Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-99.2 - EXHIBIT 99.2 - ABEONA THERAPEUTICS INC. | v459961_ex99-2.htm |
| 8-K - FORM 8-K - ABEONA THERAPEUTICS INC. | v459961_8k.htm |
EXHIBIT 99.1

NASDAQ: ABEO www.abeonatherapeutics.com

Safe Harbor Statement This presentation contains certain statements that may be forward - looking within the meaning of Section 27 a of the Securities Act of 1933 , as amended, including statements relating to the product portfolio and pipeline and clinical programs of the company, the market opportunities for the all of the company’s products and product candidates, and the company’s goals and objectives . These statements are subject to numerous risks and uncertainties, including but not limited to the risks detailed in the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10 - K for the year ended December 31 , 2015 , and other reports filed by the company with the Securities and Exchange Commission . This presentation does not constitute an offer or invitation for the sale or purchase of securities or to engage in any other transaction with Abeona Therapeutics or its affiliates . The information in this presentation is not targeted at the residents of any particular country or jurisdiction and is not intended for distribution to, or use by, any person in any jurisdiction or country where such distribution or use would be contrary to local laws or regulations . The Company undertakes no obligations to make any revisions to the forward - looking statements contained in this presentation or to update them to reflect events or circumstances occurring after the date of this presentation, whether as a result of new information, future developments or otherwise . We have filed a shelf registration statement on Form S - 3 (including a prospectus) with the SEC which was declared effective on July 23 , 2015 . Before you invest in the offering to which this communication relates, you should read the prospectus in that registration statement and the preliminary prospectus supplement related to this offering and the other documents the issuer will file with the SEC for more complete information about the issuer and this offering . You may get these documents for free by visiting EDGAR on the SEC Web site at www . sec . gov . Alternatively, you may obtain a preliminary prospectus by calling 1 - 877 - 547 - 6340 . 2
Investment Highlights A World Leader in Rare Disease Therapies Strategic Focus on Rare Diseases • Substantial unmet medical need to treat life threatening diseases caused by a defect in a single gene • Most advanced programs in neurological / lysosomal storage diseases where there are no treatment options • Orphan and Rare pediatric disease focus: shorter route to approval, and lower costs • Opportunity to secure Priority Review Voucher (PRV) for rare pediatric diseases Three Clinical Programs in Phase I/II • ABO - 102: Sanfilippo syndrome Type A – MPS IIIA. Lysosomal storage disease affecting children. • ABO - 101 : Sanfilippo syndrome Type B – MPS IIIB. Lysosomal storage disease affecting children. • EB - 101 : Recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (RDEB ). Severely fragile skin disease affecting children. Robust Pipeline With Multiple Therapies Soon Entering the Clinic • Based on strong pre - clinical results, two additional programs are expected to begin Phase I/II by the end of 2017 including: – ABO - 201: Juvenile Batten disease (CLN3) – ABO - 202: Infantile Batten disease (CLN1) Proprietary Vector Platform For New Product Development • 60+ proprietary AAV vectors that uniquely enable the delivery of genes across the blood brain barrier making IV administration possible • Next generation chimera vector platform in development with increased gene delivery efficiency, reduced antibody affinity, enhanced ability to create immune responses and target tissue specifications Several Catalysts will Drive Significant Near Term Value • Achieve fast track designation for additional programs • Initiate high dose cohort in ABO - 102 for MPS IIIA • Initiate and enroll 1 st patient in ABO - 101 for MPS IIIB Phase 1/2 clinical studies • Dose adolescents in EB - 101 trial; secure orphan drug and rare pediatric disease designations 3
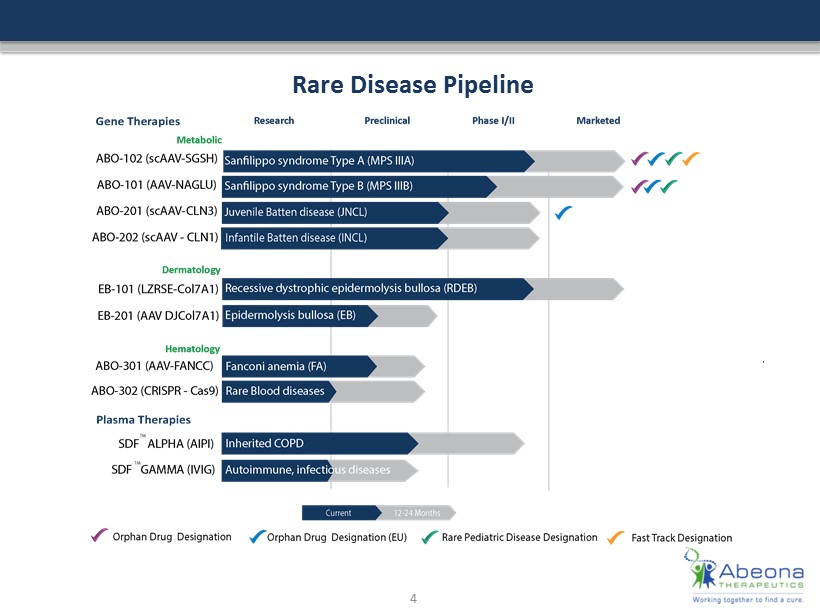
Rare Disease Pipeline 4
Focus on Gene Therapy What is Gene Therapy? • The transplantation of normal genes into cells in place of missing or defective ones in order to correct genetic disorders • Excitement in gene therapy sector due to recent European approvals of two gene therapies, impressive clinical data and anticipated first approvals of gene therapies in the US Where? • Target diseases that occur from single gene defects (mono - genetic defects) How? • Delivery, delivery, delivery: Viruses are used as transport vectors to get correct gene sequence into cells; choice of viral vector with affinity to target tissues; constructs which result in robust, uniform expression • Route of administration: Important to choose route of administration consistent with disease pathology; in Sanfilippo A, Abeona uses a single intravenous injection for whole body and CNS distribution 5 What, Where and How?

AAV Based Gene Therapy Platform Vector crosses the Blood Brain Barrier • Expressed in multiple nervous system cell types • Supra - physiological enzyme expression in brain for over a year observed in animals Self - complementary AAV (scAAV) persists as a stable episome in non - dividing cells with transgene expression for years scAAV vectors are 10 - 100 - fold more efficient than traditional single - stranded ( ss ) AAV vectors • Robust, uniform expression in all areas of brain and peripheral tissues Enables single intravenous injection therapies Sources: Keilan et al lab.; Eliason SL, Stein CS, Mao Q, et al. A knock - in reporter model of Batten disease. J Neurosci . 2007;27(37):9826 - 9834. Spinal Cord Brain 6
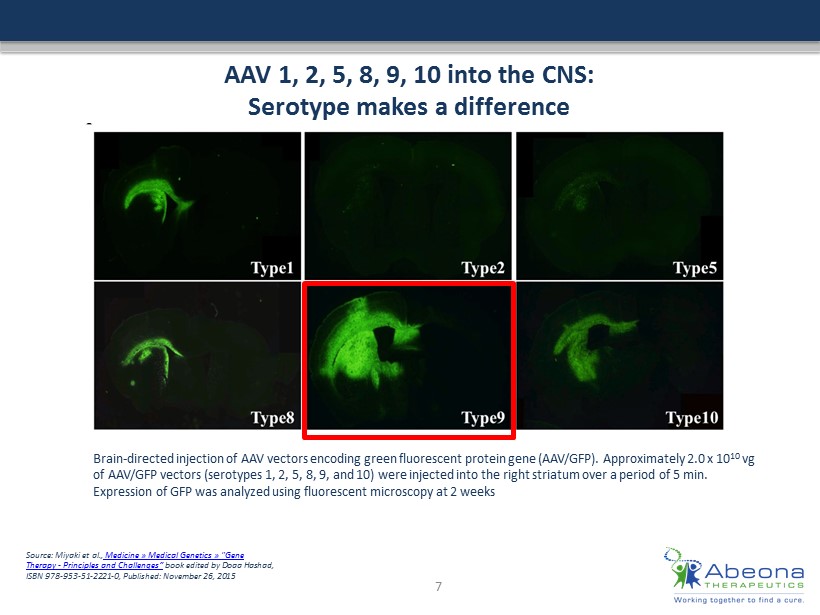
AAV 1, 2, 5, 8, 9, 10 into the CNS: Serotype makes a difference Brain - directed injection of AAV vectors encoding green fluorescent protein gene (AAV/GFP). Approximately 2.0 x 10 10 vg of AAV/GFP vectors (serotypes 1, 2, 5, 8, 9, and 10) were injected into the right striatum over a period of 5 min. Expression of GFP was analyzed using fluorescent microscopy at 2 weeks Source: Miyaki et al., Medicine » Medical Genetics » "Gene Therapy - Principles and Challenges “ book edited by Doaa Hashad, ISBN 978 - ### - ## - #### - 0, Published: November 26, 2015 7
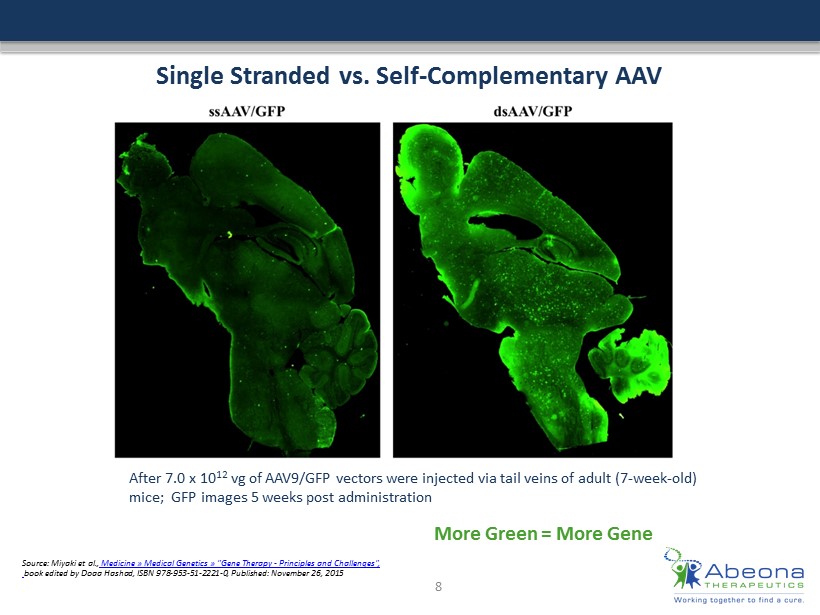
Single Stranded vs. Self - Complementary AAV Source: Miyaki et al., Medicine » Medical Genetics » "Gene Therapy - Principles and Challenges" , book edited by Doaa Hashad, ISBN 978 - ### - ## - #### - 0, Published: November 26, 2015 After 7.0 x 10 12 vg of AAV9/GFP vectors were injected via tail veins of adult (7 - week - old) mice ; GFP images 5 weeks post administration 8 More Green = More Gene

9 Global Foundation Support Investors and ongoing supporters of Abeona Original founding foundations

Clinical - Stage Programs 10

Sanfilippo Syndromes (MPS IIIA and IIIB) Rare lysosomal storage disease affecting children Sanfilippo syndrome (MPS IIIA & IIIB) is an inherited monogenic disorder that causes lysosomal enzyme deficiency • Set of four different disease states, each categorized by a missing or deficient enzyme - MPS IIIA (SGSH) - MPS IIIB (NAGLU) • Results in abnormal accumulation of glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) (sugars) • Aggressive behavior, seizures, loss of speech/vision, inability to sleep • Deterioration is severe, progressive and universally lethal • Death by end of teens – early 20’s No treatment options currently available • Incidence is estimated to be 1 in 70,000 births • Types A and B more common in North America and Europe Two ongoing clinical trials • ABO - 102 ( scAAV - SGSH) for MPS IIIA – low - dose cohort (n=3) completed, high - dose enrollment has commenced • ABO - 101 (AAV - NAGLU) for MPS IIIB – Recruitment anticipated 2Q17 • Conducted at Nationwide Children’s Hospital, Columbus, OH 11

Natural History Study 25 - patients with Sanfilippo syndrome assessed Enrollment complete : 25 subjects, 15 MPS IIIA & 10 MPS IIIB Study visits – assessments at 0 , 6 , and 12 months : • Neurocognitive (Leiter) and parental rating assessments (ABAS II) • Timed functional motor tests • Standard laboratory assessments • Serum/leukocyte NAGLU or SGSH activity • Quality of life (PedsQL) • Urine and CSF GAG (heparan sulfate) levels Study visits – assessments at baseline and 12 - month assessments • Brain, liver and spleen MRI (including DTI and 1 H spectroscopy) • CSF for standard chemistries/cell counts and NAGLU or SGSH activity All subjects through > 1 year follow up Multiple patient cross - over into clinical trials 12 Truxal , K.V. et al. "A Prospective One - Year Natural History Study Of Mucopolysaccharidosis Types IIIA And IIIB: Implications For Clinical Trial Design". Molecular Genetics and Metabolism 119.3 (2016): 239 - 248.

Phase 1/2 ABO - 102 ( scAAV - SGSH) Clinical T rial for MPS IIIA Global open - label, dose - escalation gene transfer trial Phase 1/2 open - label, dose - escalation clinical trials • Low dose: n = 3 patients; high dose: n = 3 - 6 patients • Three sites: United States, Spain and Australia Two dose cohorts of n=6 - 9 pts via intravenous injection • Cohort 1 (Low Dose): 5 X 10 12 vg/kg (n=3 subjects) – ENROLLMENT COMPLETE • Cohort 2 (High Dose): 1 X 10 13 vg/kg (n=3 - 6 subjects) – ENROLLMENT HAS COMMENCED Primary objective is determination of safety, with secondary objectives • Reduction in Urine/CSF GAG ( heparan sulfate), hepatomegaly and splenomegaly • Leukocyte SGSH enzyme activity levels • Leiter International Performance Assessment after 6 months post treatment • Parent ratings: Vineland Adaptive Behavior Assessment System and Child Behavioral Checklist • Pediatric Quality of Life Inventory 4.0 ( PedsQL ) Dosing and Short - Term Monitoring • Day - 1: subjects receive first dose of oral prednisolone elixir at 1 mg/kg/day • Day 0: subjects receive gene transfer delivered under sedation within the Procedure Center over 15 minutes • First 48 hours: Subjects monitored in PICU for 24 hours, then discharged to neurology floor for another 24 hours monitoring prior to discharge • Discharged on oral prednisolone elixir 13
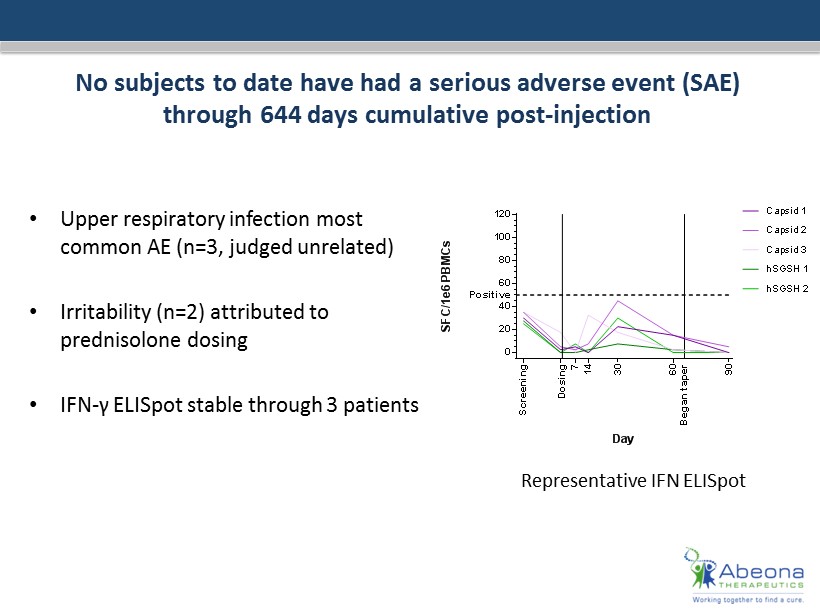
No subjects to date have had a serious adverse event (SAE ) through 644 days cumulative post - injection • Upper respiratory infection most common AE (n=3, judged unrelated) • Irritability (n=2) attributed to prednisolone dosing • IFN - γ ELISpot stable through 3 patients 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 MPS-IIIA-03 Day S F C / 1 e 6 P B M C s S c r e e n i n g D o s i n g 7 1 4 3 0 Positive Capsid 1 Capsid 2 Capsid 3 hSGSH 1 hSGSH 2 6 0 9 0 B e g a n t a p e r Representative IFN ELISpot
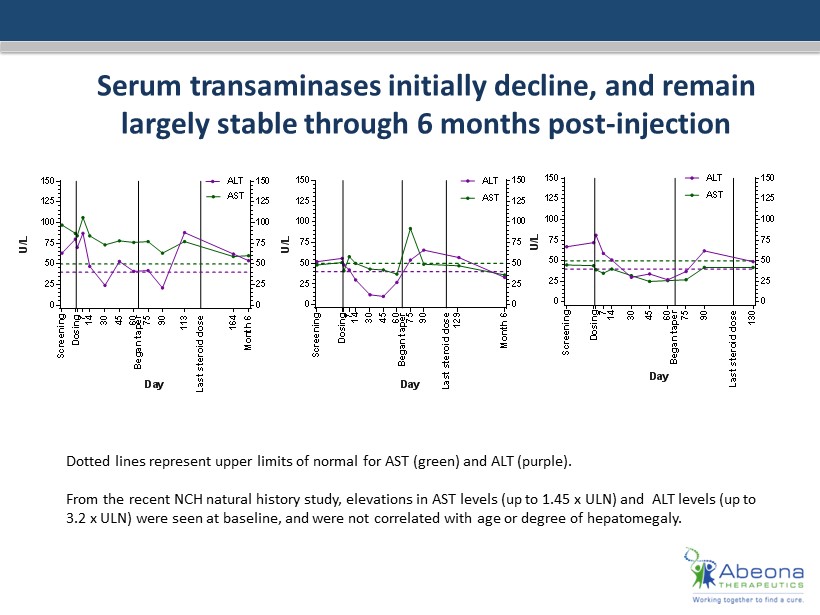
Serum transaminases initially decline, and remain largely stable through 6 months post - injection 0 25 50 75 100 125 150 0 25 50 75 100 125 150 MPS-IIIA-01 Day U / L D o s i n g S c r e e n i n g 7 1 4 3 0 4 5 6 0 7 5 B e g a n t a p e r 9 0 1 1 3 M o n t h 6 ALT AST 1 6 4 L a s t s t e r o i d d o s e 0 25 50 75 100 125 150 0 25 50 75 100 125 150 MPS-IIIA-02 Day U / L D o s i n g S c r e e n i n g 7 1 4 3 0 4 5 6 0 7 5 B e g a n t a p e r 9 0 1 2 9 M o n t h 6 AST ALT L a s t s t e r o i d d o s e 0 25 50 75 100 125 150 0 25 50 75 100 125 150 MPS-IIIA-03 Day U / L D o s i n g S c r e e n i n g 7 1 4 3 0 4 5 6 0 7 5 9 0 1 3 0 ALT AST B e g a n t a p e r L a s t s t e r o i d d o s e Dotted lines represent upper limits of normal for AST (green) and ALT (purple). From the recent NCH natural history study, elevations in AST levels (up to 1.45 x ULN) and ALT levels (up to 3.2 x ULN ) were seen at baseline, and were not correlated with age or degree of hepatomegaly .
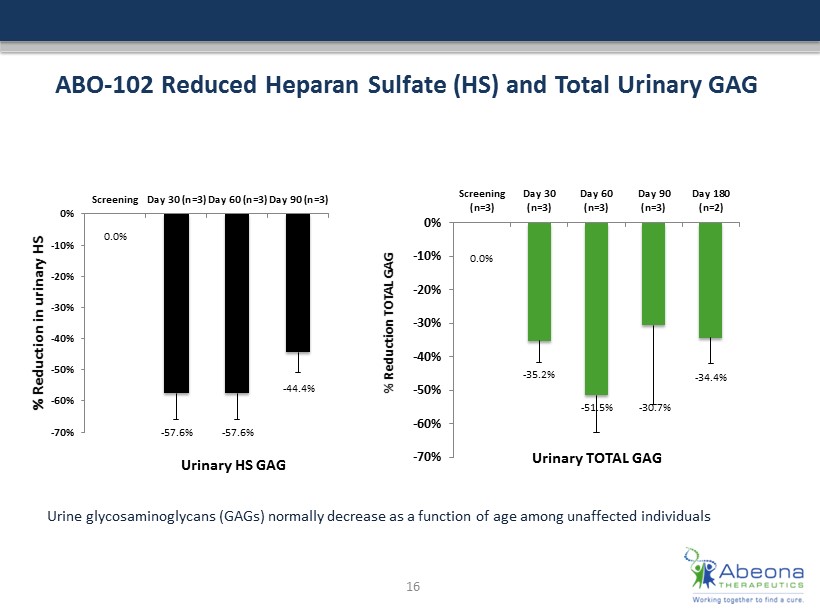
ABO - 102 Reduced Heparan Sulfate (HS) and Total Urinary GAG 0.0% - 35.2% - 51.5% - 30.7% - 34.4% -70% -60% -50% -40% -30% -20% -10% 0% Screening (n=3) Day 30 (n=3) Day 60 (n=3) Day 90 (n=3) Day 180 (n=2) % Reduction TOTAL GAG Urinary TOTAL GAG 0.0% - 57.6% - 57.6% - 44.4% -70% -60% -50% -40% -30% -20% -10% 0% Screening Day 30 (n=3) Day 60 (n=3) Day 90 (n=3) % Reduction in urinary HS Urinary HS GAG 16 Urine glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) normally decrease as a function of age among unaffected individuals
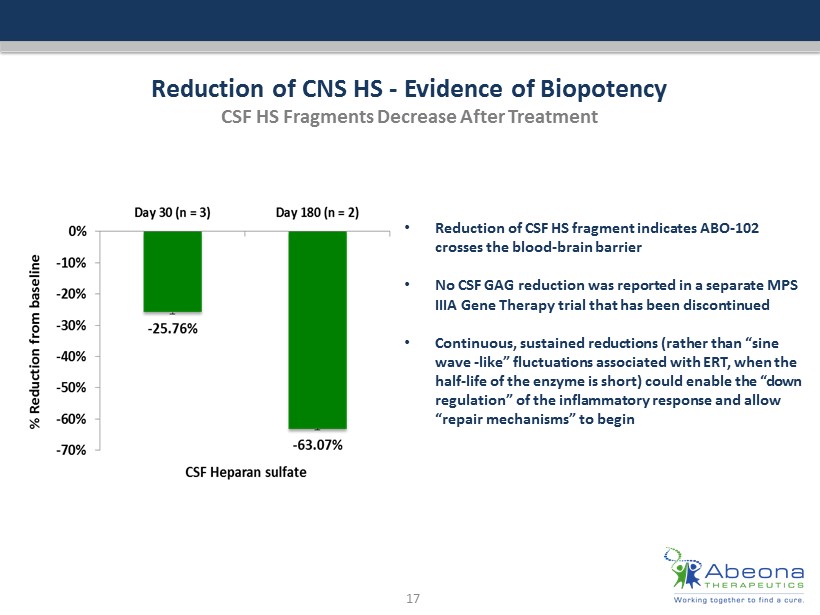
Reduction of CNS HS - Evidence of Biopotency CSF HS Fragments Decrease After Treatment 17 • Reduction of CSF HS fragment indicates ABO - 102 crosses the blood - brain barrier • No CSF GAG reduction was reported in a separate MPS IIIA Gene Therapy trial that has been discontinued • Continuous, sustained reductions (rather than “sine wave - like” fluctuations associated with ERT, when the half - life of the enzyme is short) could enable the “down regulation” of the inflammatory response and allow “repair mechanisms” to begin
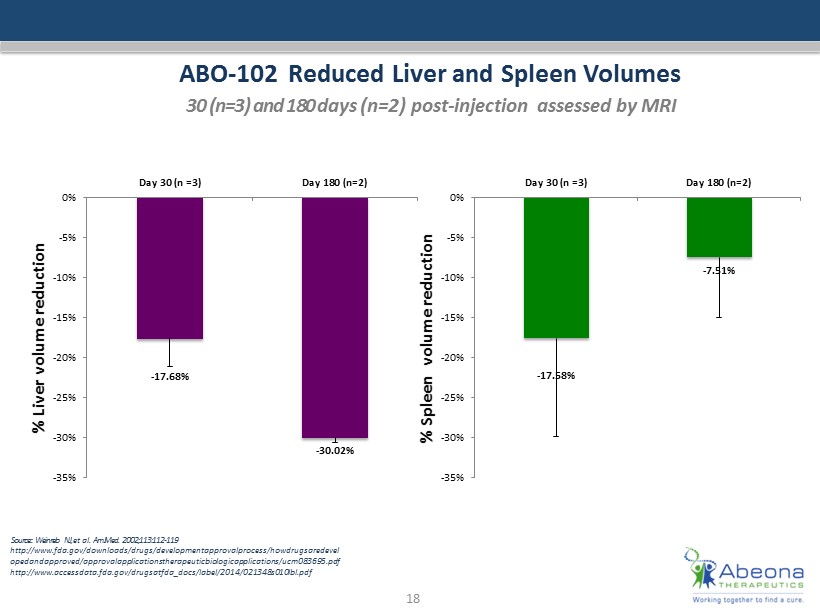
ABO - 102 Reduced Liver and Spleen Volumes 30 (n=3) and 180 d ays (n=2) post - injection a ssessed by MRI Source: : Weinreb NJ, et al. Am J Med. 2002;113:112 - 119 http:// www.fda.gov /downloads/drugs/ developmentapprovalprocess / howdrugsaredevel opedandapproved / approvalapplicationstherapeuticbiologicapplications /ucm083 695.pdf http:// www.accessdata.fda.gov / drugsatfda_docs / label /2014/021348s010lbl.pdf 18 - 17.68% - 30.02% -35% -30% -25% -20% -15% -10% -5% 0% Day 30 (n =3) Day 180 (n=2) % Liver volume reduction - 17.58% - 7.51% -35% -30% -25% -20% -15% -10% -5% 0% Day 30 (n =3) Day 180 (n=2) % Spleen volume reduction
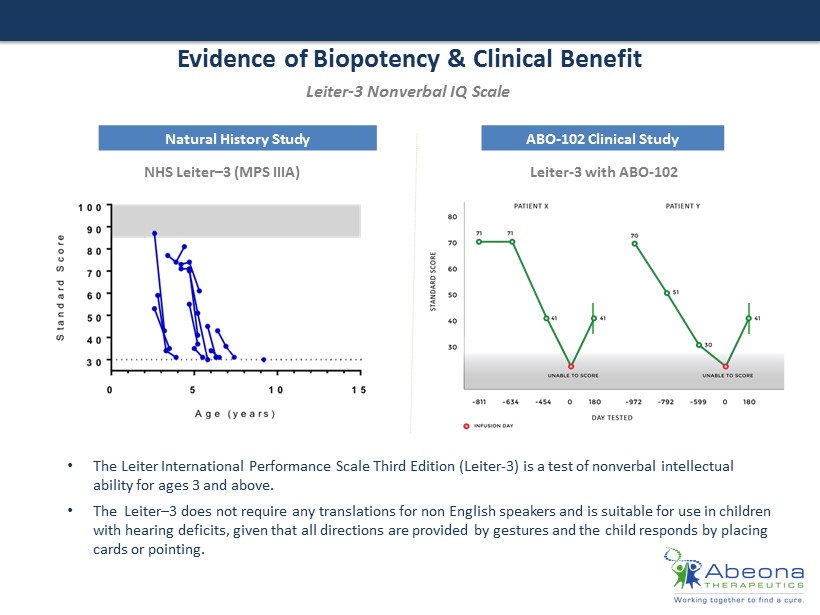
Evidence of Biopotency & Clinical Benefit Natural History Study ABO - 102 Clinical Study Leiter - 3 Nonverbal IQ Scale • The Leiter International Performance Scale Third Edition (Leiter - 3) is a test of nonverbal intellectual ability for ages 3 and above. • The Leiter – 3 does not require any translations for non English speakers and is suitable for use in children with hearing deficits, given that all directions are provided by gestures and the child responds by placing cards or pointing. Leiter - 3 with ABO - 102 NHS Leiter – 3 (MPS IIIA)
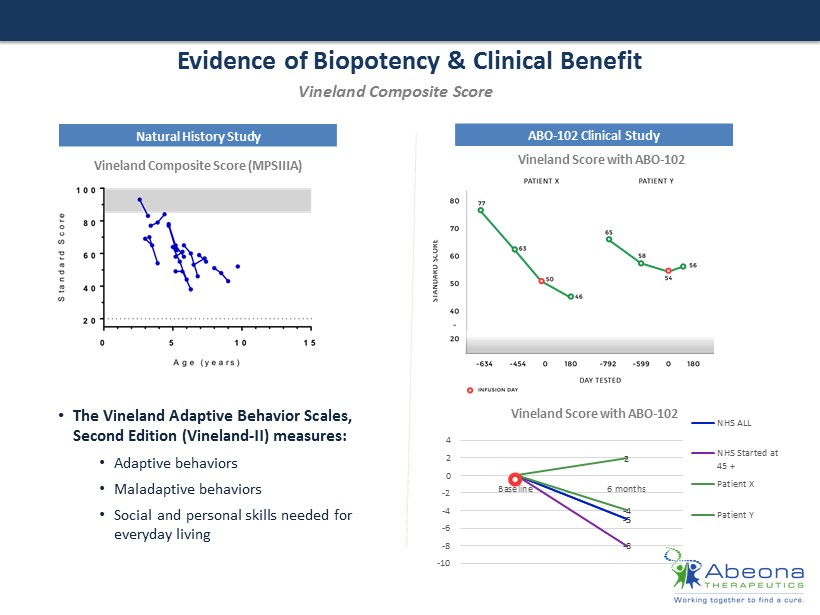
Evidence of Biopotency & Clinical Benefit Natural History Study ABO - 102 Clinical Study Vineland Composite Score (MPSIIIA) Vineland Score with ABO - 102 Vineland Score with ABO - 102 • The Vineland Adaptive Behavior Scales, Second Edition (Vineland - II) measures : • A daptive behaviors • M aladaptive behaviors • Social and personal skills needed for everyday living Vineland Composite Score 0 - 5 0 - 5 0 - 8 0 - 4 0 2 -10 -8 -6 -4 -2 0 2 4 Baseline 6 months NHS ALL NHS Started at 45 + Patient X Patient Y
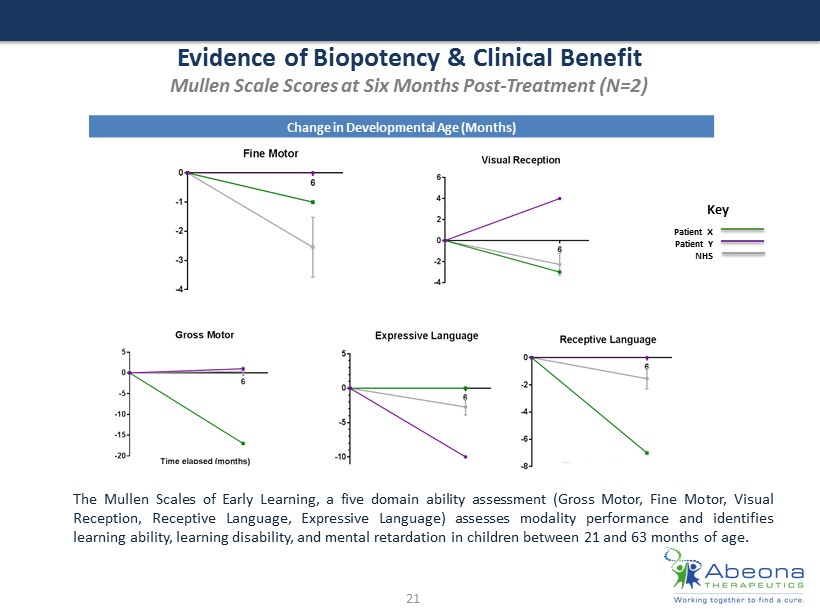
Evidence of Biopotency & Clinical Benefit Mullen Scale Scores at Six Months Post - Treatment (N=2) 21 The Mullen Scales of Early Learning, a five domain ability assessment ( Gross Motor , Fine Motor, Visual Reception, Receptive Language, Expressive Language) assesses modality performance and identifies learning ability, learning disability, and mental retardation in children between 21 and 63 months of age . Change in Developmental Age (Months) Patient X Patient Y NHS Key

Summary of ABO - 102 Clinical Data 22 ABO - 102 for MPS IIIA is Well Tolerated, and Demonstrates Biopotency and Early Signals of Neurocognitive and Behavioral Improvements • ABO - 102 is well tolerated to date, with no serious adverse events (N=4 through 650 days follow up) • All low dose subjects (N =3) tapered off immunosuppression regimen on or before 90 days (unlike other gene therapy trials by direct intracranial administration where immunosuppression has lasted 12 to 18 months) • Significant, continuous reduction in HS GAG as measured in the CSF (thought to be the key measure of biopotency /reduction of storage pathology in the CNS) in the low dose cohort (N=2) 6 months post - injection • Significant reductions in liver and spleen volumes ; potential clinical benefit in patient population where hepatosplenomegaly can lead to recurring respiratory and digestive issues • E arly positive signals of neurocognitive assessments – including early signs of improved non - verbal IQ scores, stabilization of previously declining measurements, and possible slowing of disease progression
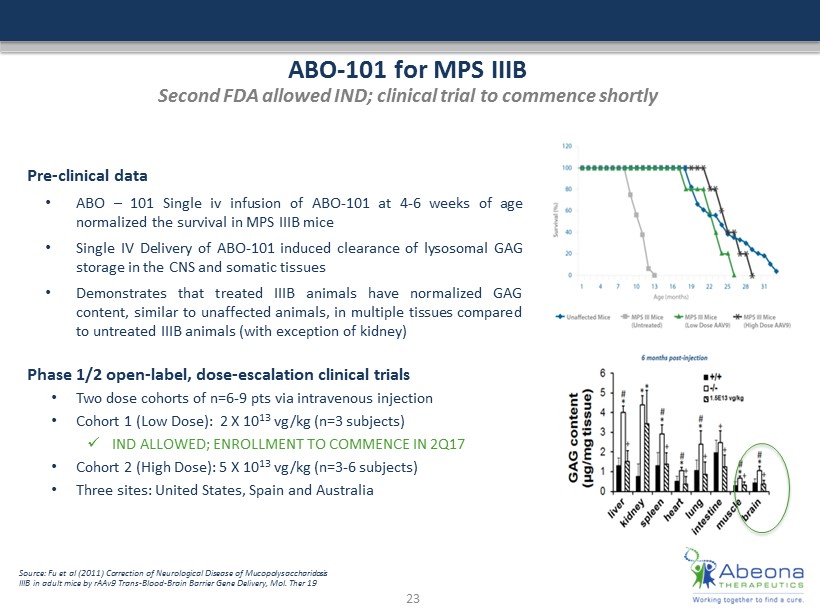
ABO - 101 for MPS IIIB Second FDA allowed IND; clinical trial to commence shortly Pre - clinical data • ABO – 101 Single iv infusion of ABO - 101 at 4 - 6 weeks of age normalized the survival in MPS IIIB mice • Single IV Delivery of ABO - 101 induced clearance of lysosomal GAG storage in the CNS and somatic tissues • Demonstrates that treated IIIB animals have normalized GAG content, similar to unaffected animals, in multiple tissues compared to untreated IIIB animals (with exception of kidney) Phase 1/2 open - label, dose - escalation clinical trials • Two dose cohorts of n=6 - 9 pts via intravenous injection • Cohort 1 (Low Dose): 2 X 10 13 vg/kg (n=3 subjects) x IND ALLOWED; ENROLLMENT TO COMMENCE IN 2Q17 • Cohort 2 (High Dose): 5 X 10 13 vg/kg (n=3 - 6 subjects) • Three sites: United States, Spain and Australia 23 Source: Fu et al (2011) Correction of Neurological Disease of Mucopolysaccharidosis IIIB in adult mice by rAAv9 Trans - Blood - Brain Barrier Gene Delivery, Mol. Ther 19
Epidermolysis Bullosa (EB) Rare and devastating skin disease Group of devastating inherited connective tissue diseases; characterized by skin blisters and erosions that can also affect internal organs • There are four forms of EB; EB - 101 targets Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (RDEB), an extremely rare form of EB, which is caused by the absence of the COL7A1 gene (encodes type 7 collagen fibril that anchors skin to the underlying stroma) • RDEB is the most severe form and is characterized by severe blistering, open wounds, and scarring in response to minor friction to skin No FDA approved therapies currently available • Prevalence of EB is estimated to be 30,000 - 40,000 of which RDEB is estimated to be 2,500 - 3,000 in the US alone • With no FDA approved treatments, any reduction in disease symptoms or improvements in wound healing could be considered clinically meaningful Ongoing clinical trial • Conducted at Stanford University School of Medicine • Phase 1 completed; strong 12 - month post treatment data on initial 4 patients • Phase 2 trial: enrolling patients 24

Abeona’s EB - 101 Approach Genetically corrected autologous skin grafts EB - 101: Ex - vivo gene therapy Gene therapy correction of patient cells To replace COL7A1 cDNA , followed by grafting EB - 101 – Gene therapy corrected skin sheets EB - 101 – Skin graft ready for application 25

EB - 101 Clinical Program Update Unprecedented wound healing in this population Phase 1 clinical trial in with Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (RDEB) - completed using genetically corrected autologous skin grafts • 5 adult patients treated with six grafts each • To date, positive 12 month post - treatment data observed; de - risked outlook for pivotal Phase 2 - All 24 grafts were well tolerated by all subjects, and no serious adverse events were reported - At 3 months, 87% (21/24 grafts) showed significant wound healing as defined by 75% healing compared with baseline - At 6 months, 67% (16/24) showed significant healing - Well tolerated with no SAEs - Phase 1 clinical trial data published in the Journal of American Medical Association (JAMA) Ongoing phase 2 clinical trial – enrolling and treating patients • Primary endpoints: - Expression of C7 and restoration of anchoring fibrils at 3 and 6 months - Absence of systemic virus at 3, 6, 12 months post grafting 26 JAMA. 2016; 2016 (17): 1808 - 1817. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.15588
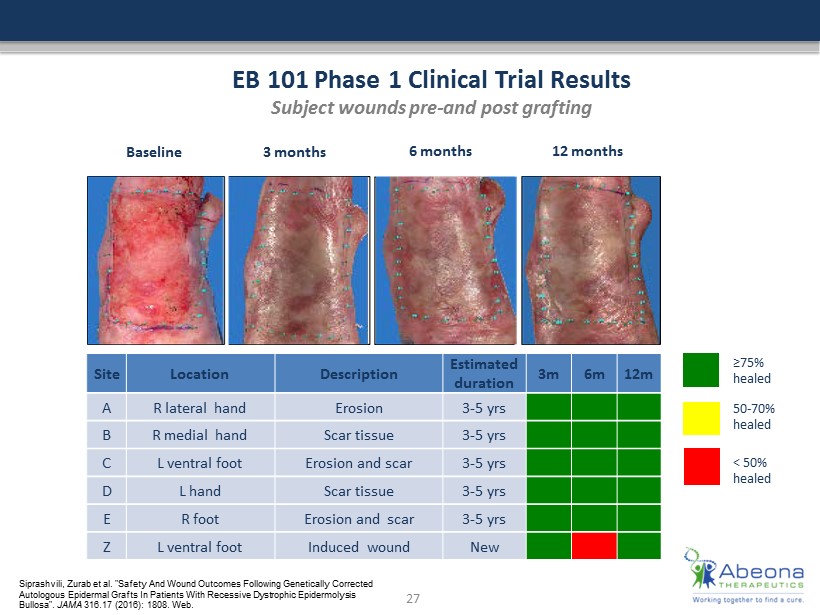
≥75% healed 50 - 70% healed < 50% healed B as e li n e 3 months 6 months 12 months EB 101 Phase 1 Clinical Trial Results Subject wounds pre - and post grafting Site Location Description Estimated duration 3m 6m 12m A R lateral hand Erosion 3 - 5 yrs B R medial hand Scar tissue 3 - 5 yrs C L ventral foot Erosion and scar 3 - 5 yrs D L hand Scar tissue 3 - 5 yrs E R foot Erosion and scar 3 - 5 yrs Z L ventral foot Induced wound New 27 Siprashvili , Zurab et al. "Safety And Wound Outcomes Following Genetically Corrected Autologous Epidermal Grafts In Patients With Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa". JAMA 316.17 (2016): 1808. Web.
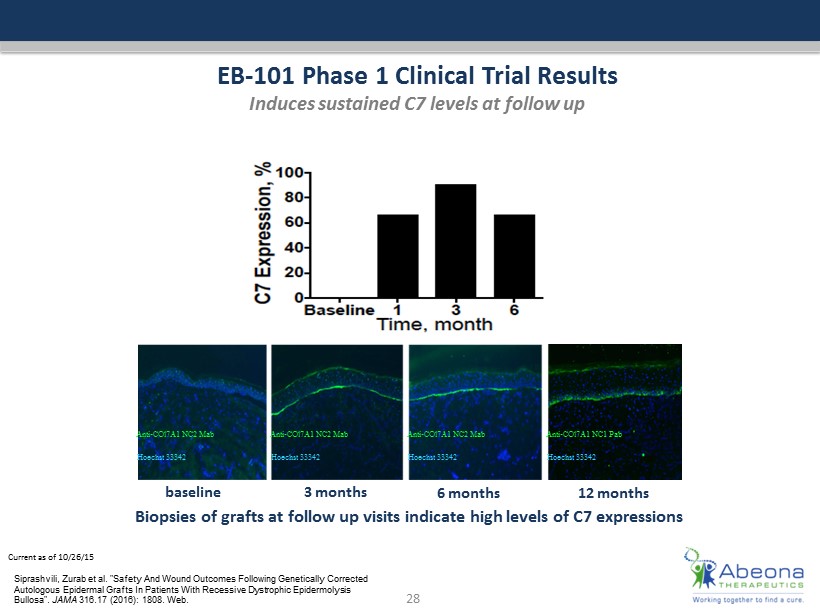
Current as of 10/26/15 EB - 101 Phase 1 Clinical Trial Results Induces sustained C7 levels at follow up Biopsies of grafts at follow up visits indicate high levels of C7 expressions Anti - COl7A1 NC2 Mab Hoechst 33342 Anti - COl7A1 NC2 Mab Hoechst 33342 Anti - COl7A1 NC2 Mab Hoechst 33342 Anti - COl7A1 NC1 Pab Hoechst 33342 28 baseline 3 months 6 months 12 months Siprashvili , Zurab et al. "Safety And Wound Outcomes Following Genetically Corrected Autologous Epidermal Grafts In Patients With Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa". JAMA 316.17 (2016): 1808. Web.

Pre - Clinical Programs 29

Gene Therapies 30

ABO – 201 for Juvenile Batten Disease – CLN3 pre - IND meeting completed, clinical trial to commence in 2017 Source: Moving towards therapies for Juvenile batten disease, Experimental Neurology, 2008 JBD - Autosomal recessive (inherited) mutation in the CLN 3 gene • Initially presents as blindness, progressing to behavioral issues, sleep disturbances, seizures, cognitive loss, motor abnormalities, premature death (late teens - early 20 s) • Neurodegeneration occurs primarily in thalamus, cortex, and hippocampus, although inclusions are observed throughout the CNS • Estimated incidence of 1 : 100 , 000 births Pre - clinical results mirrored data in MPS IIIA & B ; normalization of motor function and survival • Research conducted at the University of Nebraska Medical Center ABO - 201 : Human clinical trials anticipated in 2017 at University of Rochester Medical Center Ongoing Batten Disease Natural History Study at University of Rochester Medical Center 31

ABO – 202 for Infantile Batten Disease – CLN1 Autosomal recessive (inherited) mutation in the CLN1 gene Diagnosed between ages 6 months and 2 years – with early death before age 5 • Affected children fail to thrive and have microcephaly; also typical are short, sharp muscle contradictions called myoclonic jerks Preclinical work shows promising efficacy in INCL mice after delivery of a functioning copy of the CLN1 gene to cells of the central nervous system • Extended survival and preserved strength when administered early in the disease course • Research conducted at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill ABO – 202 Human clinical trials anticipated 2017 32

ABO - 301 – for Fanconi Anemia Fanconi anemia (FA) is a rare (1: 160,000) pediatric, autosomal recessive (inherited) disease Characterized by multiple physical abnormalities, organ defects, bone marrow failure, and a higher than normal risk of cancer — with 20 to 30 year average lifespan • The major function of bone marrow is to produce new blood cells. In FA, a DNA mutation renders the FANCC gene nonfunctional • Loss of FANCC causes patient skeletal abnormalities and leads to bone marrow failure • Higher rates of hematological diseases, such as acute myeloid leukemia (AML) or tumors of the head, neck, skin, gastrointestinal system, or genital tract ABO - 301 - demonstrates in vivo efficacy in multiple models, with no off target effects • Research conducted at University of Minnesota Next steps: Complete IND enabling pre - clinical studies; and establish safety and preliminary efficacy in human subjects 33
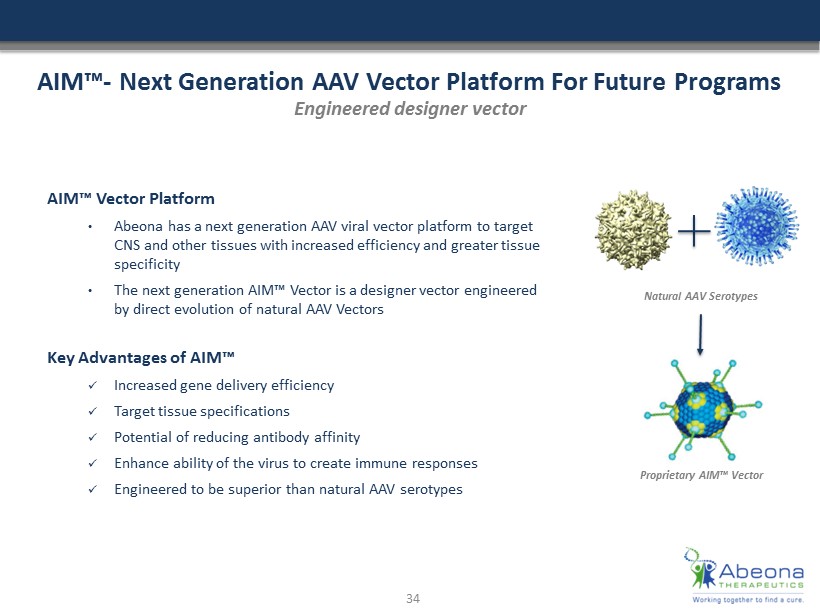
AIM™ - Next Generation AAV Vector Platform For Future Programs AIM™ Vector Platform • Abeona has a next generation AAV viral vector platform to target CNS and other tissues with increased efficiency and greater tissue specificity • The next generation AIM™ Vector is a designer vector engineered by direct evolution of natural AAV Vectors Key Advantages of AIM™ x Increased gene delivery efficiency x Target tissue specifications x Potential of reducing antibody affinity x Enhance ability of the virus to create immune responses x Engineered to be superior than natural AAV serotypes Engineered designer vector Proprietary AIM™ Vector Natural AAV Serotypes 34
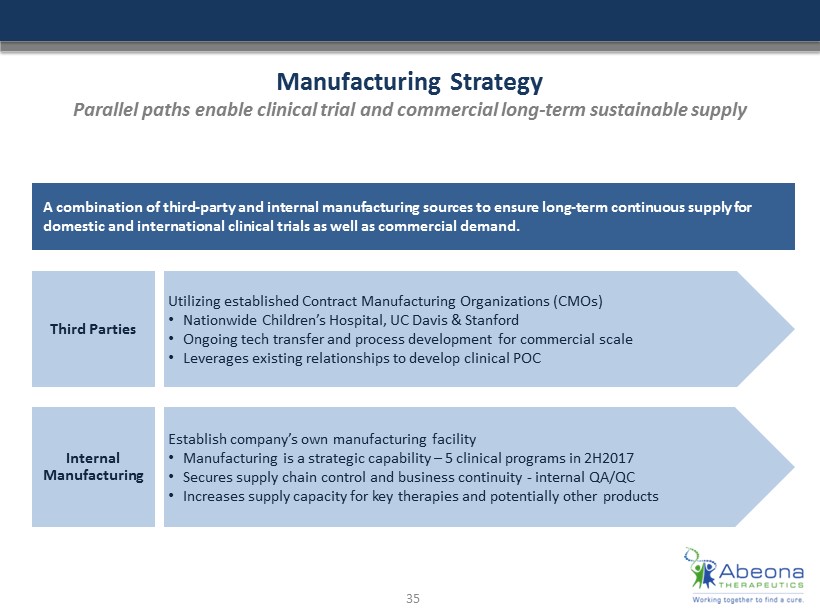
Manufacturing Strategy Parallel paths enable clinical trial and commercial long - term sustainable supply A combination of third - party and internal manufacturing sources to ensure long - term continuous supply for domestic and international clinical trials as well as commercial demand . Third Parties Utilizing established Contract Manufacturing Organizations (CMOs) • Nationwide Children’s Hospital, UC Davis & Stanford • Ongoing tech transfer and process development for commercial scale • Leverages existing relationships to develop clinical POC Internal Manufacturing Establish company’s own manufacturing facility • Manufacturing is a strategic capability – 5 clinical programs in 2H2017 • Secures supply chain control and business continuity - internal QA/QC • Increases supply capacity for key therapies and potentially other products 35

Plasma Therapy 36

Abeona Proprietary ™ SDF Process for AATD Inherited autosomal disorder that results in insufficient AAT protein production by liver • AATD may lead to liver disease • Alpha - 1 protects lungs from inflammation and damage caused by infection and inhaled irritants Prevalence – need to diagnose and treat • AATD has been identified in nearly all populations and ethnic groups • Roughly 1 in every 2,500 Americans have AATD • 5 times more prevalent than Cystic Fibrosis • Up to 3% of all people diagnosed with COPD may have undetected AATD The global market for plasma proteins is roughly $20 billion • Currently blood plasma proteins are purified using the Cohn process developed in the 1940’s Abeona’s Proprietary ™ SDF Process has demonstrated substantial improvements in yields and margins 37

Financial Overview Cash (Q3 2016): $31.2 million* Cash used in operations ( Q1 - Q3 2016 ): $9.6 million No debt Primary Common S hares outstanding: 33.5 million ** 38 * Cash, cash equivalents, and short - term investments, does not include cash from public offering of $42M, closed November 1, 2016. **End of third quarter 2016, does not include shares from public offering, closed November 1, 2016.
Investment Highlights A World Leader in Rare Disease Therapies Strategic Focus on Rare Diseases • Substantial unmet medical need to treat life threatening diseases caused by a defect in a single gene • Most advanced programs in neurological / lysosomal storage diseases where there are no treatment options • Orphan and Rare pediatric disease focus: shorter route to approval, and lower costs • Opportunity to secure Priority Review Voucher (PRV) for rare pediatric diseases Three Clinical Programs in Phase I/II • ABO - 102: Sanfilippo syndrome Type A – MPS IIIA. Lysosomal storage disease affecting children. • ABO - 101 : Sanfilippo syndrome Type B – MPS IIIB. Lysosomal storage disease affecting children. • EB - 101 : Recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (RDEB ). Severely fragile skin disease affecting children. Robust Pipeline With Multiple Therapies Soon Entering the Clinic • Based on strong pre - clinical results, two additional programs are expected to begin Phase I/II by the end of 2017 including: – ABO - 201: Juvenile Batten disease (CLN3) – ABO - 202: Infantile Batten disease (CLN1) Proprietary Vector Platform For New Product Development • 60+ proprietary AAV vectors that uniquely enable the delivery of genes across the blood brain barrier making IV administration possible • Next generation chimera vector platform in development with increased gene delivery efficiency, reduced antibody affinity, enhanced ability to create immune responses and target tissue specifications Several Catalysts will Drive Significant Near Term Value • Achieve fast track designation for additional programs • Initiate high dose cohort in ABO - 102 for MPS IIIA • Initiate and enroll 1 st patient in ABO - 101 for MPS IIIB Phase 1/2 clinical studies • Dose adolescents in EB - 101 trial; secure orphan drug and rare pediatric disease designations 39

Management & Boards Management • Tim Miller, Ph.D. - President and Chief Executive Officer & Director • Jeffrey B. Davis - Chief Operating Officer & Director • Harrison G. Wehner - Chief Financial Officer • David P. Nowotnik, Ph.D. - Senior Vice President, Research & Development • Kaye Spratt, Ph.D. - Vice President, Regulatory Board of Directors • Steven H. Rouhandeh - Executive Chairman • Mark J. Alvino - Director • Stephen B. Howell, MD - Director • Todd Wider, MD - Director Scientific Advisory Boards: Rare D isease and P lasma focused 40
Contacts 41 Investor Contact: Christine Berni - Silverstein Vice - President, Investor Relations Phone: 212.786.6212 Email: csilverstein@abeonatherapeutics.com Media Contact: Andre’a Lucca Vice - President, Communications & Operations Phone: 212.786.6208 Email: alucca@abeonatherapeutics.com
