Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-32.1 - EX-32.1 - CONTRAFECT Corp | d280078dex321.htm |
| EX-31.1 - EX-31.1 - CONTRAFECT Corp | d280078dex311.htm |
| EX-23.1 - EX-23.1 - CONTRAFECT Corp | d280078dex231.htm |
| EX-10.29 - EX-10.29 - CONTRAFECT Corp | d280078dex1029.htm |
| EX-10.28 - EX-10.28 - CONTRAFECT Corp | d280078dex1028.htm |
| EX-10.27 - EX-10.27 - CONTRAFECT Corp | d280078dex1027.htm |
Table of Contents
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, DC 20549
Form 10-K
(Mark One)
| ☒ | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2016
OR
| ☐ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
Commission File Number: 001-36577
ContraFect Corporation
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| Delaware | 39-2072586 | |
| (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) |
(IRS Employer Identification No.) | |
| 28 Wells Avenue, 3rd Floor Yonkers, NY |
10701 | |
| (Address of principal executive offices) | (Zip Code) | |
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code:
(914) 207-2300
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| Title of Class |
Name of Exchange on Which Registered | |
| Common Stock, Par Value $0.0001 per share |
NASDAQ Capital Market |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§ 232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer or a smaller reporting company. See definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. (Check one):
| Large accelerated filer | ☐ | Accelerated filer | ☒ | |||
| Non-accelerated filer | ☐ (Do not check if a smaller reporting company) | Smaller reporting company | ☐ | |||
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). Yes ☐ No ☒
As of June 30, 2016, the last business day of the registrant’s most recently completed second fiscal quarter, the aggregate market value of the registrant’s common stock held by non-affiliates of the registrant was approximately $73.4 million, based on the closing price of the registrant’s common stock on the NASDAQ Capital Market on June 30, 2016 of $2.89 per share.
As of March 7, 2017, there were 41,656,006 shares of Common Stock, $0.0001 par value per share, outstanding.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Portions of the registrant’s definitive Proxy Statement relating to its 2017 Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission are incorporated by reference into Part III of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Table of Contents
| Page | ||||||
| PART I | ||||||
| Item 1. |
1 | |||||
| Item 1A. |
30 | |||||
| Item 1B. |
59 | |||||
| Item 2. |
59 | |||||
| Item 3. |
59 | |||||
| Item 4. |
59 | |||||
| PART II | ||||||
| Item 5. |
60 | |||||
| Item 6. |
62 | |||||
| Item 7. |
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations |
62 | ||||
| Item 7A. |
73 | |||||
| Item 8. |
73 | |||||
| Item 9. |
Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure |
73 | ||||
| Item 9A. |
74 | |||||
| Item 9B. |
74 | |||||
| PART III | ||||||
| Item 10. |
76 | |||||
| Item 11. |
80 | |||||
| Item 12. |
Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters |
80 | ||||
| Item 13. |
Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence |
80 | ||||
| Item 14. |
81 | |||||
| PART IV | ||||||
| Item 15. |
82 | |||||
| Item 16. |
82 | |||||
i
Table of Contents
References to ContraFect
Throughout this Annual Report on Form 10-K, the “Company,” “ContraFect,” “we,” “us,” and “our,” except where the context requires otherwise, refer to ContraFect Corporation, and “our board of directors” refers to the board of directors of ContraFect Corporation.
All brand names or trademarks appearing in this Annual Report on Form 10-K are the property of their respective holders.
Forward Looking Information
The information in this Annual Report on Form 10-K contains forward-looking statements and information within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, or the Securities Act, and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, or the Exchange Act, which are subject to the “safe harbor” created by those sections. These forward-looking statements include, but are not limited to, statements concerning our strategy, future operations, future financial position, future revenues, projected costs, prospects and plans and objectives of management. The words “anticipates”, “believes”, “estimates”, “expects”, “intends”, “targets”, “may”, “plans”, “projects”, “potential”, “will”, “would”, “could” and similar expressions are intended to identify forward-looking statements, although not all forward-looking statements contain these identifying words. All such forward-looking statements involve significant risks and uncertainties, including, but not limited to, statements regarding:
| • | the success, cost, timing and potential indications of our product development activities and clinical trials; |
| • | our ability to advance into and through clinical development and ultimately obtain FDA approval for our product candidates; |
| • | our future marketing and sales programs; |
| • | the rate and degree of market acceptance of our product candidates and our expectations regarding the size of the commercial markets for our product candidates; |
| • | our research and development plans and ability to bring forward additional product candidates into preclinical and clinical development; |
| • | the effect of competition and proprietary rights of third parties; |
| • | the availability of and our ability to obtain additional financing; |
| • | the effects of existing and future federal, state and foreign regulations; |
| • | the seeking of joint development, licensing or distribution and collaboration and marketing arrangements with third parties; and |
| • | the period of time for which our existing cash and cash equivalents will enable us to fund our operations. |
As more fully described under the heading “Risk Factors” contained elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, many important factors affect our ability to achieve our stated objectives and to develop and commercialize any product candidates. We may not actually achieve the plans, intentions or expectations disclosed in our forward-looking statements and you should not place undue reliance on our forward-looking statements. These forward-looking statements involve risks and uncertainties that could cause our actual results to differ materially from those in the forward-looking statements, including, without limitation, the risks and uncertainties set forth in our filings with the SEC. You should read this Annual Report on Form 10-K and the documents that we have filed as exhibits to this Annual Report on Form 10-K completely and with the understanding that our actual results or events could differ materially from the plans, intentions and expectations disclosed in the forward-looking statements that we make. The forward-looking statements are applicable only as of the date on which they are made, and we do not assume any obligation to update any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise, except as required by law.
ii
Table of Contents
We are a clinical-stage biotechnology company focused on discovering and developing therapeutic protein and antibody products for the treatment of life-threatening infectious diseases, including those caused by drug-resistant pathogens, particularly those treated in hospital settings. Drug-resistant infections account for two million illnesses in the United States and 700,000 deaths worldwide each year. We intend to address drug-resistant infections using product candidates from our lysin and monoclonal antibody platforms that target conserved regions of either bacteria or viruses. Lysins are enzymes derived from naturally occurring bacteriophage which are viruses that infect bacteria. When recombinantly produced and then applied to bacteria, lysins cleave a key component of the target bacteria’s peptidoglycan cell wall, which results in rapid bacterial cell death. Lysins kill bacteria faster than conventional antibiotics, which typically require bacterial cell division and metabolism in order to kill or stop the growth of bacteria. We believe that the properties of our lysins will make them suitable for targeting antibiotic-resistant organisms, such as Staphylococcus aureus (“Staph aureus”) which causes serious infections such as bacteremia, pneumonia and osteomyelitis. In addition, our lysins have demonstrated the ability to clear biofilms in animal models, and we believe they may be useful for the treatment of biofilm-related infections in prosthetic joints, indwelling devices and catheters. Beyond our lysin programs, we are exploring therapies using monoclonal antibodies (“mAbs”) designed to bind to viral targets. Our approach to antibody therapy employs a combination of multiple mAbs to either achieve greater efficacy or provide broader coverage across pathogenic strains.
In August 2015, our most advanced lysin product candidate, CF-301, was granted fast track designation for the treatment of Staph aureus bacteremia, including endocarditis. We have concluded a Phase 1 single ascending dose study of CF-301 in healthy volunteers. The study was designed as a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in order to evaluate the safety, tolerability and pharmacokinetics of CF-301 alone, administered as a single two hour intravenous (“IV”) infusion. As specified in the protocol, an independent data safety monitoring board (the “DSMB”) reviewed the safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetic data from healthy volunteers dosed in all of the planned cohorts. CF-301 was generally well tolerated and there were no clinical adverse safety signals in the study. We intend to pursue an initial indication for the treatment of Staph aureus bacteremia, including endocarditis, caused by methicillin-resistant (“MRSA”) or methicillin-susceptible (“MSSA”) Staph aureus. We believe CF-301 may also be developed for the treatment of Staph aureus pneumonia, osteomyelitis, and biofilm-related infections in prosthetic joints, indwelling devices and catheters. Our second product candidate, CF-404, is a combination of three human mAbs for the treatment of life-threatening human influenza, including all seasonal and most pandemic varieties. We are also advancing earlier stage programs that leverage the lysin and monoclonal antibody platforms.
Our Strategy
Our strategy is to use our therapeutic products to achieve a leading market position in the treatment of life-threatening infectious diseases, including those caused by drug-resistant pathogens. We plan to pursue commercialization of therapeutic products through discovery, acquisition and development as follows:
| • | Advance our lead product candidate, CF-301, through clinical trials and demonstrate superiority of our therapy combined with standard-of-care (“SOC”) drugs over SOC alone for the treatment of Staph aureus bacteremia; |
| • | Advance additional product candidates from our lysin and antibody portfolio, including CF-404 and lysins to gram-negative bacteria; |
| • | Acquire additional foundation technologies that enable the efficient discovery of anti-infective agents; and |
| • | Acquire clinical stage therapies that treat infectious diseases through unique mechanisms of action. |
1
Table of Contents
Our Indications
Staph aureus bacteremia
In the United States (“U.S.”) alone there are approximately 120,000 cases annually of Staph aureus bacteremia, a bloodstream infection, which causes approximately 30,000 deaths. Staph aureus bacteremia can be further complicated when the infection spreads into the heart muscle, heart valves or lining of the heart, causing endocarditis. Even with current SOC antibiotic therapy, the resulting damage to the heart muscle or heart valves could require surgery to prevent stroke, heart failure or severe organ damage. Of further concern, drug-resistant strains of Staph aureus are now evolving additional resistance against SOC antibiotics, which may ultimately result in an increase in the number of cases and in mortality from Staph aureus bacteremia, including endocarditis.
Influenza
On a global basis, approximately 20% of children and 5% of adults develop symptomatic influenza annually, resulting in approximately 4 million severe cases and 375,000 deaths each year. Of further concern, despite the widespread availability of annual vaccines in the U.S., approximately 30 million people will contract influenza, resulting in an average of over 200,000 hospitalizations and up to 49,000 influenza-associated deaths each year in the U.S. alone. Because of reduced vaccine effectiveness against the predominant circulating influenza virus in the 2014-2015 season, approximately 40 million people contracted influenza, resulting in over 970,000 flu-associated hospitalizations. As a result of genetic drift and genetic shift, mutations in influenza occur each year as it circulates through the population. These mutations may result in drug-resistance of the virus and ineffectiveness of the vaccine, which causes the need for annual reformulation of the vaccine. In addition, influenza has multiple chromosomes, and the virus can grow in a variety of species, such as human, swine, bird, etc., which may result in novel strains of influenza entering into human circulation, as did the “swine flu”. These new viruses have the potential to cause worldwide pandemics.
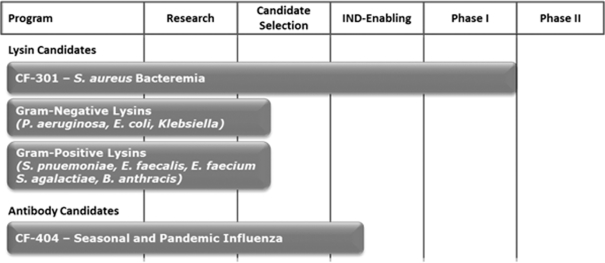
Our Pipeline
With our product candidates, we intend to treat life-threatening infections, including those caused by drug resistant pathogens. Our current pipeline of product candidates and advanced research programs is reflected in Figure 1:
2
Table of Contents
Lysins
Lysins are enzymes derived from naturally occurring bacteriophage, which are viruses that infect bacteria. When recombinantly produced and then applied to bacteria, lysins cleave a key component of the target bacteria’s peptidoglycan cell wall, resulting in rapid bacterial cell death. We believe lysins are unlike conventional antibiotics, especially regarding their mechanism and speed of action. Conventional antibiotics require bacterial cell division and metabolism to occur in order to exert their effect (i.e., cell death or cessation of growth). Based on in vitro tests, lysins, however, are fundamentally different in that they kill bacteria immediately upon contact, regardless of bacterial growth and cell division.
Bacteria can be divided into two groups based on structural differences of the bacteria’s outermost walls: (a) “gram-positive” and (b) “gram-negative”. Gram-positive bacteria have an outermost cell wall of peptidoglycan (a structure consisting of sugars and amino acids), which, when exposed to a dye known as the “Gram-stain,” absorb the dye and appear dark blue or violet when viewed under a microscope whereas Gram-negative bacteria which have an additional outer membrane, appear red under a microscope by the Gram staining technique. We have multiple research programs ongoing and have discovered lysins that selectively kill specific species of gram-positive or gram-negative bacteria.
Our pipeline of lysins includes internally discovered lysins targeting gram-positive and gram-negative organisms, as well as lysins discovered at The Rockefeller University (“Rockefeller”) which are being developed by us. We were granted a worldwide, exclusive license under Rockefeller patent rights to discover, develop, make, have made, use, import, lease, sell and offer for sale lysin products. We acquired worldwide exclusive license rights to patents for composition of matter for nine lysins from Rockefeller. Each lysin targets a specific species of bacteria, including drug-sensitive and drug-resistant forms of Staph aureus, pneumococcus, group B streptococcus, enterococcus and anthrax. Significantly, lysins have a “narrow spectrum” meaning they kill only specific species of bacteria or closely related bacteria, an attribute we believe will avoid the damaging side effects that often occur when conventional “broad spectrum” antibiotics kill the body’s normal, desirable bacteria. Table 1 sets forth the lysins for which we have acquired licenses to patents from Rockefeller, the bacteria that each lysin targets and the diseases associated with such pathogenic bacteria.
Table 1: Lysins Licensed from The Rockefeller University
| Lysin |
Bacteria | Disease | ||||
|
CF-301, CF-302 |
Staphylococcus aureus | Bacteremia* | ||||
| Abscesses* | ||||||
| Endocarditis | ||||||
| Meningitis | ||||||
| Pneumonia Skin/Skin Structure Infections | ||||||
| CF-303, CF-309 |
Pneumococcus | Pneumonia* | ||||
| Bacteremia* | ||||||
| Endocarditis* | ||||||
| Meningitis* | ||||||
| Otitis Media* | ||||||
| CF-304 |
Enterococcus | Serious Intestinal Infections | ||||
| CF-305 |
Group B Strep | Neonatal Meningitis* | ||||
|
CF-306, CF-307, CF-308 |
Bacillus Anthracis | Anthrax* | ||||
| * | Indicates published data showing lysin activity in specific disease models. |
3
Table of Contents
Our Lead Lysin Program: CF-301
CF-301: Market Opportunity
CF-301 represents a first-in-class anti-bacterial therapeutic candidate. CF-301 has been granted fast track designation for the initial indication we intend to pursue for the treatment of Staph aureus bacteremia, including endocarditis, caused by MRSA or MSSA. If we are able to obtain regulatory approval of CF-301 for this initial indication, we believe CF-301 may be further developed for the treatment of Staph aureus pneumonia, osteomyelitis, and biofilm-related infections in prosthetic joints, indwelling devices and catheters.
The issue of antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections has been widely recognized as an increasingly urgent public health threat, including by the World Health Organization, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Infectious Disease Society of America. Antibiotic resistance has limited the effectiveness of many existing drugs, and the discovery of new antibiotics to address resistance has not kept pace with the increasing incidence of difficult-to-treat microbial infections. According to the Infectious Diseases Society of America, as of 2010 the estimated cost to the U.S. healthcare system of antibiotic-resistant infections was approximately $21 billion to $34 billion annually, a substantial portion of which is due to increased length of hospital stays.
Staph aureus bacteremia is a serious bacterial infection associated with high morbidity and mortality. In the U.S. alone, there were approximately 120,000 cases of Staph aureus bacteremia, of which over 80,000 were reported as invasive MRSA infections in 2011. Of further concern, the incidence of infective endocarditis is increasing, with over 47,000 cases in 2011, due to the growth of the at-risk populations, such as adults with heart disease and prosthetic device implants, especially cardiac devices.
CF-301: Potential Advantages
Our preclinical studies to date have shown that CF-301 has the following attributes:
| • | Rapid and selective bactericidal activity. In vitro, CF-301 kills Staph aureus bacteria within seconds after contact. CF-301 exhibits potent antibacterial activity against Staph aureus strains, including methicillin sensitive staph aureus (MSSA), as well as the superbug MRSA (methicillin-resistant Staph aureus) and Staph aureus strains resistant to vancomycin, daptomycin, or linezolid. Significantly, CF-301 is highly selective against Staph aureus, which we believe will avoid the damaging side effects that often occur when conventional broad spectrum antibiotic treatments are used, which often can destroy the body’s normal, desirable bacterial flora (known as the microbiome). |
| • | Synergy with standard-of-care (SOC) antibiotics. We have discovered a strong synergy between CF-301 and several SOC antibiotics, including daptomycin, vancomycin and oxacillin. We intend to seek approval for CF-301 to be used in addition to SOC antibiotics. We believe that, if approved, the use of CF-301, in addition to (rather than as a replacement for) SOC antibiotics, will provide the best outcome for patients and may help speed adoption of our product by physicians. |
| • | Clears biofilms. In in vitro studies, CF-301 clears biofilms that protect bacterial infections in the body. Infected human tissues, such as a heart valve in endocarditis or bone in osteomyelitis, or indwelling medical devices, such as central venous catheters, prosthetic joints and pacemakers, are common sites for biofilm formation, providing an impediment to effective treatment using antibiotics alone. |
| • | Minimal resistance potential. To date, preclinical studies demonstrate that the propensity for bacteria to develop resistance to CF-301 is very low. CF-301 has also been shown to suppress the emergence of resistance to SOC antibiotics when used in combination. |
| • | Minimal competition. There are only two FDA approved drugs for the treatment of MRSA bacteremia - vancomycin and daptomycin. CF-301 works synergistically with both of these drugs and is intended to be used in addition to, not as a replacement for, SOC antibiotics. |
| • | Patent protection. Our issued composition of matter patent on CF-301 provides protection through 2032 and additional patents, if issued as we expect, could provide further protection beyond 2032. |
4
Table of Contents
CF-301: Preclinical Data
A key feature of lysins is their ability to target pathogenic antibiotic-resistant bacteria, as well as those that are antibiotic-sensitive. Table 2 sets forth our findings of CF-301’s effect on Staph aureus isolates, showing that CF-301 killed all Staph aureus isolates tested, regardless of their antibiotic-resistance profile. In this experiment, we tested 250 different drug sensitive and resistant isolates of Staph aureus. The isolates (which are classified by the particular drugs they are sensitive or resistant too) tested included MSSA, MRSA, VRSA, linezolid-resistant (“LRSA”) and daptomycin-resistant (“DRSA”) Staph aureus. The isolates were all analyzed to determine their sensitivity to CF-301 and SOC antibiotics as measured by the Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (“MIC”) value. The MIC value is the minimum dose of drug that is required to kill a standard amount of bacteria over a 24-hour period. Based on demonstrated MIC values, CF-301 was shown to be active against all the strains tested (‘+’), while subsets of the Staph aureus strains were resistant to daptomycin, vancomycin or linezolid (‘–’).
Table 2: In Vitro Sensitivity of Antibiotic-Sensitive and Antibiotic-Resistant Strains to CF-301
| Strain (n=250) |
CF-301 | Daptomycin | Vancomycin | Linezolid | ||||
| MRSA (120) |
+ | + | + | + | ||||
| MSSA (103) |
+ | + | + | + | ||||
| DRSA (8) |
+ | - | + | + | ||||
| VRSA (14) |
+ | + | - | + | ||||
| LRSA (5) |
+ | + | + | - | ||||
Lysins have been shown to kill bacteria upon contact and demonstrate bactericidal activity (defined as a 3-log drop in colony forming units (“CFU”) per mL) in minutes. The figure below compares the rate at which lysins kill bacteria to the rates at which SOC antibiotics kill bacteria (with all drugs being administered at a concentration of 1X MIC). CF-301 reduced the number of Staph aureus bacteria in tests on 62 strains (20 MSSA; 42 MRSA) by 3-logs (99.9%) within 30 minutes. In contrast, daptomycin required six hours to achieve the same level of cell killing, while vancomycin failed to achieve a 2-log, or 99%, cell kill during the same six-hour test period. The rapid bactericidal activity of lysins is one of the primary reasons we believe they could be a highly desirable therapeutic option for the treatment of rapidly advancing bacterial infections.
5
Table of Contents
Figure 2: CF 301’s Rapid Bactericidal Activity In Vitro
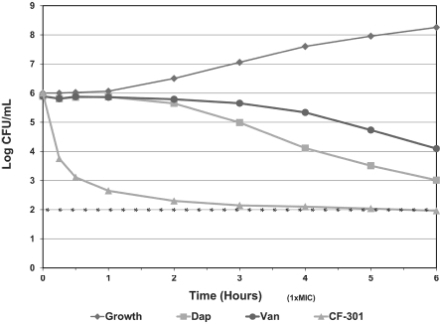
| * | The star symbols indicate the limit of detection in the plating assay. |
CF-301: Synergy with Standard-of-Care Antibiotics
Synergy is defined as the interaction of two or more agents so that their combined effect is greater than the sum of their individual effects. We discovered a strong synergy between lysins and several SOC antibiotics, including daptomycin, vancomycin and oxacillin through our in vitro testing (data not shown). In these preclinical tests, when used together, lysins and antibiotics offered a dual attack on pathogenic bacteria that was far greater than the sum of their individual contributions. The result was significantly improved killing of bacteria.
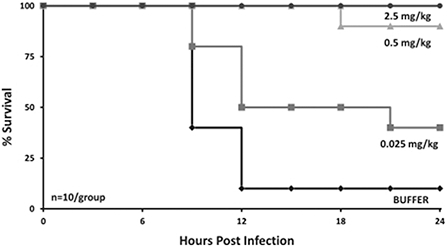
To demonstrate this synergy in vivo, we have developed animal models where CF-301 could be tested as single agent (monotherapy) or combined with a SOC antibiotic (combination therapy). Our Standard Bacteremia Model utilizes animals infected with 10 million (107) CFU of MRSA and treated 3 hours later with various doses of therapy or buffer. When used alone, CF-301 has potent anti-Staph activity that demonstrates a dose/response effect. Figure 3 below presents the dose/response of animals treated with various doses of CF-301 in the Standard Bacteremia Model. As pictured on the graph below, all mice receiving at least 0.5 mg/kg of CF-301 demonstrated at least 90% survival, whereas doses below 0.5 mg/kg resulted in lower survival rates.
6
Table of Contents
Figure 3: CF-301 Dose Response in Mice in the Standard Bacteremia Model
We also developed the Drug Failure Bacteremia Model, where the bacterial infection burden (one billion (109) CFU) was so high that SOC antibiotics used at their human equivalent doses as monotherapies failed to produce significant cure rates. We tested daptomycin, vancomycin and oxacillin in this model (data not shown for vancomycin and oxacillin). We then adjusted the dose of CF-301 so that CF-301 monotherapy would also fail to have significant cure rates under these intense infection conditions. To test whether the synergy that we had observed in vitro between CF-301 and SOC antibiotics would lead to improved efficacy in vivo, we then treated groups of animals in the Drug Failure Bacteremia Model with the drugs as monotherapies and also in combinations to evaluate if there was an improvement in efficacy.
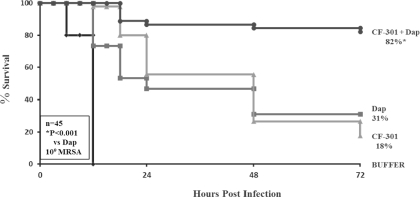
Figure 4 below presents the results of the combination of CF-301 and daptomycin when used in the Drug Failure Bacteremia Model. All control mice treated with buffer (diamonds) succumbed to bacterial infection within 18 hours. Administration of a clinical dose of daptomycin as a single agent (squares) resulted in clinical failure, as only 31% of mice survived. When CF-301 (triangles) was dosed as a single agent at this chosen dose, only 18% of mice survived. In contrast, when mice received the combination of CF-301 plus daptomycin (circles), 82% survived the bacterial challenge, demonstrating superiority of the combination therapy over the single-drug regimens.
Figure 4: Combination Therapy of CF-301 with Daptomycin in Drug Failure Bacteremia Model
7
Table of Contents
We have tested the combination of CF-301 with daptomycin, vancomycin and oxacillin in 30 different experiments (including both the Standard and Drug Failure Bacteremia Models). In each experiment, the combination therapy was shown to be superior to monotherapy with a single drug alone. As a result, we believe this provides a strong foundation on which to pursue clinical development of the combination of CF-301 and SOC antibiotics for the treatment of Staph aureus bacteremia, as CF-301’s first indication.
To further explore the activity of CF-301 in combination with SOC antibiotics for the treatment of life-threatening, drug-resistant infections, we engaged the LA Biomed Research Institute at Harbor-UCLA Medical Center (“UCLA”) to perform a study in their rat infective endocarditis model (“IE Model”). The IE Model has become a well-established experimental animal model and has been used for assessing possible efficacy of therapeutic agents in infective endocarditis. The primary endpoint of the IE Model is a reduction in the amount of bacteria (measured as CFUs) on the heart valve, in the kidney and in the spleen. Survival during the course of the treatment period was considered a secondary endpoint, as the study was not designed to see the long-term effects of the treatment on overall survival. Our study examined the activity of CF-301 alone and in combination with daptomycin, in UCLA’s prototypical high-burden biofilm-based IE Model. We worked directly with UCLA to design the study, and the description of the methods and results follows below.
Figure 5 presents the results of the combination of CF-301 alone and in combination with daptomycin as compared to both buffer and daptomycin alone in the IE Model. In this study, a single dose of CF-301 significantly increased the activity of daptomycin. This study was designed to mimic the planned clinical approach (single dose of CF-301 on top of multiple days of SOC antibiotic therapy) in a difficult to treat biofilm-based infection. In this study, a single dose of CF-301, when combined with four days of daptomycin treatment, resulted in a 3-log (99.9%) drop in bacterial burden in the cardiac vegetations and >2-log (99%) drop in the kidney and spleen of infected animals relative to daptomycin treatment alone. Importantly, in the combination treatment groups 4 of 9 animals were determined to be culture negative, whereas no animals in any other treatment arms approached this level of microbial eradication.
Figure 5: Single Dose of CF-301 with Daptomycin in Rat Infective Endocarditis Model
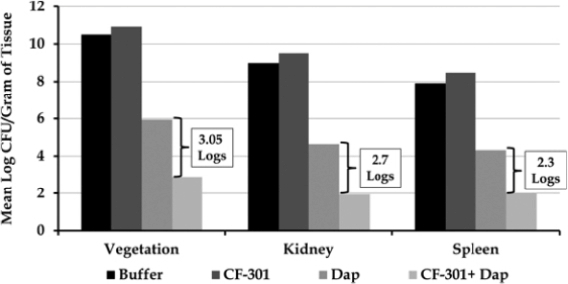
As a result, we believe this additional data strongly supports our human clinical study plan to evaluate the combination of CF-301 and SOC antibiotics for the treatment of patients with invasive Staph aureus infections, including endocarditis, caused by MSSA or MRSA.
8
Table of Contents
CF-301: Impact on Antibiotic-Resistant Biofilms
Biofilm formation is a common protective mechanism for bacteria and a key feature associated with bacterial pathogenesis. Biofilms are characterized by densely packed bacterial cells that grow in communities and are enclosed within a complex matrix of dead bacteria and excess cell wall components. Biofilm bacteria exhibit significant tolerance of various antimicrobial agents, rendering biofilm cells up to 1,000-fold less susceptible than the same bacteria grown in a planktonic, or free-floating, non-biofilm culture. Infected human tissues, such as the heart valve in endocarditis or bone in osteomyelitis, or indwelling medical devices, such as central venous catheters, prosthetic joints and pacemakers, are common sites for biofilm formation, providing a hurdle for effective treatment with antibiotics alone. Novel treatment strategies and antimicrobial agents with activity toward biofilms remain a serious unmet medical need as there is no product currently indicated for the treatment of biofilms.
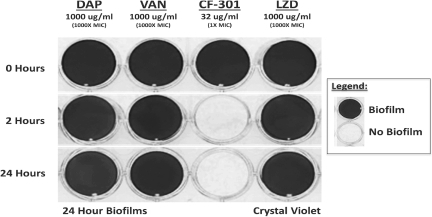
Since CF-301 disrupts the outer wall of Staph aureus by enzymatic lysis, we performed studies to determine if CF-301 would also disrupt biofilms. For this purpose, we cultured MRSA for 24 hours within wells of polystyrene dishes typically used for the culture of cells, at which point a dense biofilm formed on the dish surface. Dishes were incubated for up to 24 hours with high-dose (1,000X MIC) daptomycin, vancomycin or linezolid, or lower-dose (1XMIC) CF-301. After the four-hour treatment, dishes were washed and stained with a dye that stains the biomass of a biofilm a dark blue color. In dishes treated with CF-301, there was no visual biofilm present after two hours of treatment, whereas in dishes treated with antibiotics for up to 24 hours, the biofilm biomass remained intact (images shown in Figure 6 below). These in vitro findings demonstrate the inability of these antibiotics to penetrate and clear biofilm material whereas CF-301 effectively destroyed bacterial biofilms.
Figure 6: Sensitivity of Staph Aureus (MRSA) Biofilms to CF-301 Versus SOC Antibiotics
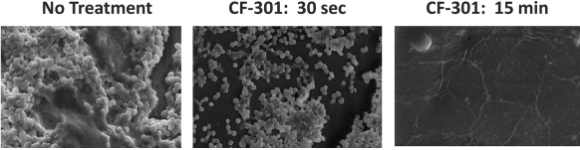
To microscopically visualize CF-301’s disruption of biofilms, we inoculated MRSA onto a medically relevant device (a catheter) where it attached to the wall of the plastic and formed a dense three-dimensional structure. We then treated the interior of the catheter with CF-301 at 1x MIC. At various time intervals after treatment the interior of the catheter was sectioned and examined by scanning electron microscopy (“SEM”), select images shown below in Figure 7. In the untreated catheter (left panel) the majority of MRSA cells (little circles in the pictures below) were found within a biofilm. However, within 30 seconds of exposure to CF-301, the dense biofilm was largely removed and only single cells were observed (middle panel). Fifteen minutes following exposure to CF-301 (right panel), the biofilm was completely stripped and residual MRSA cells which had been beneath the biofilm were killed, in effect, sterilizing the catheter. These images emphasize the rapid and potent activity of CF-301 against bacterial biofilms. Taken together with the lack of efficacy that antibiotics display against biofilms, we believe CF-301 potentially represents a new therapeutic option against what were previously untreatable biofilms.
9
Table of Contents
Figure 7: Sensitivity of Staph Aureus (MRSA) Biofilms Grown on Catheters to CF-301
CF-301: Product Development
Product development is generally accomplished in four steps, which may overlap: (1) preclinical activities to demonstrate consistent manufacturing, safety and efficacy in animals; (2) Phase 1 clinical trials, in healthy volunteers, to determine pharmacokinetics (“PK”), safety, tolerability, immunogenicity, dosing, effects in special populations, and other issues; (3) Phase 2 clinical trials in patients to determine dose, efficacy, safety, tolerability, PK and immunogenicity; and (4) Phase 3 clinical trials, the pivotal trials in patients to confirm efficacy and safety at the proposed commercial dose.
Non-Clinical Activities
Chemistry, Manufacturing and Controls
Manufacturing of CF-301 utilizes a proprietary engineered E. coli strain that expresses the product in a recombinant manner during the fermentation process. This technology allows production of up to nine grams of CF-301 per liter of fermentation broth. After fermentation, the broth containing CF-301 is separated and purified through a process containing two chromatographic columns. The resulting product has greater than 99% purity. The CF-301 produced by this process has been used in animal studies submitted in our IND and completed Phase 1 clinical trial and may be used for our planned Phase 2 clinical trial.
We intend to further optimize the manufacturing process for increased purity and yield. Once completed, we plan to begin a program to manufacture Phase 3 material. The process will then be scaled up from the current 100 liter fermentation and validated in a series of manufacturing batches to demonstrate consistency. In parallel to the validation, we intend to conduct a comparability program that demonstrates comparability between the final product used in Phase 3 and commercial manufacturing. We intend to include the results in the biologics license application (“BLA”) that we expect to submit to the FDA. Following submission, the FDA will conduct pre-approval inspections of all manufacturing facilities and determine whether it agrees that our commercial material is sufficiently comparable to our Phase 3 material.
Safety Pharmacology and Toxicology
Preclinical safety pharmacology and toxicology studies have been completed in connection with our IND application for CF-301. In these studies CF-301 was well tolerated in rats for a single two-hour IV administration of doses up to 25mg/kg (determined by us to be the no observable adverse effect level, or “NOAEL”) and that a single dose of 2.5mg/kg was not associated with any effects, adverse or not, and was therefore determined to be the no observable effect level (“NOEL”). CF-301 was also well tolerated in these studies in both rats and dogs for seven consecutive days of once daily two-hour IV infusions of up to 2.5mg/kg. In a non-GLP pilot study in rats, 1.0 mg/kg/day was well tolerated for up to seven consecutive days of once daily two-hour IV infusions or IV boluses.
10
Table of Contents
Dose dependent adverse effects were seen in both species at doses above 25 mg/kg/day for 1 day in the rat and above 2.5 mg/kg/day for seven-consecutive days in both the rat and the dog. The dose limiting toxicity observed was a localized inflammation surrounding certain blood vessels. In accordance with industry practice, we intend to study CF-301 in clinical trials at doses much lower than those that caused adverse effects in animals, and we believe these doses to be within the efficacious range of the drug.
Upon first exposure to CF-301, no hypersensitivity reaction was observed in any of our animal studies. Upon administration of a second course of CF-301, given two weeks after completion of the first course, hypersensitivity or hypersensitivity-like findings were observed in mice, rats and dogs. In a dedicated hypersensitivity studies in rats, findings of Type III hypersensitivity were observed after a two week delayed re-challenge with a second course of CF-301 and were not dose dependent. In general, Type I hypersensitivity is an allergic anaphylaxis-like response (e.g., an immediate and potentially life-threatening allergic reaction) and Type III hypersensitivity is a serum sickness-like response (e.g., fever, joint pain, protein in urine, vascular changes). While the nature of hypersensitivity reactions in rats may not necessarily be predictive of hypersensitivity reactions that may occur in humans, we have also considered the risk of hypersensitivity occurring upon first administration of CF-301 due to potential prior exposure to the active protein component of CF-301 from the environment, as it is a naturally occurring protein. Testing for anti-CF-301 antibodies was performed in Phase I subjects. No clinical hypersensitivity related to CF-301 was observed in subjects dosed in our Phase 1 study.
Clinical Studies
Phase 1. In 2015, we concluded a Phase 1 single ascending dose study in healthy volunteers. This trial was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial designed to evaluate the safety, tolerability and PK of four different intravenous doses of CF-301 alone. Subjects were randomized to receive a single IV dose of CF-301 or placebo, each administered as a two hour infusion.
In this Phase 1 trial, there were no clinical adverse safety signals, no serious adverse events (“AEs”), and no study stopping rules were met. In addition, no AEs of hypersensitivity related to CF-301 were reported. A total of five non-serious AEs were reporting during the study. Two subjects who received CF-301 reported a total of three non-serious AEs (headache, contact dermatitis, and allergic rhinitis). Two subjects who received placebo reported a total of two non-serious AEs (viral upper respiratory tract infection and viral infection). All of these events were mild in intensity and resolved. No patients withdrew from the study due to an AE. Exposure was dose dependent and intra-subject variability was low. Estimated effective exposure, based on animal models of Staph aureus infections, was attained at the 0.25mg/kg dose. Nine out of 13 subjects dosed with CF-301 developed anti-drug antibodies (ADAs) in the study. These ADAs were waning or absent by day 180, and were not correlated with markers of allergic immune response.
Phase 2. We expect to proceed into Phase 2 to assess the safety, tolerability, PK, and efficacy of CF-301 used in addition to standard-of-care (“SOC”) antibiotics. We expect the Phase 2 clinical trial to be a multicenter, double-blind, randomized study that evaluates the safety and efficacy of CF-301 used in addition to SOC antibiotics and SOC antibiotics alone in patients with Staph aureus bacteremia, including endocarditis, caused by MSSA or MRSA. The study is expected to enroll 115 patients randomized 3:2 to receive a single dose of 0.25 mg/kg of CF-301 administered via 2 hour IV infusion or placebo. The primary endpoint of early clinical response at Day 14, based on a series of objective clinical response criteria (including reduction/resolution of symptoms, lack of progression of infection, lack of need for additional antibiotics). Additional exploratory clinical, microbiologic and health resource utilization endpoints will be measured in the trial.
Phase 3. If the Phase 2 results are consistent with our expectations regarding the safety and efficacy profile of CF-301, we expect to enter into Phase 3. We expect any Phase 3 clinical trial to be a global, multicenter,
double-blind, randomized study that evaluates the efficacy and safety of CF-301 plus SOC antibiotics compared
11
Table of Contents
to SOC antibiotics alone among patients with bacteremia caused by MSSA or MRSA. Specific parameters for Phase 3 will be based on the outcomes of previously completed clinical trials and relevant guidance from regulatory authorities.
Our Lysin Discovery Platform
We employ bioinformatics and a series of metagenomic-based techniques to clone bacteriophage lysins from bacterial, viral, and environmental sources. The field of metagenomics is based on the bulk extraction of DNA/RNA from environmental samples (e.g., soil, water, etc.) without prior isolation of individual microbial sources. This is useful when one considers that less than 1% of microbes are culturable under standard laboratory conditions. Once extracted, the metagenomic DNA can then be examined using sequence-based methods or by proprietary functional screens. These functional screens for bacteriophage lysin activity form the basis for our lysin discovery work.
For the functional metagenomic work that we perform, environmental genes are expressed in a recombinant format in a standard host organism (i.e., Escherichia coli) and cells are monitored for the acquisition of a desired phenotype. We can vary both the source of environmental DNA and the way we monitor for desired phenotypes to focus only on environmental populations enriched for bacteriophage lysins that can actively kill a pathogen of interest. We sample various DNA sources including viral, prophage, and pathogen-amplified viral metagenomics. Multiple methods for both DNA library construction and for functional screening are used in parallel in order to maximize lysin identification.
We have also established additional discovery methodologies, including bioinformatics analysis of the rapidly expanding databases of bacterial genomic sequences. The highly conserved modular structure of lysins, combined with sequence homologies amongst different lysin classes, enable the rapid analysis of putative lysins from DNA databases. Such sequences can be readily synthesized and screened for lytic activity against any pathogen of interest.
The application of these methods enables the large scale identification of lysins, enabling the production of lysin banks specific for any particular pathogen. We believe the ability to rapidly identify lysins specific for any pathogen of interest, either by in vitro or in silico methods, will provide a steady pipeline of novel lysins for consideration as potential antimicrobial therapeutic candidates.
We intend to pursue preclinical and clinical development of additional lysins. In addition to the lysins we have licensed from Rockefeller and our in-house lysin discovery program, we have an active collaborative research agreement where we provide funding for the discovery of new lysins with Dr. Vincent Fischetti’s Laboratory of Bacterial Pathogenesis and Immunology at Rockefeller, where we have the first right to negotiate a license to all discoveries concerning lysins through October 2019. The primary focus of our in-house and sponsored research is the discovery of lysins to target gram-negative bacteria.
Monoclonal Antibodies
We are exploring combination therapy with mAbs that bind to target bacteria or viruses and block certain biological activities or recruit other parts of the immune system to destroy the pathogenic target. The strategies of our mAb program include: (1) targeting conserved regions of the virus or bacteria which are not prone to mutation and (b) targeting multiple proteins expressed from different genes within a bacteria or virus to prevent therapeutic escape and (c) combining mAbs to cover multiple strains for superior outcomes.
Our antibodies are generated by genetic engineering using phage display libraries, isolated directly from human blood samples or other available technologies, enabling the screening of billions of human mAbs with different binding sites. Once the best monoclonal antibodies are isolated, we use protein engineering techniques to optimize important antibody attributes such as pharmacokinetic profile, effector function engagement, antibody format (such as Fabs and bispecifics), and manufacturing efficiency. The common properties provide for a unique ability to create a therapeutic combination of mAbs.
12
Table of Contents
Our Lead mAb Program: CF-404
We intend to develop CF-404, a combination of three human mAbs against influenza, as a treatment for life-threatening seasonal and pandemic influenza infections, a disease that kills as many as 49,000 people annually in the U.S. alone. Our preclinical studies to date have shown that CF-404 may have the following attributes:
| • | Broad activity against influenza in one combination drug. CF-404 exhibits broad activity against influenza strains, including the three principal strains (H1, H3 and B). By targeting a conserved region on the virus, we believe CF-404 bypasses the effects of seasonal change, which allows (1) our mAbs to cross-react and neutralize many different influenza strains; (2) for the production of a single therapeutic combination of only three mAbs covering all human seasonal and most pandemic influenza strains; and (3) for an immediate therapeutic effect that cannot be obtained by vaccination which typically requires weeks. |
| • | Minimal resistance potential. Our mAbs react with the principal protein, hemagglutinin, on the surface of influenza at a region referred to as the hemagglutinin stalk. Because the hemagglutinin stalk is genetically stable and therefore represents a conserved region of the virus, it does not vary from one season to another. |
| • | Minimal competition. There are only four approved drugs for the treatment of influenza—Tamiflu, Relenza, Symmetrel and Flumadine—although only Tamiflu is widely used in practice. Influenza has demonstrated an increasing resistance to Tamiflu, and the clinical benefit of Tamiflu is greatest when antiviral treatment is administered early, especially within 48 hours of influenza illness onset. Based on preclinical data, we believe treatment with our mAbs may be effective even when given up to 96 hours after infection. |
Influenza Research
In preclinical studies, CF-404 cross-reacts with all strains of influenza, including the three principal strains (H1, H3 and B). These mAbs react with the principal protein, hemagglutinin, on the surface of influenza at a region referred to as the hemagglutinin stalk which is genetically stable and does not vary from one season to another. We have produced mAbs that are reactive with the stalk region of hemagglutinin for the entire natural history of the H3 influenza (1968-present), H1 influenza (1918-present; seasonal and swine flu), other strains of Type A influenza (including H5), and Type B influenza.
We have tested our mAbs in mouse models to evaluate protection against lethal infection with influenza in “proof-of-concept” experiments. These data demonstrated that our anti-H1 (CF-401), anti-H3 (CF-402) and anti-B mAbs (CF-403) were able to protect animals from lethal challenge. Importantly, our in vivo animal studies show that treatment with our mAbs appears to provide greatly enhanced potency compared to treatment with other mAbs.
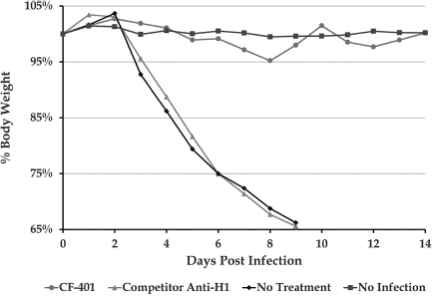
Figure 8 below shows the results of an experiment using CF-401 in a mouse model of H1N1 influenza infection, in which body weight loss is used as a proxy of disease progression (and ultimately, death). In this figure, we also demonstrate that at the same dose of 1 mg/kg, CF-401 was far superior to a competitor’s mAb currently in clinical development. Control mice treated with buffer (diamonds) succumbed to viral infection within 9 days. Administration of a single treatment, 24 hours post-infection, of a competitor’s antibody (triangles) resulted in clinical failure at an identical rate as the no treatment group. When CF-401 (circles) was administered as a single treatment, 24 hours post-infection, the mice appeared perfectly healthy, with weight changes identical to animals that did not receive challenge with influenza (squares).
13
Table of Contents
Figure 8: Effectiveness of CF-401 in Mouse Model of Influenza
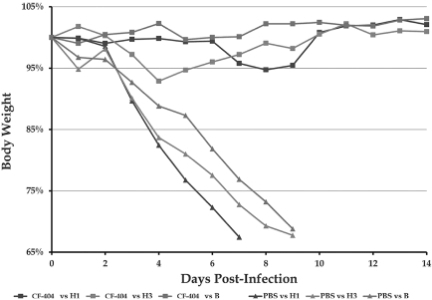
As the goal of our influenza program is to produce a combination of mAbs with efficacy against all human seasonal strains of influenza, we have formulated CF-404 and tested it in animal models of disease. Figure 9 below shows how CF-404 cured mice infected with three different strains of influenza, regardless of the strain (H1N1, H3N2 or B). Control mice treated with buffer (triangles) all succumbed to viral infection within 7-9 days. By contrast, when we administered a single treatment of CF-404 (squares) 24 hours post-infection, the infected mice appeared perfectly healthy, with weight changes comparable to healthy mice (not pictured).
Figure 9: Effectiveness of CF-404 in Mouse Model
14
Table of Contents
Currently, the SOC treatment for influenza is Tamiflu. Tamiflu, however, has several limitations, including emerging resistance. In 2009, just prior to the emergence of the pandemic H1N1 swine flu, the CDC cautioned against the use of Tamiflu for the treatment of H1N1 seasonal influenza due to nearly complete drug-resistance of the virus (in 2006 <1% of H1N1 were resistant, by 2009 that figure jumped to >98%). As previously discussed, due to the targeting of conserved regions on the hemagglutinin, we do not anticipate resistance will occur to our mAbs.
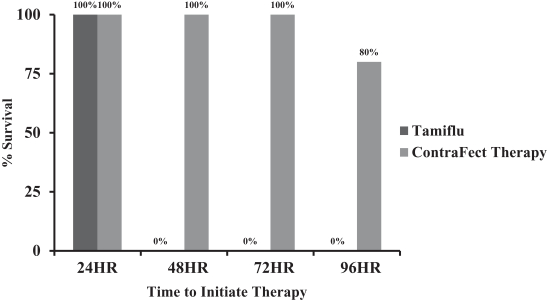
The second major limitation of Tamiflu is its narrow time window to treat a patient and still be efficacious. The clinical benefit of Tamiflu is greatest when administered early in a patient’s infection, especially within 48 hours of illness onset. To compare the time-to-treat windows of our mAbs to Tamiflu, H1N1 influenza-infected mice were treated with either a single administration of CF-401 or a 5 day course of Tamiflu beginning 24-96 hours post infection (“HPI”). Figure 10 below shows the findings of that study, including the finding that Tamiflu treatment had to have been initiated by 24 HPI to cure mice, while treatments beginning at 48, 72 or 96 HPI resulted in 100% death by day 14. In contrast, a single treatment with CF-401 resulted in 100% survival when given any time up to 72 HPI and in 80% survival when given 96 HPI. This result suggests that our mAb treatment may provide effective treatment to influenza patients at later times post-infection when Tamiflu is no longer effective.
Figure 10: CF-401 Provides Greater Therapeutic Window than Tamiflu® in Mouse Model
We believe our combination for the treatment of influenza is a novel approach addressing a high unmet medical need and would offer competitive advantages to the only product widely used on the market today if successfully developed and approved.
Intellectual Property
Our goal is to obtain, maintain and enforce patent protection for our products, formulations, processes, methods and other proprietary technologies, preserve our trade secrets, and operate without infringing on the proprietary rights of other parties, both in the United States and in other countries. Our policy is to actively seek to obtain, where appropriate, the broadest intellectual property protection possible for our product candidates, proprietary information and proprietary technology through a combination of contractual arrangements and patents, both in the United States and abroad. However, patent protection may not afford us with complete protection against competitors who seek to circumvent our patents.
15
Table of Contents
We also depend upon the skills, knowledge, experience and know-how of our management and research and development personnel, as well as that of our advisors, consultants and other contractors. To help protect our proprietary know-how, which is not patentable, and for inventions for which patents may be difficult to enforce, we currently rely and will in the future rely on trade secret protection and confidentiality agreements to protect our interests. To this end, we will require all of our employees, consultants, and other contractors (including any consultants or contractors we may retain for purposes of any of our ad hoc Clinical Advisory Boards) to enter into confidentiality agreements that prohibit the disclosure of confidential information and, where applicable, require disclosure and assignment to us of the ideas, developments, discoveries and inventions important to our business.
Our lysin portfolio consists of twelve (12) U.S. patents, fifteen (15) foreign patents and fifty-eight (58) U.S. and international patent applications that we have licensed from Rockefeller and/or developed in-house. The patents and patent applications are directed to compositions and methods for the treatment of infections caused by Group B Streptococci, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumonia, Bacillus anthracis (anthrax), Enterococcus faecalis, Enterococcus faecium and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. These patents and patent applications (if granted) would expire between 2023 and 2036.
Our influenza patent portfolio consists of two (2) foreign patents and forty-five (45) U.S. and foreign patent applications, which we have licensed from Trellis and/or developed in-house. The patent applications are directed to compositions relating to influenza antibodies as well as to pharmaceutical compositions for administration to patients and to methods for their use in conferring passive immunity against various influenza strains and clades. These patents and patent applications (if granted) would expire between 2031 and 2035.
The U.S. patent system permits the filing of provisional and non-provisional patent applications. A non-provisional patent application is examined by the United States Patent and Trademark Office (“USPTO”), and can issue as a patent once the USPTO determines that the claimed invention meets the various standards for patentability. A provisional patent application is not examined or prosecuted, and automatically expires 12 months after its filing date if a non-provisional application is not filed based on the provisional application within that 12-month period. Provisional applications are often used, among other things, to establish a priority filing date for the subsequently filed non-provisional patent application. The term of individual patents depends upon the legal term for patents in the countries in which they are filed. In most countries in which we file, the patent term is 20 years from the earliest filing date of a non-provisional patent application. In the United States, a patent’s term may be lengthened by patent term adjustment, which compensates a patentee for administrative delays by the USPTO in granting a patent. Alternatively, a patent’s term may be shortened if a patent is terminally disclaimed over another patent.
The term of a patent that covers an FDA-approved drug may also be eligible for patent term extension (“PTE”), which permits patent term restoration as compensation for the patent term lost during the FDA regulatory review process. The Drug Price Competition and Patent Term Restoration Act of 1984, or the Hatch-Waxman Amendments, permits a PTE of up to five years beyond the expiration of the patent. The length of the PTE is related to the length of time the drug is under regulatory review. Patent extension cannot extend the remaining term of a patent beyond a total of 14 years from the date of product approval and only one patent applicable to an approved drug may be extended. Similar provisions are available in Europe and certain other foreign jurisdictions to extend the term of a patent that covers an approved drug. In the future, if and when our pharmaceutical product candidates receive FDA or other regulatory approval, we may be able to apply for or receive the benefit of PTEs on patents covering those products.
License Agreements—The Rockefeller University
We have entered into the following license agreements with Rockefeller:
| • | On July 12, 2011, we entered into a license agreement for the worldwide, exclusive right to a provisional patent application, upon which a non-provisional patent application has since been filed, |
16
Table of Contents
| covering the composition of matter for the lysin PlySS2 for the treatment and prevention of diseases caused by gram-positive bacteria (the “CF-301 License”). We rebranded PlySS2 as CF-301. This license gives us the right to exclusively develop, make, have made, use, import, lease, sell and offer for sale products that would otherwise infringe a claim of this patent application or patent. |
| • | On June 1, 2011, we entered into a license agreement for the exclusive rights to Rockefeller’s interest in a joint patent application, which is presently pending, covering the method of delivering antibodies through the cell wall of a gram-positive bacteria to the periplasmic space. This intellectual property was developed as a result of the sponsored research agreement between us and Rockefeller, and was jointly discovered and filed by the two parties. |
| • | On September 23, 2010, we entered into a license agreement for the worldwide, exclusive right to develop, make, have made, use, import, lease and sell, and offer for sale products that would otherwise infringe a claim of the suite of patents and patent applications covering the composition of matter for eight individual lysin molecules for the treatment and prevention of diseases caused by gram-positive bacteria. The lysins in this suite have activity against Group B Streptococci, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumonia, Bacillus anthracis, Enterococcus faecalis and Enterococcus faecium. |
In consideration for the licenses, we paid Rockefeller license initiation fees in cash and stock and may be required to pay an annual maintenance fee, milestone payments and royalties on net sales from products to Rockefeller. We are allowed to grant sublicenses to third parties without prior approval, subject to certain conditions and the payment of a certain percentage of all payments we receive from sublicensees.
Each license agreement terminates upon the later of (i) the expiration or abandonment of the last licensed patent under the license agreement to expire or become abandoned, or (ii) 10 years after the first commercial sale of the first licensed product. Rockefeller may terminate any license agreement in the event of a breach of such agreement by us or if we challenge the validity or enforceability of the underlying patent rights. We may terminate any license agreement at any time on 60 days’ notice.
License Agreement—Trellis Bioscience LLC
On January 29, 2014, we entered into a license agreement with Trellis that gives us exclusive rights to all Trellis mAbs in the field of influenza discovered from their CellSpot platform. Particularly, the license provides us with three fully human mAbs that bind, neutralize and protect animals from all strains of H1, H3 and B influenza, and that will also cross bind, neutralize and protect animals from other seasonal or pandemic influenza strains that may arise (including H5N1 and H7N9). We have selected our three lead mAbs for the H1, H3, and B influenzas and are currently producing these antibodies at scale using manufacturing-grade expression systems and performing IND-enabling studies.
In consideration for the license, we paid Trellis licensing fees in cash and stock and may be required to make specified development and regulatory milestone payments and make additional payments upon the achievement of future sales and a royalty on net sales from products to Trellis. We are allowed to grant sublicenses to third parties.
The license agreement terminates upon the earlier of (i) our decision to terminate the agreement at will or for safety reasons, (ii) material breach by either party that is not cured within ninety (90) days, or (iii) either party’s insolvency.
On August 14, 2014, we amended the license agreement to include research conducted pursuant to a government grant.
Collaborative Research Agreements—The Rockefeller University
Beginning in October 2009, we entered into a research agreement with Rockefeller, which is now expired, where we provided funding for research focused on producing and testing monoclonal antibodies against proteins
17
Table of Contents
of Staph aureus. On October 24, 2011, we entered into a second research agreement with Rockefeller, where we provided funding for the research primarily to identify lysins, enzymes or small molecules that will kill gram-negative bacteria, and to identify and characterize lysins from Clostridia difficile to be engineered into gut commensal bacteria. This agreement expired on October 24, 2016. On October 25, 2016, we entered into a third research agreement with Rockefeller, where we provide funding for the identification of novel lysin therapeutic candidates that target Gram-negative pathogens. The research collaboration will focus on Gram-negative pathogens such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli, and Klebsiella, including antibiotic-resistant strains.
Our current agreement runs through October 24, 2019. Either party may terminate the agreement upon breach of the agreement, following 30 days written notice and failure to cure such breach. Following the expiration or termination of the agreement, each party will have a non-exclusive license to use for internal research purposes all research results, including joint intellectual property. If Rockefeller or joint intellectual property develops from these programs, we will have the right-of-first refusal to negotiate to acquire a royalty-bearing license to utilize such intellectual property for commercial purposes.
Competition
The pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries are intensely competitive. While we believe that our technology and scientific knowledge provide us with competitive advantages, we face potential competition from many different sources, including major pharmaceutical, specialty pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies and academic and research organizations in developing therapies to treat diseases.
CF-301 is a first-in-class drug candidate and we believe will be among the first lysins to enter human clinical trials. We believe there is currently no clinical competitor to CF-301 as it was designed with at least six attributes that no single antibiotic possesses, including: (1) a novel mechanism of action, (2) specificity for a target bacteria (only Staph aureus), (3) rapid speed of action, (4) activity across all drug-sensitive and drug-resistant strains of the target bacteria (including MRSA, VRSA and DRSA), (5) the ability to eradicate biofilms, and (6) synergy with antibiotics. Staph aureus bacteremia is typically treated with oxacillin, or for MRSA strains, daptomycin and vancomycin. We do not see market competition with these drugs, as our strategy is to combine CF-301 with these drugs to aim for superiority over any one of those drugs alone.
We are not aware of any other lysins in clinical development under an IND in the United States, iNtRon Biotechnology Inc., a biotechnology company located in South Korea, completed a Phase 1 human clinical trial for SAL-200, an endolysin-based drug candidate for multidrug-resistant Staph aureus infections. We will continue to monitor the advancements of SAL-200 as data become available.
CF-404 is intended for the treatment of life-threatening seasonal and pandemic influenza infections. We believe CF-404 has competitive advantages in that it potentially addresses the short-comings of currently marketed products (Tamiflu, Relenza and Rapivab) and other products in development for the following reasons: (1) it may not be prone to drug-resistance due to targeting conserved regions of the influenza virus, (2) it may provide for an increased “time-to-treat” window compared to Tamiflu, Relenza and Rapivab, which are indicated to be used within 48 hours of symptom onset, and (3) it may provide complete coverage against all seasonal and most potential pandemic strains of human influenza without the need for annual reformulation, including influenza B.
CF-404 may directly or indirectly compete with other products already in development from F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., Genentech, Inc., Johnson & Johnson, Inc., Theraclone Sciences, Inc., Toyama Chemical Co., Ltd., Romark Laboratories, L.C., Aviragen, Inc., Vectura Group plc, Far East Bio-Tec Co. Ltd, Visterra Inc., MedImmune LLC, Ansun Biopharma, Inc. and others with early stage product candidates.
Many of our competitors may have significantly greater financial resources and expertise in research and development, manufacturing, preclinical testing, conducting clinical trials, obtaining regulatory approvals and marketing approved medicines than we do. We compete with companies that have products on the market or in
18
Table of Contents
development for the same indications as our product candidates. Mergers and acquisitions in the pharmaceutical, biotechnology and diagnostic industries may result in even more resources being concentrated among a smaller number of our competitors. These competitors also compete with us in recruiting and retaining qualified scientific and management personnel and establishing clinical trial sites and patient registration for clinical trials. Smaller or early stage companies may also prove to be significant competitors, particularly through collaborative arrangements with large and established companies.
The key competitive factors affecting the success of all of our product candidates, if approved, are likely to be their efficacy, safety, convenience, price and the availability of reimbursement from government and other third-party payors. Our commercial opportunity could be reduced or eliminated if our competitors develop and commercialize medicines that are safer, more effective, have fewer or less severe side effects, are more convenient or are less expensive than any medicines that we may develop. Our competitors also may obtain FDA or other regulatory approval for their medicines more rapidly than we may obtain approval for ours, which could result in our competitors establishing a strong market position before we are able to enter the market.
Manufacturing
We do not own or operate, and currently have no plans to establish, any manufacturing facilities. We currently rely, and expect to continue to rely, on third parties for the manufacture of our product candidates for preclinical or clinical manufacturing, testing, as well as for commercial manufacture of any products that we may commercialize. We employ the services of Fujifilm UK to supply the drug substance for CF-301. We do not yet have contracts to produce a commercial supply of the drug substance for CF-301; however, we intend to pursue agreements with Fujifilm UK to do so. We employ the services of Emergent BioSolutions to produce CF-301 in its final vialed drug product form. We do not have contracts for the commercial supply of CF-301. We intend to pursue agreements with third party manufacturers regarding commercial supply of vialed drug product at an appropriate future time. We may choose to locate second fill finish third party manufacturers to supply other world regions such as the European Union or Asia.
Sales, Marketing and Distribution
We do not currently have an organization for the sales, marketing and distribution of pharmaceutical products. We may rely on licensing and co-promotion agreements with strategic partners for the commercialization of our products in the United States and other territories. If we choose to build a commercial infrastructure to support marketing in the United States, such commercial infrastructure could be expected to include a targeted sales force supported by sales management, internal sales support, an internal marketing group and distribution support. To develop the appropriate commercial infrastructure internally, we would have to invest financial and management resources, some of which would have to be deployed prior to any confirmation that any of our other products will be approved.
Research and Development Expenses
We have invested $22.1, $15.0 million and $8.9 million in research and development expenses for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively.
Government Regulation
The production, distribution, and marketing of products employing our research and intellectual property or that we may license from third parties are subject to extensive governmental regulation in the United States and in other countries. In the United States, our products will be regulated as biologics and subject to the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, as amended (the “FDC Act”), the Public Health Service Act, as amended (the “PHSA”) and the regulations of the FDA, as well as to other federal, state, and local statutes and regulations. These laws, and similar laws outside the United States, govern the research, development, clinical and preclinical testing, manufacture, safety, effectiveness, approval, labeling, distribution, sale, import, export, storage, record-
19
Table of Contents
keeping, reporting, advertising, and promotion and marketing of our products. Product development and approval within this regulatory framework, if successful, will require the expenditure of substantial resources and take years to achieve. Violations of regulatory requirements at any stage may result in various adverse consequences, including the FDA’s and other health authorities’ delay in approving or refusal to approve a product and may result in enforcement actions and administrative or judicial sanctions.
The following provides further information on certain legal and regulatory requirements that have the potential to affect our operations and the future marketing of our products.
FDA Approval Process
In the United States, pharmaceutical products are subject to extensive regulation by the FDA. The FDC Act and other federal and state statutes and regulations govern, among other things, the research, development, testing, manufacture, storage, recordkeeping, approval, labeling, promotion and marketing, distribution, post-approval monitoring and reporting, sampling, and import and export of pharmaceutical products. Biological products used for the prevention, treatment, or cure of a disease or condition of a human being are subject to regulation under the FDC Act, except the section of the FDC Act which governs the approval of new drug applications (“NDAs”). Biological products are approved for marketing under provisions of PHSA, via a BLA. However, the application process and requirements for approval of BLAs are very similar to those for NDAs, and biologics are associated with similar approval risks and costs as drugs. Failure to comply with applicable U.S. requirements may subject a company to a variety of administrative or judicial sanctions, such as FDA refusal to approve pending NDAs or BLAs, warning or untitled letters, product recalls, product seizures, total or partial suspension of production or distribution, injunctions, fines, civil penalties, and criminal prosecution.
Pharmaceutical product development for a new product or certain changes to an approved product in the United States typically involves preclinical laboratory and animal tests, the submission to the FDA of an IND, which must become effective before clinical testing may commence, and adequate and well-controlled clinical trials to establish the safety and effectiveness of the drug for each indication for which FDA approval is sought. Satisfaction of FDA pre-market approval requirements typically takes many years and the actual time required may vary substantially based upon the type, complexity, and novelty of the product or disease.
Preclinical tests include laboratory evaluation of product chemistry, formulation, and toxicity, as well as animal trials to assess the characteristics and potential safety and efficacy of the product. The conduct of the preclinical tests must comply with federal regulations and requirements, including good laboratory practices. The results of preclinical testing are submitted to the FDA as part of an IND along with other information, including information about product chemistry, manufacturing and controls, and a proposed clinical trial protocol. Long term preclinical tests, such as animal tests of reproductive toxicity and carcinogenicity, may continue after the IND is submitted.
A 30-day waiting period after the submission of each IND is required prior to the commencement of clinical testing in humans. If the FDA has neither commented on nor questioned the IND within this 30-day period, the clinical trial proposed in the IND may begin.
Clinical trials involve the administration of the investigational new drug or biologic to healthy volunteers or patients under the supervision of a qualified investigator. Clinical trials must be conducted: (i) in compliance with federal regulations; (ii) in compliance with good clinical practice (“GCP”), an international standard meant to protect the rights and health of healthy volunteers or patients and to define the roles of clinical trial sponsors, administrators, and monitors; as well as (iii) under protocols detailing the objectives of the trial, the parameters to be used in monitoring safety, and the effectiveness criteria to be evaluated. Each protocol involving testing on healthy volunteers or patients in the U.S. and subsequent protocol amendments must be submitted to the FDA as part of the IND.
The FDA may order the temporary, or permanent, discontinuation of a clinical trial at any time, or impose other sanctions, if it believes that the clinical trial either is not being conducted in accordance with FDA
20
Table of Contents
requirements or presents an unacceptable risk to the clinical trial patients. The study protocol and informed consent information for patients in clinical trials must also be submitted to an IRB for approval. An IRB may also require the clinical trial at the site to be halted, either temporarily or permanently, for failure to comply with the IRB’s requirements, or may impose other conditions.
Clinical trials to support NDAs or BLAs for marketing approval are typically conducted in three sequential phases, but the phases may overlap. In Phase 1, the initial introduction of the drug or biologic into healthy human subjects or patients, the product is tested to assess metabolism, pharmacokinetics, pharmacological actions, side effects associated with increasing doses, and, if possible, early evidence of effectiveness. Phase 2 usually involves trials in a limited patient population to determine the effectiveness of the drug or biologic for a particular indication, dosage tolerance, and optimum dosage, and to identify common adverse effects and safety risks. If a compound demonstrates evidence of effectiveness and an acceptable safety profile in Phase 2 evaluations, Phase 3 trials are undertaken to obtain the additional information about clinical efficacy and safety in a larger number of patients, typically at geographically dispersed clinical trial sites, to permit the FDA to evaluate the overall benefit-risk relationship of the drug or biologic and to provide adequate information for the labeling of the product. In most cases, the FDA requires two adequate and well-controlled Phase 3 clinical trials to demonstrate the efficacy of the drug or biologic. A single Phase 3 trial with other confirmatory evidence may be sufficient in rare instances where the study is a large multicenter trial demonstrating internal consistency and a statistically very persuasive finding of a clinically meaningful effect on mortality, irreversible morbidity or prevention of a disease with a potentially serious outcome and confirmation of the result in a second trial would be practically or ethically impossible.
After completion of the required clinical testing, an NDA or BLA is prepared and submitted to the FDA. FDA approval of the NDA or BLA is required before marketing of the product may begin in the United States. The NDA or BLA must include the results of all preclinical, clinical, and other testing and a compilation of data relating to the product’s pharmacology, chemistry, manufacture, and controls. The cost of preparing and submitting an NDA or BLA is substantial. The submission of most NDAs and BLAs is additionally subject to a substantial application user fee. For fiscal year 2017, the application user fee is $2,038,100. The manufacturer and/or sponsor under an approved NDA or BLA are also subject to annual product and establishment user fees, currently set at $94,750 per product and $512,200 per establishment. These fees are typically adjusted annually.
The FDA has 60 days from its receipt of an NDA or BLA to determine whether the application will be accepted for filing based on the agency’s threshold determination that it is sufficiently complete to permit substantive review. Once the submission is accepted for filing, the FDA begins an in-depth review. The FDA has agreed to certain performance goals in the review of NDAs and BLAs. The FDA aims to review applications for standard review drug or biologic products within twelve months of the submission of the application, and the goal is to review applications for priority review drugs or biologics in eight months of the date of submission. Priority review can be applied to applications for drugs or biologics that are intended to treat a serious disease or condition and that, if approved, would provide a significant improvement in safety or effectiveness. The review process for both standard and priority review may be extended by the FDA for three additional months to consider certain late-submitted information, or information intended to clarify information already provided in the submission.
The FDA may also refer applications for novel drug or biologic products, or drug or biologic products that present difficult questions of safety or efficacy, to an advisory committee—typically a panel that includes clinicians and other experts—for review, evaluation, and a recommendation as to whether the application should be approved. The FDA is not bound by the recommendation of an advisory committee, but it generally follows such recommendations. Before approving an NDA or BLA, the FDA will typically inspect one or more clinical sites to assure compliance with GCP. Additionally, the FDA will inspect the facility or the facilities at which the drug is manufactured. The FDA will not approve the product unless compliance with current good manufacturing practices (“cGMPs”) is satisfactory and the NDA or BLA contains data that provide substantial evidence that the drug or biologic is safe and effective in the indication studied.
21
Table of Contents
After the FDA evaluates the NDA or BLA and the manufacturing facilities, it issues either an approval letter or a complete response letter. A complete response letter generally outlines the deficiencies in the submission and may require substantial additional testing, or information, in order for the FDA to reconsider the application. If, or when, those deficiencies have been addressed to the FDA’s satisfaction in a resubmission of the NDA or BLA, the FDA will issue an approval letter. The FDA has committed to reviewing such resubmissions in two or six months depending on the type of information included.
An approval letter authorizes commercial marketing of the drug or biologic with specific prescribing information for specific indications. As a condition of NDA or BLA approval, the FDA may require a risk evaluation and mitigation strategy (“REMS”), to help ensure that the benefits of the drug or biologic outweigh the potential risks. REMS can include medication guides, communication plans for healthcare professionals, and elements to assure safe use (“ETASU”). ETASU can include, but are not limited to, special training or certification for prescribing or dispensing, dispensing only under certain circumstances, special monitoring, and the use of patient registries. The requirement for a REMS can materially affect the potential market and profitability of the product. Moreover, product approval may require substantial post-approval testing and surveillance to monitor the product’s safety or efficacy. Once granted, product approvals may be withdrawn if compliance with regulatory standards is not maintained or problems are identified following initial marketing.
Changes to some of the conditions established in an approved application, including changes in indications, labeling, or manufacturing processes or facilities, require submission and FDA approval of a new NDA or BLA or NDA or BLA supplement before the change can be implemented. An NDA or BLA supplement for a new indication typically requires clinical data similar to that in the original application, and the FDA uses the same procedures and actions in reviewing NDA or BLA supplements as it does in reviewing NDAs or BLAs.
Post-Approval Requirements
Once an NDA or BLA is approved, a product will be subject to certain post-approval requirements. For instance, the FDA closely regulates the post-approval marketing and promotion of drugs and biologics, including standards and regulations for direct-to-consumer advertising, off-label promotion, industry-sponsored scientific and educational activities and promotional activities involving the internet. Drugs and biologics may be marketed only for the approved indications and in accordance with the provisions of the approved labeling.
Adverse event reporting and submission of periodic reports is required following FDA approval of an NDA or BLA. The FDA also may require post-marketing testing, known as Phase 4 testing, REMS, and surveillance to monitor the effects of an approved product, or the FDA may place conditions on an approval that could restrict the distribution or use of the product. In addition, quality control, drug manufacture, packaging, and labeling procedures must continue to conform to cGMPs after approval. Drug and biologic manufacturers and certain of their subcontractors are required to register their establishments with the FDA and certain state agencies. Registration with the FDA subjects entities to periodic unannounced inspections by the FDA, during which the agency inspects manufacturing facilities to assess compliance with cGMPs. Accordingly, manufacturers must continue to expend time, money, and effort in the areas of production and quality-control to maintain compliance with cGMPs. Regulatory authorities may withdraw product approvals or request product recalls if a company fails to comply with regulatory standards, if it encounters problems following initial marketing, or if previously unrecognized problems are subsequently discovered.
Fast Track Designation and Accelerated Approval
The FDA administers a number of programs to facilitate the development, and expedite the review, of drugs or biologics that are intended for the treatment of serious or life-threatening diseases or conditions. For instance, a sponsor may seek the FDA’s designation of its product candidate as a “fast track” product. Fast track products are those products intended for the treatment of a serious or life-threatening disease or condition and which demonstrate the potential to address unmet medical needs for such disease or condition. Drugs that qualify as a qualified infectious disease product, or QIDP, under the Generating Antibiotic Incentives Now, or GAIN Act, are also eligible for fast track designation.
22
Table of Contents
Under the fast track program, the sponsor of a new drug or biologic candidate may request that the FDA designate the candidate for a specific indication as a fast track drug or biologic concurrent with, or after, the filing of the IND for the candidate. The FDA must determine if the drug or biologic candidate qualifies for fast track designation within 60 days of receipt of the sponsor’s request. If fast track designation is obtained, the FDA may initiate review of sections of the marketing application before the application is complete. This “rolling review” is available if the applicant provides and the FDA approves a schedule for the remaining information. However, the FDA’s time period goal for reviewing an application does not begin until the last section of the NDA or BLA is submitted. Additionally, the fast track designation may be withdrawn by the FDA if the FDA believes that the designation is no longer supported by data emerging in the clinical trial process. In addition, a product candidate that receives fast track designation is eligible for more frequent meetings with the FDA to discuss the product’s development plan and ensure collection of appropriate data needed to support approval and more frequent communications from FDA regarding such things as the design of the proposed clinical trials and use of biomarkers, as applicable. In August 2015, the FDA granted fast track designation to CF-301 for the treatment of Staph aureus bacteremia, including endocarditis.
In some cases, a fast track product may be approved under the accelerated approval program, which means that the approval may be made on the basis of either a surrogate endpoint that is reasonably likely to predict clinical benefit, or on a clinical endpoint that can be measured earlier than irreversible morbidity or mortality, that is reasonably likely to predict an effect on irreversible morbidity or mortality or other clinical benefit, taking into account the severity, rarity, or prevalence of the condition and the availability or lack of alternative treatments. In clinical trials, a surrogate endpoint is a measurement of laboratory or clinical signs of a disease or condition that substitutes for a direct measurement of how a patient feels, functions, or survives. Surrogate endpoints can often be measured more easily or more rapidly than clinical endpoints.
A drug or biologic candidate approved on this basis is subject to rigorous post-marketing compliance requirements, including the completion of Phase 4 or post-approval clinical trials to confirm the effect on the clinical endpoint. Failure to conduct required post-approval studies, or confirm a clinical benefit during post-marketing studies, will allow the FDA to withdraw the drug or biologic from the market on an expedited basis. All promotional materials for drug candidates approved under accelerated regulations are subject to prior review by the FDA.
Breakthrough Therapy Designation
The FDA is required to expedite the development and review of the application for approval of drugs that are intended to treat a serious or life-threatening disease or condition where preliminary clinical evidence indicates that the drug may demonstrate substantial improvement over existing therapies on one or more clinically significant endpoints. Under the breakthrough therapy program, the sponsor of a new drug candidate may request that the FDA designate the drug candidate for a specific indication as a breakthrough therapy concurrent with, or after, the filing of the IND for the drug candidate. The FDA must determine if the drug candidate qualifies for breakthrough therapy designation within 60 days of receipt of the sponsor’s request.
Pediatric Information
Under the Pediatric Research Equity Act (“PREA”), NDAs or BLAs or supplements to NDAs or BLAs must contain data to assess the safety and effectiveness of the drug for the claimed indications in all relevant pediatric subpopulations and to support dosing and administration for each pediatric subpopulation for which the drug is safe and effective. The FDA may grant full or partial waivers, or deferrals, for submission of data. Unless otherwise required by regulation, PREA does not apply to any drug for an indication for which orphan designation has been granted.
Additional Controls for Biologics
To help reduce the increased risk of the introduction of adventitious agents, the PHSA emphasizes the importance of manufacturing controls for products whose attributes cannot be precisely defined. The PHSA also
23
Table of Contents
provides authority to the FDA to immediately suspend licenses in situations where there exists a danger to public health, to prepare or procure products in the event of shortages and critical public health needs, and to authorize the creation and enforcement of regulations to prevent the introduction or spread of communicable diseases in the United States and between states.
After a BLA is approved, the product may also be subject to official lot release as a condition of approval. As part of the manufacturing process, the manufacturer is required to perform certain tests on each lot of the product before it is released for distribution. If the product is subject to official release by the FDA, the manufacturer submits samples of each lot of product to the FDA together with a release protocol showing a summary of the history of manufacture of the lot and the results of all of the manufacturer’s tests performed on the lot. The FDA may also perform certain confirmatory tests on lots of some products, such as viral vaccines, before releasing the lots for distribution by the manufacturer. In addition, the FDA conducts laboratory research related to the regulatory standards on the safety, purity, potency, and effectiveness of biological products. As with drugs, after approval of biologics, manufacturers must address any safety issues that arise, are subject to recalls or a halt in manufacturing, and are subject to periodic inspection after approval.
Biosimilars
The Biologics Price Competition and Innovation Act of 2009 (“BPCIA”), created an abbreviated approval pathway for biological products shown to be highly similar to or interchangeable with an FDA-licensed reference biological product. Biosimilarity sufficient to reference a prior FDA-approved product requires that there be no differences in conditions of use, route of administration, dosage form, and strength, and no clinically meaningful differences between the biological product and the reference product in terms of safety, purity, and potency. Biosimilarity must be shown through analytical studies, animal studies, and at least one clinical study, absent a waiver by the Secretary. A biosimilar product may be deemed interchangeable with a prior approved product if it meets the higher hurdle of demonstrating that it can be expected to produce the same clinical results as the reference product and, for products administered multiple times, the biologic and the reference biologic may be switched after one has been previously administered without increasing safety risks or risks of diminished efficacy relative to exclusive use of the reference biologic. To date, only four biosimilars have been licensed under the BPCIA, though no interchangeable products have been approved under the BPCIA to date. Complexities associated with the larger, and often more complex, structures of biological products, as well as the process by which such products are manufactured, pose significant hurdles to implementation which are still being evaluated by the FDA.
Under the BPCIA, an application for a biosimilar product may not be submitted to the FDA until four years following the date that the reference product was first licensed by the FDA. In addition, the approval of a biosimilar product may not be made effective by the FDA until 12 years from the date on which the reference product was first licensed. During this 12-year period of exclusivity, another company may still market a competing version of the reference product if the FDA approves a full BLA for the competing product containing that company’s own preclinical and clinical data from adequate and well-controlled trials to demonstrate the safety, and efficacy of their product. The first biologic product submitted under the abbreviated approval pathway that is determined to be interchangeable with the reference product may also enjoy a period of exclusivity. At this juncture, it is unclear whether products deemed “interchangeable” by the FDA will, in fact, be readily substituted by pharmacies, which are governed by state pharmacy law.
Disclosure of Clinical Trial Information
Sponsors of clinical trials of FDA-regulated products, including drugs, are required to register and disclose certain clinical trial information. Information related to the product, patient population, phase of investigation, study sites and investigators, and other aspects of the clinical trial is then made public as part of the registration. Sponsors are also obligated to discuss the results of their clinical trials after completion. Disclosure of the results
24
Table of Contents
of these trials can be delayed until the new product or new indication being studied has been approved. Competitors may use this publicly available information to gain knowledge regarding the progress of development programs.
Other Domestic Regulatory Requirements
In the United States, the research, manufacturing, distribution, sale, and promotion of drug and biological products are potentially subject to regulation by various federal, state, and local authorities in addition to the FDA, including the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, other divisions of the United States Department of Health and Human Services (e.g., the Office of the Inspector General), the United States Department of Justice and individual United States Attorneys’ offices within the Department of Justice, and state and local governments. For example, sales, marketing, and scientific/educational grant programs must comply with the anti-fraud and abuse provisions of the Social Security Act, the False Claims Act, the privacy and security provisions of the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, or “HIPAA”, as amended by the Health Information Technology and Clinical Health Act, or “HITECH”, and similar state laws, each as amended. Pricing and rebate programs must comply with the Medicaid rebate requirements of the Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act of 1990 and the Veterans Health Care Act of 1992, each as amended. If products are made available to authorized users of the Federal Supply Schedule of the General Services Administration, additional laws and requirements apply. All of these activities are also potentially subject to federal and state consumer protection, unfair competition, and other laws, and violations of these laws may result in imprisonment, criminal fines, civil monetary penalties and exclusion from participation in federal healthcare programs.
In addition to FDA restrictions on marketing of pharmaceutical products, several other types of state and federal laws have been applied to restrict certain marketing practices in the pharmaceutical industry in recent years. These laws include anti-kickback statutes and false claims statutes. The federal healthcare program Anti-Kickback Statute prohibits, among other things, knowingly and willfully offering, paying, soliciting or receiving remuneration to induce or in return for purchasing, leasing, ordering or arranging for the purchase, lease or order of any healthcare item or service reimbursable under Medicare, Medicaid or other federally financed healthcare programs. This statute has been interpreted to apply to arrangements between pharmaceutical manufacturers on the one hand and prescribers, purchasers and formulary managers on the other. In addition, a person or entity does not need to have actual knowledge of the statute or specific intent to violate it in order to have committed a violation. Violations of the Anti-Kickback Statute are punishable by imprisonment, criminal fines, civil monetary penalties and exclusion from participation in federal healthcare programs. Although there are a number of statutory exemptions and regulatory safe harbors protecting certain common activities from prosecution or other regulatory sanctions, the exemptions and safe harbors are drawn narrowly, and practices that involve remuneration intended to induce prescribing, purchases or recommendations may be subject to scrutiny if they do not qualify for an exemption or safe harbor.
Federal false claims laws prohibit any person from knowingly presenting, or causing to be presented, a false claim for payment to the federal government, or knowingly making, or causing to be made, a false statement to have a false claim paid. Recently, several pharmaceutical and other healthcare companies have been prosecuted under these laws for allegedly inflating drug prices they report to pricing services, which in turn were used by the government to set Medicare and Medicaid reimbursement rates, and for allegedly providing free product to customers with the expectation that the customers would bill federal programs for the product. In addition, certain marketing practices, including off-label promotion, may also violate false claims laws. The majority of states also have statutes or regulations similar to the federal anti-kickback law and false claims laws, which apply to items and services reimbursed under Medicaid and other state programs, or, in several states, apply regardless of the payor.
HIPAA also created new federal criminal statutes that prohibit among other actions, knowingly and willfully executing, or attempting to execute, a scheme to defraud any healthcare benefit program, including private third-party payors, knowingly and willfully embezzling or stealing from a healthcare benefit program, willfully obstructing a criminal investigation of a healthcare offense, and knowingly and willfully falsifying, concealing or
25
Table of Contents
covering up a material fact or making any materially false, fictitious or fraudulent statement in connection with the delivery of or payment for healthcare benefits, items or services. Similar to the federal Anti-Kickback Statute, a person or entity does not need to have actual knowledge of the statute or specific intent to violate it in order to have committed a violation.
There has also been a recent trend of increased federal and state regulation of payments made to physicians and other healthcare providers. The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, as amended by the Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act, or collectively, the Affordable Care Act, among other things, imposes new reporting requirements on drug manufacturers for payments made by them to physicians and teaching hospitals, as well as ownership and investment interests held by physicians and their immediate family members. Failure to submit required information may result in civil monetary penalties of up to an aggregate of $165,786 per year (or up to an aggregate of $1,105,241 per year for “knowing failures”), for all payments, transfers of value or ownership or investment interests that are not timely, accurately and completely reported in an annual submission. Drug manufacturers are required to submit reports to the government by the 90th day of each calendar year. Certain states also mandate implementation of compliance programs, impose restrictions on drug manufacturer marketing practices and/or require the tracking and reporting of gifts, compensation and other remuneration to physicians.
We may also be subject to data privacy and security regulation by both the federal government and the states in which we conduct our business. HIPAA, HITECH, and their respective implementing regulations, including the final omnibus rule published on January 25, 2013, imposes specified requirements relating to the privacy, security and transmission of individually identifiable health information. Among other things, HITECH makes HIPAA’s privacy and security standards directly applicable to “business associates,” defined as independent contractors or agents of covered entities that create, receive, maintain or transmit protected health information in connection with providing a service for or on behalf of a covered entity. HITECH also increased the civil and criminal penalties that may be imposed against covered entities, business associates and possibly other persons, and gave state attorneys general new authority to file civil actions for damages or injunctions in federal courts to enforce the federal HIPAA laws and seek attorney’s fees and costs associated with pursuing federal civil actions. In addition, state laws govern the privacy and security of health information in certain circumstances, many of which differ from each other in significant ways, thus complicating compliance efforts.
Moreover, ContraFect is now, and in the future may become, subject to additional federal, state, and local laws, regulations, and policies relating to safe working conditions, laboratory practices, the experimental use of animals, and/or the use, storage, handling, transportation, and disposal of human tissue, waste, and hazardous substances, including radioactive and toxic materials and infectious disease agents used in conjunction with our research work.
Physician Drug Samples
As part of the sales and marketing process, pharmaceutical companies frequently provide samples of approved drugs to physicians. The Prescription Drug Marketing Act, or the PDMA, imposes requirements and limitations upon the provision of drug samples to physicians, as well as prohibits states from licensing distributors of prescription drugs unless the state licensing program meets certain federal guidelines that include minimum standards for storage, handling and record keeping. In addition, the PDMA sets forth civil and criminal penalties for violations.
New Legislation and Regulations
From time to time, legislation is drafted, introduced and passed in Congress that could significantly change the statutory provisions governing the testing, approval, manufacturing and marketing of products regulated by the FDA. In addition to new legislation, FDA regulations and policies are often revised or interpreted by the agency in ways that may significantly affect our business and our products. It is impossible to predict whether further legislative changes will be enacted or whether FDA regulations, guidance, policies or interpretations changed or what the effect of such changes, if any, may be.
26
Table of Contents
For example, in December 2016, the 21st Century Cures act, or Cures Act, was signed into law. The Cures Act, among other things, is intended to modernize the regulation of drugs and biologics and spur innovation, but its ultimate implementation remains unclear. Among other things, the Cures Act provides a new “limited population” approval pathway for antibacterial and antifungal drugs intended to treat serious or life-threatening infections.
Foreign Regulation
In addition to regulations in the United States, we may become subject to widely varying foreign regulations, which may be quite different from those of the FDA, governing clinical trials, manufacture, product registration and approval, and pharmaceutical sales. Whether or not FDA approval has been obtained, we must obtain a separate approval for a product by the comparable regulatory authorities of foreign countries prior to the commencement of product marketing in these countries. The approval process varies from country to country, and the time may be longer or shorter than that required for FDA approval. In certain countries, regulatory authorities also establish pricing and reimbursement criteria. In addition, under current United States law, there are restrictions on the export of products not approved by the FDA, depending on the country involved and the status of the product in that country.
European Medicines Agency (EMA) – Small and Medium Enterprise (SME) Designation
The SME designation was established by EMA to promote innovation and the development of new medicinal products by smaller companies. Companies with SME status are eligible to receive financial incentives as well as administrative and regulatory support through national and regional level programs. These benefits include access to dedicated EMA personnel during the clinical development process as well as reductions in fees associated with regulatory procedures such as Scientific Advice, Marketing Authorizations, and inspections. Companies with SME status are also eligible for early application (prior to proof of concept) to the priority medicines (PRIME) scheme. PRIME provides enhanced support for the development of medicines that target an unmet medical need. In August 2016, the EMA granted SME designation to the Company.
Pharmaceutical Coverage, Pricing and Reimbursement
Our ability to commercialize our product candidates successfully will depend in part on the extent to which the United States and foreign governmental authorities, private health insurers and other third-party payors establish appropriate coverage and reimbursement levels for our product candidates and related treatments. In many of the markets where we would commercialize a product following regulatory approval, the prices of pharmaceutical products are subject to direct price controls (by law) and to drug reimbursement programs with varying price control mechanisms. Public and private health care payors control costs and influence drug pricing through a variety of mechanisms, including through negotiating discounts with the manufacturers and through the use of tiered formularies and other mechanisms that provide preferential access to certain drugs over others within a therapeutic class. Payors also set other criteria to govern the uses of a drug that will be deemed medically appropriate and therefore reimbursed or otherwise covered. In particular, many public and private health care payors limit reimbursement and coverage to the uses of a drug that are either approved by the FDA or that are supported by other appropriate evidence (for example, published medical literature) and appear in a recognized drug compendium. Drug compendia are publications that summarize the available medical evidence for particular drug products and identify which uses of a drug are supported or not supported by the available evidence, whether or not such uses have been approved by the FDA.
Healthcare Reform
In the United States, there have been a number of legislative and regulatory changes to the healthcare system in ways that could affect our future revenues and profitability and the future revenues and profitability of our potential customers. For example, the Medicare Prescription Drug, Improvement, and Modernization Act of 2003 (the “MMA”) revised the payment methodologies for many drugs, which resulted in reduced reimbursement to providers. Additionally, the MMA created an outpatient prescription drug benefit which became effective on January 1, 2006. This benefit is administered by private pharmacy benefit managers and other managed care organizations and is putting increased pressure on the pharmaceutical industry to reduce prices.
27
Table of Contents
In March 2010, the Affordable Care Act was passed, which substantially changes the way health care is financed by both governmental and private insurers, and significantly impacts the U.S. pharmaceutical industry. The Affordable Care Act, among other things, subjects biologic products to potential competition by lower-cost biosimilars, addresses a new methodology by which rebates owed by manufacturers under the Medicaid Drug Rebate Program are calculated for drugs that are inhaled, infused, instilled, implanted or injected, increases the minimum Medicaid rebates owed by manufacturers under the Medicaid Drug Rebate Program and extends the rebate program to individuals enrolled in Medicaid managed care organizations, establishes annual fees and taxes on manufacturers of certain branded prescription drugs, and a new Medicare Part D coverage gap discount program, in which manufacturers must agree to offer 50% point-of-sale discounts off negotiated prices of applicable brand drugs to eligible beneficiaries during their coverage gap period, as a condition for the manufacturer’s outpatient drugs to be covered under Medicare Part D.
We expect that the new presidential administration and U.S. Congress will seek to modify, repeal, or otherwise invalidate all, or certain provisions of, the Affordable Care Act. In January 2017, the House and Senate passed a budget resolution that authorizes congressional committees to draft legislation to repeal all or portions of the Affordable Care Act and permits such legislation to pass with a majority vote in the Senate. The President has also recently issued an executive order in which he stated that it is his administration’s policy to seek the prompt repeal of the Affordable Care Act and directed executive departments and federal agencies to waive, defer, grant exemptions from, or delay the implementation of the burdensome provisions of the Affordable Care Act to the maximum extent permitted by law. There is still uncertainty with respect to the impact the President’s administration and the U.S. Congress may have, if any, and any changes will likely take time to unfold, and could have an impact on coverage and reimbursement for healthcare items and services covered by plans that were authorized by the Affordable Care Act.
In addition, other legislative changes have been proposed and adopted in the United States since the Affordable Care Act was enacted. On August 2, 2011, the Budget Control Act of 2011 among other things, created measures for spending reductions by Congress. A Joint Select Committee on Deficit Reduction, tasked with recommending a targeted deficit reduction of at least $1.2 trillion for the years 2013 through 2021, was unable to reach required goals, thereby triggering the legislation’s automatic reduction to several government programs. This includes aggregate reductions of Medicare payments to providers of 2% per fiscal year, which went into effect in April 2013, due to subsequent legislative amendments to the statute, and will remain in effect through 2025 unless additional Congressional action is taken. On January 2, 2013, the American Taxpayer Relief Act of 2012 was signed into law, which, among other things, further reduced Medicare payments to several types of providers, including hospitals, imaging centers and cancer treatment centers, and increased the statute of limitations period for the government to recover overpayments to providers from three to five years. Recently there has also been heightened governmental scrutiny over the manner in which manufacturers set prices for their marketed products, which has resulted in several Congressional inquiries and proposed bills designed to, among other things, reform government program reimbursement methodologies. For example, the Cures Act changes the reimbursement methodology for infusion drugs and biologics furnished through durable medical equipment in an attempt to remedy over- and underpayment of certain drugs.
If additional state and federal healthcare reform measures are adopted in the future, any of which could limit the amounts that federal and state governments will pay for healthcare products and services, we could expect such measures to result in reduced demand for our product candidates or additional pricing pressures.
Segment Reporting
We are engaged solely in the discovery and development of therapeutic protein and antibody products for life-threatening, drug-resistant infectious diseases. Accordingly, we have determined that we operate in one operating segment.
28
Table of Contents
Employees
As of March 7, 2017, we had 23 full-time employees, including 11 employees with advanced degrees. Of these full-time employees, 11 employees are engaged in research and development activities. None of our employees is represented by a labor union or covered by a collective bargaining agreement. We consider our relationship with our employees to be good.
Our Corporate Information
We were incorporated under the laws of the State of Delaware in March 2008. Our executive offices are located at 28 Wells Avenue, 3rd Floor, Yonkers, NY 10701, and our telephone number is (914) 207-2300. Our website address is www.contrafect.com. References to our website are inactive textual references only and the content of our website should not be deemed incorporated by reference into this Form 10-K.
Available Information
Our Annual Reports on Form 10-K, Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, Current Reports on Form 8-K and any amendments to these reports filed or furnished pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, are available free of charge on our website located at www.contrafect.com as soon as reasonably practicable after they are filed with or furnished to the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”). These reports are also available at the SEC’s Internet website at www.sec.gov. The public may also read and copy any materials filed with the SEC at the SEC’s Public Reference Room at 100 F Street, N.E., Washington D.C. 20549. Information on the operation of the Public Reference Room may be obtained by calling the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330.
A copy of our Corporate Governance Guidelines, Code of Business Conduct and Ethics, Whistleblower Policy and the charters of the Audit Committee, Compensation Committee and Nominating and Corporate Governance Committee are posted on our website, www.contrafect.com, under “Corporate Governance” and are available in print to any person who requests copies by contacting us by calling (914) 207-2300 or by writing to ContraFect Corporation, Attn: General Counsel, 28 Wells Avenue, 3rd Floor, Yonkers, NY 10701.
29
Table of Contents
You should carefully consider the following risk factors, as well as the other information in this report, and in our other public filings. Our business, financial condition and operating results can be affected by a number of factors, whether currently known or unknown, including but not limited to those described below, any one or more of which could, directly or indirectly, cause the Company’s actual results of operations and financial condition to vary materially from past, or from anticipated future, results of operations and financial condition. Any of these factors, in whole or in part, could materially and adversely affect the Company’s business, financial condition, results of operations and common stock price. Other factors may exist that we do not consider significant based on information that is currently available. In addition, new risks may emerge at any time, and we cannot predict those risks or estimate the extent to which they may affect us. Past financial performance should not be considered to be a reliable indicator of future performance, and investors should not use historical trends to anticipate results or trends in future periods.
Risks Related to Our Financial Position and Need for Additional Capital
We have incurred significant losses since our inception and do not expect to generate revenue for at least the next several years. We expect to incur losses for at least the next several years and may never achieve or maintain profitability.
We are a clinical-stage biopharmaceutical company with no approved products, and we have not generated any revenue from product sales to date. To date, we have focused exclusively on developing our product candidates and have funded our operations primarily through the sale of common stock and warrants, convertible preferred stock and issuances of convertible debt to our investors. We have not yet demonstrated an ability to overcome many of the risks and uncertainties frequently encountered by companies in the pharmaceutical industry, and you should analyze our company in light of such risks and uncertainties.
Since inception, we have incurred significant losses. Our net losses were $28.5 million and $25.1 million for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively. We have devoted substantially all of our efforts to research and development. We expect to continue to incur significant expenses and increasing operating losses for at least the next several years. The net losses we incur may fluctuate significantly from quarter to quarter and year to year.
We anticipate that our expenses will increase substantially as clinical trials for any of our product candidates commence or progress. Our expenses will increase if and as we:
| • | seek to discover or develop additional product candidates; |
| • | seek marketing approvals for any of our product candidates that successfully complete clinical trials; |
| • | in-license or acquire other products and technologies; |
| • | maintain, expand and protect our intellectual property portfolio; |
| • | hire additional clinical, quality control and scientific personnel; and |
| • | add operational, financial and management information systems and personnel, including personnel to support our product development and planned future commercialization efforts. |
Our recurring losses from operations could raise substantial doubt regarding our ability to continue as a going concern.
We currently operate with limited resources. We believe that our cash, cash equivalents and marketable securities balance of $35.2 million as of December 31, 2016 will be sufficient to fund our projected operations
30
Table of Contents
into the second quarter of 2018. Depending on the level of cash used in or generated from operations, additional capital may be required to sustain operations. We have incurred significant losses since our inception and have never generated revenue or profit, and it is possible we will never generate revenue or profit. Meaningful revenues will likely not be available until and unless any future product candidates are approved by the FDA or comparable regulatory agencies in other countries and successfully marketed, either by us or a partner, an outcome which may not occur. There is no assurance that other financing will be available when needed to allow us to continue as a going concern. The perception that we may not be able to continue as a going concern may cause others to choose not to deal with us due to concerns about our ability to meet our contractual obligations. If we are unable to continue as a going concern, you could lose all or part of your investment in our Company.
We currently have no source of product revenue and have not yet generated any revenues from product sales.
To date, we have not completed the development of any products and have not generated any revenues from product sales. Our ability to generate revenue from product sales and achieve profitability will depend upon our ability to successfully commercialize products, including any of our current product candidates, or other product candidates that we may in-license or acquire in the future. Even if we are able to successfully achieve regulatory approval for these product candidates, we may never generate revenues that are significant enough to achieve profitability. Our ability to generate revenue from product sales from our current or future product candidates also depends on a number of additional factors, including our ability to:
| • | successfully complete development activities, including the necessary clinical trials; |
| • | complete and submit biologics license applications (“BLAs”) to the FDA, and obtain regulatory approval for indications for which there is a commercial market; |
| • | complete and submit applications to, and obtain approval from, foreign regulatory authorities; |
| • | set a commercially viable price for our products; |
| • | develop a commercial organization capable of sales, marketing and distribution for any products we intend to sell ourselves in the markets which we choose to commercialize on our own; |
| • | find suitable distribution partners to help us market, sell and distribute our products in other markets; and |
| • | obtain coverage and adequate reimbursement from third parties, including government and private payors. |
In addition, because of the numerous risks and uncertainties associated with product development, including that any of our product candidates may not advance through development or achieve the desired endpoints of applicable clinical trials, we are unable to predict the timing or amount of increased expenses, or when or if we will be able to achieve or maintain profitability. Even if we are able to complete the development and regulatory process for any product candidates, we anticipate incurring significant costs associated with commercializing these products.
Even if we are able to generate revenues from the sale of our products, we may not become profitable. If we do achieve profitability, we may not be able to sustain or increase profitability on a quarterly or annual basis. Our failure to become and remain profitable would decrease the value of our company and could impair our ability to raise capital to expand our business or continue our operations. A decline in the value of our company could also cause you to lose all or part of your investment.
We have a need for substantial additional funding. If we are unable to raise capital when needed, we could be forced to delay, reduce or eliminate our product development programs or commercialization efforts.
We expect our expenses to increase in connection with our ongoing activities, particularly as we continue the clinical development of CF-301 and preclinical development of CF-404, and, possibly, acquire and develop
31
Table of Contents
new product candidates or technologies. Accordingly, we will need to obtain substantial additional funding in connection with our continuing operations. If we are unable to raise capital when needed or on attractive terms, we could be forced to delay, reduce or eliminate our research and development programs or any future commercialization efforts.
Our future capital requirements will depend on many factors, including:
| • | the complexity, timing and results of our clinical trials of our product candidates; |
| • | the costs, timing and outcome of regulatory review of our product candidates; |
| • | the costs of developing our product candidates for additional indications; |
| • | our ability to establish scientific or business collaborations on favorable terms, if at all; |
| • | the costs of preparing, filing and prosecuting patent or other intellectual property applications, maintaining and protecting our intellectual property rights and defending against intellectual property-related claims; |
| • | the extent to which we in-license or acquire other product candidates or technologies; and |
| • | the scope, progress, results and costs of product development for our product candidates. |
Conducting clinical trials is a time-consuming, expensive and uncertain process that takes years to complete, and we may never generate the necessary data or results to obtain marketing approval and achieve product sales. In addition, if approved, CF-301, CF-404 or any other product candidate that we develop may not achieve commercial success. Accordingly, we may need to continue to rely on additional financing to achieve our business objectives. In addition, we may seek additional capital due to favorable market conditions or strategic considerations, even if we believe that we have sufficient funds for our current or future operating plans. Adequate additional financing may not be available to us on acceptable terms, or at all.
Raising additional capital may cause dilution to our stockholders, restrict our operations or require us to relinquish rights to our technologies or product candidates.
Until such time, if ever, as we can generate substantial product revenues, we may finance our cash needs through a combination of equity offerings, debt financings, collaborations, strategic alliances and marketing, distribution or licensing arrangements. We do not have any committed external source of funds. To the extent that we raise additional capital through the sale of equity or convertible debt securities, your ownership interest will be diluted, and the terms of these securities may include liquidation or other preferences that adversely affect your rights as a stockholder. Debt financing, if available, may involve agreements that include covenants limiting or restricting our ability to take specific actions, such as incurring additional debt, making capital expenditures or declaring dividends.
If we raise additional funds through collaborations, strategic alliances or marketing, distribution or licensing arrangements with third parties, we may have to relinquish valuable rights to our technologies, future revenue streams or product candidates or grant licenses on terms that may not be favorable to us. If we are unable to raise additional funds through equity or debt financings when needed, we may be required to delay, limit, reduce or terminate our product development or future commercialization efforts or grant rights to develop and market product candidates that we would otherwise prefer to develop and market ourselves.
Our short operating history may make it difficult for you to evaluate the success of our business to date and to assess our future viability.
We were incorporated in 2008 and commenced active research operations in 2010. Our operations to date have been limited to organizing and staffing our company, business planning, raising capital and acquiring and developing CF-301, CF-404 and other potential product candidates. We have not yet demonstrated our ability to successfully complete Phase 2 or Phase 3 clinical trials, obtain marketing approval, manufacture a commercial scale product, or arrange for a third-party to do so on our behalf, or conduct sales and marketing activities necessary for successful product commercialization. Consequently, any predictions you make about our future success or viability may not be as accurate as they could be if we had a longer operating history.
32
Table of Contents
In addition, we may encounter unforeseen expenses, difficulties, complications, delays and other known and unknown factors. We will need to transition from a company with a product development focus to a company capable of supporting commercial activities. We may not be successful in such a transition.
The timing of the milestone and royalty payments we are required to make under certain agreements, including to Rockefeller and Trellis, is uncertain and could adversely affect our cash flows and results of operations.
We are party to certain agreements, including with Rockefeller and Trellis, pursuant to which we have acquired licenses to certain patents and patent applications and other intellectual property related to a series of compounds, including CF-301 and CF-404, to develop and commercialize therapeutics. Under our agreements with Rockefeller and Trellis, we have obligations to achieve diligence minimums and to make payments upon achievement of specified development and regulatory milestones. We will also make additional payments upon the achievement of future sales milestones and for royalties on future net sales.
The timing of milestone payments under our licenses and sponsored research agreements is subject to factors relating to the clinical and regulatory development and commercialization of products, many of which are beyond our control. We may become obligated to make a milestone payment when we do not have the cash on hand to make such payment, which could require us to delay our clinical trials, curtail our operations, scale back our commercialization and marketing efforts or seek funds to meet these obligations on terms unfavorable to us.
Our ability to utilize our net operating loss carryforwards and certain other tax attributes may be limited.
Under Section 382 and related provisions of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended (the “Code”), if a corporation undergoes an “ownership change” (generally defined as a greater than 50% change (by value) in its equity ownership over a three year period), the corporation’s ability to use its pre-change net operating loss carryforwards and other pre-change tax attributes to offset its post-change income may be limited. As a result of our past transactions, we may have experienced an “ownership change.” At this time, we have not completed a study to assess whether an ownership change under Section 382 of the Code has occurred, or whether there have been multiple ownership changes since our formation, due to the costs and complexities associated with such a study. We may also experience ownership changes in the future as a result of subsequent shifts in our stock ownership. Thus, our ability to utilize carryforwards of our net operating losses and other tax attributes to reduce future tax liabilities may be substantially restricted. Further, U.S. tax laws limit the time during which these carryforwards may be applied against future taxes. Therefore, we may not be able to take full advantage of these carryforwards for federal or state tax purposes. As of December 31, 2016, we had federal and state net operating loss carryforwards of approximately $120.5 million and $125.3 million, respectively, and federal research and development credits of approximately $1.8 million, the use of which could be limited or eliminated by virtue of one or more “ownership changes.”
Risks Related to the Discovery, Development and Commercialization of Our Product Candidates
We are heavily dependent on the success of our leading product candidates, CF-301 and CF-404. The approval process of the FDA and comparable foreign regulatory authorities is lengthy, time consuming and inherently unpredictable, and if we are ultimately unable to obtain regulatory approval for CF-301, CF-404 or any other product candidate our business will be substantially harmed.
Our near-term business prospects are substantially dependent on our ability to develop and commercialize CF-301 and CF-404. We cannot market or sell CF-301, CF-404 or any other product candidate in the United States without FDA approval, but this approval, if ever issued, is at least several years away. To commercialize CF-301, CF-404 or any other product candidate outside of the United States, we will need applicable foreign regulatory approvals. The clinical development of CF-301, CF-404 or any other product candidate is susceptible
33
Table of Contents
to the inherent risks of any drug development program, including a failure to achieve efficacy across a broad population of patients, the potential occurrence of severe adverse events and the risks that the FDA or any applicable foreign regulatory authority will determine that a drug product is not approvable.
The process required to obtain approval for commercialization from the FDA and similar foreign authorities is unpredictable, and typically takes many years even after the commencement of clinical trials, depending on numerous factors. In addition, approval policies, regulations, or the type and amount of clinical data necessary to obtain regulatory approval may change during the course of a product’s clinical development. We may fail to obtain regulatory approval for CF-301, CF-404 or any other product candidate for many reasons, including the following:
| • | we may not be able to demonstrate to the satisfaction of the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities that CF-301, CF-404 or any other product candidate is safe and effective for any indication; |
| • | the results of clinical trials may not meet the level of clinical or statistical significance required for approval by the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities; |
| • | the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities may disagree with the design or implementation of our clinical trials; |
| • | we may not be able to demonstrate that CF-301, CF-404 or any other product candidate’s clinical and other benefits outweigh its safety risks; |
| • | the approval policies or regulations of the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities may significantly change in a manner rendering our clinical data insufficient for approval; |
| • | the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities may disagree with our interpretation of data from preclinical studies or clinical trials; |
| • | the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities may identify deficiencies in data generated at our clinical trial sites; |
| • | the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities may identify deficiencies in the clinical practices of the third-party contract research organizations (“CROs”) we use for clinical trials; and |
| • | the FDA or comparable foreign regulatory authorities may identify deficiencies in the manufacturing processes or facilities of third-party manufacturers with which we or our collaborators enter into agreements for clinical and commercial supplies. |
This lengthy approval process as well as the unpredictability of future clinical trial results may prevent us from obtaining regulatory approval to market CF-301, CF-404 or any other product candidate, which would significantly harm our business.
If clinical trials of CF-301, CF-404 or any other product candidate that we develop fail to demonstrate safety and efficacy to the satisfaction of the FDA or similar regulatory authorities outside the United States or do not otherwise produce positive results, we may incur additional costs or experience delays in completing, or ultimately be unable to complete, the development and commercialization of CF-301, CF-404 or any other product candidate.
Before obtaining marketing approval from regulatory authorities for the sale of CF-301, CF-404 or any other product candidate, we must complete preclinical development and conduct extensive clinical trials to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of our product candidates in humans. Clinical testing is expensive, difficult to design and implement, can take many years to complete and is uncertain as to outcome. A failure of one or more clinical trials can occur at any stage of testing. The outcome of preclinical testing and early clinical trials may not be predictive of the success of later clinical trials, and interim results of a clinical trial do not necessarily predict final results. Moreover, preclinical and clinical data are often susceptible to varying interpretations and analyses, and many companies that have believed their product candidates performed satisfactorily in preclinical studies and clinical trials have nonetheless failed to obtain marketing approval of their products.
34
Table of Contents
We may experience numerous unforeseen events during, or as a result of, clinical trials that could delay or prevent our ability to receive marketing approval or commercialize our product candidates, including:
| • | clinical trials of our product candidates may produce negative or inconclusive results, or significant adverse side effects, and we may decide, or regulators may require us, to conduct additional clinical trials or abandon product development programs; |
| • | the number of patients required for clinical trials of our product candidates may be larger than we anticipate, enrollment in these clinical trials may be slower than we anticipate or participants may drop out of these clinical trials at a higher rate than we anticipate; |
| • | our third-party contractors may fail to comply with regulatory requirements or meet their contractual obligations to us in a timely manner, or at all; |
| • | regulators or institutional review boards (“IRBs”) may not authorize us or our investigators to commence a clinical trial or conduct a clinical trial at a prospective trial site; |
| • | we may have delays in reaching or fail to reach agreement on acceptable clinical trial contracts or clinical trial protocols with prospective trial sites; |
| • | we may voluntarily suspend or terminate clinical trials of our product candidates for various reasons, including a finding that the participants are being exposed to unacceptable health risks; |
| • | regulators or IRBs may require that we or our investigators suspend or terminate clinical research for various reasons, including noncompliance with regulatory requirements or a finding that the participants are being exposed to unacceptable health risks; |
| • | the cost of clinical trials of our product candidates may be greater than we anticipate; |
| • | the supply or quality of our product candidates or other materials necessary to conduct clinical trials of our product candidates may be insufficient or inadequate; and |
| • | our product candidates may have undesirable side effects or other unexpected characteristics, causing us or our investigators, regulators or IRBs to suspend or terminate the trials. |
If we are required to conduct additional clinical trials or other testing of CF-301, CF-404 or any other product candidate that we develop beyond those that we contemplate, if we are unable to successfully complete clinical trials of our product candidates or other testing, if the results of these trials or tests are not positive or are only modestly positive or if there are safety concerns, we may:
| • | be delayed in obtaining marketing approval or sales revenues for our product candidates; |
| • | not obtain marketing approval at all; |
| • | obtain approval for indications or patient populations that are not as broad as intended or desired; |
| • | obtain approval with labeling that includes significant use or distribution restrictions or safety warnings, including boxed warnings; |
| • | be subject to additional post-marketing testing requirements; or |
| • | have the product removed from the market after obtaining marketing approval. |
Our product development costs will also increase if we experience delays in testing or marketing approvals. We do not know whether any clinical trials will begin as planned, will need to be restructured or will be completed on schedule, or at all. Significant clinical trial delays also could shorten any periods during which we may have the exclusive right to commercialize our product candidates or may allow our competitors to bring products to market before we do and may impair our ability to successfully commercialize our product candidates and may harm our business and results of operations.
35
Table of Contents
We may be required to suspend or discontinue clinical trials due to adverse side effects or other safety risks that could preclude approval of CF-301, CF-404 or any other product candidates.
Our clinical trials may be suspended at any time for a number of reasons. For example, it is possible that exposure to CF-301 could result in adverse clinical events such as localized inflammation in the region surrounding blood vessels, or having a hypersensitivity reaction, such as serum sickness or anaphylaxis. A clinical trial may be prevented from commencing or may be suspended or terminated by us, our collaborators, IRBs, the FDA or other regulatory authorities due to the risks of or occurrence of such adverse events, an unacceptable safety risk to participants, a failure to conduct the clinical trial in accordance with regulatory requirements or our clinical protocols, presentation of unforeseen safety issues or adverse side effects, failure to demonstrate a benefit from using the investigational drug, changes in governmental regulations or administrative actions, lack of adequate funding to continue the clinical trial, or negative or equivocal findings of the data safety monitoring board or IRBs for a clinical trial. We may voluntarily suspend or terminate our clinical trials if at any time we believe that they present an unacceptable risk to participants. If we elect or are forced to suspend or terminate any clinical trial of any product candidates that we develop, the commercial prospects of such product candidates will be harmed and our ability to generate product revenues, if at all, from any of these product candidates will be delayed or eliminated. Any of these occurrences may significantly harm our business.
Delays in clinical trials are common and have many causes, and any such delays could result in increased costs to us and jeopardize, delay or prevent our ability to obtain regulatory approval and commence product sales as currently contemplated.
We may experience delays in clinical trials of our product candidates. Our planned clinical trials might not begin on time, might need to be redesigned, might not enroll a sufficient number of patients or might not be completed on schedule, if at all. Clinical trials can be delayed for a variety of reasons, including the following:
| • | imposition of a clinical hold by the FDA or other regulatory authorities; |
| • | delays in reaching agreement on acceptable terms with prospective CROs and clinical trial sites; |
| • | delays in recruiting suitable patients to participate in a trial; |
| • | delays in having patients complete participation in a trial or return for post-treatment follow-up; |
| • | clinical sites dropping out of a trial to the detriment of enrollment; |
| • | adverse side effects in patient populations; |
| • | time required to add new sites; |
| • | delays resulting from negative or equivocal findings of the data safety monitoring board for a trial; |
| • | delays in completing, or as a result of findings from, preclinical studies; or |
| • | delays in developing adequate processes for manufacture of, or formulations for, sufficient supplies of clinical trial materials. For example, our contract manufacturer recently produced a lot of CF-301 investigational drug product that did not meet manufacturing release specifications, resulting in the delay of our Phase 2 study. |
Patient enrollment, a significant factor in the timing of clinical trials, is affected by many factors, including the size and nature of the patient population, the proximity of patients to clinical sites, the eligibility criteria for the trial, the design of the clinical trial, competing clinical trials and clinicians’ and patients’ perceptions as to the potential advantages of the drug being studied in relation to other available therapies, including any new drugs that may be approved for the indications we are investigating. Any of these delays in completing our clinical trials could increase our costs, slow down our product development and approval process and jeopardize our ability to commence product sales and generate revenues.
36
Table of Contents
We are significantly dependent on our license agreements with Rockefeller that relate to CF-301.
Under our various license agreements with Rockefeller, we are obligated to use our diligent efforts to develop and commercialize licensed products, including CF-301. Rockefeller may terminate the agreement in the event of our breach of the terms of the license agreements. In the event of such termination, Rockefeller has the right to retain its license and other rights under the agreement, subject to continuing royalties and other obligations. Our breach of the agreement, including non-payment of any milestone payment, and Rockefeller’s subsequent termination of the agreement, could result in the loss of our rights to develop and commercialize CF-301, which would seriously harm our ability to generate revenues or achieve profitability.
We rely on CROs to conduct our preclinical studies and will rely on CROs to conduct our clinical trials. If these third parties do not successfully carry out their contractual duties or meet expected deadlines, we may be delayed in obtaining, or may ultimately not be able to obtain, regulatory approval for commercialization of CF-301, CF-404 or any other product candidates.
We have relied and will continue to rely on CROs for the execution of our preclinical studies and to recruit patients and monitor and manage data for our clinical programs for CF-301, CF-404 or any other product candidate. We control only certain aspects of our CROs’ activities, but we are responsible for ensuring that each of our studies is conducted in accordance with the applicable protocol and legal, regulatory and scientific standards. Our reliance on the CROs does not relieve us of these regulatory responsibilities. We and our CROs are required to comply with the FDA’s regulations and current good clinical practices (“GCPs”), which is an international guideline meant to protect the rights and health of clinical trial subjects. The FDA enforces its regulations and GCPs through periodic inspections of trial sponsors, principal investigators and clinical trial sites. If we or our CROs fail to comply with applicable GCPs, the clinical data generated in our clinical trials may be deemed unreliable, and the FDA may require us to perform additional clinical trials before approving our product candidates. We cannot assure you that, upon inspection, the FDA will determine that any of our clinical trials comply with GCPs. In addition, to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of CF-301, CF-404 or any other product candidate to a statistically significant degree, our clinical trials will require an adequately large number of test subjects. Any clinical trial that a CRO conducts abroad on our behalf is subject to similar regulation. Accordingly, if our CROs fail to comply with these regulations or recruit a sufficient number of patients, we may have to repeat clinical trials, which would delay the regulatory approval process.
In addition, our CROs are not our employees and we cannot control whether or not they devote sufficient time and resources to our non-clinical, preclinical or clinical programs. Our CROs may also have relationships with other commercial entities, including our competitors, for whom they may also be conducting clinical studies or other drug development activities, which could impede their ability to devote appropriate time to our clinical programs. If our CROs do not successfully carry out their contractual duties or obligations or meet expected deadlines, if they need to be replaced, or if the quality or accuracy of the clinical data they obtain is compromised due to the failure to adhere to our clinical protocols or regulatory requirements, or for other reasons, our clinical trials may be extended, delayed or terminated, and we may not be able to obtain regulatory approval for or successfully commercialize CF-301, CF-404 or any other product candidate that we seek to develop. As a result, our financial results and the commercial prospects for CF-301, CF-404 or any other product candidate that we seek to develop would be harmed, our costs could increase and our ability to generate revenues could be delayed or ended.
We have no experience as a company in bringing a drug to regulatory approval.
As a company, we have never obtained regulatory approval for, or commercialized, a drug or biologic. It is possible that the FDA may refuse to accept any or all of our planned BLAs for substantive review or may conclude after review of our data that our application is insufficient to obtain regulatory approval of CF-301, CF-404 or any other product candidate. If the FDA does not accept or approve any or all of our planned BLAs, it may require that we conduct additional preclinical, clinical or manufacturing validation studies, which may be
37
Table of Contents
costly, and submit that data before it will reconsider our applications. Depending on the extent of these or any other FDA required studies, approval of any BLA or application that we submit may be significantly delayed, possibly for several years, or may require us to expend more resources than we have available. Any delay in obtaining, or an inability to obtain, regulatory approvals would prevent us from meeting our timelines for commercializing CF-301, CF-404 or any other product candidate, generating revenues and achieving and sustaining profitability.
Even if the FDA approves CF-301, CF-404 or any other product candidate, adverse effects discovered after approval could adversely affect our markets.
If we obtain regulatory approval for CF-301, CF-404 or any other product candidate that we develop, and we or others later discover that our products cause adverse effects, a number of potentially significant negative consequences could result, including:
| • | regulatory authorities may withdraw their approval of the product; |
| • | regulatory authorities may require the addition of labeling statements, such as warnings or contraindications or imposition of a risk management strategy; |
| • | we may be required to change the way the product is administered, conduct additional clinical studies or restrict the distribution of the product; |
| • | we could be sued and held liable for harm caused to patients and our liability insurance may not adequately cover those claims; and |
| • | our reputation may suffer. |
Any of these events could prevent us from maintaining market acceptance of the affected product candidate and could substantially increase the costs of, or prevent altogether, the commercialization of our product candidates.
There are underlying risks associated with the manufacture of our product candidates, which could include cost overruns, new impurities, difficulties in process or formulation development, scaling up or reproducing manufacturing processes and lack of timely availability of raw materials.
We do not currently have nor do we plan to build the infrastructure or capability internally to manufacture CF-301, CF-404 or any other product candidates.
We employ the services of Fujifilm Diosynth Biotechnologies UK LTD (“Fujifilm UK”) to supply the active pharmaceutical ingredient for CF-301 and Fujifilm Diosynth Biotechnologies U.S.A., Inc, to supply the active pharmaceutical ingredient for CF-404. We have not yet manufactured supplies for late phase human clinical trials, scaled up the process for manufacture of such supplies, validated the processes, or contractually secured our commercial supplies.
We employ the services of Emergent BioSolutions to produce CF-301 in its final vialed drug product form. We do not have contracts for the commercial supply of CF-301 drug product.
We intend to pursue agreements with third-party manufacturers regarding commercial supply at an appropriate future time. We intend to locate second fill finish third-party manufacturers to supply other world regions such as the European Union or Asia.
Late stage process development activities, including manufacturing process scale up and validation of the bulk drug substance, pose inherent risks that may be greater for biological products than for small molecules. The process will undergo scale up from the current clinical process and then be repeated under protocol successfully three times for validation.
38
Table of Contents
In addition, regulatory requirements could pose barriers to the manufacture of our active pharmaceutical ingredient and finished drug product for our product candidates. Our third-party manufacturers are required to comply with current good manufacturing practices (“cGMPs”). As a result, the manufacturing facilities and processes used by Fujifilm UK and any of our future manufacturers must pass inspection by the FDA as part of our BLA review and before approval of the applicable product candidate. Similar regulations apply to manufacturers of our products for use or sale in foreign countries. If our manufacturers cannot successfully manufacture material that conforms to our specifications and the strict regulatory requirements of the FDA and any applicable foreign regulatory authority, we will not be able to secure the applicable approval for our product candidates. If these facilities are not deemed compliant with cGMPs for the commercial manufacture of our product candidates, we may need to find alternative manufacturing facilities, which would result in significant delays of up to several years in obtaining approval. In addition, our manufacturers will be subject to ongoing periodic unannounced inspections by the FDA and corresponding state and foreign agencies for compliance with cGMPs and similar regulatory requirements.
If Fujifilm UK, or any alternate supplier of active pharmaceutical ingredient, or Emergent BioSolutions, or any alternate supplier of finished drug product for our product candidates experiences any significant difficulties in its respective manufacturing processes, does not comply with the terms of its agreement with us or does not devote sufficient time, energy and care to providing our manufacturing needs, we could experience significant interruptions in the supply of our product candidates, which could impair our ability to supply our product candidates at the levels required for our clinical trials and commercialization and prevent or delay its successful development and commercialization. For example, a lot of the CF-301 investigational drug product did not meet manufacturing release specifications, resulting in the delay of our Phase 2 study.
Developments by competitors, many of which have greater financial and other resources than we do, may render our products or technologies obsolete or non-competitive.
The pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries are intensely competitive. We compete directly and indirectly with other pharmaceutical companies, biotechnology companies and academic and research organizations in developing therapies to treat diseases. Smaller or early-stage companies may also prove to be significant competitors, particularly through collaborative arrangements with large, established companies. Many of our competitors have substantially greater financial, technical and other resources, such as larger research and development staff and experienced marketing and manufacturing organizations and well-established sales forces. We compete with companies that have products on the market or in development for the same indications as our product candidates. We may also compete with organizations that are developing similar technology platforms. Competitors may develop more effective, more affordable or more convenient products or may achieve earlier patent protection or commercialization of their products. These competing products may render our product candidates obsolete or limit our ability to generate revenue from our product candidates. Mergers and acquisitions in the biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries may result in even more resources being concentrated in our competitors. Competition may increase further as a result of advances in the commercial applicability of technologies and greater availability of capital for investment in these industries. Our competitors may succeed in developing, acquiring or licensing, on an exclusive basis, drug products that are more effective or less costly than CF-301, CF-404 and our other product candidates.
The level of commercial success of CF-301, CF-404 and any other product candidates that we develop will depend upon attaining significant market acceptance of these products among physicians and payors.
Even if CF-301, CF-404 or any other product candidates that we develop is approved by the appropriate regulatory authorities for marketing and sale, physicians may not prescribe the approved product. Market acceptance of CF-301, CF-404 and any other product candidate that we develop by physicians, patients and payors will depend on a number of factors, many of which are beyond our control, including:
| • | the indications for which the product is approved; |
39
Table of Contents
| • | acceptance by physicians and payors of each product as a safe and effective treatment; |
| • | the availability, efficacy and cost of competitive drugs; |
| • | the effectiveness of our or any third-party partner’s sales force and marketing efforts; |
| • | the extent to which the product is approved for inclusion on formularies of hospitals and managed care organizations; |
| • | whether the product is designated under physician treatment guidelines as a first-line therapy or as a second- or third-line therapy for particular infections; |
| • | the availability of adequate reimbursement by third parties, such as insurance companies and other health care payors, and/or by government health care programs, including Medicare and Medicaid; |
| • | limitations or warnings contained in a product’s FDA-approved labeling; and |
| • | prevalence and severity of adverse side effects. |
Even if the medical community accepts that our product candidates are safe and efficacious for their approved indications, physicians may not immediately be receptive to the use or may be slow to adopt our product candidates as accepted treatments for their approved indications. While we believe our product candidates may demonstrate significant advantages in clinical studies, we cannot assure you that labeling approved by the FDA will permit us to promote these advantages. In addition, our efforts to educate the medical community and third-party payors on the benefits of any product candidates that we develop may require significant resources and may never be successful.
Coverage and reimbursement may not be available for CF-301, CF-404 or any other product candidates that we develop, which could make it difficult for us to sell our products profitably.
Market acceptance and sales of CF-301, CF-404 or any other product candidate that we develop will depend on coverage and reimbursement policies and may be affected by health care reform measures. Government authorities and third-party payors, such as private health insurers and health maintenance organizations, decide which drugs they will pay for and establish reimbursement levels. We cannot be sure that reimbursement will be available for CF-301, CF-404 or any other product candidate that we develop. Also, we cannot be sure that the amount of reimbursement available, if any, will not reduce the demand for, or the price of, our products. If reimbursement is not available or is available only at limited levels, we may not be able to successfully commercialize CF-301, CF-404 or any other product candidate that we develop.
In both the United States and some foreign jurisdictions, there have been a number of legislative and regulatory proposals to change the health care system in ways that could affect our ability to sell our products profitably. In the United States, the Medicare Prescription Drug, Improvement, and Modernization Act of 2003, also called the Medicare Modernization Act (“MMA”), changed the way Medicare covers and pays for pharmaceutical products. The legislation expanded Medicare coverage for drug purchases by those covered by Medicare under a new Part D and introduced a new reimbursement methodology based on average sales prices for Medicare Part B physician-administered drugs. In addition, this legislation authorized Medicare Part D prescription drug plans to use formularies whereby they can limit the number of drugs that will be covered in any therapeutic class. As a result of this legislation and the expansion of federal coverage of drug products, we expect that there will be additional pressure to contain and reduce costs. These cost reduction initiatives and other provisions of this legislation could decrease the coverage and price that we receive for any approved products and could seriously harm our business. While the MMA applies only to drug benefits for Medicare beneficiaries, private payors often follow Medicare coverage policies and payment limitations in setting their own reimbursement rates, and therefore any reduction in Medicare reimbursement may result in a similar reduction in payments from private payors.
In March 2010, the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, as amended by the Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act (collectively, the “Affordable Care Act”), became law in the United States. The
40
Table of Contents
goal of the Affordable Care Act is to reduce the cost of health care and substantially change the way health care is financed by both governmental and private insurers. The Affordable Care Act, among other things, increased the minimum Medicaid rebates owed by manufacturers under the Medicaid Drug Rebate Program and extended the rebate program to individuals enrolled in Medicaid managed care organizations, established annual fees on manufacturers of certain branded prescription drugs, required manufacturers to participate in a discount program for certain outpatient drugs under Medicare Part D and promoted programs that increase the federal government’s comparative effectiveness research, which will impact existing government healthcare programs and will result in the development of new programs. An expansion in the government’s role in the United States healthcare industry may further lower rates of reimbursement for pharmaceutical products.
We expect that the new presidential administration and U.S. Congress will seek to modify, repeal, or otherwise invalidate all, or certain provisions of, the Affordable Care Act. In January 2017, the House and Senate passed a budget resolution that authorizes congressional committees to draft legislation to repeal all or portions of the Affordable Care Act and permits such legislation to pass with a majority vote in the Senate. President Trump has also recently issued an executive order in which he stated that it is his administration’s policy to seek the prompt repeal of the Affordable Care Act and directed executive departments and federal agencies to waive, defer, grant exemptions from, or delay the implementation of the burdensome provisions of the Affordable Care Act to the maximum extent permitted by law. There is still uncertainty with respect to the impact President Trump’s administration and the U.S. Congress may have, if any, and any changes will likely take time to unfold, and could have an impact on coverage and reimbursement for healthcare items and services covered by plans that were authorized by the Affordable Care Act. However, we cannot predict the ultimate content, timing or effect of any healthcare reform legislation or the impact of potential legislation on us.
Other legislative changes have been proposed and adopted in the United States since the Affordable Care Act was enacted. On August 2, 2011, the Budget Control Act of 2011, among other things, created measures for spending reductions by Congress. A Joint Select Committee on Deficit Reduction, tasked with recommending a targeted deficit reduction of at least $1.2 trillion for the years 2013 through 2021, was unable to reach required goals, thereby triggering the legislation’s automatic reduction to several government programs. This includes aggregate reductions of Medicare payments to providers of 2% per fiscal year, which went into effect in April 2013 and, due to subsequent legislative amendments to the statute, will remain in effect through 2025 unless additional Congressional action is taken. On January 2, 2013, the American Taxpayer Relief Act of 2012 was signed into law, or the ATRA, which, among other things, further reduced Medicare payments to several providers. Recently there has also been heightened governmental scrutiny over the manner in which manufacturers set prices for their marketed products, which has resulted in several Congressional inquiries and proposed bills designed to, among other things, reform government program reimbursement methodologies. For example, the Cures Act changes the reimbursement methodology for infusion drugs and biologics furnished through durable medical equipment in an attempt to remedy over- and underpayment of certain drugs.
While we cannot predict the impact these new laws will have in general or on our business specifically, they may result in downward pressure on pharmaceutical reimbursement, which could negatively affect market acceptance of CF-301 or any future products.
We expect to experience pricing pressures in connection with the sale of CF-301, CF-404 and any other product candidate that we develop, due to the trend toward managed health care, the increasing influence of health maintenance organizations and additional legislative proposals. If we fail to successfully secure and maintain coverage and reimbursement for our products or are significantly delayed in doing so, we will have difficulty achieving market acceptance of our products and our business will be harmed.
41
Table of Contents
Even if we obtain FDA approval of CF-301, CF-404 or any other product candidate, we may never obtain approval or commercialize our products outside of the United States, which would limit our ability to realize their full market potential.
In order to market CF-301, CF-404 or any other products outside of the United States, we must comply with numerous and varying regulatory requirements of other countries regarding safety and efficacy. Clinical trials conducted in one country may not be accepted by regulatory authorities in other countries, and regulatory approval in one country does not mean that regulatory approval will be obtained in any other country. Approval procedures vary among countries and can involve additional product testing and validation and additional administrative review periods. Seeking foreign regulatory approvals could result in significant delays, difficulties and costs for us and require additional preclinical studies or clinical trials which would be costly and time consuming. Regulatory requirements can vary widely from country to country and satisfying these and other regulatory requirements is costly, time consuming, uncertain and subject to unanticipated delays. In addition, our failure to obtain regulatory approval in the United States or any foreign country may delay or have negative effects on the process for regulatory approval in other countries. We do not have any product candidates approved for sale in the United States or any foreign country and we do not have experience as a company in obtaining regulatory approval in international markets.
We currently have no marketing and sales organization and have no experience in marketing drug products. If we are unable to establish our own marketing and sales capabilities, or enter into agreements with third parties, to market and sell our products after they are approved, we may not be able to generate revenues.
We do not have the capabilities to market, sell and distribute any of our drug products. In order to commercialize any products, we must develop these capabilities on our own or make arrangements with third parties for the marketing, sales and distribution of our products. The establishment and development of our own sales force would be expensive and time consuming and could delay any product launch, and we cannot be certain that we would be able to successfully develop this capability. As a result, we may seek one or more third parties to handle some or all of the sales, marketing or distribution for CF-301, CF-404 or any other product candidate in the United States or elsewhere. However, we may not be able to enter into arrangements with third parties to sell CF-301, CF-404 or any other product candidate on favorable terms or at all. In the event we are unable to develop our own marketing and sales force or collaborate with a third-party marketing and sales organization, we would not be able to commercialize CF-301, CF-404 or any other product candidate that we develop, which would negatively impact our ability to generate product revenues. Further, whether we commercialize products on our own or rely on a third party to do so, our ability to generate revenue will be dependent on the effectiveness of the sales force. In addition, to the extent we rely on third parties to commercialize our approved products, we may likely receive less revenues or profits than if we commercialized these products ourselves.
We may form or seek strategic alliances in the future, and we may not realize the benefits of such alliances.
We may form or seek strategic alliances, create joint ventures or collaborations or enter into licensing arrangements with third parties that we believe will complement or augment our development and commercialization efforts with respect to CF-301, CF-404 and any future product candidate that we may develop. Any of these relationships may require us to incur non-recurring and other charges, increase our near-and long-term expenditures, issue securities that dilute our existing stockholders or disrupt our management and business. In addition, we face significant competition in seeking appropriate strategic partners and the negotiation process is time-consuming and complex. Moreover, we may not be successful in our efforts to establish a strategic partnership or other alternative arrangements for CF-301, CF-404 and any future product candidate because it may be deemed to be at too early of a stage of development for collaborative effort and third parties may not view CF-301, CF-404 and any future product candidate as having the requisite potential to demonstrate safety and efficacy. Any delays in entering into new strategic partnership agreements could delay the development and commercialization of CF-301, CF-404 and any other product candidate that we develop, which would harm our business prospects, financial condition and results of operations.
42
Table of Contents
Risks Related to Regulatory Approval of Our Product Candidates and Other Legal Compliance Matters
If we are not able to obtain, or if there are delays in obtaining, required regulatory approvals, we will not be able to commercialize, or will be delayed in commercializing, CF-301, CF-404 and any future product candidate, and our ability to generate revenue will be materially impaired.
CF-301, CF-404 and any other product candidate that we develop and the activities associated with their development and commercialization, including their design, testing, manufacture, recordkeeping, labeling, storage, approval, advertising, promotion, sale, distribution, importation and exportation are subject to comprehensive regulation by the FDA and other regulatory agencies in the United States and by comparable authorities in other countries. Failure to obtain marketing approval for a product candidate will prevent us from commercializing the product candidate. We have not received approval to market any product from regulatory authorities in any jurisdiction. Securing regulatory approval requires the submission of extensive preclinical and clinical data and supporting information to the various regulatory authorities for each therapeutic indication to establish the product candidate’s safety and efficacy. Securing regulatory approval also requires the submission of information about the product manufacturing process to, and inspection of manufacturing facilities by, the relevant regulatory authority. CF-301, CF-404 and any other product candidate that we develop may not be effective, may be only moderately effective or may prove to have undesirable or unintended side effects or other characteristics that may preclude our obtaining marketing approval or prevent or limit commercial use.
The process of obtaining marketing approvals, both in the United States and abroad, is expensive, may take many years, if approval is obtained at all, and can vary substantially based upon a variety of factors, including the type, complexity and novelty of the product candidates involved. Changes in marketing approval policies during the development period, changes in or the enactment of additional statutes or regulations, or changes in regulatory review for each submitted product application, may cause delays in the approval or rejection of an application. The FDA and comparable authorities in other countries have substantial discretion in the approval process and may refuse to accept any application or may decide that our data is insufficient for approval and require additional preclinical, clinical or other studies. If we experience delays in obtaining approvals or if we fail to obtain approval of our product candidates that we develop, our ability to generate revenues will be materially impaired.
We face extensive regulatory requirements and our products may face future development and regulatory difficulties.
Even if we obtain regulatory approval in the United States, the FDA may still impose significant restrictions on the indicated uses or marketing of the approved product, or impose ongoing requirements for potentially costly post-approval studies or post-market surveillance. The holder of an approved BLA is obligated to monitor and report adverse events and any failure of a product to meet the specifications in the BLA. The holder of an approved BLA must also submit new or supplemental applications and obtain FDA approval for certain changes to the approved product, product labeling or manufacturing process. Advertising and promotional materials must comply with FDA rules and are subject to FDA review, in addition to other potentially applicable federal and state laws.
In addition, drug product manufacturers and their facilities are subject to payment of user fees and continual review and periodic inspections by the FDA and other regulatory authorities for compliance with cGMPs and adherence to commitments made in the BLA. If we or a regulatory agency discovers previously unknown problems with a product such as adverse events of unanticipated severity or frequency, or problems with the facility where the product is manufactured, a regulatory agency may impose restrictions relative to that product or the manufacturing facility, including requiring recall or withdrawal of the product from the market or suspension of manufacturing.
If the FDA or a comparable foreign regulatory authority approves any of our product candidates, the manufacturing processes, labeling, packaging, distribution, adverse event reporting, storage, advertising,
43
Table of Contents
promotion and recordkeeping for the product will be subject to extensive and ongoing regulatory requirements. These requirements include submissions of safety and other post-marketing information and reports, registration requirements and continued compliance with cGMPs and GCPs for any clinical trials that we conduct post-approval.
If we or our partners fail to comply with applicable regulatory requirements following approval of any of our future product candidates, a regulatory agency may:
| • | issue a warning or untitled letter asserting that we are in violation of the law; |
| • | seek an injunction or impose civil or criminal penalties or monetary fines; |
| • | suspend or withdraw regulatory approval; |
| • | suspend any ongoing clinical trials; |
| • | refuse to approve a pending BLA or supplements to a BLA submitted by us; |
| • | seize product; or |
| • | refuse to allow us to enter into supply contracts, including government contracts. |
Any government investigation of alleged violations of law could require us to expend significant time and resources in response and could generate negative publicity. The occurrence of any event or penalty described above may inhibit our ability to commercialize our future products and generate revenues.
In addition, we cannot predict the likelihood, nature or extent of government regulation that may arise from future legislation or administrative or executive action, either in the United States or abroad. For example, certain policies of President Trump’s administration may impact our business and industry. Namely, the administration has taken several executive actions, including the issuance of a number of Executive Orders, that could impose significant burdens on, or otherwise materially delay, FDA’s ability to engage in routine regulatory and oversight activities such as implementing statutes through rulemaking, issuance of guidance, and review and approval of marketing applications. Notably, on January 23, 2017, the President ordered a hiring freeze for all executive departments and agencies, including the FDA, which prohibits the FDA from filling employee vacancies or creating new positions. Under the terms of the order, the freeze will remain in effect until implementation of a plan to be recommended by the Director for the Office of Management and Budget, or OMB, in consultation with the Director of the Office of Personnel Management, to reduce the size of the federal workforce through attrition. An under-staffed FDA could result in delays in FDA’s responsiveness or in its ability to review submissions or applications, issue regulations or guidance, or implement or enforce regulatory requirements in a timely fashion or at all. Moreover, on January 30, 2017, the President issued an Executive Order, applicable to all executive agencies, including the FDA, which requires that for each notice of proposed rulemaking or final regulation to be issued in fiscal year 2017, the agency shall identify at least two existing regulations to be repealed, unless prohibited by law. These requirements are referred to as the “two-for-one” provisions. This Executive Order includes a budget neutrality provision that requires the total incremental cost of all new regulations in the 2017 fiscal year, including repealed regulations, to be no greater than zero, except in limited circumstances. For fiscal years 2018 and beyond, the Executive Order requires agencies to identify regulations to offset any incremental cost of a new regulation and approximate the total costs or savings associated with each new regulation or repealed regulation. In interim guidance issued by the Office of Information and Regulatory Affairs within OMB on February 2, 2017, the administration indicates that the “two-for-one” provisions may apply not only to agency regulations, but also to significant agency guidance documents. Further, on February 24, 2017, the President issued an Executive Order requiring each agency to designate a regulatory reform officer and create a regulatory reform task force to evaluate existing regulations and make recommendations regarding their repeal, replacement, or modification. It is difficult to predict how these requirements will be implemented, and the extent to which they will impact the FDA’s ability to exercise its regulatory authority. If these executive actions impose constraints on FDA’s ability to engage in oversight and implementation activities in the normal course, our business may be negatively impacted.
44
Table of Contents
If foreign approval for CF-301, CF-404 or any other product candidate is obtained, there are inherent risks in conducting business in international markets.
Commercialization of our product candidates in international markets is an element of our long-term strategy. If approved for commercialization in a foreign country, we intend to enter into agreements with third parties to market CF-301, CF-404 or any other product candidate whenever it may be approved and wherever we have the right to market it. Consequently, we expect that we will be subject to additional risks related to entering into international business relationships, including:
| • | potentially reduced protection for intellectual property rights; |
| • | the potential for so-called parallel importing, which is what happens when a local seller, faced with high or higher local prices, opts to import goods from a foreign market (with low or lower prices) rather than buying them locally; |
| • | unexpected changes in tariffs, trade barriers and regulatory requirements; |
| • | economic weakness, including inflation, or political instability in particular foreign economies and markets; |
| • | compliance with laws for employees working and traveling abroad; |
| • | foreign taxes, including withholding of payroll taxes; |
| • | foreign currency fluctuations, which could result in increased operating expenses and reduced revenues; |
| • | workforce uncertainty in countries where labor unrest is more common than in the United States; |
| • | production shortages resulting from any events affecting active pharmaceutical ingredient and/or finished drug product supply or manufacturing capabilities abroad; |
| • | business interruptions resulting from geo-political actions, including war and terrorism, or natural disasters including earthquakes, typhoons, floods and fires; and |
| • | failure to comply with the rules and regulations of the Office of Foreign Asset Control, the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act and other applicable anti-bribery rules and regulations in other jurisdictions. |
These and other risks may materially adversely affect our ability to attain or sustain revenue from international markets and therefore materially adversely affect our business.
Product liability lawsuits against us could divert our resources, cause us to incur substantial liabilities and limit commercialization of any products that we may develop.
We face an inherent risk of product liability exposure related to the testing of CF-301, CF-404 and any other product candidate that we develop in human clinical trials and we will face higher degrees of this risk if we commercially sell any products that we develop. If we cannot successfully defend ourselves against claims that our product candidates or products caused injuries, we will incur substantial liabilities. Regardless of merit or eventual outcome, liability claims may result in:
| • | distraction of our management or other internal resources from pursuing our business strategies; |
| • | decreased demand for any product candidates or products that we may develop; |
| • | injury to our reputation and significant negative media attention; |
| • | withdrawal of clinical trial participants; |
| • | significant costs to defend the related litigation; |
45
Table of Contents
| • | substantial monetary awards to trial participants or patients; |
| • | loss of revenue; and |
| • | the inability to commercialize any products that we may develop. |
We maintain product liability insurance coverage in relation to our clinical trials. Such coverage may not be adequate to cover all liabilities that we may incur. Insurance coverage is increasingly expensive. We may not be able to maintain insurance coverage at a reasonable cost or in an amount adequate to satisfy any liability that may arise.
If we fail to comply with environmental, health and safety laws and regulations, we could become subject to fines or penalties or incur costs that could have a material adverse effect on our business.
We are subject to numerous environmental, health and safety laws and regulations, including those governing laboratory procedures and the handling, use, storage, treatment and disposal of hazardous materials and wastes. From time to time and in the future, our operations may involve the use of hazardous and flammable materials, including chemicals and biological materials, and may also produce hazardous waste products. Even if we contract with third parties for the disposal of these materials and wastes, we cannot eliminate the risk of contamination or injury from these materials. In the event of contamination or injury resulting from our use of hazardous materials, we could be held liable for any resulting damages, and any liability could exceed our resources. We also could incur significant costs associated with civil or criminal fines and penalties for failure to comply with such laws and regulations.
Although we maintain workers’ compensation insurance to cover us for costs and expenses we may incur due to injuries to our employees resulting from the use of hazardous materials, this insurance may not provide adequate coverage against potential liabilities. We do not maintain insurance for environmental liability or toxic tort claims.
In addition, we may incur substantial costs in order to comply with current or future environmental, health and safety laws and regulations. These current or future laws and regulations may impair our research, development or production efforts. Failure to comply with these laws and regulations also may result in substantial fines, penalties or other sanctions.
Our product candidates may face competition sooner than anticipated.
The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, or Affordable Care Act, signed into law on March 23, 2010, includes a subtitle called the Biologics Price Competition and Innovation Act of 2009, or BPCIA, which created an abbreviated approval pathway for biological products that are biosimilar to or interchangeable with an FDA-licensed reference biological product. Under the BPCIA, an application for a biosimilar product may not be submitted to the FDA until four years following the date that the reference product was first licensed by the FDA. In addition, the approval of a biosimilar product may not be made effective by the FDA until 12 years from the date on which the reference product was first licensed. During this 12-year period of exclusivity, another company may still market a competing version of the reference product if the FDA approves a full BLA for the competing product containing the sponsor’s own preclinical data and data from adequate and well-controlled clinical trials to demonstrate the safety, purity and potency of their product. The law is complex and is still being interpreted and implemented by the FDA. As a result, its ultimate impact, implementation, and meaning are subject to uncertainty. While it is uncertain when such processes intended to implement BPCIA may be fully adopted by the FDA, any such processes could have a material adverse effect on the future commercial prospects for our biological products.
We believe that any of our product candidates approved as a biological product under a BLA should qualify for the 12-year period of exclusivity. However, there is a risk that this exclusivity could be shortened due to
46
Table of Contents
congressional action or otherwise, or that the FDA will not consider our product candidates to be reference products for competing products, potentially creating the opportunity for generic competition sooner than anticipated. Other aspects of the BPCIA, some of which may impact the BPCIA exclusivity provisions, have also been the subject of recent litigation. Moreover, the extent to which a biosimilar, once approved, will be substituted for any one of our reference products in a way that is similar to traditional generic substitution for non-biological products is not yet clear, and will depend on a number of marketplace and regulatory factors that are still developing.
Our relationships with customers and third-party payors will be subject to applicable anti-kickback, fraud and abuse and other healthcare laws and regulations, which could expose us to criminal sanctions, civil penalties, contractual damages, reputational harm and diminished profits and future earnings.
Healthcare providers, physicians and third-party payors play a primary role in the recommendation and prescription of any product candidates for which we obtain marketing approval. Our future arrangements with third-party payors and customers may expose us to broadly applicable fraud and abuse and other healthcare laws and regulations that may constrain the business or financial arrangements and relationships through which we market, sell and distribute our products for which we obtain marketing approval. Restrictions under applicable federal and state healthcare laws and regulations include the following:
| • | the federal healthcare Anti-Kickback Statute prohibits, among other things, persons from knowingly and willfully soliciting, offering, receiving or providing remuneration, directly or indirectly, in cash or in kind, to induce or reward either the referral of an individual for, or the purchase, order or recommendation of, any good or service, for which payment may be made under federal and state healthcare programs such as Medicare and Medicaid. A person or entity does not need to have actual knowledge of the federal Anti-Kickback Statute or specific intent to violate it to have committed a violation; in addition, the government may assert that a claim including items or services resulting from a violation of the federal Anti-Kickback Statute constitutes a false or fraudulent claim for purposes of the False Claims Act; |
| • | the federal False Claims Act imposes criminal and civil penalties, including through civil whistleblower or qui tam actions, against individuals or entities for knowingly presenting, or causing to be presented, to the federal government, claims for payment that are false or fraudulent or making a false statement to avoid, decrease or conceal an obligation to pay money to the federal government; |
| • | the federal Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996, as amended by the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act, imposes criminal and civil liability for executing a scheme to defraud any healthcare benefit program and also imposes obligations, including mandatory contractual terms, with respect to safeguarding the privacy, security and transmission of individually identifiable health information; |
| • | the federal false statements statute prohibits knowingly and willfully falsifying, concealing or covering up a material fact or making any materially false statement in connection with the delivery of or payment for healthcare benefits, items or services. Similar to the federal Anti-Kickback Statute, a person or entity does not need to have actual knowledge of the statute or specific intent to violate it to have committed a violation; |
| • | the federal transparency requirements under the Affordable Care Act requires certain manufacturers of drugs, devices, biologics and medical supplies for which payment is available under Medicare, Medicaid or the Children’s Health Insurance Program (with certain exceptions) to report to the Department of Health and Human Services information related to physician payments and other transfers of value and ownership and investment interests held by physicians and their immediate family members and payments or other transfers of value made to such physician owners; and |
| • | analogous state laws and regulations, such as state anti-kickback and false claims laws, and transparency laws, may apply to sales or marketing arrangements and claims involving healthcare |
47
Table of Contents
| items or services reimbursed by non-governmental third-party payors, including private insurers, and some state laws require pharmaceutical companies to comply with the pharmaceutical industry’s voluntary compliance guidelines and the relevant compliance guidance promulgated by the federal government in addition to requiring drug manufacturers to report information related to payments to physicians and other health care providers or marketing expenditures and pricing information. |
Efforts to ensure that our business arrangements with third parties will comply with applicable healthcare laws and regulations will involve substantial costs. It is possible that governmental authorities will conclude that our business practices may not comply with current or future statutes, regulations or case law involving applicable fraud and abuse or other healthcare laws and regulations. If our operations are found to be in violation of any of these laws or any other governmental regulations that may apply to us, we may be subject to significant civil, criminal and administrative penalties, damages, fines, exclusion from government funded healthcare programs, such as Medicare and Medicaid, and the curtailment or restructuring of our operations. If any of the physicians or other providers or entities with whom we expect to do business are found to be not in compliance with applicable laws, they may be subject to criminal, civil or administrative sanctions, including exclusions from government funded healthcare programs.
The adverse outcome of litigation or arbitration proceedings commenced by or against us could materially harm our business.
The adverse outcome of any litigation or arbitration proceedings commenced by or against us could have a material adverse effect on our business and impede the achievement of our development and commercialization objectives.
In the ordinary course of our operations, claims involving our actions, actions of third parties or agreements to which we are a party may be brought by and against us. The claims and charges can involve actual damages, as well as contractually agreed upon liquidated sums. These claims, if not resolved through negotiation, are often subject to lengthy and expensive litigation or arbitration proceedings.
Risks Related to Employee Matters and Managing Growth
Our future success depends on our ability to attract and retain qualified personnel, and changes in management may negatively affect our business.
We are dependent on the principal members of our management and scientific teams. Our success and the execution of our growth strategy depend largely on the continued service of these employees. Although we have formal employment agreements with our executive officers, these agreements do not prevent them from terminating their employment with us at any time. The loss of the services of any of these persons could be disruptive to our operations, impede our ability to raise additional funding or delay the achievement of our development and commercialization objectives. Additionally, we cannot be certain that changes in management will not lead to additional management departures or changes, affect our ability to hire or retain key personnel, or otherwise negatively affect our business. We do not maintain “key person” insurance for any of our executives or other employees.
Recruiting and retaining qualified scientific and clinical personnel is critical to our success. We may not be able to attract and retain these personnel on acceptable terms given the competition among numerous pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies for similar personnel. We also compete for the hiring of scientific and clinical personnel from universities and research institutions. In addition, we rely on consultants and advisors, including scientific and clinical advisors, to assist us in formulating our development and commercialization strategy. Our consultants and advisors may be employed by employers other than us and may have commitments under consulting or advisory contracts with other entities that may limit their availability to us.
48
Table of Contents
We expect to expand our development, regulatory and sales, marketing and distribution capabilities, and as a result, we may encounter difficulties in managing our growth, which could disrupt our operations.
We expect to experience growth in the number of our employees and the scope of our operations, particularly in the areas of drug discovery, drug development, regulatory affairs and commercialization. To manage our anticipated future growth, we must continue to implement and improve our managerial, operational and financial systems, expand our facilities and continue to recruit and train additional qualified personnel. Due to our limited financial resources and the various levels of experience of our management team in managing a company with significant anticipated growth, we may not be able to effectively manage the expansion of our operations or recruit and train additional qualified personnel. The physical expansion of our operations may lead to significant costs and may divert our management and business development resources. Any inability to manage growth could delay the execution of our business plans or disrupt our operations.
Risks Related to Our Intellectual Property
If we or our licensors are unable to obtain and maintain patent protection for our owned or licensed technology and products, or if the scope of the patent protection is not sufficiently broad, our competitors could develop and commercialize technology and products similar or identical to ours, and our ability to successfully commercialize our technology and products may be adversely affected.
Our success depends in large part on our and our licensors’ ability to obtain and maintain patent protection in the United States and other countries with respect to our proprietary technology and products or technology or products that may have been licensed to us. Similar to our licensors, we seek to protect our proprietary position by filing patent applications in the United States and abroad related to our novel technologies and product candidates that are important to our business. This process is expensive and time-consuming, and we or our licensors may not be able to file and prosecute all necessary or desirable patent applications at a reasonable cost or in a timely manner. It is also possible that we or our licensors will fail to identify patentable aspects of either our or their research and development output before it is too late to obtain patent protection. Moreover, if we license technology or product candidates from third parties in the future, these license agreements may not permit us to control the preparation, filing and prosecution of patent applications, or to maintain the patents, covering this intellectual property. These agreements could also give our licensors the right to enforce the licensed patents without our involvement, or to decide not to enforce the patents without our consent. Therefore, in these circumstances, we could not be certain that these patents and applications would be prosecuted and enforced in a manner consistent with the best interests of our business.
The patent position of biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies generally is highly uncertain and has in recent years been the subject of much litigation. As a result, the issuance, scope, validity, enforceability and commercial value of our patent rights and any patent rights we may license from a third party are highly uncertain. Our or our licensors’ pending and future patent applications may not result in issued patents that protect our technology or products, in whole or in part, or which effectively prevent others from commercializing competitive technologies and products. Changes in either the patent laws or interpretation of the patent laws in the United States and other countries may diminish the value of our or our licensors’ patents or narrow the scope of such patent protection.
The laws of foreign countries may not protect our rights to the same extent as the laws of the United States. For example, European patent law restricts the patentability of methods of treatment of the human body more than United States law does. Assuming the other requirements for patentability are met, historically, in the United States, the first to make the claimed invention was entitled to the patent, while outside the United States, the first to file a patent application is entitled to the patent. The United States currently uses a first-inventor-to-file system in which, assuming the other requirements for patentability are met, the first inventor to file a patent application will be entitled to the patent. Publications of discoveries in the scientific literature often
49
Table of Contents
lag behind the actual discoveries, and patent applications in the United States and other jurisdictions are typically not published until 18 months after filing, or in some cases not at all. Therefore, we cannot be certain that we were the first to make the inventions claimed in our patents or pending patent applications, or that we were the first to file for patent protection of such inventions. Moreover, we may be subject to a third party preissuance submission of prior art to the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office, or become involved in opposition, derivation, reexamination, litigation, inter partes review or interference proceedings, in the United States or elsewhere, challenging our patent rights or the patent rights of others. An adverse determination in any such submission, proceeding or litigation could reduce the scope of, or invalidate, our patent rights, allow third parties to commercialize our technology or products and compete directly with us, without payment to us, or result in our inability to manufacture or commercialize products without infringing third-party patent rights. In addition, if the breadth or strength of protection provided by our patents and patent applications is threatened, it could dissuade companies from collaborating with us to license, develop or commercialize current or future product candidates.
Even if our or our licensors’ patent applications issue as patents, they may not issue in a form that will provide us with any meaningful protection, prevent competitors from competing with us or otherwise provide us with any competitive advantage. Our competitors may be able to circumvent our owned or licensed patents by developing similar or alternative technologies or products in a non-infringing manner.
The issuance of a patent is not conclusive as to its inventorship, scope, validity or enforceability, and our owned and licensed patents may be challenged in the courts or patent offices in the United States and abroad. Such challenges may result in loss of exclusivity or freedom to operate or in patent claims being narrowed, invalidated or held unenforceable, in whole or in part, which could limit our ability to prevent others from using or commercializing similar or identical technology and products, or limit the duration of the patent protection of our technology and products. Given the amount of time required for the development, testing and regulatory review of new product candidates, patents protecting such candidates might expire before or shortly after such candidates are commercialized and such patents may not be able to claim the benefits of any patent term extension laws or regulations. As a result, our patent portfolio may not provide us with sufficient rights to exclude others from commercializing products similar or identical to ours.
We may become involved in lawsuits to protect or enforce our patents or other intellectual property, which could be expensive, time consuming and unsuccessful, and which could result in our patents or other intellectual property rights becoming invalidated.
Competitors may infringe our or our licensors’ patents, trademarks, copyrights or other intellectual property. To stop infringement or unauthorized use, we or our licensors may be required to file infringement claims, which can be expensive and time consuming. Any claims we or our licensors assert against perceived infringers could provoke these parties to assert counterclaims against us alleging that some or all of our patents or other intellectual property rights are not valid or that we or our licensors infringe their patents or other intellectual property rights. In addition, in a patent infringement proceeding, a court may decide that a patent of ours or our licensors is invalid or unenforceable, in whole or in part, construe the patent’s claims narrowly, or may refuse to stop the other party from using the technology at issue on the grounds that such patents do not cover the technology in question and therefore cannot be infringed. Similarly, if we assert trademark infringement claims, a court may determine that the marks we have asserted are invalid, unenforceable, or not infringed, or that the party against whom we have asserted trademark infringement claims has superior rights to the marks in question. In this case, we could ultimately be forced to cease use of such marks. In any infringement litigation, any award of monetary damages may be unlikely or very difficult to obtain, and any such award we may receive may not be commercially valuable. Furthermore, because of the substantial amount of discovery required in connection with intellectual property litigation, there is a risk that we could incur substantial litigation costs or that some of our confidential information could be compromised by disclosure during this type of litigation.
50
Table of Contents
Third parties may initiate legal proceedings alleging that we or our licensors are infringing their intellectual property rights, the outcome of which would be uncertain and could have a material adverse effect on the success of our business.
Our commercial success depends upon our ability to develop, manufacture, market, or sell our or our licensors’ product candidates and use our proprietary technologies without infringing the intellectual property and other proprietary rights of third parties. There is considerable intellectual property litigation in the biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries, and we may become party to, or threatened with, future adversarial proceedings or litigation regarding intellectual property rights with respect to our products and technology, including reexamination or interference proceedings before the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office. Third parties may assert infringement claims against us based on existing or future intellectual property rights.
If we or our licensors are found to infringe a third party’s intellectual property rights, we or our licensors could be enjoined from further using certain products and technology or may be required to obtain a license from such third party to continue developing and marketing such products and technology. However, we may not be able to obtain any required license on commercially reasonable terms or at all. Even if we were able to obtain a license, it could be non-exclusive, thereby giving our competitors access to the same technologies licensed to us. We could be forced, including by court order, to cease commercializing the infringing technology or product. In addition, we could be found liable for monetary damages, including treble damages and attorneys’ fees if we are found to have willfully infringed a patent or other intellectual property rights of a third party. A finding of infringement could prevent us from commercializing our product candidates or force us to cease some of our business operations, which could materially harm our business. Claims that we have misappropriated the confidential information or trade secrets of third parties could have a similar negative impact on our business.
We may be subject to claims by third parties asserting that we or our employees have misappropriated their intellectual property, or claiming ownership of what we regard as our own intellectual property.
Many of our employees were previously employed at universities or other biotechnology or pharmaceutical companies, including our competitors or potential competitors. Although we use customary non-disclosure agreements and try to ensure that our employees do not use the proprietary information or know-how of others in their work for us, we may be subject to claims that we or these employees have used or disclosed intellectual property, including trade secrets or other proprietary information, of any such employee’s former employer. Litigation may be necessary to defend against these claims.
In addition, while we typically require our employees and contractors who may be involved in the development of intellectual property to execute agreements assigning such intellectual property to us, we may be unsuccessful in executing such an agreement with each party who in fact develops intellectual property that we regard as our own, or such agreements may be inadequately drafted at times thereby not ensuring assignment to us of all potential intellectual property rights. If we fail in prosecuting or defending any such claims, in addition to paying monetary damages, we may lose valuable intellectual property rights or personnel. Even if we are successful in prosecuting or defending against such claims, litigation could result in substantial costs and be a distraction to management.
Intellectual property litigation could cause us to spend substantial resources and could distract our personnel from their normal responsibilities.
Even if resolved in our favor, litigation or other legal proceedings relating to intellectual property claims may cause us to incur significant expenses, and could distract our technical and management personnel from their normal responsibilities. In addition, there could be public announcements of the results of hearings, motions or other interim proceedings or developments and if securities analysts or investors perceive these results to be negative, it could have a substantial adverse effect on the price of our common stock. Such litigation or proceedings could substantially increase our operating losses and reduce the resources available for development,
51
Table of Contents
sales, marketing or distribution activities. We may not have sufficient financial or other resources to adequately conduct or defend such litigation or proceedings. Some of our competitors may be able to sustain the costs of such litigation or proceedings more effectively than we can because of their greater financial resources. Uncertainties resulting from the initiation and continuation of patent litigation or other proceedings could have a material adverse effect on our ability to compete in the marketplace.
In addition to seeking patents for some of our technology and products, we also rely on trade secrets, including unpatented know-how, technology and other proprietary information, to maintain our competitive position. We seek to protect these trade secrets, in part, by entering into non-disclosure and confidentiality agreements with parties who have access to them, such as our employees, corporate collaborators, outside scientific collaborators, contract manufacturers, consultants, advisors and other third parties. However, we cannot guarantee that we have executed these agreements with each party that may have or have had access to our trade secrets, nor can we guarantee that such agreements will always be adequately drafted so as to be enforceable. If we are unable to protect the confidentiality of our trade secrets, our business and competitive position would be harmed.
Enforcing a claim that a party illegally disclosed or misappropriated a trade secret is difficult, expensive and time-consuming, and the outcome is unpredictable. In addition, because of potential differences in laws in different jurisdictions, some courts inside and outside the United States are less willing or unwilling to protect trade secrets. If any of our trade secrets were to be lawfully obtained or independently developed by a competitor, we would have no right to prevent them, or those to whom they communicate it, from using that technology or information to compete with us. If any of our trade secrets were to be disclosed to or independently developed by a competitor, our competitive position would be harmed.
We have not yet registered our trademarks in all of our potential markets, and failure to secure those registrations could adversely affect our business.
Our future trademark applications may not be allowed for registration, and our registered trademarks may not be maintained or enforced. During trademark registration proceedings, we may receive rejections from the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office or other applicable foreign intellectual property offices. Although we are given an opportunity to respond to those rejections, we may be unable to overcome such rejections, or have to expend additional resources to secure registrations, such as commencing cancellation proceedings against third-party trademark registrations to remove them as obstacles to our trademark applications. In addition, in the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office and in comparable agencies in many foreign jurisdictions, third parties are given an opportunity to oppose pending trademark applications and to seek to cancel registered trademarks. Opposition or cancellation proceedings may be filed against our trademarks, and our trademarks may not survive such proceedings. If we do not secure registrations for our trademarks, we may encounter more difficulty in enforcing them against third parties than we otherwise would.
52
Table of Contents
In addition, we have not yet proposed a proprietary name for our product candidates in any jurisdiction. Any proprietary name we propose to use with our product candidates in the United States must be approved by the FDA, regardless of whether we have registered it, or applied to register it, as a trademark. The FDA typically conducts a review of proposed product names, including an evaluation of potential for confusion with other product names. If the FDA objects to any of our proposed proprietary product names, we may be required to expend significant additional resources in an effort to identify a suitable proprietary product name that would qualify under applicable trademark laws, not infringe the existing rights of third parties and be acceptable to the FDA.
Risks Related to Our Securities
The price of our common stock may be volatile and you could lose all or part of your investment.
There has been significant volatility in the market price and trading volume of equity and derivative securities, which is unrelated to the financial performance of the companies issuing the securities. In addition, equity markets have experienced significant price and volume fluctuations that have affected the market prices for the securities of biotechnology and also newly public companies for a number of reasons, including reasons that may be unrelated to the business or operating performance of the companies. These broad market fluctuations may negatively affect the market price of our common stock.
Prior to our initial public offering, there was no public market for our common stock. The trading price of our securities is likely to be highly volatile and could be subject to wide fluctuations in response to various factors, some of which are beyond our control, including limited trading volume. In addition to the factors discussed in this “Risk Factors” section and elsewhere in this Annual Report, these factors include:
| • | our ability to implement our preclinical, clinical and other development or operational plans; |
| • | adverse regulatory decisions; |
| • | strategic actions by us or our competitors, such as acquisitions or restructurings; |
| • | new laws or regulations, or new interpretations of existing laws or regulations, applicable to our business; |
| • | actual or anticipated fluctuations in our financial condition or annual or quarterly results of operations; |
| • | our cash position; |
| • | public reaction to our press releases, other public announcements and filings with the SEC; |
| • | changes in investor and financial analyst perceptions of the risks and condition of our business; |
| • | changes in, or our failure to meet, performance expectations of investors or financial analysts (including, without limitation, with respect to the status of development of our lead product candidates); |
| • | changes in market valuations of biotechnology companies; |
| • | changes in key personnel; |
| • | increased competition; |
| • | sales of common stock by us or members of our management team; |
| • | trading volume of our common stock; |
| • | issuances of debt or equity securities; |
| • | the granting or exercise of employee stock options or other equity awards; |
53
Table of Contents
| • | changes in accounting standards, policies, guidance, interpretations or principles; |
| • | ineffectiveness of our internal controls; |
| • | actions by institutional or other large shareholders; |
| • | significant lawsuits, including patent or stockholder litigation; |
| • | general political, market and economic conditions; and |
| • | other events or factors, many of which are beyond our control. |
In addition, the stock market in general, and the NASDAQ Capital Market and biotechnology companies in particular, have experienced extreme price and volume fluctuations that have often been unrelated or disproportionate to the operating performance of these companies. Broad market and industry factors may negatively affect the market price of our common stock, regardless of our actual operating performance. In the past, securities class action litigation has often been instituted against companies following periods of volatility in the market price of a company’s securities. This type of litigation, if instituted, could result in substantial costs and a diversion of management’s attention and resources, which would harm our business, operating results or financial condition.
We are required to meet the NASDAQ Capital Market’s continued listing requirements and other NASDAQ rules, or we may risk delisting. Delisting could negatively affect the price of our common stock, which could make it more difficult for us to sell securities in a future financing or for you to sell our common stock.
We are required to meet the continued listing requirements of the NASDAQ Capital Market and other NASDAQ rules, including those regarding director independence and independent committee requirements, minimum stockholders’ equity, minimum share price and certain other corporate governance requirements. In particular, we are required to maintain a minimum bid price for our listed common stock of $1.00 per share. If we do not meet these continued listing requirements, our common stock could be delisted. Delisting from the NASDAQ Capital Market would cause us to pursue eligibility for trading of these securities on other markets or exchanges, or on the “pink sheets.” In such case, our stockholders’ ability to trade, or obtain quotations of the market value of our common stock would be severely limited because of lower trading volumes and transaction delays. These factors could contribute to lower prices and larger spreads in the bid and ask prices of these securities. There can be no assurance that our securities, if delisted from the NASDAQ Capital Market in the future, would be listed on a national securities exchange, a national quotation service, the over-the-counter markets or the pink sheets. Delisting from the NASDAQ Capital Market, or even the issuance of a notice of potential delisting, would also result in negative publicity, make it more difficult for us to raise additional capital, adversely affect the market liquidity of our securities, decrease securities analysts’ coverage of us or diminish investor, supplier and employee confidence.
We may issue additional shares of common stock, warrants or other securities to finance our growth.
We may finance the development of our product pipeline or generate additional working capital through additional equity financing. Therefore, subject to the rules of the NASDAQ, we may issue additional shares of our common stock, warrants and other equity securities of equal or senior rank, with or without shareholder approval, in a number of circumstances from time to time. The issuance by us of shares of our common stock, warrants or other equity securities of equal or senior rank will have the following effects:
| • | the proportionate ownership interest in us held by our existing shareholders will decrease; |
| • | the relative voting strength of each previously outstanding share of common stock may be diminished; and |
| • | the market price of our common stock may decline. |
54
Table of Contents
In addition, if we issue shares of our common stock and/or warrants in a future offering (or, in the case of our common stock, the exercise of outstanding warrants to purchase our common stock), it could be dilutive to our security holders.
Future sales of our common stock or warrants may cause the market price of our securities to decline.
Sales of substantial amounts of shares of our common stock or warrants in the public market, or the perception that these sales may occur, could adversely affect the price of our securities and impair our ability to raise capital through the sale of additional equity securities. We have approximately 41.7 million shares of common stock outstanding. As of March 7, 2017, approximately 39.5 million shares of our outstanding common stock are freely tradable, or may become freely tradable, without restriction, in the public market unless held by our “affiliates,” as defined under Rule 144 of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”). Additionally, we have warrants to purchase approximately 2.4 million shares of common stock (“PIPE Warrants”) and warrants to purchase 14.0 million shares of our common stock (“CMPO Warrants”, and together with the PIPE Warrants, the “Warrants”) outstanding as of March 7, 2017. All shares of common stock underlying the Warrants will be freely tradable upon exercise unless held by our affiliates.
We have registered 3,358,270 shares of our common stock as of March 7, 2017 that we may issue under our employee benefit plans. These shares can be freely sold in the public market upon issuance, unless pursuant to their terms these stock awards have transfer restrictions attached to them. Additionally, pursuant to the 2014 Omnibus Incentive Plan (the “2014 Plan”), our management is authorized to grant stock options and other equity linked award to our employees, directors and consultants. The number of shares available for future grant under our 2014 Plan will automatically increase on January 1st each year, from January 1, 2015 through January 1, 2024, by an amount equal to four percent of all shares of our capital stock outstanding as of December 31st of the preceding calendar year, subject to the ability of our board of directors to take action to reduce the size of such increase in any given year. Unless our board of directors elects not to increase the number of shares underlying our 2014 Plan each year, our stockholders may experience additional dilution, which could cause our stock price to decline.
Our executive officers and directors hold a significant concentration of our common stock, which could limit the ability of our other stockholders to influence the direction of our Company.
As calculated by the SEC rules of beneficial ownership, the current executive officers and directors of our Company own 9.3% of our outstanding common stock as of March 7, 2017. Accordingly, they collectively have the ability to significantly influence or determine the election of all of our directors or the outcome of most corporate actions requiring stockholder approval such as: (i) a merger or a sale of our Company, (ii) a sale of all or substantially all of our assets and (iii) amendments to our certificate of incorporation or bylaws. This concentration of voting power and control could have a significant effect in delaying, deferring or preventing an action that might otherwise be beneficial to our other stockholders and be disadvantageous to our stockholders with interests different from those individuals. These individuals also have significant control over our business as officers and directors of our Company. There is a risk that they may exercise this ability in a manner that advances their best interests and not necessarily those of our other stockholders.
If shares of our common stock become subject to the penny stock rules, it would become more difficult to trade them.
The SEC has adopted regulations which generally define a “penny stock” to be an equity security that has a market price of less than $5.00 per share or an exercise price of less than $5.00 per share, subject to specific exemptions, including an exemption for any securities listed on a national securities exchange. The rules impose additional sales practice requirements on broker-dealers for transactions involving “penny stock”, with some exceptions. If shares of our common stock were delisted from the NASDAQ Capital Market and determined to be “penny stock”, broker-dealers may find it more difficult to trade such securities and investors may find it more difficult to acquire or dispose of such securities on the secondary market.
55
Table of Contents
There can be no assurance that we will ever provide liquidity to our investors through a sale of our company.
While acquisitions of pharmaceutical companies like ours are not uncommon, potential investors are cautioned that no assurances can be given that any form of merger, combination, or sale of our company will take place, or that any merger, combination, or sale, even if consummated, would provide liquidity or a profit for our investors. You should not invest in our company with the expectation that we will be able to sell the business in order to provide liquidity or a profit for our investors.
We incur significant increased costs as a result of operating as a public company and our management is required to devote substantial time to complying with public company regulations.
We completed an initial public offering on August 1, 2014. As a public company, we incur significant legal, accounting and other expenses, including costs associated with our public company reporting requirements under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”). We must also follow the rules, regulations and requirements subsequently adopted by the SEC and the NASDAQ and any failure by us to comply with such rules and requirements could negatively affect investor confidence in us and cause the market price of our common stock to decline. Our executive officers and other personnel will also need to devote substantial time and financial resources to comply with these rules, regulations and requirements.
We expect the rules and regulations applicable to public companies to substantially increase our legal and financial compliance costs and to make some activities more time-consuming and costly. If these requirements divert the attention of our management and personnel from other business concerns, they could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations. The increased costs will decrease our net income or increase our net loss, and may require us to reduce costs in other areas of our business. For example, we expect these rules and regulations to make it more difficult and more expensive for us to obtain director and officer liability insurance and we may be required to incur substantial costs to maintain the same or similar coverage. We cannot predict or estimate the amount or timing of additional costs we may incur to respond to these requirements. The impact of these requirements could also make it more difficult for us to attract and retain qualified persons to serve on our board of directors, our board committees or as executive officers.
If we do not develop and implement all required accounting practices and policies, we may be unable to provide the financial information required of a U.S. publicly traded company in a timely and reliable manner.
Prior to the IPO, we did not adopt all of the financial reporting and disclosure procedures and controls required of a U.S. publicly traded company because we were a privately held company. The implementation of all required accounting practices and policies and the hiring of additional financial staff have increased our operating costs and requires significant time and resources from our management and employees. If we fail to maintain effective internal controls and procedures and disclosure procedures and controls, we may be unable to provide financial information and required SEC reports that a U.S. publicly traded company is required to provide in a timely and reliable fashion. Any such delays or deficiencies could penalize us, including by limiting our ability to obtain financing, either in the public capital markets or from private sources and hurt our reputation and could thereby impede our ability to implement our strategy.
Reports published by analysts, including projections in those reports that exceed our actual results, could adversely affect the price and trading volume of our common stock.
The projections of securities research analysts may vary widely and may not accurately predict the results we actually achieve. The price of our common stock may decline if our actual results do not match the projections of these securities research analysts. Similarly, if one or more of the analysts who write reports on us downgrades our stock or publishes inaccurate or unfavorable research about our business, the price of our common stock could decline. If one or more of these analysts ceases coverage of us or fails to publish reports on us regularly, the price or trading volume of our common stock could decline.
56
Table of Contents
If securities or industry analysts do not publish research or reports about our business, the prices of our securities and trading volume could decline.
The trading market for our securities depends, in part, on the research and reports that securities or industry analysts publish about us or our business. We do not have any control over these analysts. If no securities or industry analysts commence coverage of our company, the trading prices for our securities may be negatively impacted.
We have broad discretion in the use of the net proceeds from our public offerings and private placement and may not use them effectively.
Our management has broad discretion in the application of the net proceeds from our public offerings and private placement and could spend the proceeds in ways that do not enhance the value of our common stock. Because of the number and variability of factors that will determine our use of the net proceeds from our completed offerings, their ultimate use may vary substantially from their currently intended use. The failure by our management to apply these funds effectively could delay the development of our product candidates or have a material adverse effect on our business. Pending their use, we may invest the net proceeds from the offerings in a manner that does not produce income or that loses value. If we do not apply or invest the net proceeds from the offerings in ways that enhance stockholder value, we may fail to achieve expected financial results, which could cause the price of our securities to decline.
We are an “emerging growth company,” and the reduced disclosure requirements applicable to emerging growth companies may make our common stock less attractive to investors.
We are an “emerging growth company,” as defined in the JOBS Act, and may remain an emerging growth company for up to five years. For so long as we remain an emerging growth company, we are permitted and intend to rely on exemptions from certain disclosure requirements that are applicable to other public companies that are not emerging growth companies. These exemptions include:
| • | not being required to comply with the auditor attestation requirements in the assessment of our internal control over financial reporting; |
| • | not being required to comply with any requirement that may be adopted by the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board regarding mandatory audit firm rotation or a supplement to the auditor’s report providing additional information about the audit and the financial statements; |
| • | reduced disclosure obligations regarding executive compensation; and |
| • | exemptions from the requirements of holding a nonbinding advisory vote on executive compensation and shareholder approval of any golden parachute payments not previously approved. |
We have taken advantage of certain reduced reporting burdens. We cannot predict whether investors will find our securities less attractive if we rely on these exemptions. If some investors find our securities less attractive as a result, there may be a less active trading market for our common stock, and the prices for our securities may be more volatile.
We have no present intention to pay cash dividends and, even if we change that policy, we may be restricted from paying cash dividends on our common stock.
We do not intend to pay cash dividends for the foreseeable future. We currently expect to retain all future earnings, if any, for use in the development, operation and expansion of our business. Any determination to pay cash dividends in the future will depend upon, among other things, our results of operations, plans for expansion, tax considerations, available net profits and reserves, limitations under law, financial condition, capital requirements and other factors that our board of directors considers to be relevant.
57
Table of Contents
Provisions in our corporate charter documents and under Delaware law could make an acquisition of us, which may be beneficial to our stockholders, more difficult and may prevent attempts by our stockholders to replace or remove our current management.
Provisions in our corporate charter and our bylaws may discourage, delay or prevent a merger, acquisition or other change in control of us that stockholders may consider favorable, including transactions in which you might otherwise receive a premium for your shares. These provisions could also limit the price that investors might be willing to pay in the future for our securities, thereby depressing the market prices of our securities. In addition, because our board of directors is responsible for appointing the members of our management team, these provisions may frustrate or prevent any attempts by our stockholders to replace or remove our current management by making it more difficult for stockholders to replace members of our board of directors. Among other things, these provisions:
| • | allow the authorized number of our directors to be changed only by resolution of our board of directors; |
| • | limit the manner in which stockholders can remove directors from the board of directors; |
| • | establish advance notice requirements for stockholder proposals that can be acted on at stockholder meetings and nominations to our board of directors; |
| • | require that stockholder actions must be effected at a duly called stockholder meeting and prohibit actions by our stockholders by written consent; |
| • | limit who may call stockholder meetings; |
| • | authorize our board of directors to issue preferred stock without stockholder approval, which could be used to institute a shareholder rights plan, or so-called “poison pill,” that would work to dilute the stock ownership of a potential hostile acquirer, effectively preventing acquisitions that have not been approved by our board of directors; and |
| • | require the approval of the holders of at least 75% of the votes that all our stockholders would be entitled to cast to amend or repeal certain provisions of our charter or bylaws. |
Moreover, because we are incorporated in Delaware, we are governed by the provisions of Section 203 of the Delaware General Corporation Law, which prohibits a person who owns in excess of 15% of our outstanding voting stock from merging or combining with us for a period of three years after the date of the transaction in which the person acquired in excess of 15% of our outstanding voting stock, unless the merger or combination is approved in a prescribed manner.
Risks Related to Cybersecurity
Security breaches and other disruptions could compromise our information and expose us to liability, which would cause our business and reputation to suffer.
In the ordinary course of our business, we store sensitive data, including intellectual property, proprietary business information and personally identifiable information, in our data centers and on our networks. The secure processing, maintenance and transmission of this information is critical to our operations and business strategy. Despite our security measures, our information technology and infrastructure may be vulnerable to attacks by hackers or breached due to employee error, malfeasance, or other disruptions. Any such breach could compromise our networks and the information stored there could be accessed, publicly disclosed, lost or stolen. Any such access, disclosure or other loss of information could result in legal claims or proceedings, disrupt our operations, and damage our reputation.
We maintain cyber risk insurance, but this insurance may not be sufficient to cover all of our losses from any future breaches of our systems.
58
Table of Contents
Item 1B. Unresolved Staff Comments
None
In the second quarter of 2011, we opened our corporate headquarters and laboratory in Yonkers, New York. This 15,000 sq. ft. mixed use office, laboratory space consists of open laboratory and suites for molecular biology, microbiology, tissue culture, microscopy, a vivarium, and a robotics suite. This facility is leased through December 31, 2027.
None
Item 4. Mine Safety Disclosures
None
59
Table of Contents
PART II
Item 5. Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
Market Information
Our common stock has been publicly traded on the NASDAQ Capital Market under the symbol “CFRX” since September 12, 2014. The following table sets forth the high and low sales prices of our common stock as reported on the NASDAQ Capital Market for each quarter in the years ended December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015.
| Fiscal Year Ended December 31, 2016 | High | Low | ||||||
| First Quarter |
$ | 4.62 | $ | 3.00 | ||||
| Second Quarter |
$ | 4.12 | $ | 2.10 | ||||
| Third Quarter |
$ | 3.28 | $ | 2.14 | ||||
| Fourth Quarter |
$ | 2.72 | $ | 1.35 | ||||
| Fiscal Year Ended December 31, 2015 |
||||||||
| First Quarter |
$ | 6.13 | $ | 3.50 | ||||
| Second Quarter |
$ | 6.24 | $ | 3.92 | ||||
| Third Quarter |
$ | 5.80 | $ | 3.90 | ||||
| Fourth Quarter |
$ | 5.35 | $ | 3.00 | ||||
Holders
On March 7, 2017, the last reported sale price for our common stock on the NASDAQ Capital Market was $2.10 per share. As of March 7, 2017, there were approximately 1,613 holders of record of our common stock. This number does not include beneficial owners whose shares are held by nominees in street name.
Dividends
We have not declared or paid any cash dividends on our capital stock since our inception. We intend to retain future earnings, if any, to finance the operation and expansion of our business and do not anticipate paying any cash dividends to holders of common stock in the foreseeable future.
60
Table of Contents
Performance Graph
This performance graph shall not be deemed “soliciting material” or to be “filed” with the SEC for purposes of Section 18 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended the (“Exchange Act”), or otherwise subject to the liabilities under that Section, and shall not be deemed to be incorporated by reference into any of our filings under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, or the Exchange Act.
The graph set forth below compares the cumulative total stockholder return on our common stock between September 12, 2014 (the date our common stock began trading on the NASDAQ Capital Market) and December 31, 2016, with the cumulative total return of (a) the NASDAQ Biotechnology Index and (b) the NASDAQ Composite Index, over the same period. This graph assumes the investment of $100 at the market close on September 12, 2014 in our common stock, the NASDAQ Biotechnology Index and the NASDAQ Composite Index and assumes the reinvestment of dividends, if any. The stock price performance of the following graph is not necessarily indicative of future stock price performance.
61
Table of Contents
Item 6. Selected Financial Data
The following selected financial data should be read in conjunction with Item 7, “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations”, the financial statements and the notes thereto and other financial information included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
We derived the financial data for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014 and as of December 31, 2016 and 2015 from our audited financial statements, which are included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. We derived the financial data for the years ended December 31, 2013 and 2012 and as of December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 from our audited financial statements that are not included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. The selected financial data in this section are not intended to replace our financial statements and related notes. Our historical results are not necessarily indicative of our future results.
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Statement of Operations Data |
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||||||||
| Loss from operations |
$ | (33,533,728 | ) | $ | (25,065,336 | ) | $ | (16,935,911 | ) | $ | (19,296,434 | ) | $ | (19,154,173 | ) | |||||
| Net loss attributable to common stockholders |
$ | (28,538,399 | ) | $ | (25,120,964 | ) | $ | (34,617,536 | ) | $ | (23,620,702 | ) | $ | (19,283,454 | ) | |||||
| Net loss per share of common stock, basic and diluted |
$ | (0.91 | ) | $ | (1.08 | ) | $ | (3.86 | ) | $ | (23.35 | ) | $ | (19.16 | ) | |||||
| As of December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance Sheet Data |
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||||||||
| Cash, cash equivalents and marketable securities |
$ | 35,161,154 | $ | 32,921,653 | $ | 27,393,059 | $ | 4,145,270 | $ | 7,886,264 | ||||||||||
| Total assets |
37,624,470 | 35,861,137 | 30,053,622 | 9,683,835 | 13,205,664 | |||||||||||||||
| Long-term liabilities |
13,693,419 | 1,416,443 | 1,249,046 | 16,481,765 | 1,502,946 | |||||||||||||||
| Total stockholders’ equity (deficit) |
19,512,854 | 30,675,510 | 25,581,507 | (52,910,500 | ) | (32,231,516 | ) | |||||||||||||
Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
You should read the following discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations together with our financial statements and the related notes and other financial information included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Some of the information contained in this discussion and analysis or set forth elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, including information with respect to our plans and strategy for our business, includes forward-looking statements that involve risks and uncertainties. You should review the “Risk factors” section of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for a discussion of important factors that could cause actual results to differ materially from the results described in or implied by the forward-looking statements contained in the following discussion and analysis.
Overview
We are a clinical-stage biotechnology company focused on discovering and developing therapeutic protein and antibody products for the treatment of life-threatening infectious diseases, including those caused by drug-resistant pathogens, particularly those treated in hospital settings. Drug-resistant infections account for two million illnesses in the United States and 700,000 deaths worldwide each year. We intend to address drug-resistant infections using product candidates from our lysin and monoclonal antibody platforms that target conserved regions of either bacteria or viruses. Lysins are enzymes derived from naturally occurring bacteriophage, which are viruses that infect bacteria. When recombinantly produced and then applied to bacteria, lysins cleave a key component of the target bacteria’s peptidoglycan cell wall, which results in rapid bacterial cell death. Lysins kill bacteria faster than conventional antibiotics, which typically require bacterial cell division
62
Table of Contents
and metabolism in order to kill or stop the growth of bacteria. We believe that the properties of our lysins will make them suitable for targeting antibiotic-resistant organisms, such as Staphylococcus aureus (“Staph aureus”) which causes serious infections such as bacteremia, endocarditis, pneumonia and osteomyelitis. In addition, our lysins have demonstrated the ability to clear biofilms in animal models, and we believe they may be useful for the treatment of biofilm-related infections in prosthetic joints, indwelling devices and catheters. Beyond our lysin programs, we are exploring therapies using monoclonal antibodies (“mAbs”) designed to bind to viral targets. Our approach to antibody therapy employs a combination of multiple mAbs to either achieve greater efficacy or provide broader coverage across pathogenic strains.
We have not generated any revenues and, to date, have funded our operations primarily through our IPO, our follow-on public offering, and the private placements of convertible preferred stock and convertible debt to our investors.
In August 2014, we completed our IPO, raising net proceeds of $35.0 million after underwriting discounts, commissions and offering expenses payable by us, through the issuance and sale of our units, which consisted of one share of common stock, one Class A Warrant to purchase one share of common stock at an exercise price of $4.80 per share and one Class B Warrant to purchase one-half share of common stock at an exercise price of $4.00 per full share (“Units”). As of November 2, 2015, the date of expiration of the Class B Warrants, holders of the Class B Warrants had exercised 4,812,328 Class B Warrants, resulting in the issuance of 2,406,164 shares of the Company’s common stock and the receipt by the Company of approximately $9.6 million in gross proceeds. The Class A Warrants expired on February 1, 2017. As none of the Class A Warrants were exercised prior to expiration, the Class A Warrants have been terminated and are no longer exercisable.
In June 2015, we completed a private placement of securities to institutional investors whereby the investors received an aggregate of 4,728,128 shares of our common stock and warrants to purchase an additional 2,364,066 shares of common stock at an exercise price of $8.00 per share, generating net proceeds of $18.3 million.
In July 2016, we sold 14,000,000 shares of our common stock and warrants to purchase an additional 14,000,000 shares of our common stock at a exercise price of $3.00 per share in an underwritten follow-on offering, generating net proceeds of approximately $32.0 million after underwriting discounts, commissions and offering expenses payable by us.
We have never been profitable and our net losses were $28.5 million, $25.1 million and $30.1 million for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. We expect to incur significant expenses and increasing operating losses for the foreseeable future. We expect our expenses to increase in connection with our ongoing activities, particularly as we advance our product candidates through preclinical activities and clinical trials to seek regulatory approval and, if approved, commercialize such product candidates. Additionally, we expect to incur additional costs associated with operating as a public company. Accordingly, we will need additional financing to support our continuing operations. We expect to seek to fund our operations through public or private equity, debt financings, equity-linked financings, collaborations, strategic alliances, licensing arrangements, research grants or other sources. Adequate additional financing may not be available to us on acceptable terms, or at all. Our failure to raise capital as and when needed would have a negative impact on our financial condition and our ability to pursue our business strategy. We will need to generate significant revenues to achieve profitability, and we may never do so.
Financial Operations Overview
Revenue
We have not generated any revenues to date. In the future, we may generate revenues from product sales. In addition, to the extent we enter into licensing or collaboration arrangements, we may have additional sources of revenue. We expect that any revenue we generate will fluctuate from quarter to quarter as a result of the amount
63
Table of Contents
and timing of payments that we may recognize upon the sale of our products, to the extent that any products are successfully commercialized, and the amount and timing of fees, reimbursements, milestone and other payments received under any future licensing or collaboration arrangements. If we fail to complete the development of our product candidates in a timely manner or obtain regulatory approval for them, our ability to generate future revenue, and our results of operations and financial position, would be materially adversely affected.
Research and development expenses
Research and development expenses consist primarily of costs incurred for our research activities, including our drug discovery efforts, and the development of our product candidates, which include:
| • | employee-related expenses, including salaries, benefits, travel and non-cash share-based compensation expense; |
| • | external research and development expenses incurred under arrangements with third parties such as contract research organizations, or CROs, contract manufacturers, consultants and academic institutions; and |
| • | facilities and laboratory and other supplies. |
We expense research and development costs to operations as incurred. We account for non-refundable advance payments for goods and services that will be used in future research and development activities as expenses when the service has been performed or when the goods have been received, rather than when the payment is made.
The following summarizes our most advanced current research and development programs.
CF-301: lead lysin program
CF-301 is a parenteral, potent, bactericidal lysin targeting Staph aureus bacteria, making it a highly specific therapeutic candidate for the treatment of patients with Staph aureus bacteremia. We recently concluded a Phase 1 single ascending dose study in healthy volunteers. This trial was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-escalation trial designed to evaluate the safety, tolerability and PK of four different intravenous doses of CF-301 alone. Subjects were randomized to receive a single IV dose of CF-301 or placebo, each administered as a two hour infusion. CF-301 was generally well tolerated and there were no clinical adverse safety signals in the study. We intend to initiate a Phase 2 trial in patients for treatment of Staph aureus bacteremia, including endocarditis, caused by methicillin-resistant (“MRSA”) or methicillin-susceptible (“MSSA”) Staph aureus. We have worldwide development and commercial rights to CF-301 and expect to fund the future development and commercialization costs related to this program.
Other programs
Our lead antibody-based program is CF-404 which is a potent combination of three mAbs targeting the conserved regions of the influenza virus. CF-404 cross-reacts with all human seasonal strains of influenza, making it a highly specific therapeutic candidate for the treatment of patients with life-threatening varieties of influenza. We have worldwide development and commercial rights to CF-404 and expect to fund the future development and commercialization costs related to this program.
Our discovery pipeline of lysins includes internally discovered lysins targeting gram-positive and gram-negative organisms, as well as lysins discovered at The Rockefeller University (“Rockefeller”) which are being developed by us. We were granted a world-wide, exclusive license under Rockefeller patent rights to discover, develop, make, have made, use, import, lease, sell and offer for sale lysin products. We acquired worldwide exclusive license rights to patents for composition of matter for nine lysins from Rockefeller.
64
Table of Contents
To date, a large portion of our research and development work has related to the establishment of both our lysin and antibody platform technologies, the advancement of our research projects to discovery of clinical candidates, manufacturing and preclinical testing of our clinical candidates and Phase 1 clinical testing of CF-301, the first lysin to enter clinical trials in the U.S. We currently expect to focus the majority of our resources on the CF-301 program. In the future, we intend to further leverage our employee and infrastructure resources across multiple development programs well as research projects. In the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, we recorded approximately $22.1 million, $15.0 million and $8.9 million, respectively, of research and development expenses. A breakdown of our research and development expenses by category is shown below. We do not currently utilize a formal time or laboratory project expense allocation system to allocate employee-related expenses, laboratory costs or depreciation to any particular project. Accordingly, we do not allocate these expenses to individual projects or product candidates. However, we do allocate some portions of our research and development expenses in the product development, external research and licensing and professional fees categories, by project, including CF-301 and CF-404, as shown below.
The following table summarizes our research and development expenses by category for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014:
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
| Product development |
$ | 10,331,021 | $ | 7,457,384 | $ | 1,311,452 | ||||||
| Personnel related |
4,357,177 | 3,178,451 | 2,747,487 | |||||||||
| Professional fees |
3,170,364 | 724,486 | 663,039 | |||||||||
| Laboratory costs |
2,065,064 | 1,929,799 | 1,473,739 | |||||||||
| External research and licensing costs |
1,590,668 | 1,324,425 | 1,956,861 | |||||||||
| Share-based compensation |
587,426 | 389,967 | 715,475 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total research and development expense |
$ | 22,101,720 | $ | 15,004,512 | $ | 8,868,053 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
The following table summarizes our research and development expenses by program for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014:
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
| CF-301 |
$ | 8,092,280 | $ | 4,847,190 | $ | 1,666,016 | ||||||
| CF-404 |
5,639,474 | 3,315,797 | 1,507,285 | |||||||||
| Other research and development |
3,425,363 | 3,273,107 | 2,231,790 | |||||||||
| Personnel related and share-based compensation |
4,944,603 | 3,568,418 | 3,462,962 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total research and development expense |
$ | 22,101,720 | $ | 15,004,512 | $ | 8,868,053 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
We anticipate that our research and development expenses will increase substantially in connection with the commencement of clinical trials for our product candidates. However, the successful development of future product candidates is highly uncertain. This is due to the numerous risks and uncertainties associated with developing drugs, including the uncertainty of:
| • | the scope, rate of progress and expense of our research and development activities; |
| • | clinical trial results; |
| • | the terms and timing of regulatory approvals; |
| • | our ability to market, commercialize and achieve market acceptance for our product candidates in the future; and |
| • | the expense, filing, prosecuting, defending and enforcing of patent claims and other intellectual property rights. |
65
Table of Contents
A change in the outcome of any of these variables with respect to the development of CF-301, CF-404 or any other product candidate that we may develop could mean a significant change in the costs and timing associated with the development of CF-301, CF-404 or any such product candidate. For example, if the FDA or other regulatory authority were to require us to conduct clinical trials beyond those which we currently anticipate will be required for the completion of clinical development of CF-301 or if we experience significant delays in enrollment in any clinical trials of CF-301, we could be required to expend significant additional financial resources and time on the completion of the clinical development of CF-301.
General and Administrative Expenses
General and administrative expenses consist primarily of salaries and related costs for personnel, including non-cash share-based compensation expense, in our executive, finance, legal, human resource and business development functions. Other general and administrative expenses include facility costs, insurance expenses and professional fees for legal, consulting and accounting services.
We anticipate that our general and administrative expenses will increase in future periods to support increases in our research and development activities and as a result of increased headcount, expanded infrastructure, increased legal, compliance, accounting and investor and public relations expenses associated with being a public company and increased insurance premiums, among other factors.
Interest Income
Interest income consists of interest earned on our cash and cash equivalents and available-for-sale securities.
Interest Expense
Interest expense consists primarily of cash and non-cash interest costs, including the accretion of the carrying value of our Convertible Notes due 2015 to face value and the estimated value of equity linked securities issued in conjunction with the issuance of these notes, related to our outstanding debt. We capitalize costs incurred in connection with the issuance of debt. We amortize these costs over the life of our debt agreements as interest expense in our statement of operations. Upon the closing of our IPO, we accelerated the amortization of the remaining balances of debt issuance costs and debt discount to interest expense and recognized the cost of the beneficial conversion feature of our Convertible Notes due 2015 as an additional component of interest expense.
Critical Accounting Policies and Significant Judgments and Estimates
Our management’s discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations is based on our financial statements, which we have prepared in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles. The preparation of these financial statements requires us to make estimates and judgments that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities and expenses and the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities in our financial statements. On an ongoing basis, we evaluate our estimates and judgments. We base our estimates on our limited historical experience, known trends and events and various other factors that we believe are reasonable under the circumstances, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying values of assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other sources. Actual results may differ from these estimates under different assumptions or conditions.
While our significant accounting policies are described in more detail in the notes to our financial statements included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, we believe that the following accounting policies are the most critical to aid you in fully understanding and evaluating our financial condition and results of operations.
66
Table of Contents
Fair Value of Warrant Liability
In accordance with Financial Accounting Standards Board Accounting Standards Codification Topic 820, Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures (“ASC 820”), we classify and account for our warrant liability as a level 3 financial instrument. The valuation of a level 3 financial instrument requires inputs that reflect our own assumptions that are both significant to the fair value measurement and unobservable. We calculate the fair value estimate of our warrant liability on a recurring basis at each measurement date, based on relevant market information.
We use the Black-Scholes option pricing model to estimate the fair value of our warrant liability using various assumptions that require management to apply judgment and make estimates, including:
| • | the expected term of the warrant, which we estimate to be the remaining contractual life; |
| • | the expected volatility of the underlying common stock, which we estimate based on the historical volatility of a representative peer group of publicly traded biopharmaceutical companies with similarities to us, including stage of drug development, area of therapeutic focus, number of employees and market capitalization; |
| • | the risk-free interest rate, which we based on the yield curve of U.S. Treasury securities with periods commensurate with the expected term; and |
| • | the expected dividend yield, which we estimate to be zero based on the fact that we have never paid cash dividends and have no present intention to pay cash dividends. |
These estimates may be subjective in nature and involve uncertainties and matters of significant judgment and therefore cannot be determined with precision. If factors change and different assumptions are used, our warrant liability could be materially different in the future.
Accrued research and development expenses
As part of the process of preparing our financial statements, we are required to estimate our accrued expenses. This process involves reviewing quotations and contracts, identifying services that have been performed on our behalf and estimating the level of service performed and the associated cost incurred for the service when we have not yet been invoiced or otherwise notified of the actual cost. The majority of our service providers invoice us monthly in arrears for services performed or when contractual milestones are met. We make estimates of our accrued expenses as of each balance sheet date in our financial statements based on facts and circumstances known to us at that time. We periodically confirm the accuracy of our estimates with the service providers and make adjustments if necessary. The significant estimates in our accrued research and development expenses are related to fees paid to CROs in connection with research and development activities for which we have not yet been invoiced.
We base our expenses related to CROs on our estimates of the services received and efforts expended pursuant to quotes and contracts with CROs that conduct research and development on our behalf. The financial terms of these agreements are subject to negotiation, vary from contract to contract and may result in uneven payment flows. There may be instances in which payments made to our vendors will exceed the level of services provided and result in a prepayment of the research and development expense. In accruing service fees, we estimate the time period over which services will be performed and the level of effort to be expended in each period. If the actual timing of the performance of services or the level of effort varies from our estimate, we adjust the accrual or prepayment expense accordingly. Although we do not expect our estimates to be materially different from amounts actually incurred, our understanding of the status and timing of services performed relative to the actual status and timing of services performed may vary and could result in us reporting amounts that are too high or too low in any particular period. Differences between our estimates and amounts actually incurred to date, and any resulting adjustments, have not been material.
67
Table of Contents
Stock-based compensation
We account for stock-based compensation in accordance with Financial Accounting Standards Board Accounting Standards Codification Topic 718, Compensation-Stock Compensation, which we refer to as ASC 718. ASC 718 requires the measurement and recognition of compensation expense for all stock-based payment awards made to employees and non-employee directors, including employee stock options. Compensation expense based on the grant date fair value is generally amortized over the requisite service period of the award on a straight-line basis.
We account for stock options granted to non-employees, which primarily consist of consultants and members of our scientific advisory board, using the fair value method. Stock options granted to non-employees are subject to periodic revaluation over their vesting terms and stock-based compensation expense may be recognized using an accelerated recognition model.
We use the Black-Scholes option pricing model to estimate the fair value of stock option awards using various assumptions that require management to apply judgment and make estimates, including:
| • | the expected term of the stock option award, which we calculate using the simplified method, as prescribed by the Securities and Exchange Commission Staff Accounting Bulletin No. 107, Share-Based Payment, as we have insufficient historical information regarding our stock options to provide a basis for an estimate; |
| • | the expected volatility of the underlying common stock, which we estimate based on the historical volatility of a representative peer group of publicly traded biopharmaceutical companies with similarities to us, including stage of drug development, area of therapeutic focus, number of employees and market capitalization; |
| • | the risk-free interest rate, which we based on the yield curve of U.S. Treasury securities with periods commensurate with the expected term of the options being valued; |
| • | the expected dividend yield, which we estimate to be zero based on the fact that we have never paid cash dividends and have no present intention to pay cash dividends; and |
| • | the fair value of our common stock on the date of grant. |
If factors change and different assumptions are used, our stock-based compensation expense could be materially different in the future.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
See Note 2, Recent Accounting Pronouncements, of the Notes to Financial Statements, for a discussion of the impact of new accounting standards on our Financial Statements.
Results of Operations
Comparison of years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015
The following table summarizes our results of operations for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015:
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | Dollar Change | % Change | |||||||||||||
| Operating expenses: |
||||||||||||||||
| Research and development |
$ | 22,101,720 | $ | 15,004,512 | $ | 7,097,208 | 47 | % | ||||||||
| General and administrative |
$ | 11,430,526 | $ | 10,060,825 | $ | 1,369,701 | 14 | % | ||||||||
| Other income (expense) |
$ | 4,993,847 | $ | (55,627 | ) | $ | 5,049,474 | (9,077 | )% | |||||||
68
Table of Contents
Research and Development Expenses
Research and development expense was $22.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2016, compared with $15.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2015, an increase of $7.1 million. This increase was primarily attributable to a $5.6 million increase in expenditures on our product candidates as we concluded our Phase 1 clinical study and prepared for a Phase 2 clinical trial of CF-301 and continued to progress CF-404 through IND related manufacturing activities. The increase was also due to a $1.5 million increase in expenses related to our research headcount, including salaries, benefits and laboratory costs in support of the discovery and study of additional product candidates.
General and Administrative Expenses
General and administrative expense was $11.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2016, compared with $10.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2015, an increase of $1.4 million. This increase was primarily attributable to increased severance costs of $1.4 million, including $0.5 million of non-cash share-based compensation expense, and a $0.2 million increase in accounting and filing costs related to our SEC filings. These increases were partially offset by a $0.2 million decrease in our Board of Directors fees and expenses.
Other income (expense)
Other income was $5.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2016 compared with other expense of $0.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2015, an increase of $5.0 million. In 2016, we had non-cash income of $6.3 million related to the change in fair value of our warrant liability and interest income of $0.2 million, which were partially offset by expense due to $1.5 million of issuance costs allocated to the warrants issued in our Follow-on Offering. In 2015, we had non-cash expense of more than $0.1 million related to the change in fair value of our warrant liability, which was partially offset by interest income of less than $0.1 million from our marketable securities.
Comparison of years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014
The following table summarizes our results of operations for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014:
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||
| 2015 | 2014 | Dollar Change | % Change | |||||||||||||
| Operating expenses: |
||||||||||||||||
| Research and development |
$ | 15,004,512 | $ | 8,868,053 | $ | 6,136,459 | 69 | % | ||||||||
| General and administrative |
$ | 10,060,825 | $ | 8,067,858 | $ | 1,992,967 | 25 | % | ||||||||
| Other income (expense) |
$ | (55,627 | ) | $ | (13,213,173 | ) | $ | 13,157,546 | (100 | )% | ||||||
Research and Development Expenses
Research and development expense was $15.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2015, compared with $8.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2014, an increase of $6.1 million. This increase was primarily attributable to a $4.7 million increase in expenditures on our product candidates as we initiated and concluded our Phase 1 clinical study of CF-301 and continued to progress CF-404 through IND-enabling studies and manufacturing activities. The increase was also due to a $1.4 million increase in our research headcount and related salaries, benefits and laboratory costs in support of the discovery and study of additional product candidates.
General and Administrative Expenses
General and administrative expense was $10.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2015, compared with $8.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2014, an increase of $2.0 million. This increase was primarily
69
Table of Contents
attributable to an increase in our administrative and Board of Directors headcount, resulting in an $1.0 million increase in expenses, a $0.7 million increase in costs related to being a public company, including listing fees, filing fees, insurance and investor relations expenses, $0.6 million in severance costs that did not occur in 2014, and a $0.2 million increase in expenses related to business development activities. These increases were partially offset by a $0.5 million decrease in our legal expenses.
Other income (expense)
Other expense was $0.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2015 compared with $13.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2014, a decrease of $13.1 million. In 2015, we had non-cash expense of more than $0.1 million related to the change in fair value of our warrant liability, which was partially offset by interest income of less than $0.1 million from our marketable securities. In 2014, we had non-cash interest charges of $12.4 million related to our Convertible Notes and non-cash expense of $1.2 million related to the change in fair value of our warrant and embedded derivatives liabilities, which were partially offset by $0.4 million of income from the receipt of refundable state tax credits.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Sources of Liquidity
We have financed our operations to date primarily through proceeds from sales of common stock, common stock and warrants, convertible preferred stock and convertible debt. To date, we have not generated any revenue from the sale of products. We have incurred losses and generated negative cash flows from operations since inception.
Since the date of our initial public offering, we have received gross proceeds of $76.3 million from the sale of registered securities, $9.6 million from the exercise of the Class B Warrants issued in our IPO and $20.0 million from the sale of securities in a private placement.
As of December 31, 2016, we had approximately $35.2 million in cash, cash equivalents and marketable securities. We primarily invest our cash and cash equivalents in commercial money market accounts and our marketable securities in highly rated corporate debt securities.
Cash flows
The following table shows a summary of our cash flows for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014:
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
| Net cash provided by (used in): |
||||||||||||
| Operating activities |
$ | (29,300,340 | ) | $ | (22,182,601 | ) | $ | (14,864,762 | ) | |||
| Investing activities |
$ | (8,968,567 | ) | $ | (21,600,084 | ) | $ | (1,610,536 | ) | |||
| Financing activities |
$ | 32,103,109 | $ | 28,033,013 | $ | 38,052,481 | ||||||
Net cash used in operating activities
Net cash used in operating activities resulted primarily from our net losses adjusted for non-cash charges and changes in the components of working capital. Net cash used in operating activities in the year ended December 31, 2016 increased by $7.1 million and $14.4 million as compared to the comparable periods in 2014 and 2013, respectively. This is attributable to the increase in our loss from operations in 2016 as we advanced our product candidates and expanded our research and administrative headcount.
70
Table of Contents
Net cash (used in) provided by investing activities
Net cash used in investing activities in the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014 resulted from the investment of our cash balances into marketable securities less proceeds from any maturities of those securities.
Net cash provided by financing activities
Net cash provided by financing activities in the year ended December 31, 2016 resulted primarily from the completion of a registered offering of our securities to institutional investors in July 2016, resulting in net proceeds of $32.0 million. Net cash provided by financing activities in the year ended December 31, 2015 resulted primarily from the completion of a private placement of our securities to institutional investors in June 2015, resulting in net proceeds of $18.3 million and the exercise of the Class B Warrants issued as part of the Units sold in our IPO, resulting in net proceeds of $9.7 million. Net cash provided by financing activities in the year ended December 31, 2014 resulted from the issuance of approximately 6.9 million Units on the completion of our IPO, resulting in net proceeds of $35.0 million and the issuance of approximately $3.0 million of our Convertible Notes, which were converted into common stock on the closing of our IPO.
Funding requirements
All of our product candidates are in early clinical or preclinical development. We expect to continue to incur significant expenses and increasing operating losses for the foreseeable future. We anticipate that our expenses will increase substantially if and as we:
| • | initiate the planned clinical trials of our product candidates; |
| • | continue our ongoing preclinical studies, and initiate additional preclinical studies, of our product candidates; |
| • | continue the research and development of our other product candidates and our platform technology; |
| • | seek to identify additional product candidates; |
| • | acquire or in-license other products and technologies; |
| • | seek marketing approvals for our product candidates that successfully complete clinical trials; |
| • | establish, either on our own or with strategic partners, a sales, marketing and distribution infrastructure to commercialize any products for which we may obtain marketing approval; |
| • | maintain, leverage and expand our intellectual property portfolio; and |
| • | add operational, financial and management information systems and personnel, including personnel to support our product development and future commercialization efforts. |
We believe that our existing cash and cash equivalents and marketable securities, together with interest thereon, will be sufficient to fund our operations into the second quarter of 2018. We have based this estimate on assumptions that may prove to be wrong, and we could use our available capital resources sooner than we currently expect. Because of the numerous risks and uncertainties associated with the development and commercialization of our product candidates, and the extent to which we may enter into collaborations with third parties for development and commercialization of our product candidates, we are unable to estimate the amounts of increased capital outlays and operating expenses associated with completing the development of our current product candidates. Our future capital requirements will depend on many factors, including:
| • | the progress and results of the clinical trials of our lead product candidates; |
| • | the scope, progress, results and costs of compound discovery, preclinical development, laboratory testing and clinical trials for our other product candidates; |
| • | the extent to which we acquire or in-license other products and technologies; |
71
Table of Contents
| • | the costs, timing and outcome of regulatory review of our product candidates; |
| • | the costs of future commercialization activities, including product sales, marketing, manufacturing and distribution, for any of our product candidates for which we receive marketing approval; |
| • | revenue, if any, received from commercial sales of our product candidates, should any of our product candidates receive marketing approval; |
| • | the costs of preparing, filing and prosecuting patent applications, maintaining and enforcing our intellectual property rights and defending intellectual property-related claims; and |
| • | our ability to establish any future collaboration arrangements on favorable terms, if at all. |
Until such time, if ever, as we can generate substantial product revenues, we expect to finance our cash needs through a combination of equity and debt offerings, collaborations, strategic alliances and licensing arrangements. We do not have any committed external source of funds. To the extent that we raise additional capital through the sale of equity or other securities, the ownership interest of our stockholders will be diluted, and the terms of these securities may include liquidation or other preferences that adversely affect your rights as a common stockholder. Debt financing, if available, may involve agreements that include covenants limiting or restricting our ability to take specific actions, such as incurring additional debt, making capital expenditures or declaring dividends. If we raise additional funds through collaborations, strategic alliances or licensing arrangements with third parties, we may have to relinquish valuable rights to our technologies, future revenue streams, research programs or product candidates or grant licenses on terms that may not be favorable to us. If we are unable to raise additional funds through equity or debt financings when needed, we may be required to delay, limit, reduce or terminate our product development or future commercialization efforts or grant rights to develop and market product candidates that we would otherwise prefer to develop and market ourselves.
We incur significant increased costs as a public company that we have not previously incurred, including, but not limited to, increased personnel costs, increased directors fees, increased directors and officers insurance premiums, audit and legal fees, investor relations and external communications fees, expenses for compliance with the Sarbanes-Oxley Act and rules implemented by the SEC and NASDAQ and various other costs and expenses.
Contractual Obligations and Commitments
The following table summarizes our contractual obligations at December 31, 2016 and the effect such obligations are expected to have on our liquidity and cash flows in future periods:
| Payments due by period | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Contractual obligations |
Total | Less than 1 year |
1 - 3 years | 4 - 5 years | More than 5 years |
|||||||||||||||
|
Operating lease commitments(1) |
$ | 10,626,086 | $ | 921,223 | $ | 1,790,349 | $ | 1,862,679 | $ | 6,051,835 | ||||||||||
| License and sponsored research agreements(2) |
2,355,218 | 622,282 | 1,132,936 | 400,000 | 200,000 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total contractual obligations |
$ | 12,961,304 | $ | 1,543,505 | $ | 2,903,285 | $ | 2,262,679 | $ | 6,251,835 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| (1) | Represents future minimum lease payments under non-cancelable operating leases for our principal facilities in Yonkers, New York which expire in 2027. In May 2016, we entered into a lease for facilities in Cambridge, MA which expires on May 31, 2017. The minimum lease payments above do not include certain utility costs, common area maintenance charges or real estate taxes. |
| (2) | Represents certain amounts payable under our licenses and sponsored research agreements with The Rockefeller University and Trellis Bioscience LLC. |
72
Table of Contents
We enter into contracts in the normal course of business with contract research organizations, or CROs, for clinical trials, clinical supply manufacturing, non-clinical and preclinical studies and for other services and products for operating purposes. These contracts generally provide for termination on notice, and therefore are cancelable contracts and not included in the table of contractual obligations.
The contractual obligations table also does not include any potential contingent payments upon the achievement by us of specified clinical, regulatory and commercial events, as applicable, or royalty payments we may be required to make under license agreements we have entered into with The Rockefeller University and Trellis Bioscience LLC. The occurrence and timing of these events are difficult to predict and subject to significant uncertainty. Since we are unable to reliably estimate the timing and amounts of such milestone and royalty payments, or whether they will occur at all, these contingent payments have been excluded from the table above. See “Note 15—Significant Agreements” on Page F-26 of this Annual Report for additional information.
Effects of Inflation
We do not believe that inflation or changing prices had a significant impact on our results of operations for any periods presented herein.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
We did not have during the periods presented, and we are currently not party to, any off-balance sheet arrangements.
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
Our primary exposure to market risk is interest income sensitivity, which is affected by changes in the general level of U.S. interest rates. As of December 31, 2016, we had cash, cash equivalents and marketable securities of $35.2 million. Because of the short-term maturities of our cash equivalents and marketable securities, we do not believe that an increase in market rates would have any significant impact on the fair value of our cash equivalents or marketable securities. If a 10% change in interest rates were to have immediately occurred on December 31, 2016, this change would not have had a material effect on the fair value of our investment portfolio as of that date.
While we believe our cash, cash equivalents and marketable securities do not contain excessive credit or liquidity risk, we cannot provide absolute assurance that in the future our investments will not be subject to adverse changes in market value. In addition, we maintain significant amounts of cash and cash equivalents at one or more financial institutions that are in excess of federally insured limits.
We do not own any derivative financial instruments. Accordingly, we do not believe that there is any material market risk exposure with respect to derivative, foreign currency or other financial instruments that would require disclosure under this item.
Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data
The financial statements required to be filed pursuant to this Item 8 are appended to this report. An index of those financial statements is found in Item 15 of Part IV of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Item 9. Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure
None
73
Table of Contents
Item 9A. Controls and Procedures
Limitations on Effectiveness of Controls and Procedures
In designing and evaluating our disclosure controls and procedures, management recognizes that any controls and procedures, no matter how well designed and operated, can provide only reasonable assurance of achieving the desired control objectives. In addition, the design of disclosure controls and procedures must reflect the fact that there are resource constraints and that management is required to apply judgment in evaluating the benefits of possible controls and procedures relative to their costs.
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
As required by Rule 13a-15(b) and Rule 15d-15(b) of the Exchange Act, our management, including our principal executive officer and our principal financial officer, conducted an evaluation as of the end of the period covered by this Annual Report on Form 10-K of the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rule 13a-15(e) and Rule 15d-15(e) of the Exchange Act). Based on that evaluation, our principal executive officer and principal financial officer concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures were effective at the reasonable assurance level as of December 31, 2016.
Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting, as such term is defined in Rule 13a-15(f) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended.
Our management conducted an assessment of the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting based on the criteria set forth in “Internal Control-Integrated Framework (2013)” issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. Based on this assessment, management concluded that, as of December 31, 2016, our internal control over financial reporting was effective.
This annual report does not include an attestation report of our registered public accounting firm on internal control over financial reporting due to an exemption established by the JOBS Act for “emerging growth companies”.
Changes in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
As required by Rule 13a-15(d) and Rule 15d-15(d) of the Exchange Act, our management, including our principal executive officer and our principal financial officer, conducted an evaluation of our internal control over financial reporting to determine whether any changes occurred during the quarter ended December 31, 2016 that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting. Based on that evaluation, our principal executive officer and principal financial officer concluded that there were no changes during the quarter ended December 31, 2016 that materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
As of March 14, 2017, Michael Messinger, Senior Vice President, Finance of the Company, has been unable to perform the functions of principal financial officer and principal accounting officer due to a medical emergency (the “Medical Emergency”). Steven C. Gilman, Ph.D., the Company’s Chief Executive Officer, is performing the functions of principal financial officer and principal accounting officer until the commencement of his medical leave of absence on March 16, 2017, at which point the Interim Office of the Chief Executive Officer (“Interim Office of the CEO”) will assume the duties of principal financial officer and principal accounting officer until Mr. Messinger is able to resume those functions following the resolution of the Medical Emergency.
74
Table of Contents
As previously disclosed, the Board of Directors of the Company established the Interim Office of the CEO to assume the duties of the Company’s Chief Executive Officer on an interim basis, effective March 16, 2017. The Interim Office of the CEO consists of Cara Cassino, M.D., the Company’s Chief Medical Officer and Executive Vice President of Research and Development, Natalie Bogdanos, the Company’s General Counsel and Corporate Secretary, Michael Messinger, Senior Vice President, Finance and Josh Muntner, the Company’s Senior Vice President, Business Development. Mr. Messinger is expected to serve as a member of the Interim Office of the CEO following the resolution of the Medical Emergency.
For biographical information regarding Dr. Gilman, Dr. Cassino, Ms. Bogdanos, Mr. Messinger and Mr. Muntner, see Part III, Item 10 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
On March 15, 2017, we entered into an agreement with Dr. Cassino, our Chief Medical Officer, to amend the existing employment offer letter agreement between Dr. Cassino and the Company (the “Amendment”). Pursuant to the Amendment, Dr. Cassino is eligible for an annual performance bonus of 45% of her annual base salary and a retention bonus of $150,000, which retention bonus will be payable within 60 days after the date the first patient is dosed in the CF-301 Phase 2 study, provided that Dr. Cassino remains employed with us through such date.
The Amendment also entitles Dr. Cassino to the following severance payments and benefits upon her resignation for good reason or termination by us without cause: (i) an amount equal to the sum of 18 months of Dr. Cassino’s then-current base salary plus 150% of Dr. Cassino’s then-current target annual bonus, payable over 18 months following the date of termination, (ii) payment of any earned but unpaid bonuses, (iii) payment of the applicable premiums for coverage pursuant to COBRA for 18 months from the date of termination and (iv) accelerated vesting of any then-outstanding Company stock options granted prior to June 14, 2016, with the vested portion of such stock options remaining outstanding and exercisable until the date that is two (2) years following Dr. Cassino’s employment termination date, subject to the earlier final expiration dates of such options or treatment in accordance with their contractual terms in connection with certain corporate transactions.
The foregoing description of the Amendment does not purport to be complete and is qualified in its entirety by reference to the full text of the Amendment, which is filed as an exhibit to this Annual Report on Form 10-K and incorporated herein by reference.
75
Table of Contents
PART III
Item 10. Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance
Director Biographical Information
Biographical information concerning each of our directors is set forth below:
| Name |
Age | Position | ||||
| Steven C. Gilman, Ph.D. |
64 | Director, Chairman of the Board | ||||
| Roger J. Pomerantz, M.D., F.A.C.P. |
60 | Director, Vice Chairman of the Board | ||||
| Sol J. Barer, Ph.D. |
69 | Director, Lead Independent Director | ||||
| Isaac Blech |
67 | Director | ||||
| David N. Low, Jr. |
58 | Director | ||||
| Michael J. Otto, Ph.D. |
68 | Director | ||||
| Lisa R. Ricciardi |
57 | Director | ||||
| Cary W. Sucoff, J.D. |
65 | Director | ||||
Steven C. Gilman, Ph.D. Dr. Gilman has served as Chairman of our board of directors since May 2015. In March 2016, he was appointed Interim Chief Executive Officer of the Company and in July 2016 he was appointed Chief Executive Officer of the Company. Until 2015, he served as the Executive Vice President, Research & Development and Chief Scientific Officer at Cubist Pharmaceuticals, a biopharmaceutical company, until its acquisition by Merck & Co. Prior to joining Cubist in 2008, he served as Chairman of the Board of Directors and Chief Executive Officer of ActivBiotics, a privately held biopharmaceutical company. Previously, he worked at Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Inc., where he held a number of senior leadership roles including Vice President and General Manager of the Inflammation franchise responsible for all aspects of the Inflammation business from early gene discovery to product commercialization. Prior to Millennium, he was Group Director at Pfizer Global Research and Development, where he was responsible for drug discovery of novel antibacterial agents as well as several other therapeutic areas. Dr. Gilman has also held scientific, business, and academic appointments at Wyeth, Cytogen Corporation, Temple Medical School, and Connecticut College. He currently serves on the board of directors of publicly traded companies Keryx Biopharmaceuticals, Inc., Momenta Pharmaceuticals, Inc., SCYNEXIS Inc., and Vericel Corporation. Dr. Gilman received his Ph.D. and M.S. degrees in microbiology from Pennsylvania State University, his post-doctoral training at Scripps Clinic and Research Foundation, and received a B.A. in microbiology from Miami University of Ohio. He has authored over 60 publications and is an inventor on 7 patents. We believe that Dr. Gilman’s significant scientific, executive and board leadership experience in the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries qualifies him to serve as a member of our board of directors.
Roger J. Pomerantz, M.D., F.A.C.P. Dr. Pomerantz has served as a member of our board of directors since April 2014 and was appointed Vice Chairman in May 2014. Since 2014, Dr. Pomerantz has served as President and Chief Executive Officer of Seres Therapeutics, Inc., a biotechnology company. He has also served as Chairman of the board of directors of Seres since 2013. From 2011 to 2013, he was formerly Worldwide Head of Licensing & Acquisitions, Senior Vice President at Merck & Co., Inc. where he oversaw all licensing and acquisitions at Merck Research Laboratories. Previously, he served as Senior Vice President and Global Franchise Head of Infectious Diseases at Merck. Prior to joining Merck, Dr. Pomerantz was Global Head of Infectious Diseases for Johnson & Johnson Pharmaceuticals. He joined Johnson & Johnson in 2005 as President of Tibotec Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Dr. Pomerantz received his B.A. in Biochemistry at the Johns Hopkins University and his M.D. at the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine. He received post-graduate training at the Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School and M.I.T. Dr. Pomerantz is Board Certified in both Internal Medicine and Infectious Diseases. He was Professor of Medicine, Biochemistry and Molecular Pharmacology, Chief of Infectious Diseases, and the Founding Director and Chair of the Institute for Human Virology and Biodefense at the Thomas Jefferson University and Medical School. He has developed nine drugs approved world-wide in important diseases, including HIV, HCV, and tuberculosis. We believe that
76
Table of Contents
Dr. Pomerantz’s significant scientific, executive and board leadership experience in drug development and in the pharmaceutical industry qualifies him to serve as a member of our board of directors.
Sol J. Barer, Ph.D. Dr. Barer has served as a member of our board of directors since April 2011. Dr. Barer served as our Chairman of the board of directors from February 2012 to May 2015. He was appointed Lead Independent Director in May 2015. Dr. Barer spent most of his professional career with the Celgene Corporation. He was Chairman from January 2011 until June 2011, Executive Chairman from June 2010 until January 2011 and Chairman and Chief Executive Officer from May 2006 until June 2010. Dr. Barer was the founder of the biotechnology group at the Celanese Research Company which was subsequently spun out to form Celgene. Dr. Barer serves as Chairman of the board of directors of the public companies Edge Therapeutics, InspireMD, Aevi Genomic Medicine, and Teva Pharmaceutical Industries and the private company Centrexion. He is an advisor to biotechnology/medical companies, the Israel Biotech Fund and not for profit organizations. In 2011 Dr. Barer was Chairman of the University of Medicine and Dentistry of New Jersey Governor’s Advisory Committee which resulted in sweeping changes in the structure of New Jersey’s medical schools and public research universities. He previously served as a Commissioner of the NJ Commission on Science and Technology. He was a member of the Board of Trustees of Rutgers University and served two terms as Chair of the Board of Trustees of BioNJ, the New Jersey biotechnology organization. We believe that Dr. Barer’s significant scientific, executive and board leadership experience in the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries qualifies him to serve as a member of our board of directors.
Isaac Blech. Mr. Blech has served as a member of our board of directors since August 2010. Mr. Blech’s current roles at public companies are Director of Cerecor, Inc., Director of Aevi Genomic Medicine, Inc., and Vice Chairman of Edge Therapeutics, Inc., InspireMD, SpendSmart Networks, Inc., and root9B Technologies. He is also Vice Chairman of Centrexion Corporation, Regenovation, Inc., X4 Pharmaceuticals, Sapience Therapeutics, Aridis Pharmaceuticals, WaveGuide Corporation, Alveo Health, and X-VAX Technology, Inc., which are all private companies. Over the past 35 years, Mr. Blech has helped found some of the world’s leading biotechnology companies, including Celgene Corporation, ICOS Corporation, Pathogenesis Corporation, Nova Pharmaceutical Corporation and Genetic Systems Corporation. These companies are responsible for major advances in oncology, infectious disease and cystic fibrosis. Mr. Blech earned a B.A. degree from Baruch College in 1975. We believe that Mr. Blech’s broad experience as a founder, director and major investor in numerous biotechnology companies qualifies him to serve as a member of our board of directors.
David N. Low, Jr. Mr. Low has served as a member of our board of directors since April 2014. Mr. Low has worked as an investment banker since 1987, with broad investment and advisory experience in the life sciences, biotechnology and medical technology sectors. Since 2013, Mr. Low has served as a Senior Advisor at Lazard Freres & Company, an investment bank. From 2002 to 2013, Mr. Low was a member of Lazard’s Life Sciences Group as a Managing Director. Mr. Low has advised on major M&A transactions in the life sciences, biotechnology and medical technology sectors, and has worked with private and public companies to raise capital, including emerging growth companies. Prior to joining Lazard, Mr. Low was a Managing Director at JP Morgan Chase & Co. and a Senior Vice President at Lehman Brothers. Mr. Low serves on the board of directors of the We Teach Science Foundation (as Chairman), the Philharmonia Baroque Orchestra, and the French International School. Mr. Low holds an A.B. from Harvard College, where he graduated cum laude, an M.A. from the Johns Hopkins University School of Advanced International Studies and an M.B.A. from Yale University. We believe that Mr. Low’s significant investment and financial advisory experience qualifies him to serve as a member of our board of directors.
Michael J. Otto, Ph.D. Dr. Otto has served as a member of our board of directors since April 2014. Dr. Otto served as Chief Scientific Officer of Pharmasset from October 1999 until February 2012, when the company was acquired by Gilead Sciences. He led the research team responsible for the discovery of sofosbuvir for the treatment of HCV infections. In previous capacities he has served as Associate Director of Anti-Infectives Clinical Research at Rhône-Poulenc Rorer, Vice President for Research and Development at Avid Therapeutics, Inc., Research Manager at DuPont Pharmaceuticals and Dupont Merck Pharmaceuticals and as Group Leader in
77
Table of Contents
the Virology Dept. at Sterling Drug in Rensselaer, NY. Prior to joining Sterling Drug, Dr. Otto was Research Assistant Professor at Yale University School of Medicine, Dept. of Pharmacology. Dr. Otto also served as the US editor for Antiviral Chemistry & Chemotherapy from 1989 until 2012. Dr. Otto holds a B.S. degree from Loyola University of Chicago and a Ph.D. degree in medical microbiology from The Medical College of Wisconsin. He is the author or coauthor of over 100 research papers and book chapters and named inventor on several patents and patent applications. We believe that Dr. Otto’s substantial scientific and executive leadership experience in the pharmaceutical industry qualifies him to serve as a member of our board of directors.
Cary W. Sucoff. Mr. Sucoff has served on our board of directors since May 2010. Mr. Sucoff has more than 30 years of securities industry experience encompassing supervisory, banking and sales responsibilities. He has participated in the financing of more than 100 public and private companies, raising approximately $500 million of equity capital and playing a role in securing financing for biotech companies including Amgen, Centecor, Genzyme, Genentech, Icos, PathoGenesis, Vaxgen and Biotime. Since 2011, Mr. Sucoff has owned and operated Equity Source Partners LLC, an advisory and consulting firm. In addition to ContraFect, Mr. Sucoff currently serves on the board of directors of root9B Technologies, Legacy Education Alliance, Inc. Greenwood Hall, Inc. and First Wave Technologies, Inc. In addition, Mr. Sucoff currently serves as a consultant to Sapience Therapeutics. Mr. Sucoff is the past President of New England Law/Boston, has been a member of the Board of Trustees for over 25 years and is the current Chairman of the Endowment Committee. Mr. Sucoff received a B.A. from SUNY Binghamton in 1974 and a J.D. from New England School of Law in 1977, where he was managing editor of the Law Review and graduated magna cum laude. He has been a member of the Bar of the State of New York since 1978. We believe that Mr. Sucoff’s broad financial and legal experience qualifies him to serve as a member of our board of directors.
Lisa R. Ricciardi. Ms. Ricciardi has served as a member of our board of directors since February 2017. Since 2015, Ms. Ricciardi has served as an advisor to early state biotechnology companies and investors. From July 2014 through 2015, Ms. Ricciardi served as Senior Vice President for Corporate and Business Development with Foundation Medicine, a molecular information company. From October 2010 to June 2012, she served as Senior Vice President of Business Development at Medco Health Solutions, Inc. until the business was sold. In addition, she was a Venture Partner at Essex Woodlands Health Ventures. Ms. Ricciardi held numerous executive management positions at Pfizer, including Senior Vice President in the Licensing and Development Division, closing more than 25 transactions with multi-national firms and biotechnology companies, as well as managing several key product launches in the global pharmaceuticals division. Ms. Ricciardi is currently a member of the board of directors of Chimerix Inc. and United Drug Healthcare Group, PLC in Dublin, Ireland, and was previously a member of the board of directors at Sepracor. Ms. Ricciardi earned an M.B.A. from the University of Chicago and a B.A. degree from Wesleyan University. We believe that Ms. Ricciardi’s significant life sciences, executive and board leadership experience in the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries qualifies her to serve as a member of our board of directors.
Executive Officers of the Registrant
Biographical information concerning each of our executive officers is set forth below. Information concerning Steven C. Gilman, Ph.D., our Chief Executive Officer, may be found above in the section entitled “Director Biographical Information.”
Natalie Bogdanos, J.D. Ms. Bogdanos, age 48, has served as our General Counsel and Corporate Secretary since August of 2014. She has over 18 years of experience in the legal field, almost 10 of which were serving as the chief legal officer of a publicly traded biotechnology company. Prior to joining ContraFect in 2014, Ms. Bogdanos served as Associate General Counsel at Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center (“MSKCC”), a cancer treatment and research institution, where she held a joint appointment with the Office of the General Counsel and the Office of Technology Development (“OTD”). At MSKCC, she provided legal counsel and guidance to various departments throughout the institution while having sole responsibility for the legal oversight of the OTD. She led the contracts group, managed the institution’s patent portfolio, provided regulatory guidance
78
Table of Contents
and compliance, and advised on litigation strategy. Prior to MSKCC, she was General Counsel at Enzo Biochem, Inc. (“Enzo”), a publicly traded international biotechnology and life science company, from 2003 to 2012. At Enzo, she was responsible for leading the legal department, handling contracts and complex business development agreements, ensuring SEC and regulatory compliance, overseeing litigation and managing Enzo’s portfolio of 500+ patents and patent applications. Previously, Ms. Bogdanos was an associate at Amster, Rothstein & Ebenstein from 1999 to 2003 where her practice focused on patent litigation and patent prosecution. Ms. Bogdanos has also served as a legal consultant to pharmaceutical companies and was a faculty member at the Practising Law Institute. Prior to attending law school, she was a research technician at the Public Health Research Institute where her work focused on Staphylococcus aureus. Ms. Bogdanos is an attorney licensed to practice before the United States Patent and Trademark Office. She is admitted to practice law in New York, the United States District Court, Southern and Eastern District of New York and the United States Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit. Ms. Bogdanos received her J.D. from New York Law School and her Bachelor of Arts in Biology, with honors, from Queens College of the City University of New York.
Cara Cassino, M.D. Dr. Cassino, age 55, has served as our Chief Medical Officer since September 2015 and also as Executive Vice President of Research and Development since October 2015. Dr. Cassino has over 20 years of experience as a clinician and executive in healthcare, including over 15 years of experience in pharmaceutical product development with over 20 successful regulatory submissions in the United States and globally. Prior to joining ContraFect in 2015, Dr. Cassino served as an independent consultant to various pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies, including Scynexis. Prior to that, she served as Senior Vice President at Forest Laboratories, Inc., a biopharmaceutical company (acquired by Actavis plc, now Allergan plc), where she oversaw Global Clinical Development from 2013 to 2014. While at Forest, she was responsible for pre- and post-marketing clinical activities for a portfolio of 35 compounds, and also clinical due diligence for M&A activity, including the $2.9 billion acquisition of Aptalis Pharma and the $1.1 billion acquisition of Furiex Pharmaceuticals. From 2008 to 2013, Dr. Cassino held a number of senior positions at Pfizer, including Global Medical Team Leader of Pfizer’s antibacterial franchise which included Zyvox (linezolid) and Medicines Development Group VP for Pulmonary Vascular Disease and Rare Diseases. Prior to joining Pfizer, Dr. Cassino also served as Executive Medical Director for the late stage U.S. respiratory franchise at Boehringer-Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. and was a member of the academic faculty of the Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine at New York University (NYU) School of Medicine for eight years prior to joining industry. Dr. Cassino received her B.A., summa cum laude, in Chemistry and Fine Arts from NYU where she was elected Phi Beta Kappa, followed by an M.D. from NYU School of Medicine. She completed her internship and residency in Internal Medicine at NYU/Bellevue Hospital and a fellowship in Pulmonary/Critical Care Medicine at NYU and Mount Sinai Medical Centers. Dr. Cassino is Board Certified in both internal medicine and pulmonary medicine.
Michael Messinger, CPA. Mr. Messinger, age 42, currently serves as our Senior Vice President, Finance since October 2016. He has more than 16 years of experience in finance, accounting and forecasting for clinical development. Prior to joining ContraFect in November 2012 as our Vice President, Finance, he served as Director of Finance at Lexicon Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (“Lexicon”) for eight years and also held the position of Controller for three years. Prior to working at Lexicon, Mr. Messinger served as Controller of Coelacanth Corporation (which was acquired by Lexicon) for two years. While at Lexicon, Mr. Messinger was responsible for the financial management of Lexicon’s partnership with Symphony Capital, LLC, in addition to coordinating fiscal and program management concerning Lexicon’s development programs. Mr. Messinger received his B.B.A. degree in accounting from the University of Michigan. He started his career as an auditor at Ernst & Young LLP.
Josh Muntner. Mr. Muntner, age 48, has served as the Senior Vice President of Business Development since 2015. Mr. Muntner has more than 15 years of transaction experience assisting life sciences companies with financing and M&A advisory transactions. Prior to joining ContraFect, he served as Managing Director and Co-Head of Healthcare Investment Banking at Janney Montgomery Scott, a financial services firm from 2012 to 2015. Mr. Muntner was also a Managing Director at ThinkEquity, an investment bank from 2009 to 2012.
79
Table of Contents
Previously, Mr. Muntner spent nine years at Oppenheimer & Co. and its U.S. predecessor, CIBC World Markets, in positions of increasing responsibility. Mr. Muntner also served as an investment banker at Prudential Securities. Mr. Muntner received his B.F.A. degree from Carnegie Mellon and his M.B.A. degree from The Anderson School at UCLA.
Nancy Dong. Ms. Dong, age 51, currently serves as our Vice President, Finance and Administration. She has more than 20 years of experience in accounting, strategic planning, budgeting and forecasting, organizational development, financial systems and controls and human resources. Prior to joining ContraFect in 2010 as Vice President, Controller, she served as controller at XL Marketing, a direct marketing firm, from 2009 to 2010 and at Alley Corp, a company that provides strategic advice to companies within its network, from 2007 to 2009. She also served as Vice President of Finance and Administration at DCM, a tele-services firm supporting the performing arts, from 2002 to 2007. Ms. Dong also held the positions of COO and CFO at Semaphore, a project management software development firm. Ms. Dong received her B.A. degree from Yale University and a MPPM degree from The Wharton School at the University of Pennsylvania. She started her career as a management consultant at Ernst & Young LLP.
Our board of directors has adopted a Code of Business Conduct and Ethics applicable to all officers, directors and employees, which is available on our website at http://ir.contrafect.com/governance-docs. We intend to satisfy the disclosure requirement under Item 5.05 of Form 8-K regarding amendment to, or waiver from, a provision of our Code of Business Conduct and Ethics, as well as NASDAQ’s requirement to disclose waivers with respect to directors and executive officers, by posting such information on our website at the address and location specified above.
The remaining information required by this Item 10 will be contained under the headings “Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance,” “Election of Directors – Director Biographical Information,” “Executive Officer Biographies,” and “Corporate Governance – Committees of the Board” in our definitive proxy statement to be filed with the SEC with respect to our 2017 Annual Meeting of Stockholders and is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 11. Executive Compensation
The information required by this Item 11 will be contained under the heading “Executive Compensation” in our definitive proxy statement to be filed with the SEC with respect to our 2017 Annual Meeting of Stockholders and is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters
The information required by this Item 12 will be contained under the headings “Executive Compensation – Equity Compensation Plan Information” and “Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management” in our definitive proxy statement to be filed with the SEC with respect to our 2017 Annual Meeting of Stockholders and is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence
The information required by this Item 13 will be contained under the headings “Certain Relationships and Related Transactions” and “Corporate Governance – Director Independence” in our definitive proxy statement to be filed with the SEC with respect to our 2017 Annual Meeting of Stockholders and is incorporated herein by reference.
80
Table of Contents
Item 14. Principal Accounting Fees and Services Principal Accountant Fees and Services
The information required by this Item 14 will be contained under the heading “Ratification of Appointment of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm” in our definitive proxy statement to be filed with the SEC with respect to our 2017 Annual Meeting of Stockholders and is incorporated herein by reference.
81
Table of Contents
PART IV
Item 15. Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules
| (1) | Financial Statements |
The following documents are included on pages F-1 through F-28 attached hereto and are filed as part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
| F-2 | ||||
| F-3 | ||||
| F-4 | ||||
| F-5 | ||||
| Statement of Convertible Preferred Stock and Stockholders’ Equity (Deficit) |
F-6 | |||
| F-8 | ||||
| F-9 |
| (2) | Financial Statement Schedules |
Schedules have been omitted since they are either not required or not applicable or the information is otherwise included herein.
| (3) | Exhibits |
The exhibits filed as part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K are listed in the Exhibit Index immediately preceding such Exhibits, which Exhibit Index is incorporated herein by reference.
None.
82
Table of Contents
CONTRAFECT CORPORATION
Index to Financial Statements
| F-2 | ||||
| F-3 | ||||
| F-4 | ||||
| F-5 | ||||
| Statements of Convertible Preferred Stock and Stockholders’ Equity (Deficit) |
F-6 | |||
| F-8 | ||||
| F-9 |
F-1
Table of Contents
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
The Board of Directors and Stockholders
ContraFect Corporation
We have audited the accompanying balance sheets of ContraFect Corporation as of December 31, 2016 and 2015, and the related statements of operations, comprehensive loss, convertible preferred stock and stockholders’ equity (deficit) and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2016. These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. We were not engaged to perform an audit of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Our audits included consideration of internal control over financial reporting as a basis for designing audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion. An audit also includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, and evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of ContraFect Corporation at December 31, 2016 and 2015, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2016, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
/s/ Ernst & Young LLP
Metro Park, New Jersey
March 15, 2017
F-2
Table of Contents
Balance Sheets
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Assets |
||||||||
| Current assets: |
||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 3,806,984 | $ | 9,972,781 | ||||
| Marketable securities |
31,354,170 | 22,948,872 | ||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
1,017,645 | 1,176,895 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total current assets |
36,178,799 | 34,098,548 | ||||||
| Property and equipment, net |
1,281,152 | 1,618,968 | ||||||
| Other assets |
164,519 | 143,621 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total assets |
$ | 37,624,470 | $ | 35,861,137 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Liabilities and stockholders’ equity |
||||||||
| Current liabilities: |
||||||||
| Accounts payable |
$ | 1,549,845 | $ | 1,517,417 | ||||
| Accrued liabilities |
2,868,352 | 2,251,767 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total current liabilities |
4,418,197 | 3,769,184 | ||||||
| Deferred rent |
994,439 | 972,119 | ||||||
| Warrant liabilities |
12,698,980 | 444,324 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total liabilities |
18,111,616 | 5,185,627 | ||||||
| Commitments and contingencies (Note 8) |
— | — | ||||||
| Stockholders’ equity: |
||||||||
| Preferred stock, $0.0001 par value, 25,000,000 shares authorized and none outstanding at December 31, 2016 and 2015 |
— | — | ||||||
| Common stock, $0.0001 par value, 100,000,000 shares authorized, 41,656,006 shares outstanding at December 31, 2016; 100,000,000 shares authorized, 27,482,692 shares outstanding at December 31, 2015 |
4,166 | 2,748 | ||||||
| Additional paid-in capital |
165,678,164 | 148,282,546 | ||||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss |
(51,666 | ) | (30,373 | ) | ||||
| Accumulated deficit |
(146,117,810 | ) | (117,579,411 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total stockholders’ equity |
19,512,854 | 30,675,510 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity |
$ | 37,624,470 | $ | 35,861,137 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
See accompanying notes.
F-3
Table of Contents
Statements of Operations
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
| Operating expenses: |
||||||||||||
| Research and development, including stock-based compensation of $587,426, $389,967 and $715,475, respectively |
$ | 22,101,720 | $ | 15,004,512 | $ | 8,868,053 | ||||||
| General and administrative, including stock-based compensation of $1,644,456, $1,599,895 and $1,224,704, respectively |
11,430,526 | 10,060,825 | 8,067,858 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total operating expenses |
33,532,246 | 25,065,337 | 16,935,911 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Loss from operations |
(33,532,246 | ) | (25,065,337 | ) | (16,935,911 | ) | ||||||
| Other income (expense): |
||||||||||||
| Interest income (expense), net |
216,616 | 75,693 | (12,412,620 | ) | ||||||||
| Refundable state tax credits |
— | — | 424,649 | |||||||||
| Other expense |
(1,569,341 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
| Change in fair value of warrant and embedded derivative liabilities |
6,346,572 | (131,320 | ) | (1,225,202 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total other income (expense) |
4,993,847 | (55,627 | ) | (13,213,173 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net loss |
(28,538,399 | ) | (25,120,964 | ) | (30,149,084 | ) | ||||||
| Preferred stock dividend in-kind |
— | — | (4,468,452 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net loss attributable to common stockholders |
$ | (28,538,399 | ) | $ | (25,120,964 | ) | $ | (34,617,536 | ) | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Per share information: |
||||||||||||
| Net loss per share of common stock, basic and diluted |
$ | (0.85 | ) | $ | (1.08 | ) | $ | (3.86 | ) | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Basic and diluted weighted average shares outstanding |
33,539,465 | 23,328,922 | 8,973,599 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
See accompanying notes.
F-4
Table of Contents
Statements of Comprehensive Loss
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
| Net loss |
$ | (28,538,399 | ) | $ | (25,120,964 | ) | $ | (30,149,084 | ) | |||
| Other comprehensive loss: |
||||||||||||
| Unrealized loss on available-for-sale securities |
(21,293 | ) | (29,746 | ) | (627 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Comprehensive loss |
$ | (28,559,692 | ) | $ | (25,150,710 | ) | $ | (30,149,711 | ) | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
See accompanying notes.
F-5
Table of Contents
Statement of Convertible Preferred Stock and Stockholders’ Equity (Deficit)
| Series A Convertible Preferred Stock |
Series B Convertible Preferred Stock |
Series C Convertible Preferred Stock |
Series C-1 Convertible Preferred Stock |
Common Stock | Additional Paid-In Capital |
Loan Receivable - Officer |
Accumulated Other Comprehensive Loss |
Accumulated Deficit |
Stockholders’ Equity (Deficit) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2013 |
2,200,000 | $ | 1,964,283 | 4,651,163 | $ | 10,175,750 | 9,090,909 | $ | 27,752,294 | — | $ | — | 1,011,997 | $ | 101 | $ | 4,930,310 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | (57,840,911 | ) | $ | (52,910,500 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of preferred stock for license |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 151,515 | 500,000 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of warrants for services |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 26,354 | — | — | — | 26,354 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of securities in IPO, including over-allotment |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 6,880,333 | 688 | 41,281,310 | — | — | — | 41,281,998 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock for conversion of preferred stock on closing of IPO |
(2,200,000 | ) | (1,964,283 | ) | (4,651,163 | ) | (10,175,750 | ) | (9,090,909 | ) | (27,752,294 | ) | (151,515 | ) | (500,000 | ) | 6,861,968 | 686 | 44,860,093 | — | — | (4,468,452 | ) | 40,392,327 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Financing cost of sale of securities in IPO |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (6,644,713 | ) | — | — | — | (6,644,713 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock for conversion of notes payable and for interest liabilities, recognition of beneficial conversion feature and the reclassification of note-related liabilities on closing of IPO |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 5,197,476 | 520 | 30,632,169 | — | — | — | 30,632,689 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cancellation of placement agent warrants |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 941,541 | — | — | — | 941,541 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net shares of common stock issued in relation to vesting of retention grants |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 133,109 | 13 | 532,438 | — | — | — | 532,451 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock for license |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 132,380 | 13 | 499,987 | — | — | — | 500,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Share-based compensation |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 979,071 | — | — | — | 979,071 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unrealized loss on marketable securities |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (627 | ) | — | (627 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (30,149,084 | ) | (30,149,084 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2014 |
— | $ | — | — | $ | — | — | $ | — | — | $ | — | 20,217,263 | $ | 2,021 | $ | 118,038,560 | $ | — | (627 | ) | $ | (92,458,447 | ) | $ | 25,581,507 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
F-6
Table of Contents
| Series A Convertible Preferred Stock |
Series B Convertible Preferred Stock |
Series C Convertible Preferred Stock |
Series C-1 Convertible Preferred Stock |
Common Stock | Additional Paid-In Capital |
Loan Receivable - Officer |
Accumulated Other Comprehensive Loss |
Accumulated Deficit |
Stockholders’ Equity (Deficit) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net shares issued in relation to vesting of performance grant |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 11,778 | 1 | 54,300 | — | — | — | 54,301 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock for services |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 28,445 | 3 | 167,535 | — | — | — | 167,538 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of securities in private placement |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 4,728,128 | 474 | 19,999,526 | — | — | — | 20,000,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Financing cost of sale of securities |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (1,665,554 | ) | — | — | — | (1,665,554 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock for exercise of options |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 23,235 | 2 | — | — | — | — | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock for exercise of warrants |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 2,473,843 | 247 | 9,698,317 | — | — | — | 9,698,564 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Share-based compensation |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 1,989,862 | — | — | — | 1,989,862 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unrealized loss on marketable securities |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (29,746 | ) | — | (29,746 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (25,120,964 | ) | (25,120,964 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2015 |
— | $ | — | — | $ | — | — | $ | — | — | $ | — | 27,482,692 | $ | 2,748 | $ | 148,282,546 | $ | — | $ | (30,373 | ) | $ | (117,579,411 | ) | $ | 30,675,510 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock for services |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 31,206 | 3 | 93,927 | — | — | — | 93,930 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of securities in registered offering |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 14,000,000 | 1,400 | 16,397,372 | — | — | — | 16,398,772 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Financing cost of sale of securities |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (1,383,548 | ) | — | — | — | (1,383,548 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock for exercise of options |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 2,850 | 1 | — | — | — | — | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock for exercise of warrants |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 139,258 | 14 | 55,984 | — | — | — | 55,998 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Share-based compensation |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 2,231,883 | — | — | — | 2,231,883 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unrealized loss on marketable securities |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (21,293 | ) | — | (21,293 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (28,538,399 | ) | (28,538,399 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2016 |
— | $ | — | — | $ | — | — | $ | — | — | $ | — | 41,656,006 | $ | 4,166 | $ | 165,678,164 | $ | — | $ | (51,666 | ) | $ | (146,117,810 | ) | $ | 19,512,854 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See accompanying notes.
F-7
Table of Contents
Statements of Cash Flows
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
| Cash flows from operating activities |
||||||||||||
| Net loss |
$ | (28,538,399 | ) | $ | (25,120,964 | ) | $ | (30,149,084 | ) | |||
| Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash used in operating activities: |
||||||||||||
| Depreciation |
451,008 | 537,344 | 551,323 | |||||||||
| Stock-based compensation expense |
2,231,883 | 1,989,862 | 1,511,509 | |||||||||
| Issuance of preferred stock and other costs in exchange for licensed technology |
— | — | 1,000,000 | |||||||||
| Issuance of common stock in exchange for services |
93,930 | 167,538 | — | |||||||||
| Issuance of common stock warrants in exchange for services |
— | — | 26,354 | |||||||||
| Issuance costs allocated to warrants |
1,569,341 | — | — | |||||||||
| Recognition of beneficial conversion feature |
— | — | 7,428,547 | |||||||||
| Amortization of debt issuance costs |
— | — | 1,240,391 | |||||||||
| Amortization of debt discount |
— | — | 3,550,527 | |||||||||
| Change in fair value of warrant and embedded derivative liabilities |
(6,346,572 | ) | 131,320 | 1,225,202 | ||||||||
| Increase in deferred rent |
22,320 | 36,077 | 69,675 | |||||||||
| Net amortization of premium paid on marketable securities |
428,783 | 283,915 | — | |||||||||
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities: |
||||||||||||
| Decrease (increase) in prepaid expenses and other current and non-current assets |
138,352 | (808,108 | ) | (170,377 | ) | |||||||
| Increase (decrease) in accounts payable and accrued liabilities |
649,014 | 600,415 | (1,148,829 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net cash used in operating activities |
(29,300,340 | ) | (22,182,601 | ) | (14,864,762 | ) | ||||||
| Cash flows from investing activities |
||||||||||||
| Decrease in restricted cash |
— | — | 25,000 | |||||||||
| Purchases of marketable securities |
(36,459,405 | ) | (33,524,927 | ) | (1,671,233 | ) | ||||||
| Proceeds from maturities of marketable securities |
27,604,030 | 11,933,000 | — | |||||||||
| Purchases of property and equipment |
(113,192 | ) | (8,157 | ) | — | |||||||
| Proceeds from disposal of property and equipment |
— | — | 35,697 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net cash (used in) provided by investing activities |
(8,968,567 | ) | (21,600,084 | ) | (1,610,536 | ) | ||||||
| Cash flows from financing activities |
||||||||||||
| Proceeds from issuance of convertible notes |
— | — | 3,036,350 | |||||||||
| Payment of financing costs of convertible notes |
— | — | (24,850 | ) | ||||||||
| Proceeds from issuance of equity securities |
35,000,000 | 20,000,000 | 41,281,998 | |||||||||
| Payment of financing costs of securities sold |
(2,952,889 | ) | (1,665,554 | ) | (6,241,017 | ) | ||||||
| Proceeds from exercise of warrants |
55,998 | 9,698,567 | — | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net cash provided by financing activities |
32,103,109 | 28,033,013 | 38,052,481 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents |
(6,165,798 | ) | (15,749,672 | ) | 21,577,183 | |||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of period |
9,972,781 | 25,722,453 | 4,145,270 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of period |
$ | 3,806,984 | $ | 9,972,781 | $ | 25,722,453 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Supplemental disclosures of cash flow information and non-cash investing and financing activities |
||||||||||||
| Issuance of common and preferred stock for license received |
$ | — | $ | — | $ | 1,000,000 | ||||||
| Issuance of common stock for services |
$ | 93,930 | $ | 167,538 | $ | — | ||||||
| Issuance of warrants to purchase common stock |
$ | 18,601,228 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||
| Cancellation of placement agent warrants |
$ | — | $ | — | $ | 941,541 | ||||||
See accompanying notes.
F-8
Table of Contents
Notes to Financial Statements
December 31, 2016
1. Organization and Description of Business
Organization and Business
ContraFect Corporation (the “Company”) is a clinical-stage biotechnology company focused on protein and antibody therapeutic products for life-threatening infectious diseases, particularly those treated in hospital-based settings. The Company intends to address multi-drug resistant infections using its therapeutic product candidates from its lysin and monoclonal antibody platforms to target conserved regions of either bacteria or viruses. The Company’s most advanced product candidates are CF-301, a lysin for the treatment of Staph aureus bacteremia, and CF-404, a combination of mAbs for the treatment of life-threatening seasonal and pandemic varieties of influenza.
The Company has incurred losses from operations since inception as a research and development organization and has relied on its ability to fund its operations through public and private debt and equity financings. Management believes its cash, cash equivalents and marketable securities balances as of December 31, 2016 will be sufficient to fund operations into the second quarter of 2018 and expects operating losses and negative cash flows to continue at more significant levels in the future as it initiates additional clinical trials. Transition to profitability is dependent upon the successful development, approval, and commercialization of its product candidates and achieving a level of revenues adequate to support the Company’s cost structure. The Company may never achieve profitability, and unless and until it does, the Company will continue to need to raise additional capital. Management intends to fund future operations through additional public or private equity financings, and may seek additional capital through arrangements with strategic partners or from other sources. There can be no assurances that such financing will be available to the Company on satisfactory terms, or at all.
In August 2014, the Company completed its initial public offering of 6,000,000 units, consisting of one share of common stock, one Class A Warrant to purchase one share of common stock at an exercise price of $4.80 per share and one Class B Warrant to purchase one-half share of common stock at an exercise price of $4.00 per full share (the “Units”) and closed on the underwriter’s over-allotment option for an additional 880,333 Units (the “IPO”), raising total net proceeds of $35.0 million, net of underwriting discount, commissions and offering expenses.
In June 2015, the Company completed a private placement of securities to institutional investors whereby the investors received an aggregate of 4,728,128 shares of the Company’s common stock and warrants to purchase an additional 2,364,066 shares of common stock at an exercise price of $8.00 per share. The Company received net proceeds of $18.3 million, net of expenses.
On November 2, 2015, the Company’s Class B Warrants to purchase common stock expired in accordance with their terms. As of November 2, 2015, holders of the Class B Warrants had exercised 4,812,328 Class B Warrants, resulting in the issuance of 2,406,164 shares of the Company’s common stock and the receipt by the Company of approximately $9.6 million in gross proceeds. The 2,068,005 Class B Warrants that were not exercised prior to expiration were terminated and are no longer exercisable.
On July 27, 2016, the Company completed an underwritten public offering of 14,000,000 shares of its common stock and warrants to purchase an additional 14,000,000 shares of its common stock at an exercise price of $3.00 per share (the “Follow-on Offering”). The public offering price was $2.50 per share of common stock and accompanying warrant, resulting in net proceeds to the Company of approximately $32.0 million after underwriting discounts and commissions and offering expenses payable by the Company.
The significant increases in common stock outstanding are expected to impact the year-over-year comparability of the Company’s net loss per share calculations.
F-9
Table of Contents
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Basis of Presentation
The accompanying financial information has been prepared in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (“U.S. GAAP”).
On June 2, 2016, the Company incorporated a wholly-owned subsidiary, ContraFect International Limited, in Scotland to establish legal status for interactions with the European Economic Area. This subsidiary is dormant or is otherwise non-operative.
Significant Risks and Uncertainties
The Company’s operations are subject to a number of factors that can affect its operating results and financial condition. Such factors include, but are not limited to: the results of clinical testing and trial activities of the Company’s products, the Company’s ability to obtain regulatory approval to market its products, competition from products manufactured and sold or being developed by other companies, the price of, and demand for, the Company’s products, the Company’s ability to negotiate favorable licensing or other manufacturing and marketing agreements for its products and the Company’s ability to raise capital. See “Risk Factors” contained elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K for additional risks and uncertainties.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with U.S. GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of expenses during the reporting period. The Company bases estimates and assumptions on historical experience when available and on various factors that it believes to be reasonable under the circumstances. On an ongoing basis, the Company evaluates its estimates and assumptions, including those related to accruals, fair value measurements, stock-based compensation, warrant valuation and income taxes. The Company’s actual results may differ from these estimates under different assumptions or conditions. There have been no significant changes from the Company’s original estimates in any periods presented.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
The Company considers all highly liquid investments with maturities at the date of purchase of three months or less to be cash equivalents. Cash and cash equivalents include bank demand deposits, marketable securities with maturities of three months or less at purchase, and money market funds that invest primarily in certificates of deposit, commercial paper and U.S. government and U.S. government agency obligations. Cash equivalents are reported at fair value.
Marketable Securities
Marketable securities at December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015 consisted of investments in short-term corporate debt securities. Management determines the appropriate classification of the securities at the time they are acquired and evaluates the appropriateness of such classifications at each balance sheet date. The Company classifies its marketable securities as available-for-sale pursuant to ASC 320, Investments—Debt and Equity Securities. Marketable securities are recorded at fair value, with unrealized gains and losses included as a component of accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) in stockholders’ equity (deficit) and a component of total comprehensive loss in the statements of comprehensive loss, until realized. The fair value of these securities is based on quoted prices for identical or similar assets. Realized gains and losses are included in investment income on a specific-identification basis. There were no realized gains or losses on marketable securities for the year ended December 31, 2016.
F-10
Table of Contents
The Company reviews marketable securities for other-than-temporary impairment whenever the fair value of a marketable security is less than the amortized cost and evidence indicates that a marketable security’s carrying amount is not recoverable within a reasonable period of time. Other-than-temporary impairments of investments are recognized in the statements of operations if the Company has experienced a credit loss, has the intent to sell the marketable security, or if it is more likely than not that the Company will be required to sell the marketable security before recovery of the amortized cost basis. Evidence considered in this assessment includes reasons for the impairment, compliance with the Company’s investment policy, the severity and the duration of the impairment and changes in value subsequent to the end of the period.
Marketable securities at December 31, 2016 consist of the following:
| Marketable Securities |
Amortized Cost | Unrealized Gains |
Unrealized Losses |
Fair Value | ||||||||||||
| Current: |
||||||||||||||||
| Corporate debt |
$ | 31,405,836 | $ | 24 | $ | (51,690 | ) | $ | 31,354,170 | |||||||
Marketable securities at December 31, 2015 consisted of the following:
| Marketable Securities |
Amortized Cost | Unrealized Gains |
Unrealized Losses |
Fair Value | ||||||||||||
| Current: |
||||||||||||||||
| Corporate debt |
$ | 22,979,245 | $ | 199 | $ | (30,572 | ) | $ | 22,948,872 | |||||||
At December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015, the Company held only current investments. Investments classified as current have maturities of less than one year. Investments that would be classified as non-current are those that have maturities of greater than one year and management does not intend to liquidate within the next twelve months.
At December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015, the Company held 29 and 28 debt securities, respectively, that individually and in total were in an immaterial unrealized loss position for less than one year. The aggregate fair value of debt securities in an unrealized loss position at December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015 was $29,343,892 and $21,137,424, respectively. The Company evaluated its securities for other-than-temporary impairment and considered the decline in market value for the securities to be primarily attributable to current economic and market conditions. It is not more likely than not that the Company will be required to sell the securities, and the Company does not intend to do so prior to the recovery of the amortized cost basis. Based on this analysis, these marketable securities were not considered to be other-than-temporarily impaired as of December 31, 2016 and 2015.
Concentrations of Credit Risk
Financial instruments which potentially subject the Company to credit risk consist primarily of cash, cash equivalents and marketable securities. The Company holds these investments in highly rated financial institutions, and, by policy, limits the amounts of credit exposure to any one financial institution. These amounts at times may exceed federally insured limits. The Company has not experienced any credit losses in such accounts and does not believe it is exposed to any significant credit risk on these funds. The Company has no off-balance sheet concentrations of credit risk, such as foreign currency exchange contracts, option contracts or other hedging arrangements.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
The Company’s financial instruments consist of cash and cash equivalents, marketable securities, accounts payable, accrued liabilities, notes payable, convertible notes, warrant liabilities and embedded derivatives liabilities. Fair value estimates of these instruments are made at a specific point in time, based on relevant market
F-11
Table of Contents
information. These estimates may be subjective in nature and involve uncertainties and matters of significant judgment and therefore cannot be determined with precision. The fair value of the Company’s convertible notes, warrant liabilities and embedded derivatives liabilities are based upon unobservable inputs, as described further below.
The Company is required to disclose information on all assets and liabilities reported at fair value that enables an assessment of the inputs used in determining the reported fair values. FASB ASC Topic 820, Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures (ASC 820), establishes a hierarchy of inputs used in measuring fair value that maximizes the use of observable inputs and minimizes the use of unobservable inputs by requiring that the observable inputs be used when available. Observable inputs are inputs that market participants would use in pricing the asset or liability based on market data obtained from sources independent of the Company. Unobservable inputs are inputs that reflect the Company’s assumptions about the inputs that market participants would use in pricing the asset or liability, and are developed based on the best information available in the circumstances. The fair value hierarchy applies only to the valuation inputs used in determining the reported fair value of the investments and is not a measure of the investment credit quality. The three levels of the fair value hierarchy are described below:
Level 1—Valuations based on unadjusted quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities that the Company has the ability to access at the measurement date.
Level 2—Valuations based on quoted prices for similar assets or liabilities in markets that are not active or for which all significant inputs are observable, either directly or indirectly.
Level 3—Valuations that require inputs that reflect the Company’s own assumptions that are both significant to the fair value measurement and unobservable.
To the extent that valuation is based on models or inputs that are less observable or unobservable in the market, the determination of fair value requires more judgment. Accordingly, the degree of judgment exercised by the Company in determining fair value is greatest for instruments categorized in Level 3. A financial instrument’s level within the fair value hierarchy is based on the lowest level of any input that is significant to the fair value measurement.
The Company had no liabilities classified as Level 1 or Level 2. The carrying amounts reported in the accompanying financial statements for accounts payable and accrued expenses approximate their respective fair values due to their short-term maturities. The fair value of the warrant and embedded derivative liabilities are discussed in Note 3, “Fair Value Measurements.”
Property, Office Equipment, and Leasehold Improvements
Property and equipment are recorded at cost less accumulated depreciation. Depreciation of property and equipment is provided by the straight-line method over their estimated useful lives, ranging from three to five years.
Leasehold improvements are amortized on a straight line basis over the useful life of the improvement or the initial lease term, whichever is shorter. Costs for normal repair and maintenance are charged to expense as incurred.
Deferred Rent
The Company has an operating lease for office and laboratory space. Rent expense is recorded on a straight-line basis over the initial lease term. The difference between the actual cash paid and the straight-line rent expense is recorded as deferred rent.
F-12
Table of Contents
Research and Development Costs
Research and development costs are charged to expense as incurred and are typically made up of salaries and benefits, clinical trial activities, drug development and manufacturing costs, and third-party service fees, including for clinical research organizations and investigative sites. Costs for certain development activities, such as clinical trials, are recognized based on an evaluation of the progress to completion of specific tasks using data such as patient enrollment, clinical site activations, or information provided by vendors on their actual costs incurred. Payments for these activities are based on the terms of the individual arrangements, which may differ from the pattern of costs incurred, and are reflected in the financial statements as prepaid or accrued expenses.
Share-based Compensation
The Company accounts for stock-based compensation in accordance with ASC 718, Compensation—Stock Compensation, which requires the measurement and recognition of compensation expense for all stock-based payment awards made to employees and non-employee directors, including employee stock options. Compensation expense based on the grant date fair value is generally amortized over the requisite service period of the award on a straight-line basis.
The fair value of options is calculated using the Black-Scholes option pricing model to determine the fair value of stock options on the date of grant based on key assumptions such as stock price, expected volatility and expected term. The Company’s estimates of these assumptions are primarily based on third-party valuations, historical data, peer company data and judgment regarding future trends and factors.
Income Taxes
The Company uses the asset and liability method to calculate deferred tax assets and liabilities. Deferred taxes are recognized based on the differences between the financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax bases using enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which those differences are expected to be recovered or settled. The Company records a valuation allowance against a deferred tax asset when it is more-likely-than-not that the deferred tax asset will not be realized.
The Company is subject to federal, state and local taxes and follows a recognition threshold and measurement attribute for the financial statement recognition and measurement of a tax position taken or expected to be taken in a tax return. The Company recognizes tax benefits or expenses of uncertain tax positions in the year such determination is made when the position is “more likely than not” to be sustained assuming examination by tax authorities. Management has reviewed the Company’s tax positions for all open tax years (tax years ended December 31, 2008 through December 31, 2015) and concluded that no provision for unrecognized tax benefits or expense is required in these financial statements. There are no income tax audits in progress as of December 31, 2015.
Impairment of Long-lived Assets
In accordance with ASC 360, Property, Plant, and Equipment, the Company’s policy is to review long-lived assets for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable. An impairment loss would be recognized when estimated undiscounted future cash flows expected to result from the use of the asset and its eventual disposition is less than its carrying amount. Through December 31, 2016, no impairment of long-lived assets has occurred.
Segment and Geographic Information
Operating segments are identified as components of an enterprise about which separate discrete financial information is available for evaluation by the chief operating decision maker, or decision making group, in making decisions on how to allocate resources and assess performance. The Company’s chief operating decision
F-13
Table of Contents
maker is the chief executive officer. The Company and the chief decision maker view the Company’s operations and manage its business as one operating segment. The Company operates in only one geographic segment.
Net Loss per Share Applicable to Common Stockholders
Basic net loss per share applicable to common stockholders is calculated by dividing net loss applicable to common stockholders by the weighted average shares outstanding during the period, without consideration for common stock equivalents. Net loss applicable to common stockholders is calculated by adjusting the net loss of the Company for cumulative preferred stock dividends. Diluted net loss per share applicable to common stockholders is calculated by adjusting weighted average shares outstanding for the dilutive effect of common stock equivalents outstanding for the period, determined using the treasury-stock method. For purposes of the dilutive net loss per share applicable to common stockholders calculation, stock options and warrant are considered to be common stock equivalents but are excluded from the calculation of diluted net loss per share applicable to common stockholders, as their effect would be anti-dilutive; therefore, basic and diluted net loss per share applicable to common stockholders were the same for all periods presented.
Comprehensive Income (Loss)
Comprehensive income (loss) is defined as the change in equity of a business enterprise during a period from transactions, and other events and circumstances from non-owner sources, and currently consists of net loss and changes in unrealized gains and losses on available-for-sale securities.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
In August 2014, the FASB issued a new Accounting Standards Update, Presentation of Financial Statements—Going Concern (Subtopic 205-40): Disclosure of Uncertainties about an Entity’s Ability to Continue as a Going Concern (ASU 2014-15). ASU 2014-15 provides guidance on management’s responsibility to evaluate whether there is substantial doubt about an entity’s ability to continue as a going concern within one year of the date the financial statements are issued, and, if such conditions exist, to provide related footnote disclosures. The guidance is effective for annual periods ending after December 15, 2016 and interim periods within annual periods beginning after December 15, 2016. Early adoption is permitted. The Company has adopted this guidance and there is no material impact on the financial statements and related disclosures.
In January 2016, the FASB issued a new Accounting Standards Update, Recognition and Measurement of Financial Assets and Financial Liabilities (ASU 2016-01). ASU 2016-01 amends the guidance in U.S. GAAP on the classification and measurement of financial instruments. Although the ASU retains many current requirements, it significantly revises an entity’s accounting related to (1) the classification and measurement of investments in equity securities and (2) the presentation of certain fair value changes for financial liabilities measured at fair value. The ASU also amends certain disclosure requirements associated with the fair value of financial instruments. The new standard is effective for fiscal years and interim periods within those fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, with early adoption permitted for certain changes. The Company is currently evaluating the potential effects the new standard will have of the Company’s financial statements and related disclosures.
In February 2016, the FASB issued a new Accounting Standards Update, Leases (ASU 2016-02), ASU 2016-02 is aimed at making leasing activities more transparent and comparable and requires most leases be recognized by lessees on the balance sheets as a right-of-use asset and corresponding lease liability, regardless of whether they are classified as finance or operating leases. The new standard is effective for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2018, including interim periods within that reporting period, with early adoption permitted. The Company is currently evaluating the impact of the new pronouncement on the Company’s financial statements and related disclosures.
F-14
Table of Contents
In March 2016, the FASB issued a new Accounting Standards Update, Improvements to Employee Share-Based Payment Accounting (ASU 2016-09). ASU 2016-09 requires all income tax effects of awards to be recognized in the income statement when the awards vest or are settled, thus eliminating APIC pools. Accounting for an employee’s use of shares to satisfy the employer’s statutory income tax withholding obligation and for forfeitures will change. Companies will have to elect whether to account for forfeitures by recognizing forfeitures of awards as they occur or estimating the number of awards expected to be forfeited and adjusting the estimate when it is likely to change, as is currently required. The new standard is effective for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2016, and interim periods within those fiscal years, with early adoption permitted. The Company is currently evaluating the impact of the new pronouncement on the Company’s financial statements and related disclosures.
In June 2016, the FASB issued a new Accounting Standards Update, Financial Instruments-Credit Losses (ASU 2016-13). ASU 2016-13 amends the guidance for measuring and recording credit losses on financial assets measured at amortized cost by replacing the “incurred loss” model with an “expected loss” model. Accordingly, these financial assets will be presented at the net amount expected to be collected. This new standard also requires that credit losses related to available-for-sale debt securities be recorded through an allowance for such losses rather than reducing the carrying amount under the current, other-than-temporary-impairment model. The new standard is effective for interim and annual periods beginning after December 15, 2019. The Company is currently evaluating the impact that this new standard will have on its financial statements and related disclosures.
3. Fair Value Measurements
The following fair value hierarchy table presents information about the Company’s financial assets and liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis as of December 31, 2016 and December 31, 2015:
| Fair Value Measurement As of December 31, 2016 | ||||||||||||
| Quoted Prices in Active Markets for Identical Assets (Level 1) |
Significant Other Observable Inputs (Level 2) |
Significant Unobservable Inputs (Level 3) |
||||||||||
| Cash equivalents |
$ | 3,411,058 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||
| Marketable securities |
31,354,170 | — | — | |||||||||
| Warrant liabilities |
— | — | 12,698,980 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
$ | 34,765,228 | $ | — | $ | 12,698,980 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Fair Value Measurement As of December 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||
| Quoted Prices in Active Markets for Identical Assets (Level 1) |
Significant Other Observable Inputs (Level 2) |
Significant Unobservable Inputs (Level 3) |
||||||||||
| Cash equivalents |
$ | 9,607,134 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||
| Marketable securities |
22,948,872 | — | — | |||||||||
| Warrant liabilities |
— | — | 444,324 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
$ | 32,556,006 | $ | — | $ | 444,324 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
The Company issued a warrant to the representative of the underwriter of its initial public offering (the “Representative’s Warrant”). The Company determined that this warrant should be classified as a liability and considers it as a Level 3 financial instrument (see also Note 8, “Capital Structure”). The Representative’s Warrant will be re-measured at each subsequent reporting period and changes in fair value will be recognized in
F-15
Table of Contents
the statement of operations. The following assumptions were used in a Black-Scholes option-pricing model to determine the fair value of the warrant liability:
| As of December 31, 2016 |
As of December 31, 2015 |
|||||||
| Expected volatility |
73.9 | % | 78.1 | % | ||||
| Remaining contractual term (in years) |
2.67 | 3.67 | ||||||
| Risk-free interest rate |
1.47 | % | 1.54 | % | ||||
| Expected dividend yield |
— | % | — | % | ||||
The Company issued warrants to the purchasers of its Follow-on Offering (the “CMPO Warrants”), The Company determined that these warrants should be classified as a liability and considered as a Level 3 financial instrument (see also Note 8, “Capital Structure”). The CMPO Warrants will be re-measured at each subsequent reporting period and changes in fair value will be recognized in the statement of operations. The following assumptions were used in a Black-Scholes option-pricing model to determine the fair value of the warrant liability:
| As of December 31, 2016 |
At Issuance on July 27, 2016 |
|||||||
| Expected volatility |
79.9 | % | 76.8 | % | ||||
| Remaining contractual term (in years) |
4.58 | 5.00 | ||||||
| Risk-free interest rate |
1.93 | % | 1.10 | % | ||||
| Expected dividend yield |
— | % | — | % | ||||
The following tables present a reconciliation of the Company’s financial liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis using significant unobservable inputs (Level 3) for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014:
Warrant liabilities (1)
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
| Balance at beginning of period |
$ | 444,324 | $ | 313,004 | $ | 3,088,017 | ||||||
| Issuances of convertible notes |
— | — | 865,635 | |||||||||
| Cancellation of placement agent warrants (2) |
— | — | (941,541 | ) | ||||||||
| Issuance of Representative’s Warrant |
— | — | 403,696 | |||||||||
| Issuance of CMPO Warrants |
18,601,228 | — | — | |||||||||
| Change in fair value (3) |
(6,346,572 | ) | 131,320 | 2,563,080 | ||||||||
| Conversion of convertible notes to common stock |
— | — | (5,665,883 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Balance at end of period |
$ | 12,698,980 | $ | 444,324 | $ | 313,004 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Embedded derivatives liabilities (1)
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
| Balance at beginning of period |
$ | — | $ | — | $ | 2,680,780 | ||||||
| Issuances of convertible notes |
— | — | 537,607 | |||||||||
| (Decrease) increase in fair value (3) |
— | — | (1,337,878 | ) | ||||||||
| Conversion of convertible notes to common stock |
— | — | (1,880,509 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Balance at end of period |
$ | — | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
F-16
Table of Contents
| (1) | Prior to the closing of the Company’s IPO on August 1, 2014, the Company considered its convertible note related warrant liabilities and embedded derivatives liabilities as Level 3 financial instruments. The Company determined the fair value of these liabilities immediately prior to the Company’s IPO and then reclassified the balances to additional paid-in capital on the closing of the IPO. |
| (2) | The Company reclassified the balance of the placement agent warrants to additional paid-in capital as a reduction of the offering costs upon their cancellation. |
| (3) | The change in the fair values of the warrant and embedded derivatives liabilities are recorded in other expenses in the statement of operations. |
The key inputs into the Black-Scholes option pricing model are the per share value and the expected volatility of the Company’s common stock. Significant changes in these inputs will directly increase or decrease the estimated fair value of the Company’s warrant liability.
4. Property, Equipment, and Leasehold Improvements
Property, equipment, and leasehold improvements, at cost, consist of:
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Computer equipment |
$ | 19,691 | $ | 19,691 | ||||
| Furniture |
434,697 | 434,697 | ||||||
| Lab equipment |
1,710,881 | 1,631,016 | ||||||
| Leasehold improvements |
1,855,004 | 1,821,677 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 4,020,273 | 3,907,081 | |||||||
| Less: accumulated depreciation and amortization |
(2,739,121 | ) | (2,288,113 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| $ | 1,281,152 | $ | 1,618,968 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Depreciation expense was $451,008, $537,344 and $551,323 for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively.
5. Accrued Expenses
Accrued expenses consist of the following:
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Accrued compensation costs |
$ | 1,597,414 | $ | 1,133,742 | ||||
| Accrued research and development service fees |
504,193 | 590,307 | ||||||
| Accrued professional fees |
299,912 | 317,796 | ||||||
| Accrued facilities operation expenses |
236,296 | 127,480 | ||||||
| Accrued licensing fees |
180,000 | — | ||||||
| Other accrued expenses |
50,537 | 82,442 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| $ | 2,868,352 | $ | 2,251,767 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
6. Senior Convertible Notes
The Company issued approximately $15.0 million aggregate principal amount of its 8.00% Convertible Notes due May 31, 2015 (the “Convertible Notes”) from June 2013 through June 2014. On August 1, 2014, in conjunction with the closing of the Company’s IPO, the principal amount of the Convertible Notes, and all accrued and unpaid interest thereon, automatically converted into 5,109,988 shares of common stock. Upon the closing of the offering, the Company accelerated the amortization of the remaining debt discount balance to interest expense.
F-17
Table of Contents
The Company recorded the costs directly related to the issuance of its Convertible Notes as debt issuance costs and amortized these costs to interest expense using the effective interest method of amortization until the completion of the Company’s IPO. Upon the closing of the offering, the Company accelerated the amortization of the remaining balance to interest expense.
Each purchaser of the Convertible Notes also received a warrant which included an exercise price “cap” that was analogous to “down round protection” which precluded the Company from classifying the warrants in equity (the “Note Warrants”). The Convertible Notes also included embedded derivatives (i.e. penalty provisions) that required bifurcation. As such, the Company reflected both the values of the Note Warrants and the embedded derivatives as liabilities which were re-measured at each reporting period and immediately prior to the closing of the Company’s IPO, and changes in fair value were recognized in the statement of operations. Upon the closing of the IPO, the Company reclassified the balances of the Note Warrant and embedded derivative liabilities to additional paid-in capital as the terms of the Note Warrants, including any penalty warrants, became fixed and the interest penalties were paid in the Company’s common stock, and therefore both the Note Warrants and penalties were no longer considered a liability (see Note 3, “Fair Value Measurements”).
Upon the closing of the IPO and based on the terms of the Note Warrants, the Company determined the total number of shares of the Company’s common stock underlying the Note Warrants to be 3,321,416 at an exercise price of $3.00 per share. There were 3,315,878 shares of common stock underlying the outstanding Note Warrants as of December 31, 2016 and 2015. The Note Warrants expire five years from the date of issuance.
7. Net Loss Per Share of Common Stock
Diluted loss per share is the same as basic loss per share for all periods presented because the effects of potentially dilutive items were anti-dilutive given the Company’s net loss. Basic loss per share is computed by dividing net loss available to common stockholders by the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding.
The following table sets forth the computation of basic and diluted loss per share for common stockholders:
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
| Net loss applicable to common stockholders |
$ | (28,538,399 | ) | $ | (25,120,964 | ) | $ | (34,617,536 | ) | |||
| Weighted average shares of common stock outstanding |
33,539,465 | 23,328,922 | 8,973,599 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net loss per share of common stock—basic and diluted |
$ | (0.85 | ) | $ | (1.08 | ) | $ | (3.86 | ) | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
The following potentially dilutive securities outstanding at December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014 have been excluded from the computation of diluted weighted average shares outstanding, as they would have been antidilutive given the Company’s net loss:
| December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
| Preferred stock |
— | — | — | |||||||||
| Options to purchase common stock |
4,691,746 | 4,313,755 | 3,089,327 | |||||||||
| Warrants to purchase common stock |
27,214,775 | 13,503,107 | 14,577,361 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| 31,906,521 | 17,816,862 | 17,666,688 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
8. Commitments and Contingencies
Operating Leases
In December 2010, the Company entered into a non-cancellable operating lease for office space and laboratory facilities in Yonkers, New York expiring in December 2025. In December 2011, the Company entered
F-18
Table of Contents
into an amendment which extended the terms of the lease through December 2027. The lease provides for the option to renew for two additional five-year terms. The premises were occupied in June 2011. Monthly rent payments began the date the office and laboratory facilities were ready for occupancy. A security deposit in the amount of $54,865 was paid by the Company.
In January 2012, the Company entered into a non-cancellable operating lease for additional office space and laboratory facilities in the same building in Yonkers, New York expiring in December 2027. The lease provides for an option to renew for two additional five-year terms. A security deposit in the amount of $78,238 was paid by the Company. Future minimum lease payments are as follows:
| Amount | ||||
| Year ending December 31: |
||||
| 2017 |
$ | 868,933 | ||
| 2018 |
886,311 | |||
| 2019 |
904,038 | |||
| 2020 |
922,118 | |||
| 2021 |
940,561 | |||
| Thereafter |
6,051,835 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| $ | 10,573,796 | |||
|
|
|
|||
Rent expense is recognized on the straight-line method over the terms of each lease. Rent expense for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, was approximately $880,000, $873,000 and $871,000, respectively.
In May 2016, the Company entered into a non-cancellable operating lease for office space in Cambridge, MA, expiring in May 2017. The lease provides for an option to renew for additional periods. The Company does not anticipate renewing the lease. A security deposit in the amount of $20,916 was paid by the Company. Rent expense for the year ended December 31, 2016 was approximately $76,000.
9. Capital Structure
Common Stock
As of December 31, 2016, the Company was authorized to issue 100,000,000 shares of common stock at $0.0001 par value per share.
Follow-on Offering
On July 27, 2016, the Company sold 14,000,000 shares of its common stock and warrants to purchase an additional 14,000,000 shares of its common stock in an underwritten Follow-on Offering for gross proceeds of $35.0 million. The Company received net proceeds of approximately $32.0 million after underwriting discounts, commissions and offering expenses payable by the Company.
The warrants have an exercise price of $3.00 per shares and expire five years from the date of issuance (the “CMPO Warrants”). The CMPO Warrants contain a fundamental transaction provision that obligates the Company to cash settle the CMPO Warrants under a limited set of conditions not entirely within the Company’s control. Due to this conditional obligation, the Company determined that the CMPO Warrants should be classified as a liability in the Company’s balance sheet. At issuance, the Company determined the fair value of the CMPO Warrants to be $18.6 million and reclassified this balance from equity to warrant liability. The fair value of the CMPO Warrants will be re-measured at each reporting period and changes in fair value will be recognized in the statement of operations (see Note 4, “Fair Value Measurements”). Additionally, the Company allocated approximately $1.6 million of issuance costs to the CMPO Warrants based on the proportion of the proceeds allocated to the fair value of CMPO Warrants. The allocated issuance costs were expensed as other expense in the Company’s statement of operations.
F-19
Table of Contents
Private Placement
On June 12, 2015, the Company closed a private placement of its securities with a group of institutional investors (the “PIPE”). Each investor received one share of common stock and a warrant to purchase one-half share of common stock at a price of $4.23 per common share purchased. The closing of the PIPE resulted in the issuance of an aggregate of 4,728,128 common shares and warrants to purchase an additional 2,364,066 shares of common stock at an exercise price of $8.00 per full share, which expire three years form the date of issuance (the “PIPE Warrants”). The Company received net proceeds from the PIPE of $18.3 million, after deducting expenses payable by the Company.
The placement agents in the PIPE received warrants to purchase 4% of the total number of shares of common stock sold in the PIPE (the “Placement Agent Warrants”), for a total of 189,126 shares of common stock underlying the Placement Agent Warrants. The Placement Warrants became exercisable upon issuance at an exercise price of $4.65 per share and expire on June 11, 2020.
The common stock and accompanying PIPE Warrants and Placement Agent Warrants have been classified to stockholders’ equity in the Company’s balance sheet.
Initial Public Offering
In July 2014, the shareholders approved an amended certificate of incorporation that became effectively immediately upon the closing of the Company’s IPO. The approved certificate increased the number of authorized shares of common stock to 100,000,000 shares. On August 1, 2014, the Company closed its IPO. Each Unit consisted of one share of common stock, one Class A Warrant to purchase one share of common stock at an exercise price of $4.80 per share and one Class B Warrant to purchase one-half share of common stock at an exercise price of $4.00 per full share. The closing of the IPO resulted in the sale of an aggregate of 6,880,333 Units at a public offering price of $6.00 per Unit, less underwriting discounts and commissions and the underwriter’s expenses, including 880,333 Units issued upon the exercise by the underwriters of their option to purchase additional Units at the public offering price to cover over-allotments of the Company. The Company received net proceeds from the IPO of $35.0 million, after deducting underwriting discounts, commissions, and expenses payable by the Company. Following the IPO, the units separated and the shares of common stock, Class A Warrants and Class B Warrants began to trade separately. The common stock and accompanying Class A and Class B warrants were classified to stockholders’ equity in the Company’s balance sheet.
On November 2, 2015, the Company’s Class B Warrants to purchase common stock expired in accordance with their terms. As of November 2, 2015, holders of the Class B Warrants had exercised 4,812,328 Class B Warrants, resulting in the issuance of 2,406,164 shares of the Company’s common stock and the receipt by the Company of approximately $9.6 million in gross proceeds. The 2,068,005 Class B Warrants that were not exercised prior to expiration have terminated and are no longer exercisable.
Representative’s Warrant
The Maxim Group, LLC, the representative of the underwriters in the IPO, received the Representative’s Warrant to purchase 3% of the total number of shares of common stock sold in the IPO, including those shares sold upon the exercise of the over-allotment, for a total of 206,410 shares of common stock underlying the Representative’s Warrant. The Representative’s Warrant became exercisable at an exercise price of $7.50 per share beginning 180 days after the effective date of the Company’s registration statement (January 24, 2015) and expires on August 27, 2019. The Company classified the Representative’s Warrant as a liability since it did not meet the requirements to be included in equity. The fair value of the Representative’s Warrant will be re-measured at each reporting period and changes in fair value will be recognized in the statement of operations (see Note 3, “Fair Value Measurements”).
F-20
Table of Contents
Sales Agreement
In January 2016, the Company entered into a Sales Agreement with Cowen and Company, LLC (“Cowen”) to sell shares of the Company’s common stock, with aggregate gross sales proceeds of up to $30 million, through an “at the market” equity offering program under which Cowen was to act as sales agent. On July 21, 2016, the Company terminated the Sales Agreement. The Company did not sell any shares under the program.
Voting
The holders of shares of common stock are entitled to one vote for each share of common stock held at all meetings of stockholders and written actions in lieu of meetings.
Dividends
The holders of shares of common stock are entitled to receive dividends, if and when declared by the board of directors. As of December 31, 2016, no dividends have been declared or paid on the Company’s common stock since inception.
Reserved for Future Issuance
The Company has reserved for future issuance the following number of shares of common stock as of December 31, 2016 and 2015:
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Options to purchase common stock |
4,691,746 | 4,313,755 | ||||||
| Warrants to purchase common stock |
27,214,775 | 13,503,107 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 31,906,521 | 17,816,862 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Convertible Preferred Stock
Dividends
On May 28, 2014, the board of directors declared a dividend to be paid in-kind to the holders of the Company’s preferred stock in accordance with the Company’s Fourth Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation, whereby each holder of shares of preferred stock will be entitled to a number of additional shares of the applicable series of preferred stock equal to the amount of the accrued and unpaid dividend on such holder’s shares (the “Dividend”). The Company determined that 605,645 shares of Series A preferred stock, 1,172,645 shares of Series B preferred stock, 1,379,388 shares of Series C preferred stock and 2,395 shares of Series C-1 preferred stock would be required to satisfy the Dividend.
The Company recorded the in-kind dividend payable and associated expense at fair value of the securities to be issued. The Company was able to assess the value of the preferred stock dividends in terms of its common stock to be issued upon conversion of the preferred stock on the closing of its IPO.
Conversion
On August 1, 2014, in conjunction with the closing of the Company’s IPO, all outstanding shares of the Company’s preferred stock, including the in-kind dividend payable, were automatically converted into 6,861,968 shares of its common stock.
F-21
Table of Contents
10. Stock Warrants
As of December 31, 2016 and 2015, the Company had warrants outstanding as shown in the table below.
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Note Warrants |
3,315,878 | 3,315,878 | ||||||
| Class A Warrants (1) |
6,880,333 | 6,880,333 | ||||||
| PIPE Warrants |
2,364,066 | 2,364,066 | ||||||
| CMPO Warrants |
14,000,000 | — | ||||||
| Representative’s Warrant |
206,410 | 206,410 | ||||||
| Placement Agent Warrants |
189,126 | 189,126 | ||||||
| Other warrants (2) |
258,962 | 547,294 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Warrants to purchase common stock |
27,214,775 | 13,503,107 | ||||||
| Weighted-average exercise price per share |
$ | 3.97 | $ | 5.02 | ||||
| (1) | On February 1, 2017, the Class A Warrants to purchase common stock expired in accordance with their terms. As none of the Class A Warrants were exercised prior to expiration, the Class A Warrants have been terminated and are no longer exercisable. |
| (2) | Other warrants are comprised of warrants issued prior to the Company’s IPO, generally in exchange for services rendered to the Company. |
During 2016 and 2015, the Company did not issue any warrants to purchase shares of common stock for services rendered to the Company.
During 2014, the Company issued warrants to purchase 10,714 shares of common stock at a strike price of $5.25 per share for services rendered to the Company. The Company calculated the fair value of these warrants to be $26,354 which was recognized as a component of general and administrative expenses in 2014.
The following table summarizes information regarding the Company’s warrants outstanding and the corresponding exercise price at December 31, 2016:
| Exercise Prices |
Shares Underlying Outstanding Warrants |
Expiration Date | ||||
| £ $3.00 |
17,321,591 | June 18, 2018 – September 1, 2021 | ||||
| $3.01 - $3.99 |
101,102 | September 8, 2019 – April 28, 2020 | ||||
| $4.00 - $4.99 |
7,069,459 | February 1, 2017 – June 11, 2020 | ||||
| $5.00 - $9.99 |
2,642,615 | April 30, 2018 – June 27, 2021 | ||||
| ³ $10.00 |
80,008 | April 17, 2017 – January 5, 2022 | ||||
|
|
|
|||||
| 27,214,775 | ||||||
|
|
|
|||||
11. Stock Option and Incentive Plans
Amended and Restated 2008 Equity Incentive Plan
In July 2008, the Company adopted the 2008 Equity Incentive Plan (the “Plan”). On February 26, 2013, the board of directors approved an amended and restated plan (the “Amended Plan”) to increase the number of shares of common stock available under the Amended Plan to 1,571,428 and, for new awards, to reduce the period that vested awards would remain exercisable upon termination of service from ten years to two years. The board of directors also approved an option exchange offer (the “Exchange Offer”) for eligible option holders with outstanding options with an exercise price in excess of $3.50 per share. The offering period for the Exchange
F-22
Table of Contents
Offer commenced on March 11, 2013 and expired on April 9, 2013. Participation in the Exchange Offer was voluntary. Options to purchase 647,521 shares of the Company’s common stock, held by a total of 26 participants, including 20 employees, were exchanged under the tender offer. The exchanged option grants were granted at an exercise price of $3.50 per share. The Company recorded expense associated with the modification with an immediate charge for the vested portion of option grants exchanged and additional charges as the remaining unvested portions become vested.
Upon the original adoption of the Plan, the number of shares of common stock reserved pursuant to the Plan was 214,285. On December 12, 2011, the Plan was amended to increase the number of shares of common stock available under the Plan to 900,000. The board of directors also increased the number of shares of common stock available under the Company’s Amended Plan on February 24, 2014 and April 29, 2014 to 1,857,142 and 2,357,142, respectively.
As of the closing of the Company’s IPO, there will be no further grants made under the Amended Plan.
2014 Omnibus Incentive Plan
In April 2014, the Company’s board of directors adopted the 2014 Omnibus Incentive Plan (the “2014 Plan”). The 2014 Plan was approved by the Company’s shareholders on July 3, 2014. The 2014 Plan allows for the granting of incentive and non-qualified stock options, restricted stock and stock unit awards, stock appreciation rights and other performance-based awards to the Company’s employees, members of the board of directors and consultants of the Company. On July 28, 2014, the effective date of the 2014 Plan, the number of shares of common stock reserved pursuant to the 2014 Plan was 571,429. The 2014 Plan provides for an annual increase, to be added on the first day of each fiscal year, beginning with the fiscal year ending December 31, 2015 and continuing until the expiration of the 2014 Plan, equal to the lesser of (i) 4% of the outstanding shares of common stock on December 31 immediately preceding such date or (ii) a lesser amount determined by the Company’s board of directors. Consistent with the provision for an annual increase, an additional 1,907,307 shares of common stock have been reserved under the 2014 Plan. The Company recognizes compensation expense for share-based compensation based on the fair value of the underlying instrument. The fair value of each stock option grant is estimated on the date of grant using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model. A summary of stock option activity for the year ended December 31, 2016, is summarized as follows:
| Number of Options |
Weighted Average Exercise Price |
Weighted Average Remaining Contractual Life (in years) |
Aggregate Intrinsic Value |
|||||||||||||
| Options outstanding at December 31, 2015 |
4,313,755 | $ | 4.87 | |||||||||||||
| Granted |
955,600 | 3.25 | ||||||||||||||
| Exercised |
(21,356 | ) | 3.07 | |||||||||||||
| Expired |
(115,686 | ) | 4.49 | |||||||||||||
| Forfeited |
(440,567 | ) | 4.30 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Options outstanding at December 31, 2016 |
4,691,746 | $ | 4.62 | 5.51 | $ | — | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Vested and exercisable at December 31, 2016 |
3,720,763 | $ | 4.78 | 4.89 | $ | — | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
Of the option grants outstanding to purchase 4,691,746 shares of common stock, grants to purchase 667,870 shares of common stock were issued and are outstanding outside the Company’s incentive plans.
The fair value of each option grant is estimated on the date of the grant using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model. The weighted average grant date fair value of options granted during the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014 was $3.25, $4.64 and $3.95, respectively. Total compensation expense recognized amounted to $2,231,883, $1,929,112 and $1,940,179 for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. As of December 31, 2016, the total remaining unrecognized compensation cost related to
F-23
Table of Contents
unvested stock options was $2,067,370 which will be recognized over a weighted average period of approximately 2.23 years.
The following weighted average assumptions were used to compute the fair value of stock option grants:
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
| Risk free interest rate |
1.22 | % | 1.62 | % | 1.95 | % | ||||||
| Expected dividend yield |
— | — | — | |||||||||
| Expected term (in years) |
5.01 | 5.75 | 5.96 | |||||||||
| Expected volatility |
79.5 | % | 74.4 | % | 76.3 | % | ||||||
Expected volatility—The Company estimated the expected volatility based on an average of the volatility of similar companies with publicly-traded equity securities. The companies were selected based on their enterprise value, risk profiles, position within the industry, and with historical information sufficient to meet the expected term of the associated award.
Expected term—The Company based expected term on the midpoint of the vesting period and the contractual term of each respective option grant.
Risk-free interest rate—The Company estimated the risk-free interest rate in reference to yield on U.S. Treasury securities with a maturity date commensurate with the expected term of the associated award.
Expected dividend yield—The Company estimated the expected dividend yield based on consideration of its historical dividend experience and future dividend expectations. The Company has not historically declared or paid dividends to common stockholders. Moreover, it does not intend to pay dividends in the future, but instead expects to retain any earnings to invest in its continued growth.
12. Retention Bonus Plan
On February 24, 2014, the Company adopted the ContraFect Corporation Retention Bonus Plan (the “Retention Plan”). Under the Retention Plan, participants vested in and became eligible to receive awards equal to a fixed dollar amount (the “Award Amount”), upon the earliest to occur of any of the following events: (i) the IPO; (ii) a Change of Control (as defined in the Retention Plan); (iii) May 31, 2015; and (iv) a participant’s termination of employment due to death or Disability (as defined in the Retention Plan) (each such event, a “Payment Event”). In the event of an IPO or Change of Control, participants who were then employed by the Company were eligible to receive shares of common stock in an amount equal to 1.82 times each participant’s Award Amount.
As of June 30, 2014, Award Amounts totaling $532,700 had been granted under the Retention Plan. Upon the closing of the Company’s IPO, the Company recognized a total of $954,754 of expense associated with the vesting of the grants. On September 11, 2014, the Company issued 133,109 shares of its common stock, net of shares withheld for tax obligations, in payment of the retention grants.
There are no outstanding Award Amounts as of December 31, 2016 or December 31, 2015 and the Company does not anticipate any further grants under the Retention Plan.
13. 401k Savings Plan
In 2010, the Company established a defined-contribution savings plan under Section 401(k) of the Internal Revenue Code (the 401(k) Plan). The 401(k) Plan covers all employees who meet defined minimum age and service requirements, and allows participants to defer a portion of their annual compensation on a pre-tax basis
F-24
Table of Contents
The Company did not make any contributions to the 401(k) Plan through December 31, 2014. During 2015, the Company established an employer matching program for participants in the 401(k) Plan. The Company incurred approximately $124,000 and $88,000 of expense for matching contributions to the 401(k) Plan during the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively.
14. Income Taxes
The Company has available approximately $120,534,000 and $125,270,000 of unused operating loss carryforwards for federal and state tax purposes, respectively, that may be applied against future taxable income. The net operating loss carryforwards will expire through the year 2035 if not utilized prior to that date. No provision for a deferred tax asset has been made for the tax benefits of the net operating loss carryforwards as the entire amount is offset by a valuation allowance. The valuation allowance increased by approximately $12,846,000 and $9,937,000 during the years 2016 and 2015, respectively, and was approximately $52,943,000 and $40,089,000 at December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively.
The Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended (the Code) provides for a limitation of the annual use of net operating losses and other tax attributes (such as research and development tax credit carryforwards) following certain ownership changes (as defined by the Code) that could limit the Company’s ability to utilize these carryforwards. At this time, the Company has not completed a study to assess whether an ownership change under Section 382 of the Code has occurred, or whether there have been multiple ownership changes since the Company’s formation, due to the costs and complexities associated with such a study. The Company may have experienced various ownership changes, as defined by the Code, as a result of past financing transactions. Accordingly, the Company’s ability to utilize the aforementioned carryforwards may be limited. Additionally, U.S. tax laws limit the time during which these carryforwards may be applied against future taxes. Therefore, the Company may not be able to take full advantage of these carryforwards for federal or state income tax purposes.
The Company’s reserves related to taxes are based on a determination of whether and how much of a tax benefit taken by the Company in its tax filings or positions is more likely than not to be realized following resolution of any potential contingencies present related to the tax benefit. For the three years ended December 31, 2016, the Company had no unrecognized tax benefits or related interest and penalties accrued. The Company has not, as yet, conducted a study of research and development (R&D) credit carryforwards. This study may result in an adjustment to the Company’s R&D credit carryforwards; however, until a study is completed and any adjustment is known, no amounts are being presented as an uncertain tax position. A full valuation allowance has been provided against the Company’s R&D credits and, if an adjustment is required, this adjustment would be offset by an adjustment to the valuation allowance. Thus, there would be no impact to the balance sheet or statement of operations if an adjustment were required. The Company would recognize both accrued interest and penalties related to unrecognized benefits in income tax expense. The Company’s uncertain tax positions are related to years that remain subject to examination by relevant tax authorities. Since the Company is in a loss carryforward position, the Company is generally subject to examination by the U.S. federal, state and local income tax authorities for all tax years in which a loss carryforward is available.
F-25
Table of Contents
The principal components of the Company’s deferred tax assets/liabilities for 2016 and 2015 are as follows:
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Deferred tax assets/liabilities: |
||||||||
| Net operating loss carryovers |
$ | 47,860,522 | $ | 36,414,890 | ||||
| Share-based compensation |
2,168,126 | 1,922,680 | ||||||
| R&D tax credits |
1,783,716 | 1,469,756 | ||||||
| Accrued compensation and severance |
902,688 | 147,175 | ||||||
| Depreciation |
(386,758 | ) | (496,327 | ) | ||||
| Deferred rent |
392,715 | 404,885 | ||||||
| Intangible assets |
221,783 | 225,702 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 52,942,793 | 40,088,761 | |||||||
| Valuation allowance |
(52,942,793 | ) | (40,088,761 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net deferred tax assets (liabilities) |
$ | — | $ | — | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
A reconciliation of the statutory U.S. Federal rate to the company’s effective tax rate is as follows:
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
| Federal income tax benefit at statutory rate |
(34.00 | )% | (34.00 | )% | (34.00 | )% | ||||||
| State income tax, net of federal benefit |
(5.49 | ) | (5.49 | ) | (5.70 | ) | ||||||
| Permanent item—non-deductible interest |
— | — | 14.59 | |||||||||
| Other permanent items |
(1.54 | ) | 1.99 | 1.83 | ||||||||
| Change in valuation allowance |
42.12 | 39.70 | 24.89 | |||||||||
| R&D tax credits |
(1.03 | ) | (0.99 | ) | (1.13 | ) | ||||||
| Other |
(0.06 | ) | (1.21 | ) | (0.48 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Effective income tax (benefit) expense rate |
0 | % | 0 | % | 0 | % | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
15. Significant Agreements
Rockefeller University
License Agreements
The Company has entered into the following license agreements with The Rockefeller University:
| • | On July 12, 2011, the Company entered into a license agreement for the worldwide, exclusive right to a patent covering the composition of matter for the lysin PlySS2 for the treatment and prevention of diseases caused by gram-positive bacteria (the “CF-301 License”). The Company rebranded PlySS2 as CF-301. The license gives the Company the right to exclusively develop, make, have made, use, import, lease, sell and offer for sale products that would otherwise infringe a claim of this patent application or patent. |
| • | On June 1, 2011, the Company entered into a license agreement for the exclusive rights to The Rockefeller University’s interest in a joint patent application covering the method of delivering antibodies through the cell wall of gram-positive bacteria to the periplasmic space. This intellectual property was developed as a result of the sponsored research agreement between the Company and The Rockefeller University, and was jointly discovered and filed by the two parties. |
| • | On September 23, 2010, the Company entered into a license agreement for the worldwide, exclusive right to develop, make, have made, use, import, lease, sell, and offer for sale products that would |
F-26
Table of Contents
| otherwise infringe a claim of the suite of patents and patent applications covering the composition of matter for eight individual lysin molecules for the treatment and prevention of diseases caused by gram-positive bacteria. The lysins in this suite have activity against Group B Streptococci, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pneumonia, Bacillus anthracis, Enterococcus faecalis and Enterococcus faecium. In consideration for the licenses, we paid Rockefeller license initiation fees in cash and stock and may be required to pay an annual maintenance fee, milestone payments and royalties on net sales from products to Rockefeller. We are allowed to grant sublicenses to third parties without prior approval, subject to certain conditions and the payment of a certain percentage of all payments we receive from sublicensees. |
Each license agreement terminates upon the later of (i) the expiration or abandonment of the last licensed patent under the license agreement to expire or become abandoned, or (ii) 10 years after the first commercial sale of the first licensed product. The Rockefeller University may terminate any license agreement in the event of a breach of such agreement by the Company or if the Company challenges the validity or enforceability of the underlying patent rights. The Company may terminate any license agreement at any time on 60 days’ notice.
Collaborative Research Agreements
Beginning in October 2009, we entered into a research agreement with Rockefeller where we provided funding for the research. The initial agreement focused on producing and testing monoclonal antibodies against proteins of Staphylococcus aureus. On October 24, 2011, we entered into a second research agreement with Rockefeller where we provide funding for the research, to identify lysins, enzymes or small molecules that will kill gram-negative bacteria, and identify and characterize lysins from Clostridia difficile to be engineered into gut commensal bacteria. On October 25, 2016, we entered into a third research agreement with Rockefeller, where we provide funding for the identification of novel lysin therapeutic candidates which target Gram-negative pathogens. The research collaboration will focus on Gram-negative pathogens such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli, and Klebsiella, including antibiotic-resistant strains.
Our current agreement runs through October 24, 2019. Either party may terminate the agreement upon breach of the agreement, following 30 days written notice and failure to cure such breach. Following the expiration or termination of the agreement, each party will have a non-exclusive license to use for internal research purposes all research results, including joint intellectual property. If Rockefeller or joint intellectual property develops from these programs, we will have the right-of-first refusal to negotiate to acquire a royalty-bearing license to utilize such intellectual property for commercial purposes.
Trellis Biosciences, LLC
On January 29, 2014, the Company entered into a license agreement with Trellis Biosciences, LLC (“Trellis”) that gives it exclusive rights to all Trellis mAbs in the field of influenza discovered from the Trellis CellSpot platform. Particularly, the license provides the Company with three fully human mAbs that bind, neutralize and protect animals from all strains of H1, H3 and B influenza, and that will also cross bind, neutralize and protect animals from all other seasonal or pandemic influenza strains that may arise (including H5N1 and H7N9).
In consideration for the license, the Company paid Trellis $200,000 and issued 151,515 shares of Series C-1 preferred stock, contractually valued at $500,000. On October 7, 2014, the Company issued 132,380 shares of its common stock in satisfaction of the $500,000 remaining due in stock as consideration for the license. The Company will also be required to make payments to Trellis upon the achievement of specified development and regulatory milestones and upon the achievement of future sales and for royalty on future net sales from products. The Company is allowed to grant sublicenses to third parties.
The license agreement terminates upon the earlier of (i) the Company’s decision to terminate the agreement at will or for safety reasons, (ii) material breach by either party that is not cured within ninety (90) days, or (iii) either party’s insolvency.
F-27
Table of Contents
MorphoSys AG
In June 2014, the Company and MorphoSys AG agreed to terminate their license agreement effective as of August 15, 2014 and resolve all outstanding claims thereunder. On August 11, 2014, the Company made the €1,000,000 payment to MorphoSys AG pursuant to the agreed upon settlement.
Legal Contingencies
From time to time, the Company may be involved in disputes and legal proceedings in the ordinary course of its business. These proceedings may include allegations of infringement of intellectual property, employment or other matters. The Company records a liability in its financial statements for these matters when a loss is known or considered probable and the amount can be reasonably estimated. The Company reviews these estimates each accounting period as additional information is known and adjusts the loss provision when appropriate. If a matter is both probable to result in a liability and the amounts of loss can be reasonably estimated, the Company estimates and discloses the possible loss or range of loss to the extent necessary to make the financial statements not misleading. If the loss is not probable or cannot be reasonably estimated, a liability is not recorded in the Company’s financial statements. The Company currently has no legal proceedings ongoing that management estimates could have a material effect on the Company’s financial statements.
16. Related-Party Transactions
The Company paid its non-employee directors fees for services as directors and consulting of approximately $431,000, $630,000 and $568,000 for the years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively, which were included in general and administrative expenses.
17. Subsequent Events
On February 1, 2017, the Class A Warrants to purchase common stock expired in accordance with their terms. As none of the Class A Warrants were exercised prior to expiration, the Class A Warrants have been terminated and are no longer exercisable.
F-28
Table of Contents
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| CONTRAFECT CORPORATION | ||
| By: | /s/ Steven C. Gilman, Ph.D. | |
| Steven C. Gilman, Ph.D. | ||
| President and Chief Executive Officer | ||
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| Signature |
Title |
Date | ||
| /S/ STEVEN C. GILMAN, PH.D. |
President and Chief Executive Officer, Chairman of the Board (Principal Executive Officer, Principal Financial Officer and Principal Accounting Officer) |
March 15, 2017 | ||
| Steven C. Gilman, Ph.D. | ||||
| /S/ SOL J. BARER, PH.D. |
Lead Independent Director | March 15, 2017 | ||
| Sol J. Barer, Ph.D. | ||||
| /S/ ISAAC BLECH |
Director | March 15, 2017 | ||
| Isaac Blech | ||||
| /S/ DAVID N. LOW, JR. |
Director | March 15, 2017 | ||
| David N. Low, Jr. | ||||
| /S/ MICHAEL J. OTTO, PH.D. |
Director | March 15, 2017 | ||
| Michael J. Otto, Ph.D. | ||||
| /S/ ROGER J. POMERANTZ, M.D., F.A.C.P. |
Vice Chairman of the Board | March 15, 2017 | ||
| Roger J. Pomerantz, M.D., F.A.C.P. | ||||
| /S/ LISA R. RICCIARDI |
Director | March 15, 2017 | ||
| Lisa R. Ricciardi | ||||
| /S/ CARY W. SUCOFF |
Director | March 15, 2017 | ||
| Cary W. Sucoff | ||||
Table of Contents
EXHIBIT INDEX
| Incorporated by Reference | ||||||||||||
| Exhibit No. |
Description |
Form |
File No. |
Exhibit |
Filing Date |
Filed/Furnished | ||||||
| 3.1 | Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation of ContraFect Corporation, dated August 1, 2014, and Certificate of Amendment, dated May 9, 2016 | 8-K | 001-36577 | 3.1 | May 10, 2016 | |||||||
| 3.2 | Amended and Restated Bylaws of ContraFect Corporation | 8-K | 001-36577 | 3.2 | May 10, 2016 | |||||||
| 4.1 | Form of Common Stock Certificate | S-1/A | 333-195378 | 4.1 | July 3, 2014 | |||||||
| 4.2 | Class A Warrant Agreement, dated as of July 28, 2014, by and between the Company and American Stock Transfer & Trust Company, LLC | 8-K | 001-36577 | 4.5.1 | October 29, 2015 | |||||||
| 4.3 | Specimen Class A Warrant Certificate | 8-K | 001-36577 | 4.12 | October 29, 2015 | |||||||
| 4.4 | Representative’s Warrant, dated August 27, 2014 | 8-K | 001-36577 | 4.14 | October 29, 2015 | |||||||
| 4.5 | Form of Noteholder Warrant | S-1/A | 333-195378 | 4.7 | July 3, 2014 | |||||||
| 4.6 | Specimen Unit Certificate | S-1 | 333-195378 | 4.8 | July 1, 2014 | |||||||
| 4.7 | Form of Indenture | S-3 | 333-206786 | 4.1 | September 4, 2015 | |||||||
| 4.8 | Form of Investor Warrant | 8-K | 001-36577 | 4.1 | June 12, 2015 | |||||||
| 4.9 | Form of Placement Agent Warrant | 8-K | 001-36577 | 4.2 | June 12, 2015 | |||||||
| 4.10 | Form of Warrant Agreement by and between ContraFect Corporation and American Stock Transfer & Trust Company, LLC, dated July 27, 2016 | 8-K | 001-36577 | 4.1 | July 27, 2016 | |||||||
| 4.11 | Form of Warrant Certificate | 8-K | 001-36577 | 4.2 | July 27, 2016 | |||||||
| 10.1 | License Agreement, between The Rockefeller University and ContraFect Corporation, dated July 12, 2011 | S-1 | 333-195378 | 10.1 | April 18, 2014 | |||||||
Table of Contents
| Incorporated by Reference | ||||||||||||||||||
| Exhibit No. |
Description |
Form |
File No. |
Exhibit |
Filing Date |
Filed/Furnished |
||||||||||||
| 10.2 | Lease Agreement, between Hudson View Building #3 LLC and ContraFect Corporation, dated December 1, 2010 | S-1 | 333-195378 | 10.2 | April 18, 2014 | |||||||||||||
| 10.3 | Lease Agreement, between Hudson View Building #3 LLC and ContraFect Corporation, dated January 1, 2012 | S-1 | 333-195378 | 10.3 | April 18, 2014 | |||||||||||||
| 10.4# | Form of Indemnification Agreement | S-1/A | 333-195378 | 10.4 | July 1, 2014 | |||||||||||||
| 10.5# | Employment Agreement by and between ContraFect Corporation and Julia P. Gregory dated April 29, 2014 | S-1/A | 333-195378 | 10.6 | July 1, 2014 | |||||||||||||
| 10.6# | Employment Agreement by and between ContraFect Corporation and Michael Wittekind, Ph.D. dated March 6, 2012 | S-1 | 333-195378 | 10.7 | April 18, 2014 | |||||||||||||
| 10.7# | Employment Agreement by and between ContraFect Corporation and Daniel E. Couto, dated March 21, 2011 | 10-K | 001-36577 | 10.7 | March 15, 2016 | |||||||||||||
| 10.8# | Separation and Consulting Agreement by and between ContraFect Corporation and Dr. Barry Kappel, dated April 15, 2015 | 10-K | 001-36577 | 10.8 | March 15, 2016 | |||||||||||||
| 10.9# | ContraFect Corporation Retention Bonus Plan | S-1 | 333-195378 | 10.9 | April 18, 2014 | |||||||||||||
| 10.10# | ContraFect Corporation Retention Bonus Plan Award Agreement | S-1 | 333-195378 | 10.10 | April 18, 2014 | |||||||||||||
| 10.11# | ContraFect Corporation Amended and Restated 2008 Equity Incentive Plan | S-1 | 333-195378 | 10.11 | April 18, 2014 | |||||||||||||
| 10.12# | ContraFect Corporation Form of Stock Option Agreement | S-1 | 333-195378 | 10.12 | April 18, 2014 | |||||||||||||
| 10.13# | ContraFect Corporation 2008 Equity Incentive Plan | S-1 | 333-195378 | 10.13 | April 18, 2014 | |||||||||||||
Table of Contents
| Incorporated by Reference | ||||||||||||||||||
| Exhibit No. |
Description |
Form |
File No. |
Exhibit |
Filing Date |
Filed/Furnished |
||||||||||||
| 10.14# | ContraFect Corporation 2014 Omnibus Incentive Plan | S-1/A | 333-195378 | 10.14 | July 1, 2014 | |||||||||||||
| 10.15 | License Agreement, between Trellis Bioscience LLC and ContraFect Corporation, dated January 29, 2014 | S-1/A | 333-195378 | 10.15 | July 1, 2014 | |||||||||||||
| 10.16 | Amendment to the Trellis License Agreement, dated June 15, 2014 | S-1/A | 333-195378 | 10.16 | July 1, 2014 | |||||||||||||
| 10.17 | Form of Securities Purchase Agreement between the Company and Benjamin Small, Birchview Fund, LLC, Broadfin Healthcare Master Fund, Ltd., Cormorant Global Healthcare Master Fund, LP, Jack W. Schuler, Matthew W. Strobeck, Oracle Institutional Partners, LP, Oracle Partners, LP, and Richard B. McCormick, dated June 11, 2015 | 8-K | 001-36577 | 10.1 | June 12, 2015 | |||||||||||||
| 10.18 | Form of Registration Rights Agreement among the Company, Benjamin Small, Birchview Fund, LLC, Broadfin Healthcare Master Fund, Ltd., Cormorant Global Healthcare Master Fund, LP, Jack W. Schuler, Matthew W. Strobeck, Oracle Institutional Partners, LP, Oracle Partners, LP, and Richard B. McCormick and Brookline Group LLC, dated June 11, 2015 | 8-K | 001-36577 | 10.2 | June 12, 2015 | |||||||||||||
| 10.19# | First Amendment to the Employment Agreement by and between ContraFect Corporation and Julia P. Gregory, dated August 10, 2015 | 8-K | 001-36577 | 10.1 | August 13, 2015 | |||||||||||||
| 10.20# | First Amendment to Employment Agreement by and between the Company and Michael Wittekind, PhD., dated November 12, 2015 | 10-Q | 001-36577 | 10.2 | November 12, 2015 | |||||||||||||
Table of Contents
| Incorporated by Reference | ||||||||||||
| Exhibit No. |
Description |
Form |
File No. |
Exhibit |
Filing Date |
Filed/Furnished | ||||||
| 10.21# | First Amendment to Employment Agreement by and between the Company and Daniel E. Couto, dated November 2, 2015 | 10-K | 001-36577 | 10.21 | March 15, 2016 | |||||||
| 10.22# | Separation Agreement and Release, dated March 25, 2016, between ContraFect Corporation and Julia P. Gregory | 8-K | 001-36577 | 10.1 | March 25, 2016 | |||||||
| 10.23# | Letter Agreement, dated July 21, 2016, between ContraFect Corporation and Steven C. Gilman, Ph.D. | 8-K | 001-36577 | 10.1 | July 21, 2016 | |||||||
| 10.24# | Consulting Agreement by and between the Company and Daniel E. Couto, dated May 1, 2016 | 10-Q | 001-36577 | 10.1 | August 9, 2016 | |||||||
| 10.25# | Separation and Consulting Agreement by and between ContraFect Corporation and Michael Wittekind, Ph.D., dated October 3, 2016 | 10-Q | 001-36577 | 10.1 | November 9, 2016 | |||||||
| 10.26# | Letter Agreement, dated March 13, 2017, between ContraFect Corporation and Steven C. Gilman, Ph.D. | 8-K | 001-36577 | 10.1 | March 13, 2017 | |||||||
| 10.27# | Offer Letter, dated June 26, 2014, between ContraFect Corporation and Natalie Bogdanos, as amended by Amendment No. 1, dated November 2, 2015 | * | ||||||||||
| 10.28# | Offer Letter, dated August 24, 2015, between ContraFect Corporation and Cara Cassino, M.D. | * | ||||||||||
| 10.29# | Amendment No. 1 to Offer Letter, dated March 15, 2017, between ContraFect Corporation and Cara Cassiono, M.D. | * | ||||||||||
| 23.1 | Consent of Ernst & Young LLP | * | ||||||||||
Table of Contents
| Incorporated by Reference | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Exhibit No. |
Description |
Form |
File No. |
Exhibit |
Filing Date |
Filed/Furnished | ||||||||||||||
| 31.1 | Certification of principal executive officer and principal financial officer pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a) and Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 | * | ||||||||||||||||||
| 32.1 | Certification of principal executive officer and principal financial officer pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 | ** | ||||||||||||||||||
| 101.INS | XBRL Instance Document | * | ||||||||||||||||||
| 101.SCH | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document | * | ||||||||||||||||||
| 101.CAL | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document | * | ||||||||||||||||||
| 101.DEF | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document | * | ||||||||||||||||||
| 101.LAB | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document | * | ||||||||||||||||||
| 101.PRE | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document | * | ||||||||||||||||||
| * | Filed herewith. |
| ** | Furnished herewith. |
| # | Indicates management contract or compensatory plan. |
