Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| 8-K - 8-K - Syros Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | a17-22968_18k.htm |
Cautionary note regarding forward-looking statements This presentation contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995 that involve substantial risks and uncertainties. All statements, other than statements of historical facts, contained in this presentation, including statements regarding our strategy, research and clinical development plans, future operations, future financial position, future revenues, projected costs, prospects, plans and objectives of management, are forward-looking statements. The words “anticipate,” “believe,” “estimate,” “expect,” “intend,” “may,” “plan,” “predict,” “project,” “target,” “potential,” “will,” “would,” “could,” “should,” “continue,” and similar expressions are intended to identify forward-looking statements, although not all forward-looking statements contain these identifying words. Moreover, there can be no assurance that the PK and PD and ex vivo differentiation data generated to date in the ongoing Phase 2 clinical trial of SY-1425 are predictive of the ability of such trial to meet any of its endpoints. We may not actually achieve the plans, intentions or expectations disclosed in our forward-looking statements, and you should not place undue reliance on our forward-looking statements. Actual results or events could differ materially from the plans, intentions and expectations disclosed in these forward-looking statements as a result of various important factors, including Syros’ ability to: advance the development of its programs, including SY-1425 and SY-1365, under the timelines it projects in current and future clinical trials; advance discovery programs to identify drug candidates for IND-enabling studies; obtain and maintain patent protection for its drug candidates and the freedom to operate under third party intellectual property; demonstrate in any current and future clinical trials the requisite safety, efficacy and combinability of its drug candidates; replicate scientific and non-clinical data in clinical trials; successfully develop a companion diagnostic test to identify patients with biomarkers associated with the RARA super-enhancer; obtain and maintain necessary regulatory approvals; identify, enter into and maintain collaboration agreements with third parties; manage competition; manage expenses; raise the substantial additional capital needed to achieve its business objectives; attract and retain qualified personnel; and successfully execute on its business strategies; risks described under the caption “Risk Factors” in our Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2017 that is on file with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC); and risks described in other filings that we may make with the SEC in the future. Any forward-looking statements contained in this presentation speak only as of the date this presentation is made, and we expressly disclaim any obligation to update any forward-looking statements, whether because of new information, future events or otherwise.

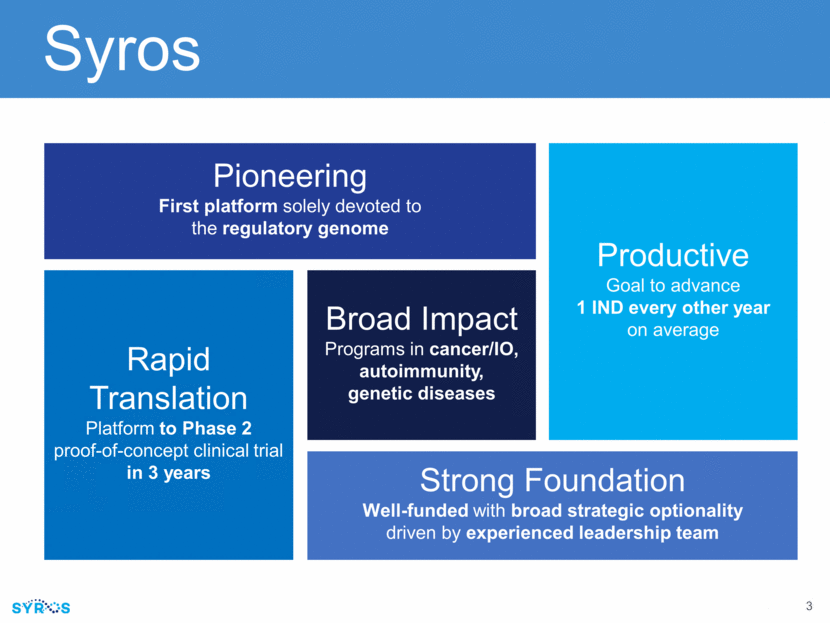
Syros Pioneering First platform solely devoted to the regulatory genome Rapid Translation Platform to Phase 2 proof-of-concept clinical trial in 3 years Productive Goal to advance 1 IND every other year on average Broad Impact Programs in cancer/IO, autoimmunity, genetic diseases Strong Foundation Well-funded with broad strategic optionality driven by experienced leadership team
Genomics 3.0 Platform
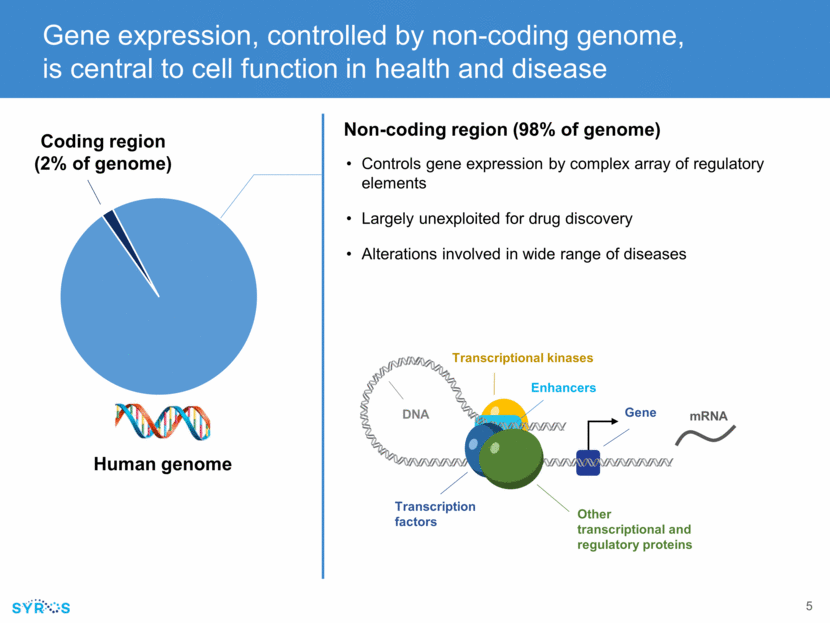
Gene expression, controlled by non-coding genome, is central to cell function in health and disease Human genome Coding region (2% of genome) Non-coding region (98% of genome) Controls gene expression by complex array of regulatory elements Largely unexploited for drug discovery Alterations involved in wide range of diseases Enhancers Transcription factors Other transcriptional and regulatory proteins Transcriptional kinases Gene DNA mRNA
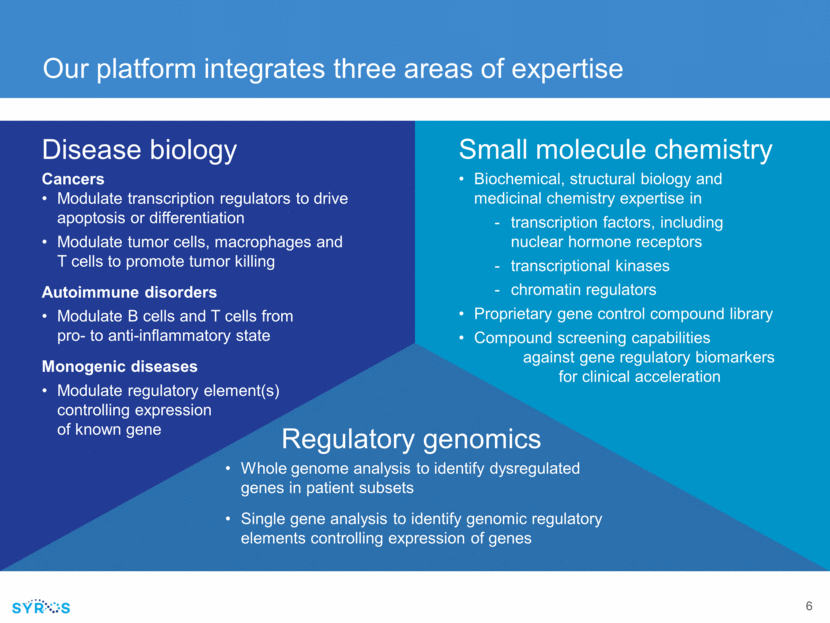
Our platform integrates three areas of expertise Disease biology Cancers Modulate transcription regulators to drive apoptosis or differentiation Modulate tumor cells, macrophages and T cells to promote tumor killing Autoimmune disorders Modulate B cells and T cells from pro- to anti-inflammatory state Monogenic diseases Modulate regulatory element(s) controlling expression of known gene Regulatory genomics Whole genome analysis to identify dysregulated genes in patient subsets Single gene analysis to identify genomic regulatory elements controlling expression of genes Small molecule chemistry Biochemical, structural biology and medicinal chemistry expertise in transcription factors, including nuclear hormone receptors transcriptional kinases chromatin regulators Proprietary gene control compound library Compound screening capabilities against gene regulatory biomarkers for clinical acceleration
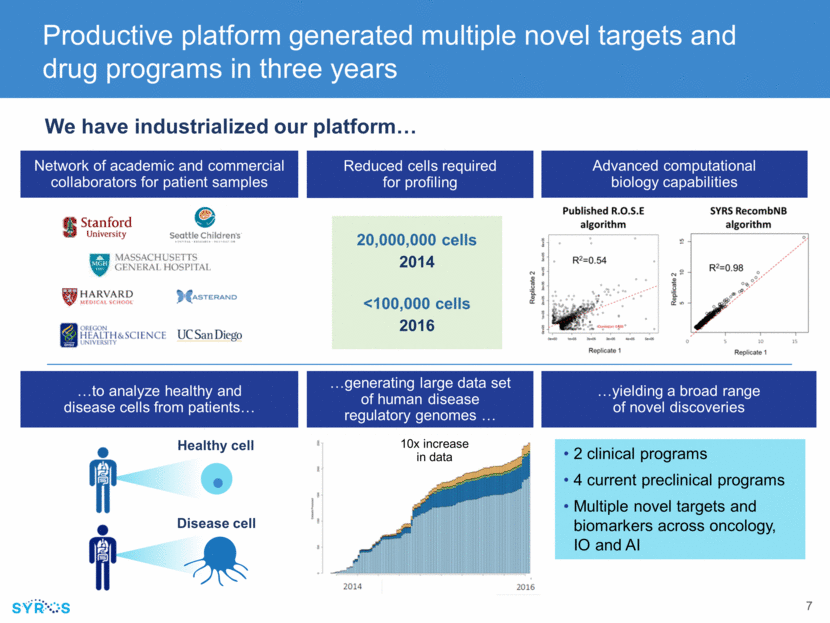
Network of academic and commercial collaborators for patient samples Productive platform generated multiple novel targets and drug programs in three years We have industrialized our platform 2014 2016 20,000,000 cells <100,000 cells Reduced cells required for profiling Advanced computational biology capabilities 2 clinical programs 4 current preclinical programs Multiple novel targets and biomarkers across oncology, IO and AI yielding a broad range of novel discoveries Healthy cell Disease cell to analyze healthy and disease cells from patients generating large data set of human disease regulatory genomes 10x increase in data
Our Programs

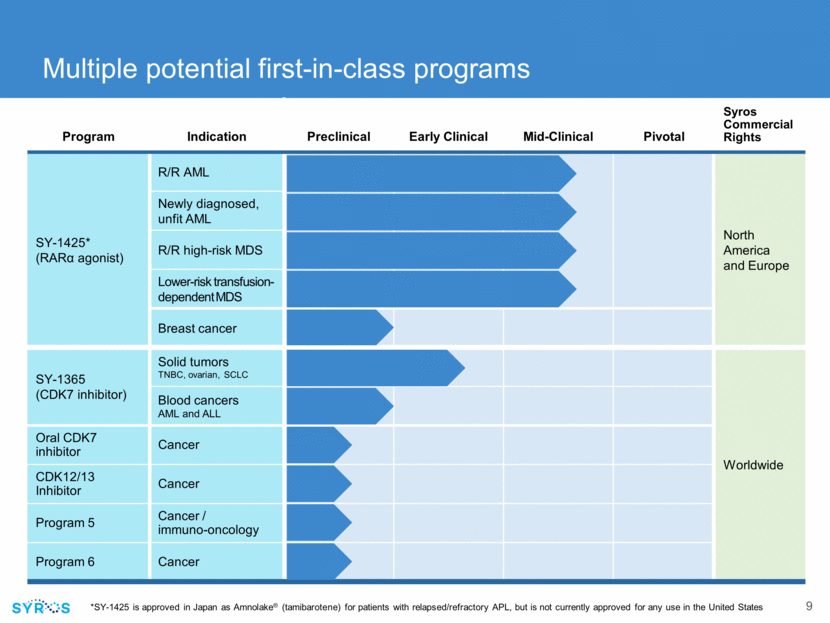
Program Indication Preclinical Early Clinical Mid-Clinical Pivotal Syros Commercial Rights SY-1425* (RAR agonist) R/R AML North America and Europe Newly diagnosed, unfit AML R/R high-risk MDS Lower-risk transfusion-dependent MDS Breast cancer SY-1365 (CDK7 inhibitor) Solid tumors TNBC, ovarian, SCLC Worldwide Blood cancers AML and ALL Oral CDK7 inhibitor Cancer CDK12/13 Inhibitor Cancer Program 5 Cancer / immuno-oncology Program 6 Cancer *SY-1425 is approved in Japan as Amnolake® (tamibarotene) for patients with relapsed/refractory APL, but is not currently approved for any use in the United States Multiple potential first-in-class programs
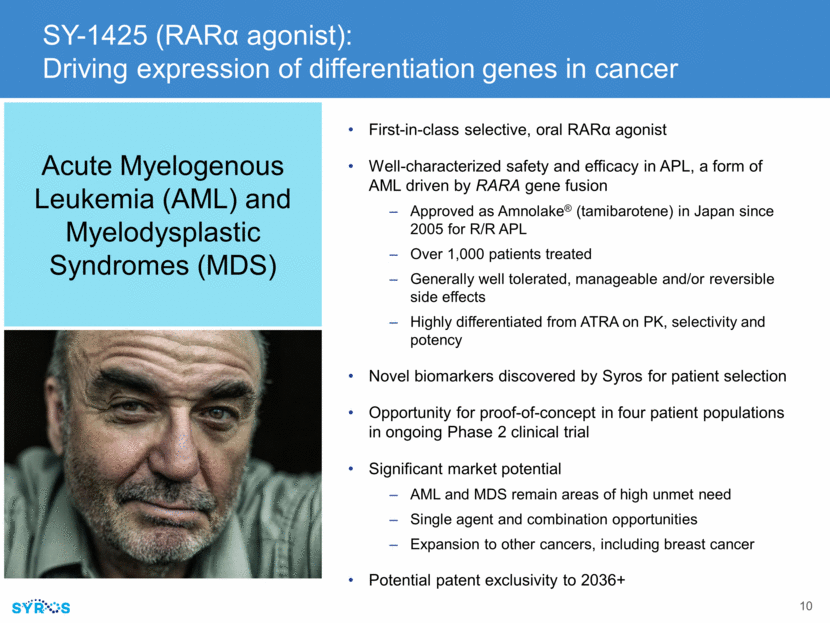
SY-1425 (RAR agonist): Driving expression of differentiation genes in cancer First-in-class selective, oral RAR agonist Well-characterized safety and efficacy in APL, a form of AML driven by RARA gene fusion Approved as Amnolake® (tamibarotene) in Japan since 2005 for R/R APL Over 1,000 patients treated Generally well tolerated, manageable and/or reversible side effects Highly differentiated from ATRA on PK, selectivity and potency Novel biomarkers discovered by Syros for patient selection Opportunity for proof-of-concept in four patient populations in ongoing Phase 2 clinical trial Significant market potential AML and MDS remain areas of high unmet need Single agent and combination opportunities Expansion to other cancers, including breast cancer Potential patent exclusivity to 2036+ Acute Myelogenous Leukemia (AML) and Myelodysplastic Syndromes (MDS)
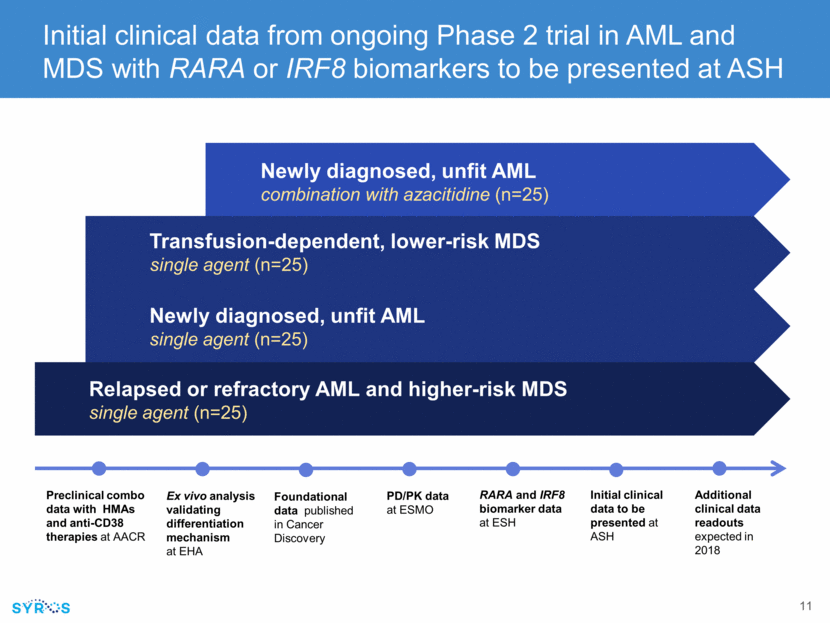
Newly diagnosed, unfit AML single agent (n=25) Relapsed or refractory AML and higher-risk MDS single agent (n=25) Initial clinical data from ongoing Phase 2 trial in AML and MDS with RARA or IRF8 biomarkers to be presented at ASH Ex vivo analysis validating differentiation mechanism at EHA PD/PK data at ESMO RARA and IRF8 biomarker data at ESH Initial clinical data to be presented at ASH Transfusion-dependent, lower-risk MDS single agent (n=25) Newly diagnosed, unfit AML combination with azacitidine (n=25) Preclinical combo data with HMAs and anti-CD38 therapies at AACR Foundational data published in Cancer Discovery Additional clinical data readouts expected in 2018
Data from ongoing Phase 2 clinical trial of SY-1425 shows favorable PK and evidence of RARa target engagement “Pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic evaluation of SY-1425 (tamibarotene) in biomarker-selected acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) patients” Dosing regimen achieves anticipated drug exposure in AML and MDS patients DHRS3 induction provides evidence of RARa target engagement Similar D1 and D15 exposure R/R AML and HR MDS LR MDS RARA+ IRF8+ Double+ C1D1 2-4h C1D15 2-4h C1D1 5-8h C1D15 5-8h C1D1 pre-dose C1D1 5-8h C1D1 pre-dose C1D1 5-8h C1D15 post-dose C1D15 post-dose RARA+ IRF8+ Double+ P D Cycle 1 Day 1 (pre-dose) PD Cycle 1 Day 1 (5-8 hours post-dose) PD Cycle 1 Day 150.03125 0.0625 0.125 0.25 0.51248 1632 DHRS 3 Fold Induction C1D 12-4h C1 D152-4hC1 D15-8hC1 D155-8h 050 100 150 200 S Y-1425 ng/m LP D Cycle 1 Day 1 (pre-dose) PD Cycle 1 Day 1 (5-8 hours post-dose) PD Cycle 1 Day 1 50.03125 0.0625 0.125 0.25 0.51 248 1632 DHR S 3 Fold Induction
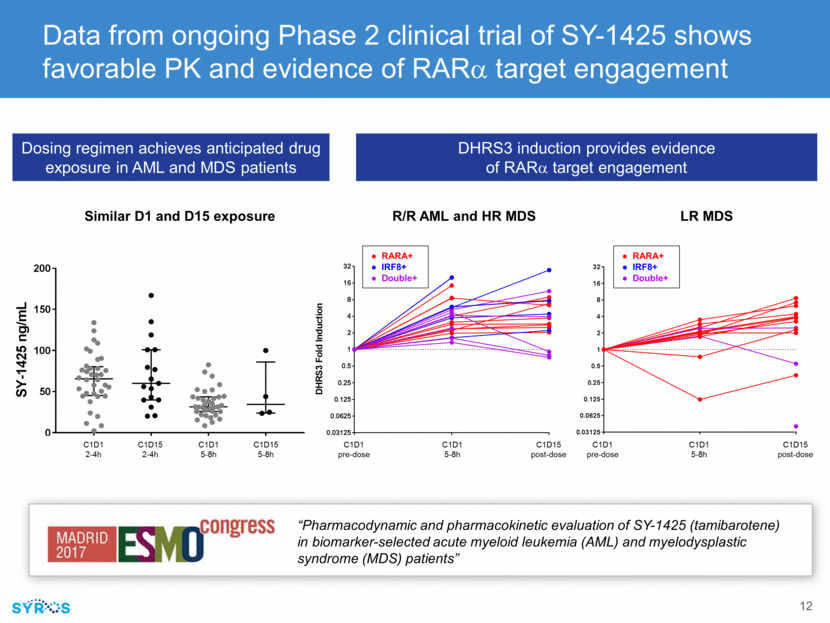
Biomarker status significantly correlated with differentiation of patient blood samples following ex vivo SY-1425 treatment “Novel RARA Pathway Activation Biomarkers in Study SY-1425-201 Define a New Subset of AML and MDS Patients and Correlate with Myeloid Differentiation” Differentiation based scoring algorithm IDE-approved clinical trial assay using qPCR for RARA and IRF8 mRNA with average turnaround time of 2.8 days ~40% of patients screened as of Aug. 31 in Phase 2 clinical trial tested biomarker-positive One-third of relapsed or refractory AML and higher-risk MDS tested positive Trending higher in lower-risk MDS and newly diagnosed AML but on small patient numbers
Foundational data support clinical development strategy for SY-1425 in AML and MDS subsets Identified six distinct patient subsets based on super-enhancer profiles, including one enriched for super-enhancer associated with RARA In preclinical studies, RARA super-enhancer is predictive of response to SY-1425 SY-1425 reduces proliferation and promotes differentiation in AML cells with high RARA expression, while having no effect on AML cells with low RARA expression SY-1425 induces transcriptional and epigenomic changes in AML cells with high RARA expression similar to those seen in APL cells treated with SY-1425 Underscores promise of platform to provide new approach for identifying drug targets in defined patient subsets with potential to lead to more precise diagnosis and better treatment “Super-Enhancer Analysis Defines Novel Epigenomic Subtypes of Non-APL AML Including an RAR Dependency Targetable by SY-1425, a Potent and Selective RAR Agonist”

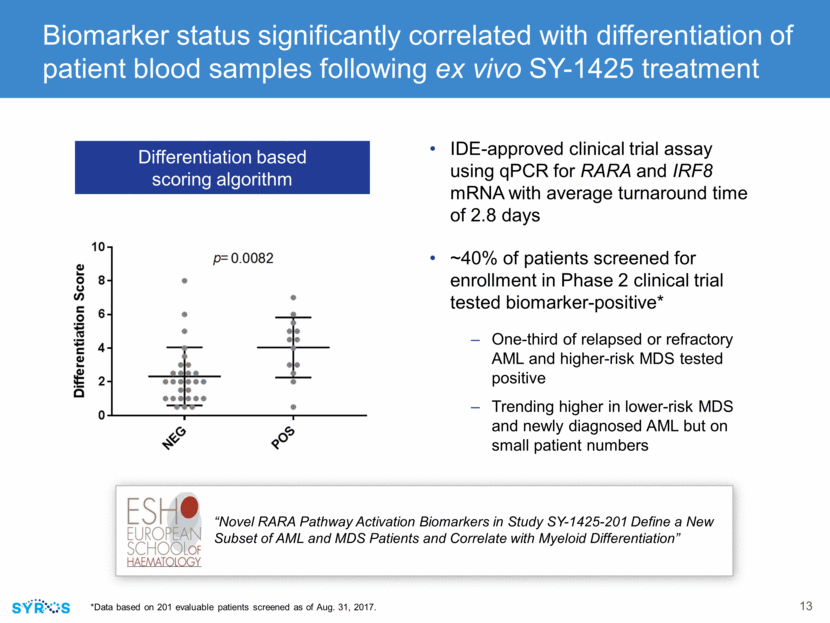
SY-1425 shows tumor growth inhibition in RARA-high models as single agent and in combination with standard-of-care agent SY-1425/Aza in RARA-high AML PDX model RARA-high AML PDX model RARA-low AML PDX model Sensitivity to SY-1425 associated with RARA biomarker Combination with azacitidine increased tumor growth inhibition “Clinical Pharmacodynamic Markers and Combinations with SY1425 (tamibarotene) in a Genomically-Defined Subset of Non-APL AML” % Peripheral Tumor Burden Vehicle (n-3) SY-1425 6mg/kg (n-3) Days Post Treatment Initiation % Peripheral Tumor Burden Vehicle (n=3) SY-1425 6mg/kg (n=3) Days Post Treatment Initiation % Peripheral Tumor Burden Vehicle (n=3) SY-1425 BID 3mg/kg (n=5) Azacitidine 2.5 mg/kg (n=5) Combination (n=5) Aza SY-1425 All mice in Aza only arm succumb to disease Days Post Treatment Initiation
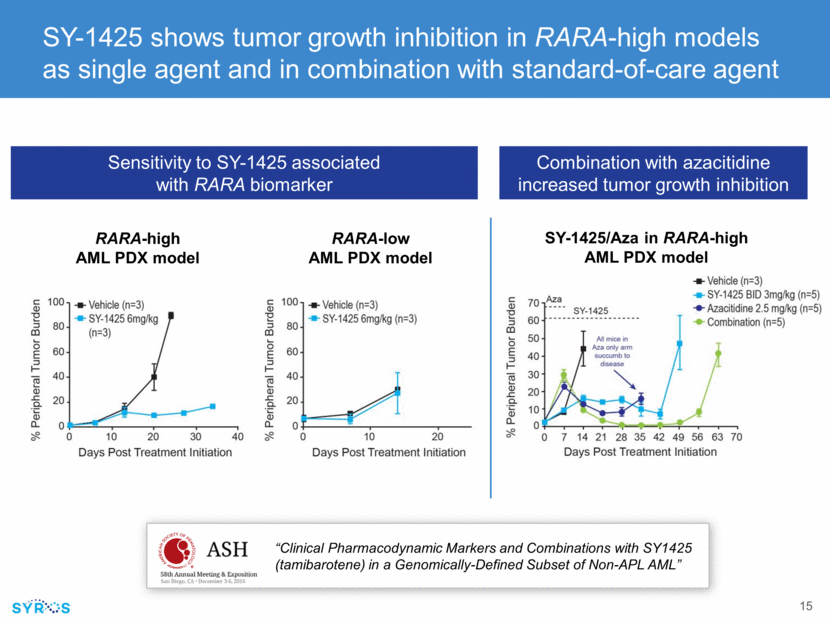
SY-1425 and AZA combination show biomarker-dependent DNA damage and induction of apoptosis Internal data on file Combo induces DNA damage Combo leads to robust reduction of tumor cells in blood, BM and spleen CR Combo induces 10-fold greater apoptosis Combo is synergistic Isobologram Vehicle Aza 2 mg/kg QD SY-1425 3 mg/kg BID Aza combo 0.005 1.01.50.00.51.01.5 Isobologram Azacitidine SY-14250 10 20 30 40 50 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 Time (hours) Normalized apoptotic cells per well (foldchange) SY-1425 50nM Aza combo Aza only Blood BM Spleen Blood BM Spleen Blood BM Spleen Blood BM Spleen 0 25 50 75 100 Tumor content in blood, bone marrow and spleen % of hC D 45+Cells/Live cells Vehicle Azacitidine (A) SY-1425 AW1; SYW2,3,4 5
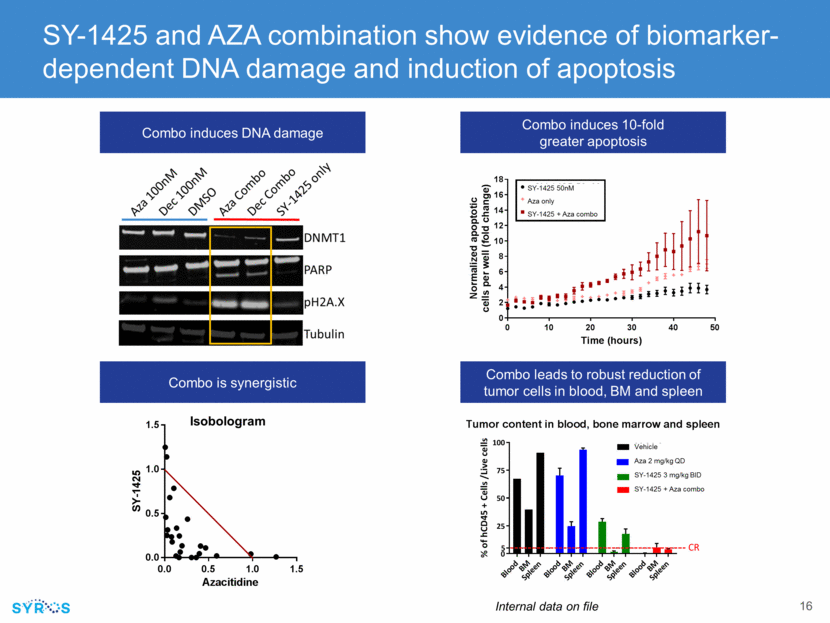
SY-1425 promotes differentiation of RARA-high AML cells and highly upregulates CD38 SY-1425 induces CD38 cell surface expression “SY-1425, a selective RAR agonist, induces high levels of CD38 expression in RARA-high AML tumors creating a susceptibility to anti-CD38 therapeutic antibody treatment” SY-1425 induces CD38 gene expression Over-expression of RARA represses diferentiation repression differentiation program sy-1425 activates differentiation activation 1425 1425 1425 1425 differentiation program differentiated cells sy-1425induces CD38 gene expression RARA-high CD38 12.5 10.0 7.5 5.0 2.5 0.0 8 4 0 4 8 Log2 fold-change mRNA RARA-low 12.5 10.0 7.5 5.0 2.5 0.0 8 4 0 4 8 Log2 fold-change mRNA SY-1425 induces CD38 cell surface expression APL AML RARA high RARA low 100 50 0 Vehicle SY-1425 Vehicle SY-1425 Vehicle SY-1425
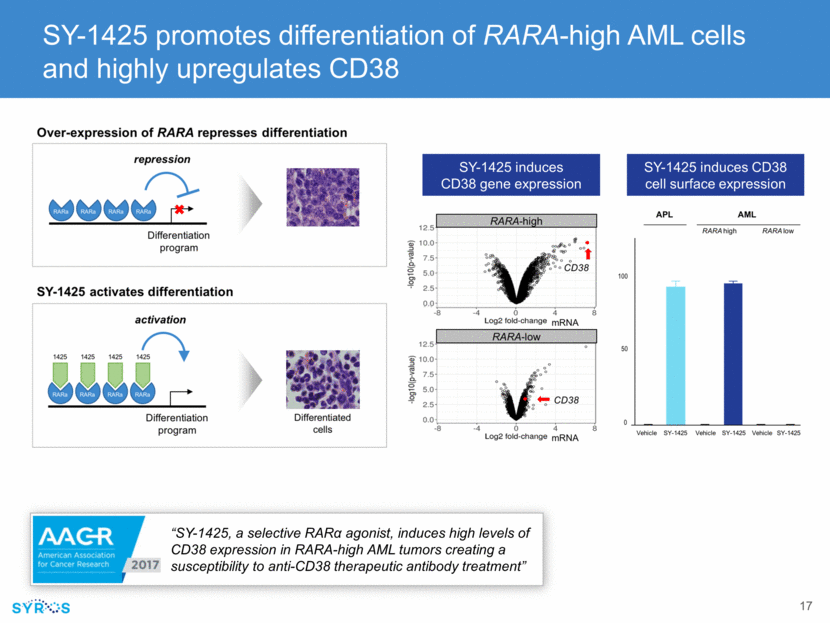
SY-1425 induces high levels of CD38 expression in RARA-high tumors creating a susceptibility to anti-CD38 therapeutic antibody treatment Cell apoptosis “SY-1425, a selective RAR agonist, induces high levels of CD38 expression in RARA-high AML tumors creating a susceptibility to anti-CD38 therapeutic antibody treatment”RARA-high AML cell line SY-1425/daratumumab SY-1425/control antibody DMSO/control antibody DMSO/daratumumab APOPTOTIC CELLS/WELL 800 700 600 500 400 300 200 100 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 25 28 30 32 34 36 HOURS Multiple Myeloma cell line APOPTOTIC CELLS/WELL SY-1425/daratumumab DMSO/daratumumab DMSO/contraol antibody SY-1425/control antibody 800 700 600 500 400 300 200 100 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 32 34 36 38 40 42 44 HOURS
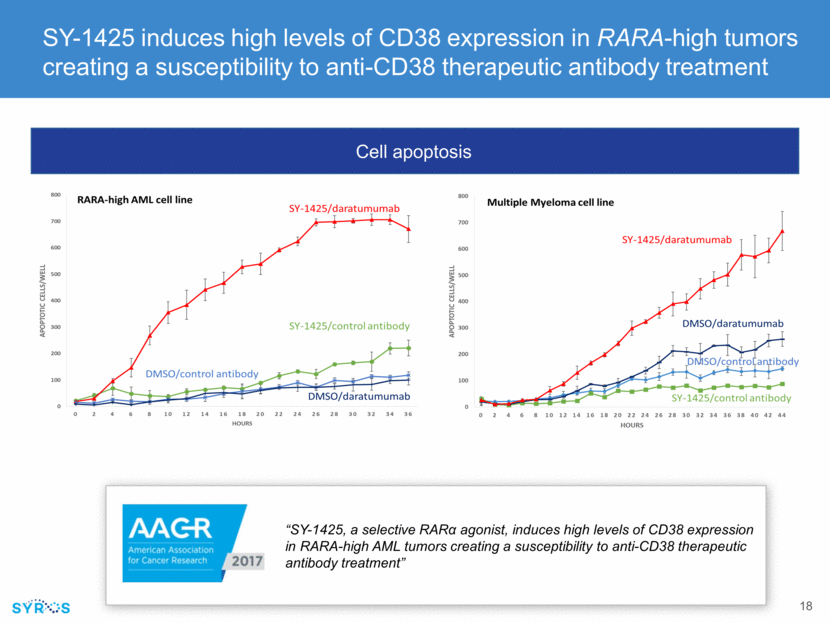
SY-1425 induces CD38 in in vivo preclinical model of AML and ex vivo in blood samples from Phase 2 study SY-1425 ATRA Vehicle “Novel RARA Pathway Activation Biomarkers in Study SY-1425-201 Define a New Subset of AML and MDS Patients and Correlate with Myeloid Differentiation” Mean fluorescent intensity (MFI) by treatment Percent composition change – radar plot Vehicle ATRA SY-1425 0 50 100 150 Mean Fluorescent Intensity (MFI) by Treatment Mean M FI
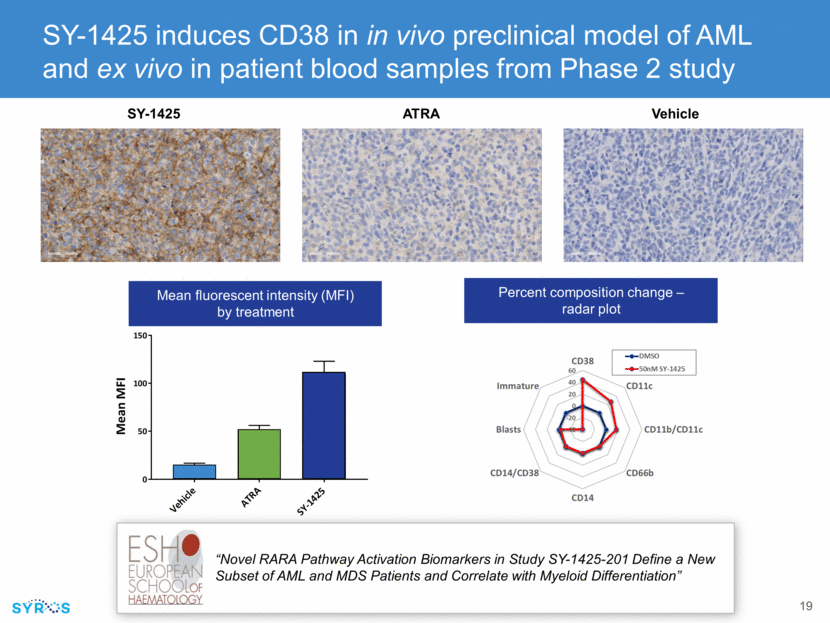
SY-1425: a potential therapy for AML and MDS patients with RARA or IRF8 biomarkers Newly diagnosed Only 40% younger, healthy patients achieve long-term remission Only 10% unfit, older patients receive achieve long-term remission Majority of patients relapse over time, with 5-year overall survival of 27%2 Relapsed or refractory Few treatment options with no approved agents Patients progress quickly in relapsed setting with few treatment options Newly diagnosed lower-risk Quality of life is significantly impacted by chronic anemia and fatigue, despite existing therapies >50% of patients require transfusions leading to increased hospitalizations and reduced survival Overall survival of 6 years Relapsed or refractory higher-risk >80% of newly diagnosed patients relapse over time Few treatment options Survival of less than 1 year AML incidence1: ~33,000 MDS incidence1: ~32,000 ~ 33% RARA or IRF8 biomarker positive ~ 33% RARA or IRF8 biomarker positive Significant need for well-tolerated oral therapies that extend survival and improve quality of life Incidence figures include annual diagnoses in the U.S., Canada and the EU 5 (UK, Germany, France, Spain and Italy); 2. ~30% of patients relapse annually Sources: Leukemia Research 52 (2017) 50–57; Expert Rev. Pharmacoecon. Outcomes Res. Early online, 1–10 (2015); Clinical Lymphoma Myeloma and Leukemia 11 (1), 2011, 10–16; Leukemia. 2015 April ; 29(4): 770–775, SEER, American Cancer Society.
RARA and IRF8 biomarkers and SY-1425 opportunity cut across mutational landscape Unique mechanism points to potential for combinations with chemo and targeted agents without anticipated overlapping toxicities Estimated frequency of RARA and IRF8 biomarkers based on Syros’ analysis of available AML patient tissue samples, and estimated frequency of IDH and FLT3 mutations based on published studies ~20% FLT3+ ~33% RARA or IRF8 biomarkers ~15% IDH+ Total AML
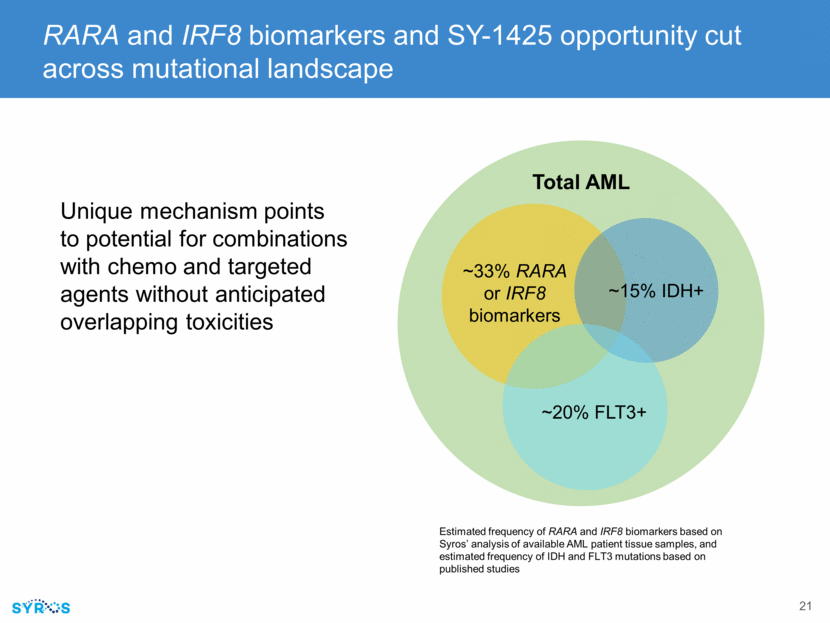
Potential to expand to other tumors with RARA biomarker, including estimated 35% of breast cancer SY-1425 shows synergy in vitro with standard-of-care agents, including lapatinib, palbociclib and tamoxifen In vivo experiments of SY-1425 in combination currently planned SY-1425 inhibits tumor growth as single agent in drug resistant RARA-high models “A novel subgroup of estrogen receptor positive breast cancer may benefit from super-enhancer guided patient selection for retinoic acid receptor agonist treatment” RARA-high CDX, trastuzumab resistant RARA-high PDX, Relapsed ER+ RARA-low PDX SY-1425 in combination with standard-of-care breast cancer therapies Vehicle SY-1425 6mpk Tamoxifen 35mgQD Vehicle SY-1425 6mpk Tumor Volume (mm3) 2000 1500 1000 500 0 0 10 20 30 Days Vehicle SY-1425 6mpk Tumor Volume (mm3) 2000 1500 1000 500 0 0 5 15 20 Days 10 0 7 14 21 28 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 Days Post Treatment Initiation Mean Tumor Volume (mm 3 Mean & SEM)
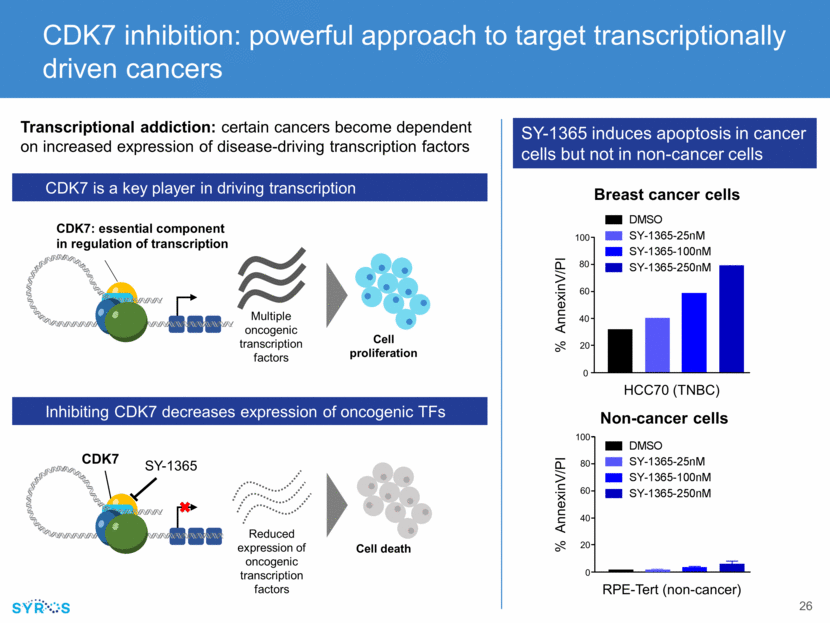
SY-1365 (CDK7 inhibitor): Controlling expression of oncogenic transcription factors First-in-class selective inhibitor of CDK7 Lowers expression of oncogenic transcription factors, including MYC CDK7 inhibition induces apoptosis and preferentially kills cancer cells over non-cancerous cells Dosing initiated in Phase 1 clinical trial of patients with advanced solid tumors Initial clinical data expected in 2018 Significant market potential Promising approach in range of difficult-to-treat cancers driven by abnormal transcription Single agent and combination therapy opportunity Difficult-to-treat solid tumors and blood cancers
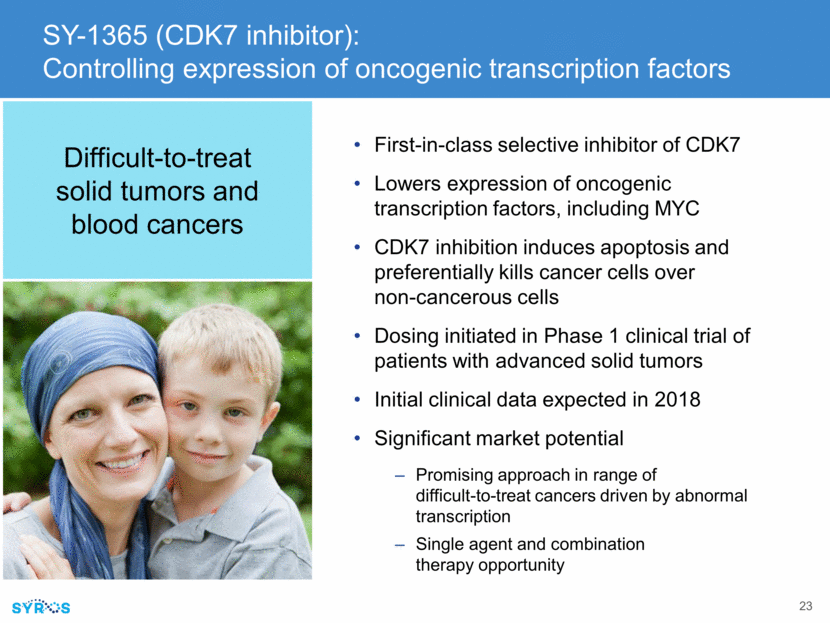
SY-1365 is a first-in-class potent and selective CDK7 inhibitor Covalent Highly potent Enzymatic IC50 = 22 nM Cellular IC50 < 20 nM Rapid clearance (1-3 hours) with sustained PD effect (55-hour half-life)* Does not significantly bind to CDK9 or cell cycle CDKs DiscoveRx kinome scan at 1mM SY-1365 7/468 kinases exhibit >90% binding Gene % Control CDK7 0.25 RSK4 2 DYRK1B 2.6 JNK3 2.7 JNK1 2.8 JNK2 3 CDK15 10 *In-house analysis
Dosing initiated in Phase 1 trial of SY-1365 in patients with advanced solid tumors Initiated Phase 1 trial in advanced solid tumor patients in May 2017, one month following IND clearance Dose escalation phase open to all-comers Expansion cohorts enriched for transcriptionally dependent tumors, including triple-negative breast, ovarian and small cell lung cancer Plan to use target engagement and downstream assays for proof-of-mechanism Strong in vivo correlation seen between target engagement and efficacy Target engagement assay to guide dose and schedule optimization Plan to use platform to identify biomarkers to predict patients most likely to respond Dose escalation Solid tumor patients enriched for transcriptionally driven tumors Acute leukemias Phase 1 program
RPE-Tert (non-cancer) 100 20 0 40 60 80 Reduced expression of oncogenic transcription factors Cell death CDK7 inhibition: powerful approach to target transcriptionally driven cancers Transcriptional addiction: certain cancers become dependent on increased expression of disease-driving transcription factors CDK7 is a key player in driving transcription Inhibiting CDK7 decreases expression of oncogenic TFs Multiple oncogenic transcription factors Cell proliferation CDK7: essential component in regulation of transcription Non-cancer cells % AnnexinV/PI SY-1365 induces apoptosis in cancer cells but not in non-cancer cells Breast cancer cells HCC70 (TNBC) % AnnexinV/PI 100 20 0 40 60 80 CDK7 SY-1365 RPE-Tert BJ-Tert 0 20 40 60 80 100 DMSO SY-1365-25nM SY-1365-100nM SY-1365-250nM RPE-Tert BJ-Tert 0 20 40 60 80 100 DMSO SY-1365-25nM SY-1365-100nM SY-1365-250nM
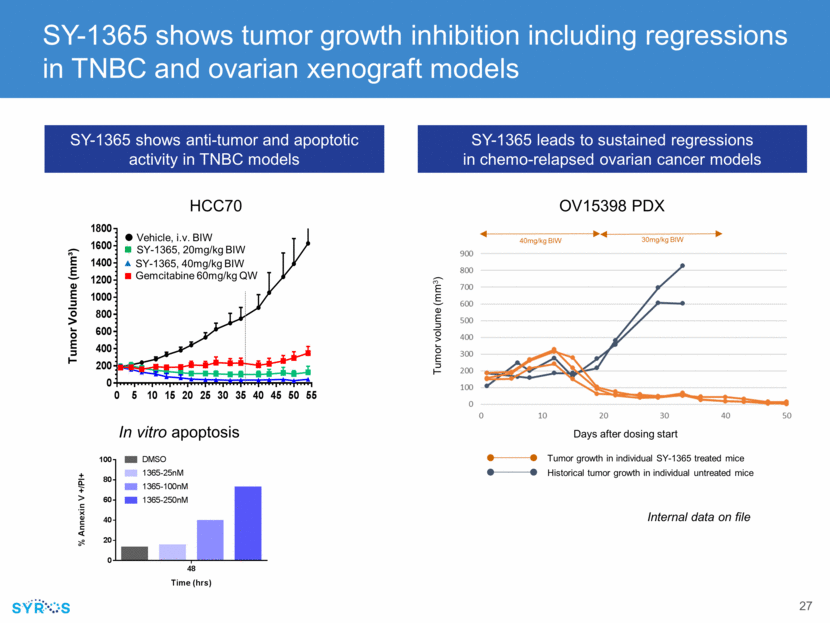
SY-1365, 20mg/kg BIW SY-1365, 40mg/kg BIW Vehicle, i.v. BIW Gemcitabine 60mg/kg QW In vitro apoptosis SY-1365 shows tumor growth inhibition including regressions in TNBC and ovarian xenograft models HCC70 Tumor Volume (mm³) OV15398 PDX SY-1365 leads to sustained regressions in chemo-relapsed ovarian cancer models Tumor volume (mm3) 40mg/kg BIW 30mg/kg BIW Days after dosing start Tumor growth in individual SY-1365 treated mice Historical tumor growth in individual untreated mice SY-1365 shows anti-tumor and apoptotic activity in TNBC models Internal data on file 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 0 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 1400 1600 1800 48 0 20 40 60 80 100 Time (hrs) % Annex in V+/PI+DMSO 1365-25nM 1365-100nM 1365-250nM
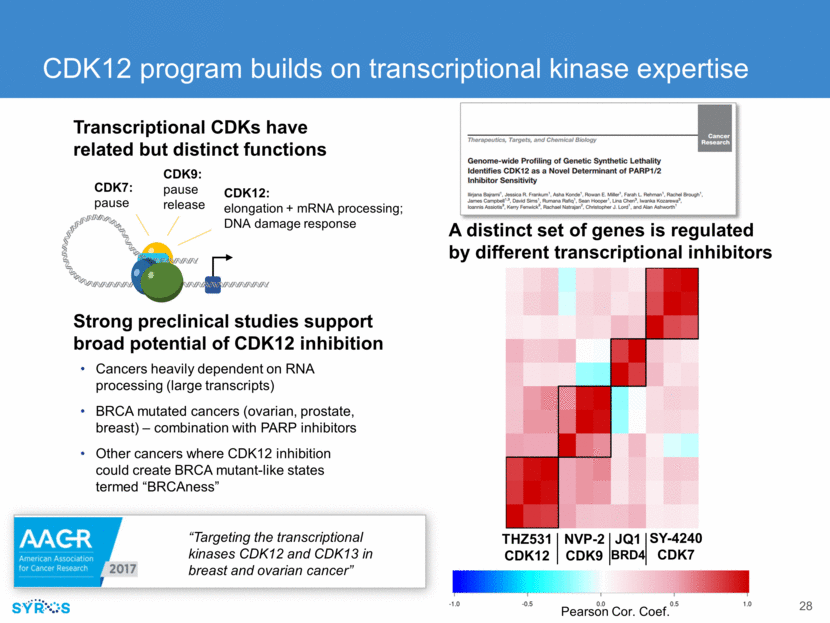
CDK12 program builds on transcriptional kinase expertise Cancers heavily dependent on RNA processing (large transcripts) BRCA mutated cancers (ovarian, prostate, breast) – combination with PARP inhibitors Other cancers where CDK12 inhibition could create BRCA mutant-like states termed “BRCAness” Transcriptional CDKs have related but distinct functions CDK7: pause CDK9: pause release CDK12: elongation + mRNA processing; DNA damage response Strong preclinical studies support broad potential of CDK12 inhibition Pearson Cor. Coef. THZ531 CDK12 NVP-2 CDK9 JQ1 BRD4 SY-4240 CDK7 A distinct set of genes is regulated by different transcriptional inhibitors “Targeting the transcriptional kinases CDK12 and CDK13 in breast and ovarian cancer”
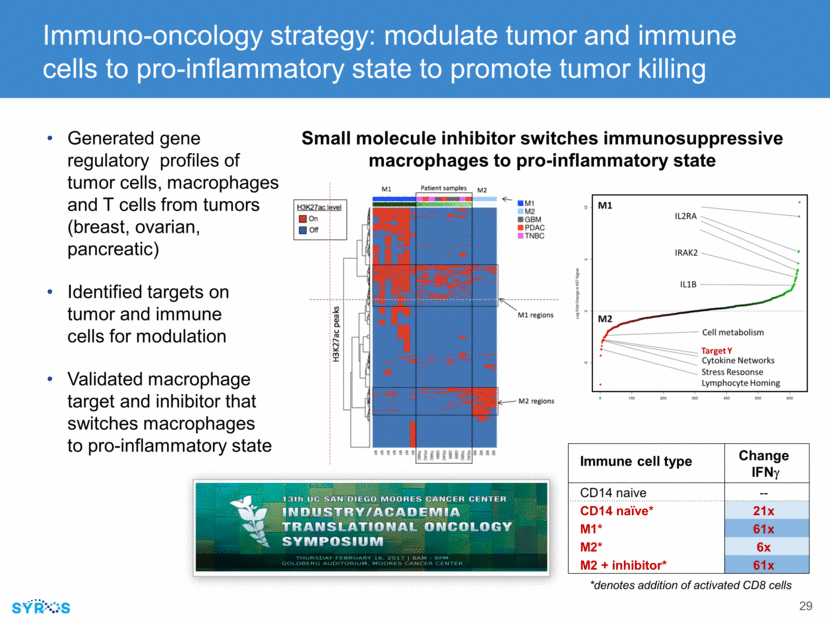
Immuno-oncology strategy: modulate tumor and immune cells to pro-inflammatory state to promote tumor killing Immune cell type Change IFNg CD14 naive -- CD14 naïve* 21x M1* 61x M2* 6x M2 + inhibitor* 61x *denotes addition of activated CD8 cells Small molecule inhibitor switches immunosuppressive macrophages to pro-inflammatory state Generated gene regulatory profiles of tumor cells, macrophages and T cells from tumors (breast, ovarian, pancreatic) Identified targets on tumor and immune cells for modulation Validated macrophage target and inhibitor that switches macrophages to pro-inflammatory state
Company Building

Strategic Collaborations In-licensing Goal to pursue strategic collaborations to maximize potential of our gene control platform SY-1425 & SY-1365 Opportunity Expand geographic reach Broaden and accelerate development Requirements Maintain development and commercialization rights and control in North America Execute at value inflection points to maximize financial return to Syros Target, Biomarker & Drug Discovery Opportunity Leverage platform potential across multiple therapeutic areas Monetize platform in areas outside of Syros core strategic focus Leverage partnerships to continue building infrastructure Current focus areas for business development Clinical-Stage Product Candidates Opportunity to accelerate platform insight into clinical development Leverage proprietary repository of gene regulatory profiles of patient disease tissue Identify novel genomically defined subsets for patient selection and stratification Oncology, including rare cancers Immuno-oncology Autoimmune Rare genetic diseases
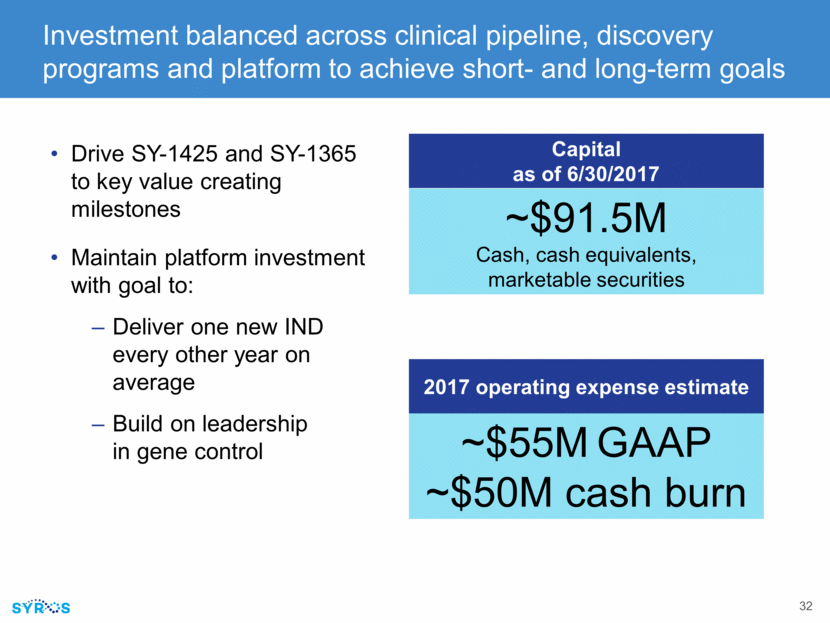
Investment balanced across clinical pipeline, discovery programs and platform to achieve short- and long-term goals Drive SY-1425 and SY-1365 to key value creating milestones Maintain platform investment with goal to: Deliver one new IND every other year on average Build on leadership in gene control 2017 operating expense estimate ~$91.5M Cash, cash equivalents, marketable securities ~$55M GAAP ~$50M cash burn Capital as of 6/30/2017
Advance one oncology/IO program to non-GLP tox for 2019 IND Enhance platform to single gene expression modulation for rare cancers and genetic diseases SY-1425 Present Phase 2 PD and clinical data Expand ongoing trial into EU Initiate combination dosing arm in ongoing trial SY-1365 Initiate Phase 1 trial Establish at least one strategic collaboration around program or platform Manage operating expense 2017 goals 2016 accomplishments set stage for breakthrough 2017

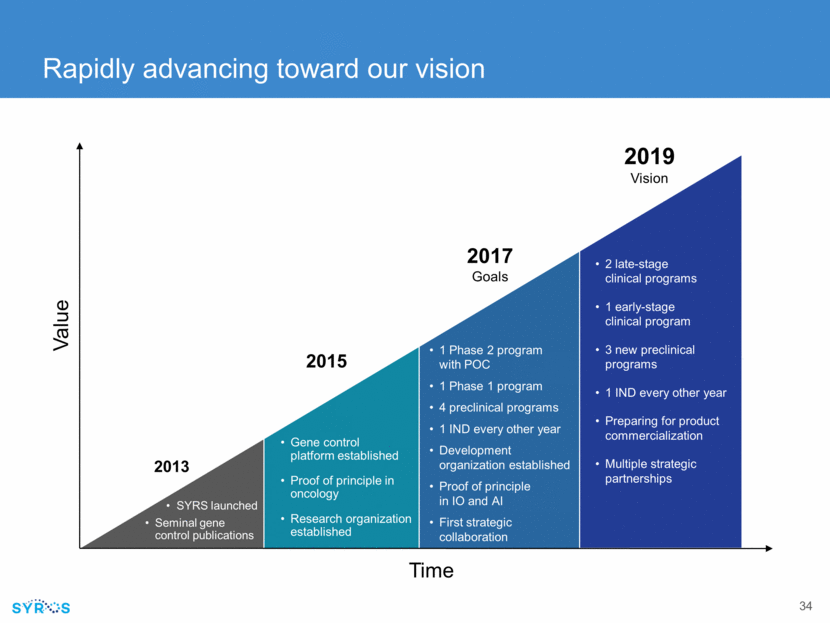
Rapidly advancing toward our vision Time Value SYRS launched Seminal gene control publications 2013 Gene control platform established Proof of principle in oncology Research organization established 2015 1 Phase 2 program with POC 1 Phase 1 program 4 preclinical programs 1 IND every other year Development organization established Proof of principle in IO and AI First strategic collaboration 2017 Goals 2 late-stage clinical programs 1 early-stage clinical program 3 new preclinical programs 1 IND every other year Preparing for product commercialization Multiple strategic partnerships 2019 Vision
expression makes a world of difference


