Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-31.1 - EX-31.1 - Phio Pharmaceuticals Corp. | d325199dex311.htm |
| EX-32.1 - EX-32.1 - Phio Pharmaceuticals Corp. | d325199dex321.htm |
| EX-23.1 - EX-23.1 - Phio Pharmaceuticals Corp. | d325199dex231.htm |
| EX-10.21 - EX-10.21 - Phio Pharmaceuticals Corp. | d325199dex1021.htm |
| EX-10.20 - EX-10.20 - Phio Pharmaceuticals Corp. | d325199dex1020.htm |
Table of Contents
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
(Mark One)
| ☒ | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2016
Or
| ☐ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from to
Commission File Number 001-36304
RXi PHARMACEUTICALS CORPORATION
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| Delaware | 45-3215903 | |
| (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) |
(I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
257 Simarano Drive, Suite 101 Marlborough, Massachusetts 01752
(Address of principal executive offices and Zip Code)
(508) 767-3861
(Registrant’s telephone number, including area code)
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| Title of each class |
Name of exchange on which registered | |
| Common stock, par value $0.0001 per share | The NASDAQ Capital Market |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act:
None.
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. ☐ Yes ☒ No
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Act. ☐ Yes ☒ No
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. ☒ Yes ☐ No
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§ 232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for any such shorter time that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). ☒ Yes ☐ No
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of the registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. (Check one):
| Large accelerated filer | ☐ | Accelerated filer | ☐ | |||
| Non-accelerated filer | ☐ (Do not check if a smaller reporting company) | Smaller reporting company | ☒ | |||
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act): ☐ Yes ☒ No
The aggregate market value of the voting common stock held by non-affiliates of the registrant, based on the closing sale price of the registrant’s common stock as reported on The NASDAQ Capital Market on June 30, 2016, was $14,012,770. Shares of common stock held by each officer and director and by each person who is known to own 10% or more of the outstanding Common Stock have been excluded in that such persons may be deemed to be affiliates of the Company. This determination of affiliate status is not necessarily a conclusive determination for other purposes.
As of March 15, 2017, RXi Pharmaceuticals Corporation had 22,045,481 shares of common stock, $0.0001 par value, outstanding.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Portions of the registrant’s definitive proxy statement for its 2017 annual meeting of stockholders, to be filed pursuant to Regulation 14A with the Securities and Exchange Commission not later than 120 days after the registrant’s fiscal year end of December 31, 2016, are incorporated by reference into Part III of this Form 10-K.
Table of Contents
RXi PHARMACEUTICALS CORPORATION
ANNUAL REPORT ON FORM 10-K
For the Fiscal Year Ended December 31, 2016
| Page | ||||||
| PART I. | ||||||
| Item 1. |
2 | |||||
| Item 1A. |
15 | |||||
| Item 1B. |
25 | |||||
| Item 2. |
25 | |||||
| Item 3. |
25 | |||||
| Item 4. |
25 | |||||
| PART II. | ||||||
| Item 5. |
26 | |||||
| Item 6. |
26 | |||||
| Item 7. |
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS |
26 | ||||
| Item 7A. |
34 | |||||
| Item 8. |
F-1 | |||||
| Item 9. |
CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE |
F-20 | ||||
| Item 9A. |
F-20 | |||||
| Item 9B. |
F-21 | |||||
| PART III. | ||||||
| Item 10. |
F-21 | |||||
| Item 11. |
F-21 | |||||
| Item 12. |
SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS |
F-21 | ||||
| Item 13. |
CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE |
F-21 | ||||
| Item 14. |
F-22 | |||||
| PART IV. | ||||||
| Item 15. |
F-22 | |||||
| Item 16. |
F-22 | |||||
Table of Contents
FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This report contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. Forward-looking statements can be identified by words such as “intends,” “believes,” “anticipates,” “indicates,” “plans,” “expects,” “suggests,” “may,” “should,” “potential,” “designed to,” “will” and similar references. Such statements include, but are not limited to, statements about: our ability to successfully develop RXI-109, Samcyprone™, and our other product candidates (collectively “our product candidates”); the future success of our clinical trials with our product candidates; the timing for the commencement and completion of clinical trials; the future success of our strategic partnerships; and our ability to implement cost-saving measures. Forward-looking statements are neither historical facts nor assurances of future performance. These statements are based only on our current beliefs, expectations and assumptions regarding the future of our business, future plans and strategies, projections, anticipated events and trends, the economy and other future conditions. Because forward-looking statements relate to the future, they are subject to inherent uncertainties, risks and changes in circumstances that are difficult to predict and many of which are outside of our control. Our actual results and financial condition may differ materially from those indicated in the forward-looking statements. Therefore, you should not rely on any of these forward-looking statements. Important factors that could cause our actual results and financial condition to differ materially from those indicated in the forward-looking statements include, among others: the risk that our clinical trials with our product candidates may not be successful in evaluating the safety and tolerability of these candidates or providing evidence of increased surgical scar reduction compared to placebo; the successful and timely completion of clinical trials; uncertainties regarding the regulatory process; the availability of funds and resources to pursue our research and development projects, including clinical trials with our product candidates; general economic conditions; and those identified in this Annual Report on Form 10-K under the heading “Risk Factors” and in other filings the Company periodically makes with the Securities and Exchange Commission. Forward-looking statements contained in this Annual Report on Form 10-K speak as of the date hereof and the Company does not undertake to update any of these forward-looking statements to reflect a change in its views or events or circumstances that occur after the date of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Table of Contents
Unless otherwise noted, (1) the term “RXi” refers to RXi Pharmaceuticals Corporation and our subsidiary, MirImmune, LLC and (2) the terms “Company,” “we,” “us” and “our” refer to the ongoing business operations of RXi and MirImmune, LLC, whether conducted through RXi or MirImmune, LLC.
| ITEM 1. | BUSINESS |
Overview
RXi is a clinical-stage company developing innovative therapeutics based on our proprietary self-delivering RNAi (sd-rxRNA®) platform and Samcyprone™, a topical immunomodulator, which address significant unmet medical needs. The Company’s clinical development programs include RXI-109, an sd-rxRNA for the treatment of dermal and ocular scarring, and Samcyprone™, for the treatment of warts. In January 2017, RXi acquired MirImmune Inc. (“MirImmune”), a privately-held company focused on the development of next generation immunotherapies for the treatment of cancer. With the acquisition of MirImmune, the Company’s development programs have expanded from dermatology and ophthalmology to also include cell-based cancer immunotherapy. The Company’s pipeline, coupled with our extensive patent portfolio, provides for product development and business development opportunities across a broad spectrum of therapeutic areas.
Our Pipeline
Our pipeline focuses on three areas: dermatology, including cosmetic product development, ophthalmology and cell-based cancer immunotherapy. Our RNAi therapies are designed to “silence,” or down-regulate, the expression of a specific gene that may be over-expressed in a disease condition and our topical immunotherapy agent, Samcyprone™, treats diseases by inducing, enhancing or suppressing an immune response in the skin. The following is a summary of our current product candidates and their development status:
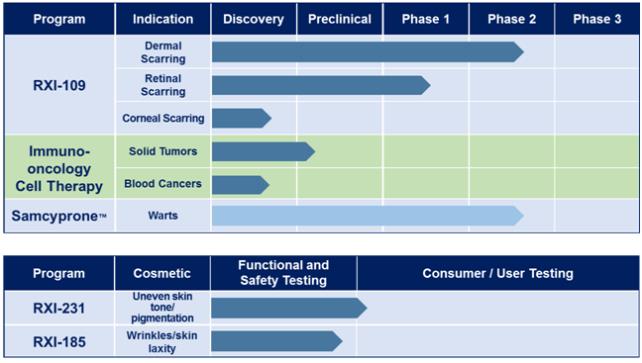
2
Table of Contents
Dermatology Franchise
RXI-109 — Dermal Scarring
The Company’s lead product candidate and first RNAi clinical product candidate, RXI-109, is a self-delivering RNAi compound (sd-rxRNA) that commenced human clinical trials in 2012. RXI-109 is designed to reduce the expression of connective tissue growth factor (“CTGF”), a critical regulator of several biological pathways involved in fibrosis, including scar formation in the skin and eye. RXI-109 is currently being evaluated in a Phase 2 clinical trial, Study 1402, to prevent or reduce dermal scarring following scar revision surgery of an existing hypertrophic scar.
The Company initially conducted two Phase 1 clinical trials evaluating RXI-109 in a surgical setting. Both trials demonstrated the safety and tolerability of RXI-109 in ascending single and multi-doses, and also provided the first evidence of clinical activity in a surgical setting. With the successful completion of the Phase 1 trials, in November 2013 the Company initiated its Phase 2 program for RXI-109 with Study 1301, a Phase 2 clinical trial evaluating the use of RXI-109 to prevent the recurrence of hypertrophic scars following scar revision surgery. Enrollment and dosing for this study have been completed.
Preliminary data observations from Study 1301 were used in the design of the Company’s second Phase 2 clinical trial in hypertrophic scars, Study 1402, which commenced in July 2014. In October 2015, we reported that preliminary data from Study 1402 demonstrated that scars at revision sites were judged to be better at three months after a treatment regimen with five mg/cm intradermal administration of RXI-109 than scars at untreated revision sites in those same subjects. Based in part on this new information, two more cohorts were added to Study 1402 in November 2015. For these two cohorts, the number of doses was increased to either eight or nine doses of RXI-109 over a six-month period to better cover the extended wound healing/scarring profile of hypertrophic scars. Enrollment of subjects into these two new cohorts completed ahead of schedule during the third quarter of 2016.
In December 2016, the Company announced that preliminary data from the first two cohorts from Study 1402 at nine months confirmed the positive differentiation of treated surgery incisions from untreated for a subset of subjects treated with five mg/cm of RXI-109 that was observed at three months. In addition, these data extend this observation to all time points, including the post-treatment follow-up period through nine months post-surgery. RXI-109 was safe and well tolerated. A complete read-out of the whole study, including all four cohorts with follow-up until nine months post-surgery, is expected in the second half of 2017.
Scarring represents a high unmet medical need as there are currently no U.S. Food and Drug Administration (“FDA”) approved therapies in the U.S. for the treatment and prevention of scars in the skin. Scar revision surgery is one treatment option, but often the scar recurs. If approved, RXI-109 could be a “first-in-class” RNAi treatment for the prevention or reduction of post-surgical dermal scarring. Given the large number of surgical procedures, there is a significant market for a scar prevention therapeutic such as RXI-109.
Samcyprone ™ — Warts
In December 2014, the Company broadened its clinical pipeline with an exclusive, global license to Samcyprone™, our second clinical candidate. Samcyprone™ is a proprietary topical formulation of the small molecule diphenylcyclopropenone (“DPCP”), an immunomodulator that works by initiating a T-cell response. The use of Samcyprone™ allows sensitization using much lower concentrations of DPCP than are used with existing compounded DPCP solutions, avoiding hyper-sensitization to subsequent challenge doses. DPCP, the active ingredient in Samcyprone™, has long been used to treat warts and has also been used for several other indications, such as to stimulate hair re-growth in alopecia areata and to clear cutaneous metastases of melanoma. In March 2015, the FDA granted Orphan Drug Designation to the Company for Samcyprone™ for the treatment of malignant melanoma stages IIb to IV. Samcyprone™ is currently being evaluated in a Phase 2a clinical trial, Study 1502, for the clearance of common warts.
Study 1502, initiated in December 2015, includes a sensitization phase in which a spot on the subject’s upper arm and one or more warts are treated with Samcyprone™. After being sensitized in this way, the subjects will enter into the treatment phase where up to four warts are treated on a once weekly basis for ten weeks with a ten-fold lower concentration of Samcyprone™ than in the sensitization phase. During the trial, the warts are scored, photographed and measured to monitor the level of clearance. The Company has added a second cohort to the study and is currently enrolling subjects to explore the opportunity to reduce the sensitization dose level and potentially reduce the treatment length. With this second cohort, enrollment is expected to be completed in the second half of 2017.
3
Table of Contents
In December 2016, the Company announced the results from a preliminary review of sensitization and wart clearance data from a subset of subjects that have completed the ten-week treatment phase of Study 1502. Results showed that greater than 90% of the subjects demonstrated a sensitization response, a prerequisite to be able to develop a therapeutic response. Additionally, more than 60% of the subjects responded to the treatment by exhibiting either complete or greater than 50% clearance of all treated warts with up to ten weekly treatments. Samcyprone™ treatment has been generally safe and well tolerated and has had drug-related adverse events relating to local reactions, which are typically expected for this type of treatment due to the sensitization and challenge responses in the skin. The complete readout of the final study is anticipated in the second half of 2017.
Cutaneous warts are extremely common, being experienced by most people at some time during their lives. Although most warts will spontaneously disappear without treatment, treatment is sought for recalcitrant warts and to prevent recurrence. There are many different treatment modalities for warts, including physical destruction and immunomodulation. However, treatment of warts is complicated by low success rates, prolonged duration of therapy and the potential for recurrence. There is a clear unmet need for new therapies for warts, and if approved, Samcyprone™ could be a more effective and convenient treatment than the currently available therapies.
Additional Dermatology Programs
In addition to our dermal scarring and wart programs, we continue to advance our preclinical and discovery programs with our sd-rxRNA technology. The Company has selected tyrosinase (“TYR”) and collagenase (“MMP1”) as targets for our self-delivering platform because they are relevant for both consumer health and therapeutic development. TYR is a key enzyme in the synthesis of melanin. Melanin is produced by melanocytes and is the pigment that gives human skin, hair and eyes their color. The inhibition of TYR can play a key role in the management of skin conditions including cutaneous hyperpigmentation disorders such as lentigines (freckles, age spots and liver spots) and possibly melanoma. MMP1 is a key enzyme involved in the breakdown of extracellular matrix. Reduction of MMP1 may be beneficial in the treatment of skin aging disorders, arthritis, acne scarring, blistering skin disorders, corneal erosions, endometriosis and possibly cancer metastasis.
Cosmetic Development
Cosmetics are compounds that affect the appearance of the skin and make no preventative or therapeutic claims. These compounds may be developed more rapidly than therapeutics, therefore the path to market may be much shorter and less expensive. In October 2015, we announced the selection of lead compounds targeting TYR and MMP1 for cosmetic development.
RXI-231 — Uneven Skin Tone and Pigmentation
RXI-231, an sd-rxRNA compound targeting TYR, is in development as a cosmetic ingredient that may improve the appearance of uneven skin tone and pigmentation. Efficacy and toxicity testing in cell culture and skin equivalents for RXI-231 was successfully completed in December 2016. The Company is currently coordinating with a U.S. clinical testing site to initiate human testing of RXI-231 in the second quarter of 2017. RXI-231 has been manufactured in sufficient quantities to support this activity. In addition to evaluating safety, the effect of RXI-231 on the appearance of skin pigmentation will be assessed.
RXI-185 — Wrinkles and Skin Laxity
RXI-185, an sd-rxRNA compound targeting MMPI, is in development as a cosmetic ingredient that may improve the appearance of wrinkles or skin laxity. Results from studies by the Company have shown a pronounced reduction in MMPI mRNA levels that correspond to a similar reduction in MMPI enzyme activity in cell culture in vitro.
Ophthalmology Franchise
RXI-109 — Retinal Scarring
As in dermal scarring, RXI-109 can also be used to target CTGF in the eye, where CTGF is known to be involved in retinal scarring. Building on the work in our dermal clinical program, the Company filed a new investigational drug application (“IND”) in July 2015 for RXI-109 as a potential therapeutic for the scarring component of retinal diseases in the eye, such as wet age-related macular degeneration (“AMD”). In November 2015, we initiated a Phase 1/2 clinical trial to evaluate the safety and clinical activity of RXI-109 in reducing the progression of retinal scarring.
4
Table of Contents
Study 1501 is a multi-dose, dose escalation study conducted in subjects with AMD with evidence of subretinal fibrosis. Each subject will receive four doses of RXI-109 by intraocular injection at one month intervals for a total dosing period of three months. The safety and tolerability of RXI-109, as well as the potential for clinical activity, will be evaluated over the course of the study using numerous assessments to monitor the health of the retina and to assess visual acuity. The first two cohorts in Study 1501 have been completely enrolled and dosing in the third cohort at the highest planned dose level has begun. To date there have been no safety issues that precluded continuation of dosing. Complete enrollment is anticipated in the first half of 2017, ahead of our original plan, with complete subject participation anticipated in the second half of 2017.
Currently, there is no effective way to prevent the formation or progression of retinal scars that may occur as a consequence of a number of debilitating ocular diseases. In advanced neo-vascular or wet-AMD, our first area of study, retinal scarring often results in continued vision loss even if the patient is being treated with an anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (“VEGF”) therapy. RXI-109 has the potential to fill this unmet medical need by reducing this continuing damage to the retina and in doing so help preserve these patients’ vision for a longer period of time.
Additional Ophthalmology Programs
In addition to the clinical trial for the use of RXI-109 as a potential therapeutic for retinal scarring, we are advancing other early-stage ophthalmology programs. Currently, the Company is directing its development efforts toward advancing RXI-109 for the treatment of corneal scarring. To date, our preclinical studies have shown that CTGF protein levels are reduced in a dose-dependent manner in both the retina and cornea following an intravitreal injection of RXI-109 in monkeys. Elevated CTGF is implicated in the formation of corneal scarring that can occur after eye injury or after certain infections, and it has been proposed that a reduction of CTGF may be an important step towards reducing corneal scarring. Scarring of the cornea can impact the transparency of the cornea, and thus negatively impact vision. We are currently working towards a non-invasive delivery formulation of RXI-109 to reduce CTGF in the front of the eye.
Cell-based Cancer Immunotherapy
In January 2017, the Company entered into a Stock Purchase Agreement (the “Stock Purchase Agreement”) pursuant to which it acquired 100% of the issued and outstanding shares of capital stock of MirImmune for an aggregate of 2,750,351 shares of common stock of the Company and 1,115,579 shares of Series C Convertible Preferred Stock (the “Series C Preferred Stock”), subject to a holdback of 3% of the aggregate closing consideration for any purchase-price adjustments. Under the terms of the Stock Purchase Agreement, if certain development or commercial milestones are achieved within two years, the Company will be required to either (i) issue to the sellers a number of shares of common stock or (ii) pay the equivalent value in cash.
Prior to its acquisition by the Company, MirImmune was a privately held biopharmaceutical company engaged in the development of cancer immunotherapies. The Company previously granted an exclusive license to MirImmune in March 2015 to utilize the Company’s novel and proprietary sd-rxRNA technology for use in developing ex vivo cell-based cancer immunotherapies.
Our approach to immunotherapy builds on well-established methodologies of adoptive cell transfer. Immune cells, such as T-lymphocytes, are isolated from specific patients or retrieved from allogeneic immune cell banks and then expanded and sometimes processed to express tumor-binding receptors. Our method will introduce a new and important step in ex vivo processing of immune cells. This step uses our sd-rxRNA technology to reduce or eliminate the expression of immunosuppressive receptors or proteins by the therapeutic immune cells, potentially making them less sensitive to tumor resistance mechanism and thus improving their ability to destroy the tumor cells.
The Company’s approach builds on current immunotherapy approaches but provides some key advantages. One major advantage is that pre-treatment with our targeted compounds allows multiple immune checkpoints to be attenuated within the same therapeutic cell, an improvement which could dramatically increase their tumor cell killing capability. In addition, these therapeutic immune cells may lack some known side effects associated with the checkpoint inhibitor toxicity while potentially improving efficacy over current immunotherapy approaches.
5
Table of Contents
Using our sd-rxRNA technology, MirImmune demonstrated in vitro that multiple sd-rxRNA compounds can be used alone or in combination to target and silence extracellular, as well as intracellular, checkpoints in immune cells. Additional in vitro data demonstrated that PD-1 silencing by sd-rxRNA in patient-derived tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) resulted in enhanced killing of melanoma tumor cells from the same patient in culture. MirImmune also showed in a mouse model of human ovarian cancer that in vivo treatment with mesothelin-targeting CAR T-cells transfected with a PD-1 targeting sd-rxRNA significantly reduced the rate of tumor growth as compared to vehicle control. Furthermore, the silencing of PD-1 in the CAR T-cells isolated from these tumors persisted for at least one month.
In December 2016, new data was provided by MirImmune demonstrating silencing of a number of undisclosed immunosuppressive targets in natural killer cells (NK cells) using our sd-rxRNA compounds. This adds to a remarkable set of immune checkpoint modulation studies in human T cells, including CAR T-cells and TILs. In immune cells tested to date, the sd-rxRNA treatment results in potent silencing while maintaining close to 100% transfection efficiency and nearly full cell viability. Moreover, the silencing effect has been validated in a number of clinically used cell treatment protocols.
MirImmune identified lead sd-rxRNA compounds for each of six different checkpoints, including PD-1, CTLA-4 and other extracellular and intracellular targets. The Company plans to build on the work completed by MirImmune prior to its acquisition by the Company to advance the potential of our sd-rxRNA platform for use in cell-based cancer immunotherapy. In 2017, the Company plans to (i) initiate an internal program to evaluate the reduction of cytokines involved in cytokine release syndrome, (ii) release data on multiple checkpoint inhibiting sd-rxRNA compounds co-transfected in CAR T-cells in mouse models for solid tumors and (iii) share preclinical results on our use of sd-rxRNA with TILs in melanoma.
Market Opportunity
As there are currently no FDA-approved drugs to prevent scar formation, a therapeutic of this type could have great benefit for trauma and surgical patients, particularly as a treatment during the surgical revision of existing unsatisfactory scars. According to the American Society for Plastic Surgery, there are approximately 180,000 scar revision surgeries in the United States every year. In addition to cosmetic and reconstructive surgeries, medical interventions which could incorporate an anti-scarring agent include treatment of scarring that results from trauma, surgery or burns (especially relating to raised or hypertrophic scarring or contracture scarring), and surgical revision of existing unsatisfactory scars. Moreover, there are over 42 million medical procedures in the U.S. each year that could potentially benefit from a therapeutic treatment that could successfully reduce or prevent scarring; thus, the market potential is quite large.
AMD is the leading cause of severe vision loss in adults over age 50. According to the National Eye Institute, in 2010 approximately 2.07 million people had AMD. The National Eye Institute further states that as the proportion of people in the U.S. age 65 and older grows larger, more people are developing age-related diseases, such as AMD. Due to the aging population, this number is expected to double to an estimated 5.44 million people in the year 2050. There is no cure for AMD and over 50% of patients start to develop scarring after 2 years on anti-VEGF therapy, the current standard of care. This represents a large number of patients with an unmet medical need that could benefit from a therapeutic treatment that could successfully reduce or prevent scarring in the retina, and thereby improve vision loss.
Overexpression of CTGF is implicated in dermal scarring, subretinal fibrosis and other fibrotic diseases. Because of this, we believe that RXI-109 or other CTGF-targeting RNAi compounds may be able to treat the fibrotic component of numerous additional indications. These indications are as wide ranging as acute spinal injury, endometriosis, organ fibrosis including liver and pulmonary fibrosis, cutaneous scleroderma and vascular restenosis, in addition to numerous ocular diseases that result in retinal scarring. If the current clinical trials of RXI-109 produce successful results, we may explore opportunities in these additional indications that can be accessed by local administration, starting with intradermal or intravitreal injection. Although the Company does not intend to develop systemic uses of RXI-109 at this time, the Company is open to business development and out-licensing opportunities for those applications.
DPCP, the active ingredient in Samcyprone™, is a small molecule that has been used since the late 1970s to stimulate regrowth of hair in patients with alopecia areata. Recent publications have supported its use as an immunomodulator for the treatment of alopecia areata, warts and cutaneous metastases of malignant melanoma, a combined market potential of over an estimated $1 billion. Although it has been used by physicians for several decades, it has never been reviewed or approved by a regulatory authority as a drug. If FDA approval is granted, Samcyprone™, RXi’s proprietary formulation of DPCP, is expected to achieve market exclusivity.
6
Table of Contents
Despite many advances, there is still a significant unmet need for cancer treatments. There are currently close to 180 therapies across various phases of development in the T-cell immunotherapy market. This growth is supported by robust and opportunistic pipelines targeting various indications. Pharmaceutical and large biotechnology companies are actively looking for complementary technology platforms that enhance their cellular pipelines. Initial clinical trials of adoptive cell transfer, our approach to immunotherapy, have shown limited success in treatment of solid tumors. One of the major issues is the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment. Multiple inhibitory receptors, or immune checkpoints, are responsible for immunosuppression. Our sd-rxRNA treatment can be seamlessly integrated in existing and new adoptive cell transfer therapies to overcome immunosuppression issues. Our sd-rxRNA compounds silence various immunosuppressive genes and boost the ability of therapeutic cells to kill tumors, while offering a safe and versatile approach to reduction of immunosuppression in therapeutic cells.
Introduction to RNAi
RNAi is a naturally occurring phenomenon where short, double-stranded RNA molecules interfere with the expression of targeted genes. The discovery of RNAi is regarded as a significant advancement in the scientific community, as evidenced by the 2006 Nobel Prize in Medicine awarded to the co-discoverers of RNAi, including Dr. Craig Mello, one of the founders of RXi.
RNAi offers a novel approach to the drug development process because RNAi compounds can potentially be designed to target any one of the thousands of human genes, many of which are “undruggable” by other modalities. The specificity of RNAi is achieved by an intrinsic, well-understood biological mechanism based on designing the sequence of an RNAi compound to match the sequence of the targeted gene. The sequence of the entire human genome is now known, and the mRNA coding sequence for many proteins is already available. Supported by numerous gene-silencing reports and our own research, we believe that this sequence information can be used to design RNAi compounds to interfere with the expression of almost any specific gene.
Our RNAi Therapeutic Platform
The first design of RNAi compounds to be pursued for the development of human therapeutics were short, double-stranded RNAs that included at least one overhanging single-stranded region and limited modifications, known as small-interfering RNA, or siRNA, which we will also refer to as classic siRNA.
We believe that classic siRNAs have drawbacks that may limit the usefulness of those agents as human therapeutics, and that we may be able to utilize the technologies we have licensed and developed internally to optimize RNAi compounds for use as human therapeutic agents. For sd-rxRNA, it is the combination of the duplex length, the nucleotide sequence and the configuration of chemical modifications that are important for effective RNAi therapeutics.
Drug delivery has been the primary challenge in developing RNAi therapeutics since its initial discovery. One conventional solution to the delivery problem involves encapsulation into a lipid-based particle, such as a liposome, to improve circulation time and cellular uptake. Scientists at RXi have used an alternative approach to delivery in which drug-like properties were built into the RNAi compound itself. These novel compounds are termed ‘self-delivering’ RNAi compounds or sd-rxRNA.
sd-rxRNAs are hybrid oligonucleotide compounds that the Company believes combine the beneficial properties of both conventional RNAi and antisense technologies. Traditional, single-stranded antisense compounds have favorable tissue distribution and cellular uptake properties. However, they do not have the intracellular potency that is a hallmark of double-stranded RNAi compounds. Conversely, the duplex structure and hydrophilic character of traditional RNAi compounds results in poor tissue distribution and cellular uptake. In an attempt to combine the best properties of both technologies, sd-rxRNA have a single-stranded phosphorothioate region, a short duplex region, and contain a variety of nuclease-stabilizing and lipophilic chemical modifications. The combination of these features allows sd-rxRNA to achieve efficient spontaneous cellular uptake and potent, long-lasting intracellular activity.
7
Table of Contents
We believe that our next generation sd-rxRNA compounds offer significant advantages over siRNAs used by other companies developing RNAi therapeutics, highlighted by the following characteristics:
| • | Efficient cellular uptake in the absence of a delivery vehicle; |
| • | Potent RNAi activity; |
| • | More resistant to nuclease degradation than unformulated oligonucleotides; |
| • | Able to suppress long non-coding RNAs, both in cytoplasm and the nucleus; |
| • | Readily manufactured; |
| • | Potentially more specific for the target gene; and |
| • | More reliable at blocking immune side effects than classic siRNA. |
Our Route of Administration
The route by which an RNAi therapeutic is brought into contact with the body depends on the intended organ or tissue to be treated. Delivery routes can be simplified into two major categories: (1) local (when a drug is delivered directly to the tissue of interest); and (2) systemic (when a drug accesses the tissue of interest through the circulatory system). Local delivery may avoid some hurdles associated with systemic approaches such as rapid clearance from circulation and inefficient tissue extravasation (crossing the endothelial barrier from the blood stream). However, the local delivery approach can only be applied to a limited number of organs or tissues (e.g., skin, eye, lung and potentially the central nervous system).
The key to therapeutic success with RNAi lies in delivering intact RNAi compounds to the target tissue and the interior of the target cells. To accomplish this, we have developed a comprehensive platform that includes chemically synthesized RNAi compounds that are optimized for stability and efficacy and combine efficient cellular uptake with a local delivery approach.
Our sd-rxRNA molecules have unique properties that improve tissue and cell uptake. We have studied sd-rxRNA molecules in animal models for dermal and ocular delivery. Direct administration of sd-rxRNA via injection with no additional delivery vehicle to the skin or to the eye demonstrates that target gene silencing can be measured after local administration. The dose levels required for these direct-injection methods are small and suitable for clinical development. The Company has a number of clinical trials currently ongoing with RXI-109, an sd-rxRNA compound, for local delivery in the skin and the eye. Other target tissues that are potentially accessible for local delivery using sd-rxRNA compounds include the lung, the central nervous system, mucosal tissues and sites of inflammation and tumor (direct administration).
We have also studied our sd-rxRNA compounds for use in the well-established methodologies of adoptive cell transfer. Immune cells are isolated from specific patients or retrieved from allogeneic immune cell banks and then expanded and possibly processed to express tumor-binding receptors. Our process involves ex vivo treatment of the immune cells with our sd-rxRNA compounds to inhibit the expression of immune checkpoint genes. The enhanced cells are then returned and used to treat the same patient.
Introduction to Samcyprone™
Immunotherapy is the treatment of disease by inducing, enhancing or suppressing an immune response. Active agents in immunotherapy are collectively called immunomodulators. They are a diverse array of recombinant, synthetic and natural preparations that help to regulate or normalize the immune system.
Our Samcyprone™ Therapeutic Pipeline
Samcyprone™, licensed by the Company in 2014, is a proprietary topical formulation of the small molecule DPCP. DPCP has been used for decades as a treatment to stimulate hair re-growth in patients with alopecia areata and more recently as a treatment for recalcitrant wart removal and as an aid in the reduction of cutaneous metastases of melanoma. As it is currently used, a doctor must prescribe DPCP to be formulated by a compounding facility, generally in acetone.
8
Table of Contents
There are no standardized methods of formulation or procedures for use. Because it works by causing an immune response, the level of response can vary greatly from person to person. Moreover, some pharmacies will not even compound it, even if it is prescribed.
Samcyprone™ works by initiating a T-cell response. T-cells or T lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell that play a key role in cell-mediated immunity. The use of Samcyprone™ will improve ease of use, allow for lower sensitizing and challenge doses than in current use and should result in an improved safety margin and a more consistent immune response.
There will be several advantages to using an FDA regulated formulation like the one we are developing. First, the amount of DPCP used in our own ointment formulation is lower than that generally used in acetone formulation. This should result in reduced side effects that happen due to accidental over-sensitization when a higher than necessary concentration is used. Second, we are developing an optimized dosing regimen so that a standardized response can be expected. And third, the ointment formulation will be easier to prescribe and to use than an acetone formulation, allowing for ease of application at the appropriate site on the skin.
Intellectual Property
We protect our proprietary information by means of United States and foreign patents, trademarks and copyrights. In addition, we rely upon trade secret protection and contractual arrangements to protect certain of our proprietary information and products. We have pending patent applications that relate to potential drug targets, compounds we are developing to modulate those targets, methods of making or using those compounds and proprietary elements of our drug discovery platform.
Much of our technology and many of our processes depend upon the knowledge, experience and skills of key scientific and technical personnel. To protect our rights to our proprietary know-how and technology, we require all employees, as well as our consultants and advisors when feasible, to enter into confidentiality agreements that require disclosure and assignment to us of ideas, developments, discoveries and inventions made by these employees, consultants and advisors in the course of their service to us, and we vigorously defend that position with partners, as well as with employees who leave the Company.
We have also obtained rights to various patents and patent applications under licenses with third parties, which require us to pay royalties, milestone payments, or both. The degree of patent protection for biotechnology products and processes, including ours, remains uncertain, both in the United States and in other important markets, because the scope of protection depends on decisions of patent offices, courts and lawmakers in these countries. There is no certainty that our existing patents or others, if obtained, will afford us substantial protection or commercial benefit. Similarly, there is no assurance that our pending patent applications or patent applications licensed from third parties will ultimately be granted as patents or that those patents that have been issued or are issued in the future will stand if they are challenged in court. We assess our license agreements on an ongoing basis, and may from time to time terminate licenses to technology that we do not intend to employ in our technology platforms, or in our product discovery or development activities.
Patents and Patent Applications
We are actively prosecuting thirty-two patent families, including those acquired from MirImmune, covering our compounds and technologies, including RXI-109 and Samcyprone™. A combined summary of these patents and patent applications is set forth below in the following table:
| Pending Applications |
Issued Patents | |||
| United States |
21 | 31 | ||
| Canada |
9 | 1 | ||
| Europe |
11 | 31 | ||
| Japan |
7 | 7 | ||
| Other Markets |
12 | 9 |
9
Table of Contents
Patents and Patent Applications Relating to RNAi
Our RNAi portfolio includes seventy-eight issued patents, fourteen of which cover our self-delivering RNAi platform. These fourteen patents broadly cover both the composition and methods of use of our self-delivering platform technology and uses of our sd-rxRNAs targeting CTGF for the treatment of fibrotic disorders (including RXI-109 for the treatment of dermal and ocular fibrosis), as well as sd-rxRNAs targeting immune checkpoint targets for ex vivo cell-based cancer immunotherapies. These patents are scheduled to expire between 2029 and 2035. Furthermore, there are fifty-seven patent applications, encompassing what we believe to be important new RNAi compounds and their use as therapeutics and/or cosmetics, chemical modifications of RNAi compounds that improve the compounds’ suitability for therapeutic uses (including delivery) and compounds directed to specific targets (i.e., that address specific disease states).
The patents and any patents that may issue from these pending patent applications will, if issued, be set to expire between 2022 and 2035, not including any patent term extensions that may be afforded under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (and the equivalent provisions in foreign jurisdictions) for any delays incurred during the regulatory approval process relating to human drug products (or processes for making or using human drug products).
Patent and Patent Applications Relating to Samcyprone™
The Samcyprone™ portfolio includes one issued patent and three patent applications. The patent and patent applications cover both the compositions and methods of use of Samcyprone™ for the treatment of warts, human papilloma virus (HPV) skin infections, skin cancer (including melanoma) and immunocompromised patients.
The patent and any patents that may issue from the pending applications will be set to expire between 2019 and 2031, not including any patent term extensions that may be afforded under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (and the equivalent provisions in foreign jurisdictions) for any delays incurred during the regulatory approval process relating to human drug products (or processed for making or using human drug products).
Intellectual Property License Agreements
We have secured exclusive and non-exclusive rights to develop therapeutics by licensing key RNAi technologies, Samcyprone™ and patent rights from third parties. These rights relate to chemistry and configuration of compounds, delivery technologies of compounds to cells and therapeutic targets. As we continue to develop our own proprietary compounds, we continue to evaluate both our in-licensed portfolio as well as the field for new technologies that could be in-licensed to further enhance our intellectual property portfolio and unique position in the RNAi and immunotherapy space.
Advirna LLC. In September 2011, we entered into an agreement with Advirna, LLC (“Advirna”) pursuant to which Advirna assigned to us its existing patent and technology rights related to sd-rxRNA technology in exchange for our agreement to issue 5% of the Company’s fully-diluted shares, pay an annual maintenance fee of $100,000 and pay a one-time milestone payment of $350,000 upon the issuance of the first patent with valid claims covering the assigned technology. The common shares of the Company were issued to Advirna in 2012 and the one-time milestone payment was paid in 2014. Additionally, we will be required to pay a 1% royalty to Advirna on any license revenue received by us with respect to future licensing of the assigned Advirna patent and technology rights. We also granted back to Advirna a license under the assigned patent and technology rights for fields of use outside human therapeutics and diagnostics.
Our rights under the Advirna agreement will expire upon the later of: (i) the expiration of the last-to-expire of the “patent rights” (as defined therein) or (ii) the abandonment of the last-to-be abandoned of such patents, unless earlier terminated in accordance with the provisions of the agreement.
We may terminate the Advirna agreement at any time upon 90 days’ written notice to Advirna, and Advirna may terminate the agreement upon 90 days’ prior written notice in the event that we cease using commercially reasonable efforts to research, develop, license or otherwise commercialize the patent rights or “royalty-bearing products” (as defined therein), provided that we may refute such claim within such 90-day period by showing budgeted expenditures for the research, development, licensing or other commercialization consistent with other technologies of similar stage of development and commercial potential as the patent rights or royalty-bearing products. Further, either party at any time
10
Table of Contents
may provide to the other party written notice of a material breach of the agreement. If the other party fails to cure the identified breach within 90 days after the date of the notice, the aggrieved party may terminate the agreement by written notice to the party in breach.
Hapten Pharmaceuticals, LLC. In December 2014, the Company entered into an Assignment and License Agreement with Hapten Pharmaceuticals, LLC (“Hapten”) under which Hapten agreed, effective at a closing that was subject to the satisfaction of certain closing conditions which occurred in February 2015, to sell and assign to us certain patent rights and related assets and rights, including an investigational new drug application and clinical data, for Hapten’s Samcyprone™ products for therapeutic and prophylactic use. Under the Assignment and License Agreement and upon the closing, Hapten received a one-time upfront cash payment of $100,000 and we issued to Hapten 20,000 shares of common stock of the Company. Pursuant to the Assignment and License Agreement, Hapten will be entitled to receive: (i) future milestone payments tied to the achievement of certain clinical and commercial objectives (all of which payments may be made at our option in cash or through the issuance of common stock) and (ii) escalating royalties based on product sales by us and any sublicensees.
We have certain customary diligence obligations under the Assignment and License Agreement requiring us to use commercially reasonable efforts to develop and commercialize one or more products covered by the Assignment and License Agreement, which obligations, if not performed, could result in rights assigned or licensed to us reverting back to Hapten.
In addition to the license agreements listed above, the Company has entered into and may enter into other license agreements that may benefit us as we develop our RNAi and Samcyprone™ pipelines.
Other Strategic Agreements
OPKO Health, Inc. In March 2013, the Company entered into an Asset Purchase Agreement with OPKO Health, Inc. (“OPKO”) (the “Asset Purchase Agreement”), in which we acquired substantially all of its RNAi-related assets, which included patents and patent applications, licenses, clinical and preclinical data and other related assets. In exchange for the assets that we purchased from OPKO, we issued 166,667 shares of our common stock and agreed to pay, if applicable: (i) up to $50 million in development and commercialization milestones for the successful development and commercialization of each “Qualified Drug” (as defined therein) and (ii) royalty payments equal to: (a) a mid-single-digit percentage of “Net Sales” (as defined therein) with respect to each Qualified Drug sold for an ophthalmologic use during the applicable “Royalty Period” (as defined therein) and (b) a low-single-digit percentage of Net Sales with respect to each Qualified Drug sold for a non-ophthalmologic use during the applicable Royalty Period.
We have certain customary diligence obligations under the Asset Purchase Agreement requiring us to use commercially reasonable efforts to develop and commercialize one or more products covered by the Asset Purchase Agreement, which obligations, if not performed, could result in assets transferred and rights assigned or licensed to us reverting back to OPKO.
MirImmune Inc. In March 2015, RXi granted an exclusive license to MirImmune to utilize the Company’s novel and proprietary sd-rxRNA technology for MirImmune’s use in developing ex vivo cell-based cancer immunotherapies to target immune inhibitory pathways (checkpoints) which are responsible for limiting the efficacy of cancer immunotherapies. Under the terms of the agreement, MirImmune was responsible for all research, development, manufacturing, regulatory and commercialization activities for the licensed products.
On October 7, 2016, RXi entered into an exclusive option agreement pursuant to which the Company had the exclusive option, but not the obligation, to purchase 100% of the outstanding capital stock of MirImmune. In January 2017, the Company exercised the option and entered into the Stock Purchase Agreement pursuant to which it acquired 100% of the outstanding shares of capital stock of MirImmune for an aggregate of 2,750,371 shares of common stock of the Company and 1,115,579 shares of Series C Preferred Stock, subject to a holdback of 3% of the aggregate closing consideration for any purchase-price adjustments. Under the terms of the Stock Purchase Agreement, if certain development or commercial milestones are achieved within two years, the Company will be required to either (i) issue to MirImmune’s shareholders a number of shares of common stock or (ii) pay the equivalent value in cash.
11
Table of Contents
Thera Neuropharma, Inc. In May 2016, RXi granted an exclusive license to Thera Neuropharma, Inc. (“Thera”) to the Company’s novel and proprietary sd-rxRNA platform to develop therapeutics for neurodegenerative diseases. Under the terms of the agreement, Thera will be responsible for all research, development, manufacturing, regulatory and commercialization activities for the licensed products. Thera’s initial focus will be on sd-rxRNA compounds targeting superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1) for use in developing innovative treatments for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), commonly known as Lou Gehrig’s disease. Upon execution of the license agreement, RXi was issued shares of common stock of Thera and was granted a five year warrant to purchase additional shares of common stock of Thera pursuant to the terms of the license agreement. The Company is eligible to receive future cash, additional equity and royalties based on the achievement of certain milestones.
Research and Development
To date, our research programs have primarily focused on developing technology necessary to make RNAi compounds available by local administration for diseases for which we intend to develop an RNAi therapeutic, identifying and testing RNAi compounds against therapeutically relevant targets in the fields of dermatology and ophthalmology and identifying lead product candidates and moving those product candidates into the clinic. With our recent acquisition of MirImmune, our research programs will also focus on developing, identifying and testing RNAi therapeutics in the field of cell-based cancer immunotherapy. Since we commenced operations, research and development has composed a significant proportion of our total operating expenses and is expected to compose the majority of our spending for the foreseeable future.
There are risks in any new field of drug discovery that preclude certainty regarding the successful development of a product. We cannot reasonably estimate or know the nature, timing and costs of the efforts necessary to complete the development of, or the period in which material net cash inflows are expected to commence from, any product candidate. Our inability to make these estimates results from the uncertainty of numerous factors, including but not limited to:
| • | Our ability to advance product candidates into preclinical research and clinical trials; |
| • | The scope and rate of progress of our preclinical program and other research and development activities; |
| • | The scope, rate of progress and cost of any clinical trials we commence; |
| • | The cost of filing, prosecuting, defending and enforcing patent claims and other intellectual property rights; |
| • | Clinical trial results; |
| • | The terms and timing of any collaborative, licensing and other arrangements that we may establish; |
| • | The cost and timing of regulatory approvals; |
| • | The cost of establishing clinical and commercial supplies of our product candidates and any products that we may develop; |
| • | The cost and timing of establishing sales, marketing and distribution capabilities; |
| • | The effect of competing technological and market developments; and |
| • | The effect of government regulation and insurance industry efforts to control healthcare costs through reimbursement policy and other cost management strategies. |
Failure to complete any stage of the development of our product candidates in a timely manner could have a material adverse effect on our operations, financial position and liquidity.
Research and Development Expense
Research and development expense consists of compensation-related costs for our employees dedicated to research and development activities, fees related to our Scientific Advisory Board members, expenses related to our ongoing research and development efforts primarily related to our clinical trials, drug manufacturing, outside contract services, licensing and patent fees and laboratory supplies and services for our research programs. We expect research and development expenses to increase as we expand our discovery, preclinical and clinical activities.
12
Table of Contents
Total research and development expense for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015 was $5,415,000 and $6,925,000, respectively.
Competition
We believe that numerous companies are investigating or plan to investigate a variety of proposed anti-scarring therapies or cell-based immunotherapies in clinical trials or are working in the RNAi area generally. Many other companies are pursuing non-RNAi-based therapies for one or more fibrotic disease indications, including ocular scarring or other indications that we may seek to pursue. The companies include large and small pharmaceuticals, chemical and biotechnology companies, as well as universities, government agencies and other private and public research organizations.
We believe that other companies currently developing anti-scarring therapies, both dermal and ocular, include CoDa Therapeutics, Inc., Sirnaomics, Inc., FirstString Research, Inc., Promedior, Inc., FibroGen, Inc., miRagen Therapeutics, Inc., Ophthotech Corporation, Vascular BioSciences, Allergan plc, and Suneva Medical, Inc.
We believe that other companies currently developing cell-based cancer immunotherapies include Juno Therapeutics, Inc., Kite Pharma, Inc., Cellectis S.A., Adaptimmune Therapeutics plc, Lion Biotechnologies, Inc., Bellicum Pharmaceuticals, Inc., and NantKwest, Inc. Many larger pharmaceutical companies such as Novartis International AG, Celgene Corporation, Pfizer Inc., GlaxoSmithKline plc, Amgen, Inc., Johnson & Johnson and EMD Serono, Inc. have entered the field through major deals with biotechnology companies and academia.
We believe that other companies working in the RNAi area, generally, include Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Benitec Biopharma Limited, Silence Therapeutics plc, Quark Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Arbutus Biopharma Corporation, Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Dicerna Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Sylentis, S.A. and Roche Innovation Center Copenhagen A/S, as well as a number of large pharmaceutical companies.
We do not believe that there are any companies developing treatments for cutaneous warts that would be considered direct competitors with the Company; however, there are several existing treatments for cutaneous warts with which Samcyprone™ could potentially compete. Current topical medicinal treatments for warts include salicylic acid, off label use of Imiquimod and Picato® and the most common ablative treatments include removal through medical procedures, such as cryotherapy, surgery or chemical peels.
Government Regulation
The United States and many other countries extensively regulate the preclinical and clinical testing, manufacturing, labeling, storage, record-keeping, advertising, promotion, export, marketing and distribution of drugs and biologic products. The FDA regulates pharmaceutical and biologic products under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, the Public Health Service Act and other federal statutes and regulations.
To obtain approval of our future product candidates from the FDA, we must, among other requirements, submit data supporting safety and efficacy for the intended indication as well as detailed information on the manufacture and composition of the product candidate. In most cases, this will require extensive laboratory tests and preclinical and clinical trials. The collection of these data, as well as the preparation of applications for review by the FDA involve significant time and expense. The FDA also may require post-marketing testing to monitor the safety and efficacy of approved products or place conditions on any approvals that could restrict the therapeutic claims and commercial applications of these products. Regulatory authorities may withdraw product approvals if we fail to comply with regulatory standards or if we encounter problems at any time following initial marketing of our products.
The first stage of the FDA approval process for a new biologic or drug involves completion of preclinical studies and the submission of the results of these studies to the FDA. These data, together with proposed clinical protocols, manufacturing information, analytical data and other information submitted to the FDA in an IND application, must become effective before human clinical trials may commence. Preclinical studies generally involve FDA regulated laboratory evaluation of product characteristics and animal studies to assess the efficacy and safety of the product candidate.
13
Table of Contents
After the IND becomes effective, a company may commence human clinical trials. These are typically conducted in three sequential phases, but the phases may overlap. Phase 1 trials consist of testing the product candidate in a small number of patients or healthy volunteers, primarily for safety at one or more doses. Phase 2 trials, in addition to safety, evaluate the efficacy of the product candidate in a patient population somewhat larger than Phase 1 trials. Phase 3 trials typically involve additional testing for safety and clinical efficacy in an expanded population at multiple test sites. A company must submit to the FDA a clinical protocol, accompanied by the approval of the Institutional Review Board (“IRB”) at the institutions participating in the trials, prior to commencement of each clinical trial.
To obtain FDA marketing authorization, a company must submit to the FDA the results of the preclinical and clinical testing, together with, among other things, detailed information on the manufacture and composition of the product candidate, in the form of a new drug application (an “NDA”), or, in the case of a biologic, a biologics license application (a “BLA”).
The amount of time taken by the FDA for approval of an NDA or BLA will depend upon a number of factors, including whether the product candidate has received priority review, the quality of the submission and studies presented, the potential contribution that the compound will make in improving the treatment of the disease in question and the workload at the FDA.
The FDA may, in some cases, confer upon an investigational product the status of a fast track product. A fast track product is defined as a new drug or biologic intended for the treatment of a serious or life threatening condition that demonstrates the potential to address unmet medical needs for this condition. The FDA can base approval of an NDA or BLA for a fast track product on an effect on a surrogate endpoint, or on another endpoint that is reasonably likely to predict clinical benefit. If a preliminary review of clinical data suggests that a fast track product may be effective, the FDA may initiate review of entire sections of a marketing application for a fast track product before the sponsor completes the application.
We anticipate that our products will be manufactured by our strategic partners, licensees or other third parties. Before approving an NDA or BLA, the FDA will inspect the facilities at which the product is manufactured and will not approve the product unless the manufacturing facilities are in compliance with the FDA’s current good manufacturing practices (“cGMP”), which are regulations that govern the manufacture, holding and distribution of a product. Manufacturers of biologics also must comply with the FDA’s general biological product standards. Our manufacturers also will be subject to regulation under the Occupational Safety and Health Act, the Nuclear Energy and Radiation Control Act, the Toxic Substance Control Act and the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act and other applicable environmental statutes. Following approval, the FDA periodically inspects drug and biologic manufacturing facilities to ensure continued compliance with the cGMP. Our manufacturers will have to continue to comply with those requirements. Failure to comply with these requirements subjects the manufacturer to possible legal or regulatory action, such as suspension of manufacturing or recall or seizure of product. Adverse patient experiences with the product must be reported to the FDA and could result in the imposition of marketing restrictions through labeling changes or market removal. Product approvals may be withdrawn if compliance with regulatory requirements is not maintained or if problems concerning safety or efficacy of the product occur following approval.
The labeling, advertising, promotion, marketing and distribution of a drug or biologic product also must be in compliance with FDA and Federal Trade Commission requirements which include, among others, standards and regulations for off-label promotion, industry sponsored scientific and educational activities, promotional activities involving the internet, and direct-to-consumer advertising. We also will be subject to a variety of federal, state and local regulations relating to the use, handling, storage and disposal of hazardous materials, including chemicals and radioactive and biological materials. In addition, we will be subject to various laws and regulations governing laboratory practices and the experimental use of animals. In each of these areas, as above, the FDA has broad regulatory and enforcement powers, including the ability to levy fines and civil penalties, suspend or delay issuance of product approvals, seize or recall products and deny or withdraw approvals.
We will also be subject to a variety of regulations governing clinical trials and sales of our products outside the United States. Whether or not FDA approval has been obtained, approval of a product candidate by the comparable regulatory authorities of foreign countries and regions must be obtained prior to the commencement of marketing the product in those countries. The approval process varies from one regulatory authority to another and the time may be longer or shorter than that required for FDA approval. In the European Union, Canada and Australia, regulatory requirements and approval processes are similar, in principle, to those in the United States.
14
Table of Contents
Environmental Compliance
Our research and development activities involve the controlled use of potentially harmful biological materials as well as hazardous materials, chemicals and various radioactive compounds. We are subject to federal, state and local laws and regulations governing the use, storage, handling and disposal of these materials and specific waste products. We are also subject to numerous environmental, health and workplace safety laws and regulations, including those governing laboratory procedures, exposure to blood-borne pathogens and the handling of bio-hazardous materials. The cost of compliance with these laws and regulations could be significant and may adversely affect capital expenditures to the extent we are required to procure expensive capital equipment to meet regulatory requirements.
Employees
As of March 15, 2017, we had fifteen full-time employees, eight of whom were engaged in research and development, and seven of whom were engaged in management, administration and finance. None of our employees are represented by a labor union or covered by a collective bargaining agreement nor have we experienced any work stoppages.
Corporate Information
RXi was incorporated in the state of Delaware in 2011. Our executive offices are located at 257 Simarano Drive, Suite 101, Marlborough, MA 01752, and our telephone number is (508) 767-3861.
Investor Information
The Company’s website address is http://www.rxipharma.com. We make available on our website, free of charge, copies of our annual reports on Form 10-K, our quarterly reports on Form 10-Q and our current reports on Form 8-K, and amendments to those reports filed or furnished pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, as soon as reasonably practicable after these reports are filed electronically with, or otherwise furnished to, the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”).
You may read and copy any materials the Company files with the SEC at the SEC’s Public Reference Room at 100 F Street, NE, Washington, DC 20549. You may obtain information on the operation of the Public Reference Room by calling the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330. The SEC maintains an Internet site that contains reports, proxy and information statements, and other information regarding RXi and other issuers that file electronically with the SEC. The SEC’s website address is http://www.sec.gov.
| ITEM 1A. | RISK FACTORS |
Risks Relating to Our Business and Industry
We are dependent on the success of our lead drug candidates, which may not receive regulatory approval or be successfully commercialized.
RXI-109, our lead drug candidate and first RNAi-based product candidate, is designed to reduce the expression of connective tissue growth factor (“CTGF”), a critical regulator of several biological pathways involved in fibrosis. Samcyprone™, our second drug candidate, is a proprietary topical formulation of the small molecule diphenylcyclopropenone (“DPCP”), an immunomodulator that works by initiating a T-cell response. We began the clinical program to reduce the formation of hypertrophic scars with RXI-109 in June 2012, and are currently conducting a Phase 2 clinical trial for RXI-109 in this indication and a Phase 1/2 clinical trial in retinal scarring. We initiated our Phase 2 clinical trial for the treatment of cutaneous warts with Samcyprone™ in December 2015. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (“FDA”) may require additional information from the Company regarding our current or planned trials at any time, and such information may be costly to provide or cause potentially significant delays in development. There is no assurance that we will be able to successfully develop RXI-109, Samcyprone™ or any other product candidate.
15
Table of Contents
We have no commercial products and currently generate no revenue from commercial sales or collaborations and may never be able to develop marketable products. The FDA or similar foreign governmental agencies must approve our non-cosmetic products in development before they can be marketed. The process for obtaining FDA approval is both time-consuming and costly, with no certainty of a successful outcome. Before obtaining regulatory approval for the sale of any drug candidate, we must conduct extensive preclinical tests and successful clinical trials to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of our product candidates in humans. For example, although the results of our Phase 1 clinical trials and preliminary results of our Phase 2 clinical trials of RXI-109 are promising, additional clinical trials will be required to establish the safety and efficacy of RXI-109. While DPCP has been used by physicians for decades, we have not yet shown safety or efficacy in humans for Samcyprone™ or for any of our other product candidates. A failure of any preclinical study or clinical trial can occur at any stage of testing. The results of preclinical and initial clinical testing of these products may not necessarily indicate the results that will be obtained from later or more extensive testing. Preliminary observations made in early stages of clinical trials with small numbers of subjects are inherently uncertain. Investors are cautioned that initial clinical trial results are not necessarily indicative of results that will be obtained when full data sets are analyzed or in subsequent clinical trials.
A number of different factors could prevent us from obtaining regulatory approval or commercializing our product candidates on a timely basis, or at all.
We, the FDA or other applicable regulatory authorities, or an Institutional Review Board (“IRB”) may suspend clinical trials of a drug candidate at any time for various reasons, including if we or they believe the subjects participating in such trials are being exposed to unacceptable health risks. Among other reasons, adverse side effects of a drug candidate on subjects in a clinical trial could result in the FDA or other regulatory authorities suspending or terminating the trial and refusing to approve a particular drug candidate for any or all indications of use.
Clinical trials of a new drug candidate require the enrollment of a sufficient number of subjects, including subjects who are suffering from the disease or condition the drug candidate is intended to treat and who meet other eligibility criteria. Rates of subject enrollment are affected by many factors, and delays in subject enrollment can result in increased costs and longer development times.
Clinical trials also require the review and oversight of IRBs, which approve and continually review clinical investigations and protect the rights and welfare of human subjects. An inability or delay in obtaining IRB approval could prevent or delay the initiation and completion of clinical trials, and the FDA may decide not to consider any data or information derived from a clinical investigation not subject to initial and continuing IRB review and approval.
Numerous factors could affect the timing, cost or outcome of our drug development efforts, including the following:
| • | Delays in filing or acceptance of initial drug applications for our product candidates; |
| • | Difficulty in securing centers to conduct clinical trials; |
| • | Conditions imposed on us by the FDA or comparable foreign authorities regarding the scope or design of our clinical trials; |
| • | Problems in engaging IRBs to oversee trials or problems in obtaining or maintaining IRB approval of studies; |
| • | Difficulty in enrolling subjects in conformity with required protocols or projected timelines; |
| • | Third-party contractors failing to comply with regulatory requirements or to meet their contractual obligations to us in a timely manner; |
| • | Our drug candidates having unexpected and different chemical and pharmacological properties in humans than in laboratory testing and interacting with human biological systems in unforeseen, ineffective or harmful ways; |
| • | The need to suspend or terminate clinical trials if the participants are being exposed to unacceptable health risks; |
| • | Insufficient or inadequate supply or quality of our drug candidates or other necessary materials necessary to conduct our clinical trials; |
16
Table of Contents
| • | Effects of our drug candidates not being the desired effects or including undesirable side effects or the drug candidates having other unexpected characteristics; |
| • | The cost of our clinical trials being greater than we anticipate; |
| • | Negative or inconclusive results from our clinical trials or the clinical trials of others for similar drug candidates or inability to generate statistically significant data confirming the efficacy of the product being tested; |
| • | Changes in the FDA’s requirements for testing during the course of that testing; |
| • | Reallocation of our limited financial and other resources to other clinical programs; and |
| • | Adverse results obtained by other companies developing similar drugs. |
It is possible that none of the product candidates that we may attempt to develop will obtain the appropriate regulatory approvals necessary to begin selling them or that any regulatory approval to market a product may be subject to limitations on the indicated uses for which we may market the product. The time required to obtain FDA and other approvals is unpredictable, but often can take years following the commencement of clinical trials, depending upon the complexity of the drug candidate. Any analysis we perform of data from clinical activities is subject to confirmation and interpretation by regulatory authorities, which could delay, limit or prevent regulatory approval. Any delay or failure in obtaining required approvals could have a material adverse effect on our ability to generate revenue from the particular drug candidate.
We also are subject to numerous foreign regulatory requirements governing the conduct of clinical trials, manufacturing and marketing authorization, pricing and third-party reimbursement. The foreign regulatory approval process includes all of the risks associated with the FDA approval described above as well as risks attributable to the satisfaction of local regulations in foreign jurisdictions. Approval by the FDA does not assure approval by regulatory authorities outside of the United States.
The approach we are taking to discover and develop novel therapeutics using RNAi is unproven and may never lead to marketable products.
RNA interference is a relatively new scientific discovery. Our RNAi technologies have been subject to only limited clinical testing. To date, no company has received regulatory approval to market therapeutics utilizing RNAi, and a number of clinical trials of RNAi technologies by other companies have been unsuccessful. The scientific evidence to support the feasibility of developing drugs based on these discoveries is both preliminary and limited. To successfully develop RNAi-based products, we must resolve a number of issues, including stabilizing the RNAi material and delivering it into target cells in the human body. We may spend large amounts of money trying to resolve these issues and may never succeed in doing so. In addition, any compounds that we develop may not demonstrate in subjects the chemical and pharmacological properties ascribed to them in laboratory studies, and they may interact with human biological systems in unforeseen, ineffective or even harmful ways.
Samcyprone™ represents a novel approach, topical immunotherapy, to the treatment of skin disorders that presents development challenges to us and may never lead to marketable products.
Although DPCP, the active ingredient in Samcyprone™, has been used by physicians for several decades to stimulate regrowth of hair in patients with alopecia areata and to clear common warts, it has never been reviewed or approved by a regulatory authority as a drug. Other immunomodulatory compounds, such as Imiquimod and Picato®, have been approved for topical use in other indications by the FDA. Our formulation of DPCP, Samcyprone™, has been subject to only limited clinical testing. Further testing may show that Samcyprone™ may interact with human biological systems in unforeseen or ineffective ways. In addition, to successfully develop Samcyprone™ we must resolve a number of development challenges, including developing a consistent process for the safe administration of the product and establishing a consistent manufacturing process in line with the good manufacturing practice regulations. We may spend significant amounts of money to resolve these development challenges and to obtain regulatory approval for Samcyprone™ and may never succeed in doing so.
We have limited experience as a company in the cell-based cancer immunotherapy field.
Prior to the Company’s acquisition of MirImmune Inc. (“MirImmune”) in January 2017, the Company’s efforts were focused on the development of therapeutics in the areas of dermatology and ophthalmology. While we are currently conducting multiple research studies using our sd-rxRNA technology for use in developing ex vivo cell-based cancer immunotherapies, we have limited experience as a company in developing immunotherapy technologies. Because of the number of companies and intense competition in immunotherapy, we may not have the ability to successfully overcome many of the risks and uncertainties that companies face in this field. In part because of this lack of experience, we cannot be certain that we will be successful in developing cell-based cancer immunotherapies.
The use of our RNAi compounds in cell-based cancer immunotherapy is a new approach to the treatment of cancer which may present us with development challenges.
Our approach to immunotherapy builds on well-established methodologies of adoptive cell transfer. Immune cells, such as T-lymphocytes, are isolated from specific patients or retrieved from allogeneic immune cell banks and then expanded and sometimes processed to express tumor-binding receptors. To successfully develop drugs based on our approach, we must overcome a number of challenges such as developing a consistent process for the safe administration of enhanced cells to be returned to the patient, developing a manufacturing process in line with good manufacturing practices and demonstrating that our therapies achieve an adequate response compared to their risks. While there have been a number of immunotherapy drugs approved by the FDA, there have been no FDA drug approvals using the approach that we are taking. We will be subjected to thorough regulatory review by the FDA and there is limited experience in this area with a few precedents. We may spend large amounts of money trying to resolve these issues and may never succeed in doing so.
17
Table of Contents
The FDA could impose a unique regulatory regime for our therapeutics.
The compounds we intend to develop may represent a new class of drug, and the FDA has not yet established any definitive policies, practices or guidelines in relation to these drugs. While we expect any product candidates that we develop will be regulated as a new drug under the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, the FDA could decide to regulate them or other products we may develop as biologics under the Public Health Service Act. The lack of policies, practices or guidelines may hinder or slow review by the FDA of any regulatory filings that we may submit. Moreover, the FDA may respond to these submissions by defining requirements that we may not have anticipated.
Even if we receive regulatory approval to market our product candidates, our product candidates may not be accepted commercially, which may prevent us from becoming profitable.
The product candidates that we are developing are based on new technologies and therapeutic approaches. For example, RNAi products may be more expensive to manufacture than traditional small molecule drugs, which may make them costlier than competing small molecule drugs. Additionally, RNAi products do not readily cross the so-called blood brain barrier, are rapidly eliminated from circulating blood and, for various applications, are likely to require injection or implantation, which will make them less convenient to administer than drugs administered orally. Key participants in the pharmaceutical marketplace, such as physicians, medical professionals working in large reference laboratories, public health laboratories and hospitals, third-party payors and consumers may not accept products intended to improve therapeutic results based on our technologies. As a result, it may be more difficult for us to convince the medical community and third-party payors to accept and use our products or to provide favorable reimbursement. If medical professionals working with large reference laboratories, public health laboratories and hospitals choose not to adopt and use our technologies, our products may not achieve broader market acceptance.
Additionally, although we expect that we will have intellectual property protection for our technology, certain governments may elect to deny patent protection for drugs targeting diseases with high unmet medical need (e.g., as in the case of HIV) and allow in their country internationally unauthorized generic competition. If this were to happen, our commercial prospects for developing any such drugs would be substantially diminished in these countries.
We are subject to significant competition and may not be able to compete successfully.
We believe that numerous companies are investigating or plan to investigate a variety of proposed anti-scarring therapies or cell-based cancer immunotherapies in clinical trials or are working in the RNAi area generally. Many other companies are pursuing non-RNAi-based therapies for one or more fibrotic disease indications, including ocular scarring or other indications that we may seek to pursue. The companies include large and small pharmaceuticals, chemical and biotechnology companies, as well as universities, government agencies and other private and public research organizations.
We do not believe that there are any companies developing treatments for cutaneous warts that would be considered direct competitors with the Company, however, there are several existing treatments with which Samcyprone™ could potentially compete.
Most of these competitors have substantially greater research and development capabilities and financial, scientific, technical, manufacturing, marketing, distribution and other resources than we have, and we may not be able to successfully compete with them. In addition, even if we are successful in developing our product candidates, in order to compete successfully we may need to be first to market or to demonstrate that our products are superior to therapies based on different technologies. A number of our competitors have already commenced clinical testing of product candidates and may be more advanced than we are in the process of developing products. If we are not first to market or are unable to demonstrate superiority, any products for which we are able to obtain approval may not be successful.
We are dependent on technologies we license, and if we lose the right to license such technologies or fail to license new technologies in the future, our ability to develop new products would be harmed.
Many patents in the fields we are pursuing have already been exclusively licensed to third parties, including our competitors. If any of our existing licenses are terminated, the development of the products contemplated by the licenses could be delayed or terminated and we may not be able to negotiate additional licenses on acceptable terms, if at all, which would have a material adverse effect on our business.
18
Table of Contents
We may be unable to protect our intellectual property rights licensed from other parties; our intellectual property rights may be inadequate to prevent third parties from using our technologies or developing competing products; and we may need to license additional intellectual property from others.
Therapeutic applications of gene silencing technologies, formulations, delivery methods and other technologies that we license from third parties are claimed in a number of pending patent applications, but there is no assurance that these applications will result in any issued patents or that those patents would withstand possible legal challenges or protect our technologies from competition. The United States Patent and Trademark Office and patent granting authorities in other countries have upheld stringent standards for the RNAi patents that have been prosecuted so far. Consequently, pending patents that we have licensed and those that we own may continue to experience long and difficult prosecution challenges and may ultimately issue with much narrower claims than those in the pending applications. Third parties may hold or seek to obtain additional patents that could make it more difficult or impossible for us to develop products based on our technologies without obtaining a license to such patents, which licenses may not be available on attractive terms, or at all.
In addition, others may challenge the patents or patent applications that we currently license or may license in the future or that we own and, as a result, these patents could be narrowed, invalidated or rendered unenforceable, which would negatively affect our ability to exclude others from using the technologies described in these patents. There is no assurance that these patent or other pending applications or issued patents we license or that we own will withstand possible legal challenges. Moreover, the laws of some foreign countries may not protect our proprietary rights to the same extent as do the laws of the United States. Any patents issued to us or our licensors may not provide us with any competitive advantages, and there is no assurance that the patents of others will not have an adverse effect on our ability to do business or to continue to use our technologies freely. Our efforts to enforce and maintain our intellectual property rights may not be successful and may result in substantial costs and diversion of management time. Even if our rights are valid, enforceable and broad in scope, competitors may develop products based on technology that is not covered by our licenses or patents or patent applications that we own.
There is no guarantee that future licenses will be available from third parties for our product candidates on timely or satisfactory terms, or at all. To the extent that we are required and are able to obtain multiple licenses from third parties to develop or commercialize a product candidate, the aggregate licensing fees and milestones and royalty payments made to these parties may materially reduce our economic returns or even cause us to abandon development or commercialization of a product candidate.
Our success depends upon our ability to obtain and maintain intellectual property protection for our products and technologies.
The applications based on RNAi technologies claim many different methods, compositions and processes relating to the discovery, development, delivery and commercialization of RNAi therapeutics. Because this field is so new, very few of these patent applications have been fully processed by government patent offices around the world, and there is a great deal of uncertainty about which patents will issue, when, to whom and with what claims. Although we are not aware of any blocking patents or other proprietary rights, it is likely that there will be significant litigation and other proceedings, such as interference and opposition proceedings in various patent offices, relating to patent rights in the RNAi field. It is possible that we may become a party to such proceedings.
We may not be able to obtain sufficient financing and may not be able to develop our product candidates.
We believe that our existing cash will likely be sufficient to fund our currently planned operations for at least the next 12 months. However, in the future, we may need to incur debt or issue equity in order to fund our planned expenditures as well as to make acquisitions and other investments. We cannot assure you that debt or equity financing will be available to us on acceptable terms or at all. If we cannot, or are limited in the ability to, incur debt, issue equity or enter into strategic collaborations, we may be unable to fund the discovery and development of our product candidates, address gaps in our product offerings or improve our technology.
19
Table of Contents
We anticipate that we will need to raise substantial amounts of money to fund a variety of future activities integral to the development of our business, which may include but is not limited to the following:
| • | To conduct research and development to successfully develop our technologies; |
| • | To obtain regulatory approval for our products; |
| • | To file and prosecute patent applications and to defend and assess patents to protect our technologies; |
| • | To retain qualified employees, particularly in light of intense competition for qualified scientists; |
| • | To manufacture products ourselves or through third parties; |
| • | To market our products, either through building our own sales and distribution capabilities or relying on third parties; and |
| • | To acquire new technologies, licenses or products. |
If we cannot obtain additional financing in the future, our operations may be restricted and we may ultimately be unable to continue to develop and potentially commercialize our product candidates.
Future financing may be obtained through, and future development efforts may be paid for by, the issuance of debt or equity, which may have an adverse effect on our stockholders or may otherwise adversely affect our business.
If we raise funds through the issuance of debt or equity, any debt securities or preferred stock issued will have rights, preferences and privileges senior to those of holders of our common stock in the event of a liquidation. In such event, there is a possibility that once all senior claims are settled, there may be no assets remaining to pay out to the holders of common stock. In addition, if we raise funds through the issuance of additional equity, whether through private placements or public offerings, such an issuance would dilute your ownership in us.
The terms of debt securities may also impose restrictions on our operations, which may include limiting our ability to incur additional indebtedness, to pay dividends on or repurchase our capital stock, or to make certain acquisitions or investments. In addition, we may be subject to covenants requiring us to satisfy certain financial tests and ratios, and our ability to satisfy such covenants may be affected by events outside of our control.
We expect to continue to incur significant research and development expenses, which may make it difficult for us to attain profitability, and may lead to uncertainty as to our ability to continue as a going concern.
We expend substantial funds to develop our technologies, and additional substantial funds will be required for further research and development, including preclinical testing and clinical trials of any product candidates, and to manufacture and market any products that are approved for commercial sale. Because the successful development of our products is uncertain, we are unable to precisely estimate the actual funds we will require to develop and potentially commercialize them. In addition, we may not be able to generate enough revenue, even if we are able to commercialize any of our product candidates, to become profitable.
If we are unable to achieve or sustain profitability or to secure additional financing, we may not be able to meet our obligations as they come due, raising substantial doubts as to our ability to continue as a going concern. Any such inability to continue as a going concern may result in our common stockholders losing their entire investment. There is no guarantee that we will become profitable or secure additional financing. Our financial statements contemplate that we will continue as a going concern and do not contain any adjustments that might result if we were unable to continue as a going concern. Changes in our operating plans, our existing and anticipated working capital needs, the acceleration or modification of our expansion plans, increased expenses, potential acquisitions or other events will all affect our ability to continue as a going concern.
We will rely upon third parties for the manufacture of our clinical and cosmetic product candidates.
We do not have the facilities or expertise to manufacture supplies of any of our potential product candidates for clinical trials or for consumer testing. Accordingly, we depend on a limited number of manufacturers to obtain supplies and we will need to either develop, contract for, or otherwise arrange for the necessary manufacturers for these supplies. If for any reason we are unable to obtain the supplies for our potential product candidates, we would have to seek to obtain it from another major manufacturer. There is no assurance that we will be able to timely secure needed supply arrangements on satisfactory terms, or at all. Our failure to secure these arrangements as needed could have a material adverse effect on our ability to complete the development of our product candidates or, if we obtain regulatory approval for our product candidates, to commercialize them.
20
Table of Contents
We may not be able to establish or maintain the third-party relationships that are necessary to develop or potentially commercialize some or all of our product candidates.
We expect to depend on collaborators, partners, licensees, clinical research organizations and other third parties to support our discovery efforts, to formulate product candidates, to manufacture our product candidates and to conduct clinical trials for some or all of our product candidates. We cannot guarantee that we will be able to successfully negotiate agreements for or maintain relationships with collaborators, partners, licensees, clinical investigators, vendors and other third parties on favorable terms, if at all. Our ability to successfully negotiate such agreements will depend on, among other things, potential partners’ evaluation of the superiority of our technology over competing technologies, the quality of the preclinical and clinical data that we have generated and the perceived risks specific to developing our product candidates. If we are unable to obtain or maintain these agreements, we may not be able to clinically develop, formulate, manufacture, obtain regulatory approvals for or commercialize our product candidates. We cannot necessarily control the amount or timing of resources that our contract partners will devote to our research and development programs, product candidates or potential product candidates, and we cannot guarantee that these parties will fulfill their obligations to us under these arrangements in a timely fashion. We may not be able to readily terminate any such agreements with contract partners even if such contract partners do not fulfill their obligations to us.
We are subject to potential liabilities from clinical testing and future product liability claims.
If any of our future products are alleged to be defective, they may expose us to claims for personal injury by subjects in clinical trials of our products. If our non-cosmetic products are approved by the FDA, users may claim that such products caused unintended adverse effects. We will seek to obtain clinical trial insurance for clinical trials that we conduct, as well as liability insurance for any products that we market. There is no assurance that we will be able to obtain insurance in the amounts we seek, or at all. We anticipate that licensees who develop our products will carry liability insurance covering the clinical testing and marketing of those products. There is no assurance, however, that any insurance maintained by us or our licensees will prove adequate in the event of a claim against us. Even if claims asserted against us are unsuccessful, they may divert management’s attention from our operations and we may have to incur substantial costs to defend such claims.
Any drugs we develop may become subject to unfavorable pricing regulations, third-party reimbursement practices or healthcare reform initiatives, which could have a material adverse effect on our business.
If approved, we intend to sell our products to physicians, plastic surgeons and dermatologists, as well as hospitals, oncologists and clinics that receive reimbursement for the healthcare services they provide to their patients from third-party payors, such as Medicare, Medicaid and other domestic and international government programs, private insurance plans and managed care programs. Most third-party payors may deny reimbursement if they determine that a medical product was not used in accordance with cost-effective treatment methods, as determined by the third-party payor, was used for an unapproved indication or if they believe the cost of the product outweighs its benefits. Third-party payors also may refuse to reimburse for experimental procedures and devices. Furthermore, because our programs are still in development, we are unable at this time to determine their cost-effectiveness and the level or method of reimbursement for them. Increasingly, the third-party payors who reimburse patients are requiring that drug companies provide them with predetermined discounts from list prices, and are challenging the prices charged for medical products. If the price we are able to charge for any products we develop is inadequate in light of our development and other costs, our profitability could be adversely affected.
We currently expect that any drugs we develop may need to be administered under the supervision of a physician. Under currently applicable law, drugs that are not usually self-administered may be eligible for coverage by the Medicare program if:
| • | They are “incidental” to a physician’s services; |
| • | They are “reasonable and necessary” for the diagnosis or treatment of the illness or injury for which they are administered according to accepted standard of medical practice; |
| • | They are not excluded as immunizations; and |
21
Table of Contents
| • | They have been approved by the FDA. |
Insurers may refuse to provide insurance coverage for newly approved drugs, including drugs in our clinical pipeline, or insurance coverage may be delayed or be more limited than the purpose for which the drugs are approved by the FDA. Moreover, eligibility for insurance coverage does not imply that any drug will be reimbursed in all cases or at a rate that covers our costs, including research, development, manufacture, sale and distribution costs. Interim payments for new drugs, if applicable, may also not be sufficient to cover our costs and may not be made permanent. Reimbursement may be based on payments for other services and may reflect budgetary constraints or imperfections in Medicare data. Net prices for drugs may be reduced by mandatory discounts or rebates required by government healthcare programs or private payors and by any future relaxation of laws that presently restrict imports of drugs from countries where they may be sold at lower prices than in the United States. Third-party payors often rely upon Medicare coverage policy and payment limitations in setting their own reimbursement rates. Our inability to promptly obtain coverage and profitable reimbursement rates from both government-funded and private payors for new drugs that we develop could have a material adverse effect on our operating results, our ability to raise capital needed to develop products and our overall financial condition.
Additionally, third-party payors are increasingly attempting to contain healthcare costs by limiting both coverage and the level of reimbursement for medical products and services. Levels of reimbursement may decrease in the future, and future legislation, regulation or reimbursement policies of third-party payors may adversely affect the demand for and price levels of our products. If our customers are not reimbursed for our products, they may reduce or discontinue purchases of our products, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Comprehensive healthcare reform legislation, which became law in 2010, and any revisions to this legislation, could adversely affect our business and financial condition. Among other provisions, the legislation provides that a “biosimilar” product may be approved by the FDA on the basis of analytical tests and certain clinical studies demonstrating that such product is highly similar to an existing, approved product and that switching between an existing product and the biosimilar product will not result in diminished safety or efficacy. This abbreviated regulatory approval process may result in increased competition if we are able to bring a product to market. The legislation also includes more stringent compliance programs for companies in various sectors of the life sciences industry with which we may need to comply and enhanced penalties for non-compliance with the new healthcare regulations. Complying with new regulations may divert management resources, and inadvertent failure to comply with new regulations may result in penalties being imposed on us.
Some states and localities have established drug importation programs for their citizens, and federal drug import legislation has been introduced in Congress. The Medicare Prescription Drug Plan legislation, which became law in 2003, required the Secretary of Health and Human Services to promulgate regulations for drug reimportation from Canada into the United States under some circumstances, including when the drugs are sold at a lower price than in the United States. The Secretary, however, retained the discretion not to implement a drug reimportation plan if the Secretary finds that the benefits do not outweigh the costs, and has so far declined to approve a reimportation plan. Proponents of drug reimportation may attempt to pass legislation that would directly allow reimportation under certain circumstances. Legislation or regulations allowing the reimportation of drugs, if enacted, could decrease the price we receive for any products that we may develop and adversely affect our future revenues and prospects for profitability.
With the new U.S. administration and Congress, there may be additional legislative changes, including repeal and replacement of certain provisions of the Affordable Care Act. It remains to be seen, however, precisely what new legislation will provide, when it will be enacted and what impact it will have on the availability of healthcare and containing or lowering the cost of healthcare. Such reforms could have an adverse effect on anticipated revenue from product candidates that we may successfully develop and for which we may obtain marketing approval and may affect our overall financial condition and ability to develop product candidates.
Even if we obtain regulatory approvals, our marketed drugs will be subject to ongoing regulatory review. If we fail to comply with continuing U.S. and foreign regulations, we could lose our approvals to market drugs and our business would be materially and adversely affected.
Following regulatory approval of any drugs we may develop, we will remain subject to continuing regulatory review, including the review of adverse drug experiences and clinical results that are reported after our drug products are
22
Table of Contents
made available to patients. This would include results from any post-marketing tests or vigilance required as a condition of approval. The manufacturer and manufacturing facilities we use to make any of our drug products will also be subject to periodic review and inspection by the FDA. The discovery of any new or previously unknown problems with the product, manufacturer or facility may result in restrictions on the drug or manufacturer or facility, including withdrawal of the drug from the market. We would continue to be subject to the FDA requirements governing the labeling, packaging, storage, advertising, promotion, recordkeeping and submission of safety and other post-market information for all of our product candidates, even those that the FDA had approved. If we fail to comply with applicable continuing regulatory requirements, we may be subject to fines, suspension or withdrawal of regulatory approval, product recalls and seizures, operating restrictions and other adverse consequences.
If we fail to attract, hire and retain qualified personnel, we may not be able to design, develop, market or sell our products or successfully manage our business.
Our business prospects are dependent on our management team and all of our employees. The loss of any of our key employees, including Drs. Cauwenbergh, Pavco and Eliseev, who serve as our Chief Executive Officer, our Chief Development Officer and our Chief Business Officer, respectively, or our inability to identify, attract, retain and integrate additional qualified key personnel, could make it difficult for us to manage our business successfully and achieve our business objectives.
Competition for skilled research, product development, regulatory and technical personnel is intense, and we may not be able to recruit and retain the personnel we need. The loss of the services of any key research, product development, regulatory and technical personnel, or our inability to hire new personnel with the requisite skills, could restrict our ability to develop our product candidates.
Risks Relating to Our Securities
The price of our common stock has been and may continue to be volatile.
The stock markets, in general, and the markets for drug delivery and pharmaceutical company stocks, in particular, have experienced extreme volatility that has often been unrelated to the operating performance of particular companies. These broad market fluctuations may adversely affect the trading price of our common stock. In addition, the limited trading volume of our stock may contribute to its volatility.
In the past, following periods of volatility in the market price of a particular company’s securities, litigation has often been brought against that company. If litigation of this type is brought against us, it could be extremely expensive and divert management’s attention and the Company’s resources.
We may not be able to regain compliance with the continued listing requirements of The Nasdaq Capital Market.
On February 2, 2017, we received written notice (the “Notification Letter”) from the Nasdaq Stock Market (“Nasdaq”) notifying us that we are not in compliance with the minimum bid price requirements set forth in Nasdaq Listing Rule 5550(a)(2) for continued listing on The Nasdaq Capital Market. Nasdaq Listing Rule 5550(a)(2) requires listed securities to maintain a minimum bid price of $1.00 per share, and Listing Rule 5810(c)(3)(A) provides that a failure to meet the minimum bid price requirement exists if the deficiency continues for a period of 30 consecutive business days. Based on the closing bid price of our common stock for the 30 consecutive business days prior to the date of the Notification Letter, we no longer meet the minimum bid price requirement.
The Notification Letter does not impact our listing on The Nasdaq Capital Market at this time. The Notification Letter states that we have 180 calendar days, or until August 1, 2017, to regain compliance with Nasdaq Listing Rule 5550(a)(2). To regain compliance, the bid price of our common stock must have a closing bid price of at least $1.00 per share for a minimum of 10 consecutive business days at any time prior to August 1, 2017. In the event that we do not regain compliance by August 1, 2017, we may be eligible for additional time to reach compliance with the minimum bid price requirement. However, if we fail to regain compliance with the minimum bid price listing requirement or fail to maintain compliance with all other applicable continued listing requirements and Nasdaq determines to delist our common stock, the delisting could adversely impact us by, among other things, reducing the liquidity and market price of our common stock; reducing the number of investors willing to hold or acquire our common stock; limiting our ability to issue additional securities in the future; and limiting our ability to fund our operations.
23
Table of Contents
We have issued preferred stock in the past and possibly may issue more preferred stock in the future, and the terms of the preferred stock may reduce the value of our common stock.
We are authorized to issue up to 10,000,000 shares of preferred stock in one or more series. There were no shares of our Series B Convertible Preferred Stock and 1,082,114 shares of Series C Convertible Preferred Stock issued and outstanding at March 15, 2017, respectively. Our Board of Directors may determine the terms of future preferred stock offerings without further action by our stockholders. The issuance of our preferred stock could affect your rights or reduce the value of our outstanding preferred stock or common stock. In particular, rights granted to holders of certain series of preferred stock may include voting rights, preferences as to dividends and liquidation, conversion and redemption rights and restrictions on our ability to merge with or sell our assets to a third party.
We may acquire other businesses or form joint ventures that may be unsuccessful and could dilute your ownership interest in the Company.
As part of our business strategy, we may pursue future acquisitions of other complementary businesses and technology licensing arrangements. We also may pursue strategic alliances. We have limited experience with respect to acquiring other companies and with respect to the formation of collaborations, strategic alliances and joint ventures. We may not be able to integrate such acquisitions successfully into our existing business, and we could assume unknown or contingent liabilities. We also could experience adverse effects on our reported results of operations from acquisition related charges, amortization of acquired technology and other intangibles and impairment charges relating to write-offs of goodwill and other intangible assets from time to time following the acquisition. Integration of an acquired company requires management resources that otherwise would be available for ongoing development of our existing business. We may not realize the anticipated benefits of any acquisition, technology license or strategic alliance. For example, in January 2017, the Company acquired 100% of the outstanding capital stock of MirImmune. The assets and development programs acquired from MirImmune are at an early stage of development and will require a significant investment of time and capital if we are to be successful in developing them. There is no assurance that we will be successful in developing such assets, and a failure to successfully develop such assets could diminish our prospects.
To finance future acquisitions, we may choose to issue shares of our common stock or preferred stock as consideration, which would dilute your ownership interest in us. Alternatively, it may be necessary for us to raise additional funds through public or private financings. Additional funds may not be available on terms that are favorable to us and, in the case of equity financings, may result in dilution to our stockholders. Any future acquisitions by us also could result in large and immediate write-offs, the incurrence of contingent liabilities or amortization of expenses related to acquired intangible assets, any of which could harm our operating results.
We do not anticipate paying cash dividends in the foreseeable future.
Our business requires significant funding. We currently plan to invest all available funds and future earnings in the development and growth of our business and do not anticipate paying any cash dividends on our common stock in the foreseeable future. As a result, capital appreciation, if any, of our common stock will be your sole source of potential gain for the foreseeable future.
Provisions of our certificate of incorporation and bylaws and Delaware law might discourage, delay or prevent a change of control of the Company or changes in our management and, as a result, depress the trading price of our common stock.
Our certificate of incorporation and bylaws contain provisions that could discourage, delay or prevent a change of control of the Company or changes in our management that the stockholders of the Company may deem advantageous. These provisions:
| • | Authorize the issuance of “blank check” preferred stock that our Board of Directors could issue to increase the number of outstanding shares and to discourage a takeover attempt; |
24
Table of Contents
| • | Prohibit stockholder action by written consent, which requires all stockholder actions to be taken at a meeting of our stockholders; |
| • | Provide that the Board of Directors is expressly authorized to adopt, alter or repeal our bylaws; and |
| • | Establish advance notice requirements for nominations for election to our Board of Directors or for proposing matters that can be acted upon by stockholders at stockholder meetings. |
Although we believe these provisions collectively provide for an opportunity to receive higher bids by requiring potential acquirers to negotiate with our Board of Directors, they would apply even if the offer may be considered beneficial by some stockholders. In addition, these provisions may frustrate or prevent any attempts by our stockholders to replace or remove our current management team by making it more difficult for stockholders to replace members of our Board of Directors, which is responsible for appointing the members of our management.
Moreover, because we are incorporated in Delaware, we are governed by the provisions of Section 203 of the Delaware General Corporation Law, which prohibits a person who owns in excess of 15% of our outstanding voting stock from merging or combining with us for a period of three years after the date of the transaction in which the person acquired in excess of 15% of our outstanding voting stock, unless the merger or combination is approved in a prescribed manner.
| ITEM 1B. | UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS |
None.
| ITEM 2. | PROPERTIES |
On December 17, 2013, we entered into a lease (the “Lease”) with 257 Simarano Drive, LLC, Brighton Properties, LLC, Robert Stubblebine 1, LLC and Robert Stubblebine 2, LLC to lease office and laboratory space in the building known as the “Main Building” located at 257 Simarano Drive, Marlborough, Massachusetts, covering approximately 7,581 square feet. The premises are used by the Company for office and laboratory space. The term of the Lease commenced on April 1, 2014 and continues for five years, expiring on March 31, 2019. The base rent for the premises during the first year of the Lease was $107,709.50 per annum, payable monthly. Each year thereafter, the base rent increases by approximately 3% over the base rent from the prior year.
We believe that our facilities are suitable for our current and future needs.
| ITEM 3. | LEGAL PROCEEDINGS |
Although we are not currently involved in any legal proceedings, from time to time, we may become a party to various legal actions and complaints arising in the ordinary course of business.
| ITEM 4. | MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES |
Not applicable.
25
Table of Contents
| ITEM 5. | MARKET FOR REGISTRANT’S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES |
Market Information
Our common stock is listed on the NASDAQ Capital Market under the symbol “RXII.” On April 14, 2016, we effected a 1-for-10 reverse stock split. The share prices in the table below are shown on a post-split basis. The following table shows the high and low per share sale prices of our common stock for the periods indicated:
| High | Low | |||||||
| 2015 |
||||||||
| First Quarter |
$ | 17.30 | $ | 6.90 | ||||
| Second Quarter |
8.70 | 3.42 | ||||||
| Third Quarter |
5.50 | 3.50 | ||||||
| Fourth Quarter |
6.49 | 3.56 | ||||||
| 2016 |
||||||||
| First Quarter |
$ | 4.00 | $ | 2.60 | ||||
| Second Quarter |
3.27 | 1.26 | ||||||
| Third Quarter |
2.67 | 1.70 | ||||||
| Fourth Quarter |
2.93 | 0.70 | ||||||
Holders
At March 15, 2017, there were approximately 106 holders of record of our common stock. Because many of our shares are held by brokers and other institutions on behalf of stockholders, we are unable to estimate the total number of individual stockholders represented by these holders of record.
Dividends
We have never paid any cash dividends and do not anticipate paying any cash dividends on our common stock in the foreseeable future. We expect to retain future earnings, if any, for use in our development activities and the operation of our business. The payment of any future dividends will be subject to the discretion of our Board of Directors and will depend, among other things, upon our results of operations, financial condition, cash requirements, prospects and other factors that our Board of Directors may deem relevant.
Securities Authorized for Issuance Under Equity Compensation Plans
We will file a definitive proxy statement, which we refer to herein as the Proxy Statement, not later than 120 days after the fiscal year end of December 31, 2016. The information required by this item is incorporated herein by reference to the information contained in the Proxy Statement.
Recent Sales of Unregistered Sales of Securities
No sales or issues of unregistered securities occurred that have not previously been disclosed in a Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q or in a Current Report on Form 8-K.
Purchases of Equity Securities by the Issuer and Affiliated Purchases
We did not repurchase any shares of our common stock during the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015.
| ITEM 6. | SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA |
As a smaller reporting company, we are not required to provide this information.
| ITEM 7. | MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS |
The following discussion of our financial condition and results of operations should be read in conjunction with our financial statements and the notes to those financial statements included in Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. This discussion contains forward-looking statements that involve significant risks and uncertainties. As a result of many factors, such as those set forth under “Risk Factors” and elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, our actual results may differ materially from those anticipated in these forward-looking statements. Please refer to the discussion under the heading “Forward-Looking Statements” above.
26
Table of Contents
Overview
RXi Pharmaceuticals Corporation (“RXi,” “we,” “our” or the “Company”) is a clinical-stage company developing innovative therapeutics based on our proprietary self-delivering RNAi (sd-rxRNA®) platform and Samcyprone™, a topical immunomodulator, which address significant unmet medical needs. The Company’s clinical development programs include RXI-109, an sd-rxRNA for the treatment of dermal and ocular scarring, and Samcyprone™, for the treatment of warts. In addition to these clinical programs, we have a pipeline of discovery and preclinical product candidates in our core therapeutic areas, as well as in other areas of interest. The Company’s pipeline, coupled with our extensive patent portfolio, provides for product development and business development opportunities across a broad spectrum of therapeutic areas.
RNAi therapies are designed to “silence,” or down-regulate, the expression of a specific gene that may be over-expressed in a disease condition. The Company’s first RNAi clinical product candidate, RXI-109, is a self-delivering RNAi compound (sd-rxRNA) that commenced human clinical trials in 2012. RXI-109 is designed to reduce the expression of connective tissue growth factor (“CTGF”), a critical regulator of several biological pathways involved in fibrosis, including scar formation in the skin and eye. RXI-109 is currently being evaluated in a Phase 2 clinical trial, Study 1402, to prevent or reduce dermal scarring following scar revision surgery of an existing hypertrophic scar and a Phase 1/2 clinical trial, Study 1501, to evaluate the safety and clinical activity of RXI-109 to prevent the progression of retinal scarring in subjects with wet age-related macular degeneration (“AMD”).
Study 1402, the Company’s Phase 2 clinical trial in hypertrophic scars, commenced in July 2014. In October 2015, we reported that preliminary data from Study 1402 demonstrated that scars at revision sites were judged to be better at three months after a treatment regimen with five mg/cm intradermal administration of RXI-109 than scars at untreated revision sites in those same subjects. Based in part on this new information, two more cohorts were added to Study 1402 in November 2015. For these two cohorts, the number of doses was increased to either eight or nine doses of RXI-109 over a six-month period to better cover the extended wound healing/scarring profile of hypertrophic scars. Enrollment of subjects into these two new cohorts completed ahead of schedule during the third quarter of 2016.
In December 2016, the Company announced that preliminary data from the first two cohorts from Study 1402 at nine months confirmed the positive differentiation from untreated surgery incisions in hypertrophic scars from the previously presented data for a subset of subjects treated with five mg/cm of RXI-109 at three months. In addition, these data extend this observation to all time points, including the post-treatment follow-up period through nine months post-surgery. RXI-109 was safe and well tolerated. Additionally, as expected, the limited three-month data available from Cohort 3 appear to align with that of the first two cohorts as these subjects all had the same dosing schedule through the third month. A complete read-out of the whole study, including all four cohorts with follow-up until nine months post-surgery, is expected in the middle of 2017.
Study 1501, the Company’s Phase 1/2 clinical trial in retinal scars, commenced in November 2015, and is a multi-dose, dose escalation study conducted in subjects with AMD with evidence of subretinal fibrosis. Each subject will receive four doses of RXI-109 by intraocular injection at one month intervals for a total dosing period of three months. The safety and tolerability of RXI-109, as well as the potential for clinical activity, will be evaluated over the course of the study using numerous assessments to monitor the health of the retina and to assess visual acuity. The first two cohorts in Study 1501 have been completely enrolled and dosing in the third cohort at the highest planned dose level has begun. To date there have been no safety issues that precluded continuation of dosing. Complete enrollment is anticipated in the first half of 2017, ahead of our original plan, with complete subject participation anticipated in the second half of 2017.
Samcyprone™, the Company’s second clinical candidate, is a proprietary topical formulation of the small molecule diphenylcyclopropenone (“DPCP”), an immunomodulator that works by initiating a T-cell response. The use of Samcyprone™ allows sensitization using much lower concentrations of DPCP than are used with existing compounded DPCP solutions, avoiding hyper-sensitization to subsequent challenge doses. Samcyprone™ is currently being evaluated in a Phase 2a clinical trial, Study 1502, for the clearance of common warts.
Study 1502 was initiated in December 2015. Study 1502 includes a sensitization phase in which a spot on the subject’s upper arm and one or more warts are treated with Samcyprone™. After being sensitized in this way, the subjects will enter into the treatment phase where up to four warts are treated on a once weekly basis for ten weeks with a ten-fold
27
Table of Contents
lower concentration of Samcyprone™ than in the sensitization phase. During the trial, the warts are scored, photographed and measured to monitor the level of clearance. The Company has added a second cohort and is currently enrolling subjects to explore the opportunity to reduce the sensitization dose level and potentially reduce the treatment length. With this second cohort, enrollment is expected to be completed in the second half of 2017.
In December 2016, the Company announced the results from a preliminary review of sensitization and wart clearance data from a subset of subjects that have completed the ten-week treatment phase of Study 1502. Results showed that greater than 90% of the subjects demonstrated a sensitization response, a prerequisite to be able to develop a therapeutic response. Additionally, more than 60% of the subjects responded to the treatment by exhibiting either complete or greater than 50% clearance of all treated warts with up to ten weekly treatments. Samcyprone™ treatment has been generally safe and well tolerated and has had drug-related adverse events relating to local reactions, which are typically expected for this type of treatment due to the sensitization and challenge responses in the skin. The complete readout of the final study is anticipated in the second half of 2017.
In addition to our clinical programs, we continue to advance our preclinical and discovery programs with our sd-rxRNA technology. In October 2015, we announced the selection of lead compounds targeting tyrosinase (“TYR”) and collagenase (“MMP1”) as targets for our self-delivering platform because they are relevant for both consumer health and therapeutic development. Cosmetics are compounds that affect the appearance of the skin and make no preventative or therapeutic claims. These compounds may be developed more rapidly than therapeutics, therefore the path to market may be much shorter and less expensive. RXI-231, an sd-rxRNA compound targeting TYR, is in development as a cosmetic ingredient that may improve the appearance of uneven skin tone and pigmentation. RXI-185, an sd-rxRNA compound targeting MMP1, is in development as a cosmetic ingredient that may improve the appearance of wrinkles or skin laxity. Efficacy and toxicity testing in cell culture and skin equivalents for RXI-231 was successfully completed in December 2016. The Company is currently coordinating with a U.S. clinical testing site to initiate human testing of RXI-231 in the second quarter of 2017. RXI-231 has been manufactured in sufficient quantities to support this activity. In addition to evaluating safety, the effect of RXI-231 on the appearance of skin pigmentation will be assessed.
On April 14, 2016, the Board of Directors of the Company approved a 1-for-10 reverse stock split of the Company’s outstanding common stock, which was effected on April 18, 2016. The number of authorized shares of the Company remain unchanged. Stockholders who would have otherwise been entitled to fractional shares as a result of the reverse stock split received a cash payment in lieu of receiving fractional shares. Shares of common stock underlying outstanding stock options and other equity instruments were proportionately reduced and the respective exercise prices, if applicable, were proportionately increased in accordance with the terms of the agreements governing such securities. All share and per share amounts in the financial statements have been retroactively adjusted for all periods presented to give effect to the reverse stock split, including reclassifying an amount equal to the reduction in par value to additional paid-in capital.
On December 21, 2016, the Company closed an underwritten public offering (the “2016 Offering”) of (i) 2,131,111 Class A Units, at a public offering price of $0.90 per unit, consisting of one share of the Company’s common stock and a five-year warrant to purchase one share of common stock at an exercise price of $0.90 per share (the “2016 Warrants”) and (ii) 8,082 Class B Units, at a public offering price of $1,000 per unit, consisting of one share of Series B Convertible Preferred Stock (the “Series B Preferred Stock”), which is convertible into 1,111.11 shares of common stock, and 1,111.11 2016 Warrants. The 2016 Offering included an over-allotment option for the underwriters to purchase an additional 1,666,666 shares of common stock and/or 2016 Warrants to purchase an additional 1,666,666 shares of common stock. The underwriters fully exercised the over-allotment option to purchase additional shares of common stock and 2016 Warrants. The total net proceeds of the 2016 Offering, including the exercise of the over-allotment option, were $10,051,000 after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and offering expenses paid by the Company.
On January 6, 2017, the Company entered into a Stock Purchase Agreement (the “Stock Purchase Agreement”) by and among the Company, RXi Merger Sub, LLC, a Delaware limited liability company and wholly owned subsidiary of the Company (“RXi Merger Sub”), MirImmune Inc. (“MirImmune”), the stockholders of MirImmune set forth on the signature pages thereto (each a “Seller” and collectively, the “Sellers”), and Alexey Wolfson, Ph.D., in his capacity as the Sellers’ Representative. Pursuant to the Stock Purchase Agreement, the Company acquired from the Sellers all of the issued and outstanding shares of capital stock of MirImmune for an aggregate of 2,750,371 shares of common stock of the Company and an aggregate of 1,115,579 shares of Series C Convertible Preferred Stock, par value $0.0001 per share (the “Series C Preferred Stock”), subject to a holdback of 3% of the aggregate closing consideration for any purchase price adjustments. The Stock Purchase Agreement contains customary representations and warranties and pre- and post-closing covenants and closing conditions.
28
Table of Contents
In connection with and promptly following the closing of the Stock Purchase Agreement, MirImmune was merged with and into RXi Merger Sub (the “Merger”), with RXi Merger Sub continuing as the surviving entity and changing its name to “MirImmune, LLC”. As a result of the Merger, MirImmune, LLC remains and will operate as a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Company.
Since inception, we have incurred significant losses. Substantially all of our losses to date have resulted from research and development expenses in connection with our clinical and research programs and from general administrative costs. At December 31, 2016, we had an accumulated deficit of $66.1 million. We expect to continue to incur significant losses for the foreseeable future, particularly as we advance our development program for RXI-109 and Samcyprone™ and begin our program in cell-based cancer immunotherapy.
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
The discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations is based upon our financial statements, which have been prepared in accordance with United States generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”). The preparation of these financial statements requires us to make estimates and judgments that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses, and related disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities. On an ongoing basis, we evaluate our estimates, including those related to the impairment of long-lived assets, certain accrued expenses and stock-based compensation. We base our estimates on historical experience and various other assumptions that are believed to be reasonable under the circumstances. Actual results may differ from these estimates under different assumptions or conditions and could have a material impact on our reported results. While our significant accounting policies are more fully described in the Notes to our financial statements included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, we believe the following accounting policies to be the most critical in understanding the judgments and estimates we use in preparing our financial statements.
Research and Development Expenses
Research and development costs are charged to expense as incurred and relate to salaries, employee benefits, facility-related expenses, supplies, stock-based compensation related to employees and non-employees involved in the Company’s research and development, external services, other operating costs and overhead related to our research and development departments, costs to acquire technology licenses and expenses associated with preclinical activities and our clinical trials.
Preclinical and clinical trial expenses relate to third-party services, subject-related fees at the sites where our clinical trials are being conducted, laboratory costs, analysis costs, toxicology studies and investigator fees. Costs associated with these expenses are generally payable on the passage of time or when certain milestones are achieved. Expense is recorded during the period incurred or in the period in which a milestone is achieved. In order to ensure that we have adequately provided for preclinical and clinical expenses during the proper period, we maintain an accrual to cover these expenses. These accruals are assessed on a quarterly basis and are based on such assumptions as expected total cost, the number of subjects and clinical trial sites and length of the study. Actual results may differ from these estimates and could have a material impact on our reported results. Our historical accrual estimates have not been materially different from our actual costs.
Stock-based Compensation
The Company follows the provisions of the Financial Accounting Standards Board (the “FASB”) Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) Topic 718, “Compensation – Stock Compensation” (“ASC 718”), which requires the measurement and recognition of compensation expense for all stock-based payment awards made to employees, officers and non-employee directors, including stock options. Stock compensation expense based on the grant date fair value estimated in accordance with the provisions of ASC 718 is recognized as an expense over the requisite service period. Determining the amount of stock-based compensation to be recorded requires us to develop highly subjective estimates to be used in calculating the grant-date fair value of stock options. We use the Black-Scholes option pricing model to value
29
Table of Contents
our option grants and determine the related compensation expense. The use of the model requires us to make estimates of the following assumptions:
Expected volatility — Due to our limited trading history, we are responsible for estimating volatility and currently use the expected volatilities of similar entities. We have considered a number of factors in making our determination as to entities that are considered similar, such as the industry, stage of development, size of the company, and financial leverage.
Expected term — We use the simplified method to estimate the expected term assumption. The simplified method is based on the vesting period and the contractual term for each grant, or for each vesting-tranche for awards with graded vesting.
Risk-free interest rate — The yield on zero-coupon U.S. Treasury securities for a period that is commensurate with the expected term assumption is used as the risk-free interest rate.
Dividend yield — We utilize a dividend yield of zero based on the fact that we have never paid cash dividends and currently have no intention to pay cash dividends.
For stock options granted as consideration for services rendered by non-employees, the Company recognizes compensation expense in accordance with the requirements of FASB ASC Topic 505-50, “Equity Based Payments to Non-Employees.” Non-employee option grants that do not vest immediately upon grant are recorded as an expense over the requisite service period of the underlying stock options. At the end of each financial reporting period prior to vesting, the value of these options, as calculated using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model, will be re-measured using the fair value of the Company’s common stock and the non-cash compensation recognized during the period will be adjusted accordingly. Since the fair market value of options granted to non-employees is subject to change in the future, the amount of the future compensation expense will include fair value re-measurements until the stock options are fully vested.
Derivative Financial Instruments
During the normal course of business we may issue warrants to vendors as consideration to perform services. We may also issue warrants as part of a debt or equity financing. Warrants and other derivative financial instruments are accounted for either as equity or as an asset or liability, depending on the characteristics of each derivative financial instrument. Warrants classified as equity are measured at fair value and recorded as additional paid in capital in stockholders’ equity at the date of issuance. No further adjustments to their valuation are made. Derivative financial instruments classified as an asset or liability are measured at fair value on the issuance date and are revalued on each subsequent balance sheet date. The changes in the fair value are recognized as current period income or loss.
Results of Operations
The following data summarizes our results of operations for the following periods indicated, in thousands:
| For the Years Ended December 31, |
||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Net revenues |
$ | 19 | $ | 34 | ||||
| Operating expenses |
(9,034 | ) | (10,271 | ) | ||||
| Operating loss |
(9,015 | ) | (10,237 | ) | ||||
| Net loss |
(8,994 | ) | (10,223 | ) | ||||
| Net loss applicable to common stockholders |
(11,069 | ) | (10,432 | ) | ||||
30
Table of Contents
Comparison of the Years Ended December 31, 2016 and 2015
Net Revenues
To date, we have primarily generated revenues through government grants. The following table summarizes our total net revenues, for the periods indicated, in thousands:
| For the Years Ended December 31, |
||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Net revenues |
$ | 19 | $ | 34 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Net revenues were approximately $19,000 for the year ended December 31, 2016, as compared with $34,000 for year ended December 31, 2015. The decrease of $15,000, or 44%, was due to the completion of a government grant from the National Cancer Institute, a division of the National Institutes of Health, in 2015. Net revenues for the year ended December 31, 2016 were due to the Company’s exclusive license agreements with MirImmune and Thera Neuropharma, Inc.
Operating Expenses
The following table summarizes our total operating expenses, for the periods indicated, in thousands:
| For the Years Ended December 31, |
||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Research and development |
$ | 5,415 | $ | 6,925 | ||||
| General and administrative |
3,619 | 3,346 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total operating expenses |
$ | 9,034 | $ | 10,271 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Research and Development Expense
Research and development expense consists of compensation-related costs for our employees dedicated to research and development activities, fees related to our Scientific Advisory Board members, expenses related to our ongoing research and development efforts primarily related to our clinical trials, drug manufacturing, outside contract services, licensing and patent fees and laboratory supplies and services for our research programs.
Total research and development expense was approximately $5,415,000 for the year ended December 31, 2016, compared with $6,925,000 for the year ended December 31, 2015. The decrease of $1,510,000, or 22%, was due to a decrease of $1,121,000 in research and development expense primarily related to cash and equity fees payable to Hapten Pharmaceuticals, LLC upon the close of the Samcyprone™ license agreement and manufacturing expenses for the RXI-109 drug product, which both occurred in 2015. An additional decrease of $389,000 in stock-based compensation expense was due to the full vesting of stock options in 2016 from stock options that were granted in 2012.
General and Administrative Expense
General and administrative expense consists primarily of compensation-related costs for our employees dedicated to general and administrative activities, legal fees, audit and tax fees, consultants, professional services and general corporate expenses.
General and administrative expense was approximately $3,619,000 for the year ended December 31, 2016, compared with $3,346,000 for the year ended December 31, 2015. The increase of $273,000, or 8%, was primarily due to an increase of $663,000 in general and administrative expense primarily related to the Company’s focus on business development activities during 2016, as compared to 2015, and an increase in legal expenses arising from the Company’s acquisition of MirImmune. These increases were offset by a decrease of $390,000 in stock-based compensation expense due to the full vesting of stock options in 2016 from stock options that were granted in 2012.
31
Table of Contents
Convertible Preferred Stock
The following table summarizes the Company’s convertible preferred stock transactions for the periods indicated, in thousands:
| For the Years Ended December 31, |
||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Accretion of Series B convertible preferred stock |
$ | 2,075 | $ | — | ||||
| Series A and Series A-1 convertible preferred stock dividends |
— | 209 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Accretion of convertible preferred stock and dividends |
$ | 2,075 | $ | 209 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Accretion of convertible preferred stock and dividends was approximately $2,075,000 for the year ended December 31, 2016, compared with $209,000 for the year ended December 31, 2015. In connection with the completion of the Company’s public offering in December 2016, the Company issued shares of Series B Convertible Preferred Stock (the “Series B Preferred Stock”). The increase of $1,866,000 was due to the one-time charge of $2,075,000 related to the beneficial conversion feature of the Series B Preferred Stock offset by a decrease of $209,000 related to the fair value of dividends on the Company’s Series A and Series A-1 Convertible Preferred Stock (the “Series A and Series A-1 Preferred Stock”).
All shares of the Series A and Series A-1 Preferred Stock were fully converted during the quarter ended June 30, 2015, resulting in no further accumulation and payment of dividends on these series of preferred stock. In November 2015, the Company filed a Certificate Eliminating the Series A Preferred Stock and a Certificate Eliminating the Series A-1 Preferred Stock from the Certificate of Incorporation of the Company with the Secretary of State of the State of Delaware. As a result, the shares of unissued Series A and Series A-1 Preferred Stock were returned to the status of authorized but unissued shares of preferred stock of the Company, without designation as to series or preferences or rights. As of December 31, 2016 and 2015, there were no shares of Series A and Series A-1 Preferred Stock authorized, issued or outstanding.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
On December 18, 2014, the Company entered into a purchase agreement (the “LPC Purchase Agreement”) with Lincoln Park Capital Fund, LLC (“LPC”), pursuant to which the Company has the right to sell to LPC up to $10.8 million in shares of the Company’s common stock, subject to certain limitations and conditions set forth in the LPC Purchase Agreement. To date, the Company has sold a total of 70,000 shares of common stock to LPC for net proceeds of approximately $216,000. Per the terms of the 2016 Offering (defined below), the Company cannot effect a transaction under the LPC Purchase Agreement for 180 days after the closing of the 2016 Offering. The LPC Purchase Agreement will expire on April 17, 2017.
On June 2, 2015, we sold 2,600,000 units in a public offering at a price of $4.00 per unit (the “2015 Offering”). Each unit consisted of one share of common stock, a 13-month overallotment purchase right to purchase one-half of one share of common stock at a price of $4.55 per full share of common stock (the “Overallotment Purchase Rights”) and a five-year warrant to purchase one-half of one share of common stock at a price of $5.20 per full share of common stock (the “2015 Warrants”). As a result of the 2015 Offering, the Company received net proceeds of approximately $9,200,000 after placement agent fees and estimated 2015 Offering expenses.
Overallotment Purchase Rights totaling 1,300,002 were issued in connection with the 2015 Offering. During the year ended December 31, 2015, 43,500 Overallotment Purchase Rights were exercised for gross proceeds of $198,000. The Company’s remaining outstanding Overallotment Purchase Rights of 1,256,502 expired on July 2, 2016 and were not exercised. As of December 31, 2016, 1,300,002 2015 Warrants were issued and outstanding.
32
Table of Contents
On December 21, 2016, the Company closed an underwritten public offering (the “2016 Offering”) of (i) 2,131,111 Class A Units, at a public offering price of $0.90 per unit, consisting of one share of the Company’s common stock and a five-year warrant to purchase one share of common stock at an exercise price of $0.90 per share (the “2016 Warrants”) and (ii) 8,082 Class B Units, at a public offering price of $1,000 per unit, consisting of one share of Series B Preferred Stock, which is convertible into 1,111.11 shares of common stock, and 1,111.11 2016 Warrants. The 2016 Offering included an over-allotment option for the underwriters to purchase an additional 1,666,666 shares of common stock and/or 2016 Warrants to purchase an additional 1,666,666 shares of common stock. The underwriters fully exercised the over-allotment option to purchase additional shares of common stock and 2016 Warrants. The total net proceeds of the 2016 Offering, including the exercise of the over-allotment option, were $10,051,000 after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and offering expenses paid by the Company.
We had cash of $12.9 million as of December 31, 2016, compared with cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments of $10.6 million as of December 31, 2015. We believe that our existing cash should be sufficient to fund our operations for at least the next twelve months. We have generated significant losses to date, have not generated any product revenue to date and may not generate product revenue in the foreseeable future, or ever. We expect to incur significant operating losses as we advance our product candidates through the drug development and regulatory process. In the future, we will be dependent on obtaining funding from third parties, such as proceeds from the issuance of debt, sale of equity, funded research and development programs and payments under partnership and collaborative research and business development agreements, in order to maintain our operations and meet our obligations to licensors. There is no guarantee that debt, additional equity or other funding will be available to us on acceptable terms, or at all. If we fail to obtain additional funding when needed, we would be forced to scale back or terminate our operations or to seek to merge with or to be acquired by another company.
The following table summarizes our cash flows for the periods indicated, in thousands:
| For the Years Ended December 31, |
||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Net cash used in operating activities |
$ | (7,760 | ) | $ | (7,317 | ) | ||
| Net cash provided by (used in) investing activities |
5,346 | (5,557 | ) | |||||
| Net cash provided by financing activities |
10,203 | 9,495 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 7,789 | $ | (3,379 | ) | |||
Net Cash Flow from Operating Activities
Net cash used in operating activities was $7,760,000 for the year ended December 31, 2016, compared with $7,317,000 for the year ended December 31, 2015. The increase in cash used in operating activities was due to changes in working capital items of $632,000 primarily attributable to payments related to the manufacturing of the RXI-109 drug product in the first quarter of 2016 and changes in non-cash expenses of $1,040,000 partially offset by a decrease in net loss of $1,229,000.
Net Cash Flow from Investing Activities
Net cash provided by investing activities was $5,346,000 for the year ended December 31, 2016, compared with net cash used in investing activities of $5,557,000 for the year ended December 31, 2015. The increase in net cash provided by investing activities was primarily related to net purchases and maturities of short-term investments as compared with the same period in 2015, offset by notes receivable owed to the Company by MirImmune and capital equipment purchases.
Net Cash Flow from Financing Activities
Net cash provided by financing activities was $10,203,000 for the year ended December 31, 2016, compared with $9,495,000 for the year ended December 31, 2015. Net cash provided by financing activities in 2016 was due to net proceeds received in connection with the 2016 Offering and net proceeds from the issuance of common stock to LPC under the LPC Purchase Agreement. Net cash provided by financing activities in 2015 was primarily due to net proceeds received from the 2015 Offering and the issuance of common stock to LPC under the LPC Purchase Agreement.
33
Table of Contents
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
In connection with certain license agreements, we are required to indemnify the licensor for certain damages arising in connection with the intellectual property rights licensed under the agreement. In addition, we are a party to a number of agreements entered into in the ordinary course of business that contain typical provisions that obligate us to indemnify the other parties to such agreements upon the occurrence of certain events. These indemnification obligations are considered off-balance sheet arrangements in accordance with ASC Topic 460, “Guarantor’s Accounting and Disclosure Requirements for Guarantees, Including Indirect Guarantees of Indebtedness of Others.” To date, we have not encountered material costs as a result of such obligations and have not accrued any liabilities related to such obligations in our financial statements. See Note 8 to our financial statements for further discussion of these indemnification agreements.
| ITEM 7A. | QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK |
As a smaller reporting company, we are not required to provide this information.
34
Table of Contents
| ITEM 8. | FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA |
| Page No. | ||||
| F-2 | ||||
| F-3 | ||||
| Statements of Operations for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015 |
F-4 | |||
| F-5 | ||||
| Statements of Cash Flows for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015 |
F-6 | |||
| F-7 | ||||
F-1
Table of Contents
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
Board of Directors and Stockholders
RXi Pharmaceuticals Corporation
Marlborough, Massachusetts
We have audited the accompanying balance sheets of RXi Pharmaceuticals Corporation (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2016 and 2015, and the related statements of operations, convertible preferred stock and stockholders’ equity and cash flows for the years then ended. These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. Our audits included consideration of internal control over financial reporting as a basis for designing audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion. An audit also includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company at December 31, 2016 and 2015 and the results of its operations and its cash flows for the years then ended, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
/s/ BDO USA, LLP
Boston, Massachusetts
March 30, 2017
F-2
Table of Contents
RXi PHARMACEUTICALS CORPORATION
BALANCE SHEETS
(Amounts in thousands, except share data)
| Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| ASSETS |
||||||||
| Current assets: |
||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 12,906 | $ | 5,117 | ||||
| Restricted cash |
50 | 50 | ||||||
| Short-term investments |
— | 5,500 | ||||||
| Prepaid expenses |
150 | 311 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total current assets |
13,106 | 10,978 | ||||||
| Property and equipment, net of accumulated depreciation of $831 and $778, in 2016 and 2015, respectively |
114 | 163 | ||||||
| Notes receivable |
150 | — | ||||||
| Other assets |
27 | 18 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total assets |
$ | 13,397 | $ | 11,159 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY |
||||||||
| Current liabilities: |
||||||||
| Accounts payable |
$ | 917 | $ | 1,163 | ||||
| Accrued expenses |
1,625 | 1,106 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total current liabilities |
2,542 | 2,269 | ||||||
| Commitments and contingencies (Note 8) |
||||||||
| Stockholders’ equity: |
||||||||
| Preferred stock, $0.0001 par value, 10,000,000 shares authorized at December 31, 2016 and 2015 |
||||||||
| Series B convertible preferred stock, $0.0001 par value; 8,100 shares authorized; 5,737 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2016 (at fair value) |
3,525 | — | ||||||
| Common stock, $0.0001 par value, 100,000,000 shares authorized; 13,003,179 and 6,534,846 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015, respectively |
1 | 1 | ||||||
| Additional paid-in capital |
73,428 | 65,994 | ||||||
| Accumulated deficit |
(66,099 | ) | (57,105 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total stockholders’ equity |
10,855 | 8,890 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity |
$ | 13,397 | $ | 11,159 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
See accompanying notes to financial statements.
F-3
Table of Contents
RXi PHARMACEUTICALS CORPORATION
STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
(Amounts in thousands, except share and per share data)
| Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Net revenues |
$ | 19 | $ | 34 | ||||
| Operating expenses: |
||||||||
| Research and development (1) |
5,415 | 6,925 | ||||||
| General and administrative (1) |
3,619 | 3,346 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total operating expenses |
9,034 | 10,271 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Operating loss |
(9,015 | ) | (10,237 | ) | ||||
| Other income (expense): |
||||||||
| Interest income, net |
15 | 16 | ||||||
| Other income (expense), net |
6 | (2 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total other income |
21 | 14 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Loss before income taxes |
(8,994 | ) | (10,223 | ) | ||||
| Provision for income taxes |
— | — | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net loss |
(8,994 | ) | (10,223 | ) | ||||
| Accretion of convertible preferred stock and dividends |
(2,075 | ) | (209 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net loss applicable to common stockholders |
$ | (11,069 | ) | $ | (10,432 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net loss per common share applicable to common stockholders: |
||||||||
| Basic and diluted |
$ | (1.64 | ) | $ | (2.10 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Weighted average common shares: basic and diluted |
6,746,080 | 4,970,382 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| (1) Non-cash stock-based compensation expenses included in operating expenses are as follows: |
||||||||
| Research and development |
$ | 243 | $ | 632 | ||||
| General and administrative |
$ | 513 | $ | 903 | ||||
See accompanying notes to financial statements.
F-4
Table of Contents
RXi PHARMACEUTICALS CORPORATION
STATEMENTS OF CONVERTIBLE PREFERRED STOCK AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
(Amounts in thousands, except share data)
| Series A Convertible Preferred Stock |
Series A-1 Convertible Preferred Stock |
Series B Convertible Preferred Stock |
Common Stock | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares Issued |
Amount | Shares Issued |
Amount | Shares Issued |
Amount | Shares Issued |
Amount | Additional Paid in Capital |
Accumulated Deficit |
Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2014 |
5,110 | $ | 5,110 | 1,578 | $ | 1,578 | — | $ | — | 2,198,427 | $ | — | $ | 48,049 | $ | (46,882 | ) | $ | 2,745 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock under Lincoln Park Capital, LLC purchase agreement |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 5,000 | — | 64 | — | 64 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock in exchange for patent and technology rights |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 20,000 | — | 228 | — | 228 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock in connection with public offering, net of offering costs of $1,198 |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 2,600,000 | 1 | 9,201 | — | 9,202 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock under employee stock purchase plan |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 6,889 | — | 31 | — | 31 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock upon exercise of warrants in connection with public offering |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 43,500 | — | 198 | — | 198 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation expense |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 1,535 | — | 1,535 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dividends issued on Series A and Series A-1 convertible preferred stock |
105 | 105 | 21 | 21 | — | — | — | — | 83 | — | 104 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fair value of Series A and Series A-1 convertible preferred stock dividends |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (209 | ) | — | (209 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Exchange of Series A convertible preferred stock into Series A-1 convertible preferred stock |
(2,000 | ) | (2,000 | ) | 2,000 | 2,000 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 2,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Conversions of Series A and Series A-1 convertible preferred stock into common stock |
(3,215 | ) | (3,215 | ) | (3,599 | ) | (3,599 | ) | — | — | 1,661,030 | — | 6,814 | — | 3,215 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (10,223 | ) | (10,223 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2015 |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 6,534,846 | 1 | 65,994 | (57,105 | ) | 8,890 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock under Lincoln Park Capital, LLC purchase agreement |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 65,000 | — | 152 | — | 152 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock and warrants in connection with 2016 public offering, net of offering costs of $431 |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 3,797,777 | — | 2,987 | — | 2,987 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of Series B convertible preferred stock and warrants in connection with 2016 public offering, net of offering costs of $1,018 |
— | — | — | — | 8,082 | 4,966 | — | — | 2,098 | 7,064 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Beneficial conversion feature related to Series B convertible preferred stock |
— | — | — | — | — | (2,075 | ) | — | — | 2,075 | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accretion of beneficial conversion feature related to Series B convertible preferred stock |
— | — | — | — | — | 2,075 | — | — | (2,075 | ) | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Conversions of Series B convertible preferred stock into common stock |
— | — | — | — | (2,345 | ) | (1,441 | ) | 2,605,556 | — | 1,441 | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation expense |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 756 | — | 756 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (8,994 | ) | (8,994 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2016 |
— | $ | — | — | $ | — | 5,737 | $ | 3,525 | 13,003,179 | $ | 1 | $ | 73,428 | $ | (66,099 | ) | $ | 10,855 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
See accompanying notes to financial statements.
F-5
Table of Contents
RXi PHARMACEUTICALS CORPORATION
STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(Amounts in thousands)
| Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Cash flows from operating activities: |
||||||||
| Net loss |
$ | (8,994 | ) | $ | (10,223 | ) | ||
| Adjustment to reconcile net loss to net cash used in operating activities: |
||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization expense |
53 | 77 | ||||||
| Non-cash stock-based compensation expense |
756 | 1,535 | ||||||
| Value of non-marketable equity securities recognized as revenue |
(9 | ) | — | |||||
| Fair value of common stock issued in exchange for patent and technology rights |
— | 228 | ||||||
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities: |
||||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other assets |
161 | 131 | ||||||
| Accounts payable |
(246 | ) | 878 | |||||
| Accrued expenses |
519 | 104 | ||||||
| Deferred revenue |
— | (47 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net cash used in operating activities |
(7,760 | ) | (7,317 | ) | ||||
| Cash flows from investing activities: |
||||||||
| Purchase of short-term investments |
(2,000 | ) | (8,000 | ) | ||||
| Maturities of short-term investments |
7,500 | 2,500 | ||||||
| Issuance of notes receivable |
(150 | ) | — | |||||
| Cash paid for purchase of property and equipment |
(4 | ) | (57 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net cash provided by (used in) investing activities |
5,346 | (5,557 | ) | |||||
| Cash flows from financing activities: |
||||||||
| Net proceeds from the issuance of common stock and/or convertible preferred stock |
10,203 | 9,266 | ||||||
| Proceeds from the issuance of common stock upon the exercise of warrants |
— | 198 | ||||||
| Proceeds from the issuance of common stock in connection with the employee stock purchase plan |
— | 31 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net cash provided by financing activities |
10,203 | 9,495 | ||||||
| Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents |
7,789 | (3,379 | ) | |||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at the beginning of period |
5,117 | 8,496 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at the end of period |
$ | 12,906 | $ | 5,117 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Supplemental disclosure of non-cash investing and financing activities: |
|
|||||||
| Series A and Series A-1 convertible preferred stock dividends |
$ | — | $ | 126 | ||||
| Fair value of Series A and Series A-1 convertible preferred stock dividends |
$ | — | $ | 209 | ||||
| Exchange of Series A convertible preferred stock into Series A-1 convertible preferred stock |
$ | — | $ | 2,000 | ||||
| Conversion of Series A and Series A-1 convertible preferred stock into common stock |
$ | — | $ | 6,814 | ||||
| Fair value of Series B convertible preferred stock beneficial conversion feature |
$ | 2,075 | $ | — | ||||
| Accretion of Series B convertible preferred stock |
$ | 2,075 | $ | — | ||||
| Conversion of Series B convertible preferred stock into common stock |
$ | 1,441 | $ | — | ||||
See accompanying notes to financial statements.
F-6
Table of Contents
RXi PHARMACEUTICALS CORPORATION
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
1. Nature of Operations
RXi Pharmaceuticals Corporation (“RXi,” “we,” “our” or the “Company”) is a clinical-stage company developing innovative therapeutics based on our proprietary self-delivering RNAi (sd-rxRNA®) platform and Samcyprone™, a topical immunomodulator, which address significant unmet medical needs. The Company’s clinical development programs include RXI-109, an sd-rxRNA for the treatment of dermal and ocular scarring, and Samcyprone™, for the treatment of warts. In addition to these clinical programs, we have a pipeline of discovery and preclinical product candidates in our core therapeutic areas, as well as in other areas of interest. The Company’s pipeline, coupled with our extensive patent portfolio, provides for product development and business development opportunities across a broad spectrum of therapeutic areas.
On April 14, 2016, the Board of Directors of the Company approved a 1-for-10 reverse stock split of the Company’s outstanding common stock, which was effected on April 18, 2016. All share and per share amounts in the financial statements have been retroactively adjusted for all periods presented to give effect to the reverse stock split, including reclassifying an amount equal to the reduction in par value to additional paid-in capital.
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Basis of Presentation
The accompanying financial statements have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“GAAP”).
Uses of Estimates in Preparation of Financial Statements
The preparation of financial statements in accordance with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ materially from these estimates.
Cash Equivalents
The Company considers all highly liquid instruments with an original maturity of three months or less to be cash equivalents. Cash equivalents consist primarily of amounts invested in certificates of deposit.
Restricted Cash
Restricted cash consists of certificates of deposit held by financial institutions as collateral for the Company’s corporate credit cards.
Short-term Investments
Short-term investments consist of certificates of deposit with original maturities ranging from over three months to one year.
Concentrations of Credit Risk
Financial instruments that potentially subject the Company to concentrations of credit risk consist principally of cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments. The Company maintains cash balances in several accounts with one bank, which at times are in excess of federally insured limits. The Company has established guidelines related to credit ratings and maturities intended to safeguard principal balances and maintain liquidity. The Company’s investments are maintained in accordance with the Company’s investment policy, which defines allowable investments, specifies credit quality standards and limits the exposure of any single issuer.
F-7
Table of Contents
Property and Equipment
Property and equipment are stated at cost and depreciated using the straight-line method based on the estimated useful lives of the related assets. The Company provides for depreciation over the assets’ estimated useful lives as follows:
| Computer equipment |
3 years | |
| Machinery & equipment |
5 years | |
| Furniture & fixtures |
5 years | |
| Leasehold improvements |
5 years |
Depreciation and amortization expense for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015 was approximately $53,000 and $77,000, respectively.
Investments in Non-marketable Equity Securities
The Company’s investments in non-marketable equity securities are accounted for under the cost method because the Company does not have the ability to exercise significant influence over the investee and the securities do not have readily determinable fair values. Our investments are carried at cost less any impairment write-downs. Annually, the Company’s cost method investments are assessed for impairment. The Company does not reassess the fair value of cost method investments if there are no identified events or changes in circumstances that may have a significant adverse effect on the fair value of the investments.
Derivative Financial Instruments
The Company follows the provisions of the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) Topic 815, “Derivatives and Hedging” (“ASC 815”). Financial instruments that meet the definition of a derivative are classified as an asset or liability and measured at fair value on the issuance date and are revalued on each subsequent balance sheet date. The changes in fair value are recognized as current period income or loss.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
The carrying amounts reported in the balance sheet for cash equivalents, restricted cash, short-term investments, notes receivable and accounts payable approximate their fair values due to their short-term nature or market rates of interest.
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets
The Company reviews long-lived assets for impairment on an interim basis if an event occurs that might reduce the fair value of such assets below their carrying values. An impairment loss would be recognized based on the difference between the carrying value of the asset and its estimated fair value, which would be determined based on either discounted future cash flows or other appropriate fair value methods. The Company believes no impairment existed as of December 31, 2016 and 2015.
Revenue Recognition
Revenue is recognized when there is persuasive evidence of an arrangement, the fee is fixed or determinable, delivery has occurred or services have been rendered and collection of the related receivable is reasonably assured. The Company may generate revenue from product sales, license agreements, collaborative research and development arrangements and government grants. Payments received prior to the recognition of revenue are recorded as deferred revenue.
F-8
Table of Contents
The Company has entered into license agreements for its proprietary sd-rxRNA technology during the ordinary course of business with start-up biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies. Under these agreements, the Company has granted exclusive licenses to the Company’s technology in exchange for potential future equity, cash and royalty payments. For each agreement, the Company determines whether the agreement includes multiple deliverables, and if so, whether they should be considered separate or a single unit of accounting and whether the delivered items have standalone value. The consideration received is allocated among the separate units of accounting, and the applicable revenue recognition guidance is applied to each of the separate units.
Upfront fees are recognized on a straight-line basis over the contracted or estimated period of performance if they do not have standalone value. If upfront fees are determined to have standalone value from other identified deliverables, the Company recognizes revenue upon delivery.
Substantive milestone payments are recognized upon achievement of the milestone. In evaluating whether a milestone has substance, the consideration earned from the achievement of a milestone is considered if the milestone is commensurate with the entity’s performance to achieve the milestone or the enhancement of value of the delivered item, if it relates solely to past performance and if it is reasonable relative to all the deliverables and payment terms within the arrangement. When a substantive milestone is achieved, revenue related to the milestone will be recognized in full. If a milestone is not considered substantive, revenue is recognized over the period of performance.
If the Company is entitled to reimbursement or payments for specific research and development services, the Company determines whether the funding would result in collaborative revenues or an offset to research and development expenses in accordance with the provisions of gross or net revenue presentation.
Research and Development Expenses
Research and development costs are charged to expense as incurred and relate to salaries, employee benefits, facility-related expenses, supplies, stock-based compensation related to employees and non-employees involved in the Company’s research and development, external services, other operating costs and overhead related to our research and development departments, costs to acquire technology licenses and expenses associated with preclinical activities and our clinical trials. Payments made by the Company in advance for research and development services not yet provided and/or for materials not yet received are recorded as prepaid expenses. Accrued liabilities are recorded related to those expenses for which vendors have not yet billed us with respect to services provided and/or materials that we have received.
Preclinical and clinical trial expenses relate to third-party services, subject-related fees at the sites where our clinical trials are being conducted, laboratory costs, analysis costs, toxicology studies and investigator fees. Costs associated with these expenses are generally payable on the passage of time or when certain milestones are achieved. Expense is recorded during the period incurred or in the period in which a milestone is achieved. In order to ensure that we have adequately provided for preclinical and clinical expenses during the proper period, we maintain an accrual to cover these expenses. These accruals are assessed on a quarterly basis and are based on such assumptions as expected total cost, the number of subjects and clinical trial sites and length of the study. Actual results may differ from these estimates and could have a material impact on our reported results. Our historical accrual estimates have not been materially different from our actual costs.
Patents and Patent Application Costs
Although the Company believes that its patents and underlying technology have continuing value, the amount of future benefits to be derived from the patents is uncertain. Patent costs are, therefore, expensed as research and development costs as incurred.
Stock-based Compensation
The Company follows the provisions of the FASB ASC Topic 718, “Compensation — Stock Compensation” (“ASC 718”), which requires the measurement and recognition of compensation expense for all stock-based payment awards made to employees, officers and non-employee directors, including stock options. Stock compensation expense based on the grant date fair value estimated in accordance with the provisions of ASC 718 is recognized as an expense over the requisite service period.
F-9
Table of Contents
For stock options granted as consideration for services rendered by non-employees, the Company recognizes compensation expense in accordance with the requirements of FASB ASC Topic 505-50, “Equity Based Payments to Non-Employees.” Non-employee option grants that do not vest immediately upon grant are recorded as an expense over the requisite service period of the underlying stock options. At the end of each financial reporting period prior to vesting, the value of these options, as calculated using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model, will be re-measured using the fair value of the Company’s common stock and the non-cash compensation recognized during the period will be adjusted accordingly. Since the fair market value of options granted to non-employees is subject to change in the future, the amount of the future compensation expense will include fair value re-measurements until the stock options are fully vested.
Income Taxes
The Company recognizes assets or liabilities for the deferred tax consequences of temporary differences between the tax basis of assets or liabilities and their reported amounts in the financial statements in accordance with FASB ASC Topic 740, “Accounting for Income Taxes” (“ASC 740”). These temporary differences will result in taxable or deductible amounts in future years when the reported amounts of the assets or liabilities are recovered or settled. ASC 740 requires that a valuation allowance be established when management determines that it is more likely than not that all or a portion of a deferred asset will not be realized. The Company evaluates the realizability of its net deferred income tax assets and valuation allowances as necessary, at least on an annual basis. During this evaluation, the Company reviews its forecasts of income in conjunction with other positive and negative evidence surrounding the realizability of its deferred income tax assets to determine if a valuation allowance is required. Adjustments to the valuation allowance will increase or decrease the Company’s income tax provision or benefit. The recognition and measurement of benefits related to the Company’s tax positions requires significant judgment, as uncertainties often exist with respect to new laws, new interpretations of existing laws, and rulings by taxing authorities. Differences between actual results and the Company’s assumptions or changes in the Company’s assumptions in future periods are recorded in the period they become known.
Comprehensive Loss
The Company’s comprehensive loss is equal to its net loss for all periods presented.
Net Loss per Share
The Company accounts for and discloses net loss per share attributable to common stockholders in accordance with FASB ASC Topic 260, “Earnings per Share.” Basic and diluted net loss per common share is computed by dividing net loss attributable to common stockholders by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding. When the effects are not dilutive, diluted earnings per share is computed by dividing the Company’s net earnings by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding and the impact of all dilutive potential common shares.
3. Recent Accounting Pronouncements
In February 2016, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) 2016-02, “Leases (Topic 842),” which requires companies that are lessees to recognize a right-of-use asset and lease liability for most leases that do not meet the definition of a short-term lease. For income statement purposes, leases will continue to be classified as either operating or financing. Classification will be based on criteria that are largely similar to those applied in current lease accounting. This standard will result in extensive qualitative and quantitative disclosure changes. This standard will be effective for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2018, including interim periods within that reporting period. The Company is currently evaluating the impact of this ASU on its financial position and results of operations.
In March 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-09, “Compensation – Stock Compensation (Topic 718) – Improvements to Employee Share-Based Payment Accounting,” which simplifies several aspects of accounting for share-based payment transactions, including the income tax consequences, classifications of awards as either equity or liabilities and classification on the statement of cash flows. This standard will be effective for annual reporting periods beginning after
F-10
Table of Contents
December 15, 2016 and interim periods within that reporting period. Early adoption is permitted. The Company adopted ASU 2016-09 in the fourth quarter of fiscal 2016 and the implementation of this standard did not have a material impact on the Company’s financial statements.
In April 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-10, “Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606) – Identifying Performance Obligations and Licensing,” which clarifies two aspects of the guidance on accounting for revenue contracts with customers: identifying performance obligations and the licensing implementation guidance. The amendments in this ASU do not change the core principles for those areas. This standard will be effective for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2017, including interim periods within that reporting period. Early adoption is not permitted. The Company is currently evaluating the potential impact the update may have on its financial position and results of operations.
In August 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-15, “Statement of Cash Flows (Topic 230) – Classification of Certain Cash Receipts and Cash Payments,” which clarifies how certain cash receipts and payments are presented and classified in the statement of cash flows. This standard will be effective for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2017, including interim periods within that reporting period. Early adoption is permitted. The amendments in ASU 2016-12 should be applied using a retrospective transition method to each period presented. The Company expects the update to have a minimal impact on its statement of cash flows and related disclosures.
In November 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-18, “Statement of Cash Flows (Topic 230) – Restricted Cash,” which requires that a statement of cash flows explain the change during the period in the total of cash, cash equivalents, and amounts generally described as restricted cash and restricted cash equivalents. With this standard, amounts generally described as restricted cash or restricted cash equivalents should be included with cash and cash equivalents when reconciling the beginning of period and end of period total amounts shown on the statement of cash flows. This standard will be effective for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2017, including interim periods within that reporting period. Early adoption is permitted. The Company expects the update to have a minimal impact on its statement of cash flows and related disclosures.
4. Notes Receivable
In October 2016, the Company entered into an exclusive option agreement (the “Option”) to acquire MirImmune Inc. (“MirImmune”), a privately-held company focused on the development of next generation immunotherapies for the treatment of cancer. As part of the Option, the Company made loans to MirImmune evidenced by convertible promissory notes (“Notes”). Under the terms of the Notes, the principal amount outstanding accrues interest at a fixed rate equal to 5%. The Notes are due upon the earlier of: (i) five years from the issuance date or (ii) an event of default, as defined in the Notes. Upon the closing of the acquisition of MirImmune by the Company, all outstanding amounts were canceled. Refer to Note 14 for further details. At December 31, 2016, a total of $150,000 in notes receivable was recorded on the Company’s balance sheet at the face amount.
5. Other Assets
In May 2016, the Company entered into an exclusive license agreement with Thera Neuropharma, Inc. (“Thera”), a privately held company, pursuant to which the Company granted certain rights to its sd-rxRNA platform for neurodegenerative diseases in exchange for an upfront equity ownership interest and the potential to receive future cash, additional equity and royalties based on the achievement of certain milestones. The Company was issued shares of common stock in Thera upon execution of the license agreement. Due to the Company’s inability to exercise significant influence over Thera and the Company owning less than 20% of the voting equity of Thera’s stock, the Company accounted for this investment using the cost method. As of December 31, 2016, the carrying value of the investment in Thera of $4,500 was included in other assets on the balance sheet. The Company has not recognized impairment expense for this investment through December 31, 2016.
The Company was also granted a five-year warrant to purchase additional shares of common stock of Thera at a price of $0.001 per share of common stock (the “Thera Warrant”) pursuant to the terms of the license agreement. The Company first assessed the Thera Warrant under ASC 815. Under the related guidance, a financial instrument shall be considered a derivative when it includes an underlying and notional amount or payment provision, an initial net
F-11
Table of Contents
investment and a net settlement. The Company determined that the Thera Warrant met all of the characteristics of a derivative. Per ASC 815, the Thera Warrant is recognized at fair value on the balance sheet and gains and losses from changes in the fair value of the Thera Warrant are recognized in the statement of operations. The fair value of the Thera Warrant at the date of issuance totaled $4,500 and was included in other assets on the balance sheet. There have been no changes to the fair value since the date of issuance.
6. Fair Value Measurements
The Company follows the provisions of FASB ASC Topic 820, “Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures,” for the Company’s financial assets and liabilities that are re-measured and reported at fair value at each reporting period and are re-measured and reported at fair value at least annually using a fair value hierarchy that is broken down into three levels. Level inputs are defined as follows:
| Level 1 | — | quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities. | ||
| Level 2 | — | other significant observable inputs for the assets or liabilities through corroboration with market data at the measurement date. | ||
| Level 3 | — | significant unobservable inputs that reflect management’s best estimate of what market participants would use to price the assets or liabilities at the measurement date. | ||
The Company categorized its restricted cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments as Level 2 hierarchy. The assets classified as Level 2 have initially been valued at the applicable transaction price and subsequently valued, at the end of each reporting period, using other market observable data. Observable market data points include quoted prices, interest rates, reportable trades and other industry and economic events.
The Company’s Thera Warrant and notes receivable are categorized as Level 3 hierarchy. The estimated fair value inputs utilizing the asset-based approach for the Thera Warrant include the stage of enterprise development, terms of existing contractual arrangements of the entity’s equity securities, the achievement of milestones and other unobservable inputs.
Financial assets measured at fair value on a recurring basis are summarized as follows, in thousands:
| Description |
December 31, 2016 | Quoted Prices In Active Markets (Level 1) |
Other Significant Observable Inputs (Level 2) |
Significant Unobservable Inputs (Level 3) |
||||||||||||
| Assets: |
||||||||||||||||
| Restricted cash |
$ | 50 | $ | — | $ | 50 | $ | — | ||||||||
| Thera Warrant |
5 | — | — | 5 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total |
$ | 55 | $ | — | $ | 50 | $ | 5 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Description |
December 31, 2015 | Quoted Prices In Active Markets (Level 1) |
Other Significant Observable Inputs (Level 2) |
Significant Unobservable Inputs (Level 3) |
||||||||||||
| Assets: |
||||||||||||||||
| Restricted cash |
$ | 50 | $ | — | $ | 50 | $ | — | ||||||||
| Cash equivalents |
2,500 | — | 2,500 | — | ||||||||||||
| Short-term investments |
5,500 | — | 5,500 | — | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total |
$ | 8,050 | $ | — | $ | 8,050 | $ | — | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
F-12
Table of Contents
There were no transfers from Level 1 to Level 2 or from Level 2 to Level 1 during the years ended December 31, 2016 or 2015. The following table presents additional information about assets measured at fair value on a recurring basis and for which the Company utilizes Level 3 inputs to determine fair value for the periods indicated, in thousands:
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Beginning balance |
$ | — | $ | — | ||||
| Thera Warrant |
5 | — | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Ending balance |
$ | 5 | $ | — | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
7. Accrued Expenses
Accrued expenses consist of the following, in thousands:
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Employee compensation and benefits |
$ | 745 | $ | 725 | ||||
| Clinical development expenses |
490 | 225 | ||||||
| Professional fees |
104 | 126 | ||||||
| Research and development costs |
276 | 20 | ||||||
| Other |
10 | 10 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total accrued expenses |
$ | 1,625 | $ | 1,106 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
8. Commitments and Contingencies
License Commitments
The Company acquires assets under development and enters into research and development arrangements with third parties that often require milestone and royalty payments based on the progress of the asset through development stages. Milestone payments may be required, for example, upon approval of the product for marketing by a regulatory agency. In certain agreements, the Company is required to make royalty payments based upon a percentage of the sales of the products licensed pursuant to such agreements. Because of the contingent nature of these payments, they are not included in the table of contractual obligations shown below (see also Note 13).
These arrangements may be material individually, and in the unlikely event that milestones for multiple products covered by these arrangements were reached in the same period, the aggregate charge to expense could be material to the results of operations. In addition, these arrangements often give the Company the discretion to unilaterally terminate development of the product, which would allow the Company to avoid making the contingent payments; however, the Company is unlikely to cease development if the compound successfully achieves clinical testing objectives.
The Company’s contractual license obligations that will require future cash payments as of December 31, 2016 are as follows, in thousands:
| Year Ending December 31, |
||||
| 2017 |
$ | 200 | ||
| 2018 |
200 | |||
| 2019 |
165 | |||
| 2020 |
165 | |||
| 2021 |
165 | |||
| Thereafter |
800 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Total |
$ | 1,695 | ||
|
|
|
|||
F-13
Table of Contents
Operating Leases
The Company leases office and laboratory space for its corporate headquarters and primary research facility in Marlborough, Massachusetts. The lease for the office and lab space will expire in March 2019. Monthly rental expense is approximately $9,500, which includes the Company’s pro rata share of annual real estate taxes and operating expenses.
Total rent expense under the Company’s operating lease was $117,000 and $118,000 for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively.
At December 31, 2016, the Company’s future minimum payments required under operating leases are as follows, in thousands:
| Year Ending December 31, |
||||
| 2017 |
$ | 117 | ||
| 2018 |
120 | |||
| 2019 |
30 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Total |
$ | 267 | ||
|
|
|
|||
The Company applies the disclosure provisions of FASB ASC Topic 460, “Guarantor’s Accounting and Disclosure Requirements for Guarantees, Including Indirect Guarantees of Indebtedness of Others” (“ASC 460”), to its agreements that contain guarantee or indemnification clauses. The Company provides: (i) indemnifications of varying scope and size to certain investors and other parties for certain losses suffered or incurred by the indemnified party in connection with various types of third-party claims; and (ii) indemnifications of varying scope and size to officers and directors against third-party claims arising from the services they provide to us. These indemnifications give rise only to the disclosure provisions of ASC 460. To date, the Company has not incurred costs as a result of these obligations and does not expect to incur material costs in the future. Accordingly, the Company has not accrued any liabilities in its financial statements related to these indemnifications.
9. Stockholders’ Equity
Purchase Agreement with Lincoln Park Capital, LLC — During the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively, the Company sold 65,000 and 5,000 shares of common stock to Lincoln Park Capital Fund, LLC (“LPC”) pursuant to a purchase agreement dated December 18, 2014 between the Company and LPC. Net proceeds to the Company totaled approximately $152,000 and $64,000 for the respective periods.
December 2016 Underwritten Public Offering — On December 21, 2016, the Company closed an underwritten public offering (the “2016 Offering”) of (i) 2,131,111 Class A Units, at a public offering price of $0.90 per unit, consisting of one share of the Company’s common stock and a five-year warrant to purchase one share of common stock at an exercise price of $0.90 per share (the “2016 Warrants”) and (ii) 8,082 Class B Units, at a public offering price of $1,000 per unit, consisting of one share of Series B Convertible Preferred Stock (the “Series B Preferred Stock”), which is convertible into 1,111.11 shares of common stock, and 1,111.11 2016 Warrants. The 2016 Offering included an over-allotment option for the underwriters to purchase an additional 1,666,666 shares of common stock and/or 2016 Warrants to purchase an additional 1,666,666 shares of common stock. The underwriters fully exercised the over-allotment option to purchase additional shares of common stock and 2016 Warrants. The total net proceeds of the 2016 Offering, including the exercise of the over-allotment option, were $10,051,000 after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and offering expenses paid by the Company.
The Company received $2,987,000 in net proceeds associated with the Class A Units, which were recorded as common stock and additional paid in capital. The Company also received $7,064,000 in net proceeds associated with the Class B Units, of which we allocated and recorded $4,966,000 to the Series B Preferred Stock and allocated $2,098,000 to the 2016 Warrants which were recorded to additional paid in capital. The Series B Preferred Stock had an effective price per share of $614.45 based on the proceeds that were allocated to them. Refer to the section below for additional disclosures on the Company’s Series B Preferred Stock.
F-14
Table of Contents
Series B Preferred Stock
Effective December 19, 2016, the Board of Directors of the Company designated 8,100 shares of its authorized preferred stock as Series B Preferred Stock. Each share of Series B Preferred Stock is convertible into 1,111.11 shares of common stock at any time at the holder’s option, subject to an ownership cap whereby conversion may not occur to the extent the holder would beneficially own more than 4.99% of the common stock then outstanding following a conversion. The Series B Preferred Stock have no voting rights, with certain exceptions as described in the Series B Convertible Preferred Stock Certificate of Designations, and shall receive dividends on an as-converted basis at the same time and in the same form as any dividends paid out on shares of the Company’s common stock. Other than as set forth in the previous sentence, no other dividends shall be paid on the Series B Preferred Stock.
Upon its issuance, the Series B Preferred Stock was assessed under FASB ASC 480, “Distinguishing Liabilities from Equity” (“ASC 480”), and it was determined that it was not within the scope of ASC 480; therefore, the Series B Preferred Stock was not considered a liability under ASC 480 and the Series B Preferred Stock was recorded in permanent equity on the Company’s balance sheet.
The Series B Preferred Stock was then assessed under FASB ASC 815. The Series B Preferred Stock is convertible into common stock at the holders’ option, subject to the terms of the Series B Convertible Preferred Stock Certificate of Designations. This embedded feature meets the definition of a derivative. The Company believes that the Series B Preferred Stock is an equity host for the purposes of assessing the embedded conversion option for potential bifurcation. The Company concluded that the conversion option feature is clearly and closely related to the preferred stock host. As such, the conversion feature did not require bifurcation under ASC 815.
The Company recognized a beneficial conversion feature on the Series B Preferred Stock. This was calculated as the number of potential conversion shares multiplied by the excess of the market price of the common stock on the issuance date over the price per conversion share based on the valuation allocated to the Series B Preferred Stock. The Series B Preferred Stock are immediately convertible and non-redeemable and therefore, the beneficial conversion feature of $2,075,000 was recorded as a one-time accretion expense and recorded as an adjustment within equity.
During the year ended December 31, 2016, 2,345 shares of Series B Preferred Stock were converted into 2,605,556 shares of common stock of the Company.
Warrants
The Company assessed the 2016 Warrants under FASB ASC 480 and determined that the 2016 Warrants were outside the scope of ASC 480. The Company next assessed the 2016 Warrants under FASB ASC 815. Under the related guidance, a reporting entity shall not consider a contract to be a derivative instrument if the contract is both (1) indexed to the entity’s own stock and (2) classified in stockholders’ equity. The Company determined that the 2016 Warrants were indexed to the Company’s stock, as the agreements do not contain any exercise contingencies and the 2016 Warrants’ settlement amount equals the difference between the fair value of the Company’s common stock price and the 2016 Warrant strike price. The Company also assessed the classification in stockholders’ equity and determined the 2016 Warrants met all of the criteria for classification as equity under ASC 815. Based on this analysis, the Company determined that the 2016 Warrants should be classified as equity.
The following table summarizes the Company’s outstanding warrants at December 31, 2016:
| Exercise prices |
Number of Shares Underlying Warrants |
Expiration | ||||||
| $39.00 |
462 | April 27, 2017 | ||||||
| $ 5.20 |
1,300,002 | June 2, 2020 | ||||||
| $ 0.90 |
12,777,777 | December 21, 2021 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total warrants outstanding |
14,078,241 | |||||||
|
|
|
|||||||
No warrants were exercised during the year ended December 31, 2016. During the year ended December 31, 2015, a total of 43,500 warrants were exercised for gross proceeds of $198,000.
F-15
Table of Contents
On July 2, 2016, 1,256,502 of the Company’s outstanding warrants with an exercise price of $4.55 expired.
10. Net Loss per Share Attributable to Common Stockholders
The following table sets forth the potential common shares excluded from the calculation of net loss per common share attributable to common stockholders because their inclusion would be anti-dilutive:
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Options to purchase common stock |
374,446 | 332,400 | ||||||
| Common stock underlying Series B Preferred Stock |
6,374,444 | — | ||||||
| Warrants to purchase common stock |
14,078,241 | 2,556,966 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total |
20,827,131 | 2,889,366 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
11. Stock-based Compensation
Stock Plans
On January 23, 2012, the Company’s Board of Directors and sole stockholder adopted the RXi Pharmaceuticals Corporation 2012 Long-Term Incentive Plan (the “2012 Incentive Plan”). Under the 2012 Incentive Plan, the Company may grant incentive stock options, nonqualified stock options, cash awards, stock appreciation rights, restricted and unrestricted stock and stock unit awards and other stock-based awards. The Company’s Board of Directors currently acts as the administrator of the Company’s 2012 Incentive Plan. The administrator has the power to select participants from among the key employees, directors and consultants of and advisors to the Company, establish the terms, conditions and vesting schedule, if applicable, of each award and to accelerate vesting or exercisability of any award.
As of December 31, 2016, an aggregate of 1,250,000 shares of common stock were reserved for issuance under the Company’s 2012 Incentive Plan, including 374,446 shares subject to outstanding common stock options granted under the 2012 Incentive Plan and 875,354 shares available for future grants. Stock options granted by the Company to employees may have different vesting parameters, but generally vest within 48 months after the option grant date and expire within ten years of issuance.
Stock-based Compensation
The Company uses the Black-Scholes option-pricing model to determine the fair value of all its option grants. For valuing options granted during the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, the following assumptions were used:
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Risk-free interest rate |
1.18 – 2.02 | % | 1.47 – 2.43 | % | ||||
| Expected volatility |
79.42 – 116.88 | % | 84.93 – 116.81 | % | ||||
| Weighted average expected volatility |
89.12 | % | 89.26 | % | ||||
| Expected lives (in years) |
5.20 – 10.00 | 5.20 – 10.00 | ||||||
| Expected dividend yield |
0.00 | % | 0.00 | % | ||||
The weighted-average fair value of options granted during the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015 was $2.15 and $4.10 per share, respectively.
The risk-free interest rate used for each grant was based upon the yield on zero-coupon U.S. Treasury securities with a term similar to the expected life of the related option. The Company’s expected stock price volatility assumption is based upon the volatility of a composition of comparable companies. The expected life assumption for employee grants was based upon the simplified method provided for under ASC 718, and the expected life assumption for non-employees was based upon the contractual term of the option. The dividend yield assumption of zero is based upon the fact that the Company has never paid cash dividends and presently has no intention of paying cash dividends.
F-16
Table of Contents
The following table summarizes the stock option activity of the Company for the year ended December 31, 2016:
| Total Number of Shares |
Weighted- Average Exercise Price Per Share |
Weighted- Average Remaining Contractual Term |
Aggregate Intrinsic Value |
|||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2015 |
332,400 | $ | 30.50 | |||||||||||||
| Granted |
58,569 | 2.91 | ||||||||||||||
| Exercised |
— | — | ||||||||||||||
| Cancelled |
(16,523 | ) | 5.88 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2016 |
374,446 | $ | 27.29 | 6.14 years | $ | — | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Exercisable at December 31, 2016 |
304,880 | $ | 30.93 | 5.61 years | $ | — | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
Stock-based compensation expense for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015 was approximately $756,000 and $1,535,000, respectively. Of this amount, the Company recognized credits to non-employee stock-based compensation expense of $1,000 and $16,800 for the same respective periods. There is no income tax benefit as the Company is currently operating at a loss and an actual income tax benefit may not be realized.
As of December 31, 2016, the compensation expense for all unvested stock options in the amount of approximately $475,000 will be recognized in the Company’s results of operations over a weighted average period of 1.47 years.
12. Income Taxes
For the years ending December 31, 2016 and 2015, all of the Company’s loss before income taxes was generated in the United States. The components of federal and state income tax expense are as follows (in thousands):
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Current |
||||||||
| Federal |
$ | — | $ | — | ||||
| State |
— | — | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total current |
— | — | ||||||
| Deferred |
||||||||
| Federal |
(2,892 | ) | (3,157 | ) | ||||
| State |
(741 | ) | (803 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total deferred |
(3,633 | ) | (3,960 | ) | ||||
| Valuation allowance |
3,633 | 3,960 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total income tax expense |
$ | — | $ | — | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
The differences between the income taxes expected at the federal statutory income tax rate and the reported income tax (benefit) expense is as follows:
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Federal statutory rate |
34.0 | % | 34.0 | % | ||||
| State income taxes, net of federal benefit |
4.6 | 4.8 | ||||||
| Non-deductible expenses |
(1.7 | ) | (1.9 | ) | ||||
| Income tax credits |
3.5 | 1.9 | ||||||
| Valuation allowance |
(40.4 | ) | (38.8 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Effective tax rate |
0.0 | % | 0.0 | % | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
F-17
Table of Contents
The components of net deferred tax assets are as follows (in thousands):
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Net operating loss carryforwards |
$ | 17,245 | $ | 13,552 | ||||
| Tax credit carryforwards |
745 | 442 | ||||||
| Stock-based compensation |
1,891 | 1,744 | ||||||
| Licensing deduction deferral |
5,385 | 5,979 | ||||||
| Other timing differences |
262 | 178 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Gross deferred tax assets |
25,528 | 21,895 | ||||||
| Valuation allowance |
(25,528 | ) | (21,895 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net deferred tax asset |
$ | — | $ | — | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
The Company’s deferred tax assets at December 31, 2016 and 2015 consisted primarily of its net operating loss carryforwards, deferred compensation, tax credit carryforwards, intangible assets capitalized for federal income tax purposes and certain accruals that for tax purposes are not deductible until future payment is made. The valuation allowance increased $3,633,000 and $3,960,000 for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively, and is primarily attributable to an increase in net operating losses, tax credits and stock-based compensation in 2016.
The Company has incurred net operating losses since inception. At December 31, 2016, the Company had federal and state net operating loss carryforwards of approximately $44,800,000 and $38,400,000, respectively, which are available to reduce future taxable income through 2036. In addition, the Company has federal and state research credits of $547,000 and $300,000, respectively, to offset future tax expense through 2036. Based on an assessment of all available evidence including, but not limited to the Company’s limited operating history in its core business and lack of profitability, uncertainties of the commercial viability of its technology, the impact of government regulation and healthcare reform initiatives, and other risks normally associated with biotechnology companies, the Company has concluded that it is more likely than not that these net operating loss carryforwards and credits will not be realized and, as a result, a full deferred income tax valuation allowance has been recorded against these assets.
Under the provisions of the Internal Revenue Code, certain substantial changes in the Company’s ownership may result in a limitation on the amount of net operating loss carryforwards and research and development credit carryforwards which could be utilized annually to offset future taxable income and taxes payable. The Company has not yet performed an analysis to determine if one or multiple ownership changes may have occurred in the past.
The Company files income tax returns in the United States, Massachusetts and New Jersey. The Company is subject to tax examinations for federal and state purposes tax years 2012 through 2016. The Company has not recorded any uncertain tax positions as of December 31, 2016 or 2015. The Company does not believe there will be any material changes in its unrecognized tax positions over the next 12 months. The Company has not incurred any interest or penalties. In the event that the Company is assessed interest or penalties at some point in the future, they will be classified in the financial statements as general and administrative expenses.
13. License Agreements
As part of its business, the Company enters into licensing agreements with third parties that often require milestone and royalty payments based on the progress of the asset through development stages. Milestone payments may be required, for example, upon approval of the product for marketing by a regulatory agency. In certain agreements, the Company is required to make royalty payments based upon a percentage of the sales of the products licensed pursuant to such agreements.
F-18
Table of Contents
The expenditures required under these arrangements may be material individually in the event that the Company develops product candidates covered by the intellectual property licensed under any such arrangement, and in the unlikely event that milestones for multiple products covered by these arrangements were reached in the same period, the aggregate charge to expense could be material to the results of operations. In addition, these arrangements often give the Company discretion to unilaterally terminate development of the product, which would allow the Company to avoid making the contingent payments; however, the Company is unlikely to cease development if the compound successfully achieves clinical testing objectives.
Advirna LLC. We have entered into an agreement with Advirna LLC (“Advirna”), pursuant to which Advirna assigned to us its existing patent and technology rights related to sd-rxRNA technology. In exchange to the Company is obligated to pay Advirna an annual maintenance fee, a milestone payment upon the issuance of the first patent with valid claims covering the assigned technology and royalties on any licensing revenue received by us with respect to future licensing of the assigned Advirna patent and technology rights. We also granted back to Advirna a license under the assigned patent and technology rights for fields of use outside human therapeutics.
Our rights under the Advirna agreement will expire upon the later of: (i) the expiration of the last-to-expire of the “patent rights” (as defined therein) included in the Advirna agreement; or (ii) the abandonment of the last-to-be abandoned of such patents, unless earlier terminated in accordance with the provisions of the agreement.
Hapten Pharmaceuticals, LLC. On December 17, 2014, the Company entered into an Assignment and License Agreement (the “Assignment and License Agreement”) with Hapten Pharmaceuticals, LLC (“Hapten”) under which Hapten agreed to sell and assign to us certain patent rights and related assets and rights, including an investigational new drug application and clinical data, for Hapten’s Samcyprone™ products for therapeutic and prophylactic use. Upon the closing of the Assignment and License Agreement in February 2015, the Company paid to Hapten a one-time upfront cash payment of $100,000 and issued to Hapten 20,000 shares of the Company’s common stock with a fair value of $228,000 which was determined using the quoted market price of the Company’s common stock on the date of issuance.
Under the Assignment and License Agreement, Hapten will be entitled to receive: (i) future milestone payments tied to the achievement of certain clinical and commercial objectives (all of which payments may be made at our option in cash or through the issuance of common stock); and (ii) escalating royalties based on product sales by us and any sublicensees.
We have certain customary diligence obligations under the Assignment and License Agreement requiring us to use commercially reasonable efforts to develop and commercialize one or more products covered by the Assignment and License Agreement, which obligations, if not performed, could result in rights assigned or licensed to us reverting back to Hapten.
14. Subsequent Events
Subsequent to December 31, 2016, 5,737 shares of Series B Preferred Stock were converted into 6,374,444 shares of common stock of the Company, as a result of which no shares of Series B Preferred Stock are outstanding.
On January 6, 2017, the Company entered into a Stock Purchase Agreement (the “Stock Purchase Agreement”) by and among the Company, RXi Merger Sub, LLC, a Delaware limited liability company and wholly owned subsidiary of the Company (“RXi Merger Sub”), MirImmune, the stockholders of MirImmune set forth on the signature pages thereto (each a “Seller” and collectively, the “Sellers”), and Alexey Wolfson, Ph.D., in his capacity as the Sellers’ Representative. Pursuant to the Stock Purchase Agreement, the Company acquired from the Sellers all of the issued and outstanding shares of capital stock of MirImmune for an aggregate of 2,750,371 shares of common stock of the Company and an aggregate of 1,115,579 shares of Series C Convertible Preferred Stock, par value $0.0001 per share (the “Series C Preferred Stock”), subject to a holdback of 3% of the aggregate closing consideration for any purchase price adjustments. The Stock Purchase Agreement contains customary representations and warranties and pre- and post-closing covenants and closing conditions.
Under the terms of the Stock Purchase Agreement, if certain development or commercial milestones are achieved within two years, the Company will be required to either: (i) issue to the Sellers a number of shares of common stock (the
F-19
Table of Contents
“Milestone Shares”) equal to the sum of 2,519,091 shares of common stock, plus an additional number of shares of common stock equal to 13% of the common stock issued upon exercise of any warrants issued under the 2016 Offering, but only to the extent that such warrants have been exercised prior to the milestone being achieved; or (ii) pay the equivalent value of the Milestone Shares in cash to the Sellers, subject to certain adjustments set forth in the Stock Purchase Agreement. In certain circumstances, if the Company has not received stockholder approval for the issuance of the Milestone Shares, the Company may be required to instead issue shares of Series C Preferred Stock in lieu of part or all of the common stock otherwise issuable as Milestone Shares.
In connection with and promptly following the closing of the Stock Purchase Agreement, MirImmune was merged with and into RXi Merger Sub (the “Merger”), with RXi Merger Sub continuing as the surviving entity and changing its name to “MirImmune, LLC”. As a result of the Merger, MirImmune, LLC remains and will operate as a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Company.
For accounting purposes, the transaction will be accounted for as an asset acquisition per the guidance in FASB ASC Topic 805, “Business Combinations.”
In connection with the Stock Purchase Agreement, on January 5, 2017, the Company filed a Certificate of Designation of Preferences, Rights and Limitations of Series C Convertible Preferred Stock (the “Series C Preferred Stock Certificate of Designation”) with the Secretary of State of the State of Delaware. The Series C Preferred Stock Certificate of Designation provides for the issuance of up to 1,800,000 shares of Series C Preferred Stock. The Series C Preferred Stock have no voting rights, with certain exceptions as described in the Series C Preferred Stock Certificate of Designations, and shall receive dividends on an as-converted basis at the same time and in the same form as any dividends paid out on shares of the Company’s common stock. Other than as set forth in the previous sentence, no other dividends shall be paid on the Series C Preferred Stock.
Upon approval by the Company’s stockholders in accordance with the stockholder approval requirements of Nasdaq Marketplace Rule 5635, each Series C Preferred Share shall be automatically converted into one share of common stock, subject to adjustment for stock splits, stock dividends, distributions, subdivisions and combinations. The Company shall not convert any of the Series C Preferred Shares into common stock to the extent that such conversion has not been approved by the Company’s stockholders in accordance with the above.
| ITEM 9. | CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE |
N/A.
| ITEM 9A. | CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES |
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Based on an evaluation as of the end of the period covered by this report, Dr. Geert Cauwenbergh, our Chief Executive Officer and acting Chief Financial Officer, has concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Exchange Act) were effective as of the end of the period covered by this report to ensure that information that we are required to disclose in reports that we file or submit under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in SEC rules and forms.
Our disclosure controls and procedures are designed to provide reasonable assurance of achieving their objectives, and Dr. Cauwenbergh has concluded that these controls and procedures are effective at the “reasonable assurance” level. We believe that a control system, no matter how well designed and operated, cannot provide absolute assurance that the objectives of the control system are met, and no evaluation of controls can provide absolute assurance that all control issues and instances of fraud, if any, within a company have been detected.
Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting. A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles.
F-20
Table of Contents
There are inherent limitations in the effectiveness of any system of internal control, including the possibility of human error and the circumvention or overriding of controls. Accordingly, even effective internal controls can provide only reasonable assurances with respect to financial statement preparation. Further, because of changes in conditions, the effectiveness of internal control may vary over time.
Our management assessed the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2016. In making this assessment, management used the criteria set forth in Internal Control – Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 framework). Based on our assessment, the Company’s Chief Executive Officer and acting Chief Financial Officer concluded that, as of December 31, 2016, our internal control over financial reporting is effective.
Attestation Report of the Registered Public Accounting Firm
This Annual Report on Form 10-K provides only management’s report. As a smaller reporting company, we are not required to provide an attestation report by our independent registered public accounting firm regarding internal control over financial reporting.
Changes in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
There were no changes in our internal control over financial reporting during the quarter ended December 31, 2016 that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
| ITEM 9B. | OTHER INFORMATION |
None.
| ITEM 10. | DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE |
We will file a definitive Proxy Statement, not later than 120 days after the fiscal year end of December 31, 2016. The information required by this item is incorporated herein by reference to the information contained in the Proxy Statement.
| ITEM 11. | EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION |
The information required by this item is incorporated herein by reference to the information contained in the Proxy Statement.
| ITEM 12. | SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS |
The information required by this item is incorporated herein by reference to the information contained in the Proxy Statement.
| ITEM 13. | CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE |
The information required by this item is incorporated herein by reference to the information contained in the Proxy Statement.
F-21
Table of Contents
| ITEM 14. | PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTANT FEES AND SERVICES |
The information required by this item is incorporated herein by reference to the information contained in the Proxy Statement.
| ITEM 15. | EXHIBITS AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES |
Financial Statements
Our financial statements are set forth in Item 8 to this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Financial Statement Schedules
Certain schedules are omitted because they are not applicable, or are not required by smaller reporting companies.
Exhibits
The exhibits listed on the Exhibit Index beginning on page II-1, which is incorporated herein by reference, are filed or furnished as part of this report or are incorporated into this report by reference.
| ITEM 16. | FORM 10-K SUMMARY |
None.
F-22
Table of Contents
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| RXi PHARMACEUTICALS CORPORATION | ||
| By: | /s/ Geert Cauwenbergh | |
| Geert Cauwenbergh, Dr. Med. Sc. | ||
| President, Chief Executive Officer and acting Chief Financial Officer | ||
| Date: March 30, 2017 | ||
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| Signatures |
Title |
Date | ||
| /s/ Geert Cauwenbergh Geert Cauwenbergh, Dr. Med. Sc. |
President, Chief Executive Officer, acting Chief Financial Officer and Director (Principal Executive Officer and Principal Financial Officer) |
March 30, 2017 | ||
| /s/ Caitlin Kontulis Caitlin Kontulis |
Director of Finance and Secretary (Principal Accounting Officer) |
March 30, 2017 | ||
| /s/ Robert J. Bitterman Robert J. Bitterman |
Director | March 30, 2017 | ||
| /s/ Keith L. Brownlie Keith L. Brownlie |
Director | March 30, 2017 | ||
| /s/ H. Paul Dorman H. Paul Dorman |
Director | March 30, 2017 | ||
| /s/ Curtis A. Lockshin Curtis A. Lockshin, Ph.D. |
Director | March 30, 2017 | ||
Table of Contents
Exhibits
EXHIBIT INDEX
| Exhibit |
Incorporated by Reference Herein | |||||
| Number |
Description |
Form |
Date | |||
| 2.1 |
Asset Purchase Agreement, dated March 1, 2013, between RXi Pharmaceuticals Corporation and OPKO Health, Inc. + | Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (File No. 000-54910) | March 15, 2013 | |||
| 2.2 |
Stock Purchase Agreement, dated January 6, 2017, by and among RXi Pharmaceuticals Corporation, RXi Merger Sub, LLC, MirImmune Inc., certain shareholders named therein and Alexey Wolfson, Ph.D., in his capacity as Sellers’ Representative. + | Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-36304) | January 10, 2017 | |||
| 3.1 |
Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation of RXi Pharmaceuticals Corporation. | Amendment No. 4 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-177498) | February 7, 2012 | |||
| 3.2 |
Certificate of Amendment to the Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation of RXi Pharmaceuticals Corporation. | Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 000-54910) | July 22, 2013 | |||
| 3.3 |
Certificate of Designations, Preferences and Rights of Series A Convertible Preferred Stock of RXi Pharmaceuticals Corporation. | Amendment No. 4 to Registration Statement Form S-1 (File No. 333-177498) | February 7, 2012 | |||
| 3.4 |
Certificate of Designations, Preferences and Rights of Series A-1 Convertible Preferred Stock of RXi Pharmaceuticals Corporation. | Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (File No. 000-54910) | August 14, 2013 | |||
| 3.5 |
Certificate of Increase, filed with the Secretary of State of the State of Delaware on January 24, 2014. | Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 000-54910) | January 24, 2014 | |||
| 3.6 |
Certificate of Amendment to the Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation of RXi Pharmaceuticals Corporation. | Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-203389) | April 13, 2015 | |||
| 3.7 |
Certificate Eliminating the Series A Convertible Preferred Stock from the Certificate of Incorporation of RXi Pharmaceuticals Corporation. | Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (File No. 001-36304) | November 12, 2015 | |||
| 3.8 |
Certificate Eliminating the Series A-1 Convertible Preferred Stock from the Certificate of Incorporation of RXi Pharmaceuticals Corporation. | Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (File No. 001-36304) | November 12, 2015 | |||
| 3.9 |
Certificate of Amendment to the Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation of RXi Pharmaceuticals Corporation. | Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-36304) | April 15, 2016 | |||
| 3.10 |
Certificate of Designation of Preferences, Rights and Limitations of Series B Convertible Preferred Stock of RXi Pharmaceuticals Corporation. | Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-36304) | December 21, 2016 | |||
| 3.11 |
Certificate of Designation of Preferences, Rights and Limitations of Series C Convertible Preferred Stock of RXi Pharmaceuticals Corporation. | Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-36304) | January 10, 2017 | |||
II-1
Table of Contents
| 3.12 |
Amended and Restated Bylaws of RXi Pharmaceuticals Corporation. | Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (File No. 333-177498) | May 14, 2012 | |||
| 4.1 |
Form of Warrant. | Amendment No. 1 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-203389) | May 21, 2015 | |||
| 4.2 |
Form of Warrant. | Amendment No. 3 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-214199) | December 14, 2016 | |||
| 10.1 |
Employment Agreement, dated September 24, 2011, between RXi Pharmaceuticals Corporation (formerly, RNCS, Inc.) and Pamela Pavco, Ph.D.* | Current Report on Form 8-K of Galena Biopharma, Inc. (File No. 001-33958) | September 26, 2011 | |||
| 10.2 |
Patent and Technology Assignment Agreement between RXi Pharmaceuticals Corporation (formerly RNCS, Inc.) and Advirna, LLC, effective as of September 24, 2011. | Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-177498) | October 25, 2011 | |||
| 10.3 |
RXi Pharmaceuticals Corporation 2012 Long Term Incentive Plan.* | Amendment No. 3 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-177498) | January 23, 2012 | |||
| 10.4 |
Form of Incentive Stock Option Award under the Company’s 2012 Long Term Incentive Plan, as amended.* | Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-191236 | September 18, 2013 | |||
| 10.5 |
Form of Non-qualified Stock Option Award under the Company’s 2012 Long Term Incentive Plan, as amended.* | Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-191236 | September 18, 2013 | |||
| 10.6 |
Form of Restricted Stock Unit Award under the Company’s 2012 Long Term Incentive Plan, as amended.* | Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-191236 | September 18, 2013 | |||
| 10.7 |
Amendment to RXi Pharmaceuticals Corporation Long-Term Incentive Plan.* | Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-191236 | September 18, 2013 | |||
| 10.8 |
Amendment to RXi Pharmaceuticals Corporation Long-Term Incentive Plan.* | Definitive Proxy Statement on Schedule 14A (file No. 001-36304) | November 4, 2016 | |||
| 10.9 |
RXi Pharmaceuticals Corporation Employee Stock Purchase Plan.* | Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-191236 | September 18, 2013 | |||
| 10.10 |
Amendment to RXi Pharmaceuticals Corporation Employee Stock Purchase Plan.* | Definitive Proxy Statement on Schedule 14A (file No. 001-36304) | November 4, 2016 | |||
| 10.11 |
Form of Indemnification Agreement.* | Amendment No. 3 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-177498) | January 23, 2012 | |||
| 10.12 |
Employment Agreement, dated April 27, 2012, between RXi Pharmaceuticals Corporation and Geert Cauwenbergh, Dr. Med. Sc.* | Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 333-177498) | May 3, 2012 | |||
II-2
Table of Contents
| 10.13 | Lease Agreement dated December 17, 2013 between RXi Pharmaceuticals Corporation and 257 Simarano Drive, LLC, Brighton Properties, LLC, Robert Stubblebine 1, LLC and Robert Stubblebine 2, LLC. | Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 000-54910) | December 20, 2013 | |||
| 10.14 | Purchase Agreement, dated as of April 22, 2014, between RXi Pharmaceuticals Corporation and Lincoln Park Capital Fund, LLC. | Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-36304) | April 23, 2014 | |||
| 10.15 | Purchase Agreement, dated as of December 18, 2014, between RXi Pharmaceuticals Corporation and Lincoln Park Capital Fund, LLC. | Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-36304) | December 19, 2014 | |||
| 10.16 | Engagement Agreement, dated February 25, 2015 between RXi Pharmaceuticals Corporation and H.C. Wainwright & Co., LLC. | Amendment No. 1 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-203389) | May 21, 2015 | |||
| 10.17 | Amendment to Engagement Agreement, dated April 20, 2015 between RXi Pharmaceuticals Corporation and H.C. Wainwright & Co., LLC. | Amendment No. 1 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-203389) | May 21, 2015 | |||
| 10.18 | Amendment to Engagement Agreement, dated May 19, 2015 between RXi Pharmaceuticals Corporation and H.C. Wainwright & Co., LLC. | Amendment No. 1 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-203389) | May 21, 2015 | |||
| 10.19 | Form of Securities Purchase Agreement. | Amendment No. 1 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-203389) | May 21, 2015 | |||
| 10.20 | Employment Agreement, dated January 6, 2017, between RXi Pharmaceuticals Corporation and Alexey Eliseev, Ph.D.**** | |||||
| 10.21 | Non-Competition Agreement, dated January 6, 2017, between RXi Pharmaceuticals Corporation and Alexey Eliseev, Ph.D.**** | |||||
| 23.1 | Consent of BDO USA, LLP, an Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm.**** | |||||
| 31.1 | Sarbanes-Oxley Act Section 302 Certification of Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer.**** | |||||
| 32.1 | Sarbanes-Oxley Act Section 906 Certification of Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer.**** | |||||
| 101 | The following financial information from the Annual Report on Form 10-K of RXi Pharmaceuticals Corporation for the year ended December 31, 2016, formatted in XBRL (eXtensible Business Reporting Language): (1) Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2016 and 2015; (2) Statements of Operations for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015; (3) Statements of Convertible Preferred Stock and Statements of Stockholders’ Equity for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015; (4) Statements of Cash Flows for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015; and (4) Notes to Financial Statements.**** | |||||
| * | Indicates a management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement. |
| **** | Filed herewith. |
| + | Confidential treatment has been requested or granted for certain portions which have been blanked out in the copy of the exhibit filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission. The omitted information has been filed separately with the Securities and Exchange Commission. |
II-3
