Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-99.2 - EX-99.2 - vTv Therapeutics Inc. | vtvt-ex992_57.htm |
| 8-K - 8-K - vTv Therapeutics Inc. | vtvt-8k_20170329.htm |
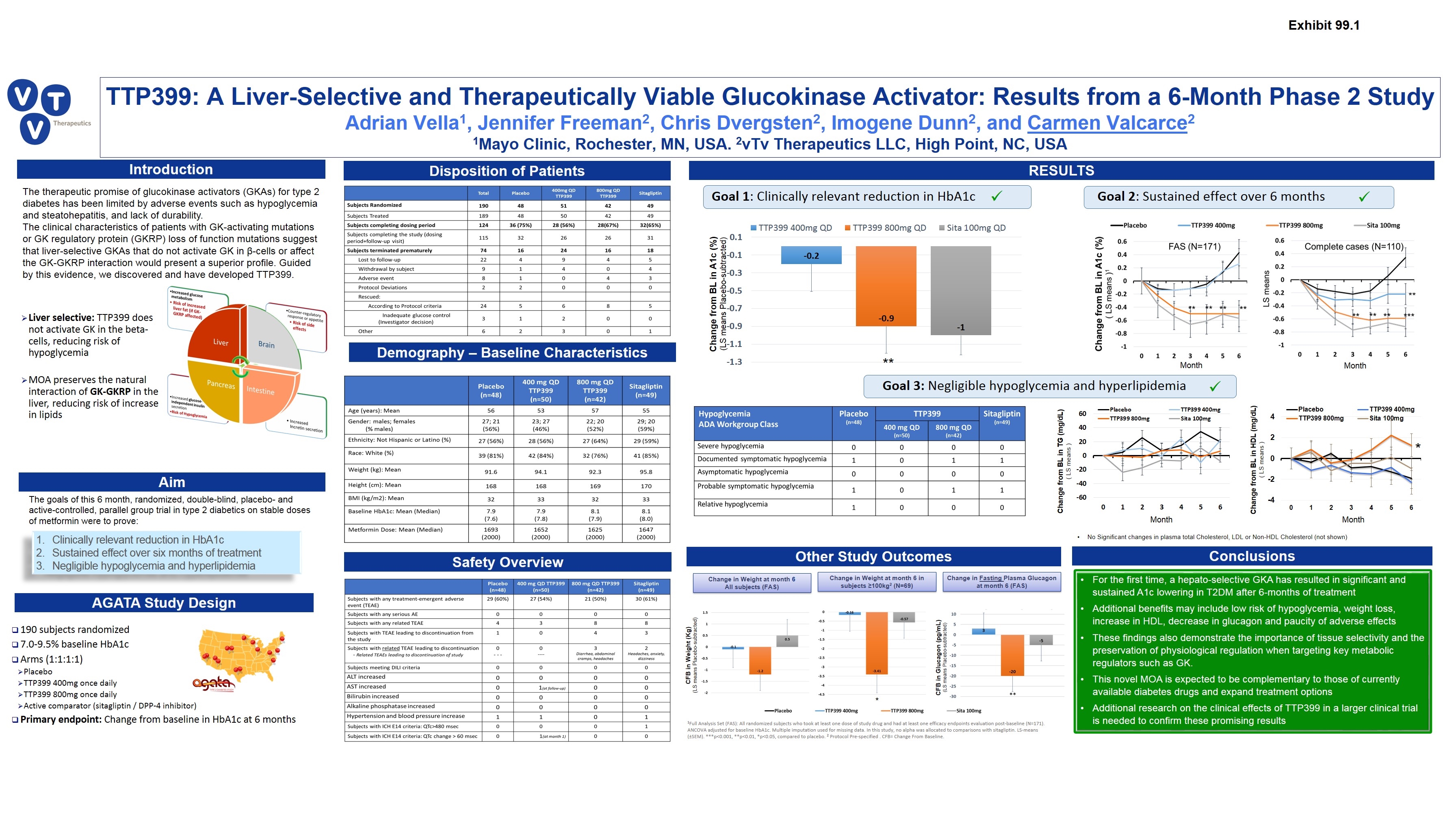
Introduction RESULTS TTP399: A Liver-Selective and Therapeutically Viable Glucokinase Activator: Results from a 6-Month Phase 2 Study Adrian Vella1, Jennifer Freeman2, Chris Dvergsten2, Imogene Dunn2, and Carmen Valcarce2 1Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, USA. 2vTv Therapeutics LLC, High Point, NC, USA Safety Overview For the first time, a hepato-selective GKA has resulted in significant and sustained A1c lowering in T2DM after 6-months of treatment Additional benefits may include low risk of hypoglycemia, weight loss, increase in HDL, decrease in glucagon and paucity of adverse effects These findings also demonstrate the importance of tissue selectivity and the preservation of physiological regulation when targeting key metabolic regulators such as GK. This novel MOA is expected to be complementary to those of currently available diabetes drugs and expand treatment options Additional research on the clinical effects of TTP399 in a larger clinical trial is needed to confirm these promising results The therapeutic promise of glucokinase activators (GKAs) for type 2 diabetes has been limited by adverse events such as hypoglycemia and steatohepatitis, and lack of durability. The clinical characteristics of patients with GK-activating mutations or GK regulatory protein (GKRP) loss of function mutations suggest that liver-selective GKAs that do not activate GK in β-cells or affect the GK-GKRP interaction would present a superior profile. Guided by this evidence, we discovered and have developed TTP399. Aim Demography – Baseline Characteristics Disposition of Patients Liver selective: TTP399 does not activate GK in the beta-cells, reducing risk of hypoglycemia MOA preserves the natural interaction of GK-GKRP in the liver, reducing risk of increase in lipids Clinically relevant reduction in HbA1c Sustained effect over six months of treatment Negligible hypoglycemia and hyperlipidemia The goals of this 6 month, randomized, double-blind, placebo- and active-controlled, parallel group trial in type 2 diabetics on stable doses of metformin were to prove: AGATA Study Design 190 subjects randomized 7.0-9.5% baseline HbA1c Arms (1:1:1:1) Placebo TTP399 400mg once daily TTP399 800mg once daily Active comparator (sitagliptin / DPP-4 inhibitor) Primary endpoint: Change from baseline in HbA1c at 6 months 1Full Analysis Set (FAS): All randomized subjects who took at least one dose of study drug and had at least one efficacy endpoints evaluation post-baseline (N=171). ANCOVA adjusted for baseline HbA1c. Multiple imputation used for missing data. In this study, no alpha was allocated to comparisons with sitagliptin. LS-means (±SEM). ***p<0.001, **p<0.01, *p<0.05, compared to placebo. 2 Protocol Pre-specified . CFB= Change From Baseline. Goal 1: Clinically relevant reduction in HbA1c Change from BL in A1c (%) (LS means Placebo-subtracted) Goal 2: Sustained effect over 6 months Goal 3: Negligible hypoglycemia and hyperlipidemia Conclusions Other Study Outcomes Change in Weight at month 6 in subjects ≥100kg2 (N=69) CFB in Glucagon (pg/mL) (LS means Placebo-subtracted) Change in Weight at month 6 All subjects (FAS) Change in Fasting Plasma Glucagon at month 6 (FAS) CFB in Weight (Kg) (LS means Placebo-subtracted) * Month Month Change from BL in TG (mg/dL) ( LS means ) Change from BL in HDL (mg/dL) ( LS means ) * No Significant changes in plasma total Cholesterol, LDL or Non-HDL Cholesterol (not shown) Month Month Exhibit 99.1
