Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-99.1 - EXHIBIT 99.1 - Aevi Genomic Medicine, Inc. | tv488321_ex99-1.htm |
| 8-K - FORM 8-K - Aevi Genomic Medicine, Inc. | tv488321_8k.htm |
Exhibit 99.2

© 2018, Aevi Genomic Medicine NASDAQ: GNMX 2017 Year - end Results and Corporate Update March 13, 2018

© 2018, Aevi Genomic Medicine 2 Forward - Looking Statement This presentation includes certain estimates and other forward - looking statements within the meaning of Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, including statements with respect to anticipated operating and financial performance, clinical results, potential partnerships, licensing opportunities and other statements of expectation. Words such as “expects,” “anticipates,” “intends,” “plans,” “believes,” “assumes,” “seeks,” “estimates,” “should” and variations of these words and similar expressions, are intended to identify these forward - looking statements. While we believe these statements are accurate, forward - looking statements are inherently uncertain and we cannot assure you that these expectations will occur and our actual results may be significantly different. These statements by the Company and its management are based on estimates, projections, beliefs and assumptions of management and are not guarantees of future performance. Important factors that could cause actual results to differ from those in the forward - looking statements include the factors described in the Company’s filings with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. The Company disclaims any obligation to update or revise any forward - looking statement based on the occurrence of future events, the receipt of new information, or otherwise.

© 2018, Aevi Genomic Medicine 3 Agenda • AEVI - 001 update • AEVI - 002 update • Financial update • Pipeline • Conclusion

© 2018, Aevi Genomic Medicine AEVI - 001 in ADHD Overview

CAG Breakthrough Discovery • 10 fold increased frequency of copy number variations (CNV’s) in the mGluR gene network detected in ADHD population vs. normal controls • These mutations were found in several related neuropsychiatric diseases 5 Research led by Dr. Hakon Hakonarson indicated ~20% of ADHD patients have underlying mGluR network mutations Elia, Glessner et al. Nature Genetic s, 2012
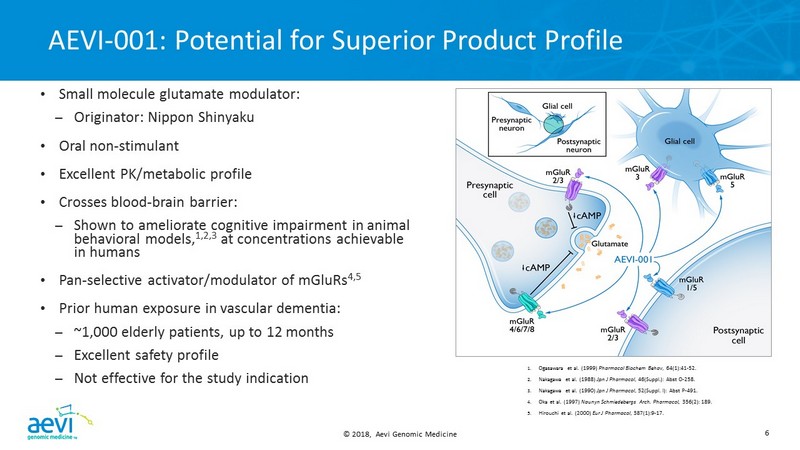
© 2018, Aevi Genomic Medicine 6 AEVI - 001: Potential for Superior Product Profile 1. Ogasawara et al. (1999) Pharmacol Biochem Behav , 64(1):41 - 52. 2. Nakagawa et al. (1988) Jpn J Pharmacol , 46(Suppl.): Abst O - 258. 3. Nakagawa et al. (1990) Jpn J Pharmacol , 52(Suppl. I): Abst P - 491. 4. Oka et al. (1997) Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol, 356(2): 189. 5. Hirouchi et al. (2000) Eur J Pharmacol , 387(1):9 - 17. • Small molecule glutamate modulator: – Originator: Nippon Shinyaku • Oral non - stimulant • Excellent PK/metabolic profile • Crosses blood - brain barrier: – Shown to ameliorate cognitive impairment in animal behavioral models, 1,2,3 at concentrations achievable in humans • Pan - selective activator/modulator of mGluRs 4,5 • Prior human exposure in vascular dementia: – ~1,000 elderly patients, up to 12 months – Excellent safety profile – Not effective for the study indication
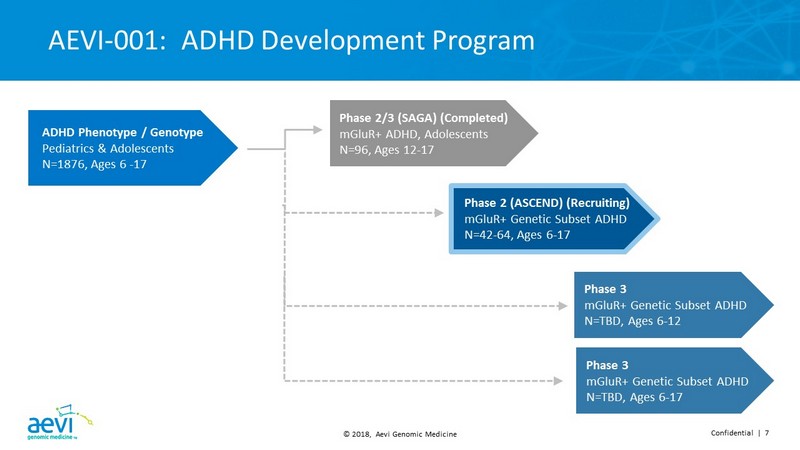
© 2018, Aevi Genomic Medicine Confidential | 7 AEVI - 001: ADHD Development Program Phase 3 mGluR + Genetic Subset ADHD N=TBD, Ages 6 - 12 Phase 3 mGluR + Genetic Subset ADHD N=TBD, Ages 6 - 17 Phase 2 (ASCEND) (Recruiting) mGluR+ Genetic Subset ADHD N=42 - 64, Ages 6 - 17 ADHD Phenotype / Genotype Pediatrics & Adolescents N=1876, Ages 6 - 17 Phase 2/3 (SAGA) (Completed) mGluR+ ADHD, Adolescents N=96, Ages 12 - 17
© 2018, Aevi Genomic Medicine 8 SAGA Responder Analysis Summary • Post - hoc analysis of patients responding to AEVI - 001 revealed a 9 - gene subset predictive of response to AEVI - 001 – accounts for approximately 10% of pediatric ADHD patients. 1 • Novel discovery: prevalence of CNTN4 mutations in ADHD • Represents approximately 5% of pediatric ADHD • All CNTN4 mutation+ patients on AEVI - 001 achieved clinical response • More severe ADHD phenotype with emotional dysregulation features • CNTN4 mutation association with neurodevelopmental diseases supports study in ASD • Clearer path to market approval and launch with a more concentrated but predictive genotype 1 Data on file and Elia, J. et al, Glutamatergic network gene mutations in children and adolescents with ADHD. Poster presented at: 6th World Congress on ADHD; April 21, 2017; Vancouver, Canada
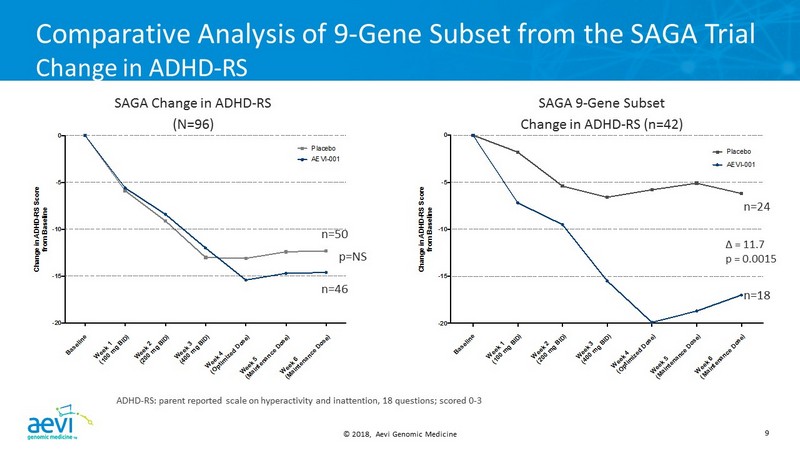
© 2018, Aevi Genomic Medicine 9 Comparative Analysis of 9 - Gene Subset from the SAGA Trial Change in ADHD - RS B a s e l i n e W e e k 1 ( 1 0 0 m g B I D ) W e e k 2 ( 2 0 0 m g B I D ) W e e k 3 ( 4 0 0 m g B I D ) W e e k 4 ( O p t i m i z e d D o s e ) W e e k 5 ( M a i n t e n a n c e D o s e ) W e e k 6 ( M a i n t e n a n c e D o s e ) -20 -15 -10 -5 0 C h a n g e i n A D H D - R S S c o r e f r o m B a s e l i n e AEVI-001 Placebo B a s e l i n e W e e k 1 ( 1 0 0 m g B I D ) W e e k 2 ( 2 0 0 m g B I D ) W e e k 3 ( 4 0 0 m g B I D ) W e e k 4 ( O p t i m i z e d D o s e ) W e e k 5 ( M a i n t e n a n c e D o s e ) W e e k 6 ( M a i n t e n a n c e D o s e ) -20 -15 -10 -5 0 C h a n g e i n A D H D - R S S c o r e f r o m B a s e l i n e AEVI-001 Placebo p=NS SAGA Change in ADHD - RS (N=96) n=50 n=46 Δ = 11.7 p = 0.0015 SAGA 9 - Gene Subset Change in ADHD - RS (n=42) n=24 n=18 ADHD - RS: parent reported scale on hyperactivity and inattention, 18 questions; scored 0 - 3
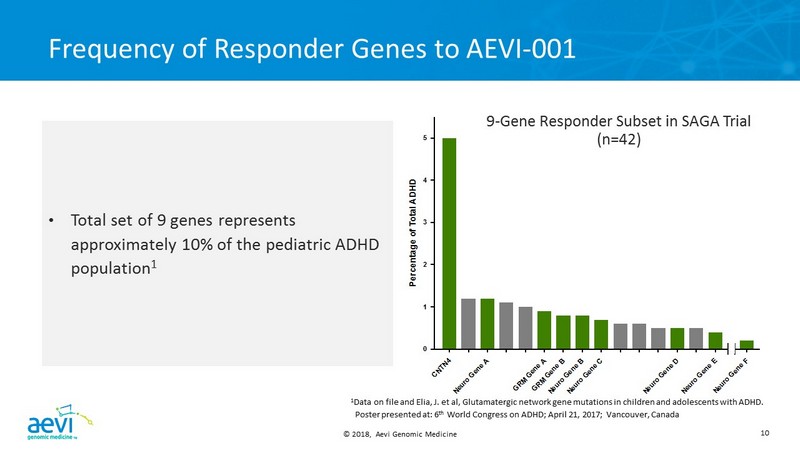
© 2018, Aevi Genomic Medicine 10 C N T N 4 N e u r o G e n e A G R M G e n e A G R M G e n e B N e u r o G e n e B N e u r o G e n e C N e u r o G e n e D N e u r o G e n e E N e u r o G e n e F 0 1 2 3 4 5 P e r c e n t a g e o f T o t a l A D H D Frequency of Responder Genes to AEVI - 001 • Total set of 9 genes represents approximately 10% of the pediatric ADHD population 1 1 Data on file and Elia, J. et al, Glutamatergic network gene mutations in children and adolescents with ADHD. Poster presented at: 6 th World Congress on ADHD; April 21, 2017; Vancouver, Canada 9 - Gene Responder Subset in SAGA Trial (n=42)
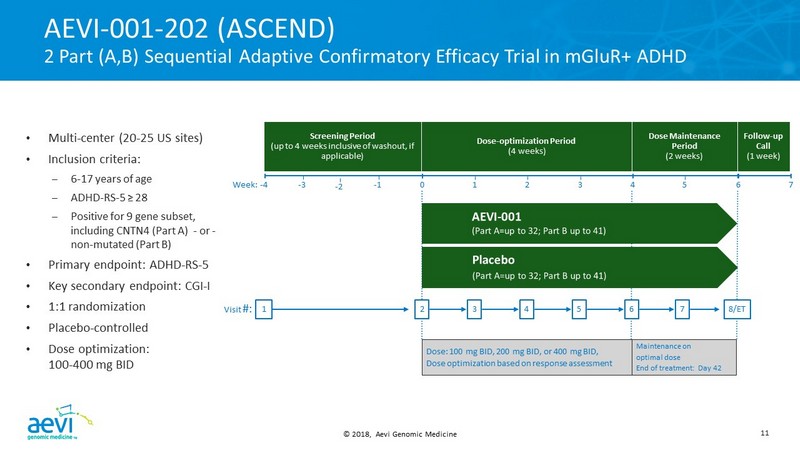
© 2018, Aevi Genomic Medicine 11 Dose - optimization Period (4 weeks) Screening Period (up to 4 weeks inclusive of washout, if applicable) Dose Maintenance Period (2 weeks) Follow - up Call (1 week) Visit #: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8/ET Dose: 100 mg BID, 200 mg BID, or 400 mg BID, Dose optimization based on response assessment Maintenance on optimal dose End of treatment: Day 42 - 2 • Multi - center (20 - 25 US sites) • Inclusion criteria: – 6 - 17 years of age – ADHD - RS - 5 ≥ 28 – Positive for 9 gene subset, including CNTN4 (Part A) - or - non - mutated (Part B) • Primary endpoint: ADHD - RS - 5 • Key secondary endpoint: CGI - I • 1:1 randomization • Placebo - controlled • Dose optimization: 100 - 400 mg BID AEVI - 001 - 202 (ASCEND) 2 Part (A,B) Sequential Adaptive Confirmatory Efficacy Trial in mGluR+ ADHD Week: - 4 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 - 3 - 1 7
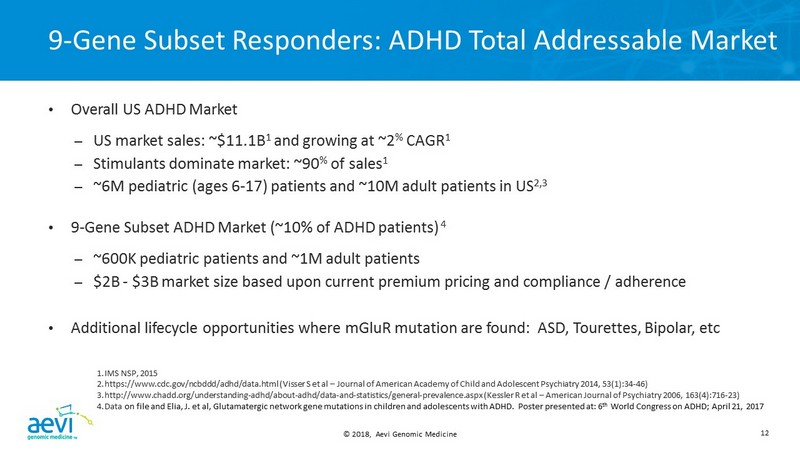
© 2018, Aevi Genomic Medicine 12 9 - Gene Subset Responders: ADHD Total Addressable Market • Overall US ADHD Market – US market sales: ~$11.1B 1 and growing at ~2 % CAGR 1 – Stimulants dominate market: ~90 % of sales 1 – ~6M pediatric (ages 6 - 17) patients and ~10M adult patients in US 2,3 • 9 - Gene Subset ADHD Market (~10% of ADHD patients) 4 – ~600K pediatric patients and ~1M adult patients – $2B - $3B market size based upon current premium pricing and compliance / adherence • Additional lifecycle opportunities where mGluR mutation are found: ASD, Tourettes , Bipolar, etc 1. IMS NSP, 2015 2. https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/adhd/data.html ( Visser S et al – Journal of American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry 2014, 53(1):34 - 46) 3. http://www.chadd.org/understanding - adhd/about - adhd/data - and - statistics/general - prevalence.aspx (Kessler R et al – American Journ al of Psychiatry 2006, 163(4):716 - 23) 4. Data on file and Elia, J. et al, Glutamatergic network gene mutations in children and adolescents with ADHD. Poster presented at: 6 th World Congress on ADHD; April 21, 2017

© 2018, Aevi Genomic Medicine AEVI - 001 in Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) Overview
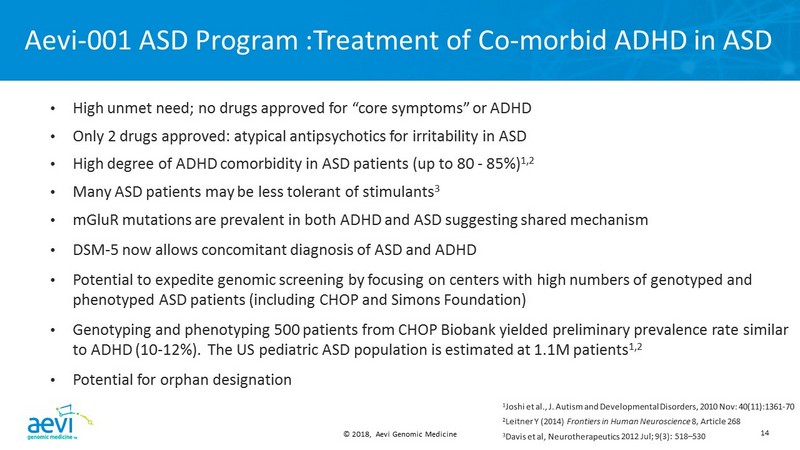
© 2018, Aevi Genomic Medicine 14 Aevi - 001 ASD Program :Treatment of Co - morbid ADHD in ASD • High unmet need; no drugs approved for “core symptoms” or ADHD • Only 2 drugs approved: atypical antipsychotics for irritability in ASD • High degree of ADHD comorbidity in ASD patients (up to 80 - 85%) 1,2 • Many ASD patients may be less tolerant of stimulants 3 • mGluR mutations are prevalent in both ADHD and ASD suggesting shared mechanism • DSM - 5 now allows concomitant diagnosis of ASD and ADHD • Potential to expedite genomic screening by focusing on centers with high numbers of genotyped and phenotyped ASD patients (including CHOP and Simons Foundation) • Genotyping and phenotyping 500 patients from CHOP Biobank yielded preliminary prevalence rate similar to ADHD (10 - 12%). The US pediatric ASD population is estimated at 1.1M patients 1,2 • Potential for orphan designation 2 Leitner Y (2014) Frontiers in Human Neuroscience 8, Article 268 2012 Jul; 9(3): 518 – 530
© 2018, Aevi Genomic Medicine 15 ASD Signal Finding Trial Overview Aevi strategy: Study AEVI - 001 in high functioning ASD patients (IQ Ͳ ሻ with comorbid ADHD and mGluR+ mutations. • Planned POC study – Inclusion criteria: 9 gene subset, ASD with comorbid ADHD, 6 - 17 years of age, IQ Ͳ • Design – Multi - center, open label ascending dose (100 - 400mg bid) – N=15 - 20 – Endpoints: ADHD - RS (primary), AIM, ABC, Vineland, Brief – Plan to initiate interventional study in 2H18 1 https:// www.cdc.gov / ncbddd / autism / data.html 2 https:// www.census.gov / quickfacts /fact/table/US/PST045216

© 2018, Aevi Genomic Medicine AEVI - 002 Program in Severe Pediatric Onset Crohn’s Disease Overview
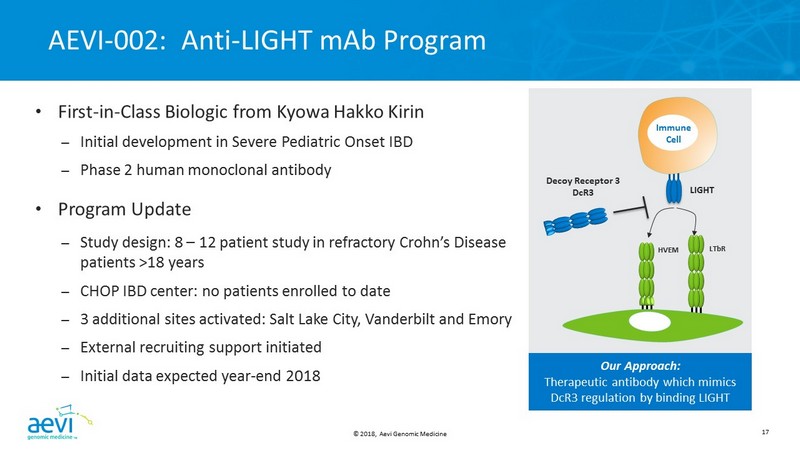
© 2018, Aevi Genomic Medicine 17 AEVI - 002: Anti - LIGHT mAb Program • First - in - Class Biologic from Kyowa Hakko Kirin – Initial development in Severe Pediatric Onset IBD – Phase 2 human monoclonal antibody • Program Update – Study design: 8 – 12 patient study in refractory Crohn’s Disease patients >18 years – CHOP IBD center: no patients enrolled to date – 3 additional sites activated: Salt Lake City, Vanderbilt and Emory – External recruiting support initiated – Initial data expected year - end 2018 Decoy Receptor 3 DcR3 LIGHT Immune Cell HVEM LT b R Our Approach: Therapeutic antibody which mimics DcR3 regulation by binding LIGHT

© 2018, Aevi Genomic Medicine AEVI - 005 Program Overview

© 2018, Aevi Genomic Medicine 19 AEVI - 005: Novel Orphan Program • Collaboration with Kyowa Hakko Kirin • First - in - class monoclonal antibody targeting a specific cell surface marker implicated in an ultra - orphan auto - immune pediatric disease – Preclinical stage • Aevi - led translational work will commence leveraging CHOP Biobank samples and genomics data. – In - vitro proof of concept in 9 - 12 months • Program expected to be ready for clinic in 18 – 24 months • Financial and other terms of the deal not disclosed
© 2018, Aevi Genomic Medicine 20 Novel Approach: Matching Molecules to Target Indications Partnered with KHK • Novel mechanism/molecule from partner • Aevi identifies appropriate biological pathways for potential therapeutic intervention in known pediatric rare/orphan diseases with potential to expand into larger syndromic diseases • CHOP/CAG provides fully curated patient derived tissue samples from biobank. • Aevi designs and conduct translational activities to biologically validate target(s) and therapeutic approach • In - vitro POC sufficient to support orphan application

© 2018, Aevi Genomic Medicine Q4 and Full Year 2017 Financial Update

© 2018, Aevi Genomic Medicine 22 Q4 and Full Year 2017 Financial Update $33.4M cash and cash equivalents at 12/31/2017 Current cash resources estimated to fund operations into early 2019, including through the receipt of: Top - line data from AEVI - 001 in the ASCEND trial in mGluR+ Genetic Subset ADHD (mid - 2018) Initial data from the signal - finding trial of AEVI - 002 in Severe Pediatric Onset Crohn’s Disease (year - end 2018) R&D expenses for 4Q 17 were $5.3M, increasing slightly from $5.1M for the same period in 2016. G&A expenses for 4Q 17 were $1.9M, decreasing from $3.4M for the same period in 2016 mainly due to decreased costs following the closure of the Company’s operations in Israel. R&D expenses for FY 17 were $25.2M, decreasing from $28.4M for the same period in 2016 mainly related to decreased spend following the closure of the Company’s operations in Israel. G&A expenses for FY 17 were $9.5M, decreasing from $13.5M for the same period in 2016 mainly due to due to severance benefits recorded in 2016 of $1.0M , decreased stock compensation expense of $2.0M, and closure of the Company’s operations in Israel of $0.9M.
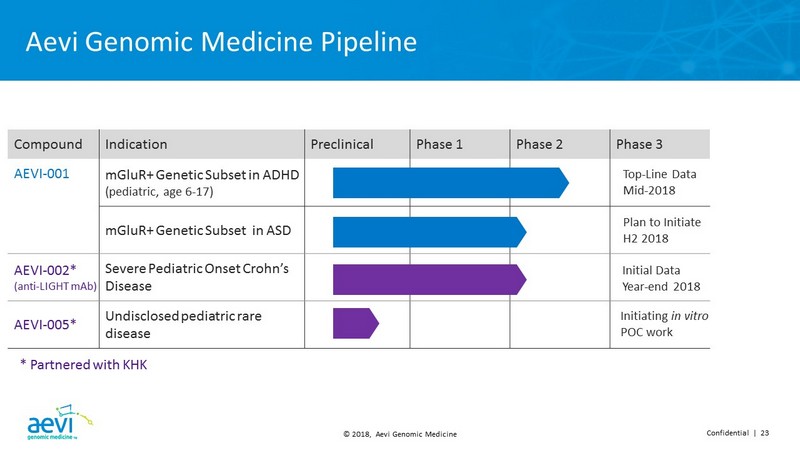
© 2018, Aevi Genomic Medicine Confidential | 23 Aevi Genomic Medicine Pipeline Compound Indication Preclinical Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3 AEVI - 001 mGluR+ Genetic Subset in ADHD (pediatric, age 6 - 17) mGluR+ Genetic Subset in ASD AEVI - 002* (anti - LIGHT mAb) Severe Pediatric Onset Crohn’s Disease AEVI - 005* Undisclosed pediatric rare disease Plan to Initiate H2 2018 Top - Line Data Mid - 2018 Initial Data Year - end 2018 Initiating in vitro POC work * Partnered with KHK

© 2018, Aevi Genomic Medicine 24 Thank you
