN are OMS721, which is in Phase 2 development by Omeros, an anti-MASP-2 antibody that inhibits the mannose-binding lectin arm of the complement system, and eculizumab, where the antibody has shown benefit in a small number of published case report studies. There are no ongoing studies of eculizumab or any other C5 inhibitor in LN.
Sales and Marketing
We hold worldwide commercialization rights to all of our complement-mediated product candidates. Subject to receiving marketing approval, we intend to independently pursue the commercialization of RA101495 SC in PNH patients in the U.S. and Europe by building a focused sales and marketing organization in these geographies. We believe that such an organization will be able to address the community of physicians who are key specialists in treating the patient populations for which our product candidates are being developed.
We also plan to build a marketing and sales management organization to create and implement marketing strategies for any products that we market through our own sales organization and to oversee and support our sales force. The responsibilities of the marketing organization would include developing educational initiatives with respect to approved products and establishing relationships with researchers and practitioners in relevant fields of medicine.
Outside of the U.S. and Europe, we may pursue the approval and commercialization of RA101495 SC for PNH patients either independently or in collaboration with others. We intend to develop and commercialize RA101495 SC for other indications independently or through collaborations with third parties.
Manufacturing
We do not currently own or operate manufacturing facilities for the production of clinical or commercial quantities of our product candidates. We intend to rely on third-party contract manufacturers to produce our products and have recruited personnel with experience to manage the third-party contract manufacturers producing our product candidates and other product candidates or products that we may develop in the future.
The process for manufacturing our product candidates consists of a multiple-stage-chemical synthesis, purification using liquid chromatography, and freeze drying into a powder form. The initial chemical synthesis process is similar to other cyclic peptide synthetic processes. For some of our products, the peptide is modified after cyclization using common synthetic processes to attach bio-distribution modifying chemical moieties. We expect the costs associated with manufacturing drug substance for our product candidates to be comparable to the current manufacturing costs for other complex and similarly sized peptide-based components, and because our product candidates are synthetic, we believe they can be manufactured in a more cost-effective manner relative to competitive biologic and monoclonal antibody therapies.
We currently engage third-party manufacturers to provide clinical supplies, nonclinical supplies and fill-finish services for RA101495 SC.
31
Government Regulation
Government authorities in the U.S., at the federal, state and local level, and in other countries and jurisdictions, including the European Union ("E.U."), extensively regulate, among other things, the research, development, testing, manufacture, quality control, approval, packaging, storage, recordkeeping, labeling, advertising, promotion, distribution, marketing, post-approval monitoring and reporting, and import and export of pharmaceutical products. The processes for obtaining regulatory approvals in the U.S. and in foreign countries and jurisdictions, along with subsequent compliance with applicable statutes and regulations and other regulatory authorities, require the expenditure of substantial time and financial resources.
Review and Approval of Drugs in the U.S.
In the U.S., the FDA regulates drugs and devices under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act ("FDCA") and implementing regulations. Although we have not yet selected the device component to use for administration of our lead product candidate, we expect that, if approved, our lead drug product candidate may be regulated as a combination product, which means that it is composed of both a drug product and device product. If marketed individually, each component would be subject to different regulatory pathways and reviewed by different centers within the FDA. A combination product, however, is assigned to a center that will have primary jurisdiction over its regulation based on a determination of the combination product's primary mode of action, which is the single mode of action that provides the most important therapeutic action. In the case of our lead product candidate, we expect the primary mode of action to be attributable to the drug component of the product, which means that the FDA's Center for Drug Evaluation and Research would have primary jurisdiction over the premarket development, review and approval. The failure to comply with applicable U.S. requirements at any time during the product development process, approval process or after approval may subject an applicant and/or sponsor to a variety of administrative or judicial sanctions, including refusal by the FDA to approve pending applications, withdrawal of an approval, imposition of a clinical hold, issuance of warning letters and other types of letters, product seizures, total or partial suspension of production or distribution, injunctions, fines, refusals of government contracts, restitution, disgorgement of profits, or civil or criminal investigations and penalties brought by the FDA and the Department of Justice or other governmental entities. In addition, an applicant may need to recall a product.
An applicant seeking approval to market and distribute a new drug product in the U.S. must typically undertake the following:
- •
- completion of nonclinical, or preclinical, laboratory tests, animal studies and formulation studies in compliance with the FDA's good
laboratory practice ("GLP") regulations;
- •
- submission to the FDA of an IND, which must take effect before human clinical trials may begin;
- •
- approval by an independent IRB representing each clinical site before each clinical trial may be initiated;
- •
- performance of adequate and well-controlled human clinical trials in accordance with good clinical practices ("GCP") to establish the safety
and efficacy of the proposed drug product for each indication;
- •
- preparation and submission to the FDA of a new drug application ("NDA");
- •
- review of the product by an FDA advisory committee, where appropriate or if applicable;
- •
- satisfactory completion of one or more FDA inspections of the manufacturing facility or facilities at which the product, or components thereof, are produced to assess compliance with current
32
- •
- satisfactory completion of FDA audits of clinical trial sites to assure compliance with GCPs and the integrity of the clinical data;
- •
- payment of user fees and securing FDA approval of the NDA; and
- •
- compliance with any post-approval requirements, including Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategies ("REMS") and post-approval studies required by the FDA.
Good Manufacturing Practices ("cGMP") requirements and to assure that the facilities, methods and controls are adequate to preserve the product's identity, strength, quality and purity;
Preclinical Studies
Preclinical studies include laboratory evaluation of the purity and stability of the manufactured drug substance or active pharmaceutical ingredient and the formulated drug or drug product, as well as in vitro and animal studies to assess the safety and activity of the drug for initial testing in humans and to establish a rationale for therapeutic use. The conduct of preclinical studies is subject to federal regulations and requirements, including GLP regulations. The results of the preclinical tests, together with manufacturing information, analytical data, any available clinical data or literature and plans for clinical trials, among other things, are submitted to the FDA as part of an IND. Some long-term preclinical testing, such as animal tests of reproductive adverse events and carcinogenicity, may continue after the IND is submitted.
Human Clinical Trials in Support of an NDA
Clinical trials involve the administration of the investigational product to human subjects under the supervision of qualified investigators in accordance with GCP requirements, which include, among other things, the requirement that all research subjects provide their informed consent in writing before their participation in any clinical trial. Clinical trials are conducted under written study protocols detailing, among other things, the inclusion and exclusion criteria, the objectives of the study, the parameters to be used in monitoring safety and the effectiveness criteria to be evaluated. A protocol for each clinical trial and any subsequent protocol amendments must be submitted to the FDA as part of the IND. An IND automatically becomes effective 30 days after receipt by the FDA, unless before that time the FDA raises concerns or questions related to a proposed clinical trial and places the trial on clinical hold. In such a case, the IND sponsor and the FDA must resolve any outstanding concerns before the clinical trial can begin. The FDA can place an IND on full or partial clinical hold at any point in development, and depending upon the scope of the hold, clinical trial(s) may not restart until resolution of the outstanding concerns to the FDA's satisfaction.
In addition, an IRB representing each institution participating in the clinical trial must review and approve the plan for any clinical trial before it commences at that institution, and the IRB must conduct a continuing review and reapprove the study at least annually. The IRB must review and approve, among other things, the study protocol and informed consent information to be provided to study subjects. An IRB must operate in compliance with FDA regulations. Information about certain clinical trials must be submitted within specific timeframes to the National Institutes of Health for public dissemination on their ClinicalTrials.gov website.
Human clinical trials are typically conducted in three sequential phases, which may overlap or be combined:
- •
- Phase 1. The drug is initially introduced into healthy human subjects or, in certain indications such as cancer, patients with the target disease or condition and tested for safety, dosage tolerance, absorption, metabolism, distribution, excretion and, if possible, to gain an early indication of its effectiveness and to determine optimal dosage.
33
- •
- Phase 2. The drug is
administered to a limited patient population to identify possible adverse effects and safety risks, to preliminarily evaluate the efficacy of the product for specific targeted diseases and to
determine dosage tolerance and optimal dosage.
- •
- Phase 3. The drug is
administered to an expanded patient population, generally at geographically dispersed clinical trial sites, in well-controlled clinical trials to generate enough data to evaluate the efficacy and
safety of the product for approval, to establish the overall risk-benefit profile of the product and to provide adequate information for the labeling of the product.
- •
- Phase 4. Post-approval studies may be conducted after initial marketing approval. These studies are used to gain additional experience from the treatment of patients in the intended therapeutic indication.
Progress reports detailing the results of the clinical trials must be submitted at least annually to the FDA and more frequently if serious adverse events occur. In addition, IND safety reports must be submitted to the FDA for any of the following: serious and unexpected suspected adverse reactions; findings from other studies or animal or in vitro testing that suggest a significant risk in humans exposed to the drug; and any clinically important increase in the case of a serious suspected adverse reaction over that listed in the protocol or investigator brochure. Phase 1, Phase 2 and Phase 3 clinical trials may not be completed successfully within any specified period, or at all. Furthermore, the FDA or the sponsor may suspend or terminate a clinical trial at any time on various grounds, including a finding that the research subjects are being exposed to an unacceptable health risk. Similarly, an IRB can suspend or terminate approval of a clinical trial at its institution, or an institution it represents, if the clinical trial is not being conducted in accordance with the IRB's requirements or if the drug has been associated with unexpected serious harm to patients. The FDA will typically inspect one or more clinical sites to assure compliance with GCP and the integrity of the clinical data submitted.
Concurrent with clinical trials, companies often complete additional animal studies and must also develop additional information about the chemistry and physical characteristics of the drug as well as finalize a process for manufacturing the product in commercial quantities in accordance with cGMP requirements. The manufacturing process must be capable of consistently producing quality batches of the drug candidate and, among other things, the applicant must develop methods for testing the identity, strength, quality, purity, and potency of the final drug. Additionally, appropriate packaging must be selected and tested and stability studies must be conducted to demonstrate that the drug candidate does not undergo unacceptable deterioration over its shelf life.
Review of an NDA by the FDA
Assuming successful completion of required clinical testing and other requirements, the results of the preclinical studies and clinical trials, together with detailed information relating to the product's chemistry, manufacture, controls and proposed labeling, among other things, are submitted to the FDA as part of an NDA requesting approval to market the drug product for one or more indications. Under the Prescription Drug User Fee Act ("PDUFA") as amended, the submission of most NDAs is additionally subject to an application user fee, currently exceeding $2.4 million. PDUFA also imposes an annual prescription drug product program fee for human drugs, currently exceeding $300,000. These fees are typically increased annually.
The FDA conducts a preliminary review of an NDA within 60 days of its receipt and informs the sponsor whether the application is sufficiently complete to permit substantive review. The FDA may request additional information rather than accept an NDA for filing. In this event, the application must be resubmitted with the additional information. The resubmitted application is also subject to review before the FDA accepts it for filing. Once the submission is accepted for filing, the FDA begins an in-depth substantive review. The FDA has agreed to specified performance goals in the review process of NDAs. Most such applications are meant to be reviewed within ten months from the date of filing,
34
and most applications for "priority review" products are meant to be reviewed within six months of filing. The review process may be extended by the FDA for three additional months to consider new information or clarification provided by the applicant to address an outstanding deficiency identified by the FDA following the original submission.
Before approving an NDA, the FDA typically will inspect the facility or facilities where the product is or will be manufactured. These pre-approval inspections may cover all facilities associated with an NDA submission, including drug component manufacturing (such as active pharmaceutical ingredients), finished drug product manufacturing, and control testing laboratories. The FDA will not approve an application unless it determines that the manufacturing processes and facilities are in compliance with cGMP requirements and adequate to assure consistent production of the product within required specifications. Additionally, before approving an NDA, the FDA will typically inspect one or more clinical sites to assure compliance with GCP.
In addition, as a condition of approval, the FDA may require an applicant to develop a REMS. REMS use risk minimization strategies beyond the professional labeling to ensure that the benefits of the product outweigh the potential risks. To determine whether a REMS is needed, the FDA will consider the size of the population likely to use the product, seriousness of the disease, the expected benefit of the product, the expected duration of treatment, the seriousness of known or potential adverse events, and whether the product is a new molecular entity. REMS can include medication guides, physician communication plans for healthcare professionals, and elements to assure safe use ("ETASU"). ETASU may include, but are not limited to, special training or certification for prescribing or dispensing, dispensing only under certain circumstances, special monitoring, or the use of patient registries. The FDA may require a REMS before approval or post-approval if it becomes aware of a serious risk associated with use of the product. The requirement for a REMS can materially affect the potential market and profitability of a product.
The FDA is required to refer an application for a novel drug to an advisory committee or explain why such referral was not made. Typically, an advisory committee is a panel of independent experts, including clinicians and other scientific experts, that reviews, evaluates and provides a recommendation as to whether the application should be approved and under what conditions. The FDA is not bound by the recommendations of an advisory committee, but it considers such recommendations carefully when making decisions.
Fast Track, Breakthrough Therapy and Priority Review Designations
The FDA is authorized to designate certain products for expedited review if they are intended to address an unmet medical need in the treatment of a serious or life-threatening disease or condition. These programs are Fast Track designation, Breakthrough Therapy designation and priority review designation.
Specifically, the FDA may designate a product for Fast Track review if it is intended, whether alone or in combination with one or more other products, for the treatment of a serious or life-threatening disease or condition, and it demonstrates the potential to address unmet medical needs for such a disease or condition. For Fast Track products, sponsors may have greater interactions with the FDA and the FDA may initiate review of sections of a Fast Track product's application before the application is complete. This rolling review may be available if the FDA determines, after preliminary evaluation of clinical data submitted by the sponsor, that a Fast Track product may be effective. The sponsor must also provide, and the FDA must approve, a schedule for the submission of the remaining information and the sponsor must pay applicable user fees. However, the FDA's time period goal for reviewing a Fast Track application does not begin until the last section of the application is submitted. In addition, the Fast Track designation may be withdrawn by the FDA if the FDA believes that the designation is no longer supported by data emerging in the clinical trial process.
35
Second, a product may be designated as a Breakthrough Therapy if it is intended, either alone or in combination with one or more other products, to treat a serious or life-threatening disease or condition and preliminary clinical evidence indicates that the product may demonstrate substantial improvement over existing therapies on one or more clinically significant endpoints, such as substantial treatment effects observed early in clinical development. The FDA may take certain actions with respect to Breakthrough Therapies, including holding meetings with the sponsor throughout the development process; providing timely advice to the sponsor regarding development and approval; involving more senior staff in the review process; assigning a cross-disciplinary project lead for the review team; and taking other steps to design the clinical trials in an efficient manner.
Third, the FDA may designate a product for priority review if it is a product that treats a serious condition and, if approved, would provide a significant improvement in safety or effectiveness. The FDA determines, on a case-by-case basis, whether the proposed product represents a significant improvement when compared with other available therapies. Significant improvement may be illustrated by evidence of increased effectiveness in the treatment of a condition, elimination or substantial reduction of a treatment-limiting adverse reaction, documented enhancement of patient compliance that is expected to lead to improvement in serious outcomes, and evidence of safety and effectiveness in a new subpopulation. A priority designation is intended to direct overall attention and resources to the evaluation of such applications, and to shorten the FDA's goal for taking action on a marketing application from ten months to six months.
Accelerated Approval Pathway
The FDA may grant accelerated approval to a product for a serious or life-threatening condition that provides meaningful therapeutic advantage to patients over existing treatments based upon a determination that the product has an effect on a surrogate endpoint that is reasonably likely to predict clinical benefit. The FDA may also grant accelerated approval for such a condition when the product has an effect on an intermediate clinical endpoint that can be measured earlier than an effect on irreversible morbidity or mortality ("IMM") and that is reasonably likely to predict an effect on irreversible morbidity or mortality or other clinical benefit, taking into account the severity, rarity, or prevalence of the condition and the availability or lack of alternative treatments. Products granted accelerated approval must meet the same statutory standards for safety and effectiveness as those granted traditional approval.
For the purposes of accelerated approval, a surrogate endpoint is a marker, such as a laboratory measurement, radiographic image, physical sign, or other measure that is thought to predict clinical benefit but is not itself a measure of clinical benefit. Surrogate endpoints can often be measured more easily or more rapidly than clinical endpoints. An intermediate clinical endpoint is a measurement of a therapeutic effect that is considered reasonably likely to predict the clinical benefit of a product, such as an effect on IMM. The FDA has limited experience with accelerated approvals based on intermediate clinical endpoints but has indicated that such endpoints generally may support accelerated approval where the therapeutic effect measured by the endpoint is not itself a clinical benefit and basis for traditional approval, if there is a basis for concluding that the therapeutic effect is reasonably likely to predict the ultimate clinical benefit of a product.
The accelerated approval pathway is most often used in settings in which the course of a disease is long and an extended period of time is required to measure the intended clinical benefit of a product, even if the effect on the surrogate or intermediate clinical endpoint occurs rapidly. Thus, accelerated approval has been used extensively in the development and approval of products for treatment of a variety of cancers in which the goal of therapy is generally to improve survival or decrease morbidity and the duration of the typical disease course requires lengthy and sometimes large trials to demonstrate a clinical or survival benefit.
36
The accelerated approval pathway is usually contingent on a sponsor's agreement to conduct, in a diligent manner, additional post-approval confirmatory studies to verify and describe the product's clinical benefit. As a result, a product candidate approved on this basis is subject to rigorous post-marketing compliance requirements, including the completion of Phase 4 or post-approval clinical trials to confirm the effect on the clinical endpoint. Failure to conduct required post-approval studies or confirm a clinical benefit during post-marketing studies, would allow the FDA to withdraw the product from the market on an expedited basis. All promotional materials for product candidates approved under accelerated regulations are subject to prior review by the FDA.
The FDA's Decision on an NDA
On the basis of the FDA's evaluation of the NDA and accompanying information, including the results of the inspection of the manufacturing facilities, the FDA may issue an approval letter or a complete response letter. An approval letter authorizes commercial marketing of the product with specific prescribing information for specific indications. A complete response letter generally outlines the deficiencies in the submission and may require substantial additional testing or information in order for the FDA to reconsider the application. If and when those deficiencies have been addressed to the FDA's satisfaction in a resubmission of the NDA, the FDA will issue an approval letter. The FDA has committed to reviewing such resubmissions in two or six months depending on the type of information included. Even with submission of this additional information, the FDA ultimately may decide that the application does not satisfy the regulatory criteria for approval.
If the FDA approves a product, it may limit the approved indications for use for the product, require that contraindications, warnings or precautions be included in the product labeling, require that post-approval studies, including Phase 4 clinical trials, be conducted to further assess the drug's safety after approval, require testing and surveillance programs to monitor the product after commercialization, or impose other conditions, including distribution restrictions or other risk management mechanisms, including REMS, which can materially affect the potential market and profitability of the product. The FDA may prevent or limit further marketing of a product based on the results of post-market studies or surveillance programs. After approval, many types of changes to the approved product, such as adding new indications, manufacturing changes and additional labeling claims, are subject to further testing requirements and FDA review and approval.
Post-Approval Requirements
Drugs manufactured or distributed pursuant to FDA approvals are subject to pervasive and continuing regulation by the FDA, including, among other things, requirements relating to recordkeeping, periodic reporting, product sampling and distribution, advertising and promotion and reporting of adverse experiences with the product. After approval, most changes to the approved product, such as adding new indications or other labeling claims, are subject to prior FDA review and approval. There also are continuing, annual user fee requirements for any marketed products and the establishments at which such products are manufactured, as well as new application fees for supplemental applications with clinical data.
In addition, drug manufacturers and other entities involved in the manufacture and distribution of approved drugs are required to register their establishments with the FDA and state agencies, and are subject to periodic unannounced inspections by the FDA and these state agencies for compliance with cGMP requirements. Changes to the manufacturing process are strictly regulated and often require prior FDA approval before being implemented. FDA regulations also require investigation and correction of any deviations from cGMP and impose reporting and documentation requirements upon the NDA holder and any third-party manufacturers that the NDA holder may decide to use. Accordingly, manufacturers must continue to expend time, money, and effort in the area of production and quality control to maintain cGMP compliance.
37
Once an approval is granted, the FDA may withdraw the approval if compliance with regulatory requirements and standards is not maintained or if problems occur after the product reaches the market. Later discovery of previously unknown problems with a product, including adverse events of unanticipated severity or frequency, or with manufacturing processes, or failure to comply with regulatory requirements, may result in revisions to the approved labeling to add new safety information; imposition of post-market studies or clinical trials to assess new safety risks; or imposition of distribution or other restrictions under a REMS program. Other potential consequences include, among other things:
- •
- restrictions on the marketing or manufacturing of the product, complete withdrawal of the product from the market or voluntary product recalls;
- •
- fines, warning letters or holds on post-approval clinical trials;
- •
- refusal of the FDA to approve pending NDAs or supplements to approved NDAs, or suspension or revocation of product approvals;
- •
- product seizure or detention, or refusal to permit the import or export of products; or
- •
- injunctions or the imposition of civil or criminal penalties.
The FDA strictly regulates marketing, labeling, advertising and promotion of products that are placed on the market. Drugs may be promoted only for the approved indications and in accordance with the provisions of the approved label. The FDA and other agencies actively enforce the laws and regulations prohibiting the promotion of off-label uses, and a company that is found to have improperly promoted off-label uses may be subject to significant liability.
In addition, the distribution of prescription pharmaceutical products is subject to the Prescription Drug Marketing Act ("PDMA"), which regulates the distribution of drugs and drug samples at the federal level, and sets minimum standards for the registration and regulation of drug distributors by the states. Both the PDMA and state laws limit the distribution of prescription pharmaceutical product samples and impose requirements to ensure accountability in distribution.
Abbreviated New Drug Applications for Generic Drugs
In 1984, with passage of the Hatch-Waxman Amendments to the FDCA, Congress authorized the FDA to approve generic drugs that are the same as drugs previously approved by the FDA under the NDA provisions of the statute. To obtain approval of a generic drug, an applicant must submit an abbreviated new drug application, or ANDA, to the agency. In support of such applications, a generic manufacturer may rely on the preclinical and clinical testing previously conducted for a drug product previously approved under an NDA, known as the reference-listed drug ("RLD").
Specifically, in order for an ANDA to be approved, the FDA must find that the generic version is identical to the RLD with respect to the active ingredients, the route of administration, the dosage form, and the strength of the drug. At the same time, the FDA must also determine that the generic drug is "bioequivalent" to the innovator drug. Under the statute, a generic drug is bioequivalent to a RLD if "the rate and extent of absorption of the drug do not show a significant difference from the rate and extent of absorption of the listed drug."
Upon approval of an ANDA, the FDA indicates whether the generic product is "therapeutically equivalent" to the RLD in its publication "Approved Drug Products with Therapeutic Equivalence Evaluations," also referred to as the "Orange Book." Physicians and pharmacists consider a therapeutic equivalent generic drug to be fully substitutable for the RLD. In addition, by operation of certain state laws and numerous health insurance programs, the FDA's designation of therapeutic equivalence often results in substitution of the generic drug without the knowledge or consent of either the prescribing physician or patient.
38
Under the Hatch-Waxman Amendments, the FDA may not approve an ANDA until any applicable period of non-patent exclusivity for the RLD has expired. The FDCA provides a period of five years of non-patent data exclusivity for a new drug containing a new chemical entity. For the purposes of this provision, a new chemical entity ("NCE") is a drug that contains no active moiety that has previously been approved by the FDA in any other NDA. An active moiety is the molecule or ion responsible for the physiological or pharmacological action of the drug substance. In cases where such NCE exclusivity has been granted, an ANDA may not be filed with the FDA until the expiration of five years unless the submission is accompanied by a Paragraph IV certification, which states the proposed generic drug will not infringe the already approved product's listed patents or that such patents are invalid or unenforceable, in which case the applicant may submit its application four years following the original product approval.
The FDCA also provides for a period of three years of exclusivity if the NDA includes reports of one or more new clinical investigations, other than bioavailability or bioequivalence studies, that were conducted by or for the applicant and are essential to the approval of the application. This three-year exclusivity period often protects changes to a previously approved drug product, such as a new dosage form, route of administration, combination or indication. Three-year exclusivity would be available for a drug product that contains a previously approved active moiety, provided the statutory requirement for a new clinical investigation is satisfied. Unlike five-year NCE exclusivity, an award of three-year exclusivity does not block the FDA from accepting ANDAs seeking approval for generic versions of the drug as of the date of approval of the original drug product. The FDA typically makes decisions about awards of data exclusivity shortly before a product is approved.
Hatch-Waxman Patent Certification and the 30-Month Stay
Upon approval of an NDA or a supplement thereto, NDA sponsors are required to list with the FDA each patent with claims that cover the applicant's product or an approved method of using the product. Each of the patents listed by the NDA sponsor is published in the Orange Book. When an ANDA applicant files its application with the FDA, the applicant is required to certify to the FDA concerning any patents listed for the reference product in the Orange Book, except for patents covering methods of use for which the ANDA applicant is not seeking approval. An applicant who submits a section 505(b)(2) NDA, which is for new or improved formulations or new uses of previously approved drug products and where at least one or more of the investigations relied upon by the applicant for approval were not conducted by or for the applicant and for which the applicant has not obtained a right of reference or use from the person by or for whom the investigations were conducted, also must certify to the FDA concerning any patents listed for the approved product in the Orange Book to the same extent that an ANDA applicant would.
Specifically, the applicant must certify with respect to each patent that:
- •
- the required patent information has not been filed;
- •
- the listed patent has expired;
- •
- the listed patent has not expired, but will expire on a particular date and approval is sought after patent expiration; or
- •
- the listed patent is invalid, unenforceable or will not be infringed by the new product.
A certification that the new product will not infringe the already approved product's listed patents or that such patents are invalid or unenforceable is called a Paragraph IV certification. If the applicant does not challenge the listed patents or indicates that it is not seeking approval of a patented method of use, the ANDA application will not be approved until all the listed patents claiming the referenced product have expired (other than method of use patents involving indications for which the ANDA applicant is not seeking approval).
39
If the ANDA applicant has provided a Paragraph IV certification to the FDA, the applicant must also send notice of the Paragraph IV certification to the NDA and patent holders once the ANDA has been accepted for filing by the FDA. The NDA and patent holders may then initiate a patent infringement lawsuit in response to the notice of the Paragraph IV certification. The filing of a patent infringement lawsuit within 45 days after the receipt of a Paragraph IV certification automatically prevents the FDA from approving the ANDA until the earlier of 30 months after the receipt of the Paragraph IV notice, expiration of the patent, or a decision in the infringement case that is favorable to the ANDA applicant.
Pediatric Studies and Exclusivity
Under the Pediatric Research Equity Act of 2003, an NDA or supplement thereto must contain data that are adequate to assess the safety and effectiveness of the drug product for the claimed indications in all relevant pediatric subpopulations, and to support dosing and administration for each pediatric subpopulation for which the product is safe and effective. With enactment of the Food and Drug Administration Safety and Innovation Act ("FDASIA") in 2012, sponsors must also submit pediatric study plans prior to the assessment data. Those plans must contain an outline of the proposed pediatric study or studies the applicant plans to conduct, including study objectives and design, any deferral or waiver requests, and other information required by regulation. The applicant, the FDA, and the FDA's internal review committee must then review the information submitted, consult with each other, and agree upon a final plan. The FDA or the applicant may request an amendment to the plan at any time.
The FDA may, on its own initiative or at the request of the applicant, grant deferrals for submission of some or all pediatric data until after approval of the product for use in adults, or full or partial waivers from the pediatric data requirements. Additional requirements and procedures relating to deferral requests and requests for extension of deferrals are contained in FDASIA. Unless otherwise required by regulation, the pediatric data requirements do not apply to products with orphan designation.
Pediatric exclusivity is another type of non-patent marketing exclusivity in the U.S. and, if granted, provides for the attachment of an additional six months of marketing protection to the term of any existing regulatory exclusivity, including the non-patent and orphan exclusivity. This six-month exclusivity may be granted if an NDA sponsor submits pediatric data that fairly respond to a written request from the FDA for such data. The data do not need to show the product to be effective in the pediatric population studied; rather, if the clinical trial is deemed to fairly respond to the FDA's request, the additional protection is granted. If reports of requested pediatric studies are submitted to and accepted by the FDA within the statutory time limits, whatever statutory or regulatory periods of exclusivity or patent protection cover the product are extended by six months. This is not a patent term extension, but it effectively extends the regulatory period during which the FDA cannot approve another application.
Orphan Drug Designation and Exclusivity
Under the Orphan Drug Act, the FDA may designate a drug product as an "orphan drug" if it is intended to treat a rare disease or condition (generally meaning that it affects fewer than 200,000 individuals in the U.S., or more in cases in which there is no reasonable expectation that the cost of developing and making a drug product available in the U.S. for treatment of the disease or condition will be recovered from sales of the product). A company must request orphan product designation before submitting an NDA. If the request is granted, the FDA will disclose the identity of the therapeutic agent and its potential use. Orphan product designation does not convey any advantage in or shorten the duration of the regulatory review and approval process.
40
If a product with orphan status receives the first FDA approval for the disease or condition for which it has such designation or for a select indication or use within the rare disease or condition for which it was designated, the product generally will be receiving orphan product exclusivity. Orphan product exclusivity means that the FDA may not approve any other applications for the same product for the same indication for seven years, except in certain limited circumstances. Competitors may receive approval of different products for the indication for which the orphan product has exclusivity and may obtain approval for the same product but for a different indication. If a drug or drug product designated as an orphan product ultimately receives marketing approval for an indication broader than what was designated in its orphan product application, it may not be entitled to exclusivity.
In July 2017, the FDA granted Orphan Drug Designation to RA101495 SC for the treatment of PNH in the U.S.
Patent Term Restoration and Extension
A patent claiming a new drug product may be eligible for a limited patent term extension under the Hatch-Waxman Amendments, which permits a patent restoration of up to five years for patent term lost during product development and the FDA regulatory review. The restoration period granted is typically one-half the time between the effective date of an IND and the submission date of an NDA, plus the time between the submission date of an NDA and the ultimate approval date. Patent term restoration cannot be used to extend the remaining term of a patent past a total of 14 years from the product's approval date. Only one patent applicable to an approved drug product is eligible for the extension, and the application for the extension must be submitted prior to the expiration of the patent in question. A patent that covers multiple drugs for which approval is sought can only be extended in connection with one of the approvals. The U.S. Patent and Trademark Office reviews and approves the application for any patent term extension or restoration in consultation with the FDA.
Europe/Rest of World Regulation
In addition to regulations in the U.S., a manufacturer is subject to a variety of regulations in other jurisdictions governing, among other things, clinical trials and any commercial sales and distribution of products, if approved. Even if a manufacturer obtains FDA approval of a product, it must still obtain the requisite approvals from regulatory authorities in foreign countries prior to the commencement of clinical trials or marketing of the product in those countries. Certain countries outside of the U.S. have a similar process that requires the submission of a clinical trial application much like the IND prior to the commencement of human clinical trials. In the E.U., for example, a clinical trial application must be submitted to each country's national health authority and an independent ethics committee, much like the FDA and IRB, respectively. Once the clinical trial application is approved in accordance with a country's requirements, clinical trial development may proceed. To obtain regulatory approval of an investigational drug under E.U. regulatory systems, a manufacturer must submit a marketing authorization application. More concretely, in the EEA (which is comprised of the 28 Member States of the E.U. plus Norway, Liechtenstein and Iceland, medicinal products can only be commercialized after obtaining a Marketing Authorization ("MA"). There are two types of marketing authorizations:
- •
- The Community MA, which is issued by the European Commission through the Centralized Procedure, based on the opinion of the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use of the European Medicines Agency ("EMA") and which is valid throughout the entire territory of the EEA. The Centralized Procedure is mandatory for certain types of products, such as biotechnology medicinal products, orphan medicinal products, and medicinal products indicated for the treatment of AIDS, cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, diabetes, auto-immune and viral diseases. The Centralized Procedure is optional for products containing a new active substance not yet authorized in the EEA, or for products that constitute a significant therapeutic, scientific or technical innovation or which are in the interest of public health in the E.U.
41
- •
- National MAs, which are issued by the competent authorities of the Member States of the EEA and only cover their respective territory, are available for products not falling within the mandatory scope of the Centralized Procedure. Where a product has already been authorized for marketing in a Member State of the EEA, this National MA can be recognized in another Member State through the Mutual Recognition Procedure. If the product has not received a National MA in any Member State at the time of application, it can be approved simultaneously in various Member States through the Decentralized Procedure.
Under the above described procedures, before granting the MA, the EMA or the competent authorities of the Member States of the EEA make an assessment of the risk-benefit balance of the product on the basis of scientific criteria concerning its quality, safety and efficacy.
In Europe, the period of orphan drug exclusivity is ten years, although it may be reduced to six years if, at the end of the fifth year, it is established that the criteria for orphan drug designation are no longer met, in other words, when it is shown on the basis of available evidence that the product is sufficiently profitable not to justify maintenance of market exclusivity. In November 2016, the European Commission has designated RA101495 SC as an orphan medicinal product for the treatment of PNH.
For other countries outside of the E.U., such as countries in Eastern Europe, Latin America or Asia, the requirements governing the conduct of clinical trials, product approval, pricing and reimbursement vary from country to country. In all cases, the clinical trials are to be conducted in accordance with GCP and the applicable regulatory requirements and the ethical principles that have their origin in the Declaration of Helsinki.
Pharmaceutical Coverage, Pricing and Reimbursement
Significant uncertainty exists as to the coverage and reimbursement status of products approved by the FDA and other government authorities. Sales of products will depend, in part, on the extent to which third-party payors, including government health programs in the U.S. such as Medicare and Medicaid, commercial health insurers and managed care organizations, provide coverage, and establish adequate reimbursement levels for, such products. The process for determining whether a payor will provide coverage for a product may be separate from the process for setting the price or reimbursement rate that the payor will pay for the product once coverage is approved. Third-party payors are increasingly challenging the prices charged, examining the medical necessity, and reviewing the cost-effectiveness of medical products and services and imposing controls to manage costs. Third-party payors may limit coverage to specific products on an approved list, or formulary, which might not include all of the approved products for a particular indication.
In order to secure coverage and reimbursement for any product approved for sale, a company may need to conduct expensive pharmacoeconomic studies in order to demonstrate the medical necessity and cost-effectiveness of the product, in addition to the costs required to obtain FDA or other comparable regulatory approvals. Nonetheless, product candidates may not be considered medically necessary or cost effective. Additionally, a payor's decision to provide coverage for a drug product does not imply that an adequate reimbursement rate will be approved. Further, one payor's determination to provide coverage for a drug product does not assure that other payors will also provide coverage for the drug product. Third-party reimbursement may not be sufficient to maintain price levels high enough to realize an appropriate return on investment in product development.
The containment of healthcare costs also has become a priority of federal, state and foreign governments and the prices of drugs have been a focus in this effort. Governments have shown significant interest in implementing cost-containment programs, including price controls, restrictions on reimbursement and requirements for substitution of generic products. Adoption of price controls and cost-containment measures, and adoption of more restrictive policies in jurisdictions with existing
42
controls and measures, could further limit our net revenue and results. Coverage policies and third-party reimbursement rates may change at any time. Even if favorable coverage and reimbursement status is attained for one or more products for which a company or its collaborators receive regulatory approval, less favorable coverage policies and reimbursement rates may be implemented in the future.
Outside the U.S., ensuring adequate coverage and payment for our product candidates will face challenges. Pricing of prescription pharmaceuticals is subject to governmental control in many countries. Pricing negotiations with governmental authorities can extend well beyond the receipt of regulatory marketing approval for a product and may require us to conduct a clinical trial that compares the cost effectiveness of our product candidates or products to other available therapies. The conduct of such a clinical trial could be expensive and result in delays in our commercialization efforts.
In the E.U., pricing and reimbursement schemes vary widely from country to country. Some countries provide that drug products may be marketed only after a reimbursement price has been agreed. Some countries may require the completion of additional studies that compare the cost-effectiveness of a particular drug candidate to currently available therapies. For example, the E.U. provides options for its member states to restrict the range of drug products for which their national health insurance systems provide reimbursement and to control the prices of medicinal products for human use. E.U. member states may approve a specific price for a drug product or it may instead adopt a system of direct or indirect controls on the profitability of the company placing the drug product on the market. Other member states allow companies to fix their own prices for drug products, but monitor and control company profits. The downward pressure on health care costs in general, particularly prescription drugs, has become intense. As a result, increasingly high barriers are being erected to the entry of new products. In addition, in some countries, cross-border imports from low-priced markets exert competitive pressure that may reduce pricing within a country. Any country that has price controls or reimbursement limitations for drug products may not allow favorable reimbursement and pricing arrangements.
Other Healthcare Laws and Regulations
Healthcare providers and third-party payors play a primary role in the recommendation and prescription of drug products that are granted regulatory approval. Arrangements with providers, consultants, third-party payors and customers are subject to broadly applicable fraud and abuse and other healthcare laws and regulations that may constrain our business and/or financial arrangements. Such restrictions under applicable federal and state healthcare laws and regulations, include, without limitation, state and federal anti-kickback, fraud and abuse, false claims, privacy and security, price reporting and physician sunshine laws. Some of our pre-commercial activities are subject to some of these laws.
The federal Anti-Kickback Statute makes it illegal for any person or entity, including a prescription drug manufacturer or a party acting on its behalf to knowingly and willfully, directly or indirectly, solicit, receive, offer, or provide any remuneration that is intended to induce the referral of business, including the purchase, order or recommendation or arranging of, any good or service for which payment may be made under a federal healthcare program, such as Medicare or Medicaid. The term "remuneration" has been broadly interpreted to include anything of value. The Anti-Kickback Statute has been interpreted to apply to arrangements between pharmaceutical manufacturers on one hand and prescribers, purchasers, formulary managers, and beneficiaries on the other. Although there are a number of statutory exceptions and regulatory safe harbors protecting some common activities from prosecution, the exceptions and safe harbors are drawn narrowly. Practices that involve remuneration that may be alleged to be intended to induce prescribing, purchases or recommendations may be subject to scrutiny if they do not qualify for an exception or safe harbor. Failure to meet all of the requirements of a particular applicable statutory exception or regulatory safe harbor does not make the conduct per se illegal under the Anti-Kickback Statute. Instead, the legality of the arrangement will be
43
evaluated on a case-by-case basis based on a cumulative review of all its facts and circumstances. Several courts have interpreted the statute's intent requirement to mean that if any one purpose of an arrangement involving remuneration is to induce referrals of federal healthcare covered business, the Anti-Kickback Statute has been violated. In addition, a person or entity does not need to have actual knowledge of the statute or specific intent to violate it in order to have committed a violation. Violations of this law are punishable by up to five years in prison, and can also result in criminal fines, civil money penalties and exclusion from participation in federal healthcare programs. Moreover, a claim including items or services resulting from a violation of the federal Anti-Kickback Statute constitutes a false or fraudulent claim for purposes of the federal civil False Claims Act.
The federal civil False Claims Act prohibits, among other things, any person or entity from knowingly presenting, or causing to be presented, for payment to, or approval by, federal programs, including Medicare and Medicaid, claims for items or services, including drugs, that are false or fraudulent or not provided as claimed. Persons and entities can be held liable under these laws if they are deemed to "cause" the submission of false or fraudulent claims by, for example, providing inaccurate billing or coding information to customers or promoting a product off-label. In addition, any of our future activities relating to the reporting of wholesaler or estimated retail prices for our products, the reporting of prices used to calculate Medicaid rebate information and other information affecting federal, state and third-party reimbursement for our products, and the sale and marketing of our products, are subject to scrutiny under this law. Penalties for federal civil False Claims Act violations may include up to three times the actual damages sustained by the government, plus mandatory civil penalties of between $11,181 and $22,363 for each separate false claim, the potential for exclusion from participation in federal healthcare programs, and, although the federal False Claims Act is a civil statute, False Claims Act violations may also implicate various federal criminal statutes.
The federal Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 ("HIPAA") created new federal criminal statutes that prohibit among other actions, knowingly and willfully executing, or attempting to execute, a scheme to defraud any healthcare benefit program, including private third-party payors, knowingly and willfully embezzling or stealing from a healthcare benefit program, willfully obstructing a criminal investigation of a healthcare offense, and knowingly and willfully falsifying, concealing or covering up a material fact or making any materially false, fictitious or fraudulent statement in connection with the delivery of or payment for healthcare benefits, items or services. Like the federal Anti-Kickback Statute a person or entity does not need to have actual knowledge of the statute or specific intent to violate it in order to have committed a violation. The civil monetary penalties statute imposes penalties against any person or entity that, among other things, is determined to have presented or caused to be presented a claim to a federal health program that the person knows or should know is for an item or service that was not provided as claimed or is false or fraudulent. Also, many states have similar fraud and abuse statutes or regulations that may be broader in scope and may apply regardless of payor, in addition to items and services reimbursed under Medicaid and other state programs. Additionally, to the extent that any of our product candidates, if approved, are sold in a foreign country, we may be subject to similar foreign laws.
HIPAA, as amended by the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act ("HITECH") and their implementing regulations, including the final omnibus rule published on January 25, 2013, mandates, among other things, the adoption of uniform standards for the electronic exchange of information in common healthcare transactions, as well as standards relating to the privacy and security of individually identifiable health information, which require the adoption of administrative, physical and technical safeguards to protect such information. Among other things, HITECH makes HIPAA's security standards directly applicable to business associates, defined as independent contractors or agents of covered entities that create, receive or obtain protected health information in connection with providing a service for or on behalf of a covered entity. HITECH also increased the civil and criminal penalties that may be imposed against covered entities and business associates, and gave state attorneys general new authority to file civil actions for damages or injunctions
44
in federal courts to enforce the federal HIPAA laws and seek attorney's fees and costs associated with pursuing federal civil actions. In addition, certain state laws govern the privacy and security of health information in certain circumstances, some of which are more stringent than HIPAA and many of which differ from each other in significant ways and may not have the same effect, thus complicating compliance efforts. Failure to comply with these laws, where applicable, can result in the imposition of significant civil and criminal penalties.
The Affordable Care Act ("ACA") imposed, among other things, new annual reporting requirements for covered manufacturers for certain payments and other transfers of value provided to physicians and teaching hospitals, as well as certain ownership and investment interests held by physicians and their immediate family members. Failure to submit timely, accurately and completely the required information for all payments, transfers of value and ownership or investment interests may result in civil monetary penalties of up to an aggregate of $165,786 per year and up to an aggregate of $1,105,241 per year for "knowing failures." Certain states also mandate implementation of compliance programs, impose restrictions on drug manufacturer marketing practices or require the tracking and reporting of gifts, compensation or other remuneration to physicians.
Because we intend to commercialize products that could be reimbursed under a federal healthcare program and other governmental healthcare programs, we intend to develop a comprehensive compliance program that establishes internal control to facilitate adherence to the rules and program requirements to which we will or may become subject. Although the development and implementation of compliance programs designed to establish internal control and facilitate compliance can mitigate the risk of investigation, prosecution, and penalties assessed for violations of these laws, the risks cannot be entirely eliminated.
If our operations are found to be in violation of any of such laws or any other governmental regulations that apply to us, we may be subject to penalties, including, without limitation, administrative, civil and criminal penalties, damages, fines, disgorgement, contractual damages, reputational harm, diminished profits and future earnings, the curtailment or restructuring of our operations, exclusion from participation in federal and state healthcare programs and individual imprisonment, any of which could adversely affect our ability to operate our business and our financial results.
Healthcare Reform
There have been a number of federal and state proposals during the last few years regarding the pricing of pharmaceutical and biopharmaceutical products, government control and other changes to the healthcare system in the U.S.
By way of example, the U.S. and state governments continue to propose and pass legislation designed to reduce the cost of healthcare. In March 2010, the U.S. Congress passed the ACA, which, among other things, includes changes to the coverage and payment for drug products under government health care programs. Among the provisions of the ACA of importance to our potential drug candidates are:
- •
- an annual, nondeductible fee on any entity that manufactures or imports specified branded prescription drugs and biologic products, apportioned
among these entities according to their market share in certain government healthcare programs;
- •
- expansion of eligibility criteria for Medicaid programs by, among other things, allowing states to offer Medicaid coverage to certain
individuals with income at or below 133% of the federal poverty level, thereby potentially increasing a manufacturer's Medicaid rebate liability;
- •
- expansion of manufacturers' rebate liability under the Medicaid Drug Rebate Program by increasing the minimum rebate for both branded and generic drugs and revising the definition of
45
- •
- a new methodology by which rebates owed by manufacturers under the Medicaid Drug Rebate Program are calculated for drugs that are inhaled,
infused, instilled, implanted or injected;
- •
- expansion of the types of entities eligible for the 340B drug discount program;
- •
- establishment of the Medicare Part D coverage gap discount program by requiring manufacturers to provide a 50% (increasing to 70%
effective January 1, 2019) point-of-sale-discount off the negotiated price of applicable brand drugs to eligible beneficiaries during their coverage gap period as a condition for the
manufacturers' outpatient drugs to be covered under Medicare Part D; and
- •
- a new Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute to oversee, identify priorities in, and conduct comparative clinical effectiveness research, along with funding for such research.
"average manufacturer price," or AMP, for calculating and reporting Medicaid drug rebates on outpatient prescription drug prices;
Some of the provisions of the Affordable Care Act ("ACA") have yet to be fully implemented, while certain provisions have been subject to judicial and Congressional challenges. For example, the Bipartisan Budget Act of 2018 among other things, amends the ACA, effective January 1, 2019, to reduce the coverage gap in most Medicare Part D plans, commonly referred to as the "donut hole." The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 includes a provision repealing, effective January 1, 2019, the tax-based shared responsibility payment imposed by the ACA on certain individuals who fail to maintain qualifying health coverage for all or part of a year that is commonly referred to as the "individual mandate." On January 22, 2018, President Trump signed a continuing resolution on appropriations for fiscal year 2018 that delayed the implementation of certain ACA-mandated fees, including the so-called "Cadillac" tax on certain high cost employer-sponsored insurance plan, the annual fee imposed on certain high cost employer-sponsored insurance plans, the annual fee imposed on certain health insurance providers based on market share, and the medical device exercise tax on non-exempt medical devices. On October 13, 2017, President Trump signed an Executive Order terminating the cost-sharing subsidies that reimburse insurers under the ACA. Several state Attorneys General filed suit to stop the administration from terminating the subsidies, but their request for a restraining order was denied by a federal judge in California on October 25, 2017. In addition, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services has recently proposed regulations that would give states greater flexibility in setting benchmarks for insurers in the individual and small group marketplaces, which may have the effect of relaxing the essential health benefits required under the ACA for plans sold through such marketplaces. Further, on January 20, 2017, President Trump signed an Executive Order directing federal agencies with authorities and responsibilities under the ACA to waive, defer, grant exemptions from, or delay the implementation of any provision of the ACA that would impose a fiscal burden on states or a cost, fee, tax, penalty or regulatory burden on individuals, healthcare providers, health insurers, or manufacturers of pharmaceuticals or medical devices. Congress also could consider subsequent legislation to modify, repeal, or replace provisions of the ACA that are repealed. Thus, the full impact of the ACA, any law replacing elements of it, or the political uncertainty surrounding its repeal or replacement on our business remains unclear. Adoption of government controls and measures, and tightening of restrictive policies in jurisdictions with existing controls and measures, could limit payments for pharmaceuticals.
Other legislative changes have been proposed and adopted in the U.S. since the ACA was enacted. For example, in August 2011, the Budget Control Act of 2011, among other things, created measures for spending reductions by Congress. A Joint Select Committee on Deficit Reduction, tasked with recommending a targeted deficit reduction of at least $1.2 trillion for the years 2012 through 2021, was unable to reach required goals, thereby triggering the legislation's automatic reduction to several government programs. This includes aggregate reductions of Medicare payments to providers of 2% per fiscal year, which went into effect in April 2013 and will remain in effect through 2027 unless additional
46
Congressional action is taken. In January 2013, President Obama signed into law the American Taxpayer Relief Act of 2012, which, among other things, further reduced Medicare payments to several providers, including hospitals, imaging centers and cancer treatment centers, and increased the statute of limitations period for the government to recover overpayments to providers from three to five years.
There have been, and likely will continue to be, legislative and regulatory proposals at the foreign, federal and state levels directed at broadening the availability of healthcare and containing or lowering the cost of healthcare. Such reforms could have an adverse effect on anticipated revenues from product candidates that we may successfully develop and for which we may obtain regulatory approval and may affect our overall financial condition and ability to develop product candidates.
Employees
As of December 31, 2017, we had 63 full-time or part-time employees, including 26 employees with M.D. or Ph.D. degrees. Of these employees, 52 employees are engaged in research and development activities and 11 employees are engaged in general and administrative activities. None of our employees are represented by labor unions or covered by collective bargaining agreements. We consider the relationship with our employees to be good.
Corporate Information
Our principal executive offices are located at 87 Cambridge Park Drive, Cambridge, MA 02140 and our telephone number is 617-401-4060. Our website address is www.rapharma.com. We do not incorporate the information on or accessible through our website into this Annual Report on Form 10-K, and you should not consider any information on, or that can be accessed through, our website a part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K or any other filing we make with the Securities and Exchange Commission.
We use various trademarks and trade names in our business, including without limitation our corporate name and logo. All other trademarks or trade names, including without limitation corporate names and logos, referred to in this report are the property of their respective owners. Solely for convenience, the trademarks and trade names in this report may be referred to without the ® and ™ symbols, but such references should not be construed as any indicator that their respective owners will not assert, to the fullest extent under applicable law, their rights thereto.
We qualify as an "emerging growth company" as defined in the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act of 2012, as amended ("JOBS Act"). As an emerging growth company, we may take advantage of specified reduced disclosure and other requirements that are otherwise applicable generally to public companies. We would cease to be an emerging growth company on the date that is the earliest of: (i) the last day of the fiscal year in which we have total annual gross revenues of $1.07 billion or more; (ii) December 31, 2021; (iii) the date on which we have issued more than $1 billion in nonconvertible debt during the previous three years; or (iv) the date on which we are deemed to be a large accelerated filer under the rules of the SEC.
Available Information
We post our Annual Report on Form 10-K, Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, Current Reports on Form 8-K, and any amendments to those reports filed or furnished pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, on the investor relations section of our public website (www.rapharma.com), free of charge, as soon as reasonably practicable after we electronically file such material with, or furnish it to, the SEC. In addition, you can read our SEC filings over the Internet at the SEC's website at https://www.sec.gov/. The contents of these websites are not incorporated into this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Further, our references to the URLs for these websites are intended to be inactive textual references only. You may also read and copy any document we file with the SEC at its public reference facility at 100 F Street, N.E., Room 1580, Washington, D.C. 20549. Please call the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330 for further information on the operation of the public reference facilities.
47
You should consider carefully the following risk factors, together with all the other information in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, including our consolidated financial statements and notes thereto, and in our other public filings with the SEC. The occurrence of any of the following risks could harm our business, financial condition, results of operations and/or growth prospects or cause our actual results to differ materially from those contained in forward-looking statements we have made in this report and those we may make from time to time. You should consider all of the risk factors described when evaluating our business.
Risks Related to Our Financial Position and Need for Additional Capital
We have a limited operating history and have incurred significant losses since our inception, and we anticipate that we will continue to incur losses for the foreseeable future.
We do not expect to generate revenue or profitability that is necessary to finance our operations in the short term. We incurred net losses of $54.4 million, $28.9 million and $13.9 million for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively. As of December 31, 2017, we had an accumulated deficit of $123.2 million. We do not expect to generate any product revenues in the foreseeable future. We do not know whether or when we will generate revenue or become profitable.
We have devoted substantially all of our financial resources and efforts to research and development, including preclinical studies and our clinical trials. Our net losses may fluctuate significantly from quarter to quarter and year to year. Net losses and negative cash flows have had, and will continue to have, an adverse effect on our stockholders' equity and working capital.
We expect to continue to incur significant expenses and increasing operating losses for the foreseeable future. We anticipate that our expenses will increase substantially if and as we:
- •
- continue to develop and conduct clinical trials with respect to our lead product candidate, RA101495 SC;
- •
- initiate and continue research, preclinical and clinical development efforts for any future product candidates;
- •
- seek to identify additional research programs and additional product candidates;
- •
- seek regulatory and marketing approvals for our product candidates that successfully complete clinical trials, if any;
- •
- establish sales, marketing, distribution and other commercial infrastructure in the future to commercialize various products for which we may
obtain marketing approval, if any;
- •
- require the manufacture of larger quantities of product candidates for clinical development and, potentially, commercialization;
- •
- maintain, expand and protect our intellectual property portfolio;
- •
- hire and retain additional personnel, such as clinical, quality control and scientific personnel;
- •
- add operational, financial and management information systems and personnel, including personnel to support our product development and help us
comply with our obligations as a public company; and
- •
- add equipment and physical infrastructure to support our research and development.
The net losses we incur may fluctuate significantly from quarter to quarter and year to year, such that a period-to-period comparison of our results of operations may not be a good indication of our
48
future performance. In any particular quarter or quarters, our operating results could be below the expectations of securities analysts or investors, which could cause our stock price to decline.
We will require substantial additional financing to achieve our goals, and a failure to obtain this necessary capital when needed on acceptable terms, or at all, could force us to delay, reduce or eliminate our product discovery and development programs or commercialization efforts.
Developing pharmaceutical products, including conducting preclinical studies and clinical trials, is a very time-consuming, expensive and uncertain process that takes years to complete. Our operations have consumed substantial amounts of cash since inception. As of December 31, 2017, our cash, cash equivalents were $70.4 million. In February 2018, we raised an additional $54.1 million in net proceeds in our underwritten public offering. Our research and development expenses were $45.3 million, $27.9 million and $15.2 million for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively. We expect our expenses to increase in connection with our ongoing activities, particularly as we initiate new clinical trials of, initiate new research and preclinical development efforts for and seek marketing approval for, our current or future product candidates or any product candidates that we acquire, if any. In addition, if we obtain marketing approval for any of our product candidates, we may incur significant commercialization expenses related to product sales, marketing, manufacturing and distribution to the extent that such sales, marketing, manufacturing and distribution are not the responsibility of a future collaborator. Furthermore, as a public company, we will incur significant additional costs associated with operating as a public company. Accordingly, we will need to obtain substantial additional funding in connection with our continuing operations. If we are unable to raise capital when needed or on attractive terms, we may be forced to delay, reduce or eliminate our research and development programs or any future commercialization efforts.
We will be required to expend significant funds in order to advance the development of RA101495 SC, as well as other product candidates we may seek to develop. In addition, while we may seek one or more collaborators for future development of our product candidates for one or more indications, we may not be able to enter into a collaboration for any of our product candidates for such indications on suitable terms, on a timely basis or at all. In any event, our existing cash and cash equivalents will not be sufficient to fund all of the efforts that we plan to undertake or to fund the completion of development of any of our product candidates. Accordingly, we will be required to obtain further funding through public or private equity offerings, debt financings, collaborations and licensing arrangements or other sources. We do not have any committed external source of funds. Adequate additional financing may not be available to us on acceptable terms, or at all. Our failure to raise capital as and when needed would have a negative impact on our financial condition and our ability to pursue our business strategy.
Our future funding requirements, both short-term and long-term, will depend on many factors, including:
- •
- the scope, progress, timing, costs and results of clinical trials of, and research and preclinical development efforts for, our current and
future product candidates;
- •
- our ability to enter into, and the terms and timing of, any collaborations, licensing or other arrangements;
- •
- the number of future product candidates that we pursue and their development requirements;
- •
- the outcome, timing and costs of seeking regulatory approvals;
- •
- the costs of commercialization activities for any of our product candidates that receive marketing approval to the extent such costs are not the responsibility of any future collaborators, including the costs and timing of establishing product sales, marketing, distribution and manufacturing capabilities;
49
- •
- subject to receipt of marketing approval, revenue, if any, received from commercial sales of our current and future product candidates;
- •
- our headcount growth and associated costs as we expand our research and development and establish a commercial infrastructure;
- •
- the costs of preparing, filing and prosecuting patent applications, maintaining and protecting our intellectual property rights including
enforcing and defending intellectual property related claims; and
- •
- the costs of operating as a public company.
We may never achieve or maintain profitability and investors may lose their entire investment.
Our ability to become and remain profitable depends on our ability to generate revenue. We do not expect to generate significant revenue unless and until we are, or any future collaborator is, able to obtain marketing approval for, and successfully commercialize, one or more of our product candidates. Successful commercialization will require achievement of key milestones, including completing clinical trials of our product candidates, obtaining marketing approval for these product candidates, manufacturing, marketing and selling those products for which we, or any of our future collaborators, may obtain marketing approval, satisfying any post-marketing requirements and obtaining reimbursement for our products from private insurance or government payors. Because of the uncertainties and risks associated with these activities, we are unable to accurately predict the timing and amount of revenues, and if or when we might achieve profitability. We and any future collaborators may never succeed in these activities and, even if we do, or any future collaborators do, we may never generate revenues that are large enough for us to achieve profitability. Even if we do achieve profitability, we may not be able to sustain or increase profitability on a quarterly or annual basis.
Because our only source of revenue to date, our research collaboration with Merck & Co., or Merck, has reached the end of its research term and identified a product candidate, to the extent we continue to receive revenue from this collaboration, we must rely on Merck's efforts to develop and commercialize that target candidate, which we do not control.
Our failure to become and remain profitable would depress the market price of our common stock and could impair our ability to raise capital, expand our business, diversify our product offerings or continue our operations. If we continue to suffer losses as we have in the past, investors may not receive any return on their investment and may lose their entire investment.
Raising additional capital may cause dilution to our stockholders, restrict our operations or require us to relinquish rights to our technologies or product candidates.
We expect our expenses to increase in connection with our planned operations. To the extent that we raise additional capital through the sale of common stock, convertible securities or other equity securities, the ownership interest of our existing stockholders may be diluted, and the terms of these securities could include liquidation or other preferences and anti-dilution protections that could adversely affect the rights of our common stockholders. In addition, debt financing, if available, may result in fixed payment obligations and may involve agreements that include restrictive covenants that limit our ability to take specific actions, such as incurring additional debt, making capital expenditures, creating liens, redeeming stock or declaring dividends, that could adversely impact our ability to conduct our business. In addition, securing financing could require a substantial amount of time and attention from our management and may divert a disproportionate amount of their attention away from day-to-day activities, which may adversely affect our management's ability to oversee the development of our product candidates.
50
If we raise additional funds through collaborations or marketing, distribution or licensing arrangements with third parties, we may have to relinquish valuable rights to our technologies, future revenue streams or product candidates or grant licenses on terms that may not be favorable to us. If we are unable to raise additional funds when needed, we may be required to delay, limit, reduce or terminate our product development or future commercialization efforts or grant rights to develop and market product candidates that we would otherwise prefer to develop and market ourselves.
We have a limited operating history and no history of commercializing pharmaceutical products, which may make it difficult to evaluate the prospects for our future viability.
We commenced operations in 2008. Our operations to date have been limited to financing and staffing our company, developing our technology and conducting preclinical research and early-stage clinical trials for our product candidates. We have not yet demonstrated an ability to successfully conduct late-stage clinical trials, obtain marketing approvals, manufacture a commercial-scale product, or arrange for a third party to do so on our behalf, or conduct sales and marketing activities necessary for successful product commercialization. Accordingly, you should consider our prospects in light of the costs, uncertainties, delays and difficulties frequently encountered by companies in the early stages of development, especially clinical-stage biopharmaceutical companies such as ours. Any predictions you make about our future success or viability may not be as accurate as they could be if we had a longer operating history or a history of successfully developing and commercializing pharmaceutical products.
We may encounter unforeseen expenses, difficulties, complications, delays and other known or unknown factors in achieving our business objectives. We will eventually need to transition from a company with a development focus to a company capable of supporting commercial activities. We may not be successful in such a transition.
We expect our financial condition and operating results to continue to fluctuate significantly from quarter to quarter and year to year due to a variety of factors, many of which are beyond our control. Accordingly, you should not rely upon the results of any quarterly or annual periods as indications of future operating performance.
Comprehensive tax reform legislation could adversely affect our business and financial condition.
The United States, or U.S., government has recently enacted comprehensive tax legislation that includes significant changes to the taxation of business entities, referenced herein as the Tax Reform Act. These changes include, among others, a permanent reduction to the corporate income tax rate, limiting interest deductions, adopting elements of a territorial tax system and introducing certain anti-base erosion provisions. The effect of the Tax Reform Act on our business, whether adverse or favorable, is uncertain, and it may not become evident for some period of time.
Risks Related to the Discovery, Development and Commercialization of Our Product Candidates
We are at a very early stage in our development efforts, our approach is unproven and we may not be able to successfully develop and commercialize any product candidates.
RA101495 SC is a novel therapeutic compound and its potential therapeutic benefit is unproven. There is only one approved therapy inhibiting C5. Our product candidates may not demonstrate in patients any or all of the pharmacological benefits we believe they may possess or compare favorably to the approved C5 inhibitor therapy. We have not yet succeeded and may never succeed in demonstrating efficacy and safety for these or any other product candidates in clinical trials or in obtaining marketing approval thereafter. For example, although we have evaluated RA101495 SC in preclinical studies and have evaluated RA101495 SC in an early-stage clinical trial and in our Phase 2 clinical trial, we have not yet advanced RA101495 SC into Phase 3 clinical development, nor have we obtained regulatory approval to sell any product based on our therapeutic approaches.
51
Our development plans include exploring the potential of complement inhibition, including C5 inhibition, to treat complement-mediated diseases for which complement inhibition has not been fully validated. This is an unproven approach to the treatment of diseases such as generalized myasthenia gravis, or gMG, atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome, or aHUS, and lupus nephritis, or LN. The scientific evidence to support the feasibility of developing products to treat such disease by C5 inhibition is both preliminary and limited. Accordingly, our focus on treating these diseases may not result in the discovery and development of commercially viable products.
If we are unsuccessful in our development efforts, we may not be able to advance the development of our product candidates, commercialize products, raise capital, expand our business or continue our operations.
Our business depends heavily upon the success of RA101495 SC, which is still under development. If we are unable to obtain regulatory approval for or successfully commercialize RA101495 SC, our business will be materially harmed.
We currently have no products approved for sale and are investing a significant portion of our efforts and financial resources in the development of our lead product candidate, RA101495 SC. Successful continued development and ultimate regulatory approval of RA101495 SC for paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria, or PNH, and, in the future, a range of debilitating autoimmune diseases including gMG, aHUS and LN is critical to the future success of our business. We will need to raise sufficient funds for, and successfully enroll and complete, our clinical development program for RA101495 SC in PNH. The future regulatory and commercial success of this product candidate is subject to a number of risks, including the following:
- •
- we may not have sufficient financial and other resources to initiate or complete the necessary clinical trials for RA101495 SC;
- •
- notwithstanding topline results from our Phase 2 clinical trial and ongoing long-term extension trial in PNH, we may not be able to
obtain adequate evidence of clinical efficacy and safety for RA101495 SC in PNH, gMG or renally impaired patients;
- •
- we do not know the degree to which RA101495 SC will be accepted as a therapy, if approved;
- •
- in our clinical programs, we may experience variability in patients, adjustments to clinical trial procedures and the need for additional
clinical trial sites, which could delay our clinical trial progress;
- •
- the results of our clinical trials may not meet the level of statistical or clinical significance required by the Food and Drug Administration,
or FDA, the European Medicines Agency, or EMA, or comparable foreign regulatory bodies for marketing approval;
- •
- notwithstanding complete enrollment in our Phase 2 clinical trial in PNH, we may have difficulty enrolling patients in trials if, for
instance, a current or future effective standard of care limits the desire of patients, physicians, or regulatory agencies to participate in or support clinical trials;
- •
- notwithstanding the lack of meaningful safety or tolerability concerns in our Phase 2 clinical trial and ongoing long-term extension
trial in PNH, patients in our clinical trials may die or suffer other adverse effects for reasons that may or may not be related to RA101495 SC, which could delay or prevent further clinical
development;
- •
- the standards implemented by regulatory agencies may change at any time;
- •
- the FDA, EMA or other foreign regulatory agencies may require endpoints for a clinical trial for the treatment of PNH, gMG, aHUS and LN that differ from the endpoints of our planned current or future trials, which may require us to conduct additional clinical trials;
52
- •
- the mechanism of action of RA101495 SC is complex and we cannot guarantee the degree to which it will translate into a medical benefit in any
indications;
- •
- if approved for PNH, gMG, aHUS and LN, RA101495 SC will likely compete with the off-label use of currently marketed products and other
therapies in development;
- •
- our intellectual property rights may not be patentable, valid or enforceable; and
- •
- we may not be able to obtain, maintain, defend or enforce our patents and other intellectual property rights.
Of the large number of drugs in development in the pharmaceutical industry, only a small percentage result in the submission of a new drug application, or NDA, to the FDA and even fewer are approved for commercialization. Furthermore, even if we do receive regulatory approval to market RA101495 SC, any such approval may be subject to limitations on the indicated uses or patient populations for which we may market the product. Accordingly, even if we are able to obtain the requisite financing to continue to fund our development programs, we cannot assure you that RA101495 SC will be successfully developed or commercialized. If we or any of our future development partners are unable to develop, or obtain regulatory approval for, or, if approved, successfully commercialize RA101495 SC, we may not be able to generate sufficient revenue to continue our business.
We face substantial competition, which may result in others discovering, developing or commercializing products before or more successfully than we do, and reducing or eliminating our commercial opportunity.
The development and commercialization of new products is highly competitive. We expect that we, and any future collaborators, will face significant competition from major pharmaceutical companies, specialty pharmaceutical companies and biotechnology companies worldwide with respect to any of our product candidates that we, or any future collaborators, may seek to develop or commercialize in the future, including from drugs that act through the complement system and drugs that use different approaches. The principal competitor for our program in PNH is eculizumab, a C5 inhibitor, which is marketed as Soliris by Alexion Pharmaceuticals and is the only drug approved for the treatment of PNH. Alexion Pharmaceuticals is also developing a next-generation C5 inhibitor named ALXN 1210 that is designed to use a less frequent intravenous dosing schedule. We are also aware that there are a number of other companies that are actively developing product candidates for the treatment of PNH, including AMY101 directed at complement component 3, or C3, inhibition that is currently in early clinical development by Amyndas Pharmaceuticals, a product candidate directed at C3 inhibition such as APL-2 that is currently in clinical development by Apellis Pharmaceuticals, product candidates directed at C5 inhibition such as ALN-CC5, an RNAi therapeutic targeting the production of C5 being developed by Alnylam that is in early clinical trials, Coversin, a small protein inhibitor of C5 being developed by Akari Pharmaceuticals that is in early clinical trials, LFG316, a monoclonal antibody inhibitor of C5 being developed by Novartis Pharma, a biosimilar product candidate ABP595 being developed by Amgen that is currently in clinical trials, RO7112689, a monoclonal antibody inhibitor of C5 being developed by F. Hoffmann-La Roche, REGN3918, a C5 antibody developed by Regeneron and other product candidates directed at other mechanisms of complement inhibition such as ACH-4471, an orally available small molecule inhibitor of complement Factor D, that is currently in development by Achillion Pharmaceuticals.
MG is currently treated with cholinesterase inhibitors and non-specific immunosuppressive agents, including azathioprine, cyclophosphamide, cyclosporine, intravenous immunoglobulin, or IVIG, mycophenolate, prednisone, and tacrolimus. Alexion Pharmaceuticals recently announced approval of eculizumab for the treatment of refractory MG in Europe and gMG in the U.S. Both rituximab, marketed by F. Hoffmann-La Roche, and belimumab, marketed by GlaxoSmithKline, which target B cell activity, are in clinical development for gMG. Anti-CD40, being developed as CFZ533 by Novartis
53
Pharma, bortezomib, and the FcRN agonist ARGX-113 developed by Argen-X, are being tested in clinical trials in gMG. A therapeutic vaccine targeting B and T-cell receptors (CV-MG-01) is in early clinical testing for gMG.
Our competitors may succeed in developing, acquiring or licensing technologies and products that are more effective, have fewer side effects or more tolerable side effects or are less costly than any product candidates that we are currently developing or that we may develop, which could render our product candidates obsolete and noncompetitive.
Our commercial opportunity could be reduced or eliminated if our competitors develop and commercialize products that are safer, more effective, have fewer or less severe side effects, are more convenient or are less expensive than any products that we, or any future collaborators, may develop. Our competitors also may obtain FDA or other marketing approval for their products before we, or any future collaborators, are able to obtain approval for ours, which could result in our competitors establishing a strong market position before we, or any future collaborators, are able to enter the market.
Many of our existing and potential future competitors have significantly greater financial resources and expertise in research and development, manufacturing, preclinical testing, conducting clinical trials, obtaining marketing approvals and marketing approved products than we do, and may be able to reduce the price at which they sell their products. Mergers and acquisitions in the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries may result in even more resources being concentrated among a smaller number of our competitors. Smaller or early stage companies may also prove to be significant competitors, particularly through collaborative arrangements with large and established companies. These competitors also compete with us in recruiting and retaining qualified scientific and management personnel and establishing clinical trial sites and patient registration for clinical trials, as well as in acquiring technologies complementary to, or necessary for, the development of our product candidates.
If clinical trials of our product candidates fail to satisfactorily demonstrate safety and efficacy to the FDA and other regulators, we, or any future collaborators, may incur additional costs or experience delays in completing, or ultimately be unable to complete, the development and commercialization of these product candidates.
We, and any future collaborators, are not permitted to commercialize, market, promote or sell any product candidate in the U.S. without obtaining marketing approval from the FDA. Foreign regulatory authorities, such as the EMA, impose similar requirements. We have not previously submitted a NDA to the FDA or similar drug approval filings to comparable foreign regulatory authorities for any of our product candidates. We, and any future collaborators, must complete extensive preclinical development and clinical trials to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of our product candidates in humans before we will be able to obtain these approvals.
Clinical testing is expensive, is difficult to design and implement, can take many years to complete and is inherently uncertain as to outcome. We cannot guarantee that any clinical trials will be conducted as planned or completed on schedule, if at all. The clinical development of our product candidates is susceptible to the risk of failure inherent at any stage of product development, including failure to demonstrate efficacy in a clinical trial or across a broad population of patients, the occurrence of adverse events that are severe or medically or commercially unacceptable, failure to comply with protocols or applicable regulatory requirements and determination by the FDA or any comparable foreign regulatory authority that a product candidate may not continue development or is not approvable. It is possible that even if one or more of our product candidates has a beneficial effect, that effect will not be detected during clinical evaluation as a result of one or more of a variety of factors, including the size, duration, design, measurements, conduct or analysis of our clinical trials. Conversely, as a result of the same factors, our clinical trials may indicate an apparent positive effect of
54
a product candidate that is greater than the actual positive effect, if any. Similarly, in our clinical trials we may fail to detect toxicity of or intolerability caused by our product candidates, or mistakenly believe that our product candidates are toxic or not well tolerated when that is not in fact the case.
Any inability to successfully complete preclinical and clinical development could result in additional costs to us, or any future collaborators, and impair our ability to generate revenues from product sales, regulatory and commercialization milestones and royalties. Moreover, if we, or any future collaborators, are required to conduct additional clinical trials or other testing of our product candidates beyond the trials and testing that we or they contemplate, if we or they are unable to successfully complete clinical trials of our product candidates or other testing or the results of these trials or tests are unfavorable, uncertain or are only modestly favorable, or there are unacceptable safety concerns associated with our product candidates, we, or any future collaborators may:
- •
- incur additional unplanned costs;
- •
- be delayed in obtaining marketing approval for our product candidates;
- •
- not obtain marketing approval at all;
- •
- obtain approval for indications or patient populations that are not as broad as intended or desired;
- •
- obtain approval with labeling that includes significant use or distribution restrictions or significant safety warnings, including boxed
warnings;
- •
- be subject to additional post-marketing testing or other requirements; or
- •
- be required to remove the product from the market after obtaining marketing approval.
Our failure to successfully complete clinical trials of our product candidates and to demonstrate the efficacy and safety necessary to obtain regulatory approval to market any of our product candidates would significantly harm our business.
Our product candidates may cause undesirable side effects or have other properties that could delay or prevent their regulatory approval, limit the commercial profile of an approved label, or result in significant negative consequences following marketing approval, if any.
Undesirable side effects caused by our product candidates could cause us or regulatory authorities to interrupt, delay or halt clinical trials and could result in a more restrictive label or the delay or denial of regulatory approval by the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities. Results of our clinical trials could reveal a high and unacceptable severity and prevalence of side effects or unexpected characteristics. To date, subjects exposed to our product candidate RA101495 SC in our Phase 1 clinical trial have experienced drug-related side effects including injection site erythema, which was reported in patients receiving the highest dose, fatigue, headache, dizziness, rash and upper respiratory tract infection. In our Phase 2 clinical trial of RA101495 SC, the most frequent adverse effect that we observed was headache.
If unacceptable side effects arise in the development of our product candidates, we, the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities, the Institutional Review Boards, or IRBs, or independent ethics committees at the institutions in which our studies are conducted, or the Data Safety Monitoring Board, or DSMB, could suspend or terminate our clinical trials or the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities could order us to cease clinical trials or deny approval of our product candidates for any or all targeted indications. Treatment-related side effects could also affect patient recruitment or the ability of enrolled patients to complete the trial or result in potential product liability claims. In addition, these side effects may not be appropriately recognized or managed by the treating medical staff. We expect to have to train medical personnel using our product candidates to understand the side
55
effect profiles for our clinical trials and upon any commercialization of any of our product candidates. Inadequate training in recognizing or managing the potential side effects of our product candidates could result in patient injury or death. Any of these occurrences may harm our business, financial condition and prospects significantly.
Moreover, clinical trials of our product candidates are conducted in carefully defined sets of patients who have agreed to enter into clinical trials. Consequently, it is possible that our clinical trials, or those of any future collaborator, may indicate an apparent positive effect of a product candidate that is greater than the actual positive effect, if any, or alternatively fail to identify undesirable side effects. If, following approval of a product candidate, we, or others, discover that the product is less effective than previously believed or causes undesirable side effects that were not previously identified, any of the following adverse events could occur:
- •
- regulatory authorities may withdraw their approval of the product or seize the product;
- •
- we, or any future collaborators, may need to recall the product, or be required to change the way the product is administered or conduct
additional clinical trials;
- •
- additional restrictions may be imposed on the marketing of, or the manufacturing processes for, the particular product;
- •
- we may be subject to fines, injunctions or the imposition of civil or criminal penalties;
- •
- regulatory authorities may require the addition of labeling statements, such as a "black box" warning or a contraindication;
- •
- we, or any future collaborators, may be required to create a Medication Guide outlining the risks of the previously unidentified side effects
for distribution to patients;
- •
- we, or any future collaborators, could be sued and held liable for harm caused to patients;
- •
- the product may become less competitive; and
- •
- our reputation may suffer.
Any of these events could harm our business and operations and could negatively impact our stock price.
If we fail to develop and commercialize other product candidates, we may be unable to grow our business.
Although the development and commercialization of RA101495 SC is our primary focus, as part of our longer-term growth strategy, we plan to evaluate the development and commercialization of other therapies for complement-mediated diseases, including rare blood, neurologic, ocular, renal and inflammatory diseases. We will evaluate internal opportunities from our current product candidates, and also may choose to in-license or acquire other product candidates as well as commercial products to treat patients suffering from immune-mediated or orphan or other disorders with high unmet medical needs and limited treatment options. These other product candidates will require additional, time-consuming development efforts prior to commercial sale, including preclinical studies, clinical trials and approval by the FDA and/or applicable foreign regulatory authorities. All product candidates are prone to the risks of failure that are inherent in pharmaceutical product development, including the possibility that the product candidate will not be shown to be sufficiently safe and effective for approval by regulatory authorities. In addition, we cannot assure you that any such products that are approved will be manufactured or produced economically, successfully commercialized or widely accepted in the marketplace or be more effective than other commercially available alternatives.
56
Our preclinical programs may not produce product candidates that are suitable for clinical trials or that can be successfully commercialized or generate revenue through partnerships.
We must successfully complete preclinical testing for RA101495 SC and our other programs, which may include demonstrating activity and comprehensive studies to show the lack of toxicity and other adverse effects in established animal models, before commencing clinical trials for any product candidate. Many pharmaceutical and biological products do not successfully complete preclinical testing and, even if preclinical testing is successfully completed, may fail in clinical trials. In addition, there can be no assurance that positive results from preclinical studies will be predictive of results obtained from subsequent preclinical studies or clinical trials. We also cannot be certain that any product candidates that do advance into clinical trials will successfully demonstrate safety and efficacy in clinical trials. Even if we achieve positive results in early clinical trials, they may not be predictive of the results in later trials.
We may expend our limited resources to pursue a particular product candidate or indication and fail to capitalize on product candidates or indications that may be more profitable or for which there is a greater likelihood of success.
Because we have limited financial and managerial resources, we intend to focus on developing product candidates for specific indications that we identify as most likely to succeed, in terms of both their potential for marketing approval and commercialization. As a result, we may forego or delay pursuit of opportunities with other product candidates or for other indications that may prove to have greater commercial potential.
Our resource allocation decisions may cause us to fail to capitalize on viable commercial products or profitable market opportunities. Our spending on current and future research and development programs and product candidates for specific indications may not yield any commercially viable product candidates. If we do not accurately evaluate the commercial potential or target market for a particular product candidate, we may relinquish valuable rights to that product candidate through collaboration, licensing or other royalty arrangements in cases in which it would have been more advantageous for us to retain sole development and commercialization rights to the product candidate.
If the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities approve generic versions of any of our product candidates that receive marketing approval, or such authorities do not grant such products appropriate periods of data exclusivity before approving generic versions of such products, the sales of such products could be adversely affected.
Once a NDA is approved, the product covered thereby becomes a "reference-listed drug" in the FDA's publication, "Approved Drug Products with Therapeutic Equivalence Evaluations," or the Orange Book. Manufacturers may seek approval of generic versions of reference-listed drugs through submission of abbreviated new drug applications, or ANDAs, in the U.S. In support of an ANDA, a generic manufacturer generally must show that its product has the same active ingredient(s), dosage form, strength, route of administration and conditions of use or labeling as the reference-listed drug and that the generic version is bioequivalent to the reference-listed drug, meaning, in part, that it is absorbed in the body at the same rate and to the same extent. Generic products may be significantly less costly to bring to market than the reference-listed drug and companies that produce generic products are generally able to offer them at lower prices. Thus, following the introduction of a generic drug, a significant percentage of the sales of any branded product or reference-listed drug may be typically lost to the generic product.
The FDA may not approve an ANDA for a generic product until any applicable period of non-patent exclusivity for the reference-listed drug has expired. The Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, or FDCA, provides a period of five years of non-patent exclusivity for a new drug containing a
57
new chemical entity, or NCE. Specifically, in cases where such exclusivity has been granted, an ANDA may not be filed with the FDA until the expiration of five years unless the submission is accompanied by a Paragraph IV certification that a patent covering the reference-listed drug is either invalid or will not be infringed by the generic product, in which case the applicant may submit its application four years following approval of the reference-listed drug. It is unclear whether the FDA will treat the active ingredients in our product candidates as NCEs and, therefore, afford them five years of NCE data exclusivity if they are approved. If any product we develop does not receive five years of NCE exclusivity, the FDA may approve generic versions of such product three years after its date of approval, subject to the requirement that the ANDA applicant certifies to any patents listed for our products in the Orange Book. Three year exclusivity is given to a drug if the NDA includes reports of one or more new clinical investigations, other than bioavailability or bioequivalence studies, that were conducted by or for the applicant and are essential to the approval of the NDA. Manufacturers may seek to launch these generic products following the expiration of the applicable marketing exclusivity period, even if we still have patent protection for our product.
Competition that our products may face from generic versions of our products could negatively impact our future revenue, profitability and cash flows and substantially limit our ability to obtain a return on our investments in those product candidates.
Even if we complete the necessary preclinical studies and clinical trials, the marketing approval process is expensive, time consuming and uncertain and may prevent us or any future collaborators from obtaining approvals for the commercialization of some or all of our product candidates. As a result, we cannot predict when or if, and in which territories, we, or any future collaborators, will obtain marketing approval to commercialize a product candidate.
The research, testing, manufacturing, labeling, approval, selling, marketing, promotion and distribution of products are subject to extensive regulation by the FDA and comparable foreign regulatory authorities. We, and any future collaborators, are not permitted to market our product candidates in the U.S. or in other countries until we, or they, receive approval of a NDA from the FDA or marketing approval from applicable regulatory authorities outside the U.S. Our product candidates are in various stages of development and are subject to the risks of failure inherent in drug development. We have not submitted an application for or received marketing approval for any of our product candidates in the U.S. or in any other jurisdiction. We have limited experience in conducting and managing the clinical trials necessary to obtain marketing approvals, including FDA approval of a NDA.
The process of obtaining marketing approvals, both in the U.S. and abroad, is lengthy, expensive and uncertain. It may take many years, if approval is obtained at all, and can vary substantially based upon a variety of factors, including the type, complexity and novelty of the product candidates involved. Securing marketing approval requires the submission of extensive preclinical and clinical data and supporting information to regulatory authorities for each therapeutic indication to establish the product candidate's safety and efficacy. Securing marketing approval also requires the submission of information about the product manufacturing process to, and inspection of manufacturing facilities by, the regulatory authorities. The FDA or other regulatory authorities may determine that our product candidates are not safe and effective, only moderately effective or have undesirable or unintended side effects, toxicities or other characteristics that preclude our obtaining marketing approval or prevent or limit commercial use. Any marketing approval we ultimately obtain may be limited or subject to restrictions or post-approval commitments that render the approved product not commercially viable.
In addition, changes in marketing approval policies during the development period, changes in or the enactment or promulgation of additional statutes, regulations or guidance or changes in regulatory review for each submitted product application, may cause delays in the approval or rejection of an application. Regulatory authorities have substantial discretion in the approval process and may refuse to
58
accept any application or may decide that our data are insufficient for approval and require additional preclinical, clinical or other studies. In addition, varying interpretations of the data obtained from preclinical and clinical testing could delay, limit or prevent marketing approval of a product candidate. Any marketing approval we, or any future collaborators, ultimately obtain may be limited or subject to restrictions or post-approval commitments that render the approved product not commercially viable.
Moreover, principal investigators for our clinical trials may serve as scientific advisors or consultants to us from time to time and receive compensation in connection with such services. Under certain circumstances, we may be required to report some of these relationships to the FDA or other regulatory authority. The FDA or other regulatory authority may conclude that a financial relationship between us and a principal investigator has created a conflict of interest or otherwise affected interpretation of the study. The FDA or other regulatory authority may therefore question the integrity of the data generated at the applicable clinical trial site and the utility of the clinical trial itself may be jeopardized. This could result in a delay in approval, or rejection, of our marketing applications by the FDA or other regulatory authority, as the case may be, and may ultimately lead to the denial of marketing approval of one or more of our product candidates.
Any delay in obtaining or failure to obtain required approvals could negatively impact our ability or that of any future collaborators to generate revenue from the particular product candidate, which likely would result in significant harm to our financial position and adversely impact our stock price.
If we encounter difficulties enrolling patients in our clinical trials, our clinical development activities could be delayed or otherwise adversely affected.
We may not be able to initiate or continue clinical trials required by the FDA, EMA or other foreign regulatory agencies for RA101495 SC if we are unable to locate and enroll a sufficient number of eligible patients to participate in these clinical trials. We will be required to identify and enroll a sufficient number of patients with PNH, gMG, aHUS and LN for each of our planned clinical trials of RA101495 SC in these indications. While we completed enrollment of patients in our Phase 2 clinical trial of RA101495 SC, there can be no assurance we will be successful in enrolling patients in our planned and future clinical trials in a timely manner or at all. Each of these is a rare disease or indication with relatively small patient populations, which could result in slow enrollment of clinical trial participants. For example, we estimate that there are approximately 16,000 PNH patients worldwide, approximately 94,000 gMG patients worldwide, 5,500 aHUS patients worldwide, and approximately 63,000 LN patients in the U.S.
Patient enrollment is affected by other factors, including:
- •
- severity of the disease under investigation;
- •
- design of the clinical trial protocol;
- •
- size and nature of the patient population;
- •
- eligibility criteria for the trial in question;
- •
- perceived risks and benefits of the product candidate under trial;
- •
- proximity and availability of clinical trial sites for prospective patients;
- •
- availability of competing therapies and clinical trials;
- •
- clinicians' and patients' perceptions as to the potential advantages of the drug being studied in relation to other available therapies,
including standard-of-care and any new drugs that may be approved for the indications we are investigating;
- •
- efforts to facilitate timely enrollment in clinical trials;
59
- •
- patient referral practices of physicians; and
- •
- our ability to monitor patients adequately during and after treatment.
Further, there are only a limited number of specialist physicians who treat patients with these diseases, and major clinical centers are concentrated in a few geographic regions. We also may encounter difficulties in identifying and enrolling such patients with a stage of disease appropriate for our ongoing or future clinical trials. For example, based on topline results from our Phase 2 trial of RA101495 SC, for the switch patient population in our future Phase 3 program design, we currently expect to target only patients that are transfusion-independent on long-term eculizumab therapy. Moreover, some or all of the above factors, as well as other unanticipated causes, may result in delays to our ability to initiate or report data from these trials. In addition, the process of finding and diagnosing patients may prove costly. Our inability to enroll a sufficient number of patients for any of our clinical trials would result in significant delays or may require us to abandon one or more clinical trials.
Ingredients, excipients and other materials necessary to manufacture RA101495 SC may not be available on commercially reasonable terms, or at all, which may adversely affect the development and commercialization of RA101495 SC.
We and our third-party manufacturers must obtain from third-party suppliers the active pharmaceutical ingredients, excipients and primary and secondary packaging materials necessary for our contract manufacturers to produce RA101495 SC for our clinical trials and, to the extent approved or commercialized, for commercial distribution. There is no guarantee that we would be able to enter into all the necessary agreements with third-party suppliers that we require for the supply of such materials on commercially reasonable terms or at all. Even if we were able to secure such agreements or guarantees, our suppliers may be unable or choose not to provide us the ingredients, excipients or materials in a timely manner or in the quantities required. If we or our third-party manufacturers are unable to obtain the quantities of these ingredients, excipients or materials that are necessary for the manufacture of commercial supplies of RA101495 SC, our ability to generate revenue from the sale of RA101495 SC would be materially and adversely affected. Further, if we or our third-party manufacturers are unable to obtain active pharmaceutical ingredients, excipients and materials as necessary for our clinical trials or for the manufacture of commercial supplies of our product candidates, if approved, potential regulatory approval or commercialization would be delayed, which would materially and adversely affect our ability to generate revenue from the sale of our product candidates.
Even if one of our product candidates receives marketing approval, it may fail to achieve the degree of market acceptance by physicians, patients, third-party payors and others in the medical community necessary for commercial success, in which case we may not generate significant revenues or become profitable.
We have never commercialized a product, and even if one of our product candidates is approved by the appropriate regulatory authorities for marketing and sale, it may nonetheless fail to gain sufficient market acceptance by physicians, patients, third-party payors and others in the medical community. Physicians are often reluctant to switch their patients from existing therapies even when new and potentially more effective or convenient treatments enter the market. Further, patients often acclimate to the therapy that they are currently taking and do not want to switch unless their physicians recommend switching products or they are required to switch therapies due to lack of reimbursement for existing therapies. Eculizumab is the only drug approved for the treatment of PNH, and even if we are able to obtain marketing approval of RA101495 SC for the treatment of PNH, we may not be able to successfully convince physicians or patients to switch from eculizumab to RA101495 SC. In addition, even if we are able to demonstrate our product candidates' safety and efficacy to the FDA and other regulators, safety concerns in the medical community may hinder market acceptance.
60
Efforts to educate the medical community and third-party payors on the benefits of our product candidates may require significant resources, including management time and financial resources, and may not be successful. If any of our product candidates is approved but does not achieve an adequate level of market acceptance, we may not generate significant revenues and we may not become profitable. The degree of market acceptance of our product candidates, if approved for commercial sale, will depend on a number of factors, including:
- •
- the efficacy and safety of the product;
- •
- the potential advantages of the product compared to competitive therapies;
- •
- the prevalence and severity of any side effects;
- •
- whether the product is designated under physician treatment guidelines as a first-, second- or third-line therapy;
- •
- our ability, or the ability of any future collaborators, to offer the product for sale at competitive prices;
- •
- the product's convenience and ease of administration compared to alternative treatments;
- •
- the willingness of the target patient population to try, and of physicians to prescribe, the product;
- •
- limitations or warnings, including distribution or use restrictions contained in the product's approved labeling;
- •
- the strength of sales, marketing and distribution support;
- •
- changes in the standard of care for the targeted indications for the product; and
- •
- availability and amount of coverage and reimbursement from government payors, managed care plans and other third-party payors.
Even if we, or any future collaborators, are able to commercialize any product candidate that we, or they, develop, the product may become subject to unfavorable pricing regulations or third-party payor coverage and reimbursement policies, any of which could harm our business.
Patients who are provided medical treatment for their conditions generally rely on third-party payors to reimburse all or part of the costs associated with their treatment. Therefore, our ability, and the ability of any future collaborators to commercialize any of our product candidates will depend in part on the extent to which coverage and reimbursement for these products and related treatments will be available from third-party payors including government health administration authorities and private health coverage insurers. Third-party payors decide which medications they will cover and establish reimbursement levels. We cannot be certain that reimbursement will be available for RA101495 SC or any of our product candidates. Also, we cannot be certain that reimbursement policies will not reduce the demand for, or the price paid for, our products. The insurance coverage and reimbursement status of newly-approved products for orphan diseases is particularly uncertain, and failure to obtain or maintain adequate coverage and reimbursement for RA101495 SC or any other product candidates could limit our ability to generate revenue.
If coverage and reimbursement are not available, or reimbursement is available only to limited levels, we, or any future collaborators, may not be able to successfully commercialize our product candidates. Even if coverage is provided, the approved reimbursement amount may not be high enough to allow us, or any future collaborators, to establish or maintain pricing sufficient to realize a sufficient return on our or their investments. In the U.S., no uniform policy of coverage and reimbursement for products exists among third-party payors and coverage and reimbursement for products can differ
61
significantly from payor to payor. As a result, the coverage determination process is often a time-consuming and costly process that will require us to provide scientific and clinical support for the use of our products to each payor separately, with no assurance that coverage and adequate reimbursement will be applied consistently or obtained in the first instance.
There is significant uncertainty related to third-party payor coverage and reimbursement of newly approved drugs. Marketing approvals, pricing and reimbursement for new drug products vary widely from country to country. Some countries require approval of the sale price of a drug before it can be marketed. In many countries, the pricing review period begins after marketing or product licensing approval is granted. In some foreign markets, prescription pharmaceutical pricing remains subject to continuing governmental control even after initial approval is granted. As a result, we, or any future collaborators, might obtain marketing approval for a product in a particular country, but then be subject to price regulations that delay commercial launch of the product, possibly for lengthy time periods, which may negatively impact the revenues we are able to generate from the sale of the product in that country. Adverse pricing limitations may hinder our ability or the ability of any future collaborators to recoup our or their investment in one or more product candidates, even if our product candidates obtain marketing approval.
The healthcare industry is acutely focused on cost containment, both in the U.S. and elsewhere. Government authorities and other third-party payors have attempted to control costs by limiting coverage and the amount of reimbursement for particular medications, which could affect our ability or that of any future collaborators to sell our product candidates profitably. These payors may not view our products, if any, as cost-effective, and coverage and reimbursement may not be available to our customers, or those of any future collaborators, or may not be sufficient to allow our products, if any, to be marketed on a competitive basis. Cost-control initiatives could cause us, or any future collaborators, to decrease the price we, or they, might establish for products, which could result in lower than anticipated product revenues. If the prices for our products, if any, decrease or if governmental and other third-party payors do not provide coverage or adequate reimbursement, our prospects for revenue and profitability will suffer.
There may also be delays in obtaining coverage and reimbursement for newly approved drugs, and coverage may be more limited than the indications for which the drug is approved by the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities. Moreover, eligibility for reimbursement does not imply that any drug will be paid for in all cases or at a rate that covers our costs, including research, development, manufacture, sale and distribution. Reimbursement rates may vary, by way of example, according to the use of the product and the clinical setting in which it is used. Reimbursement rates may also be based on reimbursement levels already set for lower cost drugs or may be incorporated into existing payments for other services.
In addition, increasingly, third-party payors are requiring higher levels of evidence of the benefits and clinical outcomes of new technologies and are challenging the prices charged. We cannot be sure that coverage will be available for any product candidate that we, or any future collaborator, commercialize and, if available, that the reimbursement rates will be adequate. Further, the net reimbursement for drug products may be subject to additional reductions if there are changes to laws that presently restrict imports of drugs from countries where they may be sold at lower prices than in the U.S. An inability to promptly obtain coverage and adequate payment rates from both government-funded and private payors for any of our product candidates for which we, or any future collaborator, obtain marketing approval could significantly harm our operating results, our ability to raise capital needed to commercialize products and our overall financial condition.
62
If any product liability lawsuits are successfully brought against us or any of our collaborative partners, we may incur substantial liabilities and may be required to limit commercialization of our product candidates.
We face an inherent risk of product liability lawsuits related to the testing of our product candidates in seriously ill patients and will face an even greater risk if product candidates are approved by regulatory authorities and introduced commercially. Product liability claims may be brought against us or our partners by participants enrolled in our clinical trials, patients, health care providers or others using, administering or selling any of our future approved products. If we cannot successfully defend ourselves against any such claims, we may incur substantial liabilities, which may result in:
- •
- decreased demand for any of our future approved products;
- •
- injury to our reputation;
- •
- withdrawal of clinical trial participants;
- •
- termination of clinical trial sites or entire trial programs;
- •
- significant litigation costs;
- •
- substantial monetary awards to or costly settlements with patients or other claimants;
- •
- product recalls or a change in the indications for which they may be used;
- •
- loss of revenue;
- •
- diversion of management and scientific resources from our business operations; and
- •
- the inability to commercialize our product candidates.
If any of our product candidates are approved for commercial sale, we will be highly dependent upon consumer perceptions of us and the safety and quality of our products. We could be adversely affected if we are subject to negative publicity associated with illness or other adverse effects resulting from patients' use or misuse of our products or any similar products distributed by other companies.
Although we maintain clinical trial liability insurance, this insurance may not fully cover potential liabilities that we may incur. The cost of any product liability litigation or other proceeding, even if resolved in our favor, could be substantial. We will need to increase our insurance coverage if we commercialize any product that receives marketing approval. In addition, insurance coverage is becoming increasingly expensive. If we are unable to maintain sufficient insurance coverage at an acceptable cost or to otherwise protect against potential product liability claims, it could prevent or inhibit the development and commercial production and sale of our product candidates, which could harm our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
We currently have no marketing, sales or distribution infrastructure with respect to our product candidates. If we are unable to develop our sales, marketing and distribution capability on our own or through collaborations with marketing partners, we will not be successful in commercializing our product candidates.
We currently have no marketing, sales or distribution capabilities and have limited sales or marketing experience within our organization. If our product candidate RA101495 SC is approved, we intend either to establish a sales and marketing organization with technical expertise and supporting distribution capabilities to commercialize RA101495 SC, or to outsource this function to a third party. Either of these options would be expensive and time consuming. Some or all of these costs may be incurred in advance of any approval of RA101495 SC. In addition, we may not be able to hire a sales force in the U.S. or other target market that is sufficient in size or has adequate expertise in the medical markets that we intend to target. These risks may be particularly pronounced due to our focus on our lead indications of PNH, gMG, aHUS and LN, each of which is a rare disease with relatively small patient populations. Any failure or delay in the development of our or third parties' internal
63
sales, marketing and distribution capabilities would adversely impact the commercialization of RA101495 SC and other future product candidates.
With respect to our existing and future product candidates, we may choose to collaborate with third parties that have direct sales forces and established distribution systems, either to augment or to serve as an alternative to our own sales force and distribution systems. Our product revenue may be lower than if we directly marketed or sold any approved products. In addition, any revenue we receive will depend in whole or in part upon the efforts of these third parties, which may not be successful and are generally not within our control. If we are unable to enter into these arrangements on acceptable terms or at all, we may not be able to successfully commercialize any approved products. If we are not successful in commercializing any approved products, our future product revenue will suffer and we may incur significant additional losses.
The route of administration, formulation or dose for RA101495 SC, which we are currently developing for SC self-administration, may be inadequate.
We are currently developing RA101495 SC for SC self-administration. Unsatisfactory drug availability due to problems relating to this route of administration or the ability of the drug to bind to its target is another potential cause of lack of efficacy of RA101495 SC if and when it is commercialized. C5, the target of RA101495 SC is predominantly found in blood. For PNH, RA101495 SC will be administered subcutaneously. In our Phase 1 study of RA101495 SC in single-ascending dose cohorts and a multiple-dose cohort, single and repeat SC doses of RA101495 SC were safe and well tolerated in healthy volunteers. In addition, while we observed promising signs that patients complied with once-daily SC self-administration at home of RA101495 SC in our Phase 2 clinical trial, there is no guarantee that patients will continue to comply in this trial or in future trials. If daily SC administration proves to be unfeasible, then we may need to research additional doses, formulations or routes of administration, which could delay commercialization of RA101495 SC and result in significant additional costs to us. Additionally, while we may offer training in SC injections, reliance on patient self-administration may lead to higher rates of user error due to poor administration procedure by patients and reduced patient compliance as compared with administration by healthcare professionals.
If we, or any future collaborators, experience any of a number of possible unforeseen events in connection with clinical trials of our product candidates, potential clinical development, marketing approval or commercialization of our product candidates could be delayed or prevented.
We, or any future collaborators, may experience numerous unforeseen events during, or as a result of, clinical trials that could delay or prevent clinical development, marketing approval or commercialization of our product candidates, including:
- •
- our product candidates may produce unfavorable or inconclusive results;
- •
- regulators may require us or any future collaborators, to conduct additional clinical trials or abandon product development programs;
- •
- the number of patients required for clinical trials of our product candidates may be larger than we, or any future collaborators, anticipate,
patient enrollment in these clinical trials may be slower than we, or any future collaborators, may anticipate or participants may drop out of these clinical trials at a higher rate than we, or any
future collaborators, anticipate;
- •
- the cost of planned clinical trials of our product candidates may be greater than we anticipate;
- •
- our third-party contractors or those of any future collaborators, including those manufacturing our product candidates or components or ingredients thereof or conducting clinical trials on our behalf or on behalf of any future collaborators, may fail to comply with regulatory requirements
64
- •
- regulators, IRBs or independent ethics committees may not authorize us, any future collaborators or our or their investigators to commence a
clinical trial or conduct a clinical trial at a prospective trial site;
- •
- delays in reaching or fail to reach agreement on acceptable clinical trial contracts or clinical trial protocols with prospective trial sites;
- •
- patients who enroll in a clinical trial may misrepresent their eligibility to do so or may otherwise not comply with the clinical trial
protocol, resulting in the need to drop the patients from the clinical trial, increase the needed enrollment size for the clinical trial or extend the clinical trial's duration;
- •
- delay, suspension or termination of clinical trials of our product candidates for various reasons, including a finding that the participants
are being exposed to unacceptable health risks, undesirable side effects or other unexpected characteristics of the product candidate;
- •
- regulators, IRBs or independent ethics committees may require that we, or any future collaborators, or our or their investigators suspend or
terminate clinical research for various reasons, including noncompliance with regulatory requirements or their standards of conduct, a finding that the participants are being exposed to unacceptable
health risks, undesirable side effects or other unexpected characteristics of the product candidate or findings of undesirable effects caused by a chemically or mechanistically similar product or
product candidate;
- •
- the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities may disagree with our, or any future collaborators', clinical trial designs or our or
their interpretation of data from preclinical studies and clinical trials;
- •
- the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities may fail to approve or subsequently find fault with the manufacturing processes or
facilities of third-party manufacturers with which we, or any future collaborators, enter into agreements for clinical and commercial supplies;
- •
- the supply or quality of raw materials or manufactured product candidates or other materials necessary to conduct clinical trials of our
product candidates may be insufficient, inadequate or not available at an acceptable cost, or we may experience interruptions in supply; and
- •
- the approval policies or regulations of the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities may significantly change in a manner rendering our clinical data insufficient to obtain marketing approval.
or meet their contractual obligations to us or any future collaborators in a timely manner or at all;
We or any future collaborators could also encounter delays if a clinical trial is suspended or terminated by us or our collaborators, by the IRBs or independent ethics committees of the institutions in which such trials are being conducted, by the DSMB for such trial or by the FDA or other regulatory authorities. Such authorities may suspend or terminate a clinical trial due to a number of factors, including failure to conduct the clinical trial in accordance with regulatory requirements or our clinical protocols, inspection of the clinical trial operations or trial site by the FDA or other regulatory authorities resulting in the imposition of a clinical hold, unforeseen safety issues or adverse side effects, failure to demonstrate a benefit from using a drug, changes in governmental regulations or administrative actions or lack of adequate funding to continue the clinical trial.
Further, conducting clinical trials in foreign countries, as we plan to do for our product candidates, presents additional risks that may delay completion of our clinical trials. These risks include the failure of enrolled patients in foreign countries to adhere to clinical protocol as a result of differences in
65
healthcare services or cultural customs, managing additional administrative burdens associated with foreign regulatory schemes, as well as political and economic risks relevant to such foreign countries.
Product development costs for us, or any future collaborators, will increase if we, or they, experience delays in testing or pursuing marketing approvals and we, or they, may be required to obtain additional funds to complete clinical trials and prepare for possible commercialization of our product candidates. We do not know whether any preclinical tests or clinical trials will begin as planned, will need to be restructured, or will be completed on schedule or at all. Significant preclinical study or clinical trial delays also could shorten any periods during which we, or any future collaborators, may have the exclusive right to commercialize our product candidates or allow our competitors, or the competitors of any future collaborators, to bring products to market before we, or any future collaborators, do and impair our ability, or the ability of any future collaborators, to successfully commercialize our product candidates and may harm our business and results of operations. In addition, many of the factors that lead to clinical trial delays may ultimately lead to the denial of marketing approval of any of our product candidates.
Results of preclinical studies and early clinical trials may not be predictive of results of future clinical trials.
The outcome of preclinical studies and early clinical trials may not be predictive of the success of later clinical trials, and interim results of clinical trials do not necessarily predict success in the results of completed clinical trials. Many companies in the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries have suffered significant setbacks in late-stage clinical trials after achieving positive results in earlier development, and we could face similar setbacks. The design of a clinical trial can determine whether its results will support approval of a product and flaws in the design of a clinical trial may not become apparent until the clinical trial is well advanced. We have limited experience in designing clinical trials and may be unable to design and execute a clinical trial to support marketing approval. In addition, preclinical and clinical data are often susceptible to varying interpretations and analyses. Many companies that believed their product candidates performed satisfactorily in preclinical studies and clinical trials have nonetheless failed to obtain marketing approval for the product candidates. Even if we, or any future collaborators, believe that the results of clinical trials for our product candidates warrant marketing approval, the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities may disagree and may not grant marketing approval of our product candidates.
In some instances, there can be significant variability in safety or efficacy results between different clinical trials of the same product candidate due to numerous factors, including changes in trial procedures set forth in protocols, differences in the size and type of the patient populations, changes in and adherence to the dosing regimen and other clinical trial protocols and the rate of dropout among clinical trial participants. If we fail to receive positive results in clinical trials of our product candidates, the development timeline and regulatory approval and commercialization prospects for our most advanced product candidates, and, correspondingly, our business and financial prospects would be negatively impacted.
From time to time, we may also publish interim, "topline" or preliminary data from our clinical studies. For example, on February 12, 2018 we announced topline data from our Phase 2 program in PNH. Interim data from clinical trials that we may complete are subject to the risk that one or more of the clinical outcomes may materially change as patient enrollment continues and more patient data become available. Preliminary or topline data remain subject to audit and verification procedures that may result in the final data being materially different from the preliminary or interim data we previously published. As a result, these data should be viewed with caution until the final data are available. Adverse changes between preliminary or interim data and final data could significantly harm our business prospects.
66
Chronic dosing of patients with RA101495 SC could lead to an immune response that causes adverse reactions or impairs the activity and/or efficacy of the drug, or causes other side effects.
There is a risk that chronic dosing of patients with RA101495 SC may lead to an immune response that causes adverse reactions or impairs the activity and/or efficacy of the drug. Patients may develop an allergic reaction to the drug and/or develop antibodies directed at the drug. Impaired drug activity could be caused by neutralization of the drug's inhibitory activity or by an increased rate of clearance of the drug from circulation. For example, one potential side effect of RA101495 SC that has occurred in patients receiving eculizumab, a humanized antibody against C5, is an increased incidence of meningococcal infections as a result of inhibition of the terminal complement system in a manner similar to RA101495 SC. As a result, patients receiving RA101495 SC will also require immunization with a meningococcal vaccine and potentially prophylactic antibiotics. While we did not observe any incidents of meningococcal infection or thromboembolic events in our topline results from our Phase 2 clinical trial of RA101495 SC and ongoing long-term extension trial, there can be no assurance that these results will be maintained as we continue the long-term extension trial.
Any immune response that causes adverse reactions or impairs the activity of the drug could cause a delay in or termination of our development of RA101495 SC, which would have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operation.
The incidence and prevalence for target patient populations of RA101495 SC have not been established with precision. If the market opportunities for RA101495 SC are smaller than we estimate or if any approval that we obtain is based on a narrower definition of the patient population, our revenue and ability to achieve profitability will be adversely affected, possibly materially.
The precise incidence and prevalence for PNH, gMG, aHUS and LN are unknown. Our projections of both the number of people who have these diseases, as well as the subset of people with these diseases who have the potential to benefit from treatment with our drug candidates, are based on estimates. For example, we estimate that there are approximately 16,000 PNH patients worldwide, approximately 94,000 gMG patients worldwide, 5,500 aHUS patients worldwide, and approximately 63,000 LN patients in the U.S.
The total addressable market opportunity for RA101945 SC will ultimately depend upon, among other things, the indication statements included in the final label for RA101945 SC, if our product candidates are approved for sale for these indications, acceptance by the medical community and patient access, drug pricing and reimbursement. The number of patients who can be treated with our product candidates may turn out to be lower than expected, patients may not be otherwise amenable to treatment with our drugs, or new patients may become increasingly difficult to identify or gain access to, all of which would adversely affect our results of operations and our business.
Risks Related to Regulatory Approval and Marketing of Our Product Candidates and Other Legal Compliance Matters
We plan to seek orphan drug designation for RA101495 SC, but we may be unable to obtain such designation or to maintain the benefits associated with orphan drug status, including market exclusivity, even if that designation is granted.
We plan to seek orphan drug designation for RA101495 SC in specific orphan indications in which there is a medically plausible basis for its use and may seek orphan drug designation for other preclinical product candidates in our pipeline or that we may develop. In the U.S., orphan drug designation entitles a party to financial incentives such as opportunities for grant funding towards clinical trial costs, tax advantages, and user-fee waivers. After the FDA grants orphan drug designation, the generic identity of the drug and its potential orphan use are disclosed publicly by the FDA. Orphan drug designation does not convey any advantage in, or shorten the duration of, the regulatory review
67
and approval process. Although we intend to seek orphan drug designation for RA101495 SC, we may never receive such designation. Moreover, obtaining orphan drug designation for one indication for RA101495 SC does not mean we will be able to obtain such designation for another indication.
If a product that has orphan drug designation subsequently receives the first FDA approval for a particular active ingredient for the disease for which it has such designation, the product is entitled to orphan drug exclusivity, which means that the FDA may not approve any other applications, including a NDA, to market the same drug for the same indication for seven years, except in limited circumstances such as if the FDA finds that the holder of the orphan drug exclusivity has not shown that it can assure the availability of sufficient quantities of the orphan drug to meet the needs of patients with the disease or condition for which the drug was designated. Similarly, the FDA can subsequently approve a drug with the same active moiety for the same condition during the exclusivity period if the FDA concludes that the later drug is clinically superior, meaning the later drug is safer, more effective, or makes a major contribution to patient care. Even if we were to obtain orphan drug designation for RA101495 SC, we may not be the first to obtain marketing approval for any particular orphan indication due to the uncertainties associated with developing pharmaceutical products, and thus approval of RA101495 SC could be blocked for seven years if another company previously obtained approval and orphan drug exclusivity for the same drug and same condition. If we do obtain exclusive marketing rights in the U.S., they may be limited if we seek approval for an indication broader than the orphan designated indication and may be lost if the FDA later determines that the request for designation was materially defective or if we are unable to assure sufficient quantities of the product to meet the needs of the relevant patients. Further, exclusivity may not effectively protect the product from competition because different drugs with different active moieties can be approved for the same condition, the same drugs can be approved for different indications and might then be used off-label in our approved indication, and different drugs for the same condition may already be approved and commercially available.
In Europe, the period of orphan drug exclusivity is ten years, although it may be reduced to six years if, at the end of the fifth year, it is established that the criteria for orphan drug designation are no longer met, in other words, when it is shown on the basis of available evidence that the product is sufficiently profitable not to justify maintenance of market exclusivity. In September 2016, the EMA's Committee for Orphan Medicinal Products adopted a positive opinion recommending RA101495 SC for the treatment of PNH for designation as an orphan medicinal product to the European Commission, which granted us orphan designation for RA101495 SC for the treatment of PNH in October 2016.
Laws and regulations governing any international operations we may have in the future may preclude us from developing, manufacturing and selling certain products outside of the U.S. and require us to develop and implement costly compliance programs.
If we further expand our operations outside of the U.S., we must dedicate additional resources to comply with numerous laws and regulations in each jurisdiction in which we plan to operate. The Foreign Corrupt Practices Act, or FCPA, prohibits any U.S. individual or business from paying, offering, authorizing payment or offering of anything of value, directly or indirectly, to any foreign official, political party or candidate for the purpose of influencing any act or decision of the foreign entity in order to assist the individual or business in obtaining or retaining business. The FCPA also obligates companies whose securities are listed in the U.S. to comply with certain accounting provisions requiring the company to maintain books and records that accurately and fairly reflect all transactions of the corporation, including international subsidiaries, and to devise and maintain an adequate system of internal accounting controls for international operations.
Compliance with the FCPA is expensive and difficult, particularly in countries in which corruption is a recognized problem. In addition, the FCPA presents particular challenges in the pharmaceutical
68
industry, because, in many countries, hospitals are operated by the government, and doctors and other hospital employees are considered foreign officials. Certain payments to hospitals in connection with clinical trials and other work have been deemed to be improper payments to government officials and have led to FCPA enforcement actions.
Various laws, regulations and executive orders also restrict the use and dissemination outside of the U.S., or the sharing with certain non-U.S. nationals, of information classified for national security purposes, as well as certain products and technical data relating to those products. If we expand our presence outside of the U.S., it will require us to dedicate additional resources to comply with these laws, and these laws may preclude us from developing, manufacturing, or selling certain products and product candidates outside of the U.S., which could limit our growth potential and increase our development costs.
The failure to comply with laws governing international business practices may result in substantial civil and criminal penalties and suspension or debarment from government contracting. The Securities and Exchange Commission, or SEC, also may suspend or bar issuers from trading securities on U.S. exchanges for violations of the FCPA's accounting provisions.
Governments outside the U.S. tend to impose strict price controls, which may adversely affect our revenues, if any.
In some countries, such as the countries of the European Union, the pricing of prescription pharmaceuticals is subject to governmental control. In these countries, pricing negotiations with governmental authorities can take considerable time after the receipt of marketing approval for a product. To obtain reimbursement or pricing approval in some countries, we, or any future collaborators, may be required to conduct a clinical trial that compares the cost-effectiveness of our product to other available therapies. If reimbursement of our products is unavailable or limited in scope or amount, or if pricing is set at unsatisfactory levels, our business could be harmed.
We are subject to extensive government regulation and the failure to comply with these regulations may have a material adverse effect on our operations and business.
Both before and after approval of any product, we and our suppliers, contract manufacturers and clinical investigators are subject to extensive regulation by governmental authorities in the U.S. and other countries, covering, among other things, testing, manufacturing, quality control, clinical trials, post-marketing studies, labeling, advertising, promotion, distribution, import and export, governmental pricing, price reporting and rebate requirements. Failure to comply with applicable requirements could result in one or more of the following actions: warning letters; unanticipated expenditures; delays in approval or refusal to approve a product candidate; product recall or seizure; interruption of manufacturing or clinical trials; operating or marketing restrictions; injunctions; criminal prosecution and civil or criminal penalties including fines and other monetary penalties; adverse publicity; and disruptions to our business. Further, government investigations into potential violations of these laws would require us to expend considerable resources and face adverse publicity and the potential disruption of our business even if we are ultimately found not to have committed a violation.
Obtaining FDA approval of our product candidates requires substantial time, effort and financial resources and may be subject to both expected and unforeseen delays, and there can be no assurance that any approval will be granted on any of our product candidates on a timely basis, if at all. The FDA may decide that our data are insufficient for approval of our product candidates and require additional preclinical, clinical or other studies or additional work related to chemistry, manufacturing and controls. In addition, we, the FDA, IRBs or independent ethics committees may suspend or terminate human clinical trials at any time on various grounds, including a finding that the patients are or would be exposed to an unacceptable health risk or because of the way in which the investigators on
69
which we rely carry out the trials. If we are required to conduct additional trials or to conduct other testing of our product candidates beyond that which we currently contemplate for regulatory approval, if we are unable to complete successfully our clinical trials or other testing, or if the results of these and other trials or tests fail to demonstrate efficacy or raise safety concerns, we may face substantial additional expenses, be delayed in obtaining marketing approval for our product candidates or may never obtain marketing approval.
We are also required to comply with extensive governmental regulatory requirements after a product has received marketing authorization. Governing regulatory authorities may require post-marketing studies that may negatively impact the commercial viability of a product. Once on the market, a product may become associated with previously undetected adverse effects and/or may develop manufacturing difficulties. As a result of any of these or other problems, a product's regulatory approval could be withdrawn, which could harm our business and operating results.
Even if we obtain FDA approval of RA101495 SC or any of our other product candidates, we or our partners may never obtain approval or commercialize our products outside of the U.S.
In order to market any products outside of the U.S., we must establish and comply with numerous and varying regulatory requirements of other countries regarding clinical trial design, safety and efficacy. Clinical trials conducted in one country may not be accepted by regulatory authorities in other countries, and regulatory approval in one country does not mean that regulatory approval will be obtained in any other country. Approval procedures vary among countries and can involve additional product testing and validation and additional administrative review periods. Seeking foreign regulatory approvals could result in significant delays, difficulties and costs for us and may require additional preclinical studies or clinical trials which would be costly and time consuming and could delay or prevent introduction of RA101495 SC or any of our other product candidates in those countries. We do not have experience in obtaining regulatory approval in international markets. If we or our partners fail to comply with regulatory requirements or to obtain and maintain required approvals, our target market will be reduced and our ability to realize the full market potential of our product candidates will be harmed.
Current and future legislation may increase the difficulty and cost for us and any future collaborators to obtain marketing approval of and commercialize our product candidates and affect the prices we, or they, may obtain.
In the U.S. and some foreign jurisdictions, there have been a number of legislative and regulatory changes and proposed changes regarding the healthcare system that could, among other things, prevent or delay marketing approval of our product candidates, restrict or regulate post-approval activities and affect our ability, or the ability of any future collaborators, to profitably sell any products for which we, or they, obtain marketing approval. We expect that current laws, as well as other healthcare reform measures that may be adopted in the future, may result in more rigorous coverage criteria and in additional downward pressure on the price that we, or any future collaborators, may receive for any approved products.
In March 2010 for example, President Obama signed into law the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, as amended by the Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act, or collectively the Affordable Care Act, or ACA. Among the provisions of the ACA of potential importance to our business and our product candidates are the following:
- •
- an annual, non-deductible fee on any entity that manufactures or imports specified branded prescription drugs and biologic products;
- •
- an increase in the statutory minimum rebates a manufacturer must pay under the Medicaid Drug Rebate Program;
70
- •
- expansion of healthcare fraud and abuse laws, including the civil False Claims Act and the federal Anti-Kickback Statute, new government
investigative powers and enhanced penalties for noncompliance;
- •
- a new Medicare Part D coverage gap discount program, in which manufacturers must agree to offer 50% (increasing to 70% effective
Janaury 1, 2019) point-of-sale discounts off negotiated prices;
- •
- extension of manufacturers' Medicaid rebate liability;
- •
- expansion of eligibility criteria for Medicaid programs;
- •
- expansion of the entities eligible for discounts under the Public Health Service pharmaceutical pricing program;
- •
- new requirements to report certain financial arrangements with physicians and teaching hospitals;
- •
- a new requirement to annually report drug samples that manufacturers and distributors provide to physicians; and
- •
- a new Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute to oversee, identify priorities in, and conduct comparative clinical effectiveness research, along with funding for such research.
The new presidential administration has indicated that enacting changes to the ACA is a legislative priority, and has alternatively discussed repealing and replacing the ACA, and amending the ACA. We do not know at this time what implications such changes, if enacted, would have on the ACA's current requirements or on our future business. Changes to the ACA or other existing health care regulations could significantly impact our business and the pharmaceutical industry.
In addition, other legislative changes have been proposed and adopted since the ACA was enacted. These changes include the Budget Control Act of 2011, which, among other things, led to aggregate reductions to Medicare payments to providers of 2% per fiscal year, which went into effect on April 1, 2013 and will remain in effect through 2027 unless additional Congressional action is taken. On January 2, 2013, the American Taxpayer Relief Act of 2012 was signed into law, which, among other things, further reduced Medicare payments to several providers and increased the statute of limitations period for the government to recover overpayments to providers from three to five years. These new laws may result in additional reductions in Medicare and other healthcare funding. We expect that additional state and federal healthcare reform measures will be adopted in the future, any of which could limit the amounts that federal and state governments will pay for healthcare products and services, which could result in reduced demand for our product candidates or additional pricing pressures.
Legislative and regulatory proposals have been made to expand post-approval requirements and restrict sales and promotional activities for pharmaceutical products. We cannot be sure whether additional legislative changes will be enacted, or whether the FDA regulations, guidance or interpretations will be changed, or what the impact of such changes on the marketing approvals of our product candidates, if any, may be. In addition, increased scrutiny by the U.S. Congress of the FDA's approval process may significantly delay or prevent marketing approval, as well as subject us and any future collaborators to more stringent product labeling and post-marketing testing and other requirements.
Our relationships with customers and third-party payors, among others, will be subject to applicable anti-kickback, fraud and abuse and other healthcare laws and regulations, which could expose us to penalties, including criminal sanctions, civil penalties, contractual damages, reputational harm, fines, disgorgement, exclusion from participation in government healthcare programs, curtailment or restricting of our operations, and diminished profits and future earnings.
71
Healthcare providers, physicians and third-party payors will play a primary role in the recommendation and prescription of any products for which we obtain marketing approval. Our future arrangements with third-party payors and customers, if any, will subject us to broadly applicable fraud and abuse and other healthcare laws and regulations. The laws and regulations may constrain the business or financial arrangements and relationships through which we market, sell and distribute any products for which we obtain marketing approval. These include the following:
- •
- Anti-kickback statute. The federal Anti-Kickback Statute prohibits, among
other things, persons and entities from knowingly and willfully soliciting, offering, receiving or providing remuneration, directly or indirectly, in cash or in kind, to induce or reward, or in return
for, either the referral of an individual for, or the purchase, order or recommendation or arranging of, any good or service, for which payment may be made under a federal healthcare program such as
Medicare and Medicaid. This statute has been interpreted to apply to arrangements between pharmaceutical manufacturers on the one hand and prescribers, purchasers and formulary managers on the other.
Although there are several statutory exceptions and regulatory safe harbors protecting certain common activities from prosecution, they are drawn narrowly, and practices that involve remuneration
intended to induce prescribing, purchasing or recommending may be subject to scrutiny if they do not qualify for an exception or safe harbor. A person or entity can be found guilty of violating the
federal Anti-Kickback Statute without actual knowledge of the statute or specific intent to violate it. In addition, the government may assert that a claim including items or services resulting from a
violation of the federal Anti-Kickback Statute constitutes a false or fraudulent claim for purposes of the federal False Claims Act or federal civil money penalties statute;
- •
- False claims laws. The federal false claims and civil monetary penalties
laws, including the federal civil False Claims Act, impose criminal and civil penalties, including through civil whistleblower or qui tam actions
against individuals or entities for, among other things, knowingly presenting, or causing to be presented false or fraudulent claims for payment by a federal healthcare program or making a false
statement or record material to payment of a false claim or avoiding, decreasing or concealing an obligation to pay money to the federal government, with potential liability including mandatory treble
damages and significant per-claim penalties, currently set at $11,181 to $22,363 per false claim;
- •
- HIPAA. The federal Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of
1996, or HIPAA, imposes criminal and civil liability for, among other things, executing a scheme to defraud any healthcare benefit program or making false statements relating to healthcare matters.
Similar to the federal Anti-Kickback Statute, a person or entity does not need to have actual knowledge of the statute or specific intent to violate it in order to have committed a violation.
Additionally, HIPAA as amended by the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act and its implementing regulations, also imposes obligations on covered entities and their
business associates, including mandatory contractual terms and technical safeguards, with respect to maintaining the privacy, security and transmission of individually identifiable health information;
- •
- Transparency requirements. The provision within the ACA commonly referred
to as the federal Physician Payments Sunshine Act requires certain manufacturers of drugs, devices, biologics, and medical supplies for which payment is available under Medicare, Medicaid, or the
Children's Health Insurance Program, with specific exceptions, to report annually to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, or CMS, information related to payments or transfers of value
made to physicians and teaching hospitals, as well as information regarding ownership and investment interests held by physicians and their immediate family members; and
- •
- Analogous state and foreign laws. Analogous state and foreign fraud and abuse laws and regulations, such as state anti-kickback and false claims laws, can apply to sales or marketing
72
arrangements, and claims involving healthcare items or services reimbursed by non-governmental third-party payors, and are generally broad and are enforced by many different foreign and state agencies as well as through private actions. Some state laws require pharmaceutical companies to comply with the pharmaceutical industry's voluntary compliance guidelines and the relevant compliance guidance promulgated by the federal government and require drug manufacturers to report information related to payments and other transfers of value to physicians and other healthcare providers or marketing expenditures. State and foreign laws also govern the privacy and security of health information in some circumstances, many of which differ from each other in significant ways and often are not pre-empted by HIPAA, thus complicating compliance efforts.
Efforts to ensure that our business arrangements with third parties, and our business generally, will comply with applicable healthcare laws and regulations will involve substantial costs. It is possible that governmental authorities will conclude that our business practices may not comply with current or future statutes, regulations or case law involving applicable fraud and abuse or other healthcare laws and regulations. If our operations are found to be in violation of any of these laws or any other governmental regulations that may apply to us, we may be subject to significant civil, criminal and administrative penalties, damages, fines, imprisonment, exclusion of products from government funded healthcare programs, such as Medicare and Medicaid, disgorgement, contractual damages, reputational harm, and the curtailment or restructuring of our operations. Defending against any such actions can be costly, time-consuming and may require significant financial and personnel resources. Therefore, even if we are successful in defending against any such actions that may be brought against us, our business may be impaired. Further, if any of the physicians or other healthcare providers or entities with whom we expect to do business is found to be not in compliance with applicable laws, they may be subject to criminal, civil or administrative sanctions, including exclusions from government funded healthcare programs.
Even if we, or any future collaborators, obtain marketing approvals for our product candidates, the terms of approvals and ongoing regulation of our products may limit how we manufacture and market our products, which could impair our ability to generate revenue.
Once marketing approval has been granted, an approved product and its manufacturer and marketer are subject to ongoing review and extensive regulation. We, and any future collaborators, must therefore comply with requirements concerning advertising and promotion for any of our product candidates for which we or they obtain marketing approval. Promotional communications with respect to prescription drugs are subject to a variety of legal and regulatory restrictions and must be consistent with the information in the product's approved labeling. Thus, we and any future collaborators will not be able to promote any products we develop for indications or uses for which they are not approved.
In addition, manufacturers of approved products and those manufacturers' facilities are required to comply with extensive FDA requirements, including ensuring that quality control and manufacturing procedures conform to current Good Manufacturing Practices, or cGMPs, which include requirements relating to quality control and quality assurance as well as the corresponding maintenance of records and documentation and reporting requirements. We, our contract manufacturers, any future collaborators and their contract manufacturers could be subject to periodic unannounced inspections by the FDA to monitor and ensure compliance with cGMPs.
Accordingly, assuming we, or any future collaborators, receive marketing approval for one or more of our product candidates, we, and any future collaborators, and our and their contract manufacturers will continue to expend time, money and effort in all areas of regulatory compliance, including manufacturing, production, product surveillance and quality control.
73
If we, and any future collaborators, are not able to comply with post-approval regulatory requirements, we, and any future collaborators, could have the marketing approvals for our products withdrawn by regulatory authorities and our, or any future collaborators', ability to market any future products could be limited, which could adversely affect our ability to achieve or sustain profitability. Further, the cost of compliance with post-approval regulations may have a negative effect on our operating results and financial condition.
Any of our product candidates for which we, or any future collaborators, obtain marketing approval in the future could be subject to post-marketing restrictions or withdrawal from the market and we, or any future collaborators, may be subject to substantial penalties if we, or they, fail to comply with regulatory requirements or if we, or they, experience unanticipated problems with our products following approval.
Any of our product candidates for which we, or any future collaborators, obtain marketing approval, as well as the manufacturing processes, post-approval studies and measures, labeling, advertising and promotional activities for such product, among other things, will be subject to ongoing requirements of and review by the FDA, the EMA and other regulatory authorities. These requirements include submissions of safety and other post-marketing information and reports, registration and listing requirements, requirements relating to manufacturing, quality control, quality assurance and corresponding maintenance of records and documents, requirements regarding the distribution of samples to physicians and recordkeeping. Even if marketing approval of a product candidate is granted, the approval may be subject to limitations on the indicated uses for which the product may be marketed or to the conditions of approval, including the requirement to implement a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy.
The FDA, the EMA and other regulatory authorities may also impose requirements for costly post-marketing studies or clinical trials and surveillance to monitor the safety or efficacy of a product. The FDA and other agencies, including the Department of Justice, closely regulate and monitor the post-approval marketing and promotion of products to ensure that they are manufactured, marketed and distributed only for the approved indications and in accordance with the provisions of the approved labeling. The FDA imposes stringent restrictions on manufacturers' communications regarding off-label use and if we, or any future collaborators, do not market any of our product candidates for which we, or they, receive marketing approval for only their approved indications, we, or they, may be subject to warnings or enforcement action for off-label marketing. Violation of the FDCA and other statutes relating to the promotion and advertising of prescription drugs may lead to investigations or allegations of violations of federal and state health care fraud and abuse laws and state consumer protection laws, including the False Claims Act.
In addition, later discovery of previously unknown adverse events or other problems with our products or their manufacturers or manufacturing processes, or failure to comply with regulatory requirements, may yield various results, including:
- •
- restrictions on the manufacturing of such products;
- •
- restrictions on the labeling or marketing of such products;
- •
- restrictions on product distribution or use;
- •
- requirements to conduct post-marketing studies or clinical trials;
- •
- warning letters or untitled letters;
- •
- withdrawal of the products from the market;
- •
- refusal to approve pending applications or supplements to approved applications that we submit;
- •
- recall of products;
74
- •
- restrictions on coverage by third-party payors;
- •
- fines, restitution or disgorgement of profits or revenues;
- •
- suspension or withdrawal of marketing approvals;
- •
- refusal to permit the import or export of products;
- •
- product seizure; or
- •
- injunctions or the imposition of civil or criminal penalties.
Additional time may be required to obtain regulatory approval for our product candidates because they are combination products.
Because certain of our product candidates are designed to be self-administered SC by patients and may be packaged as pre-filled cartridges or pens, they may be regulated as drug/device combination products that require coordination within the FDA and similar foreign regulatory agencies for review of their device and drug components. Although the FDA and similar foreign regulatory agencies have systems in place for the review and approval of combination products such as ours, we may experience delays in the development and commercialization of our product candidates due to regulatory timing constraints and uncertainties in the product development and approval process.
If we fail to comply with environmental, health and safety laws and regulations, we could become subject to fines or penalties or incur costs that could harm our business.
We are subject to numerous environmental, health and safety laws and regulations, including those governing laboratory procedures and the handling, use, storage, treatment and disposal of hazardous materials and wastes. From time to time and in the future, our operations may involve the use of hazardous and flammable materials, including chemicals and biological materials, and may also produce hazardous waste products. Even if we contract with third parties for the disposal of these materials and waste products, we cannot completely eliminate the risk of contamination or injury resulting from these materials. In the event of contamination or injury resulting from the use or disposal of our hazardous materials, we could be held liable for any resulting damages, and any liability could exceed our resources. We also could incur significant costs associated with civil or criminal fines and penalties for failure to comply with such laws and regulations.
We maintain workers' compensation insurance to cover us for costs and expenses we may incur due to injuries to our employees resulting from the use of hazardous materials, but this insurance may not provide adequate coverage against potential liabilities. However, we do not maintain insurance for environmental liability or toxic tort claims that may be asserted against us.
In addition, we may incur substantial costs in order to comply with current or future environmental, health and safety laws and regulations. Current or future environmental laws and regulations may impair our research, development or production efforts. In addition, failure to comply with these laws and regulations may result in substantial fines, penalties or other sanctions.
Risks Related to Our Dependence on Third Parties
We rely on third parties to conduct our clinical trials. If they do not perform satisfactorily, our business could be harmed.
We do not independently conduct clinical trials of any of our product candidates. We rely on third parties, such as contract research organizations, or CROs, clinical data management organizations, medical institutions and clinical investigators, to conduct these clinical trials and expect to rely on these third parties to conduct clinical trials of any other product candidate that we develop. Any of these
75
third parties may terminate their engagements with us under certain circumstances. We may not be able to enter into alternative arrangements or do so on commercially reasonable terms. In addition, there is a natural transition period when a new contract research organization begins work. As a result, delays would likely occur, which could negatively impact our ability to meet our expected clinical development timelines and harm our business, financial condition and prospects.
Further, although our reliance on these third parties for clinical development activities limits our control over these activities, we remain responsible for ensuring that each of our trials is conducted in accordance with the applicable protocol, legal and regulatory requirements and scientific standards. For example, notwithstanding the obligations of a CRO for a trial of one of our product candidates, we remain responsible for ensuring that each of our clinical trials is conducted in accordance with the general investigational plan and protocols for the trial. Moreover, the FDA requires us to comply with requirements, commonly referred to as Good Clinical Practices, or GCPs, for conducting, recording and reporting the results of clinical trials to assure that data and reported results are credible and accurate and that the rights, integrity and confidentiality of trial participants are protected. The FDA enforces these GCPs through periodic inspections of trial sponsors, principal investigators, clinical trial sites and IRBs. If we or our third-party contractors fail to comply with applicable GCPs, the clinical data generated in our clinical trials may be deemed unreliable and the FDA may require us to perform additional clinical trials before approving our product candidates, which would delay the marketing approval process. We cannot be certain that, upon inspection, the FDA will determine that any of our clinical trials comply with GCPs. We are also required to register clinical trials and post the results of completed clinical trials on a government-sponsored database, ClinicalTrials.gov, within certain timeframes. Failure to do so can result in fines, adverse publicity and civil and criminal sanctions.
Furthermore, the third parties conducting clinical trials on our behalf are not our employees, and except for remedies available to us under our agreements with such contractors, we cannot control whether or not they devote sufficient time, skill and resources to our ongoing development programs. These contractors may also have relationships with other commercial entities, including our competitors, for whom they may also be conducting clinical trials or other drug development activities, which could impede their ability to devote appropriate time to our clinical programs. If these third parties, including clinical investigators, do not successfully carry out their contractual duties, meet expected deadlines or conduct our clinical trials in accordance with regulatory requirements or our stated protocols, we may not be able to obtain, or may be delayed in obtaining, marketing approvals for our product candidates. If that occurs, we will not be able to, or may be delayed in our efforts to, successfully commercialize our product candidates. In such an event, our financial results and the commercial prospects for any product candidates that we seek to develop could be harmed, our costs could increase and our ability to generate revenues could be delayed, impaired or foreclosed.
Use of third parties to manufacture our product candidates may increase the risk that we will not have sufficient quantities of our product candidates, products, or necessary quantities at an acceptable cost.
We do not own or operate manufacturing facilities for the production of clinical or commercial quantities of our product candidates, and we lack the resources and the capabilities to do so. As a result, we currently rely on third parties for supply of the active pharmaceutical ingredients, or API, in our product candidates. Our current strategy is to outsource all manufacturing of our product candidates and products to third parties.
We currently engage third-party manufacturers to provide the API, and other third parties to provide services for the final drug product formulation of RA101495 SC that is being used in our clinical trials. Although we believe that there are several potential alternative manufacturers who could manufacture RA101495 SC, we may incur added costs and delays in identifying and qualifying any such replacement. In addition, we have not yet concluded a commercial supply contract with any commercial manufacturer. There is no assurance that we will be able to timely secure needed supply arrangements
76
on satisfactory terms, or at all. Our failure to secure these arrangements as needed could have a material adverse effect on our ability to complete the development of our product candidates or, to commercialize them, if approved. We may be unable to conclude agreements for commercial supply with third-party manufacturers, or may be unable to do so on acceptable terms. There may be difficulties in scaling up to commercial quantities and formulation of RA101495 SC and the costs of manufacturing could be prohibitive.
Even if we are able to establish and maintain arrangements with third-party manufacturers, reliance on third-party manufacturers entails additional risks, including:
- •
- reliance on third-parties for manufacturing process development, regulatory compliance and quality assurance;
- •
- limitations on supply availability resulting from capacity and scheduling constraints of third-parties;
- •
- the possible breach of manufacturing agreements by third-parties because of factors beyond our control; and
- •
- the possible termination or non-renewal of the manufacturing agreements by the third-party, at a time that is costly or inconvenient to us.
If we do not maintain our key manufacturing relationships, we may fail to find replacement manufacturers or develop our own manufacturing capabilities, which could delay or impair our ability to obtain regulatory approval for our products. If we do find replacement manufacturers, we may not be able to enter into agreements with them on terms and conditions favorable to us and there could be a substantial delay before new facilities could be qualified and registered with the FDA and other foreign regulatory authorities.
Our lead product candidate may ultimately be regulated as a drug/device combination product. Third-party manufacturers may not be able to comply with the cGMP regulatory requirements applicable to drugs and drug/device combination products, including applicable provisions of the FDA's drug cGMP regulations, device cGMP requirements embodied in the Quality System Regulation, or QSR, or similar regulatory requirements outside the U.S. Our failure, or the failure of our third-party manufacturers, to comply with applicable regulations could result in sanctions being imposed on us, including clinical holds, fines, injunctions, civil penalties, delays, suspension or withdrawal of approvals, seizures or voluntary recalls of product candidates, operating restrictions and criminal prosecutions, any of which could significantly affect supplies of our product candidates. The facilities used by our contract manufacturers to manufacture our product candidates must be evaluated by the FDA pursuant to inspections that will be conducted after we submit our NDA to the FDA. We do not control the manufacturing process of, and are completely dependent on, our contract manufacturing partners for compliance with cGMPs. If our contract manufacturers cannot successfully manufacture material that conforms to our specifications and the strict regulatory requirements of the FDA or others, we may not be able to secure and/or maintain regulatory approval for our product manufactured at these facilities. In addition, we have no control over the ability of our contract manufacturers to maintain adequate quality control, quality assurance and qualified personnel. If the FDA finds deficiencies or a comparable foreign regulatory authority does not approve these facilities for the manufacture of our product candidates or if it withdraws any such approval in the future, we may need to find alternative manufacturing facilities, which would significantly impact our ability to develop, obtain regulatory approval for or market our product candidates, if approved. Contract manufacturers may face manufacturing or quality control problems causing drug substance production and shipment delays or a situation where the contractor may not be able to maintain compliance with the applicable cGMP requirements. Any failure to comply with cGMP requirements or other FDA, EMA and comparable foreign regulatory requirements could adversely affect our clinical research
77
activities and our ability to develop our product candidates and market our products following approval.
The FDA and other foreign regulatory authorities require manufacturers to register manufacturing facilities. The FDA and corresponding foreign regulators also inspect these facilities to confirm compliance with cGMPs. Contract manufacturers may face manufacturing or quality control problems causing drug substance production and shipment delays or a situation where the contractor may not be able to maintain compliance with the applicable cGMP requirements. Any failure to comply with cGMP requirements or other FDA, EMA and comparable foreign regulatory requirements could adversely affect our clinical research activities and our ability to develop our product candidates and market our products following approval.
If our third-party manufacturer of our product candidates is unable to increase the scale of its production of our product candidates, and/or increase the product yield of its manufacturing, then our costs to manufacture the product may increase and commercialization may be delayed.
In order to produce sufficient quantities to meet the demand for clinical trials and, if approved, subsequent commercialization of RA101495 SC or any of our other product candidates in our pipeline or that we may develop, our third-party manufacturer will be required to increase its production and optimize its manufacturing processes while maintaining the quality of the product. The transition to larger scale production could prove difficult. In addition, if our third-party manufacturer is not able to optimize its manufacturing process to increase the product yield for our product candidates, or if it is unable to produce increased amounts of our product candidates while maintaining the quality of the product, then we may not be able to meet the demands of clinical trials or market demands, which could decrease our ability to generate profits and have a material adverse impact on our business and results of operation.
We may need to maintain licenses for active ingredients from third parties to develop and commercialize some of our product candidates, which could increase our development costs and delay our ability to commercialize those product candidates.
Should we decide to use active pharmaceutical ingredients in any of our product candidates that are proprietary to one or more third parties, we would need to maintain licenses to those active ingredients from those third parties. If we are unable to gain or continue to access rights to these active ingredients prior to conducting preclinical toxicology studies intended to support clinical trials, we may need to develop alternate product candidates from these programs by either accessing or developing alternate active ingredients, resulting in increased development costs and delays in commercialization of these product candidates. If we are unable to gain or maintain continued access rights to the desired active ingredients on commercially reasonable terms or develop suitable alternate active ingredients, we may not be able to commercialize product candidates from these programs.
We enter into various contracts in the normal course of our business in which we indemnify the other party to the contract. In the event we have to perform under these indemnification provisions, it could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
In the normal course of business, we periodically enter into academic, commercial, service, collaboration, licensing, consulting and other agreements that contain indemnification provisions. With respect to our academic and other research agreements, we typically indemnify the institution and related parties from losses arising from claims relating to the products, processes or services made, used, sold or performed pursuant to the agreements for which we have secured licenses, and from claims arising from our or our sublicensees' exercise of rights under the agreement. With respect to our commercial agreements, we indemnify our vendors from any third-party product liability claims that
78
could result from the production, use or consumption of the product, as well as for alleged infringements of any patent or other intellectual property right by a third party.
Should our obligation under an indemnification provision exceed applicable insurance coverage or if we were denied insurance coverage, our business, financial condition and results of operations could be adversely affected. Similarly, if we are relying on a collaborator to indemnify us and the collaborator is denied insurance coverage or the indemnification obligation exceeds the applicable insurance coverage and does not have other assets available to indemnify us, our business, financial condition and results of operations could be adversely affected.
We expect to seek to establish collaborations and, if we are not able to establish them on commercially reasonable terms, we may have to alter our development and commercialization plans.
We expect to seek one or more collaborators for the development and commercialization of one or more of our product candidates. For example, we started collaborating with Merck in 2013. Likely collaborators may include large and mid-size pharmaceutical companies, regional and national pharmaceutical companies and biotechnology companies. In addition, if we are able to obtain marketing approval for product candidates from foreign regulatory authorities, we intend to enter into strategic relationships with international biotechnology or pharmaceutical companies for the commercialization of such product candidates outside of the U.S.
We face significant competition in seeking appropriate collaborators. Whether we reach a definitive agreement for a collaboration will depend, among other things, upon our assessment of the collaborator's resources and expertise, the terms and conditions of the proposed collaboration and the proposed collaborator's evaluation of a number of factors. Those factors may include the potential differentiation of our product candidate from competing product candidates, design or results of clinical trials, the likelihood of approval by the FDA, the EMA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities and the regulatory pathway for any such approval, the potential market for the product candidate, the costs and complexities of manufacturing and delivering the product to patients and the potential of competing products. The collaborator may also consider alternative product candidates or technologies for similar indications that may be available for collaboration and whether such a collaboration could be more attractive than the one with us for our product candidate. If we elect to increase our expenditures to fund development or commercialization activities on our own, we may need to obtain additional capital, which may not be available to us on acceptable terms or at all. If we do not have sufficient funds, we may not be able to further develop our product candidates or bring them to market and generate product revenue.
Collaborations are complex and time-consuming to negotiate and document. Further, there have been a significant number of recent business combinations among large pharmaceutical companies that have resulted in a reduced number of potential future collaborators. Any collaboration agreements that we enter into in the future may contain restrictions on our ability to enter into potential collaborations or to otherwise develop specified product candidates. We may not be able to negotiate collaborations on a timely basis, on acceptable terms, or at all. If we are unable to do so, we may have to curtail the development of the product candidate for which we are seeking to collaborate, reduce or delay its development program or one or more of our other development programs, delay its potential commercialization or reduce the scope of any sales or marketing activities, or increase our expenditures and undertake development or commercialization activities at our own expense.
79
If we enter into collaborations with third parties for the development and commercialization of our product candidates, our prospects with respect to those product candidates will depend in significant part on the success of those collaborations.
We expect to enter into additional collaborations for the development and commercialization of certain of our product candidates. If we enter into such collaborations, we will have limited control over the amount and timing of resources that our collaborators will dedicate to the development or commercialization of our product candidates. Our ability to generate revenues from these arrangements will depend on any future collaborators' abilities to successfully perform the functions assigned to them in these arrangements. In addition, any future collaborators may have the right to abandon research or development projects and terminate applicable agreements, including funding obligations, prior to or upon the expiration of the agreed upon terms.
Collaborations involving our product candidates pose a number of risks, including the following:
- •
- collaborators have significant discretion in determining the efforts and resources that they will apply to these collaborations;
- •
- collaborators may not perform their obligations as expected;
- •
- collaborators may not pursue development and commercialization of our product candidates or may elect not to continue or renew development or
commercialization programs, based on clinical trial results, changes in the collaborators' strategic focus or available funding or external factors, such as an acquisition, that divert resources or
create competing priorities;
- •
- collaborators may delay clinical trials, provide insufficient funding for a clinical trial program, stop a clinical trial or abandon a product
candidate, repeat or conduct new clinical trials or require a new formulation of a product candidate for clinical testing;
- •
- collaborators could independently develop, or develop with third parties, products that compete directly or indirectly with our product
candidates;
- •
- a collaborator with marketing and distribution rights to one or more products may not commit sufficient resources to the marketing and
distribution of such product or products;
- •
- disagreements with collaborators, including disagreements over proprietary rights, including trade secrets and intellectual property rights,
contract interpretation, or the preferred course of development might cause delays or termination of the research, development or commercialization of product candidates, might lead to additional
responsibilities for us with respect to product candidates, or might result in litigation or arbitration, any of which would be time-consuming and expensive;
- •
- collaborators may not properly maintain or defend our intellectual property rights or may use our proprietary information in such a way as to
invite litigation that could jeopardize or invalidate our intellectual property or proprietary information or expose us to potential litigation;
- •
- collaborators may infringe the intellectual property rights of third parties, which may expose us to litigation and potential liability; and
- •
- collaborations may be terminated and, if terminated, may result in a need for additional capital to pursue further development or commercialization of the applicable product candidates.
Collaboration agreements may not lead to development or commercialization of product candidates in the most efficient manner or at all. If any future collaborator of ours is involved in a business combination, it could decide to delay, diminish or terminate the development or commercialization of any product candidate licensed to it by us.
80
Risks Related to Our Intellectual Property
Our success depends on our ability to protect our intellectual property and proprietary technology.
Our success depends in large part on our ability to obtain and maintain patent protection and trade secret protection in the U.S. and other countries with respect to our proprietary product candidates. If we do not adequately protect our intellectual property rights, competitors may be able to erode, negate or preempt any competitive advantage we may have, which could harm our business and ability to achieve profitability. To protect our proprietary position, we file patent applications in the U.S. and abroad related to our product candidates that are important to our business; we also license or purchase patents and/or patent applications filed by others. The patent application and approval process is expensive and time-consuming. We may not be able to file and prosecute all necessary or desirable patent applications at a reasonable cost or in a timely manner.
Agreements through which we license patent rights may not give us control over patent prosecution, maintenance or enforcement, so that we may not be able to control which claims or arguments are presented and may not be able to secure, maintain, or successfully enforce necessary or desirable patent protection from those patent rights. We have not had and do not have primary control over patent prosecution and maintenance for certain of the patents and patent applications we license, and therefore cannot guarantee that these patents and applications will be prosecuted or maintained in a manner consistent with the best interests of our business. We cannot be certain that patent prosecution, maintenance and/or enforcement activities by our licensors have been or will be conducted in compliance with applicable laws and regulations or will result in valid and enforceable patents.
If the scope of the patent protection we or our licensors obtain is not sufficiently broad, we may not be able to prevent others from developing and commercialize technology and products similar or identical to ours. The degree of patent protection we require to successfully compete in the marketplace may be unavailable or severely limited in some cases and may not adequately protect our rights or permit us to gain or keep any competitive advantage. We cannot provide any assurances that any of our licensed patents have, or that any of our pending licensed patent applications that mature into issued patents will include, claims with a scope sufficient to protect our proprietary platform or otherwise provide any competitive advantage, nor can we assure you that our licenses are or will remain in force. In addition, the laws of foreign countries may not protect our rights to the same extent as the laws of the U.S. Furthermore, patents have a limited lifespan. In the U.S., the natural expiration of a patent is generally twenty years after it is filed. Various extensions may be available; however, the life of a patent, and the protection it affords, is limited. Given the amount of time required for the development, testing and regulatory review of new product candidates, patents protecting such candidates might expire before or shortly after such candidates are commercialized. As a result, our licensed patent portfolio may not provide us with adequate and continuing patent protection sufficient to exclude others from commercializing products which are the same as or similar to our product candidates. In addition, the patent portfolio licensed to us is, or may be, licensed to third parties, such as outside our field, and such third parties may have certain enforcement rights. Thus, patents licensed to us could be put at risk of being invalidated or interpreted narrowly in litigation filed by or against another licensee or in administrative proceedings brought by or against another licensee in response to such litigation or for other reasons.
Even if they are unchallenged, our licensed patents and pending patent applications, if issued, may not provide us with any meaningful protection or prevent competitors from designing around our patent claims to circumvent our licensed patents by developing similar or alternative technologies or therapeutics in a non-infringing manner. For example, a third party may develop a competitive therapy that provides benefits similar to one or more of our product candidates but that uses a vector, expression construct or delivery modality that falls outside the scope of our patent protection or license rights. If the patent protection provided by the patents and patent applications we hold or pursue with
81
respect to our product candidates is not sufficiently broad to impede such competition, our ability to successfully commercialize our product candidates could be negatively affected, which would harm our business. These risks apply to patents and patent applications which we have in-licensed as well as those we own now or in the future.
We, or any future partners, collaborators, or licensees, may fail to identify patentable aspects of inventions made in the course of research, development and/or commercialization activities before it is too late to obtain patent protection on them. Therefore, we may miss potential opportunities to strengthen our patent position.
It is possible that defects of form or timing in the preparation or filing of our patents or patent applications may exist, or may arise in the future, for example with respect to proper priority claims, inventorship, claim scope, or requests for patent term adjustments. If we or our partners, collaborators, licensees, or licensors, whether current or future, fail to establish, maintain or protect such patents and other intellectual property rights, such rights may be reduced or eliminated. If our partners, collaborators, licensees, or licensors, are not fully cooperative or disagree with us as to the prosecution, maintenance or enforcement of any patent rights, such patent rights could be compromised. If there are material defects in the form, preparation, filing, prosecution, or enforcement of our patents or patent applications, such patents may be invalid and/or unenforceable, and such applications may never result in valid, enforceable patents. Any of these outcomes could impair our ability to prevent competition from third parties, which may have an adverse impact on our business.
The patent position of biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies generally is highly uncertain. No consistent policy regarding the breadth of claims allowed in biotechnology and pharmaceutical patents has emerged to date in the U.S. or in any foreign jurisdictions. In addition, the determination of patent rights with respect to pharmaceutical compounds commonly involves complex legal and factual questions, which has in recent years been the subject of much litigation. As a result, the issuance, scope, validity, enforceability and commercial value of our patent rights are highly uncertain.
Pending patent applications cannot be enforced against third parties practicing the technology claimed in such applications unless and until a patent issues from such applications. Assuming the other requirements for patentability are met, currently, the first inventor to file a patent application is generally entitled to the patent. However, prior to March 16, 2013, in the U.S., the first to invent was entitled to the patent. Publications of discoveries in scientific literature often lag behind the actual discoveries, and patent applications in the U.S. and other jurisdictions are not published until 18 months after filing, or in some cases not at all. Therefore, we cannot be certain that we were the first to make the inventions claimed in our patents or pending patent applications, or that we were the first to file for patent protection of such inventions. Similarly, we cannot be certain that parties from whom we do or may license or purchase patent rights were the first to make relevant claimed inventions, or were the first to file for patent protection for them. If third parties have filed patent applications on inventions claimed in our own patents or applications on or before March 15, 2013, the third parties may initiate an interference proceeding in the U.S. to determine who was the first to invent any of the subject matter covered by the patent claims of our patents or applications. If third parties have filed such applications after March 15, 2013, a derivation proceeding in the U.S. can be initiated by such third parties to determine whether our invention was derived from theirs.
Moreover, because the issuance of a patent is not conclusive as to its inventorship, scope, validity or enforceability, our patents or pending patent applications may be challenged in the courts or patent offices in the U.S. and abroad. There is no assurance that all of the potentially relevant prior art relating to our patents and patent applications has been found. If such prior art exists, it may be used to invalidate a patent, or may prevent a patent from issuing from a pending patent application. For example, such patent filings may be subject to a third-party preissuance submission of prior art to the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office, or USPTO, or to other patent offices around the world. It is often
82
the case that such third-party submissions may be made anonymously such that we would not have information regarding the name of the party challenging our intellectual property. Alternately or additionally, we may become involved in post-grant review procedures, oppositions, derivations, proceedings, reexaminations, inter partes review or interference proceedings, in the U.S. or elsewhere, challenging patents or patent applications in which we have rights, including patents on which we rely to protect our business. An adverse determination in any such challenges may result in loss of exclusivity or in patent claims being narrowed, invalidated or held unenforceable, in whole or in part, which could limit our ability to stop others from using or commercializing similar or identical technology and products, or limit the duration of the patent protection of our technology and products. In addition, given the amount of time required for the development, testing and regulatory review of new product candidates, patents protecting such candidates might expire before or shortly after such candidates are commercialized.
Pending and future patent applications may not result in patents being issued that protect our business, in whole or in part, or which effectively prevent others from commercializing competitive products. Changes in either the patent laws or interpretation of the patent laws in the U.S. and other countries may diminish the value of our patents or narrow the scope of our patent protection. In addition, the laws of foreign countries may not protect our rights to the same extent or in the same manner as the laws of the U.S. For example, patent laws in various jurisdictions, including significant commercial markets such as Europe, restrict the patentability of methods of treatment of the human body more than U.S. law does.
The patent application process is subject to numerous risks and uncertainties, and there can be no assurance that we or any of our future development partners will be successful in protecting our product candidates by obtaining and defending patents. These risks and uncertainties include the following:
- •
- the USPTO and various foreign governmental patent agencies require compliance with a number of procedural, documentary, fee payment and other
provisions during the patent process. There are situations in which noncompliance can result in abandonment or lapse of a patent or patent application, resulting in partial or complete loss of patent
rights in the relevant jurisdiction. In such an event, competitors might be able to enter the market earlier than would otherwise have been the case;
- •
- patent applications may not result in any patents being issued;
- •
- patents that may be owned or in-licensed may be challenged, invalidated, modified, revoked, circumvented, found to be unenforceable or
otherwise may not provide any competitive advantage;
- •
- our competitors, many of whom have substantially greater resources and many of whom have made significant investments in competing
technologies, may seek or may have already obtained patents that will limit, interfere with or eliminate our ability to make, use, and sell our potential product candidates;
- •
- there may be significant pressure on the U.S. government and international governmental bodies to limit the scope of patent protection both
inside and outside the U.S. for disease treatments that prove successful, as a matter of public policy regarding worldwide health concerns; and
- •
- countries other than the U.S. may have patent laws less favorable to patentees than those upheld by U.S. courts, allowing foreign competitors a better opportunity to create, develop and market competing product candidates.
Issued patents that we have or may obtain or license may not provide us with any meaningful protection, prevent competitors from competing with us or otherwise provide us with any competitive
83
advantage. Our competitors may be able to circumvent our patents by developing similar or alternative technologies or products in a non-infringing manner. Our competitors may also seek approval to market their own products similar to or otherwise competitive with our products. Alternatively, our competitors may seek to market generic versions of any approved products by submitting ANDAs to the FDA in which they claim that patents owned or licensed by us are invalid, unenforceable or not infringed. In these circumstances, we may need to defend or assert our patents, or both, including by filing lawsuits alleging patent infringement. In any of these types of proceedings, a court or other agency with jurisdiction may find our patents invalid or unenforceable, or that our competitors are competing in a non-infringing manner. Thus, even if we have valid and enforceable patents, these patents still may not provide protection against competing products or processes sufficient to achieve our business objectives.
Pursuant to the terms of some of our license agreements with third parties, some of our third-party licensors have the right, but not the obligation in certain circumstances to control enforcement of our licensed patents or defense of any claims asserting the invalidity of these patents. Even if we are permitted to pursue such enforcement or defense, we will require the cooperation of our licensors, and cannot guarantee that we would receive it and on what terms. We cannot be certain that our licensors will allocate sufficient resources or prioritize their or our enforcement of such patents or defense of such claims to protect our interests in the licensed patents. If we cannot obtain patent protection, or enforce existing or future patents against third parties, our competitive position and our financial condition could suffer.
In addition, we rely on the protection of our trade secrets and proprietary know-how. Although we have taken steps to protect our trade secrets and unpatented know-how, including entering into confidentiality agreements with third parties, and confidential information and inventions agreements with employees, consultants and advisors, we cannot provide any assurances that all such agreements have been duly executed, and third parties may still obtain this information or may come upon this or similar information independently. Additionally, if the steps taken to maintain our trade secrets are deemed inadequate, we may have insufficient recourse against third parties for misappropriating its trade secrets. If any of these events occurs or if we otherwise lose protection for our trade secrets or proprietary know-how, our business may be harmed.
It is difficult and costly to protect our intellectual property and our proprietary technologies, and we may not be able to ensure their protection.
Our commercial success will depend in part on obtaining and maintaining patent protection and trade secret protection for the use, formulation and structure of our products and product candidates, the methods used to manufacture them, the related therapeutic targets and associated methods of treatment as well as on successfully defending these patents against potential third-party challenges. Our ability to protect our products and product candidates from unauthorized making, using, selling, offering to sell or importing by third parties is dependent on the extent to which we have rights under valid and enforceable patents that cover these activities.
The patent positions of pharmaceutical, biotechnology and other life sciences companies can be highly uncertain and involve complex legal and factual questions for which important legal principles remain unresolved. Changes in either the patent laws or in interpretations of patent laws in the U.S. and other countries may diminish the value of our intellectual property. Further, the determination that a patent application or patent claim meets all of the requirements for patentability is a subjective determination based on the application of law and jurisprudence. The ultimate determination by the USPTO or by a court or other trier of fact in the U.S., or corresponding foreign national patent offices or courts, on whether a claim meets all requirements of patentability cannot be assured. For example, our lead C5 inhibitor portfolio consists of six families of patent applications that we own directed to our lead C5 inhibitor and related methods of use. Although we have conducted searches for third-party
84
publications, patents and other information that may affect the patentability of claims in our various patent applications and patents, we cannot be certain that all relevant information has been identified. Accordingly, we cannot predict the breadth of claims that may be allowed or enforced in our patents or patent applications, in our licensed patents or patent applications or in third-party patents.
We cannot provide assurances that any of our patent applications will be found to be patentable, including over our own prior art patents, or will issue as patents. Neither can we make assurances as to the scope of any claims that may issue from our pending and future patent applications nor to the outcome of any proceedings by any potential third parties that could challenge the patentability, validity or enforceability of our patents and patent applications in the U.S. or foreign jurisdictions. Any such challenge, if successful, could limit patent protection for our products and product candidates and/or materially harm our business.
The degree of future protection for our proprietary rights is uncertain because legal means afford only limited protection and may not adequately protect our rights or permit us to gain or keep our competitive advantage. For example:
- •
- we may not be able to generate sufficient data to support full patent applications that protect the entire breadth of developments in one or
more of our programs, including our PNH, gMG, aHUS and LN programs;
- •
- it is possible that one or more of our pending patent applications will not become an issued patent or, if issued, that the patent(s) will be
sufficient to protect our technology, provide us with a basis for commercially viable products or provide us with any competitive advantages;
- •
- if our pending applications issue as patents, they may be challenged by third parties as not infringed, invalid or unenforceable under U.S. or
foreign laws; or
- •
- if issued, the patents under which we hold rights may not be valid or enforceable.
In addition, to the extent that we are unable to obtain and maintain patent protection for one of our products or product candidates or in the event that such patent protection expires, it may no longer be cost-effective to extend our portfolio by pursuing additional development of a product or product candidate for follow-on indications.
We also may rely on trade secrets to protect our technologies or products, especially where we do not believe patent protection is appropriate or obtainable. For example, the patents underlying our proprietary peptide chemistry technology, which we license from third parties on a non-exclusive basis in some cases, expire by 2022. As a result, we anticipate that trade secrets will serve as the primary protection for the know-how behind our proprietary platform. Also, we cannot provide any assurances that any of our licensed patents have claims with a scope sufficient to protect our proprietary platform or otherwise provide any competitive advantage, nor can we assure you that our licenses are or will remain in full force or effect, in which case we would similarly rely on trade secrets. However, trade secrets are difficult to protect. Although we use reasonable efforts to protect our trade secrets, our employees, consultants, contractors, outside scientific collaborators and other advisers may unintentionally or willfully disclose our information to competitors. Enforcing a claim that a third-party entity illegally obtained and is using any of our trade secrets is expensive and time-consuming, and the outcome is unpredictable. In addition, courts outside the U.S. are sometimes less willing to protect trade secrets. Moreover, our competitors may independently develop equivalent knowledge, methods and know-how. Notably, proprietary technology protected by a trade secret does not preempt the patent of independently developed equivalent technology, even if such equivalent technology is invented subsequent to the technology protected by a trade secret.
85
Obtaining and maintaining patent protection depends on compliance with various procedural, document submission, fee payment and other requirements imposed by governmental patent agencies, and our patent protection could be reduced or eliminated for non-compliance with these requirements.
Periodic maintenance fees, renewal fees, annuity fees and various other governmental fees on patents and applications are required to be paid to the USPTO and various governmental patent agencies outside of the U.S. in several stages over the lifetime of the patents and applications. The USPTO and various non-U.S. governmental patent agencies require compliance with a number of procedural, documentary, fee payment and other similar provisions during the patent application process and after a patent has issued. There are situations in which non-compliance can result in abandonment or lapse of the patent or patent application, resulting in partial or complete loss of patent rights in the relevant jurisdiction. Under the terms of some of our licenses, we do not have the ability to maintain or prosecute patents in the portfolio and must therefore rely on third parties to comply with these requirements.
Patent terms may be inadequate to protect our competitive position on our products for an adequate amount of time.
Given the amount of time required for the development, testing and regulatory review of new product candidates, patents protecting such candidates might expire before or shortly after such candidates are commercialized. We expect to seek extensions of patent terms in the U.S. and, if available, in other countries where we are prosecuting patents. In the U.S., the Drug Price Competition and Patent Term Restoration Act of 1984 permits a patent term extension of up to five years beyond the normal expiration of the patent, which is limited to the approved indication (or any additional indications approved during the period of extension). However, the applicable authorities, including the FDA and the USPTO in the U.S., and any equivalent regulatory authority in other countries, may not agree with our assessment of whether such extensions are available, and may refuse to grant extensions to our patents, or may grant more limited extensions than we request. If this occurs, our competitors may be able to take advantage of our investment in development and clinical trials by referencing our clinical and preclinical data and launch their product earlier than might otherwise be the case.
Changes to the patent law in the U.S. and other jurisdictions could diminish the value of patents in general, thereby impairing our ability to protect our products.
As is the case with other biopharmaceutical companies, our success is heavily dependent on intellectual property, particularly patents. Obtaining and enforcing patents in the biopharmaceutical industry involves both technological and legal complexity and is therefore costly, time consuming and inherently uncertain. Recent patent reform legislation in the U.S., including the Leahy-Smith America Invents Act, or the America Invents Act, could increase those uncertainties and costs. The America Invents Act was signed into law on September 16, 2011, and many of the substantive changes became effective on March 16, 2013. The America Invents Act reforms U.S. patent law in part by changing the U.S. patent system from a "first to invent" system to a "first inventor to file" system, expanding the definition of prior art, and developing a post-grant review system. This legislation changes U.S. patent law in a way that may weaken our ability to obtain patent protection in the U.S. for those applications filed after March 16, 2013.
Further, the America Invents Act created new procedures to challenge the validity of issued patents in the U.S., including post-grant review and inter partes review proceedings, which some third parties have been using to cause the cancellation of selected or all claims of issued patents of competitors. For a patent with an effective filing date of March 16, 2013 or later, a petition for post-grant review can be filed by a third party in a nine-month window from issuance of the patent. A petition for inter partes review can be filed immediately following the issuance of a patent if the patent has an effective filing date prior to March 16, 2013. A petition for inter partes review can be filed after
86
the nine-month period for filing a post-grant review petition has expired for a patent with an effective filing date of March 16, 2013 or later. Post-grant review proceedings can be brought on any ground of invalidity, whereas inter partes review proceedings can only raise an invalidity challenge based on published prior art and patents. These adversarial actions at the USPTO review patent claims without the presumption of validity afforded to U.S. patents in lawsuits in U.S. federal courts and use a lower burden of proof than used in litigation in U.S. federal courts. Therefore, it is generally considered easier for a competitor or third party to have a U.S. patent invalidated in a USPTO post-grant review or inter partes review proceeding than invalidated in a litigation in a U.S. federal court. If any of our patents are challenged by a third party in such a USPTO proceeding, there is no guarantee that we or our licensors or collaborators will be successful in defending the patent, which would result in a loss of the challenged patent right to us.
In addition, recent court rulings in cases such as Association for Molecular Pathology v. Myriad Genetics, Inc., BRCA1- & BRCA2-Based Hereditary Cancer Test Patent Litigation, and Promega Corp. v. Life Technologies Corp. have narrowed the scope of patent protection available in certain circumstances and weakened the rights of patent owners in certain situations. In addition to increasing uncertainty with regard to our ability to obtain patents in the future, this combination of events has created uncertainty with respect to the value of patents once obtained. Depending on future actions by the U.S. Congress, the U.S. courts, the USPTO and the relevant law-making bodies in other countries, the laws and regulations governing patents could change in unpredictable ways that would weaken our ability to obtain new patents or to enforce our existing patents and patents that we might obtain in the future.
We may not be able to enforce our intellectual property rights throughout the world.
Filing, prosecuting, enforcing and defending patents on our product candidates in all countries throughout the world would be prohibitively expensive, and our intellectual property rights in some countries outside the U.S. can be less extensive than those in the U.S. The requirements for patentability may differ in certain countries, particularly in developing countries; thus, even in countries where we do pursue patent protection, there can be no assurance that any patents will issue with claims that cover our products.
Moreover, our ability to protect and enforce our intellectual property rights may be adversely affected by unforeseen changes in foreign intellectual property laws. Additionally, laws of some countries outside of the U.S. and Europe do not afford intellectual property protection to the same extent as the laws of the U.S. and Europe. Many companies have encountered significant problems in protecting and defending intellectual property rights in certain foreign jurisdictions. The legal systems of some countries, including India, China and other developing countries, do not favor the enforcement of patents and other intellectual property rights. This could make it difficult for us to stop the infringement of our patents or the misappropriation of our other intellectual property rights. For example, many foreign countries have compulsory licensing laws under which a patent owner must grant licenses to third parties. Consequently, we may not be able to prevent third parties from practicing our inventions in certain countries outside the U.S. and Europe. Competitors may use our technologies in jurisdictions where we have not obtained patent protection to develop and market their own products and, further, may export otherwise infringing products to territories where we have patent protection, if our ability to enforce our patents to stop infringing activities is inadequate. These products may compete with our products, and our patents or other intellectual property rights may not be effective or sufficient to prevent them from competing.
Agreements through which we license patent rights may not give us sufficient rights to permit us to pursue enforcement of our licensed patents or defense of any claims asserting the invalidity of these patents (or control of enforcement or defense) of such patent rights in all relevant jurisdictions as requirements may vary.
87
Proceedings to enforce our patent rights in foreign jurisdictions, whether or not successful, could result in substantial costs and divert our efforts and resources from other aspects of our business. Moreover, such proceedings could put our patents at risk of being invalidated or interpreted narrowly and our patent applications at risk of not issuing and could provoke third parties to assert claims against us. We may not prevail in any lawsuits that we initiate and the damages or other remedies awarded, if any, may not be commercially meaningful. Furthermore, while we intend to protect our intellectual property rights in major markets for our products, we cannot ensure that we will be able to initiate or maintain similar efforts in all jurisdictions in which we may wish to market our products. Accordingly, our efforts to protect our intellectual property rights in such countries may be inadequate.
Others may claim an ownership interest in our intellectual property which could expose it to litigation and have a significant adverse effect on its prospects.
A third party may claim an ownership interest in one or more of our or our licensors' patents or other proprietary or intellectual property rights. A third party could bring legal actions against us and seek monetary damages and/or enjoin clinical testing, manufacturing and marketing of the affected product or products. While we are presently unaware of any claims or assertions by third-parties with respect to our patents or other intellectual property, we cannot guarantee that a third-party will not assert a claim or an interest in any of such patents or intellectual property. If we become involved in any litigation, it could consume a substantial portion of our resources, and cause a significant diversion of effort by our technical and management personnel. If any of these actions are successful, in addition to any potential liability for damages, we could be required to obtain a license to continue to manufacture or market the affected product, in which case we may be required to pay substantial royalties or grant cross-licenses to our patents. We cannot, however, assure you that any such license will be available on acceptable terms, if at all. Ultimately, we could be prevented from commercializing a product, or be forced to cease some aspect of our business operations as a result of claims of patent infringement or violation of other intellectual property rights, Further, the outcome of intellectual property litigation is subject to uncertainties that cannot be adequately quantified in advance, including the demeanor and credibility of witnesses and the identity of any adverse party. This is especially true in intellectual property cases that may turn on the testimony of experts as to technical facts upon which experts may reasonably disagree.
If we are sued for infringing intellectual property rights of third parties, such litigation could be costly and time consuming and could prevent or delay us from developing or commercializing our product candidates.
Our commercial success depends, in part, on our ability to develop, manufacture, market and sell our product candidates without infringing the intellectual property and other proprietary rights of third parties. Third parties may have U.S. and non-U.S. issued patents and pending patent applications relating to compounds, methods of manufacturing compounds and/or methods of use for the treatment of the disease indications for which we are developing our product candidates or relating to the use of complement inhibition that may cover our product candidates or approach to complement inhibition. If any third-party patents or patent applications are found to cover our product candidates or their methods of use or manufacture or our approach to complement inhibition, we may not be free to manufacture or market our product candidates as planned without obtaining a license, which may not be available on commercially reasonable terms, or at all.
There is a substantial amount of intellectual property litigation in the biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries, and we may become party to, or threatened with, litigation or other adversarial proceedings regarding intellectual property rights with respect to our products candidates, including interference and post-grant proceedings before the USPTO. There may be third-party patents or patent applications with claims to compounds, starting materials, formulations, methods of manufacture or methods for treatment related to the composition, use or manufacture of our product
88
candidates. We cannot guarantee that any of our patent searches or analyses including, but not limited to, the identification of relevant patents, the scope of patent claims or the expiration of relevant patents are complete or thorough, nor can we be certain that we have identified each and every patent and pending application in the U.S. and abroad that is relevant to or necessary for the commercialization of our product candidates in any jurisdiction. Because patent applications can take many years to issue, there may be currently pending patent applications which may later result in issued patents that our product candidates or methods of making or using them may be accused of infringing. In addition, third parties may obtain patents in the future and claim that use of our technologies infringes upon these patents. Accordingly, third parties may assert infringement claims against us based intellectual property rights that exist now or arise in the future. The outcome of intellectual property litigation is subject to uncertainties that cannot be adequately quantified in advance. The pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries have produced a significant number of patents, and it may not always be clear to industry participants, including us, which patents cover various types of products or methods of use or manufacture. The scope of protection afforded by a patent is subject to interpretation by the courts, and the interpretation is not always uniform. If we were sued for patent infringement, we would need to demonstrate that our product candidates, products or methods either do not infringe the patent claims of the relevant patent or that the patent claims are invalid or unenforceable, and we may not be able to do this. Proving invalidity is difficult. For example, in the U.S., proving invalidity requires a showing of clear and convincing evidence to overcome the presumption of validity enjoyed by issued patents. Even if we are successful in these proceedings, we may incur substantial costs and the time and attention of our management and scientific personnel could be diverted in pursuing these proceedings, which could significantly harm our business and operating results. In addition, we may not have sufficient resources to bring these actions to a successful conclusion.
If we are found to infringe a third party's intellectual property rights, we could be forced, including by court order, to cease developing, manufacturing or commercializing the infringing product candidate or product. Alternatively, we may be required to obtain a license from such third party in order to use the infringing technology and continue developing, manufacturing or marketing the infringing product candidate or product. However, we may not be able to obtain any required license on commercially reasonable terms or at all. Even if we were able to obtain a license, it could be non-exclusive, thereby giving our competitors access to the same technologies licensed to us; alternatively, or additionally it could include terms that impede or destroy our ability to compete successfully in the commercial marketplace. In addition, we could be found liable for monetary damages, including treble damages and attorneys' fees if we are found to have willfully infringed a patent. A finding of infringement could prevent us from commercializing our product candidates or force us to cease some of our business operations, which could harm our business. Claims that we have misappropriated the confidential information or trade secrets of third parties could have a similar negative impact on our business.
We may be subject to claims by third parties asserting that our employees or we have misappropriated their intellectual property or claiming ownership of what we regard as our own intellectual property.
Many of our current and former employees and our licensors' current and former employees, including our senior management, were previously employed at universities or at other biotechnology or pharmaceutical companies, including some which may be competitors or potential competitors. Some of these employees, including each member of our senior management, executed proprietary rights, non-disclosure and non-competition agreements, or similar agreements, in connection with such previous employment. Although we try to ensure that our employees do not use the proprietary information or know-how of others in their work for us, we may be subject to claims that we or these employees have used, incorporated or disclosed intellectual property, including trade secrets or other proprietary information, of any such third party. Litigation may be necessary to defend against such claims. If we fail in defending any such claims, in addition to paying monetary damages, we may lose
89
valuable intellectual property rights or personnel or sustain damages. Such intellectual property rights could be awarded to a third party, and we could be required to obtain a license from such third party to commercialize our technology or products. Such a license may not be available on commercially reasonable terms or at all. Even if we are successful in defending against such claims, litigation could result in substantial costs and be a distraction to management and scientific personnel.
In addition, while we typically require our employees, consultants and contractors who may be involved in the development of intellectual property to execute agreements assigning such intellectual property to us, we may be unsuccessful in executing such an agreement with each party who in fact develops intellectual property that we regard as our own, which may result in claims by or against us related to the ownership of such intellectual property. If we fail in prosecuting or defending any such claims, in addition to paying monetary damages, we may lose valuable intellectual property rights. Even if we are successful in prosecuting or defending against such claims, litigation could result in substantial costs and be a distraction to our senior management and scientific personnel.
We may become involved in lawsuits to protect or enforce our patents or other intellectual property, which could be expensive, time consuming and unsuccessful.
Competitors may infringe our patents, trademarks, copyrights or other intellectual property. To counter infringement or unauthorized use, we may be required to file infringement claims, which can be expensive and time consuming and divert the time and attention of our management and scientific personnel. Any claims we assert against perceived infringers could provoke these parties to assert counterclaims against us alleging that we infringe their patents, in addition to counterclaims asserting that our patents are invalid or unenforceable, or both. In any patent infringement proceeding, there is a risk that a court will decide that a patent of ours is invalid or unenforceable, in whole or in part, and that we do not have the right to stop the other party from using the invention at issue. There is also a risk that, even if the validity of such patents is upheld, the court will construe the patent's claims narrowly or decide that we do not have the right to stop the other party from using the invention at issue on the grounds that our patent claims do not cover the invention. An adverse outcome in a litigation or proceeding involving one or more of our patents could limit our ability to assert those patents against those parties or other competitors and may curtail or preclude our ability to exclude third parties from making and selling similar or competitive products. Similarly, if we assert trademark infringement claims, a court may determine that the marks we have asserted are invalid or unenforceable, or that the party against whom we have asserted trademark infringement has superior rights to the marks in question. In this case, we could ultimately be forced to cease use of such trademarks thereby losing any value in the goodwill or branding associated with those marks.
Even if we establish infringement, the court may decide not to grant an injunction against further infringing activity and instead award only monetary damages, which may or may not be an adequate remedy. Furthermore, because of the substantial amount of discovery required in connection with intellectual property litigation, there is a risk that some of our confidential information could be compromised by disclosure during litigation. There could also be public announcements of the results of hearings, motions or other interim proceedings or developments. If securities analysts or investors perceive these results to be negative, it could adversely affect the price of shares of our common stock. Moreover, there can be no assurance that we will have sufficient financial or other resources to file and pursue such infringement claims, which typically last for years before they are concluded. Even if we ultimately prevail in such claims, the monetary cost of such litigation and the diversion of the attention of our management and scientific personnel could outweigh any benefit we receive as a result of the proceedings.
Additionally, for certain of our in-licensed patent rights, we do not have the right to bring suit for infringement and must rely on third parties to enforce these rights for us. If we cannot or choose not to take action against those we believe infringe our intellectual property rights, we may have difficulty
90
competing in certain markets where such potential infringers conduct their business, and our commercialization efforts may suffer as a result.
If we fail to comply with our obligations under our existing and any future intellectual property licenses with third parties, we could lose license rights that are important to our business.
We are a party to a collaboration and license agreement with Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., under which we license patent rights relating to peptides that modulate the activity of a Merck-designated non-complement cardiovascular product candidate. We are party to several other license agreements, under which we license patent rights related to our proprietary technology and other product candidates. We may enter into additional license agreements in the future. Our license agreement with Merck imposes, and we expect that future license agreements will impose, various diligence, milestone payment, royalty, insurance and other obligations on us. If we fail to comply with our obligations under these licenses, our licensors may have the right to terminate these license agreements, in which event we might not be able to market any product that is covered by these agreements, or our licensors may convert the license to a non-exclusive license, which could negatively impact the value of the product candidate being developed under the license agreement. Termination of these license agreements or reduction or elimination of our licensed rights may also result in our having to negotiate new or reinstated licenses with less favorable terms.
If we are unable to protect the confidentiality of our trade secrets, the value of our technology could be negatively impacted and our business would be harmed.
In addition to the protection afforded by patents, we also rely on trade secret protection for certain aspects of our intellectual property. For example, a majority of the patents underlying our proprietary peptide chemistry technology expire by 2022. As a result, we anticipate that we will rely on trade secrets as the primary protection for the know-how behind our proprietary platform. We seek to protect these trade secrets, in part, by entering into non-disclosure and confidentiality agreements with parties who have access to them, such as our employees, consultants, independent contractors, advisors, contract manufacturers, suppliers and other third parties. We also enter into confidentiality and invention or patent assignment agreements with employees and certain consultants. Any party with whom we have executed such an agreement may breach that agreement and disclose our proprietary information, including our trade secrets, and we may not be able to obtain adequate remedies for such breaches. Enforcing a claim that a party illegally disclosed or misappropriated a trade secret is difficult, expensive and time-consuming, and the outcome is unpredictable. Additionally, if the steps taken to maintain our trade secrets are deemed inadequate, we may have insufficient recourse against third parties for misappropriating the trade secret. Further, if any of our trade secrets were to be lawfully obtained or independently developed by a competitor, we would have no right to prevent such third party, or those to whom they communicate such technology or information, from using that technology or information to compete with us. If any of our trade secrets were to be disclosed to or independently developed by a competitor, our business and competitive position could be harmed.
If our trademarks and trade names are not adequately protected, then we may not be able to build name recognition in our marks of interest and our business may be adversely affected.
Our trademarks or trade names may be challenged, infringed, circumvented or declared generic or determined to be infringing on other marks. We rely on both registration and common law protection for our trademarks. We may not be able to protect our rights to these trademarks and trade names or may be forced to stop using these names, which we need for name recognition by potential partners or customers in our markets of interest. During trademark registration proceedings, we may receive rejections. Although we would be given an opportunity to respond to those rejections, we may be unable to overcome such rejections. In addition, in the USPTO and in comparable agencies in many
91
foreign jurisdictions, third parties are given an opportunity to oppose pending trademark applications and to seek to cancel registered trademarks. Opposition or cancellation proceedings may be filed against our trademarks, and our trademarks may not survive such proceedings. If we are unable to establish name recognition based on our trademarks and trade names, we may not be able to compete effectively and our business may be adversely affected.
Risks Related to Employee Matters and Managing Growth
We only have a limited number of employees to manage and operate our business.
As of December 31, 2017, we had 63 full-time or part-time employees. Our focus on the development of RA101495 SC requires us to optimize cash utilization and to manage and operate our business in a highly efficient manner. We cannot assure you that we will be able to hire and/or retain adequate staffing levels to develop RA101495 SC or run our operations and/or to accomplish all of the objectives that we otherwise would seek to accomplish.
Cyber-attacks or other failures in telecommunications or information technology systems could result in information theft, data corruption and significant disruption of our business operations.
We utilize information technology, or IT, systems and networks to process, transmit and store electronic information in connection with our business activities. As use of digital technologies has increased, cyber incidents, including deliberate attacks and attempts to gain unauthorized access to computer systems and networks, have increased in frequency and sophistication. These threats pose a risk to the security of our systems and networks, the confidentiality and the availability and integrity of our data. There can be no assurance that we will be successful in preventing cyber-attacks or successfully mitigating their effects. Similarly, there can be no assurance that our collaborators, CROs, third-party logistics providers, distributors and other contractors and consultants will be successful in protecting our clinical and other data that is stored on their systems. Any cyber-attack or destruction or loss of data could have a material adverse effect on our business and prospects. In addition, we may suffer reputational harm or face litigation or adverse regulatory action as a result of cyber-attacks or other data security breaches and may incur significant additional expense to implement further data protection measures.
We depend heavily on our executive officers, directors, and principal consultants and the loss of their services would materially harm our business.
Our success depends, and will likely continue to depend, upon our ability to hire, retain the services of our current executive officers, directors, principal consultants and others. In addition, we have established relationships with universities and research institutions which have historically provided, and continue to provide, us with access to research laboratories, clinical trials, facilities and patients. Our ability to compete in the biotechnology and pharmaceuticals industries depends upon our ability to attract and retain highly qualified managerial, scientific and medical personnel.
Our industry has experienced a high rate of turnover of management personnel in recent years. Any of our personnel may terminate their employment at will. If we lose one or more of our executive officers or other key employees, our ability to implement our business strategy successfully could be seriously harmed. Furthermore, replacing executive officers or other key employees may be difficult and may take an extended period of time because of the limited number of individuals in our industry with the breadth of skills and experience required to develop, gain marketing approval of and commercialize products successfully.
Competition to hire from this limited pool is intense, and we may be unable to hire, train, retain or motivate these additional key employees on acceptable terms given the competition among
92
numerous pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies for similar personnel. We also experience competition for the hiring of scientific and clinical personnel from universities and research institutions.
We rely on consultants and advisors, including scientific and clinical advisors, to assist us in formulating our research and development and commercialization strategy. Our consultants and advisors may be employed by other entities and may have commitments under consulting or advisory contracts with those entities that may limit their availability to us. If we are unable to continue to attract and retain highly qualified personnel, our ability to develop and commercialize our product candidates will be limited.
Our employees, independent contractors, consultants, collaborators and contract research organizations may engage in misconduct or other improper activities, including non-compliance with regulatory standards and requirements, which could cause significant liability for us and harm our reputation.
We are exposed to the risk that our employees, independent contractors, consultants, collaborators and contract research organizations may engage in fraudulent conduct or other illegal activity. Misconduct by those parties could include intentional, reckless and/or negligent conduct or disclosure of unauthorized activities to us that violates: (1) FDA regulations or similar regulations of comparable non-U.S. regulatory authorities, including those laws requiring the reporting of true, complete and accurate information to such authorities, (2) manufacturing standards, (3) federal and state healthcare fraud and abuse laws and regulations and similar laws and regulations established and enforced by comparable non-U.S. regulatory authorities, and (4) laws that require the reporting of financial information or data accurately. Activities subject to these laws also involve the improper use of information obtained in the course of clinical trials, which could result in regulatory sanctions and serious harm to our reputation. It is not always possible to identify and deter misconduct, and the precautions we take to detect and prevent this activity may not be effective in controlling unknown or unmanaged risks or losses or in protecting us from governmental investigations or other actions or lawsuits stemming from a failure to be in compliance with such laws, standards or regulations. If any such actions are instituted against us, and we are not successful in defending ourselves or asserting our rights, those actions could have a significant impact on our business and results of operations, including the imposition of civil, criminal and administrative penalties, damages, monetary fines, possible exclusion from participation in Medicare, Medicaid and other federal healthcare programs, contractual damages, reputational harm, diminished profits and future earnings, and curtailment of our operations, any of which could have a material adverse effect on our ability to operate our business and our results of operations.
We expect to expand our organization, and as a result, we may encounter difficulties in managing our growth, which could disrupt our operations.
We expect to experience significant growth in the number of our employees and the scope of our operations, particularly in the areas of drug manufacturing, regulatory affairs and sales, marketing and distribution, as well as to support our public company operations. To manage these growth activities, we must continue to implement and improve our managerial, operational and financial systems, expand our facilities and continue to recruit and train additional qualified personnel. Our management may need to devote a significant amount of its attention to managing these growth activities. Moreover, our expected growth could require us to relocate to a different geographic area of the country. Due to our limited financial resources and the limited experience of our management team in managing a company with such anticipated growth, we may not be able to effectively manage the expansion or relocation of our operations, retain key employees, or identify, recruit and train additional qualified personnel. Our inability to manage the expansion or relocation of our operations effectively may result in weaknesses in our infrastructure, give rise to operational mistakes, loss of business opportunities, loss of employees and reduced productivity among remaining employees. Our expected growth could also require
93
significant capital expenditures and may divert financial resources from other projects, such as the development of additional product candidates. If we are unable to effectively manage our expected growth, our expenses may increase more than expected, our ability to generate revenues could be reduced and we may not be able to implement our business strategy, including the successful commercialization of our product candidates.
Risks Related to Our Common Stock
An active trading market for our common stock may not be sustained.
In October 2016, we closed our initial public offering. Prior to that offering, there had been no public market for our common stock. Although shares of our common stock are listed and trading on The Nasdaq Global Market, an active trading market for our shares may not continue to be sustained. If an active market for our common stock does not continue, it may be difficult for our stockholders to sell their shares without depressing the market price for the shares or sell their shares at or above the prices at which they acquired their shares or sell their shares at the time they would like to sell. Any inactive trading market for our common stock may also impair our ability to raise capital to continue to fund our operations by selling shares and may impair our ability to acquire other companies or technologies by using our shares as consideration.
The price of our common stock may be volatile and fluctuate substantially.
Our stock price is likely to be highly volatile. The stock market in general and the market for smaller pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies in particular have experienced extreme volatility that has often been unrelated to the operating performance of particular companies. The market price for our common stock may be influenced by many factors, including:
- •
- the success of existing or new competitive products or technologies;
- •
- regulatory actions with respect to our product candidates or our competitors' products and product candidates;
- •
- announcements by us or our competitors of significant acquisitions, strategic partnerships, joint ventures, collaborations or capital
commitments;
- •
- the timing and results of clinical trials of RA101495 SC and any other product candidates;
- •
- commencement or termination of collaborations for our development programs;
- •
- failure or discontinuation of any of our development programs;
- •
- results of clinical trials of product candidates of our competitors;
- •
- regulatory or legal developments in the U.S. and other countries;
- •
- developments or disputes concerning patent applications, issued patents or other proprietary rights;
- •
- the recruitment or departure of key personnel;
- •
- the level of expenses related to any of our product candidates or clinical development programs;
- •
- the results of our efforts to develop additional product candidates or products;
- •
- actual or anticipated changes in estimates as to financial results or development timelines;
- •
- announcement or expectation of additional financing efforts;
- •
- sales of our common stock by us, our insiders or other stockholders;
94
- •
- variations in our financial results or those of companies that are perceived to be similar to us;
- •
- changes in estimates or recommendations by securities analysts, if any, that cover our stock;
- •
- changes in the structure of healthcare payment systems;
- •
- market conditions in the pharmaceutical and biotechnology sectors;
- •
- general economic, industry and market conditions; and
- •
- the other factors described in this "Risk Factors" section.
In the past, securities class action litigation has often been brought against a company following a decline in the market price of its securities. This risk is especially relevant for biopharmaceutical companies, which have experienced significant stock price volatility in recent years. The results of any legal proceedings are inherently uncertain and, regardless of the ultimate outcome or the merits, require substantial time and other resources to defend. Accordingly, any litigation that we could face may result in substantial costs to us, divert management's attention and resources from our company as well as harm our reputation with analysts and investors, which could substantially harm our business, financial condition and results of operations.
We have broad discretion in the use of our cash and cash equivalents and may not use them effectively.
Our management has broad discretion to use our cash and cash equivalents to fund our operations and could spend these funds in ways that do not improve our results of operations or enhance the value of our common stock. The failure by our management to apply these funds effectively could result in financial losses that could have a material adverse effect on our business, cause the price of our common stock to decline and delay the development of our product candidates. Pending our use to fund operations, we may invest our cash and cash equivalents in in short-term, investment-grade, interest-bearing securities. These investments may not yield a favorable return to our stockholders.
We are an "emerging growth company," and the reduced disclosure requirements applicable to emerging growth companies may make our common stock less attractive to investors.
We are an "emerging growth company," as defined in the JOBS Act, and may remain an emerging growth company for up to five years following our initial public offering. For so long as we remain an emerging growth company, we are permitted and plan to rely on exemptions from certain disclosure requirements that are applicable to other public companies that are not emerging growth companies. These exemptions include not being required to comply with the auditor attestation requirements of Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, or SOX Section 404, not being required to comply with any requirement that may be adopted by the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board regarding mandatory audit firm rotation or a supplement to the auditor's report providing additional information about the audit and the financial statements, reduced disclosure obligations regarding executive compensation and exemptions from the requirements of holding a nonbinding advisory vote on executive compensation and stockholder approval of any golden parachute payments not previously approved. We cannot predict whether investors will find our common stock less attractive if we rely on these exemptions. If some investors find our common stock less attractive as a result, there may be a less active trading market for our common stock and our stock price may be more volatile.
In addition, the JOBS Act provides that an emerging growth company can take advantage of an extended transition period for complying with new or revised accounting standards. This allows an emerging growth company to delay the adoption of certain accounting standards until those standards would otherwise apply to private companies. We have irrevocably elected not to avail ourselves of this exemption from new or revised accounting standards and, therefore, we will be subject to the same new or revised accounting standards as other public companies that are not emerging growth companies.
95
We will incur increased costs as a result of operating as a public company, and our management will be required to devote substantial time to new compliance initiatives and corporate governance practices.
As a public company, and particularly after we are no longer an "emerging growth company," we will incur significant legal, accounting and other expenses that we did not incur as a private company, which we anticipate could amount to between $1.0 million and $2.0 million annually. The Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, the listing requirements of the Nasdaq Global Market and other applicable securities rules and regulations impose various requirements on public companies, including establishment and maintenance of effective disclosure and financial controls and corporate governance practices. We expect that we will need to hire additional accounting, finance and other personnel in connection with our becoming, and our efforts to comply with the requirements of being, a public company and our management and other personnel will need to devote a substantial amount of time towards maintaining compliance with these requirements. These requirements will increase our legal and financial compliance costs and will make some activities more time-consuming and costly.
We are evaluating these rules and regulations, and cannot predict or estimate the amount of additional costs we may incur or the timing of such costs. These rules and regulations are often subject to varying interpretations, in many cases due to their lack of specificity, and, as a result, their application in practice may evolve over time as new guidance is provided by regulatory and governing bodies which could result in continuing uncertainty regarding compliance matters and higher costs necessitated by ongoing revisions to disclosure and governance practices.
Pursuant to SOX Section 404 we will be required to furnish a report by our management on our internal control over financial reporting beginning with our second filing of an Annual Report on Form 10-K with the SEC after we become a public company. However, while we remain an emerging growth company, we will not be required to include an attestation report on internal control over financial reporting issued by our independent registered public accounting firm. To achieve compliance with SOX Section 404 within the prescribed period, we will be engaged in a process to document and evaluate our internal control over financial reporting, which is both costly and challenging. In this regard, we will need to continue to dedicate internal resources, potentially engage outside consultants and adopt a detailed work plan to assess and document the adequacy of internal control over financial reporting, continue steps to improve control processes as appropriate, validate through testing that controls are functioning as documented and implement a continuous reporting and improvement process for internal control over financial reporting. Despite our efforts, there is a risk that we will not be able to conclude, within the prescribed timeframe or at all, that our internal control over financial reporting is effective. If we identify one or more material weaknesses, it could result in an adverse reaction in the financial markets due to a loss of confidence in the reliability of our financial statements.
A significant portion of our total outstanding shares is restricted from immediate resale but may be sold into the market in the near future, which could cause the market price of our common stock to decline significantly, even if our business is doing well.
Sales of a substantial number of shares of our common stock in the public market could occur at any time. These sales, or the perception in the market that the holders of a large number of shares of common stock intend to sell shares, could reduce the market price of our common stock. As of December 31, 2017, we have 22,626,684 shares of outstanding common stock, of which approximately 9.3 million shares are subject to restrictions on transfer under 90-day lock-up arrangements with the underwriters of this offering. These restrictions are due to expire on February 28, 2018, resulting in a substantial number of these shares becoming eligible for public sale at that time if they are registered under the Securities Act or if they qualify for an exemption from registration under the Securities Act including under Rules 144 or 701.
96
Moreover, based on filings with the SEC as of December 31, 2017, holders of an aggregate of approximately 13.4 million shares of our common stock have rights, subject to conditions, to require us to file registration statements covering their shares or to include their shares in registration statements that we may file for ourselves or other stockholders. We have also registered shares of our common stock issued and available for issuance under our equity compensation plans, which can be freely sold in the public market, subject to vesting requirements, volume limitations applicable to affiliates and lock-up agreements. If these additional shares are sold, or if it is perceived that they will be sold, in the public market, the trading price of our common stock could decline.
Our ability to use net operating losses and research and development credits to offset future taxable income may be subject to certain limitations.
As of December 31, 2017, we had federal and state net operating loss carryforwards of $55.7 million and $51.2 million, respectively, which will begin to expire in 2028. As of December 31, 2017, we also had federal research and development tax credit carryforwards of $4.4 million and state research and development tax credit carryforwards of $1.7 million, which expire at various dates through 2037 and 2032, respectively. These net operating loss and tax credit carryforwards could expire unused and be unavailable to offset future income tax liabilities. In addition, in general, under Sections 382 and 383 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended, or the Code, a corporation that undergoes an "ownership change" is subject to limitations on its ability to utilize its pre-change net operating losses or tax credits, or NOLs or credits, to offset future taxable income or taxes. For these purposes, an ownership change generally occurs where the aggregate stock ownership of one or more stockholders or groups of stockholders who owns at least 5% of a corporation's stock increases its ownership by more than 50 percentage points over its lowest ownership percentage within a specified testing period. Our existing NOLs or credits may be subject to limitations arising from previous ownership changes, our ability to utilize NOLs or credits could be further limited by Sections 382 and 383 of the Code. In addition, future changes in our stock ownership, many of which are outside of our control, could result in an ownership change under Sections 382 and 383 of the Code. Our NOLs or credits may also be impaired under state law. Accordingly, we may not be able to utilize a material portion of our NOLs or credits. The reduction of the corporate tax rate under the Tax Reform Act may cause a reduction in the economic benefit of our net operating loss carryforwards and other deferred tax assets available to us. Under the Tax Reform Act, net operating losses generated after December 31, 2017 will not be subject to expiration.
We do not anticipate paying any cash dividends on our capital stock in the foreseeable future. Accordingly, stockholders must rely on capital appreciation, if any, for any return on their investment.
We have never declared nor paid cash dividends on our capital stock. We currently plan to retain all of our future earnings, if any, to finance the operation, development and growth of our business. In addition, the terms of any future debt or credit agreements may preclude us from paying dividends. As a result, capital appreciation, if any, of our common stock will be your sole source of gain for the foreseeable future.
Concentration of ownership of our common stock among our existing executive officers, directors and principal stockholders may prevent new investors from influencing significant corporate decisions.
As of December 31, 2017, our executive officers and directors, combined with our stockholders who owned more than 5% of our outstanding common stock and their affiliates in the aggregate, beneficially own shares representing approximately 69.4% of our common stock. As a result, if these stockholders were to choose to act together, they would be able to control all matters submitted to our stockholders for approval, as well as our management and affairs. For example, these persons, if they choose to act together, would control the election of directors and approval of any merger,
97
consolidation or sale of all or substantially all of our assets. This concentration of ownership control may:
- •
- delay, defer or prevent a change in control;
- •
- entrench our management or the board of directors; or
- •
- impede a merger, consolidation, takeover or other business combination involving us that other stockholders may desire.
Some of these persons or entities may have interests different than yours. For example, because many of these stockholders purchased their shares at prices substantially below the current market price and have held their shares for a longer period, they may be more interested in selling our company to an acquirer than other investors or they may want us to pursue strategies that deviate from the interests of other stockholders.
Provisions in our corporate charter documents and under Delaware law may prevent or frustrate attempts by our stockholders to change our management or hinder efforts to acquire a controlling interest in us.
Provisions in our corporate charter and our bylaws may discourage, delay or prevent a merger, acquisition or other change in control of us that stockholders may consider favorable, including transactions in which you might otherwise receive a premium for your shares. These provisions could also limit the price that investors might be willing to pay in the future for shares of our common stock, thereby depressing the market price of our common stock. In addition, because our board of directors is responsible for appointing the members of our management team, these provisions may frustrate or prevent any attempts by our stockholders to replace or remove our current management by making it more difficult for stockholders to replace members of our board of directors. Among other things, these provisions:
- •
- establish a classified board of directors such that all members of the board are not elected at one time;
- •
- allow the authorized number of our directors to be changed only by resolution of our board of directors;
- •
- limit the manner in which stockholders can remove directors from the board;
- •
- establish advance notice requirements for nominations for election to the board of directors or for proposing matters that can be acted on at
stockholder meetings;
- •
- require that stockholder actions must be effected at a duly called stockholder meeting and prohibit actions by our stockholders by written
consent;
- •
- limit who may call a special meeting of stockholders;
- •
- authorize our board of directors to issue preferred stock without stockholder approval, which could be used to institute a "poison pill" that
would work to dilute the stock ownership of a potential hostile acquirer, effectively preventing acquisitions that have not been approved by our board of directors; and
- •
- require the approval of the holders of at least 75% of the votes that all our stockholders would be entitled to cast to amend or repeal certain provisions of our charter or bylaws.
Moreover, because we are incorporated in Delaware, we are governed by the provisions of Section 203 of the General Corporation Law of the State of Delaware, which prohibits a person who owns in excess of 15% of our outstanding voting stock from merging or combining with us for a period of three years after the date of the transaction in which the person acquired in excess of 15% of our outstanding voting stock, unless the merger or combination is approved in a prescribed manner. This
98
could discourage, delay or prevent someone from acquiring us or merging with us, whether or not it is desired by, or beneficial to, our stockholders. This could also have the effect of discouraging others from making tender offers for our common stock, including transactions that may be in your best interests. These provisions may also prevent changes in our management or limit the price that investors are willing to pay for our stock.
If securities or industry analysts do not publish research or publish inaccurate or unfavorable research about our business, our share price and trading volume could decline.
The trading market for our common stock may be influenced, in part, by the research and reports that industry or securities analysts publish about us or our business. If no or few securities or industry analysts maintain coverage of us, or one or more of the analysts who cover us issues an adverse opinion about our company, our stock price would likely decline. If one or more of these analysts ceases research coverage of us or fails to regularly publish reports on us, we could lose visibility in the financial markets, which in turn could cause our stock price or trading volume to decline.
ITEM 1B. UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS
None.
We lease approximately 27,000 square feet of office and laboratory space in Cambridge, Massachusetts, which serves as our corporate headquarters under a lease that expires in April 2023. We have an option to extend the lease term for five additional years. We believe that this office and laboratory space is sufficient to meet our current needs and that suitable additional space or alternative space will be available as needed on commercially reasonable terms.
We are not currently subject to any material legal proceedings. From time to time, we may be subject to various legal proceedings and claims that arise in the ordinary course of our business activities. Although the results of litigation and claims cannot be predicted with certainty, as of the date of this report, we do not believe we are party to any claim or litigation the outcome of which, if determined adversely to us, would individually or in the aggregate be reasonably expected to have a material adverse effect on our business. Regardless of the outcome, litigation can have an adverse impact on us because of defense and settlement costs, diversion of management resources and other factors.
ITEM 4. MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES
Not applicable.
99
ITEM 5. MARKET FOR REGISTRANT'S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES
Market Information
Our common stock has been trading on The Nasdaq Global Market under the symbol "RARX" since it began trading on October 26, 2016. Prior to this date, there was no public market for our common stock. The following table sets forth the high and low intra-day sale prices of our common stock for the periods indicated as reported by The Nasdaq Global Market.
Fiscal 2017
|
High | Low | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Fourth quarter |
$ | 17.90 | $ | 7.15 | |||
Third quarter |
19.03 | 12.16 | |||||
Second quarter |
27.84 | 15.13 | |||||
First quarter |
24.12 | 13.83 | |||||
Fiscal 2016
|
High | Low | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Fourth quarter (from and after October 26, 2016) |
$ | 16.56 | $ | 12.05 | |||
Holders of Common Stock
As of March 2, 2018, we had 15 stockholders of record. The number of holders is based upon the actual number of holders registered in our records at such date and excludes holders in "street name" or persons, partnerships, associations, corporations, or other entities identified in security positions listings maintained by depository trust companies.
Stock Performance Graph
The following graph shows a comparison from October 26, 2016, the date on which our common stock first began trading on the Nasdaq Global Market, of the cumulative total return on an assumed investment of $100.00 on October 26, 2016, in our common stock as compared to the same investment in the Nasdaq Composite Index and the Nasdaq Biotechnology Index, all through December 31, 2017. These returns are based on historical results and are not intended to suggest future performance. We have not paid any dividends on the common stock, and no dividends are included in the representation of our performance. Information used in the graph was obtained from the Nasdaq Stock Market LLC, a source believed to be reliable, but we are not responsible for any errors or omissions in such information.
100
Comparison of Cumulative Total Return*
- *
- $100 invested on October 26, 2016
Cumulative Total Return Comparison
| |
|
December 31, | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
October 26, 2016 |
|||||||||
| |
2016 | 2017 | ||||||||
Ra Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (RARX) |
$ | 100 | $ | 116.85 | $ | 65.38 | ||||
Nasdaq Composite (^IXIC) |
100 | 102.53 | 131.49 | |||||||
Nasdaq Biotechnology (^NBI) |
100 | 99.92 | 120.96 | |||||||
The performance graph in this Item 5 shall not be deemed "soliciting material" or be deemed "filed" for purposes of Section 18 of the Exchange Act, or otherwise subject to the liabilities under that Section, and shall not be deemed to be incorporated by reference into any of our filings under the Securities Act, whether made before or after the date hereof and irrespective of any general incorporation language in any such filing.
Dividend Policy
We have never declared or paid cash dividends on our common stock, and we do not expect to pay any cash dividends on our common stock in the foreseeable future. Payment of future dividends, if any, on our common stock will be at the discretion of our board of directors after taking into account various factors, including our financial condition, operating results, anticipated cash needs, and plans for expansion.
Securities Authorized for Issuance under Equity Compensation Plans
Information about our equity compensation plans is incorporated herein by reference to Item 11 of Part III of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Recent Sales of Unregistered Securities
None.
Use of Proceeds from Public Offering of Common Stock
In October 2016, we issued and sold 7,049,230 shares of our common stock in our IPO, and in November 2016, we issued and sold 1,057,385 shares of common stock to the underwriters under the
101
underwriters' option to purchase additional shares of common stock, at a public offering price of $13.00 per share, for aggregate gross proceeds of $105.4 million. All of the shares issued and sold in the IPO were registered under the Securities Act pursuant to a Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333- 213917), which was declared effective by the SEC on October 26, 2016. Credit Suisse Securities (USA) LLC, Jeffries LLC and BMO Capital Markets Corp. acted as joint book-running managers of the offering and as representatives of the underwriters. SunTrust Robinson Humphrey, Inc. acted as manager for the offering.
We received net proceeds from the IPO, including the exercise of the underwriter's over-allotment, of approximately $95.6 million, after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions of approximately $7.4 million and offering-related expenses of approximately $2.4 million payable by us. None of the expenses associated with the IPO were paid to directors, officers, persons owning 10% or more of any class of equity securities, or to their associates, or to our affiliates.
There has been no material change in the planned use of proceeds from our IPO as described in our final prospectus filed with the SEC pursuant to Rule 424(b) of the Securities Act on October 26, 2016. We are holding the balance of the net proceeds from the IPO in investments in primarily money market funds. As of December 31, 2017, we used approximately $25.2 million of proceeds from the IPO.
Purchases of Equity Securities by the Issuer and Affiliated Purchases
None.
ITEM 6. SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA
The selected financial data set forth below is derived from our audited financial statements and should be read in conjunction with "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations" contained in Item 7 and "Financial Statements and Supplementary Data" contained in Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
102
Consolidated Statement of Operations Data:
| |
Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
| |
(in thousands, except per share amounts) |
||||||||||||
Revenue |
$ | — | $ | 4,928 | $ | 4,094 | $ | 4,830 | |||||
Operating expenses: |
|||||||||||||
Research and development(1) |
45,251 | 27,928 | 15,217 | 10,016 | |||||||||
General and administrative(1) |
9,778 | 5,024 | 2,233 | 1,924 | |||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total operating expenses |
55,029 | 32,952 | 17,450 | 11,940 | |||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Loss from operations |
(55,029 | ) | (28,024 | ) | (13,356 | ) | (7,110 | ) | |||||
Other income (expense), net |
571 | (858 | ) | (606 | ) | 1,607 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Loss from operations before benefit from income taxes |
(54,458 | ) | (28,882 | ) | (13,962 | ) | (5,503 | ) | |||||
Benefit from income taxes |
(19 | ) | (18 | ) | (19 | ) | (27 | ) | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net loss from operations |
(54,439 | ) | (28,864 | ) | (13,943 | ) | (5,476 | ) | |||||
Gain on extinguishment of redeemable convertible preferred shares |
— | — | 1,673 | — | |||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net loss attributable to common stockholders |
$ | (54,439 | ) | $ | (28,864 | ) | $ | (12,270 | ) | $ | (5,476 | ) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net loss per common share—basic and diluted |
$ | (2.41 | ) | $ | (6.98 | ) | $ | (24.68 | ) | $ | (12.46 | ) | |
Weighted average number of common shares outstanding—basic and diluted(2) |
22,591 | 4,135 | 497 | 440 | |||||||||
Consolidated Balance Sheet Data:
| |
December 31, | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
| |
(in thousands) |
||||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents(2) |
$ | 70,381 | $ | 117,812 | $ | 19,386 | $ | 4,039 | |||||
Working capital |
64,263 | 112,765 | 13,248 | 1,642 | |||||||||
Total assets |
80,197 | 126,818 | 24,342 | 7,315 | |||||||||
Redeemable convertible preferred stock(2) |
— | — | 53,675 | 28,984 | |||||||||
Accumulated deficit |
(123,214 | ) | (68,764 | ) | (39,900 | ) | (25,957 | ) | |||||
Total stockholders' equity (deficit) |
69,184 | 117,222 | (37,199 | ) | (25,714 | ) | |||||||
- (1)
- Includes non-cash stock-based compensation expense as indicated in the following table:
| |
Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
| |
(in thousands) |
||||||||||||
Research and development |
$ | 3,081 | $ | 361 | $ | 58 | $ | 58 | |||||
General and administrative |
2,492 | 665 | 94 | 30 | |||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total |
$ | 5,573 | $ | 1,026 | $ | 152 | $ | 88 | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
- (2)
- In October 2016, we completed an initial public offering in which we issued 8,106,615 shares of common stock, resulting in net proceeds of $95.6 million, after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and offering costs. Upon the closing of our initial public offering, all of the outstanding shares of redeemable convertible preferred stock automatically converted into 13,623,933 shares of common stock and outstanding warrants net exercised into 221,573 shares of common stock.
103
ITEM 7. MANAGEMENT'S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
The following discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations should be read together with our consolidated financial statements and related notes appearing elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Some of the information contained in this discussion and analysis or set forth elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, including information with respect to our plans and strategy for our business and related financing, includes forward-looking statements that involve risks and uncertainties and should be read together with the "Risk Factors" section of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for a discussion of important factors that could cause actual results to differ materially from the results described in or implied by the forward-looking statements contained in the following discussion and analysis.
Overview
We are a clinical-stage biopharmaceutical company using our proprietary peptide chemistry platform to develop novel therapeutics for the treatment of serious diseases that are caused by excessive or uncontrolled activation of the complement system, a critical component of the immune system. The complement system, which consists of approximately 30 interacting proteins, offers a target-rich opportunity for us to leverage our proprietary peptide chemistry platform, which was pioneered by Nobel Laureate Dr. Jack Szostak and allows us to inhibit certain uncontrolled complement pathway factors involved in complement-mediated diseases. Known as our Extreme Diversity platform, our proprietary macrocyclic peptide chemistry technology allows us to produce synthetic macrocyclic peptides that combine the diversity and specificity of antibodies with the pharmacological properties of small molecules. We believe this chemistry technology will allow us to pursue challenging targets for which only monoclonal antibodies have been developed.
We are developing our lead product candidate, RA101495 SC, a convenient self-administered subcutaneous ("SC") injection, which is an injection into the tissue under the skin, for the treatment of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria, or PNH. PNH is a rare, chronic, life-threatening, blood disorder where red blood cells are mistakenly attacked and destroyed by the complement system. We initiated our Phase 2 clinical program for RA101495 SC in PNH patients in the second quarter of 2017, released interim data in June 2017 and December 2017, completed dosing and announced our topline data in February 2018. The global, dose-finding, twelve-week open label Phase 2 program was designed to evaluate the safety, tolerability, preliminary efficacy, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of RA101495 SC in patients with PNH.
We enrolled a total of 29 patients across three cohorts in the Phase 2 clinical program in PNH. The first cohort enrolled 10 patients who had not previously been treated with eculizumab. We refer to these patients as eculizumab naïve patients. The second cohort enrolled 16 patients, who, prior to the trial, were treated with an eculizumab regimen and, in connection with the trial, were switched over to treatment with RA101495 SC. We refer to these patients as eculizumab switch patients. The third cohort enrolled three patients. These patients are United States ("U.S.") based and were inadequate responders to eculizumab and who were also switching over to RA101495 SC. We refer to these patients as eculizumab inadequate responders.
The primary efficacy endpoint was the change in LDH levels, from baseline to the mean level from week 6 to week 12 of the trial. Patients in all three cohorts were eligible to enter a long-term extension study following the completion of the initial 12-week dosing period. A total of 21 patients completed the initial 12-week dosing period and 16 of those patients (or 76%) are continuing treatment with RA101495 SC in our long-term extension study (8 naïve patients and 8 switch patients, including all 3 inadequate responders). The data cut-off date for the December 4, 2017 interim results was
104
November 30, 2017 and the data cut-off date for the topline data published on February 12, 2018 was February 7, 2018.
Eculizumab Naïve Cohort
All 10 eculizumab naïve patients successfully completed 12 weeks of dosing. RA101495 SC met the primary endpoint, demonstrating a rapid, robust, and sustained reduction in LDH levels from baseline to the mean of Weeks 6-12 (p=0.002) and near-complete suppression of complement activity. Fifty percent of eculizumab naïve patients (3/6) who were transfusion-dependent prior to enrollment remained transfusion-free while on study. Meaningful improvements in standard measures of quality of life, as shown by the Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy ("FACIT") fatigue score were observed, as well as a high level of patient satisfaction with SC self-administration based on patient surveys. Eight of the 10 patients in the naïve cohort continue in the long-term extension study, with the longest treated patients (n=2) dosed through 36 weeks.
The clinically meaningful reduction in mean LDH observed during the 12-week Phase 2 dosing period has been sustained in the long-term extension study.
Eculizumab Switch Cohort
In eculizumab switch patients, transfusion-independent patients (n=5) switching to RA101495 SC maintained an overall stable mean LDH level, with one patient withdrawing early due to breakthrough hemolysis and reverting to eculizumab without complications. Among switch patients who were transfusion-dependent at baseline (n=11), breakthrough hemolysis occurred after switching in seven patients (7/11), who all reverted to eculizumab treatment without complications. Persistent transfusion-dependence, which occurs in up to 20 percent of the eculizumab-treated population, is most commonly attributable to extravascular hemolysis driven by intense C3 deposition on erythrocytes. This condition, a unique complication of long-term eculizumab therapy in certain PNH patients, may not be adequately addressed by inhibition at the level of C5, and published data suggest that targeting complement upstream of C5 (e.g. Factor D or C3) may have greater utility in this small subset of PNH patients.
Eculizumab Inadequate Responder Cohort
In our U.S.-based cohort of patients who were inadequate responders to eculizumab and have a history of elevated LDH levels, all three patients (two transfusion-independent, one transfusion-dependent) have completed 12 weeks of dosing and maintained stable mean LDH levels.
Pooled Data (Eculizumab Switch and Inadequate Responder Cohorts)
In transfusion-independent patients switching from eculizumab to RA101495 SC, pooled from both the switch cohort and the U.S.-based inadequate responder cohort (collectively, n=7), mean LDH and hemoglobin levels have remained stable in patients enrolled in the long-term extension study through the data cut-off date of February 7, 2018.
Across all cohorts, no major safety or tolerability concerns have been reported after more than 500 patient weeks of cumulative exposure across all cohorts. No meningococcal infections or thromboembolic events have been observed. Out of more than 3,500 doses administered to date, only nine mild (grade 1) injection site reactions have occurred in a total of five patients. As of February 7, 2018, full compliance with once daily SC self-administration of RA101495 SC has been observed.
We are also developing RA101495, administered SC, to treat other debilitating complement mediated diseases such as generalized myasthenia gravis ("gMG") atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome ("aHUS") and lupus nephritis ("LN"). We initiated a Phase 2 clinical trial with RA101495 SC for gMG in the fourth quarter of 2017 and a Phase 1b clinical trial evaluating RA101495 SC in patients with
105
renal impairment, supporting development in aHUS and LN, in the first quarter of 2018. We also have preclinical programs targeting selective inhibition of other complement factors for diseases with no approved therapies, including a Factor D program for ocular and renal diseases, an oral small molecule C5 inhibitor and other complement inhibitors for certain autoimmune and central nervous system ("CNS") diseases. In addition to our focus on developing novel therapeutics to treat complement mediated diseases, we have validated our Extreme Diversity platform by successfully identifying and delivering orally available cyclic peptides for a non-complement cardiovascular target with a large market opportunity in a collaboration with Merck & Co., Inc. ("Merck").
Since our inception in June 2008, we have devoted substantially all of our resources to organizing and staffing our company, business planning, raising capital, acquiring and developing our proprietary chemistry technology, identifying potential product candidates and conducting preclinical studies of our product candidates and a clinical trial of our lead product candidate, RA101495 SC. To date, we have not generated any product revenue and have financed our operations primarily through the public offering and the private placement of our securities and revenue from our collaboration with Merck. As of December 31, 2017, we had received an aggregate of $181.0 million in net proceeds from the issuance of equity and debt securities and $17.5 million in payments in connection with our collaboration and license agreement with Merck (the "Merck Agreement"). As of December 31, 2017, our principal source of liquidity was cash and cash equivalents, which totaled $70.4 million.
On October 31, 2016, we completed an initial public offering ("IPO"), in which we issued and sold 7,049,230 shares of our common stock at a public offering price of $13.00 per share, resulting in net proceeds to us of $82.8 million after deducting $6.4 million of underwriting discounts and commissions and offering costs of $2.4 million. On November 29, 2016, we completed the sale of an additional 1,057,385 shares of common stock to the underwriters under the underwriters' option in the IPO to purchase additional shares of common stock at the public offering price of $13.00 per share, resulting in additional net proceeds to us of $12.8 million after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions of $1.0 million.
In February 2018, we completed a follow-on public offering of 9,660,000 shares of our common stock, including the full exercise of the underwriter's over-allotment of 1,260,000 shares, at $6.00 per share and received aggregate net proceeds of $54.1 million, after deducting $3.5 million of underwriting discounts and commissions and approximately $0.4 million of offering expenses.
As of December 31, 2017, we had an accumulated deficit of $123.2 million. Our net losses were $54.4 million, $28.9 million and $13.9 million for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively. We have incurred significant net operating losses in every year since our inception and expect to continue to incur increasing net operating losses and significant expenses for the foreseeable future. Our net losses may fluctuate significantly from quarter to quarter and year to year. We anticipate that our expenses will increase significantly as we:
- •
- continue to advance our lead program, RA101495 SC, through clinical development by establishing clinical proof-of-concept activity using
convenient SC administration in PNH, gMG, and patients in complement-mediated renal diseases, such as aHUS and LN;
- •
- continue our current research programs and development activities;
- •
- seek to identify additional research programs and additional product candidates;
- •
- initiate preclinical testing and clinical trials for any product candidates we identify and develop, maintain, expand and protect our
intellectual property portfolio;
- •
- hire additional research, clinical and scientific personnel; and
- •
- incur additional costs associated with operating as a public company, including expanding our operational, finance and management teams.
106
We believe that our available cash and cash equivalents as of December 31, 2017, and the net proceeds of $54.1 million from the equity offering closed in February 2018, will enable us to fund our operating expenses and capital expenditure requirements through the end of 2019. We do not expect to generate revenue from product sales unless and until we successfully complete development and obtain regulatory approval for a product candidate, which we expect will take a number of years and is subject to significant uncertainty. Additionally, we believe that our available funds as of December 31, 2017, and the net proceeds of $54.1 million from the equity offering closed in February 2018, will be sufficient to enable us to prepare and plan for the initiation of our Phase 3 clinical trials of RA101495 SC for the treatment of PNH, obtain top line data from our ongoing Phase 2 clinical trial in gMG, complete the Phase 1b clinical trial clinical trial evaluating RA101495 SC in patients with renal impairment, supporting further development in aHUS and LN, and advance our other preclinical pipeline programs. We expect that these funds will not, however, be sufficient to enable us to complete our Phase 3 clinical study in PNH. It is also possible that we will not achieve the progress that we expect with respect to RA101495 SC because the actual costs and timing of clinical development activities are difficult to predict and are subject to substantial risks and delays. We will be required to obtain further funding through public or private equity offerings, debt financings, collaborations and licensing arrangements or other sources. Adequate additional financing may not be available to us on acceptable terms, or at all. Our failure to raise capital as and when needed would have a negative impact on our financial condition and our ability to pursue our business strategy.
Financial Overview
Revenue
We have derived all of our revenue to date from the Merck Agreement, which we entered into in April 2013. Under the Merck Agreement, we collaborated with Merck and used our proprietary drug discovery technology platform to identify orally available cyclic peptides for non-complement targets nominated by Merck and provided specific research and development services. At the signing, Merck paid us an upfront, non-refundable, license fee payment of $4.5 million. In addition, during the research term, which ended in April 2016, Merck reimbursed us for research and development services provided by us in accordance with a pre-specified number of our full-time equivalent employees ("FTEs") working under the Merck Agreement. At the conclusion of the research term, Merck elected to continue the development of a non-complement cardiovascular program target with a large market opportunity, for which we had received $3.5 million in preclinical milestone payments as of December 31, 2017. We are also entitled to receive future aggregate milestone payments of up to $61.5 million and low-to-mid single digit percentage royalties on any future sales for this program target. For additional information about the Merck Agreement, see Item 8, "Financial Statements and Supplementary Data" within this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
To date, we have not generated any revenue from product sales and do not expect to do so in the near future. We expect that our revenue will be less than our expenses for the foreseeable future and that we will experience increasing losses as we continue our development of, and seek regulatory approvals for, our product candidates and begin to commercialize any approved products. Our ability to generate revenue for each product candidate for which we receive regulatory approval will depend on numerous factors, including competition, commercial manufacturing capability and market acceptance of our products.
107
Research and Development Expenses
Research and development expenses consist primarily of costs incurred for our research activities, including development of our proprietary chemistry technology platform, and our preclinical and clinical candidates, which include:
- •
- employee-related expenses, including salaries, benefits, and stock-based compensation expense;
- •
- expenses incurred under agreements with contract research organizations ("CROs"), contract manufacturing organizations ("CMOs"), and
independent contractors that conduct research and development, preclinical and clinical activities on our behalf;
- •
- costs of purchasing lab supplies and non-capital equipment used in our preclinical activities and in manufacturing preclinical study and
clinical trial materials;
- •
- consulting, licensing and professional fees related to research and development activities: and;
- •
- facility costs, depreciation, and other expenses, which include direct and allocated expenses for rent and maintenance of facilities, insurance, and other supplies.
We expense research and development costs as incurred. We recognize costs for certain development activities, such as preclinical studies and clinical trials, based on an evaluation of the progress to completion of specific tasks using information provided to us by our vendors such as patient enrollment or clinical site activations for services received and efforts expended.
Research and development activities are central to our business model. We expect research and development costs to increase significantly for the foreseeable future as our current development programs progress and new programs are added.
The following table sets forth our research and development expenses related to our product pipeline:
| |
Year Ended December, 31 |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
2017 | 2016 | |||||
| |
(in thousands) |
||||||
RA101495 SC |
$ | 21,554 | $ | 12,520 | |||
Other pipeline programs |
3,320 | 676 | |||||
| | | | | | | | |
Allocated costs |
24,874 | 13,196 | |||||
Unallocated costs |
20,377 | 14,732 | |||||
| | | | | | | | |
Total |
$ | 45,251 | $ | 27,928 | |||
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
The expenses allocated to our product pipeline in the table above relate to CRO and CMO costs associated with our pre-clinical studies and clinical trials. We do not allocate compensation, benefits and other employee-related expenses, costs related to facilities, depreciation, share-based compensation, research and development support services, laboratory supplies and certain other costs directly to programs.
Historically, we had not provided program costs because we have not tracked or recorded our research and development expenses on a program-by-program basis. Beginning in the first quarter of 2017, we began to allocate costs related to our third-party vendors directly to programs. Amounts for the year ended December 31, 2016 in the table above were reclassified to conform to the current period's presentation. Amounts for the year ended December 31, 2015 were not tracked on a program-by-program basis and are excluded from the table above.
108
Because of the numerous risks and uncertainties associated with product development, we cannot determine with certainty the duration and completion costs of the current or future preclinical studies and clinical trials or if, when, or to what extent we will generate revenues from the commercialization and sale of our product candidates. We may never succeed in achieving regulatory approval for our product candidates. The duration, costs, and timing of preclinical studies and clinical trials and development of our product candidates will depend on a variety of factors, including:
- •
- successful completion of preclinical studies and Investigational New Drug-enabling studies;
- •
- successful enrollment in, and completion of, clinical trials;
- •
- receipt of marketing approvals from applicable regulatory authorities;
- •
- establishing commercial manufacturing capabilities or making arrangements with third-party manufacturers;
- •
- obtaining and maintaining patent and trade secret protection and non-patent exclusivity;
- •
- launching commercial sales of the product, if and when approved, whether alone or in collaboration with others;
- •
- acceptance of the product, if and when approved, by patients, the medical community and third-party payors;
- •
- effectively competing with other therapies and treatment options;
- •
- a continued acceptable safety profile following approval;
- •
- enforcing and defending intellectual property and proprietary rights and claims; and
- •
- achieving desirable medicinal properties for the intended indications.
A change in the outcome of any of these factors could mean a significant change in the costs and timing associated with the development of our current and future preclinical and clinical product candidates. For example, if the Food and Drug Administration ("FDA"), or another regulatory authority were to require us to conduct clinical trials beyond those that we currently anticipate will be required for the completion of clinical development, or if we experience significant delays in execution of or enrollment in any of our preclinical studies or clinical trials, we could be required to expend significant additional financial resources and time on the completion of preclinical and clinical development. We expect our research and development expenses to increase for the foreseeable future as we continue the development of product candidates.
General and Administrative Expenses
General and administrative expenses consist primarily of employee related expenses, including salaries, benefits, and stock-based compensation, for personnel in executive, finance, facility operations and administrative functions. Other significant costs include facility costs not otherwise included in research and development expenses, legal fees relating to patent and corporate matters, and fees for accounting, tax and consulting services.
We anticipate that our general and administrative expenses will increase in the future to support continued research and development activities, potential commercialization of our product candidates and increased costs of operating as a public company. These increases will likely include increased costs related to the hiring of additional personnel and fees to outside consultants, lawyers and accountants, among other expenses. Additionally, we anticipate increased costs associated with being a public company, including expenses related to services associated with maintaining compliance with exchange listing and Securities and Exchange Commission ("SEC"), requirements, director and officer insurance costs and investor and public relations costs.
109
Other Income (Expense), Net
Other income (expense), net primarily consists of interest income earned on our cash and cash equivalents and changes in in fair value of preferred stock tranche rights.
Income Taxes
We have not recorded a provision for federal or state income taxes as we have had cumulative net operating losses since inception.
The U.S. government has recently enacted comprehensive tax legislation that includes significant changes to the taxation of business entities ("Tax Reform Act"). These changes include, among others, a permanent reduction to the corporate income tax rate, limiting interest deductions, adopting elements of a territorial tax system and introducing certain anti-base erosion provisions. In addition, federal net operating losses generated after December 31, 2017 will not be subject to expiration.
Critical Accounting Policies and Significant Judgments and Estimates
Our discussion and analysis of our liquidity, capital resources and results of operations is based upon our consolidated financial statements prepared in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles in the U.S. The preparation of these financial statements requires us to make certain estimates and assumptions that may affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities, the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reported periods and related disclosures. These estimates and assumptions are monitored and analyzed by us for changes in facts and circumstances, and material changes in these estimates could occur in the future. We base our estimates on our historical experience, trends in the industry and various other factors that are believed to be reasonable under the circumstances. Actual results may differ from our estimates under different assumptions or conditions.
We believe that our application of the following accounting policies, each of which require significant judgments and estimates on the part of management, is the most critical to aid in fully understanding and evaluating our reported financial results: (1) revenue recognition, (2) research and development costs, and (3) stock-based compensation.
Revenue Recognition
We have derived all of our revenue to date from our Merck Agreement. The terms of the Merck Agreement contain multiple deliverables, which included licenses and research and development activities, including participation on the joint steering committee. Payments to us under the agreement include: (i) an upfront nonrefundable license fee; (ii) payments for research and development services performed by our employees, including reimbursement for certain lab supplies and reagents; (iii) payments based upon the achievement of certain development (pre-clinical and clinical), regulatory and commercial milestones; and (iv) royalties on net product sales, if any.
Multiple element arrangements, such as the Merck Agreement, are analyzed to determine whether the deliverables can be separated or whether they must be accounted for as a single unit of accounting. We account for those components as separate elements when the following criteria are met:
- •
- the delivered items have value to the customer on a stand-alone basis; and
- •
- if there is a general right of return relative to the delivered items, delivery or performance of the undelivered items is considered probable and within our control.
This evaluation requires subjective determinations and requires us to make judgments about the individual deliverables and whether such deliverables are separable from the other aspects of the contractual relationship. In determining the units of accounting, we evaluate certain criteria, including
110
whether the deliverables have standalone value, based on consideration of the relevant facts and circumstances for each arrangement. Factors considered in this determination include the research, manufacturing and commercialization capabilities of the partner and the availability of research and manufacturing expertise in the general marketplace. In addition, we consider whether the collaborator can use the license or other deliverables for their intended purpose without the receipt of the remaining elements, and whether the value of the deliverable is dependent on the undelivered items and whether there are other vendors that can provide the undelivered items.
The consideration received is allocated among the separate units of accounting using the relative selling price method, and the applicable revenue recognition criteria are applied to each of the separate units.
We determine the estimated selling price for deliverables using vendor-specific objective evidence ("VSOE") of selling price, if available, third-party evidence ("TPE") of selling price if VSOE is not available, or best estimate of selling price ("BESP") if neither VSOE nor TPE is available. Determining the BESP for a deliverable requires significant judgment. We use BESP to estimate the selling price for licenses to our proprietary technology, since we often do not have VSOE or TPE of selling price for these deliverables. In those circumstances where we utilize BESP to determine the estimated selling price of a license to our proprietary technology, we consider market conditions as well as entity-specific factors, including those factors contemplated in negotiating the agreements as well as internally developed models that include assumptions related to the market opportunity, estimated development costs, probability of success and the time needed to commercialize a product candidate pursuant to the license. In validating our BESP, we evaluate whether changes in the key assumptions used to determine the BESP will have a significant effect on the allocation of arrangement consideration between multiple deliverables.
We recognize revenue allocated to each unit of accounting when there is persuasive evidence that an arrangement exists, services have been rendered or delivery has occurred, the price is fixed or determinable, and collection is reasonably assured.
We recognize revenue allocated to the license upon delivery, when we believe the license to our intellectual property has standalone value. When we recognize revenue allocated to the license upon delivery, we may experience significant fluctuations in our collaborative arrangements revenues from quarter to quarter and year to year depending on the timing of transactions. When we believe the license to our intellectual property does not have standalone value from the other deliverables to be provided in the arrangement, it is combined with other deliverables, such as research and development activities in the Merck Agreement, and the revenue of the combined unit of accounting is recorded based on the method appropriate for the last delivered item.
At the inception of each arrangement that includes precommercial milestone payments, we evaluate whether each precommercial milestone is substantive, in accordance with ASU 2010-17, Revenue Recognition—Milestone Method. This evaluation includes an assessment of whether (a) the consideration is commensurate with either (1) the entity's performance to achieve the milestone, or (2) the enhancement of the value of the delivered item(s) as a result of a specific outcome resulting from the entity's performance to achieve the milestone, (b) the consideration relates solely to past performance and (c) the consideration is reasonable relative to all of the deliverables and payment terms within the arrangement. We evaluate factors such as the scientific, clinical, regulatory, commercial and other risks that must be overcome to achieve the respective milestone, the level of effort and investment required and whether the milestone consideration is reasonable relative to all deliverables and payment terms in the arrangement in making this assessment. If a substantive precommercial milestone was achieved and collection of the related receivable was reasonably assured, we would recognize revenue related to the milestone in its entirety in the period in which the milestone was achieved. If we achieve milestones that we consider substantive, we may experience significant
111
fluctuations in our collaborative arrangements revenue from quarter to quarter and year to year depending on the timing of achieving such substantive milestones. In those circumstances where a precommercial milestone is not substantive, we recognize as revenue on the date the milestone is achieved an amount equal to the applicable percentage of the performance period that had elapsed as of the date the milestone was achieved, with the balance being deferred and recognized over the remaining period of performance. Commercial milestones are accounted for as royalties and are recorded as revenue upon achievement of the milestone, assuming all other revenue recognition criteria are met.
We may receive royalty revenues under our current or future multiple element arrangements. If we do not have any future performance obligations under these agreements, we record these revenues as earned.
Research and Development Expenses
We expense research and development costs to operations as incurred. We defer and capitalize nonrefundable advance payments we make for research and development activities until the related goods are received or the related services are performed.
Research and development expenses comprise costs incurred in performing research and development activities, including salaries, benefits and other employee-related expenses, share-based compensation expense, laboratory supplies and other direct expenses, facilities cost, overhead costs, third-party contract costs relating to pre-clinical studies and clinical trial activities and related contract manufacturing expenses, and other outside costs.
As part of the process of preparing our consolidated financial statements, we are required to estimate certain of our research and development expenses, including estimates of third-party contract costs relating to pre-clinical studies and clinical trial activities and related contract manufacturing expenses. This process involves reviewing open contracts and purchase orders, communicating with our personnel to identify services that have been performed for us and estimating the level of service performed and the associated cost incurred for the service when we have not yet been invoiced or otherwise notified of the actual cost.
The majority of our service providers invoice us monthly in arrears for services performed or when contractual milestones are met. We make estimates of our accrued expenses as of each balance sheet date in our financial statements based on facts and circumstances known to us at that time. We periodically confirm the accuracy of our estimates with the service providers to gauge the reasonableness of our estimates. Differences between actual and estimated expenses recorded have not been material and are adjusted for in the period in which they become known. However, if we incorrectly estimate activity levels associated with such research and development activities at a given point in time, we could be required to record material adjustments in future periods. Examples of estimated research and development expenses include fees paid to:
- •
- CROs in connection with clinical trials;
- •
- CMOs with respect to clinical materials, intermediates, drug substance and drug product;
- •
- vendors in connection with preclinical development activities; and
- •
- vendors related to manufacturing, development and distribution of clinical supplies.
We base our expenses related to clinical trials on our estimates of the services received and efforts expended pursuant to contracts with multiple CROs that conduct and manage clinical trials on our behalf. The financial terms of these agreements are subject to negotiation, vary from contract to contract and may result in uneven payment flows. There may be instances in which payments made to our vendors will exceed the level of services provided and result in a prepayment of the clinical
112
expense. Payments under some of these contracts depend on factors such as the successful enrollment of subjects and the completion of clinical trial milestones. In accruing service fees, we estimate the time period over which services will be performed, enrollment of subjects and the level of effort to be expended in each period.
Stock-Based Compensation
Our share-based compensation programs grant awards which may include stock options, restricted stock awards ("RSAs"), restricted stock units ("RSUs"), and other stock-based awards.
Share-based compensation is recognized as an expense in the financial statements based on the grant date fair value over the requisite service period. For awards granted to employees and directors that vest based on service conditions, we use the straight-line method to allocate compensation expense to reporting periods. Beginning in the first quarter of 2017, we do not adjust stock-based compensation for estimated forfeitures and account for forfeitures when they occur.
The fair value of the RSUs and RSAs is based on the market value of our common stock on the date of grant. The fair value of options is calculated using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model, which requires the use of subjective assumptions, including volatility and expected term.
Due to the lack of a public market for the trading of our common stock prior to the IPO in October 2016 and a lack of historical and implied volatility data, we have based our estimate of expected volatility on the historical volatility of a group of similar companies that are publicly traded. We selected companies with comparable characteristics to us, including enterprise value, risk profiles, position within the industry and with historical share price information sufficient to meet the expected term of the stock-based awards. We will continue to apply this process until a sufficient amount of historical information regarding the volatility of its own stock price becomes available. Due to the lack of Company specific historical option activity, the Company estimates the expected term using the "simplified" method.
Result of Operations
Comparison of the Years Ended December 31, 2017 and 2016
The following table summarizes our results of operations:
| |
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
2017 | 2016 | $ Change | % Change | |||||||||
| |
(in thousands, except percentages) |
||||||||||||
Revenue |
$ | — | $ | 4,928 | $ | (4,928 | ) | (100.0 | )% | ||||
Operating expenses: |
|||||||||||||
Research and development |
45,251 | 27,928 | 17,323 | 62.0 | % | ||||||||
General and administrative |
9,778 | 5,024 | 4,754 | 94.6 | % | ||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total operating expenses |
55,029 | 32,952 | 22,077 | 67.0 | % | ||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Loss from operations |
(55,029 | ) | (28,024 | ) | (27,005 | ) | 96.4 | % | |||||
Other income (expense), net |
571 | (858 | ) | 1,429 | (166.6 | )% | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net loss before benefit from income taxes |
(54,458 | ) | (28,882 | ) | (25,576 | ) | 88.6 | % | |||||
Benefit from income taxes |
(19 | ) | (18 | ) | (1 | ) | (5.6 | )% | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net loss |
$ | (54,439 | ) | $ | (28,864 | ) | $ | (25,575 | ) | 88.6 | % | ||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
113
Revenue
Revenue decreased by $4.9 million to zero for the year ended December 31, 2017, from $4.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2016, which included a $3.0 million pre-clinical milestone payment and $1.9 million in non-refundable license fees earned and reimbursement of research and development services provided by us in accordance with a pre-specified number of our FTEs working under the Merck Agreement. The research term of the Merck Agreement expired in April 2016.
Research and Development Expenses
Research and development expenses increased by $17.3 million to $45.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2017, from $27.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2016. This increase was primarily attributable to a $11.7 million increase in CRO and CMO expenses for preclinical studies and clinical trials for RA101495 SC; a $5.5 million increase in employee-related costs associated with compensation, benefits, non-cash stock-based compensation and other employee-related expenses, including costs for additional personnel to support our increased research and development activities; a $0.3 million increase in laboratory supply and reagent expenses; and a $0.2 million increase in depreciation expense; partially offset by a $0.4 million net decrease in other expenses, primarily attributable to lower external consulting and legal expenses.
General and Administrative Expenses
General and administrative expenses increased by $4.8 million to $9.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2017, from $5.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2016. This increase was primarily attributable to $3.1 million increase in employee-related costs associated compensation, benefits, non-cash stock-based compensation for executive and administrative personnel, including costs for additional personnel to support our increased activities; a $0.9 million increase in insurance, legal and audit costs, primarily due to operating as a public company; a $0.4 million increase in patent costs; and a $0.4 million net increase in other expenses.
Other Income (Expense), Net
Other income (expense), net increased by $1.4 million to $0.6 million in other income, net during the year ended December 31, 2017, from approximately $0.8 million in other expense, net for the year ended December 31, 2016. This increase was due primarily to the Series B-2 Preferred Stock Tranche Rights fair value adjustment of $1.0 million recognized during the year ended December 31, 2016 and a $0.5 million increase in interest income; partially offset by $0.1 million net increase in other expenses.
114
Comparison of the Years Ended December 31, 2016 and 2015
The following table summarizes our results of operations:
| |
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
2016 | 2015 | $ Change | % Change | |||||||||
| |
(in thousands, except percentages) |
||||||||||||
Revenue |
$ | 4,928 | $ | 4,094 | $ | 834 | 20.4 | % | |||||
Operating expenses: |
|||||||||||||
Research and development |
27,928 | 15,217 | 12,711 | 83.5 | % | ||||||||
General and administrative |
5,024 | 2,233 | 2,791 | 125.0 | % | ||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total operating expenses |
32,952 | 17,450 | 15,502 | 88.8 | % | ||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Loss from operations |
(28,024 | ) | (13,356 | ) | (14,668 | ) | 109.8 | % | |||||
Other income (expense), net |
(858 | ) | (606 | ) | (252 | ) | 41.6 | % | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net loss before income taxes |
(28,882 | ) | (13,962 | ) | (14,920 | ) | 106.9 | % | |||||
Benefit from income taxes |
(18 | ) | (19 | ) | 1 | 5.3 | % | ||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net loss |
$ | (28,864 | ) | $ | (13,943 | ) | $ | (14,921 | ) | 107.0 | % | ||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Revenue
Revenue increased by $0.8 million to $4.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2016, from $4.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2015. This increase is primarily attributable to the recognition of a $3.0 million milestone payment from Merck in June 2016 and an increase of $0.2 million in connection with recognition of the remaining deferred revenue related to the upfront non-refundable license fee earned at the expiration of the research term of the Merck Agreement on March 31, 2016. These increases were offset in part by $2.2 million decrease in FTE revenue related to a decrease in the number of FTEs providing research and development services under the Merck Agreement and $0.2 million decrease related to lower reimbursable lab supply and reagent expenses for the year ended December 31, 2016.
Research and Development Expenses
Research and development expenses increased by $12.7 million to $27.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2016, from $15.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2015. This increase is primarily attributable to $6.6 million increase in CRO and CMO expenses in connection with our pre-clinical studies and clinical trials for RA101495 SC, $3.3 million increase in employee-related costs associated with salaries, bonus, benefits, travel and non-cash stock-based compensation including costs for additional personnel to support our increased research and development activities, $1.3 million increase in facilities costs including rent, moving expenses related to our new facility, and depreciation expense, $0.8 million increase in consulting expenses and $0.7 million increase in lab-supply and reagent expenses.
General and Administrative Expenses
General and administrative expenses increased by $2.8 million to $5.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2016, from $2.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2015. The increase in general and administrative expenses was primarily attributable to $1.4 million increase in employee-related costs, including salary, bonus, benefits, travel, insurance and non-cash stock-based compensation for executive and administrative personnel including for additional personnel to support our increased activities, $0.8 million increase in consulting and professional fees, including increased market research,
115
accounting, legal and audit fees, approximately $0.3 million in increased facilities related costs and depreciation and $0.2 million in patent costs.
Other Income (Expense), Net
Other expense, net increased by $0.3 million to $0.9 million in other expense, net during the year ended December 31, 2016 from $0.6 million in other expense, net for the year ended December 31, 2015. This increase was primarily attributable to increase in the fair value of the Series B-2 Preferred Stock Tranche Rights of $1.0 million recognized during the year ended December 31, 2016, offset by other expense of $0.6 million related to the loss upon debt extinguishment of the Convertible Notes during the year ended December 31, 2015 and interest income of $0.1 million recognized during the year ended December 31, 2016.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Overview
We have funded our operations from inception through December 31, 2017 primarily through the public offering and the private placement of our securities and revenue from our collaboration with Merck. As of December 31, 2017, we had received an aggregate of $181.0 million in net proceeds from the issuance of equity and debt securities and $17.5 million in payments in connection with our collaboration and license agreement with Merck. As of December 31, 2017, we had cash and cash equivalents of $70.4 million.
On October 31, 2016, we completed an initial public offering ("IPO"), in which we issued and sold 7,049,230 shares of common stock at a public offering price of $13.00 per share, resulting in net proceeds to us of $82.8 million after deducting $6.4 million of underwriting discounts and commissions and offering costs of $2.4 million. On November 29, 2016, we completed the sale of an additional 1,057,385 shares of common stock to the underwriters under the underwriters' option in the IPO to purchase additional shares of common stock at the public offering price of $13.00 per share, resulting in net proceeds to us of $12.8 million after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions of $1.0 million. The shares began trading on the Nasdaq Global Market on October 26, 2016.
In February 2018, we completed a follow-on public offering of 9,660,000 shares of our common stock, including the full exercise of the underwriter's over-allotment of 1,260,000 shares, at $6.00 per share and received aggregate net proceeds of $54.1 million, after deducting $3.5 million of underwriting discounts and commissions and approximately $0.4 million of offering expenses.
Cash Flows
Comparison of the Years Ended December 31, 2017 and 2016
The following table summarizes our sources and uses of cash:
| |
Year Ended December 31, |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
2017 | 2016 | |||||
| |
(in thousands) |
||||||
Net cash provided by (used in): |
|||||||
Operating activities |
$ | (46,779 | ) | $ | (21,843 | ) | |
Investing activities |
(1,412 | ) | (4,967 | ) | |||
Financing activities |
760 | 125,236 | |||||
| | | | | | | | |
Net increase (decrease) in cash |
$ | (47,431 | ) | $ | 98,426 | ||
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
116
Net Cash Used in Operating Activities
Cash flows used in operating activities represent the cash receipts and disbursements related to all of our activities other than investing and financing activities. Operating cash flow is derived by adjusting our net loss for (1) non-cash operating items such as depreciation and amortization, stock-based compensation and changes in fair value of preferred stock tranche rights as well as (2) changes in operating assets and liabilities, which reflect timing differences between the receipt and payment of cash associated with transactions and when they are recognized in our results of operations.
Net cash used in operating activities was $46.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2017 compared to $21.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2016. The increase in net cash used in operations was primarily attributable to a $25.6 million increase in our net loss as a result of higher operating expenses, primarily in connection with our pre-clinical studies and clinical trials related to our lead program RA101495 SC and other research and development pipeline programs; and a net increase in operating assets; partially offset by higher non-cash expenses, including depreciation, amortization and stock-based compensation and a net increase in operating liabilities.
Net Cash Used in Investing Activities
Net cash used in investing activities was $1.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2017 compared to $5.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2016. The decrease in cash used in investing activities was primarily due to a reduction in purchases of property and equipment.
Net Cash Provided by Financing Activities
Net cash provided by financing activities was $0.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2017 compared to $125.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2016. The decrease in cash provided by financing activities was primarily due to the net proceeds of $95.6 million from our IPO completed in October 2016; and the Series B-2 Preferred Stock financing completed in June 2016, which resulted in net proceeds of $29.2 million; partially offset by proceeds of $0.7 million from the disgorgement of a stockholder's short-swing profits and an increase of $0.2 million in proceeds from exercises of stock options.
Comparison of the Years Ended December 31, 2016 and 2015
The following table summarizes our sources and uses of cash:
| |
Year Ended December 31, |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
2016 | 2015 | |||||
| |
(in thousands) |
||||||
Net cash provided by (used in): |
|||||||
Operating activities |
$ | (21,843 | ) | $ | (12,017 | ) | |
Investing activities |
(4,967 | ) | (1,664 | ) | |||
Financing activities |
125,236 | 29,028 | |||||
| | | | | | | | |
Net increase in cash |
$ | 98,426 | $ | 15,347 | |||
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
The use of cash in all periods resulted primarily from our net losses adjusted for non-cash charges and changes in components of working capital.
Net cash used in operating activities was $21.8 million during the year ended December 31, 2016 compared to $12.0 million during the year ended December 31, 2015. The increase in net cash used in operations was primarily due to an increase in our net loss of $14.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2016, as compared to the year ended December 31, 2015 due to an increase in our
117
operating expenses in connection with our lead program RA101495 SC and other research and development pipeline programs, offset in part by an increase in accrued expenses, accounts payable, deferred rent, deferred revenue and other non-current liabilities of $4.5 million and an increase in prepaid expenses and other assets of approximately $0.9 million.
Net cash used in investing activities was $5.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2016 compared to $1.7 million during the year ended December 31, 2015. The increase in cash used in investing activities was primarily due to increased purchases of property and equipment related to the cost of new leasehold improvements in our new leased facility in Cambridge, Massachusetts.
Net cash provided by financing activities was $125.2 million during the year ended December 31, 2016 compared to $29.0 million during the year ended December 31, 2015. The increase in cash provided by financing activities was due to net proceeds from our IPO of $95.9 million.
Funding Requirements
We expect our expenses to increase in connection with our ongoing activities, particularly as we initiate Phase 3 clinical trials of RA101495 SC in PNH, continue clinical trials of RA101495 SC in additional indications, including gMG, aHUS and LN, advance the development of pipeline programs, initiate new research and preclinical development efforts and seek marketing approval for any product candidates that we successfully develop. In addition, if we obtain marketing approval for any of our product candidates, we expect to incur significant commercialization expenses related to establishing sales, marketing, distribution and other commercial infrastructure to commercialize such products. Furthermore, we anticipate increased costs associated with being and operating as a public company. Accordingly, we will need to obtain substantial additional funding in connection with our continuing operations. If we are unable to raise capital when needed or on attractive terms, we would be forced to delay, reduce or eliminate our research and development programs or future commercialization efforts.
We believe that, our cash and cash equivalents as of December 31, 2017, in addition to the net proceeds of $54.1 million from the equity offering closed in February 2018, will enable us to fund our operating expenses and capital expenditure requirements through the end of 2019. We have based our projections of operating capital requirements on assumptions that may prove to be incorrect and we may use all of our available capital resources sooner than we expect. Because of the numerous risks and uncertainties associated with the development and commercialization of RA101495 SC and the research, development and commercialization of other potential product candidates, we are unable to estimate the exact amount of our operating capital requirements. Our future capital requirements will depend on many factors, including:
- •
- the scope, progress, timing, costs and results of clinical trials of RA101495 SC;
- •
- research and preclinical development efforts for any future product candidates that we may develop;
- •
- our ability to enter into and the terms and timing of any collaborations, licensing agreements or other arrangements;
- •
- the number of future product candidates that we pursue and their development requirements;
- •
- the outcome, timing and costs of seeking regulatory approvals;
- •
- the costs of commercialization activities for any of our product candidates that receive marketing approval to the extent such costs are not the responsibility of any future collaborators, including the costs and timing of establishing product sales, marketing, distribution and manufacturing capabilities;
118
- •
- subject to receipt of marketing approval, revenue, if any, received from commercial sales of our current and future product candidates;
- •
- our headcount growth and associated costs as we expand our research and development and establish a commercial infrastructure;
- •
- the costs of preparing, filing and prosecuting patent applications, maintaining and protecting our intellectual property rights and defending
against intellectual property related claims; and
- •
- the costs of operating as a public company.
Identifying potential product candidates and conducting preclinical studies and clinical trials is a time-consuming, expensive and uncertain process that takes many years to complete, and we may never generate the necessary data or results required to obtain marketing approval and achieve product sales. In addition, our product candidates, if approved, may not achieve commercial success. Accordingly, we will need to continue to rely on additional financing to achieve our business objectives. Adequate additional financing may not be available to us on acceptable terms, or at all.
Until such time, if ever, as we can generate substantial product revenues, we expect to finance our cash needs through a combination of equity offerings, debt financings, collaborations, strategic alliances and licensing arrangements. To the extent that we raise additional capital through the sale of equity or convertible debt securities, the ownership interest of our existing stockholders will be diluted, and the terms of these securities may include liquidation or other preferences that adversely affect the rights of a common stockholder. Debt financing, if available, may involve agreements that include covenants limiting or restricting our ability to take specific actions, such as incurring additional debt, making capital expenditures or declaring dividends.
If we raise funds through additional collaborations, strategic alliances or licensing arrangements with third parties, we may have to relinquish valuable rights to our technologies, future revenue streams, research programs or product candidates or to grant licenses on terms that may not be favorable to us. If we are unable to raise additional funds through equity or debt financings when needed, we may be required to delay, limit, reduce or terminate our product development or future commercialization efforts or grant rights to develop and market product candidates that we would otherwise prefer to develop and market ourselves.
Contractual Commitments and Obligations
Minimum future payments of our contractual obligations as of December 31, 2017 are as follows:
| |
Payments Due by Period | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
Total | Less than 1 Year |
1 - 3 Years |
3 - 5 Years |
More Than 5 Years |
|||||||||||
| |
(in thousands) |
|||||||||||||||
Operating leases |
$ | 7,619 | $ | 1,254 | $ | 2,845 | $ | 3,007 | $ | 513 | ||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total contractual cash obligations |
$ | 7,619 | $ | 1,254 | $ | 2,845 | $ | 3,007 | $ | 513 | ||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
As of December 31, 2017, we had several ongoing clinical and nonclinical for our various pipeline programs. We enter into contracts in the normal course of business with CROs and clinical sites for the conduct of clinical trials, professional consultants for expert advice and other vendors for clinical supply manufacturing or other services. These contracts are not included in the table above as generally they are cancellable, with notice, at the Company's option and do not have significant cancellation penalties.
119
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
As of December 31, 2017, we did not have any significant off-balance sheet arrangements, as defined in Item 303(a)(4)(ii) of SEC Regulation S-K promulgated under the Exchange Act.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
For a discussion of recently adopted or issued accounting pronouncements please refer to Item 8, "Financial Statements and Supplementary Data" within this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
JOBS Act
The Jumpstart our Business Startups Act of 2012 (the "JOBS Act") permits an "emerging growth company" such as us to take advantage of an extended transition period to comply with new or revised accounting standards applicable to public companies. We have chosen to "opt out" of this provision and will comply with new or revised accounting standards as required when they are adopted. This decision to opt out of the extended transition period under the JOBS Act is irrevocable.
ITEM 7A. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK
Interest Rate Risk
We are exposed to market risk related to changes in interest rates. As of December 31, 2017, we had cash and cash equivalents of $70.4 million, consisting primarily of money market funds. Our primary exposure to market risk is interest rate sensitivity, which is affected by changes in the general level of U.S. interest rates, particularly because our cash equivalents are in held in short-term money market funds. Due to short-term duration of our investment portfolio and the low risk profile of our investments, an immediate 100 basis point change in interest rates would not have a material effect on the fair market value of our portfolio.
Foreign Currency Risk
We are also exposed to market risk related to changes in foreign currency exchange rates. From time to time, we engage contract research organizations, or CROs, and investigational sites globally. We are therefore subject to fluctuations in foreign currency rates in connection with these engagements. We do not currently hedge our foreign currency exchange rate risk. As of December 31, 2017, we had minimal or no assets or liabilities denominated in foreign currencies.
Effects of Inflation
We do not believe that inflation and changing prices during the three months ended December 31, 2017 had a significant impact on our results of operations or financial condition.
ITEM 8. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
The consolidated financial statements together with the report of our independent registered public accounting firm, appear at page F-1 through F-28 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
ITEM 9. CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE
None.
120
ITEM 9A. CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Our management, with the participation of our principal executive officer and principal financial officer, evaluated the effectiveness of the design and operation of our disclosure controls and procedures as of December 31, 2017. The term "disclosure controls and procedures," as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, or the Exchange Act, means controls and other procedures of a company that are designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed by a company in the reports that it files or submits under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized and reported, within the time periods specified in the Securities and Exchange Commission's rules and forms. Disclosure controls and procedures include, without limitation, controls and procedures designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed by a company in the reports that it files or submits under the Exchange Act is accumulated and communicated to the company's management, including its principal executive and principal financial officers, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure. Our management recognizes that any controls and procedures, no matter how well designed and operated, can provide only reasonable assurance of achieving their objectives and our management necessarily applies its judgment in evaluating the cost-benefit relationship of possible controls and procedures. Based on the evaluation of our disclosure controls and procedures as of December 31, 2017, our principal executive officer and principal financial officer concluded that, as of such date, our disclosure controls and procedures were effective at the reasonable assurance level.
Management's Annual Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended). Our internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, we conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting based on the framework in Internal Control—Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. Based on our assessment and those criteria, management concluded that the Company maintained effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017.
The effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017 has not been audited by Deloitte & Touche LLP, our independent registered public accounting firm due to a transition period established by the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act, or JOBS Act, for emerging growth companies.
Changes in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
No change in our internal control over financial reporting occurred during the quarter ended December 31, 2017, that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
None.
121
ITEM 10. DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
Except as set forth below, the information required by this item will be contained in our definitive proxy statement to be filed with the SEC in connection with the Annual Meeting of Stockholders within 120 days after the conclusion of our fiscal year ended December 31, 2017, or the Proxy Statement, and is incorporated in this Annual Report on Form 10-K by reference.
We have adopted a written code of business conduct and ethics that applies to our directors, officers and employees, including our principal executive officer, principal financial officer, principal accounting officer or controller, or persons performing similar functions. A current copy of the code has been posted on the investor relations section of our website, which is located at www.rapharma.com. If we make any substantive amendments to, or grant any waivers from, the code of business conduct and ethics for any officer or director, we will disclose the nature of such amendment or waiver on our website or in a current report on Form 8-K.
ITEM 11. EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION
The information required by this item will be contained in the Proxy Statement and is incorporated in this Annual Report on Form 10-K by reference.
ITEM 12. SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS
The information required by this item will be contained in the Proxy Statement and is incorporated in this Annual Report on Form 10-K by reference.
ITEM 13. CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE
The information required by this item will be contained in the Proxy Statement and is incorporated in this Annual Report on Form 10-K by reference.
ITEM 14. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING FEES AND SERVICES
The information required by this item will be contained in the Proxy Statement and is incorporated in this Annual Report on Form 10-K by reference.
122
ITEM 15. EXHIBITS AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES
- (a)
- The
following documents are filed as part of this report:
- (1)
- Financial Statements
- (2)
- Financial Statement Schedules
Financial Statements—See Index to Consolidated Financial Statements at Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, beginning on page F-1.
Financial statement schedules have been omitted in this Annual Report on Form 10-K because they are not applicable, not required under the instructions, or the information requested is set forth in the consolidated financial statements or related notes thereto.
- (b)
- Exhibits.
The exhibits listed in the accompanying index to exhibits are filed as part of, or incorporated by reference into, this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
None.
123
Index to Consolidated Financial Statements
F-1
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To
the Stockholders and the Board of Directors of
Ra Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Cambridge, Massachusetts
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Ra Pharmaceuticals, Inc. and subsidiaries (the "Company") as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, the related consolidated statements of operations, redeemable convertible preferred stock and stockholders' equity (deficit), and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2017, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the "financial statements"). In our opinion, the financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2017, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company's management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company's financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB) and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. As part of our audits, we are required to obtain an understanding of internal control over financial reporting but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company's internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion.
Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
/s/ Deloitte & Touche LLP
Boston,
Massachusetts
March 14, 2018
We have served as the Company's auditor since 2013.
F-2
RA PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(In thousands, except per share data)
| |
December 31, | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
2017 | 2016 | |||||
Assets |
|||||||
Current assets: |
|||||||
Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 70,381 | $ | 117,812 | |||
Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
2,496 | 1,690 | |||||
| | | | | | | | |
Total current assets |
72,877 | 119,502 | |||||
Property and equipment, net |
5,606 | 5,537 | |||||
Goodwill |
183 | 183 | |||||
Intangible assets, net |
197 | 262 | |||||
Restricted cash |
1,334 | 1,334 | |||||
| | | | | | | | |
Total assets |
$ | 80,197 | $ | 126,818 | |||
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity |
|||||||
Current liabilities: |
|||||||
Accounts payable |
$ | 4,348 | $ | 3,252 | |||
Accrued expenses |
3,937 | 3,182 | |||||
Deferred rent |
329 | 303 | |||||
| | | | | | | | |
Total current liabilities |
8,614 | 6,737 | |||||
Deferred rent, net of current portion |
2,359 | 2,800 | |||||
Deferred tax liabilities |
40 | 59 | |||||
| | | | | | | | |
Total liabilities |
11,013 | 9,596 | |||||
Commitments and contingencies (Note 4 and 7) |
|||||||
Stockholders' equity: |
|||||||
Preferred stock, $0.001 par value; 5,000 shares authorized; no shares issued and outstanding |
— | — | |||||
Common stock, $0.001 par value; 150,000 shares authorized; 22,626 and 22,546 shares issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively |
23 | 23 | |||||
Additional paid-in capital |
192,375 | 185,963 | |||||
Accumulated deficit |
(123,214 | ) | (68,764 | ) | |||
| | | | | | | | |
Total stockholders' equity |
69,184 | 117,222 | |||||
| | | | | | | | |
Total liabilities and stockholders' equity |
$ | 80,197 | $ | 126,818 | |||
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the consolidated financial statements.
F-3
RA PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
(in thousands, except per share data)
| |
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
Revenue |
$ | — | $ | 4,928 | $ | 4,094 | ||||
Operating expenses: |
||||||||||
Research and development |
45,251 | 27,928 | 15,217 | |||||||
General and administrative |
9,778 | 5,024 | 2,233 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Total operating expenses |
55,029 | 32,952 | 17,450 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Loss from operations |
(55,029 | ) | (28,024 | ) | (13,356 | ) | ||||
Other income (expense): |
||||||||||
Interest income |
645 | 109 | — | |||||||
Interest expense with related parties |
— | — | (159 | ) | ||||||
Loss on debt extinguishment with related parties |
— | — | (602 | ) | ||||||
Other income (expense), net |
(74 | ) | (967 | ) | 155 | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Total other income (expense), net |
571 | (858 | ) | (606 | ) | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Loss from operations before benefit from income taxes |
(54,458 | ) | (28,882 | ) | (13,962 | ) | ||||
Benefit from income taxes |
(19 | ) | (18 | ) | (19 | ) | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Net loss |
$ | (54,439 | ) | $ | (28,864 | ) | $ | (13,943 | ) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Reconciliation of net loss to net loss attributable to common stockholders: |
||||||||||
Net loss |
$ | (54,439 | ) | $ | (28,864 | ) | $ | (13,943 | ) | |
Gain on extinguishment of redeemable convertible preferred shares |
— | — | 1,673 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Net loss attributable to common stockholders |
$ | (54,439 | ) | $ | (28,864 | ) | $ | (12,270 | ) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Net loss per share attributable to common stockholders—basic and diluted |
$ | (2.41 | ) | $ | (6.98 | ) | $ | (24.68 | ) | |
Weighted average number of common shares outstanding—basic and diluted |
22,591 | 4,135 | 497 | |||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the consolidated financial statements.
F-4
RA PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF REDEEMABLE CONVERTIBLE PREFERRED STOCK AND STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY (DEFICIT)
(in thousands)
| |
Series A Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock |
Series B-1 Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock |
Series B-2 Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock |
|
|
|
|
|
Total Stockholders' Equity (Deficit) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
|
|
|
Additional Paid-In Capital |
Accumulated Deficit |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |
|
Common Stock | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |
Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount |
|
Shares | Amount | Amount | Amount | Amount | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
December 31, 2014 |
34,441 | $ | 28,984 | — | $ | — | — | $ | — | 474 | $ | — | $ | 243 | $ | (25,957 | ) | $ | (25,714 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
Sale of Series B-1 convertible preferred stock, net of $2,694 discount associated with preferred stock tranche rights, issuance costs of $193 and the conversion of convertible notes |
— | — | 31,565 | 26,364 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Extinguishment of Series A convertible preferred stock |
— | (1,673 | ) | — | — | — | — | — | — | 1,673 | — | 1,673 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of common stock warrants |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 548 | — | 548 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Exercise of common stock warrants |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 11 | — | 1 | — | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Exercise of common stock options |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 52 | 1 | 83 | — | 84 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Stock-based compensation |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 152 | — | 152 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net loss |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (13,943 | ) | (13,943 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
December 31, 2015 |
34,441 | 27,311 | 31,565 | 26,364 | — | — | 537 | 1 | 2,700 | (39,900 | ) | (37,199 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Sale of Series B-2 convertible preferred stock, net of issuance costs of $22 |
— | — | — | — | 29,362 | 32,808 | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Conversion of redeemable convertible preferred stock into common stock |
(34,441 | ) | (27,331 | ) | (31,565 | ) | (26,364 | ) | (29,362 | ) | (32,808 | ) | 13,624 | 14 | 86,469 | — | 86,483 | |||||||||||||||||||
Exercise of common stock warrants |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 221 | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of common stock from initial public offering, net of underwriters discounts and issuance costs |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 8,107 | 8 | 95,659 | — | 95,667 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Exercise of common stock options |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 57 | — | 109 | — | 109 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Stock-based compensation |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 1,026 | — | 1,026 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net loss |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (28,864 | ) | (28,864 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
December 31, 2016 |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 22,546 | 23 | 185,963 | (68,764 | ) | 117,222 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Exercise of common stock options |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 80 | — | 266 | — | 266 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Stock-based compensation |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 5,573 | — | 5,573 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Proceeds from disgorgement of stockholder's short-swing profits |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 670 | — | 670 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Other, net |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (97 | ) | (11 | ) | (108 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Net loss |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (54,439 | ) | (54,439 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
December 31, 2017 |
— | $ | — | — | $ | — | — | $ | — | 22,626 | $ | 23 | $ | 192,375 | $ | (123,214 | ) | $ | 69,184 | |||||||||||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the consolidated financial statements.
F-5
RA PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(in thousands)
| |
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
Cash flows from operating activities |
||||||||||
Net loss |
$ | (54,439 | ) | $ | (28,864 | ) | $ | (13,943 | ) | |
Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash used in operating activities: |
||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization |
1,524 | 1,274 | 897 | |||||||
Stock-based compensation |
5,573 | 1,026 | 152 | |||||||
Non-cash interest expense with stockholders |
— | — | 109 | |||||||
Loss on debt extinguishment with stockholders |
— | — | 602 | |||||||
Accretion of discount and debt issuance costs of convertible notes with stockholders |
— | — | 50 | |||||||
Change in fair value of preferred stock tranche rights |
— | 960 | (74 | ) | ||||||
Other, net |
8 | 84 | (95 | ) | ||||||
Changes in operating assets and liabilities: |
||||||||||
Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
(1,023 | ) | (890 | ) | (392 | ) | ||||
Accounts payable and accrued expenses |
2,012 | 4,018 | 1,102 | |||||||
Deferred rent |
(415 | ) | 2,389 | 517 | ||||||
Deferred revenue |
— | (1,862 | ) | (883 | ) | |||||
Other, net |
(19 | ) | 22 | (59 | ) | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Net cash used in operating activities |
(46,779 | ) | (21,843 | ) | (12,017 | ) | ||||
Cash flows from investing activities |
||||||||||
Purchase of property and equipment |
(1,412 | ) | (5,105 | ) | (331 | ) | ||||
Other, net |
— | 9 | 1 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Net cash used in investing activities |
(1,412 | ) | (5,096 | ) | (330 | ) | ||||
Cash flows from financing activities |
||||||||||
Proceeds from common stock offering, net of underwriter discounts |
— | 98,009 | — | |||||||
Payment of common stock offering costs |
(176 | ) | (2,110 | ) | — | |||||
Proceeds from issuance of preferred stock |
— | 29,250 | 24,142 | |||||||
Payment of preferred stock issuance costs |
— | (22 | ) | (193 | ) | |||||
Proceeds from issuance of convertible notes with stockholders |
— | — | 5,000 | |||||||
Proceeds from disgorgement of stockholder's short-swing profits |
670 | — | — | |||||||
Proceeds from exercise of stock options |
266 | 109 | 84 | |||||||
Other, net |
— | — | (5 | ) | ||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Net cash provided by financing activities |
760 | 125,236 | 29,028 | |||||||
Net change in cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash |
(47,431 | ) | 98,297 | 16,681 | ||||||
Cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash, beginning of period |
119,146 | 20,849 | 4,168 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash, end of period |
$ | 71,715 | $ | 119,146 | $ | 20,849 | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Noncash investing and financing activity: |
||||||||||
Conversion of redeemable convertible preferred stock into common stock |
$ | — | $ | 86,483 | $ | — | ||||
Reclassification of Series B-2 tranche right liability to the balance of Series B-2 redeemable convertible preferred stock |
$ | — | $ | 3,580 | $ | — | ||||
Conversion of convertible notes with stockholders into Series B-1 redeemable convertible preferred stock |
$ | — | $ | — | $ | 5,109 | ||||
Gain on extinguishment of Series A redeemable convertible preferred stock |
$ | — | $ | — | $ | 1,673 | ||||
Common stock offering costs incurred but unpaid at period end |
$ | 139 | $ | 232 | $ | — | ||||
Changes in liabilities and prepaid expenses related to fixed asset additions |
$ | 124 | $ | 127 | $ | 484 | ||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the consolidated financial statements.
F-6
RA PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
1. Nature of Business
The Company is a clinical-stage biopharmaceutical company using its proprietary peptide chemistry platform to create novel therapeutics to treat life-threatening diseases that are caused by excessive or uncontrolled activation of the complement system, an essential component of the body's innate immune system. The Company's lead product candidate, RA101495 SC, is being developed as a convenient self-administered subcutaneous ("SC") injection, which is an injection into the tissue under the skin, for the treatment of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria ("PNH"), a rare, chronic, life-threatening, blood disorder where red blood cells are mistakenly attacked and destroyed by the complement system. The Company is also developing RA101495 SC, administered SC, to treat other debilitating complement-mediated diseases such as generalized myasthenia gravis ("gMG"), atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome ("aHUS"), and lupus nephritis ("LN"). Additionally, the Company is pursuing discovery and preclinical programs targeting selective inhibition of other uncontrolled complement pathway factors to treat a variety of ocular, renal and inflammatory diseases. In addition to its focus on developing novel therapeutics to treat complement-mediated diseases, the Company has validated its Extreme Diversity platform by successfully identifying and delivering orally-available cyclic peptides for a non-complement cardiovascular target with a large market opportunity in a collaboration with Merck & Co., Inc. ("Merck").
The Company was incorporated in Delaware on June 27, 2008 and is located in Cambridge, Massachusetts. During 2011, the Company acquired Cosmix Verwaltungs GmbH ("Cosmix"), organized in Germany. In January 2016, the Company formed a wholly-owned subsidiary organized in the United Kingdom ("UK"), Ra Europe Limited, for the purpose of conducting clinical trials in Europe and the UK.
The Company is subject to risks common to other life science companies in the development stage including, but not limited to, uncertainty of product development and commercialization, lack of marketing and sales history, development by its competitors of new technological innovations, dependence on key personnel, market acceptance of products, product liability, protection of proprietary technology, ability to raise additional financing, and compliance with Food and Drug Administration and other government regulations. If the Company does not successfully commercialize any of its product candidates, it will be unable to generate recurring product revenue or achieve profitability. If the Company is unable to raise capital when needed or on attractive terms, it would be forced to delay, reduce, eliminate or out-license certain of its research and development programs or future commercialization efforts.
Since inception, the Company has incurred net losses and negative cash flows from operations, and has an accumulated deficit of $123.2 million and $68.8 million as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively. The Company has financed its operations to date through the public offering and the private placement of its securities and funding from its collaboration and license agreement with Merck (the "Merck Agreement").
Public Offerings
On October 31, 2016, the Company completed an initial public offering ("IPO"), in which the Company issued and sold 7,049,230 shares of common stock at a public offering price of $13.00 per share, resulting in net proceeds of $82.8 million after deducting $6.4 million of underwriting discounts and commissions and offering costs of $2.4 million. On November 29, 2016, the Company completed the sale of an additional 1,057,385 shares of common stock to the underwriters under the underwriters'
F-7
RA PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
1. Nature of Business (Continued)
option in the IPO to purchase additional shares at the public offering price of $13.00 per share, resulting in net proceeds of $12.8 million after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions of $1.0 million. The shares began trading on the Nasdaq Global Market on October 26, 2016.
In February 2018, the Company completed a follow-on public offering of 9,660,000 shares of common stock, including the full exercise of the underwriter's over-allotment of 1,260,000 shares, at $6.00 per share and received aggregate net proceeds of $54.1 million, after deducting $3.5 million of underwriting discounts and commissions and approximately $0.4 million of offering expenses.
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Principles of Consolidation
The Company's consolidated financial statements reflect its financial statements and those of its subsidiaries in which the Company holds a controlling financial interest, including Cosmix and Ra Europe Limited. Intercompany balances and transactions are eliminated in consolidation.
Reclassifications
Certain reclassifications have been made to prior year amounts to conform to the current year presentation. These reclassifications have no impact on the Company's net loss or cash flows.
Segment Information
Operating segments are defined as components of an enterprise for which separate financial information is available for evaluation by the chief operating decision maker in deciding how to allocate resources and in assessing performance. The Company operates in one operating segment, the business of developing peptide-based drugs for a variety of therapeutic uses.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of consolidated financial statements requires that the Company make estimates and judgments that may affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues, expenses and related disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities. On an on-going basis, the Company evaluates its estimates, judgments and methodologies. The Company bases its estimates on historical experience and on various other assumptions that are believed to be reasonable, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying values of assets and liabilities. Actual results may differ from these estimates under different assumptions or conditions. Changes in estimates are reflected in reported results in the period in which they become known.
Cash Equivalents
The Company considers all highly liquid investments with a maturity when purchased of three months or less to be cash equivalents. As of December 31, 2017 and 2016, cash equivalents were comprised of money market funds.
F-8
RA PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (Continued)
Fair Value Measurements
The accounting standard for fair value measurements defines fair value, establishes a framework for measuring fair value in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States ("U.S. GAAP"), and requires certain disclosures about fair value measurements. Under this standard, fair value is the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. The Company has certain financial assets and liabilities recorded at fair value which have been classified as Level 1, 2 or 3 within the fair value hierarchy:
- •
- Level 1—Fair values are determined utilizing prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical assets or liabilities that
the Company has the ability to access.
- •
- Level 2—Fair values are determined by utilizing quoted prices for identical or similar assets and liabilities in active
markets or other market observable inputs such as interest rates, yield curves, and foreign currency spot rates.
- •
- Level 3—Prices or valuations that require inputs that are both significant to the fair value measurement and unobservable.
The fair value hierarchy level is determined by asset and liability class based on the lowest level of significant input. The observability of inputs may change for certain assets or liabilities. This condition could cause an asset or liability to be reclassified between levels. The Company recognizes transfers between levels within the fair value hierarchy, if any, at the end of each reporting period.
Valuation methodologies used for assets measured or disclosed at fair value are as follows:
- •
- Cash equivalents—Valued at market prices determined through third-party pricing services.
Concentrations of Credit Risk
Financial instruments, which potentially subject the Company to concentrations of credit risk, consist principally of cash and cash equivalents and restricted cash. The Company places these investments in highly rated financial institutions and limits the amounts of credit exposure to any one financial institution.
Concentrations of Suppliers
The Company currently engages third-party manufacturers to provide clinical supplies, nonclinical supplies and fill-finish services for RA101495 SC.
If any of the Company's suppliers were to limit or terminate production or otherwise fail to meet the quality or delivery requirements needed to satisfy the supply commitments, the process of locating and qualifying alternate sources could require up to several months, during which time the Company's production could be delayed. Such delays could have a material adverse effect on the Company's business and ongoing clinical and nonclinical studies.
F-9
RA PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (Continued)
Property and Equipment
Property and equipment, including leasehold improvements, are recorded at cost, and are depreciated when placed into service using the straight-line method based on their estimated useful lives as follows:
Asset
|
Estimated useful life | |
|---|---|---|
Computer equipment and software |
3 years | |
Furniture, fixtures, and other |
5 years | |
Laboratory equipment |
5 years | |
Leasehold improvements |
Shorter of useful life or term of lease |
Costs for assets not yet placed into service is capitalized as construction in progress. Maintenance and repair costs are expensed as incurred.
Impairment of Long-lived Assets
Long-lived assets to be held and used are reviewed for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of the assets or asset group may not be recoverable. Determination of recoverability is based on an estimate of undiscounted future cash flows resulting from the use of the asset and its eventual disposition. In the event that such cash flows are not expected to be sufficient to recover the carrying amount of the assets, the assets are written-down to their fair values. Long-lived assets to be disposed of are carried at fair value less costs to sell.
Operating Leases
The Company leases office and laboratory facilities under a non-cancelable operating lease agreement. The Company recognizes rent expense under such leases on a straight-line basis over the term of the lease with the difference between the expense and the payments recorded as deferred rent on the consolidated balance sheets. Any reimbursements by the landlord for tenant improvements are considered lease incentives, the balance of which is recorded as a lease incentive obligation within deferred rent on the consolidated balance sheets, and are amortized over the life of the lease. Lease renewal periods are considered on a lease-by-lease basis in determining the lease term.
Revenue Recognition
The Company has derived all of its revenue to date from the Merck Agreement. Refer to Note 9, "Revenue Recognition." The terms of the Merck Agreement contain multiple deliverables, which include licenses, research and development activities and participation on the joint steering committee. Payments under the agreement include: (i) an upfront nonrefundable license fee; (ii) payments for research and development services performed by the Company, including reimbursement for certain lab supplies and reagents; (iii) payments based upon the achievement of certain development (pre-clinical and clinical), regulatory and commercial milestones; and (iv) royalties on net product sales, if any.
In order to account for multiple element arrangements, such as the Merck Agreement, the Company identifies the deliverables and evaluates which deliverables represent separate units of
F-10
RA PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (Continued)
accounting. The Company accounts for those components as separate elements when the following criteria are met:
- •
- the delivered items have value to the customer on a stand-alone basis; and
- •
- if there is a general right of return relative to the delivered items, delivery or performance of the undelivered items is considered probable and within the Company's control.
This evaluation requires subjective determinations and requires the Company to make judgments about the individual deliverables and whether such deliverables are separable from the other aspects of the contractual relationship. In determining the units of accounting, the Company evaluates certain criteria, including whether the deliverables have standalone value, based on consideration of the relevant facts and circumstances for each arrangement. Factors considered in this determination include the research, manufacturing and commercialization capabilities of the partner and the availability of research and manufacturing expertise in the general marketplace. In addition, the Company considers whether the collaborator can use the license or other deliverables for their intended purpose without the receipt of the remaining elements, and whether the value of the deliverable is dependent on the undelivered items and whether there are other vendors that can provide the undelivered items.
The consideration received is allocated among the separate units of accounting using the relative selling price method, and the applicable revenue recognition criteria are applied to each of the separate units.
The Company determines the estimated selling price for deliverables using vendor-specific objective evidence ("VSOE") of selling price, if available, third-party evidence ("TPE") of selling price if VSOE is not available, or best estimate of selling price ("BESP") if neither VSOE nor TPE is available. Determining the BESP for a deliverable requires significant judgment. The Company uses BESP to estimate the selling price for licenses to its proprietary technology, since it often does not have VSOE or TPE of selling price for these deliverables. In those circumstances where the Company utilizes BESP to determine the estimated selling price of a license to its proprietary technology, it considers market conditions as well as entity-specific factors, including those factors contemplated in negotiating the agreements as well as internally developed models that include assumptions related to the market opportunity, estimated development costs, probability of success and the time needed to commercialize a product candidate pursuant to the license. In validating our BESP, the Company evaluates whether changes in the key assumptions used to determine the BESP will have a significant effect on the allocation of arrangement consideration between multiple deliverables.
The Company recognizes revenue when there is persuasive evidence that an arrangement exists, services have been rendered or delivery has occurred, the price is fixed or determinable, and collection is reasonably assured.
The Company recognizes revenue allocated to the license upon delivery, when it believes the license to its intellectual property has standalone value. When the Company recognizes revenue allocated to the license upon delivery, it may experience significant fluctuations in its collaborative arrangements revenues from quarter to quarter and year to year depending on the timing of transactions. When the Company believes the license to its intellectual property does not have standalone value from the other deliverables to be provided in the arrangement, such as research and development activities in the Merck Agreement, the license is combined with other deliverables and the
F-11
RA PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (Continued)
revenue of the combined unit of accounting is recorded based on the method appropriate for the last delivered item.
At the inception of each arrangement that includes precommercial milestone payments, the Company evaluates whether each precommercial milestone is substantive, in accordance with ASU 2010-17, "Revenue Recognition—Milestone Method." This evaluation includes an assessment of whether (a) the consideration is commensurate with either (1) the entity's performance to achieve the milestone, or (2) the enhancement of the value of the delivered item(s) as a result of a specific outcome resulting from the entity's performance to achieve the milestone, (b) the consideration relates solely to past performance and (c) the consideration is reasonable relative to all of the deliverables and payment terms within the arrangement. The Company evaluates factors such as the scientific, clinical, regulatory, commercial and other risks that must be overcome to achieve the respective milestone, the level of effort and investment required and whether the milestone consideration is reasonable relative to all deliverables and payment terms in the arrangement in making this assessment. If a substantive pre-commercial milestone were achieved and collection of the related receivable was reasonably assured, the Company would recognize revenue related to the milestone in its entirety in the period in which the milestone was achieved. If the Company achieves milestones that it considers substantive, it may experience significant fluctuations in its collaborative arrangements revenue from quarter to quarter and year to year depending on the timing of achieving such substantive milestones. In those circumstances where a pre-commercial milestone is not substantive, the Company recognizes as revenue on the date the milestone is achieved an amount equal to the applicable percentage of the performance period that had elapsed as of the date the milestone was achieved, with the balance being deferred and recognized over the remaining period of performance. Commercial milestones are accounted for as royalties and are recorded as revenue upon achievement of the milestone, assuming all other revenue recognition criteria are met.
The Company may receive royalty revenues under its current or future multiple element arrangements. If the Company does not have any future performance obligations under these agreements, such as under the Merck Agreement, it records these revenues as earned.
Research and Development Expenses
The Company expenses research and development costs to operations as incurred. The Company defers and capitalizes nonrefundable advance payments made by the Company for research and development activities until the related goods are received or the related services are performed.
Research and development expenses comprise costs incurred in performing research and development activities, including salaries, benefits and other employee-related expenses, share-based compensation expense, laboratory supplies and other direct expenses, facilities cost, overhead costs, third-party contract costs relating to pre-clinical studies and clinical trial activities and related contract manufacturing expenses, and other outside costs.
Stock-Based Compensation
The Company's share-based compensation programs grant awards which may include stock options, restricted stock awards (RSAs), restricted stock units (RSUs), and other stock-based awards.
F-12
RA PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (Continued)
Share-based compensation is recognized as an expense in the financial statements based on the grant date fair value over the requisite service period. For awards granted to employees and directors that vest based on service conditions, the Company uses the straight-line method to allocate compensation expense to reporting periods.
The fair value of the RSUs and RSAs is based on the market value of the Company's common stock on the date of grant. The fair value of options is calculated using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model, which requires the use of subjective assumptions, including volatility and expected term.
Due to the lack of a public market for the trading of its common stock prior to the IPO in October 2016 and a lack of Company-specific historical and implied volatility data, the Company has based its estimate of expected volatility on the historical volatility of a group of similar companies that are publicly traded. The Company selected companies with comparable characteristics to it, including enterprise value, risk profiles, position within the industry and with historical share price information sufficient to meet the expected term of the stock-based awards. The Company will continue to apply this process until a sufficient amount of historical information regarding the volatility of its own stock price becomes available. Due to the lack of Company specific historical option activity, the Company estimates the expected term using the "simplified" method.
Income Taxes
The Company provides for income taxes under the liability method. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are determined based on differences between financial reporting and tax bases of assets and liabilities and are measured using the enacted tax rates in effect when the differences are expected to reverse. Deferred tax assets are reduced by a valuation allowance to reflect the uncertainty associated with their ultimate realization.
When uncertain tax positions exist, the Company recognizes the tax benefit of tax positions to the extent that the benefit will more likely than not be realized. The determination as to whether the tax benefit will more likely than not be realized is based upon the technical merits of the tax position as well as consideration of the available facts and circumstances. The Company's practice is to recognize interest and/or penalties related to uncertain tax positions in income tax expense.
Net Loss Per Share Attributable to Common Stockholders
The Company calculates basic net income (loss) per share attributable to common stockholders and diluted net loss per share attributable to common stockholders by dividing the net income (loss) attributable to common stockholders by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding during the period. Diluted net income per share attributable to common stockholders is computed by dividing net income attributable to common stockholders by the diluted number of shares outstanding during the period.
Except where the result would be antidilutive to net income, diluted net income per share attributable to common stockholders is computed assuming the conversion of redeemable convertible preferred stock, the exercise of warrants, the exercise of common stock options and the vesting of RSUs and RSAs (using the treasury stock method), as well as their related income tax effects.
During periods of income, the Company allocates participating securities a proportional share of income determined by dividing total weighted average participating securities by the sum of the total
F-13
RA PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (Continued)
weighted average common shares and participating securities (the "two class method"). Prior to converting into common shares, shares of the Company's redeemable convertible preferred stock were entitled to participate in any dividends declared by the Company and were therefore considered to be participating securities. During periods of loss, the Company allocates no loss to participating securities because they have no contractual obligation to share in the losses of the Company.
Newly Adopted Accounting Pronouncements
In November 2015, the Financial Accounting Standards Board ("FASB") issued Accounting Standards Update ("ASU") 2015-17, "Balance Sheet Classification of Deferred Taxes," that requires companies to classify all deferred tax assets and liabilities, along with any valuation allowance, as noncurrent on the balance sheet instead of separating deferred taxes into current and noncurrent amounts. The guidance does not change the existing requirement that only permits offsetting within a jurisdiction. The ASU is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2016, and interim periods within those fiscal years. The adoption of ASU 2015-17 during the quarter ended March 31, 2017 did not have a significant impact on the Company's consolidated financial statements and related disclosures.
In March 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-09, "Improvements to Employee Share-Based Payment Accounting." The standard reduces complexity in several aspects of the accounting for employee share-based compensation, including the income tax consequences, classification of awards as either equity or liabilities, and classification on the statement of cash flows. The ASU is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2016, and interim periods within those fiscal years. The adoption of ASU 2016-09 during the quarter ended March 31, 2017 did not have a significant impact on the Company's consolidated financial statements and related disclosures. Upon adoption, the Company elected to account for forfeitures when they occur and recorded a cumulative effect adjustment of $11,200 to accumulated deficit.
In August 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-15, "Classification of Certain Cash Receipts and Cash Payments." The standard addresses the classification of certain transactions within the statement of cash flows, including cash payments for debt prepayment or debt extinguishment costs, contingent consideration payments made after a business combination, and distributions received from equity method investments. The ASU is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, and interim periods within those fiscal years. Early adoption is permitted. The adoption of this standard during the quarter ended December 31, 2017 did not have a significant impact on the Company's consolidated financial statements and related disclosures.
In November 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-18, "Restricted Cash." The standard addresses the classification and presentation of restricted cash and restricted cash equivalents within the statement of cash flows. The ASU is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, and interim periods within those fiscal years. Early adoption is permitted. The Company adopted this standard during the quarter ended December 31, 2017. The Company historically excluded the restricted cash balance from cash and cash equivalents within the consolidated statements of cash flows, reflecting transfers between cash and cash equivalents and restricted cash within cash flows from investing activities. As a result of the adoption of this standard, the Company combined restricted cash balances of $1.3 million, $1.5 million and $0.1 million as of December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively, with
F-14
RA PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (Continued)
cash and cash equivalents when reconciling the beginning and ending balances within the consolidated statements of cash flows for the fiscal years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015.
As of December 31, 2017, cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash of $71.7 million, as reported within the consolidated statement of cash flows, included $70.4 million of cash and cash equivalents and $1.3 million of restricted cash, as reported within the consolidated balance sheets. As of December 31, 2016, cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash of $119.1 million, as reported within the consolidated statement of cash flows, included $117.8 million of cash and cash equivalents and $1.3 million of restricted cash, as reported within the consolidated balance sheets.
In January 2017, the FASB issued ASU 2017-04, "Simplifying the Test for Goodwill Impairment." The standard simplifies the accounting for goodwill impairment by removing Step 2 of the goodwill impairment test, which requires a hypothetical purchase price allocation. The ASU is effective for annual or interim goodwill impairment tests in fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2019 and should be applied on a prospective basis. Early adoption is permitted for interim or annual goodwill impairment tests performed on testing dates after January 1, 2017. The adoption of this standard during the quarter ended December 31, 2017 did not have a significant impact on the Company's consolidated financial statements and related disclosures.
In May 2017, the FASB issued ASU 2017-09, "Scope of Modification Accounting." The standard clarifies when changes to the terms or conditions of a share-based payment award must be accounted for as modifications. The ASU is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, and interim periods within those fiscal years. Early adoption is permitted. The adoption of this standard during the quarter ended December 31, 2017 did not have a significant impact on the Company's consolidated financial statements and related disclosures.
Newly Issued Accounting Pronouncements
In May 2014, the FASB issued ASU 2014-09, "Revenue from Contracts with Customers." The standard, including subsequently issued amendments, will replace most existing revenue recognition guidance in U.S. GAAP when it becomes effective and permits the use of either the retrospective or cumulative effect transition method. The standard will require an entity to recognize the amount of revenue to which it expects to be entitled for the transfer of promised goods or services to customers. The standard will be effective for annual and interim periods beginning after December 15, 2017. The Company has one contract subject to the new standard, the Merck Agreement, and all performance obligations were completed upon the expiration of the research term in April 2016. See Note 9 "Revenue Recognition." The new standard will be adopted on January 1, 2018 using the retrospective method. The Company concluded that the adoption of ASU 2014-09 will not have a significant impact on its consolidated financial statements for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016, 2015, 2014 and 2013.
In February 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-02, "Leases." The standard established the principles that lessees and lessors will apply to report useful information to users of financial statements about the amount, timing and uncertainty of cash flows arising from a lease. The ASU is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2018, and interim periods within those fiscal years. Early adoption is permitted. The Company is still evaluating the full impact this standard will have on its consolidated financial statements and related disclosures but expects to recognize substantially all of its leases on the balance sheet by recording a right-to-use asset and a corresponding lease liability.
F-15
RA PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
3. Fair Value Measurements
Assets measured at fair value on a recurring basis are summarized below:
| |
December 31, 2017 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total | |||||||||
| |
(in thousands) |
||||||||||||
Cash equivalents—money market funds |
$ | 70,449 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 70,449 | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total assets |
$ | 70,449 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 70,449 | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| |
December 31, 2016 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total | |||||||||
| |
(in thousands) |
||||||||||||
Cash equivalents—money market funds |
$ | 117,708 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 117,708 | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total assets |
$ | 117,708 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 117,708 | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
There were no transfers between fair value levels during the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016.
4. Supplemental Balance Sheet Information
Property and equipment, net
Property and equipment, net consists of the following:
| |
December 31, | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
2017 | 2016 | |||||
| |
(in thousands) |
||||||
Computer equipment and software |
$ | 20 | $ | — | |||
Furniture, fixtures and other |
378 | 365 | |||||
Laboratory equipment |
5,116 | 3,642 | |||||
Leasehold improvements |
3,753 | 3,732 | |||||
| | | | | | | | |
|
9,267 | 7,739 | |||||
Accumulated depreciation |
(3,661 | ) | (2,202 | ) | |||
| | | | | | | | |
Property and equipment, net |
$ | 5,606 | $ | 5,537 | |||
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
Depreciation expense was $1.5 million, $1.2 million and $0.8 million for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016, and 2015, respectively.
Restricted Cash
The Company is contingently liable under an unused letter of credit with a bank, related to the Company's facility leases. Refer to Note 7, "Commitments and Contingencies." As a result, as of December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, the Company had restricted cash as presented in the table below,
F-16
RA PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
4. Supplemental Balance Sheet Information (Continued)
securing the letters of credit. The cash will be restricted until the termination or modification of the lease arrangement.
| |
December 31, | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| |
(in thousands) |
|||||||||
Restricted cash |
$ | 1,334 | $ | 1,334 | $ | 1,463 | ||||
Accrued expenses
Accrued expenses consist of the following:
| |
December 31, | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
2017 | 2016 | |||||
| |
(in thousands) |
||||||
Payroll and employee-related costs |
$ | 2,063 | $ | 1,451 | |||
Research and development costs |
1,464 | 1,326 | |||||
Other |
410 | 405 | |||||
| | | | | | | | |
Total |
$ | 3,937 | $ | 3,182 | |||
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
5. Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets
In February 2011, the Company recorded goodwill of $0.2 million and intangible assets of $0.7 million upon the acquisition of Cosmix. Based on the Company's step zero of the goodwill impairment test, completed as of October 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, goodwill was not impaired.
Intangible assets are amortized over the pattern in which the economic benefits of the intangible assets are utilized, over an estimated useful life of approximately nine years.
Intangible assets were $0.2 million and $0.3 million as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively. Amortization expense of intangible assets for each of the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 was approximately $0.1 million and was recorded as a component of research and development expense in the Company's consolidated statements of operations.
Estimated amortization expense for intangible assets for the remaining three years is as follows:
Year Ended December 31,
|
Amortization Expense |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
(in thousands) |
|||
2018 |
$ | 66 | ||
2019 |
66 | |||
2020 |
65 | |||
6. Convertible Notes
On April 1, 2015, the Company entered into a Convertible Note Purchase Agreement (the "Note Agreement") with the holders of its existing Series A Preferred Stock and issued Convertible Notes and warrants to purchase 221,521 shares of the Company's common stock. In connection with the issuance, the Company received gross proceeds of $5.0 million and incurred insignificant issuance costs. The Convertible Notes bore interest at a rate of 8% per annum and were payable in full at the earliest of March 2018 ("Maturity Date"), an event of default as defined in the Note Agreement, or the sale of the Company.
F-17
RA PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
6. Convertible Notes (Continued)
The Convertible Notes included certain features resulting in automatic conversion or possible early redemption. In the event the Company sold or issued shares ("Equity Securities") resulting in cash proceeds to the Company of no less than $5.0 million ("Qualified Financing"), the Convertible Notes would automatically convert into the Equity Securities at a conversion price equal to the price per share paid by the investors purchasing the Equity Securities. In the event of the Company undergoing a change in control prior to the Maturity Date, the Convertible Notes would automatically convert into the right to receive 3 times the outstanding principal, plus accrued interest. Lastly, the Convertible Notes included a put feature, at the option of the holders, whereby upon an event of default, repayment of the Convertible Notes could be accelerated in the amount of outstanding principal, plus accrued interest. Each of these three features were embedded derivatives that required bifurcation.
The embedded derivatives were valued upon issuance using a "with and without" income valuation approach. The Company recorded approximately $0.1 million as the fair value of the combined embedded derivative liability on April 1, 2015, resulting in a debt discount. The debt discount was amortized as interest expense over the life of the Convertible Notes under the effective interest method. Changes in the estimated fair value of the embedded features were recorded as a component of other income (expense), net in the consolidated statement of operations.
On July 10, 2015, the Company completed a Series B-1 preferred stock financing, which resulted in the automatic conversion of the Convertible Notes into 5,512,743 shares of Series B-1 preferred stock at a conversion price of $0.92667 per share. Upon conversion, the Company recorded the difference between the fair value of the Series B-1 preferred stock issued and the carrying value of the Convertible Notes plus accrued interest as a $0.6 million loss on debt extinguishment in its consolidated statement of operations.
The Company allocated $0.5 million of the proceeds from the Convertible Notes to the common stock warrants based on a relative fair value basis and recognized this amount as additional paid-in capital with a corresponding debt discount upon issuance. In October 2016, upon the closing of the IPO, all of the outstanding warrants net exercised, in accordance with their terms, into shares of common stock.
7. Commitments and Contingencies
License Agreement
In 2010, the Company entered into an exclusive license agreement with an individual. The Company is required to pay an annual license fee of approximately $15,000 until the first commercial sale of a licensed product. The Company is also obligated to pay royalties of 0.25% on net sales of licensed products sold or transferred by the Company. The royalty obligations will continue on a country-by-country basis until the expiration of the last valid patent claim in the applicable country. The Company has the right to terminate the agreement for any reason upon a thirty-day notice.
Lease Commitments
In September 2015, the Company entered into an operating lease for laboratory and office space at its headquarters in Cambridge, Massachusetts. The lease expires in April 2023 and contains various clauses for renewal at the Company's option and certain rent escalation clauses. Rent expense under the lease was $1.0 million, $1.1 million and $0.6 million for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016
F-18
RA PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
7. Commitments and Contingencies (Continued)
and 2015, respectively. The Company is also obligated to pay operating costs, including property taxes, insurance, maintenance and other operating expenses. In connection with the lease, the Company was provided tenant improvements allowance totaling approximately $2.7 million by the landlord as reimbursement for capital improvements to the facility. As of December 31, 2017, the Company had an unamortized lease incentive obligation of $1.9 million recorded in deferred rent in the consolidated balance sheet.
Future minimum commitments due under this operating lease agreement are as follows:
Year Ended December 31,
|
Minimum Lease Payments |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
(in thousands) |
|||
2018 |
$ | 1,254 | ||
2019 |
1,403 | |||
2020 |
1,442 | |||
2021 |
1,483 | |||
2022 |
1,524 | |||
Thereafter |
513 | |||
| | | | | |
Total |
$ | 7,619 | ||
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
The Company is contractually obligated to return leased office and laboratory space in good order, repair and condition excluding ordinary wear and tear upon termination of the lease agreement. The Company's asset retirement obligations were not significant as of December 31, 2017 and 2016.
Other Funding Commitments
As of December 31, 2017, the Company had several ongoing clinical and nonclinical studies for its various pipeline programs. The Company enters into contracts in the normal course of business with contract research organizations and clinical sites for the conduct of clinical trials, professional consultants for expert advice and other vendors for clinical supply manufacturing or other services. These contracts are not included in the table above as generally they are cancellable, with notice, at the Company's option and do not have significant cancellation penalties.
Guarantees
The Company enters into certain agreements with other parties in the ordinary course of business that contain indemnification provisions. These typically include agreements with directors and officers, business partners, contractors, landlords and clinical sites. Under these provisions, the Company generally indemnifies and holds harmless the indemnified party for losses suffered or incurred by the indemnified party as a result of the Company's activities. These indemnification provisions generally survive termination of the underlying agreement. The maximum potential amount of future payments the Company could be required to make under these indemnification provisions is unlimited. However, to date the Company has not incurred material costs to defend lawsuits or settle claims related to these indemnification provisions. As a result, the estimated fair value of these obligations is minimal.
F-19
RA PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
7. Commitments and Contingencies (Continued)
Litigation
The Company is not a party to any known litigation and does not have contingency reserves established for any litigation liabilities.
8. Redeemable Convertible Preferred Stock
Series A Preferred Stock
In February 2010, the Company issued 12,887,999 shares of Series A Preferred Stock pursuant to the Series A Preferred Stock agreement at a price of $0.80176 per share. Additionally, investors were granted the right to purchase up to an additional 21,552,566 shares of the Company's Series A Preferred Stock at a price of $0.80176 per share, in two subsequent closings upon the Company meeting certain milestone criteria. In February 2012 and March 2014, the board of directors waived certain milestone events provided for in the Series A Preferred Stock agreement and the Company issued 10,776,283 and 10,776,283 shares, respectively, of Series A Preferred Stock at a price of $0.80176 per share. In October 2016, upon the closing of the Company's IPO, all outstanding shares of Series A Preferred Stock converted into 4,920,074 shares of the Company's common stock.
Series B Preferred Stock
In July 2015, the Company issued 31,564,630 shares of Series B-1 Preferred Stock pursuant to the Series B Preferred Stock agreement at a price of $0.92667 per share. Additionally, investors were granted the right to purchase up to an additional 29,362,452 shares of the Company's Series B-2 Preferred Stock at a price of $0.99617, in any number of subsequent closings upon the request of each investor or in a mandatory closing upon the Company meeting certain milestone criteria. In June 2016, the board of directors and required certain investors waived certain milestone events provided for in the Series B Preferred Stock agreement and the Company issued 29,362,452 shares of Series B-2 Preferred Stock at a price of $0.99617 per share. In October 2016, upon the closing of the Company's IPO, all outstanding shares of Series B-1 and B-2 Preferred Stock converted into 8,703,859 shares of the Company's common stock.
Series A and Series B-2 Preferred Stock Tranche Rights
The Company determined that the rights of the investors to purchase additional shares of Series A and Series B-2 Preferred Stock met the definition of a freestanding financial instrument and were recognized as a liability at fair value upon the initial issuance of Series A and Series B-1 Preferred Stock in February 2010 and July 2015, respectively. The Company adjusted the carrying value of the Series A and Series B-2 Preferred Stock Tranche Rights liability to its estimated fair value at each subsequent reporting date and immediately prior to the subsequent issuances through charges to other income (expense), net in the condensed consolidated statement of operations. The Series A Preferred Stock Tranche Rights liability was extinguished in March 2014 and the Series B-2 Preferred Stock Tranche Rights liability was extinguished in June 2016. During the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, the Company adjusted the Series B-2 Preferred Stock Tranche Rights liability to its fair value and recorded other expense of $1.0 million and other income of $0.1 million, respectively.
F-20
RA PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
9. Revenue Recognition
In April 2013, the Company entered into a multi-target collaboration and license agreement with Merck to use its proprietary drug discovery technology platform to identify orally available cyclic peptides for non-complement program targets nominated by Merck and provide specific research and development services. Under the agreement, the Company granted Merck licenses under certain of its intellectual property rights to manufacture, develop and commercialize compounds and products directed to selected program targets. The agreement consists of a research phase, where the Company and Merck collaborated on identifying and pre-clinically developing orally available cyclic peptides suitable for further development by Merck, and a development and commercialization phase pursuant to which Merck has sole discretion and responsibility, including financial responsibility, for further development and commercialization of these peptides, on a program-by-program basis, from the collaboration. The research term ended in April 2016.
At the signing of the Merck Agreement, Merck made an upfront nonrefundable, technology license fee of $4.5 million. In addition, the Merck Agreement provides for reimbursement of research and development services provided by the Company and includes milestone payments that could total up to $65.0 million.
The Company has identified two deliverables in connection with the Merck Agreement: (1) rights to access the Company's technology platform for each program target, and (2) the research and development services provided during the research term. The Company has determined that none of the deliverables have standalone value. Since the separability criteria have not been met for any of the deliverables, the deliverables were accounted for as a single combined unit of accounting. The Company has recognized revenue in connection with the upfront non-refundable license fee ratably over the research term. Payments for research and development services and reimbursement for certain lab supplies and reagents have been recognized as services are performed. The research term ended in April 2016.
The Company has determined that the $3.5 million in milestone payments received was substantive in nature as they were commensurate with the enhancement of value resulting from the Company's performance under the Merck Agreement, related solely to past performance and were reasonable relative to all of the deliverables and payment terms within the arrangement. Accordingly, the Company has accounted for these milestone payments under the milestone method. The Company is entitled to receive future aggregate milestone payments of up to $61.5 million for the non-complement cardiovascular target selected, consisting of remaining preclinical and clinical milestones of $16.5 million, regulatory milestones of $19.0 million, and commercial milestones of $26.0 million, and low-to-mid single digit percentage royalties on future sales, if any. Following the end of the research term, any future milestone payments will be recognized as revenue upon achievement, assuming all other revenue recognition criteria are met, as no further performance obligations exist for the Company under the Merck Agreement. As of December 31, 2017, the Company had no remaining precommercial milestones that were deemed substantive.
During the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, the Company recognized revenue of $4.2 million and $1.0 million related to upfront, non-refundable payments, respectively, and revenue of approximately $0.7 million and $3.1 million related to research and development services and reimbursable expenses, respectively. No revenue was recognized during the year ended December 31, 2017.
F-21
RA PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
10. Stock Incentive Plans
In February 2010, the Company adopted the 2010 Stock Incentive Plan (the "2010 Plan") under which it was able to grant stock options and restricted stock grants to employees, consultants and directors. The Company had reserved 2,495,607 shares of common stock under the 2010 Plan, prior to the establishment of the 2016 Stock Award and Incentive Plan (the "2016 Plan"), as described below. As of December 31, 2017, options to purchase 1,870,783 shares of common stock were outstanding under the 2010 Plan.
In October 2016, the Company's stockholders approved the 2016 Plan under which stock options, RSAs, RSUs, and other stock-based awards may be granted to employees, officers, directors, or consultants of the Company. There were 1,401,109 shares of common stock reserved for issuance under the 2016 Plan at the time of approval, including 1,300,000 shares initially reserved plus the 101,109 shares available for issuance under the 2010 Plan. The number of shares available for future grant will automatically increase on the first day of each fiscal year by an amount equal to the lesser of: (i) 2,000,000; (ii) 4% of the number of outstanding shares of common stock on immediately preceding December 31; and (iii) an amount determined by the administrator appointed by the board of directors. Awards that are returned to the Company's equity plans as a result of their expiration, cancellation, termination or repurchase are automatically made available for issuance under the 2016 Plan. As of December 31, 2017, there were 847,866 shares available for future grant under the 2016 Plan and on January 1, 2018, this number increased by 905,067 shares.
Stock Options
Stock options granted to employees and directors under the Company's equity plans generally have a ten-year term and vest over a period of four years, provided the individual continues to serve at the Company through the vesting dates. Options granted under all equity plans are exercisable at a price per share not less than the fair market value of the underlying common stock on the date of grant and not less than 110% of the fair market value for participants who own more than 10% of the Company's voting power.
The weighted average assumptions used to estimate the grant date fair value of the stock options using the Black-Scholes option pricing model were as follows:
| |
Year Ended December 31, |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
Expected life (in years) |
6.0 | 6.1 | 6.1 | |||||||
Expected volatility |
77.5 | % | 82.9 | % | 74.5 | % | ||||
Risk-free interest rate |
2.0 | % | 1.3 | % | 1.9 | % | ||||
Expected dividend yield |
— | % | — | % | — | % | ||||
F-22
RA PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
10. Stock Incentive Plans (Continued)
The following table summarizes the stock option activity of the Company's share-based plans:
| |
Number of Shares |
Weighted Average Exercise Price |
Weighted Average Contractual Life |
Aggregate Intrinsic Value |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
(in thousands) |
|
(in years) |
(in thousands) |
|||||||||
Options outstanding as of December 31, 2016 |
2,168 | $ | 4.27 | ||||||||||
Granted |
1,656 | $ | 17.16 | ||||||||||
Exercised |
(81 | ) | $ | 3.31 | |||||||||
Cancelled |
(273 | ) | $ | 10.04 | |||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Options outstanding as of December 31, 2017 |
3,470 | $ | 9.99 | 8.5 | $ | 8,529 | |||||||
Options exercisable as of December 31, 2017 |
1,031 | $ | 6.11 | 8.0 | $ | 4,056 | |||||||
Options vested and expected to vest as of December 31, 2017 |
3,283 | $ | 9.87 | 8.5 | $ | 8,236 | |||||||
The total intrinsic values of options exercised totaled $1.4 million, $0.1 million and $0.1 million the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively. The intrinsic value was calculated as the difference between the fair value of the Company's common stock and the exercise price of the option. The weighted-average grant date fair value of stock options granted was $11.57, $3.74 and $1.89 for years ending December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively.
Stock-Based Compensation
The following table provides stock-based compensation by the financial statement line item in which it is presented:
| |
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| |
(in thousands) |
|||||||||
Research and development |
$ | 3,081 | $ | 361 | $ | 58 | ||||
General and administrative |
2,492 | 665 | 94 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Total |
$ | 5,573 | $ | 1,026 | $ | 152 | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
As of December 31, 2017, there was approximately $17.5 million of unrecognized share-based compensation, which is expected to be recognized over a weighted average period of approximately 2.7 years.
2016 ESPP
In October 2016, the Company's stockholders approved the 2016 Employee Stock Purchase Plan (the "2016 ESPP"), which gives eligible employees the right to purchase shares of common stock at the lower of 85% of the fair market value on the first or last day of an offering period. There were 175,000 shares of common stock initially reserved for issuance pursuant to the 2016 ESPP. The number of shares of common stock that may be issued under the 2016 ESPP will automatically increase on each
F-23
RA PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
10. Stock Incentive Plans (Continued)
January 1 equal to the lesser of: (i) 300,000, (ii) 1% of the Company's shares of common stock outstanding on the immediately preceding December 31 or (iii) an amount determined by the administrator of the 2016 ESPP appointed by the Company's board of directors. As of December 31, 2017, there were 400,461 shares available for future grant under the 2016 ESPP and on January 1, 2018, this number increased by 226,266 shares.
11. 401(k) Savings Plan
In 2010, the Company adopted a tax-qualified employee savings and retirement 401(k) Plan, covering all qualified employees. Eligible employees may make pretax contributions to the 401(k) Plan up to statutory limits. At the election of its board of directors, the Company may elect to match employee contributions. Currently, the Company makes matching contributions at a rate of 50% of the first 6% of employee contributions. The Company recorded $0.2 million, $0.1 million and less than $0.1 million of expenses related to its 401(k) match for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively.
12. Income Taxes
The following table presents domestic and foreign components of loss from operations before income taxes:
| |
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| |
(in thousands) |
|||||||||
Domestic |
$ | (54,452 | ) | $ | (28,886 | ) | $ | (13,961 | ) | |
Foreign |
(6 | ) | 4 | (1 | ) | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Total |
$ | (54,458 | ) | $ | (28,882 | ) | $ | (13,962 | ) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
The Company recorded no current or deferred tax expense for federal and state purposes and no current foreign tax expense for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015. A foreign deferred tax benefit of approximately $19,000, $18,000 and $19,000 has been recorded for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016, and 2015, respectively.
F-24
RA PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
12. Income Taxes (Continued)
A reconciliation setting forth the differences between the effective tax rate of the Company for the periods ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 and the U.S. federal statutory tax rate is as follows:
| |
December 31, | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| |
(in thousands) |
|||||||||
Income tax benefit at U.S. federal statutory rate |
$ | (18,515 | ) | $ | (9,820 | ) | $ | (4,749 | ) | |
State income taxes, net of federal tax benefit |
(2,644 | ) | (1,525 | ) | (737 | ) | ||||
Nondeductible / nontaxable permanent items |
1,297 | 256 | 272 | |||||||
Tax credits |
(2,283 | ) | (1,261 | ) | (857 | ) | ||||
Change in U.S. federal tax rate |
13,645 | — | — | |||||||
Other |
289 | 125 | 7 | |||||||
Change in valuation allowance |
8,192 | 12,207 | 6,045 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Income tax benefit |
$ | (19 | ) | $ | (18 | ) | $ | (19 | ) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Effective tax rate |
0.04 | % | 0.06 | % | 0.14 | % | ||||
The significant components of the Company's deferred tax assets are as follows:
| |
December 31, 2017 |
December 31, 2016 |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
(in thousands) |
||||||
Deferred tax assets: |
|||||||
Net operating losses |
$ | 14,956 | $ | 17,501 | |||
R&D credits |
5,747 | 3,498 | |||||
Accrued expenses |
545 | 80 | |||||
Deferred rent |
734 | 1,100 | |||||
Equity compensation |
934 | 218 | |||||
Capitalized R&D costs |
13,961 | 6,316 | |||||
Other deferred tax assets |
189 | 270 | |||||
| | | | | | | | |
Total deferred tax assets |
37,066 | 28,983 | |||||
Deferred tax liabilities: |
|||||||
Depreciation related |
(33 | ) | (145 | ) | |||
Purchased intangibles |
(57 | ) | (76 | ) | |||
| | | | | | | | |
Total deferred tax liabilities |
(90 | ) | (221 | ) | |||
Valuation allowance |
(37,016 | ) | (28,821 | ) | |||
| | | | | | | | |
Net deferred tax liabilities |
$ | (40 | ) | $ | (59 | ) | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
In December 2017, the U.S. government enacted comprehensive tax legislation ("Tax Reform Act") that includes significant changes to the taxation of business entities. These changes include, among others, (1) a permanent reduction to the corporate income tax rate from 34% to 21%, (2) limiting interest deductions, (3) adopting elements of a territorial tax system and (4) introducing certain anti-base erosion provisions. In addition, under the Tax Reform Act, federal net operating losses generated after December 31, 2017 will not be subject to expiration. In December 2017, the SEC issued guidance, which directs taxpayers to consider the impact of the U.S. legislation as "provisional" when it does not have the necessary information available, prepared or analyzed (including computations) in
F-25
RA PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
12. Income Taxes (Continued)
reasonable detail to complete its accounting for the change in tax law. As of December 31, 2017, the Company recognized a provisional amount of $0 for the transition tax. The Company re-measured certain deferred tax assets and liabilities based on the rates at which they are anticipated to reverse in the future, which is generally 21%. The provisional amount recorded related to the re-measurement of the deferred tax balance was a tax expense of $13.6 million, which was fully offset by an adjustment to the valuation allowance.
Management of the Company has evaluated the positive and negative evidence bearing upon the realizability of its deferred tax assets. Management has considered the Company's history of operating losses and concluded, in accordance with the applicable accounting standards, that it is more likely than not that the Company will not realize the benefit of its deferred tax assets. Accordingly, with the exception of the deferred tax assets recorded at Cosmix, a full valuation allowance for the net deferred tax asset was recorded as of December 31, 2017 and 2016. Management reevaluates the positive and negative evidence on a quarterly basis.
The valuation allowance increased by $8.2 million during the year ended December 31, 2017, primarily due to an increase in capitalized research and development costs, research and development credits and stock-based compensation expense; partially offset by a decrease in net operating losses and a lower U.S. federal tax rate due to the Tax Reform Act. The valuation allowance increased by $12.2 million during the year ended December 31, 2016, primarily due to an increase net operating losses, research and development credits and stock-based compensation expense.
Subject to the limitations described below, as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, the Company had federal net operating loss carryforwards of $55.7 million and $45.1 million, respectively, and state net operating loss carryforwards of $51.2 million and $40.9 million, respectively. The net operating loss carryforwards expire at various dates beginning in 2028 through 2037 for U.S. federal and state purposes. As of both December 31, 2017 and 2016, the Company has trade net operating loss carryforwards of less than $0.1 million at its German subsidiary. There is no expiration of the German net operating loss carryforwards.
As of December 31, 2017 and 2016, the Company had research and development credits for federal income tax purposes of $4.4 million and $2.5 million, respectively, and research and development credits for state income tax purposes of $1.7 million and $1.5 million, respectively. If not utilized, the available research and development credits for federal and state income tax purposes expire at various dates through 2037 and 2032, respectively.
Utilization of net operating loss carryforwards and research and development credit carryforwards may be subject to a substantial annual limitation due to ownership change limitations that could occur in the future in accordance with Section 382 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 ("IRC Section 382") and with Section 383 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as well as similar state provisions. These ownership changes may limit the amount of net operating loss carryforwards and research and development credit carryforwards that can be utilized annually to offset future taxable income and taxes, respectively. In general, an ownership change, as defined by IRC Section 382, results from transactions increasing the ownership of certain stockholders or public groups in the stock of a corporation by more than 50 percentage points over a three-year period. The Company has completed several financings since its inception which may result in a change in control as defined by IRC Section 382 or could result in a change in control in the future.
F-26
RA PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
12. Income Taxes (Continued)
As of December 31, 2017 and 2016, the Company had no unrecognized tax benefits and no accrued interest or penalties related to uncertain tax positions.
The Company files income tax returns in the U.S. federal, Massachusetts and foreign jurisdictions. The statute of limitations for assessment by the Internal Revenue Service and state tax authorities remains open for all years since the Company's inception. There are currently no federal or state income tax audits in progress.
13. Net Loss Per Share Attributable to Common Stockholders
Basic and diluted net loss per share attributable to common stockholders are calculated as follows:
| |
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| |
(in thousands) |
|||||||||
Numerator: |
||||||||||
Net loss |
$ | (54,439 | ) | $ | (28,864 | ) | $ | (13,943 | ) | |
Gain on extinguishment of redeemable convertible preferred shares |
— | — | 1,673 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Net loss attributable to common stockholders |
$ | (54,439 | ) | $ | (28,864 | ) | $ | (12,270 | ) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Denominator: |
||||||||||
Weighted average number of common shares outstanding—basic and diluted |
22,591 | 4,135 | 497 | |||||||
The following common stock equivalents were excluded from the calculation of net loss per share attributable to common stockholders due to their anti-dilutive effect:
| |
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| |
(in thousands) |
|||||||||
Convertible preferred stock |
— | — | 9,429 | |||||||
Common stock warrants |
— | — | 223 | |||||||
Outstanding stock options |
3,470 | 2,168 | 835 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Total |
3,470 | 2,168 | 10,487 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
F-27
RA PHARMACEUTICALS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
14. Quarterly Financial Data (unaudited)
The following table contains selected quarterly financial information for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016. The Company believes that the following information reflects all normal recurring adjustments necessary for a fair statement of the information for the periods presented.
| |
First Quarter |
Second Quarter |
Third Quarter |
Fourth Quarter |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
(in thousands, except per share data) |
||||||||||||
Year Ended December 31, 2017 |
|||||||||||||
Revenue |
$ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | |||||
Operating expenses |
11,481 | 12,812 | 15,414 | 15,322 | |||||||||
Net loss attributable to common stockholders |
(11,360 | ) | (12,663 | ) | (15,275 | ) | (15,141 | ) | |||||
Net loss per share attributable to common stockholders—basic and diluted |
$ | (0.50 | ) | $ | (0.56 | ) | $ | (0.68 | ) | $ | (0.67 | ) | |
Weighted average number of common shares outstanding—basic and diluted |
22,549 | 22,575 | 22,614 | 22,626 | |||||||||
Year Ended December 31, 2016 |
|||||||||||||
Revenue |
$ | 1,884 | $ | 3,044 | $ | — | $ | — | |||||
Operating expenses |
6,248 | 7,590 | 8,121 | 10,993 | |||||||||
Net loss attributable to common stockholders |
(5,056 | ) | (4,806 | ) | (8,114 | ) | (10,888 | ) | |||||
Net loss per share attributable to common stockholders—basic and diluted |
$ | (9.42 | ) | $ | (8.90 | ) | $ | (14.22 | ) | $ | (0.73 | ) | |
Weighted average number of common shares outstanding—basic and diluted |
537 | 540 | 571 | 14,816 | (a) | ||||||||
- (a)
- During the fourth quarter 2016, the Company completed an IPO, which resulted in the issuance of 8,106,615 shares of common stock. Upon the closing of the IPO, all of the outstanding shares of convertible preferred stock automatically converted into 13,623,933 shares of common stock and outstanding warrants net exercised into 221,573 shares of common stock.
15. Subsequent Events
In February 2018, the Company completed a follow-on equity offering. See Note 1, "Nature of Business."
F-28
124
- *
- Filed
herewith.
- **
- Furnished
herewith.
- †
- An
order for confidential treatment of certain provisions has been granted by the Securities and Exchange Commission. Omitted material for which
confidential treatment has been granted has been filed separately with the Securities and Exchange Commission.
- #
- Indicates a management contract or any compensatory plan, contract or arrangement.
125
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| RA PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. | ||||
Date: March 14, 2018 |
By: |
/s/ DOUGLAS A. TRECO |
||
Date: March 14, 2018 |
By: |
/s/ DAVID C. LUBNER |
||
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, this Report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the Registrant in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
Signature
|
Title
|
Date
|
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| /s/ DOUGLAS A. TRECO Douglas A. Treco, Ph.D. |
Chief Executive Officer and Director (Principal Executive Officer) |
March 14, 2018 | ||
/s/ DAVID C. LUBNER David C. Lubner |
Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) |
March 14, 2018 |
||
/s/ EDWARD T. MATHERS Edward T. Mathers |
Director |
March 14, 2018 |
||
/s/ ROBERT HEFT Robert Heft |
Director |
March 14, 2018 |
||
/s/ JASON LETTMANN Jason Lettmann |
Director |
March 14, 2018 |
126
Signature
|
Title
|
Date
|
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| /s/ RAJEEV SHAH Rajeev Shah |
Director | March 14, 2018 | ||
/s/ TIMOTHY PEARSON Timothy Pearson |
Director |
March 14, 2018 |
||
/s/ PETER TUXEN BISGAARD Peter Tuxen Bisgaard |
Director |
March 14, 2018 |
127
