Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-32.1 - EXHIBIT 32.1 - LA JOLLA PHARMACEUTICAL CO | exhibit321fy201710-k.htm |
| EX-31.2 - EXHIBIT 31.2 - LA JOLLA PHARMACEUTICAL CO | exhibit312fy201710-k.htm |
| EX-31.1 - EXHIBIT 31.1 - LA JOLLA PHARMACEUTICAL CO | exhibit311fy201710-k.htm |
| EX-23.1 - EXHIBIT 23.1 - LA JOLLA PHARMACEUTICAL CO | exhibit231fy2017.htm |
| EX-21.1 - EXHIBIT 21.1 - LA JOLLA PHARMACEUTICAL CO | exhibit211fy2017.htm |
| EX-10.16 - EXHIBIT 10.16 - LA JOLLA PHARMACEUTICAL CO | exhibit1016.htm |
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
WASHINGTON, DC 20549
FORM 10-K
x ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2017
OR
o TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the transition period from to
Commission file number: 1-36282
LA JOLLA PHARMACEUTICAL COMPANY
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
California | 33-0361285 | |
(State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | (I.R.S. Employer Identification Number) | |
4550 Towne Centre Court, San Diego, CA 92121
(Address of principal executive offices, including Zip Code)
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code: (858) 207-4264
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
Title of each class | Name of each exchange on which registered | |
Common Stock, Par Value $0.0001 per share | The Nasdaq Capital Market | |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes o No x
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Act. Yes o No x
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant: (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes x No o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate website, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes x No o
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of the Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. x
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. (Check one):
Large accelerated filer | o | Accelerated filer | x | |
Non-accelerated filer | o | (Do not check if a smaller reporting company) | Smaller reporting company | o |
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13a of the Exchange Act. o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes o No x
The aggregate market value of voting and non-voting common stock held by non-affiliates of the registrant as of June 30, 2017 totaled approximately $512,864,000. As of February 16, 2018, there were 22,168,242 shares of the Company’s common stock outstanding.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Certain information required to be disclosed in Part III of this report is incorporated by reference from the registrant’s definitive Proxy Statement for the 2018 Annual Meeting of Shareholders, which proxy statement is expected to be filed no later than 120 days after the end of the fiscal year covered by this report.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This report contains forward-looking statements as that term is defined in the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. Forward-looking statements can be identified by words such as “intends,” “believes,” “anticipates,” “indicates,” “plans,” “expects,” “suggests,” “may,” “should,” “potential,” “designed to,” “will” and similar references. In addition, any statements that refer to expectations, intentions, projections or other characterizations of future events or circumstances are forward-looking statements. These statements relate to future events or the Company’s anticipated future results of operations. These statements are only predictions and involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors, which may cause actual results to be materially different from these forward-looking statements. The Company cautions readers not to place undue reliance on any such forward-looking statements, which speak only as of the date they were made. Certain of these risks, uncertainties, and other factors are described in greater detail in the Company’s filings with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), all of which are available free of charge on the SEC’s website www.sec.gov. Actual results may differ materially from those expressed or implied in such statements. These risks include, but are not limited to, risks relating to: our ability to successfully commercialize GIAPREZATM (angiotensin II); the timing for commencement of preclinical studies and clinical trials; the anticipated timing for completion of such studies and trials, and the anticipated timing for regulatory actions; the success of future development activities for our product candidates; potential indications for which our product candidates may be developed; and the expected duration over which the Company’s cash balances will fund its operations.
Important factors that could cause our actual results and financial condition to differ materially from those indicated in the forward-looking statements include, among others:
• | our ability to successfully commercialize, market and achieve market acceptance of GIAPREZATM (angiotensin II), formerly known as LJPC-501, and other product candidates, including our positioning relative to competing products; |
• | our ability to meet the demand for GIAPREZA in a timely manner; |
• | any limitations or unfavorable warning or cautionary language that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) may ultimately impose on the label for GIAPREZA; |
• | potential market sizes for our products, including the market for the treatment of septic or other distributive shock; |
• | the anticipated treatment of future data by the FDA, European Medicines Agency (EMA) or other regulatory authorities, including whether such data will be sufficient for approval of GIAPREZA in the EMA or for approval of LJPC-401 by either the FDA or the EMA; |
• | the cost of producing and selling GIAPREZA; |
• | unforeseen safety issues from the administration of product and product candidates in patients; |
• | the timing, costs, conduct and outcome of preclinical studies and clinical trials; |
• | the success of future development activities for LJPC-401; |
• | the risk that our clinical trials with our product candidates may not be successful in evaluating their safety and tolerability or providing evidence of efficacy; |
• | the successful and timely completion of clinical trials; |
• | our plans and timing with respect to seeking regulatory approvals and uncertainties regarding the regulatory process; |
• | the availability of funds and resources to pursue our research and development projects, including clinical trials with our product candidates; |
• | uncertainties associated with obtaining and enforcing patents and the availability of regulatory exclusivity; |
• | the potential commercialization of any of our product candidates that receive regulatory approval; |
• | the uncertainty of obtaining raw materials or finished products supplies from third parties (some of which may be single sourced) and other related supply and manufacturing difficulties, interruptions and delays; |
• | our estimates for future performance; |
• | our ability to hire and retain our key employees; |
• | our estimates regarding our capital requirements and our needs for, and ability to obtain, additional financing; |
• | the expected duration over which the Company’s cash balances will fund its operations; and |
• | those risk factors identified in this Annual Report on Form 10-K under the heading “Risk Factors” and in other filings the Company periodically makes with the SEC. |
Forward-looking statements contained in this Annual Report on Form 10-K speak as of the date hereof, and we do not undertake to update any of these forward-looking statements to reflect a change in our views or events or circumstances that occur after the date of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. In addition, please see the “Risk Factors” section of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. These risk factors may be updated from time to time by our future filings under the Exchange Act.
PART I
In this report, all references to “we,” “our,” “us,” “La Jolla” and “the Company” refer to La Jolla Pharmaceutical Company, a California corporation, and our subsidiaries on a consolidated basis.
Item 1. Business.
Overview
La Jolla Pharmaceutical Company is a biopharmaceutical company focused on the discovery, development and commercialization of innovative therapies intended to significantly improve outcomes in patients suffering from life-threatening diseases.
GIAPREZATM (angiotensin II), formerly known as LJPC-501, was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) on December 21, 2017 as a vasoconstrictor to increase blood pressure in adults with septic or other distributive shock. GIAPREZA is our first commercial product.
LJPC-401, a clinical-stage investigational product, is our proprietary formulation of synthetic human hepcidin. LJPC-401 is being developed for the potential treatment of conditions characterized by iron overload, such as hereditary hemochromatosis, beta thalassemia, sickle cell disease and myelodysplastic syndrome.
GIAPREZATM (angiotensin II)
GIAPREZATM (angiotensin II), injection for intravenous infusion, was approved by the FDA on December 21, 2017 as a vasoconstrictor indicated to increase blood pressure in adults with septic or other distributive shock. Angiotensin II is the major bioactive component of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS). The RAAS is one of three central regulators of blood pressure.
There are approximately 800,000 distributive shock cases in the U.S. each year. Of these cases, an estimated 90% are septic shock patients. Approximately 300,000 patients do not achieve adequate blood pressure response with initial vasopressor therapy and require additional therapy for low blood pressure. The Center for Disease Control estimates that approximately 250,000 people in the U.S. die each year from septic shock. The inability to achieve or maintain adequate blood pressure results in inadequate blood flow to the body’s organs and tissue and is associated with a mortality rate exceeding most acute conditions requiring hospitalization.
In March 2015, we initiated a Phase 3 study of GIAPREZA in adult patients with septic or other distributive shock who remain hypotensive despite fluid and vasopressor therapy, known as the ATHOS-3 (Angiotensin II for the Treatment of High-Output Shock) Phase 3 study. In ATHOS-3, patients were randomized in a 1:1 fashion to receive either: (i) GIAPREZA plus standard-of-care vasopressors; or (ii) placebo plus standard-of-care vasopressors. Randomized patients received their assigned treatment via continuous IV infusion for up to 7 days. The primary efficacy endpoint was the percentage of patients with a MAP ≥ 75 mmHg or a 10 mmHg increase from baseline MAP at three hours following the initiation of study treatment without an increase in standard-of-care vasopressors.
The ATHOS-3 Phase 3 study completed enrollment of 344 patients in the fourth quarter of 2016. In February 2017, we reported positive top-line results from ATHOS-3. In May 2017, the results of ATHOS-3 were published by The New England Journal of Medicine.
The analysis of the primary efficacy endpoint, defined as the percentage of patients achieving a pre-specified target blood pressure response, was highly statistically significant: 23% of the 158 placebo-treated patients had a blood pressure response compared to 70% of the 163 GIAPREZA-treated patients (p<0.00001). In addition, a trend toward longer survival was observed: 22% reduction in mortality risk through day 28 [hazard ratio=0.78 (0.57-1.07), p=0.12] for GIAPREZA-treated patients.
Throughout ATHOS-3, safety outcomes were followed by an independent Data Safety Monitoring Board (DSMB). The DSMB recommended that the study continue as originally planned. In this critically ill patient population: 92% of placebo-treated patients compared to 87% of GIAPREZA-treated patients experienced at least one adverse event, and 22% of placebo-treated patients compared to 14% of GIAPREZA-treated patients discontinued treatment due to an adverse event.
1
In September 2017, an analysis from ATHOS-3 entitled “Baseline angiotensin levels and ACE effects in patients with vasodilatory shock treated with angiotensin II” was presented during the 30th European Society of Intensive Care Medicine Annual Congress. The pre-specified analysis showed that a relatively low angiotensin II state (as measured by the ratio of angiotensin I to angiotensin II) predicted increased mortality in patients with vasodilatory shock, suggesting that a low angiotensin II state is a negative prognostic indicator of outcomes. Furthermore, the analysis showed a statistically significant treatment effect of GIAPREZA compared to placebo on mortality in these patients with a relatively low angiotensin II state (relative risk reduction of 36%; HR=0.64; 95% CI: 0.41-1.00; p=0.047).
In September 2017, we reported that the European Medicines Agency’s (EMA) Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) issued favorable Scientific Advice regarding the EU regulatory pathway for GIAPREZA. Based on this Advice, we intend to submit a Marketing Authorization Application (MAA) for GIAPREZA in the third quarter of 2018.
On December 21, 2017, the FDA approved GIAPREZA to increase blood pressure in adults with septic or other distributive shock.
LJPC-401
LJPC-401, a clinical-stage investigational product, is our proprietary formulation of synthetic human hepcidin. Hepcidin, an endogenous peptide hormone, is the body’s naturally occurring regulator of iron absorption and distribution. In healthy individuals, hepcidin prevents excessive iron accumulation in vital organs, such as the liver and heart, where it can cause significant damage and even result in death. We are developing LJPC-401 for the potential treatment of iron overload, which occurs as a result of diseases such as hereditary hemochromatosis (HH), beta thalassemia, sickle cell disease (SCD) and myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS).
HH is a disease characterized by a genetic deficiency in hepcidin. HH is the most common genetic disease in Caucasians and causes liver cirrhosis, liver cancer, heart disease and/or failure, diabetes, arthritis and joint pain. The current standard treatment for HH is a blood removal procedure known as phlebotomy. Each phlebotomy procedure, which is usually conducted at a hospital, medical office or blood center, typically involves the removal of approximately a pint of blood. The required frequency of procedures varies by patient but often ranges from one to two times per week for an initial period after diagnosis and once every one to three months for life. Since most of the body’s iron is stored in red blood cells, chronic removal of blood can effectively lower iron levels if a phlebotomy regimen is adhered to. However, phlebotomy procedures may cause and may be associated with pain, bruising and scarring at the venous puncture site, fatigue and dizziness during and following the procedure and disruption of daily activities. Furthermore, phlebotomy is not appropriate in patients with poor venous access, anemia or heart disease.
Beta thalassemia, SCD and MDS are genetic diseases of the blood that can cause life-threatening anemia and usually require frequent and life-long blood transfusions. These blood transfusions cause excessive iron accumulation in the body, which is toxic to vital organs, such as the liver and heart. In addition, the underlying anemia causes excessive iron accumulation independent of blood transfusions.
In 2015, the EMA Committee for Orphan Medicinal Products (COMP) designated LJPC-401 as an orphan medicinal product for the treatment of beta thalassemia intermedia and major. In 2016, the EMA COMP designated LJPC-401 as an orphan medicinal product for the treatment of SCD.
In September 2016, we reported positive results from a Phase 1 study of LJPC-401 in patients at risk of iron overload suffering from HH, thalassemia and SCD. In this study, single, escalating doses of LJPC-401 were associated with a dose-dependent, statistically significant reduction in serum iron. LJPC-401 was well-tolerated with no dose-limiting toxicities. Injection-site reactions were the most commonly reported adverse event and were all mild or moderate in severity, self-limiting and fully resolved.
In September 2016, we reached agreement with the EMA on the design of a pivotal study of LJPC-401 for the treatment of beta thalassemia patients suffering from iron overload, a major unmet need in an orphan patient population. This study, which we refer to as LJ401-BT01, was initiated in December 2017. LJ401-BT01 is designed to enroll approximately 100 patients across 9 countries, including the U.S. Patients will be randomized 1:1 to receive either: (i) weekly subcutaneous injections of LJPC‑401, while continuing standard-of-care chelation therapy (LJPC‑401 treatment arm); or (ii) a continuation of standard-of-care chelation therapy only (observation arm). After 6 months of treatment, patients randomized to the observation arm will cross over to receive LJPC‑401 (plus standard-of-care chelation therapy) for 6 months, while patients randomized to
2
the LJPC-401 treatment arm will continue with LJPC-401 (plus standard-of-care chelation therapy) for an additional 6 months (for a total of one year). The primary efficacy endpoint of this study is the change in iron content in the heart after 6 months, as measured by cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). If this study is successful, we would anticipate filing an MAA for LJPC-401 in Europe.
In December 2017, we announced the initiation of LJ401-HH01, a Phase 2 clinical study of LJPC‑401 in patients with HH. LJ401-HH01 is a multinational, multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, Phase 2 study that is designed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of LJPC-401 as a treatment for HH. Approximately 60 patients will be randomized to receive weekly subcutaneous injections of either LJPC‑401 or placebo for 12 weeks. The primary efficacy endpoint of the study is the change in transferrin saturation, a standard measurement of iron levels in the body and one of the two key measurements used to detect iron overload, from baseline to end of treatment. Secondary efficacy endpoints include: (i) the change in serum ferritin, the other key measurement used to detect iron overload, from baseline to end of treatment; and (ii) the requirement for and frequency of phlebotomy procedures used during the study.
Manufacturing
We do not currently own or operate manufacturing facilities for the production of commercial or clinical quantities of GIAPREZA or any of our product candidates. We rely on a small number of third-party manufacturers to produce our compounds and expect to continue to do so to meet our commercial needs and the requirements of our product candidates.
In order to meet our commercial needs, we are currently negotiating or have entered into long-term commercial supply agreements with certain third-party manufacturers. Historically, we have not had long-term agreements with any third parties and will likely continue to not have long-term arrangements as they relate to our clinical and preclinical product candidates. In all of our manufacturing and processing agreements, we require that third-party contract manufacturers produce active pharmaceutical ingredients (API) and finished products in accordance with the FDA’s current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP) and all other applicable laws and regulations. We maintain confidentiality agreements with potential and existing manufacturers in order to protect our proprietary rights related to our product and product candidates.
With regard to GIAPREZA, we have utilized third parties to manufacture the API, formulate, fill and finish, and perform the analytical release testing of the drug product. We have also completed our commercial scale-up of manufacturing process development and the validation of commercial production runs. The commercial success of GIAPREZA will depend in part on the ability of our contract manufacturers to produce cGMP-compliant API and drug product in commercial quantities and at competitive costs. Further, some of the critical materials and components used in manufacturing GIAPREZA are sourced from single suppliers. An interruption in the supply of key materials could significantly delay our sales or increase our expenses.
We plan to continue to scale up manufacturing through multiple third-party manufacturers as required, with the objectives of realizing important economies of scale and security of supply. These scale-up activities will take time to implement, require additional capital investment, process development, validation and FDA review.
Patents and Proprietary Technologies
Patents and other proprietary rights are important to our business. As part of our strategy to protect our current product and product candidates and to provide a foundation for future products, we have filed a number of patent applications and have licensed rights from third parties for other patent applications related to our product candidates.
As of December 31, 2017, we owned or had the rights to 24 issued patents (12 U.S. and 12 foreign) and 109 pending applications (36 U.S. and 73 foreign). These patents and patent applications owned or licensed by us cover GIAPREZA, LJPC-401 and other product candidates.
United States | Foreign | |||||||||||
Description | Issued | Pending | Expiration | Issued | Pending | Expiration | ||||||
GIAPREZA | 3 | 10 | 2029 - 2038 | — | 42 | 2034 - 2037 | ||||||
LJPC-401 | 2 | 8 | 2022 - 2038 | 5 | 6 | 2022 - 2037 | ||||||
Other | 7 | 18 | 2022 - 2038 | 7 | 25 | 2022 - 2037 | ||||||
3
In addition to those above, we plan to file additional patent applications that, if issued, would provide further protection for GIAPREZA and LJPC-401. Although we believe the bases for these patents and patent applications are sound, they are untested, and there is no assurance that they will not be successfully challenged. There can be no assurance that any patent previously issued will be of commercial value, that any patent applications will result in issued patents of commercial value, or that our technology will not be held to infringe patents held by others.
Material Contract
In December 2014, the Company entered into a patent license agreement with the George Washington University (GW), which the parties amended and restated on March 1, 2016. Pursuant to the amended and restated license agreement, GW exclusively licensed to the Company certain intellectual property rights relating to GIAPREZA, including the exclusive rights to certain issued patents and patent applications covering GIAPREZA. Under the license agreement, the Company is obligated to use commercially reasonable efforts to develop, commercialize, market and sell GIAPREZA. The Company has paid a one-time license initiation fee, annual maintenance fees, an amendment fee and additional payments following the achievement of certain development and regulatory milestones, including FDA approval. The Company may be obligated to make additional milestone payments of up to $1.6 million in the aggregate. Following the commencement of commercial sales of GIAPREZA, the Company is obligated to pay tiered royalties in the low- to mid-single digits on products covered by the licensed rights. The patents and patent applications covered by the GW license agreement expire between 2029 and 2038, and the obligation to pay royalties under this agreement extend through the last-to-expire patent covering GIAPREZA.
Sales and Marketing
Our U.S.-based sales and marketing team consisted of 130 employees as of February 16, 2018. The sales and marketing infrastructure includes marketing, commercial insights, commercial operations and sales training. La Jolla has deployed a hospital market access team, clinical nurse educator team and specialized hospital sales team to focus on a targeted group of hospitals and hospital systems that treat high rates of distributive shock. These teams work to educate critical care physicians, ICU nurses and hospital pharmacists, with the goal of ensuring that they understand the clinical value of, and adopt, GIAPREZA as part of their clinical pathway for the management of distributive shock.
Customers
GIAPREZA is distributed in the U.S. through a limited number of specialty distributors that subsequently resell GIAPREZA to hospitals. Due to the relatively short lead-time required to fill orders for our product, backlog is not material to our business. We have engaged a third-party logistics service provider to act as our logistics and supply-chain manager for the commercial distribution of GIAPREZA to our specialty-distributor customers.
Competition
The biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries are subject to rapid technological change. Competition from domestic and foreign biotechnology companies, large pharmaceutical and specialty pharmaceutical companies, generic drug companies and other institutions, is intense and expected to increase. A number of companies are pursuing the development of pharmaceuticals in our targeted areas. However, we are not currently aware of any other angiotensin II drug product in development. We believe that the key competitive factors that will affect the commercial success of GIAPREZA, as well as future product candidates that we may develop, are: efficacy, safety and tolerability profiles; convenience in dosing; and price and reimbursement.
Government Regulation
Pharmaceutical Regulation
Pharmaceutical products in the U.S., including GIAPREZA, are subject to extensive government regulation. Likewise, if we seek to market and distribute products abroad, they would also be subject to extensive foreign government regulation.
In the U.S., the FDA regulates pharmaceutical products. FDA regulations govern the testing, research and development activities, manufacturing, quality, storage, advertising, promotion, labeling, sale and distribution of pharmaceutical products. Accordingly, there is a rigorous process for the approval of new drugs and ongoing oversight of marketed products. We are also subject to foreign regulatory requirements governing clinical trials and drug products if products are tested or marketed abroad. The approval process outside the U.S. varies from jurisdiction to jurisdiction and the time required may be longer or shorter than that required for FDA approval.
4
See Item 1A. Risk Factors of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for a discussion of the factors that could adversely impact our development of commercial products and industry regulation.
Regulation in the U.S.
The FDA testing and approval process requires substantial time, effort and money. We cannot assure you that any of our product candidates will ever obtain approval. The FDA approval process for new drugs includes, without limitation:
• | preclinical studies; |
• | submission in the U.S. of an IND for clinical trials conducted in the U.S.; |
• | adequate and well-controlled human clinical trials to establish safety and efficacy of the product; |
• | review of an NDA in the U.S.; and |
• | inspection of the facilities used in the manufacturing of the drug to assess compliance with the FDA’s current cGMP regulations. |
The FDA monitors the progress of trials conducted in the U.S. under an IND and may, at its discretion, re-evaluate, alter, suspend or terminate testing based on the data accumulated to that point and the FDA’s benefit-risk assessment with regard to the patients enrolled in the trial. The FDA may also withdraw approval for an IND for that drug if deemed warranted. Furthermore, even after regulatory approval is obtained, under certain circumstances, such as later discovery of previously unknown problems, the FDA can withdraw approval or subject the drug to additional restrictions.
Preclinical Testing
The testing and approval process requires substantial time, effort and financial resources, and we cannot be certain that any approvals for our product candidates will be granted on a timely basis, if at all. Preclinical studies include laboratory evaluation of the product, as well as animal studies to assess the potential safety and effectiveness of the product. Most of these studies must be performed according to Good Laboratory Practices, a system of management controls for laboratories and research organizations to ensure the consistency and reliability of results.
An IND is the request for authorization from the FDA to administer an investigational new drug product to humans. The IND includes information regarding the preclinical studies, the investigational product’s chemistry and manufacturing, supporting data and literature, and the investigational plan and protocol(s). Clinical trials may begin 30 days after an IND is received, unless the FDA raises concerns or questions about the conduct of the clinical trials. If concerns or questions are raised, an IND sponsor and the FDA must resolve any outstanding concerns before clinical trials can proceed. An IND must become effective before human clinical trials begin.
Clinical Trials
Clinical trials involve the administration of the product candidate that is the subject of the trial to volunteers or patients under the supervision of a qualified principal investigator and in accordance with a clinical trial protocol, which sets forth details, such as the study objectives and the safety and effectiveness criteria to be evaluated. Each clinical trial must be reviewed and approved by an independent institutional review board (IRB) in the U.S. or ethics committee in the European Union (EU) at each institution at which the study will be conducted. The IRB or ethics committee will consider, among other things, ethical factors, safety of human subjects and the possible liability of the institution arising from the conduct of the proposed clinical trial. In addition, clinical trials in the U.S. must be performed according to good clinical practices, which are enumerated in FDA regulations and guidance documents. Some studies include oversight by an independent group of experts, known as a data safety monitoring board, which provides authorization for whether a study may move forward based on certain data from the study and may stop the clinical trial if it determines that there is an unacceptable safety risk for subjects or on other grounds.
The FDA may order the temporary, or permanent, discontinuation of a clinical trial at any time, or impose other sanctions, if it believes that the clinical trial is not being conducted in accordance with FDA requirements or presents an unacceptable risk to the clinical trial patients. An IRB may also require the clinical trial at the site to be halted, either temporarily or permanently, for failure to comply with the IRB’s requirements, or may impose other conditions.
5
Clinical trials in the U.S. typically are conducted in sequential phases: Phases 1, 2, 3 and 4. The phases may overlap. The FDA may require that we suspend clinical trials at any time on various grounds, including if the FDA makes a finding that the subjects participating in the trial are being exposed to an unacceptable health risk.
In Phase 1 clinical trials, the investigational product is usually tested on a small number of healthy volunteers to determine safety, any adverse effects, proper dosage, absorption, metabolism, distribution, excretion and other drug effects. Phase 1b clinical trials may also evaluate efficacy with respect to trial participants.
In Phase 2 clinical trials, the investigational product is usually tested on a limited number of patients (generally up to several hundred) to preliminarily evaluate the efficacy of the drug for specific, targeted indications, determine dosage tolerance and optimal dosage, and identify possible adverse effects and safety risks. Multiple Phase 2 clinical trials may be conducted to obtain information prior to beginning Phase 3 clinical studies and support proof of concept.
In Phase 3 clinical studies, the investigational product is administered to an expanded patient population to support efficacy claims, provide evidence of clinical efficacy and to further test for safety, generally at multiple clinical sites.
In Phase 4 clinical studies or other post-approval commitments, additional studies and patient follow-up are conducted to gain experience from the treatment of patients in the intended therapeutic indication. FDA may require a commitment to conduct post-approval Phase 4 studies as a condition of approval. Additional studies and follow-up may be conducted to document a clinical benefit where drugs are approved under accelerated approval regulations and based on surrogate endpoints. In clinical trials, surrogate endpoints are alternative measurements of the symptoms of a disease or condition that are substituted for measurements of observable clinical symptoms. Failure to timely conduct Phase 4 clinical trials and follow-up could result in withdrawal of approval for products approved under accelerated approval regulations.
We cannot assure you that any of our current or future clinical studies will result in approval to market our product candidates.
Clinical Data Review and Approval in the U.S.
The data from the clinical studies, together with preclinical data and other supporting information that establishes a product candidate’s safety, are submitted to the FDA in the form of an NDA, or NDA supplement (for approval of a new indication if the product candidate is already approved for another indication). Under applicable laws and FDA regulations, FDA reviews the NDA within 60 days of receipt of the NDA to determine whether the application will be accepted for filing based on FDA’s threshold determination that the NDA is sufficiently complete to permit substantive review. If deemed complete, the FDA will “file” the NDA, thereby triggering substantive review of the application. The FDA can refuse to file any NDA that it deems incomplete or not properly reviewable.
The FDA has established internal substantive review goals of ten months for most NDAs. The FDA has various programs, including Fast Track, priority review, and accelerated approval, which are intended to expedite or simplify the process for reviewing drugs, and/or provide for approval based on surrogate endpoints. Even if a drug qualifies for one or more of these programs, the FDA may later decide that the drug no longer meets the conditions for qualification or that the period for FDA review or approval will not be shortened. Generally, drugs that may be eligible for these programs are those for serious or life-threatening conditions, those with the potential to address unmet medical needs, and those that offer meaningful benefits over existing treatments. For example, Fast Track is a process designed to facilitate the development, and expedite the review, of drugs to treat serious diseases and fill an unmet medical need. The request may be made at the time of IND submission and generally no later than the pre-NDA meeting. The FDA will respond within 60 calendar days of receipt of the request. Priority review, which is requested at the time of an NDA submission, is designed to give drugs that offer major advances in treatment or provide a treatment where no adequate therapy exists, an initial review within six months as compared to a standard review time of ten months. Although Fast Track and priority review do not affect the standards for approval, the FDA will attempt to facilitate early and frequent meetings with a sponsor of a Fast Track designated drug and expedite review of the application for a drug designated for priority review. Accelerated approval provides an earlier approval of drugs to treat serious diseases, and that fill an unmet medical need based on a surrogate endpoint. The FDA, however, is not legally required to complete its review within these periods, and these performance goals may change over time.
If the FDA approves the NDA, it will issue an approval letter authorizing the commercial marketing of the drug with prescribing information for specific indications. As a condition of NDA approval, the FDA may require a risk evaluation and mitigation strategy (REMS) to help ensure that the benefits of the drug outweigh the potential risks. REMS can include medication guides, communication plans for healthcare professionals, and elements to assure safe use. Additionally, the FDA
6
will inspect the facility or the facilities at which the drug is manufactured. Moreover, product approval may require substantial post-approval testing and surveillance to monitor the drug's safety or efficacy. Once granted, product approvals may be withdrawn if compliance with regulatory standards is not maintained or problems are identified following initial marketing. In many cases, the outcome of the review, even if generally favorable, is not an actual approval, but a “complete response” that generally outlines the deficiencies in the submission, which may require substantial additional testing, or information, in order for the FDA to reconsider the application. If, or when, those deficiencies have been addressed to the FDA's satisfaction in a resubmission of the NDA, the FDA will issue an approval letter.
Satisfaction of FDA requirements or similar requirements of state, local, and foreign regulatory agencies typically take several years and requires the expenditure of substantial financial resources. Information generated in this process is susceptible to varying interpretations that could delay, limit or prevent regulatory approval at any stage of the process. Accordingly, the actual time and expense required to bring a product to market may vary substantially. We cannot assure you that we will submit applications for required authorizations to manufacture and/or market potential products or that any such application will be reviewed and approved by the appropriate regulatory authorities in a timely manner, if at all. Data obtained from clinical activities is not always conclusive and may be susceptible to varying interpretations, which could delay, limit or prevent regulatory approval. Success in early stage clinical trials does not ensure success in later stage clinical trials. Even if a product candidate receives regulatory approval, the approval may be significantly limited to specific disease states, patient populations and dosages, or have conditions placed on it that restrict the commercial applications, advertising, promotion or distribution of these products.
Once issued, the FDA may withdraw product approval if ongoing regulatory standards are not met or if safety problems occur after the product reaches the market. In addition, the FDA may require testing and surveillance programs to monitor the safety or effectiveness of approved products which have been commercialized, and the FDA has the power to prevent or limit further marketing of a product based on the results of these post-marketing programs. The FDA may also request or require additional Phase 4 clinical trials after a product is approved. The results of Phase 4 clinical trials can confirm the effectiveness of a product candidate and can provide important safety information to augment the FDA’s voluntary adverse drug reaction reporting system. Any products manufactured or distributed by us pursuant to FDA approvals would be subject to continuing regulation by the FDA, including record-keeping requirements and reporting of adverse experiences with the drug. Drug manufacturers and their subcontractors are required to register their establishments with the FDA and certain state agencies and are subject to periodic unannounced inspections by the FDA and certain state agencies for compliance with cGMP, which impose certain procedural and documentation requirements on us and our third-party manufacturers. We cannot be certain that we, or our present or future suppliers, will be able to comply with the cGMP regulations and other FDA regulatory requirements.
In addition, both before and after approval is sought, we are required to comply with a number of FDA requirements. For example, we are required to report certain adverse reactions and production problems, if any, to the FDA, and to comply with certain limitations and other requirements concerning advertising and promotion for our products. In addition, quality control and manufacturing procedures must continue to conform to cGMP after approval, and the FDA periodically inspects manufacturing facilities to assess compliance with continuing cGMP. In addition, discovery of problems, such as safety problems, may result in changes in labeling or restrictions on a product manufacturer or NDA holder, including removal of the product from the market.
The FDA closely regulates the marketing and promotion of drugs. Approval may be subject to post-marketing surveillance and other record-keeping and reporting obligations, and involve ongoing requirements. Product approvals may be withdrawn if compliance with regulatory standards is not maintained or if problems occur following initial marketing. A company can make only those claims relating to safety and efficacy that are approved by the FDA. Failure to comply with these requirements can result in adverse publicity, warning letters, corrective advertising and potential civil and criminal penalties.
Clinical Trial Conduct and Product Approval Regulation in Non-U.S. Jurisdictions
In addition to regulations in the U.S., we may be subject to a variety of foreign regulations governing clinical trials and commercial sales and distribution of our products. Our clinical trials conducted in the EU must be done under a clinical trial application (CTA), which must be supported by an Investigational Medicinal Product Dossier (IMPD), and the oversight of an ethics committee. If we market our products in foreign countries, we also will be subject to foreign regulatory requirements governing marketing approval for pharmaceutical products. The requirements governing the conduct of clinical trials, product approval, pricing and reimbursement vary widely from country to country. Whether or not FDA approval has been obtained, approval of a product by the comparable regulatory authorities of foreign countries must be obtained before manufacturing or marketing the product in those countries. The approval process varies from country to country and the time required for such
7
approvals may differ substantially from that required for FDA approval. There is no assurance that any future FDA approval of any of our product candidates will result in similar foreign approvals or vice versa. The process for clinical trials in the EU is similar, and trials are heavily scrutinized by the designated ethics committee.
Section 505(b)(2) Applications
Some of our product candidates may be eligible for submission of applications for approval under the FDA’s Section 505(b)(2) approval process, which provides an alternate path to FDA approval for new or improved formulations or new uses of previously approved products. Section 505(b)(2) was enacted as part of the Drug Price Competition and Patent Term Restoration Act of 1984, also known as the Hatch-Waxman Act, and allows approval of NDAs that rely, at least in part, on studies that were not conducted by or for the applicant and to which the applicant has not obtained a right of reference. Such studies can be provided by published literature, or the FDA can rely on previous findings of safety and efficacy for a previously approved drug. If the 505(b)(2) applicant can establish that reliance on the FDA's previous approval is scientifically appropriate, it may eliminate the need to conduct certain preclinical studies or clinical trials of the new product. Section 505(b)(2) applications may be submitted for drug products that represent a modification (e.g., a new indication or new dosage form) of an eligible approved drug. In such cases, the additional information in 505(b)(2) applications necessary to support the change from the previously approved drug is frequently provided by new studies submitted by the applicant. Because a Section 505(b)(2) application relies in part on previous studies or previous FDA findings of safety and effectiveness, preparing 505(b)(2) applications is generally less costly and time-consuming than preparing an NDA based entirely on new data and information from a full set of clinical trials. The FDA may approve the new product candidate for all, or some, of the label indications for which the referenced product has been approved, as well as for any new indication sought by the Section 505(b)(2) applicant. The law governing Section 505(b)(2) or FDA’s current policies may change in such a way as to adversely affect our applications for approval that seek to utilize the Section 505(b)(2) approach. Such changes could result in additional costs associated with additional studies or clinical trials and delays.
The FDA provides that reviews and/or approvals of applications submitted under Section 505(b)(2) will be delayed in various circumstances. For example, the holder of the NDA for the listed drug may be entitled to a period of market exclusivity during which the FDA will not approve, and may not even review, a Section 505(b)(2) application from other sponsors. If the listed drug is claimed by one or more patents that the NDA holder has listed with the FDA, the Section 505(b)(2) applicant must submit a certification with respect to each such patent. If the 505(b)(2) applicant certifies that a listed patent is invalid, unenforceable or not infringed by the product that is the subject of the Section 505(b)(2) application, it must notify the patent holder and the NDA holder. If, within 45 days of providing this notice, the NDA holder sues the 505(b)(2) applicant for patent infringement, the FDA will not approve the Section 505(b)(2) application until the earlier of a court decision favorable to the Section 505(b)(2) applicant or the expiration of 30 months. The regulations governing marketing exclusivity and patent protection are complex, and it is often unclear how they will be applied in particular circumstances.
Drug Enforcement Agency Regulation
Our research and development processes involve the controlled use of hazardous materials, including chemicals. Some of these hazardous materials are considered to be controlled substances and subject to regulation by the U.S. Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA). Controlled substances are those drugs that appear on one of five schedules promulgated and administered by the DEA under the Controlled Substances Act (CSA). The CSA governs, among other things, the distribution, recordkeeping, handling, security and disposal of controlled substances. We must be registered by the DEA in order to engage in these activities, and are subject to periodic and ongoing inspections by the DEA and similar state drug enforcement authorities to assess ongoing compliance with the DEA’s regulations. Any failure to comply with these regulations could lead to a variety of sanctions, including the revocation, or a denial of renewal, of the DEA registration, injunctions or civil or criminal penalties.
Third-Party Payor Coverage and Reimbursement
Commercial success of GIAPREZA, and any of our other product candidates that are approved or commercialized for any indication will depend, in part, on the availability of coverage and reimbursement from third-party payors at the federal, state and private levels. Government payor programs, including Medicare and Medicaid, private healthcare insurance companies and managed care plans have attempted to control costs by limiting coverage and the amount of reimbursement for particular procedures or drug treatments. The U.S. Congress and state legislatures, from time to time, propose and adopt initiatives aimed at cost containment. Ongoing federal and state government initiatives directed at lowering the total cost of healthcare will likely continue to focus on healthcare reform, the cost of prescription pharmaceuticals and on the reform of the Medicare and Medicaid payment systems.
8
Examples of how limits on drug coverage and reimbursement in the U.S. may cause reduced payments for drugs in the future include:
• | changing Medicare reimbursement methodologies; |
• | fluctuating decisions on which drugs to include in formularies; |
• | revising drug rebate calculations under the Medicaid program or requiring that new or additional rebates be provided to Medicare, Medicaid, other federal or state healthcare programs; and |
• | reforming drug importation laws. |
Some third-party payors also require pre-approval of coverage for new drug therapies before they will reimburse healthcare providers that use such therapies. While we cannot predict whether any proposed cost-containment measures will be adopted or otherwise implemented in the future, the announcement or adoption of these proposals could have a material adverse effect on our ability to obtain adequate prices for our product candidates and to operate profitably.
Reimbursement systems in international markets vary significantly by country and, within some countries, by region. Reimbursement approvals must be obtained on a country-by-country basis. In many foreign markets, including markets in which we hope to sell our products, the pricing of prescription pharmaceuticals is subject to government pricing control. In these markets, once marketing approval is received, pricing negotiations could take significant additional time. As in the U.S., the lack of satisfactory reimbursement or inadequate government pricing of any of our products would limit widespread use and lower potential product revenues.
Anti-Kickback, Fraud and Abuse and False Claims Regulation
On commercial launch of a product in the U.S., we will be subject to healthcare fraud and abuse regulation and enforcement by both the federal government and the states in which we conduct our business. Healthcare providers, physicians and third-party payors play a primary role in the recommendation and prescription of any product candidates for which we obtain marketing approval. Arrangements with third-party payors and customers may expose us to applicable fraud and abuse and other healthcare laws and regulations that may constrain the business or financial arrangements and relationships through which we market, sell and distribute our products for which we obtain marketing approval.
Regulations under applicable federal and state healthcare laws and regulations include the federal healthcare programs’ Anti-Kickback Law, which prohibits, among other things, persons from knowingly and willfully soliciting, receiving, offering or paying remuneration, directly or indirectly, in exchange for or to induce either the referral or purchase of any good or service for which payment may be made under federal healthcare programs such as the Medicare and Medicaid programs. Remuneration has been broadly defined to include anything of value, including cash, improper discounts, and free or reduced-price items and services. Many states have similar laws that apply to their state healthcare programs as well as private payors. In addition, the False Claims Act (FCA) imposes liability on persons who, among other things, present or cause to be presented false or fraudulent claims for payment by a federal healthcare program. The FCA has been used to prosecute persons submitting claims for payment that are inaccurate or fraudulent, that are for services not provided as claimed, or for services that are not medically necessary. Actions under the FCA may be brought by the Attorney General or as a qui tam action by a private individual in the name of the government. Violations of the FCA can result in significant monetary penalties and treble damages. The federal government is using the FCA, and the accompanying threat of significant liability, in its investigation and prosecution of pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies throughout the country, for example, in connection with the promotion of products for unapproved uses and other sales and marketing practices.
The risk of being found in violation of these laws is increased by the fact that many of them have not been fully interpreted by the regulatory authorities or the courts, and their provisions are open to a variety of interpretations. Moreover, recent healthcare reform legislation has strengthened many of these laws. For example, the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA), among other things, amends the intent requirement of the federal anti-kickback and criminal healthcare fraud statutes to clarify that a person or entity does not need to have actual knowledge of this statute or specific intent to violate it. In addition, PPACA provides that a claim including items or services resulting from a violation of the federal anti-kickback statute constitutes a false or fraudulent claim for purposes of the false claims statutes.
The continuing interpretation and application of these laws could have a material adverse impact on our business and our ability to compete should we commence marketing a product.
9
Federal and State Sunshine Laws
We must comply with federal “sunshine” laws that require transparency regarding financial arrangements with healthcare providers. This would include the reporting and disclosure requirements imposed by the PPACA on drug manufacturers regarding any “payment or transfer of value” made or distributed to physicians and teaching hospitals. Failure to submit required information can result in civil monetary penalties. A number of states have laws that require the implementation of commercial compliance programs, impose restrictions on drug manufacturer marketing practices, and/or require pharmaceutical companies to track and report payments, gifts and other benefits provided to physicians and other healthcare professionals and entities.
Foreign Corrupt Practices Act
We are subject to the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act of 1997 (FCPA). The FCPA and other similar anti-bribery laws in other jurisdictions, such as the U.K. Bribery Act, generally prohibit companies and their intermediaries from providing money or anything of value to officials of foreign governments, foreign political parties, or international organizations with the intent to obtain or retain business or seek a business advantage. Recently, there has been a substantial increase in anti-bribery law enforcement activity by U.S. regulators, with more frequent and aggressive investigations and enforcement proceedings by both the Department of Justice and the SEC. A determination that our operations or activities are not, or were not, in compliance with U.S. or foreign laws or regulations could result in the imposition of substantial fines, interruptions of business, loss of supplier, vendor or other third-party relationships, termination of necessary licenses and permits, and other legal or equitable sanctions. Other internal or government investigations or legal or regulatory proceedings, including lawsuits brought by private litigants, may also follow as a consequence.
Patient Privacy and Data Security
We are required to comply, as applicable, with numerous federal and state laws, including state security breach notification laws, state health information privacy laws and federal and state consumer protection laws, and to govern the collection, use and disclosure of personal information. Other countries also have, or are developing, laws governing the collection, use and transmission of personal information. In addition, most healthcare providers who may prescribe products we may sell in the future and from whom we may obtain patient health information are subject to privacy and security requirements under the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA), as amended by the Health Information Technology and Clinical Health Act (HITECH), and its implementing regulations. We are not a HIPAA covered entity, do not currently intend to become one, and we do not operate as a business associate to any covered entities. Therefore, these privacy and security requirements do not apply to us. However, we could be subject to civil and criminal penalties if we knowingly obtain individually identifiable health information from a covered entity in a manner that is not authorized or permitted by HIPAA or for aiding and abetting the violation of HIPAA. The legislative and regulatory landscape for privacy and data protection continues to evolve, and there has been an increasing amount of focus on privacy and data protection issues with the potential to affect our business, including recently enacted laws in a majority of states requiring security breach notification. These laws could create liability for us or increase our cost of doing business, and any failure to comply could result in harm to our reputation and potential fines and penalties.
In addition, state laws govern the privacy and security of health information in certain circumstances, many of which differ from each other in significant ways and may not have the same effect, thus complicating compliance efforts.
Environmental, Health and Safety Laws
Our operations and those of our third-party manufacturers are subject to complex and increasingly stringent environmental, health and safety laws and regulations. Further, in the future, we may open manufacturing facilities that would likely be subject to environmental and health and safety authorities in the relevant jurisdictions. These authorities typically administer laws which regulate, among other matters, the emission of pollutants into the air (including the workplace), the discharge of pollutants into bodies of water, the storage, use, handling and disposal of hazardous substances, the exposure of persons to hazardous substances, and the general health, safety and welfare of employees and members of the public. Violations of these laws could subject us to strict liability, fines, or liability to third parties.
10
Other Laws
We are subject to a variety of financial disclosure and securities trading regulations as a public company in the U.S., including laws relating to the oversight activities of the SEC and the regulations of The Nasdaq Capital Market, on which our shares are traded. We are also subject to various laws, regulations and recommendations relating to safe working conditions, laboratory practices and the experimental use of animals.
Employees
As of February 16, 2018, we employed 309 regular, full-time employees, 147 of whom are engaged in research and clinical development activities, and 162 of whom are in sales and marketing, finance, information technology, human resources and administration. None of our employees are covered by a collective bargaining agreement.
Company Information
La Jolla was incorporated in Delaware in 1989 and reincorporated in California in 2012. Our common stock trades on The Nasdaq Capital Market, under the symbol “LJPC.” Our principal office is located at 4550 Towne Centre Court, San Diego, CA 92121. Our telephone number is (858) 207-4264. Our website address is www.ljpc.com. No portion of our website is incorporated herein by reference.
Available Information
You are advised to read this Annual Report on Form 10-K in conjunction with other reports and documents that we file from time to time with the SEC. In particular, please read our definitive proxy statements, our Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q and any Current Reports on Form 8-K that we may file from time to time. You may obtain copies of these reports after the date of this Annual Report directly from us or from the SEC at the SEC’s Public Reference Room at 100 F Street, N.E. Washington, D.C. 20549. In addition, the SEC maintains information for electronic filers (including us) at its website at www.sec.gov. The public may obtain information regarding the operation of the Public Reference Room by calling the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330. We make our periodic and current reports available on our internet website at www.ljpc.com, free of charge, as soon as reasonably practicable after such material is electronically filed with, or furnished to, the SEC.
11
Item 1A. Risk Factors.
An investment in our common stock involves a high degree of risk. You should carefully consider the risks described below and the other information before deciding to invest in our common stock. The risks described below are not the only ones facing our Company. Additional risks not presently known to us or that we currently consider immaterial may also adversely affect our business. We have attempted to identify below the major factors that could cause differences between actual and planned or expected results, but we cannot assure you that we have identified all of those factors.
If any of the following risks actually happen, our business, financial condition and operating results could be materially adversely affected. In this case, the trading price of our common stock could decline, and you could lose all or part of your investment.
I. RISK FACTORS RELATING TO THE COMPANY AND THE INDUSTRY IN WHICH WE OPERATE
We are substantially dependent on the commercial success of GIAPREZATM (angiotensin II).
The near-term success of our business is largely dependent on our ability to successfully commercialize our recently approved product, GIAPREZATM (angiotensin II), our only commercial product. Although members of our management team have prior experience launching new products, GIAPREZA is the first product that the Company will have launched.
Even if our sales organization performs as expected, the revenue that we may receive from sales of GIAPREZA may be less than anticipated due to factors that are outside of our control. These factors that may impact revenue include:
• | the perception of physicians and other members of the healthcare community of the safety and efficacy and cost-competitiveness relative to that of competing products; |
• | our ability to maintain successful sales, marketing and educational programs for certain physicians and other healthcare providers; |
• | our ability to raise patient and physician awareness; |
• | the cost-effectiveness of our product; |
• | acceptance by institutional formulary committees; |
• | patient and physician satisfaction with our product; |
• | the size of the potential market for our product; |
• | our ability to obtain adequate reimbursement from government and third-party payors; |
• | unfavorable publicity concerning our product or similar products; |
• | the introduction, availability and acceptance of competing treatments; |
• | adverse event information relating to our product or similar classes of drugs; |
• | product liability litigation alleging injuries relating to the product or similar classes of drugs; |
• | our ability to maintain and defend our patents for GIAPREZA; |
• | our ability to have GIAPREZA manufactured at a commercial production level successfully and on a timely basis; |
• | the availability of raw materials; |
• | our ability to access third parties to manufacture and distribute our product on acceptable terms or at all; |
• | regulatory developments related to the manufacture or continued use of our product; |
• | any post-approval study requirements and the results thereof; |
• | the extent and effectiveness of sales and marketing and distribution support for our product; |
• | our competitors’ activities, including decisions as to the timing of competing product launches, generic entrants, pricing and discounting; and |
• | any other material adverse developments with respect to the potential commercialization of our product. |
12
Our business will be adversely affected if, due to these or other factors, our commercialization of GIAPREZA does not achieve the acceptance and demand necessary to sustain revenue growth. If we are unable to successfully commercialize GIAPREZA, our business and results of operations will suffer.
If we are unable to develop and maintain sales, marketing and distribution capabilities to sell and market GIAPREZA or any other products we may develop, our product sales may be hindered.
We are in the process of establishing an internal sales organization for the sale, marketing and distribution of GIAPREZA. In order to successfully commercialize any other product we may develop, we must increase our sales, marketing, distribution and other non-technical capabilities. The development of a sales organization to market GIAPREZA, or any other product we may develop, is expensive and time-consuming, and we cannot be certain that we will be able to successfully develop this capacity or that this function will execute as expected. If we are unable to establish adequate sales, marketing and distribution capabilities, we may not be able to generate product revenue and our business and results of operations will suffer.
If we fail to comply with our reporting and payment obligations under U.S. governmental pricing and contracting programs, we could be subject to additional reimbursement requirements, penalties and fines, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
The Medicare program and certain government pricing programs, including the Medicaid drug rebate program, the Public Health Services’ 340B drug pricing program, and the pricing program under the Veterans Health Care Act of 1992 impact the reimbursement we may receive from sales of GIAPREZA, or any other products that are approved for marketing. Pricing and rebate calculations vary among programs. The calculations are complex and are often subject to interpretation by manufacturers, governmental or regulatory agencies, and the courts. We are required to submit a number of different pricing calculations to government agencies on a quarterly basis. Failure to comply with our reporting and payment obligations under U.S. governmental pricing and contracting programs may result in additional payments, penalties and fines due to government agencies, which may have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
We have only limited assets and will need to raise additional capital before we can expect to become profitable.
As of December 31, 2017, we had minimal revenue sources and available cash and cash equivalents of $90.9 million. To fund future operations to the point where we are able to generate positive cash flow from the sales or out-licensing of our product and product candidates, we will need to raise significant additional capital. The amount and timing of future funding requirements will depend on many factors, including the success of our commercialization efforts for GIAPREZA, the timing and results of our ongoing development efforts, the potential expansion of our current development programs, potential new development programs and related general and administrative support. We anticipate that we will seek to fund our operations through equity, debt or royalty-based financings or other sources, such as potential collaboration agreements. We cannot provide assurance that additional financing will be available to us on favorable terms, or at all. Although we have previously been successful in obtaining financing through equity offerings, there can be no assurance that we will be able to do so in the future. If we are unable to raise additional capital to fund our clinical development, commercialization efforts, and other business activities, we could be forced to abandon one or more programs and curtail or cease our operations.
We have never generated any revenue from product sales and may never be profitable.
We have a single product approved for commercialization and have never generated any revenue from product sales. Our ability to generate revenue and achieve profitability depends on our ability, alone or with strategic collaboration partners, to successfully commercialize GIAPREZA and to complete the development of, and obtain the regulatory and marketing approvals necessary to commercialize our other product candidates in development. Our ability to generate revenue from product sales depends heavily on our success in many areas, including but not limited to:
• | successfully completing research and nonclinical and clinical development of our product candidates; |
• | obtaining regulatory and marketing approvals for product candidates for which we complete clinical trials; |
• | launching and commercializing product candidates for which we obtain regulatory and marketing approval, either directly or with a collaborator or distributor; |
• | obtaining market acceptance of our product candidates as viable treatment options; |
• | addressing any competing technological and market developments; |
• | identifying, assessing, acquiring or developing new product candidates; |
13
• | negotiating favorable terms in any collaboration, licensing or other arrangements into which we may enter; |
• | maintaining, protecting and expanding our portfolio of intellectual property rights, including patents, trade secrets and know-how; and |
• | attracting, hiring and retaining qualified personnel. |
We anticipate incurring significant costs associated with commercializing GIAPREZA and any other approved product candidate. Our expenses could increase beyond expectations if we are required by the FDA, the EMA or other regulatory agencies, domestic or foreign, to change our manufacturing processes or assays, or to perform additional clinical, nonclinical or other types of studies in addition to those that we currently anticipate. In cases such as GIAPREZA where we are successful in obtaining regulatory approvals to market our product candidates, our revenue will be dependent, in part, on the size of the markets in the territories for which we gain regulatory approval, the accepted price for the product, the ability to get reimbursement at any price, and whether we own the commercial rights for that territory. If the number of our addressable patients is not as significant as we estimate, the indication approved by regulatory authorities is narrower than we expect, or the reasonably accepted population for treatment is narrowed by competition, physician choice or treatment guidelines, we may be unable to generate significant revenue from sales of approved products.
Results from any future clinical trials we may undertake may not be sufficient to obtain regulatory approvals to market our product candidates in the U.S. or other countries on a timely basis, if at all.
Product candidates are subject to extensive government regulations related to development, clinical trials, manufacturing and commercialization. In order to sell any product that is under development, we must first receive regulatory approval. To obtain regulatory approval, we must conduct clinical trials and toxicology studies that demonstrate that our product candidates are safe and effective. The process of obtaining FDA and foreign regulatory approvals is costly, time-consuming, uncertain and subject to unanticipated delays.
The FDA, EMA and other foreign regulatory authorities have substantial discretion in the approval process and may not agree that we have demonstrated that our product candidates are safe and effective. If our product candidates are ultimately not found to be safe and effective, we would be unable to obtain regulatory approval to manufacture, market and sell them. We can provide no assurances that the FDA, EMA or other foreign regulatory authorities will approve our product candidates or, if approved, what the scope of the approved indication might be.
Clinical drug development involves a lengthy and expensive process with an uncertain outcome, and results of earlier studies may not be predictive of future study results.
Clinical testing is expensive and can take many years to complete, and its outcome is inherently uncertain. Failure can occur at any time during the clinical trial process. The results of nonclinical studies and early clinical trials of our product candidates may not be predictive of the results of later-stage clinical trials. Product candidates that have shown promising results in early-stage clinical trials may still suffer significant setbacks in subsequent clinical trials. For example, the safety or efficacy results generated to date in our clinical trials do not ensure that later clinical trials will demonstrate similar results. There is a high failure rate for drugs proceeding through clinical trials, and product candidates in later stages of clinical trials may fail to show the desired safety and efficacy, despite having progressed through nonclinical studies and initial clinical trials. A number of companies in the biopharmaceutical industry have suffered significant setbacks in advanced clinical trials due to lack of efficacy or adverse safety profiles, notwithstanding promising results in earlier studies. Moreover, nonclinical and clinical data are often susceptible to varying interpretations and analyses. We do not know whether any clinical trials we may conduct will demonstrate consistent or adequate efficacy and safety sufficient to obtain regulatory approval to market our product candidates.
Future clinical trials that we may undertake may be delayed or halted.
Any clinical trials of our product candidates that we may conduct in the future may be delayed or halted for various reasons, including:
• | we do not have sufficient financial resources; |
• | supplies of drug product are not sufficient to treat the patients in the studies; |
• | patients do not enroll in the studies at the rate we expect; |
• | the product candidates are not effective; |
• | patients experience negative side effects or other safety concerns are raised during treatment; |
14
• | the trials are not conducted in accordance with applicable clinical practices; |
• | there is political unrest at foreign clinical sites; or |
• | there are natural disasters at any of our clinical sites. |
If any future trials are delayed or halted, we may incur significant additional expenses, and our potential approval of our product candidates may be delayed, which could have a severe negative effect on our business.
We rely on third parties to conduct our preclinical and clinical trials. If these third parties do not successfully carry out their contractual duties or meet expected deadlines, we may not be able to obtain regulatory approval for or commercialize our product candidates and our business could be substantially harmed.
We have agreements with third-party contract research organizations (CROs) to monitor and manage data for our preclinical and clinical programs. We rely heavily on these parties for execution of our preclinical and clinical trials, and control only certain aspects of their activities. Nevertheless, we are responsible for ensuring that each of our studies is conducted in accordance with the applicable protocol, legal, regulatory and scientific standards, and our reliance on CROs does not relieve us of our regulatory responsibilities. We and our CROs are required to comply with current good clinical practices (cGCPs), which are regulations and guidelines enforced by the FDA, EMA and other foreign regulatory authorities for products in clinical development. Regulatory authorities enforce these cGCPs through periodic inspections of trial sponsors, principal investigators and trial sites. If we or any of these CROs fail to comply with applicable cGCP regulations, the clinical data generated in our clinical trials may be deemed unreliable and the FDA, EMA and other foreign regulatory authorities may require us to perform additional clinical trials before approving our marketing applications. We cannot assure you that, on inspection, such regulatory authorities will determine that any of our clinical trials comply with the cGCP regulations. In addition, our clinical trials must be conducted with product produced under cGMP regulations and will require a large number of test subjects. Our or our CROs’ failure to comply with these regulations may require us to repeat clinical trials, which would delay the regulatory approval process.
If any of our relationships with these third-party CROs terminate, we may not be able to enter into arrangements with alternative CROs or to do so on commercially reasonable terms. In addition, our CROs are not our employees, and except for remedies available to us under our agreements with such CROs, we cannot control whether or not they devote sufficient time and resources to our ongoing preclinical and clinical programs. If CROs do not successfully carry out their contractual duties or obligations or meet expected deadlines, if they need to be replaced or if the quality or accuracy of the clinical data they obtain is compromised due to the failure to adhere to our clinical protocols, regulatory requirements or for other reasons, our clinical trials may be extended, delayed or terminated and we may not be able to obtain regulatory approval for or successfully commercialize our product candidates. As a result, we may incur significant additional expenses, and our potential approval of our product candidates may be delayed, which could have a severe negative effect on our business.
If the third-party manufacturers on which we rely fail to produce the materials that we require on a timely basis, or to comply with stringent regulations applicable to pharmaceutical drug manufacturers, we may face commercial supply shortages, delays in the trials, regulatory submissions, required approvals or commercialization of our product and product candidates.
We do not manufacture GIAPREZA or any of our product candidates, nor do we plan to develop any capacity to do so. Instead, we contract with third-party manufacturers to manufacture and supply GIAPREZA and all of our product candidates. The manufacture of pharmaceutical products requires significant expertise and capital investment, including the development of advanced manufacturing techniques and process controls. Manufacturers of pharmaceutical products often encounter difficulties in production, which include difficulties with production costs and yields, quality control and assurance and shortages of qualified personnel, as well as compliance with strictly enforced federal, state and foreign regulations. The third-party manufacturers we contract with may not perform as agreed or may terminate their agreements with us. Although we believe that we could identify and qualify alternate suppliers if necessary, the steps needed for a pharmaceutical manufacturer to implement a validated manufacturing process can be time-consuming and costly. As a result, and because we currently have only a single manufacturer for GIAPREZA, termination of this manufacturing relationship or a disruption in their manufacturing facilities could adversely affect the available commercial supply of GIAPREZA. Further, certain critical materials used in manufacturing GIAPREZA have historically been sourced from single suppliers. An interruption in the supply of a key material could also significantly impact our ability to meet the demand for GIAPREZA.
Any facilities in which our product or product candidates are manufactured or tested for their ability to meet required specifications must be inspected by and approved by the FDA and/or the EMA before a commercial product can be
15
manufactured. Failure of such a facility to be approved could delay the commercial sale or approval of one or more of our products or product candidates.
Any of these factors could cause us to delay or suspend any future commercial sales, clinical trials, regulatory submissions, required approvals or commercialization of one or more of our products or product candidates, entail higher costs and result in our being unable to effectively commercialize products.
Our success in developing and marketing our product and product candidates depends significantly on our ability to obtain patent protection and operate without infringing on the rights of others.
We depend on patents and other intellectual property to prevent others from improperly benefiting from products or technologies that we sell, develop or acquire. Our patents and patent applications cover various technologies, product and product candidates. The patent position of biotechnology firms like ours is highly uncertain and involves complex legal and factual questions, and no consistent policy has emerged regarding the breadth of claims covered in biotechnology patents or the protection afforded by these patents. Additionally, recent U.S. Supreme Court and Federal Circuit opinions further limit the scope of patentable inventions in the life sciences space and have added increased uncertainty around the validity of certain issued patents and the successful prosecution of certain pending patent applications. We intend to continue to file patent applications as we believe is appropriate to obtain patents covering both our products and processes. There can be no assurance, however, that any additional patents will be issued, that the scope of any patent that has issued or may issue will be sufficient to protect our technology, or that any current or future issued patent will be held not invalid if subsequently challenged. There is a substantial backlog of biotechnology patent applications at the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO), which may delay the review and issuance of any patents.
Others, including our competitors, could have patents or patent applications pending that relate to compounds or processes that overlap or compete with our intellectual property or which may affect our freedom to operate.
There can be no assurance that third-party patents will not ultimately be found to impact the sales of GIAPREZA or the advancement of our product candidates. While we intend to challenge the issuance and validity of this patent, we may not be successful. If the USPTO or any foreign counterpart issues or has issued any other patents containing competitive or conflicting claims, and if these claims are valid, the protection provided by our existing patents or any future patents that may be issued could be significantly reduced, and our ability to prevent competitors from developing products or technologies identical or similar to ours could be negatively affected. In addition, there can be no guarantee that we would be able to obtain licenses to these patents on commercially reasonable terms, if at all, or that we would be able to develop or obtain alternative technology. Our failure to obtain a license to a technology or process that may be required to develop or commercialize one or more of our product candidates may have a material adverse effect on our business.
We do not have complete patent protection for GIAPREZA or our other product candidates, as the active pharmaceutical ingredients in GIAPREZA and our other product candidates are known compounds that are not themselves covered by composition of matter patents, and thus may only be protected by formulation or method-of-use patents (to the extent that such patents are granted and are enforceable) and/or regulatory exclusivity (to the extent available). Therefore, it is possible that a competitor could develop the same or similar technology if we fail to obtain protection of this type. We may have to incur significant expense and management time in defending or enforcing our patents. If we cannot obtain and maintain effective patent rights and/or regulatory exclusivity for our product candidates, we may not be able to compete effectively and our business and results of operations would be harmed.
Patent policy and rule changes could increase the uncertainties and costs surrounding the prosecution of our patent applications and the enforcement or defense of our issued patents.
Changes in either the patent laws or interpretation of the patent laws in the U.S. and other countries may diminish the value of our patents or narrow the scope of our patent protection. The laws of foreign countries may not protect our rights to the same extent as the laws of the U.S. Publications of discoveries in the scientific literature often lag behind the actual discoveries, and patent applications in the U.S. and other jurisdictions are typically not published until 18 months after filing, or in some cases not at all. We therefore cannot be certain that we or our licensors were the first to make the inventions claimed in our owned and licensed patents or pending applications, or that we or our licensor were the first to file for patent protection of such inventions.
Assuming the other requirements for patentability are met, in the U.S. prior to March 15, 2013, the first to make the claimed invention is entitled to the patent, while outside the U.S., the first to file a patent application is entitled to the patent. After March 15, 2013, under the Leahy-Smith America Invents Act (Leahy-Smith Act), enacted on September 16, 2011, the
16
U.S. has moved to a first-to-file system. The Leahy-Smith Act also includes a number of significant changes that affect the way patent applications will be prosecuted and may also affect patent litigation. The effects of these changes are currently unclear as the USPTO must still implement various regulations, the courts have yet to address any of these provisions and the applicability of the act and new regulations on specific patents discussed herein have not been determined and would need to be reviewed. In general, the Leahy-Smith Act and its implementation could increase the uncertainties and costs surrounding the prosecution of our patent applications and the enforcement or defense of our issued patents, all of which could have a material adverse effect on our business and financial condition.
If our product candidates infringe the rights of others, we could be subject to expensive litigation or be required to obtain licenses from others to develop or market them.
Our competitors or others may have patent rights that they choose to assert against us or our licensees, suppliers, customers or potential collaborators. Moreover, we may not know about patents or patent applications that our products would infringe. For example, because patent applications do not publish for at least 18 months, if at all, and can take many years to issue, there may be currently pending applications unknown to us that may later result in issued patents that our product candidates would infringe. In addition, if third parties file patent applications or obtain patents claiming technology also claimed by us or our licensors in issued patents or pending applications, we may have to participate in interference proceedings in the USPTO to determine priority of invention. If third parties file oppositions in foreign countries, we may also have to participate in opposition proceedings in foreign tribunals to defend the patentability of our foreign patent applications.
If a third party claims that we infringe its proprietary rights, any of the following may occur:
• | we may become involved in time-consuming and expensive litigation, even if the claim is without merit; |
• | we may become liable for substantial damages for past infringement if a court decides that our technology infringes a competitor’s patent; |
• | a court may prohibit us from selling or licensing our product without a license from the patent holder, which may not be available on commercially acceptable terms, if at all, or which may require us to pay substantial royalties or grant cross licenses to our patents; and |
• | we may have to redesign our product candidates or technology so that they do not infringe patent rights of others, which may not be possible or commercially feasible. |
If any of these events occur, our business and prospects will suffer and the market price of our common stock will likely decline substantially.
The patent protection and patent prosecution for some of our product and product candidates is dependent on third parties.
While we normally seek and gain the right to fully prosecute the patents relating to our product and product candidates, there may be times when patents relating to our product candidates are controlled by our licensors. If any of our future licensing partners fail to appropriately prosecute and maintain patent protection for patents covering any of our product candidates, our ability to develop and commercialize those product candidates may be materially adversely affected and we may not be able to prevent competitors from making, using, selling and importing competing products. In addition, even where we now have the right to control patent prosecution of patents and patent applications we have licensed from third parties, we may still be adversely affected or prejudiced by actions or inactions of our licensors and their counsel that took place prior to us assuming control over patent prosecution.
In addition to patent protection, we will need to successfully preserve our trade secrets. If we are unable to maintain effective proprietary rights for our product candidates or any future product candidates, we may not be able to compete effectively in our markets.
In addition to the protection afforded by patents, we rely on trade secret protection and confidentiality agreements to protect proprietary know-how that is not patentable or that we elect not to patent, processes for which patents are difficult to enforce and any other elements of our product candidate discovery and development processes that involve information or technology that is not covered by patents. However, trade secrets can be difficult to protect. We seek to protect our proprietary technology and processes, in part, by entering into confidentiality agreements with our employees, consultants, scientific advisors, and contractors. We also seek to preserve the integrity and confidentiality of our data and trade secrets by maintaining physical security of our premises and physical and electronic security of our information technology systems. While we have confidence in these individuals, organizations and systems, agreements or security measures may be breached, and we may not
17
have adequate remedies for any breach. In addition, our trade secrets may otherwise become known or be independently discovered by competitors.
Although we expect all of our employees and consultants to assign their inventions to us, and all of our employees, consultants, advisors, and any third parties who have access to our proprietary know-how, information, or technology to enter into confidentiality agreements, we cannot provide any assurances that all such agreements have been duly executed, that our trade secrets and other confidential proprietary information will not be disclosed or that competitors will not otherwise gain access to our trade secrets or independently develop substantially equivalent information and techniques. Misappropriation or unauthorized disclosure of our trade secrets could impair our competitive position and may have a material adverse effect on our business. Additionally, if the steps taken to maintain our trade secrets are deemed inadequate, we may have insufficient recourse against third parties for misappropriating our trade secrets.
If we fail to obtain orphan or other regulatory exclusivity for our product and product candidates, we may face greater commercial competition and our revenue will be reduced.
Regulatory authorities in some jurisdictions, including the U.S. and EU may designate drugs for relatively small patient populations as orphan drugs. Our business strategy for certain of our product and product candidates includes seeking orphan drug designation. Under the Orphan Drug Act, the FDA may designate a product as an orphan drug if it is intended to treat a rare disease or condition, defined as a patient population of fewer than 200,000 in the U.S., or a patient population greater than 200,000 in the U.S. where there is no reasonable expectation that the cost of developing the drug will be recovered from sales in the U.S. In the EU, the EMA’s Committee for Orphan Medicinal Products grants orphan drug designation to promote the development of products that are intended for the diagnosis, prevention, or treatment of a life-threatening or chronically debilitating condition affecting not more than 5 in 10,000 persons in the EU. If orphan drug status is granted, we may be eligible for a period of commercial exclusivity, which would afford us additional protection from generic competition, beyond that protection that may be afforded by patents. Even if a particular disease has a small patient population that we believe may be eligible for orphan status, it is possible that the FDA or EMA may not grant orphan status. If we do not obtain orphan drug exclusivity for our drug products and biologic products, particularly for any products that do not have broad patent protection, our competitors may then sell the same drug to treat the same condition sooner than if we had obtained orphan drug exclusivity and our revenue could be reduced.
Because a number of companies compete with us, many of which have greater resources than we do, and because we face rapid changes in technology in our industry, we cannot be certain that our products will be accepted in the marketplace or capture market share.
Competition from domestic and foreign biotechnology companies, large pharmaceutical companies and other institutions is intense and is expected to increase. A number of companies and institutions are pursuing the development of pharmaceuticals in our targeted areas. Many of these companies are very large and have financial, technical, sales and distribution and other resources substantially greater than ours. The greater resources of these competitors could enable them to develop or market competing products more quickly or effectively, making it extremely difficult for us to develop a share of the market for our products. These competitors also include companies that are conducting clinical trials and preclinical studies in the field of cancer therapeutics. Our competitors may develop or obtain regulatory approval for products more rapidly than we do. Also, the biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries are subject to rapid changes in technology. Our competitors may develop and market technologies and products that are more effective or less costly than those we are developing or that would render our technology and proposed products obsolete or noncompetitive.
Our product and product candidates may cause undesirable side effects or have other properties that could delay or prevent their market acceptance or regulatory approval, limit the commercial profile of an approved label, or result in significant negative consequences following marketing approval, if any.
Undesirable side effects caused by our product or product candidates could cause us or regulatory authorities to interrupt, delay, or halt clinical trials and commercial sales and could result in a more restrictive label or the delay or denial of regulatory approval by the FDA or other comparable foreign authorities. Results of our studies could reveal a high and unacceptable severity and prevalence of undesirable side effects. In such an event, our studies could be suspended or terminated, and the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities could order us to cease further development of or deny or withdraw approval of our product or product candidates for any or all targeted indications.
The drug-related side effects could affect commercial sales, patient recruitment, the ability of enrolled patients to complete the study, or result in potential product liability claims. We carry product liability insurance in the amount of $10.0 million in the aggregate. We believe our product liability insurance coverage is sufficient in light of our clinical programs;
18
however, we may not be able to maintain insurance coverage at a reasonable cost or in sufficient amounts to protect us against losses due to liability. A successful product liability claim or series of claims brought against us could cause our stock price to decline and, if judgments exceed our insurance coverage, could adversely affect our results of operations and business. In addition, regardless of merit or eventual outcome, product liability claims may result in impairment of our business reputation, withdrawal of clinical trial participants, costs due to related litigation, distraction of management’s attention from our primary business, initiation of investigations by regulators, substantial monetary awards to patients or other claimants, the inability to commercialize our product candidates and decreased demand for our product candidates, if approved for commercial sale.
Additionally, if one or more of our product candidates receives marketing approval, and we or others later identify undesirable side effects caused by such products, a number of potentially significant negative consequences could result, including but not limited to:
• | regulatory authorities may withdraw approvals of such product; |
• | regulatory authorities may require additional warnings on the label; |
• | we may be required to create a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) plan, which could include a medication guide outlining the risks of such side effects for distribution to patients, a communication plan for healthcare providers, and/or other elements to assure safe use; |
• | we could be sued and held liable for harm caused to patients; and |
• | our reputation may suffer. |
Any of these events could prevent us from achieving or maintaining market acceptance of the particular product and could significantly harm our business, results of operations, and prospects.
Our product and product candidates are subject to regulatory scrutiny.
As an approved product, GIAPREZA is subject to ongoing regulatory requirements for manufacturing, labeling, packaging, storage, advertising, promotion, sampling, record-keeping, pharmacovigilance, conduct of post-marketing studies and submission of safety, efficacy and other post-market information, including both federal and state requirements in the U.S. and requirements of comparable foreign regulatory authorities.
Manufacturers and manufacturers’ facilities are required to comply with extensive FDA, and comparable foreign regulatory authorities, requirements, including ensuring that quality control and manufacturing procedures conform to cGMP regulations. As such, we and our contract manufacturers will be subject to continual review and inspections to assess compliance with cGMP and adherence to commitments made in any NDA, biologic license application (BLA), or market authorization application (MAA). Accordingly, we and others with whom we work must continue to expend time, money, and effort in all areas of regulatory compliance, including manufacturing, production and quality control.
Any regulatory approvals that we have received or may receive for our product and product candidates are and may be subject to limitations on the approved indicated uses for which the product may be marketed or to the conditions of approval, or contain requirements for potentially costly post-marketing testing, including Phase 4 clinical trials, and surveillance to monitor the safety and efficacy of the product candidate. We will be required to report certain adverse reactions and production problems, if any, to the FDA and comparable foreign regulatory authorities. Any new legislation addressing drug safety issues could result in delays in product development or commercialization, or increased costs to assure compliance. We will have to comply with requirements concerning advertising and promotion for our products. Promotional communications with respect to prescription drugs are subject to a variety of legal and regulatory restrictions and must be consistent with the information in the product’s approved label. As such, we may not promote our products for indications or uses for which they do not have approval. The holder of an approved NDA, BLA, or MAA must submit new or supplemental applications and obtain approval for certain changes to the approved product, product labeling or manufacturing process. We could also be asked to conduct post-marketing clinical trials to verify the safety and efficacy of our products in general or in specific patient subsets. If original marketing approval were obtained via the accelerated approval pathway, we could be required to conduct a successful post-marketing clinical trial to confirm clinical benefit for our products. An unsuccessful post-marketing study or failure to complete such a study could result in the withdrawal of marketing approval.
If a regulatory agency discovers previously unknown problems with a product, such as adverse events of unanticipated severity or frequency, or problems with the facility where the product is manufactured, or disagrees with the promotion, marketing or labeling of a product, such regulatory agency may impose restrictions on that product or us, including requiring withdrawal of the product from the market. If we fail to comply with applicable regulatory requirements, a regulatory agency or enforcement authority may, among other things:
19
• | issue warning letters; |
• | impose civil or criminal penalties; |
• | suspend or withdraw regulatory approval; |
• | suspend any of our ongoing clinical trials; |
• | refuse to approve pending applications or supplements to approved applications submitted by us; |
• | impose restrictions on our operations, including closing our contract manufacturers’ facilities; or |
• | seize or detain products, or require a product recall. |
Any government investigation of alleged violations of law could require us to expend significant time and resources in response, and could generate negative publicity. Any failure to comply with ongoing regulatory requirements may significantly and adversely affect our ability to commercialize and generate revenue from our products. If regulatory sanctions are applied or if regulatory approval is withdrawn, the value of our Company and our operating results will be adversely affected.
We may not be successful in our efforts to identify, license, discover, develop, or commercialize additional product candidates.
Although a substantial amount of our effort will focus on the continued clinical testing, potential approval, and commercialization of our existing product candidates, the success of our business also depends on our ability to identify, license, discover, develop or commercialize additional product candidates. Research programs to identify new product candidates require substantial technical, financial and human resources. We may focus our efforts and resources on potential programs or product candidates that ultimately prove to be unsuccessful. Our research programs or licensing efforts may fail to yield additional product candidates for clinical development and commercialization for a number of reasons, including but not limited to the following:
• | our research or business development methodology or search criteria and process may be unsuccessful in identifying potential product candidates; |
• | we may not be able or willing to assemble sufficient resources to acquire or discover additional product candidates; |
• | our product candidates may not succeed in preclinical or clinical testing; |
• | our potential product candidates may be shown to have harmful side effects or may have other characteristics that may make the products unmarketable or unlikely to receive marketing approval; |
• | competitors may develop alternatives that render our product candidates obsolete or less attractive; |
• | product candidates we develop may be covered by third parties’ patents or other exclusive rights; |
• | the market for a product candidate may change during our program so that such a product may become unreasonable to continue to develop; |
• | a product candidate may not be capable of being produced in commercial quantities at an acceptable cost, or at all; and |
• | a product candidate may not be accepted as safe and effective by patients, the medical community or third-party payors. |
If any of these events occur, we may be forced to abandon our development efforts for a program or programs, or we may not be able to identify, license, discover, develop or commercialize additional product candidates, which would have a material adverse effect on our business and could potentially cause us to cease operations.
If the market opportunities for our products are smaller than we believe, our revenue may be adversely affected, and our business may suffer.
Our estimates of the potential market opportunity for each of our products include several key assumptions based on our industry knowledge, industry publications, third-party research reports and other surveys. For example, GIAPREZA was approved for use in adult patients with septic or other distributive shock. However, determining the approximate number of hypotension patients in a given market requires numerous estimates and assumptions. While we believe that our internal assumptions are reasonable, no independent source has verified such assumptions. If any of these assumptions proves to be inaccurate, then the actual market for our product candidates could be smaller than our estimates of our potential market opportunity. If the actual market for our products is smaller than we estimate, our product revenue may be limited and it may be more difficult for us to achieve or maintain profitability.
20
We are subject to federal and state healthcare fraud and abuse laws, false claims laws and health information privacy and security laws. If we are unable to comply, or have not fully complied, with such laws, we could face substantial penalties.
Our operations are subject to various federal and state fraud and abuse laws, including, without limitation, the federal Anti-Kickback Statute, the federal FCA and physician sunshine laws and regulations. These laws impact, among other things, our sales, marketing and education programs. In addition, we are subject to patient privacy regulation by both the federal government and the states in which we conduct our business. The laws that affect our ability to operate include:
• | the federal Anti-Kickback Statute, which prohibits, among other things, persons from knowingly and willfully soliciting, receiving, offering or paying remuneration, directly or indirectly, to induce, or in return for, the purchase or recommendation of an item or service reimbursable under a federal healthcare program, such as the Medicare and Medicaid programs; |
• | federal civil and criminal false claims laws and civil monetary penalty laws, which prohibit, among other things, individuals or entities from knowingly presenting, or causing to be presented, claims for payment from Medicare, Medicaid or other third-party payors that are false or fraudulent; |
• | HIPAA, which created new federal criminal statutes that prohibit executing a scheme to defraud any healthcare benefit program and making false statements relating to healthcare matters; |
• | HIPAA, as amended by the federal Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act and its implementing regulations, which imposes certain requirements relating to the privacy, security and transmission of individually identifiable health information; |
• | the federal physician sunshine requirements under the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act and the Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act of 2010 (Health Care Reform Laws) require manufacturers of drugs, devices, biologics, and medical supplies to report annually to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services information related to payments and other transfers of value to physicians, other healthcare providers, and teaching hospitals, and ownership and investment interests held by physicians and other healthcare providers and their immediate family members and applicable group purchasing organizations; and |
• | state law equivalents of each of the above federal laws, such as anti-kickback and false claims laws that may apply to items or services reimbursed by any third-party payor, including commercial insurers; state laws to comply with the pharmaceutical industry’s voluntary compliance guidelines and the relevant compliance guidance promulgated by the federal government, or otherwise restrict payments that may be made to healthcare providers and other potential referral sources; state laws that require drug manufacturers to report information related to payments and other transfers of value to physicians and other healthcare providers or marketing expenditures; and state laws governing the privacy and security of health information in certain circumstances, many of which differ from each other in significant ways and may not have the same effect, thus complicating compliance efforts. |
Because of the breadth of these laws and the narrowness of the statutory exceptions and safe harbors available, our business activities could be subject to challenge under one or more of such laws. In addition, recent healthcare reform legislation has strengthened these laws. For example, the Health Care Reform Laws, among other things, amends the intent requirement of the federal anti-kickback and criminal healthcare fraud statutes. A person or entity no longer needs to have actual knowledge of this statute or specific intent to violate it. Moreover, the Health Care Reform Laws provides that the government may assert that a claim including items or services resulting from a violation of the federal anti-kickback statute constitutes a false or fraudulent claim for purposes of the False Claims Act.
If our operations are found to be in violation of any of the laws described above or any other governmental regulations that apply to us, we may be subject to penalties, including civil and criminal penalties, damages, fines, exclusion from participation in government healthcare programs, such as Medicare and Medicaid, imprisonment and the curtailment or restructuring of our operations, any of which could adversely affect our ability to operate our business and our results of operations.
21
Current and future legislation may increase the difficulty and cost needed to obtain marketing approval, and the subsequent commercialization, of our product candidates and affect the prices we may obtain.
In the U.S. and some foreign jurisdictions, there have been a number of legislative and regulatory changes and proposed changes regarding the healthcare system that could prevent or delay marketing approval of our product candidates, restrict or regulate post-approval activities and affect our ability to profitably sell any product candidates for which we obtain marketing approval.
For example, in 2010, President Obama signed into law the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, as amended by the Health Care and Education Affordability Reconciliation Act, (collectively, the PPACA). Among the provisions of the PPACA of importance to our potential product candidates are the following:
• | an annual, nondeductible fee on any entity that manufactures or imports specified branded prescription drugs and biologic agents; |
• | an increase in the statutory minimum rebates a manufacturer must pay under the Medicaid Drug Rebate Program; |
• | expansion of healthcare fraud and abuse laws, including the False Claims Act and the Anti-Kickback Statute, new government investigative powers, and enhanced penalties for noncompliance; |
• | a new Medicare Part D coverage gap discount program, in which manufacturers must agree to offer 50% point-of-sale discounts off negotiated prices; |
• | extension of manufacturers’ Medicaid rebate liability; |
• | expansion of eligibility criteria for Medicaid programs; |
• | new requirements to report financial arrangements with physicians and teaching hospitals; |
• | a new requirement to annually report drug samples that manufacturers and distributors provide to physicians; and |
• | a new Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute to oversee, identify priorities in, and conduct comparative clinical effectiveness research, along with funding for such research. |
In addition, other legislative changes have been proposed and adopted since the PPACA was enacted. These changes included aggregate reductions of Medicare payments to providers of up to 2% per fiscal year. Additionally, in January 2013, President Obama signed into law the American Taxpayer Relief Act of 2012, which, among other things, reduced Medicare payments to several providers, and increased the statute of limitations period for the government to recover overpayments to providers from three to five years. Further, while the healthcare reform agenda and policies of the new Trump administration are not fully known, it is possible that additional regulatory changes, as well as the repeal (in whole or in part) of the PPACA, could negatively affect insurance coverage and drug prices. These new laws may result in additional reductions in Medicare and other healthcare funding.
We expect that the PPACA, as well as other healthcare reform measures that may be adopted in the future, may result in more rigorous coverage criteria and additional downward pressure on the price that we receive for any approved product. Any reduction in reimbursement from Medicare or other government programs may result in a similar reduction in payments from private payers. The implementation of cost containment measures or other healthcare reforms may prevent us from being able to generate revenue, attain profitability, or commercialize our products.
Legislative and regulatory proposals have been made to expand post-approval requirements and restrict sales and promotional activities for pharmaceutical products. Additionally, legislation has been introduced to repeal the PPACA. We cannot be sure whether additional legislative changes will be enacted, or whether the FDA regulations, guidance or interpretations will be changed, or what the impact of such changes on the marketing approvals of our product candidates, if any, may be. In addition, increased scrutiny by the U.S. Congress of the FDA’s approval process may significantly delay or prevent marketing approval, as well as subject us to more stringent product labeling and post-marketing testing and other requirements.
Governments outside the U.S. tend to impose strict price controls, which may adversely affect our revenues, if any.
In some countries, particularly the countries of the European Union, the pricing of prescription pharmaceuticals is subject to governmental control. In these countries, pricing negotiations with governmental authorities can take considerable time after the receipt of marketing approval for a product. To obtain reimbursement or pricing approval in some countries, we may be required to conduct a clinical trial that compares the cost-effectiveness of our product candidate to other available
22
therapies. If reimbursement of our products is unavailable or limited in scope or amount, or if pricing is set at unsatisfactory levels, our business could be harmed, possibly materially.
We rely on certain key employees, and the loss of their service could negatively impact our future success.
We have only a small number of employees, and we rely on the services of certain key employees, including George F. Tidmarsh, M.D. Ph.D., who serves as our President and Chief Executive Officer. The loss of the services of Dr. Tidmarsh or other key employees could negatively affect our ability to execute on our business plan and development activities and could cause a decline in our stock price.
II. RISK FACTORS RELATED SPECIFICALLY TO OUR STOCK
As of December 31, 2017, we had approximately 22.2 million shares of common stock outstanding and currently may be required to issue up to a total of approximately 13.6 million additional shares of common stock upon conversion of existing convertible preferred stock and upon exercise of outstanding stock option grants and warrants. Such an issuance would be significantly dilutive to our existing common shareholders. You will experience further dilution if we issue additional equity securities in future fundraising transactions.
As of December 31, 2017, there were approximately 3,906 shares of Series C-12 Convertible Preferred Stock and approximately 2,737 shares of Series F Convertible Preferred Stock issued and outstanding. In light of the conversion rate of our preferred stock (approximately 1,724 shares of common stock are issuable upon the conversion of one share of Series C-12 Convertible Preferred Stock, and approximately 286 shares of common stock are issuable upon the conversion of one share of Series F Convertible Preferred Stock), the presence of such a large number of convertible preferred shares may dilute the ownership of our existing shareholders and provide the preferred investors with a sizeable interest in the Company.
Assuming the conversion of all preferred stock into common stock at the current conversion rates, and the exercise of all outstanding options and warrants, we would have approximately 35.8 million shares of common stock issued and outstanding following any such conversion and exercise, although the issuance of the common stock upon the conversion of our preferred stock is limited by a 9.999% beneficial ownership cap for each preferred shareholder, which such cap may be amended or waived by each such holder with no less than 61 days’ notice to the Company. With approximately 22.2 million shares of common stock issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2017, the issuance of this number of shares of common stock underlying the convertible preferred stock and outstanding stock options and warrants would represent approximately 38% dilution to our existing shareholders.
In addition, we may choose to raise additional capital due to market conditions or strategic considerations, even if we believe we have sufficient funds for our current or future operating plans. To the extent that additional capital is raised through the sale of equity or convertible debt securities, the issuance of these securities could result in further dilution to our shareholders or result in downward pressure on the price of our common stock.
The price of our common stock has been, and will be, volatile and may decline.
Our stock has historically experienced significant price and volume volatility and could continue to be volatile. Market prices for securities of biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies, including ours, have historically been highly volatile, and the market has from time to time experienced significant price and volume fluctuations that are unrelated to the operating performance of particular companies. The following factors, among others, can have a significant effect on the market price of our securities:
• | significant conversions of preferred stock into common stock and sales of those shares of common stock; |
• | results from our preclinical studies and clinical trials; |
• | limited financial resources; |
• | announcements regarding financings, mergers or other strategic transactions; |
• | future sales of significant amounts of our capital stock by us or our shareholders; |
• | developments in patent or other proprietary rights; |
• | developments concerning potential agreements with collaborators; and |
23
• | general market conditions and comments by securities analysts. |
The realization of any of the risks described in these “Risk Factors” could have a negative effect on the market price of our common stock. In addition, class action litigation is sometimes instituted against companies whose securities have experienced periods of volatility in market price. Any such litigation brought against us could result in substantial costs and a diversion of management’s attention and resources, which could hurt our business, operating results and financial condition.
Because we do not expect to pay dividends on our common stock in the foreseeable future, you must rely on stock appreciation for any return on your investment.
We have paid no cash dividends on our common stock to date, and we currently intend to retain our future earnings, if any, to fund the development and growth of our business. As a result, we do not expect to pay any cash dividends on our common stock in the foreseeable future, and payment of cash dividends, if any, will also depend on our financial condition, results of operations, capital requirements and other factors and will be at the discretion of our board of directors. Furthermore, we may in the future become subject to contractual restrictions on, or prohibitions against, the payment of dividends. Accordingly, the success of your investment in our common stock will likely depend entirely upon any future appreciation. There is no guarantee that our common stock will appreciate in value or even maintain the price at which you purchased your shares, and you may not realize a return on your investment in our common stock.
Item 1B. Unresolved Staff Comments.
None.
Item 2. Properties.
On December 29, 2016, the Company entered into an agreement with BMR-Axiom LP to lease 83,008 square feet of office and laboratory space as the Company’s new corporate headquarters located at 4550 Towne Centre Court, San Diego, California (the Lease) for a period of ten years commencing on October 30, 2017. The Lease provides an option to extend the Lease for an additional 5 years at the end of the initial term. The annual rent is subject to escalation during the term. In addition to rent, the Lease requires the Company to pay certain taxes, insurance, and operating costs relating to the leased premises. The Lease contains customary default provisions, representations, warranties and covenants. The Company also leases a total of 3,713 square feet of office space with a lease term through March 2018.
Item 3. Legal Proceedings.
We are not currently a party to any material legal proceedings.
Item 4. Mine Safety Disclosures.
None.
24
PART II
Item 5. Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Shareholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities.
Information about Our Common Stock
Our common stock trades on The Nasdaq Capital Market, under the symbol “LJPC.” Set forth below are the high and low sales prices for our common stock for each full quarterly period within the two most recent fiscal years.
Prices | |||||||
High | Low | ||||||
Year Ended December 31, 2017 | |||||||
First Quarter | $ | 39.28 | $ | 16.71 | |||
Second Quarter | $ | 36.73 | $ | 25.01 | |||
Third Quarter | $ | 37.97 | $ | 27.54 | |||
Fourth Quarter | $ | 36.99 | $ | 22.68 | |||
Year Ended December 31, 2016 | |||||||
First Quarter | $ | 26.44 | $ | 12.68 | |||
Second Quarter | $ | 23.80 | $ | 14.24 | |||
Third Quarter | $ | 28.20 | $ | 15.55 | |||
Fourth Quarter | $ | 24.54 | $ | 14.63 | |||
Stock Performance Graph
The graph below compares the cumulative total shareholder returns on our common stock for the last 5 fiscal years with the cumulative total shareholder returns on the Nasdaq Composite Index and the Nasdaq Biotechnology Index for the same period. The graph assumes that $100 was invested on December 31, 2012 in our common stock and in each index and that all dividends were reinvested. No cash dividends have been declared on our common stock. Shareholder returns over the indicated period should not be considered indicative of future shareholder returns.
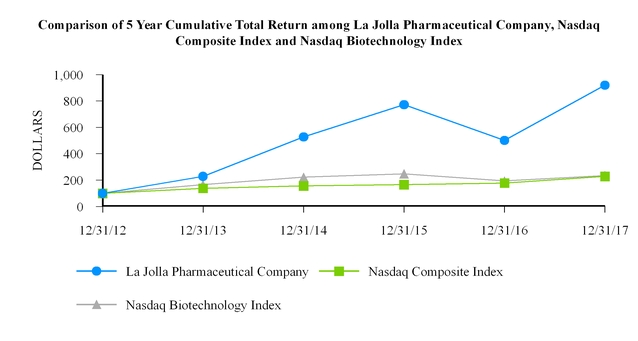
Holders
As of February 16, 2018, the number of shares of common stock outstanding was 22,168,242, and there were three holders of record. We have approximately 4,000 beneficial holders of our common stock.
25
Dividends
We have never paid dividends on our common stock, and we do not anticipate paying dividends in the foreseeable future.
Item 6. Selected Financial Data.
The following table sets forth selected historical consolidated financial data for each of our last 5 fiscal years during the year ended December 31, 2017. This information should be read in conjunction with “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and the consolidated financial statements and related notes included in Item 15 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Statement of Operations Data
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||||||||
(in thousands, except per share amounts) | |||||||||||||||||||
Total revenue | $ | — | $ | 616 | $ | 1,057 | $ | — | $ | — | |||||||||
Loss from operations | $ | (115,427 | ) | $ | (78,372 | ) | $ | (41,969 | ) | $ | (21,340 | ) | $ | (17,941 | ) | ||||
Net loss | $ | (114,803 | ) | $ | (78,185 | ) | $ | (41,912 | ) | $ | (21,313 | ) | $ | (17,935 | ) | ||||
Net loss attributable to common shareholders | $ | (114,803 | ) | $ | (78,185 | ) | $ | (41,912 | ) | $ | (21,313 | ) | $ | (18,736 | ) | ||||
Basic and diluted net loss per share | $ | (5.41 | ) | $ | (4.54 | ) | $ | (2.68 | ) | $ | (2.00 | ) | $ | (12.16 | ) | ||||
Weighted-average common shares outstanding - basic and diluted | 21,215 | 17,228 | 15,651 | 10,667 | 1,540 | ||||||||||||||
Balance Sheet Data
December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||||||||
(in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 90,915 | $ | 65,726 | $ | 126,467 | $ | 48,555 | $ | 8,629 | |||||||||
Working capital | $ | 75,510 | $ | 57,673 | $ | 122,725 | $ | 48,177 | $ | 7,615 | |||||||||
Total assets | $ | 119,539 | $ | 70,795 | $ | 129,347 | $ | 50,536 | $ | 8,747 | |||||||||
Total current liabilities | $ | 18,552 | $ | 9,758 | $ | 4,820 | $ | 2,080 | $ | 1,094 | |||||||||
Accumulated deficit | $ | (721,514 | ) | $ | (606,711 | ) | $ | (528,526 | ) | $ | (486,614 | ) | $ | (465,301 | ) | ||||
Total shareholders’ equity | $ | 88,202 | $ | 61,037 | $ | 124,527 | $ | 48,456 | $ | 7,653 | |||||||||
Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.
Introduction
Management’s discussion and analysis of financial condition and results of operations is provided as a supplement to the accompanying consolidated financial statements and notes, included in Item 15 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, to help provide an understanding of our financial condition, the changes in our financial condition and our results of operations. Our discussion is organized as follows:
• | Business Overview. This section provides a general description of our business and significant events and transactions that we believe are important in understanding our financial condition and results of operations. |
• | Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates. This section provides a description of our significant accounting policies, including the critical accounting policies and estimates, which are summarized in Note 2 to the accompanying consolidated financial statements included in Item 15 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. |
• | Results of Operations. This section provides an analysis of our results of operations presented in the accompanying consolidated statements of operations by comparing the results for the year ended December 31, 2017 to the results for the year ended December 31, 2016 and for the year ended December 31, 2016 to the results for the year ended December 31, 2015. |
26
• | Liquidity and Capital Resources. This section provides an analysis of our historical cash flows, as well as our future capital requirements. |
Business Overview
La Jolla Pharmaceutical Company is a biopharmaceutical company focused on the discovery, development and commercialization of innovative therapies intended to significantly improve outcomes in patients suffering from life-threatening diseases.
GIAPREZATM (angiotensin II), formerly known as LJPC-501, was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) on December 21, 2017 as a vasoconstrictor to increase blood pressure in adults with septic or other distributive shock. GIAPREZA is our first commercial product.
LJPC-401, a clinical-stage investigational product, is our proprietary formulation of synthetic human hepcidin. LJPC-401 is being developed for the potential treatment of conditions characterized by iron overload, such as hereditary hemochromatosis, beta thalassemia, sickle cell disease and myelodysplastic syndrome.
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
The discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations are based on our consolidated financial statements, which have been prepared in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP). The preparation of these consolidated financial statements requires us to make estimates and judgments that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses, and related disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities. We evaluate our estimates on an ongoing basis. We base our estimates on historical experience and on other assumptions that we believe to be reasonable under the circumstances, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying values of assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other sources. Actual results may differ materially from these estimates under different assumptions or conditions.
We believe the following critical accounting policies involve significant judgments and estimates used in the preparation of our consolidated financial statements (see also Note 2 to our consolidated financial statements included in Item 15 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K).
Revenue Recognition
In accordance with GAAP, we recognize revenue when all of the following criteria are met: (1) persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists; (2) delivery has occurred or services have been rendered; (3) the seller’s price to the buyer is fixed or determinable; and (4) collectibility is reasonably assured. We recognized revenue from payments received under a services agreement with a related party. Under the terms of this services agreement, we receive payments from this related party for research and development services that the Company provides at what the Company believes is a negotiated, arms-length rate.
Clinical Trial Expense
Payments in connection with our clinical trials are often made under contracts with multiple contract research organizations that conduct and manage clinical trials on our behalf. The financial terms of these agreements are subject to negotiation and vary from contract to contract and may result in uneven payment flows. Generally, these agreements set forth the scope of work to be performed at a fixed fee, unit price or on a time and materials basis. Payments under these contracts depend on factors such as the successful enrollment or treatment of patients or the completion of other clinical trial milestones. We amortize prepayments to expense based on estimates regarding work performed, including actual level of patient enrollment, completion of patient studies and progress of the clinical trials.
Expenses related to clinical trials are accrued based on estimates regarding work performed, including actual level of patient enrollment, completion of patient studies and progress of the clinical trials. Other incidental costs related to patient enrollment or treatment are accrued when reasonably certain. If the contracted amounts are modified, the accruals are modified accordingly on a prospective basis. Revisions in the scope of a contract are charged to research and development expense in the period in which the facts that give rise to the revision occur.
27
Share-based Compensation Expense
We generally grant share-based awards under our shareholder-approved, share-based compensation plan. We have granted, and may in the future grant, stock options and restricted stock awards to employees, directors, consultants and advisors under our 2013 Equity Incentive Plan.
We estimate the fair value of stock options granted using the Black-Scholes option pricing model (Black-Scholes model). This fair value is then amortized over the requisite service periods of the awards. The Black-Scholes model requires the input of subjective assumptions, including each option’s expected life and the price volatility of the underlying stock. Expected volatility is based on our historical stock price volatility. The expected life of employee stock options represents the average of the contractual term of the options and the weighted-average vesting period, as permitted under the “simplified” method.
Share-based compensation expense has been reduced for actual forfeitures as they occur. Changes in assumptions used under the Black-Scholes option pricing model could materially affect our net loss and net loss per share.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
Recent accounting pronouncements are disclosed in Note 2 to the accompanying consolidated financial statements included in Item 15 of this Annual Report on form 10-K.
Results of Operations
The following summarizes the results of our operations for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 (in thousands):
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
Contract revenue - related party | $ | — | $ | 616 | $ | 1,057 | |||||
Research and development expense | (84,575 | ) | (62,288 | ) | (29,092 | ) | |||||
General and administrative expense | (30,852 | ) | (16,700 | ) | (13,934 | ) | |||||
Other income, net | 624 | 187 | 57 | ||||||||
Net loss attributable to common shareholders | $ | (114,803 | ) | $ | (78,185 | ) | $ | (41,912 | ) | ||
Contract Revenue - Related Party
During the year ended December 31, 2015, we entered into a services agreement with a related party. Pursuant to the services agreement, we provide certain services to this related party, including, but not limited to, research and development and clinical study design and management for projects undertaken. Contract revenue is a function of the availability of potential projects identified by our customer and our ability and willingness to take on such projects. As such, this revenue may be significantly reduced in future periods, as has happened for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016. In exchange for providing such services, we receive payments at a negotiated, arms-length rate. As a result, the consideration received by us for our services is considered to be no less favorable to us than comparable terms that we could obtain from an unaffiliated third party in an arms-length transaction. The services agreement may be canceled by either party upon 60-days’ written notice to the other party. In addition, we have a non-voting profit interest in the related party, which provides us with the potential to receive a portion of the future distributions of profits, if any.
28
Research and Development Expense
The following summarizes our research and development expense for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 (in thousands):
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
Clinical development costs | $ | 34,420 | $ | 32,798 | $ | 13,074 | |||||
Personnel and related costs | 26,735 | 13,570 | 6,630 | ||||||||
Share-based compensation expense | 11,980 | 5,657 | 4,084 | ||||||||
In-licensing and technology purchase costs | 2,097 | 847 | 754 | ||||||||
Other research and development costs | 9,343 | 9,416 | 4,550 | ||||||||
Total research and development expense | $ | 84,575 | $ | 62,288 | $ | 29,092 | |||||
Years Ended December 31, 2017 and 2016
During the year ended December 31, 2017, we incurred $84.6 million in research and development expense compared to $62.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2016. The increase was primarily due to increased personnel and related costs and share-based compensation expense as a result of increased headcount associated with the development of GIAPREZA and LJPC-401. We anticipate research and development expense to increase throughout 2018, due to the continuation of our clinical development of LJPC-401, the initiation of additional clinical trials and ongoing development of our product candidates.
Years Ended December 31, 2016 and 2015
During the year ended December 31, 2016, we incurred $62.3 million in research and development expense compared to $29.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2015. The increase was primarily due to increased development activities associated with GIAPREZA, clinical development costs associated with LJPC-401 and preclinical costs associated with other programs. Increases in personnel and related costs and share-based compensation expense associated with the support of our increased development activities also contributed to the increase in research and development expense.
General and Administrative Expense
The following summarizes our general and administrative expense for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 (in thousands):
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
Personnel and related costs | $ | 9,367 | $ | 4,020 | $ | 2,458 | |||||
Share-based compensation expense | 9,815 | 8,889 | 8,988 | ||||||||
Other pre-commercialization activities | 5,033 | — | — | ||||||||
Other general and administrative | 6,637 | 3,791 | 2,488 | ||||||||
Total general and administrative expense | $ | 30,852 | $ | 16,700 | $ | 13,934 | |||||
Years Ended December 31, 2017 and 2016
During the year ended December 31, 2017, we incurred $30.9 million in general and administrative expense compared to $16.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2016. The increase was primarily due to increased personnel costs and professional and outside service costs associated with our increased development and pre-commercialization activities. We anticipate general and administrative expense to increase throughout 2018 due to planned increases in personnel to support the product launch of GIAPREZA and the development of our product candidates.
29
Years Ended December 31, 2016 and 2015
During the year ended December 31, 2016, we incurred $16.7 million in general and administrative expense compared to $13.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2015. The increase was primarily due to increases in personnel costs and facilities costs associated with the support of our increased development activities. In addition, there were increased expenses for professional and outside service costs.
Sales and Marketing Expense
In 2018, we will begin to incur sales and marketing expenses to support the commercialization of GIAPREZA. The commercial launch process requires the expenditure of substantial resources. Sales and marketing expense will primarily consist of salaries and related costs, share-based compensation expense and other related costs for sales operations, marketing and market access. Other sales and marketing costs will include advertising, speaker programs, medical education and other consulting costs.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Since January 2012, when the Company was effectively restarted with new assets and a new management team, through December 31, 2017, our cash used for operating activities was $188.5 million. From inception through December 31, 2017, we have incurred a cumulative net loss of $721.5 million and have financed our operations through public and private offerings of securities, revenues from collaborative agreements, equipment financings and interest income on invested cash balances. From inception through December 31, 2017, we have raised $706.3 million in net proceeds from sales of equity securities.
As of December 31, 2017, we had $90.9 million in cash and cash equivalents, compared to $65.7 million in cash and cash equivalents as of December 31, 2016. Cash used for operating activities for the year ended December 31, 2017 was $84.9 million, compared to $58.7 million for the same period in 2016. The increase in cash used for operating activities was a result of the increase in our net loss, primarily offset by changes in working capital and increases in share-based compensation and depreciation expense. For the year ended December 31, 2017, we used $9.2 million of cash for investing activities, compared to $2.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2016. The increase in cash used for investing activities was a result of purchases of property and equipment. Cash provided by financing activities for the year ended December 31, 2017 was $119.3 million, compared to $0.1 million for the same period in 2016. The increase in cash provided by financing activities was due to $117.5 million of proceeds from the March 2017 common stock offering and an increase of $2.7 million of proceeds from the exercise of stock options for common stock.
We have a history of incurring significant operating losses and negative cash flows from operations. We do not have sufficient capital to fund our planned operations during the twelve-month period subsequent to the issuance of the financial statements included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. These factors raise substantial doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern within one year from the date this Annual Report on Form 10-K is filed with the SEC. The accompanying consolidated financial statements do not include any adjustments relating to the recoverability of assets and classification of liabilities that might be necessary should we be unable to continue as a going concern. We anticipate that we will need to raise additional capital in order to fund these future operations. We will seek to fund our operations through equity, debt or royalty-based financings or other sources, such as potential collaboration agreements. We cannot be certain that additional funding will be available to us on acceptable terms, or at all.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
We have no off-balance sheet arrangements that have, or are reasonably likely to have, a current or future effect on our financial condition, changes in our financial condition, expenses, results of operations, liquidity, capital expenditures or capital resources.
30
Contractual Obligations
Contractual obligations represent future minimum cash commitments and liabilities under agreements with third parties. See Note 9 Commitments and Contingencies in the Notes to consolidated financial statements included in Item 15 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. The following table represents our contractual obligations as of December 31, 2017, aggregated by type (amounts in thousands):
Payments Due by Period | ||||||||||||||||||||
Contractual Obligations | Total | Less Than 1 Year | 1 - 3 Years | 3 - 5 Years | More Than 5 Years | |||||||||||||||
License agreements | $ | 795 | $ | 142 | $ | 295 | $ | 305 | $ | 53 | ||||||||||
Leases | 41,231 | 1,945 | 8,021 | 8,510 | 22,755 | |||||||||||||||
Purchase obligations | 3,855 | 1,092 | 1,842 | 921 | — | |||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 45,881 | $ | 3,179 | $ | 10,158 | $ | 9,736 | $ | 22,808 | ||||||||||
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk.
Our exposure to market risk for changes in interest rates relates primarily to interest earned on our cash equivalents and investments. The primary objective of our investment activities is to preserve our capital to fund operations. A secondary objective is to maximize income from our investments without assuming significant risk. Our investment policy provides for investments in low-risk, investment-grade debt instruments. As of December 31, 2017, we had cash and cash equivalents of $90.9 million, which includes money market funds. A hypothetical 10% change in interest rates during any of the periods presented would not have had a material impact on our consolidated financial statements. To date, we have not experienced a loss of principal on any of our investments.
We face foreign exchange risk as a result of entering into transactions denominated in currencies other than U.S. dollars. Due to the uncertain timing of expected payments in foreign currencies, we do not utilize any forward exchange contracts. All foreign transactions settle on the applicable spot exchange basis at the time such payments are made. An adverse movement in foreign exchange rates could have an effect on payments made to foreign suppliers and for license agreements. A hypothetical 10% change in foreign exchange rates during any of the periods presented would not have had a material impact on our financial statements.
Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.
The financial statements required by this item are set forth at the end of this Annual Report on Form 10-K beginning on page F-3 and are incorporated herein by reference.
Item 9. Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure.
None.
Item 9A. Controls and Procedures.
(a) Disclosure Controls and Procedures; Changes in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Our management, with the participation of our principal executive and principal financial officer, has evaluated the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Exchange Act) as of December 31, 2017. Based on this evaluation, our principal executive and principal financial officer concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures were effective as of December 31, 2017.
There was no change in our internal control over financial reporting during the quarter ended December 31, 2017 that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
(b) Management Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting as defined in Rule 13a-15(f) of the Exchange Act. Our management used the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) (COSO framework) to evaluate the effectiveness of
31
internal control over financial reporting. Management believes that the COSO framework is a suitable framework for its evaluation of financial reporting because it is free from bias, permits reasonably consistent qualitative and quantitative measurements of our internal control over financial reporting, is sufficiently complete so that those relevant factors that would alter a conclusion about the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting are not omitted and is relevant to an evaluation of internal control over financial reporting.
Management has assessed the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017 and has concluded that such internal control over financial reporting was effective.
(c) Attestation report of the independent registered public accounting firm
The effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting has been audited by Squar Milner LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, as stated in their attestation report appearing below, which expresses an unqualified opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017.
32
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Shareholders and the Board of Directors of La Jolla Pharmaceutical Company
Opinion on the Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
We have audited La Jolla Pharmaceutical Company's (the Company) internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017, based on criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission in 2013. In our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017, based on criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission in 2013.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the consolidated balance sheets of La Jolla Pharmaceutical Company as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, and the related consolidated statements of operations, shareholders’ equity, and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2017, and the related notes to the consolidated financial statements of the Company and our report dated February 22, 2018 expressed an unqualified opinion.
Basis for Opinion
The Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audit also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
A company's internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company's internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of the company's assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
/s/ SQUAR MILNER LLP
San Diego, California
February 22, 2018
33
Item 9B. Other Information.
None.
PART III
Item 10. Directors, Executive Officer and Corporate Governance.
The information required by this Item is expected to be in our definitive Proxy Statement for the 2018 Annual Meeting of Shareholders, which we expect to be filed with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) within 120 days of the end of our fiscal year ended December 31, 2017 and is incorporated herein by reference.
We have adopted a Code of Business Conduct and Ethics that applies to all of our directors, officers and employees, including our principal executive, principal financial and principal accounting officers, or persons performing similar functions. Our Code of Business Conduct and Ethics is posted on our website located at www.ljpc.com in the Corporate Governance section under “Investor Relations”. We intend to disclose future amendments to certain provisions of the Code of Business Conduct and Ethics, and waivers of the Code of Business Conduct and Ethics granted to executive officers and directors, on the website within 4 business days following the date of the amendment or waiver.
Item 11. Executive Compensation.
The information required by this Item is expected to be in our definitive Proxy Statement for the 2018 Annual Meeting of Shareholders, which we expect to be filed with the SEC within 120 days of the end of our fiscal year ended December 31, 2017 and is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Shareholder Matters.
The information required by this Item is expected to be in our definitive Proxy Statement for the 2018 Annual Meeting of Shareholders, which we expect to be filed with the SEC within 120 days of the end of our fiscal year ended December 31, 2017 and is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence.
The information required by this Item is expected to be in our definitive Proxy Statement for the 2018 Annual Meeting of Shareholders, which we expect to be filed with the SEC within 120 days of the end of our fiscal year ended December 31, 2017 and is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 14. Principal Accountant Fees and Services.
The information required by this Item is expected to be in our definitive Proxy Statement for the 2018 Annual Meeting of Shareholders, which we expect to be filed with the SEC within 120 days of the end of our fiscal year ended December 31, 2017 and is incorporated herein by reference.
34
PART IV
Item 15. Exhibits, Financial Statement Schedules.
(a) Documents filed as part of this report.
1. | The following financial statements of La Jolla Pharmaceutical Company are filed as part of this report under Item 8 — Financial Statements and Supplementary Data: |
2. | Financial Statement Schedules. |
The following financial statement schedules of La Jolla Pharmaceutical Company are filed as part of this report under Item 8 — Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.
None.
3. | Exhibits. |
List of Exhibit required by Item 601 of Regulation S-K. See part (b) below.
(b) Exhibits:
35
8-K | 9/25/2013 | |||||||
10-K | 2/25/2016 | |||||||
8-K | 4/10/2015 | |||||||
10-K | 2/25/2016 | |||||||
10-K | 2/23/2017 | |||||||
X | ||||||||
X | ||||||||
X | ||||||||
X | ||||||||
X | ||||||||
X | ||||||||
X | ||||||||
101.INS | XBRL Instance Document | X | ||||||
101.SCH | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document | X | ||||||
101.CAL | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document | X | ||||||
101.DEF | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document | X | ||||||
101.LAB | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document | X | ||||||
101.PRE | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document | X | ||||||
* | This exhibit is a management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement. |
† | Confidential treatment has been requested with respect to certain portions of the exhibit, which portions have been omitted and filed separately with the Securities and Exchange Commission. |
Item 16. Form 10-K Summary.
None.
36
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned hereunto duly authorized.
La Jolla Pharmaceutical Company | ||
Date: | February 22, 2018 | /s/ George F. Tidmarsh |
George F. Tidmarsh, M.D., Ph.D. | ||
President, Chief Executive Officer and Secretary | ||
(Principal Executive Officer) | ||
POWER OF ATTORNEY
KNOW ALL MEN BY THESE PRESENT, that each person whose signature appears below constitutes and appoints each of George F. Tidmarsh, M.D., Ph.D. and Dennis M. Mulroy as his or her true and lawful attorney-in-fact and agent, with full power of substitution for him or her, and in his or her name in any and all capacities, to sign any and all amendments to this Annual Report on Form 10-K, and to file the same, with exhibits thereto and other documents in connection therewith, with the Securities and Exchange Commission, granting unto said attorney-in-fact and agent full power and authority to do and perform each and every act and thing requisite and necessary to be done therewith, as fully to all intents and purposes as he might or could do in person, hereby ratifying and confirming all that said attorney-in-fact and agent, his substitute or substitutes, may lawfully do or cause to be done by virtue hereof.
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
Signature | Title | Date | |||
/s/ George F. Tidmarsh | Director, President, Chief Executive Officer and Secretary (Principal Executive Officer) | February 22, 2018 | |||
George F. Tidmarsh, M.D., Ph.D. | |||||
/s/ Dennis M. Mulroy | Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) | February 22, 2018 | |||
Dennis M. Mulroy | |||||
/s/ Kevin C. Tang | Chairman of the Board and Director | February 22, 2018 | |||
Kevin C. Tang | |||||
/s/ Laura L. Douglass | Director | February 22, 2018 | |||
Laura L. Douglass | |||||
/s/ Craig A. Johnson | Director | February 22, 2018 | |||
Craig A. Johnson | |||||
/s/ Robert H. Rosen | |||||
Director | February 22, 2018 | ||||
Robert H. Rosen | |||||
37
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Shareholders and the Board of Directors of La Jolla Pharmaceutical Company
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of La Jolla Pharmaceutical Company (the Company) as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, the related consolidated statements of operations, shareholders’ equity, and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2017, and the related notes to the consolidated financial statements (collectively the financial statements). In our opinion, the financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company at December 31, 2017 and 2016, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2017, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the Company's internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017, based on criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission in 2013, and our report dated February 22, 2018 expressed an unqualified opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
Going Concern Uncertainty
The accompanying financial statements have been prepared assuming that the Company will continue as a going concern. As discussed in Note 1 to the financial statements, the Company has a history of significant recurring losses from operations through December 31, 2017 and does not have sufficient working capital at December 31, 2017 to fund its planned operations during the twelve-month period subsequent to the issuance of these financial statements. This raises substantial doubt about the Company's ability to continue as a going concern. Management's plans in regard to these matters also are described in Note 1. The financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of this uncertainty.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company's management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company's financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audits to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
/s/ SQUAR MILNER LLP
We have served as the Company's auditor since 2012.
San Diego, California
February 22, 2018
F - 1
LA JOLLA PHARMACEUTICAL COMPANY
Consolidated Balance Sheets
(in thousands, except share and par value amounts)
December 31, 2017 | December 31, 2016 | ||||||
ASSETS | |||||||
Current assets: | |||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 90,915 | $ | 65,726 | |||
Restricted cash, current portion | — | 200 | |||||
Prepaid expenses and other current assets | 3,147 | 1,505 | |||||
Total current assets | 94,062 | 67,431 | |||||
Property and equipment, net | 24,568 | 3,145 | |||||
Restricted cash, less current portion | 909 | — | |||||
Other assets | — | 219 | |||||
Total assets | $ | 119,539 | $ | 70,795 | |||
LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY | |||||||
Current liabilities: | |||||||
Accounts payable | $ | 11,484 | $ | 6,652 | |||
Accrued clinical and other expenses | 703 | 905 | |||||
Accrued payroll and related expenses | 4,995 | 2,077 | |||||
Deferred rent, current portion | 1,370 | 124 | |||||
Total current liabilities | 18,552 | 9,758 | |||||
Deferred rent, less current portion | 12,785 | — | |||||
Total liabilities | 31,337 | 9,758 | |||||
Commitments and contingencies (Note 9) | |||||||
Shareholders’ equity: | |||||||
Common Stock, $0.0001 par value; 100,000,000 shares authorized, 22,167,529 and 18,261,557 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016, respectively | 2 | 2 | |||||
Series C-12 Convertible Preferred Stock, $0.0001 par value; 11,000 shares authorized, 3,906 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016, and a liquidation preference of $3,906 at December 31, 2017 and 2016 | 3,906 | 3,906 | |||||
Series F Convertible Preferred Stock, $0.0001 par value; 10,000 shares authorized, 2,737 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016, and a liquidation preference of $2,737 at December 31, 2017 and 2016 | 2,737 | 2,737 | |||||
Additional paid-in capital | 803,071 | 661,103 | |||||
Accumulated deficit | (721,514 | ) | (606,711 | ) | |||
Total shareholders’ equity | 88,202 | 61,037 | |||||
Total liabilities and shareholders’ equity | $ | 119,539 | $ | 70,795 | |||
See accompanying notes to the consolidated financial statements.
F - 2
LA JOLLA PHARMACEUTICAL COMPANY
Consolidated Statements of Operations
(in thousands, except per share amounts)
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
Revenue | |||||||||||
Contract revenue - related party | $ | — | $ | 616 | $ | 1,057 | |||||
Total revenue | — | 616 | 1,057 | ||||||||
Operating expenses | |||||||||||
Research and development | 84,575 | 62,288 | 29,092 | ||||||||
General and administrative | 30,852 | 16,700 | 13,934 | ||||||||
Total operating expenses | 115,427 | 78,988 | 43,026 | ||||||||
Loss from operations | (115,427 | ) | (78,372 | ) | (41,969 | ) | |||||
Other income, net | 624 | 187 | 57 | ||||||||
Net loss | (114,803 | ) | (78,185 | ) | (41,912 | ) | |||||
Net loss attributable to common shareholders | $ | (114,803 | ) | $ | (78,185 | ) | $ | (41,912 | ) | ||
Basic and diluted net loss per share | $ | (5.41 | ) | $ | (4.54 | ) | $ | (2.68 | ) | ||
Weighted-average common shares outstanding - basic and diluted | 21,215 | 17,228 | 15,651 | ||||||||
See accompanying notes to the consolidated financial statements.
F - 3
La Jolla Pharmaceutical Company
Consolidated Statements of Shareholders’ Equity
For the Years Ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015
(in thousands)
Series C-12 Convertible Preferred Stock | Series F Convertible Preferred Stock | Common Stock | Additional Paid-in Capital | Accumulated Deficit | Total Shareholders’ Equity | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2014 | 4 | $ | 3,917 | 3 | $ | 2,798 | 15,226 | $ | 2 | $ | 528,353 | $ | (486,614 | ) | $ | 48,456 | |||||||||||||||||
Issuance of common stock for September 2015 financing | — | — | — | — | 2,933 | — | 104,596 | — | 104,596 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Conversion of Series F Convertible Preferred Stock into common stock | — | — | — | (61 | ) | 17 | — | 61 | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Conversion of Series C-12 Convertible Preferred Stock into common stock | — | (11 | ) | — | — | 19 | — | 11 | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Share-based compensation expense | — | — | — | — | — | — | 11,551 | — | 11,551 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Third party share-based compensation expense | — | — | — | — | — | — | 1,521 | — | 1,521 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Exercise of stock options for common stock | — | — | — | — | 45 | — | 315 | — | 315 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of restricted stock awards | — | — | — | — | 4 | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net loss | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (41,912 | ) | (41,912 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2015 | 4 | 3,906 | 3 | 2,737 | 18,244 | 2 | 646,408 | (528,526 | ) | 124,527 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Share-based compensation expense | — | — | — | — | — | — | 14,349 | — | 14,349 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Third party share-based compensation expense | — | — | — | — | — | — | 197 | — | 197 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Exercise of stock options for common stock | — | — | — | — | 17 | — | 149 | — | 149 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net loss | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (78,185 | ) | (78,185 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2016 | 4 | 3,906 | 3 | 2,737 | 18,261 | 2 | 661,103 | (606,711 | ) | 61,037 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of common stock for March 2017 financing | — | — | — | — | 3,731 | — | 117,480 | — | 117,480 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Share-based compensation expense | — | — | — | — | — | — | 20,776 | — | 20,776 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Third party share-based compensation expense | — | — | — | — | — | — | 1,019 | — | 1,019 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Exercise of stock options for common stock | — | — | — | — | 175 | — | 2,693 | — | 2,693 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net loss | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (114,803 | ) | (114,803 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at December 31, 2017 | 4 | $ | 3,906 | 3 | $ | 2,737 | 22,167 | $ | 2 | $ | 803,071 | $ | (721,514 | ) | $ | 88,202 | |||||||||||||||||
See accompanying notes to the consolidated financial statements.
F - 4
LA JOLLA PHARMACEUTICAL COMPANY
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
(in thousands)
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
Operating activities | |||||||||||
Net loss | $ | (114,803 | ) | $ | (78,185 | ) | $ | (41,912 | ) | ||
Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash used for operating activities: | |||||||||||
Share-based compensation expense | 20,776 | 14,349 | 11,551 | ||||||||
Third party share-based compensation expense | 1,019 | 197 | 1,521 | ||||||||
Depreciation expense | 1,268 | 730 | 347 | ||||||||
Loss on disposal of property and equipment | 199 | 75 | 16 | ||||||||
Changes in operating assets and liabilities: | |||||||||||
Restricted cash, current portion | 200 | 37 | (200 | ) | |||||||
Prepaid expenses and other current assets | (1,642 | ) | (664 | ) | 824 | ||||||
Other assets | 219 | (149 | ) | (70 | ) | ||||||
Accounts payable | 4,832 | 3,600 | 2,322 | ||||||||
Accrued clinical and other expenses | (202 | ) | 227 | (248 | ) | ||||||
Accrued payroll and related expenses | 2,918 | 987 | 666 | ||||||||
Deferred rent | 335 | 124 | — | ||||||||
Net cash used for operating activities | (84,881 | ) | (58,672 | ) | (25,183 | ) | |||||
Investing activities | |||||||||||
Purchase of property and equipment | (9,194 | ) | (2,218 | ) | (1,816 | ) | |||||
Net cash used for investing activities | (9,194 | ) | (2,218 | ) | (1,816 | ) | |||||
Financing activities | |||||||||||
Net proceeds from the issuance of common stock | 117,480 | — | 104,596 | ||||||||
Net proceeds from the exercise of stock options for common stock | 2,693 | 149 | 315 | ||||||||
Restricted cash, long term | (909 | ) | — | — | |||||||
Net cash provided by financing activities | 119,264 | 149 | 104,911 | ||||||||
Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | 25,189 | (60,741 | ) | 77,912 | |||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of period | 65,726 | 126,467 | 48,555 | ||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at end of period | $ | 90,915 | $ | 65,726 | $ | 126,467 | |||||
Supplemental disclosure of cash flow information | |||||||||||
Non-cash investing and financing activity: | |||||||||||
Capitalized landlord funded tenant improvements | $ | 13,696 | $ | — | $ | — | |||||
Conversion of Series C-12 Convertible Preferred Stock into common stock | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 11 | |||||
Conversion of Series F Convertible Preferred Stock into common stock | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 61 | |||||
See accompanying notes to the consolidated financial statements.
F - 5
La Jolla Pharmaceutical Company
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
1. Business
La Jolla Pharmaceutical Company (collectively with its subsidiaries, the Company) is a biopharmaceutical company focused on the discovery, development and commercialization of innovative therapies intended to significantly improve outcomes in patients suffering from life-threatening diseases. The Company was incorporated in 1989 as a Delaware corporation and reincorporated in California in 2012.
GIAPREZATM (angiotensin II), formerly known as LJPC-501, was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) on December 21, 2017 as a vasoconstrictor to increase blood pressure in adults with septic or other distributive shock. GIAPREZA is the Company’s first commercial product.
LJPC-401, a clinical stage investigational product, is our proprietary formulation of synthetic human hepcidin. LJPC-401 is being developed for the potential treatment of conditions characterized by iron overload, such as hereditary hemochromatosis, beta thalassemia, sickle cell disease and myelodysplastic syndrome.
As of December 31, 2017, the Company had $90.9 million in cash and cash equivalents, compared to $65.7 million in cash and cash equivalents at December 31, 2016. The Company has a history of incurring significant operating losses and negative cash flows from operations. As of December 31, 2017, the Company does not have sufficient capital to fund its planned operations during the twelve-month period subsequent to the issuance of these financial statements. These factors raise substantial doubt about the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern within one year from the date this Annual Report on Form 10-K is filed with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). The accompanying consolidated financial statements do not include any adjustments relating to the recoverability of assets and classification of liabilities that might be necessary should the Company be unable to continue as a going concern. The Company anticipates that it will need to raise additional capital in order to fund these future operations. The Company will seek to fund its operations through equity, debt or royalty-based financings or other sources, such as potential collaboration agreements. The Company cannot be certain that additional funding will be available to us on acceptable terms, or at all.
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Basis of Presentation and Use of Estimates
The consolidated financial statements of the Company have been prepared in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) and include the accounts of the Company and its wholly owned subsidiaries. All intercompany transactions and balances have been eliminated in consolidation. The preparation of financial statements requires that management make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues, expenses and related disclosures. Actual results could differ materially from those estimates.
Certain amounts previously reported in the financial statements have been reclassified to conform to the current year presentation. Such reclassifications did not affect net loss, shareholders’ equity or cash flows.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
The Company considers all highly liquid investments with a maturity from the date of purchase of less than three months to be cash equivalents. The carrying value of the Company’s money market funds is included in cash equivalents and approximates the fair value.
Restricted Cash
Cash is classified as restricted cash when certain funds are reserved for a specific purpose and are not available for immediate or general business use. Under the terms of the Company’s building lease, the Company has provided a standby letter of credit of $0.9 million in lieu of a security deposit during the term of such lease, subject to periodic decreases during the first 5 years of the lease. There is a requirement to maintain a $0.9 million collateral cash account pledged as security for such letter of credit. Previously under the terms of the Company’s credit card arrangements, there was a requirement to maintain a $0.2 million collateral cash account pledged as security for such credit cards.
F - 6
La Jolla Pharmaceutical Company
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Concentrations of Credit Risk
Financial instruments that potentially subject the Company to concentrations of credit risk consist primarily of cash equivalents. The Company invests excess cash in money market accounts. This investment strategy is consistent with the Company’s policy to ensure safety of principal and maintain liquidity.
Property and Equipment
Property and equipment is stated at cost less accumulated depreciation and amortization. Depreciation is computed using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the assets, which range from two to seven years. Amortization of leasehold improvements is recorded over the shorter of the lease term or the estimated useful life of the related assets. Maintenance and repairs are charged to operating expense as incurred. When assets are sold, or otherwise disposed of, the cost and related accumulated depreciation are removed from the accounts, and any gain or loss is included in operating expense.
Lease incentives are amortized on a straight-line basis over the lease term as a reduction to rent expense. Leasehold improvements are capitalized and amortized over the shorter of the lease term or expected useful lives.
Revenue Recognition
The Company recognizes revenue when all of the following criteria are met: (1) persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists; (2) delivery has occurred or services have been rendered; (3) the seller’s price to the buyer is fixed or determinable; and (4) collectibility is reasonably assured. The Company has recognized revenue from payments received under a services agreement with a related party. Under the terms of this services agreement, the Company receives payments from this related party for research and development services that the Company provides at a negotiated, arms-length rate.
Research and Development Expense
Research and development expense includes salaries and benefits, facilities and other overhead costs, research-related manufacturing costs, contract service and clinical and preclinical-related service costs performed by clinical research organizations, research institutions and other outside service providers. Research and development expense is expensed as incurred when these expenditures relate to the Company’s research and development efforts and have no alternative future uses.
In accordance with certain research and development agreements, the Company is obligated to make certain upfront payments upon execution of the agreement. Advance payments, including nonrefundable amounts, for materials or services that will be used or rendered for future research and development activities are deferred and capitalized. Such amounts are recognized as an expense as the related goods are delivered or the related services are performed.
Acquisition or milestone payments that the Company makes in connection with in-licensed technology are expensed as incurred when there is uncertainty in receiving future economic benefits from the licensed technology. The Company considers the future economic benefits from the licensed technology to be uncertain until such licensed technology is incorporated into products that are approved for marketing by the FDA or when other significant risk factors are abated. For accounting purposes, management has viewed future economic benefits for all of the Company’s licensed technology to be uncertain.
Clinical Trial Expenses
Payments in connection with the Company’s clinical trials are often made under contracts with multiple contract research organizations that conduct and manage clinical trials on the Company’s behalf. The financial terms of these contracts are subject to negotiation, vary from contract to contract and may result in uneven payment flows. Generally, these contracts set forth the scope of work to be performed at a fixed fee, unit price or on a time and materials basis. Payments under these contracts depend on factors such as the successful enrollment or treatment of patients or the completion of other clinical trial milestones. The Company amortizes prepaid clinical trial costs to expense based on estimates regarding work performed, including actual level of patient enrollment, completion of patient studies and progress of the clinical trials.
Expenses related to clinical trials are accrued based on estimates regarding work performed, including actual level of patient enrollment, completion of patient studies and progress of the clinical trials. Other incidental costs related to patient enrollment or treatment are accrued when reasonably certain. If the contracted amounts are modified, the accruals are modified accordingly on a prospective basis. Revisions in the scope of a contract are charged to research and development expense in the period in which the facts that give rise to the revision occur.
F - 7
La Jolla Pharmaceutical Company
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Patent Costs
Legal costs in connection with approved patents and patent applications are expensed as incurred, as recoverability of such expenditures is uncertain. These costs are recorded in general and administrative expense in the consolidated statements of operations.
Share-based Compensation
The Company accounts for share-based payment arrangements in accordance with Accounting Standards Codification (ASC) 718, Compensation - Stock Compensation and ASC 505-50, Equity - Equity Based Payments to Non-Employees, which requires the recognition of compensation expense, using a fair-value based method, for all costs related to share-based payments, including stock options and restricted stock awards. These standards require companies to estimate the fair value of share-based payment awards on the date of the grant using an option-pricing model. The Company has elected to account for forfeitures as they occur.
Income Taxes
The Company accounts for income taxes using the asset and liability method. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are determined based on the differences between the financial statement carrying amounts and the income tax basis of assets and liabilities. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates applicable to taxable income in the years in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized in income in the period that includes the enactment date. A valuation allowance is applied against any deferred tax asset if, based on available evidence, it is more likely than not that some or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized. For uncertain tax positions that meet a “more likely than not” threshold, the Company recognizes the benefit of uncertain tax positions in the consolidated financial statements. The Company’s practice is to recognize interest and penalties, if any, related to uncertain tax positions in income tax expense in the consolidated statements of operations.
Net Loss Per Share
Basic net loss per share is calculated based on the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding, excluding unvested restricted stock awards. Diluted net loss per share is calculated using the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding plus common stock equivalents. Convertible preferred stock, stock options, warrants and unvested restricted stock awards are considered common stock equivalents and are included in the calculation of diluted net loss per share using the treasury stock method when their effect is dilutive. Common stock equivalents are excluded from the calculation of diluted net loss per share when their effect is anti-dilutive. As of December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, there were common stock equivalents of 13.6 million shares, 10.7 million shares and 10.0 million shares, respectively, which were excluded from the calculation of diluted net loss per share because their effect was anti-dilutive.
Comprehensive Loss
Comprehensive loss is defined as a change in equity during a period from transactions and other events and circumstances from non-owner sources. There have been no items qualifying as other comprehensive loss, and, therefore, comprehensive loss for the periods reported was comprised solely of the Company’s net loss.
Segment Reporting
Operating segments are identified as components of an enterprise about which separate discrete financial information is available for evaluation by the chief operating decision-maker in making decisions regarding resource allocation and assessing performance. Management views its operations and manages its business in one operating segment.
Fair Value Measurements
The Company follows the provisions of ASC 820-10, Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures, which defines fair value, establishes a framework for measuring fair value in GAAP and requires certain disclosures about fair value measurements. Broadly, the ASC 820-10 framework clarifies that fair value is an exit price, representing the amount that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants. As such, fair
F - 8
La Jolla Pharmaceutical Company
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
value is a market-based measurement that should be determined based on assumptions that market participants would use in pricing an asset or liability.
As a basis for considering such assumptions, ASC 820-10 establishes a three-tier fair value hierarchy which prioritizes the inputs used in measuring fair value as follows: Level 1) observable inputs such as quoted prices in active markets; Level 2) inputs other than the quoted prices in active markets that are observable either directly or indirectly; and Level 3) unobservable inputs in which there is little or no market data, which require us to develop our own assumptions. The hierarchy requires the Company to use observable market data, when available, and to minimize the use of unobservable inputs when determining fair value.
Cash equivalents consist of money market accounts with maturities of 90 days or less. Due to the high ratings and short-term nature of these funds, the Company considers the inputs to the value of all cash and cash equivalents as Level 1.
The Company’s consolidated financial instruments include cash and cash equivalents, prepaid expenses, accounts payable and accrued expenses. The carrying amounts reported in the balance sheets for cash equivalents, prepaid expenses, accounts payable and accrued expenses approximate fair values because of the short-term nature of these instruments.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
In May 2017, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) issued Accounting Standard Update (ASU) 2017-09, Compensation - Stock Compensation (Topic 718), Scope of Modification Accounting. The new standard clarifies when to account for a change to the terms or conditions of a share-based payment award as a modification. ASU 2017-09 will be effective for the Company in the first quarter of 2018. Early adoption is permitted, including adoption in an interim period for which financial statements have not yet been issued. The Company plans to adopt the ASU in the first quarter of 2018 and expects the standard to have no material impact on the Company’s financial position or results of operations.
In November 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-18, Statement of Cash Flows (Topic 230): Restricted Cash. The new standard update clarifies the presentation of restricted cash and cash equivalents, and requires companies to include restricted cash and cash equivalents in the beginning and ending cash and cash equivalents on the statement of cash flows. Additional disclosures will be required to describe the amount and detail of the restriction by balance sheet line item. ASU 2016-18 will be effective for the Company in the first quarter of 2018. The Company plans to adopt the ASU in the first quarter of 2018, which will require inclusion of the Company’s restricted cash balances in cash and cash equivalents on the statement of cash flows with retrospective application of each prior period presented.
In February 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-02, Leases (Topic 842). The new standard requires lessees to recognize most leases on their balance sheets as lease liabilities with corresponding right-of-use assets and eliminates certain real estate-specific provisions. ASU 2016-02 will be effective for the Company in the first quarter of 2019 and will be adopted with modified retrospective application for the Company's new 10-year lease agreement for its corporate headquarters, which commenced October 30, 2017. This lease will be recognized on the balance sheet as a lease liability with a corresponding right-of-use asset, which will require modified retrospective application back to the fourth quarter of 2017 and for all of 2018. By 2019, all of the Company’s prior existing leases will have ended. Those leases will not require modified retrospective disclosures applied within the consolidated financial statements upon adoption in 2019.
In May 2014, the FASB issued ASU 2014-09, Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606). The new standard is based on the principle that revenue should be recognized to depict the transfer of promised goods or services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration to which the entity expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods or services. Since its initial release, the FASB has issued several amendments to the standard, which include clarification of accounting guidance related to identification of performance obligations and principal versus agent considerations. Topic 606 will be effective for the Company in the first quarter of 2018 and allows for a full retrospective or a modified retrospective adoption approach. The Company currently does not have, and has never had any, contracts that are within the scope of Topic 606 or its predecessor guidance, ASC 605 Revenue Recognition. Accordingly, there will not be any retrospective impact to the financial statements upon the adoption of Topic 606, which the Company will implement when it has contracts within its scope. The Company anticipates that initial sales subject to Topic 606 will begin in the first quarter of 2018, and that such sales will be to a limited number of customers, which are pharmaceutical specialty distributors. The Contract Revenue - Related Party reported in our results of operations for 2015 and 2016, which represents expense reimbursements from a related party, will not be impacted by the adoption of the new guidance.
F - 9
La Jolla Pharmaceutical Company
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
3. Balance Sheet Account Details
Property and Equipment
Property and equipment, net consists of the following (in thousands):
December 31, | |||||||
2017 | 2016 | ||||||
Lab equipment | $ | 7,812 | $ | 2,610 | |||
Furniture and fixtures | 2,282 | 389 | |||||
Computer hardware | 1,238 | 457 | |||||
Software | 619 | 309 | |||||
Leasehold improvements | 14,852 | 464 | |||||
Total property and equipment, gross | 26,803 | 4,229 | |||||
Accumulated depreciation and amortization | (2,235 | ) | (1,084 | ) | |||
Total property and equipment, net | $ | 24,568 | $ | 3,145 | |||
Accrued Clinical and Other Expenses
Accrued clinical and other expenses consist of the following (in thousands):
December 31, | |||||||
2017 | 2016 | ||||||
Accrued clinical trials | $ | 577 | $ | 828 | |||
Accrued other | 126 | 77 | |||||
Total accrued clinical and other expenses | $ | 703 | $ | 905 | |||
4. Licensed Technology
The George Washington University
In December 2014, the Company entered into a patent license agreement with the George Washington University (GW), which the parties amended and restated on March 1, 2016. Pursuant to this license agreement, GW exclusively licensed to the Company certain intellectual property rights relating to GIAPREZA, including the exclusive rights to certain issued patents and patent applications covering GIAPREZA. Under this license agreement, the Company is obligated to use commercially reasonable efforts to develop, commercialize, market and sell GIAPREZA. The Company has paid a one-time license initiation fee, annual maintenance fees, an amendment fee and additional payments following the achievement of certain development and regulatory milestones including FDA approval. The Company may be obligated to make additional milestone payments of up to $0.5 million in the aggregate. Following the commencement of commercial sales of GIAPREZA, the Company is obligated to pay tiered royalties in the low- to mid- single digits on products covered by the licensed rights. The patents and patent applications covered by the GW license agreement expire between 2029 and 2038, and the obligation to pay royalties under this agreement extend through the last-to-expire patent covering GIAPREZA.
Inserm Transfert SA
In February 2014, the Company entered into a license agreement with Inserm Transfert SA (Inserm). Pursuant to this license agreement, Inserm exclusively licensed to the Company certain intellectual property rights relating to LJPC-401. Under this license agreement, the Company has paid a one-time license initiation fee, annual maintenance fees and additional payments following the achievement of certain development milestones. The Company may be obligated to make additional payments of up to $4.1 million upon the achievement of certain development milestones and regulatory approval on products covered by the licensed patent rights. Following the commencement of commercial sales of a product covered by the licensed intellectual property, the Company will be obligated to pay tiered royalties in the low- to mid- single digits on products covered by the licensed rights. The patents and patent applications covered by the Inserm license agreement expire between 2022 and
F - 10
La Jolla Pharmaceutical Company
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
2038, and the obligation to pay royalties under this agreement extend through the last-to-expire patent covering a licensed product.
Other In-Licensed Technology
The Company continues to seek additional technology for potential new development programs and, as a result, has entered into various licensing agreements for intellectual property rights. In 2015, the Company formed foreign subsidiaries to acquire and in-license various early-stage technology from Indiana University Research and Technology Corporation, Vanderbilt University and the Board of Trustees of the Leland Stanford Junior University.
The Company has incurred licensing and milestone fees of $1.6 million, $0.5 million and $0.8 million recorded in research and development expense in connection with its licensing agreements for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively. See Note 9 for future minimum licensing payment commitments.
5. Contract Revenue - Related Party
During the year ended December 31, 2015, the Company entered into a services agreement with a related party. Pursuant to the services agreement, the Company provides certain services to this related party, including, but not limited to, research and development and clinical study design and management for projects undertaken. In exchange for providing such services, the Company receives payments at a negotiated, arms-length rate. As a result, the consideration received by the Company for its services is considered to be no less favorable to the Company than comparable terms that the Company could
obtain from an unaffiliated third party in an arms-length transaction. The services agreement may be canceled by either party upon 60-days’ written notice to the other party.
The Company had no contract revenue during the year ended December 31, 2017. During the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, the Company recognized approximately $0.6 million and $1.1 million of contract revenue for services and costs provided under the services agreement, respectively.
In addition, the Company has a non-voting profit interest in the related party, which provides the Company with the potential to receive a portion of the future distributions of profits, if any. Investment funds affiliated with the Chairman of the Company’s board of directors have a controlling interest in, and the Company’s Chief Executive Officer (CEO) has a non-voting profit interest in, the related party.
6. Shareholders’ Equity
Common Stock
2015 Common Stock Offering
In September 2015, the Company offered and sold an aggregate of 2,932,500 shares of common stock in an underwritten offering at a public offering price of $38.00 per share, with gross proceeds of approximately $111.4 million. The Company received net proceeds of approximately $104.6 million, net of approximately $6.8 million in underwriting commissions, discounts and other issuance costs.
2017 Common Stock Offering
In March 2017, the Company offered and sold an aggregate of 3,731,344 shares of common stock in an underwritten public offering at a price of $33.50 per share, with gross proceeds of approximately $125.0 million. The Company received net proceeds of approximately $117.5 million, net of approximately $7.5 million in underwriting commissions, discounts and other issuance costs.
Preferred Stock
As of December 31, 2017, the Company is authorized to issue 8,000,000 shares of preferred stock, with a par value of $0.0001 per share, in one or more series, of which 11,000 are designated as Series C-12 Convertible Preferred Stock (Series C-12 Preferred) and 10,000 are designated as Series F Convertible Preferred Stock (Series F Preferred). During the year ended December 31, 2015, the Company issued 19,134 and 17,360 shares of common stock upon the conversion of Series C-12 Preferred and Series F Preferred, respectively. The Series C-12 Preferred is convertible into common stock at a rate of
F - 11
La Jolla Pharmaceutical Company
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
approximately 1,724 shares of common stock for each share of Series C-12 Preferred, and the Series F Preferred is convertible into common stock at a rate of approximately 286 shares of common stock for each share of Series F Preferred.
As of December 31, 2017 and 2016, there were 3,906 shares of Series C-12 Preferred and 2,737 shares of Series F Preferred issued and outstanding. As such, as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, the issued and outstanding Series C-12 Preferred and Series F Preferred were convertible into 6,735,378 and 782,032 shares of common stock, respectively.
The holders of preferred stock do not have voting rights, other than for general protective rights required by the California General Corporation Law. The Series C-12 Preferred and the Series F Preferred do not have dividends. The Series C-12 Preferred and the Series F Preferred have a liquidation preference in an amount equal to $1,000 per share. As of December 31, 2017 and 2016, the aggregate liquidation preference was approximately $3.9 million and $2.7 million on the Series C-12 Preferred and Series F Preferred, respectively.
Share-based Compensation Expense
Stock Options
2013 Equity Incentive Plan
In September 2013, the Company adopted an equity compensation plan entitled the 2013 Equity Incentive Plan (2013 Equity Plan). The 2013 Equity Plan is an omnibus equity compensation plan that permits the issuance of various types of equity-based compensation awards, including stock options, restricted stock awards, stock appreciation rights and restricted stock units, as well as cash awards, to employees, directors and eligible consultants of the Company. The 2013 Equity Plan has a ten-year term and permits the issuance of incentive stock options under Section 422 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended (IRC). The administrator under the plan has broad discretion to establish the terms of awards, including the size, term, exercise price and vesting conditions. Generally, grants to employees vest over four years, with 25% vesting on the one-year anniversary and the remainder vesting either quarterly or monthly thereafter; grants to non-employee directors generally vest over one year on the one-year anniversary.
At the 2015, 2016 and 2017 annual meetings of shareholders, the Company’s shareholders approved and adopted an amendment to the 2013 Equity Plan to increase the number of shares of common stock authorized for issuance up to a total of 3,100,000, 4,600,000 and 8,100,000 shares, respectively.
As of December 31, 2017, there were 1,875,732 shares available for future grants under the 2013 Equity Plan.
F - 12
La Jolla Pharmaceutical Company
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Stock Option Activity
The Company’s 2013 Equity Plan stock option activity for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 was comprised of the following:
Outstanding Stock Options and 2013 Equity Plans | ||||||||||||
Shares Underlying Stock Options | Weighted- Average Exercise Price per Share | Weighted- Average Remaining Contractual Term | Aggregate Intrinsic Value | |||||||||
Outstanding at December 31, 2014 | 618,900 | $ | 9.54 | |||||||||
Granted | 1,769,785 | $ | 25.89 | |||||||||
Exercised | (51,814 | ) | $ | 10.81 | ||||||||
Forfeited | (18,186 | ) | $ | 7.80 | ||||||||
Outstanding at December 31, 2015 | 2,318,685 | $ | 22.01 | |||||||||
Granted | 483,200 | $ | 17.83 | |||||||||
Exercised | (17,548 | ) | $ | 8.52 | ||||||||
Forfeited | (156,875 | ) | $ | 26.35 | ||||||||
Outstanding at December 31, 2016 | 2,627,462 | $ | 21.07 | |||||||||
Granted | 3,704,725 | $ | 25.94 | |||||||||
Exercised | (174,628 | ) | $ | 15.42 | ||||||||
Forfeited | (120,257 | ) | $ | 22.82 | ||||||||
Outstanding at December 31, 2017 | 6,037,302 | $ | 24.19 | 8.76 years | $ | 49,399,882 | ||||||
Vested and expected to vest at December 31, 2017 | 6,037,302 | $ | 24.19 | 8.76 years | $ | 49,399,882 | ||||||
Exercisable at December 31, 2017 | 1,536,369 | $ | 20.94 | 7.36 years | $ | 17,799,721 | ||||||
In April 2015, the Company made a stock option grant to the Company’s Chief Financial Officer upon his hiring to purchase 60,000 shares of common stock at an exercise price equal to the fair market value of the Company’s common stock on the grant date. This grant was awarded as an Inducement Grant outside of the 2013 Equity Plan and is included in the table above. The stock option vests and becomes exercisable with respect to 25% of the underlying shares on the first anniversary of the grant date, and then with respect to the remaining shares, on a quarterly basis over the next three years, subject to continued service during that time.
As of December 31, 2017, the Company has reserved 7,853,034 shares of common stock for future issuance upon exercise of all outstanding stock options granted or to be granted under the 2013 Equity Plan, which excludes the 60,000 shares underlying the stock option discussed above that was issued in April 2015.
The weighted-average grant date fair values of the stock options granted was $23.80, $15.33 and $22.56 per underlying share for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively. As of December 31, 2017, $96.0 million of total unrecognized share-based compensation expense related to non-vested stock options remains and is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of approximately 3.3 years. During the year ended December 31, 2017, stock options to purchase 174,628 shares of common stock were exercised with an intrinsic value of $3.3 million. During the year ended December 31, 2016, stock options to purchase 17,548 shares of common stock were exercised with an intrinsic value of $0.1 million. During the year ended December 31, 2015, stock options to purchase 51,814 shares of common stock were exercised with an intrinsic value of $0.9 million.
Restricted Stock Award Activity
Restricted stock awards (RSAs) are grants that entitle the holder to acquire shares of common stock for no cash consideration or at a fixed price, which is typically nominal. The Company accounts for RSAs as issued and outstanding common stock, even though: (a) shares covered by an RSA cannot be sold, pledged or otherwise disposed of until the award vests; and (b) any unvested shares may be reacquired by the Company for the original purchase price following the awardee’s termination of service. The valuation of RSAs is based on the fair market value of the underlying shares on the grant date.
F - 13
La Jolla Pharmaceutical Company
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
In September 2013, the Company issued RSAs consisting of 1,327,048 shares to the Company’s CEO, 79,622 shares to a director and an aggregate of 336,185 shares to three non-officer employees. The RSA grants to the CEO, director and one of the employees were for the replacement of canceled stock options and restricted stock units granted in April 2012, which was done in order to complete the capital restructuring that took place in September 2013. These RSAs were granted outside of the 2013 Equity Plan, but are governed in all respects by the 2013 Equity Plan. These RSAs were granted with a combination of performance-based and time-based vesting components. As of December 31, 2017, all performance-based and time-based vesting conditions had been satisfied. In July 2015, the vesting conditions for 1,042,680 shares of unvested and outstanding RSAs awarded to the CEO were amended to provide that vesting and delivery of the shares were deferred until March 15, 2017, subject to the CEO’s continued service with the Company through such date. In December 2016, vesting and delivery was accelerated for 500,000 shares of the RSAs that had been deferred until March 15, 2017. As of December 31, 2017, the remaining 542,680 shares of the RSAs had vested and been delivered.
In August 2015, the Company issued a fully vested RSA representing the right to acquire 4,000 shares of common stock with a grant date fair value of approximately $0.1 million.
The Company’s RSA activity for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 was comprised of the following:
Number of Shares | Weighted- Average Grant Date Fair Market Value | |||||
Unvested at December 31, 2014 | 1,279,007 | $ | 12.86 | |||
Granted | 4,000 | $ | 23.12 | |||
Vested | (210,108 | ) | $ | 12.41 | ||
Unvested at December 31, 2015 | 1,072,899 | $ | 13.00 | |||
Vested | (530,219 | ) | $ | 12.78 | ||
Unvested at December 31, 2016 | 542,680 | $ | 13.22 | |||
Vested | (542,680 | ) | $ | 13.22 | ||
Unvested at December 31, 2017 | — | — | ||||
Stock Option Valuation
The fair value of each stock option award is estimated on the grant date using a Black-Scholes option pricing model (Black-Scholes model), which uses the assumptions noted in the following table. Expected volatility is based on historical volatility of the Company’s common stock. In determining the expected life of employee stock options, the Company uses the “simplified” method. The expected life assumptions for non-employees’ options are based upon the contractual term of the stock options. The risk-free interest rate is based on the U.S. Treasury yield for a period consistent with the expected term of the stock options in effect at the time of the grants. The dividend yield assumption is based on the expectation of no future dividend payments by the Company.
The Company estimated the fair value of each stock option grant on the grant date using the Black-Scholes model with the following weighted-average assumptions:
Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||
Volatility | 139 | % | 143 | % | 149 | % | ||
Expected life (years) | 6.12 | 5.80 | 5.28 | |||||
Risk-free interest rate | 2.1 | % | 1.4 | % | 1.5 | % | ||
Dividend yield | — | — | — | |||||
F - 14
La Jolla Pharmaceutical Company
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Share-Based Compensation Expense
Total share-based compensation expense related to all share-based awards for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 was comprised of the following (in thousands):
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
Research and development: | |||||||||||
Stock options | $ | 11,904 | $ | 5,599 | $ | 2,428 | |||||
Restricted stock | — | 30 | 1,600 | ||||||||
Warrants | 76 | 28 | 56 | ||||||||
Research and development share-based compensation expense | 11,980 | 5,657 | 4,084 | ||||||||
General and administrative: | |||||||||||
Stock options | 8,837 | 6,539 | 3,693 | ||||||||
Restricted stock | 409 | 2,161 | 4,265 | ||||||||
Warrants | 569 | 189 | 1,030 | ||||||||
General and administrative share-based compensation expense | 9,815 | 8,889 | 8,988 | ||||||||
Total share-based compensation expense included in expenses | $ | 21,795 | $ | 14,546 | $ | 13,072 | |||||
Share-based compensation expense recognized for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 is reduced by actual forfeitures in the period that the forfeiture occurs.
Third Party Share-based Compensation Expense
The Company initially estimates the fair value of stock options and warrants issued to non-employees, other than non-employee directors, on the grant date using the Black-Scholes model. Thereafter, the Company re-measures the fair value using the Black-Scholes model as of each balance sheet date as the stock options and warrants vest.
In December 2014, the Company granted warrants to purchase 51,000 shares of common stock to two outside third parties at an exercise price equal to the fair market value of the stock on the grant dates. One grant vests 25% on each anniversary date over four years. The other grant vested 100% on the one-year anniversary of the grant. In January 2016, the Company granted a warrant to purchase 17,000 shares of common stock to an outside third party at an exercise price equal to the fair market value of the stock on the date of each grant. The grant vested 100% on the one-year anniversary of the grant. In January 2017, the Company granted a warrant to purchase 25,013 shares of common stock to an outside third party at an exercise price equal to the fair market value of the stock on the date of each grant. The grant vests 100% on the one-year anniversary of the grant. The Company recognized compensation expense for these warrant grants of approximately $0.6 million, $0.2 million and $1.1 million for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively.
In February 2015, the Company granted a stock option to purchase 60,000 shares of common stock to a consultant at an exercise price equal to the fair market value of the Company’s common stock on the grant date. This grant was made from the 2013 Equity Plan. The stock option vested with respect to 25% of the underlying shares on the grant date with the remainder to vest quarterly over three years. The Company recognized third-party compensation expense for this stock option grant of approximately $0.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2015. In July 2015, this consultant became an employee of the Company.
In August and November 2015, the Company granted stock options to purchase 50,000 shares of common stock to two consultants at exercise prices equal to the fair market value of the Company’s common stock on the grant dates. These grants were made from the 2013 Equity Plan. The vesting of these stock options was contingent on the achievement of a performance milestone by the end of 2016, at which time any unvested shares underlying the options would be canceled. The milestone was achieved in the fourth quarter of 2016 at a 75% achievement level, with 25% of the options canceling. The Company recognized compensation (benefit) expense for these stock option grants of approximately $(0.1) million and $0.1 million for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively.
F - 15
La Jolla Pharmaceutical Company
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
In September 2016, the Company granted a stock option to purchase 35,000 shares of common stock to a consultant at an exercise price equal to the fair market value of the Company’s common stock on the grant date. This grant was made from the 2013 Equity Plan. The stock option will vest with respect to 25% of the underlying shares on the one-year anniversary of the grant, with the remainder to vest monthly over the next three years, subject to continued service during that time. In January 2017, this consultant became an employee of the Company.
In February 2017, the Company granted stock options to purchase 42,000 shares of common stock to three consultants at exercise prices equal to the fair market value of the Company’s common stock on the grant dates. These grants were made from the 2013 Equity Plan. Two of the stock options will vest with respect to 25% of the underlying shares on the one-year anniversary of the grant, with the remainder to vest monthly over the next three years, subject to continued service during that time. The other stock option will vest with respect to 25% of the underlying shares on the one-year anniversary of the grant, with the remainder to vest monthly over the next two years, subject to continued service during that time. In addition, an employee converted to a consultant during April 2017. Two of his options were modified and are continuing to vest over the next two years. The Company recognized third-party compensation expense for these stock option grants of approximately $0.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2017.
7. Defined Contribution Plan
The Company has a defined contribution plan (401k Plan) covering substantially all of the Company’s employees. The 401k Plan was established to provide retirement benefits for employees and is employee funded up to the elective annual deferral limits.
Effective January 1, 2015, the 401k Plan was amended. As a result, all employees are eligible to participate with no minimum service requirement, and the Company made matching contributions of $0.7 million, $0.4 million and $0.2 million for the years December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively.
8. Income Taxes
The Company did not record a provision for income taxes for the years ended December 2017, 2016 and 2015 due to a full valuation allowance against its deferred tax assets.
On December 22, 2017, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (2017 Tax Act) was enacted. The 2017 Tax Act includes a number of changes to existing U.S. tax laws that impact the Company, most notably a reduction of the U.S. corporate tax rate from 34% to 21%, for tax years beginning after December 31, 2017. The 2017 Tax Act also provides for the implementation of a territorial tax system, a one-time transition tax on certain foreign earnings, the acceleration of depreciation for certain assets placed into service after September 27, 2017 and other prospective changes beginning in 2018, including repeal of the domestic manufacturing deduction, acceleration of tax revenue recognition, capitalization of research and development expenditures, additional limitations on executive compensation and limitations on the deductibility of interest.
Pursuant to the SEC Staff Accounting Bulletin No. 118, Income Tax Accounting Implications of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, the Company has not finalized its accounting for the income tax effects of the 2017 Tax Act. This includes a provisional amount related to the re-measurement of deferred tax assets based on the rates at which they are expected to reverse in the future, which is generally 21% plus the applicable state tax rate, with a corresponding change to the valuation allowance as of December 31, 2017. The impact of the 2017 Tax Act may differ from this estimate during the one-year measurement period due to, among other things, further refinement of the Company’s calculation, changes in interpretations and assumptions the Company has made, additional guidance that may be issued and actions the Company may take as a result of the 2017 Tax Act.
Significant components of the Company’s deferred tax assets are as follows (in thousands):
December 31, | |||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
Deferred tax assets: | |||||||||||
Capitalized research and development and other | $ | 7,379 | $ | 9,380 | $ | 33,894 | |||||
Valuation allowance | (7,379 | ) | (9,380 | ) | (33,894 | ) | |||||
Net deferred tax assets | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | |||||
F - 16
La Jolla Pharmaceutical Company
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
The difference between the provision for income taxes and income taxes computed using the effective U.S. federal statutory rate is as follows (in thousands):
December 31, | |||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||
Income tax benefit at statutory federal rate | $ | (39,033 | ) | $ | (26,583 | ) | $ | (14,250 | ) | ||
Research and development credits | (2,691 | ) | (1,240 | ) | 1,128 | ||||||
Foreign rate differential | 1,249 | — | — | ||||||||
Expired tax attributes | 2,228 | (5 | ) | 31 | |||||||
Impact of the 2017 Tax Act | 71,199 | — | — | ||||||||
Stock-based compensation | 2,253 | — | — | ||||||||
Change in valuation allowance | (35,246 | ) | 25,091 | 12,042 | |||||||
Other permanent differences | 41 | 2,737 | 1,049 | ||||||||
Provision for income taxes | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | |||||
The Company has established a valuation allowance against its federal and state deferred tax assets due to the uncertainty surrounding the realization of such assets. Management periodically evaluates the recoverability of the deferred tax assets. At such time as it is determined that it is more likely than not that deferred assets are realizable, the valuation allowance will be reduced accordingly and recorded as a tax benefit.
Pursuant to Section 382 and 383 of the IRC, utilization of the Company’s federal net operating loss and research and development credit carryforwards may be subject to annual limitations in the event of any significant future changes in its ownership structure. These annual limitations may result in the expiration of net operating loss and research and development credit carryforwards prior to utilization. The Company has not completed an IRC Section 382 and 383 analysis regarding the limitation of net operating loss and research and development credit carryforwards. The Company does not presently plan to complete an IRC Section 382 and 383 analysis; and until this analysis has been completed, the Company has removed the deferred tax assets for net operating losses and research and development credits generated through 2017 from its deferred tax assets and has recorded a corresponding increase to its valuation allowance.
As of December 31, 2017, the Company has estimated federal and California net operating loss carryforwards of approximately $537.1 million and $323.5 million, respectively. The difference between the federal and California tax net operating loss carryforwards is primarily attributable to the capitalization of research and development expenses for California income tax purposes. In addition, the Company has estimated federal and California research and development tax credit carryforwards of approximately $21.0 million and $13.4 million, respectively. The federal net operating loss carryforwards, federal research tax credit carryforwards and California net operating loss carryforwards will begin to expire in 2018, if not utilized. California research and development credit carryforwards will carry forward indefinitely until utilized. The Company believes that, in May 2010 and February 2009, it experienced ownership changes at times when its enterprise value was minimal. As a result of the ownership changes and low enterprise values at such times, the Company’s federal and California net operating loss carryforwards and federal research and development credit carryforwards as of December 31, 2017 will likely be subject to annual limitations under IRC Section 382 and 383 and, more likely than not, will expire unused.
There were no unrecognized tax benefits as of the December 31, 2017 and 2016. The Company does not anticipate there will be a significant change in unrecognized tax benefits within the next 12 months.
The Company had no accrual for interest or penalties on the Company’s consolidated balance sheets as of December 31, 2017 or December 31, 2016, and has not recognized interest and/or penalties in the consolidated statements of operations for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015.
The Company is subject to taxation in the U.S. and various state jurisdictions. The Company’s tax returns since inception are subject to examination by the U.S. and various state tax authorities. The Company is not currently undergoing a tax audit in any federal or state jurisdiction.
F - 17
La Jolla Pharmaceutical Company
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
9. Commitments and Contingencies
Leases
On December 29, 2016, the Company entered into an agreement with BMR-Axiom LP to lease office and laboratory space as the Company’s new corporate headquarters located at 4550 Towne Centre Court, San Diego, California (Lease) for a period of ten years commencing on October 30, 2017.
The Lease provides an option to extend the Lease for an additional 5.0 years at the end of the initial term. The Company has provided a standby letter of credit for $0.9 million in lieu of a security deposit. This amount will decrease to $0.6 million after year two of the lease and decrease to $0.3 million after year 5 of the lease term. The Lease provided an allowance for tenant improvements of $13.7 million, which was classified as deferred rent on the Company’s balance sheet and will be amortized as an offset to rent expense with a corresponding charge to depreciation expense on a straight-line basis over the term of the lease. The annual rent under the Lease is subject to escalation during the term. In addition to rent, the Lease requires the Company to pay certain taxes, insurance and operating costs relating to the leased premises. The Lease contains customary default provisions, representations, warranties and covenants.
Annual future minimum payments under operating leases as of December 31, 2017 are as follows (in thousands):
2018 | $ | 1,945 | |
2019 | 3,951 | ||
2020 | 4,070 | ||
2021 | 4,192 | ||
2022 | 4,318 | ||
Thereafter | 22,755 | ||
Total future minimum lease payments | $ | 41,231 | |
Rent expense was $1.7 million, $1.1 million and $0.7 million for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, respectively.
Licensing Agreements
In the normal course of business, the Company enters into licensing agreements under which the Company commits to certain annual maintenance payments. Annual future minimum licensing payments under the Company’s agreements as of December 31, 2017 are as follows (in thousands):
2018 | $ | 142 | |
2019 | 147 | ||
2020 | 148 | ||
2021 | 147 | ||
2022 | 158 | ||
Thereafter | 53 | ||
Total future minimum license payments | $ | 795 | |
F - 18
La Jolla Pharmaceutical Company
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Supply Agreements
In the normal course of business, the Company enters into agreements for the manufacturing and supply of its clinical and commercial products. In 2017, the Company entered into agreements arranging for the manufacture and supply of GIAPREZA through 2022. During this time, the Company will be obligated to make certain minimum purchases. Annual future minimum payments for manufacturing and supply agreements as of December 31, 2017 are as follows (in thousands):
2018 | $ | 1,092 | |
2019 | 921 | ||
2020 | 921 | ||
2021 | 921 | ||
Total future minimum manufacturing and supply agreement payments | $ | 3,855 | |
10. Quarterly Financial Information (unaudited)
The following is a summary of the quarterly results of operations for the years ended December 31, 2017 and 2016 (in thousands, except per share amounts):
First Quarter | Second Quarter | Third Quarter | Fourth Quarter | ||||||||||||
2017 | |||||||||||||||
Total revenue | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | |||||||
Loss from operations | $ | (23,268 | ) | $ | (26,830 | ) | $ | (26,483 | ) | $ | (38,846 | ) | |||
Net loss | $ | (23,240 | ) | $ | (26,729 | ) | $ | (26,288 | ) | $ | (38,546 | ) | |||
Basic and diluted net loss per share | $ | (1.26 | ) | $ | (1.21 | ) | $ | (1.19 | ) | $ | (1.74 | ) | |||
Weighted-average common shares outstanding - basic and diluted | 18,410 | 22,123 | 22,125 | 22,151 | |||||||||||
2016 | |||||||||||||||
Total revenue | $ | 234 | $ | 253 | $ | 44 | $ | 85 | |||||||
Loss from operations | $ | (16,534 | ) | $ | (15,617 | ) | $ | (21,297 | ) | $ | (24,924 | ) | |||
Net loss | $ | (16,481 | ) | $ | (15,566 | ) | $ | (21,251 | ) | $ | (24,887 | ) | |||
Basic and diluted net loss per share | $ | (0.96 | ) | $ | (0.90 | ) | $ | (1.23 | ) | $ | (1.44 | ) | |||
Weighted-average common shares outstanding - basic and diluted | 17,210 | 17,211 | 17,211 | 17,280 | |||||||||||
F - 19
