Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-31.2 - EXHIBIT 31.2 SECTION 302 CFO CERTIFICATION - TRACTOR SUPPLY CO /DE/ | a201710-kex312.htm |
| EX-32 - EXHIBIT 32 SECTION 906 CERTIFICATION - TRACTOR SUPPLY CO /DE/ | a201710-kex32.htm |
| EX-31.1 - EXHIBIT 31.1 SECTION 302 CEO CERTIFICATION - TRACTOR SUPPLY CO /DE/ | a201710-kex311.htm |
| EX-23 - EXHIBIT 23 CONSENT - TRACTOR SUPPLY CO /DE/ | a201710-kex23.htm |
| EX-21 - EXHIBIT 21 SUBSIDIARIES LIST - TRACTOR SUPPLY CO /DE/ | a201710-kex21.htm |
| EX-10.34 - EXHIBIT 10.34 FORM OF PERFORMANCE SHARE UNIT AGREEMENT FOR CEO - TRACTOR SUPPLY CO /DE/ | a201710-kex1034performance.htm |
| EX-10.33 - EXHIBIT 10.33 FORM OF PERFORMANCE SHARE UNIT AGREEMENT FOR OFFICERS - TRACTOR SUPPLY CO /DE/ | a201710-kex1033performance.htm |
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
WASHINGTON, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
(Mark One)
ý | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended December 30, 2017
or
o | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from________to________.
Commission file number 000-23314

TRACTOR SUPPLY COMPANY
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
Delaware | 13-3139732 | |
(State or Other Jurisdiction of Incorporation or Organization) | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) | |
5401 Virginia Way, Brentwood, Tennessee | 37027 | |
(Address of Principal Executive Offices) | (Zip Code) | |
Registrant’s Telephone Number, Including Area Code: | (615) 440-4000 | |
Securities Registered Pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
Title of each class | Name of each exchange on which registered | |
Common Stock, $.008 par value | NASDAQ Global Select Market | |
Securities Registered Pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act.
YES þ NO o
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act.
YES o NO þ
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days.
YES þ NO o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files).
YES þ NO o
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K (§229.405 of this chapter) is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act:
Large accelerated filer | þ | Accelerated filer | o | |
Non-accelerated filer | o (Do not check if a smaller reporting company) | Smaller reporting company | o | |
Emerging growth company | o | |||
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act.)
YES o NO þ
The aggregate market value of the Common Stock held by non-affiliates of the registrant, based on the closing price of the Common Stock on The NASDAQ Global Select Market on July 1, 2017, the last business day of the registrant’s most recently completed second fiscal quarter, was approximately $6.2 billion. For purposes of this response, the registrant has assumed that its directors, executive officers, and beneficial owners of 5% or more of its Common Stock are affiliates of the registrant.
Indicate the number of shares outstanding of each of the registrant’s classes of common stock as of the latest practicable date.
Class | Outstanding at January 27, 2018 | |
Common Stock, $.008 par value | 125,116,910 | |
Portions of the Registrant’s definitive Proxy Statement for its 2018 Annual Meeting of Stockholders are incorporated by reference into Part III hereof.
Item no. | Form 10-K Report Page | |
i
FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS OR INFORMATION
This Form 10-K and statements included or incorporated by reference in this Form 10-K include certain historical and forward-looking information. The forward-looking statements included are made pursuant to the safe harbor provisions of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995 (the “Act”). All statements, other than statements of historical facts, which address activities, events or developments that we expect or anticipate will or may occur in the future, including such things as future capital expenditures (including their amount and nature), business strategy, expansion and growth of the business operations and other such matters are forward-looking statements. To take advantage of the safe harbor provided by the Act, we are identifying certain factors that could cause actual results to differ materially from those expressed in any forward-looking statements, whether oral or written. These factors include, without limitation, national, regional and local economic conditions affecting consumer spending, weather conditions, the seasonal nature of the business, the timing and acceptance of new products in the stores, the timing and mix of goods sold, purchase price volatility (including inflationary and deflationary pressures), the ability to increase sales at existing stores, the ability to manage growth and identify suitable locations, failure of an acquisition to produce anticipated results, the ability to successfully manage expenses and execute key gross margin enhancing initiatives, increases in fuel and other transportation costs, increases in wages due to competitive pressures or minimum wage laws and regulations, the availability of favorable credit sources, capital market conditions in general, the ability to open new stores in the manner and number currently contemplated, the impact of new stores on the business, competition, effective merchandising and marketing initiatives, the ability to retain vendors, reliance on foreign suppliers, the ability to attract, train and retain qualified employees, product liability and other claims, changes in federal, state or local regulations, potential judgments, fines, legal fees and other costs, breach of information systems or theft of employee or customer data, ongoing and potential future legal or regulatory proceedings, management of the Company’s information systems, failure to develop and implement new technologies, the failure of customer-facing technology systems, business disruption resulting from a natural or other disaster or implementation of new technologies, including but not limited to, new supply chain technologies, effective tax rate changes, including expected effects of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, and results of examination by taxing authorities, the ability to maintain an effective system of internal control over financial reporting, changes in accounting standards, assumptions and estimates, and those described in Item 1A. “Risk Factors.” Forward-looking statements are based on currently available information and are based on our current expectations and projections about future events. We undertake no obligation to release publicly any revisions to these forward-looking statements to reflect events or circumstances after the date hereof or to reflect the occurrence of unanticipated events.
ii
PART I
Item 1. | Business |
Overview
Tractor Supply Company (the “Company” or “we”) is the largest operator of rural lifestyle retail stores in the United States (“U.S.”). The Company is focused on supplying the needs of recreational farmers and ranchers and others who enjoy the rural lifestyle (which we refer to as the “Out Here” lifestyle), as well as tradesmen and small businesses. We operate retail stores under the names Tractor Supply Company, Del’s Feed & Farm Supply and Petsense and operate websites under the names TractorSupply.com and Petsense.com. Our stores are located primarily in towns outlying major metropolitan markets and in rural communities.
Tractor Supply Company has one reportable industry segment which is the retail sale of products that support the rural lifestyle. At December 30, 2017, we operated 1,853 retail stores in 49 states (1,685 Tractor Supply and Del’s retail stores and 168 Petsense retail stores). Our Tractor Supply stores typically range in size from 15,000 to 20,000 square feet of inside selling space, along with additional outside selling space, and our Petsense stores have approximately 5,500 square feet of inside selling space. For Tractor Supply retail locations, we use a standard design for most new built-to-suit locations that includes approximately 15,500 square feet of inside selling space.
Business Strategy
We believe our sales and earnings growth is the result of executing our business strategy, which includes the following key components:
Market Niche
We have identified a specialized market niche: supplying the lifestyle needs of recreational farmers and ranchers and others who enjoy the rural lifestyle, as well as tradesmen and small businesses. By focusing our product assortment on these core customers, we believe we are differentiated from general merchandise, home center and other specialty retailers. We cater to the rural lifestyle and often serve a market by being a trip consolidator for many basic maintenance needs for farm, ranch and rural customers.
Customers
Our target customers are home, land, pet and livestock owners who generally have above average income and below average cost of living. We seek to serve a customer base that primarily lives in towns outlying major metropolitan markets and in rural communities. This customer base includes recreational farmers and ranchers and others who enjoy the rural lifestyle, as well as tradesmen and small businesses.
Customer Service
We are committed to providing our customers reliable product availability and a high level of in-store service through our motivated, well-trained store team members. We believe the ability of our store team members to provide friendly, responsive and seasoned advice helps our customers find the right products to satisfy their everyday needs as well as the specialty items needed to complete their rural lifestyle projects. We also engage with our customers through our e-commerce website (TractorSupply.com), which provides the opportunity to allow customers to shop at a time and place that fits their schedule while delivering enhanced product information, research and decision tools that support product selection and informational needs in specific subject areas. Additionally, we maintain a customer solutions center at our Store Support Center located in Brentwood, Tennessee to support our in-store and online customers as well as our store team members. We believe this commitment to customer service promotes strong customer loyalty and repeat shopping.
We use a third-party provider to measure our level of customer service. This process allows customers to provide feedback on their shopping experience. Based on the third-party provider’s data, we believe our customer satisfaction scores to be among the best-in-class. We carefully evaluate the feedback we receive from our customers and implement improvements at the individual store level based on that feedback.
1
Store Personnel and Training
We seek to hire store team members with farming and ranching backgrounds, with particular emphasis on general maintenance, equine and welding. We endeavor to staff our stores with courteous, highly motivated team members and devote considerable resources to training store team members, often in cooperation with our vendors. Our training programs include:
• | a thorough on-boarding process to prepare new team members for their new role; |
• | productive workplace environment training that is intended to educate team members on company policies and procedures covering topics such as harassment, discrimination, and retaliation; |
• | new store opening training that prepares our store managers to open new stores to Company standards; |
• | a management training program which covers all aspects of our store operations, delivering superior service and managing the team member experience; |
• | structured training on customer service and selling skills; |
• | online product knowledge training produced in conjunction with key vendors; |
• | leadership development programs that prepare leaders to expand their current contributions; and |
• | an annual store manager meeting with vendor product presentations. |
Store Environment
Our stores are designed and managed to make shopping an enjoyable experience and to maximize sales and operating efficiencies. Stores are strategically arranged to provide an open environment for optimal product placement and visual display. In addition, these layouts allow for departmental space to be easily re-allocated and visual displays to be changed for seasonal products and promotions. Display and product placement information is routinely sent to stores to ensure quality and uniformity among the stores. Informative signs are located in key product categories to assist customers with purchasing decisions and merchandise location. These signs provide customers with a comparison of product qualities, clear pricing, useful information regarding product benefits, and suggestions for appropriate accessories. Our store layouts and visual displays are designed to provide our customers a feeling of familiarity and enhance the shopping experience. Also, our store team members wear highly visible red vests, aprons or smocks with nametags, and our customer service and checkout counters are conveniently located near the front of the store.
Merchandising and Purchasing
We offer an extensive assortment of products for those seeking to enjoy the “Out Here” lifestyle, as well as tradesmen and small businesses. Our product assortment is tailored to meet the needs of our customers in various geographic markets. Our full line of product offerings includes a broad selection of high quality, reputable brand name and exclusive brand products and is supported by a strong in-stock inventory position with an average of 15,500 to 20,000 products per store. No one product accounted for more than 10% of our sales during 2017. Our comprehensive selection of merchandise is comprised of the following major product categories:
• | Equine, livestock, pet and small animal products, including items necessary for their health, care, growth and containment; |
• | Hardware, truck, towing and tool products; |
• | Seasonal products, including heating, lawn and garden items, power equipment, gifts and toys; |
• | Work/recreational clothing and footwear; and |
• | Maintenance products for agricultural and rural use. |
The following table indicates the percentage of net sales represented by each of our major product categories during fiscal 2017, 2016 and 2015:
Percent of Net Sales | ||||||||
Product Category: | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||
Livestock and Pet | 47 | % | 46 | % | 44 | % | ||
Hardware, Tools and Truck | 22 | 22 | 23 | |||||
Seasonal, Gift and Toy Products | 19 | 19 | 20 | |||||
Clothing and Footwear | 8 | 8 | 8 | |||||
Agriculture | 4 | 5 | 5 | |||||
Total | 100 | % | 100 | % | 100 | % | ||
Our buying team continuously reviews and updates our product assortment to respond to customer needs and to offer new, relevant products. We are focused on providing key products that our customers use on a regular basis for their lifestyle and maintenance
2
needs with emphasis on consumable, usable, and edible (“C.U.E.”) products. Examples of C.U.E. product categories include, but are not limited to, livestock feed and bedding, pet food, lubricants, and various seasonal products, such as heating, pest control and twine.
Our products are sourced through both domestic and international vendors. Our business is not dependent upon any one vendor or particular group of vendors. We purchase our products from a group of approximately 900 vendors, with no one vendor representing more than 10% of our purchases during fiscal 2017. Approximately 350 core vendors accounted for 90% of our merchandise purchases during fiscal 2017. We have not experienced any significant difficulty in obtaining satisfactory alternative sources of supply for our products, and we believe that adequate sources of supply exist at substantially similar costs for nearly all of our products. We have no material long-term contractual commitments with any of our product vendors.
Our buying teams focus on merchandise procurement, vendor line reviews and testing of new products and programs. We also employ a dedicated inventory management team that focuses exclusively on forecasting and inventory replenishment, a committed merchandise planning team that concentrates on assortment planning and a specialized pricing team that seeks to optimize market-specific pricing for our products. Through the combined efforts of these teams, we continue to focus on improving our overall inventory productivity and in-stock position.
Intellectual Property
Our subsidiary, Tractor Supply Co. of Texas, LP (“TSCT”), owns registrations with the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office (“USPTO”) for various service marks including TSC®, Tractor Supply Co.®, TSC Tractor Supply Co.® and the trapezium design for retail store services. We consider these service marks, and the accompanying goodwill and name recognition, to be valuable assets of our business. TSCT also owns several other service marks for retail services, some of which have been registered with the USPTO and some of which are the subject of applications for registration pending before the USPTO.
In addition to selling products that bear nationally-known manufacturer brands, we also sell products manufactured for us under a number of exclusive brands that we consider to be important to our business. These exclusive brands are manufactured for us by a number of vendors and provide an alternative to the national brands, which helps provide value for our customers and positions us as a destination store.
Our exclusive brands represented approximately 32% of our total sales in both fiscal 2017 and 2016 and 31% in fiscal 2015. Our exclusive brands include:
Ÿ 4health® (pet foods and supplies) | Ÿ JobSmart® (tools) |
Ÿ Bit & Bridle® (apparel and footwear) | Ÿ Paws & Claws® (pet foods and supplies) |
Ÿ Blue Mountain® (apparel) | Ÿ Producer’s Pride® (livestock and horse feed and supplies) |
Ÿ C.E. Schmidt® (apparel and footwear) | Ÿ Red Shed® (gifts, collectibles, and outdoor furniture) |
Ÿ Countyline® (livestock, farm and ranch equipment) | Ÿ Redstone® (heating products) |
Ÿ Dumor® (livestock and horse feed and supplies) | Ÿ Retriever® (pet foods and supplies) |
Ÿ Equistages® (horse feed) | Ÿ Royal Wing® (bird feed and supplies) |
Ÿ Groundwork® (lawn and garden supplies) | Ÿ Traveller® (truck and automotive products) |
Ÿ Huskee® (outdoor power equipment) | Ÿ TSC Tractor Supply Co® (trailers, truck tool boxes and animal |
bedding) | |
The exclusive brands identified above have been registered as trademarks with the USPTO for certain products and are the subject of applications for registration pending before the USPTO for other products.
Our trademark and service mark registrations have various expiration dates; however, provided that we continue to use the marks and renew the registrations in a timely manner, the registrations are potentially perpetual in duration.
We believe our intellectual property, which includes the trademarks and service marks identified above, together with certain trade names, domain names, patents and copyrights, has significant value and is an important component of our merchandising and marketing strategies.
3
Distribution
We currently operate a distribution network for supplying stores with merchandise and delivering product ordered through TractorSupply.com. In fiscal 2017, our Tractor Supply stores received approximately 74% of merchandise through this network while the remaining merchandise shipped directly to the stores from our vendors or directly to our customers. We believe this flow facilitates the prompt and efficient distribution of merchandise in order to enhance in-stocks, minimize freight costs and improve the inventory turn rate. Our distribution facilities, located in Arizona, Georgia, Indiana, Kentucky, Maryland, Nebraska, Texas, and Washington, represent total distribution capacity of 5.0 million square feet. In fiscal 2017, we began construction on a new northeast distribution center in Frankfort, New York, as well as an expansion of our existing distribution center in Waverly, Nebraska, which will provide additional distribution capacity once construction is completed.
We select the locations of our distribution facilities in an effort to minimize logistics costs and optimize the distance from distribution facilities to our stores. Our distribution centers utilize warehouse and labor management tools that support the planning, control and processing of inventory. We manage our inbound and outbound transportation activity in-house through the use of a transportation management system. We utilize multiple common carriers for store and direct to customer deliveries. We manage our transportation costs through carrier negotiations, the monitoring of transportation routes, and the scheduling of deliveries.
Marketing
We utilize an “everyday value price” philosophy to consistently offer our products at competitive prices complemented by strategically planned promotions throughout the year. To drive store traffic and position ourselves as a destination store, we promote broad selections of merchandise with newspaper circulars, customer targeted direct mail as well as e-mail, digital and social media initiatives. In addition, our Neighbor’s Club loyalty program enhances our ability to create engagement with our best customers. Vendors frequently support these specific programs by offering temporary cost reductions and honoring coupons. Our vendors also provide assistance with product presentation and fixture design, brochures, support for in-store events and point-of-purchase materials for customer education and product knowledge for our team members.
Omni-Channel
We connect with our customers in their manner of choosing, whether that is in store, on our e-commerce website (TractorSupply.com), e-mail, social media, direct mail or through our customer solutions center. Our goal is to be available anytime, anywhere and in any way our customers choose to engage with our brand. We provide our customers the opportunity to shop in a manner that fits their lifestyle and is most convenient for them. We offer an expansive product assortment, search capabilities and information that is relevant for their lifestyle. We provide our customers the ability to have products shipped direct to our retail stores, their homes or offices. We maintain two fulfillment centers within our distribution center network to support our e-commerce activities. In 2017, we completed the expansion of our buy online and pick up in store program which provides convenient customer pick up in our store locations. We also began providing additional convenience through flexible payment options and simplified checkout. We are focused on delivering an enhanced mobile and tablet experience, improving the site response time and expanding our product offerings for vendor direct to customer shipments, allowing us to serve our customers at any time. Digital capabilities have further enhanced customer service and allowed us to target markets outside of our current retail store locations.
Management and Team Members
As of December 30, 2017, we employed approximately 14,000 full-time and 14,000 part-time Tractor Supply team members. We also employ additional part-time team members during peak periods. We are not party to any collective bargaining agreements.
At the end of fiscal 2017, our store operations were organized into ten regions. Each region is led by a regional vice president, and the region is further organized into districts, each of which is led by a district manager. We have two internal advisory boards, one comprised of store managers and the other comprised of district managers. These groups bring a grassroots perspective to operational initiatives and generate chain-wide endorsement of proposed best-practice solutions.
All of our team members participate in one of various bonus incentive programs, which provide the opportunity to receive additional compensation based upon team and/or Company performance. In addition to bonus incentive programs, we provide our eligible team members the opportunity to participate in an employee stock purchase plan and a 401(k) retirement savings plan. We also share in the cost of health insurance provided to eligible team members, and team members receive a discount on merchandise purchased from the Company.
We encourage a promote-from-within environment when internal resources permit. We also provide internal leadership development programs designed to prepare our high-potential team members for greater responsibility. Our current team of district managers and store managers have an average tenure of approximately nine and six years, respectively. We believe internal
4
promotions, coupled with the hiring of individuals with previous retail experience, will provide the management structure necessary to support our planned growth.
Continuous Improvement
We are committed to a continuous improvement program to drive change throughout our organization. Using data analytics and team member engagement, we examine business processes and identify opportunities to reduce costs, drive innovation, and improve effectiveness. We have implemented numerous continuous improvement projects (with team members from multiple areas of our business) to evaluate key operations and implement process changes. Team members are empowered and expected to challenge current paradigms and improve processes. Our management encourages the participation of all team members in decision-making, regularly solicits input and suggestions from our team members and incorporates suggestions into our improvement activities.
Management Information and Control Systems
We have invested resources in management information and control systems to provide legendary customer service. This includes use of digital technologies to integrate the customer experience in store, online, and through our customer solutions center, offering customers the ability to shop anytime, anywhere, and in any way they choose. Our key platforms include a point-of-sale system, in-store mobility and digital technology system, an e-commerce platform, a supply chain management and replenishment system, a transportation management system, warehouse and labor management tools, a price optimization system, a vendor purchase order control system, a merchandise presentation system, and a customer loyalty system. These systems are integrated through an enterprise resource planning (“ERP”) system. This ERP system tracks merchandise from initial order through ultimate sale and interfaces with our financial systems.
We continue to invest in technology to support store, online, and distribution facility expansion. We also continue to evaluate and improve the functionality of our systems to maximize their effectiveness. Such efforts include ongoing hardware and software evaluations, refreshes and upgrades to support optimal software configurations and application performance. We plan to continue to invest in information technology and implement efficiency-driving system enhancements, as well as evaluate use of technologies to improve productivity such as artificial intelligence, automation software, and other technologies. We also maintain and continue to strengthen the security of our information systems to help protect and prevent unauthorized access to personal information of our customers, employees and vendors or other confidential Company data. Collectively, these efforts are directed toward improving business processes, maintaining secure, efficient and stable systems, and enabling the continued growth and success of our business.
Petsense
Petsense is a small-box pet specialty supply retailer focused on meeting the needs of pet owners, primarily in small and mid-sized communities, and offering a variety of pet products and services. At December 30, 2017, we operated a total of 168 Petsense stores in 26 states, with 400 full-time and 900 part-time team members, and an e-commerce website (Petsense.com). The Petsense name is registered with the USPTO.
Growth Strategy
Tractor Supply believes we can grow our business by being the most dependable supplier of relevant products and services for the “Out Here” lifestyle, creating customer loyalty through personalized experiences and providing convenience that our customers expect at anytime, anywhere, and in any way they choose. Our long-term growth strategy is to: (1) drive profitable growth through new store openings and by expanding omni-channel capabilities, thus tying together our website product content, social media, digital and online shopping experience, attracting new customers and driving loyalty, (2) build customer-centric engagement by leveraging analytics to deliver legendary customer service, seasoned advice and personalized experiences, (3) offer relevant assortments and services across all channels through exclusive and national brands and continue to introduce new products through our test and learn strategy, (4) enhance our core and foundational capabilities by investing in infrastructure and process improvements which will support growth, scale and agility while improving the customer experience, and (5) expand through selective acquisitions, as such opportunities arise, to add complementary businesses and to enhance penetration into new and existing markets to supplement organic growth.
Achieving this strategy will require a foundational focus on: (1) organizing, optimizing and empowering our team members for growth by developing skills, talent and leadership across the organization, and (2) implementing operational efficiency initiatives to align our cost structure to support new business capabilities for margin improvement and cost reductions.
Over the past five years, we have experienced considerable sales growth, resulting in a compounded annual growth rate of approximately 9.2%. We plan to open approximately 80 new Tractor Supply and 20 new Petsense stores in fiscal 2018, a selling square footage increase of approximately 5.0%. In fiscal 2017, we opened 101 new Tractor Supply stores and 25 new Petsense
5
stores. In fiscal 2016, we opened 113 new Tractor Supply stores and began operating 143 Petsense stores. This represents a selling square footage increase of approximately 6.3% during fiscal 2017 and 10.8% during fiscal 2016.
At December 30, 2017, we operated 1,853 retail stores in 49 states (1,685 Tractor Supply and Del’s retail stores and 168 Petsense retail stores). Given the size of the communities that we target, we believe that there is ample opportunity for new store growth in many existing and new markets. We have developed a proven method for selecting store sites and have identified approximately 800 additional markets for new Tractor Supply stores. We also believe that there is opportunity for up to 1,000 Petsense stores. Approximately 40% of our Tractor Supply stores are in freestanding buildings and 60% are located in strip shopping centers. We lease approximately 93% of our stores and own the remaining 7%.
Competition
We operate in a competitive retail industry. The principal competitive factors include location of stores, fulfillment options, price, quality of merchandise, in-stock consistency, merchandise assortment and presentation, product knowledge and customer service. We compete with general merchandise retailers, home center retailers, specialty and discount retailers, independently owned retail farm and ranch stores, numerous privately-held regional farm store chains and farm cooperatives, as well as internet-based retailers. However, we believe we successfully differentiate ourselves from many of these retailers by focusing on our specialized market niche for customers living the rural lifestyle. See further discussion of competition in 1A, “Risk Factors” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Seasonality and Weather
Our business is seasonal. Historically, our sales and profits are the highest in the second and fourth fiscal quarters due to the sale of seasonal products. We experience our highest inventory and accounts payable balances during our first fiscal quarter for purchases of seasonal products to support the higher sales volume of the spring selling season, and again during our third fiscal quarter to support the higher sales volume of the cold-weather selling season. We believe that our business can be more accurately assessed by focusing on the performance of the halves, not the quarters, due to the fact that different weather patterns from year-to-year can shift the timing of sales and profits between quarters, particularly between the first and second fiscal quarters and the third and fourth fiscal quarters.
Historically, weather conditions, including unseasonably warm weather in the fall and winter months and unseasonably cool weather in the spring and summer months, have affected the timing and volume of our sales and results of operations. In addition, extreme weather conditions, including snow and ice storms, flood and wind damage, hurricanes, tornadoes, extreme rain and droughts, have impacted operating results both negatively and positively, depending on the severity and length of these conditions. Our strategy is to manage product flow and adjust merchandise assortments and depth of inventory to capitalize on seasonal demand trends.
Stewardship and Compliance with Environmental Matters
Our operations are subject to numerous federal, state and local laws and regulations, enacted or adopted, regulating the discharge of materials into the environment or otherwise relating to the protection of the environment. We are committed to complying with all applicable environmental laws and regulations. We are also committed to becoming a more environmentally sustainable company. This commitment is demonstrated through our Stewardship Program, which is our environmental sustainability program. Through this program, the Company has implemented a number of initiatives designed to reduce our impact on the environment. These initiatives include the installation of energy management systems, LED lighting, high efficiency heating/air conditioning systems in our stores, and recycling programs in our stores, distribution facilities and the Store Support Center. Our Store Support Center, opened in 2014, and our distribution center in Casa Grande, Arizona, opened in 2015, were each awarded LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) Silver certification for environmentally sustainable design, construction and operation. We also installed solar arrays at the Store Support Center in Brentwood, Tennessee and our store in Hendersonville, Tennessee.
Executive Officers of the Registrant
Pursuant to General Instruction G(3) of Form 10-K, the following list is included in Part I of this Report in lieu of being included in the Proxy Statement for the Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be held on May 10, 2018.
6
The following is a list of the names and ages of all executive officers of the registrant, indicating all positions and offices with the registrant held by each such person and each person’s principal occupations and employment during at least the past five years:
Name | Position | Age |
Gregory A. Sandfort | Chief Executive Officer | 62 |
Steve K. Barbarick | President – Chief Merchandising Officer | 50 |
Benjamin F. Parrish, Jr. | Executive Vice President – General Counsel and Corporate Secretary | 61 |
Kurt D. Barton | Senior Vice President – Chief Financial Officer and Treasurer | 46 |
Chad M. Frazell | Senior Vice President – Human Resources | 45 |
Robert D. Mills | Senior Vice President – Chief Information Officer | 45 |
Gregory A. Sandfort has served as Chief Executive Officer since December 2012. He served as President and Chief Executive Officer of the Company from December 2012 to May 2016. Prior to that time, he served as President and Chief Operating Officer of the Company since February 2012. Mr. Sandfort previously served as President and Chief Merchandising Officer of the Company since February 2009, after having served as Executive Vice President – Chief Merchandising Officer of the Company since November 2007. Mr. Sandfort served as President and Chief Operating Officer at Michaels Stores, Inc. from March 2006 to August 2007 and as Executive Vice President – General Merchandise Manager at Michaels Stores, Inc. from January 2004 to February 2006. Mr. Sandfort has served as a director of the Company since February 2013.
Steve K. Barbarick has served as President and Chief Merchandising Officer since May 2016, prior to which he served as Executive Vice President – Chief Merchandising Officer for the Company since September 2012. Prior to that time, he served as Senior Vice President – Merchandising since February 2011. Mr. Barbarick previously served as Vice President – Merchandising since June 2009, after having served as Vice President and Divisional Merchandise Manager since 2003.
Benjamin F. Parrish, Jr. has served as Executive Vice President – General Counsel and Corporate Secretary of the Company since February 2016, after having served as Senior Vice President – General Counsel and Corporate Secretary of the Company since October 2010. Mr. Parrish previously served as Executive Vice President and General Counsel of MV Transportation, Inc. from September 2008 until he joined the Company. He served as Senior Vice President and General Counsel of Central Parking Corporation from 1998 to 2008.
Kurt D. Barton has served as Senior Vice President – Chief Financial Officer and Treasurer since March 2017, after having served as Senior Vice President – Controller of the Company since February 2016. Mr. Barton served as Vice President - Controller from February 2009 after having previously served as Director, Internal Audit from July 2002 to February 2009. Mr. Barton has served in various other leadership roles in accounting since he joined the Company in 1999. Mr. Barton, a Certified Public Accountant, began his career in public accounting in 1993, spending six years at Ernst & Young, LLP.
Chad M. Frazell has served as Senior Vice President - Human Resources since August 2014. Mr. Frazell previously served as Senior Vice President, Human Resources for Shopko Stores Operating Co., LLC from April 2011 until he joined the Company. From 2008 to 2011, Mr. Frazell served as Vice President, Human Resources for Kohl’s Corporation, where he began as a store manager in 1999. Prior to 1999, Mr. Frazell served as a store manager and assistant manager for Target Corporation. He began his career with Wal-Mart Stores, Inc., where he served as an assistant manager and sales associate.
Robert D. Mills has served as Senior Vice President - Chief Information Officer since February 2014. Mr. Mills previously served as Chief Information Officer for Ulta Beauty from October 2011 until he joined the Company. From 2005 to 2011, Mr. Mills was Vice President, Chief Information Officer for the online business unit at Sears Holdings Corporation where he began as an Information Technology Customer Relationship Leader in 2001. Prior to 2001, Mr. Mills held roles at Allstate Insurance, Rockwell International Telecommunications Division, and Household Finance Corporation.
Additional Information
We file reports with the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”), including Annual Reports on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, current reports on Form 8-K and other reports as required. The public may read and copy any materials the Company files with the SEC at the SEC’s Public Reference Room at 100 F Street, NE, Washington, DC 20549. The public may obtain information on the operation of the Public Reference Room by calling the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330. We are an electronic filer and the SEC maintains an Internet site at sec.gov that contains the reports, proxy and information statements, and other information filed electronically.
7
We make available, free of charge through our Internet website, TractorSupply.com, our Annual Report on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, current reports on Form 8-K and all amendments to those reports as soon as reasonably practicable after such material is electronically filed with or furnished to the SEC. The information provided on our website is not part of this report, and is therefore not incorporated by reference unless such information is otherwise specifically referenced elsewhere in this report.
Item 1A. Risk Factors
Our business faces many risks. Those risks of which we are currently aware and deem to be material are described below. If any of the events or circumstances described in the following risk factors occur, our business, financial condition or results of operations may significantly suffer, and the trading price of our common stock could decline. These risk factors should be read in conjunction with the other information in this Form 10-K.
General economic conditions may adversely affect our financial performance.
Our results of operations may be sensitive to changes in overall economic conditions that impact consumer spending, including discretionary spending. A weakening of economic conditions affecting disposable consumer income such as lower employment levels, uncertainty or changes in business or political conditions, higher interest rates, higher tax rates, higher fuel and energy costs, higher labor and healthcare costs, the impact of natural disasters or acts of terrorism, and other matters could reduce consumer spending or cause consumers to shift their spending to competitors. A general reduction in the level of discretionary spending, shifts in consumer discretionary spending to our competitors or shifts in discretionary spending to less profitable products sold by us could result in lower net sales, slower inventory turnover, greater markdowns on inventory, and a reduction in profitability due to lower margins.
Failure to protect our reputation could have a material adverse effect on our brand name.
Our success depends in part on the value and strength of the Tractor Supply name. The Tractor Supply name is integral to our business as well as to the implementation of our strategies for expanding our business. Maintaining, promoting, and positioning our brand will depend largely on the success of our marketing and merchandising efforts and our ability to provide high quality merchandise and a consistent, high quality customer experience. Our brand could be adversely affected if we fail to achieve these objectives or if our public image or reputation were to be tarnished by negative publicity. Failure to comply or accusation of failure to comply with ethical, social, product, labor, data privacy, and environmental standards could also jeopardize our reputation and potentially lead to various adverse consumer actions. Any of these events could result in decreased revenue or otherwise adversely affect our business.
We may be unable to increase sales at our existing stores.
We experience fluctuations in our comparable store sales, defined as sales in stores which have been open for at least twelve months. Various factors affect comparable store sales, including the general retail sales environment, our ability to efficiently source and distribute products, changes in our merchandise assortment, competition, proximity of our locations to one another or to the locations of other retailers, increased presence of online retailers, current economic conditions, customer satisfaction with our products, the timing of promotional events, the release of new merchandise, the success of marketing programs and weather conditions. These factors may cause our comparable store sales results to differ materially from prior periods and from expectations. Past comparable store sales are not an indication of future results, and there can be no assurance that our comparable store sales will not decrease in the future.
Purchase price volatility, including inflationary and deflationary pressures, may adversely affect our financial performance.
Although we cannot determine the full effect of inflation and deflation on our operations, we believe our sales and results of operations are affected by both. We are subject to market risk with respect to the pricing of certain products and services, which include, among other items, grain, corn, steel, petroleum, cotton and other commodities as well as diesel fuel and transportation services. Therefore, we may experience both inflationary and deflationary pressure on product cost, which may impact consumer demand and, as a result, sales and gross margin. Our strategy is to reduce or mitigate the effects of purchase price volatility principally by taking advantage of vendor incentive programs, economies of scale from increased volume of purchases, adjusting retail prices and selectively buying from the most competitive vendors while maintaining product quality. Should our strategy to mitigate purchase price volatility not be effective, our financial performance could be adversely impacted.
Weather conditions may have a significant impact on our financial results.
Weather conditions affect the demand for, and in some cases the supply of, products, which in turn has an impact on prices. Historically, weather conditions, including unseasonably warm weather in the fall and winter months and unseasonably cool weather in the spring and summer months, have affected the timing and volume of our sales and results of operations. In addition, extreme weather conditions, including snow and ice storms, flood and wind damage, hurricanes, tornadoes, extreme rain and
8
droughts, have impacted operating results. While extreme weather conditions can positively impact our operating results by increasing demand in affected locations for products needed to cope with the weather condition and its effects, they can also negatively affect our business depending on the severity and length of these conditions as a result of store closings or the inability of customers to shop at our stores due to weather conditions. Our strategy is to manage product flow and adjust merchandise assortments and depth of inventory to capitalize on seasonal demand trends. Should such a strategy not be effective, the weather may have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
Our merchandising and marketing initiatives may not provide expected results.
We believe our past performance has been based on, and future success will depend upon, in part, the ability to develop and execute merchandising initiatives with effective marketing programs. These merchandising initiatives and marketing programs may not deliver expected results, and there is no assurance that we will correctly identify and respond in a timely manner to evolving trends and consumer preferences and expectations. If we misjudge the market or our marketing programs are not successful, we may overstock unpopular products and be forced to take inventory price reductions that have a material adverse effect on our profitability. Failure to execute and promote such initiatives in a timely manner could harm our ability to grow the business and could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations and financial condition. Shortages of key merchandise could also have a material adverse impact on operating results and financial condition.
Capital required for growth may not be available.
The construction or acquisition of new stores, store support center facilities, distribution facilities or other facilities, the remodeling and renovation of existing facilities and investments in information technology require significant amounts of capital. In the past, our growth has been funded through internally generated cash flow and bank borrowings. Disruptions in the capital and credit markets could adversely affect the ability of the banks to meet their commitments. Our access to funds under our debt facilities is dependent on the ability of the banks that are parties to the facility to meet their funding commitments. Those banks may not be able to meet their funding commitments to us if they experience shortages of capital and liquidity or if they experience excessive volumes of borrowing requests within a short period of time. In addition, tight lending practices may make it difficult for our real estate developers to obtain financing under acceptable loan terms and conditions. Unfavorable lending practices could impact the timing of our store openings and materially adversely affect our ability to open new stores in desirable locations.
Longer term disruptions in the capital and credit markets as a result of uncertainty, changing or increased regulation, reduced funding alternatives, or failures of significant financial institutions could adversely affect our access to liquidity needed for our business. Any disruption could require us to take measures to conserve cash until the markets stabilize or until alternative credit arrangements or other funding for our business needs can be arranged. Such measures could include deferring capital expenditures and reducing or eliminating future share repurchases, cash dividends or other discretionary uses of cash.
Failure to open and manage new stores in the number and manner currently contemplated could adversely affect our financial performance.
An integral part of our business strategy includes the expansion of our store base through new store openings. This expansion strategy is dependent on our ability to find suitable locations, and we face competition from many retailers for such sites. If we are unable to implement this strategy, our ability to increase our sales, profitability, and cash flow could be impaired significantly. To the extent that we are unable to open new stores in the manner we anticipate (due to, among other reasons, site approval or unforeseen delays in construction), our sales growth may be impeded.
As we execute this expansion strategy, we may also experience managerial or operational challenges which may prevent any expected increase in sales, profitability or cash flow. Our ability to manage our planned expansion depends on the adequacy of our existing information systems, the efficiency and expansion of our distribution systems, the adequacy of the hiring and training process for new personnel (especially store managers), the effectiveness of our controls and procedures, and the ability to identify customer demand and build market awareness in different geographic areas. There can be no assurance that we will be able to achieve our planned expansion, that the new stores will be effectively integrated into our existing operations or that such stores will be profitable.
Although we have a rigorous real estate site selection and approval process, there can be no assurance that our new store openings will be successful or result in incremental sales and profitability for the Company. New stores build their sales volumes and refine their merchandise selection over time and, as a result, generally have lower gross margins and higher operating expenses as a percentage of net sales than our more mature stores. As we continue to open new stores, there may be a negative impact on our results from a lower contribution margin of these new stores until their sales levels ramp to chain average, if at all, as well as from the impact of related pre-opening costs.
9
Our failure to attract and retain qualified team members, increases in wage and labor costs and changes in laws and other labor issues could adversely affect our financial performance.
Our ability to continue expanding operations depends on our ability to attract and retain a large and growing number of qualified team members. Our ability to meet labor needs while controlling wage and related labor costs is subject to numerous external factors, including the availability of a sufficient number of qualified persons in the work force, unemployment levels, prevailing wage rates, changing demographics, health and other insurance costs, changes in employment legislation and the potential for changes in local labor practices or union activities. If we are unable to locate, attract or retain qualified personnel, or if costs of labor or related costs increase significantly, our financial performance could be adversely affected.
We are subject to federal, state, and local laws governing employment practices and working conditions. These laws cover wage and hour practices, labor relations, paid and family leave, workplace safety and immigration, among others. The laws and regulations being passed at the state and local level create unique challenges for a multi-state employer. We must continue to monitor and adapt our employment practices to comply with these various laws and regulations. If our costs of labor or related costs increase significantly as new or revised labor laws, rules or regulations or healthcare laws are adopted or implemented, our financial performance could be adversely affected.
We may pursue strategic acquisitions and the failure of an acquisition to produce the anticipated results or the inability to fully integrate the acquired companies could have an adverse impact on our business.
We may, from time to time, acquire businesses we believe to be complementary to our business. The success of an acquisition is based on our ability to make accurate assumptions regarding the valuation, operations, growth potential, integration and other factors relating to the target business. Acquisitions may result in difficulties in assimilating acquired companies and may result in the diversion of our capital and our management’s attention from other business issues and opportunities. We may not be able to successfully integrate an organization that we acquire, including their personnel, financial systems, distribution, operations and general operating procedures. If we fail to successfully integrate acquisitions, we could experience increased costs associated with operating inefficiencies which could have an adverse effect on our financial results. Also, while we employ several different methodologies to assess potential business opportunities, the new businesses may not meet our expectations and, therefore, adversely affect our financial performance.
Competition may hinder our ability to execute our business strategy and adversely affect our operations.
We operate in the highly competitive retail merchandise sector with numerous competitors. These competitors include general merchandise retailers, home center retailers, specialty and discount retailers, independently owned retail farm and ranch stores, numerous privately-held regional farm store chains and farm cooperatives, as well as internet-based retailers. We compete for customers, merchandise, real estate locations, and employees. This competitive environment subjects us to various other risks, including the inability to continue our store and sales growth and to provide attractive merchandise to our customers at competitive prices that allow us to maintain our profitability. Our failure to compete effectively in this environment could adversely impact our financial performance.
We face risks associated with vendors from whom our products are sourced.
The products we sell are sourced from a variety of domestic and international vendors. We have agreements with our vendors in which the vendors agree to comply with applicable laws, including labor and environmental laws, and to indemnify us against certain liabilities and costs. Our ability to recover liabilities and costs under these vendor agreements is dependent upon the financial condition and integrity of the vendors. We rely on long-term relationships with our suppliers but have no long-term contracts with such suppliers. Our future success will depend in large measure upon our ability to maintain our existing supplier relationships or to develop new ones. This reliance exposes us to the risk of inadequate and untimely supplies of various products due to political, economic, social, or environmental conditions, transportation delays, or changes in laws and regulations affecting distribution. Our vendors may be forced to reduce their production, shut down their operations or file for bankruptcy protection, which could make it difficult for us to serve the market’s needs and could have a material adverse effect on our business.
While the Company selects these third-party vendors carefully, it does not control their actions. Any problems caused by these third parties, including those resulting from breakdowns or other disruptions in communication services provided by a vendor, failure of a vendor to handle current or higher volumes, and cyber attacks or security breaches at a vendor could adversely affect the Company’s ability to deliver products and services to its customers and otherwise conduct its business.
We rely on foreign manufacturers for various products that we sell. In addition, many of our domestic suppliers purchase a portion of their products from foreign sources. As an importer, our business is subject to the risks generally associated with doing business internationally, such as domestic and foreign governmental regulations, economic disruptions, delays in shipments, transportation capacity and costs, currency exchange rates and changes in political or economic conditions in countries from which we purchase products. If any such factors were to render the conduct of business in particular countries undesirable or impractical or if additional
10
U.S. quotas, duties, taxes or other charges or restrictions were imposed upon the importation of our products in the future, our financial condition and results of operations could be materially adversely affected.
The current political landscape in the U.S. has introduced greater uncertainty with respect to tax and trade policies, tariffs and regulations affecting trade between the U.S. and other countries. We source a portion of our merchandise from manufacturers located outside the U.S., primarily in Asia and Central America. Major developments in tax policy or trade relations, such as the disallowance of tax deductions for imported merchandise or the imposition of tariffs on imported products, could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and liquidity.
A significant disruption to our distribution network or to the timely receipt of inventory could adversely impact sales or increase our transportation costs, which would decrease our profits.
We rely on our distribution and transportation network to provide goods to our stores in a timely and cost-effective manner through deliveries to our distribution facilities from vendors and then from the distribution facilities or direct ship vendors to our stores by various means of transportation, including shipments by sea, air, rail and truck. Any disruption, unanticipated expense or operational failure related to this process could affect store operations negatively. For example, unexpected delivery delays (including delays due to weather, fuel shortages or other reasons) or increases in transportation costs (including increased fuel costs or a decrease in transportation capacity for overseas shipments) could significantly decrease our ability to provide adequate product for sale, or products at a desired price, resulting in lower sales and profitability. In addition, labor shortages or work stoppages in the transportation industry or long-term disruptions to the national and international transportation infrastructure that lead to delays or interruptions of deliveries could negatively affect our business. Also, a fire, tornado, or other disaster at one of our distribution facilities could disrupt our timely receiving, processing and shipment of merchandise to our stores which could adversely affect our business.
The implementation of our supply chain initiatives could disrupt our operations in the near term, and these initiatives might not provide the anticipated benefits or might fail.
We maintain a network of distribution facilities and have plans to build new facilities and expand existing facilities to support our growth objectives. Delays in opening new or expanded distribution facilities could adversely affect our future operations by slowing store growth, which may in turn reduce revenue growth. In addition, distribution-related construction or expansion projects entail risks which could cause delays and cost overruns, such as: shortages of materials; shortages of skilled labor or work stoppages; unforeseen construction, scheduling, engineering, environmental or geological problems; weather interference; fires or other casualty losses; and unanticipated cost increases. The completion date and ultimate cost of future projects could differ significantly from initial expectations due to construction-related or other reasons. We cannot guarantee that all projects will be completed on time or within established budgets.
We continue to make significant technology investments in our supply chain. These initiatives are designed to streamline our distribution process so that we can optimize the delivery of goods and services to our stores and distribution facilities in a timely manner and at a reasonable cost. The cost and potential problems and interruptions associated with the implementation of these initiatives, including those associated with managing third-party service providers and employing new web-based tools and services, could disrupt or reduce the efficiency of our operations in the near term. In addition, our improved supply chain technology might not provide the anticipated benefits, it might take longer than expected to realize the anticipated benefits, or the initiatives might fail altogether.
We are subject to personal injury, workers’ compensation, product liability, discrimination, harassment, wrongful termination and other claims in the ordinary course of business.
Our business involves a risk of personal injury, workers’ compensation, product liability, discrimination, harassment, wrongful termination and other claims in the ordinary course of business. Product liability claims from customers and product recalls for merchandise alleged to be defective or harmful could lead to the disposal or write-off of merchandise inventories, the incurrence of fines or penalties and damage to our reputation. We maintain general liability and workers’ compensation insurance with a self-insured retention for each policy type and a deductible for each occurrence. We also maintain umbrella limits above the primary general liability and product liability coverage. In many cases, we have indemnification rights against the manufacturers of the products and their products liability insurance as well as the property owners of our leased buildings. Our ability to recover costs and damages under such insurance or indemnification arrangements is subject to the financial viability of the insurers, manufacturers and landlords and the specific allegations of a claim. No assurance can be given that our insurance coverage or the manufacturers’ or landlords’ indemnity will be available or sufficient in any claims brought against us.
Additionally, we are subject to U.S. federal, state and local employment laws that expose us to potential liability if we are determined to have violated such employment laws, including but not limited to, laws pertaining to minimum wage rates, overtime pay,
11
discrimination, harassment, and wrongful termination. Compliance with these laws, including the remediation of any alleged violation, may have a material adverse effect on our business or results of operations.
Failure to maintain an effective system of internal control over financial reporting could materially impact our business and results.
The Company’s management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting. An internal control system, no matter how well designed and operated, can provide only reasonable, not absolute, assurance that the objectives of the control system are met. Further, the design of a control system must reflect the fact that there are resource constraints, and the benefits of controls must be considered relative to their costs. Because of the inherent limitations in all internal
control systems, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Any failure to maintain an effective system of internal control over financial reporting could limit our ability to report our financial results accurately and timely or to detect and prevent fraud, and could expose us to litigation or adversely affect the market price of our common stock.
Any failure to maintain the security of the information relating to our business, customers, employees and vendors that we hold, whether as a result of cybersecurity attacks or otherwise, could damage our reputation with customers, employees and vendors, could cause us to incur substantial additional costs and to become subject to litigation, and could adversely affect our operating results, financial condition and liquidity.
We receive certain personal and other confidential information about our customers, employees and vendors. We also rely on business partners to provide services to us that may include important business information or data about our customers, employees and vendors. In addition, our online operations at TractorSupply.com and Petsense.com depend upon the secure transmission of confidential information over public networks, including information permitting cashless payments. While we maintain substantial security measures to help protect and prevent unauthorized access to such information, it is possible that unauthorized parties (through cybersecurity attacks, which are rapidly evolving and becoming increasingly sophisticated, or by other means) might compromise our security measures and obtain and misuse the personal information of customers, employees and vendors that we hold or other confidential Company data. It is possible that such a compromise could go undetected by us. Such an occurrence could materially adversely affect our reputation with our customers, employees, and vendors, as well as our operations, results of operations, financial condition and liquidity, and could result in significant legal and financial exposure beyond the scope or limits of insurance coverage. Moreover, a security breach could require that we expend significant additional resources to respond to the breach and could result in a disruption of our operations.
In addition, states and the federal government are increasingly enacting laws and regulations relating to data breaches and theft of employee and customer data. These laws will likely increase the costs of doing business and, if we fail to comply with these laws and regulations or to implement appropriate safeguards or to detect and provide prompt notice of unauthorized access as required by some of these new laws, we could be subject to potential claims for damages and other remedies, which could harm our business.
Our business and operations could suffer material losses in the event of system interruptions or failures.
Our information technology systems, some of which are dependent on services provided by third parties, serve an important role in the operation and administration of our business. These systems are vulnerable to damages from any number of sources, including, but not limited to, human error, cybersecurity attacks, computer viruses, unauthorized access, fire, flood, power outages, telecommunication failures, facility or equipment damage, natural disasters, terrorism, and war. In addition, we continually make investments in technology to implement new processes and systems as well as to maintain and update our existing processes and systems. Implementing process and system changes increases the risk of disruption. If our information technology systems are interrupted or fail and our redundant systems or recovery plans are not adequate to address such interruptions or failures on a timely basis, our revenues and profits could be reduced and the reputation of our brand and our business could be materially adversely affected. Additionally, remediation of any problems with our systems could result in significant, unplanned expenses.
As customer-facing technology systems become an increasingly important part of our sales and marketing strategy, the failure of those systems to perform effectively and reliably could keep us from delivering positive customer experiences.
Through our continued information technology enhancements, we are able to provide an improved overall shopping environment and an omni-channel experience that empowers our customers to shop and interact with us from computers, tablets, smart phones and other mobile communication devices. We use our website both as a sales channel for our products and also as a method of providing product, project and other relevant information to our customers to drive both in-store and online sales. Omni-channel retailing is continually evolving and expanding, and we must effectively respond to changing customer expectations and new developments. Disruptions, failures or other performance issues with these customer-facing technology systems could impair the benefits that they provide to our online and in-store business and negatively affect our relationship with our customers.
12
If we are unable to maintain or upgrade our management information systems and software programs or if we are unable to convert to alternate systems in an efficient and timely manner, our operations may be disrupted or become less efficient and our strategic business initiatives may not be successful.
We depend on management information systems for many aspects of our business. We rely on certain software vendors to maintain and periodically upgrade many of these systems so that we can continue to support our business. We could be materially adversely affected if we experienced a disruption or data loss relating to our management information systems and are unable to recover timely. We could also be adversely impacted if we are unable to improve, upgrade, maintain and expand our management information systems, particularly in light of the contemplated continued store growth.
The success of our strategic business initiatives designed to increase our sales and improve margin is dependent in varying degrees on the timely delivery and the functionality of information technology systems to support them. Extended delays or cost overruns in securing, developing and otherwise implementing technology solutions to support the strategic business initiatives would delay and possibly even prevent us from realizing the projected benefits of those initiatives.
We cannot provide any guaranty of future dividend payments or that we will continue to repurchase our common stock pursuant to our stock repurchase program.
Although our Board of Directors has indicated an intention to pay future quarterly cash dividends on our common stock, any determination to pay or increase cash dividends on our common stock in the future will be based primarily upon our financial condition, results of operations, business requirements, and our Board of Directors’ continuing determination that the declaration of dividends is in the best interests of our stockholders and is in compliance with all laws and agreements applicable to the dividend. Furthermore, although our Board of Directors has authorized a share repurchase program of up to $3 billion through December 2020, we may discontinue this program at any time or significantly reduce repurchases under the program.
The market price for our common stock might be volatile and could result in a decline in value.
The price at which our common stock trades may be volatile and could be subject to significant fluctuations in response to our operating results, general trends and prospects for the retail industry, announcements by our competitors, analyst recommendations, our ability to meet or exceed analysts’ or investors’ expectations, the condition of the financial markets and other factors. The Company’s stock price is dependent in part on the multiple of earnings that investors are willing to pay. That multiple is in part dependent on investors’ perception of the Company’s future earnings growth prospects. If investor perceptions of the Company’s earnings growth prospects change, the Company’s earnings multiple may decline and its stock price could be adversely affected.
In addition, the stock market in recent years has experienced extreme price and volume fluctuations that often have been unrelated or disproportionate to the operating performance of companies. These fluctuations, as well as general economic and market conditions, may adversely affect the market price of our common stock notwithstanding our actual operating performance.
Our costs of doing business could increase as a result of federal, state, local or foreign laws and regulations.
We are subject to numerous federal, state, local and foreign laws and governmental regulations including those relating to environmental protection, personal injury, intellectual property, consumer product safety, building, land use and zoning requirements, workplace regulations, wage and hour, privacy and information security and employment law matters. If we fail to comply with existing or future laws or regulations, or if these laws or regulations are violated by importers, manufacturers or distributors, we may be subject to governmental or judicial fines or sanctions, while incurring substantial legal fees and costs. In addition, our capital expenditures could increase due to remediation measures that may be required if we are found to be noncompliant with any existing or future laws or regulations.
We are also subject to the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (the “FCPA”), which prohibits U.S. companies and their intermediaries from making improper payments to foreign officials for the purposes of obtaining or retaining business, and the anti-bribery laws of other jurisdictions. Failure to comply with the FCPA and similar laws could subject us to, among other things, penalties and legal expenses that could harm our reputation and have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Potential noncompliance with environmental regulations could materially impact our results of operations or financial condition.
Our business is subject to various federal, state and local laws, regulations and other requirements pertaining to protection of the environment and public health, including, for example, regulations governing the management of waste materials and waste waters. Governmental agencies on the federal, state and local levels have, in recent years, increasingly focused on the retail sector’s compliance with such laws and regulations, and have at times pursued enforcement activities. We periodically receive information requests and notices of potential noncompliance with environmental laws and regulations from governmental agencies, which are addressed on a case-by-case basis with the relevant agency. Any of these events could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations or financial condition.
13
Effective tax rate changes and results of examinations by taxing authorities could materially impact our results.
Our future effective tax rates could be adversely affected by legislative tax reform, changes in statutory rates or changes in tax laws, or interpretations thereof. Additionally, our future effective tax rates could be adversely affected by the earnings mix being lower than historical results in states where we have lower statutory rates and higher than historical results in states where we have higher statutory rates or by changes in the measurement of our deferred tax assets and liabilities.
We are subject to periodic audits and examinations by the Internal Revenue Service (“IRS”), as well as state and local taxing authorities. Like many retailers, a portion of our sales are to tax-exempt customers. The business activities of our customers and the intended use of the unique products sold by us create a challenging and complex compliance environment. These circumstances create risk that we could be challenged as to the propriety of our sales tax compliance. Our results could be materially impacted by the determinations and expenses related to these and other proceedings by the IRS and other state and local taxing authorities.
Item 1B. Unresolved Staff Comments
None.
Item 2. Properties
At December 30, 2017, the Company operated 1,853 stores in 49 states. The Company leases approximately 93% of its stores. Store leases typically have initial terms of 10 to 15 years, with two to four renewal periods of five years each, exercisable at our option. No single lease is material to Company operations.
The following is a count of store locations by state:
State | Number of Stores | State | Number of Stores | |||
Texas | 210 | Maryland | 22 | |||
North Carolina | 94 | New Hampshire | 21 | |||
Pennsylvania | 93 | Maine | 20 | |||
Tennessee | 91 | Massachusetts | 20 | |||
Ohio | 90 | Wisconsin | 20 | |||
Georgia | 83 | Connecticut | 19 | |||
Michigan | 83 | Washington | 19 | |||
New York | 77 | Nebraska | 18 | |||
Kentucky | 69 | Illinois | 17 | |||
Florida | 63 | New Jersey | 17 | |||
California | 59 | Utah | 15 | |||
Indiana | 57 | North Dakota | 14 | |||
Alabama | 56 | Minnesota | 12 | |||
Virginia | 55 | Iowa | 9 | |||
Oklahoma | 53 | South Dakota | 9 | |||
Louisiana | 44 | Wyoming | 8 | |||
South Carolina | 44 | Vermont | 7 | |||
Mississippi | 39 | Montana | 6 | |||
Arkansas | 35 | Delaware | 5 | |||
Arizona | 34 | Idaho | 4 | |||
Missouri | 30 | Rhode Island | 4 | |||
New Mexico | 28 | Nevada | 3 | |||
West Virginia | 28 | Oregon | 3 | |||
Colorado | 22 | Hawaii | 2 | |||
Kansas | 22 | |||||
1,853 | ||||||
14
The following is a list of distribution locations including the approximate square footage and if the location is leased or owned:
Distribution Facility Location | Approximate Square Footage | Owned/Leased Facility | ||
Franklin, Kentucky | 833,000 | Owned | ||
Pendleton, Indiana | 764,000 | Owned | ||
Macon, Georgia | 684,000 | Owned | ||
Waco, Texas | 666,000 | Owned | ||
Casa Grande, Arizona | 650,000 | Owned | ||
Hagerstown, Maryland (a) | 482,000 | Owned | ||
Hagerstown, Maryland (a) | 309,000 | Leased | ||
Waverly, Nebraska | 422,000 | Owned | ||
Seguin, Texas (b) | 71,000 | Owned | ||
Lakewood, Washington | 64,000 | Leased | ||
Longview, Texas (b) | 63,000 | Owned | ||
(a) The leased facility in Hagerstown is treated as an extension of the existing owned Hagerstown location and is not considered a separate distribution center.
(b) This is a mixing center designed to process certain high-volume bulk products.
The Company’s Store Support Center occupies approximately 260,000 square feet of owned building space in Brentwood, Tennessee, and the Company’s Merchandising Innovation Center occupies approximately 32,000 square feet of leased building space in Nashville, Tennessee. The Company also leases approximately 8,000 square feet of building space for the Petsense corporate headquarters located in Scottsdale, Arizona.
In fiscal 2017, we began construction on a new northeast distribution center in Frankfort, New York, as well as an expansion of our existing distribution center in Waverly, Nebraska, which will provide additional distribution capacity once construction is completed.
Item 3. Legal Proceedings
Item 103 of SEC Regulation S-K requires disclosure of certain environmental legal proceedings if the proceeding reasonably involves potential monetary sanctions of $100,000 or more. We periodically receive information requests and notices of potential noncompliance with environmental laws and regulations from governmental agencies, which are addressed on a case-by-case basis with the relevant agency. The Company received a subpoena from the District Attorney of Yolo County, California, requesting records and information regarding its hazardous waste management and disposal practices in California. The Company and the Office of the District Attorney of Yolo County engaged in settlement discussions which resulted in the settlement of the matter. A consent decree reflecting the terms of settlement was filed with the Yolo County Superior Court on June 23, 2017. Under the settlement, the Company agreed to a compliance plan and also agreed to pay a civil penalty and fund supplemental environmental projects furthering consumer protection and environmental enforcement in California. The civil penalty did not differ materially from the amount accrued. The cost of the settlement and the compliance with the consent decree will not have a material effect on our consolidated financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
The Company is also involved in various litigation matters arising in the ordinary course of business. The Company believes that any estimated loss related to such matters has been adequately provided for in accrued liabilities to the extent probable and reasonably estimable. Accordingly, the Company currently expects these matters will be resolved without material adverse effect on its consolidated financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
Item 4. Mine Safety Disclosures
Not applicable.
15
PART II
Item 5. | Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities |
The Company’s common stock trades on the Nasdaq Global Select Market under the symbol, “TSCO.”
The table below sets forth the high and low sales prices of our common stock as reported by the Nasdaq Global Select Market for each fiscal quarter of the periods indicated:
Price Range | |||||||
2017 | 2016 | ||||||
High | Low | High | Low | ||||
First Quarter | $78.25 | $67.70 | $90.76 | $78.05 | |||
Second Quarter | $71.53 | $52.09 | $97.25 | $86.44 | |||
Third Quarter | $63.40 | $49.87 | $95.39 | $66.77 | |||
Fourth Quarter | $75.64 | $54.76 | $78.17 | $61.50 | |||
As of February 2, 2018, the number of record holders of our common stock was 585 (excluding individual participants in nominee security position listings), and the estimated number of beneficial holders of our common stock was approximately 200,000.
Common Stock Dividends
During 2017 and 2016, the Company’s Board of Directors declared the following cash dividends:
Date Declared | Dividend Amount Per Share | Stockholders of Record Date | Date Paid | |||
November 6, 2017 | $0.27 | November 20, 2017 | December 5, 2017 | |||
August 7, 2017 | $0.27 | August 21, 2017 | September 6, 2017 | |||
May 8, 2017 | $0.27 | May 22, 2017 | June 6, 2017 | |||
February 8, 2017 | $0.24 | February 27, 2017 | March 14, 2017 | |||
October 31, 2016 | $0.24 | November 14, 2016 | November 29, 2016 | |||
August 1, 2016 | $0.24 | August 15, 2016 | August 30, 2016 | |||
May 2, 2016 | $0.24 | May 16, 2016 | June 1, 2016 | |||
February 3, 2016 | $0.20 | February 22, 2016 | March 8, 2016 | |||
It is the present intention of the Board of Directors to continue to pay a quarterly cash dividend; however, the declaration and payment of future dividends will be determined by the Board of Directors in its sole discretion and will depend upon the earnings, financial condition and capital needs of the Company, as well as other factors which the Board of Directors deem relevant.
On February 7, 2018, our Board of Directors declared a quarterly cash dividend of $0.27 per share of the Company’s common stock. The dividend will be paid on March 13, 2018, to stockholders of record as of the close of business on February 26, 2018.
16
Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
The Company’s Board of Directors has authorized common stock repurchases under a share repurchase program of up to $3 billion, exclusive of any fees, commissions or other expenses related to such repurchases through December 31, 2020. Additionally, the Company withholds shares from vested restricted stock units to satisfy employees’ minimum statutory tax withholding requirements. Stock purchase activity during fiscal 2017 is set forth in the table below:
Period | Total Number of Shares Purchased | Average Price Paid Per Share | Total Number of Shares Purchased as Part of Publicly Announced Plans or Programs | Maximum Dollar Value of Shares That May Yet Be Purchased Under the Plans or Programs | ||||||||||
First Quarter (a) | 1,605,165 | $ | 71.77 | 1,596,167 | $ | 1,124,516,565 | ||||||||
Second Quarter | 2,209,506 | 60.47 | 2,209,506 | 990,943,666 | ||||||||||
Third Quarter (a) | 1,427,570 | 55.08 | 1,425,371 | 912,461,301 | ||||||||||
Fourth Quarter: | ||||||||||||||
10/1/17 – 10/28/17 | 315,000 | 58.98 | 315,000 | 893,885,189 | ||||||||||
10/29/17 – 11/25/17 (a) | 259,359 | 61.08 | 258,801 | 878,077,270 | ||||||||||
11/26/17 – 12/30/17 | 119,900 | 69.77 | 119,900 | 869,713,394 | ||||||||||
694,259 | 61.63 | 693,701 | 869,713,394 | |||||||||||
As of December 30, 2017 | 5,936,500 | $ | 62.36 | 5,924,745 | $ | 869,713,394 | ||||||||
(a) The total number of shares purchased and average price paid per share include shares withheld from vested restricted stock units to satisfy employees’ minimum statutory tax withholding requirements of 8,998 during the first quarter, 2,199 during the third quarter and 558 during the fourth quarter.
We expect to implement the balance of the repurchase program through purchases made from time to time either in the open market or through private transactions, in accordance with regulations of the SEC and other applicable legal requirements. The timing and amount of any common stock repurchased under the program will depend on a variety of factors including price, corporate and regulatory requirements, capital availability and other market conditions.
Any additional stock repurchase programs will be subject to the discretion of our Board of Directors and subject to our results of operations, financial condition, cash requirements and other factors deemed relevant by our Board of Directors. The program may be limited or terminated at any time, without prior notice.
17
STOCK PERFORMANCE GRAPH
This performance graph shall not be deemed “filed” for purposes of Section 18 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”) or otherwise subject to the liabilities under that Section and shall not be deemed to be incorporated by reference into any filing of Tractor Supply Company under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, or the Exchange Act.
The following graph compares the cumulative total stockholder return on our common stock from December 29, 2012 to December 30, 2017 (the Company’s fiscal year-end), with the cumulative total returns of the S&P 500 Index and the S&P Retail Index over the same period. The comparison assumes that $100 was invested on December 29, 2012, in our common stock and in each of the foregoing indices and in each case assumes reinvestment of dividends. The historical stock price performance shown on this graph is not indicative of future performance.
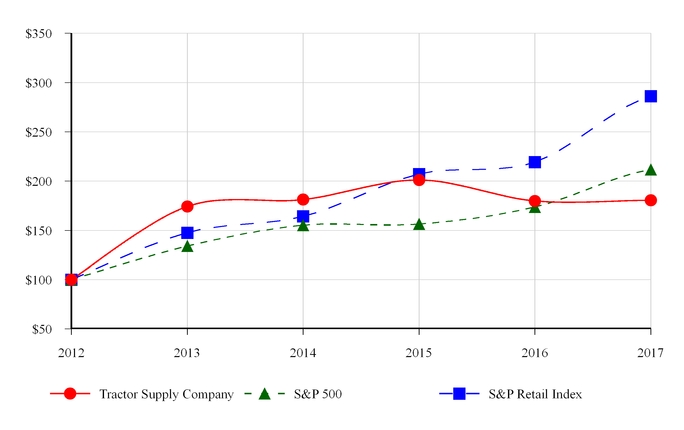
12/29/2012 | 12/28/2013 | 12/27/2014 | 12/26/2015 | 12/31/2016 | 12/30/2017 | |||||||||||||||||||
Tractor Supply Company | $ | 100.00 | $ | 174.14 | $ | 181.29 | $ | 201.04 | $ | 179.94 | $ | 180.52 | ||||||||||||
S&P 500 | $ | 100.00 | $ | 134.11 | $ | 155.24 | $ | 156.43 | $ | 173.74 | $ | 211.67 | ||||||||||||
S&P Retail Index | $ | 100.00 | $ | 147.73 | $ | 164.24 | $ | 207.15 | $ | 219.43 | $ | 286.13 | ||||||||||||
18
Item 6. | Selected Financial Data |
FIVE YEAR SELECTED FINANCIAL AND OPERATING HIGHLIGHTS (a)(b)
The following selected financial data is derived from the Consolidated Financial Statements of Tractor Supply Company and provides summary historical financial information for the fiscal periods ended and as of the dates indicated (in thousands, except per share amounts and selected operating and other data):
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||||||||
(52 weeks) | (53 weeks) | (52 weeks) | (52 weeks) | (52 weeks) | |||||||||||||||
Operating Results: | |||||||||||||||||||
Net sales | $ | 7,256,382 | $ | 6,779,579 | $ | 6,226,507 | $ | 5,711,715 | $ | 5,164,784 | |||||||||
Gross profit | 2,491,965 | 2,325,202 | 2,143,174 | 1,950,415 | 1,753,609 | ||||||||||||||
Selling, general and administrative expenses | 1,639,749 | 1,488,164 | 1,369,097 | 1,246,308 | 1,138,934 | ||||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 165,834 | 142,958 | 123,569 | 114,635 | 100,025 | ||||||||||||||
Operating income | 686,382 | 694,080 | 650,508 | 589,472 | 514,650 | ||||||||||||||
Interest expense, net | 13,859 | 5,810 | 2,891 | 1,885 | 557 | ||||||||||||||
Income before income taxes | 672,523 | 688,270 | 647,617 | 587,587 | 514,093 | ||||||||||||||
Income tax expense | 249,924 | 251,150 | 237,222 | 216,702 | 185,859 | ||||||||||||||
Net income | $ | 422,599 | $ | 437,120 | $ | 410,395 | $ | 370,885 | $ | 328,234 | |||||||||
Net income per share – basic (c) | $ | 3.31 | $ | 3.29 | $ | 3.03 | $ | 2.69 | $ | 2.35 | |||||||||
Net income per share – diluted (c) | $ | 3.30 | $ | 3.27 | $ | 3.00 | $ | 2.66 | $ | 2.32 | |||||||||
Weighted average shares – diluted (c) | 128,204 | 133,813 | 136,845 | 139,435 | 141,723 | ||||||||||||||
Dividends declared per common share outstanding | $ | 1.05 | $ | 0.92 | $ | 0.76 | $ | 0.61 | $ | 0.49 | |||||||||
Operating Data (percent of net sales): | |||||||||||||||||||
Gross margin | 34.3 | % | 34.3 | % | 34.4 | % | 34.1 | % | 34.0 | % | |||||||||
Selling, general and administrative expenses | 22.6 | % | 22.0 | % | 22.0 | % | 21.8 | % | 22.1 | % | |||||||||
Operating income | 9.4 | % | 10.2 | % | 10.4 | % | 10.3 | % | 10.0 | % | |||||||||
Net income | 5.8 | % | 6.4 | % | 6.6 | % | 6.5 | % | 6.4 | % | |||||||||
Store, Sales and Other Data: | |||||||||||||||||||
Stores open at end of year | 1,853 | 1,738 | 1,488 | 1,382 | 1,276 | ||||||||||||||
Comparable store sales increase (d) | 2.7 | % | 1.6 | % | 3.1 | % | 3.8 | % | 4.8 | % | |||||||||
New store sales (as a % of net sales) (e) | 5.6 | % | 5.6 | % | 5.6 | % | 6.2 | % | 5.4 | % | |||||||||
Average transaction value | $ | 44.61 | $ | 44.42 | $ | 44.87 | $ | 44.84 | $ | 44.48 | |||||||||
Comparable store average transaction value increase (decrease) (c) | 0.5 | % | (0.9 | )% | (0.2 | )% | 0.6 | % | — | % | |||||||||
Comparable store average transaction count increase (d) | 2.2 | % | 2.6 | % | 3.3 | % | 3.2 | % | 4.7 | % | |||||||||
Total selling square footage (000’s) | 28,180 | 26,511 | 23,938 | 22,176 | 20,470 | ||||||||||||||
Total team members | 29,300 | 26,000 | 23,000 | 21,100 | 19,200 | ||||||||||||||
Capital expenditures (000’s) | $ | 250,401 | $ | 226,017 | $ | 236,496 | $ | 160,613 | $ | 218,200 | |||||||||
Balance Sheet Data (at end of period): | |||||||||||||||||||
Average inventory per store (f) | $ | 735.4 | $ | 741.7 | $ | 820.1 | $ | 752.7 | $ | 723.5 | |||||||||
Inventory turns | 3.24 | 3.19 | 3.23 | 3.32 | 3.29 | ||||||||||||||
Working capital (g) | $ | 806,154 | $ | 740,615 | $ | 768,177 | $ | 670,897 | $ | 677,107 | |||||||||
Total assets | $ | 2,868,769 | $ | 2,674,942 | $ | 2,370,826 | $ | 2,034,571 | $ | 1,903,391 | |||||||||
Long-term debt, less current portion (h) | $ | 433,686 | $ | 289,769 | $ | 166,992 | $ | 4,957 | $ | 1,200 | |||||||||
Stockholders’ equity | $ | 1,418,673 | $ | 1,453,218 | $ | 1,393,294 | $ | 1,293,561 | $ | 1,246,894 | |||||||||
(a) Our fiscal year includes 52 or 53 weeks and ends on the last Saturday of the calendar year. References to fiscal year mean the year in which that fiscal year ended. Fiscal year 2016 consisted of 53 weeks while all other fiscal years presented consisted of 52 weeks.
(b) Beginning in the fourth quarter ended December 31, 2016, selected financial and operating information includes the consolidation of Petsense, unless otherwise noted.
(c) Basic net income per share is calculated based on the weighted average number of common shares outstanding applied to net income. Diluted net income per share is calculated using the treasury stock method for stock options and restricted stock units.
(d) Comparable store metrics are calculated on an annual basis using sales generated from all stores open at least one year and all online sales, excluding certain adjustments to net sales. Beginning in fiscal 2015, stores closed during the year are removed from our comparable store metrics calculations. This change in the calculation methodology did not have a material impact on the comparable store metrics reported in prior periods presented due to the minimal number of stores closed in those periods. Stores relocated during the years being compared are not removed from our comparable store metrics. If the effect of relocated stores on our comparable store metrics becomes material, we would remove relocated stores from the calculations. Acquired Petsense stores are considered comparable stores beginning in the fourth quarter of fiscal 2017.
(e) New stores sales metrics are based on stores open for less than one year.
(f) Assumes average inventory cost, excluding inventory in-transit.
(g) Working capital for 2017, 2016 and 2015 reflects deferred tax assets as non-current as a result of the adoption of ASU 2015-17 (which is discussed in Note 15 to the Consolidated Financial Statements). Years prior to 2015 have not been adjusted to reflect the adoption of this guidance.
(h) Long-term debt includes amounts outstanding under the Company’s debt facilities and capital lease obligations, excluding the current portions.
19
Item 7. | Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations |
The following discussion and analysis is intended to provide the reader with information that will assist in understanding the significant factors affecting our consolidated operating results, financial condition, liquidity and capital resources during the three-year period ended December 30, 2017 (our fiscal years 2017, 2016 and 2015). This discussion should be read in conjunction with our Consolidated Financial Statements and Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements included elsewhere in this report. This discussion contains forward-looking statements. See “Forward-Looking Statements” and “Risk Factors” included elsewhere in this report.
Tractor Supply reports its financial results in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“U.S. GAAP”). Tractor Supply also uses certain non-GAAP measures that fall within the meaning of Securities and Exchange Commission Regulation G and Regulation S-K Item 10(e), which may provide users of the financial information with additional meaningful comparison to prior reported results. Non-GAAP measures do not have standardized definitions and are not defined by U.S. GAAP. Therefore, Tractor Supply’s non-GAAP measures are unlikely to be comparable to similar measures presented by other companies. The presentation of these non-GAAP measures should not be considered in isolation from, as a substitute for, or as superior to the financial information presented in accordance with U.S. GAAP.
Overview
Founded in 1938, Tractor Supply Company is the largest operator of rural lifestyle retail stores in the United States (“U.S.”). The Company is focused on supplying the needs of recreational farmers and ranchers and others who enjoy the rural lifestyle (which we refer to as the “Out Here” lifestyle), as well as tradesmen and small businesses. As of December 30, 2017, we operated 1,853 retail stores in 49 states under the names Tractor Supply Company, Del’s Feed & Farm Supply and Petsense. We also operate websites under the names TractorSupply.com and Petsense.com. Our stores are located primarily in towns outlying major metropolitan markets and in rural communities, and they offer the following comprehensive selection of merchandise:
• | Equine, livestock, pet and small animal products, including items necessary for their health, care, growth and containment; |
• | Hardware, truck, towing and tool products; |
• | Seasonal products, including heating, lawn and garden items, power equipment, gifts and toys; |
• | Work/recreational clothing and footwear; and |
• | Maintenance products for agricultural and rural use. |
Tractor Supply believes we can grow our business by being the most dependable supplier of relevant products and services for the “Out Here” lifestyle, creating customer loyalty through personalized experiences and providing convenience that our customers expect at anytime, anywhere, and in any way they choose. Our long-term growth strategy is to: (1) drive profitable growth through new store openings and by expanding omni-channel capabilities, thus tying together our website product content, social media, digital and online shopping experience, attracting new customers and driving loyalty, (2) build customer-centric engagement by leveraging analytics to deliver legendary customer service, seasoned advice and personalized experiences, (3) offer relevant assortments and services across all channels through exclusive and national brands and continue to introduce new products through our test and learn strategy, (4) enhance our core and foundational capabilities by investing in infrastructure and process improvements which will support growth, scale and agility while improving the customer experience, and (5) expand through selective acquisitions, as such opportunities arise, to add complementary businesses and to enhance penetration into new and existing markets to supplement organic growth.
Achieving this strategy will require a foundational focus on: (1) organizing, optimizing and empowering our team members for growth by developing skills, talent and leadership across the organization, and (2) implementing operational efficiency initiatives to align our cost structure to support new business capabilities for margin improvement and cost reductions.
Over the past five years, we have experienced considerable growth in stores, growing from 1,176 stores at the end of 2012 to 1,853 stores (1,685 Tractor Supply and Del’s retail stores and 168 Petsense retail stores) at the end of fiscal 2017, and in sales, with a compounded annual growth rate of approximately 9.2%. Given the size of the communities that we target, we believe that there is ample opportunity for new store growth in existing and new markets. We have developed a proven method for selecting store sites and have identified approximately 800 additional opportunities for new Tractor Supply stores. We also believe that there is opportunity for up to 1,000 Petsense stores.
Executive Summary
In 2017, we opened 101 new Tractor Supply stores in 39 states and 25 new Petsense stores in 11 states. In 2016, we opened 113 new Tractor Supply stores and began operating 143 Petsense stores. This resulted in a selling square footage increase of approximately 6.3% in fiscal 2017 and approximately 10.8% in fiscal 2016.
20
Net sales increased 7.0% to $7.26 billion in fiscal 2017 (52 weeks) from $6.78 billion in fiscal 2016 (53 weeks). Comparable store sales increased 2.7% in fiscal 2017 versus a 1.6% increase in fiscal 2016. Gross profit increased 7.2% to $2.49 billion in fiscal 2017 from $2.33 billion in fiscal 2016, and gross margin remained flat to prior year at 34.3% as a percentage of net sales. Operating income decreased 80 basis points to 9.4% of net sales in fiscal 2017 from 10.2% of net sales in fiscal 2016. For fiscal 2017, net income was $422.6 million, or $3.30 per diluted share, compared to $437.1 million, or $3.27 per diluted share, in fiscal 2016. Excluding the impact of the revaluation of the Company’s net deferred tax asset resulting in a one-time, non-cash charge of approximately $4.9 million, or $0.03 per diluted share, adjusted net income for fiscal 2017 was $427.5 million, or $3.33 per diluted share.
We ended the year with $109.1 million in cash and outstanding debt of $426.1 million, after returning $503.2 million to our stockholders through stock repurchases and quarterly cash dividends.
Significant Accounting Policies and Estimates
Management’s discussion and analysis of our financial position and results of operations are based upon our Consolidated Financial Statements, which have been prepared in accordance with U.S. GAAP. The preparation of these financial statements requires management to make informed estimates and judgments that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses and related disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities. Our financial position and/or results of operations may be materially different when reported under different conditions or when using different assumptions in the application of such policies. In the event estimates or assumptions prove to be different from actual amounts, adjustments are made in subsequent periods to reflect more current information. Our significant accounting policies are disclosed in Note 1 to our Consolidated Financial Statements. The following discussion addresses our most critical accounting policies, which are those that are both important to the portrayal of our financial condition and results of operations and that require significant judgment or use of complex estimates.
Description | Judgments and Uncertainties | Effect if Actual Results Differ from Assumptions | ||
Inventory Valuation: | ||||
Inventory Impairment | ||||
We identify potentially excess and slow-moving inventory by evaluating turn rates, historical and expected future sales trends, age of merchandise, overall inventory levels, current cost of inventory and other benchmarks. We have established an inventory valuation reserve to recognize the estimated impairment in value (i.e., an inability to realize the full carrying value) based on our aggregate assessment of these valuation indicators under prevailing market conditions and current merchandising strategies. | We do not believe our merchandise inventories are subject to significant risk of obsolescence in the near term. However, changes in market conditions or consumer purchasing patterns could result in the need for additional reserves. Our impairment reserve contains uncertainties because the calculation requires management to make assumptions and to apply judgment regarding forecasted customer demand and the promotional environment. | We have not made any material changes in the accounting methodology used to recognize inventory impairment reserves in the financial periods presented. We do not believe there is a reasonable likelihood that there will be a material change in the future estimates or assumptions we use to calculate impairment. However, if assumptions regarding consumer demand or clearance potential for certain products are inaccurate, we may be exposed to losses or gains that could be material. A 10% change in our impairment reserve as of December 30, 2017, would have affected net income by approximately $0.5 million in fiscal 2017. | ||
21
Description | Judgments and Uncertainties | Effect if Actual Results Differ from Assumptions | ||
Shrinkage | ||||
We perform physical inventories at least once a year for each store that has been open more than 12 months, and we have established a reserve for estimating inventory shrinkage between physical inventory counts. The reserve is established by assessing the chain-wide average shrinkage experience rate, applied to the related periods’ sales volumes. Such assessments are updated on a regular basis for the most recent individual store experiences. | The estimated store inventory shrink rate is based on historical experience. We believe historical rates are a reasonably accurate reflection of future trends. Our shrinkage reserve contains uncertainties because the calculation requires management to make assumptions and to apply judgment regarding future shrinkage trends, the effect of loss prevention measures and new merchandising strategies. | We have not made any material changes in the accounting methodology used to recognize shrinkage in the financial periods presented. We do not believe there is a reasonable likelihood that there will be a material change in the future estimates or assumptions we use to calculate our shrinkage reserve. However, if our estimates regarding inventory losses are inaccurate, we may be exposed to losses or gains that could be material. A 10% change in our shrinkage reserve as of December 30, 2017, would have affected net income by approximately $1.7 million in fiscal 2017. | ||
Vendor Funding | ||||
We receive funding from substantially all of our significant merchandise vendors, in support of our business initiatives, through a variety of programs and arrangements, including vendor support funds (“vendor support”) and volume-based rebate funds (“volume rebates”). The amounts received are subject to terms of vendor agreements, most of which are “evergreen”, reflecting the on-going relationship with our significant merchandise vendors. Certain of our agreements, primarily volume rebates, are renegotiated annually, based on expected annual purchases of the vendor’s product. Vendor funding is initially deferred as a reduction of the purchase price of inventory, and then recognized as a reduction of cost of merchandise as the related inventory is sold. During interim periods, the amount of vendor support and volume rebates is estimated based upon initial commitments and anticipated purchase levels with applicable vendors. | The estimated purchase volume (and related vendor funding) is based on our current knowledge of inventory levels, sales trends and expected customer demand, as well as planned new store openings and relocations. Although we believe we can reasonably estimate purchase volume and related volume rebates at interim periods, it is possible that actual year-end results could be different from previously estimated amounts. Our allocation methodology contains uncertainties because the calculation requires management to make assumptions and to apply judgment regarding customer demand, purchasing activity, target thresholds, vendor attrition and collectability. | We have not made any material changes in the accounting methodology used to establish our vendor funding reserves in the financial periods presented. At the end of each fiscal year, a significant portion of the actual purchase activity is known. Thus, we do not believe there is a reasonable likelihood that there will be a material change in the amounts recorded as vendor funding. We do not believe there is a significant collectability risk related to vendor funding amounts due to us at the end of fiscal 2017. If a 10% reserve had been applied against our outstanding vendor funding due as of December 30, 2017, net income would have been affected by approximately $1.4 million in fiscal 2017. Although it is unlikely that there will be any significant reduction in historical levels of vendor funding, if such a reduction were to occur in future periods, the Company could experience a higher inventory balance and higher cost of sales. | ||
Freight | ||||
We incur various types of transportation and delivery costs in connection with inventory purchases and distribution. Such costs are included as a component of the overall cost of inventories (on an aggregate basis) and recognized as a component of cost of merchandise sold as the related inventory is sold. | We allocate freight as a component of total cost of sales without regard to inventory mix or unique freight burden of certain categories. This assumption has been consistently applied for all years presented. | We have not made any material changes in the accounting methodology used to establish our capitalized freight balance or freight allocation in the financial periods presented. If a 10% increase or decrease had been applied against our current inventory capitalized freight balance as of December 30, 2017, net income would have been affected by approximately $7.8 million in fiscal 2017. | ||
22
Description | Judgments and Uncertainties | Effect if Actual Results Differ from Assumptions | ||
Self-Insurance Reserves: | ||||
We self-insure a significant portion of our employee medical insurance, workers’ compensation insurance and general liability (including product liability) insurance plans. We have stop-loss insurance policies to protect from individual losses over specified dollar values. Provisions for losses related to our self-insured liabilities are based upon periodic independent actuarially determined estimates that consider a number of factors including historical claims experience, demographic factors and severity factors. | The full extent of certain claims, especially workers’ compensation and general liability claims, may not become fully determined for several years. Our self-insured liabilities contain uncertainties because management is required to make assumptions and to apply judgment to estimate the ultimate cost to settle reported claims and claims incurred but not reported as of the balance sheet date based upon historical data and experience, including actuarial calculations. | We have not made any material changes in the accounting methodology used to establish our self-insurance reserves in the financial periods presented. We do not believe there is a reasonable likelihood that there will be a material change in the assumptions we use to calculate insurance reserves. However, if we experience a significant increase in the number of claims or the cost associated with these claims, we may be exposed to losses that could be material. A 10% change in our self-insurance reserves as of December 30, 2017, would have affected net income by approximately $3.6 million in fiscal 2017. | ||
Sales Tax Audit Reserve: | ||||
A portion of our sales are to tax-exempt customers, predominantly agricultural-based. We obtain exemption information as a necessary part of each tax-exempt transaction. Many of the states in which we conduct business will perform audits to verify our compliance with applicable sales tax laws. The business activities of our customers and the intended use of the unique products sold by us create a challenging and complex tax compliance environment. These circumstances also create some risk that we could be challenged as to the accuracy of our sales tax compliance. When establishing our sales tax audit reserve, we review our past audit experience and assessments with applicable states to continually determine if we have potential exposure for non-compliance. Any estimated liability is based on an initial assessment of compliance risk as well as our historical experience with each respective state. | We continually reassess the exposure based on historical audit results, changes in policies, preliminary and final assessments made by state sales tax auditors and additional documentation that may be provided to reduce the assessment. Our sales tax audit reserve contains uncertainties because management is required to make assumptions and to apply judgment regarding the complexity of agricultural-based exemptions, the ambiguity in state tax regulations, the number of ongoing audits and the length of time required to settle with the state taxing authorities. | We have not made any material changes to our sales tax audit assessment methodology in the financial periods presented. We do not believe there is a reasonable likelihood that there will be a material change in the future estimates or assumptions we use to calculate the sales tax liability reserve. However, if our estimates regarding the ultimate sales tax liability are inaccurate, we may be exposed to losses or gains that could be material. A 10% change in our sales tax audit reserve as of December 30, 2017, would have affected net income by approximately $0.9 million in fiscal 2017. | ||
23
Description | Judgments and Uncertainties | Effect if Actual Results Differ from Assumptions | ||
Tax Contingencies: | ||||
Our income tax returns are periodically audited by U.S. federal and state tax authorities. These audits include questions regarding our tax filing positions, including the timing and amount of deductions and the allocation of income among various tax jurisdictions. At any time, multiple tax years are subject to audit by the various tax authorities. In evaluating the exposures associated with our various tax filing positions, we record a liability for uncertain tax positions taken or expected to be taken in a tax return. A number of years may elapse before a particular matter, for which we have established a reserve, is audited and fully resolved or clarified. We recognize the effect of income tax positions only if those positions are more likely than not of being sustained. Recognized income tax positions are measured at the largest amount that is greater than 50% likely of being realized. Changes in recognition or measurement are reflected in the period in which the change in judgment occurs. We adjust our tax contingencies reserve and income tax provision in the period in which actual results of a settlement with tax authorities differs from our established reserve, the statute of limitations expires for the relevant tax authority to examine the tax position or when more information becomes available. | Our tax contingencies reserve contains uncertainties because management is required to make assumptions and to apply judgment to estimate the exposures associated with our various filing positions and whether or not the minimum requirements for recognition of tax benefits have been met. The effective income tax rate is also affected by changes in tax law, the tax jurisdiction of new stores or business ventures, the level of earnings and the results of tax audits. | We have not made any material changes in the accounting methodology used to establish our tax contingencies in the financial periods presented. We do not believe there is a reasonable likelihood that there will be a material change in the reserves established for tax benefits not recognized. Although management believes that the judgments and estimates discussed herein are reasonable, actual results could differ, and we may be exposed to losses or gains that could be material. To the extent we prevail in matters for which reserves have been established, or are required to pay amounts in excess of our reserves, our effective income tax rate in a given financial statement period could be materially affected. An unfavorable tax settlement would require use of our cash and would result in an increase in our effective income tax rate in the period of resolution. A favorable tax settlement would be recognized as a reduction in our effective income tax rate in the period of resolution. A 10% change in our uncertain tax position reserve as of December 30, 2017, would have affected net income by approximately $0.1 million in fiscal 2017. | ||
24
Description | Judgments and Uncertainties | Effect if Actual Results Differ from Assumptions | ||
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets: | ||||
Long-lived assets are evaluated for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying value may not be recoverable. When evaluating long-lived assets for potential impairment, we first compare the carrying value of the asset to the asset’s estimated future cash flows (undiscounted and without interest charges). The evaluation for long-lived assets is performed at the lowest level of identifiable cash flows, which is generally the individual store level. The significant assumptions used to determine estimated undiscounted cash flows include cash inflows and outflows directly resulting from the use of those assets in operations, including margin on net sales, payroll and related items, occupancy costs, insurance allocations and other costs to operate a store. If the estimated future cash flows are less than the carrying value of the asset, we calculate an impairment loss. The impairment loss calculation compares the carrying value of the asset to the asset’s estimated fair value, which may be based on an estimated future cash flow model. We recognize an impairment loss if the amount of the asset’s carrying value exceeds the asset’s estimated fair value. If we recognize an impairment loss, the adjusted carrying amount of the asset becomes its new cost basis. For a depreciable long-lived asset, the new cost basis will be depreciated (amortized) over the remaining estimated useful life of that asset. | Our impairment loss calculations contain uncertainties because they require management to make assumptions and to apply judgment to estimate future cash flows and asset fair values. | We have not made any material changes in our impairment loss assessment methodology in the financial periods presented. We do not believe there is a reasonable likelihood that there will be a material change in the estimates or assumptions we use to calculate long-lived asset impairment losses. None of these estimates and assumptions are significantly sensitive, and a 10% change in any of these estimates would not have a material impact on our analysis. However, if actual results are not consistent with our estimates and assumptions used in estimating future cash flows and asset fair values, we may be exposed to losses that could be material. | ||
25
Description | Judgments and Uncertainties | Effect if Actual Results Differ from Assumptions | ||
Impairment of Goodwill and Other Indefinite-Lived Intangible Assets: | ||||
Goodwill and other indefinite-lived intangible assets are evaluated for impairment annually, or whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying value may not be recoverable. In accordance with the accounting standards, an entity has the option first to assess qualitative factors to determine whether events and circumstances indicate that it is more likely than not that goodwill or an indefinite-lived intangible asset is impaired. If after such assessment an entity concludes that the asset is not impaired, then the entity is not required to take further action. However, if an entity concludes otherwise, then it is required to determine the fair value of the asset using a quantitative impairment test, and if impaired, the associated assets must be written down to fair value. The quantitative impairment test for goodwill compares the fair value of a reporting unit with the carrying value of its net assets, including goodwill. If the fair value of the reporting unit is less than the carrying value of the reporting unit, an impairment charge would be recorded to the Company’s operations, for the amount, if any, in which the carrying amount exceeds the reporting unit’s fair value. We determine fair values for each reporting unit using the market approach, when available and appropriate, or the income approach, or a combination of both. If multiple valuation methodologies are used, the results are weighted appropriately. The quantitative impairment test for other indefinite-lived intangible assets involves comparing the carrying amount of the asset to the sum of the discounted cash flows expected to be generated by the asset. If the implied fair value of the indefinite-lived intangible asset is less than the carrying value, an impairment charge would be recorded to the Company’s operations. | Our impairment loss calculation contains uncertainties because they require management to make assumptions and to apply judgment to qualitative factors as well as estimate future cash flows and asset fair values, including forecasting prospective financial information and selecting the discount rate that reflects the risk inherent in future cash flows. | The valuation approaches utilized to estimate fair value for the purposes of the impairment tests of goodwill and other indefinite-lived intangible assets require the use of assumptions and estimates, which involve a degree of uncertainty. If actual results are not consistent with our estimates and assumptions used in estimating future cash flows and asset fair values, we may be exposed to non-cash impairment losses that could be material. | ||
26
Quarterly Financial Data
Our unaudited quarterly operating results for each fiscal quarter of 2017 and 2016 are shown below (in thousands, except per share amounts):
First Quarter | Second Quarter | Third Quarter | Fourth Quarter | Total | ||||||||||||||||
2017 | (13 weeks) | (13 weeks) | (13 weeks) | (13 weeks) | (52 weeks) | |||||||||||||||
Net sales | $ | 1,564,078 | $ | 2,017,762 | $ | 1,721,704 | $ | 1,952,838 | $ | 7,256,382 | ||||||||||
Gross profit | 518,203 | 704,708 | 600,456 | 668,598 | 2,491,965 | |||||||||||||||
Operating income | 96,362 | 257,925 | 148,253 | 183,842 | 686,382 | |||||||||||||||
Net income | 60,311 | 160,649 | 91,896 | 109,743 | 422,599 | |||||||||||||||
Net income per share: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Basic | $ | 0.46 | $ | 1.25 | $ | 0.73 | $ | 0.87 | $ | 3.31 | ||||||||||
Diluted | $ | 0.46 | $ | 1.25 | $ | 0.72 | $ | 0.87 | $ | 3.30 | ||||||||||
Comparable store sales (decrease) increase (a) | (2.2 | )% | 2.2 | % | 6.6 | % | 4.0 | % | 2.7 | % | ||||||||||
First Quarter | Second Quarter | Third Quarter | Fourth Quarter | Total | ||||||||||||||||
2016 (b) | (13 weeks) | (13 weeks) | (13 weeks) | (14 weeks) | (53 weeks) | |||||||||||||||
Net sales | $ | 1,467,797 | $ | 1,852,534 | $ | 1,542,706 | $ | 1,916,542 | $ | 6,779,579 | ||||||||||
Gross profit | 494,444 | 649,222 | 535,274 | 646,262 | 2,325,202 | |||||||||||||||
Operating income | 108,195 | 249,249 | 142,020 | 194,616 | 694,080 | |||||||||||||||
Net income | 67,668 | 156,425 | 89,444 | 123,583 | 437,120 | |||||||||||||||
Net income per share: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Basic | $ | 0.51 | $ | 1.17 | $ | 0.67 | $ | 0.94 | $ | 3.29 | ||||||||||
Diluted | $ | 0.50 | $ | 1.16 | $ | 0.67 | $ | 0.94 | $ | 3.27 | ||||||||||
Comparable store sales increase (decrease) (a) | 4.9 | % | (0.5 | )% | (0.6 | )% | 3.1 | % | 1.6 | % | ||||||||||
(a) Comparable store metrics are calculated using sales generated from all stores open at least one year and all online sales, excluding certain adjustments to net sales. Closed stores are removed from our comparable store metrics calculations. Stores relocated during the periods being compared are not removed from our comparable store metrics. If the effect of relocated stores on our comparable store metrics becomes material, we would remove relocated stores from the calculations. Acquired Petsense stores are considered comparable stores beginning in the fourth quarter of fiscal 2017.
(b) Beginning in the fourth quarter ended December 31, 2016, selected financial and operating information includes the consolidation of Petsense, unless otherwise noted.
Results of Operations
The following table sets forth, for the periods indicated, certain items in our Consolidated Statements of Income expressed as a percentage of net sales.
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||
Net sales | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | ||
Cost of merchandise sold (a) | 65.7 | 65.7 | 65.6 | |||||
Gross margin (a) | 34.3 | 34.3 | 34.4 | |||||
Selling, general and administrative expenses (a) | 22.6 | 22.0 | 22.0 | |||||
Depreciation and amortization | 2.3 | 2.1 | 2.0 | |||||
Operating income | 9.4 | 10.2 | 10.4 | |||||
Interest expense, net | 0.2 | 0.1 | — | |||||
Income before income taxes | 9.2 | 10.1 | 10.4 | |||||
Income tax provision | 3.4 | 3.7 | 3.8 | |||||
Net income | 5.8 | % | 6.4 | % | 6.6 | % | ||
(a) Our gross margin amounts may not be comparable to those of other retailers since some retailers include all of the costs related to their distribution network in cost of merchandise sold and others (like our Company) exclude a portion of these distribution network costs from gross margin and instead include them in selling, general and administrative expenses; refer to Note 1 – Significant Accounting Policies, of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, included in Item 8 Financial Statements and Supplementary Data, of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
27
Fiscal 2017 Compared to Fiscal 2016
Net sales increased 7.0% to $7.26 billion in fiscal 2017 from $6.78 billion in fiscal 2016. The prior year included an extra sales week as a part of the Company’s 53-week calendar in 2016, which negatively impacted the overall sales increase by approximately 1.6 percentage points. Comparable store sales for fiscal 2017 were $6.85 billion, a 2.7% increase over fiscal 2016. This compares to a 1.6% comparable store sales increase in the prior year. The comparable store transaction count increased 2.2% and comparable store average ticket increased 0.5% for fiscal 2017.
Comparable store metrics are calculated on an annual basis using sales generated from all stores open at least one year and all online sales, excluding certain adjustments to net sales. Stores closed during the year are removed from our comparable store metrics calculations. Stores relocated during the years being compared are not removed from our comparable store metrics. If the effect of relocated stores on our comparable store metrics becomes material, we would remove relocated stores from the calculations. Acquired Petsense stores are considered comparable beginning in the fourth quarter of fiscal 2017.
The comparable store sales increase was driven by an increase in traffic counts and the year-round strength of consumable, usable and edible ("C.U.E.") products, primarily animal- and pet-related merchandise. Warmer than normal weather patterns early in the first quarter negatively impacted the sales of winter seasonal items and winter storms in March had an unfavorable impact on the start to the spring selling season. Beginning in the second quarter, we experienced broad-based improvement through the remainder of the year in all geographic regions and major product categories driven by strength in sales of everyday basic items in C.U.E. and year-round products. The third quarter experienced an additional benefit from an extended spring and summer selling season and strong sales of emergency response products related to hurricanes during the quarter while the fourth quarter experienced an additional benefit from solid sales in cold weather and other seasonal products.
In addition to comparable store sales growth in fiscal 2017, sales from stores opened less than one year, including Petsense, were $405.0 million in fiscal 2017, which represented 6.0 percentage points of the 7.0% increase over fiscal 2016 net sales. Sales from stores opened less than one year, including Petsense, were $378.9 million in fiscal 2016, which represented 6.1 percentage points of the 8.9% increase over fiscal 2015 net sales.
The following table summarizes our store growth during fiscal 2017 and 2016:
Tractor Supply | 2017 | 2016 | |||
Store count, beginning of period | 1,595 | 1,488 | |||
New stores opened | 101 | 113 | |||
Stores closed | (11 | ) | (6 | ) | |
Store count, end of period | 1,685 | 1,595 | |||
Petsense | |||||
Beginning of period | 143 | — | |||
Stores acquired | — | 136 | |||
New stores opened | 25 | 8 | |||
Stores closed | — | (1 | ) | ||
End of period | 168 | 143 | |||
Consolidated end of period | 1,853 | 1,738 | |||
Stores relocated | 3 | 3 | |||
28
The following table indicates the percentage of net sales represented by each of our major product categories during fiscal 2017 and 2016:
Percent of Net Sales | |||||
Product Category: | 2017 | 2016 | |||
Livestock and Pet | 47 | % | 46 | % | |
Hardware, Tools and Truck | 22 | 22 | |||
Seasonal, Gift and Toy Products | 19 | 19 | |||
Clothing and Footwear | 8 | 8 | |||
Agriculture | 4 | 5 | |||
Total | 100 | % | 100 | % | |
Gross profit increased 7.2% to $2.49 billion in fiscal 2017 compared to $2.33 billion in fiscal 2016. As a percent of net sales, gross margin remained flat to prior year at 34.3%. Gross margin percentage was negatively impacted by higher markdowns on cold weather merchandise and targeted promotional activity in the first quarter, as well as a higher freight expense throughout the year due to higher carrier costs, increased average fuel costs and a shift in product mix towards more freight intensive products. These declines in gross margin were offset by strong sell-through rates and solid price and inventory management, particularly in the back half of the year.
Total selling, general and administrative (“SG&A”) expenses, including depreciation and amortization, for fiscal 2017 increased 10.7% to $1.81 billion from $1.63 billion in fiscal 2016. SG&A expenses, as a percent of net sales, increased 80 basis points to 24.9% in fiscal 2017 from 24.1% in fiscal 2016. The increase in SG&A as a percent of net sales was primarily attributable to higher store payroll from wage inflation and our continued effort to enhance customer service, increased incentive compensation at the store level from the strong year-over-year growth in comparable store sales, the deleverage of occupancy and other fixed costs resulting from the integration of Petsense expenses and the 53rd week of sales in fiscal 2016 that did not reoccur in fiscal 2017, and investments in infrastructure and technology to support our strategic long-term growth initiatives.
Our effective tax rate increased to 37.2% for fiscal 2017 compared to 36.5% in fiscal 2016. On December 22, 2017, the U.S. government enacted comprehensive tax legislation commonly referred to as the Tax Cut and Jobs Act (the “Act”). The Act makes broad and complex changes to the U.S. tax code including, but not limited to, a reduction of the federal income tax rate from 35% to 21% effective for tax years beginning after December 31, 2017. We have made a reasonable estimate of the effects of the Act on our existing deferred tax balances as of December 30, 2017, and recognized a provisional amount of $4.9 million, which is included as a component of income tax expense from continuing operations. However, we are still analyzing certain aspects of the Act and refining our calculations, which could potentially affect the measurement of these balances in future periods. Excluding the impacts of the Act, our effective income tax rate in 2017 would have been 36.4%.
For fiscal 2017, net income was $422.6 million, or $3.30 per diluted share, compared to $437.1 million, or $3.27 per diluted share, in fiscal 2016. Excluding the impact of the revaluation of the Company’s net deferred tax asset resulting in a one-time, non-cash charge of approximately $4.9 million, or $0.03 per diluted share, adjusted net income for fiscal 2017 was $427.5 million, or $3.33 per diluted share. Adjusted net income is a non-GAAP measure which has been provided in order to enhance comparability for the periods presented.
During fiscal 2017, we repurchased approximately 5.9 million shares of the Company’s common stock at a total cost of $369.4 million as part of our $3 billion share repurchase program. In fiscal 2016, we repurchased approximately 4.4 million shares at a total cost of $331.7 million.
Fiscal 2016 Compared to Fiscal 2015
Net sales increased 8.9% to $6.78 billion in fiscal 2016 from $6.23 billion in fiscal 2015. The fourth quarter included an extra sales week as a part of the Company’s 53-week calendar in 2016, which represented 1.6 percentage points of the overall 8.9% sales increase over prior year. Comparable store sales for fiscal 2016 were $6.41 billion, a 1.6% increase over fiscal 2015. This compares to a 3.1% comparable store sales increase in the prior year. The comparable store transaction count increased 2.6%, while comparable store average ticket decreased 0.9% for fiscal 2016.
Comparable store metrics are calculated on an annual basis using sales generated from all stores open at least one year and all online sales, excluding certain adjustments to net sales. Stores closed during the year are removed from our comparable store metrics calculations. Stores relocated during the years being compared are not removed from our comparable store metrics. If
29
the effect of relocated stores on our comparable store metrics becomes material, we would remove relocated stores from the calculations. Petsense stores are not considered comparable stores until 12 months after the date of acquisition.
The comparable store sales increase was driven by an increase in traffic counts and the year-round strength of C.U.E. products, principally animal- and pet-related merchandise. Livestock equipment and hardline products such as fencing and trailers also performed well throughout the year. The full year sales performance was negatively impacted by unpredictable weather patterns during the spring selling season and unseasonably warm weather in the key cold months of the year which drove softness in cold weather seasonal categories and big ticket items such as log splitters and stoves. Additionally, the Company believes that economic conditions in the energy producing markets negatively impacted consumer spending primarily in the Midwest and South Central regions.
In addition to comparable store sales growth in fiscal 2016, sales from stores opened less than one year, including Petsense, were $378.9 million in fiscal 2016, which represented 6.1 percentage points of the 8.9% increase over fiscal 2015 net sales. Sales from stores opened less than one year were $351.0 million in fiscal 2015, which represented 6.1 percentage points of the 9.0% increase over fiscal 2014 net sales.
The following table summarizes our store growth during fiscal 2016 and 2015:
Tractor Supply | 2016 | 2015 | |||
Store count, beginning of period | 1,488 | 1,382 | |||
New stores opened | 113 | 114 | |||
Stores closed | (6 | ) | (8 | ) | |
Store count, end of period | 1,595 | 1,488 | |||
Petsense | |||||
Beginning of period | — | — | |||
Stores acquired | 136 | — | |||
New stores opened | 8 | — | |||
Stores closed | (1 | ) | — | ||
End of period | 143 | — | |||
Consolidated end of period | 1,738 | 1,488 | |||
Stores relocated | 3 | 6 | |||
The following table indicates the percentage of net sales represented by each of our major product categories during fiscal 2016 and 2015:
Percent of Net Sales | |||||
Product Category: | 2016 | 2015 | |||
Livestock and Pet | 46 | % | 44 | % | |
Hardware, Tools and Truck | 22 | 23 | |||
Seasonal, Gift and Toy Products | 19 | 20 | |||
Clothing and Footwear | 8 | 8 | |||
Agriculture | 5 | 5 | |||
Total | 100 | % | 100 | % | |
Gross profit increased 8.5% to $2.33 billion in fiscal 2016 compared to $2.14 billion in fiscal 2015. As a percent of net sales, gross margin decreased 10 basis points to 34.3% for fiscal 2016 compared to 34.4% for fiscal 2015. This decrease in gross margin percentage principally reflects a higher mix of C.U.E. products, which generally carry below chain average gross margin, partially offset by benefits from our key margin driving initiatives. Freight expense as a percent of net sales experienced a marginal increase in fiscal 2016 as compared to the prior year due principally to an increase in inbound miles and domestic transportation costs, partially offset by lower diesel fuel prices and import container costs.
SG&A expenses, including depreciation and amortization, as a percent of net sales increased 10 basis points to 24.1% in fiscal 2016 from 24.0% in fiscal 2015. SG&A expenses as a percent of net sales increased due to incremental costs associated with our
30
new distribution facilities that began operations in late fiscal 2015, as well as acquisition and operating expenses associated with the Petsense purchase. These increases were partially offset by leverage of occupancy costs from the 53rd week of sales in fiscal 2016, as well as lower year-over-year incentive compensation expense. Total SG&A expenses, including depreciation and amortization, for fiscal 2016 increased 9.3% to $1.63 billion from $1.49 billion in fiscal 2015. The increase in SG&A expenses primarily reflects new store growth, incremental costs from operating the new distribution facilities, variable costs associated with our comparable store sales growth and the extra sales week during the year and incremental expenses associated with the Petsense acquisition and its operations.
Our effective tax rate decreased to 36.5% for fiscal 2016 compared to 36.6% in fiscal 2015. The decrease in the effective income tax rate was due principally to the availability of federal and state tax incentives.
As a result of the foregoing factors, net income for fiscal 2016 increased 6.5% to $437.1 million, or $3.27 per diluted share, as compared to net income of $410.4 million, or $3.00 per diluted share, in fiscal 2015.
During fiscal 2016, we repurchased approximately 4.4 million shares of the Company’s common stock at a total cost of $331.7 million as part of our $3 billion share repurchase program. In fiscal 2015, we repurchased approximately 3.4 million shares at a total cost of $292.7 million.
Fiscal 2018 Outlook
Our guidance for fiscal 2018 anticipates net sales of $7.69 billion to $7.77 billion, reflecting a comparable store sales increase of 2.0% to 3.0% as well as the opening of approximately 80 Tractor Supply stores and 20 Petsense stores. At the mid-point of our guidance range, we anticipate that operating profit as a percentage of net sales will decrease from 9.4% in fiscal 2017 to 8.8% in fiscal 2018. Included in this estimate are anticipated cost pressures associated with rising diesel fuel prices and transportation costs, wage investments for our team members in our stores and distribution centers, investments to support our growth strategy, and incremental pre-opening and other operating expenses from our new distribution center which is currently under construction in Frankfort, New York. Lastly, as a result of the Act reducing the statutory federal income tax rate from 35% to 21%, our effective tax rate in fiscal 2018 is expected to range from 23.0% to 23.5%. As a result of the foregoing factors, we estimate net income for fiscal 2018 of $490 million to $515 million, or $3.95 to $4.15 per diluted share.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
In addition to normal operating expenses, our primary ongoing cash requirements are for new store expansion, remodeling and relocation programs, distribution facility capacity and improvements, information technology, inventory purchases, repayment of
existing borrowings under our debt facilities, share repurchases, cash dividends and selective acquisitions as opportunities arise.
Our primary ongoing sources of liquidity are existing cash balances, cash provided from operations, remaining funds available under our debt facilities, capital and operating leases and normal trade credit. Our inventory and accounts payable levels typically build in the first and third fiscal quarters to support the higher sales volume of the spring and cold-weather selling seasons, respectively.
We believe that our existing cash balances, expected cash flow from future operations, funds available under our debt facilities, operating and capital leases and normal trade credit will be sufficient to fund our operations and our capital expenditure needs, including new store openings, store acquisitions, relocations and renovations and distribution facility capacity, through the end of fiscal 2018.
31
Working Capital
At December 30, 2017, the Company had working capital of $806.2 million, which increased $65.6 million from December 31, 2016. The shifts in working capital were attributable to changes in the following components of current assets and current liabilities (in millions):
2017 | 2016 | Variance | |||||||||
Current assets: | |||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 109.1 | $ | 53.9 | $ | 55.2 | |||||
Inventories | 1,453.2 | 1,369.7 | 83.5 | ||||||||
Prepaid expenses and other current assets | 88.3 | 90.6 | (2.3 | ) | |||||||
Income taxes receivable | 4.8 | 3.6 | 1.2 | ||||||||
Total current assets | 1,655.4 | 1,517.8 | 137.6 | ||||||||
Current liabilities: | |||||||||||
Accounts payable | 576.6 | 519.5 | 57.1 | ||||||||
Accrued employee compensation | 31.6 | 25.2 | 6.4 | ||||||||
Other accrued expenses | 201.7 | 215.7 | (14.0 | ) | |||||||
Current portion of long-term debt | 25.0 | 10.0 | 15.0 | ||||||||
Current portion of capital lease obligation | 3.5 | 1.3 | 2.2 | ||||||||
Income taxes payable | 10.8 | 5.5 | 5.3 | ||||||||
Total current liabilities | 849.2 | 777.2 | 72.0 | ||||||||
Working capital | $ | 806.2 | $ | 740.6 | $ | 65.6 | |||||
In comparison to December 31, 2016, working capital as of December 30, 2017 was impacted most significantly by changes in our cash, inventory and accounts payable.
• | The cash balance increased primarily due to strong inventory turns at the end of fiscal 2017 stemming from the sale of cold weather seasonal merchandise. |
• | The increase in inventory resulted from the purchase of additional inventory to support new store growth. We actively manage our inventory balances and in-stock levels at our stores. Average inventory per store decreased slightly year-over-year principally due to an improvement in inventory turns of seasonal and cold-weather merchandise at the end of fiscal 2017 as compared to fiscal 2016. |
• | Accounts payable increased primarily as a result of new store growth along with timing of payments to vendors. |
Debt
The following table summarizes the Company’s outstanding debt as of the dates indicated (in millions):
December 30, 2017 | December 31, 2016 | |||||||
Senior Notes | $ | 150.0 | $ | — | ||||
Senior Credit Facility: | ||||||||
February 2016 Term Loan | 180.0 | 190.0 | ||||||
June 2017 Term Loan | 97.5 | — | ||||||
Revolving credit loans | — | 85.0 | ||||||
Total outstanding borrowings | 427.5 | 275.0 | ||||||
Less: unamortized debt issuance costs | (1.4 | ) | (1.1 | ) | ||||
Total debt | 426.1 | 273.9 | ||||||
Less: current portion of long-term debt | (25.0 | ) | (10.0 | ) | ||||
Long-term debt | $ | 401.1 | $ | 263.9 | ||||
Outstanding letters of credit | $ | 39.6 | $ | 44.3 | ||||
32
Senior Notes
On August 14, 2017, the Company entered into a note purchase and private shelf agreement (the “Note Purchase Agreement”), pursuant to which the Company agreed to sell $150 million aggregate principal amount of senior unsecured notes due August 14, 2029 (the “2029 Notes”) in a private placement. The 2029 Notes bear interest at 3.70% per annum with interest payable semi-annually in arrears on each annual and semi-annual anniversary of the issuance date. The obligations under the Note Purchase Agreement are unsecured, but guaranteed by each of the Company’s material subsidiaries.
The Company may from time to time issue and sell additional senior unsecured notes (the “Shelf Notes”) pursuant to the Note Purchase Agreement, in an aggregate principal amount of up to $150 million. The Shelf Notes will have a maturity date of no more than 12 years after the date of original issuance and may be issued through August 14, 2020, unless earlier terminated in accordance with the terms of the Note Purchase Agreement.
Pursuant to the Note Purchase Agreement, the 2029 Notes and any Shelf Notes (collectively, the "Notes") are redeemable by the Company, in whole at any time or in part from time to time, at 100% of the principal amount of the Notes being redeemed, together with accrued and unpaid interest thereon and a make whole amount calculated by discounting all remaining scheduled payments on the Notes by the yield on the U.S. Treasury security with a maturity equal to the remaining average life of the Notes plus 0.50%.
Senior Credit Facility
On February 19, 2016, the Company entered into a senior credit facility (the “2016 Senior Credit Facility”) consisting of a $200 million term loan (the “February 2016 Term Loan”) and a $500 million revolving credit facility (the “Revolver”) with a sublimit of $50 million for swingline loans. This agreement is unsecured. On February 16, 2018, the maturity date was extended from February 19, 2021 to February 19, 2022.
On June 15, 2017, pursuant to an accordion feature available under the 2016 Senior Credit Facility, the Company entered into an incremental term loan agreement (the “June 2017 Term Loan”) which increased the term loan capacity under the 2016 Senior Credit Facility by $100 million. This agreement is unsecured and matures on June 15, 2022.
The February 2016 Term Loan of $200 million requires quarterly payments totaling $10 million per year in years one and two and $20 million per year in years three through the maturity date, with the remaining balance due in full on the maturity date of February 19, 2022. The June 2017 Term Loan of $100 million requires quarterly payments totaling $5 million per year in years one and two and $10 million per year in years three through the maturity date, with the remaining balance due in full on the maturity date of June 15, 2022. The 2016 Senior Credit Facility also contains a $500 million revolving credit facility (with a sublimit of $50 million for swingline loans).
Borrowings under the February 2016 Term Loan and Revolver bear interest at either the bank’s base rate (4.500% at December 30, 2017) or the London Inter-Bank Offer Rate (“LIBOR”) (1.564% at December 30, 2017) plus an additional amount ranging from 0.500% to 1.125% per annum (0.750% at December 30, 2017), adjusted quarterly based on our leverage ratio. The Company is also required to pay, quarterly in arrears, a commitment fee for unused capacity ranging from 0.075% to 0.200% per annum (0.125% at December 30, 2017), adjusted quarterly based on the Company’s leverage ratio. Borrowings under the June 2017 Term Loan bear interest at either the bank’s base rate (4.500% at December 30, 2017) or LIBOR (1.564% at December 30, 2017) plus an additional 1.000% per annum. As further described in Note 6 to the Consolidated Financial Statements, the Company has entered into interest rate swap agreements in order to hedge our exposure to variable rate interest payments associated with each of the term loans under the 2016 Senior Credit Facility.
Proceeds from the 2016 Senior Credit Facility may be used for working capital, capital expenditures, dividends, share repurchases, and other matters. There are no compensating balance requirements associated with the 2016 Senior Credit Facility.
Covenants and Default Provisions of the Debt Agreements
The 2016 Senior Credit Facility and the Note Purchase Agreement (collectively, the “Debt Agreements”) require quarterly compliance with respect to two material covenants: a fixed charge coverage ratio and a leverage ratio. Both ratios are calculated on a trailing twelve-month basis at the end of each fiscal quarter. The fixed charge coverage ratio compares earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, amortization, share-based compensation and rent expense (“consolidated EBITDAR”) to the sum of interest paid and rental expense (excluding any straight-line rent adjustments). The fixed charge coverage ratio shall be greater than or equal to 2.00 to 1.0 as of the last day of each fiscal quarter. The leverage ratio compares rental expense (excluding any straight-line rent adjustments) multiplied by a factor of six plus total debt to consolidated EBITDAR. The leverage ratio shall be less than
33
or equal to 4.00 to 1.0 as of the last day of each fiscal quarter. The Debt Agreements also contain certain other restrictions regarding additional indebtedness, capital expenditures, business operations, guarantees, investments, mergers, consolidations and sales of assets, transactions with subsidiaries or affiliates, and liens. As of December 30, 2017, the Company was in compliance with all debt covenants.
The Debt Agreements contain customary events of default, including payment defaults, breaches of representations and warranties, covenant defaults, cross-defaults to other material indebtedness, certain events of bankruptcy and insolvency, material judgments, certain ERISA events and invalidity of loan documents. Upon certain changes of control, payment under the Debt Agreements could become due and payable. In addition, under the Note Purchase Agreement, upon an event of default or change of control, the make whole payment described above may become due and payable.
The Note Purchase Agreement also requires that, in the event the Company amends its 2016 Senior Credit Facility, or any subsequent credit facility of $100 million or greater, such that it contains covenant or default provisions that are not provided in the Note Purchase Agreement or that are similar to those contained in the Note Purchase Agreement but which contain percentages, amounts, formulas or grace periods that are more restrictive than those set forth in the Note Purchase Agreement or are otherwise more beneficial to the lenders thereunder, the Note Purchase Agreement shall be automatically amended to include such additional or amended covenants and/or default provisions.
Interest Rate Swaps
The Company entered into an interest rate swap agreement which became effective on March 31, 2016, with a maturity date of February 19, 2021. The notional amount of this swap agreement began at $197.5 million (the principal amount of the February 2016 Term Loan borrowings as of March 31, 2016) and will amortize at the same time and in the same amount as the February 2016 Term Loan borrowings as described in Note 5 to the Consolidated Financial Statements, up to the maturity date of the interest rate swap agreement on February 19, 2021. As of December 30, 2017, the notional amount of the interest rate swap was $180.0 million.
The Company entered into a second interest rate swap agreement which became effective on June 30, 2017, with a maturity date of June 15, 2022. The notional amount of this swap agreement began at $100 million (the principal amount of the June 2017 Term Loan borrowings as of June 30, 2017) and will amortize at the same time and in the same amount as the June 2017 Term Loan borrowings as described in Note 5 to the Consolidated Financial Statements. As of December 30, 2017, the notional amount of the interest rate swap was $97.5 million.
The Company’s interest rate swap agreements are executed for risk management and are not held for trading purposes. The objective of the interest rate swap agreements is to mitigate interest rate risk associated with future changes in interest rates. To accomplish this objective, the interest rate swap agreements are intended to hedge the variable cash flows associated with the variable rate term loan borrowings under the 2016 Senior Credit Facility. Both interest rate swap agreements entitle the Company to receive, at specified intervals, a variable rate of interest based on LIBOR in exchange for the payment of a fixed rate of interest throughout the life of the agreement, without exchange of the underlying notional amount.
Sources and Uses of Cash
Our primary source of liquidity is cash provided by operations and funds available under our debt facilities. Principal uses of cash for investing activities are capital expenditures and selective acquisitions, while principal uses of cash for financing activities are repurchase of the Company’s common stock and cash dividends paid to stockholders.
The following table presents a summary of cash flows provided by or used in operating, investing and financing activities for the last three fiscal years (in millions):
2017 | 2016(a) | 2015(a) | |||||||||
(52 weeks) | (53 weeks) | (52 weeks) | |||||||||
Net cash provided by operating activities | $ | 631.5 | $ | 650.7 | $ | 456.2 | |||||
Net cash used in investing activities | (238.0 | ) | (369.3 | ) | (235.9 | ) | |||||
Net cash used in financing activities | (338.3 | ) | (291.3 | ) | (207.6 | ) | |||||
Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | $ | 55.2 | $ | (9.9 | ) | $ | 12.7 | ||||
(a) As a result of the adoption of ASU 2016-09 (discussed in Note 15 to the Consolidated Financial Statements), excess tax benefits on stock options exercised are no longer presented as a separate line item in the statement of cash flows. The presentation of fiscal 2016 and fiscal 2015 have been adjusted to conform to the current presentation.
34
Operating Activities
Operating activities provided net cash of $631.5 million, $650.7 million and $456.2 million in fiscal 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively. The $19.2 million decrease in net cash provided by operating activities in fiscal 2017 compared to fiscal 2016 was due to changes in the following (in millions):
2017 | 2016(a) | Variance | |||||||||
(52 weeks) | (53 weeks) | ||||||||||
Net income | $ | 422.6 | $ | 437.1 | $ | (14.5 | ) | ||||
Depreciation and amortization | 165.8 | 143.0 | 22.8 | ||||||||
Share-based compensation expense | 29.2 | 23.6 | 5.6 | ||||||||
Deferred income taxes | 26.7 | 10.0 | 16.7 | ||||||||
Inventories and accounts payable | (26.5 | ) | 14.8 | (41.3 | ) | ||||||
Prepaid expenses and other current assets | 2.3 | 1.8 | 0.5 | ||||||||
Accrued expenses | (3.9 | ) | 2.1 | (6.0 | ) | ||||||
Income taxes | 4.2 | 11.8 | (7.6 | ) | |||||||
Other, net | 11.1 | 6.5 | 4.6 | ||||||||
Net cash provided by operating activities | $ | 631.5 | $ | 650.7 | $ | (19.2 | ) | ||||
(a) As a result of the adoption of ASU 2016-09 (discussed in Note 15 to the Consolidated Financial Statements), excess tax benefits on stock options exercised are no longer presented as a separate line item in the statement of cash flows. The presentation of fiscal 2016 has been adjusted to conform to the current presentation.
The $19.2 million decrease in net cash provided by operating activities in fiscal 2017 compared with fiscal 2016 primarily reflects the timing of receipts and payments in relation to inventory and accounts payable partially offset by increased depreciation and amortization due to new store growth and investments in information technology and infrastructure.
The $194.5 million increase in net cash provided by operating activities in fiscal 2016 over fiscal 2015 was due to changes in the following (in millions):
2016(a) | 2015(a) | Variance | |||||||||
(53 weeks) | (52 weeks) | ||||||||||
Net income | $ | 437.1 | $ | 410.4 | $ | 26.7 | |||||
Depreciation and amortization | 143.0 | 123.6 | 19.4 | ||||||||
Stock compensation expense | 23.6 | 19.4 | 4.2 | ||||||||
Deferred income taxes | 10.0 | (5.5 | ) | 15.5 | |||||||
Inventories and accounts payable | 14.8 | (112.5 | ) | 127.3 | |||||||
Prepaid expenses and other current assets | 1.8 | (21.1 | ) | 22.9 | |||||||
Accrued expenses | 2.1 | 16.9 | (14.8 | ) | |||||||
Income taxes payable | 11.8 | 16.3 | (4.5 | ) | |||||||
Other, net | 6.5 | 8.7 | (2.2 | ) | |||||||
Net cash provided by operating activities | $ | 650.7 | $ | 456.2 | $ | 194.5 | |||||
(a) As a result of the adoption of ASU 2016-09 (discussed in Note 15 to the Consolidated Financial Statements), excess tax benefits on stock options exercised are no longer presented as a separate line item in the statement of cash flows. The presentation of fiscal 2016 and fiscal 2015 has been adjusted to conform to the current presentation.
The $194.5 million increase in net cash provided by operating activities in fiscal 2016 compared with fiscal 2015 primarily reflects incremental profitability and the impact of effective management of inventory and accounts payable levels. Average inventory per store decreased year-over-year principally due to an improvement in inventory turns of seasonal and cold-weather merchandise at the end of fiscal 2016 compared to fiscal 2015. Additionally, the timing of payments to vendors more closely aligned with receipt of inventory at the end of fiscal 2016 in comparison with the end of fiscal 2015, resulting in an improvement in cash flow year-over-year.
35
Investing Activities
Investing activities used cash of $238.0 million, $369.3 million and $235.9 million in fiscal 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively. Fiscal 2016 had a significant cash outflow from investing activities related to the acquisition of Petsense. Other than cash flows related to the acquisition of Petsense, cash flows from investing activities in the years presented are primarily composed of capital expenditures. Capital expenditures for fiscal 2017, 2016 and 2015 were as follows (in millions):
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
(52 weeks) | (53 weeks) | (52 weeks) | |||||||||
Information technology | $ | 82.1 | $ | 40.5 | $ | 35.8 | |||||
New and relocated stores and stores not yet opened | 79.3 | 111.2 | 96.7 | ||||||||
Distribution center capacity and improvements | 45.8 | 21.0 | 80.2 | ||||||||
Existing stores | 43.0 | 53.1 | 23.1 | ||||||||
Corporate and other | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.7 | ||||||||
Total capital expenditures | $ | 250.4 | $ | 226.0 | $ | 236.5 | |||||
The above table reflects an investment in 101 new Tractor Supply stores and three store relocations, as well as 25 new Petsense stores during fiscal 2017. In 2016, we opened 113 new Tractor Supply stores, had three store relocations and began operating 143 Petsense stores as compared to 114 new Tractor Supply stores and six store relocations in fiscal 2015. Existing store expenditures were higher in fiscal 2016 and fiscal 2017, as compared to fiscal 2015, due to the investment in the chain-wide LED lighting retrofit initiative, which was completed in fiscal 2017.
The sustained increase in spending on information technology represents continued support of our store growth and our omni-channel platform, as well as improvements in security and compliance, enhancements to our customer relationship management database and other strategic initiatives.
Spending for distribution center capacity and improvements increased in fiscal 2017 as we began construction of a new northeast distribution center in Frankfort, New York, and expansion of our distribution center in Waverly, Nebraska. Distribution center spending was also higher in fiscal 2015 as a result of the construction of two mixing centers in Texas and the southwest distribution center in Casa Grande, Arizona, all of which began operations in fiscal 2015.
We currently estimate that capital expenditures in fiscal 2018 will range between $260 million and $300 million.
• | We plan to open approximately 80 Tractor Supply stores and 20 Petsense stores in fiscal 2018. |
• | We plan to continue to invest in the development of our new northeast distribution center. We also plan to invest in two additional mixing centers and an East Coast import center. |
• | Additionally, we will continue to enhance our digital and omni-channel capabilities to better serve our customers. |
Financing Activities
Financing activities used cash of $338.3 million, $291.3 million and $207.6 million in fiscal 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively.
The $47.0 million increase in net cash used in financing activities in fiscal 2017 compared to fiscal 2016 was due to changes in the following (in millions):
2017 | 2016(a) | Variance | |||||||||
(52 weeks) | (53 weeks) | ||||||||||
Net borrowings and repayments under debt facilities | $ | 152.5 | $ | 125.0 | $ | 27.5 | |||||
Repurchase of common stock | (369.4 | ) | (331.7 | ) | (37.7 | ) | |||||
Net proceeds from issuance of common stock | 16.3 | 41.0 | (24.7 | ) | |||||||
Cash dividends paid to stockholders | (133.8 | ) | (122.3 | ) | (11.5 | ) | |||||
Other, net | (3.9 | ) | (3.3 | ) | (0.6 | ) | |||||
Net cash used in financing activities | $ | (338.3 | ) | $ | (291.3 | ) | $ | (47.0 | ) | ||
(a) As a result of the adoption of ASU 2016-09 (discussed in Note 15 to the Consolidated Financial Statements), excess tax benefits on stock options exercised are no longer presented as a separate line item in the statement of cash flows. The presentation of fiscal 2016 has been adjusted to conform to the current presentation.
36
The increase in net cash used in financing activities in fiscal 2017 compared to fiscal 2016 is largely due to incremental share repurchases of common stock and a reduction in proceeds from the issuance of common stock, partially offset by an increase in borrowings, net of repayments, under our debt facilities.
The $83.7 million increase in net cash used in financing activities in fiscal 2016 compared to fiscal 2015 was due to changes in the following (in millions):
2016(a) | 2015(a) | Variance | |||||||||
(53 weeks) | (52 weeks) | ||||||||||
Net borrowings and repayments under debt facilities | $ | 125.0 | $ | 150.0 | $ | (25.0 | ) | ||||
Repurchase of common stock | (331.7 | ) | (292.7 | ) | (39.0 | ) | |||||
Net proceeds from issuance of common stock | 41.0 | 41.7 | (0.7 | ) | |||||||
Cash dividends paid to stockholders | (122.3 | ) | (103.1 | ) | (19.2 | ) | |||||
Other, net | (3.3 | ) | (3.5 | ) | 0.2 | ||||||
Net cash used in financing activities | $ | (291.3 | ) | $ | (207.6 | ) | $ | (83.7 | ) | ||
(a) As a result of the adoption of ASU 2016-09 (discussed in Note 15 to the Consolidated Financial Statements), excess tax benefits on stock options exercised are no longer presented as a separate line item in the statement of cash flows. The presentation of fiscal 2016 and fiscal 2015 has been adjusted to conform to the current presentation.
The increase in net cash used in financing activities in fiscal 2016 as compared to fiscal 2015 is due to incremental share repurchases of common stock, fewer borrowings, net of repayments, under our debt facilities, and an increase in quarterly cash dividends paid to stockholders.
Repurchase of Common Stock
The Company’s Board of Directors has authorized common stock repurchases under a share repurchase program of up to $3 billion, exclusive of any fees, commissions or other expenses related to such repurchases through December 31, 2020. The repurchases may be made from time to time on the open market or in privately negotiated transactions. The timing and amount of any shares repurchased under the program will depend on a variety of factors, including price, corporate and regulatory requirements, capital availability and other market conditions. Repurchased shares are accounted for at cost and will be held in treasury for future issuance. The program may be limited or terminated at any time without prior notice.
We repurchased approximately 5.9 million, 4.4 million and 3.4 million shares of common stock under the share repurchase program at a total cost of $369.4 million, $331.7 million and $292.7 million in fiscal 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively. As of December 30, 2017, we had remaining authorization under the share repurchase program of $0.9 billion, exclusive of any fees, commissions, or other expenses.
Cash Dividends Paid to Stockholders
We paid cash dividends totaling $133.8 million, $122.3 million and $103.1 million in fiscal 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively. In fiscal 2017, we declared and paid cash dividends to stockholders of $1.05 per common share outstanding as compared to $0.92 and $0.76 per common share outstanding in fiscal 2016 and fiscal 2015, respectively. These payments reflect an increase in the quarterly dividend in the second quarter of fiscal 2017 to $0.27 per share from $0.24 per share and an increase in the quarterly dividend in the second quarter of fiscal 2016 to $0.24 per share from $0.20 per share.
It is the present intention of the Board of Directors to continue to pay a quarterly cash dividend; however, the declaration and payment of future dividends will be determined by the Board of Directors in its sole discretion and will depend upon the earnings, financial condition and capital needs of the Company, as well as other factors which the Board of Directors deem relevant.
37
Significant Contractual Obligations and Commercial Commitments
The following table reflects our future obligations and commitments as of December 30, 2017 (in thousands):
Payment Due by Period | ||||||||||||||||||||
Total | 2018 | 2019-2020 | 2021-2022 | Thereafter | ||||||||||||||||
Operating leases | $ | 2,680,687 | $ | 324,813 | $ | 611,835 | $ | 524,991 | $ | 1,219,048 | ||||||||||
Capital leases(a) | 48,265 | 5,201 | 10,449 | 9,466 | 23,149 | |||||||||||||||
Long-term debt (b) | 512,400 | 36,222 | 78,280 | 211,114 | 186,784 | |||||||||||||||
Construction commitments (c) | 55,000 | 55,000 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
$ | 3,296,352 | $ | 421,236 | $ | 700,564 | $ | 745,571 | $ | 1,428,981 | |||||||||||
(a) Capital lease obligations include related interest.
(b) Long-term debt obligations include an estimate of related interest after consideration of the interest rate swap agreements. See Notes 5 and 6 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information regarding our interest rates.
(c) Represents contractual commitments related to the ongoing construction of a new distribution center in Frankfort, New York, and the expansion of our existing distribution center in Waverly, Nebraska.
At December 30, 2017, there were $39.6 million outstanding letters of credit under the 2016 Senior Credit Facility.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
Our off-balance sheet arrangements are limited to operating leases and outstanding letters of credit. The balances for these arrangements are previously discussed. We typically lease buildings for retail stores rather than acquiring these assets through purchases. Letters of credit allow us to purchase inventory, primarily sourced overseas, in a timely manner and support certain risk management programs.
New Accounting Pronouncements
Refer to Note 15 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for recently adopted accounting pronouncements and recently issued accounting pronouncements not yet adopted as of December 30, 2017.
38
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
Interest Rate Risk
We are exposed to interest rate changes, primarily as a result of borrowings under our 2016 Senior Credit Facility (as discussed in Note 5 to the Consolidated Financial Statements), which bear interest based on variable rates.
As discussed in Note 6 to the Consolidated Financial Statements, we entered into interest rate swap agreements which are intended to mitigate interest rate risk associated with future changes in interest rates for the term loan borrowings under the 2016 Senior Credit Facility. As a result of the interest rate swaps, our exposure to interest rate volatility is minimized. The interest rate swap agreements have been executed for risk management purposes and are not held for trading purposes.
A 1% change in interest rates on our variable rate debt in excess of that amount covered by the interest rate swaps would have affected interest expense by approximately $2.1 million, $1.5 million, and $1.1 million in the fiscal years ended December 30, 2017, December 31, 2016, and December 26, 2015, respectively. As of December 30, 2017, we have no outstanding variable rate debt other than the borrowings which are covered by interest rate swaps; therefore, on a prospective basis, a 1% change in interest rates on our variable rate debt, in excess of that amount covered by the interest rate swaps, would result in no additional interest expense.
Purchase Price Volatility
Although we cannot determine the full effect of inflation and deflation on our operations, we believe our sales and results of operations are affected by both. We are subject to market risk with respect to the pricing of certain products and services, which include, among other items, grain, corn, steel, petroleum, cotton and other commodities as well as transportation services. Therefore, we may experience both inflationary and deflationary pressure on product cost, which may impact consumer demand and, as a result, sales and gross margin. Our strategy is to reduce or mitigate the effects of purchase price volatility, principally by taking advantage of vendor incentive programs, economies of scale from increased volume of purchases, adjusting retail prices and selectively buying from the most competitive vendors without sacrificing quality.
39
Item 8. | Financial Statements and Supplementary Data |
INDEX
TRACTOR SUPPLY COMPANY
Page | |
40
Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Rules 13a-15(f) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended). The Company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Therefore, even those systems determined to be effective can provide only reasonable assurance with respect to financial statement preparation and presentation.
Management assessed the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 30, 2017. In making this assessment, management used the criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 framework) (the COSO criteria). Based on this assessment, management believes that, as of December 30, 2017, the Company’s internal control over financial reporting is effective based on those criteria.
Ernst & Young LLP, the independent registered public accounting firm which also audited the Company’s Consolidated Financial Statements, has issued a report on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting, which is included herein.
/s/ Gregory A. Sandfort | /s/ Kurt D. Barton | |||
Gregory A. Sandfort Chief Executive Officer | Kurt D. Barton Senior Vice President - Chief Financial Officer and Treasurer | |||
February 22, 2018 | February 22, 2018 | |||
41
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Shareholders and the Board of Directors of Tractor Supply Company
Opinion on the Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
We have audited Tractor Supply Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 30, 2017, based on criteria established in Internal Control-Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 framework) (the COSO criteria). In our opinion, Tractor Supply Company’s (the Company) maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 30, 2017, based on the COSO criteria.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the consolidated balance sheets of Tractor Supply Company as of December 30, 2017 and December 31, 2016, and the related consolidated statements of income, comprehensive income, stockholders’ equity, and cash flows for each of the three fiscal years in the period ended December 30, 2017, and the related notes and our report dated February 22, 2018, expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
Basis for Opinion
The Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting, and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting included in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with the respect to the Company in accordance with U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects.
Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
/s/ Ernst & Young LLP
Nashville, Tennessee
February 22, 2018
42
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Shareholders and the Board of Directors of Tractor Supply Company
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Tractor Supply Company (the Company) as of December 30, 2017 and December 31, 2016, the related consolidated statements of income, comprehensive income, stockholders' equity, and cash flows for each of the three fiscal years in the period ended December 30, 2017, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the “financial statements”). In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company at December 30, 2017 and December 31, 2016, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three fiscal years in the period ended December 30, 2017, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the Company's internal control over financial reporting as of December 30, 2017, based on criteria established in Internal Control-Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 framework) and our report dated February 22, 2018, expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures include examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
/s/ Ernst & Young LLP
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2001.
Nashville, Tennessee
February 22, 2018
43
TRACTOR SUPPLY COMPANY
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF INCOME
(in thousands, except per share amounts)
Fiscal Year | |||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
(52 weeks) | (53 weeks) | (52 weeks) | |||||||||
Net sales | $ | 7,256,382 | $ | 6,779,579 | $ | 6,226,507 | |||||
Cost of merchandise sold | 4,764,417 | 4,454,377 | 4,083,333 | ||||||||
Gross profit | 2,491,965 | 2,325,202 | 2,143,174 | ||||||||
Selling, general and administrative expenses | 1,639,749 | 1,488,164 | 1,369,097 | ||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 165,834 | 142,958 | 123,569 | ||||||||
Operating income | 686,382 | 694,080 | 650,508 | ||||||||
Interest expense, net | 13,859 | 5,810 | 2,891 | ||||||||
Income before income taxes | 672,523 | 688,270 | 647,617 | ||||||||
Income tax expense | 249,924 | 251,150 | 237,222 | ||||||||
Net income | $ | 422,599 | $ | 437,120 | $ | 410,395 | |||||
Net income per share – basic | $ | 3.31 | $ | 3.29 | $ | 3.03 | |||||
Net income per share – diluted | $ | 3.30 | $ | 3.27 | $ | 3.00 | |||||
Weighted average shares outstanding | |||||||||||
Basic | 127,588 | 132,905 | 135,582 | ||||||||
Diluted | 128,204 | 133,813 | 136,845 | ||||||||
Dividends declared per common share outstanding | $ | 1.05 | $ | 0.92 | $ | 0.76 | |||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
44
TRACTOR SUPPLY COMPANY
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
(in thousands)
Fiscal Year | |||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
(52 weeks) | (53 weeks) | (52 weeks) | |||||||||
Net income | $ | 422,599 | $ | 437,120 | $ | 410,395 | |||||
Other comprehensive income: | |||||||||||
Change in fair value of interest rate swaps, net of taxes | 1,371 | 1,392 | — | ||||||||
Total other comprehensive income | 1,371 | 1,392 | — | ||||||||
Total comprehensive income | $ | 423,970 | $ | 438,512 | $ | 410,395 | |||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
45
TRACTOR SUPPLY COMPANY
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(in thousands, except per share amounts)
December 30, 2017 | December 31, 2016 | ||||||
ASSETS | |||||||
Current assets: | |||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 109,148 | $ | 53,916 | |||
Inventories | 1,453,208 | 1,369,656 | |||||
Prepaid expenses and other current assets | 88,252 | 90,557 | |||||
Income taxes receivable | 4,760 | 3,680 | |||||
Total current assets | 1,655,368 | 1,517,809 | |||||
Property and equipment: | |||||||
Land | 99,336 | 94,940 | |||||
Buildings and improvements | 1,037,730 | 965,582 | |||||
Furniture, fixtures and equipment | 605,957 | 567,653 | |||||
Computer software and hardware | 266,898 | 224,370 | |||||
Construction in progress | 83,816 | 21,320 | |||||
Property and equipment, gross | 2,093,737 | 1,873,865 | |||||
Accumulated depreciation and amortization | (1,049,234 | ) | (911,557 | ) | |||
Property and equipment, net | 1,044,503 | 962,308 | |||||
Goodwill and other intangible assets | 124,492 | 125,717 | |||||
Deferred income taxes | 18,494 | 45,218 | |||||
Other assets | 25,912 | 23,890 | |||||
Total assets | $ | 2,868,769 | $ | 2,674,942 | |||
LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | |||||||
Current liabilities: | |||||||
Accounts payable | $ | 576,568 | $ | 519,522 | |||
Accrued employee compensation | 31,673 | 25,246 | |||||
Other accrued expenses | 201,656 | 215,650 | |||||
Current portion of long-term debt | 25,000 | 10,000 | |||||
Current portion of capital lease obligations | 3,545 | 1,294 | |||||
Income taxes payable | 10,772 | 5,482 | |||||
Total current liabilities | 849,214 | 777,194 | |||||
Long-term debt | 401,069 | 263,850 | |||||
Capital lease obligations, less current maturities | 32,617 | 25,919 | |||||
Deferred rent | 105,906 | 100,078 | |||||
Other long-term liabilities | 61,290 | 54,683 | |||||
Total liabilities | 1,450,096 | 1,221,724 | |||||
Stockholders’ equity: | |||||||
Preferred Stock, $1.00 par value; 40 shares authorized; no shares issued | — | — | |||||
Common Stock, $0.008 par value; 400,000 shares authorized at December 30, 2017 and December 31, 2016; 170,375 shares issued and 125,303 shares outstanding at December 30, 2017 and 169,943 shares issued and 130,795 shares outstanding at December 31, 2016 | 1,363 | 1,360 | |||||
Additional paid-in capital | 716,228 | 671,515 | |||||
Treasury stock, at cost, 45,072 shares at December 30, 2017 and 39,148 shares at December 31, 2016 | (2,130,901 | ) | (1,761,498 | ) | |||
Accumulated other comprehensive income | 2,763 | 1,392 | |||||
Retained earnings | 2,829,220 | 2,540,449 | |||||
Total stockholders’ equity | 1,418,673 | 1,453,218 | |||||
Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity | $ | 2,868,769 | $ | 2,674,942 | |||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
46
TRACTOR SUPPLY COMPANY
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
(in thousands)
Common Stock | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Shares | Dollars | Additional Paid-in Capital | Treasury Stock | Accum. Other Comp. Income | Retained Earnings | Total Stockholders’ Equity | ||||||||||||||||||||
Stockholders' equity at December 27, 2014 | 136,382 | $ | 1,342 | $ | 510,997 | $ | (1,137,085 | ) | $ | — | $ | 1,918,307 | $ | 1,293,561 | ||||||||||||
Issuance of common stock under employee stock purchase plan | 68 | 1 | 4,709 | 4,710 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Exercise of stock options and restricted stock units | 1,190 | 9 | 36,970 | 36,979 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Share-based compensation | 19,420 | 19,420 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Tax benefit of stock options exercised | 27,032 | 27,032 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Repurchase of shares to satisfy tax obligations | (2,997 | ) | (2,997 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Repurchase of common stock | (3,416 | ) | (292,705 | ) | (292,705 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||
Dividends paid | (103,101 | ) | (103,101 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Net income | 410,395 | 410,395 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Stockholders' equity at December 26, 2015 | 134,224 | 1,352 | 596,131 | (1,429,790 | ) | — | 2,225,601 | 1,393,294 | ||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of common stock under employee stock purchase plan | 70 | 1 | 4,808 | 4,809 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Exercise of stock options and restricted stock units | 899 | 7 | 36,194 | 36,201 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Share-based compensation | 23,554 | 23,554 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Tax benefit of stock options exercised | 11,671 | 11,671 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Repurchase of shares to satisfy tax obligations | (843 | ) | (843 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Repurchase of common stock | (4,398 | ) | (331,708 | ) | (331,708 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||
Dividends paid | (122,272 | ) | (122,272 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Change in fair value of interest rate swaps, net of taxes | 1,392 | 1,392 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net income | 437,120 | 437,120 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Stockholders' equity at December 31, 2016 | 130,795 | 1,360 | 671,515 | (1,761,498 | ) | 1,392 | 2,540,449 | 1,453,218 | ||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of common stock under employee stock purchase plan | 83 | 1 | 4,282 | 4,283 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Exercise of stock options and restricted stock units | 349 | 2 | 12,045 | 12,047 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Share-based compensation | 29,202 | 29,202 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Repurchase of shares to satisfy tax obligations | (816 | ) | (816 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Repurchase of common stock | (5,924 | ) | (369,403 | ) | (369,403 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||
Dividends paid | (133,828 | ) | (133,828 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Change in fair value of interest rate swaps, net of taxes | 1,371 | 1,371 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net income | 422,599 | 422,599 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Stockholders' equity at December 30, 2017 | 125,303 | $ | 1,363 | $ | 716,228 | $ | (2,130,901 | ) | $ | 2,763 | $ | 2,829,220 | $ | 1,418,673 | ||||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
47
TRACTOR SUPPLY COMPANY
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(in thousands)
Fiscal Year | |||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
(52 weeks) | (53 weeks) | (52 weeks) | |||||||||
Cash flows from operating activities: | |||||||||||
Net income | $ | 422,599 | $ | 437,120 | $ | 410,395 | |||||
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: | |||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 165,834 | 142,958 | 123,569 | ||||||||
Loss on disposition of property and equipment | 460 | 579 | 315 | ||||||||
Share-based compensation expense | 29,202 | 23,554 | 19,420 | ||||||||
Deferred income taxes | 26,724 | 9,976 | (5,450 | ) | |||||||
Change in assets and liabilities: | |||||||||||
Inventories | (83,552 | ) | (67,650 | ) | (168,925 | ) | |||||
Prepaid expenses and other current assets | 2,305 | 1,782 | (21,066 | ) | |||||||
Accounts payable | 57,046 | 82,477 | 56,426 | ||||||||
Accrued employee compensation | 6,427 | (18,237 | ) | 5,628 | |||||||
Other accrued expenses | (10,338 | ) | 20,368 | 11,252 | |||||||
Income taxes | 4,210 | 11,787 | 16,282 | ||||||||
Other | 10,533 | 5,997 | 8,366 | ||||||||
Net cash provided by operating activities | 631,450 | 650,711 | 456,212 | ||||||||
Cash flows from investing activities: | |||||||||||
Capital expenditures | (250,401 | ) | (226,017 | ) | (236,496 | ) | |||||
Proceeds from sale of property and equipment | 11,220 | 362 | 584 | ||||||||
Acquisition of Petsense, net of cash acquired | 1,225 | (143,610 | ) | — | |||||||
Net cash used in investing activities | (237,956 | ) | (369,265 | ) | (235,912 | ) | |||||
Cash flows from financing activities: | |||||||||||
Borrowings under debt facilities | 1,180,000 | 945,000 | 680,000 | ||||||||
Repayments under debt facilities | (1,027,500 | ) | (820,000 | ) | (530,000 | ) | |||||
Debt issuance costs | (599 | ) | (1,380 | ) | — | ||||||
Principal payments under capital lease obligations | (2,446 | ) | (1,150 | ) | (507 | ) | |||||
Repurchase of shares to satisfy tax obligations | (816 | ) | (843 | ) | (2,997 | ) | |||||
Repurchase of common stock | (369,403 | ) | (331,708 | ) | (292,705 | ) | |||||
Net proceeds from issuance of common stock | 16,330 | 41,010 | 41,689 | ||||||||
Cash dividends paid to stockholders | (133,828 | ) | (122,272 | ) | (103,101 | ) | |||||
Net cash used in financing activities | (338,262 | ) | (291,343 | ) | (207,621 | ) | |||||
Net change in cash and cash equivalents | 55,232 | (9,897 | ) | 12,679 | |||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of year | 53,916 | 63,813 | 51,134 | ||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at end of year | $ | 109,148 | $ | 53,916 | $ | 63,813 | |||||
Supplemental disclosures of cash flow information: | |||||||||||
Cash paid during the year for: | |||||||||||
Interest | $ | 10,481 | $ | 6,124 | $ | 2,283 | |||||
Income taxes | 219,081 | 232,258 | 226,968 | ||||||||
Supplemental disclosures of non-cash activities: | |||||||||||
Property and equipment acquired through capital lease | $ | 11,395 | $ | 10,493 | $ | 13,207 | |||||
Non-cash accruals for construction in progress | 8,647 | 12,303 | 16,050 | ||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
48
TRACTOR SUPPLY COMPANY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 1 – Significant Accounting Policies:
Nature of Business
Founded in 1938, Tractor Supply Company (the “Company” or “we”) is the largest operator of rural lifestyle retail stores in the United States (“U.S.”). The Company is focused on supplying the needs of recreational farmers and ranchers and those who enjoy the rural lifestyle (which we refer to as the “Out Here” lifestyle), as well as tradesmen and small businesses. Stores are located primarily in towns outlying major metropolitan markets and in rural communities. At December 30, 2017, the Company operated a total of 1,853 retail stores in 49 states (1,685 Tractor Supply and Del’s retail stores and 168 Petsense retail stores) and also offered a number of products online at TractorSupply.com and Petsense.com.
Basis of Presentation
In the first quarter of fiscal 2017, the Company adopted accounting guidance which affected the presentation in the statement of cash flows of excess tax benefits or deficiencies from the exercise of stock options as discussed in Note 15. The Company has elected to apply the amendments using a retrospective transition method for all periods presented and therefore the presentation of previously reported excess tax benefits on the Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows has been changed to conform to the presentation used in the current period. As a result, $11.7 million and $27.0 million of excess tax benefits related to share-based awards which were previously classified as cash flows from financing activities have been reclassified as cash flows from operating activities in the Consolidated Statement of Cash Flows for the years ended December 31, 2016, and December 26, 2015, respectively. Additionally, beginning in fiscal 2017, the Statement of Stockholders’ Equity is no longer impacted by the excess tax benefits or deficiencies from the exercise of stock options.
Fiscal Year
The Company’s fiscal year includes 52 or 53 weeks and ends on the last Saturday of the calendar year. The fiscal year ended December 30, 2017 consisted of 52 weeks, the fiscal year ended December 31, 2016 consisted of 53 weeks and the fiscal year ended December 26, 2015 consisted of 52 weeks.
Principles of Consolidation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company and its subsidiaries. All intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated.
Management Estimates
The preparation of consolidated financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States (“U.S. GAAP”) inherently requires estimates and assumptions by management of the Company that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities, revenues and expenses and related disclosures. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Significant estimates and assumptions by management primarily impact the following key financial statement areas:
Inventory Valuation
Inventory Impairment Risk
The Company identifies potentially excess and slow-moving inventory by evaluating turn rates, historical and expected future sales trends, age of merchandise, overall inventory levels, current cost of inventory and other benchmarks. The Company has established an inventory valuation reserve to recognize the estimated impairment in value (i.e., an inability to realize the full carrying value) based on the Company’s aggregate assessment of these valuation indicators under prevailing market conditions and current merchandising strategies. The Company does not believe its merchandise inventories are subject to significant risk of obsolescence in the near term. However, changes in market conditions or consumer purchasing patterns could result in the need for additional reserves.
49
Shrinkage
The Company performs physical inventories at least once a year for each store that has been open more than 12 months, and the Company has established a reserve for estimating inventory shrinkage between physical inventory counts. The reserve is established by assessing the chain-wide average shrinkage experience rate, applied to the related periods’ sales volumes. Such assessments are updated on a regular basis for the most recent individual store experiences. The estimated store inventory shrink rate is based on historical experience. The Company believes historical rates are a reasonably accurate reflection of future trends.
Vendor Funding
The Company receives funding from substantially all of its significant merchandise vendors, in support of its business initiatives, through a variety of programs and arrangements, including guaranteed vendor support funds (“vendor support”) and volume-based rebate funds (“volume rebates”). The amounts received are subject to terms of vendor agreements, most of which are “evergreen,” reflecting the on-going relationship with our significant merchandise vendors. Certain of the Company’s agreements, primarily volume rebates, are renegotiated annually, based on expected annual purchases of the vendor’s product. Vendor funding is initially deferred as a reduction of the purchase price of inventory, and then recognized as a reduction of cost of merchandise as the related inventory is sold.
During interim periods, the amount of vendor support and volume rebates are estimated based upon initial commitments and anticipated purchase levels with applicable vendors. The estimated purchase volume (and related vendor funding) is based on the Company’s current knowledge of inventory levels, sales trends and expected customer demand, as well as planned new store openings and relocations. Although the Company believes it can reasonably estimate purchase volume and related volume rebates at interim periods, it is possible that actual year-end results could be different from previously estimated amounts.
Freight
The Company incurs various types of transportation and delivery costs in connection with inventory purchases and distribution. Such costs are included as a component of the overall cost of inventories (on an aggregate basis) and recognized as a component of cost of merchandise sold as the related inventory is sold.
Self-Insurance Reserves
The Company self-insures a significant portion of its employee medical insurance, workers’ compensation insurance and general liability (including product liability) insurance plans. The Company has stop-loss insurance policies to protect it from individual losses over specified dollar values. For self-insured employee medical claims, we have a stop loss limit of $300,000 per person per year. Our deductible or self-insured retention, as applicable, for each claim involving workers’ compensation insurance and general liability insurance is limited to $500,000 and our Texas Work Injury Policy is limited to $750,000. Further, we maintain a commercially reasonable umbrella/excess policy that covers liabilities in excess of the primary insurance policy limits.
The full extent of certain claims, especially workers’ compensation and general liability claims, may not become fully determined for several years. Therefore, the Company estimates potential obligations based upon historical claims experience, industry factors, severity factors and other actuarial assumptions. Although the Company believes the reserves established for these obligations are reasonably estimated, any significant change in the number of claims or costs associated with claims made under these plans could have a material effect on the Company’s financial results. At December 30, 2017, the Company had recorded net insurance reserves of $57.9 million compared to $54.3 million at December 31, 2016.
Sales Tax Audit Reserve
A portion of the Company’s sales are to tax-exempt customers, predominantly agricultural-based. The Company obtains exemption information as a necessary part of each tax-exempt transaction. Many of the states in which the Company conducts business will perform audits to verify the Company’s compliance with applicable sales tax laws. The business activities of the Company’s customers and the intended use of the unique products sold by the Company create a challenging and complex tax compliance environment. These circumstances also create some risk that the Company could be challenged as to the accuracy of the Company’s sales tax compliance.
The Company reviews past audit experience and assessments with applicable states to continually determine if it has potential exposure for non-compliance. Any estimated liability is based on an initial assessment of compliance risk and historical experience with each state. The Company continually reassesses the exposure based on historical audit results, changes in policies, preliminary and final assessments made by state sales tax auditors and additional documentation that may be provided to reduce the assessment. The reserve for these tax audits can fluctuate depending on numerous factors, including the
50
complexity of agricultural-based exemptions, the ambiguity in state tax regulations, the number of ongoing audits and the length of time required to settle with the state taxing authorities.
Tax Contingencies
The Company’s income tax returns are periodically audited by U.S. federal and state tax authorities. These audits include questions regarding tax filing positions, including the timing and amount of deductions and the allocation of income among various tax jurisdictions. At any time, multiple tax years are subject to audit by the various tax authorities. In evaluating the exposures associated with the Company’s various tax filing positions, the Company records a liability for uncertain tax positions taken or expected to be taken in a tax return. A number of years may elapse before a particular matter, for which the Company has established a reserve, is audited and fully resolved or clarified. The Company recognizes the effect of income tax positions only if those positions are more likely than not of being sustained. Recognized income tax positions are measured at the largest amount that is greater than 50% likely of being realized. Changes in recognition or measurement are reflected in the period in which the change in judgment occurs. The Company adjusts its tax contingencies reserve and income tax provision in the period in which actual results of a settlement with tax authorities differs from the established reserve, the statute of limitations expires for the relevant tax authority to examine the tax position or when more information becomes available.
The Company’s tax contingencies reserve contains uncertainties because management is required to make assumptions and apply judgment to estimate the exposures associated with the Company’s various filing positions and whether or not the minimum requirements for recognition of tax benefits have been met.
The effective income tax rate is also affected by changes in tax law, the tax jurisdiction of new stores or business ventures, the level of earnings and the results of tax audits.
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets
Long-lived assets are evaluated for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying value may not be recoverable.
When evaluating long-lived assets for potential impairment, the Company first compares the carrying value of the asset to the asset’s estimated undiscounted future cash flows. The evaluation for long-lived assets is performed at the lowest level of identifiable cash flows, which is generally the individual store level. The significant assumptions used to determine estimated undiscounted cash flows include cash inflows and outflows directly resulting from the use of those assets in operations, including margin on net sales, payroll and related items, occupancy costs, insurance allocations and other costs to operate a store. If the estimated future cash flows are less than the carrying value of the asset, the Company calculates an impairment loss. The impairment loss calculation compares the carrying value of the asset to the asset’s estimated fair value, which may be based on an estimated future cash flow model. The Company recognizes an impairment loss if the amount of the asset’s carrying value exceeds the asset’s estimated fair value. If the Company recognizes an impairment loss, the adjusted carrying amount of the asset becomes its new cost basis. For a depreciable long-lived asset, the new cost basis will be depreciated (amortized) over the remaining estimated useful life of that asset.
No significant impairment charges were recognized in fiscal 2017, 2016 or 2015. Impairment charges are included in selling, general and administrative (“SG&A”) expenses in the Consolidated Statements of Income.
Impairment of Indefinite-Lived Intangible Assets
Goodwill and other indefinite-lived intangible assets are evaluated for impairment annually, or whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying value may not be recoverable.
In accordance with the accounting standards, an entity has the option first to assess qualitative factors to determine whether events and circumstances indicate that it is more likely than not that goodwill or an indefinite-lived intangible asset is impaired. If after such assessment an entity concludes that the asset is not impaired, then the entity is not required to take further action. However, if an entity concludes otherwise, then it is required to determine the fair value of the asset using a quantitative impairment test, and if impaired, the associated assets must be written down to fair value.
The quantitative impairment test for goodwill compares the fair value of a reporting unit with the carrying value of its net assets, including goodwill. If the fair value of the reporting unit is less than the carrying value of the reporting unit, an impairment charge would be recorded to the Company’s operations, for the amount, if any, in which the carrying amount exceeds the reporting unit’s fair value. We determine fair values for each reporting unit using the market approach, when available and appropriate, or the income approach, or a combination of both. If multiple valuation methodologies are used, the results are weighted appropriately.
51
The quantitative impairment test for other indefinite-lived intangible assets involves comparing the carrying amount of the asset to the sum of the discounted cash flows expected to be generated by the asset. If the implied fair value of the indefinite-lived intangible asset is less than the carrying value, an impairment charge would be recorded to the Company’s operations.
No significant impairment charges were recognized in fiscal 2017, 2016 or 2015. Impairment charges are included in SG&A expenses in the Consolidated Statements of Income.
Revenue Recognition and Sales Returns
The Company recognizes revenue at the time the customer takes possession of merchandise. If the Company receives payment before completion of its customer obligations (as per the Company’s special order and layaway programs), the revenue is deferred until the customer takes possession of the merchandise and the sale is complete.
The Company is required to collect certain taxes and fees from customers on behalf of government agencies and remit such collections to the applicable governmental agency on a periodic basis. These taxes and fees are collected from customers at the time of purchase, but are not included in net sales. The Company records a liability upon collection from the customer and relieves the liability when payments are remitted to the applicable governmental agency.
The Company estimates a liability for sales returns based on a rolling average of historical return trends, and the Company believes that its estimate for sales returns is an accurate reflection of future returns associated with past sales. However, as with any estimate, refund activity may vary from estimated amounts. At December 30, 2017, the Company had a liability of $3.8 million reserved for sales returns compared to $4.2 million at December 31, 2016.
The Company recognizes revenue when a gift card or merchandise return card is redeemed by the customer and recognizes income when the likelihood of the gift card or merchandise return card being redeemed by the customer is remote (referred to as “breakage”). The gift cards and merchandise return card breakage rate is based upon historical redemption patterns and income is recognized for unredeemed gift cards and merchandise return cards in proportion to those historical redemption patterns. The Company recognized breakage income of $2.4 million, $1.9 million and $1.6 million in fiscal 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively.
Cost of Merchandise Sold
Cost of merchandise sold includes the total cost of products sold; freight expenses associated with moving merchandise inventories from vendors to distribution facilities, from distribution facilities to retail stores, from one distribution facility to another, and directly to our customers; vendor support; damaged, junked or defective product; cash discounts from payments to merchandise vendors; and adjustments for shrinkage (physical inventory losses), lower of cost or net realizable value, slow moving product and excess inventory quantities.
Selling, General and Administrative Expenses
SG&A expenses include payroll and benefit costs for retail, distribution facility and corporate employees; share-based compensation expenses; occupancy costs of retail, distribution and corporate facilities; advertising; tender costs, including bank charges and costs associated with credit and debit card interchange fees; outside service fees; and other administrative costs, such as computer maintenance, supplies, travel and lodging.
Advertising Costs
Advertising costs consist of expenses incurred in connection with newspaper circulars and customer-targeted direct mail, as well as limited television, radio, digital and social media offerings and other promotions. Costs are expensed when incurred with the exception of television advertising and circular and direct mail promotions, which are expensed upon first showing. Advertising expenses for fiscal 2017, 2016 and 2015 were approximately $81.3 million, $84.2 million and $73.9 million, respectively. Prepaid advertising costs were approximately $1.1 million and $2.1 million at December 30, 2017, and December 31, 2016, respectively.
Warehousing and Distribution Facility Costs
Costs incurred at the Company’s distribution facilities for receiving, warehousing and preparing product for delivery are expensed as incurred and are included in SG&A expenses in the Consolidated Statements of Income. Because the Company does not include these costs in cost of sales, the Company’s gross margin may not be comparable to other retailers that include these costs in the calculation of gross margin. Distribution facility costs including depreciation for fiscal 2017, 2016 and 2015 were approximately $182.1 million, $166.8 million and $145.4 million, respectively.
52
Pre-opening Costs
Non-capital expenditures incurred in connection with opening new stores, primarily payroll and rent, are expensed as incurred. Pre-opening costs were approximately $10.8 million, $9.9 million and $9.6 million in fiscal 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively.
Share-Based Compensation
The Company has share-based compensation plans covering certain members of management and non-employee directors, which include incentive and non-qualified stock options and restricted stock units. In addition, the Company offers an Employee Stock Purchase Plan (“ESPP”) to most employees that work at least 20 hours per week.
The Company estimates the fair value of its stock option awards at the date of grant utilizing a Black-Scholes option pricing model. The Black-Scholes option valuation model was developed for use in estimating the fair value of short-term traded options that have no vesting restrictions and are fully transferable. However, key assumptions used in the Black-Scholes model are adjusted to incorporate the unique characteristics of the Company’s stock option awards. Option pricing models and generally accepted valuation techniques require management to make subjective assumptions including expected stock price volatility, expected dividend yield, risk-free interest rate and expected life. The Company relies on historical volatility trends to estimate future volatility assumptions. The risk-free interest rates used were actual U.S. Treasury Constant Maturity rates for bonds matching the expected term of the option on the date of grant. The expected term of the option on the date of grant was estimated based on the Company’s historical experience for similar options.
In addition to the key assumptions used in the Black-Scholes model, the estimated forfeiture rate at the time of valuation (which is based on historical experience for similar options) is a critical assumption, as it reduces expense ratably over the vesting period. The Company adjusts this estimate periodically, based on the extent to which actual forfeitures differ, or are expected to differ, from the previous estimate.
The fair value of the Company’s restricted stock unit awards is the closing price of the Company’s common stock the day preceding the grant date, discounted for the expected dividend yield over the term of the award.
The Company believes its estimates are reasonable in the context of historical experience. Future results will depend on, among other matters, levels of share-based compensation granted in the future, actual forfeiture rates and the timing of option exercises.
Depreciation and Amortization
Depreciation includes expenses related to all retail, distribution facility and corporate assets. Amortization includes expenses related to definite-lived intangible assets.
Income Taxes
The Company uses the asset and liability method to account for income taxes whereby deferred tax assets and liabilities are determined based on differences between the financial carrying amounts of assets and liabilities and their tax bases. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using the enacted tax rates and laws that are anticipated to be in effect when temporary differences reverse or are settled. The effect of a tax rate change is recognized in the period in which the law is enacted in the provision for income taxes. The Company records a valuation allowance when it is more likely than not that a deferred tax asset will not be realized.
Net Income Per Share
Basic net income per share is calculated by dividing net income by the weighted average number of shares outstanding during the period. Diluted net income per share is calculated by dividing net income by the weighted average diluted shares outstanding. Dilutive shares are computed using the treasury stock method for stock options and restricted stock units.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
Temporary cash investments, with a maturity of three months or less when purchased, are considered to be cash equivalents. The majority of payments due from banks for customer credit cards are classified as cash and cash equivalents, as they generally settle within 24-48 hours.
53
Sales generated through the Company’s private label credit cards are not reflected as accounts receivable. Under an agreement with Citi Cards, a division of Citigroup, consumer and business credit is extended directly to customers by Citigroup. All credit program and related services are performed and controlled directly by Citigroup. Payments due from Citigroup are classified as cash and cash equivalents as they generally settle within 24-48 hours.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
Fair value is defined as the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability (an exit price) in an orderly transaction between market participants on the measurement date. The Company uses a three-tier fair value hierarchy, which prioritizes the inputs used in measuring fair value. These tiers include: Level 1, defined as observable inputs such as quoted prices in active markets; Level 2, defined as inputs other than quoted prices in active markets that are either directly or indirectly observable; and Level 3, defined as unobservable inputs in which little or no market data exists, therefore requiring an entity to develop its own assumptions.
The Company’s financial instruments consist of cash and cash equivalents, short-term receivables, trade payables, debt instruments and interest rate swaps. Due to their short-term nature, the carrying values of cash and cash equivalents, short-term receivables and trade payables approximate current fair value at each balance sheet date. The Company had $427.5 million in borrowings under our debt facilities (as discussed in Note 5) at December 30, 2017, and $275.0 million in borrowings as of December 31, 2016. Based on current market interest rates (Level 2 inputs), the carrying value of our borrowings under our debt facilities approximates fair value for each period reported. The fair value of the Company’s interest rate swaps is determined based on the present value of expected future cash flows using forward rate curves (a Level 2 input). As described in further detail in Note 6, the fair value of the interest rate swaps, excluding accrued interest, was a $5.2 million asset at December 30, 2017, and was a $2.8 million asset at December 31, 2016.
Derivative Financial Instruments
The Company accounts for derivative financial instruments in accordance with applicable accounting standards for such instruments and hedging activities, which require that all derivatives are recorded on the balance sheet at fair value. The accounting for changes in the fair value of derivatives depends on the intended use of the derivative, whether the Company has elected to designate a derivative in a hedging relationship and apply hedge accounting and whether the hedging relationship has satisfied the criteria necessary to apply hedge accounting.
Derivatives designated and qualifying as a hedge of the exposure to changes in the fair value of an asset, liability, or firm commitment attributable to a particular risk are considered fair value hedges. Derivatives designated and qualifying as a hedge of the exposure to variability in expected future cash flows, or other types of forecasted transactions, are considered cash flow hedges. Hedge accounting generally provides for the matching of the timing of gain or loss recognition on the hedging instrument with the recognition of the changes in the fair value of the hedged asset or liability that are attributable to the hedged risk in a fair value hedge or the earnings effect of the hedged forecasted transactions in a cash flow hedge. The Company may enter into derivative contracts that are intended to economically hedge a certain portion of its risk, even though hedge accounting does not apply or the Company elects not to apply the hedge accounting standards.
Inventories
Inventories are stated at the lower of cost, as determined by the average cost method, or net realizable value. Inventory cost consists of the direct cost of merchandise including freight. Inventories are net of shrinkage, obsolescence, other valuations and vendor allowances.
Property and Equipment
Property and equipment are carried at cost. Depreciation is recorded using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the assets. Improvements to leased premises are amortized using the straight-line method over the initial term of the lease or the useful life of the improvement, whichever is less. The following estimated useful lives are generally applied:
Life | |
Buildings | 30 – 35 years |
Leasehold and building improvements | 1 – 35 years |
Furniture, fixtures and equipment | 5 – 10 years |
Computer software and hardware | 3 – 5 years |
54
The Company entered into agreements with various governmental entities in the states of Kentucky, Georgia and Tennessee to implement tax abatement plans related to its distribution center in Franklin, Kentucky (Simpson County), its distribution center in Macon, Georgia (Bibb County), and its Store Support Center in Brentwood, Tennessee (Williamson County). The tax abatement plans provide for reduction of real property taxes for specified time frames by legally transferring title to its real property in exchange for industrial revenue bonds. This property was then leased back to the Company. No cash was exchanged.
The lease payments are equal to the amount of the payments on the bonds. The tax abatement period extends through the term of the lease, which coincides with the maturity date of the bonds. At any time, the Company has the option to purchase the real property by paying off the bonds, plus $1. The terms and amounts authorized and drawn under each industrial revenue bond agreement are outlined as follows, as of December 30, 2017:
Bond Term | Bond Authorized Amount (in millions) | Amount Drawn (in millions) | ||
Franklin, Kentucky Distribution Center | 30 years | $54.0 | $51.8 | |
Macon, Georgia Distribution Center | 15 years | $58.0 | $49.9 | |
Brentwood, Tennessee Store Support Center | 10 years | $78.0 | $75.3 | |
Due to the form of these transactions, the Company has not recorded the bonds or the lease obligation associated with the sale lease-back transaction. The original cost of the Company’s property and equipment is recorded on the balance sheet and is being depreciated over its estimated useful life.
Capitalized Software Costs
The Company capitalizes certain costs related to the acquisition and development of software and amortizes these costs using the straight-line method over the estimated useful life of the software, which is three to five years. Computer software consists of software developed for internal use and third-party software purchased for internal use. A subsequent addition, modification or upgrade to internal-use software is capitalized to the extent that it enhances the software’s functionality or extends its useful life. These costs are included in computer software and hardware in the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheets. Certain software costs not meeting the criteria for capitalization are expensed as incurred.
Store Closing Costs
The Company regularly evaluates the performance of its stores and periodically closes those that are under-performing. The Company records a liability for costs associated with an exit or disposal activity when the liability is incurred, usually in the period the store closes. Store closing costs were not significant to the results of operations for any of the fiscal years presented.
Leases
Assets under capital leases are amortized in accordance with the Company’s normal depreciation policy for owned assets or over the lease term, if shorter, and the related charge to operations is included in depreciation expense in the Consolidated Statements of Income.
Certain operating leases include rent increases during the lease term. For these leases, the Company recognizes the related rental expense on a straight-line basis over the term of the lease (which includes the pre-opening period of construction, renovation, fixturing and merchandise placement) and records the difference between the expense charged to operations and amounts paid as a deferred rent liability.
The Company occasionally receives reimbursements from landlords to be used towards improving the related store to be leased. Leasehold improvements are recorded at their gross costs, including items reimbursed by landlords. Related reimbursements are deferred and amortized on a straight-line basis as a reduction of rent expense over the applicable lease term.
Note 2 - Share-Based Compensation:
Share-based compensation includes stock option and restricted stock unit awards and certain transactions under the Company’s ESPP. Share-based compensation expense is recognized based on the grant date fair value of all stock option and restricted stock unit awards plus a discount on shares purchased by employees as a part of the ESPP. The discount under the ESPP represents the difference between the purchase date market value and the employee’s purchase price.
55
There were no significant modifications to the Company’s share-based compensation plans during fiscal 2017. At December 30, 2017, the Company had approximately 2.3 million shares available for future equity awards under the Company’s 2009 Stock Incentive Plan.
Share-based compensation expense, including changes in expense for modifications of awards, was $29.2 million, $23.6 million and $19.4 million for fiscal 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively.
Stock Options
Under the Company’s 2009 Stock Incentive Plan, options may be granted to current or prospective officers or employees, non-employee directors and consultants. The per share exercise price of options granted shall not be less than the fair market value of the stock on the date of grant and such options will expire no later than ten years from the date of grant. Vesting of options commences at various anniversary dates following the dates of grant.
The fair value is separately estimated for each option grant. The fair value of each option is recognized as compensation expense ratably over the vesting period. The Company has estimated the fair value of all stock option awards as of the date of the grant by applying a Black-Scholes pricing valuation model. The application of this valuation model involves assumptions that are judgmental and highly sensitive in the determination of compensation expense. The ranges of key assumptions used in determining the fair value of options granted during fiscal 2017, 2016 and 2015, as well as a summary of the methodology applied to develop each assumption, are as follows:
Fiscal Year | |||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||
Expected price volatility | 25.1 - 26.0% | 25.5 - 27.9% | 27.3 – 28.8% | ||||
Risk-free interest rate | 1.7 - 1.9% | 0.9 - 1.3% | 1.2 – 1.5% | ||||
Weighted average expected lives (in years) | 4.4 | 4.4 | 4.5 | ||||
Forfeiture rate | 7.2 | % | 7.1 | % | 6.9% | ||
Dividend yield | 1.3 | % | 0.9 | % | 1.0% | ||
Expected Price Volatility — This is a measure of the amount by which a price has fluctuated or is expected to fluctuate. The Company applies a historical volatility rate. To calculate historical changes in market value, the Company uses daily market value changes from the date of grant over a past period generally representative of the expected life of the options to determine volatility. The Company believes the use of historical price volatility provides an appropriate indicator of future volatility. An increase in the expected volatility will increase compensation expense.
Risk-Free Interest Rate — This is the U.S. Treasury Constant Maturity rate over a term equal to the expected life of the option. An increase in the risk-free interest rate will increase compensation expense.
Weighted Average Expected Lives — This is the period of time over which the options granted are expected to remain outstanding and is based on historical experience. Options granted generally have a maximum term of ten years. An increase in the expected life will increase compensation expense.
Forfeiture Rate — This is the estimated percentage of options granted that are expected to be forfeited or canceled before becoming fully vested. This estimate is based on historical experience. An increase in the forfeiture rate will decrease compensation expense.
Dividend Yield —This is the estimated dividend yield for the weighted average expected life of the option granted. An increase in the dividend yield will decrease compensation expense.
56
The Company issues shares for options when exercised. A summary of stock option activity is as follows:
Options | Weighted Average Exercise Price | Weighted Average Fair Value | Weighted Average Remaining Contractual Term | Aggregate Intrinsic Value (in thousands) | ||||||||||||
Outstanding December 27, 2014 | 4,083,426 | $ | 41.93 | 7.2 | $ | 146,967 | ||||||||||
Granted | 1,080,490 | 83.70 | $ | 19.53 | ||||||||||||
Exercised | (1,116,828 | ) | 33.11 | |||||||||||||
Canceled | (185,582 | ) | 67.28 | |||||||||||||
Outstanding December 26, 2015 | 3,861,506 | $ | 54.95 | 7.1 | $ | 119,050 | ||||||||||
Granted | 1,150,941 | 86.05 | $ | 19.27 | ||||||||||||
Exercised | (851,118 | ) | 42.53 | |||||||||||||
Canceled | (187,582 | ) | 80.01 | |||||||||||||
Outstanding December 31, 2016 | 3,973,747 | $ | 65.43 | 6.9 | $ | 59,601 | ||||||||||
Granted | 1,625,140 | 72.11 | $ | 14.56 | ||||||||||||
Exercised | (309,904 | ) | 38.87 | |||||||||||||
Canceled | (290,457 | ) | 79.08 | |||||||||||||
Outstanding December 30, 2017 | 4,998,526 | $ | 68.46 | 6.9 | $ | 50,145 | ||||||||||
Exercisable at December 30, 2017 | 2,582,283 | $ | 60.46 | 5.3 | $ | 45,939 | ||||||||||
The aggregate intrinsic values in the table above represent the total difference between the Company’s closing stock price at each year-end and the option exercise price, multiplied by the number of in-the-money options at each year-end. As of December 30, 2017, total unrecognized compensation expense related to non-vested stock options was approximately $19.8 million with a weighted average expense recognition period of 1.9 years.
There were no material modifications to options in fiscal 2017, 2016 or 2015.
Other information relative to option activity during fiscal 2017, 2016 and 2015 is as follows (in thousands):
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
Total fair value of stock options vested | $ | 15,996 | $ | 15,184 | $ | 13,207 | |||||
Total intrinsic value of stock options exercised | $ | 9,237 | $ | 39,696 | $ | 60,082 | |||||
57
Restricted Stock Units
The Company issues shares for restricted stock unit awards once vesting occurs and related restrictions lapse. The units vest over a one to four-year term; some plan participants have elected to defer receipt of shares of common stock upon vesting of restricted stock units, and as a result, shares are not issued until a later date. The status of restricted stock units is presented below:
Restricted Stock Units | Shares | Weighted Average Grant Date Fair Value | |||||
Restricted at December 27, 2014 | 277,347 | $ | 42.64 | ||||
Granted | 56,052 | 84.86 | |||||
Exercised | (107,548 | ) | 25.97 | ||||
Forfeited | (6,234 | ) | 63.57 | ||||
Restricted at December 26, 2015 | 219,617 | $ | 60.99 | ||||
Granted | 59,586 | 83.22 | |||||
Exercised | (58,503 | ) | 52.51 | ||||
Forfeited | (26,669 | ) | 76.51 | ||||
Restricted at December 31, 2016 | 194,031 | $ | 68.04 | ||||
Granted | 85,049 | 66.34 | |||||
Exercised | (51,069 | ) | 64.64 | ||||
Forfeited | (4,781 | ) | 79.65 | ||||
Restricted at December 30, 2017 | 223,230 | $ | 67.92 | ||||
Other information relative to restricted stock unit activity during fiscal 2017, 2016 and 2015 is as follows (in thousands):
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
Total grant date fair value of restricted stock units vested and issued | $ | 3,301 | $ | 3,072 | $ | 2,793 | |||||
Total intrinsic value of restricted stock units vested and issued | $ | 3,465 | $ | 5,104 | $ | 9,139 | |||||
For the majority of restricted stock units granted, the number of shares issued on the date the restricted stock units vest is net of shares withheld by the Company for the minimum statutory tax withholding requirements, which the Company pays on behalf of its employees. The Company issued 39,314, 48,267 and 72,206 shares as a result of vested restricted stock units during fiscal 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively. Although shares withheld are not issued, they are treated similar to common stock repurchases as they reduce the number of shares that would have been issued upon vesting. The amounts are net of 11,755, 10,236 and 35,342 shares withheld to satisfy $0.8 million of employees’ tax obligations during both fiscal 2017 and 2016, and $3.0 million during fiscal 2015.
There were no material modifications to restricted stock units in fiscal 2017, 2016 or 2015.
As of December 30, 2017, total unrecognized compensation expense related to non-vested restricted stock units was approximately $4.3 million with a weighted average expense recognition period of 1.6 years.
Employee Stock Purchase Plan
The ESPP provides Company employees the opportunity to purchase, through payroll deductions, shares of common stock at a 15% discount. Pursuant to the terms of the ESPP, the Company issued 83,155, 69,562 and 68,428 shares of common stock during fiscal 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively. The total cost related to the ESPP, including the compensation expense calculations, was approximately $1.0 million in fiscal 2017 and $1.1 million in both fiscal 2016 and 2015. There is a maximum of 16.0 million shares of common stock that are reserved under the ESPP. At December 30, 2017, there were approximately 12.0 million remaining shares of common stock reserved for future issuance under the ESPP.
58
Note 3 - Acquisition of Petsense:
On September 29, 2016, the Company completed the acquisition of Petsense. Headquartered in Scottsdale, Arizona, Petsense is a small-box pet specialty supply retailer focused on meeting the needs of pet owners, primarily in small and mid-size communities, and offering a variety of pet products and services. Pursuant to the agreement governing the transaction, the Company acquired all the outstanding equity interests in Petsense for an all-cash purchase price which was financed with cash on-hand and revolver borrowings under the 2016 Senior Credit Facility (as defined in Note 5).
The total consideration transferred in connection with the Petsense acquisition has been allocated to the assets acquired and liabilities assumed based upon their respective fair values. The fair value of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed is estimated based on either one or a combination of the following methodologies: the income approach, the cost approach or the market approach as determined based on the nature of the asset or liability and the level of inputs available. With respect to assets and liabilities, the determination of fair value requires management to make subjective judgments as to projections of future operating performance, the appropriate discount rate to apply, long-term growth rates, etc. (i.e. unobservable inputs classified as Level 3 inputs under the fair value hierarchy), which affect the amounts recorded in the purchase price allocation. The excess of the consideration transferred over the fair value of the identifiable assets, net of liabilities, is recorded as goodwill, which is indicative of the expected continued growth and development of the pet specialty retail business acquired.
The table below summarizes the consideration transferred and allocation of the purchase price for the Petsense acquisition (in thousands):
Consideration transferred | $ | 144,476 | |
Assets acquired: | |||
Current assets | $ | 21,875 | |
Property and equipment | 25,519 | ||
Other intangible assets - tradename | 31,300 | ||
Other assets | 428 | ||
Liabilities assumed: | |||
Current liabilities | (12,091 | ) | |
Long-term liabilities | (5,489 | ) | |
Total identifiable net assets acquired | 61,542 | ||
Excess of consideration transferred over identifiable net assets acquired (goodwill) | $ | 82,934 | |
In September 2017, the Company finalized the working capital settlement pursuant to the agreement governing the transaction. As a result, the values of the consideration transferred, assets acquired and liabilities assumed as reflected in the table above are considered final. The working capital settlement reduced both the consideration transferred and goodwill by $1.2 million from the preliminary values.
The resulting goodwill of $82.9 million and tradename of $31.3 million are amortized for income tax purposes.
The results of operations of Petsense have been included in the Consolidated Financial Statements since the date of acquisition.
59
Note 4 - Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets:
Goodwill
The Company had approximately $93.2 million and $94.4 million of goodwill at December 30, 2017 and December 31, 2016, respectively. The changes in the carrying amount of goodwill for the years ended December 30, 2017 and December 31, 2016 are as follows (in thousands):
2017 | 2016 | ||||||
Balance, beginning of year | $ | 94,417 | $ | 10,258 | |||
Goodwill acquired as part of acquisition | — | 84,159 | |||||
Working capital settlement | (1,225 | ) | — | ||||
Impairment loss | — | — | |||||
Balance, end of year | $ | 93,192 | $ | 94,417 | |||
Goodwill is allocated to each identified reporting unit, which is defined as an operating segment or one level below the operating segment.
Goodwill is not amortized, but is evaluated for impairment annually and whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate the carrying value of goodwill may not be recoverable. The Company completes its impairment evaluation by performing valuation analyses and considering other publicly available market information, as appropriate.
The test used to identify the potential for goodwill impairment compares the fair value of a reporting unit with its carrying value. An impairment charge would be recorded to the Company’s operations for the amount, if any, in which the carrying value exceeds the fair value.
In the fourth quarter of fiscal 2017, the Company completed its annual impairment testing of goodwill and no impairment was identified. The Company determined that the fair value of each reporting unit (including goodwill) was in excess of the carrying value of the respective reporting unit. In reaching this conclusion, the fair value of each reporting unit was determined based on either a market or an income approach. Under the market approach, the fair value is based on observed market data.
Other Intangible Assets
The Company had approximately $31.3 million of intangible assets other than goodwill at December 30, 2017 and December 31, 2016. The intangible asset balance represents the estimated fair value of the Petsense tradename, which is not subject to amortization as it has an indefinite useful life on the basis that it is expected to contribute cash flows beyond the foreseeable horizon.
With respect to intangible assets, we evaluate for impairment annually and whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying value may not be recoverable. We recognize an impairment loss only if the carrying amount is not recoverable through its discounted cash flows and measure the impairment loss based on the difference between the carrying value and fair value. In the fourth quarter of fiscal 2017, the Company completed its annual impairment testing of intangible assets and no impairment was identified.
60
Note 5 - Debt:
The following table summarizes the Company’s outstanding debt as of the dates indicated (in millions):
December 30, 2017 | December 31, 2016 | |||||||
Senior Notes | $ | 150.0 | $ | — | ||||
Senior Credit Facility: | ||||||||
February 2016 Term Loan | 180.0 | 190.0 | ||||||
June 2017 Term Loan | 97.5 | — | ||||||
Revolving credit loans | — | 85.0 | ||||||
Total outstanding borrowings | 427.5 | 275.0 | ||||||
Less: unamortized debt issuance costs | (1.4 | ) | (1.1 | ) | ||||
Total debt | 426.1 | 273.9 | ||||||
Less: current portion of long-term debt | (25.0 | ) | (10.0 | ) | ||||
Long-term debt | $ | 401.1 | $ | 263.9 | ||||
Outstanding letters of credit | $ | 39.6 | $ | 44.3 | ||||
Senior Notes
On August 14, 2017, the Company entered into a note purchase and private shelf agreement (the “Note Purchase Agreement”), pursuant to which the Company agreed to sell $150 million aggregate principal amount of senior unsecured notes due August 14, 2029 (the “2029 Notes”) in a private placement. The 2029 Notes bear interest at 3.70% per annum with interest payable semi-annually in arrears on each annual and semi-annual anniversary of the issuance date. The obligations under the Note Purchase Agreement are unsecured, but guaranteed by each of the Company’s material subsidiaries.
The Company may from time to time issue and sell additional senior unsecured notes (the “Shelf Notes”) pursuant to the Note Purchase Agreement, in an aggregate principal amount of up to $150 million. The Shelf Notes will have a maturity date of no more than 12 years after the date of original issuance and may be issued through August 14, 2020, unless earlier terminated in accordance with the terms of the Note Purchase Agreement.
Pursuant to the Note Purchase Agreement, the 2029 Notes and any Shelf Notes (collectively, the "Notes") are redeemable by the Company, in whole at any time or in part from time to time, at 100% of the principal amount of the Notes being redeemed, together with accrued and unpaid interest thereon and a make whole amount calculated by discounting all remaining scheduled payments on the Notes by the yield on the U.S. Treasury security with a maturity equal to the remaining average life of the Notes plus 0.50%.
Senior Credit Facility
On February 19, 2016, the Company entered into a senior credit facility (the “2016 Senior Credit Facility”) consisting of a $200 million term loan (the “February 2016 Term Loan”) and a $500 million revolving credit facility (the “Revolver”) with a sublimit of $50 million for swingline loans. This agreement is unsecured. On February 16, 2018, the maturity date was extended from February 19, 2021 to February 19, 2022.
On June 15, 2017, pursuant to an accordion feature available under the 2016 Senior Credit Facility, the Company entered into an incremental term loan agreement (the “June 2017 Term Loan”) which increased the term loan capacity under the 2016 Senior Credit Facility by $100 million. This agreement is unsecured and matures on June 15, 2022.
The February 2016 Term Loan of $200 million requires quarterly payments totaling $10 million per year in years one and two and $20 million per year in years three through the maturity date, with the remaining balance due in full on the maturity date of February 19, 2022. The June 2017 Term Loan of $100 million requires quarterly payments totaling $5 million per year in years one and two and $10 million per year in years three through the maturity date, with the remaining balance due in full on the maturity date of June 15, 2022. The 2016 Senior Credit Facility also contains a $500 million revolving credit facility (with a sublimit of $50 million for swingline loans).
61
Borrowings under the February 2016 Term Loan and Revolver bear interest at either the bank’s base rate (4.500% at December 30, 2017) or the London Inter-Bank Offer Rate (“LIBOR”) (1.564% at December 30, 2017) plus an additional amount ranging from 0.500% to 1.125% per annum (0.750% at December 30, 2017), adjusted quarterly based on our leverage ratio. The Company is also required to pay, quarterly in arrears, a commitment fee for unused capacity ranging from 0.075% to 0.200% per annum (0.125% at December 30, 2017), adjusted quarterly based on the Company’s leverage ratio. Borrowings under the June 2017 Term Loan bear interest at either the bank’s base rate (4.500% at December 30, 2017) or LIBOR (1.564% at December 30, 2017) plus an additional 1.000% per annum. As further described in Note 6, the Company has entered into interest rate swap agreements in order to hedge our exposure to variable rate interest payments associated with each of the term loans under the 2016 Senior Credit Facility.
Proceeds from the 2016 Senior Credit Facility may be used for working capital, capital expenditures, dividends, share repurchases, and other matters. There are no compensating balance requirements associated with the 2016 Senior Credit Facility.
Covenants and Default Provisions of the Debt Agreements
The 2016 Senior Credit Facility and the Note Purchase Agreement (collectively, the “Debt Agreements”) require quarterly compliance with respect to two material covenants: a fixed charge coverage ratio and a leverage ratio. Both ratios are calculated on a trailing twelve-month basis at the end of each fiscal quarter. The fixed charge coverage ratio compares earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, amortization, share-based compensation and rent expense (“consolidated EBITDAR”) to the sum of interest paid and rental expense (excluding any straight-line rent adjustments). The fixed charge coverage ratio shall be greater than or equal to 2.00 to 1.0 as of the last day of each fiscal quarter. The leverage ratio compares rental expense (excluding any straight-line rent adjustments) multiplied by a factor of six plus total debt to consolidated EBITDAR. The leverage ratio shall be less than or equal to 4.00 to 1.0 as of the last day of each fiscal quarter. The Debt Agreements also contain certain other restrictions regarding additional indebtedness, capital expenditures, business operations, guarantees, investments, mergers, consolidations and sales of assets, transactions with subsidiaries or affiliates, and liens. As of December 30, 2017, the Company was in compliance with all debt covenants.
The Debt Agreements contain customary events of default, including payment defaults, breaches of representations and warranties, covenant defaults, cross-defaults to other material indebtedness, certain events of bankruptcy and insolvency, material judgments, certain ERISA events and invalidity of loan documents. Upon certain changes of control, payment under the Debt Agreements could become due and payable. In addition, under the Note Purchase Agreement, upon an event of default or change of control, the make whole payment described above may become due and payable.
The Note Purchase Agreement also requires that, in the event the Company amends its 2016 Senior Credit Facility, or any subsequent credit facility of $100 million or greater, such that it contains covenant or default provisions that are not provided in the Note Purchase Agreement or that are similar to those contained in the Note Purchase Agreement but which contain percentages, amounts, formulas or grace periods that are more restrictive than those set forth in the Note Purchase Agreement or are otherwise more beneficial to the lenders thereunder, the Note Purchase Agreement shall be automatically amended to include such additional or amended covenants and/or default provisions.
Note 6 - Interest Rate Swaps:
The Company entered into an interest rate swap agreement which became effective on March 31, 2016, with a maturity date of February 19, 2021. The notional amount of this swap agreement began at $197.5 million (the principal amount of the February 2016 Term Loan borrowings as of March 31, 2016) and will amortize at the same time and in the same amount as the February 2016 Term Loan borrowings as described in Note 5, up to the maturity date of the interest rate swap agreement on February 19, 2021. As of December 30, 2017, the notional amount of the interest rate swap was $180.0 million.
The Company entered into a second interest rate swap agreement which became effective on June 30, 2017, with a maturity date of June 15, 2022. The notional amount of this swap agreement began at $100 million (the principal amount of the June 2017 Term Loan borrowings as of June 30, 2017) and will amortize at the same time and in the same amount as the June 2017 Term Loan borrowings as described in Note 5. As of December 30, 2017, the notional amount of the interest rate swap was $97.5 million.
The Company’s interest rate swap agreements are executed for risk management and are not held for trading purposes. The objective of the interest rate swap agreements is to mitigate interest rate risk associated with future changes in interest rates. To accomplish this objective, the interest rate swap agreements are intended to hedge the variable cash flows associated with the variable rate term loan borrowings under the 2016 Senior Credit Facility. Both interest rate swap agreements entitle the Company to receive,
62
at specified intervals, a variable rate of interest based on LIBOR in exchange for the payment of a fixed rate of interest throughout the life of the agreement, without exchange of the underlying notional amount.
The Company has designated its interest rate swap agreements as cash flow hedges and accounts for the underlying activity in accordance with hedge accounting. The interest rate swaps are presented within the consolidated balance sheets at fair value. In accordance with hedge accounting, the effective portion of gains and losses on interest rate swaps that are designated and qualify as cash flow hedges are recorded as a component of Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) (“OCI” or “OCL”, respectively) and reclassified into earnings in the period during which the hedged transactions affect earnings. The ineffective portion of gains and losses on interest rate swaps, if any, are recognized in current earnings.
The assets and liabilities measured at fair value related to the Company’s interest rate swaps, excluding accrued interest, were as follows (in thousands):
Balance Sheet Location | 2017 | 2016 | ||||||||
Interest rate swaps (short-term portion) | Other current assets / (Other accrued expenses) | $ | 900 | $ | (398 | ) | ||||
Interest rate swaps (long-term portion) | Other assets | 4,252 | 3,215 | |||||||
Total net assets | $ | 5,152 | $ | 2,817 | ||||||
The offset to the interest rate swap asset or liability is recorded as a component of equity, net of deferred taxes, in Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) (“AOCI” or “AOCL,” respectively), and will be reclassified into earnings over the term of the underlying debt as interest payments are made.
The following table summarizes the changes in AOCI/AOCL, net of tax, related to the Company’s interest rate swaps (in thousands):
2017 | 2016 | |||||||
Beginning fiscal year AOCI balance | $ | 1,392 | $ | — | ||||
Current fiscal period gain recognized in OCI | 1,371 | 1,392 | ||||||
Amounts reclassified from AOCI (AOCL) into current fiscal period earnings | — | — | ||||||
Other comprehensive gain, net of tax | 1,371 | 1,392 | ||||||
Ending fiscal period AOCI balance | $ | 2,763 | $ | 1,392 | ||||
As of December 30, 2017, the estimated pre-tax portion of AOCI that is expected to be reclassified into earnings over the next twelve months is $0.9 million. Cash flows related to the interest rate swaps are included in operating activities on the consolidated statements of cash flows.
The following table summarizes the impact of pre-tax gains and losses derived from the Company’s interest rate swaps (in thousands):
Financial Statement Location | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||
Effective portion of gains recognized in OCI during the period | Other comprehensive income | $ | 2,240 | $ | 2,283 | $ | — | |||||||
Amounts reclassified from AOCI (AOCL) into earnings | Interest expense, net | — | — | — | ||||||||||
Ineffective portion of gains recognized in earnings during the period | Interest expense, net | 95 | 534 | — | ||||||||||
The following table summarizes the impact of taxes affecting AOCI/AOCL as a result of the Company’s interest rate swaps (in thousands):
2017 | 2016 | |||||||
Income tax expense of interest rate swaps on AOCI | $ | 869 | $ | 891 | ||||
63
Credit-risk-related contingent features
In accordance with the underlying interest rate swap agreements, the Company could be declared in default on its interest rate swap obligations if repayment of the underlying indebtedness (i.e., the Company’s term loan) is accelerated by the lender due to the Company's default on such indebtedness.
If the Company had breached any of the provisions in the underlying agreements at December 30, 2017, it could have been required to post full collateral or settle its obligations under the Company’s interest rate swap agreements. However, as of December 30, 2017, the Company had not breached any of these provisions or posted any collateral related to the underlying interest rate swap agreements. Further, as of December 30, 2017, the net balance of each of the Company’s interest rate swaps were in a net asset position and therefore the Company would have no obligation upon default.
Note 7 - Leases:
The Company leases the majority of its retail store locations, two distribution sites, its Merchandise Innovation Center, transportation equipment and other equipment under various non-cancellable operating leases. The leases have varying terms and expire at various dates through 2037. Store leases typically have initial terms of between 10 and 15 years, with two to four optional renewal periods of five years each. Some leases require the payment of contingent rent that is based upon store sales above agreed-upon sales levels for the year. The sales levels vary for each store and are established in the lease agreements. Generally, most of the leases also require that the Company pays associated taxes, insurance and maintenance costs.
Total rent expense for fiscal 2017, 2016 and 2015 was approximately $319.5 million, $293.0 million and $262.1 million, respectively. Total contingent rent expense for fiscal 2017, 2016 and 2015 was insignificant.
Future minimum payments, by year and in the aggregate, under leases with initial or remaining terms of one year or more consist of the following (in thousands):
Capital Leases | Operating Leases | ||||||
2018 | $ | 5,201 | $ | 324,813 | |||
2019 | 5,215 | 315,062 | |||||
2020 | 5,234 | 296,773 | |||||
2021 | 5,294 | 273,932 | |||||
2022 | 4,172 | 251,059 | |||||
Thereafter | 23,149 | 1,219,048 | |||||
Total minimum lease payments | 48,265 | $ | 2,680,687 | ||||
Amount representing interest | (12,103 | ) | |||||
Present value of minimum lease payments | 36,162 | ||||||
Less: current portion | (3,545 | ) | |||||
Long-term capital lease obligations | $ | 32,617 | |||||
Assets under capital leases were as follows (in thousands):
2017 | 2016 | ||||||
Building and improvements, gross | $ | 29,324 | $ | 29,324 | |||
Computer software and hardware | 11,388 | — | |||||
Less: accumulated depreciation and amortization | (6,462 | ) | (3,381 | ) | |||
Assets under capital lease, net | $ | 34,250 | $ | 25,943 | |||
Note 8 - Capital Stock and Dividends:
Capital Stock
The authorized capital stock of the Company consists of common stock and preferred stock. The Company is authorized to issue 400 million shares of common stock. The Company is also authorized to issue 40,000 shares of preferred stock, with such designations, rights and preferences as may be determined from time to time by the Board of Directors.
64
Dividends
During fiscal 2017 and 2016, the Company’s Board of Directors declared the following cash dividends:
Date Declared | Dividend Amount Per Share | Stockholders of Record Date | Date Paid | |||
November 6, 2017 | $0.27 | November 20, 2017 | December 5, 2017 | |||
August 7, 2017 | $0.27 | August 21, 2017 | September 6, 2017 | |||
May 8, 2017 | $0.27 | May 22, 2017 | June 6, 2017 | |||
February 8, 2017 | $0.24 | February 27, 2017 | March 14, 2017 | |||
October 31, 2016 | $0.24 | November 14, 2016 | November 29, 2016 | |||
August 1, 2016 | $0.24 | August 15, 2016 | August 30, 2016 | |||
May 2, 2016 | $0.24 | May 16, 2016 | June 1, 2016 | |||
February 3, 2016 | $0.20 | February 22, 2016 | March 8, 2016 | |||
It is the present intention of the Board of Directors to continue to pay a quarterly cash dividend; however, the declaration and payment of future dividends will be determined by the Board of Directors in its sole discretion and will depend upon the earnings, financial condition and capital needs of the Company, as well as other factors which the Board of Directors deem relevant.
On February 7, 2018, the Company’s Board of Directors declared a quarterly cash dividend of $0.27 per share of common stock. The dividend will be paid on March 13, 2018, to stockholders of record as of the close of business on February 26, 2018.
Note 9 - Treasury Stock:
The Company’s Board of Directors has authorized common stock repurchases under a share repurchase program of up to $3 billion, exclusive of any fees, commissions or other expenses related to such repurchases through December 31, 2020. The repurchases may be made from time to time on the open market or in privately negotiated transactions. The timing and amount of any shares repurchased under the program will depend on a variety of factors, including price, corporate and regulatory requirements, capital availability and other market conditions. Repurchased shares are accounted for at cost and will be held in treasury for future issuance. The program may be limited or terminated at any time without prior notice.
The Company repurchased approximately 5.9 million, 4.4 million and 3.4 million shares of common stock under the share repurchase program at a total cost of $369.4 million, $331.7 million and $292.7 million in fiscal 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively. As of December 30, 2017, the Company had remaining authorization under the share repurchase program of $0.9 billion, exclusive of any fees, commissions or other expenses.
65
Note 10 - Net Income Per Share:
Net income per share is calculated as follows (in thousands, except per share amounts):
2017 | ||||||||||
Net Income | Shares | Per Share Amount | ||||||||
Basic net income per share | $ | 422,599 | 127,588 | $ | 3.31 | |||||
Dilutive stock options and restricted stock units outstanding | — | 616 | (0.01 | ) | ||||||
Diluted net income per share | $ | 422,599 | 128,204 | $ | 3.30 | |||||
2016 | ||||||||||
Net Income | Shares | Per Share Amount | ||||||||
Basic net income per share | $ | 437,120 | 132,905 | $ | 3.29 | |||||
Dilutive stock options and restricted stock units outstanding | — | 908 | (0.02 | ) | ||||||
Diluted net income per share | $ | 437,120 | 133,813 | $ | 3.27 | |||||
2015 | ||||||||||
Net Income | Shares | Per Share Amount | ||||||||
Basic net income per share | $ | 410,395 | 135,582 | $ | 3.03 | |||||
Dilutive stock options and restricted stock units outstanding | — | 1,263 | (0.03 | ) | ||||||
Diluted net income per share | $ | 410,395 | 136,845 | $ | 3.00 | |||||
Anti-dilutive stock options excluded from the above calculations totaled approximately 3.9 million, 1.9 million and 0.9 million in fiscal 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively.
Note 11 – Income Taxes:
The provision for income taxes consists of the following (in thousands):
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
Current tax expense: | |||||||||||
Federal | $ | 207,986 | $ | 221,207 | $ | 225,253 | |||||
State | 14,516 | 20,858 | 17,419 | ||||||||
Total current | 222,502 | 242,065 | 242,672 | ||||||||
Deferred tax expense (benefit): | |||||||||||
Federal | 22,469 | 12,256 | (7,017 | ) | |||||||
State | 4,953 | (3,171 | ) | 1,567 | |||||||
Total deferred | 27,422 | 9,085 | (5,450 | ) | |||||||
Total provision | $ | 249,924 | $ | 251,150 | $ | 237,222 | |||||
66
Deferred income taxes reflect the net tax effects of temporary differences between the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities for financial reporting purposes and the amounts used for income tax purposes. Significant components of the deferred tax assets and liabilities are as follows (in thousands):
2017 | 2016 | ||||||
Tax assets: | |||||||
Inventory valuation | $ | 13,029 | $ | 19,713 | |||
Accrued employee benefits costs | 7,092 | 14,120 | |||||
Accrued sales tax audit reserve | 3,479 | 4,317 | |||||
Rent expenses in excess of cash payments required | 24,728 | 35,391 | |||||
Deferred compensation | 20,299 | 23,978 | |||||
Workers’ compensation insurance | 9,153 | 13,565 | |||||
General liability insurance | 4,265 | 5,332 | |||||
Lease exit obligations | 1,829 | 2,617 | |||||
Income tax credits | 4,206 | 4,265 | |||||
Other | 6,997 | 7,311 | |||||
95,077 | 130,609 | ||||||
Tax liabilities: | |||||||
Inventory basis difference | (4,141 | ) | (4,600 | ) | |||
Prepaid expenses | (1,423 | ) | (2,912 | ) | |||
Depreciation | (65,650 | ) | (73,336 | ) | |||
Amortization | (3,818 | ) | (2,419 | ) | |||
Other | (1,551 | ) | (2,124 | ) | |||
(76,583 | ) | (85,391 | ) | ||||
Net deferred tax asset | $ | 18,494 | $ | 45,218 | |||
On December 22, 2017, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 (the “Act”) was signed into law making significant changes to the Internal Revenue Code. Under the provisions of the Act, the U.S. corporate income tax rate decreased from 35% to 21% effective for tax years beginning after December 31, 2017. This change required the Company to remeasure our deferred tax assets and liabilities based on the rates at which they are expected to reverse in the future, which generally is 21% for federal income tax purposes. We have made a reasonable estimate of the effects on our existing deferred tax balances as of December 30, 2017, and recognized a provisional expense amount of $4.9 million, which is included as a component of income tax expense from continuing operations. However, we are still analyzing certain aspects of the Act and refining our calculations, which could potentially affect the measurement of these balances. We will recognize any changes to this provisional amount as we refine our estimates of our cumulative temporary differences as well as interpretations of the application of the Act.
The Company has evaluated the need for a valuation allowance for all or a portion of the deferred tax assets. The Company believes that all of the deferred tax assets will more likely than not be realized through future earnings. The Company had state tax credit carryforwards of $5.1 million and $7.5 million as of December 30, 2017 and December 31, 2016, respectively, with varying dates of expiration between 2017 and 2030. The Company provided no valuation allowance as of December 30, 2017 and December 31, 2016 for state tax credit carryforwards, as the Company believes it is more likely than not that all of these credits will be utilized before their expiration dates.
67
A reconciliation of the provision for income taxes to the amounts computed at the federal statutory rate is as follows (in thousands):
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
Tax provision at statutory rate | $ | 235,383 | $ | 240,894 | $ | 226,666 | |||||
Tax effect of: | |||||||||||
State income taxes, net of federal tax benefits | 14,320 | 15,527 | 13,976 | ||||||||
Tax credits, net of federal tax benefits | (5,060 | ) | (7,227 | ) | (3,763 | ) | |||||
Stock-based compensation programs | (1,040 | ) | — | — | |||||||
Enactment of tax legislation | 4,856 | — | — | ||||||||
Other | 1,465 | 1,956 | 343 | ||||||||
Total income tax expense | $ | 249,924 | $ | 251,150 | $ | 237,222 | |||||
The Company and its affiliates file income tax returns in the U.S. and various state and local jurisdictions. With few exceptions, the Company is no longer subject to federal, state and local income tax examinations by tax authorities for years before 2012. Various states have completed an examination of our income tax returns for 2011 through 2014 with minimal adjustments.
The total amount of unrecognized tax positions that, if recognized, would decrease the effective tax rate, is $1.7 million at December 30, 2017. In addition, the Company recognizes current interest and penalties accrued related to these uncertain tax positions as interest expense, and the amount is not material to the Consolidated Statements of Income. The Company has considered the reasonably possible expected net change in uncertain tax positions during the next 12 months and does not expect any material changes to our liability for uncertain tax positions through December 29, 2018.
A reconciliation of the beginning and ending gross amount of unrecognized tax benefits (exclusive of interest and penalties) is as follows (in thousands):
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
Balance at beginning of year | $ | 1,579 | $ | 2,922 | $ | 3,500 | |||||
Additions based on tax positions related to the current year | 527 | 460 | 869 | ||||||||
Additions for tax positions of prior years | 14 | 139 | — | ||||||||
Reductions for tax positions of prior years | (127 | ) | (1,829 | ) | (1,447 | ) | |||||
Reductions due to audit results | — | (113 | ) | — | |||||||
Balance at end of year | $ | 1,993 | $ | 1,579 | $ | 2,922 | |||||
Note 12 - Retirement Benefit Plans:
The Company has a defined contribution benefit plan, the Tractor Supply Company 401(k) Retirement Savings Plan (the “401(k) Plan”), which provides retirement benefits for eligible employees. The Company matches (in cash) 100% of the employee’s elective contributions up to 3% of eligible compensation plus 50% of the employee’s elective contributions from 3% to 6% of eligible compensation. In no event shall the total Company match made on behalf of the employee exceed 4.5% of the employee’s eligible compensation. All current contributions are immediately vested. Company contributions to the 401(k) Plan during fiscal 2017, 2016 and 2015, were approximately $7.4 million, $6.6 million and $5.9 million, respectively.
The Company offers, through a deferred compensation program, the opportunity for certain qualifying employees to elect to defer a portion of their annual base salary and/or their annual incentive bonus. Under the deferred compensation program, a percentage of the participants’ salary deferral is matched by the Company, limited to a maximum annual matching contribution of $4,500. The Company’s contributions, including accrued interest, during fiscal 2017, 2016 and 2015, were $0.5 million, $0.6 million and $0.5 million, respectively.
Note 13 – Commitments and Contingencies:
Construction and Real Estate Commitments
At December 30, 2017, the Company had contractual commitments of approximately $55 million related to the ongoing construction of its new distribution center in Frankfort, New York, and the expansion of its existing distribution center in Waverly, Nebraska. There were no material commitments related to construction projects extending greater than twelve months.
68
Letters of Credit
At December 30, 2017, there were $39.6 million outstanding letters of credit under the 2016 Senior Credit Facility.
Litigation
Item 103 of SEC Regulation S-K requires disclosure of certain environmental legal proceedings if the proceeding reasonably involves potential monetary sanctions of $100,000 or more. We periodically receive information requests and notices of potential noncompliance with environmental laws and regulations from governmental agencies, which are addressed on a case-by-case basis with the relevant agency. The Company received a subpoena from the District Attorney of Yolo County, California, requesting records and information regarding its hazardous waste management and disposal practices in California. The Company and the Office of the District Attorney of Yolo County engaged in settlement discussions which resulted in the settlement of the matter. A consent decree reflecting the terms of settlement was filed with the Yolo County Superior Court on June 23, 2017. Under the settlement, the Company agreed to a compliance plan and also agreed to pay a civil penalty and fund supplemental environmental projects furthering consumer protection and environmental enforcement in California. The civil penalty did not differ materially from the amount accrued. The cost of the settlement and the compliance with the consent decree will not have a material effect on our consolidated financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
The Company is also involved in various litigation matters arising in the ordinary course of business. The Company believes that any estimated loss related to such matters has been adequately provided for in accrued liabilities to the extent probable and reasonably estimable. Accordingly, the Company currently expects these matters will be resolved without material adverse effect on its consolidated financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
Note 14 – Segment Reporting:
The Company has one reportable segment which is the retail sale of products that support the rural lifestyle. The following table indicates the percentage of net sales represented by each major product category during fiscal 2017, 2016, and 2015:
Percent of Net Sales | ||||||||
Product Category: | 2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||
Livestock and Pet | 47 | % | 46 | % | 44 | % | ||
Hardware, Tools and Truck | 22 | 22 | 23 | |||||
Seasonal, Gift and Toy Products | 19 | 19 | 20 | |||||
Clothing and Footwear | 8 | 8 | 8 | |||||
Agriculture | 4 | 5 | 5 | |||||
Total | 100 | % | 100 | % | 100 | % | ||
Note 15 – New Accounting Pronouncements:
New Accounting Pronouncements Recently Adopted
In July 2015, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) 2015-11, "Inventory (Topic 330): Simplifying the Measurement of Inventory.” This update requires an entity that determines the cost of inventory by methods other than last-in, first-out and the retail inventory method to measure inventory at the lower of cost and net realizable value. The Company adopted this guidance in the first quarter of fiscal 2017 using a prospective application. The adoption of this guidance did not have a material impact to our Consolidated Financial Statements and related disclosures.
In March 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-04, “Liabilities - Extinguishments of Liabilities (Subtopic 405-20): Recognition of Breakage for Certain Prepaid Stored-Value Products.” This update requires that liabilities related to the sale of prepaid stored-value products (gift cards) be adjusted periodically to reflect breakage. The Company adopted this guidance in the first quarter of fiscal 2017. The Company was recording gift card breakage prior to the adoption of this guidance; therefore, the adoption of this guidance did not have a material impact to our Consolidated Financial Statements and related disclosures.
In March 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-09, “Compensation - Stock Compensation (Topic 718): Improvements to Employee Share-Based Payment Accounting.” The update addresses several aspects of the accounting for share-based compensation transactions including: (a) income tax consequences when awards vest or are settled, (b) classification of awards as either equity or liabilities, (c) a policy election to account for forfeitures as they occur rather than on an estimated basis and (d) classification
69
of excess tax impacts on the statement of cash flows. The inclusion of excess tax benefits and deficiencies as a component of our income tax expense will increase volatility within our provision for income taxes as the amount of excess tax benefits or deficiencies from share-based compensation awards is dependent on our stock price at the date the awards are exercised or settled. The Company adopted this guidance in the first quarter of fiscal 2017, which did not have a material impact to our Consolidated Financial Statements and related disclosures. The Company has elected to continue estimating forfeitures of share-based awards. The Company has elected to apply the amendments related to the presentation of excess tax benefits on the statement of cash flows using a retrospective transition method, and as a result, excess tax benefits related to share-based awards which had been previously classified as cash flows from financing activities will be reclassified as cash flows from operating activities.
In August 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-15, “Statement of Cash Flows (Topic 230): Classification of Certain Cash Receipts and Cash Payments.” This update clarifies and provides specific guidance on eight cash flow classification issues that are not currently addressed by U.S. GAAP and thereby reduces the current and potential future diversity in practice. The Company adopted this guidance in the first quarter of fiscal 2017. The adoption of this guidance did not impact the classification of any of the Company’s cash flow activity and therefore did not have a material impact to our Consolidated Financial Statements and related disclosures.
In January 2017, the FASB issued ASU 2017-04, “Intangibles - Goodwill and Other (Topic 350): Simplifying the Test for Goodwill Impairment.” This update simplifies the measurement of goodwill by eliminating the second step from the goodwill impairment test, which requires the comparison of the implied fair value of goodwill with the current carrying amount of goodwill. Instead, under the amendments in this guidance, an entity shall perform a goodwill impairment test by comparing the fair value of each reporting unit with its carrying amount and an impairment charge is to be recorded for the amount, if any, in which the carrying value exceeds the reporting unit’s fair value. The Company adopted this guidance in the first quarter of fiscal 2017 using a prospective application. The adoption of this guidance did not have a material impact to our Consolidated Financial Statements and related disclosures.
New Accounting Pronouncements Not Yet Adopted
In May 2014, the FASB issued ASU 2014-09, “Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606).” ASU 2014-09 amends the guidance for revenue recognition to replace numerous, industry-specific requirements and converges areas under this topic with those of the International Financial Reporting Standards. The ASU implements a five-step process for customer contract revenue recognition that focuses on transfer of control, as opposed to transfer of risk and rewards. The amendment also requires enhanced disclosures regarding the nature, amount, timing and uncertainty of revenues and cash flows from contracts with customers. Other major provisions include the capitalization and amortization of certain contract costs, ensuring the time value of money is considered in the transaction price, and allowing estimates of variable consideration to be recognized before contingencies are resolved in certain circumstances. In August 2015, the FASB issued ASU 2015-14, “Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606): Deferral of the Effective Date,” which implemented a one-year deferral of ASU 2014-09. As a result of the deferral, the amendments in ASU 2014-09 are effective for reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2017. In March 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-08, “Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606): Principal versus Agent Considerations (Reporting Revenue Gross versus Net),” which further clarifies the implementation guidance on principal versus agent considerations. In April 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-10, “Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606): Identifying Performance Obligations and Licensing,” which further clarifies the aspects of (a) identifying performance obligations and (b) the licensing implementation guidance. In May 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-12 “Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606): Narrow-Scope Improvements and Practical Expedients,” which provides implementation guidance in regards to (a) assessing the collectability criterion, (b) the presentation of taxes collected from customers, (c) noncash consideration, (d) contract modification at transition, (e) completed contracts at transition and (f) other technical corrections. In December 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-20, “Technical Corrections and Improvements to Topic 606, Revenue from Contracts with Customers,” which is intended to clarify the codification and to correct unintended application of guidance pertaining to Topic 606 and other Topics amended by ASU 2014-09 to increase stakeholders’ awareness of the proposals and to expedite improvements to ASU 2014-09. The effective date and transition requirements for ASU 2016-08, ASU 2016-10, ASU 2016-12 and ASU 2016-20 are the same as the effective date and transition requirements of ASU 2014-09. Entities that transition to these standards may either retrospectively restate each prior reporting period or reflect the cumulative effect of initially applying the updates with an adjustment to retained earnings at the date of adoption. The Company will adopt this guidance in the first quarter of fiscal 2018 using the modified retrospective transition method. Based on an evaluation of the standard as a whole, the Company has identified customer incentives and principal versus agent considerations as the areas that will most likely be affected by the new revenue recognition guidance. The adoption of this guidance is not expected to have a material impact on our Consolidated Financial Statements and related disclosures.
In February 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-02, “Leases (Topic 842).” This update requires a dual approach for lessee accounting under which a lessee will account for leases as finance leases or operating leases. Both finance leases and operating leases will
70
result in the lessee recognizing a right-of-use asset and a corresponding lease liability on its balance sheet, with differing methodology for income statement recognition. This guidance is effective for public business entities for fiscal years, and interim periods within those years, beginning after December 15, 2018, with early adoption permitted. A modified retrospective approach is required for all leases existing or entered into after the beginning of the earliest comparative period in the consolidated financial statements. The Company is currently assessing the impact that adoption of this guidance will have on its Consolidated Financial Statements and related disclosures.
In May 2017, the FASB issued ASU 2017-09, “Compensation - Stock Compensation (Topic 718): Scope of Modification Accounting.” This update provides guidance about which changes to the terms or conditions of a share-based payment award require an entity to apply modification accounting in Topic 718. An entity should account for the effects of a modification unless (a) the fair value of the modified award is the same as the fair value of the original award immediately before the original award is modified, (b) the vesting conditions of the modified award are the same as the vesting conditions of the original award immediately before the original award is modified or (c) the classification of the modified award as an equity instrument or a liability instrument is the same as the classification of the original award immediately before the original award is modified. The amendments in ASU 2017-09 are effective for public business entities for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2017, including interim periods within those annual periods. Early adoption is permitted, including adoption in any interim period, for public business entities for reporting periods for which financial statements have not been issued. The amendments in ASU 2017-09 should be applied prospectively to an award modified on or after the adoption date. The Company plans to adopt this guidance in the first quarter of fiscal 2018. The adoption of this guidance is not expected to have a material impact on our Consolidated Financial Statements and related disclosures.
In August 2017, the FASB issued ASU 2017-12, “Derivatives and Hedging (Topic 815): Targeted Improvements to Accounting for Hedging Activities,” which amends and simplifies existing guidance in order to allow companies to more accurately present the economic effects of risk management activities in the financial statements. This update expands and refines hedge accounting for both nonfinancial and financial risk components and aligns the recognition and presentation of the effects of the hedging instrument and the hedged item in the financial statements. Additionally, the amendments in ASU 2017-12 provide new guidance about income statement classification and eliminates the requirement to separately measure and report hedge ineffectiveness. This guidance is effective for public business entities for fiscal years, and interim periods within those years, beginning after December 15, 2018, with early adoption permitted. The amendments in ASU 2017-12 require that an entity with cash flow or net investment hedges existing at the date of adoption apply a cumulative-effect adjustment to eliminate the separate measurement of ineffectiveness to the opening balance of retained earnings as of the beginning of the fiscal year that the entity adopts this guidance. The amended presentation and disclosure guidance is adopted prospectively. The adoption of this guidance is not expected to have a material impact on our Consolidated Financial Statements and related disclosures.
In February 2018, the FASB issued ASU 2018-02, “Income Statement - Reporting Comprehensive Income (Topic 220): Reclassification of Certain Tax Effects from Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income,” which allows a reclassification from accumulated other comprehensive income to retained earnings for stranded tax effects resulting from the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act. This guidance is effective for all entities for fiscal years, and interim periods within those years, beginning after December 15, 2018, with early adoption permitted. The amendments in ASU 2018-02 should be applied either in the period of adoption or retrospectively to each period in which the effect of the change in the U.S. federal corporate income tax rate in the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act is recognized. The adoption of this guidance is not expected to have a material impact on our Consolidated Financial Statements and related disclosures.
Item 9. | Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure |
None
Item 9A. | Controls and Procedures |
Disclosure Controls and Procedures
We carried out an evaluation required by the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “1934 Act”), under the supervision and with the participation of our principal executive officer and principal financial officer, of the effectiveness of the design and operation of our disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rule 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the 1934 Act) as of December 30, 2017. Based on this evaluation, our principal executive officer and principal financial officer concluded that, as of December 30, 2017, our disclosure controls and procedures were effective.
71
Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
A report of the Company’s management on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting (as such term is defined in Rule 13a-15(f) under the 1934 Act) and a report of Ernst & Young LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting are included in Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
There were no changes in our internal control over financial reporting that occurred during our last fiscal quarter that have materially affected or are reasonably likely to materially affect our internal control over financial reporting.
Item 9B. | Other Information |
None.
PART III
Item 10. | Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance |
The information set forth under the caption “Executive Officers of the Registrant” in Part I of this Form 10-K is incorporated herein by reference.
The information set forth under the captions “Item 1: Election of Directors,” “Board Meetings and Committees,” and “Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance” in our Proxy Statement for our Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be held on May 10, 2018, is incorporated herein by reference.
The Company has a Code of Ethics which covers all exempt employees, officers and directors of the Company, including the principal executive officer, principal financial officer, principal accounting officer and controller. The Code of Ethics is available in the “Corporate Governance” section of the Company’s website at TractorSupply.com. A copy of the Code of Ethics can also be obtained, free of charge, upon written request to the Corporate Secretary, Tractor Supply Company, 5401 Virginia Way, Brentwood, TN 37027. The Company intends to post amendments to or waivers, if any, from its Code of Ethics (to the extent applicable to its principal executive officer, principal financial officer, principal accounting officer or controller) on its website.
Item 11. Executive Compensation
The information set forth under the captions “Corporate Governance – Compensation Committee Interlocks and Insider Participation,” “Compensation of Directors,” and “Executive Compensation” in our Proxy Statement for our Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be held on May 10, 2018, is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters
The information set forth under the caption “Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management” in our Proxy Statement for our Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be held on May 10, 2018, is incorporated herein by reference.
72
Following is a summary of our equity compensation plans as of December 30, 2017, under which equity securities are authorized for issuance, aggregated as follows:
Plan Category | Number of Securities to be Issued Upon Exercise of Outstanding Options, Warrants, and Rights | Weighted Average Exercise Price of Outstanding Options, Warrants and Rights | Number of Securities Remaining Available for Future Issuance | |||||||
Equity compensation plans approved by security holders: | ||||||||||
Stock Incentive Plans | 5,221,756 | (a) | $ | 65.53 | (b) | 2,277,812 | ||||
Employee Stock Purchase Plan | — | — | 12,010,832 | |||||||
Equity compensation plans not approved by security holders | — | — | — | |||||||
Total | 5,221,756 | $ | 65.53 | 14,288,644 | ||||||
(a) Includes 4,998,526 outstanding stock options, 184,312 unvested restricted stock units and 38,918 restricted stock units which have vested but the receipt of which have been deferred by the recipient. The 2006 Stock Incentive Plan was superseded in May 2009 by the 2009 Stock Incentive Plan. Shares available under the 2009 Stock Incentive Plan are reduced by one share for each share issued pursuant to the exercise of a stock option and by two shares for each share issued pursuant to a full-value award (e.g., restricted stock unit).
(b) Restricted stock units have a weighted average exercise price of zero.
The information set forth in Note 2 to the “Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements” contained in this Form 10-K provides further information with respect to the material features of each plan.
Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence
The information set forth under the captions “Corporate Governance – Director Independence and Board Operations” and “Related – Party Transactions” in our Proxy Statement for our Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be held on May 10, 2018, is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 14. Principal Accountant Fees and Services
The information set forth under the caption “Item 2 – Ratification of Reappointment of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm” in our Proxy Statement for our Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be held on May 10, 2018, is incorporated herein by reference.
PART IV
Item 15. Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules
(a) (1) Financial Statements
See Consolidated Financial Statements under Item 8 on pages 40 through 71 of this Form 10-K.
(a) (2) Financial Statement Schedules
All schedules for which provision is made in the applicable accounting regulations of the SEC are not required under the related instructions, are inapplicable or the information is included in the Consolidated Financial Statements and, therefore, have been omitted.
(a) (3) Exhibits
The exhibits listed in the Index to Exhibits, which appears on pages 75 through 77 of this Form 10-K, are incorporated herein by reference or filed as part of this Form 10-K.
Item 16. Form 10-K Summary
None.
73
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the Registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
TRACTOR SUPPLY COMPANY | |||
Date: | February 22, 2018 | By: | /s/ Kurt D. Barton Senior Vice President – Chief Financial Officer and Treasurer |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the Registrant in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
Signature | Title | Date | |
/s/ Kurt D. Barton Kurt D. Barton | Senior Vice President – Chief Financial Officer and Treasurer (Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) | February 22, 2018 | |
/s/ Gregory A. Sandfort Gregory A. Sandfort | Chief Executive Officer and Director (Principal Executive Officer) | February 22, 2018 | |
/s/ Cynthia T. Jamison Cynthia T. Jamison | Chairman of the Board | February 22, 2018 | |
/s/ Johnston C. Adams Johnston C. Adams | Director | February 22, 2018 | |
/s/ Peter D. Bewley Peter D. Bewley | Director | February 22, 2018 | |
/s/ Thomas A. Kingsbury Thomas A. Kingsbury | Director | February 22, 2018 | |
/s/ Ramkumar Krishnan Ramkumar Krishnan | Director | February 22, 2018 | |
/s/ George MacKenzie George MacKenzie | Director | February 22, 2018 | |
/s/ Edna K. Morris Edna K. Morris | Director | February 22, 2018 | |
/s/ Mark J. Weikel Mark J. Weikel | Director | February 22, 2018 | |
74
EXHIBIT INDEX
3.1 | |
3.2 | |
4.1 | Form of Specimen Certificate representing the Company’s Common Stock, par value $.008 per share (filed as Exhibit 4.2 to Amendment No. 1 to Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form S-1, Registration No. 33-73028, filed in paper form with the Commission on January 31, 1994, and incorporated herein by reference). |
10.1 | Certificate of Insurance relating to the Medical Expense Reimbursement Plan of the Company (filed as Exhibit 10.33 to Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form S-1, Registration No. 33-73028, filed in paper form with the Commission on December 17, 1993, and incorporated herein by reference). |
10.2 | Summary Plan Description of the Executive Life Insurance Plan of the Company (filed as Exhibit 10.34 to Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form S-1, Registration No. 33-73028, filed in paper form with the Commission on December 17, 1993, and incorporated herein by reference).+ |
10.3 | |
10.4 | |
10.5 | |
10.6 | |
10.7 | |
10.8 | |
10.9 | |
10.10 | |
10.11 | |
10.12 | |
10.13 | |
10.14 | |
75
10.15 | |
10.16 | |
10.17 | |
10.18 | |
10.19 | |
10.20 | |
10.21 | |
10.22 | |
10.23 | |
10.24 | |
10.25 | |
10.26 | |
10.27 | |
10.28 | |
10.29 | |
10.30 | |
76
10.31 | |
10.32 | |
10.33* | |
10.34* | |
21* | |
23* | |
31.1* | |
31.2* | |
32* | |
101* | The following financial information from our Annual Report on Form 10-K for fiscal 2017, filed with the SEC on February 22, 2018, formatted in Extensible Business Reporting Language (XBRL): (i) the Consolidated Balance Sheets at December 30, 2017 and December 31, 2016, (ii) the Consolidated Statements of Income for the fiscal years ended December 30, 2017, December 31, 2016, and December 26, 2015, (iii) the Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income for the fiscal years ended December 30, 2017, December 31, 2016, and December 26, 2015, (iv) the Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the fiscal years ended December 30, 2017, December 31, 2016, and December 26, 2015, (v) the Consolidated Statements of Stockholders’ Equity for the fiscal years ended December 30, 2017, December 31, 2016, and December 26, 2015, and (vi) the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. |
* Filed herewith
+ Management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement
77
