Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| 8-K - 8-K - Astria Therapeutics, Inc. | a17-15370_18k.htm |
Exhibit 99.1
Catabasis Pharmaceuticals Corporate Update June 19, 2017

Forward Looking Statements This presentation contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of The Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995, including statements regarding our expectations and beliefs about our business, future financial and operating performance, clinical trial plans, product development plans and prospects. The words “believe”, “anticipate”, “plans,” “expect”, “could”, “should”, “will”, “would”, “may”, “intend” and similar expressions are intended to identify forward-looking statements, although not all forward-looking statements contain these identifying words. The forward-looking statements contained in this presentation and in remarks made during this presentation and the following Q&A session are subject to important risks and uncertainties that may cause actual events or results to differ materially from our current expectations and beliefs, including: uncertainties inherent in the initiation and completion of preclinical studies and clinical trials and clinical development of our product candidates; availability and timing of results from preclinical studies and clinical trials; whether interim results from a clinical trial will be predictive of the final results of the trial or the results of future trials; expectations for regulatory approvals to conduct trials or to market products; availability of funding sufficient for our foreseeable and unforeseeable operating expenses and capital expenditure requirements; other matters that could affect the availability or commercial potential of our product candidates; and general economic and market conditions. These and other risks are described under the caption “Risk Factors” in our Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the period ended March 31, 2017, which is on file with the Securities and Exchange Commission, and in other filings that we may make with the Securities and Exchange Commission in the future. In addition, the forward-looking statements included in this presentation represent our views as of the date of this presentation. We anticipate that subsequent events and developments will cause our views to change. However, while we may elect to update these forward-looking statements at some point in the future, we specifically disclaim any obligation to do so. These forward-looking statements should not be relied upon as representing our views as of any date subsequent to the date of this presentation. 2

Advancing Rare Disease Pipeline: Preparing for Phase 3 Trial in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Edasalonexent completed placebo-controlled Phase 2 MoveDMD trial – – – Oral inhibitor of NF-KB for all patients with DMD regardless of mutation Open-label extension results expected in Q3 2017 Phase 3 trial plan expected in H2 2017 DMD is characterized by predictable, sequential loss of mobility and function – Therapeutic goal is to delay the loss of function MoveDMD Phase 2 results consistent with goal of DMD treatment – – A primary exploratory biomarker endpoint, not a pivotal endpoint, was not met Clinically meaningful improvements observed in well established and pre-specified functional assessments Functional assessments have precedence as endpoints in pivotal trials in DMD Safe and well tolerated – – Additional programs derived from SMART Linker technology including CAT-5571 for cystic fibrosis 3

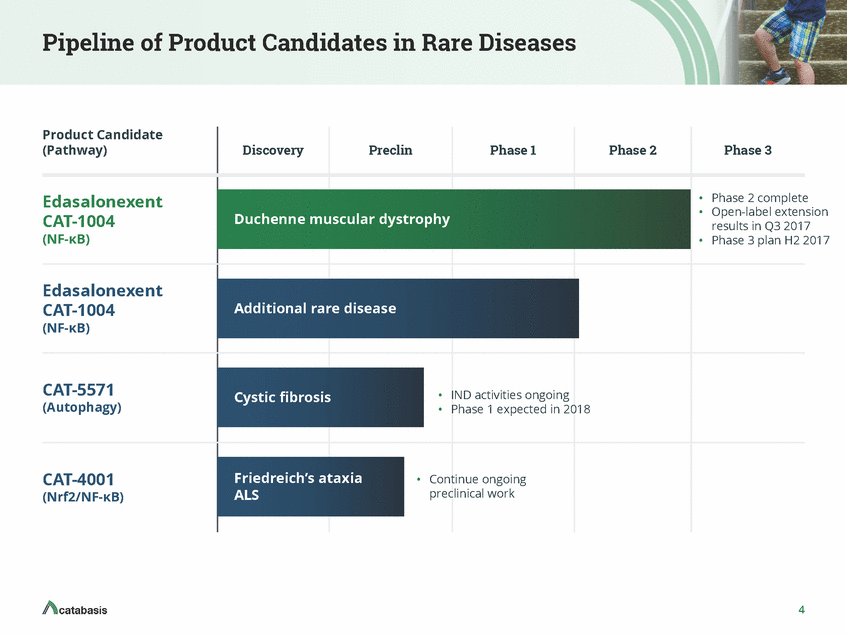
Pipeline of Product Candidates in Rare Diseases Product Candidate (Pathway) Discovery Preclin Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3 • • Phase 2 complete Open-label extension results in Q3 2017 Phase 3 plan H2 2017 Edasalonexent CAT-1004 (NF-KB) Duchenne muscular dystrophy • Edasalonexent CAT-1004 (NF-KB) Additional rare disease CAT-5571 (Autophagy) • IND activities ongoing • Phase 1 expected in 2018 Cystic fibrosis Friedreich’s ataxia ALS CAT-4001 (Nrf2/NF-KB) • Continue ongoing preclinical work 4
DMD Today 5

Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: Preserving Function Is the Goal of Treatment DMD is a rare recessive X-linked genetic disorder characterized by dystrophin deficiency in muscle tissue and subsequent chronic activation of NF-KB that results in muscle degeneration and prevents muscle regeneration Overall decline in DMD is characterized by a predictable cascade of discrete losses of function and mobility milestones Preserving or extending each individual functional capability delays overall decline and prolongs life Current therapeutic modalities delay loss of function and forestall additional serious decline in mobility 6
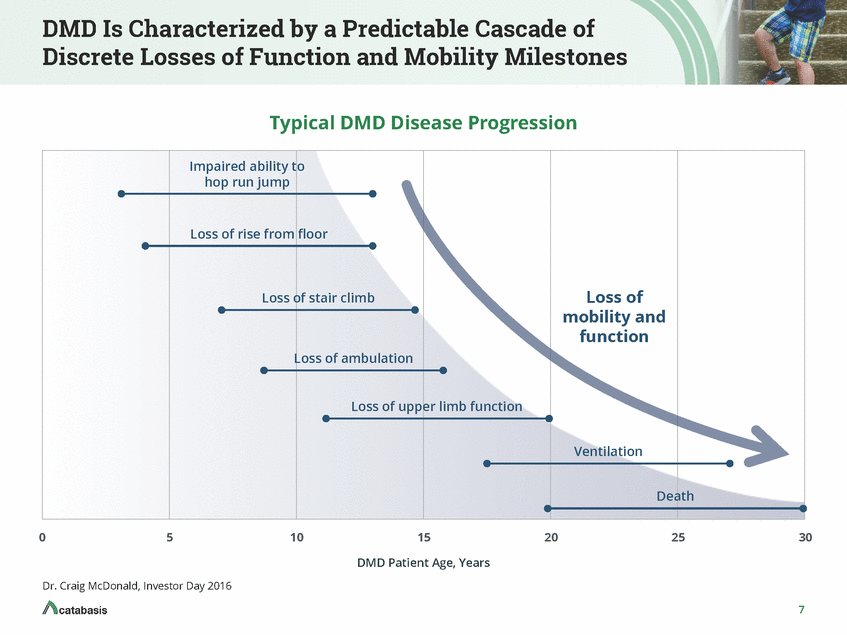
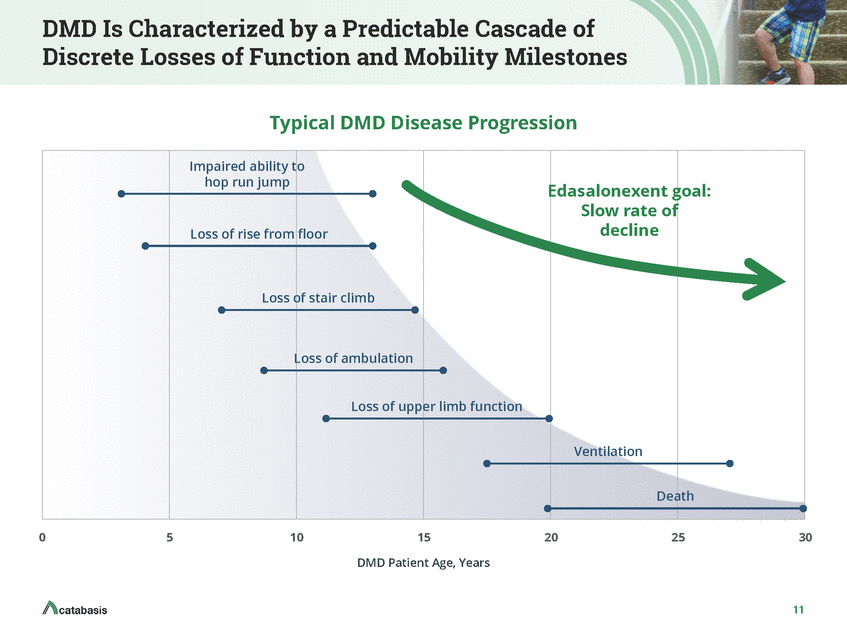
DMD Is Characterized by a Predictable Cascade of Discrete Losses of Function and Mobility Milestones Typical DMD Disease Progression Impaired ability to hop run jump Loss of rise from floor Loss of mobility and function Loss of stair climb Loss of ambulation Loss of upper limb function Ventilation Death 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 DMD Patient Age, Years Dr. Craig McDonald, Investor Day 2016 7
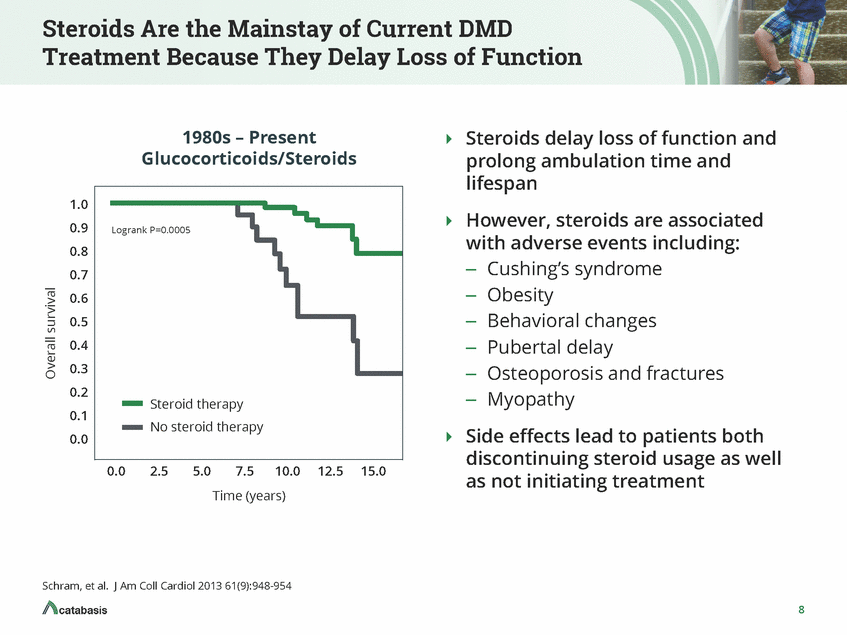
Steroids Are the Mainstay of Current DMD Treatment Because They Delay Loss of Function 1980s – Present Glucocorticoids/Steroids Steroids delay loss of function and prolong ambulation time and lifespan 1.0 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0.0 However, steroids are associated Logrank P=0.0005 with adverse events including: Cushing’s syndrome Obesity Behavioral changes Pubertal delay Osteoporosis and fractures Myopathy – – – – – – Steroid therapy No steroid therapy Side effects lead to patients both discontinuing steroid usage as well as not initiating treatment 0.0 2.5 5.0 7.5 10.0 12.5 15.0 Time (years) Schram, et al. J Am Coll Cardiol 2013 61(9):948-954 8 Overall survival
Edasalonexent (CAT-1004) Program Oral small molecule designed to inhibit NF-KB for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy 9
Edasalonexent: Potential to Slow Disease Progression for All Boys with DMD Investigational disease-modifying product candidate for all patients with DMD regardless of mutation Oral inhibitor of NF-KB, a protein that is chronically activated in DMD and drives muscle degeneration and suppresses muscle regeneration Reduction in rate of functional decline in MoveDMD Phase 2 – Clinically meaningful improvements observed in well established and pre-specified functional assessments – Functional assessments have precedence as endpoints in pivotal trials in DMD – Safe and well tolerated Edasalonexent currently in open-label extension portion of MoveDMD trial – Open-label extension results expected in Q3 2017 – Phase 3 trial plan expected in H2 2017 Developing as monotherapy and also potentially combinable with any dystrophin targeted therapy 10

DMD Is Characterized by a Predictable Cascade of Discrete Losses of Function and Mobility Milestones Typical DMD Disease Progression Impaired ability to hop run jump Edasalonexent goal: Slow rate of decline Loss of rise from floor Loss of stair climb Loss of ambulation Loss of upper limb function Ventilation Death 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 DMD Patient Age, Years 11
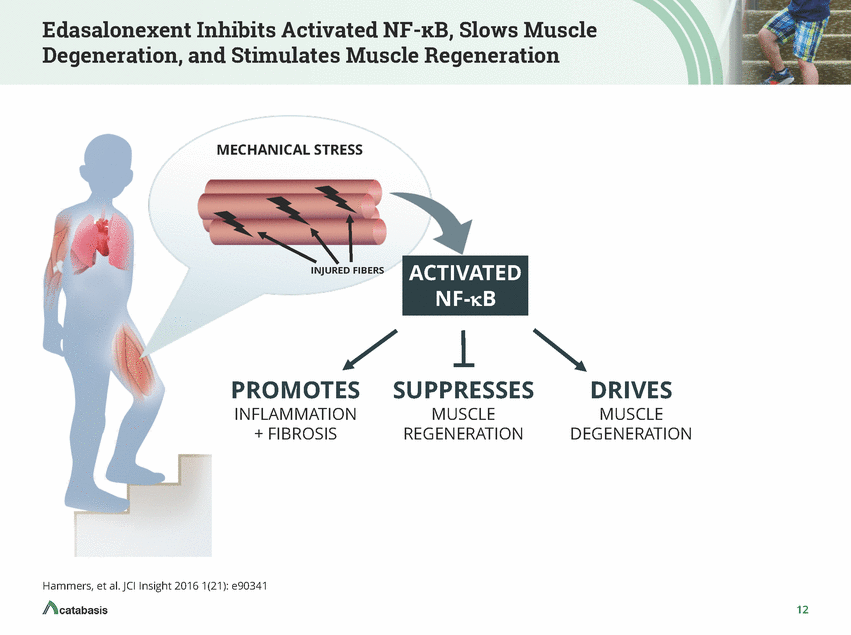
Edasalonexent Inhibits Activated NF-KB, Slows Muscle Degeneration, and Stimulates Muscle Regeneration MECHANICAL STRESS IVATED INJURED FIBERS NF-kB PROMOTES SUPPRESSES DRIVES MUSCLE DEGENERATION INFLAMMATION MUSCLE + FIBROSIS REGENERATION Hammers, et al. JCI Insight 2016 1(21): e90341 12 ACT
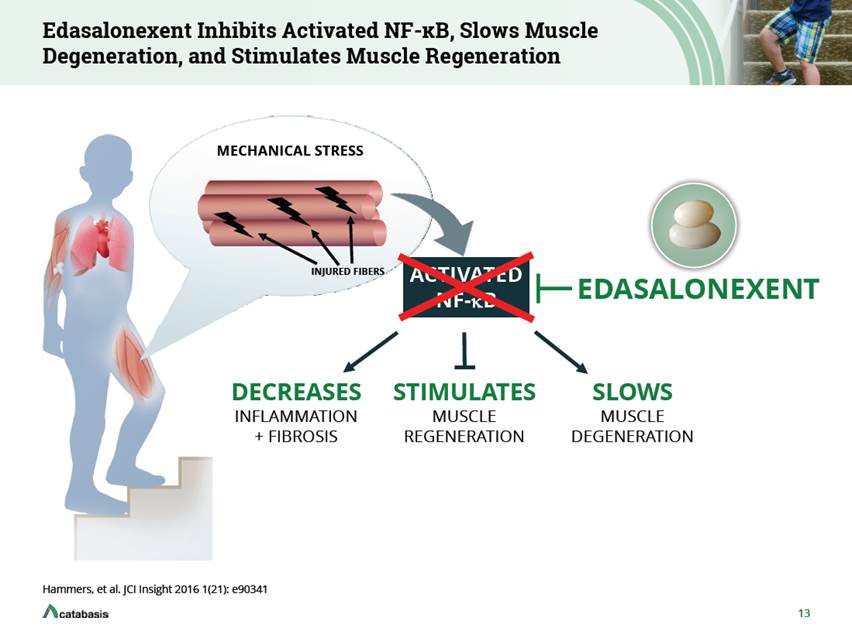
Edasalonexent Inhibits Activated NF-KB, Slows Muscle Degeneration, and Stimulates Muscle Regeneration MECHANICAL STRESS INJURED FIBERS EDASALONEXENT DECREASES INFLAMMATION + FIBROSIS STIMULATES MUSCLE REGENERATION SLOWS MUSCLE DEGENERATION Hammers, et al. JCI Insight 2016 1(21): e90341 13 ACTIVATED NF-KB
MoveDMD Phase 2 Demonstrated Favorable Delay in Loss of Function in Critical Function and Mobility Parameters TWO PRE-SPECIFIED ANALYSES Placebo-Controlled Crossover Edasa Edasa Pooled (n=20) Edasa Pooled (n=12) 67 mg/kg/day (n=10) + + - + + + + - + + + + + + +* 10-meter walk/run 4-stair Climb Time to stand NSAA PODCI * p < 0.05 Placebo-Controlled: Comparison of change from baseline between treatments and placebo during 12-week Crossover: Comparison of rate of change for off-treatment period (average of 8 months) to 12 weeks active treatment 14 Edasa 100 mg/kg/day (n=10) + + + + +
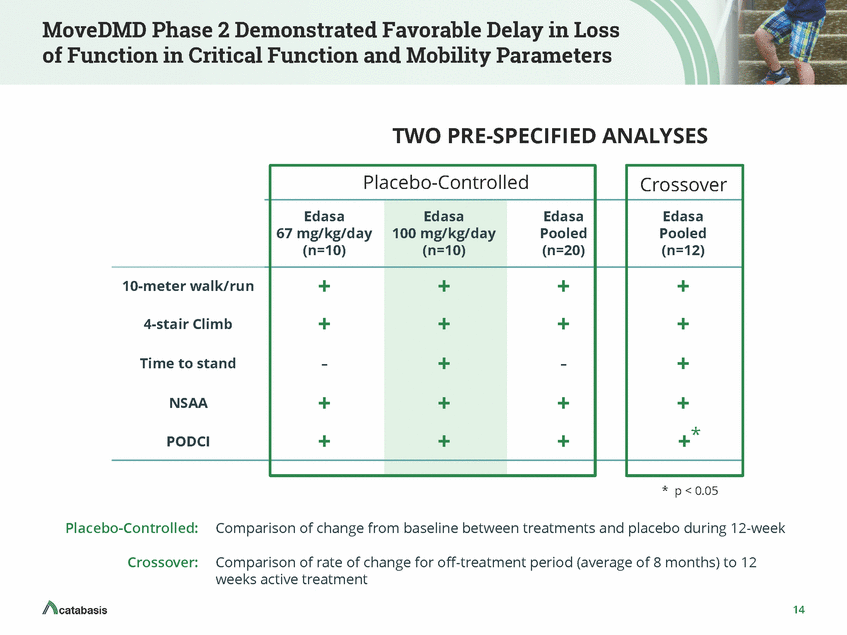
Composite Score for Phase 2 Functional Assessments Edasalonexent Preserves Function by Slowing Rate of Decline Max. possible score 5 p < 0.05 0 Min. possible score - 5 Placebo Edasalonexent (n=11) (n=20) Individual scores for 4-stair climb, 10-meter walk/run, time to stand, NSAA and PODCI were pooled –+1 for improvement, -1 for decline, 0 for no change Post-hoc analysis: average composite scores by individual improved vs. placebo 15 Composite Functional Score
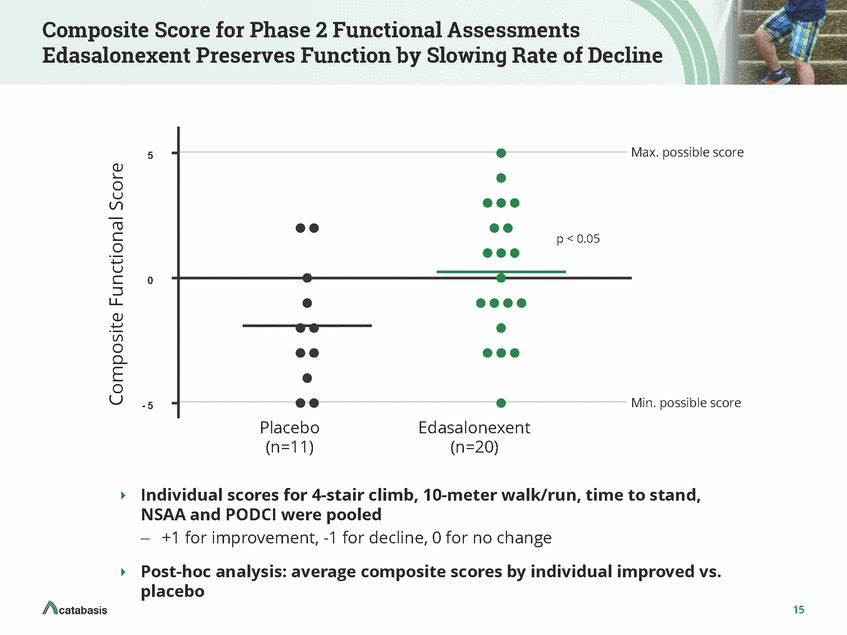
Timed Function Test: 10-meter Walk/Run Speed: Rate of Loss of Function Slowed Placebo-Controlled Crossover 0 . 0 0 5 0 . 0 0 5 0 . 0 0 0 0 . 0 0 0 - 0 . 0 0 5 - 0 . 0 0 5 - 0 . 0 1 0 - 0 . 0 1 0 p NS - 0 . 0 1 5 - 0 . 0 1 5 - 0 . 0 2 0 - 0 . 0 2 0 Placebo (n=11) Edasalonexent Placebo (n=12) Edasalonexent (n=12) (n=20) • There was a ~6% decline in function in the • There was a ~8% decline in function in the off treatment period The rate of decline in 10-meter walk/run was improved by 50% in edasalonexent crossover period vs. off-treatment period placebo over the 12 week trial period • • The change in 10-meter walk/run speed was improved by >80% in edasalonexent group compared to placebo Error bars in chart denote SEM, change in speed normalized to 12 weeks 16 Change in Speed Change in Speed
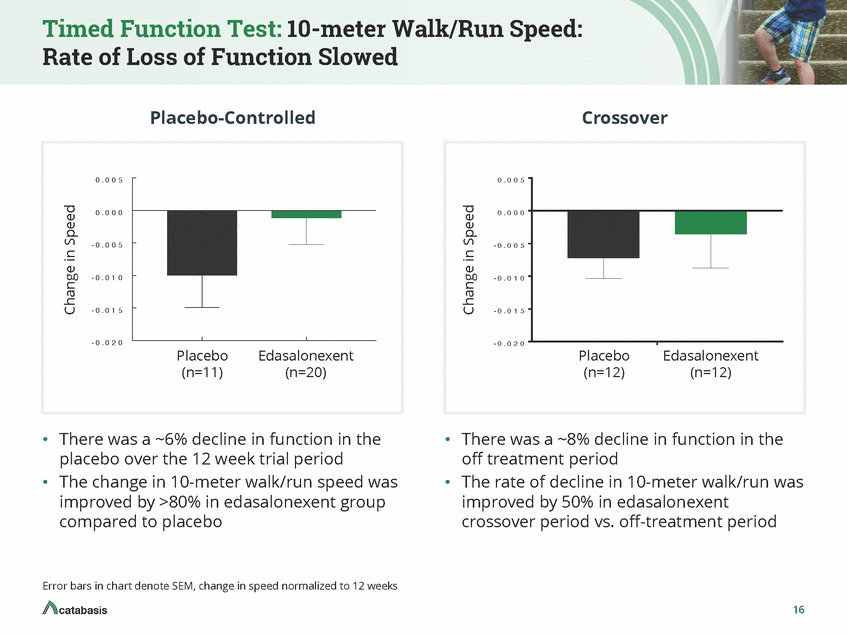
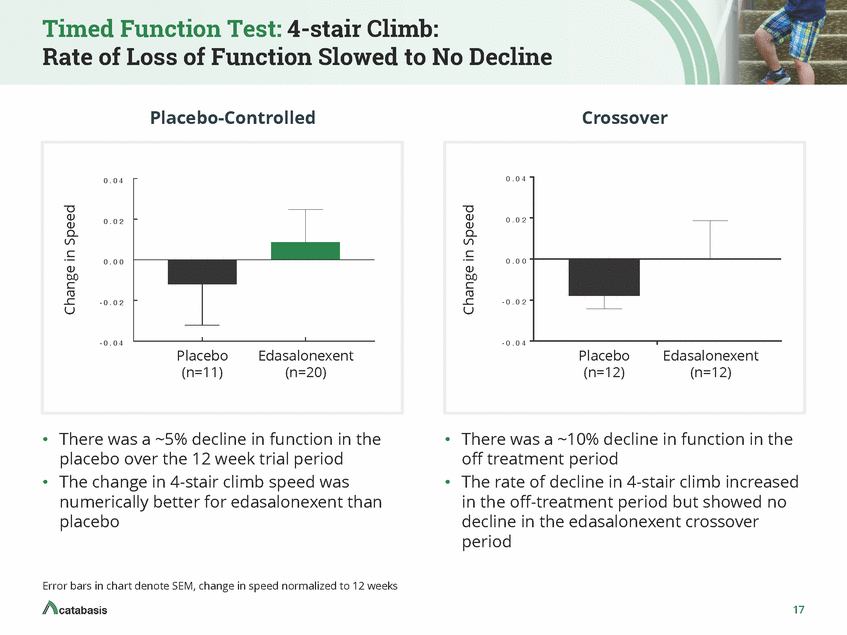
Timed Function Test: 4-stair Climb: Rate of Loss of Function Slowed to No Decline Placebo-Controlled Crossover 0 . 0 4 0 . 0 4 0 . 0 2 0 . 0 2 0 . 0 0 0 . 0 0 - 0 . 0 2 - 0 . 0 2 - 0 . 0 4 - 0 . 0 4 Placebo (n=11) Edasalonexent Placebo (n=12) Edasalonexent (n=12) (n=20) • There was a ~5% decline in function in the • There was a ~10% decline in function in the off treatment period The rate of decline in 4-stair climb increased in the off-treatment period but showed no decline in the edasalonexent crossover placebo over the 12 week trial period • • The change in 4-stair climb speed was numerically better for edasalonexent than placebo period Error bars in chart denote SEM, change in speed normalized to 12 weeks 17 Change in Speed Change in Speed
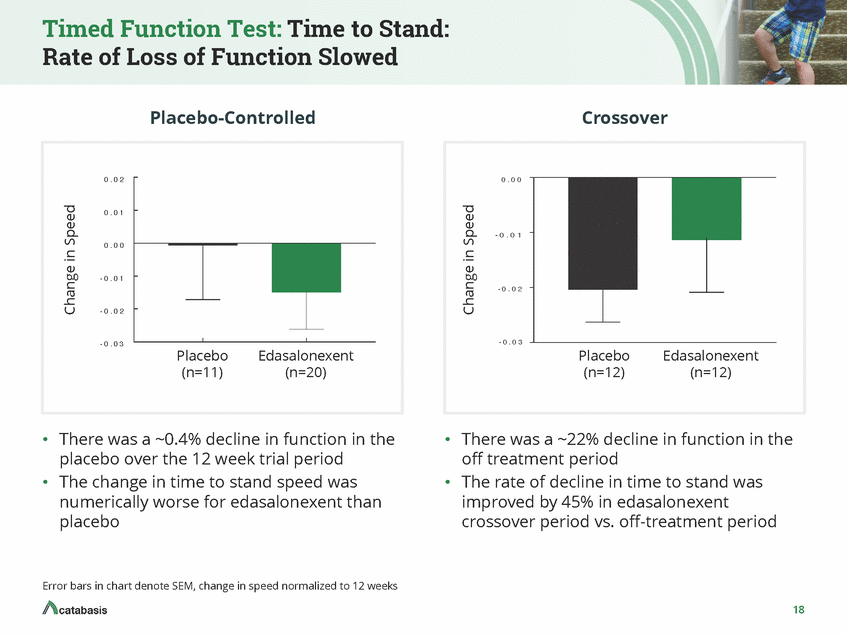
Timed Function Test: Time to Stand: Rate of Loss of Function Slowed Placebo-Controlled Crossover 0 . 0 2 00 ..00 00 0 0 . 0 1 --0 . 0 01 1 0 . 0 0 - 0 . 0 1 --00 ..00 02 2 - 0 . 0 2 - -00. .00033 - 0 . 0 3 Placebo (n=11) Edasalonexent Placebo (n=12) Edasalonexent (n=12) (n=20) • There was a ~0.4% decline in function in the • There was a ~22% decline in function in the off treatment period The rate of decline in time to stand was improved by 45% in edasalonexent crossover period vs. off-treatment period placebo over the 12 week trial period • • The change in time to stand speed was numerically worse for edasalonexent than placebo Error bars in chart denote SEM, change in speed normalized to 12 weeks 18 Change in Speed Change in Speed
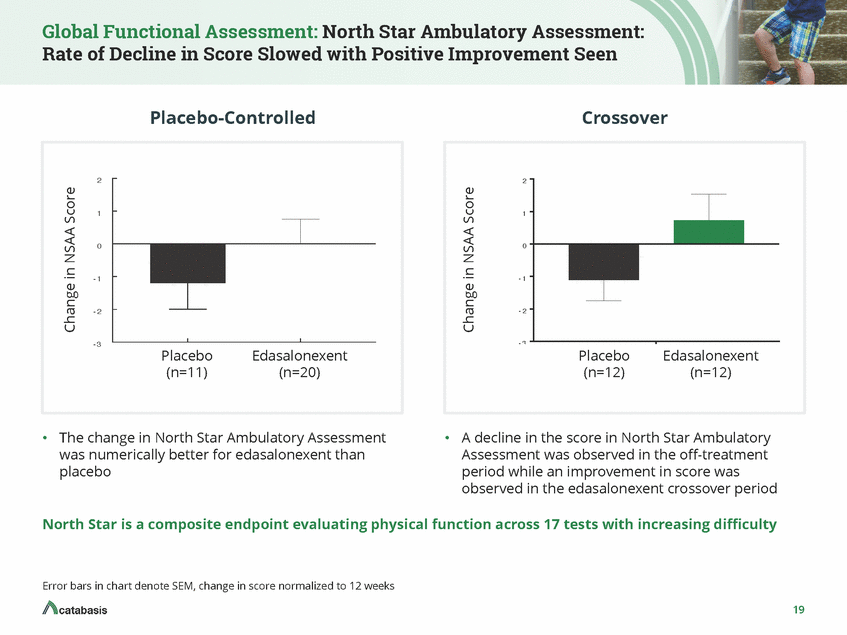
Global Functional Assessment: North Star Ambulatory Assessment: Rate of Decline in Score Slowed with Positive Improvement Seen Placebo-Controlled Crossover 2 2 1 1 0 0 - 1 - 1 - 2 - 2 - 3 Placebo (n=11) Edasalonexent (n=20) Placebo (n=12) Edasalonexent (n=12) •The change in North Star Ambulatory Assessment was numerically better for edasalonexent than • A decline in the score in North Star Ambulatory Assessment was observed in the off-treatment period while an improvement in score was observed in the edasalonexent crossover period placebo North Star is a composite endpoint evaluating physical function across 17 tests with increasing difficulty Error bars in chart denote SEM, change in score normalized to 12 weeks 19 Change in NSAA Score Change in NSAA Score
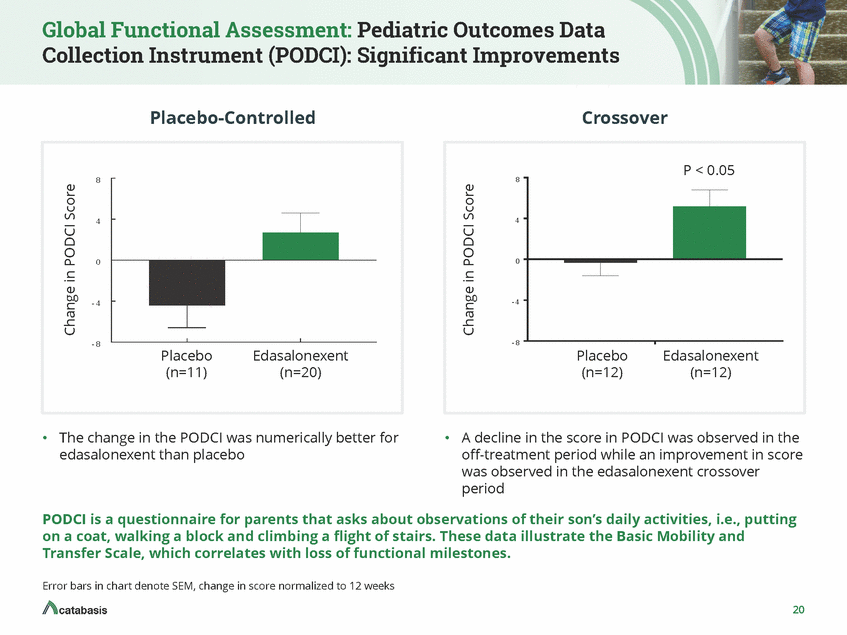
Global Functional Assessment: Pediatric Outcomes Data Collection Instrument (PODCI): Significant Improvements Placebo-Controlled Crossover pP <=00..0015 8 8 4 4 0 0 - 4 - 4 - 8 - 8 Placebo (n=11) Edasalonexent Placebo (n=12) Edasalonexent (n=12) (n=20) •The change in the PODCI was numerically better for •A decline in the score in PODCI was observed in the off-treatment period while an improvement in score was observed in the edasalonexent crossover edasalonexent than placebo period PODCI is a questionnaire for parents that asks about observations of their son’s daily activities, i.e., putting on a coat, walking a block and climbing a flight of stairs. These data illustrate the Basic Mobility and Transfer Scale, which correlates with loss of functional milestones. Error bars in chart denote SEM, change in score normalized to 12 weeks 20 Change in PODCI Score Change in PODCI Score
Key Takeaways from Phase 2 Data Reduction in rate of functional decline in MoveDMD Phase 2 – Reduction in rates of decline in well established timed function tests – Improvements in scores on validated global functional assessments No safety signals identified and well-tolerated Functional improvements observed in Phase 2 provide necessary information for Phase 3 trial design Expect results from open-label extension of MoveDMD trial in Q3 2017 Expect to announce Phase 3 trial plan in H2 2017 21

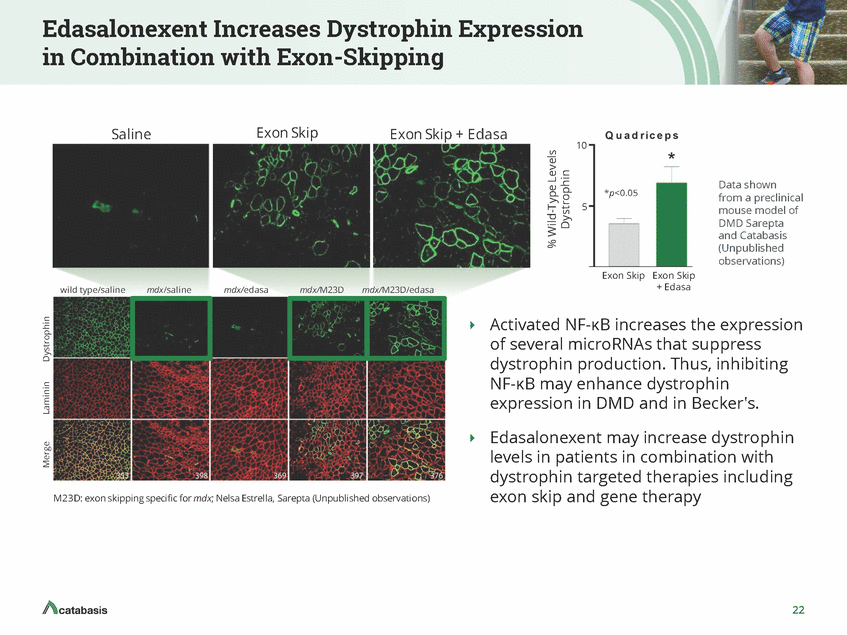
Edasalonexent Increases Dystrophin Expression in Combination with Exon-Skipping Exon Skip Saline Exon Skip + Edasa 10 Data shown from a preclinical mouse model of DMD Sarepta and Catabasis (Unpublished observations) *p<0.05 5 Exon Skip Exon Skip + Edasa wild type/saline mdx/saline mdx/edasa mdx/M23D mdx/M23D/edasa Activated NF-KB increases the expression of several microRNAs that suppress dystrophin production. Thus, inhibiting NF-KB may enhance dystrophin expression in DMD and in Becker's. Edasalonexent may increase dystrophin levels in patients in combination with dystrophin targeted therapies including exon skip and gene therapy M23D: exon skipping specific for mdx; Nelsa Estrella, Sarepta (Unpublished observations) 22 Merge Laminin Dystrophin % Wild-Type Levels Dystrophin
SMART Pipeline 23
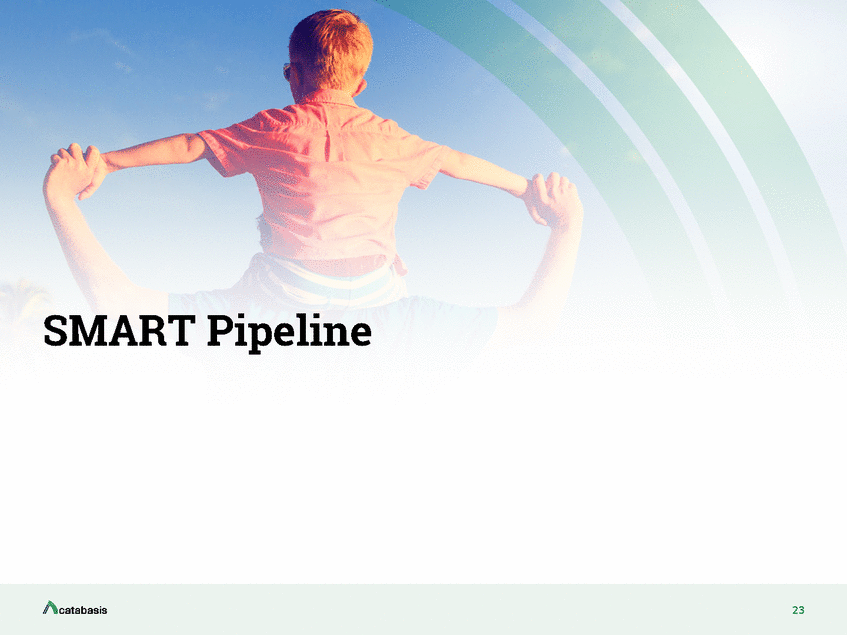
The Intersection Of Pathway Biology and the SMART Linker Platform BIFUNCTIONAL CONJUGATES of known bioactives engineered with proprietary, enzyme-cleavable small chemical linkers CELLULAR UPTAKE by endocytosis SMART linker conjugate Outside cell Inside cell (“SMART linkers”) Enzyme-specific cleavage of SMART linker Multi-node pathway modulation Release of bioactives BIOACTIVES “REACTIVATED” upon cleavage and freed to interact with intended intracellular targets Disease pathway 24
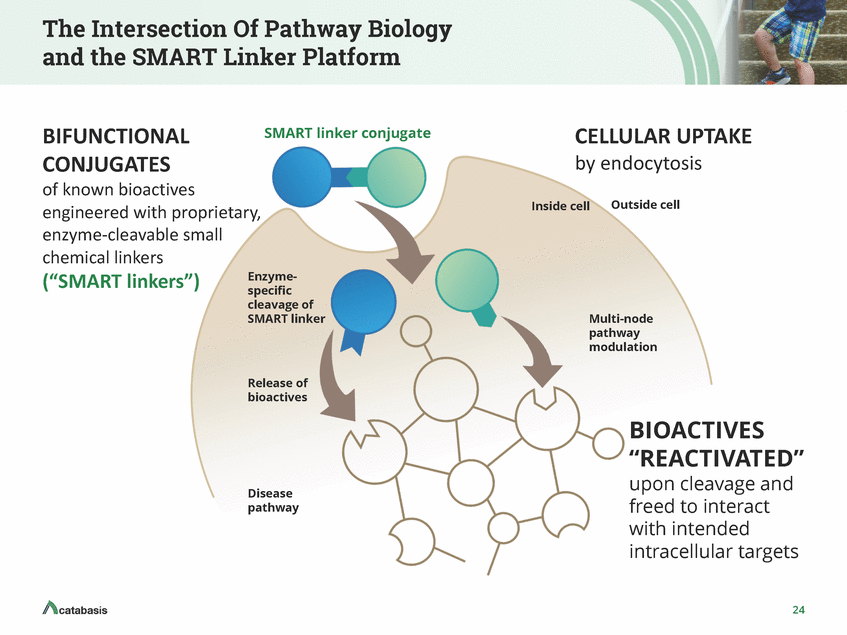
CAT-5571: Breaking the Spiral of Cystic Fibrosis Progression Obstruction CFTR Dysfunction Respiratory Tract Infection Obstruction Structural damage Respiratory Tract Infection Obstruction Bronchiectasis Respiratory Tract Infection Inflammation Pulmonary Insufficiency Inflammation Respiratory Failure Inflammation AT-5571 is designed to address impaired autophagy and improve host defense in CF patients, strengthening their ability to clear persistent serious lung infections 25
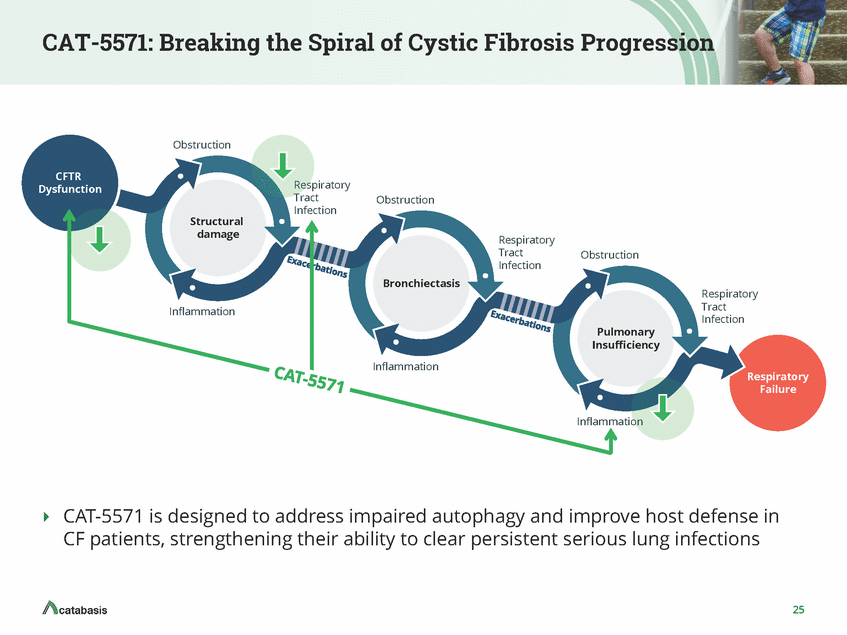
CAT-5571 Reduces Pulmonary Infection and Inflammation and Increases CFTR Function in Presence of F508del CFTR CAT-5571 reduces pulmonary P. aeruginosa infection and inflammation in mice with delF508 mutation P u l m o n a r y B a c t e r i a l L o a d P u l m o n a r y N e u t r o p h i l l i a 1 ´ 1 0 0 6 4 0 3 0 1 ´ 1 0 0 5 2 0 1 ´ 1 0 0 4 1 0 1 ´ 1 0 0 3 0 V e h i c l e C A T - 5 5 7 1 V e h i c l e C A T - 5 5 7 1 * p < 0.05 CAT-5571 significantly reduces the intracellular bacterial load of P. cenocepacia aeruginosa and B. CAT-5571 also increases CFTR cell surface trafficking and enhances CFTR function in homozygous delF508 human bronchial epithelial cells CAT-5571 could play an important role in improving clinical outcomes in combination with current CF therapies Pediatric Pulmonology. 2016 Supplement 45. 276-7. 26 C F U / m l L u n g N e u t r o p h i l s ( % W B C s ) * *
Catabasis in 2017: Anticipated Events and Priorities Report results from the open-label extension of the MoveDMD trial in Q3 2017 Announce Phase 3 trial plan for edasalonexent in DMD in H2 2017 Continue IND-enabling activities to initiate Phase 1 trial for CAT-5571 in 2018 Continue ongoing preclinical research for CAT-4001 in ALS and FA 27

Catabasis Pharmaceuticals Corporate Update June 19, 2017

