Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-32.3 - EXHIBIT 32.3 - KKR & Co. Inc. | kkr-2017331xex323.htm |
| EX-32.2 - EXHIBIT 32.2 - KKR & Co. Inc. | kkr-2017331xex322.htm |
| EX-32.1 - EXHIBIT 32.1 - KKR & Co. Inc. | kkr-2017331xex321.htm |
| EX-31.3 - EXHIBIT 31.3 - KKR & Co. Inc. | kkr-2017331xex313.htm |
| EX-31.2 - EXHIBIT 31.2 - KKR & Co. Inc. | kkr-2017331xex312.htm |
| EX-31.1 - EXHIBIT 31.1 - KKR & Co. Inc. | kkr-2017331xex311.htm |
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
WASHINGTON, D.C. 20549
Form 10-Q
ý QUARTERLY REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934.
For the quarterly period ended March 31, 2017
Or
o TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934.
For the Transition period from to .
Commission File Number 001-34820
KKR & CO. L.P.
(Exact name of Registrant as specified in its charter)
Delaware | 26-0426107 | |
(State or other Jurisdiction of Incorporation or Organization) | (I.R.S. Employer Identification Number) | |
9 West 57th Street, Suite 4200
New York, New York 10019
Telephone: (212) 750-8300
(Address, zip code, and telephone number, including
area code, of registrant’s principal executive office.)
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ý No o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes ý No o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company,” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
Large accelerated filer x | Accelerated filer o | Non-accelerated filer o | Smaller reporting company o | Emerging growth company o | ||||
(Do not check if a smaller reporting company) | ||||||||
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes o No ý
As of May 3, 2017, there were 461,797,801 Common Units of the registrant outstanding.
KKR & CO. L.P.
FORM 10-Q
For the Quarter Ended March 31, 2017
INDEX
Page No. | ||
PART I—FINANCIAL INFORMATION | ||
Item 1. | Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements (Unaudited) | |
Item 2. | Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations | |
Item 3. | Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk | |
Item 4. | Controls and Procedures | |
PART II—OTHER INFORMATION | ||
Item 1. | Legal Proceedings | |
Item 1A. | Risk Factors | |
Item 2. | Unregistered Sales of Equity Securities and Use of Proceeds | |
Item 3. | Defaults Upon Senior Securities | |
Item 4. | Mine Safety Disclosures | |
Item 5. | Other Information | |
Item 6. | Exhibits | |
SIGNATURES | ||
2
CAUTIONARY NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This report contains forward looking statements within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, or the Securities Act, and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, or the Exchange Act, which reflect our current views with respect to, among other things, our operations and financial performance. You can identify these forward looking statements by the use of words such as "outlook," "believe," "expect," "potential," "continue," "may," "should," "seek," "approximately," "predict," "intend," "will," "plan," "estimate," "anticipate," the negative version of these words, other comparable words or other statements that do not relate strictly to historical or factual matters. Without limiting the foregoing, statements regarding the declaration and payment of distributions on common or preferred units of KKR, the timing, manner and volume of repurchases of common units pursuant to a repurchase program, the announced transaction to combine Prisma Capital Partners LP and certain of its affiliates ("KKR Prisma") and Pacific Alternative Asset Management Company, LLC and the expected synergies from the acquisitions or strategic partnerships, may constitute forward-looking statements. Forward looking statements are subject to various risks and uncertainties. Accordingly, there are or will be important factors that could cause actual outcomes or results to differ materially from those indicated in these statements or cause the benefits and anticipated synergies from transactions to not be realized. We believe these factors include those described under the section entitled "Risk Factors" in our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2016 filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on February 24, 2017. These factors should be read in conjunction with the other cautionary statements that are included in this report and in our other periodic filings. We do not undertake any obligation to publicly update or review any forward looking statement, whether as a result of new information, future developments or otherwise.
In this report, references to "KKR," "we," "us," "our" and "our partnership" refer to KKR & Co. L.P. and its consolidated subsidiaries. Prior to KKR & Co. L.P. becoming listed on the New York Stock Exchange ("NYSE") on July 15, 2010, KKR Group Holdings L.P. ("Group Holdings") consolidated the financial results of KKR Management Holdings L.P. and KKR Fund Holdings L.P. (together, the "KKR Group Partnerships") and their consolidated subsidiaries. On August 5, 2014, KKR International Holdings L.P. became a KKR Group Partnership. Each KKR Group Partnership has an identical number of partner interests and, when held together, one Class A partner interest in each of the KKR Group Partnerships together represents one KKR Group Partnership Unit. In connection with KKR's issuance of Series A Preferred Units and Series B Preferred Units, the KKR Group Partnerships issued preferred units with economic terms designed to mirror those of the Series A Preferred Units and Series B Preferred Units, respectively.
References to "our Managing Partner" are to KKR Management LLC, which acts as our general partner and unless otherwise indicated, references to equity interests in KKR's business, or to percentage interests in KKR's business, reflect the aggregate equity of the KKR Group Partnerships and are net of amounts that have been allocated to our principals and other employees and non-employee operating consultants in respect of the carried interest from KKR's business as part of our "carry pool" and certain minority interests. References to "principals" are to our senior employees and non-employee operating consultants who hold interests in KKR's business through KKR Holdings L.P., which we refer to as "KKR Holdings," and references to our "senior principals" are to our senior employees who hold interests in our Managing Partner entitling them to vote for the election of its directors.
References to non-employee operating consultants include employees of KKR Capstone and are not employees of KKR. KKR Capstone refers to a group of entities that are owned and controlled by their senior management. KKR Capstone is not a subsidiary or affiliate of KKR. KKR Capstone operates under several consulting agreements with KKR and uses the "KKR" name under license from KKR.
Prior to October 1, 2009, KKR's business was conducted through multiple entities for which there was no single holding entity, but were under common control of senior KKR principals, and in which senior principals and KKR's other principals and individuals held ownership interests (collectively, the "Predecessor Owners"). On October 1, 2009, we completed the acquisition of all of the assets and liabilities of KKR & Co. (Guernsey) L.P. (f/k/a KKR Private Equity Investors, L.P. or "KPE") and, in connection with such acquisition, completed a series of transactions pursuant to which the business of KKR was reorganized into a holding company structure. The reorganization involved a contribution of certain equity interests in KKR's business that were held by KKR's Predecessor Owners to the KKR Group Partnerships in exchange for equity interests in the KKR Group Partnerships held through KKR Holdings. We refer to the acquisition of the assets and liabilities of KPE and to our subsequent reorganization into a holding company structure as the "KPE Transaction."
3
In this report, the term "GAAP" refers to accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
We disclose certain financial measures in this report that are calculated and presented using methodologies other than in accordance with GAAP. We believe that providing these performance measures on a supplemental basis to our GAAP results is helpful to unitholders in assessing the overall performance of KKR's businesses. These financial measures should not be considered as a substitute for similar financial measures calculated in accordance with GAAP, if available. We caution readers that these non-GAAP financial measures may differ from the calculations of other investment managers, and as a result, may not be comparable to similar measures presented by other investment managers. Reconciliations of these non-GAAP financial measures to the most directly comparable financial measures calculated and presented in accordance with GAAP, where applicable, are included within "Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements (Unaudited)—Note 14. Segment Reporting" and later in this report under "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations — Segment Operating and Performance Measures" and "— Segment Balance Sheet."
This report uses the terms assets under management or AUM, fee paying assets under management or FPAUM, economic net income or ENI, fee related earnings or FRE, distributable earnings, capital invested, syndicated capital and book value. You should note that our calculations of these financial measures and other financial measures may differ from the calculations of other investment managers and, as a result, our financial measures may not be comparable to similar measures presented by other investment managers. These and other financial measures are defined in the section "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition & Results of Operations—Segment Operating and Performance Measures" and "— Segment Balance Sheet."
References to "our funds" or "our vehicles" refer to investment funds, vehicles and accounts advised, sponsored or managed by one or more subsidiaries of KKR including CLO and CMBS vehicles, unless the context requires otherwise. They do not include investment funds, vehicles or accounts of any hedge fund manager with which we have formed a strategic partnership where we have acquired a non-controlling interest.
Unless otherwise indicated, references in this report to our fully exchanged and diluted common units outstanding, or to our common units outstanding on a fully exchanged and diluted basis, reflect (i) actual common units outstanding, (ii) common units into which KKR Group Partnership Units not held by us are exchangeable pursuant to the terms of the exchange agreement described in this report, (iii) common units issuable in respect of exchangeable equity securities issued in connection with the acquisition of Avoca Capital ("Avoca"), and (iv) common units issuable pursuant to any equity awards actually granted from the KKR & Co. L.P. 2010 Equity Incentive Plan, which we refer to as our "Equity Incentive Plan," but do not reflect common units available for issuance pursuant to our Equity Incentive Plan for which equity awards have not yet been granted.
4
KKR & CO. L.P.
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION (UNAUDITED)
(Amounts in Thousands, Except Unit Data)
March 31, 2017 | December 31, 2016 | ||||||
Assets | |||||||
Cash and Cash Equivalents | $ | 2,758,398 | $ | 2,508,902 | |||
Cash and Cash Equivalents Held at Consolidated Entities | 1,599,897 | 1,624,758 | |||||
Restricted Cash and Cash Equivalents | 128,815 | 212,155 | |||||
Investments | 34,225,324 | 31,409,765 | |||||
Due from Affiliates | 323,335 | 250,452 | |||||
Other Assets | 2,599,943 | 2,996,865 | |||||
Total Assets | $ | 41,635,712 | $ | 39,002,897 | |||
Liabilities and Equity | |||||||
Debt Obligations | $ | 19,625,439 | $ | 18,544,075 | |||
Due to Affiliates | 385,374 | 359,479 | |||||
Accounts Payable, Accrued Expenses and Other Liabilities | 3,337,101 | 2,981,260 | |||||
Total Liabilities | 23,347,914 | 21,884,814 | |||||
Commitments and Contingencies | |||||||
Redeemable Noncontrolling Interests | 781,428 | 632,348 | |||||
Equity | |||||||
Series A Preferred Units (13,800,000 units issued and outstanding as of March 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016) | 332,988 | 332,988 | |||||
Series B Preferred Units (6,200,000 units issued and outstanding as of March 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016) | 149,566 | 149,566 | |||||
KKR & Co. L.P. Capital - Common Unitholders (455,570,965 and 452,380,335 common units issued and outstanding as of March 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016, respectively) | 5,755,354 | 5,457,279 | |||||
Total KKR & Co. L.P. Partners' Capital | 6,237,908 | 5,939,833 | |||||
Noncontrolling Interests | 11,268,462 | 10,545,902 | |||||
Total Equity | 17,506,370 | 16,485,735 | |||||
Total Liabilities and Equity | $ | 41,635,712 | $ | 39,002,897 | |||
See notes to condensed consolidated financial statements.
5
KKR & CO. L.P.
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION (Continued) (UNAUDITED)
(Amounts in Thousands)
The following presents the portion of the consolidated balances presented in the condensed consolidated statements of financial condition attributable to consolidated variable interest entities (“VIEs”) as of March 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016. KKR's consolidated VIEs consist primarily of certain collateralized financing entities (“CFEs”) holding collateralized loan obligations ("CLOs") and commercial real estate mortgage-backed securities ("CMBS”) and certain investment funds. With respect to consolidated VIEs, the following assets may only be used to settle obligations of these consolidated VIEs and the following liabilities are only the obligations of these consolidated VIEs. The noteholders, limited partners and other creditors of these VIEs have no recourse to KKR’s general assets. Additionally, KKR has no right to the benefits from, nor does KKR bear the risks associated with, the assets held by these VIEs beyond KKR’s beneficial interest therein and any fees generated from the VIEs. There are neither explicit arrangements nor does KKR hold implicit variable interests that would require KKR to provide any material ongoing financial support to the consolidated VIEs, beyond amounts previously committed, if any.
March 31, 2017 | |||||||||||
Consolidated CFEs | Consolidated KKR Funds and Other Entities | Total | |||||||||
Assets | |||||||||||
Cash and Cash Equivalents Held at Consolidated Entities | $ | 1,223,262 | $ | 376,635 | $ | 1,599,897 | |||||
Restricted Cash and Cash Equivalents | — | 98,702 | 98,702 | ||||||||
Investments | 14,526,323 | 9,857,892 | 24,384,215 | ||||||||
Due from Affiliates | — | 5,323 | 5,323 | ||||||||
Other Assets | 353,463 | 395,831 | 749,294 | ||||||||
Total Assets | $ | 16,103,048 | $ | 10,734,383 | $ | 26,837,431 | |||||
Liabilities | |||||||||||
Debt Obligations | $ | 14,283,962 | $ | 1,645,008 | $ | 15,928,970 | |||||
Accounts Payable, Accrued Expenses and Other Liabilities | 1,053,107 | 255,538 | 1,308,645 | ||||||||
Total Liabilities | $ | 15,337,069 | $ | 1,900,546 | $ | 17,237,615 | |||||
December 31, 2016 | |||||||||||
Consolidated CFEs | Consolidated KKR Funds and Other Entities | Total | |||||||||
Assets | |||||||||||
Cash and Cash Equivalents Held at Consolidated Entities | $ | 1,158,641 | $ | 466,117 | $ | 1,624,758 | |||||
Restricted Cash and Cash Equivalents | 86,777 | 95,105 | 181,882 | ||||||||
Investments | 13,950,897 | 8,979,341 | 22,930,238 | ||||||||
Due from Affiliates | — | 5,555 | 5,555 | ||||||||
Other Assets | 153,283 | 430,326 | 583,609 | ||||||||
Total Assets | $ | 15,349,598 | $ | 9,976,444 | $ | 25,326,042 | |||||
Liabilities | |||||||||||
Debt Obligations | $ | 13,858,288 | $ | 1,612,799 | $ | 15,471,087 | |||||
Accounts Payable, Accrued Expenses and Other Liabilities | 722,714 | 316,121 | 1,038,835 | ||||||||
Total Liabilities | $ | 14,581,002 | $ | 1,928,920 | $ | 16,509,922 | |||||
See notes to condensed consolidated financial statements.
6
KKR & CO. L.P.
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS (UNAUDITED)
(Amounts in Thousands, Except Unit Data)
Three Months Ended March 31, | |||||||
2017 | 2016 | ||||||
Revenues | |||||||
Fees and Other | $ | 715,952 | $ | 162,805 | |||
Expenses | |||||||
Compensation and Benefits | 402,963 | 125,489 | |||||
Occupancy and Related Charges | 14,851 | 16,566 | |||||
General, Administrative and Other | 122,200 | 166,268 | |||||
Total Expenses | 540,014 | 308,323 | |||||
Investment Income (Loss) | |||||||
Net Gains (Losses) from Investment Activities | 558,448 | (735,223 | ) | ||||
Dividend Income | 9,924 | 63,213 | |||||
Interest Income | 280,980 | 230,476 | |||||
Interest Expense | (186,854 | ) | (171,394 | ) | |||
Total Investment Income (Loss) | 662,498 | (612,928 | ) | ||||
Income (Loss) Before Taxes | 838,436 | (758,446 | ) | ||||
Income Tax / (Benefit) | 40,542 | 1,890 | |||||
Net Income (Loss) | 797,894 | (760,336 | ) | ||||
Net Income (Loss) Attributable to Redeemable Noncontrolling Interests | 20,933 | (38 | ) | ||||
Net Income (Loss) Attributable to Noncontrolling Interests | 509,277 | (430,359 | ) | ||||
Net Income (Loss) Attributable to KKR & Co. L.P. | 267,684 | (329,939 | ) | ||||
Net Income Attributable to Series A Preferred Unitholders | 5,822 | — | |||||
Net Income Attributable to Series B Preferred Unitholders | 2,519 | — | |||||
Net Income (Loss) Attributable to KKR & Co. L.P. Common Unitholders | $ | 259,343 | $ | (329,939 | ) | ||
Net Income (Loss) Attributable to KKR & Co. L.P. Per Common Unit | |||||||
Basic | $ | 0.57 | $ | (0.73 | ) | ||
Diluted | $ | 0.52 | $ | (0.73 | ) | ||
Weighted Average Common Units Outstanding | |||||||
Basic | 453,695,846 | 450,262,143 | |||||
Diluted | 496,684,340 | 450,262,143 | |||||
See notes to condensed consolidated financial statements.
7
KKR & CO. L.P.
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME (LOSS) (UNAUDITED)
(Amounts in Thousands)
Three Months Ended March 31, | |||||||
2017 | 2016 | ||||||
Net Income (Loss) | $ | 797,894 | $ | (760,336 | ) | ||
Other Comprehensive Income (Loss), Net of Tax: | |||||||
Foreign Currency Translation Adjustments | 16,576 | 8,434 | |||||
Comprehensive Income (Loss) | 814,470 | (751,902 | ) | ||||
Less: Comprehensive Income (Loss) Attributable to Redeemable Noncontrolling Interests | 20,933 | (38 | ) | ||||
Less: Comprehensive Income (Loss) Attributable to Noncontrolling Interests | 520,109 | (426,773 | ) | ||||
Comprehensive Income (Loss) Attributable to KKR & Co. L.P. | $ | 273,428 | $ | (325,091 | ) | ||
See notes to condensed consolidated financial statements.
8
KKR & CO. L.P.
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN EQUITY (UNAUDITED)
(Amounts in Thousands, Except Unit Data)
KKR & Co. L.P. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Common Units | Capital - Common Unitholders | Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) | Total Capital - Common Units | Capital - Series A Preferred Units | Noncontrolling Interests | Total Equity | Redeemable Noncontrolling Interests | |||||||||||||||||||
Balance at January 1, 2016 | 457,834,875 | $ | 5,575,981 | $ | (28,799 | ) | $ | 5,547,182 | $ | — | $ | 43,731,774 | $ | 49,278,956 | $ | 188,629 | ||||||||||
Net Income (Loss) | (329,939 | ) | (329,939 | ) | (430,359 | ) | (760,298 | ) | (38 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
Other Comprehensive Income (Loss)- Foreign Currency Translation (Net of Tax) | 4,848 | 4,848 | 3,586 | 8,434 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Deconsolidation of Funds | — | (34,190,890 | ) | (34,190,890 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
Exchange of KKR Holdings L.P. Units and Other Securities to KKR & Co. L.P. Common Units | 2,513,530 | 29,633 | (253 | ) | 29,380 | (29,380 | ) | — | ||||||||||||||||||
Tax Effects Resulting from Exchange of KKR Holdings L.P. Units and delivery of KKR & Co. L.P. Common Units | 1,048 | (137 | ) | 911 | 911 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Equity Based Compensation | 49,961 | 49,961 | 13,862 | 63,823 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Unit Repurchases | (14,221,835 | ) | (194,957 | ) | (194,957 | ) | (194,957 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
Equity Issued in connection with Preferred Unit Offering | — | 332,988 | 332,988 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Capital Contributions | — | 507,870 | 507,870 | 59,500 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Capital Distributions | (72,033 | ) | (72,033 | ) | (297,241 | ) | (369,274 | ) | (17,329 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
Balance at March 31, 2016 | 446,126,570 | $ | 5,059,694 | $ | (24,341 | ) | $ | 5,035,353 | $ | 332,988 | $ | 9,309,222 | $ | 14,677,563 | $ | 230,762 | ||||||||||
KKR & Co. L.P. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Common Units | Capital - Common Unitholders | Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) | Total Capital - Common Units | Capital - Series A Preferred Units | Capital - Series B Preferred Units | Noncontrolling Interests | Total Equity | Redeemable Noncontrolling Interests | |||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at January 1, 2017 | 452,380,335 | $ | 5,506,375 | $ | (49,096 | ) | $ | 5,457,279 | $ | 332,988 | $ | 149,566 | $ | 10,545,902 | $ | 16,485,735 | $ | 632,348 | |||||||||||
Net Income (Loss) | 259,343 | 259,343 | 5,822 | 2,519 | 509,277 | 776,961 | 20,933 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Other Comprehensive Income (Loss)- Foreign Currency Translation (Net of Tax) | 5,744 | 5,744 | 10,832 | 16,576 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Changes in Consolidation | — | (71,657 | ) | (71,657 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Transfer of interests under common control (See Note 15) | 12,269 | (1,988 | ) | 10,281 | (10,281 | ) | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Exchange of KKR Holdings L.P. Units and Other Securities to KKR & Co. L.P. Common Units | 3,190,630 | 43,564 | (388 | ) | 43,176 | (43,176 | ) | — | |||||||||||||||||||||
Tax Effects Resulting from Exchange of KKR Holdings L.P. Units | 1,802 | 167 | 1,969 | 1,969 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Equity Based Compensation | 49,943 | 49,943 | 61,093 | 111,036 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Unit Repurchases | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Capital Contributions | — | 528,833 | 528,833 | 128,499 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Capital Distributions | (72,381 | ) | (72,381 | ) | (5,822 | ) | (2,519 | ) | (262,361 | ) | (343,083 | ) | (352 | ) | |||||||||||||||
Balance at March 31, 2017 | 455,570,965 | $ | 5,800,915 | $ | (45,561 | ) | $ | 5,755,354 | $ | 332,988 | $ | 149,566 | $ | 11,268,462 | $ | 17,506,370 | $ | 781,428 | |||||||||||
See notes to condensed consolidated financial statements.
9
KKR & CO. L.P.
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS (UNAUDITED)
(Amounts in Thousands)
Three Months Ended March 31, | |||||||
2017 | 2016 | ||||||
Operating Activities | |||||||
Net Income (Loss) | $ | 797,894 | $ | (760,336 | ) | ||
Adjustments to Reconcile Net Income (Loss) to Net Cash Provided (Used) by Operating Activities: | |||||||
Equity Based Compensation | 111,036 | 63,823 | |||||
Net Realized (Gains) Losses on Investments | (146,164 | ) | 43,283 | ||||
Change in Unrealized (Gains) Losses on Investments | (412,284 | ) | 691,940 | ||||
Carried Interest Allocated as a result of Changes in Fund Fair Value | (335,773 | ) | 116,956 | ||||
Other Non-Cash Amounts | 38,087 | 34,921 | |||||
Cash Flows Due to Changes in Operating Assets and Liabilities: | |||||||
Change in Cash and Cash Equivalents Held at Consolidated Entities | 31,060 | 329,656 | |||||
Change in Due from / to Affiliates | (48,964 | ) | (78,798 | ) | |||
Change in Other Assets | 539,623 | 114,332 | |||||
Change in Accounts Payable, Accrued Expenses and Other Liabilities | 310,776 | (3,882 | ) | ||||
Investments Purchased | (8,345,252 | ) | (3,314,089 | ) | |||
Proceeds from Investments | 6,341,592 | 2,023,404 | |||||
Net Cash Provided (Used) by Operating Activities | (1,118,369 | ) | (738,790 | ) | |||
Investing Activities | |||||||
Change in Restricted Cash and Cash Equivalents | 83,340 | 65,062 | |||||
Purchase of Fixed Assets | (21,384 | ) | (1,470 | ) | |||
Development of Oil and Natural Gas Properties | (177 | ) | (957 | ) | |||
Net Cash Provided (Used) by Investing Activities | 61,779 | 62,635 | |||||
Financing Activities | |||||||
Distributions to Partners | (72,381 | ) | (72,033 | ) | |||
Distributions to Redeemable Noncontrolling Interests | (352 | ) | (17,329 | ) | |||
Contributions from Redeemable Noncontrolling Interests | 128,499 | 59,500 | |||||
Distributions to Noncontrolling Interests | (262,361 | ) | (297,241 | ) | |||
Contributions from Noncontrolling Interests | 520,269 | 507,870 | |||||
Issuance of Preferred Units (net of issuance costs) | — | 332,988 | |||||
Preferred Unit Distributions | (8,341 | ) | — | ||||
Unit Repurchases | — | (194,957 | ) | ||||
Proceeds from Debt Obligations | 2,160,958 | 1,251,139 | |||||
Repayment of Debt Obligations | (1,154,415 | ) | (657,461 | ) | |||
Financing Costs Paid | (5,790 | ) | (3,168 | ) | |||
Net Cash Provided (Used) by Financing Activities | 1,306,086 | 909,308 | |||||
Net Increase/(Decrease) in Cash and Cash Equivalents | 249,496 | 233,153 | |||||
Cash and Cash Equivalents, Beginning of Period | 2,508,902 | 1,047,740 | |||||
Cash and Cash Equivalents, End of Period | $ | 2,758,398 | $ | 1,280,893 | |||
See notes to condensed consolidated financial statements.
10
KKR & CO. L.P.
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS (Continued) (UNAUDITED)
(Amounts in Thousands)
Three Months Ended March 31, | |||||||
2017 | 2016 | ||||||
Supplemental Disclosures of Cash Flow Information | |||||||
Payments for Interest | $ | 197,242 | $ | 164,818 | |||
Payments for Income Taxes | $ | 9,687 | $ | 11,460 | |||
Supplemental Disclosures of Non-Cash Investing and Financing Activities | |||||||
Non-Cash Contributions of Equity Based Compensation | $ | 111,036 | $ | 63,823 | |||
Non-Cash Contributions from Noncontrolling Interests | $ | 8,564 | $ | — | |||
Debt Obligations - Net Gains (Losses), Translation and Other | $ | (78,860 | ) | $ | (328,860 | ) | |
Tax Effects Resulting from Exchange of KKR Holdings L.P. Units and delivery of KKR & Co. L.P. Common Units | $ | 1,969 | $ | 911 | |||
Changes in Consolidation | |||||||
Cash and Cash Equivalents Held at Consolidated Entities | $ | (1,254 | ) | $ | (355,702 | ) | |
Restricted Cash and Cash Equivalents | $ | — | $ | (145,264 | ) | ||
Investments | $ | (70,403 | ) | $ | (35,967,251 | ) | |
Due From Affiliates | $ | — | $ | 147,427 | |||
Other Assets | $ | — | $ | (622,001 | ) | ||
Debt Obligations | $ | — | $ | (2,813,305 | ) | ||
Due to Affiliates | $ | — | $ | 330,270 | |||
Accounts Payable, Accrued Expenses and Other Liabilities | $ | — | $ | (268,866 | ) | ||
Noncontrolling Interests | $ | (71,657 | ) | $ | (34,190,890 | ) | |
See notes to condensed consolidated financial statements.
11
KKR & CO. L.P.
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (UNAUDITED)
(All Amounts in Thousands, Except Unit, Per Unit Data, and Except Where Noted)
1. ORGANIZATION
KKR & Co. L.P. (NYSE: KKR), together with its consolidated subsidiaries (“KKR”), is a leading global investment firm that manages investments across multiple asset classes including private equity, energy, infrastructure, real estate, growth equity, credit and hedge funds. KKR aims to generate attractive investment returns by following a patient and disciplined investment approach, employing world class people, and driving growth and value creation at the asset level. KKR invests its own capital alongside the capital it manages for fund investors and brings debt and equity investment opportunities to others through its capital markets business.
KKR & Co. L.P. was formed as a Delaware limited partnership on June 25, 2007 and its general partner is KKR Management LLC (the “Managing Partner”). KKR & Co. L.P. is the parent company of KKR Group Limited, which is the non-economic general partner of KKR Group Holdings L.P. (“Group Holdings”), and KKR & Co. L.P. is the sole limited partner of Group Holdings. Group Holdings holds a controlling economic interest in each of (i) KKR Management Holdings L.P. (“Management Holdings”) through KKR Management Holdings Corp., a Delaware corporation which is a domestic corporation for U.S. federal income tax purposes, (ii) KKR Fund Holdings L.P. (“Fund Holdings”) directly and through KKR Fund Holdings GP Limited, a Cayman Island limited company which is a disregarded entity for U.S. federal income tax purposes, and (iii) KKR International Holdings L.P. (“International Holdings”, and together with Management Holdings and Fund Holdings, the “KKR Group Partnerships”) directly and through KKR Fund Holdings GP Limited. Group Holdings also owns certain economic interests in Management Holdings through a wholly owned Delaware corporate subsidiary of KKR Management Holdings Corp. and certain economic interests in Fund Holdings through a Delaware partnership of which Group Holdings is the general partner with a 99% economic interest and KKR Management Holdings Corp. is a limited partner with a 1% economic interest. KKR & Co. L.P., through its indirect controlling economic interests in the KKR Group Partnerships, is the holding partnership for the KKR business.
KKR & Co. L.P. both indirectly controls the KKR Group Partnerships and indirectly holds Class A partner units in each KKR Group Partnership (collectively, “KKR Group Partnership Units”) representing economic interests in KKR’s business. The remaining KKR Group Partnership Units are held by KKR Holdings L.P. (“KKR Holdings”), which is not a subsidiary of KKR. As of March 31, 2017, KKR & Co. L.P. held approximately 56.5% of the KKR Group Partnership Units and principals through KKR Holdings held approximately 43.5% of the KKR Group Partnership Units. The percentage ownership in the KKR Group Partnerships will continue to change as KKR Holdings and/or principals exchange units in the KKR Group Partnerships for KKR & Co. L.P. common units or when KKR & Co. L.P. otherwise issues or repurchases KKR & Co. L.P. common units. The KKR Group Partnerships also have outstanding equity interests that provide for the carry pool and preferred units with economic terms that mirror the preferred units issued by KKR & Co. L.P.
PAAMCO Prisma
On February 6, 2017, KKR and Pacific Alternative Asset Management Company, LLC (“PAAMCO”) announced that they entered into a strategic transaction to create a new liquid alternatives investment firm by combining PAAMCO and KKR Prisma. Under the terms of the agreement, the entire businesses of both PAAMCO and KKR Prisma will be contributed to a newly formed company that will operate independently from KKR, and KKR will retain a 39.9% stake as a long-term strategic partner. This transaction is subject to the satisfaction of customary closing conditions, including the receipt of requisite regulatory approvals.
12
2. SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Basis of Presentation
The accompanying unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements of KKR & Co. L.P. have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“GAAP”) for interim financial information and the instructions to Form 10-Q. The condensed consolidated financial statements (referred to hereafter as the “financial statements”), including these notes, are unaudited and exclude some of the disclosures required in annual financial statements. Management believes it has made all necessary adjustments (consisting of only normal recurring items) such that the financial statements are presented fairly and that estimates made in preparing the financial statements are reasonable and prudent. The operating results presented for interim periods are not necessarily indicative of the results that may be expected for any other interim period or for the entire year. The December 31, 2016 condensed consolidated balance sheet data was derived from audited consolidated financial statements included in KKR’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2016, which include all disclosures required by GAAP. These financial statements should be read in conjunction with the audited consolidated financial statements included in KKR & Co. L.P.’s Annual Report on Form 10-K filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”).
KKR & Co. L.P. consolidates the financial results of the KKR Group Partnerships and their consolidated subsidiaries, which include the accounts of KKR’s investment management and capital markets companies, the general partners of certain unconsolidated investment funds, general partners of consolidated investment funds and their respective consolidated investment funds and certain other entities including CFEs. References in the accompanying financial statements to “principals” are to KKR’s senior employees and non‑employee operating consultants who hold interests in KKR’s business through KKR Holdings.
All intercompany transactions and balances have been eliminated.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of the financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities, the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of fees, expenses and investment income (loss) during the reporting periods. Such estimates include but are not limited to the valuation of investments and financial instruments. Actual results could differ from those estimates, and such differences could be material to the financial statements.
Principles of Consolidation
The types of entities KKR assesses for consolidation include (i) subsidiaries, including management companies, broker-dealers and general partners of investment funds that KKR manages, (ii) entities that have all the attributes of an investment company, like investment funds, (iii) CFEs and (iv) other entities, including entities that employ non-employee operating consultants. Each of these entities is assessed for consolidation on a case by case basis depending on the specific facts and circumstances surrounding that entity.
Pursuant to its consolidation policy, KKR first considers whether an entity is considered a VIE and therefore whether to apply the consolidation guidance under the VIE model. Entities that do not qualify as VIEs are assessed for consolidation as voting interest entities (“VOEs”) under the voting interest model.
KKR’s funds are, for GAAP purposes, investment companies and therefore are not required to consolidate their investments in portfolio companies even if majority-owned and controlled. Rather, the consolidated funds and vehicles reflect their investments at fair value as described below in “Fair Value Measurements.”
An entity in which KKR holds a variable interest is a VIE if any one of the following conditions exist: (a) the total equity investment at risk is not sufficient to permit the legal entity to finance its activities without additional subordinated financial support, (b) the holders of the equity investment at risk (as a group) lack either the direct or indirect ability through voting rights or similar rights to make decisions about a legal entity’s activities that have a significant effect on the success of the legal entity or the obligation to absorb the expected losses or right to receive the expected residual returns, or (c) the voting rights of some investors are disproportionate to their obligation to absorb the expected losses of the legal entity, their rights to receive the expected residual returns of the legal entity, or both and substantially all of the legal entity’s activities either involve or are conducted on behalf of an investor with disproportionately few voting rights. Limited partnerships and other similar entities where unaffiliated limited partners have not been granted (i) substantive participatory rights or (ii) substantive rights to either
13
dissolve the partnership or remove the general partner (“kick-out rights”) are VIEs under condition (b) above. KKR’s investment funds that are not CFEs (i) are generally limited partnerships, (ii) generally provide KKR with operational discretion and control, and (iii) generally have fund investors with no substantive rights to impact ongoing governance and operating activities of the fund, including the ability to remove the general partner, and as such the limited partners do not hold kick-out rights. Accordingly, most of KKR’s investment funds are categorized as VIEs.
KKR consolidates all VIEs in which it is the primary beneficiary. A reporting entity is determined to be the primary beneficiary if it holds a controlling financial interest in a VIE. A controlling financial interest is defined as (a) the power to direct the activities of a VIE that most significantly impact the VIE’s economic performance and (b) the obligation to absorb losses of the VIE that could potentially be significant to the VIE or the right to receive benefits from the VIE that could potentially be significant to the VIE. The consolidation guidance requires an analysis to determine (i) whether an entity in which KKR holds a variable interest is a VIE and (ii) whether KKR’s involvement, through holding interests directly or indirectly in the entity or contractually through other variable interests (for example, management and performance related fees), would give it a controlling financial interest. Performance of that analysis requires the exercise of judgment. Fees earned by KKR that are customary and commensurate with the level of effort required to provide those services, and where KKR does not hold other economic interests in the entity that would absorb more than an insignificant amount of the expected losses or returns of the entity, would not be considered variable interests. KKR factors in all economic interests including interests held through related parties, to determine if it holds a variable interest. KKR determines whether it is the primary beneficiary of a VIE at the time it becomes involved with a VIE and reconsiders that conclusion periodically.
For entities that are determined not to be VIEs, these entities are generally considered VOEs and are evaluated under the voting interest model. KKR consolidates VOEs it controls through a majority voting interest or through other means.
The consolidation assessment, including the determination as to whether an entity qualifies as a VIE or VOE depends on the facts and circumstances surrounding each entity and therefore certain of KKR’s investment funds may qualify as VIEs whereas others may qualify as VOEs.
With respect to CLOs (which are generally VIEs), in its role as collateral manager, KKR generally has the power to direct the activities of the CLO that most significantly impact the economic performance of the entity. In some, but not all cases, KKR, through its residual interest in the CLO may have variable interests that represent an obligation to absorb losses of, or a right to receive benefits from, the CLO that could potentially be significant to the CLO. In cases where KKR has both the power to direct the activities of the CLO that most significantly impact the CLO's economic performance and the obligation to absorb losses of the CLO or the right to receive benefits from the CLO that could potentially be significant to the CLO, KKR is deemed to be the primary beneficiary and consolidates the CLO.
With respect to CMBS vehicles (which are generally VIEs), KKR holds unrated and non-investment grade rated securities issued by the CMBS, which are the most subordinate tranche of the CMBS vehicle. The economic performance of the CMBS is most significantly impacted by the performance of the underlying assets. Thus, the activities that most significantly impact the CMBS economic performance are the activities that most significantly impact the performance of the underlying assets. The special servicer has the ability to manage the CMBS assets that are delinquent or in default to improve the economic performance of the CMBS. KKR generally has the right to unilaterally appoint and remove the special servicer for the CMBS and as such is considered the controlling class of the CMBS vehicle. These rights give KKR the ability to direct the activities that most significantly impact the economic performance of the CMBS. Additionally, as the holder of the most subordinate tranche, KKR is in a first loss position and has the right to receive benefits, including the actual residual returns of the CMBS, if any. In these cases, KKR is deemed to be the primary beneficiary and consolidates the CMBS.
Redeemable Noncontrolling Interests
Redeemable Noncontrolling Interests represent noncontrolling interests of certain investment funds and vehicles that are subject to periodic redemption by fund investors following the expiration of a specified period of time (typically between one and three years), or may be withdrawn subject to a redemption fee during the period when capital may not be otherwise withdrawn. Fund investors interests subject to redemption as described above are presented as Redeemable Noncontrolling Interests in the accompanying condensed consolidated statements of financial condition and presented as Net Income (Loss) Attributable to Redeemable Noncontrolling Interests in the accompanying condensed consolidated statements of operations.
When redeemable amounts become legally payable to fund investors, they are classified as a liability and included in Accounts Payable, Accrued Expenses and Other Liabilities in the accompanying condensed consolidated statements of financial condition. For all consolidated investment vehicles and funds in which redemption rights have not been granted, noncontrolling
14
interests are presented within Equity in the accompanying condensed consolidated statements of financial condition as noncontrolling interests.
Noncontrolling Interests
Noncontrolling interests represent (i) noncontrolling interests in consolidated entities and (ii) noncontrolling interests held by KKR Holdings.
Noncontrolling Interests in Consolidated Entities
Noncontrolling interests in consolidated entities represent the non-redeemable ownership interests in KKR that are held primarily by:
(i) | third party fund investors in KKR’s funds; |
(ii) | third parties entitled to up to 1% of the carried interest received by certain general partners of KKR’s funds and 1% of KKR’s other profits (losses) through and including December 31, 2015; |
(iii) | certain former principals and their designees representing a portion of the carried interest received by the general partners of KKR’s private equity funds that was allocated to them with respect to private equity investments made during such former principals’ tenure with KKR prior to October 1, 2009; |
(iv) | certain principals and former principals representing all of the capital invested by or on behalf of the general partners of KKR’s private equity funds prior to October 1, 2009 and any returns thereon; |
(v) | third parties in KKR’s capital markets business; |
(vi) | holders of exchangeable equity securities representing ownership interests in a subsidiary of a KKR Group Partnership issued in connection with the acquisition of Avoca; and |
(vii) | holders of the 7.375% Series A LLC Preferred Shares of KFN whose rights are limited to the assets of KFN. |
Noncontrolling Interests held by KKR Holdings
Noncontrolling interests held by KKR Holdings include economic interests held by principals in the KKR Group Partnerships. Such principals receive financial benefits from KKR’s business in the form of distributions received from KKR Holdings and through their direct and indirect participation in the value of KKR Group Partnership Units held by KKR Holdings. These financial benefits are not paid by KKR & Co. L.P. and are borne by KKR Holdings.
The following table presents the calculation of noncontrolling interests held by KKR Holdings:
Three Months Ended March 31, | |||||||
2017 | 2016 | ||||||
Balance at the beginning of the period | $ | 4,293,337 | $ | 4,347,153 | |||
Net income (loss) attributable to noncontrolling interests held by KKR Holdings (1) | 216,432 | (271,575 | ) | ||||
Other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax (2) | 4,920 | 3,730 | |||||
Impact of the exchange of KKR Holdings units to KKR & Co. L.P. common units (3) | (35,904 | ) | (29,380 | ) | |||
Equity based compensation | 61,093 | 10,606 | |||||
Capital contributions | 37 | 69 | |||||
Capital distributions | (56,637 | ) | (61,673 | ) | |||
Transfer of interests under common control (See Note 15) | 7,919 | — | |||||
Balance at the end of the period | $ | 4,491,197 | $ | 3,998,930 | |||
(1) | Refer to the table below for calculation of Net income (loss) attributable to noncontrolling interests held by KKR Holdings. |
(2) | Calculated on a pro rata basis based on the weighted average KKR Group Partnership Units held by KKR Holdings during the reporting period. |
15
(3) | Calculated based on the proportion of KKR Holdings units exchanged for KKR & Co. L.P. common units pursuant to the exchange agreement during the reporting period. The exchange agreement provides for the exchange of KKR Group Partnership Units held by KKR Holdings for KKR & Co. L.P. common units. |
Net income (loss) attributable to KKR & Co. L.P. after allocation to noncontrolling interests held by KKR Holdings, with the exception of certain tax assets and liabilities that are directly allocable to KKR Management Holdings Corp., is attributed based on the percentage of the weighted average KKR Group Partnership Units held by KKR and KKR Holdings, each of which hold equity of the KKR Group Partnerships. However, primarily because of the (i) contribution of certain expenses borne entirely by KKR Holdings, (ii) the periodic exchange of KKR Holdings units for KKR & Co. L.P. common units pursuant to the exchange agreement and (iii) the contribution of certain expenses borne entirely by KKR associated with the KKR & Co. L.P. 2010 Equity Incentive Plan (“Equity Incentive Plan”), equity allocations shown in the condensed consolidated statement of changes in equity differ from their respective pro-rata ownership interests in KKR’s net assets.
The following table presents net income (loss) attributable to noncontrolling interests held by KKR Holdings:
Three Months Ended March 31, | |||||||
2017 | 2016 | ||||||
Net income (loss) | $ | 797,894 | $ | (760,336 | ) | ||
Less: Net income (loss) attributable to Redeemable Noncontrolling Interests | 20,933 | (38 | ) | ||||
Less: Net income (loss) attributable to Noncontrolling Interests in consolidated entities | 292,845 | (158,784 | ) | ||||
Less: Net income (loss) attributable to Series A and Series B Preferred Unitholders | 8,341 | — | |||||
Plus: Income tax / (benefit) attributable to KKR Management Holdings Corp. | 19,160 | (9,385 | ) | ||||
Net income (loss) attributable to KKR & Co. L.P. Common Unitholders and KKR Holdings | $ | 494,935 | $ | (610,899 | ) | ||
Net income (loss) attributable to noncontrolling interests held by KKR Holdings | $ | 216,432 | $ | (271,575 | ) | ||
Investments
Investments consist primarily of private equity, real assets, credit, investments of consolidated CFEs, equity method, carried interest and other investments. Investments denominated in currencies other than the entity's functional currency are valued based on the spot rate of the respective currency at the end of the reporting period with changes related to exchange rate movements reflected as a component of Net Gains (Losses) from Investment Activities in the consolidated statements of operations. Security and loan transactions are recorded on a trade date basis. Further disclosure on investments is presented in Note 4 “Investments.”
The following describes the types of securities held within each investment class.
Private Equity - Consists primarily of equity investments in operating businesses, including growth equity investments.
Real Assets - Consists primarily of investments in (i) energy related assets, principally oil and natural gas producing properties, (ii) infrastructure assets, and (iii) real estate, principally residential and commercial real estate assets and businesses.
Credit - Consists primarily of investments in below investment grade corporate debt securities (primarily high yield bonds and syndicated bank loans), distressed and opportunistic debt and interests in unconsolidated CLOs.
Investments of Consolidated CFEs - Consists primarily of (i) investments in below investment grade corporate debt securities (primarily high yield bonds and syndicated bank loans) held directly by the consolidated CLOs and (ii) investments in originated, fixed-rate mortgage loans held directly by the consolidated CMBS vehicles.
Equity Method - Consists primarily of (i) certain investments in private equity funds, real assets funds and credit funds, which are not consolidated and (ii) certain investments in operating companies in which KKR is deemed to exert significant influence under GAAP.
16
Carried Interest - Consists of carried interest from unconsolidated investment funds that are allocated to KKR as the general partner of the investment fund based on cumulative fund performance to date, and where applicable, subject to a preferred return.
Other - Consists primarily of investments in common stock, preferred stock, warrants and options of companies that are not private equity, real assets, credit or investments of consolidated CFEs.
Investments held by Consolidated Investment Funds
The consolidated investment funds are, for GAAP purposes, investment companies and reflect their investments and other financial instruments, including portfolio companies that are majority-owned and controlled by KKR's investment funds, at fair value. KKR has retained this specialized accounting for the consolidated funds in consolidation. Accordingly, the unrealized gains and losses resulting from changes in fair value of the investments and other financial instruments held by the consolidated investment funds are reflected as a component of Net Gains (Losses) from Investment Activities in the condensed consolidated statements of operations.
Certain energy investments are made through consolidated investment funds, including investments in working and royalty interests in oil and natural gas producing properties as well as investments in operating companies that operate in the energy industry. Since these investments are held through consolidated investment funds, such investments are reflected at fair value as of the end of the reporting period.
Investments in operating companies that are held through KKR’s consolidated investment funds are generally classified within private equity investments and investments in working and royalty interests in oil and natural gas producing properties are generally classified as real asset investments.
Energy Investments held directly by KKR
Certain energy investments are made by KKR directly in working and royalty interests in oil and natural gas producing properties and not through investment funds. Oil and natural gas producing activities are accounted for under the successful efforts method of accounting and such working interests are consolidated based on the proportion of the working interests held by KKR. Accordingly, KKR reflects its proportionate share of the underlying statements of financial condition and statements of operations of the consolidated working interests on a gross basis and changes in the value of these working interests are not reflected as unrealized gains and losses in the consolidated statements of operations. Under the successful efforts method, exploration costs, other than the costs of drilling exploratory wells, are charged to expense as incurred. Costs that are associated with the drilling of successful exploration wells are capitalized if proved reserves are found. Lease acquisition costs are capitalized when incurred. Costs associated with the drilling of exploratory wells that do not find proved reserves, geological and geophysical costs and costs of certain nonproducing leasehold costs are charged to expense as incurred.
Expenditures for repairs and maintenance, including workovers, are charged to expense as incurred.
The capitalized costs of producing oil and natural gas properties are depleted on a field-by-field basis using the units-of production method based on the ratio of current production to estimated total net proved oil, natural gas and natural gas liquid reserves. Proved developed reserves are used in computing depletion rates for drilling and development costs and total proved reserves are used for depletion rates of leasehold costs.
Estimated dismantlement and abandonment costs for oil and natural gas properties, net of salvage value, are capitalized at their estimated net present value and amortized on a unit-of-production basis over the remaining life of the related proved developed reserves.
Whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amounts of oil and natural gas properties may not be recoverable, KKR evaluates oil and natural gas properties and related equipment and facilities for impairment on a field-by-field basis. The determination of recoverability is made based upon estimated undiscounted future net cash flows. The amount of impairment loss, if any, is determined by comparing the fair value, as determined by a discounted cash flow analysis, with the carrying value of the related asset. Any impairment in value is recognized when incurred and is recorded in General, Administrative, and Other expense in the condensed consolidated statements of operations.
17
Fair Value Option
For certain investments and other financial instruments, KKR has elected the fair value option. Such election is irrevocable and is applied on a financial instrument by financial instrument basis at initial recognition. KKR has elected the fair value option for certain private equity, real assets, credit, investments of consolidated CFEs, equity method and other financial instruments not held through a consolidated investment fund with gains and losses recorded in net income. Accounting for these investments at fair value is consistent with how KKR accounts for its investments held through consolidated investment funds. Changes in the fair value of such instruments are recognized in Net Gains (Losses) from Investment Activities in the consolidated statements of operations. Interest income on interest bearing credit securities on which the fair value option has been elected is based on stated coupon rates adjusted for the accretion of purchase discounts and the amortization of purchase premiums. This interest income is recorded within Interest Income in the condensed consolidated statements of operations.
Equity Method
For certain investments in entities over which KKR exercises significant influence but which do not meet the requirements for consolidation and for which KKR has not elected the fair value option, KKR uses the equity method of accounting. KKR’s share of earnings (losses) from these investments is reflected as a component of Net Gains (Losses) from Investment Activities in the condensed consolidated statements of operations. For equity method investments, KKR records its proportionate share of the investee's earnings or losses based on the most recently available financial information of the investee, which in certain cases may lag the date of KKR's financial statements by no more than three calendar months. KKR evaluates its equity method investments for which KKR has not elected the fair value option for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amounts of such investments may not be recoverable.
The carrying value of equity method investments in private equity funds, real assets funds and credit funds, which are not consolidated, approximate fair value, because the underlying investments of the unconsolidated investment funds are reported at fair value.
The carrying value of equity method investments in certain operating companies, which KKR is determined to exert significant influence under GAAP and for which KKR has not elected the fair value option, is determined based on the amounts invested by KKR, adjusted for the equity in earnings or losses of the investee allocated based on KKR’s respective ownership percentage, less distributions.
Financial Instruments held by Consolidated CFEs
KKR measures both the financial assets and financial liabilities of the consolidated CFEs in its financial statements using the more observable of the fair value of the financial assets and the fair value of the financial liabilities which results in KKR’s consolidated net income (loss) reflecting KKR’s own economic interests in the consolidated CFEs including (i) changes in the fair value of the beneficial interests retained by KKR and (ii) beneficial interests that represent compensation for services rendered.
For the consolidated CLO entities, KKR has determined that the fair value of the financial assets of the consolidated CLOs is more observable than the fair value of the financial liabilities of the consolidated CLOs. As a result, the financial assets of the consolidated CLOs are being measured at fair value and the financial liabilities are being measured as: (1) the sum of the fair value of the financial assets and the carrying value of any nonfinancial assets that are incidental to the operations of the CLOs less (2) the sum of the fair value of any beneficial interests retained by KKR (other than those that represent compensation for services) and KKR’s carrying value of any beneficial interests that represent compensation for services. The resulting amount is allocated to the individual financial liabilities (other than the beneficial interests retained by KKR).
For the consolidated CMBS vehicles, KKR has determined that the fair value of the financial liabilities of the consolidated CMBS vehicles is more observable than the fair value of the financial assets of the consolidated CMBS vehicles. As a result, the financial liabilities of the consolidated CMBS vehicles are being measured at fair value and the financial assets are being measured in consolidation as: (1) the sum of the fair value of the financial liabilities (other than the beneficial interests retained by KKR), the fair value of the beneficial interests retained by KKR and the carrying value of any nonfinancial liabilities that are incidental to the operations of the CMBS vehicles less (2) the carrying value of any nonfinancial assets that are incidental to the operations of the CMBS vehicles. The resulting amount is allocated to the individual financial assets.
18
Fair Value Measurements
Fair value is the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. Except for certain of KKR's equity method investments (see "Equity Method" above in this Note 2 "Summary of Significant Accounting Policies") and debt obligations (as described in Note 10 "Debt Obligations"), KKR's investments and other financial instruments are recorded at fair value or at amounts whose carrying values approximate fair value. Where available, fair value is based on observable market prices or parameters or derived from such prices or parameters. Where observable prices or inputs are not available, valuation techniques are applied. These valuation techniques involve varying levels of management estimation and judgment, the degree of which is dependent on a variety of factors.
GAAP establishes a hierarchical disclosure framework which prioritizes and ranks the level of market price observability used in measuring financial instruments at fair value. Market price observability is affected by a number of factors, including the type of financial instrument, the characteristics specific to the financial instrument and the state of the marketplace, including the existence and transparency of transactions between market participants. Financial instruments with readily available quoted prices in active markets generally will have a higher degree of market price observability and a lesser degree of judgment used in measuring fair value.
Investments and financial instruments measured and reported at fair value are classified and disclosed based on the observability of inputs used in the determination of fair values, as follows:
Level I - Pricing inputs are unadjusted, quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities as of the measurement date. The types of financial instruments included in this category are publicly-listed equities, credit investments and securities sold short.
Level II - Pricing inputs are other than quoted prices in active markets, which are either directly or indirectly observable as of the measurement date, and fair value is determined through the use of models or other valuation methodologies. The types of financial instruments included in this category are credit investments, investments and debt obligations of consolidated CLO entities, convertible debt securities indexed to publicly-listed securities, less liquid and restricted equity securities and certain over-the-counter derivatives such as foreign currency option and forward contracts.
Level III - Pricing inputs are unobservable for the financial instruments and include situations where there is little, if any, market activity for the financial instrument. The inputs into the determination of fair value require significant management judgment or estimation. The types of financial instruments generally included in this category are private portfolio companies, real assets investments, credit investments, equity method investments for which the fair value option was elected and investments and debt obligations of consolidated CMBS entities.
In certain cases, the inputs used to measure fair value may fall into different levels of the fair value hierarchy. In such cases, the level in the fair value hierarchy within which the fair value measurement in its entirety falls has been determined based on the lowest level input that is significant to the fair value measurement in its entirety. KKR’s assessment of the significance of a particular input to the fair value measurement in its entirety requires judgment and consideration of factors specific to the asset.
A significant decrease in the volume and level of activity for the asset or liability is an indication that transactions or quoted prices may not be representative of fair value because in such market conditions there may be increased instances of transactions that are not orderly. In those circumstances, further analysis of transactions or quoted prices is needed, and a significant adjustment to the transactions or quoted prices may be necessary to estimate fair value.
The availability of observable inputs can vary depending on the financial asset or liability and is affected by a wide variety of factors, including, for example, the type of instrument, whether the instrument has recently been issued, whether the instrument is traded on an active exchange or in the secondary market, and current market conditions. To the extent that valuation is based on models or inputs that are less observable or unobservable in the market, the determination of fair value requires more judgment. Accordingly, the degree of judgment exercised by KKR in determining fair value is greatest for instruments categorized in Level III. The variability and availability of the observable inputs affected by the factors described above may cause transfers between Levels I, II, and III, which KKR recognizes at the beginning of the reporting period.
Investments and other financial instruments that have readily observable market prices (such as those traded on a securities exchange) are stated at the last quoted sales price as of the reporting date. KKR does not adjust the quoted price for these investments, even in situations where KKR holds a large position and a sale could reasonably affect the quoted price.
19
Management’s determination of fair value is based upon the methodologies and processes described below and may incorporate assumptions that are management’s best estimates after consideration of a variety of internal and external factors.
Level II Valuation Methodologies
Credit Investments: These instruments generally have bid and ask prices that can be observed in the marketplace. Bid prices reflect the highest price that KKR and others are willing to pay for an instrument. Ask prices represent the lowest price that KKR and others are willing to accept for an instrument. For financial assets and liabilities whose inputs are based on bid-ask prices obtained from third party pricing services, fair value may not always be a predetermined point in the bid-ask range. KKR’s policy is generally to allow for mid-market pricing and adjusting to the point within the bid-ask range that meets KKR’s best estimate of fair value.
Investments and Debt Obligations of Consolidated CLO Vehicles: Investments of consolidated CLO vehicles are reported within Investments of Consolidated CFEs and are valued using the same valuation methodology as described above for credit investments. Under ASU 2014-13, KKR measures CLO debt obligations on the basis of the fair value of the financial assets of the CLO.
Securities indexed to publicly-listed securities: The securities are typically valued using standard convertible security pricing models. The key inputs into these models that require some amount of judgment are the credit spreads utilized and the volatility assumed. To the extent the company being valued has other outstanding debt securities that are publicly-traded, the implied credit spread on the company’s other outstanding debt securities would be utilized in the valuation. To the extent the company being valued does not have other outstanding debt securities that are publicly-traded, the credit spread will be estimated based on the implied credit spreads observed in comparable publicly-traded debt securities. In certain cases, an additional spread will be added to reflect an illiquidity discount due to the fact that the security being valued is not publicly-traded. The volatility assumption is based upon the historically observed volatility of the underlying equity security into which the convertible debt security is convertible and/or the volatility implied by the prices of options on the underlying equity security.
Restricted Equity Securities: The valuation of certain equity securities is based on an observable price for an identical security adjusted for the effect of a restriction.
Derivatives: The valuation incorporates observable inputs comprising yield curves, foreign currency rates and credit spreads.
Level III Valuation Methodologies
Investments and financial instruments categorized as Level III consist primarily of the following:
Private Equity Investments: KKR generally employs two valuation methodologies when determining the fair value of a private equity investment. The first methodology is typically a market comparables analysis that considers key financial inputs and recent public and private transactions and other available measures. The second methodology utilized is typically a discounted cash flow analysis, which incorporates significant assumptions and judgments. Estimates of key inputs used in this methodology include the weighted average cost of capital for the investment and assumed inputs used to calculate terminal values, such as exit EBITDA multiples. Other inputs are also used in both methodologies. In addition, when a definitive agreement has been executed to sell an investment, KKR generally considers a significant determinant of fair value to be the consideration to be received by KKR pursuant to the executed definitive agreement.
Upon completion of the valuations conducted using these methodologies, a weighting is ascribed to each method, and an illiquidity discount is typically applied where appropriate. The ultimate fair value recorded for a particular investment will generally be within a range suggested by the two methodologies, except that the value may be higher or lower than such range in the case of investments being sold pursuant to an executed definitive agreement.
When determining the weighting ascribed to each valuation methodology, KKR considers, among other factors, the availability of direct market comparables, the applicability of a discounted cash flow analysis, the expected hold period and manner of realization for the investment, and in the case of investments being sold pursuant to an executed definitive agreement, an estimated probability of such sale being completed. These factors can result in different weightings among investments in the portfolio and in certain instances may result in up to a 100% weighting to a single methodology.
20
When an illiquidity discount is to be applied, KKR seeks to take a uniform approach across its portfolio and generally applies a minimum 5% discount to all private equity investments. KKR then evaluates such private equity investments to determine if factors exist that could make it more challenging to monetize the investment and, therefore, justify applying a higher illiquidity discount. These factors generally include (i) whether KKR is unable to sell the portfolio company or conduct an initial public offering of the portfolio company due to the consent rights of a third party or similar factors, (ii) whether the portfolio company is undergoing significant restructuring activity or similar factors and (iii) characteristics about the portfolio company regarding its size and/or whether the portfolio company is experiencing, or expected to experience, a significant decline in earnings. These factors generally make it less likely that a portfolio company would be sold or publicly offered in the near term at a price indicated by using just a market multiples and/or discounted cash flow analysis, and these factors tend to reduce the number of opportunities to sell an investment and/or increase the time horizon over which an investment may be monetized. Depending on the applicability of these factors, KKR determines the amount of any incremental illiquidity discount to be applied above the 5% minimum, and during the time KKR holds the investment, the illiquidity discount may be increased or decreased, from time to time, based on changes to these factors. The amount of illiquidity discount applied at any time requires considerable judgment about what a market participant would consider and is based on the facts and circumstances of each individual investment. Accordingly, the illiquidity discount ultimately considered by a market participant upon the realization of any investment may be higher or lower than that estimated by KKR in its valuations.
In the case of growth equity investments, enterprise values may be determined using the market comparables analysis and discounted cash flow analysis described above. A scenario analysis may also be conducted to subject the estimated enterprise values to a downside, base and upside case, which involves significant assumptions and judgments. A milestone analysis may also be conducted to assess the current level of progress towards value drivers that we have determined to be important, which involves significant assumptions and judgments. The enterprise value in each case may then be allocated across the investment’s capital structure to reflect the terms of the security and subjected to probability weightings. In certain cases, the values of growth equity investments may be based on recent or expected financings.
Real Assets Investments: Real asset investments in infrastructure, energy and real estate are valued using one or more of the discounted cash flow analysis, market comparables analysis and direct income capitalization, which in each case incorporates significant assumptions and judgments. Infrastructure investments are generally valued using the discounted cash flow analysis. Key inputs used in this methodology can include the weighted average cost of capital and assumed inputs used to calculate terminal values, such as exit EBITDA multiples. Energy investments are generally valued using a discounted cash flow analysis. Key inputs used in this methodology that require estimates include the weighted average cost of capital. In addition, the valuations of energy investments generally incorporate both commodity prices as quoted on indices and long-term commodity price forecasts, which may be substantially different from commodity prices on certain indices for equivalent future dates. Certain energy investments do not include an illiquidity discount. Long-term commodity price forecasts are utilized to capture the value of the investments across a range of commodity prices within the energy investment portfolio associated with future development and to reflect a range of price expectations. Real estate investments are generally valued using a combination of direct income capitalization and discounted cash flow analysis. Key inputs used in such methodologies that require estimates include an unlevered discount rate and current capitalization rate. The valuations of real assets investments also use other inputs.
Credit Investments: Credit investments are valued using values obtained from dealers or market makers, and where these values are not available, credit investments are generally valued by KKR based on ranges of valuations determined by an independent valuation firm. Valuation models are based on discounted cash flow analyses, for which the key inputs are determined based on market comparables, which incorporate similar instruments from similar issuers.
Other Investments: With respect to other investments including equity method investments for which the fair value election has been made, KKR generally employs the same valuation methodologies as described above for private equity investments when valuing these other investments.
Investments and Debt Obligations of Consolidated CMBS Vehicles: Under ASU 2014-13, KKR measures CMBS investments, which are reported within Investments of Consolidated CFEs on the basis of the fair value of the financial liabilities of the CMBS. Debt obligations of consolidated CMBS vehicles are valued based on discounted cash flow analyses. The key input is the expected yield of each CMBS security using both observable and unobservable factors, which may include recently offered or completed trades and published yields of similar securities, security-specific characteristics (e.g. securities ratings issued by nationally recognized statistical rating organizations, credit support by other subordinate securities issued by the CMBS and coupon type) and other characteristics.
Key unobservable inputs that have a significant impact on KKR’s Level III investment valuations as described above are included in Note 5 “Fair Value Measurements.” KKR utilizes several unobservable pricing inputs and assumptions in
21
determining the fair value of its Level III investments. These unobservable pricing inputs and assumptions may differ by investment and in the application of KKR’s valuation methodologies. KKR’s reported fair value estimates could vary materially if KKR had chosen to incorporate different unobservable pricing inputs and other assumptions or, for applicable investments, if KKR only used either the discounted cash flow methodology or the market comparables methodology instead of assigning a weighting to both methodologies.
Level III Valuation Process
The valuation process involved for Level III measurements is completed on a quarterly basis and is designed to subject the valuation of Level III investments to an appropriate level of consistency, oversight, and review.
For Private Markets investments classified as Level III, investment professionals prepare preliminary valuations based on their evaluation of financial and operating data, company specific developments, market valuations of comparable companies and other factors. These preliminary valuations are reviewed by an independent valuation firm engaged by KKR to perform certain procedures in order to assess the reasonableness of KKR’s valuations annually for all Level III investments in Private Markets and quarterly for investments other than certain investments, which have values less than pre-set value thresholds and which in the aggregate comprise less than 5% of the total value of KKR’s Level III Private Markets investments. The valuations of certain real asset investments are determined solely by an independent valuation firm without the preparation of preliminary valuations by our investment professionals, and instead such independent valuation firm relies principally on valuation information available to it as a broker or valuation firm. For credit investments and debt obligations of consolidated CMBS vehicles, an independent valuation firm is generally engaged by KKR with respect to investments classified as Level III. The valuation firm either provides a valuation range from which KKR’s investment professionals select a point in the range to determine the preliminary valuation or performs certain procedures in order to assess the reasonableness and provide positive assurance of KKR’s valuations. After reflecting any input from the independent valuation firm, the valuation proposals are submitted to their respective valuation sub-committees.
KKR has a global valuation committee comprised of senior employees including investment professionals and professionals from business operations functions, and includes KKR's Chief Financial Officer, General Counsel and Chief Compliance Officer. The global valuation committee is assisted by valuation sub-committees and investment professionals for each business strategy. All preliminary Level III valuations are reviewed and approved by the valuation sub-committees for private equity, real estate, energy and infrastructure, and credit, as applicable. When Level III valuations are required to be performed on hedge fund investments, a valuation sub-committee for hedge funds reviews these valuations. The valuation sub-committees are responsible for the review and approval of valuations in their respective business lines on a quarterly basis. The members of the valuation sub-committees are comprised of investment professionals, including the heads of each respective strategy, and professionals from business operations functions such as legal, compliance and finance, who are not primarily responsible for the management of the investments.
The global valuation committee provides general oversight of the valuation sub-committees. The global valuation committee is responsible for coordinating and implementing the firm’s valuation process to ensure consistency in the application of valuation principles across portfolio investments and between periods. All valuations are subject to approval by the global valuation committee. When valuations are approved by the global valuation committee after reflecting any input from it, the valuations of Level III investments, as well as the valuations of Level I and Level II investments, are presented to the audit committee of the board of directors of the general partner of KKR & Co. L.P. and are then reported to the board of directors.
Fees and Other
Fees and other consist primarily of (i) transaction fees earned in connection with successful investment transactions and from capital markets activities, (ii) management and incentive fees from providing investment management services to unconsolidated funds, CLOs, other vehicles, and separately managed accounts, (iii) monitoring fees from providing services to portfolio companies, (iv) carried interest allocations to general partners of unconsolidated funds, (v) revenue earned by oil and gas-producing entities that are consolidated and (vi) consulting fees earned by consolidated entities that employ non-employee operating consultants.
22
For the three months ended March 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively, fees and other consisted of the following:
Three Months Ended March 31, | |||||||
2017 | 2016 | ||||||
Management Fees | $ | 161,182 | $ | 156,330 | |||
Transaction Fees | 243,658 | 97,268 | |||||
Monitoring Fees | 36,769 | 28,103 | |||||
Fee Credits | (88,078 | ) | (22,379 | ) | |||
Carried Interest | 335,773 | (116,956 | ) | ||||
Incentive Fees | 273 | (2,008 | ) | ||||
Oil and Gas Revenue | 17,273 | 13,561 | |||||
Consulting Fees | 9,102 | 8,886 | |||||
Total Fees and Other | $ | 715,952 | $ | 162,805 | |||
All revenues presented in the table above, except for oil and gas revenue and certain transaction fees earned by KKR's Capital Markets business, are earned from KKR investment funds and portfolio companies. Consulting fees are earned by certain consolidated entities that employ non-employee operating consultants from providing advisory and other services to portfolio companies and other companies. These fees are separately negotiated with each company for which services are provided and are not shared with KKR.
Management Fees
Management fees are recognized in the period during which the related services are performed in accordance with the contractual terms of the related agreement. Management fees earned from private equity funds and certain investment funds are based upon a percentage of capital committed or capital invested during the investment period, and thereafter generally based on remaining invested capital or net asset value. For certain other investment funds, CLOs, and separately managed accounts, management fees are based upon the net asset value, gross assets or as otherwise defined in the respective agreements.
Management fees received from KKR’s consolidated funds and vehicles are eliminated in consolidation. However, because these amounts are funded by, and earned from, noncontrolling interests, KKR’s allocated share of the net income from KKR’s consolidated funds and vehicles is increased by the amount of fees that are eliminated. Accordingly, the elimination of these fees does not have an effect on the net income (loss) attributable to KKR or KKR partners’ capital.
Transaction Fees
Transaction fees are earned by KKR primarily in connection with successful investment transactions and capital markets activities. Transaction fees are recognized in the period when the transaction closes. Fees are typically paid on or shortly after the closing of a transaction.
In connection with pursuing successful portfolio company investments, KKR receives reimbursement for certain transaction‑related expenses. Transaction‑related expenses, which are reimbursed by third parties, are typically deferred until the transaction is consummated and are recorded in Other Assets on the consolidated statements of financial condition on the date incurred. The costs of successfully completed transactions are borne by the KKR investment funds and included as a component of the investment’s cost basis. Subsequent to closing, investments are recorded at fair value each reporting period as described in the section above titled “Investments”. Upon reimbursement from a third party, the cash receipt is recorded and the deferred amounts are relieved. No fees or expenses are recorded for these reimbursements.
Monitoring Fees
Monitoring fees are earned by KKR for services provided to portfolio companies and are recognized as services are rendered. These fees are generally paid based on a fixed periodic schedule by the portfolio companies either in advance or in arrears and are separately negotiated for each portfolio company.
In connection with the monitoring of portfolio companies and certain unconsolidated funds, KKR receives reimbursement for certain expenses incurred on behalf of these entities. Costs incurred in monitoring these entities are classified as general, administrative and other expenses and reimbursements of such costs are classified as monitoring fees. In addition, certain
23
monitoring fee provisions may provide for a termination payment following an initial public offering or change of control. These termination payments are recognized in the period when the related transaction closes.
Fee Credits
Agreements with the fund investors of certain of its investment funds require KKR to share with these fund investors an agreed upon percentage of certain fees, including monitoring and transaction fees received from portfolio companies (“Fee Credits”). Fund investors receive Fee Credits only with respect to monitoring and transaction fees that are allocable to the fund’s investment in the portfolio company and not, for example, any fees allocable to capital invested through co-investment vehicles. Fee Credits are calculated after deducting certain fund-related expenses and generally amount to 80% for older funds, or 100% for our newer funds, of allocable monitoring and transaction fees after fund-related expenses are recovered, although the actual percentage may vary from fund to fund as well as among different classes of investors within a fund.
Carried Interest
For certain investment fund structures, carried interest is allocated to the general partner based on cumulative fund performance to date, and where applicable, subject to a preferred return to limited partners. At the end of each reporting period, KKR calculates the carried interest that would be due to KKR for each fund, pursuant to the fund agreements, as if the fair value of the underlying investments were realized as of such date, irrespective of whether such amounts have been realized. As the fair value of underlying investments varies between reporting periods, it is necessary to make adjustments to amounts recorded as carried interest to reflect either (a) positive performance resulting in an increase in the carried interest allocated to the general partner or (b) negative performance that would cause the amount due to KKR to be less than the amount previously recognized as revenue, resulting in a negative adjustment to carried interest allocated to the general partner. In each case, it is necessary to calculate the carried interest on cumulative results compared to the carried interest recorded to date and make the required positive or negative adjustments. KKR ceases to record negative carried interest allocations once previously recognized carried interest allocations for a fund have been fully reversed. KKR is not obligated to pay guaranteed returns or hurdles, and therefore, cannot have negative carried interest over the life of a fund. Accrued but unpaid carried interest as of the reporting date is reflected in Investments in the condensed consolidated statements of financial condition.
Incentive Fees
Incentive fees earned on the performance of certain hedge fund structures are recognized based on fund performance, subject to the achievement of minimum return levels, and/or high water marks, in accordance with the respective terms set out in each fund’s governing agreements. Incentive fee rates generally range from 5% to 20%. KKR does not record performance‑based incentive fees until the end of each fund’s measurement period (which is generally one year) when the performance‑based incentive fees become fixed and determinable.
Oil and Gas Revenue Recognition
Oil and gas revenues are recognized when production is sold to a purchaser at fixed or determinable prices, when delivery has occurred and title has transferred and collectability of the revenue is reasonably assured. The oil and gas producing entities consolidated by KKR follow the sales method of accounting for natural gas revenues. Under this method of accounting, revenues are recognized based on volumes sold, which may differ from the volume to which the entity is entitled based on KKR’s working interest. An imbalance is recognized as a liability only when the estimated remaining reserves will not be sufficient to enable the under-produced owners to recoup their entitled share through future production. Under the sales method, no receivables are recorded when these entities have taken less than their share of production and no payables are recorded when it has taken more than its share of production unless reserves are not sufficient.
Consulting Fees
Consulting fees are earned by certain consolidated entities that employ non‑employee operating consultants from providing advisory and other services to portfolio companies and other companies and are recognized as the services are rendered. These fees are separately negotiated with each company for which services are provided and are not shared with KKR.
24
Recently Issued Accounting Pronouncements
Revenue from Contracts with Customers
In May 2014, the FASB issued ASU No. 2014-09, Revenue from Contracts with Customers Topic 606 (“ASU 2014-09”) which has subsequently been amended by ASU 2016-08, ASU 2016-10, and ASU 2016-12. These ASUs outline a single comprehensive model for entities to use in accounting for revenue arising from contracts with customers and supersedes most current revenue recognition guidance, including industry-specific guidance. Revenue recorded under ASU 2014-09 will depict the transfer of promised goods or services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration to which the entity expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods or services. In July 2015, the FASB deferred the effective date of ASU 2014-09 to annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2017. Early adoption will be permitted as of annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2016, including interim reporting periods within those annual periods. A full retrospective or modified retrospective approach is required.
Carried interest is a capital allocation to the general partner based on fund performance, and where applicable, subject to a preferred return to limited partners. KKR has concluded that capital allocation-based carried interest represents income from equity method investments that is not in the scope of ASU 2014-09. Accordingly, in connection with the adoption of ASU 2014-09, KKR will account for such carried interest as a financial instrument under the equity method of accounting within the scope of ASC 323, Investments - Equity Method and Joint Ventures (“ASC 323”). In accordance with ASC 323, KKR will record equity method income (losses) based on the change in KKR’s proportionate claim on the net assets of the investment fund, including performance-based capital allocations, assuming the investment fund was liquidated as of each reporting date pursuant to each investment fund's governing agreements. As carried interest and the related general partner investments are considered to be a single unit of account under KKR’s new accounting policy, the equity method income associated with the general partner interests will be combined with the associated carried interest and reported in a single line within the statement of operations. KKR expects to apply this change in accounting on a full retrospective basis. The pattern and amount of recognition under the new policy is not expected to differ materially from KKR’s existing recognition. As it pertains to incentive fees, KKR expects the recognition of incentive fees, which are a form of variable consideration, to be deferred until such fees are no longer subject to significant reversal, which is consistent with KKR’s existing recognition treatment. Additionally, KKR is currently in the process of implementing the new revenue guidance and is continuing to evaluate the effect this guidance will have on other revenue streams. KKR expects to adopt the new revenue recognition guidance effective January 1, 2018.
Financial Instruments
In January 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-01, Financial Instruments (Topic 825): Recognition and Measurement of Financial Assets and Liabilities (“ASU 2016-01”). The amended guidance (i) requires equity investments (except those accounted for under the equity method of accounting or those that result in consolidation of the investee) to be measured at fair value with changes in fair value recognized in net income; (ii) eliminates the requirement to disclose the method(s) and significant assumptions used to estimate the fair value that is currently required to be disclosed for financial instruments measured at fair value; (iii) requires an entity to present separately in other comprehensive income the portion of the total change in the fair value of a liability resulting from a change in the instrument-specific credit risk when the entity has elected to measure the liability at fair value in accordance with the fair value option for financial instruments and (iv) requires separate presentation of financial assets and financial liabilities by measurement category and form of financial asset (that is, securities or loans and receivables) on the balance sheet or the accompanying notes to the financial statements. ASU 2016-01 is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, including interim periods within those fiscal years. The amended guidance should be applied by means of a cumulative-effect adjustment to the balance sheet as of the beginning of the fiscal year of adoption. The amended guidance related to equity securities without readily determinable fair values (including the disclosure requirements) should be applied prospectively to equity investments that exist as of the date of adoption. KKR is currently evaluating the impact of this guidance on the financial statements.
25
Leases
In February 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-02, Leases (Topic 842). The guidance requires the recognition of lease assets and lease liabilities for those leases classified as operating leases under previous GAAP. The guidance retains a distinction between finance leases and operating leases. The classification criteria for distinguishing between finance leases and operating leases are substantially similar to the classification criteria for distinguishing between capital leases and operating leases under previous GAAP. The recognition, measurement and presentation of expenses and cash flows arising from a lease by a lessee have not changed significantly from previous GAAP. For operating leases, a lessee is required to do the following: (a) recognize a right-of-use asset and a lease liability, initially measured at the present value of the lease payments, in the Statement of Financial Condition, (b) recognize a single lease cost, calculated so that the cost of the lease is allocated over the lease term on a generally straight-line basis, and (c) classify all cash payments within operating activities in the statement of cash flows. The guidance is effective for fiscal periods beginning after December 15, 2018. Early application is permitted. KKR is currently evaluating the impact of this guidance on the financial statements.
Investments
In March 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-07, Investments - Equity Method and Joint Ventures (Topic 323): Simplifying the Transition to the Equity Method of Accounting ("ASU 2016-07"), which simplifies the equity method of accounting by eliminating the requirement to retrospectively apply the equity method to an investment that subsequently qualifies for such accounting as a result of an increase in the level of ownership interest or degree of influence. ASU 2016-07 is effective for all entities for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2016, including interim periods within those fiscal years, with early adoption permitted for all entities. Entities are required to apply the guidance prospectively to increases in the level of ownership interest or degree of influence occurring after the ASU’s effective date. Additional transition disclosures are not required upon adoption. This guidance has been adopted as of January 1, 2017 and did not have a material impact on KKR's results of operations or financial condition.
Equity-Based Compensation
In March 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-09, Compensation - Stock Compensation (Topic 718): Improvements to Employee Shared-Based Payment Accounting ("ASU 2016-09"), which simplifies several aspects of the accounting for employee share-based payment transactions for both public and nonpublic entities, including the accounting for income taxes, forfeitures, and statutory tax withholding requirements, as well as classification in the statement of cash flows. ASU 2016-09 is effective for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2016, including interim periods within those annual reporting periods. KKR adopted ASU 2016-09 on January 1, 2017 and will apply prospective application. In connection with this adoption, the most significant impacts to KKR relate to the following: (i) with respect to the tax impact of equity based compensation charges, KKR has accounted for the difference between the deduction for tax purposes and the compensation cost recognized for financial reporting purposes as an income tax expense or benefit in the statement of operations, (ii) KKR has classified this difference with other income tax cash flows as an operating activity in the statement of cash flows and (iii) KKR has made an election to continue to estimate the number of equity compensation awards that are expected to vest, net of forfeitures, over the life of an equity award and not account for forfeitures as they occur.
Cash Flow Classification
In August 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-15, Statement of Cash Flows (Topic 230): Classification of Certain Cash Receipts and Cash Payments (“ASU 2016-15”), which amends the guidance on the classification of certain cash receipts and payments in the statement of cash flows. The amended guidance adds or clarifies guidance on eight cash flow matters: (i) debt prepayment or debt extinguishment costs, (ii) settlement of zero-coupon debt instruments or other debt instruments with coupon interest rates that are insignificant in relation to the effective interest rate of the borrowing, (iii) contingent consideration payments made after a business combination, (iv) proceeds from the settlement of insurance claims, (v) proceeds from the settlement of corporate-owned life insurance policies, (vi) distributions received from equity method investees, (vii) beneficial interests in securitization transactions and (viii) separately identifiable cash flows and application of the predominance principle. The guidance in the ASU is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, including interim periods within those fiscal years. Early adoption is permitted. The guidance must be applied retrospectively to all periods presented but may be applied prospectively from the earliest date practicable if retrospective application would be impracticable. KKR is currently evaluating the impact of this guidance on the financial statements.
In November 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-18, Statement of Cash Flows (Topic 230): Restricted Cash (“ASU 2016-18”), which amends the guidance to add or clarify guidance on the classification and presentation of restricted cash in the statement of cash flows. The amended guidance requires the following: (i) restricted cash and restricted cash equivalents should
26
be included in the cash and cash-equivalents balances in the statement of cash flows; (ii) changes in restricted cash and restricted cash equivalents that result from transfers between cash, cash equivalents, and restricted cash and restricted cash equivalents should not be presented as cash flow activities in the statement of cash flows; (iii) a reconciliation between the statement of financial position and the statement of cash flows must be disclosed when the statement of financial position includes more than one line item for cash, cash equivalents, restricted cash, and restricted cash equivalents; and (iv) the nature of the restrictions must be disclosed for material restricted cash and restricted cash equivalents amounts. The guidance in this ASU is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, including interim periods therein. Early adoption is permitted. The guidance must be applied retrospectively to all periods presented. KKR is currently evaluating the impact of this guidance on the financial statements.
Income Taxes
In October 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-16, Income Taxes (Topic 740): Intra-entity Transfers of Assets Other Than Inventory ("ASU 2016-16"), which removed the prohibition in ASC 740 against the immediate recognition of the current and deferred income tax effects of intra-entity transfers of assets other than inventory. ASU 2016-16 is effective for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2017, including interim periods within those annual reporting periods. KKR is currently evaluating the impact of this guidance on the financial statements.
Goodwill
In January 2017, the FASB issued ASU No. 2017-04, Intangibles - Goodwill and Other (Topic 350): Simplifying the Test for Goodwill Impairment (“ASU 2017-04”). This guidance simplifies the accounting for goodwill impairments by eliminating the second step from the goodwill impairment test. The ASU requires goodwill impairments to be measured on the basis of the fair value of a reporting unit relative to the reporting unit’s carrying amount rather than on the basis of the implied amount of goodwill relative to the goodwill balance of the reporting unit. The ASU also (i) clarifies the requirements for excluding and allocating foreign currency translation adjustments to reporting units related to an entity’s testing of reporting units for goodwill impairment; and (ii) clarifies that an entity should consider income tax effects from any tax deductible goodwill on the carrying amount of the reporting unit when measuring the goodwill impairment loss, if applicable. The guidance is effective for fiscal periods beginning after December 15, 2019. Early adoption is allowed for entities as of January 1, 2017, for annual and any interim impairment tests occurring after January 1, 2017. KKR is currently evaluating the impact of this guidance on the financial statements.
Clarifying the Definition of a Business
In January 2017, the FASB issued ASU No. 2017-01, Business Combinations (Topic 805): Clarifying the Definition of a Business (“ASU 2017-01”). This guidance amends the definition of a business and provides a threshold which must be considered to determine whether a transaction is an asset acquisition or a business combination. ASU 2017-01 is effective for fiscal years and interim periods beginning after December 15, 2017. Early adoption is permitted. KKR is currently evaluating the impact of this guidance on the financial statements.
Other Income
In February 2017, the FASB issued ASU No. 2017-05, Other Income—Gains and Losses from the Derecognition of Nonfinancial Assets (Subtopic 610-20): Clarifying the Scope of Asset Derecognition Guidance and Accounting for Partial Sales of Nonfinancial Assets ("ASU 2017-05"). The ASU conforms the derecognition guidance on nonfinancial assets with the model for transactions in the new revenue standard (ASC 606, as amended). The effective date of the new guidance is aligned with the requirements in the new revenue standard, which is effective for annual and interim reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2017. The ASU allows an entity to use a full or modified retrospective adoption approach. KKR is currently evaluating the impact of this guidance on the financial statements.
27
3. NET GAINS (LOSSES) FROM INVESTMENT ACTIVITIES
Net Gains (Losses) from Investment Activities in the condensed consolidated statements of operations consist primarily of the realized and unrealized gains and losses on investments (including foreign exchange gains and losses attributable to foreign denominated investments and related activities) and other financial instruments, including those for which the fair value option has been elected. Unrealized gains or losses result from changes in the fair value of these investments and other financial instruments during a period. Upon disposition of an investment or financial instrument, previously recognized unrealized gains or losses are reversed and an offsetting realized gain or loss is recognized in the current period.
The following table summarizes total Net Gains (Losses) from Investment Activities:
Three Months Ended March 31, 2017 | Three Months Ended March 31, 2016 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Net Realized Gains (Losses) | Net Unrealized Gains (Losses) | Total | Net Realized Gains (Losses) | Net Unrealized Gains (Losses) | Total | ||||||||||||||||||
Private Equity (1) | $ | 106,813 | $ | 3,288 | $ | 110,101 | $ | (2,127 | ) | $ | (212,361 | ) | $ | (214,488 | ) | ||||||||
Credit and Other (1) | (222,408 | ) | 448,246 | 225,838 | (40,504 | ) | (237,050 | ) | (277,554 | ) | |||||||||||||
Investments of Consolidated CFEs (1) | (1,103 | ) | 12,983 | 11,880 | (36,989 | ) | 219,184 | 182,195 | |||||||||||||||
Real Assets (1) | 3,060 | 6,798 | 9,858 | 12,355 | (123,138 | ) | (110,783 | ) | |||||||||||||||
Foreign Exchange Forward Contracts and Options (2) | 9,986 | (58,263 | ) | (48,277 | ) | 17,761 | (46,200 | ) | (28,439 | ) | |||||||||||||
Securities Sold Short (2) | 246,787 | 42,270 | 289,057 | 15,159 | (17,335 | ) | (2,176 | ) | |||||||||||||||
Other Derivatives (2) | (5,760 | ) | (4,847 | ) | (10,607 | ) | (16,513 | ) | 4,356 | (12,157 | ) | ||||||||||||
Debt Obligations and Other (3) | 8,789 | (38,191 | ) | (29,402 | ) | 7,575 | (279,396 | ) | (271,821 | ) | |||||||||||||
Net Gains (Losses) From Investment Activities | $ | 146,164 | $ | 412,284 | $ | 558,448 | $ | (43,283 | ) | $ | (691,940 | ) | $ | (735,223 | ) | ||||||||
(1) | See Note 4 "Investments." |
(2) | See Note 8 "Other Assets and Accounts Payable, Accrued Expenses and Other Liabilities." |
(3) | See Note 10 "Debt Obligations." |
4. INVESTMENTS
Investments consist of the following:
March 31, 2017 | December 31, 2016 | ||||||
Private Equity | $ | 3,360,415 | $ | 2,915,667 | |||
Credit | 5,931,557 | 4,847,936 | |||||
Investments of Consolidated CFEs | 14,526,323 | 13,950,897 | |||||
Real Assets | 2,045,587 | 1,807,128 | |||||
Equity Method | 2,830,603 | 2,728,995 | |||||
Carried Interest | 2,495,992 | 2,384,177 | |||||
Other | 3,034,847 | 2,774,965 | |||||
Total Investments | $ | 34,225,324 | $ | 31,409,765 | |||
As of March 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016, there were no investments which represented greater than 5% of total investments. In addition, as of March 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016, investments totaling $17.2 billion and $16.1 billion, respectively, were pledged as direct collateral against various financing arrangements. See Note 10 “Debt Obligations.” The majority of the securities underlying private equity investments represent equity securities.
28
Carried Interest
Carried interest allocated to the general partner in respect of performance of investment funds that are not consolidated were as follows:
Balance at December 31, 2016 | $ | 2,384,177 | ||
Carried Interest Allocated as a result of Changes in Fund Fair Value | 335,773 | |||
Cash Proceeds Received | (223,958 | ) | ||
Balance at March 31, 2017 | $ | 2,495,992 | ||
5. FAIR VALUE MEASUREMENTS
The following tables summarize the valuation of KKR's assets and liabilities by the fair value hierarchy. Carried Interest and Equity Method Investments for which the fair value option has not been elected have been excluded from the tables below.
Assets, at fair value:
March 31, 2017 | |||||||||||||||
Level I | Level II | Level III | Total | ||||||||||||
Private Equity | $ | 1,266,597 | $ | 92,614 | $ | 2,001,204 | $ | 3,360,415 | |||||||
Credit | — | 2,028,534 | 3,903,023 | 5,931,557 | |||||||||||
Investments of Consolidated CFEs | — | 9,099,771 | 5,426,552 | 14,526,323 | |||||||||||
Real Assets | — | — | 2,045,587 | 2,045,587 | |||||||||||
Equity Method | — | 215,431 | 593,227 | 808,658 | |||||||||||
Other | 1,179,786 | 48,680 | 1,806,381 | 3,034,847 | |||||||||||
Total | 2,446,383 | 11,485,030 | 15,775,974 | 29,707,387 | |||||||||||
Foreign Exchange Contracts and Options | — | 176,201 | — | 176,201 | |||||||||||
Other Derivatives | — | 23,632 | 61,603 | (1) | 85,235 | ||||||||||
Total Assets | $ | 2,446,383 | $ | 11,684,863 | $ | 15,837,577 | $ | 29,968,823 | |||||||
December 31, 2016 | |||||||||||||||
Level I | Level II | Level III | Total | ||||||||||||
Private Equity | $ | 1,240,108 | $ | 116,000 | $ | 1,559,559 | $ | 2,915,667 | |||||||
Credit | — | 1,557,575 | 3,290,361 | 4,847,936 | |||||||||||
Investments of Consolidated CFEs | — | 8,544,677 | 5,406,220 | 13,950,897 | |||||||||||
Real Assets | — | — | 1,807,128 | 1,807,128 | |||||||||||
Equity Method | — | 220,896 | 570,522 | 791,418 | |||||||||||
Other | 994,677 | 12,715 | 1,767,573 | 2,774,965 | |||||||||||
Total | 2,234,785 | 10,451,863 | 14,401,363 | 27,088,011 | |||||||||||
Foreign Exchange Contracts and Options | — | 240,627 | — | 240,627 | |||||||||||
Other Derivatives | — | 81,593 | — | 81,593 | |||||||||||
Total Assets | $ | 2,234,785 | $ | 10,774,083 | $ | 14,401,363 | $ | 27,410,231 | |||||||
(1) | Includes derivative assets that were valued using a third party valuation firm. The approach used to estimate the fair value of these derivative assets was generally the discounted cash flow method, which includes consideration of the current portfolio, projected portfolio construction, projected portfolio realizations, portfolio volatility (based on the volatility, correlation, and size of each underlying asset class), and the discounting of future cash flows to the reporting date. |
29
Liabilities, at fair value:
March 31, 2017 | |||||||||||||||
Level I | Level II | Level III | Total | ||||||||||||
Securities Sold Short | $ | 572,993 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 572,993 | |||||||
Foreign Exchange Contracts and Options | — | 69,503 | — | 69,503 | |||||||||||
Unfunded Revolver Commitments | — | 9,201 | — | 9,201 | |||||||||||
Other Derivatives | — | 36,366 | 56,000 | (1) | 92,366 | ||||||||||
Debt Obligations of Consolidated CFEs | — | 8,970,392 | 5,313,570 | 14,283,962 | |||||||||||
Total Liabilities | $ | 572,993 | $ | 9,085,462 | $ | 5,369,570 | $ | 15,028,025 | |||||||
December 31, 2016 | |||||||||||||||
Level I | Level II | Level III | Total | ||||||||||||
Securities Sold Short | $ | 644,196 | $ | 3,038 | $ | — | $ | 647,234 | |||||||
Foreign Exchange Contracts and Options | — | 75,218 | — | 75,218 | |||||||||||
Unfunded Revolver Commitments | — | 9,023 | — | 9,023 | |||||||||||
Other Derivatives | — | 44,015 | 56,000 | (1) | 100,015 | ||||||||||
Debt Obligations of Consolidated CFEs | — | 8,563,547 | 5,294,741 | 13,858,288 | |||||||||||
Total Liabilities | $ | 644,196 | $ | 8,694,841 | $ | 5,350,741 | $ | 14,689,778 | |||||||
(1) | Includes options issued in connection with the acquisition of the 24.9% equity interest in Marshall Wace LLP and its affiliates to increase KKR's ownership interest to 39.9% in periodic increments from 2017 to 2019. The option is valued using a Monte-Carlo simulation valuation methodology. Key inputs used in this methodology that require estimates include Marshall Wace's dividend yield, assets under management volatility and equity volatility. |
30
The following tables summarize changes in investments and debt obligations reported at fair value for which Level III inputs have been used to determine fair value for the three months ended March 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively:
Three Months Ended March 31, 2017 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Level III Investments | Level III Debt Obligations | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Private Equity | Credit | Investments of Consolidated CFEs | Real Assets | Equity Method | Other | Total | Debt Obligations of Consolidated CFEs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance, Beg. of Period | $ | 1,559,559 | $ | 3,290,361 | $ | 5,406,220 | $ | 1,807,128 | $ | 570,522 | $ | 1,767,573 | $ | 14,401,363 | $ | 5,294,741 | |||||||||||||||
Transfers Out Due to Deconsolidation of Funds | — | (95,962 | ) | — | — | — | — | (95,962 | ) | — | |||||||||||||||||||||
Transfers In | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Transfers Out | — | — | — | — | — | (1,496 | ) | (1,496 | ) | — | |||||||||||||||||||||
Asset Purchases / Debt Issuances | 429,644 | 596,862 | — | 250,278 | 9,556 | 15,119 | 1,301,459 | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Sales / Paydowns | (22,629 | ) | (168,858 | ) | (8,940 | ) | (21,677 | ) | (12,678 | ) | (8,128 | ) | (242,910 | ) | — | ||||||||||||||||
Settlements | — | (11,075 | ) | — | — | — | — | (11,075 | ) | (8,940 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||
Net Realized Gains (Losses) | — | (9,243 | ) | — | 3,060 | — | (19,530 | ) | (25,713 | ) | — | ||||||||||||||||||||
Net Unrealized Gains (Losses) | 34,630 | 280,039 | 29,272 | 6,798 | 25,827 | 52,843 | 429,409 | 27,769 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Change in Other Comprehensive Income | — | 20,899 | — | — | — | — | 20,899 | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance, End of Period | $ | 2,001,204 | $ | 3,903,023 | $ | 5,426,552 | $ | 2,045,587 | $ | 593,227 | $ | 1,806,381 | $ | 15,775,974 | $ | 5,313,570 | |||||||||||||||
Changes in Net Unrealized Gains (Losses) Included in Net Gains (Losses) from Investment Activities related to Level III Assets and Liabilities still held as of the Reporting Date | $ | 34,630 | $ | 280,039 | $ | 29,272 | $ | 6,798 | $ | 25,827 | $ | 52,843 | $ | 429,409 | $ | 27,769 | |||||||||||||||
Three Months Ended March 31, 2016 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Level III Investments | Level III Debt Obligations | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Private Equity | Credit | Investments of Consolidated CFEs | Real Assets | Equity Method | Other | Total | Debt Obligations of Consolidated CFEs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance, Beg. of Period | $ | 18,903,538 | $ | 5,012,355 | $ | — | $ | 4,048,281 | $ | 891,606 | $ | 2,581,188 | $ | 31,436,968 | $ | — | |||||||||||||||
Transfers Out Due to Deconsolidation of Funds | (17,806,748 | ) | (710,348 | ) | — | (2,628,999 | ) | — | (2,026,793 | ) | (23,172,888 | ) | — | ||||||||||||||||||
Transfers In | — | 2,447 | 4,343,829 | — | — | — | 4,346,276 | 4,272,081 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Transfers Out | — | — | — | (55,781 | ) | (311,270 | ) | — | (367,051 | ) | — | ||||||||||||||||||||
Asset Purchases / Debt Issuances | 235,541 | 344,055 | 1,026,801 | 224,519 | 8,231 | 33,926 | 1,873,073 | 990,450 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Sales / Paydowns | — | (286,104 | ) | (7,278 | ) | (58,619 | ) | (57,560 | ) | (55,528 | ) | (465,089 | ) | — | |||||||||||||||||
Settlements | — | 1,247 | — | — | — | — | 1,247 | (7,278 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Net Realized Gains (Losses) | — | 11,391 | — | 13,602 | (1,991 | ) | (24,613 | ) | (1,611 | ) | — | ||||||||||||||||||||
Net Unrealized Gains (Losses) | (18,630 | ) | (121,708 | ) | 187,130 | (116,310 | ) | (73,071 | ) | (3,854 | ) | (146,443 | ) | 191,905 | |||||||||||||||||
Change in Other Comprehensive Income | — | 3,241 | — | — | — | — | 3,241 | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance, End of Period | $ | 1,313,701 | $ | 4,256,576 | $ | 5,550,482 | $ | 1,426,693 | $ | 455,945 | $ | 504,326 | $ | 13,507,723 | $ | 5,447,158 | |||||||||||||||
Changes in Net Unrealized Gains (Losses) Included in Net Gains (Losses) from Investment Activities related to Level III Assets and Liabilities still held as of the Reporting Date | $ | (18,630 | ) | $ | (121,708 | ) | $ | 187,130 | $ | (116,310 | ) | $ | (73,071 | ) | $ | (3,854 | ) | $ | (146,443 | ) | $ | 191,905 | |||||||||
31
Total realized and unrealized gains and losses recorded for Level III assets and liabilities are reported in Net Gains (Losses) from Investment Activities in the accompanying condensed consolidated statements of operations.
The following table summarizes the fair value transfers between fair value levels for the three months ended March 31, 2017 and 2016:
Three Months Ended March 31, | ||||||||
2017 | 2016 | |||||||
Assets, at fair value: | ||||||||
Transfers from Level II to Level III (1) | $ | — | $ | 4,346,276 | ||||
Transfers from Level III to Level II (2) | $ | — | $ | 367,051 | ||||
Transfers from Level III to Level I (3) | $ | 1,496 | $ | — | ||||
Liabilities, at fair value: | ||||||||
Transfers from Level II to Level III (4) | $ | — | $ | 4,272,081 | ||||
(1) | Transfers out of Level II into Level III are principally attributable to certain investments that experienced an insignificant level of market activity during the period and thus were valued in the absence of observable inputs. |
(2) | Transfers out of Level III into Level II are principally attributable to certain investments that experienced a higher level of market activity during the period and thus were valued using observable inputs. |
(3) | Transfers out of Level III into Level I are attributable to portfolio companies that are valued using their publicly traded market price. |
(4) | Transfers out of Level II into Level III are principally attributable to debt obligations of CMBS vehicles due to an insignificant level of market activity during the period and thus were valued in the absence of observable inputs. |
32
The following table presents additional information about valuation methodologies and significant unobservable inputs used for investments and debt obligations that are measured at fair value and categorized within Level III as of March 31, 2017:
Fair Value March 31, 2017 | Valuation Methodologies | Unobservable Input(s) (1) | Weighted Average (2) | Range | Impact to Valuation from an Increase in Input (3) | ||||||||
Private Equity | $ | 2,001,204 | |||||||||||
Private Equity | $ | 949,325 | Inputs to market comparables, discounted cash flow and transaction price | Illiquidity Discount | 9.1% | 5.0% - 15.0% | Decrease | ||||||
Weight Ascribed to Market Comparables | 45.3% | 0.0% - 50.0% | (4) | ||||||||||
Weight Ascribed to Discounted Cash Flow | 47.5% | 12.5% - 100.0% | (5) | ||||||||||
Weight Ascribed to Transaction Price | 7.2% | 0.0% - 75.0% | (6) | ||||||||||
Market comparables | Enterprise Value/LTM EBITDA Multiple | 13.2x | 6.4x - 23.2x | Increase | |||||||||
Enterprise Value/Forward EBITDA Multiple | 12.0x | 7.4x - 24.9x | Increase | ||||||||||
Discounted cash flow | Weighted Average Cost of Capital | 10.8% | 8.1% - 14.3% | Decrease | |||||||||
Enterprise Value/LTM EBITDA Exit Multiple | 10.5x | 8.0x - 14.4x | Increase | ||||||||||
Growth Equity | $ | 1,051,879 | Inputs to market comparables, discounted cash flow and milestones | Illiquidity Discount | 14.0% | 10.0% - 20.0% | Decrease | ||||||
Weight Ascribed to Market Comparables | 48.4% | 0.0% - 100.0% | (4) | ||||||||||
Weight Ascribed to Discounted Cash Flow | 22.7% | 0.0% - 100.0% | (5) | ||||||||||
Weight Ascribed to Milestones | 28.9% | 0.0% - 100.0% | (6) | ||||||||||
Scenario Weighting | Base | 53.3% | 30.0% - 80.0% | Increase | |||||||||
Downside | 23.2% | 10.0% - 40.0% | Decrease | ||||||||||
Upside | 23.5% | 10.0% - 33.3% | Increase | ||||||||||
Credit | $ | 3,903,023 | Yield Analysis | Yield | 12.1% | 5.1% - 35.1% | Decrease | ||||||
Net Leverage | 7.3x | 0.6x - 30.5x | Decrease | ||||||||||
EBITDA Multiple | 14.9x | 0.1x - 39.0x | Increase | ||||||||||
Investments of Consolidated CFEs | $ | 5,426,552 | (9) | ||||||||||
Debt Obligations of Consolidated CFEs | $ | 5,313,570 | Discounted cash flow | Yield | 5.5% | 1.9% - 27.1% | Decrease | ||||||
Real Assets | $ | 2,045,587 | (10) | ||||||||||
Energy | $ | 1,067,845 | Discounted cash flow | Weighted Average Cost of Capital | 10.9% | 8.8% - 17.6% | Decrease | ||||||
Average Price Per BOE (8) | $43.01 | $35.68 - $48.46 | Increase | ||||||||||
Real Estate | $ | 808,603 | Inputs to direct income capitalization and discounted cash flow | Weight Ascribed to Direct Income Capitalization | 33.0% | 0.0% - 75.0% | (7) | ||||||
Weight Ascribed to Discounted Cash Flow | 67.0% | 25.0% - 100.0% | (5) | ||||||||||
Direct income capitalization | Current Capitalization Rate | 6.2% | 4.2% - 12.0% | Decrease | |||||||||
Discounted cash flow | Unlevered Discount Rate | 9.3% | 5.5% - 20.0% | Decrease | |||||||||
Other | $ | 1,806,381 | Inputs to market comparables, discounted cash flow and transaction price | Illiquidity Discount | 9.8% | 5.0% - 15.0% | Decrease | ||||||
Weight Ascribed to Market Comparables | 24.5% | 0.0% - 100.0% | (4) | ||||||||||
Weight Ascribed to Discounted Cash Flow | 47.2% | 0.0% - 100.0% | (5) | ||||||||||
Weight Ascribed to Transaction Price | 28.3% | 0.0% - 100.0% | (6) | ||||||||||
Market comparables | Enterprise Value/LTM EBITDA Multiple | 11.5x | 0.1x - 21.0x | Increase | |||||||||
Enterprise Value/Forward EBITDA Multiple | 10.0x | 0.6x - 13.4x | Increase | ||||||||||
Discounted cash flow | Weighted Average Cost of Capital | 11.2% | 5.9% - 17.9% | Decrease | |||||||||
Enterprise Value/LTM EBITDA Exit Multiple | 8.2x | 4.5x - 9.0x | Increase | ||||||||||
33
(1) | In determining certain of these inputs, management evaluates a variety of factors including economic conditions, industry and market developments, market valuations of comparable companies and company specific developments including exit strategies and realization opportunities. Management has determined that market participants would take these inputs into account when valuing the investments and debt obligations. LTM means last twelve months and EBITDA means earnings before interest taxes depreciation and amortization. |
(2) | Inputs were weighted based on the fair value of the investments included in the range. |
(3) | Unless otherwise noted, this column represents the directional change in the fair value of the Level III investments that would result from an increase to the corresponding unobservable input. A decrease to the unobservable input would have the opposite effect. Significant increases and decreases in these inputs in isolation could result in significantly higher or lower fair value measurements. |
(4) | The directional change from an increase in the weight ascribed to the market comparables approach would increase the fair value of the Level III investments if the market comparables approach results in a higher valuation than the discounted cash flow approach and transaction price. The opposite would be true if the market comparables approach results in a lower valuation than the discounted cash flow approach and transaction price. |
(5) | The directional change from an increase in the weight ascribed to the discounted cash flow approach would increase the fair value of the Level III investments if the discounted cash flow approach results in a higher valuation than the market comparables approach, transaction price and direct income capitalization approach. The opposite would be true if the discounted cash flow approach results in a lower valuation than the market comparables approach and transaction price. |
(6) | The directional change from an increase in the weight ascribed to the transaction price or milestones would increase the fair value of the Level III investments if the transaction price results in a higher valuation than the market comparables and discounted cash flow approach. The opposite would be true if the transaction price results in a lower valuation than the market comparables approach and discounted cash flow approach. |
(7) | The directional change from an increase in the weight ascribed to the direct income capitalization approach would increase the fair value of the Level III investments if the direct income capitalization approach results in a higher valuation than the discounted cash flow approach. The opposite would be true if the direct income capitalization approach results in a lower valuation than the discounted cash flow approach. |
(8) | The total energy fair value amount includes multiple investments (in multiple locations throughout North America) that are held in multiple investment funds and produce varying quantities of oil, condensate, natural gas liquids, and natural gas. Commodity price may be measured using a common volumetric equivalent where one barrel of oil equivalent, or BOE, is determined using the ratio of six thousand cubic feet of natural gas to one barrel of oil, condensate or natural gas liquids. The price per BOE is provided to show the aggregate of all price inputs for the various investments over a common volumetric equivalent although the valuations for specific investments may use price inputs specific to the asset for purposes of our valuations. The discounted cash flows include forecasted production of liquids (oil, condensate, and natural gas liquids) and natural gas with a forecasted revenue ratio of approximately 85% liquids and 15% natural gas. |
(9) | KKR measures CMBS investments on the basis of the fair value of the financial liabilities of the CMBS vehicle. See Note 2 "Summary of Significant Accounting Policies." |
(10) | Includes one Infrastructure investment for $169.1 million that was valued using a discounted cash flow analysis. The significant inputs used included the weighted average cost of capital 7.5% and the enterprise value/LTM EBITDA Exit Multiple 11.0x. |
The table above excludes equity method investments in the amount of $593.2 million, comprised primarily of interests in real estate joint ventures, which were valued using Level III value methodologies which are generally the same as those shown for real estate investments.
In the table above, certain private equity investments may be valued at cost for a period of time after an acquisition as the best indicator of fair value. In addition, certain valuations of private equity investments may be entirely or partially derived by reference to observable valuation measures for a pending or consummated transaction.
The various unobservable inputs used to determine the Level III valuations may have similar or diverging impacts on valuation. Significant increases and decreases in these inputs in isolation and interrelationships between those inputs could result in significantly higher or lower fair value measurements as noted in the table above.
34
6. FAIR VALUE OPTION
The following table summarizes the financial instruments for which the fair value option has been elected:
March 31, 2017 | December 31, 2016 | ||||||
Assets | |||||||
Private Equity | $ | 416,604 | $ | 96,721 | |||
Credit | 2,008,481 | 1,392,525 | |||||
Investments of Consolidated CFEs | 14,526,323 | 13,950,897 | |||||
Real Assets | 281,547 | 247,376 | |||||
Equity Method | 808,658 | 791,418 | |||||
Other | 266,499 | 240,343 | |||||
Total | $ | 18,308,112 | $ | 16,719,280 | |||
Liabilities | |||||||
Debt Obligations of Consolidated CFEs | $ | 14,283,962 | $ | 13,858,288 | |||
Total | $ | 14,283,962 | $ | 13,858,288 | |||
The following table presents the realized and net change in unrealized gains (losses) on financial instruments on which the fair value option was elected:
Three Months Ended March 31, 2017 | Three Months Ended March 31, 2016 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Net Realized Gains (Losses) | Net Unrealized Gains (Losses) | Total | Net Realized Gains (Losses) | Net Unrealized Gains (Losses) | Total | ||||||||||||||||||
Assets | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Private Equity | $ | — | $ | 362 | $ | 362 | $ | — | $ | (3,144 | ) | $ | (3,144 | ) | |||||||||
Credit | (239,098 | ) | 55,870 | (183,228 | ) | (5,196 | ) | (45,641 | ) | (50,837 | ) | ||||||||||||
Investments of Consolidated CFEs | (1,103 | ) | 12,983 | 11,880 | (36,989 | ) | 219,184 | 182,195 | |||||||||||||||
Real Assets | (216 | ) | 6,788 | 6,572 | — | 5,240 | 5,240 | ||||||||||||||||
Equity Method | — | 20,362 | 20,362 | (1,991 | ) | (93,293 | ) | (95,284 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Other | (18,799 | ) | 17,281 | (1,518 | ) | (1,816 | ) | (10,502 | ) | (12,318 | ) | ||||||||||||
Total | $ | (259,216 | ) | $ | 113,646 | $ | (145,570 | ) | $ | (45,992 | ) | $ | 71,844 | $ | 25,852 | ||||||||
Liabilities | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Debt Obligations of Consolidated CFEs | 4,825 | (11,058 | ) | (6,233 | ) | — | (267,456 | ) | (267,456 | ) | |||||||||||||
Total | $ | 4,825 | $ | (11,058 | ) | $ | (6,233 | ) | $ | — | $ | (267,456 | ) | $ | (267,456 | ) | |||||||
35
7. NET INCOME (LOSS) ATTRIBUTABLE TO KKR & CO. L.P. PER COMMON UNIT
For the three months ended March 31, 2017 and 2016, basic and diluted Net Income (Loss) attributable to KKR & Co. L.P. per common unit were calculated as follows:
Three Months Ended March 31, | |||||||
2017 | 2016 | ||||||
Net Income (Loss) Attributable to KKR & Co. L.P. Common Unitholders | $ | 259,343 | $ | (329,939 | ) | ||
Basic Net Income (Loss) Per Common Unit | |||||||
Weighted Average Common Units Outstanding - Basic | 453,695,846 | 450,262,143 | |||||
Net Income (Loss) Attributable to KKR & Co. L.P. Per Common Unit - Basic | $ | 0.57 | $ | (0.73 | ) | ||
Diluted Net Income (Loss) Per Common Unit | |||||||
Weighted Average Common Units Outstanding - Basic | 453,695,846 | 450,262,143 | |||||
Weighted Average Unvested Common Units and Other Exchangeable Securities | 42,988,494 | — | |||||
Weighted Average Common Units Outstanding - Diluted | 496,684,340 | 450,262,143 | |||||
Net Income (Loss) Attributable to KKR & Co. L.P. Per Common Unit - Diluted | $ | 0.52 | $ | (0.73 | ) | ||
Weighted Average Common Units Outstanding—Diluted primarily includes unvested equity awards that have been granted under the Equity Incentive Plan as well as exchangeable equity securities issued in connection with the acquisition of Avoca. Vesting or exchanges of these equity interests dilute KKR and KKR Holdings pro rata in accordance with their respective ownership interests in the KKR Group Partnerships.
For the three months ended March 31, 2016, equity awards granted under the Equity Incentive Plan as well as exchangeable equity securities issued in connection with the acquisition of Avoca have been excluded from the calculation of diluted Net Income (Loss) attributable to KKR & Co. L.P. per common unit since these equity awards and exchangeable equity securities would be anti-dilutive, having the effect of decreasing the loss per common unit.
Three Months Ended March 31, | |||||
2017 | 2016 | ||||
Weighted Average KKR Holdings Units Outstanding | 352,586,584 | 360,317,628 | |||
For the three months ended March 31, 2017 and 2016, KKR Holdings units have been excluded from the calculation of Net Income (Loss) attributable to KKR & Co. L.P. per common unit - diluted since the exchange of these units would not dilute KKR’s respective ownership interests in the KKR Group Partnerships.
36
8. OTHER ASSETS AND ACCOUNTS PAYABLE, ACCRUED EXPENSES AND OTHER LIABILITIES
Other Assets consist of the following:
March 31, 2017 | December 31, 2016 | ||||||
Unsettled Investment Sales (1) | $ | 325,187 | $ | 144,600 | |||
Receivables | 174,204 | 49,279 | |||||
Due from Broker (2) | 389,183 | 1,084,602 | |||||
Oil & Gas Assets, net (3) | 270,624 | 276,694 | |||||
Deferred Tax Assets, net | 275,975 | 286,948 | |||||
Interest Receivable | 206,081 | 158,511 | |||||
Fixed Assets, net (4) | 300,646 | 283,262 | |||||
Foreign Exchange Contracts and Options (5) | 176,201 | 240,627 | |||||
Intangible Assets, net (6) | 128,952 | 135,024 | |||||
Goodwill (6) | 89,000 | 89,000 | |||||
Derivative Assets | 85,235 | 81,593 | |||||
Deferred Transaction Related Expenses | 28,684 | 17,688 | |||||
Prepaid Taxes | 46,718 | 46,996 | |||||
Prepaid Expenses | 18,011 | 17,761 | |||||
Deferred Financing Costs | 8,474 | 10,507 | |||||
Other | 76,768 | 73,773 | |||||
Total | $ | 2,599,943 | $ | 2,996,865 | |||
(1) | Represents amounts due from third parties for investments sold for which cash settlement has not occurred. |
(2) | Represents amounts held at clearing brokers resulting from securities transactions. |
(3) | Includes proved and unproved oil and natural gas properties under the successful efforts method of accounting, which is net of impairment write-downs, accumulated depreciation, depletion and amortization. |
(4) | Net of accumulated depreciation and amortization of $145,852 and $141,911 as of March 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016, respectively. Depreciation and amortization expense of $4,197 and $3,916 for the three months ended March 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively, is included in General, Administrative and Other in the accompanying consolidated statements of operations. |
(5) | Represents derivative financial instruments used to manage foreign exchange risk arising from certain foreign currency denominated investments. |
(6) | See Note 16 “Goodwill and Intangible Assets.” |
37
Accounts Payable, Accrued Expenses and Other Liabilities consist of the following:
March 31, 2017 | December 31, 2016 | ||||||
Amounts Payable to Carry Pool (1) | $ | 1,035,671 | $ | 987,994 | |||
Unsettled Investment Purchases (2) | 1,060,496 | 722,076 | |||||
Securities Sold Short (3) | 572,993 | 647,234 | |||||
Derivative Liabilities | 92,366 | 100,015 | |||||
Accrued Compensation and Benefits | 99,709 | 20,764 | |||||
Interest Payable | 120,931 | 114,894 | |||||
Foreign Exchange Contracts and Options (4) | 69,503 | 75,218 | |||||
Accounts Payable and Accrued Expenses | 117,997 | 114,854 | |||||
Deferred Rent | 20,534 | 19,144 | |||||
Taxes Payable | 26,802 | 12,514 | |||||
Redemptions Payable | 589 | 4,021 | |||||
Due to Broker (5) | 36,729 | 83,206 | |||||
Other Liabilities | 82,781 | 79,326 | |||||
Total | $ | 3,337,101 | $ | 2,981,260 | |||
(1) | Represents the amount of carried interest payable to principals, professionals and other individuals with respect to KKR’s active funds and co-investment vehicles that provide for carried interest. |
(2) | Represents amounts owed to third parties for investment purchases for which cash settlement has not occurred. |
(3) | Represents the obligations of KKR to deliver a specified security at a future point in time. Such securities are measured at fair value with changes in fair value recorded in Net Gains (Losses) from Investment Activities in the accompanying consolidated statements of operations. See Note 3 “Net Gains (Losses) from Investment Activities” for the net changes in fair value associated with these instruments. |
(4) | Represents derivative financial instruments used to manage foreign exchange risk arising from certain foreign currency denominated investments. |
(5) | Represents amounts owed for securities transactions initiated at clearing brokers. |
38
9. VARIABLE INTEREST ENTITIES
Consolidated VIEs
KKR consolidates certain VIEs in which it is determined that KKR is the primary beneficiary as described in Note 2 "Summary of Significant Accounting Policies" and which are predominately CFEs and certain investment funds. The primary purpose of these VIEs is to provide strategy specific investment opportunities to earn capital gains, current income or both in exchange for management and performance based fees or carried interest. KKR’s investment strategies for these VIEs differ by product; however, the fundamental risks have similar characteristics, including loss of invested capital and loss of management fees and carried interests. KKR does not provide performance guarantees and has no other financial obligation to provide funding to these consolidated VIEs, beyond amounts previously committed, if any.
Unconsolidated VIEs
KKR holds variable interests in certain VIEs which are not consolidated as it has been determined that KKR is not the primary beneficiary. VIEs that are not consolidated include certain investment funds sponsored by KKR and certain CLO vehicles.
Investments in Unconsolidated Investment Funds
KKR’s investment strategies differ by investment fund; however, the fundamental risks have similar characteristics, including loss of invested capital and loss of management fees and carried interests. KKR’s maximum exposure to loss as a result of its investments in the unconsolidated investment funds is the carrying value of such investments, including KKR's capital interest and any unrealized carried interest, which was approximately $3.8 billion at March 31, 2017. Accordingly, disaggregation of KKR’s involvement by type of unconsolidated investment fund would not provide more useful information. For these unconsolidated investment funds in which KKR is the sponsor, KKR may have an obligation as general partner to provide commitments to such investment funds. As of March 31, 2017, KKR's commitments to these unconsolidated investment funds was $2.7 billion. KKR has not provided any financial support other than its obligated amount as of March 31, 2017.
Investments in Unconsolidated CLO Vehicles
KKR provides collateral management services for, and has made nominal investments in, certain CLO vehicles that it does not consolidate. KKR’s investments in the unconsolidated CLO vehicles, if any, are carried at fair value in the consolidated statements of financial condition. KKR earns management fees, including subordinated collateral management fees, for managing the collateral of the CLO vehicles. As of March 31, 2017, combined assets under management in the pools of unconsolidated CLO vehicles were $0.8 billion. KKR’s maximum exposure to loss as a result of its investments in the residual interests of unconsolidated CLO vehicles is the carrying value of such investments, which was $1.0 million as of March 31, 2017. CLO investors in the CLO vehicles may only use the assets of the CLO to settle the debt of the related CLO, and otherwise have no recourse against KKR for any losses sustained in the CLO structures.
As of March 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016, the maximum exposure to loss, before allocations to the carry pool and noncontrolling interests, if any, for those VIEs in which KKR is determined not to be the primary beneficiary but in which it has a variable interest is as follows:
March 31, 2017 | December 31, 2016 | ||||||
Investments | $ | 3,830,373 | $ | 3,632,162 | |||
Due from (to) Affiliates, net | (47,294 | ) | (60,604 | ) | |||
Maximum Exposure to Loss | $ | 3,783,079 | $ | 3,571,558 | |||
39
10. DEBT OBLIGATIONS
KKR borrows and enters into credit agreements and issues debt for its general operating and investment purposes and certain of its investment funds borrow to meet financing needs of their operating and investing activities. KKR consolidates and reports KFN's debt obligations which are non-recourse to KKR beyond the assets of KFN.
Fund financing facilities have been established for the benefit of certain investment funds. When an investment fund borrows from the facility in which it participates, the proceeds from the borrowings are limited for their intended use by the borrowing investment fund. KKR’s obligations with respect to these financing arrangements are generally limited to KKR’s pro-rata equity interest in such funds.
In addition, certain consolidated CFE vehicles issue debt securities to third party investors which are collateralized by assets held by the CFE vehicle. Debt securities issued by CFEs are supported solely by the assets held at the CFEs and are not collateralized by assets of any other KKR entity. CFEs also may have warehouse facilities with banks to provide liquidity to the CFE. The CFE's debt obligations are non-recourse to KKR beyond the assets of the CFE.
KKR’s borrowings consisted of the following:
March 31, 2017 | December 31, 2016 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Financing Available | Borrowing Outstanding | Fair Value | Financing Available | Borrowing Outstanding | Fair Value | |||||||||||||||||||
Revolving Credit Facilities: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Corporate Credit Agreement | $ | 1,000,000 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 1,000,000 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||||||
KCM Credit Agreement | 500,000 | — | — | 500,000 | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
Notes Issued: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
KKR Issued 6.375% Notes Due 2020 (1) | — | 497,950 | 562,475 | (10) | — | 497,804 | 562,960 | (10) | ||||||||||||||||
KKR Issued 5.500% Notes Due 2043 (2) | — | 491,242 | 521,560 | (10) | — | 491,158 | 502,800 | (10) | ||||||||||||||||
KKR Issued 5.125% Notes Due 2044 (3) | — | 990,101 | 990,320 | (10) | — | 990,009 | 955,240 | (10) | ||||||||||||||||
KFN Issued 5.500% Notes Due 2032 (4) | — | 367,845 | 367,845 | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
KFN Issued 7.500% Notes Due 2042 (5) | — | 122,908 | 117,576 | (11) | — | 123,008 | 116,699 | (11) | ||||||||||||||||
KFN Issued Junior Subordinated Notes (6) | — | 234,979 | 200,793 | — | 250,154 | 210,084 | ||||||||||||||||||
Other Consolidated Debt Obligations: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Fund Financing Facilities and Other (7) | 1,929,633 | 2,636,452 | 2,636,452 | (12) | 2,039,532 | 2,333,654 | 2,333,654 | (12) | ||||||||||||||||
CLO Senior Secured Notes (8) | — | 8,692,761 | 8,692,761 | — | 8,279,812 | 8,279,812 | ||||||||||||||||||
CLO Subordinated Notes (8) | — | 277,631 | 277,631 | — | 283,735 | 283,735 | ||||||||||||||||||
CMBS Debt Obligations (9) | — | 5,313,570 | 5,313,570 | — | 5,294,741 | 5,294,741 | ||||||||||||||||||
$ | 3,429,633 | $ | 19,625,439 | $ | 19,680,983 | $ | 3,539,532 | $ | 18,544,075 | $ | 18,539,725 | |||||||||||||
(1) | $500 million aggregate principal amount of 6.375% senior notes of KKR due 2020. Borrowing outstanding is presented net of i) unamortized note discount and ii) unamortized debt issuance costs of $1.3 million and $1.4 million as of March 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016, respectively. |
(2) | $500 million aggregate principal amount of 5.500% senior notes of KKR due 2043. Borrowing outstanding is presented net of i) unamortized note discount and ii) unamortized debt issuance costs of $3.8 million and $3.9 million as of March 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016, respectively. |
(3) | $1.0 billion aggregate principal amount of 5.125% senior notes of KKR due 2044. Borrowing outstanding is presented net of i) unamortized note discount (net of premium) and ii) unamortized debt issuance costs of $8.6 million and $8.6 million as of March 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016, respectively. |
(4) | KKR consolidates KFN and thus reports KFN’s outstanding $375 million aggregate principal amount of 5.500% senior unsecured notes due 2032. Borrowing outstanding is presented net of i) unamortized note discount and ii) unamortized debt issuance costs of $4.5 million as of March 31, 2017. These debt obligations are classified as Level III within the fair value hierarchy and valued using the same valuation methodologies as KKR’s Level III credit investments. |
(5) | KKR consolidates KFN and thus reports KFN’s outstanding $115 million aggregate principal amount of 7.500% senior notes due 2042. Borrowing outstanding is presented net of unamortized note premium as of March 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016. |
(6) | KKR consolidates KFN and thus reports KFN’s outstanding $264.8 million aggregate principal amount of junior subordinated notes. The weighted average interest rate is 3.5% and the weighted average years to maturity is 20.0 years as of March 31, 2017. These debt obligations are classified as Level III within the fair value hierarchy and valued using the same valuation methodologies as KKR’s Level III credit investments. |
40
(7) | Certain of KKR’s consolidated investment funds have entered into financing arrangements with major financial institutions, generally to enable such investment funds to make investments prior to or without receiving capital from fund limited partners. The weighted average interest rate is 2.8% and 2.4% as of March 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016, respectively. In addition, the weighted average years to maturity is 3.6 years and 2.4 years as of March 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016, respectively. |
(8) | CLO debt obligations are carried at fair value and are classified as Level II within the fair value hierarchy. See Note 5 “Fair Value Measurements.” |
(9) | CMBS debt obligations are carried at fair value and are classified as Level III within the fair value hierarchy. See Note 5 “Fair Value Measurements.” |
(10) | The notes are classified as Level II within the fair value hierarchy and fair value is determined by third party broker quotes. |
(11) | The notes are classified as Level I within the fair value hierarchy and fair value is determined by quoted prices in active markets since the debt is publicly listed. See Note 19 "Subsequent Events." |
(12) | Carrying value approximates fair value given the fund financing facilities’ interest rates are variable. |
Notes Issued
KFN Issued 5.500% Notes Due 2032
On March 30, 2017, KFN issued $375.0 million par amount of 5.500% Senior Unsecured Notes (“KFN 2032 Senior Unsecured Notes”) in a private placement, resulting in net proceeds to KFN of $368.6 million. Interest on the KFN 2032 Senior Unsecured Notes is payable semi-annually on March 30th and September 30th. The KFN 2032 Senior Unsecured Notes will mature on March 30, 2032. KFN may redeem the KFN 2032 Senior Unsecured Notes in whole, but not in part, at a redemption price equal to 100% of the outstanding principal amount plus accrued and unpaid interest to, but excluding, the date of redemption on or after March 30, 2022 and annually thereafter, after providing notice to noteholders of such redemption not less than 30 and no more than 60 business days prior to such redemption date. At any time prior to March 30, 2022, KFN may redeem the KFN 2032 Senior Unsecured Notes in whole, but not in part, at a redemption price equal to (i) 100% of the outstanding principal amount, (ii) plus accrued and unpaid interest to, but excluding, the date of redemption, (iii) plus the excess, if any, of (a) the sum of the present values of the remaining scheduled payments of principal and interest on the Notes (as if the Notes matured on March 30, 2022), discounted to the redemption date on a semi-annual basis (assuming a 360-day year of twelve 30-day months) at a rate equal to the sum of the applicable treasury rate plus 50 basis points, minus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, on the KFN 2032 Senior Unsecured Notes being redeemed to, but excluding, the redemption date over (b) the principal amount of the KFN 2032 Senior Unsecured Notes being redeemed.
Other Consolidated Debt Obligations
Debt Obligations of Consolidated CFEs
As of March 31, 2017, debt obligations of consolidated CFEs consisted of the following:
Borrowing Outstanding | Weighted Average Interest Rate | Weighted Average Remaining Maturity in Years | ||||||
Senior Secured Notes of Consolidated CLOs | $ | 8,692,761 | 2.6 | % | 10.9 | |||
Subordinated Notes of Consolidated CLOs | 277,631 | (1) | 11.3 | |||||
Debt Obligations of Consolidated CMBS Vehicles | 5,313,570 | 4.4 | % | 31.8 | ||||
$ | 14,283,962 | |||||||
(1) | The subordinated notes do not have contractual interest rates but instead receive a pro rata amount of the net distributions from the excess cash flows of the respective CLO vehicle. Accordingly, weighted average borrowing rates for the subordinated notes are based on cash distributions during the period, if any. |
Debt obligations of consolidated CFEs are collateralized by assets held by each respective CFE vehicle and assets of one CFE vehicle may not be used to satisfy the liabilities of another. As of March 31, 2017, the fair value of the consolidated CFE assets was $16.1 billion. This collateral consisted of Cash and Cash Equivalents Held at Consolidated Entities, Investments, and Other Assets.
41
11. INCOME TAXES
The consolidated entities of KKR are generally treated as partnerships or disregarded entities for U.S. and non-U.S. tax purposes. The taxes payable on the income generated by partnerships and disregarded entities are generally paid by the fund investors, unitholders, principals and other third parties who beneficially own such partnerships and disregarded entities and are generally not payable by KKR. However, certain consolidated entities are or are treated as corporations for U.S. and non-U.S. tax purposes and are therefore subject to U.S. federal, state and/or local income taxes and/or non-U.S. taxes at the entity-level. In addition, certain consolidated entities which are treated as partnerships for U.S. tax purposes are subject to the New York City Unincorporated Business Tax or other local taxes.
The effective tax rates were 4.84% and (0.25)% for the three months ended March 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively. The effective tax rate differs from the statutory rate primarily due to the following: (i) a substantial portion of the reported net income (loss) before taxes is not attributable to KKR but rather is attributable to noncontrolling interests held in KKR’s consolidated entities by KKR Holdings or by third parties, (ii) a significant portion of the amount of the reported net income (loss) before taxes attributable to KKR is from certain entities that are not subject to U.S. federal, state or local income taxes and/or non-U.S. taxes, and (iii) certain compensation charges attributable to KKR are not deductible for tax purposes.
During the three month period ended March 31, 2017, there were no material changes to KKR’s uncertain tax positions and KKR believes there will be no significant increase or decrease to the uncertain tax positions within 12 months of the reporting date.
42
12. EQUITY BASED COMPENSATION
The following table summarizes the expense associated with equity based compensation for the three months ended March 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively.
Three Months Ended March 31, | |||||||
2017 | 2016 | ||||||
Equity Incentive Plan Units | $ | 49,943 | $ | 49,961 | |||
KKR Holdings Principal Awards | 44,979 | 6,548 | |||||
Other Exchangeable Securities | — | 3,256 | |||||
Discretionary Compensation | 16,114 | 4,058 | |||||
Total | $ | 111,036 | $ | 63,823 | |||
Equity Incentive Plan
Under the Equity Incentive Plan, KKR is permitted to grant equity awards representing ownership interests in KKR & Co. L.P. common units. Vested awards under the Equity Incentive Plan dilute KKR & Co. L.P. common unitholders and KKR Holdings pro rata in accordance with their respective percentage interests in the KKR Group Partnerships.
The total number of common units that may be issued under the Equity Incentive Plan is equivalent to 15% of the number of fully diluted common units outstanding, subject to annual adjustment. Equity awards have been granted under the Equity Incentive Plan and are generally subject to service based vesting, typically over a three to five year period from the date of grant. In certain cases, these awards are subject to transfer restrictions and/or minimum retained ownership requirements. The transfer restriction period, if applicable, lasts for (i) one year with respect to one-half of the interests vesting on any vesting date and (ii) two years with respect to the other one-half of the interests vesting on such vesting date. While providing services to KKR, if applicable, certain of these awards are also subject to minimum retained ownership rules requiring the award recipient to continuously hold common unit equivalents equal to at least 15% of their cumulatively vested awards that have the minimum retained ownership requirement.
Expense associated with the vesting of these awards is based on the closing price of the KKR & Co. L.P. common units on the date of grant, discounted for the lack of participation rights in the expected distributions on unvested units. Beginning with the financial results reported for the first quarter of 2017, KKR intends to make quarterly distributions to common unitholders of $0.17 per common unit per quarter or $0.68 per year. Therefore, for units granted on or after January 1, 2017, the discount for lack of participation rights in the expected distributions on unvested units is based on the $0.68 annual distribution. KKR has made equal quarterly distributions to holders of its common units of $0.16 per common unit per quarter or $0.64 per year in respect of financial results reported for the first quarter of 2016 through the fourth quarter of 2016. Accordingly, for units granted subsequent to December 31, 2015 but before January 1, 2017, the discount for the lack of participation rights in the expected distributions on unvested units was based on the $0.64 annual distribution. The discount range for awards granted prior to December 31, 2015 was based on management’s estimates of future distributions that the unvested equity awards would not be entitled to receive between the grant date and the vesting date which ranged from 8% to 56%.
Expense is recognized on a straight line basis over the life of the award and assumes a forfeiture rate of up to 8% annually based upon expected turnover by class of recipient.
43
As of March 31, 2017, there was approximately $341.5 million of estimated unrecognized expense related to unvested awards. That cost is expected to be recognized as follows:
Year | Unrecognized Expense (in millions) | |||
2017 | $ | 126.7 | ||
2018 | 123.9 | |||
2019 | 70.8 | |||
2020 | 18.8 | |||
2021 | 1.3 | |||
Total | $ | 341.5 | ||
A summary of the status of unvested awards granted under the Equity Incentive Plan from January 1, 2017 through March 31, 2017 is presented below:
Units | Weighted Average Grant Date Fair Value | |||||
Balance, January 1, 2017 | 37,498,333 | $ | 13.85 | |||
Granted | 1,314,929 | 14.34 | ||||
Vested | (91 | ) | 15.02 | |||
Forfeited | (282,598 | ) | 13.97 | |||
Balance, March 31, 2017 | 38,530,573 | $ | 13.87 | |||
The weighted average remaining vesting period over which unvested awards are expected to vest is 1.3 years.
A summary of the remaining vesting tranches of awards granted under the Equity Incentive Plan is presented below:
Vesting Date | Units | ||
April 1, 2017 | 8,284,291 | ||
October 1, 2017 | 3,691,353 | ||
April 1, 2018 | 10,292,257 | ||
October 1, 2018 | 3,093,771 | ||
April 1, 2019 | 6,988,171 | ||
October 1, 2019 | 1,643,236 | ||
April 1, 2020 | 3,663,683 | ||
October 1, 2020 | 365,351 | ||
April 1, 2021 | 508,460 | ||
38,530,573 | |||
KKR Holdings Awards
KKR Holdings units are exchangeable for KKR Group Partnership Units and allow for their exchange into common units of KKR & Co. L.P. on a one-for one basis. As of March 31, 2017 and 2016, KKR Holdings owned approximately 43.5% or 350,909,471 and 44.6%, or 358,815,903 units respectively, of outstanding KKR Group Partnership Units. Awards for KKR Holdings units that have been granted are generally subject to service based vesting, typically over a three to five year period from the date of grant. They are also subject to transfer restrictions which last for (i) one year with respect to one-half of the interests vesting on any vesting date and (ii) two years with respect to the other one-half of the interests vesting on such vesting date. While providing services to KKR, the recipients are also subject to minimum retained ownership rules requiring them to continuously hold 25% of their vested interests. Upon separation from KKR, award recipients are subject to the terms of a confidentiality and restrictive covenants agreement that would require the forfeiture of certain vested and unvested units should the terms of the agreement be violated. Holders of KKR Holdings units are not entitled to participate in distributions made on KKR Group Partnership Units underlying their KKR Holdings units until such units are vested.
44
Because KKR Holdings is a partnership, all of the 350,909,471 KKR Holdings units have been legally allocated, but the allocation of 7,559,065 of these units has not been communicated to each respective principal and the final allocation and terms of vesting for these units are subject to change and the exercise of judgment by the general partner of KKR Holdings. It was therefore determined that the grant date and service inception date had not occurred and these units do not yet meet the criteria for recognition of compensation expense.
The fair value of awards granted out of KKR Holdings is generally based on the closing price of KKR & Co L.P. common units on the date of grant. KKR determined this to be the best evidence of fair value as a KKR & Co. L.P. common unit is traded in an active market and has an observable market price. Additionally, a KKR Holdings unit is an instrument with terms and conditions similar to those of a KKR & Co. L.P. common unit. Specifically, units in both KKR Holdings and KKR & Co. L.P. represent ownership interests in KKR Group Partnership Units and, subject to any vesting, minimum retained ownership requirements and transfer restrictions, each KKR Holdings unit is exchangeable into a KKR Group Partnership Unit and then into a KKR & Co. L.P. common unit on a one-for-one basis.
In February 2016, approximately 28.9 million KKR Holdings units were granted that were originally subject to market condition and service-based vesting that were subsequently modified in November 2016 to eliminate the market condition vesting and instead require only service-based vesting in equal annual installments over a five year period. At the date of modification, total future compensation expense amounted to $320.9 million, net of estimated forfeitures, to be recognized over the remaining vesting period of the modified awards.
The awards described above were granted from outstanding but previously unallocated units of KKR Holdings, and consequently these grants did not increase the number of KKR Holdings units outstanding or outstanding KKR common units on a fully-diluted basis. If and when vested, these awards will not dilute KKR's respective ownership interests in the KKR Group Partnerships.
KKR Holdings Awards give rise to equity-based compensation in the consolidated statements of operations based on the grant-date fair value of the award discounted for the lack of participation rights in the expected distributions on unvested units. Beginning with the financial results reported for the first quarter of 2017, KKR intends to make quarterly distributions to common unitholders of $0.17 per common unit per quarter or $0.68 per year. Therefore, for awards granted on or after January 1, 2017, the discount for lack of participation rights in the expected distributions on unvested units is based on the $0.68 annual distribution. KKR has made equal quarterly distributions to holders of its common units of $0.16 per common unit per quarter or $0.64 per year in respect of financial results reported for the first quarter of 2016 through the fourth quarter of 2016. Accordingly, for awards granted subsequent to December 31, 2015 but before January 1, 2017, the discount for the lack of participation rights in the expected distributions on unvested units was based on the $0.64 annual distribution.
Expense is recognized on a straight line basis over the life of the award and assumes a forfeiture rate of up to 8% annually based on expected turnover by class of recipient.
As of March 31, 2017, there was approximately $263.6 million of estimated unrecognized expense related to unvested KKR Holdings awards. That cost is expected to be recognized as follows:
Year | Unrecognized Expense (in millions) | |||
2017 | 61.5 | |||
2018 | 67.2 | |||
2019 | 61.0 | |||
2020 | 55.8 | |||
2021 | 18.1 | |||
Total | $ | 263.6 | ||
45
A summary of the status of unvested awards granted under the KKR Holdings Plan from January 1, 2017 through March 31, 2017 is presented below:
Units | Weighted Average Grant Date Fair Value | |||||
Balance, January 1, 2017 | 28,245,886 | $ | 12.10 | |||
Granted | — | — | ||||
Vested | — | — | ||||
Forfeited | — | — | ||||
Balance, March 31, 2017 | 28,245,886 | $ | 12.10 | |||
The weighted average remaining vesting period over which unvested awards are expected to vest is 2.0 years.
A summary of the remaining vesting tranches of awards granted under the KKR Holdings Plan is presented below:
Vesting Date | Units | ||
April 1, 2017 | 768,939 | ||
May 1, 2017 | 5,200,000 | ||
October 1, 2017 | 111,293 | ||
April 1, 2018 | 824,999 | ||
May 1, 2018 | 5,200,000 | ||
April 1, 2019 | 349,143 | ||
May 1, 2019 | 5,200,000 | ||
April 1, 2020 | 191,512 | ||
May 1, 2020 | 5,200,000 | ||
May 1, 2021 | 5,200,000 | ||
28,245,886 | |||
Other Exchangeable Securities
As of October 1, 2016, all equity securities of a subsidiary of a KKR Group Partnership and of KKR & Co. L.P. both of which are exchangeable into common units of KKR & Co. L.P. on a one-for-one basis issued in connection with the acquisition of Avoca ("Other Exchangeable Securities") have either vested or forfeited, and there is no unrecognized expense associated with Other Exchangeable Securities as of March 31, 2017.
Discretionary Compensation
KKR employees and certain employees of certain consolidated entities are eligible to receive discretionary cash bonuses. While cash bonuses paid to most employees are borne by KKR and certain consolidated entities and result in customary compensation and benefits expense, cash bonuses that are paid to certain principals are currently borne by KKR Holdings. These compensation charges are currently recorded based on the amount of cash expected to be paid by KKR Holdings.
46
13. RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
Due from Affiliates consists of:
March 31, 2017 | December 31, 2016 | ||||||
Amounts due from portfolio companies | $ | 108,303 | $ | 66,940 | |||
Amounts due from unconsolidated investment funds | 207,390 | 170,219 | |||||
Amounts due from related entities | 7,642 | 13,293 | |||||
Due from Affiliates | $ | 323,335 | $ | 250,452 | |||
Due to Affiliates consists of:
March 31, 2017 | December 31, 2016 | ||||||
Amounts due to KKR Holdings in connection with the tax receivable agreement | $ | 130,153 | $ | 128,091 | |||
Amounts due to unconsolidated investment funds | 254,684 | 230,823 | |||||
Amounts due to related entities | 537 | 565 | |||||
Due to Affiliates | $ | 385,374 | $ | 359,479 | |||
47
14. SEGMENT REPORTING
KKR operates through four reportable business segments. These segments, which are differentiated primarily by their business objectives and investment strategies, are presented below. These financial results represent the combined financial results of the KKR Group Partnerships on a segment basis. KKR earns the majority of its fees from subsidiaries located in the United States.
Private Markets
Through KKR’s Private Markets segment, KKR manages and sponsors private equity funds and co-investment vehicles, which invest capital for long-term appreciation, either through controlling ownership of a company or strategic minority positions. KKR also manages and sponsors investment funds and co-investment vehicles that invest capital in real assets, such as infrastructure, energy and real estate, and growth equity investments.
Public Markets
KKR operates and reports its combined credit and hedge funds businesses through the Public Markets segment. KKR’s credit business invests capital in leveraged credit strategies, such as leveraged loans and high yield bonds, and alternative credit strategies such as special situations, mezzanine or corporate credit opportunities, direct lending, and revolving credit. KKR’s Public Markets segment also includes its hedge funds business, which includes customized hedge fund portfolios, hedge fund-of-fund solutions and strategic partnerships consisting of minority stakes in other hedge fund managers.
Capital Markets
KKR’s global capital markets business supports the firm, portfolio companies, and third-party clients by developing and implementing both traditional and non-traditional capital solutions for investments or companies seeking financing. These services include arranging debt and equity financing for transactions, placing and underwriting securities offerings and providing other types of capital markets services.
Principal Activities
Through KKR's Principal Activities segment, we manage the firm’s assets and deploy capital to support and grow our businesses.
KKR's Principal Activities segment uses its balance sheet assets to support KKR's investment management and capital markets businesses, including to make capital commitments as general partner to its funds, to seed new businesses or investments for new funds or to bridge capital selectively for its funds’ investments.
The Principal Activities segment also provides the required capital to fund the various commitments of KKR's Capital Markets business or to meet regulatory capital requirements.
Key Performance Measure - Economic Net Income (“ENI”)
ENI is used by management in making operating and resource deployment decisions as well as assessing the overall performance of each of KKR’s reportable business segments. The reportable segments for KKR’s business are presented prior to giving effect to the allocation of income (loss) between KKR & Co. L.P. and KKR Holdings and as such represents the business in total. In addition, KKR’s reportable segments are presented without giving effect to the consolidation of the funds that KKR manages.
ENI is a measure of profitability for KKR’s reportable segments and is used by management as an alternative measurement of the operating and investment earnings of KKR and its business segments. ENI is comprised of total segment revenues; less total segment expenses and certain economic interests in KKR’s segments held by third parties.
48
The following tables present the financial data for KKR’s reportable segments:
As of and for the Three Months Ended March 31, 2017 | |||||||||||||||||||
Private Markets | Public Markets | Capital Markets | Principal Activities | Total Reportable Segments | |||||||||||||||
Segment Revenues | |||||||||||||||||||
Management, Monitoring and Transaction Fees, Net | |||||||||||||||||||
Management Fees | $ | 123,512 | $ | 84,772 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 208,284 | |||||||||
Monitoring Fees | 13,220 | — | — | — | 13,220 | ||||||||||||||
Transaction Fees | 117,882 | 4,056 | 121,097 | — | 243,035 | ||||||||||||||
Fee Credits | (85,650 | ) | (3,367 | ) | — | — | (89,017 | ) | |||||||||||
Total Management, Monitoring and Transaction Fees, Net | 168,964 | 85,461 | 121,097 | — | 375,522 | ||||||||||||||
Performance Income (Loss) | |||||||||||||||||||
Realized Incentive Fees | — | 1,686 | — | — | 1,686 | ||||||||||||||
Realized Carried Interest | 206,204 | — | — | — | 206,204 | ||||||||||||||
Unrealized Carried Interest | 123,506 | 17,120 | — | — | 140,626 | ||||||||||||||
Total Performance Income (Loss) | 329,710 | 18,806 | — | — | 348,516 | ||||||||||||||
Investment Income (Loss) | |||||||||||||||||||
Net Realized Gains (Losses) | — | — | — | 79,451 | 79,451 | ||||||||||||||
Net Unrealized Gains (Losses) | — | — | — | 204,036 | 204,036 | ||||||||||||||
Total Realized and Unrealized | — | — | — | 283,487 | 283,487 | ||||||||||||||
Interest Income and Dividends | — | — | — | 56,882 | 56,882 | ||||||||||||||
Interest Expense | — | — | — | (41,709 | ) | (41,709 | ) | ||||||||||||
Net Interest and Dividends | — | — | — | 15,173 | 15,173 | ||||||||||||||
Total Investment Income (Loss) | — | — | — | 298,660 | 298,660 | ||||||||||||||
Total Segment Revenues | 498,674 | 104,267 | 121,097 | 298,660 | 1,022,698 | ||||||||||||||
Segment Expenses | |||||||||||||||||||
Compensation and Benefits | |||||||||||||||||||
Cash Compensation and Benefits | 60,008 | 19,784 | 22,561 | 37,082 | 139,435 | ||||||||||||||
Realized Performance Income Compensation | 87,393 | 674 | — | — | 88,067 | ||||||||||||||
Unrealized Performance Income Compensation | 50,366 | 6,848 | — | — | 57,214 | ||||||||||||||
Total Compensation and Benefits | 197,767 | 27,306 | 22,561 | 37,082 | 284,716 | ||||||||||||||
Occupancy and Related Charges | 8,107 | 1,856 | 664 | 3,742 | 14,369 | ||||||||||||||
Other Operating Expenses | 26,887 | 8,338 | 5,328 | 12,945 | 53,498 | ||||||||||||||
Total Segment Expenses | 232,761 | 37,500 | 28,553 | 53,769 | 352,583 | ||||||||||||||
Income (Loss) attributable to noncontrolling interests | — | — | 1,584 | — | 1,584 | ||||||||||||||
Economic Net Income (Loss) | $ | 265,913 | $ | 66,767 | $ | 90,960 | $ | 244,891 | $ | 668,531 | |||||||||
Total Assets | $ | 1,815,404 | $ | 1,191,199 | $ | 573,162 | $ | 10,758,695 | $ | 14,338,460 | |||||||||
49
As of and for the Three Months Ended March 31, 2016 | |||||||||||||||||||
Private Markets | Public Markets | Capital Markets | Principal Activities | Total Reportable Segments | |||||||||||||||
Segment Revenues | |||||||||||||||||||
Management, Monitoring and Transaction Fees, Net | |||||||||||||||||||
Management Fees | $ | 117,798 | $ | 76,802 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 194,600 | |||||||||
Monitoring Fees | 12,037 | — | — | — | 12,037 | ||||||||||||||
Transaction Fees | 37,398 | 1,132 | 57,555 | — | 96,085 | ||||||||||||||
Fee Credits | (22,596 | ) | (211 | ) | — | — | (22,807 | ) | |||||||||||
Total Management, Monitoring and Transaction Fees, Net | 144,637 | 77,723 | 57,555 | — | 279,915 | ||||||||||||||
Performance Income (Loss) | |||||||||||||||||||
Realized Incentive Fees | — | 1,593 | — | — | 1,593 | ||||||||||||||
Realized Carried Interest | 93,450 | 3,838 | — | — | 97,288 | ||||||||||||||
Unrealized Carried Interest | (194,699 | ) | (29,106 | ) | — | — | (223,805 | ) | |||||||||||
Total Performance Income (Loss) | (101,249 | ) | (23,675 | ) | — | — | (124,924 | ) | |||||||||||
Investment Income (Loss) | |||||||||||||||||||
Net Realized Gains (Losses) | — | — | — | (24,183 | ) | (24,183 | ) | ||||||||||||
Net Unrealized Gains (Losses) | — | — | — | (564,991 | ) | (564,991 | ) | ||||||||||||
Total Realized and Unrealized | — | — | — | (589,174 | ) | (589,174 | ) | ||||||||||||
Interest Income and Dividends | — | — | — | 108,120 | 108,120 | ||||||||||||||
Interest Expense | — | — | — | (48,544 | ) | (48,544 | ) | ||||||||||||
Net Interest and Dividends | — | — | — | 59,576 | 59,576 | ||||||||||||||
Total Investment Income (Loss) | — | — | — | (529,598 | ) | (529,598 | ) | ||||||||||||
Total Segment Revenues | 43,388 | 54,048 | 57,555 | (529,598 | ) | (374,607 | ) | ||||||||||||
Segment Expenses | |||||||||||||||||||
Compensation and Benefits | |||||||||||||||||||
Cash Compensation and Benefits | 48,967 | 19,054 | 8,168 | 24,710 | 100,899 | ||||||||||||||
Realized Performance Income Compensation | 37,380 | 2,172 | — | — | 39,552 | ||||||||||||||
Unrealized Performance Income Compensation | (75,000 | ) | (11,642 | ) | — | — | (86,642 | ) | |||||||||||
Total Compensation and Benefits | 11,347 | 9,584 | 8,168 | 24,710 | 53,809 | ||||||||||||||
Occupancy and Related Charges | 8,925 | 2,675 | 628 | 3,722 | 15,950 | ||||||||||||||
Other Operating Expenses | 37,126 | 9,278 | 4,096 | 11,386 | 61,886 | ||||||||||||||
Total Segment Expenses | 57,398 | 21,537 | 12,892 | 39,818 | 131,645 | ||||||||||||||
Income (Loss) attributable to noncontrolling interests | — | — | 667 | — | 667 | ||||||||||||||
Economic Net Income (Loss) | $ | (14,010 | ) | $ | 32,511 | $ | 43,996 | $ | (569,416 | ) | $ | (506,919 | ) | ||||||
Total Assets | $ | 1,738,931 | $ | 1,080,077 | $ | 306,996 | $ | 9,663,781 | $ | 12,789,785 | |||||||||
50
The following tables reconcile KKR’s total reportable segments to the most directly comparable financial measures calculated and presented in accordance with GAAP:
Fees and Other
Three Months Ended | |||||||
March 31, 2017 | March 31, 2016 | ||||||
Total Segment Revenues | $ | 1,022,698 | $ | (374,607 | ) | ||
Management fees relating to consolidated funds and placement fees | (47,102 | ) | (38,270 | ) | |||
Fee credits relating to consolidated funds | 939 | 428 | |||||
Net realized and unrealized carried interest - consolidated funds | (11,057 | ) | 9,561 | ||||
Total investment income (loss) | (298,660 | ) | 529,598 | ||||
Revenue earned by oil & gas producing entities | 17,273 | 13,561 | |||||
Reimbursable expenses | 23,549 | 15,881 | |||||
Other | 8,312 | 6,653 | |||||
Fees and Other | $ | 715,952 | $ | 162,805 | |||
Expenses
Three Months Ended | |||||||
March 31, 2017 | March 31, 2016 | ||||||
Total Segment Expenses | $ | 352,583 | $ | 131,645 | |||
Equity based compensation | 111,036 | 63,823 | |||||
Reimbursable expenses and placement fees | 36,123 | 24,107 | |||||
Operating expenses relating to consolidated funds, CFEs and other entities | 13,430 | 43,671 | |||||
Expenses incurred by oil & gas producing entities | 11,177 | 17,826 | |||||
Intangible amortization | 6,366 | 17,393 | |||||
Other | 9,299 | 9,858 | |||||
Total Expenses | $ | 540,014 | $ | 308,323 | |||
Net Income (Loss) Attributable to KKR & Co. L.P. Common Unitholders
Three Months Ended | |||||||
March 31, 2017 | March 31, 2016 | ||||||
Economic net income (loss) | $ | 668,531 | $ | (506,919 | ) | ||
Income tax | (40,542 | ) | (1,890 | ) | |||
Amortization of intangibles, placement fees and other, net (1) | (32,837 | ) | (28,882 | ) | |||
Equity based compensation | (111,036 | ) | (63,823 | ) | |||
Net income (loss) attributable to noncontrolling interests held by KKR Holdings | (216,432 | ) | 271,575 | ||||
Preferred Unit Distributions | (8,341 | ) | — | ||||
Net income (loss) Attributable to KKR & Co. L.P. Common Unitholders | $ | 259,343 | $ | (329,939 | ) | ||
(1) Other primarily represents the statement of operations impact of the accounting convention differences for (i) direct interests in oil & natural gas properties outside of investment funds and (ii) certain interests in consolidated CLOs and other entities. On a segment basis, direct interests in oil & natural gas properties outside of investment funds are carried at fair value with changes in fair value recorded in Economic Net Income (Loss) and certain interests in consolidated CLOs and other entities are carried at cost. See Note 2 "Summary of Significant Accounting Policies" for the GAAP accounting for these direct interests in oil and natural gas producing properties outside investment funds and interests in consolidated CLOs and other entities.
The items that reconcile KKR’s total reportable segments to the corresponding consolidated amounts calculated and presented in accordance with GAAP for net income (loss) attributable to redeemable noncontrolling interests and income (loss) attributable to noncontrolling interests are primarily attributable to the impact of KKR Holdings L.P., KKR's consolidated funds and certain other entities.
51
Assets
As of March 31, | |||||||
2017 | 2016 | ||||||
Total Segment Assets | $ | 14,338,460 | $ | 12,789,785 | |||
Impact of Consolidation of Investment Vehicles and Other Entities (1) | 25,963,256 | 20,236,392 | |||||
Carry Pool Reclassification to Liabilities | 1,035,671 | 1,113,450 | |||||
Impact of KKR Management Holdings Corp. | 298,325 | 288,956 | |||||
Total Assets | $ | 41,635,712 | $ | 34,428,583 | |||
(1) Includes accounting basis difference for oil & natural gas properties of $7,700 and $78,416 as of March 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively. | |||||||
52
15. EQUITY
Reorganization of India Capital Markets and Corporate NBFC
On March 30, 2017, KKR completed a transaction in which KKR’s Indian capital markets and credit asset management business, KKR Capital Markets India Private Limited (“KCM India”), was combined with KKR’s corporate non-bank financial company, KKR India Financial Services Private Limited (the “Corporate NBFC”), to create KKR India Financial Investments Pte. Ltd. or “KIFL”.
Prior to the completion of this transaction, KKR owned all of KCM India and a controlling financial interest in the Corporate NBFC and as such, the results of both entities were consolidated in KKR’s financial statements with a noncontrolling interest reflecting a third party's interest in the Corporate NBFC. As of the date of the completion of this transaction, KKR owns 60% in the combined business and thus continues to consolidate KIFL.
Since both KCM India and the Corporate NBFC were under the common control of KKR both prior to and following this transaction, this transaction is accounted for as a transfer of interests under common control. As such, no new basis of accounting was established upon completion of this transaction and KKR carried forward the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities subsequent to the transaction. The difference between KKR’s carrying value before and after the transaction was treated as a reallocation of equity interests from noncontrolling interests to KKR equity and no gain or loss was recognized in the consolidated financial statements. This reallocation amounted to an increase to KKR’s equity of $10.3 million and to KKR Holdings of $7.9 million.
Unit Repurchase Program
Since October 27, 2015, KKR has authorized a total of $750.0 million to repurchase its common units, of which $459.0 million has been spent to repurchase 31.7 million common units as of April 21, 2017. Under this common unit repurchase program, common units may be repurchased from time to time in open market transactions, in privately negotiated transactions or otherwise. The timing, manner, price and amount of any unit repurchases will be determined by KKR in its discretion and will depend on a variety of factors, including legal requirements, price and economic and market conditions. KKR expects that the program, which has no expiration date, will be in effect until the maximum approved dollar amount has been used to repurchase common units. The program does not require KKR to repurchase any specific number of common units, and the program may be suspended, extended, modified or discontinued at any time. See condensed consolidated statements of changes in equity for the amount of common units repurchased during the three months ended March 31, 2017 and 2016.
Distribution Policy
Under KKR's distribution policy for its common units, KKR intends to make equal quarterly distributions to holders of its common units in an amount of $0.17 per common unit per quarter. The declaration and payment of any distributions are subject to the discretion of the board of directors of the general partner of KKR and the terms of its limited partnership agreement. There can be no assurance that distributions will be made as intended or at all, that unitholders will receive sufficient distributions to satisfy payment of their tax liabilities as limited partners of KKR or that any particular distribution policy will be maintained.
53
16. GOODWILL AND INTANGIBLE ASSETS
Goodwill
Goodwill from the acquisition of Prisma Capital Partners LP and its affiliates represents the excess of acquisition costs over the fair value of net tangible and intangible assets acquired and is primarily attributed to synergies expected to arise after the acquisition of Prisma. As of March 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016, the carrying value of goodwill was $89.0 million. Goodwill is recorded in Other Assets in the consolidated statements of financial condition. The carrying values of goodwill allocated to the Public Markets and Principal Activities segments were $59.0 million and $30.0 million, respectively. All of the goodwill is currently expected to be deductible for tax purposes. See Note 8 “Other Assets and Accounts Payable, Accrued Expenses and Other Liabilities.”
Intangible Assets
Intangible Assets, Net consists of the following:
March 31, 2017 | December 31, 2016 | ||||||
Finite-Lived Intangible Assets | $ | 252,013 | $ | 251,768 | |||
Accumulated Amortization | (123,061 | ) | (116,744 | ) | |||
Intangible Assets, Net | $ | 128,952 | $ | 135,024 | |||
Changes in Intangible Assets, Net consists of the following:
Three Months Ended | |||
March 31, 2017 | |||
Balance, Beginning of Period | $ | 135,024 | |
Amortization Expense | (6,356 | ) | |
Foreign Exchange | 284 | ||
Balance, End of Period | $ | 128,952 | |
54
17. COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
Debt Covenants
Borrowings of KKR contain various debt covenants. These covenants do not, in management’s opinion, materially restrict KKR’s operating business or investment strategies. KKR is in compliance with its debt covenants in all material respects as of March 31, 2017.
Funding Commitments
As of March 31, 2017, KKR had unfunded commitments consisting of (i) $3,522.3 million to its active private equity and other investment vehicles. In addition to the uncalled commitments to KKR's investment funds, KKR has entered into contractual commitments with respect to (i) the purchase of investments and other assets in its Principal Activities segment, and (ii) underwriting transactions, debt financing, and syndications in KKR's Capital Markets segment. As of March 31, 2017, these commitments amounted to $1,396.3 million and $1,027.8 million, respectively. Whether these amounts are actually funded, in whole or in part, depends on the contractual terms of such commitments, including the satisfaction or waiver of any conditions to closing or funding. In the case of purchases of investments or assets in our Principal Activities segment, the amount to be funded includes amounts that are intended to be syndicated to third parties, and the actual amounts to be funded may be less than shown.
Contingent Repayment Guarantees
The partnership documents governing KKR’s carry-paying funds, including funds relating to private equity, infrastructure, energy, real estate, mezzanine, direct lending and special situations investments, generally include a “clawback” provision that, if triggered, may give rise to a contingent obligation requiring the general partner to return amounts to the fund for distribution to the fund investors at the end of the life of the fund. Under a clawback obligation, upon the liquidation of a fund, the general partner is required to return, typically on an after-tax basis, previously distributed carry to the extent that, due to the diminished performance of later investments, the aggregate amount of carry distributions received by the general partner during the term of the fund exceed the amount to which the general partner was ultimately entitled, including the effects of any performance thresholds. Excluding carried interest received by the general partners of funds that were not contributed to KKR in the acquisition of the assets and liabilities of KKR & Co. (Guernsey) L.P. (formerly known as KKR Private Equity Investors, L.P.) on October 1, 2009 (the “KPE Transaction”), as of March 31, 2017, no carried interest was subject to this clawback obligation, assuming that all applicable carry paying funds were liquidated at their March 31, 2017 fair values. Had the investments in such funds been liquidated at zero value, the clawback obligation would have been $2,193.6 million. Carried interest is recognized in the statement of operations based on the contractual conditions set forth in the agreements governing the fund as if the fund were terminated and liquidated at the reporting date and the fund’s investments were realized at the then estimated fair values. Amounts earned pursuant to carried interest are earned by the general partner of those funds to the extent that cumulative investment returns are positive and where applicable, preferred return thresholds have been met. If these investment amounts earned decrease or turn negative in subsequent periods, recognized carried interest will be reversed and to the extent that the aggregate amount of carry distributions received by the general partner during the term of the fund exceed the amount to which the general partner was ultimately entitled, a clawback obligation would be recorded. For funds that are consolidated, this clawback obligation, if any, is reflected as an increase in noncontrolling interests in the consolidated statements of financial condition. For funds that are not consolidated, this clawback obligation, if any, is reflected as a reduction of KKR’s investment balance as this is where carried interest is initially recorded.
Prior to the KPE Transaction in 2009, certain principals who received carried interest distributions with respect to certain private equity funds contributed to KKR had personally guaranteed, on a several basis and subject to a cap, the contingent obligations of the general partners of such private equity funds to repay amounts to fund investors pursuant to the general partners’ clawback obligations. The terms of the KPE Transaction require that principals remain responsible for any clawback obligations relating to carry distributions received prior to the KPE Transaction, up to a maximum of $223.6 million. Through investment realizations, the principals' potential exposure has been reduced to $86.8 million as of March 31, 2017. Using valuations as of March 31, 2017, no amounts are due with respect to the clawback obligation required to be funded by principals. Carry distributions arising subsequent to the KPE Transaction may give rise to clawback obligations that may be allocated generally to KKR and persons who participate in the carry pool. In addition, guarantees of or similar arrangements relating to clawback obligations in favor of third party investors in an individual investment partnership by entities KKR owns may limit distributions of carried interest more generally.
55
Indemnifications and Other Guarantees
KKR may incur contingent liabilities for claims that may be made against it in the future. KKR enters into contracts that contain a variety of representations, warranties and covenants, including indemnifications. For example, certain of KKR’s investment funds and KFN have provided certain indemnities relating to environmental and other matters and have provided nonrecourse carve-out guarantees for fraud, willful misconduct and other customary wrongful acts, each in connection with the financing of certain real estate investments that KKR has made. In addition, KKR has also provided credit support to certain of its subsidiaries’ obligations in connection with a limited number of investment vehicles that KKR manages. For example, KKR has guaranteed the obligations of a general partner to post collateral on behalf of its investment vehicle in connection with such vehicle’s derivative transactions, and KKR has also agreed to be liable for certain investment losses and/or for providing liquidity in the events specified in the governing documents of another investment vehicle. KKR also may become liable for certain fees payable to sellers of businesses or assets if a transaction does not close, subject to certain conditions, if any, specified in the acquisition agreements for such businesses or assets. KKR’s maximum exposure under these arrangements is currently unknown and KKR's liabilities for these matters would require a claim to be made against KKR in the future.
Litigation
From time to time, KKR is involved in various legal proceedings, lawsuits and claims incidental to the conduct of KKR’s business. KKR’s business is also subject to extensive regulation, which may result in regulatory proceedings against it.
KKR currently is and expects to continue to become, from time to time, subject to examinations, inquiries and investigations by various U.S. and non U.S. governmental and regulatory agencies, including but not limited to the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission, or SEC, Department of Justice, state attorney generals, Financial Industry Regulatory Authority, or FINRA, and the U.K. Financial Conduct Authority. Such examinations, inquiries and investigations may result in the commencement of civil, criminal or administrative proceedings against KKR or its personnel.
Moreover, in the ordinary course of business, KKR is and can be both the defendant and the plaintiff in numerous lawsuits with respect to acquisitions, bankruptcy, insolvency and other types of proceedings. Such lawsuits may involve claims that adversely affect the value of certain investments owned by KKR’s funds.
KKR establishes an accrued liability for legal proceedings only when those matters present loss contingencies that are both probable and reasonably estimable. In such cases, there may be an exposure to loss in excess of any amounts accrued. No loss contingency is recorded for matters where such losses are either not probable or reasonably estimable (or both) at the time of determination. Such matters may be subject to many uncertainties, including among others (i) the proceedings may be in early stages; (ii) damages sought may be unspecified, unsupportable, unexplained or uncertain; (iii) discovery may not have been started or is incomplete; (iv) there may be uncertainty as to the outcome of pending appeals or motions; (v) there may be significant factual issues to be resolved; or (vi) there may be novel legal issues or unsettled legal theories to be presented or a large number of parties. Consequently, management is unable to estimate a range of potential loss, if any, related to these matters. In addition, loss contingencies may be, in part or in whole, subject to insurance or other payments such as contributions and/or indemnity, which may reduce any ultimate loss.
It is not possible to predict the ultimate outcome of all pending legal proceedings, and some of the matters discussed above seek or may seek potentially large and/or indeterminate amounts. As of such date, based on information known by management, management has not concluded that the final resolutions of the matters above will have a material effect upon the financial statements. However, given the potentially large and/or indeterminate amounts sought or may be sought in certain of these matters and the inherent unpredictability of investigations and litigations, it is possible that an adverse outcome in certain matters could, from time to time, have a material effect on KKR’s financial results in any particular period.
56
18. REGULATORY CAPITAL REQUIREMENTS
KKR has registered broker-dealer subsidiaries which are subject to the minimum net capital requirements of the SEC and the FINRA. Additionally, KKR entities based in London and Dublin are subject to the regulatory capital requirements of the U.K. Financial Conduct Authority and the Central Bank of Ireland, respectively. In addition, KKR has an entity based in Hong Kong which is subject to the capital requirements of the Hong Kong Securities and Futures Ordinance, an entity based in Tokyo subject to the capital requirements of Financial Services Authority of Japan, and two entities based in Mumbai which are subject to capital requirements of the Reserve Bank of India or RBI and the Securities and Exchange Board of India or SEBI. All of these entities have continuously operated in excess of their respective minimum regulatory capital requirements.
The regulatory capital requirements referred to above may restrict KKR’s ability to withdraw capital from its registered broker-dealer entities. At March 31, 2017, approximately $148.4 million of cash at KKR’s registered broker-dealer entities may be restricted as to the payment of cash dividends and advances to KKR.
19. SUBSEQUENT EVENTS
Common Unit Distribution
A distribution of $0.17 per KKR & Co. L.P. common unit was announced on April 27, 2017, and will be paid on May 23, 2017 to common unitholders of record as of the close of business on May 8, 2017. KKR Holdings will receive its pro rata share of the distribution from the KKR Group Partnerships.
Preferred Unit Distributions
A distribution of $0.421875 per Series A Preferred Unit has been declared as announced on April 27, 2017 and set aside for payment on June 15, 2017 to holders of record of Series A Preferred Units as of the close of business on June 1, 2017.
A distribution of $0.406250 per Series B Preferred Unit has been declared as announced on April 27, 2017 and set aside for payment on June 15, 2017 to holders of record of Series B Preferred Units as of the close of business on June 1, 2017.
KFN Redemption
On April 24, 2017, KFN redeemed all of its outstanding 7.500% Senior Notes due 2042 (the “KFN 2042 Notes”) for cash, in accordance with the optional redemption provisions provided in the documents governing the KFN 2042 Notes. As of March 31, 2017, there was $115 million aggregate principal amount of the KFN 2042 Notes outstanding. The redemption price was equal to 100% of the principal amount of the KFN 2042 Notes plus unpaid interest accrued thereon to, but excluding, the redemption date, in accordance with the terms of the KFN 2042 Notes.
Short Term Credit Agreement
On April 20, 2017 a subsidiary of KKR Capital Markets entered into a short term credit agreement with HSBC Bank USA and borrowed approximately $486 million. The loan is non-recourse to KKR beyond certain assets of the subsidiary of KKR Capital Markets and matures 75 days from issuance. As of May 3, 2017, approximately $157 million remained outstanding on such loan.
57
ITEM 2. MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
The following discussion and analysis should be read in conjunction with the unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements of KKR & Co. L.P., together with its consolidated subsidiaries, and the related notes included elsewhere in this report and our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2016, filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on February 24, 2017 (our "Annual Report"), including the audited consolidated financial statements and the related notes and “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” contained therein. The historical condensed consolidated financial data discussed below reflects the historical results and financial position of KKR. In addition, this discussion and analysis contains forward looking statements and involves numerous risks and uncertainties, including those described under “Cautionary Note Regarding Forward-looking Statements” and “Risk Factors" in this report, our Annual Report and other quarterly reports. Actual results may differ materially from those contained in any forward looking statements.
Overview
We are a leading global investment firm that manages investments across multiple asset classes including private equity, energy, infrastructure, real estate, growth equity, credit and hedge funds. We aim to generate attractive investment returns by following a patient and disciplined investment approach, employing world‑class people, and driving growth and value creation in the assets we manage. We invest our own capital alongside the capital we manage for fund investors and bring debt and equity investment opportunities to others through our capital markets business.
Our business offers a broad range of investment management services to our fund investors and provides capital markets services to our firm, our portfolio companies and third parties. Throughout our history, we have consistently been a leader in the private equity industry, having completed more than 290 private equity investments in portfolio companies with a total transaction value in excess of $545 billion as of March 31, 2017. We have grown our firm by expanding our geographical presence and building businesses in areas, such as credit, special situations, hedge funds, collateralized loan obligations (“CLOs”), capital markets, infrastructure, energy, real estate and growth equity. Our balance sheet has provided a significant source of capital in the growth and expansion of our business, and has allowed us to further align our interests with those of our fund investors. These efforts build on our core principles and industry expertise, allowing us to leverage the intellectual capital and synergies in our businesses, and to capitalize on a broader range of the opportunities we source. Additionally, we have increased our focus on meeting the needs of our existing fund investors and in developing relationships with new investors in our funds.
We conduct our business with offices throughout the world, providing us with a pre-eminent global platform for sourcing transactions, raising capital and carrying out capital markets activities. Our growth has been driven by value that we have created through our operationally focused investment approach, the expansion of our existing businesses, our entry into new lines of business, innovation in the products that we offer investors in our funds, an increased focus on providing tailored solutions to our clients and the integration of capital markets distribution activities.
As a global investment firm, we earn management, monitoring, transaction, incentive fees and carried interest for providing investment management, monitoring and other services to our funds, vehicles, CLOs, managed accounts and portfolio companies, and we generate transaction-specific income from capital markets transactions. We earn additional investment income from investing our own capital alongside that of our fund investors, from other assets on our balance sheet and from the carried interest we receive from our funds and certain of our other investment vehicles. A carried interest entitles the sponsor of a fund to a specified percentage of investment gains that are generated on third-party capital that is invested.
Our investment teams have deep industry knowledge and are supported by a substantial and diversified capital base, an integrated global investment platform, the expertise of operating consultants, senior advisors and other advisors and a worldwide network of business relationships that provide a significant source of investment opportunities, specialized knowledge during due diligence and substantial resources for creating and realizing value for stakeholders. These teams invest capital, a substantial portion of which is of a long duration and not subject to redemption. As of March 31, 2017, approximately 76% of our fee paying assets under management are not subject to redemption for at least 8 years from inception, providing us with significant flexibility to grow investments and select exit opportunities. We believe that these aspects of our business will help us continue to expand and grow our business and deliver strong investment performance in a variety of economic and financial conditions.
58
Recent Developments
PAAMCO Prisma
On February 6, 2017, KKR and Pacific Alternative Asset Management Company, LLC (“PAAMCO”) announced that they entered into a strategic transaction to create a new liquid alternatives investment firm by combining PAAMCO and KKR Prisma. Under the terms of the agreement, the entire businesses of both PAAMCO and KKR Prisma will be contributed to a newly formed company that will operate independently from KKR, and KKR will retain a 39.9% stake as a long-term strategic partner. This transaction is subject to the satisfaction of customary closing conditions, including the receipt of requisite regulatory approvals.
KFN Redemption
On April 24, 2017 KFN redeemed all of its outstanding 7.500% Senior Notes due 2042 (the “KFN 2042 Notes”) for cash, in accordance with the optional redemption provisions provided in the documents governing the KFN 2042 Notes. As of March 31, 2017, there was $115 million aggregate principal amount of the KFN 2042 Notes outstanding. The redemption price was equal to 100% of the principal amount of the KFN 2042 Notes plus unpaid interest accrued thereon to, but excluding, the redemption date, in accordance with the terms of the KFN 2042 Notes.
KFN Issued 5.500% Notes Due 2032
On March 30, 2017, KFN issued $375.0 million par amount of 5.500% Senior Unsecured Notes (“KFN 2032 Senior Unsecured Notes”) in a private placement, resulting in net proceeds to KFN of $368.6 million. Interest on the KFN 2032 Senior Unsecured Notes is payable semi-annually on March 30th and September 30th. The KFN 2032 Senior Unsecured Notes will mature on March 30, 2032. KFN may redeem the KFN 2032 Senior Unsecured Notes in whole, but not in part, at a redemption price equal to 100% of the outstanding principal amount plus accrued and unpaid interest to, but excluding, the date of redemption on or after March 30, 2022 and annually thereafter, after providing notice to noteholders of such redemption not less than 30 and no more than 60 business days prior to such redemption date. At any time prior to the March 30, 2022, KFN may redeem the KFN 2032 Senior Unsecured Notes in whole, but not in part, at a redemption price equal to (i) 100% of the outstanding principal amount, (ii) plus accrued and unpaid interest to, but excluding, the date of redemption, (iii) plus the excess, if any, of (a) the sum of the present values of the remaining scheduled payments of principal and interest on the KFN 2032 Senior Unsecured Notes (as if the Notes matured on the March 30, 2022), discounted to the redemption date on a semi-annual basis (assuming a 360-day year of twelve 30-day months) at a rate equal to the sum of the applicable treasury rate plus 50 basis points, minus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, on the KFN 2032 Senior Unsecured Notes being redeemed to, but excluding, the redemption date over (b) the principal amount of the KFN 2032 Senior Unsecured Notes being redeemed.
Business Segments
Private Markets
Through our Private Markets segment, we manage and sponsor private equity funds and co-investment vehicles that invest capital for long-term appreciation, either through controlling ownership of a company or strategic minority positions. We also manage and sponsor investment funds and co-investment vehicles that invest capital in real assets, such as infrastructure, energy and real estate, and growth equity investments. These funds, vehicles and accounts are managed by Kohlberg Kravis Roberts & Co. L.P., an SEC registered investment adviser. As of March 31, 2017, the segment had $80.2 billion of AUM and FPAUM of $56.7 billion, consisting of $43.5 billion in private equity and growth equity and $13.2 billion in real assets (including infrastructure, energy and real estate) and other strategies.
59
The table below presents information as of March 31, 2017 relating to our current private equity, growth equity and real asset funds and other investment vehicles for which we have the ability to earn carried interest. This data does not reflect acquisitions or disposals of investments, changes in investment values or distributions occurring after March 31, 2017.
Investment Period (1) | Amount ($ in millions) | |||||||||||||||||||||
Commencement Date | End Date | Commitment (2) | Uncalled Commitments | Percentage Committed by General Partner | Invested | Realized | Remaining Cost (3) | Remaining Fair Value | ||||||||||||||
Private Markets | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Private Equity and Growth Equity | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Asian Fund III (4) | 4/2017 | 4/2023 | $ | 5,787.8 | $ | 5,787.8 | 8.6% | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | |||||||
Americas Fund XII (4) | 1/2017 | 1/2023 | 13,500.0 | 13,500.0 | 7.4% | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||
Next Generation Technology Growth Fund (4) | 3/2016 | 3/2021 | 658.9 | 568.2 | 22.5% | 90.7 | — | 90.7 | 114.6 | |||||||||||||
European Fund IV (4) | 12/2014 | 12/2020 | 3,444.6 | 2,271.6 | 5.8% | 1,181.8 | — | 1,181.8 | 1,268.2 | |||||||||||||
Asian Fund II (4) | 4/2013 | 4/2017 | 5,825.0 | 2,022.9 | 1.3% | 4,687.2 | 948.1 | 3,778.5 | 6,032.0 | |||||||||||||
North America Fund XI (4) | 9/2012 | 1/2017 | 8,718.4 | 1,242.0 | 2.9% | 8,790.8 | 3,549.7 | 6,527.5 | 10,203.6 | |||||||||||||
China Growth Fund | 11/2010 | 11/2016 | 1,010.0 | — | 1.0% | 1,010.0 | 442.9 | 764.3 | 962.6 | |||||||||||||
E2 Investors (Annex Fund) | 8/2009 | 11/2013 | 195.8 | — | 4.9% | 195.8 | 195.7 | 18.1 | 1.8 | |||||||||||||
European Fund III | 3/2008 | 3/2014 | 6,113.6 | 786.3 | 4.7% | 5,327.3 | 6,198.0 | 2,417.9 | 3,571.1 | |||||||||||||
Asian Fund | 7/2007 | 4/2013 | 3,983.3 | — | 2.5% | 3,945.9 | 7,506.0 | 924.0 | 977.9 | |||||||||||||
2006 Fund | 9/2006 | 9/2012 | 17,642.2 | 337.7 | 2.1% | 17,304.5 | 23,366.2 | 6,190.5 | 9,517.4 | |||||||||||||
European Fund II | 11/2005 | 10/2008 | 5,750.8 | — | 2.1% | 5,750.8 | 8,455.4 | — | 70.4 | |||||||||||||
Millennium Fund | 12/2002 | 12/2008 | 6,000.0 | — | 2.5% | 6,000.0 | 13,305.4 | 444.9 | 629.0 | |||||||||||||
Total Private Equity and Growth Equity | 78,630.4 | 26,516.5 | 54,284.8 | 63,967.4 | 22,338.2 | 33,348.6 | ||||||||||||||||
Co-Investment Vehicles and Other (4) | Various | Various | 8,300.1 | 3,214.5 | Various | 5,281.2 | 3,153.7 | 3,841.8 | 4,912.2 | |||||||||||||
Total Private Equity and Growth Equity | 86,930.5 | 29,731.0 | 59,566.0 | 67,121.1 | 26,180.0 | 38,260.8 | ||||||||||||||||
Real Assets | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Energy Income and Growth Fund | 9/2013 | 9/2018 | 1,974.2 | 746.4 | 12.9% | 1,253.9 | 222.5 | 1,080.4 | 1,016.1 | |||||||||||||
Natural Resources Fund | Various | Various | 887.4 | 2.8 | Various | 884.5 | 96.6 | 809.9 | 183.2 | |||||||||||||
Global Energy Opportunities (4) | Various | Various | 979.2 | 645.6 | Various | 373.0 | 58.8 | 258.9 | 266.8 | |||||||||||||
Global Infrastructure Investors (4) | 9/2011 | 10/2014 | 1,039.9 | 75.9 | 4.8% | 994.9 | 656.3 | 649.5 | 858.1 | |||||||||||||
Global Infrastructure Investors II (4) | 10/2014 | 10/2020 | 3,025.8 | 1,805.5 | 4.1% | 1,263.1 | 45.4 | 1,217.8 | 1,267.4 | |||||||||||||
Real Estate Partners Americas (4) | 5/2013 | 5/2017 | 1,229.1 | 668.6 | 16.3% | 898.5 | 633.5 | 560.1 | 629.3 | |||||||||||||
Real Estate Partners Europe (4) | 9/2015 | 6/2020 | 691.7 | 569.3 | 9.1% | 122.4 | — | 122.4 | 130.7 | |||||||||||||
Co-Investment Vehicles and Other | Various | Various | 1,829.6 | 687.7 | Various | 1,141.9 | 466.3 | 1,139.6 | 1,340.2 | |||||||||||||
Real Assets | $ | 11,656.9 | $ | 5,201.8 | $ | 6,932.2 | $ | 2,179.4 | $ | 5,838.6 | $ | 5,691.8 | ||||||||||
Unallocated Commitments | 138.9 | 138.9 | Various | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Private Markets Total | $ | 98,726.3 | $ | 35,071.7 | $ | 66,498.2 | $ | 69,300.5 | $ | 32,018.6 | $ | 43,952.6 | ||||||||||
(1) | The commencement date represents the date on which the general partner of the applicable fund commenced investment of the fund’s capital or the date of the first closing. The end date represents the earlier of (i) the date on which the general partner of the applicable fund was or will be required by the fund’s governing agreement to cease making investments on behalf of the fund, unless extended by a vote of the fund investors or (ii) the date on which the last investment was made. |
(2) | The commitment represents the aggregate capital commitments to the fund, including capital commitments by third-party fund investors and the general partner. Foreign currency commitments have been converted into U.S. dollars based on (i) the foreign exchange rate at the date of purchase for each investment and (ii) the exchange rate that prevailed on March 31, 2017, in the case of uncalled commitments. |
(3) | The remaining cost represents the initial investment of the general partner and limited partners, with the limited partners’ investment reduced for any return of capital and realized gains from which the general partner did not receive a carried interest. |
(4) | The “Invested” and “Realized” columns include the amounts of any realized investments that restored the unused capital commitments of the fund investors, if any. |
60
The tables below present information as of March 31, 2017 relating to the historical performance of certain of our Private Markets investment vehicles since inception, which we believe illustrates the benefits of our investment approach. The information presented under Total Investments includes all of the investments made by the specified investment vehicle, while the information presented under Realized/Partially Realized Investments includes only those investments that have been disposed of or have otherwise generated disposition proceeds or current income including dividends that have been distributed by the relevant fund. This data does not reflect additional capital raised since March 31, 2017 or acquisitions or disposals of investments, changes in investment values or distributions occurring after that date. Past performance is no guarantee of future results.
Amount | Fair Value of Investments | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Private Markets Investment Funds | Commitment | Invested (5) | Realized (5) | Unrealized | Total Value | Gross IRR (5) | Net IRR (5) | Multiple of Invested Capital (5) | |||||||||||||||||
($ in millions) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total Investments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Legacy Funds (1) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
1976 Fund | $ | 31.4 | $ | 31.4 | $ | 537.2 | $ | — | $ | 537.2 | 39.5 | % | 35.5 | % | 17.1 | ||||||||||
1980 Fund | 356.8 | 356.8 | 1,827.8 | — | 1,827.8 | 29.0 | % | 25.8 | % | 5.1 | |||||||||||||||
1982 Fund | 327.6 | 327.6 | 1,290.7 | — | 1,290.7 | 48.1 | % | 39.2 | % | 3.9 | |||||||||||||||
1984 Fund | 1,000.0 | 1,000.0 | 5,963.5 | — | 5,963.5 | 34.5 | % | 28.9 | % | 6.0 | |||||||||||||||
1986 Fund | 671.8 | 671.8 | 9,080.7 | — | 9,080.7 | 34.4 | % | 28.9 | % | 13.5 | |||||||||||||||
1987 Fund | 6,129.6 | 6,129.6 | 14,949.2 | — | 14,949.2 | 12.1 | % | 8.9 | % | 2.4 | |||||||||||||||
1993 Fund | 1,945.7 | 1,945.7 | 4,143.3 | — | 4,143.3 | 23.6 | % | 16.8 | % | 2.1 | |||||||||||||||
1996 Fund | 6,011.6 | 6,011.6 | 12,476.9 | — | 12,476.9 | 18.0 | % | 13.3 | % | 2.1 | |||||||||||||||
Subtotal - Legacy Funds | 16,474.5 | 16,474.5 | 50,269.3 | — | 50,269.3 | 26.1 | % | 19.9 | % | 3.1 | |||||||||||||||
Included Funds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
European Fund (1999) (2) | 3,085.4 | 3,085.4 | 8,757.7 | — | 8,757.7 | 26.9 | % | 20.2 | % | 2.8 | |||||||||||||||
Millennium Fund (2002) | 6,000.0 | 6,000.0 | 13,305.4 | 629.0 | 13,934.4 | 22.0 | % | 16.0 | % | 2.3 | |||||||||||||||
European Fund II (2005) (2) | 5,750.8 | 5,750.8 | 8,455.4 | 70.4 | 8,525.8 | 6.1 | % | 4.5 | % | 1.5 | |||||||||||||||
2006 Fund (2006) | 17,642.2 | 17,304.5 | 23,366.2 | 9,517.4 | 32,883.6 | 11.4 | % | 8.8 | % | 1.9 | |||||||||||||||
Asian Fund (2007) | 3,983.3 | 3,945.9 | 7,506.0 | 977.9 | 8,483.9 | 18.9 | % | 13.7 | % | 2.2 | |||||||||||||||
European Fund III (2008) (2) | 6,113.6 | 5,327.3 | 6,198.0 | 3,571.1 | 9,769.1 | 16.0 | % | 10.7 | % | 1.8 | |||||||||||||||
E2 Investors (Annex Fund) (2009) (2) | 195.8 | 195.8 | 195.7 | 1.8 | 197.5 | 0.3 | % | (0.5 | )% | 1.0 | |||||||||||||||
China Growth Fund (2010) | 1,010.0 | 1,010.0 | 442.9 | 962.6 | 1,405.5 | 13.9 | % | 7.8 | % | 1.4 | |||||||||||||||
Natural Resources Fund (2010) | 887.4 | 884.5 | 96.6 | 183.2 | 279.8 | (32.8 | )% | (35.4 | )% | 0.3 | |||||||||||||||
Global Infrastructure Investors (2011) (2) | 1,039.9 | 994.9 | 656.3 | 858.1 | 1,514.4 | 13.8 | % | 11.8 | % | 1.5 | |||||||||||||||
North America Fund XI (2012) | 8,718.4 | 8,790.8 | 3,549.7 | 10,203.6 | 13,753.3 | 25.2 | % | 19.3 | % | 1.6 | |||||||||||||||
Asian Fund II (2013) | 5,825.0 | 4,687.2 | 948.1 | 6,032.0 | 6,980.1 | 29.1 | % | 20.6 | % | 1.5 | |||||||||||||||
Real Estate Partners Americas (2013) | 1,229.1 | 898.5 | 633.5 | 629.3 | 1,262.8 | 21.8 | % | 16.1 | % | 1.4 | |||||||||||||||
Energy Income and Growth Fund (2013) | 1,974.2 | 1,253.9 | 222.5 | 1,016.1 | 1,238.6 | (0.8 | )% | (3.9 | )% | 1.0 | |||||||||||||||
Global Infrastructure Investors II (2014) (2) | 3,025.8 | 1,263.1 | 45.4 | 1,267.4 | 1,312.8 | 4.9 | % | 1.5 | % | 1.0 | |||||||||||||||
European Fund IV (2015) (2) | 3,444.6 | 1,181.8 | — | 1,268.2 | 1,268.2 | 6.6 | % | 0.5 | % | 1.1 | |||||||||||||||
Real Estate Partners Europe (2015) (2) (3) | 691.7 | 122.4 | — | 130.7 | 130.7 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
Next Generation Technology Growth Fund (2016) (3) | 658.9 | 90.7 | — | 114.6 | 114.6 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
Americas Fund XII (2017) (3) | 13,500.0 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
Asian Fund III (2017) (3) | 5,787.8 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
Subtotal - Included Funds | 90,563.9 | 62,787.5 | 74,379.4 | 37,433.4 | 111,812.8 | 15.4 | % | 11.3 | % | 1.8 | |||||||||||||||
All Funds | $ | 107,038.4 | $ | 79,262.0 | $ | 124,648.7 | $ | 37,433.4 | $ | 162,082.1 | 25.6 | % | 18.8 | % | 2.0 | ||||||||||
61
Amount | Fair Value of Investments | |||||||||||||||||||
Private Markets Investment Funds | Commitment | Invested (5) | Realized (5) | Unrealized | Total Value | Multiple of Invested Capital (5) | ||||||||||||||
($ in millions) | ||||||||||||||||||||
Realized/Partially Realized Investments (4) | ||||||||||||||||||||
Legacy Funds (1) | ||||||||||||||||||||
1976 Fund | $ | 31.4 | $ | 31.4 | $ | 537.2 | $ | — | $ | 537.2 | 17.1 | |||||||||
1980 Fund | 356.8 | 356.8 | 1,827.8 | — | 1,827.8 | 5.1 | ||||||||||||||
1982 Fund | 327.6 | 327.6 | 1,290.7 | — | 1,290.7 | 3.9 | ||||||||||||||
1984 Fund | 1,000.0 | 1,000.0 | 5,963.5 | — | 5,963.5 | 6.0 | ||||||||||||||
1986 Fund | 671.8 | 671.8 | 9,080.7 | — | 9,080.7 | 13.5 | ||||||||||||||
1987 Fund | 6,129.6 | 6,129.6 | 14,949.2 | — | 14,949.2 | 2.4 | ||||||||||||||
1993 Fund | 1,945.7 | 1,945.7 | 4,143.3 | — | 4,143.3 | 2.1 | ||||||||||||||
1996 Fund | 6,011.6 | 6,011.6 | 12,476.9 | — | 12,476.9 | 2.1 | ||||||||||||||
Subtotal - Legacy Funds | 16,474.5 | 16,474.5 | 50,269.3 | — | 50,269.3 | 3.1 | ||||||||||||||
Included Funds | ||||||||||||||||||||
European Fund (1999) (2) | 3,085.4 | 3,085.4 | 8,757.7 | — | 8,757.7 | 2.8 | ||||||||||||||
Millennium Fund (2002) | 6,000.0 | 5,599.4 | 13,305.4 | 510.1 | 13,815.5 | 2.5 | ||||||||||||||
European Fund II (2005) (2) | 5,750.8 | 5,245.4 | 8,455.4 | 70.4 | 8,525.8 | 1.6 | ||||||||||||||
2006 Fund (2006) | 17,642.2 | 12,615.1 | 23,366.2 | 5,033.2 | 28,399.4 | 2.3 | ||||||||||||||
Asian Fund (2007) | 3,983.3 | 3,267.2 | 7,506.0 | 421.9 | 7,927.9 | 2.4 | ||||||||||||||
European Fund III (2008) (2) | 6,113.6 | 3,351.1 | 6,198.0 | 1,220.7 | 7,418.7 | 2.2 | ||||||||||||||
E2 Investors (Annex Fund) (2009) (2) | 195.8 | 94.8 | 195.7 | — | 195.7 | 2.1 | ||||||||||||||
China Growth Fund (2010) | 1,010.0 | 427.5 | 442.9 | 267.4 | 710.3 | 1.7 | ||||||||||||||
Natural Resources Fund (2010) | 887.4 | 884.6 | 96.6 | 183.0 | 279.6 | 0.3 | ||||||||||||||
Global Infrastructure Investors (2011) (2) | 1,039.9 | 974.6 | 656.3 | 782.6 | 1,438.9 | 1.5 | ||||||||||||||
North America Fund XI (2012) | 8,718.4 | 4,213.5 | 3,549.7 | 4,889.6 | 8,439.3 | 2.0 | ||||||||||||||
Asian Fund II (2013) | 5,825.0 | 2,194.9 | 948.1 | 3,320.4 | 4,268.5 | 1.9 | ||||||||||||||
Real Estate Partners Americas (2013) | 1,229.1 | 688.5 | 633.5 | 389.9 | 1,023.4 | 1.5 | ||||||||||||||
Energy Income and Growth Fund (2013) | 1,974.2 | 1,253.9 | 222.5 | 1,016.1 | 1,238.6 | 1.0 | ||||||||||||||
Global Infrastructure Investors II (2014) (2) | 3,025.8 | 501.7 | 45.4 | 490.0 | 535.4 | 1.1 | ||||||||||||||
European Fund IV (2015) (2) | 3,444.6 | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||
Real Estate Partners Europe (2015) (2) (3) (4) | 691.7 | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||
Next Generation Technology Growth Fund (2016) (3) (4) | 658.9 | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||
Americas Fund XII (2017) (3) (4) | 13,500.0 | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||
Asian Fund III (2017) (3) (4) | 5,787.8 | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||
Subtotal - Included Funds | 90,563.9 | 44,397.6 | 74,379.4 | 18,595.3 | 92,974.7 | 2.1 | ||||||||||||||
All Realized/Partially Realized Investments | $ | 107,038.4 | $ | 60,872.1 | $ | 124,648.7 | $ | 18,595.3 | $ | 143,244.0 | 2.4 | |||||||||
(1) | These funds were not contributed to KKR as part of the KPE Transaction. |
(2) | The capital commitments of the European Fund, European Fund II, European Fund III, E2 Investors (Annex Fund), European Fund IV, Global Infrastructure Investors, Global Infrastructure Investors II and Real Estate Partners Europe include euro-denominated commitments of €196.5 million, €2,597.5 million, €2,882.8 million, €55.5 million, €1,626.1 million, €30.0 million, €243.8 million and €276.6 million, respectively. Such amounts have been converted into U.S. dollars based on (i) the foreign exchange rate at the date of purchase for each investment and (ii) the exchange rate prevailing on March 31, 2017 in the case of unfunded commitments. |
(3) | The gross IRR, net IRR and multiple of invested capital are calculated for our investment funds that made their first investment at least 24 months prior to March 31, 2017. None of the Real Estate Partners Europe, Next Generation Technology Growth Fund, Americas Fund XII or Asian Fund III has invested for at least 24 months as of March 31, 2017. We therefore have not calculated gross IRRs, net IRRs and multiples of invested capital with respect to those funds. |
(4) | An investment is considered partially realized when it has been disposed of or has otherwise generated disposition proceeds or current income that has been distributed by the relevant fund. In periods prior to the three months ended September 30, 2015, realized proceeds excluded current income such as dividends and interest. Realizations have not been shown for those investment funds that made their first investment more recently than 24 months prior to March 31, 2017. We therefore have not calculated gross IRRs, net IRRs and multiples of invested capital with respect to the investments of those funds. |
(5) | IRRs measure the aggregate annual compounded returns generated by a fund’s investments over a holding period. Net IRRs are calculated after giving effect to the allocation of realized and unrealized carried interest and the payment of any applicable management fees. Gross IRRs are calculated before giving effect to the allocation of carried interest and the payment of any applicable management fees. |
The multiples of invested capital measure the aggregate value generated by a fund’s investments in absolute terms. Each multiple of invested capital is calculated by adding together the total realized and unrealized values of a fund’s investments and dividing by the total amount of capital invested by the fund. Such amounts do not give effect to the allocation of any realized and unrealized returns on a fund’s investments to the fund’s general partner pursuant to a carried interest or the payment of any applicable management fees.
62
KKR Private Markets funds may utilize third party financing facilities to provide liquidity to such funds. In such event IRRs are calculated from the time capital contributions are due from fund investors to the time fund investors receive a related distribution from the fund, and the use of such financing facilities generally decreases the amount of invested capital that would otherwise be used to calculate IRRs and multiples of invested capital, which tends to increase IRRs and multiples when fair value grows over time and decrease IRRs and multiples when fair value decreases over time. KKR Private Markets funds also generally provide in certain circumstances, which vary depending on the relevant fund documents, for a portion of capital returned to investors to be restored to unused commitments as recycled capital. For KKR's Private Markets funds that have a preferred return, we take into account recycled capital in the calculation of IRRs and multiples of invested capital because the calculation of the preferred return includes the effect of recycled capital. For KKR's Private Markets funds that do not have a preferred return, we do not take recycled capital into account in the calculation of IRRs and multiples of invested capital. The inclusion of recycled capital generally causes invested and realized amounts to be higher and IRRs and multiples of invested capital to be lower than had recycled capital not been included. The inclusion of recycled capital would reduce the composite net IRR of all Included Funds by 0.1% and the composite net IRR of all Legacy Funds by 0.5%, and would reduce the composite multiple of invested capital of Included Funds by less than 0.1 and the composite multiple of invested capital of Legacy Funds by 0.4.
Public Markets
We operate and report our combined credit and hedge funds businesses through the Public Markets segment. Our credit business advises funds, CLOs, separately managed accounts, and investment companies registered under the Investment Company Act of 1940, or the Investment Company Act, including business development companies or BDCs, and alternative investments funds or AIFs, which invest capital in (i) leveraged credit strategies, including leveraged loans, high yield bonds and opportunistic credit, and (ii) alternative credit strategies, including special situations strategy and private credit strategies such as private credit opportunities, direct lending and revolving credit investment strategies. The funds, accounts, registered investment companies, BDCs and CLOs in our leveraged credit and alternative credit strategies, including special situations and private credit strategies are managed by KKR Credit Advisors (US) LLC, which is an SEC‑registered investment adviser, KKR Credit Advisors (Ireland) Unlimited Company, regulated by the Central Bank of Ireland, and KKR Credit Advisors (UK) LLP, regulated by the United Kingdom Financial Conduct Authority, or FCA. Our Public Markets segment also includes our hedge funds business. Through our hedge fund business we offer a variety of investment strategies including customized hedge fund portfolios, hedge fund-of-fund solutions and direct hedge funds that are managed by Prisma Capital Partners LP (KKR Prisma or Prisma), an SEC-registered investment adviser. KKR Prisma also provides hedge fund advisory services to institutional investors. In addition, our hedge fund business includes strategic partnerships consisting of minority stakes in other hedge fund managers.
As of March 31, 2017, this segment had $57.4 billion of AUM, comprised of $20.2 billion of assets managed in our leveraged credit strategies, $7.3 billion of assets managed in our special situations strategy, $8.9 billion of assets managed in our private credit strategies, $20.0 billion of assets managed through our hedge fund business and $1.0 billion of assets managed in other strategies. Our private credit strategies include $2.4 billion of assets managed in our private opportunistic credit strategy, $5.9 billion of assets managed in our direct lending strategy and $0.6 billion of assets managed in our revolving credit strategy.
Credit
Performance
We generally review our performance in our credit business by investment strategy. Our leveraged credit strategies principally invest in leveraged loans and high yield bonds, or a combination of both. In certain cases, these strategies have meaningful track records and may be compared to widely-known indices. The following table presents information regarding larger leveraged credit strategies managed by KKR from inception to March 31, 2017. Past performance is no guarantee of future results.
63
Leveraged Credit Strategies: Inception-to-Date Annualized Gross Performance vs. Benchmark by Strategy
($ in millions) | Inception Date | Gross Returns | Net Returns | Benchmark (1) | Benchmark Gross Returns | ||||||||
Bank Loans Plus High Yield | Jul 2008 | 8.50 | % | 7.85 | % | 65% S&P/ LSTA, 35% BoAML HY Master II Index (2) | 6.53 | % | |||||
Opportunistic Credit (3) | May 2008 | 13.30 | % | 11.22 | % | BoAML HY Master II Index (3) | 8.21 | % | |||||
Bank Loans | Apr 2011 | 5.62 | % | 4.99 | % | S&P/ LSTA Loan Index (4) | 4.29 | % | |||||
High Yield | Apr 2011 | 7.00 | % | 6.41 | % | BoAML HY Master II Index (5) | 6.64 | % | |||||
Bank Loans Conservative | Apr 2011 | 4.90 | % | 4.28 | % | S&P/ LSTA BB-B Loan Index (6) | 4.29 | % | |||||
European Leveraged Loans (7) | Sep 2009 | 5.75 | % | 5.22 | % | CS Inst West European Leveraged Loan Index (8) | 4.96 | % | |||||
High Yield Conservative | Apr 2011 | 6.44 | % | 5.87 | % | BoAML HY BB-B Constrained | 6.53 | % | |||||
European Credit Opportunities (7) | Sept 2007 | 5.80 | % | 4.89 | % | S&P LSTA European Leveraged Loans (All Loans) | 4.43 | % | |||||
(1) | The Benchmarks referred to herein include the S&P/LSTA Leveraged Loan Index (the “S&P/LSTA Loan Index”), S&P/LSTA U.S. B/BB Ratings Loan Index (the '"S&P/ LSTA BB-B Loan Index"), the Bank of America Merrill Lynch High Yield Master II Index (the “BoAML HY Master II Index”), the BofA Merrill Lynch BB-B US High Yield Index (the “BoAML HY BB-B Constrained"), the Credit Suisse Institutional Western European Leveraged Loan Index (the “CS Inst European Leveraged Loan Index"), and S&P LSTA European Leveraged Loans (All Loans). The S&P/LSTA Loan Index is a daily tradable index for the U.S. loan market that seeks to mirror the market-weighted performance of the largest institutional loans that meet certain criteria. The S&P/ LSTA BB-B Loan Index is comprised of loans in the S&P/LSTA Loan Index, whose rating is BB+, BB, BB-, B+, B or B-. The BoAML HY Master II Index is an index for high yield corporate bonds. It is designed to measure the broad high yield market, including lower-rated securities. The BOAML HY BB-B Constrained is a subset of the BoAML HY Master II Index including all securities rated BB1 through B3, inclusive. The CS Inst European Leveraged Loan Index contains only institutional loan facilities priced above 90, excluding TL and TLa facilities and loans rated CC, C or are in default. The S&P European Leveraged Loan Index reflects the market-weighted performance of institutional leveraged loan portfolios investing in European credits. While the returns of these strategies reflect the reinvestment of income and dividends, none of the indices presented in the chart above reflect such reinvestment, which has the effect of increasing the reported relative performance of these strategies as compared to the indices. Furthermore, these indices are not subject to management fees, incentive allocations or expenses. |
(2) | Performance is based on a blended composite of Bank Loans Plus High Yield strategy accounts. The Benchmark used for purposes of comparison for the Bank Loans Plus High Yield strategy is based on 65% S&P/LSTA Loan Index and 35% BoAML HY Master II Index. |
(3) | The Opportunistic Credit strategy invests in high yield securities and corporate loans with no preset allocation. The Benchmark used for purposes of comparison for the Opportunistic Credit strategy presented herein is based on the BoAML HY Master II Index. Funds within this strategy may utilize third party financing facilities to enhance investment returns. In cases where financing facilities are used, the amounts drawn on the facility are deducted from the assets of the fund in the calculation of net asset value, which tends to increase returns when net asset value grows over time and decrease returns when net asset value decreases over time. |
(4) | Performance is based on a composite of portfolios that primarily invest in leveraged loans. The Benchmark used for purposes of comparison for the Bank Loans strategy is based on the S&P/LSTA Loan Index. |
(5) | Performance is based on a composite of portfolios that primarily invest in high yield securities. The Benchmark used for purposes of comparison for the High Yield strategy is based on the BoAML HY Master II Index. |
(6) | Performance is based on a composite of portfolios that primarily invest in leveraged loans rated B-/Baa3 or higher. The Benchmark used for purposes of comparison for the Bank Loans strategy is based on the S&P/LSTA BB/B Loan Index. |
(7) | The returns presented are calculated based on local currency. |
(8) | Performance is based on a composite of portfolios that primarily invest in higher quality leveraged loans. The Benchmark used for purposes of comparison for the European Senior Loans strategy is based on the CS Inst West European Leveraged Loan Index. |
64
Our alternative credit strategies primarily invest in more illiquid instruments through private investment funds, BDCs and separately managed accounts. The following table presents information regarding our Public Markets alternative credit commingled funds where investors are subject to capital commitments from inception to March 31, 2017. Some of these funds have been investing for less than 24 months, and thus their performance is less meaningful and not included below. Past performance is no guarantee of future results.
Credit Strategies: Fund Performance
Amount | Fair Value of Investments | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Public Markets Investment Funds | Inception Date | Commitment | Invested (1) | Realized (1) | Unrealized | Total Value | Gross IRR (2) | Net IRR (2) | Multiple of Invested Capital (3) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
($ in Millions) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Special Situations Fund | Dec-12 | $ | 2,274.3 | $ | 2,165.2 | $ | 542.2 | $ | 2,194.9 | $ | 2,737.1 | 9.5 | % | 7.6 | % | 1.3 | |||||||||||||||
Special Situations Fund II | Dec-14 | 3,195.4 | 922.4 | — | 868.3 | 868.3 | (4.1 | )% | (7.4 | )% | 0.9 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Mezzanine Partners | Mar-10 | 1,022.8 | 913.9 | 782.9 | 453.2 | 1,236.1 | 11.9 | % | 8.0 | % | 1.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Private Credit Opportunities Partners II | Dec-15 | 548.1 | — | — | 14.7 | 14.7 | N/A | N/A | N/A | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Lending Partners | Dec-11 | 460.2 | 405.3 | 260.0 | 255.2 | 515.2 | 8.2 | % | 6.8 | % | 1.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Lending Partners II | Jun-14 | 1,335.9 | 867.1 | 163.9 | 946.3 | 1,110.2 | 17.5 | % | 14.9 | % | 1.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Lending Partners Europe | Mar-15 | 847.6 | 244.9 | 21.7 | 270.9 | 292.6 | 32.9 | % | 23.1 | % | 1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Revolving Credit Partners | May-15 | 510.0 | — | 16.1 | (11.1 | ) | 5.0 | N/A | N/A | N/A | |||||||||||||||||||||
All Funds | $ | 10,194.3 | $ | 5,518.8 | $ | 1,786.8 | $ | 4,992.4 | $ | 6,779.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
(1) Recycled capital is excluded from the amounts invested and realized.
(2) These credit funds utilize third party financing facilities to provide liquidity to such funds, and in such event IRRs are calculated from the time capital contributions are due from fund investors to the time fund investors receive a related distribution from the fund. The use of such financing facilities generally decreases the amount of invested capital that would otherwise be used to calculate IRRs, which tends to increase IRRs when fair value grows over time and decrease IRRs when fair value decreases over time. IRRs measure the aggregate annual compounded returns generated by a fund’s investments over a holding period and are calculated taking into account recycled capital. Net IRRs presented are calculated after giving effect to the allocation of realized and unrealized carried interest and the payment of any applicable management fees. Gross IRRs are calculated before giving effect to the allocation of carried interest and the payment of any applicable management fees.
(3) The multiples of invested capital measure the aggregate value generated by a fund’s investments in absolute terms. Each multiple of invested capital is calculated by adding together the total realized and unrealized values of a fund’s investments and dividing by the total amount of capital invested by the investors. The use of financing facilities generally decreases the amount of invested capital that would otherwise be used to calculate multiples of invested capital, which tends to increase multiples when fair value grows over time and decrease multiples when fair value decreases over time. Such amounts do not give effect to the allocation of any realized and unrealized returns on a fund’s investments to the fund’s general partner pursuant to a carried interest or the payment of any applicable management fees and are calculated without taking into account recycled capital.
For the period beginning in June 2004 through March 31, 2017, our hedge fund-of-funds low volatility strategy, which consists of the majority of our hedge fund-of-funds AUM and FPAUM, generated a gross annualized return of 6.4%. Within our hedge funds business, as of March 31, 2017, KKR Prisma managed $9.6 billion of AUM and our strategic partnerships with other hedge fund managers accounted for $10.4 billion of AUM.
65
Public Markets Vehicle Structures
The table below presents information as of March 31, 2017, based on the investment funds, vehicles or accounts offered by our Public Markets segment. Our funds, vehicles and accounts have been sorted based upon their primary investment strategies. However, the AUM and FPAUM presented for each line in the table includes certain investments from non-primary investment strategies, which is permitted by their investment mandates, for purposes of presenting the fees and other terms for such funds, vehicles and accounts.
($ in millions) | AUM | FPAUM | Typical Management Fee Rate | Incentive Fee / Carried Interest | Preferred Return | Duration of Capital | ||||||||||
Leveraged Credit: | ||||||||||||||||
Leveraged Credit SMAs/Funds | $ | 9,522 | $ | 8,890 | 0.35%-1.50% | Various (1) | Various (1) | Subject to redemptions | ||||||||
CLO’s | 9,355 | 9,355 | 0.40%-0.50% | Various (1) | Various (1) | 10-14 Years (2) | ||||||||||
Total Leveraged Credit | 18,877 | 18,245 | ||||||||||||||
Alternative Credit: (3) | ||||||||||||||||
Special Situations | 8,246 | 4,703 | 0.90%-1.75% (4) | 10.00-20.00% | 8.00-12.00% | 8-15 Years (2) | ||||||||||
Private Credit | 6,036 | 3,669 | 0.50%-1.50% | 10.00-20.00% | 5.00-8.00% | 8-15 Years (2) | ||||||||||
Total Alternative Credit | 14,282 | 8,372 | ||||||||||||||
Hedge Funds (5) | 20,011 | 19,598 | 0.50%-2.00% | Various (1) | Various (1) | Subject to redemptions | ||||||||||
Business Development Companies (6) | 4,249 | 4,249 | 1.00% | 10.00% | 7.00% | 7 years | ||||||||||
Total | $ | 57,419 | $ | 50,464 | ||||||||||||
(1) | Certain funds and CLOs are subject to a performance fee in which the manager or general partner of the funds share in up to 20% (in the majority of our hedge fund solutions business, up to 10%) of the net profits earned by investors in excess of performance hurdles (generally tied to a benchmark or index) and subject to a provision requiring the funds and vehicles to regain prior losses before any performance fee is earned. |
(2) | Duration of capital is measured from inception. Inception dates for CLOs were between 2005 and 2016 and for separately managed accounts and funds investing in alternative credit strategies from 2009 through 2016. |
(3) | Our alternative credit funds generally have investment periods of 3 to 5 years and our newer alternative credit funds generally earn fees on invested capital during the investment period. |
(4) | Lower fees on uninvested capital in certain vehicles. |
(5) | Hedge Funds include KKR's hedge fund solutions platform and KKR's pro-rata portion of AUM and FPAUM of strategic partnerships, which consist of minority stakes in other hedge fund managers. |
(6) | Consists of Corporate Capital Trust (CCT) and Corporate Capital Trust II, which are BDCs sub-advised by KKR. These vehicles invest in both leveraged credit and private credit strategies. On April 6, 2017, CCT filed a preliminary proxy statement with the SEC to call a meeting of CCT shareholders to vote, among other things, on a proposal for KKR Credit Advisors (US) LLC to become CCT’s sole investment adviser subject to the listing of CCT’s shares on a national securities exchange. |
Capital Markets
Our capital markets business supports our firm, our portfolio companies and third-party clients by developing and implementing both traditional and non-traditional capital solutions for investments or companies seeking financing. These services include arranging debt and equity financing, placing and underwriting securities offerings and providing other types of capital markets services. When we underwrite an offering of securities or a loan on a firm commitment basis, we commit to buy and sell an issue of securities or indebtedness and generate revenue by purchasing the securities or indebtedness at a discount or for a fee. When we act in an agency capacity or best efforts basis, we generate revenue for arranging financing or placing securities or debt with capital markets investors. We may also provide issuers with capital markets advice on security selection, access to markets, marketing considerations, securities pricing, and other aspects of capital markets transactions in exchange for a fee. When we are sole arrangers of a credit facility, we generally advance amounts to the borrower on behalf of other lenders, for which such lenders are expected to repay us promptly. KKR Capital Markets LLC is an SEC-registered broker-dealer and a FINRA member, and we are also registered or authorized to carry out certain broker-dealer activities in various countries in North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific and the Middle East.
66
Principal Activities
Through our Principal Activities segment, we manage the firm’s own assets on our balance sheet and deploy capital to support and grow our businesses. Our Principal Activities segment uses our balance sheet assets to support our investment management and capital markets businesses. Typically, the funds in our Private Markets and Public Markets businesses contractually require us, as general partner of the funds, to make sizable capital commitments from time to time. We believe our general partner commitments are indicative of the conviction we have in a given fund’s strategy, which assists us in raising new funds from limited partners. We also use our balance sheet to acquire investments in order to help establish a track record for fundraising purposes in new strategies. We may also use our own capital to seed investments for new funds, to bridge capital selectively for our funds’ investments or finance strategic acquisitions and partnerships, although the financial results of an acquired business or strategic partnership may be reported in our other segments.
Our Principal Activities segment also provides the required capital to fund the various commitments of our Capital Markets business when underwriting or syndicating securities, or when providing term loan commitments for transactions involving our portfolio companies and for third parties. Our Principal Activities segment also holds assets that may be utilized to satisfy regulatory requirements for our Capital Markets business and risk retention requirements for our CLO business.
We also make opportunistic investments through our Principal Activities segment, which include co-investments alongside our Private Markets and Public Markets funds, as well as make Principal Activities investments that do not involve our Private Markets or Public Markets funds.
We endeavor to use our balance sheet strategically and opportunistically to generate an attractive risk-adjusted return on equity in a manner that is consistent with our fiduciary duties and in compliance with applicable laws.
The chart below presents the holdings of our Principal Activities segment by asset class as of March 31, 2017.
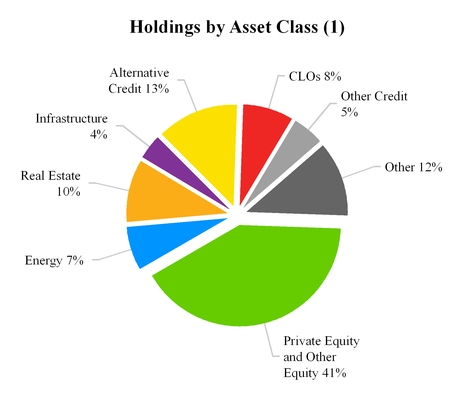
(1) General partner commitments in our funds are included in the various asset classes shown above. Assets and revenues of other asset managers with which KKR has formed strategic partnerships where KKR does not hold more than 50% ownership interest are not included in our Principal Activities segment but are reported in the financial results of our other segments. Private Equity and Other Equity includes KKR private equity funds, co-investments alongside such KKR sponsored private equity funds and other opportunistic investments. However, equity investments in other asset classes, such as real estate, special situations and energy appear in these other asset classes. Other Credit consists of liquid credit and specialty finance strategies.
67
Business Environment
Market Conditions
Global Economic Conditions. As a global investment firm, we are affected by financial and economic conditions globally. Global and regional economic conditions have a substantial impact on our financial condition and results of operations, impacting the values of the investments we make, our ability to exit these investments profitably and our ability to make new investments. Financial and economic conditions in the United States and the European Union are significant contributors to the global economy. According to Bureau of Economic Analysis as of March 31, 2017, real GDP in the United States increased at a seasonally adjusted annualized rate of 0.7% for the quarter ended March 31, 2017 compared to 2.1% for the quarter ended December 31, 2016. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the U.S. unemployment rate was 4.5% as of March 31, 2017, down from 4.7% as of December 31, 2016. For the quarter ended March 31, 2017, Bloomberg estimates suggest that Euro Area real GDP growth was 0.4% on a quarter over quarter basis, compared to actual quarter over quarter growth of 0.5% as of December 31, 2016. Euro Area core inflation was 0.7% on a year over year basis as of March 31, 2017, compared to 0.9% as of December 31, 2016. Following the June 2016 referendum held in the United Kingdom in which voters approved an exit from the European Union, commonly referred to as “Brexit,” the United Kingdom triggered Article 50 to formally begin the exit process. Continuing controversy and uncertainty surrounding key issues such as immigration, austerity, and globalization and risk of countries exiting the European Union could impair economic growth in the region and lead to financial market volatility. These and other key issues could have adverse repercussions across financial markets, which could adversely affect the valuations of our investments. In addition, on a quarter over quarter, seasonally adjusted basis, China’s National Bureau of Statistics indicated that real GDP grew 1.3% in the quarter ended March 31, 2017, less than the 1.7% reported for the quarter ended December 31, 2016. A slowdown in China's growth could adversely impact the valuations of our investments in China and could also adversely impact the global economy, particularly other emerging markets. For a further discussion of how market conditions may affect our businesses, see “Risk Factors- Risks Related to Our Business - Difficult market conditions can adversely affect our business in many ways, including by reducing the value or performance of the investments that we manage or by reducing the ability of our funds to raise or deploy capital, each of which could negatively impact our net income and cash flow and adversely affect our financial condition” in our Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Global Equity and Credit Markets. Global equity and credit markets have a substantial effect on our financial condition and results of operations. In general, a climate of reasonable interest rates and high levels of liquidity in the debt and equity capital markets provide a positive environment for us to generate attractive investment returns, which also impacts our ability to generate incentive fees and carried interest. Periods of volatility and dislocation in the capital markets present substantial risks, but also can present us with opportunities to invest at reduced valuations that position us for future growth and investment returns.
Many of our investments are in equities, so a change in global equity prices or in market volatility directly impacts the value of our investments and our profitability as well as our ability to realize investment gains and the receptiveness of fund investors to our investment products. For the quarter ended March 31, 2017, global equity markets were positive, with the S&P 500 Index up 6.1% and the MSCI World Index up 6.5% on a total return basis including dividends. Equity market volatility as evidenced by the Chicago Board Options Exchange Market Volatility Index, or the VIX, a measure of volatility, ended at 12.4 as of March 31, 2017 decreasing from 14.0 as of December 31, 2016. For a further discussion of our valuation methods, see “Risk Factors-Risks Related to the Assets We Manage - Our investments are impacted by various economic conditions that are difficult to quantify or predict, and may have a significant impact on the valuation of our investments and, therefore, on the investment income we realize and our financial condition and results of operations” in our Annual Report on Form 10-K and “-Critical Accounting Policies-Fair Value Measurements-Level III Valuation Methodologies” in this report.
Many of our investments are also in credit instruments, and our funds and their portfolio companies also rely on credit financing and the ability to refinance existing debt. Consequently, any decrease in the value of credit instruments that we have invested in or any increase in the cost of credit financing reduces our returns and decreases our net income. In particular due in part to holdings of credit instruments such as CLOs on our balance sheet, the performance of the credit markets has had an amplified impact on our financial results, as we directly bear the full extent of losses from credit instruments on our balance sheet. Credit markets can also impact valuations because a discounted cash flow analysis is generally used as one of the methodologies used to ascertain the fair value of our investments that do not have readily observable market prices. In addition, with respect to our credit instruments, tightened credit spreads are generally expected to lead to an increase in the value of these investments, if not offset by hedging or other factors. During the quarter ended March 31, 2017, US Investment Grade corporate bond spreads (BofAML US Corporate Index) tightened by 6 basis points and US High-Yield corporate bond spreads (BofAML HY Master II Index) tightened by 30 basis points. For a further discussion of how market conditions may affect our businesses, see “Risk Factors- Risks Related to Our Business - Difficult market conditions can adversely affect our business in many ways, including by reducing the value or performance of the investments that we manage or by reducing the ability of
68
our funds to raise or deploy capital, each of which could negatively impact our net income and cash flow and adversely affect our financial condition" and "Risks Related to the Assets We Manage - Our investments are impacted by various economic conditions that are difficult to quantify or predict, and may have a significant impact on the valuation of our investments and, therefore, on the investment income we realize and our financial condition and results of operations" in our Annual Report on Form 10-K.
The sub-investment grade credit indices rose during the quarter ended March 31, 2017, with the S&P/LSTA Leveraged Loan Index up 1.1% and the BoAML HY Master II Index up 2.7%. For the quarter ended March 31, 2017, 10-year government bond yields fell 6 basis points in the United States, rose 25 basis points in China, rose 2 basis points in Japan and rose 12 basis points in Germany. For further discussion of the impact of global credit markets on our financial condition and results of operations, see “Risk Factors - Risks Related to the Assets We Manage -Changes in the debt financing markets may negatively impact the ability of our investment funds, their portfolio companies and strategies pursued with our balance sheet assets to obtain attractive financing for their investments or refinance existing debt and may increase the cost of such financing if it is obtained, which could lead to lower-yielding investments and potentially decrease our net income,” “- Our investments are impacted by various economic conditions that are difficult to quantify or predict, and may have a significant impact on the valuation of our investments and, therefore, on the investment income we realize and our financial condition and results of operations” and “- Because we hold interests in some of our portfolio companies both through our management of private equity funds as well as through separate investments in those funds and direct co-investments, fluctuation in the fair values of these portfolio companies may have a disproportionate impact on the investment income earned by us” in our Annual Report on Form 10-K and “-Critical Accounting Policies-Fair Value Measurements-Level III Valuation Methodologies” in this report.
Foreign Exchange Rates. Foreign exchange rates have a substantial impact on the valuations of our investments that are denominated in currencies other than the U.S. dollar. Currency volatility can also affect our businesses and investments, which deal in cross‑border trade. The appreciation or depreciation of the U.S. dollar is expected to contribute to a decrease or increase, respectively, in the U.S. dollar value of our non‑U.S. investments to the extent unhedged. In addition, an appreciating U.S. dollar would be expected to make the exports of U.S. based companies less competitive, which may lead to a decline in their export revenues, if any, while a depreciating U.S. dollar would be expected to have the opposite effect. Moreover, when selecting investments for our investment funds that are denominated in U.S. dollars, an appreciating U.S. dollar may create opportunities to invest at more attractive U.S. dollar prices in certain countries outside of the U.S., while a depreciating U.S. dollar would be expected to have the opposite effect. For the quarter ended March 31, 2017, the euro rose 1.3%, the China renminbi rose 1.0%, and the British pound rose 1.7% respectively, relative to the U.S. dollar. See “Risk Factors- Risks Related to Our Business - Difficult market conditions can adversely affect our business in many ways, including by reducing the value or performance of the investments that we manage or by reducing the ability of our funds to raise or deploy capital, each of which could negatively impact our net income and cash flow and adversely affect our financial condition” in our Annual Report on Form 10-K. In China, the continued potential for greater depreciation of China's currency, the yuan, remains a large source of uncertainty. For additional information regarding our foreign exchange rate risk, see “-Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosure About Market Risk - Exchange Rate Risk” in our Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Commodity Markets. Our Private Markets portfolio contains energy real asset investments and certain of our Public Markets strategies and products, including direct lending, special situations and CLOs, have meaningful investments in the energy sector. The value of these investments is heavily influenced by the price of natural gas and oil. During the quarter ended March 31, 2017, the long-term price of WTI crude decreased approximately 8%, while the long-term price of natural gas was relatively stable. The long-term price of WTI crude oil declined from approximately $56 per barrel to $51 per barrel, and the long-term price of natural gas decreased from approximately $2.87 per mcf to $2.84 per mcf as of December 31, 2016 and March 31, 2017, respectively. When commodity prices decline or if a decline is not offset by other factors, we would expect the value of our energy real asset investments to be adversely impacted. In addition, because we hold certain energy assets on our balance sheet, which had a fair value of $0.6 billion as of March 31, 2017, these price movements would have an amplified impact on our financial results, as we would directly bear the full extent of such gains or losses. For additional information regarding our energy real assets, see “-Critical Accounting Policies-Fair Value Measurements-Level III Valuation Methodologies-Real Asset Investments” in this report and “Risk Factors - Risks Related to the Assets We Manage - Because we hold interests in some of our portfolio companies both through our management of private equity funds as well as through separate investments in those funds and direct co-investments, fluctuation in the fair values of these portfolio companies may have a disproportionate impact on the investment income earned by us” in our Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Basis of Accounting
We consolidate the financial results of the KKR Group Partnerships and their consolidated subsidiaries, which include the accounts of our investment management and capital markets companies, the general partners of unconsolidated funds and
69
vehicles, general partners of certain funds that are consolidated and their respective consolidated funds and certain other entities including certain consolidated CLOs and commercial real estate mortgage-backed securities, or "CMBS". We refer to CLOs and CMBS as collateralized financing entities or CFEs.
When an entity is consolidated, we reflect the accounts of the consolidated entity, including its assets, liabilities, fees, expenses, investment income, cash flows and other amounts, on a gross basis. While the consolidation of a consolidated fund or entity does not have an effect on the amounts of Net Income Attributable to KKR or KKR's partners' capital that KKR reports, the consolidation does significantly impact the financial statement presentation under GAAP. This is due to the fact that the accounts of the consolidated entities are reflected on a gross basis while the allocable share of those amounts that are attributable to third parties are reflected as single line items. The single line items in which the accounts attributable to third parties are recorded are presented as noncontrolling interests on the consolidated statements of financial condition and net income attributable to noncontrolling interests on the consolidated statements of operations.
For a further discussion of our consolidation policies, see "Item 1. Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements (Unaudited)--Summary of Significant Accounting Policies."
Key Financial Measures Under GAAP
Fees and Other
Fees and other consist primarily of (i) transaction fees earned in connection with successful investment transactions and from capital markets activities, (ii) management and incentive fees from providing investment management services to unconsolidated funds, CLOs, other vehicles and separately managed accounts, (iii) monitoring fees from providing services to portfolio companies, (iv) carried interest allocations to general partners of unconsolidated funds, (v) revenue earned by oil and gas-producing entities that are consolidated and (vi) consulting fees earned by entities that employ non-employee operating consultants. These fees are based on the contractual terms of the governing agreements and are recognized when earned, which coincides with the period during which the related services are performed and in the case of transaction fees, upon closing of the transaction. Monitoring fees may provide for a termination payment following an initial public offering or change of control. These termination payments are recognized in the period when the related transaction closes.
For a further discussion of our fee policies, see "Item 1. Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements (Unaudited)--Summary of Significant Accounting Policies."
Expenses
Compensation and Benefits
Compensation and benefits expense includes cash compensation consisting of salaries, bonuses, and benefits, as well as equity-based compensation consisting of charges associated with the vesting of equity-based awards, carry pool allocations and other performance-based income compensation. All employees and employees of certain consolidated entities receive a base salary that is paid by KKR or its consolidated entities, and is accounted for as compensation and benefits expense. These employees are also eligible to receive discretionary cash bonuses based on performance, overall profitability and other matters. While cash bonuses paid to most employees are borne by KKR and certain consolidated entities and result in customary compensation and benefits expense, cash bonuses that are paid to certain employees are currently borne by KKR Holdings. These bonuses have historically been funded with distributions that KKR Holdings receives on KKR Group Partnership Units held by KKR Holdings but are not then passed on to holders of unvested units of KKR Holdings. Because employees are not entitled to receive distributions on units that are unvested, any amounts allocated to employees in excess of an employee's vested equity interests are reflected as employee compensation and benefits expense. These compensation charges are currently recorded based on the amount of cash expected to be paid by KKR Holdings. Because KKR makes only fixed quarterly distributions, the distributions made on KKR Group Partnership Units underlying any unvested KKR Holdings units are generally insufficient to fund annual cash bonus compensation to the same extent as in periods prior to the fourth quarter of 2015. In addition, substantially all units in KKR Holdings have been allocated and will vest over a 5 year period, thus decreasing the amount of distributions received by KKR Holdings that are available for annual cash bonus compensation. We, therefore, expect to pay an increasing portion and eventually all of the cash bonus payments currently borne by KKR Holdings from other sources, including cash from our operations, the carry pool and other performance-based income compensation as described below. See "Risks Related to Our Business - If we cannot retain and motivate our principals and other key personnel and recruit, retain and motivate new principals and other key personnel, our business, results and financial condition could be adversely affected" in our Annual Report on Form 10-K regarding the adequacy of such distributions to fund future discretionary cash bonuses.
70
With respect to KKR’s investment funds that provide for carried interest, KKR allocates 40% of the carried interest earned from such funds to its carry pool for employees and non-employee operating consultants. In addition, our carry pool is supplemented by allocating performance-based income to compensation equal to 40% of the incentive fees earned from investment funds that provide for incentive fees and, beginning with the quarter ended September 30, 2016, for investment funds that have a preferred return, also includes 40% of the management fees that would have been subject to a management fee refund. Because of the different ways management fees are refunded in preferred return and non-preferred return funds, this calculation of 40% of the portion of the management fees subject to refund for funds that have a preferred return is designed to allocate to compensation an amount comparable to the amount that would have been allocated to the carry pool had the fund not had a preferred return. For a discussion of how management fees are refunded for preferred return funds and non-preferred funds see "--Fair Value Measurements--Recognition of Carried Interest in the Statement of Operations".
The amounts allocated to the carry pool and other performance-based income compensation are accounted for as compensatory profit-sharing arrangements and recorded as compensation and benefits expense for KKR employees and general, administrative and other expense for certain non-employee consultants and service providers in the consolidated statements of operations prepared in accordance with U.S. GAAP.
General, Administrative and Other
General, administrative and other expense consists primarily of professional fees paid to legal advisors, accountants, advisors and consultants, insurance costs, travel and related expenses, communications and information services, depreciation and amortization charges, changes in fair value of contingent consideration, expenses incurred by oil and gas-producing entities (including impairment charges) that are consolidated and other general and operating expenses which are not borne by fund investors and are not offset by credits attributable to fund investors' noncontrolling interests in consolidated funds. General, administrative and other expense also consists of costs incurred in connection with pursuing potential investments that do not result in completed transactions, a substantial portion of which are borne by fund investors.
Investment Income (Loss)
Net Gains (Losses) from Investment Activities
Net gains (losses) from investment activities consist of realized and unrealized gains and losses arising from our investment activities. A large portion of our net gains (losses) from investment activities are related to our private equity investments. Fluctuations in net gains (losses) from investment activities between reporting periods is driven primarily by changes in the fair value of our investment portfolio as well as the realization of investments. The fair value of, as well as the ability to recognize gains from, our private equity and other investments is significantly impacted by the global financial markets, which, in turn, affects the net gains (losses) from investment activities recognized in any given period. Upon the disposition of an investment, previously recognized unrealized gains and losses are reversed and an offsetting realized gain or loss is recognized in the current period. Since our investments are carried at fair value, fluctuations between periods could be significant due to changes to the inputs to our valuation process over time. For a further discussion of our fair value measurements and fair value of investments, see "—Critical Accounting Policies—Fair Value Measurements."
Dividend Income
Dividend income consists primarily of distributions that we and our consolidated investment funds receive from portfolio companies in which they invest. Dividend income is recognized primarily in connection with (i) dispositions of operations by portfolio companies, (ii) distributions of excess cash generated from operations from portfolio companies and (iii) other significant refinancings undertaken by portfolio companies.
Interest Income
Interest income consists primarily of interest that is received on our credit instruments in which we and our consolidated funds and other entities invest as well as interest on our cash balances and other investments.
Interest Expense
Interest expense is incurred from debt issued by KKR, including debt issued by KFN which was consolidated upon completion of the acquisition of KFN, credit facilities entered into by KKR, debt securities issued by consolidated CFEs and financing arrangements at our consolidated funds entered into primarily with the objective of managing cash flow. KFN's debt
71
obligations are non-recourse to KKR beyond the assets of KFN. Debt securities issued by consolidated CFEs are supported solely by the investments held at the CFE and are not collateralized by assets of any other KKR entity. Our obligations under financing arrangements at our consolidated funds are generally limited to our pro-rata equity interest in such funds. However, in some circumstances, we may provide limited guarantees of the obligations of our general partners in an amount equal to its pro rata equity interest in such funds. We also may provide other kinds of guarantees. See "—Liquidity".
Income Taxes
The KKR Group Partnerships and certain of their subsidiaries operate in the United States as partnerships for U.S. federal income tax purposes and as corporate entities in non-U.S. jurisdictions. Accordingly, these entities, in some cases, are subject to New York City unincorporated business taxes, or non-U.S. income taxes. Furthermore, we hold our interest in one of the KKR Group Partnerships through KKR Management Holdings Corp., which is treated as a corporation for U.S. federal income tax purposes, and certain other subsidiaries of the KKR Group Partnerships are treated as corporations for U.S. federal income tax purposes. Accordingly, certain subsidiaries of KKR, including KKR Management Holdings Corp., are subject to U.S. federal, state and local corporate income taxes at the entity level and the related tax provision attributable to KKR's share of this income is reflected in the financial statements. We also generate certain interest income to our unitholders and interest deductions to KKR Management Holdings Corp.
We use the asset and liability method to account for income taxes in accordance with GAAP. Under this method, deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the expected future tax consequences of differences between the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities and their respective tax basis using currently enacted tax rates. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized in income in the period when the change is enacted. Deferred tax assets are reduced by a valuation allowance when it is more likely than not that all or a portion of the deferred tax assets will not be realized.
Tax laws are complex and subject to different interpretations by the taxpayer and respective governmental taxing authorities. Significant judgment is required in determining tax expense and in evaluating tax positions including evaluating uncertainties. We review our tax positions quarterly and adjust our tax balances as new information becomes available.
Net Income (Loss) Attributable to Noncontrolling Interests
Net income (loss) attributable to noncontrolling interests primarily represents the ownership interests that certain third parties hold in entities that are consolidated in the financial statements as well as the ownership interests in our KKR Group Partnerships that are held by KKR Holdings. The allocable share of income and expense attributable to these interests is accounted for as net income (loss) attributable to noncontrolling interests. Given the consolidation of certain of our investment funds and the significant ownership interests in our KKR Group Partnerships held by KKR Holdings, we expect a portion of net income (loss) will continue to be attributed to noncontrolling interests in our business.
For a further discussion of our noncontrolling interests policies, see "Item 1. Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements (Unaudited)--Summary of Significant Accounting Policies."
Segment Operating and Performance Measures
The segment key performance measures that follow are used by management in making operating and resource deployment decisions as well as assessing the overall performance of each of KKR's reportable business segments. The reportable segments for KKR's business are presented prior to giving effect to the allocation of income (loss) between KKR & Co. L.P. and KKR Holdings L.P. and as such represent the business in total. In addition, KKR's reportable segments are presented without giving effect to the consolidation of the investment funds and CFEs that KKR manages as well as other consolidated entities that are not subsidiaries of KKR & Co. L.P.
We disclose the following financial measures in this report that are calculated and presented using methodologies other than in accordance with GAAP. We believe that providing these performance measures on a supplemental basis to our GAAP results is helpful to unitholders in assessing the overall performance of KKR's businesses. These financial measures should not be considered as a substitute for similar financial measures calculated in accordance with GAAP, if available. We caution readers that these non-GAAP financial measures may differ from the calculations of other investment managers, and as a result, may not be comparable to similar measures presented by other investment managers. Reconciliations of these non-GAAP financial measures to the most directly comparable financial measures calculated and presented in accordance with GAAP, where applicable, are included within "Financial Statements and Supplementary Data — Note 14. Segment Reporting" and later in this report under "—Segment Balance Sheet."
72
Adjusted Units
Adjusted units are used as a measure of the total common equity ownership of KKR that is held by KKR & Co. L.P. (including equity awards issued under the KKR & Co. L.P. 2010 Equity Incentive Plan (the "Equity Incentive Plan"), but excluding preferred units), KKR Holdings and other holders of securities exchangeable into common units of KKR & Co. L.P. and represent the fully diluted common unit count using the if-converted method. We believe this measure is useful to unitholders as it provides an indication of the total common equity ownership of KKR as if all outstanding KKR Holdings units, equity awards issued under the Equity Incentive Plan and other exchangeable securities had been exchanged for common units of KKR & Co. L.P. The Series A and Series B Preferred Units are not exchangeable for common units of KKR & Co. L.P.
Adjusted Units Eligible for Distribution
Adjusted units eligible for distribution represents the portion of total adjusted units that is eligible to receive a distribution. We believe this measure is useful to unitholders as it provides insight into the calculation of amounts available for distribution on a per unit basis. Adjusted units eligible for distribution is used in the calculation of after-tax distributable earnings per unit.
After-Tax Distributable Earnings
After-tax distributable earnings is used by management as an operating measure of the earnings excluding mark-to-market gains (losses) of KKR. KKR believes this measure is useful to unitholders as it provides a supplemental measure to assess performance, excluding the impact of mark-to-market gains (losses). After-tax distributable earnings excludes certain realized investment losses to the extent unrealized losses on these investments were recognized prior to the combination with KPE on October 1, 2009. After-tax distributable earnings does not represent and is not used to calculate actual distributions under KKR’s distribution policy.
73
The following table presents our after-tax distributable earnings on common units for the three months ended March 31, 2017 and 2016 as described above. For a discussion of the components that drove the changes in our distributable earnings, see“—Segment Analysis.”
Three Months Ended | ||||||||
($ in thousands except per unit data) | March 31, 2017 | March 31, 2016 | ||||||
Revenues | ||||||||
Management, Monitoring and Transaction Fees, Net | $ | 375,522 | $ | 279,915 | ||||
Realized Performance Income (loss) | 207,890 | 98,881 | ||||||
Realized Investment Income (loss) | 94,624 | 35,393 | ||||||
Total Distributable Segment Revenues | 678,036 | 414,189 | ||||||
Expenses | ||||||||
Cash Compensation and Benefits | 139,435 | 100,899 | ||||||
Realized Performance Income Compensation | 88,067 | 39,552 | ||||||
Occupancy and Related Charges | 14,369 | 15,950 | ||||||
Other Operating Expenses | 53,498 | 61,886 | ||||||
Total Distributable Segment Expenses | 295,369 | 218,287 | ||||||
Distributable Earnings Before Taxes, Noncontrolling Interests and Preferred Distributions | 382,667 | 195,902 | ||||||
Less: Corporate and local income taxes paid | 26,275 | 26,503 | ||||||
Less: Income attributable to segment noncontrolling interests | 1,584 | 667 | ||||||
Less: Preferred Distributions | 8,341 | — | ||||||
After-tax Distributable Earnings | $ | 346,467 | $ | 168,732 | ||||
Per Adjusted Unit Eligible for Distribution | $ | 0.43 | $ | 0.21 | ||||
Assets Under Management ("AUM")
Assets under management ("AUM") represent the assets managed by KKR or by its strategic partners from which KKR is entitled to receive fees or a carried interest (either currently or upon deployment of capital) and general partner capital. We believe this measure is useful to unitholders as it provides additional insight into KKR's capital raising activities and the overall activity in its investment funds and strategic partnerships. KKR calculates the amount of AUM as of any date as the sum of: (i) the fair value of the investments of KKR's investment funds; (ii) uncalled capital commitments from these funds, including uncalled capital commitments from which KKR is currently not earning management fees or carried interest; (iii) the fair value of investments in KKR's co-investment vehicles; (iv) the par value of outstanding CLOs (excluding CLOs wholly-owned by KKR); (v) KKR's pro-rata portion of the AUM managed by strategic partnerships in which KKR holds a minority ownership interest and (vi) the fair value of other assets managed by KKR. The pro-rata portion of the AUM managed by strategic partnerships is calculated based on KKR’s percentage ownership interest in such entities multiplied by such entity’s respective AUM. KKR's definition of AUM is not based on any definition of AUM that may be set forth in the agreements governing the investment funds, vehicles or accounts that it manages or calculated pursuant to any regulatory definitions.
Book Value
Book value is a measure of the net assets of KKR’s reportable segments and is used by management primarily in assessing the unrealized value of KKR’s investments and other assets, including carried interest. We believe this measure is useful to unitholders as it provides additional insight into the assets and liabilities of KKR excluding the assets and liabilities that are allocated to noncontrolling interest holders and to the holders of the Series A and Series B Preferred Units.
74
Capital Invested
Capital invested is the aggregate amount of capital invested by (i) KKR’s investment funds, (ii) KKR's Principal Activities segment as a co-investment, if any, alongside KKR’s investment funds, and (iii) the Principal Activities segment in connection with a syndication transaction conducted by KKR's Capital Markets segment, if any. Capital invested is used as a measure of investment activity at KKR during a given period. We believe this measure is useful to unitholders as it provides a measure of capital deployment across KKR’s business segments. Capital invested includes investments made using investment financing arrangements like credit facilities, as applicable. Capital invested excludes (i) investments in liquid credit strategies, (ii) capital invested by KKR’s Principal Activities segment that is not a co-investment alongside KKR’s investment funds, and (iii) capital invested by the Principal Activities segment that is not invested in connection with a syndication transaction by KKR’s Capital Markets segment. Capital syndicated by our Capital Markets segment to third parties other than KKR’s investment funds or Principal Activities segment is not included in capital invested. See also syndicated capital. In the fourth quarter of 2016, the capital invested metric was changed to include capital invested by KKR's Principal Activities segment and all prior periods in this report have been adjusted.
Economic Net Income (Loss) (“ENI”)
Economic net income (loss) is a measure of profitability for KKR’s reportable segments and is used by management as an alternative measurement of the operating and investment earnings of KKR and its business segments. We believe this measure is useful to unitholders as it provides additional insight into the overall profitability of KKR’s businesses inclusive of carried interest, incentive fees and related carry pool allocations and investment income. ENI is comprised of total segment revenues less total segment expenses and certain economic interests in KKR’s segments held by third parties. Pre-tax Economic Net Income (Loss) represents Economic Net Income (Loss) after equity-based compensation. After-tax Economic Net Income (Loss) represents Economic Net Income (Loss) after equity-based compensation, provision for income taxes and preferred distributions.
Fee Paying AUM ("FPAUM")
Fee paying AUM represents only those assets under management of KKR or its strategic partners from which KKR receives management fees. We believe this measure is useful to unitholders as it provides additional insight into the capital base upon which KKR earns management fees. FPAUM is the sum of all of the individual fee bases that are used to calculate KKR's fees and differs from AUM in the following respects: (i) assets and commitments from which KKR does not receive a fee are excluded (i.e. assets and commitments with respect to which it receives only carried interest or is otherwise not currently receiving a fee) and (ii) certain assets, primarily in its private equity funds, are reflected based on capital commitments and invested capital as opposed to fair value because fees are not impacted by changes in the fair value of underlying investments.
Fee Related Earnings ("FRE")
Fee related earnings is a measure of the operating earnings of KKR and its business segments before performance income, related performance income compensation and investment income. KKR believes this measure may be useful to unitholders as it provides additional insight into the operating profitability of KKR's fee generating management companies and capital markets businesses.
Outstanding Adjusted Units
Outstanding adjusted units represents the portion of total adjusted units that would receive assets of KKR if it were to be liquidated as of a particular date. Outstanding adjusted units is used to calculate book value per outstanding adjusted unit, which we believe is useful to unitholders as it provides a measure of net assets of KKR’s reportable segments on a per unit basis.
Syndicated Capital
Syndicated capital is generally the aggregate amount of capital in transactions originated by KKR and its investment funds and carry-yielding co-investment vehicles, which has been distributed to third parties in exchange for a fee. It does not include (i) capital invested in such transactions by KKR investment funds and carry-yielding co-investment vehicles, which is instead reported in capital invested and (ii) debt capital that is arranged as part of the acquisition financing of transactions originated by KKR investment funds and (iii) debt capital that is either underwritten or arranged on a best efforts basis. Syndicated capital is used as a measure of investment activity for KKR during a given period, and we believe that this measure is useful to
75
unitholders as it provides additional insight into levels of syndication activity in KKR's Capital Markets segment and across its investment platform.
Uncalled Commitments
Uncalled commitments are used as a measure of unfunded capital commitments that KKR’s investment funds and carry-paying co-investment vehicles have received from partners to contribute capital to fund future investments. We believe this measure is useful to unitholders as it provides additional insight into the amount of capital that is available to KKR’s investment funds to make future investments. Uncalled commitments are not reduced for investments completed using fund-level investment financing arrangements.
A reconciliation of Net Income (Loss) Attributable to KKR & Co. L.P. Common Unitholders on a GAAP basis to ENI, FRE and After-tax Distributable Earnings is provided below.
Three Months Ended | ||||||||
($ in thousands) | March 31, 2017 | March 31, 2016 | ||||||
Net Income (Loss) Attributable to KKR & Co. L.P. Common Unitholders | $ | 259,343 | $ | (329,939 | ) | |||
Plus: Preferred Distributions | 8,341 | — | ||||||
Plus: Net income (loss) attributable to noncontrolling interests held by KKR Holdings L.P. | 216,432 | (271,575 | ) | |||||
Plus: Non-cash equity-based charges | 111,036 | 63,823 | ||||||
Plus: Amortization of intangibles, placement fees and other, net | 32,837 | 28,882 | ||||||
Plus: Income tax (benefit) | 40,542 | 1,890 | ||||||
Economic Net Income (Loss) | 668,531 | (506,919 | ) | |||||
Plus: Income attributable to segment noncontrolling interests | 1,584 | 667 | ||||||
Less: Total investment income (loss) | 298,660 | (529,598 | ) | |||||
Less: Net performance income (loss) | 203,235 | (77,834 | ) | |||||
Plus: Expenses of Principal Activities Segment | 53,769 | 39,818 | ||||||
Fee Related Earnings | 221,989 | 140,998 | ||||||
Plus: Net interest and dividends | 15,173 | 59,576 | ||||||
Less: Expenses of Principal Activities Segment | 53,769 | 39,818 | ||||||
Plus: Realized performance income (loss), net | 119,823 | 59,329 | ||||||
Plus: Net realized gains (losses) | 79,451 | (24,183 | ) | |||||
Less: Corporate and local income taxes paid | 26,275 | 26,503 | ||||||
Less: Preferred Distributions | 8,341 | — | ||||||
Less: Income attributable to segment noncontrolling interests | 1,584 | 667 | ||||||
After-tax Distributable Earnings | $ | 346,467 | $ | 168,732 | ||||
76
Unaudited Condensed Consolidated Results of Operations
The following is a discussion of our condensed consolidated results of operations for the three months ended March 31, 2017 and 2016. You should read this discussion in conjunction with the condensed consolidated financial statements and related notes included elsewhere in this report. For a more detailed discussion of the factors that affected the results of operations of our four business segments in these periods, see “—Segment Analysis.”
Three months ended March 31, 2017 compared to three months ended March 31, 2016
Three Months Ended | |||||||||||
March 31, 2017 | March 31, 2016 | Change | |||||||||
($ in thousands) | |||||||||||
Revenues | |||||||||||
Fees and Other | $ | 715,952 | $ | 162,805 | $ | 553,147 | |||||
Expenses | |||||||||||
Compensation and Benefits | 402,963 | 125,489 | 277,474 | ||||||||
Occupancy and Related Charges | 14,851 | 16,566 | (1,715 | ) | |||||||
General, Administrative and Other | 122,200 | 166,268 | (44,068 | ) | |||||||
Total Expenses | 540,014 | 308,323 | 231,691 | ||||||||
Investment Income (Loss) | |||||||||||
Net Gains (Losses) from Investment Activities | 558,448 | (735,223 | ) | 1,293,671 | |||||||
Dividend Income | 9,924 | 63,213 | (53,289 | ) | |||||||
Interest Income | 280,980 | 230,476 | 50,504 | ||||||||
Interest Expense | (186,854 | ) | (171,394 | ) | (15,460 | ) | |||||
Total Investment Income (Loss) | 662,498 | (612,928 | ) | 1,275,426 | |||||||
Income (Loss) Before Taxes | 838,436 | (758,446 | ) | 1,596,882 | |||||||
Income Taxes | 40,542 | 1,890 | 38,652 | ||||||||
Net Income (Loss) | 797,894 | (760,336 | ) | 1,558,230 | |||||||
Net Income (Loss) Attributable to Redeemable Noncontrolling Interests | 20,933 | (38 | ) | 20,971 | |||||||
Net Income (Loss) Attributable to Noncontrolling Interests | 509,277 | (430,359 | ) | 939,636 | |||||||
Net Income (Loss) Attributable to KKR & Co. L.P. | 267,684 | (329,939 | ) | 597,623 | |||||||
Less: Net Income Attributable to Series A Preferred Unitholders | 5,822 | — | 5,822 | ||||||||
Less: Net Income Attributable to Series B Preferred Unitholders | 2,519 | — | 2,519 | ||||||||
Net Income (Loss) Attributable to KKR & Co. L.P. Common Unitholders | $ | 259,343 | $ | (329,939 | ) | $ | 589,282 | ||||
77
Fees and Other
For the three months ended March 31, 2017 and 2016, fees and other consisted of the following:
Three Months Ended | ||||||||||||
March 31, 2017 | March 31, 2016 | Change | ||||||||||
Management Fees | $ | 161,182 | $ | 156,330 | $ | 4,852 | ||||||
Transaction Fees | 243,658 | 97,268 | 146,390 | |||||||||
Monitoring Fees | 36,769 | 28,103 | 8,666 | |||||||||
Fee Credits | (88,078 | ) | (22,379 | ) | (65,699 | ) | ||||||
Carried Interest | 335,773 | (116,956 | ) | 452,729 | ||||||||
Incentive Fees | 273 | (2,008 | ) | 2,281 | ||||||||
Oil and Gas Revenue | 17,273 | 13,561 | 3,712 | |||||||||
Consulting Fees | 9,102 | 8,886 | 216 | |||||||||
Total Fees and Other | $ | 715,952 | $ | 162,805 | $ | 553,147 | ||||||
Management fees, transaction fees, monitoring fees and fee credits all increased in the three months ended March 31, 2017 compared to the three months ended March 31, 2016. For a more detailed discussion of the factors that affected our management fees, transaction fees, monitoring fees and fee credits during the period, see “—Segment Analysis.”
The carried interest gains earned during the three months ended March 31, 2017 were due primarily to an overall increase in the value of our private equity and alternative credit portfolios. For a more detailed discussion of the factors that affected our Private Markets and Public Markets carried interest during the period, see “—Segment Analysis -- Private Markets -- Segment Revenues -- Performance Income and —Segment Analysis -- Public Markets -- Segment Revenues -- Performance Income.”
The increase in oil and gas revenue was due primarily to a higher price of oil in the three months ended March 31, 2017 compared to the three months ended March 31, 2016.
Compensation and Benefits Expenses
The increase was primarily due to higher carry pool allocations reflecting a higher level of appreciation in the value of our private equity portfolio during the three months ended March 31, 2017 compared to the three months ended March 31, 2016 as well as an increase in management and transaction fees.
General Administrative and Other Expenses
The decrease was primarily due to (i) a lower level of financing costs incurred relating to debt at new consolidated CLOs for which the fair value option has been elected and (ii) a decrease in depreciation, depletion and amortization of our consolidated oil and gas producing entities caused by a lower cost basis due to previously recorded impairments, resulting in a lower unit of production depletion rate compared to the prior period. These decreases were partially offset by an increase in placement fees incurred in connection with capital raising activity, the most significant of which relates to Asia Fund III.
78
Net Gains (Losses) from Investment Activities
The following is a summary of net gains (losses) from investment activities:
Three Months Ended March 31, | |||||||
2017 | 2016 | ||||||
($ in thousands) | |||||||
Private Equity Investments | $ | 110,101 | $ | (214,488 | ) | ||
Credit & Other Investments | 225,838 | (277,554 | ) | ||||
Investments of Consolidated CFE's | 11,880 | 182,195 | |||||
Real Assets Investments | 9,858 | (110,783 | ) | ||||
Debt Obligations | (29,402 | ) | (271,821 | ) | |||
Other Net Gains (Losses) from Investment Activities | 230,173 | (42,772 | ) | ||||
Net Gains (Losses) from Investment Activities | $ | 558,448 | $ | (735,223 | ) | ||
The net gains from investment activities for the three months ended March 31, 2017 were comprised of net realized gains of $146.2 million and net unrealized gains of $412.3 million. For the three months ended March 31, 2017, net realized gains were comprised primarily of realized gains on sales of private equity investments held directly by KKR, including the final sale of Galenica AG (VTX: GALN) and HCA Holdings, Inc. (NYSE: HCA) and a partial sale of US Foods Holding Corp. (NYSE: USFD). For the three months ended March 31, 2017, net unrealized gains were driven primarily by (i) mark-to-market gains in our private equity portfolio held directly by KKR including unrealized gains in First Data Corporation (NYSE: FDC), (ii) mark-to-market gains on alternative credit assets in our consolidated special situations funds and KFN and (iii) mark-to-market gains on investments held through consolidated CMBS structures. Offsetting these unrealized gains were unrealized losses, the most significant of which were unrealized losses relating to (i) the reversal of unrealized gains on the final sale of Galenica AG and HCA Holdings, Inc. and the partial sale of US Foods Holding Corp., and (ii) mark-to-market losses on debt held through consolidated CMBS. For a discussion of other factors that affected KKR's investment income, see "--Segment Analysis."
The net loss from investment activities for the three months ended March 31, 2016 was comprised of net realized losses of $43.3 million and net unrealized losses of $691.9 million. For the three months ended March 31, 2016, net realized losses were comprised primarily of the loss from the redemption of limited partner interests in a fund managed by BlackGold Capital Management offset by gains on sales of private equity investments, including the sales of Masan Consumer Corporation (consumer products sector), Dalmia Cement (manufacturing sector) and SunGard Data Systems, Inc (technology sector). For the three months ended March 31, 2016, net unrealized losses were driven primarily by net unrealized losses in (i) our private equity portfolio and other investments held directly by KKR including unrealized losses in First Data Corporation (NYSE: FDC), WMI Holdings Corp. (NASDAQ: WMIH), and Walgreens Boots Alliance, Inc. (NASDAQ: WBA), (ii) our credit and CLO portfolios held directly by KKR and through consolidated funds and (iii) energy investments held through consolidated funds. These unrealized losses were offset by unrealized gains relating to investments held through consolidated CMBS structures.
Dividend Income
During the three months ended March 31, 2017 we received dividends of $9.9 million from various investments across a variety of investment strategies. During the three months ended March 31, 2016 we received dividends of $63.2 million comprised of $23.4 million from US Foods Holding Corp., $24.6 million from real estate investments held directly and through our consolidated real estate funds and an aggregate of $15.2 million of dividends from other investments. Significant dividends from portfolio companies are generally not recurring quarterly dividends, and while they may occur in the future, their size and frequency are variable. For a discussion of other factors that affected KKR's dividend income, see "--Segment Analysis."
Interest Income
The increase in interest income was primarily due to higher interest earned related to (i) our recent CMBS loans acquired by KKR Real Estate Finance Trust Inc., (ii) an increase in credit investments in our consolidated special situations funds and (iii) the consolidation of six additional CLOs since the three months ended March 31, 2016. For a discussion of other factors that affected KKR's interest income, see "--Segment Analysis."
Interest Expense
79
The increase in interest expense was primarily due to (i) increased CMBS borrowings by KKR Real Estate Finance Trust Inc., and (ii) the consolidation of six additional CLOs since the three months ended March 31, 2016. These increases were partially offset by a decrease in interest expense associated with the redemption and paydown of KFN's 8.375% senior notes due 2041 and other debt at KFN after the first quarter of 2016. Replacing KFN’s 8.375% senior notes due 2041 (which were redeemed in November 2016) and the KFN 2042 Notes (which were redeemed in April 2017 as discussed in “-Recent Developments”) with the KFN 2032 Notes (which were issued in March 2017) represents an annualized interest expense savings of $9.7 million when calculated in the aggregate. For a discussion of other factors that affected KKR's interest expense, see "--Segment Analysis."
Income (Loss) Before Taxes
The increase in income (loss) before taxes for the three months ended March 31, 2017, was due primarily to carried interest gains accrued by certain fund entities and net gains from investment activities, in each case as described above, as compared to losses in the prior period.
Income Taxes
The increase in income taxes is due primarily to a higher level of fees earned by our management companies and carried interest gains accrued by certain general partner entities subject to corporate income tax during the three months ended March 31, 2017 compared to carried interest losses at such general partner entities in the prior period.
Net Income (Loss) Attributable to Noncontrolling Interests
Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests for the three months ended March 31, 2017 relates primarily to net income attributable to KKR Holdings L.P. representing its ownership interests in the KKR Group Partnerships as well as third party limited partner interests in those investment funds that we consolidate. The increase from the prior period is due primarily to carried interest gains accrued by certain consolidated fund entities and mark-to-market gains in our private equity portfolio attributable to third party limited partners in our consolidated investment funds compared to losses recognized in the prior period.
Net Income (Loss) Attributable to KKR & Co. L.P.
The increase for the three months ended March 31, 2017, was due primarily to investment and carried interest gains in the current period as compared to losses in the prior period and to a lesser extent, increased fee income.
80
Condensed Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition
The following table provides the condensed consolidated statements of financial condition on a GAAP Basis as of March 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016.
(Amounts in thousands, except common unit and per common unit amounts) | ||||||||
As of | As of | |||||||
March 31, 2017 | December 31, 2016 | |||||||
Assets | ||||||||
Cash and Cash Equivalents | $ | 2,758,398 | $ | 2,508,902 | ||||
Investments | 34,225,324 | 31,409,765 | ||||||
Other | 4,651,990 | 5,084,230 | ||||||
Total Assets | 41,635,712 | 39,002,897 | ||||||
Liabilities and Equity | ||||||||
Debt Obligations | 19,625,439 | 18,544,075 | ||||||
Other Liabilities | 3,722,475 | 3,340,739 | ||||||
Total Liabilities | 23,347,914 | 21,884,814 | ||||||
Redeemable Noncontrolling Interests | 781,428 | 632,348 | ||||||
Equity | ||||||||
Series A Preferred Units | 332,988 | 332,988 | ||||||
Series B Preferred Units | 149,566 | 149,566 | ||||||
KKR & Co. L.P. Capital - Common Unitholders | 5,755,354 | 5,457,279 | ||||||
Noncontrolling Interests | 11,268,462 | 10,545,902 | ||||||
Total Equity | 17,506,370 | 16,485,735 | ||||||
Total Liabilities and Equity | $ | 41,635,712 | $ | 39,002,897 | ||||
KKR & Co. L.P. Capital Per Outstanding Common Unit - Basic | $ | 12.63 | $ | 12.06 | ||||
81
Condensed Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
The accompanying condensed consolidated statements of cash flows include the cash flows of our consolidated entities which include certain consolidated investment funds and CFEs notwithstanding the fact that we may hold only a minority economic interest in those funds and CFEs.
The assets of our consolidated funds and CFEs, on a gross basis, can be substantially larger than the assets of our business and, accordingly, could have a substantial effect on the cash flows reflected in our condensed consolidated statements of cash flows. The primary cash flow activities of our consolidated funds and CFEs involve: (i) capital contributions from fund investors; (ii) using the capital of fund investors to make investments; (iii) financing certain investments with indebtedness; (iv) generating cash flows through the realization of investments; and (v) distributing cash flows from the realization of investments to fund investors. Because our consolidated funds and CFEs are treated as investment companies for accounting purposes, certain of these cash flow amounts are included in our cash flows from operations.
Net Cash Provided (Used) by Operating Activities
Our net cash provided (used) by operating activities was $(1.1) billion and $(0.7) billion during the three months ended March 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively. These amounts primarily included: (i) proceeds from sales of investments net of purchases of investments of $(2.0) billion and $(1.3) billion during the three months ended March 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively; (ii) net realized gains (losses) on investments of $146.2 million and $(43.3) million during the three months ended March 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively; (iii) change in unrealized gains (losses) on investments of $412.3 million and (691.9) million during the three months ended March 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively; and (iv) carried interest allocated as a result of changes in fund fair value of $(335.8) million and $117.0 million during the three months ended March 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively. Investment funds are, for GAAP purposes, investment companies and reflect their investments and other financial instruments at fair value.
Net Cash Provided (Used) by Investing Activities
Our net cash provided (used) by investing activities was $61.8 million and $62.6 million during the three months ended March 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively. Our investing activities included: (i) a change in restricted cash and cash equivalents (that primarily funds collateral requirements) of $83.3 million and $65.1 million during the three months ended March 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively; (ii) the purchase of fixed assets of $(21.4) million and $(1.5) million during the three months ended March 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively; and (iii) development of oil and natural gas properties of $(0.2) million and $(1.0) million for the three months ended March 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively.
Net Cash Provided (Used) by Financing Activities
Our net cash provided (used) by financing activities was $1.3 billion and $0.9 billion during the three months ended March 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively. Our financing activities primarily included: (i) distributions to, net of contributions by, our noncontrolling and redeemable noncontrolling interests of $0.4 billion and $0.3 billion during the three months ended March 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively; (ii) proceeds received net of repayment of debt obligations of $1.0 billion and $0.6 billion during the three months ended March 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively; (iii) distributions to our partners of $(72.4) million and $(72.0) million during the three months ended March 31, 2017 and 2016, respectively; (iv) unit repurchases of $(195.0) million during the three months ended March 31, 2016; (v) issuance of Preferred Units of $333.0 million during the three months ended March 31, 2016; and (vi) Preferred Units distributions of $(8.3) million during the three months ended March 31, 2017.
82
Segment Analysis
The following is a discussion of the results of our four reportable business segments for the three months ended March 31, 2017 and 2016. You should read this discussion in conjunction with the information included under “—Basis of Financial Presentation—Segment Operating and Performance Measures” and the condensed consolidated financial statements and related notes included elsewhere in this report.
Expense Allocations
Certain expenses are allocated among our operating segments. Specifically, as described below, (i) a portion of expenses, except for broken deal expenses, originating in our Private Markets, Public Markets or Capital Markets segments are reflected in the Principal Activities segment and (ii) corporate expenses are allocated across all segments.
Expenses Allocated to Principal Activities
KKR allocates certain expenses to its Principal Activities segment. The Principal Activities segments incurs its own direct costs, and an allocation from the other segments is also made to reflect the estimated amount of costs that are necessary to operate our Principal Activities segment, which are incremental to those costs incurred directly by the Principal Activities segment. These allocable expenses consist of a portion of our cash compensation and benefits, occupancy and related charges and other operating expenses that are initially recognized within our Private Markets, Public Markets and Capital Markets segments. Consistent with prior years, the total amount of expenses (other than its direct costs) that is allocated to Principal Activities is based on the proportion of revenue earned by Principal Activities, relative to other operating segments revenue, over the preceding four calendar years. Beginning in 2017, however, KKR has determined that this allocation percentage will not be less than the allocation percentage calculated using the cumulative amount of such revenues since 2009 (the year we completed the KPE transaction). For 2017, KKR determined that this allocation percentage is 25.7%. This allocation percentage is expected to be updated annually or more frequently if there are material changes to our business.
Below is a summary of the allocation to Principal Activities, relative to other operating segments, for the 2017 and 2016 periods.
• | 2017 Allocation: 25.7%, based on cumulative revenues earned since 2009 |
• | 2016 Allocation: 22.6%, based on revenues earned in 2015, 2014, 2013 and 2012 |
Once the total amount of expense to be allocated to the Principal Activities segment is estimated for each reporting period, the amount of this expense will be allocated from the Private Markets, Public Markets and Capital Markets segments based on the proportion of headcount in each of these three segments.
Allocations of Corporate Expenses
Corporate expenses are allocated to each of the Private Markets, Public Markets, Capital Markets and Principal Activities segments based on the proportion of revenues earned by each segment over the preceding four calendar years. However, to the extent that expenses allocated to Principal Activities, as described above, is based on the cumulative amount of such revenues since 2009, corporate expenses will be allocated in the same manner.
83
Below is a summary of the allocations percentages used for corporate expenses to each of our operating segments for the 2017 and 2016 periods.
Expense Allocation | ||||||
Segment | 2017 | 2016 | ||||
Private Markets | 59.6 | % | 61.6 | % | ||
Public Markets | 9.0 | % | 10.1 | % | ||
Capital Markets | 5.7 | % | 5.7 | % | ||
Principal Activities | 25.7 | % | 22.6 | % | ||
Total Reportable Segments | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | ||
Allocation basis | Cumulative revenue since 2009 | Revenue earned in 2015, 2014, 2013 & 2012 | ||||
84
Private Markets Segment
The following tables set forth information regarding the results of operations and certain key operating metrics for our Private Markets segment for the three months ended March 31, 2017 and 2016.
Three months ended March 31, 2017 compared to three months ended March 31, 2016
Three Months Ended | |||||||||||
March 31, 2017 | March 31, 2016 | Change | |||||||||
($ in thousands) | |||||||||||
Segment Revenues | |||||||||||
Management, Monitoring and Transaction Fees, Net | |||||||||||
Management Fees | $ | 123,512 | $ | 117,798 | $ | 5,714 | |||||
Monitoring Fees | 13,220 | 12,037 | 1,183 | ||||||||
Transaction Fees | 117,882 | 37,398 | 80,484 | ||||||||
Fee Credits | (85,650 | ) | (22,596 | ) | (63,054 | ) | |||||
Total Management, Monitoring and Transaction Fees, Net | 168,964 | 144,637 | 24,327 | ||||||||
Performance Income | |||||||||||
Realized Incentive Fees | — | — | — | ||||||||
Realized Carried Interest | 206,204 | 93,450 | 112,754 | ||||||||
Unrealized Carried Interest | 123,506 | (194,699 | ) | 318,205 | |||||||
Total Performance Income | 329,710 | (101,249 | ) | 430,959 | |||||||
Investment Income (Loss) | |||||||||||
Net Realized Gains (Losses) | — | — | — | ||||||||
Net Unrealized Gains (Losses) | — | — | — | ||||||||
Total Realized and Unrealized | — | — | — | ||||||||
Interest Income and Dividends | — | — | — | ||||||||
Interest Expense | — | — | — | ||||||||
Net Interest and Dividends | — | — | — | ||||||||
Total Investment Income (Loss) | — | — | — | ||||||||
Total Segment Revenues | 498,674 | 43,388 | 455,286 | ||||||||
Segment Expenses | |||||||||||
Compensation and Benefits | |||||||||||
Cash Compensation and Benefits | 60,008 | 48,967 | 11,041 | ||||||||
Realized Performance Income Compensation | 87,393 | 37,380 | 50,013 | ||||||||
Unrealized Performance Income Compensation | 50,366 | (75,000 | ) | 125,366 | |||||||
Total Compensation and Benefits | 197,767 | 11,347 | 186,420 | ||||||||
Occupancy and related charges | 8,107 | 8,925 | (818 | ) | |||||||
Other operating expenses | 26,887 | 37,126 | (10,239 | ) | |||||||
Total Segment Expenses | 232,761 | 57,398 | 175,363 | ||||||||
Income (Loss) attributable to noncontrolling interests | — | — | — | ||||||||
Economic Net Income (Loss) | $ | 265,913 | $ | (14,010 | ) | $ | 279,923 | ||||
Assets Under Management | $ | 80,197,600 | $ | 71,056,700 | $ | 9,140,900 | |||||
Fee Paying Assets Under Management | $ | 56,667,600 | $ | 46,008,000 | $ | 10,659,600 | |||||
Capital Invested | $ | 4,484,200 | $ | 2,084,200 | $ | 2,400,000 | |||||
Uncalled Commitments | $ | 35,071,700 | $ | 26,903,200 | $ | 8,168,500 | |||||
85
Segment Revenues
Management, Monitoring and Transaction Fees, Net
The net increase was primarily due to an increase in transaction fees of $80.5 million, partially offset by a corresponding increase in fee credits of $63.1 million, and an increase in management fees of $5.7 million. The increase in transaction fees was primarily attributable to an increase in both the number and size of transaction fee-generating investments. During the three months ended March 31, 2017, there were 13 investments that paid an average fee of $9.1 million compared to 10 transaction fee-generating investments paying an average fee of $3.7 million during the three months ended March 31, 2016. The majority of these transaction fees were paid by companies located in the Asia-Pacific region. Transaction fees vary by investment based upon a number of factors, the most significant of which are transaction size, the particular discussions as to the amount of the fees, the complexity of the transaction and KKR’s role in the transaction. The increase in fee credits is due primarily to a higher level of transaction fees. The increase in management fees was primarily due to (i) Americas Fund XII entering its investment period in the first quarter of 2017, which accrues management fees on a higher fee base than its predecessor fund North America Fund XI, which entered its post investment period and (ii) new capital raised in our Next Generation Technology Growth Fund and Real Estate Partners Europe. This net increase was partially offset by decreases due to (i) North America Fund XI entering its post investment period during which it earns fees at a lower rate and based on invested capital rather than committed capital and (ii) lower invested capital as a result of realizations primarily in our 2006 Fund and China Growth Fund. Recurring monitoring fees remained relatively flat during the three months ended March 31, 2017, compared to the same period in 2016. For the three months ended March 31, 2017, we had 48 portfolio companies that were paying an average monitoring fee of $0.3 million compared with 44 portfolio companies that were paying an average monitoring fee of $0.3 million for the three months ended March 31, 2016.
Performance Income
The net increase is attributable to net carried interest gains in the three months ended March 31, 2017, compared to net carried interest losses in the three months ended March 31, 2016, primarily reflecting appreciation in value of our private equity portfolio in the current period compared to net reductions in value in the prior period.
Realized carried interest for the three months ended March 31, 2017, consisted primarily of realized gains from the final sales of Galenica AG (VTX: GALN) and HCA Holdings, Inc. (NYSE: HCA) and the partial sale of US Foods Holding Corp. (NYSE: USFD).
Realized carried interest for the three months ended March 31, 2016 consisted primarily of dividends received from US Foods Holding Corp. and realized gains from the sale of Masan Consumer Corporation (consumer products sector).
86
The following table presents performance income by investment vehicle for the three months ended March 31, 2017 and 2016:
Three Months Ended March 31, | |||||||||||||||||||
2017 | 2016 | ||||||||||||||||||
($ in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||||
Realized Carried Interest | Unrealized Carried Interest | Total Carried Interest | Realized Carried Interest | Unrealized Carried Interest | Total Carried Interest | ||||||||||||||
North America Fund XI | $ | 24,519 | $ | 133,044 | $ | 157,563 | $ | — | $ | (11,007 | ) | $ | (11,007 | ) | |||||
2006 Fund | 111,823 | (63,848 | ) | 47,975 | 55,890 | (162,716 | ) | (106,826 | ) | ||||||||||
Asian Fund II | — | 32,642 | 32,642 | — | (15,150 | ) | (15,150 | ) | |||||||||||
European Fund III | — | 30,636 | 30,636 | — | 38,440 | 38,440 | |||||||||||||
Co-Investment Vehicles and Other | 2,303 | 21,023 | 23,326 | 404 | (17,213 | ) | (16,809 | ) | |||||||||||
Global Infrastructure Investors | — | 15,702 | 15,702 | — | 4,803 | 4,803 | |||||||||||||
Asian Fund | 14,293 | (2,299 | ) | 11,994 | 30,937 | (2,876 | ) | 28,061 | |||||||||||
Millennium Fund | 28,266 | (20,087 | ) | 8,179 | 4,236 | (5,315 | ) | (1,079 | ) | ||||||||||
Real Estate Partners Americas | — | 3,991 | 3,991 | — | 424 | 424 | |||||||||||||
China Growth Fund | 6,891 | (3,014 | ) | 3,877 | — | (5,728 | ) | (5,728 | ) | ||||||||||
European Fund IV | — | 1,730 | 1,730 | — | (526 | ) | (526 | ) | |||||||||||
European Fund | — | — | — | — | (1,532 | ) | (1,532 | ) | |||||||||||
E2 Investors | — | (306 | ) | (306 | ) | — | 258 | 258 | |||||||||||
European Fund II | 18,109 | (23,282 | ) | (5,173 | ) | 1,983 | (12,030 | ) | (10,047 | ) | |||||||||
Management Fee Refunds | — | (2,426 | ) | (2,426 | ) | — | (4,531 | ) | (4,531 | ) | |||||||||
Total (1) | $ | 206,204 | $ | 123,506 | $ | 329,710 | $ | 93,450 | $ | (194,699 | ) | $ | (101,249 | ) | |||||
(1) The above table excludes any funds for which there was no carried interest during either of the periods presented.
Unrealized carried interest reflects the difference between total carried interest and realized carried interest. The recognition of realized carried interest results in the reversal of accumulated unrealized carried interest, generally resulting in minimal impact on total performance income. Additionally, because unrealized carried interest can be reversed upon a realization event, in periods where there is significant realized carried interest, unrealized carried interest can be negative even in periods of portfolio appreciation.
For the three months ended March 31, 2017, the value of our private equity investment portfolio increased 4.7%. This was comprised of a 4.2% increase in the share prices of various publicly held or publicly indexed investments and a 5.0% increase in value of our privately held investments. The most significant increases in share prices of various publicly held or publicly indexed investments were gains in First Data Corporation (NYSE: FDC), PRA Health Sciences, Inc. (NASDAQ: PRAH) and Qingdao Haier (CH: 600690). These increases were partially offset by decreased share prices of various publicly held investments, the most significant of which were losses in Laureate Education, Inc. (NASDAQ: LAUR), Pets at Home Ltd. (LSE: PETS) and Fujian Sunner Development Co. Ltd (SZ: 002299). Our privately held investments contributed the remainder of the change in value, the most significant of which were gains relating to Gardner Denver, Inc. (manufacturing sector), PortAventura (hotels/leisure sector) and Weld North (education sector). The unrealized gains on our privately held investments were partially offset by unrealized losses relating primarily to Westbrick Energy Ltd. (energy sector) and Santanol Pty Ltd (forestry sector). The increased valuations of individual companies in our privately held investments, in the aggregate, generally related to (i) in the case of PortAventura, a valuation that reflects a pending realization event, (ii) an increase in the value of market comparables and (iii) individual company performance. The decreased valuations of individual companies in our privately held investments, in the aggregate, generally related to (i) individual company performance or, in certain cases, an unfavorable business outlook and (ii) a decrease in the value of market comparables.
Subsequent to March 31, 2017 realization activity such as dividends and agreements to sell, including partial sales and secondary sales, are expected, with respect to the following private equity portfolio companies: Panasonic Healthcare Co. Ltd (healthcare sector), Capsugel (manufacturing sector), Gland Pharma Limited (manufacturing sector), Dalmia Cement (industrial sector), PortAventura, Ambea Mehiläinen (healthcare sector), SBI Life Insurance (financial services Sector), Visma
87
AS (technology sector), China Greenland Rundong (retail sector), two infrastructure investments and two real estate investments. These transactions, if consummated as of March 31, 2017 and, based on the then anticipated realization values, represent distributable earnings of approximately $250 million. Some or all of these transactions are subject to the satisfaction of closing conditions prior to their completion, and there can be no assurance if or when any of these transactions will be completed.
For the three months ended March 31, 2016, the value of our private equity investment portfolio decreased 0.9%. This was comprised of a 7.1% decrease in the share prices of various publicly held or publicly indexed investments and a 3.8% increase in value of our privately held investments. The most significant decreases in share prices of various publicly held or publicly indexed investments were losses in First Data Corporation (NYSE: FDC), Qingdao Haier (CH: 600690) and Engility Holdings, Inc. (NYSE: EGL). These decreases were partially offset by increased share prices of various publicly held investments, the most significant of which were HCA Holdings, Inc. (NYSE: HCA), Fujian Sunner Development (SZE: 002299) and Zimmer Biomet Holdings, Inc. (NYSE: ZBH). Our privately held investments contributed the remainder of the change in value, the most significant of which were gains relating to Alliance Tire Group B.V. (manufacturing sector), US Foods Holding Corp. (prior to its public listing) and Scout24 Schweiz (media sector). The unrealized gains on our privately held investments were partially offset by unrealized losses relating primarily to Aricent Group (technology sector), KKR Debt Investors 2006 Sarl (KDI) (financial services sector), a vehicle created to invest opportunistically in the credit markets, and Sonos (technology sector). The increased valuations of individual companies in our privately held investments, in the aggregate, generally related to (i) in the case of Alliance Tire Group B.V. and Scout24 Schweiz, valuations that reflect agreements to sell these investments, (ii) an increase in the value of market comparables and (iii) individual company performance. The decreased valuations of individual companies in our privately held investments, in the aggregate, generally related to (i) individual company performance or, in certain cases, an unfavorable business outlook, (ii) a decrease in the value of market comparables and (iii) in the case of KDI a valuation that reflects price movements of the underlying credit assets in the portfolio.
Segment Expenses
Compensation and Benefits
The net increase was due primarily to higher performance income compensation resulting from gains in our private equity portfolio in the current period compared to losses in the prior period as described above as well as increased cash compensation and benefits in connection with a higher level of fees.
Occupancy and Other Operating Expenses
The decrease is primarily due to a decrease in expenses for unconsummated transactions, also known as broken deal expenses and other expenses that are creditable to our investment funds.
Economic Net Income (Loss)
The increase was primarily due to performance income gains in the current period compared to losses in the prior period and higher transaction fees partially offset by the increase in compensation and benefits as described above.
Assets Under Management
The following table reflects the changes in our Private Markets AUM from December 31, 2016 to March 31, 2017:
($ in thousands) | |||
December 31, 2016 | $ | 73,815,500 | |
New Capital Raised | 6,290,900 | ||
Distributions and Other | (1,866,500 | ) | |
Change in Value | 1,957,700 | ||
March 31, 2017 | $ | 80,197,600 | |
AUM for the Private Markets segment was $80.2 billion at March 31, 2017, an increase of $6.4 billion, compared to $73.8 billion at December 31, 2016. The increase was primarily attributable to new capital raised primarily in our Asian Fund III, Americas Fund XII and Health Care Strategic Growth Fund and to a lesser extent, an increase in the value of our Private Markets portfolio. These increases were offset by distributions to Private Markets fund investors primarily as a result of realizations most notably in our 2006 Fund, Millennium Fund and Asian Fund.
88
The increase in the value of our Private Markets portfolio was driven primarily by net gains of $0.8 billion in our North America Fund XI, $0.3 billion in our 2006 Fund and $0.2 billion in our European Fund III. The drivers of the overall change in value for Private Markets were a 4.2% increase in the share prices of various publicly held or publicly indexed investments and a 5.0% increase in value of our privately held investments. The most significant increases in share prices of various publicly held or publicly indexed investments were gains in First Data Corporation (NYSE: FDC), PRA Health Sciences, Inc. (NASDAQ: PRAH) and Qingdao Haier (CH: 600690). These increases were partially offset by decreased share prices of various publicly held investments, the most significant of which were losses in Laureate Education, Inc. (NASDAQ: LAUR), Pets at Home Ltd. (LSE: PETS) and Fujian Sunner Development Co. Ltd (SZ: 002299). Our privately held investments contributed the remainder of the change in value, the most significant of which were gains relating to Gardner Denver, Inc. (manufacturing sector), PortAventura (hotels/leisure sector) and Weld North (education sector). The unrealized gains on our privately held investments were partially offset by unrealized losses relating primarily to Westbrick Energy Ltd. (energy sector) and Santanol Pty Ltd (forestry sector). The increased valuations of individual companies in our privately held investments, in the aggregate, generally related to (i) in the case of PortAventura, a valuation that reflects a pending realization event, (ii) an increase in the value of market comparables and (iii) individual company performance. The decreased valuations of individual companies in our privately held investments, in the aggregate, generally related to (i) individual company performance or, in certain cases, an unfavorable business outlook and (ii) a decrease in the value of market comparables.
Certain investments included in our AUM are denominated in currencies other than the U.S. dollar. Those investments expose our AUM to the risk that the value of the investments will be affected by changes in exchange rates between the currency in which the investments are denominated and the currency in which the investments are made. Our policy is to minimize these risks in certain cases by employing hedging techniques, including using foreign currency options and foreign exchange forward contracts to reduce exposure to changes in exchange rates when a meaningful amount of capital has been invested in currencies other than the currencies in which the investments are denominated. We do not, however, hedge our currency exposure in all currencies or all investments. See “-Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk -- Exchange Rate Risk” of our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2016 and “Risk Factors-Risks Related to the Assets We Manage--We make investments in companies that are based outside of the United States, which may expose us to additional risks not typically associated with investing in companies that are based in the United States.” of our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2016.
Fee-Paying Assets Under Management
The following table reflects the changes in our Private Markets FPAUM from December 31, 2016 to March 31, 2017:
($ in thousands) | |||
December 31, 2016 | $ | 52,204,800 | |
New Capital Raised | 6,913,600 | ||
Distributions and Other | (545,500 | ) | |
Net Changes in Fee Base of Certain Funds | (2,041,500 | ) | |
Change in Value | 136,200 | ||
March 31, 2017 | $ | 56,667,600 | |
FPAUM in our Private Markets segment was $56.7 billion at March 31, 2017, an increase of $4.5 billion, compared to $52.2 billion at December 31, 2016. The increase was primarily attributable to new capital raised in our Asian Fund III and Americas Fund XII and capital invested in our North America Fund XI. These increases were partially offset by net changes in the fee base of our Asian Fund II as a result of it entering into its post investment period during which it earns fees based on invested capital rather than committed capital. Distributions and other activity primarily related to realizations in our 2006 Fund. Uncalled capital commitments from investment funds from which KKR is currently not earning management fees amounted to approximately $7.2 billion at March 31, 2017, which includes capital commitments reserved for follow-on investments for funds that have completed their investment periods. This capital will generally begin to earn management fees upon deployment of the capital or upon the commencement of the fund's investment period. The average annual management fee rate associated with this capital is approximately 0.8%. We will not begin earning fees on this capital until it is deployed or the related investment period commences, neither of which is guaranteed. If and when such management fees are earned, which will occur over an extended period of time, a portion of existing FPAUM may cease paying fees or pay lower fees, thus offsetting a portion of any new management fees earned. Based on the amount of capital remaining in the Asian Fund II, as of March 31, 2017, and assuming that Asian Fund III had reached its $8.5 billion limit on fee paying limited partner capital on such date, the increase in management fees from Asian Fund III entering its investment period would initially exceed the reduction in management fees from the Asian Fund II entering its post-investment period by approximately $60 million on an
89
annualized basis. Management fees from the Asian Fund II would decrease over time as the investments in the Asian Fund II are realized, which would cause management fees from such fund to decrease over time. As of March 31, 2017, there were fee paying limited partner commitments of $5.3 billion for Asian Fund III, and there can be no assurance if or when the $8.5 billion limit will be reached.
Capital Invested
The increase in capital invested was driven primarily by a $1.4 billion increase in capital invested in our private equity platform and a $1.0 billion increase in capital invested in our real assets and other platforms. Generally, the portfolio companies acquired through our private equity funds have higher transaction values and result in higher capital invested relative to transactions in our real assets funds. The number of large private equity investments made in any quarter is volatile and consequently, a significant amount of capital invested in one quarter or a few quarters may not be indicative of a similar level of capital deployment in future quarters. Geographically, the largest amount of capital was deployed in private equity transactions in Asia during the three months ended March 31, 2017, which totaled approximately $1.9 billion. As of April 27, 2017, our Private Markets business had announced transactions that were subject to closing conditions which aggregated approximately $3 billion. Some or all of these transactions are subject to the satisfaction of closing conditions prior to their completion, and there can be no assurance if or when any of these transactions will be completed.
Uncalled Commitments
As of March 31, 2017, our Private Markets segment had $35.1 billion of remaining uncalled capital commitments that could be called for investments in new transactions. The increase is due primarily to new capital raised in Americas Fund XII and Asian Fund III, partially offset by capital called from fund investors to fund investments during the period.
90
Public Markets Segment
The following tables set forth information regarding the results of operations and certain key operating metrics for our Public Markets segment for the three months ended March 31, 2017 and 2016.
Three months ended March 31, 2017 compared to three months ended March 31, 2016
Three Months Ended | ||||||||||||
March 31, 2017 | March 31, 2016 | Change | ||||||||||
($ in thousands) | ||||||||||||
Segment Revenues | ||||||||||||
Management, Monitoring and Transaction Fees, Net | ||||||||||||
Management Fees | $ | 84,772 | $ | 76,802 | $ | 7,970 | ||||||
Monitoring Fees | — | — | — | |||||||||
Transaction Fees | 4,056 | 1,132 | 2,924 | |||||||||
Fee Credits | (3,367 | ) | (211 | ) | (3,156 | ) | ||||||
Total Management, Monitoring and Transaction Fees, Net | 85,461 | 77,723 | 7,738 | |||||||||
Performance Income | ||||||||||||
Realized Incentive Fees | 1,686 | 1,593 | 93 | |||||||||
Realized Carried Interest | — | 3,838 | (3,838 | ) | ||||||||
Unrealized Carried Interest | 17,120 | (29,106 | ) | 46,226 | ||||||||
Total Performance Income | 18,806 | (23,675 | ) | 42,481 | ||||||||
Investment Income (Loss) | ||||||||||||
Net Realized Gains (Losses) | — | — | — | |||||||||
Net Unrealized Gains (Losses) | — | — | — | |||||||||
Total Realized and Unrealized | — | — | — | |||||||||
Interest Income and Dividends | — | — | — | |||||||||
Interest Expense | — | — | — | |||||||||
Net Interest and Dividends | — | — | — | |||||||||
Total Investment Income (Loss) | — | — | — | |||||||||
Total Segment Revenues | 104,267 | 54,048 | 50,219 | |||||||||
Segment Expenses | ||||||||||||
Compensation and Benefits | ||||||||||||
Cash Compensation and Benefits | 19,784 | 19,054 | 730 | |||||||||
Realized Performance Income Compensation | 674 | 2,172 | (1,498 | ) | ||||||||
Unrealized Performance Income Compensation | 6,848 | (11,642 | ) | 18,490 | ||||||||
Total Compensation and Benefits | 27,306 | 9,584 | 17,722 | |||||||||
Occupancy and related charges | 1,856 | 2,675 | (819 | ) | ||||||||
Other operating expenses | 8,338 | 9,278 | (940 | ) | ||||||||
Total Segment Expenses | 37,500 | 21,537 | 15,963 | |||||||||
Income (Loss) attributable to noncontrolling interests | — | — | — | |||||||||
Economic Net Income (Loss) | $ | 66,767 | $ | 32,511 | $ | 34,256 | ||||||
Assets Under Management | $ | 57,418,700 | $ | 55,332,200 | $ | 2,086,500 | ||||||
Fee Paying Assets Under Management | $ | 50,463,500 | $ | 47,711,700 | $ | 2,751,800 | ||||||
Capital Invested | $ | 893,600 | $ | 418,300 | $ | 475,300 | ||||||
Uncalled Commitments | $ | 6,151,100 | $ | 7,593,100 | $ | (1,442,000 | ) | |||||
91
Segment Revenues
Management, Monitoring and Transaction Fees, Net
The net increase was primarily due to an increase in management fees of $8.0 million relating primarily to an increase in capital invested in our Special Situations Fund II, Lending Partners II Fund, and Lending Partners Europe Fund as well as new capital raised in our liquid credit strategies. This increase was partially offset by a decrease in management fees in our hedge funds solutions business as a result of a reduction in fee paying AUM due to redemptions.
Performance Income
The net increase was primarily attributable to net carried interest gains in the three months ended March 31, 2017, compared to net carried interest losses during the three months ended March 31, 2016. The carried interest gains in the current period were primarily the result of increases in the value of our credit portfolio, with the most significant carried interest gains arising in funds investing in our direct lending strategies and certain separately managed accounts investing in our special situations strategies. In the prior period carried interest losses were experienced in our Mezzanine Fund and our direct lending strategies.
Segment Expenses
Compensation and Benefits
The increase was primarily due to higher net performance income compensation in connection with net carried interest gains for the three months ended March 31, 2017, as compared to net carried interest losses for the three months ended March 31, 2016, as described above.
Occupancy and Other Operating Expenses
The decrease was primarily driven by changes in the amount of expense allocated to Principal Activities and the amount of corporate expenses allocated to Public Markets from the prior period. See "--Segment Analysis--Expense Allocations."
Economic Net Income (Loss)
The increase is primarily attributable to the increase in performance income and management fees partially offset by an increase in compensation and benefits expense as described above.
Assets Under Management
The following table reflects the changes in our Public Markets AUM from December 31, 2016 to March 31, 2017:
($ in thousands) | |||
December 31, 2016 | $ | 55,740,200 | |
New Capital Raised | 2,249,200 | ||
Distributions | (671,400 | ) | |
Redemptions | (1,037,800 | ) | |
Change in Value | 1,138,500 | ||
March 31, 2017 | $ | 57,418,700 | |
AUM in our Public Markets segment totaled $57.4 billion at March 31, 2017, an increase of $1.7 billion compared to AUM of $55.7 billion at December 31, 2016. The increase for the period was primarily due to new capital raised of $2.2 billion across multiple strategies most notably $0.6 billion in our CLO strategies, $1.0 billion in our liquid credit strategies and $0.6 billion in our strategic partnerships. The increases due to change in value were driven primarily by our private credit strategy and our hedge funds business, which includes our strategic partnerships platform and hedge fund solutions platform. Partially offsetting these increases were redemptions and distributions of $1.7 billion from certain investment vehicles across multiple strategies including our hedge fund solutions business, our strategic partnerships and our CLOs. For the three months ended March 31, 2017, within our hedge funds business, new capital raised has outpaced redemptions within our strategic partnership platform, while redemptions have outpaced new capital raised in our hedge fund solutions platform.
92
Fee-Paying Assets Under Management
The following table reflects the changes in our Public Markets FPAUM from December 31, 2016 to March 31, 2017:
($ in thousands) | |||
December 31, 2016 | $ | 49,268,600 | |
New Capital Raised | 2,664,800 | ||
Distributions | (1,102,900 | ) | |
Redemptions | (1,037,800 | ) | |
Change in Value | 670,800 | ||
March 31, 2017 | $ | 50,463,500 | |
FPAUM in our Public Markets segment was $50.5 billion at March 31, 2017, an increase of $1.2 billion compared to FPAUM of $49.3 billion at December 31, 2016. The increase was primarily due to new capital raised of $2.7 billion across multiple strategies most notably $0.6 billion in our CLOs, $0.6 billion in our strategic partnership platform and $1.0 billion in our liquid credit strategies. New capital raised includes capital that was raised in previous periods but began earning fees upon deployment of capital. Partially offsetting these increases were redemptions and distributions of $2.1 billion from certain investment vehicles across multiple strategies driven by $1.0 billion from our hedge funds business, $0.4 billion from our Special Situations II Fund, and $0.3 billion from our CLOs. For the three months ended March 31, 2017, within our hedge fund business, new capital raised has outpaced redemptions within our strategic partnership platform, while redemptions have outpaced new capital raised in our hedge fund solutions platform. Uncalled capital commitments from investment funds from which KKR is currently not earning management fees amounted to approximately $4.1 billion. This capital will generally begin to earn management fees upon deployment of the capital or upon the commencement of the fund's investment period. The average annual management fee rate associated with this capital is approximately 1.2%. We will not begin earnings fees on this capital until it is deployed or the related investment period commences, neither of which is guaranteed. If and when such management fees are earned, which will occur over an extended period of time, a portion of existing FPAUM may cease paying fees or pay lower fees, thus offsetting a portion of any new management fees earned.
Capital Invested
Capital invested increased for the three months ended March 31, 2017, compared to the three months ended March 31, 2016. The increase is primarily due to a higher level of net capital deployed in our direct lending and special situations strategies.
Uncalled Commitments
As of March 31, 2017, our Public Markets segment had $6.2 billion of uncalled capital commitments that could be called for investments in new transactions. The decrease from March 31, 2016, is due to capital called from limited partners to fund investments during the period, partially offset by new capital raised primarily in Private Credit Opportunities Partners II Fund.
93
Capital Markets
The following tables set forth information regarding the results of operations and certain key operating metrics for our Capital Markets segment for the three months ended March 31, 2017 and 2016.
Three months ended March 31, 2017 compared to three months ended March 31, 2016
Three Months Ended | ||||||||||||
March 31, 2017 | March 31, 2016 | Change | ||||||||||
($ in thousands) | ||||||||||||
Segment Revenues | ||||||||||||
Management, Monitoring and Transaction Fees, Net | ||||||||||||
Management Fees | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||
Monitoring Fees | — | — | — | |||||||||
Transaction Fees | 121,097 | 57,555 | 63,542 | |||||||||
Fee Credits | — | — | — | |||||||||
Total Management, Monitoring and Transaction Fees, Net | 121,097 | 57,555 | 63,542 | |||||||||
Performance Income | ||||||||||||
Realized Incentive Fees | — | — | — | |||||||||
Realized Carried Interest | — | — | — | |||||||||
Unrealized Carried Interest | — | — | — | |||||||||
Total Performance Income | — | — | — | |||||||||
Investment Income (Loss) | ||||||||||||
Net Realized Gains (Losses) | — | — | — | |||||||||
Net Unrealized Gains (Losses) | — | — | — | |||||||||
Total Realized and Unrealized | — | — | — | |||||||||
Interest Income and Dividends | — | — | — | |||||||||
Interest Expense | — | — | — | |||||||||
Net Interest and Dividends | — | — | — | |||||||||
Total Investment Income (Loss) | — | — | — | |||||||||
Total Segment Revenues | 121,097 | 57,555 | 63,542 | |||||||||
Segment Expenses | ||||||||||||
Compensation and Benefits | ||||||||||||
Cash Compensation and Benefits | 22,561 | 8,168 | 14,393 | |||||||||
Realized Performance Income Compensation | — | — | — | |||||||||
Unrealized Performance Income Compensation | — | — | — | |||||||||
Total Compensation and Benefits | 22,561 | 8,168 | 14,393 | |||||||||
Occupancy and related charges | 664 | 628 | 36 | |||||||||
Other operating expenses | 5,328 | 4,096 | 1,232 | |||||||||
Total Segment Expenses | 28,553 | 12,892 | 15,661 | |||||||||
Income (Loss) attributable to noncontrolling interests | 1,584 | 667 | 917 | |||||||||
Economic Net Income (Loss) | $ | 90,960 | $ | 43,996 | $ | 46,964 | ||||||
Syndicated Capital | $ | 1,181,300 | $ | 665,300 | $ | 516,000 | ||||||
94
Segment Revenues
Management, Monitoring and Transaction Fees, Net
Transaction fees increased due primarily to an increase in both the number and size of capital markets transactions for the three months ended March 31, 2017, compared to the three months ended March 31, 2016. Overall, we completed 47 capital markets transactions for the three months ended March 31, 2017, of which 7 represented equity offerings and 40 represented debt offerings, as compared to 20 transactions for the three months ended March 31, 2016, of which 5 represented equity offerings and 15 represented debt offerings. We earned fees in connection with underwriting, syndication and other capital markets services. While each of the capital markets transactions that we undertake in this segment is separately negotiated, our fee rates are generally higher with respect to underwriting or syndicating equity offerings than with respect to debt offerings, and the amount of fees that we collect for like transactions generally correlates with overall transaction sizes. Our capital markets fees are sourced from our Private Markets and Public Markets businesses as well as third party companies. For the three months ended March 31, 2017, approximately 20% of our transaction fees were earned from unaffiliated third parties as compared to approximately 10% for the three months ended March 31, 2016. Our transaction fees are comprised of fees earned from North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific, including India. For the three months ended March 31, 2017, approximately 54% of our transaction fees were sourced internationally as compared to approximately 50% for the three months ended March 31, 2016. Our capital markets business is dependent on the overall capital markets environment, which is influenced by equity prices, credit spreads and volatility. Our capital markets business does not generate management or monitoring fees.
Segment Expenses
Compensation and Benefits
The increase compared to the prior period is primarily related to the increase in transaction fees noted above.
Occupancy and Other Operating Expenses
The overall increase was primarily due to increased transaction costs in connection with a reorganization of our India business.
Economic Net Income (Loss)
The increase is primarily attributable to the increase in transaction fees as described above.
Syndicated Capital
The increase is primarily due to an increase in the average size of syndication transactions in the three months ended March 31, 2017, as compared to the three months ended March 31, 2016. Overall, we completed 5 syndication transactions for each of the three months ended March 31, 2017, and March 31, 2016.
95
Principal Activities
The following tables set forth information regarding the results of operations and certain key operating metrics for our Principal Activities segment for the three months ended March 31, 2017 and 2016.
Three months ended March 31, 2017 compared to three months ended March 31, 2016
Three Months Ended | ||||||||||||
March 31, 2017 | March 31, 2016 | Change | ||||||||||
($ in thousands) | ||||||||||||
Segment Revenues | ||||||||||||
Management, Monitoring and Transaction Fees, Net | ||||||||||||
Management Fees | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||
Monitoring Fees | — | — | — | |||||||||
Transaction Fees | — | — | — | |||||||||
Fee Credits | — | — | — | |||||||||
Total Management, Monitoring and Transaction Fees, Net | — | — | — | |||||||||
Performance Income | ||||||||||||
Realized Incentive Fees | — | — | — | |||||||||
Realized Carried Interest | — | — | — | |||||||||
Unrealized Carried Interest | — | — | — | |||||||||
Total Performance Income | — | — | — | |||||||||
Investment Income (Loss) | ||||||||||||
Net Realized Gains (Losses) | 79,451 | (24,183 | ) | 103,634 | ||||||||
Net Unrealized Gains (Losses) | 204,036 | (564,991 | ) | 769,027 | ||||||||
Total Realized and Unrealized | 283,487 | (589,174 | ) | 872,661 | ||||||||
Interest Income and Dividends | 56,882 | 108,120 | (51,238 | ) | ||||||||
Interest Expense | (41,709 | ) | (48,544 | ) | 6,835 | |||||||
Net Interest and Dividends | 15,173 | 59,576 | (44,403 | ) | ||||||||
Total Investment Income (Loss) | 298,660 | (529,598 | ) | 828,258 | ||||||||
Total Segment Revenues | 298,660 | (529,598 | ) | 828,258 | ||||||||
Segment Expenses | ||||||||||||
Compensation and Benefits | ||||||||||||
Cash Compensation and Benefits | 37,082 | 24,710 | 12,372 | |||||||||
Realized Performance Income Compensation | — | — | — | |||||||||
Unrealized Performance Income Compensation | — | — | — | |||||||||
Total Compensation and Benefits | 37,082 | 24,710 | 12,372 | |||||||||
Occupancy and related charges | 3,742 | 3,722 | 20 | |||||||||
Other operating expenses | 12,945 | 11,386 | 1,559 | |||||||||
Total Segment Expenses | 53,769 | 39,818 | 13,951 | |||||||||
Income (Loss) attributable to noncontrolling interests | — | — | — | |||||||||
Economic Net Income (Loss) | $ | 244,891 | $ | (569,416 | ) | $ | 814,307 | |||||
96
Segment Revenues
Investment Income
The net increase is primarily due to realized and unrealized gains during the quarter ended March 31, 2017, compared to realized and unrealized losses in the prior period, partially offset by a decrease in net interest and dividends of $44.4 million.
For the quarter ended March 31, 2017, net realized gains were primarily comprised of gains from the sale of private equity investments including the sales or partial sales of HCA Holdings, Inc. and Galenica AG, partially offset by losses on the sale of Fortune Creek Partnership (energy sector) and an alternative energy investment in our special situations strategy. Net unrealized gains were primarily attributable to mark to market gains on various Private Markets investments including First Data Corporation and credit investments, the most significant of which was an oil field services investment in our special situations strategy. These increases were partially offset by unrealized losses due to the reversal of unrealized gains on the sales of private equity investments.
As of March 31, 2017, $260.2 million of investments in CLOs and our $289.7 million investment in KKR Real Estate Finance Trust Inc., our real estate investment trust or REIT, were carried at cost. As of March 31, 2017, the cumulative net unrealized gain or loss relating to changes in fair value for these investments was an $8.5 million gain for CLOs and a $15.2 million gain for the real estate investment trust.
Since April 30, 2014, the date we completed our acquisition of KFN, the amount of invested capital in our CLOs has decreased. During 2014 and through 2016, the notes issued by all six legacy CLOs held by KFN have been called for redemption. These legacy CLOs held by KFN, which were issued prior to 2012, were larger in total transaction size relative to those that were issued subsequently. The size of new CLOs and the frequency of CLO issuances will depend on market conditions. CLO issuances typically increase when the spread between the value of CLO assets and liabilities generates an attractive return to KKR and other subordinated note holders, such as KKR. In the case where demand for loans leads to tighter spreads or if interest rates for the liabilities increase, the return to subordinated note holders would be less attractive, and the issuance of CLOs would be expected to generally decline. Consequently, since April 30, 2014, the amount of interest income and dividends from our CLOs has declined. While the size of our CLO portfolio has declined compared to prior years, along with the levels of associated interest income and dividends, as we have called for redemption all notes issued by all six legacy CLOs held by KFN, we do not expect the rate of decline in the near term to be as significant as in past quarters. Based on the above factors combined with alternative investment opportunities, we may selectively redeploy capital to other assets outside of CLOs and credit into other asset classes such as private equity.
For the three months ended March 31, 2016, net realized losses were comprised primarily of the loss from the redemption of limited partner interests in a fund managed by BlackGold Capital Management, offset by gains on sales of private equity investments, including the sales of Masan Consumer Corporation, Dalmia Cement and SunGard Data Systems, Inc. (technology sector). Net unrealized losses were primarily attributable to mark to market losses on various Private Markets investments including First Data Corporation, WMI Holdings Corp. (NASDAQ: WMIH), and Walgreens Boots Alliance, Inc. (NASDAQ: WBA) and energy investments including direct energy investments and energy funds as well as credit investments and CLOs.
For the three months ended March 31, 2017, net interest and dividends were comprised of (i) $38.5 million of interest income which consists primarily of interest that is received from our Public Markets investments including CLOs and other credit investments and to a lesser extent our cash balances and other assets, (ii) $18.4 million of dividend income from distributions received primarily through our private equity investments and real estate investments including our investment in our REIT and (iii) $41.7 million of interest expense primarily relating to the senior notes outstanding for KKR and KFN.
For the three months ended March 31, 2016, net interest and dividends were comprised of (i) $51.7 million of interest income which consists primarily of interest that is received from our Public Markets investments including CLOs and to a lesser extent our cash balances and other assets, (ii) $56.4 million of dividend income from distributions received through our private equity investments, real estate funds and Public Markets investments and, (iii) $48.5 million of interest expense primarily relating to the senior notes outstanding for KKR and KFN.
The net decrease in net interest and dividends is due primarily to the lower amount of capital invested in CLOs described above, as well as a lower level of dividends in the 2017 period, partially offset by lower interest expense due to the redemption and paydown of KFN's 8.375% senior notes due 2041 and other debt after the first quarter of 2016. Replacing KFN’s 8.375% senior notes due 2041 (which were redeemed in November 2016) and the KFN 2042 Notes (which were redeemed in April 2017 as discussed in “-Recent Developments”) with the KFN 2032 Notes (which were issued in March 2017) represents an annualized interest expense savings of $9.7 million when calculated in the aggregate.
97
Segment Expenses
Compensation and Benefits
The increase was primarily due to a greater amount of compensation and benefits expenses allocated from the other operating segments to Principal Activities, as well as a greater amount of corporate compensation allocated to Principal Activities, in each case as a result of an increase in the proportion of revenue earned by Principal Activities relative to other operating segments as well as an increase in the absolute amount of compensation recorded. See "-Segment Analysis" for a discussion of expense allocations among segments.
Occupancy and Other Operating Expenses
The increase was primarily due to a greater amount of occupancy and other expenses allocated from the other operating segments to Principal Activities, as well as a greater amount of corporate occupancy and other expenses allocated to Principal Activities, in each case as a result of an increase in the proportion of revenue earned by Principal Activities relative to other operating segments.
Economic Net Income (Loss)
Economic net income for the three months ended March 31, 2017 was primarily driven by the net investment income as described above.
Segment Balance Sheet
Our segment balance sheet is the balance sheet of KKR & Co. L.P. and its subsidiaries on a segment basis which includes, but is not limited to, our investment management companies, broker-dealer companies, general partners of our investment funds and KFN. Our segment balance sheet excludes the assets and liabilities of our investment funds and CFEs and other consolidated entities that are not subsidiaries of KKR & Co. L.P.
Investments
Investments is a term used solely for purposes of financial presentation of a portion of KKR's balance sheet and includes majority ownership of subsidiaries that operate KKR's asset management and other businesses, including the general partner interests of KKR's investment funds.
Cash and Short-Term Investments
Cash and short-term investments represent cash and liquid short-term investments in high-grade, short-duration cash management strategies used by KKR to generate additional yield on our excess liquidity and is used by management in evaluating KKR's liquidity position. We believe this measure is useful to unitholders as it provides additional insight into KKR's available liquidity. Cash and short-term investments differ from cash and cash equivalents on a GAAP basis as a result of the inclusion of liquid short-term investments in cash and short-term investments. The impact that these liquid short-term investments have on cash and cash equivalents on a GAAP basis is reflected in the consolidated statements of cash flows within cash flows from operating activities. Accordingly, the exclusion of these investments from cash and cash equivalents on a GAAP basis has no impact on cash provided (used) by operating activities, investing activities or financing activities.
98
The following tables present information with respect to our segment balance sheet as of March 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016:
As of | As of | |||||||
March 31, 2017 | December 31, 2016 | |||||||
($ in thousands, except per unit amounts) | ||||||||
Cash and Short-term Investments | $ | 3,383,032 | $ | 3,387,673 | ||||
Investments | 7,709,739 | 6,958,873 | ||||||
Unrealized Carry (1) | 1,306,737 | 1,213,692 | ||||||
Other Assets | 1,777,727 | 1,611,678 | ||||||
Corporate Real Estate | 161,225 | 161,225 | ||||||
Total Assets | $ | 14,338,460 | $ | 13,333,141 | ||||
Debt Obligations - KKR (ex-KFN) | $ | 2,000,000 | $ | 2,000,000 | ||||
Debt Obligations - KFN | 754,767 | 398,560 | ||||||
Preferred Shares - KFN | 373,750 | 373,750 | ||||||
Other Liabilities | 362,426 | 244,676 | ||||||
Total Liabilities | 3,490,943 | 3,016,986 | ||||||
Noncontrolling Interests | 21,167 | 19,564 | ||||||
Preferred Units | 500,000 | 500,000 | ||||||
Book Value | $ | 10,326,350 | $ | 9,796,591 | ||||
Book Value Per Outstanding Adjusted Unit | $ | 12.80 | $ | 12.15 | ||||
(1) Unrealized Carry | ||||||||
Private Markets | $ | 1,222,184 | $ | 1,141,610 | ||||
Public Markets | 84,553 | 72,082 | ||||||
Total | $ | 1,306,737 | $ | 1,213,692 | ||||
99
The following table presents the holdings of our segment balance sheet by asset class as of March 31, 2017:
As of March 31, 2017 | ||||||||||||
Investments | Cost | Fair Value | Fair Value as a Percentage of Total Investments | |||||||||
Private Equity Co-Investments and Other Equity | $ | 1,737,193 | $ | 1,981,106 | 25.7 | % | ||||||
Private Equity Funds | 952,781 | 1,150,455 | 14.9 | % | ||||||||
Private Equity Total | 2,689,974 | 3,131,561 | 40.6 | % | ||||||||
Energy | 970,902 | 572,895 | 7.4 | % | ||||||||
Real Estate (1) | 730,104 | 769,919 | 10.0 | % | ||||||||
Infrastructure | 252,171 | 273,199 | 3.6 | % | ||||||||
Real Assets Total | 1,953,177 | 1,616,013 | 21.0 | % | ||||||||
Special Situations | 835,329 | 852,955 | 11.1 | % | ||||||||
Direct Lending | 127,784 | 124,016 | 1.6 | % | ||||||||
Mezzanine | 24,381 | 24,931 | 0.3 | % | ||||||||
Alternative Credit Total | 987,494 | 1,001,902 | 13.0 | % | ||||||||
CLOs (1) | 966,830 | 596,706 | 7.7 | % | ||||||||
Liquid Credit | 151,335 | 160,637 | 2.1 | % | ||||||||
Specialty Finance | 292,442 | 221,659 | 2.9 | % | ||||||||
Credit Total | 2,398,101 | 1,980,904 | 25.7 | % | ||||||||
Other | 964,098 | 981,261 | 12.7 | % | ||||||||
Total Investments | $ | 8,005,350 | $ | 7,709,739 | 100.0 | % | ||||||
As of March 31, 2017 | ||||||||||||
Significant Investments: (2) | Cost | Fair Value | Fair Value as a Percentage of Total Investments | |||||||||
First Data Corporation (NYSE: FDC) | $ | 1,031,827 | $ | 1,191,388 | 15.5 | % | ||||||
KKR Real Estate Finance Trust Inc. | 289,723 | 289,723 | 3.8 | % | ||||||||
WMIH Corp. (NASDAQ: WMIH) | 221,412 | 215,431 | 2.8 | % | ||||||||
Oil Field Services Investment | 137,567 | 161,887 | 2.1 | % | ||||||||
Natural Gas Midstream Investment | 150,224 | 158,218 | 2.0 | % | ||||||||
Total Significant Investments | 1,830,753 | 2,016,647 | 26.2 | % | ||||||||
Other Investments | 6,174,597 | 5,693,092 | 73.8 | % | ||||||||
Total Investments | $ | 8,005,350 | $ | 7,709,739 | 100.0 | % | ||||||
(1) Includes approximately $260.2 million and $289.7 million of CLOs and our ownership of KKR Real Estate Finance Trust Inc., respectively, that are not held for investment purposes and are held at cost. | ||||||||||||
(2) The significant investments include the top five investments (other than investments expected to be syndicated or transferred in connection with new fundraising) based on their fair values as of March 31, 2017. The fair value figures include the co-investment and the limited partner and/or general partner interests held by KKR in the underlying investment, if applicable. | ||||||||||||
100
The following tables provide reconciliations of KKR’s GAAP Condensed Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition to Total Reportable Segments Balance Sheet as of March 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016.
As of March 31, 2017 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
(Amounts in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION (GAAP BASIS) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | TOTAL REPORTABLE SEGMENTS BALANCE SHEET | |||||||||||||||||
Assets | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Cash and Cash Equivalents | $ | 2,758,398 | — | — | 624,634 | — | — | $ | 3,383,032 | Cash and Short-term Investments | |||||||||||||
Investments | 34,225,324 | (24,173,177 | ) | (1,035,671 | ) | (1,306,737 | ) | — | — | 7,709,739 | Investments | ||||||||||||
— | — | 1,306,737 | — | — | 1,306,737 | Unrealized Carry | |||||||||||||||||
Other Assets | 4,651,990 | (1,790,079 | ) | — | (785,859 | ) | — | (298,325 | ) | 1,777,727 | Other Assets | ||||||||||||
— | — | 161,225 | — | — | 161,225 | Corporate Real Estate | |||||||||||||||||
Total Assets | $ | 41,635,712 | (25,963,256 | ) | (1,035,671 | ) | — | — | (298,325 | ) | $ | 14,338,460 | |||||||||||
Liabilities and Equity | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Debt Obligations | 19,625,439 | (16,870,672 | ) | — | (754,767 | ) | — | — | 2,000,000 | Debt Obligations - KKR (ex-KFN) | |||||||||||||
— | — | 754,767 | — | — | 754,767 | Debt Obligations - KFN | |||||||||||||||||
— | — | 373,750 | — | — | 373,750 | Preferred Shares - KFN | |||||||||||||||||
Other Liabilities | 3,722,475 | (2,159,286 | ) | (1,035,671 | ) | — | — | (165,092 | ) | 362,426 | Other Liabilities | ||||||||||||
Total Liabilities | 23,347,914 | (19,029,958 | ) | (1,035,671 | ) | 373,750 | — | (165,092 | ) | 3,490,943 | |||||||||||||
Redeemable Noncontrolling Interests | 781,428 | (781,428 | ) | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Equity | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Series A Preferred Units | 332,988 | — | — | (332,988 | ) | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Series B Preferred Units | 149,566 | — | — | (149,566 | ) | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
KKR & Co. L.P. Capital - Common Unitholders | 5,755,354 | 140,248 | — | (17,446 | ) | 4,581,427 | (133,233 | ) | 10,326,350 | Book Value | |||||||||||||
Noncontrolling Interests | 11,268,462 | (6,292,118 | ) | — | (373,750 | ) | (4,581,427 | ) | — | 21,167 | Noncontrolling Interests | ||||||||||||
— | — | 500,000 | — | — | 500,000 | Preferred Units | |||||||||||||||||
Total Liabilities and Equity | $ | 41,635,712 | (25,963,256 | ) | (1,035,671 | ) | — | — | (298,325 | ) | $ | 14,338,460 | |||||||||||
1 | IMPACT OF CONSOLIDATION OF INVESTMENT VEHICLES AND OTHER ENTITIES | ||||||||||||||||||||||
2 | CARRY POOL RECLASSIFICATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||
3 | OTHER RECLASSIFICATIONS | ||||||||||||||||||||||
4 | NONCONTROLLING INTERESTS HELD BY KKR HOLDINGS L.P. AND OTHER | ||||||||||||||||||||||
5 | EQUITY IMPACT OF KKR MANAGEMENT HOLDINGS CORP. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
101
As of December 31, 2016 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
(Amounts in thousands) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION (GAAP BASIS) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | TOTAL REPORTABLE SEGMENTS BALANCE SHEET | |||||||||||||||||
Assets | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Cash and Cash Equivalents | $ | 2,508,902 | — | — | 878,771 | — | — | $ | 3,387,673 | Cash and Short-term Investments | |||||||||||||
Investments | 31,409,765 | (22,249,206 | ) | (987,994 | ) | (1,213,692 | ) | — | — | 6,958,873 | Investments | ||||||||||||
— | — | 1,213,692 | — | — | 1,213,692 | Unrealized Carry | |||||||||||||||||
Other Assets | 5,084,230 | (2,118,364 | ) | — | (1,039,996 | ) | — | (314,192 | ) | 1,611,678 | Other Assets | ||||||||||||
— | — | 161,225 | — | — | 161,225 | Corporate Real Estate | |||||||||||||||||
Total Assets | $ | 39,002,897 | (24,367,570 | ) | (987,994 | ) | — | — | (314,192 | ) | $ | 13,333,141 | |||||||||||
Liabilities and Equity | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Debt Obligations | 18,544,075 | (16,145,515 | ) | — | (398,560 | ) | — | — | 2,000,000 | Debt Obligations - KKR (ex-KFN) | |||||||||||||
— | — | 398,560 | — | — | 398,560 | Debt Obligations - KFN | |||||||||||||||||
— | — | 373,750 | — | — | 373,750 | Preferred Shares - KFN | |||||||||||||||||
Other Liabilities | 3,340,739 | (1,945,039 | ) | (987,994 | ) | — | — | (163,030 | ) | 244,676 | Other Liabilities | ||||||||||||
Total Liabilities | 21,884,814 | (18,090,554 | ) | (987,994 | ) | 373,750 | — | (163,030 | ) | 3,016,986 | |||||||||||||
Redeemable Noncontrolling Interests | 632,348 | (632,348 | ) | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||
Equity | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Series A Preferred Units | 332,988 | — | — | (332,988 | ) | — | — | ||||||||||||||||
Series B Preferred Units | 149,566 | — | — | (149,566 | ) | — | — | ||||||||||||||||
KKR & Co. L.P. Capital - Common Unitholders | 5,457,279 | 118,635 | — | (17,446 | ) | 4,389,285 | (151,162 | ) | 9,796,591 | Book Value | |||||||||||||
Noncontrolling Interests | 10,545,902 | (5,763,303 | ) | — | (373,750 | ) | (4,389,285 | ) | — | 19,564 | Noncontrolling Interests | ||||||||||||
— | — | 500,000 | — | — | 500,000 | Preferred Units | |||||||||||||||||
Total Liabilities and Equity | $ | 39,002,897 | (24,367,570 | ) | (987,994 | ) | — | — | (314,192 | ) | $ | 13,333,141 | |||||||||||
1 | IMPACT OF CONSOLIDATION OF INVESTMENT VEHICLES AND OTHER ENTITIES | ||||||||||||||||||||||
2 | CARRY POOL RECLASSIFICATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||
3 | OTHER RECLASSIFICATIONS | ||||||||||||||||||||||
4 | NONCONTROLLING INTERESTS HELD BY KKR HOLDINGS L.P. AND OTHER | ||||||||||||||||||||||
5 | EQUITY IMPACT OF KKR MANAGEMENT HOLDINGS CORP. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
102
The following tables provide reconciliations of KKR’s GAAP Common Units Outstanding to Adjusted Units, Adjusted Units Eligible for Distribution and Outstanding Adjusted Units:
As of | As of | |||
March 31, 2017 | December 31, 2016 | |||
GAAP Common Units Outstanding - Basic | 455,570,965 | 452,380,335 | ||
Adjustments: | ||||
Unvested Common Units (1) | 38,551,767 | 37,519,436 | ||
Other Exchangeable Securities (2) | 4,257,617 | 4,600,320 | ||
GAAP Common Units Outstanding - Diluted | 498,380,349 | 494,500,091 | ||
Adjustments: | ||||
KKR Holdings Units (3) | 350,909,471 | 353,757,398 | ||
Adjusted Units | 849,289,820 | 848,257,489 | ||
Adjustments: | ||||
Unvested Common Units | (38,551,767 | ) | (37,519,436 | ) |
Adjusted Units Eligible for Distribution | 810,738,053 | 810,738,053 | ||
Adjustments: | ||||
Vested Other Exchangeable Securities (2) | (4,257,617 | ) | (4,600,320 | ) |
Outstanding Adjusted Units | 806,480,436 | 806,137,733 | ||
(1) Represents equity awards granted under the Equity Incentive Plan. The issuance of common units of KKR & Co. L.P. pursuant to awards under the Equity Incentive Plan dilutes KKR common unitholders and KKR Holdings pro rata in accordance with their respective percentage interests in the KKR business. Year-end 2016 equity awards were granted before December 31, 2016 (except for awards to our named executive officers), rather than, as has been historical practice, after the end of the year. As a result, adjusted units increased in the fourth quarter of 2016, rather than in the first quarter of 2017.
(2) Represents securities in a subsidiary of a KKR Group Partnership and of KKR & Co. L.P. that are exchangeable into KKR & Co. L.P. common units issued in connection with the acquisition of Avoca.
(3) Common units that may be issued by KKR & Co. L.P. upon exchange of units in KKR Holdings L.P. for KKR common units.
Liquidity
We manage our liquidity and capital requirements by focusing on our cash flows before the consolidation of our funds and CFEs and the effect of changes in short term assets and liabilities, which we anticipate will be settled for cash within one year. Our primary cash flow activities on a segment basis typically involve: (i) generating cash flow from operations; (ii) generating income from investment activities, by investing in investments that generate yield (namely interest and dividends) as well as the sale of investments and other assets; (iii) funding capital commitments that we have made to, and advancing capital to, our funds and CLOs; (iv) developing and funding new investment strategies, investment products and other growth initiatives, including acquisitions of other investments, assets and businesses; (v) underwriting and funding commitments in our capital markets business; (vi) distributing cash flow to our unitholders, certain holders of certain exchangeable securities and holders of our Series A and Series B Preferred Units; and (vii) paying borrowings, interest payments and repayments under credit agreements, our senior notes and other borrowing arrangements. See "-Liquidity - Liquidity Needs - Distributions."
Sources of Liquidity
Our primary sources of liquidity consist of amounts received from: (i) our operating activities, including the fees earned from our funds, portfolio companies, and capital markets transactions; (ii) realizations on carried interest from our investment funds; (iii) interest and dividends from investments that generate yield, including our investments in CLOs; (iv) realizations on and sales of investments and other assets, including the transfers of investments for fund formations and (v) borrowings under our credit facilities, debt offerings and other borrowing arrangements. In addition, we may generate cash proceeds from sales of equity securities.
With respect to our private equity funds, carried interest is distributed to the general partner of a private equity fund with a clawback provision only after all of the following are met: (i) a realization event has occurred (e.g., sale of a portfolio company,
103
dividend, etc.); (ii) the vehicle has achieved positive overall investment returns since its inception, in excess of performance hurdles where applicable; and (iii) with respect to investments with a fair value below cost, cost has been returned to fund investors in an amount sufficient to reduce remaining cost to the investments' fair value. As of March 31, 2017, certain of our funds had met the first and second criteria, as described above, but did not meet the third criteria. In these cases, carried interest accrues on the consolidated statement of operations, but will not be distributed in cash to us as the general partner of an investment fund upon a realization event. For a fund that has a fair value above cost, overall, but has one or more investments where fair value is below cost, the shortfall between cost and fair value for such investments is referred to as a "netting hole." When netting holes are present, realized gains on individual investments that would otherwise allow the general partner to receive carried interest distributions are instead used to return invested capital to our funds' limited partners in an amount equal to the netting hole. Once netting holes have been filled with either (a) return of capital equal to the netting hole for those investments where fair value is below cost, or (b) increases in the fair value of those investments where fair value is below cost, then realized carried interest will be distributed to the general partner upon a realization event. A fund that is in a position to pay cash carry refers to a fund for which carried interest is expected to be paid to the general partner upon the next material realization event, which includes funds with no netting holes as well as funds with a netting hole that is sufficiently small in size such that the next material realization event would be expected to result in the payment of carried interest.
As of March 31, 2017, a netting hole in excess of $50 million existed at our European Fund IV for $102.8 million. In accordance with the criteria set forth above, other funds currently have and may in the future develop netting holes, and netting holes for those and other funds may otherwise increase or decrease in the future.
We have access to funding under various credit facilities, other borrowing arrangements and other sources of liquidity that we have entered into with major financial institutions or which we receive from the capital markets. The following describes these sources of liquidity.
Revolving Credit Agreements, Senior Notes, KFN Debt Obligations & KFN Securities
For a discussion of KKR's debt obligations, including our revolving credit agreements, senior notes, KFN debt obligations and KFN securities, see Note 10 "Debt Obligations" to the audited financial statements included in our Annual Report on Form 10-K. The information presented below supplements and updates, and should be read in conjunction with, such information. No amounts were borrowed under our corporate credit agreement with HSBC Bank USA for the three months ended March 31, 2017 and a total of $325 million was borrowed and $325 million was repaid under the KCM Credit Agreement with a major financial institution for the three months ended March 31, 2017.
KFN Redemption
On April 24, 2017 KFN redeemed all of its outstanding 7.500% Senior Notes due 2042. See discussion under "--Recent Developments."
KFN Issued 5.500% Senior Unsecured Notes Due 2032
On March 30, 2017, KFN issued $375.0 million par amount of 5.500% Senior Unsecured Notes. See discussion under "--Recent Developments."
Preferred Units
For a discussion of KKR's Series A and Series B Preferred Units, see Note 15 "Equity" to the audited financial statements and "--Liquidity Needs--Preferred Units" in the management's discussion and analysis of financial condition and results of operations, each of which is included in our Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Common Units
On May 16, 2014, KKR & Co. L.P. filed a registration statement with the Securities and Exchange Commission for the sale by us from time to time of up to 5,000,000 common units of KKR & Co. L.P. to generate cash proceeds (a) up to (1) the amount of withholding taxes, social benefit payments or similar payments payable by us in respect of awards granted pursuant to the Equity Incentive Plan, and (2) the amount of cash delivered in respect of awards granted pursuant to the Equity Incentive Plan that are settled in cash instead of common units; and (b) to the extent the net proceeds from the sale of common units exceeds the amounts due under clause (a), for general corporate purposes. The administrator of the Equity Incentive Plan is expected to reduce the maximum number of common units eligible to be issued under the Equity Incentive Plan by the number of common units issued and sold pursuant to this Registration Statement, as applicable, unless such reduction is already
104
provided for with respect to such awards under the terms of the Equity Incentive Plan. The Securities and Exchange Commission declared the registration statement effective on June 4, 2014, and will expire on June 4, 2017. As of March 31, 2017, 4,173,039 common units have been issued and sold under the registration statement and are included in our basic common units outstanding as of March 31, 2017.
Liquidity Needs
We expect that our primary liquidity needs will consist of cash required to:
• | continue to grow our business, including seeding new strategies, funding our capital commitments made to existing and future funds, co-investments and any net capital requirements of our capital markets companies and otherwise supporting investment vehicles which we sponsor; |
• | warehouse investments in portfolio companies or other investments for the benefit of one or more of our funds, vehicles, accounts or CLOs pending the contribution of committed capital by the investors in such vehicles, and advancing capital to them for operational or other needs; |
• | service debt obligations including the payment of obligations upon maturity or redemption, as well as any contingent liabilities that may give rise to future cash payments; |
• | fund cash operating expenses, including litigation matters; |
• | pay amounts that may become due under our tax receivable agreement with KKR Holdings; |
• | make cash distributions in accordance with our distribution policy for our common units or the terms of our preferred units; |
• | underwrite commitments, advance loan proceeds and fund syndication commitments within our capital markets business; |
• | make future purchase price payments in connection with our proprietary investments, such as our strategic partnership with Marshall Wace, to the extent not paid by newly issued common units; |
• | acquire other assets for our Principal Activities segment, including other businesses, investments and assets; and |
• | repurchase KKR & Co. L.P. common units pursuant to the unit repurchase program announced on October 27, 2015 and subsequently increased on February 9, 2017. |
KKR & Co. L.P. Unit Repurchase Program
On October 27, 2015, KKR announced the authorization of a program providing for the repurchase by KKR of up to $500 million in the aggregate of its outstanding common units. On February 9, 2017, KKR announced the authorization of an incremental $250 million under this unit repurchase program. Under this unit repurchase program, units may be repurchased from time to time in open market transactions, in privately negotiated transactions or otherwise. The timing, manner, price and amount of any unit repurchases will be determined by KKR in its discretion and will depend on a variety of factors, including legal requirements, price and economic and market conditions. KKR expects that the program, which has no expiration date, will be in effect until the maximum approved dollar amount has been used to repurchase common units. The program does not require KKR to repurchase any specific number of common units, and the program may be suspended, extended, modified or discontinued at any time. Since inception of the unit repurchase program through April 27, 2017, KKR has repurchased and canceled approximately 31.7 million outstanding common units for approximately $459 million. There is $291 million remaining as of April 27, 2017 under the current repurchase program. No units were repurchased during the first quarter of 2017.
In addition to the purchases of common units above, (1) cash was used to pay the amount of withholding taxes, social benefit payments or similar payments payable by us in respect of awards granted pursuant to the Equity Incentive Plan and (2) cash was delivered in respect of certain awards granted pursuant to the Equity Incentive Plan and Other Exchangeable Securities. During 2017, KKR canceled equity awards representing 2.1 million common units to satisfy tax and cash-settlement obligations of $37.8 million in connection with their vesting. See "--Item 2. Unregistered Sales of Equity Securities and Use of Proceeds."
105
Capital Commitments
The agreements governing our active investment funds generally require the general partners of the funds to make minimum capital commitments to such funds, which usually range from 2% to 8% of a fund's total capital commitments at final closing; however, the size of our general partner commitment to certain funds pursuing newer strategies may exceed this range. The following table presents our uncalled commitments to our active investment funds as of March 31, 2017:
Uncalled Commitments | |||
Private Markets | ($ in thousands) | ||
Americas Fund XII | $ | 1,000,000 | |
Asian Fund III | 500,000 | ||
European Fund IV | 128,600 | ||
Next Generation Technology Growth Fund | 127,900 | ||
Real Estate Partners Americas | 108,800 | ||
Energy Income and Growth | 96,500 | ||
Global Infrastructure Investors II | 74,500 | ||
Real Estate Partners Europe | 52,300 | ||
North America Fund XI | 33,600 | ||
Asian Fund II | 25,800 | ||
Other Private Markets Vehicles | 983,500 | ||
Total Private Markets Commitments | 3,131,500 | ||
Public Markets | |||
Special Situations Fund II | 203,700 | ||
Lending Partners Europe | 30,400 | ||
Lending Partners II | 17,500 | ||
Special Situations Fund | 12,000 | ||
Lending Partners | 8,300 | ||
Mezzanine Partners | 4,700 | ||
Other Public Markets Vehicles | 114,200 | ||
Total Public Markets Commitments | 390,800 | ||
Total Uncalled Commitments | $ | 3,522,300 | |
Other Commitments
In addition to the uncalled commitments to our investment funds as shown above, KKR has entered into contractual commitments with respect to (i) the purchase of investments and other assets in its Principal Activities segment, and (ii) underwriting transactions, debt financing, and syndications in our Capital Markets segment. As of March 31, 2017, these commitments amounted to $1,396.3 million and $1,027.8 million, respectively. Whether these amounts are actually funded, in whole or in part, depends on the contractual terms of such commitments, including the satisfaction or waiver of any conditions to closing or funding. In the case of purchases of investments or assets in our Principal Activities segment, the amount to be funded include amounts that are intended to be syndicated to third parties, and the actual amounts to be funded may be less than shown.
Prisma Capital Partners
On October 1, 2012, KKR acquired all of the equity interests of Prisma subject to potential purchase price payments in 2014 and 2017. At the time of the acquisition, KKR may have become contingently obligated to make future purchase price payments in 2017 based on whether the Prisma business grows to achieve certain operating performance metrics when measured in such year. During the fourth quarter of 2016, KKR determined that it was no longer probable that the sellers (certain of whom are employees of KKR) of Prisma Capital Partners LP and its affiliates would be entitled to any future additional payment under the contingent consideration arrangement. Consequently, as of December 31, 2016, KKR has reduced
106
the fair value of the contingent consideration liability to zero. Additionally, on February 6, 2017, KKR and Pacific Alternative Asset Management Company, LLC, or PAAMCO, announced that they entered into a strategic transaction to create a new liquid alternatives investment firm by combining PAAMCO and KKR Prisma. Under the terms of the agreement, the entire businesses of both PAAMCO and KKR Prisma will be contributed to a newly formed company that will operate independently from KKR, and KKR will retain a 39.9% stake as a long-term strategic partner. This transaction is subject to the satisfaction of customary closing conditions, including the receipt of requisite regulatory approvals.
Investment in Marshall Wace LLP
On November 2, 2015, KKR entered into a long-term strategic relationship with Marshall Wace LLP and its affiliates and acquired a 24.9% interest in Marshall Wace through a combination of cash and common units. Subject to the exercise of a put option by Marshall Wace or a call option by KKR, at subsequent closings to occur in the second, third and fourth years following the initial closing described above, and subject to satisfaction or waiver of certain closing conditions, including regulatory approvals, KKR may at each such closing subscribe (or be required to subscribe) for an incremental 5% equity interest, for ultimate aggregate ownership of up to 39.9% of Marshall Wace. The exercise of such options would require the use of cash and/or KKR common units. KKR's investment in Marshall Wace is accounted for using the equity method of accounting.
Tax Receivable Agreement
We and certain intermediate holding companies that are taxable corporations for U.S. federal, state and local income tax purposes, may be required to acquire KKR Group Partnership Units from time to time pursuant to our exchange agreement with KKR Holdings. KKR Management Holdings L.P. made an election under Section 754 of the Internal Revenue Code that will remain in effect for each taxable year in which an exchange of KKR Group Partnership Units for common units occurs, which may result in an increase in our intermediate holding companies' share of the tax basis of the assets of the KKR Group Partnerships at the time of an exchange of KKR Group Partnership Units. Certain of these exchanges are expected to result in an increase in our intermediate holding companies' share of the tax basis of the tangible and intangible assets of the KKR Group Partnerships, primarily attributable to a portion of the goodwill inherent in our business that would not otherwise have been available. This increase in tax basis may increase depreciation and amortization deductions for tax purposes and therefore reduce the amount of income tax our intermediate holding companies would otherwise be required to pay in the future. This increase in tax basis may also decrease gain (or increase loss) on future dispositions of certain capital assets to the extent tax basis is allocated to those capital assets.
We have entered into a tax receivable agreement with KKR Holdings, which requires our intermediate holding companies to pay to KKR Holdings, or to current and former principals who have exchanged KKR Holdings units for KKR common units as transferees of KKR Group Partnership Units, 85% of the amount of cash savings, if any, in U.S. federal, state and local income tax that the intermediate holding companies realize as a result of the increase in tax basis described above, as well as 85% of the amount of any such savings the intermediate holding companies realize as a result of increases in tax basis that arise due to future payments under the agreement. We expect our intermediate holding companies to benefit from the remaining 15% of cash savings, if any, in income tax that they realize. A termination of the agreement or a change of control could give rise to similar payments based on tax savings that we would be deemed to realize in connection with such events. In the event that other of our current or future subsidiaries become taxable as corporations and acquire KKR Group Partnership Units in the future, or if we become taxable as a corporation for U.S. federal income tax purposes, we expect that each will become subject to a tax receivable agreement with substantially similar terms.
These payment obligations are obligations of our intermediate holding companies and not the KKR Group Partnerships. As such, cash payments received by common unitholders may vary from those received by holders of KKR Group Partnership Units held by KKR Holdings and its current and former principals to the extent payments are made to those parties under the tax receivable agreement. Payments made under the tax receivable agreement are required to be made within 90 days of the filing of the tax returns of our intermediate holding companies, which may result in a timing difference between the tax savings received by KKR's intermediate holdings companies and the cash payments made to the selling holders of KKR Group Partnership Units.
For the three months ended March 31, 2017 and 2016, no cash payments have been made under the tax receivable agreement. As of March 31, 2017, $4.2 million of cumulative income tax savings have been realized. See "-Liquidity-Other Liquidity Needs- Contractual Obligations, Commitments and Contingencies" for a discussion of amounts payable and cumulative cash payments made under this agreement.
107
Distributions
A distribution of $0.17 per common unit has been declared, which will be paid on May 23, 2017 to holders of record of common units as of the close of business on May 8, 2017. Under KKR's current distribution policy for its common units, KKR intends to make equal quarterly distributions to holders of common units in an amount of $0.17 per common unit per quarter, beginning with the financial results reported for the first quarter of 2017.
A distribution of $0.421875 per Series A Preferred Unit has been declared and set aside for payment on June 15, 2017 to holders of record of Series A Preferred Units as of the close of business on June 1, 2017. A distribution of $0.406250 per Series B Preferred Unit has been declared and set aside for payment on June 15, 2017 to holders of record of Series B Preferred Units as of the close of business on June 1, 2017.
The declaration and payment of any future distributions on preferred or common units are subject to the discretion of the board of directors of the general partner of KKR & Co. L.P. and the terms of its limited partnership agreement. There can be no assurance that future distributions will be made as intended or at all, that unitholders will receive sufficient distributions to satisfy payment of their tax liabilities as limited partners of KKR & Co. L.P. or that any particular distribution policy for common units will be maintained. Furthermore, the declaration and payment of distributions by the KKR Group Partnerships and our other subsidiaries may also be subject to legal, contractual and regulatory restrictions, including restrictions contained in our debt agreements and the preferred units of the KKR Group Partnerships.
When KKR & Co. L.P. receives distributions from the KKR Group Partnerships (the holding companies of the KKR business), KKR Holdings receives its pro rata share of such distributions from the KKR Group Partnerships.
Other Liquidity Needs
We may also be required to fund various underwriting, syndications and fronting commitments in our capital markets business in connection with the underwriting of loans, securities or other financial instruments, which has increased in significance in the first quarter of 2017 and may continue to be significant in future quarters. We generally expect that these commitments will be syndicated to third parties or otherwise fulfilled or terminated, although we may in some instances elect to retain a portion of the commitments for our own investment.
Contractual Obligations, Commitments and Contingencies on a Consolidated Basis
In the ordinary course of business, we and our consolidated funds and CFEs enter into contractual arrangements that may require future cash payments. The following table sets forth information relating to anticipated future cash payments as of March 31, 2017.
Payments due by Period | ||||||||||||||||||||
Types of Contractual Obligations | <1 Year | 1-3 Years | 3-5 Years | >5 Years | Total | |||||||||||||||
($ in millions) | ||||||||||||||||||||
Uncalled commitments to investment funds (1) | $ | 6,251.3 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 6,251.3 | ||||||||||
Debt payment obligations (2) | 765.8 | 1,231.7 | 1,325.4 | 16,080.8 | 19,403.7 | |||||||||||||||
Interest obligations on debt (3) | 694.7 | 1,351.4 | 1,228.7 | 4,295.2 | 7,570.0 | |||||||||||||||
Underwriting commitments (4) | 875.9 | — | — | — | 875.9 | |||||||||||||||
Lending commitments (5) | 151.9 | — | — | — | 151.9 | |||||||||||||||
Purchase commitments (6) | 1,366.1 | 30.2 | — | — | 1,396.3 | |||||||||||||||
Lease obligations | 51.3 | 94.4 | 45.4 | 10.6 | 201.7 | |||||||||||||||
Corporate real estate (7) | — | 292.5 | — | — | 292.5 | |||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 10,157.0 | $ | 3,000.2 | $ | 2,599.5 | $ | 20,386.6 | $ | 36,143.3 | ||||||||||
(1) | These uncalled commitments represent amounts committed by our consolidated investment funds, which include amounts committed by KKR and our fund investors, to fund the purchase price paid for each investment made by our investment funds which are actively investing. Because capital contributions are due on demand, the above commitments have been presented as falling due within one year. However, given the size of such commitments and the pace at which our investment funds make investments, we expect that the capital commitments presented above will be called over a period of several years. See "—Liquidity—Liquidity Needs." |
108
(2) | Amounts include (i) the 2020 Senior Notes, 2043 Senior Notes and 2044 Senior Notes of $2.0 billion gross of unamortized discount, (ii) KFN 2032 Senior notes of $0.4 billion gross of unamortized discount, (iii) KFN 2042 Senior Notes of $0.1 billion (redeemed in full on April 24, 2017), net of unamortized premium, (iv) KFN Junior Subordinated Notes of $0.3 billion, gross of unamortized discount, (v) financing arrangements entered into by our consolidated funds with the objective of providing liquidity to the funds of $2.6 billion, (vi) debt securities issued by our consolidated CLOs of $9.0 billion and (vii) debt securities issued by our consolidated CMBS entities of $5.0 billion. KFN's debt obligations are non-recourse to KKR beyond the assets of KFN. Debt securities issued by consolidated CLOs and CMBS entities are supported solely by the investments held at the CLO and CMBS vehicles and are not collateralized by assets of any other KKR entity. Obligations under financing arrangements entered into by our consolidated funds are generally limited to our pro-rata equity interest in such funds. Our management companies bear no obligations to repay any financing arrangements at our consolidated funds. |
(3) | These interest obligations on debt represent estimated interest to be paid over the maturity of the related debt obligation, which has been calculated assuming the debt outstanding at March 31, 2017 is not repaid until its maturity. Future interest rates are assumed to be those in effect as of March 31, 2017, including both variable and fixed rates, as applicable, provided for by the relevant debt agreements. The amounts presented above include accrued interest on outstanding indebtedness. |
(4) | Represents various commitments in our capital markets business in connection with the underwriting of loans, securities and other financial instruments. These commitments are shown net of amounts syndicated. |
(5) | Represents obligations in our capital markets business to lend under various revolving credit facilities. |
(6) | Represents commitments of KKR and KFN to fund the purchase of various investments. |
(7) | Represents the purchase price due upon delivery of a new KKR office being constructed, all or a portion of which represents construction financing obtained by the developer and may be refinanced upon delivery of the completed office. |
The commitment table above excludes contractual amounts owed under the tax receivable agreement because the ultimate amount and timing of the amounts due are not presently known. As of March 31, 2017, a payable of $130.2 million has been recorded in due to affiliates in the condensed consolidated financial statements representing management's best estimate of the amounts currently expected to be owed under the tax receivable agreement. As of March 31, 2017, approximately $24.0 million of cumulative cash payments have been made under the tax receivable agreement. See "—Liquidity Needs—Tax Receivable Agreement."
Contractual Obligations, Commitments and Contingencies on an Unconsolidated Basis
In the ordinary course of business, we enter into contractual arrangements that may require future cash payments. The following table sets forth information relating to anticipated future cash payments as of March 31, 2017 on an unconsolidated basis before the consolidation of funds and CFEs. This table differs from the table presented above which sets forth contractual commitments on a consolidated basis principally because this table excludes the obligations of our consolidated funds and CFEs.
Payments due by Period | ||||||||||||||||||||
Types of Contractual Obligations | <1 Year | 1-3 Years | 3-5 Years | >5 Years | Total | |||||||||||||||
($ in millions) | ||||||||||||||||||||
Uncalled commitments to investment funds (1) | $ | 3,522.3 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 3,522.3 | ||||||||||
Debt payment obligations (2) | — | — | 500.0 | 2,254.8 | 2,754.8 | |||||||||||||||
Interest obligations on debt (3) | 151.1 | 298.4 | 250.4 | 2,241.8 | 2,941.7 | |||||||||||||||
Underwriting commitments (4) | 875.9 | — | — | — | 875.9 | |||||||||||||||
Lending commitments (5) | 151.9 | — | — | — | 151.9 | |||||||||||||||
Purchase commitments (6) | 1,366.1 | 30.2 | — | — | 1,396.3 | |||||||||||||||
Lease obligations | 51.3 | 94.4 | 45.4 | 10.6 | 201.7 | |||||||||||||||
Corporate real estate (7) | — | 292.5 | — | — | 292.5 | |||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 6,118.6 | $ | 715.5 | $ | 795.8 | $ | 4,507.2 | $ | 12,137.1 | ||||||||||
109
(1) | These uncalled commitments represent amounts committed by us to fund a portion of the purchase price paid for each investment made by our investment funds which are actively investing. Because capital contributions are due on demand, the above commitments have been presented as falling due within one year. However, given the size of such commitments and the pace at which our investment funds make investments, we expect that the capital commitments presented above will be called over a period of several years. See "—Liquidity—Liquidity Needs." |
(2) | Represents the 2020 Senior Notes, 2043 Senior Notes, 2044 Senior Notes, KFN 2032 Senior Notes, KFN 2042 Senior Notes (redeemed in full on April 24, 2017) and KFN Junior Subordinated Notes which are presented gross of unamortized discounts and net of unamortized premiums. KFN's debt obligations are non-recourse to KKR beyond the assets of KFN. |
(3) | These interest obligations on debt represent estimated interest to be paid over the maturity of the related debt obligation, which has been calculated assuming the debt outstanding at March 31, 2017 is not repaid until its maturity. Future interest rates are assumed to be those in effect as of March 31, 2017, including both variable and fixed rates, as applicable, provided for by the relevant debt agreements. The amounts presented above include accrued interest on outstanding indebtedness. |
(4) | Represents various commitments in our capital markets business in connection with the underwriting of loans, securities and other financial instruments. These commitments are shown net of amounts syndicated. |
(5) | Represents obligations in our capital markets business to lend under various revolving credit facilities. |
(6) | Represents commitments of KKR and KFN to fund the purchase of various investments. |
(7) | Represents the purchase price due upon delivery of a new KKR office being constructed in New York, all or a portion of which represents construction financing obtained by the developer and may be refinanced upon delivery of the completed office. |
The commitment table above excludes contractual amounts owed under the tax receivable agreement, because the ultimate amount and timing of the amounts due are not presently known. As of March 31, 2017, a payable of $130.2 million has been recorded in due to affiliates in the condensed consolidated financial statements representing management's best estimate of the amounts currently expected to be owed under the tax receivable agreement. As of March 31, 2017, approximately $24.0 million of cumulative cash payments have been made under the tax receivable agreement. See "—Liquidity Needs—Tax Receivable Agreement."
We may incur contingent liabilities for claims that may be made against us in the future. We enter into contracts that contain a variety of representations, warranties and covenants, including indemnifications. For example, certain of our investment funds and KFN have provided certain indemnities relating to environmental and other matters and have provided nonrecourse carve-out guarantees for fraud, willful misconduct and other customary wrongful acts, each in connection with the financing of certain real estate investments that we have made. In addition, we have also provided credit support to certain of our subsidiaries’ obligations in connection with a limited number of investment vehicles that we manage. For example, KKR has guaranteed the obligations of a general partner to post collateral on behalf of its investment vehicle in connection with such vehicle’s derivative transactions, and we have also agreed to be liable for certain investment losses and/or for providing liquidity in the events specified in the governing documents of another investment vehicle. Our maximum exposure under these arrangements is currently unknown as our liabilities for these matters would require a claim to be made against us in the future.
The partnership documents governing our carry-paying funds, including funds and vehicles relating to private equity, mezzanine, infrastructure, energy, direct lending and special situations investments, generally include a "clawback" provision that, if triggered, may give rise to a contingent obligation requiring the general partner to return amounts to the fund for distribution to the fund investors at the end of the life of the fund. Under a clawback obligation, upon the liquidation of a fund, the general partner is required to return, typically on an after-tax basis, previously distributed carry to the extent that, due to the diminished performance of later investments, the aggregate amount of carry distributions received by the general partner during the term of the fund exceed the amount to which the general partner was ultimately entitled, including the effects of any performance thresholds. Excluding carried interest received by the general partners of funds that were not contributed to us in the KPE Transaction, as of March 31, 2017, no carried interest was subject to this clawback obligation, assuming that all applicable carry paying funds were liquidated at their March 31, 2017 fair values. Had the investments in such funds been liquidated at zero value, the clawback obligation would have been $2,193.6 million. Carried interest is recognized in the
110
statement of operations based on the contractual conditions set forth in the agreements governing the fund as if the fund were terminated and liquidated at the reporting date and the fund's investments were realized at the then estimated fair values. Amounts earned pursuant to carried interest are earned by the general partner of those funds to the extent that cumulative investment returns are positive and where applicable, preferred return thresholds have been met. If these investment amounts earned decrease or turn negative in subsequent periods, recognized carried interest will be reversed and to the extent that the aggregate amount of carry distributions received by the general partner during the term of the fund exceed the amount to which the general partner was ultimately entitled, a clawback obligation would be recorded. For funds that are consolidated, this clawback obligation, if any, is reflected as an increase in noncontrolling interests in the consolidated statements of financial condition. For funds that are not consolidated, this clawback obligation, if any, is reflected as a reduction of our investment balance as this is where carried interest is initially recorded.
Prior to the KPE Transaction in 2009, certain principals who received carried interest distributions with respect to certain private equity funds contributed to us had personally guaranteed, on a several basis and subject to a cap, the contingent obligations of the general partners of such private equity funds to repay amounts to fund investors pursuant to the general partners' clawback obligations. The terms of the KPE Transaction require that principals remain responsible for any clawback obligations relating to carry distributions received prior to the KPE Transaction, up to a maximum of $223.6 million. Through investment realizations, the principals' potential exposure has been reduced to $86.8 million as of March 31, 2017. Using valuations as of March 31, 2017, no amounts are due with respect to the clawback obligation required to be funded by principals. Carry distributions arising subsequent to the KPE Transaction may give rise to clawback obligations that may be allocated generally to us and to persons who participate in the carry pool. In addition, guarantees of or similar arrangements relating to clawback obligations in favor of third party investors in an individual investment partnership by entities we own may limit distributions of carried interest more generally.
Off Balance Sheet Arrangements
Other than contractual commitments and other legal contingencies incurred in the normal course of our business, we do not have any off-balance sheet financings or liabilities.
Critical Accounting Policies
The preparation of our condensed consolidated financial statements in accordance with GAAP requires our management to make estimates and judgments that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities, disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities, and reported amounts of fees, expenses and investment income. Our management bases these estimates and judgments on available information, historical experience and other assumptions that we believe are reasonable under the circumstances. However, these estimates, judgments and assumptions are often subjective and may be impacted negatively based on changing circumstances or changes in our analyses. If actual amounts are ultimately different from those estimated, judged or assumed, revisions are included in the condensed consolidated financial statements in the period in which the actual amounts become known. We believe our critical accounting policies could potentially produce materially different results if we were to change underlying estimates, judgments or assumptions.
The following discussion details certain of our critical accounting policies. For a full discussion of all critical accounting policies, please see the notes to the condensed consolidated financial statements "--Item 1. Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements (Unaudited)--Summary of Significant Accounting Policies."
Fair Value Measurements
Fair value is the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date under current market conditions. Except for certain of KKR's equity method investments and debt obligations, KKR's investments and other financial instruments are recorded at fair value or at amounts whose carrying values approximate fair value. Where available, fair value is based on observable market prices or parameters or derived from such prices or parameters. Where observable prices or inputs are not available, valuation techniques are applied. These valuation techniques involve varying levels of management estimation and judgment, the degree of which is dependent on a variety of factors.
GAAP establishes a hierarchical disclosure framework which prioritizes and ranks the level of market price observability used in measuring financial instruments at fair value. Market price observability is affected by a number of factors, including the type of financial instrument, the characteristics specific to the financial instrument and the state of the marketplace, including the existence and transparency of transactions between market participants. Financial instruments with readily
111
available quoted prices in active markets generally will have a higher degree of market price observability and a lesser degree of judgment used in measuring fair value.
112
Financial instruments measured and reported at fair value are classified and disclosed based on the observability of inputs used in the determination of fair values, as follows:
Level I
Pricing inputs are unadjusted, quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities as of the measurement date. The types of financial instruments included in this category are publicly-listed equities, credit investments and securities sold short.
We classified 8.2% of total investments measured and reported at fair value as Level I at March 31, 2017.
Level II
Pricing inputs are other than quoted prices in active markets, which are either directly or indirectly observable as of the measurement date, and fair value is determined through the use of models or other valuation methodologies. The types of financial instruments included in this category are credit investments, investments and debt obligations of consolidated CLO entities, convertible debt securities indexed to publicly-listed securities, less liquid and restricted equity securities and certain over-the-counter derivatives such as foreign currency option and forward contracts.
We classified 38.7% of total investments measured and reported at fair value as Level II at March 31, 2017.
Level III
Pricing inputs are unobservable for the financial instruments and include situations where there is little, if any, market activity for the financial instrument. The inputs into the determination of fair value require significant management judgment or estimation. The types of financial instruments generally included in this category are private portfolio companies, real assets investments, credit investments, equity method investments for which the fair value option was elected and investments and debt obligations of consolidated CMBS entities.
We classified 53.1% of total investments measured and reported at fair value as Level III at March 31, 2017. The valuation of our Level III investments at March 31, 2017 represents management's best estimate of the amounts that we would anticipate realizing on the sale of these investments in an orderly transaction at such date.
In certain cases, the inputs used to measure fair value may fall into different levels of the fair value hierarchy. In such cases, the level in the fair value hierarchy within which the fair value measurement in its entirety falls has been determined based on the lowest level input that is significant to the fair value measurement in its entirety. Our assessment of the significance of a particular input to the fair value measurement in its entirety requires judgment and consideration of factors specific to the asset.
A significant decrease in the volume and level of activity for the asset or liability is an indication that transactions or quoted prices may not be representative of fair value because in such market conditions there may be increased instances of transactions that are not orderly. In those circumstances, further analysis of transactions or quoted prices is needed, and a significant adjustment to the transactions or quoted prices may be necessary to estimate fair value.
The availability of observable inputs can vary depending on the financial asset or liability and is affected by a wide variety of factors, including, for example, the type of instrument, whether the instrument has recently been issued, whether the instrument is traded on an active exchange or in the secondary market, and current market conditions. To the extent that valuation is based on models or inputs that are less observable or unobservable in the market, the determination of fair value requires more judgment. Accordingly, the degree of judgment exercised by us in determining fair value is greatest for instruments categorized in Level III. The variability and availability of the observable inputs affected by the factors described above may cause transfers between Levels I, II, and III, which we recognize at the beginning of the reporting period.
Investments and other financial instruments that have readily observable market prices (such as those traded on a securities exchange) are stated at the last quoted sales price as of the reporting date. We do not adjust the quoted price for these investments, even in situations where we hold a large position and a sale could reasonably affect the quoted price.
Management’s determination of fair value is based upon the methodologies and processes described below and may incorporate assumptions that are management’s best estimates after consideration of a variety of internal and external factors.
113
Level II Valuation Methodologies
Credit Investments: These instruments generally have bid and ask prices that can be observed in the marketplace. Bid prices reflect the highest price that KKR and others are willing to pay for an instrument. Ask prices represent the lowest price that KKR and others are willing to accept for an instrument. For financial assets and liabilities whose inputs are based on bid-ask prices obtained from third party pricing services, fair value may not always be a predetermined point in the bid-ask range. KKR’s policy is generally to allow for mid-market pricing and adjusting to the point within the bid-ask range that meets KKR’s best estimate of fair value.
Investments and Debt Obligations of Consolidated CLO Vehicles: Investments of consolidated CLO vehicles are valued using the same valuation methodology as described above for credit investments. Under ASU 2014-13, KKR measures CLO debt obligations on the basis of the fair value of the financial assets of the CLO.
Securities indexed to publicly-listed securities: The securities are typically valued using standard convertible security pricing models. The key inputs into these models that require some amount of judgment are the credit spreads utilized and the volatility assumed. To the extent the company being valued has other outstanding debt securities that are publicly-traded, the implied credit spread on the company’s other outstanding debt securities would be utilized in the valuation. To the extent the company being valued does not have other outstanding debt securities that are publicly-traded, the credit spread will be estimated based on the implied credit spreads observed in comparable publicly-traded debt securities. In certain cases, an additional spread will be added to reflect an illiquidity discount due to the fact that the security being valued is not publicly-traded. The volatility assumption is based upon the historically observed volatility of the underlying equity security into which the convertible debt security is convertible and/or the volatility implied by the prices of options on the underlying equity security.
Restricted Equity Securities: The valuation of certain equity securities is based on an observable price for an identical security adjusted for the effect of a restriction.
Derivatives: The valuation incorporates observable inputs comprising yield curves, foreign currency rates and credit spreads.
Level III Valuation Methodologies
Financial assets and liabilities categorized as Level III consist primarily of the following:
Private Equity Investments: We generally employ two valuation methodologies when determining the fair value of a private equity investment. The first methodology is typically a market comparables analysis that considers key financial inputs and recent public and private transactions and other available measures. The second methodology utilized is typically a discounted cash flow analysis, which incorporates significant assumptions and judgments. Estimates of key inputs used in this methodology include the weighted average cost of capital for the investment and assumed inputs used to calculate terminal values, such as exit EBITDA multiples. In certain cases the results of the discounted cash flow approach can be significantly impacted by these estimates. Other inputs are also used in both methodologies. Also, as discussed in greater detail under "—Business Environment" in this report and "Risk Factors—Risks Related to the Assets We Manage—Our investments are impacted by various economic conditions that are difficult to quantify or predict, but may have a significant adverse impact on the value of our investments" in our Annual Report on Form 10-K, a change in interest rates could have a significant impact on valuations. In addition, when a definitive agreement has been executed to sell an investment, KKR generally considers a significant determinant of fair value to be the consideration to be received by KKR pursuant to the executed definitive agreement.
Upon completion of the valuations conducted using these methodologies, a weighting is ascribed to each method, and an illiquidity discount is typically applied where appropriate. The ultimate fair value recorded for a particular investment will generally be within a range suggested by the two methodologies, except that the value may be higher or lower than such range in the case of investments being sold pursuant to an executed definitive agreement.
When determining the weighting ascribed to each valuation methodology, we consider, among other factors, the availability of direct market comparables, the applicability of a discounted cash flow analysis, the expected hold period and manner of realization for the investment, and in the case of investments being sold pursuant to an executed definitive agreement, we estimated probability of such a sale being completed. These factors can result in different weightings among investments in the portfolio and in certain instances may result in up to a 100% weighting to a single methodology. Across the total Level III private equity investment portfolio, including investments in both consolidated and unconsolidated investment
114
funds, approximately 64% of the fair value is derived from investments that are valued based exactly 50% on market comparables and 50% on a discounted cash flow analysis. Less than 5% of the fair value of this Level III private equity investment portfolio is derived from investments that are valued either based 100% on market comparables or 100% on a discounted cash flow analysis. As of March 31, 2017, the overall weights ascribed to the market comparables methodology, the discounted cash flow methodology and a methodology based on pending sales for this portfolio of Level III private equity investments were 36%, 43% and 21%, respectively.
When an illiquidity discount is to be applied, we seek to take a uniform approach across our portfolio and generally apply a minimum 5% discount to all private equity investments. We then evaluate such private equity investments to determine if factors exist that could make it more challenging to monetize the investment and, therefore, justify applying a higher illiquidity discount. These factors generally include (i) whether we are unable to freely sell the portfolio company or conduct an initial public offering of the portfolio company due to the consent rights of a third party or similar factors, (ii) whether the portfolio company is undergoing significant restructuring activity or similar factors and (iii) characteristics about the portfolio company regarding its size and/or whether the portfolio company is experiencing, or expected to experience, a significant decline in earnings. These factors generally make it less likely that a portfolio company would be sold or publicly offered in the near term at a price indicated by using just a market multiples and/or discounted cash flow analysis, and these factors tend to reduce the number of opportunities to sell an investment and/or increase the time horizon over which an investment may be monetized. Depending on the applicability of these factors, we determine the amount of any incremental illiquidity discount to be applied above the 5% minimum, and during the time we hold the investment, the illiquidity discount may be increased or decreased, from time to time, based on changes to these factors. The amount of illiquidity discount applied at any time requires considerable judgment about what a market participant would consider and is based on the facts and circumstances of each individual investment. Accordingly, the illiquidity discount ultimately considered by a market participant upon the realization of any investment may be higher or lower than that estimated by us in our valuations.
In the case of growth equity investments, enterprise values may be determined using the market comparables analysis and discounted cash flow analysis described above. A scenario analysis may also be conducted to subject the estimated enterprise values to a downside, base and upside case, which involves significant assumptions and judgments. A milestone analysis may also be conducted to assess the current level of progress towards value drivers that we have determined to be important, which involves significant assumptions and judgments. The enterprise value in each case may then be allocated across the investment’s capital structure to reflect the terms of the security and subjected to probability weightings. In certain cases, the values of growth equity investments may be based on recent or expected financings.
Real Assets Investments: Real asset investments in infrastructure, energy and real estate are valued using one or more of the discounted cash flow analysis, market comparables analysis and direct income capitalization, which in each case incorporates significant assumptions and judgments. Infrastructure investments are generally valued using the discounted cash flow analysis. Key inputs used in this methodology can include the weighted average cost of capital and assumed inputs used to calculate terminal values, such as exit EBITDA multiples. Energy investments are generally valued using a discounted cash flow analysis. Key inputs used in this methodology that require estimates include the weighted average cost of capital. In addition, the valuations of energy investments generally incorporate both commodity prices as quoted on indices and long-term commodity price forecasts, which may be substantially different from, and are currently higher than, commodity prices on certain indices for equivalent future dates. Certain energy investments do not include an illiquidity discount. Long-term commodity price forecasts are utilized to capture the value of the investments across a range of commodity prices within the energy investment portfolio associated with future development and to reflect a range of price expectations. Real estate investments are generally valued using a combination of direct income capitalization and discounted cash flow analysis. Key inputs used in such methodologies that require estimates include an unlevered discount rate and current capitalization rate, and certain real estate investments do not include a minimum illiquidity discount. The valuations of real assets investments also use other inputs.
On a segment basis, our energy real asset investments in oil and gas producing properties as of March 31, 2017 had a fair value of approximately $573 million. Based on this fair value, we estimate that an immediate, hypothetical 10% decline in the fair value of these energy investments from one or more adverse movements to the investments' valuation inputs would result in a decline in investment income of $57.3 million and a decline in net income attributable to KKR & Co. L.P. of $32.4 million, after deducting amounts that are attributable to noncontrolling interests held by KKR Holdings L.P. As of March 31, 2017, if we were to value our energy investments using only the commodity prices as quoted on indices and did not use long-term commodity price forecasts, and also held all other inputs to their valuation constant, we estimate that investment income would have been approximately $65 million lower, resulting in a lower amount of net income attributable to KKR & Co. L.P. of approximately 56.5% of the overall decrease in investment income, after deducting amounts that are attributable to noncontrolling interests held by KKR Holdings L.P.
115
These hypothetical declines relate only to investment income. There would be no current impact on KKR's carried interest since all of the investment funds which hold these types of energy investments have investment values that are either below their cost or not currently accruing carried interest. Additionally, there would be no impact on fees since fees earned from investment funds which hold investments in oil and gas producing properties are based on either committed capital or capital invested.
For GAAP purposes, where KKR holds energy investments consisting of working interests in oil and gas producing properties directly and not through an investment fund, such working interests are consolidated based on the proportion of the working interests held by us. Accordingly, we reflect the assets, liabilities, revenues, expenses, investment income and cash flows of the consolidated working interests on a gross basis and changes in the value of these energy investments are not reflected as unrealized gains and losses in the consolidated statements of operations. Accordingly, a change in fair value for these investments does not result in a decrease in net gains (losses) from investment activities, but may result in an impairment charge reflected in general, administrative and other expenses. For segment purposes, these directly held working interests are treated as investments and changes in value are reflected in our segment results as unrealized gains and losses.
Credit Investments: Credit investments are valued using values obtained from dealers or market makers, and where these values are not available, credit investments are generally valued by us based on ranges of valuations determined by an independent valuation firm. Valuation models are based on discounted cash flow analyses, for which the key inputs are determined based on market comparables, which incorporate similar instruments from similar issuers.
Other Investments: With respect to other investments including equity method investments for which the fair value election has been made, we generally employ the same valuation methodologies as described above for private equity investments when valuing these other investments.
Investments and Debt Obligations of Consolidated CMBS Vehicles: Under ASU 2014-13, we measure CMBS investments on the basis of the fair value of the financial liabilities of the CMBS. Debt obligations of consolidated CMBS vehicles are valued based on discounted cash flow analyses. The key input is the expected yield of each CMBS security using both observable and unobservable factors, which may include recently offered or completed trades and published yields of similar securities, security-specific characteristics (e.g. securities ratings issued by nationally recognized statistical rating organizations, credit support by other subordinate securities issued by the CMBS and coupon type) and other characteristics.
Key unobservable inputs that have a significant impact on our Level III investment valuations as described above are included in Note 5 "Fair Value Measurements" of the financial statements included elsewhere in this report. We utilize several unobservable pricing inputs and assumptions in determining the fair value of our Level III investments. These unobservable pricing inputs and assumptions may differ by investment and in the application of our valuation methodologies. Our reported fair value estimates could vary materially if we had chosen to incorporate different unobservable pricing inputs and other assumptions or, for applicable investments, if we only used either the discounted cash flow methodology or the market comparables methodology instead of assigning a weighting to both methodologies. For valuations determined for periods other than at year end, various inputs may be estimated prior to the end of the relevant period.
Level III Valuation Process
The valuation process involved for Level III measurements is completed on a quarterly basis and is designed to subject the valuation of Level III investments to an appropriate level of consistency, oversight, and review.
For Private Markets investments classified as Level III, investment professionals prepare preliminary valuations based on their evaluation of financial and operating data, company specific developments, market valuations of comparable companies and other factors. These preliminary valuations are reviewed by an independent valuation firm engaged by KKR to perform certain procedures in order to assess the reasonableness of KKR’s valuations annually for all Level III investments in Private Markets and quarterly for investments other than certain investments, which have values less than pre-set value thresholds and which in the aggregate comprise less than 5% of the total value of KKR’s Level III Private Markets investments. The valuations of certain real asset investments are determined solely by an independent valuation firm without the preparation of preliminary valuations by our investment professionals, and instead such independent valuation firm relies on valuation information available to it as a broker or valuation firm. For credit investments and debt obligations of consolidated CMBS vehicles, an independent valuation firm is generally engaged by KKR with respect to most investments classified as Level III. The valuation firm either provides a valuation range from which KKR’s investment professionals select a point in the range to determine the preliminary valuation or performs certain procedures in order to assess the reasonableness and provide positive assurance of KKR’s valuations. After reflecting any input from the independent valuation firm, the valuation proposals are
116
submitted to their respective valuation sub-committees. As of March 31, 2017, less than 6% of the total value of our Level III credit investments are not valued with the engagement of an independent valuation firm.
KKR has a global valuation committee comprised of senior employees including investment professionals and professionals from business operations functions, and includes our Chief Financial Officer, General Counsel and Chief Compliance Officer. The global valuation committee is assisted by valuation sub-committees and investment professionals for each business strategy. All preliminary Level III valuations are reviewed and approved by the valuation sub-committees for private equity, real estate, energy and infrastructure and credit, as applicable. When Level III valuations are required to be performed on hedge fund investments, a valuation sub-committee for hedge funds reviews these valuations. The valuation sub-committees are responsible for the review and approval of valuations in their respective business lines on a quarterly basis. The members of the valuation sub-committees are comprised of investment professionals, including the heads of each respective strategy, and professionals from business operations functions such as legal, compliance and finance, who are not primarily responsible for the management of the investments.
The global valuation committee provides general oversight of the valuation sub-committees. The global valuation committee is responsible for coordinating and implementing the firm’s valuation process to ensure consistency in the application of valuation principles across portfolio investments and between periods. All valuations are subject to approval by the global valuation committee. When valuations are approved by the global valuation committee after reflecting any input from it, the valuations of Level III investments, as well as the valuations of Level I and Level II investments, are presented to the audit committee of the board of directors of the general partner of KKR & Co. L.P. and are then reported to the board of directors.
As of March 31, 2017, upon completion by, where applicable, an independent valuation firm of certain limited procedures requested to be performed by them on certain investments, the independent valuation firm concluded that the fair values, as determined by KKR, of those investments reviewed by them were reasonable. The limited procedures did not involve an audit, review, compilation or any other form of examination or attestation under generally accepted auditing standards and were not conducted on all Level III investments. We are responsible for determining the fair value of investments in good faith, and the limited procedures performed by an independent valuation firm are supplementary to the inquiries and procedures that we are required to undertake to determine the fair value of the commensurate investments.
As described above, Level II and Level III investments were valued using internal models with significant unobservable inputs and our determinations of the fair values of these investments may differ materially from the values that would have resulted if readily observable inputs had existed. Additional external factors may cause those values, and the values of investments for which readily observable inputs exist, to increase or decrease over time, which may create volatility in our earnings and the amounts of assets and partners' capital that we report from time to time.
Changes in the fair value of investments impacts the amount of carried interest that is recognized as well as the amount of investment income that is recognized for investments held directly and through our consolidated funds as described below. We estimate that an immediate 10% decrease in the fair value of investments held directly and through consolidated investment funds generally would result in a commensurate change in the amount of net gains (losses) from investment activities for investments held directly and through investment funds and a more significant impact to the amount of carried interest recognized, regardless of whether the investment was valued using observable market prices or management estimates with significant unobservable pricing inputs. With respect to consolidated investment funds, the impact that the consequential decrease in investment income would have on net income attributable to KKR would generally be significantly less than the amount described above, given that a majority of the change in fair value of our consolidated funds would be attributable to noncontrolling interests and therefore we are only impacted to the extent of our carried interest and our balance sheet investments.
As of March 31, 2017, there were no investments which represented greater than 5% of total investments on a GAAP basis. On a segment basis, as of March 31, 2017, investments which represented greater than 5% of total reportable segments investments consisted of only First Data Corporation valued at $1,191.4 million. Our investment income can be impacted by volatility in the public markets related to our holdings of publicly traded securities, including our sizable holdings of First Data Corporation (NYSE: FDC). For the quarter ended March 31, 2017, the increase in the stock price of First Data Corporation increased economic net income on a segment basis by approximately $124 million. See "--Business Environment" for a discussion on the impact of global equity markets on our financial condition and "--Segment Balance Sheet" for additional information regarding our largest holdings on a segment basis in our Annual Report on Form 10-K.
117
Recognition of Investment Income
Investment income consists primarily of the net impact of: (i) realized and unrealized gains and losses on investments, (ii) dividends, (iii) interest income, (iv) interest expense and (v) foreign exchange gains and losses relating to mark-to-market activity on foreign exchange forward contracts, foreign currency options, foreign denominated debt and debt securities issued by consolidated CFEs. Unrealized gains or losses resulting from the aforementioned activities are included in net gains (losses) from investment activities. Upon disposition of an instrument that is marked-to-market, previously recognized unrealized gains or losses are reversed and a realized gain or loss is recognized. While this reversal generally does not significantly impact the net amounts of gains (losses) that we recognize from investment activities, it affects the manner in which we classify our gains and losses for reporting purposes.
Certain of our investment funds are consolidated. When a fund is consolidated, the portion of our funds' investment income that is allocable to our carried interests and capital investments is not shown in the condensed consolidated financial statements. For funds that are consolidated, all investment income (loss), including the portion of a funds' investment income (loss) that is allocable to KKR's carried interest, is included in investment income (loss) on the consolidated statements of operations. The carried interest that KKR retains in net income (loss) attributable to KKR & Co. L.P. is reflected as an adjustment to net income (loss) attributable to noncontrolling interests. However, because certain of our funds remain consolidated and because we hold a minority economic interest in these funds' investments, our share of the investment income is less than the total amount of investment income presented in the condensed consolidated financial statements for these consolidated funds.
Recognition of Carried Interest in the Statement of Operations
Carried interest entitles the general partner of a fund to a greater allocable share of the fund's earnings from investments relative to the capital contributed by the general partner and correspondingly reduces noncontrolling interests' attributable share of those earnings. Carried interest is earned by the general partner of those funds to the extent that cumulative investment returns are positive and where applicable, preferred return thresholds have been met. If these investment returns decrease or turn negative in subsequent periods, recognized carried interest will be reversed and reflected as losses in the statement of operations. For funds that are not consolidated, amounts earned pursuant to carried interest are included in fees and other in the consolidated statements of operations. Amounts earned pursuant to carried interest at consolidated funds are eliminated from fees and other upon consolidation of the fund and are included as investment income (loss) in net gains (losses) from investment activities along with all of the other investment gains and losses at the consolidated fund.
Carried interest is recognized in the statement of operations based on the contractual conditions set forth in the agreements governing the fund as if the fund were terminated and liquidated at the reporting date and the fund's investments were realized at the then estimated fair values. Due to the extended durations of our private equity funds, we believe that this approach results in income recognition that best reflects our periodic performance in the management of those funds. Amounts earned pursuant to carried interest are earned by the general partner of those funds to the extent that cumulative investment returns are positive and where applicable, preferred return thresholds have been met. If these investment amounts earned decrease or turn negative in subsequent periods, recognized carried interest will be reversed and to the extent that the aggregate amount of carry distributions received by the general partner during the term of the fund exceed the amount to which the general partner was ultimately entitled, a clawback obligation would be recorded. For funds that are not consolidated, this clawback obligation, if any, is reflected as a reduction of our investment balance as this is where carried interest is initially recorded. For funds that are consolidated, this clawback obligation, if any, is reflected as an increase in noncontrolling interests in the consolidated statements of financial condition.
Prior to January 1, 2016, most of our historical private equity funds that provide for carried interest do not have a preferred return. For these funds, the management company is required to refund up to 20% of any management fees earned from its limited partners in the event that the fund recognizes carried interest. At such time as the fund recognizes carried interest in an amount sufficient to cover 20% of the management fees earned or a portion thereof, a liability due to the fund’s limited partners is recorded and revenue is reduced for the amount of the carried interest recognized, not to exceed 20% of the management fees earned. The refunds to the limited partners are paid, and liabilities relieved, at such time that the underlying investment is sold and the associated carried interest is realized. In the event that a fund’s carried interest is not sufficient to cover all or a portion of the amount that represents 20% of the earned management fees, such management fees would be retained and not returned to the funds’ limited partners.
Most of our newer investment funds that provide for carried interest, however, have a preferred return. In this case, the management company does not refund the management fees earned from the limited partners of the fund as described above. Instead, the management fee is effectively returned to the limited partners through a reduction of the realized gain on which
118
carried interest is calculated. To calculate the carried interest, KKR calculates whether a preferred return has been achieved based on an amount that includes all of the management fees paid by the limited partners as well as the other capital contributions and expenses paid by them to date. To the extent the fund has exceeded the preferred return at the time of a realization event, and subject to any other conditions for the payment of carried interest like netting holes, carried interest is distributed to the general partner. Until the preferred return is achieved, no carried interest is recorded. Thereafter, the general partner is entitled to a catch up allocation such that the general partner’s carried interest is paid in respect of all of the fund’s net gains, including the net gains used to pay the preferred return, until the general partner has received the full percentage amount of carried interest that the general partner is entitled to under the terms of the fund. In general, investment funds that entitle the management company to receive an incentive fee have a preferred return and are calculated on a similar basis that takes into account management fees paid.
Recently Issued Accounting Pronouncements
For a full discussion of recently issued accounting pronouncements, please see the notes to the condensed consolidated financial statements "--Item 1. Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements (Unaudited)--Summary of Significant Accounting Policies."
ITEM 3. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK
There was no material change in our market risks during the three months ended March 31, 2017. For additional information, please refer to our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2016, filed with the SEC on February 24, 2017.
ITEM 4. CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
We maintain disclosure controls and procedures (as such term is defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Exchange Act) that are designed to ensure that the information required to be disclosed by us in the reports filed or submitted by us under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and forms and such information is accumulated and communicated to management, including the Co-Chief Executive Officers and the Chief Financial Officer, as appropriate, to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure. Any controls and procedures, no matter how well designed and operated, can provide only reasonable assurances of achieving the desired controls.
As of the period ended March 31, 2017, we carried out an evaluation, under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including the Co-Chief Executive Officers and the Chief Financial Officer, of the effectiveness of the design and operation of our disclosure controls and procedures. Based upon that evaluation, our Co-Chief Executive Officers and Chief Financial Officer have concluded that, as of the period ended March 31, 2017, our disclosure controls and procedures were effective to accomplish their objectives at the reasonable assurance level.
Changes in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
No changes in our internal control over financial reporting (as such term is defined in Rule 13a-15(f) of the Exchange Act) occurred during the three months ended March 31, 2017 that materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
119
PART II. OTHER INFORMATION
ITEM 1. LEGAL PROCEEDINGS.
The section entitled “Litigation” appearing in Note 17 “Commitments and Contingencies” of our financial statements included elsewhere in this report is incorporated herein by reference.
ITEM 1A. RISK FACTORS.
For a discussion of our potential risks and uncertainties, see the information under the heading “Risk Factors” in our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2016 filed with the SEC on February 24, 2017.
120
ITEM 2. UNREGISTERED SALES OF EQUITY SECURITIES AND USE OF PROCEEDS.
Common Unit Repurchases in the First Quarter of 2017
The table below sets forth the information with respect to purchases made by or on behalf of KKR & Co. L.P. or any “affiliated purchaser” (as defined in Rule 10b-18(a)(3) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934) of our common units during the first quarter of 2017.
Issuer Purchases of Common Units | ||||||||||||||
(amounts in thousands, except unit and per unit amounts) | ||||||||||||||
Total Number of Units Purchased | Average Price Paid Per Units | Cumulative Number of Units Purchased as Part of Publicly Announced Plans or Programs (1) | Approximate Dollar Value of Units that May Yet Be Purchased Under the Plans or Programs(2) | |||||||||||
Month #1 January 1, 2017 to January 31, 2017) | — | $ | — | 31,674,162 | $ | 41,225 | ||||||||
Month #2 (February 1, 2017 to February 28, 2017) | — | $ | — | 31,674,162 | $ | 291,225 | ||||||||
Month #3 (March 1, 2017 to March 31, 2017) | — | $ | — | 31,674,162 | $ | 291,225 | ||||||||
Total through March 31, 2017 | — | |||||||||||||
Purchases subsequent to March 31, 2017: | ||||||||||||||
(April 1, 2017 to April 27, 2017) | — | $ | — | 31,674,162 | $ | 291,225 | ||||||||
Total through April 27, 2017 | — | |||||||||||||
(1) As announced On October 27, 2015 and February 9, 2017, KKR is authorized to repurchase up to $750 million in the aggregate of its outstanding common units. Under this unit repurchase program, units may be repurchased from time to time in open market transactions, in privately negotiated transactions or otherwise. The timing, manner, price and amount of any unit repurchases will be determined by KKR in its discretion and will depend on a variety of factors, including legal requirements, price and economic and market conditions. KKR expects that the program, which has no expiration date, will be in effect until the maximum approved dollar amount has been used to repurchase common units. The program does not require KKR to repurchase any specific number of common units, and the program may be suspended, extended, modified or discontinued at any time. | ||||||||||||||
In addition to the purchases of common units above, (1) cash was used to pay the amount of withholding taxes, social benefit payments or similar payments payable by us in respect of awards granted pursuant to the Equity Incentive Plan and (2) cash was delivered in respect of certain awards granted pursuant to the Equity Incentive Plan and Other Exchangeable Securities. During 2017, KKR canceled equity awards representing 2.1 million common units to satisfy tax and cash-settlement obligations of $37.8 million in connection with their vesting, bringing cumulative cancellations of equity awards representing 7.2 million common units to satisfy tax obligations of approximately $116.7 million.
During the first quarter of 2017, 3,190,630 KKR Group Partnership Units were exchanged by (i) KKR Holdings and (ii) holders of other exchangeable securities issued in connection with the acquisition of Avoca for an equal number of our common units. This resulted in an increase in our ownership of the KKR Group Partnerships and a corresponding decrease in the ownership of the KKR Group Partnerships by KKR Holdings and holders of the other exchangeable security holders.
ITEM 3. DEFAULTS UPON SENIOR SECURITIES.
Not applicable.
ITEM 4. MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES.
Not applicable.
121
ITEM 5. OTHER INFORMATION.
None.
ITEM 6. EXHIBITS.
Required exhibits are listed in the Index to Exhibits and are incorporated herein by reference.
122
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned thereunto duly authorized.
KKR & CO. L.P. | |||
By: KKR Management LLC | |||
Its General Partner | |||
By: | /s/ William J. Janetschek | ||
William J. Janetschek | |||
Chief Financial Officer | |||
(principal financial and accounting officer of KKR Management LLC and authorized signatory) | |||
DATE: | May 5, 2017 | ||
123
INDEX TO EXHIBITS
The following is a list of all exhibits filed or furnished as part of this report:
Exhibit No. | Description of Exhibit | |
Indenture dated as of March 30, 2017 among KKR Financial Holdings LLC and The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N. A., as trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the KKR Financial Holdings LLC Current Report on Form 8-K filed on March 30, 2017). | ||
First Supplemental Indenture dated as of March 30, 2017 among KKR Financial Holdings LLC and The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N. A., as trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.2 to the KKR Financial Holdings LLC Current Report on Form 8-K filed on March 30, 2017). | ||
Form of 5.50% Senior Note due 2032 of KKR Financial Holdings LLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.2 to the KKR Financial Holdings LLC Current Report on Form 8-K filed on March 30, 2017). | ||
31.1 | Certification of Co-Chief Executive Officer pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a) or Rule 15d-14(a) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, as adopted pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes- Oxley Act of 2002. | |
31.2 | Certification of Co-Chief Executive Officer pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a) or Rule 15d-14(a) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, as adopted pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | |
31.3 | Certification of Chief Financial Officer pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a) or Rule 15d-14(a) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, as adopted pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | |
32.1 | Certification of Co-Chief Executive Officer pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | |
32.2 | Certification of Co-Chief Executive Officer pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | |
32.3 | Certification of Chief Financial Officer pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | |
101 | Interactive data files pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T: (i) the Condensed Consolidated Statements of Financial Condition as of March 31, 2017 and December 31, 2016, (ii) the Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations for the three months ended March 31, 2017 and March 31, 2016, (iii) the Condensed Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income for the three months ended March 31, 2017 and March 31, 2016; (iv) the Condensed Consolidated Statements of Changes in Equity for the three months ended March 31, 2017 and March 31, 2016, (v) the Condensed Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the three months ended March 31, 2017 and March 31, 2016, and (vi) the Notes to the Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements. | |
The agreements and other documents filed as exhibits to this report are not intended to provide factual information or other disclosure other than with respect to the terms of the agreements or other documents themselves, and you should not rely on them for that purpose. In particular, any representations and warranties made by us in these agreements or other documents were made solely within the specific context of the relevant agreement or document and may not describe the actual state of affairs as of the date they were made or at any other time.
124
