Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-32.2 - CERTIFICATION PURSUANT TO SECTION 906 OF THE SARBANES-OXLEY ACT OF 2002 - NEW YORK TIMES CO | ex322_12312017.htm |
| EX-21 - SUBSIDIARIES OF THE COMPANY - NEW YORK TIMES CO | ex21_12312017.htm |
| EX-32.1 - CERTIFICATION PURSUANT TO SECTION 906 OF THE SARBANES-OXLEY ACT OF 2002 - NEW YORK TIMES CO | ex321_12312017.htm |
| EX-31.2 - RULE 13A-14(A)/15D-14(A) CERTIFICATION - NEW YORK TIMES CO | ex312_12312017.htm |
| EX-31.1 - RULE 13A-14(A)/15D-14(A) CERTIFICATION - NEW YORK TIMES CO | ex311_12312017.htm |
| EX-23.1 - CONSENT OF ERNST & YOUNG LLP - NEW YORK TIMES CO | ex231_12312017.htm |
| EX-10.17 - LETTER AGREEMENT - NEW YORK TIMES CO | ex1017_12312017.htm |
| EX-10.16 - LETTER AGREEMENT - NEW YORK TIMES CO | ex1016_12312017.htm |
UNITED STATES SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
WASHINGTON, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
Annual Report pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2017 | Commission file number 1-5837 | |||
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
New York | 13-1102020 | |
(State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) | |
620 Eighth Avenue, New York, N.Y. | 10018 | |
(Address of principal executive offices) | (Zip code) | |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
Title of each class | Name of each exchange on which registered | |
Class A Common Stock of $.10 par value | New York Stock Exchange | |
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes þ No ¨
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Exchange Act. Yes ¨ No þ
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes þ No ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files).
Yes þ No ¨
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. þ
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. (Check one):
Large accelerated filer | þ | Accelerated filer | ¨ | |
Non-accelerated filer | ¨ | Smaller reporting company | ¨ | |
Emerging growth company | ¨ | |||
If an emerging growth company, indicate by the check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes ¨ No þ
The aggregate worldwide market value of Class A Common Stock held by non-affiliates, based on the closing price on June 25, 2017, the last business day of the registrant’s most recently completed second quarter, as reported on the New York Stock Exchange, was approximately $2.7 billion. As of such date, non-affiliates held 66,205 shares of Class B Common Stock. There is no active market for such stock.
The number of outstanding shares of each class of the registrant’s common stock as of February 23, 2018 (exclusive of treasury shares), was as follows: 164,017,902 shares of Class A Common Stock and 803,763 shares of Class B Common Stock.
Documents incorporated by reference
Portions of the Proxy Statement relating to the registrant’s 2018 Annual Meeting of Stockholders, to be held on April 19, 2018, are incorporated by reference into Part III of this report.
INDEX TO THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY 2017 ANNUAL REPORT ON FORM 10-K |
ITEM NO. | ||||||
16 | ||||||
PART I |
FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS |
This Annual Report on Form 10-K, including the sections titled “Item 1A — Risk Factors” and “Item 7 —Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations,” contains forward-looking statements that relate to future events or our future financial performance. We may also make written and oral forward-looking statements in our Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) filings and otherwise. We have tried, where possible, to identify such statements by using words such as “believe,” “expect,” “intend,” “estimate,” “anticipate,” “will,” “could,” “project,” “plan” and similar expressions in connection with any discussion of future operating or financial performance. Any forward-looking statements are and will be based upon our then-current expectations, estimates and assumptions regarding future events and are applicable only as of the dates of such statements. We undertake no obligation to update or revise any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise.
By their nature, forward-looking statements are subject to risks and uncertainties that could cause actual results to differ materially from those anticipated in any such statements. You should bear this in mind as you consider forward-looking statements. Factors that we think could, individually or in the aggregate, cause our actual results to differ materially from expected and historical results include those described in “Item 1A — Risk Factors” below, as well as other risks and factors identified from time to time in our SEC filings.
ITEM 1. BUSINESS |
OVERVIEW
The New York Times Company (the “Company”) was incorporated on August 26, 1896, under the laws of the State of New York. The Company and its consolidated subsidiaries are referred to collectively in this Annual Report on Form 10-K as “we,” “our” and “us.”
We are a global media organization focused on creating, collecting and distributing high-quality news and information. Our continued commitment to premium content and journalistic excellence makes The New York Times brand a trusted source of news and information for readers and viewers across various platforms. Recognized widely for the quality of our reporting and content, our publications have been awarded many industry and peer accolades, including 122 Pulitzer Prizes and citations, more than any other news organization.
The Company includes newspapers, print and digital products and investments. We have one reportable segment with businesses that include:
• | our newspaper, The New York Times (“The Times”); |
• | our websites, including NYTimes.com; |
• | our mobile applications, including The Times’s core news applications, as well as interest-specific applications, including our Crossword and Cooking products; and |
• | related businesses, such as The Times news services division; our product review and recommendation website, Wirecutter; our digital archive distribution; NYT Live (our live events business); our digital marketing agencies and other products and services under The Times brand. |
We generate revenues principally from subscriptions and advertising. Subscription revenues consist of revenues from subscriptions to our print and digital products (which include our news products, as well as our Crossword and Cooking products) and single-copy sales of our print newspaper. Advertising revenue is derived from the sale of our advertising products and services on our print and digital platforms. Revenue information for the Company appears under “Item 7 — Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.” Revenues, operating profit and identifiable assets of our foreign operations are not significant.
During 2017, we continued to make significant investments in our journalism, while taking further steps to position our organization to operate more efficiently in a digital environment. During the year, The Times continued to break stories and produce investigative reports that sparked global conversations on wide-ranging topics. We also launched groundbreaking digital journalism projects and a popular daily news podcast, The Daily, and created
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 1
special inserts in our print newspaper, including a monthly section dedicated to children. In addition, we continued to create innovative digital advertising solutions across our platforms and expand our creative services offerings.
We believe that the significant growth over the last year in subscriptions to our products demonstrates the success of our “subscription-first” strategy and the willingness of our readers to pay for high-quality journalism. We had approximately 3.6 million subscriptions to our products as of December 31, 2017, more than at any point in our history.
During the year, we exited our joint venture investments in Women in the World, LLC, a live-event conference business, and Donahue Malbaie Inc. (“Malbaie”), a Canadian newsprint company, and we are in the process of exiting our joint venture investment in Madison Paper Industries (“Madison”), a partnership that previously operated a paper mill. These investments were accounted for under the equity method. For additional information on these investments, see “Item 7 — Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and Note 5 of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
The Company sold the New England Media Group in 2013 and the results of operations for this business have been presented as discontinued operations for all periods presented. See Note 13 of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information regarding our discontinued operations.
PRODUCTS
The Company’s principal business consists of distributing content generated by our newsroom through our digital and print platforms. In addition, we distribute selected content on third-party platforms.
Our core news website, NYTimes.com, was launched in 1996. Since 2011, we have charged consumers for content provided on this website and our core news mobile application. Digital subscriptions can be purchased individually or through group corporate or group education subscriptions. Our metered model offers users free access to a set number of articles per month and then charges users for access to content beyond that limit. In addition to subscriptions to our news product, we offer standalone subscriptions to other digital products, namely our Crossword and Cooking products. Certain digital news product subscription packages include complimentary access to our Crossword and Cooking products.
The Times’s print edition, a daily (Mon. - Sat.) and Sunday newspaper in the United States, commenced publication in 1851. The Times also has an international edition that is tailored and edited for global audiences. First published in 2013 and previously called the International New York Times, the international edition succeeded the International Herald Tribune, a leading daily newspaper that commenced publishing in Paris in 1887. Our print newspapers are sold in the United States and around the world through individual home-delivery subscriptions, bulk subscriptions (primarily by schools and hotels) and single-copy sales. All print home-delivery subscribers are entitled to receive unlimited digital access.
SUBSCRIPTIONS AND AUDIENCE
Our content reaches a broad audience through our print, web and mobile platforms. As of December 31, 2017, we had approximately 3.6 million paid subscriptions across 208 countries and territories to our print and digital products.
Paid digital-only subscriptions totaled approximately 2,644,000 as of December 31, 2017, an increase of approximately 42% compared with December 25, 2016. This amount includes standalone paid subscriptions to our Crossword and Cooking products, which totaled approximately 413,000 as of December 31, 2017.
The number of paid digital-only subscriptions also includes estimated group corporate and group education subscriptions (which collectively represent approximately 7% of total paid digital subscriptions to our news products). The number of paid group subscriptions is derived using the value of the relevant contract and a discounted basic subscription rate. The actual number of users who have access to our products through group subscriptions is substantially higher.
In the United States, The Times had the largest daily and Sunday print circulation of all seven-day newspapers for the three-month period ended September 30, 2017, according to data collected by the Alliance for Audited Media (“AAM”), an independent agency that audits circulation of most U.S. newspapers and magazines.
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2017, The Times’s average print circulation (which includes paid and qualified circulation of the newspaper in print) was approximately 540,000 for weekday (Monday to Friday) and
P. 2 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
1,066,000 for Sunday. (Under AAM’s reporting guidance, qualified circulation represents copies available for individual consumers that are either non-paid or paid by someone other than the individual, such as copies delivered to schools and colleges and copies purchased by businesses for free distribution.)
Internationally, average circulation for the international edition of our newspaper (which includes paid circulation of the newspaper in print and electronic replica editions) for the fiscal years ended December 31, 2017, and December 25, 2016, was approximately 173,000 (estimated) and 197,000, respectively. These figures follow the guidance of Office de Justification de la Diffusion, an agency based in Paris and a member of the International Federation of Audit Bureaux of Circulations that audits the circulation of most newspapers and magazines in France. The final 2017 figure will not be available until April 2018.
According to comScore Media Metrix, an online audience measurement service, in 2017, NYTimes.com had a monthly average of approximately 97 million unique visitors in the United States on either desktop/laptop computers or mobile devices. Globally, including the United States, NYTimes.com had a 2017 monthly average of approximately 136 million unique visitors on either desktop/laptop computers or mobile devices, according to internal data estimates.
ADVERTISING
We have a comprehensive portfolio of advertising products and services that we provide across print, web and mobile platforms. Our advertising revenue is divided into three main categories:
Display Advertising
Display advertising is principally from advertisers promoting products, services or brands, such as financial institutions, movie studios, department stores, American and international fashion and technology. In print, column-inch ads are priced according to established rates, with premiums for color and positioning. The Times had the largest market share in 2017 in print advertising revenue among a national newspaper set that consists of USA Today, The Wall Street Journal and The Times, according to MediaRadar, an independent agency that measures advertising sales volume and estimates advertising revenue.
On our web and mobile platforms, display advertising comprises banners, video, rich media and other interactive ads. Display advertising also includes branded content on The Times’s platforms. Branded content is longer form marketing content that is distinct from The Times’s editorial content. In 2017, digital and print display advertising represented approximately 87% of our advertising revenues.
Classified and Other Advertising
Classified advertising includes line ads sold in the major categories of real estate, help wanted, automotive and other. In print, classified advertisers pay on a per-line basis. On our web and mobile platforms, classified advertisers pay on either a per-listing basis for bundled listing packages, or as an add-on to their print ad.
Other advertising primarily includes creative services fees associated with our branded content studio and our digital marketing agencies, including HelloSociety and Fake Love, each of which the Company acquired in 2016; advertising revenue generated by our product review and recommendation website, Wirecutter, which the Company also acquired in 2016; revenues from preprinted advertising, also known as free-standing inserts; revenues generated from branded bags in which our newspapers are delivered; and advertising revenues from our news services business. In 2017, digital and print classified and other advertising represented approximately 13% of our advertising revenues.
Our business is affected in part by seasonal patterns in advertising, with generally higher advertising volume in the fourth quarter due to holiday advertising.
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 3
COMPETITION
Our print, web and mobile products compete for subscriptions and advertising with other media in their respective markets. Competition for subscription revenue and readership is generally based upon platform, format, content, quality, service, timeliness and price, while competition for advertising is generally based upon audience levels and demographics, advertising rates, service, targeting capabilities and advertising results.
Our print newspaper competes for subscriptions and advertising primarily with national newspapers such as The Wall Street Journal and The Washington Post; newspapers of general circulation in New York City and its suburbs; other daily and weekly newspapers and television stations and networks in markets in which The Times is circulated; and some national news and lifestyle magazines. The international edition of our newspaper competes with international sources of English-language news, including the Financial Times, Time, Bloomberg Business Week and The Economist.
As our industry continues to experience a shift from print to digital media, our products face competition for audience, subscriptions and advertising from a wide variety of digital media, including news and other information websites and mobile applications, news aggregation sites, sites that cover niche content, social media platforms, and other forms of media. In addition, we compete for advertising on digital advertising networks and exchanges and real-time bidding and other programmatic buying channels.
Our websites and mobile applications most directly compete for audience, subscriptions and advertising with other U.S. news and information websites and mobile applications, including The Washington Post, The Wall Street Journal, CNN, Yahoo! News, Buzzfeed, HuffPost, Vox and Vice. We also compete for audience and advertising against customized news feeds and news aggregation websites such as Facebook Newsfeed, Apple News and Google News. Internationally, our websites and mobile applications compete against international online sources of English-language news, including BBC News, CNN, The Guardian, the Financial Times, The Wall Street Journal, The Economist, HuffPost and Reuters.
OTHER BUSINESSES
We derive revenue from other businesses, which primarily include:
• | The Times news services division, which transmits articles, graphics and photographs from The Times and other publications to approximately 1,800 newspapers, magazines and websites in over 100 countries and territories worldwide. It also comprises a number of other businesses that primarily include digital archive distribution, which licenses electronic databases to resellers in the business, professional and library markets; magazine licensing; news digests; book development and rights and permissions; |
• | The Company’s NYT Live business, a platform for our live journalism that convenes thought leaders from business, academia and government at conferences and events to discuss topics ranging from education to sustainability to the luxury business; and |
• | Wirecutter, a product review and recommendation website acquired in October 2016 that serves as a guide to technology gear, home products and other consumer goods. This website generates affiliate referral revenue (revenue generated by offering direct links to merchants in exchange for a portion of the sale price), which we record as other revenues. |
PRINT PRODUCTION AND DISTRIBUTION
The Times is currently printed at our production and distribution facility in College Point, N.Y., as well as under contract at 26 remote print sites across the United States. We also utilize excess printing capacity at our College Point facility for commercial printing. The Times is delivered to newsstands and retail outlets in the New York metropolitan area through a combination of third-party wholesalers and our own drivers. In other markets in the United States and Canada, The Times is delivered through agreements with other newspapers and third-party delivery agents.
The international edition of The Times is printed under contract at 39 sites throughout the world and is sold in over 130 countries and territories. It is distributed through agreements with other newspapers and third-party delivery agents.
P. 4 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
RAW MATERIALS
The primary raw materials we use are newsprint and coated paper, which we purchase from a number of North American and European producers. A significant portion of our newsprint is purchased from Resolute Forest Products Inc., a large global manufacturer of paper, market pulp and wood products with which we shared ownership in Malbaie before we sold our interest in the fourth quarter of 2017.
In 2017 and 2016, we used the following types and quantities of paper:
(In metric tons) | 2017 | 2016 | ||||
Newsprint | 90,500 | 97,800 | ||||
Coated and Supercalendared Paper(1) | 16,500 | 19,500 | ||||
(1) The Times uses a mix of coated and supercalendered paper for The New York Times Magazine, and coated paper for T: The New York Times Style Magazine.
EMPLOYEES AND LABOR RELATIONS
We had approximately 3,790 full-time equivalent employees as of December 31, 2017.
As of December 31, 2017, nearly half of our full-time equivalent employees were represented by unions. The following is a list of collective bargaining agreements covering various categories of the Company’s employees and their corresponding expiration dates. As indicated below, one collective bargaining agreement, under which less than 1% of our full-time equivalent employees are covered, will expire within one year and negotiations for a new contract are ongoing. We cannot predict the timing or the outcome of these negotiations.
Employee Category | Expiration Date |
Machinists | March 30, 2018 |
Mailers | March 30, 2019 |
Typographers | March 30, 2020 |
Drivers | March 30, 2020 |
NewsGuild of New York | March 30, 2021 |
Paperhandlers | March 30, 2021 |
Pressmen | March 30, 2021 |
Stereotypers | March 30, 2021 |
AVAILABLE INFORMATION
Our Annual Report on Form 10-K, Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, Current Reports on Form 8-K, and all amendments to those reports, and the Proxy Statement for our Annual Meeting of Stockholders are made available, free of charge, on our website at http://www.nytco.com, as soon as reasonably practicable after such reports have been filed with or furnished to the SEC.
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 5
ITEM 1A. RISK FACTORS |
You should carefully consider the risk factors described below, as well as the other information included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Our business, financial condition or results of operations could be materially adversely affected by any or all of these risks, or by other risks or uncertainties not presently known or currently deemed immaterial, that may adversely affect us in the future.
We face significant competition in all aspects of our business.
We operate in a highly competitive environment. We compete for subscription and advertising revenue with both traditional publishers and other content providers. Competition among companies offering online content is intense, and new competitors can quickly emerge. Some of our current and potential competitors may have greater resources than we do, which may allow them to compete more effectively than us.
Our ability to compete effectively depends on many factors both within and beyond our control, including among others:
• | our ability to continue delivering high-quality journalism and content that is interesting and relevant to our audience; |
• | the popularity, usefulness, ease of use, performance and reliability of our digital products compared with those of our competitors; |
• | the engagement of our current users with our print and digital products, and our ability to reach new users; |
• | our ability to develop, maintain and monetize our products; |
• | the pricing of our products; |
• | our marketing and selling efforts, including our ability to differentiate our products from those of our competitors; |
• | our ability to provide marketers with a compelling return on their investments; |
• | our ability to attract, retain, and motivate talented employees, including journalists and product and technology specialists; |
• | our ability to manage and grow our operations in a cost-effective manner; and |
• | our reputation and brand strength relative to those of our competitors. |
Our success depends on our ability to respond and adapt to changes in technology and consumer behavior.
Technology in the media industry continues to evolve rapidly. Advances in technology have led to an increased number of methods for the delivery and consumption of news and other content. These developments are also driving changes in the preferences and expectations of consumers as they seek more control over how they consume content.
Changes in technology and consumer behavior pose a number of challenges that could adversely affect our revenues and competitive position. For example, among others:
• | we may be unable to develop products for mobile devices or other digital platforms that consumers find engaging, that work with a variety of operating systems and networks and that achieve a high level of market acceptance; |
• | we may introduce new products or services, or make changes to existing products and services, that are not favorably received by consumers; |
• | there may be changes in user sentiment about the quality or usefulness of our existing products or concerns related to privacy, security or other factors; |
• | news aggregation websites and customized news feeds may reduce our traffic levels by creating a disincentive for users to visit our websites or use our digital products; |
• | consumers’ increased reliance on mobile devices for the consumption of news and other content may contribute to a decline in engagement with our products; |
P. 6 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
• | changes implemented by social media platforms and search engines, including those affecting how content is displayed and/or prioritized, could affect our business; |
• | failure to successfully manage changes in search engine optimization and social media traffic to increase our digital presence and visibility may reduce our traffic levels; |
• | we may be unable to maintain or update our technology infrastructure in a way that meets market and consumer demands; and |
• | the distribution of our content on delivery platforms of third parties may lead to limitations on monetization of our products, the loss of control over distribution of our content and loss of a direct relationship with our audience. |
Responding to these changes may require significant investment. We may be limited in our ability to invest funds and resources in digital products, services or opportunities, and we may incur expense in building, maintaining and evolving our technology infrastructure.
Unless we are able to use new and existing technologies to distinguish our products and services from those of our competitors and develop in a timely manner compelling new products and services that engage users across platforms, our business, financial condition and prospects may be adversely affected.
Our advertising revenues are affected by numerous factors, including economic conditions, market dynamics, audience fragmentation and evolving digital advertising trends.
We derive substantial revenues from the sale of advertising in our products. Advertising spending is sensitive to overall economic conditions, and our advertising revenues could be adversely affected if advertisers respond to weak and uneven economic conditions by reducing their budgets or shifting spending patterns or priorities, or if they are forced to consolidate or cease operations.
In determining whether to buy advertising, our advertisers consider the demand for our products, demographics of our reader base, advertising rates, results observed by advertisers, and alternative advertising options.
Although print advertising revenue continues to represent a majority of our total advertising revenue (57% of our total advertising revenues in 2017), the overall proportion continues to decline. The increased popularity of digital media among consumers, particularly as a source for news and other content, has driven a corresponding shift in demand from print advertising to digital advertising. However, our digital advertising revenue has not replaced, and may not replace in full, print advertising revenue lost as a result of the shift.
The increasing number of digital media options available, including through social networking platforms and news aggregation websites, has expanded consumer choice significantly, resulting in audience fragmentation. Competition from new content providers and platforms, some of which charge lower rates than we do or have greater audience reach and targeting capabilities, and the significant increase in inventory of digital advertising space, have affected and will likely continue to affect our ability to attract and retain advertisers and to maintain or increase our advertising rates. In recent years, large digital platforms, such as Facebook, Google and Amazon, which have greater audience reach and targeting capabilities than we do, have commanded an increased share of the digital display advertising market, and we anticipate that this trend will continue.
The digital advertising market itself continues to undergo significant change. Digital advertising networks and exchanges, real-time bidding and other programmatic buying channels that allow advertisers to buy audiences at scale are playing a more significant role in the advertising marketplace and may cause further downward pricing pressure. New delivery platforms may also lead to a loss of distribution and pricing control and loss of a direct relationship with consumers. In addition, changes in the standards for the delivery of digital advertising could also negatively affect our digital advertising revenues.
Technologies have been developed, and will likely continue to be developed, that enable consumers to circumvent digital advertising on websites and mobile devices. Advertisements blocked by these technologies are treated as not delivered and any revenue we would otherwise receive from the advertiser for that advertisement is lost. Increased adoption of these technologies could adversely affect our advertising revenues, particularly if we are unable to develop effective solutions to mitigate their impact.
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 7
As the digital advertising market continues to evolve, our ability to compete successfully for advertising budgets will depend on, among other things, our ability to engage and grow digital audiences and prove the value of our advertising and the effectiveness of our platforms to advertisers.
We may experience further downward pressure on our advertising revenue margins.
The character of our digital advertising business continues to change, as demand for newer forms of advertising, such as branded content and other customized advertising, and video advertising, increases. The margin on revenues from some of these newer advertising forms is generally lower than the margin on revenues we generate from our print advertising and traditional digital display advertising. Consequently, we may experience further downward pressure on our advertising revenue margins as a greater percentage of advertising revenues comes from these newer forms.
The inability of the Company to retain and grow our subscriber base could adversely affect our results of operations and business.
Revenue from subscriptions to our print and digital products makes up a majority of our total revenue. Subscription revenue is sensitive to discretionary spending available to subscribers in the markets we serve, as well as economic conditions. To the extent poor economic conditions lead consumers to reduce spending on discretionary activities, our ability to retain current and obtain new subscribers could be hindered, thereby reducing our subscription revenue. In addition, the growth rate of new subscriptions to our news products that are driven by significant news events, such as an election, may not be sustainable.
Print subscriptions have declined over the last several years, primarily due to increased competition from digital media formats (which are often free to users), higher subscription rates and a growing preference among many consumers to receive all or a portion of their news from sources other than a print newspaper. If we are unable to offset continued revenue declines resulting from falling print subscriptions with revenue from home-delivery price increases, our print subscription revenue will be adversely affected.
Subscriptions to content provided on our digital platforms generate substantial revenue for us, and our future growth depends upon our ability to retain and grow our digital subscription base and audience. To do so will require us to evolve our subscription model, address changing consumer demands and developments in technology and improve our digital product offering while continuing to deliver high-quality journalism and content that is interesting and relevant to readers. There is no assurance that we will be able to successfully maintain and increase our digital subscriber base or that we will be able to do so without taking steps such as reducing pricing or incurring subscription acquisition costs that would affect our margin or profitability.
Failure to execute cost-control measures successfully could adversely affect our profitability.
Over the last several years, we have taken steps to reduce operating costs across the Company, and we plan to continue our cost-management efforts. Some of these cost management efforts require significant up-front investment. If we do not achieve expected savings from these efforts, our total operating costs will be greater than anticipated. In addition, if we do not manage cost-management efforts properly, such efforts may affect the quality of our products and therefore our ability to generate future revenues. And to the extent our cost-management efforts result in reductions in staff and employee compensation and benefits, our ability to attract and retain key employees could be adversely affected.
Significant portions of our expenses are fixed costs that neither increase nor decrease proportionately with revenues. In addition, our ability to make short-term adjustments to manage our costs or to make changes to our business strategy may be limited by certain of our collective bargaining agreements. If we are not able to implement further cost-control efforts or reduce our fixed costs sufficiently in response to a decline in our revenues, our results of operations will be adversely affected.
P. 8 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
The size and volatility of our pension plan obligations may adversely affect our operations, financial condition and liquidity.
We sponsor several single-employer defined benefit pension plans. Although we have frozen participation and benefits under all but two of these qualified pension plans, and have taken other steps to reduce the size and volatility of our pension plan obligations, our results of operations will be affected by the amount of income or expense we record for, and the contributions we are required to make to, these plans.
We are required to make contributions to our plans to comply with minimum funding requirements imposed by laws governing those plans. As of December 31, 2017, our qualified defined benefit pension plans were underfunded by approximately $69 million. Our obligation to make additional contributions to our plans, and the timing of any such contributions, depends on a number of factors, many of which are beyond our control. These include: legislative changes; assumptions about mortality; and economic conditions, including a low interest rate environment or sustained volatility and disruption in the stock and bond markets, which impact discount rates and returns on plan assets.
As a result of required contributions to our qualified pension plans, we may have less cash available for working capital and other corporate uses, which may have an adverse impact on our results of operations, financial condition and liquidity.
In addition, the Company sponsors several non-qualified pension plans, with unfunded obligations totaling $245 million. Although we have frozen participation and benefits under these plans, and have taken other steps to reduce the size and volatility of our obligations under these plans, a number of factors, including changes in discount rates or mortality tables, may have an adverse impact on our results of operations and financial condition.
Our participation in multiemployer pension plans may subject us to liabilities that could materially adversely affect our results of operations, financial condition and cash flows.
We participate in, and make periodic contributions to, various multiemployer pension plans that cover many of our current and former production and delivery union employees. Our required contributions to these plans could increase because of a shrinking contribution base as a result of the insolvency or withdrawal of other companies that currently contribute to these plans, the inability or failure of withdrawing companies to pay their withdrawal liability, low interest rates, lower than expected returns on pension fund assets or other funding deficiencies. Our withdrawal liability for any multiemployer pension plan will depend on the nature and timing of any triggering event and the extent of that plan’s funding of vested benefits.
If a multiemployer pension plan in which we participate has significant underfunded liabilities, such underfunding will increase the size of our potential withdrawal liability. In addition, under federal pension law, special funding rules apply to multiemployer pension plans that are classified as “endangered,” “critical” or “critical and declining.” If plans in which we participate are in critical status, benefit reductions may apply and/or we could be required to make additional contributions.
We have recorded significant withdrawal liabilities with respect to multiemployer pension plans in which we formerly participated (primarily in connection with the sales of the New England Media Group in 2013 and the Regional Media Group in 2012) and may record additional liabilities in the future. In addition, we have recorded withdrawal liabilities for actual and estimated partial withdrawals from several plans in which we continue to participate. Until demand letters from some of the multiemployer plans’ trustees are received, the exact amount of the withdrawal liability will not be fully known and, as such, a difference from the recorded estimate could have an adverse effect on our results of operations, financial condition and cash flows. Several of the multiemployer plans in which we participate are specific to the newspaper industry, which continues to undergo significant pressure. A withdrawal by a significant percentage of participating employers may result in a mass withdrawal declaration by the trustees of one or more of these plans, which would require us to record additional withdrawal liabilities.
If, in the future, we elect to withdraw from these plans or if we trigger a partial withdrawal due to declines in contribution base units or a partial cessation of our obligation to contribute, additional liabilities would need to be recorded that could have an adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition or cash flows.
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 9
Security breaches and other network and information systems disruptions could affect our ability to conduct our business effectively and damage our reputation.
Our systems store and process confidential subscriber, employee and other sensitive personal and Company data, and therefore maintaining our network security is of critical importance. In addition, we rely on the technology and systems provided by third-party vendors (including cloud-based service providers) for a variety of operations, including encryption and authentication technology, employee email, domain name registration, content delivery to customers, administrative functions (including payroll processing and certain finance and accounting functions) and other operations.
We regularly face attempts by third parties to breach our security and compromise our information technology systems, and we believe these attempts are increasing in number and in technical sophistication. These attackers may use a blend of technology and social engineering techniques (including denial of service attacks, phishing attempts intended to induce our employees and users to disclose information or unwittingly provide access to systems or data and other techniques), with the goal of service disruption or data exfiltration. Information security threats are constantly evolving, increasing the difficulty of detecting and successfully defending against them. To date, no incidents have had, either individually or in the aggregate, a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition or results of operations.
In addition, our systems, and those of third parties upon which our business relies, may be vulnerable to interruption or damage that can result from natural disasters, fires, power outages, acts of terrorism or other similar events.
We have implemented controls and taken other preventative measures designed to strengthen our systems against attacks, including measures designed to reduce the impact of a security breach at our third-party vendors. Although the costs of the controls and other measures we have taken to date have not had a material effect on our financial condition, results of operations or liquidity, there can be no assurance as to the costs of additional controls and measures that we may conclude are necessary in the future.
There can also be no assurance that the actions, measures and controls we have implemented will be effective against future attacks or be sufficient to prevent a future security breach or other disruption to our network or information systems, or those of our third-party providers. Such an event could result in a disruption of our services, improper disclosure of personal data or confidential information, or theft or misuse of our intellectual property, all of which could harm our reputation, require us to expend resources to remedy such a security breach or defend against further attacks, divert management’s attention and resources or subject us to liability under laws that protect personal data, or otherwise adversely affect our business.
Our brand and reputation are key assets of the Company, and negative perceptions or publicity could adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
The New York Times brand is a key asset of the Company, and we believe that it contributes significantly to the success of our business. We also believe that our continued success depends on our ability to preserve, grow and leverage the value of our brand. We believe that we have a powerful and trusted brand with an excellent reputation for high-quality journalism and content, but our brand could be damaged by incidents that erode consumer trust. For example, to the extent consumers perceive our journalism to be less reliable, whether as a result of negative publicity or otherwise, our ability to attract readers and advertisers may be hindered. In addition, we may introduce new products or services that users do not like and which may negatively affect our brand. We also may fail to provide adequate customer service, which could erode confidence in our brand. Our reputation could also be damaged by failures of third-party vendors we rely on in many contexts. Maintaining and enhancing our brand may require us to make significant investments, which may not be successful. To the extent our brand and reputation are damaged by these or other incidents, our revenues and profitability could be adversely affected.
Our international operations expose us to economic and other risks inherent in foreign operations.
We have news bureaus and other offices around the world, and our print, web and mobile products are generally available globally. We are focused on further expanding the international scope of our business, and face the inherent risks associated with doing business abroad, including:
• | effectively managing and staffing foreign operations, including complying with local laws and regulations in each different jurisdiction; |
P. 10 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
• | ensuring the safety and security of our journalists and other employees working in foreign locations; |
• | navigating local customs and practices; |
• | government policies and regulations that restrict the digital flow of information, which could block access to, or the functionality of, our products; |
• | protecting and enforcing our intellectual property and other rights under varying legal regimes; |
• | complying with international laws and regulations, including those governing consumer privacy and the collection, use, retention, sharing and security of consumer and staff data; |
• | economic uncertainty, volatility in local markets and political or social instability; |
• | restrictions on foreign ownership, foreign investment or repatriation of funds; |
• | higher-than-anticipated costs of entry; and |
• | currency exchange rate fluctuations. |
Adverse developments in any of these areas could have an adverse impact on our business, financial condition and results of operations. We may, for example, incur increased costs necessary to comply with existing and newly adopted laws and regulations or penalties for any failure to comply. In addition, we have limited experience in developing and marketing our digital products in international regions and could be at a disadvantage compared with local and multinational competitors.
A significant increase in the price of newsprint, or significant disruptions in our newsprint supply chain or newspaper printing and distribution channels, would have an adverse effect on our operating results.
The cost of raw materials, of which newsprint is the major component, represented approximately 4% of our total operating costs in 2017. The price of newsprint has historically been volatile and could increase as a result of various factors, including:
•a reduction in the number of newsprint suppliers due to restructurings, bankruptcies and consolidations;
•increases in supplier operating expenses due to rising raw material or energy costs or other factors;
•currency volatility;
•duties on certain paper imports from Canada into United States; and
•inability to maintain existing relationships with our newsprint suppliers.
We also rely on suppliers for deliveries of newsprint, and the availability of our newsprint supply may be affected by various factors, including labor unrest, transportation issues and other disruptions that may affect deliveries of newsprint.
Outside the New York area, The Times is printed and distributed under contracts with print and distribution partners across the United States and internationally. Financial pressures, newspaper industry economics or other circumstances affecting these print and distribution partners could lead to reduced operations or consolidations of print sites and/or distribution routes, which could increase the cost of printing and distributing our newspapers.
If newsprint prices increase significantly or we experience significant disruptions in our newsprint supply chain or newspaper printing and distribution channels, our operating results may be adversely affected.
Acquisitions, divestitures, investments and other transactions could adversely affect our costs, revenues, profitability and financial position.
In order to position our business to take advantage of growth opportunities, we engage in discussions, evaluate opportunities and enter into agreements for possible acquisitions, divestitures, investments and other transactions. We may also consider the acquisition of, or investment in, specific properties, businesses or technologies that fall outside our traditional lines of business and diversify our portfolio, including those that may operate in new and developing industries, if we deem such properties sufficiently attractive.
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 11
Acquisitions involve significant risks and uncertainties, including:
• | difficulties in integrating acquired operations (including cultural challenges associated with integrating employees from the acquired company into our organization); |
• | diversion of management attention from other business concerns or resources; |
• | use of resources that are needed in other parts of our business; |
• | possible dilution of our brand or harm to our reputation; |
• | the potential loss of key employees; |
• | risks associated with integrating financial reporting and internal control systems; and |
• | other unanticipated problems and liabilities. |
Competition for certain types of acquisitions, particularly digital properties, is significant. Even if successfully negotiated, closed and integrated, certain acquisitions or investments may prove not to advance our business strategy and may fall short of expected return on investment targets, which could adversely affect our business, results of operations and financial condition.
In addition, we have divested and may in the future divest certain assets or businesses that no longer fit with our strategic direction or growth targets. Divestitures involve significant risks and uncertainties that could adversely affect our business, results of operations and financial condition. These include, among others, the inability to find potential buyers on favorable terms, disruption to our business and/or diversion of management attention from other business concerns, loss of key employees and possible retention of certain liabilities related to the divested business.
Finally, we have made investments in companies, and we may make similar investments in the future. Investments in these businesses subject us to the operating and financial risks of these businesses and to the risk that we do not have sole control over the operations of these businesses. Our investments are generally illiquid and the absence of a market may inhibit our ability to dispose of them. In addition, if the book value of an investment were to exceed its fair value, we would be required to recognize an impairment charge related to the investment.
A significant number of our employees are unionized, and our business and results of operations could be adversely affected if labor agreements were to further restrict our ability to maximize the efficiency of our operations.
Nearly half of our full-time equivalent work force is unionized. As a result, we are required to negotiate the wage, benefits and other terms and conditions of employment with many of our employees collectively. Our results could be adversely affected if future labor negotiations or contracts were to further restrict our ability to maximize the efficiency of our operations. If we are unable to negotiate labor contracts on reasonable terms, or if we were to experience labor unrest or other business interruptions in connection with labor negotiations or otherwise, our ability to produce and deliver our products could be impaired. In addition, our ability to make adjustments to control compensation and benefits costs, change our strategy or otherwise adapt to changing business needs may be limited by the terms and duration of our collective bargaining agreements.
Failure to comply with laws and regulations, including with respect to privacy, data protection and consumer marketing practices, could adversely affect our business.
Our business is subject to government regulation in the jurisdictions in which we operate, and our websites, which are available worldwide, may be subject to laws regulating the Internet even in jurisdictions where we do not do business. Among others, we are subject to laws and regulations with respect to online privacy and the collection and use of consumer data, as well as laws and regulations with respect to consumer marketing practices.
Various federal and state laws and regulations, as well as the laws of foreign jurisdictions, govern the collection, use, retention, processing, sharing and security of the data we receive from and about our users. Failure to protect confidential user data, provide users with adequate notice of our privacy policies or obtain valid consent could subject us to liabilities imposed by these jurisdictions. Existing privacy-related laws and regulations are evolving and subject to potentially differing interpretations, and various federal and state legislative and regulatory bodies, as well as foreign legislative and regulatory bodies, may expand current or enact new laws regarding privacy and data protection. For example, the General Data Protection Regulation recently adopted by the European Union will impose more stringent data protection requirements, and significant penalties for noncompliance, beginning on May 25, 2018. In addition, the European Union’s forthcoming ePrivacy Regulation is expected to impose stricter data protection and
P. 12 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
data collection requirements, which we expect will require certain changes in our marketing and advertising practices. The actions needed to comply with existing and newly adopted laws and regulations, or penalties for any failure to comply, could adversely affect our results of operations.
In addition, various federal and state laws and regulations, as well as the laws of foreign jurisdictions, govern the manner in which we market our subscription products, including with respect to pricing and subscription renewals. These laws and regulations often differ across jurisdictions. Failure to comply with these laws and regulations could result in claims against us by governmental entities or others, damage to our reputation and/or increased costs to change our practices.
Any failure, or perceived failure, by us to comply with laws and regulations that govern our business operations, as well as any failure, or perceived failure, by us to comply with our own posted policies, could result in claims against us by governmental entities or others and/or increased costs to change our practices. They could also result in negative publicity and a loss of confidence in us by our users and advertisers. All of these potential consequences could adversely affect our business and results of operations.
Our business may suffer if we cannot protect our intellectual property.
Our business depends on our intellectual property, including our valuable brands, content, services and internally developed technology. We believe our proprietary trademarks and other intellectual property rights are important to our continued success and our competitive position. Unauthorized parties may attempt to copy or otherwise unlawfully obtain and use our content, services, technology and other intellectual property, and we cannot be certain that the steps we have taken to protect our proprietary rights will prevent any misappropriation or confusion among consumers and merchants, or unauthorized use of these rights.
Advancements in technology have made the unauthorized duplication and wide dissemination of content easier, making the enforcement of intellectual property rights more challenging. In addition, as our business and the risk of misappropriation of our intellectual property rights have become more global in scope, we may not be able to protect our proprietary rights in a cost-effective manner in a multitude of jurisdictions with varying laws.
If we are unable to procure, protect and enforce our intellectual property rights, including maintaining and monetizing our intellectual property rights to our content, we may not realize the full value of these assets, and our business and profitability may suffer. In addition, if we must litigate in the United States or elsewhere to enforce our intellectual property rights or determine the validity and scope of the proprietary rights of others, such litigation may be costly and divert the attention of our management.
We have been, and may be in the future, subject to claims of intellectual property infringement that could adversely affect our business.
We periodically receive claims from third parties alleging infringement, misappropriation or other violations of their intellectual property rights. These third parties often include patent holding companies seeking to monetize patents they have purchased or otherwise obtained through asserting claims of infringement or misuse. Even if we believe that these claims of intellectual property infringement are without merit, defending against the claims can be time-consuming, be expensive to litigate or settle, and cause diversion of management attention.
These intellectual property infringement claims, if successful, may require us to enter into royalty or licensing agreements on unfavorable terms, use more costly alternative technology or otherwise incur substantial monetary liability. Additionally, these claims may require us to significantly alter certain of our operations. The occurrence of any of these events as a result of these claims could result in substantially increased costs or otherwise adversely affect our business.
We may not have access to the capital markets on terms that are acceptable to us or may otherwise be limited in our financing options.
From time to time the Company may need or desire to access the long-term and short-term capital markets to obtain financing. The Company’s access to, and the availability of, financing on acceptable terms and conditions in the future will be impacted by many factors, including, but not limited to: (1) the Company’s financial performance; (2) the Company’s credit ratings or absence of a credit rating; (3) liquidity of the overall capital markets and (4) the state of the economy. There can be no assurance that the Company will continue to have access to the capital markets on terms acceptable to it.
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 13
In addition, macroeconomic conditions, such as continued or increased volatility or disruption in the credit markets, could adversely affect our ability to obtain financing to support operations or to fund acquisitions or other capital-intensive initiatives.
Our Class B Common Stock is principally held by descendants of Adolph S. Ochs, through a family trust, and this control could create conflicts of interest or inhibit potential changes of control.
We have two classes of stock: Class A Common Stock and Class B Common Stock. Holders of Class A Common Stock are entitled to elect 30% of the Board of Directors and to vote, with holders of Class B Common Stock, on the reservation of shares for equity grants, certain material acquisitions and the ratification of the selection of our auditors. Holders of Class B Common Stock are entitled to elect the remainder of the Board of Directors and to vote on all other matters. Our Class B Common Stock is principally held by descendants of Adolph S. Ochs, who purchased The Times in 1896. A family trust holds approximately 90% of the Class B Common Stock. As a result, the trust has the ability to elect 70% of the Board of Directors and to direct the outcome of any matter that does not require a vote of the Class A Common Stock. Under the terms of the trust agreement, the trustees are directed to retain the Class B Common Stock held in trust and to vote such stock against any merger, sale of assets or other transaction pursuant to which control of The Times passes from the trustees, unless they determine that the primary objective of the trust can be achieved better by the implementation of such transaction. Because this concentrated control could discourage others from initiating any potential merger, takeover or other change of control transaction that may otherwise be beneficial to our businesses, the market price of our Class A Common Stock could be adversely affected.
Adverse results from litigation or governmental investigations can impact our business practices and operating results.
From time to time, we are party to litigation and regulatory, environmental and other proceedings with governmental authorities and administrative agencies. See Note 18 of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements regarding certain matters. Adverse outcomes in lawsuits or investigations could result in significant monetary damages or injunctive relief that could adversely affect our results of operations or financial condition as well as our ability to conduct our business as it is presently being conducted. In addition, regardless of merit or outcome, such proceedings can have an adverse impact on the Company as a result of legal costs, diversion of management and other personnel, and other factors.
ITEM 1B. UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS |
None.
P. 14 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
ITEM 2. PROPERTIES |
Our principal executive offices are located in our New York headquarters building in the Times Square area. The building was completed in 2007 and consists of approximately 1.54 million gross square feet, of which approximately 828,000 gross square feet of space have been allocated to us. We owned a leasehold condominium interest representing approximately 58% of the New York headquarters building until March 2009, when we entered into an agreement to sell and simultaneously lease back 21 floors, or approximately 750,000 rentable square feet, currently occupied by us (the “Condo Interest”). The sale price for the Condo Interest was $225.0 million. The lease term is 15 years, and we have three renewal options that could extend the term for an additional 20 years. We have an option to repurchase the Condo Interest for $250.0 million in 2019, and we have provided notice of our intent to exercise this option. We continue to own a leasehold condominium interest in seven floors in our New York headquarters building, totaling approximately 216,000 rentable square feet that were not included in the sale-leaseback transaction, all of which are currently leased to third parties.
We are engaged in a plan to consolidate the Company’s operations in our headquarters building from the 17 floors we previously occupied to 10, and to lease the remaining seven floors to third parties. We believe this plan will generate meaningful rental income to the Company and result in a more collaborative workspace.
In addition, we have a printing and distribution facility with 570,000 gross square feet located in College Point, N.Y., on a 31-acre site owned by the City of New York for which we have a ground lease. We have an option to purchase the property before the lease ends in 2019 for $6.9 million. As of December 31, 2017, we also owned other properties with an aggregate of approximately 3,000 gross square feet and leased other properties with an aggregate of approximately 205,000 rentable square feet in various locations.
ITEM 3. LEGAL PROCEEDINGS |
We are involved in various legal actions incidental to our business that are now pending against us. These actions are generally for amounts greatly in excess of the payments, if any, that may be required to be made. See Note 18 of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements for a description of certain matters, which is incorporated herein by reference. Although the Company cannot predict the outcome of these matters, it is possible that an unfavorable outcome in one or more matters could be material to the Company’s consolidated results of operations or cash flows for an individual reporting period. However, based on currently available information, management does not believe that the ultimate resolution of these matters, individually or in the aggregate, is likely to have a material effect on the Company’s financial position.
ITEM 4. MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES |
Not applicable.
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 15
EXECUTIVE OFFICERS OF THE REGISTRANT
Name | Age | Employed By Registrant Since | Recent Position(s) Held as of February 27, 2018 | |||
Mark Thompson | 60 | 2012 | President and Chief Executive Officer (since 2012); Director-General, British Broadcasting Corporation (2004 to 2012) | |||
A.G. Sulzberger | 37 | 2009 | Publisher of The Times (since 2018); Deputy Publisher (2016 to 2017); Associate Editor (2015-2016); Assistant Editor (2012-2015) | |||
R. Anthony Benten | 54 | 1989 | Senior Vice President, Treasurer (since December 2016) and Corporate Controller (since 2007); Senior Vice President, Finance (2008 to 2016) | |||
Diane Brayton | 49 | 2004 | Executive Vice President, General Counsel (since January 2017) and Secretary (since 2011); Deputy General Counsel (2016); Assistant Secretary (2009 to 2011) and Assistant General Counsel (2009 to 2016) | |||
James M. Follo(1) | 58 | 2007 | Executive Vice President (since 2013) and Chief Financial Officer (since 2007); Senior Vice President (2007 to 2013) | |||
Meredith Kopit Levien | 46 | 2013 | Executive Vice President (since 2013) and Chief Operating Officer (since 2017); Chief Revenue Officer (2015 to 2017); Executive Vice President, Advertising (2013 to 2015); Chief Revenue Officer, Forbes Media LLC (2011 to 2013) | |||
(1) Mr. Follo will retire from the Company effective February 28, 2018. As previously disclosed, Roland Caputo, currently Executive Vice President, Print Products and Services Group, will serve as Interim Chief Financial Officer following Mr. Follo’s retirement and until the Company appoints a permanent Chief Financial Officer.
P. 16 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
PART II |
ITEM 5. MARKET FOR THE REGISTRANT’S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES |
MARKET INFORMATION
The Class A Common Stock is listed on the New York Stock Exchange. The Class B Common Stock is unlisted and is not actively traded.
The number of security holders of record as of February 23, 2018, was as follows: Class A Common Stock: 5,662; Class B Common Stock: 21.
We have paid quarterly dividends of $0.04 per share on the Class A and Class B Common Stock since late 2013. We currently expect to continue to pay comparable cash dividends in the future, although changes in our dividend program may be considered by our Board of Directors in light of our earnings, capital requirements, financial condition and other factors considered relevant. In addition, our Board of Directors will consider restrictions in any future indebtedness. See also “Item 7 — Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations — Liquidity and Capital Resources — Third-Party Financing.”
The following table sets forth, for the periods indicated, the high and low closing sales prices for the Class A Common Stock as reported on the New York Stock Exchange.
2017 | 2016 | |||||||||||||||
Quarters | High | Low | High | Low | ||||||||||||
First Quarter | $ | 16.25 | $ | 13.05 | $ | 13.74 | $ | 12.25 | ||||||||
Second Quarter | 17.90 | 14.20 | 13.12 | 11.80 | ||||||||||||
Third Quarter | 19.95 | 17.35 | 13.17 | 11.54 | ||||||||||||
Fourth Quarter | 20.00 | 17.10 | 14.10 | 10.80 | ||||||||||||
ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES(1)
Period | Total number of shares of Class A Common Stock purchased (a) | Average price paid per share of Class A Common Stock (b) | Total number of shares of Class A Common Stock purchased as part of publicly announced plans or programs (c) | Maximum number (or approximate dollar value) of shares of Class A Common Stock that may yet be purchased under the plans or programs (d) | ||||||||||
September 25, 2017 - October 29, 2017 | — | $ | — | — | $ | 16,236,612 | ||||||||
October 30, 2017 - November 26, 2017 | — | $ | — | — | $ | 16,236,612 | ||||||||
November 27, 2017 - December 31, 2017 | — | $ | — | — | $ | 16,236,612 | ||||||||
Total for the fourth quarter of 2017 | — | $ | — | — | $ | 16,236,612 | ||||||||
(1) | On January 13, 2015, the Board of Directors approved an authorization of $101.1 million to repurchase shares of the Company’s Class A Common Stock. As of December 31, 2017, repurchases under this authorization totaled $84.9 million (excluding commissions), and $16.2 million remained under this authorization. All purchases were made pursuant to our publicly announced share repurchase program. Our Board of Directors has authorized us to purchase shares from time to time, subject to market conditions and other factors. There is no expiration date with respect to this authorization. |
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 17
UNREGISTERED SALES OF EQUITY SECURITIES
On September 26, 2017, and December 28, 2017, we issued 2,170 and 5,000 shares, respectively, of Class A Common Stock to holders of Class B Common Stock upon the conversion of such Class B Common Stock into Class A Common Stock. The conversions, which were in accordance with our Certificate of Incorporation, did not involve a public offering and were exempt from registration pursuant to Section 3(a)(9) of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended.
PERFORMANCE PRESENTATION
The following graph shows the annual cumulative total stockholder return for the five fiscal years ended December 31, 2017, on an assumed investment of $100 on December 30, 2012, in the Company, the Standard & Poor’s S&P 400 MidCap Stock Index and the Standard & Poor’s S&P 1500 Publishing and Printing Index. Stockholder return is measured by dividing (a) the sum of (i) the cumulative amount of dividends declared for the measurement period, assuming reinvestment of dividends, and (ii) the difference between the issuer’s share price at the end and the beginning of the measurement period, by (b) the share price at the beginning of the measurement period. As a result, stockholder return includes both dividends and stock appreciation.
Stock Performance Comparison Between the S&P 400 Midcap Index, S&P 1500 Publishing & Printing Index and The New York Times Company’s Class A Common Stock
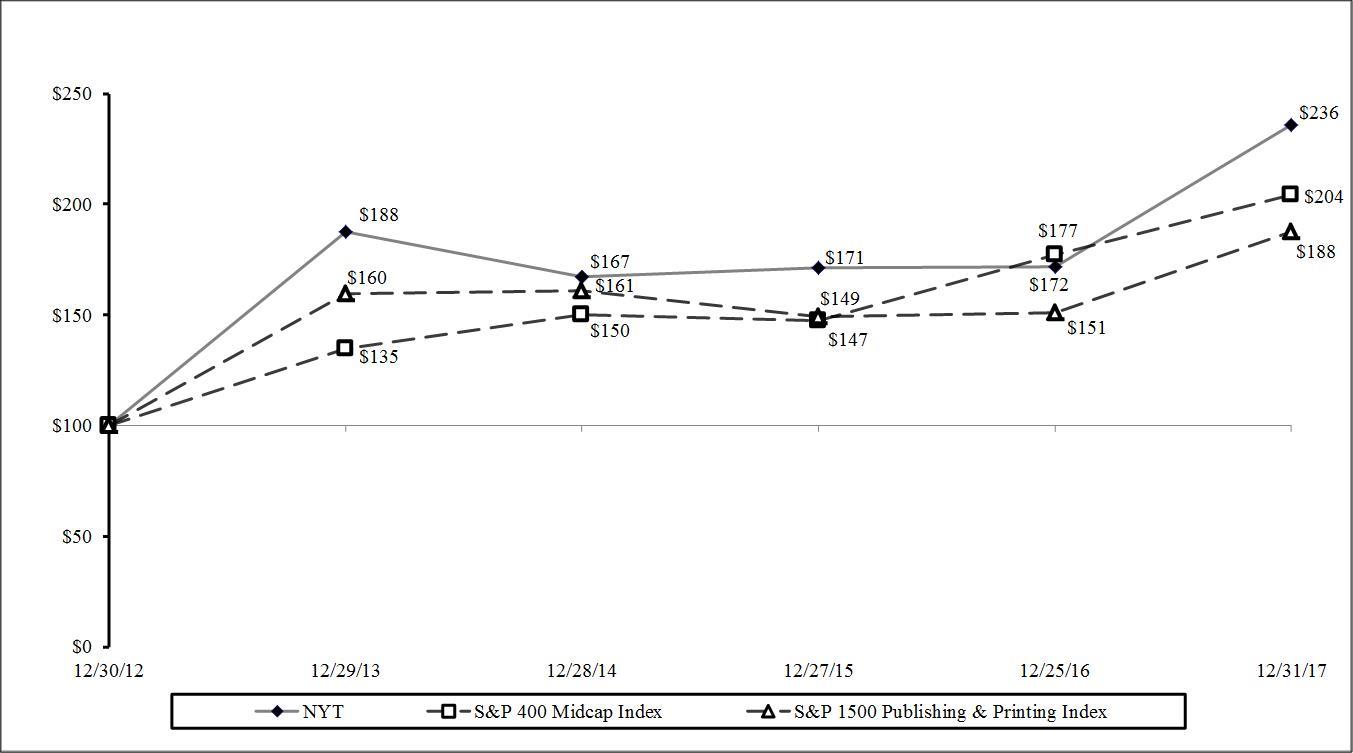
P. 18 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
ITEM 6. SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA |
The Selected Financial Data should be read in conjunction with “Item 7 — Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and the Consolidated Financial Statements and the related Notes in Item 8. The results of operations for the New England Media Group, which was sold in 2013, have been presented as discontinued operations for all periods presented (see Note 13 of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements). The pages following the table show certain items included in Selected Financial Data. All per share amounts on those pages are on a diluted basis. Fiscal year 2017 comprised 53 weeks and all other fiscal years presented in the table below comprised 52 weeks.
As of and for the Years Ended | ||||||||||||||||||||
(In thousands) | December 31, 2017 | December 25, 2016 | December 27, 2015 | December 28, 2014 | December 29, 2013 | |||||||||||||||
(53 Weeks) | (52 Weeks) | (52 Weeks) | (52 Weeks) | (52 Weeks) | ||||||||||||||||
Statement of Operations Data | ||||||||||||||||||||
Revenues | $ | 1,675,639 | $ | 1,555,342 | $ | 1,579,215 | $ | 1,588,528 | $ | 1,577,230 | ||||||||||
Operating costs | 1,488,131 | 1,410,910 | 1,393,246 | 1,484,505 | 1,411,744 | |||||||||||||||
Headquarters redesign and consolidation | 10,090 | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Restructuring charge | — | 14,804 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Multiemployer pension plan withdrawal expense | — | 6,730 | 9,055 | — | 6,171 | |||||||||||||||
Postretirement benefit plan settlement gain | (37,057 | ) | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||
Pension settlement expense | 102,109 | 21,294 | 40,329 | 9,525 | 3,228 | |||||||||||||||
Early termination charge and other expenses | — | — | — | 2,550 | — | |||||||||||||||
Operating profit | 112,366 | 101,604 | 136,585 | 91,948 | 156,087 | |||||||||||||||
Gain/(loss) from joint ventures | 18,641 | (36,273 | ) | (783 | ) | (8,368 | ) | (3,215 | ) | |||||||||||
Interest expense and other, net | 19,783 | 34,805 | 36,050 | 53,730 | 58,073 | |||||||||||||||
Income from continuing operations before income taxes | 111,224 | 30,526 | 96,752 | 29,850 | 94,799 | |||||||||||||||
Income from continuing operations | 7,268 | 26,105 | 62,842 | 33,391 | 56,907 | |||||||||||||||
(Loss)/income from discontinued operations, net of income taxes | (431 | ) | (2,273 | ) | — | (1,086 | ) | 7,949 | ||||||||||||
Net income attributable to The New York Times Company common stockholders | 4,296 | 29,068 | 63,246 | 33,307 | 65,105 | |||||||||||||||
Balance Sheet Data | ||||||||||||||||||||
Cash, cash equivalents and marketable securities | $ | 732,911 | $ | 737,526 | $ | 904,551 | $ | 981,170 | $ | 1,023,780 | ||||||||||
Property, plant and equipment, net | 640,939 | 596,743 | 632,439 | 665,758 | 713,356 | |||||||||||||||
Total assets | 2,099,780 | 2,185,395 | 2,417,690 | 2,566,474 | 2,572,552 | |||||||||||||||
Total debt and capital lease obligations | 250,209 | 246,978 | 431,228 | 650,120 | 684,163 | |||||||||||||||
Total New York Times Company stockholders’ equity | 897,279 | 847,815 | 826,751 | 726,328 | 842,910 | |||||||||||||||
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 19
As of and for the Years Ended | ||||||||||||||||||||
(In thousands, except ratios, per share and employee data) | December 31, 2017 | December 25, 2016 | December 27, 2015 | December 28, 2014 | December 29, 2013 | |||||||||||||||
(53 Weeks) | (52 Weeks) | (52 Weeks) | (52 Weeks) | (52 Weeks) | ||||||||||||||||
Per Share of Common Stock | ||||||||||||||||||||
Basic earnings/(loss) per share attributable to The New York Times Company common stockholders: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Income from continuing operations | $ | 0.03 | $ | 0.19 | $ | 0.38 | $ | 0.23 | $ | 0.38 | ||||||||||
(Loss)/income from discontinued operations, net of income taxes | — | (0.01 | ) | — | (0.01 | ) | 0.05 | |||||||||||||
Net income | $ | 0.03 | $ | 0.18 | $ | 0.38 | $ | 0.22 | $ | 0.43 | ||||||||||
Diluted earnings/(loss) per share attributable to The New York Times Company common stockholders: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Income from continuing operations | $ | 0.03 | $ | 0.19 | $ | 0.38 | $ | 0.21 | $ | 0.36 | ||||||||||
(Loss)/income from discontinued operations, net of income taxes | — | (0.01 | ) | — | (0.01 | ) | 0.05 | |||||||||||||
Net income | $ | 0.03 | $ | 0.18 | $ | 0.38 | $ | 0.20 | $ | 0.41 | ||||||||||
Dividends declared per share | $ | 0.16 | $ | 0.16 | $ | 0.16 | $ | 0.16 | $ | 0.08 | ||||||||||
New York Times Company stockholders’ equity per share | $ | 5.46 | $ | 5.21 | $ | 4.97 | $ | 4.50 | $ | 5.34 | ||||||||||
Average basic shares outstanding | 161,926 | 161,128 | 164,390 | 150,673 | 149,755 | |||||||||||||||
Average diluted shares outstanding | 164,263 | 162,817 | 166,423 | 161,323 | 157,774 | |||||||||||||||
Key Ratios | ||||||||||||||||||||
Operating profit to revenues | 6.7 | % | 6.5 | % | 8.6 | % | 5.8 | % | 9.9 | % | ||||||||||
Return on average common stockholders’ equity | 0.5 | % | 3.5 | % | 8.1 | % | 4.2 | % | 8.7 | % | ||||||||||
Return on average total assets | 0.2 | % | 1.3 | % | 2.5 | % | 1.3 | % | 2.4 | % | ||||||||||
Total debt and capital lease obligations to total capitalization | 21.8 | % | 22.6 | % | 34.3 | % | 47.2 | % | 44.8 | % | ||||||||||
Current assets to current liabilities | 1.80 | 2.00 | 1.53 | 1.91 | 3.36 | |||||||||||||||
Full-Time Equivalent Employees | 3,789 | 3,710 | 3,560 | 3,588 | 3,529 | |||||||||||||||
The items below are included in the Selected Financial Data.
2017 (53-week fiscal year)
The items below had a net unfavorable effect on our Income from continuing operations of $127.3 million, or $.77 per share:
• | $102.1 million pre-tax pension settlement charges ($61.5 million after tax, or $.37 per share) in connection with the transfer of certain pension benefit obligations to insurers. See Note 9 of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements for more information on this item. |
• | a $68.7 million charge ($.42 per share) primarily attributable to the remeasurement of our net deferred tax assets required as a result of recent tax legislation. See Note 12 of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements for more information on this item. |
• | a $37.1 million pre-tax gain ($22.3 million after tax, or $.14 per share) primarily in connection with the settlement of contractual funding obligations for a postretirement plan. See Note 10 of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements for more information on this item. |
• | a $23.9 million pre-tax charge ($14.4 million after tax, or $.09 per share) for severance costs. |
P. 20 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
• | a $15.3 million net pre-tax gain ($7.8 million after tax and net of noncontrolling interest, or $.05 per share) from joint ventures consisting of (i) a $30.1 million gain related to the sale of the remaining assets of Madison Paper Industries, in which the Company has an investment through a subsidiary, (ii) an $8.4 million loss reflecting our proportionate share of Madison’s settlement of pension obligations, and (iii) a $6.4 million loss from the sale of our 49% equity interest in Donahue Malbaie Inc., a Canadian newsprint company. See Note 5 of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements for more information on this item. |
• | $11.2 million of pre-tax expenses ($6.7 million after tax, or $.04 per share) for non-operating retirement costs. |
• | a $10.1 million pre-tax charge ($6.1 million after tax, or $.04 per share) in connection with the ongoing redesign and consolidation of space in our headquarters building. See Note 7 of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements for more information on this item. |
2016
The items below had a net unfavorable effect on our Income from continuing operations of $65.4 million, or $.40 per share:
• | a $37.5 million pre-tax loss ($22.8 million after tax and net of noncontrolling interest, or $.14 per share) from joint ventures related to the announced closure of the paper mill operated by Madison. |
• | a $21.3 million pre-tax pension settlement charge ($12.8 million after tax, or $.08 per share) in connection with lump-sum payments made under an immediate pension benefits offer to certain former employees. |
• | an $18.8 million pre-tax charge ($11.3 million after tax, or $.07 per share) for severance costs. |
• | $15.9 million of pre-tax expenses ($9.5 million after tax, or $.06 per share) for non-operating retirement costs. |
• | a $14.8 million pre-tax charge ($8.8 million after tax, or $.05 per share) in connection with the streamlining of the Company’s international print operations (primarily consisting of severance costs). |
• | a $6.7 million pre-tax charge ($4.0 million after tax or $.02 per share) for a partial withdrawal obligation under a multiemployer pension plan following an unfavorable arbitration decision. |
• | a $3.8 million income tax benefit ($.02 per share) primarily due to a reduction in the Company’s reserve for uncertain tax positions. |
2015
The items below had a net unfavorable effect on our Income from continuing operations of $54.1 million, or $.32 per share:
• | a $40.3 million pre-tax pension settlement charge ($24.0 million after tax, or $.14 per share) in connection with lump-sum payments made under an immediate pension benefits offer to certain former employees. |
• | $34.4 million of pre-tax expenses ($20.5 million after tax, or $.12 per share) for non-operating retirement costs. |
• | a $9.1 million pre-tax charge ($5.4 million after tax, or $.03 per share) for partial withdrawal obligations under multiemployer pension plans. |
• | a $7.0 million pre-tax charge ($4.2 million after tax, or $.03 per share) for severance costs. |
2014
The items below had a net unfavorable effect on our Income from continuing operations of $35.1 million, or $.22 per share:
• | $36.7 million of pre-tax expenses ($21.7 million after tax, or $.13 per share) for non-operating retirement costs. |
• | a $36.1 million pre-tax charge ($21.4 million after tax, or $.13 per share) for severance costs. |
• | a $21.1 million income tax benefit ($.13 per share) primarily due to reductions in the Company’s reserve for uncertain tax positions. |
• | a $9.5 million pre-tax pension settlement charge ($5.7 million after tax, or $.04 per share) in connection with lump-sum payments made under an immediate pension benefits offer to certain former employees. |
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 21
• | a $9.2 million pre-tax charge ($5.9 million after tax or $.04 per share) for an impairment related to the Company’s investment in a joint venture. |
• | a $2.6 million pre-tax charge ($1.5 million after tax, or $.01 per share) for the early termination of a distribution agreement. |
2013
The items below had a net unfavorable effect on our Income from continuing operations of $25.2 million, or $.16 per share:
• | $20.8 million of pre-tax expenses ($12.3 million after tax, or $.08 per share) for non-operating retirement costs. |
• | a $12.4 million pre-tax charge ($7.3 million after tax, or $.05 per share) for severance costs. |
• | a $6.2 million pre-tax charge ($3.7 million after tax, or $.02 per share) for a partial withdrawal obligation under multiemployer pension plans. |
• | a $3.2 million pre-tax pension settlement charge ($1.9 million after tax, or $.01 per share) in connection with lump-sum payments under an immediate pension benefit offer to certain former employees. |
P. 22 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
ITEM 7. MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS |
The following discussion and analysis provides information that management believes is relevant to an assessment and understanding of our consolidated financial condition as of December 31, 2017, and results of operations for the three years ended December 31, 2017. This item should be read in conjunction with our Consolidated Financial Statements and the related Notes included in this Annual Report.
EXECUTIVE OVERVIEW
We are a global media organization that includes newspapers, print and digital products and investments. We have one reportable segment with businesses that include our newspaper, websites, mobile applications and related businesses.
We generate revenues principally from subscriptions and advertising. Other revenues primarily consist of revenues from news services/syndication, digital archive licensing, building rental income, affiliate referrals, NYT Live (our live events business) and retail commerce. Our main operating costs are employee-related costs.
In the accompanying analysis of financial information, we present certain information derived from consolidated financial information but not presented in our financial statements prepared in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States of America (“GAAP”). We are presenting in this report supplemental non-GAAP financial performance measures that exclude depreciation, amortization, severance, non-operating retirement costs and certain identified special items, as applicable. These non-GAAP financial measures should not be considered in isolation from or as a substitute for the related GAAP measures, and should be read in conjunction with financial information presented on a GAAP basis. For further information and reconciliations of these non-GAAP measures to the most directly comparable GAAP measures, see “—Results of Operations—Non-GAAP Financial Measures.”
Fiscal year 2017 comprised 53 weeks, while all other fiscal years presented in this Item 7 comprised 52 weeks.
2017 Financial Highlights
In 2017, diluted earnings per share from continuing operations were $0.03, compared with $0.19 for 2016. Diluted earnings per share from continuing operations excluding severance, non-operating retirement costs and special items discussed below (or “adjusted diluted earnings per share,” a non-GAAP measure) were $0.80 for 2017, compared with $0.57 for 2016.
Operating profit in 2017 was $112.4 million, compared with $101.6 million for 2016. The increase was mainly driven by higher subscription revenues, a postretirement benefit settlement gain and higher digital advertising revenues, partially offset by a pension settlement charge, lower print advertising revenues and higher operating costs. Operating profit before depreciation, amortization, severance, non-operating retirement costs and special items discussed below (or “adjusted operating profit,” a non-GAAP measure) was $284.5 million and $240.9 million for 2017 and 2016, respectively.
Total revenues increased 7.7% to $1.68 billion in 2017 from $1.56 billion in 2016 primarily driven by a significant increase in digital subscription revenue, as well as increased digital advertising revenue, partially offset by a decrease in print advertising revenue.
Subscription revenues increased 14.5% in 2017 compared with 2016, and surpassed $1 billion for the first time in our history. This increase was primarily due to significant growth in the number of subscriptions to the Company’s digital subscription products, as well as the 2017 increase in home-delivery prices for The New York Times newspaper, which more than offset a decline in print copies sold. Revenue from our digital-only subscription products, which include our news product, as well as our Crossword product and Cooking product (which first launched as a paid digital product in the third quarter of 2017), increased 46.2% in 2017 compared with 2016.
Paid digital-only subscriptions totaled approximately 2,644,000 as of December 31, 2017, a 41.8% increase compared with year-end 2016. News product subscriptions totaled approximately 2,231,000 at the end of 2017, a 37.9% increase compared with 2016. Other product subscriptions, which include subscriptions to our Crossword product and Cooking product, totaled approximately 413,000 at the end of 2017, a 67.2% increase compared with 2016.
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 23
Total advertising revenues decreased 3.8% in 2017 compared with 2016, reflecting a 13.9% decrease in print advertising revenues, offset by an 14.2% increase in digital advertising revenues. The decrease in print advertising revenues resulted from a continued decline in display advertising, primarily in the luxury, travel and real estate categories. The increase in digital advertising revenues primarily reflected increases in revenue from smartphone advertising and branded content, partially offset by a continued decrease in traditional website display advertising.
Other revenues increased 15.6% in 2017 compared with 2016, largely due to affiliate referral revenue associated with the product review and recommendation website, Wirecutter, which the Company acquired in October 2016.
Operating costs increased in 2017 to $1.49 billion from $1.41 billion in 2016, driven by higher marketing and compensation costs, partially offset by a decline in outside printing costs and raw materials expense. Operating costs before depreciation, amortization, severance and non-operating retirement costs (or “adjusted operating costs,” a non-GAAP measure) increased in 2017 to $1.39 billion from $1.31 billion in 2016.
Non-operating retirement costs, excluding special items, decreased to $11.2 million in 2017 from $15.9 million in 2016, primarily due to lower multiemployer pension plan withdrawal expense.
Business Environment
We believe that a number of factors and industry trends have had, and will continue to have, an adverse effect on our business and prospects. These include the following:
Competition in our industry
We operate in a highly competitive environment. Our print and digital products compete for subscription and advertising revenue with both traditional and other content providers. Competition among companies offering online content is intense, and new competitors can quickly emerge. Some of our current and potential competitors may have greater resources than we do, which may allow them to compete more effectively than us.
Our ability to compete effectively depends on, among other things, our ability to continue delivering high-quality journalism and content that is interesting and relevant to our audience; the popularity, ease of use and performance of our products compared to those of our competitors; the engagement of our current users with our print and digital products, and our ability to reach new users; our ability to develop, maintain and monetize our products, and the pricing of our products; our ability to attract, retain and motivate talented employees, including journalists and product and technology specialists; and our ability to manage and grow our business in a cost-effective manner.
Evolving subscription model
Subscription revenue is a significant source of revenue for us and an increasingly important driver as the overall composition of our revenues has shifted in response to our “subscription-first” strategy and transformations in our industry. The largest portion of our subscription revenue is currently from our print newspaper, where we have experienced declining print circulation volume in recent years. This is due to, among other factors, increased competition from digital media formats (which are often free to users), higher print subscription and single-copy prices and a growing preference among some consumers to receive their news from sources other than a print newspaper.
Advances in technology have led to an increased number of methods for the delivery and consumption of news and other content. These developments are also driving changes in the preferences and expectations of consumers as they seek more control over how they consume content. Our ability to retain and continue to build on our digital subscription base depends on, among other things, our ability to evolve our subscription model, address changing consumer demands and developments in technology and improve our digital product offering while continuing to deliver high-quality journalism and content that is interesting and relevant to readers.
Advertising market dynamics
We derive substantial revenue from the sale of advertising in our print and digital products. In determining whether to buy advertising, our advertisers consider the demand for our products, demographics of our reader base, advertising rates, results observed by advertisers, and alternative advertising options.
During 2017, the Company, along with others in the industry, continued to experience significant pressure on print advertising revenue. Although print advertising revenue represents a majority of our total advertising revenue,
P. 24 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
the overall proportion continues to decline. The increased popularity of digital media among consumers, particularly as a source for news and other content, has driven a corresponding shift in demand from print advertising to digital advertising. However, our digital advertising revenue has not replaced, and may not replace in full, print advertising revenue lost as a result of the shift.
The digital advertising market continues to undergo significant changes. The increasing number of digital media options available, including through social networking platforms and news aggregation websites, has resulted in audience fragmentation and increased competition for advertising. Competition from new content providers and platforms, some of which charge lower rates than we do or have greater audience reach and targeting capabilities, and the significant increase in inventory of digital advertising space, have affected and will likely continue to affect our ability to attract and retain advertisers and to maintain or increase our advertising rates. In recent years, large digital platforms, such as Facebook, Google and Amazon, which have greater audience reach and targeting capabilities than we do, have commanded an increased share of the digital display advertising market, and we anticipate that this trend will continue.
In addition, digital advertising networks and exchanges, real-time bidding and other programmatic buying channels that allow advertisers to buy audiences at scale are playing a more significant role in the advertising marketplace and may cause further downward pricing pressure.
The character of our digital advertising business also continues to change, as demand for newer forms of advertising, such as branded content and other customized advertising, and video advertising, increases. The margin on revenues from some of these newer advertising forms is generally lower than the margin on revenues we generate from our print advertising and traditional digital display advertising. Consequently, we may experience further downward pressure on our advertising revenue margins as a greater percentage of advertising revenues comes from these newer forms.
In addition, technologies have been and will continue to be developed that enable consumers to block digital advertising on websites and mobile devices. Advertisements blocked by these technologies are treated as not delivered and any revenue we would otherwise receive from the advertiser for that advertisement is lost.
As the digital advertising market continues to evolve, our ability to compete successfully for advertising budgets will depend on, among other things, our ability to engage and grow our audience and prove the value of our advertising and the effectiveness of our platforms to advertisers.
Economic conditions
Global, national and local economic conditions affect various aspects of our business. Our subscription revenue is sensitive to discretionary spending available to subscribers in the markets we serve, and to the extent poor economic conditions lead consumers to reduce spending on discretionary activities, our ability to retain current subscribers and obtain new subscribers could be hindered.
In addition, the level of advertising sales in any period may be affected by advertisers’ decisions to increase or decrease their advertising expenditures in response to anticipated consumer demand and general economic conditions. Changes in spending patterns and priorities, including shifts in marketing strategies and/or budget cuts of key advertisers in response to economic conditions could have an effect on our advertising revenues.
Fixed costs
A significant portion of our costs are fixed, and therefore we are limited in our ability to reduce these costs in the short term. Employee-related costs and raw materials together accounted for approximately half of our total operating costs in 2017. Changes in employee-related costs and the price and availability of newsprint can materially affect our operating results.
For a discussion of these and other factors that could affect our business, results of operations and financial condition, see “Item 1A — Risk Factors.”
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 25
Our Strategy
We are operating during a period of transformation for our industry and amidst uncertain economic conditions. We anticipate that the challenges we currently face will continue, and we believe that the following elements are key to our efforts to address them.
Providing journalism worth paying for
We believe that The Times’s original and high-quality content and journalistic excellence set us apart from other news organizations, and that our readers are willing to pay for trustworthy, insightful and differentiated content.
During 2017, The Times again broke stories and produced investigative reports that sparked global conversations on wide-ranging topics. Our ground-breaking journalism continues to be recognized, most notably in the number of Pulitzer prizes The Times has received — more than any other news organization. In addition, we have continued to make significant investments in our newsroom, adding journalistic talent across a wide range of areas — from our business coverage to our opinion page — and investing in new forms of visual and multimedia journalism.
We believe that the significant growth over the last year in subscriptions to our products demonstrates the success of our “subscription-first” strategy and the willingness of our readers to pay for high-quality journalism. As of December 31, 2017, we had approximately 3.6 million total subscriptions to our products, more than at any point in our history.
As we look ahead to further executing on our strategic priorities, we remain committed to providing high-quality, trustworthy and differentiated content that we believe sets us apart.
Strengthening engagement by becoming an essential part of readers’ daily lives
We continue to focus on deepening the engagement of readers by making The Times an indispensable part of their daily lives. And we continue to communicate the value of independent, high-quality journalism and why it matters.
During 2017, we developed and enhanced products spanning a broad range of topics, interests, formats and platforms. Among other things, we introduced The Daily podcast in early 2017, which became one of the most downloaded podcasts of the year, and launched a monthly insert in our print newspaper dedicated to children. And we continued to make investments in our lifestyle products and services, such as our Crossword and Cooking products and Wirecutter.
We also continued our efforts to reach and engage readers around the world, investing in, among other things, a news bureau in Australia, and opportunities to reach more readers in the United Kingdom, Europe and Canada. In addition, we continued to experiment with reaching new readers on third-party platforms, while remaining focused on building engagement with readers on our own platforms.
Looking ahead, we will continue to explore opportunities to deeply engage readers and further innovate our products, while remaining committed to creating quality content and a quality user experience, regardless of the distribution model or platform.
Creating marketing solutions as compelling as our journalism
We are focused on continuing to grow our digital advertising revenue by developing innovative and compelling advertising offerings that integrate well with the user experience and provide value to advertisers. We believe we have a powerful brand that, because of the quality of our journalism, attracts educated, affluent and influential audiences, and provides a safe and trusted platform for advertisers’ brands.
During 2017, the digital advertising market continued to shift away from traditional desktop display advertising and towards newer advertising forms, such as branded content and other customized forms of advertising, as well as programmatic, video and mobile advertising. We adapted to this market shift, introducing innovative digital advertising solutions for our mobile and other platforms, and providing advertisers new ways of reaching our audience. Looking ahead, we will continue to focus on leveraging our brand in developing and refining our advertising offerings.
P. 26 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
Transforming our operations to deliver on our goals
We are focused on becoming a more effective and efficient organization and have taken and continue to take a number of steps to achieve this. Among other things, we realigned our organizational structure to accelerate our digital transformation, and continue to optimize our product, technology and data systems to improve the speed with which we are able to develop, enhance and deliver our digital products. In addition, we introduced a new editing process in our newsroom intended to further streamline this function, and continued to optimize our print operations and supply chain.
We are also engaged in a plan to redesign our headquarters building and consolidate our operations within a smaller number of floors, and to lease the remaining floors to third parties. We believe this plan will generate meaningful rental income for the Company and result in a more collaborative workspace.
Looking ahead, we will continue to focus on optimizing our organizational and cost structure to ensure that we are operating more efficiently and effectively across functions.
Effectively managing our liquidity and our non-operating costs
We have continued to strengthen our liquidity position and further de-leverage and de-risk our balance sheet. As of December 31, 2017, the Company had cash and cash equivalents and marketable securities of approximately $733 million, which exceeded our total debt and capital lease obligations by approximately $483 million. We believe our cash balance and cash provided by operations, in combination with other sources of cash, will be sufficient to meet our financing needs over the next 12 months.
In March 2009, we entered into an agreement to sell and simultaneously lease back the Condo Interest in our headquarters building. The sale price for the Condo Interest was $225.0 million less transaction costs, for net proceeds of approximately $211 million. We have an option, exercisable in 2019, to repurchase the Condo Interest for $250.0 million, and we have provided notice of our intent to exercise this option. We believe exercising this option is in the best interest of the Company given that the market value of the Condo Interest exceeds the exercise price.
In addition, we remain focused on managing our pension plan obligations. Our qualified pension plans were underfunded (meaning the present value of future benefits obligations exceeded the fair value of plan assets) as of December 31, 2017, by approximately $69 million, compared with approximately $222 million as of December 25, 2016. We made contributions of approximately $128 million, including discretionary contributions of $120 million, to certain qualified pension plans in 2017, compared with approximately $8 million in 2016. We expect contributions made in 2018 to satisfy minimum funding requirements to total approximately $8 million.
We have taken steps over the last several years to reduce the size and volatility of our pension obligations, including freezing accruals under most of our qualified defined benefit pension plans, which cover both our non-union employees and those covered by certain collective bargaining agreements, and making immediate pension benefits offers in the form of lump-sum payments to certain former employees. During 2017, we entered into agreements to transfer certain future benefit obligations and administrative costs to insurers, which allowed us to reduce our overall qualified pension plan obligations by approximately $263 million. See Note 9 of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information on these actions. We will continue to look for ways to reduce the size and volatility of our pension obligations.
While we have made significant progress in our liability-driven investment strategy to reduce the funding volatility of our qualified pension plans, the size of our pension plan obligations relative to the size of our current operations will continue to have a significant impact on our reported financial results. We expect to continue to experience volatility in our retirement-related costs, including pension, multiemployer pension and retiree medical costs.
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 27
RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
Overview
Fiscal year 2017 comprised 53 weeks and fiscal years 2016 and 2015 each comprised 52 weeks. The following table presents our consolidated financial results:
Years Ended | % Change | |||||||||||||||||
(In thousands) | December 31, 2017 | December 25, 2016 | December 27, 2015 | 2017 vs. 2016 | 2016 vs. 2015 | |||||||||||||
(53 weeks) | (52 weeks) | (52 weeks) | ||||||||||||||||
Revenues | ||||||||||||||||||
Subscription | $ | 1,008,431 | $ | 880,543 | $ | 851,790 | 14.5 | 3.4 | ||||||||||
Advertising | 558,513 | 580,732 | 638,709 | (3.8 | ) | (9.1 | ) | |||||||||||
Other | 108,695 | 94,067 | 88,716 | 15.6 | 6.0 | |||||||||||||
Total revenues | 1,675,639 | 1,555,342 | 1,579,215 | 7.7 | (1.5 | ) | ||||||||||||
Operating costs | ||||||||||||||||||
Production costs: | ||||||||||||||||||
Wages and benefits | 362,750 | 363,051 | 354,516 | (0.1 | ) | 2.4 | ||||||||||||
Raw materials | 66,304 | 72,325 | 77,176 | (8.3 | ) | (6.3 | ) | |||||||||||
Other production costs | 186,352 | 192,728 | 186,120 | (3.3 | ) | 3.6 | ||||||||||||
Total production costs | 615,406 | 628,104 | 617,812 | (2.0 | ) | 1.7 | ||||||||||||
Selling, general and administrative costs | 810,854 | 721,083 | 713,837 | 12.4 | 1.0 | |||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 61,871 | 61,723 | 61,597 | 0.2 | 0.2 | |||||||||||||
Total operating costs | 1,488,131 | 1,410,910 | 1,393,246 | 5.5 | 1.3 | |||||||||||||
Headquarters redesign and consolidation | 10,090 | — | — | * | * | |||||||||||||
Restructuring charge | — | 14,804 | — | * | * | |||||||||||||
Multiemployer pension plan withdrawal expense | — | 6,730 | 9,055 | * | (25.7 | ) | ||||||||||||
Postretirement benefit plan settlement gain | (37,057 | ) | — | — | * | * | ||||||||||||
Pension settlement expense | 102,109 | 21,294 | 40,329 | * | (47.2 | ) | ||||||||||||
Operating profit | 112,366 | 101,604 | 136,585 | 10.6 | (25.6 | ) | ||||||||||||
Gain/(loss) from joint ventures | 18,641 | (36,273 | ) | (783 | ) | * | * | |||||||||||
Interest expense and other, net | 19,783 | 34,805 | 39,050 | (43.2 | ) | (10.9 | ) | |||||||||||
Income from continuing operations before income taxes | 111,224 | 30,526 | 96,752 | * | (6.3 | ) | ||||||||||||
Income tax expense | 103,956 | 4,421 | 33,910 | * | (87.0 | ) | ||||||||||||
Income from continuing operations | 7,268 | 26,105 | 62,842 | (72.2 | ) | (58.5 | ) | |||||||||||
Loss from discontinued operations, net of income taxes | (431 | ) | (2,273 | ) | — | (81.0 | ) | * | ||||||||||
Net income | 6,837 | 23,832 | 62,842 | (71.3 | ) | (62.1 | ) | |||||||||||
Net (income)/loss attributable to the noncontrolling interest | (2,541 | ) | 5,236 | 404 | * | * | ||||||||||||
Net income attributable to The New York Times Company common stockholders | $ | 4,296 | $ | 29,068 | $ | 63,246 | (85.2 | ) | (54.0 | ) | ||||||||
* Represents a change equal to or in excess of 100% or one that is not meaningful.
P. 28 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
Revenues
Subscription, advertising and other revenues were as follows:
Years Ended | % Change | |||||||||||||||||
(In thousands) | December 31, 2017 | December 25, 2016 | December 27, 2015 | 2017 vs. 2016 | 2016 vs. 2015 | |||||||||||||
(53 weeks) | (52 weeks) | (52 weeks) | ||||||||||||||||
Subscription | $ | 1,008,431 | $ | 880,543 | $ | 851,790 | 14.5 | 3.4 | ||||||||||
Advertising | 558,513 | 580,732 | 638,709 | (3.8 | ) | (9.1 | ) | |||||||||||
Other | 108,695 | 94,067 | 88,716 | 15.6 | 6.0 | |||||||||||||
Total | $ | 1,675,639 | $ | 1,555,342 | $ | 1,579,215 | 7.7 | (1.5 | ) | |||||||||
Subscription Revenues
In 2017, the Company renamed “circulation revenues” as “subscription revenues.” Subscription revenues consist of revenues from subscriptions to our print and digital products (which include our news product, as well as our Crossword and Cooking products), and single-copy and bulk sales of our print products (which represent approximately 10% of these revenues). Our Cooking product first launched as a paid digital product in the third quarter of 2017. Subscription revenues are based on both the number of copies of the printed newspaper sold and digital-only subscriptions, and the rates charged to the respective customers.
The following tables summarize digital-only subscription revenues for the years ended December 31, 2017, December 25, 2016, and December 27, 2015:
Years Ended | % Change | |||||||||||||||
(In thousands) | December 31, 2017 | December 25, 2016 | December 27, 2015 | 2017 vs. 2016 | 2016 vs. 2015 | |||||||||||
(53 weeks) | (52 weeks) | (52 weeks) | ||||||||||||||
Digital-only subscription revenues: | ||||||||||||||||
News product subscription revenues(1) | $ | 325,956 | $ | 223,459 | $ | 192,657 | 45.9 | 16.0 | ||||||||
Other product subscription revenues(2) | 14,387 | 9,369 | 6,286 | 53.6 | 49.0 | |||||||||||
Total digital-only subscription revenues | $ | 340,343 | $ | 232,828 | $ | 198,943 | 46.2 | 17.0 | ||||||||
(1) Includes revenues from subscriptions to the Company’s news product. News product subscription packages that include access to the Company’s Crossword and Cooking products are also included in this category.
(2) Includes revenues from standalone subscriptions to the Company’s Crossword and Cooking products.
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 29
The following tables summarize digital-only subscriptions as of December 31, 2017, December 25, 2016, and December 27, 2015:
As of | % Change | ||||||||||||
(In thousands) | December 31, 2017 | December 25, 2016 | December 27, 2015 | 2017 vs. 2016 | 2016 vs. 2015 | ||||||||
(53 weeks) | (52 weeks) | (52 weeks) | |||||||||||
Digital-only subscriptions(1): | |||||||||||||
News product subscriptions(2) | 2,231 | 1,618 | 1,094 | 37.9 | 47.9 | ||||||||
Other product subscriptions(3) | 413 | 247 | 176 | 67.2 | 40.3 | ||||||||
Total digital-only subscriptions | 2,644 | 1,865 | 1,270 | 41.8 | 46.9 | ||||||||
(1) Reflects certain immaterial prior-period corrections.
(2) Includes subscriptions to the Company’s news product. News product subscription packages that include access to the Company’s Crossword and Cooking products are also included in this category.
(3) Includes standalone subscriptions to the Company’s Crossword and Cooking products.
2017 Compared with 2016
Subscription revenues increased 14.5% in 2017 compared with 2016. The increase was primarily driven by significant growth in the number of digital-only subscription products, which led to digital-only subscription revenue growth of approximately 46%, as well as an increase of approximately 6% in home-delivery prices for The New York Times newspaper, which more than offset a decline of approximately 1% in print copies sold.
2016 Compared with 2015
Subscription revenues increased in 2016 compared with 2015 primarily due to growth in the number of subscriptions to the Company’s digital-only subscription products and the January 2016 print home-delivery price increase for The Times, partially offset by a reduction in the number of print copies sold. Digital-only subscription revenues were $232.8 million in 2016 compared with $198.9 million in 2015, an increase of 17.0%.
Advertising Revenues
Advertising revenues are derived from the sale of our advertising products and services on our print, web and mobile platforms. These revenues are primarily determined by the volume, rate and mix of advertisements. Display advertising revenue is principally from advertisers promoting products, services or brands in print in the form of column-inch ads, and on our web and mobile platforms in the form of banners, video, rich media and other interactive ads. Display advertising also includes branded content on The Times’s platforms. Classified advertising revenue includes line-ads sold in the major categories of real estate, help wanted, automotive and other. Other advertising revenue primarily includes creative services fees associated with, among other things, our digital marketing agencies and our branded content studio; advertising revenue generated by our product review and recommendation website, Wirecutter; revenue from preprinted advertising, also known as free-standing inserts; and revenue generated from branded bags in which our newspapers are delivered.
2017 Compared with 2016
Years Ended | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
December 31, 2017 | December 25, 2016 | % Change | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(53 weeks) | (52 weeks) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(In thousands) | Print | Digital | Total | Print | Digital | Total | Print | Digital | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Display | $ | 285,679 | $ | 198,658 | $ | 484,337 | $ | 335,652 | $ | 181,545 | $ | 517,197 | (14.9 | )% | 9.4 | % | (6.4 | )% | |||||||||||||||
Classified and Other | 34,543 | 39,633 | 74,176 | $ | 36,328 | 27,207 | 63,535 | (4.9 | )% | 45.7 | % | 16.7 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||
Total advertising | $ | 320,222 | $ | 238,291 | $ | 558,513 | $ | 371,980 | $ | 208,752 | $ | 580,732 | (13.9 | )% | 14.2 | % | (3.8 | )% | |||||||||||||||
P. 30 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
Print advertising revenues, which represented 57% of total advertising revenues in 2017, declined 13.9% to $320.2 million in 2017 compared with $372.0 million in 2016. The decrease was driven by a continued decline in display advertising, primarily in the luxury, travel and real estate categories.
Digital advertising revenues, which represented 43% of total advertising revenues in 2017, increased 14.2% to $238.3 million in 2017 compared with $208.8 million in 2016. The increase in digital advertising revenues primarily reflected increases in revenue from smartphone advertising and branded content, partially offset by a continued decline in traditional website display advertising.
Classified and Other advertising revenues increased 16.7% in 2017 compared with 2016 largely due to increased revenue associated with our digital marketing agencies, HelloSociety and Fake Love, each acquired in 2016, and our branded content studio.
2016 Compared with 2015
Years Ended | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
December 25, 2016 | December 27, 2015 | % Change | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(52 weeks) | (52 weeks) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(In thousands) | Print | Digital | Total | Print | Digital | Total | Print | Digital | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Display | $ | 335,652 | $ | 181,545 | $ | 517,197 | $ | 400,596 | $ | 178,557 | $ | 579,153 | (16.2 | )% | 1.7 | % | (10.7 | )% | |||||||||||||||
Classified and Other | 36,328 | 27,207 | 63,535 | $ | 40,972 | 18,584 | 59,556 | (11.3 | )% | 46.4 | % | 6.7 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||
Total advertising | $ | 371,980 | $ | 208,752 | $ | 580,732 | $ | 441,568 | $ | 197,141 | $ | 638,709 | (15.8 | )% | 5.9 | % | (9.1 | )% | |||||||||||||||
Print advertising revenues, which represented 64% of total advertising revenues in 2016, declined 15.8% to $372.0 million in 2016 compared with $441.6 million in 2015. The decrease was driven by a continued decline in display advertising, primarily in the luxury goods, entertainment, retail and technology categories.
Digital advertising revenues, which represented 36% of total advertising revenues in 2016, increased 5.9% to $208.8 million in 2016 compared with $197.1 million in 2015 due to an increase in revenue from smartphone advertising, our programmatic buying channels and branded content distribution. Revenues from our digital marketing agencies, HelloSociety and Fake Love, each acquired in 2016, also contributed favorably to this increase. This increase was partially offset by a decline in traditional desktop display advertising.
Classified and Other advertising revenues increased 6.7% in 2016 compared with 2015 due to an increase in creative services fees related to branded content campaign launches during 2016. This was partially offset by a decrease in the real estate, help wanted and other categories.
Other Revenues
Other revenues primarily consist of revenues from news services/syndication, digital archive licensing, building rental income, affiliate referrals, NYT Live (our live events business) and retail commerce. Digital other revenues consists primarily of digital archive licensing revenue and affiliate referral revenue. Building rental income consists of revenue from the lease of floors in our New York headquarters building, which totaled $16.7 million, $17.1 million and $16.9 million in 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively.
2017 Compared with 2016
Other revenues increased 15.6% in 2017 compared with 2016 largely due to affiliate referral revenue associated with the product review and recommendation website, Wirecutter, which the Company acquired in October 2016. Digital other revenues totaled $41.7 million in 2017, an 83.7% increase compared with 2016, driven primarily by affiliate referral revenue associated with Wirecutter.
2016 Compared with 2015
Other revenues increased 6.0% in 2016 compared with 2015 largely due to affiliate referral revenue associated with our acquisition in October 2016 of Wirecutter, as well as from our NYT Live business. Digital other revenues totaled $22.7 million in 2016, a 14.1% increase compared with 2015, driven primarily by affiliate referral revenue associated with Wirecutter.
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 31
Operating Costs
Operating costs were as follows:
Years Ended | % Change | |||||||||||||||||
(In thousands) | December 31, 2017 | December 25, 2016 | December 27, 2015 | 2017 vs. 2016 | 2016 vs. 2015 | |||||||||||||
(53 weeks) | (52 weeks) | (52 weeks) | ||||||||||||||||
Production costs: | ||||||||||||||||||
Wages and benefits | $ | 362,750 | $ | 363,051 | $ | 354,516 | (0.1 | ) | 2.4 | |||||||||
Raw materials | 66,304 | 72,325 | 77,176 | (8.3 | ) | (6.3 | ) | |||||||||||
Other production costs | 186,352 | 192,728 | 186,120 | (3.3 | ) | 3.6 | ||||||||||||
Total production costs | 615,406 | 628,104 | 617,812 | (2.0 | ) | 1.7 | ||||||||||||
Selling, general and administrative costs | 810,854 | 721,083 | 713,837 | 12.4 | 1.0 | |||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 61,871 | 61,723 | 61,597 | 0.2 | 0.2 | |||||||||||||
Total operating costs | $ | 1,488,131 | $ | 1,410,910 | $ | 1,393,246 | 5.5 | 1.3 | ||||||||||
The components of operating costs as a percentage of total operating costs were as follows:
Years Ended | |||||||||
December 31, 2017 | December 25, 2016 | December 27, 2015 | |||||||
(53 weeks) | (52 weeks) | (52 weeks) | |||||||
Components of operating costs as a percentage of total operating costs | |||||||||
Wages and benefits | 46 | % | 45 | % | 44 | % | |||
Raw materials | 4 | % | 5 | % | 6 | % | |||
Other operating costs | 46 | % | 46 | % | 46 | % | |||
Depreciation and amortization | 4 | % | 4 | % | 4 | % | |||
Total | 100 | % | 100 | % | 100 | % | |||
The components of operating costs as a percentage of total revenues were as follows:
Years Ended | |||||||||
December 31, 2017 | December 25, 2016 | December 27, 2015 | |||||||
(53 weeks) | (52 weeks) | (52 weeks) | |||||||
Components of operating costs as a percentage of total revenues | |||||||||
Wages and benefits | 40 | % | 41 | % | 39 | % | |||
Raw materials | 4 | % | 5 | % | 5 | % | |||
Other operating costs | 41 | % | 41 | % | 40 | % | |||
Depreciation and amortization | 4 | % | 4 | % | 4 | % | |||
Total | 89 | % | 91 | % | 88 | % | |||
P. 32 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
Production Costs
Production costs include items such as labor costs, raw materials and machinery and equipment expenses related to news-gathering and production activity, as well as costs related to producing branded content.
2017 Compared with 2016
Production costs decreased in 2017 compared with 2016, primarily driven by a decrease in other production costs (approximately $6 million) and raw materials expense (approximately $6 million). Other production costs decreased primarily as a result of lower outside printing expenses (approximately $5 million). Raw materials expense decreased primarily due to lower newsprint consumption (approximately $6 million).
2016 Compared with 2015
Production costs increased in 2016 compared with 2015 primarily due to higher wages and benefits (approximately $9 million) and other production costs (approximately $7 million), which consisted mainly of outside services (approximately $9 million) and travel and entertainment (approximately $2 million), offset by lower outside printing expenses (approximately $5 million). Newsprint expense declined 6.6% in 2016 compared with 2015, with 6.1% from lower consumption and 0.5% from lower pricing.
Selling, General and Administrative Costs
Selling, general and administrative costs include costs associated with the selling, marketing and distribution of products as well as administrative expenses.
2017 Compared with 2016
Selling, general and administrative costs increased in 2017 compared with 2016, primarily due to an increase in compensation costs (approximately $47 million), promotion and marketing costs (approximately $26 million) and severance costs (approximately $5 million). Compensation costs increased primarily as a result of higher incentive compensation, increased hiring to support growth initiatives, and higher benefit costs. Promotion and marketing costs increased due to increased spending to promote our subscription business and brand. Severance costs increased due to a workforce reduction announced in the second quarter of 2017 primarily affecting our newsroom.
2016 Compared with 2015
Selling, general and administrative costs increased in 2016 compared with 2015 primarily due to an increase in severance costs (approximately $12 million), compensation costs (approximately $11 million) and promotion costs (approximately $8 million), partially offset by a decrease in non-operating retirement costs (approximately $19 million) and distribution costs (approximately $6 million). Compensation costs increased primarily as a result of increased hiring to support growth initiatives and business acquisitions. Distribution costs decreased primarily as a result of fewer print copies produced and lower transportation costs.
Depreciation and Amortization
2017 Compared with 2016
Depreciation and amortization costs were flat in 2017 compared with 2016.
2016 Compared with 2015
Depreciation and amortization costs were flat in 2016 compared with 2015.
Other Items
See Note 7 of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements for more information regarding other items.
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 33
NON-OPERATING ITEMS
Investments in Joint Ventures
See Note 5 of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements for information regarding our joint venture investments.
Interest Expense and Other, Net
See Note 6 of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements for information regarding interest expense and other.
Income Taxes
See Note 12 of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements for information regarding income taxes.
Discontinued Operations
See Note 13 of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements for information regarding discontinued operations.
Non-GAAP Financial Measures
We have included in this report certain supplemental financial information derived from consolidated financial information but not presented in our financial statements prepared in accordance with GAAP. Specifically, we have referred to the following non-GAAP financial measures in this report:
• | diluted earnings per share from continuing operations excluding severance, non-operating retirement costs and the impact of special items (or adjusted diluted earnings per share from continuing operations); |
• | operating profit before depreciation, amortization, severance, non-operating retirement costs and special items (or adjusted operating profit); and |
• | operating costs before depreciation, amortization, severance and non-operating retirement costs (or adjusted operating costs). |
The special items in 2017 consisted of:
• | $102.1 million pre-tax pension settlement charges ($61.5 million after tax, or $.38 per share) in connection with the transfer of certain pension benefit obligations to insurers. |
• | a $68.7 million charge ($.42 per share) primarily attributable to the remeasurement of our net deferred tax assets required as a result of recent tax legislation. |
• | a $37.1 million pre-tax gain ($22.3 million after tax, or $.14 per share) primarily in connection with the settlement of contractual funding obligations for a postretirement plan. |
• | a $15.3 million pre-tax net gain ($7.8 million after tax and net of noncontrolling interest, or $.05 per share) from joint ventures consisting of (i) a $30.1 million gain related to the sale of the remaining assets of Madison, (ii) an $8.4 million loss reflecting our proportionate share of Madison’s settlement of pension obligations, and (iii) a $6.4 million loss from the sale of our 49% equity interest in Malbaie. |
• | a $10.1 million pre-tax charge ($6.1 million after tax, or $.04 per share) in connection with the ongoing redesign and consolidation of space in our headquarters building. |
The special items in 2016 consisted of:
• | a $37.5 million pre-tax loss ($22.8 million after tax and net of noncontrolling interest, or $.14 per share) from joint ventures related to the announced closure of the paper mill operated by Madison. |
• | a $21.3 million pre-tax pension settlement charge ($12.8 million after tax, or $.08 per share) in connection with lump-sum payments made under an immediate pension benefits offer to certain former employees; |
• | a $14.8 million pre-tax charge ($8.8 million after tax, or $.05 per share) in connection with the streamlining of the Company’s international print operations (primarily consisting of severance costs); |
P. 34 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
• | a $6.7 million pre-tax charge ($4.0 million after tax, or $.02 per share) for a partial withdrawal obligation under a multiemployer pension plan following an unfavorable arbitration decision; and |
• | a $3.8 million income tax benefit ($.02 per share) primarily due to a reduction in the Company’s reserve for uncertain tax positions. |
The special items in 2015 consisted of:
• | a $40.3 million pre-tax pension settlement charge ($24.0 million after tax, or $.14 per share) in connection with lump-sum payments made under an immediate pension benefits offer to certain former employees; and |
• | a $9.1 million pre-tax charge ($5.4 million after tax, or $.03 per share) for partial withdrawal obligations under multiemployer pension plans. |
We have included these non-GAAP financial measures because management reviews them on a regular basis and uses them to evaluate and manage the performance of our operations. We believe that, for the reasons outlined below, these non-GAAP financial measures provide useful information to investors as a supplement to reported diluted earnings/(loss) per share from continuing operations, operating profit/(loss) and operating costs. However, these measures should be evaluated only in conjunction with the comparable GAAP financial measures and should not be viewed as alternative or superior measures of GAAP results.
Adjusted diluted earnings per share provides useful information in evaluating our period-to-period performance because it eliminates items that we do not consider to be indicative of earnings from ongoing operating activities. Adjusted operating profit is useful in evaluating the ongoing performance of our businesses as it excludes the significant non-cash impact of depreciation and amortization as well as items not indicative of ongoing operating activities. Total operating costs include depreciation, amortization, severance and non-operating retirement costs. Adjusted operating costs, which exclude these items, provide investors with helpful supplemental information on our underlying operating costs that is used by management in its financial and operational decision-making.
Management considers special items, which may include impairment charges, pension settlement charges and other items that arise from time to time, to be outside the ordinary course of our operations. Management believes that excluding these items provides a better understanding of the underlying trends in the Company’s operating performance and allows more accurate comparisons of the Company’s operating results to historical performance. In addition, management excludes severance costs, which may fluctuate significantly from quarter to quarter, because it believes these costs do not necessarily reflect expected future operating costs and do not contribute to a meaningful comparison of the Company’s operating results to historical performance.
Non-operating retirement costs include:
• | interest cost, expected return on plan assets and amortization of actuarial gain and loss components of pension expense; |
• | interest cost and amortization of actuarial gain and loss components of retiree medical expense; and |
• | all expenses associated with multiemployer pension plan withdrawal obligations not otherwise included as special items. |
These non-operating retirement costs are primarily tied to financial market performance and changes in market interest rates and investment performance. Non-operating retirement costs do not include service costs and amortization of prior service costs for pension and retiree medical benefits, which we believe reflect the ongoing operating costs of providing pension and retiree medical benefits to our employees. We consider non-operating retirement costs to be outside the performance of our ongoing core business operations and believe that presenting operating results excluding non-operating retirement costs, in addition to our GAAP operating results, provides increased transparency and a better understanding of the underlying trends in our operating business performance.
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 35
Reconciliations of non-GAAP financial measures from, respectively, diluted earnings per share from continuing operations, operating profit and operating costs, the most directly comparable GAAP items, as well as details on the components of non-operating retirement costs, are set out in the tables below.
Reconciliation of diluted earnings per share from continuing operations excluding severance, non-operating retirement costs and special items (or adjusted diluted earnings per share from continuing operations) | ||||||||||||||||||
Years Ended | % Change | |||||||||||||||||
December 31, 2017 | December 25, 2016 | December 27, 2015 | 2017 vs. 2016 | 2016 vs. 2015 | ||||||||||||||
(53 weeks) | (52 weeks) | (52 weeks) | ||||||||||||||||
Diluted earnings per share from continuing operations | $ | 0.03 | $ | 0.19 | $ | 0.38 | (84.2 | %) | (50.0 | %) | ||||||||
Add: | ||||||||||||||||||
Severance | 0.15 | 0.12 | 0.04 | 25.0 | % | * | ||||||||||||
Non-operating retirement costs | 0.07 | 0.10 | 0.21 | (30.0 | %) | (52.4 | %) | |||||||||||
Special items: | ||||||||||||||||||
Headquarters redesign and consolidation | 0.06 | — | — | * | * | |||||||||||||
Restructuring charge | — | 0.09 | — | * | * | |||||||||||||
Pension settlement expense | 0.62 | 0.13 | 0.24 | * | (45.8 | )% | ||||||||||||
Multiemployer pension plan withdrawal expense | — | 0.04 | 0.05 | * | (20.0 | )% | ||||||||||||
Postretirement benefit plan settlement gain | (0.23 | ) | — | — | * | * | ||||||||||||
Loss in joint ventures, net of tax and noncontrolling interest | (0.08 | ) | 0.18 | — | * | * | ||||||||||||
Income tax expense of special items | (0.24 | ) | (0.26 | ) | (0.22 | ) | (7.7 | )% | 18.2 | % | ||||||||
Reduction in reserve for uncertain tax positions | — | (0.02 | ) | — | * | * | ||||||||||||
Deferred tax asset remeasurement adjustment | 0.42 | — | — | * | * | |||||||||||||
Adjusted diluted earnings per share from continuing operations (1) | $ | 0.80 | $ | 0.57 | $ | 0.71 | 40.4 | % | (19.7 | )% | ||||||||
(1) Amounts may not add due to rounding.
* Represents a change equal to or in excess of 100% or one that is not meaningful.
P. 36 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
Reconciliation of operating profit before depreciation & amortization, severance, non-operating retirement costs and special items (or adjusted operating profit) | ||||||||||||||||||
Years Ended | % Change | |||||||||||||||||
(In thousands) | December 31, 2017 | December 25, 2016 | December 27, 2015 | 2017 vs. 2016 | 2016 vs. 2015 | |||||||||||||
(53 weeks) | (52 weeks) | (52 weeks) | ||||||||||||||||
Operating profit | $ | 112,366 | $ | 101,604 | $ | 136,585 | 10.6 | % | (25.6 | )% | ||||||||
Add: | ||||||||||||||||||
Depreciation & amortization | 61,871 | 61,723 | 61,597 | 0.2 | % | 0.2 | % | |||||||||||
Severance | 23,949 | 18,829 | 7,035 | 27.2 | % | * | ||||||||||||
Non-operating retirement costs | 11,152 | 15,880 | 34,383 | (29.8 | )% | (53.8 | )% | |||||||||||
Special items: | ||||||||||||||||||
Headquarters redesign and consolidation | 10,090 | — | — | * | * | |||||||||||||
Restructuring charge | — | 14,804 | — | * | * | |||||||||||||
Multiemployer pension plan withdrawal expense | — | 6,730 | 9,055 | * | (25.7 | )% | ||||||||||||
Postretirement benefit plan settlement gain | (37,057 | ) | — | — | * | * | ||||||||||||
Pension settlement expense | 102,109 | 21,294 | 40,329 | * | (47.2 | )% | ||||||||||||
Adjusted operating profit | $ | 284,480 | $ | 240,864 | $ | 288,984 | 18.1 | % | (16.7 | )% | ||||||||
* Represents a change equal to or in excess of 100% or one that is not meaningful.
Reconciliation of operating costs before depreciation & amortization, severance and non-operating retirement costs (or adjusted operating costs) | ||||||||||||||||||
Years Ended | % Change | |||||||||||||||||
(In thousands) | December 31, 2017 | December 25, 2016 | December 27, 2015 | 2017 vs. 2016 | 2016 vs. 2015 | |||||||||||||
(53 weeks) | (52 weeks) | (52 weeks) | ||||||||||||||||
Operating costs | $ | 1,488,131 | $ | 1,410,910 | $ | 1,393,246 | 5.5 | % | 1.3 | % | ||||||||
Less: | ||||||||||||||||||
Depreciation & amortization | 61,871 | 61,723 | 61,597 | 0.2 | % | 0.2 | % | |||||||||||
Severance | 23,949 | 18,829 | 7,035 | 27.2 | % | * | ||||||||||||
Non-operating retirement costs | 11,152 | 15,880 | 34,383 | (29.8 | )% | (53.8 | )% | |||||||||||
Adjusted operating costs | $ | 1,391,159 | $ | 1,314,478 | $ | 1,290,231 | 5.8 | % | 1.9 | % | ||||||||
* Represents a change equal to or in excess of 100% or one that is not meaningful.
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 37
LIQUIDITY AND CAPITAL RESOURCES
Overview
The following table presents information about our financial position.
Financial Position Summary
% Change | |||||||||||
(In thousands, except ratios) | December 31, 2017 | December 25, 2016 | 2017 vs. 2016 | ||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 182,911 | $ | 100,692 | 81.7 | ||||||
Marketable securities | 550,000 | 636,834 | (13.6 | ) | |||||||
Long-term debt and capital lease obligations | 250,209 | 246,978 | 1.3 | ||||||||
Total New York Times Company stockholders’ equity | 897,279 | 847,815 | 5.8 | ||||||||
Ratios: | |||||||||||
Total debt and capital lease obligations to total capitalization | 21.8 | % | 22.6 | % | |||||||
Current assets to current liabilities | 1.80 | 2.00 | |||||||||
Our primary sources of cash inflows from operations were revenues from subscription and advertising sales. Subscription and advertising revenues provided about 60% and 33%, respectively, of total revenues in 2017. The remaining cash inflows were primarily from other revenue sources such as news services/syndication, digital archive licensing, building rental income, affiliate referrals, NYT Live (our live events business) and retail commerce.
Our primary sources of cash outflows were for employee compensation and benefits and other operating expenses. We believe our cash and cash equivalents, marketable securities balance and cash provided by operations, in combination with other sources of cash, will be sufficient to meet our financing needs over the next 12 months.
We have continued to strengthen our liquidity position and our debt profile. As of December 31, 2017, we had cash, cash equivalents and marketable securities of $732.9 million and total debt and capital lease obligations of $250.2 million. Accordingly, our cash, cash equivalents and marketable securities exceeded total debt and capital lease obligations by $482.7 million. Included within marketable securities is approximately $63 million of securities used as collateral for letters of credit issued by the Company in connection with the leasing of floors in our headquarters building. See Note 18 of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements for more information regarding these letters of credit. Our cash, cash equivalent and marketable securities balances decreased in 2017 primarily due to contributions of approximately $128 million to certain qualified pension plans, partially offset by higher revenues.
We have paid quarterly dividends of $0.04 per share on the Class A and Class B Common Stock since late 2013. We currently expect to continue to pay comparable cash dividends in the future, although changes in our dividend program will be considered by our Board of Directors in light of our earnings, capital requirements, financial condition and other factors considered relevant.
In March 2009, we entered into an agreement to sell and simultaneously lease back the Condo Interest in our headquarters building. The sale price for the Condo Interest was $225.0 million less transaction costs, for net proceeds of approximately $211 million. We have an option, exercisable in 2019, to repurchase the Condo Interest for $250.0 million, and we have provided notice of our intent to exercise this option. We believe that exercising this option is in the best interest of the Company given that the market value of the Condo Interest exceeds the exercise price.
During 2017, we made contributions of approximately $128 million to certain qualified pension plans funded by cash on hand. This included $120 million of discretionary contributions and $8 million of contributions to satisfy minimum funding requirements. As of December 31, 2017, the underfunded balance of our qualified pension plans was approximately $69 million, a reduction of approximately $153 million from December 25, 2016. We expect contributions made to satisfy minimum funding requirements to total approximately $8 million in 2018.
As part of our continued effort to reduce the size and volatility of our pension obligations, in 2017, the Company entered into arrangements with insurers to transfer certain future benefit obligations and administrative
P. 38 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
costs for certain qualified pension plans. These transactions allowed us to reduce our overall qualified pension plan obligations by approximately $263 million. See Note 9 of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements for more information.
The Company and UPM-Kymmene Corporation (“UPM”), a Finnish paper manufacturing company, are partners through subsidiary companies in Madison, which previously operated a supercalendered paper mill in Maine. The paper mill closed in May 2016 and the Company’s joint venture in Madison is currently being liquidated. In the fourth quarter of 2016, Madison sold certain assets at the mill site and we recognized a gain of $3.9 million related to the sale. In 2017 we recognized a net gain of $20.8 million, reflecting our proportionate share of the gain recognized by Madison related to the sale of the remaining assets of the paper mill, partially offset by a loss related to our share of Madison’s settlement of pension obligations. The Company’s proportionate share of the gain was $11.6 million after tax and net of noncontrolling interest. In 2018, we expect to receive a cash distribution of approximately $12 million related to the wind down of our Madison investment. See Note 5 of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements for more information on the Company’s investment in Madison.
In early 2015, entities controlled by Carlos Slim Helú, a beneficial owner of our Class A Common Stock, exercised warrants to purchase 15.9 million shares of our Class A Common Stock at a price of $6.3572 per share, and the Company received cash proceeds of approximately $101.1 million from this exercise. Concurrently, the Board of Directors terminated an existing authorization to repurchase shares of the Company’s Class A Common Stock and approved a new repurchase authorization of $101.1 million, equal to the cash proceeds received by the Company from the warrant exercise. As of December 31, 2017, total repurchases under this authorization totaled $84.9 million (excluding commissions) and $16.2 million remained under this authorization. Our Board of Directors has authorized us to purchase shares from time to time, subject to market conditions and other factors. There is no expiration date with respect to this authorization.
Capital Resources
Sources and Uses of Cash
Cash flows provided by/(used in) by category were as follows:
Years Ended | % Change | |||||||||||||||||
(In thousands) | December 31, 2017 | December 25, 2016 | December 27, 2015 | 2017 vs. 2016 | 2016 vs. 2015 | |||||||||||||
Operating activities | $ | 86,712 | $ | 103,876 | $ | 179,075 | (16.5 | ) | (42.0 | ) | ||||||||
Investing activities | $ | 21,019 | $ | 128,272 | $ | (30,703 | ) | (83.6 | ) | * | ||||||||
Financing activities | $ | (26,019 | ) | $ | (237,024 | ) | $ | (217,960 | ) | (89.0 | ) | 8.7 | ||||||
* Represents an increase or decrease in excess of 100%.
Operating Activities
Cash from operating activities is generated by cash receipts from subscriptions, advertising sales and other revenue. Operating cash outflows include payments for employee compensation, pension and other benefits, raw materials, interest and income taxes.
Net cash provided by operating activities decreased in 2017 compared with 2016 due to contributions totaling approximately $128 million to certain qualified pension plans, partially offset by higher revenues and lower tax payments.
Net cash provided by operating activities decreased in 2016 compared with 2015 due to higher income tax payments, higher employee compensation payments, higher marketing costs and an overall decline in revenues. We made income tax payments of approximately $45 million in 2016 compared with approximately $21 million in 2015.
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 39
Investing Activities
Cash from investing activities generally includes proceeds from marketable securities that have matured and the sale of assets, investments or a business. Cash used in investing activities generally includes purchases of marketable securities, payments for capital projects, restricted cash (the majority of which is set aside to collateralize workers’ compensation obligations), acquisitions of new businesses and investments.
Net cash provided by investing activities in 2017 was primarily related to maturities and disposals of marketable securities of $548.5 million and proceeds from the sale of our 49% share in Malbaie of $15.6 million, offset by purchases of marketable securities of $466.5 million and capital expenditures of $84.8 million.
Net cash provided by investing activities in 2016 was primarily due to maturities of marketable securities, offset by purchases of marketable securities and a cash distribution of $38.0 million from the liquidation of certain investments related to our corporate-owned life insurance, consideration paid for acquisitions of $40.4 million and payments for capital expenditures of $30.1 million.
Net cash used in investing activities in 2015 was primarily due to purchases of marketable securities, offset by maturities of marketable securities and payments for capital expenditures.
Payments for capital expenditures were approximately $85 million, $30 million and $27 million in 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively.
Financing Activities
Cash from financing activities generally includes borrowings under third-party financing arrangements, the issuance of long-term debt and funds from stock option exercises. Cash used in financing activities generally includes the repayment of amounts outstanding under third-party financing arrangements, the payment of dividends and the payment of long-term debt and capital lease obligations.
Net cash used in financing activities in 2017 was primarily related to dividend payments ($26.0 million).
Net cash used in financing activities in 2016 was primarily related to the repayment, at maturity, of the $189.2 million remaining principal amount under our 6.625% senior notes in December 2016, dividend payments of $25.9 million and share repurchases of $15.7 million.
Net cash used in financing activities in 2015 was primarily related to the repayment, at maturity, of $223.7 million remaining under our 5.0% senior notes, share repurchases of $69.3 million and dividend payments of $26.6 million, partially offset by $101.1 million of proceeds from the exercise of warrants.
See “— Third-Party Financing” below and our Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for additional information on our sources and uses of cash.
Restricted Cash
We were required to maintain $18.0 million of restricted cash as of December 31, 2017 and $24.9 million as of December 25, 2016, the majority of which is set aside to collateralize workers’ compensation obligations.
Capital Expenditures
Capital expenditures totaled approximately $104 million, $26 million and $29 million in 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively. The cash payments related to the capital expenditures totaled approximately $85 million, $30 million and $27 million in 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively. The increase was primarily driven by the ongoing redesign and consolidation of space in our headquarters building and certain improvements at our printing and distribution facility in College Point, New York.
Third-Party Financing
As of December 31, 2017, our current indebtedness consisted of the repurchase option related to a sale-leaseback of a portion of our New York headquarters. See Note 6 for information regarding our total debt and capital lease obligations. See Note 8 for information regarding the fair value of our long-term debt.
P. 40 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
Contractual Obligations
The information provided is based on management’s best estimate and assumptions of our contractual obligations as of December 31, 2017. Actual payments in future periods may vary from those reflected in the table.
Payment due in | ||||||||||||||||||||
(In thousands) | Total | 2018 | 2019-2020 | 2021-2022 | Later Years | |||||||||||||||
Debt(1) | $ | 303,086 | $ | 27,554 | $ | 275,532 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||||
Capital leases(2) | 7,797 | 552 | 7,245 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Operating leases(2) | 52,681 | 10,738 | 13,685 | 9,703 | 18,555 | |||||||||||||||
Benefit plans(3) | 475,546 | 52,177 | 98,159 | 94,201 | 231,009 | |||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 839,110 | $ | 91,021 | $ | 394,621 | $ | 103,904 | $ | 249,564 | ||||||||||
(1) | Includes estimated interest payments on long-term debt. See Note 6 of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information related to our debt. |
(2) | See Note 18 of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information related to our capital and operating leases. |
(3) | The Company's general funding policy with respect to qualified pension plans is to contribute amounts at least sufficient to satisfy the minimum amount required by applicable law and regulations. Contributions for our qualified pension plans and future benefit payments for our unfunded pension and other postretirement benefit payments have been estimated over a 10-year period; therefore, the amounts included in the “Later Years” column only include payments for the period of 2023-2027. For our funded qualified pension plans, estimating funding depends on several variables, including the performance of the plans' investments, assumptions for discount rates, expected long-term rates of return on assets, rates of compensation increases and other factors. Thus, our actual contributions could vary substantially from these estimates. While benefit payments under these plans are expected to continue beyond 2027, we have included in this table only those benefit payments estimated over the next 10 years. Benefit plans in the table above also include estimated payments for multiemployer pension plan withdrawal liabilities. See Notes 9 and 10 of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information related to our pension and other postretirement benefits plans. |
“Other Liabilities — Other” in our Consolidated Balance Sheets include liabilities related to (1) deferred compensation, primarily related to our deferred executive compensation plan (the “DEC”) and (2) various other liabilities, including our contingent tax liability for uncertain tax positions. These liabilities are not included in the table above primarily because the future payments are not determinable. See Note 11 of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information.
The DEC enables certain eligible executives to elect to defer a portion of their compensation on a pre-tax basis. The deferred amounts are invested at the executives’ option in various mutual funds. The fair value of deferred compensation is based on the mutual fund investments elected by the executives and on quoted prices in active markets for identical assets. The DEC was frozen effective December 31, 2015, and no new contributions may be made into the plan. See Note 11 of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information on “Other Liabilities — Other.”
Our liability for uncertain tax positions was approximately $19.3 million, including approximately $2.2 million of accrued interest as of December 31, 2017. Until formal resolutions are reached between us and the tax authorities, the timing and amount of a possible audit settlement for uncertain tax benefits is not practicable. Therefore, we do not include this obligation in the table of contractual obligations. See Note 12 of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information regarding income taxes.
We have a contract through the end of 2022 with Resolute, a major paper supplier, to purchase newsprint. The contract requires us to purchase annually the lesser of a fixed number of tons or a percentage of our total newsprint requirement at market rate in an arm’s length transaction. Since the quantities of newsprint purchased annually under this contract are based on our total newsprint requirement, the amount of the related payments for these purchases is excluded from the table above.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
We did not have any material off-balance sheet arrangements as of December 31, 2017.
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 41
CRITICAL ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Our Consolidated Financial Statements are prepared in accordance with GAAP. The preparation of these financial statements requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the amounts reported in the Consolidated Financial Statements for the periods presented.
We continually evaluate the policies and estimates we use to prepare our Consolidated Financial Statements. In general, management’s estimates are based on historical experience, information from third-party professionals and various other assumptions that are believed to be reasonable under the facts and circumstances. Actual results may differ from those estimates made by management.
Our critical accounting policies include our accounting for goodwill and intangibles, retirement benefits and income taxes. Specific risks related to our critical accounting policies are discussed below.
Goodwill and Intangibles
We evaluate whether there has been an impairment of goodwill or intangibles assets not amortized on an annual basis or in an interim period if certain circumstances indicate that a possible impairment may exist.
(In thousands) | December 31, 2017 | December 25, 2016 | ||||||
Goodwill | $ | 143,549 | $ | 134,517 | ||||
Intangibles | $ | 8,161 | $ | 10,634 | ||||
Total assets | $ | 2,099,780 | $ | 2,185,395 | ||||
Percentage of goodwill and intangibles to total assets | 7 | % | 7 | % | ||||
The impairment analysis is considered critical because of the significance of goodwill and intangibles to our Consolidated Balance Sheets.
We test for goodwill impairment at the reporting unit level, which is our operating segment. We first perform a qualitative assessment to determine whether it is more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying value. The qualitative assessment includes, but is not limited to, the results of our most recent quantitative impairment test, consideration of industry, market and macroeconomic conditions, cost factors, cash flows, changes in key management personnel and our share price. The result of this assessment determines whether it is necessary to perform the goodwill impairment two-step test. For the 2017 annual impairment testing, based on our qualitative assessment, we concluded that it is more likely than not that goodwill is not impaired.
If we determine that it is more likely than not that the fair value of our reporting unit is less than its carrying value, in the first step we compare the fair value of the reporting unit with its carrying amount, including goodwill. Fair value is calculated by a combination of a discounted cash flow model and a market approach model. In calculating fair value for the reporting unit, we generally weigh the results of the discounted cash flow model more heavily than the market approach because the discounted cash flow model is specific to our business and long-term projections. If the fair value exceeds the carrying amount, goodwill is not considered impaired. If the carrying amount exceeds the fair value, the second step must be performed to measure the amount of the impairment loss, if any. In the second step, we compare the implied fair value of the reporting unit’s goodwill with the carrying amount of that goodwill. An impairment loss would be recognized in an amount equal to the excess of the carrying amount of the goodwill over the implied fair value of the goodwill.
Intangible assets that are not amortized (i.e., trade names) are tested for impairment at the asset level by comparing the fair value of the asset with its carrying amount. If the fair value, which is based on future cash flows, exceeds the carrying value, the asset is not considered impaired. If the carrying amount exceeds the fair value, an impairment loss would be recognized in an amount equal to the excess of the carrying amount of the asset over the fair value of the asset.
Intangible assets that are amortized (i.e., customer lists, non-competes, etc.) are tested for impairment at the asset level associated with the lowest level of cash flows. An impairment exists if the carrying value of the asset (1) is not recoverable (the carrying value of the asset is greater than the sum of undiscounted cash flows) and (2) is greater than its fair value.
P. 42 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
The discounted cash flow analysis requires us to make various judgments, estimates and assumptions, many of which are interdependent, about future revenues, operating margins, growth rates, capital expenditures, working capital, discount rates and royalty rates. The starting point for the assumptions used in our discounted cash flow analysis is the annual long-range financial forecast. The annual planning process that we undertake to prepare the long-range financial forecast takes into consideration a multitude of factors, including historical growth rates and operating performance, related industry trends, macroeconomic conditions, and marketplace data, among others. Assumptions are also made for perpetual growth rates for periods beyond the long-range financial forecast period. Our estimates of fair value are sensitive to changes in all of these variables, certain of which relate to broader macroeconomic conditions outside our control.
The market approach analysis includes applying a multiple, based on comparable market transactions, to certain operating metrics of the reporting unit.
The significant estimates and assumptions used by management in assessing the recoverability of goodwill and intangibles are estimated future cash flows, discount rates, growth rates, as well as other factors. Any changes in these estimates or assumptions could result in an impairment charge. The estimates, based on reasonable and supportable assumptions and projections, require management’s subjective judgment. Depending on the assumptions and estimates used, the estimated results of the impairment tests can vary within a range of outcomes.
In addition to annual testing, management uses certain indicators to evaluate whether the carrying value of our reporting unit or intangibles may not be recoverable and an interim impairment test may be required. These indicators include: (1) current-period operating or cash flow declines combined with a history of operating or cash flow declines or a projection/forecast that demonstrates continuing declines in the cash flow or the inability to improve our operations to forecasted levels, (2) a significant adverse change in the business climate, whether structural or technological, (3) significant impairments and (4) a decline in our stock price and market capitalization.
Management has applied what it believes to be the most appropriate valuation methodology for its impairment testing. Additionally, management believes that the likelihood of an impairment of goodwill is remote due to the excess market capitalization relative to the Company’s net book value. See Note 4 of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
Retirement Benefits
Our single-employer pension and other postretirement benefit costs and obligations are accounted for using actuarial valuations. We recognize the funded status of these plans – measured as the difference between plan assets, if funded, and the benefit obligation – on the balance sheet and recognize changes in the funded status that arise during the period but are not recognized as components of net periodic pension cost, within other comprehensive income/(loss), net of tax. The assets related to our funded pension plans are measured at fair value.
We also recognize the present value of liabilities associated with the withdrawal from multiemployer pension plans.
We consider accounting for retirement plans critical to our operations because management is required to make significant subjective judgments about a number of actuarial assumptions, which include discount rates, long-term return on plan assets and mortality rates. These assumptions may have an effect on the amount and timing of future contributions. Depending on the assumptions and estimates used, the impact from our pension and other postretirement benefits could vary within a range of outcomes and could have a material effect on our Consolidated Financial Statements.
See “— Pensions and Other Postretirement Benefits” below for more information on our retirement benefits.
Income Taxes
We consider accounting for income taxes critical to our operating results because management is required to make significant subjective judgments in developing our provision for income taxes, including the determination of deferred tax assets and liabilities, and any valuation allowances that may be required against deferred tax assets.
Income taxes are recognized for the following: (1) amount of taxes payable for the current year and (2) deferred tax assets and liabilities for the future tax consequence of events that have been recognized differently in the financial statements than for tax purposes. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are established using statutory tax rates and are adjusted for tax rate changes in the period of enactment.
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 43
We assess whether our deferred tax assets shall be reduced by a valuation allowance if it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized. Our process includes collecting positive (i.e., sources of taxable income) and negative (i.e., recent historical losses) evidence and assessing, based on the evidence, whether it is more likely than not that the deferred tax assets will not be realized.
We recognize in our financial statements the impact of a tax position if that tax position is more likely than not of being sustained on audit, based on the technical merits of the tax position. This involves the identification of potential uncertain tax positions, the evaluation of tax law and an assessment of whether a liability for uncertain tax positions is necessary. Different conclusions reached in this assessment can have a material impact on the Consolidated Financial Statements.
We operate within multiple taxing jurisdictions and are subject to audit in these jurisdictions. These audits can involve complex issues, which could require an extended period of time to resolve. Until formal resolutions are reached between us and the tax authorities, the timing and amount of a possible audit settlement for uncertain tax benefits is difficult to predict.
On December 22, 2017, federal tax legislation commonly referred to as the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (the “Act”) was signed into law making significant changes to the Internal Revenue Code. Changes include, but are not limited to, a federal corporate tax rate decrease from 35% to 21% for tax years beginning after December 31, 2017, a one-time transition tax on the mandatory deemed repatriation of foreign earnings and numerous domestic and international-related provisions effective in 2018.
We have estimated our provision for income taxes in accordance with the Act and guidance available as of the date of this filing and as a result have recorded $68.7 million as additional income tax expense in the fourth quarter of 2017, the period in which the legislation was enacted.
On December 22, 2017, Staff Accounting Bulletin No. 118 ("SAB 118") was issued to address the application of GAAP in situations when a registrant does not have the necessary information available, prepared, or analyzed (including computations) in reasonable detail to complete the accounting for certain income tax effects of the Act. In accordance with SAB 118, we have determined that the $68.7 million of additional income tax expense recorded in connection with the remeasurement of certain deferred tax assets and liabilities, the one-time transition tax on the mandatory deemed repatriation of foreign earnings, and deferred tax assets related to executive compensation deductions was a provisional amount and a reasonable estimate at December 31, 2017. Provisional estimates were also made with regard to the Company’s deductions under the Act’s new expensing provisions and state and local income taxes related to foreign earnings subject to the one-time transition tax. The ultimate impact of the Act may differ from the provisional amount recognized due to, among other things, changes in estimates resulting from the receipt or calculation of final data, changes in interpretations of the Act, and additional regulatory guidance that may be issued. The accounting for the impact of the Act is expected to be completed by the fourth quarter of fiscal year 2018.
PENSIONS AND OTHER POSTRETIREMENT BENEFITS
We sponsor several single-employer defined benefit pension plans, the majority of which have been frozen. We also participated in two joint Company and Guild-sponsored plans covering employees who are members of The NewsGuild of New York. Effective January 1, 2018, the sponsorship of one of these plans, the Newspaper Guild of New York - The New York Times Pension Plan, which is frozen, was transferred exclusively to the Company. Our pension liability also includes our multiemployer pension plan withdrawal obligations. Our liability for postretirement obligations includes our liability to provide health benefits to eligible retired employees.
The table below includes the liability for all of these plans.
(In thousands) | December 31, 2017 | December 25, 2016 | ||||||
Pension and other postretirement liabilities (includes current portion) | $ | 476,965 | $ | 640,650 | ||||
Total liabilities | $ | 1,202,417 | $ | 1,341,151 | ||||
Percentage of pension and other postretirement liabilities to total liabilities | 39.7 | % | 47.8 | % | ||||
P. 44 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
Pension Benefits
Our Company-sponsored defined benefit pension plans include qualified plans (funded) as well as non-qualified plans (unfunded). These plans provide participating employees with retirement benefits in accordance with benefit formulas detailed in each plan. All of our non-qualified plans, which provide enhanced retirement benefits to select employees, are currently frozen, except for a foreign-based pension plan discussed below.
Our joint Company and Guild-sponsored plan is a qualified plan and is included in the table below.
We also have a foreign-based pension plan for certain non-U.S. employees (the “foreign plan”). The information for the foreign plan is combined with the information for U.S. non-qualified plans. The benefit obligation of the foreign plan is immaterial to our total benefit obligation.
The funded status of our qualified and non-qualified pension plans as of December 31, 2017 is as follows:
December 31, 2017 | ||||||||||||
(In thousands) | Qualified Plans | Non-Qualified Plans | All Plans | |||||||||
Pension obligation | $ | 1,636,488 | $ | 245,302 | $ | 1,881,790 | ||||||
Fair value of plan assets | 1,567,411 | — | 1,567,411 | |||||||||
Pension underfunded/unfunded obligation, net | $ | (69,077 | ) | $ | (245,302 | ) | $ | (314,379 | ) | |||
We made contributions of approximately $128 million to certain qualified pension plans in 2017. We expect contributions made to satisfy minimum funding requirements to total approximately $8 million in 2018.
Pension expense is calculated using a number of actuarial assumptions, including an expected long-term rate of return on assets (for qualified plans) and a discount rate. Our methodology in selecting these actuarial assumptions is discussed below.
In determining the expected long-term rate of return on assets, we evaluated input from our investment consultants, actuaries and investment management firms, including our review of asset class return expectations, as well as long-term historical asset class returns. Projected returns by such consultants and economists are based on broad equity and bond indices. Our objective is to select an average rate of earnings expected on existing plan assets and expected contributions to the plan (less plan expenses to be incurred) during the year. The expected long-term rate of return determined on this basis was 6.75% at the beginning of 2017. Our plan assets had an average rate of return of approximately 16.59% in 2017 and an average annual return of approximately 7.57% over the three-year period 2015-2017. We regularly review our actual asset allocation and periodically rebalance our investments to meet our investment strategy.
The market-related value of plan assets is multiplied by the expected long-term rate of return on assets to compute the expected return on plan assets, a component of net periodic pension cost. The market-related value of plan assets is a calculated value that recognizes changes in fair value over three years.
Based on the composition of our assets at the end of the year, we estimated our 2018 expected long-term rate of return to be 5.70%. If we had decreased our expected long-term rate of return on our plan assets by 50 basis points to 6.25% in 2017, pension expense would have increased by approximately $8 million in 2017 for our qualified pension plans. Our funding requirements would not have been materially affected.
We determined our discount rate using a Ryan ALM, Inc. Curve (the “Ryan Curve”). The Ryan Curve provides the bonds included in the curve and allows adjustments for certain outliers (i.e., bonds on “watch”). We believe the Ryan Curve allows us to calculate an appropriate discount rate.
To determine our discount rate, we project a cash flow based on annual accrued benefits. For active participants, the benefits under the respective pension plans are projected to the date of termination. The projected plan cash flow is discounted to the measurement date, which is the last day of our fiscal year, using the annual spot rates provided in the Ryan Curve. A single discount rate is then computed so that the present value of the benefit cash flow equals the present value computed using the Ryan Curve rates.
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 45
The weighted-average discount rate determined on this basis was 3.75% for our qualified plans and 3.67% for our non-qualified plans as of December 31, 2017.
If we had decreased the expected discount rate by 50 basis points for our qualified plans and our non-qualified plans in 2017, pension expense would have increased by approximately $1 million as of December 31, 2017 and our pension obligation would have increased by approximately $117 million.
We will continue to evaluate all of our actuarial assumptions, generally on an annual basis, and will adjust as necessary. Actual pension expense will depend on future investment performance, changes in future discount rates, the level of contributions we make and various other factors.
We also recognize the present value of pension liabilities associated with the withdrawal from multiemployer pension plans. Our multiemployer pension plan withdrawal liability was approximately $108 million as of December 31, 2017. This liability represents the present value of the obligations related to complete and partial withdrawals that have already occurred as well as an estimate of future partial withdrawals that we considered probable and reasonably estimable. For those plans that have yet to provide us with a demand letter, the actual liability will not be known until they complete a final assessment of the withdrawal liability and issue a demand to us. Therefore, the estimate of our multiemployer pension plan liability will be adjusted as more information becomes available that allows us to refine our estimates.
See Note 9 of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information regarding our pension plans.
Other Postretirement Benefits
We provide health benefits to retired employees (and their eligible dependents) who meet the definition of an eligible participant and certain age and service requirements, as outlined in the plan document. While we offer pre-age 65 retiree medical coverage to employees who meet certain retiree medical eligibility requirements, we do not provide post-age 65 retiree medical benefits for employees who retired on or after March 1, 2009. We accrue the costs of postretirement benefits during the employees’ active years of service and our policy is to pay our portion of insurance premiums and claims from our assets.
The annual postretirement expense was calculated using a number of actuarial assumptions, including a health-care cost trend rate and a discount rate. The health-care cost trend rate was 7.60% as of December 31, 2017. A one-percentage point change in the assumed health-care cost trend rate would result in an increase of $0.1 million or a decrease of $0.1 million in our 2017 service and interest costs, respectively, two factors included in the calculation of postretirement expense. A one-percentage point change in the assumed health-care cost trend rate would result in an increase of approximately $2 million or a decrease of approximately $2 million in our accumulated benefit obligation as of December 31, 2017.
See Note 10 of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information regarding our other postretirement benefits.
Change in Discount Rate Methodology
Beginning in 2016, we changed the approach used to calculate the service and interest components of net periodic benefit cost for benefit plans to provide a more precise measurement of service and interest costs. Prior to this change, we calculated these service and interest components utilizing a single weighted-average discount rate derived from the yield curve used to measure the benefit obligation at the beginning of the period. We have elected to utilize an approach that discounts the individual expected cash flows using the applicable spot rates derived from the yield curve over the projected cash flow period. The spot rates used to estimate 2016 service and interest costs ranged from 1.32% to 4.79%. Service costs and interest costs for our benefit plans were reduced by approximately $19 million in 2016 due to the change in methodology.
See Notes 9 and 10 of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements for more information regarding our pension benefits and other postretirement benefits, respectively.
RECENT ACCOUNTING PRONOUNCEMENTS
See Note 2 of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements for information regarding recent accounting pronouncements.
P. 46 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
ITEM 7A. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK |
Our market risk is principally associated with the following:
• | Our exposure to changes in interest rates relates primarily to interest earned and market value on our cash and cash equivalents, and marketable securities. Our cash and cash equivalents and marketable securities consist of cash, money market fund, certificates of deposit, U.S. Treasury securities, U.S. government agency securities, commercial paper, and corporate debt securities. Our investment policy and strategy are focused on preservation of capital and supporting our liquidity requirements. Changes in U.S. interest rates affect the interest earned on our cash and cash equivalents and marketable securities, and the market value of those securities. A hypothetical 100 basis point increase in interest rates would have resulted in a decrease of approximately $5 million in the market value of our marketable debt securities as of December 31, 2017 and December 25, 2016. Any realized gains or losses resulting from such interest rate changes would only occur if we sold the investments prior to maturity. |
• | Newsprint is a commodity subject to supply and demand market conditions. The cost of raw materials, of which newsprint expense is a major component, represented approximately 4% and 5% of our total operating costs in 2017 and 2016, respectively. Based on the number of newsprint tons consumed in 2017 and 2016, a $10 per ton increase in newsprint prices would have resulted in additional newsprint expense of $0.9 million (pre-tax) in 2017 and 2016. |
• | The discount rate used to measure the benefit obligations for our qualified pension plans is determined by using the Ryan Curve, which provides rates for the bonds included in the curve and allows adjustments for certain outliers (i.e., bonds on “watch”). Broad equity and bond indices are used in the determination of the expected long-term rate of return on pension plan assets. Therefore, interest rate fluctuations and volatility of the debt and equity markets can have a significant impact on asset values, the funded status of our pension plans and future anticipated contributions. See “Item 7 — Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations — Pensions and Other Postretirement Benefits.” |
• | A significant portion of our employees are unionized and our results could be adversely affected if future labor negotiations or contracts were to further restrict our ability to maximize the efficiency of our operations. In addition, if we are unable to negotiate labor contracts on reasonable terms, or if we were to experience labor unrest or other business interruptions in connection with labor negotiations or otherwise, our ability to produce and deliver our products could be impaired. |
See Notes 6, 9 and 18 of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 47
ITEM 8. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA |
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY 2017 FINANCIAL REPORT
INDEX | PAGE |
Consolidated Statements of Operations for the years ended December 31, 2017, December 25, 2016 and December 27, 2015 | |
Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income/(Loss) for the years ended December 31, 2017, December 25, 2016 and December 27, 2015 | |
Consolidated Statements of Changes in Stockholders’ Equity for the years ended December 31, 2017, December 25, 2016 and December 27, 2015 | |
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the years ended December 31, 2017, December 25, 2016 and December 27, 2015 | |
4. Goodwill and Intangibles | |
P. 48 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
REPORT OF MANAGEMENT
Management’s Responsibility for the Financial Statements
The Company’s consolidated financial statements were prepared by management, who is responsible for their integrity and objectivity. The consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“GAAP”) and, as such, include amounts based on management’s best estimates and judgments.
Management is further responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting as defined in Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. The Company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with GAAP. The Company follows and continuously monitors its policies and procedures for internal control over financial reporting to ensure that this objective is met (see “Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting” below).
The consolidated financial statements were audited by Ernst & Young LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, in 2017, 2016 and 2015. Its audits were conducted in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) and its report is shown on Page 50.
The Audit Committee of the Board of Directors, which is composed solely of independent directors, meets regularly with the independent registered public accounting firm, internal auditors and management to discuss specific accounting, financial reporting and internal control matters. Both the independent registered public accounting firm and the internal auditors have full and free access to the Audit Committee. Each year the Audit Committee selects, subject to ratification by stockholders, the firm which is to perform audit and other related work for the Company.
Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Management of the Company is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting as defined in Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. The Company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with GAAP. The Company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that:
• | pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the Company; |
• | provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with GAAP, and that receipts and expenditures of the Company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the Company; and |
• | provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of the Company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements. |
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Our management, with the participation of our principal executive officer and principal financial officer, assessed the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017. In making this assessment, management used the criteria set forth by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission in Internal Control — Integrated Framework (2013 framework). Based on its assessment, management concluded that the Company’s internal control over financial reporting was effective as of December 31, 2017.
The Company’s independent registered public accounting firm, Ernst & Young LLP, that audited the consolidated financial statements of the Company included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, has issued an attestation report on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017, which is included on Page 51 in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 49
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders of
The New York Times Company
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of The New York Times Company as of December 31, 2017 and December 25, 2016, and the related consolidated statements of operations, comprehensive income/ (loss), changes in stockholders’ equity, and cash flows for each of the three fiscal years in the period ended December 31, 2017, and the related notes and the financial statement schedule listed at Item 15(A)(2) of The New York Times Company’s 2017 Annual Report on Form 10-K (collectively referred to as the “consolidated financial statements”). In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the consolidated financial position of The New York Times Company at December 31, 2017 and December 25, 2016, and the consolidated results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three fiscal years in the period ended December 31, 2017, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), The New York Times Company's internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017, based on criteria established in Internal Control-Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 framework), and our report dated February 27, 2018 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of The New York Times Company's management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on The New York Times Company’s financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to The New York Times Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
/s/ Ernst & Young LLP
We have served as The New York Times Company’s auditor since 2007.
New York, New York
February 27, 2018
P. 50 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders of
The New York Times Company
Opinion on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
We have audited The New York Times Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017, based on criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 framework) (the COSO criteria). In our opinion, The New York Times Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017, based on the COSO criteria.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of The New York Times Company as of December 31, 2017 and December 25, 2016, and the related consolidated statements of operations, comprehensive income/ (loss), changes in stockholders’ equity, and cash flows for each of the three fiscal years in the period ended December 31, 2017, and the related notes and the financial statement schedule listed at Item 15(A)(2) and our report dated February 27, 2018 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
Basis for Opinion
The New York Times Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting included in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on The New York Times Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to The New York Times Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects.
Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 51
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
/s/ Ernst & Young LLP
New York, New York
February 27, 2018
P. 52 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(In thousands) | December 31, 2017 | December 25, 2016 | ||||||
Assets | ||||||||
Current assets | ||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 182,911 | $ | 100,692 | ||||
Short-term marketable securities | 308,589 | 449,535 | ||||||
Accounts receivable (net of allowances of $14,542 in 2017 and $16,815 in 2016) | 184,885 | 197,355 | ||||||
Prepaid expenses | 22,851 | 15,948 | ||||||
Other current assets | 50,463 | 32,648 | ||||||
Total current assets | 749,699 | 796,178 | ||||||
Long-term marketable securities | 241,411 | 187,299 | ||||||
Investments in joint ventures | 1,736 | 15,614 | ||||||
Property, plant and equipment: | ||||||||
Equipment | 528,111 | 523,104 | ||||||
Buildings, building equipment and improvements | 674,056 | 641,383 | ||||||
Software | 232,791 | 212,118 | ||||||
Land | 105,710 | 105,710 | ||||||
Assets in progress | 45,672 | 18,164 | ||||||
Total, at cost | 1,586,340 | 1,500,479 | ||||||
Less: accumulated depreciation and amortization | (945,401 | ) | (903,736 | ) | ||||
Property, plant and equipment, net | 640,939 | 596,743 | ||||||
Goodwill | 143,549 | 134,517 | ||||||
Deferred income taxes | 153,046 | 301,342 | ||||||
Miscellaneous assets | 169,400 | 153,702 | ||||||
Total assets | $ | 2,099,780 | $ | 2,185,395 | ||||
See Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 53
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS — continued
(In thousands, except share and per share data) | December 31, 2017 | December 25, 2016 | ||||||
Liabilities and stockholders’ equity | ||||||||
Current liabilities | ||||||||
Accounts payable | $ | 125,479 | $ | 104,463 | ||||
Accrued payroll and other related liabilities | 104,614 | 96,463 | ||||||
Unexpired subscriptions revenue | 75,054 | 66,686 | ||||||
Accrued expenses and other | 110,510 | 131,125 | ||||||
Total current liabilities | 415,657 | 398,737 | ||||||
Other liabilities | ||||||||
Long-term debt and capital lease obligations | 250,209 | 246,978 | ||||||
Pension benefits obligation | 405,422 | 558,790 | ||||||
Postretirement benefits obligation | 48,816 | 57,999 | ||||||
Other | 82,313 | 78,647 | ||||||
Total other liabilities | 786,760 | 942,414 | ||||||
Stockholders’ equity | ||||||||
Common stock of $.10 par value: | ||||||||
Class A – authorized: 300,000,000 shares; issued: 2017 – 170,276,449; 2016 – 169,206,879 (including treasury shares: 2017 –8,870,801; 2016 – 8,870,801) | 17,028 | 16,921 | ||||||
Class B – convertible – authorized and issued shares: 2017 – 803,763; 2016 – 816,632 (including treasury shares: 2017 – none; 2016 – none) | 80 | 82 | ||||||
Additional paid-in capital | 164,275 | 149,928 | ||||||
Retained earnings | 1,310,136 | 1,331,911 | ||||||
Common stock held in treasury, at cost | (171,211 | ) | (171,211 | ) | ||||
Accumulated other comprehensive loss, net of income taxes: | ||||||||
Foreign currency translation adjustments | 6,328 | (1,822 | ) | |||||
Funded status of benefit plans | (427,819 | ) | (477,994 | ) | ||||
Unrealized loss on available-for-sale securities | (1,538 | ) | — | |||||
Total accumulated other comprehensive loss, net of income taxes | (423,029 | ) | (479,816 | ) | ||||
Total New York Times Company stockholders’ equity | 897,279 | 847,815 | ||||||
Noncontrolling interest | 84 | (3,571 | ) | |||||
Total stockholders’ equity | 897,363 | 844,244 | ||||||
Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity | $ | 2,099,780 | $ | 2,185,395 | ||||
See Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
P. 54 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
Years Ended | ||||||||||||
(In thousands) | December 31, 2017 | December 25, 2016 | December 27, 2015 | |||||||||
(53 weeks) | (52 weeks) | (52 weeks) | ||||||||||
Revenues | ||||||||||||
Subscription | $ | 1,008,431 | $ | 880,543 | $ | 851,790 | ||||||
Advertising | 558,513 | 580,732 | 638,709 | |||||||||
Other | 108,695 | 94,067 | 88,716 | |||||||||
Total revenues | 1,675,639 | 1,555,342 | 1,579,215 | |||||||||
Operating costs | ||||||||||||
Production costs: | ||||||||||||
Wages and benefits | 362,750 | 363,051 | 354,516 | |||||||||
Raw materials | 66,304 | 72,325 | 77,176 | |||||||||
Other production costs | 186,352 | 192,728 | 186,120 | |||||||||
Total production costs | 615,406 | 628,104 | 617,812 | |||||||||
Selling, general and administrative costs | 810,854 | 721,083 | 713,837 | |||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 61,871 | 61,723 | 61,597 | |||||||||
Total operating costs | 1,488,131 | 1,410,910 | 1,393,246 | |||||||||
Headquarters redesign and consolidation | 10,090 | — | — | |||||||||
Restructuring charge | — | 14,804 | — | |||||||||
Multiemployer pension plan withdrawal expense | — | 6,730 | 9,055 | |||||||||
Postretirement benefit plan settlement gain | (37,057 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
Pension settlement expense | 102,109 | 21,294 | 40,329 | |||||||||
Operating profit | 112,366 | 101,604 | 136,585 | |||||||||
Gain/(loss) from joint ventures | 18,641 | (36,273 | ) | (783 | ) | |||||||
Interest expense and other, net | 19,783 | 34,805 | 39,050 | |||||||||
Income from continuing operations before income taxes | 111,224 | 30,526 | 96,752 | |||||||||
Income tax expense | 103,956 | 4,421 | 33,910 | |||||||||
Income from continuing operations | 7,268 | 26,105 | 62,842 | |||||||||
Loss from discontinued operations, net of income taxes | (431 | ) | (2,273 | ) | — | |||||||
Net income | 6,837 | 23,832 | 62,842 | |||||||||
Net (income)/loss attributable to the noncontrolling interest | (2,541 | ) | 5,236 | 404 | ||||||||
Net income attributable to The New York Times Company common stockholders | $ | 4,296 | $ | 29,068 | $ | 63,246 | ||||||
Amounts attributable to The New York Times Company common stockholders: | ||||||||||||
Income from continuing operations | $ | 4,727 | $ | 31,341 | $ | 63,246 | ||||||
Loss from discontinued operations, net of income taxes | (431 | ) | (2,273 | ) | — | |||||||
Net income | $ | 4,296 | $ | 29,068 | $ | 63,246 | ||||||
See Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 55
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS — continued
Years Ended | ||||||||||||
(In thousands, except per share data) | December 31, 2017 | December 25, 2016 | December 27, 2015 | |||||||||
(53 weeks) | (52 weeks) | (52 weeks) | ||||||||||
Average number of common shares outstanding: | ||||||||||||
Basic | 161,926 | 161,128 | 164,390 | |||||||||
Diluted | 164,263 | 162,817 | 166,423 | |||||||||
Basic earnings per share attributable to The New York Times Company common stockholders: | ||||||||||||
Income from continuing operations | $ | 0.03 | $ | 0.19 | $ | 0.38 | ||||||
Loss from discontinued operations, net of income taxes | — | (0.01 | ) | — | ||||||||
Net income | $ | 0.03 | $ | 0.18 | $ | 0.38 | ||||||
Diluted earnings per share attributable to The New York Times Company common stockholders: | ||||||||||||
Income from continuing operations | $ | 0.03 | $ | 0.19 | $ | 0.38 | ||||||
Loss from discontinued operations, net of income taxes | — | (0.01 | ) | — | ||||||||
Net income | $ | 0.03 | $ | 0.18 | $ | 0.38 | ||||||
Dividends declared per share | $ | 0.16 | $ | 0.16 | $ | 0.16 | ||||||
See Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
P. 56 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME/(LOSS)
Years Ended | ||||||||||||
(In thousands) | December 31, 2017 | December 25, 2016 | December 27, 2015 | |||||||||
(53 weeks) | (52 weeks) | (52 weeks) | ||||||||||
Net income | $ | 6,837 | $ | 23,832 | $ | 62,842 | ||||||
Other comprehensive income/(loss), before tax: | ||||||||||||
Foreign currency translation adjustments-income/(loss) | 12,110 | (3,070 | ) | (8,803 | ) | |||||||
Pension and postretirement benefits obligation | 89,881 | 51,405 | 50,579 | |||||||||
Net unrealized loss on available-for-sale securities | (2,545 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
Other comprehensive income, before tax | 99,446 | 48,335 | 41,776 | |||||||||
Income tax expense | 41,545 | 19,096 | 16,988 | |||||||||
Other comprehensive income, net of tax | 57,901 | 29,239 | 24,788 | |||||||||
Comprehensive income | 64,738 | 53,071 | 87,630 | |||||||||
Comprehensive (income)/loss attributable to the noncontrolling interest | (3,655 | ) | 5,275 | 317 | ||||||||
Comprehensive income attributable to The New York Times Company common stockholders | $ | 61,083 | $ | 58,346 | $ | 87,947 | ||||||
See Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 57
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
(In thousands, except share and per share data) | Capital Stock Class A and Class B Common | Additional Paid-in Capital | Retained Earnings | Common Stock Held in Treasury, at Cost | Accumulated Other Comprehensive Loss, Net of Income Taxes | Total New York Times Company Stockholders’ Equity | Non- controlling Interest | Total Stock- holders’ Equity | |||||||||||||||||
Balance, December 28, 2014 | $ | 15,252 | $ | 39,217 | $ | 1,291,907 | $ | (86,253 | ) | $ | (533,795 | ) | $ | 726,328 | $ | 2,021 | $ | 728,349 | |||||||
Net income/(loss) | — | — | 63,246 | — | — | 63,246 | (404 | ) | 62,842 | ||||||||||||||||
Dividends | — | — | (26,409 | ) | — | — | (26,409 | ) | — | (26,409 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Other comprehensive income | — | — | — | — | 24,701 | 24,701 | 87 | 24,788 | |||||||||||||||||
Issuance of shares: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Stock options – 341,362 Class A shares | 34 | 1,909 | — | — | — | 1,943 | — | 1,943 | |||||||||||||||||
Restricted stock units vested – 233,901 Class A shares | 23 | (2,207 | ) | — | — | — | (2,184 | ) | — | (2,184 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Performance-based awards – 87,134 Class A shares | 9 | (1,574 | ) | — | — | — | (1,565 | ) | — | (1,565 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Warrants - 15,900,000 Class A Shares | 1,590 | 99,474 | — | 19 | — | 101,083 | — | 101,083 | |||||||||||||||||
Share repurchases - 5,511,233 Class A shares | — | — | — | (69,921 | ) | — | (69,921 | ) | — | (69,921 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Stock-based compensation | — | 10,431 | — | — | — | 10,431 | — | 10,431 | |||||||||||||||||
Income tax shortfall related to share-based payments | — | (902 | ) | — | — | — | (902 | ) | — | (902 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Balance, December 27, 2015 | 16,908 | 146,348 | 1,328,744 | (156,155 | ) | (509,094 | ) | 826,751 | 1,704 | 828,455 | |||||||||||||||
Net income/(loss) | — | — | 29,068 | — | — | 29,068 | (5,236 | ) | 23,832 | ||||||||||||||||
Dividends | — | — | (25,901 | ) | — | — | (25,901 | ) | — | (25,901 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Other comprehensive income/(loss) | — | — | — | — | 29,278 | 29,278 | (39 | ) | 29,239 | ||||||||||||||||
Issuance of shares: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Stock options – 114,652 Class A shares | 12 | 750 | — | — | — | 762 | — | 762 | |||||||||||||||||
Restricted stock units vested – 304,171 Class A shares | 30 | (2,769 | ) | — | — | — | (2,739 | ) | — | (2,739 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Performance-based awards – 524,520 Class A shares | 53 | (6,941 | ) | — | — | — | (6,888 | ) | — | (6,888 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Share Repurchases – 1,179,672 Class A shares | — | — | — | (15,056 | ) | — | (15,056 | ) | — | (15,056 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Stock-based compensation | — | 12,622 | — | — | — | 12,622 | — | 12,622 | |||||||||||||||||
Income tax shortfall related to share-based payments | — | (82 | ) | — | — | — | (82 | ) | — | (82 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Balance, December 25, 2016 | 17,003 | 149,928 | 1,331,911 | (171,211 | ) | (479,816 | ) | 847,815 | (3,571 | ) | 844,244 | ||||||||||||||
Net income | — | — | 4,296 | — | — | 4,296 | 2,541 | 6,837 | |||||||||||||||||
Dividends | — | — | (26,071 | ) | — | — | (26,071 | ) | — | (26,071 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Other comprehensive income | — | — | — | — | 56,787 | 56,787 | 1,114 | 57,901 | |||||||||||||||||
Issuance of shares: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Stock options – 657,704 Class A shares | 66 | 4,535 | — | — | — | 4,601 | — | 4,601 | |||||||||||||||||
Restricted stock units vested – 283,116 Class A shares | 28 | (2,743 | ) | — | — | — | (2,715 | ) | — | (2,715 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Performance-based awards – 115,881 Class A shares | 11 | (1,360 | ) | — | — | — | (1,349 | ) | — | (1,349 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Stock-based compensation | — | 13,915 | — | — | — | 13,915 | — | 13,915 | |||||||||||||||||
Balance, December 31, 2017 | $ | 17,108 | $ | 164,275 | $ | 1,310,136 | $ | (171,211 | ) | $ | (423,029 | ) | $ | 897,279 | $ | 84 | $ | 897,363 | |||||||
See Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
P. 58 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
See Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
Years Ended | ||||||||||||
(In thousands) | December 31, 2017 | December 25, 2016 | December 27, 2015 | |||||||||
Cash flows from operating activities | ||||||||||||
Net income | $ | 6,837 | $ | 23,832 | $ | 62,842 | ||||||
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: | ||||||||||||
Restructuring charge | — | 14,804 | — | |||||||||
Pension settlement expense | 102,109 | 21,294 | 40,329 | |||||||||
Multiemployer pension plan charges | — | 11,701 | 9,055 | |||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 61,871 | 61,723 | 61,597 | |||||||||
Stock-based compensation expense | 14,809 | 12,430 | 10,588 | |||||||||
Undistributed (income)/loss of joint ventures | (18,641 | ) | 36,273 | 783 | ||||||||
Deferred income taxes | 105,174 | (13,128 | ) | (10,102 | ) | |||||||
Long-term retirement benefit obligations | (184,418 | ) | (55,228 | ) | (15,404 | ) | ||||||
Uncertain tax positions | (4,343 | ) | 5,089 | 1,627 | ||||||||
Other – net | 2,991 | (564 | ) | 11,494 | ||||||||
Changes in operating assets and liabilities: | ||||||||||||
Accounts receivable – net | 12,470 | 9,825 | 5,510 | |||||||||
Other current assets | (30,527 | ) | 1,599 | 22,141 | ||||||||
Accounts payable, accrued payroll and other liabilities | 10,012 | (32,276 | ) | (22,833 | ) | |||||||
Unexpired subscriptions | 8,368 | 6,502 | 1,448 | |||||||||
Net cash provided by operating activities | 86,712 | 103,876 | 179,075 | |||||||||
Cash flows from investing activities | ||||||||||||
Purchases of marketable securities | (466,522 | ) | (566,846 | ) | (818,865 | ) | ||||||
Maturities/disposals of marketable securities | 548,461 | 725,365 | 818,262 | |||||||||
Cash distribution from corporate-owned life insurance | — | 38,000 | — | |||||||||
Business acquisitions | — | (40,410 | ) | — | ||||||||
(Purchases)/proceeds from investments | 15,591 | (1,955 | ) | (5,068 | ) | |||||||
Capital expenditures | (84,753 | ) | (30,095 | ) | (26,965 | ) | ||||||
Change in restricted cash | 6,919 | 3,804 | 1,521 | |||||||||
Other-net | 1,323 | 409 | 412 | |||||||||
Net cash provided by/(used in) investing activities | 21,019 | 128,272 | (30,703 | ) | ||||||||
Cash flows from financing activities | ||||||||||||
Long-term obligations: | ||||||||||||
Repayment of debt and capital lease obligations | (552 | ) | (189,768 | ) | (223,648 | ) | ||||||
Dividends paid | (26,004 | ) | (25,897 | ) | (26,599 | ) | ||||||
Capital shares: | ||||||||||||
Stock issuances | 4,601 | 761 | 103,026 | |||||||||
Repurchases | — | (15,684 | ) | (69,293 | ) | |||||||
Windfall tax benefit related to share-based payments | — | 3,193 | 2,303 | |||||||||
Share-based compensation tax withholding | (4,064 | ) | (9,629 | ) | (3,749 | ) | ||||||
Net cash used in financing activities | (26,019 | ) | (237,024 | ) | (217,960 | ) | ||||||
Net increase/(decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | 81,712 | (4,876 | ) | (69,588 | ) | |||||||
Effect of exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents | 507 | (208 | ) | (1,243 | ) | |||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at the beginning of the year | 100,692 | 105,776 | 176,607 | |||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at the end of the year | $ | 182,911 | $ | 100,692 | $ | 105,776 | ||||||
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 59
SUPPLEMENTAL DISCLOSURES TO CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
Cash Flow Information
Years Ended | ||||||||||||
(In thousands) | December 31, 2017 | December 25, 2016 | December 27, 2015 | |||||||||
Cash payments | ||||||||||||
Interest, net of capitalized interest | $ | 27,732 | $ | 39,487 | $ | 41,449 | ||||||
Income tax payments – net | $ | 21,552 | $ | 44,896 | $ | 21,078 | ||||||
See Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
P. 60 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
1. Basis of Presentation
Nature of Operations
The New York Times Company is a global media organization that includes newspapers, print and digital products and investments (see Note 5). The New York Times Company and its consolidated subsidiaries are referred to collectively as the “Company,” “we,” “our” and “us.” Our major sources of revenue are subscription and advertising.
Principles of Consolidation
The accompanying Consolidated Financial Statements have been prepared in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States of America (“GAAP”) and include the accounts of our Company and our wholly and majority-owned subsidiaries after elimination of all significant intercompany transactions.
The portion of the net income or loss and equity of a subsidiary attributable to the owners of a subsidiary other than the Company (a noncontrolling interest) is included as a component of consolidated stockholders‘ equity in our Consolidated Balance Sheets, within net income or loss in our Consolidated Statements of Operations, within comprehensive income or loss in our Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income/(Loss) and as a component of consolidated stockholders’ equity in our Consolidated Statements of Changes in Stockholders’ Equity.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the amounts reported in our Consolidated Financial Statements. Actual results could differ from these estimates.
Fiscal Year
Our fiscal year end is the last Sunday in December. Fiscal year 2017 comprised 53 weeks and fiscal years 2016 and 2015 each comprised 52 weeks. Our fiscal years ended as of December 31, 2017, December 25, 2016, and December 27, 2015, respectively.
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Cash and Cash Equivalents
We consider all highly liquid debt instruments with original maturities of three months or less to be cash equivalents.
Marketable Securities
We have investments in marketable debt securities. We determine the appropriate classification of our investments at the date of purchase and reevaluate the classifications at the balance sheet date. Marketable debt securities with maturities of 12 months or less are classified as short-term. Marketable debt securities with maturities greater than 12 months are classified as long-term. Historically, we have accounted for all marketable securities as held-to-maturity (“HTM”) and stated at amortized cost as we had the intent and ability to hold our marketable debt securities until maturity. However, on June 29, 2017, our Board of Directors approved a change to the Company’s cash reserve investment policy to allow the Company to sell marketable securities prior to maturity. Beginning in the third quarter of 2017, the Company reclassified all marketable securities from HTM to available-for-sale (“AFS”).
AFS securities are reported at fair value. Unrealized gains and losses, after applicable income taxes, are reported in accumulated other comprehensive income/(loss).
We conduct an other-than-temporary impairment (“OTTI”) analysis on a quarterly basis or more often if a potential loss-triggering event occurs. We consider factors such as the duration, severity and the reason for the decline in value, the potential recovery period and whether we intend to sell. For AFS securities, we also consider whether (i) it is more likely than not that we will be required to sell the debt securities before recovery of their amortized cost basis and (ii) the amortized cost basis cannot be recovered as a result of credit losses.
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 61
Concentration of Risk
Financial instruments, which potentially subject us to concentration of risk, are cash and cash equivalents and marketable securities. Cash is placed with major financial institutions. As of December 31, 2017, we had cash balances at financial institutions in excess of federal insurance limits. We periodically evaluate the credit standing of these financial institutions as part of our ongoing investment strategy.
Our marketable securities portfolio consists of investment-grade securities diversified among security types, issuers and industries. Our cash equivalents and marketable securities are primarily managed by third-party investment managers who are required to adhere to investment policies approved by our Board of Directors designed to mitigate risk. Included within marketable securities is approximately $63 million of securities used as collateral for letters of credit issued by the Company in connection with the leasing of floors in our headquarters building.
Accounts Receivable
Credit is extended to our advertisers and our subscribers based upon an evaluation of the customer’s financial condition, and collateral is not required from such customers. Allowances for estimated credit losses, rebates, returns, rate adjustments and discounts are generally established based on historical experience.
Inventories
Inventories are included within Other current assets of the Consolidated Balance Sheets. Inventories are stated at the lower of cost or net realizable value. Inventory cost is generally based on the last-in, first-out (“LIFO”) method for newsprint and other paper grades and the first-in, first-out (“FIFO”) method for other inventories.
Investments
Investments in which we have at least a 20%, but not more than a 50%, interest are generally accounted for under the equity method. Investment interests below 20% are generally accounted for under the cost method, except if we could exercise significant influence, the investment would be accounted for under the equity method.
We evaluate whether there has been an impairment of our cost and equity method investments annually or in an interim period if circumstances indicate that a possible impairment may exist.
Property, Plant and Equipment
Property, plant and equipment are stated at cost. Depreciation is computed by the straight-line method over the shorter of estimated asset service lives or lease terms as follows: buildings, building equipment and improvements – 10 to 40 years; equipment – 3 to 30 years; and software – 2 to 5 years. We capitalize interest costs and certain staffing costs as part of the cost of major projects.
We evaluate whether there has been an impairment of long-lived assets, primarily property, plant and equipment, if certain circumstances indicate that a possible impairment may exist. These assets are tested for impairment at the asset group level associated with the lowest level of cash flows. An impairment exists if the carrying value of the asset (1) is not recoverable (the carrying value of the asset is greater than the sum of undiscounted cash flows) and (2) is greater than its fair value.
Goodwill and Intangibles
Goodwill is the excess of cost over the fair value of tangible and intangible net assets acquired. Goodwill is not amortized but tested for impairment annually or in an interim period if certain circumstances indicate a possible impairment may exist. Our annual impairment testing date is the first day of our fiscal fourth quarter.
We test for goodwill impairment at the reporting unit level, which is our single operating segment. We first perform a qualitative assessment to determine whether it is more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying value. The qualitative assessment includes, but is not limited to, the results of our most recent quantitative impairment test, consideration of industry, market and macroeconomic conditions, cost factors, cash flows, changes in key management personnel and our share price. The result of this assessment determines whether it is necessary to perform the goodwill impairment two-step test. For the 2017 annual impairment testing, based on our qualitative assessment, we concluded that it is more likely than not that goodwill is not impaired.
If we determine that it is more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying value, in the first step, we compare the fair value of the reporting unit with its carrying amount, including goodwill.
P. 62 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
Fair value is calculated by a combination of a discounted cash flow model and a market approach model. In calculating fair value for our reporting unit, we generally weigh the results of the discounted cash flow model more heavily than the market approach because the discounted cash flow model is specific to our business and long-term projections. If the fair value exceeds the carrying amount, goodwill is not considered impaired. If the carrying amount exceeds the fair value, the second step must be performed to measure the amount of the impairment loss, if any. In the second step, we compare the implied fair value of the reporting unit’s goodwill with the carrying amount of that goodwill. An impairment loss would be recognized in an amount equal to the excess of the carrying amount of the goodwill over the implied fair value of the goodwill.
Intangible assets that are not amortized (i.e., trade names) are tested for impairment at the asset level by comparing the fair value of the asset with its carrying amount. If the fair value, which is based on future cash flows, exceeds the carrying value, the asset is not considered impaired. If the carrying amount exceeds the fair value, an impairment loss would be recognized in an amount equal to the excess of the carrying amount of the asset over the fair value of the asset.
Intangible assets that are amortized (i.e., customer lists, non-competes, etc.) are tested for impairment at the asset level associated with the lowest level of cash flows. An impairment exists if the carrying value of the asset (1) is not recoverable (the carrying value of the asset is greater than the sum of undiscounted cash flows) and (2) is greater than its fair value.
The discounted cash flow analysis requires us to make various judgments, estimates and assumptions, many of which are interdependent, about future revenues, operating margins, growth rates, capital expenditures, working capital, discount rates and royalty rates. The starting point for the assumptions used in our discounted cash flow analysis is the annual long-range financial forecast. The annual planning process that we undertake to prepare the long-range financial forecast takes into consideration a multitude of factors, including historical growth rates and operating performance, related industry trends, macroeconomic conditions, and marketplace data, among others. Assumptions are also made for perpetual growth rates for periods beyond the long-range financial forecast period. Our estimates of fair value are sensitive to changes in all of these variables, certain of which relate to broader macroeconomic conditions outside our control.
The market approach analysis includes applying a multiple, based on comparable market transactions, to certain operating metrics of the reporting unit.
The significant estimates and assumptions used by management in assessing the recoverability of goodwill acquired and intangibles are estimated future cash flows, discount rates, growth rates, as well as other factors. Any changes in these estimates or assumptions could result in an impairment charge. The estimates, based on reasonable and supportable assumptions and projections, require management’s subjective judgment. Depending on the assumptions and estimates used, the estimated results of the impairment tests can vary within a range of outcomes.
In addition to annual testing, management uses certain indicators to evaluate whether the carrying value of our reporting unit or intangibles may not be recoverable and an interim impairment test may be required. These indicators include: (1) current-period operating or cash flow declines combined with a history of operating or cash flow declines or a projection/forecast that demonstrates continuing declines in the cash flow or the inability to improve our operations to forecasted levels, (2) a significant adverse change in the business climate, whether structural or technological, (3) significant impairments and (4) a decline in our stock price and market capitalization.
Management has applied what it believes to be the most appropriate valuation methodology for its impairment testing. Additionally, management believes that the likelihood of an impairment of goodwill is remote due to the excess market capitalization relative to its net book value. See Note 4.
Self-Insurance
We self-insure for workers’ compensation costs, automobile and general liability claims, up to certain deductible limits, as well as for certain employee medical and disability benefits. Employee medical costs above a certain threshold are insured by a third party. The recorded liabilities for self-insured risks are primarily calculated using actuarial methods. The liabilities include amounts for actual claims, claim growth and claims incurred but not yet reported. The recorded liabilities for self-insured risks were approximately $38 million as of December 31, 2017 and December 25, 2016.
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 63
Pension and Other Postretirement Benefits
Our single-employer pension and other postretirement benefit costs are accounted for using actuarial valuations. We recognize the funded status of these plans – measured as the difference between plan assets, if funded, and the benefit obligation – on the balance sheet and recognize changes in the funded status that arise during the period but are not recognized as components of net periodic pension cost, within other comprehensive income/(loss), net of income taxes. The assets related to our funded pension plans are measured at fair value.
We make significant subjective judgments about a number of actuarial assumptions, which include discount rates, health-care cost trend rates, long-term return on plan assets and mortality rates. Depending on the assumptions and estimates used, the impact from our pension and other postretirement benefits could vary within a range of outcomes and could have a material effect on our Consolidated Financial Statements.
We have elected the practical expedient to use the month-end that is closest to our fiscal year-end or interim period-end for measuring the single-employer pension plan assets and obligations as well as other postretirement benefit plan assets and obligations.
We also recognize the present value of pension liabilities associated with the withdrawal from multiemployer pension plans. We record liabilities for obligations related to complete, partial and estimated withdrawals from multiemployer pension plans. The actual liability for estimated withdrawals is not known until each plan completes a final assessment of the withdrawal liability and issues a demand to us. Therefore, we adjust the estimate of our multiemployer pension plan liability as more information becomes available that allows us to refine our estimates.
See Notes 9 and 10 for additional information regarding pension and other postretirement benefits.
Revenue Recognition
In 2017, the Company renamed “circulation revenues” as “subscription revenues.” Subscription revenues include single-copy and subscription revenues. Subscription revenues are based on the number of copies of the printed newspaper (through home-delivery subscriptions and single-copy sales) and digital subscriptions sold and the rates charged to the respective customers. Single-copy revenue is recognized based on date of publication, net of provisions for related returns. Proceeds from subscription revenues are deferred at the time of sale and are recognized in earnings on a pro rata basis over the terms of the subscriptions. The deferred proceeds are recorded within unexpired subscription revenue in the Consolidated Balance Sheets. When our digital subscriptions are sold through third parties, we are a principal in the transaction and, therefore, revenues and related costs to third parties for these sales are reported on a gross basis. Several factors are considered to determine whether we are a principal, most notably whether we are the primary obligor to the customer and have determined the selling price and product specifications.
Advertising revenues are recognized when advertisements are published in newspapers or placed on digital platforms or, with respect to certain digital advertising, each time a user clicks on certain advertisements, net of provisions for estimated rebates and rate adjustments.
We recognize a rebate obligation as a reduction of revenues, based on the amount of estimated rebates that will be earned and claimed, related to the underlying revenue transactions during the period. Measurement of the rebate obligation is estimated based on the historical experience of the number of customers that ultimately earn and use the rebate. We recognize an obligation for rate adjustments as a reduction of revenues, based on the amount of estimated post-billing adjustments that will be claimed. Measurement of the rate adjustment obligation is estimated based on historical experience of credits actually issued.
Other revenues are recognized when the delivery occurs, services are rendered or purchases are made.
Income Taxes
Income taxes are recognized for the following: (1) amount of taxes payable for the current year and (2) deferred tax assets and liabilities for the future tax consequence of events that have been recognized differently in the financial statements than for tax purposes. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are established using statutory tax rates and are adjusted for tax rate changes in the period of enactment.
We assess whether our deferred tax assets should be reduced by a valuation allowance if it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized. Our process includes collecting positive (i.e.,
P. 64 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
sources of taxable income) and negative (i.e., recent historical losses) evidence and assessing, based on the evidence, whether it is more likely than not that the deferred tax assets will not be realized.
We recognize in our financial statements the impact of a tax position if that tax position is more likely than not of being sustained on audit, based on the technical merits of the tax position. This involves the identification of potential uncertain tax positions, the evaluation of tax law and an assessment of whether a liability for uncertain tax positions is necessary. Different conclusions reached in this assessment can have a material impact on our Consolidated Financial Statements.
We operate within multiple taxing jurisdictions and are subject to audit in these jurisdictions. These audits can involve complex issues, which could require an extended period of time to resolve. Until formal resolutions are reached between us and the tax authorities, the timing and amount of a possible audit settlement for uncertain tax benefits is difficult to predict.
On December 22, 2017, federal tax legislation commonly referred to as the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (the “Act”) was signed into law making significant changes to the Internal Revenue Code. Changes include, but are not limited to, a federal corporate tax rate decrease from 35% to 21% for tax years beginning after December 31, 2017, a one-time transition tax on the mandatory deemed repatriation of foreign earnings and numerous domestic and international-related provisions effective in 2018.
We have estimated our provision for income taxes in accordance with the Act and guidance available as of the date of this filing and as a result have recorded $68.7 million as additional income tax expense in the fourth quarter of 2017, the period in which the legislation was enacted.
On December 22, 2017, Staff Accounting Bulletin No. 118 ("SAB 118") was issued to address the application of GAAP in situations when a registrant does not have the necessary information available, prepared, or analyzed (including computations) in reasonable detail to complete the accounting for certain income tax effects of the Act. In accordance with SAB 118, we have determined that the $68.7 million of additional income tax expense recorded in connection with the remeasurement of certain deferred tax assets and liabilities, the one-time transition tax on the mandatory deemed repatriation of foreign earnings, and deferred tax assets related to executive compensation deductions was a provisional amount and a reasonable estimate at December 31, 2017. Provisional estimates were also made with regard to the Company’s deductions under the Act’s new expensing provisions and state and local income taxes related to foreign earnings subject to the one-time transition tax. The ultimate impact of the Act may differ from the provisional amount recognized due to, among other things, changes in estimates resulting from the receipt or calculation of final data, changes in interpretations of the Act, and additional regulatory guidance that may be issued. The accounting for the impact of the Act is expected to be completed by the fourth quarter of fiscal year 2018.
Stock-Based Compensation
We establish fair value based on market data for our stock-based awards to determine our cost and recognize the related expense over the appropriate vesting period. We recognize stock-based compensation expense for outstanding stock-settled long-term performance awards, stock-settled and cash-settled restricted stock units, stock options and stock appreciation rights. See Note 15 for additional information related to stock-based compensation expense.
Earnings/(Loss) Per Share
Basic earnings/(loss) per share is calculated by dividing net earnings/(loss) available to common stockholders by the weighted-average common stock outstanding. Diluted earnings/(loss) per share is calculated similarly, except that it includes the dilutive effect of the assumed exercise of securities, including outstanding warrants and the effect of shares issuable under our Company’s stock-based incentive plans if such effect is dilutive.
The two-class method is an earnings allocation method for computing earnings/(loss) per share when a company’s capital structure includes either two or more classes of common stock or common stock and participating securities. This method determines earnings/(loss) per share based on dividends declared on common stock and participating securities (i.e., distributed earnings), as well as participation rights of participating securities in any undistributed earnings.
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 65
Foreign Currency Translation
The assets and liabilities of foreign companies are translated at period-end exchange rates. Results of operations are translated at average rates of exchange in effect during the year. The resulting translation adjustment is included as a separate component in the Stockholders’ Equity section of our Consolidated Balance Sheets, in the caption “Accumulated other comprehensive loss, net of income taxes.”
Recently Adopted Accounting Pronouncements
In March 2016, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) 2016-09, “Compensation-Stock Compensation,” which provides guidance on accounting for share-based payment transactions, including the income tax consequences, classification of awards as either equity or liabilities, and classification on the statement of cash flows. This guidance became effective for the Company for fiscal years beginning after December 25, 2016.
As a result of the adoption of ASU 2016-09 in the first quarter of 2017, we recognized excess tax windfalls in income tax expense rather than additional paid-in capital of $3.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2017. Excess tax shortfalls and/or windfalls for share-based payments are now included in net cash from operating activities rather than net cash from financing activities. The changes have been applied prospectively in accordance with the ASU and prior periods have not been adjusted. Additionally, the presentation of employee taxes paid to taxing authorities for share-based transactions are now included in net cash from financing activities rather than net cash from operating activities. This change was applied retrospectively and as a result, we reclassified $9.6 million and $3.7 million for the years ended December 25, 2016 and December 27, 2015, respectively, in our Statement of Cash Flows from operating activities to financing activities. No other material changes resulted from the adoption of this standard.
Recently Issued Accounting Pronouncements
In February 2018, the FASB issued ASU 2018-02, “Income Statement - Reporting Comprehensive Income (Topic 220): Reclassification of Certain Tax Effect from Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income.” The new guidance provides financial statement preparers with an option to reclassify stranded tax effects within Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income to retained earnings in each period in which the effect of the change in the U.S. federal corporate income tax rate in the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act is recorded. The amendments are effective for all organizations for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2018, and interim periods within those fiscal years. Early adoption is permitted. We are currently in the process of evaluating the impact of this guidance on our consolidated financial statements.
In March 2017, the FASB issued ASU 2017-07, “Compensation - Retirement Benefits (Topic 715): Improving the Presentation of Net Periodic Pension Cost and Net Periodic Postretirement Benefit Cost.” The new guidance requires the service cost component to be presented separately from the other components of net benefit costs related to single-employer pension plans and other postretirement benefits plans. Service cost will be presented with other employee compensation cost within operations. The other components of net benefit cost, such as interest cost, amortization of prior service cost and gains or losses are required to be presented outside of operations. The new guidance is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, and interim periods within those fiscal years. Early adoption is permitted. The guidance should be applied retrospectively for the presentation of the service cost component in the income statement and allows a practical expedient for the estimation basis for applying the retrospective presentation requirements. Since the changes required in ASU 2017-07 only change the Consolidated Statements of Operations classification of the components of net periodic benefit cost, no changes will be made to net income. Upon adoption of the ASU during the first quarter of 2018, the Company will separately present the components of net periodic benefit cost or income related to single-employer pension plans and other postretirement benefits plans, excluding the service cost component, in non-operating expenses on a retrospective basis. Refer to Note 9 and Note 10 for components of net periodic benefit cost related to single-employer pension plans and other postretirement benefits, respectively.
In January 2017, the FASB issued ASU 2017-04, Intangibles - Goodwill and Other (Topic 350): Simplifying the Test for Goodwill Impairment, which eliminates step two from the goodwill impairment test. Under ASU 2017-04, an entity should recognize an impairment charge for the amount by which the carrying amount of a reporting unit exceeds its fair value up to the amount of goodwill allocated to that reporting unit. This guidance will be effective for us in the first quarter of 2020 on a prospective basis, and early adoption is permitted. The Company is in the process
P. 66 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
of evaluating the impact that this guidance will have on its consolidated financial statements. However, we do not expect the adoption of the standard to have a material effect on our consolidated financial statements.
In January 2017, the FASB issued ASU 2017-01, Business Combinations (Topic 805) : Clarifying the Definition of a Business, which provides guidance to assist companies with evaluating whether transactions should be accounted for as acquisitions (or disposals) of assets or businesses. The guidance is effective for interim and annual periods beginning after December 15, 2017. The adoption of this standard is not expected to have a material impact on the consolidated financial statements of the Company.
In November 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-18, “Statement of Cash Flow: Restricted Cash,” which amends the guidance in Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) 230 on the classification and presentation of restricted cash in the statement of cash flows. The key requirements of the ASU are: (1) all entities should include in their cash and cash-equivalent balances in the statements of cash flows those amounts that are deemed to be restricted cash and restricted cash equivalents, (2) a reconciliation between the statement of financial position and the statement of cash flows must be disclosed when the statement of financial position includes more than one line item for cash, cash equivalents, restricted cash, and restricted cash equivalents, (3) changes in restricted cash and restricted cash equivalents that result from transfers between cash, cash equivalents, and restricted cash and restricted cash equivalents should not be presented as cash flow activities in the statement of cash flows and (4) an entity with a material balance of amounts generally described as restricted cash and restricted cash equivalents must disclose information about the nature of the restrictions. This guidance becomes effective for Company for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, and interim periods within those fiscal years. Early adoption is permitted. Upon adoption of the standard during the first quarter of 2018, the Company will include the restricted cash balance with cash and cash equivalents balances in the statements of cash flows on a retrospective basis. Cash flows provided by investing activities will decrease by $6.9 million and $3.8 million for the fiscal years ended December 31, 2017 and December 25, 2016, respectively. The Company will add a reconciliation from Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheets to Condensed Consolidated Statement of Cash Flows in the first quarter of 2018.
In August 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-15, “Statement of Cash Flows: Classification of Certain Cash Receipts and Cash Payments,” which amends the guidance in ASC 230 on the classification of certain cash receipts and cash payments in the statement of cash flows. The primary purpose of this ASU is to reduce the diversity in practice that has resulted from the lack of consistent principles on this topic. The ASU’s amendments add or clarify guidance on eight cash flows issues: debt prepayment or debt extinguishment costs, settlement of zero-coupon debt instruments or other debt instruments with coupon interest rates that are insignificant in relation to the effective interest rate of the borrowing, contingent consideration payments made after a business combination, proceeds from the settlement of insurance claims, proceeds from the settlement of corporate-owned life insurance policies, including bank-owned life insurance policies, distributions received from equity method investees, beneficial interests in securitization transactions, and separately identifiable cash flows and application of the predominance principle. This guidance becomes effective for the Company for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, and interim periods within those fiscal years. Early adoption is permitted, including adoption in an interim period. All amendments must be adopted in the same period. Since proceeds and premiums of corporate-owned life insurance policies and the return on equity investment are currently classified as cash flows from investing activities, we do not expect the adoption of the standard to have a material effect on our consolidated financial statements.
In June 2016, FASB issued ASU 2016-13, “Financial Instruments - Credit Losses.” The new guidance introduces an approach based on expected losses to estimate credit losses on certain types of financial instruments. It also modifies the impairment model for available-for-sale (AFS) debt securities and provides for a simplified accounting model for purchased financial assets with credit deterioration since their origination. The new guidance is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2019, and interim periods within those fiscal years. Early adoption is permitted for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2018, and interim periods within those fiscal years. We are currently in the process of evaluating the impact of this guidance on our consolidated financial statements.
In February 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-02, “Leases,” which provides guidance on accounting for leases and disclosure of key information about leasing arrangements. The guidance requires lessees to recognize the following for all operating and finance leases at the commencement date: (1) a lease liability, which is the obligation to make lease payments arising from a lease, measured on a discounted basis and (2) a right-of-use asset representing the lessee’s right to use, or control the use of, the underlying asset for the lease term. A lessee is permitted to make an accounting policy election not to recognize lease assets and lease liabilities for short-term leases with a term of 12 months or less. The guidance does not fundamentally change lessor accounting; however, some changes have been
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 67
made to align that guidance with the lessee guidance and other areas within GAAP. This guidance becomes effective for the Company for fiscal years beginning after December 30, 2018. Early application is permitted. This guidance is expected to be applied on a modified retrospective basis for leases existing at, or entered into after, the earliest period presented in the financial statements. We are currently in the process of evaluating the impact of the new leasing guidance and expect that most of our operating lease commitments will be subject to the new standard. The adoption of the standard will have the most significant change on our balance sheet as it will require us to record right-of-use assets and lease liabilities. Based upon our initial evaluation, we do not expect the adoption of the standard to have a material effect on our results of operations and liquidity.
In January 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-01, “Financial Instruments-Overall: Recognition and Measurement of Financial Assets and Financial Liabilities” which addresses certain aspects of recognition, measurement, presentation, and disclosure of financial instruments including requirements to measure most equity investments at fair value with changes in fair value recognized in net income, to perform a qualitative assessment of equity investments without readily determinable fair values, and to separately present financial assets and liabilities by measurement category and by type of financial asset on the balance sheet or the accompanying notes to the financial statements. The new guidance is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, and interim periods within those fiscal years. Early adoption is permitted. The amendments related to equity securities without readily determinable fair values for which the measurement alternative is applied should be applied prospectively to equity investments that exist as of the date of adoption. We expect to elect the measurement alternative, defined as cost, less impairments, adjusted by observable price changes. Starting the fourth quarter of 2017, we have renamed “Interest expense, net” as “Interest expense and other, net” to account for non-operational income or expense and any impairments or remeasurement of our non-equity method investments as a result of adopting this ASU. We anticipate that the adoption of the standard may increase the volatility of our Interest expense and other, net, as a result of the remeasurement of our equity investments upon the occurrence of observable price changes and impairments.
In May 2014, the FASB issued ASU 2014-09, “Revenue from Contracts with Customers,” which prescribes a single comprehensive model for entities to use in the accounting of revenue arising from contracts with customers. The new guidance will supersede virtually all existing revenue guidance under GAAP and is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 31, 2017. There are two transition options available to entities: the full retrospective approach or the modified retrospective approach. Under the full retrospective approach, the Company would restate prior periods in compliance with ASC 250, “Accounting Changes and Error Corrections.” Alternatively, the Company may elect the modified retrospective approach, which allows for the new revenue standard to be applied to existing contracts as of the effective date with a cumulative catch-up adjustment recorded to retained earnings. We will adopt the new standard using the modified retrospective method beginning January 1, 2018.
Subsequently, in March 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-08, “Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606): Principal versus Agent Considerations (Reporting Revenue Gross versus Net),” which clarifies the implementation guidance on principal versus agent considerations in ASU 2014-09. In April 2016, the FASB also issued ASU 2016-10, “Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606): Identifying Performance Obligations and Licensing,” to reduce the cost and complexity of applying the guidance on identifying promised goods or services when identifying a performance obligation and improve the operability and understandability of the licensing implementation guidance. In May 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-12, “Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606): Narrow-Scope Improvements and Practical Expedients,” to reduce the cost and complexity of applying the guidance to address certain issues on assessing collectability, presentation of sales taxes, noncash consideration, and completed contracts and contract modifications at transition. The amendments in ASU 2016-08, 2016-10, and 2016-12 do not change the core principle of ASU 2014-09.
Based upon our evaluation, the adoption of the standards will not have a material effect on our financial condition or results of operations. Our subscription and advertising revenues will not be impacted by the new guidance. The most significant changes will be primarily related to how we account for certain licensing arrangements in the other revenue category for which archival and updated content is included. Under the current revenue guidance, licensing revenue is generally recognized based on the annual minimum guarantee amount specified in the contractual agreement with the licensee as a single deliverable. Based on the guidance of Topic 606, the Company has determined that the archival content and updated content included in these licensing arrangements represent two separate performance obligations. As such, a portion of the total contract consideration related to the archival content will be recognized at the commencement of the contract when control of the archival content is
P. 68 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
transferred. Based on the modified retroactive approach, the remaining contractual consideration will be recognized proportionately over the term of the contract when updated content is transferred to the licensee, in line with when the control of the new content is transferred. The net impact of these changes will accelerate the revenue of contracts not completed as of January 1, 2018 and we expect that the adjustment to opening retained earnings will be an increase in the range of approximately $3 million to $6 million.
The Company considers the applicability and impact of all recently issued accounting pronouncements. Recent accounting pronouncements not specifically identified in our disclosures are either not applicable to the Company or are not expected to have a material effect on our financial condition or results of operations.
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 69
3. Marketable Securities
As noted in Note 2, the Company reclassified all marketable securities from HTM to AFS in the third quarter of 2017, following a change to the Company’s cash reserve investment policy that allows the Company to sell marketable securities prior to maturity. This change resulted in recording a $2.5 million net unrealized loss in other comprehensive income. The reclassification of the investment portfolio to AFS was made to provide increased flexibility in the use of our investments to support current operations.
The following table presents the amortized cost, gross unrealized gains and losses, and fair market value of our AFS securities as of December 31, 2017:
December 31, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||
(In thousands) | Amortized Cost | Gross unrealized gains | Gross unrealized losses | Fair Value | ||||||||||||
Short-term AFS securities | ||||||||||||||||
Corporate debt securities | $ | 150,334 | $ | — | $ | (227 | ) | $ | 150,107 | |||||||
U.S. Treasury securities | 70,985 | — | (34 | ) | 70,951 | |||||||||||
U.S. governmental agency securities | 45,819 | — | (179 | ) | 45,640 | |||||||||||
Certificates of deposit | 9,300 | — | — | 9,300 | ||||||||||||
Commercial paper | 32,591 | — | — | 32,591 | ||||||||||||
Total short-term AFS securities | $ | 309,029 | $ | — | $ | (440 | ) | $ | 308,589 | |||||||
Long-term AFS securities | ||||||||||||||||
U.S. governmental agency securities | $ | 97,798 | $ | — | $ | (1,019 | ) | $ | 96,779 | |||||||
Corporate debt securities | 92,687 | — | (683 | ) | 92,004 | |||||||||||
U.S. Treasury securities | 53,031 | — | (403 | ) | 52,628 | |||||||||||
Total long-term AFS securities | $ | 243,516 | $ | — | $ | (2,105 | ) | $ | 241,411 | |||||||
P. 70 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
The following table represents the AFS securities as of December 31, 2017 that were in an unrealized loss position, aggregated by investment category and the length of time that individual securities have been in a continuous loss position:
December 31, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Less than 12 Months | 12 Months or Greater | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||
(In thousands) | Fair Value | Gross unrealized losses | Fair Value | Gross unrealized losses | Fair Value | Gross unrealized losses | ||||||||||||||||||
Short-term AFS securities | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Corporate debt securities | $ | 140,111 | $ | (199 | ) | $ | 9,996 | $ | (28 | ) | $ | 150,107 | $ | (227 | ) | |||||||||
U.S. Treasury securities | 70,951 | (34 | ) | — | — | 70,951 | (34 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
U.S. governmental agency securities | 19,770 | (50 | ) | 25,870 | (129 | ) | 45,640 | (179 | ) | |||||||||||||||
Total short-term AFS securities | $ | 230,832 | $ | (283 | ) | $ | 35,866 | $ | (157 | ) | $ | 266,698 | $ | (440 | ) | |||||||||
Long-term AFS securities | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
U.S. governmental agency securities | $ | 23,998 | $ | (125 | ) | $ | 72,781 | $ | (894 | ) | $ | 96,779 | $ | (1,019 | ) | |||||||||
Corporate debt securities | 81,118 | (579 | ) | 10,886 | (104 | ) | 92,004 | (683 | ) | |||||||||||||||
U.S. Treasury securities | 52,628 | (403 | ) | — | — | 52,628 | (403 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
Total long-term AFS securities | $ | 157,744 | $ | (1,107 | ) | $ | 83,667 | $ | (998 | ) | $ | 241,411 | $ | (2,105 | ) | |||||||||
We periodically review our AFS securities for OTTI. See Note 2 for factors we consider when assessing AFS securities for OTTI. As of December 31, 2017, we did not intend to sell and it was not likely that we would be required to sell these investments before recovery of their amortized cost basis, which may be at maturity. Unrealized losses related to these investments are primarily due to interest rate fluctuations as opposed to changes in credit quality. Therefore, as of December 31, 2017, we have recognized no OTTI loss.
The following table presents the amortized cost of our HTM securities as of December 25, 2016:
December 25, 2016 | ||||
(In thousands) | Amortized Cost | |||
Short-term HTM securities (1) | ||||
U.S. Treasury securities | $ | 150,623 | ||
Corporate debt securities | 150,599 | |||
U.S. governmental agency securities | 64,135 | |||
Commercial paper | 84,178 | |||
Total short-term HTM securities | $ | 449,535 | ||
Long-term HTM securities (1) | ||||
U.S. governmental agency securities | $ | 110,732 | ||
Corporate debt securities | 61,775 | |||
U.S. Treasury securities | 14,792 | |||
Total long-term HTM securities | $ | 187,299 | ||
(1) All HTM securities were recorded at amortized cost and not adjusted to fair value in accordance with the HTM accounting treatment. As of December 25, 2016, the amortized cost approximated fair value because of the short-term maturity and highly liquid nature of these investments.
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 71
Marketable debt securities
As of December 31, 2017, our short-term and long-term marketable securities had remaining maturities of less than 1 month to 12 months and 13 months to 35 months, respectively. See Note 8 for additional information regarding the fair value hierarchy of our marketable securities.
Letters of credit
We issued letters of credit totaling $56.0 million as of December 31, 2017, to secure commitments under certain sub-lease agreements associated with the rental of floors in our headquarters building. The letters of credit will expire in 2019, and are collateralized by marketable securities, with a fair value of $63.1 million, held in our investment portfolios. No amounts were outstanding on these letters of credit as of December 31, 2017. See Note 18 for additional information regarding the securities commitment.
4. Goodwill and Intangibles
In 2016, the Company acquired two digital marketing agencies, HelloSociety, LLC and Fake Love, LLC for an aggregate of $15.4 million, in separate all-cash transactions. Also in 2016, the Company acquired Submarine Leisure Club, Inc., which owned the product review and recommendation websites The Wirecutter and The Sweethome, in an all-cash transaction. We paid $25.0 million, including a payment made for a non-compete agreement, and also entered into a consulting agreement and retention agreements that will likely require payments over the three years following the acquisition.
The Company allocated the purchase prices for these acquisitions based on the final valuation of assets acquired and liabilities assumed, resulting in allocations to goodwill, intangibles, property, plant and equipment and other miscellaneous assets.
The aggregate carrying amount of intangible assets of $8.2 million related to these acquisitions has been included in “Miscellaneous Assets” in our Consolidated Balance Sheets. The estimated useful lives for these assets range from 3 to 7 years and are amortized on a straight-line basis.
The changes in the carrying amount of goodwill as of December 31, 2017, and since December 27, 2015, were as follows:
(In thousands) | Total Company | |||
Balance as of December 27, 2015 | $ | 109,085 | ||
Business acquisitions | 28,529 | |||
Foreign currency translation | (3,097 | ) | ||
Balance as of December 25, 2016 | 134,517 | |||
Measurement Period Adjustment (1) | (198 | ) | ||
Foreign currency translation | 9,230 | |||
Balance as of December 31, 2017 | $ | 143,549 | ||
(1) Includes measurement period adjustment in connection with the Submarine Leisure Club, Inc. acquisition.
The foreign currency translation line item reflects changes in goodwill resulting from fluctuating exchange rates related to the consolidation of certain international subsidiaries.
5. Investments
Investments in Joint Ventures
As of December 31, 2017, our investment in joint ventures of $1.7 million consisted of a 40% equity ownership interest in Madison Paper Industries (“Madison”), a partnership that previously operated a supercalendered paper mill in Maine. In the fourth quarter of 2017, we sold our 49% equity interest in Donohue Malbaie Inc. (“Malbaie”), a Canadian newsprint company, for $20 million Canadian dollar ($15.6 million USD). In the third quarter of 2017, we sold our 30% ownership in Women in the World Media, LLC, a live event conference business, for a nominal amount.
P. 72 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
These investments are accounted for under the equity method, and are recorded in “Investments in joint ventures” in our Consolidated Balance Sheets. Our proportionate shares of the operating results of our investments are recorded in “Gain/(loss) from joint ventures” in our Consolidated Statements of Operations.
In 2017, we had a gain from joint ventures of $18.6 million compared with a loss of $36.3 million in 2016. The gain was primarily due to the sale of the remaining assets of the paper mill previously operated by Madison, partially offset by our proportionate share of the loss recognized by Madison resulting from Madison’s settlement of pension obligations, as well as the sale of our investment in Malbaie.
In 2016, we had a loss from joint ventures of $36.3 million compared with a loss of $0.8 million in 2015. The increase was primarily due to losses related to the shutdown of the paper mill previously operated by Madison, as described below, partially offset by increased income from our investment in Malbaie, which benefited from higher newsprint prices and the impact of a significantly weakened Canadian dollar.
Madison
The Company and UPM-Kymmene Corporation (“UPM”), a Finnish paper manufacturing company, are partners through subsidiary companies in Madison. The Company’s 40% ownership of Madison is through an 80%-owned consolidated subsidiary that owns 50% of Madison. UPM owns 60% of Madison, including a 10% interest through a 20% noncontrolling interest in the consolidated subsidiary of the Company. In 2016, the paper mill closed and we recognized $41.4 million in losses from joint ventures related to the closure. The Company’s proportionate share of the loss was $20.1 million after tax and net of noncontrolling interest. As a result of the mill closure, we wrote our investment down to zero.
The Company’s joint venture in Madison is currently being liquidated. In the fourth quarter of 2016, Madison sold certain assets at the mill site and we recognized a gain of $3.9 million related to the sale. In 2017 we recognized a gain of $20.8 million, primarily related to the sale of the remaining assets, partially offset by the loss related to our proportionate share of Madison’s settlement of certain pension obligations. The Company’s proportionate share of the gain was $11.6 million after tax and net of noncontrolling interest. We expect to receive our proportionate share of a cash distribution from the wind down of our Madison investment in 2018.
The following table presents summarized unaudited balance sheet information for Madison, which follows a calendar year:
(In thousands) | December 31, 2017 | December 31, 2016 | ||||||
Current assets | $ | 35,764 | $ | 3,766 | ||||
Noncurrent assets | 9,640 | 8,944 | ||||||
Total assets | 45,404 | 12,710 | ||||||
Current liabilities | 137 | 1,373 | ||||||
Noncurrent liabilities | 4,070 | 29,386 | ||||||
Total liabilities | 4,207 | 30,759 | ||||||
Total equity | $ | 41,197 | $ | (18,049 | ) | |||
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 73
The following table presents summarized unaudited income statement information for Madison, which follows a calendar year:
For the Twelve Months Ended | ||||||||||||
(In thousands) | December 31, 2017 | December 31, 2016 | December 31, 2015 | |||||||||
Revenues | $ | — | $ | 40,523 | $ | 133,319 | ||||||
Income/(Expenses): | ||||||||||||
Cost of sales (1) | (13,396 | ) | (63,439 | ) | (126,292 | ) | ||||||
General and administrative income/(expense) and other (2) | 55,058 | (62,759 | ) | (13,550 | ) | |||||||
Total income/(expense) | 41,662 | (126,198 | ) | (139,842 | ) | |||||||
Operating income/(loss) | 41,662 | (85,675 | ) | (6,523 | ) | |||||||
Other income/(expense) | 18 | 2 | 689 | |||||||||
Net income/(loss) | $ | 41,680 | $ | (85,673 | ) | $ | (5,834 | ) | ||||
(1) Primarily represents Madison’s settlement of its pension obligations in 2017.
(2) Primarily represents gains/(losses) from the sale of assets and closure of Madison in 2017 and 2016.
We received no distributions from Madison in 2017, 2016, or 2015.
Malbaie
We had a 49% equity interest in Malbaie, which we sold during the fourth quarter of 2017 for $20 million Canadian dollars ($15.6 million USD). We recognized a loss of $6.4 million before tax as a result of the sale. The other 51% equity interest was owned by Resolute FP Canada Inc., a subsidiary of Resolute Forest Products Inc. (“Resolute”), a Delaware corporation. Resolute is a large global manufacturer of paper, market pulp and wood products.
Other than from the sale of our equity interest in 2017, we received no distributions from Malbaie in 2017, 2016 or 2015.
Other
We purchased newsprint from Malbaie, and previously purchased supercalendered paper from Madison, at competitive prices. These purchases totaled approximately $11 million in 2017, $14 million in 2016 and $12 million in 2015.
Cost Method Investments
The aggregate carrying amount of cost method investments included in “Miscellaneous assets’’ in our Consolidated Balance Sheets were $13.6 million for December 31, 2017 and December 25, 2016.
P. 74 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
6. Debt Obligations
Our indebtedness primarily consisted of the repurchase option related to a sale-leaseback of a portion of our New York headquarters. Our total debt and capital lease obligations consisted of the following:
(In thousands) | December 31, 2017 | December 25, 2016 | ||||||
Option to repurchase ownership interest in headquarters building in 2019: | ||||||||
Principal amount | $ | 250,000 | $ | 250,000 | ||||
Less unamortized discount based on imputed interest rate of 13.0% | 6,596 | 9,801 | ||||||
Total option to repurchase ownership interest in headquarters building in 2019 | 243,404 | 240,199 | ||||||
Capital lease obligations | 6,805 | 6,779 | ||||||
Total long-term debt and capital lease obligations | $ | 250,209 | $ | 246,978 | ||||
See Note 8 for information regarding the fair value of our long-term debt.
The aggregate face amount of maturities of debt over the next five years and thereafter is as follows:
(In thousands) | Amount | |||
2018 | $ | — | ||
2019 | 250,000 | |||
2020 | — | |||
2021 | — | |||
2022 | — | |||
Thereafter | — | |||
Total face amount of maturities | 250,000 | |||
Less: Unamortized debt costs and discount | (6,596 | ) | ||
Carrying value of debt (excludes capital leases) | $ | 243,404 | ||
“Interest expense and other, net,” as shown in the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Operations was as follows:
(In thousands) | December 31, 2017 | December 25, 2016 | December 27, 2015 | |||||||||
Interest expense | $ | 27,732 | $ | 39,487 | $ | 41,973 | ||||||
Amortization of debt costs and discount on debt | 3,205 | 4,897 | 4,756 | |||||||||
Capitalized interest | (1,257 | ) | (559 | ) | (338 | ) | ||||||
Interest income and other expense, net | (9,897 | ) | (9,020 | ) | (7,341 | ) | ||||||
Total interest expense and other, net | $ | 19,783 | $ | 34,805 | $ | 39,050 | ||||||
6.625% Notes
In November 2010, we issued $225.0 million aggregate principal amount of 6.625% senior unsecured notes due December 15, 2016 (“6.625% Notes”). During 2014, we repurchased $18.4 million principal amount of the 6.625% Notes. In December 2016, the Company repaid, at maturity, the remaining principal amount of the 6.625% Notes.
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 75
Sale-Leaseback Financing
In March 2009, we entered into an agreement to sell and simultaneously lease back a portion of our leasehold condominium interest in our Company’s headquarters building located at 620 Eighth Avenue in New York City (the “Condo Interest”). The sale price for the Condo Interest was $225.0 million less transaction costs, for net proceeds of approximately $211 million. The lease term is 15 years, and we have three renewal options that could extend the term for an additional 20 years. We have an option, exercisable in 2019, to repurchase the Condo Interest for $250.0 million. In January 2018, we delivered notice of our intent to exercise this option. See Note 19 for more detail on this notice.
The transaction is accounted for as a financing transaction. As such, we have continued to depreciate the Condo Interest and account for the rental payments as interest expense. The difference between the purchase option price of $250.0 million and the net sale proceeds of approximately $211 million, or approximately $39 million, is being amortized over a 10-year period through interest expense. The effective interest rate on this transaction was approximately 13%.
7. Other
Advertising Expenses
Advertising expense to promote our brand, subscription products and marketing services were $118.6 million, $89.8 million and $83.4 million for the fiscal years ended December 31, 2017, December 25, 2016 and December 27, 2015, respectively. We expense our advertising costs as incurred.
Capitalized Computer Software Costs
Amortization of capitalized computer software costs included in “Depreciation and amortization” in our Consolidated Statements of Operations was $12.8 million, $11.5 million and $11.9 million for the fiscal years ended December 31, 2017, December 25, 2016 and December 27, 2015, respectively. The unamortized computer software costs were $28.1 million and $19.0 million as of December 31, 2017 and December 25, 2016, respectively.
Headquarters Redesign and Consolidation
In December 2016, we announced plans to redesign our headquarters building, consolidate our operations within a smaller number of floors and lease the additional floors to third parties. These changes are expected to generate additional rental income and result in a more collaborative workspace. We incurred $10.1 million of total costs related to these measures for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2017 . The capital expenditures related to these measures were approximately $62 million for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2017.
Severance Costs
On May 31, 2017, we announced certain measures designed to streamline our editing process and allow us to make further investments in the newsroom. These measures resulted in a workforce reduction primarily affecting our newsroom. We recognized severance costs of $23.9 million for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2017, substantially all of which were related to this workforce reduction. We recognized severance costs of $18.8 million in 2016 and $7.0 million in 2015. These costs are recorded in “Selling, general and administrative costs” in our Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Additionally, during the second quarter of 2016, we announced certain measures to streamline our international print operations and support future growth efforts. These measures included a redesign of our international print newspaper and the relocation of certain editing and production operations conducted in Paris to our locations in Hong Kong and New York. During the third and second quarters of 2016, we incurred $2.9 million and $11.9 million, respectively, of total costs related to the measures, primarily related to relocation and severance charges. These costs were recorded in “Restructuring charge” in our Consolidated Statements of Operations.
We had a severance liability of $18.8 million and $23.2 million included in “Accrued expenses and other” in our Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2017 and December 25, 2016, respectively.
P. 76 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
8. Fair Value Measurements
Fair value is the price that would be received upon the sale of an asset or paid upon transfer of a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. The transaction would be in the principal or most advantageous market for the asset or liability, based on assumptions that a market participant would use in pricing the asset or liability. The fair value hierarchy consists of three levels:
Level 1–quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities that the reporting entity has the ability to access at the measurement date;
Level 2–inputs other than quoted prices included within Level 1 that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly; and
Level 3–unobservable inputs for the asset or liability.
Assets/Liabilities Measured and Recorded at Fair Value on a Recurring Basis
As of December 31, 2017 and December 25, 2016, we had assets related to our qualified pension plans measured at fair value. The required disclosures regarding such assets are presented in Note 9.
The following table summarizes our financial assets and liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis as of December 31, 2017 and December 25, 2016:
(In thousands) | December 31, 2017 | December 25, 2016 (3) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Assets: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Short-term AFS securities(1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
U.S Treasury securities | $ | 70,951 | $ | — | $ | 70,951 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||||||||||
Corporate debt securities | 150,107 | — | 150,107 | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
U.S. governmental agency securities | 45,640 | — | 45,640 | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Certificates of deposit | 9,300 | — | 9,300 | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Commercial paper | 32,591 | — | 32,591 | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total short-term AFS securities | $ | 308,589 | $ | — | $ | 308,589 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||||||||||
Long-term AFS securities(1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
U.S. governmental agency securities | $ | 96,779 | $ | — | $ | 96,779 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||||||||||
Corporate debt securities | 92,004 | — | 92,004 | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
U.S Treasury securities | 52,628 | — | 52,628 | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total long-term AFS securities | $ | 241,411 | $ | — | $ | 241,411 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||||||||||
Liabilities: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Deferred compensation(2) | $ | 29,526 | $ | 29,526 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 31,006 | $ | 31,006 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||||||||||
(1) Our marketable securities, which include U.S. Treasury securities, corporate debt securities, U.S. government agency securities, municipal securities, certificates of deposit and commercial paper, are recorded at fair value (see Note 3). We classified these investments as Level 2 since the fair value is based on market observable inputs for investments with similar terms and maturities.
(2) The deferred compensation liability, included in “Other liabilities—Other” in our Consolidated Balance Sheets, consists of deferrals under The New York Times Company Deferred Executive Compensation Plan (the “DEC”), which enables certain eligible executives to elect to defer a portion of their compensation on a pre-tax basis. The deferred amounts are invested at the executives’ option in various mutual funds. The fair value of deferred compensation is based on the mutual fund investments elected by the executives and on quoted prices in active markets for identical assets. Participation in the DEC was frozen effective December 31, 2015. Refer to Note 11 for detail.
(3) As noted in Note 2, in the third quarter of 2017, we reclassified our marketable securities from HTM to AFS. Prior to being classified as AFS, the securities were recorded at amortized cost and not adjusted to fair value in accordance with the HTM accounting treatment. As of December 25, 2016, the amortized cost approximated fair value because of the short-term maturity and highly liquid nature of these
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 77
investments. We classified these investments as Level 2 since the fair value estimates are based on market observable inputs for investments with similar terms and maturities.
Financial Instruments Disclosed, But Not Reported, at Fair Value
The carrying value of our long-term debt was approximately $243 million as of December 31, 2017 and approximately $240 million as of December 25, 2016. The fair value of our long-term debt was approximately $279 million and $298 million as of December 31, 2017, and December 25, 2016, respectively. We estimate the fair value of our debt utilizing market quotations for debt that have quoted prices in active markets. Since our debt does not trade in an active market, the fair value estimates are based on market observable inputs based on borrowing rates currently available for debt with similar terms and average maturities (Level 2).
Assets Measured and Recorded at Fair Value on a Non-Recurring Basis
Certain non-financial assets, such as goodwill, intangible assets, property, plant and equipment and certain investments are only recorded at fair value if an impairment charge is recognized. Goodwill and intangible assets are initially recorded at fair value in purchase accounting. We classified all of these measurements as Level 3, as we used unobservable inputs within the valuation methodologies that were significant to the fair value measurements, and the valuations required management‘s judgment due to the absence of quoted market prices. There was no impairment recognized in 2017, 2016 and 2015.
9. Pension Benefits
Single-Employer Plans
We sponsor several single-employer defined benefit pension plans, the majority of which have been frozen. We also participated in two joint Company and Guild-sponsored plans covering employees who are members of The NewsGuild of New York. Effective January 1, 2018, the sponsorship of one of these plans, the Newspaper Guild of New York - The New York Times Pension Plan, which is frozen, was transferred exclusively to the Company.
We also have a foreign-based pension plan for certain employees (the “foreign plan”). The information for the foreign plan is combined with the information for U.S. non-qualified plans. The benefit obligation of the foreign plan is immaterial to our total benefit obligation.
Net Periodic Pension Cost
The components of net periodic pension cost were as follows:
December 31, 2017 | December 25, 2016 | December 27, 2015 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(In thousands) | Qualified Plans | Non- Qualified Plans | All Plans | Qualified Plans | Non- Qualified Plans | All Plans | Qualified Plans | Non- Qualified Plans | All Plans | |||||||||||||||||||||
Service cost | $ | 9,720 | $ | 79 | $ | 9,799 | $ | 8,991 | $ | 143 | $ | 9,134 | $ | 11,932 | $ | 157 | $ | 12,089 | ||||||||||||
Interest cost | 60,742 | 7,840 | 68,582 | 66,293 | 8,172 | 74,465 | 74,536 | 10,060 | 84,596 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Expected return on plan assets | (102,900 | ) | — | (102,900 | ) | (111,159 | ) | — | (111,159 | ) | (115,261 | ) | — | (115,261 | ) | |||||||||||||||
Amortization and other costs | 29,051 | 4,318 | 33,369 | 28,274 | 4,184 | 32,458 | 36,442 | 5,081 | 41,523 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Amortization of prior service (credit)/cost | (1,945 | ) | — | (1,945 | ) | (1,945 | ) | — | (1,945 | ) | (1,945 | ) | — | (1,945 | ) | |||||||||||||||
Effect of settlement/curtailment | 102,109 | — | 102,109 | 21,294 | (1,599 | ) | 19,695 | 40,329 | — | 40,329 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Net periodic pension cost | $ | 96,777 | $ | 12,237 | $ | 109,014 | $ | 11,748 | $ | 10,900 | $ | 22,648 | $ | 46,033 | $ | 15,298 | $ | 61,331 | ||||||||||||
Over the past several years the Company has taken steps to reduce the size and volatility of our pension obligations. In the fourth quarter of 2017, the Company entered into agreements with two insurance companies to transfer future benefit obligations and annuity administration for certain retirees (or their beneficiaries) in two of the Company’s qualified pension plans. This transfer of plan assets and obligations reduced the Company’s qualified pension plan obligations by $263.3 million. As a result of these agreements, the Company recorded pension settlement charges of $102.1 million. Additionally, during the fourth quarter of 2017, the Company made discretionary contributions totaling $120 million to certain qualified pension plans.
P. 78 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
In the fourth quarter of 2016, we recorded a pension settlement charge of $21.3 million in connection with a lump-sum payment offer made to certain former employees who participated in certain qualified pension plans. These lump-sum payments totaled $49.5 million and were made with cash from the qualified pension plans, not with Company cash. The effect of this lump-sum payment offer was to reduce our pension obligations by $52.2 million. In addition, we recorded a $1.6 million curtailment related to the streamlining of the Company’s international print operations. See Note 7 for more information on the streamlining of the Company’s international print operations.
In the first quarter of 2015, we recorded a pension settlement charge of $40.3 million in connection with a lump-sum payment offer made to certain former employees who participated in certain qualified pension plans. These lump-sum payments totaled $98.3 million and were made with cash from the qualified pension plans, not with Company cash. The effect of this lump-sum payment offer was to reduce our pension obligations by $142.8 million.
Other changes in plan assets and benefit obligations recognized in other comprehensive income/loss were as follows:
(In thousands) | December 31, 2017 | December 25, 2016 | December 27, 2015 | |||||||||
Net actuarial loss/(gain) | $ | 22,600 | $ | (4,289 | ) | $ | 31,044 | |||||
Amortization of loss | (33,369 | ) | (32,458 | ) | (41,523 | ) | ||||||
Amortization of prior service credit | 1,945 | 1,945 | 1,945 | |||||||||
Effect of curtailment | — | — | (1,264 | ) | ||||||||
Effect of settlement | (102,109 | ) | (21,294 | ) | (40,329 | ) | ||||||
Total recognized in other comprehensive (income)/loss | (110,933 | ) | (56,096 | ) | (50,127 | ) | ||||||
Net periodic pension cost | 109,014 | 22,648 | 61,331 | |||||||||
Total recognized in net periodic benefit cost and other comprehensive (income)/loss | $ | (1,919 | ) | $ | (33,448 | ) | $ | 11,204 | ||||
Actuarial gains and losses are amortized using a corridor approach. The gain or loss corridor is equal to 10% of the greater of the projected benefit obligation and the market-related value of assets. Gains and losses in excess of the corridor are generally amortized over the future working lifetime for the ongoing plans and average life expectancy for the frozen plans.
The estimated actuarial loss and prior service credit that will be amortized from accumulated other comprehensive loss into net periodic pension cost over the next fiscal year is approximately $32 million and $2 million, respectively.
In the fourth quarter of 2015, the Company’s ERISA Management Committee made a decision to freeze the accrual of benefits under the Retirement Annuity Plan For Craft Employees of The New York Times Companies with respect to all participants covered by a collective bargaining agreement between the Company and The New York Newspaper Printing Pressmen’s Union No. 2N/1SE, effective as of the close of business on December 31, 2015. As a result, we recorded a curtailment of $1.3 million in 2015.
We also contribute to defined contribution benefit plans. The amount of cost recognized for defined contribution benefit plans was approximately $23 million for 2017, $15 million for 2016 and $16 million for 2015.
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 79
Benefit Obligation and Plan Assets
The changes in the benefit obligation and plan assets and other amounts recognized in other comprehensive loss were as follows:
December 31, 2017 | December 25, 2016 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
(In thousands) | Qualified Plans | Non- Qualified Plans | All Plans | Qualified Plans | Non- Qualified Plans | All Plans | ||||||||||||||||||
Change in benefit obligation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Benefit obligation at beginning of year | $ | 1,798,652 | $ | 240,399 | $ | 2,039,051 | $ | 1,851,910 | $ | 247,087 | $ | 2,098,997 | ||||||||||||
Service cost | 9,720 | 79 | 9,799 | 8,991 | 143 | 9,134 | ||||||||||||||||||
Interest cost | 60,742 | 7,840 | 68,582 | 66,293 | 8,172 | 74,465 | ||||||||||||||||||
Plan participants’ contributions | 9 | — | 9 | 9 | — | 9 | ||||||||||||||||||
Actuarial loss | 142,980 | 15,342 | 158,322 | 23,994 | 2,695 | 26,689 | ||||||||||||||||||
Curtailments | — | — | — | — | (1,599 | ) | (1,599 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
Settlements | (269,287 | ) | — | (269,287 | ) | (48,413 | ) | — | (48,413 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Benefits paid | (106,328 | ) | (18,510 | ) | (124,838 | ) | (104,132 | ) | (15,992 | ) | (120,124 | ) | ||||||||||||
Effects of change in currency conversion | — | 152 | 152 | — | (107 | ) | (107 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
Benefit obligation at end of year | 1,636,488 | 245,302 | 1,881,790 | 1,798,652 | 240,399 | 2,039,051 | ||||||||||||||||||
Change in plan assets | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Fair value of plan assets at beginning of year | 1,576,760 | — | 1,576,760 | 1,579,356 | — | 1,579,356 | ||||||||||||||||||
Actual return on plan assets | 238,622 | — | 238,622 | 142,137 | — | 142,137 | ||||||||||||||||||
Employer contributions | 127,635 | 18,510 | 146,145 | 7,803 | 15,992 | 23,795 | ||||||||||||||||||
Plan participants’ contributions | 9 | — | 9 | 9 | — | 9 | ||||||||||||||||||
Settlements | (269,287 | ) | — | (269,287 | ) | (48,413 | ) | — | (48,413 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Benefits paid | (106,328 | ) | (18,510 | ) | (124,838 | ) | (104,132 | ) | (15,992 | ) | (120,124 | ) | ||||||||||||
Fair value of plan assets at end of year | 1,567,411 | — | 1,567,411 | 1,576,760 | — | 1,576,760 | ||||||||||||||||||
Net amount recognized | $ | (69,077 | ) | $ | (245,302 | ) | $ | (314,379 | ) | $ | (221,892 | ) | $ | (240,399 | ) | $ | (462,291 | ) | ||||||
Amount recognized in the Consolidated Balance Sheets | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Current liabilities | $ | — | $ | (16,901 | ) | $ | (16,901 | ) | $ | — | $ | (16,818 | ) | $ | (16,818 | ) | ||||||||
Noncurrent liabilities | (69,077 | ) | (228,401 | ) | (297,478 | ) | (221,892 | ) | (223,581 | ) | (445,473 | ) | ||||||||||||
Net amount recognized | $ | (69,077 | ) | $ | (245,302 | ) | $ | (314,379 | ) | $ | (221,892 | ) | $ | (240,399 | ) | $ | (462,291 | ) | ||||||
Amount recognized in accumulated other comprehensive loss | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Actuarial loss | $ | 641,194 | $ | 109,880 | $ | 751,074 | $ | 765,096 | $ | 98,855 | $ | 863,951 | ||||||||||||
Prior service credit | (20,731 | ) | — | (20,731 | ) | (22,676 | ) | — | (22,676 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 620,463 | $ | 109,880 | $ | 730,343 | $ | 742,420 | $ | 98,855 | $ | 841,275 | ||||||||||||
P. 80 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
Information for pension plans with an accumulated benefit obligation in excess of plan assets was as follows:
(In thousands) | December 31, 2017 | December 25, 2016 | ||||||
Projected benefit obligation | $ | 1,881,790 | $ | 2,039,051 | ||||
Accumulated benefit obligation | $ | 1,874,445 | $ | 2,034,636 | ||||
Fair value of plan assets | $ | 1,567,411 | $ | 1,576,760 | ||||
Assumptions
Weighted-average assumptions used in the actuarial computations to determine benefit obligations for qualified pension plans were as follows:
December 31, 2017 | December 25, 2016 | |||||
Discount rate | 3.75 | % | 4.31 | % | ||
Rate of increase in compensation levels | 2.95 | % | 2.95 | % | ||
The rate of increase in compensation levels is applicable only for qualified pension plans that have not been frozen.
Weighted-average assumptions used in the actuarial computations to determine net periodic pension cost for qualified plans were as follows:
December 31, 2017 | December 25, 2016 | December 27, 2015 | |||||||
Discount rate for determining projected benefit obligation | 4.31 | % | 4.60 | % | 4.05 | % | |||
Discount rate in effect for determining service cost | 4.74 | % | 5.78 | % | 4.05 | % | |||
Discount rate in effect for determining interest cost | 3.54 | % | 3.68 | % | 4.05 | % | |||
Rate of increase in compensation levels | 2.95 | % | 2.91 | % | 2.89 | % | |||
Expected long-term rate of return on assets | 6.73 | % | 7.01 | % | 7.01 | % | |||
Weighted-average assumptions used in the actuarial computations to determine benefit obligations for non-qualified plans were as follows:
December 31, 2017 | December 25, 2016 | |||||
Discount rate | 3.67 | % | 4.17 | % | ||
Rate of increase in compensation levels | 2.50 | % | 2.50 | % | ||
The rate of increase in compensation levels is applicable only for the non-qualified pension plans that have not been frozen.
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 81
Weighted-average assumptions used in the actuarial computations to determine net periodic pension cost for non-qualified plans were as follows:
December 31, 2017 | December 25, 2016 | December 27, 2015 | |||||||
Discount rate for determining projected benefit obligation | 4.17 | % | 4.40 | % | 3.90 | % | |||
Discount rate in effect for determining interest cost | 3.39 | % | 3.44 | % | 3.90 | % | |||
Rate of increase in compensation levels | 2.50 | % | 2.50 | % | 2.50 | % | |||
We determined our discount rate using a Ryan ALM, Inc. Curve (the “Ryan Curve”). The Ryan Curve provides the bonds included in the curve and allows adjustments for certain outliers (i.e., bonds on “watch”). We believe the Ryan Curve allows us to calculate an appropriate discount rate.
To determine our discount rate, we project a cash flow based on annual accrued benefits. The projected plan cash flow is discounted to the measurement date, which is the last day of our fiscal year, using the annual spot rates provided in the Ryan Curve.
In determining the expected long-term rate of return on assets, we evaluated input from our investment consultants, actuaries and investment management firms, including our review of asset class return expectations, as well as long-term historical asset class returns. Projected returns by such consultants and economists are based on broad equity and bond indices. Our objective is to select an average rate of earnings expected on existing plan assets and expected contributions to the plan during the year, less expense expected to be incurred by the plan during the year.
The market-related value of plan assets is multiplied by the expected long-term rate of return on assets to compute the expected return on plan assets, a component of net periodic pension cost. The market-related value of plan assets is a calculated value that recognizes changes in fair value over three years.
During the fourth quarters of 2017 and 2016, we adopted new mortality tables released by the Society of Actuaries (“SOA”) and revised the mortality assumptions used in determining our pension obligations. The net impact to our qualified and non-qualified pension obligations resulting from the new mortality assumptions in 2017 and 2016 was a decrease of $15.4 million and $34.7 million, respectively.
Beginning in 2016, we changed the approach used to calculate the service and interest components of net periodic benefit cost for benefit plans to provide a more precise measurement of service and interest costs. Prior to this change, we calculated these service and interest components utilizing a single weighted-average discount rate derived from the yield curve used to measure the benefit obligation at the beginning of the period. We have elected to utilize an approach that discounts the individual expected cash flows using the applicable spot rates derived from the yield curve over the projected cash flow period. The spot rates used to estimate 2016 service and interest costs ranged from 1.32% to 4.79%. Service costs and interest costs for our benefit plans were reduced by approximately $18 million in 2016 due to the change in methodology.
Plan Assets
Company-Sponsored Pension Plans
The assets underlying the Company-sponsored qualified pension plans are managed by professional investment managers. These investment managers are selected and monitored by the pension investment committee, composed of certain senior executives, who are appointed by the Finance Committee of the Board of Directors of the Company. The Finance Committee is responsible for adopting our investment policy, which includes rules regarding the selection and retention of qualified advisors and investment managers. The pension investment committee is responsible for implementing and monitoring compliance with our investment policy, selecting and monitoring investment managers and communicating the investment guidelines and performance objectives to the investment managers.
Our contributions are made on a basis determined by the actuaries in accordance with the funding requirements and limitations of the Employee Retirement Income Security Act (“ERISA”) and the Internal Revenue Code.
P. 82 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
Investment Policy and Strategy
The primary long-term investment objective is to allocate assets in a manner that produces a total rate of return that meets or exceeds the growth of our pension liabilities. Our investment objective is to transition the asset mix to hedge liabilities and minimize volatility in the funded status of the plans.
Asset Allocation Guidelines
In accordance with our asset allocation strategy, for substantially all of our Company-sponsored pension plan assets, investments are categorized into long duration fixed income investments whose value is highly correlated to that of the pension plan obligations (“Long Duration Assets”) or other investments, such as equities and high-yield fixed income securities, whose return over time is expected to exceed the rate of growth in our pension plan obligations (“Return-Seeking Assets”).
The proportional allocation of assets between Long Duration Assets and Return-Seeking Assets is dependent on the funded status of each pension plan. Under our policy, for example, a funded status between 95% and 97.5% requires an allocation of total assets of 53% to 63% to Long Duration Assets and 37% to 47% to Return-Seeking Assets. As a plan's funded status increases, the allocation to Long Duration Assets will increase and the allocation to Return-Seeking Assets will decrease.
The following asset allocation guidelines apply to the Return-Seeking Assets:
Asset Category | Percentage Range | Actual | ||||
Public Equity | 70% | - | 90% | 83 | % | |
Growth Fixed Income | 0% | - | 15% | 6 | % | |
Alternatives | 0% | - | 15% | 8 | % | |
Cash | 0% | - | 10% | 3 | % | |
The asset allocations by asset category for both Long Duration and Return-Seeking Assets, as of December 31, 2017, were as follows:
Asset Category | Percentage Range | Actual | ||||
Long Duration | 53% | - | 63% | 56 | % | |
Public Equity | 26% | - | 42% | 36 | % | |
Growth Fixed Income | 0% | - | 7% | 3 | % | |
Alternatives | 0% | - | 7% | 4 | % | |
Cash | 0% | - | 5% | 1 | % | |
The specified target allocation of assets and ranges set forth above are maintained and reviewed on a periodic basis by the pension investment committee. The pension investment committee may direct the transfer of assets between investment managers in order to rebalance the portfolio in accordance with approved asset allocation ranges to accomplish the investment objectives for the pension plan assets.
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 83
Fair Value of Plan Assets
The fair value of the assets underlying our Company-sponsored qualified pension plans and the joint-sponsored Guild-Times Adjustable Pension Plan by asset category are as follows:
December 31, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||||
(In thousands) | Quoted Prices Markets for Identical Assets | Significant Observable Inputs | Significant Unobservable Inputs | Investment Measured at Net Asset Value (3) | ||||||||||||||||
Asset Category | (Level 1) | (Level 2) | (Level 3) | Total | ||||||||||||||||
Equity Securities: | ||||||||||||||||||||
U.S. Equities | $ | 65,466 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 65,466 | ||||||||||
International Equities | 62,256 | — | — | — | 62,256 | |||||||||||||||
Mutual Funds | 44,173 | — | — | — | 44,173 | |||||||||||||||
Registered Investment Companies | 42,868 | — | — | — | 42,868 | |||||||||||||||
Common/Collective Funds(1) | — | — | — | 601,896 | 601,896 | |||||||||||||||
Fixed Income Securities: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Corporate Bonds | — | 416,201 | — | — | 416,201 | |||||||||||||||
U.S. Treasury and Other Government Securities | — | 144,085 | — | — | 144,085 | |||||||||||||||
Group Annuity Contract | — | — | — | 45,005 | 45,005 | |||||||||||||||
Municipal and Provincial Bonds | — | 36,674 | — | — | 36,674 | |||||||||||||||
Government Sponsored Enterprises(2) | — | 11,364 | — | — | 11,364 | |||||||||||||||
Other | — | 10,883 | — | — | 10,883 | |||||||||||||||
Cash and Cash Equivalents | — | — | — | 32,352 | 32,352 | |||||||||||||||
Private Equity | — | — | — | 20,289 | 20,289 | |||||||||||||||
Hedge Fund | — | — | — | 33,899 | 33,899 | |||||||||||||||
Assets at Fair Value | 214,763 | 619,207 | — | 733,441 | 1,567,411 | |||||||||||||||
Other Assets | — | |||||||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 214,763 | $ | 619,207 | $ | — | $ | 733,441 | $ | 1,567,411 | ||||||||||
(1) | The underlying assets of the common/collective funds are primarily comprised of equity and fixed income securities. The fair value in the above table represents our ownership share of the net asset value (“NAV”) of the underlying funds. |
(2) | Represents investments that are not backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. government. |
(3) | Certain investments that are measured at fair value using the NAV per share (or its equivalent) have not been classified in the fair value hierarchy. |
P. 84 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
Fair Value Measurement at December 25, 2016 | ||||||||||||||||||||
(In thousands) | Quoted Prices Markets for Identical Assets | Significant Observable Inputs | Significant Unobservable Inputs | Investment Measured at Net Asset Value (3) | ||||||||||||||||
Asset Category | (Level 1) | (Level 2) | (Level 3) | Total | ||||||||||||||||
Equity Securities: | ||||||||||||||||||||
U.S. Equities | $ | 61,327 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 61,327 | ||||||||||
International Equities | 48,494 | — | — | — | 48,494 | |||||||||||||||
Mutual Funds | 49,869 | — | — | — | 49,869 | |||||||||||||||
Registered Investment Companies | 30,870 | — | — | — | 30,870 | |||||||||||||||
Common/Collective Funds (1) | — | — | — | 701,577 | 701,577 | |||||||||||||||
Fixed Income Securities: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Corporate Bonds | — | 376,289 | — | — | 376,289 | |||||||||||||||
U.S. Treasury and Other Government Securities | — | 128,179 | — | — | 128,179 | |||||||||||||||
Group Annuity Contract | — | — | — | 54,872 | 54,872 | |||||||||||||||
Municipal and Provincial Bonds | — | 33,115 | — | — | 33,115 | |||||||||||||||
Government Sponsored Enterprises (2) | — | 7,227 | — | — | 7,227 | |||||||||||||||
Other | — | 4,486 | — | — | 4,486 | |||||||||||||||
Cash and Cash Equivalents | — | — | — | 22,829 | 22,829 | |||||||||||||||
Private Equity | — | — | — | 24,931 | 24,931 | |||||||||||||||
Hedge Fund | — | — | — | 31,939 | 31,939 | |||||||||||||||
Assets at Fair Value | 190,560 | 549,296 | — | 836,148 | 1,576,004 | |||||||||||||||
Other Assets | — | — | — | — | 756 | |||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 190,560 | $ | 549,296 | $ | — | $ | 836,148 | $ | 1,576,760 | ||||||||||
(1) | The underlying assets of the common/collective funds are primarily comprised of equity and fixed income securities. The fair value in the above table represents our ownership share of the net asset value (“NAV”) of the underlying funds. |
(2) | Represents investments that are not backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. government. |
(3) | Certain investments that are measured at fair value using the NAV per share (or its equivalent) have not been classified in the fair value hierarchy. |
Level 1 and Level 2 Investments
Where quoted prices are available in an active market for identical assets, such as equity securities traded on an exchange, transactions for the asset occur with such frequency that the pricing information is available on an ongoing/daily basis. We classify these types of investments as Level 1 where the fair value represents the closing/last trade price for these particular securities.
For our investments where pricing data may not be readily available, fair values are estimated by using quoted prices for similar assets, in both active and not active markets, and observable inputs, other than quoted prices, such as interest rates and credit risk. We classify these types of investments as Level 2 because we are able to reasonably estimate the fair value through inputs that are observable, either directly or indirectly. There are no restrictions on our ability to sell any of our Level 1 and Level 2 investments.
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 85
Cash Flows
In 2017, we made contributions to qualified pension plans of $127.6 million. We expect contributions made to satisfy minimum funding requirements to total approximately $8 million in 2018.
The following benefit payments, which reflect future service for plans that have not been frozen, are expected to be paid:
Plans | ||||||||||||
(In thousands) | Qualified | Non- Qualified | Total | |||||||||
2018 | $ | 84,216 | $ | 17,181 | $ | 101,397 | ||||||
2019 | 85,816 | 17,068 | 102,884 | |||||||||
2020 | 87,162 | 16,794 | 103,956 | |||||||||
2021 | 89,169 | 16,583 | 105,752 | |||||||||
2022 | 91,192 | 16,389 | 107,581 | |||||||||
2023-2027(1) | 479,738 | 78,560 | 558,298 | |||||||||
(1) | While benefit payments under these plans are expected to continue beyond 2027, we have presented in this table only those benefit payments estimated over the next 10 years. |
Multiemployer Plans
We contribute to a number of multiemployer defined benefit pension plans under the terms of various collective bargaining agreements that cover our union-represented employees. In recent years, certain events, such as amendments to various collective bargaining agreements and the sale of the New England Media Group, resulted in withdrawals from multiemployer pension plans. These actions, along with a reduction in covered employees, have resulted in us estimating withdrawal liabilities to the respective plans for our proportionate share of any unfunded vested benefits. In 2016 and 2015, we recorded $6.7 million and $9.1 million in charges for partial withdrawal obligations under multiemployer pension plans, respectively. There was no such charge in 2017.
Our multiemployer pension plan withdrawal liability was approximately $108 million as of December 31, 2017 and approximately $113 million as of December 25, 2016. This liability represents the present value of the obligations related to complete and partial withdrawals that have already occurred as well as an estimate of future partial withdrawals that we considered probable and reasonably estimable. For those plans that have yet to provide us with a demand letter, the actual liability will not be fully known until they complete a final assessment of the withdrawal liability and issue a demand to us. Therefore, the estimate of our multiemployer pension plan liability will be adjusted as more information becomes available that allows us to refine our estimates.
The risks of participating in multiemployer plans are different from single-employer plans in the following aspects:
• | Assets contributed to the multiemployer plan by one employer may be used to provide benefits to employees of other participating employers. |
• | If a participating employer stops contributing to the plan, the unfunded obligations of the plan may be borne by the remaining participating employers. |
• | If we elect to withdraw from these plans or if we trigger a partial withdrawal due to declines in contribution base units or a partial cessation of our obligation to contribute, we may be assessed a withdrawal liability based on a calculated share of the underfunded status of the plan. |
• | If a multiemployer plan from which we have withdrawn subsequently experiences a mass withdrawal, we may be required to make additional contributions under applicable law. |
Our participation in significant plans for the fiscal period ended December 31, 2017, is outlined in the table below. The “EIN/Pension Plan Number” column provides the Employer Identification Number (“EIN”) and the three-digit plan number. The zone status is based on the latest information that we received from the plan and is
P. 86 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
certified by the plan’s actuary. A plan is generally classified in critical status if a funding deficiency is projected within four years or five years, depending on other criteria. A plan in critical status is classified in critical and declining status if it is projected to become insolvent in the next 15 or 20 years, depending on other criteria. A plan is classified in endangered status if its funded percentage is less than 80% or a funding deficiency is projected within seven years. If the plan satisfies both of these triggers, it is classified in seriously endangered status. A plan not classified in any other status is classified in the green zone. The “FIP/RP Status Pending/Implemented” column indicates plans for which a financial improvement plan (“FIP”) or a rehabilitation plan (“RP”) is either pending or has been implemented. The “Surcharge Imposed” column includes plans in a red zone status that are required to pay a surcharge in excess of regular contributions. The last column lists the expiration date(s) of the collective bargaining agreement(s) to which the plans are subject.
EIN/Pension Plan Number | Pension Protection Act Zone Status | FIP/RP Status Pending/Implemented | (In thousands) Contributions of the Company | Surcharge Imposed | Collective Bargaining Agreement Expiration Date | ||||||||||
Pension Fund | 2017 | 2016 | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||
CWA/ITU Negotiated Pension Plan | 13-6212879-001 | Critical and Declining as of 1/01/17 | Critical and Declining as of 1/01/16 | Implemented | $ | 425 | $ | 486 | $ | 543 | No | (1) | |||
Newspaper and Mail Deliverers’-Publishers’ Pension Fund | 13-6122251-001 | Green as of 6/01/17 | Green as of 6/01/16 | N/A | 995 | 1,040 | 1,038 | No | 3/30/2020(2) | ||||||
GCIU-Employer Retirement Benefit Plan | 91-6024903-001 | Critical and Declining as of 1/01/17 | Critical and Declining as of 1/01/16 | Implemented | 39 | 43 | 57 | Yes | 3/30/2021(3) | ||||||
Pressmen’s Publishers’ Pension Fund | 13-6121627-001 | Green as of 4/01/17 | Green as of 4/01/16 | N/A | 963 | 1,001 | 1,033 | No | 3/30/2021(4) | ||||||
Paper-Handlers’-Publishers’ Pension Fund | 13-6104795-001 | Critical and Declining as of 4/01/17 | Critical and Declining as of 4/01/16 | Implemented | 88 | 100 | 97 | Yes | 3/30/2021(5) | ||||||
Contributions for individually significant plans | $ | 2,510 | $ | 2,670 | $ | 2,768 | |||||||||
Total Contributions | $ | 2,510 | $ | 2,670 | $ | 2,768 | |||||||||
(1) | There are two collective bargaining agreements requiring contributions to this plan: Mailers which expires March 30, 2019, and Typographers which expires March 30, 2020. |
(2) | Elections under the Preservation of Access to Care for Medicare Beneficiaries and Pension Relief Act of 2010: Extended Amortization of Net Investment Losses (IRS Section 431(b)(8)(A)) and the Expanded Smoothing Period (IRS Section 431(b)(8)(B)). |
(3) | We previously had two collective bargaining agreements requiring contributions to this plan. With the sale of the New England Media Group only one collective bargaining agreement remains for the Stereotypers, which expires March 30, 2021. The method for calculating actuarial value of assets was changed retroactive to January 1, 2009, as elected by the Board of Trustees and as permitted by IRS Notice 2010-83. This election includes smoothing 2008 investment losses over ten years. |
(4) | The Plan sponsor elected two provisions of funding relief under the Preservation of Access to Care for Medicare Beneficiaries and Pension Relief Act of 2010 (PRA 2010) to more slowly absorb the 2008 plan year investment loss, retroactively effective as of April 1, 2009. These included extended amortization under the prospective method and 10-year smoothing of the asset loss for the plan year beginning April 1, 2008. |
(5) | Board of Trustees elected funding relief. This election includes smoothing the March 31, 2009 investment losses over 10 years. |
The rehabilitation plan for the GCIU-Employer Retirement Benefit Plan includes minimum annual contributions no less than the total annual contribution made by us from September 1, 2008 through August 31, 2009.
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 87
The Company was listed in the plans’ respective Forms 5500 as providing more than 5% of the total contributions for the following plans and plan years:
Pension Fund | Year Contributions to Plan Exceeded More Than 5 Percent of Total Contributions (as of Plan’s Year-End) |
CWA/ITU Negotiated Pension Plan | 12/31/2016 & 12/31/2015(1) |
Newspaper and Mail Deliverers’-Publishers’ Pension Fund | 5/31/2016 & 5/31/2015(1) |
Pressmen’s Publisher’s Pension Fund | 3/31/2017 & 3/31/2016 |
Paper-Handlers’-Publishers’ Pension Fund | 3/31/2017 & 3/31/2016 |
(1) Forms 5500 for the plans’ year ended 12/31/17 and 5/31/17 were not available as of the date we filed our financial statements.
The Company received a notice and demand for payment of withdrawal liability from the Newspaper and Mail Deliverers’-Publishers’ Pension Fund in September 2013 and December 2014 associated with partial withdrawals. See Note 18 for further information.
10. Other Postretirement Benefits
We provide health benefits to retired employees (and their eligible dependents) who meet the definition of an eligible participant and certain age and service requirements, as outlined in the plan document. While we offer pre-age 65 retiree medical coverage to employees who meet certain retiree medical eligibility requirements, we do not provide post-age 65 retiree medical benefits for employees who retired on or after March 1, 2009. We accrue the costs of postretirement benefits during the employees’ active years of service and our policy is to pay our portion of insurance premiums and claims from our assets.
Net Periodic Other Postretirement Benefit Income
The components of net periodic postretirement benefit income were as follows:
(In thousands) | December 31, 2017 | December 25, 2016 | December 27, 2015 | |||||||||
Service cost | $ | 367 | $ | 417 | $ | 588 | ||||||
Interest cost | 1,881 | 1,979 | 2,794 | |||||||||
Amortization and other costs | 3,621 | 4,105 | 5,197 | |||||||||
Amortization of prior service credit | (7,755 | ) | (8,440 | ) | (9,495 | ) | ||||||
Effect of settlement/curtailment (1) | (32,737 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
Net periodic postretirement benefit income | $ | (34,623 | ) | $ | (1,939 | ) | $ | (916 | ) | |||
(1) In the fourth quarter of 2017, the Company recorded a gain in connection with the settlement of a funding obligation related to a postretirement plan.
P. 88 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
The changes in the benefit obligations recognized in other comprehensive income/loss were as follows:
(In thousands) | December 31, 2017 | December 25, 2016 | December 27, 2015 | |||||||||
Net actuarial loss/(gain) | $ | (6,625 | ) | $ | 28 | $ | (5,543 | ) | ||||
Prior service cost | — | — | 1,145 | |||||||||
Amortization of loss | (3,621 | ) | (4,105 | ) | (5,197 | ) | ||||||
Amortization of prior service credit | 7,755 | 8,440 | 9,495 | |||||||||
Effect of curtailment | 6,502 | — | — | |||||||||
Effect of settlement | 26,235 | — | — | |||||||||
Total recognized in other comprehensive loss/(income) | 30,246 | 4,363 | (100 | ) | ||||||||
Net periodic postretirement benefit income | (34,623 | ) | (1,939 | ) | (916 | ) | ||||||
Total recognized in net periodic postretirement benefit income and other comprehensive (income)/loss | $ | (4,377 | ) | $ | 2,424 | $ | (1,016 | ) | ||||
Actuarial gains and losses are amortized using a corridor approach. The gain or loss corridor is equal to 10% of the accumulated postretirement benefit obligation. Gains and losses in excess of the corridor are generally amortized over the average remaining service period to expected retirement of active participants.
The estimated actuarial loss and prior service credit that will be amortized from accumulated other comprehensive loss into net periodic benefit cost over the next fiscal year is approximately $5 million and $6 million, respectively.
In connection with collective bargaining agreements, we contribute to several multiemployer welfare plans. These plans provide medical benefits to active and retired employees covered under the respective collective bargaining agreement. Contributions are made in accordance with the formula in the relevant agreement. Postretirement costs related to these plans are not reflected above and were approximately $15 million in 2017, $15 million in 2016 and $16 million in 2015.
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 89
The changes in the benefit obligation and plan assets and other amounts recognized in other comprehensive income/loss were as follows:
(In thousands) | December 31, 2017 | December 25, 2016 | ||||||
Change in benefit obligation | ||||||||
Benefit obligation at beginning of year | $ | 65,042 | $ | 71,047 | ||||
Service cost | 367 | 417 | ||||||
Interest cost | 1,881 | 1,979 | ||||||
Plan participants’ contributions | 4,007 | 4,409 | ||||||
Actuarial loss | 3,703 | 28 | ||||||
Curtailments/settlements | (10,328 | ) | — | |||||
Benefits paid | (10,030 | ) | (12,838 | ) | ||||
Benefit obligation at the end of year | 54,642 | 65,042 | ||||||
Change in plan assets | ||||||||
Fair value of plan assets at beginning of year | — | — | ||||||
Employer contributions | 6,023 | 8,429 | ||||||
Plan participants’ contributions | 4,007 | 4,409 | ||||||
Benefits paid | (10,030 | ) | (12,838 | ) | ||||
Fair value of plan assets at end of year | — | — | ||||||
Net amount recognized | $ | (54,642 | ) | $ | (65,042 | ) | ||
Amount recognized in the Consolidated Balance Sheets | ||||||||
Current liabilities | $ | (5,826 | ) | $ | (7,043 | ) | ||
Noncurrent liabilities | (48,816 | ) | (57,999 | ) | ||||
Net amount recognized | $ | (54,642 | ) | $ | (65,042 | ) | ||
Amount recognized in accumulated other comprehensive loss | ||||||||
Actuarial loss | $ | 38,512 | $ | 22,522 | ||||
Prior service credit | (18,613 | ) | (32,870 | ) | ||||
Total | $ | 19,899 | $ | (10,348 | ) | |||
Weighted-average assumptions used in the actuarial computations to determine the postretirement benefit obligations were as follows:
December 31, 2017 | December 25, 2016 | |||||
Discount rate | 3.46 | % | 3.94 | % | ||
Estimated increase in compensation level | 3.50 | % | 3.50 | % | ||
P. 90 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
Weighted-average assumptions used in the actuarial computations to determine net periodic postretirement cost were as follows:
December 31, 2017 | December 25, 2016 | December 27, 2015 | |||||||
Discount rate for determining projected benefit obligation | 3.93 | % | 4.05 | % | 3.74 | % | |||
Discount rate in effect for determining service cost | 4.08 | % | 4.24 | % | 3.74 | % | |||
Discount rate in effect for determining interest cost | 3.21 | % | 2.96 | % | 3.74 | % | |||
Estimated increase in compensation level | 3.50 | % | 3.50 | % | 3.50 | % | |||
The assumed health-care cost trend rates were as follows:
December 31, 2017 | December 25, 2016 | |||||
Health-care cost trend rate | 7.60 | % | 8.00 | % | ||
Rate to which the cost trend rate is assumed to decline (ultimate trend rate) | 5.00 | % | 5.00 | % | ||
Year that the rate reaches the ultimate trend rate | 2025 | 2025 | ||||
Because our health-care plans are capped for most participants, the assumed health-care cost trend rates do not have a significant effect on the amounts reported for the health-care plans. A one-percentage point change in assumed health-care cost trend rates would have the following effects:
One-Percentage Point | ||||||||
(In thousands) | Increase | Decrease | ||||||
Effect on total service and interest cost for 2017 | $ | 62 | $ | (53 | ) | |||
Effect on accumulated postretirement benefit obligation as of December 31, 2017 | $ | 2,200 | $ | (1,865 | ) | |||
The following benefit payments (net of plan participant contributions) under our Company’s postretirement plans, which reflect expected future services, are expected to be paid:
(In thousands) | Amount | ||
2018 | $ | 5,968 | |
2019 | 5,589 | ||
2020 | 5,286 | ||
2021 | 4,988 | ||
2022 | 4,655 | ||
2023-2027 (1) | 19,045 | ||
(1) | While benefit payments under these plans are expected to continue beyond 2027, we have presented in this table only those benefit payments estimated over the next 10 years. |
We accrue the cost of certain benefits provided to former or inactive employees after employment, but before retirement. The cost is recognized only when it is probable and can be estimated. Benefits include life insurance, disability benefits and health-care continuation coverage. The accrued obligation for these benefits amounted to $11.3 million as of December 31, 2017 and $11.4 million as of December 25, 2016.
During the fourth quarters of 2017 and 2016, we adopted new mortality tables released by the SOA and revised the mortality assumptions used in determining our postretirement benefit obligations. The net impact to our postretirement obligations resulting from the new mortality assumptions in 2017 and 2016 was a decrease of $0.6 million and $1.2 million, respectively.
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 91
Beginning in 2016, we changed the approach used to calculate the service and interest components of net periodic benefit cost for benefit plans to provide a more precise measurement of service and interest costs. Prior to this change, we calculated these service and interest components utilizing a single weighted-average discount rate derived from the yield curve used to measure the benefit obligation at the beginning of the period. We have elected to utilize an approach that discounts the individual expected cash flows using the applicable spot rates derived from the yield curve over the projected cash flow period. The spot rates used to estimate 2016 service and interest costs ranged from 1.32% to 4.79%. Service costs and interest costs for our benefit plans were reduced by approximately $1 million in 2016 due to the change in methodology.
11. Other Liabilities
The components of the “Other Liabilities — Other” balance in our Consolidated Balance Sheets were as follows:
(In thousands) | December 31, 2017 | December 25, 2016 | ||||||
Deferred compensation | $ | 29,526 | $ | 31,006 | ||||
Other liabilities | 52,787 | 47,641 | ||||||
Total | $ | 82,313 | $ | 78,647 | ||||
Deferred compensation consists primarily of deferrals under our DEC. The DEC enabled certain eligible executives to elect to defer a portion of their compensation on a pre-tax basis. Participation in the DEC was frozen effective December 31, 2015, and no new contributions may be made into the plan.
We invest deferred compensation in life insurance products designed to closely mirror the performance of the investment funds that the participants select. Our investments in life insurance products are included in “Miscellaneous assets” in our Consolidated Balance Sheets, and were $40.3 million as of December 31, 2017 and $34.8 million as of December 25, 2016.
Other liabilities in the preceding table primarily included our post employment liabilities, our contingent tax liability for uncertain tax positions and self-insurance liabilities as of December 31, 2017 and December 25, 2016.
P. 92 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
12. Income Taxes
Reconciliations between the effective tax rate on income from continuing operations before income taxes and the federal statutory rate are presented below.
December 31, 2017 | December 25, 2016 | December 27, 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||
(In thousands) | Amount | % of Pre-tax | Amount | % of Pre-tax | Amount | % of Pre-tax | |||||||||||||||
Tax at federal statutory rate | $ | 38,928 | 35.0 | $ | 10,685 | 35.0 | $ | 33,863 | 35.0 | ||||||||||||
State and local taxes, net | 4,800 | 4.3 | 3,095 | 10.1 | 5,093 | 5.2 | |||||||||||||||
Effect of enacted changes in tax laws | 68,747 | 61.8 | — | — | 1,801 | 1.8 | |||||||||||||||
Reduction in uncertain tax positions | (2,277 | ) | (2.0 | ) | (4,534 | ) | (14.9 | ) | (2,545 | ) | (2.6 | ) | |||||||||
Loss/(gain) on Company-owned life insurance | (1,916 | ) | (1.7 | ) | (736 | ) | (2.4 | ) | 75 | 0.1 | |||||||||||
Nondeductible expense, net | 1,021 | 0.9 | 1,115 | 3.7 | 880 | 0.9 | |||||||||||||||
Domestic manufacturing deduction | — | — | (1,820 | ) | (6.0 | ) | (2,651 | ) | (2.7 | ) | |||||||||||
Foreign Earnings and Dividends | 458 | 0.4 | (2,418 | ) | (7.9 | ) | (1,214 | ) | (1.3 | ) | |||||||||||
Other, net | (5,805 | ) | (5.2 | ) | (966 | ) | (3.2 | ) | (1,392 | ) | (1.4 | ) | |||||||||
Income tax expense | $ | 103,956 | 93.5 | $ | 4,421 | 14.4 | $ | 33,910 | 35.0 | ||||||||||||
The components of income tax expense as shown in our Consolidated Statements of Operations were as follows:
(In thousands) | December 31, 2017 | December 25, 2016 | December 27, 2015 | |||||||||
Current tax expense/(benefit) | ||||||||||||
Federal | $ | (252 | ) | $ | 22,864 | $ | 41,199 | |||||
Foreign | 458 | 312 | 485 | |||||||||
State and local | 350 | (3,295 | ) | 5,919 | ||||||||
Total current tax expense | 556 | 19,881 | 47,603 | |||||||||
Deferred tax expense | ||||||||||||
Federal | 105,905 | (16,625 | ) | (14,554 | ) | |||||||
State and local | (2,505 | ) | 1,165 | 861 | ||||||||
Total deferred tax expense/(benefit) | 103,400 | (15,460 | ) | (13,693 | ) | |||||||
Income tax expense/(benefit) | $ | 103,956 | $ | 4,421 | $ | 33,910 | ||||||
State tax operating loss carryforwards totaled $4.7 million as of December 31, 2017 and $3.4 million as of December 25, 2016. Such loss carryforwards expire in accordance with provisions of applicable tax laws and have remaining lives up to 20 years.
On December 22, 2017, federal tax legislation commonly referred to as the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (the “Act”) was signed into law making significant changes to the Internal Revenue Code. Changes include, but are not limited to, a federal corporate tax rate decrease from 35% to 21% for tax years beginning after December 31, 2017, a one-time transition tax on the mandatory deemed repatriation of foreign earnings and numerous domestic and international-related provisions effective in 2018.
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 93
We have estimated our provision for income taxes in accordance with the Act and guidance available as of the date of this filing and as a result have recorded $68.7 million as additional income tax expense in the fourth quarter of 2017, the period in which the legislation was enacted.
On December 22, 2017, Staff Accounting Bulletin No. 118 ("SAB 118") was issued to address the application of GAAP in situations when a registrant does not have the necessary information available, prepared, or analyzed (including computations) in reasonable detail to complete the accounting for certain income tax effects of the Act. In accordance with SAB 118, we have determined that the $68.7 million of additional income tax expense recorded in connection with the remeasurement of certain deferred tax assets and liabilities, the one-time transition tax on the mandatory deemed repatriation of foreign earnings, and deferred tax assets related to executive compensation deductions was a provisional amount and a reasonable estimate at December 31, 2017. Provisional estimates were also made with regard to the Company’s deductions under the Act’s new expensing provisions and state and local income taxes related to foreign earnings subject to the one-time transition tax. The ultimate impact of the Act may differ from the provisional amount recognized due to, among other things, changes in estimates resulting from the receipt or calculation of final data, changes in interpretations of the Act, and additional regulatory guidance that may be issued. The accounting for the impact of the Act is expected to be completed by the fourth quarter of fiscal year 2018.
The components of the net deferred tax assets and liabilities recognized in our Consolidated Balance Sheets were as follows:
(In thousands) | December 31, 2017 | December 25, 2016 | ||||||
Deferred tax assets | ||||||||
Retirement, postemployment and deferred compensation plans | $ | 140,657 | $ | 275,611 | ||||
Accruals for other employee benefits, compensation, insurance and other | 16,883 | 34,466 | ||||||
Accounts receivable allowances | 1,391 | 2,450 | ||||||
Net operating losses | 6,228 | 2,598 | ||||||
Investment in joint ventures | — | 5,329 | ||||||
Other | 30,295 | 39,943 | ||||||
Gross deferred tax assets | $ | 195,454 | $ | 360,397 | ||||
Deferred tax liabilities | ||||||||
Property, plant and equipment | $ | 31,043 | $ | 46,284 | ||||
Intangible assets | 7,300 | 11,975 | ||||||
Investments in joint ventures | 615 | — | ||||||
Other | 3,450 | 796 | ||||||
Gross deferred tax liabilities | 42,408 | 59,055 | ||||||
Net deferred tax asset | $ | 153,046 | $ | 301,342 | ||||
We assess whether a valuation allowance should be established against deferred tax assets based on the consideration of both positive and negative evidence using a “more likely than not” standard. In making such judgments, significant weight is given to evidence that can be objectively verified. We evaluated our deferred tax assets for recoverability using a consistent approach that considers our three-year historical cumulative income/(loss), including an assessment of the degree to which any such losses were due to items that are unusual in nature (i.e., impairments of nondeductible goodwill and intangible assets).
We had an income tax receivable of $25.4 million as of December 31, 2017 versus accrued income taxes payable of $1.9 million as of December 25, 2016.
Income tax benefits related to the exercise or vesting of equity awards reduced current taxes payable by $13.7 million in 2017, $8.6 million in 2016 and $4.4 million in 2015.
P. 94 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
As of December 31, 2017 and December 25, 2016, “Accumulated other comprehensive loss, net of income taxes” in our Consolidated Balance Sheets and for the years then ended in our Consolidated Statements of Changes in Stockholders’ Equity was net of deferred tax assets of approximately $196 million and $331 million, respectively.
A reconciliation of unrecognized tax benefits is as follows:
(In thousands) | December 31, 2017 | December 25, 2016 | December 27, 2015 | |||||||||
Balance at beginning of year | $ | 10,028 | $ | 13,941 | $ | 16,324 | ||||||
Gross additions to tax positions taken during the current year | 9,009 | 997 | 1,151 | |||||||||
Gross additions to tax positions taken during the prior year | 103 | — | 282 | |||||||||
Gross reductions to tax positions taken during the prior year | (372 | ) | (3,042 | ) | (37 | ) | ||||||
Reductions from lapse of applicable statutes of limitations | (1,682 | ) | (1,868 | ) | (3,779 | ) | ||||||
Balance at end of year | $ | 17,086 | $ | 10,028 | $ | 13,941 | ||||||
The total amount of unrecognized tax benefits that would, if recognized, affect the effective income tax rate was approximately $7 million as of December 31, 2017 and December 25, 2016.
In 2017 and 2016, we recorded a $2.3 million and $4.5 million income tax benefit, respectively, primarily due to a reduction in the Company’s reserve for uncertain tax positions.
We also recognize accrued interest expense and penalties related to the unrecognized tax benefits within income tax expense or benefit. The total amount of accrued interest and penalties was approximately $2 million and $3 million as of December 31, 2017 and December 25, 2016, respectively. The total amount of accrued interest and penalties was a net benefit of $0.1 million in 2017, a net benefit of $0.9 million in 2016 and a net benefit of $0.1 million in 2015.
With few exceptions, we are no longer subject to U.S. federal, state and local, or non-U.S. income tax examinations by tax authorities for years prior to 2010. Management believes that our accrual for tax liabilities is adequate for all open audit years. This assessment relies on estimates and assumptions and may involve a series of complex judgments about future events.
It is reasonably possible that certain income tax examinations may be concluded, or statutes of limitation may lapse, during the next 12 months, which could result in a decrease in unrecognized tax benefits of $3.3 million that would, if recognized, impact the effective tax rate.
13. Discontinued Operations
New England Media Group
In the fourth quarter of 2013, we completed the sale of substantially all of the assets and operating liabilities of the New England Media Group — consisting of The Boston Globe, BostonGlobe.com, Boston.com, the T&G, Telegram.com and related properties — and our 49% equity interest in Metro Boston, for approximately $70.0 million in cash, subject to customary adjustments. The net after-tax proceeds from the sale, including a tax benefit, were approximately $74.0 million. In the forth quarter of 2016, the Company reached a settlement with respect to litigation involving NEMG T&G, Inc., a subsidiary of the Company that was a part of New England Media Group. As a result of the settlement, the Company recorded charges of $0.7 million ($0.4 million after tax) and $3.7 million ($2.3 million after tax) for the fiscal years ended December 31, 2017 and December 25, 2016, respectively. The results of operations of the New England Media Group have been classified as discontinued operations for all periods presented.
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 95
14. Earnings/(Loss) Per Share
We compute earnings/(loss) per share using a two-class method, an earnings allocation method used when a company’s capital structure includes either two or more classes of common stock or common stock and participating securities. This method determines earnings/(loss) per share based on dividends declared on common stock and participating securities (i.e., distributed earnings), as well as participation rights of participating securities in any undistributed earnings.
Earnings/(loss) per share is computed using both basic shares and diluted shares. The difference between basic and diluted shares is that diluted shares include the dilutive effect of the assumed exercise of outstanding securities. Our stock options, stock-settled long-term performance awards and restricted stock units could have the most significant impact on diluted shares. The decrease in our basic shares is primarily due to repurchases of the Company’s Class A Common Stock.
Securities that could potentially be dilutive are excluded from the computation of diluted earnings per share when a loss from continuing operations exists or when the exercise price exceeds the market value of our Class A Common Stock, because their inclusion would result in an anti-dilutive effect on per share amounts.
The number of stock options excluded from the computation of diluted earnings per share because they were anti-dilutive was approximately 2 million in 2017, 4 million in 2016 and 5 million in 2015.
There were no anti-dilutive stock-settled long-term performance awards and restricted stock units excluded from the computation of diluted earnings per share for the year ended 2017, 2016 and 2015.
15. Stock-Based Awards
As of December 31, 2017, the Company was authorized to grant stock-based compensation under its 2010 Incentive Compensation Plan (the “2010 Incentive Plan”), which became effective April 27, 2010, and was amended and restated effective April 30, 2014. The 2010 Incentive Plan replaced the 1991 Executive Stock Incentive Plan (the “1991 Incentive Plan”). In addition, through April 30, 2014, the Company maintained its 2004 Non-Employee Directors’ Stock Incentive Plan (the “2004 Directors’ Plan”).
The Company’s long-term incentive compensation program provides executives the opportunity to earn cash and shares of Class A Common Stock at the end of three-year performance cycles based in part on the achievement of financial goals tied to a financial metric and in part on stock price performance relative to companies in the Standard & Poor’s 500 Stock Index, with the majority of the target award to be settled in the Company’s Class A Common Stock. In addition, the Company grants time-vested restricted stock units annually to a number of employees. These are settled in shares of Class A Common Stock.
We recognize stock-based compensation expense for these stock-settled long-term performance awards and restricted stock units, as well as any stock options and stock appreciation rights (together, “Stock-Based Awards”). Stock-based compensation expense was $14.8 million in 2017, $12.4 million in 2016 and $10.6 million in 2015.
Stock-based compensation expense is recognized over the period from the date of grant to the date when the award is no longer contingent on the employee providing additional service. Awards under the 1991 Incentive Plan and 2010 Incentive Plan generally vest over a stated vesting period or, with respect to awards granted prior to December 28, 2014, upon the retirement of an employee or director, as the case may be.
Prior to 2012, under our 2004 Directors’ Plan, each non-employee director of the Company received annual grants of non-qualified stock options with 10-year terms to purchase 4,000 shares of Class A Common Stock from the Company at the average market price of such shares on the date of grants. These grants were replaced with annual grants of cash-settled phantom stock units in 2012, and, accordingly, no grants of stock options have since been made under this plan. Under its terms, the 2004 Directors’ Plan terminated as of April 30, 2014.
In 2015, the annual grants of phantom stock units were replaced with annual grants of restricted stock units under the 2010 Incentive Plan. Restricted stock units are awarded on the date of the annual meeting of stockholders and vest on the date of the subsequent year’s annual meeting, with the shares to be delivered upon a director’s cessation of membership on the Board of Directors. Each non-employee director is credited with additional restricted stock units with a value equal to the amount of all dividends paid on the Company’s Class A Common Stock. The Company’s directors are considered employees for purposes of stock-based compensation.
P. 96 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
Stock Options
The 1991 Incentive Plan provided, and the 2010 Incentive Plan provides, for grants of both incentive and non-qualified stock options at an exercise price equal to the fair market value (as defined in each plan, respectively) of our Class A Common Stock on the date of grant. Stock options have generally been granted with a 3-year vesting period and a 10-year term and vest in equal annual installments. Due to a change in the Company’s long-term incentive compensation, no grants of stock options were made in 2017, 2016 or 2015.
The 2004 Directors’ Plan provided for grants of stock options to non-employee directors at an exercise price equal to the fair market value (as defined in the 2004 Directors’ Plan) of our Class A Common Stock on the date of grant. Prior to 2012, stock options were granted with a 1-year vesting period and a 10-year term. No grants of stock options were made in 2017, 2016 or 2015. The Company’s directors are considered employees for purposes of stock-based compensation.
Changes in our Company’s stock options in 2017 were as follows:
December 31, 2017 | |||||||||||||
(Shares in thousands) | Options | Weighted Average Exercise Price | Weighted Average Remaining Contractual Term (Years) | Aggregate Intrinsic Value $(000s) | |||||||||
Options outstanding at beginning of year | 4,518 | $ | 14 | 3 | $ | 12,797 | |||||||
Exercised | (658 | ) | 7 | ||||||||||
Forfeited/Expired | (86 | ) | 24 | ||||||||||
Options outstanding at end of period (1) | 3,774 | $ | 15 | 2 | $ | 17,597 | |||||||
Options exercisable at end of period | 3,774 | $ | 15 | 2 | $ | 17,597 | |||||||
(1) All outstanding options are vested as of December 31, 2017.
The total intrinsic value for stock options exercised was $7.0 million in 2017, $0.7 million in 2016 and $2.7 million in 2015.
The fair value of the stock options granted was estimated on the date of grant using a Black-Scholes valuation model that uses the following assumptions. The risk-free rate is based on the U.S. Treasury yield curve in effect at the time of grant. The expected life (estimated period of time outstanding) of stock options granted was determined using the average of the vesting period and term. Expected volatility was based on historical volatility for a period equal to the stock option’s expected life, ending on the date of grant, and calculated on a monthly basis. Dividend yield was based on expected Company dividends, if applicable on the date of grant. The fair value for stock options granted with different vesting periods and on different dates is calculated separately.
Restricted Stock Units
The 2010 Incentive Plan provides for grants of other stock-based awards, including restricted stock units.
Outstanding stock-settled restricted stock units have been granted with a stated vesting period up to 5 years. Each restricted stock unit represents our obligation to deliver to the holder one share of Class A Common Stock upon vesting. The fair value of stock-settled restricted stock units is the average market price on the grant date. Changes in our Company’s stock-settled restricted stock units in 2017 were as follows:
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 97
December 31, 2017 | |||||||
(Shares in thousands) | Restricted Stock Units | Weighted Average Grant-Date Fair Value | |||||
Unvested stock-settled restricted stock units at beginning of period | 1,008 | $ | 14 | ||||
Granted | 466 | 16 | |||||
Vested | (505 | ) | 14 | ||||
Forfeited | (83 | ) | 14 | ||||
Unvested stock-settled restricted stock units at end of period | 886 | $ | 15 | ||||
Unvested stock-settled restricted stock units expected to vest at end of period | 840 | $ | 15 | ||||
The intrinsic value of stock-settled restricted stock units vested was $7.9 million in 2017, $7.3 million in 2016 and $5.5 million in 2015.
Long-Term Incentive Compensation
The 2010 Incentive Plan provides for grants of cash and stock-settled awards to key executives payable at the end of a multi-year performance period.
Cash-settled awards have been granted with three-year performance periods and are based on the achievement of specified financial performance measures. Cash-settled awards have been classified as a liability because we incurred a liability payable in cash. There were payments of approximately $3 million in 2017, $4 million in 2016 and $3 million in 2015.
Stock-settled awards have been granted with three-year performance periods and are based on relative Total Shareholder Return (“TSR”), which is calculated at stock appreciation plus deemed reinvested dividends, and another performance measure. Stock-settled awards are payable in Class A Common Stock and are classified within equity. The fair value of TSR awards is determined at the date of grant using a Monte Carlo simulation model. The fair value of awards under the other performance measure is determined by the average market price on the grant date.
Unrecognized Compensation Expense
As of December 31, 2017, unrecognized compensation expense related to the unvested portion of our Stock-Based Awards was approximately $13 million and is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of 1.45 years.
Reserved Shares
We generally issue shares for the exercise of stock options and vesting of stock-settled restricted stock units from unissued reserved shares.
P. 98 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
Shares of Class A Common Stock reserved for issuance were as follows:
(Shares in thousands) | December 31, 2017 | December 25, 2016 | |||
Stock options, stock–settled restricted stock units and stock-settled performance awards | |||||
Stock options and stock-settled restricted stock units | 4,772 | 5,588 | |||
Stock-settled performance awards(1) | 2,559 | 3,159 | |||
Outstanding | 7,331 | 8,747 | |||
Available | 7,188 | 6,914 | |||
Employee Stock Purchase Plan(2) | |||||
Available | 6,410 | 6,410 | |||
401(k) Company stock match(3) | |||||
Available | 3,045 | 3,045 | |||
Total Outstanding | 7,331 | 8,747 | |||
Total Available | 16,643 | 16,369 | |||
(1) | The number of shares actually earned at the end of the multi-year performance period will vary, based on actual performance, from 0% to 200% of the target number of performance awards granted. The maximum number of shares that could be issued is included in the table above. |
(2) | We have not had an offering under the Employee Stock Purchase Plan since 2010. |
(3) | Effective 2014, we no longer offer a Company stock match under the Company’s 401(k) plan. |
16. Stockholders’ Equity
Shares of our Company’s Class A and Class B Common Stock are entitled to equal participation in the event of liquidation and in dividend declarations. The Class B Common Stock is convertible at the holders’ option on a share-for-share basis into Class A Common Stock. Upon conversion, the previously outstanding shares of Class B Common Stock that were converted are automatically and immediately retired, resulting in a reduction of authorized Class B Common Stock. As provided for in our Company’s Certificate of Incorporation, the Class A Common Stock has limited voting rights, including the right to elect 30% of the Board of Directors, and the Class A and Class B Common Stock have the right to vote together on the reservation of our Company shares for stock options and other stock-based plans, on the ratification of the selection of a registered public accounting firm and, in certain circumstances, on acquisitions of the stock or assets of other companies. Otherwise, except as provided by the laws of the State of New York, all voting power is vested solely and exclusively in the holders of the Class B Common Stock.
There were 803,763 shares as of December 31, 2017 and 816,632 as of December 25, 2016 of Class B Common Stock issued and outstanding that may be converted into shares of Class A Common Stock.
The Adolph Ochs family trust holds approximately 90% of the Class B Common Stock and, as a result, has the ability to elect 70% of the Board of Directors and to direct the outcome of any matter that does not require a vote of the Class A Common Stock.
On January 14, 2015, entities controlled by Carlos Slim Helú, a beneficial owner of our Class A Common Stock, exercised warrants to purchase 15.9 million shares of our Class A Common Stock at a price of $6.3572 per share, and the Company received cash proceeds of approximately $101.1 million from this exercise. Concurrently, the Board of Directors terminated an existing authorization to repurchase shares of the Company’s Class A Common Stock and approved a new repurchase authorization of $101.1 million, equal to the cash proceeds received by the Company from the warrant exercise. As of December 31, 2017, total repurchases under this authorization totaled $84.9 million (excluding commissions) and $16.2 million remained under this authorization. Our Board of Directors has authorized us to purchase shares from time to time, subject to market conditions and other factors. There is no expiration date with respect to this authorization.
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 99
We may issue preferred stock in one or more series. The Board of Directors is authorized to set the distinguishing characteristics of each series of preferred stock prior to issuance, including the granting of limited or full voting rights; however, the consideration received must be at least $100 per share. No shares of preferred stock were issued or outstanding as of December 31, 2017.
The following table summarizes the changes in AOCI by component as of December 31, 2017:
(In thousands) | Foreign Currency Translation Adjustments | Funded Status of Benefit Plans | Net unrealized loss on available-for-sale Securities | Total Accumulated Other Comprehensive Loss | ||||||||||||
Balance as of December 25, 2016 | $ | (1,822 | ) | $ | (477,994 | ) | $ | — | $ | (479,816 | ) | |||||
Other comprehensive income/(loss) before reclassifications, before tax(1) | 10,810 | (7,895 | ) | (2,545 | ) | 370 | ||||||||||
Amounts reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive loss, before tax(1) | 1,300 | 96,662 | — | 97,962 | ||||||||||||
Income tax (benefit)/expense(1) | 3,960 | 38,592 | (1,007 | ) | 41,545 | |||||||||||
Net current-period other comprehensive (loss)/income, net of tax | 8,150 | 50,175 | (1,538 | ) | 56,787 | |||||||||||
Balance as of December 31, 2017 | $ | 6,328 | $ | (427,819 | ) | $ | (1,538 | ) | $ | (423,029 | ) | |||||
(1) | All amounts are shown net of noncontrolling interest. |
The following table summarizes the reclassifications from AOCI for the period ended December 31, 2017:
(In thousands) | Amounts reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive loss | Affect line item in the statement where net income is presented | ||||
Detail about accumulated other comprehensive loss components | ||||||
Funded status of benefit plans: | ||||||
Amortization of prior service credit(1) | $ | (9,700 | ) | Selling, general & administrative costs | ||
Amortization of actuarial loss(1) | 36,990 | Selling, general & administrative costs | ||||
Postretirement benefit plan settlement gain | (32,737 | ) | Postretirement benefit plan settlement gain | |||
Pension settlement charge | 102,109 | Pension settlement charge | ||||
Total reclassification, before tax(2) | 96,662 | |||||
Income tax expense | 38,592 | Income tax expense | ||||
Total reclassification, net of tax | $ | 58,070 | ||||
(1) | These accumulated other comprehensive income components are included in the computation of net periodic benefit cost for pension and other retirement benefits. See Notes 9 and 10 for additional information. |
(2) | There were no reclassifications relating to noncontrolling interest for the year ended December 31, 2017. |
17. Segment Information
We have one reportable segment that includes The New York Times, NYTimes.com and related businesses. Therefore, all required segment information can be found in the Consolidated Financial Statements.
Our operating segment generated revenues principally from subscriptions and advertising. Other revenues primarily consists of revenues from news services/syndication, digital archive licensing, building rental income, affiliate referrals, NYT Live (our live events business), and retail commerce.
P. 100 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
18. Commitments and Contingent Liabilities
Operating Leases
Operating lease commitments are primarily for office space and equipment. Certain office space leases provide for rent adjustments relating to changes in real estate taxes and other operating costs.
Rental expense amounted to approximately $19 million in 2017 and $16 million in 2016 and 2015. The increase in rental expense is related to additional costs incurred due to the headquarter redesign and consolidation. The approximate minimum rental commitments as of December 31, 2017 were as follows:
(In thousands) | Amount | ||
2018 | $ | 10,738 | |
2019 | 7,532 | ||
2020 | 6,153 | ||
2021 | 4,972 | ||
2022 | 4,731 | ||
Later years | 18,555 | ||
Total minimum lease payments | $ | 52,681 | |
Capital Leases
Future minimum lease payments for all capital leases, and the present value of the minimum lease payments as of December 31, 2017, were as follows:
(In thousands) | Amount | ||
2018 | $ | 552 | |
2019 | 7,245 | ||
2020 | — | ||
2021 | — | ||
2022 | — | ||
Later years | — | ||
Total minimum lease payments | 7,797 | ||
Less: imputed interest | (992 | ) | |
Present value of net minimum lease payments including current maturities | $ | 6,805 | |
Restricted Cash
We were required to maintain $18.0 million of restricted cash as of December 31, 2017 and $24.9 million as of December 25, 2016, the majority of which is set aside to collateralize workers’ compensation obligations. The decrease reflects the settlement of certain litigation described below.
Newspaper and Mail Deliverers – Publishers’ Pension Fund
In September 2013, the Newspaper and Mail Deliverers-Publishers’ Pension Fund (the “NMDU Fund”) assessed a partial withdrawal liability against the Company in the gross amount of approximately $26 million for the plan years ending May 31, 2012 and 2013 (the “Initial Assessment”), an amount that was increased to a gross amount of approximately $34 million in December 2014, when the NMDU Fund issued a revised partial withdrawal liability assessment for the plan year ending May 31, 2013 (the “Revised Assessment”). The NMDU Fund claimed that when City & Suburban Delivery Systems, Inc., a retail and newsstand distribution subsidiary of the Company and the
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 101
largest contributor to the NMDU Fund, ceased operations in 2009, it triggered a decline of more than 70% in contribution base units in each of these two plan years.
The Company disagreed with both the NMDU Fund’s determination that a partial withdrawal occurred and the methodology by which it calculated the withdrawal liability, and the parties engaged in arbitration proceedings to resolve the matter. In June 2016, the arbitrator issued an interim award and opinion that supported the NMDU Fund’s determination that a partial withdrawal had occurred, and concluded that the methodology used to calculate the Initial Assessment was correct. However, the arbitrator also concluded that the NMDU Fund’s calculation of the Revised Assessment was incorrect. In July 2017, the arbitrator issued a final award and opinion reflecting the same conclusions, which the Company has appealed.
Due to requirements of the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974 that sponsors make payments demanded by plans during arbitration and any resultant appeals, the Company had been making payments to the NMDU Fund since September 2013 relating to the Initial Assessment and February 2015 relating to the Revised Assessment based on the NMDU Fund’s demand. As a result, as of December 31, 2017, we have paid $15.3 million relating to the Initial Assessment since the receipt of the initial demand letter. We also paid $5.0 million related to the Revised Assessment, which was refunded in July 2016 based on the arbitrator’s ruling. The Company recognized $0.4 million of expense for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2017. The Company recognized $10.7 million of expense (inclusive of a special item of $6.7 million) and $6.8 million for the fiscal years ended December 25, 2016 and December 27, 2015, respectively. The Company had a liability of $6.5 million as of December 31, 2017, related to this matter. Management believes it is reasonably possible that the total loss in this matter could exceed the liability established by a range of zero to approximately $10 million.
NEMG T&G, Inc.
The Company was involved in class action litigation brought on behalf of individuals who, from 2006 to 2011, delivered newspapers at NEMG T&G, Inc., a subsidiary of the Company (“T&G”). T&G was a part of the New England Media Group, which the Company sold in 2013. The plaintiffs asserted several claims against T&G, including a challenge to their classification as independent contractors, and sought unspecified damages. In December 2016, the Company reached a settlement with respect to the claims, which was approved by the court in May 2017. As a result of the settlement, the Company recorded charges of $0.7 million ($0.4 million after tax) and $3.7 million ($2.3 million after tax) for the fiscal years ended December 31, 2017 and December 25, 2016, respectively, within discontinued operations.
Other
We are involved in various legal actions incidental to our business that are now pending against us. These actions are generally for amounts greatly in excess of the payments, if any, that may be required to be made. Although the Company cannot predict the outcome of these matters, it is possible that an unfavorable outcome in one or more matters could be material to the Company’s consolidated results of operations or cash flows for an individual reporting period. However, based on currently available information, management does not believe that the ultimate resolution of these matters, individually or in the aggregate, is likely to have a material effect on the Company’s financial position.
Letter of Credit Commitment
The Company issued $56 million letters of credit in connection with a sub-lease entered into in the fourth quarter of 2017 for approximately four floors of our headquarters building. A portion of the letters of credit will expire prorata through the second quarter of 2019, while the remaining portion of letters of credit will expire upon the Company’s repurchase of the Condo Interest in our headquarters building in 2019. Approximately $63 million of marketable securities were used as collateral for the letters of credit.
P. 102 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
19. Subsequent Events
Notice of Intent to Exercise Repurchase Option Under Lease Agreement
On January 30, 2018, the Company provided notice to an affiliate of W.P. Carey & Co. LLC of the Company’s intention to exercise its option under the Lease Agreement, dated March 6, 2009, by and between the parties (the “Lease”) to repurchase a portion of the Company’s leasehold condominium interest in the Company’s headquarters building located at 620 Eighth Avenue, New York, New York (the “Condo Interest”).
The Lease was part of a transaction in 2009 under which the Company sold and simultaneously leased back approximately 750,000 rentable square feet, comprising the Condo Interest. The sale price for the Condo Interest was approximately $225 million. Under the Lease, the Company has an option exercisable in 2019 to repurchase the Condo Interest for approximately $250 million.
The Company has accounted for the transaction as a financing transaction, and has continued to depreciate the Condo Interest and account for the rental payments as interest expense. The difference between the purchase option price and the net sale proceeds from the transaction is being amortized over the 10-year period of 2009-2019 through interest expense.
Quarterly Dividend
On February 21, 2018, our Board of Directors approved a dividend of $0.04 per share on our Class A and Class B common stock. The dividend is payable on April 19, 2018, to all stockholders of record as of the close of business on April 4, 2018. Our Board of Directors will continue to evaluate the appropriate dividend level on an ongoing basis in light of our earnings, capital requirements, financial condition and other relevant factors.
SCHEDULE II – VALUATION AND QUALIFYING ACCOUNTS
For the Years Ended December 31, 2017, December 25, 2016, and December 27, 2015:
(In thousands) | Balance at beginning of period | Additions charged to operating costs and other | Deductions(1) | Balance at end of period | ||||||||||||
Accounts receivable allowances: | ||||||||||||||||
Year ended December 31, 2017 | $ | 16,815 | $ | 11,747 | $ | 14,020 | $ | 14,542 | ||||||||
Year ended December 25, 2016 | $ | 13,485 | $ | 17,154 | $ | 13,824 | $ | 16,815 | ||||||||
Year ended December 27, 2015 | $ | 12,860 | $ | 13,999 | $ | 13,374 | $ | 13,485 | ||||||||
Valuation allowance for deferred tax assets: | ||||||||||||||||
Year ended December 31, 2017 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||
Year ended December 25, 2016 | $ | 36,204 | $ | — | $ | 36,204 | $ | — | ||||||||
Year ended December 27, 2015 | $ | 41,136 | $ | — | $ | 4,932 | $ | 36,204 | ||||||||
(1) | Includes write-offs, net of recoveries. |
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 103
QUARTERLY INFORMATION (UNAUDITED)
Quarterly financial information for each quarter in the years ended December 31, 2017 and December 25, 2016 is included in the following tables. See Note 13 of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information regarding discontinued operations.
2017 Quarters | |||||||||||||||
(In thousands, except per share data) | March 26, 2017 | June 25, 2017 | September 24, 2017 | December 31, 2017 | Full Year | ||||||||||
(13 weeks) | (13 weeks) | (13 weeks) | (14 weeks) | (53 weeks) | |||||||||||
Revenues | $ | 398,804 | $ | 407,074 | $ | 385,635 | $ | 484,126 | $ | 1,675,639 | |||||
Operating costs | 367,393 | 377,420 | 350,080 | 393,238 | 1,488,131 | ||||||||||
Headquarters redesign and consolidation(1) | 2,402 | 1,985 | 2,542 | 3,161 | 10,090 | ||||||||||
Postretirement benefit plan settlement gain (2) | — | — | — | (37,057 | ) | (37,057 | ) | ||||||||
Pension settlement expense(3) | — | — | — | 102,109 | 102,109 | ||||||||||
Operating profit | 29,009 | 27,669 | 33,013 | 22,675 | 112,366 | ||||||||||
Gain/(loss) from joint ventures | 173 | (266 | ) | 31,557 | (12,823 | ) | 18,641 | ||||||||
Interest expense and other, net | 5,325 | 5,133 | 4,660 | 4,665 | 19,783 | ||||||||||
Income from continuing operations before income taxes | 23,857 | 22,270 | 59,910 | 5,187 | 111,224 | ||||||||||
Income tax expense (4) | 10,742 | 6,711 | 23,420 | 63,083 | 103,956 | ||||||||||
Income/(loss) from continuing operations | 13,115 | 15,559 | 36,490 | (57,896 | ) | 7,268 | |||||||||
(Loss)/income from discontinued operations, net of income taxes | — | — | (488 | ) | 57 | (431 | ) | ||||||||
Net income/(loss) | 13,115 | 15,559 | 36,002 | (57,839 | ) | 6,837 | |||||||||
Net (income)/loss attributable to the noncontrolling interest | 66 | 40 | (3,673 | ) | 1,026 | (2,541 | ) | ||||||||
Net income/(loss) attributable to The New York Times Company common stockholders | $ | 13,181 | $ | 15,599 | $ | 32,329 | $ | (56,813 | ) | $ | 4,296 | ||||
Amounts attributable to The New York Times Company common stockholders: | |||||||||||||||
Income/(loss) from continuing operations | $ | 13,181 | $ | 15,599 | $ | 32,817 | $ | (56,870 | ) | $ | 4,727 | ||||
(Loss)/income from discontinued operations, net of income taxes | $ | — | $ | — | $ | (488 | ) | $ | 57 | $ | (431 | ) | |||
Net income/(loss) | $ | 13,181 | $ | 15,599 | $ | 32,329 | $ | (56,813 | ) | $ | 4,296 | ||||
Average number of common shares outstanding: | |||||||||||||||
Basic | 161,402 | 161,787 | 162,173 | 162,311 | 161,926 | ||||||||||
Diluted | 162,592 | 163,808 | 164,405 | 162,311 | 164,263 | ||||||||||
Basic earnings/(loss) per share attributable to The New York Times Company common stockholders: | |||||||||||||||
Income/(loss) from continuing operations | $ | 0.08 | $ | 0.10 | $ | 0.20 | $ | (0.35 | ) | $ | 0.03 | ||||
(Loss) from discontinued operations, net of income taxes | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | |||||
Net income/(loss) | $ | 0.08 | $ | 0.10 | $ | 0.20 | $ | (0.35 | ) | $ | 0.03 | ||||
Diluted earnings/(loss) per share attributable to The New York Times Company common stockholders: | |||||||||||||||
Income/(loss) from continuing operations | $ | 0.08 | $ | 0.09 | $ | 0.20 | $ | (0.35 | ) | $ | 0.03 | ||||
(Loss) from discontinued operations, net of income taxes | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | |||||
Net income/(loss) | $ | 0.08 | $ | 0.09 | $ | 0.20 | $ | (0.35 | ) | $ | 0.03 | ||||
Dividends declared per share | $ | 0.04 | $ | — | $ | 0.08 | $ | 0.04 | $ | 0.16 | |||||
(1) | We recognized expenses related to the ongoing redesign and consolidation of space in our headquarters building. |
(2) | We recorded a gain in the fourth quarter primarily in connection with the settlement of contractual funding obligations from a postretirement plan. |
(3) | We recorded a pension settlement charge in the fourth quarter in connection with the purchase of group annuity contracts. |
(4) | We recorded a $68.7 million charge in the fourth quarter primarily attributable to the remeasurement of our net deferred tax assets required as a result of recent tax legislation. |
P. 104 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
2016 Quarters | |||||||||||||||
(In thousands, except per share data) | March 26, 2016 | June 26, 2016 | September 25, 2016 | December 25, 2016 | Full Year | ||||||||||
(13 weeks) | (13 weeks) | (13 weeks) | (13 weeks) | (52 weeks) | |||||||||||
Revenues | $ | 379,515 | $ | 372,630 | $ | 363,547 | $ | 439,650 | $ | 1,555,342 | |||||
Operating costs | 351,580 | 339,933 | 356,596 | 362,801 | 1,410,910 | ||||||||||
Restructuring charge(1) | — | 11,855 | 2,949 | — | 14,804 | ||||||||||
Multiemployer pension plan withdrawal expense(2) | — | 11,701 | (4,971 | ) | — | 6,730 | |||||||||
Pension settlement expense(3) | — | — | — | 21,294 | 21,294 | ||||||||||
Operating (loss)/profit | 27,935 | 9,141 | 8,973 | 55,555 | 101,604 | ||||||||||
(Loss)/income from joint ventures | (41,896 | ) | (412 | ) | 463 | 5,572 | (36,273 | ) | |||||||
Interest expense and other, net | 8,826 | 9,097 | 9,032 | 7,850 | 34,805 | ||||||||||
(Loss)/income from continuing operations before income taxes | (22,787 | ) | (368 | ) | 404 | 53,277 | 30,526 | ||||||||
Income tax (benefit)/expense | (9,201 | ) | 124 | 121 | 13,377 | 4,421 | |||||||||
Income/(loss) from continuing operations | (13,586 | ) | (492 | ) | 283 | 39,900 | 26,105 | ||||||||
(Loss) from discontinued operations, net of income taxes | — | — | — | (2,273 | ) | (2,273 | ) | ||||||||
Net (loss)/income | (13,586 | ) | (492 | ) | 283 | 37,627 | 23,832 | ||||||||
Net income attributable to the noncontrolling interest | 5,315 | 281 | 123 | (483 | ) | 5,236 | |||||||||
Net (loss)/income attributable to The New York Times Company common stockholders | $ | (8,271 | ) | $ | (211 | ) | $ | 406 | $ | 37,144 | $ | 29,068 | |||
Amounts attributable to The New York Times Company common stockholders: | |||||||||||||||
(Loss)/income from continuing operations | $ | (8,271 | ) | $ | (211 | ) | $ | 406 | $ | 39,417 | $ | 31,341 | |||
(Loss) from discontinued operations, net of income taxes | — | — | — | (2,273 | ) | (2,273 | ) | ||||||||
Net (loss)/income | $ | (8,271 | ) | $ | (211 | ) | $ | 406 | $ | 37,144 | $ | 29,068 | |||
Average number of common shares outstanding: | |||||||||||||||
Basic | 161,003 | 161,128 | 161,185 | 161,235 | 161,128 | ||||||||||
Diluted | 161,003 | 161,128 | 162,945 | 162,862 | 162,817 | ||||||||||
Basic earnings/(loss) per share attributable to The New York Times Company common stockholders: | |||||||||||||||
(Loss)/income from continuing operations | $ | (0.05 | ) | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 0.24 | $ | 0.19 | ||||
(Loss) from discontinued operations, net of income taxes | — | — | — | (0.01 | ) | (0.01 | ) | ||||||||
Net (loss)/income | $ | (0.05 | ) | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 0.23 | $ | 0.18 | ||||
Diluted earnings/(loss) per share attributable to The New York Times Company common stockholders: | |||||||||||||||
Income/(loss) from continuing operations | $ | (0.05 | ) | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 0.24 | $ | 0.19 | ||||
(Loss) from discontinued operations, net of income taxes | — | — | — | (0.01 | ) | (0.01 | ) | ||||||||
Net (loss)/income | $ | (0.05 | ) | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 0.23 | $ | 0.18 | ||||
Dividends declared per share | $ | 0.04 | $ | — | $ | 0.08 | $ | 0.04 | $ | 0.16 | |||||
(1) | We recorded restructuring charges in the second and third quarters associated with the streamlining of the Company’s international print operations. |
(2) | We recorded a charge in the second quarter related to a partial withdrawal obligation under a multiemployer pension plan following an unfavorable arbitration decision, of which $5 million was reimbursed to the Company in the third quarter. |
(3) | We recorded a pension settlement charge in the fourth quarter related to a lump-sum payment offer to certain former employees who participated in a qualified pension plan. |
Earnings/(loss) per share amounts for the quarters do not necessarily equal the respective year-end amounts for earnings or loss per share due to the weighted-average number of shares outstanding used in the computations for the respective periods. Earnings/(loss) per share amounts for the respective quarters and years have been computed using the average number of common shares outstanding.
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 105
One of our largest sources of revenue is advertising. Our business has historically experienced higher advertising volume in the fourth quarter than the remaining quarters because of holiday advertising.
ITEM 9. CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE |
Not applicable.
ITEM 9A. CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES |
EVALUATION OF DISCLOSURE CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES
Our management, with the participation of our principal executive officer and our principal financial officer, evaluated the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934) as of December 31, 2017. Based upon such evaluation, our principal executive officer and principal financial officer concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures were effective to ensure that the information required to be disclosed by us in the reports that we file or submit under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and forms, and is accumulated and communicated to our management, including our principal executive officer and principal financial officer, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
MANAGEMENT’S REPORT ON INTERNAL CONTROL OVER FINANCIAL REPORTING
Management’s report on internal control over financial reporting and the attestation report of our independent registered public accounting firm on our internal control over financial reporting are set forth in Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K and are incorporated by reference herein.
CHANGES IN INTERNAL CONTROL OVER FINANCIAL REPORTING
There were no changes in our internal control over financial reporting during the quarter ended December 31, 2017, that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
ITEM 9B. OTHER INFORMATION |
Not applicable.
P. 106 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
PART III |
ITEM 10. DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE |
In addition to the information set forth under the caption “Executive Officers of the Registrant” in Part I of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, the information required by this item is incorporated by reference to the sections titled “Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance,” “Proposal Number 1 — Election of Directors,” “Interests of Related Persons in Certain Transactions of the Company,” “Board of Directors and Corporate Governance,” beginning with the section titled “Independent Directors,” but only up to and including the section titled “Audit Committee Financial Experts,” “Board Committees” and “Nominating & Governance Committee” of our Proxy Statement for the 2018 Annual Meeting of Stockholders.
The Board of Directors has adopted a code of ethics that applies to the principal executive officer, principal financial officer and principal accounting officer. The current version of such code of ethics can be found on the Corporate Governance section of our website at http://investors.nytco.com/investors/corporate-governance. We intend to post any amendments to or waivers from the code of ethics that apply to our principal executive officer, principal financial officer or principal accounting officer on our website.
ITEM 11. EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION |
The information required by this item is incorporated by reference to the sections titled “Compensation Committee,” “Directors’ Compensation,” “Directors’ and Officers’ Liability Insurance” and “Compensation of Executive Officers” of our Proxy Statement for the 2018 Annual Meeting of Stockholders.
ITEM 12. SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS |
The information required by this item is incorporated by reference to the sections titled “Principal Holders of Common Stock,” “Security Ownership of Management and Directors” and “The 1997 Trust” of our Proxy Statement for the 2018 Annual Meeting of Stockholders.
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 107
Equity Compensation Plan Information
The following table presents information regarding our existing equity compensation plans as of December 31, 2017.
Plan category | Number of securities to be issued upon exercise of outstanding options, warrants and rights (a) | Weighted average exercise price of outstanding options, warrants and rights (b) | Number of securities remaining available for future issuance under equity compensation plans (excluding securities reflected in column (a)) (c) | |||||||
Equity compensation plans approved by security holders | ||||||||||
Stock options and stock-based awards | 7,331,057 | (1) | $ | 14.71 | (2) | 7,187,603 | (3) | |||
Employee Stock Purchase Plan | — | — | 6,409,741 | (4) | ||||||
Total | 7,331,057 | 13,597,344 | ||||||||
Equity compensation plans not approved by security holders | None | None | None | |||||||
(1) | Includes (i) 3,773,928 shares of Class A stock to be issued upon the exercise of outstanding stock options granted under the 1991 Incentive Plan, the 2010 Incentive Plan, and the 2004 Non-Employee Directors’ Stock Incentive Plan, at a weighted-average exercise price of $14.71 per share, and with a weighted-average remaining term of 2 years; (ii) 886,243 shares of Class A stock issuable upon the vesting of outstanding stock-settled restricted stock units granted under the 2010 Incentive Plan; (iii) 111,480 shares of Class A stock related to vested stock-settled restricted stock units granted under the 2010 Incentive Plan issuable to non-employee directors upon retirement from the Board; and (iv) 2,559,406, shares of Class A stock that would be issuable at maximum performance pursuant to outstanding stock-settled performance awards under the 2010 Incentive Plan. Under the terms of the performance awards, shares of Class A stock are to be issued at the end of three-year performance cycles based on the Company’s achievement against specified performance targets. The shares included in the table represent the maximum number of shares that would be issued under the outstanding performance awards; assuming target performance, the number of shares that would be issued under the outstanding performance awards is 1,279,703. |
(2) | Excludes shares of Class A stock issuable upon vesting of stock-settled restricted stock units and shares issuable pursuant to stock-settled performance awards. |
(3) | Includes shares of Class A stock available for future stock options to be granted under the 2010 Incentive Plan. As of December 31, 2017, the 2010 Incentive Plan had 7,187,603 shares of Class A stock remaining available for issuance upon the grant, exercise or other settlement of share-based awards. Stock options granted under the 2010 Incentive Plan must provide for an exercise price of 100% of the fair market value (as defined in the 2010 Incentive Plan) on the date of grant. The 2004 Non-Employee Directors’ Stock Incentive Plan terminated on April 30, 2014. |
(4) | Includes shares of Class A stock available for future issuance under the Company’s Employee Stock Purchase Plan (“ESPP”). We have not had an offering under the ESPP since 2010. |
ITEM 13. CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE |
The information required by this item is incorporated by reference to the sections titled “Interests of Related Persons in Certain Transactions of the Company,” “Board of Directors and Corporate Governance — Independent Directors,” “Board of Directors and Corporate Governance — Board Committees” and “Board of Directors and Corporate Governance — Policy on Transactions with Related Persons” of our Proxy Statement for the 2018 Annual Meeting of Stockholders.
ITEM 14. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTANT FEES AND SERVICES |
The information required by this item is incorporated by reference to the section titled “Proposal Number 3 — Selection of Auditors,” beginning with the section titled “Audit Committee’s Pre-Approval Policies and Procedures,” but only up to and not including the section titled “Recommendation and Vote Required” of our Proxy Statement for the 2018 Annual Meeting of Stockholders.
P. 108 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
PART IV |
ITEM 15. EXHIBITS AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES |
(A) DOCUMENTS FILED AS PART OF THIS REPORT
(1) Financial Statements
As listed in the index to financial information in “Item 8 — Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.”
(2) Supplemental Schedules
The following additional consolidated financial information is filed as part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K and should be read in conjunction with the Consolidated Financial Statements set forth in “Item 8 — Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.” Schedules not included with this additional consolidated financial information have been omitted either because they are not applicable or because the required information is shown in the Consolidated Financial Statements.
Page | |
Consolidated Schedule for the Three Years Ended December 31, 2017 | |
II – Valuation and Qualifying Accounts | |
Separate financial statements of associated companies accounted for by the equity method are omitted in accordance with permission granted by the Securities and Exchange Commission pursuant to Rule 3-13 of Regulation S-X.
(3) Exhibits
The exhibits listed in the accompanying index are filed as part of this report.
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 109
INDEX TO EXHIBITS |
Exhibit numbers 10.18 through 10.27 are management contracts or compensatory plans or arrangements.
Exhibit Number | Description of Exhibit | |
(3.1) | ||
(3.2) | ||
(4) | The Company agrees to furnish to the Commission upon request a copy of any instrument with respect to long-term debt of the Company and any subsidiary for which consolidated or unconsolidated financial statements are required to be filed, and for which the amount of securities authorized thereunder does not exceed 10% of the total assets of the Company and its subsidiaries on a consolidated basis. | |
(4.1) | ||
(10.1) | ||
(10.2) | ||
(10.3) | ||
(10.4) | ||
(10.5) | ||
(10.6) | ||
(10.7) | ||
(10.8) | ||
(10.9) | ||
(10.10) | ||
(10.11) | ||
(10.12) | ||
(10.13) | ||
(10.14) | ||
P. 110 – THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY
Exhibit Number | Description of Exhibit | |
(10.15) | ||
(10.16)* | ||
(10.17)* | ||
(10.18) | ||
(10.19) | ||
(10.20) | ||
(10.21) | ||
(10.22) | ||
(10.23) | ||
(10.24) | ||
(10.25) | ||
(10.26) | ||
(10.27) | ||
(21) | ||
(23.1) | ||
(24) | Power of Attorney (included as part of signature page). | |
(31.1) | ||
(31.2) | ||
(32.1) | ||
(32.2) | ||
(101.INS) | XBRL Instance Document. | |
(101.SCH) | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document. | |
(101.CAL) | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document. | |
(101.DEF) | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document. | |
(101.LAB) | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document. | |
(101.PRE) | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document. | |
* Portions of this exhibit (indicated by asterisks) have been omitted pursuant to a confidential treatment request submitted separately to the SEC pursuant to Rule 24b-2 under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended.
ITEM 16. FORM 10-K SUMMARY |
None.
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 111
SIGNATURES |
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
Date: February 27, 2018
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY (Registrant) | |||
BY: | /s/ James M. Follo | ||
James M. Follo | |||
Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer | |||
We, the undersigned directors and officers of The New York Times Company, hereby severally constitute Diane Brayton and James M. Follo, and each of them singly, our true and lawful attorneys with full power to them and each of them to sign for us, in our names in the capacities indicated below, any and all amendments to this Annual Report on Form 10-K filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission.
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
Signature | Title | Date |
/s/ Mark Thompson | Chief Executive Officer, President and Director (principal executive officer) | February 27, 2018 |
/s/ James M. Follo | Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer (principal financial officer) | February 27, 2018 |
/s/ R. Anthony Benten | Senior Vice President, Treasurer and Corporate Controller (principal accounting officer) | February 27, 2018 |
/s/ A.G. Sulzberger | Publisher and Director | February 27, 2018 |
/s/ Arthur Sulzberger, Jr. | Chairman of the Board | February 27, 2018 |
/s/ Raul E. Cesan | Director | February 27, 2018 |
/s/ Robert E. Denham | Director | February 27, 2018 |
/s/ Rachel Glaser | Director | February 27, 2018 |
/s/ Hays N. Golden | Director | February 27, 2018 |
/s/ Steven B. Green | Director | February 27, 2018 |
/s/ Joichi Ito | Director | February 27, 2018 |
/s/ James A. Kohlberg | Director | February 27, 2018 |
/s/ Brian P. McAndrews | Director | February 27, 2018 |
/s/ Doreen A. Toben | Director | February 27, 2018 |
/s/ Rebecca Van Dyck | Director | February 27, 2018 |
THE NEW YORK TIMES COMPANY – P. 112
