Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| 8-K - 8-K - Pulmatrix, Inc. | d437893d8k.htm |

Engineering Respiratory Products for Major Unmet Pulmonary Diseases August 2017 NASDAQ: PULM Exhibit 99.1

Disclaimers & Forward Looking Statements This presentation contains forward-looking statements. Forward-looking statements may be identified by the use of forward-looking terms such as “anticipates,” “assumes,” “believes,” “can,” “could,” “estimates,” “expects,” “forecasts,” “guides,” “intends,” “is confident that,” “may,” “plans,” “seeks,” “projects,” “targets,” and “would” or the negative of such terms or other variations on such terms or comparable terminology. These statements are not guarantees of future performance, are based on current expectations of future events and are subject to risks and uncertainties that could cause actual results to differ materially from those expressed or implied by such statements, including risks that we will not have sufficient working capital, that we will have delays in obtaining, or we will be unable to obtain, FDA or other regulatory approvals for our products, unable to establish collaborations, or that our products will not be commercially viable, among other risks. A discussion of these and other factors, including risks and uncertainties with respect to the Company, is set forth in the Company’s filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), including the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K and its quarterly reports on Form 10-Q. Investors and security holders are urged to read these documents free of charge on the SEC’s website at http://www.sec.gov. Forward-looking statements contained in this presentation are made as of this date, and the Company undertakes no obligation to publicly update any forward-looking statement, whether as a result of new information, future events, or otherwise.
Executive Summary Pulmatrix and iSPERSE™ Technology De-risked portfolio targeting large markets with high unmet need: PUR1800 (Phase 2): Narrow spectrum kinase inhibitor (NSKI) for Acute Exacerbations of COPD (AECOPD) PUR1900 (Phase 1): Inhaled reformulation of oral anti-fungal for Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis (ABPA) in severe asthma PUR0200 (Out-license opportunity): Spiriva® HandiHaler® U.S. branded alternative (E.U. substitutable) Two meaningful clinical milestones and value inflection points in 2018 Projected U.S. peak revenue potential for PUR1800 and PUR1900 exceeds $2.3B Pulmatrix is a clinical stage pulmonary bio-pharma company Experienced team with a proven record of product development and value creation iSPERSE™ proprietary lung delivery platform uses small, dense, dispersible particles to deliver drug to the deepest parts of the lung Patent protection into the 2030’s and technology can be adapted for any medical product Products and Milestones

Experienced Leadership Team with Record of Success Management Team Proven fundraising and capital management ability Experienced R&D team focused on pulmonary drug delivery and the role of inhaled particles Commercialization and partnership experience Board of Directors Diverse Collective Experience at Leading Respiratory Companies Strong Background in Product Development and Commercialization Robert Clarke, PhD CEO David Hava, PhD CSO Bill Duke, MBA CFO Ted Raad, MBA CBO Mark Iwicki Chairman Steve Gillis, PhD BOD Investor Matthew Sherman BOD Terry McGuire BOD Investor Michael Higgins BOD-Audit Chair Amit Munshi BOD
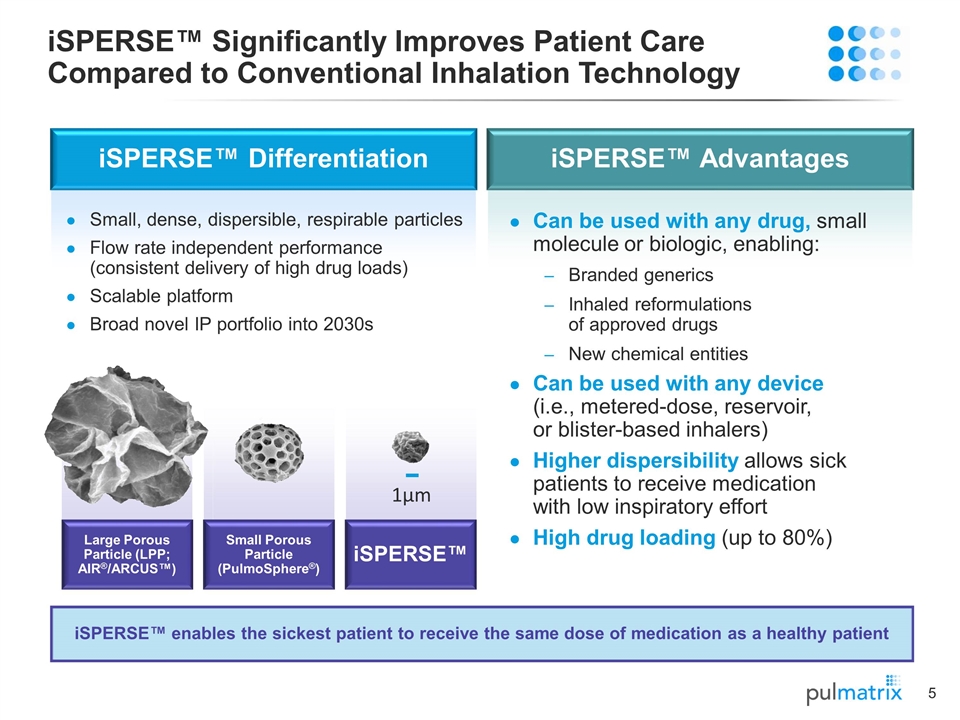
Large Porous Particle (LPP; AIR®/ARCUS™) iSPERSE™ Significantly Improves Patient Care Compared to Conventional Inhalation Technology 1µm iSPERSE™ enables the sickest patient to receive the same dose of medication as a healthy patient iSPERSE™ Differentiation iSPERSE™ Advantages Small, dense, dispersible, respirable particles Flow rate independent performance (consistent delivery of high drug loads) Scalable platform Broad novel IP portfolio into 2030s Can be used with any drug, small molecule or biologic, enabling: Branded generics Inhaled reformulations of approved drugs New chemical entities Can be used with any device (i.e., metered-dose, reservoir, or blister-based inhalers) Higher dispersibility allows sick patients to receive medication with low inspiratory effort High drug loading (up to 80%) Small Porous Particle (PulmoSphere®) iSPERSE™
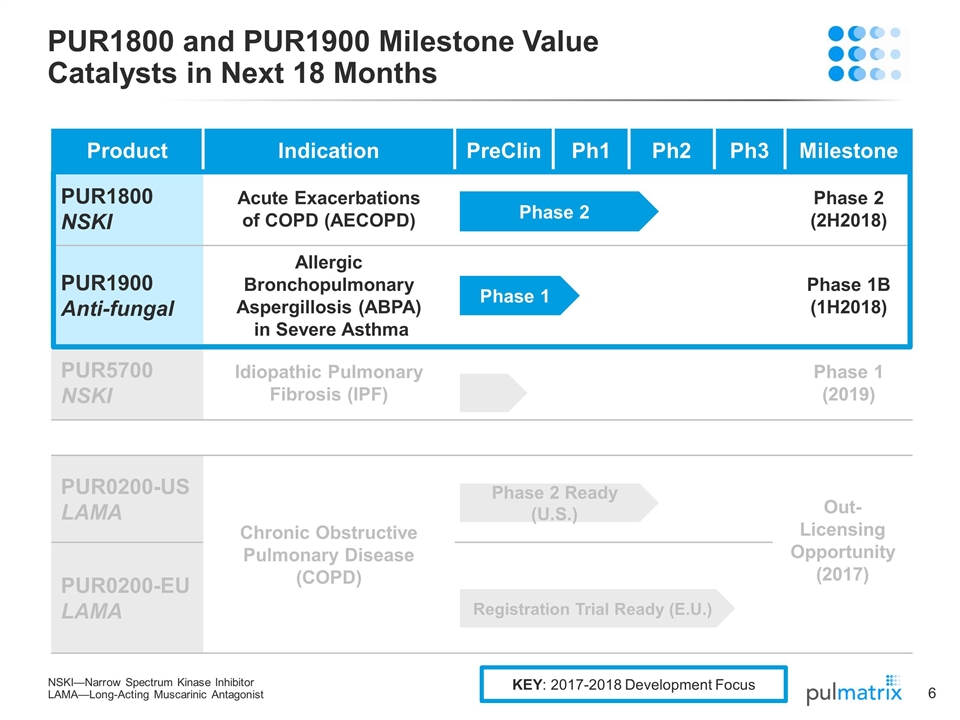
Product Indication PreClin Ph1 Ph2 Ph3 Milestone PUR1800 NSKI Acute Exacerbations of COPD (AECOPD) Phase 2 (2H2018) PUR1900 Anti-fungal Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis (ABPA) in Severe Asthma Phase 1B (1H2018) PUR5700 NSKI Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) Phase 1 (2019) PUR0200-US LAMA Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Out-Licensing Opportunity (2017) PUR0200-EU LAMA PUR1800 and PUR1900 Milestone Value Catalysts in Next 18 Months NSKI—Narrow Spectrum Kinase Inhibitor LAMA—Long-Acting Muscarinic Antagonist Phase 2 Ready (U.S.) Registration Trial Ready (E.U.) Phase 2 Phase 1 KEY: 2017-2018 Development Focus
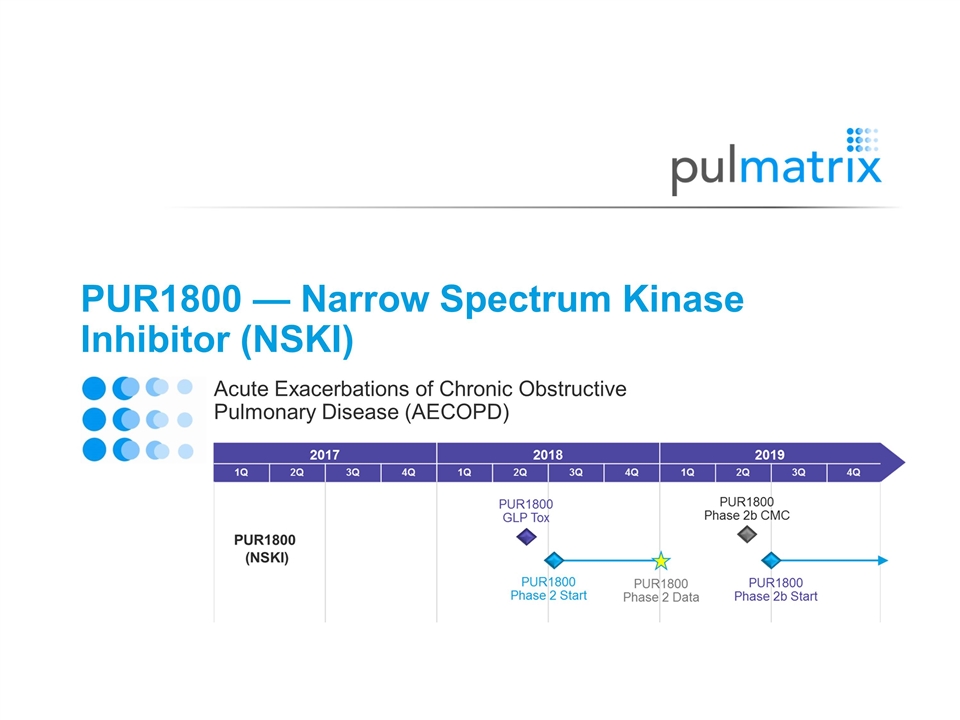
PUR1800 — Narrow Spectrum Kinase Inhibitor (NSKI) Acute Exacerbations of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (AECOPD)
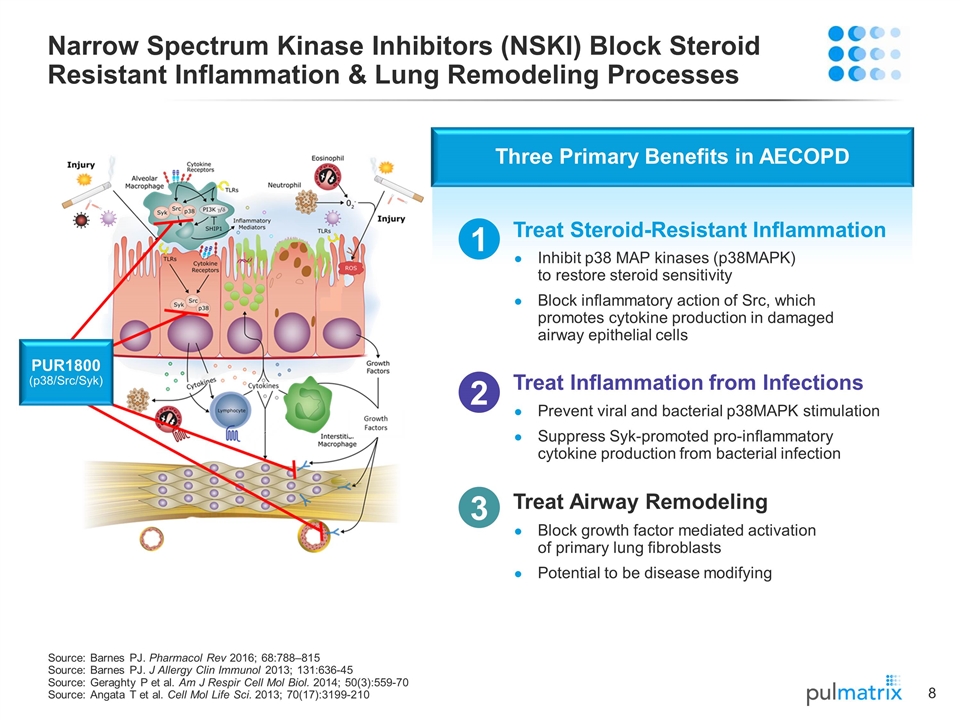
Narrow Spectrum Kinase Inhibitors (NSKI) Block Steroid Resistant Inflammation & Lung Remodeling Processes Source: Barnes PJ. Pharmacol Rev 2016; 68:788–815 Source: Barnes PJ. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2013; 131:636-45 Source: Geraghty P et al. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2014; 50(3):559-70 Source: Angata T et al. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013; 70(17):3199-210 Three Primary Benefits in AECOPD Treat Steroid-Resistant Inflammation 1 Inhibit p38 MAP kinases (p38MAPK) to restore steroid sensitivity Block inflammatory action of Src, which promotes cytokine production in damaged airway epithelial cells 2 Treat Inflammation from Infections Prevent viral and bacterial p38MAPK stimulation Suppress Syk-promoted pro-inflammatory cytokine production from bacterial infection Treat Airway Remodeling Block growth factor mediated activation of primary lung fibroblasts Potential to be disease modifying 3 PUR1800 (p38/Src/Syk)
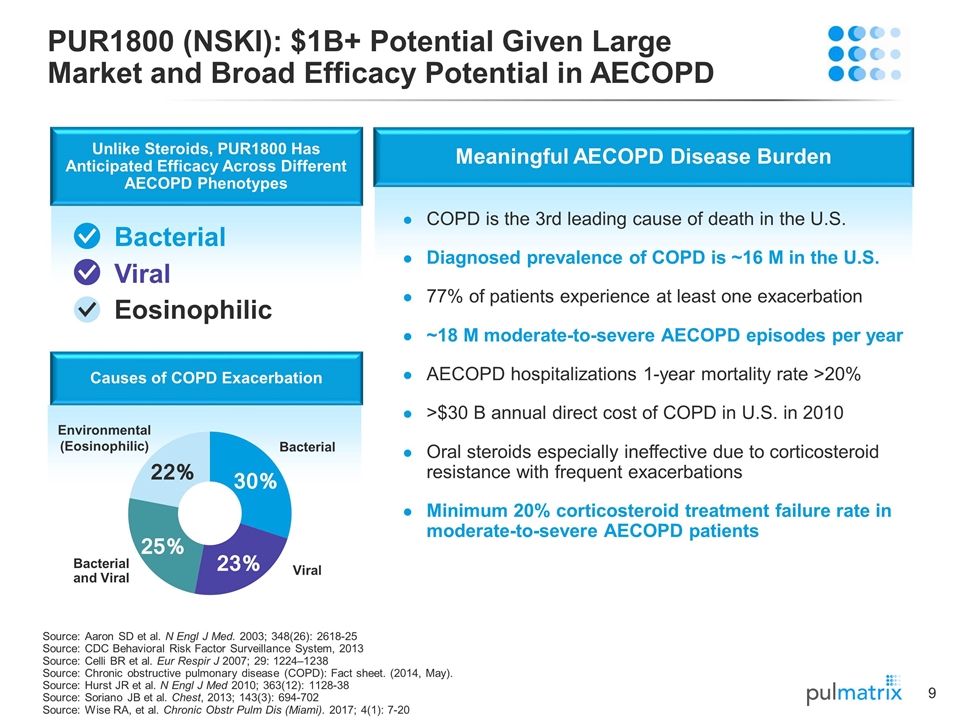
PUR1800 (NSKI): $1B+ Potential Given Large Market and Broad Efficacy Potential in AECOPD Meaningful AECOPD Disease Burden Unlike Steroids, PUR1800 Has Anticipated Efficacy Across Different AECOPD Phenotypes COPD is the 3rd leading cause of death in the U.S. Diagnosed prevalence of COPD is ~16 M in the U.S. 77% of patients experience at least one exacerbation ~18 M moderate-to-severe AECOPD episodes per year AECOPD hospitalizations 1-year mortality rate >20% >$30 B annual direct cost of COPD in U.S. in 2010 Oral steroids especially ineffective due to corticosteroid resistance with frequent exacerbations Minimum 20% corticosteroid treatment failure rate in moderate-to-severe AECOPD patients Causes of COPD Exacerbation Bacterial Eosinophilic Viral Environmental (Eosinophilic) Bacterial Viral Bacterial and Viral Source: Aaron SD et al. N Engl J Med. 2003; 348(26): 2618-25 Source: CDC Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System, 2013 Source: Celli BR et al. Eur Respir J 2007; 29: 1224–1238 Source: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): Fact sheet. (2014, May). Source: Hurst JR et al. N Engl J Med 2010; 363(12): 1128-38 Source: Soriano JB et al. Chest, 2013; 143(3): 694-702 Source: Wise RA, et al. Chronic Obstr Pulm Dis (Miami). 2017; 4(1): 7-20
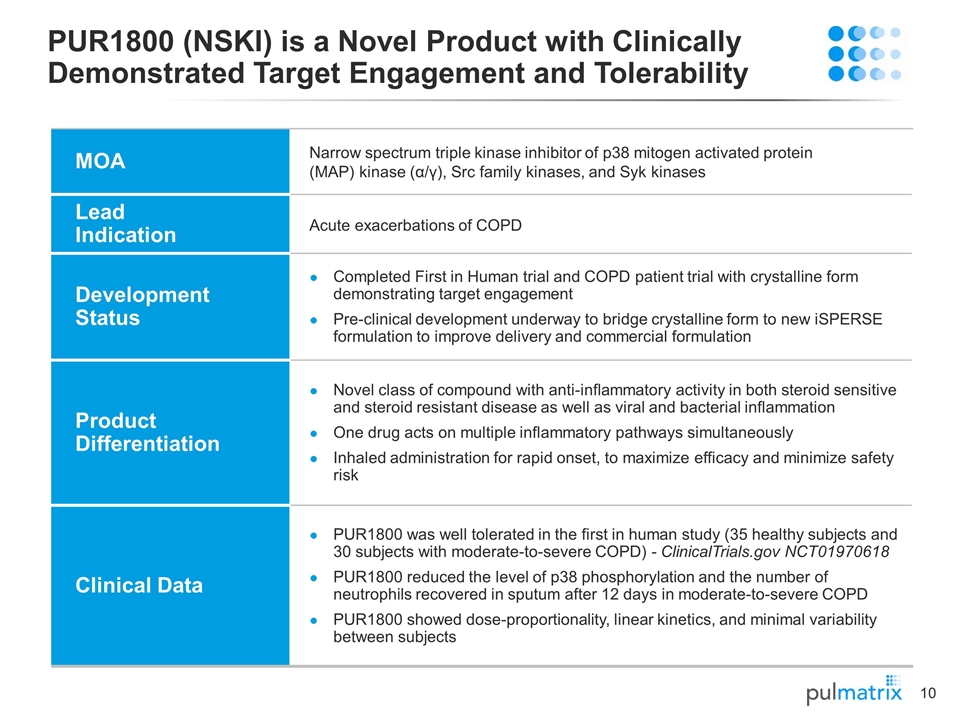
PUR1800 (NSKI) is a Novel Product with Clinically Demonstrated Target Engagement and Tolerability MOA Narrow spectrum triple kinase inhibitor of p38 mitogen activated protein (MAP) kinase (α/γ), Src family kinases, and Syk kinases Lead Indication Acute exacerbations of COPD Development Status Completed First in Human trial and COPD patient trial with crystalline form demonstrating target engagement Pre-clinical development underway to bridge crystalline form to new iSPERSE formulation to improve delivery and commercial formulation Product Differentiation Novel class of compound with anti-inflammatory activity in both steroid sensitive and steroid resistant disease as well as viral and bacterial inflammation One drug acts on multiple inflammatory pathways simultaneously Inhaled administration for rapid onset, to maximize efficacy and minimize safety risk Clinical Data PUR1800 was well tolerated in the first in human study (35 healthy subjects and 30 subjects with moderate-to-severe COPD) - ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01970618 PUR1800 reduced the level of p38 phosphorylation and the number of neutrophils recovered in sputum after 12 days in moderate-to-severe COPD PUR1800 showed dose-proportionality, linear kinetics, and minimal variability between subjects
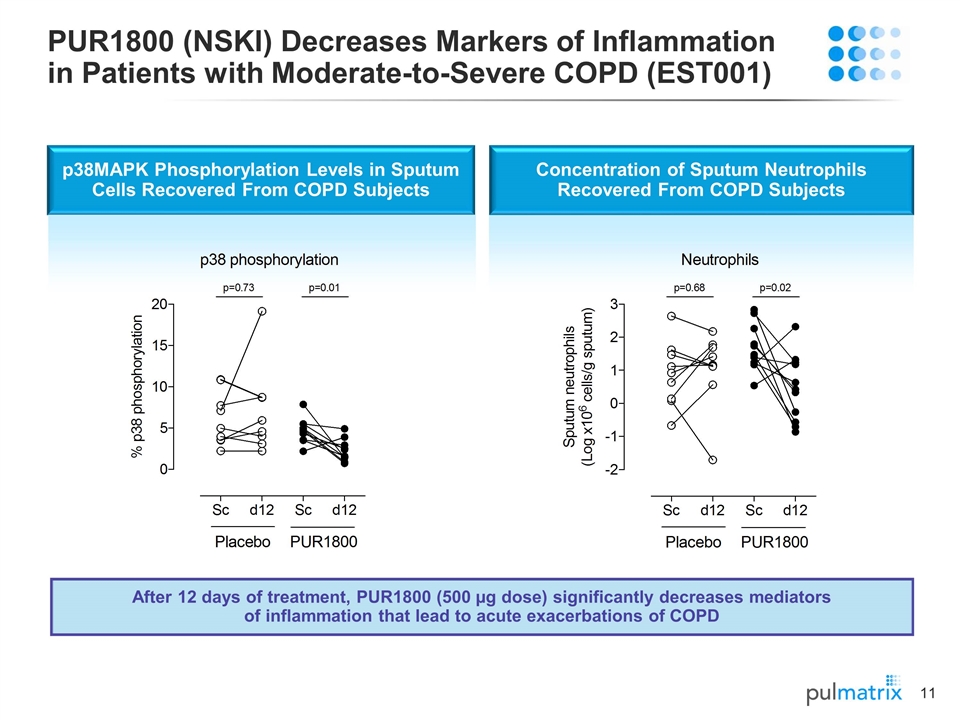
PUR1800 (NSKI) Decreases Markers of Inflammation in Patients with Moderate-to-Severe COPD (EST001) p38MAPK Phosphorylation Levels in Sputum Cells Recovered From COPD Subjects Concentration of Sputum Neutrophils Recovered From COPD Subjects After 12 days of treatment, PUR1800 (500 µg dose) significantly decreases mediators of inflammation that lead to acute exacerbations of COPD
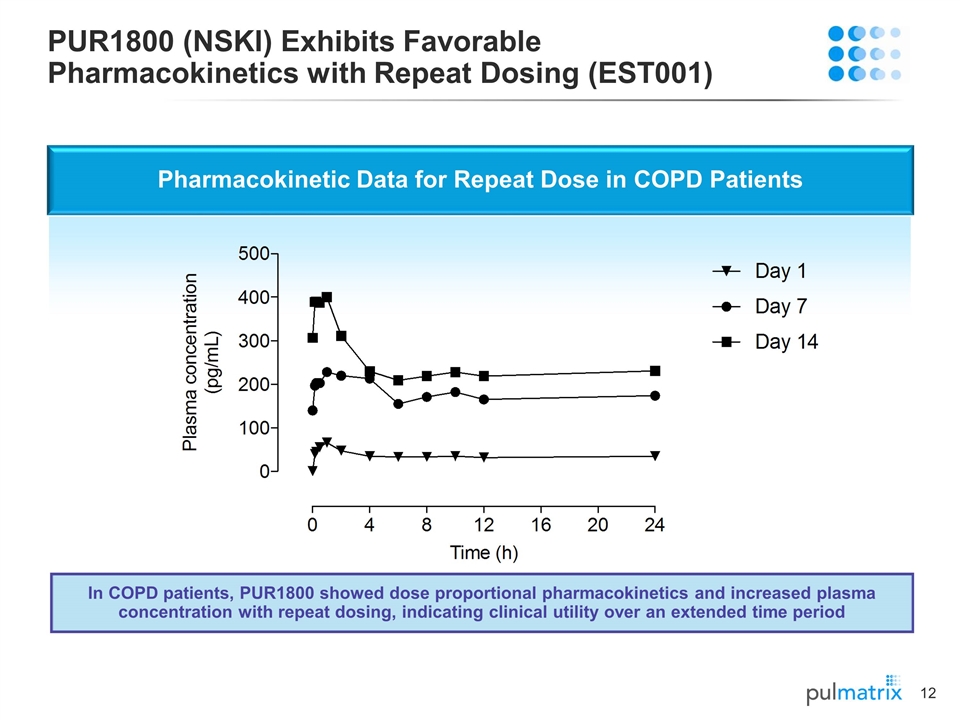
PUR1800 (NSKI) Exhibits Favorable Pharmacokinetics with Repeat Dosing (EST001) Pharmacokinetic Data for Repeat Dose in COPD Patients In COPD patients, PUR1800 showed dose proportional pharmacokinetics and increased plasma concentration with repeat dosing, indicating clinical utility over an extended time period
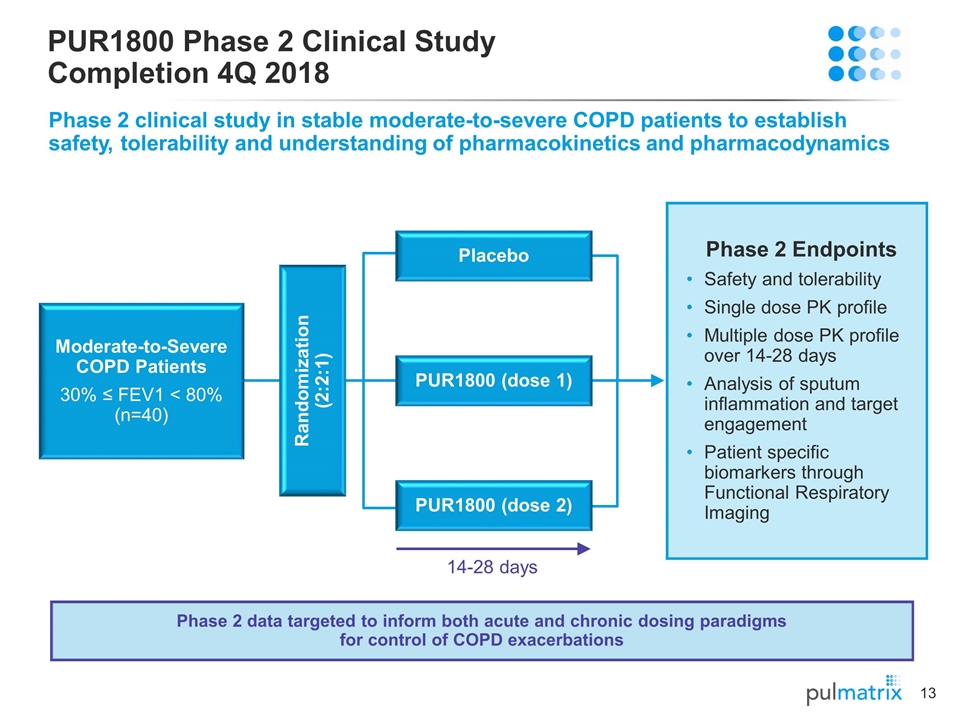
Moderate-to-Severe COPD Patients 30% ≤ FEV1 < 80% (n=40) Randomization (2:2:1) 14-28 days Phase 2 Endpoints Safety and tolerability Single dose PK profile Multiple dose PK profile over 14-28 days Analysis of sputum inflammation and target engagement Patient specific biomarkers through Functional Respiratory Imaging PUR1800 Phase 2 Clinical Study Completion 4Q 2018 Phase 2 clinical study in stable moderate-to-severe COPD patients to establish safety, tolerability and understanding of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics Placebo PUR1800 (dose 1) PUR1800 (dose 2) Phase 2 data targeted to inform both acute and chronic dosing paradigms for control of COPD exacerbations
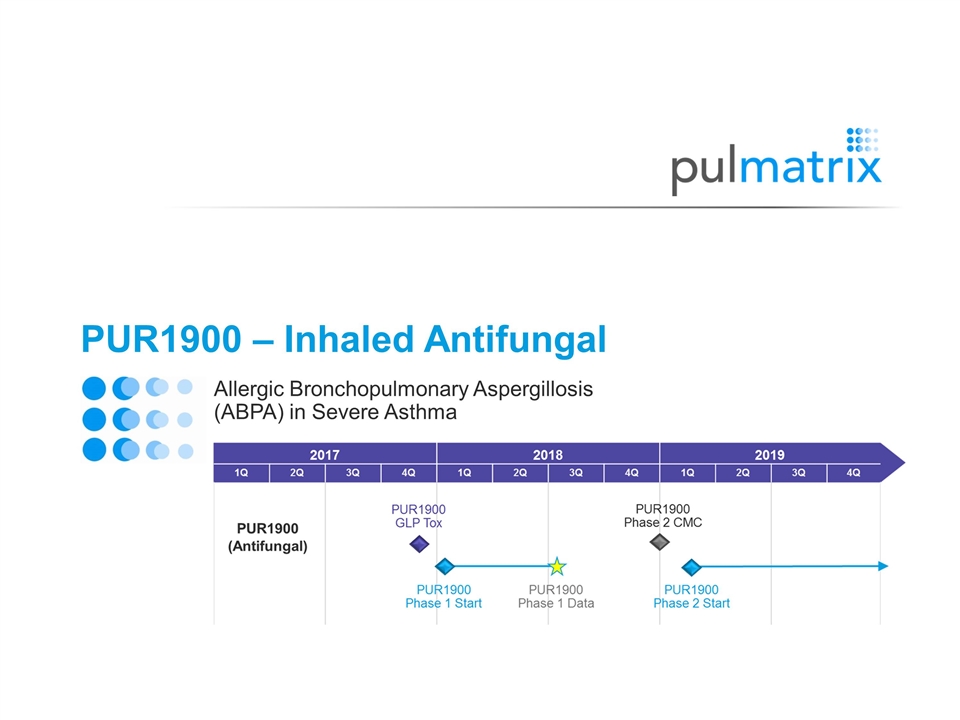
PUR1900 – Inhaled Antifungal Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis (ABPA) in Severe Asthma
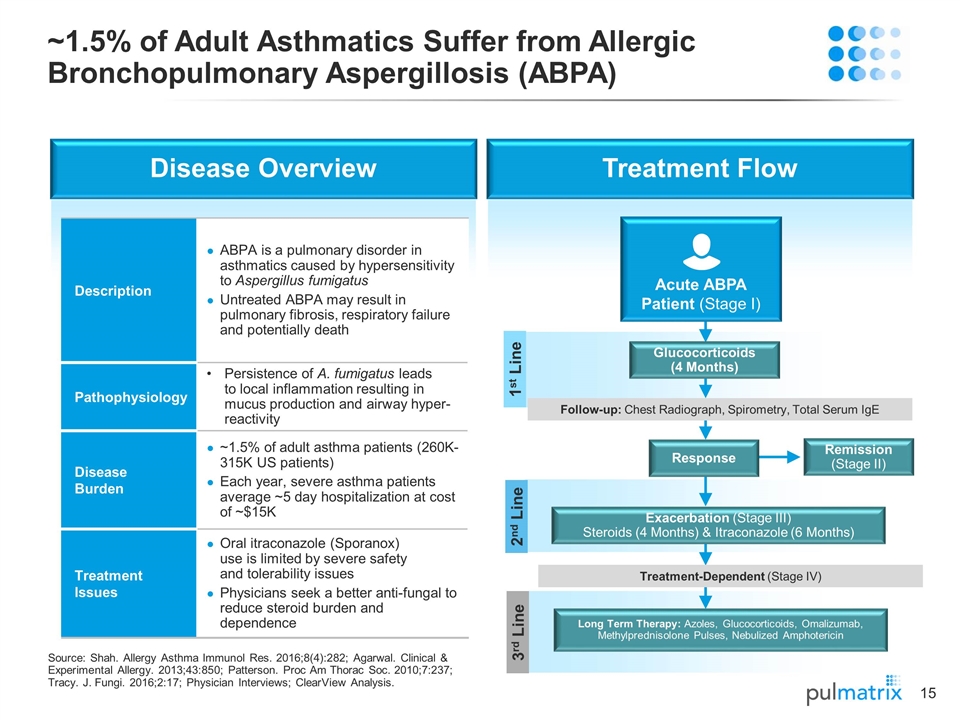
2nd Line Disease Overview Treatment Flow ~1.5% of Adult Asthmatics Suffer from Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis (ABPA) Source: Shah. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2016;8(4):282; Agarwal. Clinical & Experimental Allergy. 2013;43:850; Patterson. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2010;7:237; Tracy. J. Fungi. 2016;2:17; Physician Interviews; ClearView Analysis. Description ABPA is a pulmonary disorder in asthmatics caused by hypersensitivity to Aspergillus fumigatus Untreated ABPA may result in pulmonary fibrosis, respiratory failure and potentially death Pathophysiology Persistence of A. fumigatus leads to local inflammation resulting in mucus production and airway hyper- reactivity Disease Burden ~1.5% of adult asthma patients (260K-315K US patients) Each year, severe asthma patients average ~5 day hospitalization at cost of ~$15K Treatment Issues Oral itraconazole (Sporanox) use is limited by severe safety and tolerability issues Physicians seek a better anti-fungal to reduce steroid burden and dependence 1st Line Follow-up: Chest Radiograph, Spirometry, Total Serum IgE 3rd Line Glucocorticoids (4 Months) Acute ABPA Patient (Stage I) Remission (Stage II) Response Exacerbation (Stage III) Steroids (4 Months) & Itraconazole (6 Months) Long Term Therapy: Azoles, Glucocorticoids, Omalizumab, Methylprednisolone Pulses, Nebulized Amphotericin Treatment-Dependent (Stage IV)
PUR1900 (Antifungal) First in Class Inhaled Delivery Expected to Improve Safety & Efficacy MOA Triazole that inhibits P450-dependent synthesis of ergosterol, a key component of fungal cell wall biosynthesis Lead Indication Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis (ABPA) in Asthma Other Potential Indications Cystic fibrosis; immunocompromised patients (HIV-AIDS, cancer, transplant) Development Status 28-day GLP toxicology studies ongoing to support First in Human trial in Q1 2018 Product Differentiation Itraconazole, an oral anti-fungal currently marketed as Sporanox, has an established MOA and demonstrated efficacy in the treatment of ABPA Oral itraconazole use is limited by poor pharmacokinetics and safety concerns associated with high plasma concentrations Inhaled delivery achieves higher lung concentrations and lower systemic exposure than oral therapy leading to improved efficacy and safety profile Regulatory Milestones FDA Orphan drug designation and Qualified Infectious Disease Product (QIDP) designation granted in 2016
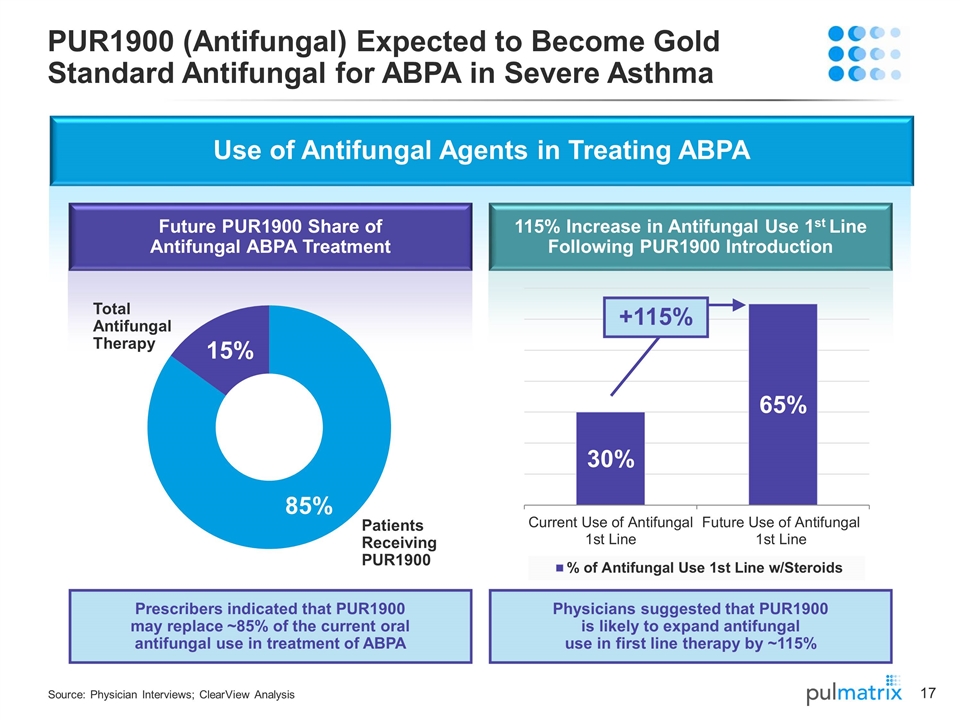
Use of Antifungal Agents in Treating ABPA Prescribers indicated that PUR1900 may replace ~85% of the current oral antifungal use in treatment of ABPA +115% PUR1900 (Antifungal) Expected to Become Gold Standard Antifungal for ABPA in Severe Asthma Source: Physician Interviews; ClearView Analysis Future PUR1900 Share of Antifungal ABPA Treatment 115% Increase in Antifungal Use 1st Line Following PUR1900 Introduction Physicians suggested that PUR1900 is likely to expand antifungal use in first line therapy by ~115% Patients Receiving PUR1900 Total Antifungal Therapy
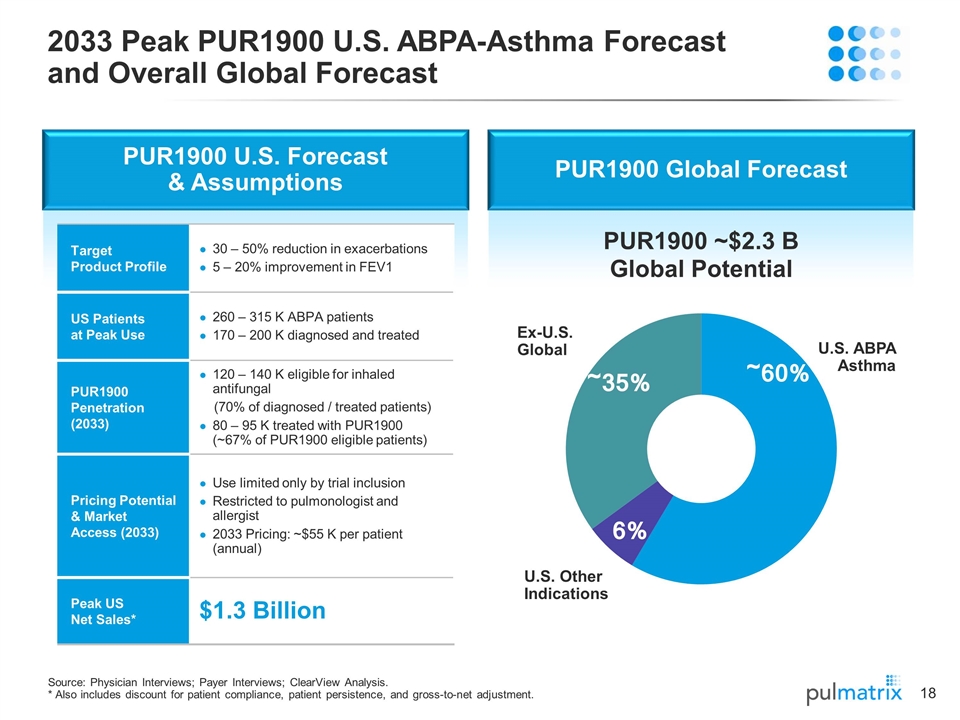
PUR1900 Global Forecast 2033 Peak PUR1900 U.S. ABPA-Asthma Forecast and Overall Global Forecast Source: Physician Interviews; Payer Interviews; ClearView Analysis. * Also includes discount for patient compliance, patient persistence, and gross-to-net adjustment. U.S. Other Indications U.S. ABPA Asthma Ex-U.S. Global PUR1900 U.S. Forecast & Assumptions Target Product Profile 30 – 50% reduction in exacerbations 5 – 20% improvement in FEV1 US Patients at Peak Use 260 – 315 K ABPA patients 170 – 200 K diagnosed and treated PUR1900 Penetration (2033) 120 – 140 K eligible for inhaled antifungal (70% of diagnosed / treated patients) 80 – 95 K treated with PUR1900 (~67% of PUR1900 eligible patients) Pricing Potential & Market Access (2033) Use limited only by trial inclusion Restricted to pulmonologist and allergist 2033 Pricing: ~$55 K per patient (annual) Peak US Net Sales* $1.3 Billion
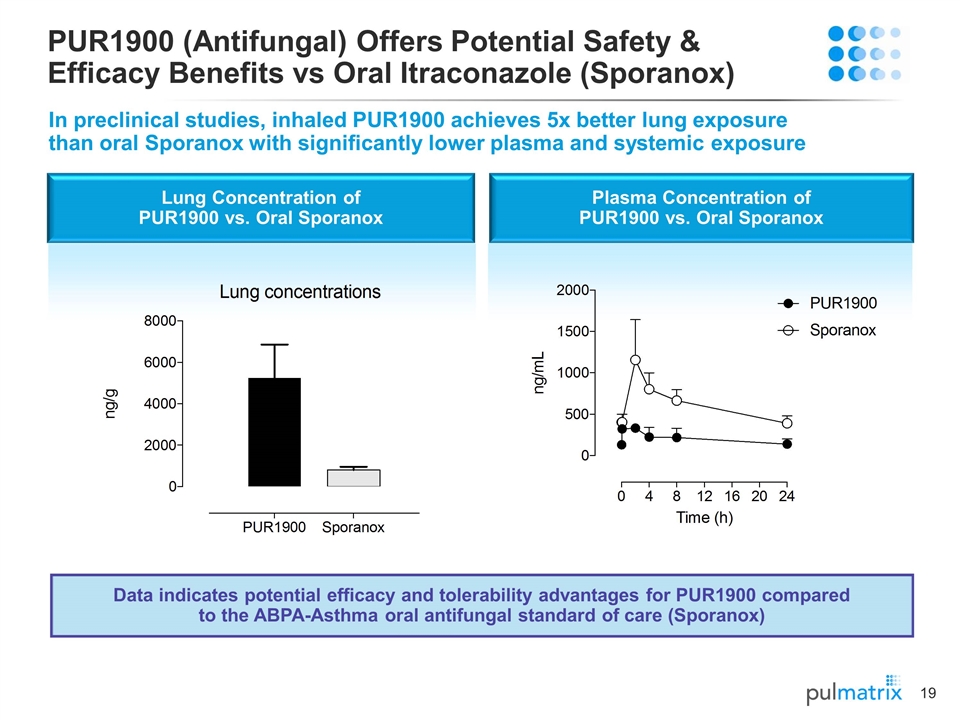
Plasma Concentration of PUR1900 vs. Oral Sporanox Lung Concentration of PUR1900 vs. Oral Sporanox PUR1900 (Antifungal) Offers Potential Safety & Efficacy Benefits vs Oral Itraconazole (Sporanox) In preclinical studies, inhaled PUR1900 achieves 5x better lung exposure than oral Sporanox with significantly lower plasma and systemic exposure Data indicates potential efficacy and tolerability advantages for PUR1900 compared to the ABPA-Asthma oral antifungal standard of care (Sporanox)
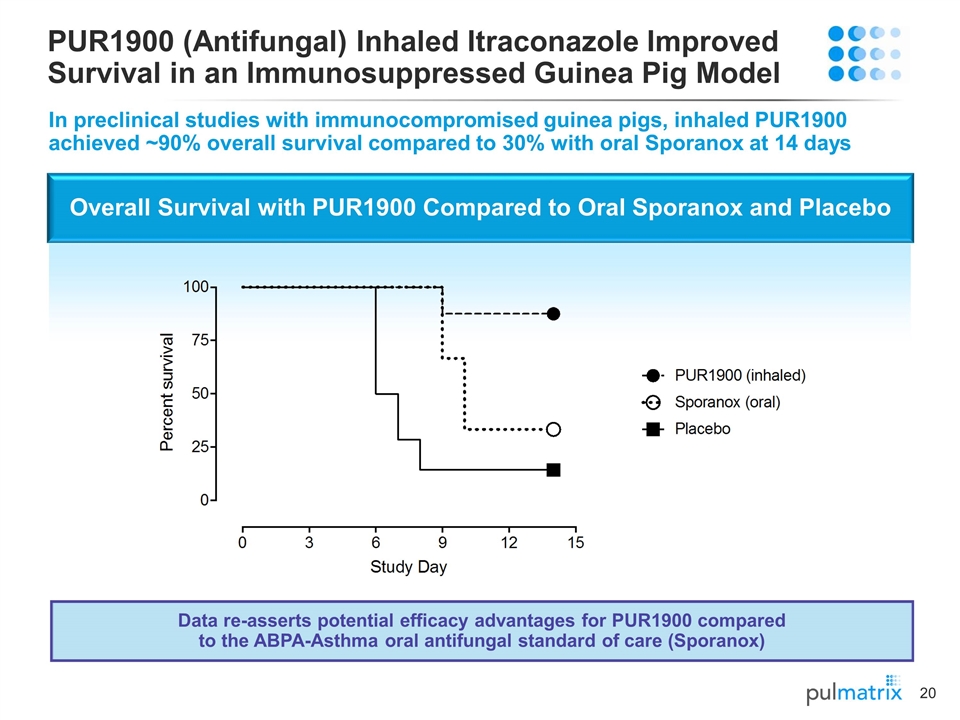
Overall Survival with PUR1900 Compared to Oral Sporanox and Placebo PUR1900 (Antifungal) Inhaled Itraconazole Improved Survival in an Immunosuppressed Guinea Pig Model In preclinical studies with immunocompromised guinea pigs, inhaled PUR1900 achieved ~90% overall survival compared to 30% with oral Sporanox at 14 days Data re-asserts potential efficacy advantages for PUR1900 compared to the ABPA-Asthma oral antifungal standard of care (Sporanox)
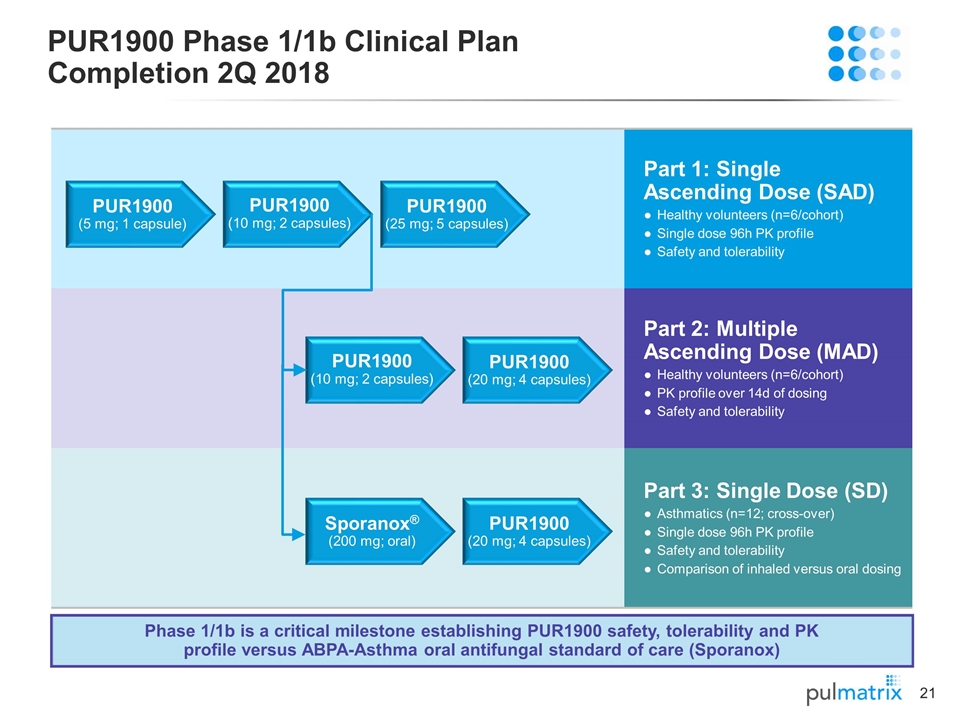
Part 1: Single Ascending Dose (SAD) Healthy volunteers (n=6/cohort) Single dose 96h PK profile Safety and tolerability Part 2: Multiple Ascending Dose (MAD) Healthy volunteers (n=6/cohort) PK profile over 14d of dosing Safety and tolerability Part 3: Single Dose (SD) Asthmatics (n=12; cross-over) Single dose 96h PK profile Safety and tolerability Comparison of inhaled versus oral dosing PUR1900 Phase 1/1b Clinical Plan Completion 2Q 2018 PUR1900 (25 mg; 5 capsules) PUR1900 (10 mg; 2 capsules) PUR1900 (5 mg; 1 capsule) PUR1900 (20 mg; 4 capsules) PUR1900 (10 mg; 2 capsules) PUR1900 (20 mg; 4 capsules) Sporanox® (200 mg; oral) Phase 1/1b is a critical milestone establishing PUR1900 safety, tolerability and PK profile versus ABPA-Asthma oral antifungal standard of care (Sporanox)

PUR0200 – iSPERSE™ Reformulation of Spiriva® Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
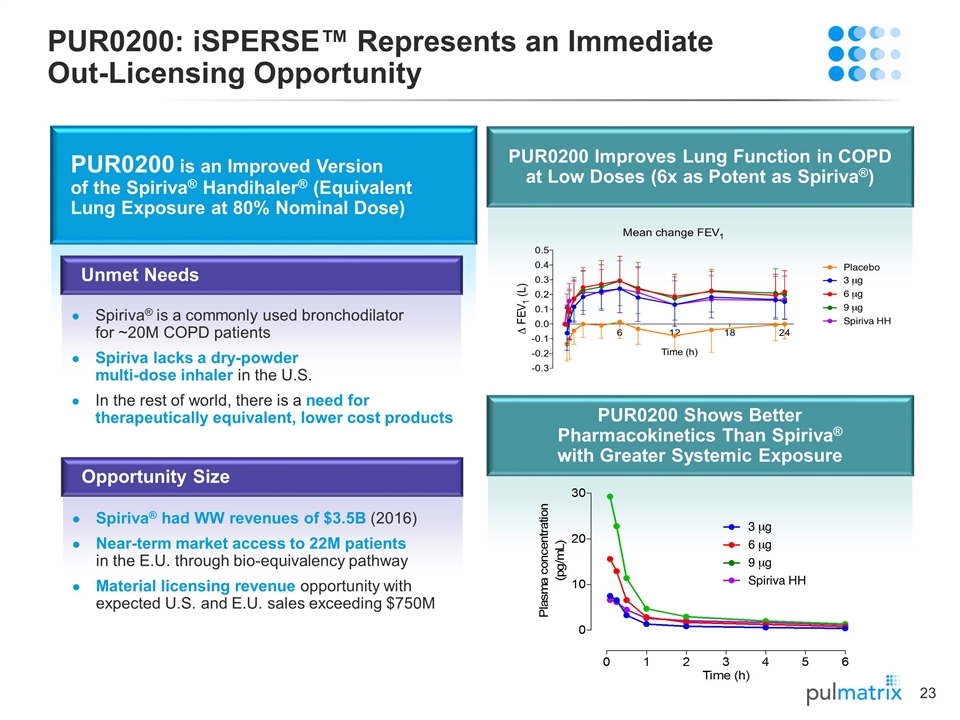
PUR0200: iSPERSE™ Represents an Immediate Out-Licensing Opportunity PUR0200 is an Improved Version of the Spiriva® Handihaler® (Equivalent Lung Exposure at 80% Nominal Dose) Spiriva® is a commonly used bronchodilator for ~20M COPD patients Spiriva lacks a dry-powder multi-dose inhaler in the U.S. In the rest of world, there is a need for therapeutically equivalent, lower cost products Unmet Needs Spiriva® had WW revenues of $3.5B (2016) Near-term market access to 22M patients in the E.U. through bio-equivalency pathway Material licensing revenue opportunity with expected U.S. and E.U. sales exceeding $750M Opportunity Size PUR0200 Improves Lung Function in COPD at Low Doses (6x as Potent as Spiriva®) PUR0200 Shows Better Pharmacokinetics Than Spiriva® with Greater Systemic Exposure

Summary & Development Plan
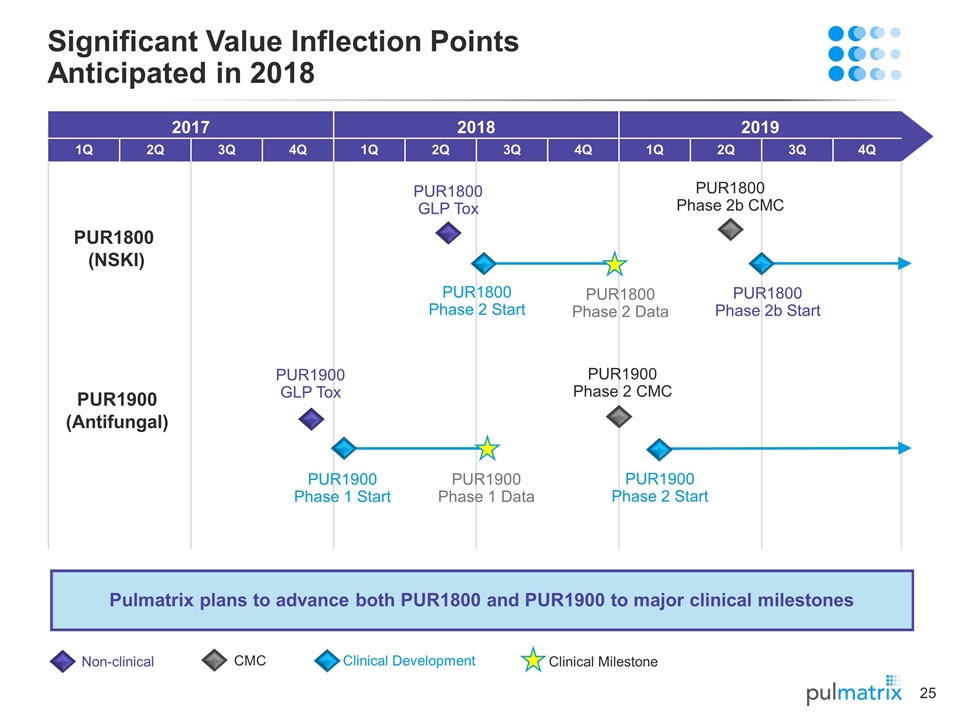
2017 2018 2019 1Q 2Q 3Q 4Q 1Q 2Q 3Q 4Q 1Q 2Q 3Q 4Q Pulmatrix plans to advance both PUR1800 and PUR1900 to major clinical milestones Significant Value Inflection Points Anticipated in 2018 PUR1800 (NSKI) PUR1800 Phase 2b Start PUR1800 Phase 2 Data PUR1800 Phase 2b CMC PUR1800 GLP Tox Non-clinical CMC Clinical Development Clinical Milestone PUR1800 Phase 2 Start PUR1900 (Antifungal) PUR1900 Phase 1 Data PUR1900 Phase 2 Start PUR1900 Phase 2 CMC PUR1900 GLP Tox PUR1900 Phase 1 Start
Clear Corporate Strategy with Value Creation Milestones in 2018 Target iSPERSE™ technology toward major respiratory diseases PUR1800 novel narrow spectrum kinase inhibitor (NSKI) for AECOPD Phase 2 data expected in 4Q 2018 >$1B U.S. potential revenue opportunity Significantly reduced development risk with the 505(b)(2) pathway PUR1900 inhaled Itraconazole for ABPA using iSPERSE™ technology Phase 1/1b data expected in 2Q 2018 ~$1.3B U.S. potential revenue opportunity iSPERSE™ Enabled Novel Products Focused on High Unmet Need iSPERSE™ Reformulated and Improved Existing Products Experienced Management Team and Board of Directors Pulmatrix Team Proven Record of Successful Respiratory Product Development Significant Value Creation Experience Two Key Strategies to Create Value

Engineering Respiratory Products for Major Unmet Needs August 2017
