Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-32.1 - EXHIBIT 32.1 - ROPER TECHNOLOGIES INC | a201710-kex321.htm |
| EX-31.2 - EXHIBIT 31.2 - ROPER TECHNOLOGIES INC | a201710-kex312.htm |
| EX-31.1 - EXHIBIT 31.1 - ROPER TECHNOLOGIES INC | a201710-kex311.htm |
| EX-23.1 - EXHIBIT 23.1 - ROPER TECHNOLOGIES INC | a201710-kex231.htm |
| EX-21.1 - EXHIBIT 21.1 - ROPER TECHNOLOGIES INC | a201710-kex211.htm |
| EX-10.23 - EXHIBIT 10.23 - ROPER TECHNOLOGIES INC | a201710-kex1023.htm |
| EX-10.22 - EXHIBIT 10.22 - ROPER TECHNOLOGIES INC | a201710-kex1022.htm |
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
--------------------------
FORM 10-K
þ ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2017
☐ TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the transition period from ___ to ___
Commission File Number 1-12273
ROPER TECHNOLOGIES, INC.
(Exact name of Registrant as specified in its charter)
----------------
Delaware | 51-0263969 |
(State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
----------------
6901 Professional Parkway East, Suite 200
Sarasota, Florida 34240
(Address of principal executive offices) (Zip Code)
Registrant's telephone number, including area code: (941) 556-2601
----------------
SECURITIES REGISTERED PURSUANT TO SECTION 12(b) OF THE ACT:
Title of Each Class | Name of Each Exchange On Which Registered | |
Common Stock, $0.01 Par Value | New York Stock Exchange | |
SECURITIES REGISTERED PURSUANT TO SECTION 12(g) OF THE ACT: None
----------------
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. þ Yes ☐ No
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. ☐ Yes þ No
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. þ Yes ☐ No
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K (§229.405) is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant's knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§223.405) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). þ Yes ☐ No
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). þ Large accelerated filer ☐ Accelerated filer ☐ Non-accelerated filer ☐ Smaller reporting company ☐ Emerging growth company
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12-b2 of the Act). ☐ Yes þ No
Based on the closing sale price on the New York Stock Exchange on June 30, 2017, the aggregate market value of the voting and non-voting common stock held by non-affiliates of the registrant was: $23,224,859,776.
Number of shares of registrant's Common Stock outstanding as of February 16, 2018: 102,826,454.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Portions of the registrant's Proxy Statement to be furnished to Stockholders in connection with its Annual Meeting of Stockholders are incorporated by reference into Part III of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
ROPER TECHNOLOGIES, INC.
FORM 10-K FOR THE FISCAL YEAR ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2017
Table of Contents
Page | ||
2
Information About Forward-Looking Statements
This Annual Report on Form 10-K ("Annual Report") includes and incorporates by reference "forward-looking statements" within the meaning of the federal securities laws. In addition, we, or our executive officers on our behalf, may from time to time make forward-looking statements in reports and other documents we file with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission ("SEC") or in connection with oral statements made to the press, potential investors or others. All statements that are not historical facts are "forward-looking statements." Forward-looking statements may be indicated by words or phrases such as "anticipate," "estimate," "plans," "expects," "projects," "should," "will," "believes" or "intends" and similar words and phrases. These statements reflect management's current beliefs and are not guarantees of future performance. They involve risks and uncertainties that could cause actual results to differ materially from those expressed or implied in any forward-looking statement.
Examples of forward-looking statements in this report include but are not limited to statements regarding operating results, the success of our operating plans, our expectations regarding our ability to generate cash and reduce debt and associated interest expense, profit and cash flow expectations, the prospects for newly acquired businesses to be integrated and contribute to future growth and our expectations regarding growth through acquisitions. Important assumptions relating to the forward-looking statements include, among others, demand for our products, the cost, timing and success of product upgrades and new product introductions, raw material costs, expected pricing levels, expected outcomes of pending litigation, competitive conditions and general economic conditions. These assumptions could prove inaccurate. Although we believe that the estimates and projections reflected in the forward-looking statements are reasonable, our expectations may prove to be incorrect. Important factors that could cause actual results to differ materially from estimates or projections contained in the forward-looking statements include, but are not limited to:
• | general economic conditions; |
• | difficulty making acquisitions and successfully integrating acquired businesses; |
• | any unforeseen liabilities associated with future acquisitions; |
• | limitations on our business imposed by our indebtedness; |
• | unfavorable changes in foreign exchange rates; |
• | difficulties associated with exports; |
• | risks and costs associated with our international sales and operations; |
• | rising interest rates; |
• | product liability and insurance risks; |
• | increased warranty exposure; |
• | future competition; |
• | the cyclical nature of some of our markets; |
• | reduction of business with large customers; |
• | risks associated with government contracts; |
• | changes in the supply of, or price for, raw materials, parts and components; |
• | environmental compliance costs and liabilities; |
• | risks and costs associated with asbestos-related litigation; |
• | potential write-offs of our goodwill and other intangible assets; |
• | our ability to successfully develop new products; |
• | failure to protect our intellectual property; |
• | the effect of, or change in, government regulations (including tax); |
• | economic disruption caused by terrorist attacks, including cybersecurity threats, health crises or other unforeseen events; and |
• | the factors discussed in Item 1A to this Annual Report under the heading "Risk Factors." |
We believe these forward-looking statements are reasonable. However, you should not place undue reliance on any forward-looking statements, which are based on current expectations. Further, forward-looking statements speak only as of the date they are made, and we undertake no obligation to publicly update any of them in light of new information or future events.
3
PART I
ITEM 1. | BUSINESS |
Our Business
Roper Technologies, Inc. ("Roper," the "Company," "we," "our" or "us") is a diversified technology company. We operate businesses that design and develop software (both license and software-as-a-service) and engineered products and solutions for a variety of niche end markets.
We pursue consistent and sustainable growth in earnings and cash flow by emphasizing continuous improvement in the operating performance of our existing businesses and by acquiring other businesses that offer high value-added software, services, engineered products and solutions that we believe are capable of achieving growth and maintaining high margins. We compete in many niche markets and believe we are the market leader or a competitive alternative to the market leader in most of these markets.
We were incorporated on December 17, 1981 under the laws of the State of Delaware.
Market Share, Market Expansion, and Product Development
Leadership with Engineered Content for Niche Markets - We maintain a leading position in many of our markets. We believe our market positions are attributable to the technical sophistication of our products and software, the applications expertise used to create our advanced products and systems, and our distribution and service capabilities. Our operating units grow their businesses through new product development and development of new applications and services to satisfy customer needs. In addition, our operating units grow our customer base by expanding our access to customers and entering adjacent markets.
Diversified End Markets and Geographic Reach - We have a global presence, with sales to customers outside the U.S. totaling $1.3 billion in 2017. Information regarding our international operations is set forth in Note 13 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements included in this Annual Report.
Research and Development - We conduct applied research and development to improve the quality and performance of our products and to develop new technologies and products. Our research and development spending was $281 million in 2017 as compared to $195 million and $164 million in 2016 and 2015, respectively.
Our Business Segments
Our operations are reported in four segments based upon common customers, markets, sales channels, technologies and common cost opportunities. The segments are: RF Technology, Medical & Scientific Imaging, Industrial Technology and Energy Systems & Controls. Financial information about our business segments is presented in Note 13 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements included in this Annual Report.
RF Technology
Our RF Technology segment provides radio frequency identification ("RFID") communication technology and software solutions. This segment had net revenues of $1.86 billion for the year ended December 31, 2017, representing 40.4% of our total net revenues.
Comprehensive Application Management Software - We provide 1) enterprise software and information solutions for government contractors, professional services firms and other project-based businesses, 2) comprehensive management software solutions for law and other professional services firms, including business development, calendar/docket matter management, time and billing and case management and 3) preconstruction project management solutions for construction industry professionals.
Software-as-a-Service - We maintain electronic marketplaces that connect 1) available capacity of trucking units with the available loads of freight to be moved from location to location throughout North America, 2) food suppliers, distributors and vendors, primarily in the perishable food sector and 3) construction industry professionals.
Card Systems/Integrated Security Solutions - We provide software, card systems and integrated security solutions primarily to education and health care markets. We also provide an integrated nutrition management solution used by food service customers.
4
Toll and Traffic Systems - We manufacture and sell toll tags and monitoring systems as well as provide transaction and violation processing services for toll and traffic systems to both governmental and private sector entities. In addition, we provide intelligent traffic systems that assist customers in improving traffic flow and infrastructure utilization.
RFID Card Readers - We design, develop and manufacture RFID card readers that support most smart cards worldwide. The readers are used in numerous applications and OEM solutions including secure printing and single sign-on across several vertical markets including healthcare, manufacturing and government.
Metering and Remote Monitoring - We manufacture and sell meter reading, data logging and pressure control products for use primarily in water and gas applications. We also provide network monitoring, leakage reduction and pressure control services in water and gas distribution networks.
Medical and Scientific Imaging
Our Medical & Scientific Imaging segment offers products and software in medical applications, and high performance digital imaging products. For 2017, this segment had net revenues of $1.41 billion, representing 30.6% of our total net revenues.
Medical Products and Software - We provide diagnostic and laboratory software solutions to healthcare providers and services and technologies to support the diverse and complex needs of alternate site health care providers who deliver services outside of an acute care hospital setting. We also manufacture and sell patient positioning devices and related software for use in radiation oncology and 3-D measurement technology in computer-assisted surgery, and we supply diagnostic and therapeutic disposable products used in ultrasound imaging for minimally invasive medical procedures. We design and manufacture a non-invasive instrument for portable ultrasound bladder volume measurement and a video laryngoscope designed to enable rapid intubation in difficult situations. In addition, we provide a cloud-based financial analytics and performance software platform to healthcare providers.
Digital Imaging Products and Software - We manufacture and sell extremely sensitive, high-performance electron filters, charged couple device ("CCD") and complementary metal oxide semiconductor ("CMOS") cameras, detectors and related software for a variety of scientific and industrial uses, which require high resolution and/or high speed digital video, including electron microscopy and spectroscopy applications. We sell these products for use within academic, government research, semiconductor, security and other end-user markets such as biological and material science. They are frequently incorporated into products by original equipment manufacturers ("OEMs").
Industrial Technology
Our Industrial Technology segment produces primarily water meter and meter reading technology, fluid handling pumps, and materials analysis solutions. For 2017, this segment had net revenues of $784 million, representing 17.0% of our total net revenues.
Water Meter and Automatic Meter Reading Products and Systems - We manufacture and distribute water meter products serving the residential, commercial and industrial water management markets, and several lines of automatic meter reading products and systems serving these markets.
Fluid Handling Pumps - We manufacture and sell a wide variety of pumps. These pumps vary significantly in complexity and in pumping method employed, which allows for the movement and application of a diverse range of low and high viscosity liquids, high solids content slurries and chemicals. Our pumps are used in end markets such as oil and gas, agricultural, water and wastewater, chemical and general industrial.
Materials Analysis Equipment and Consumables - We manufacture and sell equipment and supply consumables necessary to prepare material samples for testing and analysis. These products are used mostly within the material science, steel, automotive, electronics, mining and research end-user markets.
The Industrial Technology segment companies' revenues reflect a combination of standard products and specially engineered, application-specific products. Standard products are typically shipped within two weeks of receipt of order. Application-specific products typically ship within 6 to 12 weeks following receipt of order. However, larger project orders and blanket purchase orders for certain OEMs may extend shipment for longer periods.
5
Energy Systems & Controls
Our Energy Systems & Controls segment principally produces control systems, testing equipment, valves and sensors. For 2017, this segment had net revenues of $551 million, representing 12.0% of our total net revenues.
Control Systems - We manufacture control systems and provide related engineering and commissioning services for turbomachinery applications, primarily in energy markets.
Fluid Properties Testing Equipment - We manufacture and sell test equipment to determine physical and elemental properties, such as sulfur and nitrogen content, flash point, viscosity, freeze point and distillation range of liquids and gases primarily for the petroleum industry.
Sensors, Controls and Valves - We manufacture sensors and control equipment including pressure sensors, temperature sensors, measurement instruments and control software for global rubber, plastics and process industries. We also manufacture and distribute valves, sensors, switches and control products used on engines, compressors, turbines and other powered equipment for the oil and gas, pipeline, power generation, marine engine and general industrial markets. Many of these products are designed for use in hazardous environments.
Non-destructive Inspection and Measurement Instrumentation - We manufacture non-destructive inspection and measurement solutions including measurement probes, robotics, vibration sensors, switches and transmitters. These solutions are applied principally in nuclear energy markets. Many of these products are designed for use in hazardous environments.
The Energy Systems & Controls segment companies' revenues reflect a combination of standard products and large engineered projects. Standard products generally ship within two weeks of receipt of order, and large engineered projects may have lead times of several months. As such, backlog may fluctuate depending upon the timing of large project awards.
Materials and Suppliers
We believe most materials and supplies we use are readily available from numerous sources and suppliers throughout the world. However, some components and sub-assemblies are currently available from a limited number of suppliers. Some high-performance components for digital imaging products can be in short supply and/or suppliers have occasional difficulty manufacturing such components to our specifications. We regularly investigate and identify alternative sources where possible, and we believe these conditions equally affect our competitors. Supply shortages have not had a material adverse effect on our revenues although delays in shipments have occurred following such supply interruptions.
Backlog
Our backlog includes only firm unfilled orders expected to be recognized as revenue within twelve months. Backlog was $1.7 billion at December 31, 2017, and $1.6 billion at December 31, 2016.
Distribution and Sales
Distribution and sales occur through direct sales offices, manufacturers' representatives and distributors. In addition, our Medical & Scientific Imaging segment also sells through value added resellers ("VARs") and OEMs.
Environmental Matters and Other Governmental Regulation
Our operations and properties are subject to laws and regulations relating to environmental protection, including those governing air emissions, water discharges, waste management and workplace safety. We use, generate and dispose of hazardous substances and waste in our operations and could be subject to material liabilities relating to the investigation and clean-up of contaminated properties and related claims. We are required to conform our operations and properties to these laws and adapt to regulatory requirements in all countries as these requirements change. In connection with our acquisitions, we may assume significant environmental liabilities, some of which we may not be aware of, or may not be quantifiable, at the time of acquisition. In addition, new laws and regulations, the discovery of previously unknown contamination or the imposition of new requirements could increase our costs or subject us to new or increased liabilities.
Customers
No customer accounted for 10% or more of net revenues for 2017 for any of our segments or for our company as a whole.
6
Competition
Generally, our products and solutions face significant competition, usually from a limited number of competitors. We believe that we are a leader in most of our markets, and no single company competes with us over a significant number of product lines. Competitors might be large or small in size, often depending on the size of the niche market we serve. We compete primarily on product quality, performance, innovation, technology, price, applications expertise, system and service flexibility, distribution channel access and customer service capabilities.
Patents and Trademarks
In addition to trade secrets, unpatented know-how, and other intellectual property rights, we own or license the rights under a number of patents, trademarks and copyrights relating to certain of our products and businesses. We also employ various methods, including confidentiality and non-disclosure agreements with individuals and companies we do business with, employees, distributors, representatives and customers to protect our trade secrets and know-how. We believe our operating units are not substantially dependent on any single patent, trademark, copyright, or other item of intellectual property or group of patents, trademarks or copyrights.
Employees
As of December 31, 2017, we had 14,236 employees, with 9,425 located in the United States. We have 187 employees who are subject to collective bargaining agreements. We have not experienced any work stoppages and consider our relations with our employees to be good.
Available Information
All reports we file electronically with the SEC, including our annual reports on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, current reports on Form 8-K and our annual proxy statements, as well as any amendments to those reports, are accessible at no cost on our website at www.ropertech.com as soon as reasonably practicable after we electronically file such material with, or furnish it to, the SEC. These filings are also accessible on the SEC's website at www.sec.gov. You may also read and copy any material we file with the SEC at the SEC's Public Reference Room at 100 F Street, N.E., Washington, D.C. 20549. You may obtain information on the operation of the Public Reference Room by calling the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330. Our Corporate Governance Guidelines; the charters of our Audit Committee, Compensation Committee, and Nominating and Governance Committee; and our Business Code of Ethics and Standards of Conduct are also available on our website. Any amendment to the Business Code of Ethics and Standards of Conduct and any waiver applicable to our directors, executive officers or senior financial officers will be posted on our website within the time period required by the SEC and the New York Stock Exchange (the "NYSE"). The information posted on our website is not incorporated into this Annual Report.
We have included the Chief Executive Officer and the Chief Financial Officer certifications regarding our public disclosure required by Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 as Exhibits 31.1 and 31.2 of this report. Additionally, we filed with the NYSE the Chief Executive Officer certification regarding our compliance with the NYSE's Corporate Governance Listing Standards (the "Listing Standards") pursuant to Section 303A.12(a) of the Listing Standards. We filed the certification with the NYSE on June 29, 2017 and our Chief Executive Officer indicated that he was not aware of any violations of the Listing Standards by us.
7
ITEM 1A. | RISK FACTORS |
Risks Relating to Our Business
Our indebtedness may affect our business and may restrict our operating flexibility.
As of December 31, 2017, we had $5.2 billion in total consolidated indebtedness. In addition, we had $1.2 billion undrawn availability under our senior unsecured credit facility. Subject to restrictions contained in our credit facility, we may incur additional indebtedness in the future, including indebtedness incurred to finance acquisitions.
Our level of indebtedness and the debt servicing costs associated with that indebtedness could have important effects on our operations and business strategy. For example, our indebtedness could:
• | limit our ability to borrow additional funds; |
• | limit our ability to complete future acquisitions; |
• | limit our ability to pay dividends; |
• | limit our ability to make capital expenditures; |
• | place us at a competitive disadvantage relative to our competitors, some of which have lower debt service obligations and greater financial resources; and |
• | increase our vulnerability to general adverse economic and industry conditions. |
Our ability to make scheduled principal payments of, to pay interest on, or to refinance our indebtedness and to satisfy our other debt obligations will depend upon our future operating performance, which may be affected by factors beyond our control. In addition, there can be no assurance that future borrowings or equity financing will be available to us on favorable terms for the payment or refinancing of our indebtedness. If we are unable to service our indebtedness, our business, financial condition and results of operations would be materially adversely affected.
Our credit facility contains covenants requiring us to achieve certain financial and operating results and maintain compliance with specified financial ratios. Our ability to meet the financial covenants or requirements in our credit facility may be affected by events beyond our control, and we may not be able to satisfy such covenants and requirements. A breach of these covenants or our inability to comply with the financial ratios, tests or other restrictions contained in our facility could result in an event of default under this facility. Upon the occurrence of an event of default under our credit facility, and the expiration of any grace periods, the lenders could elect to declare all amounts outstanding under the facility, together with accrued interest, to be immediately due and payable. If this were to occur, our assets may not be sufficient to fully repay the amounts due under this facility or our other indebtedness.
Unfavorable changes in foreign exchange rates may harm our business.
Several of our operating companies have transactions and balances denominated in currencies other than the U.S. dollar. Most of these transactions and balances are denominated in euros, Canadian dollars, British pounds or Danish kroner. Sales by our operating companies whose functional currency is not the U.S. dollar represented 17% and 20% of our total net revenues for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively. Unfavorable changes in exchange rates between the U.S. dollar and those currencies could significantly reduce our reported revenues and earnings.
8
We export a significant portion of our products. Difficulties associated with the export of our products could harm our business.
Sales to customers outside the U.S. by our businesses located in the U.S. account for a significant portion of our net revenues. These sales accounted for 11% of our net revenues for the year ended December 31, 2017 and 12% for the year ended December 31, 2016. We are subject to risks that could limit our ability to export our products or otherwise reduce the demand for these products in our foreign markets. Such risks include, without limitation, the following:
• | unfavorable changes in or noncompliance with U.S. and other jurisdictions' export requirements; |
• | restrictions on the export of technology and related products; |
• | unfavorable changes in or noncompliance with U.S. and other jurisdictions' export policies to certain countries; |
• | unfavorable changes in the import policies of our foreign markets; and |
• | a general economic downturn in our foreign markets. |
The occurrence of any of these events could reduce the foreign demand for our products or could limit our ability to export our products and, therefore, could have a material negative effect on our future sales and earnings.
Economic, political and other risks associated with our international operations could adversely affect our business.
As of and for the year ended December 31, 2017, 20% of our net revenues and 18% of our long-lived assets, excluding goodwill and intangibles, were attributable to operations outside the U.S. We expect our international operations to contribute materially to our business for the foreseeable future. Our international operations are subject to varying degrees of risk inherent in doing business outside the U.S. including, without limitation, the following:
• | adverse changes in a specific country's or region's political or economic conditions, particularly in emerging markets; |
• | oil price volatility; |
• | trade protection measures and import or export requirements; |
• | subsidies or increased access to capital for firms that are currently, or may emerge as, competitors in countries in which we have operations; |
• | partial or total expropriation; |
• | potentially negative consequences from changes in tax laws; |
• | difficulty in staffing and managing widespread operations; |
• | differing labor regulations; |
• | differing protection of intellectual property; and |
• | differing and unexpected changes in regulatory requirements. |
Our growth strategy includes acquisitions. We may not be able to identify suitable acquisition candidates, complete acquisitions or integrate acquisitions successfully.
Our future growth is likely to depend to some degree on our ability to acquire and successfully integrate new businesses. We intend to seek additional acquisition opportunities, both to expand into new markets and to enhance our position in existing markets. There are no assurances, however, that we will be able to successfully identify suitable candidates, negotiate appropriate terms, obtain financing on acceptable terms, complete proposed acquisitions, successfully integrate acquired businesses or expand into new markets. Once acquired, operations may not achieve anticipated levels of revenues or profitability.
Acquisitions involve risks, including difficulties in the integration of the operations, technologies, services and products of the acquired companies and the diversion of management's attention from other business concerns. Although our management will endeavor to evaluate the risks inherent in any particular transaction, there are no assurances that we will properly ascertain all such risks. In addition, prior acquisitions have resulted, and future acquisitions could result, in the incurrence of substantial additional indebtedness and other expenses. Future acquisitions may also result in potentially dilutive issuances of equity securities. Difficulties encountered with acquisitions may have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
9
Our technology is important to our success and our failure to protect this technology could put us at a competitive disadvantage.
Many of our products rely on proprietary technology; therefore we believe that the development and protection of intellectual property rights through patents, copyrights, trade secrets, trademarks, confidentiality agreements and other contractual provisions are important to the future success of our business. Despite our efforts to protect proprietary rights, unauthorized parties or competitors may copy or otherwise obtain and use our products or technology. Actions to enforce these rights may result in substantial costs and diversion of resources, and we make no assurances that any such actions will be successful.
Product liability, insurance risks and increased insurance costs could harm our operating results.
Our business exposes us to product liability risks in the design, manufacturing and distribution of our products. In addition, certain of our products are used in hazardous environments. We currently have product liability insurance; however, we may not be able to maintain our insurance at a reasonable cost or in sufficient amounts to adequately protect us against losses. We also maintain other insurance policies, including directors' and officers' liability insurance. We believe we have adequately accrued estimated losses, principally related to deductible amounts under our insurance policies, with respect to all product liability and other claims, based upon our past experience and available facts. However, a successful product liability or other claim or series of claims brought against us could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations. In addition, a significant increase in our insurance costs could have an adverse impact on our operating results.
Our operating results could be adversely affected by a reduction of business with our large customers.
In some of our businesses, we derive a significant amount of revenue from large customers. The loss or reduction of any significant contracts with any of these customers could reduce our revenues and cash flows. Additionally, many of our customers are government entities. In many situations, government entities can unilaterally terminate or modify our existing contracts without cause and without penalty to the government agency.
We face intense competition. If we do not compete effectively, our business may suffer.
We face intense competition from numerous competitors. Our products compete primarily on the basis of product quality, performance, innovation, technology, price, applications expertise, system and service flexibility, distribution channel access and established customer service capabilities. We may not be able to compete effectively on all of these fronts or with all of our competitors. In addition, new competitors may emerge, and product lines may be threatened by new technologies or market trends that reduce the value of these product lines. To remain competitive, we must develop new products, respond to new technologies and enhance our existing products in a timely manner. We anticipate that we may have to adjust prices to stay competitive.
Changes in the supply of, or price for, raw materials, parts and components used in our products could affect our business.
The availability and prices of raw materials, parts and components are subject to curtailment or change due to, among other things, suppliers' allocations to other purchasers, interruptions in production by suppliers, changes in exchange rates and prevailing price levels. Some high-performance components for digital imaging products may be in short supply and/or suppliers may have occasional difficulty manufacturing these components to meet our specifications. In addition, some of our products are provided by sole source suppliers. Any change in the supply of, or price for, these parts and components, as well as any increases in commodity prices, particularly copper, could affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Environmental compliance costs and liabilities could increase our expenses and adversely affect our financial condition.
Our operations and properties are subject to laws and regulations relating to environmental protection, including air emissions, water discharges, waste management and workplace safety. These laws and regulations can result in the imposition of substantial fines and sanctions for violations and could, in certain instances, require the installation of pollution control equipment or operational changes to limit pollution emissions and/or decrease the likelihood of accidental hazardous substance releases. We must conform our operations and properties to these laws and adapt to regulatory requirements in the countries in which we operate as these requirements change.
We use and generate hazardous substances and wastes in some of our operations and, as a result, could be subject to potentially material liabilities relating to the investigation and clean-up of contaminated properties and to claims alleging personal injury. We have experienced, and expect to continue to experience, costs relating to compliance with environmental laws and regulations. In connection with our acquisitions, we may assume significant environmental liabilities, some of which we may not be aware of at the time of acquisition. In addition, new laws and regulations, stricter enforcement of existing laws and regulations, the discovery of previously unknown contamination or the imposition of new clean-up requirements could require us to incur costs or become
10
the basis for new or increased liabilities that could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Some of the industries in which we operate are cyclical, and, accordingly, our business is subject to changes in the economy.
Some of the business areas in which we operate are subject to specific industry and general economic cycles. Certain businesses are subject to industry cycles, including but not limited to, the industrial and energy markets. Accordingly, a downturn in these or other markets in which we participate could materially adversely affect us. If demand changes and we fail to respond accordingly, our results of operations could be materially adversely affected. The business cycles of our different operations may occur contemporaneously. Consequently, the effect of an economic downturn may have a magnified negative effect on our business.
Our goodwill and intangible assets are a significant amount of our total assets, and any write-off of our intangible assets would negatively affect our results of operations.
Our total assets reflect substantial intangible assets, primarily goodwill. At December 31, 2017, goodwill totaled $8.8 billion compared to $6.9 billion of stockholders' equity, and represented 62% of our total assets of $14.3 billion. The goodwill results from our acquisitions, representing the excess of cost over the fair value of the net assets we have acquired. We assess at least annually whether there has been an impairment in the value of our goodwill and indefinite economic life intangible assets. If future operating performance at one or more of our business units were to fall significantly below current levels, if competing or alternative technologies emerge, if interest rates rise or if business valuations decline, we could incur a non-cash charge to operating earnings. Any determination requiring the write-off of a significant portion of goodwill or unamortized intangible assets would negatively affect our results of operations, the effect of which could be material.
We depend on our ability to develop new products, and any failure to develop or market new products could adversely affect our business.
The future success of our business will depend, in part, on our ability to design and manufacture new competitive products and to enhance existing products so that we maintain our margin profile. This product development may require substantial internal investment. There can be no assurance that unforeseen problems will not occur with respect to the development, performance or market acceptance of new technologies or products or that we will otherwise be able to successfully develop and market new products. Failure of our products to gain market acceptance or our failure to successfully develop and market new products could reduce our margins, which would have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
We rely on information and technology for many of our business operations which could fail and cause disruption to our business operations.
Our business operations are dependent upon information technology networks and systems to securely transmit, process and store electronic information and to communicate among our locations around the world and with clients and vendors. A shutdown of, or inability to access, one or more of our facilities, a power outage or a failure of one or more of our information technology, telecommunications or other systems could significantly impair our ability to perform such functions on a timely basis. Computer viruses, cyber-attacks, other external hazards and human error could result in the misappropriation of assets or sensitive information, corruption of data or operational disruption. If sustained or repeated, such a business interruption, system failure, service denial or data loss and damage could result in a deterioration of our ability to perform necessary business functions.
A breach in the security of our software could harm our reputation, result in a loss of current and potential customers, and subject us to material claims, which could materially harm our operating results and financial condition.
If our security measures are breached, an unauthorized party may obtain access to our data or our users' or customers' data. In addition, cyber-attacks and similar acts could lead to interruptions and delays in customer processing or a loss or breach of customers' data. Because the techniques used to obtain unauthorized access, disable or degrade service, or sabotage systems change frequently and often are not recognized until launched against a target, we may be unable to anticipate these techniques or to implement adequate preventative measures. The risk that these types of events could seriously harm our business is likely to increase as we expand the number of web-based products and services we offer, and operate in more countries.
Regulatory authorities around the world have adopted and are considering further adoptions of legislative and regulatory proposals concerning data protection. In addition the interpretation and application of consumer and data protection laws in the United States, Europe and elsewhere are often uncertain and in flux. It is possible that these laws may be interpreted and applied in a manner
11
that is inconsistent with our data practices. If so, in addition to the possibility of fines, this could result in an order requiring that we change our data practices, which could have an adverse effect on our business and results of operations.
Any security breaches for which we are, or are perceived to be, responsible, in whole or in part, could subject us to legal claims or legal proceedings, including regulatory investigations, which could harm our reputation and result in significant litigation costs and damage awards or settlement amounts. Any imposition of liability, particularly liability that is not covered by insurance or is in excess of insurance coverage, could materially harm our operating results and financial condition. Security breaches also could cause us to lose current and potential customers, which could have an adverse effect on our business. Moreover, we might be required to expend significant financial and other resources to protect further against security breaches or to rectify problems caused by any security breach.
Any business disruptions due to political instability, armed hostilities, incidents of terrorism or natural disasters could adversely impact our financial performance.
If terrorist activity, armed conflict, political instability or natural disasters occur in the U.S. or other locations, such events may negatively impact our operations, cause general economic conditions to deteriorate or cause demand for our products to decline. A prolonged economic slowdown or recession could reduce the demand for our products, and therefore, negatively affect our future sales and profits. Any of these events could have a significant impact on our business, financial condition or results of operations.
ITEM 1B. | UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS |
None
12
ITEM 2. | PROPERTIES |
Our corporate offices, consisting of 29,000 square feet of leased space, are located at 6901 Professional Parkway East, Sarasota, Florida. We have 128 principal locations around the world to support our operations, of which 49 are manufacturing, assembly and testing facilities, and the remaining 79 locations provide sales, programming, service and administrative support functions. We consider our facilities to be in good operating condition and adequate for their present use and believe we have sufficient capacity to meet our anticipated operating requirements.
The following table summarizes the size, location and usage of our principal properties as of December 31, 2017 (amounts in thousands of square feet).
Office | Office & Manufacturing | |||
Segment | Region | Leased | Leased | Owned |
RF Technology | ||||
U.S. | 1,163 | 108 | — | |
Canada | 30 | — | — | |
Europe | 82 | — | 16 | |
Asia-Pacific | 116 | — | — | |
Medical & Scientific Imaging | ||||
U.S. | 325 | 275 | 120 | |
Canada | — | 140 | — | |
Europe | 68 | 28 | — | |
Asia-Pacific | 21 | — | — | |
Mexico | — | 43 | — | |
Industrial Technology | ||||
U.S. | 18 | 260 | 478 | |
Canada | 36 | — | — | |
Europe | 13 | 136 | 43 | |
Asia-Pacific | 21 | — | — | |
Mexico | — | 60 | — | |
Energy Systems & Controls | ||||
U.S. | — | 322 | — | |
Canada | — | 56 | — | |
Europe | 29 | 20 | 128 | |
Asia-Pacific | — | 28 | 33 | |
13
ITEM 3. | LEGAL PROCEEDINGS |
Information pertaining to legal proceedings can be found in Note 12 to the Consolidated Financial Statements included in this Annual Report, and is incorporated by reference herein.
ITEM 4. | MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES |
None
14
PART II
ITEM 5. | MARKET FOR REGISTRANT'S COMMON EQUITY RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES |
Our common stock trades on the NYSE under the symbol "ROP". The table below sets forth the range of high and low sales prices for our common stock as reported by the NYSE as well as cash dividends declared during each of our 2017 and 2016 quarters.
High | Low | Cash Dividends Declared | ||||||||||
2017 | 4th Quarter | $ | 267.83 | $ | 243.45 | $ | 0.4125 | |||||
3rd Quarter | 247.54 | 226.81 | 0.35 | |||||||||
2nd Quarter | 235.50 | 204.62 | 0.35 | |||||||||
1st Quarter | 214.44 | 183.74 | 0.35 | |||||||||
2016 | 4th Quarter | $ | 188.04 | $ | 167.91 | $ | 0.35 | |||||
3rd Quarter | 182.84 | 163.33 | 0.30 | |||||||||
2nd Quarter | 184.66 | 164.77 | 0.30 | |||||||||
1st Quarter | 187.56 | 158.89 | 0.30 | |||||||||
Based on information available to us and our transfer agent, we believe that as of February 16, 2018 there were 136 record holders of our common stock.
Dividends – We have declared a cash dividend in each quarter since our February 1992 initial public offering and we have annually increased our dividend rate since our initial public offering. In December 2017, our Board of Directors increased the quarterly dividend paid January 23, 2018 to $0.4125 per share from $0.35 per share, an increase of 18%. This is the twenty-fifth consecutive year in which Roper has increased its dividend. The timing, declaration and payment of future dividends will be at the sole discretion of our Board of Directors and will depend upon our profitability, financial condition, capital needs, future prospects and other factors deemed relevant by our Board of Directors.
Recent Sales of Unregistered Securities - In 2017, there were no sales of unregistered securities.
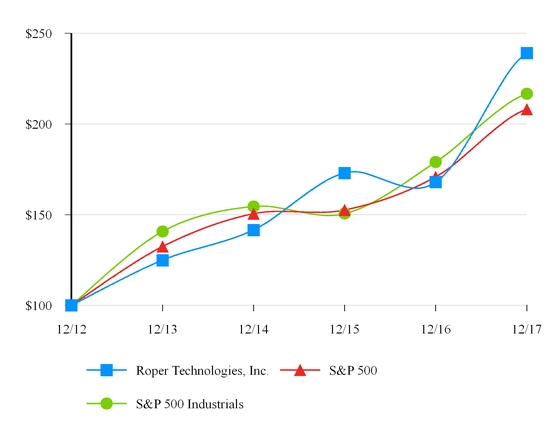
Performance Graph - This performance graph shall not be deemed "filed" for purposes of Section 18 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the "Exchange Act") or otherwise subject to the liabilities under that Section and shall not be deemed to be incorporated by reference into any of our filings under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, or under the Exchange Act.
15
The following graph compares, for the five year period ended December 31, 2017, the cumulative total stockholder return for our common stock, the Standard and Poor's 500 Stock Index (the "S&P 500") and the Standard and Poor's 500 Industrials Index (the "S&P 500 Industrials"). Measurement points are the last trading day of each of our fiscal years ended December 31, 2012, 2013, 2014, 2015, 2016 and 2017. The graph assumes that $100 was invested on December 31, 2012 in our common stock, the S&P 500 and the S&P 500 Industrials and assumes reinvestment of any dividends. The stock price performance on the following graph is not necessarily indicative of future stock price performance.
12/31/2012 | 12/31/2013 | 12/31/2014 | 12/31/2015 | 12/31/2016 | 12/31/2017 | ||||||||||||||||||
Roper Technologies, Inc. | $ | 100.00 | $ | 124.89 | $ | 141.61 | $ | 172.94 | $ | 167.96 | $ | 239.15 | |||||||||||
S&P 500 | 100.00 | 132.39 | 150.51 | 152.59 | 170.84 | 208.14 | |||||||||||||||||
S&P 500 Industrials | 100.00 | 140.68 | 154.50 | 150.59 | 178.99 | 216.64 | |||||||||||||||||
The information set forth in Item 12 under the heading "Securities Authorized for Issuance under Equity Compensation Plans" is incorporated herein by reference.
16
ITEM 6. | SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA |
You should read the table below in conjunction with "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations" and our Consolidated Financial Statements and related notes included in this Annual Report (amounts in thousands, except per share data).
As of and for the Years ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||
2017 (1) | 2016 (2) | 2015 (3) | 2014 (4) | 2013 (5) | |||||||||||||||
Operations data: | |||||||||||||||||||
Net revenues | $ | 4,607,471 | $ | 3,789,925 | $ | 3,582,395 | $ | 3,549,494 | $ | 3,238,128 | |||||||||
Gross profit | 2,864,796 | 2,332,410 | 2,164,646 | 2,101,899 | 1,882,928 | ||||||||||||||
Income from operations | 1,210,244 | 1,054,563 | 1,027,918 | 999,473 | 842,361 | ||||||||||||||
Net earnings (6) | 971,772 | 658,645 | 696,067 | 646,033 | 538,293 | ||||||||||||||
Per share data: | |||||||||||||||||||
Basic earnings per share | $ | 9.51 | $ | 6.50 | $ | 6.92 | $ | 6.47 | $ | 5.43 | |||||||||
Diluted earnings per share | $ | 9.39 | $ | 6.43 | $ | 6.85 | $ | 6.40 | $ | 5.37 | |||||||||
Dividends declared per share | $ | 1.4625 | $ | 1.2500 | $ | 1.0500 | $ | 0.8500 | $ | 0.6950 | |||||||||
Balance sheet data: | |||||||||||||||||||
Working capital (7) | $ | (270,007 | ) | $ | 331,229 | $ | 897,919 | $ | 884,158 | $ | 730,246 | ||||||||
Total assets (8) | 14,316,413 | 14,324,927 | 10,168,365 | 8,400,185 | 8,169,120 | ||||||||||||||
Long-term debt, net of current portion (8) | 4,354,611 | 5,808,561 | 3,264,417 | 2,190,282 | 2,437,975 | ||||||||||||||
Stockholders' equity | 6,863,564 | 5,788,865 | 5,298,947 | 4,755,360 | 4,213,050 | ||||||||||||||
(1) | Includes results from the acquisitions of Phase Technology from June 21, 2017, Handshake Software, Inc. from August 4, 2017, Workbook Software A/S from September 15, 2017 and Onvia, Inc. from November 17, 2017. |
(2) | Includes results from the acquisitions of CliniSys Group Ltd. from January 7, 2016, PCI Medical Inc. from March 17, 2016, GeneInsight Inc. from April 1, 2016, iSqFt Holdings Inc. (d/b/a ConstructConnect) from October 31, 2016, UNIConnect LC from November 10, 2016 and Deltek, Inc. from December 28, 2016. |
(3) | Includes results from the acquisitions of Strata Decision Technologies LLC from January 21, 2015, SoftWriters Inc. from February 9, 2015, Data Innovations LLC from March 4, 2015, On Center Software LLC from July 20, 2015, RF IDeas Inc. from September 1, 2015, Atlantic Health Partners LLC from September 4, 2015, Aderant Holdings Inc. from October 21, 2015, Atlas Database Software Corp. from October 26, 2015, Black Diamond Advanced Technologies through March 20, 2015 and Abel Pumps through October 2, 2015. |
(4) | Includes results from the acquisitions of Foodlink Holdings Inc. from July 2, 2014, Innovative Product Achievements LLC from August 5, 2014, Strategic Healthcare Programs Holdings LLC from August 14, 2014. |
(5) | Includes results from the acquisitions of Managed Health Care Associates Inc. from May 1, 2013 and Advanced Sensors Ltd. from October 4, 2013. |
(6) | The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 (“the Tax Act”) was signed into U.S. law on December 22, 2017, which was prior to the end of the Company’s 2017 reporting period and resulted in a one-time net income tax benefit of $215.4 million. |
(7) | At December 31, 2017, there were $799 million of senior notes, net of debt issuance costs, due October 1, 2018, and at December 31, 2016, there were $399 million of senior notes, net of debt issuance costs, due November 15, 2017, thus requiring classification as short-term debt, included in working capital. |
(8) | Total assets and Long-term debt, net of current portion for 2013 and 2014 have been adjusted due to the retrospective adoption of an accounting standard update which requires that our senior notes be shown net of debt issuance costs. The adjustment amounts were $12,749 and $15,861 for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively. |
17
ITEM 7. | MANAGEMENT'S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS |
You should read the following discussion in conjunction with "Selected Financial Data" and our Consolidated Financial Statements and related notes included in this Annual Report.
Overview
We are a diversified technology company. We operate businesses that design and develop software (both license and software-as-a-service) and engineered products and solutions for a variety of niche end markets.
We pursue consistent and sustainable growth in earnings and cash flow by emphasizing continuous improvement in the operating performance of our existing businesses and by acquiring other carefully selected businesses. Our acquisitions have represented both additions to existing businesses and new strategic platforms.
Application of Critical Accounting Policies
Our Consolidated Financial Statements are prepared in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States ("GAAP"). A discussion of our significant accounting policies can also be found in the notes to our Consolidated Financial Statements for the year ended December 31, 2017 included in this Annual Report.
GAAP offers acceptable alternative methods for accounting for certain issues affecting our financial results, such as determining inventory cost, depreciating long-lived assets and recognizing revenue. We have not changed the application of acceptable accounting methods or the significant estimates affecting the application of these principles in the last three years in a manner that had a material effect on our financial statements.
The preparation of financial statements in accordance with GAAP requires the use of estimates, assumptions, judgments and interpretations that can affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses, the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities and other supplemental disclosures.
The development of accounting estimates is the responsibility of our management. Our management discusses those areas that require significant judgments with the Audit Committee of our Board of Directors. The Audit Committee has reviewed all financial disclosures in our annual filings with the SEC. Although we believe the positions we have taken with regard to uncertainties are reasonable, others might reach different conclusions and our positions can change over time as more information becomes available. If an accounting estimate changes, its effects are accounted for prospectively or through a cumulative catch up adjustment.
Our most significant accounting uncertainties are encountered in the areas of accounts receivable collectibility, inventory valuation, future warranty obligations, revenue recognition (percentage-of-completion), income taxes and goodwill and indefinite-lived impairment analyses. These issues affect each of our business segments and are evaluated using a combination of historical experience, current conditions and relatively short-term forecasting.
Accounts receivable collectibility is based on the economic circumstances of customers and credits given to customers after shipment of products, including in certain cases credits for returned products. Accounts receivable are regularly reviewed to determine customers who have not paid within agreed upon terms, whether these amounts are consistent with past experiences, what historical experience has been with amounts deemed uncollectible and the impact that economic conditions might have on collection efforts in general and with specific customers. The returns and other sales credit allowance is an estimate of customer returns, exchanges, discounts or other forms of anticipated concessions and is treated as a reduction in revenue. The returns and other sales credits histories are analyzed to determine likely future rates for such credits. At December 31, 2017, our allowance for doubtful accounts receivable was $10.3 million and our allowance for sales returns and sales credits was $2.4 million, for a total of $12.7 million, or 1.9% of total gross accounts receivable, as compared to a total of $14.5 million, or 2.3% of total gross accounts receivable, at December 31, 2016. This percentage is influenced by the risk profile of the underlying receivables, and the timing of write-offs of accounts deemed uncollectible.
We regularly compare inventory quantities on hand against anticipated future usage, which we determine as a function of historical usage or forecasts related to specific items in order to evaluate obsolescence and excessive quantities. When we use historical usage, this information is also qualitatively compared to business trends to evaluate the reasonableness of using historical information as an estimate of future usage. At December 31, 2017, inventory reserves for excess and obsolete inventory were $38.1 million, or 15.7% of gross inventory cost, as compared to $37.2 million, or 17.0% of gross inventory cost, at December 31,
18
2016. The inventory reserve as a percent of gross inventory cost will continue to fluctuate based upon specific identification of reserves needed based upon changes in our business as well as the physical disposal of obsolete inventory.
Most of our product-based revenues are covered by warranty provisions that generally provide for the repair or replacement of qualifying defective items for a specified period after the time of sale, typically 12 to 24 months. Future warranty obligations are evaluated using, among other factors, historical cost experience, product evolution and customer feedback. Our expense for warranty obligations was less than 1% of net revenues for each of the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015.
Revenues related to the use of the percentage-of-completion method of accounting are dependent on total costs incurred compared with total estimated costs for a project. During the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 we recognized revenue of $249 million, $241 million and $253 million, respectively, using this method. Percentage-of-completion is used primarily for major turn-key, longer term toll and traffic and energy projects and installations of large software application projects. At December 31, 2017, $253 million of revenue related to unfinished percentage-of-completion contracts had yet to be recognized.
Income taxes can be affected by estimates of whether and within which jurisdictions future earnings will occur and if, how and when cash is repatriated to the U.S., combined with other aspects of an overall income tax strategy. Additionally, taxing jurisdictions could retroactively disagree with our tax treatment of certain items, and some historical transactions have income tax effects going forward. Accounting rules require these future effects to be evaluated using current laws, rules and regulations, each of which can change at any time and in an unpredictable manner. During 2017, our effective income tax rate was 6.1%, as compared to the 2016 rate of 30.0%. The decrease was due primarily to the recognition of a $215 million net income tax benefit related to the Tax Act as well as increased excess tax benefits related to equity compensation in 2017 as compared to 2016. We expect the effective tax rate for 2018 to be between 21% and 23%.
We account for goodwill in a purchase business combination as the excess of the cost over the estimated fair value of net assets acquired. Goodwill, which is not amortized, is tested for impairment on an annual basis in conjunction with our annual forecast process during the fourth quarter (or an interim basis if an event occurs or circumstances change that would more likely than not reduce the fair value of a reporting unit below its carrying value).
When testing goodwill for impairment, we have the option to first assess qualitative factors to determine whether the existence of events or circumstances leads to a determination that it is more likely than not that the estimated fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying amount. If we elect to perform a qualitative assessment and determine that an impairment is more likely than not, we are then required to perform the quantitative impairment test; otherwise, no further analysis is required. Under the qualitative assessment, we consider various qualitative factors, including macroeconomic conditions, relevant industry and market trends, cost factors, overall financial performance, other entity-specific events and events affecting the reporting unit that could indicate a potential change in the fair value of our reporting unit or the composition of its carrying values. We also consider the specific future outlook for the reporting unit.
We also may elect not to perform the qualitative assessment and, instead, proceed directly to the quantitative impairment test. The quantitative assessment utilizes both an income approach (discounted cash flows) and a market approach consisting of a comparable company earnings multiples methodology to estimate the fair value of a reporting unit. To determine the reasonableness of the estimated fair values, we review the assumptions to ensure that neither the income approach nor the market approach provides significantly different valuations. If the estimated fair value exceeds the carrying value, no further work is required and no impairment loss is recognized. If the carrying value exceeds the estimated fair value, a non-cash impairment loss is recognized in the amount of that excess.
Key assumptions used in the income and market approaches are updated when the analysis is performed for each reporting unit. Various assumptions are utilized including forecasted operating results, strategic plans, economic projections, anticipated future cash flows, the weighted-average cost of capital, comparable transactions, market data and earnings multiples. While we use reasonable and timely information to prepare our cash flow and discount rate assumptions, actual future cash flows or market conditions could differ significantly and could result in future non-cash impairment charges related to recorded goodwill balances.
Recently acquired reporting units generally represent a higher inherent risk of impairment, which typically decreases as the businesses are integrated into our enterprise. Negative industry or economic trends, disruptions to our business, actual results significantly below projections, unexpected significant changes or planned changes in the use of the assets, divestitures and market capitalization declines may have a negative effect on the fair value of our reporting units.
We have 33 reporting units with individual goodwill amounts ranging from zero to $2.3 billion. In 2017, we performed our annual impairment test in the fourth quarter for all reporting units. We conducted our analysis qualitatively and assessed whether it was more likely than not that the respective fair value of these reporting units was less than the carrying amount. We determined that
19
impairment of goodwill was not likely in 31 of our reporting units and thus we were not required to perform a quantitative analysis for these reporting units. For the remaining two reporting units, the Company performed its quantitative analysis and concluded that the fair value of each of these two reporting units was substantially in excess of its carrying value, with no impairment indicated as of October 1, 2017.
Business combinations can also result in other intangible assets being recognized. Amortization of intangible assets, if applicable, occurs over their estimated useful lives. Trade names that are determined to have an indefinite useful economic life are not amortized, but separately tested for impairment during the fourth quarter of the fiscal year or on an interim basis if an event occurs that indicates the fair value is more likely than not below the carrying value. We first qualitatively assess whether the existence of events or circumstances leads to a determination that it is more likely than not that the estimated fair value of the indefinite-lived trade name is less than its carrying amount. If necessary, we conduct a quantitative review using the relief-from-royalty method, which we believe to be an acceptable methodology due to its common use by valuation specialists in determining the fair value of intangible assets. This methodology assumes that, in lieu of ownership, a third-party would be willing to pay a royalty in order to exploit the related benefits of these assets. The fair value of each trade name is determined by applying a royalty rate to a projection of net revenues discounted using a risk-adjusted rate of capital. Each royalty rate is determined based on the profitability of the trade name to which it relates and observed market royalty rates. Revenue growth rates are determined after considering current and future economic conditions, recent sales trends, discussions with customers, planned timing of new product launches or other variables. Trade names resulting from recent acquisitions generally represent the highest risk of impairment, which typically decreases as the businesses are integrated into our enterprise and positioned for improved future sales growth.
The assessment of fair value for impairment purposes requires significant judgments to be made by management. Although our forecasts are based on assumptions that are considered reasonable by management and consistent with the plans and estimates management uses to operate the underlying businesses, there is significant judgment in determining the expected results attributable to the reporting units. Changes in estimates or the application of alternative assumptions could produce significantly different results. No impairment resulted from the annual reviews performed in 2017.
We evaluate whether there has been an impairment of identifiable intangible assets with definite useful economic lives, or of the remaining life of such assets, when certain indicators of impairment are present. In the event that facts and circumstances indicate that the cost or remaining period of amortization of any asset may be impaired, an evaluation of recoverability would be performed. If an evaluation is required, the estimated future gross, undiscounted cash flows associated with the asset would be compared to the asset's carrying amount to determine if a write-down to fair value or a revision in the remaining amortization period is required.
20
Results of Operations
The following table sets forth selected information for the years indicated. Dollar amounts are in thousands and percentages are of net revenues. Percentages may not foot due to rounding.
Years ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
Net revenues: | |||||||||||
RF Technology (1) | $ | 1,862,126 | $ | 1,210,264 | $ | 1,033,951 | |||||
Medical & Scientific Imaging (2) | 1,410,349 | 1,362,813 | 1,215,318 | ||||||||
Industrial Technology (3) | 783,707 | 706,625 | 745,381 | ||||||||
Energy Systems & Controls (4) | 551,289 | 510,223 | 587,745 | ||||||||
Total | $ | 4,607,471 | $ | 3,789,925 | $ | 3,582,395 | |||||
Gross margin: | |||||||||||
RF Technology | 61.1 | % | 56.7 | % | 53.4 | % | |||||
Medical & Scientific Imaging | 72.0 | 73.2 | 74.0 | ||||||||
Industrial Technology | 50.6 | 50.6 | 49.8 | ||||||||
Energy Systems & Controls | 57.4 | 57.1 | 58.1 | ||||||||
Total | 62.2 | % | 61.5 | % | 60.4 | % | |||||
Segment operating margin: | |||||||||||
RF Technology | 25.7 | % | 30.8 | % | 30.2 | % | |||||
Medical & Scientific Imaging | 34.5 | 35.0 | 36.4 | ||||||||
Industrial Technology | 30.0 | 28.7 | 28.8 | ||||||||
Energy Systems & Controls | 27.4 | 25.4 | 27.6 | ||||||||
Total | 29.3 | % | 31.2 | % | 31.6 | % | |||||
Corporate administrative expenses | (3.1 | )% | (3.4 | )% | (2.9 | )% | |||||
Income from continuing operations | 26.3 | 27.8 | 28.7 | ||||||||
Interest expense, net | (3.9 | ) | (2.9 | ) | (2.4 | ) | |||||
Other income/(expense) | 0.1 | (0.1 | ) | 1.6 | |||||||
Income from continuing operations before taxes | 22.5 | 24.8 | 28.0 | ||||||||
Income taxes | (1.4 | ) | (7.4 | ) | (8.5 | ) | |||||
Net earnings | 21.1 | % | 17.4 | % | 19.4 | % | |||||
(1) | Includes results from the acquisitions of Foodlink Holdings Inc. from July 2, 2014, On Center Software LLC from July 20, 2015, RF Ideas Inc. from September 1, 2015, Aderant Holdings Inc. from October 21, 2015, Black Diamond Advanced Technologies through March 20, 2015, ConstructConnect from October 31, 2016, Deltek, Inc. from December 28, 2016, Handshake Software, Inc. from August 4, 2017, Workbook Software A/S from September 15, 2017 and Onvia, Inc. from November 17, 2017. |
(2) | Includes results from the acquisitions of Strata Decision Technologies LLC from January 21, 2015, SoftWriters Inc. from February 9, 2015, Data Innovations LLC from March 4, 2015, Atlantic Health Partners LLC from September 4, 2015, Atlas Database Software Corp. from October 26, 2015, CliniSys from January 7, 2016, PCI Medical from March 17, 2016, GeneInsight from April 1, 2016 and UNIConnect from November 10, 2016. |
(3) | Includes results from Abel Pumps through October 2, 2015. |
(4) | Includes results from the acquisition of Phase Technology from June 21, 2017. |
21
Year Ended December 31, 2017 Compared to Year Ended December 31, 2016
Net revenues for the year ended December 31, 2017 were $4.61 billion as compared to $3.79 billion for the year ended December 31, 2016, an increase of 21.6%. The increase was the result of contributions from acquisitions of 16.3%, organic growth of 5.3% and no impact from foreign exchange.
In our RF Technology segment, net revenues for the year ended December 31, 2017 increased by $651.9 million or 54% over the year ended December 31, 2016. Acquisitions accounted for 51% and organic revenues increased by 3%. The increase in organic revenues was due primarily to growth in our software businesses. Gross margin was 61.1% for the year ended December 31, 2017 as compared to 56.7% for the year ended December 31, 2016, due primarily to an increased percentage of revenues from our software businesses, which have a higher gross margin. Selling, general and administrative ("SG&A") expenses as a percentage of revenues in the year ended December 31, 2017 increased to 35.3%, as compared to 25.9% in the year ended December 31, 2016, due primarily to an increased percentage of revenues from our software businesses, which have a higher SG&A structure, including amortization of acquired intangibles. The resulting operating margin was 25.7% in 2017 as compared to 30.8% in 2016.
Our Medical & Scientific Imaging segment reported a $47.5 million or 3% increase in net revenues for the year ended December 31, 2017 over the year ended December 31, 2016, all of which was attributable to organic growth. The growth in organic revenues was due primarily to increased sales in our medical products businesses, led by NDI, and our alternate site healthcare businesses. Gross margin decreased to 72.0% for the year ended December 31, 2017 from 73.2% for the year ended December 31, 2016, due primarily to an unfavorable sales mix at both our software and medical products businesses. SG&A expenses as a percentage of net revenues decreased to 37.5% in the year ended December 31, 2017, as compared to 38.2% in the year ended December 31, 2016, due primarily to operating leverage on higher sales. The resulting operating margin was 34.5% in the year ended December 31, 2017 as compared to 35.0% in the year ended December 31, 2016.
Net revenues for our Industrial Technology segment increased by $77.1 million or 11% for the year ended December 31, 2017 from the year ended December 31, 2016, all of which was attributable to organic growth. The growth in organic revenues was broad-based, due primarily to our fluid handling, water meter technology and materials testing businesses. Gross margin was consistent at 50.6% for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016. SG&A expenses as a percentage of net revenues were 20.6% in the year ended December 31, 2017, as compared to 21.9% in the year ended December 31, 2016, due primarily to operating leverage on higher sales volume. The resulting operating margin was 30.0% in the year ended December 31, 2017 as compared to 28.7% in the year ended December 31, 2016.
In our Energy Systems & Controls segment, net revenues for the year ended December 31, 2017 increased by $41.1 million or 8% from the year ended December 31, 2016. Organic sales increased by 7% and the benefit from foreign exchange and acquisitions totaled 1%. The growth in organic revenues was due primarily to increased sales in pressure sensors and valves businesses serving energy markets as well as businesses serving industrial end markets. Gross margin increased to 57.4% in the year ended December 31, 2017 as compared to 57.1% in the year ended December 31, 2016 and SG&A expenses as a percentage of net revenues decreased to 30.0% in the year ended December 31, 2017, as compared to 31.7% in the year ended December 31, 2016, both of which were due to operating leverage on higher sales volume. As a result, operating margin was 27.4% in the year ended December 31, 2017 as compared to 25.4% in the year ended December 31, 2016.
Corporate expenses increased by $14.3 million to $141.8 million, or 3.1% of revenues, in 2017 as compared to $127.5 million, or 3.4% of revenues, in 2016. The dollar increase was due primarily to increased incentive compensation and professional services.
Interest expense increased $69.0 million, or 61.9%, for the year ended December 31, 2017 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2016. The increase was due primarily to higher average debt balances to fund acquisitions at the end of 2016.
Other income, net, of $5.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2017 was composed primarily of a $9.4 million gain on sale of a product line in our Energy Systems & Controls segment, offset in part by a $1.8 million charge on a minority investment and foreign exchange losses at our non-U.S. based companies. Other expense of $1.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2016 was composed primarily of foreign exchange losses at our non-U.S. based companies, offset in part by royalty income.
During 2017, our effective income tax rate was 6.1% as compared to our 2016 rate of 30.0%. The decrease was due primarily to the recognition of a $215 million net income tax benefit related to the Tax Act as well as increased excess tax benefits related to equity compensation in 2017 as compared to 2016.
The following table summarizes order backlog information at December 31, 2017 and 2016 (dollar amounts in thousands). We include in backlog only orders that are expected to be recognized as revenue within twelve months.
22
2017 | 2016 | change | ||||||||
RF Technology | $ | 991,382 | $ | 991,212 | — | % | ||||
Medical & Scientific Imaging | 467,836 | 423,616 | 10.4 | |||||||
Industrial Technology | 110,841 | 65,259 | 69.8 | |||||||
Energy Systems & Controls | 102,293 | 92,309 | 10.8 | |||||||
Total | $ | 1,672,352 | $ | 1,572,396 | 6.4 | % | ||||
Year Ended December 31, 2016 Compared to Year Ended December 31, 2015
Net revenues for the year ended December 31, 2016 were $3.79 billion as compared to $3.58 billion for the year ended December 31, 2015, an increase of 5.8%. The increase was the result of contributions from acquisitions of 6.8%, negative organic growth of 0.3% and a negative foreign exchange impact of 0.7%.
In our RF Technology segment, net revenues for the year ended December 31, 2016 increased by $176 million or 17% over the year ended December 31, 2015. Acquisitions net of the divestiture of the Black Diamond Advanced Technology business added 15%, organic revenues increased by 3%, and the negative foreign exchange impact was 1%. The increase in organic revenues was due primarily to increased sales in our software businesses, offset in part by the completion of large service contracts in our toll and traffic businesses in 2015. Gross margin was 56.7% in 2016 as compared to 53.4% in the prior year due to product mix in our toll and traffic businesses as well as an increased percentage of revenues at our software businesses which have a higher gross margin. SG&A expenses as a percentage of net revenues in the year ended December 31, 2016 increased to 25.9%, as compared to 23.3% in the prior year due primarily to an increased percentage of net revenues at our software businesses which have a higher SG&A structure. Operating margin was 30.8% in 2016 as compared to 30.2% in 2015.
Our Medical & Scientific Imaging segment reported a $147 million or 12% increase in net revenues for the year ended December 31, 2016 over the year ended December 31, 2015. Acquisitions contributed 9%, organic revenues increased 4% and the negative foreign exchange impact was 1%. The increase in organic revenues was due to increased sales in our medical businesses, led by NDI and Verathon. Gross margin decreased to 73.2% in the year ended December 31, 2016 from 74.0% in the year ended December 31, 2015, due primarily to product mix. SG&A expenses as a percentage of net revenues increased to 38.2% in the year ended December 31, 2016 as compared to 37.7% in the year ended December 31, 2015, due to a higher SG&A structure in our medical businesses. Operating margin was 35.0% in the year ended December 31, 2016 as compared to 36.4% in the year ended December 31, 2015.
Net revenues for our Industrial Technology segment decreased by $39 million or 5.2% for the year ended December 31, 2016 from the year ended December 31, 2015. The divestiture of the Abel Pumps business in 2015 accounted for a negative 3.1%, organic revenues decreased by 1.5% and the negative foreign exchange impact was 0.6%. The decrease in organic revenues was due primarily to decreased sales in those fluid handling businesses that serve oil and gas markets, offset in part by increased sales in our water metering business. Gross margin increased to 50.6% for the year ended December 31, 2016 as compared to 49.8% in the year ended December 31, 2015 due to product mix. SG&A expenses as a percentage of net revenues were 21.9%, as compared to 21.0% in the prior year, due primarily to negative leverage on lower sales volume. The resulting operating margin was 28.7% in the year ended December 31, 2016 as compared to 28.8% in the year ended December 31, 2015.
In our Energy Systems & Controls segment, net revenues for the year ended December 31, 2016 decreased by $78 million or 13% from the year ended December 31, 2015. Organic revenues decreased by 12% due to decreased sales in oil and gas products, including safety systems and valves, and the negative foreign exchange impact was 1%. Gross margin decreased to 57.1% in the year ended December 31, 2016 as compared to 58.1% in the year ended December 31, 2015 and SG&A expenses as a percentage of net revenues increased to 31.7% as compared to 30.5% in the prior year, both of which were due to negative leverage on lower sales volume. Operating margin was 25.4% in the year ended December 31, 2016 as compared to 27.6% in the year ended December 31, 2015.
Corporate expenses increased by $24.7 million to $127.5 million, or 3.4% of net revenues, in 2016 as compared to $102.8 million, or 2.9% of net revenues, in 2015. The increase was due primarily to increased equity compensation costs as a result of both an increase in the number of shares granted in the current year and increases in our common stock price and increased costs related to acquisitions.
Interest expense increased $27.3 million, or 32.5%, for the year ended December 31, 2016 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2015. The increase was due primarily to higher average debt balances to fund current year acquisitions as well as higher average interest rates throughout 2016.
23
Other expense of $1.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2016 was composed primarily of foreign exchange losses at our non-U.S. based companies, offset in part by royalty income. Other income of $58.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2015 was composed primarily of the $70.9 million gain from the divestiture of Abel Pumps (see Note 2 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements included in this Annual Report), offset in part by a $9.5 million impairment charge on a minority investment.
During 2016, our effective income tax rate was 30.0%, which was 60 basis points lower than the 2015 rate of 30.6%. The decrease was due to the recognition of $15.3 million in excess tax benefits in the current year in accordance with an ASU related to stock compensation adopted in the first quarter of 2016 (see Note 1 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements included in this Annual Report), as well as the non-recurrence of the 2015 taxable gain on the divestiture of Abel Pumps which was partially offset by discrete tax benefits from settlements of tax matters in 2015.
The following table summarizes order backlog information at December 31, 2016 and 2015 (dollar amounts in thousands). We include in backlog only orders that are expected to be recognized as revenue within twelve months.
2016 | 2015 | change | ||||||||
RF Technology | $ | 991,212 | $ | 538,877 | 83.9 | % | ||||
Medical & Scientific Imaging | 423,616 | 373,213 | 13.5 | % | ||||||
Industrial Technology | 65,259 | 68,002 | (4.0 | )% | ||||||
Energy Systems & Controls | 92,309 | 90,365 | 2.2 | % | ||||||
Total | $ | 1,572,396 | $ | 1,070,457 | 46.9 | % | ||||
Financial Condition, Liquidity and Capital Resources
Selected cash flows for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 are as follows (in millions):
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
Cash provided by/(used in): | |||||||||||
Operating activities | $ | 1,234 | $ | 964 | $ | 929 | |||||
Investing activities | (210 | ) | (3,753 | ) | (1,698 | ) | |||||
Financing activities | (1,170 | ) | 2,805 | 996 | |||||||
Operating activities - The increase in cash provided by operating activities in 2017 and in 2016 was primarily due to increased earnings net of non-cash expenses and higher deferred revenue balances due to an increased percentage of revenue from software and other subscription based products. The increase in cash provided by operating activities in 2016 was offset in part by income tax payments in the first quarter of 2016 related to the gain on the sale of the Abel Pumps business in the fourth quarter of 2015.
Investing activities - Cash used in investing activities during 2017, 2016 and 2015 was primarily for business acquisitions. Cash received from investing activities in 2015 was primarily proceeds from the sale of the Abel Pumps business.
Financing activities - Cash used in/provided by financing activities in all periods presented was primarily debt repayments/borrowings as well as dividends paid to stockholders. Cash used in financing activities during 2017 was primarily from the pay-down of revolving debt borrowings of $660 million and the repayment of $400 million of senior notes. Cash provided by financing activities during 2016 was primarily from the issuance of $1.2 billion of senior notes and revolving debt borrowings for acquisitions.
Cash and cash equivalents increased as a result of the effects of foreign currency exchange rate changes during the year ended December 31, 2017 by $59 million as compared to decreases during the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015 of $38 million and $59 million, respectively. The increase for the year ended December 31, 2017 was due primarily to the strengthening of functional currencies of our European subsidiaries against the U.S. dollar, while the decreases for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015 were due primarily to the weakening of functional currencies of our European subsidiaries against the U.S. dollar.
Net working capital (current assets, excluding cash, less total current liabilities, excluding debt) was a negative $140 million at December 31, 2017 compared to negative $25 million at December 31, 2016, due primarily to increased deferred revenues. This deferred revenue increase is due to a higher percentage of revenue from software and subscription-based services along with the impact of fair value purchase accounting resulting from 2016 acquisitions.
24
Total debt was $5.2 billion at December 31, 2017 (43.0% of total capital) compared to $6.2 billion at December 31, 2016 (51.8% of total capital). Our decreased debt at December 31, 2017 compared to December 31, 2016 was due primarily to the pay-down of revolving debt borrowings of $660 million and the repayment of $400 million of senior notes.
On September 23, 2016, we entered into a five-year unsecured credit facility (the "2016 Facility") with JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., as administrative agent, and a syndicate of lenders, which replaced our previous unsecured credit facility, dated as of July 27, 2012, as amended as of October 28, 2015 (the "2012 Facility"). The 2016 Facility comprises a five year $2.5 billion revolving credit facility, which includes availability of up to $150 million for letters of credit. We may also, subject to compliance with specified conditions, request term loans or additional revolving credit commitments in an aggregate amount not to exceed $500 million.
The 2016 Facility contains various affirmative and negative covenants which, among other things, limit our ability to incur new debt, enter into certain mergers and acquisitions, sell assets and grant liens, make restricted payments (including the payment of dividends on our common stock) and capital expenditures, or change our line of business. We also are subject to financial covenants which require us to limit our consolidated total leverage ratio and to maintain a consolidated interest coverage ratio. The most restrictive covenant is the consolidated total leverage ratio which is limited to 3.5 to 1.
On December 2, 2016, we amended the 2016 Facility to allow the consolidated total leverage ratio be increased, no more than twice during the term of the 2016 Facility, to 4.0 to 1 for a consecutive four quarter fiscal period per increase (or, for any portion of such four quarter fiscal period in which the maximum would be 4.25 to 1 pursuant to the 2016 facility amendment, 4.25 to 1). In conjunction with the Deltek acquistion (see Note 2 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements included in this Annual Report), we increased the maximum consolidated total leverage ratio covenant to 4.25 to 1 through June 30, 2017 and 4.00 to 1 through December 31, 2017.
At December 31, 2017, we had $3.9 billion of senior unsecured notes and $1.3 billion of outstanding revolver borrowings. In addition, we had $3.1 million of other debt in the form of capital leases and several smaller facilities that allow for borrowings or the issuance of letters of credit in foreign locations to support our non-U.S. businesses. We had $75.9 million of outstanding letters of credit at December 31, 2017, of which $33.1 million was covered by our lending group, thereby reducing our revolving credit capacity commensurately.
We may redeem some or all of these notes at any time or from time to time, at 100% of their principal amount, plus a make-whole premium based on a spread to U.S. Treasury securities.
We were in compliance with all debt covenants related to our credit facility throughout the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016.
See Note 8 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements included in this Annual Report for additional information regarding our credit facility and senior notes.
Cash and cash equivalents at our foreign subsidiaries at December 31, 2017 totaled $592 million. The Tax Act included a one-time deemed mandatory repatriation tax on all undistributed foreign earnings, resulting in a charge of $110.7 million as of December 31, 2017. The Company will elect to pay the liability over 8 years. In addition, the introduction of a modified territorial taxation system resulted in a one-time estimated charge of $28.7 million due to the Company’s change in its indefinite reinvestment assertion on foreign earnings. The Company now intends to distribute all historical earnings subject to the deemed repatriation tax and has provided for deferred taxes related to the future state and foreign tax cost to repatriate. See Note 7 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements included in this Annual Report for additional information regarding income taxes.
Capital expenditures of $48.8 million, $37.3 million and $36.3 million were incurred during 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively. Capitalized software expenditures of $10.8 million, $2.8 million and $2.4 million were incurred during 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively. The increases in 2017 as compared to 2016 was due primarily to our 2016 acquisitions. In the future, we expect the aggregate of capital expenditures and capitalized software expenditures as a percentage of annual net revenues to be between 1.0% and 1.5%.
25
Contractual Cash Obligations and Other Commercial Commitments and Contingencies
The following tables quantify our contractual cash obligations and commercial commitments at December 31, 2017 (in thousands).
Payments Due in Fiscal Year | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Contractual Cash Obligations 1 | Total | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | Thereafter | ||||||||||||||||||||
Total debt | $ | 5,170,009 | $ | 800,009 | $ | 500,000 | $ | 600,000 | $ | 1,770,000 | $ | 500,000 | $ | 1,000,000 | |||||||||||||
Senior note interest | 579,657 | 129,325 | 106,608 | 85,025 | 67,269 | 51,822 | 139,608 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Capital leases | 3,140 | 1,494 | 1,061 | 529 | 47 | 9 | — | ||||||||||||||||||||
Operating leases | 272,285 | 61,109 | 49,563 | 42,109 | 35,473 | 26,014 | 58,017 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 6,025,091 | $ | 991,937 | $ | 657,232 | $ | 727,663 | $ | 1,872,789 | $ | 577,845 | $ | 1,197,625 | |||||||||||||
Amounts Expiring in Fiscal Year | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Other Commercial Commitments | Total Amount Committed | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | Thereafter | ||||||||||||||||||||
Standby letters of credit and bank guarantees | $ | 75,898 | $ | 28,614 | $ | 1,921 | $ | 723 | $ | 34,006 | $ | 10,351 | $ | 283 | |||||||||||||
1 We have excluded the liability for uncertain tax positions and other income tax liabilities resulting from the Tax Act considered "provisional." See Note 7 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements included in this Annual Report.
As of December 31, 2017, we had $573.4 million of outstanding surety bonds. Certain contracts, primarily those involving public sector customers, require us to provide a surety bond as a guarantee of its performance of contractual obligations.
We believe that internally generated cash flows and the remaining availability under our credit facility will be adequate to finance normal operating requirements. Although we maintain an active acquisition program, any future acquisitions will be dependent on numerous factors and it is not feasible to reasonably estimate if or when any such acquisitions will occur and what the impact will be on our activities, financial condition and results of operations. We may also explore alternatives to attract additional capital resources.
We anticipate that our businesses will generate positive cash flows from operating activities, and that these cash flows will permit the reduction of currently outstanding debt in accordance with the repayment schedule. However, the rate at which we can reduce our debt during 2018 (and reduce the associated interest expense) will be affected by, among other things, the financing and operating requirements of any new acquisitions and the financial performance of our existing companies. None of these factors can be predicted with certainty.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
At December 31, 2017 and 2016, we did not have any relationships with unconsolidated entities or financial partnerships, such as entities often referred to as structured finance or special purpose entities, which would have been established for the purpose of facilitating off-balance sheet arrangements or other contractually narrow or limited purposes.
Recently Issued Accounting Standards
See Note 1 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements included in this Annual Report for information regarding the effect of new accounting pronouncements on our consolidated financial statements.
26
ITEM 7A. | QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK |
We are exposed to interest rate risks on our outstanding revolving credit borrowings, and to foreign currency exchange risks on our transactions denominated in currencies other than the U.S. dollar. We are also exposed to equity market risks pertaining to the traded price of our common stock.
At December 31, 2017, we had $3.9 billion of fixed rate borrowings with interest rates ranging from 2.05% to 6.25%. At December 31, 2017, the prevailing market rates for our long-term notes were between 0.05% higher and 3.85% lower than the fixed rates on our debt instruments. Our credit facility contains a $2.5 billion variable-rate revolver with $1.27 billion of outstanding borrowings at December 31, 2017.
Several of our businesses have transactions and balances denominated in currencies other than the U.S. dollar. Most of these transactions or balances are denominated in euros, Canadian dollars, British pounds or Danish kroner. Net revenues recognized by companies whose functional currency was not the U.S. dollar were 17% of our total revenues in 2017 and 68% of these revenues were recognized by companies with a European functional currency. If these currency exchange rates had been 10% different throughout 2017 compared to currency exchange rates actually experienced, the impact on our net earnings would have been approximately 1%.
The trading price of our common stock influences the valuation of stock award grants and the effects these grants have on our results of operations. The stock price also influences the computation of potentially dilutive common stock to determine diluted earnings per share. The stock price also affects our employees' perceptions of programs that involve our common stock. We believe the quantification of the effects of these changing prices on our future earnings and cash flows is not readily determinable.
27
ITEM 8. | FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA |
INDEX TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
Page | |
Consolidated Financial Statements: | |
Supplementary Data: | |
28
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Stockholders of Roper Technologies, Inc.:
Opinions on the Financial Statements and Internal Control over Financial Reporting
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Roper Technologies, Inc. and its subsidiaries (the "Company") as of December 31, 2017, and 2016, and the related consolidated statements of earnings, of comprehensive income, of stockholders' equity, and of cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2017, including the related notes and financial statement schedule listed in the accompanying index (collectively referred to as the “consolidated financial statements”). We also have audited the Company's internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017, based on criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO).
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2017 in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. Also in our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017, based on criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the COSO.
Basis for Opinions
The Company's management is responsible for these consolidated financial statements, for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting, and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Management's Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express opinions on the Company’s consolidated financial statements and on the Company's internal control over financial reporting based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) ("PCAOB") and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audits to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the consolidated financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud, and whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects.
Our audits of the consolidated financial statements included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the consolidated financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the consolidated financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the consolidated financial statements. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audits also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinions.
As described in Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting, management has excluded acquisitions completed in 2017 from its assessment of internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017 because they were acquired by the Company in purchase business combinations during 2017. We have also excluded acquisitions completed in 2017 from our audit of internal control over financial reporting. These acquisitions are wholly-owned subsidiaries whose total assets and total revenues excluded from management’s assessment and our audit of internal control over financial reporting represent less than 1% of the related consolidated financial statement amounts as of and for the year ended December 31, 2017.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control over Financial Reporting
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (i) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (ii) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are
29
being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (iii) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
/S/ PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP
Certified Public Accountants
Tampa, Florida
February 23, 2018
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2002.
30
ROPER TECHNOLOGIES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
December 31, 2017 and 2016
(in thousands, except per share data)
2017 | 2016 | ||||||
Assets | |||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 671,327 | $ | 757,200 | |||
Accounts receivable, net | 641,662 | 619,854 | |||||
Inventories, net | 204,933 | 181,952 | |||||
Income taxes receivable | 24,365 | 31,679 | |||||
Unbilled receivables | 143,634 | 129,965 | |||||
Other current assets | 73,481 | 55,851 | |||||
Total current assets | 1,759,402 | 1,776,501 | |||||
Property, plant and equipment, net | 142,535 | 141,318 | |||||
Goodwill | 8,820,313 | 8,647,142 | |||||
Other intangible assets, net | 3,475,218 | 3,655,843 | |||||
Deferred taxes | 30,726 | 30,620 | |||||
Other assets | 88,219 | 73,503 | |||||
Total assets | $ | 14,316,413 | $ | 14,324,927 | |||
Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity | |||||||
Accounts payable | $ | 171,073 | $ | 152,067 | |||
Accrued compensation | 198,020 | 161,730 | |||||
Deferred revenue | 566,447 | 488,399 | |||||
Other accrued liabilities | 266,574 | 219,339 | |||||
Income taxes payable | 26,351 | 22,762 | |||||
Current portion of long-term debt, net | 800,944 | 400,975 | |||||
Total current liabilities | 2,029,409 | 1,445,272 | |||||
Long-term debt, net of current portion | 4,354,611 | 5,808,561 | |||||
Deferred taxes | 829,657 | 1,178,205 | |||||
Other liabilities | 239,172 | 104,024 | |||||
Total liabilities | 7,452,849 | 8,536,062 | |||||
Commitments and contingencies (Note 12) | |||||||
Stockholders' equity: | |||||||
Preferred stock, $0.01 par value per share; 1,000 shares authorized; none outstanding | — | — | |||||
Common stock, $0.01 par value per share; 350,000 shares authorized; 104,379 shares issued and 102,493 outstanding at December 31, 2017 and 103,578 shares issued and 101,672 outstanding at December 31, 2016 | 1,044 | 1,036 | |||||
Additional paid-in capital | 1,602,869 | 1,489,067 | |||||
Retained earnings | 5,464,571 | 4,642,402 | |||||
Accumulated other comprehensive loss | (186,214 | ) | (324,739 | ) | |||
Treasury stock, 1,886 shares at December 31, 2017 and 1,906 shares at December 31, 2016 | (18,706 | ) | (18,901 | ) | |||
Total stockholders' equity | 6,863,564 | 5,788,865 | |||||
Total liabilities and stockholders' equity | $ | 14,316,413 | $ | 14,324,927 | |||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
31
ROPER TECHNOLOGIES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF EARNINGS
Years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
(Dollar and share amounts in thousands, except per share data)
Years ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
Net revenues | $ | 4,607,471 | $ | 3,789,925 | $ | 3,582,395 | |||||
Cost of sales | 1,742,675 | 1,457,515 | 1,417,749 | ||||||||
Gross profit | 2,864,796 | 2,332,410 | 2,164,646 | ||||||||
Selling, general and administrative expenses | 1,654,552 | 1,277,847 | 1,136,728 | ||||||||
Income from operations | 1,210,244 | 1,054,563 | 1,027,918 | ||||||||
Interest expense, net | 180,566 | 111,559 | 84,225 | ||||||||
Loss on extinguishment of debt | — | 871 | — | ||||||||
Other income/(expense), net | 5,045 | (1,481 | ) | 58,652 | |||||||
Earnings before income taxes | 1,034,723 | 940,652 | 1,002,345 | ||||||||
Income taxes | 62,951 | 282,007 | 306,278 | ||||||||
Net earnings | $ | 971,772 | $ | 658,645 | $ | 696,067 | |||||
Earnings per share: | |||||||||||
Basic | $ | 9.51 | $ | 6.50 | $ | 6.92 | |||||
Diluted | $ | 9.39 | $ | 6.43 | $ | 6.85 | |||||
Weighted-average common shares outstanding: | |||||||||||
Basic | 102,168 | 101,291 | 100,616 | ||||||||
Diluted | 103,522 | 102,464 | 101,597 | ||||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
32
ROPER TECHNOLOGIES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
Years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
(in thousands)
Years ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
Net earnings | $ | 971,772 | $ | 658,645 | $ | 696,067 | |||||
Other comprehensive income, net of tax: | |||||||||||
Foreign currency translation adjustments | 138,525 | (111,960 | ) | (139,789 | ) | ||||||
Unrecognized pension gain | — | — | (1,063 | ) | |||||||
Total other comprehensive income/(loss), net of tax | 138,525 | (111,960 | ) | (140,852 | ) | ||||||
Comprehensive income | $ | 1,110,297 | $ | 546,685 | $ | 555,215 | |||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
33
ROPER TECHNOLOGIES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY
Years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
(in thousands, except per share data)
Common Stock | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Shares | Amount | Additional paid-in capital | Retained earnings | Accumulated other comprehensive earnings | Treasury stock | Total stockholders' equity | ||||||||||||||||||||
Balances at December 31, 2014 | 100,126 | $ | 1,021 | $ | 1,325,338 | $ | 3,520,201 | $ | (71,927 | ) | $ | (19,273 | ) | $ | 4,755,360 | |||||||||||
Net earnings | — | — | — | 696,067 | — | — | 696,067 | |||||||||||||||||||
Stock option exercises | 402 | 4 | 33,002 | — | — | — | 33,006 | |||||||||||||||||||
Treasury stock sold | 18 | — | 2,710 | — | — | 179 | 2,889 | |||||||||||||||||||
Currency translation adjustments, net of $6,658 tax | — | — | — | — | (139,789 | ) | — | (139,789 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
Stock based compensation | — | — | 61,766 | — | — | — | 61,766 | |||||||||||||||||||
Restricted stock activity | 324 | 3 | (14,697 | ) | — | — | — | (14,694 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
Stock option tax benefit, net of shortfalls | — | — | 22,175 | — | — | — | 22,175 | |||||||||||||||||||
Conversion of senior subordinated convertible notes | — | — | (11,032 | ) | — | — | — | (11,032 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
Post-retirement benefit plan adjustments | — | — | — | — | (1,063 | ) | — | (1,063 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
Dividends declared ($1.05 per share) | — | — | — | (105,738 | ) | — | — | (105,738 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
Balances at December 31, 2015 | 100,870 | $ | 1,028 | $ | 1,419,262 | $ | 4,110,530 | $ | (212,779 | ) | $ | (19,094 | ) | $ | 5,298,947 | |||||||||||
Net earnings | — | — | — | 658,645 | — | — | 658,645 | |||||||||||||||||||
Stock option exercises | 372 | 4 | 27,970 | — | — | — | 27,974 | |||||||||||||||||||
Treasury stock sold | 19 | — | 3,147 | — | — | 193 | 3,340 | |||||||||||||||||||
Currency translation adjustments, net of $2,570 tax | — | — | — | — | (111,960 | ) | — | (111,960 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
Stock based compensation | — | — | 77,860 | — | — | — | 77,860 | |||||||||||||||||||
Restricted stock activity | 411 | 4 | (17,980 | ) | — | — | — | (17,976 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
Stock option tax benefit, net of shortfalls | — | — | (8,081 | ) | — | — | — | (8,081 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
Conversion of senior subordinated convertible notes | — | — | (13,111 | ) | — | — | — | (13,111 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
Dividends declared ($1.25 per share) | — | — | — | (126,773 | ) | — | — | (126,773 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
Balances at December 31, 2016 | 101,672 | $ | 1,036 | $ | 1,489,067 | $ | 4,642,402 | $ | (324,739 | ) | $ | (18,901 | ) | $ | 5,788,865 | |||||||||||
Net earnings | — | — | — | 971,772 | — | — | 971,772 | |||||||||||||||||||
Stock option exercises | 645 | 6 | 61,317 | — | — | — | 61,323 | |||||||||||||||||||
Treasury stock sold | 20 | — | 4,003 | — | — | 195 | 4,198 | |||||||||||||||||||
Currency translation adjustments, net of $4,899 tax | — | — | — | — | 138,525 | — | 138,525 | |||||||||||||||||||
Stock based compensation | — | — | 81,324 | — | — | — | 81,324 | |||||||||||||||||||
Restricted stock activity | 156 | 2 | (32,842 | ) | — | — | — | (32,840 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
Dividends declared ($1.4625 per share) | — | — | — | (149,603 | ) | — | — | (149,603 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
Balances at December 31, 2017 | 102,493 | $ | 1,044 | $ | 1,602,869 | $ | 5,464,571 | $ | (186,214 | ) | $ | (18,706 | ) | $ | 6,863,564 | |||||||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
34
ROPER TECHNOLOGIES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
Years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
(in thousands)
Years ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
Cash flows from operating activities: | |||||||||||
Net earnings | $ | 971,772 | $ | 658,645 | $ | 696,067 | |||||
Adjustments to reconcile net earnings to cash flows from operating activities: | |||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization of property, plant and equipment | 49,513 | 37,299 | 38,185 | ||||||||
Amortization of intangible assets | 295,452 | 203,154 | 166,076 | ||||||||
Amortization of deferred financing costs | 7,227 | 5,612 | 4,136 | ||||||||
Non-cash stock compensation | 83,075 | 78,827 | 61,766 | ||||||||
Gain on disposal of a business | — | — | (70,860 | ) | |||||||
Gain on sale of assets | (9,393 | ) | — | — | |||||||
Changes in operating assets and liabilities, net of acquired businesses: | |||||||||||
Accounts receivable | (6,673 | ) | (20,734 | ) | 52,597 | ||||||
Unbilled receivables | (13,493 | ) | (1,202 | ) | (21,844 | ) | |||||
Inventories | (15,363 | ) | 6,353 | (1,150 | ) | ||||||
Accounts payable and accrued liabilities | 73,333 | 20,176 | (8,392 | ) | |||||||
Deferred revenue | 74,881 | 25,190 | 8,239 | ||||||||
Income taxes | (256,971 | ) | (47,589 | ) | 3,069 | ||||||
Other, net | (18,878 | ) | (1,946 | ) | 936 | ||||||
Cash provided by operating activities | 1,234,482 | 963,785 | 928,825 | ||||||||
Cash flows from investing activities: | |||||||||||
Acquisitions of businesses, net of cash acquired | (153,736 | ) | (3,721,758 | ) | (1,762,883 | ) | |||||
Capital expenditures | (48,752 | ) | (37,305 | ) | (36,260 | ) | |||||
Capitalized software expenditures | (10,784 | ) | (2,801 | ) | (2,439 | ) | |||||
Proceeds from disposal of a business | — | — | 105,624 | ||||||||
Proceeds from sale of assets | 10,628 | 870 | 1,126 | ||||||||
Other, net | (6,932 | ) | 8,138 | (3,500 | ) | ||||||
Cash used in investing activities | (209,576 | ) | (3,752,856 | ) | (1,698,332 | ) | |||||
Cash flows from financing activities: | |||||||||||
Proceeds from senior notes | — | 1,200,000 | 900,000 | ||||||||
Payment of senior notes | (400,000 | ) | — | — | |||||||
Borrowings/(payments) under revolving line of credit, net | (660,000 | ) | 1,750,000 | 180,000 | |||||||
Principal payments on convertible notes | — | (4,284 | ) | (4,006 | ) | ||||||
Debt issuance costs | — | (17,266 | ) | (8,044 | ) | ||||||
Cash dividends to stockholders | (142,753 | ) | (121,130 | ) | (100,334 | ) | |||||
Treasury stock sales | 4,198 | 3,340 | 2,889 | ||||||||
Stock award tax excess windfall benefit | — | — | 22,228 | ||||||||
Proceeds from stock based compensation, net | 28,487 | 9,998 | 18,312 | ||||||||
Redemption premium on convertible debt | — | (14,166 | ) | (13,126 | ) | ||||||
Other | 51 | (1,229 | ) | (1,677 | ) | ||||||
Cash provided by/(used in) financing activities | (1,170,017 | ) | 2,805,263 | 996,242 | |||||||
Effect of exchange rate changes on cash | 59,238 | (37,503 | ) | (58,654 | ) | ||||||
Net increase/(decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | (85,873 | ) | (21,311 | ) | 168,081 | ||||||
Cash and cash equivalents, beginning of year | 757,200 | 778,511 | 610,430 | ||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents, end of year | $ | 671,327 | $ | 757,200 | $ | 778,511 | |||||
Supplemental disclosures: | |||||||||||
Cash paid for: | |||||||||||
Interest | $ | 175,021 | $ | 104,928 | $ | 79,225 | |||||
Income taxes, net of refunds received | $ | 320,235 | $ | 329,596 | $ | 280,801 | |||||
Noncash investing activities: | |||||||||||
Net assets of businesses acquired: | |||||||||||
Fair value of assets, including goodwill | $ | 177,276 | $ | 4,433,085 | $ | 1,876,984 | |||||
Liabilities assumed | (23,540 | ) | (711,327 | ) | (114,101 | ) | |||||
Cash paid, net of cash acquired | $ | 153,736 | $ | 3,721,758 | $ | 1,762,883 | |||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
35
ROPER TECHNOLOGIES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
(1) Summary of Accounting Policies
Basis of Presentation - These financial statements present consolidated information for Roper Technologies, Inc. and its subsidiaries ("Roper," the "Company," "we," "our" or "us"). All significant intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated.
Nature of the Business - Roper is a diversified technology company. The Company operates businesses that design and develop software (both license and software-as-a-service) and engineered products and solutions for a variety of niche end markets.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements - The Financial Accounting Standards Board ("FASB") establishes changes to accounting principles under GAAP in the form of accounting standards updates ("ASUs") to the FASB's Accounting Standards Codification. The Company considers the applicability and impact of all ASUs. Any ASUs not listed below were assessed and determined to be either not applicable or are expected to have an immaterial impact on the Company's results of operations, financial position or cash flows.
Recently Adopted Accounting Pronouncements
In January 2017, the FASB issued an update simplifying the test for goodwill impairment. This update, effective on a prospective basis for goodwill impairment tests performed in fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2019, eliminates Step 2 from the goodwill impairment test. Under the amendments in the update, an entity should perform its goodwill impairment test by comparing the fair value of a reporting unit with its carrying amount and recognize an impairment charge for the amount by which the carrying amount exceeds the reporting unit's fair value; however, the loss recognized should not exceed the total amount of goodwill allocated to that reporting unit. Additionally, an entity should consider income tax effects from any tax deductible goodwill on the carrying amount of the reporting unit when measuring the goodwill impairment loss, if applicable. Early adoption is permitted for interim or annual impairment tests performed on testing dates after January 1, 2017. The Company elected to early adopt this standard for it's annual goodwill impairment testing during the fourth quarter of 2017. The update did not have an impact on the Company's results of operations, financial position or cash flows.
In July 2015, the FASB issued an update providing guidance to simplify the measurement of inventory. This update, effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2016, requires that inventory within the scope of the update be measured at the lower of cost and net realizable value. The update did not have a material impact on the Company's results of operations, financial position or cash flows.
In March 2016, the FASB issued an update on stock compensation. The ASU simplifies several aspects of the accounting for employee share-based payment awards, including the accounting for income taxes, forfeitures, and statutory tax withholding requirements, as well as classification in the statement of cash flows. This standard is effective for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2016. The Company elected to early adopt this standard on a prospective basis in the quarter ended March 31, 2016. The impact of the early adoption resulted in the following:
• | The Company recorded tax benefits of $15.3 million within income tax expense for the year ended December 31, 2016 related to the excess tax benefit on share-based awards. Prior to adoption this amount would have been recorded as a reduction of additional paid-in capital. This change adds volatility to the Company's effective tax rate. |
• | The Company no longer reclassifies the excess tax benefit from operating activities to financing activities in the statement of cash flows. The Company elected to apply this change in presentation prospectively and thus prior periods have not been adjusted. |
• | The Company elected not to change its policy on accounting for forfeitures and continued to estimate the total number of awards for which the requisite service period will not be rendered. |
• | The Company excluded the excess tax benefits from the assumed proceeds available to repurchase shares in the computation of its diluted earnings per share since adoption. This resulted in an increase in diluted weighted average common shares outstanding of 278,829 shares for the year ended December 31, 2016. |
In March 2016, the FASB issued an update amending the equity method of accounting, eliminating the requirement that an entity retroactively adopt the equity method of accounting if an investment qualifies for the equity method as a result of an increase in the level of ownership or degree of influence. The amendments in the update, to be applied prospectively, are effective for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2016, and interim periods within those annual periods. Early adoption is permitted. The
36
Company elected to early adopt on a prospective basis effective January 1, 2016. The update did not have a material impact on its results of operations, financial condition or cash flows.
In September 2015, the FASB issued an update providing guidance to simplify the accounting for measurement period adjustments. This update, effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2015, including interim periods within those fiscal years, requires that an acquirer recognize adjustments to provisional amounts that are identified during the measurement period in the reporting period in which the adjustment amounts are determined. The Company adopted the update effective January 1, 2016. The update did not have a material impact on its results of operations, financial condition or cash flows.
In April 2015, the FASB issued an update providing guidance to determine whether the fee paid by an entity for a cloud computing arrangement includes a software license. If a cloud computing arrangement includes a software license, then the software license element of the arrangement should be accounted for consistently with the acquisition of other software licenses. A cloud computing arrangement that does not include a software license should be accounted for as a service contract. The update is effective for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2015, and may be adopted prospectively or retrospectively. The Company adopted the update prospectively effective January 1, 2016. The update did not have a material impact on its results of operations, financial condition or cash flows.
In June 2014, the FASB issued an update to the accounting for stock compensation. This update, effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2015, modifies the accounting for share-based payments when the terms of an award provide that a performance target could be achieved after the requisite service period. The Company adopted the update prospectively effective January 1, 2016. The update did not have a material impact on its results of operations, financial condition or cash flows.
Recently Released Accounting Pronouncements
In August 2016, the FASB issued an update clarifying the classification of certain cash receipts and cash payments in the statement of cash flows. This update, effective for annual reporting periods after December 15, 2017, including interim periods within those annual periods, addresses the following eight specific cash flow issues: Debt prepayment or debt extinguishment costs; settlement of zero-coupon debt instruments or other debt instruments with coupon interest rates that are insignificant in relation to the effective interest rate of the borrowing; contingent consideration payments made after a business combination; proceeds from the settlement of insurance claims; proceeds from the settlement of corporate-owned life insurance policies (including bank-owned life insurance policies); distributions received from equity method investees; beneficial interests in securitization transactions; and separately identifiable cash flows and application of the predominance principle. The Company does not expect the update to have a material impact on its results of operations, financial condition or cash flows.
In February 2016, the FASB issued an update on lease accounting. The update, effective for annual reporting periods after December 15, 2018, including interim periods within those annual periods, provides amendments to current lease accounting. These amendments include the recognition of lease assets and lease liabilities on the balance sheet and disclosing other key information about leasing arrangements. The Company is evaluating the impact of the update on its results of operations, financial condition and cash flows.
In May 2014, the FASB issued updates on accounting and disclosures for revenue from contracts with customers. These updates, effective for annual reporting periods after December 15, 2017, create a single, comprehensive revenue recognition model for all contracts with customers. The model is based on changes in contract assets (rights to receive consideration) and liabilities (obligations to provide a good or service). Revenue will be recognized based on the satisfaction of performance obligations, which occurs when control of a good or service transfers to a customer and enhanced disclosures will be required regarding the nature, amount, timing and uncertainty of revenue and cash flows arising from an entity's contracts with customers. Either a retrospective or cumulative effect transition method is permitted. The Company has elected to adopt using the modified retrospective transition method. The Company has completed its assessment to identify differences between the existing standard and new standard on its customer contracts. Based on this assessment, the impact of the new standard is due primarily to the acceleration of recognition of revenues and associated costs for certain of our software license contracts. Under existing guidance, these contracts are recognized ratably over the contractual term of post-contract support services in the event vendor-specific objective evidence is unavailable. The new standard requires recognition at once upon the transfer of control of the software license. The opening balance sheet adjustment as of January 1, 2018 under the modified retrospective transition method will be less than 1% of the Company's 2017 annual revenues, prior to the effects of income taxes. The Company believes it is following an appropriate timeline to allow for proper recognition, presentation and disclosure upon adoption effective the beginning of fiscal year 2018.
Accounts Receivable - Accounts receivable are stated net of an allowance for doubtful accounts and sales allowances of $12.7 million and $14.5 million at December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively. Outstanding accounts receivable balances are reviewed periodically, and allowances are provided at such time that management believes it is probable that an account receivable is
37
uncollectible. The returns and other sales credit allowance is an estimate of customer returns, exchanges, discounts or other forms of anticipated concessions and is treated as a reduction in revenue.
Cash and Cash Equivalents - Roper considers highly liquid financial instruments with remaining maturities at acquisition of three months or less to be cash equivalents. Roper had no cash equivalents at December 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016.
Contingencies - Management continually assesses the probability of any adverse judgments or outcomes to its potential contingencies. Disclosure of the contingency is made if there is at least a reasonable possibility that a loss or an additional loss may have been incurred. In the assessment of contingencies as of December 31, 2017, management concluded that there were no matters for which there was a reasonable possibility of a material loss.
Earnings per Share - Basic earnings per share were calculated using net earnings and the weighted-average number of shares of common stock outstanding during the respective year. Diluted earnings per share were calculated using net earnings and the weighted-average number of shares of common stock and potential common stock outstanding during the respective year. Potentially dilutive common stock consisted of stock options and the premium over the conversion price on Roper's senior subordinated convertible notes based upon the trading price of the Company's common stock. Effective January 1, 2016, Roper adopted the provisions of an accounting standards update on a prospective basis which increased the number of potentially dilutive stock options as there is no longer a tax benefit in the calculation of dilutive stock options. See the caption "Recent Accounting Pronouncements" elsewhere in this Note for additional information regarding the ASU. The effects of potential common stock were determined using the treasury stock method (in thousands):
Years ended December 31, | ||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||
Basic weighted-average shares outstanding | 102,168 | 101,291 | 100,616 | |||||
Effect of potential common stock: | ||||||||
Common stock awards | 1,354 | 1,126 | 887 | |||||
Senior subordinated convertible notes | — | 47 | 94 | |||||
Diluted weighted-average shares outstanding | 103,522 | 102,464 | 101,597 | |||||
As of and for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, there were 477,898, 1,144,350 and 618,220 outstanding stock options, respectively, that were not included in the determination of diluted earnings per share because doing so would have been antidilutive.
Estimates - The preparation of financial statements in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States ("GAAP") requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Foreign Currency Translation and Transactions - Assets and liabilities of subsidiaries whose functional currency is not the U.S. dollar were translated at the exchange rate in effect at the balance sheet date, and revenues and expenses were translated at average exchange rates for the period in which those entities were included in Roper's financial results. Translation adjustments are reflected as a component of other comprehensive income. Foreign currency transaction gains and losses are recorded in the consolidated statement of earnings as other income/(expense). Foreign currency transaction losses were $1.4 million, $2.9 million and $0.7 million for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015.
Goodwill and Other Intangibles - Roper accounts for goodwill in a purchase business combination as the excess of the cost over the estimated fair value of net assets acquired. Business combinations can also result in other intangible assets being recognized. Amortization of intangible assets, if applicable, occurs over their estimated useful lives. Goodwill, which is not amortized, is tested for impairment on an annual basis (or an interim basis if an event occurs or circumstances change that would more likely than not reduce the fair value of a reporting unit below its carrying value). When testing goodwill for impairment, the Company has the option to first assess qualitative factors to determine whether the existence of events or circumstances leads to a determination that it is more likely than not that the estimated fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying amount. If the Company elects to perform a qualitative assessment and determines that an impairment is more likely than not, then performance of the quantitative impairment test is required. The quantitative process utilizes both an income approach (discounted cash flows) and a market approach consisting of a comparable public company earnings multiples methodology to estimate the fair value of a reporting unit. To determine the reasonableness of the estimated fair values, the Company reviews the assumptions to ensure that neither the income approach nor the market approach provides significantly different valuations. If the estimated fair value exceeds the carrying value, no further work is required and no impairment loss is recognized. If the carrying value exceeds the estimated fair value, a non-cash impairment loss is recognized in the amount of that excess.
38
When performing the quantitative assessment, key assumptions used in the income and market methodologies are updated when the analysis is performed for each reporting unit. Various assumptions are utilized including forecasted operating results, strategic plans, economic projections, anticipated future cash flows, the weighted-average cost of capital, comparable transactions, market data and earnings multiples. The assumptions that have the most significant effect on the fair value calculations are the anticipated future cash flows, discount rates, and the earnings multiples. While the Company uses reasonable and timely information to prepare its cash flow and discount rate assumptions, actual future cash flows or market conditions could differ significantly resulting in future impairment charges related to recorded goodwill balances.
Roper has 33 reporting units with individual goodwill amounts ranging from zero to $2.3 billion. In 2017, the Company performed its annual impairment test in the fourth quarter for all reporting units. The Company conducted its analysis qualitatively and assessed whether it was more likely than not that the respective fair value of these reporting units was less than the carrying amount. The Company determined that impairment of goodwill was not likely in 31 of its reporting units and thus was not required to perform a quantitative analysis for these reporting units. For the remaining two reporting units, the Company performed its quantitative analysis and concluded that the fair value of each of these two reporting units was substantially in excess of its carrying value, with no impairment indicated as of October 1, 2017.
Recently acquired reporting units generally represent a higher inherent risk of impairment, which typically decreases as the businesses are integrated into the enterprise. Negative industry or economic trends, disruptions to its business, actual results significantly below expected results, unexpected significant changes or planned changes in the use of the assets, divestitures and market capitalization declines may have a negative effect on the fair value of Roper's reporting units.
The following events or circumstances, although not comprehensive, would be considered to determine whether interim testing of goodwill would be required:
• | a significant adverse change in legal factors or in the business climate; |
• | an adverse action or assessment by a regulator; |
• | unanticipated competition; |
• | a loss of key personnel; |
• | a more-likely-than-not expectation that a reporting unit or a significant portion of a reporting unit will be sold or otherwise disposed of; |
• | the testing for recoverability under the Impairment or Disposal of Long-Lived Assets of a significant asset group within a reporting unit; and |
• | recognition of a goodwill impairment loss in the financial statements of a subsidiary that is a component of a reporting unit. |
Business combinations can also result in other intangible assets being recognized. Amortization of intangible assets, if applicable, occurs over their estimated useful lives. Trade names that are determined to have an indefinite useful economic life are not amortized, but separately tested for impairment during the fourth quarter of the fiscal year or on an interim basis if an event occurs that indicates the fair value is more likely than not below the carrying value. Roper first qualitatively assesses whether the existence of events or circumstances leads to a determination that it is more likely than not that the estimated fair value of an indefinite-lived trade name is less than its carrying amount. If necessary, Roper conducts a quantitative review using the relief-from-royalty method. This methodology assumes that, in lieu of ownership, a third party would be willing to pay a royalty in order to exploit the related benefits of these assets. The fair value of each trade name is determined by applying a royalty rate to a projection of net revenues discounted using a risk adjusted rate of capital. Each royalty rate is determined based on the profitability of the trade name to which it relates and observed market royalty rates. Revenue growth rates are determined after considering current and future economic conditions, recent sales trends, discussions with customers, planned timing of new product launches or other variables. Trade names resulting from recent acquisitions generally represent the highest risk of impairment, which typically decreases as the businesses are integrated into Roper's enterprise.
The assessment of fair value for impairment purposes requires significant judgments to be made by management. Although forecasts are based on assumptions that are considered reasonable by management and consistent with the plans and estimates management uses to operate the underlying businesses, there is significant judgment in determining the expected results attributable to the reporting units. Changes in estimates or the application of alternative assumptions could produce significantly different results. No impairment resulted from the annual testing performed in 2017.
Roper evaluates whether there has been an impairment of identifiable intangible assets with definite useful economic lives, or of the remaining life of such assets, when certain indicators of impairment are present. In the event that facts and circumstances indicate that the cost or remaining period of amortization of any asset may be impaired, an evaluation of recoverability would be performed. If an evaluation is required, the estimated future gross, undiscounted cash flows associated with the asset would be
39
compared to the asset's carrying amount to determine if a write-down to fair value or a revision in the remaining amortization period is required.
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets - The Company determines whether there has been an impairment of long-lived assets, excluding goodwill and identifiable intangible assets that are determined to have indefinite useful economic lives, when certain indicators of impairment are present. In the event that facts and circumstances indicate that the cost or life of any long-lived assets may be impaired, an evaluation of recoverability would be performed. If an evaluation is required, the estimated future gross, undiscounted cash flows associated with the asset would be compared to the asset's carrying amount to determine if a write-down to fair value or revision to remaining life is required. Future adverse changes in market conditions or poor operating results of underlying long-lived assets could result in losses or an inability to recover the carrying value of the long-lived assets that may not be reflected in the assets' current carrying value, thereby possibly requiring an impairment charge or acceleration of depreciation or amortization expense in the future.
Income Taxes - The Company recognizes in the consolidated financial statements only those tax positions determined to be "more likely than not" of being sustained upon examination based on the technical merits of the positions. Interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits are classified as a component of income tax expense.
The Company records a valuation allowance to reduce its deferred tax assets if, based on the weight of available evidence, both positive and negative, for each respective tax jurisdiction, it is more likely than not that some portion or all of such deferred tax assets will not be realized. Available evidence which is considered in determining the amount of valuation allowance required includes, but is not limited to, the Company’s estimate of future taxable income and any applicable tax-planning strategies.
Certain assets and liabilities have different bases for financial reporting and income tax purposes. Deferred income taxes have been provided for these differences at the enacted tax rates expected to be paid. See Note 7 for information regarding income taxes.
Interest Rate Risk - The Company manages interest rate risk by maintaining a combination of fixed- and variable-rate debt, which may include interest rate swaps to convert fixed-rate debt to variable-rate debt, or to convert variable-rate debt to fixed-rate debt. Interest rate swaps are recorded at fair value in the balance sheet as an asset or liability, and the changes in fair values of both the swap and the hedged item are recorded as interest expense in current earnings. There were no interest rate swaps outstanding at December 31, 2017 or December 31, 2016.
Inventories - Inventories are valued at the lower of cost and net realizable value. Cost is determined using the first-in, first-out method. The Company writes down its inventory for estimated obsolescence or excess inventory equal to the difference between the cost of inventory and the estimated net realizable value based upon assumptions about future demand and market conditions.
Other Comprehensive Income - Comprehensive income includes net earnings and all other non-owner sources of changes in a company's net assets.
Product Warranties - The Company sells certain of its products to customers with a product warranty that allows customers to return a defective product during a specified warranty period following the purchase in exchange for a replacement product, repair at no cost to the customer or the issuance of a credit to the customer. The Company accrues its estimated exposure to warranty claims based upon current and historical product sales data, warranty costs incurred and any other related information known to the Company.
Property, Plant and Equipment and Depreciation and Amortization - Property, plant and equipment is stated at cost less accumulated depreciation and amortization. Depreciation and amortization are provided for using principally the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the assets as follows:
Buildings | 20-30 years |
Machinery | 8-12 years |
Other equipment | 3-5 years |
Research and Development - Research and development ("R&D") costs include salaries and benefits, rents, supplies, and other costs related to products under development. Research and development costs are expensed in the period incurred and totaled $281.1 million, $195.4 million and $164.2 million for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively.
40
Revenue Recognition - The Company recognizes revenue when all of the following criteria are met:
• | persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists; |
• | delivery has occurred or services have been rendered; |
• | the seller's price to the buyer is fixed or determinable; and |
• | collectibility is reasonably assured. |
In addition, the Company recognizes revenue from the sale of product when title and risk of loss pass to the customer, which is generally when product is shipped. The Company recognizes revenue from services when such services are rendered or, if applicable, upon customer acceptance. Revenues under certain relatively long-term and relatively large-value construction and software projects are recognized under the percentage-of-completion method using the ratio of costs incurred to total estimated costs as the measure of performance. The Company recognized revenues of $249 million, $241 million and $253 million for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively, using this method. Estimated losses on any projects are recognized as soon as such losses become known.
Capitalized Software - The Company accounts for capitalized software under applicable accounting guidance which, among other provisions, requires capitalization of certain internal-use software costs once certain criteria are met. Overhead, general and administrative and training costs are not capitalized. Capitalized software balances, net of accumulated amortization, were $14.0 million and $4.4 million at December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively.
Stock-Based Compensation - The Company recognizes expense for the grant date fair value of its employee stock awards on a straight-line basis (or, in the case of performance-based awards, on a graded basis) over the employee's requisite service period (generally the vesting period of the award). The fair value of option awards is estimated using the Black-Scholes option valuation model.
(2) Business Acquisitions and Divestitures
Roper completed four business acquisitions in the year ended December 31, 2017, with an aggregate purchase price of $152 million, net of cash acquired. The results of operations of the acquired businesses did not have a material impact on Roper's consolidated results of operations.
Acquisition of Phase Technology - On June 21, 2017, Roper acquired the assets of Phase Technology, a business engaged in the design, manufacture, marketing and sales of test instruments. Phase Technology is reported in the Energy Systems & Controls segment.
The results of the following acquisitions are reported in the RF Technology segment:
Acquisition of Handshake Software, Inc. - On August 4, 2017, Roper acquired 100% of the shares of Handshake Software, Inc., a provider of search products, portals and services for legal professionals.
Acquisition of Workbook Software A/S - On September 15, 2017, Roper acquired 100% of the shares of Workbook Software A/S, a provider of software solutions for customer relationship management, project management and finance/accounting.
Acquisition of Onvia, Inc. - On November 17, 2017, Roper acquired 100% of the outstanding shares of Onvia, Inc. ("Onvia") common stock for $9.00 per share in an all-cash tender offer. Onvia provides enterprise, mid-market and small business customers with sales lead generation technologies into federal, state and local government markets.
The Company recorded $83 million in goodwill and $85 million of other identifiable intangibles in connection with the acquisitions; however, purchase price allocations are preliminary pending final tax-related adjustments. The amortizable intangible assets include primarily customer relationships of $68 million (15 year weighted average useful life) and technology of $13 million (6 year weighted average useful life).
Sale of Product Line - On May 15, 2017, Roper completed the sale of a product line in our Energy Systems & Controls segment for $10.4 million. The pretax gain on the sale was $9.4 million, which is reported in Other income/(expense), net in the consolidated statements of earnings.
41
2016 Acquisitions – During the year ended December 31, 2016, Roper completed six business combinations. Roper acquired the businesses in order to both expand and complement its existing technologies. The results of operations of the acquired companies have been included in Roper's consolidated results since the date of each acquisition.
The largest of the 2016 acquisitions was Deltek Inc., a global provider of enterprise software and information solutions for government contractors, professional services firms and other project-based businesses. Roper acquired 100% of the shares of Project Diamond Holdings Corp. (the parent company of Deltek) on December 27, 2016, in a $2.8 billion all-cash transaction. Deltek is reported in the RF Technology segment.
The following table (in thousands) summarizes the fair values of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed at the date of acquisition.
Accounts receivable | $ | 94,506 | |
Other current assets | 37,558 | ||
Identifiable intangibles | 972,000 | ||
Goodwill | 2,234,549 | ||
Other assets | 43,098 | ||
Total assets acquired | 3,381,711 | ||
Deferred revenue | 166,393 | ||
Other current liabilities | 57,433 | ||
Long-term deferred tax liability | 349,810 | ||
Other liabilities | 7,935 | ||
Net assets acquired | $ | 2,800,140 | |
The majority of the goodwill is not expected to be deductible for tax purposes. Of the $972 million of acquired intangible assets acquired, $145 million was assigned to trade names that are not subject to amortization and $62 million was assigned to in process research and development. The remaining $765 million of acquired intangible assets have a weighted-average useful life of 12 years. The intangible assets that make up that amount include customer relationships of $625 million (13 year weighted-average useful life) and unpatented technology of $140 million (6 year weighted-average useful life).
The Company expensed transaction costs of $4.3 million related to the Deltek acquisition as corporate general and adminstrative expenses, as incurred.
Roper's results for the year ended December 31, 2016 included results from Deltek between December 28, 2016 and December 31, 2016. In that period, Deltek contributed $7.9 million in revenue and $0.8 million of earnings to Roper's results. The following unaudited pro forma summary presents consolidated information as if the acquisition of Deltek had occurred on January 1, 2015 (amounts in millions, except per share data):
Pro forma Year ended December 31, | |||||||
2016 | 2015 | ||||||
Net revenues | $ | 4,268,052 | $ | 4,012,030 | |||
Net income | 656,404 | 647,089 | |||||
Earnings per share, basic | 6.48 | 6.43 | |||||
Earnings per share, diluted | 6.41 | 6.37 | |||||
Pro forma earnings were adjusted by $47.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2016 for non-recurring acquisition and other costs. Adjustments were also made for recurring changes in amortization, interest expense and taxes related to the acquisition.
During the year ended December 31, 2016, Roper completed five other acquisitions which were immaterial. The aggregate purchase price of these acquisitions totaled $920 million of cash. The Company recorded $372 million in other identifiable intangibles and $642 million in goodwill in connection with these acquisitions. Supplemental pro forma information has not been provided as the acquisitions did not have a material impact on Roper's consolidated results of operations individually or in aggregate.
The results of the following acquisitions are reported in the Medical & Scientific Imaging segment:
42
– | Clinisys - On January 7, 2016, Roper acquired 100% of the shares of CliniSys Group Ltd. ("CliniSys"), a provider of clinical laboratory software headquartered in the United Kingdom. |
– | PCI Medical - On March 17, 2016, Roper acquired the assets of PCI Medical Inc., a provider of medical probe and scope disinfection products. |
– | GeneInsight - On April 1, 2016, the Company acquired 100% of the shares of GeneInsight Inc., a provider of software for managing the analysis, interpretation and reporting of genetic tests. |
– | UNIConnect - On November 10, 2016, Roper acquired the assets of UNIConnect LC, a provider of process management software for molecular laboratories. |
ConstructConnect - On October 31, 2016, Roper acquired 100% of the shares of iSqFt Holdings Inc. (d/b/a ConstructConnect), a provider of cloud-based data, collaboration, and workflow automation solutions to the commercial construction industry. ConstructConnect is reported in the RF Technology segment.
The Company expensed transaction costs of $4.2 million related to the acquisitions as corporate general and adminstrative expenses, as incurred.
The majority of the goodwill recorded for these five companies is not expected to be deductible for tax purposes. Of the $372 million of intangible assets acquired, $34 million was assigned to trade names that are not subject to amortization. The remaining $338 million of acquired intangible assets have a weighted-average useful life of 12 years. The intangible assets that make up that amount include customer relationships of $242 million (14 year weighted-average useful life), unpatented technology of $66 million (6 year weighted-average useful life) and software of $30 million (9 year weighted-average useful life).
2015 Acquisitions – During the year ended December 31, 2015, Roper completed eight business combinations. The results of operations of the acquired companies have been included in Roper's consolidated results since the date of each acquisition. Supplemental pro forma information has not been provided as the acquisitions did not have a material impact on Roper's consolidated results of operations individually or in aggregate.
The results of the following acquisitions are reported in the Medical & Scientific Imaging segment:
– | Strata - On January 21, 2015, Roper acquired 100% of the shares of Strata Decision Technologies LLC ("Strata"), a provider of planning and budget software for health care providers. |
– | Softwriters - On February 9, 2015, Roper acquired 100% of the shares of Softwriters Inc., a provider of long-term care pharmacy operating software. |
– | Data Innovations - On March 4, 2015, Roper acquired 100% of the shares of Data Innovations LLC, a provider of clinical and blood laboratory middleware. |
– | AHP - On September 4, 2015, Roper acquired the assets of Atlantic Health Partners LLC ("AHP"), a group purchasing organization specializing in vaccines for the physician marketplace. |
– | Atlas - On October 26, 2015, Roper acquired 100% of the shares of Atlas Database Software Corp. ("Atlas"), a provider of clinical process integration to private and public health sectors. |
The results of the following acquisitions are reported in the RF Technology segment:
– | On Center - On July 20, 2015, Roper acquired 100% of the shares of On Center Software LLC ("On Center"), a provider of construction automation technology. |
– | RF IDeas - On September 1, 2015, Roper acquired 100% of the shares of RF IDeas, Inc., a provider of proprietary identification card technology solutions. |
– | Aderant - On October 21, 2015, Roper acquired 100% of the shares of Aderant Holdings, Inc. ("Aderant"), a provider of comprehensive software solutions for law and other professional services firms. |
The aggregate purchase price for the 2015 acquisitions was $1.8 billion, paid in cash. Roper purchased the businesses to expand upon existing software, supply chain and medical platforms.
The Company expensed transaction costs of $5.9 million related to the acquisitions as corporate general and administrative expenses, as incurred.
43
The Company recorded $1.2 billion in goodwill and $731 million in other identifiable intangibles in connection with the acquisitions. The majority of the goodwill recorded is not expected to be deductible for tax purposes. Of the $731 million of intangible assets acquired, $51 million was assigned to trade names that are not subject to amortization. The remaining $680 million of acquired intangible assets have a weighted-average useful life of 17 years. The intangible assets that make up that amount include customer relationships of $541 million (19 year weighted-average useful life), unpatented technology of $100 million (8 year weighted-average useful life) and software of $39 million (6 year weighted-average useful life).
Divestiture of Abel - On October 2, 2015, Roper completed the sale of Abel Pumps ("Abel") for $106 million (€95 million), net of cash divested. The pretax gain on the divestiture was $70.9 million, which is reported as Other income/(expense), net on the consolidated statement of earnings. The gain resulted in tax expense of $46 million as well as a future tax benefit of $11 million.
The year to date pretax income of Abel was $5.9 million for the period ended October 2, 2015. Abel was reported in the Industrial Technology segment.
(3) Inventories
The components of inventories at December 31 were as follows (in thousands):
2017 | 2016 | ||||||
Raw materials and supplies | $ | 132,949 | $ | 113,632 | |||
Work in process | 27,649 | 24,290 | |||||
Finished products | 82,445 | 81,263 | |||||
Inventory reserves | (38,110 | ) | (37,233 | ) | |||
$ | 204,933 | $ | 181,952 | ||||
(4) Property, Plant and Equipment
The components of property, plant and equipment at December 31 were as follows (in thousands):
2017 | 2016 | ||||||
Land | $ | 2,471 | $ | 2,404 | |||
Buildings | 90,683 | 88,201 | |||||
Machinery and other equipment | 226,320 | 221,325 | |||||
Computer equipment | 77,508 | 70,110 | |||||
Software | 62,387 | 54,451 | |||||
459,369 | 436,491 | ||||||
Accumulated depreciation | (316,834 | ) | (295,173 | ) | |||
$ | 142,535 | $ | 141,318 | ||||
Depreciation and amortization expense related to property, plant and equipment was $49,513, $37,299 and $38,185 for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively.
44
(5) Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets
The carrying value of goodwill by segment was as follows (in thousands):
RF Technology | Medical & Scientific Imaging | Industrial Technology | Energy Systems & Controls | Total | |||||||||||||||
Balances at December 31, 2015 | $ | 1,993,299 | $ | 3,039,197 | $ | 374,033 | $ | 418,197 | $ | 5,824,726 | |||||||||
Goodwill acquired | 2,710,223 | 166,768 | — | — | 2,876,991 | ||||||||||||||
Currency translation adjustments | (15,118 | ) | (19,100 | ) | (10,055 | ) | (7,774 | ) | (52,047 | ) | |||||||||
Reclassifications and other | (734 | ) | (1,794 | ) | — | — | (2,528 | ) | |||||||||||
Balances at December 31, 2016 | $ | 4,687,670 | $ | 3,185,071 | $ | 363,978 | $ | 410,423 | $ | 8,647,142 | |||||||||
Goodwill acquired | 63,490 | — | — | 19,169 | 82,659 | ||||||||||||||
Currency translation adjustments | 19,337 | 17,582 | 13,540 | 8,395 | 58,854 | ||||||||||||||
Reclassifications and other | 28,394 | 3,264 | — | — | 31,658 | ||||||||||||||
Balances at December 31, 2017 | $ | 4,798,891 | $ | 3,205,917 | $ | 377,518 | $ | 437,987 | $ | 8,820,313 | |||||||||
Reclassifications and other during the year ended December 31, 2017 were due primarily to tax adjustments for 2016 acquisitions. See Note 2 for information regarding acquisitions.
Other intangible assets were comprised of (in thousands):
Cost | Accum. amort. | Net book value | |||||||||
Assets subject to amortization: | |||||||||||
Customer related intangibles | $ | 3,272,081 | $ | (712,718 | ) | $ | 2,559,363 | ||||
Unpatented technology | 462,152 | (144,025 | ) | 318,127 | |||||||
Software | 184,761 | (56,882 | ) | 127,879 | |||||||
Patents and other protective rights | 24,656 | (20,399 | ) | 4,257 | |||||||
Trade names | 6,591 | (653 | ) | 5,938 | |||||||
Assets not subject to amortization: | |||||||||||
Trade names | 578,279 | — | 578,279 | ||||||||
In process research and development | 62,000 | — | 62,000 | ||||||||
Balances at December 31, 2016 | $ | 4,590,520 | $ | (934,677 | ) | $ | 3,655,843 | ||||
Assets subject to amortization: | |||||||||||
Customer related intangibles | $ | 3,355,232 | $ | (913,680 | ) | $ | 2,441,552 | ||||
Unpatented technology | 544,046 | (207,678 | ) | 336,368 | |||||||
Software | 184,703 | (84,825 | ) | 99,878 | |||||||
Patents and other protective rights | 26,090 | (22,729 | ) | 3,361 | |||||||
Trade names | 6,635 | (1,731 | ) | 4,904 | |||||||
Assets not subject to amortization: | |||||||||||
Trade names | 587,737 | — | 587,737 | ||||||||
In process research and development | 1,418 | — | 1,418 | ||||||||
Balances at December 31, 2017 | $ | 4,705,861 | $ | (1,230,643 | ) | $ | 3,475,218 | ||||
Amortization expense of other intangible assets was $294 million, $201 million, and $164 million during the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively. Amortization expense is expected to be $294 million in 2018, $282 million in 2019, $276 million in 2020, $264 million in 2021 and $260 million in 2022.
45
(6) Accrued Liabilities
Accrued liabilities at December 31 were as follows (in thousands):
2017 | 2016 | ||||||
Interest | $ | 20,060 | $ | 21,742 | |||
Customer deposits | 29,236 | 16,707 | |||||
Commissions | 8,341 | 9,144 | |||||
Warranty | 10,587 | 10,548 | |||||
Accrued dividend | 42,921 | 36,077 | |||||
Rebates | 29,996 | 19,414 | |||||
Billings in excess of cost | 23,284 | 12,381 | |||||
Other | 102,149 | 93,326 | |||||
$ | 266,574 | $ | 219,339 | ||||
(7) Income Taxes
Earnings before income taxes for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 consisted of the following components (in thousands):
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
United States | $ | 783,654 | $ | 721,000 | $ | 710,614 | |||||
Other | 251,069 | 219,652 | 291,731 | ||||||||
$ | 1,034,723 | $ | 940,652 | $ | 1,002,345 | ||||||
Components of income tax expense for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 were as follows (in thousands):
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
Current: | |||||||||||
Federal | $ | 316,031 | $ | 239,217 | $ | 229,224 | |||||
State | 29,768 | 21,779 | 22,041 | ||||||||
Foreign | 89,894 | 54,937 | 71,507 | ||||||||
Deferred: | |||||||||||
Federal | (358,300 | ) | (26,760 | ) | 6,710 | ||||||
State | (3,670 | ) | 189 | (16,844 | ) | ||||||
Foreign | (10,772 | ) | (7,355 | ) | (6,360 | ) | |||||
$ | 62,951 | $ | 282,007 | $ | 306,278 | ||||||
Reconciliations between the statutory federal income tax rate and the effective income tax rate for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 were as follows:
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||
Federal statutory rate | 35.0 | % | 35.0 | % | 35.0 | % | ||
Foreign rate differential | (2.6 | ) | (3.2 | ) | (3.3 | ) | ||
R&D tax credits | (0.8 | ) | (0.7 | ) | (0.5 | ) | ||
State taxes, net of federal benefit | 1.9 | 1.9 | 2.0 | |||||
Section 199 deduction | (1.3 | ) | (1.5 | ) | (1.3 | ) | ||
Stock-based compensation | (3.9 | ) | (1.6 | ) | — | |||
Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 | (20.8 | ) | — | — | ||||
Other, net | (1.4 | ) | 0.1 | (1.3 | ) | |||
6.1 | % | 30.0 | % | 30.6 | % | |||
The deferred income tax balance sheet accounts arise from temporary differences between the amount of assets and liabilities recognized for financial reporting and tax purposes.
46
Components of the deferred tax assets and liabilities at December 31 were as follows (in thousands):
2017 | 2016 | ||||||
Deferred tax assets: | |||||||
Reserves and accrued expenses | $ | 121,509 | $ | 186,120 | |||
Inventories | 5,094 | 8,967 | |||||
Net operating loss carryforwards | 71,774 | 87,010 | |||||
R&D credits | 9,570 | 7,933 | |||||
Foreign tax credits | — | 9,203 | |||||
Valuation allowance | (25,690 | ) | (26,009 | ) | |||
Total deferred tax assets | $ | 182,257 | $ | 273,224 | |||
Deferred tax liabilities: | |||||||
Reserves and accrued expenses | $ | 39,566 | $ | 13,915 | |||
Amortizable intangible assets | 935,874 | 1,400,792 | |||||
Plant and equipment | 5,748 | 6,102 | |||||
Total deferred tax liabilities | $ | 981,188 | $ | 1,420,809 | |||
As of December 31, 2017, the Company had approximately $29.2 million of tax-effected U.S. federal net operating loss carryforwards that if not utilized will expire in years 2021 through 2037. The U.S. federal net operating loss carryforwards decreased from 2016 to 2017 primarily due to reduction in U.S. federal corporate tax rate for tax years beginning after December 31, 2017. The Company has approximately $26.1 million of tax-effected state net operating loss carryforwards (without regard to federal benefit of state) that if not utilized will expire in years 2018 through 2037. The state net operating loss carryforwards are primarily related to Florida and New Jersey, but the Company has smaller net operating losses in various other states. The Company has approximately $22.0 million of tax-effected foreign net operating loss carryforwards. Some of these net operating loss carryforwards have an indefinite carryforward period and those that do not if not utilized will begin to expire in 2018. Additionally, the Company has $11.3 million of U.S. federal and state research and development tax credit carryforwards (without regard to federal benefit of state) that will expire in years 2018 through 2037.
As of December 31, 2017, the Company determined that a total valuation allowance of $25.7 million was necessary to reduce U.S. federal and state deferred tax assets by $9.5 million and foreign deferred tax assets by $16.2 million, where it was more likely than not that all of such deferred tax assets will not be realized. As of December 31, 2017, based on the Company's estimates of future taxable income and any applicable tax-planning strategies within various tax jurisdictions, the Company believes that it is more likely than not that the remaining net deferred tax assets will be realized.
The Company recognizes in the consolidated financial statements only those tax positions determined to be "more likely than not" of being sustained upon examination based on the technical merits of the positions. A reconciliation of the beginning and ending amount of unrecognized tax benefits is as follows (in thousands):
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
Beginning balance | $ | 38,678 | $ | 26,140 | $ | 28,567 | |||||
Additions for tax positions of prior periods | 24,804 | 3,450 | 3,525 | ||||||||
Additions for tax positions of the current period | 4,174 | 9,012 | 3,299 | ||||||||
Additions due to acquisitions | — | 5,049 | 6,177 | ||||||||
Reductions for tax positions of prior periods | (11,162 | ) | (1,165 | ) | (12,206 | ) | |||||
Reductions attributable to settlements with taxing authorities | (1,536 | ) | (568 | ) | (142 | ) | |||||
Reductions attributable to lapses of applicable statute of limitations | (2,769 | ) | (3,240 | ) | (3,080 | ) | |||||
Ending balance | $ | 52,189 | $ | 38,678 | $ | 26,140 | |||||
The total amount of unrecognized tax benefits that, if recognized, would affect the effective tax rate is $50.4 million. Interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits are classified as a component of income tax expense and totaled an expense of $1.3 million in 2017. Accrued interest and penalties were $5.1 million at December 31, 2017 and $3.8 million at December 31, 2016. During the next twelve months, it is reasonably possible that the unrecognized tax benefits may decrease by a net $2.3 million, mainly due to anticipated statute of limitations lapses in various jurisdictions.
47
The Company and its subsidiaries are subject to U.S. federal income tax as well as income tax in multiple state, city and foreign jurisdictions. The Company's federal income tax returns for 2015 through the current period remain subject to examination and the relevant state, city and foreign statutes vary. The Company does not expect the assessment of any significant additional tax in excess of amounts reserved.
The Tax Act was signed into U.S. law on December 22, 2017, which was prior to the end of the Company’s 2017 reporting period. The Tax Act contains provisions which impact the Company’s current and future income taxes including a reduction in the US federal corporate income tax rate from 35% to 21%, a one-time deemed mandatory repatriation tax imposed on all undistributed foreign earnings, and the introduction of a modified territorial taxation system.
The SEC released Staff Accounting Bulletin No. 118 (“SAB 118”) on December 22, 2017 to provide guidance where the accounting under ASC 740, Income Taxes, is incomplete for certain income tax effects of the Tax Act upon issuance of financial statements for the reporting period in which the Tax Act was enacted. SAB 118 provides that if a Company can determine a reasonable estimate, it should be reported as a provisional amount and adjusted during a measurement period. If a Company is unable to determine a reasonable estimate, no related provisional amounts would be recorded until a reasonable estimate can be determined, within the measurement period. The measurement period extends until all necessary information has been obtained, prepared, and analyzed, but no longer than 12-months from the date of enactment of the Tax Act.
The reduction in the US federal corporate income tax rate from 35% to 21% and certain immaterial changes in tax basis resulted in a one-time estimated benefit of $379.0 million due to remeasurement of the Company’s deferred taxes. This estimate is a provisional amount that will be finalized during the measurement period once all information pertaining to the deferred tax assets and liabilities has been obtained and analyzed. The reduction in tax rate will also impact the Company’s current tax expense in future periods beginning in 2018.
The one-time deemed mandatory repatriation tax on all undistributed foreign earnings resulted in a one-time estimated charge of $110.7 million. The Company will elect to pay the liability over 8 years. This federal and state tax estimate is a provisional amount that will be finalized during the measurement period once all information pertaining to the historical foreign earnings and profits with available tax credits has been obtained and analyzed.
The introduction of a modified territorial taxation system resulted in a one-time estimated charge of $28.7 million due to the Company’s change in its indefinite reinvestment assertion on foreign earnings. The Company now intends to distribute all historical earnings subject to the deemed repatriation tax and has provided for deferred taxes related to the future state and foreign tax cost to repatriate. This estimate is a provisional amount that will be finalized during the measurement period once all information pertaining to the underlying calculation has been obtained and analyzed, and interpretations to the legislation have been decided. The Company also incurred a one-time estimated charge of $24.2 million resulting from the write-off of indirect benefits associated with uncertain tax positions. The Company is currently unable to estimate the amount of these indirect benefits which will be utilizable due to uncertainty surrounding interpretations to the legislations and timing of the related tax payments. This amount will be finalized during the measurement period as information becomes available.
In January 2018, the FASB released guidance on accounting for taxes on the global intangible low-taxed income (“GILTI”) provisions of the Tax Act. The Company is still evaluating its position whether to account for deferred taxes related to GILTI inclusions or to treat any taxes on GILTI inclusions as a period cost. The Company will perform an analysis during the measurement period and will disclose the policy election in its financial statements once its analysis has been finalized.
(8) Long-Term Debt
On September 23, 2016, Roper entered into a five-year $2.5 billion unsecured credit facility (the "2016 Facility") with JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., as administrative agent, and a syndicate of lenders, which replaced its previous $1.85 billion unsecured credit facility dated as of July 27, 2012, as amended as of October 28, 2015 (the "2012 Facility"). The 2016 Facility comprises a five year $2.5 billion revolving credit facility, which includes availability of up to $150 million for letters of credit. Roper may also, subject to compliance with specified conditions, request term loans or additional revolving credit commitments in an aggregate amount not to exceed $500 million. At December 31, 2017, there were $1.3 billion of outstanding borrowings under the 2016 Facility.
The 2016 Facility contains affirmative and negative covenants which, among other things, limit Roper's ability to incur new debt, enter into certain mergers and acquisitions, sell assets and grant liens, make restricted payments (including the payment of dividends on our common stock) and capital expenditures, or change its line of business. Roper is also subject to financial covenants which require the Company to limit its consolidated total leverage ratio and to maintain a consolidated interest coverage ratio. The most restrictive covenant is the consolidated total leverage ratio which is limited to 3.5 to 1.
48
On December 2, 2016, Roper amended the 2016 facility to allow the consolidated total leverage ratio be increased, no more than twice during the term of the 2016 facility, to 4.0 to 1 for a consecutive four quarter fiscal period per increase (or, for any portion of such four quarter fiscal period in which the maximum would be 4.25 to 1 pursuant to the 2016 facility amendment, 4.25 to 1). In conjunction with the Deltek acquistion (see Note 2), the Company increased the maximum consolidated total leverage ratio covenant to 4.25 to 1 through June 30, 2017 and 4.00 to 1 through December 31, 2017.
The Company was in compliance with its debt covenants throughout the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016.
On November 15, 2017, $400 million of senior notes due 2017 matured and were repaid using cash on hand and revolver borrowings from the 2016 Facility.
On December 19, 2016, the Company completed a public offering of $500 million aggregate principal amount of 2.80% senior unsecured notes due December 15, 2021 and $700 million aggregate principal amount of 3.80% senior unsecured notes due December 15, 2026. The notes bear interest at a fixed rate of 2.80% and 3.80% per year, respectively, payable semi-annually in arrears on June 15 and December 15 of each year, beginning June 15, 2017.
On December 7, 2015, the Company completed a public offering of $600 million aggregate principal amount of 3.00% senior unsecured notes due December 15, 2020 and $300 million aggregate principal amount of 3.85% senior unsecured notes due December 15, 2025. The notes bear interest at a fixed rate of 3.00% and 3.85% per year, respectively, payable semi-annually in arrears on June 15 and December 15 of each year, beginning June 15, 2016.
On June 6, 2013, the Company completed a public offering of $800 million aggregate principal amount of 2.05% senior unsecured notes due October 1, 2018. The notes bear interest at a fixed rate of 2.05% per year, payable semi-annually in arrears on April 1 and October 1 of each year, beginning October 1, 2013.
On November 21, 2012, the Company completed a public offering of $500 million aggregate principal amount of 3.125% senior unsecured notes due November 15, 2022. The notes bear interest at a fixed rate of 3.125% per year, payable semi-annually in arrears on May 15 and November 15 of each year, beginning May 15, 2013.
In September 2009, the Company completed a public offering of $500 million aggregate principal amount of 6.25% senior unsecured notes due September 1, 2019. The notes bear interest at a fixed rate of 6.25% per year, payable semi-annually in arrears on March 1 and September 1 of each year, beginning March 1, 2010.
Roper may redeem some or all of these notes at any time or from time to time, at 100% of their principal amount, plus a make-whole premium based on a spread to U.S. Treasury securities.
The Company's senior notes are unsecured senior obligations of the Company and rank equally in right of payment with all of Roper's existing and future unsecured and unsubordinated indebtedness. The notes are effectively subordinated to any of its existing and future secured indebtedness to the extent of the value of the collateral securing such indebtedness. The notes are not guaranteed by any of Roper's subsidiaries and are effectively subordinated to all existing and future indebtedness and other liabilities of Roper's subsidiaries.
49
Total debt at December 31 consisted of the following (in thousands):
2017 | 2016 | ||||||
2016 Facility | $ | 1,270,000 | $ | 1,930,000 | |||
$400 million 1.850% senior notes due 2017 | — | 400,000 | |||||
$800 million 2.050% senior notes due 2018 | 800,000 | 800,000 | |||||
$500 million 6.250% senior notes due 2019 | 500,000 | 500,000 | |||||
$600 million 3.000% senior notes due 2020 | 600,000 | 600,000 | |||||
$500 million 2.800% senior notes due 2021 | 500,000 | 500,000 | |||||
$500 million 3.125% senior notes due 2022 | 500,000 | 500,000 | |||||
$300 million 3.850% senior notes due 2025 | 300,000 | 300,000 | |||||
$700 million 3.800% senior notes due 2026 | 700,000 | 700,000 | |||||
Other | 3,149 | 2,989 | |||||
Less unamortized debt issuance costs | (17,594 | ) | (23,453 | ) | |||
Total debt | 5,155,555 | 6,209,536 | |||||
Less current portion, net of issuance costs | 800,944 | 400,975 | |||||
Long-term debt | $ | 4,354,611 | $ | 5,808,561 | |||
The 2016 Facility and Roper's $3.9 billion senior notes provide substantially all of Roper's daily external financing requirements. The interest rate on the borrowings under the 2016 Facility is calculated based upon various recognized indices plus a margin as defined in the credit agreement. At December 31, 2017, Roper's fixed debt consisted of $3.9 billion of senior notes, $3.1 million of other debt in the form of capital leases, several smaller facilities that allow for borrowings or the issuance of letters of credit in foreign locations to support Roper's non-U.S. businesses and $75.9 million of outstanding letters of credit at December 31, 2017.
Future maturities of total debt during each of the next five years ending December 31 and thereafter were as follows (in thousands):
2018 | $ | 801,503 | |
2019 | 501,061 | ||
2020 | 600,529 | ||
2021 | 1,770,047 | ||
2022 | 500,009 | ||
Thereafter | 1,000,000 | ||
Total | $ | 5,173,149 | |
(9) Fair Value
Roper's debt at December 31, 2017 included $3.9 billion of fixed-rate senior notes with the following fair values (in millions):
$800 million 2.050% senior notes due 2018 | 800 | |
$500 million 6.250% senior notes due 2019 | 531 | |
$600 million 3.000% senior notes due 2020 | 608 | |
$500 million 2.800% senior notes due 2021 | 501 | |
$500 million 3.125% senior notes due 2022 | 505 | |
$300 million 3.850% senior notes due 2025 | 311 | |
$700 million 3.800% senior notes due 2026 | 723 | |
The fair values of the senior notes are based on the trading prices of the notes, which the Company has determined to be Level 2 in the FASB fair value hierarchy. Most of Roper's other borrowings at December 31, 2017 were at various interest rates that adjust relatively frequently under its credit facility. The estimated fair value for these borrowings at December 31, 2017 approximated the carrying value of these borrowings.
50
(10) Retirement and Other Benefit Plans
Roper maintains four defined contribution retirement plans under the provisions of Section 401(k) of the IRC covering substantially all U.S. employees. Roper partially matches employee contributions. Costs related to all such plans were $27.6 million, $23.7 million and $20.4 million for 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively.
Roper also maintains various defined benefit retirement plans covering employees of non-U.S. and certain U.S. subsidiaries and a plan that supplements certain employees for the contribution ceiling applicable to the Section 401(k) plans. The costs and accumulated benefit obligations associated with each of these plans were not material.
(11) Stock-Based Compensation
The Roper Technologies, Inc. 2016 Incentive Plan ("2016 Plan") is a stock-based compensation plan used to grant incentive stock options, nonqualified stock options, restricted stock, stock appreciation rights or equivalent instruments to Roper's employees, officers and directors. At December 31, 2017, 7,802,395 shares were available to grant under the 2016 Plan.
Under the Roper Technologies, Inc., Employee Stock Purchase Plan ("ESPP"), all employees in the U.S. and Canada are eligible to designate up to 10% of eligible earnings to purchase Roper's common stock at a 5% discount to the average closing price of its common stock at the beginning and end of a quarterly offering period. Common stock sold to the employees may be either treasury stock, stock purchased on the open market, or newly issued shares.
Stock based compensation expense for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 was as follows (in millions):
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
Stock based compensation | $ | 83.1 | $ | 78.8 | $ | 61.8 | |||||
Tax benefit recognized in net earnings | 29.1 | 27.6 | 21.6 | ||||||||
Windfall tax benefit, net | — | — | 22.2 | ||||||||
Windfall tax benefits are no longer calculated due to the adoption of the ASU related to stock compensation (see Note 1), as all tax benefits are recognized in net income.
Stock Options – Stock options are typically granted at prices not less than 100% of market value of the underlying stock at the date of grant. Stock options typically vest over a period of three to five years from the grant date and expire ten years after the grant date. The Company recorded $18.3 million, $20.1 million, and $15.3 million of compensation expense relating to outstanding options during 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively, as a component of general and administrative expenses, primarily at corporate.
The Company estimates the fair value of its option awards using the Black-Scholes option valuation model. The stock volatility for each grant is measured using the weighted-average of historical daily price changes of the Company's common stock over the most recent period equal to the expected life of the grant. The expected term of options granted is derived from historical data to estimate option exercises and employee forfeitures, and represents the period of time that options granted are expected to be outstanding. The risk-free rate for periods within the contractual life of the option is based on the U.S. Treasury yield curve in effect at the time of grant. The weighted-average fair value of options granted in 2017, 2016 and 2015 were calculated using the following weighted-average assumptions:
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||
Weighted-average fair value ($) | 40.87 | 34.57 | 33.98 | |||||
Risk-free interest rate (%) | 2.03 | 1.44 | 1.53 | |||||
Average expected option life (years) | 5.26 | 5.20 | 5.10 | |||||
Expected volatility (%) | 18.74 | 21.35 | 22.17 | |||||
Expected dividend yield (%) | 0.67 | 0.70 | 0.62 | |||||
The following table summarizes the Company's activities with respect to its share-based compensation plans for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016:
51
Number of shares | Weighted-average exercise price per share | Weighted-average contractual term | Aggregate intrinsic value | |||||||||
Outstanding at January 1, 2016 | 3,117,616 | $ | 104.54 | |||||||||
Granted | 743,250 | 172.23 | ||||||||||
Exercised | (371,853 | ) | 75.23 | |||||||||
Canceled | (69,416 | ) | 159.97 | |||||||||
Outstanding at December 31, 2016 | 3,419,597 | 121.31 | 6.15 | $ | 211,369,740 | |||||||
Granted | 608,598 | 210.56 | ||||||||||
Exercised | (644,610 | ) | 95.14 | |||||||||
Canceled | (187,721 | ) | 170.75 | |||||||||
Outstanding at December 31, 2017 | 3,195,864 | 140.68 | 6.09 | $ | 368,589,147 | |||||||
Exercisable at December 31, 2017 | 1,766,869 | $ | 103.48 | 4.12 | $ | 269,474,477 | ||||||
The following table summarizes information for stock options outstanding at December 31, 2017:
Outstanding options | Exercisable options | |||||||||||||||
Exercise price | Number | Average exercise price | Average remaining life (years) | Number | Average exercise price | |||||||||||
$40.57 - 52.37 | 147,840 | $ | 47.38 | 1.7 | 147,840 | $ | 47.38 | |||||||||
52.37 - 78.56 | 500,259 | 61.18 | 1.2 | 500,259 | 61.18 | |||||||||||
78.56 - 104.75 | 172,777 | 93.83 | 4.1 | 172,777 | 93.83 | |||||||||||
104.75 - 130.94 | 342,805 | 117.51 | 5.2 | 342,805 | 117.51 | |||||||||||
130.94 - 157.12 | 481,652 | 139.21 | 6.4 | 430,101 | 138.27 | |||||||||||
157.12 - 183.31 | 870,883 | 169.61 | 7.8 | 151,337 | 166.74 | |||||||||||
183.31 - 209.50 | 225,450 | 187.64 | 8.7 | 21,750 | 185.47 | |||||||||||
209.50 - 235.68 | 434,398 | 215.02 | 9.3 | — | — | |||||||||||
235.68 - 261.87 | 19,800 | 253.01 | 9.8 | — | — | |||||||||||
$40.57 - 261.87 | 3,195,864 | $ | 140.68 | 6.1 | 1,766,869 | $ | 103.48 | |||||||||
At December 31, 2017, there was $29.6 million of total unrecognized compensation expense related to nonvested options granted under the Company's share-based compensation plans. That cost is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of 2.1 years. The total intrinsic value of options exercised in 2017, 2016 and 2015 was $90.6 million, $38.9 million and $36.9 million, respectively. Cash received from option exercises under all plans in 2017 and 2016 was $61.3 million and $28.0 million, respectively.
Restricted Stock Grants - During 2017 and 2016, the Company granted 410,267 and 555,730 shares, respectively, of restricted stock to certain employee and director participants under its share-based compensation plans. Restricted stock grants generally vest over a period of 1 to 3 years. The Company recorded $63.0 million, $57.8 million and $46.5 million of compensation expense related to outstanding shares of restricted stock held by employees and directors during 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively. A summary of the Company's nonvested shares activity for 2017 and 2016 is as follows:
52
Number of shares | Weighted-average grant date fair value | |||||
Nonvested at December 31, 2015 | 709,275 | $ | 146.64 | |||
Granted | 555,730 | 172.67 | ||||
Vested | (287,233 | ) | 141.27 | |||
Forfeited | (25,100 | ) | 139.56 | |||
Nonvested at December 31, 2016 | 952,672 | $ | 164.62 | |||
Granted | 410,267 | 205.88 | ||||
Vested | (387,452 | ) | 155.95 | |||
Forfeited | (116,491 | ) | 173.53 | |||
Nonvested at December 31, 2017 | 858,996 | $ | 187.01 | |||
At December 31, 2017, there was $90.8 million of total unrecognized compensation expense related to nonvested awards granted to both employees and directors under the Company's share-based compensation plans. That cost is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of 2.2 years. Unrecognized compensation expense related to nonvested shares of restricted stock grants is recorded as a reduction to additional paid-in capital in stockholder's equity at December 31, 2017.
Employee Stock Purchase Plan - During 2017, 2016 and 2015, participants of the ESPP purchased 19,683, 19,448 and 18,132 shares, respectively, of Roper's common stock for total consideration of $4.2 million, $3.3 million, and $2.9 million, respectively. All of these shares were purchased from Roper's treasury shares.
(12) Contingencies
Roper, in the ordinary course of business, is the subject of, or a party to, various pending or threatened legal actions, including product liability and employment practices that, in general, are based upon claims of the kind that have been customary over the past several years and which the Company is vigorously defending. After analyzing the Company's contingent liabilities on a gross basis and, based upon past experience with resolution of its product liability and employment practices claims and the limits of the primary, excess, and umbrella liability insurance coverages that are available with respect to pending claims, management believes that adequate provision has been made to cover any potential liability not covered by insurance, and that the ultimate liability, if any, arising from these actions should not have a material adverse effect on Roper's consolidated financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
Roper or its subsidiaries have been named defendants along with numerous industrial companies in asbestos-related litigation claims in certain U.S. states. No significant resources have been required by Roper to respond to these cases and Roper believes it has valid defenses to such claims and, if required, intends to defend them vigorously. Given the state of these claims it is not possible to determine the potential liability, if any.
Roper's rent expense was $58.6 million, $44.9 million and $40.2 million for 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively. Roper's future minimum property lease commitments are as follows (in millions):
2018 | $ | 54.3 | |
2019 | 44.7 | ||
2020 | 39.6 | ||
2021 | 34.6 | ||
2022 | 25.7 | ||
Thereafter | 58.0 | ||
Total | $ | 256.9 | |
53
A summary of the Company's warranty accrual activity is presented below (in thousands):
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
Balance, beginning of year | $ | 10,548 | $ | 10,183 | $ | 9,537 | |||||
Additions charged to costs and expenses | 10,820 | 15,950 | 14,284 | ||||||||
Deductions | (11,170 | ) | (15,513 | ) | (13,059 | ) | |||||
Other | 389 | (72 | ) | (579 | ) | ||||||
Balance, end of year | $ | 10,587 | $ | 10,548 | $ | 10,183 | |||||
Other included warranty balances at acquired businesses at the dates of acquisition, the effects of foreign currency translation adjustments, reclassifications and other.
As of December 31, 2017, Roper had $75.9 million of letters of credit issued to guarantee its performance under certain services contracts or to support certain insurance programs and $573.4 million of outstanding surety bonds. Certain contracts, primarily those involving public sector customers, require Roper to provide a surety bond as a guarantee of its performance of contractual obligations.
(13) Segment and Geographic Area Information
Roper's operations are reported in four segments around common customers, markets, sales channels, technologies and common cost opportunities. The segments are: RF Technology, Medical & Scientific Imaging, Industrial Technology and Energy Systems & Controls. The RF Technology segment provides comprehensive application management software, software-as-a-service applications and products and systems that utilize RFID communication technology. The Medical & Scientific Imaging segment offers medical products and software and high performance digital imaging products and software. Products included within the Industrial Technology segment are water and fluid handling pumps, flow measurement and metering equipment, industrial valves and controls, materials analysis equipment and consumables and industrial leak testing. The Energy Systems & Controls segment's products include control systems, equipment and consumables for fluid properties testing, vibration sensors and other non-destructive inspection and measurement products and services. Roper's management structure and internal reporting are aligned consistently with these four segments.
There were no material transactions between Roper's business segments during 2017, 2016 and 2015. Sales between geographic areas are primarily of finished products and are accounted for at prices intended to represent third-party prices. Operating profit by business segment and by geographic area is defined as net revenues less operating costs and expenses. These costs and expenses do not include unallocated corporate administrative expenses. Items below income from operations on Roper's statement of earnings are not allocated to business segments.
Identifiable assets are those assets used primarily in the operations of each business segment or geographic area. Corporate assets are principally comprised of cash and cash equivalents, deferred tax assets, recoverable insurance claims, deferred compensation assets and property and equipment.
54
Selected financial information by business segment for 2017, 2016 and 2015 follows (in thousands):
RF Technology | Medical & Scientific Imaging | Industrial Technology | Energy Systems & Controls | Corporate | Total | ||||||||||||||||||
2017 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Net revenues | $ | 1,862,126 | $ | 1,410,349 | $ | 783,707 | $ | 551,289 | $ | — | $ | 4,607,471 | |||||||||||
Operating profit | 479,295 | 486,575 | 235,018 | 151,163 | (141,807 | ) | 1,210,244 | ||||||||||||||||
Assets: | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Operating assets | 518,423 | 309,235 | 195,413 | 175,775 | 7,399 | 1,206,245 | |||||||||||||||||
Intangible assets, net | 6,660,898 | 4,590,768 | 499,490 | 544,375 | — | 12,295,531 | |||||||||||||||||
Other | 192,041 | 131,078 | 76,193 | 196,528 | 218,797 | 814,637 | |||||||||||||||||
Total | 14,316,413 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Capital expenditures | 20,079 | 18,791 | 5,707 | 3,155 | 1,020 | 48,752 | |||||||||||||||||
Capitalized software expenditures | 9,989 | 792 | 3 | — | — | 10,784 | |||||||||||||||||
Depreciation and other amortization | 191,876 | 118,643 | 17,109 | 16,747 | 590 | 344,965 | |||||||||||||||||
2016 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Net revenues | $ | 1,210,264 | $ | 1,362,813 | $ | 706,625 | $ | 510,223 | $ | — | $ | 3,789,925 | |||||||||||
Operating profit | 372,467 | 477,548 | 202,451 | 129,602 | (127,505 | ) | 1,054,563 | ||||||||||||||||
Assets: | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Operating assets | 487,936 | 282,437 | 182,430 | 164,349 | 11,788 | 1,128,940 | |||||||||||||||||
Intangible assets, net | 6,634,964 | 4,660,298 | 493,924 | 513,799 | — | 12,302,985 | |||||||||||||||||
Other | 156,413 | 154,838 | 88,130 | 134,976 | 358,645 | 893,002 | |||||||||||||||||
Total | 14,324,927 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Capital expenditures | 11,536 | 16,098 | 6,590 | 2,218 | 863 | 37,305 | |||||||||||||||||
Capitalized software expenditures | 6 | 2,749 | 15 | 31 | — | 2,801 | |||||||||||||||||
Depreciation and other amortization | 82,653 | 119,248 | 18,573 | 19,701 | 278 | 240,453 | |||||||||||||||||
2015 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Net revenues | $ | 1,033,951 | $ | 1,215,318 | $ | 745,381 | $ | 587,745 | $ | — | $ | 3,582,395 | |||||||||||
Operating profit | 312,112 | 441,931 | 214,538 | 162,128 | (102,791 | ) | 1,027,918 | ||||||||||||||||
Assets: | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Operating assets | 293,004 | 265,520 | 182,544 | 194,898 | 9,080 | 945,046 | |||||||||||||||||
Intangible assets, net | 2,848,911 | 4,451,028 | 513,155 | 540,628 | — | 8,353,722 | |||||||||||||||||
Other | 117,596 | 121,461 | 67,832 | 113,014 | 449,694 | 869,597 | |||||||||||||||||
Total | 10,168,365 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Capital expenditures | 10,758 | 12,642 | 9,179 | 3,276 | 405 | 36,260 | |||||||||||||||||
Capitalized software expenditures | — | 2,368 | 48 | 23 | — | 2,439 | |||||||||||||||||
Depreciation and other amortization | 56,877 | 105,928 | 19,912 | 21,254 | 290 | 204,261 | |||||||||||||||||
55
Summarized data for Roper's U.S. and foreign operations (principally in Canada, Europe and Asia) for 2017, 2016 and 2015, based upon the country of origin of the Roper entity making the sale, was as follows (in thousands):
United States | Non-U.S. | Eliminations | Total | ||||||||||||
2017 | |||||||||||||||
Sales to unaffiliated customers | $ | 3,679,133 | $ | 928,338 | $ | — | $ | 4,607,471 | |||||||
Sales between geographic areas | 133,193 | 187,765 | (320,958 | ) | — | ||||||||||
Net revenues | $ | 3,812,326 | $ | 1,116,103 | $ | (320,958 | ) | $ | 4,607,471 | ||||||
Long-lived assets | $ | 144,013 | $ | 31,431 | $ | — | $ | 175,444 | |||||||
2016 | |||||||||||||||
Sales to unaffiliated customers | $ | 2,978,496 | $ | 811,429 | $ | — | $ | 3,789,925 | |||||||
Sales between geographic areas | 137,276 | 109,370 | (246,646 | ) | — | ||||||||||
Net revenues | $ | 3,115,772 | $ | 920,799 | $ | (246,646 | ) | $ | 3,789,925 | ||||||
Long-lived assets | $ | 145,996 | $ | 21,020 | $ | — | $ | 167,016 | |||||||
2015 | |||||||||||||||
Sales to unaffiliated customers | $ | 2,829,752 | $ | 752,643 | $ | — | $ | 3,582,395 | |||||||
Sales between geographic areas | 135,363 | 119,006 | (254,369 | ) | — | ||||||||||
Net revenues | $ | 2,965,115 | $ | 871,649 | $ | (254,369 | ) | $ | 3,582,395 | ||||||
Long-lived assets | $ | 133,522 | $ | 21,960 | $ | — | $ | 155,482 | |||||||
Export sales from the U.S. during the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 were $513 million, $460 million and $481 million, respectively. In the year ended December 31, 2017, these exports were shipped primarily to Asia (34%), Europe (21%), Canada (17%), Middle East (16%) and other (12%).
Sales to customers outside the U.S. accounted for a significant portion of Roper's revenues. Sales are attributed to geographic areas based upon the location where the product is ultimately shipped. Roper's net revenues for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 are shown below by region, except for Canada, which is presented separately as it is the only country in which Roper has had greater than 4% of total revenues for any of the three years presented (in thousands):
RF Technology | Medical & Scientific Imaging | Industrial Technology | Energy Systems & Controls | Total | |||||||||||||||
2017 | |||||||||||||||||||
Canada | $ | 73,356 | $ | 23,501 | $ | 64,079 | $ | 26,171 | $ | 187,107 | |||||||||
Europe | 140,348 | 244,031 | 92,427 | 119,434 | 596,240 | ||||||||||||||
Asia | 10,180 | 119,150 | 58,286 | 137,693 | 325,309 | ||||||||||||||
Middle East | 61,356 | 11,051 | 4,833 | 35,238 | 112,478 | ||||||||||||||
Rest of the world | 26,243 | 22,708 | 21,485 | 49,592 | 120,028 | ||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 311,483 | $ | 420,441 | $ | 241,110 | $ | 368,128 | $ | 1,341,162 | |||||||||
2016 | |||||||||||||||||||
Canada | $ | 52,703 | $ | 21,993 | $ | 60,551 | $ | 22,360 | $ | 157,607 | |||||||||
Europe | 71,673 | 228,058 | 89,229 | 119,032 | 507,992 | ||||||||||||||
Asia | 11,988 | 111,843 | 52,087 | 126,769 | 302,687 | ||||||||||||||
Middle East | 50,605 | 10,107 | 2,997 | 37,491 | 101,200 | ||||||||||||||
Rest of the world | 17,067 | 21,549 | 20,675 | 46,202 | 105,493 | ||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 204,036 | $ | 393,550 | $ | 225,539 | $ | 351,854 | $ | 1,174,979 | |||||||||
2015 | |||||||||||||||||||
Canada | $ | 45,506 | $ | 23,737 | $ | 65,826 | $ | 23,883 | $ | 158,952 | |||||||||
Europe | 57,581 | 167,698 | 97,938 | 129,021 | 452,238 | ||||||||||||||
Asia | 10,019 | 112,732 | 60,817 | 132,088 | 315,656 | ||||||||||||||
Middle East | 54,165 | 15,877 | 4,220 | 50,227 | 124,489 | ||||||||||||||
Rest of the world | 10,761 | 20,417 | 24,471 | 55,074 | 110,723 | ||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 178,032 | $ | 340,461 | $ | 253,272 | $ | 390,293 | $ | 1,162,058 | |||||||||
56
(14) Concentration of Risk
Financial instruments which potentially subject the Company to credit risk consist primarily of cash, trade receivables and unbilled receivables.
The Company maintains cash with various major financial institutions around the world. The Company limits the amount of credit exposure with any one financial institution and believes that no significant concentration of credit risk exists with respect to cash balances.
Trade and unbilled receivables subject the Company to the potential for credit risk with customers. To reduce credit risk, the Company performs ongoing evaluations of its customers' financial condition.
(15) Quarterly Financial Data (unaudited)
First Quarter | Second Quarter | Third Quarter | Fourth Quarter | ||||||||||||
(in thousands, except per share data) | |||||||||||||||
2017 | |||||||||||||||
Net revenues | $ | 1,086,305 | $ | 1,134,671 | $ | 1,159,912 | $ | 1,226,583 | |||||||
Gross profit | 667,614 | 705,650 | 726,420 | 765,112 | |||||||||||
Income from operations | 258,256 | 294,258 | 310,747 | 346,983 | |||||||||||
Net earnings | 158,071 | 179,556 | 190,273 | 443,872 | |||||||||||
Earnings per share: | |||||||||||||||
Basic | $ | 1.55 | $ | 1.76 | $ | 1.86 | 4.33 | ||||||||
Diluted | $ | 1.53 | $ | 1.74 | $ | 1.84 | 4.27 | ||||||||
2016 | |||||||||||||||
Net revenues | $ | 902,423 | $ | 931,558 | $ | 945,144 | $ | 1,010,800 | |||||||
Gross profit | 559,519 | 567,520 | 578,493 | 626,878 | |||||||||||
Income from operations | 244,991 | 253,078 | 267,390 | 289,104 | |||||||||||
Net earnings | 151,416 | 158,069 | 167,079 | 182,081 | |||||||||||
Earnings per share: | |||||||||||||||
Basic | $ | 1.50 | $ | 1.56 | $ | 1.65 | $ | 1.79 | |||||||
Diluted | $ | 1.48 | $ | 1.54 | $ | 1.63 | $ | 1.78 | |||||||
The sum of the four quarters may not agree with the total for the year due to rounding.
57
ROPER TECHNOLOGIES, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Schedule II – Consolidated Valuation and Qualifying Accounts
Years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
Balance at beginning of year | Additions charged to costs and expenses | Deductions | Other | Balance at end of year | |||||||||||||||
(in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||||
Allowance for doubtful accounts and sales allowances | |||||||||||||||||||
2017 | $ | 14,489 | $ | 4,262 | $ | (5,919 | ) | $ | (144 | ) | $ | 12,688 | |||||||
2016 | 12,404 | 1,791 | (2,794 | ) | 3,088 | 14,489 | |||||||||||||
2015 | 13,694 | 1,536 | (4,128 | ) | 1,302 | 12,404 | |||||||||||||
Reserve for inventory obsolescence | |||||||||||||||||||
2017 | $ | 37,233 | $ | 5,291 | $ | (6,331 | ) | $ | 1,917 | $ | 38,110 | ||||||||
2016 | 34,040 | 10,071 | (6,540 | ) | (338 | ) | 37,233 | ||||||||||||
2015 | 38,879 | 8,616 | (9,049 | ) | (4,406 | ) | 34,040 | ||||||||||||
Deductions from the allowance for doubtful accounts represented the net write-off of uncollectible accounts receivable. Deductions from the inventory obsolescence reserve represented the disposal of obsolete items.
Other included the allowance for doubtful accounts and reserve for inventory obsolescence of acquired businesses at the dates of acquisition, the effects of foreign currency translation adjustments for those companies whose functional currency was not the U.S. dollar, reclassifications and other.
58
ITEM 9. | CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE |
There have been no changes in accountants or disagreements with accountants on accounting and financial disclosures.
ITEM 9A. | CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES |
Management's Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate control over financial reporting, as such term is defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f). Under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including our principal executive officer and principal financial officer, we conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting based on the framework in Internal Control-Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. Based on our evaluation under the framework in Internal Control-Integrated Framework, our management concluded that our internal control over financial reporting was effective as of December 31, 2017. Our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017 has been audited by PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, as stated in their report which is included herein.
Our management excluded acquisitions completed during 2017 from its assessment of internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017. These acquisitions are wholly-owned subsidiaries whose assets and revenues each represent less than 1% of the related consolidated financial statement amounts as of and for the year ended December 31, 2017.
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
As required by SEC rules, we have evaluated the effectiveness of the design and operation of our disclosure controls and procedures as of the end of the period covered by this report. This evaluation was carried out under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including our principal executive officer and principal financial officer. Based on this evaluation, we have concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures were effective as of December 31, 2017.
Disclosure controls and procedures are our controls and other procedures designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed by us in the reports that we file or submit under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized and reported, within the time periods specified in the SEC's rules and forms. Disclosure controls and procedures include, without limitation, controls and procedures designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed by us in the reports that we file or submit under the Exchange Act are accumulated and communicated to our management, including our principal executive officer and principal financial officer, as appropriate, to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
There was no change in our internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the fourth quarter of 2017 that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
ITEM 9B. | OTHER INFORMATION |
There were no disclosures of any information required to be filed on Form 8-K during the fourth quarter of 2017 that were not filed.
59
PART III
Except as otherwise indicated, the following information required by the Instructions to Form 10-K is incorporated herein by reference from the sections of the Roper Proxy Statement for the annual meeting of shareholders ("2018 Proxy Statement"), as specified below:
ITEM 10. | DIRECTORS EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE |
We incorporate the information required by this item by reference to our 2018 Proxy Statement.
ITEM 11. | EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION |
We incorporate the information required by this item by reference to our 2018 Proxy Statement.
ITEM 12. | SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS |
Other than the information set forth below, we incorporate the information required by this item by reference to our 2018 Proxy Statement.
Securities Authorized for Issuance under Equity Compensation Plans
The following table provides information as of December 31, 2017 regarding compensation plans (including individual compensation arrangements) under which our equity securities are authorized for issuance.
Plan Category | (a) Number of Securities to be Issued Upon Exercise of Outstanding Options, Warrants and Rights | (b) Weighted-Average Exercise Price of Outstanding Options, Warrants and Rights | (c) Number of Securities Remaining Available for Future Issuance Under Equity Compensation Plans (Excluding Securities Reflected in Column (a)) | ||||||
Equity Compensation Plans Approved by Shareholders (1) | |||||||||
Stock options | 3,195,864 | $ | 140.68 | ||||||
Restricted stock awards (2) | 858,996 | — | |||||||
Subtotal | 4,054,860 | 7,802,395 | |||||||
Equity Compensation Plans Not Approved by Shareholders | — | — | — | ||||||
Total | 4,054,860 | $ | — | 7,802,395 | |||||
(1) | Consists of the Amended and Restated 2006 Incentive Plan (no additional equity awards may be granted under this plan) and the 2016 Incentive Plan. |
(2) | The weighted-average exercise price is not applicable to restricted stock awards. |
ITEM 13. | CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE |
We incorporate the information required by this item by reference to our 2018 Proxy Statement.
ITEM 14. | PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTANT FEES AND SERVICES |
We incorporate the information required by this item by reference to our 2018 Proxy Statement.
60
PART IV
ITEM 15. | EXHIBITS AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES |
(a) | The following documents are filed as a part of this Annual Report. |
(1) | Consolidated Financial Statements: The following consolidated financial statements are included in Part II, Item 8 of this report. |
Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2017 and 2016
Consolidated Statements of Earnings for the Years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income for the Years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
Consolidated Statements of Stockholders' Equity for the Years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the Years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(2) | Consolidated Valuation and Qualifying Accounts for the Years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 |
(b) | Exhibits |
Exhibit No. | Description of Exhibit | ||
(a)3.1 | |||
(b)3.2 | |||
(c)4.2 | |||
4.3 | |||
(d)4.4 | |||
(e)4.5 | |||
(f)4.6 | |||
(g)4.7 | |||
(h)4.8 | |||
(i)4.9 | |||
(j)4.10 | |||
(k)4.11 | |||
4.12 | |||
(l)4.13 | |||
4.14 | |||
(m)10.01 | |||
(n)10.02 | |||
(o)10.03 | |||
(p)10.04 | |||
(q)10.05 | |||
(r)10.06 | |||
(s)10.07 | |||
(t)10.08 | |||
(u)10.09 | |||
(u)10.10 | |||
(u)10.11 | |||
(v)10.12 | |||
(w)10.13 | |||
(x)10.14 | |||
(y)10.15 | |||
(z)10.16 | |||
(aa)10.17 | |||
(bb)10.18 | |||
(cc)10.19 | |||
(dd)10.20 | |||
10.21 | |||
10.22 | |||
10.23 | |||
21.1 | |||
23.1 | |||
31.1 | |||
31.2 | |||
32.1 | |||
101.INS | XBRL Instance Document, furnished herewith. | ||
101.SCH | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document, furnished herewith. | ||
101.CAL | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document, furnished herewith. | ||
101.DEF | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document, furnished herewith. | ||
101.LAB | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document, furnished herewith. | ||
101.PRE | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document, furnished herewith. | ||
a) | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on April 24, 2015 (file no. 1-12273). | ||
b) | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 3.2 to the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed March 14, 2016 (file no. 1-12273). | ||
c) | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 4.2 to the Company's Pre-Effective Amendment No. 1 to the Registration Statement on Form S-3 filed November 28, 2003 (file no. 333-110491). | ||
d) | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed January 13, 2004 (file no. 1-12273). | ||
e) | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed December 7, 2004 (file no. 1-12273). | ||
f) | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 4.2 to the Company's Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed on November 7, 2008 (file no. 1-12273). | ||
g) | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 4.2 to the Registration Statement on Form S-3/ASR filed November 25, 2015 (file no. 333-208200). | ||
h) | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed June 6, 2013 (file no. 1-12273). | ||
i) | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed September 2, 2009 (file no. 1-12273). | ||
j) | Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed November 21, 2012 (file no. 1-12273). | ||
k) | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed December 7, 2015 (file no. 1-12273). | ||
l) | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed December 19, 2016 (file no. 1-12273). | ||
m) | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.04 to the Company's Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed August 31, 1999 (file no. 1-12273). | ||
n) | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company's Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed March 5, 2017. (file no. 1-12273). | ||
o) | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.06 to the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K filed March 2, 2009 (file no. 1-12273). | ||
p) | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.07 to the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K filed March 2, 2009 (file no. 1-12273). | ||
q) | Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed September 23, 2016 (file no. 1-12273). | ||
r) | Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed December 7, 2016 (file no. 1-12273). | ||
s) | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company's Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q filed August 9, 2006 (file no. 1-12273). | ||
t) | Incorporated herein by reference to Appendix A to the Company's Definitive Proxy Statement on Schedule 14A filed April 30, 2012 (file no. 1-12273). | ||
u) | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibits 10.2, 10.3 and 10.4 to the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K filed December 6, 2006 (file no. 1-12273). | ||
v) | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.21 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K filed March 2, 2009 (file no. 1-12273). | ||
w) | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.17 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K filed on February 27, 2017 (file no. 1-12273). | ||
x) | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10 to the Current Report on Form 8-K filed November 20, 2015 (file no. 1-12273). | ||
y) | Incorporated by reference to Appendix B to the Company’s Definitive Proxy Statement on Schedule 14A filed April 26, 2016 (file no. 1-12273). | ||
z) | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.20 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K filed on February 27, 2017 (file no. 1-12273). | ||
aa) | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.21 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K filed on February 27, 2017 (file no. 1-12273). | ||
bb) | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.22 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K filed on February 27, 2017 (file no. 1-12273). | ||
cc) | Incorporated herein by reference to Exhibit 10.23 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K filed on February 27, 2017 (file no. 1-12273). | ||
dd) | Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Company’s Form 10-Q filed August 5, 2016 (file no. 1-12273). | ||
† | Management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement. | ||
ITEM 16. | FORM 10-K SUMMARY |
None
61
Signatures
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, Roper has duly caused this Report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, therewith duly authorized.
ROPER TECHNOLOGIES, INC.
(Registrant)
By: | /S/ BRIAN D. JELLISON | February 23, 2018 | |
Brian D. Jellison, President and Chief Executive Officer | |||
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this Report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of Roper and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
/S/ BRIAN D. JELLISON | President, Chief Executive Officer and | ||
Brian D. Jellison | Chairman of the Board of Directors | February 23, 2018 | |
(Principal Executive Officer) | |||
/S/ ROBERT C. CRISCI | Vice President, Chief Financial Officer | ||
Robert C. Crisci | (Principal Financial Officer) | February 23, 2018 | |
/S/ JASON P. CONLEY | Vice President and Controller | ||
Jason P. Conley | (Principal Accounting Officer) | February 23, 2018 | |
/S/ AMY WOODS BRINKLEY | |||
Amy Woods Brinkley | Director | February 23, 2018 | |
/S/ JOHN F. FORT, III | |||
John F. Fort, III | Director | February 23, 2018 | |
/S/ ROBERT D. JOHNSON | |||
Robert D. Johnson | Director | February 23, 2018 | |
/S/ ROBERT E. KNOWLING | |||
Robert E. Knowling | Director | February 23, 2018 | |
/S/ WILBUR J. PREZZANO | |||
Wilbur J. Prezzano | Director | February 23, 2018 | |
/S/ LAURA G. THATCHER | |||
Laura G. Thatcher | Director | February 23, 2018 | |
/S/ RICHARD F. WALLMAN | |||
Richard F. Wallman | Director | February 23, 2018 | |
/S/ CHRISTOPHER WRIGHT | |||
Christopher Wright | Director | February 23, 2018 | |
62
