Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-32.2 - EXHIBIT 32.2 - AES CORP | aes09302017exhibit322.htm |
| EX-32.1 - EXHIBIT 32.1 - AES CORP | aes09302017exhibit321.htm |
| EX-31.2 - EXHIBIT 31.2 - AES CORP | aes09302017exhibit312.htm |
| EX-31.1 - EXHIBIT 31.1 - AES CORP | aes09302017exhibit311.htm |
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
WASHINGTON, D.C. 20549
______________________________________________________________________________________________
FORM 10-Q
(Mark One)
x | QUARTERLY REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the Quarterly Period Ended September 30, 2017
or
¨ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
Commission file number 1-12291

THE AES CORPORATION
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
Delaware | 54 1163725 | |
(State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) | |
4300 Wilson Boulevard Arlington, Virginia | 22203 | |
(Address of principal executive offices) | (Zip Code) | |
(703) 522-1315
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code:
______________________________________________________________________________________________
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes x No ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes x No ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer”, “accelerated filer”, “smaller reporting company”, and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
Large accelerated filer x | Accelerated filer ¨ | Smaller reporting company ¨ | Emerging growth company ¨ | |||
Non-accelerated filer ¨ | (Do not check if a smaller reporting company) | |||||
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes ¨ No x
______________________________________________________________________________________________
The number of shares outstanding of Registrant’s Common Stock, par value $0.01 per share, on October 27, 2017 was 660,386,566.
THE AES CORPORATION
FORM 10-Q
FOR THE QUARTERLY PERIOD ENDED SEPTEMBER 30, 2017
TABLE OF CONTENTS
ITEM 1. | ||
ITEM 2. | ||
ITEM 3. | ||
ITEM 4. | ||
ITEM 1. | ||
ITEM 1A. | ||
ITEM 2. | ||
ITEM 3. | ||
ITEM 4. | ||
ITEM 5. | ||
ITEM 6. | ||
GLOSSARY OF TERMS
The following terms and acronyms appear in the text of this report and have the definitions indicated below:
Adjusted EPS | Adjusted Earnings Per Share, a non-GAAP measure |
Adjusted PTC | Adjusted Pretax Contribution, a non-GAAP measure of operating performance |
AFS | Available For Sale |
AOCL | Accumulated Other Comprehensive Loss |
ASC | Accounting Standards Codification |
ASU | Accounting Standards Update |
BNDES | Brazilian Development Bank |
CAA | United States Clean Air Act |
CAMMESA | Wholesale Electric Market Administrator in Argentina |
CDPQ | La Caisse de depot et placement du Quebec |
CHP | Combined Heat and Power |
COFINS | Contribution for the Financing of Social Security |
DP&L | The Dayton Power & Light Company |
DPL | DPL Inc. |
DPLER | DPL Energy Resources, Inc. |
DPP | Dominican Power Partners, LDC |
EPA | United States Environmental Protection Agency |
EPC | Engineering, Procurement and Construction |
EURIBOR | Euro Interbank Offered Rate |
FASB | Financial Accounting Standards Board |
FERC | Federal Energy Regulatory Commission |
FX | Foreign Exchange |
GAAP | Generally Accepted Accounting Principles in the United States |
GHG | Greenhouse Gas |
IPALCO | IPALCO Enterprises, Inc. |
IPL | Indianapolis Power & Light Company |
kWh | Kilowatt Hours |
LIBOR | London Interbank Offered Rate |
LNG | Liquid Natural Gas |
MATS | Mercury and Air Toxics Standards |
MMI | Mini Maritsa Iztok (state-owned electricity public supplier in Bulgaria) |
MW | Megawatts |
MWh | Megawatt Hours |
NCI | Noncontrolling Interest |
NEK | Natsionalna Elektricheska Kompania (state-owned electricity public supplier in Bulgaria) |
NM | Not Meaningful |
NOV | Notice of Violation |
NOX | Nitrogen Oxides |
NPDES | National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System |
PIS | Program of Social Integration |
PJM | PJM Interconnection, LLC |
PPA | Power Purchase Agreement |
PREPA | Puerto Rico Electric Power Authority |
RSU | Restricted Stock Unit |
SIC | Central Interconnected Electricity System |
SING | Norte Grande Interconnected Electricity System |
SBU | Strategic Business Unit |
SEC | United States Securities and Exchange Commission |
SO2 | Sulfur Dioxide |
U.S. | United States |
USD | United States Dollar |
VAT | Value-Added Tax |
VIE | Variable Interest Entity |
1
PART I: FINANCIAL INFORMATION
ITEM 1. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
THE AES CORPORATION
Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheets
(Unaudited)
September 30, 2017 | December 31, 2016 | ||||||
(in millions, except share and per share data) | |||||||
ASSETS | |||||||
CURRENT ASSETS | |||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 1,398 | $ | 1,305 | |||
Restricted cash | 437 | 278 | |||||
Short-term investments | 563 | 798 | |||||
Accounts receivable, net of allowance for doubtful accounts of $90 and $111, respectively | 2,357 | 2,166 | |||||
Inventory | 660 | 630 | |||||
Prepaid expenses | 89 | 83 | |||||
Other current assets | 1,080 | 1,151 | |||||
Current assets of held-for-sale businesses | 76 | — | |||||
Total current assets | 6,660 | 6,411 | |||||
NONCURRENT ASSETS | |||||||
Property, Plant and Equipment: | |||||||
Land | 798 | 779 | |||||
Electric generation, distribution assets and other | 29,916 | 28,539 | |||||
Accumulated depreciation | (10,199 | ) | (9,528 | ) | |||
Construction in progress | 3,841 | 3,057 | |||||
Property, plant and equipment, net | 24,356 | 22,847 | |||||
Other Assets: | |||||||
Investments in and advances to affiliates | 1,164 | 621 | |||||
Debt service reserves and other deposits | 786 | 593 | |||||
Goodwill | 1,157 | 1,157 | |||||
Other intangible assets, net of accumulated amortization of $563 and $519, respectively | 474 | 359 | |||||
Deferred income taxes | 760 | 781 | |||||
Service concession assets, net of accumulated amortization of $182 and $114, respectively | 1,382 | 1,445 | |||||
Other noncurrent assets | 2,095 | 1,905 | |||||
Total other assets | 7,818 | 6,861 | |||||
TOTAL ASSETS | $ | 38,834 | $ | 36,119 | |||
LIABILITIES AND EQUITY | |||||||
CURRENT LIABILITIES | |||||||
Accounts payable | $ | 2,091 | $ | 1,656 | |||
Accrued interest | 353 | 247 | |||||
Accrued and other liabilities | 2,020 | 2,066 | |||||
Non-recourse debt, includes $439 and $273, respectively, related to variable interest entities | 2,257 | 1,303 | |||||
Current liabilities of held-for-sale businesses | 15 | — | |||||
Total current liabilities | 6,736 | 5,272 | |||||
NONCURRENT LIABILITIES | |||||||
Recourse debt | 4,954 | 4,671 | |||||
Non-recourse debt, includes $1,305 and $1,502, respectively, related to variable interest entities | 14,822 | 14,489 | |||||
Deferred income taxes | 742 | 804 | |||||
Pension and other postretirement liabilities | 1,387 | 1,396 | |||||
Other noncurrent liabilities | 3,047 | 3,005 | |||||
Total noncurrent liabilities | 24,952 | 24,365 | |||||
Commitments and Contingencies (see Note 8) | |||||||
Redeemable stock of subsidiaries | 967 | 782 | |||||
EQUITY | |||||||
THE AES CORPORATION STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | |||||||
Common stock ($0.01 par value, 1,200,000,000 shares authorized; 816,312,913 issued and 660,386,566 outstanding at September 30, 2017 and 816,061,123 issued and 659,182,232 outstanding at December 31, 2016) | 8 | 8 | |||||
Additional paid-in capital | 8,670 | 8,592 | |||||
Accumulated deficit | (934 | ) | (1,146 | ) | |||
Accumulated other comprehensive loss | (2,666 | ) | (2,756 | ) | |||
Treasury stock, at cost (155,926,347 and 156,878,891 shares at September 30, 2017 and December 31, 2016, respectively) | (1,892 | ) | (1,904 | ) | |||
Total AES Corporation stockholders’ equity | 3,186 | 2,794 | |||||
NONCONTROLLING INTERESTS | 2,993 | 2,906 | |||||
Total equity | 6,179 | 5,700 | |||||
TOTAL LIABILITIES AND EQUITY | $ | 38,834 | $ | 36,119 | |||
See Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements.
2
THE AES CORPORATION
Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations
(Unaudited)
Three Months Ended September 30, | Nine Months Ended September 30, | ||||||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2017 | 2016 | ||||||||||||
(in millions, except per share data) | |||||||||||||||
Revenue: | |||||||||||||||
Regulated | $ | 1,793 | $ | 1,785 | $ | 5,157 | $ | 4,926 | |||||||
Non-Regulated | 1,839 | 1,757 | 5,437 | 5,116 | |||||||||||
Total revenue | 3,632 | 3,542 | 10,594 | 10,042 | |||||||||||
Cost of Sales: | |||||||||||||||
Regulated | (1,574 | ) | (1,623 | ) | (4,640 | ) | (4,521 | ) | |||||||
Non-Regulated | (1,347 | ) | (1,231 | ) | (3,980 | ) | (3,750 | ) | |||||||
Total cost of sales | (2,921 | ) | (2,854 | ) | (8,620 | ) | (8,271 | ) | |||||||
Operating margin | 711 | 688 | 1,974 | 1,771 | |||||||||||
General and administrative expenses | (52 | ) | (40 | ) | (155 | ) | (135 | ) | |||||||
Interest expense | (353 | ) | (354 | ) | (1,034 | ) | (1,086 | ) | |||||||
Interest income | 101 | 110 | 291 | 365 | |||||||||||
Loss on extinguishment of debt | (49 | ) | (16 | ) | (44 | ) | (12 | ) | |||||||
Other expense | (47 | ) | (13 | ) | (95 | ) | (42 | ) | |||||||
Other income | 18 | 18 | 105 | 43 | |||||||||||
Gain (loss) on disposal and sale of businesses | (1 | ) | — | (49 | ) | 30 | |||||||||
Asset impairment expense | (2 | ) | (79 | ) | (260 | ) | (473 | ) | |||||||
Foreign currency transaction gains (losses) | 21 | (20 | ) | 13 | (16 | ) | |||||||||
INCOME FROM CONTINUING OPERATIONS BEFORE TAXES AND EQUITY IN EARNINGS OF AFFILIATES | 347 | 294 | 746 | 445 | |||||||||||
Income tax expense | (110 | ) | (75 | ) | (270 | ) | (165 | ) | |||||||
Net equity in earnings of affiliates | 24 | 11 | 33 | 25 | |||||||||||
INCOME FROM CONTINUING OPERATIONS | 261 | 230 | 509 | 305 | |||||||||||
Loss from operations of discontinued businesses, net of income tax benefit of $4 for the nine months ended September 30, 2016 | — | (1 | ) | — | (7 | ) | |||||||||
Net loss from disposal and impairments of discontinued businesses, net of income tax benefit of $401 for the nine months ended September 30, 2016 | — | — | — | (382 | ) | ||||||||||
NET INCOME (LOSS) | 261 | 229 | 509 | (84 | ) | ||||||||||
Less: Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests and redeemable stock of subsidiaries | (109 | ) | (54 | ) | (328 | ) | (97 | ) | |||||||
NET INCOME (LOSS) ATTRIBUTABLE TO THE AES CORPORATION | $ | 152 | $ | 175 | $ | 181 | $ | (181 | ) | ||||||
AMOUNTS ATTRIBUTABLE TO THE AES CORPORATION COMMON STOCKHOLDERS: | |||||||||||||||
Income from continuing operations, net of tax | $ | 152 | $ | 176 | $ | 181 | $ | 208 | |||||||
Loss from discontinued operations, net of tax | — | (1 | ) | — | (389 | ) | |||||||||
NET INCOME (LOSS) ATTRIBUTABLE TO THE AES CORPORATION | $ | 152 | $ | 175 | $ | 181 | $ | (181 | ) | ||||||
BASIC EARNINGS PER SHARE: | |||||||||||||||
Income from continuing operations attributable to The AES Corporation common stockholders, net of tax | $ | 0.23 | $ | 0.26 | $ | 0.28 | $ | 0.31 | |||||||
Loss from discontinued operations attributable to The AES Corporation common stockholders, net of tax | — | — | — | (0.59 | ) | ||||||||||
NET INCOME (LOSS) ATTRIBUTABLE TO THE AES CORPORATION COMMON STOCKHOLDERS | $ | 0.23 | $ | 0.26 | $ | 0.28 | $ | (0.28 | ) | ||||||
DILUTED EARNINGS PER SHARE: | |||||||||||||||
Income from continuing operations attributable to The AES Corporation common stockholders, net of tax | $ | 0.23 | $ | 0.26 | $ | 0.27 | $ | 0.31 | |||||||
Loss from discontinued operations attributable to The AES Corporation common stockholders, net of tax | — | — | — | (0.59 | ) | ||||||||||
NET INCOME (LOSS) ATTRIBUTABLE TO THE AES CORPORATION COMMON STOCKHOLDERS | $ | 0.23 | $ | 0.26 | $ | 0.27 | $ | (0.28 | ) | ||||||
DILUTED SHARES OUTSTANDING | 663 | 662 | 662 | 662 | |||||||||||
DIVIDENDS DECLARED PER COMMON SHARE | $ | 0.12 | $ | 0.11 | $ | 0.24 | $ | 0.22 | |||||||
See Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements.
3
THE AES CORPORATION
Condensed Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income (Loss)
(Unaudited)
Three Months Ended September 30, | Nine Months Ended September 30, | ||||||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2017 | 2016 | ||||||||||||
(in millions) | |||||||||||||||
NET INCOME (LOSS) | $ | 261 | $ | 229 | $ | 509 | $ | (84 | ) | ||||||
Foreign currency translation activity: | |||||||||||||||
Foreign currency translation adjustments, net of income tax benefit (expense) of $1, $(1), $0 and $0, respectively | 80 | (16 | ) | 29 | 232 | ||||||||||
Reclassification to earnings, net of $0 income tax | — | — | 98 | — | |||||||||||
Total foreign currency translation adjustments | 80 | (16 | ) | 127 | 232 | ||||||||||
Derivative activity: | |||||||||||||||
Change in derivative fair value, net of income tax benefit (expense) of $(6), $(7), $15 and $39, respectively | 5 | 19 | (42 | ) | (138 | ) | |||||||||
Reclassification to earnings, net of income tax benefit (expense) of $5, $(4), $(6) and $(5), respectively | 1 | 21 | 50 | 23 | |||||||||||
Total change in fair value of derivatives | 6 | 40 | 8 | (115 | ) | ||||||||||
Pension activity: | |||||||||||||||
Reclassification to earnings due to amortization of net actuarial loss, net of income tax expense of $4, $2, $10 and $4, respectively | 7 | 3 | 20 | 10 | |||||||||||
Total pension adjustments | 7 | 3 | 20 | 10 | |||||||||||
OTHER COMPREHENSIVE INCOME | 93 | 27 | 155 | 127 | |||||||||||
COMPREHENSIVE INCOME | 354 | 256 | 664 | 43 | |||||||||||
Less: Comprehensive income attributable to noncontrolling interests | (127 | ) | (66 | ) | (360 | ) | (94 | ) | |||||||
COMPREHENSIVE INCOME (LOSS) ATTRIBUTABLE TO THE AES CORPORATION | $ | 227 | $ | 190 | $ | 304 | $ | (51 | ) | ||||||
See Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements.
4
THE AES CORPORATION
Condensed Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
(Unaudited)
Nine Months Ended September 30, | |||||||
2017 | 2016 | ||||||
(in millions) | |||||||
OPERATING ACTIVITIES: | |||||||
Net income (loss) | $ | 509 | $ | (84 | ) | ||
Adjustments to net income (loss): | |||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 884 | 877 | |||||
Loss (gain) on sales and disposals of businesses | 49 | (30 | ) | ||||
Impairment expenses | 260 | 475 | |||||
Deferred income taxes | (3 | ) | (475 | ) | |||
Provisions for contingencies | 30 | 28 | |||||
Loss on extinguishment of debt | 44 | 12 | |||||
Loss on sales of assets | 34 | 26 | |||||
Impairments of discontinued operations | — | 783 | |||||
Other | 61 | 106 | |||||
Changes in operating assets and liabilities | |||||||
(Increase) decrease in accounts receivable | (279 | ) | 335 | ||||
(Increase) decrease in inventory | (66 | ) | 36 | ||||
(Increase) decrease in prepaid expenses and other current assets | 140 | 670 | |||||
(Increase) decrease in other assets | (266 | ) | (237 | ) | |||
Increase (decrease) in accounts payable and other current liabilities | 162 | (567 | ) | ||||
Increase (decrease) in income tax payables, net and other tax payables | (4 | ) | (270 | ) | |||
Increase (decrease) in other liabilities | 134 | 497 | |||||
Net cash provided by operating activities | 1,689 | 2,182 | |||||
INVESTING ACTIVITIES: | |||||||
Capital expenditures | (1,587 | ) | (1,770 | ) | |||
Acquisitions of businesses, net of cash acquired, and equity method investments | (606 | ) | (61 | ) | |||
Proceeds from the sale of businesses, net of cash sold, and equity method investments | 39 | 157 | |||||
Sale of short-term investments | 2,942 | 3,747 | |||||
Purchase of short-term investments | (2,673 | ) | (3,797 | ) | |||
Increase in restricted cash, debt service reserves. and other assets | (311 | ) | (123 | ) | |||
Other investing | (86 | ) | (22 | ) | |||
Net cash used in investing activities | (2,282 | ) | (1,869 | ) | |||
FINANCING ACTIVITIES: | |||||||
Borrowings under the revolving credit facilities | 1,489 | 1,079 | |||||
Repayments under the revolving credit facilities | (851 | ) | (856 | ) | |||
Issuance of recourse debt | 1,025 | 500 | |||||
Repayments of recourse debt | (1,353 | ) | (808 | ) | |||
Issuance of non-recourse debt | 2,703 | 2,118 | |||||
Repayments of non-recourse debt | (1,731 | ) | (1,720 | ) | |||
Payments for financing fees | (96 | ) | (86 | ) | |||
Distributions to noncontrolling interests | (263 | ) | (356 | ) | |||
Contributions from noncontrolling interests and redeemable security holders | 59 | 154 | |||||
Proceeds from the sale of redeemable stock of subsidiaries | — | 134 | |||||
Dividends paid on AES common stock | (238 | ) | (218 | ) | |||
Payments for financed capital expenditures | (100 | ) | (108 | ) | |||
Purchase of treasury stock | — | (79 | ) | ||||
Proceeds from sales to noncontrolling interests | 60 | — | |||||
Other financing | (26 | ) | (12 | ) | |||
Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities | 678 | (258 | ) | ||||
Effect of exchange rate changes on cash | 9 | 7 | |||||
(Increase) decrease in cash of discontinued operations and held-for-sale businesses | (1 | ) | 6 | ||||
Total increase in cash and cash equivalents | 93 | 68 | |||||
Cash and cash equivalents, beginning | 1,305 | 1,257 | |||||
Cash and cash equivalents, ending | $ | 1,398 | $ | 1,325 | |||
SUPPLEMENTAL DISCLOSURES: | |||||||
Cash payments for interest, net of amounts capitalized | $ | 797 | $ | 837 | |||
Cash payments for income taxes, net of refunds | $ | 291 | $ | 425 | |||
SCHEDULE OF NON-CASH INVESTING AND FINANCING ACTIVITIES: | |||||||
Assets acquired through capital lease and other liabilities | $ | — | $ | 5 | |||
Reclassification of Alto Maipo loans and accounts payable into equity (see Note 11—Equity) | $ | 279 | $ | — | |||
See Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements.
5
THE AES CORPORATION
Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements
For the Three and Nine Months Ended September 30, 2017 and 2016
1. FINANCIAL STATEMENT PRESENTATION
Consolidation — In this Quarterly Report the terms “AES,” “the Company,” “us” or “we” refer to the consolidated entity, including its subsidiaries and affiliates. The terms “The AES Corporation” or “the Parent Company” refer only to the publicly held holding company, The AES Corporation, excluding its subsidiaries and affiliates. Furthermore, VIEs in which the Company has a variable interest have been consolidated where the Company is the primary beneficiary. Investments in which the Company has the ability to exercise significant influence, but not control, are accounted for using the equity method of accounting. All intercompany transactions and balances have been eliminated in consolidation.
Interim Financial Presentation — The accompanying unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements and footnotes have been prepared in accordance with GAAP, as contained in the FASB ASC, for interim financial information and Article 10 of Regulation S-X issued by the SEC. Accordingly, they do not include all the information and footnotes required by GAAP for annual fiscal reporting periods. In the opinion of management, the interim financial information includes all adjustments of a normal recurring nature necessary for a fair presentation of the results of operations, financial position, comprehensive income and cash flows. The results of operations for the three and nine months ended September 30, 2017, are not necessarily indicative of expected results for the year ending December 31, 2017. The accompanying condensed consolidated financial statements are unaudited and should be read in conjunction with the 2016 audited consolidated financial statements and notes thereto, which are included in the 2016 Form 10-K filed with the SEC on February 27, 2017 (the “2016 Form 10-K”).
New Accounting Pronouncements — The following table provides a brief description of recent accounting pronouncements that had or may have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements. Accounting pronouncements not listed below were assessed and determined to be either not applicable or are expected to have no material impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
New Accounting Standards Adopted | |||
ASU Number and Name | Description | Date of Adoption | Effect on the financial statements upon adoption |
2016-09, Compensation — Stock Compensation (Topic 718): Improvements to Employee Share-Based Payment Accounting | The standard simplifies the following aspects of accounting for share-based payments awards: accounting for income taxes, classification of excess tax benefits on the statement of cash flows, forfeitures, statutory tax withholding requirements, classification of awards as either equity or liabilities and classification of employee taxes paid on statement of cash flows when an employer withholds shares for tax-withholding purposes. Transition method: The recognition of excess tax benefits and tax deficiencies arising from vesting or settlement were applied retrospectively. The elimination of the requirement that excess tax benefits be realized before they are recognized was adopted on a modified retrospective basis. | January 1, 2017 | The recognition of excess tax benefits in the provision for income taxes in the period when the awards vest or are settled, rather than in paid-in-capital in the period when the excess tax benefits are realized, resulted in a decrease of $31 million to deferred tax liabilities, offset by an increase to retained earnings. |
New Accounting Standards Issued But Not Yet Effective | |||
ASU Number and Name | Description | Date of Adoption | Effect on the financial statements upon adoption |
2017-12, Derivatives and Hedging (Topic 815): Targeted improvements to Accounting for Hedging Activities | The standard updates the hedge accounting model to expand the ability to hedge risk, reduce complexity, and ease certain documentation and assessment requirements. It also eliminates the requirement to separately measure and report hedge ineffectiveness, and generally requires the change in fair value of a hedging instrument to be presented in the same income statement line as the hedged item. Transition method: modified retrospective and prospective for presentation and disclosures. | January 1, 2019. Early adoption is permitted. | The Company is currently evaluating the impact of adopting the standard on its consolidated financial statements. |
2017-11, Earnings Per Share (Topic 260); Distinguishing Liabilities from Equity (Topic 480); Derivatives and Hedging (Topic 815): Accounting for Certain Financial Instruments and Certain Mandatorily Redeemable Noncontrolling Interests | Part 1 of this standard changes the classification of certain equity-linked financial instruments when assessing whether the instrument is indexed to an entity’s own stock. Transition method: retrospective. | January 1, 2019. Early adoption is permitted. | The Company is currently evaluating the impact of adopting the standard on its consolidated financial statements. |
6
2017-08, Receivables — Nonrefundable Fees and Other Costs (Subtopic 310-20): Premium Amortization on Purchased Callable Debt Securities | This standard shortens the period of amortization for the premium on certain callable debt securities to the earliest call date. Transition method: modified retrospective. | January 1, 2019. Early adoption is permitted. | The Company is currently evaluating the impact of adopting the standard on its consolidated financial statements. |
2017-07, Compensation — Retirement Benefits (Topic 715): Improving the Presentation of Net Periodic Pension Cost and Net Periodic Postretirement Benefit Cost | This standard changes the presentation of non-service cost associated with defined benefit plans and updates the guidance so that only the service cost component will be eligible for capitalization. Transition method: Retrospective for presentation of non-service cost expense. Prospective for the change in capitalization. | January 1, 2018. Early adoption is permitted. | The Company expects the adoption of this standard to result in a $144 million reclassification of non-service pension costs from Cost of Sales to Other Expense for 2016. The Company plans to adopt the standard as of January 1, 2018. |
2017-05, Other Income — Gains and Losses from the Derecognition of Nonfinancial Assets (Topic 610-20) | This standard clarifies the scope and application of ASC 610-20 on the sale, transfer, and derecognition of nonfinancial assets and in substance nonfinancial assets to non-customers, including partial sales. It also clarifies that the derecognition of businesses is under scope of ASC 810. The standard must be adopted concurrently with ASC 606, however an entity will not have to apply the same transition method as ASC 606. Transition method: full or modified retrospective. Under a modified retrospective approach, the guidance shall be applied to all contracts that are not completed as of the initial application date (January 1, 2018). The Company is in the process of identifying contracts that would not be completed as of January 1, 2018. Based on the assessment of contracts already executed as of September 30, 2017, the contracts that may require any type of assessment under the new standard are limited. | January 1, 2018. Early adoption is permitted only as of January 1, 2017. | The Company is currently evaluating the impact of adopting the standard on its consolidated financial statements, will adopt the standard on January 1, 2018, and plans to use the modified retrospective approach. |
2017-04, Intangibles — Goodwill and Other (Topic 350): Simplifying the Test for Goodwill Impairment | This standard simplifies the accounting for goodwill impairment by removing the requirement to calculate the implied fair value. Instead, it requires that an entity records an impairment charge based on the excess of a reporting unit's carrying amount over its fair value. Transition method: prospective. | January 1, 2020. Early adoption is permitted as of January 1, 2017. | The Company is currently evaluating the impact of adopting the standard on its consolidated financial statements. |
2016-18, Statement of Cash Flows (Topic 230): Restricted Cash (a consensus of the FASB Emerging Issues Task Force) | This standard requires that a statement of cash flows explain the change during the period in the total of cash, cash equivalents, and amounts generally described as restricted cash or restricted cash equivalents. Therefore, amounts generally described as restricted cash and restricted cash equivalents should be included with cash and cash equivalents when reconciling the beginning-of-period and end-of-period total amounts shown on the statement of cash flows. Transition method: retrospective. | January 1, 2018. Early adoption is permitted. | The Company has performed a preliminary evaluation. However, foreign exchange impacts on movements related to restricted cash have not been quantified. |
2016-16, Income Taxes (Topic 740): Intra-Entity Transfers of Assets Other Than Inventory | This standard requires that an entity recognizes the income tax consequences of an intra-entity transfer of an asset other than inventory when the transfer occurs. Transition method: modified retrospective. | January 1, 2018. Early adoption is permitted. | The Company is currently evaluating the impact of adopting the standard on its consolidated financial statements. |
2016-13, Financial Instruments — Credit Losses (Topic 326): Measurement of Credit Losses on Financial Instruments | The standard updates the impairment model for financial assets measured at amortized cost to an expected loss model rather than an incurred loss model. It also allows for the presentation of credit losses on available-for-sale debt securities as an allowance rather than a write down. Transition method: various. | January 1, 2020. Early adoption is permitted only as of January 1, 2019. | The Company is currently evaluating the impact of adopting the standard on its consolidated financial statements. |
7
2016-02, Leases (Topic 842) | This standard requires lessees to recognize assets and liabilities for most leases but recognize expenses in a manner similar to today’s accounting. For Lessors, the guidance modifies the lease classification criteria and the accounting for sales-type and direct financing leases. The guidance also eliminates today’s real estate-specific provisions. Transition method: modified retrospective at the beginning of the earliest comparative period presented in the financial statements (January 1, 2017). The Company has established a task force focused on the identification of contracts that would be under the scope of the new standard and on the assessment and measurement of the right-of-use asset and related liability. The implementation team is in the process of evaluating changes to our business processes, systems and controls to support recognition and disclosure under the new standard. | January 1, 2019. Early adoption is permitted. | The Company is currently evaluating the impact of adopting the standard on its consolidated financial statements and intends to adopt the standard as of January 1, 2019. |
2014-09, 2015-14, 2016-08, 2016-10, 2016-12, 2016-20, 2017-13, Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606) | See discussion of the ASU below. | January 1, 2018. Early adoption is permitted only as of January 1, 2017. | The Company will adopt the standard on January 1, 2018; see below for the evaluation of the impact of its adoption on the consolidated financial statements. |
ASU 2014-09 and its subsequent corresponding updates provide the principles an entity must apply to measure and recognize revenue. The core principle is that an entity shall recognize revenue to depict the transfer of promised goods or services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration to which the entity expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods or services. Amendments to the standard were issued that provide further clarification of the principle and to provide certain transition expedients. The standard will replace most existing revenue recognition guidance in GAAP.
In 2016, the Company established a cross-functional implementation team and is in the process of evaluating and implementing changes to our business processes, systems, and controls to support recognition and disclosure under the new standard. At this time, we do not expect any significant impact on our financial systems or a material change to controls as a result of the implementation of the new revenue recognition standard.
Given the complexity and diversity of our non-regulated arrangements, the Company is assessing the standard on a contract-by-contract basis and is in the process of completing the contract assessments by applying the interpretations reached during 2017 on key issues. These issues include the application of the practical expedient for measuring progress towards satisfaction of a performance obligation, when variable quantities would be considered variable consideration versus an option to acquire additional goods and services and how to allocate variable consideration to one or more, but not all, distinct goods or services promised in a series of distinct goods or services that forms part of a single performance obligation. Additionally, the Company is working on the application of the standard to contracts that are under the scope of Service Concession Arrangements (Topic 853) and assessing the gross versus net presentation for spot energy sales and purchases. Through this assessment, the Company to date has identified limited situations where revenue recognized under ASC 606 could differ from that recognized under ASC 605 and where the presentation of sales to and purchases from the energy spot markets will change. The main change that the Company is expecting to have is related to a contract under the scope of Topic 853. The Company will continue its work to complete the assessment of the full population of contracts and determine the overall impact to the consolidated financial statements.
The standard requires retrospective application and allows either a full retrospective adoption in which all periods are presented under the new standard or a modified retrospective approach in which the cumulative effect of initially applying the guidance is recognized at the date of initial application. Although we had previously been working toward adopting the standard using the full retrospective method, given the limited impact of the situations where revenue recognized under ASC 606 differs from that recognized under ASC 605, we now expect to use the modified retrospective approach. However, the Company will continue to assess this conclusion which is dependent on the final impact to the financial statements.
We are continuing to work with various non-authoritative industry groups, and monitoring the FASB and Transition Resource Group activity, as we finalize our accounting policy on these and other industry specific interpretative issues, which is expected in 2017.
8
2. INVENTORY
The following table summarizes the Company’s inventory balances as of the periods indicated (in millions):
September 30, 2017 | December 31, 2016 | ||||||
Fuel and other raw materials | $ | 350 | $ | 302 | |||
Spare parts and supplies | 310 | 328 | |||||
Total | $ | 660 | $ | 630 | |||
3. FAIR VALUE
The fair value of current financial assets and liabilities, debt service reserves and other deposits approximate their reported carrying amounts. The estimated fair values of the Company’s assets and liabilities have been determined using available market information. By virtue of these amounts being estimates and based on hypothetical transactions to sell assets or transfer liabilities, the use of different market assumptions and/or estimation methodologies may have a material effect on the estimated fair value amounts. The Company made no changes during the period to the fair valuation techniques described in Note 4—Fair Value in Item 8.—Financial Statements and Supplementary Data of its 2016 Form 10-K.
Recurring Measurements — The following table presents, by level within the fair value hierarchy, the Company’s financial assets and liabilities that were measured at fair value on a recurring basis as of the dates indicated (in millions). For the Company’s investments in marketable debt and equity securities, the security classes presented are determined based on the nature and risk of the security and are consistent with how the Company manages, monitors and measures its marketable securities:
September 30, 2017 | December 31, 2016 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Assets | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
AVAILABLE FOR SALE: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Debt securities: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Unsecured debentures | $ | — | $ | 157 | $ | — | $ | 157 | $ | — | $ | 360 | $ | — | $ | 360 | |||||||||||||||
Certificates of deposit | — | 340 | — | 340 | — | 372 | — | 372 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Government debt securities | — | — | — | — | — | 9 | — | 9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Subtotal | — | 497 | — | 497 | — | 741 | — | 741 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Equity securities: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Mutual funds | — | 54 | — | 54 | — | 49 | — | 49 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Subtotal | — | 54 | — | 54 | — | 49 | — | 49 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Total available for sale | — | 551 | — | 551 | — | 790 | — | 790 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
TRADING: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Equity securities: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Mutual funds | 20 | — | — | 20 | 16 | — | — | 16 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Total trading | 20 | — | — | 20 | 16 | — | — | 16 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
DERIVATIVES: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Interest rate derivatives | — | 13 | — | 13 | — | 18 | — | 18 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Cross-currency derivatives | — | 14 | — | 14 | — | 4 | — | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Foreign currency derivatives | — | 37 | 242 | 279 | — | 54 | 255 | 309 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Commodity derivatives | — | 44 | 8 | 52 | — | 38 | 7 | 45 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Total derivatives — assets | — | 108 | 250 | 358 | — | 114 | 262 | 376 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
TOTAL ASSETS | $ | 20 | $ | 659 | $ | 250 | $ | 929 | $ | 16 | $ | 904 | $ | 262 | $ | 1,182 | |||||||||||||||
Liabilities | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
DERIVATIVES: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Interest rate derivatives | $ | — | $ | 104 | $ | 192 | $ | 296 | $ | — | $ | 121 | $ | 179 | $ | 300 | |||||||||||||||
Cross-currency derivatives | — | 5 | — | 5 | — | 18 | — | 18 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Foreign currency derivatives | — | 42 | — | 42 | — | 64 | — | 64 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Commodity derivatives | — | 16 | 2 | 18 | — | 40 | 2 | 42 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Total derivatives — liabilities | — | 167 | 194 | 361 | — | 243 | 181 | 424 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
TOTAL LIABILITIES | $ | — | $ | 167 | $ | 194 | $ | 361 | $ | — | $ | 243 | $ | 181 | $ | 424 | |||||||||||||||
As of September 30, 2017, all AFS debt securities had stated maturities within one year. For the three and nine months ended September 30, 2017 and 2016, no other-than-temporary impairments of marketable securities were recognized in earnings or Other Comprehensive Income (Loss). Gains and losses on the sale of investments are determined using the specific-identification method. The following table presents gross proceeds from the sale of AFS securities during the periods indicated (in millions):
Three Months Ended September 30, | Nine Months Ended September 30, | ||||||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2017 | 2016 | ||||||||||||
Gross proceeds from sale of AFS securities | $ | 1,020 | $ | 812 | $ | 2,982 | $ | 3,216 | |||||||
9
The following tables present a reconciliation of net derivative assets and liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis using significant unobservable inputs (Level 3) for the three and nine months ended September 30, 2017 and 2016 (presented net by type of derivative in millions). Transfers between Level 3 and Level 2 are determined as of the end of the reporting period and principally result from changes in the significance of unobservable inputs used to calculate the credit valuation adjustment.
Three Months Ended September 30, 2017 | Interest Rate | Foreign Currency | Commodity | Total | |||||||||||
Balance at July 1 | $ | (195 | ) | $ | 239 | $ | 9 | $ | 53 | ||||||
Total realized and unrealized gains (losses): | |||||||||||||||
Included in earnings | (5 | ) | 12 | — | 7 | ||||||||||
Included in other comprehensive income — derivative activity | (2 | ) | — | — | (2 | ) | |||||||||
Settlements | 10 | (9 | ) | (3 | ) | (2 | ) | ||||||||
Balance at September 30 | $ | (192 | ) | $ | 242 | $ | 6 | $ | 56 | ||||||
Total gains (losses) for the period included in earnings attributable to the change in unrealized gains (losses) relating to assets and liabilities held at the end of the period | $ | (1 | ) | $ | 3 | $ | — | $ | 2 | ||||||
Three Months Ended September 30, 2016 | Interest Rate | Foreign Currency | Commodity | Total | |||||||||||
Balance at July 1 | $ | (421 | ) | $ | 271 | $ | 11 | $ | (139 | ) | |||||
Total realized and unrealized gains (losses): | |||||||||||||||
Included in earnings | (1 | ) | 12 | 1 | 12 | ||||||||||
Included in other comprehensive income — derivative activity | 6 | — | — | 6 | |||||||||||
Included in other comprehensive income — foreign currency translation activity | — | (5 | ) | — | (5 | ) | |||||||||
Settlements | 17 | (4 | ) | (3 | ) | 10 | |||||||||
Transfers of liabilities into Level 3 | (2 | ) | — | — | (2 | ) | |||||||||
Transfers of liabilities out of Level 3 | 94 | — | — | 94 | |||||||||||
Balance at September 30 | $ | (307 | ) | $ | 274 | $ | 9 | $ | (24 | ) | |||||
Total gains for the period included in earnings attributable to the change in unrealized gains (losses) relating to assets and liabilities held at the end of the period | $ | — | $ | 8 | $ | 1 | $ | 9 | |||||||
Nine Months Ended September 30, 2017 | Interest Rate | Foreign Currency | Commodity | Total | |||||||||||
Balance at January 1 | $ | (179 | ) | $ | 255 | $ | 5 | $ | 81 | ||||||
Total realized and unrealized gains (losses): | |||||||||||||||
Included in earnings | (5 | ) | 12 | (1 | ) | 6 | |||||||||
Included in other comprehensive income — derivative activity | (29 | ) | — | — | (29 | ) | |||||||||
Included in regulatory liabilities | — | — | 10 | 10 | |||||||||||
Settlements | 28 | (25 | ) | (8 | ) | (5 | ) | ||||||||
Transfers of liabilities into Level 3 | (7 | ) | — | — | (7 | ) | |||||||||
Balance at September 30 | $ | (192 | ) | $ | 242 | $ | 6 | $ | 56 | ||||||
Total losses for the period included in earnings attributable to the change in unrealized gains (losses) relating to assets and liabilities held at the end of the period | $ | — | $ | (12 | ) | $ | — | $ | (12 | ) | |||||
Nine Months Ended September 30, 2016 | Interest Rate | Foreign Currency | Commodity | Total | |||||||||||
Balance at January 1 | $ | (304 | ) | $ | 277 | $ | 3 | $ | (24 | ) | |||||
Total realized and unrealized gains (losses): | |||||||||||||||
Included in earnings | — | 30 | 3 | 33 | |||||||||||
Included in other comprehensive income — derivative activity | (172 | ) | 6 | — | (166 | ) | |||||||||
Included in other comprehensive income — foreign currency translation activity | (3 | ) | (43 | ) | — | (46 | ) | ||||||||
Included in regulatory liabilities | — | — | 11 | 11 | |||||||||||
Settlements | 56 | (8 | ) | (8 | ) | 40 | |||||||||
Transfers of liabilities into Level 3 | (2 | ) | — | — | (2 | ) | |||||||||
Transfers of assets out of Level 3 | 118 | 12 | — | 130 | |||||||||||
Balance at September 30 | $ | (307 | ) | $ | 274 | $ | 9 | $ | (24 | ) | |||||
Total gains for the period included in earnings attributable to the change in unrealized gains (losses) relating to assets and liabilities held at the end of the period | $ | 5 | $ | 25 | $ | 3 | $ | 33 | |||||||
The following table summarizes the significant unobservable inputs used for Level 3 derivative assets (liabilities) as of September 30, 2017 (in millions, except range amounts):
Type of Derivative | Fair Value | Unobservable Input | Amount or Range (Weighted Average) | |||||
Interest rate | $ | (192 | ) | Subsidiaries’ credit spreads | 2.4% to 5.1% (4.7%) | |||
Foreign currency: | ||||||||
Argentine Peso | 242 | Argentine Peso to USD currency exchange rate after one year (1) | 21.3 to 47.8 (33.8) | |||||
Commodity: | ||||||||
Other | 6 | |||||||
Total | $ | 56 | ||||||
_____________________________
(1) | During the nine months ended September 30, 2017, the Company began utilizing the interest rate differential approach to construct the remaining portion of the forward curve after one year (beyond the traded points). In previous periods, the Company used the purchasing price parity approach to construct the forward curve. |
10
For interest rate derivatives and foreign currency derivatives, increases (decreases) in the estimates of the Company’s own credit spreads would decrease (increase) the value of the derivatives in a liability position. For foreign currency derivatives, increases (decreases) in the estimate of the above exchange rate would increase (decrease) the value of the derivative.
Nonrecurring Measurements
When evaluating impairment of long-lived assets and equity method investments, the Company measures fair value using the applicable fair value measurement guidance. Impairment expense is measured by comparing the fair value at the evaluation date to the then-latest available carrying amount. The following table summarizes our major categories of assets and liabilities measured at fair value on a nonrecurring basis and their level within the fair value hierarchy (in millions):
Nine Months Ended September 30, 2017 | Measurement Date | Carrying Amount (1) | Fair Value | Pretax Loss | |||||||||||||||||
Assets | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | ||||||||||||||||||
Long-lived assets held and used: (2) | |||||||||||||||||||||
DPL | 02/28/2017 | $ | 77 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 11 | $ | 66 | ||||||||||
Tait Energy Storage | 02/28/2017 | 15 | — | — | 7 | 8 | |||||||||||||||
Dispositions and held-for-sale businesses: (3) | |||||||||||||||||||||
Kazakhstan Hydroelectric | 06/30/2017 | 190 | — | 92 | — | 92 | |||||||||||||||
Kazakhstan CHPs | 03/31/2017 | 171 | — | 29 | — | 94 | |||||||||||||||
Nine Months Ended September 30, 2016 | Measurement Date | Carrying Amount (1) | Fair Value | Pretax Loss | |||||||||||||||||
Assets | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | ||||||||||||||||||
Long-lived assets held and used: (2) | |||||||||||||||||||||
Buffalo Gap I | 08/31/2016 | $ | 113 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 35 | $ | 78 | ||||||||||
DPL | 06/30/2016 | 324 | — | — | 89 | 235 | |||||||||||||||
Buffalo Gap II | 03/31/2016 | 251 | — | — | 92 | 159 | |||||||||||||||
Discontinued operations and held-for-sale businesses: (3) | |||||||||||||||||||||
Sul | 06/30/2016 | 1,581 | — | 470 | — | 783 | |||||||||||||||
_____________________________
(1) | Represents the carrying values at the dates of measurement, before fair value adjustment. |
(2) | See Note 14—Asset Impairment Expense for further information. |
(3) | Per the Company’s policy, pretax loss is limited to the impairment of long-lived assets. Any additional loss will be recognized on completion of the sale. See Note 16—Held-for-Sale Businesses and Dispositions for further information. |
The following table summarizes the significant unobservable inputs used in the Level 3 measurement on a nonrecurring basis during the nine months ended September 30, 2017 (in millions, except range amounts):
Fair Value | Valuation Technique | Unobservable Input | Range (Weighted Average) | ||||||
Long-lived assets held and used: | |||||||||
DPL | $ | 11 | Discounted cash flow | Pretax operating margin (through remaining life) | 10% to 22% (15%) | ||||
Weighted average cost of capital | 7% | ||||||||
Tait Energy Storage | 7 | Discounted cash flow | Annual pretax operating margin | 46% to 85% (80%) | |||||
Weighted average cost of capital | 9% | ||||||||
Financial Instruments not Measured at Fair Value in the Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheets
The following table presents (in millions) the carrying amount, fair value and fair value hierarchy of the Company’s financial assets and liabilities that are not measured at fair value in the Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheets as of September 30, 2017 and December 31, 2016, but for which fair value is disclosed:
September 30, 2017 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Carrying Amount | Fair Value | |||||||||||||||||||
Total | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | |||||||||||||||||
Assets: | Accounts receivable — noncurrent (1) | $ | 200 | $ | 262 | $ | — | $ | 6 | $ | 256 | |||||||||
Liabilities: | Non-recourse debt | 17,079 | 17,706 | — | 15,479 | 2,227 | ||||||||||||||
Recourse debt | 4,958 | 5,266 | — | 5,266 | — | |||||||||||||||
December 31, 2016 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Carrying Amount | Fair Value | |||||||||||||||||||
Total | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | |||||||||||||||||
Assets: | Accounts receivable — noncurrent (1) | $ | 264 | $ | 350 | $ | — | $ | 20 | $ | 330 | |||||||||
Liabilities: | Non-recourse debt | 15,792 | 16,188 | — | 15,120 | 1,068 | ||||||||||||||
Recourse debt | 4,671 | 4,899 | — | 4,899 | — | |||||||||||||||
_____________________________
(1) | These amounts primarily relate to amounts due from CAMMESA, the administrator of the wholesale electricity market in Argentina, and are included in Other noncurrent assets in the accompanying Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheets. The fair value and carrying amount of these receivables exclude VAT of $38 million and $24 million as of September 30, 2017 and December 31, 2016, respectively. |
11
4. DERIVATIVE INSTRUMENTS AND HEDGING ACTIVITIES
There are no changes to the information disclosed in Note 1—General and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies—Derivatives and Hedging Activities of Item 8.—Financial Statements and Supplementary Data in the 2016 Form 10-K.
Volume of Activity — The following table presents the Company’s maximum notional (in millions) over the remaining contractual period by type of derivative as of September 30, 2017, regardless of whether they are in qualifying cash flow hedging relationships, and the dates through which the maturities for each type of derivative range:
Derivatives | Maximum Notional Translated to USD | Latest Maturity | ||||
Interest Rate (LIBOR and EURIBOR) | $ | 4,557 | 2035 | |||
Cross-Currency Swaps (Chilean Unidad de Fomento and Chilean Peso) | 394 | 2029 | ||||
Foreign Currency: | ||||||
Argentine Peso | 233 | 2026 | ||||
Chilean Peso | 504 | 2020 | ||||
Colombian Peso | 255 | 2019 | ||||
Others, primarily with weighted average remaining maturities of a year or less | 326 | 2020 | ||||
Accounting and Reporting — Assets and Liabilities — The following tables present the fair value of assets and liabilities related to the Company’s derivative instruments as of September 30, 2017 and December 31, 2016 (in millions):
Fair Value | September 30, 2017 | December 31, 2016 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Assets | Designated | Not Designated | Total | Designated | Not Designated | Total | |||||||||||||||||
Interest rate derivatives | $ | 13 | $ | — | $ | 13 | $ | 18 | $ | — | $ | 18 | |||||||||||
Cross-currency derivatives | 14 | — | 14 | 4 | — | 4 | |||||||||||||||||
Foreign currency derivatives | 5 | 274 | 279 | 9 | 300 | 309 | |||||||||||||||||
Commodity derivatives | 7 | 45 | 52 | 20 | 25 | 45 | |||||||||||||||||
Total assets | $ | 39 | $ | 319 | $ | 358 | $ | 51 | $ | 325 | $ | 376 | |||||||||||
Liabilities | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Interest rate derivatives | $ | 151 | $ | 145 | $ | 296 | $ | 295 | $ | 5 | $ | 300 | |||||||||||
Cross-currency derivatives | 5 | — | 5 | 18 | — | 18 | |||||||||||||||||
Foreign currency derivatives | 7 | 35 | 42 | 19 | 45 | 64 | |||||||||||||||||
Commodity derivatives | 5 | 13 | 18 | 26 | 16 | 42 | |||||||||||||||||
Total liabilities | $ | 168 | $ | 193 | $ | 361 | $ | 358 | $ | 66 | $ | 424 | |||||||||||
September 30, 2017 | December 31, 2016 | ||||||||||||||
Fair Value | Assets | Liabilities | Assets | Liabilities | |||||||||||
Current | $ | 101 | $ | 221 | $ | 99 | $ | 155 | |||||||
Noncurrent | 257 | 140 | 277 | 269 | |||||||||||
Total | $ | 358 | $ | 361 | $ | 376 | $ | 424 | |||||||
Credit Risk-Related Contingent Features (1) | September 30, 2017 | December 31, 2016 | |||||||||||||
Present value of liabilities subject to collateralization | $ | 12 | $ | 41 | |||||||||||
Cash collateral held by third parties or in escrow | 5 | 18 | |||||||||||||
_____________________________
(1) | Based on the credit rating of certain subsidiaries |
12
Earnings and Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) — The next table presents (in millions) the pretax gains (losses) recognized in AOCL and earnings related to all derivative instruments for the periods indicated:
Three Months Ended September 30, | Nine Months Ended September 30, | ||||||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2017 | 2016 | ||||||||||||
Effective portion of cash flow hedges | |||||||||||||||
Gains (losses) recognized in AOCL | |||||||||||||||
Interest rate derivatives | $ | (6 | ) | $ | 7 | $ | (79 | ) | $ | (213 | ) | ||||
Cross-currency derivatives | 12 | 15 | 14 | 12 | |||||||||||
Foreign currency derivatives | (4 | ) | (6 | ) | (15 | ) | (11 | ) | |||||||
Commodity derivatives | 9 | 10 | 23 | 35 | |||||||||||
Total | $ | 11 | $ | 26 | $ | (57 | ) | $ | (177 | ) | |||||
Gains (losses) reclassified from AOCL into earnings | |||||||||||||||
Interest rate derivatives | $ | (19 | ) | $ | (26 | ) | $ | (63 | ) | $ | (81 | ) | |||
Cross-currency derivatives | 14 | 4 | 18 | 14 | |||||||||||
Foreign currency derivatives | (1 | ) | (7 | ) | (24 | ) | (3 | ) | |||||||
Commodity derivatives | 10 | 4 | 13 | 42 | |||||||||||
Total | $ | 4 | $ | (25 | ) | $ | (56 | ) | $ | (28 | ) | ||||
Gains (losses) recognized in earnings related to | |||||||||||||||
Ineffective portion of cash flow hedges | $ | 4 | $ | (2 | ) | $ | 4 | $ | — | ||||||
Not designated as hedging instruments: | |||||||||||||||
Foreign currency derivatives | $ | 5 | $ | (6 | ) | $ | (13 | ) | $ | 10 | |||||
Commodity derivatives and other | 1 | 7 | 7 | (11 | ) | ||||||||||
Total | $ | 6 | $ | 1 | $ | (6 | ) | $ | (1 | ) | |||||
Pretax losses reclassified to earnings as a result of discontinuance of cash flow hedge because it was probable that the forecasted transaction would not occur | $ | — | $ | — | $ | (16 | ) | $ | — | ||||||
AOCL is expected to decrease pretax income from continuing operations for the twelve months ended September 30, 2018, by $67 million, primarily due to interest rate derivatives.
5. FINANCING RECEIVABLES
Financing receivables are defined as receivables with contractual maturities of greater than one year. The Company’s financing receivables are primarily related to amended agreements or government resolutions that are due from CAMMESA, the administrator of the wholesale electricity market in Argentina. The following table presents financing receivables by country as of the dates indicated (in millions):
September 30, 2017 | December 31, 2016 | ||||||
Argentina | $ | 216 | $ | 236 | |||
Brazil | 9 | 8 | |||||
United States | 6 | 20 | |||||
Other | 7 | — | |||||
Total | $ | 238 | $ | 264 | |||
Argentina — Collection of the principal and interest on these receivables is subject to various business risks and uncertainties, including, but not limited to, the operation of power plants which generate cash for payments of these receivables, regulatory changes that could impact the timing and amount of collections, and economic conditions in Argentina. The Company monitors these risks, including the credit ratings of the Argentine government, on a quarterly basis to assess the collectability of these receivables. The Company accrues interest on these receivables once the recognition criteria have been met. The Company’s collection estimates are based on assumptions that it believes to be reasonable but are inherently uncertain. Actual future cash flows could differ from these estimates. The decrease in Argentina financing receivables was primarily due to planned collections, as well as the recognition of a $15 million allowance on a non-trade receivable.
6. INVESTMENTS IN AND ADVANCES TO AFFILIATES
Summarized Financial Information — The following table summarizes financial information of the Company’s 50%-or-less-owned affiliates that are accounted for using the equity method (in millions):
Nine Months Ended September 30, | |||||||
50%-or-less-Owned Affiliates | 2017 | 2016 | |||||
Revenue | $ | 532 | $ | 439 | |||
Operating margin | 91 | 108 | |||||
Net income | 44 | 46 | |||||
sPower — In February 2017, the Company and Alberta Investment Management Corporation (“AIMCo”) entered into an agreement to acquire FTP Power LLC (“sPower”). On July 25, 2017, AES closed on the acquisition
13
of its 48% ownership interest in sPower for $461 million. As the Company does not control sPower, it was accounted for as an equity method investment. The sPower portfolio includes solar and wind projects in operation, under construction, and in development located in the United States. The sPower equity method investment is reported in the US SBU reportable segment.
7. DEBT
Recourse Debt
In August 2017, the Company issued $500 million aggregate principal amount of 5.125% senior notes due in 2027. The Company used these proceeds to redeem at par $240 million aggregate principal of its existing LIBOR + 3.00% senior unsecured notes due in 2019 and repurchased $217 million of its existing 8.00% senior unsecured notes due in 2020. As a result of the latter transactions, the Company recognized a loss on extinguishment of debt of $36 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2017.
In May 2017, the Company closed on $525 million aggregate principal LIBOR + 2.00% secured term loan due in 2022. In June 2017, the Company used these proceeds to redeem at par all $517 million aggregate principal of its existing Term Convertible Securities. As a result of the latter transaction, the Company recognized a loss on extinguishment of debt of $6 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2017.
In March 2017, the Company redeemed via tender offers $276 million aggregate principal of its existing 7.375% senior unsecured notes due in 2021 and $24 million of its existing 8.00% senior unsecured notes due in 2020. As a result of these transactions, the Company recognized a loss on extinguishment of debt of $47 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2017.
In July 2016, the Company redeemed in full the $181 million balance of its 8.00% outstanding senior unsecured notes due 2017 using proceeds from its senior secured credit facility. As a result, the Company recognized a loss on extinguishment of debt of $16 million for the three and nine months ended September 30, 2016.
In May 2016, the Company issued $500 million aggregate principal amount of 6.00% senior notes due in 2026. The Company used these proceeds to redeem at par $495 million aggregate principal of its existing LIBOR + 3.00% senior unsecured notes due 2019. As a result of the latter transaction, the Company recognized a loss on extinguishment of debt of $4 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2016.
In January 2016, the Company redeemed $125 million of its senior unsecured notes outstanding. The repayment included a portion of the 7.375% senior notes due in 2021, the 4.875% senior notes due in 2023, the 5.5% senior notes due in 2024, the 5.5% senior notes due in 2025 and the floating rate senior notes due in 2019. As a result of these transactions, the Company recognized a net gain on extinguishment of debt of $7 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2016.
Non-Recourse Debt
During the nine months ended September 30, 2017, the Company’s subsidiaries had the following significant debt transactions:
Subsidiary | Issuances | Repayments | Gain (Loss) on Extinguishment of Debt | |||||||||
Tietê | $ | 585 | $ | (293 | ) | $ | (5 | ) | ||||
IPALCO | 532 | (480 | ) | (9 | ) | |||||||
Southland | 360 | — | — | |||||||||
AES Argentina | 307 | (181 | ) | 65 | ||||||||
Los Mina | 278 | (259 | ) | (4 | ) | |||||||
Gener | 243 | (78 | ) | — | ||||||||
Colon | 220 | — | — | |||||||||
Eletropaulo | 189 | (147 | ) | — | ||||||||
Other | 261 | (509 | ) | (3 | ) | |||||||
Total | $ | 2,975 | $ | (1,947 | ) | $ | 44 | |||||
Southland — In June 2017, AES Southland Energy LLC closed on $2 billion of aggregate principal long-term non-recourse debt financing to fund the Southland re-powering construction projects (“the Southland financing”). The Southland financing consists of $1.5 billion senior secured notes, amortizing through 2040, and $492 million senior secured term loan, amortizing through 2027. The long term debt financing has a combined weighted average cost of approximately 4.5%. As of September 30, 2017, $360 million of the senior secured notes were outstanding under the Southland financing.
14
AES Argentina — In February 2017, AES Argentina issued $300 million aggregate principal of unsecured and unsubordinated notes due in 2024. The net proceeds from this issuance were used for the prepayment of $75 million of non-recourse debt related to the construction of the San Nicolas Plant resulting in a gain on extinguishment of debt of approximately $65 million.
Non-Recourse Debt in Default — The current portion of non-recourse debt includes the following subsidiary debt in default as of September 30, 2017 (in millions).
Subsidiary | Primary Nature of Default | Debt in Default | Net Assets | |||||||
Alto Maipo (Chile) | Covenant | $ | 623 | $ | 352 | |||||
AES Puerto Rico | Covenant | 365 | 566 | |||||||
AES Ilumina | Covenant | 36 | 56 | |||||||
$ | 1,024 | |||||||||
The above defaults are not payment defaults. All of the subsidiary non-recourse debt defaults were triggered by failure to comply with covenants and/or other conditions such as (but not limited to) failure to meet information covenants, complete construction or other milestones in an allocated time, meet certain minimum or maximum financial ratios, or other requirements contained in the non-recourse debt documents of the applicable subsidiary.
The AES Corporation’s recourse debt agreements include cross-default clauses that will trigger if a subsidiary or group of subsidiaries for which the non-recourse debt is in default provides more than 20% or more of the Parent Company’s total cash distributions from businesses for the four most recently completed fiscal quarters. As of September 30, 2017, the Company has no defaults which result in or are at risk of triggering a cross-default under the recourse debt of the Parent Company. In the event the Parent Company is not in compliance with the financial covenants of its senior secured revolving credit facility, restricted payments will be limited to regular quarterly shareholder dividends at the then-prevailing rate. Payment defaults and bankruptcy defaults would preclude the making of any restricted payments.
8. COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
Guarantees, Letters of Credit and Commitments — In connection with certain project financings, acquisitions and dispositions, power purchases and other agreements, the Parent Company has expressly undertaken limited obligations and commitments, most of which will only be effective or will be terminated upon the occurrence of future events. In the normal course of business, the Parent Company has entered into various agreements, mainly guarantees and letters of credit, to provide financial or performance assurance to third parties on behalf of AES businesses. These agreements are entered into primarily to support or enhance the creditworthiness otherwise achieved by a business on a stand-alone basis, thereby facilitating the availability of sufficient credit to accomplish their intended business purposes. Most of the contingent obligations relate to future performance commitments which the Company or its businesses expect to fulfill within the normal course of business. The expiration dates of these guarantees vary from less than one year to more than 17 years.
The following table summarizes the Parent Company’s contingent contractual obligations as of September 30, 2017. Amounts presented in the following table represent the Parent Company’s current undiscounted exposure to guarantees and the range of maximum undiscounted potential exposure. The maximum exposure is not reduced by the amounts, if any, that could be recovered under the recourse or collateralization provisions in the guarantees.
Contingent Contractual Obligations | Amount (in millions) | Number of Agreements | Maximum Exposure Range for Each Agreement (in millions) | ||||||
Guarantees and commitments | $ | 806 | 21 | <$1 — 272 | |||||
Letters of credit under the unsecured credit facility | 125 | 5 | $2 — 73 | ||||||
Asset sale related indemnities (1) | 27 | 1 | $27 | ||||||
Letters of credit under the senior secured credit facility | 9 | 17 | <$1 — 2 | ||||||
Total | $ | 967 | 44 | ||||||
_____________________________
(1) | Excludes normal and customary representations and warranties in agreements for the sale of assets (including ownership in associated legal entities) where the associated risk is considered to be nominal. |
During the nine months ended September 30, 2017, the Company paid letter of credit fees ranging from 0.25% to 2.25% per annum on the outstanding amounts of letters of credit.
Contingencies
Environmental — The Company periodically reviews its obligations as they relate to compliance with environmental laws, including site restoration and remediation. As of September 30, 2017 and December 31, 2016, the Company had recognized liabilities of $9 million and $12 million, respectively, for projected environmental
15
remediation costs. Due to the uncertainties associated with environmental assessment and remediation activities, future costs of compliance or remediation could be higher or lower than the amount currently accrued. Moreover, where no liability has been recognized, it is reasonably possible that the Company may be required to incur remediation costs or make expenditures in amounts that could be material but could not be estimated as of September 30, 2017. In aggregate, the Company estimates the range of potential losses related to environmental matters, where estimable, to be up to $19 million. The amounts considered reasonably possible do not include amounts accrued as discussed above.
Litigation — The Company is involved in certain claims, suits and legal proceedings in the normal course of business. The Company accrues for litigation and claims when it is probable that a liability has been incurred and the amount of loss can be reasonably estimated. The Company has recognized aggregate liabilities for all claims of approximately $174 million and $179 million as of September 30, 2017 and December 31, 2016, respectively. These amounts are reported on the Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheets within Accrued and other liabilities and Other noncurrent liabilities. A significant portion of these accrued liabilities relate to labor and employment, non-income tax and customer disputes in international jurisdictions. Certain of the Company’s subsidiaries, principally in Brazil, are defendants in a number of labor and employment lawsuits. The complaints generally seek unspecified monetary damages, injunctive relief, or other relief. The subsidiaries have denied any liability and intend to vigorously defend themselves in all of these proceedings. There can be no assurance that these accrued liabilities will be adequate to cover all existing and future claims or that we will have the liquidity to pay such claims as they arise.
Where no accrued liability has been recognized, it is reasonably possible that some matters could be decided unfavorably to the Company and could require the Company to pay damages or make expenditures in amounts that could be material but could not be estimated as of September 30, 2017. The material contingencies where a loss is reasonably possible primarily include claims under financing agreements, including the Eletrobrás case; disputes with offtakers, suppliers and EPC contractors; alleged violation of monopoly laws and regulations; income tax and non-income tax matters with tax authorities; and regulatory matters. In October 2017, Eletropaulo and Eletrobrás entered into a memorandum of understanding to engage in settlement discussions. If settlement is achieved, it will be subject to the approval of the Eletropaulo Board of Directors and the majority of non-AES board members of Eletropaulo. As such, no contingency has been recorded as it does not meet the criteria under ASC 450. In aggregate, the Company estimates the range of potential losses, where estimable, related to these reasonably possible material contingencies to be between $1.6 billion and $1.9 billion. The amounts considered reasonably possible do not include the amounts accrued, as discussed above. These material contingencies do not include income tax-related contingencies which are considered part of our uncertain tax positions.
9. PENSION PLANS
Total pension cost and employer contributions were as follows for the periods indicated (in millions):
Three Months Ended September 30, | Nine Months Ended September 30, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2017 | 2016 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
U.S. | Foreign | U.S. | Foreign | U.S. | Foreign | U.S. | Foreign | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Service cost | $ | 3 | $ | 4 | $ | 3 | $ | 3 | $ | 10 | $ | 11 | $ | 9 | $ | 9 | |||||||||||||||
Interest cost | 10 | 99 | 10 | 92 | 31 | 296 | 30 | 255 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Expected return on plan assets | (17 | ) | (73 | ) | (17 | ) | (59 | ) | (52 | ) | (219 | ) | (50 | ) | (164 | ) | |||||||||||||||
Amortization of prior service cost | 1 | — | 2 | — | 4 | — | 6 | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Amortization of net loss | 5 | 10 | 5 | 5 | 14 | 31 | 14 | 14 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Curtailment loss recognized | — | — | — | — | 4 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Total pension cost | $ | 2 | $ | 40 | $ | 3 | $ | 41 | $ | 11 | $ | 119 | $ | 9 | $ | 114 | |||||||||||||||
Nine Months Ended September 30, 2017 | Remainder of 2017 (Expected) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
U.S. | Foreign | U.S. | Foreign | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total employer contributions | $ | 14 | $ | 118 | $ | — | $ | 41 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
16
10. REDEEMABLE STOCK OF SUBSIDIARIES
The following table summarizes the Company’s redeemable stock of subsidiaries balances as of the periods indicated (in millions):
September 30, 2017 | December 31, 2016 | ||||||
IPALCO common stock | $ | 618 | $ | 618 | |||
Eletropaulo preferred stock | 152 | — | |||||
Colon quotas (1) | 137 | 100 | |||||
IPL preferred stock | 60 | 60 | |||||
Other common stock | — | 4 | |||||
Redeemable stock of subsidiaries | $ | 967 | $ | 782 | |||
_____________________________
(1) | Characteristics of quotas are similar to common stock. |
Eletropaulo — In September 2017, Eletropaulo obtained shareholder approval for the transfer of Eletropaulo’s shares to Novo Mercado, which is a listing segment of the Brazilian stock exchange with the highest standards of corporate governance. Certain preferred shareholders who did not vote in favor of the share transfer to the Novo Mercado have withdrawal rights which allow the shareholder to receive a cash payment for tendering their shares to Eletropaulo over a 30-day withdrawal rights window that expired on October 30, 2017. Due to these withdrawal rights, these shares were probable of becoming redeemable as of September 30, 2017 and the corresponding non-controlling interest was reclassified to temporary equity.
Colon — Our partner in Colon made capital contributions of $30 million and $106 million during the nine months ended September 30, 2017 and 2016, respectively. Any subsequent adjustments to allocate earnings and dividends to our partner, or measure the investment at fair value, will be classified as temporary equity each reporting period as it is probable that the shares will become redeemable.
IPALCO — In March 2016, CDPQ exercised its final purchase option by investing $134 million in IPALCO. The company also recognized an increase to additional paid-in capital and a reduction to retained earnings of $84 million for the excess of the fair value of the shares over their book value. In June 2016, CDPQ contributed an additional $24 million to IPALCO. Any subsequent adjustments to allocate earnings and dividends to CDPQ will be classified as NCI within permanent equity as it is not probable that the shares will become redeemable.
11. EQUITY
Changes in Equity — The following table is a reconciliation of the beginning and ending equity attributable to stockholders of The AES Corporation, NCI and total equity as of the periods indicated (in millions):
Nine Months Ended September 30, 2017 | Nine Months Ended September 30, 2016 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
The Parent Company Stockholders’ Equity | NCI | Total Equity | The Parent Company Stockholders’ Equity | NCI | Total Equity | ||||||||||||||||||
Balance at the beginning of the period | $ | 2,794 | $ | 2,906 | $ | 5,700 | $ | 3,149 | $ | 3,022 | $ | 6,171 | |||||||||||
Net income (loss) (1) | 181 | 328 | 509 | (181 | ) | 97 | (84 | ) | |||||||||||||||
Total foreign currency translation adjustment, net of income tax | 117 | 10 | 127 | 179 | 53 | 232 | |||||||||||||||||
Total change in derivative fair value, net of income tax | 5 | 3 | 8 | (52 | ) | (63 | ) | (115 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Total pension adjustments, net of income tax | 1 | 19 | 20 | 3 | 7 | 10 | |||||||||||||||||
Cumulative effect of a change in accounting principle (2) | 31 | — | 31 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
Fair value adjustment (3) | (19 | ) | — | (19 | ) | (4 | ) | — | (4 | ) | |||||||||||||
Disposition of businesses | — | — | — | — | 18 | 18 | |||||||||||||||||
Distributions to noncontrolling interests | — | (261 | ) | (261 | ) | (2 | ) | (293 | ) | (295 | ) | ||||||||||||
Contributions from noncontrolling interests | — | 17 | 17 | — | 23 | 23 | |||||||||||||||||
Dividends declared on common stock | (158 | ) | — | (158 | ) | (144 | ) | — | (144 | ) | |||||||||||||
Purchase of treasury stock | — | — | — | (79 | ) | — | (79 | ) | |||||||||||||||
Issuance and exercise of stock-based compensation benefit plans | 12 | — | 12 | 15 | — | 15 | |||||||||||||||||
Sale of subsidiary shares to noncontrolling interests | 22 | 47 | 69 | — | 17 | 17 | |||||||||||||||||
Acquisition of subsidiary shares from noncontrolling interests | 200 | (85 | ) | 115 | (2 | ) | (3 | ) | (5 | ) | |||||||||||||
Less: Net loss attributable to redeemable stock of subsidiaries | — | 9 | 9 | — | 8 | 8 | |||||||||||||||||
Balance at the end of the period | $ | 3,186 | $ | 2,993 | $ | 6,179 | $ | 2,882 | $ | 2,886 | $ | 5,768 | |||||||||||
_____________________________
(1) | Net income attributable to noncontrolling interest of $337 million and net loss attributable to redeemable stocks of subsidiaries of $9 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2017. Net income attributable to noncontrolling interest of $105 million and net loss attributable to redeemable stock of subsidiaries of $8 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2016. |
(2) | See Note 1—Financial Statement Presentation, New Accounting Standards Adopted for further information. |
(3) | Adjustment to record the of redeemable stock of Colon at fair value. |
17
Equity Transactions with Noncontrolling Interests
Dominican Republic — On September 28, 2017, Linda Group, an investor-based group in the Dominican Republic acquired an additional 5% of our Dominican Republic business for $60 million, pre tax. This transaction resulted in a net increase of $25 million to the Company’s additional paid-in capital and noncontrolling interest, respectively. No gain or loss was recognized in net income as the sale was not considered a sale of in-substance real estate. As the Company maintained control after the sale, our businesses in the Dominican Republic continue to be consolidated by the Company within the MCAC SBU reportable segment.
Alto Maipo — On March 17, 2017, AES Gener completed the legal and financial restructuring of Alto Maipo. As part of this restructuring, AES indirectly acquired the 40% ownership interest of the noncontrolling shareholder, for a de minimis payment, and sold a 6.7% interest in the project to the construction contractor. This transaction resulted in a $196 million increase to the Parent Company’s Stockholders’ Equity due to an increase in additional-paid-in capital of $229 million, offset by the reclassification of accumulated other comprehensive losses from NCI to the Parent Company Stockholders’ Equity of $33 million. No gain or loss was recognized in net income as the sale was not considered to be a sale of in-substance real estate. After completion of the sale, the Company has an effective 62% economic interest in Alto Maipo. As the Company maintained control of the partnership after the sale, Alto Maipo continues to be consolidated by the Company within the Andes SBU reportable segment.
Jordan — On February 18, 2016, the Company completed the sale of 40% of its interest in a wholly owned subsidiary in Jordan which owns a controlling interest in the Jordan IPP4 gas-fired plant, for $21 million. The transaction was accounted for as a sale of in-substance real estate and a pretax gain of $4 million, net of transaction costs, was recognized in net income. The cash proceeds from the sale are reflected in Proceeds from the sale of businesses, net of cash sold, and equity investments on the Consolidated Statement of Cash Flows for the period ended September 30, 2016. After completion of the sale, the Company has a 36% economic interest in Jordan IPP4 and will continue to manage and operate the plant, with 40% owned by Mitsui Ltd. and 24% owned by Nebras Power Q.S.C. As the Company maintained control after the sale, Jordan IPP4 continues to be consolidated by the Company within the Eurasia SBU reportable segment.
Deconsolidations
UK Wind — During the second quarter of 2016, the Company determined it no longer had control of its wind development projects in the United Kingdom (“UK Wind”) as the Company no longer held seats on the board of directors. In accordance with the accounting guidance, UK Wind was deconsolidated and a loss on deconsolidation of $20 million was recorded to Gain (loss) on disposal and sale of businesses in the Condensed Consolidated Statement of Operations to write off the Company’s noncontrolling interest in the project. The UK Wind projects were reported in the Eurasia SBU reportable segment.
Accumulated Other Comprehensive Loss — The following table summarizes the changes in AOCL by component, net of tax and NCI, for the nine months ended September 30, 2017 (in millions):
Foreign currency translation adjustment, net | Unrealized derivative gains (losses), net | Unfunded pension obligations, net | Total | ||||||||||||
Balance at the beginning of the period | $ | (2,147 | ) | $ | (323 | ) | $ | (286 | ) | $ | (2,756 | ) | |||
Other comprehensive income (loss) before reclassifications | 19 | (35 | ) | (3 | ) | (19 | ) | ||||||||
Amount reclassified to earnings | 98 | 40 | 4 | 142 | |||||||||||
Other comprehensive income | 117 | 5 | 1 | 123 | |||||||||||
Reclassification from NCI due to Alto Maipo Restructuring | — | (33 | ) | — | (33 | ) | |||||||||
Balance at the end of the period | $ | (2,030 | ) | $ | (351 | ) | $ | (285 | ) | $ | (2,666 | ) | |||
18
Reclassifications out of AOCL are presented in the following table. Amounts for the periods indicated are in millions and those in parenthesis indicate debits to the Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations:
Details About AOCL Components | Affected Line Item in the Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations | Three Months Ended September 30, | Nine Months Ended September 30, | |||||||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2017 | 2016 | |||||||||||||||
Foreign currency translation adjustment, net | ||||||||||||||||||
Loss on disposal and sale of businesses | $ | — | $ | — | $ | (98 | ) | $ | — | |||||||||
Net income (loss) attributable to The AES Corporation | $ | — | $ | — | $ | (98 | ) | $ | — | |||||||||
Unrealized derivative gains (losses), net | ||||||||||||||||||
Non-regulated revenue | $ | 12 | $ | 20 | $ | 22 | $ | 94 | ||||||||||
Non-regulated cost of sales | (2 | ) | (17 | ) | (11 | ) | (54 | ) | ||||||||||
Interest expense | (20 | ) | (25 | ) | (63 | ) | (86 | ) | ||||||||||
Foreign currency transaction gains (losses) | 14 | (3 | ) | (4 | ) | 18 | ||||||||||||
Income (loss) from continuing operations before taxes and equity in earnings of affiliates | 4 | (25 | ) | (56 | ) | (28 | ) | |||||||||||
Income tax benefit (expense) | (5 | ) | 4 | 6 | 5 | |||||||||||||
Loss from continuing operations | (1 | ) | (21 | ) | (50 | ) | (23 | ) | ||||||||||
Less: Net loss from operations attributable to noncontrolling interests and redeemable stock of subsidiaries | 1 | 5 | 10 | 4 | ||||||||||||||
Net income (loss) attributable to The AES Corporation | $ | — | $ | (16 | ) | $ | (40 | ) | $ | (19 | ) | |||||||
Amortization of defined benefit pension actuarial loss, net | ||||||||||||||||||
Regulated cost of sales | $ | (10 | ) | $ | (4 | ) | $ | (30 | ) | $ | (13 | ) | ||||||
General and administrative expenses | — | — | 1 | — | ||||||||||||||
Other expense | (1 | ) | — | (1 | ) | — | ||||||||||||
Loss from continuing operations before taxes and equity in earnings of affiliates | (11 | ) | (4 | ) | (30 | ) | (13 | ) | ||||||||||
Income tax benefit | 4 | 2 | 10 | 4 | ||||||||||||||
Loss from continuing operations | (7 | ) | (2 | ) | (20 | ) | (9 | ) | ||||||||||
Net loss from disposal and impairments of discontinued businesses | — | (1 | ) | — | (1 | ) | ||||||||||||
Net loss | (7 | ) | (3 | ) | (20 | ) | (10 | ) | ||||||||||
Less: Net loss from operations attributable to noncontrolling interests and redeemable stock of subsidiaries | 6 | 2 | 16 | 7 | ||||||||||||||
Net income (loss) attributable to The AES Corporation | $ | (1 | ) | $ | (1 | ) | $ | (4 | ) | $ | (3 | ) | ||||||
Total reclassifications for the period, net of income tax and noncontrolling interests | $ | (1 | ) | $ | (17 | ) | $ | (142 | ) | $ | (22 | ) | ||||||
Common Stock Dividends — The Company paid dividends of $0.12 per outstanding share to its common stockholders during the first, second and third quarters of 2017 for dividends declared in December 2016, February 2017, and July 2017, respectively.
On October 6, 2017, the Board of Directors declared a quarterly common stock dividend of $0.12 per share payable on November 15, 2017, to shareholders of record at the close of business on November 1, 2017.
12. SEGMENTS
The segment reporting structure uses the Company’s management reporting structure as its foundation to reflect how the Company manages the businesses internally and is organized by geographic regions which provides a socio-political-economic understanding of our business. During the third quarter of 2017, the Europe and Asia SBUs were merged in order to leverage scale and are now reported as part of the Eurasia SBU. The management reporting structure is organized by five SBUs led by our President and Chief Executive Officer: US, Andes, Brazil, MCAC, and Eurasia SBUs. Using the accounting guidance on segment reporting, the Company determined that it has five operating and five reportable segments corresponding to its SBUs. All prior period results have been retrospectively revised to reflect the new segment reporting structure.
Corporate and Other — Corporate overhead costs which are not directly associated with the operations of our five reportable segments are included in “Corporate and Other.” Also included are certain intercompany charges such as self-insurance premiums which are fully eliminated in consolidation.
The Company uses Adjusted PTC as its primary segment performance measure. Adjusted PTC, a non-GAAP measure, is defined by the Company as pretax income from continuing operations attributable to The AES Corporation excluding gains or losses of the consolidated entity due to (a) unrealized gains or losses related to derivative transactions; (b) unrealized foreign currency gains or losses; (c) gains or losses and associated benefits and costs due to dispositions and acquisitions of business interests, including early plant closures, and the tax impact from the repatriation of sales proceeds; (d) losses due to impairments; and (e) gains, losses and costs due to the early retirement of debt. Adjusted PTC also includes net equity in earnings of affiliates on an after-tax basis
19
adjusted for the same gains or losses excluded from consolidated entities. The Company has concluded that Adjusted PTC better reflects the underlying business performance of the Company and is the most relevant measure considered in the Company’s internal evaluation of the financial performance of its segments. Additionally, given its large number of businesses and complexity, the Company has concluded that Adjusted PTC is a more transparent measure that better assists investors in determining which businesses have the greatest impact on the Company’s results.
Revenue and Adjusted PTC are presented before inter-segment eliminations, which includes the effect of intercompany transactions with other segments except for interest, charges for certain management fees, and the write-off of intercompany balances, as applicable. All intra-segment activity has been eliminated within the segment. Inter-segment activity has been eliminated within the total consolidated results.
The following tables present financial information by segment for the periods indicated (in millions):
Three Months Ended September 30, | Nine Months Ended September 30, | ||||||||||||||
Total Revenue | 2017 | 2016 | 2017 | 2016 | |||||||||||
US SBU | $ | 852 | $ | 916 | $ | 2,445 | $ | 2,582 | |||||||
Andes SBU | 689 | 667 | 1,979 | 1,864 | |||||||||||
Brazil SBU | 1,085 | 1,027 | 3,106 | 2,761 | |||||||||||
MCAC SBU | 630 | 547 | 1,851 | 1,596 | |||||||||||
Eurasia SBU | 380 | 386 | 1,204 | 1,249 | |||||||||||
Corporate and Other | 9 | 6 | 29 | 8 | |||||||||||
Eliminations | (13 | ) | (7 | ) | (20 | ) | (18 | ) | |||||||
Total Revenue | $ | 3,632 | $ | 3,542 | $ | 10,594 | $ | 10,042 | |||||||
Three Months Ended September 30, | Nine Months Ended September 30, | ||||||||||||||
Total Adjusted PTC | 2017 | 2016 | 2017 | 2016 | |||||||||||
Reconciliation from Income from Continuing Operations before Taxes and Equity In Earnings of Affiliates: | |||||||||||||||
Income from continuing operations before taxes and equity in earnings of affiliates | $ | 347 | $ | 294 | $ | 746 | $ | 445 | |||||||
Add: Net equity in earnings of affiliates | 24 | 11 | 33 | 25 | |||||||||||
Less: Income from continuing operations before taxes, attributable to noncontrolling interests | (148 | ) | (82 | ) | (454 | ) | (196 | ) | |||||||
Pretax contribution | 223 | 223 | 325 | 274 | |||||||||||
Unrealized derivative losses (gains) | (8 | ) | 5 | (7 | ) | 1 | |||||||||
Unrealized foreign currency transaction losses (gains) | (21 | ) | 3 | (54 | ) | 12 | |||||||||
Disposition/acquisition losses (gains) | 1 | (3 | ) | 107 | (5 | ) | |||||||||
Impairment expense | 2 | 24 | 264 | 309 | |||||||||||
Losses on extinguishment of debt | 48 | 20 | 43 | 26 | |||||||||||
Total Adjusted PTC | $ | 245 | $ | 272 | $ | 678 | $ | 617 | |||||||
Three Months Ended September 30, | Nine Months Ended September 30, | ||||||||||||||
Total Adjusted PTC | 2017 | 2016 | 2017 | 2016 | |||||||||||
US SBU | $ | 129 | $ | 114 | $ | 240 | $ | 257 | |||||||
Andes SBU | 62 | 134 | 232 | 279 | |||||||||||
Brazil SBU | 12 | 6 | 64 | 18 | |||||||||||
MCAC SBU | 98 | 74 | 256 | 197 | |||||||||||
Eurasia SBU | 61 | 46 | 218 | 197 | |||||||||||
Corporate and Other | (117 | ) | (102 | ) | (332 | ) | (331 | ) | |||||||
Total Adjusted PTC | $ | 245 | $ | 272 | $ | 678 | $ | 617 | |||||||
Total Assets | September 30, 2017 | December 31, 2016 | |||||
US SBU | $ | 10,104 | $ | 9,333 | |||
Andes SBU | 9,339 | 8,971 | |||||
Brazil SBU | 7,416 | 6,448 | |||||
MCAC SBU | 5,640 | 5,162 | |||||
Eurasia SBU | 5,938 | 5,777 | |||||
Assets of held-for-sale businesses | 76 | — | |||||
Corporate and Other | 321 | 428 | |||||
Total Assets | $ | 38,834 | $ | 36,119 | |||
13. OTHER INCOME AND EXPENSE
Other income generally includes gains on asset sales and liability extinguishments, favorable judgments on contingencies, gains on contract terminations, allowance for funds used during construction and other income from miscellaneous transactions. Other expense generally includes losses on asset sales and dispositions, losses on
20
legal contingencies, and losses from other miscellaneous transactions. The components are summarized as follows (in millions):
Three Months Ended September 30, | Nine Months Ended September 30, | |||||||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2017 | 2016 | |||||||||||||
Other Income | Legal settlements (1) | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 60 | $ | — | |||||||
Allowance for funds used during construction (US Utilities) | 7 | 8 | 20 | 22 | ||||||||||||
Gain on sale of assets | 2 | — | 3 | 3 | ||||||||||||
Other | 9 | 10 | 22 | 18 | ||||||||||||
Total other income | $ | 18 | $ | 18 | $ | 105 | $ | 43 | ||||||||
Other Expense | Loss on sale and disposal of assets | $ | 16 | $ | 12 | $ | 54 | $ | 26 | |||||||
Water rights write-off | 15 | — | 18 | 7 | ||||||||||||
Allowance for other receivables (2) | 15 | — | 15 | — | ||||||||||||
Legal contingencies and settlements | 1 | 1 | 2 | 5 | ||||||||||||
Other | — | — | 6 | 4 | ||||||||||||
Total other expense | $ | 47 | $ | 13 | $ | 95 | $ | 42 | ||||||||
_____________________________
(1) | In December 2016, the Company and YPF entered into a settlement agreement in which all parties agreed to give up any and all legal action related to gas supply contracts that were terminated in 2008 and have been in dispute since 2009. In January 2017, the YPF board approved the agreement and paid the Company $60 million, thereby resolving all uncertainties around the dispute. |
(2) | During the third quarter of 2017, we recognized a full allowance on a non-trade receivable in Andes due to collection uncertainties. |
14. ASSET IMPAIRMENT EXPENSE
Three Months Ended September 30, | Nine Months Ended September 30, | ||||||||||||||
(in millions) | 2017 | 2016 | 2017 | 2016 | |||||||||||
Kazakhstan Hydroelectric | $ | 2 | $ | — | $ | 92 | $ | — | |||||||
Kazakhstan CHPs | — | — | 94 | — | |||||||||||
Buffalo Gap I | — | 78 | — | 78 | |||||||||||
DPL | — | — | 66 | 235 | |||||||||||
Tait Energy Storage | — | — | 8 | — | |||||||||||
Buffalo Gap II | — | — | — | 159 | |||||||||||
Other | — | 1 | — | 1 | |||||||||||
Total | $ | 2 | $ | 79 | $ | 260 | $ | 473 | |||||||
Kazakhstan Hydroelectric — In April 2017, the Republic of Kazakhstan stated the concession would not be extended for Shulbinsk HPP and Ust-Kamenogorsk HPP, two hydroelectric plants in Kazakhstan, and initiated the process to transfer these plants back to the government. The fair value of the asset group was determined to be below carrying value. As a result, the Company recognized asset impairment expense of $92 million during the nine months ended September 30, 2017. The Kazakhstan hydroelectric plants are reported in the Eurasia SBU reportable segment. See Note 16—Held-for-Sale Businesses and Dispositions of this Form 10-Q for further information.
DPL — On March 17, 2017, the board of directors of DPL approved the retirement of the DPL operated and co-owned Stuart Station coal-fired and diesel-fired generating units, and the Killen Station coal-fired generating unit and combustion turbine on or before June 1, 2018. The Company performed a long-lived asset impairment analysis and determined that the carrying amounts of the facilities were not recoverable. The Stuart Station and Killen Station were determined to have fair values of $3 million and $8 million, respectively, using the income approach. As a result, the Company recognized a total asset impairment expense of $66 million. DPL is reported in the US SBU reportable segment.
During the second quarter of 2016, the Company tested the recoverability of its long-lived generation assets at DPL. Uncertainty created by the Supreme Court of Ohio’s June 20, 2016 opinion, lower expectations of future revenue resulting from the most recent PJM capacity auction, and higher anticipated environmental compliance costs resulting from third party studies were collectively determined to be an impairment indicator for these assets. The Company performed a long-lived asset impairment analysis and determined that the carrying amount of Killen, a coal-fired generation facility, and certain DPL peaking generation facilities were not recoverable. The Killen and DPL peaking generation asset groups were determined to have a fair value of $84 million and $5 million, respectively, using the income approach. As a result, the Company recognized a total asset impairment expense of $235 million. DPL is reported in the US SBU reportable segment.
Kazakhstan CHPs — In January 2017, the Company entered into an agreement for the sale of Ust-Kamenogorsk CHP and Sogrinsk CHP, its combined heating and power coal plants in Kazakhstan. The fair value of the Kazakhstan asset group was determined to be below carrying value. As a result, the Company recognized asset
21
impairment expense of $94 million during the three months ended March 31, 2017. The Company completed the sale of its interest in the Kazakhstan CHP plants on April 7, 2017. Prior to their sale, the plants were reported in the Eurasia SBU reportable segment. See Note 16—Held-for-Sale Businesses and Dispositions of this Form 10-Q for further information.
Buffalo Gap I — During the third quarter of 2016, the Company tested the recoverability of its long-lived assets at Buffalo Gap I. As a result of decreases in wind production, management underwent a process to enhance the methodology for forecasting wind dispatch. The change in management’s estimate of dispatch resulted in lower forecasted revenues from September 2016 through the end of the asset group’s useful life. The Company determined that the carrying amount of the Buffalo Gap I asset group was not recoverable. The Buffalo Gap I asset group was determined to have a fair value of $35 million using the income approach. As a result, the Company recognized an asset impairment expense of $78 million ($23 million attributable to AES). Buffalo Gap I is reported in the US SBU reportable segment.
Buffalo Gap II — During the first quarter of 2016, the Company tested the recoverability of its long-lived assets at Buffalo Gap II. Impairment indicators were identified based on a decline in forward power curves. The Company determined that the carrying amount was not recoverable. The Buffalo Gap II asset group was determined to have a fair value of $92 million using the income approach. As a result, the Company recognized asset impairment expense of $159 million ($49 million attributable to AES). Buffalo Gap II is reported in the US SBU reportable segment.
15. DISCONTINUED OPERATIONS
Brazil Distribution — Due to a portfolio evaluation in the first half of 2016, management decided to pursue a strategic shift of its distribution companies in Brazil, Sul and Eletropaulo. In June 2016, the Company executed an agreement for the sale of Sul and reported its results of operations and financial position as discontinued operations. The disposal of Sul was completed in October 2016. Prior to its classification as discontinued operations, Sul was reported in the Brazil SBU reportable segment. In December 2016, Eletropaulo underwent a corporate restructuring which is expected to, among other things, provide more liquidity of its shares. AES is continuing to pursue strategic options for Eletropaulo in order to complete its strategic shift to reduce AES’ exposure to the Brazilian distribution businesses, including preparation for listing its shares into the Novo Mercado, which is a listing segment of the Brazilian stock exchange with the highest standards of corporate governance.
As the sale of Sul was completed during 2016, there were no assets or liabilities of discontinued operations at September 30, 2017 or December 31, 2016. There were no significant losses from discontinued operations or cash flows used in operating or investing activities of discontinued operations for the three and nine months ended September 30, 2017.
The following table summarizes the major line items constituting the loss from discontinued operations for the three and nine months ended September 30, 2016 (in millions):
Three Months Ended September 30, 2016 | Nine Months Ended September 30, 2016 | ||||||
Loss from discontinued operations, net of tax | |||||||
Revenue — regulated | $ | 213 | $ | 632 | |||
Cost of sales | (200 | ) | (608 | ) | |||
Asset impairment expense | — | (783 | ) | ||||
Other income and expense items that are not major, net | (14 | ) | (35 | ) | |||
Pretax loss from discontinued operations | $ | (1 | ) | $ | (794 | ) | |
Income tax benefit | — | 405 | |||||
Loss from discontinued operations, net of tax | $ | (1 | ) | $ | (389 | ) | |
The following table summarizes the operating and investing cash flows from discontinued operations for the nine months ended September 30, 2016 (in millions):
Nine Months Ended September 30, 2016 | |||
Cash flows provided by operating activities of discontinued operations | $ | 68 | |
Cash flows used in investing activities of discontinued operations | (63 | ) | |
22
16. HELD-FOR-SALE BUSINESSES AND DISPOSITIONS
Held-for-Sale Businesses
Kazakhstan Hydroelectric — Affiliates of the Company (the “Affiliates”) previously operated Shulbinsk HPP and Ust-Kamenogorsk HPP (the “HPPs”), two hydroelectric plants in Kazakhstan, under a concession agreement with the Republic of Kazakhstan (“RoK”). In April 2017, the RoK initiated the process to transfer these plants back to the RoK. Management considered it probable that the transfer would occur, and these plants met the held-for-sale criteria in the second quarter of 2017. For the nine months ended September 30, 2017, impairment charges of $92 million were recorded and were limited to the carrying value of the long lived assets. As of September 30, 2017, the remaining carrying value of the asset group, which was classified as held-for-sale, totaled $114 million, which included cumulative translation losses of $103 million.
On September 29, 2017, rather than paying the Affiliates, the RoK deposited $77 million into an escrow account that was not established in accordance with the requirements of the concession agreement. The amount deposited by the RoK equaled the Affiliates’ calculation of the transfer payment. In return, the RoK asserted that the Affiliates would be required to transfer the HPPs and that arbitration would be necessary to determine the correct transfer payment. On October 2, 2017, the Affiliates transferred 100% of the shares in the plants to the RoK, under protest and with a reservation of rights. As such, the HPPs remained classified as held-for-sale as of September 30, 2017. The Company expects to record a loss on disposal of at least $37 million in the fourth quarter of 2017. The Affiliates will proceed with arbitration to recover the $77 million that was placed in escrow, unless the parties can resolve the dispute prior to the initiation of arbitration. Additional losses may be incurred if some or all of the disputed consideration is not subsequently paid by the RoK. The transfer does not meet the criteria to be reported as discontinued operations. The Kazakhstan HPPs are reported in the Eurasia SBU reportable segment. Excluding the impairment charge, pretax income attributable to AES was as follows:
Three Months Ended September 30, | Nine Months Ended September 30, | ||||||||||||||
(in millions) | 2017 | 2016 | 2017 | 2016 | |||||||||||
Kazakhstan Hydroelectric | $ | 12 | $ | 10 | $ | 33 | $ | 28 | |||||||
Zimmer and Miami Fort — In April 2017, DP&L and AES Ohio Generation entered into an agreement for the sale of DP&L’s undivided interest in Zimmer and Miami Fort for $50 million in cash and the assumption of certain liabilities, including environmental, subject to predefined closing adjustments. The sale is subject to approval by the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission and is expected to close in the fourth quarter of 2017. Accordingly, Zimmer and Miami Fort remained classified as held-for-sale as of September 30, 2017, but did not meet the criteria to be reported as discontinued operations. Zimmer and Miami Fort are reported in the US SBU reportable segment. Their combined pretax income (loss) attributable to AES was as follows:
Three Months Ended September 30, | Nine Months Ended September 30, | ||||||||||||||
(in millions) | 2017 | 2016 | 2017 | 2016 | |||||||||||
Zimmer and Miami Fort | $ | 11 | $ | 1 | $ | 19 | $ | (10 | ) | ||||||
Dispositions
Kazakhstan CHPs — In April 2017, the Company completed the sale of Ust-Kamenogorsk CHP and Sogrinsk CHP, its combined heating and power coal plants in Kazakhstan, for net proceeds of $24 million. The carrying value of the asset group of $171 million was greater than its fair value less costs to sell of $29 million. The Company recognized an impairment charge of $94 million, which was limited to the carrying value of the long lived assets, and recognized a pretax loss on sale of $49 million, primarily related to cumulative translation losses. The sale did not meet the criteria to be reported as discontinued operations. Prior to their sale, the Kazakhstan CHP plants were reported in the Eurasia SBU reportable segment. Excluding the impairment charge and loss on sale, pretax income (loss) attributable to AES was as follows:
Three Months Ended September 30, | Nine Months Ended September 30, | ||||||||||||||
(in millions) | 2017 | 2016 | 2017 | 2016 | |||||||||||
Kazakhstan CHPs | $ | — | $ | (2 | ) | $ | 13 | $ | 5 | ||||||
DPLER — On January 1, 2016, the Company completed the sale of its interest in DPLER, a competitive retail marketer selling electricity to customers in Ohio. Upon completion, proceeds of $76 million were received and a gain on sale of $49 million was recognized. The sale of DPLER did not meet the criteria to be reported as a discontinued operation. Prior to its sale, DPLER was reported in the US SBU reportable segment.
23
Kelanitissa — On January 27, 2016, the Company completed the sale of its interest in Kelanitissa, a diesel-fired generation station in Sri Lanka. Upon completion, proceeds of $18 million were received and a loss on sale of $5 million was recognized. The sale of Kelanitissa did not meet the criteria to be reported as a discontinued operation. Prior to its sale, Kelanitissa was reported in the Eurasia SBU reportable segment.
UK Wind — During the second quarter of 2016, the Company deconsolidated UK Wind and recorded a loss on deconsolidation of $20 million to Gain (loss) on disposal and sale of businesses in the Condensed Consolidated Statement of Operations. Prior to deconsolidation, UK Wind was reported in the Eurasia SBU reportable segment.
17. ACQUISITIONS
Alto Sertão II — On August 3, 2017, the Company completed the acquisition of 100% of the Alto Sertão II Wind Complex (“Alto Sertão II”) from Renova Energia S.A. for $189 million, subject to customary purchase price adjustments, plus the assumption of $363 million of non-recourse debt, and up to $32 million of contingent consideration. At closing, the Company made an initial cash payment of $143 million, which excludes holdbacks related to indemnifications and purchase price adjustments. As of September 30, 2017, the purchase price allocation for Alto Sertão II is preliminary. The Company is in the process of assessing the fair value of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed in the acquisition, and expects to complete the purchase price allocation within the one year measurement period. Alto Sertão II is a wind farm with total installed capacity of 386 MW reported in the Brazil SBU reportable segment.
Bauru Solar Complex — On September 25, 2017, AES Tietê executed an investment agreement with Cobra do Brasil to provide approximately $150 million of non-convertible debentures in project financing for the construction of photovoltaic solar plants in Brazil with total forecasted capacity of 180 MW. Upon completion of the project, expected to be concluded in the first half of 2018, and subject to the solar plants’ compliance with certain technical specifications defined in the agreement, Tietê expects to acquire the solar complex in exchange for the non-convertible debentures and an additional investment of approximately $60 million.
18. EARNINGS PER SHARE
Basic and diluted earnings per share are based on the weighted average number of shares of common stock and potential common stock outstanding during the period. Potential common stock, for purposes of determining diluted earnings per share, includes the effects of dilutive RSUs, stock options and convertible securities. The effect of such potential common stock is computed using the treasury stock method or the if-converted method, as applicable.
The following table is a reconciliation of the numerator and denominator of the basic and diluted earnings per share computation for income from continuing operations for the three and nine months ended September 30, 2017 and 2016, where income or loss represents the numerator and weighted average shares represent the denominator.
Three Months Ended September 30, | 2017 | 2016 | |||||||||||||||||||
(in millions, except per share data) | Income | Shares | $ per Share | Income | Shares | $ per Share | |||||||||||||||
BASIC EARNINGS PER SHARE | |||||||||||||||||||||
Income from continuing operations attributable to The AES Corporation common stockholders, net of tax (1) | $ | 152 | 660 | $ | 0.23 | $ | 171 | 659 | $ | 0.26 | |||||||||||
EFFECT OF DILUTIVE SECURITIES | |||||||||||||||||||||
Restricted stock units | — | 3 | — | — | 3 | — | |||||||||||||||
DILUTED EARNINGS PER SHARE | $ | 152 | 663 | $ | 0.23 | $ | 171 | 662 | $ | 0.26 | |||||||||||
Nine Months Ended September 30, | 2017 | 2016 | |||||||||||||||||||
(in millions, except per share data) | Income | Shares | $ per Share | Income | Shares | $ per Share | |||||||||||||||
BASIC EARNINGS PER SHARE | |||||||||||||||||||||
Income from continuing operations attributable to The AES Corporation common stockholders, net of tax (2) | $ | 181 | 660 | $ | 0.28 | $ | 203 | 660 | $ | 0.31 | |||||||||||
EFFECT OF DILUTIVE SECURITIES | |||||||||||||||||||||
Restricted stock units | — | 2 | (0.01 | ) | — | 2 | — | ||||||||||||||
DILUTED EARNINGS PER SHARE | $ | 181 | 662 | $ | 0.27 | $ | 203 | 662 | $ | 0.31 | |||||||||||
_____________________________
(1) | Income from continuing operations, net of tax, of $176 million less the $5 million adjustment to retained earnings to record the DP&L redeemable preferred stock at its redemption value as of September 30, 2016. |
(2) | Income from continuing operations, net of tax, of $208 million less the $5 million adjustment to retained earnings to record the DP&L redeemable preferred stock at its redemption value as of September 30, 2016. |
24
For the three and nine months ended September 30, 2017 and 2016, respectively, the calculation of diluted earnings per share excluded 6 million and 7 million outstanding stock awards that could potentially dilute basic earnings per share in the future. All 15 million shares of potential common stock associated with convertible debentures (“TECONs”) were omitted from the earnings per share calculation for the three and nine months ended September 30, 2016. The company redeemed all of its existing TECONs in June 2017. The stock awards and convertible debentures were excluded from the calculation because they were anti-dilutive.
19. RISKS AND UNCERTAINTIES
Alto Maipo — As disclosed in Note 26—Risks and Uncertainties in Item 8.—Financial Statements and Supplementary Data of the 2016 Form 10-K, as of December 31, 2016, the Company has 531 MW under construction at Alto Maipo. Increased project costs, or delays in construction, could have an adverse impact on the Company. Alto Maipo has experienced construction difficulties, which have resulted in an increase in projected cost for the project of up to 22% of the original $2 billion budget. These overages led to a series of negotiations with the intention of restructuring the project’s existing financial structure and obtaining additional funding. On March 17, 2017, AES Gener completed the legal and financial restructuring of Alto Maipo, and through the Company’s 67% ownership interest in AES Gener, AES now has an effective 62% indirect economic interest in Alto Maipo. See Note 11—Equity for additional information regarding the restructuring.
Following the restructuring described above, the project continued to face construction difficulties including greater than expected costs and slower than anticipated productivity by construction contractors towards agreed-upon milestones. Furthermore, during the second quarter of 2017, as a result of the failure to perform by one of its construction contractors, Constructora Nuevo Maipo S.A. (“CNM”), Alto Maipo terminated CNM’s contract and is seeking a permanent replacement contractor to complete CNM’s work. Alto Maipo has hired a temporary replacement contractor to complete a portion of CNM’s work while the search for a permanent replacement contractor continues. As a result of the termination of CNM, Alto Maipo’s construction debt of $623 million and derivative liabilities of $139 million are in technical default and presented as current in the balance sheet as of September 30, 2017.
Construction at the project is continuing and Alto Maipo is working to resolve the challenges described above. Alto Maipo is seeking a permanent replacement contractor to complete CNM’s work, and continues to negotiate with lenders and other parties. However, there can be no assurance that Alto Maipo will succeed in these efforts and if there are further delays or cost overruns, or if Alto Maipo is unable to reach an agreement with the non-recourse lenders, there is a risk that these lenders may seek to exercise remedies available as a result of the default noted above, or that Alto Maipo may not be able to meet its contractual or other obligations and may be unable to continue with the project. If any of the above occur, there could be a material impairment for the Company.
The carrying value of the long-lived assets and deferred tax assets of Alto Maipo as of September 30, 2017 was approximately $1.4 billion and $60 million, respectively. Through its 67% ownership interest in Gener, the Parent Company has invested approximately $360 million in Alto Maipo and has an additional equity commitment of $55 million to be funded as part of the March 2017 restructuring described above. Even though certain of the construction difficulties have not been formally resolved, construction costs continue to be capitalized as management believes the project is probable of completion. Management believes the carrying value of the long-lived asset group is recoverable and was not impaired as of September 30, 2017. In addition, management believes it is more likely than not that the deferred tax assets will be realized, they could be reduced if estimates of future taxable income are decreased.
Puerto Rico — In September 2017, Puerto Rico was severely impacted by Hurricanes Irma and Maria, disrupting the operations of AES Puerto Rico and AES Ilumina. Puerto Rico’s infrastructure was severely damaged, including electric infrastructure and transmission lines. The extensive structural damage caused by hurricane winds and flooding is expected to take considerable time to repair. Although a more detailed assessment of the damage to its facilities is still ongoing, the Company sustained modest damage to its 24 MW AES Ilumina solar plant, resulting in an estimated $6 million loss, and minor damage to its 524 MW AES Puerto Rico thermal plants.
Our subsidiaries in Puerto Rico have long-term PPAs with state-owned PREPA. As a result of the Hurricanes, PREPA has declared an event of Force Majeure. However, both units of AES Puerto Rico and approximately 75% of AES Ilumina are available to generate electricity which, in accordance with the PPAs, will allow AES Puerto Rico to invoice capacity, even under Force Majeure.
Starting prior to the hurricanes, PREPA has been facing economic challenges that could impact the Company, and on July 2, 2017, filed for bankruptcy under Title III. As a result of the bankruptcy filing, AES Puerto Rico and
25
AES Ilumina’s non-recourse debt of $365 million and $36 million, respectively, are in default and have been classified as current as of September 30, 2017. In addition, the Company's receivable balances in Puerto Rico as of September 30, 2017 totaled $63 million, of which $30 million was overdue. After the filing of Title III protection, and up until the disruption caused by the hurricanes, AES in Puerto Rico was collecting the overdue amounts from PREPA in line with historic payment patterns.
Considering the information available as of the filing date, Management believes the carrying amount of our assets in Puerto Rico of $622 million is recoverable as of September 30, 2017.
20. SUBSEQUENT EVENTS
Kazakhstan Hydroelectric — On October 2, 2017, the Company transferred 100% of shares in Shulbinsk HPP and Ust-Kamenogorsk HPP to the Republic of Kazakhstan in accordance with the termination of the concession agreement. The Company expects to record a loss on disposal of at least $37 million in the fourth quarter of 2017. See Note 16—Held-for-Sale Businesses and Dispositions for further discussion.
Eletropaulo — In September 2017, the majority of Eletropaulo’s shareholders approved the transfer of Eletropaulo’s shares to the Novo Mercado. However, shareholders holding approximately 3 million shares, representing 2.7% of the total preferred shares, have indicated their preference to exercise withdrawal rights, which allows them to redeem their shares and receive a cash payment at book value for tendering their shares to Eletropaulo. Eletropaulo has now received all third party approvals to migrate to the Novo Mercado. The migration will be submitted to the Eletropaulo Board for confirmation that the costs associated with the exercise of the withdrawal rights are not significant enough to prevent migration. Once confirmed and the preferred shares are converted into ordinary shares, AES will no longer control Eletropaulo. Losing control will result in deconsolidation of Eletropaulo and the recording of an equity method investment for the remaining interest held in Eletropaulo. As of September 30, 2017, Eletropaulo had cumulative translation losses attributable to AES of $452 million and pension losses attributable to AES in other comprehensive income of $243 million, both of which will be recognized in earnings if Eletropaulo is deconsolidated. See Note 15—Discontinued Operations for further discussion.
26
ITEM 2. MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
The condensed consolidated financial statements included in Item 1.—Financial Statements of this Form 10-Q and the discussions contained herein should be read in conjunction with our 2016 Form 10-K.
FORWARD-LOOKING INFORMATION
The following discussion may contain forward-looking statements regarding us, our business, prospects and our results of operations that are subject to certain risks and uncertainties posed by many factors and events that could cause our actual business, prospects and results of operations to differ materially from those that may be anticipated by such forward-looking statements. Factors that could cause or contribute to such differences include, but are not limited to, those described in Item 1A.—Risk Factors and Item 7.—Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations of our 2016 Form 10-K and subsequent filings with the SEC. Readers are cautioned not to place undue reliance on these forward-looking statements which speak only as of the date of this report. We undertake no obligation to revise any forward-looking statements in order to reflect events or circumstances that may subsequently arise. If we do update one or more forward-looking statements, no inference should be drawn that we will make additional updates with respect to those or other forward-looking statements. Readers are urged to carefully review and consider the various disclosures made by us in this report and in our other reports filed with the SEC that advise of the risks and factors that may affect our business.
Overview of Our Business — We are a diversified power generation and utility company organized into the following five market-oriented SBUs: US (United States); Andes (Chile, Colombia and Argentina); Brazil; MCAC (Mexico, Central America and the Caribbean); and Eurasia (Europe and Asia). During the third quarter of 2017, the Europe and Asia SBUs were merged in order to leverage scale and are now reported as part of the Eurasia SBU. For additional information regarding our business, see Item 1.—Business of our 2016 Form 10-K.
Within our five SBUs, we have two lines of business. The first business line is generation, where we own and/or operate power plants to generate and sell power to customers such as utilities, industrial users and other intermediaries. The second business line is utilities, where we own and/or operate utilities to generate or purchase, distribute, transmit and sell electricity to end-user customers in the residential, commercial, industrial and governmental sectors within a defined service area. In certain circumstances, our utilities also generate and sell electricity on the wholesale market.
27
Executive Summary
Compared with last year, the results for the three and nine months ended September 30, 2017 reflect higher margins resulting from increased tariffs, lower fixed costs, and revenue associated with a favorable opinion on the basis calculation for PIS and COFINS taxes from prior years at Eletropaulo. In addition, operating margins increased due to higher contract capacity and the commencement of the Los Mina combined cycle operations at the MCAC SBU.
Net cash provided by operating activities decreased for the three months ended September 30, 2017compared to the prior year primarily driven by lower collections of net regulatory assets and current year sales at Eletropaulo, and the absence of Sul’s operating cash flow in 2017. In addition to the quarterly drivers, net cash provided by operating activities decreased for the nine months ended September 30, 2017 due to the collection of overdue receivables at Maritza in Bulgaria in 2016.
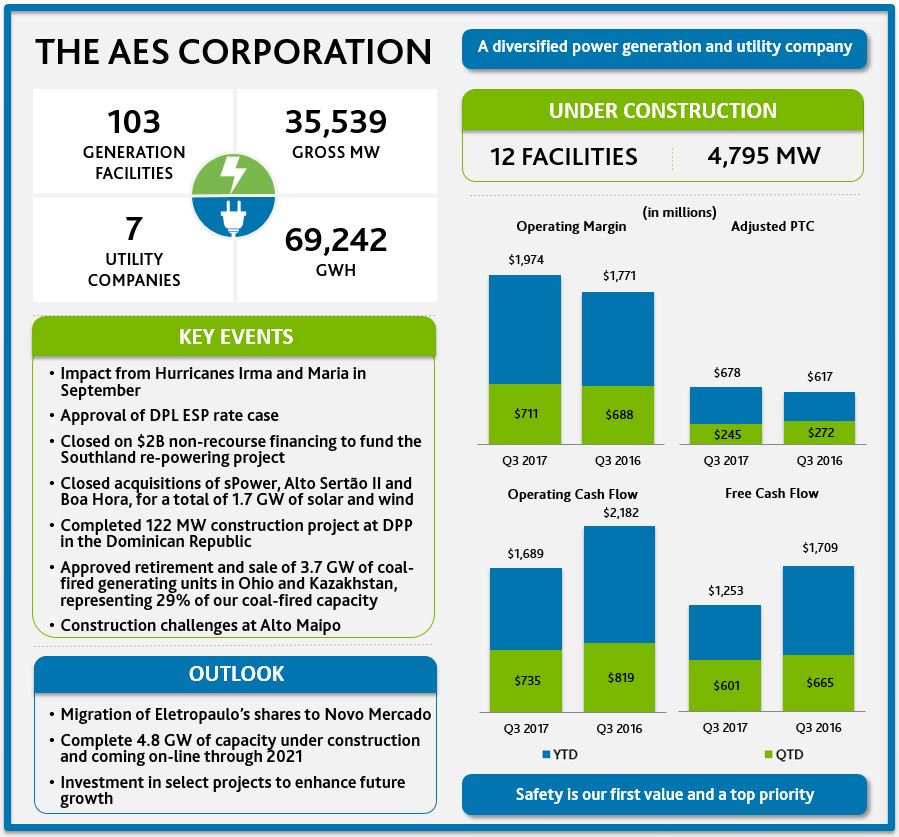
28
Overview of Q3 2017 Results and Strategic Performance
Strategic Priorities — We continue to make progress towards meeting our strategic goals to maximize value for our shareholders.
Leveraging Our Platforms | |||||||
Focusing our growth in markets where we already operate and have a competitive advantage to realize attractive risk-adjusted returns | |||||||
● | 4,795 MW currently under construction | ||||||
○ | Represents $8.7 billion in total capital expenditures | ||||||
○ | Majority of AES’ $1.5 billion in equity already funded | ||||||
○ | Expected to come on-line through 2021 | ||||||
● | Completed 122 MW conversion at DPP in the Dominican Republic | ||||||
● | Completed $2.0 billion non-recourse financing for 1,384 MW Southland re-powering project in California | ||||||
● | Will continue to advance select projects from our development pipeline | ||||||
Reducing Complexity | |||||||
Exiting businesses and markets where we do not have a competitive advantage, simplifying our portfolio and reducing risk | |||||||
● | Announced the sale or shutdown of 3,737 MW of merchant coal-fired generation in Ohio and Kazakhstan | ||||||
Performance Excellence | |||||||
Striving to be the low-cost manager of a portfolio of assets and deriving synergies and scale from our businesses | |||||||
● | Expect to achieve a total of $400 million in savings through 2020 | ||||||
○ | Includes overhead reductions, procurement efficiencies and operational improvements | ||||||
Expanding Access to Capital | |||||||
Optimizing risk-adjusted returns in existing businesses and growth projects | |||||||
● | Building strategic partnerships at the project and business level with an aim to optimize our risk-adjusted returns in our business and growth projects | ||||||
● | Adjust our global exposure to commodity, fuel, country and other macroeconomic risks | ||||||
Allocating Capital in a Disciplined Manner | |||||||
Maximizing risk-adjusted returns to our shareholders by investing our free cash flow to strengthen our credit and deliver attractive growth in cash flow and earnings | |||||||
● | Prepaid $300 million and refinanced $1 billion of Parent Company bonds | ||||||
● | Closed the acquisition of sPower, the largest independent solar developer in the United States | ||||||
Q3 2017 Strategic Performance
Earnings Per Share and Free Cash Flow Results in Q3 2017 (in millions, except per share amounts):
Three Months Ended September 30, | Nine Months Ended September 30, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | $ Change | % Change | 2017 | 2016 | $ Change | % Change | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Diluted earnings per share from continuing operations | $ | 0.23 | $ | 0.26 | $ | (0.03 | ) | -12 | % | $ | 0.27 | $ | 0.31 | $ | (0.04 | ) | -13 | % | |||||||||||
Adjusted EPS (a non-GAAP measure) (1) | 0.24 | 0.32 | (0.08 | ) | -25 | % | 0.66 | 0.64 | 0.02 | 3 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
Net cash provided by operating activities | 735 | 819 | (84 | ) | -10 | % | 1,689 | 2,182 | (493 | ) | -23 | % | |||||||||||||||||
Free Cash Flow (a non-GAAP measure) (1) | 601 | 665 | (64 | ) | -10 | % | 1,253 | 1,709 | (456 | ) | -27 | % | |||||||||||||||||
_____________________________
(1) | See Item 2.—SBU Performance Analysis—Non-GAAP Measures for reconciliation and definition. |
Three Months Ended September 30, 2017
Diluted earnings per share from continuing operations decreased $0.03, or 12% to income of $0.23. This was primarily driven by lower margin at our Andes SBU, higher losses on extinguishment of debt, higher income tax expense, unfavorable impact at Andes SBU from the full recognition of a non-trade receivable allowance and the write-off of water rights related to a business development project that is no longer pursued, and losses due to damages caused by hurricanes Irma and Maria. These decreases were partially offset by prior year impairments at Buffalo Gap I, unrealized foreign currency transaction gains and higher margin at our MCAC SBU.
Adjusted EPS, a non-GAAP measure, decreased $0.08, or 25%, to $0.24, primarily driven by lower margin at
29
our Andes SBU, higher income tax expense, unfavorable impact at Andes SBU from the full recognition of a non-trade receivable allowance and the write-off water rights related to a business development project that is no longer pursued, and losses due to the damages caused by hurricanes Irma and Maria. These decreases were partially offset by higher margins at our MCAC SBU.
Net cash provided by operating activities decreased by $84 million, or 10%, to $735 million, primarily driven by lower collections of net regulatory assets and current year sales at Eletropaulo, delay in collections at Gener, and the absence of Sul’s operating cash flow in 2017. These decreases were partially offset by the timing of payments for energy purchases at Eletropaulo.
Free cash flow, a non-GAAP measure, decreased by $64 million, or 10%, to $601 million, primarily driven by an $84 million decrease in net cash provided by operating activities, which was partially offset by a decrease of $18 million in maintenance (net of reinsurance proceeds) and non-recoverable environmental expenditures.
Nine Months Ended September 30, 2017
Diluted earnings per share from continuing operations decreased $0.04, or 13%, to $0.27. This was primarily driven by impairments at DPL and Kazakhstan CHPs and hydroelectric plants, losses incurred for the disposition of the Kazakhstan CHPs and higher income tax expense. These decreases were partially offset by prior year impairments at DPL and Buffalo Gap I and II, higher margins at our MCAC, Eurasia and Brazil SBUs and the favorable impact of the YPF legal settlement at AES Uruguaiana in 2017.
Adjusted EPS, a non-GAAP measure, increased $0.02, or 3%, to $0.66, primarily driven by higher margins at our MCAC, Eurasia and Brazil SBUs, the favorable impact of the YPF legal settlement at AES Uruguaiana, which was partially offset by higher income tax expense.
Net cash provided by operating activities decreased by $493 million, or 23%, to $1,689 million, primarily driven by lower collections of net regulatory assets and current year sales at Eletropaulo, the 2016 collection of overdue receivables at Maritza, and the absence of Sul’s operating cash flow in 2017. These decreases were partially offset by the timing of payments for energy purchases at Eletropaulo.
Free cash flow, a non-GAAP measure, decreased by $456 million, or 27%, to $1,253 million, primarily driven by a $493 million decrease in net cash provided by operating activities (exclusive of lower service concession asset expenditures of $22 million), which was partially offset by a decrease of $59 million in maintenance (net of reinsurance proceeds) and non-recoverable environmental expenditures.
30
Review of Consolidated Results of Operations
Three Months Ended September 30, | Nine Months Ended September 30, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
(in millions, except per share amounts) | 2017 | 2016 | $ change | % change | 2017 | 2016 | $ change | % change | |||||||||||||||||||||
Revenue: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
US SBU | $ | 852 | $ | 916 | $ | (64 | ) | -7 | % | $ | 2,445 | $ | 2,582 | $ | (137 | ) | -5 | % | |||||||||||
Andes SBU | 689 | 667 | 22 | 3 | % | 1,979 | 1,864 | 115 | 6 | % | |||||||||||||||||||
Brazil SBU | 1,085 | 1,027 | 58 | 6 | % | 3,106 | 2,761 | 345 | 12 | % | |||||||||||||||||||
MCAC SBU | 630 | 547 | 83 | 15 | % | 1,851 | 1,596 | 255 | 16 | % | |||||||||||||||||||
Eurasia SBU | 380 | 386 | (6 | ) | -2 | % | 1,204 | 1,249 | (45 | ) | -4 | % | |||||||||||||||||
Corporate and Other | 9 | 6 | 3 | 50 | % | 29 | 8 | 21 | NM | ||||||||||||||||||||
Intersegment eliminations | (13 | ) | (7 | ) | (6 | ) | -86 | % | (20 | ) | (18 | ) | (2 | ) | -11 | % | |||||||||||||
Total Revenue | 3,632 | 3,542 | 90 | 3 | % | 10,594 | 10,042 | 552 | 5 | % | |||||||||||||||||||
Operating Margin: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
US SBU | 184 | 189 | (5 | ) | -3 | % | 421 | 436 | (15 | ) | -3 | % | |||||||||||||||||
Andes SBU | 151 | 203 | (52 | ) | -26 | % | 452 | 466 | (14 | ) | -3 | % | |||||||||||||||||
Brazil SBU | 107 | 53 | 54 | NM | 311 | 174 | 137 | 79 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||
MCAC SBU | 165 | 140 | 25 | 18 | % | 430 | 370 | 60 | 16 | % | |||||||||||||||||||
Eurasia SBU | 102 | 95 | 7 | 7 | % | 343 | 308 | 35 | 11 | % | |||||||||||||||||||
Corporate and Other | 2 | 7 | (5 | ) | -71 | % | 17 | 11 | 6 | 55 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
Intersegment eliminations | — | 1 | (1 | ) | 100 | % | — | 6 | (6 | ) | 100 | % | |||||||||||||||||
Total Operating Margin | 711 | 688 | 23 | 3 | % | 1,974 | 1,771 | 203 | 11 | % | |||||||||||||||||||
General and administrative expenses | (52 | ) | (40 | ) | (12 | ) | 30 | % | (155 | ) | (135 | ) | (20 | ) | 15 | % | |||||||||||||
Interest expense | (353 | ) | (354 | ) | 1 | — | % | (1,034 | ) | (1,086 | ) | 52 | -5 | % | |||||||||||||||
Interest income | 101 | 110 | (9 | ) | -8 | % | 291 | 365 | (74 | ) | -20 | % | |||||||||||||||||
Loss on extinguishment of debt | (49 | ) | (16 | ) | (33 | ) | NM | (44 | ) | (12 | ) | (32 | ) | NM | |||||||||||||||
Other expense | (47 | ) | (13 | ) | (34 | ) | NM | (95 | ) | (42 | ) | (53 | ) | NM | |||||||||||||||
Other income | 18 | 18 | — | — | % | 105 | 43 | 62 | NM | ||||||||||||||||||||
Gain (loss) on disposal and sale of businesses | (1 | ) | — | (1 | ) | NM | (49 | ) | 30 | (79 | ) | NM | |||||||||||||||||
Asset impairment expense | (2 | ) | (79 | ) | 77 | -97 | % | (260 | ) | (473 | ) | 213 | -45 | % | |||||||||||||||
Foreign currency transaction gains (losses) | 21 | (20 | ) | 41 | NM | 13 | (16 | ) | 29 | NM | |||||||||||||||||||
Income tax expense | (110 | ) | (75 | ) | (35 | ) | 47 | % | (270 | ) | (165 | ) | (105 | ) | 64 | % | |||||||||||||
Net equity in earnings of affiliates | 24 | 11 | 13 | NM | 33 | 25 | 8 | 32 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||
INCOME FROM CONTINUING OPERATIONS | 261 | 230 | 31 | 13 | % | 509 | 305 | 204 | 67 | % | |||||||||||||||||||
Loss from operations of discontinued businesses, net of income tax benefit of $4 for the nine months ended September 30, 2016 | — | (1 | ) | 1 | -100 | % | — | (7 | ) | 7 | -100 | % | |||||||||||||||||
Net loss from disposal and impairments of discontinued businesses, net of income tax benefit of $401 for the nine months ended September 30, 2016 | — | — | — | — | % | — | (382 | ) | 382 | -100 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
NET INCOME (LOSS) | 261 | 229 | 32 | 14 | % | 509 | (84 | ) | 593 | NM | |||||||||||||||||||
Less: Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests and redeemable stock of subsidiaries | (109 | ) | (54 | ) | (55 | ) | NM | (328 | ) | (97 | ) | (231 | ) | NM | |||||||||||||||
NET INCOME (LOSS) ATTRIBUTABLE TO THE AES CORPORATION | $ | 152 | $ | 175 | $ | (23 | ) | -13 | % | $ | 181 | $ | (181 | ) | $ | 362 | NM | ||||||||||||
AMOUNTS ATTRIBUTABLE TO THE AES CORPORATION COMMON STOCKHOLDERS: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Income from continuing operations, net of tax | $ | 152 | $ | 176 | $ | (24 | ) | -14 | % | $ | 181 | $ | 208 | $ | (27 | ) | -13 | % | |||||||||||
Loss from discontinued operations, net of tax | — | (1 | ) | 1 | -100 | % | — | (389 | ) | 389 | -100 | % | |||||||||||||||||
NET INCOME (LOSS) ATTRIBUTABLE TO THE AES CORPORATION | $ | 152 | $ | 175 | $ | (23 | ) | -13 | % | $ | 181 | $ | (181 | ) | $ | 362 | NM | ||||||||||||
Net cash provided by operating activities | $ | 735 | $ | 819 | $ | (84 | ) | -10 | % | $ | 1,689 | $ | 2,182 | $ | (493 | ) | -23 | % | |||||||||||
DIVIDENDS DECLARED PER COMMON SHARE | $ | 0.12 | $ | 0.11 | $ | 0.01 | 9 | % | $ | 0.24 | $ | 0.22 | $ | 0.02 | 9 | % | |||||||||||||
Components of Revenue, Cost of Sales, Operating Margin, and Operating Cash Flow — Revenue includes revenue earned from the sale of energy from our utilities and the production and sale of energy from our generation plants, which are classified as regulated and non-regulated, respectively, on the Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations. Revenue also includes the gains or losses on derivatives associated with the sale of electricity.
Cost of sales includes costs incurred directly by the businesses in the ordinary course of business. Examples include electricity and fuel purchases, operations and maintenance costs, depreciation and amortization expense, bad debt expense and recoveries, and general administrative and support costs (including employee-related costs directly associated with the operations of the business). Cost of sales also includes the gains or losses on derivatives (including embedded derivatives other than foreign currency embedded derivatives) associated with the purchase of electricity or fuel.
Operating margin is defined as revenue less cost of sales.
31
Consolidated Revenue and Operating Margin
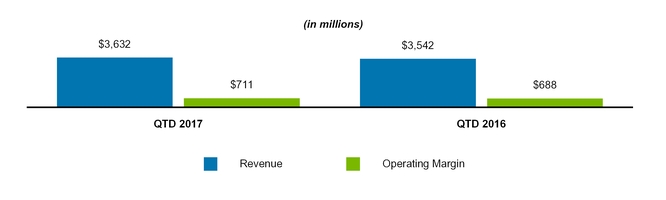
Three months ended September 30, 2017
Consolidated Revenue — Revenue increased $90 million, or 3%, for the three months ended September 30, 2017, as compared to the three months ended September 30, 2016. This increase was driven by:
• | The favorable FX impact of $37 million, primarily in Brazil of $31 million. |
Excluding the FX impact mentioned above:
• | $81 million in MCAC primarily due to higher contract energy sales resulting from the commencement of the combined cycle operations at Los Mina in June 2017, higher rates in the Dominican Republic, as well as higher pass through costs in El Salvador; and |
• | $28 million in Brazil primarily due to the acquisition of the Alto Sertão II wind farm in Tietê, and the one time recognition of revenue associated with a favorable opinion on the basis calculation for PIS and COFINS taxes from prior years as well as higher tariffs, partially offset by lower demand at Eletropaulo. |
These positive impacts were partially offset by a decrease of $64 million in the U.S. mainly due to lower wholesale volume and price, lower tariffs, and the unfavorable impact of mild weather at DPL.
Consolidated Operating Margin — Operating margin increased $23 million, or 3%, for the three months ended September 30, 2017, as compared to the three months ended September 30, 2016. This increase was driven by:
• | The favorable FX impact of $10 million, primarily in Andes and in Brazil. |
Excluding the FX impact mentioned above:
• | $52 million in Brazil primarily due to the one time recognition of revenue associated with a favorable opinion on the basis calculation for PIS and COFINS taxes from prior years, lower fixed cost, and higher tariffs, partially offset by lower demand at Eletropaulo, as well as the acquisition of the Alto Sertão II wind farm, partially offset by net unfavorable impact of volume and prices at Tietê; and |
• | $25 million in MCAC primarily due to the commencement of the combined cycle operations at Los Mina in June 2017, and higher availability in the Dominican Republic. |
These positive impacts were partially offset by a decrease of $56 million in Andes,primarily at Gener, driven by lower availability and higher fixed costs due to major maintenance at Ventanas, the unfavorable impact of new regulation on emissions, and lower contract margin in the SING market, partially offset by start of operations of Cochrane Units I and II in July and October 2016, respectively.
32
(in millions)
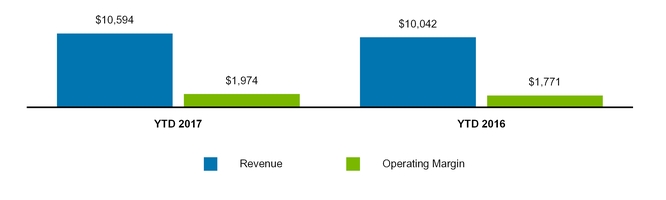
Nine months ended September 30, 2017
Consolidated Revenue — Revenue increased $552 million, or 5%, for the nine months ended September 30, 2017, as compared to the nine months ended September 30, 2016. This increase was driven by:
• | The favorable FX impact of $293 million, primarily in Brazil of $312 million, partially offset by the unfavorable FX impact of $19 million in Eurasia. |
Excluding the FX impact mentioned above:
• | $262 million in MCAC primarily due to higher LNG sales, higher contract rates, and higher contract energy sales resulting from the commencement of the combined cycle operations at Los Mina in June 2017, as well as higher pass through costs in El Salvador; and |
• | $109 million in Andes primarily due to the start of commercial operations at Cochrane as well as higher availability in Argentina, partially offset by lower spot sales at Chivor. |
These positive impacts were partially offset by a decrease of $137 million in the U.S. mainly due to lower tariffs, lower wholesale volume and price, and the unfavorable impact of mild weather at DPL.
Consolidated Operating Margin — Operating margin increased $203 million, or 11%, for the nine months ended September 30, 2017, as compared to the nine months ended September 30, 2016. This increase was driven by:
• | The favorable impact of FX of $42 million, primarily in Brazil of $29 million and in Andes of $15 million. |
Excluding the FX impact mentioned above:
• | $108 million in Brazil primarily due to higher tariffs, lower fixed costs, and the one time recognition of revenue associated with a favorable opinion on the basis calculation for PIS and COFINS taxes from prior years, partially offset by lower demand at Eletropaulo; |
• | $59 million in MCAC due to higher contract capacity and the commencement of the Los Mina combined cycle operations in June 2017 in the Dominican Republic as well as higher availability and lower maintenance in Mexico; and |
• | $39 million in Eurasia primarily due to higher derivative valuation adjustments and higher capacity income in Northern Ireland. |
These positive impacts were partially offset by a decrease of $28 million in Andes, primarily at Gener, driven by the impact of new regulation on emissions, lower availability and higher fixed costs due to maintenance activities, and lower contract margin in the SING market, partially offset by start of operations of Cochrane Units I and II in July and October 2016, respectively, as well as higher availability at Argentina.
See Item 2.—SBU Performance Analysis of this Form 10-Q for additional discussion and analysis of operating results for each SBU.
Consolidated Results of Operations — Other
General and administrative expenses
General and administrative expenses increased $12 million, or 30%, to $52 million for the three months ended September 30, 2017, as compared to $40 million for the three months ended September 30, 2016, primarily due to
33
business development activity and increased people costs.
General and administrative expenses increased $20 million, or 15%, to $155 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2017, as compared to $135 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2016, primarily due to increased professional fees and business development activity.
Interest expense
Interest expense decreased $1 million to $353 million for the three months ended September 30, 2017, as compared to $354 million for the three months ended September 30, 2016, with no significant drivers.
Interest expense decreased $52 million, or 5%, to $1,034 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2017, as compared to $1,086 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2016. This decrease was primarily due to a $61 million decrease at Eletropaulo attributable to lower debt balances, interest rates and regulatory liabilities, and a $23 million decrease at the Parent Company due to lower average debt balances. These decreases were partially offset by a $28 million increase at Cochrane primarily due to lower capitalized interest in 2017 as a result of the plant starting commercial operations in the second half of 2016.
Interest income
Interest income decreased $9 million, or 8%, to $101 million for the three months ended September 30, 2017, as compared to $110 million for the three months ended September 30, 2016. This decrease was primarily due to lower regulatory assets and interest rates at Eletropaulo.
Interest income decreased $74 million, or 20%, to $291 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2017, as compared to $365 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2016. This decrease was primarily due to lower regulatory assets and interest rates at Eletropaulo.
Loss on extinguishment of debt
Loss on extinguishment of debt increased $33 million to $49 million for the three months ended September 30, 2017, as compared to $16 million for the three months ended September 30, 2016. This increase was primarily due to a $36 million loss at the Parent Company resulting from the redemption and repurchase of senior notes in 2017.
Loss on extinguishment of debt increased $32 million to $44 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2017, as compared to $12 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2016. This increase was primarily due to losses of $92 million at the Parent Company, as a result of the redemption and repurchase of senior notes, partially offset by a gain of $65 million at Alicura, as a result of the prepayment of non-recourse debt related to the construction of the San Nicolas Plant, in the current period.
See Note 7—Debt included in Item 1.—Financial Statements of this Form 10-Q for further information.
Other income and expense
Other income remained flat at $18 million for the three months ended September 30, 2017, as compared to the three months ended September 30, 2016.
Other income increased $62 million to $105 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2017, as compared to $43 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2016. This increase was primarily due to the favorable settlement of legal proceeding at Uruguaiana related to YPF's breach of the parties’ gas supply agreement.
Other expense increased $34 million to $47 million for the three months ended September 30, 2017, as compared to $13 million for the three months ended September 30, 2016, primarily due to the write-off of water rights in the Andes SBU for projects that are no longer being pursued, and the recognition of a full allowance on a non-trade receivable in Andes SBU.
Other expense increased $53 million to $95 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2017, as compared to $42 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2016. This increase was primarily due to the loss on disposal of assets at DPL as a result of the decision made in 2017 to close the coal-fired and diesel-fired generating units at Stuart and Killen on or before June 1, 2018, higher assets write-off at Brazil SBU, the write-off of water rights in the Andes SBU for projects that are no longer being pursued, and the recognition of a full allowance on a non-trade receivable in Andes SBU.
See Note 13—Other Income and Expense included in Item 1.—Financial Statements of this Form 10-Q for further information.
34
Gain (loss) on disposal and sale of businesses
Loss on disposal and sale of businesses was $1 million for the three months ended September 30, 2017, with no loss in the comparative three months ended September 30, 2016.
Loss on disposal and sale of businesses was $49 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2017, as compared to a gain of $30 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2016. The 2017 negative impact was due to a $49 million loss on sale of Kazakhstan CHPs in 2017. The 2016 positive impact was primarily due to the $49 million gain on sale of DPLER, partially offset by the $20 million loss on deconsolidation of UK Wind in 2016.
See Note 16—Held-for-Sale Businesses and Dispositions included in Item 1.—Financial Statements of this Form 10-Q for further information.
Asset impairment expense
Asset impairment expense decreased $77 million, or 97%, to $2 million for the three months ended September 30, 2017, as compared to $79 million for the three months ended September 30, 2016. This was due to the prior year impairment at Buffalo Gap I, resulting from lower forecasted revenues due to decreases in wind production.
Asset impairment expense decreased $213 million, or 45%, to $260 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2017, as compared to $473 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2016. This was primarily due to the prior year impairments at Buffalo Gap I, resulting from lower forecasted revenues due to decreases in wind production, DPL, resulting from lower forecasted revenues from the PJM capacity auction and higher anticipated environmental compliance costs, and Buffalo Gap II, due to a decline in forward power curves. These were partially offset by impairments in the current year at Kazakhstan, resulting from the sale of the CHPs and the expiration of the HPPs concession agreement on October 2017 and their classification as held-for-sale, and at DPL as a result of the decision to close the coal-fired and diesel-fired generating units at Stuart and Killen on or before June 1, 2018.
See Note 14—Asset Impairment Expense included in Item 1.—Financial Statements of this Form 10-Q for further information.
Foreign currency transaction gains (losses)
Three Months Ended September 30, | Nine Months Ended September 30, | |||||||||||||||
(in millions) | 2017 | 2016 | 2017 | 2016 | ||||||||||||
Corporate | $ | 4 | $ | (23 | ) | $ | (1 | ) | $ | (29 | ) | |||||
Argentina | 9 | 8 | 4 | 9 | ||||||||||||
Colombia | (15 | ) | (3 | ) | (26 | ) | (4 | ) | ||||||||
United Kingdom | — | 1 | (3 | ) | 10 | |||||||||||
Chile | 9 | (2 | ) | 4 | (4 | ) | ||||||||||
Bulgaria | 5 | — | 1 | 12 | (3 | ) | ||||||||||
Philippines | 4 | — | 10 | 8 | ||||||||||||
Other | 5 | (2 | ) | 13 | (3 | ) | ||||||||||
Total (1) | $ | 21 | $ | (20 | ) | $ | 13 | $ | (16 | ) | ||||||
___________________________________________
(1) | Foreign currency derivative contracts gains and losses had no net impact for the 3 months ended September 30, 2017. Includes $15 million of losses on foreign currency derivative contracts for the 3 months ended September 30, 2016, and $37 million of losses and $8 million of gains on foreign currency derivative contracts for the nine months ended September 30, 2017 and 2016, respectively. |
The Company recognized net foreign currency transaction gains of $21 million for the three months ended September 30, 2017, primarily due to appreciation of the peso at Chile, and foreign currency derivatives related to government receivables at Argentina, partially offset foreign currency derivatives losses at Colombia due to a change in functional currency.
The Company recognized net foreign currency transaction losses of $20 million for the three months ended September 30, 2016, primarily at the Parent company due to foreign currency swaps and options, partially offset by remeasurement gains on intercompany notes.
The Company recognized net foreign currency transaction gains of $13 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2017, primarily due to the amortization of frozen embedded derivatives at Philippines, and appreciation of the euro at Bulgaria, partially offset by foreign currency derivatives losses at Columbia due to change a in functional currency.
The Company recognized net foreign currency transaction losses of $16 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2016, primarily at the Parent company due to foreign currency swaps and options, partially offset by remeasurement gains on intercompany notes and remeasurement gains on intercompany debt at United Kingdom.
35
Income tax expense
Income tax expense increased $35 million, or 47%, to $110 million for the three months ended September 30, 2017, compared to $75 million for the three months ended September 30, 2016. The Company’s effective tax rates were 32% and 26% for the three months ended September 30, 2017 and 2016, respectively. This net increase was due, in part, due to the prior year resolution of an audit settlement at certain of our operating subsidiaries in the Dominican Republic as well as the prior year devaluation of the Peso impacting certain of our Mexican subsidiaries.
Income tax expense increased $105 million, or 64%, to $270 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2017, compared to $165 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2016. The Company’s effective tax rates were 36% and 37% for the nine months ended September 30, 2017 and 2016, respectively. This net decrease was principally due to the unfavorable impact of Chilean income tax law reform enacted during the first quarter of 2016 and the 2016 asset impairments recorded at Buffalo Gap I, Buffalo Gap II, and DPL partially offset by the tax impacts of the 2017 appreciation of the Mexican Peso compared to the 2016 depreciation of the Peso.
Our effective tax rate reflects the tax effect of significant operations outside the U.S. which are generally taxed at lower rates than the U.S. statutory rate of 35%. A future proportionate change in the composition of income before income taxes from foreign and domestic tax jurisdictions could impact our periodic effective tax rate. In certain periods, however, our effective tax rate may be higher than 35% due to various discrete tax expense impacts.
Net equity in earnings of affiliates
Net equity in earnings of affiliates increased $13 million, to $24 million for the three months ended September 30, 2017, compared to $11 million for the three months ended September 30, 2016. This increase was primarily due to the purchase of the sPower equity method investment in July 2017.
Net equity in earnings of affiliates increased $8 million, or 32%, to $33 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2017, compared to $25 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2016. This increase was primarily due to the purchase of the sPower equity method investment, partially offset by a fixed asset impairment at Distributed Energy in 2017.
Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests and redeemable stock of subsidiaries
Net income attributable to NCI increased $55 million to $109 million for the three months ended September 30, 2017, as compared to $54 million for the three months ended September 30, 2016. This increase was primarily due to asset impairment expense at Buffalo Gap I in 2016 and higher operating margin at Eletropaulo due to the one time recognition of revenue associated with a favorable opinion on the basis calculation for PIS and COFINS taxes from prior years, lower fixed cost, and higher tariffs, partially offset by lower demand, partially offset by lower operating margin at Tietê.
Net income attributable to NCI increased $231 million to $328 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2017, as compared to $97 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2016. This increase was primarily due to asset impairment at Buffalo Gap I and II in 2016, higher operating margin at Eletropaulo primarily due to higher tariffs, lower fixed costs, and the one time recognition of revenue associated with a favorable opinion on the basis calculation for PIS and COFINS taxes from prior years, partially offset by lower demand, and favorable YPF legal settlement at AES Uruguaiana.
Discontinued operations
Net loss from discontinued operations was $1 million and $389 million for the three and nine months ended September 30, 2016, respectively, due to the operations from Sul being classified as discontinued operations starting in the second quarter of 2016. The sale of Sul closed in the fourth quarter of 2016. See Note 15—Discontinued Operations included in Item 1.—Financial Statements of this Form 10-Q for further information regarding the Sul discontinued operations.
Net income (loss) attributable to The AES Corporation
Net income attributable to The AES Corporation decreased $23 million to $152 million for the three months ended September 30, 2017, as compared to $175 million for the three months ended September 30, 2016. Key drivers of the decrease were:
• | Lower margin at our Andes SBU; |
• | Higher loss on extinguishment debt; |
• | Higher income tax expense; |
36
• | Unfavorable impact at Andes SBU from the full recognition of a non-trade receivable allowance and the write-off of water rights to a business development project that is no longer pursued; and |
• | Losses due to damages caused by hurricanes Irma and Maria. |
These decreases were partially offset by:
• | Prior year impairments at Buffalo Gap I; |
• | Unrealized foreign currency transaction gains; and |
• | Higher margin at our MCAC SBU. |
Net income attributable to The AES Corporation was $181 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2017, compared to a net loss attributable to The AES Corporation of $181 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2016. The $362 million positive impact was primarily driven by the following increases:
• | Prior year loss from discontinued operations of $389 million as a result of the sale of Sul (See Note 15. Discontinued Operations included in Item 1.— Financial Statements of this Form 10-Q for further information.) |
• | Prior year impairments at DPL and Buffalo Gap I and II; |
• | Higher margins at our MCAC, Eurasia and Brazil SBUs in the current year; and |
• | The favorable impact of the YPF legal settlement at AES Uruguaiana. |
These increases were partially offset by:
• | Current year impairments at Kazakhstan CHPs and hydroelectric plants, and DPL; |
• | Higher income tax expense; and |
• | Current year loss on sale of Kazakhstan CHPs. |
SBU Performance Analysis
Non-GAAP Measures
Adjusted Operating Margin, Adjusted PTC, Adjusted EPS, and Consolidated Free Cash Flow (“Free Cash Flow”) are non-GAAP supplemental measures that are used by management and external users of our consolidated financial statements such as investors, industry analysts and lenders. The Adjusted Operating Margin, Adjusted PTC, and Consolidated Free Cash Flow by SBU for the three and nine months ended September 30, 2017 and September 30, 2016, are shown below. The percentages represent the contribution by each SBU to the gross metric, excluding Corporate.
For the year beginning January 1, 2017, the Company changed the definition of Adjusted PTC and Adjusted EPS to exclude associated benefits and costs due to acquisitions, dispositions, and early plant closures; including the tax impact of decisions made at the time of sale to repatriate sales proceeds. We believe excluding these benefits and costs better reflect the business performance by removing the variability caused by strategic decisions to dispose of or acquire business interests or close plants early. The Company has also reflected these changes in the comparative periods ending September 30, 2016.
Adjusted Operating Margin
Operating Margin is defined as revenue less cost of sales. We define Adjusted Operating Margin as Operating Margin, adjusted for the impact of NCI, excluding unrealized gains or losses related to derivative transactions.
The GAAP measure most comparable to Adjusted Operating Margin is Operating Margin. We believe that Adjusted Operating Margin better reflects the underlying business performance of the Company. Factors in this determination include the impact of NCI, where AES consolidates the results of a subsidiary that is not wholly owned by the Company, as well as the variability due to unrealized derivatives gains or losses. Adjusted Operating Margin should not be construed as an alternative to Operating Margin, which is determined in accordance with GAAP.
37
Reconciliation of Adjusted Operating Margin (in millions) | Three Months Ended September 30, | Nine Months Ended September 30, | |||||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2017 | 2016 | ||||||||||||
Operating Margin | $ | 711 | $ | 688 | $ | 1,974 | $ | 1,771 | |||||||
Noncontrolling interests adjustment | (222 | ) | (187 | ) | (630 | ) | (502 | ) | |||||||
Derivatives adjustment | (6 | ) | (10 | ) | (16 | ) | 4 | ||||||||
Total Adjusted Operating Margin | $ | 483 | $ | 491 | $ | 1,328 | $ | 1,273 | |||||||
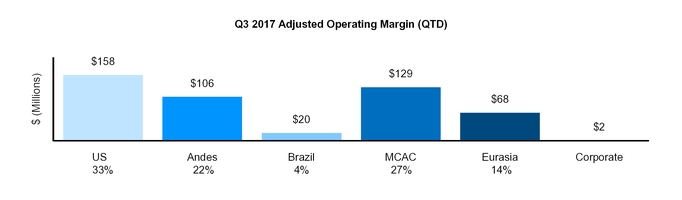
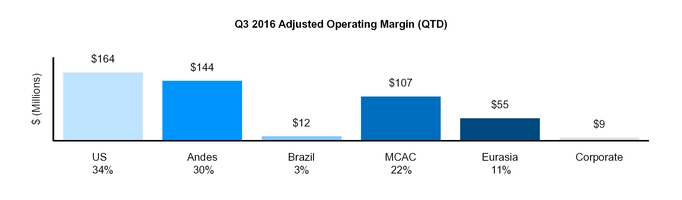
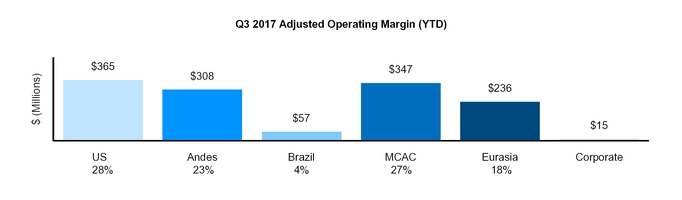
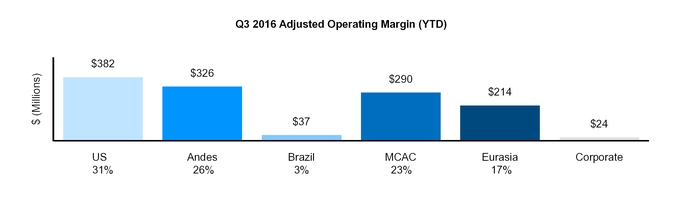
38
Adjusted PTC
We define Adjusted PTC as pretax income from continuing operations attributable to The AES Corporation excluding gains or losses of the consolidated entity due to (a) unrealized gains or losses related to derivative transactions; (b) unrealized foreign currency gains or losses; (c) gains or losses and associated benefits and costs due to dispositions and acquisitions of business interests, including early plant closures, and the tax impact from the repatriation of sales proceeds; (d) losses due to impairments; and (e) gains, losses and costs due to the early retirement of debt. Adjusted PTC also includes net equity in earnings of affiliates on an after-tax basis adjusted for the same gains or losses excluded from consolidated entities.
Adjusted PTC reflects the impact of NCI and excludes the items specified in the definition above. In addition to the revenue and cost of sales reflected in Operating Margin, Adjusted PTC includes the other components of our income statement, such as general and administrative expenses in the corporate segment, as well as business development costs, interest expense and interest income, other expense and other income, realized foreign currency transaction gains and losses, and net equity in earnings of affiliates.
The GAAP measure most comparable to Adjusted PTC is income from continuing operations attributable to The AES Corporation. We believe that Adjusted PTC better reflects the underlying business performance of the Company and is the most relevant measure considered in the Company’s internal evaluation of the financial performance of its segments. Factors in this determination include the variability due to unrealized gains or losses related to derivative transactions, unrealized foreign currency gains or losses, losses due to impairments and strategic decisions to dispose of or acquire business interests or retire debt, which affect results in a given period or periods. In addition, earnings before tax represents the business performance of the Company before the application of statutory income tax rates and tax adjustments, including the effects of tax planning, corresponding to the various jurisdictions in which the Company operates. Adjusted PTC should not be construed as an alternative to income from continuing operations attributable to The AES Corporation, which is determined in accordance with GAAP.
Reconciliation of Adjusted PTC (in millions) | Three Months Ended September 30, | Nine Months Ended September 30, | |||||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2017 | 2016 | ||||||||||||
Income from continuing operations, net of tax, attributable to The AES Corporation | $ | 152 | $ | 176 | $ | 181 | $ | 208 | |||||||
Income tax expense attributable to The AES Corporation | 71 | 47 | 144 | 66 | |||||||||||
Pretax contribution | 223 | 223 | 325 | 274 | |||||||||||
Unrealized derivative losses (gains) | (8 | ) | 5 | (7 | ) | 1 | |||||||||
Unrealized foreign currency transaction losses (gains) | (21 | ) | 3 | (54 | ) | 12 | |||||||||
Disposition/acquisition losses (gains) | 1 | (3 | ) | 107 | (5 | ) | |||||||||
Impairment expense | 2 | 24 | 264 | 309 | |||||||||||
Losses on extinguishment of debt | 48 | 20 | 43 | 26 | |||||||||||
Total Adjusted PTC | $ | 245 | $ | 272 | $ | 678 | $ | 617 | |||||||
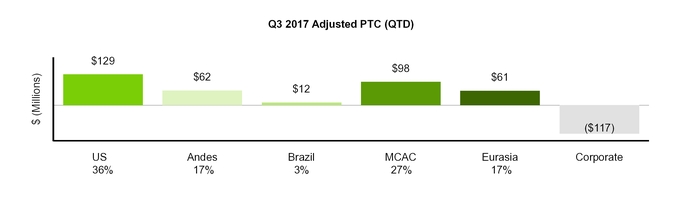
39
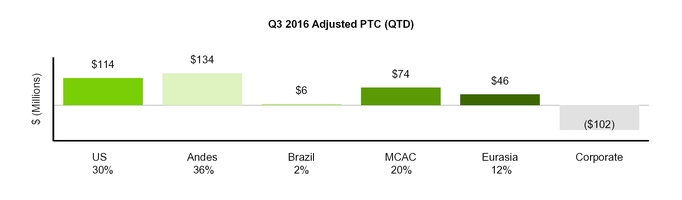
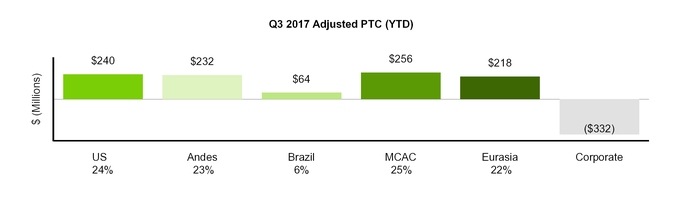
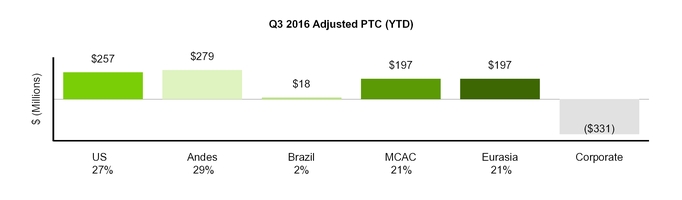
Adjusted EPS
We define Adjusted EPS as diluted earnings per share from continuing operations excluding gains or losses of both consolidated entities and entities accounted for under the equity method due to (a) unrealized gains or losses related to derivative transactions; (b) unrealized foreign currency gains or losses; (c) gains or losses and associated benefits and costs due to dispositions and acquisitions of business interests, including early plant closures, and the tax impact from the repatriation of sales proceeds; (d) losses due to impairments; and (e) gains, losses and costs due to the early retirement of debt.
The GAAP measure most comparable to Adjusted EPS is diluted earnings per share from continuing operations. We believe that Adjusted EPS better reflects the underlying business performance of the Company and is considered in the Company’s internal evaluation of financial performance. Factors in this determination include the variability due to unrealized gains or losses related to derivative transactions, unrealized foreign currency gains or losses, losses due to impairments and strategic decisions to dispose of or acquire business interests or retire debt, which affect results in a given period or periods. Adjusted EPS should not be construed as an alternative to diluted earnings per share from continuing operations, which is determined in accordance with GAAP.
40
Reconciliation of Adjusted EPS | Three Months Ended September 30, | Nine Months Ended September 30, | ||||||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2017 | 2016 | |||||||||||||
Diluted earnings per share from continuing operations | $ | 0.23 | $ | 0.26 | $ | 0.27 | $ | 0.31 | ||||||||
Unrealized derivative gains | (0.01 | ) | — | (0.01 | ) | — | ||||||||||
Unrealized foreign currency transaction losses (gains) | (0.03 | ) | 0.01 | (0.07 | ) | 0.01 | ||||||||||
Disposition/acquisition losses (gains) | — | — | 0.16 | (1) | — | (2) | ||||||||||
Impairment expense | — | 0.03 | (3) | 0.40 | (4) | 0.47 | (5) | |||||||||
Losses on extinguishment of debt | 0.07 | (6) | 0.04 | (7) | 0.06 | (8) | 0.05 | (9) | ||||||||
Less: Net income tax benefit | (0.02 | ) | (10) | (0.02 | ) | (0.15 | ) | (11) | (0.20 | ) | (11) | |||||
Adjusted EPS | $ | 0.24 | $ | 0.32 | $ | 0.66 | $ | 0.64 | ||||||||
_____________________________
(1) | Amount primarily relates to loss on sale of Kazakhstan CHPs of $48 million, or $0.07 per share, realized derivative losses associated with the sale of Sul of $38 million, or $0.06 per share; costs associated with early plant closure of DPL of $20 million, or $0.03 per share. |
(2) | Net impact of zero relates to the gain on sale of DPLER of $22 million, or $0.03 per share; offset by the loss on deconsolidation of UK Wind of $20 million, or $0.03 per share. |
(3) | Amount primarily relates to the asset impairment at Buffalo Gap I of $78 million ($23 million, or $0.03 per share, net of NCI). |
(4) | Amount primarily relates to asset impairment at Kazakhstan hydroelectric plants of $92 million, or $0.14 per share, at Kazakhstan CHPs of $94 million, or $0.14 per share, and DPL of $66 million, or $0.10 per share. |
(5) | Amount primarily relates to asset impairments at DPL of $235 million, or $0.36 per share; $159 million at Buffalo Gap II ($49 million, or $0.07 per share, net of NCI); and $78 million at Buffalo Gap I ($23 million, or $0.03 per share, net of NCI). |
(6) | Amount primarily relates to the losses on early retirement of debt at the Parent Company of $38 million, or $0.06 per share |
(7) | Amount primarily relates to losses on early retirement of debt at the Parent Company of $17 million, or $0.02 per share; and an adjustment of $5 million, or $0.01 per share to record the DP&L redeemable preferred stock at its redemption value. |
(8) | Amount primarily relates to losses on early retirement of debt at the Parent Company of $92 million, or $0.14 per share, partially offset by the the gain on early retirement of debt at Alicura of $65 million, or $0.10 per share. |
(9) | Amount primarily relates to losses on early retirement of debt at the Parent Company of $19 million, or $0.03 per share; and an adjustment of $5 million, or $0.01 per share, to record the DP&L redeemable preferred stock at its redemption value. |
(10) | Amount primarily relates to the income tax benefit associated with losses on early retirement of debt of $16 million, or $0.02 per share in the three months ended September 30, 2017. |
(11) | Amount primarily relates to the income tax benefit associated with asset impairment losses of $82 million, or $0.12 per share and $123 million, or $0.19 per share in the nine months ended September 30, 2017 and 2016, respectively. |
Free Cash Flow
We define Free Cash Flow as net cash from operating activities (adjusted for service concession asset capital expenditures) less maintenance capital expenditures (including non-recoverable environmental capital expenditures), net of reinsurance proceeds from third parties.
We also exclude environmental capital expenditures that are expected to be recovered through regulatory, contractual or other mechanisms. An example of recoverable environmental capital expenditures is IPL's investment in MATS-related environmental upgrades that are recovered through a tracker. See Item 1.—US SBU—IPL—Environmental Matters included in our 2016 Form 10-K for details of these investments.
The GAAP measure most comparable to Free Cash Flow is net cash provided by operating activities. We believe that Free Cash Flow is a useful measure for evaluating our financial condition because it represents the amount of cash generated by the business after the funding of maintenance capital expenditures that may be available for investing in growth opportunities or for repaying debt.
The presentation of Free Cash Flow has material limitations. Free Cash Flow should not be construed as an alternative to net cash from operating activities, which is determined in accordance with GAAP. Free Cash Flow does not represent our cash flow available for discretionary payments because it excludes certain payments that are required or to which we have committed, such as debt service requirements and dividend payments. Our definition of Free Cash Flow may not be comparable to similarly titled measures presented by other companies.
Calculation of Free Cash Flow (in millions) | Three Months Ended September 30, | Nine Months Ended September 30, | ||||||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | 2017 | 2016 | |||||||||||||
Net Cash provided by operating activities | $ | 735 | $ | 819 | $ | 1,689 | $ | 2,182 | ||||||||
Add: capital expenditures related to service concession assets (1) | 3 | 1 | 5 | 27 | ||||||||||||
Less: maintenance capital expenditures, net of reinsurance proceeds | (129 | ) | (144 | ) | (423 | ) | (464 | ) | ||||||||
Less: non-recoverable environmental capital expenditures (2) | (8 | ) | (11 | ) | (18 | ) | (36 | ) | ||||||||
Free Cash Flow | $ | 601 | $ | 665 | $ | 1,253 | $ | 1,709 | ||||||||
_____________________________
(1) | Service concession asset expenditures are included in net cash provided by operating activities, but are excluded from the free cash flow non-GAAP metric. |
(2) | Excludes IPL's recoverable environmental capital expenditures of $10 million and $32 million for the three months ended September 30, 2017 and 2016, as well as, $39 million and $162 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2017 and 2016, respectively. |
41
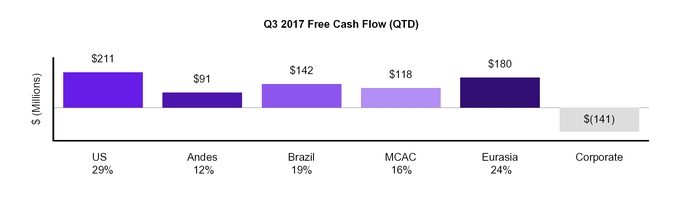
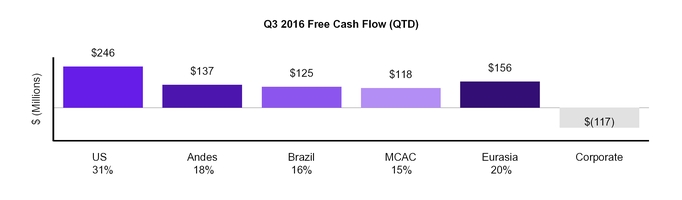
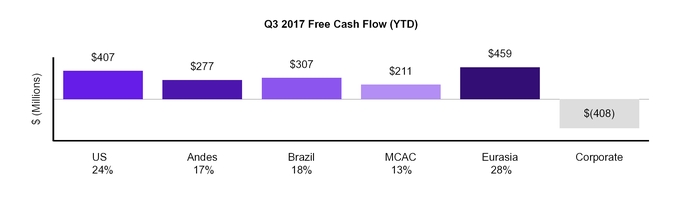
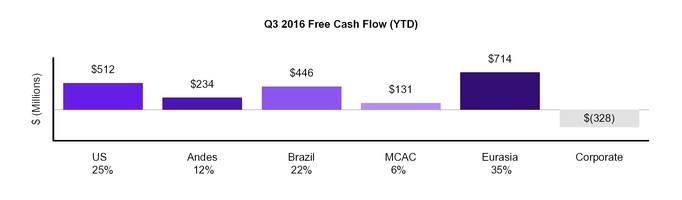
42
US SBU
The following table summarizes Operating Margin, Adjusted Operating Margin, Adjusted PTC, and Free Cash Flow (in millions) for the periods indicated:
Three Months Ended September 30, | Nine Months Ended September 30, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | $ Change | % Change | 2017 | 2016 | $ Change | % Change | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Operating Margin | $ | 184 | $ | 189 | $ | (5 | ) | -3 | % | $ | 421 | $ | 436 | $ | (15 | ) | -3 | % | |||||||||||
Noncontrolling Interests Adjustment (1) | (23 | ) | (26 | ) | (56 | ) | (59 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
Derivatives Adjustment | (3 | ) | 1 | — | 5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Adjusted Operating Margin | $ | 158 | $ | 164 | $ | (6 | ) | -4 | % | $ | 365 | $ | 382 | $ | (17 | ) | -4 | % | |||||||||||
Adjusted PTC | $ | 129 | $ | 114 | $ | 15 | 13 | % | $ | 240 | $ | 257 | $ | (17 | ) | -7 | % | ||||||||||||
Free Cash Flow | $ | 211 | $ | 246 | $ | (35 | ) | -14 | % | $ | 407 | $ | 512 | $ | (105 | ) | -21 | % | |||||||||||
Free Cash Flow Attributable to NCI | $ | 18 | $ | 27 | $ | (9 | ) | -33 | % | $ | 32 | $ | 43 | $ | (11 | ) | -26 | % | |||||||||||
_____________________________
(1) | See Item 1.—Business included in our 2016 Form 10-K for the respective ownership interest for key businesses. |
Operating Margin for the three months ended September 30, 2017, decreased by $5 million, or 3%, which was driven primarily by the following (in millions):
IPL | |||
Lower retail margin primarily due to weather | $ | (10 | ) |
Other | (3 | ) | |
Total IPL Decrease | (13 | ) | |
US Generation | |||
Warrior Run primarily due to higher availability and lower maintenance cost due to major outages in 2016 | 6 | ||
Other | 4 | ||
Total US Generation Increase | 10 | ||
Other Business Drivers | (2 | ) | |
Total US SBU Operating Margin Decrease | $ | (5 | ) |
Adjusted Operating Margin decreased by $6 million for the US SBU due to the drivers above, adjusted for NCI and excluding unrealized gains and losses on derivatives.
Adjusted PTC increased by $15 million, driven by earnings from equity affiliates due to the 2017 acquisition of sPower and an increase in insurance recoveries at DPL, partially offset by the $6 million decrease in Adjusted Operating Margin described above.
Free Cash Flow decreased by $35 million, of which $9 million was attributable to NCI. The decrease in Free Cash Flow was primarily driven by:
• | Additional inventory purchases of $20 million primarily due to inventory optimization efforts at DPL and IPL that occurred in 2016; |
• | Higher payments of $13 million for general accounts payable at DPL due to timing; |
• | Higher interest payments of $13 million primarily at DPL and IPL due to timing; and |
• | $9 million decrease in Operating Margin (net of lower depreciation of $4 million). |
These negative impacts were partially offset by an increase of $12 million in insurance proceeds at DPL.
Operating Margin for the nine months ended September 30, 2017, decreased by $15 million, or 3%, which was driven primarily by the following (in millions):
IPL | |||
Decrease due to implementation of new base rates in Q2 2016 which resulted in a favorable change in accrual | $ | (18 | ) |
Other | (1 | ) | |
Total IPL Decrease | (19 | ) | |
DPL | |||
Lower retail margin due to lower regulated rates | (26 | ) | |
Lower depreciation expense driven by lower PP&E carrying values from impairments in 2016 and 2017 | 19 | ||
Total DPL Decrease | (7 | ) | |
US Generation | |||
Warrior Run primarily due to higher availability and lower maintenance cost due to major outages in 2016, partially offset by a decrease in energy price under the PPA | 4 | ||
Other | 7 | ||
Total US Generation Increase | 11 | ||
Total US SBU Operating Margin Decrease | $ | (15 | ) |
Adjusted Operating Margin decreased by $17 million for the US SBU due to the drivers above, adjusted for NCI and excluding unrealized gains and losses on derivatives.
43
Adjusted PTC decreased by $17 million, driven by the $17 million decrease in Adjusted Operating Margin described above as well as a 2016 gain on contract termination at DP&L, offset by the Company's share of earnings under the HLBV allocation of noncontrolling interest at Distributed Energy due to new project growth, earnings from equity affiliates due to the 2017 acquisition of sPower, and an increase in insurance recoveries at DPL.
Free Cash Flow decreased by $105 million, of which $11 million was attributable to NCI. The decrease in Free Cash Flow was primarily driven by:
• | Additional inventory purchases of $66 million primarily due to inventory optimization efforts in 2016 at DPL and IPL; |
• | Timing of payments for purchased power and general accounts payable of $42 million at DPL; |
• | $41 million decrease in Operating Margin (net of lower depreciation of $26 million); |
• | Higher interest payments of $19 million primarily at DPL and IPL due to timing; and |
• | Lower collections at DPL of $11 million primarily due to the settlement of DPLER’s receivable balances resulting from its sale in 2016. |
These negative impacts were partially offset by:
• | Higher collections at IPL of $32 million due to higher receivable balances in December 2016 resulting from favorable weather and the impacts from the 2016 rate order; |
• | $30 million of lower maintenance and non-recoverable environmental capital expenditures; and |
• | Increase of $12 million in insurance proceeds at DPL. |
ANDES SBU
The following table summarizes Operating Margin, Adjusted Operating Margin, Adjusted PTC, and Free Cash Flow (in millions) for the periods indicated:
Three Months Ended September 30, | Nine Months Ended September 30, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | $ Change | % Change | 2017 | 2016 | $ Change | % Change | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Operating Margin | $ | 151 | $ | 203 | $ | (52 | ) | -26 | % | $ | 452 | $ | 466 | $ | (14 | ) | -3 | % | |||||||||||
Noncontrolling Interests Adjustment (1) | (46 | ) | (59 | ) | (144 | ) | (140 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
Derivatives Adjustment | 1 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Adjusted Operating Margin | $ | 106 | $ | 144 | $ | (38 | ) | -26 | % | $ | 308 | $ | 326 | $ | (18 | ) | -6 | % | |||||||||||
Adjusted PTC | $ | 62 | $ | 134 | $ | (72 | ) | -54 | % | $ | 232 | $ | 279 | $ | (47 | ) | -17 | % | |||||||||||
Free Cash Flow | $ | 91 | $ | 137 | $ | (46 | ) | -34 | % | $ | 277 | $ | 234 | $ | 43 | 18 | % | ||||||||||||
Free Cash Flow Attributable to NCI | $ | 33 | $ | 45 | $ | (12 | ) | -27 | % | $ | 98 | $ | 82 | $ | 16 | 20 | % | ||||||||||||
_____________________________
(1) | See Item 1.—Business included in our 2016 Form 10-K for the respective ownership interest for key businesses. |
Including favorable FX and remeasurement impacts of $5 million, Operating Margin for the three months ended September 30, 2017, decreased by $52 million, or 26%, which was driven primarily by the following (in millions):
Gener | |||
Lower availability of efficient generation resulting in higher replacement energy and fixed costs mainly associated with major maintenance at Ventanas Complex | $ | (29 | ) |
Negative impact of new regulation on emissions (green taxes) | (13 | ) | |
Lower margin at the SING market primarily associated with lower contract sales and increase in coal prices at Norgener | (8 | ) | |
Start of operations at Cochrane Units I and II in July and October 2016, respectively | 17 | ||
Other | (3 | ) | |
Total Gener Decrease | (36 | ) | |
Chivor | |||
Lower spot sales mainly associated to lower generation and lower prices | (16 | ) | |
Other | 1 | ||
Total Chivor Decrease | (15 | ) | |
Other Business Drivers | (1 | ) | |
Total Andes SBU Operating Margin Decrease | $ | (52 | ) |
Adjusted Operating Margin decreased by $38 million due to the drivers above, adjusted for the impact of NCI and excluding unrealized gains and losses on derivatives.
Adjusted PTC decreased by $72 million, mainly driven by the full allowance of a non-trade receivable in Argentina due to collection uncertainties, higher interest expense primarily associated with the issuance of debt in February 2017 at Argentina, and the write-off of water rights at Gener resulting from a business development project that is no longer pursued.
44
Free Cash Flow decreased by $46 million, of which $12 million was attributable to NCI. The decrease in Free Cash Flow was primarily driven by:
• | Higher working capital requirements of $59 million primarily due to delay in collections at Gener; and |
• | $32 million decrease in Operating Margin (net of higher depreciation of $7 million and $13 million of environmental tax accruals in Chile impacting margin but not free cash flow). |
These negative impacts were offset by higher collections of $44 million from account receivables in Argentina due to the impact of major maintenance performed in Q2 2016 and from financing receivables due to the commencement of operations of the Guillermo Brown Plant in October 2016.
Including favorable FX and remeasurement impacts of $15 million, Operating Margin for the nine months ended September 30, 2017, decreased by $14 million, or 3%, which was driven primarily by the following (in millions):
Gener | |||
Negative impact of new regulation on Emissions (Green Taxes) | $ | (37 | ) |
Lower availability of efficient generation resulting in higher replacement energy and fixed costs mainly associated with major maintenance at Ventanas Complex | (50 | ) | |
Lower margin at the SING market primarily associated with lower contract sales and increase in coal prices at Norgener partially offset by higher spot sales | (25 | ) | |
Start of operations at Cochrane Units I and II in July and October 2016, respectively | 64 | ||
Other | (6 | ) | |
Total Gener Decrease | (54 | ) | |
Argentina | |||
Higher capacity payments primarily associated to changes in regulation in 2017 | 32 | ||
Higher fixed costs mainly associated with higher people costs driven by inflation | (9 | ) | |
Other | 3 | ||
Total Argentina Increase | 26 | ||
Chivor | |||
Higher contract sales primarily associated to an increase in contracted capacity | 20 | ||
Lower spot sales mainly associated to lower generation | (12 | ) | |
Favorable FX impact | 7 | ||
Other | (1 | ) | |
Total Chivor Increase | 14 | ||
Total Andes SBU Operating Margin Decrease | $ | (14 | ) |
Adjusted Operating Margin decreased by $18 million due to the drivers above, adjusted for the impact of NCI.
Adjusted PTC decreased by $47 million, driven by the decrease of $18 million in Adjusted Operating Margin plus the full allowance of a non-trade receivable in Argentina due to collection uncertainties, higher interest expenses mainly associated to lower interest capitalization on construction projects and the issuance of debt at Argentina, and the write-off of water rights at Gener resulting from a business development project that is no longer pursued. These negative impacts were partially offset by foreign currency gains in Argentina associated with collections of financing receivables and lower foreign currency losses associated with the sale of Argentina’s sovereign bonds at Termoandes and prepayment of financial debt denominated in U.S. dollars in 2017 at Argentina.
Free Cash Flow increased by $43 million, of which $16 million was attributable to NCI. The increase in Free Cash Flow was primarily driven by:
• | Lower tax payments of $57 million primarily at Chivor and Argentina; |
• | $55 million increase in Operating Margin (net of higher depreciation of $32 million and $37 million of environmental tax accruals in Chile impacting margin but not free cash flow); |
• | Higher collections of $50 million from financing receivables in Argentina due to the commencement of operations of the Guillermo Brown Plant in October 2016; and |
• | $5 million of lower maintenance and non-recoverable environmental capital expenditures. |
These positive impacts were partially offset by:
• | Higher working capital requirements of $60 million primarily due to delay in collections at Gener and Argentina; |
• | Lower collections of prior period sales of $35 million at Chivor primarily due to higher receivables in Q1 2016 related to higher sales in Q4 2015; |
• | Higher interest payments of $14 million primarily associated with interest at Cochrane which is no longer capitalized; and |
• | Lower VAT refunds of $14 million at Alto Maipo and Cochrane due to the timing of construction activities. |
45
BRAZIL SBU
The following table summarizes Operating Margin, Adjusted Operating Margin, Adjusted PTC, and Free Cash Flow (in millions) for the periods indicated:
Three Months Ended September 30, | Nine Months Ended September 30, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | $ Change | % Change | 2017 | 2016 | $ Change | % Change | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Operating Margin | $ | 107 | $ | 53 | $ | 54 | NM | $ | 311 | $ | 174 | $ | 137 | 79 | % | ||||||||||||||
Noncontrolling Interests Adjustment (1) | (87 | ) | (41 | ) | (254 | ) | (137 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
Adjusted Operating Margin | $ | 20 | $ | 12 | $ | 8 | 67 | % | $ | 57 | $ | 37 | $ | 20 | 54 | % | |||||||||||||
Adjusted PTC | $ | 12 | $ | 6 | $ | 6 | 100 | % | $ | 64 | $ | 18 | $ | 46 | NM | ||||||||||||||
Free Cash Flow | $ | 142 | $ | 125 | $ | 17 | 14 | % | $ | 307 | $ | 446 | $ | (139 | ) | -31 | % | ||||||||||||
Free Cash Flow Attributable to NCI | $ | 116 | $ | 101 | $ | 15 | 15 | % | $ | 233 | $ | 340 | $ | (107 | ) | -31 | % | ||||||||||||
_____________________________
(1) | See Item 1.—Business included in our 2016 Form 10-K for the respective ownership interest for key businesses. |
Including favorable FX impacts of $3 million, Operating Margin for the three months ended September 30, 2017, increased by $54 million, which was driven primarily by the following (in millions):
Eletropaulo | |||
Revenue associated with a favorable opinion on the basis calculation for PIS and COFINS taxes from prior years | $ | 50 | |
Lower fixed costs mainly due to lower bad debt and regulatory penalties | 34 | ||
Higher tariffs due to annual tariff reset | 20 | ||
Lower volume mainly due to lower demand resulting from economic decline and migration to free market | (30 | ) | |
Other | (2 | ) | |
Total Eletropaulo Increase | 72 | ||
Tietê | |||
Net impact of volume and prices of bilateral contracts due to higher energy purchased | (45 | ) | |
Net impact of volume and prices of lower energy purchased in spot market | 13 | ||
Higher volume due to acquisition of new wind entities - Alto Sertão II | 12 | ||
Other | 2 | ||
Total Tietê Decrease | (18 | ) | |
Total Brazil SBU Operating Margin Increase | $ | 54 | |
Adjusted Operating Margin increased by $8 million, primarily due to the drivers discussed above, adjusted for the impact of noncontrolling interests.
Adjusted PTC increased by $6 million, mainly driven by the increase of $8 million in Adjusted Operating Margin as described above, partially offset by $2 million due to higher interest expense from debt issued to acquire new wind entities at Tietê.
Free Cash Flow increased by $17 million, of which $15 million was attributable to NCI. The increase in Free Cash Flow was primarily driven by:
•$166 million of lower payments for energy purchases at Eletropaulo due to lower energy costs and lower regulatory charges;
• | $65 million increase in Operating Margin (net of increased depreciation of $11 million); and |
• | Favorable timing of $24 million in higher energy purchased for resale at Tietê. |
These positive impacts were partially offset by:
• | $181 million in lower collections of costs deferred in net regulatory assets at Eletropaulo due to higher energy costs in Q3 2017; |
• | $22 million in lower collections of energy sales at Eletropaulo due primarily to higher tariffs in 2017; |
• | $15 million of higher maintenance capital expenditures at Eletropaulo; |
• | $7 million in lower collections on energy sales at Tietê; and |
• | $6 million of higher interest payments resulting from the assumption of debt for the acquisition of Alto Sertão II. |
46
Including favorable FX impacts of $29 million, Operating Margin for the nine months ended September 30, 2017, increased by $137 million, which was driven primarily by the following (in millions):
Eletropaulo | |||
Higher tariffs due to annual tariff reset | $ | 84 | |
Lower volume mainly due to lower demand resulting from slow economic growth and migration to free market | (61 | ) | |
Lower fixed costs mainly due to lower bad debt and lower regulatory penalties | 54 | ||
Revenue associated with a favorable opinion on the basis calculation for PIS and COFINS taxes from prior years | 50 | ||
Total Eletropaulo Increase | 127 | ||
Tietê | |||
Net impact of volume and prices of bilateral contracts due to higher energy purchased | (70 | ) | |
Net impact of volume and prices of lower energy purchased in spot market | 57 | ||
Favorable FX impacts | 20 | ||
Higher volume due to acquisition of new wind entities - Alto Sertão II | 12 | ||
Other | (3 | ) | |
Total Tietê Increase | 16 | ||
Other Business Drivers | (6 | ) | |
Total Brazil SBU Operating Margin Increase | $ | 137 | |
Adjusted Operating Margin increased by $20 million, primarily due to the drivers discussed above, adjusted for the impact of noncontrolling interests.
Adjusted PTC increased by $46 million, driven by the increase of $20 million in Adjusted Operating Margin as described above, as well as a $28 million increase from the settlement of a legal dispute with YPF at Uruguaiana.
Free Cash Flow decreased by $139 million, of which $107 million was attributable to NCI. The decrease in Free Cash Flow was primarily driven by:
• | $556 million of higher collections in 2016 of costs deferred in net regulatory assets at Eletropaulo, as a result of unfavorable hydrology in prior periods; |
• | $193 million in lower collections on energy sales at Eletropaulo due primarily to higher tariff flags in 2016; |
• | $55 million higher maintenance capital expenditures at Eletropaulo; |
• | $32 million decrease due to the sale of Sul in October 2016; |
• | $20 million in lower collections on energy sales at Tietê; |
• | $13 million of higher pension payments in 2017 driven by the debt renegotiation in prior year at Eletropaulo; and |
• | $6 million of higher interest payments at Alto Sertão II. |
These negative impacts were partially offset by:
• | Favorable timing of $401 million in payments for energy purchases at Eletropaulo due to lower energy costs and lower regulatory charges; |
• | $167 million increase in Operating Margin (net of increased depreciation of $30 million); |
• | $60 million collected from a legal dispute settlement with YPF at Uruguaiana; |
• | $58 million of lower tax payments at Tietê ; |
• | Favorable timing of $32 million in higher energy purchased for resale at Tietê; and |
• | $11 million of lower interest payments at Tietê. |
MCAC SBU
The following table summarizes Operating Margin, Adjusted Operating Margin, Adjusted PTC, and Free Cash Flow (in millions) for the periods indicated:
Three Months Ended September 30, | Nine Months Ended September 30, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | $ Change | % Change | 2017 | 2016 | $ Change | % Change | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Operating Margin | $ | 165 | $ | 140 | $ | 25 | 18 | % | $ | 430 | $ | 370 | $ | 60 | 16 | % | |||||||||||||
Noncontrolling Interests Adjustment (1) | (35 | ) | (31 | ) | (82 | ) | (77 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
Derivatives Adjustment | (1 | ) | (2 | ) | (1 | ) | (3 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
Adjusted Operating Margin | $ | 129 | $ | 107 | $ | 22 | 21 | % | $ | 347 | $ | 290 | $ | 57 | 20 | % | |||||||||||||
Adjusted PTC | $ | 98 | $ | 74 | $ | 24 | 32 | % | $ | 256 | $ | 197 | $ | 59 | 30 | % | |||||||||||||
Free Cash Flow | $ | 118 | $ | 118 | $ | — | — | % | $ | 211 | $ | 131 | $ | 80 | 61 | % | |||||||||||||
Free Cash Flow Attributable to NCI | $ | 14 | $ | 27 | $ | (13 | ) | -48 | % | $ | 20 | $ | 33 | $ | (13 | ) | -39 | % | |||||||||||
_____________________________
(1) | See Item 1.—Business included in our 2016 Form 10-K for the respective ownership interest for key businesses. |
47
Operating Margin for the three months ended September 30, 2017, increased by $25 million, or 18%, which was driven primarily by the following (in millions):
Dominican Republic | |||
Higher contracted energy sales mainly driven by Los Mina combined cycle commencement of operations in June 2017 | $ | 14 | |
Higher availability driven by Los Mina combined cycle interconnection in 2016 | 5 | ||
Other | 6 | ||
Total Dominican Republic Increase | 25 | ||
Total MCAC SBU Operating Margin Increase | $ | 25 | |
Adjusted Operating Margin increased by $22 million due to the drivers above, adjusted for the impact of NCI and excluding unrealized gains and losses on derivatives.
Adjusted PTC increased by $24 million, driven by the increase of $22 million in Adjusted Operating Margin as described above.
Free Cash Flow is aligned in both periods, driven by $28 million increase in Operating Margin (net of increased depreciation of $3 million), offset by higher working capital requirements due to unfavorable timing of collections, mainly in the Dominican Republic.
Including favorable FX impacts of $1 million, Operating Margin for the nine months ended September 30, 2017, increased by $60 million, or 16%, which was driven primarily by the following (in millions):
Dominican Republic | |||
Higher energy sales mainly driven by higher contracted capacity | $ | 32 | |
Higher availability driven by greater major maintenance scope in 2016 | 13 | ||
Other | (7 | ) | |
Total Dominican Republic Increase | 38 | ||
Mexico | |||
Lower maintenance and higher availability | 17 | ||
Other | 4 | ||
Total Mexico Increase | 21 | ||
Other Business Drivers | 1 | ||
Total MCAC SBU Operating Margin Increase | $ | 60 | |
Adjusted Operating Margin increased by $57 million due to the drivers above, adjusted for the impact of NCI and excluding unrealized gains and losses on derivatives.
Adjusted PTC increased by $59 million, driven by the increase of $57 million in Adjusted Operating Margin as described above.
Free Cash Flow increased by $80 million, of which a $13 million decrease was attributable to NCI. The increase in Free Cash Flow was driven by:
• | $68 million increase in Operating Margin (net of increased depreciation of $8 million); |
• | Lower working capital requirements of $36 million in AES Puerto Rico primarily due to higher collections of energy sales; |
• | Lower tax payments of $10 million in the Dominican Republic primarily due to lower withholding taxes on dividends paid in 2016 to AES Affiliates; |
• | Lower tax payments of $16 million in El Salvador; and |
• | $7 million of lower maintenance and non-recoverable environmental capital expenditures. |
These positive impacts were partially offset by:
• | Higher working capital requirements of $42 million in the Dominican Republic primarily due to lower collections of energy sales at Itabo; and |
• | $13 million of higher interest payments in the Dominican Republic primarily due to an increase in net debt and average interest rates. |
48
EURASIA SBU
The following table summarizes Operating Margin, Adjusted Operating Margin, Adjusted PTC, and Free Cash Flow (in millions) for the periods indicated:
Three Months Ended September 30, | Nine Months Ended September 30, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | $ Change | % Change | 2017 | 2016 | $ Change | % Change | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Operating Margin | $ | 102 | $ | 95 | $ | 7 | 7 | % | $ | 343 | $ | 308 | $ | 35 | 11 | % | |||||||||||||
Noncontrolling Interests Adjustment (1) | (30 | ) | (30 | ) | (94 | ) | (89 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
Derivatives Adjustment | (4 | ) | (10 | ) | (13 | ) | (5 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
Adjusted Operating Margin | $ | 68 | $ | 55 | $ | 13 | 24 | % | $ | 236 | $ | 214 | $ | 22 | 10 | % | |||||||||||||
Adjusted PTC | $ | 61 | $ | 46 | $ | 15 | 33 | % | $ | 218 | $ | 197 | $ | 21 | 11 | % | |||||||||||||
Free Cash Flow | $ | 180 | $ | 156 | $ | 24 | 15 | % | $ | 459 | $ | 714 | $ | (255 | ) | -36 | % | ||||||||||||
Free Cash Flow Attributable to NCI | $ | 56 | $ | 65 | $ | (9 | ) | -14 | % | $ | 145 | $ | 142 | $ | 3 | 2 | % | ||||||||||||
_____________________________
(1) | See Item 1.—Business included in our 2016 Form 10-K for the respective ownership interest for key businesses. |
Including favorable FX impacts of $2 million, Operating Margin for the three months ended September 30, 2017, increased by $7 million, or 7%, which was driven primarily by the following (in millions):
Ballylumford | |||
Higher energy and capacity prices | $ | 4 | |
Other | 4 | ||
Total Ballylumford Increase | 8 | ||
Other Business Drivers | (1 | ) | |
Total Eurasia SBU Operating Margin Increase | $ | 7 | |
Adjusted Operating Margin increased by $13 million due to the drivers above, adjusted for NCI and excluding unrealized gains and losses on derivatives.
Adjusted PTC increased by $15 million, mainly driven by the increase of $13 million in Adjusted Operating Margin described above.
Free Cash Flow increased by $24 million, of which a $9 million decrease was attributable to NCI. The increase in Free Cash Flow was primarily driven by:
• | Increase in CO2 allowances of $9 million at Maritza due to decreased prices in 2016; |
• | Lower working capital requirements of $8 million at Kilroot primarily due to a decrease in rates and VAT received in 2017; and |
• | $5 million of lower maintenance and non-recoverable environmental capital expenditures. |
Including unfavorable FX impacts of $3 million, Operating Margin for the nine months ended September 30, 2017 increased by $35 million, or 11%, which was driven primarily by the following (in millions):
Kilroot | |||
Higher fair value adjustments of commodity swaps | $ | 10 | |
Favorable capacity prices due to fixed EUR/GBP rate set by the Regulator | 9 | ||
Unfavorable clean-dark spread leading to lower dispatch | (6 | ) | |
Other | (3 | ) | |
Total Kilroot Increase | 10 | ||
Ballylumford | |||
Higher energy and capacity prices | 7 | ||
Settlement with offtaker on previous gas transportation charges billed in April 2017 | 4 | ||
Lower maintenance costs due to outages in 2016 | 3 | ||
Other | 6 | ||
Total Ballylumford Increase | 20 | ||
Other Business Drivers | 5 | ||
Total Eurasia SBU Operating Margin Increase | $ | 35 | |
Adjusted Operating Margin increased by $22 million due to the drivers above, adjusted for NCI and excluding unrealized gains and losses on derivatives.
Adjusted PTC increased by $21 million, mainly driven by the increase of $22 million in Adjusted Operating Margin described above.
49
Free Cash Flow decreased by $255 million, of which a $3 million increase was attributable to NCI. The decrease in Free Cash Flow was primarily driven by:
• | Lower collections of $376 million at Maritza, primarily due to the collection of overdue receivables from NEK in April 2016; |
• | $9 million of higher non-cash mark-to-market valuation adjustments to commodity swaps at Kilroot impacting margin but not free cash flow; and |
• | Lower coal purchases of $9 million at Mong Duong due to the reserve shutdown in 2017. |
These negative impacts were partially offset by:
• | The settlement of $73 million in payables to Maritza’s fuel supplier; |
• | $21 million of lower maintenance and non-recoverable environmental capital expenditures; |
• | $19 million increase in operating margin (net of $16 million of lower depreciation); |
• | Lower working capital requirements of $19 million at Masinloc due to the timing of payments for coal purchases; and |
• | Increase in CO2 allowances of $17 million at Maritza due to decreased prices in 2016. |
Key Trends and Uncertainties
During the remainder of 2017 and beyond, we expect to face the following challenges at certain of our businesses. Management expects that improved operating performance at certain businesses, growth from new businesses and global cost reduction initiatives may lessen or offset their impact. If these favorable effects do not occur, or if the challenges described below and elsewhere in this section impact us more significantly than we currently anticipate, or if volatile foreign currencies and commodities move more unfavorably, then these adverse factors (or other adverse factors unknown to us) may have a material impact on our operating margin, net income attributable to The AES Corporation and cash flows. We continue to monitor our operations and address challenges as they arise.
Hurricanes Irma and Maria
In September 2017, Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands were severely impacted by Hurricanes Irma and Maria, disrupting the operations of AES Puerto Rico, AES Ilumina, and certain Distributed Energy assets. Puerto Rico’s infrastructure was severely damaged, including electric infrastructure and transmission lines. The extensive structural damage caused by hurricane winds and flooding is expected to take significant time to repair.
On October 24, 2017, the U.S. Congress approved a $37 billion emergency disaster relief bill which will allow the US Government to help victims from the hurricanes and assist with the infrastructure rebuild in the affected areas through the Federal Emergency Management Agency. This supplemental appropriation includes an allocation of $5 billion for the Disaster Assistance Direct Loan Program to assist local governments, like Puerto Rico, in providing essential services, such as reestablishing electricity.
Although a more detailed assessment of the damage to its facilities is still ongoing, the Company sustained modest damage to its 24 MW AES Ilumina solar plant, resulting in an estimated $6 million loss, and minor damage to its 524 MW AES Puerto Rico thermal plants, both located in Puerto Rico. The Company’s 5 MW solar plant in the U.S. Virgin Islands has been materially damaged, resulting in an estimated $9 million loss, and is not available to generate electricity.
As a result of the Hurricanes, PREPA has declared an event of Force Majeure. However, both units of AES Puerto Rico and approximately 75% of AES Ilumina are available to generate electricity which, in accordance with the PPAs, will allow AES Puerto Rico to invoice capacity, even under Force Majeure.
The Company maintains an insurance program, subject to an annual cap, which provides coverage for property damage, business interruption, and costs associated with clean-up and recovery. However, it is possible that any losses not covered by insurance could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition, results of operations, or cash flows.
Macroeconomic and Political
During the past few years, economic conditions in some countries where our subsidiaries conduct business have destabilized. Changes in global economic conditions could have an adverse impact on our businesses in the event these recent trends continue.
Puerto Rico — As discussed in Item 7—Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Key Trends and Uncertainties of the 2016 Form 10-K our subsidiaries in Puerto Rico have
50
long- term PPAs with state-owned PREPA, which has been facing economic challenges that could impact the Company.
In order to address these challenges, on June 30, 2016, the Puerto Rico Oversight, Management, and Economic Stability Act (“PROMESA”) was signed into law. PROMESA created a structure for exercising federal oversight over the fiscal affairs of U.S. territories and allowed for the establishment of an Oversight Board with broad powers of budgetary and financial control over Puerto Rico. PROMESA also created procedures for adjusting debts accumulated by the Puerto Rico government and, potentially, other territories (“Title III”). Finally, PROMESA expedites the approval of key energy projects and other critical projects in Puerto Rico.
PREPA entered into preliminary Restructuring Support Agreements (“RSAs”) with their lenders. Under PROMESEA, PREPA submitted the RSA to the Oversight Board for approval on April 28, 2017, which the board denied on June 28, 2017. As a consequence, on July 2, 2017, the Oversight Board filed for bankruptcy on behalf of PREPA under Title III.
As a result of the bankruptcy filing, AES Puerto Rico and AES Ilumina’s non-recourse debt of $365 million and $36 million, respectively, are in default and have been classified as current as of September 30, 2017. In addition, the Company's receivable balances in Puerto Rico as of September 30, 2017 totaled $63 million, of which $30 million was overdue. After the filing of Title III protection, and up until the disruption caused by the hurricanes, AES in Puerto Rico was collecting the overdue amounts from PREPA in line with historic payment patterns.
Additionally, on July 18, 2017, Moody's downgraded AES Puerto Rico to Caa1 from B3 due to the heightened default risk for AES Puerto Rico as a result of PREPA's bankruptcy protection. This protection gives PREPA the ability to renegotiate contracts, which could impact the value of our assets in Puerto Rico or otherwise have a material impact on the Company. In this regard, PREPA had requested the Company to renegotiate its 24 MW AES Ilumina’s PPA. After the event of the hurricanes Maria and Irma, these negotiations were put on hold.
Considering the information available as of the filing date, Management believes the carrying amount of our assets in Puerto Rico of $622 million is recoverable as of September 30, 2017.
Brazil — The political landscape in Brazil remains uncertain. As disclosed in the Company’s Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2016, Brazilian President Michael Temer was seeking to implement economic reforms in Brazil that would improve the economic outlook in Brazil, which may benefit our businesses in the country. During 2017, corruption investigations were formally started against President Temer. These investigations could delay the reform plans which may have benefited our businesses in Brazil.
Regulatory
DP&L ESP Rate Case — On October 20, 2017, PUCO issued a final decision approving the DP&L ESP rate case. The ESP establishes DP&L’s framework for providing retail service on a go forward basis including rate structures, non-bypassable charges and other specific rate recovery true-up mechanisms. The agreement establishes a six-year settlement that provides a framework for energy rates and defines components which include, but are not limited to, the following:
• | Bypassable standard offer energy rates for DP&L’s customers based on competitive bid auctions; |
• | The establishment of a three-year non-bypassable Distribution Modernization Rider designed to collect $105 million in revenue per year which could be extended by PUCO for an additional two years. The Distribution Modernization Rider will be used for debt repayments as well as modernization and maintenance of transmission and distribution infrastructure; |
• | The establishment of a non-bypassable Distribution Investment Rider to recover incremental distribution capital investments, the amount of which is to be established in a separate DP&L distribution rate case; |
• | A non-bypassable Reconciliation Rider permitting DP&L to defer, recover, or credit the net proceeds from selling energy and capacity received as part of DP&L’s investment in the Ohio Valley Electric Corporation; |
• | Implementation by DP&L of a Smart Grid Rider, Economic Development Rider, Economic Development Fund, Regulatory Compliance Rider and certain other new or modified rates, riders and competitive retail market enhancements, with tariffs consistent with the order to be effective November 1, 2017; |
• | A commitment to commence the sale process of the Company’s ownership interests in the Zimmer, Miami Fort and Conesville coal-fired generation plants with all sales proceeds used to pay debt of DPL and DP&L; and |
• | Restrictions on DPL making dividend or tax sharing payments. |
51
In connection with the sale or closure of our generation plants as contemplated by the ESP settlement or otherwise, DPL and DP&L may incur certain cash and non-cash charges, which could be material to the Company.
Proposed U.S. Market Reforms — The U.S. Department of Energy (“DOE”) issued a Notice of Proposed Rule Making (“NOPR”) on September 29, 2017, which directed the FERC to exercise its authority to set just and reasonable rates that recognize the “resiliency” value provided by generation plants with certain characteristics, including having 90-days or more of on-site fuel and operating in markets where they do not receive rate base treatment through state ratemaking. Nuclear and coal-fired generation plants are most likely to be able to meet the requirements. As proposed, the DOE would value resiliency through rates that recover “compensable costs” that are defined to include the recovery of operating and fuel expenses, debt service and a fair return on equity. The FERC is proceeding on an expedited basis, as requested by the DOE, but the timing and outcome of the proposed rule, including effects on wholesale energy markets, remains uncertain.
International Trade Commission — In April 2017, Suniva, a bankrupt solar photovoltaic panel manufacturer with a factory in Georgia filed a petition with the U.S. International Trade Commission (“ITC”) asserting that solar panels imported into the U.S. were causing substantial injury to domestic manufacturers. Subsequent to filing, SolarWorld Americas, a large U.S. manufacturer of solar panels, joined as a co-petitioner. The ITC accepted the petition and on September 22, 2107 determined that serious injury has been caused by foreign solar photovoltaic panels. On October 31, 2017, the ITC announced its proposed recommendations for remedies. These proposed recommendations include tariffs at various levels, a quota system and licensing fees. The ITC's final recommendations will be provided to the U.S. President by November 13, 2017. A final decision, either to accept, revise or reject some or all of the ITC's recommendations, will be made by the U.S. President in late 2017 or early 2018. AES is still evaluating the impact these recommended remedies will have, but they will likely increase the cost of solar photovoltaic panels and may impact the value of future solar development projects in the U.S., including those of our solar businesses. In the absence of the U.S. President's final decision, it is difficult to predict the outcome of the recommended remedies, but the impact on our solar businesses and AES could be material.
Alto Maipo
As disclosed in the Company’s Form 10-Q for the period ended March 31, 2017, Alto Maipo has experienced construction difficulties which have resulted in an increase in projected cost for the project of up to 22% of the original $2 billion budget. These overages led to a series of negotiations with the intention of restructuring the project’s existing financial structure and obtaining additional funding. On March 17, 2017, AES Gener completed a legal and financial restructuring of Alto Maipo. As a part of this restructuring, AES Gener simultaneously acquired a 40% ownership interest from Minera Los Pelambres (“MLP”), a noncontrolling shareholder, for a nominal consideration, and sold a 6.7% interest to one of the construction contractors. Through its 67% ownership interest in AES Gener, the Company now has an effective 62% indirect economic interest in Alto Maipo. Additionally, certain construction milestones were amended and if Alto Maipo is unable to meet these milestones, there could be a material impact to the financing and value of the project. For additional information on risks regarding construction and development, refer to Item 1A.—Risk Factors—Our Business is Subject to Substantial Development Uncertainties of the 2016 Form 10-K.
Following the restructuring described above, the project continued to face construction difficulties including greater than expected costs and slower than anticipated productivity by construction contractors towards agreed-upon milestones. Furthermore, during the second quarter of 2017, as a result of the failure to perform by one of its construction contractors, Constructora Nuevo Maipo S.A. (“CNM”), Alto Maipo terminated CNM’s contract. Alto Maipo has hired a temporary replacement contractor to complete a portion of CNM’s work while the search for a permanent replacement contractor continues. Alto Maipo is currently a party to legal proceedings concerning the termination of CNM and related matters, including, but not limited to, Alto Maipo’s draws on letters of credit securing CNM’s performance under the parties’ construction contract totaling $73 million (the “LC Funds”). The LC Funds were collected by Alto Maipo and are available to be utilized for on-going construction costs, but CNM may require Alto Maipo to escrow the LC Funds. The Company cannot anticipate the outcome of the legal proceedings. As a result of the termination of CNM, Alto Maipo’s construction debt of $623 million and derivative liabilities of $139 million are in technical default and presented as current in the balance sheet as of September 30, 2017.
Construction at the project is continuing and Alto Maipo is working to resolve the challenges described above. Alto Maipo is seeking a permanent replacement contractor to complete CNM’s work, and continues to maintain negotiations with lenders and other parties. However, there can be no assurance that Alto Maipo will succeed in these efforts and if there are further delays or cost overruns, or if Alto Maipo is unable to reach an agreement with the non-recourse lenders or other parties, there is a risk these lenders may seek to exercise remedies available as a result of the default noted above, or Alto Maipo may not be able to meet its contractual or
52
other obligations and may be unable to continue with the project. If any of the above occur, there could be a material impairment for the Company.
The carrying value of long-lived assets and deferred tax assets of Alto Maipo as of September 30, 2017 was approximately $1.4 billion and $60 million, respectively. Through its 67% ownership interest in AES Gener, the Parent Company has invested approximately $360 million in Alto Maipo and has an additional equity funding commitment of $55 million required as part of the March 2017 restructuring described above. Even though certain construction difficulties have not been formally resolved, construction costs continue to be capitalized as management believes the project is probable of completion. Management believes the carrying value of the long-lived asset group is recoverable and was not impaired as of September 30, 2017. In addition, management believes it is more likely than not the deferred tax assets will be realized; however, they could be reduced if estimates of future taxable income are decreased.
Eletropaulo
AES is continuing to pursue strategic options for Eletropaulo to reduce the Company’s exposure to the Brazilian distribution market. In preparation for this strategic shift, the Company is pursuing the transfer of Eletropaulo’s shares to the Novo Mercado, a listing segment of the Brazilian stock exchange with the highest governance standards, including the requirement for the company to trade exclusively in ordinary shares. On September 12, 2017, the required majority of Eletropaulo’s shareholders approved the conversion of the current preferred shares into ordinary shares and the transfer to the Novo Mercado. However, shareholders holding approximately 3 million shares, representing 2.7% of the total preferred shares, have indicated their preference to exercise withdrawal rights, which allows them to redeem their shares and receive a cash payment at book value for tendering their shares to Eletropaulo. Eletropaulo has now received all third party approvals to migrate to the Novo Mercado. The migration will be submitted to the Eletropaulo Board for confirmation that the costs associated with the exercise of the withdrawal rights are not significant enough to prevent migration. Once confirmed, and the preferred shares are converted into ordinary shares, AES will no longer control Eletropaulo. Losing control will result in deconsolidation of Eletropaulo and the recording of an equity method investment for the remaining interest held in Eletropaulo. As of September 30, 2017, Eletropaulo had cumulative translation losses attributable to AES of $452 million and pension losses attributable to AES in other comprehensive income of $243 million, both of which will be recognized in earnings if Eletropaulo is deconsolidated.
Changuinola Tunnel Leak
Increased water levels were noted in a creek near the Changuinola power plant, a 223 MW hydroelectric power facility in Panama. After the completion of an assessment, the Company has confirmed loss of water in specific sections of the tunnel. The plant is in operation and can generate up to its maximum capacity. Repairs will be needed to ensure the long term performance of the facility, during which time the affected units of the plant will be out of service. Subject to final inspection, the repairs may take up to 10 months to complete and it is expected to commence during the first quarter of 2019. The Company has notified its insurers of a potential claim and is asserting claims against its construction contractor. However, there can be no assurance of collection. The Company has not identified any indicators of impairment and believes the carrying value of the long-lived asset group is recoverable as of September 30, 2017.
Impairments
Long-lived Assets — During the nine months ended September 30, 2017, the Company recognized asset impairment expense of $186 million at the Kazakhstan CHP and Hydroelectric plants, $66 million at the Stuart and Killen Stations at DPL, and $8 million at Tait Energy Storage in the PJM market. See Note 14—Asset Impairment Expense included in Item 1.—Financial Statements of this Form 10-Q for further information. After recognizing these asset impairment expenses, the carrying value of the long-lived asset groups, including those that were assessed and not impaired, excluding Alto Maipo, totaled $809 million at September 30, 2017.
Events or changes in circumstances that may necessitate further recoverability tests and potential impairments of long-lived assets may include, but are not limited to, adverse changes in the regulatory environment, unfavorable changes in power prices or fuel costs, increased competition due to additional capacity in the grid, technological advancements, declining trends in demand, or an expectation it is more likely than not the asset will be disposed of before the end of its estimated useful life.
Functional Currency
Argentina — In February 2017, the Argentina Ministry of Energy issued Resolution 19/2017, which established changes to the energy price framework. As a result of this resolution, tariffs are priced in USD rather than Argentine Pesos, and the retention of unpaid amounts and accumulation of receivables with CAMMESA was eliminated. Concurrent with the establishment of the new price framework, AES Argentina issued $300 million of bonds denominated in USD. Given these significant changes in economic facts and circumstances, the Company changed
53
the functional currency of the Argentina businesses from the Argentine Peso to the USD effective February 2017. Changes to the energy framework could have a material impact on the Company.
Chivor — In May 2017, the Company repaid its outstanding USD denominated debt held at Chivor. In addition, the Company updated Chivor’s future financing strategy to align with Colombian Peso denominated operational cash flows of the business. Given these changes, the Colombian Peso is now regarded as the currency of the economic environment in which Chivor primarily operates. Therefore, the Company changed the functional currency of the Chivor business from USD to the Columbian Peso effective May 2017.
Foreign Exchange and Commodities
Our businesses are exposed to and proactively manage market risk. Our primary market risk exposure is to the price of commodities, particularly electricity, oil, natural gas, coal, and environmental credits, and FX rates. Volatility in these prices and FX rates could have a material impact on our results. For additional information, refer to Item 3.—Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk.
Environmental
The Company is subject to numerous environmental laws and regulations in the jurisdictions in which it operates. The Company faces certain risks and uncertainties related to these environmental laws and regulations, including existing and potential GHG legislation or regulations, and actual or potential laws and regulations pertaining to water discharges, waste management (including disposal of coal combustion byproducts) and certain air emissions, such as SO2, NOx, particulate matter and mercury. Such risks and uncertainties could result in increased capital expenditures or other compliance costs which could have a material adverse effect on certain of our U.S. or international subsidiaries and our consolidated results of operations. For further information about these risks, see Item 1A.—Risk Factors—Our businesses are subject to stringent environmental laws and regulations; Our businesses are subject to enforcement initiatives from environmental regulatory agencies; and Regulators, politicians, non-governmental organizations and other private parties have expressed concern about greenhouse gas, or GHG, emissions and the potential risks associated with climate change and are taking actions which could have a material adverse impact on our consolidated results of operations, financial condition and cash flows included in the 2016 Form 10-K. The following discussion of the impact of environmental laws and regulations on the Company updates the discussion provided in Item 1.—Business—Environmental and Land Use Regulations of the 2016 Form 10-K.
Update to Greenhouse Gas Emissions Discussion — We refer to the discussion in Item 1.—Business—United States Environmental and Land-Use Regulations—Greenhouse Gas Emissions in the Company’s 2016 Form 10-K for a discussion of certain recent developments, including the EPA’s CO2 emissions rules for new electric generating units, or GHG NSPS, as well as the CO2 emissions rules for existing power plants, called the CPP. Both the GHG NSPS and the CPP are being challenged by several states and industry groups in the D.C. Circuit. The challenges to the CPP have been fully briefed and argued, but oral arguments have not yet taken place on the GHG NSPS. On March 28, 2017, the EPA filed a motion in the D.C. Circuit to hold the challenges to both the CPP and the GHG NSPS in abeyance in light of an Executive Order signed the same day. On April 28, 2017, the D.C. Circuit issued orders holding the challenges to both rules in abeyance for 60 days, with subsequent extensions granted by the court. The most recent extension was set to expire on October 10, 2017. EPA filed a status report and requested that the court continue to hold the case in abeyance in light of EPA’s announcement that it would propose to repeal the CPP in accordance with an Executive Order that instructed the EPA Administrator to review the GHG NSPS and CPP and “if appropriate...as soon as practicable...publish for notice and comment proposed rules suspending, revising, or rescinding those rules.” On October 16, 2017, the EPA published in the Federal Register a proposed rule that would rescind the CPP. Some states and environmental groups have opposed EPA’s most recent request to continue to hold the CPP appeals in abeyance and the D.C. Circuit has not yet acted upon EPA’s request.
By order of the U.S. Supreme Court, the CPP has been stayed pending resolution of the challenges to the rule. Due to the future uncertainty of the CPP, we cannot at this time determine the impact on our operations or consolidated financial results, but we believe the cost to comply with the CPP, should it be upheld and implemented in its current or a substantially similar form, could be material. The GHG NSPS remains in effect at this time, and, absent further action from the EPA that rescinds or substantively revises the NSPS, it could impact any Company plans to construct and/or modify or reconstruct electric generating units in some locations, which may have a material impact on our business, financial condition or results of operations.
Updates to Water Discharges Regulations Discussion — As further discussed in Item 1.—Business—United States Environmental and Land-Use Regulations—Water Discharges in the Company’s 2016 Form 10-K, the EPA published its final effluent limitations guideline (“ELG”) rule in November 2015 to reduce toxic pollutants discharged
54
into waters of the United States by power plants. These effluent limitations for existing and new sources include dry handling of fly ash, closed-loop or dry handling of bottom ash, and more stringent effluent limitations for flue gas desulfurization wastewater. The required compliance time lines for existing sources was to be established between November 1, 2018 and December 31, 2023. On September 18, 2017, the EPA published a final rule delaying certain compliance dates of the ELG rule for two years while it administratively reconsiders the rule. While we are still evaluating the effects of the rule, we anticipate that the implementation of its current requirements could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations, financial condition and cash flows, and a postponement or reconsideration of the rule that leads to less stringent requirements would likely offset some or all of the adverse effects of the rule.
As further discussed in Item 1.—Business—United States Environmental and Land-Use Regulations—Water Discharges in the Company’s 2016 Form 10-K and in Item 1.—Management’s Discussion and Analysis—Key Trends and Uncertainties—Updates to Water Discharges Discussion in the Company’s Form 10-Q for the fiscal quarter ended March 31, 2017, the EPA published a final rule in June 2015 defining federal jurisdiction over waters of the U.S. This rule, which became effective on August 28, 2015, may expand or otherwise change the number and types of waters or features subject to federal permitting. On October 9, 2015, the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Sixth Circuit (the “Sixth Circuit”) issued an order to temporarily stay the “Waters of the U.S.” rule nationwide. The Sixth Circuit’s stay remains in place pending the outcome of various legal challenges, including a challenge to the U.S. Supreme Court that will determine whether the Sixth Circuit has jurisdiction over the rule. On June 27, 2017, the EPA proposed a rule that would rescind the “Waters of the U.S.” rule and re-codify the definition of “Waters of the United States” that existed prior to the 2015 rule. We cannot predict the outcome of this judicial or regulatory process, but if the “Waters of the United States” rule is ultimately implemented in its current or substantially similar form and survives the legal challenges, it could have a material impact on our business, financial condition or results of operations.
Capital Resources and Liquidity
Overview — As of September 30, 2017, the Company had unrestricted cash and cash equivalents of $1.4 billion, of which $81 million was held at the Parent Company and qualified holding companies. The Company also had $563 million in short-term investments, held primarily at subsidiaries. In addition, we had restricted cash and debt service reserves of $1.2 billion. The Company also had non-recourse and recourse aggregate principal amounts of debt outstanding of $17.1 billion and $5.0 billion, respectively.
We expect current maturities of non-recourse debt to be repaid from net cash provided by operating activities of the subsidiary to which the debt relates, through opportunistic refinancing activity, or some combination thereof. We have $4 million of recourse debt which matures within the next twelve months. From time to time, we may elect to repurchase our outstanding debt through cash purchases, privately negotiated transactions or otherwise when management believes that such securities are attractively priced. Such repurchases, if any, will depend on prevailing market conditions, our liquidity requirements and other factors. The amounts involved in any such repurchases may be material.
We rely mainly on long-term debt obligations to fund our construction activities. We have, to the extent available at acceptable terms, utilized non-recourse debt to fund a significant portion of the capital expenditures and investments required to construct and acquire our electric power plants, distribution companies and related assets. Our non-recourse financing is designed to limit cross-default risk to the Parent Company or other subsidiaries and affiliates. Our non-recourse long-term debt is a combination of fixed and variable interest rate instruments. Debt is typically denominated in the currency that matches the currency of the revenue expected to be generated from the benefiting project, thereby reducing currency risk. In certain cases, the currency is matched through the use of derivative instruments. The majority of our non-recourse debt is funded by international commercial banks, with debt capacity supplemented by multilaterals and local regional banks.
Given our long-term debt obligations, the Company is subject to interest rate risk on debt balances that accrue interest at variable rates. When possible, the Company will borrow funds at fixed interest rates or hedge its variable rate debt to fix its interest costs on such obligations. In addition, the Company has historically tried to maintain at least 70% of its consolidated long-term obligations at fixed interest rates, including fixing the interest rate through the use of interest rate swaps. These efforts apply to the notional amount of the swaps compared to the amount of related underlying debt. Presently, the Parent Company’s only material unhedged exposure to variable interest rate debt relates to indebtedness under its $522 million outstanding secured term loan due 2022 and drawings of $540 million under its senior secured credit facility. On a consolidated basis, of the Company’s $22.0 billion of total debt outstanding as of September 30, 2017, approximately $4.1 billion bore interest at variable rates that were not
55
subject to a derivative instrument which fixed the interest rate. Brazil holds $1.9 billion of our floating rate non-recourse exposure as we have no ability to fix local debt interest rates efficiently.
In addition to utilizing non-recourse debt at a subsidiary level when available, the Parent Company provides a portion, or in certain instances all, of the remaining long-term financing or credit required to fund development, construction or acquisition of a particular project. These investments have generally taken the form of equity investments or intercompany loans, which are subordinated to the project’s non-recourse loans. We generally obtain the funds for these investments from our cash flows from operations, proceeds from the sales of assets and/or the proceeds from our issuances of debt, common stock and other securities. Similarly, in certain of our businesses, the Parent Company may provide financial guarantees or other credit support for the benefit of counterparties who have entered into contracts for the purchase or sale of electricity, equipment or other services with our subsidiaries or lenders. In such circumstances, if a business defaults on its payment or supply obligation, the Parent Company will be responsible for the business’ obligations up to the amount provided for in the relevant guarantee or other credit support. At September 30, 2017, the Parent Company had provided outstanding financial and performance-related guarantees or other credit support commitments to or for the benefit of our businesses, which were limited by the terms of the agreements, of approximately $833 million in aggregate (excluding those collateralized by letters of credit and other obligations discussed below).
As a result of the Parent Company’s below investment grade rating, counterparties may be unwilling to accept our general unsecured commitments to provide credit support. Accordingly, with respect to both new and existing commitments, the Parent Company may be required to provide some other form of assurance, such as a letter of credit, to backstop or replace our credit support. The Parent Company may not be able to provide adequate assurances to such counterparties. To the extent we are required and able to provide letters of credit or other collateral to such counterparties, this will reduce the amount of credit available to us to meet our other liquidity needs. At September 30, 2017, we had $125 million in letters of credit outstanding provided under our unsecured credit facility and $9 million in letters of credit outstanding provided under our senior secured credit facility. These letters of credit operate to guarantee performance relating to certain project development and construction activities and business operations. During the quarter ended September 30, 2017, the Company paid letter of credit fees ranging from 0.25% to 2.25% per annum on the outstanding amounts.
We expect to continue to seek, where possible, non-recourse debt financing in connection with the assets or businesses that we or our affiliates may develop, construct or acquire. However, depending on local and global market conditions and the unique characteristics of individual businesses, non-recourse debt may not be available on economically attractive terms or at all. If we decide not to provide any additional funding or credit support to a subsidiary project that is under construction or has near-term debt payment obligations and that subsidiary is unable to obtain additional non-recourse debt, such subsidiary may become insolvent, and we may lose our investment in that subsidiary. Additionally, if any of our subsidiaries lose a significant customer, the subsidiary may need to withdraw from a project or restructure the non-recourse debt financing. If we or the subsidiary choose not to proceed with a project or are unable to successfully complete a restructuring of the non-recourse debt, we may lose our investment in that subsidiary.
Many of our subsidiaries depend on timely and continued access to capital markets to manage their liquidity needs. The inability to raise capital on favorable terms, to refinance existing indebtedness or to fund operations and other commitments during times of political or economic uncertainty may have material adverse effects on the financial condition and results of operations of those subsidiaries. In addition, changes in the timing of tariff increases or delays in the regulatory determinations under the relevant concessions could affect the cash flows and results of operations of our businesses.
Long-Term Receivables — As of September 30, 2017, the Company had approximately $238 million of accounts receivable classified as Noncurrent assets—other, primarily related to certain of its generation businesses in Argentina and the United States, and its utility business in Brazil. These noncurrent receivables mostly consist of accounts receivable in Argentina that, pursuant to amended agreements or government resolutions, have collection periods that extend beyond September 30, 2018, or one year from the latest balance sheet date. The majority of Argentinian receivables have been converted into long-term financing for the construction of power plants. See Note 5—Financing Receivables included in Part I—Item 1.—Financial Statements of this Form 10-Q and Item 1.—Business—Argentina—Regulatory Framework included in our 2016 Form 10-K for further information.
56
Consolidated Cash Flows
The following table reflects the changes in operating, investing, and financing cash flows for the comparative three and nine month periods (in millions):
Three Months Ended September 30, | Nine Months Ended September 30, | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Cash flows provided by (used in): | 2017 | 2016 | $ Change | 2017 | 2016 | $ Change | ||||||||||||||||||
Operating activities | $ | 735 | $ | 819 | $ | (84 | ) | $ | 1,689 | $ | 2,182 | $ | (493 | ) | ||||||||||
Investing activities | (1,174 | ) | (543 | ) | (631 | ) | (2,282 | ) | (1,869 | ) | (413 | ) | ||||||||||||
Financing activities | 614 | (215 | ) | 829 | 678 | (258 | ) | 936 | ||||||||||||||||
Operating Activities
The following table summarizes the key components of our consolidated operating cash flows (in millions):
Three Months Ended September 30, | Nine Months Ended September 30, | |||||||||||||||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | $ Change | 2017 | 2016 | $ Change | |||||||||||||||||||
Net income (loss) | $ | 261 | $ | 229 | $ | 32 | $ | 509 | $ | (84 | ) | $ | 593 | |||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 303 | 291 | 12 | 884 | 877 | 7 | ||||||||||||||||||
Impairment expenses | 2 | 79 | (77 | ) | 260 | 475 | (215 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
Loss on extinguishment of debt | 49 | 16 | 33 | 44 | 12 | 32 | ||||||||||||||||||
Other adjustments to net income | 5 | 14 | (9 | ) | 171 | 438 | (267 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
Non-cash adjustments to net income (loss) | 359 | 400 | (41 | ) | 1,359 | 1,802 | (443 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
Net income, adjusted for non-cash items | $ | 620 | $ | 629 | $ | (9 | ) | $ | 1,868 | $ | 1,718 | $ | 150 | |||||||||||
Net change in operating assets and liabilities (1) | $ | 115 | $ | 190 | $ | (75 | ) | $ | (179 | ) | $ | 464 | $ | (643 | ) | |||||||||
Net cash provided by operating activities (2) | $ | 735 | $ | 819 | $ | (84 | ) | $ | 1,689 | $ | 2,182 | $ | (493 | ) | ||||||||||
_____________________________
(1) | Refer to the table below for explanations of the variance in operating assets and liabilities (also generally referred to as “working capital” in the Segment Operating Cash Flow Analysis). |
(2) | Amounts included in the table above include the results of discontinued operations, where applicable. |
Net change in operating assets and liabilities decreased by $75 million for the three months ended September 30, 2017, compared to the three months ended September 30, 2016, which was primarily driven by (in millions):
Increases in: | |||
Accounts receivable, primarily at Gener and Itabo | $ | (128 | ) |
Prepaid expenses and other current assets, primarily short-term regulatory assets at Eletropaulo and Sul | (213 | ) | |
Inventory, primarily at IPL, Eletropaulo, Itabo and Gener | (47 | ) | |
Accounts payable and other current liabilities, primarily at Eletropaulo | 306 | ||
Other | 7 | ||
Total decrease in cash from changes in operating assets and liabilities | $ | (75 | ) |
Net change in operating assets and liabilities decreased by $643 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2017, compared to the nine months ended September 30, 2016, which was primarily driven by (in millions):
Increases in: | |||
Accounts receivable, primarily at Maritza and Eletropaulo | $ | (614 | ) |
Prepaid expenses and other current assets, primarily short-term regulatory assets at Eletropaulo and Sul | (530 | ) | |
Inventory, primarily at Gener, IPL and DPL | (102 | ) | |
Accounts payable and other current liabilities, primarily at Eletropaulo, Maritza and Gener | 729 | ||
Income taxes payable, net, and other taxes payable, primarily at Gener,Tietê and Eletropaulo | 266 | ||
Decreases in: | |||
Other liabilities, primarily due to higher deferrals into regulatory liabilities related to energy costs in 2016 compared to 2017 at Eletropaulo | (363 | ) | |
Other | (29 | ) | |
Total decrease in cash from changes in operating assets and liabilities | $ | (643 | ) |
57
Investing Activities
Net cash used in investing activities increased by $631 million for the three months ended September 30, 2017, compared to the three months ended September 30, 2016, which was primarily driven by (in millions):
Decreases In: | |||
Capital expenditures (1) | $ | 51 | |
Short-term investments | 221 | ||
Increases in: | |||
Acquisitions of businesses, net of cash acquired, and equity method investees (related to the acquisitions of sPower and Alto Sertão II in 2017, partially offset by the acquisition of Distributed Energy in 2016) | (554 | ) | |
Restricted cash, debt service and other assets | (318 | ) | |
Other investing activities | (31 | ) | |
Total increase in net cash used in investing activities | $ | (631 | ) |
_____________________________
(1) | Refer to the tables below for a breakout of capital expenditures by type and primary business driver. |
Net cash used in investing activities increased by $413 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2017, compared to the nine months ended September 30, 2016, which was primarily driven by (in millions):
Decreases in: | |||
Capital expenditures (1) | $ | 183 | |
Proceeds from the sales of businesses, net of cash sold, and equity method investments (primarily related to the sales of DPLER, Kelanitissa and Jordan in 2016 and the receipt of contingent sales proceeds in 2016 from the sale of Cameroon, partially offset by the sale of Kazakhstan CHPs in 2017) | (118 | ) | |
Short-term investments | 319 | ||
Increases in: | |||
Acquisitions of businesses, net of cash acquired, and equity method investees (related to the acquisitions of sPower and Alto Sertão II in 2017, partially offset by the acquisition of Distributed Energy in 2016) | (545 | ) | |
Restricted cash, debt service and other assets | (188 | ) | |
Other investing activities | (64 | ) | |
Total increase in net cash used in investing activities | $ | (413 | ) |
_____________________________
(1) | Refer to the tables below for a breakout of capital expenditures by type and primary business driver. |
Capital Expenditures
The following table summarizes the Company's capital expenditures for growth investments, maintenance, and environmental reported in investing cash activities for the periods indicated (in millions):
Three Months Ended September 30, | Nine Months Ended September 30, | |||||||||||||||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | $ Change | 2017 | 2016 | $ Change | |||||||||||||||||||
Growth Investments | $ | (310 | ) | $ | (339 | ) | $ | 29 | $ | (1,109 | ) | $ | (1,126 | ) | $ | 17 | ||||||||
Maintenance | (137 | ) | (141 | ) | 4 | (423 | ) | (458 | ) | 35 | ||||||||||||||
Environmental (1) | (17 | ) | (35 | ) | 18 | (55 | ) | (186 | ) | 131 | ||||||||||||||
Total capital expenditures | $ | (464 | ) | $ | (515 | ) | $ | 51 | $ | (1,587 | ) | $ | (1,770 | ) | $ | 183 | ||||||||
_____________________________
(1) | Includes both recoverable and non-recoverable environmental capital expenditures. See Non-GAAP Measures—Free Cash Flow for more information. |
Cash used for capital expenditures decreased by $51 million for the three months ended September 30, 2017, compared to the three months ended September 30, 2016, which was primarily driven by (in millions):
Decreases in: | |||
Growth expenditures at the Andes SBU, primarily due to slower than anticipated productivity by construction contractors at Alto Maipo | $ | 137 | |
Maintenance and environmental expenditures at the US SBU, primarily due to lower spending at IPALCO on the NPDES compliance and Harding Street refueling projects and decreased spending on CCR compliance | 19 | ||
Growth expenditures at the Eurasia SBU, primarily due to timing of payments to contractors for Unit 3 expansion at Masinloc | 18 | ||
Increases in: | |||
Growth expenditures at the US SBU, primarily due to increased spending at Southland repowering | (130 | ) | |
Other capital expenditures | 7 | ||
Total decrease in net cash used for capital expenditures | $ | 51 | |
58
Cash used for capital expenditures decreased by $183 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2017, compared to the nine months ended September 30, 2016, which was primarily driven by (in millions):
Decreases in: | |||
Growth expenditures at the Andes SBU, primarily due to the completion of the Cochrane project | $ | 85 | |
Maintenance and environmental expenditures at the US SBU, primarily due to lower spending at IPALCO on the NPDES and MATS compliance and Harding Street refueling projects, decreased spending on CCR compliance and also, decreased spending at DPL on Stuart and Killen facilities due to planned plant closures | 152 | ||
Increases in: | |||
Growth expenditures at the US SBU, primarily due to increased spending at Southland repowering and various Distributed Energy projects, offset by lower spending related to CCGT at IPALCO | (18 | ) | |
Growth, maintenance and environmental expenditures at the Brazil SBU, primarily due to the quality indicator recovery plan and increase in productivity commitments at Eletropaulo, offset by absence of spending at Sul due to its sale in 2016 | (43 | ) | |
Other capital expenditures | 7 | ||
Total decrease in net cash used for capital expenditures | $ | 183 | |
Financing Activities
Net cash provided by financing activities increased $829 million for the three months ended September 30, 2017, compared to the three months ended September 30, 2016, which was primarily driven by (in millions):
Increases in: | |||
Borrowings under the revolving credit facilities, at the Parent Company | $ | 384 | |
Issuance of recourse debt at the Parent Company (1) | 204 | ||
Issuance of non-recourse debt, primarily at the US, MCAC, and Brazil SBUs (1) | 204 | ||
Proceeds from sale of noncontrolling interests related to the sell down of Dominican Republic business in 2017 | 60 | ||
Other financing activities | (23 | ) | |
Total increase in net cash provided by financing activities | $ | 829 | |
_____________________________
(1) | See Note 7—Debt in Item 1—Financial Statements of this Form 10-Q for more information regarding significant non-recourse debt transactions. |
Net cash provided by financing activities increased $936 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2017, compared to the nine months ended September 30, 2016, which was primarily driven by (in millions):
Decreases in: | |||
Proceeds from the sale of redeemable stock of subsidiaries at IPALCO | $ | (134 | ) |
Increases in: | |||
Borrowings under the revolving credit facilities, primarily at the Parent Company and net decrease in repayment at the US SBU | 415 | ||
Issuance of non-recourse debt, primarily at the Brazil, MCAC, and US SBUs (1) | 574 | ||
Proceeds from sale of noncontrolling interests related to the sell down of Dominican Republic business in 2017 | 60 | ||
Other financing activities | 21 | ||
Total increase in net cash provided by financing activities | $ | 936 | |
_____________________________
(1) | See Note 7—Debt in Item 1—Financial Statements of this Form 10-Q for more information regarding significant non-recourse debt transactions. |
Segment Operating Cash Flow Analysis
Operating Cash Flow by SBU (1)
Three Months Ended September 30, | Nine Months Ended September 30, | |||||||||||||||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | $ Change | 2017 | 2016 | $ Change | |||||||||||||||||||
US SBU | $ | 241 | $ | 291 | $ | (50 | ) | $ | 544 | $ | 691 | $ | (147 | ) | ||||||||||
Andes SBU | 110 | 157 | (47 | ) | 338 | 300 | 38 | |||||||||||||||||
Brazil SBU | 194 | 173 | 21 | 463 | 582 | (119 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
MCAC SBU | 141 | 142 | (1 | ) | 275 | 202 | 73 | |||||||||||||||||
Eurasia SBU | 188 | 171 | 17 | 475 | 729 | (254 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
Corporate and Other | (139 | ) | (115 | ) | (24 | ) | (406 | ) | (322 | ) | (84 | ) | ||||||||||||
Total SBUs | $ | 735 | $ | 819 | $ | (84 | ) | $ | 1,689 | $ | 2,182 | $ | (493 | ) | ||||||||||
_____________________________
(1) | Operating cash flow as presented above include the effects of intercompany transactions with other segments except for interest, tax sharing, charges for management fees and transfer pricing. |
59
US SBU
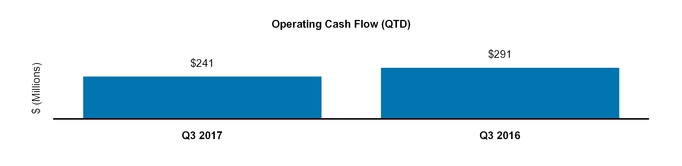
The decrease in Operating Cash Flow of $50 million was driven primarily by the following (in millions):
US SBU Q3 2017 vs. Q3 2016 (QTD) | ||||
Lower operating margin, net of lower depreciation of $4 million | $ | (9 | ) | |
Higher payments for inventory purchases primarily due to inventory optimization efforts at DPL and IPL that occurred in 2016 | (20 | ) | ||
Timing of payments for general accounts payable at DPL | (13 | ) | ||
Timing of interest payments primarily at DPL and IPL | (13 | ) | ||
Other | 5 | |||
Total US SBU Operating Cash Decrease | $ | (50 | ) | |
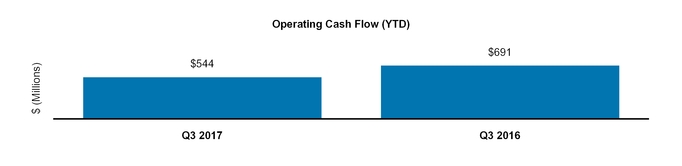
The decrease in Operating Cash Flow of $147 million was driven primarily by the following (in millions):
US SBU Q3 2017 vs. Q3 2016 (YTD) | ||||
Lower operating margin, net of lower depreciation of $26 | $ | (41 | ) | |
Higher payments for inventory purchases primarily due to inventory optimization efforts at DPL and IPL that occurred in 2016 | (66 | ) | ||
Timing of payments for purchased power and general accounts payable at DPL | (42 | ) | ||
Timing of interest payments primarily at DPL and IPL | (19 | ) | ||
Lower collections at DPL, primarily due to the settlement of receivable balances at DPLER upon its sale in Q1 2016 | (11 | ) | ||
Higher collections at IPL, primarily due to higher A/R balances in December 2016 resulting from favorable weather and the 2016 rate order | 32 | |||
Total US SBU Operating Cash Decrease | $ | (147 | ) | |
60
ANDES SBU
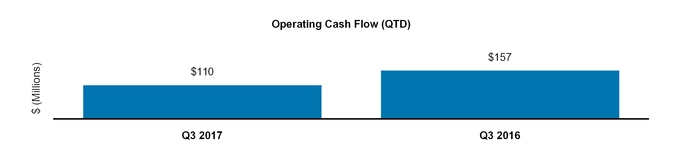
The decrease in Operating Cash Flow of $47 million was driven primarily by the following (in millions):
Andes SBU Q3 2017 vs. Q3 2016 (QTD) | ||||
Lower operating margin, net of increased depreciation of $7 | $ | (45 | ) | |
Increase in other working capital requirements primarily due to delay in collections at Gener | (59 | ) | ||
Increase in collections of financing receivables in Argentina, resulting primarily from the commencement of commercial operations at the Guillermo Brown plant and the impact of major maintenance in 2016 | 44 | |||
Environmental tax accruals in Chile impacting margin but not operating cash flow | 13 | |||
Total Andes SBU Operating Cash Decrease | $ | (47 | ) | |
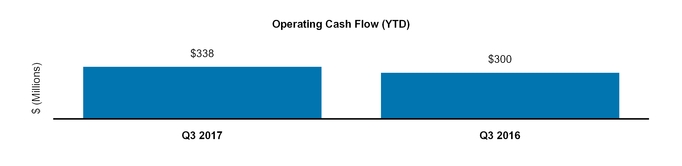
The increase in Operating Cash Flow of $38 million was driven primarily by the following (in millions):
Andes SBU Q3 2017 vs. Q3 2016 (YTD) | ||||
Higher operating margin, net of increased depreciation of $32 | $ | 18 | ||
Lower tax payments at Chivor and Argentina | 57 | |||
Increase in collections of financing receivables in Argentina, resulting primarily from the commencement of commercial operations at the Guillermo Brown plant | 50 | |||
Environmental tax accruals in Chile impacting margin but not operating cash flow | 37 | |||
Increase in other working capital requirements primarily due to delay in collections at Gener | (60 | ) | ||
Lower collections at Chivor, primarily due higher receivables in Q1 2016 resulting from higher sales in Q4 2015 | (35 | ) | ||
Increase in interest payments to reflect the cessation of capitalization of interest for the Cochrane project | (14 | ) | ||
Lower VAT refunds, primarily at Alto Maipo and Cochrane | (14 | ) | ||
Other | (1 | ) | ||
Total Andes SBU Operating Cash Increase | $ | 38 | ||
61
BRAZIL SBU
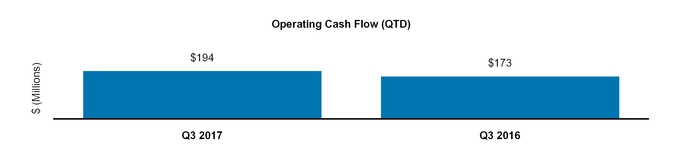
The increase in Operating Cash Flow of $21 million was driven primarily by the following (in millions):
Brazil SBU Q3 2017 vs. Q3 2016 (QTD) | ||||
Higher operating margin, net of increased depreciation of $11 | $ | 65 | ||
Lower payments for energy purchases at Eletropaulo due to lower energy costs and lower regulatory charges | 166 | |||
Timing of payments at Tietê for energy to be resold | 24 | |||
Lower collections of costs deferred in net regulatory assets at Eletropaulo due to higher energy costs | (181 | ) | ||
Higher accounts receivable balances at Eletropaulo due primarily to higher tariffs in 2017 | (22 | ) | ||
Lack of AES Sul’s operating cash flow, which was sold in 2016 | (13 | ) | ||
Lower collections at Tietê, due to higher energy sales under bilateral contracts | (7 | ) | ||
Higher interest payments resulting from the assumption of debt for the acquisition of Alto Sertão II | (6 | ) | ||
Other | (5 | ) | ||
Total Brazil SBU Operating Cash Increase | $ | 21 | ||
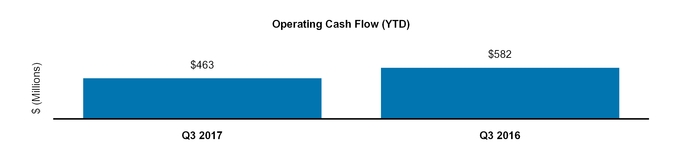
The decrease in Operating Cash Flow of $119 million was driven primarily by the following (in millions):
Brazil SBU Q3 2017 vs. Q3 2016 (YTD) | ||||
Higher operating margin, net of increased depreciation of $30 | $ | 167 | ||
Higher collections in 2016 of costs deferred in net regulatory assets at Eletropaulo as a result of unfavorable hydrology in prior periods | (556 | ) | ||
Lower collections of accounts receivable at Eletropaulo due primarily to higher tariff flags in 2016 | (193 | ) | ||
Lack of AES Sul’s operating cash flow, which was sold in 2016 | (68 | ) | ||
Lower collections at Tietê, due to higher energy sales under bilateral contracts | (20 | ) | ||
Increase in pension contributions at Eletropaulo | (13 | ) | ||
Timing of payments for energy purchases at Eletropaulo due to lower energy costs and lower regulatory charges | 401 | |||
Receipt of YPF legal settlement at Uruguaiana | 60 | |||
Lower tax payments at Tietê | 58 | |||
Timing of payments at Tietê for energy to be resold | 32 | |||
Lower interest payments at Tietê | 11 | |||
Other | 2 | |||
Total Brazil SBU Operating Cash Decrease | $ | (119 | ) | |
62
MCAC SBU
The decrease in Operating Cash Flow of $1 million was driven primarily by the following (in millions):
MCAC SBU Q3 2017 vs. Q3 2016 (QTD) | ||||
Higher operating margin, net of increased depreciation of $3 | $ | 28 | ||
Higher working capital requirements in the Dominican Republic, primarily due to an increase in days outstanding of accounts receivable | (68 | ) | ||
Lower working capital requirements in El Salvador, primarily due to lower energy pricing reducing overall accounts receivable balances and an increase in Accounts Payable days outstanding related to energy purchases | 25 | |||
Lower working capital requirements in Puerto Rico, primarily due to higher collections and lower sales in September 2017 due to Hurricane Maria | 19 | |||
Other | (5 | ) | ||
Total MCAC SBU Operating Cash Decrease | $ | (1 | ) | |
The increase in Operating Cash Flow of $73 million was driven primarily by the following (in millions):
MCAC SBU Q3 2017 vs. Q3 2016 (YTD) | ||||
Higher operating margin, net of increased depreciation of $8 | $ | 68 | ||
Lower working capital requirements in AES Puerto Rico, primarily due to higher collections | 36 | |||
Lower tax payments in El Salvador | 16 | |||
Lower tax payments in the Dominican Republic, primarily due to lower withholding taxes on dividends paid in 2016 to AES affiliates | 10 | |||
Higher working capital requirements in the Dominican Republic, primarily due to an increase in accounts receivable days outstanding at Itabo | (42 | ) | ||
Higher interest payments in the Dominican Republic, primarily due to an increase in net debt and higher average interest rates | (13 | ) | ||
Other | (2 | ) | ||
Total MCAC SBU Operating Cash Increase | $ | 73 | ||
63
EURASIA SBU
The increase in Operating Cash Flow of $17 million was driven primarily by the following (in millions):
Eurasia SBU Q3 2017 vs. Q3 2016 (QTD) | ||||
Increase in C02 allowances at Maritza due to decreased prices in 2016 | $ | 9 | ||
Lower working capital requirements at Kilroot primarily due to a decrease in rates and net VAT payments received in 2017 | 8 | |||
Total Eurasia SBU Operating Cash Increase | $ | 17 | ||
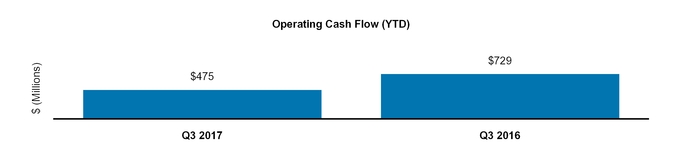
The decrease in Operating Cash Flow of $254 million was driven primarily by the following (in millions):
Eurasia SBU Q3 2017 vs. Q3 2016 (YTD) | ||||
Higher operating margin, net of lower depreciation of $16 | $ | 19 | ||
Lower collections at Maritza, primarily due to the collection of overdue receivables from NEK in 2016 | (376 | ) | ||
Lower payments to fuel suppliers at Maritza, due primarily to the settlement of overdue invoices in 2016 pursuant to the tripartite agreement with NEK and MMI | 73 | |||
Decrease in service concession asset expenditures at Mong Duong | 22 | |||
Lower working capital requirements at Masinloc due to the timing of payments for coal purchases | 19 | |||
Increase in C02 allowances at Maritza due to decreased prices in 2016 | 17 | |||
Higher mark-to-market valuation of commodity swaps at Kilroot impacting margin but not operating cash flow | (9 | ) | ||
Lower coal purchases at Mong Duong due to the reserve shutdown in 2017 | (9 | ) | ||
Other | (10 | ) | ||
Total Eurasia SBU Operating Cash Decrease | $ | (254 | ) | |
64
CORPORATE AND OTHER
The decrease in Operating Cash Flow of $24 million was driven primarily by the following (in millions):
Corporate and Other Q3 2017 vs. Q3 2016 (QTD) | ||||
Timing of insurance recoveries | $ | (15 | ) | |
Lower payments for interest expense, primarily due to timing of refinancings and draws on Revolver debt | 10 | |||
Other | (19 | ) | ||
Total Corporate and Other Operating Cash Decrease | $ | (24 | ) | |
The decrease in Operating Cash Flow of $84 million was driven primarily by the following (in millions):
Corporate and Other Q3 2017 vs. Q3 2016 (YTD) | ||||
Timing of intercompany settlements with SBUs | $ | (39 | ) | |
Higher realized losses on oil derivatives | (22 | ) | ||
Higher payments for people-related costs and associated payroll taxes | (14 | ) | ||
Other | (9 | ) | ||
Total Corporate and Other Operating Cash Decrease | $ | (84 | ) | |
65
Parent Company Liquidity
The following discussion is included as a useful measure of the liquidity available to The AES Corporation, or the Parent Company, given the non-recourse nature of most of our indebtedness. Parent Company Liquidity as outlined below is a non-GAAP measure and should not be construed as an alternative to cash and cash equivalents, which is determined in accordance with GAAP as a measure of liquidity. Cash and cash equivalents is disclosed in the Condensed Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows. Parent Company Liquidity may differ from similarly titled measures used by other companies. The principal sources of liquidity at the Parent Company level are dividends and other distributions from our subsidiaries, including refinancing proceeds, proceeds from debt and equity financings at the Parent Company level, including availability under our credit facility, and proceeds from asset sales. Cash requirements at the Parent Company level are primarily to fund interest, principal repayments of debt, construction commitments, other equity commitments, common stock repurchases, acquisitions, taxes, Parent Company overhead and development costs, and dividends on common stock.
The Company defines Parent Company Liquidity as cash available to the Parent Company plus available borrowings under existing credit facility. The cash held at qualified holding companies represents cash sent to subsidiaries of the Company domiciled outside of the U.S. Such subsidiaries have no contractual restrictions on their ability to send cash to the Parent Company. Parent Company Liquidity is reconciled to its most directly comparable GAAP financial measure, cash and cash equivalents, at the periods indicated as follows (in millions):
September 30, 2017 | December 31, 2016 | ||||||
Consolidated cash and cash equivalents | $ | 1,398 | $ | 1,305 | |||
Less: Cash and cash equivalents at subsidiaries | (1,317 | ) | (1,205 | ) | |||
Parent Company and qualified holding companies’ cash and cash equivalents | 81 | 100 | |||||
Commitments under Parent Company credit facilities | 1,100 | 800 | |||||
Less: Letters of credit under the credit facilities | (9 | ) | (6 | ) | |||
Less: Borrowings under the credit facilities | (540 | ) | — | ||||
Borrowings available under Parent Company credit facilities | 551 | 794 | |||||
Total Parent Company Liquidity | $ | 632 | $ | 894 | |||
The Company paid dividends of $0.12 per share to its common stockholders during each of the first, second and third quarters of 2017 for dividends declared in December 2016, February 2017, and July 2017, respectively. While we intend to continue payment of dividends, and believe we will have sufficient liquidity to do so, we can provide no assurance that we will continue to pay dividends, or if continued, the amount of such dividends.
Recourse Debt
Our total recourse debt was $5.0 billion and $4.7 billion as of September 30, 2017 and December 31, 2016, respectively. See Note 7—Debt in Item 1.—Financial Statements of this Form 10-Q and Note 11—Debt in Item 8.—Financial Statements and Supplementary Data of our 2016 Form 10-K for additional detail.
While we believe that our sources of liquidity will be adequate to meet our needs for the foreseeable future, this belief is based on a number of material assumptions, including, without limitation, assumptions about our ability to access the capital markets, the operating and financial performance of our subsidiaries, currency exchange rates, power market pool prices, and the ability of our subsidiaries to pay dividends. In addition, our subsidiaries’ ability to declare and pay cash dividends to us (at the Parent Company level) is subject to certain limitations contained in loans, governmental provisions and other agreements. We can provide no assurance that these sources will be available when needed or that the actual cash requirements will not be greater than anticipated. We have met our interim needs for shorter-term and working capital financing at the Parent Company level with our senior secured credit facility. See Item 1A.—Risk Factors—The AES Corporation is a holding company and its ability to make payments on its outstanding indebtedness, including its public debt securities, is dependent upon the receipt of funds from its subsidiaries by way of dividends, fees, interest, loans or otherwise of the Company’s 2016 Form 10-K for additional information.
Various debt instruments at the Parent Company level, including our senior secured credit facility, contain certain restrictive covenants. The covenants provide for — among other items — limitations on other indebtedness; liens, investments and guarantees; limitations on dividends, stock repurchases and other equity transactions; restrictions and limitations on mergers and acquisitions, sales of assets, leases, transactions with affiliates and off-balance sheet and derivative arrangements; maintenance of certain financial ratios; and financial and other reporting requirements. As of September 30, 2017, we were in compliance with these covenants at the Parent Company level.
Non-Recourse Debt
While the lenders under our non-recourse debt financings generally do not have direct recourse to the Parent
66
Company, defaults thereunder can still have important consequences for our results of operations and liquidity, including, without limitation:
• | reducing our cash flows as the subsidiary will typically be prohibited from distributing cash to the Parent Company during the time period of any default; |
• | triggering our obligation to make payments under any financial guarantee, letter of credit or other credit support we have provided to or on behalf of such subsidiary; |
• | causing us to record a loss in the event the lender forecloses on the assets; and |
• | triggering defaults in our outstanding debt at the Parent Company. |
For example, our senior secured credit facility and outstanding debt securities at the Parent Company include events of default for certain bankruptcy-related events involving material subsidiaries. In addition, our revolving credit agreement at the Parent Company includes events of default related to payment defaults and accelerations of outstanding debt of material subsidiaries.
Some of our subsidiaries are currently in default with respect to all or a portion of their outstanding indebtedness. The total non-recourse debt classified as current in the accompanying Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheets amounts to $2.3 billion. The portion of current debt related to such defaults was $1.0 billion at September 30, 2017, all of which was non-recourse debt related to three subsidiaries — Alto Maipo, AES Puerto Rico, and AES Ilumina. See Note 7—Debt in Item 1.—Financial Statements of this Form 10-Q for additional detail.
None of the subsidiaries that are currently in default are subsidiaries that met the applicable definition of materiality under AES’ corporate debt agreements as of September 30, 2017, in order for such defaults to trigger an event of default or permit acceleration under AES’ indebtedness. However, as a result of additional dispositions of assets, other significant reductions in asset carrying values or other matters in the future that may impact our financial position and results of operations or the financial position of the individual subsidiary, it is possible that one or more of these subsidiaries could fall within the definition of a “material subsidiary” and thereby upon an acceleration trigger an event of default and possible acceleration of the indebtedness under the Parent Company’s outstanding debt securities. A material subsidiary is defined in the Company’s senior secured credit facility as any business that contributed 20% or more of the Parent Company’s total cash distributions from businesses for the four most recently ended fiscal quarters. As of September 30, 2017, none of the defaults listed above individually or in the aggregate results in or is at risk of triggering a cross-default under the recourse debt of the Company.
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
The condensed consolidated financial statements of AES are prepared in conformity with U.S. GAAP, which requires the use of estimates, judgments and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenue and expenses during the periods presented. The Company’s significant accounting policies are described in Note 1—General and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies of our 2016 Form 10-K. The Company’s critical accounting estimates are described in Item 7.—Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations in the 2016 Form 10-K. An accounting estimate is considered critical if the estimate requires management to make an assumption about matters that were highly uncertain at the time the estimate was made, different estimates reasonably could have been used, or if changes in the estimate that would have a material impact on the Company’s financial condition or results of operations are reasonably likely to occur from period to period. Management believes that the accounting estimates employed are appropriate and resulting balances are reasonable; however, actual results could differ from the original estimates, requiring adjustments to these balances in future periods. The Company has reviewed and determined that these remain as critical accounting policies as of and for the nine months ended September 30, 2017.
ITEM 3. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK
Overview Regarding Market Risks — Our businesses are exposed to and proactively manage market risk. Our primary market risk exposure is to the price of commodities, particularly electricity, oil, natural gas, coal and environmental credits. In addition, our businesses are exposed to lower electricity prices due to increased competition, including from renewable sources such as wind and solar, as a result of lower costs of entry and lower variable costs. We operate in multiple countries and as such, are subject to volatility in exchange rates at varying degrees at the subsidiary level and between our functional currency, the U.S. Dollar, and currencies of the countries in which we operate. We are also exposed to interest rate fluctuations due to our issuance of debt and related financial instruments.
67
The disclosures presented in this Item 3 are based upon a number of assumptions; actual effects may differ. The safe harbor provided in Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933 and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 shall apply to the disclosures contained in this Item 3. For further information regarding market risk, see Item 1A.—Risk Factors, Our financial position and results of operations may fluctuate significantly due to fluctuations in currency exchange rates experienced at our foreign operations; Our businesses may incur substantial costs and liabilities and be exposed to price volatility as a result of risks associated with the electricity markets, which could have a material adverse effect on our financial performance; and We may not be adequately hedged against our exposure to changes in commodity prices or interest rates of the 2016 Form 10-K.
Commodity Price Risk — Although we prefer to hedge our exposure to the impact of market fluctuations in the price of electricity, fuels and environmental credits, some of our generation businesses operate under short-term sales or under contract sales that leave an unhedged exposure on some of our capacity or through imperfect fuel pass-throughs. In our utility businesses, we may be exposed to commodity price movements depending on our excess or shortfall of generation relative to load obligations and sharing or pass-through mechanisms. These businesses subject our operational results to the volatility of prices for electricity, fuels and environmental credits in competitive markets. We employ risk management strategies to hedge our financial performance against the effects of fluctuations in energy commodity prices. The implementation of these strategies can involve the use of physical and financial commodity contracts, futures, swaps and options. At our generation businesses for 2017-2019, 75% to 80% of our variable margin is hedged against changes in commodity prices. At our utility businesses for 2017-2019, 85% to 90% of our variable margin is insulated from changes in commodity prices.
The portion of our sales and purchases that are not subject to such agreements or contracted businesses where indexation is not perfectly matched to business drivers will be exposed to commodity price risk. When hedging the output of our generation assets, we utilize contract sales that lock in the spread per MWh between variable costs and the price at which the electricity can be sold.
AES businesses will see changes in variable margin performance as global commodity prices shift. For 2017, we project pretax earnings exposure on a 10% move in commodity prices would be approximately $5 million for U.S. power (DPL), and less than $5 million for natural gas, oil, and coal, respectively. Our estimates exclude correlation of oil with coal or natural gas. For example, a decline in oil or natural gas prices can be accompanied by a decline in coal price if commodity prices are correlated. In aggregate, the Company’s downside exposure occurs with lower oil, lower natural gas, and higher coal prices. Exposures at individual businesses will change as new contracts or financial hedges are executed, and our sensitivity to changes in commodity prices generally increases in later years with reduced hedge levels at some of our businesses.
Commodity prices affect our businesses differently depending on the local market characteristics and risk management strategies. Spot power prices, contract indexation provisions and generation costs can be directly or indirectly affected by movements in the price of natural gas, oil and coal. We have some natural offsets across our businesses such that low commodity prices may benefit certain businesses and be a cost to others. Exposures are not perfectly linear or symmetric. The sensitivities are affected by a number of local or indirect market factors. Examples of these factors include hydrology, local energy market supply/demand balances, regional fuel supply issues, regional competition, bidding strategies and regulatory interventions such as price caps. Operational flexibility changes the shape of our sensitivities. For instance, certain power plants may limit downside exposure by reducing dispatch in low market environments. Volume variation also affects our commodity exposure. The volume sold under contracts or retail concessions can vary based on weather and economic conditions resulting in a higher or lower volume of sales in spot markets. Thermal unit availability and hydrology can affect the generation output available for sale and can affect the marginal unit setting power prices.
In the US SBU, the generation businesses are largely contracted but may have residual risk to the extent contracts are not perfectly indexed to the business drivers. IPL primarily generates energy to meet its retail customer demand however it opportunistically sells surplus economic energy into wholesale markets at market prices. Additionally, at DPL, competitive retail markets permit our customers to select alternative energy suppliers or elect to remain in aggregated customer pools for which energy is supplied by third party suppliers through a competitive auction process. DPL participates in these auctions held by other utilities and sells the remainder of its economic energy into the wholesale market. Given that natural gas-fired generators generally get energy prices for many markets, higher natural gas prices tend to expand our coal fixed margins. Our non-contracted generation margins are impacted by many factors, including the growth in natural gas-fired generation plants, new energy supply from renewable sources, and increasing energy efficiency.
In the Andes SBU, our business in Chile owns assets in the central and northern regions of the country and has a portfolio of contract sales in both. In the central region, the contract sales generally cover the efficient generation from our coal-fired and hydroelectric assets. Any residual spot price risk will primarily be driven by the
68
amount of hydrological inflows. In the case of low hydroelectric generation, spot price exposure is capped by the ability to dispatch our natural gas/diesel assets the price of which depends on fuel pricing at the time required. There is a small amount of coal generation in the northern region that is not covered by the portfolio of contract sales and therefore subject to spot price risk. In both regions, generators with oil or oil-linked fuel generally set power prices. In Colombia, we operate under a short-term sales strategy and have commodity exposure to unhedged volumes. Because we own hydroelectric assets there, contracts are not indexed to fuel.
In the Brazil SBU, the hydroelectric generating facility is covered by contract sales. Under normal hydrological volatility, spot price risk is mitigated through a regulated sharing mechanism across all hydroelectric generators in the country. Under drier conditions, the sharing mechanism may not be sufficient to cover the business' contract position, and therefore it may have to purchase power at spot prices driven by the cost of thermal generation.
In the MCAC SBU, our businesses have commodity exposure on unhedged volumes. Panama is highly contracted under a portfolio of fixed volume contract sales. To the extent hydrological inflows are greater than or less than the contract sales volume, the business will be sensitive to changes in spot power prices which may be driven by oil prices in some time periods. In the Dominican Republic, we own natural gas-fired assets contracted under a portfolio of contract sales and a coal-fired asset contracted with a single contract, and both contract and spot prices may move with commodity prices. Additionally, the contract levels do not always match our generation availability and our assets may be sellers of spot prices in excess of contract levels or a net buyer in the spot market to satisfy contract obligations.
In the Eurasia SBU, our Kilroot facility operates on a short-term sales strategy. To the extent that sales are unhedged, the commodity risk at our Kilroot business is to the clean dark spread, which is the difference between electricity price and our coal-based variable dispatch cost, including emissions. Natural gas-fired generators set power prices for many periods, so higher natural gas prices generally expand margins and higher coal or emissions prices reduce them. Similarly, increased wind generators displaces higher cost generation, reducing Kilroot's margins, and vice versa. Our Masinloc business is a coal-fired generation facility which hedges its output under a portfolio of contract sales that are indexed to fuel prices, with generation in excess of contract volume or shortfalls of generation relative to contract volumes settled in the spot market. Low oil prices may be a driver of margin compression since oil affects spot power sale prices sold in the spot market. Our Mong Duong business has minimal exposure to commodity price risk as it has no merchant exposure and fuel is subject to a pass-through mechanism.
Foreign Exchange Rate Risk — In the normal course of business, we are exposed to foreign currency risk and other foreign operations risks that arise from investments in foreign subsidiaries and affiliates. A key component of these risks stems from the fact that some of our foreign subsidiaries and affiliates utilize currencies other than our consolidated reporting currency, the U.S. Dollar ("USD"). Additionally, certain of our foreign subsidiaries and affiliates have entered into monetary obligations in the USD or currencies other than their own functional currencies. Certain of our foreign subsidiaries calculate and pay taxes in currencies other than their own functional currency. We have varying degrees of exposure to changes in the exchange rate between the USD and the following currencies: Argentine Peso, British Pound, Brazilian Real, Chilean Peso, Colombian Peso, Dominican Peso, Euro, Indian Rupee, Mexican Peso and Philippine Peso. These subsidiaries and affiliates have attempted to limit potential foreign exchange exposure by entering into revenue contracts that adjust to changes in foreign exchange rates. We also use foreign currency forwards, swaps and options, where possible, to manage our risk related to certain foreign currency fluctuations.
AES enters into cash flow hedges to protect economic value of the business and minimize impact of foreign exchange rate fluctuations to AES portfolio. While protecting cash flows, the hedging strategy is also designed to reduce forward looking earnings foreign exchange volatility. Due to variation of timing and amount between cash distribution and earnings exposure, the hedge impact may not fully cover the earnings exposure on a realized basis which could result in greater volatility in earnings. The largest foreign exchange risks over a 12-month forward- looking period stem from the following currencies: Brazilian Real, Euro, Colombian Peso, British Pound, and Kazakhstani Tenge. As of September 30, 2017, assuming a 10% USD appreciation, cash distributions attributable to foreign subsidiaries exposed to movement in the exchange rate of the Brazilian Real, British Pound, Colombian Peso, and Euro each are projected to be reduced by less than $5 million for 2017. These numbers have been produced by applying a one-time 10% USD appreciation to forecasted exposed cash distributions for 2017 coming from the respective subsidiaries exposed to the currencies listed above, net of the impact of outstanding hedges and holding all other variables constant. The numbers presented above are net of any transactional gains/losses. These sensitivities may change in the future as new hedges are executed or existing hedges are unwound. Additionally, updates to the forecasted cash distributions exposed to foreign exchange risk may result in further
69
modification. The sensitivities presented do not capture the impacts of any administrative market restrictions or currency inconvertibility.
Interest Rate Risk — We are exposed to risk resulting from changes in interest rates as a result of our issuance of variable and fixed-rate debt, as well as interest rate swap, cap, floor and option agreements.
Decisions on the fixed-floating debt mix are made to be consistent with the risk factors faced by individual businesses or plants. Depending on whether a plant’s capacity payments or revenue stream is fixed or varies with inflation, we partially hedge against interest rate fluctuations by arranging fixed-rate or variable-rate financing. In certain cases, particularly for non-recourse financing, we execute interest rate swap, cap and floor agreements to effectively fix or limit the interest rate exposure on the underlying financing. Most of our interest rate risk is related to non-recourse financings at our businesses.
As of September 30, 2017, the portfolio’s pretax earnings exposure for 2017 to a one-time 100-basis-point increase in interest rates for our Argentine Peso, Brazilian Real, Colombian Peso, Euro, and USD denominated debt would be approximately $10 million on interest expense for the debt denominated in these currencies. These amounts do not take into account the historical correlation between these interest rates.
ITEM 4. CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures — The Company, under the supervision and with the participation of its management, including the Company’s Chief Executive Officer (“CEO”) and Chief Financial Officer (“CFO”), evaluated the effectiveness of its “disclosure controls and procedures,” as such term is defined in Rule 13a-15(e) under the Securities Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”), as of the end of the period covered by this Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q. Based on that evaluation, our CEO and CFO have concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures were effective as of September 30, 2017, to ensure that information required to be disclosed by the Company in reports that we file or submit under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in SEC rules and forms, and include controls and procedures designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed by us in such reports is accumulated and communicated to our management, including our CEO and CFO, as appropriate, to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosures.
Changes in Internal Controls over Financial Reporting — There were no changes that occurred during the fiscal quarter covered by this Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
70
PART II: OTHER INFORMATION
ITEM 1. LEGAL PROCEEDINGS
The Company is involved in certain claims, suits and legal proceedings in the normal course of business. The Company has accrued for litigation and claims where it is probable that a liability has been incurred and the amount of loss can be reasonably estimated. The Company believes, based upon information it currently possesses and taking into account established reserves for estimated liabilities and its insurance coverage, that the ultimate outcome of these proceedings and actions is unlikely to have a material adverse effect on the Company's financial statements. It is reasonably possible, however, that some matters could be decided unfavorably to the Company and could require the Company to pay damages or make expenditures in amounts that could be material but cannot be estimated as of September 30, 2017.
In 1989, Centrais Elétricas Brasileiras S.A. (“Eletrobrás”) filed suit in the Fifth District Court in the state of Rio de Janeiro (“FDC”) against Eletropaulo Eletricidade de São Paulo S.A. (“EEDSP”) relating to the methodology for calculating monetary adjustments under the parties' financing agreement. In April 1999, the FDC found in favor of Eletrobrás and in September 2001, Eletrobrás initiated an execution suit in the FDC to collect approximately R$2.03 billion ($641 million) from Eletropaulo as estimated by Eletropaulo (or approximately R$2.76 billion ($872 million) as of June 2017, as estimated by Eletrobrás, and possibly legal costs) and a lesser amount from an unrelated company, Companhia de Transmissão de Energia Elétrica Paulista (“CTEEP”) (Eletropaulo and CTEEP were spun off of EEDSP pursuant to its privatization in 1998). In November 2002, the FDC rejected Eletropaulo's defenses in the execution suit. On appeal, the case was remanded to the FDC for further proceedings to determine whether Eletropaulo is liable for the debt. In December 2012, the FDC issued a decision that Eletropaulo is liable for the debt. However, that decision was annulled on appeal and the case was remanded to the FDC for further proceedings. On remand at the FDC, the FDC appointed an accounting expert to analyze the issues in the case. In September 2015, the expert issued a preliminary report concluding that Eletropaulo is liable for the debt, without quantifying the debt. Eletropaulo thereafter submitted questions to the expert and reports rebutting the expert's preliminary report (“Rebuttal Reports”). In April 2016, Eletrobrás requested that the expert determine both the criteria to calculate the debt and the amount of the debt. In April 2017, the FDC ordered the expert to comment on Eletropaulo’s Rebuttal Reports and to analyze the questions presented by the parties. It is unclear when the expert will issue his comments. Pursuant to a memorandum of understanding, in October 2017, Eletropaulo and Eletrobrás requested that the FDC suspend the case for 60 days to allow Eletropaulo and Eletrobrás to engage in settlement discussions. If settlement is achieved, it will be subject to the approval of the Eletropaulo Board of Directors and the majority of non-AES board members of Eletropaulo. If settlement is not achieved, the case will proceed and, ultimately, a decision will be issued by the FDC, which will be free to reject or adopt in whole or in part the expert's report. If the FDC again determines that Eletropaulo is liable for the debt, Eletrobrás will be entitled to resume the execution suit in the FDC. If Eletrobrás does so, Eletropaulo will be required to provide security for its alleged liability. In addition, in February 2008, CTEEP filed a lawsuit in the FDC against Eletrobrás and Eletropaulo seeking a declaration that CTEEP is not liable for any debt under the financing agreement. In June 2016, the FDC dismissed CTEEP’s lawsuit, on the ground that CTEEP’s claim would be decided in the FDC lawsuit initiated by Eletrobrás. Eletropaulo believes it has meritorious defenses to the claims asserted against it and will defend itself vigorously in these proceedings; however, there can be no assurances that it will be successful in its efforts. If Eletrobrás requests the seizure of the security noted above and the FDC grants such request (or if a court determines that Eletropaulo is liable for the debt), Eletropaulo's results of operations may be materially adversely affected and, in turn, the Company's results of operations may also be materially adversely affected. Eletropaulo and the Company could face a loss of earnings and/or cash flows and may have to provide loans or equity to support affected businesses or projects, restructure them, write down their value, and/or face the possibility that Eletropaulo cannot continue operations or provide returns consistent with our expectations, any of which could have a material impact on the Company.
In September 1996, a public civil action was asserted against Eletropaulo and Associação Desportiva Cultural Eletropaulo (the “Associação”) relating to alleged environmental damage caused by construction of the Associação near Guarapiranga Reservoir. The initial decision that was upheld by the Appellate Court of the state of São Paulo in 2006 found that Eletropaulo should repair the alleged environmental damage by demolishing certain construction and reforesting the area, and either sponsor an environmental project which would cost approximately R$2 million ($632 thousand) as of December 31, 2015, or pay an indemnification amount of approximately R$15 million ($5 million). Eletropaulo has appealed this decision to the Supreme Court and the Supreme Court affirmed the decision of the Appellate Court. Following the Supreme Court's decision, the case has been remanded to the court of first instance for further proceedings and to monitor compliance by the defendants with the terms of the decision. In January 2014, Eletropaulo informed the court that it intended to comply with the court's decision by donating a green area inside a protection zone and restore watersheds, the aggregate cost of which is expected to be
71
approximately R$2 million ($632 thousand). Eletropaulo also requested that the court add the current owner of the land where the Associação facilities are located, Empresa Metropolitana de Águas e Energia S.A. (“EMAE”), as a party to the lawsuit and order EMAE to perform the demolition and reforestation aspects of the court's decision. In July 2014, the court requested the Secretary of the Environment for the State of São Paulo to notify the court of its opinion regarding the acceptability of the green areas to be donated by Eletropaulo to the State of São Paulo. In January 2015, the Secretary of the Environment for the State of São Paulo notified Eletropaulo and the court that it would not accept Eletropaulo's proposed green areas donation. Instead of such green areas donation, the Secretary of the Environment proposed in March 2015 that Eletropaulo undertake an environmental project to offset the alleged environmental damage. Since March 2015, Eletropaulo and the Secretary of Environment have been working together to define an environmental project, which will be submitted for approval by the Public Prosecutor. The cost of such project is currently estimated to be R$3 million ($1 million).
In December 2001, Grid Corporation of Odisha (“GRIDCO”) served a notice to arbitrate pursuant to the Indian Arbitration and Conciliation Act of 1996 on the Company, AES Orissa Distribution Private Limited (“AES ODPL”), and Jyoti Structures (“Jyoti”) pursuant to the terms of the shareholders agreement between GRIDCO, the Company, AES ODPL, Jyoti and the Central Electricity Supply Company of Orissa Ltd. (“CESCO”), an affiliate of the Company. In the arbitration, GRIDCO asserted that a comfort letter issued by the Company in connection with the Company's indirect investment in CESCO obligates the Company to provide additional financial support to cover all of CESCO's financial obligations to GRIDCO. GRIDCO appeared to be seeking approximately $189 million in damages, plus undisclosed penalties and interest, but a detailed alleged damage analysis was not filed by GRIDCO. The Company counterclaimed against GRIDCO for damages. In June 2007, a 2-to-1 majority of the arbitral tribunal rendered its award rejecting GRIDCO's claims and holding that none of the respondents, the Company, AES ODPL, or Jyoti, had any liability to GRIDCO. The respondents' counterclaims were also rejected. A majority of the tribunal later awarded the respondents, including the Company, some of their costs relating to the arbitration. GRIDCO filed challenges of the tribunal's awards with the local Indian court. GRIDCO's challenge of the costs award has been dismissed by the court, but its challenge of the liability award remains pending. A hearing on the liability award is scheduled for November 2, 2017. The Company believes that it has meritorious defenses to the claims asserted against it and will defend itself vigorously in these proceedings; however, there can be no assurances that it will be successful in its efforts.
In March 2003, the office of the Federal Public Prosecutor for the State of São Paulo, Brazil (“MPF”) notified Eletropaulo that it had commenced an inquiry into the BNDES financings provided to AES Elpa and AES Transgás, the rationing loan provided to Eletropaulo, changes in the control of Eletropaulo, sales of assets by Eletropaulo, and the quality of service provided by Eletropaulo to its customers. The MPF requested various documents from Eletropaulo relating to these matters. In July 2004, the MPF filed a public civil lawsuit in the Federal Court of São Paulo (“FCSP”) alleging that BNDES violated Law 8429/92 (the Administrative Misconduct Act) and BNDES's internal rules by (1) approving the AES Elpa and AES Transgás loans; (2) extending the payment terms on the AES Elpa and AES Transgás loans; (3) authorizing the sale of Eletropaulo's preferred shares at a stock-market auction; (4) accepting Eletropaulo's preferred shares to secure the loan provided to Eletropaulo; and (5) allowing the restructurings of Light Serviços de Eletricidade S.A. and Eletropaulo. The MPF also named AES Elpa and AES Transgás as defendants in the lawsuit because they allegedly benefited from BNDES's alleged violations. In May 2006, the FCSP ruled that the MPF could pursue its claims based on the first, second, and fourth alleged violations noted above. The MPF subsequently filed an interlocutory appeal with the Federal Court of Appeals (“FCA”) seeking to require the FCSP to consider all five alleged violations. In April 2015, the FCA issued a decision holding that the FCSP should consider all five alleged violations. AES Elpa and AES Brasiliana (the successor of AES Transgás) have appealed the April 2015 decision to the Superior Court of Justice. The lawsuit remains pending before the FCSP. AES Elpa and AES Brasiliana believe they have meritorious defenses to the allegations asserted against them and will defend themselves vigorously in these proceedings; however, there can be no assurances that they will be successful in their efforts.
Pursuant to their environmental audit, AES Sul and AES Florestal discovered 200 barrels of solid creosote waste and other contaminants at a pole factory that AES Florestal had been operating. The conclusion of the audit was that a prior operator of the pole factory, Companhia Estadual de Energia (“CEEE”), had been using those contaminants to treat the poles that were manufactured at the factory. On their initiative, AES Sul and AES Florestal communicated with Brazilian authorities and CEEE about the adoption of containment and remediation measures. In March 2008, the State Attorney of the state of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil filed a public civil action against AES Sul, AES Florestal and CEEE seeking an order requiring the companies to recover the contaminated area located on the grounds of the pole factory and an indemnity payment of approximately R$6 million ($2 million) to the state's Environmental Fund. In October 2011, the State Attorney Office filed a request for an injunction ordering the defendant companies to contain and remove the contamination immediately. The court granted injunctive relief on
72
October 18, 2011, but determined only that defendant CEEE was required to proceed with the removal work. In May 2012, CEEE began the removal work in compliance with the injunction. The removal costs are estimated to be approximately R$60 million ($19 million) and the work was completed in February 2014. In parallel with the removal activities, a court-appointed expert investigation took place, which was concluded in May 2014. The court-appointed expert final report was presented to the State Attorneys in October 2014, and in January 2015 to the defendant companies. In March 2015, AES Sul and AES Florestal submitted comments and supplementary questions regarding the expert report. The Company believes that it has meritorious defenses to the claims asserted against it and will defend itself vigorously in these proceedings; however, there can be no assurances that it will be successful in its efforts.
In May 2008, the Tax Authority initiated a collection suit against Eletropaulo, seeking to collect approximately R$230 million ($73 million) in PIS taxes (as estimated by Eletropaulo) for the period of March 1996 to December 1998. Unfavorable decisions on the merits were issued by the First Instance Court (“FIC”) and the Second Instance Court (“SIC”) in January 2011 and April 2015, respectively. Subsequently, Eletropaulo requested that the SIC remit the case to the Superior Court of Justice (“STJ”) and the Supreme Federal Court (“STF”). In March 2017, the SIC rejected Eletropaulo’s request. Eletropaulo has requested that an SIC panel review the March 2017 decision. In addition, Eletropaulo has appealed that decision to the STJ and STF. Also, in April 2017, in a related execution proceeding, the FIC asked the Tax Authority to advise on whether it intends to pursue collection. In August 2017, the Tax Authority requested that Eletropaulo replace its bank guarantee with a cash deposit of the amount in dispute into a judicial account (currently, the bank guarantee is in place as security for Eletropaulo’s alleged obligation). Eletropaulo contested the Tax Authority’s request. In September 2017, the FIC denied the Tax Authority’s request. The Tax Authority is expected to appeal. Eletropaulo believes it has meritorious defenses and will defend itself vigorously in these proceedings; however, there can be no assurances that it will be successful in its efforts.
In October 2009, IPL received an NOV and Finding of Violation from the EPA pursuant to the CAA Section 113(a). The NOV alleges violations of the CAA at IPL's three primarily coal-fired electric generating facilities dating back to 1986. The alleged violations primarily pertain to the Prevention of Significant Deterioration and nonattainment New Source Review requirements under the CAA. IPL management previously met with EPA staff regarding possible resolutions of the NOV. At this time, we cannot predict the ultimate resolution of this matter. However, settlements and litigated outcomes of similar cases have required companies to pay civil penalties, install additional pollution control technology on coal-fired electric generating units, retire existing generating units, and invest in additional environmental projects. A similar outcome in this case could have a material impact to IPL and could, in turn, have a material impact on the Company. IPL would seek recovery of any operating or capital expenditures related to air pollution control technology to reduce regulated air emissions; however, there can be no assurances that it would be successful in that regard.
In June 2011, the São Paulo Municipal Tax Authority (the “Tax Authority”) filed 60 tax assessments in São Paulo administrative court against Eletropaulo, seeking to collect services tax (“ISS”) on revenues for services rendered by Eletropaulo. Eletropaulo challenged the assessments on the grounds that the revenues at issue were not subject to ISS. In October 2013, the First Instance Administrative Court (“FIAC”) determined that Eletropaulo was liable for ISS, interest, and related penalties totaling approximately R$3.3 billion ($1 billion) as estimated by Eletropaulo. Eletropaulo thereafter appealed to the Second Instance Administrative Court (“SIAC”). In January 2016, the Tax Authority nullified most of the ISS sought from Eletropaulo. In January 2017, the SIAC issued a decision confirming the reduction and rejecting certain other amounts of ISS as time-barred, but finding that Eletropaulo was liable for the remainder of ISS totaling approximately R$200 million ($63 million). The Tax Authority appealed the SIAC’s decision on the time-barred amounts, totaling approximately R$16 million ($5 million) (“Time-Barred Amounts”), to the Municipal Council of Taxes (“MCT Proceeding”). With respect to the R$200 million, in March 2017, the Tax Authority canceled most of that amount (“March 2017 Cancelation”), and initiated an execution lawsuit to collect the remainder of approximately R$70 million ($22 million) (“Execution Lawsuit”). The Time-Barred Amounts and the March 2017 Cancelation will be reviewed in the ongoing MCT Proceeding. The Execution Lawsuit is also ongoing. Eletropaulo believes it has meritorious defenses and will defend itself vigorously in these proceedings; however, there can be no assurances that it will be successful in its efforts.
In January 2012, the Brazil Federal Tax Authority issued an assessment alleging that AES Tietê had paid PIS and COFINS taxes from 2007 to 2010 at a lower rate than the tax authority believed was applicable. AES Tietê challenged the assessment on the grounds that the tax rate was set in the applicable legislation. In April 2013, the FIAC determined that AES Tietê should have calculated the taxes at the higher rate and that AES Tietê was liable for unpaid taxes, interest, and penalties totaling approximately R$1.16 billion ($366 million) as estimated by AES Tietê. AES Tietê appealed to the SIAC. In January 2015, the SIAC issued a decision in AES Tietê's favor, finding that AES Tietê was not liable for unpaid taxes. The public prosecutor subsequently filed an appeal, which was denied as untimely. The Tax Authority thereafter filed a motion for clarification of the SIAC's decision, which was
73
denied in September 2016. The Tax Authority later filed a special appeal (“Special Appeal”), which was rejected as untimely in October 2016. The Tax Authority thereafter filed an interlocutory appeal with the Superior Administrative Court (“SAC”). In March 2017, the President of the SAC determined that the SAC would analyze the Special Appeal on timeliness and, if required, the merits. AES Tietê has challenged the Special Appeal. AES Tietê believes it has meritorious defenses to the claim and will defend itself vigorously in these proceedings; however, there can be no assurances that it will be successful in its efforts.
In January 2015, DPL received NOVs from the EPA alleging violations of opacity at Stuart and Killen Stations, and in October 2015, IPL received a similar NOV alleging violations at Petersburg Station. In February 2017, EPA issued a second NOV for DPL Stuart Station, alleging violations of opacity in 2016. Moreover, in February 2016, IPL received an NOV from the EPA alleging violations of New Source Review (“NSR”) and other CAA regulations, the Indiana SIP, and the Title V operating permit at Petersburg Station. It is too early to determine whether the NOVs could have a material impact on our business, financial condition or results of our operations. IPL would seek recovery of any operating or capital expenditures, but not fines or penalties, related to air pollution control technology to reduce regulated air emissions; however, there can be no assurances that we would be successful in this regard.
In September 2015, AES Southland Development, LLC and AES Redondo Beach, LLC filed a lawsuit against the California Coastal Commission (the “CCC”) over the CCC's determination that the site of AES Redondo Beach included approximately 5.93 acres of CCC-jurisdictional wetlands. The CCC has asserted that AES Redondo Beach has improperly installed and operated water pumps affecting the alleged wetlands in violation of the California Coastal Act and Redondo Beach Local Coastal Program and has ordered AES Redondo Beach to restore the site. Additional potential outcomes of the CCC determination could include an order requiring AES Redondo Beach to fund a wetland mitigation project and/or pay fines or penalties. AES Redondo Beach believes that it has meritorious arguments and intends to vigorously prosecute such lawsuit, but there can be no assurances that it will be successful.
In October 2015, Ganadera Guerra, S.A. (“GG”) and Constructora Tymsa, S.A. (“CT”) filed separate lawsuits against AES Panama in the local courts of Panama. The claimants allege that AES Panama profited from a hydropower facility (La Estrella) being partially located on land owned initially by GG and currently by CT, and that AES Panama must pay compensation for its use of the land. The damages sought from AES Panama are approximately $685 million (GG) and $100 million (CT). In October 2016, the court dismissed GG's claim because of GG's failure to comply with a court order requiring GG to disclose certain information. GG has refiled its lawsuit. Also, there are ongoing administrative proceedings concerning whether AES Panama is entitled to acquire an easement over the land and whether AES Panama can continue to occupy the land. AES Panama believes it has meritorious defenses and claims and will assert them vigorously; however, there can be no assurances that it will be successful in its efforts.
In January 2017, the Superintendencia del Medio Ambiente (“SMA”) issued a Formulation of Charges asserting that Alto Maipo is in violation of certain conditions of the Environmental Approval Resolution (“RCA”) governing Alto Maipo’s hydropower project, for, among other things, operating vehicles at unauthorized times and failing to mitigate the impact of water intrusion during tunnel construction. In February 2017, Alto Maipo submitted a compliance plan to the SMA which, if approved by the agency, would resolve the matter without materially impacting construction of the project. In June 2017, the SMA issued a resolution detailing its comments on the compliance plan. Alto Maipo responded to the SMA’s comments in July 2017. The SMA is expected to issue its decision on Alto Maipo’s compliance plan in the near future. The outcome of this matter is uncertain, but an adverse decision by the SMA could have a negative impact on the construction of the project. Alto Maipo will pursue its interests vigorously in this matter; however, there can be no assurance that it will be successful in its efforts.
In June 2017, Alto Maipo terminated one of its contractors, Constructora Nuevo Maipo S.A. (“CNM”), given CNM’s stoppage of tunneling works, its failure to produce a completion plan, and its other breaches of contract. Alto Maipo also initiated arbitration against CNM to recover completion costs and other damages relating to these breaches. CNM subsequently initiated a separate arbitration, seeking a declaration that its termination was wrongful, damages, and other relief. CNM has not supported its alleged damages, but it has asserted that it is entitled to recover over $20 million in damages, legal costs, and the amounts drawn by Alto Maipo under letters of credit. The arbitrations have been consolidated into a single action, which is ongoing. As noted above, Alto Maipo drew on letters of credit securing CNM’s obligations, totaling approximately $73 million. Initially, the issuing bank did not pay Alto Maipo because CNM obtained an ex parte injunction from a Chilean court prohibiting the bank from honoring the draws. However, at Alto Maipo’s request, the Chilean court later removed the injunction. Accordingly, in July 2017, the bank paid Alto Maipo in full. CNM is attempting to seek relief in the Chilean court of appeals and the arbitration in relation to the draws on the letters of credit. To date, CNM has been unable to obtain such relief. Alto
74
Maipo believes it has meritorious claims and defenses and will assert them vigorously in these proceedings; however, there can be no assurances that it will be successful in its efforts.
In October 2017, the Ministry of Justice (“MOJ”) of the Republic of Kazakhstan (“ROK”) filed a lawsuit in the Economic Court of Kazakhstan against Tau Power BV (an AES affiliate), Altai Power LLP (an AES affiliate), the Company, and two hydropower plants (“HPPs”) previously under concession to Tau Power. In its lawsuit, the MOJ references a 2013 treaty arbitration award against the ROK concerning the ROK’s energy laws. While its lawsuit is unclear, the MOJ appears to seek relief relating to the net income distributed by the HPPs during certain years of the concession period. There is a hearing on this matter in the Economic Court on November 1, 2017. The AES defendants believe that the lawsuit is without merit and they will assert their defenses vigorously; however, there can be no assurances that they will be successful in their efforts.
ITEM 1A. RISK FACTORS
There have been no material changes to the risk factors disclosed in Part I—Item 1A.—Risk Factors of our 2016 Form 10-K.
ITEM 2. UNREGISTERED SALES OF EQUITY SECURITIES AND USE OF PROCEEDS
No repurchases were made by the AES Corporation of its common stock during the third quarter of 2017.
The Board has authorized the Company to repurchase stock through a variety of methods, including open market repurchases, purchases by contract (including, without limitation, accelerated stock repurchase programs or 10b5-1 plans) and/or privately negotiated transactions. There can be no assurances as to the amount, timing or prices of repurchases, which may vary based on market conditions and other factors. The Program does not have an expiration date and can be modified or terminated by the Board of Directors at any time. As of September 30, 2017, $246 million remained available for repurchase under the Program.
ITEM 3. DEFAULTS UPON SENIOR SECURITIES
None.
ITEM 4. MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES
Not applicable.
ITEM 5. OTHER INFORMATION
None.
ITEM 6. EXHIBITS
4.1 | ||
31.1 | ||
31.2 | ||
32.1 | ||
32.2 | ||
101.INS | XBRL Instance Document (filed herewith). | |
101.SCH | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document (filed herewith). | |
101.CAL | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document (filed herewith). | |
101.DEF | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document (filed herewith). | |
101.LAB | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document (filed herewith). | |
101.PRE | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document (filed herewith). | |
75
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned thereunto duly authorized.
THE AES CORPORATION (Registrant) | |||||
Date: | November 1, 2017 | By: | /s/ THOMAS M. O’FLYNN | ||
Name: | Thomas M. O’Flynn | ||||
Title: | Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial Officer) | ||||
By: | /s/ FABIAN E. SOUZA | ||||
Name: | Fabian E. Souza | ||||
Title: | Vice President and Controller (Principal Accounting Officer) | ||||
76
