Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-31.2 - EX-31.2 - AIR LEASE CORP | al-20171231ex312cc77ca.htm |
| EX-32.2 - EX-32.2 - AIR LEASE CORP | al-20171231ex322baaf1c.htm |
| EX-32.1 - EX-32.1 - AIR LEASE CORP | al-20171231ex321ff43f0.htm |
| EX-31.1 - EX-31.1 - AIR LEASE CORP | al-20171231ex3110e5c96.htm |
| EX-23.1 - EX-23.1 - AIR LEASE CORP | al-20171231ex2319e1c2d.htm |
| EX-21.1 - EX-21.1 - AIR LEASE CORP | al-20171231ex211e906b3.htm |
| EX-12.1 - EX-12.1 - AIR LEASE CORP | al-20171231ex121565f8e.htm |
| EX-10.99 - EX-10.99 - AIR LEASE CORP | al-20171231ex1099927e4.htm |
| EX-10.80 - EX-10.80 - AIR LEASE CORP | al-20171231ex1080302d3.htm |
| EX-10.79 - EX-10.79 - AIR LEASE CORP | al-20171231ex10792ebbc.htm |
| EX-10.75 - EX-10.75 - AIR LEASE CORP | al-20171231ex107504f3f.htm |
| EX-10.37 - EX-10.37 - AIR LEASE CORP | al-20171231ex103778984.htm |
| EX-10.12 - EX-10.12 - AIR LEASE CORP | al-20171231ex1012b098c.htm |
| EX-10.11 - EX-10.11 - AIR LEASE CORP | al-20171231ex1011e824c.htm |
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10‑K
|
(Mark One) |
|
|
☒ |
ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
|
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2017 |
|
|
☐ |
TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
|
For the transition period from to |
|
Commission File Number 001-35121
AIR LEASE CORPORATION
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
|
Delaware |
27‑1840403 |
|
2000 Avenue of the Stars, Suite 1000N |
90067 |
(Registrant’s telephone number, including area code): (310) 553-0555
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
|
Title of each class |
|
Name of each exchange |
|
Class A Common Stock |
|
New York |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well‑known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Exchange Act. Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate website, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S‑T (§ 232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S‑K is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10‑K or any amendment to this Form 10‑K. ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company,” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. (Check One):
|
Large accelerated filer ☒ |
Accelerated filer ☐ |
Non‑accelerated filer ☐ |
Smaller reporting company ☐ |
|
|
|
|
Emerging growth company ☐ |
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the Registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes ☐ No ☒
The aggregate market value of registrant’s voting stock held by non‑affiliates was approximately $3.6 billion on June 30, 2017, based upon the last reported sales price on the New York Stock Exchange. As of February 21, 2018, there were 103,621,629 shares of Class A common stock outstanding.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Designated portions of the Proxy Statement relating to registrant’s 2018 Annual Meeting of Shareholders have been incorporated by reference into Part III of this report.
Form 10‑K
For the Fiscal Year Ended December 31, 2017
INDEX
2
FORWARD LOOKING STATEMENTS
This Annual Report on Form 10‑K and other publicly available documents may contain or incorporate statements that constitute forward‑looking statements within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. Those statements appear in a number of places in this Form 10‑K and include statements regarding, among other matters, the state of the airline industry, our access to the capital markets, our ability to restructure leases and repossess aircraft, the structure of our leases, regulatory matters pertaining to compliance with governmental regulations, and other factors affecting our financial condition or results of operations. Words such as “expects,” “anticipates,” “intends,” “plans,” “believes,” “seeks,” “estimates” and “should,” and variations of these words and similar expressions, are used in many cases to identify these forward‑looking statements. Any such forward‑looking statements are not guarantees of future performance and involve risks, uncertainties, and other factors that may cause our actual results, performance or achievements, or industry results to vary materially from our future results, performance or achievements, or those of our industry, expressed or implied in such forward‑looking statements. Such factors include, among others, general commercial aviation industry, economic, and business conditions, which will, among other things, affect demand for aircraft, availability, and creditworthiness of current and prospective lessees, lease rates, availability and cost of financing and operating expenses, governmental actions and initiatives, and environmental and safety requirements, as well as the factors discussed under “Item 1A. Risk Factors,” in this Annual Report on Form 10‑K. We do not intend and undertake no obligation to update any forward‑looking information to reflect actual results or future events or circumstances.
3
Overview
Air Lease Corporation (the “Company”, “ALC”, “we”, “our” or “us”) is a leading aircraft leasing company that was founded by aircraft leasing industry pioneer, Steven F. Udvar-Házy. We are principally engaged in purchasing new commercial jet transport aircraft directly from aircraft manufacturers, such as The Boeing Company (“Boeing”) and Airbus S.A.S. (“Airbus”), and leasing those aircraft to airlines throughout the world with the intention to generate attractive returns on equity. In addition to our leasing activities, we sell aircraft from our operating lease portfolio to third parties, including other leasing companies, financial services companies, and airlines. We also provide fleet management services to investors and owners of aircraft portfolios for a management fee. Our operating performance is driven by the growth of our fleet, the terms of our leases, the interest rates on our debt, and the aggregate amount of our indebtedness, supplemented by the gains from our aircraft sales and trading activities and our management fees.
We currently have relationships with over 200 airlines across 70 countries. We operate our business on a global basis, providing aircraft to airline customers in every major geographical region, including markets such as Asia, the Pacific Rim, Latin America, the Middle East, Europe, Africa, and North America. Many of these markets are experiencing increased demand for passenger airline travel and have lower market saturation than more mature markets such as the United States and Western Europe. We expect that these markets will also present significant replacement opportunities in upcoming years as many airlines look to replace aging aircraft with new, modern technology, fuel efficient jet aircraft. An important focus of our strategy is meeting the needs of this replacement market. Airlines in some of these markets have fewer financing alternatives, enabling us to command relatively higher lease rates compared to those in more mature markets.
We mitigate the risks of owning and leasing aircraft through careful management and diversification of our leases and lessees by geography, lease term, and aircraft age and type. We believe that diversification of our operating lease portfolio reduces the risks associated with individual lessee defaults and adverse geopolitical and regional economic events. We mitigate the risks associated with cyclical variations in the airline industry by managing customer concentrations and lease maturities in our operating lease portfolio to minimize periods of concentrated lease expirations. In order to maximize residual values and minimize the risk of obsolescence, our strategy is to own an aircraft during the first third of its expected 25 year useful life.
We ended 2017 with 244 owned aircraft and 50 aircraft in our managed fleet portfolio. As of December, 31, 2017, the net book value of our fleet increased by 10.3%, as compared to December 31, 2016, to $13.3 billion, with a weighted average lease term remaining of 6.8 years and a weighted average age of 3.8 years. We have a globally diversified customer base comprised of 91 airlines in 55 countries. As of February 22, 2018, all of our aircraft in our operating lease portfolio were subject to lease agreements.
During 2017, we increased our total commitments with Airbus and Boeing by a net 35 aircraft. As of December 31, 2017, we had commitments to purchase 368 aircraft from Airbus and Boeing for delivery through 2023, with an estimated aggregate commitment of $27.0 billion. We ended 2017 with $23.4 billion in committed minimum future rental payments and placed 79% of our order book on long-term leases for aircraft delivering through 2020. This includes $10.1 billion in contracted minimum rental payments on the aircraft in our existing fleet and $13.3 billion in minimum future rental payments related to aircraft which will deliver between 2018 and 2022.
We finance the purchase of aircraft and our business with available cash balances, internally generated funds, including aircraft sales and trading activities, and debt financings. Our debt financing strategy is focused on raising unsecured debt in the global bank and debt capital markets, with a limited utilization of export credit or other forms of secured financing. In 2017, we issued $2.2 billion senior unsecured notes with an average interest rate of 3.16%, with maturities ranging from 2022 to 2027 and in January 2018, we issued (i) $550.0 million in aggregate principal amount of senior unsecured notes due 2021 that bear interest at a rate of 2.50% and (ii) $700.0 million in aggregate principal amount of senior unsecured notes due 2025 that bear interest at a rate of 3.25%. In 2017, we increased our unsecured
4
revolving credit facility capacity to approximately $3.8 billion, representing an 18.6% increase from 2016 and extended the final maturity to May 5, 2021. In February 2018, we further increased the capacity of our unsecured revolving credit facility by 4.7% to approximately $3.9 billion. Borrowings under our unsecured revolving credit facility will bear interest at LIBOR plus a margin of 1.05% per year. We ended 2017 with total debt outstanding, net of discounts and issuance costs, of $9.7 billion, of which 85.4% was at a fixed rate and 94.6% of which was unsecured. Our composite cost of funds decreased to 3.20% as of December 31, 2017 from 3.42% as of December 31, 2016.
On December 22, 2017, the U.S. Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (the “Tax Reform Act”) was signed into law. The Tax Reform Act significantly revised the U.S. corporate income tax law by, among other things, lowering the U.S. corporate tax rate from 35% to 21% effective January 1, 2018. As a result of the Tax Reform Act, we recorded an estimated tax benefit of $354.1 million or $3.16 per diluted share due to the remeasurement of deferred tax assets and liabilities for the quarter ended December 31, 2017.
In 2017, total revenues increased by 6.9% to $1.5 billion, compared to 2016. The increase in our total revenues is primarily due to the $1.2 billion increase in the net book value of our operating lease portfolio. Our net income for the year ended December 31, 2017 was $756.2 million, or $6.82 per diluted share compared to $374.9 million, or $3.44 per diluted share for the year ended December 31, 2016. The increase in our net income and diluted earnings per share for the year ended December 31, 2017 was due to the $1.2 billion increase in the net book value of our operating lease portfolio, and the re-measurement of our U.S. deferred tax liabilities associated with the enactment of the Tax Reform Act, resulting in a tax benefit of $354.1 million. Our pre-tax profit margin for the year ended December 31, 2017 was 40.2% as compared to 40.9% for the year ended December 31, 2016.
Our adjusted net income before income taxes excludes the effects of certain non-cash items, one-time or non-recurring items, such as settlement expense, net of recoveries, that are not expected to continue in the future and certain other items. Our adjusted net income before income taxes for the year ended December 31, 2017 was $657.8 million or $5.94 per diluted share, compared to $622.9 million, or $5.67 per diluted share for the year ended December 31, 2016. Our adjusted margin before income taxes for the year ended December 31, 2017 was 43.4% compared to 44.1% for the year ended December 31, 2016. Adjusted net income before income taxes, adjusted margin before income taxes and adjusted diluted earnings per share before income taxes are measures of financial and operational performance that are not defined by Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (“GAAP”). See Note 2 in “Item 6. Selected Financial Data” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for a discussion of adjusted net income before income taxes and adjusted diluted earnings per share before income taxes as non-GAAP measures and reconciliation of these measures to net income.
Operations to Date
Current Fleet
Our fleet, based on net book value, increased by 10.3% to $13.3 billion as of December 31, 2017 compared to $12.0 billion as of December 31, 2016. As of December 31, 2017, we owned 244 aircraft, comprised of 188 narrowbody jet aircraft and 56 widebody jet aircraft, with a weighted average age of 3.8 years. As of December 31, 2016, we owned 237 aircraft, comprised of 188 narrowbody jet aircraft and 49 widebody jet aircraft, with a weighted average age of 3.8 years. In addition, we also managed 50 jet aircraft for third party owners on a fee basis as of December 31, 2017 compared to 30 jet aircraft as of December 31, 2016.
5
Geographic Diversification
Over 95% of our aircraft are operated internationally. The following table sets forth the dollar amount and percentage of our rental of flight equipment revenues attributable to the respective geographical regions based on each airline’s principal place of business:
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
Year Ended |
|
Year Ended |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
December 31, 2017 |
|
December 31, 2016 |
|
December 31, 2015 |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
Amount of |
|
|
|
Amount of |
|
|
|
Amount of |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
Rental |
|
|
|
Rental |
|
|
|
Rental |
|
|
|
|||
|
Region |
|
Revenue |
|
% of Total |
|
Revenue |
|
% of Total |
|
Revenue |
|
% of Total |
|
|||
|
|
|
(in thousands, except percentages) |
|
|||||||||||||
|
Europe |
|
$ |
450,628 |
|
31.1 |
% |
$ |
400,491 |
|
29.9 |
% |
$ |
380,295 |
|
32.4 |
% |
|
Asia (excluding China) |
|
|
332,284 |
|
22.9 |
% |
|
308,658 |
|
23.1 |
% |
|
223,284 |
|
19.0 |
% |
|
China |
|
|
324,147 |
|
22.3 |
% |
|
293,206 |
|
21.9 |
% |
|
265,450 |
|
22.6 |
% |
|
The Middle East and Africa |
|
|
116,799 |
|
8.1 |
% |
|
106,300 |
|
7.9 |
% |
|
90,416 |
|
7.7 |
% |
|
Central America, South America, and Mexico |
|
|
102,205 |
|
7.0 |
% |
|
112,068 |
|
8.4 |
% |
|
114,672 |
|
9.8 |
% |
|
U.S. and Canada |
|
|
76,685 |
|
5.3 |
% |
|
69,918 |
|
5.2 |
% |
|
54,294 |
|
4.6 |
% |
|
Pacific, Australia, and New Zealand |
|
|
47,987 |
|
3.3 |
% |
|
48,361 |
|
3.6 |
% |
|
46,133 |
|
3.9 |
% |
|
Total |
|
$ |
1,450,735 |
|
100.0 |
% |
$ |
1,339,002 |
|
100.0 |
% |
$ |
1,174,544 |
|
100.0 |
% |
The following table sets forth the regional concentration based on each airline's principal place of business of our flight equipment subject to operating lease based on net book value as of December 31, 2017 and 2016:
|
|
|
December 31, 2017 |
|
December 31, 2016 |
|
||||||
|
|
|
Net Book |
|
|
|
Net Book |
|
|
|
||
|
Region |
|
Value |
|
% of Total |
|
Value |
|
% of Total |
|
||
|
|
|
(in thousands, except percentages) |
|
||||||||
|
Europe |
|
$ |
4,205,431 |
|
31.7 |
% |
$ |
3,547,294 |
|
29.5 |
% |
|
Asia (excluding China) |
|
|
2,981,339 |
|
22.4 |
% |
|
2,739,554 |
|
22.7 |
% |
|
China |
|
|
2,720,124 |
|
20.5 |
% |
|
2,779,546 |
|
23.0 |
% |
|
The Middle East and Africa |
|
|
1,481,825 |
|
11.2 |
% |
|
935,968 |
|
7.8 |
% |
|
Central America, South America, and Mexico |
|
|
926,732 |
|
7.0 |
% |
|
937,287 |
|
7.8 |
% |
|
U.S. and Canada |
|
|
599,367 |
|
4.5 |
% |
|
647,743 |
|
5.4 |
% |
|
Pacific, Australia, and New Zealand |
|
|
365,432 |
|
2.7 |
% |
|
454,533 |
|
3.8 |
% |
|
Total |
|
$ |
13,280,250 |
|
100.0 |
% |
$ |
12,041,925 |
|
100.0 |
% |
At December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, we owned and managed leased aircraft to customers in the following regions based on each airline's principal place of business:
|
|
|
December 31, 2017 |
|
December 31, 2016 |
|
December 31, 2015 |
|
||||||
|
|
|
Number of |
|
|
|
Number of |
|
|
|
Number of |
|
|
|
|
Region |
|
Customers(1) |
|
% of Total |
|
Customers(1) |
|
% of Total |
|
Customers(1) |
|
% of Total |
|
|
Europe |
|
31 |
|
34.0 |
% |
27 |
|
31.8 |
% |
27 |
|
30.0 |
% |
|
Asia (excluding China) |
|
18 |
|
19.8 |
% |
18 |
|
21.2 |
% |
19 |
|
21.1 |
% |
|
U.S. and Canada |
|
11 |
|
12.1 |
% |
12 |
|
14.1 |
% |
11 |
|
12.2 |
% |
|
The Middle East and Africa |
|
11 |
|
12.1 |
% |
7 |
|
8.2 |
% |
8 |
|
8.9 |
% |
|
China |
|
9 |
|
9.9 |
% |
9 |
|
10.6 |
% |
12 |
|
13.4 |
% |
|
Central America, South America, and Mexico |
|
9 |
|
9.9 |
% |
9 |
|
10.6 |
% |
11 |
|
12.2 |
% |
|
Pacific, Australia, and New Zealand |
|
2 |
|
2.2 |
% |
3 |
|
3.5 |
% |
2 |
|
2.2 |
% |
|
Total |
|
91 |
|
100.0 |
% |
85 |
|
100.0 |
% |
90 |
|
100.0 |
% |
|
(1) |
A customer is an airline with its own operating certificate. |
6
For the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016, and 2015, China was the only individual country that represented at least 10% of our rental revenue based on each airline's principal place of business. In 2017, 2016, and 2015, no rental revenue from any individual airline represented 10% or more of our rental revenue.
Aircraft Acquisition Strategy
We seek to acquire the most highly in demand and widely distributed, modern technology, fuel efficient narrowbody and widebody commercial jet transport aircraft. Our strategy is to order new aircraft directly from the manufacturers. When placing new aircraft orders with the manufacturers, we strategically target the replacement of aging aircraft with modern technology aircraft. Additionally, we look to supplement our order pipeline with opportunistic purchases of aircraft in the secondary market and participate in sale-leaseback transactions with airlines.
Prior to ordering aircraft, we evaluate the market for specific types of aircraft. We consider the overall demand for the aircraft type in the marketplace based on our deep knowledge of the aviation industry and our customer relationships. It is important to assess the airplane’s economic viability, the operating performance characteristics, engine variant options, intended utilization by our customers, and which aircraft types it will replace or compete with in the global market. Additionally, we study the effects of global airline passenger traffic growth in order to determine the likely demand for our new aircraft.
For new aircraft deliveries, we source many components separately, which include seats, safety equipment, avionics, galleys, cabin finishes, engines, and other equipment. Often times we are able to achieve lower pricing through direct bulk purchase contracts with the component manufacturers than would be achievable if the airframe manufacturers sourced the components for the airplane. Manufacturers such as Boeing and Airbus install this buyer furnished equipment in our aircraft during the final assembly process at their facilities. With this purchasing strategy, we are able to meet specific customer configuration requirements and lower the total acquisition cost of the aircraft.
Aircraft Leasing Strategy
The airline industry is a complex industry with constantly evolving competition, code shares (where two or more airlines share the same flight), alliances, and passenger traffic patterns. This requires frequent updating and flexibility within an airline’s fleet. The operating lease allows airlines to effectively adapt and manage their fleets through varying market conditions without bearing the full financial risk associated with these capital intensive assets which have an expected useful life of 25 years. This fleet flexibility enables airlines to more effectively operate and compete in their respective markets. We work closely with our airline customers throughout the world to help optimize their long-term aircraft fleet strategies.
We work to mitigate the risks associated with owning and leasing aircraft and cyclical variations in the airline industry through careful management of our fleet, including managing customer concentrations by geography and region, entering into long term leases, staggering lease maturities, balancing aircraft type exposures, and maintaining a young fleet age. We believe that diversification of our operating lease portfolio reduces the risks associated with individual customer defaults and the impact of adverse geopolitical and regional economic events. In order to maximize residual values and minimize the risk of obsolescence, our strategy is generally to own an aircraft for approximately the first third of its expected 25 year useful life.
Our management team identifies prospective airline customers based upon industry knowledge and long‑standing relationships. Prior to leasing an aircraft, we evaluate the competitive positioning of the airline, the strength and quality of the management team, and the financial performance of the airline. Management obtains and reviews relevant business materials from all prospective customers before entering into a lease agreement. Under certain circumstances, the customer may be required to obtain guarantees or other financial support from a sovereign entity or a financial institution. We work closely with our existing customers and potential lessees to develop customized lease structures that address their specific needs. We typically enter into a lease agreement 18 to 36 months in advance of the delivery of a new aircraft from our order book. Once the aircraft has been delivered and operated by the airline, we look
7
to remarket the aircraft and sign a follow-on lease six to 12 months ahead of the scheduled expiry of the initial lease term. Our leases typically contain the following key provisions:
|
· |
our leases are primarily structured as operating leases, whereby we retain the residual rights to the aircraft; |
|
· |
our leases are triple net leases, whereby the lessee is responsible for all operating costs including taxes, insurance, and aircraft maintenance; |
|
· |
our leases typically require all payments be made in U.S. dollars; |
|
· |
our leases are typically for fixed rates and terms; |
|
· |
our leases typically require cash security deposits and maintenance reserve payments; and |
|
· |
our leases contain provisions which require payment whether or not the aircraft is operated, irrespective of the circumstances. |
The lessee is responsible for compliance with applicable laws and regulations with respect to the aircraft. We require our lessees to comply with the standards of either the U.S. Federal Aviation Administration (“FAA”) or its equivalent in foreign jurisdictions. As a function of these laws and the provisions in our lease contracts, the lessees are responsible to perform all maintenance of the aircraft and return the aircraft and its components in a specified return condition. Generally, we receive a cash deposit and maintenance reserves as security for the lessee’s performance of obligations under the lease and the condition of the aircraft upon return. In addition, most leases contain extensive provisions regarding our remedies and rights in the event of a default by a lessee. The lessee generally is required to continue to make lease payments under all circumstances, including periods during which the aircraft is not in operation due to maintenance or grounding.
Some foreign countries have currency and exchange laws regulating the international transfer of currencies. When necessary, we may require, as a condition to any foreign transaction, that the lessee or purchaser in a foreign country obtain the necessary approvals of the appropriate government agency, finance ministry, or central bank for the remittance of all funds contractually owed in U.S. dollars. We attempt to minimize our currency and exchange risks by negotiating the designated payment currency in our leases to be U.S. dollars. To meet the needs of certain of our airline customers, we have agreed to accept certain lease payments in a foreign currency. After we agree to the rental payment currency with an airline, the negotiated currency typically remains for the term of the lease. We may enter into contracts to mitigate our foreign currency risk, but we expect that the economic risk arising from foreign currency denominated leases will be insignificant to us.
We may, in connection with the lease of used aircraft, agree to contribute specific additional amounts to the cost of certain first major maintenance events or modifications, which usually reflect the usage of the aircraft prior to the commencement of the lease. We may be obligated under the leases to make reimbursements of maintenance reserves previously received to lessees for expenses incurred for certain planned major maintenance. We also, on occasion, may contribute towards aircraft modifications and recover any such costs over the life of the lease.
Monitoring
During the lease term, we closely follow the operating and financial performance of our lessees. We maintain a high level of communication with the lessee and frequently evaluate the state of the market in which the lessee operates, including the impact of changes in passenger air travel and preferences, emerging competition, new government regulations, regional catastrophes, and other unforeseen shocks that are relevant to the airline’s market. This enables us to identify lessees that may be experiencing operating and financial difficulties. This identification assists us in assessing the lessee’s ability to fulfill its obligations under the lease. This monitoring also identifies candidates, where appropriate, to restructure the lease prior to the lessee’s insolvency or the initiation of bankruptcy or similar proceedings. Once an
8
insolvency or bankruptcy occurs, we typically have less control over, and would most likely incur greater costs in connection with, the restructuring of the lease or the repossession of the aircraft.
During the life of the lease, situations may lead us to restructure leases with our lessees. When we repossess an aircraft leased in a foreign country, we generally expect to export the aircraft from the lessee’s jurisdiction. In some very limited situations, the lessees may not fully cooperate in returning the aircraft. In those cases, we will take appropriate legal action, a process that could ultimately delay the return and export of the aircraft. In addition, in connection with the repossession of an aircraft, we may be required to pay outstanding mechanics’ liens, airport charges, and navigation fees and other amounts secured by liens on the repossessed aircraft. These charges could relate to other aircraft that we do not own but were operated by the lessee.
Remarketing
Our lease agreements are generally structured to require lessees to notify us nine to 12 months in advance of the lease’s expiration if a lessee desires to renew or extend the lease. Requiring lessees to provide us with such advance notice provides our management team with an extended period of time to consider a broad set of alternatives with respect to the aircraft, including assessing general market and competitive conditions and preparing to remarket or sell the aircraft. If a lessee fails to provide us with notice, the lease will automatically expire at the end of the term, and the lessee will be required to return the aircraft pursuant to the conditions in the lease. Our leases contain detailed provisions regarding the required condition of the aircraft and its components upon redelivery at the end of the lease term.
Aircraft Sales & Trading Strategy
Our strategy is to maintain a portfolio of young aircraft with a widely diversified customer base. In order to achieve this profile, we primarily order new planes directly from the manufacturers, place them on long term leases, and sell the aircraft when they near the end of the first third of their expected 25 year economic useful lives. We typically sell aircraft that are currently operated by an airline with multiple years of lease term remaining on the contract, in order to achieve the maximum disposition value of the aircraft. Buyers of the aircraft may include leasing companies, financial institutions, and airlines. We also, from time to time, buy and sell aircraft on an opportunistic basis for trading profits. In the past three years ended December 31, 2017, we sold 101 aircraft. Additionally, we may provide management services to buyers of our aircraft asset for a fee.
Aircraft Management Strategy
We supplement our core business model by providing fleet management services to third party investors and owners of aircraft portfolios for a management fee. This allows us to better serve our airline customers and expand our existing airline customer base by providing additional leasing opportunities beyond our own aircraft portfolio, new order pipeline, and customer or regional concentration limits.
Financing Strategy
We finance the purchase of aircraft and our business with available cash balances, internally generated funds, including aircraft sales and trading activity, and debt financings. We have structured the Company to have investment grade credit metrics and our debt financing strategy has focused on funding our business on an unsecured basis. Unsecured financing provides us with operational flexibility when selling or transitioning aircraft from one airline to another. We may, to a limited extent, utilize export credit or other forms of secured financing.
Insurance
We require our lessees to carry those types of insurance that are customary in the air transportation industry, including comprehensive liability insurance, aircraft all‑risk hull insurance, and war‑risk insurance covering risks such as hijacking, terrorism (but excluding coverage for weapons of mass destruction and nuclear events), confiscation, expropriation, seizure, and nationalization. We generally require a certificate of insurance from the lessee’s insurance broker prior to delivery of an aircraft. Generally, all certificates of insurance contain a breach of warranty endorsement
9
so that our interests are not prejudiced by any act or omission of the lessee. Lease agreements generally require hull and liability limits to be in U.S. dollars, which are shown on the certificate of insurance.
Insurance premiums are to be paid by the lessee, with coverage acknowledged by the broker or carrier. The territorial coverage, in each case, should be suitable for the lessee’s area of operations. We generally require that the certificates of insurance contain, among other provisions, a provision prohibiting cancellation or material change without at least 30 days’ advance written notice to the insurance broker (who would be obligated to give us prompt notice), except in the case of hull war insurance policies, which customarily only provide seven days’ advance written notice for cancellation and may be subject to shorter notice under certain market conditions. Furthermore, the insurance is primary and not contributory, and we require that all insurance carriers be required to waive rights of subrogation against us.
The stipulated loss value schedule under aircraft hull insurance policies is on an agreed‑value basis acceptable to us and usually exceeds the book value of the aircraft. In cases where we believe that the agreed value stated in the lease is not sufficient, we make arrangements to cover such deficiency, which would include the purchase of additional “Total Loss Only” coverage for the deficiency.
Aircraft hull policies generally contain standard clauses covering aircraft engines. The lessee is required to pay all deductibles. Furthermore, the hull war policies generally contain full war risk endorsements, including, but not limited to, confiscation (where available), seizure, hijacking and similar forms of retention or terrorist acts.
The comprehensive liability insurance listed on certificates of insurance generally include provisions for bodily injury, property damage, passenger liability, cargo liability, and such other provisions reasonably necessary in commercial passenger and cargo airline operations. We expect that such certificates of insurance list combined comprehensive single liability limits of not less than $500.0 million for Airbus and Boeing aircraft and $200.0 million for Embraer S.A. (“Embraer”). As a standard in the industry, airline operator's policies contain a sublimit for third-party war risk liability generally in the amount of at least $150.0 million. We require each lessee to purchase higher limits of third-party war risk liability or obtain an indemnity from its respective government.
The international aviation insurance market has exclusions for physical damage to aircraft hulls caused by dirty bombs, bio‑hazardous materials, and electromagnetic pulsing. Exclusions for the same type of perils could be introduced into liability policies in the future.
We cannot assure you that our lessees will be adequately insured against all risks, that lessees will at all times comply with their obligations to maintain insurance, that any particular claim will be paid, or that lessees will be able to obtain adequate insurance coverage at commercially reasonable rates in the future.
Separately, we purchase contingent liability insurance and contingent hull insurance on all aircraft in our fleet and maintain other insurance covering the specific needs of our business operations. While we believe our insurance is adequate both as to coverages and amounts, we cannot assure you that we are adequately insured against all risks.
Competition
The leasing, remarketing, and sale of aircraft is highly competitive. We are one of the largest aircraft lessors operating on a global scale. We face competition from aircraft manufacturers, banks, financial institutions, other leasing companies, aircraft brokers, and airlines. Some of our competitors may have greater operating and financial resources and access to lower capital costs than we have. Competition for leasing transactions is based on a number of factors, including delivery dates, lease rates, lease terms, other lease provisions, aircraft condition, and the availability in the marketplace of the types of aircraft required to meet the needs of airline customers. Competition in the purchase and sale of used aircraft is based principally on the availability of used aircraft, price, the terms of the lease to which an aircraft is subject, and the creditworthiness of the lessee, if any.
10
Government Regulation
The air transportation industry is highly regulated. We do not operate commercial aircraft, and thus may not be directly subject to many industry laws and regulations, such as regulations of the U.S. Department of State (the “DOS”), the U.S. Department of Transportation, or their counterpart organizations in foreign countries regarding the operation of aircraft for public transportation of passengers and property. As discussed below, however, we are subject to government regulation in a number of respects. In addition, our lessees are subject to extensive regulation under the laws of the jurisdictions in which they are registered or operate. These laws govern, among other things, the registration, operation, maintenance, and condition of the aircraft.
We are required to register our aircraft with an aviation authority mutually agreed upon with our lessee. Each aircraft registered to fly must have a Certificate of Airworthiness, which is a certificate demonstrating the aircraft’s compliance with applicable government rules and regulations and that the aircraft is considered airworthy. Each airline we lease to must have a valid operation certificate to operate our aircraft. Our lessees are obligated to maintain the Certificates of Airworthiness for the aircraft they lease.
Our involvement with the civil aviation authorities of foreign jurisdictions consists largely of requests to register and deregister our aircraft on those countries’ registries.
We are also subject to the regulatory authority of the DOS and the U.S. Department of Commerce (the “DOC”) to the extent such authority relates to the export of aircraft for lease and sale to foreign entities and the export of parts to be installed on our aircraft. We may be required to obtain export licenses for parts installed in aircraft exported to foreign countries. The DOC and the U.S. Department of the Treasury (through its Office of Foreign Assets Control, or "OFAC") impose restrictions on the operation of U.S.-made goods, such as aircraft and engines, in sanctioned countries, as well as on the ability of U.S. companies to conduct business with entities in those countries. The U.S. Patriot Act of 2001 (the “Patriot Act”) prohibits financial transactions by U.S. persons, including U.S. individuals, entities, and charitable organizations, with individuals and organizations designated as terrorists and terrorist supporters by the U.S. Secretary of State or the U.S. Secretary of the Treasury. The U.S. Customs and Border Protection, a law enforcement agency of the U.S. Department of Homeland Security, enforces regulations related to the import of aircraft into the United States for maintenance or lease and the importation of parts into the U.S. for installation.
Jurisdictions in which aircraft are registered as well as jurisdictions in which they operate may impose regulations relating to noise and emission standards. In addition, most countries’ aviation laws require aircraft to be maintained under an approved maintenance program with defined procedures and intervals for inspection, maintenance and repair. To the extent that aircraft are not subject to a lease or a lessee is not in compliance, we are required to comply with such requirements, possibly at our own expense.
Employees
As of December 31, 2017, we had 87 full-time employees. On average, our senior management team has approximately 27 years of experience in the commercial aviation industry. None of our employees are represented by a union or collective bargaining agreements.
Access to Our Information
We file annual, quarterly, current reports, proxy statements and other information with the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”). We make our public SEC filings available, at no cost, through our website at www.airleasecorp.com as soon as reasonably practicable after the report is electronically filed with, or furnished to, the SEC. The information contained on or connected to our website is not incorporated by reference into this Annual Report on Form 10‑K and should not be considered part of this or any other report filed with the SEC. We will also provide these reports in electronic or paper format free of charge upon written request made to Investor Relations at 2000 Avenue of the Stars, Suite 1000N, Los Angeles, California 90067. Our SEC filings are also available free of charge on the SEC’s website at www.sec.gov. The public may also read and copy any document we file with the SEC at the
11
SEC’s public reference room located at 100 F Street NE, Washington, DC 20549. Please call the SEC at 1‑800‑SEC‑0330 for further information on the operation of the public reference room.
Corporate Information
Air Lease Corporation incorporated in Delaware and launched in February 2010. Our website is www.airleasecorp.com. We may post information that is important to investors on our website. Information included or referred to on, or otherwise accessible through, our website is not intended to form a part of or be incorporated by reference into this report.
Executive Officers of the Company
Set forth below is certain information concerning each of our executive officers as of February 22, 2018, including his/her age, current position with the Company and business experience during the past five years.
|
Name |
|
Age |
|
Company Position |
|
Prior Positions |
|
Steven F. Udvar‑Házy |
|
71 |
|
Executive Chairman of the Board of Directors (since July 2016) |
|
Chairman and Chief Executive Officer, February 2010-June 2016 |
|
John L. Plueger |
|
63 |
|
Chief Executive Officer, President and Director (since July 2016) |
|
President, Chief Operating Officer and Director, March 2010-June 2016 |
|
Carol H. Forsyte |
|
55 |
|
Executive Vice President, General Counsel, Corporate Secretary and Chief Compliance Officer (since September 2012) |
|
|
|
Gregory B. Willis |
|
39 |
|
Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer (since July 2016) |
|
Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer, March 2012-June 2016 |
|
Marc H. Baer |
|
53 |
|
Executive Vice President, Marketing (since April 2010) |
|
|
|
Jie Chen |
|
54 |
|
Executive Vice President and Managing Director of Asia (since August 2010) |
|
|
|
Alex A. Khatibi |
|
57 |
|
Executive Vice President (since April 2010) |
|
|
|
Kishore Korde |
|
44 |
|
Executive Vice President, Marketing (since May 2015) |
|
Senior Vice President, Marketing, 2010-May 2015 |
|
Grant A. Levy |
|
55 |
|
Executive Vice President (since April 2010) |
|
|
|
John D. Poerschke |
|
56 |
|
Executive Vice President of Aircraft Procurement and Specifications (since February 2017) |
|
Senior Vice President of Aircraft Procurement and Specifications, March 2010-February 2017 |
12
The following important risk factors, and those risk factors described elsewhere in this report or in our other filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission, could cause our actual results to differ materially from those stated in forward-looking statements contained in this document and elsewhere. These risks are not presented in order of importance or probability of occurrence. Further, the risks described below are not the only risks that we face. Additional risks and uncertainties not currently known to us or that we currently deem immaterial may also impair our business operations. Any of these risks may have a material adverse effect on our business, reputation, financial condition, results of operations, profitability, cash flows or liquidity.
Risks Relating to Our Business
We cannot assure you that we will be able to enter into profitable leases for any aircraft acquired, which failure to do so would negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
We cannot assure you that we will be able to enter into profitable leases upon the acquisition of the aircraft we purchase in the future. Our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations depend upon our management team’s judgment and ability to evaluate the ability of lessees and other counterparties to perform their obligations to us and to negotiate transaction documents. We cannot assure you that our management team will be able to perform such functions in a manner that will achieve our investment objectives, which would negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
Our business model depends on the continual leasing and remarketing of our aircraft, and we may not be able to do so on favorable terms, which would negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
Our business model depends on the continual leasing and remarketing of our aircraft in order to generate sufficient revenues to finance our growth and operations, pay our debt service obligations and generate cash flows from operations. Our ability to lease and remarket our aircraft will depend on general market and competitive conditions at the time the leases are entered into and expire. If we are not able to lease or remarket an aircraft or to do so on favorable terms, we may be required to attempt to sell the aircraft to provide funds for our debt service obligations or operating expenses. Our ability to lease, remarket or sell the aircraft on favorable terms or without significant off-lease time and costs could be negatively affected by depressed conditions in the aviation industry, government and environmental regulations, increased operating costs including the price and availability of jet fuel, airline bankruptcies, the effects of terrorism, war, natural disasters and/or epidemic diseases on airline passenger traffic trends, declines in the values of aircraft, and various other general market and competitive conditions and factors which are outside of our control. If we are unable to lease and remarket our aircraft on favorable terms, or at all, our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations would be negatively impacted.
Our success depends in large part on our ability to obtain capital on favorable terms to finance our growth through the purchase of aircraft and to repay our outstanding debt obligations as they mature. If we are not able to obtain capital on terms acceptable to us, or at all, it would significantly impact our ability to compete effectively in the commercial aircraft leasing market and would negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
Growing our fleet will require substantial additional capital. Accordingly, we will need to obtain additional financing, which may not be available to us on favorable terms or at all. Further, we must continue to have access to the capital markets and other sources of financing in order to repay our outstanding obligations as they mature. Our access to sources of financing will depend upon a number of factors over which we have limited control, including:
|
· |
general market conditions; |
|
· |
the market’s view of the quality of our assets; |
13
|
· |
the market’s perception of our growth potential; |
|
· |
interest rate fluctuations; |
|
· |
our current and potential future earnings and cash distributions; and |
|
· |
the market price of our Class A common stock. |
Weaknesses in the capital and credit markets could negatively affect our ability to obtain financing or could increase the costs of financing. For instance, during the 2008 financial crisis, many companies experienced downward pressure on their share prices and had limited or no access to the credit markets, often without regard to their underlying financial strength. If financial market disruption and volatility were to occur again, we cannot assure you that we will be able to access capital, which could negatively affect our financial condition and results of operations.
In addition, if there are new regulatory capital requirements imposed on our private lenders, they may be required to limit, or increase the cost of, financing they provide to us. In general, this could potentially increase our financing costs and reduce our liquidity or require us to sell assets at an inopportune time or price.
If we are unable to raise additional funds or obtain capital on terms acceptable to us, we may not be able to satisfy funding requirements for any aircraft acquisition commitments then in place. If we are unable to satisfy our purchase commitments, we may be forced to forfeit our deposits. Further, we would be exposed to potential breach of contract claims by our lessees and manufacturers. These risks may also be increased by the volatility and disruption in the capital and credit markets. Depending on market conditions at the time, we may have to rely more heavily on additional equity issuances, which may be dilutive to our stockholders, or on less efficient forms of debt financing that require a larger portion of our cash flow from operations, thereby reducing funds available for our operations, future business opportunities and other purposes. Further, because our charter permits the issuance of preferred stock, if our board of directors approves the issuance of preferred stock in a future financing transaction, such preferred stockholders may have rights, preferences or privileges senior to existing stockholders, and you will not have the ability to approve such a transaction. These risks would negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
Incurring significant costs resulting from lease defaults could negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
Based on historical rates of airline defaults and bankruptcies, some of our lessees are likely to default on their lease obligations or file for bankruptcy in the ordinary course of our business. Those costs likely would include legal and other expenses associated with court or other governmental proceedings, including the cost of posting security bonds or letters of credit necessary to effect repossession of the aircraft, particularly if the lessee is contesting the proceedings or is in bankruptcy. In addition, during any such proceedings the relevant aircraft would likely not be generating revenue. We could also incur substantial maintenance, refurbishment or repair costs if a defaulting lessee fails to pay such costs and where such maintenance, refurbishment or repairs are necessary to put the aircraft in suitable condition for remarketing or sale. We may also incur storage costs associated with any aircraft that we repossess and are unable to place immediately with another lessee. Even if we are able to immediately place a repossessed aircraft with another lessee, we may not be able to do so at a similar or favorable lease rate. It may also be necessary to pay off liens, taxes and other governmental charges on the aircraft to obtain clear possession and to remarket the aircraft effectively, including, in some cases, liens that the lessee might have incurred in connection with the operation of its other aircraft. We could also incur other costs in connection with the physical possession of the aircraft.
We may suffer other negative consequences as a result of a lessee default, the related termination of the lease and the repossession of the related aircraft. It is likely that our rights upon a lessee default will vary significantly depending upon the jurisdiction and the applicable law, including the need to obtain a court order for repossession of the aircraft and/or consents for deregistration or export of the aircraft. We anticipate that when a defaulting lessee is in bankruptcy, protective administration, insolvency or similar proceedings, additional limitations may apply. Certain jurisdictions give rights to the trustee in bankruptcy or a similar officer to assume or reject the lease or to assign it to a third party, or entitle the lessee or another third party to retain possession of the aircraft without paying lease rentals or
14
performing all or some of the obligations under the relevant lease. In addition, certain of our lessees are owned, in whole or in part, by government‑related entities, which could complicate our efforts to repossess our aircraft in that lessee’s domicile. Accordingly, we may be delayed in, or prevented from, enforcing certain of our rights under a lease and in remarketing the affected aircraft.
If we repossess an aircraft, we may not necessarily be able to export or deregister and profitably redeploy the aircraft. An aircraft cannot be registered in two countries at the same time. Before an aviation authority will register an aircraft that has previously been registered in another country, it must receive confirmation that the aircraft has been deregistered by that country's aviation authority. In order to deregister an aircraft, the lessee must comply with applicable laws and regulations, and the relevant governmental authority must enforce these laws and regulations. For instance, where a lessee or other operator flies only domestic routes in the jurisdiction in which the aircraft is registered, repossession may be more difficult, especially if the jurisdiction permits the lessee or the other operator to resist deregistration. We may also incur significant costs in retrieving or recreating aircraft records required for registration of the aircraft, and in obtaining the Certificate of Airworthiness for an aircraft. If, upon a lessee default, we incur significant costs in connection with repossessing our aircraft, are delayed in repossessing our aircraft or are unable to obtain possession of our aircraft as a result of lessee defaults, our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations would be negatively affected.
If our lessees fail to discharge aircraft liens, we may be obligated to pay the aircraft liens, which would negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
In the normal course of their business, our lessees are likely to incur aircraft liens that secure the payment of airport fees and taxes, customs duties, air navigation charges, including charges imposed by Eurocontrol, the European Organization for the Safety of Air Navigation, landing charges, crew wages, salvage or other liens that may attach to our aircraft. These liens may secure substantial sums that may, in certain jurisdictions or for certain types of liens, particularly liens on entire fleets of aircraft, exceed the value of the particular aircraft to which the liens have attached. Aircraft may also be subject to mechanics’ liens as a result of routine maintenance performed by third parties on behalf of our lessees. Although we anticipate that the financial obligations relating to these liens are the responsibility of our lessees, if they fail to fulfill such obligations, the liens may attach to our aircraft and ultimately become our responsibility. In some jurisdictions, aircraft liens may give the holder thereof the right to detain or, in limited cases, sell or cause the forfeiture of the aircraft.
Until they are discharged, these liens could impair our ability to repossess, remarket or sell our aircraft. Our lessees may not comply with the anticipated obligations under their leases to discharge aircraft liens arising during the terms of the leases. If they do not, we may find it necessary to pay the claims secured by such aircraft liens in order to repossess the aircraft. Such payments would negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
If our lessees fail to perform as expected and we decide to restructure or reschedule our leases, the restructuring and rescheduling would likely result in less favorable leases, which would negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
A lessee’s ability to perform its obligations under its lease will depend primarily on the lessee’s financial condition and cash flow, which may be affected by factors outside our control, including:
|
· |
competition; |
|
· |
passenger and air cargo rates; |
|
· |
passenger and air cargo demand; |
|
· |
geopolitical and other events, including war, acts of terrorism, outbreaks of epidemic diseases and natural disasters; |
15
|
· |
increases in operating costs, including the price and availability of jet fuel and labor costs; |
|
· |
labor difficulties, including pilot shortages; |
|
· |
economic conditions and currency fluctuations in the countries and regions in which the lessee operates; and |
|
· |
governmental regulation and associated fees affecting the air transportation business. |
Many of our airline customers do not have investment grade credit profiles. We anticipate that some of our lessees will experience a weakened financial condition or suffer liquidity problems. This could lead to a lessee experiencing difficulties in performing under the terms of our lease agreement. This could result in the lessee seeking relief under some of the terms of our lease agreement, or it could result in us electing to repossess the aircraft.
Any future downturns in the airline industry could greatly exacerbate the weakened financial condition of some of these lessees and further increase the risk of delayed, missed or reduced rental payments. We may not correctly assess the credit risk of a lessee, or may not charge lease rates which correctly reflect the related risks, and as a result, lessees may not be able to satisfy their financial and other obligations under their leases. A delayed, missed or reduced rental payment from a lessee would decrease our revenues and cash flow. If we, in the exercise of our remedies under a lease, repossess an aircraft, we may not receive all or any of the past-due or deferred payments and we may not be able to remarket the aircraft promptly or at favorable rates, if at all.
It is likely that restructurings and/or repossessions with some of our lessees will occur in the future. The terms and conditions of possible lease restructurings or rescheduling may result in a significant reduction of lease revenue, which may negatively affect our financial results and growth prospects. If any request for payment restructuring or rescheduling is made and granted, reduced or deferred rental payments may be payable over all or some part of the remaining term of the lease. The terms of any revised payment schedules may be unfavorable and such payments may not be made. Our default levels would likely increase over time if economic conditions deteriorate. If lessees of a significant number of our aircraft defaulted on their leases, it would negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
Failure to obtain certain required licenses, consents and approvals could negatively affect our ability to remarket or sell aircraft, which would negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
Airlines are subject to extensive regulation under the laws of the jurisdictions in which they are registered and in which they operate. As a result, we expect that certain aspects of our leases will require licenses, consents or approvals, including consents from governmental or regulatory authorities for certain payments under our leases and for the import, export or deregistration of the aircraft. Subsequent changes in applicable law or administrative practice may increase such requirements and governmental consent, once given, could be withdrawn. Furthermore, consents needed in connection with the future remarketing or sale of an aircraft may not be forthcoming. Any of these events could negatively affect our ability to remarket or sell aircraft, which would negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
Our aircraft require routine maintenance, and if they are not properly maintained, their value may decline and we may not be able to lease or remarket such aircraft at favorable rates, if at all, which would negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
We may be exposed to increased maintenance costs for our aircraft associated with a lessee’s failure to properly maintain the aircraft or pay supplemental maintenance rent. If an aircraft is not properly maintained, its market value may decline, which would result in lower revenues from its lease or sale. We enter into leases pursuant to which the lessees are primarily responsible for many obligations, which include maintaining the aircraft and complying with all governmental requirements applicable to the lessee and the aircraft, including operational, maintenance, government agency oversight, registration requirements, service bulletins issued by aircraft manufacturers and airworthiness directives issued by aviation authorities. Failure of a lessee to perform required maintenance, or comply with the
16
applicable service bulletins and airworthiness directives during the term of a lease could result in a decrease in value of an aircraft, an inability to remarket an aircraft at favorable rates, if at all, or a potential grounding of an aircraft. Maintenance failures by a lessee would also likely require us to incur maintenance and modification costs upon the termination of the applicable lease, which could be substantial, to restore the aircraft to an acceptable condition prior to remarketing or sale. Even if we are entitled to receive supplemental maintenance rents, these rents may not cover the entire cost of actual maintenance required. Any failure by our lessees to meet their obligations to perform required scheduled maintenance or our inability to maintain our aircraft would negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
If we experience abnormally high maintenance or obsolescence issues with any of our aircraft or aircraft that we acquire, it would negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
Aircraft are long-lived assets, requiring long lead times to develop and manufacture, with particular types and models becoming obsolete or less in demand over time when newer, more advanced aircraft are manufactured. The weighted average age of our fleet was 3.8 years as of December 31, 2017. Our existing fleet, as well as the aircraft that we have ordered, have exposure to obsolescence, particularly if unanticipated events occur which shorten the life cycle of such aircraft types. These events include but are not limited to government regulation or changes in our airline customers’ preferences, including for instance, an increased demand for more fuel efficient aircraft. These events may shorten the life cycle for aircraft types in our fleet and, accordingly, may negatively impact lease rates, trigger impairment charges, increase depreciation expense or result in losses related to aircraft asset value guarantees, if we provide such guarantees.
Further, variable expenses like fuel, crew size or aging aircraft corrosion control or modification programs and airworthiness directives could make the operation of older aircraft more costly to our lessees and may result in increased lessee defaults or attempts to renegotiate lease terms. We may also incur some of these increased maintenance expenses and regulatory costs upon acquisition or remarketing of our aircraft. Any of these expenses or costs would negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
If we acquire a high concentration of a particular model of aircraft, our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations would be negatively affected by changes in market demand or problems specific to that aircraft model.
If we acquire a high concentration of a particular model of aircraft, our business and financial results could be negatively affected if the market demand for that model of aircraft declines. There are several scenarios which could adversely affect the demand for an aircraft. These scenarios include but are not limited to, if the aircraft model is redesigned or replaced by its manufacturer, or if this aircraft model experiences design or technical problems, which could ultimately lead to the grounding of the aircraft model. This could lead to the decline in value and lease rates of such aircraft model, and ultimately we may not be able to lease such aircraft model on favorable terms or at all. For instance, our fleet consists of a number of widebody aircraft and many of our new purchases will consist of newer, more fuel efficient models. Any changes in demand for these models or other models in our fleet could negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
The introduction of superior aircraft technology or a new line of aircraft, in particular more fuel efficient aircraft, could cause the aircraft that we own to become outdated or obsolete or oversupplied and therefore less desirable, which would negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
As manufacturers introduce technological innovations and new types of aircraft, some of the aircraft in our fleet could become less desirable to potential lessees. In particular, the introduction recently of more fuel efficient aircraft has made some older models less attractive and more difficult to lease. Technological innovations, increased fuel efficiency, improved operating economics and new models may increase the rate of obsolescence of existing aircraft faster than currently anticipated by our management. New aircraft manufacturers could emerge to produce aircraft that compete with the aircraft we own. The introduction of new technologies or introduction of a new type of aircraft, in particular more fuel efficient models, may negatively affect the value of the aircraft in our fleet.
17
In addition, the imposition of increased regulation regarding stringent noise or emissions restrictions may make some of our aircraft less desirable and accordingly less valuable in the marketplace. The development of new aircraft and engine options could decrease the desirability of certain aircraft in our fleet and/or aircraft that we have ordered. This could, in turn, reduce both future residual values and lease rates for certain types of aircraft in our portfolio. Any of these risks may negatively affect our ability to lease or sell our aircraft on favorable terms, if at all, which would negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
We are indirectly subject to many of the economic and political risks associated with emerging markets, including China, which could negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
Our business strategy emphasizes leasing aircraft to lessees outside of the United States, including to airlines in emerging market countries. Emerging market countries have less developed economies and infrastructure and are often more vulnerable to economic and geopolitical challenges and may experience significant fluctuations in gross domestic product, interest rates and currency exchange rates, as well as civil disturbances, government instability, nationalization and expropriation of private assets and the imposition of taxes or other charges by government authorities. The occurrence of any of these events in markets served by our lessees and the resulting economic instability that may arise, particularly if combined with high fuel prices, could negatively affect the value of our aircraft subject to lease in such countries, or the ability of our lessees, which operate in these markets, to meet their lease obligations. As a result, lessees that operate in emerging market countries may be more likely to default than lessees that operate in developed countries. In addition, legal systems in emerging market countries may be less developed, which could make it more difficult for us to enforce our legal rights in such countries.
Further, demand for aircraft is dependent on passenger and cargo traffic, which in turn is dependent on general business and economic conditions. A decrease in passenger or cargo traffic may have a negative effect on our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations. Weak or negative economic growth in emerging markets may have an indirect effect on the value of the assets that we acquire if airlines and other potential lessees are negatively affected. Economic downturns can affect the values of the assets we purchase, which may have a negative effect on our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
From time to time, the aircraft industry has experienced periods of oversupply during which lease rates and aircraft values have declined, and any future oversupply could negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
The aircraft leasing business has experienced periods of aircraft oversupply following the September 11, 2001 terrorist attacks and the 2008 financial crisis. The oversupply of a specific type of aircraft is likely to depress the lease rates for and the value of that type of aircraft, including upon sale. Further, over recent years, the airline industry has committed to a significant number of aircraft deliveries through order placements with manufacturers, and in response, aircraft manufacturers have raised their production output. The increase in these production levels could result in an oversupply of relatively new aircraft if growth in airline traffic does not meet airline industry expectations.
The supply and demand for aircraft is affected by various cyclical and non-cyclical factors that are outside of our control, including:
|
· |
passenger and air cargo demand; |
|
· |
airline operating costs, including fuel costs; |
|
· |
general economic conditions; |
|
· |
geopolitical events, including war, prolonged armed conflict and acts of terrorism; |
|
· |
outbreaks of communicable diseases and natural disasters; |
18
|
· |
governmental regulation, including new airworthiness directives, statutory limits on the age of aircraft, and restrictions in certain jurisdictions on the age of aircraft for import, climate change initiatives and environmental regulation, and other factors leading to obsolescence of aircraft models; |
|
· |
interest and foreign exchange rates; |
|
· |
tariffs and other restrictions on trade; |
|
· |
the availability of credit; |
|
· |
airline restructurings and bankruptcies; |
|
· |
airline fleet planning that reduces capacity or changes the type of aircraft in demand; |
|
· |
manufacturer production levels and technological innovation; |
|
· |
discounting by manufacturers on aircraft types nearing end of production; |
|
· |
manufacturers merging or exiting the industry or ceasing to produce aircraft types; |
|
· |
new-entrant manufacturers producing additional aircraft models, or existing manufacturers producing new engine models or new aircraft models, in competition with existing aircraft models; |
|
· |
retirement and obsolescence of aircraft models; |
|
· |
reintroduction into service of aircraft previously in storage; and |
|
· |
airport and air traffic control infrastructure constraints. |
In addition, operating lessors may be sold or merged with other entities. These types of transactions may call for a reduction in the fleet of the new entity, which could increase supply levels of used and older aircraft in the market. Furthermore, recent and future political developments could result in increased regulation of trade, which could adversely impact demand for aircraft.
Any of these factors may produce sharp and prolonged decreases in aircraft lease rates and values. They may have a negative effect on our ability to lease or remarket the aircraft in our fleet or in our order book. Any of these factors could negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
The value of the aircraft we acquire and the market rates for leases could decline, which would have a negative effect on our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
Aircraft values and market rates for leases have from time to time experienced sharp decreases due to a number of factors including, but not limited to, decreases in passenger and air cargo demand, increases in fuel costs, government regulation and increases in interest rates. Operating leases place the risk of realization of residual values on aircraft lessors because only a portion of the equipment’s value is covered by contractual cash flows at lease inception. In addition to factors linked to the aviation industry generally, many other factors may affect the value of the aircraft that we acquire and market rates for leases, including:
|
· |
the particular maintenance, damage, operating history and documentary records of the aircraft; |
|
· |
the geographical area where the aircraft is based and operates; |
19
|
· |
the number of operators using that type of aircraft; |
|
· |
aircraft age; |
|
· |
the regulatory authority under which the aircraft is operated; |
|
· |
whether an aircraft is subject to a lease and, if so, whether the lease terms are favorable to the lessor; |
|
· |
any renegotiation of an existing lease on less favorable terms; |
|
· |
the negotiability of clear title free from mechanics’ liens and encumbrances; |
|
· |
any tax, customs, regulatory and other legal requirements that must be satisfied before the aircraft can be purchased, sold or remarketed; |
|
· |
grounding orders or other regulatory action that could prevent or limit utilization of our aircraft; |
|
· |
compatibility of aircraft configurations or specifications with other aircraft owned by operators of that type; |
|
· |
comparative value based on newly manufactured competitive aircraft; and |
|
· |
the availability of spare parts. |
Any decrease in the value of aircraft that we acquire and market rates for leases, which may result from the above factors or other unanticipated factors, would have a negative effect on our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
Competition from other aircraft lessors, including lessors with greater resources or a lower cost of capital than ours, could negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
The aircraft leasing industry is highly competitive. Some of our competitors may have greater resources or a lower cost of capital than ours or may provide certain financial services, maintenance services or other inducements to potential lessees that we cannot provide; accordingly, they may be able to compete more effectively in one or more of the markets we conduct business in.
In addition, we may encounter competition from other entities in the acquisition of aircraft such as:
|
· |
airlines; |
|
· |
financial institutions; |
|
· |
special purpose vehicles formed for the purpose of acquiring, leasing and selling aircraft; |
|
· |
aircraft brokers; |
|
· |
public and private partnerships, investors and funds with more capital to invest in aircraft; and |
|
· |
other aircraft leasing companies that we do not currently consider our major competitors. |
Competition for a leasing transaction is based principally upon lease rates, delivery dates, lease terms, reputation, management expertise, aircraft condition, specifications and configuration and the availability of the types of aircraft necessary to meet the needs of the customer. Competition in the purchase and sale of aircraft is based principally
20
on the availability of the aircraft, the price, and where applicable the terms of the lease to which an aircraft is subject and the creditworthiness of the lessee. We will not always be able to compete successfully with our competitors, which could negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
The failure of any manufacturer to meet its delivery obligations to us would negatively affect our cash flow and results of operations.
The supply of commercial aircraft is dominated by a few airframe manufacturers and a limited number of engine manufacturers. As a result, we are dependent on the success of these manufacturers in remaining financially stable, producing products and related components which meet the airlines’ demands and fulfilling any contractual obligations they may have to us.
Should the manufacturers fail to respond appropriately to changes in the market environment or fail to fulfill any contractual obligations they might have to us, we may experience:
|
· |
missed or late delivery of aircraft and a potential inability to meet our contractual obligations owed to any of our then lessees, resulting in potential lost or delayed revenues, lower growth rates and strained customer relationships; |
|
· |
an inability to acquire aircraft and related components on terms which will allow us to lease those aircraft to airline customers at a profit, resulting in lower growth rates or a contraction in our aircraft fleet; |
|
· |
a market environment with too many aircraft available, potentially creating downward pressure on demand for the anticipated aircraft in our fleet and reduced market lease rates and sale prices; |
|
· |
reduced demand for a particular manufacturer's product as a result of poor customer support, creating downward pressure on demand for those aircraft and engines in our fleet and reduced market lease rates and sale prices for those aircraft and engines; and |
|
· |
a reduction in our competitiveness due to deep discounting by the manufacturers, which may lead to reduced market lease rates and aircraft values and may affect our ability to remarket or sell at a profit, or at all, some of the aircraft in our fleet. |
There have been recent well‑publicized delays by airframe and engine manufacturers in meeting stated deadlines in bringing new aircraft to market. If there are manufacturing delays for aircraft for which we have made future lease commitments, some or all of our affected lessees could elect to terminate their lease arrangements with respect to such delayed aircraft. Any such termination could strain our relations with those lessees going forward and would negatively affect our cash flow and results of operations.
Aircraft have limited economic useful lives and depreciate over time, which would negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
We depreciate our aircraft for accounting purposes on a straight-line basis to the aircraft’s residual value over its estimated useful life. If reduced demand for an aircraft causes a decline in its projected lease rates, or if we dispose of the aircraft for a price that is less than its depreciated book value on our balance sheet, then we will recognize a loss on the sale of the aircraft or potentially record an impairment charge. For this reason, our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations would be negatively affected.
Failure to close our aircraft acquisition commitments could negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
As of December 31, 2017, we had entered into binding purchase commitments to acquire a total of 368 new aircraft for delivery through 2023. If we are unable to maintain our financing sources or find new sources of financing or
21
if the various conditions to our existing commitments are not satisfied, we may be unable to close the purchase of some or all of the aircraft which we have commitments to acquire. If our aircraft acquisition commitments are not closed for these or other reasons, we will be subject to several risks, including the following:
|
· |
forfeiting deposits and progress payments and having to pay and expense certain significant costs relating to these commitments, such as actual damages, and legal, accounting and financial advisory expenses, not realizing any of the benefits of completing the transactions and damage to our reputation and relationship with aircraft manufacturers; |
|
· |
defaulting on our lease commitments, which could result in monetary damages and damage to our reputation and relationships with lessees; and |
|
· |
failing to capitalize on other aircraft acquisition opportunities that were not pursued due to our management’s focus on these commitments. |
If we determine that the capital we require to satisfy these commitments may not be available to us, either at all or on terms we deem attractive, we may eliminate or reduce any dividend program that may be in place at that time in order to preserve capital to apply to these commitments. These risks would negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
Certain of the agreements governing our indebtedness may limit our operational flexibility, our ability to effectively compete and our ability to grow our business as currently planned, which would negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
Certain of the agreements governing our indebtedness, including our credit facilities, contain financial and non-financial covenants, such as requirements that we comply with one or more of the following covenants: maximum debt-to-equity ratios, dividend restrictions, limitations on the ability of our subsidiaries to incur debt, minimum net worth and interest coverage ratios, change of control provisions, and prohibitions against our disposing of our aircraft or other aviation assets without a lender’s prior consent. Complying with such covenants may at times necessitate that we forego other opportunities, such as using available cash to grow our aircraft fleet or promptly disposing of less profitable aircraft or other aviation assets. Moreover, our failure to comply with any of these covenants would likely constitute a default under such agreements and could give rise to an acceleration of some, if not all, of our then outstanding indebtedness, which would have a negative effect on our business and our ability to continue as a going concern. If we were unable to repay the indebtedness when due and payable, secured lenders could proceed against, among other things, the aircraft securing such indebtedness, if any.
In addition, we cannot assure you that our business will generate cash flow from operations in an amount sufficient to enable us to service our debt and grow our operations as planned. We cannot assure you that we will be able to refinance any of our debt on favorable terms, if at all. In addition, we cannot assure you that in the future we will be able to access long‑term financing or credit support on attractive terms, if at all, or qualify for guarantees, or obtain attractive terms for such guarantees, from the export credit agencies. Any inability to generate sufficient cash flow, maintain our existing fleet and facilities, or access long‑term financing or credit support would negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
Negative changes in our credit ratings may limit our ability to obtain financing or increase our borrowing costs which would negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
We are currently subject to periodic review by independent credit rating agencies S&P, Fitch and Kroll, each of which currently maintains investment grade credit ratings with respect to us and certain of our debt securities, and we may become subject to periodic review by other independent credit rating agencies in the future. An increase in the level of our outstanding indebtedness, or other events that could have a negative impact on our business, properties, financial condition, results of operations or prospects, may cause S&P, Fitch or Kroll, or, in the future, other rating agencies, to downgrade or withdraw the credit rating with respect to us or our debt securities, which could negatively impact our ability to secure financing and increase our borrowing costs.
22
We cannot assure you that these credit ratings will remain in effect for any given period of time or that a rating will not be lowered, suspended or withdrawn entirely by the applicable rating agency, if, in such rating agency’s sole judgment, circumstances so warrant. Ratings are not a recommendation to buy, sell or hold any security. Each agency’s rating should be evaluated independently of any other agency’s rating. Actual or anticipated changes or downgrades in our credit ratings, including any announcement that our ratings are under further review for a downgrade, could increase our corporate borrowing costs and limit our access to the capital markets which would negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
An increase in our borrowing costs would negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
We finance many of the aircraft in our fleet through a combination of short-and long-term debt financings. As these debt financings mature, we may have to refinance these existing commitments by entering into new financings, which could result in higher borrowing costs, or repay them by using cash on hand or cash from the sale of our assets. Moreover, an increase in interest rates under the various debt financing facilities we have in place would have a negative effect on our earnings and could make our aircraft leasing contracts unprofitable.
A limited percentage of our debt financings bear interest at a floating rate, such that our interest expense would vary with changes in the applicable reference rate. As a result, our inability to sufficiently protect ourselves from changes in our cost of borrowing, as reflected in our composite interest rate, may have a direct, negative impact on our net income. Our lease rental stream is generally fixed over the life of our leases, whereas we have used floating-rate debt to finance a significant portion of our aircraft acquisitions. As of December 31, 2017, we had $1.4 billion in floating-rate debt. If interest rates increase, we would be obligated to make higher interest payments to the lenders of our floating-rate debt. Further, as we continue to incur fixed-rate debt, increased interest rates prevailing in the market at the time of the incurrence of such debt would also increase our interest expense. If our composite interest rate were to increase by 1.0%, we would expect to incur additional interest expense on our existing indebtedness as of December 31, 2017, of approximately $14.3 million on an annualized basis, which would negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
As such, if interest rates were to rise sharply, we would not be able to fully offset immediately the negative impact on our net income by increasing lease rates, even if the market were able to bear such increases in lease rates. Our leases are generally for multiple years with fixed lease rates over the life of the lease and, therefore, lags will exist because our lease rates with respect to a particular aircraft cannot generally be increased until the expiration of the lease.
The interest rates that we obtain on our debt financings have several components, including credit spreads, swap spreads, duration, and new issue premiums. These are all incremental to the underlying risk-free rates, as applicable. Volatility in our perceived risk of default or in a market sector’s risk of default will negatively impact our cost of funds.
We currently are not involved in any interest rate hedging activities, but we are contemplating engaging in hedging activities in the future. Any such hedging activities will require us to incur additional costs, and there can be no assurance that we will be able to successfully protect ourselves from any or all negative interest rate fluctuations at a reasonable cost.
Our substantial indebtedness incurred to acquire our aircraft requires significant debt service payments which would negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
We and our subsidiaries have a significant amount of indebtedness. As of December 31, 2017, our total consolidated indebtedness, net of discounts and issuance costs, was approximately $9.7 billion and our interest payments were $301.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2017. Furthermore, we expect this amount to grow as we acquire more aircraft. Our level of debt could have important consequences, including the following:
|
· |
making it more difficult for us to satisfy our payment obligations with respect to our debt; |
23
|
· |
limiting our ability to obtain additional financing to fund the acquisition of aircraft or for other corporate requirements; |
|
· |
requiring a substantial portion of our cash flows to be dedicated to debt service payments instead of other purposes, thereby reducing the amount of cash flows available for dividends, aircraft acquisitions and other general corporate purposes; |
|
· |
increasing our vulnerability to general negative economic and industry conditions; |
|
· |
exposing us to the risk of increased interest rates as certain of our borrowings, including borrowings under our various credit facilities, are at variable rates of interest; |
|
· |
limiting our flexibility in planning for and reacting to changes in the aircraft industry; |
|
· |
placing us at a disadvantage compared to other competitors; and |
|
· |
increasing our cost of borrowing. |
In addition, certain agreements governing our existing indebtedness contain financial maintenance covenants that require us to satisfy certain ratios and maintain minimum net worth, and other restrictive covenants that limit our ability to engage in activities that may be in our long‑term best interest. Our failure to comply with those covenants could result in an event of default which, if not cured or waived, may result in the acceleration of some or all our debt, which would negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
Creditors of any subsidiaries we form for purposes of financing will have priority over our stockholders in the event of a distribution of such subsidiaries’ assets.
Some of the aircraft we acquire are held in special-purpose, bankruptcy-remote subsidiaries of our Company. Liens on those assets will be held by a collateral agent for the benefit of the lenders under the respective facility. In addition, funds generated from the lease of aircraft generally are applied first to amounts due to lenders, with certain exceptions. Creditors of our subsidiaries will have priority over us, our stockholders and our creditors relating to debt that is not guaranteed or secured by our subsidiaries or their assets in any distribution of any such subsidiaries’ assets in a liquidation, reorganization or otherwise.
Defaults by one or more of our significant airline customers would negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
The airline industry is cyclical, economically sensitive and highly competitive. Our lessees are affected by a number of factors over which we and they have limited control, including fare levels, air cargo rates, passenger air travel and air cargo demand, fuel prices and shortages, political or economic instability, currency fluctuations in the countries and regions in which the lessees operate, availability of financing and other circumstances affecting airline liquidity, terrorist activities, cyber risk, changes in national policy, competitive pressures, labor costs, labor actions, pilot shortages, aircraft accidents, insurance costs, recessions, health concerns, and other political or economic events negatively affecting the world or regional trading markets. Our lessees’ abilities to react to and cope with the volatile competitive environment in which they operate, as well as our own competitive environment, will likely affect our revenues and income. The loss of one or more of our significant airline customers or their inability to make operating lease payments due to financial difficulties, bankruptcy or otherwise could have a material negative effect on our cash flow and earnings. This, in turn, could result in a breach of the covenants contained in any of our long-term debt facilities, possibly resulting in accelerated amortization or defaults and would negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations. In the event that a lessee defaults under a lease, any security deposit paid or letter of credit provided by the lessee may not be sufficient to cover the lessee’s outstanding or unpaid lease obligations and required maintenance and transition expenses.
24
The appreciation of the U.S. dollar could negatively impact many of our lessees’ ability to honor the terms of their leases and could therefore materially adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Many of our lessees are exposed to currency risk due to the fact that they earn revenues in their local currencies while a significant portion of their liabilities and expenses are denominated in U.S. dollars, including their lease payments to us, as well as fuel, debt service, and other expenses. For the year ended December 31, 2017, less than 3% of our revenues were derived from customers who have their principal place of business in the U.S. While we attempt to minimize our currency and exchange risks by negotiating the designated payment currency in our leases to be U.S. dollars, the ability of our lessees to make lease payments to us in U.S. dollars may be adversely impacted in the event of an appreciating U.S. dollar.
Our lessees may not be able to increase their revenues sufficiently to offset the impact of exchange rates on their lease payments and other expenses denominated in U.S. dollars. This is particularly true for non-U.S. airlines whose operations are primarily domestic. Currency volatility, particularly as witnessed recently in other emerging market countries, could impact the ability of some of our customers to meet their contractual obligations in a timely manner. Shifts in foreign exchange rates can be significant, are difficult to predict, and can occur quickly.
Certain of our subsidiaries may be restricted in their ability to make distributions to us which would negatively affect our financial condition and cash flow.
The subsidiaries that hold our aircraft are legally distinct from us, and some of these subsidiaries are restricted from paying dividends or otherwise making funds available to us pursuant to agreements governing our indebtedness. Some of our principal debt facilities have financial covenants. If we are unable to comply with these covenants, then the amounts outstanding under these facilities may become immediately due and payable, cash generated by our subsidiaries affected by these facilities may be unavailable to us and/or we may be unable to draw additional amounts under these facilities. The events that could cause some of our subsidiaries not to be in compliance with their loan agreements, such as a lessee default, may be beyond our control, but they nevertheless could have a substantial negative impact on the amount of our cash flow available to fund working capital, make capital expenditures and satisfy other cash needs. For these reasons our financial condition and cash flow would be negatively affected. For a description of the operating and financial restrictions in our debt facilities, see the section titled “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Liquidity and Capital Resources.”
Our aircraft may not at all times be adequately insured either as a result of lessees failing to maintain sufficient insurance during the course of a lease or insurers not being willing to cover certain risks which would negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
We do not directly control the operation of any aircraft we acquire. Nevertheless, because we hold title, directly or indirectly, to such aircraft, we could be sued or held strictly liable for losses resulting from the operation of such aircraft, or may be held liable for those losses on other legal theories, in certain jurisdictions around the world, or claims may be made against us as the owner of an aircraft requiring us to expend resources in our defense. We require our lessees to obtain specified levels of insurance and indemnify us for, and insure against, liabilities arising out of their use and operation of the aircraft. Lessees are also required to maintain public liability, property damage and all risk hull and war risk insurance on the aircraft at agreed upon levels. Some lessees may fail to maintain adequate insurance coverage during a lease term, which, although in contravention of the lease terms, would necessitate our taking some corrective action such as terminating the lease or securing insurance for the aircraft, either of which could negatively affect our financial results. Moreover, even if our lessees retain specified levels of insurance, and indemnify us for, and insure against, liabilities arising out of their use and operation of the aircraft, we cannot assure you that we will not have any liability.
In addition, there are certain risks or liabilities that our lessees may face, for which insurers may be unwilling to provide coverage or the cost to obtain such coverage may be prohibitively expensive. For example, following the terrorist attacks of September 11, 2001, non-government aviation insurers significantly reduced the amount of insurance coverage available for claims resulting from acts of terrorism, war, dirty bombs, bio-hazardous materials, electromagnetic pulsing or similar events. At the same time, they significantly increased the premiums for such third-
25
party war risk and terrorism liability insurance and coverage in general. Accordingly, we anticipate that our lessees’ insurance or other coverage may not be sufficient to cover all claims that could or will be asserted against us arising from the operation of our aircraft by our lessees. Inadequate insurance coverage or default by lessees in fulfilling their indemnification or insurance obligations will reduce the proceeds that would be received by us in the event that we are sued and are required to make payments to claimants. Moreover, our lessees’ insurance coverage is dependent on the financial condition of insurance companies, which might not be able to pay claims. A reduction in insurance proceeds otherwise payable to us as a result of any of these factors would negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
The death, incapacity or departure of key officers could harm our business and negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
We believe our senior management’s reputation and relationships with lessees, manufacturers, buyers and financiers of aircraft are a critical element to the success of our business. We depend on the diligence, skill and network of business contacts of our management team. We believe there are only a limited number of available qualified executives in the aircraft industry, and we therefore have encountered, and will likely continue to encounter, intense competition for qualified employees from other companies in our industry. Our future success will depend, to a significant extent, upon the continued service of our senior management personnel, particularly: Mr. Udvar-Házy, our founder, and Executive Chairman of the Board; Mr. Plueger, our Chief Executive Officer and President; and our other senior officers, each of whose services are critical to the success of our business strategies. We do not have employment agreements with Mr. Udvar-Házy or Mr. Plueger. If we were to lose the services of any of the members of our senior management team, it could negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
Conflicts of interest may arise between us and clients who will utilize our fleet management services, which could negatively affect our business interests, cash flow and results of operations.
Conflicts of interest may arise between us and third‑party aircraft owners, financiers and operating lessors who hire us to perform fleet management services such as leasing, re‑leasing, lease management and sales services. These conflicts may arise because services we anticipate providing for these clients are also services we will provide for our own fleet, including the placement of aircraft with lessees. We expect our fleet management services agreements will provide that we will use our reasonable commercial efforts in providing services, but, to the extent that we are in competition with the client for leasing opportunities, we will give priority to our own fleet. Nevertheless, despite these contractual waivers, competing with our fleet management clients in practice may result in strained relationships with them, which could negatively affect our business interests, cash flow and results of operations.
We may on occasion enter into strategic ventures with the intent that we would serve as the manager of such strategic ventures; however, entering into strategic relationships poses risks in that we most likely would not have complete control over the enterprise, and our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations could be negatively affected if we encounter disputes, deadlock or other conflicts of interest with our strategic partners.
In addition to our Blackbird Capital I, LLC and Blackbird Capital II, LLC joint ventures discussed in Note 12 of Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements included in Part II, Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, for which we own non-controlling interests, we may on occasion enter into strategic ventures with third parties to take advantage of favorable financing opportunities or tax benefits, to share capital and/or operating risk, and/or to earn fleet management fees. Strategic ventures involve significant risks that may not be present with other methods of ownership, including that:
|
· |
we may not realize a satisfactory return on our investment; |
|
· |
the strategic ventures may divert management’s attention from our core business; |
|
· |
our strategic venture partners could have investment goals that are not consistent with our investment objectives, including the timing, terms and strategies for any investments; |
26
|
· |
our strategic venture partners might fail to fund their share of required capital contributions or fail to fulfill their other obligations; |
|
· |
our strategic venture partners may have competing interests in our markets that could create conflict of interest issues, particularly if aircraft owned by the strategic ventures are being marketed for lease or sale at a time when we also have comparable aircraft available for lease or sale. |
Although we anticipate that we would serve as the manager of any such strategic ventures, it has been our management’s experience that most strategic venture agreements will provide the non‑managing strategic partner certain veto rights over various significant actions, including the right to remove us as the manager under certain circumstances. If we were to be removed as the manager from a strategic venture that generates significant management fees, our financial results and growth prospects could be materially and negatively affected. In addition, if we were unable to resolve a dispute with a significant strategic partner that retains material managerial veto rights, we might reach an impasse that could require us to dissolve the strategic venture at a time and in a manner that could result in our losing some or all of our original investment in the strategic venture, which could have a negative effect on our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
Our business and earnings are affected by general business, financial market and economic conditions throughout the world, which could have a negative effect on our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
Our business and earnings are affected by general business, financial market and economic conditions throughout the world. As an aircraft leasing business with exposure to emerging markets, we are particularly exposed to downturns in these emerging markets. A recession or worsening of economic conditions, particularly if combined with high fuel prices, may have a material negative effect on the ability of our lessees to meet their financial and other obligations under our operating leases, which, if our lessees default on their obligations to us, could have a material negative effect on our cash flow and results of operations. General business and economic conditions that could affect us include the level and volatility of short-term and long-term interest rates, inflation, employment levels, bankruptcies, restructurings and mergers in the airline industry, demand for passenger and cargo air travel, volatility in both debt and equity capital markets, liquidity of the global financial markets, volatility in foreign exchange rates, the availability and cost of credit, investor confidence and the strength of the global economy and the local economies in which we operate. For these reasons our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations could be negatively affected.
Because our leases are concentrated in certain geographical regions, we have concentrated exposure to the political and economic risks associated with those regions.
Through our lessees and the countries in which they operate, we are exposed to the specific economic and political conditions and associated risks of those jurisdictions. For example, we have large concentrations of lessees in China, and therefore have increased exposure to the economic and political conditions in that country. These risks can include economic recessions, burdensome local regulations or, in extreme cases, increased risks of requisition of our aircraft. An adverse political or economic event in any region or country in which our lessees are concentrated or where we have a large number of aircraft could affect the ability of our lessees in that region or country to meet their obligations to us, or expose us to various legal or political risks associated with the affected jurisdictions, all of which could have a material and adverse effect on our financial results.
Economic conditions and regulatory changes in the United States, United Kingdom and Europe could have an adverse effect on our business and results of operations.
Following a referendum in June 2016 in which voters in the United Kingdom, or U.K., approved an exit from the European Union, or E.U., it is expected that the U.K. government will initiate a process, often referred to as Brexit, to leave the E.U. and will begin negotiating the terms of the U.K.'s future relationship with the E.U. The effects of Brexit will likely depend on the agreements that the U.K. is able to make to retain access to E.U. markets, either during a transitional period or more permanently. We lease aircraft to airlines in the E.U., including the U.K. We and the aviation industry face uncertainty regarding the impact of Brexit. Adverse consequences, such as instability in financial markets, deterioration in economic conditions, volatility in currency exchange rates or adverse changes in regulation of the
27
aviation industry or bilateral agreements governing air travel, could negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations. These impacts may include increased costs of financing; downward pressure on demand for our aircraft and reduced market lease rates and lease margins; and a higher incidence, in the U.K. in particular and the E.U. generally, of lessee defaults or other events resulting in our lessees' failing to perform under our lease agreements.
In the United States, any negative economic effects of instability resulting from changes in the political environment, international relations, existing trade agreements, import and export regulations, immigration, tariffs and customs duties as well as regulatory, environmental or tax policy changes, may negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations. For example, unanticipated impacts of the Tax Cuts and Job Act of 2017 (the “Tax Act”), including as a result of changes in assumptions we make in our interpretation of the Tax Act and guidance related to application of the Tax Act that may be issued in the future may negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations. Additionally, in the E.U., several countries will hold general and/or presidential elections in 2018, including Italy, Sweden and Ireland, and the outcome of these elections could create significant changes in, or create uncertainty regarding, laws, regulations and policies affecting our business.
Any of the above effects of Brexit and U.S. political changes, and others that we may not be able to anticipate, could negatively impact our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
Terrorist attacks, war or armed hostilities between countries or non-state actors, or the fear of such attacks, even if not made directly on the airline industry, could negatively affect lessees and the airline industry, which would negatively affect our cash flow and results of operations.
Terrorist attacks, war or armed hostilities between countries or non-state actors, or the fear of such events, have historically had a negative impact on the aviation industry and could result in:
|
· |
higher costs to the airlines due to the increased security measures; |
|
· |
decreased passenger demand and revenue due to the inconvenience of additional security measures or concerns about the safety of flying; |
|
· |
the imposition of ''no-fly zone'' or other restrictions on commercial airline traffic in certain regions; |
|
· |
uncertainty of the price and availability of jet fuel and the cost and practicability of obtaining fuel hedges; |
|
· |
higher financing costs and difficulty in raising the desired amount of proceeds on favorable terms, if at all; |
|
· |
significantly higher costs of aviation insurance coverage for future claims caused by acts of war, terrorism, sabotage, hijacking and other similar perils, or the unavailability of certain types of insurance; |
|
· |
inability of airlines to reduce their operating costs and conserve financial resources, taking into account the increased costs incurred as a consequence of such events; |
|
· |
special charges recognized by some operators, such as those related to the impairment of aircraft and engines and other long-lived assets stemming from the grounding of aircraft as a result of terrorist attacks, economic conditions and airline reorganizations; and |
|
· |
an airline's becoming insolvent and/or ceasing operations. |
For example, as a result of the September 11, 2001 terrorist attacks in the United States and subsequent terrorist attacks abroad, notably in the Middle East, Southeast Asia and Europe, increased security restrictions were implemented on air travel, costs for aircraft insurance and security measures increased, passenger and cargo demand for air travel decreased, and operators faced difficulties in acquiring war risk and other insurance at reasonable costs. Further, international sanctions against Russia and other countries, uncertainty regarding tensions between the United States and
28
North Korea, the situations in Iraq, Afghanistan, Egypt and Syria, the Israeli/Palestinian conflict, political instability in the Middle East and North Africa, the dispute between Japan and China, the recent tensions in the South China Sea and additional international hostilities could lead to further instability in these regions.
Terrorist attacks, war or armed hostilities between countries or non-state actors, large protests or government instability, or the fear of such events, could adversely affect the aviation industry and the financial condition and liquidity of our lessees, as well as aircraft values and rental rates. In addition, such events may cause certain aviation insurance to become available only at significantly increased premiums or with reduced amounts of coverage insufficient to comply with the current requirements of aircraft lenders and lessors or by applicable government regulations, or not to be available at all. Although some governments provide for limited coverage under government programs for specified types of aviation insurance, these programs may not be available at the relevant time or governments may not pay under these programs in a timely fashion.
Such events are likely to cause our lessees to incur higher costs and to generate lower revenues, which could result in a material adverse effect on their financial condition and liquidity, including their ability to make rental and other lease payments to us or to obtain the types and amounts of insurance we require. This in turn could lead to aircraft groundings or additional lease restructurings and repossessions, increase our cost of remarketing or selling aircraft, impair our ability to remarket or otherwise dispose of aircraft on favorable terms or at all, or reduce the proceeds we receive for our aircraft in a disposition.
Changes in fuel costs could materially negatively affect our lessees and by extension the demand for our aircraft which would negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
Fuel costs represent a major expense to airlines, and fuel prices fluctuate widely depending primarily on international market conditions, geopolitical and environmental events, regulatory changes (including those related to greenhouse gas emissions) and currency exchange rates. If airlines are unable to increase ticket prices to offset fuel price increases, their cash flows will suffer. Political unrest in the Middle East and North Africa has historically generated uncertainty regarding the predictability of the world’s future oil supply, which has led to significant increases in fuel costs. Fuel costs may rise in the future. Other events can also significantly affect fuel availability and prices, including natural disasters, decisions by the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries regarding their members’ oil output, and the increase in global demand for fuel from countries such as China.
High fuel costs would likely have a material negative impact on airline profitability. Due to the competitive nature of the airline industry, airlines may not be able to pass on increases in fuel prices to their passengers by increasing fares. If airlines are successful in increasing fares, demand for air travel may be negatively affected. Higher and more volatile fuel prices may also have an impact on consumer confidence and spending, and thus may adversely impact demand for air transportation. In addition, airlines may not be able to manage fuel cost risk by appropriately hedging their exposure to fuel price fluctuations. The profitability and liquidity of those airlines that do hedge their fuel costs can also be adversely affected by swift movements in fuel prices, if such airlines are required to post cash collateral under their hedge agreements. If fuel prices increase, they are likely to cause our lessees to incur higher costs. A sustained period of lower fuel costs may adversely affect regional economies that depend on oil revenue, including those in which certain of our lessees operate. Consequently, these conditions may:
|
· |
affect our lessees’ ability to make rental and other lease payments; |
|
· |
result in lease restructurings and aircraft repossessions; |
|
· |
increase our costs of maintaining and marketing aircraft; |
|
· |
impair our ability to remarket aircraft or otherwise sell our aircraft on a timely basis at favorable rates; or |
|
· |
reduce the sale proceeds received in the event of an aircraft sale. |
29
Such effects would materially negatively affect demand for our aircraft, which would negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
A deterioration in the financial condition of the airline industry would have a negative impact on our ability to lease our aircraft which would negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
The financial condition of the airline industry is of particular importance to us because our aircraft are primarily leased to passenger airlines and we plan to continue to lease our aircraft to passenger airlines. Our ability to achieve our primary business objectives will depend on the financial condition and growth of the airline industry as well as the financial strength of our lessees and the lessees’ ability to manage their respective risks. However, these risks are generally out of our control, but because these risks have a significant impact on our intended airline customers, they will affect us as well. We may experience:
|
· |
downward pressure on demand for our aircraft and reduced market lease rates and lease margins; |
|
· |
a higher incidence of lessee defaults, lease restructurings, repossessions and airline bankruptcies and restructurings, resulting in lower lease margins due to maintenance and legal costs associated with repossession, as well as lost revenue for the time our aircraft are off lease and possibly lower lease rates from our new lessees; |
|
· |
an inability to lease aircraft on commercially acceptable terms, resulting in lower lease margins due to aircraft not earning revenue and resulting in storage, insurance and maintenance costs; |
|
· |
a loss if the aircraft are damaged or destroyed by an event specifically excluded from insurance policies such as dirty bombs, bio-hazardous materials and electromagnetic pulsing; and |
|
· |
any changes in the general business, financial market, and economic conditions or the local economies in which lessees operate that negatively affect lessees. |
For these reasons our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations would be negatively affected.
Epidemic diseases may hinder airline travel and reduce the demand for aircraft which would negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
Epidemic diseases, such as severe acute respiratory syndrome, bird flu, swine flu, the Zika virus, Ebola or other pandemic diseases negatively affected passenger demand for air travel in recent years. These epidemic diseases and other pandemic diseases, or the fear of such events, could provoke responses, including government-imposed travel restrictions, which could negatively affect passenger demand for air travel and the financial condition of the aviation industry. The consequences of these events may reduce the demand for aircraft and/or impair our lessees’ ability to satisfy their lease payment obligations to us, which in turn would negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
Natural disasters and other natural phenomena may disrupt air travel and reduce the demand for aircraft which would negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
Air travel can be disrupted, sometimes severely, by the occurrence of natural disasters and other natural phenomena. A natural disaster or other natural phenomena could cause disruption to air travel and could result in a reduced demand for aircraft and/or impair our lessees’ ability to satisfy their lease payment obligations to us, which in turn would negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
30
The effects of various environmental regulations may negatively affect the airline industry, which may in turn cause lessees to default on their lease payment obligations to us which would negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
The airline industry is subject to increasingly stringent federal, state, local and international environmental laws and regulations concerning emissions to the air, discharges to surface and subsurface waters, safe drinking water, aircraft noise, the management of hazardous substances, oils and waste materials and other regulations affecting aircraft operations. Governmental regulations regarding aircraft and engine noise and emissions levels apply based on where the relevant aircraft is registered and operated. For example, jurisdictions throughout the world have adopted noise regulations which require all aircraft to comply with noise level standards. In addition to the current requirements, the United States and the International Civil Aviation Organization (the “ICAO”) have specific standards for noise levels which applies to engines manufactured or certified on or after January 1, 2006. Currently, U.S. regulations would not require any phase-out of aircraft that qualify with the older standards applicable to engines manufactured or certified prior to January 1, 2006, but the European Union has established a framework for the imposition of operating limitations on aircraft that do not comply with the new standards and incorporates aviation-related emissions into the European union’s Emission Trading Scheme (the “ETS”). ICAO has also adopted new, more stringent noise level standards to apply to new airplane type design with a maximum certificated takeoff weight of 55,000 kg or more on or after December 31, 2017; or with maximum certificated takeoff weight of less than 55,000 kg on or after December 31, 2020. Additionally, the U.S. has adopted new noise regulations, effective November 3, 2017, to harmonize with the new ICAO standards. These regulations could limit the economic life of the aircraft and engines, reduce their value, limit our ability to lease or sell the non-compliant aircraft and engines or, if engine modifications are permitted, require us to make significant additional investments in the aircraft and engines to make them compliant.
In addition to more stringent noise restrictions, the United States and other jurisdictions are beginning to impose more stringent limits on nitrogen oxide, carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide emissions from engines, consistent with current ICAO standards. These limits generally apply only to engines manufactured after 1999. Because aircraft engines are replaced from time to time in the normal course, it is likely that the number of such engines would increase over time. On October 6, 2016, 191 member states of the ICAO adopted the Carbon Offset and Reduction Scheme for International Aviation (“CORSIA”) which calls for a global market measure to help the aviation industry meet its goal of carbon-neutral growth after 2020. Baseline emissions levels will be measured in 2019-2020, after which airlines will purchase offsets for any increase in emissions from that level. The plan starts with a voluntary phase-in from 2021 through 2026, during which only routes between countries that choose to participate will be covered. At least 65 countries have indicated that they will participate in the voluntary phase, including the United States, Canada, China, and 28 EU countries. Concerns over global warming could result in more stringent limitations on the operation of aircraft powered by older, non-compliant engines, as well as newer engines. Future regulatory actions that may be taken by the U.S. government, other foreign governments or the ICAO to address concerns about climate change, noise and emissions from the aviation sector may include the imposition of requirements to purchase additional emission offsets or credits, which could require participation in emission trading (such as is required in the EU and by the CORSIA), substantial taxes on emissions and growth restrictions on airline operations, among other potential regulatory actions.
European countries generally have relatively strict environmental regulations that can restrict operational flexibility and decrease aircraft productivity. The European Parliament has confirmed that all emissions from flights within the European Union are subject to the ETS requirement, even those emissions that are emitted outside of the European Union. The European Union suspended the enforcement of the ETS requirements for international flights outside of the European Union due to a proposal issued by the ICAO in October 2013 to develop a global program to reduce international aviation emissions, which would be enforced by 2020. In response to this, the European Commission amended the ETS legislation through the end of 2017 so that only flights or portions thereof that take place in European regional airspace are subject to the ETS requirements. On December 13, 2017, the European Commission further amended the ETS legislation to extend the derogation of the ETS requirements through the end of 2023. The United States, China and other countries continue to oppose the inclusion of aviation emissions from outside of the E.U. in the ETS. Similar measures may be implemented in other jurisdictions as a result of environmental concerns.
The potential impact of ETS and the new ICAO carbon standards on costs has not been completely identified. Limitations on emissions such as the ones in the European Union could favor younger, more fuel efficient aircraft since
31
they generally produce lower levels of emissions per passenger, which could adversely affect our ability to remarket or otherwise dispose of less efficient aircraft on a timely basis, at favorable terms, or at all. Concerns over global warming also could result in more stringent limitations on the operation of aircraft. Any of these regulations could limit the economic life of the aircraft and engines, reduce their value, limit our ability to lease or sell the compliant aircraft and engines or, if engine modifications are permitted, require us to make significant additional investments in the aircraft and engines to make them compliant, which would negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations. Further, compliance with current or future regulations, taxes or duties imposed to deal with environmental concerns could cause lessees to incur higher costs and to generate lower net revenues, resulting in a negative impact on their financial conditions. For example, the United Kingdom doubled its air passenger duties, effective February 1, 2007, in recognition of the environmental costs of air travel. Consequently, such compliance may affect lessees’ ability to make rental and other lease payments and reduce the value we receive for the aircraft upon any disposition, which would negatively affect our financial condition, cash flow and results of operations.
We operate in multiple jurisdictions and may become subject to a wide range of income and other taxes which would negatively affect our cash flow and results of operations.
We operate in multiple jurisdictions and may become subject to a wide range of income and other taxes. If we are unable to execute our business in jurisdictions with favorable tax treatment, our operations may be subject to significant income and other taxes.
Moreover, as our aircraft are operated by our lessees in multiple states and foreign jurisdictions, we may have nexus or taxable presence as a result of our aircraft landings in various states or foreign jurisdictions. Such landings may result in us being subject to various foreign, state and local taxes in such states or foreign jurisdictions. For these reasons our cash flow and results of operations would be negatively affected.
We are subject to various risks and requirements associated with transacting business in foreign countries which would negatively affect our cash flow and results of operations.
Our international operations expose us to trade and economic sanctions and other restrictions imposed by the United States or other governments or organizations. The U.S. Departments of Justice, Commerce, State and Treasury and other foreign agencies and authorities have a broad range of civil and criminal penalties they may seek to impose against corporations and individuals for violations of economic sanctions laws, export control laws, the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (“FCPA”) and other federal statutes and regulations, including the International Traffic in Arms Regulations and those established by the Office of Foreign Assets Control (“OFAC”), and, increasingly, similar or more restrictive foreign laws, rules and regulations, including the U.K. Bribery Act (“UKBA”), which may also apply to us. Under these laws and regulations, the government may require export licenses, may seek to impose modifications to business practices, including cessation of business activities in sanctioned countries or with sanctioned persons or entities, and modifications to compliance programs, which may increase compliance costs, and may subject us to fines, penalties and other sanctions. A violation of these laws or regulations could negatively impact our business, operating results, and financial condition. Further, events in Ukraine and Crimea have resulted in the European Union and the United States imposing escalating sanctions on Russia and certain businesses and sectors and individuals in Russia, including the airline industry. For instance, the United States has imposed restrictions prohibiting U.S. individuals and entities, including their foreign branches or subsidiaries owned or controlled by such individuals or entities, from providing financial services or assistance in the form of new equity or debt with certain maturities to specified Russian individuals and entities. Additionally, the European Union has enacted similar restrictions in which citizens of European Union member states and corporations domiciled in European Union member states are prohibited from dealing with financial instruments having a maturity greater than 30 days with certain Russian entities. Russia has imposed its own sanctions on certain individuals in the United States and may impose other sanctions on the United States and the European Union and/or certain businesses or individuals from these regions. We cannot assure you that the current sanctions or any further sanctions imposed by the European Union, the United States or other international interests will not materially adversely affect our operations.
In 2016, the United States and European Union lifted certain nuclear-related secondary sanctions as provided by the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (“JCPOA”) with Iran. Among other things, the sale or lease of civil passenger
32
aircraft to most Iranian airlines is now permitted, subject to receipt of an appropriate license. Transactions with sanctioned individuals and entities, including aircraft sale and lease transactions with such persons, remain prohibited, and the United States retains the authority to revoke the sanctions relief provided by the JCPOA if Iran fails to meet its commitments thereunder.
We have in place training programs for our employees with respect to FCPA, OFAC, UKBA, export controls and similar laws and regulations. There can be no assurance that our employees, consultants, sales agents, or associates will not engage in unlawful conduct for which we may be held responsible, nor can there be assurance that our business partners will not engage in conduct which could materially affect their ability to perform their contractual obligations to us or even result in our being held liable for such conduct. Moreover, while we believe that we have been in compliance with all applicable sanctions laws and regulations, and intend to maintain such compliance, there can be no assurance that we will be in compliance in the future, particularly as the scope of certain laws may be unclear and may be subject to change. Violations of the FCPA, OFAC, UKBA and other export control regulations, and similar laws and regulations may result in severe criminal or civil sanctions, and we may be subject to other liabilities, which could negatively affect our cash flow and results of operations.
A cyber‑attack that bypasses our information technology, or IT, security systems, causing an IT security breach, may lead to a material disruption of our IT systems and the loss of business information which may hinder our ability to conduct our business effectively and may result in lost revenues and additional costs.
Parts of our business depend on the secure operation of our computer systems to manage, process, store, and transmit information associated with aircraft leasing. We have, from time to time, experienced threats to our data and systems, including malware and computer virus attacks. A cyber‑attack could adversely impact our daily operations and lead to the loss of sensitive information, including our own proprietary information and that of our customers, suppliers and employees. Such losses could harm our reputation and result in competitive disadvantages, litigation, regulatory enforcement actions, lost revenues, additional costs and liability. While we devote substantial resources to maintaining adequate levels of cyber‑security, our resources and technical sophistication may not be adequate to prevent all types of cyber‑attacks.
Material damage to, or interruptions in, our information systems as a result of external factors, staffing shortages and difficulties in updating our existing software or developing or implementing new software could have a material adverse effect on our business or results of operations.
We depend largely upon our information technology systems in the conduct of all aspects of our operations. Such systems are subject to damage or interruption from power outages, computer and telecommunications failures, computer viruses, security breaches, fire and natural disasters. Damage or interruption to our information systems may require a significant investment to fix or replace them, and we may suffer interruptions in our operations in the interim. Potential problems and interruptions associated with the implementation of new or upgraded systems and technology or with maintenance or adequate support of existing systems could also disrupt or reduce the efficiency of our operations. Any material interruptions or failures in our information systems may have a material adverse effect on our business or results of operations.
Our financial reporting for lease revenue may be impacted by a proposed new model for lease accounting.
In February 2016, the Financial Accounting Standards Board ("FASB") issued Accounting Standards Update ("ASU") No. 2016-02 ("ASU 2016-02"), “Leases (Topic 842)”. The standard requires lessees to recognize most leases on their balance sheets as lease liabilities with corresponding right-of-use assets. Lessor accounting for operating leases would remain substantially unchanged. The standard will be effective for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2018 for public entities. We plan to adopt the standard on its required effective date of January 1, 2019. We believe the standard will not have a material impact on our consolidated financial statements. We do not believe that the adoption of the standard will significantly impact our existing or potential lessees' economic decisions to lease aircraft.
33
Risks Related to Our Class A Common Stock
The price of our Class A common stock historically has been volatile. This volatility may negatively affect the price of our Class A common stock.
The Company’s stock continues to experience substantial price volatility. This volatility may negatively affect the price of our Class A common stock at any point in time. Our stock price is likely to continue to be volatile and subject to significant price and volume fluctuations in response to market and other factors, including:
|
· |
variations in our quarterly or annual operating results; |
|
· |
actual or perceived reduction in our growth or expected future growth; |
|
· |
announcements concerning our competitors, the airline industry or the economy in general; |
|
· |
announcements concerning the availability of the type of aircraft we own; |
|
· |
general and industry-specific economic conditions; |
|
· |
changes in the price of aircraft fuel; |
|
· |
changes in financial estimates or recommendations by securities analysts or failure to meet analysts’ performance expectations; |
|
· |
additions or departures of key members of management; |
|
· |
any increased indebtedness we may incur in the future; |
|
· |
speculation or reports by the press or investment community with respect to us or our industry in general or the decision to suspend or terminate coverage in the future; |
|
· |
changes in market valuations of similar companies; |
|
· |
changes in or elimination of our dividend; |
|
· |
announcements by us or our competitors of significant contracts, acquisitions, dispositions, strategic partnerships, joint ventures or capital commitments; |
|
· |
changes or proposed changes in laws or regulations affecting the airline industry or enforcement of these laws and regulations, or announcements relating to these matters; and |
|
· |
general market, political and economic conditions, including any such conditions and local conditions in the markets in which our lessees are located. |
Broad market and industry factors may decrease the market price of our Class A common stock, regardless of our actual operating performance. The stock market in general has from time to time experienced extreme price and volume fluctuations, including periods of sharp decline. In the past, following periods of volatility in the overall market and the market price of a company’s securities, securities class action litigation has often been instituted against these companies. Such litigation, if instituted against us, could result in substantial costs and a diversion of our management’s attention and resources.
34
Provisions in Delaware law and our restated certificate of incorporation and amended and restated bylaws may inhibit a takeover of us, which could cause the market price of our Class A common stock to decline and could entrench management.
Our restated certificate of incorporation and amended and restated bylaws contain provisions that may discourage unsolicited takeover proposals that stockholders may consider to be in their best interests, including the ability of our board of directors to designate the terms of and issue new series of preferred stock, a prohibition on our stockholders from calling special meetings of the stockholders, and advance notice requirements for stockholder proposals and director nominations. In addition, Section 203 of the Delaware General Corporation Law, which we have not opted out of, prohibits a public Delaware corporation from engaging in certain business combinations with an “interested stockholder” (as defined in such section) for a period of three years following the time that such stockholder became an interested stockholder without the prior consent of our board of directors. The effect of Section 203 of the Delaware General Corporation Law, as well as these charter and bylaws provisions, may make the removal of management more difficult. It may also impede a merger, takeover or other business combination or discourage a potential acquirer from making a tender offer for our Class A common stock, which, under certain circumstances, could reduce the market price of our Class A common stock.
Future offerings of debt or equity securities by us may adversely affect the market price of our Class A common stock.
In the future, we may attempt to obtain financing or to further increase our capital resources by issuing additional shares of Class A common stock or offering debt or additional equity securities, including commercial paper, medium‑term notes, senior or subordinated notes or preferred shares. Issuing additional shares of Class A common stock or other additional equity offerings may dilute the economic and voting rights of our existing stockholders or reduce the market price of our Class A common stock, or both. Upon liquidation, holders of such debt securities and preferred shares, if issued, and lenders with respect to other borrowings, would receive a distribution of our available assets prior to the holders of our Class A common stock. Preferred shares, if issued, could have a preference with respect to liquidating distributions or a preference with respect to dividend payments that could limit our ability to pay dividends to the holders of our Class A common stock. Because our decision to issue securities in any future offering will depend on market conditions and other factors beyond our control, we cannot predict or estimate the amount, timing or nature of our future offerings. Thus, holders of our Class A common stock bear the risk of our future offerings reducing the market price of our Class A common stock and diluting their shareholdings in us.
We may not be able to pay or maintain dividends, or we may choose not to pay dividends, and the failure to pay or maintain dividends may negatively affect our share price.
Current dividends may not be indicative of the amount of any future quarterly dividends. Our ability to pay, maintain or increase cash dividends to our shareholders is subject to the discretion of our Board of Directors and will depend on many factors, including our ability to comply with covenants in our financing documents that limit our ability to pay dividends and make certain other restricted payments to shareholders; the difficulty we may experience in raising and the cost of additional capital and our ability to finance our aircraft acquisition commitments; our ability to re-finance our long-term financings before excess cash flows are no longer made available to us to pay dividends and for other purposes; our ability to negotiate and enforce favorable lease rates and other contractual terms; the level of demand for our aircraft; the economic condition of the commercial aviation industry generally; the financial condition and liquidity of our lessees; unexpected or increased expenses; the level and timing of capital expenditures, principal repayments and other capital needs; the value of our aircraft portfolio; our compliance with loan to value, interest rate coverage and other financial tests in our financings; our results of operations, financial condition and liquidity; general business conditions; restrictions imposed by our debt agreements; legal restrictions on the payment of dividends; and other factors that our Board of Directors deems relevant. Some of these factors are beyond our control, and a change in any such factor could affect our ability to pay dividends on our common stock. In the future we may choose not to pay dividends or may not be able to pay dividends, maintain our current level of dividends, or increase them over time. The failure to maintain or pay dividends may negatively affect our share price.
35
ITEM 1B. UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS
None.
Flight Equipment
As of December 31, 2017, our operating lease portfolio consisted of 244 aircraft, comprised of 188 narrowbody jet aircraft and 56 widebody jet aircraft, with a weighted average age of 3.8 years.
The following table shows the scheduled lease terminations (for the minimum non-cancellable period which does not include contracted unexercised lease extension options) of our operating lease portfolio as of December 31, 2017, updated through February 22, 2018:
|
Aircraft Type |
|
2018 |
|
2019 |
|
2020 |
|
2021 |
|
2022 |
|
Thereafter |
|
Total |
|
|
Airbus A319-100 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
1 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
1 |
|
|
Airbus A320-200 |
|
3 |
|
3 |
|
7 |
|
6 |
|
1 |
|
20 |
|
40 |
|
|
Airbus A320-200neo |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
5 |
|
5 |
|
|
Airbus A321-200 |
|
1 |
|
— |
|
1 |
|
— |
|
1 |
|
26 |
|
29 |
|
|
Airbus A321-200neo |
|
— |
|
1 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
4 |
|
5 |
|
|
Airbus A330-200 |
|
— |
|
4 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
2 |
|
9 |
|
15 |
|
|
Airbus A330-300 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
1 |
|
— |
|
1 |
|
3 |
|
5 |
|
|
Airbus A350-900 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
2 |
|
2 |
|
|
Boeing 737-700 |
|
— |
|
2 |
|
— |
|
1 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
3 |
|
|
Boeing 737-800 |
|
1 |
|
10 |
|
7 |
|
6 |
|
11 |
|
67 |
|
102 |
|
|
Boeing 737-8 MAX |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
2 |
|
2 |
|
|
Boeing 767-300ER |
|
— |
|
1 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
1 |
|
|
Boeing 777-200ER |
|
— |
|
— |
|
1 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
1 |
|
|
Boeing 777-300ER |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
4 |
|
4 |
|
16 |
|
24 |
|
|
Boeing 787-9 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
8 |
|
8 |
|
|
Embraer E190 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
1 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
1 |
|
|
Total |
|
5 |
|
21 |
|
18 |
|
18 |
|
20 |
|
162 |
|
244 |
|
Commitments
As of December 31, 2017, we had committed to purchase the following new aircraft at an estimated aggregate purchase price (including adjustment for anticipated inflation) of approximately $27.0 billion for delivery as shown below. The recorded basis of aircraft may be adjusted upon delivery to reflect changes in, among other items, actual inflation and the final cost of buyer furnished equipment.
|
Aircraft Type |
|
2018 |
|
2019 |
|
2020 |
|
2021 |
|
2022 |
|
Thereafter |
|
Total |
|
|
Airbus A321-200 |
|
2 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
2 |
|
|
Airbus A320/321neo(1) |
|
14 |
|
35 |
|
27 |
|
22 |
|
25 |
|
25 |
|
148 |
|
|
Airbus A330-900neo |
|
5 |
|
5 |
|
4 |
|
7 |
|
6 |
|
2 |
|
29 |
|
|
Airbus A350-900/1000 |
|
4 |
|
2 |
|
4 |
|
5 |
|
3 |
|
— |
|
18 |
|
|
Boeing 737-7/8/9 MAX |
|
12 |
|
27 |
|
27 |
|
35 |
|
27 |
|
— |
|
128 |
|
|
Boeing 787-9/10 |
|
7 |
|
12 |
|
9 |
|
7 |
|
8 |
|
— |
|
43 |
|
|
Total(2) |
|
44 |
|
81 |
|
71 |
|
76 |
|
69 |
|
27 |
|
368 |
|
|
(1) Our Airbus A320/321neo aircraft orders include 55 long-range variants. |
|
(2) |
In addition to the aircraft from our orderbook, we have a commitment to purchase one used Boeing 737-800 aircraft from an airline, which is scheduled for delivery in 2018. |
36
Airbus has informed us to expect several month delivery delays relating to certain aircraft scheduled for delivery in 2018 and 2019. The delays have been reflected in our commitment schedules above. Our leases contain lessee cancellation clauses related to aircraft delivery delays, typically for aircraft delays greater than one year. Our purchase agreements contain similar clauses. As of February 22, 2018, none of our lease contracts are subject to cancellation.
As of December 31, 2017, the Company had a non-binding commitment to acquire up to five A350-1000 aircraft. Deliveries of these aircraft are scheduled to commence in 2023 and continue through 2024.
Our new aircraft are being purchased pursuant to binding purchase agreements with each of Airbus and Boeing. These agreements establish pricing formulas (which include certain price adjustments based upon inflation and other factors) and various other terms with respect to the purchase of aircraft. Under certain circumstances, we have the right to alter the mix of aircraft types that we ultimately acquire.
New Lease Placements
Our current lease placements are progressing well and are in line with our expectations. As of February 22, 2018, we had entered into contracts for the lease of new aircraft scheduled to be delivered through 2023 as follows:
|
|
|
Number of |
|
Number |
|
|
|
|
Delivery Year |
|
Aircraft |
|
Leased |
|
% Leased |
|
|
2018 |
|
44 |
|
44 |
|
100.0 |
% |
|
2019 |
|
81 |
|
77 |
|
95.1 |
% |
|
2020 |
|
71 |
|
33 |
|
46.5 |
% |
|
2021 |
|
76 |
|
6 |
|
7.9 |
% |
|
2022 |
|
69 |
|
2 |
|
2.9 |
% |
|
Thereafter |
|
27 |
|
— |
|
— |
% |
|
Total |
|
368 |
|
162 |
|
|
|
Our lease commitments for the 44 aircraft to be delivered in 2018 are comprised of 43 binding leases and one non-binding letter of intent. Our lease commitments for 77 of the 81 aircraft to be delivered in 2019 are comprised of 70 binding leases and seven non-binding letters of intent. Our lease commitments for 33 of the 71 aircraft to be delivered in 2020 are comprised of 27 binding leases and six non-binding letters of intent. Our lease commitments for six of the 76 aircraft to be delivered in 2021 are all comprised of binding leases. Finally, our lease commitments for two of the 69 aircraft to be delivered in 2022 are all comprised of binding leases. While our management’s historical experience is that non-binding letters of intent for aircraft leases generally lead to binding contracts, we are not certain that we will ultimately execute binding agreements for all or any of the letters of intent. While we actively seek lease placements for the aircraft that are scheduled to be delivered through 2023, in making our lease placement decisions, we also take into consideration the anticipated growth in the aircraft leasing market and anticipated improvements in lease rates, which could lead us to determine that entering into particular lease arrangements at a later date would be more beneficial to us.
Facilities
We lease our principal executive office at 2000 Avenue of the Stars, Suite 1000N, Los Angeles, California 90067. We also lease offices at 3rd Floor, Kilmore House, Park Lane, Spencer Dock, Dublin 1, Ireland. We do not own any real estate. We believe our current facilities are adequate for our current needs and for the foreseeable future.
From time to time, we may be involved in litigation and claims incidental to the conduct of our business in the ordinary course. Our industry is also subject to scrutiny by government regulators, which could result in enforcement proceedings or litigation related to regulatory compliance matters. We are not presently a party to any enforcement proceedings or litigation related to regulatory compliance matters or material legal proceedings. We maintain insurance
37
policies in amounts and with the coverage and deductibles we believe are adequate, based on the nature and risks of our business, historical experience and industry standards.
ITEM 4. MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES
Not applicable.
38
ITEM 5. MARKET FOR REGISTRANT’S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES
Market Information
Our Class A common stock has been quoted on the New York Stock Exchange (the “NYSE”) under the symbol “AL” since April 19, 2011. Prior to that time, there was no public market for our stock. As of December 31, 2017, there were 103,621,629 shares of Class A common stock outstanding held by approximately 215 holders of record.
As of February 21, 2018, the closing price of our Class A common stock was $45.51 per share as reported by the NYSE. The table below sets forth for the indicated periods the high and low sales prices for our Class A common stock as reported on the NYSE.
|
Fiscal Year 2017 Quarters Ended: |
|
High |
|
Low |
|
||
|
March 31, 2017 |
|
$ |
40.12 |
|
$ |
34.64 |
|
|
June 30, 2017 |
|
$ |
38.74 |
|
$ |
34.91 |
|
|
September 30, 2017 |
|
$ |
42.74 |
|
$ |
37.91 |
|
|
December 31, 2017 |
|
$ |
48.31 |
|
$ |
41.12 |
|
|
Fiscal Year 2016 Quarters Ended: |
|
High |
|
Low |
|
||
|
March 31, 2016 |
|
$ |
32.85 |
|
$ |
22.73 |
|
|
June 30, 2016 |
|
$ |
32.38 |
|
$ |
24.93 |
|
|
September 30, 2016 |
|
$ |
29.95 |
|
$ |
25.63 |
|
|
December 31, 2016 |
|
$ |
37.02 |
|
$ |
28.21 |
|
Dividends
The following table sets forth the dividends declared for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015:
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
Year Ended |
|
Year Ended |
|
|||
|
|
|
December 31, 2017 |
|
December 31, 2016 |
|
December 31, 2015 |
|
|||
|
Dividends declared per share |
|
$ |
0.325 |
|
$ |
0.225 |
|
$ |
0.170 |
|
While the Board of Directors paid a quarterly cash dividend in 2017 and currently expects to continue paying a quarterly cash dividend of $0.10 per share for the foreseeable future, the cash dividend policy can be changed at any time at the discretion of the Board of Directors. On February 20, 2018, our board of directors approved a quarterly cash dividend of $0.10 per share on our outstanding common stock. The dividend will be paid on April 6, 2018 to holders of record of our common stock as of March 20, 2018.
39
Stock Authorized for Issuance Under Equity Compensation Plans
Set forth below is certain information about the Class A common stock authorized for issuance under the Company’s equity compensation plan.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Number of securities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
remaining available for |
|
|
|
|
Number of securities to be |
|
Weighted-average exercise |
|
future issuance under |
|
|
|
|
|
issued upon exercise of |
|
price of outstanding |
|
equity compensation plans |
|
|
|
|
|
outstanding options, |
|
options, warrants and |
|
(excluding securities |
|
|
|
Plan Category |
|
warrants and rights |
|
rights |
|
reflected in column (a)) |
|
|
|
|
|
(a) |
|
|
(b) |
|
(c) |
|
|
Equity compensation plans approved by security holders |
|
2,858,158 |
|
$ |
20.37 |
|
5,795,999 |
|
|
Equity compensation plans not approved by security holders |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
Total |
|
2,858,158 |
|
$ |
20.37 |
|
5,795,999 |
|
Performance Graph
The graph below compares the 5-year cumulative return of the Company’s Class A common stock, the S&P Midcap 400 Index, the Russell 2000 Index and a customized peer group. The peer group consists of three companies: Aircastle Limited (NYSE: AYR), AerCap Holdings NV (NYSE: AER) and FLY Leasing Limited (NYSE: FLY). The peer group investment is weighted by market capitalization as of December 31, 2012, and is adjusted monthly. An investment of $100, with reinvestment of all dividends, is assumed to have been made in our Class A common stock, in the peer group and in the S&P Midcap 400 Index and in the Russell 2000 Index on December 31, 2012, and the relative performance of each is tracked through December 31, 2017. The stock price performance shown in the graph is not necessarily indicative of future stock price performance.
40
Comparison of 5 Year Cumulative Total Return
Assumes Initial Investment of $100
December 31, 2017
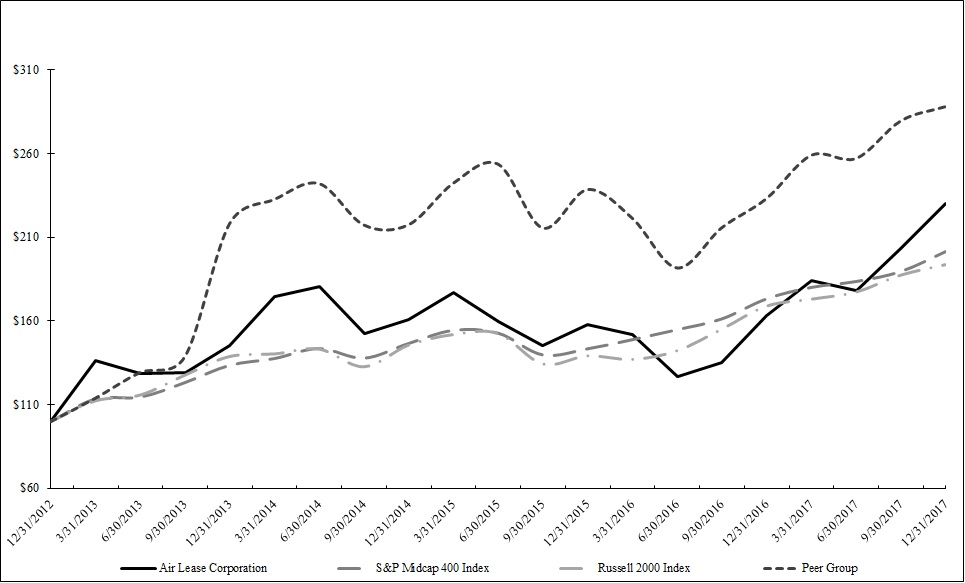
Company Purchases of Stock
The Company did not purchase any shares of its Class A common stock during 2017.
Unregistered Sales of Equity Securities and Use of Proceeds
On December 4, 2017, a holder of our 3.875% convertible senior notes due 2018 ("Convertible Notes") converted $2,000 in principal amount of our Convertible Notes and received 67 shares of Class A Common Stock at a per share conversion price of $29.48. The shares were issued in reliance on an exemption from registration under Section 3(a)(9) of the Securities Act of 1933 (the “1933 Act”).
On March 9, 2017, a holder of warrants performed a cashless exercise of 268,125 warrants, resulting in the issuance of 131,001 shares of Class A common stock. The shares were issued in reliance on an exemption from registration under Section 3(a)(9) of the 1933 Act. As of December 31, 2017, we did not have any warrants outstanding.
41
ITEM 6. SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA
The following selected consolidated financial data should be read in conjunction with “Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and our consolidated financial statements and the related notes appearing in “Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
Year Ended |
|
Year Ended |
|
Year Ended |
|
Year Ended |
|
|||||
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
December 31, |
|
December 31, |
|
December 31, |
|
December 31, |
|
|||||
|
|
|
2017 |
|
2016 |
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
|
2013 |
|
|||||
|
|
|
(in thousands, except share and per share amounts) |
|
|||||||||||||
|
Operating data: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rentals of flight equipment |
|
$ |
1,450,735 |
|
$ |
1,339,002 |
|
$ |
1,174,544 |
|
$ |
991,241 |
|
$ |
836,516 |
|
|
Aircraft sales, trading and other(1) |
|
|
65,645 |
|
|
80,053 |
|
|
48,296 |
|
|
59,252 |
|
|
22,159 |
|
|
Total revenues |
|
|
1,516,380 |
|
|
1,419,055 |
|
|
1,222,840 |
|
|
1,050,493 |
|
|
858,675 |
|
|
Expenses(1) |
|
|
906,850 |
|
|
838,817 |
|
|
829,887 |
|
|
655,717 |
|
|
565,233 |
|
|
Income before taxes |
|
|
609,530 |
|
|
580,238 |
|
|
392,953 |
|
|
394,776 |
|
|
293,442 |
|
|
Income tax benefit/(expense)(3) |
|
|
146,622 |
|
|
(205,313) |
|
|
(139,562) |
|
|
(138,778) |
|
|
(103,031) |
|
|
Net income |
|
$ |
756,152 |
|
$ |
374,925 |
|
$ |
253,391 |
|
$ |
255,998 |
|
$ |
190,411 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Adjusted net income before income taxes(2) |
|
$ |
657,838 |
|
$ |
622,871 |
|
$ |
507,982 |
|
$ |
438,596 |
|
$ |
338,683 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net income per share: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic |
|
$ |
7.33 |
|
$ |
3.65 |
|
$ |
2.47 |
|
$ |
2.51 |
|
$ |
1.88 |
|
|
Diluted |
|
$ |
6.82 |
|
$ |
3.44 |
|
$ |
2.34 |
|
$ |
2.38 |
|
$ |
1.80 |
|
|
Adjusted diluted earnings per share before income taxes(2) |
|
$ |
5.94 |
|
$ |
5.67 |
|
$ |
4.64 |
|
$ |
4.03 |
|
$ |
3.16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash dividends declared per share: |
|
$ |
0.325 |
|
$ |
0.225 |
|
$ |
0.170 |
|
$ |
0.130 |
|
$ |
0.105 |
|
|
Weighted average shares outstanding: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic |
|
|
103,189,175 |
|
|
102,801,161 |
|
|
102,547,774 |
|
|
102,142,828 |
|
|
101,529,137 |
|
|
Diluted |
|
|
111,657,564 |
|
|
110,798,727 |
|
|
110,628,865 |
|
|
110,192,771 |
|
|
108,963,550 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash flow data: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net cash flows provided by (used in): |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operating activities |
|
$ |
1,059,713 |
|
$ |
1,020,078 |
|
$ |
839,795 |
|
$ |
769,018 |
|
$ |
654,213 |
|
|
Investing activities |
|
|
(2,143,951) |
|
|
(2,005,516) |
|
|
(2,152,801) |
|
|
(1,805,657) |
|
|
(2,185,894) |
|
|
Financing activities |
|
|
1,101,640 |
|
|
1,103,565 |
|
|
1,186,862 |
|
|
1,049,285 |
|
|
1,571,765 |
|
42
|
|
|
As of December 31, |
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
2017 |
|
2016 |
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
|
2013 |
|
|||||
|
|
|
(in thousands, except aircraft data) |
|
|||||||||||||
|
Balance sheet data: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Flight equipment subject to operating leases (net of accumulated depreciation) |
|
$ |
13,280,250 |
|
$ |
12,041,925 |
|
$ |
10,813,475 |
|
$ |
8,953,804 |
|
$ |
7,613,135 |
|
|
Total assets |
|
|
15,614,164 |
|
|
13,975,616 |
|
|
12,355,098 |
|
|
10,691,180 |
|
|
9,242,355 |
|
|
Total debt, net of discounts and issuance costs |
|
|
9,698,785 |
|
|
8,713,874 |
|
|
7,712,421 |
|
|
6,630,758 |
|
|
5,763,068 |
|
|
Total liabilities |
|
|
11,486,722 |
|
|
10,593,429 |
|
|
9,335,186 |
|
|
7,919,118 |
|
|
6,718,921 |
|
|
Shareholders’ equity |
|
|
4,127,442 |
|
|
3,382,187 |
|
|
3,019,912 |
|
|
2,772,062 |
|
|
2,523,434 |
|
|
Other operating data: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aircraft lease portfolio at period end: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Owned |
|
|
244 |
|
|
237 |
|
|
240 |
|
|
213 |
|
|
193 |
|
|
Managed |
|
|
50 |
|
|
30 |
|
|
29 |
|
|
17 |
|
|
4 |
|
|
(1) |
Expenses for the year ended December 31, 2015 included settlement expense of $72.0 million. Other income for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015 included income recovery on a settlement of $1.0 million, $5.25 million and $4.5 million, respectively. |
|
(2) |
Adjusted net income before income taxes (defined as net income excluding the effects of certain non-cash items, one-time or non-recurring items, such as settlement expense, net of recoveries, that are not expected to continue in the future and certain other items), adjusted margin before income taxes (defined as adjusted net income before income taxes divided by total revenues, excluding insurance recoveries) and adjusted diluted earnings per share before income taxes (defined as adjusted net income before income taxes divided by the weighted average diluted common shares outstanding) are measures of operating performance that are not defined by GAAP and should not be considered as an alternative to net income, pre-tax profit margin, earnings per share, and diluted earnings per share, or any other performance measures derived in accordance with GAAP. Adjusted net income before income taxes, adjusted margin before income taxes and adjusted diluted earnings per share before income taxes, are presented as supplemental disclosure because management believes they provide useful information on our earnings from ongoing operations. |
Management and our board of directors use adjusted net income before income taxes, adjusted margin before income taxes and adjusted diluted earnings per share before income taxes to assess our consolidated financial and operating performance. Management believes these measures are helpful in evaluating the operating performance of our ongoing operations and identifying trends in our performance, because they remove the effects of certain non-cash items, one-time or non-recurring items that are not expected to continue in the future and certain other items from our operating results. Adjusted net income before income taxes, adjusted margin before income taxes and adjusted diluted earnings per share before income taxes, however, should not be considered in isolation or as a substitute for analysis of our operating results or cash flows as reported under GAAP. Adjusted net income before income taxes, adjusted margin before income taxes and adjusted diluted earnings per share before income taxes do not reflect our cash expenditures or changes in our cash requirements for our working capital needs. In addition, our calculation of adjusted net income before income taxes, adjusted margin before income taxes and adjusted diluted earnings per share before income taxes may differ from the adjusted net income before income taxes, adjusted margin before income taxes and adjusted diluted earnings per share before income taxes or analogous calculations of other companies in our industry, limiting their usefulness as a comparative measure.
43
The following tables show the reconciliation of net income to adjusted net income before income taxes and adjusted margin before income taxes (in thousands, except percentages):
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
2017 |
|
2016 |
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
|
2013 |
|
|||||
|
|
|
(unaudited) |
|
|||||||||||||
|
Reconciliation of net income to adjusted net income before income taxes: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net income |
|
$ |
756,152 |
|
$ |
374,925 |
|
$ |
253,391 |
|
$ |
255,998 |
|
$ |
190,411 |
|
|
Amortization of debt discounts and issuance costs |
|
|
29,454 |
|
|
30,942 |
|
|
30,507 |
|
|
27,772 |
|
|
23,627 |
|
|
Stock-based compensation |
|
|
19,804 |
|
|
16,941 |
|
|
17,022 |
|
|
16,048 |
|
|
21,614 |
|
|
Settlement |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
72,000 |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
Insurance recovery on settlement |
|
|
(950) |
|
|
(5,250) |
|
|
(4,500) |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
Provision for income taxes |
|
|
(146,622) |
|
|
205,313 |
|
|
139,562 |
|
|
138,778 |
|
|
103,031 |
|
|
Adjusted net income before income taxes |
|
$ |
657,838 |
|
$ |
622,871 |
|
$ |
507,982 |
|
$ |
438,596 |
|
$ |
338,683 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Reconciliation of denominator of adjusted margin before income taxes: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total revenues |
|
|
1,516,380 |
|
|
1,419,055 |
|
|
1,222,840 |
|
|
1,050,493 |
|
|
858,675 |
|
|
Insurance recovery on settlement |
|
|
(950) |
|
|
(5,250) |
|
|
(4,500) |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
Total revenues, excluding insurance recovery on settlement |
|
|
1,515,430 |
|
|
1,413,805 |
|
|
1,218,340 |
|
|
1,050,493 |
|
|
858,675 |
|
|
Adjusted margin before income taxes |
|
|
43.4 |
% |
|
44.1 |
% |
|
41.7 |
% |
|
41.8 |
% |
|
39.4 |
% |
The following table shows the reconciliation of net income to adjusted diluted earnings per share before income taxes (in thousands, except share and per share data):
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
2017 |
|
2016 |
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
|
2013 |
|
|||||
|
|
|
(unaudited) |
|
|||||||||||||
|
Reconciliation of net income to adjusted diluted earnings per share before income taxes: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net income |
|
$ |
756,152 |
|
$ |
374,925 |
|
$ |
253,391 |
|
$ |
255,998 |
|
$ |
190,411 |
|
|
Amortization of debt discounts and issuance costs |
|
|
29,454 |
|
|
30,942 |
|
|
30,507 |
|
|
27,772 |
|
|
23,627 |
|
|
Stock-based compensation |
|
|
19,804 |
|
|
16,941 |
|
|
17,022 |
|
|
16,048 |
|
|
21,614 |
|
|
Settlement |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
72,000 |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
Insurance recovery on settlement |
|
|
(950) |
|
|
(5,250) |
|
|
(4,500) |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
Provision for income taxes |
|
|
(146,622) |
|
|
205,313 |
|
|
139,562 |
|
|
138,778 |
|
|
103,031 |
|
|
Adjusted net income before income taxes |
|
$ |
657,838 |
|
$ |
622,871 |
|
$ |
507,982 |
|
$ |
438,596 |
|
$ |
338,683 |
|
|
Assumed conversion of convertible senior notes |
|
|
5,842 |
|
|
5,780 |
|
|
5,806 |
|
|
5,811 |
|
|
5,783 |
|
|
Adjusted net income before income taxes plus assumed conversions |
|
$ |
663,680 |
|
$ |
628,651 |
|
$ |
513,788 |
|
$ |
444,407 |
|
$ |
344,466 |
|
|
Weighted-average diluted shares outstanding |
|
|
111,657,564 |
|
|
110,798,727 |
|
|
110,628,865 |
|
|
110,192,771 |
|
|
108,963,550 |
|
|
Adjusted diluted earnings per share before income taxes |
|
$ |
5.94 |
|
$ |
5.67 |
|
$ |
4.64 |
|
$ |
4.03 |
|
$ |
3.16 |
|
44
|
(3) |
On December 22, 2017, the U.S. Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (the “Tax Reform Act”) was signed into law. The Tax Reform Act significantly revised the U.S. corporate income tax law by, among other things, lowering the U.S. corporate tax rate from 35% to 21%, effective January 1, 2018. Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) 740 requires that the impact of tax legislation be recognized in the period in which the law was enacted. As a result of the Tax Reform Act, we recorded an estimated tax benefit of $354.1 million due to the remeasurement of deferred tax assets and liabilities in the year ended December 31, 2017. |
ITEM 7. MANAGEMENT'S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
Overview
Air Lease Corporation is a leading aircraft leasing company that was founded by aircraft leasing industry pioneer, Steven F. Udvar-Házy. We are principally engaged in purchasing new commercial jet transport aircraft directly from aircraft manufacturers, such as Boeing and Airbus, and leasing those aircraft to airlines throughout the world. In addition to our leasing activities, we sell aircraft from our operating lease portfolio to third parties, including other leasing companies, financial services companies, and airlines. We also provide fleet management services to investors and owners of aircraft portfolios for a management fee. Our operating performance is driven by the growth of our fleet, the terms of our leases, the interest rates on our debt, and the aggregate amount of our indebtedness, supplemented by the gains of our aircraft sales and trading activities and our management fees.
During the year ended December 31, 2017, we purchased and took delivery of 30 aircraft from our new order pipeline, purchased 10 incremental aircraft, sold 31 aircraft and received insurance proceeds relating to the insured losses of two aircraft, ending the year with a total of 244 owned aircraft with a net book value of $13.3 billion. The weighted average lease term remaining on our operating lease portfolio was 6.8 years and the weighted average age of our fleet was 3.8 years as of December 31, 2017. Our fleet grew by 10.3% based on net book value of $13.3 billion as of December 31, 2017 compared to $12.0 billion as of December 31, 2016. In addition, our managed fleet increased to 50 aircraft as of December 31, 2017 from 30 aircraft as of December 31, 2016. We have a globally diversified customer base comprised of 91 airlines in 55 countries. As of February 22, 2018, all of our aircraft in our operating lease portfolio were subject to lease agreements.
During 2017, we increased our total commitments with Airbus and Boeing by a net 35 aircraft. As of December 31, 2017, we had commitments to purchase 368 aircraft from Airbus and Boeing for delivery through 2023, with an estimated aggregate commitment of $27.0 billion. We ended 2017 with $23.4 billion in committed minimum future rental payments and placed 79% of our order book on long-term leases for aircraft delivering through 2020. This includes $10.1 billion in contracted minimum rental payments on the aircraft in our existing fleet and $13.3 billion in minimum future rental payments related to aircraft which will deliver between 2018 and 2022.
We finance the purchase of aircraft and our business with available cash balances, internally generated funds, including aircraft sales and trading activities, and debt financings. Our debt financing strategy is focused on raising unsecured debt in the global bank and debt capital markets, with a limited utilization of export credit or other forms of secured financing. In 2017, we issued $2.2 billion senior unsecured notes with an average interest rate of 3.16%, with maturities ranging from 2022 to 2027 and in January 2018, we issued (i) $550.0 million in aggregate principal amount of senior unsecured notes due 2021 that bear interest at a rate of 2.50% and (ii) $700.0 million in aggregate principal amount of senior unsecured notes due 2025 that bear interest at a rate of 3.25%. In 2017, we increased our unsecured revolving credit facility capacity to approximately $3.8 billion, representing an 18.6% increase from 2016 and extended the final maturity to May 5, 2021. In February 2018, we further increased the capacity of our unsecured revolving credit facility by 4.7% to approximately $3.9 billion. Borrowings under our unsecured revolving credit facility will bear interest at LIBOR plus a margin of 1.05% per year. We ended 2017 with total debt outstanding of $9.7 billion, of which 85.4% was at a fixed rate and 94.6% of which was unsecured. Our composite cost of funds decreased to 3.20% as of December 31, 2017 from 3.42% as of December 31, 2016.
On December 22, 2017, the Tax Reform Act was signed into law. The Tax Reform Act significantly revised the U.S. corporate income tax law by, among other things, lowering the U.S. corporate tax rate from 35% to 21%,
45
effective January 1, 2018. As a result of the Tax Reform Act, we recorded an estimated tax benefit of $354.1 million or $3.16 per diluted share due to the remeasurement of deferred tax assets and liabilities for the quarter ended December 31, 2017.
In 2017, total revenues increased by 6.9% to $1.5 billion, compared to 2016. The increase in our total revenues is primarily due to the $1.2 billion increase in the net book value of our operating lease portfolio. Our net income for the year ended December 31, 2017 was $756.2 million, or $6.82 per diluted share compared to $374.9 million, or $3.44 per diluted share for the year ended December 31, 2016. The increase in our net income and diluted earnings per share for the year ended December 31, 2017 was due to the $1.2 billion increase in the net book value of our operating lease portfolio, and the re-measurement of our U.S. deferred tax liabilities associated with the enactment of the Tax Reform Act, resulting in a tax benefit of $354.1 million. Our pre-tax profit margin for the year ended December 31, 2017 was 40.2% as compared to 40.9% for the year ended December 31, 2016.
Our adjusted net income before income taxes excludes the effects of certain non-cash items, one-time or non-recurring items, such as settlement expense, net of recoveries, that are not expected to continue in the future and certain other items. Our adjusted net income before income taxes for the year ended December 31, 2017 was $657.8 million or $5.94 per diluted share, compared to $622.9 million, or $5.67 per diluted share for the year ended December 31, 2016. Our adjusted margin before income taxes for the year ended December 31, 2017 was 43.4% compared to 44.1% for the year ended December 31, 2016. Adjusted net income before income taxes, adjusted margin before income taxes and adjusted diluted earnings per share before income taxes are measures of financial and operational performance that are not defined by Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (“GAAP”). See Note 2 in “Item 6. Selected Financial Data” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for a discussion of adjusted net income before income taxes and adjusted diluted earnings per share before income taxes as non-GAAP measures and reconciliation of these measures to net income.
Our Fleet
We have continued to build one of the world’s youngest operating lease portfolios, including the most fuel-efficient commercial jet transport aircraft. Our fleet, based on net book value, increased by 10.3%, to $13.3 billion as of December 31, 2017 compared to $12.0 billion as of December 31, 2016. During the year ended December 31, 2017, we took delivery of 30 aircraft from our new order pipeline, purchased 10 incremental aircraft, and sold 31 aircraft and received insurance proceeds relating to the insured losses of two aircraft, ending the year with a total of 244 aircraft. Our weighted average fleet age and weighted average remaining lease term as of December 31, 2017 were 3.8 years and 6.8 years, respectively. We also managed 50 aircraft as of December 31, 2017.
Portfolio metrics of our fleet as of December 31, 2017 and 2016 are as follows:
|
|
|
December 31, 2017 |
|
December 31, 2016 |
|
||
|
Aggregate net book value |
|
$ |
13.3 |
billion |
$ |
12.0 |
billion |
|
Weighted-average fleet age(1) |
|
|
3.8 |
years |
|
3.8 |
years |
|
Weighted average remaining lease term(1) |
|
|
6.8 |
years |
|
6.9 |
years |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Owned fleet |
|
|
244 |
|
|
237 |
|
|
Managed fleet |
|
|
50 |
|
|
30 |
|
|
Order book |
|
|
368 |
|
|
363 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current fleet contracted rentals |
|
$ |
10.1 |
billion |
$ |
9.4 |
billion |
|
Committed fleet rentals |
|
$ |
13.3 |
billion |
$ |
14.4 |
billion |
|
Total committed rentals |
|
$ |
23.4 |
billion |
$ |
23.8 |
billion |
|
(1) Weighted‑average fleet age and remaining lease term calculated based on net book value. |
46
The following table sets forth the net book value and percentage of the net book value of our flight equipment subject to operating lease in the indicated regions based on each airline's principal place of business as of December 31, 2017 and 2016:
|
|
|
December 31, 2017 |
|
December 31, 2016 |
|
||||||
|
|
|
Net Book |
|
|
|
Net Book |
|
|
|
||
|
Region |
Value |
% of Total |
Value |
%of Total |
|||||||
|
|
|
(in thousands, except percentages) |
|
||||||||
|
Europe |
|
$ |
4,205,431 |
|
31.7 |
% |
$ |
3,547,294 |
|
29.5 |
% |
|
Asia (excluding China) |
|
|
2,981,339 |
|
22.4 |
% |
|
2,739,554 |
|
22.7 |
% |
|
China |
|
|
2,720,124 |
|
20.5 |
% |
|
2,779,546 |
|
23.0 |
% |
|
The Middle East and Africa |
|
|
1,481,825 |
|
11.2 |
% |
|
935,968 |
|
7.8 |
% |
|
Central America, South America, and Mexico |
|
|
926,732 |
|
7.0 |
% |
|
937,287 |
|
7.8 |
% |
|
U.S. and Canada |
|
|
599,367 |
|
4.5 |
% |
|
647,743 |
|
5.4 |
% |
|
Pacific, Australia, and New Zealand |
|
|
365,432 |
|
2.7 |
% |
|
454,533 |
|
3.8 |
% |
|
Total |
|
$ |
13,280,250 |
|
100.0 |
% |
$ |
12,041,925 |
|
100.0 |
% |
The following table sets forth the number of aircraft we leased by aircraft type as of December 31, 2017 and 2016:
|
|
|
December 31, 2017 |
|
December 31, 2016 |
|
||||
|
|
|
Number of |
|
|
|
Number of |
|
|
|
|
Aircraft type |
|
Aircraft(1) |
|
% of Total |
|
Aircraft(1) |
|
% of Total |
|
|
Airbus A319-100 |
|
1 |
|
0.4 |
% |
3 |
|
1.3 |
% |
|
Airbus A320-200 |
|
40 |
|
16.4 |
% |
44 |
|
18.6 |
% |
|
Airbus A320-200neo |
|
5 |
|
2.1 |
% |
1 |
|
0.4 |
% |
|
Airbus A321-200 |
|
29 |
|
11.9 |
% |
31 |
|
13.1 |
% |
|
Airbus A321-200neo |
|
5 |
|
2.1 |
% |
— |
|
— |
% |
|
Airbus A330-200 |
|
15 |
|
6.2 |
% |
17 |
|
7.2 |
% |
|
Airbus A330-300 |
|
5 |
|
2.0 |
% |
5 |
|
2.1 |
% |
|
Airbus A350-900 |
|
2 |
|
0.9 |
% |
— |
|
— |
% |
|
Boeing 737-700 |
|
3 |
|
1.2 |
% |
8 |
|
3.4 |
% |
|
Boeing 737-800 |
|
102 |
|
41.8 |
% |
95 |
|
40.1 |
% |
|
Boeing 737-8 MAX |
|
2 |
|
0.8 |
% |
— |
|
— |
% |
|
Boeing 767-300ER |
|
1 |
|
0.4 |
% |
1 |
|
0.4 |
% |
|
Boeing 777-200ER |
|
1 |
|
0.4 |
% |
1 |
|
0.4 |
% |
|
Boeing 777-300ER |
|
24 |
|
9.8 |
% |
22 |
|
9.3 |
% |
|
Boeing 787-9 |
|
8 |
|
3.3 |
% |
3 |
|
1.3 |
% |
|
Embraer E190 |
|
1 |
|
0.3 |
% |
6 |
|
2.4 |
% |
|
Total |
|
244 |
|
100.0 |
% |
237 |
|
100.0 |
% |
|
(1) |
We did not have any aircraft held for sale as of December 31, 2017. As of December 31, 2016, we had six aircraft held for sale. |
47
As of December 31, 2017, we had contracted to buy 368 new aircraft for delivery through 2023, with an estimated aggregate purchase price (including adjustments for inflation) of $27.0 billion, for delivery as follows:
|
Aircraft Type |
|
2018 |
|
2019 |
|
2020 |
|
2021 |
|
2022 |
|
Thereafter |
|
Total |
|
|
Airbus A321-200 |
|
2 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
2 |
|
|
Airbus A320/321neo(1) |
|
14 |
|
35 |
|
27 |
|
22 |
|
25 |
|
25 |
|
148 |
|
|
Airbus A330-900neo |
|
5 |
|
5 |
|
4 |
|
7 |
|
6 |
|
2 |
|
29 |
|
|
Airbus A350-900/1000 |
|
4 |
|
2 |
|
4 |
|
5 |
|
3 |
|
— |
|
18 |
|
|
Boeing 737-7/8/9 MAX |
|
12 |
|
27 |
|
27 |
|
35 |
|
27 |
|
— |
|
128 |
|
|
Boeing 787-9/10 |
|
7 |
|
12 |
|
9 |
|
7 |
|
8 |
|
— |
|
43 |
|
|
Total(2) |
|
44 |
|
81 |
|
71 |
|
76 |
|
69 |
|
27 |
|
368 |
|
|
(1) |
Our Airbus A320/321neo aircraft orders include 55 long-range variants. |
|
(2) |
In addition to the aircraft from our orderbook, we have a commitment to purchase one used Boeing 737-800 aircraft from an airline, which is scheduled for delivery in 2018. |
Airbus has informed us to expect several month delivery delays relating to certain aircraft scheduled for delivery in 2018 and 2019. The delays have been reflected in our commitment schedules above. Our leases contain lessee cancellation clauses related to aircraft delivery delays, typically for aircraft delays greater than one year. Our purchase agreements contain similar clauses. As of February 22, 2018, none of our lease contracts are subject to cancellation.
Our lease placements are progressing in line with expectations. As of December 31, 2017, we have entered into contracts for the lease of new aircraft scheduled to be delivered as follows:
|
|
|
Number of |
|
Number |
|
|
|
|
Delivery Year |
|
Aircraft |
|
Leased |
|
% Leased |
|
|
2018 |
|
44 |
|
44 |
|
100.0 |
% |
|
2019 |
|
81 |
|
77 |
|
95.1 |
% |
|
2020 |
|
71 |
|
33 |
|
46.5 |
% |
|
2021 |
|
76 |
|
6 |
|
7.9 |
% |
|
2022 |
|
69 |
|
2 |
|
2.9 |
% |
|
Thereafter |
|
27 |
|
— |
|
— |
% |
|
Total |
|
368 |
|
162 |
|
|
|
As of December 31, 2017, the Company had a non-binding commitment to acquire up to five A350-1000 aircraft. Deliveries of these aircraft are scheduled to commence in 2023 and continue through 2024.
Aircraft Industry and Sources of Revenues
Our revenues are principally derived from operating leases with scheduled and charter airlines. In each of the last four calendar years, we derived more than 95% of our revenues from airlines domiciled outside of the U.S., and we anticipate that most of our revenues in the future will be generated from foreign customers.
Demand for air travel has consistently grown in terms of both passenger traffic and number of aircraft in service. The International Air Transport Association (“IATA”) reported passenger traffic up 7.6% year over year in 2017, exceeding the 10-year average annual growth rate. The number of aircraft in service has grown steadily and the number of leased aircraft in the global fleet has increased. The long-term outlook for aircraft demand remains robust due to increased passenger traffic and the need to replace aging aircraft.
From time to time, our airline customers face financial difficulties. In May 2017, Alitalia, an Italian airline, began the process to file a petition to begin an Extraordinary Administration proceeding in the Italian Bankruptcy Court. Extraordinary Administrative proceedings are aimed at enabling a debtor in financial difficulty to restructure its
48
operations, including its debt, in order to continue its activities. While the Extraordinary Administrative proceeding is pending, the airline is permitted to operate and we understand that Alitalia intends to continue its normal operations. Alitalia operates four of our Airbus A330-200s. In October 2017, the Italian government granted an additional loan to Alitalia and extended the term for the sale of Alitalia and the repayment date of its loans to April 2018.
In August 2017, Air Berlin filed to commence insolvency proceedings under self-administration, and at the time of the filing, two A321-200 aircraft and one A320-200 aircraft from our fleet were on lease with Air Berlin. In September 2017, we learned that VIM Airlines was unlikely to continue as a going concern, and at that time, one Boeing 777-300ER from our fleet was on lease with VIM Airlines. Finally, in October 2017, Monarch Airlines filed for bankruptcy, and at the time of the filing, two Boeing 737-800 aircraft from our fleet were on lease with Monarch Airlines. As of February 22, 2018, all of these aircraft are subject to new lease agreements.
The success of the commercial airline industry is linked to the strength of global economic development, which may be negatively impacted by macroeconomic conditions, geopolitical and policy risks. Nevertheless, across a variety of global economic conditions, the leasing industry has remained resilient over time. We remain optimistic about the long-term growth prospects for air transportation. We see a growing demand for aircraft leasing in the broader industry and a role for us in helping airlines modernize their fleets to support the growth of the airline industry. However, with the growth in aircraft leasing worldwide, we are witnessing an increase in competition among aircraft lessors resulting in more variation in lease rates.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Overview
We finance the purchase of aircraft and our business with available cash balances, internally generated funds, including aircraft sales and trading activity, and debt financings. We have structured ourselves with the goal to maintain investment grade credit metrics and our debt financing strategy has focused on funding our business on an unsecured basis. Unsecured financing provides us with operational flexibility when selling or transitioning aircraft from one airline to another. We may, to a limited extent, utilize export credit financing in support of our new aircraft deliveries.
During the year ended December 31, 2017, we incurred additional debt financing and capacity aggregating $2.8 billion, which included $2.2 billion in senior unsecured notes, $587.7 million in additional capacity to our unsecured revolving credit facility which now totals approximately $3.8 billion and $20.0 million in additional debt facilities. We ended 2017 with total debt outstanding, net of discounts and issuance costs, of $9.7 billion compared to $8.7 billion in 2016. We ended 2017 with total unsecured debt outstanding of $9.3 billion compared to $8.1 billion in 2016, increasing our unsecured debt as a percentage of total debt to 94.6% as of December 31, 2017 compared to 92.4% as of December 31, 2016. Our fixed rate debt as a percentage of total debt increased to 85.4% as of December 31, 2017 from 83.5% as of December 31, 2016. In January 2018, we issued $550.0 million in aggregate principal amount of senior unsecured notes due 2021 that bear interest at a rate of 2.50% and $700.0 million in aggregate principal amount of senior unsecured notes due 2025 that bear interest at a rate of 3.25%. Also, in February 2018, we further increased the capacity of our unsecured revolving credit facility by 4.7% to $3.9 billion.
We increased our cash flows from operations by 3.9% or $39.6 million to $1.1 billion in 2017 as compared to $1.0 billion in 2016. Our cash flows from operations increased primarily because of the lease of additional aircraft in 2017. Our cash flow used in investing activities was $2.1 billion for the year ended December 31, 2017, which increased primarily from the purchase of aircraft, partially offset by proceeds on the sale of aircraft. Our cash flow provided by financing activities was $1.1 billion for the year ended December 31, 2017, which resulted primarily from the net proceeds received from the issuance of our unsecured notes in 2017, partially offset by the repayment of outstanding debt.
We ended 2017 with available liquidity of $3.2 billion which is comprised of unrestricted cash of $292.2 million and undrawn balances under our unsecured revolving credit facility of $2.9 billion. We believe that we have sufficient liquidity to satisfy the operating requirements of our business through the next twelve months.
49
Our financing plan for 2018 is focused on funding the purchase of aircraft and our business with available cash balances, internally generated funds, including aircraft sales and trading activities, and debt financings. Our debt financing plan will remain focused on continuing to raise unsecured debt in the global bank and investment grade capital markets. In addition, we may utilize, to a limited extent, export credit financing in support of our new aircraft deliveries.
Our liquidity plans are subject to a number of risks and uncertainties, including those described in “Item 1A. Risk Factors” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Debt
Our debt financing was comprised of the following at December 31, 2017 and 2016:
|
|
|
December 31, 2017 |
|
December 31, 2016 |
|
||
|
|
|
(in thousands, except percentages) |
|
||||
|
Unsecured |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Senior notes |
|
$ |
8,019,871 |
|
$ |
6,953,343 |
|
|
Revolving credit facility |
|
|
847,000 |
|
|
766,000 |
|
|
Term financings |
|
|
203,704 |
|
|
211,346 |
|
|
Convertible senior notes |
|
|
199,983 |
|
|
199,995 |
|
|
Total unsecured debt financing |
|
|
9,270,558 |
|
|
8,130,684 |
|
|
Secured |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Term financings |
|
|
484,036 |
|
|
619,767 |
|
|
Export credit financing |
|
|
44,920 |
|
|
51,574 |
|
|
Total secured debt financing |
|
|
528,956 |
|
|
671,341 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total debt financing |
|
|
9,799,514 |
|
|
8,802,025 |
|
|
Less: Debt discounts and issuance costs |
|
|
(100,729) |
|
|
(88,151) |
|
|
Debt financing, net of discounts and issuance costs |
|
$ |
9,698,785 |
|
$ |
8,713,874 |
|
|
Selected interest rates and ratios: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Composite interest rate(1) |
|
|
3.20 |
% |
|
3.42 |
% |
|
Composite interest rate on fixed-rate debt(1) |
|
|
3.27 |
% |
|
3.69 |
% |
|
Percentage of total debt at fixed-rate |
|
|
85.42 |
% |
|
83.48 |
% |
|
(1) |
This rate does not include the effect of upfront fees, undrawn fees or issuance cost amortization. |
Senior unsecured notes
We issued $2.2 billion in aggregate principal amount of senior unsecured notes during 2017, comprised of (i) $500.0 million in aggregate principal amount of 3.625% notes due 2027; (ii) $600.0 million in aggregate principal amount of 2.625% notes due 2022; (iii) $500.0 million in aggregate principal amount of 3.625% notes due 2027; and (iv) $600.0 million in aggregate principal amount of 2.750% notes due 2023.
Furthermore, in January 2018 we issued (i) $550.0 million in aggregate principal amount of senior unsecured notes due 2021 that bear interest at a rate of 2.50% and (ii) $700.0 million in aggregate principal amount of senior unsecured notes due 2025 that bear interest at a rate of 3.25%.
As of December 31, 2017, we had $8.0 billion in aggregate principal amount of senior unsecured notes outstanding with remaining terms ranging from 0.1 years to 9.9 years and bearing interest at fixed rates ranging from 2.125% to 7.375%. As of December 31, 2016, we had $7.0 billion in aggregate principal amount of senior unsecured notes outstanding bearing interest at fixed rates ranging from 2.125% to 7.375%.
Registered notes. Of our $8.0 billion aggregate principal amount of senior unsecured notes as of December 31, 2017, approximately $7.8 billion of such notes have been registered with the SEC. All of our registered notes may be redeemed in part or in full at any time and from time to time prior to maturity at specified redemption prices. Our registered notes also require us to offer to purchase all of the notes at a purchase price equal to 101% of the principal
50
amount of the notes, plus accrued and unpaid interest if a change of control repurchase event (as defined in the applicable indenture or supplemental indenture) occurs.
Of the $7.8 billion in aggregate principal amount of registered notes, we have approximately $7.4 billion in aggregate principal amount of registered notes that were issued during or after November 2013. Each of the indentures governing these registered notes requires us to comply with certain covenants, including restrictions on our ability to (i) incur liens on assets and (ii) merge, consolidate or transfer all or substantially all of our assets.
For the approximately $400.0 million in aggregate principal amount of registered notes that were issued prior to November 2013, each of the indentures governing those registered notes contain financial maintenance covenants relating to our consolidated net worth, consolidated unencumbered assets and interest coverage, and other additional covenants that, among other things, (i) limit our ability and the ability of our subsidiaries to pay dividends on or purchase certain equity interests, prepay subordinated obligations, alter their lines of business, and engage in affiliate transactions; (ii) limit the ability of our subsidiaries to incur unsecured indebtedness; and (iii) limit our ability and the ability of each note guarantor subsidiary, if any, to consolidate, merge, or sell all or substantially all of its assets. The covenants contained in all of the indentures governing our registered notes are subject to a number of important exceptions and qualifications set forth in the applicable indenture, including, with respect to the indentures governing our registered notes issued before November 2013, the suspension of the financial maintenance covenant relating to interest coverage and the covenant that limits our payment of dividends on or purchases of certain equity interests and prepayments of subordinated indebtedness when such registered notes are rated investment grade (as defined in the applicable indenture). As of December 31, 2017, such registered notes were investment grade rated as defined in the applicable indenture. We believe that we were in compliance with all covenants contained in the indentures governing our registered notes as of December 31, 2017.
The indentures governing our registered notes also provide for customary events of default. If any event of default occurs, any amount then outstanding under the relevant indentures may immediately become due and payable. These events of default are subject to a number of important exceptions and qualifications set forth in the indentures.
Unregistered notes. Of our $8.0 billion aggregate principal amount of senior unsecured notes as of December 31, 2017, approximately $244.9 million of such notes have not been registered with the SEC and are governed by various purchase agreements. Our unregistered notes, like our registered notes, may be redeemed in part or in full at any time and from time to time prior to maturity at specified redemption prices. Our unregistered notes also require us to offer to purchase all of the notes at a purchase price equal to 100% of the principal amount of the notes, plus accrued and unpaid interest if a change of control (as defined in the applicable purchase agreement) occurs.
The purchase agreements governing our unregistered notes contain financial maintenance covenants relating to our consolidated net worth, consolidated unencumbered assets, interest coverage, and consolidated leverage ratio. In addition, the purchase agreements contain covenants that, among other things, (i) limit our ability and the ability of our subsidiaries to pay dividends on or purchase certain equity interests, prepay subordinated obligations, alter their lines of business, and engage in affiliate transactions; (ii) limit the ability of our subsidiaries to incur unsecured indebtedness; and (iii) limit our ability and the ability of each note guarantor subsidiary, if any, to consolidate, merge or sell all or substantially all of its assets. These covenants are subject to a number of important exceptions and qualifications set forth in the applicable purchase agreement, including, with respect to the purchase agreement governing certain tranches of unregistered notes, the suspension of the financial maintenance covenant relating to interest coverage and the covenant that limits our ability to pay dividends on or purchase certain equity interests and prepay subordinated indebtedness when the unregistered notes governed by such purchase agreement are rated investment grade (as defined in the applicable purchase agreement). As of December 31, 2017, such unregistered notes were investment grade rated as defined in the applicable purchase agreement. We believe that we were in compliance with all covenants contained in the purchase agreements governing our unregistered notes as of December 31, 2017.
The purchase agreements also provide for customary events of default. If any event of default occurs, any amount then outstanding under the relevant purchase agreement may immediately become due and payable. These events of default are subject to a number of important exceptions and qualifications set forth in the purchase agreements.
51
Unsecured revolving credit facility
We have a senior unsecured revolving credit facility governed by a second amended and restated credit agreement, dated May 5, 2014 (as amended, modified and supplemented thereafter), with JP Morgan Chase Bank, N.A., as administrative agent, and the lenders from time to time party thereto. The unsecured revolving credit facility currently provides us with financing capacity of up to $3.8 billion subject to the terms and conditions set forth therein. Lenders hold revolving commitments totaling approximately $3.2 billion that mature on May 5, 2021, commitments totaling $217.7 million that mature on May 5, 2020, commitments totaling $290.0 million that mature on May 5, 2019, and commitments totaling $55.0 million that mature on May 5, 2018. The unsecured revolving credit facility contains an uncommitted accordion feature under which its aggregate principal amount can be increased to $4.0 billion under certain circumstances.
As of December 31, 2017, borrowings under the unsecured revolving credit facility will generally bear interest at either (a) LIBOR plus a margin of 1.05% per year or (b) an alternative base rate plus a margin of 0.05% per year, subject, in each case, to increases or decreases based on declines in the credit ratings for our debt. We are required to pay a facility fee of 20 basis points per year (also subject to increases or decreases based on declines in the credit ratings for our debt) in respect of total commitments under the unsecured revolving credit facility. Borrowings under the unsecured revolving credit facility are used to finance our working capital needs in the ordinary course of business and for other general corporate purposes.
The total amount outstanding under our unsecured revolving credit facility was $847.0 million and $766.0 million as of December 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016, respectively.
The unsecured revolving credit facility provides for certain covenants, including covenants that limit our subsidiaries’ ability to incur, create, or assume certain unsecured indebtedness, and our and our subsidiaries’ abilities to declare or make certain dividends and distributions and to engage in certain mergers, consolidations, and asset sales. The unsecured revolving credit facility also requires us to comply with certain financial maintenance covenants (measured at the end of each fiscal quarter) including a maximum consolidated leverage ratio, minimum consolidated shareholders’ equity, and minimum consolidated unencumbered assets, as well as an interest coverage test that will be suspended when the unsecured revolving credit facility or certain of our other indebtedness is rated investment grade (as defined in the unsecured revolving credit facility). The covenant limiting our and our subsidiaries' abilities to declare or make certain dividends and distributions will also be suspended when the unsecured revolving credit facility or certain of our other indebtedness is rated investment grade (as defined in the unsecured revolving credit facility). As of December 31, 2017, such investment grade rating as defined in the unsecured revolving credit facility was achieved. We believe we were in compliance with all covenants contained in our unsecured revolving credit facility as of December 31, 2017. In addition, the unsecured revolving credit facility contains customary events of default. In the case of an event of default, the lenders may terminate the commitments under the unsecured revolving credit facility and require immediate repayment of all outstanding borrowings and the cash collateralization of all outstanding letters of credit. Such termination and acceleration will occur automatically in the event of certain bankruptcy events. These provisions are subject to a number of important exceptions and qualifications set forth in the credit agreement governing the unsecured revolving credit facility.
Unsecured term financings
From time to time, we enter into unsecured term facilities. During 2017, we entered into two additional unsecured term facilities aggregating $20.0 million, both with terms of five years and bearing interest at fixed rates of 2.75% per annum. The outstanding balance on our unsecured term facilities as of December 31, 2017 was $203.7 million, bearing interest at fixed rates ranging from 2.75% to 3.50% and one facility bearing interest at a floating rate of LIBOR plus 1.00%. As of December 31, 2017, the remaining maturities of all unsecured term facilities ranged from approximately 0.1 years to approximately 4.6 years. As of December 31, 2016, the outstanding balance on our unsecured term facilities was $211.3 million.
52
Convertible senior notes
In November 2011, we issued $200.0 million in aggregate principal amount of 3.875% convertible senior notes due 2018 in an offering exempt from registration under the Securities Act. The convertible notes are senior unsecured obligations of the Company and bear interest at a rate of 3.875% per annum, payable in arrears on June 1 and December 1 of each year. As of December 31, 2017, the convertible notes are convertible at the option of the holder into shares of our Class A common stock at a price of $29.42 per share.
Secured term financings
We fund some aircraft purchases through secured term financings. Our various consolidated entities will borrow through secured bank facilities to purchase an aircraft. The aircraft are then leased by our entities to airlines. We guarantee the obligations of the entities under certain of the loan agreements. The loans may be secured by a pledge of the shares of the entities, the aircraft, the lease receivables, security deposits, maintenance reserves or a combination thereof. Included in our secured term financings are two prior warehouse facilities that we refinanced into secured term loans in March 2014 and June 2016.
The secured term facilities contain customary covenants for financings of these types, including covenants that limit the borrowers’ actions to those of special purpose entities engaged in the ownership and leasing of a particular aircraft and restrict their ability to incur, create, or assume certain indebtedness, to incur or assume certain liens, to purchase, hold or acquire certain investments, to declare or make certain dividends and distributions, and to engage in certain mergers, consolidations and asset sales. The secured term facilities also contain limitations on our ability to transfer the equity interests of such subsidiaries or to incur, create or assume liens on such equity interests or the collateral securing such secured term facilities. Certain of the facilities require us to comply with certain financial maintenance covenants. In addition, the secured term facilities contain customary events of default for such financings. In the case of an event of default, the lenders may require immediate repayment of all outstanding loans. Such termination and acceleration will occur automatically in the event of certain bankruptcy events. These provisions are subject to a number of important exceptions and qualifications set forth in the loan agreements governing the secured term facilities. We believe we were in compliance with the covenants contained in our secured term facilities as of December 31, 2017.
As of December 31, 2017, the outstanding balance on our secured term facilities was $484.0 million and we had pledged 19 aircraft as collateral with a net book value of $1.1 billion. The outstanding balance under our secured term facilities as of December 31, 2017 was comprised of $2.6 million fixed rate debt consisting of one facility with an interest rate of 4.58% and $481.5 million floating rate debt with interest rates ranging from LIBOR plus 1.15% to LIBOR plus 2.99%. As of December 31, 2017, the remaining maturities of all secured term facilities ranged from approximately 0.2 years to approximately 5.6 years.
As of December 31, 2016, the outstanding balance on our secured term facilities was $619.8 million and we had pledged 23 aircraft as collateral with a net book value of $1.3 billion. The outstanding balance under our secured term facilities as of December 31, 2016 was comprised of $31.7 million fixed rate debt and $588.1 million floating rate debt, with interest rates ranging from 4.34% to 5.36% and LIBOR plus 1.15% to LIBOR plus 2.99%, respectively.
Export credit financings
In March 2013, we issued $76.5 million in secured notes due 2024 guaranteed by the Export-Import Bank of the United States. The notes mature on August 15, 2024 and bear interest at a rate of 1.617% per annum. We used the proceeds of the offering to refinance a portion of the purchase price of two Boeing aircraft, which serve as collateral for the notes, and the related premium charged by Export-Import Bank for its guarantee of the notes. As of December 31, 2017 and 2016, we had $44.9 million and $51.6 million in export credit financing outstanding, respectively.
53
Credit Ratings
Our investment grade credit ratings help us to lower our cost of funds and broaden our access to attractively priced capital. Our long-term debt financing strategy is focused on continuing to raise unsecured debt in the global bank and investment grade capital markets.
In 2017, Kroll Bond Rating Agency, Standard and Poor's, and Fitch Ratings reaffirmed their issuer and senior unsecured debt ratings and outlook. The following table summarizes our current credit ratings:
|
|
|
Long-term |
|
Corporate |
|
|
|
Date of Last |
|
|
Rating Agency |
|
Debt |
|
Rating |
|
Outlook |
|
Ratings Action |
|
|
Kroll Bond Ratings |
|
A− |
|
A− |
|
Stable Outlook |
|
December 15, 2017 |
|
|
Standard and Poor's |
|
BBB |
|
BBB |
|
Stable Outlook |
|
November 12, 2017 |
|
|
Fitch Ratings |
|
BBB |
|
BBB |
|
Stable Outlook |
|
July 24, 2017 |
|
While a ratings downgrade would not result in a default under any of our debt agreements, it could adversely affect our ability to issue debt and obtain new financings, or renew existing financings, and it would increase the cost of our financings.
54
Results of Operations
|
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
Year Ended |
|
Year Ended |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
December 31, 2017 |
|
December 31, 2016 |
|
December 31, 2015 |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
(in thousands, except share and per share amounts and percentages) |
|
|||||||
|
Revenues |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rental of flight equipment |
|
|
$ |
1,450,735 |
|
$ |
1,339,002 |
|
$ |
1,174,544 |
|
|
Aircraft sales, trading, and other |
|
|
|
65,645 |
|
|
80,053 |
|
|
48,296 |
|
|
Total revenues |
|
|
|
1,516,380 |
|
|
1,419,055 |
|
|
1,222,840 |
|
|
Expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest |
|
|
|
257,917 |
|
|
255,259 |
|
|
235,637 |
|
|
Amortization of debt discounts and issuance costs |
|
|
|
29,454 |
|
|
30,942 |
|
|
30,507 |
|
|
Interest expense |
|
|
|
287,371 |
|
|
286,201 |
|
|
266,144 |
|
|
Depreciation of flight equipment |
|
|
|
508,352 |
|
|
452,682 |
|
|
397,760 |
|
|
Settlement |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
72,000 |
|
|
Selling, general, and administrative |
|
|
|
91,323 |
|
|
82,993 |
|
|
76,961 |
|
|
Stock-based compensation |
|
|
|
19,804 |
|
|
16,941 |
|
|
17,022 |
|
|
Total expenses |
|
|
|
906,850 |
|
|
838,817 |
|
|
829,887 |
|
|
Income before taxes |
|
|
|
609,530 |
|
|
580,238 |
|
|
392,953 |
|
|
Income tax benefit/(expense) |
|
|
|
146,622 |
|
|
(205,313) |
|
|
(139,562) |
|
|
Net income |
|
|
$ |
756,152 |
|
$ |
374,925 |
|
$ |
253,391 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net income per share of Class A and B common stock |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic |
|
|
$ |
7.33 |
|
$ |
3.65 |
|
$ |
2.47 |
|
|
Diluted |
|
|
$ |
6.82 |
|
$ |
3.44 |
|
$ |
2.34 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted-average shares outstanding |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic |
|
|
|
103,189,175 |
|
|
102,801,161 |
|
|
102,547,774 |
|
|
Diluted |
|
|
|
111,657,564 |
|
|
110,798,727 |
|
|
110,628,865 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other financial data |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pre-tax profit margin |
|
|
|
40.2 |
% |
|
40.9 |
% |
|
32.1 |
% |
|
Adjusted net income before income taxes(1) |
|
|
$ |
657,838 |
|
$ |
622,871 |
|
$ |
507,982 |
|
|
Adjusted margin before income taxes(1) |
|
|
|
43.4 |
% |
|
44.1 |
% |
|
41.7 |
% |
|
Adjusted diluted earnings per share before income taxes(1) |
|
|
$ |
5.94 |
|
$ |
5.67 |
|
$ |
4.64 |
|
|
(1) |
Adjusted net income before income taxes (defined as net income excluding the effects of certain non-cash items, one-time or non-recurring items, such as settlement expense, net of recoveries, that are not expected to continue in the future and certain other items), adjusted margin before income taxes (defined as adjusted net income before income taxes divided by total revenues, excluding insurance recoveries), and adjusted diluted earnings per share before income taxes (defined as adjusted net income before income taxes divided by the weighted average diluted common shares outstanding) are measures of operating performance that are not defined by GAAP and should not be considered as an alternative to net income, pre-tax profit margin, earnings per share, and diluted earnings per share, or any other performance measures derived in accordance with GAAP. Adjusted net income before income taxes, adjusted margin before income taxes, and adjusted diluted earnings per share before income taxes, are presented as supplemental disclosure because management believes they provide useful information on our earnings from ongoing operations. |
Management and our board of directors use adjusted net income before income taxes, adjusted margin before income taxes and adjusted diluted earnings per share before income taxes to assess our consolidated financial and operating performance. Management believes these measures are helpful in evaluating the operating performance of our ongoing operations and identifying trends in our performance, because they remove the effects of certain non-cash items, one-time or non-recurring items that are not expected to continue in the future and certain other items
55
from our operating results. Adjusted net income before income taxes, adjusted margin before income taxes and adjusted diluted earnings per share before income taxes, however, should not be considered in isolation or as a substitute for analysis of our operating results or cash flows as reported under GAAP. Adjusted net income before income taxes, adjusted margin before income taxes and adjusted diluted earnings per share before income taxes do not reflect our cash expenditures or changes in our cash requirements for our working capital needs. In addition, our calculation of adjusted net income before income taxes, adjusted margin before income taxes and adjusted diluted earnings per share before income taxes may differ from the adjusted net income before income taxes, adjusted margin before income taxes and adjusted diluted earnings per share before income taxes or analogous calculations of other companies in our industry, limiting their usefulness as a comparative measure.
The following tables show the reconciliation of net income to adjusted net income before income taxes and adjusted margin before income taxes (in thousands, except percentages):
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
2017 |
|
2016 |
|
2015 |
|
|||
|
|
|
(unaudited) |
|
|||||||
|
Reconciliation of net income to adjusted net income before income taxes: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net income |
|
$ |
756,152 |
|
$ |
374,925 |
|
$ |
253,391 |
|
|
Amortization of debt discounts and issuance costs |
|
|
29,454 |
|
|
30,942 |
|
|
30,507 |
|
|
Stock-based compensation |
|
|
19,804 |
|
|
16,941 |
|
|
17,022 |
|
|
Settlement |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
72,000 |
|
|
Insurance recovery on settlement |
|
|
(950) |
|
|
(5,250) |
|
|
(4,500) |
|
|
Provision for income taxes |
|
|
(146,622) |
|
|
205,313 |
|
|
139,562 |
|
|
Adjusted net income before income taxes |
|
$ |
657,838 |
|
$ |
622,871 |
|
$ |
507,982 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Reconciliation of denominator of adjusted margin before income taxes: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total revenues |
|
|
1,516,380 |
|
|
1,419,055 |
|
|
1,222,840 |
|
|
Insurance recovery on settlement |
|
|
(950) |
|
|
(5,250) |
|
|
(4,500) |
|
|
Total revenues, excluding insurance recovery on settlement |
|
|
1,515,430 |
|
|
1,413,805 |
|
|
1,218,340 |
|
|
Adjusted margin before income taxes |
|
|
43.4 |
% |
|
44.1 |
% |
|
41.7 |
% |
56
The following table shows the reconciliation of net income to adjusted diluted earnings per share before income taxes (in thousands, except share and per share amounts):
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
2017 |
|
2016 |
|
2015 |
|
|||
|
|
|
(unaudited) |
|
|||||||
|
Reconciliation of net income to adjusted diluted earnings per share before income taxes: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net income |
|
$ |
756,152 |
|
$ |
374,925 |
|
$ |
253,391 |
|
|
Amortization of debt discounts and issuance costs |
|
|
29,454 |
|
|
30,942 |
|
|
30,507 |
|
|
Stock-based compensation |
|
|
19,804 |
|
|
16,941 |
|
|
17,022 |
|
|
Settlement |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
72,000 |
|
|
Insurance recovery on settlement |
|
|
(950) |
|
|
(5,250) |
|
|
(4,500) |
|
|
Provision for income taxes |
|
|
(146,622) |
|
|
205,313 |
|
|
139,562 |
|
|
Adjusted net income before income taxes |
|
$ |
657,838 |
|
$ |
622,871 |
|
$ |
507,982 |
|
|
Assumed conversion of convertible senior notes |
|
|
5,842 |
|
|
5,780 |
|
|
5,806 |
|
|
Adjusted net income before income taxes plus assumed conversions |
|
$ |
663,680 |
|
$ |
628,651 |
|
$ |
513,788 |
|
|
Weighted-average diluted shares outstanding |
|
|
111,657,564 |
|
|
110,798,727 |
|
|
110,628,865 |
|
|
Adjusted diluted earnings per share before income taxes |
|
$ |
5.94 |
|
$ |
5.67 |
|
$ |
4.64 |
|
2017 Compared to 2016
Rental revenue
As of December 31, 2017, we owned 244 aircraft, with a net book value of $13.3 billion, and recorded $1.5 billion in rental revenue for the year then ended, which included overhaul revenue, net of amortization of initial direct costs, of $21.6 million. In the prior year, as of December 31, 2016, we owned 237 aircraft with a net book value of $12.0 billion and recorded $1.3 billion in rental revenue for the year ended December 31, 2016, which included overhaul revenue, net of amortization of initial direct costs, of $11.3 million. The increase in rental revenue was primarily due to the increase in net book value of our operating lease portfolio to $13.3 billion as of December 31, 2017 from $12.0 billion as of December 31, 2016.
Aircraft sales, trading, and other revenue
Aircraft sales, trading, and other revenue totaled $65.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2017 compared to $80.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2016. During the year ended December 31, 2017, we sold 31 aircraft from our operating lease portfolio and received insurance proceeds relating to the losses of two insured aircraft, recording gains on aircraft sales and trading activity of $38.5 million. In addition, we received insurance proceeds of $1.0 million in connection with a litigation settlement. During the year ended December 31, 2016, we sold 46 aircraft from our operating lease portfolio recording gains on aircraft sales and trading activity of $61.5 million and received $5.25 million of insurance proceeds in connection with the litigation settlement.
Interest expense
Interest expense totaled $287.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2017 compared to $286.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2016. The change was primarily due to an increase in our average outstanding debt balances, partially offset by a decrease in our composite cost of funds. We expect that our interest expense will increase as our average debt balance outstanding continues to increase. Interest expense will also be impacted by changes in our composite cost of funds.
57
Depreciation expense
We recorded $508.4 million in depreciation expense of flight equipment for the year ended December 31, 2017 compared to $452.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2016. The increase in depreciation expense for 2017, compared to 2016, was primarily attributable to the increase in book value of our operating lease portfolio net of sales.
Selling, general, and administrative expenses
We recorded selling, general, and administrative expenses of $91.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2017 compared to $83.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2016. Selling, general, and administrative expense as a percentage of total revenue increased to 6.0% for the year ended December 31, 2017 compared to 5.8% for the year ended December 31, 2016. However, as we continue to add new aircraft to our portfolio, we expect over the long-term, selling, general, and administrative expense to decrease as a percentage of our revenue.
Stock-based compensation expense
Stock-based compensation expense totaled $19.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2017 compared to $16.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2016.
Taxes
For the year ended December 31, 2017, we reported an effective tax rate of -24.0%, as compared to 35.4% for the year ended December 31, 2016. The change in effective tax rate is primarily due to the impact of the Tax Reform Act. Our estimated impact of the Tax Reform Act resulted in an estimated net tax benefit of $354.1 million or $3.16 per diluted share for the quarter ended December 31, 2017. This resulted from the re-measurement of our U.S. deferred tax liabilities at the new statutory rate of 21%, partially offset by other impacts of the Tax Reform Act. In addition to the effects from the Tax Reform Act, we recorded a $10.9 million tax benefit from the utilization of foreign tax credits.
The $354.1 million benefit resulting from the remeasurement of deferred tax assets and liabilities is a provisional amount and a reasonable estimate by our management of the impact of the Tax Reform Act. Based on our initial assessment of the Tax Reform Act, we believe that the most significant impact on our financial statements is the remeasurement of deferred taxes. We do not expect other provisions of the Tax Reform Act to have a material impact on our consolidated financial statements for the fiscal year ending December 31, 2018. Quantifying all of the impacts of the Tax Reform Act, however, requires significant judgment by our management, including the inherent complexities involved in determining the timing of reversals of our deferred tax assets and liabilities. Accordingly, we will continue to analyze the impacts of the Tax Reform Act and, if necessary, record any further adjustments to our deferred tax assets and liabilities in future periods.
Net income
For the year ended December 31, 2017, we reported consolidated net income of $756.2 million, or $6.82 per diluted share, compared to a consolidated net income of $374.9 million, or $3.44 per diluted share, for the year ended December 31, 2016. Our net income and diluted earnings per share for the year ended December 31, 2017 include our estimated tax benefit of $354.1 million associated with the enactment of the Tax Reform Act. The increase in net income for 2017, compared to 2016, was also due to the increase in net book value of our operating lease portfolio.
Adjusted net income before income taxes
For the year ended December 31, 2017, we recorded adjusted net income before income taxes of $657.8 million, or $5.94 per diluted share, compared to an adjusted net income before income taxes of $622.9 million, or $5.67 per diluted share, for the year ended December 31, 2016. The increase in adjusted net income before income taxes for 2017, compared to 2016, was primarily attributable to the increase in net book value of our operating lease portfolio.
58
Adjusted net income before income taxes is a measure of financial and operational performance that is not defined by GAAP. See Note 2 in “Item 6. Selected Financial Data” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for a discussion of adjusted net income before income taxes as a non-GAAP measure and a reconciliation of this measure to net income.
2016 Compared to 2015
Rental revenue
As of December 31, 2016, we owned 237 aircraft, with a net book value of $12.0 billion, and recorded $1.3 billion in rental revenue for the year then ended, which included overhaul revenue, net of amortization of initial direct costs, of $11.3 million. In the prior year, as of December 31, 2015, we owned 240 aircraft with a net book value of $10.8 billion and recorded $1.2 billion in rental revenue for the year ended December 31, 2015, which included overhaul revenue, net of amortization of initial direct costs, of $24.9 million. The increase in rental revenue was primarily due to the increase in net book value of our operating lease portfolio to $12.0 billion as of December 31, 2016 from $10.8 billion as of December 31, 2015.
Aircraft sales, trading, and other revenue
Aircraft sales, trading, and other revenue totaled $80.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2016 compared to $48.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2015. During the year ended December 31, 2016, we sold 46 aircraft from our operating lease portfolio, recording gains on aircraft sales and trading activity of $61.5 million. In addition, we received insurance proceeds of $5.25 million in connection with a litigation settlement. During the year ended December 31, 2015, we sold 24 aircraft from our operating lease portfolio recording gains on aircraft sales and trading activity of $33.9 million and received $4.5 million of insurance proceeds in connection with a litigation settlement.
Interest expense
Interest expense totaled $286.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2016 compared to $266.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2015. The change was primarily due to an increase in our average outstanding debt balances, partially offset by a decrease in our composite cost of funds, resulting in a $19.6 million increase in interest and a $0.4 million increase in amortization of our discounts and deferred debt issue costs. We expect that our interest expense will increase as our average debt balance outstanding continues to increase. Interest expense will also be impacted by changes in our composite cost of funds.
Depreciation expense
We recorded $452.7 million in depreciation expense of flight equipment for the year ended December 31, 2016 compared to $397.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2015. The increase in depreciation expense for 2016, compared to 2015, was primarily attributable to the increase in book value of our operating lease portfolio net of sales.
Settlement expense
We recorded settlement expense of $72.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2015 as a result of the Settlement Agreement entered into by and between the Company, certain executive officers and employees of the Company, AIG, ILFC, and AerCap Holdings N.V., to settle all ongoing litigation.
Selling, general, and administrative expenses
We recorded selling, general, and administrative expenses of $83.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2016 compared to $77.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2015. Selling, general, and administrative expense as a percentage of total revenue decreased to 5.8% for the year ended December 31, 2016 compared to 6.3% for the year ended December 31, 2015. As we continue to add new aircraft to our portfolio, we expect over the long-term, selling, general, and administrative expense to decrease as a percentage of our revenue.
59
Stock based compensation expense
Stock based compensation expense totaled $16.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2016 compared to $17.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2015.
Taxes
The effective tax rate for the year ended December 31, 2016 was 35.4% compared to 35.5% for the year ended December 31, 2015. The change in effective tax rate for the respective periods is due to the effect of changes in permanent differences.
Net income
For the year ended December 31, 2016, we reported consolidated net income of $374.9 million, or $3.44 per diluted share, compared to a consolidated net income of $253.4 million, or $2.34 per diluted share, for the year ended December 31, 2015. The increase in net income for 2016, compared to 2015, was primarily attributable to the increase in net book value of our operating lease portfolio and the settlement expense incurred in 2015 related to the AIG/ILFC litigation.
Adjusted net income before income taxes
For the year ended December 31, 2016, we recorded adjusted net income before income taxes of $622.9 million, or $5.67 per diluted share, compared to an adjusted net income before income taxes of $508.0 million, or $4.64 per diluted share, for the year ended December 31, 2015. The increase in adjusted net income before income taxes for 2016, compared to 2015, was primarily attributable to the increase in net book value of our operating lease portfolio.
Adjusted net income before income taxes is a measure of financial and operational performance that is not defined by GAAP. See Note 2 in “Item 6. Selected Financial Data” of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for a discussion of adjusted net income before income taxes as a non-GAAP measure and a reconciliation of this measure to net income.
Contractual Obligations
Our contractual obligations as of December 31, 2017 are as follows:
|
|
|
2018 |
|
2019 |
|
2020 |
|
2021 |
|
2022 |
|
Thereafter |
|
Total |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
(in thousands) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
Long-term debt obligations |
|
$ |
1,556,665 |
|
$ |
1,043,758 |
|
$ |
1,226,540 |
|
$ |
1,847,849 |
|
$ |
1,226,884 |
|
$ |
2,897,818 |
|
$ |
9,799,514 |
|
|
Interest payments on debt outstanding(1) |
|
|
305,940 |
|
|
260,815 |
|
|
223,432 |
|
|
164,256 |
|
|
125,711 |
|
|
747,610 |
|
|
1,827,764 |
|
|
Purchase commitments |
|
|
4,029,636 |
|
|
5,798,963 |
|
|
5,506,214 |
|
|
5,538,285 |
|
|
4,678,092 |
|
|
1,478,734 |
|
|
27,029,924 |
|
|
Operating leases |
|
|
2,926 |
|
|
3,232 |
|
|
3,111 |
|
|
2,946 |
|
|
3,034 |
|
|
3,770 |
|
|
19,019 |
|
|
Total |
|
$ |
5,895,167 |
|
$ |
7,106,768 |
|
$ |
6,959,297 |
|
$ |
7,553,336 |
|
$ |
6,033,721 |
|
$ |
5,127,932 |
|
$ |
38,676,221 |
|
|
(1) |
Future interest payments on floating rate debt are estimated using floating rates in effect at December 31, 2017. |
60
Off‑balance Sheet Arrangements
We have not established any unconsolidated entities for the purpose of facilitating off-balance sheet arrangements or for other contractually narrow or limited purposes. We have, however, from time to time established subsidiaries and created partnership arrangements or trusts for the purpose of leasing aircraft or facilitating borrowing arrangements all of which are consolidated. We have investments in two joint ventures in which we own 9.5% of the equity of each joint venture. We account for our investment in these joint ventures using the equity method of accounting due to our level of influence and involvement in the joint ventures.
Critical Accounting Policies
We believe the following critical accounting policies can have a significant impact on our results of operations, financial position, and financial statement disclosures, and may require subjective and complex estimates and judgments.
Lease revenue
We lease flight equipment principally under operating leases and report rental income ratably over the life of each lease. Rentals received, but unearned, under the lease agreements are recorded in Rentals received in advance on our Consolidated Balance Sheets until earned. The difference between the rental income recorded and the cash received under the provisions of the lease is included in Lease receivables, as a component of Other assets on our Consolidated Balance Sheets. An allowance for doubtful accounts will be recognized for past-due rentals based on management’s assessment of collectability. Our management team monitors all lessees with past due lease payments (if any) and discusses relevant operational and financial issues facing those lessees with our marketing executives in order to determine an appropriate allowance for doubtful accounts. In addition, if collection is not reasonably assured, we will not recognize rental income for amounts due under our lease contracts and will recognize revenue for such lessees on a cash basis. Should a lessee’s credit quality deteriorate, we may be required to record an allowance for doubtful accounts and/or stop recognizing revenue until cash is received.
Our aircraft lease agreements typically contain provisions which require the lessee to make additional contingent rental payments based on either the usage of the aircraft, measured on the basis of hours or cycles flown per month (a cycle is one take-off and landing), or calendar-based time (“Maintenance Reserves”). These payments represent contributions to the cost of major future maintenance events (“Qualifying Events”) associated with the aircraft and typically cover major airframe structural checks, engine overhauls, the replacement of life limited parts contained in each engine, landing gear overhauls and overhauls of the auxiliary power unit. These Maintenance Reserves are generally collected monthly based on reports of usage by the lessee or collected as fixed monthly rates.
In accordance with our lease agreements, Maintenance Reserves are subject to reimbursement to the lessee upon the occurrence of a Qualifying Event. The reimbursable amount is capped by the amount of Maintenance Reserves payments received by the Company, net of previous reimbursements. The Company is only required to reimburse for Qualifying Events during the lease term. The Company is not required to reimburse for routine maintenance or additional maintenance costs incurred during a Qualifying Event. All amounts of Maintenance Reserves unclaimed by the lessee at the end of the lease term are retained by the Company.
We record as rental revenue the portion of Maintenance Reserves that we are virtually certain we will not reimburse to the lessee as a component of “Rental of flight equipment” in our Consolidated Statements of Income. Maintenance Reserves which we may be required to reimburse to the lessee are reflected in our overhaul reserve liability, as a component of “Security deposits and maintenance reserves on flight equipment leases” in our Consolidated Balance Sheets.
Estimating when we are virtually certain that Maintenance Reserves payments will not be reimbursed requires judgments to be made as to the timing and cost of future maintenance events. In order to determine virtual certainty with respect to this contingency, our Technical Asset Management department analyzes the terms of the lease, utilizes available cost estimates published by the equipment manufacturers, and thoroughly evaluates an airline’s Maintenance Planning Document (“MPD”). The MPD describes the required inspections and the frequency of those inspections. Our
61
Technical Asset Management department utilizes this information, combined with their cumulative industry experience, to determine when major Qualifying Events are expected to occur for each relevant component of the aircraft, and translates this information into a determination of how much we will ultimately be required to reimburse to the lessee. We record Maintenance Reserves revenue as the aircraft is operated when we determine that a Qualifying Event will occur outside the non-cancellable lease term or after we have collected Maintenance Reserves equal to the amount that we expect to reimburse to the lessee as the aircraft is operated.
Should such estimates be inaccurate, we may be required to reverse revenue previously recognized. In addition, if we can no longer make accurate estimates with respect to a particular lease, we will stop recognizing any Maintenance Reserves revenue until the end of such lease.
Any Maintenance Reserves or end of lease payments collected that were not reimbursed to the lessee during the term of the lease for a Qualifying Event are recognized as Rental revenues at the end of the lease. Leases that contain provisions which require us to pay a portion of a lessee's major maintenance based on the usage of the aircraft and major life-limited components that were incurred prior to the current lease are recorded as lease incentives based on estimated payments we expect to pay the lessee. These lease incentives are amortized as a reduction of Rental revenues over the term of the lease.
All of our lease agreements are triple net leases whereby the lessee is responsible for all taxes, insurance, and aircraft maintenance. In the future, we may incur repair and maintenance expenses for off-lease aircraft. We recognize repair and maintenance in our Consolidated Statements of Income for all such expenditures.
Lessee-specific modifications such as those related to modifications of the aircraft cabin are expected to be capitalized as initial direct costs and amortized over the term of the lease into rental revenue in our Consolidated Statements of Income.
Flight equipment
Flight equipment under operating lease is stated at cost less accumulated depreciation. Purchases, major additions and modifications, and interest on deposits during the construction phase are capitalized. We generally depreciate passenger aircraft on a straight-line basis over a 25-year life from the date of manufacture to a 15% residual value. Changes in the assumption of useful lives or residual values for aircraft could have a significant impact on our results of operations and financial condition. At the time flight equipment is retired or sold, the cost and accumulated depreciation are removed from the related accounts and the difference, net of proceeds, is recorded as a gain or loss.
Major aircraft improvements and modifications incurred during an off-lease period are capitalized and depreciated over the remaining life of the flight equipment. In addition, costs paid by the Company for scheduled maintenance and overhauls are capitalized and depreciated over a period to the next scheduled maintenance or overhaul event. Miscellaneous repairs are expensed when incurred.
Our management team evaluates on a quarterly basis the need to perform an impairment test whenever facts or circumstances indicate a potential impairment has occurred. An assessment is performed whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an aircraft may not be recoverable. Recoverability of an aircraft’s carrying amount is measured by comparing the carrying amount of the aircraft to future undiscounted net cash flows expected to be generated by the aircraft. The undiscounted cash flows consist of cash flows from currently contracted leases, future projected lease rates, and estimated residual or scrap values for each aircraft. We develop assumptions used in the recoverability analysis based on our knowledge of active lease contracts, current and future expectations of the global demand for a particular aircraft type, and historical experience in the aircraft leasing market and aviation industry, as well as information received from third-party industry sources. The factors considered in estimating the undiscounted cash flows are affected by changes in future periods due to changes in contracted lease rates, economic conditions, technology, and airline demand for a particular aircraft type. In the event that an aircraft does not meet the recoverability test, the aircraft will be recorded at fair value in accordance with our Fair Value Policy, resulting in an impairment charge. Deterioration of future lease rates and the residual values of our aircraft could result in impairment charges which could have a significant impact on our results of operations and financial condition.
62
We record flight equipment at fair value if we determine the carrying value may not be recoverable. We principally use the income approach to measure the fair value of aircraft. The income approach is based on the present value of cash flows from contractual lease agreements and projected future lease payments, including contingent rentals, net of expenses, which extend to the end of the aircraft’s economic life in its highest and best use configuration, as well as a disposition value based on expectations of market participants. These valuations are considered Level 3 valuations, as the valuations contain significant non observable inputs.
Maintenance Rights
We identify, measure, and account for maintenance right assets and liabilities associated with our acquisitions of aircraft with in-place leases. A maintenance right asset represents the fair value of our contractual right under a lease to receive an aircraft in an improved maintenance condition as compared to the maintenance condition on the acquisition date. A maintenance right liability represents our obligation to pay the lessee for the difference between the lease end contractual maintenance condition of the aircraft and the actual maintenance condition of the aircraft on the acquisition date.
Our aircraft are typically subject to triple-net leases pursuant to which the lessee is responsible for maintenance, which is accomplished through one of two types of provisions in its leases: (i) end of lease return conditions (“EOL Leases”) or (ii) periodic maintenance payments (“MR Leases”).
(i) EOL Leases
Under EOL Leases, the lessee is obligated to comply with certain return conditions which require the lessee to perform maintenance on the aircraft or make cash compensation payments at the end of the lease to bring the aircraft into a specified maintenance condition.
Maintenance right assets in EOL Leases represent the difference in value between the contractual right to receive an aircraft in an improved maintenance condition as compared to the maintenance condition on the acquisition date. Maintenance right liabilities exist in EOL Leases if, on the acquisition date, the maintenance condition of the aircraft is greater than the contractual return condition in the lease and we are required to pay the lessee in cash for the improved maintenance condition. Maintenance right assets, net will be recorded as a component of flight equipment subject to operating leases on our Consolidated Balance Sheets.
When we record maintenance right assets with respect to EOL Leases, the following accounting scenarios exist: (i) the aircraft is returned at lease expiry in the contractually specified maintenance condition without any cash payment to us by the lessee, the maintenance right asset is relieved, and an aircraft improvement is recorded to the extent the improvement is substantiated and deemed to meet our capitalization policy; (ii) the lessee pays us cash compensation at lease expiry in excess of the value of the maintenance right asset, the maintenance right asset is relieved, and any excess is recognized as end of lease income; or (iii) the lessee pays us cash compensation at lease expiry that is less than the value of the maintenance right asset, the cash is applied to the maintenance right asset and the balance of such asset is relieved and recorded as an aircraft improvement to the extent the improvement is substantiated and meets our capitalization policy. Any aircraft improvement will be depreciated over a period to the next scheduled maintenance event in accordance with our policy with respect to major maintenance and included in depreciation of flight equipment on our Consolidated Statements of Income.
When we record maintenance right liabilities with respect to EOL Leases, the following accounting scenarios exist: (i) the aircraft is returned at lease expiry in the contractually specified maintenance condition without any cash payment by us to the lessee, the maintenance right liability is relieved, and end of lease income is recognized; (ii) we pay the lessee cash compensation at lease expiry of less than the value of the maintenance right liability, the maintenance right liability is relieved and any difference is recognized as end of lease income; or (iii) we pay the lessee cash compensation at lease expiry in excess of the value of the maintenance right liability, the maintenance right liability is relieved, and the excess amount is recorded as an aircraft improvement asset to the extent that it meets our capitalization policy.
63
(ii) MR Leases
Under MR Leases, the lessee is required to make periodic payments to the Company for maintenance based upon planned usage of the aircraft. When a Qualifying Event occurs during the lease term, we are required to reimburse the lessee for the costs associated with such maintenance. At the end of lease, we are entitled to retain any cash receipts in excess of the required reimbursements to the lessee.
Maintenance right assets in MR Leases represent the right to receive an aircraft in an improved condition relative to the actual condition on the acquisition date. The aircraft is improved by the performance of a Qualifying Event paid for by the lessee who is reimbursed by us from the periodic maintenance payments that it receives. Maintenance right assets, net will be recorded as a component of flight equipment subject to operating leases on our Consolidated Balance Sheets.
When we record maintenance right assets with respect to MR Leases, the following accounting scenarios exist: (i) the aircraft is returned at lease expiry and no Qualifying Event has been performed by the lessee since the acquisition date, the maintenance right asset is offset by the amount of the associated maintenance payment liability, and any excess is recorded as end of lease income; or (ii) we have reimbursed the lessee for the performance of a Qualifying Event, the maintenance right asset is relieved, and an aircraft improvement is recorded to the extent of that it meets our capitalization policy.
When flight equipment is sold, maintenance rights are included in the calculation of the disposition gain or loss.
Income taxes
We use the asset and liability method of accounting for income taxes. Under the asset and liability method, deferred income taxes are recognized for the tax consequences of “temporary differences” by applying enacted statutory tax rates applicable to future years to differences between the financial statement carrying amounts and the tax basis of existing assets and liabilities. The effect on deferred taxes of a change in the tax rates is recognized in income in the period that includes the enactment date. We record a valuation allowance for deferred tax assets when the probability of realization of the full value of the asset is less than 50%. Based on the timing of reversal of deferred tax liabilities, future anticipated taxable income based on lease and debt arrangements in place at the balance sheet date, and tax planning strategies available to us, our management considers the deferred tax asset recoverable. Should events occur in the future that make the likelihood of recovery of deferred tax assets less than 50%, a deferred tax valuation allowance will be required that could have a significant impact on our results of operations and financial condition.
We recognize the impact of a tax position, if that position has a probability of greater than 50% that it would be sustained on audit, based on the technical merits of the position. Recognized income tax positions are measured at the largest amount that has a probability of more than 50% of being realized. Changes in recognition or measurement are reflected in the period in which the change in judgment occurs. As our business develops, we may take tax positions that have a probability of less than 50% of being sustained on audit which will require us to reserve for such positions. If these tax positions are audited by a taxing authority, there can be no assurance that the ultimate resolution of such tax positions will not result in further losses. Such losses could have a significant impact on our results of operations and financial condition.
ITEM 7A. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK
Market risk represents the risk of changes in value of a financial instrument, caused by fluctuations in interest rates and foreign exchange rates. Changes in these factors could cause fluctuations in our results of operations and cash flows. We are exposed to the market risks described below.
Interest Rate Risk
The nature of our business exposes us to market risk arising from changes in interest rates. Changes, both increases and decreases, in our cost of borrowing, as reflected in our composite interest rate, directly impact our net
64
income. Our lease rental stream is generally fixed over the life of our leases, whereas we have used floating‑rate debt to finance a significant portion of our aircraft acquisitions. As of December 31, 2017 and 2016, we had $1.4 billion and $1.5 billion in floating‑rate debt, respectively. If interest rates increase, we would be obligated to make higher interest payments to our lenders. If we incur significant fixed‑rate debt in the future, increased interest rates prevailing in the market at the time of the incurrence of such debt would also increase our interest expense. If our composite rate were to increase by 1.0%, we would expect to incur additional interest expense on our existing indebtedness as of December 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016 of approximately $14.3 million and $14.5 million, each on an annualized basis, which would put downward pressure on our operating margins. The decrease in additional interest expense the Company would incur is primarily due to a decrease in the floating‑rate debt outstanding as of December 31, 2017 compared to December 31, 2016.
We also have interest rate risk on our forward lease placements. This is caused by us setting a fixed lease rate in advance of the delivery date of an aircraft. The delivery date is when a majority of the financing for an aircraft is arranged. We partially mitigate the risk of an increasing interest rate environment between the lease signing date and the delivery date of the aircraft by having interest rate adjusters in a majority of our forward lease contracts which would adjust the final lease rate upward if certain benchmark interest rates are higher at the time of delivery of the aircraft than at the lease signing date.
Foreign Exchange Rate Risk
The Company attempts to minimize currency and exchange risks by entering into aircraft purchase agreements and a majority of lease agreements and debt agreements with U.S. dollars as the designated payment currency. Thus, most of our revenue and expenses are denominated in U.S. dollars. As of December 31, 2017 and 2016, approximately 1.0% of our lease revenues were denominated in Euros. As our principal currency is the U.S. dollar, fluctuations in the U.S. dollar as compared to other major currencies should not have a significant impact on our future operating results.
65
ITEM 8. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
Air Lease Corporation
INDEX TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Contents
|
|
|
Page |
|
|
|
67 |
|
|
|
Financial Statements |
|
|
|
|
|
69 |
|
|
|
|
70 |
|
|
|
|
71 |
|
|
|
|
72 |
|
|
|
|
73 |
|
66
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Shareholders and Board of Directors
Air Lease Corporation:
Opinion on the Consolidated Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Air Lease Corporation and subsidiaries (the Company) as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, the related consolidated statements of income, shareholders’ equity, and cash flows for each of the years in the three‑year period ended December 31, 2017, and the related notes (collectively, the consolidated financial statements). In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the years in the three‑year period ended December 31, 2017, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017, based on criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission, and our report dated February 22, 2018 expressed an unqualified opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
Basis for Opinion
These consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these consolidated financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the consolidated financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the consolidated financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the consolidated financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the consolidated financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
/s/ KPMG LLP
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2010.
Los Angeles, California
February 22, 2018
67
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Shareholders and Board of Directors
Air Lease Corporation:
Opinion on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
We have audited Air Lease Corporation and subsidiaries’ (the Company) internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017, based on criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. In our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017, based on criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the consolidated balance sheets of the Company as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, the related consolidated statements of income, shareholders’ equity, and cash flows for each of the years in the three-year period ended December 31, 2017, and the related notes (collectively, the consolidated financial statements), and our report dated February 22, 2018 expressed an unqualified opinion on those consolidated financial statements.
Basis for Opinion
The Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audit also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
/s/ KPMG LLP
Los Angeles, California
February 22, 2018
68
Air Lease Corporation and Subsidiaries
|
|
|
December 31, 2017 |
|
December 31, 2016 |
|
||
|
|
|
(in thousands, except share and par value amounts) |
|
||||
|
Assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents |
|
$ |
292,204 |
|
$ |
274,802 |
|
|
Restricted cash |
|
|
16,078 |
|
|
16,000 |
|
|
Flight equipment subject to operating leases |
|
|
15,100,040 |
|
|
13,597,530 |
|
|
Less accumulated depreciation |
|
|
(1,819,790) |
|
|
(1,555,605) |
|
|
|
|
|
13,280,250 |
|
|
12,041,925 |
|
|
Deposits on flight equipment purchases |
|
|
1,562,776 |
|
|
1,290,676 |
|
|
Other assets |
|
|
462,856 |
|
|
352,213 |
|
|
Total assets |
|
$ |
15,614,164 |
|
$ |
13,975,616 |
|
|
Liabilities and Shareholders’ Equity |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accrued interest and other payables |
|
$ |
309,182 |
|
$ |
256,775 |
|
|
Debt financing, net of discounts and issuance costs |
|
|
9,698,785 |
|
|
8,713,874 |
|
|
Security deposits and maintenance reserves on flight equipment leases |
|
|
856,140 |
|
|
856,335 |
|
|
Rentals received in advance |
|
|
104,820 |
|
|
99,385 |
|
|
Deferred tax liability |
|
|
517,795 |
|
|
667,060 |
|
|
Total liabilities |
|
$ |
11,486,722 |
|
$ |
10,593,429 |
|
|
Shareholders’ Equity |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Preferred Stock, $0.01 par value; 50,000,000 shares authorized; no shares issued or outstanding |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
Class A common stock, $0.01 par value; authorized 500,000,000 shares; issued and outstanding 103,621,629 and 102,844,477 shares at December 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016, respectively |
|
|
1,036 |
|
|
1,010 |
|
|
Class B Non-Voting common stock, $0.01 par value; authorized 10,000,000 shares; no shares issued or outstanding |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
Paid-in capital |
|
|
2,260,064 |
|
|
2,237,866 |
|
|
Retained earnings |
|
|
1,866,342 |
|
|
1,143,311 |
|
|
Total shareholders’ equity |
|
$ |
4,127,442 |
|
$ |
3,382,187 |
|
|
Total liabilities and shareholders’ equity |
|
$ |
15,614,164 |
|
$ |
13,975,616 |
|
(See Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements)
69
Air Lease Corporation and Subsidiaries
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF INCOME
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
Year Ended |
|
Year Ended |
|
|||
|
|
|
December 31, 2017 |
|
December 31, 2016 |
|
December 31, 2015 |
|
|||
|
|
|
(in thousands, except share and per share amounts) |
||||||||
|
Revenues |
|
|
||||||||
|
Rental of flight equipment |
|
$ |
1,450,735 |
|
$ |
1,339,002 |
|
$ |
1,174,544 |
|
|
Aircraft sales, trading, and other |
|
|
65,645 |
|
|
80,053 |
|
|
48,296 |
|
|
Total revenues |
|
|
1,516,380 |
|
|
1,419,055 |
|
|
1,222,840 |
|
|
Expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest |
|
|
257,917 |
|
|
255,259 |
|
|
235,637 |
|
|
Amortization of debt discounts and issuance costs |
|
|
29,454 |
|
|
30,942 |
|
|
30,507 |
|
|
Interest expense |
|
|
287,371 |
|
|
286,201 |
|
|
266,144 |
|
|
Depreciation of flight equipment |
|
|
508,352 |
|
|
452,682 |
|
|
397,760 |
|
|
Settlement |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
72,000 |
|
|
Selling, general, and administrative |
|
|
91,323 |
|
|
82,993 |
|
|
76,961 |
|
|
Stock-based compensation |
|
|
19,804 |
|
|
16,941 |
|
|
17,022 |
|
|
Total expenses |
|
|
906,850 |
|
|
838,817 |
|
|
829,887 |
|
|
Income before taxes |
|
|
609,530 |
|
|
580,238 |
|
|
392,953 |
|
|
Income tax benefit/(expense) |
|
|
146,622 |
|
|
(205,313) |
|
|
(139,562) |
|
|
Net income |
|
$ |
756,152 |
|
$ |
374,925 |
|
$ |
253,391 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net income per share of Class A and Class B common stock: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic |
|
$ |
7.33 |
|
$ |
3.65 |
|
$ |
2.47 |
|
|
Diluted |
|
$ |
6.82 |
|
$ |
3.44 |
|
$ |
2.34 |
|
|
Weighted-average shares outstanding |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic |
|
|
103,189,175 |
|
|
102,801,161 |
|
|
102,547,774 |
|
|
Diluted |
|
|
111,657,564 |
|
|
110,798,727 |
|
|
110,628,865 |
|
(See Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements)
70
Air Lease Corporation and Subsidiaries
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Class A |
|
Class B Non-Voting |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
Preferred Stock |
|
Common Stock |
|
Common Stock |
|
Paid-in |
|
Retained |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
Shares |
|
Amount |
|
Shares |
|
Amount |
|
Shares |
|
Amount |
|
Capital |
|
Earnings |
|
Total |
|
||||||
|
|
|
(in thousands, except share and per share amounts) |
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
Balance at December 31, 2014 |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
102,392,208 |
|
$ |
1,010 |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
$ |
2,215,479 |
|
$ |
555,573 |
|
$ |
2,772,062 |
|
|
Issuance of common stock upon exercise of options and vesting of restricted stock units |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
321,395 |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
177 |
|
|
— |
|
|
177 |
|
|
Stock-based compensation expense |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
17,022 |
|
|
— |
|
|
17,022 |
|
|
Cash dividends (declared $0.17 per share) |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
(17,438) |
|
|
(17,438) |
|
|
Tax withholdings on stock based compensation |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
(130,934) |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
(5,302) |
|
|
— |
|
|
(5,302) |
|
|
Net income |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
253,391 |
|
|
253,391 |
|
|
Balance at December 31, 2015 |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
102,582,669 |
|
$ |
1,010 |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
$ |
2,227,376 |
|
$ |
791,526 |
|
$ |
3,019,912 |
|
|
Issuance of common stock upon exercise of options and vesting of restricted stock units |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
452,759 |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
96 |
|
|
— |
|
|
96 |
|
|
Stock-based compensation expense |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
16,941 |
|
|
— |
|
|
16,941 |
|
|
Cash dividends (declared $0.225 per share) |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
(23,140) |
|
|
(23,140) |
|
|
Tax withholdings on stock based compensation |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
(190,951) |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
(6,547) |
|
|
— |
|
|
(6,547) |
|
|
Net income |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
374,925 |
|
|
374,925 |
|
|
Balance at December 31, 2016 |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
102,844,477 |
|
$ |
1,010 |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
$ |
2,237,866 |
|
$ |
1,143,311 |
|
$ |
3,382,187 |
|
|
Cumulative effect adjustment upon adoption of ASU 2016-09 |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
458 |
|
|
458 |
|
|
Issuance of common stock upon exercise of options and vesting of restricted stock units |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
942,088 |
|
|
26 |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
9,320 |
|
|
— |
|
|
9,346 |
|
|
Stock-based compensation expense |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
19,804 |
|
|
— |
|
|
19,804 |
|
|
Cash dividends (declared $0.325 per share) |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
(33,579) |
|
|
(33,579) |
|
|
Tax withholdings on stock based compensation |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
(164,936) |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
(6,926) |
|
|
— |
|
|
(6,926) |
|
|
Net income |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
756,152 |
|
|
756,152 |
|
|
Balance at December 31, 2017 |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
103,621,629 |
|
$ |
1,036 |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
$ |
2,260,064 |
|
$ |
1,866,342 |
|
$ |
4,127,442 |
|
(See Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements)
71
Air Lease Corporation and Subsidiaries
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
Year Ended |
|
Year Ended |
|
|||
|
|
|
December 31, 2017 |
|
December 31, 2016 |
|
December 31, 2015 |
|
|||
|
|
|
(in thousands) |
|
|||||||
|
Operating Activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net income |
|
$ |
756,152 |
|
$ |
374,925 |
|
$ |
253,391 |
|
|
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Depreciation of flight equipment |
|
|
508,352 |
|
|
452,682 |
|
|
397,760 |
|
|
Stock-based compensation |
|
|
19,804 |
|
|
16,941 |
|
|
17,022 |
|
|
Deferred taxes |
|
|
(146,622) |
|
|
205,313 |
|
|
138,608 |
|
|
Amortization of discounts and debt issuance costs |
|
|
29,454 |
|
|
30,942 |
|
|
30,507 |
|
|
Gain on aircraft sales, trading and other activity |
|
|
(55,073) |
|
|
(58,880) |
|
|
(41,072) |
|
|
Changes in operating assets and liabilities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other assets |
|
|
(108,622) |
|
|
(55,728) |
|
|
11,336 |
|
|
Accrued interest and other payables |
|
|
50,832 |
|
|
45,983 |
|
|
16,635 |
|
|
Rentals received in advance |
|
|
5,436 |
|
|
7,900 |
|
|
15,608 |
|
|
Net cash provided by operating activities |
|
|
1,059,713 |
|
|
1,020,078 |
|
|
839,795 |
|
|
Investing Activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Acquisition of flight equipment under operating lease |
|
|
(1,972,009) |
|
|
(1,914,093) |
|
|
(2,088,646) |
|
|
Payments for deposits on flight equipment purchases |
|
|
(773,981) |
|
|
(868,091) |
|
|
(597,170) |
|
|
Proceeds from aircraft sales, trading and other activity |
|
|
779,489 |
|
|
988,040 |
|
|
752,747 |
|
|
Acquisition of furnishings, equipment and other assets |
|
|
(177,450) |
|
|
(211,372) |
|
|
(219,732) |
|
|
Net cash used in investing activities |
|
|
(2,143,951) |
|
|
(2,005,516) |
|
|
(2,152,801) |
|
|
Financing Activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Issuance of common stock upon exercise of options |
|
|
9,264 |
|
|
20 |
|
|
60 |
|
|
Cash dividends paid |
|
|
(30,933) |
|
|
(20,555) |
|
|
(16,405) |
|
|
Tax withholdings on stock-based compensation |
|
|
(6,926) |
|
|
(5,890) |
|
|
(5,302) |
|
|
Net change in unsecured revolving facilities |
|
|
81,000 |
|
|
46,000 |
|
|
151,000 |
|
|
Proceeds from debt financings |
|
|
2,183,824 |
|
|
2,021,966 |
|
|
1,232,384 |
|
|
Payments in reduction of debt financings |
|
|
(1,303,499) |
|
|
(1,093,910) |
|
|
(328,248) |
|
|
Net change in restricted cash |
|
|
(78) |
|
|
528 |
|
|
(9,059) |
|
|
Debt issuance costs |
|
|
(5,855) |
|
|
(5,042) |
|
|
(4,518) |
|
|
Security deposits and maintenance reserve receipts |
|
|
226,064 |
|
|
218,754 |
|
|
218,380 |
|
|
Security deposits and maintenance reserve disbursements |
|
|
(51,221) |
|
|
(58,306) |
|
|
(51,430) |
|
|
Net cash provided by financing activities |
|
|
1,101,640 |
|
|
1,103,565 |
|
|
1,186,862 |
|
|
Net increase (decrease) in cash |
|
|
17,402 |
|
|
118,127 |
|
|
(126,144) |
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of period |
|
|
274,802 |
|
|
156,675 |
|
|
282,819 |
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents at end of period |
|
$ |
292,204 |
|
$ |
274,802 |
|
$ |
156,675 |
|
|
Supplemental Disclosure of Cash Flow Information |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash paid during the period for interest, including capitalized interest of $46,049, $40,883 and $40,118 at December 31, 2017 and 2016 and 2015, respectively |
|
$ |
301,741 |
|
$ |
293,969 |
|
$ |
259,968 |
|
|
Supplemental Disclosure of Noncash Activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Buyer furnished equipment, capitalized interest, deposits on flight equipment purchases and seller financing applied to acquisition of flight equipment and other assets applied to payments for deposits on flight equipment purchases |
|
$ |
644,206 |
|
$ |
873,828 |
|
$ |
944,469 |
|
|
Cash dividends declared, not yet paid |
|
$ |
10,359 |
|
$ |
7,714 |
|
$ |
5,129 |
|
(See Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements)
72
Note 1. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Organization
Air Lease Corporation is a leading aircraft leasing company that was founded by aircraft leasing industry pioneer, Steven F. Udvar‑Házy. We are principally engaged in purchasing new commercial jet transport aircraft directly from the manufacturers, such as Boeing and Airbus. We lease these aircraft to airlines throughout the world to generate attractive returns on equity. As of December 31, 2017 we owned a fleet of 244 aircraft and had 368 aircraft on order with the manufacturers. In addition to our leasing activities, we sell aircraft from our fleet to other leasing companies, financial services companies, and airlines. We also provide fleet management services to investors and owners of aircraft portfolios for a management fee.
Principles of consolidation
The Company consolidates financial statements of all entities in which we have a controlling financial interest, including the account of any Variable Interest Entity in which we have a controlling financial interest and for which we are the primary beneficiary. All material intercompany balances are eliminated in consolidation.
Rental of flight equipment
The Company leases flight equipment principally under operating leases and reports rental income ratably over the life of each lease. Rentals received, but unearned, under the lease agreements are recorded in Rentals received in advance on the Company’s Consolidated Balance Sheets until earned. The difference between the rental income recorded and the cash received under the provisions of the lease is included in Lease receivables, as a component of Other assets on the Company’s Consolidated Balance Sheet. An allowance for doubtful accounts will be recognized for past‑due rentals based on management’s assessment of collectability. Management monitors all lessees with past due lease payments and discuss relevant operational and financial issues facing those lessees in order to determine an appropriate allowance for doubtful accounts. In addition, if collection is not reasonably assured, the Company will not recognize rental income for amounts due under the Company’s lease contracts and will recognize revenue for such lessees on a cash basis. As of December 31, 2017 and 2016, the Company had no such allowance, and no leases were on a cash basis.
All of the Company’s lease agreements are triple net leases whereby the lessee is responsible for all taxes, insurance, and aircraft maintenance. In the future, we may incur repair and maintenance expenses for off‑lease aircraft. We recognize repair and maintenance expense in our Consolidated Statements of Income for all such expenditures. In many operating lease contracts, the lessee is obligated to make periodic payments, which are calculated with reference to the utilization of the airframe, engines, and other major life‑limited components during the lease. In these leases, we will make a payment to the lessee to compensate the lessee for the cost of the Qualifying Event incurred, up to the maximum of the amount of Maintenance Reserves payment made by the lessee during the lease term, net of previous reimbursements. These payments are made upon the lessee’s presentation of invoices evidencing the completion of such Qualifying Event. The Company records as “Rental of flight equipment” revenue, the portion of Maintenance Reserves that is virtually certain will not be reimbursed to the lessee. Maintenance Reserves payments which we may be required to reimburse to the lessee are reflected in our overhaul reserve liability, as a component of “Security deposits and overhaul reserves on flight equipment leases” in our Consolidated Balance Sheets.
Any Maintenance Reserves or end of lease payments collected that were not reimbursed to the lessee during the term of the lease for a Qualifying Event are recognized as Rental revenues at the end of the lease. Leases that contain provisions which require us to pay a portion of a lessee's major maintenance based on the usage of the aircraft and major life-limited components that were incurred prior to the current lease are recorded as lease incentives based on estimated
73
Air Lease Corporation and Subsidiaries
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
payments we expect to pay the lessee. These lease incentives are amortized as a reduction of Rental revenues over the term of the lease.
Lessee‑specific modifications are capitalized as initial direct costs and amortized over the term of the lease into rental revenue in our Consolidated Statements of Income.
Initial direct costs
The Company records as period costs those internal and other costs incurred in connection with identifying, negotiating, and delivering aircraft to the Company's lessees. Amounts paid by us to lessees and/or other parties in connection with originating lease transactions are capitalized as lease incentives and are amortized over the lease term. Additionally, regarding the extension of leases that contain maintenance reserve provisions, the Company considers maintenance reserves that were previously recorded as revenue and no longer meet the virtual certainty criteria as a function of the extended lease term as lease incentives and capitalizes such reserves. The amortization of lease incentives are recorded as a reduction of lease revenue in the Consolidated Statement of Income.
Cash and cash equivalents
The Company considers cash and cash equivalents to be cash on hand and highly liquid investments with original maturity dates of 90 days or less.
Restricted cash
Restricted cash consists of pledged security deposits, maintenance reserves, and rental payments related to secured aircraft financing arrangements.
Flight equipment
Flight equipment under operating lease is stated at cost less accumulated depreciation. Purchases, major additions and modifications, and interest on deposits during the construction phase are capitalized. The Company generally depreciates passenger aircraft on a straight‑line basis over a 25‑year life from the date of manufacture to a 15% residual value. Changes in the assumption of useful lives or residual values for aircraft could have a significant impact on the Company’s results of operations and financial condition.
Major aircraft improvements and modifications incurred during an off-lease period are capitalized and depreciated over the remaining life of the flight equipment. In addition, costs paid by us for scheduled maintenance and overhauls are capitalized and depreciated over a period to the next scheduled maintenance or overhaul event. Miscellaneous repairs are expensed when incurred.
Management evaluates on a quarterly basis the need to perform an impairment test whenever facts or circumstances indicate a potential impairment has occurred. An assessment is performed whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an aircraft may not be recoverable. Recoverability of an aircraft’s carrying amount is measured by comparing the carrying amount of the aircraft to future undiscounted net cash flows expected to be generated by the aircraft. The undiscounted cash flows consist of cash flows from currently contracted leases, future projected lease rates, and estimated residual or scrap values for each aircraft. We develop assumptions used in the recoverability analysis based on our knowledge of active lease contracts, current and future expectations of the global demand for a particular aircraft type, and historical experience in the aircraft leasing market and aviation industry, as well as information received from third‑party industry sources. The factors considered in estimating the undiscounted cash flows are affected by changes in future periods due to changes in contracted lease rates, economic conditions, technology, and airline demand for a particular aircraft type. In the event that an aircraft does not meet the
74
Air Lease Corporation and Subsidiaries
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
recoverability test, the aircraft will be recorded at fair value in accordance with the Company’s Fair Value Policy, resulting in an impairment charge. Our Fair Value Policy is described below under “Fair Value Measurements”.
Maintenance Rights
The Company identifies, measures, and accounts for maintenance right assets and liabilities associated with its acquisitions of aircraft with in-place leases. A maintenance right asset represents the fair value of the Company’s contractual right under a lease to receive an aircraft in an improved maintenance condition as compared to the maintenance condition on the acquisition date. A maintenance right liability represents the Company’s obligation to pay the lessee for the difference between the lease end contractual maintenance condition of the aircraft and the actual maintenance condition of the aircraft on the acquisition date.
The Company’s aircraft are typically subject to triple-net leases pursuant to which the lessee is responsible for maintenance, which is accomplished through one of two types of provisions in its leases: (i) end of lease return conditions (“EOL Leases”) or (ii) periodic maintenance payments (“MR Leases”).
(i) EOL Leases
Under EOL Leases, the lessee is obligated to comply with certain return conditions which require the lessee to perform maintenance on the aircraft or make cash compensation payments at the end of the lease to bring the aircraft into a specified maintenance condition.
Maintenance right assets in EOL Leases represent the difference in value between the contractual right to receive an aircraft in an improved maintenance condition as compared to the maintenance condition on the acquisition date. Maintenance right liabilities exist in EOL Leases if, on the acquisition date, the maintenance condition of the aircraft is greater than the contractual return condition in the lease and the Company is required to pay the lessee in cash for the improved maintenance condition. Maintenance rights, net of accumulated amortization, are recorded as a component of flight equipment subject to operating leases on the Consolidated Balance Sheets.
When the Company has recorded maintenance right assets with respect to EOL Leases, the following accounting scenarios exist: (i) the aircraft is returned at lease expiry in the contractually specified maintenance condition without any cash payment to the Company by the lessee, the maintenance right asset is relieved, and an aircraft improvement is recorded to the extent the improvement is substantiated and deemed to meet the Company’s capitalization policy; (ii) the lessee pays the Company cash compensation at lease expiry in excess of the value of the maintenance right asset, the maintenance right asset is relieved, and any excess is recognized as end of lease income; or (iii) the lessee pays the Company cash compensation at lease expiry that is less than the value of the maintenance right asset, the cash is applied to the maintenance right asset, and the balance of such asset is relieved and recorded as an aircraft improvement to the extent the improvement is substantiated and meets the Company’s capitalization policy. Any aircraft improvement will be depreciated over a period to the next scheduled maintenance event in accordance with the Company’s policy with respect to major maintenance and included in depreciation of flight equipment on the Company’s Consolidated Statements of Income.
When the Company has recorded maintenance right liabilities with respect to EOL Leases, the following accounting scenarios exist: (i) the aircraft is returned at lease expiry in the contractually specified maintenance condition without any cash payment by the Company to the lessee, the maintenance right liability is relieved, and end of lease income is recognized; (ii) the Company pays the lessee cash compensation at lease expiry of less than the value of the maintenance right liability, the maintenance right liability is relieved, and any difference is recognized as end of lease income; or (iii) the Company pays the lessee cash compensation at lease expiry in excess of the value of the maintenance right liability, the maintenance right liability is relieved, and the excess amount is recorded as an aircraft improvement to the extent of that it meets our capitalization policy.
75
Air Lease Corporation and Subsidiaries
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
(ii) MR Leases
Under MR Leases, the lessee is required to make periodic payments to us for maintenance based upon planned usage of the aircraft. When a Qualifying Event occurs during the lease term, the Company is required to reimburse the lessee for the costs associated with such an event. At the end of lease, the Company is entitled to retain any cash receipts in excess of the required reimbursements to the lessee.
Maintenance right assets in MR Leases represent the right to receive an aircraft in an improved condition relative to the actual condition on the acquisition date. The aircraft is improved by the performance of a Qualifying Event paid for by the lessee who is reimbursed by the Company from the periodic maintenance payments that it receives. Maintenance rights, net of accumulated amortization, are recorded as a component of flight equipment subject to operating leases on the Consolidated Balance Sheets.
When the Company has recorded maintenance right assets with respect to MR Leases, the following accounting scenarios exist: (i) the aircraft is returned at lease expiry and no Qualifying Event has been performed by the lessee since the acquisition date, the maintenance right asset is offset by the amount of the associated maintenance payment liability, and any excess is recorded as end of lease income; or (ii) the Company has reimbursed the lessee for the performance of a Qualifying Event, the maintenance right asset is relieved, and an aircraft improvement is recorded to the extent of that it meets our capitalization policy.
There are no maintenance right liabilities for MR Leases.
When flight equipment is sold, maintenance rights are included in the calculation of the disposition gain or loss.
For the year ended December 31, 2017, the Company did not purchase any aircraft in the secondary market subject to an existing lease. For the year ended December 31, 2016, the Company purchased one aircraft in the secondary market subject to an existing lease. The total cost for the aircraft was $33.7 million, which included maintenance rights assets of $3.2 million. As of December 31, 2017 and 2016, the Company had maintenance rights assets, net of accumulated amortization of $44.6 million and $95.1 million, respectively. Maintenance rights assets are included under flight equipment subject to operating leases in our Consolidated Balance Sheets.
Flight equipment held for sale
Management evaluates all contemplated aircraft sale transactions to determine whether all the required criteria have been met under Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (“GAAP”) to classify aircraft as flight equipment held for sale. Management uses judgment in evaluating these criteria. Due to the significant uncertainties of potential sale transactions, the held for sale criteria generally will not be met unless the aircraft is subject to a signed sale agreement, or management has made a specific determination and obtained appropriate approvals to sell a particular aircraft or group of aircraft. Aircraft classified as flight equipment held for sale are recognized at the lower of their carrying amount or estimated fair value less estimated costs to sell. At the time aircraft are classified as flight equipment held for sale, depreciation expense is no longer recognized.
Capitalized interest
The Company may borrow funds to finance deposits on new flight equipment purchases. The Company capitalizes interest expense on such borrowings. The capitalized amount is calculated using our composite borrowing rate and is recorded as an increase to the cost of the flight equipment on our Consolidated Balance Sheets at the time of purchase.
76
Air Lease Corporation and Subsidiaries
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Fair value measurements
Fair value is the amount that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. The Company measures the fair value of certain assets on a non-recurring basis, principally our flight equipment, when GAAP requires the application of fair value, including events or changes in circumstances that indicate that the carrying amounts of assets may not be recoverable.
The Company records flight equipment at fair value when we determine the carrying value may not be recoverable. The Company principally uses the income approach to measure the fair value of flight equipment. The income approach is based on the present value of cash flows from contractual lease agreements and projected future lease payments, including contingent rentals, net of expenses, which extend to the end of the aircraft’s economic life in its highest and best use configuration, as well as a disposition value based on expectations of market participants. These valuations are considered Level 3 valuations, as the valuations contain significant non‑observable inputs.
Income taxes
The Company uses the asset and liability method of accounting for income taxes. Under the asset and liability method, deferred income taxes are recognized for the tax consequences of “temporary differences” by applying enacted statutory tax rates applicable to future years to differences between the financial statement carrying amounts and the tax basis of existing assets and liabilities. The effect on deferred taxes of a change in the tax rates is recognized in income in the period that includes the enactment date. The Company records a valuation allowance for deferred tax assets when the probability of realization of the full value of the asset is less than 50%. The Company recognizes the impact of a tax position, if that position is more than 50% likely to be sustained on audit, based on the technical merits of the position. Recognized income tax positions are measured at the largest amount that is greater than 50% likely to be realized. Changes in recognition or measurement are reflected in the period in which the change in judgment occurs.
The Company recognizes interest and penalties for uncertain tax positions in income tax expense.
Deferred costs
The Company incurs debt issuance costs in connection with debt financings. Those costs are deferred and amortized over the life of the specific loan using the effective interest method and charged to interest expense. The Company also incurs costs in connection with equity offerings. Such costs are deferred until the equity offering is completed and either netted against the equity raised, or expensed if the equity offering is abandoned.
Investments
Our investment in the Blackbird Capital I, LLC and Blackbird Capital II, LLC joint ventures, where we own 9.5% of the equity of each venture, is accounted for using the equity method of accounting due to our level of influence and involvement in the joint ventures. The investments are recorded at the amount invested plus or minus our 9.5% share of net income or loss, less any distributions or return of capital received from the entity.
Stock‑based compensation
Stock‑based compensation cost is measured at the grant date based on the fair value of the award. Stock-based compensation expense is recognized over the requisite service periods of the awards on a straight-line basis.
Effective as of January 1, 2017, the Company adopted a change in accounting policy in accordance with Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) 2016-09 (“ASU 2016-09”), “Compensation-Stock Compensation (Topic 718),” wherein all excess tax benefits and tax deficiencies related to employee stock compensation will be recognized within
77
Air Lease Corporation and Subsidiaries
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
income tax expense on the Consolidated Statement of Income. Previously, only net tax deficiencies were recognized as tax expense. In connection with the adoption of ASU 2016-09, the Company recorded excess tax benefits relating to prior periods of $0.5 million on a modified retrospective basis through a cumulative effect adjustment to retained earnings.
In addition, ASU 2016-09 requires excess tax benefits and deficiencies to be classified as operating activities on the Statement of Cash Flow. Previously, these items were classified as financing activities. We have elected to present the cash flow statement on a prospective transition method and there were no adjustments to the Consolidated Statement of Cash Flows for the year ended December 31, 2017 as a result of this adoption.
Finally, ASU 2016-09 provides an accounting policy election to account for forfeitures as they occur or to account for forfeitures on an estimated basis. We elected to change our policy from estimating forfeitures to accounting for forfeitures as they are incurred. This change in accounting policy was made on a prospective basis.
Use of estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the amounts reported in the financial statements and accompanying notes. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Reclassifications
Certain reclassifications have been made in the 2015 and 2016 consolidated financial statements to conform to the classifications in 2017.
Recently issued accounting pronouncements
In May 2014, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB") issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) No. 2014-09 (“ASU 2014-09”), “Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606)”. The amendments in ASU 2014-09 supersede most of the current revenue recognition requirements. The guidance requires entities to recognize revenue when it transfers promised goods or services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration to which the entity expects to be entitled to in exchange for those goods or services. ASU 2014-09 will be effective for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2017 for public entities, including interim periods within that reporting period, and is required to be applied using either a full retrospective approach or a modified retrospective approach. The standard will not have a material impact on our consolidated financial statements and will not have an impact on our historical consolidated financial statements. We plan to adopt the standard on a modified retrospective approach on its required effective date of January 1, 2018.
In February 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-02 (“ASU 2016-02”), “Leases (Topic 842)”. The amendments in ASU 2016-02 set out the principles for the recognition, measurement, presentation and disclosure of leases for both lessees and lessors. ASU 2016-02 will be effective for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2018 for public entities and is required to be applied using the modified retrospective transition approach. Early adoption is permitted. Based on our initial evaluation of the guidance we noted that Lessor accounting is similar to the current model but the guidance will impact us in scenarios where we are the Lessee. We do not expect the impact of this standard to have a material impact on our consolidated financial statements. We will adopt the standard on January 1, 2019.
In August 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-15 (“ASU 2016-15”), “Statement of Cash Flows (Topic 230)”. The amendments in ASU 2016-15 addresses eight classification issues related to the statement of cash flows. ASU 2016-15 will be effective for interim and annual periods beginning after December 15, 2017 for public entities and is required to be adopted using a retrospective transition method to each period presented. Early adoption is permitted.
78
Air Lease Corporation and Subsidiaries
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
We have concluded our evaluation of this guidance and determined that the standard will not have a material impact on our financial statements.
In October 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-16 (“ASU 2016-16”), “Income Taxes (Topic 740)”. The ASU 2016-16 requires entities to recognize the income tax consequences of many intercompany asset transfers at the transaction date. ASU 2016-16 will be effective for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2017 for public entities and is required to be adopted using a modified retrospective transition approach. Early adoption is only permitted as of the beginning of an annual reporting period. We have concluded our evaluation of this guidance and determined that the standard will not have a material impact on our financial statements.
Note 2. Debt Financing
The Company’s consolidated debt as of December 31, 2017 and 2016 is summarized below:
|
|
|
December 31, 2017 |
|
December 31, 2016 |
|
||
|
|
|
(in thousands) |
|
||||
|
Unsecured |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Senior notes |
|
$ |
8,019,871 |
|
$ |
6,953,343 |
|
|
Revolving credit facility |
|
|
847,000 |
|
|
766,000 |
|
|
Term financings |
|
|
203,704 |
|
|
211,346 |
|
|
Convertible senior notes |
|
|
199,983 |
|
|
199,995 |
|
|
Total unsecured debt financing |
|
|
9,270,558 |
|
|
8,130,684 |
|
|
Secured |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Term financings |
|
|
484,036 |
|
|
619,767 |
|
|
Export credit financing |
|
|
44,920 |
|
|
51,574 |
|
|
Total secured debt financing |
|
|
528,956 |
|
|
671,341 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total debt financing |
|
|
9,799,514 |
|
|
8,802,025 |
|
|
Less: Debt discounts and issuance costs |
|
|
(100,729) |
|
|
(88,151) |
|
|
Debt financing, net of discounts and issuance costs |
|
$ |
9,698,785 |
|
$ |
8,713,874 |
|
At December 31, 2017, management of the Company believes it is in compliance in all material respects with the covenants in its debt agreements, including its financial covenants concerning debt-to-equity, tangible net equity, and interest coverage ratios.
The Company’s secured obligations as of December 31, 2017 and 2016 are summarized below:
|
|
|
December 31, 2017 |
|
December 31, 2016 |
|
||
|
|
|
(in thousands) |
|
||||
|
Nonrecourse |
|
$ |
205,906 |
|
$ |
245,155 |
|
|
Recourse |
|
|
323,050 |
|
|
426,186 |
|
|
Total |
|
$ |
528,956 |
|
$ |
671,341 |
|
|
Number of aircraft pledged as collateral |
|
|
21 |
|
|
25 |
|
|
Net book value of aircraft pledged as collateral |
|
$ |
1,184,264 |
|
$ |
1,421,657 |
|
Senior unsecured notes
As of December 31, 2017, the Company had $8.0 billion in aggregate principal amount of senior unsecured notes outstanding with remaining terms ranging from 0.1 years to 9.9 years and bearing interest at fixed rates ranging
79
Air Lease Corporation and Subsidiaries
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
from 2.125% to 7.375%. As of December 31, 2016, the Company had $7.0 billion in aggregate principal amount of senior unsecured notes outstanding bearing interest at fixed rates ranging from 2.125% to 7.375%.
During the year ended December 31, 2017, the Company issued $2.2 billion in aggregate principal amount of senior unsecured notes.
In March 2017, the Company issued $500.0 million in aggregate principal amount of senior unsecured notes due 2027 that bear interest at a rate of 3.625%.
In June 2017, the Company issued $600.0 million in aggregate principal amount of senior unsecured notes due 2022 that bear interest at a rate of 2.625%.
In November 2017, the Company issued (i) $500.0 million in aggregate principal amount of senior unsecured notes due 2027 that bear interest at a rate of 3.625% and (ii) $600.0 million in aggregate principal amount of senior unsecured notes due 2023 that bear interest at a rate of 2.750%.
Furthermore, in January 2018 the Company issued (i) $550.0 million in aggregate principal amount of senior unsecured notes due 2021 that bear interest at a rate of 2.50% and (ii) $700.0 million in aggregate principal amount of senior unsecured notes due 2025 that bear interest at a rate of 3.25%.
Unsecured revolving credit facility
The total amount outstanding under the Company's unsecured revolving credit facility was $847.0 million and $766.0 million as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively.
During the first three months of 2017, we increased the aggregate capacity of our unsecured revolving credit facility by $300.0 million to $3.5 billion.
In May 2017, the Company amended and extended its four-year unsecured revolving credit facility whereby, among other things, the Company extended the final maturity date from May 5, 2020 to May 5, 2021 and increased the total revolving commitments to approximately $3.7 billion from approximately $3.5 billion at an interest rate of LIBOR plus 1.05% with a 0.20% facility fee. Lenders hold revolving commitments totaling approximately $3.1 billion that mature on May 5, 2021, commitments totaling $217.7 million that mature on May 5, 2020, commitments totaling $290.0 million that mature on May 5, 2019, and commitments totaling $55.0 million that mature on May 5, 2018.
In November 2017, we executed a commitment increase to our unsecured revolving credit facility. This increased the aggregate facility capacity by $50.0 million to $3.8 billion.
Furthermore, in February 2018, we increased the capacity of our unsecured revolving credit facility by 4.7% to $3.9 billion.
Unsecured term financings
From time to time, the Company enters into unsecured term facilities. During 2017, the Company entered into two additional unsecured term facilities aggregating $20.0 million, both with terms of five years and bearing interest at fixed rates of 2.75% per annum. The outstanding balance on our unsecured term facilities as of December 31, 2017 was $203.7 million, bearing interest at fixed rates ranging from 2.75% to 3.50% and one facility bearing interest at a floating rate of LIBOR plus 1.00%. As of December 31, 2017, the remaining maturities of all unsecured term facilities ranged from approximately 0.1 years to approximately 4.6 years. As of December 31, 2016, the outstanding balance on our unsecured term facilities was $211.3 million.
80
Air Lease Corporation and Subsidiaries
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Convertible senior notes
In November 2011, the Company issued $200.0 million in aggregate principal amount of 3.875% convertible senior notes due 2018 in an offering exempt from registration under the Securities Act. The convertible notes were sold to Qualified Institutional Buyers in reliance upon Rule 144A under the Securities Act. The convertible notes are senior unsecured obligations of the Company and bear interest at a rate of 3.875% per annum, payable semi‑annually in arrears on June 1 and December 1 of each year, commencing on June 1, 2012. As of December 31, 2017, the convertible notes are convertible at the option of the holder into shares of our Class A common stock at a price of $29.42 per share.
Secured term financing
We fund some aircraft purchases through secured term financings. Our various consolidated entities will borrow through secured bank facilities to purchase an aircraft. The aircraft are then leased by our entities to airlines. We may guarantee the obligations of the entities under the loan agreements. The loans may be secured by a pledge of the shares of the entities, the aircraft, the lease receivables, security deposits, maintenance reserves, or a combination thereof.
As of December 31, 2017, the outstanding balance on our secured term facilities was $484.0 million and we had pledged 19 aircraft as collateral with a net book value of $1.1 billion. The outstanding balance under our secured term facilities as of December 31, 2017 was comprised of $2.6 million fixed rate debt consisting of one facility with an interest rate of 4.58% and $481.5 million floating rate debt with interest rates ranging from LIBOR plus 1.15% to LIBOR plus 2.99%. As of December 31, 2017, the remaining maturities of all secured term facilities ranged from approximately 0.2 years to approximately 5.6 years.
As of December 31, 2016, the outstanding balance on our secured term facilities was $619.8 million and we had pledged 23 aircraft as collateral with a net book value of $1.3 billion. The outstanding balance under our secured term facilities as of December 31, 2016 was comprised of $31.7 million fixed rate debt and $588.1 million floating rate debt, with interest rates ranging from 4.34% to 5.36% and LIBOR plus 1.15% to LIBOR plus 2.99%, respectively.
Export credit financings
As of December 31, 2017, the Company had $44.9 million in export credit financing outstanding. As of December 31, 2016, the Company had $51.6 million in export credit financing outstanding.
In March 2013, the Company issued $76.5 million in secured notes due 2024 guaranteed by the Ex‑Im Bank. The notes will mature on August 15, 2024 and bear interest at a rate of 1.617% per annum.
Maturities
Maturities of debt outstanding as of December 31, 2017 are as follows:
|
Years ending December 31, |
|
(in thousands) |
|
|
|
2018 |
|
$ |
1,556,665 |
|
|
2019 |
|
|
1,043,758 |
|
|
2020 |
|
|
1,226,540 |
|
|
2021 |
|
|
1,847,849 |
|
|
2022 |
|
|
1,226,884 |
|
|
Thereafter |
|
|
2,897,818 |
|
|
Total |
|
$ |
9,799,514 |
|
81
Air Lease Corporation and Subsidiaries
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Note 3. Interest Expense
The following table shows the components of interest for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015:
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
Year Ended |
|
Year Ended |
|
|||
|
|
|
December 31, 2017 |
|
December 31, 2016 |
|
December 31, 2015 |
|
|||
|
|
|
(in thousands) |
|
|||||||
|
Interest on borrowings |
|
$ |
303,966 |
|
$ |
296,142 |
|
$ |
275,755 |
|
|
Less capitalized interest |
|
|
(46,049) |
|
|
(40,883) |
|
|
(40,118) |
|
|
Interest |
|
|
257,917 |
|
|
255,259 |
|
|
235,637 |
|
|
Amortization of discounts and deferred debt issue costs |
|
|
29,454 |
|
|
30,942 |
|
|
30,507 |
|
|
Interest expense |
|
$ |
287,371 |
|
$ |
286,201 |
|
$ |
266,144 |
|
Note 4. Shareholders’ Equity
In 2010, the Company authorized 500,000,000 shares of Class A common stock, $0.01 par value per share, of which 103,621,629 and 102,844,477 shares were issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively. As of December 31, 2017 and 2016, the Company had authorized 10,000,000 shares of Class B Non‑Voting common stock, $0.01 par value per share, of which no shares were outstanding as of December 31, 2017 and 2016.
On June 4, 2010, the Company issued 482,625 warrants for the purchase of up to 482,625 shares of Class A common stock to two institutional investors (the “Committed Investors”). The warrants had a seven-year term and an exercise price of $20 per share. The Company used the BSM option pricing model to determine the fair value of warrants. The fair value of warrants was calculated on the date of grant by an option‑pricing model using a number of complex and subjective variables. These variables include expected stock price volatility over the term of the warrant, projected exercise behavior, a risk‑free interest rate, and expected dividends. The warrants had a fair value at the grant date of $5.6 million. The warrants are classified as an equity instrument and the proceeds from the issuance of common stock to the Committed Investors was split between the warrants and the stock based on fair value of the warrants and recorded as an increase to Paid‑in capital on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. On March 9, 2017, a Committed Investor performed a cashless exercise of the remaining 268,125 warrants, resulting in the issuance of 131,001 shares of Class A common stock. As of December 31, 2017, the Company did not have any warrants outstanding.
As of December 31, 2017 and 2016 the Company had authorized 50,000,000 shares of preferred stock, $0.01 par value per share, of which no shares were issued or outstanding.
82
Air Lease Corporation and Subsidiaries
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Note 5. Rental Income
At December 31, 2017, minimum future rentals on non‑cancellable operating leases of flight equipment in our fleet, which have been delivered as of December 31, 2017, are as follows:
|
Years ending December 31, |
|
(in thousands) |
|
|
|
2018 |
|
$ |
1,500,266 |
|
|
2019 |
|
|
1,453,702 |
|
|
2020 |
|
|
1,352,817 |
|
|
2021 |
|
|
1,252,878 |
|
|
2022 |
|
|
1,133,860 |
|
|
Thereafter |
|
|
3,405,496 |
|
|
Total |
|
$ |
10,099,019 |
|
The Company recorded $40.9 million, $29.0 million, and $34.0 million in maintenance reserve revenue based on our lessees’ usage of the aircraft for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016, and 2015, respectively.
The following table shows the scheduled lease terminations (for the minimum non‑cancellable period which does not include contracted unexercised lease extension options) of our operating lease portfolio as of December 31, 2017, updated through February 22, 2018:
|
Aircraft Type |
|
2018 |
|
2019 |
|
2020 |
|
2021 |
|
2022 |
|
Thereafter |
|
Total |
|
Airbus A319-100 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
1 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
1 |
|
Airbus A320-200 |
|
3 |
|
3 |
|
7 |
|
6 |
|
1 |
|
20 |
|
40 |
|
Airbus A320-200neo |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
5 |
|
5 |
|
Airbus A321-200 |
|
1 |
|
— |
|
1 |
|
— |
|
1 |
|
26 |
|
29 |
|
Airbus A321-200neo |
|
— |
|
1 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
4 |
|
5 |
|
Airbus A330-200 |
|
— |
|
4 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
2 |
|
9 |
|
15 |
|
Airbus A330-300 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
1 |
|
— |
|
1 |
|
3 |
|
5 |
|
Airbus A350-900 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
2 |
|
2 |
|
Boeing 737-700 |
|
— |
|
2 |
|
— |
|
1 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
3 |
|
Boeing 737-800 |
|
1 |
|
10 |
|
7 |
|
6 |
|
11 |
|
67 |
|
102 |
|
Boeing 737-8 MAX |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
2 |
|
2 |
|
Boeing 767-300ER |
|
— |
|
1 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
1 |
|
Boeing 777-200ER |
|
— |
|
— |
|
1 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
1 |
|
Boeing 777-300ER |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
4 |
|
4 |
|
16 |
|
24 |
|
Boeing 787-9 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
8 |
|
8 |
|
Embraer E190 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
1 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
1 |
|
Total |
|
5 |
|
21 |
|
18 |
|
18 |
|
20 |
|
162 |
|
244 |
Note 6. Concentration of Risk
Geographical and credit risks
As of December 31, 2017, all of the Company's rental of flight equipment revenues were generated by leasing flight equipment to foreign and domestic airlines, and the Company leased and managed aircraft to 91 customers whose principal places of business are located in 55 countries as of December 31, 2017 compared to 85 lessees in 51 countries as of December 31, 2016.
83
Air Lease Corporation and Subsidiaries
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Over 95% of our aircraft are operated internationally. The following table sets forth the regional concentration based on each airline's principal place of business of our aircraft portfolio based on net book value as of December 31, 2017 and 2016:
|
|
|
December 31, 2017 |
|
December 31, 2016 |
|
||||||
|
|
|
Net Book |
|
|
|
Net Book |
|
|
|
||
|
Region |
|
Value(1) |
|
% of Total |
|
Value(1) |
|
% of Total |
|
||
|
|
|
(in thousands, except percentages) |
|
||||||||
|
Europe |
|
$ |
4,205,431 |
|
31.7 |
% |
$ |
3,547,294 |
|
29.5 |
% |
|
Asia (excluding China) |
|
|
2,981,339 |
|
22.4 |
% |
|
2,739,554 |
|
22.7 |
% |
|
China |
|
|
2,720,124 |
|
20.5 |
% |
|
2,779,546 |
|
23.0 |
% |
|
The Middle East and Africa |
|
|
1,481,825 |
|
11.2 |
% |
|
935,968 |
|
7.8 |
% |
|
Central America, South America, and Mexico |
|
|
926,732 |
|
7.0 |
% |
|
937,287 |
|
7.8 |
% |
|
U.S. and Canada |
|
|
599,367 |
|
4.5 |
% |
|
647,743 |
|
5.4 |
% |
|
Pacific, Australia, and New Zealand |
|
|
365,432 |
|
2.7 |
% |
|
454,533 |
|
3.8 |
% |
|
Total |
|
$ |
13,280,250 |
|
100.0 |
% |
$ |
12,041,925 |
|
100.0 |
% |
|
(1) |
We did not have any aircraft held for sale as of December 31, 2017. As of December 31, 2016, we had six aircraft held for sale. |
At December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, we owned and managed leased aircraft to customers in the following regions based on each airline's principal place of business:
|
|
|
December 31, 2017 |
|
December 31, 2016 |
|
December 31, 2015 |
|
||||||
|
|
|
Number of |
|
|
|
Number of |
|
|
|
Number of |
|
|
|
|
Region |
|
Customers(1) |
|
% of Total |
|
Customers(1) |
|
% of Total |
|
Customers(1) |
|
% of Total |
|
|
Europe |
|
31 |
|
34.0 |
% |
27 |
|
31.8 |
% |
27 |
|
30.0 |
% |
|
Asia (excluding China) |
|
18 |
|
19.8 |
% |
18 |
|
21.2 |
% |
19 |
|
21.1 |
% |
|
U.S. and Canada |
|
11 |
|
12.1 |
% |
12 |
|
14.1 |
% |
11 |
|
12.2 |
% |
|
The Middle East and Africa |
|
11 |
|
12.1 |
% |
7 |
|
8.2 |
% |
8 |
|
8.9 |
% |
|
China |
|
9 |
|
9.9 |
% |
9 |
|
10.6 |
% |
12 |
|
13.4 |
% |
|
Central America, South America, and Mexico |
|
9 |
|
9.9 |
% |
9 |
|
10.6 |
% |
11 |
|
12.2 |
% |
|
Pacific, Australia, and New Zealand |
|
2 |
|
2.2 |
% |
3 |
|
3.5 |
% |
2 |
|
2.2 |
% |
|
Total |
|
91 |
|
100.0 |
% |
85 |
|
100.0 |
% |
90 |
|
100.0 |
% |
|
(1) |
A customer is an airline with its own operating certificate. |
84
Air Lease Corporation and Subsidiaries
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
The following table sets forth the dollar amount and percentage of our rental of flight equipment revenues attributable to the indicated regions based on each airline’s principal place of business:
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
Year Ended |
|
Year Ended |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
December 31, 2017 |
|
December 31, 2016 |
|
December 31, 2015 |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
Amount of |
|
|
|
Amount of |
|
|
|
Amount of |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
Rental |
|
|
|
Rental |
|
|
|
Rental |
|
|
|
|||
|
Region |
|
Revenue |
|
% of Total |
|
Revenue |
|
% of Total |
|
Revenue |
|
% of Total |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
(in thousands, except percentages) |
|
||||||||||||
|
Europe |
|
$ |
450,628 |
|
31.1 |
% |
$ |
400,491 |
|
29.9 |
% |
$ |
380,295 |
|
32.4 |
% |
|
Asia (excluding China) |
|
|
332,284 |
|
22.9 |
% |
|
308,658 |
|
23.1 |
% |
|
223,284 |
|
19.0 |
% |
|
China |
|
|
324,147 |
|
22.3 |
% |
|
293,206 |
|
21.9 |
% |
|
265,450 |
|
22.6 |
% |
|
The Middle East and Africa |
|
|
116,799 |
|
8.1 |
% |
|
106,300 |
|
7.9 |
% |
|
90,416 |
|
7.7 |
% |
|
Central America, South America, and Mexico |
|
|
102,205 |
|
7.0 |
% |
|
112,068 |
|
8.4 |
% |
|
114,672 |
|
9.8 |
% |
|
U.S. and Canada |
|
|
76,685 |
|
5.3 |
% |
|
69,918 |
|
5.2 |
% |
|
54,294 |
|
4.6 |
% |
|
Pacific, Australia, and New Zealand |
|
|
47,987 |
|
3.3 |
% |
|
48,361 |
|
3.6 |
% |
|
46,133 |
|
3.9 |
% |
|
Total |
|
$ |
1,450,735 |
|
100.0 |
% |
$ |
1,339,002 |
|
100.0 |
% |
$ |
1,174,544 |
|
100.0 |
% |
Based on our lease placements of future new aircraft deliveries, we anticipate that a growing percentage of our aircraft will be located in the Asia, the Central America, South America, and Mexico, and the Middle East and Africa regions.
For the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016, and 2015, China was the only individual country that represented at least 10% of our rental revenue based on each airline's principal place of business. In 2017, 2016, and 2015, no individual airline represented at least 10% of our rental revenue.
Currency risk
The Company attempts to minimize currency and exchange risks by entering into aircraft purchase agreements and a majority of lease agreements and debt agreements with U.S. dollars as the designated payment currency.
Note 7. Income Taxes
The provision for income taxes consists of the following:
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||
|
|
|
2017 |
|
2016 |
|
2015 |
|
|||
|
|
|
(in thousands) |
|
|||||||
|
Current: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Federal |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
State |
|
|
380 |
|
|
30 |
|
|
— |
|
|
Foreign |
|
|
3,853 |
|
|
848 |
|
|
1,003 |
|
|
Deferred: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Federal |
|
|
(150,850) |
|
|
203,882 |
|
|
138,517 |
|
|
State |
|
|
(5) |
|
|
553 |
|
|
42 |
|
|
Foreign |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
Provision for income taxes |
|
$ |
(146,622) |
|
$ |
205,313 |
|
$ |
139,562 |
|
85
Air Lease Corporation and Subsidiaries
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Differences between the provision for income taxes and income taxes at the statutory federal income tax rate are as follows:
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||||||||||
|
|
|
2017 |
|
2016 |
|
2015 |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
Amount |
|
Percent |
|
Amount |
|
Percent |
|
Amount |
|
Percent |
|
|||
|
|
|
(in thousands, except percentages) |
|
|||||||||||||
|
Income taxes at statutory federal rate |
|
$ |
213,336 |
|
35.0 |
% |
$ |
203,083 |
|
35.0 |
% |
$ |
137,541 |
|
35.0 |
% |
|
Impact of tax legislation |
|
|
(354,127) |
|
(58.1) |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
Foreign tax credit |
|
|
(10,873) |
|
(1.8) |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
State income taxes, net of federal income tax effect and other |
|
|
5,042 |
|
0.9 |
|
|
2,230 |
|
0.4 |
|
|
2,021 |
|
0.5 |
|
|
Provision for income taxes |
|
$ |
(146,622) |
|
(24.0) |
% |
$ |
205,313 |
|
35.4 |
% |
$ |
139,562 |
|
35.5 |
% |
On December 22, 2017, the U.S. Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (the “Tax Reform Act”) was signed into law. The Tax Reform Act significantly revised the U.S. corporate income tax law by, among other things, lowering the U.S. corporate tax rate from 35% to 21%, effective January 1, 2018, repealing the Alternative Minimum Tax (“AMT”), changes to tax depreciation, limitations on interest expense deductions, and limitations on utilization of net operating losses. Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) 740 requires that the impact of tax legislation be recognized in the period in which the law was enacted. As a result of the Tax Reform Act, the Company recorded an estimated tax benefit of $354.1 million due to the remeasurement of deferred tax assets and liabilities in the year ended December 31, 2017.
On December 22, 2017, Staff Accounting Bulletin No. 118 (“SAB 118”) was issued to address the application of US GAAP in situations when a registrant does not have the necessary information available, prepared, or analyzed (including computations) in reasonable detail to complete the accounting for certain income tax effects of the Tax Reform Act. In accordance with SAB 118, the Company has determined that the $354.1 million benefit resulting from the remeasurement of certain deferred tax assets and liabilities is a provisional amount and a reasonable estimate of the impact of the Tax Reform Act on the Consolidated Financial Statements as of December 31, 2017. The estimated adjustment of $354.1 million is based upon the current interpretation of the Tax Reform Act. We expect additional clarification and interpretation guidance that may refine our estimate of the expected reversal of deferred tax balances or could potentially give rise to new deferred tax accounts. Once the Company finalizes certain tax positions when it files its 2017 U.S. Federal Income Tax Return, it will be able to conclude whether any further adjustments are required to its net deferred tax liability as of December 31, 2017. Any subsequent adjustments to the $354.1 million benefit will be recorded as a component of tax expense or benefit in the reporting period in which any adjustments are determined, which will be no later than the fourth quarter of 2018. We expect to complete our analysis within the measurement period in accordance with SAB 118.
The Company recorded a $10.9 million benefit related to foreign taxes expensed in the current year, as well as prior years, that may now be claimed as a Foreign Tax Credit (“FTC”). The Company has determined there will be sufficient foreign source income projected to utilize these credits.
In the first quarter of 2017, the Company adopted ASU 2016-09, Improvements to Employee Share-Based Payment Accounting, which requires all excess tax benefits and tax deficiencies to be recognized in the income statement when the awards vest or are settled. Upon adoption of ASU 2016-09, the Company recognized $0.5 million of previously unrecognized windfall tax benefits in retained earnings.
Prior to the adoption of ASU 2016-09, the tax effect of deductions in excess compensation cost (“windfalls”) related to the exercise of nonqualified stock options and vesting of restricted stock unit awards were recorded in equity and any tax deficiencies (“shortfalls”) were recorded in equity to the extent of previously recognized windfalls. The exercise of nonqualified stock options and vesting of restricted stock unit awards resulted in an increase to additional paid-in capital in the amount of $8.5 million through December 31, 2016.
86
Air Lease Corporation and Subsidiaries
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
As of December 31, 2017 and 2016, the Company’s net deferred tax assets (liabilities) are as follows:
|
|
|
December 31, 2017 |
|
December 31, 2016 |
|
||
|
|
|
(in thousands) |
|
||||
|
Assets (Liabilities) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Equity compensation |
|
$ |
12,744 |
|
$ |
21,477 |
|
|
Net operating losses |
|
|
10,143 |
|
|
48,215 |
|
|
Foreign tax credit |
|
|
14,577 |
|
|
— |
|
|
Rents received in advance |
|
|
22,076 |
|
|
34,883 |
|
|
Accrued bonus |
|
|
1,777 |
|
|
4,631 |
|
|
Straight-line rents |
|
|
(1,967) |
|
|
3,057 |
|
|
Other |
|
|
1,912 |
|
|
7,877 |
|
|
Aircraft depreciation |
|
|
(579,057) |
|
|
(787,200) |
|
|
Net deferred tax assets/(liabilities) |
|
$ |
(517,795) |
|
$ |
(667,060) |
|
The Company has net operating loss carry forwards (“NOLs”) for federal and state income tax purposes of $54.1 million and $150.9 million as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively, which are available to offset future taxable income in future periods. The Company has FTCs for federal income tax purposes of $14.6 million as of December 31, 2017, which are available to offset future taxable income in future periods. The Company generated $75.6 million of NOLs for federal income tax purposes for the year ended December 31, 2016. There were no NOLs generated for the year ended December 31, 2017. The Company's loss and tax credit carryforwards expire in the following periods:
|
|
|
NOL |
|
Tax Credit |
||
|
|
|
Carryforwards |
|
Carryforwards |
||
|
|
|
(in thousands) |
||||
|
2018-2022 |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
20 |
|
Thereafter |
|
|
54,115 |
|
|
14,558 |
|
Total carryforwards |
|
$ |
54,115 |
|
$ |
14,578 |
The Company has not recorded a deferred tax valuation allowance as of December 31, 2017 and 2016 as realization of the deferred tax asset is considered more likely than not. In assessing the realizability of the deferred tax assets, management considered whether future taxable income will be sufficient during the periods in which those temporary differences are deductible before NOLs and FTCs expire. Management considers the scheduled reversal of deferred tax liabilities, projected taxable income, and tax planning strategies in making this assessment. Management anticipates the timing differences on aircraft depreciation will reverse and be available for offsetting the reversal of deferred tax assets. As of December 31, 2017 and 2016 the Company has not recorded any liability for unrecognized tax benefits.
The Company files income tax returns in the U.S. and various state and foreign jurisdictions. The Company is subject to examinations by the major tax jurisdictions for the 2013 tax year and forward.
87
Air Lease Corporation and Subsidiaries
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Note 8. Commitments and Contingencies
Aircraft Acquisition
As of December 31, 2017, we had commitments to acquire a total of 368 new aircraft for delivery through 2023 as follows:
|
Aircraft Type |
|
2018 |
|
2019 |
|
2020 |
|
2021 |
|
2022 |
|
Thereafter |
|
Total |
|
|
Airbus A321-200 |
|
2 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
2 |
|
|
Airbus A320/321neo(1) |
|
14 |
|
35 |
|
27 |
|
22 |
|
25 |
|
25 |
|
148 |
|
|
Airbus A330-900neo |
|
5 |
|
5 |
|
4 |
|
7 |
|
6 |
|
2 |
|
29 |
|
|
Airbus A350-900/1000 |
|
4 |
|
2 |
|
4 |
|
5 |
|
3 |
|
— |
|
18 |
|
|
Boeing 737-7/8/9 MAX |
|
12 |
|
27 |
|
27 |
|
35 |
|
27 |
|
— |
|
128 |
|
|
Boeing 787-9/10 |
|
7 |
|
12 |
|
9 |
|
7 |
|
8 |
|
— |
|
43 |
|
|
Total(2) |
|
44 |
|
81 |
|
71 |
|
76 |
|
69 |
|
27 |
|
368 |
|
|
(1) |
Our Airbus A320/321neo aircraft orders include 55 long-range variants. |
|
(2) |
In addition to the aircraft from our orderbook, we have a commitment to purchase one used Boeing 737-800 aircraft from an airline, which is scheduled for delivery in 2018. |
Airbus has informed us to expect several month delivery delays relating to certain aircraft scheduled for delivery in 2018 and 2019. The delays have been reflected in our commitment schedules above. Our leases contain lessee cancellation clauses related to aircraft delivery delays, typically for aircraft delays greater than one year. Our purchase agreements contain similar clauses. As of February 22, 2018, none of our lease contracts are subject to cancellation.
Commitments for the acquisition of these aircraft and other equipment at an estimated aggregate purchase price (including adjustments for inflation) of approximately $27.0 billion as of December 31, 2017 are as follows:
|
Years ending December 31, |
|
(in thousands) |
|
|
2018 |
|
$ |
4,029,636 |
|
2019 |
|
|
5,798,963 |
|
2020 |
|
|
5,506,214 |
|
2021 |
|
|
5,538,285 |
|
2022 |
|
|
4,678,092 |
|
Thereafter |
|
|
1,478,734 |
|
Total |
|
$ |
27,029,924 |
As of December 31, 2017, the Company had a non-binding commitment to acquire up to five A350-1000 aircraft. Deliveries of these aircraft are scheduled to commence in 2023 and continue through 2024.
We have made non‑refundable deposits on the aircraft for which we have commitments to purchase of $1.6 billion and $1.3 billion as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively, which are subject to manufacturer performance commitments. If we are unable to satisfy our purchase commitments, we may be forced to forfeit our deposits. Further, we would be exposed to breach of contract claims by our lessees and manufacturers.
88
Air Lease Corporation and Subsidiaries
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Office Lease
The Company’s lease for office space provides for step rentals over the term of the lease. Those rentals are considered in the evaluation of recording rent expense on a straight‑line basis over the term of the lease. Tenant improvement allowances received from the lessor are deferred and amortized in selling, general and administrative expenses against rent expense. The Company recorded office lease expense (net of sublease income) of $2.3 million, $2.2 million, and $2.0 million for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016, and 2015, respectively.
Commitments for minimum rentals under the non‑cancellable lease term at December 31, 2017 are as follows:
|
Years ending December 31, |
|
(in thousands) |
|
|
|
2018 |
|
$ |
2,926 |
|
|
2019 |
|
|
3,232 |
|
|
2020 |
|
|
3,111 |
|
|
2021 |
|
|
2,946 |
|
|
2022 |
|
|
3,034 |
|
|
Thereafter |
|
|
3,770 |
|
|
Total |
|
$ |
19,019 |
|
Note 9. Net Earnings Per Share
Basic net earnings per share is computed by dividing net income by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding for the period. Diluted earnings per share reflects the potential dilution that would occur if securities or other contracts to issue common stock were exercised or converted into common stock; however, potential common equivalent shares are excluded if the effect of including these shares would be anti‑dilutive. The Company’s two classes of common stock, Class A and Class B Non‑Voting, have equal rights to dividends and income, and therefore, basic and diluted earnings per share are the same for each class of common stock. As of December 31, 2017, we did not have any Class B Non-Voting common stock outstanding.
Diluted net earnings per share takes into account the potential conversion of stock options, restricted stock units, and warrants using the treasury stock method and convertible notes using the if-converted method. For the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016, and 2015, the Company did not exclude any potentially dilutive securities, whose effect would have been anti-dilutive, from the computation of diluted earnings per share. In addition, the Company excluded 1,085,049, 1,005,697, and 993,092 shares related to restricted stock units for which the performance metric had yet to be achieved as of December 31, 2017, 2016, and 2015, respectively.
89
Air Lease Corporation and Subsidiaries
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
The following table sets forth the reconciliation of basic and diluted net income per share:
|
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
Year Ended |
|
Year Ended |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
December 31, 2017 |
|
December 31, 2016 |
|
December 31, 2015 |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
(in thousands, except share and per share amounts) |
|
|||||||
|
Basic net income per share: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Numerator |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net income |
|
|
$ |
756,152 |
|
$ |
374,925 |
|
$ |
253,391 |
|
|
Denominator |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted-average common shares outstanding |
|
|
|
103,189,175 |
|
|
102,801,161 |
|
|
102,547,774 |
|
|
Basic net income per share |
|
|
$ |
7.33 |
|
$ |
3.65 |
|
$ |
2.47 |
|
|
Diluted net income per share: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Numerator |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net income |
|
|
$ |
756,152 |
|
$ |
374,925 |
|
$ |
253,391 |
|
|
Assumed conversion of convertible senior notes |
|
|
|
5,842 |
|
|
5,780 |
|
|
5,806 |
|
|
Net income plus assumed conversions |
|
|
$ |
761,994 |
|
$ |
380,705 |
|
$ |
259,197 |
|
|
Denominator |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Number of shares used in basic computation |
|
|
|
103,189,175 |
|
|
102,801,161 |
|
|
102,547,774 |
|
|
Weighted-average effect of dilutive securities |
|
|
|
8,468,389 |
|
|
7,997,566 |
|
|
8,081,091 |
|
|
Number of shares used in per share computation |
|
|
|
111,657,564 |
|
|
110,798,727 |
|
|
110,628,865 |
|
|
Diluted net income per share |
|
|
$ |
6.82 |
|
$ |
3.44 |
|
$ |
2.34 |
|
Note 10. Fair Value Measurements
Assets and Liabilities Measured at Fair Value on a Recurring and Non‑recurring Basis
The Company had no assets or liabilities which were measured at fair value on a recurring or non‑recurring basis as of December 31, 2017 or 2016.
Financial Instruments Not Measured at Fair Values
The fair value of debt financing is estimated based on the quoted market prices for the same or similar issues, or on the current rates offered to the Company for debt of the same remaining maturities, which would be categorized as a Level 2 measurement in the fair value hierarchy. The estimated fair value of debt financing as of December 31, 2017 was $10.0 billion compared to a book value of $9.8 billion. The estimated fair value of debt financing as of December 31, 2016 was $8.9 billion compared to a book value of $8.8 billion.
The following financial instruments are not measured at fair value on the Company’s consolidated balance sheet at December 31, 2017, but require disclosure of their fair values: cash and cash equivalents and restricted cash. The estimated fair value of such instruments at December 31, 2017 and 2016 approximates their carrying value as reported on the consolidated balance sheet. The fair value of all these instruments would be categorized as Level 1 in the fair value hierarchy.
Note 11. Stock‑based Compensation
On May 7, 2014, the stockholders of the Company approved the Air Lease Corporation 2014 Equity Incentive Plan (the “2014 Plan”). Upon approval of the 2014 Plan, no new awards may be granted under the Amended and Restated 2010 Equity Incentive Plan (the “2010 Plan”). As of December 31, 2017, the number of stock options (“Stock Options”) and restricted stock units (“RSUs”) authorized under the 2014 Plan is approximately 5,795,999, which includes 795,999 shares which were previously reserved for issuance under the 2010 Plan. Stock Options are generally
90
Air Lease Corporation and Subsidiaries
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
granted for a term of 10 years and generally vest over a three year period. The Company has issued RSUs with four different vesting criteria: those RSUs that vest based on the attainment of book‑value goals, those RSUs that vest based on the attainment of Total Shareholder Return (“TSR”) goals, and time based RSUs that vest ratably over a time period of three years and RSUs that cliff vest at the end of a one or two year period. Book value RSUs generally vest ratably over three years, if the performance condition has been met. Book value RSUs for which the performance metric has not been met are forfeited. The TSR RSUs vest at the end of a three year period. The number of TSR RSUs that will ultimately vest is based upon the percentile ranking of the Company’s TSR among a peer group. The number of shares that will ultimately vest will range from 0% to 200% of the RSUs initially granted depending on the extent to which the TSR metric is achieved. For disclosure purposes, we have assumed the TSR RSUs will ultimately vest at 100%. As of December 31, 2017, the Company had 1,163,700 unvested RSUs outstanding of which 640,886 are TSR RSUs.
The Company recorded $19.8 million, $16.9 million, and $17.0 million of stock‑based compensation expense for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016, and 2015, respectively.
Stock Options
The Company uses the BSM option pricing model to determine the fair value of stock options. The fair value of stock‑based payment awards on the date of grant is determined by an option‑pricing model using a number of complex and subjective variables. These variables include expected stock price volatility over the term of the awards, a risk‑free interest rate, and expected dividends.
Estimated volatility of the Company’s common stock for new grants is determined by using historical volatility of the Company’s peer group. Due to our limited operating history at the time of grant, there was no historical exercise data to provide a reasonable basis which the Company could use to estimate expected terms. Accordingly, the Company used the “simplified method” as permitted under Staff Accounting Bulletin No. 110. The risk‑free interest rate used in the option valuation model was derived from U.S. Treasury zero‑coupon issues with remaining terms similar to the expected term on the options. In accordance with ASC Topic 718, Compensation—Stock Compensation, the Company estimated forfeitures at the time of grant and revises those estimates in subsequent periods if actual forfeitures differ from those estimates. During the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016, and 2015, the Company did not grant any Stock Options.
91
Air Lease Corporation and Subsidiaries
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
A summary of stock option activity in accordance with the Company’s stock option plan for the year ended December 31, 2017 follows:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Remaining |
|
Aggregate |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Exercise |
|
Contractual Term |
|
Intrinsic Value |
|
||
|
|
|
Shares |
|
Price |
|
(in years) |
|
(in thousands)(1) |
|
||
|
Balance at December 31, 2014 |
|
3,312,158 |
|
$ |
20.40 |
|
5.49 |
|
|
46,077 |
|
|
Granted |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
Exercised |
|
(3,000) |
|
$ |
20.00 |
|
— |
|
|
49 |
|
|
Forfeited/canceled |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
Balance at December 31, 2015 |
|
3,309,158 |
|
$ |
20.40 |
|
4.50 |
|
|
43,287 |
|
|
Granted |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
Exercised |
|
(1,000) |
|
$ |
20.00 |
|
— |
|
|
14 |
|
|
Forfeited/canceled |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
Balance at December 31, 2016 |
|
3,308,158 |
|
$ |
20.40 |
|
3.50 |
|
|
46,086 |
|
|
Granted |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
Exercised |
|
(450,000) |
|
$ |
20.59 |
|
— |
|
|
9,397 |
|
|
Forfeited/canceled |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
Balance at December 31, 2017 |
|
2,858,158 |
|
$ |
20.37 |
|
2.49 |
|
|
79,230 |
|
|
Vested and exercisable as of December 31, 2017 |
|
2,858,158 |
|
$ |
20.37 |
|
2.49 |
|
|
79,230 |
|
|
(1) |
The aggregate intrinsic value is calculated as the difference between the exercise price of the underlying awards and the closing stock price of our Class A common stock as of the respective date. |
As of December 31, 2017, 2016, and 2015, all of the Company’s outstanding employee stock options had fully vested and there were no unrecognized compensation costs related to outstanding employee stock options. As a result, there was no stock-based compensation expense related to Stock Options for the year ended December 31, 2017, 2016, and 2015.
The following table summarizes additional information regarding outstanding, exercisable and vested stock options at December 31, 2017:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Options Exercisable |
||
|
|
|
Options Outstanding |
|
and Vested |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted- |
|
|
|
Weighted |
|
|
|
|
|
Average |
|
|
|
Average |
|
|
|
Number of |
|
Remaining Life |
|
Number of |
|
Remaining Life |
|
Range of exercise prices |
|
Shares |
|
(in years) |
|
Shares |
|
(in years) |
|
$20.00 |
|
2,738,158 |
|
2.46 |
|
2,738,158 |
|
2.46 |
|
$28.80 |
|
120,000 |
|
3.32 |
|
120,000 |
|
3.32 |
|
$20.00 - $28.80 |
|
2,858,158 |
|
2.49 |
|
2,858,158 |
|
2.49 |
Restricted Stock Units
Compensation cost for stock awards is measured at the grant date based on fair value and recognized over the vesting period. The fair value of book value and time based RSUs is determined based on the closing market price of the Company’s Class A common stock on the date of grant, while the fair value of TSR RSUs is determined at the grant date using a Monte Carlo simulation model. Included in the Monte Carlo simulation model were certain assumptions regarding a number of highly complex and subjective variables, such as expected volatility, risk‑free interest rate and expected dividends. To appropriately value the award, the risk‑free interest rate is estimated for the time period from the
92
Air Lease Corporation and Subsidiaries
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
valuation date until the vesting date and the historical volatilities were estimated based on a historical timeframe equal to the time from the valuation date until the end date of the performance period.
During the year ended December 31, 2017, the Company granted 505,545 RSUs of which 228,938 are TSR RSUs. The following table summarizes the activities for our unvested RSUs for the year ended December 31, 2017:
|
|
|
Unvested Restricted Stock Units |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Average |
|
|
|
|
|
Number of |
|
Grant-Date |
|
|
|
|
|
Shares |
|
Fair Value |
|
|
|
Unvested at December 31, 2016 |
|
1,129,045 |
|
$ |
37.47 |
|
|
Granted |
|
505,545 |
|
$ |
45.05 |
|
|
Vested |
|
(367,016) |
|
$ |
36.07 |
|
|
Forfeited/canceled |
|
(103,874) |
|
$ |
48.22 |
|
|
Unvested at December 31, 2017 |
|
1,163,700 |
|
$ |
40.24 |
|
At December 31, 2017, the outstanding RSUs are expected to vest as follows: 2018—452,169; 2019—406,764; and 2020—304,767. The Company recorded $19.8 million, $16.9 million, and $17.0 million of stock‑based compensation expense related to RSUs for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016, and 2015, respectively.
As of December 31, 2017 there was $46.8 million of unrecognized compensation cost, adjusted for estimated forfeitures, related to unvested stock‑based payments granted to employees. Total unrecognized compensation cost will be adjusted for future changes in estimated forfeitures and is expected to be recognized over a weighted average remaining period of 1.74 years.
Note 12. Investments
On November 4, 2014, a wholly owned subsidiary of the Company entered into an agreement with a co-investment vehicle arranged by Napier Park to participate in a joint venture and formed Blackbird Capital I, LLC (“Blackbird I”) for the purpose of investing in commercial aircraft and leasing them to airlines around the globe. We will also provide management services to the joint venture for a fee based upon aircraft assets under management. The Company's non-controlling interest in Blackbird I is 9.5% and it is accounted for as an investment under the equity method of accounting. The Company's investment in Blackbird I was $32.3 million and $25.1 million as of December 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively, and is included in other assets on the Consolidated Balance Sheets.
On August 1, 2017, a wholly owned subsidiary of the Company entered into an agreement with a co-investment vehicle arranged by Napier Park to participate in a joint venture and formed Blackbird Capital II, LLC (''Blackbird II'') for the purpose of investing in commercial aircraft and leasing them to airlines around the globe. We provide management services to the joint venture for a fee based upon aircraft assets under management. The Company’s non-controlling interest in Blackbird II is 9.5% and will be accounted for as an investment under the equity method of accounting. The Company's investment in Blackbird II was $3.3 million as of December 31, 2017. As of December 31, 2017, the Company's total unfunded commitment to Blackbird II was $19.0 million.
Note 13. Litigation
On April 24, 2012, the Company was named as a defendant in a complaint filed in the Superior Court of the State of California for the County of Los Angeles by AIG and ILFC (the “AIG/ILFC Complaint”). The complaint also named as defendants certain executive officers and employees of the Company.
93
Air Lease Corporation and Subsidiaries
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
Among other things, the complaint, as amended, alleges breach of fiduciary duty, misappropriation of trade secrets, the wrongful recruitment of ILFC employees, and the wrongful diversion of potential ILFC leasing opportunities.
On August 15, 2013, the Company filed a cross‑complaint against ILFC and AIG. The cross‑complaint, as amended, alleges breach of contract for the sale of goods in connection with an agreement entered into by AIG, acting on behalf of ILFC, in January 2010 to sell 25 aircraft to the entity that became Air Lease Corporation.
The matters set forth in the AIG/ILFC Complaint are collectively referred to as the "litigation."
On April 22, 2015, the Company and certain executive officers and employees of the Company entered into a settlement agreement and release ("the Settlement Agreement") with AIG, ILFC, and ILFC’s parent, AerCap Holdings N.V., to settle all ongoing litigation. Pursuant to the terms of the Settlement Agreement, (i) all claims and counterclaims asserted in the litigation were dismissed with prejudice, (ii) each of the parties to the litigation received full releases of all claims and counterclaims asserted in the litigation, and (iii) the Company agreed to pay AIG the sum of $72.0 million. The Company recorded settlement expense of $72.0 million on the Consolidated Statement of Income for the year ended December 31, 2015. The parties to the Settlement Agreement agreed that the settlement was intended solely as a compromise of disputed claims, and that no party admits any wrongdoing or liability with respect to any matter alleged in the litigation. On April 24, 2015, the parties filed a request for dismissal which was entered on April 29, 2015. For the years ended December 2017, 2016, and 2015, we received $1.0 million, $5.25 million, and $4.5 million in insurance recoveries related to this matter, respectively, which are included in aircraft sales, trading and other revenue in our Consolidated Statements of Income.
Note 14. Quarterly Financial Data (unaudited)
The following table presents our unaudited quarterly results of operations for the two‑year period ended December 31, 2017.
|
|
|
Quarter Ended |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
Mar 31, |
|
Jun 30, |
|
Sep 30, |
|
Dec 31, |
|
Mar 31, |
|
Jun 30, |
|
Sep 30, |
|
Dec 31, |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
2016 |
|
2016 |
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
|
2017 |
|
2017 |
|
2017 |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
(in thousands, except per share amounts) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Revenues |
|
$ |
343,328 |
|
$ |
350,139 |
|
$ |
355,101 |
|
$ |
370,487 |
|
$ |
360,187 |
|
$ |
380,957 |
|
$ |
376,765 |
|
$ |
398,471 |
|
|
Income before taxes |
|
|
143,991 |
|
|
142,271 |
|
|
144,573 |
|
|
149,403 |
|
|
133,878 |
|
|
155,869 |
|
|
154,119 |
|
|
165,664 |
|
|
Net income |
|
|
92,858 |
|
|
91,803 |
|
|
93,276 |
|
|
96,988 |
|
|
84,937 |
|
|
100,925 |
|
|
99,188 |
|
|
471,102 |
|
|
Net income per share: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic |
|
$ |
0.90 |
|
$ |
0.89 |
|
$ |
0.91 |
|
$ |
0.94 |
|
$ |
0.83 |
|
$ |
0.98 |
|
$ |
0.96 |
|
$ |
4.56 |
|
|
Diluted |
|
$ |
0.85 |
|
$ |
0.84 |
|
$ |
0.86 |
|
$ |
0.89 |
|
$ |
0.78 |
|
$ |
0.92 |
|
$ |
0.90 |
|
$ |
4.22 |
|
The sum of quarterly earnings per share amounts may not equal the annual amount reported since per share amounts are computed independently for each period presented.
Note 15. Subsequent Events
On February 20, 2018, our board of directors approved a quarterly cash dividend of $0.10 per share on our outstanding common stock. The dividend will be paid on April 6, 2018 to holders of record of our common stock as of March 20, 2018.
94
Air Lease Corporation and Subsidiaries
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
In January 2018, we issued (i) $550.0 million in aggregate principal amount of senior unsecured notes due 2021 that bear interest at a rate of 2.50% and (ii) $700.0 million in aggregate principal amount of senior unsecured notes due 2025 that bear interest at a rate of 3.25%.
95
ITEM 9. CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE
None.
ITEM 9A. CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
We maintain disclosure controls and procedures that are designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed in our filings under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the periods specified in the rules and forms of the Securities and Exchange Commission, and such information is accumulated and communicated to our management, including the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer (collectively, the “Certifying Officers”), as appropriate, to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure. In designing and evaluating the disclosure controls and procedures, management recognized that any controls and procedures, no matter how well designed and operated, can provide only reasonable assurance of achieving the desired control objectives, as the Company’s controls are designed to do, and management necessarily was required to apply its judgment in evaluating the risk related to controls and procedures.
We have evaluated, under the supervision and with the participation of management, including the Certifying Officers, the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures, as defined in Rules 13a‑15(e) and 15d‑15(e) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, as of December 31, 2017. Based on that evaluation, our Certifying Officers have concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures were effective at December 31, 2017.
Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting. The Company’s internal control system was designed to provide reasonable assurance to the Company’s management and Board of Directors regarding the preparation and fair presentation of published financial statements.
Our management assessed the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017. In making this assessment, it used the criteria set forth by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO) in Internal Control—Integrated Framework (2013). Based upon its assessment, our management believes that, as of December 31, 2017, the Company’s internal control over financial reporting is effective based on these criteria.
KPMG LLP, the independent registered public accounting firm that audited the consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report on Form 10‑K, has issued an audit report on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2017, which is included herein.
Changes in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
There were no changes in our internal control over financial reporting during the quarter ended December 31, 2017 that materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
None.
96
ITEM 10. DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
Executive Officers of the Company
Except as set forth below or as contained in Part I above, under “Executive Officers of the Company”, the other information required by this item is incorporated by reference to the “Corporate Governance and Board Matters”, the “Proposal 1: Election of Directors” and “Other Matters” sections of our Proxy Statement for the 2018 Annual Meeting of Stockholders (the “2018 Proxy Statement”), which will be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission no later than April 30, 2018.
Code of Business Conduct and Ethics
We have adopted a Code of Business Conduct and Ethics for our directors, officers (including our principal executive officer, principal financial officer and principal accounting officer) and employees. The Code of Business Conduct and Ethics is available on our website at www.airleasecorp.com under the Investors tab.
Within the time period required by the Securities and Exchange Commission and the New York Stock Exchange, we will post on our website at www.airleasecorp.com under the Investors tab any amendment to our Code of Business Conduct and Ethics.
Corporate Governance Guidelines
We have adopted Corporate Governance Guidelines that are available on our website at www.airleasecorp.com under the Investors tab.
ITEM 11. EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION
The information required by this item is incorporated by reference to the “Corporate Governance and Board Matters” and the “Executive Compensation” sections of the 2018 Proxy Statement.
ITEM 12. SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS
The information required by this item is incorporated by reference to the “Other Matters” section of the 2018 Proxy Statement, except for the information required by Item 201(d) of Regulation S‑K, which is provided in Item 5 of Part II above.
ITEM 13. CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE
The information required by this item is incorporated by reference to the “Corporate Governance and Board Matters” and the “Proposal 1: Election of Directors” sections of our 2018 Proxy Statement.
ITEM 14. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING FEES AND SERVICES
The information required by this item is incorporated by reference to the “Independent Auditor Fees and Services” section of our 2018 Proxy Statement.
97
ITEM 15. EXHIBITS, FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES
(a)
1. Consolidated Financial Statements
The following documents are filed as part of this Annual Report on Form 10‑K:
|
|
|
Page |
|
|
|
67 |
|
|
|
Financial Statements |
|
|
|
|
|
69 |
|
|
|
|
70 |
|
|
|
|
71 |
|
|
|
|
72 |
|
|
|
|
73 |
|
2. Financial Statement Schedules
Financial statement schedules have been omitted as they are not required, not applicable, or the required information is otherwise included in the consolidated financial statements or the notes thereto.
3. Exhibits
|
Exhibit |
|
|
|
|
|
Incorporated by Reference |
||||
|
Number |
|
Exhibit Description |
|
Form |
|
File No. |
|
Exhibit |
|
Filing Date |
|
3.1 |
|
Restated Certificate of Incorporation of Air Lease Corporation |
|
S‑1 |
|
333‑171734 |
|
3.1 |
|
January 14, 2011 |
|
3.2 |
|
|
8‑K |
|
001‑35121 |
|
3.2 |
|
June 20, 2016 |
|
|
4.1 |
|
|
S‑1 |
|
333‑171734 |
|
4.1 |
|
March 25, 2011 |
|
|
4.2 |
|
|
S‑1 |
|
333‑171734 |
|
4.2 |
|
January 14, 2011 |
|
|
4.3 |
|
|
S‑3 |
|
333‑184382 |
|
4.4 |
|
October 12, 2012 |
|
|
4.4 |
|
|
8-K |
|
001-35121 |
|
4.2 |
|
February 5, 2013 |
|
98
|
Exhibit |
|
|
|
|
|
Incorporated by Reference |
||||
|
Number |
|
Exhibit Description |
|
Form |
|
File No. |
|
Exhibit |
|
Filing Date |
|
4.5 |
|
|
8-K |
|
001-35121 |
|
4.2 |
|
November 19, 2013 |
|
|
4.6 |
|
|
8-K |
|
001-35121 |
|
4.2 |
|
January 23, 2014 |
|
|
4.7 |
|
|
8-K |
|
001-35121 |
|
4.2 |
|
March 11, 2014 |
|
|
4.8 |
|
|
8-K |
|
001-35121 |
|
4.2 |
|
September 16, 2014 |
|
|
4.9 |
|
|
8-K |
|
001-35121 |
|
4.3 |
|
September 16, 2014 |
|
|
4.10 |
|
|
8-K |
|
001-35121 |
|
4.2 |
|
January 14, 2015 |
|
|
4.11 |
|
|
8-K |
|
001-35121 |
|
4.2 |
|
August 18, 2015 |
|
|
4.12 |
|
|
8-K |
|
001-35121 |
|
4.2 |
|
April 11, 2016 |
|
99
|
Exhibit |
|
|
|
|
|
Incorporated by Reference |
||||
|
Number |
|
Exhibit Description |
|
Form |
|
File No. |
|
Exhibit |
|
Filing Date |
|
4.13 |
|
|
8-K |
|
001-35121 |
|
4.2 |
|
August 15, 2016 |
|
|
4.14 |
|
|
8-K |
|
001-35121 |
|
4.2 |
|
October 3, 2016 |
|
|
4.15 |
|
|
8-K |
|
001-35121 |
|
4.2 |
|
March 8, 2017 |
|
|
4.16 |
|
|
8-K |
|
001-35121 |
|
4.2 |
|
June 12, 2017 |
|
|
4.17 |
|
|
8-K |
|
001-35121 |
|
4.2 |
|
November 20, 2017 |
|
|
4.18 |
8-K |
001-35121 |
4.3 |
November 20, 2017 |
||||||
|
Certain instruments defining the rights of holders of long‑term debt of Air Lease Corporation and all of its subsidiaries for which consolidated or unconsolidated financial statements are required to be filed are being omitted pursuant to paragraph (b)(4)(iii)(A) of Item 601 of Regulation S‑K. Air Lease Corporation agrees to furnish a copy of any such instrument to the Securities and Exchange Commission upon request. |
||||||||||
|
10.1 |
|
|
8‑K |
|
001‑35121 |
|
10.1 |
|
June 24, 2013 |
|
100
|
Exhibit |
|
|
|
|
|
Incorporated by Reference |
||||
|
Number |
|
Exhibit Description |
|
Form |
|
File No. |
|
Exhibit |
|
Filing Date |
|
10.2 |
|
|
8-K |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.1 |
|
July 29, 2014 |
|
|
10.3 |
|
|
10-Q |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.5 |
|
May 8, 2014 |
|
|
10.4 |
|
|
8-K |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.1 |
|
June 2, 2015 |
|
|
10.5 |
|
|
8-K |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.2 |
|
June 2, 2015 |
|
|
10.6 |
|
|
10-K |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.7 |
|
February 25, 2016 |
|
|
10.7 |
|
|
10-K |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.8 |
|
February 25, 2016 |
|
|
10.8 |
|
|
8-K |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.1 |
|
June 1, 2016 |
|
|
10.9 |
|
|
8-K |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.2 |
|
June 1, 2016 |
|
101
|
Exhibit |
|
|
|
|
|
Incorporated by Reference |
||||
|
Number |
|
Exhibit Description |
|
Form |
|
File No. |
|
Exhibit |
|
Filing Date |
|
10.10 |
|
|
10-K |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.10 |
|
February 23, 2017 |
|
|
10.11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Filed herewith |
|
|
10.12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Filed herewith |
|
|
10.13 |
|
|
10-K |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.11 |
|
February 23, 2017 |
|
|
10.14 |
|
|
10-K |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.12 |
|
February 23, 2017 |
|
|
10.15 |
|
|
10-Q |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.3 |
|
May 4, 2017 |
|
|
10.16 |
|
|
10-Q |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.4 |
|
May 4, 2017 |
|
102
|
Exhibit |
|
|
|
|
|
Incorporated by Reference |
||||
|
Number |
|
Exhibit Description |
|
Form |
|
File No. |
|
Exhibit |
|
Filing Date |
|
10.17
|
|
|
10-Q |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.5 |
|
May 4, 2017 |
|
|
10.18 |
|
|
10-Q |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.8 |
|
November 9, 2017 |
|
|
10.19 |
|
|
S‑1 |
|
333‑171734 |
|
10.2 |
|
January 14, 2011 |
|
|
10.20† |
|
|
10‑Q |
|
001‑35121 |
|
10.3 |
|
November 7, 2013 |
|
|
10.21† |
|
|
10-Q |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.2 |
|
November 6, 2014 |
|
|
10.22† |
|
|
10-Q |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.19 |
|
August 4, 2016 |
|
|
10.23† |
|
|
10-Q |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.20 |
|
August 4, 2016 |
|
|
10.24† |
|
|
10-Q |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.21 |
|
August 4, 2016 |
|
|
10.25† |
|
|
10-Q |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.22 |
|
August 4, 2016 |
|
|
10.26† |
|
|
10-K |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.21 |
|
February 23, 2017 |
|
103
|
Exhibit |
|
|
|
|
|
Incorporated by Reference |
||||
|
Number |
|
Exhibit Description |
|
Form |
|
File No. |
|
Exhibit |
|
Filing Date |
|
10.27† |
|
|
10-Q |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.6 |
|
November 9, 2017 |
|
|
10.28† |
|
|
10-Q |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.7 |
|
November 9, 2017 |
|
|
10.29† |
|
|
10‑Q |
|
001‑35121 |
|
10.2 |
|
May 9, 2013 |
|
|
10.30† |
|
|
10-Q |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.2 |
|
May 7, 2015 |
|
|
10.31† |
|
|
10-Q |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.3 |
|
May 7, 2015 |
|
|
10.32† |
|
|
10‑Q |
|
001‑35121 |
|
10.1 |
|
November 5, 2015 |
|
|
10.33† |
|
|
10‑Q |
|
001‑35121 |
|
10.15 |
|
August 4, 2016 |
|
|
10.34† |
|
|
10‑Q |
|
001‑35121 |
|
10.16 |
|
August 4, 2016 |
|
|
10.35† |
|
|
10-K |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.28 |
|
February 23, 2017 |
|
|
10.36† |
|
|
10‑Q |
|
001‑35121 |
|
10.1 |
|
November 9, 2017 |
|
|
10.37† |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Filed herewith |
|
|
10.38† |
|
|
10‑Q |
|
001‑35121 |
|
10.1 |
|
November 7, 2013 |
|
|
10.39† |
|
|
10‑Q |
|
001‑35121 |
|
10.12 |
|
May 4, 2017 |
|
104
|
Exhibit |
|
|
|
|
|
Incorporated by Reference |
||||
|
Number |
|
Exhibit Description |
|
Form |
|
File No. |
|
Exhibit |
|
Filing Date |
|
10.40† |
|
|
10‑Q |
|
001‑35121 |
|
10.2 |
|
November 7, 2013 |
|
|
10.41† |
|
|
10-Q |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.1 |
|
November 6, 2014 |
|
|
10.42† |
|
|
10‑Q |
|
001‑35121 |
|
10.13 |
|
May 4, 2017 |
|
|
10.43† |
|
|
10-Q |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.18 |
|
August 4, 2016 |
|
|
10.44† |
|
|
10-K |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.35 |
|
February 23, 2017 |
|
|
10.45† |
|
|
10-K |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.36 |
|
February 23, 2017 |
|
|
10.46† |
|
|
10‑Q |
|
001‑35121 |
|
10.14 |
|
May 4, 2017 |
|
|
10.47† |
|
|
10‑Q |
|
001‑35121 |
|
10.15 |
|
May 4, 2017 |
|
|
10.48† |
|
|
10‑Q |
|
001‑35121 |
|
10.7 |
|
August 3, 2017 |
|
|
10.49† |
|
|
10‑Q |
|
001‑35121 |
|
10.8 |
|
August 3, 2017 |
|
|
10.50† |
|
|
10‑Q |
|
001‑35121 |
|
10.9 |
|
August 3, 2017 |
|
|
10.51† |
|
|
10‑Q |
|
001‑35121 |
|
10.10 |
|
August 3, 2017 |
|
|
10.52† |
|
|
10‑Q |
|
001‑35121 |
|
10.4 |
|
November 9, 2017 |
|
105
|
Exhibit |
|
|
|
|
|
Incorporated by Reference |
||||
|
Number |
|
Exhibit Description |
|
Form |
|
File No. |
|
Exhibit |
|
Filing Date |
|
10.53† |
|
|
10‑Q |
|
001‑35121 |
|
10.5 |
|
November 9, 2017 |
|
|
10.54† |
|
|
10-Q |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.2 |
|
August 9, 2012 |
|
|
10.55† |
|
|
10-Q |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.7 |
|
August 4, 2016 |
|
|
10.56† |
|
|
10-Q |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.4 |
|
November 6, 2014 |
|
|
10.57† |
|
|
10-Q |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.5 |
|
November 6, 2014 |
|
|
10.58† |
|
|
10-Q |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.8 |
|
August 4, 2016 |
|
|
10.59† |
|
|
10-Q/A |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.4 |
|
September 2, 2016 |
|
|
10.60† |
|
|
10-Q |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.9 |
|
August 4, 2016 |
|
|
10.61† |
|
|
10-Q |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.10 |
|
August 4, 2016 |
|
|
10.62† |
|
|
10-Q |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.11 |
|
August 4, 2016 |
|
|
10.63† |
|
|
10-Q |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.12 |
|
August 4, 2016 |
|
|
10.64† |
|
|
10-Q |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.13 |
|
August 4, 2016 |
|
|
10.65† |
|
|
10-Q |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.14 |
|
August 4, 2016 |
|
106
|
Exhibit |
|
|
|
|
|
Incorporated by Reference |
||||
|
Number |
|
Exhibit Description |
|
Form |
|
File No. |
|
Exhibit |
|
Filing Date |
|
10.66† |
|
|
10-Q |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.9 |
|
May 4, 2017 |
|
|
10.67† |
|
|
10-Q |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.10 |
|
May 4, 2017 |
|
|
10.68† |
|
|
10-Q |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.11 |
|
May 4, 2017 |
|
|
10.69† |
|
|
10-Q |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.3 |
|
August 3, 2017 |
|
|
10.70† |
|
|
10-Q |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.4 |
|
August 3, 2017 |
|
|
10.71† |
|
|
10-Q |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.5 |
|
August 3, 2017 |
|
|
10.72† |
|
|
10-Q |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.6 |
|
August 3, 2017 |
|
|
10.73† |
|
|
10-Q |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.2 |
|
November 9, 2017 |
|
|
10.74† |
|
|
10-Q |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.3 |
|
November 9, 2017 |
|
|
10.75† |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Filed herewith |
|
|
10.76† |
|
|
10-Q/A |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.1 |
|
September 2, 2016 |
|
|
10.77† |
|
|
10-Q |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.17 |
|
August 4, 2016 |
|
|
10.78† |
|
|
10-Q |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.2 |
|
August 3, 2017 |
|
107
|
Exhibit |
|
|
|
|
|
Incorporated by Reference |
||||
|
Number |
|
Exhibit Description |
|
Form |
|
File No. |
|
Exhibit |
|
Filing Date |
|
10.79† |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Filed herewith |
|
|
10.80† |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Filed herewith |
|
|
10.81§ |
|
|
10‑Q |
|
001‑35121 |
|
10.3 |
|
May 9, 2013 |
|
|
10.82§ |
|
|
S‑1/A |
|
333‑171734 |
|
10.5 |
|
February 22, 2011 |
|
|
10.83§ |
|
|
10‑Q |
|
001‑35121 |
|
10.4 |
|
May 9, 2013 |
|
|
10.84§ |
|
Air Lease Corporation Amended and Restated Deferred Bonus Plan |
|
S‑1 |
|
333‑171734 |
|
10.17 |
|
February 22, 2011 |
|
10.85§ |
|
|
10-Q |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.1 |
|
May 8, 2014 |
|
|
10.86§ |
|
|
10-Q |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.2 |
|
May 8, 2014 |
|
|
10.87§ |
|
|
S-8 |
|
333-195755 |
|
4.5 |
|
May 7, 2014 |
|
|
10.88§ |
|
|
S-8 |
|
333-195755 |
|
4.6 |
|
May 7, 2014 |
|
|
10.89§ |
|
|
10-K |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.4 |
|
February 26, 2015 |
|
|
10.90§ |
|
|
10-K |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.41 |
|
February 26, 2015 |
|
|
10.91§ |
|
|
10-Q |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.1 |
|
May 5, 2016 |
|
|
10.92§ |
|
|
10-Q |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.1 |
|
August 4, 2016 |
|
108
|
Exhibit |
|
|
|
|
|
Incorporated by Reference |
||||
|
Number |
|
Exhibit Description |
|
Form |
|
File No. |
|
Exhibit |
|
Filing Date |
|
10.93§ |
|
|
10-Q |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.6 |
|
May 4, 2017 |
|
|
10.94§ |
|
|
10-Q |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.7 |
|
May 4, 2017 |
|
|
10.95§ |
|
|
10-Q |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.8 |
|
May 4, 2017 |
|
|
10.96§ |
|
|
10-Q |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.2 |
|
August 4, 2016 |
|
|
10.97§ |
|
|
10-Q |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.3 |
|
August 4, 2016 |
|
|
10.98 |
|
Form of Indemnification Agreement with directors and officers |
|
S‑1 |
|
333‑171734 |
|
10.12 |
|
February 22, 2011 |
|
10.99§ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Filed herewith |
|
|
10.100§ |
|
|
10-Q |
|
001-35121 |
|
10.1 |
|
May 4, 2017 |
|
|
12.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Filed herewith |
|
|
21.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Filed herewith |
|
|
23.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Filed herewith |
|
|
31.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Filed herewith |
|
|
31.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Filed herewith |
|
109
|
Exhibit |
|
|
|
|
|
Incorporated by Reference |
||||
|
Number |
|
Exhibit Description |
|
Form |
|
File No. |
|
Exhibit |
|
Filing Date |
|
32.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Furnished herewith |
|
|
32.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Furnished herewith |
|
|
101 |
|
The following materials from Air Lease Corporation’s Annual Report on Form 10‑K for the year ended December 31, 2017, formatted in eXtensible Business Reporting Language (XBRL): (i) Consolidated Statements of Income, (ii) Consolidated Balance Sheets, (iii) Consolidated Statements of Stockholders’ Equity, (iv) Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows, and (v) Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Filed herewith |
†The Company has omitted confidential portions of the referenced exhibit and filed such confidential portions separately with the Securities and Exchange Commission pursuant to a request for confidential treatment under Rule 406 promulgated under the Securities Act of 1933.
§Management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement.
None
110
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized, on February 22, 2018.
|
|
Air Lease Corporation |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
By: |
/s/ Gregory B. Willis |
|
|
|
Gregory B. Willis Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial Officer and Principal Accounting Officer) |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated:
|
Signature |
|
Title |
|
Date |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Steven F. Udvar‑Házy |
|
Executive Chairman of the Board of Directors |
|
February 22, 2018 |
|
Steven F. Udvar‑Házy |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ John L. Plueger |
|
Chief Executive Officer and President (Principal Executive Officer) |
|
February 22, 2018 |
|
John L. Plueger |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Matthew J. Hart |
|
Director |
|
February 22, 2018 |
|
Matthew J. Hart |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Cheryl Gordon Krongard |
|
Director |
|
February 22, 2018 |
|
Cheryl Gordon Krongard |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Director |
|
February 22, 2018 |
|
Marshall O. Larsen |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Robert A. Milton |
|
Director |
|
February 22, 2018 |
|
Robert A. Milton |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Ian M. Saines |
|
Director |
|
February 22, 2018 |
|
Ian M. Saines |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Dr. Ronald D. Sugar |
|
Director |
|
February 22, 2018 |
|
Dr. Ronald D. Sugar |
|
|
111
