Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-10.69 - EX-10.69 - IQVIA HOLDINGS INC. | d321341dex1069.htm |
| EX-32.2 - EX-32.2 - IQVIA HOLDINGS INC. | d321341dex322.htm |
| EX-32.1 - EX-32.1 - IQVIA HOLDINGS INC. | d321341dex321.htm |
| EX-31.2 - EX-31.2 - IQVIA HOLDINGS INC. | d321341dex312.htm |
| EX-31.1 - EX-31.1 - IQVIA HOLDINGS INC. | d321341dex311.htm |
| EX-23.1 - EX-23.1 - IQVIA HOLDINGS INC. | d321341dex231.htm |
| EX-21.1 - EX-21.1 - IQVIA HOLDINGS INC. | d321341dex211.htm |
| EX-10.104 - EX-10.104 - IQVIA HOLDINGS INC. | d321341dex10104.htm |
| EX-10.78 - EX-10.78 - IQVIA HOLDINGS INC. | d321341dex1078.htm |
| EX-10.76 - EX-10.76 - IQVIA HOLDINGS INC. | d321341dex1076.htm |
| EX-10.47 - EX-10.47 - IQVIA HOLDINGS INC. | d321341dex1047.htm |
| EX-10.45 - EX-10.45 - IQVIA HOLDINGS INC. | d321341dex1045.htm |
| EX-10.41 - EX-10.41 - IQVIA HOLDINGS INC. | d321341dex1041.htm |
| EX-10.27 - EX-10.27 - IQVIA HOLDINGS INC. | d321341dex1027.htm |
Table of Contents
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
(Mark One)
| ☒ | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2016
or
| ☐ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from to .
Commission File Number: 001-35907
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| Delaware (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) |

|
27-1341991 (I.R.S. Employer Identification Number) |
4820 Emperor Blvd., Durham, North Carolina 27703
and
83 Wooster Heights Road, Danbury, Connecticut 06810
(Address of principal executive offices and Zip Code)
(919) 998-2000 and (203) 448-4600
(Registrant’s telephone number, including area code)
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| Title of Each Class: |
Name of Each Exchange on which Registered | |
| Common Stock, par value $0.01 per share | New York Stock Exchange |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or section 15(d) of the Exchange Act. Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding twelve months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| Large accelerated filer | ☒ | Accelerated filer | ☐ | |||||
| Non-accelerated filer | ☐ | (Do not check if a smaller reporting company) | Smaller reporting company | ☐ | ||||
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes ☐ No ☒
The aggregate market value of the voting and non-voting common stock held by non-affiliates of the registrant, based upon the closing sale price as reported on the New York Stock Exchange on June 30, 2016, the last business day of the registrant’s most recently completed second quarter, was approximately $5,770,018,162, (which does not give effect to the business combination of Quintiles Transnational Holdings Inc. and IMS Health Holdings, Inc. completed on October 3, 2016).
Indicate the number of shares outstanding of each of the issuer’s classes of Common Stock, as of the latest practicable date.
| Class |
Number of Shares Outstanding | |
| Common Stock $0.01 par value | 235,719,111 shares outstanding as of February 9, 2017 |
Portions of the registrant’s Proxy Statement for the 2017 Annual Meeting of Stockholders are incorporated herein by reference in Part III of this Annual Report on Form 10-K to the extent stated herein. Such proxy statement will be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission within 120 days of the registrant’s fiscal year ended December 31, 2016.
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC.
FORM 10-K
2
Table of Contents
FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This Annual Report on Form 10-K contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (“Securities Act”), and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”). Such forward-looking statements reflect, among other things, our current expectations, our forecasts and our anticipated results of operations, all of which are subject to known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors that may cause our actual results, performance or achievements, market trends, or industry results to differ materially from those expressed or implied by such forward-looking statements. Therefore, any statements contained herein that are not statements of historical fact may be forward-looking statements and should be evaluated as such. Without limiting the foregoing, the words “anticipates,” “believes,” “estimates,” “expects,” “intends,” “may,” “plans,” “projects,” “should,” “targets,” “will” and the negative thereof and similar words and expressions are intended to identify forward-looking statements. These forward-looking statements are subject to a number of risks, uncertainties and assumptions, including those described in Part I, Item 1A, “Risk Factors.” We assume no obligation to update any such forward-looking information to reflect actual results or changes in the factors affecting such forward-looking information.
GENERAL
When we use the terms “QuintilesIMS,” the “Company,” “we,” “us” or “our” in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, we mean Quintiles IMS Holdings, Inc. and its subsidiaries on a consolidated basis, unless we state or the context implies otherwise.
On October 3, 2016, Quintiles Transnational Holdings Inc. (“Quintiles”) completed its previously announced merger of equals transaction (the “Merger”) with IMS Health Holdings, Inc. (“IMS Health”). Pursuant to the terms of the merger agreement dated as of May 3, 2016 between Quintiles and IMS Health (the “Merger Agreement”), IMS Health was merged with and into Quintiles, and the separate corporate existence of IMS Health ceased, with Quintiles continuing as the surviving corporation. Immediately prior to the completion of the Merger, Quintiles reincorporated as a Delaware corporation. Quintiles changed its name to Quintiles IMS Holdings, Inc. At the effective time of the Merger, each issued and outstanding share of IMS Health common stock was automatically converted into 0.3840 of a share of the Company’s common stock.
INDUSTRY AND MARKET DATA
This annual report on Form 10-K includes market data and forecasts with respect to the healthcare industry. In some cases, we rely on and refer to market data and certain industry forecasts that were obtained from third party surveys, market research, consultant surveys, publicly available information and industry publications and surveys that we believe to be reliable. However, we have not independently verified data from industry analyses and cannot guarantee their accuracy or completeness. We believe that data regarding the industry, market size and its market position and market share within such industry provide general guidance but are inherently imprecise. Other industry and market data included in this annual report are from QuintilesIMS analyses and have been identified accordingly, including, for example, QuintilesIMS Market Prognosis, which is a subscription-based service that provides five-year pharmaceutical market forecasts at the national, regional and global levels. We are a leading global information provider for the healthcare industry and we maintain databases, produce market analyses and deliver information to clients in the ordinary course of our business. Our information is widely referenced in the industry and used by governments, payers, academia, the life sciences industry, the financial community and others. Most of this information is available on a subscription basis. Other reports and information are available publicly through our QuintilesIMS Institute for Healthcare Informatics (the “QuintilesIMS Institute”). All such information is based upon our own market research, internal databases and published reports and has not been verified by any independent sources. Our estimates and assumptions involve risks and uncertainties and are subject to change based on various factors, including those discussed in the “Risk Factors” section. These and other factors could cause results to differ materially from those expressed in the estimates and assumptions.
3
Table of Contents
TRADEMARKS AND SERVICE MARKS
We own or have rights to trademarks and service marks that we use in connection with the operation of our business, including QuintilesIMS, Quintiles, the Quintiles logo, IMS Health, IMS, the IMS logo, IMS One, MIDAS, One Key, Xponent, DDD, MD360 Provider Performance Management and E360. All other trademarks or service marks appearing in this annual report that are not identified as marks owned by us are the property of their respective owners.
Solely for convenience, the trademarks, service marks and trade names referred to in this annual report are listed without the ®, (sm) and (TM) symbols, but we will assert, to the fullest extent under applicable law, our rights or the rights of the applicable licensors to these trademarks, service marks and trade names. We do not intend our use or display of other companies’ trademarks or service marks to imply an endorsement or sponsorship of us by such other companies.
4
Table of Contents
Our Company
We are a leading worldwide integrated information and technology-enabled healthcare service provider, dedicated to helping our clients improve their clinical, scientific and commercial results. Formed through the merger of Quintiles and IMS Health, QuintilesIMS’s over 50,000 employees conduct operations in more than 100 countries. Our broad range of healthcare information, technology and service solutions span the entire product lifecycle, from clinical to commercial operations, bringing clients an opportunity to realize the full potential of innovations and advanced healthcare outcomes.
Following the Merger, we have one of the largest and most comprehensive collections of healthcare information in the world, which includes more than 530 million comprehensive, longitudinal, anonymous patient records spanning sales, prescription and promotional data, medical claims, electronic medical records and social media. Our scaled and growing data set contains over 20 petabytes of proprietary data sourced from more than 100,000 data suppliers and covering over 800,000 data feeds globally. Based on this data, we deliver information and insights on over 85% of the world’s pharmaceuticals, as measured by 2015 sales. We standardize, organize, structure and integrate this data by applying our sophisticated analytics and leveraging our global technology infrastructure. This helps our clients run their organizations more efficiently and make better decisions to improve their clinical, commercial and financial performance. The breadth of the intelligent, actionable information we provide is not comprehensively available from any other source and our scope of information would be difficult and costly for another party to replicate.
We leverage our proprietary information assets to develop clinical and commercial capabilities with a talented healthcare-focused workforce that enables us to grow our relationships with healthcare stakeholders throughout the life science’s value chain. This set of capabilities includes:
| • | A leading healthcare-specific global IT infrastructure, representing what we believe is one of the largest and most sophisticated information technology infrastructures in healthcare. By processing over 65 billion healthcare transactions annually, our infrastructure connects complex healthcare data while applying a wide range of privacy, security, operational, legal and contractual protections for data in response to local law, supplier requirements and industry leading practices; |
| • | Data-enriched clinical development, which improves clinical trial design, site identification and patient recruitment by empowering therapeutic, scientific, and domain experts with expansive levels of information, including product level tracking in 90 markets, and information about treatments and outcomes on more than 530 million anonymous patients; |
| • | Robust real-world insights ecosystem, with sophisticated retrospective database analytics, prospective real-world data collection technology platforms and scientific expertise, which enables us to address critical healthcare issues of cost, value and patient outcomes; |
| • | A growing set of proprietary commercial applications, which support our clients’ sales operations, sales management, multi-channel marketing and performance management; and |
| • | A staff of more than 50,000 employees across the globe, including approximately 16,000 Commercial Services employees, approximately 27,000 Research & Development Solutions employees and approximately 7,000 Integrated Engagement Services employees. |
5
Table of Contents
Our mission-critical relationships with our life science clients consist of four important decision-making processes related to their product portfolios: Research and Development, Pre-Launch, Launch and In-Market. We continue to develop software and services applications to further deepen our level of client integration by enabling our clients to enhance and/or automate many components of these key decision-making processes.

| • Market opportunity assessment |
• Drug pricing optimization |
• Market access |
• Commercial operations | |||
| • Project management and clinical monitoring |
• Launch readiness |
• Health technology assessment |
• Sales force effectiveness | |||
| • Clinical trial support services |
• Commercial planning |
• Commercial readiness |
• Sales force alignment | |||
| • Patient recruitment |
• Brand positioning |
• Forecasting |
• Multi-channel marketing | |||
| • Clinical trial laboratory services |
• Message testing |
• Resource allocation |
• Client relationship management | |||
| • Strategic clinical trial planning and design |
• Influence networks |
• Contract sales force |
• Lifecycle management | |||
| • Territory design |
• Observational studies |
|||||
| • Stakeholder engagement |
||||||
6
Table of Contents
We believe that a powerful component of our value proposition is the breadth and depth of intelligence we provide to help our clients address fundamental operational questions.
| User | Illustrative Questions | |||||
| Research & Development | Which study centers have the target patients? | Are there enough patients for my clinical trial? | How long will trial enrollment take to hit target patient volumes? | |||
| Sales | Which providers generate the highest return on representative visit? | Does my sales representative drive appropriate prescribing? | How much should I pay my sales representative next month? | |||
| Marketing | What share of patients is appropriately treated? | Which underserved patient populations will benefit most from my new drug? | Is my brand gaining market share quickly enough to hit revenue forecasts? | |||
| Real-World Evidence/Pharmacovigilance | What is the likely impact of new therapies on costs and outcomes? | Are new therapies performing better against existing standards of care in real-world settings? | Does real-world data indicate adverse events not detected in clinical trials? | |||
Our Market Opportunity
We compete in a market of greater than $230 billion consisting of outsourced research and development, real-world evidence and connected health and technology enabled commercial operations markets for the life sciences companies and the broader healthcare industry. The following sets forth our estimates for the size of our principal markets:
| • | Outsourced research and development: Biopharmaceutical spending on drug development totaled approximately $100 billion in 2016. Of that amount, we estimate that our addressable market (clinical development spending excluding preclinical spending) was approximately $56 billion. The portion of this addressable market that was outsourced in 2016, based on our estimates, was approximately $24 billion; |
| • | Real-World Evidence and connected health: Total addressable market of approximately $80 billion based on 2016 sales that consists of two relatively equal parts. First, the market for Real-World Evidence of approximately $40 billion includes traditionally defined analytic platforms and implementation, medical and scientific analytic services, observation studies and market access. Second, the market for connected healthcare of approximately $40 billion includes areas such as revenue cycle management, payer analytics and clinical decision support services; and |
| • | Technology enabled commercial operations: Total addressable market of approximately $50 billion based on 2016 sales that includes information, data warehousing, IT outsourcing, software applications and other services in the broader market for IT services. This addressable market also includes commercial services such as recruiting, training, deploying and managing global sales forces, channel management, patient engagement services, market access consulting, brand communication, advisory services, and health information analytics and technology consulting. |
In deriving estimates of the size of the various markets described above, we review third-party sources, which include estimates and forecasts of spending in various market segments, in combination with internal QuintilesIMS research and analysis informed by our experience serving these market segments, as well as projected growth rates for each of these segments.
7
Table of Contents
We believe there are six key trends affecting our end markets that will create increasing demand for research and development services and commercial solutions:
Growth and innovation in the life sciences industry. The life sciences industry is a large and critical part of the global healthcare system, and, according to the latest information available from the QuintilesIMS Market Prognosis service, is estimated to have generated approximately $1.1 trillion in revenue in 2016. According to our research, revenue growth in the life sciences industry globally is expected to range from 4% to 7% between 2017 and 2021. According to the QuintilesIMS Institute, it is estimated that spending on pharmaceuticals in emerging markets will expand at a 6-9% compound annual growth rate (“CAGR”) through 2021. The growth of emerging markets is making these geographies strategically important to life sciences organizations and, consistent with their approach in the developed markets, we expect these organizations to apply a high degree of sophistication to their commercial operations in these countries. For global companies, this requires highly localized knowledge and information assets, the development of market access strategies and performance benchmarking. In addition, local players are learning that they need to compete on the basis of improved information and analytics.
Growth in Research and Development. Spending trends in research and development are impacted as a result of several factors, including major biopharmaceutical companies’ efforts to replenish revenues lost from the so-called “patent cliff” of recent years, increased access to capital by the small and midcap biotechnology industry, and recent increases in pharmaceutical approvals by regulatory authorities. The QuintilesIMS Institute also estimates that 225 new molecular entities (“NMEs”) are expected to be approved between 2017 and 2021, compared to 184 between 2011 and 2015, and 146 between 2006 and 2010. We believe that further research and development spending, combined with the continued need for cost efficiency across the healthcare landscape, will continue to create opportunities for biopharmaceutical services companies, particularly those with a global reach and broad service offerings, to help biopharmaceutical companies with their pre- and post-launch solutions development and commercialization needs.
Increased Complexity in Research and Development. Biopharmaceutical companies face environments in which it has become increasingly difficult to operate. Improved standards of care in many therapeutic areas and the emergence of new types of therapies, such as biologics, genetically targeted therapies, gene and stem cell therapies, and other treatment modalities have led to more complex development and regulatory pathways. For example, the United States and European countries have recently released guidelines for the development of “biosimilar” products. We believe that our global clinical development capabilities, including our expertise in biomarkers and genomics and our global laboratory network, position us well to help biopharmaceutical companies manage the complexities inherent in an environment where this type of expertise is important.
Regulators require clinical trials involving local populations as part of the process for approving new pharmaceutical products, especially in certain Asian and emerging markets. Understanding the epidemiological and physiological differences in different ethnic populations and being able to conduct clinical trials locally in certain geographies will be important to pharmaceutical product growth strategies, both for multinational and local/regional biopharmaceutical companies. We believe that our global clinical development capabilities and unmatched presence in Asia and other emerging markets make us a strong partner for biopharmaceutical companies managing the complexities of international drug development.
Financial pressures driving the need for increased efficiency. Despite expected accelerating growth in the global life sciences market, we believe our clients will face increased operating margin pressure due to their changing product mix, pricing and reimbursement challenges, and rising costs of compliance. Product portfolios for life sciences companies have shifted toward specialty products with lower peak market sales potential than traditional primary care medicines. We believe that the need for biopharmaceutical companies to maximize productivity and lower costs across their processes from research and development through commercial
8
Table of Contents
operations will cause them to look to partners as they enter into outsourcing arrangements to improve efficiency. Further, our clients are looking for new ways to simplify processes and drive operational efficiencies by using automation, consolidating vendors and adopting new technology options such as hosted and cloud-based applications. This provides opportunities for technology services vendors to capture and consolidate internal spending by providing lower-cost and variable-cost options that lower clients’ research and development, selling, marketing and administrative costs.
Evolving need to integrate and structure expanding sources of data. Over the past decade, many health systems around the world have focused on digitizing medical records. While such records theoretically enhance access to data, relevant information is often unintegrated, unstructured, siloed in disparate software systems, or entered inconsistently. In addition, new sources of data from the internet, such as social media and information on limited patient pools, and information resulting from enhanced diagnostic technologies are creating new sources of healthcare data.
In order to derive valuable insights from existing and expanding sources of information, clients need access to statistically significant data sets organized into databases that can be queried and analyzed. For example, real-world evidence studies demonstrate practical and clinical efficacies, which we believe require the aggregation and integration of large clinical data sets across all care settings, types of therapies and patient cohorts. Longitudinal studies require analysis of anonymous patient diagnoses, treatments, procedures and laboratory test results to identify types of patients that will likely best respond to particular therapies. Finally, manufacturers also require the ability to analyze social media activity to identify the specific patient and advocacy groups that influence the adoption of new orphan drugs. This information is highly relevant to all healthcare stakeholders and we believe the opportunity to more broadly apply healthcare data can only be realized through structuring, organizing and integrating new and existing forms of data in conjunction with sophisticated analytics.
Need for demonstrated value in healthcare. Participants in the healthcare industry are focused on improving quality and reducing costs, both of which require assessment of quality and value of therapies and providers. As a result, physicians no longer make prescribing decisions in isolation, but rather in the context of guidance and rules from payers, integrated delivery networks and governments. We believe life sciences companies are working to bring alignment across constituents on the value of their treatments in order to successfully develop and commercialize new therapies.
There is increasing pressure on life sciences companies to support and justify the value of their therapies. Many new drugs that are being approved are more expensive than existing therapies, and will likely receive heightened scrutiny by regulators and payers to determine whether the existing treatment options would be sufficient. Additionally, many new specialty drugs are molecular-based therapies and require a more detailed understanding of clinical factors and influencers that demonstrate therapeutic value. As a result, leading life sciences companies are utilizing more sophisticated outcome research and data analytics services.
We believe we are well positioned to take advantage of these global trends in healthcare. Beyond our proprietary information assets, we have developed key capabilities to assess opportunities to develop and commercialize therapies, support and defend the value of medicines and help our clients operate more efficiently through the application of insight-driven decision-making and cost-efficient technology solutions.
Our Growth Strategy
We believe we are well positioned for continued growth across the markets we serve. Our strategy for achieving growth includes:
Continue to innovate by leveraging our information, technology and service capabilities. As a leader in the development and commercialization of new pharmaceutical therapies, we can empower our therapeutic,
9
Table of Contents
scientific and domain experts with expansive levels of information including product level tracking in 90 markets and information about treatments and outcomes on more than 530 million anonymous patients. Further, we have the ability to optimize the clinical trial process and enable our clients to reduce costs and get their products to market more quickly by running their clinical trials more efficiently and effectively through more informed site selection and faster patient recruitment practices.
Build upon our extensive client relationships. We have a diversified base of over 5,000 clients in over 100 countries, and through the Merger have expanded our client value proposition to address a broader market for research and development and commercial operations which we estimate to be $230 billion in 2016. Through the combined offerings of research and development and commercial services we built a platform that allows us to be a more complete partner to our clients.
Expand portfolio through strategic acquisitions. We have and expect to continue to acquire assets and businesses that strengthen our value proposition to clients. We have developed an internal capability to source, evaluate and integrate acquisitions that have created value for stockholders. As the global healthcare landscape evolves, we expect that there will be a growing number of acquisition opportunities across the life sciences, payer and provider sectors. We expect to continue to invest in or explore opportunities for strategic acquisitions to grow our platform and enhance our ability to provide more services to our clients.
Expand the penetration of our offerings to the broader healthcare marketplace. We believe that substantial opportunities exist to expand penetration of our addressable market and further integrate our offerings in a broader cross-section of the healthcare marketplace, particularly connected healthcare.
Our Offerings
We offer hundreds of distinct services, applications and solutions to help our clients make critical decisions and perform better. Following the Merger, we now have three operating segments: Commercial Solutions, Research & Development Solutions and Integrated Engagement Services. Their offerings complement each other and can provide enhanced value to our clients when delivered together, with each driving demand for the other.
For financial information regarding our segments, see Part II, Item 7 “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Consolidated Results of Operations-Segment Results of Operations and Note 22 to our audited consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Please refer to Note 21 to our audited consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K for further details regarding our foreign and domestic operations in 2016, 2015 and 2014. For a discussion of risks attendant to our foreign operations, see “Risk Factors — Our business is subject to international economic, political and other risks that could negatively affect our results of operations and financial condition.”
Our principal Commercial Solutions offerings include:
National information offerings. Our national offerings comprise unique services in more than 80 countries that provide consistent country level performance metrics related to sales of pharmaceutical products, prescribing trends, medical treatment and promotional activity across multiple channels including retail, hospital and mail order. These solutions are an integral part of critical processes in life science companies around the world and are also used extensively by the investment and financial sectors that deal with life science companies.
Sub-national information offerings. Our sub-national offerings comprise unique services in more than 60 countries that provide a consistent measurement of sales or prescribing activity at the regional, zip code and individual prescriber level (depending on regulation in the relevant country). These solutions are used extensively, with a majority of pharmaceutical sales organizations within these countries dependent on these services to set goals, determine resourcing, measure performance and calculate compensation.
10
Table of Contents
OneKey. Our widely used reference database that tracks more than 14 million healthcare professionals in more than 70 countries, providing a comprehensive view of health care practitioners that is critical for the commercial success of our clients’ marketing and sales initiatives.
Real-World Insights. We enable clients to use anonymous patient-level data to understand treatments, outcomes, and costs to inform and advance healthcare decision making. With patient privacy and security safeguards, we offer data assets that integrate medical claims, prescriptions, electronic medical records, biomarkers and government statistics as needed for research requirements. Our proprietary technologies and advanced analytic skills enable us to help payer, government, and biopharmaceutical clients manage and use this information to understand the effectiveness and economic efficiency of drugs in real-world use.
Technology solutions. We provide an extensive range of cloud-based applications and associated implementation services. SaaS solutions support a wide range of commercial and regulatory processes, including multi-channel marketing, customer relationship management (“CRM”), performance management, incentive compensation, territory alignment, roster management, call planning, compliance reporting and master data management. These solutions are used by healthcare companies to manage, optimize and execute their commercial strategies in an orchestrated manner while addressing their regulatory obligations. Using proprietary algorithms, we combine our country-level data, healthcare expertise and therapeutic knowledge in over 100 countries to create our Global Market Insight family of offerings such as MIDAS, Analytics Link and Disease Insights, which provides a leading source of insight into international market dynamics and are used by most large pharmaceutical companies.
Workflow analytics and consulting services. We provide a broad set of strategic and implementation consulting services, including advanced analytics and commercial processes outsourcing services to help the commercial operations of life sciences companies successfully transform their commercial models, engage more effectively with the healthcare stakeholders and reduce their operating costs. We also help our client’s R&D function to address strategic challenges in the drug development process. Our global teams leverage local market knowledge, deep scientific and therapeutic area expertise and our global information resources to assist our clients with R&D strategy, portfolio, brand and commercial strategy, as well as pricing and market access and launch excellence.
Our principal Research & Development Solutions offerings include:
Project Management and Clinical Monitoring. Drawing upon our years of experience, our site databases, our site relationships and our highly trained staff, Clinical Solutions & Services enables the efficient conduct and coordination of multi-site clinical trials (generally Phase II-IV). Clinical Solutions & Services’ service offerings include protocol design, feasibility and operational planning, site start up and patient recruitment.
Clinical Trial Support Services. Each clinical trial requires a number of concurrent services and data streams. We offer a broad range of functional services and consultation to support clinical trials through specialized expertise that help clients efficiently collect, analyze and report the quality data and evidence they need to gain regulatory approval.
Q2 Solutions. We provide our clients globally scaled end-to-end clinical trial laboratory and research services through our majority-owned joint venture with Quest Diagnostics Incorporated (“Quest”) which was formed on July 1, 2015. We offer clinical trial, genomic, and bioanalytical laboratory service offerings within the joint venture, which is referred to as Q2 Solutions.
Strategic Planning and Design. Through our strategic planning and design services, we offer consultation services to improve decisions and performance including portfolio, program and protocol planning and design, biomarker consultation, benefit-risk management, regulatory affairs, biostatistics, modeling and simulation, and personalized medicine.
11
Table of Contents
Our Research & Development Solutions segment is the world’s largest provider of biopharmaceutical development services. We are positioned at the intersection of business services and healthcare. We use the breadth and depth of our service offerings, our global footprint and our therapeutic, scientific and analytics expertise to help biopharmaceutical companies, as well as other healthcare clients to be more successful in an increasingly complex healthcare environment.
Our Research & Development Solutions backlog was $9.5 billion at December 31, 2016 as compared to $8.9 billion at December 31, 2015. We expect $2.9 billion of this to convert to revenue over the next 12 months. See Part II, Item 7, “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations – Backlog and Net New Business Reporting” for more detail.
Our principal Integrated Engagement Services offerings include:
Health Care Provider Engagement Services. We partner with biopharmaceutical companies and other life sciences providers (e.g., medical device companies) to develop and deploy tailored stakeholder engagement solutions, including contract sales and market access professionals, which maximize brand value at all stages of the product lifecycle from initial market entry to brands nearing patent expiry.
Patient Engagement Services. Our nurse-based programs directly engage with patients to help improve their disease and medication understanding through interventional and non-interventional support, while also providing assistance in navigating complex reimbursement coverage issues. Our patient engagement services combine insight from clinical trials and social listening, behavioral design, personal and innovative eHealth multichannel interactions across multiple sites (e.g., the physician’s office, hospital, pharmacy, home), that act as an extension of the Health Care Provider prescribed treatment course which can lead to improved adherence and better overall outcomes.
Medical Affairs Services. We provide a range of scientific strategy and medical affairs services to help biopharmaceutical companies plan and transition from the clinical trial setting to commercialization. Beginning in the clinical trial stage, our services can deploy educators to clinical trial sites to accelerate patient recruitment and improve retention, assist in translation of complex clinical trial data into a compelling scientific platform and publication strategy, and, provide field medical teams to facilitate scientific engagement with key opinion leaders and healthcare decision makers, before and after product approval.
Our Clients
Sales to companies in life sciences, including pharmaceutical companies, biotechnology companies, device and diagnostic companies, and consumer health companies, accounted for the majority of our revenues. Nearly all of the top 100 global pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies, measured by revenue, are clients, and many of these companies subscribe to reports and services in many countries. Other clients include payers, government and regulatory agencies, providers, pharmaceutical distributors, and pharmacies. Our client base is broad in scope and enables us to avoid dependence on any single client. No single client accounted for 10% or more of our combined company revenues in 2016, 2015 or 2014.
Our Competition
Our Commercial Solutions business competes with a broad and diverse set of businesses. While we believe no competitor provides the combination of geographical reach and breadth of its services, we generally compete in the countries in which we operate with other information, analytics, technology, services and consulting companies, as well as with the in-house capabilities of our clients. Also, we compete with certain government agencies, private payers and other healthcare stakeholders that provide their data directly to others. In addition to country-by-country competition, we have a number of regional and global competitors in the marketplace as well. Our offerings compete with various firms, including Accenture, Cognizant Technology Solutions, Covance, Deloitte, Evidera, GfK, LexisNexis Risk Solutions, IBM, Infosys, inVentiv Health, Kantar Health, McKinsey, Nielsen, OptumInsight, Parexel, Press Ganey, RTI Health Solutions, Symphony Health Solutions, Synovate
12
Table of Contents
Healthcare, The Advisory Board, Trizetto, Veeva, Verisk, and ZS Associates. We also compete with a broad range of new entrants and start-ups that are looking to bring new technologies and business models to healthcare information services and technology services.
The markets for Research & Development Solutions offerings are highly competitive, and we compete against traditional contract research organizations (“CROs”), the in-house research and development departments of biopharmaceutical companies, universities and teaching hospitals. Among the traditional CROs, there are several-hundred small, limited-service providers, several medium-sized firms and only a few full-service companies with global capabilities. Consolidation among CROs likely will result in greater competition among the larger CROs for customers, clinical personnel and acquisition candidates. Our primary competitors include Pharmaceutical Product Development, Inc., PAREXEL International Corporation, ICON plc, inVentiv Health, Inc., INC Research, PRA International, and Covance Inc., the drug development business of Laboratory Corporation of America Holdings, among others. Competitive factors include: previous experience and relationships; medical and scientific experience in specific therapeutic areas; the quality of contract research; speed to completion; the ability to organize and manage large scale clinical trials on a global basis; the ability to manage large and complex medical databases; the ability to provide statistical, regulatory and consulting services; the ability to recruit investigators and patients expeditiously; the ability to deploy and integrate IT systems to improve the efficiency of contract research; risk and reward sharing; the ability to form strategic alliances; a global presence with strategically located facilities and breadth of service offerings; financial strength and stability; and price.
The market for our Integrated Engagement Services competes in the post-approval arena. We compete against the in-house sales and marketing departments of biopharmaceutical companies, other contract pharmaceutical sales and service organizations and consulting firms. Integrated Engagement Services’ primary competitor in the United States is Publicis. Outside of the United States, Integrated Engagement Services typically competes against single country or more regionally focused service providers, such as United Drug plc, inVentiv, EPS Corporation and CMIC HOLDINGS Co., Ltd in Japan. The primary competitive factors affecting Integrated Engagement Services are breadth of service offering and ability to deploy in an integrated manner, quality and track record, i.e. the proven ability to quickly assemble, train and manage large qualified teams on a global footprint and price. Also, we compete with certain government agencies, private payers and other healthcare stakeholders that provide their data directly to others.
Government Regulation
Many aspects of our businesses are regulated by federal and state laws, rules and regulations. Accordingly, we maintain a comprehensive compliance program and we believe we operate our business in substantial compliance with all existing legal requirements material to the operation of our businesses. There are, however, significant uncertainties involving the application of various legal requirements, the violation of which could result in, among other things, sanctions. See “Part I—Item 1A—Risk Factors” for additional detail.
Good Clinical Practice
Good Clinical Practice (“GCP”) regulations and guidelines contain the industry standards for the conduct of clinical trials with respect to the integrity of the data and safety of the research subjects. The United States Food and Drug Administration (“FDA”), the European Medicines Agency (“EMA”), Japan’s Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare and many other regulatory authorities require that study results and data submitted to such authorities be based on clinical trials conducted in accordance with GCP provisions. Records for clinical trials must be maintained for specified periods for inspection by the FDA and other regulators.
Regulation of Drugs, Biologics and Medical Devices
In the United States, pharmaceutical, biological and medical device products are subject to extensive regulation by the FDA. The Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (“FDC Act”), the Public Health Service Act (“PHS Act”), and other federal and state statutes and regulations, govern, among other things, the research, development, testing, manufacture, storage, recordkeeping, approval, labeling, promotion and marketing, distribution, post-approval monitoring and reporting, sampling, and import and export of pharmaceutical,
13
Table of Contents
biological and medical device products. Failure to comply with applicable United States requirements may subject a company to a variety of administrative or judicial sanctions, such as FDA refusal to approve a pending new drug application (“NDA”) for a new drug, a biologics license application (“BLA”) for a new biological product pre-market approval (“PMA”) or clearance for a new medical device, warning or untitled letters, product recalls, product seizures, total or partial suspension of production or distribution, injunctions, fines, civil penalties, and criminal prosecution.
Regulation of Patient Information
Our information management services relate to the diagnosis and treatment of disease and are, therefore, subject to substantial governmental regulation. In addition, the confidentiality of patient-specific information and the circumstances under which such patient-specific records may be released for inclusion in our databases or used in other aspects of our business is heavily regulated. Federal, state and foreign governments are contemplating or have proposed or adopted additional legislation governing the possession, use and dissemination of personal data, such as personal health information and personal financial data, as well as security breach notification rules for loss or theft of such data. Additional legislation or regulation of this type might, among other things, require us to implement new security measures and processes or bring within the legislation or regulation de-identified health or other personal data, each of which may require substantial expenditures or limit our ability to offer some of our services.
In particular, personal health-related information is recognized in many countries such as the United States, the European Union, or EU, and several countries in Asia, as a special, sensitive category of personal information, subject to additional mandatory protections. Violations of data protection regulations are subject to administrative penalties, civil money penalties and criminal prosecution, including corporate fines and personal liability.
Regulation of Promotion, Marketing and Distribution of Pharmaceutical Products and Medical Devices
Our services are subject to detailed and comprehensive regulation in each geographic market in which we operate. Such regulation relates, among other things, to the distribution of drug samples, the marketing and promotion of approved products, the qualifications of sales representatives and the use of healthcare professionals in sales functions.
In the United States, our services are subject to numerous federal and state laws pertaining to promotional activities involving pharmaceutical products and medical devices, such as the FDA’s regulations against “off-label promotion,” which require sales representatives to restrict promotion of the approved product they are detailing to the approved labeling for the product, and the Prescription Drug Marketing Act which imposes licensing, personnel record keeping, packaging, labeling, product handling and facility storage and security requirements. Other federal and state laws prohibit manufacturers, suppliers and providers from offering, giving or receiving kickbacks or other remuneration in connection with ordering or recommending the purchase or rental of healthcare items and services. The sale or distribution of pharmaceutical products and devices is also governed by the United States Federal Trade Commission Act and state consumer protection laws. We are subject to similar regulations currently in effect in the other countries where we offer Integrated Healthcare Services.
We are also subject to various laws and regulations that may apply to certain drug and device promotional practices, including, among others, various aspects of the Medicare program. Violations of these laws and regulations may result in criminal and/or civil penalties, including possibly as an “aider and abettor.”
14
Table of Contents
Regulation of Laboratories
Our United States “central” laboratories are subject to licensing and regulation under federal, state and local laws relating to hazard communication and employee right-to-know regulations, and the safety and health of laboratory employees. Additionally, our United States laboratories are subject to applicable federal and state laws and regulations and licensing requirements relating to the handling, storage and disposal of hazardous waste, radioactive materials and laboratory specimens, including the regulations of the Environmental Protection Agency, the Nuclear Regulatory Commission, the Department of Transportation, the National Fire Protection Agency and the United States Drug Enforcement Administration (“DEA”). The use of controlled substances in testing for drugs with a potential for abuse is regulated in the United States by the DEA and by similar regulatory bodies in other parts of the world. Our United States laboratories using controlled substances for testing purposes are licensed by the DEA. The regulations of the United States Department of Transportation, Public Health Service and Postal Service apply to the surface and air transportation of laboratory specimens. Our laboratories also are subject to International Air Transport Association regulations, which govern international shipments of laboratory specimens. Furthermore, when the materials are sent to a foreign country, the transportation of such materials becomes subject to the laws, rules and regulations of such foreign country. Our laboratories outside the United States are subject to applicable national laws governing matters such as licensing, the handling and disposal of medical specimens, hazardous waste and radioactive materials, as well as the health and safety of laboratory employees.
In addition to its comprehensive regulation of safety in the workplace, the United States Occupational Safety and Health Administration has established extensive requirements relating to workplace safety for healthcare employers whose workers may be exposed to blood-borne pathogens such as HIV and the hepatitis B virus. Although we believe that we are currently in compliance in all material respects with such federal, state and local laws, failure to comply with such laws could subject us to denial of the right to conduct business, fines, criminal penalties and other enforcement actions.
Further, laboratories that analyze human blood or other biological samples for the diagnosis and treatment of clinical trial subjects must comply with Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (“CLIA”), as well as requirements established by various states. The failure to meet these requirements may result in civil penalties and suspension or revocation of the CLIA certification.
Our Intellectual Property
In addition to our proprietary data sets described above, we develop and use a number of proprietary methodologies, analytics, systems, technologies and other intellectual property in the conduct of our business. We rely upon a combination of legal, technical, and administrative safeguards to protect our proprietary and confidential information and trade secrets, and patent, copyright and trademark laws to protect other intellectual property rights. We consider our trademark and related names, marks and logos to be of material importance to our business, and we have registered or applied for registration for certain of these trademarks including QuintilesIMS, Quintiles, IMS Health and IMS, in the United States and other jurisdictions and aggressively seek to protect them. Trademarks and service marks generally may be renewed indefinitely so long as they are in use and/or their registrations are properly maintained, and so long as they have not been found to have become generic. Although we believe the ownership of our patents, trademarks and service marks is an important factor in our business and that our success does depend in part on the ownership thereof, we rely primarily on the innovative skills, technical competence and marketing abilities of our employees.
Our Employees
As of December 31, 2016, we have over 50,000 employees worldwide. Almost all of these employees are full-time. None of our employees are covered by a collective bargaining agreement or are represented by a labor
union. Employees in certain locations outside of the United States are represented by works councils as required
15
Table of Contents
by local laws. We believe that our relations with our employees are good and have been maintained in a normal and customary manner.
Available Information
Our website address is www.quintilesims.com, and our investor relations website is located at http://ir.quintilesims.com. Information on our website is not incorporated by reference herein. Copies of our annual reports on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, current reports on Form 8-K and our Proxy Statements for our annual meetings of stockholders, and any amendments to those reports, as well as Section 16 reports filed by our insiders, are available free of charge on our website as soon as reasonably practicable after we file the reports with, or furnish the reports to, the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”). Our SEC filings are also available for reading and copying at the SEC’s Public Reference Room at 100 F Street, NE, Washington, D.C. 20549. Information on the operation of the Public Reference Room may be obtained by calling the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330. In addition, the SEC maintains an Internet site (http://www.sec.gov) containing reports, proxy and information statements, and other information regarding issuers that file electronically with the SEC. Information on the SEC’s website does not constitute part of this report. Also posted on our website are our certificate of incorporation and by-laws, the charters for our Audit Committee, Leadership Development and Compensation Committee and Nominating and Governance Committee, our Corporate Governance Guidelines, and our Code of Conduct governing our directors, officers and employees. Copies of our SEC reports and corporate governance information are available in print upon the request of any stockholder to our Investor Relations Department. Within the time period required by the SEC and the New York Stock Exchange (“NYSE”), we will post on our website any amendment to the Code of Business Conduct or the Code of Ethics for Chief Executive Officer and Senior Financial Officers or any waiver of either such policy applicable to any of our senior financial officers, executive officers or directors.
16
Table of Contents
Item 1A. Risk Factors
We operate in a rapidly changing environment that involves a number of risks, some of which are beyond our control. You should consider carefully the risks and uncertainties described below together with the other information included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, including our consolidated financial statements and related notes included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, in evaluating our company. The occurrence of any of the following risks may materially and adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations and future prospects.
Risks Relating to Our Business
The potential loss or delay of our large contracts or of multiple contracts could adversely affect our results.
Most of our Research & Development Solutions clients can terminate our contracts upon 30 to 90 days notice. Our clients may delay, terminate or reduce the scope of our contracts for a variety of reasons beyond our control, including but not limited to:
| • | decisions to forego or terminate a particular clinical trial; |
| • | lack of available financing, budgetary limits or changing priorities; |
| • | actions by regulatory authorities; |
| • | production problems resulting in shortages of the drug being tested; |
| • | failure of products being tested to satisfy safety requirements or efficacy criteria; |
| • | unexpected or undesired clinical results for products; |
| • | insufficient patient enrollment in a clinical trial; |
| • | insufficient investigator recruitment; |
| • | shift of business to a competitor or internal resources; |
| • | product withdrawal following market launch; or |
| • | shut down of manufacturing facilities. |
As a result, contract terminations, delays and alterations are a regular part of our Research & Development Solutions business. In the event of termination, our contracts often provide for fees for winding down the project, but these fees may not be sufficient for us to maintain our margins, and termination may result in lower resource utilization rates. In addition, we may not realize the full benefits of our backlog of contractually committed services if our clients cancel, delay or reduce their commitments under our contracts with them, which may occur if, among other things, a client decides to shift its business to a competitor or revoke our status as a preferred provider. Thus, the loss or delay of a large contract or the loss or delay of multiple contracts could adversely affect our revenues and profitability. We believe the risk of loss or delay of multiple contracts potentially has greater effect where we are party to broader partnering arrangements with global biopharmaceutical companies.
17
Table of Contents
We depend on third parties for data and support services. Our suppliers or providers might restrict our use of or refuse to license data or provide services, which could lead to our inability to access certain data or provide certain services and, as a result, materially and adversely affect our operating results and financial condition.
Each of our Commercial Solutions information services is derived from data we collect from third parties. These data suppliers are numerous and diverse, reflecting the broad scope of information that we collect and use in our business.
Although we typically enter into long-term contractual arrangements with many of these suppliers of data, at the time of entry into a new contract or renewal of an existing contract, suppliers may increase restrictions on our use of such data, increase the price they charge us for data or refuse altogether to license the data to us. In addition, during the term of any data supply contract, suppliers may fail to adhere to our data quality control standards or fail to deliver data. Further, although no single individual data supplier is material to our business, if a number of suppliers collectively representing a significant amount of data that we use for one or more of our services were to impose additional contractual restrictions on our use of or access to data, fail to adhere to our quality-control standards, repeatedly fail to deliver data or refuse to provide data, now or in the future, our ability to provide those services to our clients could be materially adversely impacted, which may harm our operating results and financial condition.
Additionally, we depend on third parties for support services to our business. Such support services include, but are not limited to, third-party transportation providers, suppliers of drugs for patients participating in clinical trials, suppliers of kits for use in our clinical trial laboratories business, suppliers of reagents for use in our testing equipment and providers of maintenance contracts for our equipment. The failure of any of these third parties to adequately provide the critical support services could have a material adverse effect on our business.
If we fail to perform our services in accordance with contractual requirements, regulatory standards and ethical considerations, we could be subject to significant costs or liability and our reputation could be harmed.
In connection with our Research & Development Solutions business, we contract with biopharmaceutical companies to perform a wide range of services to assist them in bringing new drugs to market. Our services include monitoring clinical trials, data and laboratory analysis, electronic data capture, patient recruitment and other related services. Such services are complex and subject to contractual requirements, regulatory standards and ethical considerations. For example, we must adhere to regulatory requirements such as the FDA and current GCP, Good Laboratory Practice and Good Manufacturing Practice requirements. If we fail to perform our services in accordance with these requirements, regulatory agencies may take action against us for failure to comply with applicable regulations governing clinical trials or sales and marketing practices. Such actions may include sanctions, such as injunctions or failure of such regulatory authorities to grant marketing approval of products, delay, suspension or withdrawal of approvals, license revocation, product seizures or recalls, operational restrictions, civil or criminal penalties or prosecutions, damages or fines. Clients may also bring claims against us for breach of our contractual obligations and patients in the clinical trials and patients taking drugs approved on the basis of those clinical trials may bring personal injury claims against us for negligence. Any such action could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations, financial condition and reputation.
Such consequences could arise if, among other things, the following occur:
Improper performance of our services. The performance of clinical development services is complex and time-consuming. For example, we may make mistakes in conducting a clinical trial that could negatively impact
18
Table of Contents
or obviate the usefulness of the clinical trial or cause the results of the clinical trial to be reported improperly. If the clinical trial results are compromised, we could be subject to significant costs or liability, which could have an adverse impact on our ability to perform our services. As examples:
| • | non-compliance generally could result in the termination of ongoing clinical trials or sales and marketing projects or the disqualification of data for submission to regulatory authorities; |
| • | compromise of data from a particular clinical trial, such as failure to verify that informed consent was obtained from patients, could require us to repeat the clinical trial under the terms of our contract at no further cost to our client, but at a substantial cost to us; and |
| • | breach of a contractual term could result in liability for damages or termination of the contract. |
Large clinical trials can cost up to hundreds of millions of dollars, and while we endeavor to contractually limit our exposure to such risks, improper performance of our services could have an adverse effect on our financial condition, damage our reputation and result in the cancellation of current contracts by or failure to obtain future contracts from the affected client or other clients.
Investigation of clients. From time to time, one or more of our clients are audited or investigated by regulatory authorities or enforcement agencies with respect to regulatory compliance of their clinical trials, programs or the marketing and sale of their drugs. In these situations, we have often provided services to our clients with respect to the clinical trials, programs or activities being audited or investigated, and we are called upon to respond to requests for information by the authorities and agencies. There is a risk that either our clients or regulatory authorities could claim that we performed our services improperly or that we are responsible for clinical trial or program compliance. If our clients or regulatory authorities make such claims against us and prove them, we could be subject to damages, fines or penalties. In addition, negative publicity regarding regulatory compliance of our clients’ clinical trials, programs or drugs could have an adverse effect on our business and reputation.
Insufficient client funding to complete a clinical trial. As noted above, clinical trials can cost hundreds of millions of dollars. There is a risk that we may initiate a clinical trial for a client, and then the client becomes unwilling or unable to fund the completion of the clinical trial. In such a situation, notwithstanding the client’s ability or willingness to pay for or otherwise facilitate the completion of the clinical trial, we may be ethically bound to complete or wind down the clinical trial at our own expense.
Security breaches and unauthorized use of our IT systems and information, or the IT systems or information in the possession of our vendors, could expose us, our clients, our data suppliers or others to risk of loss.
We rely upon the security of our computer and communications systems infrastructure to protect us from cyberattacks and unauthorized access. Cyberattacks can include malware, computer viruses, hacking or other significant disruption of our computer, communications and related systems. Although we take steps to manage and avoid these risks and to prevent their recurrence, our preventive and remedial actions may not be successful. Such attacks, whether successful or unsuccessful, could result in our incurring costs related to, for example, rebuilding internal systems, defending against litigation, responding to regulatory inquiries or actions, paying damages or fines, or taking other remedial steps with respect to third parties. Publicity about vulnerabilities and attempted or successful incursions could damage our reputation with clients and data suppliers and reduce demand for our services.
We also store proprietary and sensitive information in connection with our business, which could be compromised by a cyberattack. To the extent that any disruption or security breach results in a loss or damage to our data, an inappropriate disclosure of proprietary or sensitive information, an inability to access data sources, or an inability to process data or provide our offerings to our clients, it could cause significant damage to our
19
Table of Contents
reputation, affect our relationships with our data suppliers and clients (including loss of suppliers and clients), lead to claims against us and ultimately harm our business. We may be required to incur significant costs to alleviate, remedy or protect against damage caused by these disruptions or security breaches in the future. We may also face inquiry or increased scrutiny from government agencies as a result of any such disruption or breach. While we have insurance coverage for certain instances of a cyber security breach, our coverage may not be sufficient if we suffer a significant attack or multiple attacks. Any such breach or disruption could have a material adverse effect on our operating results and our reputation as a provider of mission-critical services.
Some of our vendors have significant responsibility for the security of certain of our data centers and computer-based platforms. Also, our data suppliers have responsibility for security of their own computer and communications environments. These third parties face risks relating to cyber security similar to ours, which could disrupt their businesses and therefore materially impact ours. Accordingly, we are subject to any flaw in or breaches to their computer and communications systems or those that they operate for us, which could result in a material adverse effect on our business, operations and financial results.
Failure to meet productivity objectives under our internal business transformation initiatives could adversely impact our competitiveness and harm our operating results.
We are pursuing business transformation initiatives to update technology, increase innovation and obtain operating efficiencies. As part of these initiatives, we seek to improve our productivity, flexibility, quality, functionality and cost savings by investing in the development and implementation of global platforms and integration of our business processes and functions to achieve economies of scale. For example, we hired and trained more than 500 people to form a center of excellence (“COE”) in Manila, The Philippines for standardizing and cleaning data received from data suppliers, developed updated tools for standardizing and cleaning data, are moving local standardizing and cleaning from countries around the world to the Manila COE, and retired local standardizing and cleaning systems. These various initiatives may not yield their intended gains, which may impact our competitiveness and our ability to meet our growth objectives and, as a result, materially and adversely affect our business, operating results and financial condition.
If we are unsuccessful at investing in growth opportunities, our business could be materially and adversely affected.
We continue to invest significantly in growth opportunities, including the development and acquisition of new data, technologies and services to meet our clients’ needs. For example, we are expanding our services and technology offerings, such as the development of a cloud-based platform with a growing number of applications to support commercial operations for life sciences companies (e.g., multi-channel marketing, marketing campaign management, customer relationship management, incentive compensation management, targeting and segmentation, performance management and other applications). We also continue to invest significantly in growth opportunities in emerging markets, such as the development, launch and enhancement of services in China, India, Russia, Turkey and other countries. We believe healthcare spending in these emerging markets will continue to grow over the next five years, and we consider our presence in these markets to be an important focus of our growth strategy.
There is no assurance that our investment plans or growth strategy will be successful or will produce a sufficient or any return on our investments. Further, if we are unable to develop new technologies and services, clients do not purchase our new technologies and services, our new technologies and services do not work as intended or there are delays in the availability or adoption of our new technologies and services, then we may not be able to grow our business or growth may occur slower than anticipated. Additionally, although we expect continued growth in healthcare spending in emerging markets, such spending may occur more slowly or not at all, and we may not benefit from our investments in these markets.
20
Table of Contents
We plan to fund growth opportunities with cash from operations or from future financings. There can be no assurance that those sources will be available in sufficient amounts to fund future growth opportunities when needed.
Any of the foregoing could have a material and adverse effect on our operating results and financial condition.
Data protection, privacy and similar laws restrict access, use and disclosure of information, and failure to comply with or adapt to changes in these laws could materially and adversely harm our business.
Patient health information is among the most sensitive of personal information and it is critical that information about an individual’s healthcare is properly protected from inappropriate access, use and disclosure. Laws restricting access, use and disclosure of such information include the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (“HIPAA”), the European Union (“EU”) Data Protection Directive (which will be superseded by the General Data Protection Regulation), Canada’s Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act and other data protection, privacy and similar national, state/provincial and local laws. We have established frameworks, models, processes and technologies to manage privacy for many data types, from a variety of sources, and under myriad privacy and data protection laws worldwide. In addition, we rely on our data suppliers to deliver information to us in a form and in a manner that complies with applicable privacy and data protection laws. These laws are complex and there is no assurance that the safeguards and controls employed by us or our data suppliers will be sufficient to prevent a breach of these laws, or that claims will not be filed against us or our data suppliers despite such safeguards and controls. For example, in February 2014, a group of individuals filed a civil lawsuit in Korea against IMS Health Korea Ltd., our wholly-owned subsidiary (“IMS Korea”), the Korean Pharmaceutical Association (“KPA”), and a KPA affiliate that supplies data to IMS Korea. The lawsuit alleges the KPA affiliate collected plaintiffs’ personal information without the necessary consent in violation of applicable privacy laws and transferred such information to IMS Korea for sale to clients. In addition, in July 2015, indictments were issued by the Seoul Central District Prosecutors’ Office in South Korea against IMS Korea and two of its employees, among others, alleging improper handling of sensitive health information in violation of applicable privacy laws. Alleged or actual failure to comply with such laws may result in, among other things, negative publicity, damage to our reputation, civil and criminal liability, data being blocked from use or liability under contractual provisions.
Laws and expectations relating to privacy continue to evolve, and we continue to adapt to changing needs. Nevertheless, changes in these laws (including newly released interpretations of these laws by courts and regulatory bodies) may limit our data access, use and disclosure, and may require increased expenditures by us or may dictate that we not offer certain types of services. Any of the foregoing may have a material adverse impact on our ability to provide services to our clients or maintain our profitability.
There is ongoing concern from privacy advocates, regulators and others regarding data protection and privacy issues, and the number of jurisdictions with data protection and privacy laws has been increasing. Also, there are ongoing public policy discussions regarding whether the standards for de-identified, anonymous or pseudonomized health information are sufficient, and the risk of re-identification sufficiently small, to adequately protect patient privacy. These discussions may lead to further restrictions on the use of such information. There can be no assurance that these initiatives or future initiatives will not adversely affect our ability to access and use data or to develop or market current or future services.
Data protection, privacy and similar laws protect more than patient information, and although they vary by jurisdiction, these laws can extend to employee information, business contact information, provider information and other information relating to identifiable individuals. Failure to comply with these laws may result in, among other things, civil and criminal liability, negative publicity, damage to our reputation and liability under contractual provisions. In addition, compliance with such laws may require increased costs to us or may dictate that we not offer certain types of services.
21
Table of Contents
The occurrence of any of the foregoing could impact our ability to provide the same level of service to our clients, require us to modify our offerings or increase our costs, which could materially and adversely affect our operating results and financial condition.
Current and proposed laws and regulations regarding the protection of personal data could result in increased risks of liability or increased cost to us or could limit our service offerings.
The confidentiality, collection, use and disclosure of personal data, including clinical trial patient-specific information, are subject to governmental regulation generally in the country that the personal data were collected or used. For example, United States federal regulations under Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (“HIPAA”) and as amended in 2014 by the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health (“HITECH”) Act, require individuals’ written authorization, in addition to any required informed consent, before Protected Health Information may be used for research. We are both directly and indirectly affected by the privacy provisions surrounding individual authorizations because many investigators with whom we are involved in clinical trials are directly subject to them as a HIPAA “covered entity” and because we obtain identifiable health information from third parties that are subject to such regulations. As there are some instances where we are a HIPAA “business associate” of a “covered entity,” we can also be directly liable for mishandling protected health information. Under HIPAA’s enforcement scheme, we can be subject to up to $1.5 million in annual civil penalties for each HIPAA violation.
In the EU personal data includes any information that relates to an identified or identifiable natural person with health information carrying additional obligations, including obtaining the explicit consent from the individual for collection, use or disclosure of the information. In addition, we are subject to EU rules with respect to cross-border transfers of such data out of the EU. The United States, the EU and its member states, and other countries where we have operations, such as Japan, South Korea, Malaysia, the Philippines, Russia and Singapore, continue to issue new privacy and data protection rules and regulations that relate to personal data and health information. Failure to comply with certain certification/registration and annual re-certification/registration provisions associated with these data protection and privacy regulations and rules in various jurisdictions, or to resolve any serious privacy complaints, could subject us to regulatory sanctions, criminal prosecution or civil liability. Federal, state and foreign governments are contemplating or have proposed or adopted additional legislation governing the collection, possession, use or dissemination of personal data, such as personal health information, and personal financial data as well as security breach notification rules for loss or theft of such data. Additional legislation or regulation of this type might, among other things, require us to implement new security measures and processes or bring within the legislation other personal data, each of which may require substantial expenditures or limit our ability to offer some of our services. Additionally, if we violate applicable laws, regulations or duties relating to the use, privacy or security of personal data, we could be subject to civil liability or criminal prosecution, be forced to alter our business practices and suffer reputational harm.
Our success depends on our ability to protect our intellectual property rights.
Our success depends, in part, upon our ability to develop, use and protect our proprietary methodologies, analytics, systems, technologies and other intellectual property. Existing laws of the various countries in which we provide services or solutions offer only limited protection of our intellectual property rights, and the protection in some countries may be very limited. We rely upon a combination of trade secrets, confidentiality policies, nondisclosure, invention assignment and other contractual arrangements, and patent, copyright and trademark laws, to protect our intellectual property rights. These laws are subject to change at any time and certain agreements may not be fully enforceable, which could further restrict our ability to protect our innovations. Our intellectual property rights may not prevent competitors from independently developing services similar to or duplicative of ours. Further, the steps we take in this regard might not be adequate to prevent or deter infringement or other misappropriation of our intellectual property by competitors, former employees or other third parties, and we might not be able to detect unauthorized use of, or take appropriate and timely steps to enforce, our intellectual property rights.
22
Table of Contents
Our ability to obtain, protect and enforce our intellectual property rights is subject to general litigation or third-party opposition risks, as well as the uncertainty as to the scope of protection, registrability, patentability, validity and enforceability of our intellectual property rights in each applicable country. Governments may adopt regulations, and government agencies or courts may render decisions, requiring compulsory licensing of intellectual property rights. When we seek to enforce our intellectual property rights we may be subject to claims that the intellectual property rights are invalid or unenforceable. Litigation may be necessary in the future to enforce our intellectual property rights and to protect our confidential and proprietary information. Litigation brought to protect and enforce our intellectual property rights could be costly, time consuming and distracting to management and could result in the impairment or loss of portions of our intellectual property rights. Furthermore, our efforts to enforce our intellectual property rights may be met with defenses, counterclaims and countersuits attacking the validity and enforceability of our intellectual property rights. Our inability to protect our proprietary technology against unauthorized copying or use, as well as any costly litigation or diversion of our management’s attention and resources, could delay further sales or the implementation of our solutions, impair the functionality of our solutions, delay introductions of new solutions, result in our substituting inferior or more costly technologies into our solutions, or injure our reputation and harm our operating results and financial condition.
Depending on the circumstances, we might need to grant a specific client greater rights in intellectual property developed in connection with a contract than we otherwise generally do. In certain situations, we might forego all rights to the use of intellectual property we create, which would limit our ability to reuse that intellectual property for other clients. Any limitation on our ability to provide a service or solution could cause us to lose revenue-generating opportunities and require us to incur additional expenses to develop or license new or modified solutions for future projects.
The theft or unauthorized use or publication of our trade secrets and other confidential business information could reduce the differentiation of our services and harm our business; the value of our investment in development or business acquisitions could be reduced; and third parties might make claims against us related to losses of their confidential or proprietary information. In addition, we may not be able to discover or determine the extent of any unauthorized use of our proprietary rights. Third parties that license our proprietary rights also may take actions that diminish the value of our proprietary rights or reputation. The protection of our intellectual property may require the expenditure of significant financial and managerial resources. Moreover, the steps we take to protect our intellectual property may not adequately protect our rights or prevent third parties from infringing or misappropriating our proprietary rights. These incidents and claims could harm our business, reduce revenue, increase expenses and harm our reputation.
We may be subject to claims by others that we are infringing on their intellectual property rights.
Third parties may assert claims that we or our clients infringe their intellectual property rights and these claims, with or without merit, could be expensive to litigate, cause us to incur substantial costs and divert management resources and attention in defending the claim. In some jurisdictions, plaintiffs can also seek injunctive relief that may limit the operation of our business or prevent the marketing and selling of our services that infringe on the plaintiff’s intellectual property rights. To resolve these claims, we may enter into licensing agreements with restrictive terms or significant fees, stop selling, be required to implement costly redesigns to the affected services, or pay damages to satisfy contractual obligations to others. If we do not resolve these claims in advance of a trial, there is no guarantee that we will be successful in court. These outcomes may have a material adverse impact on our business, operating results and financial condition.
In addition, certain contracts with our suppliers or clients contain provisions whereby we indemnify, subject to certain limitations, the counterparty for damages suffered as a result of claims related to intellectual property infringement and the use of our data. Claims made under these provisions could be expensive to litigate and could result in significant payments.
23
Table of Contents
We rely on licenses from third parties to certain technology and intellectual property rights for some of our services and the licenses we currently have could terminate or expire.
Some of our Commercial Solutions services rely on technology or intellectual property rights owned and controlled by others. Our licenses to this technology or these intellectual property rights could be terminated or could expire. We may be unable to replace these licenses in a timely manner. Failure to renew these licenses, or renewals of these licenses on less advantageous terms, could harm our operating results and financial condition.
Our financial results may be adversely affected if we underprice our contracts, overrun our cost estimates or fail to receive approval for or experience delays in documenting change orders.
Most of our Research & Development Solutions contracts are either fee for service contracts or fixed-fee contracts. Our past financial results have been, and our future financial results may be, adversely impacted if we initially underprice our contracts or otherwise overrun our cost estimates and are unable to successfully negotiate a change order. Change orders typically occur when the scope of work we perform needs to be modified from that originally contemplated by our contract with the client. Modifications can occur, for example, when there is a change in a key clinical trial assumption or parameter or a significant change in timing. Where we are not successful in converting out-of-scope work into change orders under our current contracts, we bear the cost of the additional work. Such underpricing, significant cost overruns or delay in documentation of change orders could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition or cash flows.
The relationship of backlog to revenues varies over time.
Backlog, on an “as-contracted” basis, represents future revenues for our Research & Development Solutions business from work not yet completed or performed under signed binding commitments and signed contracts. Once work begins on a project, revenue is recognized over the duration of the project. Projects may be terminated or delayed by the client or delayed by regulatory authorities for reasons beyond our control. To the extent projects are delayed, the timing of our revenue could be affected. In the event that a client cancels a contract, we typically would be entitled to receive payment for all services performed up to the cancellation date and subsequent client-authorized services related to terminating the canceled project. Typically, however, we have no contractual right to the full amount of the revenue reflected in our backlog in the event of a contract cancellation. The duration of the projects included in our backlog, and the related revenue recognition, range from a few weeks to many years. Our backlog may not be indicative of our future revenues from our Research & Development Solutions business, and we may not realize all the anticipated future revenue reflected in our backlog. A number of factors may affect backlog, including:
| • | the size, complexity and duration of the projects; |
| • | the cancellation or delay of projects; and |
| • | change in the scope of work during the course of a project. |
Although an increase in backlog will generally result in an increase in revenues to be recognized over time (depending on the level of cancellations), an increase in backlog at a particular point in time does not necessarily correspond directly to an increase in revenues during a particular period. Computing backlog on an “as-contracted basis” rather than an “as awarded” basis may result in additions to the backlog later in the sales cycle than using the “as awarded” basis and may result in different rates of conversion from backlog to revenue than experienced using the “as awarded” basis. The extent to which contracts in backlog will result in revenue depends on many factors, including but not limited to delivery against projected schedules, the need for scope changes (change orders), contract cancellations and the nature, duration, size, complexity and phase of the contracts, each of which factors can vary significantly from time to time.
The rate at which our backlog converts to revenue may vary over time for a variety of reasons. The revenue recognition on larger, more global projects could be slower than on smaller, less global projects for a variety of
24
Table of Contents
reasons, including but not limited to an extended period of negotiation between the time the project is awarded to us and the actual execution of the contract, as well as an increased timeframe for obtaining the necessary regulatory approvals. Additionally, the increased complexity of clinical trials and the need to enroll precise patient populations could extend the length of clinical trials causing revenue to be recognized over a longer period of time. Further, delayed projects will remain in backlog, unless otherwise canceled by the client, and will not generate revenue at the rate originally expected. Thus, the relationship of backlog to realized revenues may vary over time.
Our business depends on the continued effectiveness and availability of our information systems, including the information systems we use to provide our services to our clients, and failures of these systems may materially limit our operations.
Due to the global nature of our business and our reliance on information systems to provide our services, we intend to increase our use of web-enabled and other integrated information systems in delivering our services. We also provide access to similar information systems to certain of our clients in connection with the services we provide them. As the breadth and complexity of our information systems continue to grow, we will increasingly be exposed to the risks inherent in the development, integration and ongoing operation of evolving information systems, including:
| • | disruption, impairment or failure of data centers, telecommunications facilities or other key infrastructure platforms; |
| • | security breaches of, cyberattacks on and other failures or malfunctions in our critical application systems or their associated hardware; and |
| • | excessive costs, excessive delays or other deficiencies in systems development and deployment. |
The materialization of any of these risks may impede the processing of data, the delivery of databases and services, and the day-to-day management of our business and could result in the corruption, loss or unauthorized disclosure of proprietary, confidential or other data. While we have disaster recovery plans in place, they might not adequately protect us in the event of a system failure. While many of our operations have disaster recovery plans in place, we currently do not have excess or standby computer processing or network capacity everywhere in the world to avoid disruption in the receipt, processing and delivery of data in the event of a system failure. Despite any precautions we take, damage from fire, floods, hurricanes, power loss, telecommunications failures, computer viruses, break-ins and similar events at our various computer facilities could result in interruptions in the flow of data to our servers and from our servers to our clients. Corruption or loss of data may result in the need to repeat a clinical trial at no cost to the client, but at significant cost to us, the termination of a contract or damage to our reputation.
In addition, any failure by our computer environment to provide sufficient processing or network capacity to transfer data could result in interruptions in our service. In the event of a delay in the delivery of data, we could be required to transfer our data collection operations to an alternative provider of server hosting services. Such a transfer could result in significant delays in our ability to deliver services to our clients, and increase our costs. Additionally, significant delays in system enhancements or inadequate performance of new or upgraded systems once completed could damage our reputation and harm our business. Finally, long-term disruptions in the infrastructure caused by events such as natural disasters, the outbreak of war, the escalation of hostilities and acts of terrorism, particularly involving cities in which we have offices, could adversely affect our businesses. Although we carry property and business interruption insurance, our coverage might not be adequate to compensate us for all losses that may occur.
We have continued to undertake significant programs to optimize business processes with respect to our services. Our inability to effectively manage the implementation and adapt to new processes designed into new or upgraded systems in a timely and cost-effective manner may result in disruption to our business and negatively affect our operations.
25
Table of Contents
We have entered into agreements with certain vendors to provide systems development and integration services that develop or license to us the IT platform for programs to optimize our business processes. If such vendors fail to perform as required or if there are substantial delays in developing, implementing and updating the IT platform, our client delivery may be impaired, and we may have to make substantial further investments, internally or with third parties, to achieve our objectives. Additionally, our progress may be limited by parties with existing or claimed patents who seek to enjoin us from using preferred technology or seek license payments from us. Meeting our objectives is dependent on a number of factors which may not take place as we anticipate, including obtaining adequate technology-enabled services, creating IT-enabled services that our clients will find desirable and implementing our business model with respect to these services. Also, increased IT-related expenditures may negatively impact our profitability.
We may experience challenges with the acquisition, development, enhancement or deployment of technology necessary for our business.
We operate in businesses that require sophisticated computer systems and software for data collection, data processing, cloud-based platforms, analytics, cryptography, statistical projections and forecasting, mobile computing, social media analytics and other applications and technologies, particularly our Commercial Solutions business. We seek to address our technology risks by increasing our reliance on the use of innovations by cross-industry technology leaders and adapt these for our biopharmaceutical and healthcare industry clients. Some of these technologies supporting the industries we serve are changing rapidly and we must continue to adapt to these changes in a timely and effective manner at an acceptable cost. We also must continue to deliver data to our clients in forms that are easy to use while simultaneously providing clear answers to complex questions. There can be no guarantee that we will be able to develop, acquire or integrate new technologies, that these new technologies will meet our clients’ needs or achieve expected investment goals, or that we will be able to do so as quickly or cost-effectively as our competitors. Significant technological change could render our services obsolete. Moreover, the introduction of new services embodying new technologies could render existing services obsolete. Our continued success will depend on our ability to adapt to changing technologies, manage and process ever-increasing amounts of data and information and improve the performance, features and reliability of our services in response to changing client and industry demands. We may experience difficulties that could delay or prevent the successful design, development, testing, introduction or marketing of our services. New services, or enhancements to existing services, may not adequately meet the requirements of current and prospective clients or achieve any degree of significant market acceptance. Any of these failures could have a material adverse effect on our operating results and financial condition.
Consolidation in the industries in which our clients operate may reduce the volume of services purchased by consolidated clients following an acquisition or merger, which could materially harm our operating results and financial condition.
Mergers or consolidations among our clients have in the past and could in the future reduce the number of our clients and potential clients. When companies consolidate, overlapping services previously purchased separately are usually purchased only once by the combined entity, leading to loss of revenue. Other services that were previously purchased by one of the merged or consolidated entities may be deemed unnecessary or cancelled. If our clients merge with or are acquired by other entities that are not our clients, or that use fewer of our services, they may discontinue or reduce their use of our services. There can be no assurance as to the degree to which we may be able to address the revenue impact of such consolidation. Any of these developments could materially harm our operating results and financial condition.
We may be adversely affected by client or therapeutic concentration.
Although we did not have any client that represented 10% or more of our revenues in 2016, 2015 and 2014, we derive the majority of our revenues from a number of large clients. If any large client decreases or terminates its relationship with us, our business, results of operations or financial condition could be materially adversely affected.
26
Table of Contents
Additionally, conducting multiple clinical trials for different clients in a single therapeutic class involving drugs with the same or similar chemical action has in the past and may in the future adversely affect our business if some or all of the clinical trials are canceled because of new scientific information or regulatory judgments that affect the drugs as a class or if industry consolidation results in the rationalization of drug development pipelines. Similarly, marketing and selling drugs for different biopharmaceutical companies with similar chemical actions subjects us to risk if new scientific information or regulatory judgment prejudices the drugs as a class, which may lead to compelled or voluntary prescription limitations or withdrawal of some or all of such drugs from the market.
Our business is subject to international economic, political and other risks that could negatively affect our results of operations and financial condition.
We have significant operations in countries that may require complex arrangements to deliver services throughout the world for our clients. Additionally, we have established operations in locations remote from our most developed business centers. As a result, we are subject to heightened risks inherent in conducting business internationally, including the following:
| • | required compliance with a variety of local laws and regulations which may be materially different than those to which we are subject in the United States or which may change unexpectedly; for example, conducting a single clinical trial across multiple countries is complex, and issues in one country, such as a failure to comply with local regulations or restrictions, may affect the progress of the clinical trial in the other countries, for example, by limiting the amount of data necessary for a clinical trial to proceed, resulting in delays or potential cancellation of contracts, which in turn may result in loss of revenue; |
| • | the United States or foreign countries could enact legislation or impose regulations or other restrictions, including unfavorable labor regulations, tax policies or economic sanctions, which could have an adverse effect on our ability to conduct business in or expatriate profits from the countries in which we operate, including hiring, retaining and overseeing qualified management personnel for managing operations in multiple countries, differing employment practices and labor issues, and tax-related risks, including the imposition of taxes and the lack of beneficial treaties, that result in a higher effective tax rate for us; |
| • | foreign countries are expanding or may expand their regulatory framework with respect to patient informed consent, protection and compensation in clinical trials, which could delay or inhibit our ability to conduct clinical trials in such jurisdictions; |
| • | the regulatory or judicial authorities of foreign countries may not enforce legal rights and recognize business procedures in a manner in which we are accustomed or would reasonably expect; |
| • | local, economic, political and social conditions, including potential hyperinflationary conditions, political instability, and potential nationalization, repatriation, expropriation, price controls or other restrictive government actions, including changes in political and economic conditions may lead to changes in the business environment in which we operate, as well as changes in foreign currency exchange rates; |
| • | immigration laws are subject to legislative change and varying standards of application and enforcement due to political forces, economic conditions or other events and local immigration laws may require us to meet certain other legal requirements as a condition to obtaining or maintaining entry visas, which may impact our ability to provide services to our clients; |
| • | potential violations of local laws or anti-bribery laws, such as the United States Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (“FCPA”), and the UK Bribery Act, may cause difficulty in managing foreign operations, as well as significant consequences to us if those laws are violated; |
| • | clients in foreign jurisdictions may have longer payment cycles, and it may be more difficult to collect receivables in foreign jurisdictions; and |
27
Table of Contents
| • | natural disasters, pandemics or international conflict, including terrorist acts, could interrupt our services, endanger our personnel or cause project delays or loss of clinical trial materials or results. |
These risks and uncertainties could negatively impact our ability to, among other things, perform large, global projects for our clients. Furthermore, our ability to deal with these issues could be affected by applicable United States laws and the need to protect our assets. Any such risks could have an adverse impact on our financial condition and results of operations.
Exchange rate fluctuations may affect our results of operations and financial condition.
Because a large portion of our revenues and expenses are denominated in currencies other than the United States dollar and our financial statements are reported in United States dollars, changes in foreign currency exchange rates could significantly affect our results of operations and financial condition. Exchange rate fluctuations between local currencies and the United States dollar create risk in several ways, including:
| • | Foreign Currency Translation Risk. The revenue and expenses of our foreign operations are generally denominated in local currencies and translated into United States dollars for financial reporting purposes. Accordingly, exchange rate fluctuations will affect the translation of foreign results into United States dollars for purposes of reporting our consolidated results. |
| • | Foreign Currency Transaction Risk. We are subject to foreign currency transaction risk for fluctuations in exchange rates during the period of time between the consummation and cash settlement of a transaction. We earn revenue from our service contracts over a period of several months and, in some cases, over several years. Accordingly, exchange rate fluctuations during this period may affect our profitability with respect to such contracts. |
We may limit these risks through exchange rate fluctuation provisions stated in our service contracts, or we may hedge our transaction risk with foreign currency exchange contracts or options. We have not, however, hedged all of our foreign currency transaction risk, and we may experience fluctuations in financial results from our operations outside the United States and foreign currency transaction risk associated with our service contracts.
Due to the global nature of our business, we may be exposed to liabilities under the United States Foreign Corrupt Practices Act and various non-United States anti-corruption laws, and any allegation or determination that we violated these laws could have a material adverse effect on our business.
We are required to comply with the FCPA and other United States and non-United States anti-corruption laws, which prohibit companies from engaging in bribery including corruptly or improperly offering, promising, or providing money or anything else of value to non-United States officials and certain other recipients. In addition, the FCPA imposes certain books, records, and accounting control obligations on public companies and other issuers. We operate in parts of the world in which corruption can be common and compliance with anti-bribery laws may conflict with local customs and practices. Our global operations face the risk of unauthorized payments or offers being made by employees, consultants, sales agents, and other business partners outside of our control or without our authorization. It is our policy to implement safeguards to prohibit these practices by our employees and business partners with respect to our operations. However, irrespective of these safeguards, or as a result of monitoring compliance with such safeguards, it is possible that we or certain other parties may discover or receive information at some point that certain employees, consultants, sales agents, or other business partners may have engaged in corrupt conduct for which we might be held responsible. Violations of the FCPA or other non-United States anti-corruption laws may result in restatements of, or irregularities in, our financial statements as well as severe criminal or civil sanctions, and we may be subject to other liabilities, which could negatively affect our business, operating results and financial condition. In some cases, companies that violate the FCPA may be debarred by the United States government and/or lose their United States export privileges. Changes in anti-corruption laws or enforcement priorities could also result in increased compliance requirements and related costs which could adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations. In
28
Table of Contents
addition, the United States or other governments may seek to hold us liable for successor liability FCPA violations or violations of other anti-corruption laws committed by companies in which we invest or that we acquired or will acquire.
We face risks related to sales to government entities.
We derive a portion of our revenue from sales to government entities in the United States. In general, our contracts with United States government entities are terminable at will by the government entity at any time. Government demand and payment for our services may be affected by public-sector budgetary cycles and funding authorizations. Government contracts are subject to oversight, including special rules on accounting, expenses, reviews and security. Failure to comply with these rules could result in civil and criminal penalties and sanctions, including termination of contracts, fines and suspensions, or debarment from future business with the United States government. As a result, failure to comply with these rules could have an adverse effect on our future business, reputation, operating results and financial condition.
If we are unable to successfully develop and market new services or enter new markets, our growth, results of operations or financial condition could be adversely affected.
A key element of our growth strategy is the successful development and marketing of new services or entering new markets that complement or expand our existing business. As we develop new services or enter new markets, including services targeted at participants in the broader healthcare industry, we may not have or adequately build the competencies necessary to perform such services satisfactorily, may not receive market acceptance for such services or may face increased competition. If we are unable to succeed in developing new services, entering new markets or attracting a client base for our new services or in new markets, we will be unable to implement this element of our growth strategy, and our future business, reputation, results of operations and financial condition could be adversely affected.
Our Research & Development Solutions business could subject us to potential liability that may adversely affect our results of operations and financial condition.
Our Research & Development Solutions business involves the testing of new drugs on patients in clinical trials and, if marketing approval is granted, the availability of these drugs to be prescribed to patients. Our involvement in the clinical trials and development process creates a risk of liability for personal injury to or death of patients, particularly those with life-threatening illnesses, resulting from adverse reactions to the drugs administered during testing or after product launch, respectively. For example, we have from time to time been sued and may be sued in the future by individuals alleging personal injury due to their participation in clinical trials and seeking damages from us under a variety of legal theories. Although we maintain the types and amounts of insurance we view as customary in the industries and countries in which we operate, if we are required to pay damages or incur defense costs in connection with any personal injury claim that is outside the scope of indemnification agreements we have with our clients, if any indemnification agreement is not performed in accordance with its terms or if our liability exceeds the amount of any applicable indemnification limits or available insurance coverage, our financial condition, results of operations and reputation could be materially and adversely affected. We maintain professional liability insurance, including liability for completed operations coverage. In the future, we may not be able to get adequate insurance for these types of risks at reasonable rates.
We also contract with physicians to serve as investigators in conducting clinical trials. If the investigators commit errors or make omissions during a clinical trial that result in harm to clinical trial patients or after a clinical trial to a patient using the drug after it has received regulatory approval, claims for personal injury or liability damages may result. Additionally, if the investigators engage in fraudulent behavior, clinical trial data may be compromised, which may require us to repeat the clinical trial or subject us to liability. We do not believe we are legally responsible for the medical care rendered by such third-party investigators, and we would
29
Table of Contents
vigorously defend any claims brought against us. However, it is possible we could be found liable for claims with respect to the actions of third-party investigators, which may adversely affect our financial condition, results of operations and reputation.
Some of our Research & Development Solutions services involve direct interaction with clinical trial subjects or volunteers and operation of Phase I clinical facilities, which could create potential liability that may adversely affect our results of operations and financial condition.
We operate facilities where Phase I clinical trials are conducted, which ordinarily involve testing an investigational drug on a limited number of healthy individuals, typically 20 to 80 persons, to determine such drug’s basic safety. Failure to operate such a facility in accordance with applicable regulations could result in that facility being shut down, which could disrupt our operations. Additionally, we face risks associated with adverse events resulting from the administration of such drugs to healthy volunteers and the professional malpractice of medical care providers. Occasionally, physicians employed at our Phase I clinical facilities act as principal investigators in later-phase clinical trials at those same facilities. We also directly employ nurses and other trained employees who assist in implementing the testing involved in our clinical trials, such as drawing blood from healthy volunteers. Any professional malpractice or negligence by such investigators, nurses or other employees could potentially result in liability to us in the event of personal injury to or death of a healthy volunteer in clinical trials. This liability, particularly if it were to exceed the limits of any indemnification agreements and insurance coverage we may have, may adversely affect our financial condition, results of operations and reputation.
Our Integrated Engagement Services business could result in liability to us if a drug causes harm to a patient. While we are generally indemnified and insured against such risks, we may still suffer financial losses.
When we market drugs under contract for a biopharmaceutical company, we could suffer liability for harm allegedly caused by those drugs, either as a result of a lawsuit against the biopharmaceutical company to which we are joined, a lawsuit naming us or any of our subsidiaries or an action launched by a regulatory body. While we are generally indemnified by the biopharmaceutical company for the action of the drugs we market on its behalf, and we carry insurance to cover harm caused by our negligence in performing services, it is possible that we could nonetheless incur financial losses, regulatory penalties or both. In particular, any claim could result in potential liability for us if the claim is outside the scope of the indemnification agreement we have with the biopharmaceutical company, the biopharmaceutical company does not abide by the indemnification agreement as required or the liability exceeds the amount of any applicable indemnification limits or available insurance coverage. Such a finding could have an adverse impact on our financial condition, results of operations and reputation. Furthermore, negative publicity associated with harm caused by drugs we helped to market could have an adverse effect on our business and reputation.
Our insurance may not cover all of our indemnification obligations and other liabilities associated with our operations.
We maintain insurance designed to provide coverage for ordinary risks associated with our operations and our ordinary indemnification obligations. The coverage provided by such insurance may not be adequate for all claims we may make or may be contested by our insurance carriers. If our insurance is not adequate or available to pay liabilities associated with our operations, or if we are unable to purchase adequate insurance at reasonable rates in the future, our profitability may be adversely impacted.
If we are unable to attract suitable investigators and patients for our clinical trials, our clinical development business might suffer.
The timely recruitment of investigators and patients for clinical trials is essential to our Research & Development Solutions business. Investigators are typically located at hospitals, clinics or other sites and supervise
30
Table of Contents
the administration of the investigational drug to patients during the course of a clinical trial. Patients generally include people from the communities in which the clinical trials are conducted. Our clinical development business could be adversely affected if we are unable to attract suitable and willing investigators or patients for clinical trials on a consistent basis. For example, if we are unable to engage investigators to conduct clinical trials as planned or enroll sufficient patients in clinical trials, we might need to expend additional funds to obtain access to resources or else be compelled to delay or modify the clinical trial plans, which may result in additional costs to us.
If we lose the services of key personnel or are unable to recruit additional qualified personnel, our business could be adversely affected.
Our success substantially depends on the collective performance, contributions and expertise of our personnel including senior management and key personnel, qualified professional, scientific and technical operating staff and qualified sales representatives for our contract sales services. There is significant and increasing competition for qualified personnel, particularly those with higher educational degrees, such as a medical degree, a Ph.D. or an equivalent degree, or relevant experience in the industry and in the locations in which we operate. In addition, the departure of our key employees, or our inability to continue to identify, attract and retain qualified personnel or replace any departed personnel in a timely fashion, may impact our ability to grow our business and compete effectively in our industry and may negatively affect our ability to meet financial and operational goals.
Disruptions in the credit and capital markets and unfavorable general economic conditions could negatively affect our business, results of operations and financial condition.
Disruptions in the credit and capital markets could have negative effects on our business that may be difficult to predict or anticipate, including the ability of our clients, vendors, contractors and financing sources to meet their contractual obligations. Although we are unable to quantify the impact it has had on us, we are aware of a limited number of instances in our Research & Development Solutions business during the past several years where cancellations, changes in scope and failure to pay timely were attributable, at least in part, to difficulty in our clients’ ability to obtain financing. In the future such actions by our clients could, if they involve a significant amount of business with us, have a material adverse effect on our results of operations.
Our effective income tax rate may fluctuate, which may adversely affect our operations, earnings and earnings per share.
Our effective income tax rate is influenced by our projected profitability in the various taxing jurisdictions in which we operate. Changes in the distribution of profits and losses among taxing jurisdictions may have a significant impact on our effective income tax rate, which in turn could have an adverse effect on our net income and earnings per share. Factors that may affect our effective income tax rate include, but are not limited to:
| • | the requirement to exclude from our quarterly worldwide effective income tax calculations losses in jurisdictions where no income tax benefit can be recognized; |
| • | actual and projected full year pre-tax income; |
| • | changes in the valuation of deferred tax assets and liabilities; |
| • | the repatriation of foreign earnings to the United States; |
| • | changes in tax laws in various taxing jurisdictions; |
| • | audits by taxing authorities; and |
| • | the establishment of valuation allowances against deferred income tax assets if we determined that it is more likely than not that future income tax benefits will not be realized. |
31
Table of Contents
These changes may cause fluctuations in our effective income tax rate that could adversely affect our results of operations and cause fluctuations in our earnings and earnings per share. Additional information regarding our income taxes is presented in Note 18 to our audited consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Our relationships with existing or potential clients who are in competition with each other may adversely impact the degree to which other clients or potential clients use our services, which may adversely affect our results of operations.
The biopharmaceutical industry is highly competitive, with biopharmaceutical companies each seeking to persuade payers, providers and patients that their drug therapies are better and more cost-effective than competing therapies marketed or being developed by competing firms. In addition to the adverse competitive interests that biopharmaceutical companies have with each other, biopharmaceutical companies also have adverse interests with respect to drug selection and reimbursement with other participants in the healthcare industry, including payers and providers. Biopharmaceutical companies also compete to be first to market with new drug therapies. We regularly provide services to biopharmaceutical companies who compete with each other, and we sometimes provide services or funding to such clients regarding competing drugs in development. Our existing or future relationships with our biopharmaceutical clients may therefore deter other biopharmaceutical clients from using our services or may result in our clients seeking to place limits on our ability to serve other biopharmaceutical industry participants in connection with drug development activities. In addition, our further expansion into the broader healthcare market may adversely impact our relationships with biopharmaceutical clients, and such clients may elect not to use our services, reduce the scope of services that we provide to them or seek to place restrictions on our ability to serve clients in the broader healthcare market with interests that are adverse to theirs. A loss of clients or reductions in the level of revenues from a client could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations, business and prospects.
If we are unable to successfully identify, acquire and integrate existing businesses, services and technologies, our business, results of operations and financial condition could be adversely impacted.
We anticipate that a portion of our future growth may come from acquiring existing businesses, services or technologies. The success of any acquisition will depend upon, among other things, our ability to effectively integrate acquired personnel, operations, services and technologies into our business and to retain the key personnel and clients of our acquired businesses. In addition, we may be unable to identify suitable acquisition opportunities or obtain any necessary financing on commercially acceptable terms. We may also spend time and money investigating and negotiating with potential acquisition targets but not complete the transaction. Any future acquisition could involve other risks, including, among others, the assumption of additional liabilities and expenses, difficulties and expenses in connection with integrating the acquired companies and achieving the expected benefits, issuances of potentially dilutive securities or interest-bearing debt, loss of key employees of the acquired companies, transaction costs, diversion of management’s attention from other business concerns and, with respect to the acquisition of foreign companies, the inability to overcome differences in foreign business practices, language and customs. Our failure to identify potential acquisitions, complete targeted acquisitions and integrate completed acquisitions could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Investments in our clients’ businesses or drugs and our related commercial rights strategies could have a negative impact on our financial performance.
We may enter into arrangements with our clients or other drug companies in which we take on some of the risk of the potential success or failure of their businesses or drugs, including making strategic investments in our clients or other drug companies, providing financing to clients or other drug companies or acquiring an interest in the revenues from clients’ drugs or in entities developing a limited number of drugs. Our financial results would be adversely affected if these investments or the underlying drugs result in losses or do not achieve the level of success that we anticipate and/or our return or payment from the drug investment or financing is less than our direct and indirect costs with respect to these arrangements.
32
Table of Contents
Our results of operations may be adversely affected if we fail to realize the full value of our goodwill and intangible assets.
We assess the realizability of our indefinite-lived intangible assets and goodwill annually and conduct an interim evaluation whenever events or changes in circumstances, such as operating losses or a significant decline in earnings associated with the acquired business or asset, indicate that these assets may be impaired. For example, we recognized $28 million of impairment losses during the year ended December 31, 2016, for goodwill and intangible assets in our Encore reporting unit. Our ability to realize the value of the goodwill and indefinite-lived intangible assets will depend on the future cash flows of the businesses we have acquired, which in turn depend in part on how well we have integrated these businesses into our own business. If we are not able to realize the value of the goodwill and indefinite-lived intangible assets, we may be required to incur material charges relating to the impairment of those assets. Such impairment charges could materially and adversely affect our operating results and financial condition.
We face risks arising from the restructuring of our operations.
From time to time, we have adopted restructuring plans to improve our operating efficiency through various means such as reduction of overcapacity, elimination of non-billable support roles or other realignment of resources. In addition, we have provided guidance of cost synergies of annualized savings exiting 2019 of $200 million in connection with the Merger. Restructuring presents significant potential risks of events occurring that could adversely affect us, including:
| • | actual or perceived disruption of service or reduction in service standards to clients; |
| • | the failure to preserve supplier relationships and distribution, sales and other important relationships and to resolve conflicts that may arise; |
| • | loss of sales as we reduce or eliminate staffing on non-core services; |
| • | diversion of management attention from ongoing business activities; and |
| • | the failure to maintain employee morale and retain key employees. |
Further, any such restructuring would result in charges that, if material, could harm our results of operations and significantly reduce our cash position or increase debt. In addition, we may incur certain unforeseen costs once any restructuring activities are implemented. Further, if we determine to effect any restructuring, we can give no assurance that any projected cost reductions resulting from such restructuring activities will be achieved within the expected timeframe, or at all.
Because of these and other factors, we cannot predict whether we will realize the purpose and anticipated benefits of these measures and, if we do not, our business and results of operations may be adversely affected.
Additionally, there may be delays in implementing the restructuring activities or a failure to achieve the anticipated levels of cost savings and efficiency as a result of the restructuring activities, each of which could materially and adversely impact our business and results of operations. Further restructuring or reorganization activities may also be required in the future beyond what is currently planned, which could further enhance the risks associated with these activities.
Risks Relating to Our Industry
The biopharmaceutical services industry is highly competitive.
The biopharmaceutical services industry is highly competitive. Our business often competes with other biopharmaceutical services companies, internal discovery departments, development departments, sales and marketing departments, information technology departments and other departments within our clients, some of
33
Table of Contents
which could be considered large biopharmaceutical services companies in their own right with greater resources than ours. We also compete with universities, teaching hospitals, governments agencies and others. If we do not compete successfully, our business will suffer. The industry is highly fragmented, with numerous smaller specialized companies and a handful of companies with global capabilities similar to certain of our own capabilities. Increased competition has led to price and other forms of competition, such as acceptance of less favorable contract terms, that could adversely affect our operating results. There are few barriers to entry for companies considering offering any one or more of the services we offer. Because of their size and focus, these companies might compete effectively against us, which could have a material adverse impact on our business.
Our future growth and success will depend on our ability to successfully compete with other companies that provide similar services in the same markets, some of which may have financial, marketing, technical and other advantages. We also expect that competition will continue to increase as a result of consolidation among these various companies. Large technology companies with substantial resources, technical expertise and greater brand power could also decide to enter or further expand in the markets where our business operates and compete with us. If one or more of our competitors or potential competitors were to merge or partner with another of our competitors, or if a new entrant emerged with substantial resources, the change in the competitive landscape could adversely affect our ability to compete effectively. We compete on the basis of various factors, including breadth and depth of services, reputation, reliability, quality, innovation, security, price and industry expertise and experience. In addition, our ability to compete successfully may be impacted by the growing availability of health information from social media, government health information systems and other free or low-cost sources. For example, the United Kingdom’s National Health Service started releasing large volumes of data beginning in December 2011 at little or no charge, reducing the demand for our information services derived from similar data. In addition, consolidation or integration of wholesalers, retail pharmacies, health networks, payers or other healthcare stakeholders may lead any of them to provide information services directly to clients or indirectly through a designated service provider, resulting in increased competition from firms that may have lower costs to market (e.g., no data supply costs). Any of the above may result in lower demand for our services, which could result in a material adverse impact on our operating results and financial condition.
Outsourcing trends in the biopharmaceutical industry and changes in aggregate spending and research and development budgets could adversely affect our operating results and growth rate.
Economic factors and industry trends that affect biopharmaceutical companies affect our Research & Development Solutions business. Biopharmaceutical companies continue to seek long-term strategic collaborations with global contract research organizations with favorable pricing terms. Competition for these collaborations is intense and we may decide to forego an opportunity or we may not be selected, in which case a competitor may enter into the collaboration and our business with the client, if any, may be limited. In addition, if the biopharmaceutical industry reduces its outsourcing of clinical trials and sales and marketing projects or such outsourcing fails to grow at projected rates, our operations and financial condition could be materially and adversely affected. We may also be negatively impacted by consolidation and other factors in the biopharmaceutical industry, which may slow decision making by our clients or result in the delay or cancellation of clinical trials. Our commercial services may be affected by reductions in new drug launches and increases in the number of drugs losing patent protection. All of these events could adversely affect our business, results of operations or financial condition.
Our business may be materially and adversely impacted by factors affecting the biopharmaceutical and healthcare industries.
The vast majority of our revenue is generated from sales to the biopharmaceutical and healthcare industries. The clients we serve in these industries are commonly subject to financial pressures, including, but not limited to, increased costs, reduced demand for their products, reductions in pricing and reimbursement for products and services, formulary approval and placement, government approval to market their products and limits on the manner by which they market their products, loss of patent exclusivity (whether due to patent
34
Table of Contents
expiration or as a result of a successful legal challenge) and the proliferation of or changes to regulations applicable to these industries. To the extent our clients face such pressures, or they change how they utilize our offerings, the demand for our services, or the prices our clients are willing to pay for those services, may decline. Any such decline could have a material adverse effect on our business, operating results and financial condition.
We may be affected by healthcare reform and potential additional reforms.
The United States Congress continues to consider healthcare reform legislation and impose health industry cost containment measures, which may significantly impact the biopharmaceutical industry. In addition, numerous government bodies are considering or have adopted various healthcare reforms and may undertake, or are in the process of undertaking, efforts to control growing healthcare costs through legislation, regulation and voluntary agreements with medical care providers and biopharmaceutical companies. We are uncertain as to the effects of these recent reforms on our business and are unable to predict what legislative proposals, if any, will be adopted in the future. If regulatory cost containment efforts limit the profitability of new drugs, our clients may reduce their research and development spending or promotional, marketing and sales expenditures, which could reduce the business they outsource to us. Similarly, if regulatory requirements are relaxed or simplified drug approval procedures are adopted, the demand for our services could decrease.
Foreign and domestic government bodies may also adopt healthcare legislation or regulations that are more burdensome than existing regulations. For example, product safety concerns and recommendations by the Drug Safety Oversight Board could change the regulatory environment for drug products, and new or heightened regulatory and licensing requirements may increase our expenses or limit or delay our ability to offer some of our services. Additionally, new or heightened regulatory requirements may have a negative impact on the ability of our clients to conduct industry-sponsored clinical trials, which could reduce the need for our services.
Actions by government regulators or clients to limit a prescription’s scope or withdraw an approved drug from the market could adversely affect our business and result in a loss of revenues.
Government regulators have the authority, after approving a drug, to regulate or limit its scope of prescription or withdraw it from the market completely based on safety concerns. Similarly, clients may act to voluntarily limit the scope of prescription of drugs or withdraw them from the market. In the past, we have provided services with respect to drugs that have been limited and/or withdrawn. If we are providing services to clients for drugs that are limited or withdrawn, we may be required to narrow the scope of or terminate our services with respect to such drugs, which would prevent earning the full amount of revenues anticipated under the related service contracts with negative impacts to our financial results.
If we do not keep pace with rapid technological changes, our services may become less competitive or obsolete.
The biopharmaceutical industry is subject to rapid technological changes. Our current competitors or other businesses might develop technologies or services that are more effective or commercially attractive than, or render obsolete, our current or future technologies and services. If our competitors introduce superior technologies or services and if we cannot make enhancements to remain competitive, our competitive position would be harmed. If we are unable to compete successfully, we may lose clients or be unable to attract new clients, which could lead to a decrease in our revenue and financial condition.
Laws restricting biopharmaceutical sales and marketing practices may adversely impact demand for our services.
There have been a significant number of laws, legislative initiatives and regulatory actions over the years that seek to limit biopharmaceutical sales and marketing practices. For example, three states in 2006 and 2007 passed laws restricting the use of prescriber identifiable information for the purpose of promoting branded
35
Table of Contents
prescription medicines. Although these laws were subsequently declared to be unconstitutional based on a decision of the U.S. Supreme Court in Sorrell v. IMS Health in 2011, we are unable to predict whether, and in what form, other initiatives may be introduced or actions taken at the state or Federal levels to limit biopharmaceutical sales and marketing practices. In addition, while we will continue to seek to adapt our services to comply with the requirements of these laws (to the extent applicable to our services), if enacted, there can be no assurance that our efforts to adapt our offerings will be successful and provide the same financial contribution to us. There can also be no assurance that future legislative initiatives will not adversely affect our ability to develop or market current or future offerings, or that any future laws will not diminish the demand for our services, all of which could, over time, result in a material adverse impact on our operating results and financial condition.
Our Research & Development Solutions clients face intense competition from lower cost generic products, which may lower the amount that they spend on our services.
Our Research & Development Solutions clients face increasing competition from lower cost generic products, which in turn may affect their ability to pursue research and development activities with us. In the United States, EU and Japan, political pressure to reduce spending on prescription drugs has led to legislation and other measures which encourages the use of generic products. In addition, proposals emerge from time to time in the United States and other countries for legislation to further encourage the early and rapid approval of generic drugs. Loss of patent protection for a product typically is followed promptly by generic substitutes, reducing our clients’ sales of that product and their overall profitability. Availability of generic substitutes for our clients’ drugs may adversely affect their results of operations and cash flow, which in turn may mean that they would not have surplus capital to invest in research and development and drug commercialization, including in our services. If competition from generic products impacts our clients’ finances such that they decide to curtail our services, our revenues may decline and this could have a material adverse effect on our business.
Risks Relating to Our Indebtedness
Restrictions imposed in the Senior Secured Credit Facilities and other outstanding indebtedness, including the indentures governing Quintiles IMS Holdings, Inc. outstanding notes, may limit our ability to operate our business and to finance our future operations or capital needs or to engage in other business activities.
The terms of the Senior Secured Credit Facilities restrict QuintilesIMS and its restricted subsidiaries from engaging in specified types of transactions. These covenants restrict the ability of QuintilesIMS and its restricted subsidiaries, among other things, to:
| • | incur liens; |
| • | make investments and loans; |
| • | incur indebtedness or guarantees; |
| • | issue preferred stock of a restricted subsidiary; |
| • | issue disqualified equity; |
| • | engage in mergers, acquisitions and asset sales; |
| • | declare dividends, make payments or redeem or repurchase equity interests; |
| • | alter the business QuintilesIMS and its restricted subsidiaries conduct; |
| • | make restricted payments; |
| • | enter into agreements limiting restricted subsidiary distributions; |
36
Table of Contents
| • | prepay, redeem or purchase certain indebtedness; and |
| • | engage in certain transactions with affiliates. |
In addition, the revolving credit facility and the new term loans under our senior secured credit facility require QuintilesIMS to comply with a quarterly maximum senior secured net leverage ratio test and minimum interest coverage ratio test, which become more restrictive over time. QuintilesIMS’s ability to comply with these financial covenants can be affected by events beyond our control, and QuintilesIMS may not be able to satisfy them. Additionally, the restrictions contained in the indentures governing the outstanding notes could also limit our ability to plan for or react to market conditions, meet capital needs or make acquisitions or otherwise restrict our activities or business plans.
A breach of any of these covenants could result in a default under the Senior Secured Credit Facilities or the indentures governing the outstanding notes, which could trigger acceleration of our indebtedness and may result in the acceleration of or default under any other debt to which a cross-acceleration or cross-default provision applies, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, operations and financial results. In the event of any default under the Senior Secured Credit Facilities, the applicable lenders could elect to terminate borrowing commitments and declare all borrowings and loans outstanding, together with accrued and unpaid interest and any fees and other obligations, to be due and payable. In addition, or in the alternative, the applicable lenders could exercise their rights under the security documents entered into in connection with the Senior Secured Credit Facilities. QuintilesIMS and the other subsidiary guarantors have pledged substantially all of their tangible and intangible assets (subject to customary exceptions) as collateral under the Senior Secured Credit Facilities, including the stock and the assets of certain of our current and future wholly owned United States subsidiaries and a portion of the stock of certain of our non-United States subsidiaries.
If we were unable to repay or otherwise refinance these borrowings and loans when due, the applicable lenders could proceed against the collateral granted to them to secure that indebtedness, which could force us into bankruptcy or liquidation. In the event the applicable lenders accelerate the repayment of our borrowings, we and our subsidiaries may not have sufficient assets to repay that indebtedness. Any acceleration of amounts due under the credit agreement governing the Senior Secured Credit Facilities or the exercise by the applicable lenders of their rights under the security documents would likely have a material adverse effect on us.
Despite our level of indebtedness, we are able to incur more debt and undertake additional obligations. Incurring such debt or undertaking such additional obligations could further exacerbate the risks to our financial condition.
Although our credit agreement, which governs the senior credit facilities of our wholly owned subsidiary through which we conduct our operations, Quintiles IMS Incorporated (“OpCo”), contains restrictions on the incurrence of additional indebtedness, these restrictions are subject to a number of qualifications and exceptions and the indebtedness incurred in compliance with these restrictions could increase. In addition, the receivables financing agreement for our special purpose subsidiary, Quintiles Funding, LLC (“Quintiles Funding”) limits borrowing based on the amount of receivables purchased by Quintiles Funding from certain of our other subsidiaries, but when supported by the value of such purchased receivables, the debt under our receivables financing facility can increase.
While the credit agreement also contains restrictions on our and our restricted subsidiaries’ ability to make loans and investments, these restrictions are subject to a number of qualifications and exceptions, and the investments incurred in compliance with these restrictions could be substantial.
37
Table of Contents
Restrictive covenants in our other indebtedness may limit our flexibility in our current and future operations, particularly our ability to respond to changes in our business or to pursue our business strategies.
The terms contained in certain of our indebtedness, including credit facilities and any future indebtedness of ours, may include a number of restrictive covenants that impose significant operating and financial restrictions, including restrictions on our and our restricted subsidiaries’ ability to take actions that we believe may be in our interest. These agreements, among other things, limit our ability to:
| • | incur additional debt; |
| • | provide guarantees in respect of obligations of other persons; |
| • | issue redeemable stock and preferred stock; |
| • | pay dividends or distributions or redeem or repurchase capital stock; |
| • | prepay, redeem or repurchase debt; |
| • | make loans, investments and capital expenditures; |
| • | enter into transactions with affiliates; |
| • | create or incur liens; |
| • | make distributions from our subsidiaries; |
| • | sell assets and capital stock of our subsidiaries; |
| • | make acquisitions; and |
| • | consolidate or merge with or into, or sell substantially all of our assets to, another person. |
A breach of the covenants or restrictions under the agreements governing our other indebtedness could result in a default under the applicable indebtedness. Such default may allow the creditors to accelerate the related debt and may result in the acceleration of any other debt to which a cross-acceleration or cross-default provision applies. In the event our lenders and noteholders accelerate the repayment of our borrowings, we cannot assure that we and our subsidiaries would have sufficient assets to repay such indebtedness.
Our financial results, our substantial indebtedness and our credit ratings could adversely affect the availability and terms of future financing.
Interest rate fluctuations may affect our results of operations and financial condition.
Because we have variable rate debt, fluctuations in interest rates affect our business. We attempt to minimize interest rate risk and lower our overall borrowing costs through the utilization of derivative financial instruments, primarily interest rate caps and swaps. We have entered into interest rate caps and swaps with financial institutions that have reset dates and critical terms that match those of our senior secured term loan credit facility. Accordingly, any change in market value associated with the interest rate caps and swaps is offset by the opposite market impact on the related debt. Because we do not attempt to hedge all of our variable rate debt, we may incur higher interest costs for the portion of our variable rate debt which is not hedged.
38
Table of Contents
Risks Relating to Ownership of Our Common Stock
The parties to the Shareholders Agreement continue to have significant influence over us after the Merger, including control over decisions that require the approval of stockholders, which could limit the ability of other stockholders to influence the outcome of matters submitted to stockholders for a vote.
As of February 9, 2017, certain of the largest post-merger stockholders own approximately 41.4% of the outstanding shares of our common stock. These stockholders are parties to a Shareholders Agreement dated May 3, 2016 (the “Shareholders Agreement”) that superseded and replaced the Quintiles’ Amended and Restated Shareholders Agreement dated February 5, 2015 and the Quintiles’ Second Amended and Restated Registration Rights Agreement, dated May 14, 2013, as amended and the IMS Health Amended and Restated Shareholders Agreement dated as of April 9, 2014.
The parties to the Shareholders Agreement, other than Dr. Dennis Gillings and certain of his affiliates (the “DG Shareholders”) (who have agreed separately to vote in favor of the merger and the transactions contemplated thereby), have agreed to vote for individuals designated to the Surviving Corporation board of directors upon completion of the Merger as follows:
| • | Ari Bousbib (as our Chief Executive Officer); |
| • | one individual designated by the TPG-Q Funds and the TPG-I Funds (collectively “TPG Shareholders”) (until the time at which the TPG Shareholders beneficially own, as a group, less than 5% of our outstanding common stock); |
| • | another individual designated by the TPG Shareholders (until the earlier of (i) the seven year anniversary of completion of the merger and (ii) time at which the TPG Shareholders beneficially own, as a group, 5% or more but less than 12% of our outstanding common stock); |
| • | one individual designated by each of Bain Capital Investors, LLC (“Bain Capital”), the LGP Shareholders and the CPP Shareholder (each until the earlier of (i) the day after our 2018 annual meeting of stockholders or (ii) the time at which such stockholder group beneficially owns less than 2.5% of our outstanding common stock); |
| • | four individuals who are non-stockholder, independent directors; and |
| • | until the Company’s 2018 annual meeting of stockholders, the vacancy resulting from Thomas H. Pike’s resignation may be filled by remaining Quintiles Nominees (as defined in the Shareholders Agreement). |
The Shareholders Agreement provides that we will use our best efforts to cause Dr. Gillings to be elected as the Lead Director through our 2018 annual meeting of stockholders and to be elected as a director so that he may serve as a director until the day after our 2021 annual meeting of stockholders (provided that the DG Shareholders, as a group, continue to beneficially own at least 2.5% of our outstanding common stock), including using its best efforts to support his nomination for the slate of director nominees for a three-year term at our 2017 and 2020 annual meetings of stockholders.
As a result, the parties to the Shareholders Agreement potentially have the ability to influence decisions of our company to enter into any corporate transaction (and the terms thereof), any change in the composition of our board of directors and any transaction that requires stockholder approval regardless of whether others believe that such change or transaction is in the best interests of our company. Additionally, the parties to the Shareholders Agreement are in the business of making investments in companies and may from time to time acquire and hold interests in businesses that compete directly or indirectly with us. One or more of the parties to the Shareholders Agreement may also pursue acquisition opportunities that may be complementary to our businesses and, as a result, those acquisition opportunities may not be available to us. So long as the parties to the Shareholders Agreement continue to own a significant amount of our equity, if they exercise their stockholder rights collectively, they will be able to significantly influence our decisions.
39
Table of Contents
Provisions of the corporate governance documents of QuintilesIMS could make an acquisition of QuintilesIMS difficult and may prevent attempts by its stockholders to replace or remove its management, even if beneficial to its stockholders.
In addition to the beneficial ownership of a large percentage of QuintilesIMS common stock by the parties to the Shareholders Agreement, our certificate of incorporation and Delaware bylaws and the General Corporation Law of Delaware (“DGCL”) contain provisions that could make it difficult for a third party to acquire QuintilesIMS even if doing so might be beneficial to its stockholders, including:
| • | the division of the board of directors into three classes and the election of each class for three-year terms; |
| • | subject to the Shareholders Agreement, the sole ability of the board of directors to fill a vacancy created by the death or resignation of a director or the expansion of the board of directors; |
| • | advance notice requirements for stockholder proposals and director nominations; |
| • | limitations on the ability of stockholders to call special meetings and to take action by written consent; |
| • | the approval of holders of at least seventy-five percent (75%) of the outstanding shares of QuintilesIMS entitled to vote on any amendment, alteration, change, addition or repeal of the Delaware bylaws is required to amend, alter, change, add to or repeal the Delaware bylaws; |
| • | the required approval of holders of at least seventy-five percent (75%) of the outstanding shares of QuintilesIMS to remove directors, which removal may only be for cause, subject to different requirements in the case of directors elected by a voting group of stockholders and the terms of the Shareholders Agreement; and |
| • | the ability of the board of directors to issue new series of, and designate the terms of, preferred stock, without stockholder approval, which could be used to, among other things, institute a rights plan that would have the effect of significantly diluting the stock ownership of a potential hostile acquirer, likely preventing acquisitions that have not been approved by the board of directors. |
In addition, QuintilesIMS is subject to Section 203 of the DGCL regulating corporate takeovers, although our board of directors adopted a resolution approving the Merger pursuant to which shares of common stock were acquired, by among others, the TPG Shareholders. Section 203, subject to certain exceptions, prohibits a Delaware corporation from engaging in any “business combination” with any “interested stockholder” for a period of three years following the date that such stockholder became an interested stockholder unless:
| • | prior to such date, the board of directors of the corporation approved either the business combination or the transaction that resulted in the stockholder becoming an interested stockholder; |
| • | upon consummation of the transaction that resulted in the stockholder becoming an interested stockholder, the interested stockholder owned at least 85% of the voting stock of the corporation outstanding at the time the transaction commenced, excluding those shares owned by persons who are directors and also officers, and employee stock plans in which employee participants do not have the right to determine confidentially whether shares held subject to the plan will be tendered in a tender or exchange offer; or |
| • | on or subsequent to such date, the business combination is approved by the board of directors and authorized at an annual or special meeting of stockholders, and not by written consent, by the affirmative vote of at least two-thirds of the outstanding voting stock that is not owned by the interested stockholder. |
In general, Section 203 defines “business combination” to include mergers or consolidations between a Delaware corporation and an interested stockholder, transactions with an interested stockholder involving the
40
Table of Contents
assets or stock of the corporation or its majority-owned subsidiaries and transactions which increase an interested stockholder’s percentage ownership of stock. In general, Section 203 defines an “interested stockholder” as any entity or person beneficially owning 15% or more of the outstanding voting stock of the corporation and any entity or person affiliated with or controlling or controlled by such entity or person. These provisions may frustrate or prevent any attempts by stockholders to replace members of the board of directors. Because QuintilesIMS’s board is responsible for appointing the members of management, these provisions could in turn affect any attempt to replace current members of management. As a result, stockholders of QuintilesIMS may lose their ability to sell their stock for a price in excess of the prevailing market price due to these protective measures, and efforts by stockholders to change the direction or management of QuintilesIMS may be unsuccessful.
Our operating results and share price may be volatile, which could cause the value of our stockholders’ investments to decline.
Our quarterly and annual operating results may fluctuate in the future, and such fluctuations may be significant. In addition, securities markets worldwide have experienced, and are likely to continue to experience, significant price and volume fluctuations. This market volatility, as well as general economic, market or political conditions, could subject the market price of our shares to wide price fluctuations regardless of our operating performance. Our operating results and the trading price of our shares may fluctuate in response to various factors, including:
| • | market conditions in the broader stock market; |
| • | actual or anticipated fluctuations in our quarterly and annual financial and operating results; |
| • | introduction of new services by us or our competitors; |
| • | issuance of new or changed securities analysts’ reports or recommendations; |
| • | sales, or anticipated sales, of large blocks of our stock; |
| • | additions or departures of key personnel; |
| • | regulatory or political developments; |
| • | litigation and governmental investigations; |
| • | changing economic conditions; and |
| • | exchange rate fluctuations. |
These and other factors, many of which are beyond our control, may cause our operating results and the market price for our shares to fluctuate substantially. While we believe that operating results for any particular quarter are not necessarily a meaningful indication of future results, fluctuations in our quarterly operating results could limit or prevent investors from readily selling their shares and may otherwise negatively affect the market price and liquidity of our shares. In addition, in the past, when the market price of a stock has been volatile, holders of that stock have sometimes instituted securities class action litigation against the company that issued the stock. If any of our stockholders brought a lawsuit against us, we could incur substantial costs defending the lawsuit. Such a lawsuit could also divert the time and attention of our management from our business, which could significantly harm our profitability and reputation.
There may be sales of a substantial amount of our common stock by our current stockholders, and these sales could cause the price of our common stock to fall.
As of February 9, 2017, there were 235,719,111 shares of common stock outstanding. Approximately 41.4% of the outstanding shares of our common stock is held by parties to the Shareholders Agreement).
41
Table of Contents
Sales of substantial amounts of our common stock in the public market, or the perception that such sales will occur, could adversely affect the market price of our common stock and make it difficult for us to raise funds through securities offerings in the future. For example, as restrictions on resale end, the market price of our common stock could decline if the holders of currently restricted shares sell them or are perceived by the market as intending to sell them.
Stockholders that are a party to the Shareholders Agreement may require us to register their shares for resale under the federal securities laws, subject to certain requirements. Under the Shareholders Agreement, we are required to pay the registration expenses associated with the registration of such shares, not including the underwriting discounts, commissions and transfer taxes. Registration of those shares would allow those stockholders to immediately resell their shares in the public market. Any such sales or the anticipation of such sales may cause the market price of our common stock to decline.
In addition, we may use our cash, cash generated from operations or dispositions of assets or businesses and/or proceeds from any new financing arrangements or issuances of debt or equity securities to repurchase shares, including the repurchase of shares from our stockholders that are a party to the Shareholders Agreement.
Since we have no current plans to pay regular cash dividends on our common stock, stockholders may not receive any return on investment unless they sell their common stock for a price greater than that which they paid for it.
Although we have previously declared dividends to our stockholders prior to our initial public offering in May 2013, we do not currently anticipate paying any regular cash dividends on our common stock. Any decision to declare and pay dividends in the future will be made at the discretion of our Board and will depend on, among other things, our results of operations, financial condition, cash requirements, contractual restrictions and other factors that our Board may deem relevant. In addition, our ability to pay dividends is, and may be, limited by covenants of existing and any future outstanding indebtedness we or our subsidiaries incur, including under our existing credit facilities. Therefore, any return on investment in our common stock is solely dependent upon the appreciation of the price of our common stock on the open market, which may not occur.
Our certificate of incorporation contains a provision renouncing any interest and expectancy in certain corporate opportunities identified by certain of our affiliates, even if such corporate opportunities are ones that we might reasonably be deemed to have pursued or had the ability or desire to pursue.
Our certificate of incorporation provides that our company renounces any interest or expectancy in the business opportunities of the TPG Shareholders, the Bain Shareholders, CPP Investment Board Private Holdings Inc. (“CPP Shareholder”), and Leonard Green & Partners, L.P. (“LGP Shareholders”), and their affiliates (other than our company and our subsidiaries) and all of their respective partners, principals, directors, officers, members, managers, managing directors and/or employees, and each such person will have no obligation to offer us such opportunities. This provision applies to these stockholders (and associated parties) only for so long as a nominee designated by the stockholder under the Shareholders Agreement continues to serve on the board. Stockholders are deemed to have notice of and have consented to this provision of our certificate of incorporation.
Therefore, a director or officer of our company who also serves as a director, officer, member, manager, or employee of such stockholders may pursue certain business opportunities, including acquisitions, that may be complementary to its business and, as a result, such opportunities may not be available to us. These potential conflicts of interest could have a material adverse effect on the business, financial condition, results of operations, or prospects of our company if attractive corporate opportunities are allocated by such stockholders to themselves or their other affiliates instead of to us.
42
Table of Contents
Risks Relating to the Merger
QuintilesIMS may be unable to fully realize the competitive and operating synergies that are projected to be achieved through the combination of Quintiles’ services and IMS Health’s offerings.
Part of the strategic rationale for the Merger is the opportunity for us to potentially drive additional revenue and earnings through the utilization by Quintiles of IMS Health’s data assets and capabilities in accelerating clinical trials. However, the utilization of data in the two companies’ markets is still evolving and subject to a number of risks and uncertainties, including the following:
| • | government regulatory agencies and legislative bodies, including agencies and legislatures regulating the use of personal data, may impose new conditions or restrictions which affect our use of IMS Health data; |
| • | Our clients may decide that they will not award additional business to QuintilesIMS based on its data capabilities; |
| • | implementation of any operational plans to create new data services and solutions for our clients will likely be complex and technically challenging to implement, and may be subject to delays and cost overruns and there is no assurance that the implementation can be carried out effectively; |
| • | clinical research is a complex and evolving area, and creating effective approaches involving the use of third party data to drive more effective and efficient research outcomes is difficult and challenging; and |
| • | third parties outside of the control of the Company (including suppliers, regulators, and clients) may impose restrictions or conditions which affect the projected data synergies arising from the transaction. |
We are unable to predict the extent to which these factors will inhibit our business plans and any one of them could result in decreased or delays in our performance.
We may fail to realize all of the anticipated benefits of the Merger or those benefits may take longer to realize than expected. We may also encounter significant difficulties in integrating the two businesses.
Our ability to realize the anticipated benefits of the transaction will depend, to a large extent, on our ability to integrate the two businesses. The combination of two independent businesses is a complex, costly and time-consuming process. As a result, we are required to devote significant management attention and resources to integrating their business practices and operations. The integration process may disrupt the businesses and, if implemented ineffectively, would restrict the realization of the full-expected benefits. The failure to meet the challenges involved in integrating the two businesses and to realize the anticipated benefits of the transaction could cause an interruption of or a loss of momentum in, the activities of QuintilesIMS and could adversely affect the results of operations of QuintilesIMS.
In addition, the overall integration of the businesses may result in material unanticipated problems, expenses, liabilities, competitive responses, loss of client relationships, and diversion of management’s attention. The difficulties of combining the operations of the companies include, among others:
| • | difficulties in achieving anticipated cost savings, synergies, business opportunities and growth prospects from the combination; |
| • | difficulties in the integration of the companies’ businesses; |
| • | difficulties in managing the expanded operations of a significantly larger and more complex company; |
| • | challenges in attracting and retaining key personnel; and |
| • | potential unknown liabilities and unforeseen increased expenses or delays associated with the merger. |
43
Table of Contents
Many of these factors will be outside of our control and any one of them could result in increased costs, decreases in the amount of expected revenues and diversion of management’s time and energy, which could materially impact our business, financial condition and results of operations. In addition, even if the operations of the businesses of Quintiles and IMS Health are integrated successfully, the full benefits of the transaction may not be realized, including the synergies, cost savings or sales or growth opportunities that are expected. These benefits may not be achieved within the anticipated time frame, or at all. Further, additional unanticipated costs may be incurred in the integration of the businesses of Quintiles and IMS Health. All of these factors could negatively impact our earnings per share, decrease or delay the expected accretive effect of the transaction and negatively impact the price of our shares. As a result, there is no assurance that the combination of Quintiles and IMS Health will result in the realization of the full benefits anticipated from the Merger.
The future results of QuintilesIMS will suffer if we do not effectively manage its expanded operations following the completion of the Merger.
Following the completion of the Merger, the size of the business of QuintilesIMS increased significantly beyond the current size of either Quintiles’ or IMS Health’s business. Our future success depends, in part, upon our ability to manage this expanded business, which poses substantial challenges for management, including challenges related to the management and monitoring of new operations and associated increased costs and complexity. If we are unsuccessful in managing our integrated operations, or if we do not realize the expected operating efficiencies, cost savings and other benefits currently anticipated from the Merger, the operations and financial condition of QuintilesIMS could be adversely affected and we may not be able to take advantage of business development opportunities.
If the Merger does not qualify as a reorganization under Section 368(a) of the Internal Revenue Code, IMS Health and the IMS Health stockholders may be required to pay substantial United States federal income taxes.
It was a condition of the Merger that legal opinions from tax counsel were received that the Merger will be treated for United States federal income tax purposes as a “reorganization” within the meaning of Section 368(a) of the Internal Revenue Code. These opinions were based on certain assumptions and representations as to factual matters from Quintiles and IMS Health, as well as certain covenants and undertakings by Quintiles and IMS Health. If any of the assumptions, representations, covenants or undertakings is incorrect, incomplete, inaccurate or is violated in any material respect, the validity of the conclusions reached by tax counsel would be jeopardized. Additionally, an opinion of counsel is not binding on the Internal Revenue Service (“IRS”) or any court, so there can be no certainty that the IRS will not challenge the conclusions reflected in the opinions or that a court will not sustain such a challenge. If the IRS or a court determines that the Merger should not be treated as a “reorganization,” a holder of IMS Health common stock that is a United States holder would generally recognize a gain or loss upon the exchange of IMS Health common stock for QuintilesIMS common stock pursuant to the Merger. In addition, if the Merger is not treated as a “reorganization,” IMS Health would recognize a gain or loss, measured generally by the difference between the fair market value of IMS Health’s assets and IMS Health’s adjusted tax basis in such assets.
Item 1B. Unresolved Staff Comments
None.
As of December 31, 2016, we had approximately 273 offices located in approximately 82 countries. Our executive headquarters are located adjacent to Research Triangle Park, North Carolina, and in Danbury, Connecticut. We own facilities in Barcelona, Spain; Buenos Aires, Argentina; Caracas, Venezuela; Los Ruices, Venezuela; Lisbon, Portugal and Bangalore, India. All of our other offices are leased. Our properties are
44
Table of Contents
geographically distributed to meet our worldwide operating requirements, and none of our properties are individually material to our business operations. Many of our leases have an option to renew, and we believe that we will be able to successfully renew expiring leases on terms satisfactory to us. We believe that our facilities are adequate for our operations and that suitable additional space will be available if needed.
We are involved in a variety of legal and tax proceedings, claims and litigation that arise from time to time in the ordinary course of business. These actions may be commenced by various parties, including competitors, clients, current or former employees, government agencies or others. We record a provision with respect to a proceeding, claim or litigation when it is probable that a liability has been incurred and the amount of the loss can be reasonably estimated. However, even in instances where we have recorded an estimated liability, we are unable to predict with certainty the final outcome of the matter or whether resolution of the matter will materially affect our operating results, financial position or cash flows. As additional information becomes available, we adjust our assessment and estimates of such liabilities accordingly.
Further, we routinely enter into agreements with our suppliers to acquire data and with our clients to sell data, all in the normal course of business. In these agreements, we sometimes agree to indemnify and hold harmless the other party for any damages such other party may suffer as a result of potential intellectual property infringement and other claims related to the use of the data. We have not accrued liability with respect to these matters, as the exposure is considered remote.
Based on our review of the latest information available, management does not expect the impact of pending legal and tax proceedings, claims and litigation, either individually or in the aggregate, to have a material adverse effect on our operating results, financial position or cash flows. However, one or more unfavorable outcomes in any claim or litigation against us could have a material adverse effect for the period in which it is resolved. The following is a summary of the more significant legal matters involving the company.
Our wholly-owned subsidiary, IMS Government Solutions Inc., is primarily engaged in providing services under contracts with the United States government. United States government contracts are subject to extensive legal and regulatory requirements and, from time to time, agencies of the United States government have the ability to investigate whether contractors’ operations are being conducted in accordance with such requirements. IMS Government Solutions discovered potential noncompliance with various contract clauses and requirements under its General Services Administration Contract (the “GSA Contract”) which was awarded in 2002 to its predecessor company, Synchronous Knowledge Inc. (Synchronous Knowledge Inc. was acquired by IMS Health in May 2005). The potential noncompliance arose from two primary areas: first, at the direction of the government, work performed under one task order was invoiced under another task order without the appropriate modifications to the orders being made; and second, personnel who did not meet strict compliance with the labor categories component of the qualification requirements of the GSA Contract were assigned to contracts. Upon discovery of the potential noncompliance, we began remediation efforts, promptly disclosed the potential noncompliance to the United States government, and were accepted into the Department of Defense Voluntary Disclosure Program. We filed a Voluntary Disclosure Program Report on August 29, 2008. We are currently unable to determine the outcome of all of these matters pending the resolution of the Voluntary Disclosure Program process and the ultimate liability arising from these matters could exceed our current reserves.
On February 13, 2014, a group of approximately 1,200 medical doctors and 900 private individuals filed a civil lawsuit with the Seoul Central District Court against IMS Korea and two other defendants, KPA and the Korean Pharmaceutical Information Center (“KPIC”). The civil lawsuit alleges KPA and KPIC collected their personal information in violation of applicable privacy laws without the necessary consent through a software system installed on pharmacy computer systems in Korea, and that personal information was transferred to IMS Korea and sold to pharmaceutical companies. The plaintiffs are claiming damages in the aggregate amount of approximately $6 million plus interest. We believe the lawsuit is without merit, reject plaintiffs’ claims and intend to vigorously defend our position.
45
Table of Contents
On July 23, 2015, indictments were issued by the Seoul Central District Prosecutors’ Office in South Korea against 24 individuals and companies alleging improper handling of sensitive health information in violation of, among others, South Korea’s Personal Information Protection Act. IMS Korea and two of its employees were among the individuals and organizations indicted. Although there is no assertion that IMS Korea used patient identified health information in any of its offerings, prosecutors allege that certain of IMS Korea’s data suppliers should have obtained patient consent when they converted sensitive patient information into non-identified data and that IMS Korea had not taken adequate precautions to reduce the risk of re-identification. We believe the indictment is without merit, that we acted in compliance with all applicable laws at all times and intend to vigorously defend our position.
For additional information, see Note 13 to our audited consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K and “Risk factors—Risks Related to our Business—Litigation or regulatory proceedings could have a material adverse effect on our operating results and financial condition.”
Item 4. Mine Safety Disclosures
Not applicable.
46
Table of Contents
Item 5. Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
Market Information for Common Stock
Our common stock trades on the NYSE under the symbol “Q.” The following table sets forth the high and low sales prices per share of our common stock as reported by the NYSE for the periods indicated.
| High | Low | |||||||
| Fiscal Year 2015 |
||||||||
| First Quarter |
$ | 69.97 | $ | 56.46 | ||||
| Second Quarter |
$ | 73.82 | $ | 63.63 | ||||
| Third Quarter |
$ | 80.45 | $ | 67.47 | ||||
| Fourth Quarter |
$ | 72.68 | $ | 63.62 | ||||
| High | Low | |||||||
| Fiscal Year 2016 |
||||||||
| First Quarter |
$ | 67.92 | $ | 55.01 | ||||
| Second Quarter |
$ | 71.44 | $ | 61.21 | ||||
| Third Quarter |
$ | 81.26 | $ | 65.01 | ||||
| Fourth Quarter |
$ | 81.45 | $ | 70.10 | ||||
Holders of Record
On February 9, 2017, we had approximately 60 stockholders of record as reported by our transfer agent. Holders of record are defined as those stockholders whose shares are registered in their names in our stock records and do not include beneficial owners of common stock whose shares are held in the names of brokers, dealers or clearing agencies.
Dividend Policy
We do not currently intend to pay dividends on our common stock, and no dividends were declared or paid in 2016 or 2015. However, we expect to reevaluate our dividend policy on a regular basis and may, subject to compliance with the covenants contained in our credit facilities and other considerations, determine to pay dividends in the future. The declaration, amount and payment of any future dividends on shares of our common stock will be at the sole discretion of our Board, which may take into account general and economic conditions, our financial condition and results of operations, our available cash and current and anticipated cash needs, capital requirements, contractual, legal, tax and regulatory restrictions, the implications of the payment of dividends by us to our stockholders or by our subsidiaries to us, and any other factors that our Board may deem relevant. Our long-term debt arrangements contain usual and customary restrictive covenants that, among other things, place limitations on our ability to declare dividends. For additional information regarding these restrictive covenants, see Part II, Item 7 “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Liquidity and Capital Resources” and Note 11 to our audited consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Recent Sales of Unregistered Securities
We did not sell any unregistered equity securities in 2016.
47
Table of Contents
Purchases of Equity Securities by the Issuer
On October 30, 2013, our Board approved an equity repurchase program (“Repurchase Program”) authorizing the repurchase of up to $125 million of either our common stock or vested in-the-money employee stock options, or a combination thereof. During 2015, our Board increased the share repurchase authorization under the Repurchase Program by $600 million, which increased the total amount that has been authorized under the Repurchase Program to $725 million. On November 1, 2016, our Board increased the stock repurchase authorization under the Repurchase Program by $1.5 billion, which increased the total amount that has been authorized under the Repurchase Program to $2.225 billion. The Repurchase Program does not obligate us to repurchase any particular amount of common stock or vested in-the-money employee stock options, and it could be modified, extended, suspended or discontinued at any time. The timing and amount of repurchases are determined by our management based on a variety of factors such as the market price of our common stock, our corporate requirements, and overall market conditions. Purchases of our common stock may be made in open market transactions effected through a broker-dealer at prevailing market prices, in block trades, or in privately negotiated transactions. We may also repurchase shares of our common stock pursuant to a trading plan meeting the requirements of Rule 10b5-1 under the Exchange Act, which would permit shares of our common stock to be repurchased when we might otherwise be precluded from doing so by law. Repurchases of vested in-the-money employee stock options were made through transactions between us and our employees (other than our executive officers, who were not eligible to participate in the program), and this aspect of the Repurchase Program expired in November 2013. The Repurchase Program for common stock does not have an end date.
From inception through December 31, 2016, we have repurchased a total of $1,678 million of our securities under the Repurchase Program, consisting of $59 million of stock options and $1,619 million of common stock. As of December 31, 2016, we have remaining authorization to repurchase up to $547 million of our common stock under the Repurchase Program. In addition, from time to time, we have repurchased and may continue to repurchase common stock through private or other transactions outside of the Repurchase Program. For additional information regarding our equity repurchases, see Part II, Item 7 “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Liquidity and Capital Resources” and Note 14 to our audited consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
The following table summarizes the equity repurchase program activity for the three months ended December 31, 2016 and the approximate dollar value of shares that may yet be purchased pursuant to the Repurchase Program:
| Period |
Total Number of Shares Purchased |
Average Price Paid per Share |
Total Number of Shares Purchased as Part of Publicly Announced Plans or Programs |
Approximate Dollar Value of Shares That May Yet Be Purchased Under the Plans or Programs | ||||||||||||
| (in millions, except per share data) | ||||||||||||||||
| October 1, 2016 – October 31, 2016 |
— | $ | — | — | $ | 47 | ||||||||||
| November 1, 2016 – November 30, 2016 |
7.4 | $ | 78.13 | 7.4 | $ | 967 | ||||||||||
| December 1, 2016 – December 31, 2016 |
5.4 | $ | 77.41 | 5.4 | $ | 547 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| 12.8 | 12.8 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
During the year ended December 31, 2016, we repurchased 14.3 million shares of our common stock at an average market price per share of $76.57 for an aggregate purchase price of $1,098 million under the Repurchase Program.
48
Table of Contents
Stock Performance Graph
This performance graph shall not be deemed “filed” for purposes of Section 18 of the Exchange Act, or incorporated by reference into any filing of Quintiles IMS Holdings, Inc. under the Exchange Act or under the Securities Act, except as shall be expressly set forth by specific reference in such filing.
The following graph shows a comparison from May 9, 2013 (the date our common stock commenced trading on the NYSE) through December 31, 2016 of the cumulative total return for our common stock, the Standard & Poor’s 500 Stock Index (“S&P 500”) and a select peer group. The peer group consists of Cerner Corporation, Charles River Laboratories, Inc., Dun & Bradstreet Corporation, Equifax Inc., ICON plc, IHS Markit Ltd., INC Research Holdings, Laboratory Corporation of America Holdings, Nielsen N.V., Parexel International Corporation, Inc., PRA Health Sciences, Inc., Thomson Reuters Corporation and Verisk Analytics, Inc. The companies in our peer group are publicly traded information services, information technology or contract research companies, and thus share similar business model characteristics to QuintilesIMS, or provide services to similar customers as QuintilesIMS. Many of these companies are also used by our compensation committee for purposes of compensation benchmarking.
The graph assumes that $100 was invested in QuintilesIMS, the S&P 500 and the peer group as of the close of market on May 9, 2013, assumes the reinvestments of dividends, if any. The S&P 500 and our peer group are included for comparative purposes only. They do not necessarily reflect management’s opinion that the S&P 500 and our peer group are an appropriate measure of the relative performance of the stock involved, and they are not intended to forecast or be indicative of possible future performance of our common stock.
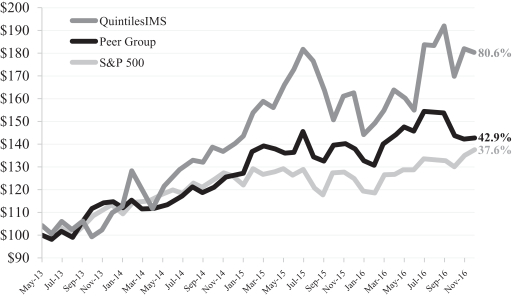
|
|
5/9/2013 | 12/31/2013 | 12/31/2014 | 12/31/2015 | 12/31/2016 | |||||||||||||||
| Q |
$ | 100 | $ | 110 | $ | 140 | $ | 163 | $ | 181 | ||||||||||
| Peer Group |
$ | 100 | $ | 116 | $ | 143 | $ | 151 | $ | 143 | ||||||||||
| S&P 500 |
$ | 100 | $ | 114 | $ | 127 | $ | 126 | $ | 138 | ||||||||||
Item 6. Selected Financial Data
We have derived the following consolidated statements of income data for 2016, 2015 and 2014 and consolidated balance sheet data as of December 31, 2016 and 2015 from our audited consolidated financial
49
Table of Contents
statements included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. We have derived the following consolidated statements of income data for 2013 and 2012 and consolidated balance sheet data as of December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 from our audited consolidated financial statements not included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. You should read the consolidated financial data set forth below in conjunction with our consolidated financial statements and related notes included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K and the information under Part II, Item 7, “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.” On October 3, 2016, we completed a merger of equals transaction with IMS Health. Pursuant to the terms of the merger agreement dated as of May 3, 2016 between Quintiles and IMS Health, IMS Health was merged with and into Quintiles, and the separate corporate existence of IMS Health ceased, with Quintiles continuing as the surviving corporation. We have included the results of operations of acquired businesses, including IMS Health, from the date of acquisition. As a result, our period to period results of operations vary depending on the dates and sizes of the acquisitions. Accordingly, this selected financial data is not necessarily comparable or indicative of our future results. You should read this selected consolidated financial data in conjunction with our audited consolidated financial statements and related footnotes included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||
| (in millions, except per share data) |
2016(5) | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||||||||
| Statement of Income Data: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Revenues |
$ | 5,364 | $ | 4,326 | $ | 4,165 | $ | 3,808 | $ | 3,692 | ||||||||||
| Reimbursed expenses |
1,514 | 1,411 | 1,295 | 1,291 | 1,173 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
| Total revenues |
6,878 | 5,737 | 5,460 | 5,099 | 4,865 | |||||||||||||||
| Costs of revenue, exclusive of depreciation and amortization |
3,236 | 2,705 | 2,664 | 2,452 | 2,443 | |||||||||||||||
| Costs of revenue, reimbursed expenses |
1,514 | 1,411 | 1,295 | 1,291 | 1,173 | |||||||||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative expenses |
1,011 | 815 | 781 | 772 | 736 | |||||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
289 | 128 | 121 | 108 | 98 | |||||||||||||||
| Restructuring costs |
71 | 30 | 9 | 14 | 19 | |||||||||||||||
| Merger related costs(1) |
87 | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
| Impairment charges(2) |
28 | 2 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
| Income from operations |
642 | 646 | 590 | 462 | 396 | |||||||||||||||
| Interest expense, net |
140 | 97 | 97 | 119 | 132 | |||||||||||||||
| Loss on extinguishment of debt |
31 | 8 | — | 20 | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| Other (income) expense, net |
(8 | ) | 2 | (8 | ) | — | (4 | ) | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
| Income before income taxes and equity in earnings (losses) of unconsolidated affiliates |
479 | 539 | 501 | 323 | 267 | |||||||||||||||
| Income tax expense(3) |
345 | 159 | 149 | 96 | 93 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
| Income before equity in earnings (losses) of unconsolidated affiliates |
134 | 380 | 352 | 227 | 174 | |||||||||||||||
| Equity in earnings (losses) of unconsolidated affiliates |
(4 | ) | 8 | 5 | (1 | ) | 3 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
| Net income |
130 | 388 | 357 | 226 | 177 | |||||||||||||||
| Net (income) loss attributable to non-controlling interests |
(15 | ) | (1 | ) | — | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
| Net income attributable to Quintiles IMS Holdings, Inc. |
$ | 115 | $ | 387 | $ | 357 | $ | 227 | $ | 178 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
50
Table of Contents
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||
| (in millions, except per share data) |
2016(5) | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||||||||
| Earnings per share attributable to common stockholders: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic |
$ | 0.77 | $ | 3.15 | $ | 2.78 | $ | 1.83 | $ | 1.53 | ||||||||||
| Diluted |
$ | 0.76 | $ | 3.08 | $ | 2.72 | $ | 1.77 | $ | 1.51 | ||||||||||
| Cash dividends declared per common share |
$ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 4.91 | ||||||||||
| Weighted average common shares outstanding: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic |
149.1 | 123.0 | 128.0 | 124.1 | 115.7 | |||||||||||||||
| Diluted |
152.0 | 125.6 | 131.1 | 127.9 | 117.8 | |||||||||||||||
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||
| (in millions) |
2016(5) | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||||||||
| Statement of Cash Flow Data: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Net cash provided by (used in): |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating activities |
$ | 860 | $ | 476 | $ | 433 | $ | 393 | $ | 336 | ||||||||||
| Investing activities |
1,731 | (67 | ) | (173 | ) | (236 | ) | (132 | ) | |||||||||||
| Financing activities |
(2,284 | ) | (249 | ) | (130 | ) | 71 | (147 | ) | |||||||||||
| Other Financial Data: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Capital expenditures |
$ | (164 | ) | $ | (78 | ) | $ | (83 | ) | $ | (88 | ) | $ | (71 | ) | |||||
| Cash dividend paid to common stockholders |
— | — | — | — | (568 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| As of December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||
| (in millions) |
2016(5) | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||||||||
| Balance Sheet Data: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 1,198 | $ | 977 | $ | 867 | $ | 777 | $ | 568 | ||||||||||
| Investments in debt, equity and other securities |
53 | 33 | 35 | 40 | 36 | |||||||||||||||
| Trade accounts receivable and unbilled services, net |
1,707 | 1,166 | 975 | 924 | 745 | |||||||||||||||
| Property and equipment, net |
406 | 188 | 190 | 200 | 194 | |||||||||||||||
| Total assets |
21,208 | 3,926 | 3,296 | 3,054 | 2,476 | |||||||||||||||
| Total long-term liabilities |
9,643 | 2,668 | 2,528 | 2,239 | 2,526 | |||||||||||||||
| Total debt and capital leases (4) |
7,219 | 2,501 | 2,306 | 2,061 | 2,445 | |||||||||||||||
| Total stockholders’ equity (deficit) |
8,860 | (336 | ) | (704 | ) | (667 | ) | (1,359 | ) | |||||||||||
| (1) | Merger related costs include the direct and incremental costs associated with our merger with IMS Health Holdings, Inc., on October 3, 2016 (the “Merger”). |
| (2) | In 2016, we recognized $28 million of impairment losses for other than temporary declines in fair value of goodwill ($23 million) and identifiable intangible assets ($5 million) in our Encore reporting unit. In 2015, we wrote down $2 million related to long-lived assets. |
51
Table of Contents
| (3) | Income tax expense in 2016 includes $252 million related to a change in our indefinitely reinvested assertion on our cumulative foreign earnings as a result of the Merger. |
| (4) | Excludes $19 million, $33 million, $22 million, $28 million and $47 million of unamortized discounts and debt issuance costs as of December 31, 2016, 2015, 2014, 2013 and 2012. |
| (5) | Includes the acquisition of IMS Health effective October 3, 2016. |
52
Table of Contents
Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
You should read the following discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations together with our consolidated financial statements and the related notes included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Some of the information contained in this discussion and analysis or set forth elsewhere in this Annual Report, including information with respect to our plans and strategy for our business, includes forward-looking statements that involve risks and uncertainties. You should read the “Risk Factors” section of this Annual Report for a discussion of important factors that could cause actual results to differ materially from the results described in or implied by the forward-looking statements contained in the following discussion and analysis.
Overview
Quintiles IMS Holdings, Inc. (“QuintilesIMS”, the “Company”, “we”, “our” and/or “us”) is a leading worldwide integrated information and technology-enabled healthcare service provider, dedicated to helping its clients improve their clinical, scientific and commercial results. Formed through the merger (the “Merger”) of Quintiles Transnational Holdings Inc. (“Quintiles”) and IMS Health Holdings, Inc. (“IMS Health”) on October 3, 2016, QuintilesIMS’s more than 50,000 employees conduct operations in over 100 countries. Companies seeking to improve real-world patient outcomes through treatment innovations, care provision and access can utilize our broad range of healthcare information, technology and service solutions to drive new insights and approaches. Our solutions span clinical to commercial, bringing our clients an opportunity to realize the full potential of innovations and advanced healthcare outcomes.
Following the merger with IMS Health, we manage our business through three reportable segments, Commercial Solutions (substantially IMS Health’s legacy businesses plus Quintiles’ legacy Real-World Late Phase, Payer/Provider and Advisory businesses), Research & Development Solutions (substantially Quintiles’ legacy Product Development segment) and Integrated Engagement Services (substantially Quintiles’ legacy Integrated Healthcare Services segment). Historical segment reporting has been revised to reflect these changes to the Company’s segment structure.
For a description of our service offerings within our segments, refer to “Business” within Part I, Item 1, of this Annual Report of Form 10-K.
Industry Outlook
For information about the industry outlook and markets that we operate in, refer to “Our Market Outlook” within Part I, Item I of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Business Combinations
We have completed and will continue to consider strategic business combinations to enhance our capabilities and offerings in certain areas. In October 2016, we completed the merger with IMS Health to better serve our clients across their entire product lifecycle by (i) improving clinical trial design, recruitment, and execution; (ii) creating real-world information solutions based on the use of medicines by actual patients in normal situations; and (iii) increasing the efficiency of healthcare companies’ commercial organizations through enhanced analytics and outsourcing services. In July 2015, we combined our global clinical trials laboratory operations in our Research & Development Solutions segment with the clinical trials laboratory operations of Quest with the resulting combined business referred to as Q2 Solutions. We own 60% of Q2 Solutions and Quest owns the remaining 40%.
These transactions were accounted for as business combinations and the acquired results of operations are included in our consolidated financial information since the acquisition date with a non-controlling interest for
53
Table of Contents
the portion which we do not own. See Note 15 to our audited consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K for additional information with respect to these business combinations.
Sources of Revenue
Total revenues are comprised of revenues from the provision of our services and revenues from reimbursed expenses that are incurred while providing our services. We do not have any material product revenues. Our segment revenues expressed as a percent of 2016 revenues (excluding reimbursed expense revenue) are as follows:
| Commercial Solutions |
20.4 | % | ||
| Research & Development Solutions |
64.7 | % | ||
| Integrated Engagement Services |
14.9 | % |
Reimbursed expenses are comprised primarily of payments to physicians (investigators) who oversee clinical trials and travel expenses for our clinical monitors principally within our Research & Development Solutions segment and travel expenses for our sales representatives within our Integrated Engagement Services segment. Reimbursed expenses may fluctuate from period-to-period due, in part, to where we are in the lifecycle of the many contracts that are in progress at a particular point in time. As reimbursed expenses are pass-through costs to our clients with little to no profit and we believe that the fluctuations from period-to-period are not meaningful to our underlying performance, we do not provide any analysis of the fluctuations in these items or their impact on our financial results. We have collection risk on contractually reimbursable expenses, and, from time to time, are unable to obtain reimbursement from the client for costs incurred. When such an expense is not reimbursed, it is classified as costs of revenue on the consolidated statements of income.
Costs and Expenses
Our costs and expenses are comprised primarily of our costs of revenue, reimbursed expenses and selling, general and administrative expenses. Costs of revenue include compensation and benefits for billable employees and personnel involved in production, data management and delivery, and the costs of acquiring and processing data for our information offerings; costs of staff directly involved with delivering technology-related services offerings and engagements, related accommodations and the costs of data purchased specifically for technology services engagements; and other expenses directly related to service contracts such as courier fees, laboratory supplies, professional services and travel expenses. As noted above, reimbursed expenses are comprised principally of payments to investigators who oversee clinical trials and travel expenses for our clinical monitors and sales representatives. Selling, general and administrative expenses include costs related to sales, marketing, and administrative functions (including human resources, legal, finance and general management) for compensation and benefits, travel, professional services, training and expenses for information technology (“IT”), facilities and depreciation and amortization.
Foreign Currency Translation
In 2016, approximately 36% of our revenues were denominated in currencies other than the United States dollar. Because a large portion of our revenues and expenses are denominated in currencies other than the United States dollar and our financial statements are reported in United States dollars, changes in foreign currency exchange rates can significantly affect our results of operations. The revenue and expenses of our foreign operations are generally denominated in local currencies and translated into United States dollars for financial reporting purposes. Accordingly, exchange rate fluctuations will affect the translation of foreign results into United States dollars for purposes of reporting our consolidated results. As a result, we believe that providing the
54
Table of Contents
impact of fluctuations in foreign currency rates on certain financial results can facilitate the analysis of period-to-period comparisons of business performance that excludes the effects of foreign currency rate fluctuations. The constant currency information assumes the same foreign currency exchange rates that were in effect for the comparable prior-year period were used in translation of the current period results.
Consolidated Results of Operations
Year ended December 31, 2016 compared to the year ended December 31, 2015 and the year ended December 31, 2015 compared to the year ended December 31, 2014
Summary Results of Operations
The following tables present a summary of our results of operations:
| Year Ended December 31, 2015 |
Change | Year Ended December 31, 2016 | ||||||||||||||
| (in millions) |
Currency Impact |
Constant Currency |
||||||||||||||
| Revenues |
$ | 4,326 | $ | (6 | ) | $ | 1,044 | $ | 5,364 | |||||||
| Costs of revenue |
2,705 | (35 | ) | 566 | 3,236 | |||||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative expenses |
815 | (19 | ) | 215 | 1,011 | |||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
128 | (3 | ) | 164 | 289 | |||||||||||
| Restructuring costs |
30 | 1 | 40 | 71 | ||||||||||||
| Merger related costs |
— | (1 | ) | 88 | 87 | |||||||||||
| Impairment charges |
2 | — | 26 | 28 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
| Income from operations |
$ | 646 | $ | 51 | $ | (55 | ) | $ | 642 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
| Year Ended December 31, 2014 |
Change | Year Ended December 31, 2015 | ||||||||||||||
| (in millions) |
Currency Impact |
Constant Currency |
||||||||||||||
| Revenues |
$ | 4,165 | $ | (211 | ) | $ | 372 | $ | 4,326 | |||||||
| Costs of revenue |
2,664 | (196 | ) | 237 | 2,705 | |||||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative expenses |
781 | (37 | ) | 71 | 815 | |||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
121 | (4 | ) | 11 | 128 | |||||||||||
| Restructuring costs |
9 | (4 | ) | 25 | 30 | |||||||||||
| Impairment charges |
— | — | 2 | 2 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
| Income from operations |
$ | 590 | $ | 30 | $ | 26 | $ | 646 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
55
Table of Contents
Consolidated Results of Operations
For information regarding our results of operations for Commercial Solutions, Research & Development Solutions and Integrated Engagement Services, refer to “Segment Results of Operations” later in this section.
Revenues
| Change | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Year Ended December 31, | 2016 vs. 2015 | 2015 vs. 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (dollars in millions) |
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | $ | % | $ | % | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Revenues |
$ | 5,364 | $ | 4,326 | $ | 4,165 | $ | 1,038 | 24.0 | % | $ | 161 | 3.9 | % | ||||||||||||||
2016 compared to 2015
In 2016, our revenues increased $1,038 million, or 24.0%, as compared to the same period in 2015. This increase was comprised of constant currency revenue growth of approximately $1,044 million, or 24.1%, and a negative impact of approximately $6 million from the effects of foreign currency fluctuations. The constant currency revenue growth was comprised of a $774 million increase in Commercial Solutions, which includes $806 million from the merger with IMS Health, partially offset by a decline in the legacy service offerings, a $336 million increase in Research & Development Solutions, which includes the incremental impact from the businesses that Quest contributed to Q2 Solutions, and a $66 million decrease in Integrated Engagement Services. The revenue contributed by the Merger in 2016 was negatively impacted by approximately $55 million as a result of adjusting the acquired IMS Health unearned income to fair value as required by purchase accounting.
2015 compared to 2014
In 2015, our revenues increased $161 million, or 3.9%, as compared to 2014. This increase was comprised of constant currency revenue growth of approximately $372 million, or 8.9%, and a negative impact of approximately $211 million from the effects of foreign currency fluctuations. The constant currency revenue growth was comprised of a $98 million increase in Commercial Solutions, which includes the impact from the Encore acquisition which closed in July 2014, a $239 million increase in Research & Development Solutions, which includes the incremental impact from the businesses that Quest contributed to Q2 Solutions, and a $35 million increase in Integrated Engagement Services.
Costs of Revenue, exclusive of Depreciation and Amortization
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| (dollars in millions) |
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
| Costs of revenue |
$ | 3,236 | $ | 2,705 | $ | 2,664 | ||||||
| % of revenues |
60.3 | % | 62.5 | % | 64.0 | % | ||||||
2016 compared to 2015
When compared to 2015, costs of revenue in 2016 increased $531 million. This increase included a constant currency increase in expenses of approximately $566 million, or 20.9%, partially offset by a positive impact of approximately $35 million from the effects of foreign currency fluctuations. The constant currency growth was comprised of a $406 million increase in Commercial Solutions, which includes $438 million from the merger with IMS Health, partially offset by a decline in the legacy service offerings, a $220 million increase in Research & Development Solutions, which includes the incremental impact from the businesses that Quest contributed to Q2 Solutions, and a $60 million decrease in Integrated Engagement Services.
56
Table of Contents
2015 compared to 2014
When compared to 2014, costs of revenue in 2015 increased $41 million. This increase included a constant currency increase in expenses of approximately $238 million, or 8.9%, partially offset by a positive impact of approximately $197 million from the effects of foreign currency fluctuations. The constant currency growth was comprised of a $71 million increase in Commercial Solutions, which included the impact from the Encore acquisition which closed in July 2014, a $146 million increase in Research & Development Solutions, which included the incremental impact from the businesses that Quest contributed to Q2 Solutions, and a $21 million increase in Integrated Engagement Services.
The decrease in costs of revenue as a percent of revenues for 2015 was primarily as a result of an improvement in constant currency profit margin in the Commercial Solutions, Research & Development Solutions and Integrated Engagement Services segments (as more fully described in the segment discussion later in this section). For 2015, this constant currency profit margin expansion was partially offset by the effect from a higher proportion of consolidated revenues being contributed by our lower margin Integrated Engagement Services segment when compared to 2014 as well as a negative impact from foreign currency fluctuations.
Selling, General and Administrative Expenses, exclusive of Depreciation and Amortization
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| (dollars in millions) |
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative expenses |
$ | 1,011 | $ | 815 | $ | 781 | ||||||
| % of revenues |
18.8 | % | 18.8 | % | 18.8 | % | ||||||
2016 compared to 2015
The $196 million increase in selling, general and administrative expenses in 2016 included a constant currency increase of $215 million, or 26.4%, partially offset by a positive impact of approximately $19 million from the effects of foreign currency fluctuations. The constant currency growth was comprised of a $151 million increase in Commercial Solutions, which includes $158 million from the merger with IMS Health, partially offset by a decline in the legacy service offerings, a $32 million increase in Research & Development Solutions, which includes the incremental impact from the businesses that Quest contributed to Q2 Solutions, a $3 million increase in Integrated Engagement Services, and a $29 million increase in general corporate and unallocated expenses, which includes $37 million from the merger with IMS Health. The constant currency increase in general corporate and unallocated expenses in 2016 was primarily due to higher stock-based compensation expense.
2015 compared to 2014
The $34 million increase in selling, general and administrative expenses in 2015 included a constant currency increase of $74 million, or 9.5%, partially offset by a positive impact of approximately $42 million from the effects of foreign currency fluctuations. The constant currency growth was comprised of a $14 million increase in Commercial Solutions, which included the impact from the Encore acquisition which closed in July 2014, a $40 million increase in Research & Development Solutions, which included the incremental impact from the businesses that Quest contributed to Q2 Solutions, a $4 million increase in Integrated Engagement Services, and a $14 million increase in general corporate and unallocated expenses. The constant currency increase in general corporate and unallocated expenses in 2015 was primarily due to higher stock-based compensation expense and costs associated with the Q2 Solutions transaction.
57
Table of Contents
Depreciation and Amortization
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| (dollars in millions) |
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
$ | 289 | $ | 128 | $ | 121 | ||||||
| % of revenues |
5.4 | % | 3.0 | % | 2.9 | % | ||||||
2016 compared to 2015
The $161 million increase in depreciation and amortization in 2016 was primarily the result of the merger with IMS Health.
2015 compared to 2014
The $7 million increase in depreciation and amortization in 2015 included a constant currency increase of $11 million, or 9.0%, partially offset by a positive impact of approximately $4 million from the effects of foreign currency fluctuations. The constant currency growth was primarily due to the incremental impact from the businesses that Quest contributed to Q2 Solutions.
Restructuring Costs
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| (in millions) |
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
| Restructuring costs |
$ | 71 | $ | 30 | $ | 9 | ||||||
During 2016, we recognized $71 million of restructuring charges, net of reversals for changes in estimates, under our existing restructuring plans. The remaining actions under these plans are expected to occur throughout 2017, and are expected to consist of severance, facility closure and other exit-related costs.
During 2015, we recognized $30 million of restructuring charges, net of reversals for changes in estimates, associated with both the February 2015 restructuring plan and the Q2 Solutions restructuring plan.
During 2014, we recognized $9 million of restructuring charges, net of reversals for changes in estimates, which was primarily related to our 2014 restructuring plans.
Merger Related Costs
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| (in millions) |
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
| Merger related costs |
$ | 87 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||
During 2016 we recognized $87 million of merger related costs. Merger related costs include the direct and incremental costs associated with the Merger such as (i) investment banking, legal, accounting and consulting fees, (ii) incremental compensation costs triggered under change in control provisions in executive employment agreements, (iii) compensation and related costs of employees 100% dedicated to merger-related integration activities and (iv) severance and other termination costs associated with employees whose positions became redundant as a result of the Merger.
58
Table of Contents
Impairment Charges
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| (in millions) |
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
| Impairment charges |
$ | 28 | $ | 2 | $ | — | ||||||
During 2016, we recognized $28 million of impairment losses for other than temporary declines in fair value of goodwill ($23 million) and identifiable intangible assets ($5 million) in our Encore reporting unit. See Note 17 to our audited consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K for additional information with respect to impairment charges. During the fourth quarter of 2015, we exited a training facility in Japan, resulting in a $2 million impairment of the land and building.
Interest Income and Interest Expense
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| (in millions) |
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
| Interest income |
$ | (4 | ) | $ | (4 | ) | $ | (4 | ) | |||
| Interest expense |
$ | 144 | $ | 101 | $ | 101 | ||||||
Interest income included interest received primarily from bank balances and investments.
Interest expense during 2016 was higher than 2015 due to an increase in the average debt outstanding, primarily as a result of the debt acquired from the Merger.
Interest expense during 2015 reflects the increase in the average debt outstanding, primarily as a result of the $275 million term loan that was issued under the receivables financing facility in December 2014 and our new senior secured credit agreement and senior notes, both of which are described in Liquidity and Capital Resources. This increase was offset by a decrease in the average rate of interest incurred on our debt as compared to 2014.
Loss on Extinguishment of Debt
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| (in millions) |
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
| Loss on extinguishment of debt |
$ | 31 | $ | 8 | $ | — | ||||||
In the fourth quarter of 2016, we recognized a $31 million loss on extinguishment of debt related to the refinancing of our senior secured credit facilities. The loss on extinguishment of debt included an $8 million call premium, $9 million of unamortized debt issuance costs and $14 million of unamortized discount.
In May 2015, we recognized an $8 million loss on extinguishment of debt related to the refinancing of our senior secured credit facilities. The loss on extinguishment of debt included $1 million of unamortized debt issuance costs, $1 million of unamortized discount and $6 million of related fees and expenses.
See “—Liquidity and Capital Resources” for more information on these transactions.
59
Table of Contents
Other (Income), Expense Net
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| (in millions) |
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
| Other (income), expense net |
$ | (8) | $ | 2 | $ | (8) | ||||||
Other (income) expense, net for 2016 primarily consisted of a gain on the sale of a cost basis investment partially offset by foreign currency net losses.
Other (income), expense net for 2015 primarily consisted of $6 million of expense related to the change in fair value of contingent consideration related to an acquisition, partially offset by $5 million of foreign currency net gains.
Other (income), expense net for 2014 included income of approximately $9 million due to changes in the estimated fair value of contingent consideration from an acquisition as well as a gain from the sale of marketable equity securities of approximately $5 million, partially offset by other expenses, primarily consisting of $5 million of foreign currency net losses.
Income Tax Expense
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| (dollars in millions) |
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
| Income tax expense |
$ | 345 | $ | 159 | $ | 149 | ||||||
| Effective income tax rate |
72.0 | % | 29.5 | % | 29.7 | % | ||||||
The increase in the 2016 effective income tax rate was due to a change in our permanent reinvestment assertion on the majority of our cumulative foreign earnings. Due to the Merger, we reevaluated our indefinite reinvestment assertion based on the need for cash in the United States, including funding the Repurchase Program and potential acquisitions. Accordingly, we changed our assertion with respect to $2,801 million of foreign earnings, including $1,865 million of IMS Health’s previously undistributed historical foreign earnings. We intend to use these acquired foreign earnings to fund cash needs in the United States. Deferred income taxes of $625 million were recorded in 2016 related to non-indefinitely reinvested foreign earnings. Of that amount, $373 million was recorded through purchase accounting related to IMS Health’s historical foreign earnings and the remainder of $252 million was recorded through deferred income tax expense.
The decrease in the 2015 effective income tax rate was due to an income tax benefit related to the reversal of uncertain tax positions for tax years whose statute of limitations expired in 2015 and also a change in the relative mix of the profitability between taxing jurisdictions. These benefits were partially offset by additional income tax expense related to an increase in the amount of current year earnings of our foreign subsidiaries not considered permanently reinvested.
Equity in Earnings (Losses) of Unconsolidated Affiliates
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| (in millions) |
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
| Equity in (losses) earnings of unconsolidated affiliates |
$ | (4) | $ | 8 | $ | 5 | ||||||
Equity in earnings (losses) of unconsolidated affiliates primarily included (losses) earnings from our investment in NovaQuest Pharma Opportunities Fund III, L.P. (“Fund III”). The earnings from Fund III in 2014 were partially offset by losses and write-downs incurred on another equity method investment.
60
Table of Contents
Net (Income) Loss Attributable to Non-controlling Interests
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| (in millions) |
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
| Net income attributable to non-controlling interests |
$ | (15) | $ | (1) | $ | — | ||||||
Net income attributable to non-controlling interests in 2016 and 2015 primarily included Quest’s interest in Q2 Solutions.
Segment Results of Operations
Revenues and profit by segment are as follows (dollars in millions):
| Segment Revenues | Segment Profit | Segment Profit Margin | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial Solutions |
$ | 1,096 | $ | 323 | $ | 230 | $ | 236 | $ | 19 | $ | 4 | 21.5 | % | 5.9 | % | 1.7 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
| Research & Development Solutions |
3,472 | 3,159 | 3,050 | 942 | 824 | 744 | 27.1 | % | 26.1 | % | 24.4 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Integrated Engagement Services |
796 | 844 | 885 | 75 | 78 | 78 | 9.4 | % | 9.2 | % | 8.8 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Total |
5,364 | 4,326 | 4,165 | 1,253 | 921 | 826 | 23.4 | % | 21.3 | % | 19.8 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General corporate and unallocated |
(136 | ) | (115 | ) | (106 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
(289 | ) | (128 | ) | (121 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Restructuring costs |
(71 | ) | (30 | ) | (9 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Merger related costs |
(87 | ) | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Impairment charges |
(28 | ) | (2 | ) | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Consolidated |
$ | 5,364 | $ | 4,326 | $ | 4,165 | $ | 642 | $ | 646 | $ | 590 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
Certain costs are not allocated to our segments and are reported as general corporate and unallocated expenses. These costs primarily consist of stock-based compensation, and expenses for corporate overhead functions such as senior leadership, finance, human resources, information technology, facilities and legal. We do not allocate depreciation and amortization, restructuring costs, merger related costs or impairment charges to our segments.
61
Table of Contents
Commercial Solutions
| Change | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (dollars in millions) |
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2016 vs. 2015 | 2015 vs. 2014 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Revenues |
$ | 1,096 | $ | 323 | $ | 230 | $ | 773 | 239.3 | % | $ | 93 | 40.4 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Costs of revenue |
644 | 239 | 174 | 405 | 169.5 | 65 | 37.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| as a percentage of revenues |
58.8 | % | 74.0 | % | 75.7 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative expenses |
216 | 65 | 52 | 151 | 232.3 | 13 | 25.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| as a percentage of revenues |
19.7 | % | 20.1 | % | 22.6 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
| Segment profit |
$ | 236 | $ | 19 | $ | 4 | $ | 217 | 1,142.1 | % | $ | 15 | 375.0 | % | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
| as a percentage of revenues |
21.5 | % | 5.9 | % | 1.7 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Revenues
2016 compared to 2015
Commercial Solutions’ revenues were $1,096 million in 2016, an increase of $773 million over 2015, which includes the incremental impact from the Merger of $806 million. The constant currency revenue increase was due to the incremental impact from the Merger and from growth in real-world and late phase research services, partially offset by lower revenues from payer provider and advisory services. The revenue contributed by the Merger in 2016 was negatively impacted by approximately $55 million as a result of adjusting the acquired IMS Health unearned income to fair value as required by purchase accounting.
2015 compared to 2014
Commercial Solutions’ revenues were $323 million in 2015, an increase of $93 million, or 40.4%, over 2014. This increase was comprised of constant currency revenue growth of $98 million, or 42.7%, including $44 million from the Encore acquisition which closed in July 2014, partially offset by a negative impact of approximately $5 million due to the effects of foreign currency fluctuations. The increase in constant currency revenues was due to the impact from the Encore acquisition which closed in July 2014, as well as growth in real-world and late phase research services, partially offset by lower revenue from advisory services.
Costs of Revenue, exclusive of Depreciation and Amortization
2016 compared to 2015
Commercial Solutions’ costs of revenue increased approximately $405 million in 2016. This increase was comprised of a $407 million constant currency increase, which includes $438 million from the Merger, offset by lower costs in payer provider and advisory services due to lower revenue volumes, and $2 million due to the negative effects of foreign currency fluctuations.
2015 compared to 2014
Commercial Solutions’ costs of revenue increased approximately $65 million in 2015. This increase was comprised of a $71 million constant currency increase, or 41.1%, partially offset by a reduction of $6 million from the positive effects of foreign currency fluctuations. The constant currency increase for 2015 was due to the impact of the Encore acquisition and costs to support the growth in real-world and late phase research services.
62
Table of Contents
Selling, General and Administrative Expenses, exclusive of Depreciation and Amortization
2016 compared to 2015
Commercial Solutions’ selling, general and administrative expenses increased approximately $151 million in 2016 as compared to 2015. This increase was primarily due to $158 million from the Merger, an increase in bad debt expense and cost reductions in various other areas.
2015 compared to 2014
Commercial Solutions’ selling, general and administrative expenses increased approximately $13 million, or 25.0%, in 2015 as compared to 2014. This increase was comprised of a $14 million constant currency increase, or 26.9%, partially offset by a reduction of $1 million from the positive effects of foreign currency fluctuations. The constant currency increase was primarily due to the impact from the Encore acquisition which closed in July 2014.
Research & Development Solutions
| Change | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (dollars in millions) |
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2016 vs. 2015 | 2015 vs. 2014 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Revenues |
$ | 3,472 | $ | 3,159 | $ | 3,050 | $ | 313 | 9.9 | % | $ | 109 | 3.6 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Costs of revenue |
1,953 | 1,779 | 1,764 | 174 | 9.8 | 15 | 0.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| as a percentage of revenues |
56.3 | % | 56.3 | % | 57.8 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative expenses |
577 | 556 | 542 | 21 | 3.8 | 14 | 2.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| as a percentage of revenues |
16.6 | % | 17.6 | % | 17.8 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
| Segment profit |
$ | 942 | $ | 824 | $ | 744 | $ | 118 | 14.3 | % | $ | 80 | 10.8 | % | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
| as a percentage of revenues |
27.1 | % | 26.1 | % | 24.4 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Backlog and Net New Business
Beginning with the third quarter of 2016, we began reporting net new business and backlog on an as-contracted basis (signed binding commitments and signed contracts during the period). We only report backlog and net new business for the Research & Development Solutions segment on a rolling basis for the last twelve months. Previously, net new business included non-binding written awards, which was consistent with industry practice. We believe the as-contracted method is a more precise approach as it requires a higher threshold and less judgment for backlog inclusion. Net new business totaled $4.3 billion for both the 12 months ended December 31, 2016 and 2015. Ending backlog was $9.5 billion at December 31, 2016, and we expect $2.9 billion of this backlog to convert to revenue in the next 12 months.
Net new business under sole provider arrangements is recorded over the life of the arrangement as projects are awarded. Consistent with our methodology for calculating net new business during a particular period, backlog represents, at a particular point in time, future service revenues from work not yet completed or performed under signed contracts. Once work begins on a project, service revenues are recognized over the duration of the project. Net new business and backlog denominated in foreign currencies are valued each month using the actual average foreign exchange rates in effect during the month.
63
Table of Contents
We believe that backlog and net new business may not be consistent indicators of future revenues because they have been and likely will be affected by a number of factors, including the variable size and duration of projects, many of which are performed over several years, cancellations, and changes to the scope of work during the course of projects. Projects that have been delayed remain in backlog, but the timing of the revenue generated may differ from the timing originally expected. Additionally, projects may be terminated or delayed by the customer or delayed by regulatory authorities. In the event that a client cancels a contract, we typically would be entitled to receive payment for all services performed up to the cancellation date and subsequent client-authorized services related to terminating the canceled project. However, we typically do not have a contractual right to the full amount of the revenue reflected in our backlog or net new business contracts in the event of cancellation. For more details regarding risks related to our backlog, see Part I, Item IA, “Risk Factors—The relationship of backlog to revenues varies over time.”
Revenues
2016 compared to 2015
Research & Development Solutions’ revenues were $3,472 million in 2016, an increase of $313 million, or 9.9%, over 2015. This increase was comprised of constant currency revenue growth of $335 million, or 10.6%, partially offset by a negative impact of approximately $22 million from the effects of foreign currency fluctuations. The constant currency revenue growth primarily included volume-related increases in our services and the incremental impact from the businesses that Quest contributed to Q2 Solutions.
The volume-related revenue growth was related to increases in revenue from both our clinical solutions and services and our clinical trial support services. This growth was due largely to execution on the higher backlog in place as we entered the year. The 2016 growth was negatively impacted by $17 million of non-recurring revenue recognized in the second quarter of 2015 related to the early close out of a client arrangement. The constant currency revenue growth in 2016 was negatively impacted by $27 million of foreign currency exchange rate adjustments associated with client contracts and losses on foreign exchange forward contracts.
2015 compared to 2014
Research & Development Solutions’ revenues were $3,159 million in 2015, an increase of $109 million, or 3.6%, over 2014. This increase was comprised of constant currency revenue growth of $239 million, or 7.8%, partially offset by a negative impact of approximately $130 million from the effects of foreign currency fluctuations. The constant currency revenue growth included a volume-related increase in our services and the incremental impact from the businesses that Quest contributed to Q2 Solutions.
The volume-related revenue growth was related to an increase in revenue from both clinical solutions and services and clinical trial support services. This growth was due largely to execution on the higher backlog in place as we entered the year. In addition, we recognized $17 million of revenue in the second quarter of 2015 as a result of the release of deferred revenue upon the early close out of a client arrangement. The constant currency revenue growth in 2015 was negatively impacted by contract cancellations in 2014 as well as $28 million of foreign currency exchange rate adjustments associated with client contracts and losses on foreign exchange forward contracts
Costs of Revenue, exclusive of Depreciation and Amortization
2016 compared to 2015
Research & Development Solutions’ costs of revenue increased approximately $174 million in 2016 over 2015. This increase included constant currency growth of $219 million, or 12.3%, which includes the incremental impact from the businesses that Quest contributed to Q2 Solutions, partially offset by $45 million from the positive effects of foreign currency fluctuations.
64
Table of Contents
The constant currency costs of revenue growth was primarily due to the impact from the Q2 Solutions transaction and an increase in compensation and related expenses. The increase in compensation and related expenses resulted from (i) an increase in billable headcount resulting from the higher volume of constant currency revenue, (ii) our continued investment in our global delivery network (“GDN”) which is a coordinated global delivery model that enables us to provide standardized, centrally-managed services from seven hub locations across five countries, (iii) annual merit increases and (iv) an increase in competition for qualified personnel in certain markets. The constant currency growth for 2016 also included a $12 million reserve for certain potentially non-reimbursable expenses. These increases in cost were partially offset by $17 million of expense recognized in the second quarter of 2015 related to the early close out of a client arrangement that did not recur in 2016 and a $15 million increase in the benefit from research and development credits received in Europe.
2015 compared to 2014
Research & Development Solutions’ costs of revenue increased approximately $15 million in 2015 over 2014. This increase included a constant currency increase of $146 million, or 8.3%, which included the incremental impact from the businesses that Quest contributed to Q2 Solutions, partially offset by $131 million from the positive effects of foreign currency fluctuations.
The constant currency costs of revenue growth was primarily due to the impact from the Q2 Solutions transaction and an increase in compensation and related expenses. The increase in compensation and related expenses resulted from an increase in billable headcount as a result of the ramp up of new projects as well as annual merit increases and an increase in competition for qualified personnel in certain markets. Also contributing to the constant currency increase was $17 million of expense recognized in the second quarter of 2015 as a result of the release of deferred contract costs upon the early close out of a client arrangement. Costs of revenue growth was partially offset by an $8 million increase in the benefit from research and development credits received in Europe. As a percent of revenues, Research & Development Solutions’ costs of revenue were 56.3% and 57.8% in 2015 and 2014, respectively. The decrease in costs of revenue as a percentage of revenues reflected a favorable impact from the effects of foreign currency fluctuations and a closer alignment of resources with project requirements, including cost efficiencies gained from restructuring actions taken in prior years, which more than offset the impact of the constant currency costs of revenue growth noted above.
Selling, General and Administrative Expenses, exclusive of Depreciation and Amortization
2016 compared to 2015
Research & Development Solutions’ selling, general and administrative expenses increased approximately $21 million, or 3.8%, in 2016 as compared to 2015. This increase was caused by constant currency growth of $32 million, partially offset by a reduction of $11 million from foreign currency fluctuations. As a percent of revenues, Research & Development Solutions’ selling, general and administrative expenses were 16.6% and 17.6% in 2016 and 2015, respectively. The constant currency increase was primarily due to the incremental impact from the businesses that Quest contributed to Q2 Solutions, higher compensation and related expenses due to annual merit increases and an increase in headcount and an increase in bad debt expense.
2015 compared to 2014
Research & Development Solutions’ selling, general and administrative expenses increased approximately $14 million, or 2.6%, in 2015 as compared to 2014. This increase was primarily caused by a constant currency increase of $40 million, which included the incremental impact from the businesses that Quest contributed to Q2 Solutions, partially offset by a reduction of $26 million from the positive effects of foreign currency fluctuations. As a percent of revenues, Research & Development Solutions’ selling, general and administrative expenses were 17.6% and 17.8% in 2015 and 2014, respectively. The constant currency increase was primarily due to the incremental impact from the businesses that Quest contributed to Q2 Solutions, higher compensation and related expenses due to annual merit increases and an increase in headcount.
65
Table of Contents
Integrated Engagement Services
| Change | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (dollars in millions) |
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2016 vs. 2015 | 2015 vs. 2014 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Revenues |
$ | 796 | $ | 844 | $ | 885 | $ | (48 | ) | (5.7 | )% | $ | (41 | ) | (4.6 | )% | ||||||||||||
| Costs of revenue |
639 | 687 | 726 | (48 | ) | (7.0 | ) | (39 | ) | (5.4 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
| as a percentage of revenues |
80.3 | % | 81.4 | % | 82.0 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative expenses |
82 | 79 | 81 | 3 | 3.8 | (2 | ) | (2.5 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
| as a percentage of revenues |
10.3 | % | 9.4 | % | 9.2 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
| Segment profit |
$ | 75 | $ | 78 | $ | 78 | $ | (3 | ) | (3.8 | )% | $ | — | 0.0 | % | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
| as a percentage of revenues |
9.4 | % | 9.2 | % | 8.8 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Revenues
2016 compared to 2015
Integrated Engagement Services’ revenues were $796 million in 2016, a decrease of $48 million, or 5.7%, over 2015. This decrease was comprised of a constant currency revenue decrease of $67 million, or 7.9%, partially offset by a positive impact of approximately $19 million due to the effects of foreign currency fluctuations. The decline in constant currency revenues for 2016 was due to a decrease in commercial services in North America (primarily as a result of cancellations that occurred in 2015 and earlier this year), Japan and Europe. The decline in Europe was partially offset by a $10 million benefit from the acceleration of revenue due to a contract modification on a sales force arrangement that fixed a portion of the contract price that previously was not determinable until future sales-based royalties were known.
2015 compared to 2014
Integrated Engagement Services’ revenues were $844 million in 2015, a decrease of $41 million, or 4.6%, over 2014. This decrease was comprised of constant currency revenue growth of $35 million, or 4.0%, partially offset by a negative impact of approximately $76 million due to the effects of foreign currency fluctuations. The increase in constant currency revenues was due to an increase in commercial services in North America, partially offset by a decline in Europe due to the loss of revenue from an agreement to distribute pharmaceutical products in Italy that ended in the fourth quarter of 2014.
Costs of Revenue, exclusive of Depreciation and Amortization
2016 compared to 2015
Integrated Engagement Services’ costs of revenue decreased approximately $48 million in 2016. This decrease was comprised of a $60 million constant currency decrease, or 8.7%, partially offset by $11 million due to the positive effects of foreign currency fluctuations. The constant currency decrease for 2016 was due to a decrease in compensation and related expenses resulting from a decrease in billable headcount.
2015 compared to 2014
Integrated Engagement Services’ costs of revenue decreased approximately $39 million in 2015. This increase was comprised of a $21 million constant currency increase, or 2.9%, more than offset by a reduction of $60 million from the positive effects of foreign currency fluctuations. The constant currency increase for 2015 was due to an increase in compensation and related expenses resulting from an increase in billable headcount
66
Table of Contents
needed to support the higher volume of constant currency revenue and annual merit increases. These increases in compensation and related expenses were partially offset by a decline in other expenses directly related to the agreement to distribute pharmaceutical products in Italy, which ended in the fourth quarter of 2014.
Selling, General and Administrative Expenses, exclusive of Depreciation and Amortization
2016 compared to 2015
Integrated Engagement Services’ selling, general and administrative expenses increased approximately $3 million in 2016 as compared to 2015. This increase was due to a higher level of bad debt expense.
2015 compared to 2014
Integrated Engagement Services’ selling, general and administrative expenses decreased approximately $2 million in 2015 as compared to 2014. This decrease was comprised of a $4 million constant currency increase, or 5.0%, partially offset by a reduction of $6 million from the positive effects of foreign currency fluctuations. The constant currency increase was primarily due to an increase in compensation and related expenses.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Overview
We assess our liquidity in terms of our ability to generate cash to fund our operating, investing and financing activities. Our principal source of liquidity is operating cash flows. In addition to operating cash flows, other significant factors that affect our overall management of liquidity include: capital expenditures, acquisitions, investments, debt service requirements, dividends, equity repurchases, adequacy of our revolving credit and receivables financing facilities and access to the capital markets.
We manage our worldwide cash requirements by monitoring the funds available among our subsidiaries and determining the extent to which those funds can be accessed on a cost effective basis. The repatriation of cash balances from certain of our subsidiaries could have adverse tax consequences; however, those balances are generally available without legal restrictions to fund ordinary business operations. We have and expect to transfer cash from those subsidiaries to the United States and to other international subsidiaries when it is cost effective to do so. Since the Merger, through December 31, 2016, we have transferred $615 million from foreign subsidiaries to the United States.
Due to the Merger, we reevaluated our indefinite reinvestment assertion based on the need for cash in the United States, including funding the Repurchase Program and potential acquisitions. Accordingly, we changed our assertion with respect to $2,801 million of foreign earnings, including $1,865 million of IMS Health’s previously undistributed historical foreign earnings. We intend to use these acquired foreign earnings to fund cash needs in the United States.
We had a cash balance of $1,198 million at December 31, 2016 ($237 million of which was in the United States), an increase from $977 million at December 31, 2015.
Based on our current operating plan, we believe that our available cash and cash equivalents, future cash flows from operations and our ability to access funds under our revolving credit and receivables financing facilities will enable us to fund our operating requirements and capital expenditures and meet debt obligations for at least the next 12 months. We regularly evaluate our debt arrangements, as well as market conditions, and from time to time we may explore opportunities to modify our existing debt arrangements or pursue additional financing arrangements that could result in the issuance of new debt securities by us or our affiliates. For example, in September 2016, IMS Health issued approximately $1,750 million in senior notes (as discussed below) and we used the proceeds to repay certain outstanding indebtedness, including our senior secured credit facilities, following the Merger. We may use our existing cash, cash generated from operations or dispositions of assets or businesses and/or proceeds from any new financing arrangements or issuances of debt or equity
67
Table of Contents
securities to repay or reduce some of our outstanding obligations, to repurchase shares from our stockholders or for other purposes. As part of our ongoing business strategy, we also continually evaluate new acquisition, expansion and investment possibilities or other strategic growth opportunities, as well as potential dispositions of assets or businesses, as appropriate, including dispositions that may cause us to recognize a loss on certain assets. Should we elect to pursue any such transaction, we may seek to obtain debt or equity financing to facilitate those activities. Our ability to enter into any such potential transactions and our use of cash or proceeds is limited to varying degrees by the terms and restrictions contained in our existing debt arrangements. We cannot provide assurances that we will be able to complete any such financing arrangements or other transactions on favorable terms or at all.
Equity Repurchases
Since 2013, we have repurchased approximately $2,093 million of our equity securities as discussed further below.
Equity Repurchase Program
On October 30, 2013, our Board approved the Repurchase Program authorizing the repurchase of up to $125 million of either our common stock or vested in-the-money employee stock options, or a combination thereof. During 2015, our Board increased the stock repurchase authorization under the Repurchase Program by $600 million, which increased the total amount that has been authorized under the Repurchase Program to $725 million. On November 1, 2016, our Board increased the stock repurchase authorization under the Repurchase Program by $1.5 billion, which increased the total amount that has been authorized under the Repurchase Program to $2.225 billion. The Repurchase Program does not obligate us to repurchase any particular amount of common stock or vested in-the-money employee stock options, and may be modified, extended, suspended or discontinued at any time. The Repurchase Program for common stock does not have an end date. In 2016, we repurchased 14.3 million shares of our common stock at an average market price per share of $76.57 for an aggregate purchase price of $1,098 million under the Repurchase Program. From inception through December 31, 2016, we have repurchased a total of $1,678 million of our securities under the Repurchase Program, consisting of $59 million of stock options and $1,619 million of common stock. As of December 31, 2016, we have remaining authorization to repurchase up to $547 million of our common stock under the Repurchase Program. On February 12, 2017, our Board increased this authorization by $1.0 billion. Additional information regarding the Repurchase Program is presented in Part II, Item 5 “Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities” and Notes 14 and 27 to our audited consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
In addition, from time to time, we have repurchased and may continue to repurchase common stock through private or other transactions outside of the Repurchase Program.
Other Equity Repurchases
On May 28, 2014, we completed the repurchase of 3.3 million shares of our common stock for $50.23 per share from TPG Quintiles Holdco, L.P., one of our existing stockholders, in a private transaction for an aggregate purchase price of approximately $165 million. The repurchase price per share of common stock was equal to 98% of the closing market price of our common stock on the NYSE on May 27, 2014 (which was $51.26). The repurchase of shares from our existing stockholder was authorized in compliance with our related party transactions approval policy. We funded this private repurchase transaction with cash on hand. This private repurchase transaction was separate from and in addition to the Repurchase Program.
On November 10, 2014, we completed the repurchase of 4.3 million shares of our common stock for $58.09 per share for an aggregate purchase price of approximately $250 million. We funded this repurchase transaction with a combination of cash on hand and a $150 million draw on our revolving credit facility which was subsequently repaid. This repurchase transaction was separate from and in addition to the Repurchase Program.
68
Table of Contents
Debt
The following table presents a summary of debt refinancing activities just prior to and after the merger of Quintiles and IMS Health on October 3, 2016:
| (in millions) |
Legacy Quintiles |
Legacy IMS Health |
Refinancing Proceeds (Repayments) |
QuintilesIMS | ||||||||||||
| Senior Secured Credit Facilities: |
||||||||||||||||
| Term Loans A and B due through 2022 |
$ | 1,389 | $ | — | $ | (1,389 | ) | $ | — | |||||||
| Term Loans A due 2021 |
— | — | 1,350 | 1,350 | ||||||||||||
| Term Loans B due 2021 |
— | 2,516 | — | 2,516 | ||||||||||||
| Term Loans A due 2019 |
— | 884 | (884 | ) | — | |||||||||||
| 4.875% Senior Notes due 2023 |
800 | — | — | 800 | ||||||||||||
| 5.0% Senior Notes due 2026 |
— | — | 1,050 | 1,050 | ||||||||||||
| 3.5% Senior Notes due 2024 |
— | — | 698 | 698 | ||||||||||||
| 4.125% Senior Notes due 2023 |
— | 307 | — | 307 | ||||||||||||
| 6.0% Senior Notes due 2020 |
— | 500 | (500 | ) | — | |||||||||||
| Receivables financing facility due 2018 |
275 | — | — | 275 | ||||||||||||
| Revolving Credit Facility |
— | 298 | (298 | ) | — | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
| Total debt refinancing activities |
$ | 2,464 | $ | 4,505 | $ | 27 | $ | 6,996 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
As of December 31, 2016, we had $7.2 billion of total indebtedness, excluding $656 million of additional available borrowings under our revolving credit facilities. The summary of debt refinancing activities presented in the above table do not reflect amounts drawn on our Revolving Credit Facility unrelated to the Merger during 2016. See Note 11 to our audited consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in the Annual Report on Form 10-K for additional details regarding our credit arrangements.
Senior Secured Credit Agreement and Senior Notes
At December 31, 2016, our senior secured credit facility provides financing of up to approximately $4,772 million, which consisted of $4,147 million principal amount of debt outstanding (as disclosed in Note 11 to our audited consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in the Annual Report on Form 10-K) and $625 million of commitments that expire in 2021. The revolving credit facility is comprised of a $450 million senior secured revolving facility available in U.S. Dollars, a $400 million senior secured revolving facility available in U.S. Dollars, Euros, Swiss Francs and other foreign currencies and a $150 million senior secured revolving facility available in U.S. Dollars and Yen. The term A loans and revolving credit facility mature in October 2021, while the term B loans mature in March 2021. Under certain circumstances, the maturity date of the term A loans and the senior secured revolving facility may be accelerated to 2020. We are required to make scheduled quarterly payments on the term A loans equal to 1.25% of the original principal amount, with the remaining balance paid at maturity. We are required to make scheduled quarterly payments on the term B loans equal to approximately 0.25% of the original principal amount, with the remaining balance paid at maturity. In addition, beginning with fiscal year ending December 31, 2017, we are required to apply 50% of excess cash flow (as defined in our senior secured credit facility), subject to a reduction to 25% or 0% depending upon our senior secured first lien net leverage ratio, for prepayment of the Term Loans, with any such prepayment to be applied toward principal payments due in subsequent quarters. We are also required to pay an annual commitment fee that ranges from 0.30% to 0.40% in respect of any unused commitments under the revolving credit facility. The senior secured credit facility is collateralized by substantially all of our assets and the assets of our material domestic subsidiaries including 100% of the equity interests of substantially all of our material domestic subsidiaries and 66% of the equity interests of substantially all of our first-tier material foreign subsidiaries and their domestic subsidiaries.
69
Table of Contents
On October 3, 2016, we refinanced the term A loans due 2019 (approximately $884 million) assumed in the Merger with a term A loan facility due in 2021 for an aggregate principal amount of approximately $1,350 million comprised of both U.S. Dollar denominated term A loans and Euro denominated term A loans. Additionally, the revolving credit facility was refinanced to an aggregate principal amount equal to $1,000 million. The additional proceeds were used, in part, to fund the redemption on November 1, 2016 of $500 million of 6% Senior Notes due 2020 assumed in the Merger, at a redemption price equal to 101.5% of the aggregate outstanding principal amount plus accrued interest to the redemption date. We incurred a loss on extinguishment of debt of approximately $8 million related to the aggregate payments for make-whole premiums.
On September 28, 2016, IMS Health issued senior unsecured notes totaling principal amount of $1,750 million, which consisted of (i) $1,050 million of 5% senior notes due October 2026 (the “5% Dollar Notes”) and (ii) €625 million of 3.5% senior notes due October 2024 (the “3.5% Euro Notes” and, together with the 5% Dollar Notes, the “2016 Notes”). The proceeds of the 2016 Notes, which we assumed upon closing of the Merger, were used on October 3, 2016 to repay in full ($1,389 million) the term loans outstanding under the Quintiles Transnational senior secured credit facilities. Interest on the 2016 Notes is payable semi-annually, beginning on April 15, 2017. The notes are guaranteed on a senior unsecured basis by our wholly-owned domestic restricted subsidiaries (excluding IMS Japan K.K.) and, subject to certain exceptions, each of our future domestic subsidiaries that guarantees our other indebtedness or indebtedness of any of the guarantors. The 5% Dollar Notes and the 3.5% Euro Notes may be redeemed, either together or separately, prior to their final stated maturity, subject to a customary make-whole premium, at any time prior to October 15, 2021 with respect to the 5% Dollar Notes and October 15, 2019 with respect to the 3.5% Euro Notes (in each case subject to a customary “equity claw” redemption right) and thereafter subject to annually declining redemption premiums at any time prior to October 15, 2024 with respect to the 5% Dollar Notes and October 15, 2021 with respect to the 3.5% Euro Notes.
We also assumed in the Merger €275 million aggregate principal amount of its 4.125% Senior Notes due in April 2023 (the “4.125% Senior Notes”). Interest on the 4.125% Senior Notes is payable semi-annually each year and commenced on October 1, 2015. The 4.125% Senior Notes are guaranteed on a senior unsecured basis by IMS Health’s wholly-owned domestic subsidiaries that are guarantors under the senior secured credit facilities. We may redeem the 4.125% Senior Notes, in whole or in part, at any time prior to April 1, 2018 at a price equal to 100% of the principal amount thereof, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to the date of redemption, plus a “make-whole” premium. On or after April 1, 2018, we may redeem all or a portion of the 4.125% Senior Notes at predetermined redemption prices set forth in the indenture governing the 4.125% Senior Notes plus accrued and unpaid interest to the date of redemption.
2015 Financing Transactions
On May 12, 2015, through its wholly-owned subsidiary, Quintiles Transnational, entered into new senior secured credit facilities, which consisted of a $500 million revolving credit facility and $1.45 billion of term loans. In addition, Quintiles Transnational issued $800 million of 4.875% senior secured notes due 2023 (the “4.875% Senior Notes”) in a private placement. The term loans, in the amount of $1,389 million, were repaid in full on October 3, 2016, as discussed above. Interest on the 4.875% Senior Notes is paid semiannually on May 15 and November 15 of each year until maturity. The Senior Notes are unsecured senior obligations of QuintilesIMS and are effectively subordinated in right of payment to all secured obligations of QuintilesIMS, to the extent of the value of any collateral. Also on May 12, 2015, an outstanding term loan was repaid with proceeds from the new credit facilities entered into that day and we recognized an $8 million loss on extinguishment of debt, which included $1 million of unamortized debt issuance costs, $1 million of unamortized discount and $6 million of related fees and expenses.
Receivables Financing Facility
On December 5, 2014, we entered into a four-year arrangement to securitize certain of our accounts receivable. Under the receivables financing facility, certain of our accounts receivable are sold on a non-recourse basis by certain of our consolidated subsidiaries to another of our consolidated subsidiaries, a bankruptcy-remote
70
Table of Contents
special purpose entity (“SPE”). The SPE obtained a term loan and revolving loan commitment from a third party lender, secured by liens on the assets of the SPE, to finance the purchase of the accounts receivable, which included a $275 million term loan and a $25 million revolving loan commitment. The revolving loan commitment may be increased by an additional $35 million as amounts are repaid under the term loan. QuintilesIMS has guaranteed the performance of the obligations of existing and future subsidiaries that sell and service the accounts receivable under the receivables financing facility. The assets of the SPE are not available to satisfy any of our obligations or any obligations of our subsidiaries. As of December 31, 2016, the full $25 million of revolving loan commitment was available under the receivables financing facility.
We used the proceeds from the term loan under the receivables financing facility to repay in full the amount outstanding on the then outstanding revolving credit facility under its then outstanding senior secured credit agreement ($150 million), to repay $25 million of the then outstanding Term Loan B-3, to pay related fees and expenses and the remainder was used for general working capital purposes.
Restrictive Covenants
Our debt agreements provide for certain covenants and events of default customary for similar instruments, including a covenant not to exceed a specified ratio of consolidated senior secured net indebtedness to Consolidated EBITDA, as defined in the senior secured credit facility and a covenant to maintain a specified minimum interest coverage ratio. If an event of default occurs under any of the Company’s or the Company’s subsidiaries’ financing arrangements, the creditors under such financing arrangements will be entitled to take various actions, including the acceleration of amounts due under such arrangements, and in the case of the lenders under the revolving credit facility and New Term Loans, other actions permitted to be taken by a secured creditor. Our long-term debt arrangements contain usual and customary restrictive covenants that, among other things, place limitations on our ability to declare dividends. For additional information regarding these restrictive covenants, see Part II, Item 5 “Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities—Dividend Policy” and Note 11 to our audited consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. At December 31, 2016, the Company was in compliance with the financial covenants under the Company’s financing arrangements.
Years ended December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014
Cash Flow from Operating Activities
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| (in millions) |
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
| Net cash provided by operating activities |
$ | 860 | $ | 476 | $ | 433 | ||||||
2016 compared to 2015
Cash provided by operating activities increased $384 million in 2016 as compared to 2015. The increase in cash provided by operating activities reflects the increase in net income as adjusted for non-cash items necessary to reconcile net income to cash provided by operating activities. Also contributing to the increase were lower payments for income taxes ($15 million), and lower cash used in days sales outstanding (“DSO”) and accounts payable and accrued expenses. The lower cash used in DSO reflects a two-day increase in DSO in 2016 compared to a seven-day increase in DSO in 2015. DSO can shift significantly at each reporting period depending on the timing of cash receipts under contractual payment terms relative to the recognition of revenue over a project lifecycle.
71
Table of Contents
2015 compared to 2014
Cash provided by operating activities increased $43 million in 2015 as compared to 2014. The increase in cash provided by operating activities primarily reflects the increase in net income as adjusted for non-cash items necessary to reconcile net income to cash provided by operating activities. Also contributing to the increase was an increase in accounts payable and accrued expenses ($59 million) as well as lower payments for interest ($12 million) and income taxes ($18 million). These improvements in operating cash flow were partially offset by higher cash used in DSO. The higher cash used in DSO reflects a seven-day increase in DSO in 2015 compared to a two-day increase in DSO in 2014.
Cash Flow from Investing Activities
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| (in millions) |
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
| Net cash provided by (used in) investing activities |
$ | 1,731 | $ | (67) | $ | (173) | ||||||
2016 compared to 2015
Cash provided by investing activities increased $1,798 million in 2016 as compared 2015. This increase was primarily related to cash from the acquisition of businesses, including the merger with IMS Health ($1,887 million) partially offset by higher cash used for the acquisition of property, equipment and software ($86 million).
2015 compared to 2014
Cash used in investing activities decreased $106 million in 2015 as compared to 2014. This decrease was primarily related to cash acquired in the Q2 Solutions transaction ($32 million) compared to cash used for the acquisition of businesses ($92 million) in 2014, partially offset by the termination of interest rate swaps in connection with the refinancing transaction in 2015 ($11 million) and higher cash used for investments.
Cash Flow from Financing Activities
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| (in millions) |
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
| Net cash used in financing activities |
$ | (2,284) | $ | (249) | $ | (130) | ||||||
2016 compared to 2015
Cash used in financing activities increased $2,035 million in 2016 as compared to 2015. The increase in cash used in financing activities was primarily related to lower net borrowing under our credit facilities ($1,488 million) and higher cash used to repurchase common stock ($582 million).
2015 compared to 2014
Cash used in financing activities increased $119 million in 2015 as compared to 2014. The increase in cash used in financing activities in 2015 was primarily related to higher cash used to repurchase common stock ($100 million) and lower cash provided by debt issuances, net of repayments ($75 million), partially offset by higher cash from stock issued under employee stock purchase and option plans ($29 million), and an increase in the excess income tax benefits from stock-based award activities ($19 million).
72
Table of Contents
Contingencies
We are exposed to certain known contingencies that are material to our investors. The facts and circumstances surrounding these contingencies and a discussion of their effect on us are in Note 13 to our audited consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. These contingencies may have a material effect on our liquidity, capital resources or results of operations. In addition, even where our reserves are adequate, the incurrence of any of these liabilities may have a material effect on our liquidity and the amount of cash available to us for other purposes.
We believe that we have made appropriate arrangements in respect of the future effect on us of these known contingencies. We also believe that the amount of cash available to us from our operations, together with cash from financing, will be sufficient for us to pay any known contingencies as they become due without materially affecting our ability to conduct our operations and invest in the growth of our business.
Contractual Obligations and Commitments
Below is a summary of our future payment commitments by year under contractual obligations as of December 31, 2016 (in millions):
| 2017 | 2018 - 2019 | 2020 - 2021 | Thereafter | Total | ||||||||||||||||
| Long-term debt, including interest(1) |
$ | 371 | $ | 991 | $ | 4,313 | $ | 3,070 | $ | 8,745 | ||||||||||
| Operating leases |
171 | 217 | 131 | 159 | 678 | |||||||||||||||
| Data acquisition and telecommunication services |
261 | 224 | 160 | 7 | 652 | |||||||||||||||
| Purchase obligations(2) |
28 | 20 | 4 | — | 52 | |||||||||||||||
| Commitments to unconsolidated affiliates(3) |
— | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
| Benefit obligations(4) |
33 | 42 | 47 | 141 | 263 | |||||||||||||||
| Uncertain income tax positions(5) |
2 | — | — | — | 2 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
| Total |
$ | 866 | $ | 1,494 | $ | 4,655 | $ | 3,377 | $ | 10,392 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
| (1) | Interest payments on our debt are based on the interest rates in effect on December 31, 2016. |
| (2) | Purchase obligations are defined as agreements to purchase goods or services that are enforceable and legally binding and that specify all significant terms, including fixed or minimum quantities to be purchased, fixed, minimum or variable pricing provisions and the approximate timing of the transactions. |
| (3) | We are currently committed to invest $70 million in private equity funds. As of December 31, 2016, we have funded approximately $51 million of these commitments and we have approximately $19 million remaining to be funded. |
| (4) | Amounts represent expected future benefit payments for our pension and postretirement benefit plans, as well as expected contributions for 2016 for our funded pension benefit plans. We made cash contributions totaling approximately $10 million to our defined benefit plans in 2016, and we estimate that we will make contributions totaling approximately $23 million in 2017. Due to the potential impact of future plan investment performance, changes in interest rates, changes in other economic and demographic assumptions and changes in legislation in foreign jurisdictions, we are not able to reasonably estimate the timing and amount of contributions that may be required to fund our defined benefit plans for periods beyond 2017. |
| (5) | As of December 31, 2016, our liability related to uncertain income tax positions was approximately $75 million, $73 million of which has not been included in the above table as we are unable to predict when these liabilities will be paid due to the uncertainties in the timing of the settlement of the income tax positions. |
Application of Critical Accounting Policies
Note 1 to the audited consolidated financial statements provided elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K describes the significant accounting policies used in the preparation of the consolidated financial statements. The preparation of our consolidated financial statements requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities, and the disclosure of contingent assets and
73
Table of Contents
liabilities at the date of the financial statements, as well as the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the period. Our estimates are based on historical experience and various other assumptions we believe are reasonable under the circumstances. We evaluate our estimates on an ongoing basis and make changes to the estimates and related disclosures as experience develops or new information becomes known. Actual results may differ from those estimates.
We believe the following critical accounting policies affect our more significant judgments and estimates used in the preparation of our consolidated financial statements.
Revenue Recognition
We recognize revenue when all of the following conditions are satisfied: (1) there is persuasive evidence of an arrangement, (2) the service offering has been delivered to the client, (3) the collection of fees is probable and (4) the arrangement consideration is fixed or determinable. We do not recognize revenue with respect to start-up activities including contract and scope negotiation, feasibility analysis and conflict of interest review associated with contracts. The costs for these activities are expensed as incurred. For contracts in which portions of revenue are contingent upon the occurrence of uncertain future events we recognize the revenue only after it has been earned and the contingency has been resolved.
For arrangements that include multiple elements, arrangement consideration is allocated to units of accounting based on the relative selling price. The best evidence of selling price of a unit of accounting is vendor-specific objective evidence (“VSOE”) which is the price we charge when the deliverable is sold separately. When VSOE is not available to determine selling price, we use relevant third-party evidence (“TPE”) of selling price, if available. When neither VSOE nor TPE of selling price exists, we use our best estimate of selling price considering all relevant information that is available without undue cost and effort.
We derive the majority of our revenues in the Commercial Solutions segment from various information and technology service offerings. Our revenue arrangements may include multiple elements. A typical information offerings arrangement (primarily under fixed-price contracts) may include an ongoing subscription-based deliverable for which revenue is recognized ratably as earned over the contract period and/or a one-time delivery of data offerings for which revenue is recognized upon delivery, assuming all other criteria are met. Our subscription arrangements typically have terms ranging from one to three years and are generally non-cancelable and do not contain refund-type provisions. We also offer technology services offerings that enable our clients to make informed business decisions. Technology services offerings consist of a mix of small and large-scale services and consulting projects, multi-year outsourcing contracts and SaaS licenses. These arrangements typically have terms ranging from several weeks to three years, with a majority having terms of one year or less. Revenues for services engagements where deliverables occur ratably over time are recognized on a straight-line basis over the term of the arrangement. Revenues from time and material contracts are recognized as the services are provided. Revenues from fixed price ad hoc services and consulting contracts are recognized either over the contract term based on the ratio of the number of hours incurred for services provided during the period compared to the total estimated hours to be incurred over the entire arrangement (efforts based), or upon delivery (completed contract).
The majority of revenue in our Research & Development Solutions segment and Integrated Engagement Services segment is recognized based on objective contractual criteria and does not require significant estimates or judgments. However, at any point in time we are working on thousands of active client projects, which are governed by individual contracts. Most projects are customized based on the needs of the client, the type of services being provided, therapeutic indication of the drug, geographic locations and other variables. Project specific terms related to pricing, billing terms and the scope and type of services to be provided are generally negotiated and contracted on a project-by-project basis. Changes in the scope of work are common, especially under long-term contracts, and generally result in a change in contract value. In such situations, we enter into
74
Table of Contents
negotiations for a contract amendment to reflect the change in scope and the related price. Depending on the complexity of the amendment, the negotiation process can take from a few weeks for a simple adjustment to several months for a complex amendment. Management may authorize the project team to commence work on activities outside the contract scope while we negotiate and finalize the contract amendment. In these limited cases, if we are not able to obtain a contract amendment from the client, our profit margin on the arrangement may be impacted. This result occurs because our costs of delivery are expensed as they are incurred, while revenue is not recognized unless the client has agreed to the changes in scope and renegotiated pricing terms, the contract value is amended and all other revenue recognition criteria are met. Most contracts are terminable upon 30 to 90 days notice by the client. Our risk of material loss in these situations is mitigated as these contracts generally require payment to us for expenses to wind down the clinical trial or project, fees earned to date and, in some cases, a termination fee or a payment of some portion of the fees or profits that could have been earned under the contract if it had not been terminated early. In addition, our contract terms provide for payment terms that generally correspond with performance of the services. Termination fees are included in revenues when realization is assured.
Accounts Receivable and Unbilled Services
Accounts receivable represents amounts billed to clients. Revenues recognized in excess of billings are classified as unbilled services. The realization of these amounts is based on the client’s willingness and ability to pay us. We have an allowance for doubtful accounts based on management’s estimate of probable losses we expect to incur resulting from a client failing to pay us. Our allowance for doubtful accounts, and losses from clients failing to pay us, have not been material to our results of operations. If any of these estimates change or actual results differs from expected results, then an adjustment is recorded in the period in which the amounts become reasonably estimable. These adjustments could have a material effect on our results of operations.
Investments in Unconsolidated Affiliates—Equity Method Investments
We have investments in unconsolidated affiliates that are accounted for under the equity method of accounting. Periodically, we review our investments for a decline in value which we believe may be other than temporary. Should we identify such a decline, we will record a loss through earnings to establish a new cost basis for the investment. These losses could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations.
Income Taxes
Certain items of income and expense are not recognized on our income tax returns and financial statements in the same year, which creates timing differences. The income tax effect of these timing differences results in (1) deferred income tax assets that create a reduction in future income taxes and (2) deferred income tax liabilities that create an increase in future income taxes. Recognition of deferred income tax assets is based on management’s belief that it is more likely than not that the income tax benefit associated with certain temporary differences, income tax operating loss and capital loss carryforwards and income tax credits, would be realized. We recorded a valuation allowance to reduce our deferred income tax assets for those deferred income tax items for which it was more likely than not that realization would not occur. We determined the amount of the valuation allowance based, in part, on our assessment of future taxable income and in light of our ongoing income tax strategies. If our estimate of future taxable income or tax strategies changes at any time in the future, we would record an adjustment to our valuation allowance. Recording such an adjustment could have a material effect on our financial position.
Income tax expense is based on the distribution of profit before income tax among the various taxing jurisdictions in which we operate, adjusted as required by the income tax laws of each taxing jurisdiction. Changes in the distribution of profits and losses among taxing jurisdictions may have a significant impact on our effective income tax rate. We do not consider the undistributed earnings of most of our foreign subsidiaries to be
75
Table of Contents
indefinitely reinvested outside of the United States. Accordingly, we have provided a deferred income tax liability related to those undistributed earnings. The associated foreign income taxes on our foreign earnings could be available as a credit in the United States on our income taxes. We recognize foreign tax credits to the extent that the recognition is supported by projected foreign source income.
Business Combinations
We use the acquisition method to account for business combinations, and accordingly, the identifiable assets acquired, the liabilities assumed and any non-controlling interest in the acquiree are recorded at their estimated fair values on the date of the acquisition. We use significant judgments, estimates and assumptions in determining the estimated fair value of assets acquired, liabilities assumed and non-controlling interest including expected future cash flows; discount rates that reflect the risk associated with the expected future cash flows; and estimated useful lives.
When a business combination involves contingent consideration, we recognize a liability equal to the estimated fair value of the contingent consideration obligation at the date of the acquisition. The estimate of fair value of a contingent consideration liability requires subjective assumptions to be made regarding future business results including revenues and net new business, discount rates that reflect the risk associated with the expected future cash flows and probabilities assigned to various potential business result scenarios. We reassess the estimated fair value of the contingent consideration each financial reporting period over the term of the arrangement. Any resulting changes are recognized in earnings and could have a material effect on our results of operations.
Goodwill, Tangible and Identifiable Intangible Assets
We have recorded and allocated to our reporting units the excess of the cost over the fair value of the net assets acquired, known as goodwill. The recoverability of the goodwill and indefinite-lived intangible assets are evaluated annually for impairment, or if and when events or circumstances indicate a possible impairment. We review the carrying values of other identifiable intangible assets if the facts and circumstances indicate a possible impairment. Goodwill and indefinite-lived intangible assets are not amortized, and other identifiable intangible assets are amortized over their estimated useful lives. We believe that the risk of an impairment to goodwill or indefinite-lived intangible assets is currently very low.
For goodwill, we perform a qualitative analysis to determine whether it is more likely than not that the estimated fair value of a reporting unit is less than its book value. This includes a qualitative analysis of macroeconomic conditions, industry and market considerations, internal cost factors, financial performance, fair value history and other company specific events. If this qualitative analysis indicates that it is more likely than not that estimated fair value is less than the book value for the respective reporting unit, we apply a two-step impairment test in which we determine whether the estimated fair value of the reporting unit is in excess of its carrying value. If the carrying value of the net assets assigned to the reporting unit exceeds the estimated fair value of the reporting unit, we perform the second step of the impairment test to determine the implied estimated fair value of the reporting unit’s goodwill. We determine the implied estimated fair value of goodwill by determining the present value of the estimated future cash flows for each reporting unit and comparing the reporting unit’s risk profile and growth prospects to selected, reasonably similar publicly traded companies. The inherent subjectivity of applying a discounted cash flow and market comparables approach to valuing our assets and liabilities could have a significant impact on our analysis. Any future impairment could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition or results of operations.
For indefinite-lived intangible assets, we perform a qualitative analysis to determine whether it is more likely than not that the estimated fair value of the indefinite-lived intangible asset is less than its carrying value. If this qualitative analysis indicates that it is more likely than not that the estimated fair value is less than the carrying value of the indefinite-lived intangible asset, we determine the estimated fair value of the indefinite-
76
Table of Contents
lived intangible asset (trade name) by determining the present value of the estimated royalty payments on an after-tax basis that it would be required to pay the owner for the right to use such trade name. If the carrying amount exceeds the estimated fair value, an impairment loss is recognized in an amount equal to the excess. Any future impairment could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition or results of operations.
We review the carrying values of property and equipment if the facts and circumstances suggest that a potential impairment may have occurred. If this review indicates that carrying values will not be recoverable, as determined based on undiscounted cash flows over the remaining depreciation or amortization period, we will reduce carrying values to estimated fair value. The inherent subjectivity of our estimates of future cash flows could have a significant impact on our analysis. Any future write-offs of long-lived assets could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition or results of operations.
Stock-based Compensation
We measure compensation cost for most stock-based payment awards (stock options and stock appreciation rights) granted to employees and non-employee directors at fair value using the Black-Scholes-Merton option-pricing model. Stock-based compensation expense includes stock-based awards granted to employees and non-employee directors and has been reported in selling, general and administrative expenses in our consolidated statements of income based upon the classification of the individuals who were granted stock-based awards.
The Black-Scholes-Merton option-pricing model requires the use of subjective assumptions, including share price volatility, the expected life of the award, risk-free interest rate and the fair value of the underlying common shares on the date of grant. In developing our assumptions, we take into account the following:
| • | We calculate expected volatility based on reported data for selected reasonably similar publicly traded companies for which the historical information is available. We plan to continue to use the guideline peer group volatility information until the historical volatility of our common shares is relevant to measure expected volatility for future award grants; |
| • | We determine the risk-free interest rate by reference to implied yields available from United States Treasury securities with a remaining term equal to the expected life assumed at the date of grant; |
| • | We estimate the dividend yield to be zero as we do not currently anticipate paying any future dividends; |
| • | We estimate the average expected life of the award based on our historical experience; and |
| • | We estimate forfeitures based on our historical analysis of actual forfeitures. |
Pensions and Other Postretirement Benefits
We provide retirement benefits to certain employees, including defined benefit pension plans and postretirement medical plans. The determination of benefit obligations and expense is based on actuarial models. In order to measure benefit costs and obligations using these models, critical assumptions are made with regard to the discount rate, expected return on plan assets, cash balance crediting rate, lump sum conversion rate and the assumed rate of compensation increases. In addition, retiree medical care cost trend rates are a key assumption used exclusively in determining costs for our postretirement health care and life insurance benefit plans. Management reviews these critical assumptions at least annually. Other assumptions involve demographic factors such as the turnover, retirement and mortality rates. Management reviews these assumptions periodically and updates them when its experience deems it appropriate to do so.
The discount rate is the rate at which the benefit obligations could be effectively settled and is determined annually by management. For United States plans, the discount rate is based on results of a modeling process in
77
Table of Contents
which the plans’ expected cash flow (determined on a projected benefit obligation basis) is matched with spot rates developed from a yield curve comprised of high-grade (Moody’s Aa and above, or Standard and Poor’s AA and above) non-callable corporate bonds to develop the present value of the expected cash flow, and then determining the single rate (discount rate) which when applied to the expected cash flow derives that same present value. In the United Kingdom specifically, the discount rate is set based on the yields on a universe of high quality non-callable corporate bonds denominated in the British Pound, appropriate to the duration of plan liabilities. For the other non-United States plans, the discount rate is based on the current yield of an index of high quality corporate bonds. As a sensitivity measure, a 25 basis point increase in the discount rate for either our United States plan or our United Kingdom plans, absent any offsetting changes in other assumptions, would result in less than $1 million increase in pension expense within the Consolidated Statements of Income.
Under the United States qualified retirement plan, participants have a notional retirement account that increases with pay and investment credits. The rate used to determine the investment credit (cash balance crediting rate) varies monthly. At retirement, the account is converted to a monthly retirement benefit.
In selecting an expected return on plan asset assumption, we consider the returns being earned by each plan investment category in the fund, the rates of return expected to be available for reinvestment and long-term economic forecasts for the type of investments held by the plan. The actual return on plan assets will vary from year to year versus this assumption. We believe it is appropriate to use long-term expected forecasts in selecting the expected return on plan assets. As such, there can be no assurance that our actual return on plan assets will approximate the long-term expected forecasts. As a sensitivity measure, a 25 basis point change in the expected return on assets (“EROA”) assumption for our United States plan, absent any offsetting changes in other assumptions, would result in a less than $1 million increase or decrease in pension expense. For our United Kingdom plans, a 25 basis point change in the EROA assumption, absent any offsetting changes in other assumptions, would result in a less than $1 million increase or decrease in pension expense. While we believe that the assumptions used are reasonable, differences in actual experience or changes in assumptions may materially affect our pension and postretirement obligations and future expense.
We utilize a corridor approach to amortizing unrecognized gains and losses in the pension and postretirement plans. Amortization occurs when the accumulated unrecognized net gain or loss balance exceeds the criterion of 10% of the larger of the beginning balances of the projected benefit obligation or the market-related value of the plan assets. The excess unrecognized gain or loss balance is then amortized using the straight-line method over the average remaining service-life of active employees expected to receive benefits. At December 31, 2016, the weighted-average remaining service-life of active employees was approximately 13 years.
Foreign Currency
We have significant investments in non-United States countries. Therefore, changes in the value of foreign currencies affect our Consolidated Financial Statements when translated into United States Dollars. For all operations outside the United States where we have designated the local currency as the functional currency, assets and liabilities are translated using end-of-period exchange rates; revenues, expenses and cash flows are translated using average rates of exchange prevailing during the period the transactions occurred. Translation gains and losses are included as an adjustment to the accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) component of stockholders’ deficit. In addition, gains and losses from foreign currency transactions, such as those resulting from the settlement and revaluation of third-party and intercompany foreign receivables and payables, are included in the determination of net income (loss).
For operations in countries that are considered to be highly inflationary or where the United States Dollar is designated as the functional currency, monetary assets and liabilities are remeasured using end-of-period exchange rates, whereas non-monetary accounts are remeasured using historical exchange rates, and all remeasurement and transaction adjustments are recognized in other expense (income), net.
78
Table of Contents
Recently Issued Accounting Standards
Information relating to recently issued accounting standards is included in Note 1 to our audited consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
Market risk is the potential loss arising from adverse changes in market rates and prices. In the ordinary course of business, we are exposed to various market risks and we regularly evaluate our exposure to such changes. Our overall risk management strategy seeks to balance the magnitude of the exposure and the cost and availability of appropriate financial instruments. The following analyses present the sensitivity of our financial instruments to hypothetical changes that are reasonably possible over a one-year period.
Foreign Currency Exchange Rates
We transact business in more than 100 countries and are subject to risks associated with fluctuating foreign currency exchange rates. Our objective is to reduce earnings and cash flow volatility associated with foreign currency exchange rate movements. Accordingly, we enter into foreign currency forward contracts to minimize the impact of foreign exchange movements on non–functional currency assets and liabilities. We also enter into foreign currency forward contracts to hedge certain forecasted foreign currency cash flows related to service contracts and to hedge non-United States Dollar anticipated intercompany royalties. It is our policy to enter into foreign currency transactions only to the extent necessary to meet its objectives as stated above. We do not enter into foreign currency transactions for investment or speculative purposes. The principal currencies hedged are the Euro, the British Pound, the Japanese Yen, the Swiss Franc and the Canadian Dollar.
The contractual value of our foreign exchange derivative instruments, all of which were foreign exchange forward contracts, was approximately $489 million at December 31, 2016. The fair value of these contracts is subject to change as a result of potential changes in foreign exchange rates. We assess our market risk based on changes in foreign exchange rates utilizing a sensitivity analysis. The sensitivity analysis measures the potential loss in fair values based on a hypothetical 10% change in foreign currency exchange rates. The potential loss in fair value for foreign exchange forward contracts based on a hypothetical 10% decrease in the value of the United States Dollar or, in the case of non-dollar-related contracts, the currency being purchased, was $39 million at December 31, 2016. However, the change in the fair value of the foreign exchange forward contracts would likely be offset by a change in the fair value of the future service contract revenue, royalty or balance sheet exposure being hedged. The estimated fair values of the foreign exchange forward contracts were determined based on quoted market prices.
Exchange rate fluctuations affect the United States Dollar value of foreign currency revenue and expenses and may have a significant effect on our results. Excluding the impacts from any outstanding or future hedging transactions, a hypothetical 10% change in average exchange rates used to translate all foreign currencies to the United States Dollar would have impacted income before income taxes for 2016 by approximately $65 million. The actual impact of exchange rate movements in the future could differ materially from this hypothetical analysis, based on the mix of foreign currencies and the timing and magnitude of individual exchange rate movements.
Additionally commencing in 2016, we designated a portion of our foreign currency denominated debt as a hedge of our net investment in foreign subsidiaries to reduce the volatility in stockholders’ equity caused by changes in the Euro exchange rate with respect to the United States Dollar. As of December 31, 2016, these borrowings (net of original issue discount) were €2,025 million ($2,131 million). A hypothetical 10% decrease in the value of the United States Dollar would lead to a potential loss in fair value of $213 million. However, this change in fair value would be offset by the change in fair value of the hedged portion of our net investment in foreign subsidiaries.
79
Table of Contents
Interest Rates
Because we have variable rate debt, fluctuations in interest rates affect our business. We attempt to minimize interest rate risk and lower our overall borrowing costs through the utilization of derivative financial instruments, primarily interest rate caps and swaps. We have entered into interest rate caps and swaps with financial institutions that have reset dates and critical terms that match the underlying debt. Accordingly, any change in market value associated with the interest rate caps and swaps is offset by the opposite market impact on the related debt. As of December 31, 2016, we had approximately $4.4 billion of variable rate indebtedness and interest rate caps and swaps with a notional value of $1.9 billion. Because we do not attempt to hedge all of our variable rate debt, we may incur higher interest costs for the portion of our variable rate debt which is not hedged. Each quarter-point increase or decrease in the variable interest rate would result in our interest expense changing by approximately $6 million per year under our unhedged variable rate debt.
Marketable Securities
At December 31, 2016, we held investments in marketable equity securities. These investments are classified as either trading securities or available-for-sale securities and are recorded at fair value in the financial statements. These securities are subject to price risk. As of December 31, 2016, the fair value of these investments was $40 million based on the quoted market value of the securities. The potential loss in fair value resulting from a hypothetical decrease of 10% in quoted market values was approximately $4 million at December 31, 2016.
80
Table of Contents
Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data
MANAGEMENT’S REPORT ON INTERNAL CONTROL OVER FINANCIAL REPORTING
The management of Quintiles IMS Holdings, Inc. (the “Company”) is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting. Internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Management assessed the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2016. In making this assessment, management used the framework established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). As a result of this assessment and based on the criteria in the COSO framework, management has concluded that, as of December 31, 2016, the Company’s internal control over financial reporting was effective.
The effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2016 has been audited by PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, as stated in their report which appears herein.
| /s/ Ari Bousbib | /s/ Michael R. McDonnell | |||
| Ari Bousbib Chairman, Chief Executive Officer and President (Principal Executive Officer) |
Michael R. McDonnell Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial Officer) | |||
February 16, 2017
81
Table of Contents
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders of Quintiles IMS Holdings, Inc.:
In our opinion, the accompanying consolidated balance sheets and the related consolidated statements of income, comprehensive income, cash flows and stockholders’ equity (deficit), present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of Quintiles IMS Holdings, Inc. and its subsidiaries at December 31, 2016 and 2015, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2016 in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. In addition, in our opinion, the financial statement schedules listed in the index appearing under Item 15(a)(2) present fairly, in all material respects, the information set forth therein when read in conjunction with the related consolidated financial statements. Also in our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2016, based on criteria established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). The Company’s management is responsible for these financial statements and financial statement schedules, for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express opinions on these financial statements, on the financial statement schedules, and on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our integrated audits. We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audits to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement and whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audits of the financial statements included examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, and evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audits also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinions.
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (i) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (ii) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (iii) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
/s/ PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP
Raleigh, North Carolina
February 16, 2017
82
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF INCOME
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| (in millions, except per share data) |
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
| Revenues |
$ | 5,364 | $ | 4,326 | $ | 4,165 | ||||||
| Reimbursed expenses |
1,514 | 1,411 | 1,295 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| Total revenues |
6,878 | 5,737 | 5,460 | |||||||||
| Costs of revenue, exclusive of depreciation and amortization |
3,236 | 2,705 | 2,664 | |||||||||
| Costs of revenue, reimbursed expenses |
1,514 | 1,411 | 1,295 | |||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative expenses |
1,011 | 815 | 781 | |||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
289 | 128 | 121 | |||||||||
| Restructuring costs |
71 | 30 | 9 | |||||||||
| Merger related costs |
87 | — | — | |||||||||
| Impairment charges |
28 | 2 | — | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| Income from operations |
642 | 646 | 590 | |||||||||
| Interest income |
(4 | ) | (4 | ) | (4 | ) | ||||||
| Interest expense |
144 | 101 | 101 | |||||||||
| Loss on extinguishment of debt |
31 | 8 | — | |||||||||
| Other (income), expense net |
(8 | ) | 2 | (8 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| Income before income taxes and equity in (losses) earnings of unconsolidated affiliates |
479 | 539 | 501 | |||||||||
| Income tax expense |
345 | 159 | 149 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| Income before equity in (losses) earnings of unconsolidated affiliates |
134 | 380 | 352 | |||||||||
| Equity in (losses) earnings of unconsolidated affiliates |
(4 | ) | 8 | 5 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| Net income |
130 | 388 | 357 | |||||||||
| Net (income) loss attributable to non-controlling interests |
(15 | ) | (1 | ) | — | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| Net income attributable to Quintiles IMS Holdings, Inc. |
$ | 115 | $ | 387 | $ | 357 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| Earnings per share attributable to common stockholders: |
||||||||||||
| Basic |
$ | 0.77 | $ | 3.15 | $ | 2.78 | ||||||
| Diluted |
$ | 0.76 | $ | 3.08 | $ | 2.72 | ||||||
| Weighted average common shares outstanding: |
||||||||||||
| Basic |
149.1 | 123.0 | 128.0 | |||||||||
| Diluted |
152.0 | 125.6 | 131.1 | |||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
83
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| (in millions) |
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
| Net income |
$ | 130 | $ | 388 | $ | 357 | ||||||
| Comprehensive income adjustments: |
||||||||||||
| Unrealized (losses) gains on available-for-sale securities |
— | — | (1 | ) | ||||||||
| Unrealized (losses) gains on derivative instruments, net of income taxes of $3, ($4) and ($2) |
(7 | ) | (9 | ) | (5 | ) | ||||||
| Defined benefit plan adjustments, net of income taxes of $11, $— and ($3) |
23 | — | (7 | ) | ||||||||
| Foreign currency translation, net of income taxes of $(9), ($5) and ($2) |
(513 | ) | (60 | ) | (48 | ) | ||||||
| Reclassification adjustments: |
||||||||||||
| Gains on marketable securities included in net income, net of income taxes of $—, $— and ($2) |
— | — | (3 | ) | ||||||||
| Losses on derivative instruments included in net income, net of income taxes of $7, $6 and $4 |
21 | 12 | 5 | |||||||||
| Amortization of actuarial losses and prior service costs included in net income |
1 | 1 | — | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| Comprehensive (loss) income |
(345 | ) | 332 | 298 | ||||||||
| Comprehensive loss (income) attributable to non-controlling interests |
1 | 3 | — | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| Comprehensive (loss) income attributable to Quintiles IMS Holdings, Inc. |
$ | (344 | ) | $ | 335 | $ | 298 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
84
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
| December 31, | ||||||||
| (in millions, except per share data) |
2016 | 2015 | ||||||
| ASSETS | ||||||||
| Current assets: |
||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 1,198 | $ | 977 | ||||
| Trade accounts receivable and unbilled services, net |
1,707 | 1,166 | ||||||
| Prepaid expenses |
123 | 51 | ||||||
| Deferred income taxes |
— | 101 | ||||||
| Income taxes receivable |
34 | 34 | ||||||
| Investments in debt, equity and other securities |
40 | — | ||||||
| Other current assets and receivables |
235 | 83 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Total current assets |
3,337 | 2,412 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Property and equipment, net |
406 | 188 | ||||||
| Investments in debt, equity and other securities |
13 | 33 | ||||||
| Investments in unconsolidated affiliates |
69 | 52 | ||||||
| Goodwill |
10,727 | 720 | ||||||
| Other identifiable intangibles, net |
6,390 | 368 | ||||||
| Deferred income taxes |
89 | 43 | ||||||
| Deposits and other assets |
177 | 110 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Total assets |
$ | 21,208 | $ | 3,926 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY (DEFICIT) | ||||||||
| Current liabilities: |
||||||||
| Accounts payable |
$ | 250 | $ | 145 | ||||
| Accrued expenses |
1,493 | 761 | ||||||
| Unearned income |
774 | 585 | ||||||
| Income taxes payable |
76 | 35 | ||||||
| Current portion of long-term debt and obligations held under capital leases |
92 | 49 | ||||||
| Other current liabilities |
20 | 19 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Total current liabilities |
2,705 | 1,594 | ||||||
| Long-term debt and obligations held under capital leases, less current portion |
7,108 | 2,419 | ||||||
| Deferred income taxes |
2,133 | 66 | ||||||
| Other liabilities |
402 | 183 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Total liabilities |
12,348 | 4,262 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Commitments and contingencies (Note 1) |
||||||||
| Stockholders’ equity (deficit): |
||||||||
| Common stock and additional paid-in capital, 400.0 and 300.0 shares authorized at December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively, $0.01 par value, 248.3 and 119.4 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively |
10,602 | 9 | ||||||
| Accumulated deficit |
(399 | ) | (462 | ) | ||||
| Treasury stock, at cost, 12.9 shares at December 31, 2016 |
(1,000 | ) | — | |||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss |
(570 | ) | (111 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Equity (deficit) attributable to Quintiles IMS Holdings, Inc.’s stockholders |
8,633 | (564 | ) | |||||
| Non-controlling interests |
227 | 228 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Total stockholders’ equity (deficit) |
8,860 | (336 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity (deficit) |
$ | 21,208 | $ | 3,926 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
85
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| (in millions) |
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
| Operating activities: |
||||||||||||
| Net income |
$ | 130 | $ | 388 | $ | 357 | ||||||
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to cash provided by operating activities: |
||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
289 | 128 | 121 | |||||||||
| Amortization of debt issuance costs and discount |
30 | 9 | 7 | |||||||||
| Amortization of accumulated other comprehensive loss on terminated interest rate swaps |
3 | 8 | — | |||||||||
| Stock-based compensation |
80 | 38 | 30 | |||||||||
| Impairment of goodwill, identifiable intangible and long-lived assets |
28 | 2 | — | |||||||||
| Gain on disposals of property and equipment, net |
(1 | ) | (1 | ) | (1 | ) | ||||||
| Loss (Earnings) from unconsolidated affiliates |
8 | (8 | ) | (4 | ) | |||||||
| (Gain) Loss on investments, net |
(13 | ) | 1 | (5 | ) | |||||||
| Provision for (benefit from) deferred income taxes |
135 | 18 | (6 | ) | ||||||||
| Excess income tax benefits from stock-based award activities |
(41 | ) | (39 | ) | (20 | ) | ||||||
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities: |
||||||||||||
| Accounts receivable and unbilled services |
(62 | ) | (246 | ) | (79 | ) | ||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other assets |
(8 | ) | 15 | (41 | ) | |||||||
| Accounts payable and accrued expenses |
160 | 104 | 46 | |||||||||
| Unearned income |
52 | 54 | 20 | |||||||||
| Income taxes payable and other liabilities |
70 | 5 | 8 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| Net cash provided by operating activities |
860 | 476 | 433 | |||||||||
| Investing activities: |
||||||||||||
| Acquisition of property, equipment and software |
(164 | ) | (78 | ) | (83 | ) | ||||||
| Net cash assumed from (paid for) acquisition of businesses |
1,887 | 32 | (92 | ) | ||||||||
| Purchase of trading securities |
(40 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
| Proceeds from corporate owned life insurance policies |
21 | — | — | |||||||||
| Proceeds from sale of equity securities |
41 | — | 6 | |||||||||
| Investments in unconsolidated affiliates, net of payments received |
(17 | ) | (12 | ) | (4 | ) | ||||||
| Termination of interest rate swaps |
— | (11 | ) | — | ||||||||
| Other |
3 | 2 | — | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| Net cash provided by (used in) investing activities |
1,731 | (67 | ) | (173 | ) | |||||||
| Financing activities: |
||||||||||||
| Proceeds from issuance of debt |
466 | 2,249 | 275 | |||||||||
| Payment of debt issuance costs |
(7 | ) | (22 | ) | (1 | ) | ||||||
| Repayment of debt |
(1,949 | ) | (2,057 | ) | (30 | ) | ||||||
| Proceeds from revolving credit facility |
172 | — | 150 | |||||||||
| Repayment of revolving credit facility |
— | — | (150 | ) | ||||||||
| Principal payments on capital lease obligations |
(2 | ) | (4 | ) | (3 | ) | ||||||
| Payment of contingent consideration |
(5 | ) | (3 | ) | (3 | ) | ||||||
| Stock issued under employee stock purchase and option plans |
97 | 64 | 35 | |||||||||
| Repurchase of common stock |
(1,097 | ) | (515 | ) | (415 | ) | ||||||
| Repurchase of stock options |
— | — | (8 | ) | ||||||||
| Excess income tax benefits from stock-based award activities |
41 | 39 | 20 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| Net cash used in financing activities |
(2,284 | ) | (249 | ) | (130 | ) | ||||||
| Effect of foreign currency exchange rate changes on cash |
(86 | ) | (50 | ) | (40 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| Increase in cash and cash equivalents |
221 | 110 | 90 | |||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of period |
977 | 867 | 777 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of period |
$ | 1,198 | $ | 977 | $ | 867 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
86
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY (DEFICIT)
| (in millions) |
Common Stock Shares |
Treasury Stock Shares |
Common Stock |
Additional Paid-In Capital |
Accumulated Deficit |
Treasury Stock |
Accumulated Other Comprehensive (Loss) Income |
Non- controlling Interests |
Total | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2013 |
129.6 | — | $ | 1 | $ | 477 | $ | (1,145 | ) | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | (667 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock |
2.1 | — | — | 35 | — | — | — | — | 35 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurchase of common stock |
(7.6 | ) | — | — | (415 | ) | — | — | — | — | (415 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation |
— | — | — | 26 | — | — | — | — | 26 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Income tax benefits from stock-based award activities |
— | — | — | 20 | — | — | — | — | 20 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income |
— | — | — | — | 357 | — | — | — | 357 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unrealized loss on marketable securities, net of tax |
— | — | — | — | — | — | (1 | ) | — | (1 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unrealized loss on derivative instruments, net of tax |
— | — | — | — | — | — | (5 | ) | — | (5 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Defined benefit plan adjustments, net of tax |
— | — | — | — | — | — | (7 | ) | — | (7 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation, net of tax |
— | — | — | — | — | — | (48 | ) | — | (48 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reclassification adjustments, net of tax |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 2 | — | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2014 |
124.1 | — | 1 | 143 | (788 | ) | — | (59 | ) | — | (703 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock |
3.1 | — | — | 65 | — | — | — | — | 65 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurchase of common stock |
(7.8 | ) | — | — | (455 | ) | (61 | ) | — | — | — | (516 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation |
— | — | — | 31 | — | — | — | — | 31 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Income tax benefits from stock-based award activities |
— | — | — | 39 | — | — | — | — | 39 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Q2 Solutions business combination |
— | — | — | 423 | — | — | — | — | 423 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-controlling interest related to Q2 Solutions transaction |
— | — | — | (231 | ) | — | — | — | 231 | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Deferred tax impact of the Q2 Solutions transaction |
— | — | — | (7 | ) | — | — | — | — | (7 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income |
— | — | — | — | 387 | — | — | 1 | 388 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unrealized loss on derivative instruments, net of tax |
— | — | — | — | — | — | (9 | ) | — | (9 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation, net of tax |
— | — | — | — | — | — | (56 | ) | (4 | ) | (60 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reclassification adjustments, net of tax |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 13 | — | 13 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2015 |
119.4 | — | 1 | 8 | (462 | ) | — | (111 | ) | 228 | (336 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock |
130.4 | — | 1 | 10,522 | — | — | — | — | 10,523 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurchase of common stock before October 3, 2016 |
(1.5 | ) | — | — | (46 | ) | (52 | ) | — | — | — | (98 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurchase of common stock on or after October 3, 2016 |
— | (12.9 | ) | — | — | — | (1,000 | ) | — | — | (1,000 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation |
— | — | — | 76 | — | — | — | — | 76 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Income tax benefits from stock-based award activities |
— | — | — | 41 | — | — | — | — | 41 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Investment by non-controlling interest |
— | — | — | (1 | ) | — | — | — | — | (1 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income |
— | — | — | — | 115 | — | — | 15 | 130 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unrealized gain on derivative instruments, net of tax |
— | — | — | — | — | — | (7 | ) | — | (7 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Defined benefit plan adjustments, net of tax |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 23 | — | 23 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation, net of tax |
— | — | — | — | — | — | (497 | ) | (16 | ) | (513 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reclassification adjustments, net of tax |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 22 | — | 22 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2016 |
248.3 | (12.9 | ) | $ | 2 | $ | 10,600 | $ | (399 | ) | $ | (1,000 | ) | $ | (570 | ) | $ | 227 | $ | 8,860 | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
87
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
1. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
The Company
Conducting business in more than 100 countries with over 50,000 employees, Quintiles IMS Holdings, Inc. (together with its subsidiaries, the “Company” or “QuintilesIMS”) is a leading integrated information and technology-enabled healthcare service provider worldwide, dedicated to helping its clients improve their clinical, scientific and commercial results.
On October 3, 2016, Quintiles Transnational Holdings Inc. (“Quintiles”) completed its previously announced merger of equals transaction (the “Merger”) with IMS Health Holdings, Inc. (“IMS Health”). Pursuant to the terms of the merger agreement dated as of May 3, 2016 between Quintiles and IMS Health (the “Merger Agreement”), IMS Health was merged with and into Quintiles, and the separate corporate existence of IMS Health ceased, with Quintiles continuing as the surviving corporation (the “Surviving Corporation”). Immediately prior to the completion of the Merger, Quintiles reincorporated as a Delaware corporation. The Surviving Corporation changed its name to Quintiles IMS Holdings, Inc. At the effective time of the Merger, each issued and outstanding share of IMS Health common stock, par value $0.01 per share (“IMS Health common stock”), was automatically converted into 0.3840 of a share of the Company’s common stock, par value $0.01 per share. In addition, immediately following the effective time of the Merger, Quintiles Transnational Corp (“Quintiles Corp.”), a direct subsidiary of Quintiles, was merged with and into IMS Health Incorporated, following which IMS Health Incorporated will continue as a direct, wholly-owned subsidiary of the Surviving Corporation. See Note 15 for additional information regarding the Merger.
Reclassifications
Certain prior period amounts have been reclassified to conform to the current presentation, including the reclassification of depreciation and amortization from costs of revenue and selling, general and administrative expenses to a separate caption on the accompanying consolidated statements of income. These changes had no effect on previously reported total revenues, net income, comprehensive income, stockholders’ deficit or cash flows.
Principles of Consolidation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements include the accounts and operations of the Company, its subsidiaries and investments in which the Company has control. Amounts pertaining to the non-controlling ownership interests held by third parties in the operating results and financial position of the Company’s majority-owned subsidiaries are reported as non-controlling interests. Intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States of America (“GAAP”) requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities, and the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities, at the date of the financial statements, as well as the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the period. These estimates are based on historical experience and various other assumptions believed reasonable under the circumstances. The Company evaluates its estimates on an ongoing basis and makes changes to the estimates and related disclosures as experience develops or new information becomes known. Actual results may differ from those estimates.
88
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
Foreign Currencies
The Company’s financial statements are reported in United States dollars and, accordingly, the Company’s results of operations are impacted by fluctuations in exchange rates that affect the translation of its revenues and expenses denominated in foreign currencies into United States dollars for purposes of reporting its consolidated financial results. Assets and liabilities recorded in foreign currencies on the books of foreign subsidiaries are translated at the exchange rate on the balance sheet date. Revenues, costs and expenses are translated at average rates of exchange during the year. Translation adjustments resulting from this process are charged or credited to the accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) (“AOCI”) component of stockholders’ equity (deficit). The Company is subject to foreign currency transaction risk for fluctuations in exchange rates during the period of time between the consummation and cash settlement of a transaction. The Company earns revenue from its service contracts over a period of several months and, in some cases, over a period of several years. Accordingly, exchange rate fluctuations during this period may affect the Company’s profitability with respect to such contracts.
For operations in countries that are considered to be highly inflationary or where the United States Dollar is designated as the functional currency, monetary assets and liabilities are remeasured using end-of-period exchange rates, whereas non-monetary accounts are remeasured using historical exchange rates, and all remeasurement and transaction adjustments are recognized in other expense (income), net. Other expense (income), net, includes foreign currency net losses (gains) for 2016, 2015 and 2014 of approximately $6 million, ($5) million and $5 million, respectively.
Cash Equivalents
The Company considers all highly liquid investments with an initial maturity of three months or less when purchased to be cash equivalents.
Investments in Marketable Securities
Investments in marketable securities are classified as either trading or available-for-sale and measured at fair market value. Realized and unrealized gains and losses on trading securities are included in other expense (income), net, on the accompanying consolidated statements of income. Realized gains and losses on available-for-sale securities are included in other expense (income), net, on the accompanying consolidated statements of income. Unrealized gains and losses, net of deferred income taxes, on available-for-sale securities are included in the AOCI component of stockholders’ equity (deficit) until realized. Any gains or losses from the sales of investments or other-than-temporary declines in fair value are computed by specific identification.
Equity Method Investments
The Company’s investments in and advances to unconsolidated affiliates are accounted for under the equity method if the Company exercises significant influence or has an investment in a limited partnership that is considered to be greater than minor. These investments and advances are classified as investments in and advances to unconsolidated affiliates on the accompanying consolidated balance sheets. The Company records its pro rata share of the earnings, adjusted for accretion of basis difference, of these investments in equity in earnings of unconsolidated affiliates on the accompanying consolidated statements of income. The Company reviews its investments in and advances to unconsolidated affiliates for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amounts may not be recoverable.
89
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
Derivatives
The Company uses derivative instruments to manage exposures to interest rates and foreign currencies. Derivatives are recorded on the balance sheet at fair value at each balance sheet date utilizing pricing models for non-exchange-traded contracts. At inception, the Company designates whether or not the derivative instrument is an effective hedge of an asset, liability or firm commitment which is then classified as either a cash flow hedge or a fair value hedge. If determined to be an effective cash flow hedge, changes in the fair value of the derivative instrument are recorded as a component of AOCI until realized. The Company includes the impact from these hedges in the same line item as the hedged item on the consolidated statements of cash flows. Changes in fair value of effective fair value hedges are recorded in earnings as an offset to the changes in the fair value of the related hedged item. Hedge ineffectiveness, if any, is immediately recognized in earnings. Changes in the fair values of derivative instruments that are not an effective hedge are recognized in earnings. When it is probable that a hedged forecasted transaction will not occur, the Company discontinues hedge accounting for the affected portion of the forecasted transaction, and reclassifies gains or losses that were accumulated in AOCI to earnings in other expense (income), net for foreign exchange derivatives and interest expense for interest rate derivatives on the consolidated statements of income. Cash flows are classified consistent with the underlying hedged item. The Company has entered, and may in the future enter, into derivative contracts (caps, swaps, forwards, calls or puts, warrants, for example) related to its debt, investments in marketable equity securities and forecasted foreign currency transactions.
Billed and Unbilled Services and Unearned Income
In general, prerequisites for billings and payments are established by contractual provisions including predetermined payment schedules, which may or may not correspond to the timing of the performance of services under the contract. Unbilled services arise when services have been rendered for which revenue has been recognized but the clients have not been billed.
In some cases, payments received are in excess of revenue recognized. Payments received in advance of services being provided are deferred as unearned income on the consolidated balance sheet. As the contracted services are subsequently performed and the associated revenue is recognized, the unearned income balance is reduced by the amount of the revenue recognized during the period.
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
The Company’s allowance for doubtful accounts is determined based on a variety of factors that affect the potential collectability of the related receivables, including length of time the receivables are past due, client credit ratings, financial stability of the client, specific one-time events and past client history. In addition, in circumstances where the Company is made aware of a specific client’s inability to meet its financial obligations, a specific allowance is established. The accounts are individually evaluated on a regular basis and reserves are established as deemed appropriate based on the above criteria.
Receivables Financing Facility
Advances received under the Company’s receivables financing facility are accounted for as borrowings secured by the receivables and included in net cash provided by financing activities. The Company services the collateralized accounts receivable and the cash flows for the underlying receivables are included in cash provided by operating activities. The collateralized accounts receivable are included in trade accounts receivable and unbilled services, net.
90
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
Business Combinations
Business combinations are accounted for using the acquisition method of accounting. The identifiable assets acquired, the liabilities assumed, and any non-controlling interest in the acquiree are recorded at their estimated fair values on the date of the acquisition. Goodwill represents the excess of the purchase price over the estimated fair value of the net assets acquired, including the amount assigned to identifiable intangible assets. When a business combination involves contingent consideration, the Company recognizes a liability equal to the estimated fair value of the contingent consideration obligation at the date of the acquisition. Subsequent changes in the estimated fair value of the contingent consideration are recognized in earnings in the period of the change. Acquisition-related costs are expensed as incurred. The consolidated financial statements include the results of operations of business combinations since the acquisition date.
Long-Lived Assets
Property and equipment are stated at cost and are depreciated using the straight-line method over the shorter of the asset’s estimated useful life or the lease term, if related to leased property, as follows:
| Buildings and leasehold improvements |
3 - 40 years | |
| Equipment |
3 - 10 years | |
| Furniture and fixtures |
5 - 10 years | |
| Motor vehicles |
3 - 5 years |
Definite-lived identifiable intangible assets are amortized primarily using an accelerated method that reflects the pattern in which the Company expects to benefit from the use of the asset over its estimated remaining useful life as follows:
| Trademarks and trade names |
2 - 10 years | |
| Contract backlog and client relationships |
3 - 25 years | |
| Software and related assets |
2 - 9 years | |
| Databases |
1 - 5 years | |
| Non-compete agreements and other |
1 - 5 years |
Goodwill and indefinite-lived identifiable intangible assets, which consist of certain trade names, are not amortized but evaluated for impairment annually, or more frequently if events or changes in circumstances indicate an impairment.
Included in software and related items is the capitalized cost of internal-use software used in supporting the Company’s business. Qualifying costs incurred during the application development stage are capitalized and amortized over their estimated useful lives. Costs are capitalized from completion of the preliminary project stage and when it is considered probable that the software will be used to perform its intended function, up until the time the software is placed into service. The Company recognized $44 million, $38 million and $33 million of amortization expense in 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively, related to software and related assets.
The carrying values of property, equipment and intangible and other long-lived assets are reviewed for recoverability if the facts and circumstances suggest that a potential impairment may have occurred. If this review indicates that carrying values will not be recoverable, as determined based on undiscounted cash flow
91
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
projections, the Company will record an impairment charge to reduce carrying values to estimated fair value. See Note 17 for information regarding the impairment charge recognized in 2016. During 2015, the Company recognized a $2 million impairment charge for long-lived assets related to a facility closure in Japan. There were no events, facts or circumstances in 2014 that resulted in any impairment charges to the Company’s property, equipment, intangible or other long-lived assets.
Revenue Recognition
The Company recognizes revenue when all of the following conditions are satisfied: (1) there is persuasive evidence of an arrangement; (2) the service offering has been delivered to the client; (3) the collection of the fees is probable; and (4) the arrangement consideration is fixed or determinable. The Company’s arrangements are primarily service contracts that range in duration from a few months to several years.
In some cases, contracts provide for consideration that is contingent upon the occurrence of uncertain future events. The Company recognizes contingent revenue when the contingency has been resolved and all other criteria for revenue recognition have been met. The Company treats cash payments to clients as incentives to induce the clients to enter into such a service agreement with the Company. The related asset is amortized as a reduction of revenue over the period the services are performed. The Company records revenues net of any tax assessments by governmental authorities, such as value added taxes, that are imposed on and concurrent with specific revenue generating transactions. The Company does not recognize revenue with respect to start-up activities including contract and scope negotiation, feasibility analysis and conflict of interest review associated with contracts. The costs for these activities are expensed as incurred.
For the arrangements that include multiple elements, arrangement consideration is allocated to units of accounting based on the relative selling price. The best evidence of selling price of a unit of accounting is vendor-specific objective evidence (“VSOE”), which is the price the Company charges when the deliverable is sold separately. When VSOE is not available to determine selling price, management uses relevant third-party evidence (“TPE”) of selling price, if available. When neither VSOE nor TPE of selling price exists, management uses its best estimate of selling price considering all relevant information that is available without undue cost and effort.
The Company derives the majority of its revenues in the Commercial Solutions segment from various information and technology service offerings. A typical information offerings arrangement (primarily under fixed-price contracts) may include an ongoing subscription-based deliverable for which revenue is recognized ratably as earned over the contract period, and/or a one-time delivery of data offerings for which revenue is recognized upon delivery, assuming all other criteria are met. The Company’s subscription arrangements typically have terms ranging from one to three years and are generally non-cancelable and do not contain refund-type provisions. Technology services offerings consist of a mix of small and large-scale services and consulting projects, multi-year outsourcing contracts and Software-as-a-Service (“SaaS”) licenses. These arrangements typically have terms ranging from several weeks to three years, with a majority having terms of one year or less. Revenues for services engagements where deliverables occur ratably over time are recognized on a straight-line basis over the term of the arrangement. Revenues from time and material contracts are recognized as the services are provided. Revenues from fixed price ad hoc services and consulting contracts are recognized either over the contract term based on the ratio of the number of hours incurred for services provided during the period compared to the total estimated hours to be incurred over the entire arrangement (efforts based), or upon delivery (completed contract).
The majority of the Company’s contracts within the Research & Development Solutions segment are service contracts for clinical research that represent a single unit of accounting. The Company recognizes
92
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
revenue on its clinical research services contracts as services are performed primarily on a proportional performance basis, generally using output measures that are specific to the service provided. Examples of output measures include among others, number of investigators enrolled, number of site initiation visits and number of monitoring visits completed. Revenue is determined by dividing the actual units of work completed by the total units of work required under the contract and multiplying that ratio by the total contract value. The total contract value, or total contractual payments, represents the aggregate contracted price for each of the agreed upon services to be provided. Changes in the scope of work are common, especially under long-term contracts, and generally result in a change in contract value. Once the client has agreed to the changes in scope and renegotiated pricing terms, the contract value is amended and revenue is recognized, as described above. To the extent that contracts involve multiple elements, the Company follows the allocation methodology described above and recognizes revenue for each unit of accounting on a proportional performance basis. Most contracts may be terminated upon 30 to 90 days notice by the client, however, in the event of termination, contract provisions typically require payment for services rendered through the date of termination, as well as for subsequent services rendered to close out the contract.
The Company derives the majority of its revenues in its Integrated Engagement Services segment on a fee-for-service basis to clients within the biopharmaceutical industry. Fees on these arrangements are billed based on a contractual per-diem or hourly rate basis and revenue is recognized primarily on a time and materials basis. Some of the Company’s Integrated Engagement Services contracts are multiple element arrangements, with elements including recruiting, training and deployment of sales representatives. The nature of the terms of these multiple element arrangements will vary based on the customized needs of the Company’s clients. For contracts that have multiple elements, the Company follows the allocation methodology described above and recognizes revenue for each unit of accounting on a time and materials basis. The Company’s Integrated Engagement Services contracts sometimes include variable fees that are based on a percentage of service sales (royalty payments). The Company recognizes revenue on royalty payments when the variable components become fixed or determinable and all other revenue recognition criteria have been met, which generally only occurs upon the sale of the underlying service(s) and upon the Company’s receipt of information necessary to make a reasonable estimate.
Reimbursed Expenses
The Company includes reimbursed expenses in total revenues and costs of revenue as the Company is deemed to be the primary obligor in the applicable arrangements. These costs include such items as payments to investigators and travel expenses for the Company’s clinical monitors and sales representatives.
The Company has collection risk on contractually reimbursable expenses, and, from time to time, is unable to obtain reimbursement from the client for costs incurred. When such an expense is not reimbursed, it is classified as costs of revenue on the consolidated statements of income.
Expenses
Our costs and expenses are comprised primarily of our costs of revenue, reimbursed expenses and selling, general and administrative expenses. Costs of revenue include compensation and benefits for billable employees and personnel involved in production, data management and delivery, and the costs of acquiring and processing data for our information offerings; costs of staff directly involved with delivering technology-related services offerings and engagements, related accommodations and the costs of data purchased specifically for technology services engagements; and other expenses directly related to service contracts such as courier fees, laboratory supplies, professional services and travel expenses. As noted above, reimbursed expenses are comprised principally of payments to investigators who oversee clinical trials and travel expenses for our clinical monitors
93
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
and sales representatives. Selling, general and administrative expenses include costs related to sales, marketing, and administrative functions (including human resources, legal, finance and general management) for compensation and benefits, travel, professional services, training and expenses for information technology (“IT”), facilities and depreciation and amortization.
Concentration of Credit Risk
Financial instruments that subject the Company to credit risk primarily consist of cash and cash equivalents, marketable securities and accounts receivable. The Company maintains its cash and cash equivalent balances with high-quality financial institutions and, consequently, the Company believes that such funds are subject to minimal credit risk. Investment policies have been implemented that limit purchases of marketable securities to investment grade securities. Substantially all revenues for Commercial Solutions, Research & Development Solutions and Integrated Engagement Services are earned by performing services under contracts with various pharmaceutical, biotechnology, medical device and healthcare companies. The concentration of credit risk is equal to the outstanding accounts receivable and unbilled services balances, less the unearned income related thereto, and such risk is subject to the financial and industry conditions of the Company’s clients. The Company does not require collateral or other securities to support client receivables. Credit losses have been immaterial and reasonably within management’s expectations. No client accounted for 10.0% or more of consolidated revenues in 2016, 2015 or 2014.
Restructuring Costs
Restructuring costs, which primarily include termination benefits and facility closure costs, are recorded at estimated fair value. Key assumptions in determining the restructuring costs include the terms and payments that may be negotiated to terminate certain contractual obligations and the timing of employees leaving the Company.
Merger Related Costs
Merger related costs include the direct and incremental costs associated with business combinations including (i) acquisition related costs such as investment banking, legal, accounting and consulting fees (see Footnote 15), (ii) incremental compensation costs triggered under change in control provisions in executive employment agreements, (iii) compensation and related costs of employees 100% dedicated to merger-related integration activities and (iv) severance and other termination costs associated with redundant employees. During 2016, the Company recognized $87 million of merger related costs, which includes $36 million of acquisition related costs. All of these costs are related to the merger with IMS Health. Merger related costs for all other business combinations have been immaterial and are included within selling, general and administrative expenses on the consolidated statements of income.
Legal Costs
Legal costs are expensed as incurred.
Debt Fees
Fees incurred to issue debt are generally deferred and amortized as a component of interest expense over the estimated term of the related debt using the effective interest rate method.
Contingencies
The Company records accruals for claims, suits, investigations and proceedings when it is probable that a liability has been incurred and the amount of the loss can be reasonably estimated. The Company reviews claims,
94
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
suits, investigations and proceedings at least quarterly and records or adjusts accruals related to such matters to reflect the impact and status of any settlements, rulings, advice of counsel or other information pertinent to a particular matter. Legal costs associated with contingencies are charged to expense as incurred.
The Company is party to legal proceedings incidental to its business. While the outcome of these matters could differ from management’s expectations, the Company does not believe the resolution of these matters has a reasonable possibility of having a material adverse effect to the Company’s financial statements.
Income Taxes
Income tax expense includes United States federal, state and international income taxes. Certain items of income and expense are not reported in income tax returns and GAAP financial statements in the same year. The income tax effects of these differences are reported as deferred income taxes. Valuation allowances are provided to reduce the related deferred income tax assets to an amount which will, more likely than not, be realized. In addition, the Company does not consider the undistributed foreign earnings of most of its foreign subsidiaries to be permanently reinvested. To the extent undistributed foreign earnings are not permanently reinvested, the Company records deferred income taxes on these earnings. Interest and penalties related to unrecognized income tax benefits are recognized as a component of income tax expense as discussed further in Note 18.
Pensions and Other Postretirement Benefits
The Company provides retirement benefits to certain employees, including defined benefit pension plans and postretirement medical plans. The determination of benefit obligations and expense is based on actuarial models. In order to measure benefit costs and obligations using these models, critical assumptions are made with regard to the discount rate, expected return on plan assets, cash balance crediting rate, lump sum conversion rate and the assumed rate of compensation increases. In addition, retiree medical care cost trend rates are a key assumption used exclusively in determining costs for the Company’s postretirement health care and life insurance benefit plans. Management reviews these critical assumptions at least annually. Other assumptions involve demographic factors such as the turnover, retirement and mortality rates. Management reviews these assumptions periodically and updates them when their experience deems it appropriate to do so.
The discount rate is the rate at which the benefit obligations could be effectively settled and is determined annually by management. For United States plans, the discount rate is based on results of a modeling process in which the plans’ expected cash flow (determined on a projected benefit obligation basis) is matched with spot rates developed from a yield curve comprised of high-grade (Moody’s Aa and above, or Standard and Poor’s AA and above) non-callable corporate bonds to develop the present value of the expected cash flow, and then determining the single rate (discount rate) which when applied to the expected cash flow derives that same present value. In the United Kingdom specifically, the discount rate is set based on the yields on a universe of high quality non-callable corporate bonds denominated in the British Pound, appropriate to the duration of plan liabilities. For the non-United States plans, the discount rate is based on the current yield of an index of high quality corporate bonds.
The Company estimates the service and interest cost components of net periodic benefit cost for our United States and United Kingdom pension benefit plans by utilizing a full yield curve approach in the estimation of these components by applying the specific spot rates along the yield curve used in the determination of the benefit obligation to each of the underlying projected cash flows based on time until payment.
Under the United States qualified retirement plan, participants have a notional retirement account that increases with pay and investment credits. The rate used to determine the investment credit (cash balance crediting rate) varies monthly. At retirement, the account is converted to a monthly retirement benefit.
95
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
In selecting an expected return on plan asset assumption, the Company considers the returns being earned by each plan investment category in the fund, the rates of return expected to be available for reinvestment and long-term economic forecasts for the type of investments held by the plan. The actual return on plan assets will vary from year to year versus this assumption. The Company believes it is appropriate to use long-term expected forecasts in selecting the expected return on plan assets. As such, there can be no assurance that the Company’s actual return on plan assets will approximate the long-term expected forecasts. While the Company believes that the assumptions used are reasonable, differences in actual experience or changes in assumptions may materially affect its pension and postretirement benefit obligations and future expense.
The Company’s estimated long-term rate of return on plan assets is based on the principles of capital market theory which maintain that over the long run, prudent investment risk taking is rewarded with incremental returns and that combining non-correlated assets can maximize risk adjusted portfolio returns. Long-term return estimates are developed by asset category based on actual class return data, historical relationships between asset classes and risk factors and peer plan data. Long-term return estimates for the Company’s United Kingdom pension plans are developed by asset category based on actual class return data, historical relationships between asset classes and risk factors.
The Company utilizes a corridor approach to amortizing unrecognized gains and losses in the pension and postretirement benefit plans. Amortization occurs when the accumulated unrecognized net gain or loss balance exceeds the criterion of 10% of the larger of the beginning balances of the projected benefit obligation or the market-related value of the plan assets. The excess unrecognized gain or loss balance is then amortized using the straight-line method over the average remaining service-life of active employees expected to receive benefits.
Employee Stock Compensation
The Company accounts for stock-based compensation for stock options and stock appreciation rights under the fair value method and uses the Black-Scholes-Merton model to estimate the value of such stock-based awards granted to its employees and non-executive directors. Expected volatility is based upon the historical volatility of a peer group for a period equal to the expected term, as the Company does not have adequate history to calculate its own volatility and believes the expected volatility will approximate the historical volatility of the peer group. The Company does not currently anticipate paying dividends. The expected term represents the period of time the grants are expected to be outstanding. The risk-free interest rate is based on the United States Treasury yield curve in effect at the time of the grant.
The Company accounts for its stock-based compensation for restricted stock awards, restricted stock units and performance awards based on the closing market price of the Company’s common stock on the date of grant.
Earnings Per Share
The calculation of earnings per share is based on the weighted average number of common shares or common stock equivalents outstanding during the applicable period. The dilutive effect of common stock equivalents is excluded from basic earnings per share and is included in the calculation of diluted earnings per share. Potentially dilutive securities include outstanding stock options and unvested restricted stock units, restricted stock and performance shares.
Employee equity share options, restricted stock units, restricted stock, performance shares and similar equity instruments granted by the Company are treated as potential common shares outstanding in computing diluted earnings per share. Diluted shares outstanding are calculated based on the average share price for each
96
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
fiscal period using the treasury stock method. Under the treasury stock method, the amount the employee must pay for exercising stock options, the amount of compensation cost for future service that the Company has not yet recognized, and the amount of benefits that would be recorded in additional paid-in capital when the award becomes deductible for tax purposes are assumed to be used to repurchase shares.
Treasury Stock
The Company records treasury stock purchases under the cost method. Upon reissuance of treasury stock, amounts in excess of the acquisition cost are credited to additional paid in capital. If the Company reissues treasury stock at an amount below its acquisition cost and additional paid in capital associated with prior treasury stock transactions is insufficient to cover the difference between the acquisition cost and the reissue price, this difference is recorded in retained earnings.
Recently Issued Accounting Standards
Accounting pronouncement adopted
In November 2015, the United States Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued new accounting guidance which removed the requirement that deferred income tax assets and liabilities be classified as either current or non-current in a classified statement of financial position and instead requires deferred income tax assets and liabilities to be classified as non-current. The Company adopted this new accounting guidance prospectively on January 1, 2016.
Accounting pronouncements being evaluated
In August 2016, the FASB issued new accounting guidance which eliminates the diversity in practice related to the cash flow classification of certain cash receipts and payments, including debt prepayment or extinguishment payments, payments upon maturity of a zero coupon bond, payment of contingent liabilities arising from a business combination, proceeds from insurance settlements, distributions received from certain equity method investees, and cash flows related to beneficial interests obtained in a financial asset securitization. The new guidance designates the appropriate cash flow statement classification, including requirements to allocate certain components of these cash receipts and payments among operating, investing and financing activities. This new accounting guidance will be effective for the Company on January 1, 2018. Early adoption is permitted. The Company is currently evaluating the impact of this new accounting guidance on its consolidated financial statements.
In March 2016, the FASB issued new accounting guidance which simplifies several aspects of the accounting for employee stock-based payment transactions, including the accounting for income taxes, forfeitures, statutory tax withholding requirements, and the classification of excess income tax benefits on the statement of cash flows. The Company will adopt this new accounting guidance as required on January 1, 2017. Under the new accounting guidance, excess income tax benefits related to stock-based awards will be reflected as a reduction of income tax expense on the statements of income and as cash provided from operating activities on the statements of cash flows. Under existing guidance, these tax benefits are reflected directly in additional paid-in capital and as cash provided from financing activities. The Company recognized $41 million of such income tax benefits in 2016. The Company does not expect the adoption of this new accounting guidance to impact the recognition of its stock-based compensation expense or its presentation of cash flows related to employee taxes paid for withheld shares.
In February 2016, the FASB issued new accounting guidance which requires lessees to recognize almost all leases on their balance sheet as a right-of-use asset and a lease liability. The income statement will reflect lease
97
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
expense for operating leases, and amortization and interest expense for financing leases. The new accounting guidance will be effective for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2018. Early adoption is permitted. The Company is currently evaluating the impact of this new accounting guidance on its consolidated financial statements.
In January 2016, the FASB issued new accounting guidance which modifies how entities measure equity investments and present changes in the fair value of financial liabilities. The new accounting guidance will be effective for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2017. Early adoption of the presentation guidance is permitted; however, early adoption of the recognition and measurement guidance is not permitted. The adoption of this new accounting guidance is not expected to have a material effect on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
In May 2014, the FASB and the International Accounting Standards Board issued a converged standard on the recognition of revenue from contracts with clients. The objective of the new standard is to establish a single comprehensive revenue recognition model that is designed to create greater comparability of financial statements across industries and jurisdictions. Under the new standard, companies will recognize revenue to depict the transfer of goods or services to clients in amounts that reflect the consideration to which the company expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods or services. The new standard also will require expanded disclosures on revenue recognition, including information about changes in assets and liabilities that result from contracts with clients. The new standard allows for either a retrospective or prospective approach to transition upon adoption. The new standard will be effective for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2017. Early adoption is permitted for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2016. The Company is currently evaluating the impact of this new accounting guidance on its consolidated financial statements, the date of adoption and the transition approach to implement the new standard.
2. Accounts Receivable and Unbilled Services
Accounts receivable and unbilled services consist of the following (in millions):
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Trade: |
||||||||
| Billed |
$ | 998 | $ | 554 | ||||
| Unbilled services |
723 | 614 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| 1,721 | 1,168 | |||||||
| Allowance for doubtful accounts |
(14 | ) | (2 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| $ | 1,707 | $ | 1,166 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
3. Investments – Debt, Equity and Other Securities
Current
The Company’s short-term investments in debt, equity and other securities consist primarily of trading investments in mutual funds that are measured at fair value with realized and unrealized gains and losses recorded in other expense (income), net, on the accompanying consolidated statements of income. Net realized and unrealized gains were approximately $3 million during the year ended December 31, 2016.
98
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
Long-term
The Company’s long-term investments in debt, equity and other securities consist primarily of cost method investments.
The Company is party to a joint venture with the Samsung Group to provide biopharmaceutical contract manufacturing services in South Korea. The Company’s investment in the joint venture totaled $27 million at December 31, 2015. During the second quarter of 2016, the Company exercised its right to sell a portion of its ownership interest in the joint venture to the Samsung Group in exchange for approximately $26 million. As of December 31, 2016, the Company’s investment in the joint venture totaled approximately $1 million (representing an ownership interest of less than 1%).
The Company reviews the carrying value of each individual investment at each balance sheet date to determine whether or not an other-than-temporary decline in fair value has occurred. The Company employs alternative valuation techniques including the following: (i) the review of financial statements, including assessments of liquidity, (ii) the review of valuations available to the Company prepared by independent third parties used in raising capital, (iii) the review of publicly available information including press releases and (iv) direct communications with the investee’s management, as appropriate. If the review indicates that such a decline in fair value has occurred, the Company adjusts the carrying value to the estimated fair value of the investment and recognizes a loss for the amount of the adjustment.
4. Investments in and Advances to Unconsolidated Affiliates
The Company accounts for its investments in and advances to unconsolidated affiliates under the equity method of accounting and records its pro rata share of its losses or earnings from these investments in equity in earnings (losses) of unconsolidated affiliates. The following is a summary of the Company’s investments in and advances to unconsolidated affiliates (in millions):
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| NovaQuest Pharma Opportunities Fund III, L.P. |
$ | 43 | $ | 40 | ||||
| NovaQuest Pharma Opportunities Fund IV, L.P. |
6 | 2 | ||||||
| CenduitTM |
11 | 9 | ||||||
| Other |
9 | 1 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| $ | 69 | $ | 52 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
NovaQuest Pharma Opportunities Funds
The Company has committed to invest up to $50 million as a limited partner in NovaQuest Pharma Opportunities Fund III, L.P. (“Fund III”). As of December 31, 2016, the Company has funded approximately $43 million and has approximately $7 million of remaining funding commitments. As of December 31, 2016 and 2015, the Company had a 10.9% ownership interest in Fund III.
The Company has committed to invest up to $20 million as a limited partner in NovaQuest Pharma Opportunities Fund IV, L.P. (“Fund IV”). As of December 31, 2016, the Company has funded approximately $8 million and has approximately $12 million of remaining funding commitments. As of December 31, 2016 and 2015, the Company had a 2.3% ownership interest in Fund IV.
99
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
Cenduit™
In May 2007, the Company and Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. (“Thermo Fisher”) completed the formation of a joint venture, Cenduit™. The Company contributed its Interactive Response Technology operations in India and the United States. Thermo Fisher contributed its Fisher Clinical Services Interactive Response Technology operations in three locations — the United Kingdom, the United States and Switzerland. Additionally, each company contributed $4 million in initial capital. The Company and Thermo Fisher each own 50% of Cenduit™.
See Note 20 for information regarding related party transactions.
5. Variable Interest Entities
As of December 31, 2016, the Company’s investments in unconsolidated variable interest entities (“VIEs”) and its estimated maximum exposure to loss were as follows (in millions):
| Investments in Unconsolidated VIEs |
Maximum Exposure to Loss | |||||||
| NovaQuest Pharma Opportunities Fund III, L.P. |
$ | 43 | $ | 51 | ||||
| NovaQuest Pharma Opportunities Fund IV, L.P. |
6 | 18 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| $ | 49 | $ | 69 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
The Company’s maximum exposure to loss on Fund III and Fund IV (collectively “the Funds”) is limited to its investments and remaining funding commitments.
The Company has determined that the Funds are VIEs but that the Company is not the primary beneficiary as it does not have a controlling financial interest in either of the Funds. However, because the Company has determined that it has the ability to exercise significant influence, it accounts for its investments in the Funds under the equity method of accounting and records its pro rata share of the Funds’ earnings and losses in equity in (losses) earnings of unconsolidated affiliates on the accompanying consolidated statements of income. The investment assets of unconsolidated VIEs are included in investments in and advances to unconsolidated affiliates on the accompanying consolidated balance sheets.
6. Derivatives
Foreign Exchange Risk Management
The Company transacts business in more than 100 countries and is subject to risks associated with fluctuating foreign exchange rates. The Company’s objective is to reduce earnings and cash flow volatility associated with foreign exchange rate movements. Accordingly, the Company enters into foreign currency forward contracts to minimize the impact of foreign exchange movements on non-functional currency assets and liabilities (“Balance Sheet Hedging”) to (i) hedge certain forecasted foreign exchange cash flows arising from service contracts (“Service Contract Hedging”) and (ii) hedge non-United States Dollar anticipated intercompany royalties (“Royalty Hedging”). It is the Company’s policy to enter into foreign currency transactions only to the extent necessary to meet its objectives as stated above. The Company does not enter into foreign currency transactions for investment or speculative purposes. The principal currencies hedged are the Euro, the British Pound, the Japanese Yen, the Swiss Franc and the Canadian Dollar.
Balance Sheet Hedging contracts entered into for balance sheet risk management purposes are not designated as hedges and are carried at fair value, with changes in the fair value recorded to other expense (income), net in the accompanying consolidated statements of income. These contracts do not subject the Company to material balance sheet risk because gains and losses on these derivatives are intended to offset gains and losses on the assets and liabilities being hedged.
100
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
Service Contract Hedging and Royalty Hedging contracts are designated as hedges and are carried at fair value, with changes in the fair value recorded to AOCI. The change in fair value is reclassified from AOCI to earnings in the period in which the hedged transaction occurs. These contracts have various expiration dates through November 2017.
As of December 31, 2016, the Company had 62 open Service Contract Hedging and Royalty Hedging contracts to hedge certain forecasted foreign currency cash flow transactions occurring in 2017 with notional amounts totaling $300 million. As of December 31, 2015, the Company had 15 open Service Contract Hedging contracts to hedge certain forecasted foreign currency cash flow transactions occurring in 2016. For accounting purposes these hedges are deemed to be highly effective. As of December 31, 2016 and 2015, the Company had recorded gross unrealized gains (losses) of $1 million and ($5 million), respectively, related to these contracts. Upon expiration of the hedge instruments in 2017, the Company will reclassify the unrealized gains and losses on the derivative instruments included in AOCI into earnings. The unrealized gains (losses) are included in other current assets and liabilities on the accompanying consolidated balance sheets as of December 31, 2016 and 2015.
Interest Rate Risk Management
The Company purchases interest rate caps and has entered into interest rate swap agreements for purposes of managing its risk in interest rate fluctuations.
On June 9, 2011, the Company entered into six interest rate swaps which expired between September 30, 2013 and March 31, 2016, in an effort to limit its exposure to changes in the variable interest rate on its senior secured credit facilities. During May 2015, in conjunction with the debt refinancing described in Note 11, the Company terminated the remaining open interest rate swaps for a cash payment to the counterparty of $12 million, which included $1 million of accrued interest. Since the hedged forecasted cash transactions continued to be probable of occurring, the accumulated loss ($3 million at December 31, 2015) related to the terminated interest rate swaps in AOCI was reclassified to earnings as a component of interest expense in the same periods as the hedged forecasted transactions occurred over the first three months of 2016.
In April 2014, the IMS Health purchased United States Dollar denominated interest rate caps (“2014 Caps”) with a total notional value of $1 billion at strike rates ranging between 2% and 3%. These caps were effective at various times between April 2014 and April 2016, and expire at various times between April 2017 and April 2019. The total premiums paid were $21 million. The 2014 Caps are designated as cash flow hedges.
IMS Health also entered into United States Dollar and Euro denominated interest rate swap agreements in April 2014 (“2014 Swaps”) to hedge interest rate exposure on notional amounts of approximately $600 million of its borrowings. The 2014 Swaps were effective between April and June 2014, and expire at various times from March 2017 through March 2021. On these agreements, the Company pays a fixed rate ranging from 1.4% to 2.1% and receives a variable rate of interest equal to the greater of three-month United States Dollar London Interbank Offered Rate (“LIBOR”) or three-month Euro Interbank Offered Rate (“EURIBOR”), and 1%. The 2014 Swaps are designated as cash flow hedges.
On June 3, 2015, the Company entered into seven forward starting interest rate swaps (“2015 Swaps”) in an effort to limit its exposure to changes in the variable interest rate on its senior secured credit facilities. Interest on the swaps began accruing on June 30, 2016 and the interest rate swaps expire between March 31, 2017 and March 31, 2020. Payments on the 2015 Swaps, together with the variable rate of interest incurred on the underlying debt, result in a fixed rate of interest of 2.1% plus the applicable margin on the affected borrowings.
The critical terms of the 2014 Swaps and 2015 Swaps are substantially the same as the underlying borrowings. These interest rate swaps are being accounted for as cash flow hedges as these transactions were
101
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
executed to hedge the Company’s interest payments, and for accounting purposes these hedges are deemed to be highly effective. As such, changes in the fair value of these derivative instruments are recorded as unrealized gains (losses) on derivatives included in AOCI. The fair value of these interest rate swaps represents the present value of the anticipated net payments the Company will make to the counterparty, which, when they occur, are reflected as interest expense on the consolidated statements of income. These interest rate swaps will result in a total debt mix of approximately 52% fixed rate debt and 48% variable rate debt, before the additional protection arising from the interest rate caps.
Net Investment Risk Management
Beginning in the 2016, the Company designated its foreign currency denominated debt as a hedge of its net investment in foreign subsidiaries to reduce the volatility in stockholders’ equity caused by changes in the Euro exchange rate with respect to the United States Dollar. As of December 31, 2016, these borrowings (net of original issue discount) were €2,025 million ($2,131 million). The effective portion of foreign exchange gains or losses on the remeasurement of the debt is recognized in the cumulative translation adjustment component of AOCI with the related offset in long-term debt. Those amounts would be reclassified from AOCI to earnings upon the sale or substantial liquidation of these net investments. The amount of foreign exchange gains (losses) related to the net investment hedge included in cumulative translation adjustment for the year ended December 31, 2016 was $131 million.
The fair values of the Company’s derivative instruments and the line items on the accompanying consolidated balance sheets to which they were recorded are summarized in the following table (in millions):
| December 31, 2016 | December 31, 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance Sheet Classification |
Assets | Liabilities | Notional | Assets | Liabilities | Notional | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Derivatives designated as hedging instruments: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign exchange forward contracts |
|
Other current assets and liabilities |
|
$ | 11 | $ | 9 | $ | 300 | $ | — | $ | 5 | $ | 118 | |||||||||||||
| Interest rate swaps |
|
Other current liabilities |
|
— | 15 | 945 | — | 6 | 440 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Interest rate caps |
|
Deposits and other assets |
|
1 | — | 1,000 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||
| Derivatives not designated as hedging instruments: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign exchange forward contracts |
|
Other current liabilities |
|
— | 1 | 189 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
| Total derivatives |
$ | 12 | $ | 25 | $ | — | $ | 11 | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
102
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
The effect of the Company’s cash flow hedging instruments on other comprehensive income (loss) is summarized in the following table (in millions):
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
| Foreign exchange forward contracts |
$ | 16 | $ | (1 | ) | $ | (8 | ) | ||||
| Interest rate derivatives |
8 | 6 | 10 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| Total |
$ | 24 | $ | 5 | $ | 2 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
The Company expects $2 million of pre-tax unrealized losses related to its foreign exchange contracts and interest rate derivatives included in AOCI at December 31, 2016 to be reclassified into earnings within the next twelve months.
7. Fair Value Measurements
The Company records certain assets and liabilities at fair value. Fair value is defined as the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in the principal or most advantageous market for the asset or liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. A three-level fair value hierarchy that prioritizes the inputs used to measure fair value is described below. This hierarchy requires entities to maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs. The three levels of inputs used to measure fair value are as follows:
| • | Level 1—Quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities. |
| • | Level 2—Observable inputs other than quoted prices included in Level 1, such as quoted prices for similar assets and liabilities in active markets; quoted prices for identical or similar assets and liabilities in markets that are not active; or other inputs that are observable or can be corroborated by observable market data. |
| • | Level 3—Unobservable inputs that are supported by little or no market activity. This includes certain pricing models, discounted cash flow methodologies and similar techniques that use significant unobservable inputs. |
The carrying values of cash, cash equivalents, accounts receivable and accounts payable approximated their fair values at December 31, 2016 and 2015 due to their short-term nature. At December 31, 2016 and 2015, the fair value of total debt approximated $7,298 million and $2,499 million, respectively, as determined under Level 2 measurements based on quoted prices for these financial instruments.
103
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
Recurring Fair Value Measurements
The following table summarizes the fair value of the Company’s financial assets and liabilities that are measured on a recurring basis as of December 31, 2016 (in millions):
| Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total | |||||||||||||
| Assets: |
||||||||||||||||
| Trading securities |
$ | 40 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 40 | ||||||||
| Derivatives |
— | 12 | — | 12 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
| Total |
$ | 40 | $ | 12 | $ | — | $ | 52 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
| Liabilities: |
||||||||||||||||
| Derivatives |
$ | — | $ | 25 | $ | — | $ | 25 | ||||||||
| Contingent consideration |
— | — | 18 | 18 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
| Total |
$ | — | $ | 25 | $ | 18 | $ | 43 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
The following table summarizes the fair value of the Company’s financial assets and liabilities that are measured on a recurring basis as of December 31, 2015 (in millions):
| Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total | |||||||||||||
| Liabilities: |
||||||||||||||||
| Derivatives |
$ | — | $ | 11 | $ | — | $ | 11 | ||||||||
| Contingent consideration |
— | — | 4 | 4 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
| Total |
$ | — | $ | 11 | $ | 4 | $ | 15 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
Below is a summary of the valuation techniques used in determining fair value:
Marketable securities—The Company values trading and available-for-sale securities using the quoted market value of the securities held.
Derivatives—Derivatives consist of foreign exchange contracts and interest rate caps and swaps. The fair value of foreign exchange contracts is based on observable market inputs of spot and forward rates or using other observable inputs. The fair value of the interest rate caps and swaps is the estimated amount that the Company would receive or pay to terminate such agreements, taking into account market interest rates and the remaining time to maturities or using market inputs with mid-market pricing as a practical expedient for bid-ask spread.
Contingent consideration—The Company values contingent consideration related to business combinations using a weighted probability calculation of potential payment scenarios discounted at rates reflective of the risks associated with the expected future cash flows. Key assumptions used to estimate the fair value of contingent consideration include revenue, net new business and operating forecasts and the probability of achieving the specific targets.
104
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
The following table summarizes the changes in Level 3 financial assets and liabilities measured on a recurring basis for the year ended December 31 (in millions):
| Contingent Consideration – Accrued Expenses | ||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
| Balance as of January 1 |
$ | 4 | $ | 1 | $ | 13 | ||||||
| Business combinations |
19 | — | — | |||||||||
| Contingent consideration paid |
(4 | ) | (3 | ) | (3 | ) | ||||||
| Revaluations included in earnings and foreign currency translation adjustments |
(1 | ) | 6 | (9 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| Balance as of December 31 |
$ | 18 | $ | 4 | $ | 1 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
The revaluation for the contingent consideration is recognized in other expense (income), net on the accompanying consolidated statements of income.
Non-recurring Fair Value Measurements
Certain assets are carried on the accompanying consolidated balance sheets at cost and are not remeasured to fair value on a recurring basis. These assets include cost and equity method investments and loans that are written down to fair value for declines which are deemed to be other-than-temporary, and goodwill and identifiable intangible assets which are tested for impairment annually and when a triggering event occurs. See Note 17 for additional information.
As of December 31, 2016, assets carried on the balance sheet and not remeasured to fair value on a recurring basis totaled approximately $17,199 million and were identified as Level 3. These assets are comprised of cost and equity method investments of $82 million, goodwill of $10,727 million and other identifiable intangibles, net of $6,390 million.
Cost and Equity Method Investments—The inputs available for valuing investments in non-public portfolio companies are generally not easily observable. The valuation of non-public investments requires significant judgment by the Company due to the absence of quoted market values, inherent lack of liquidity and the long-term nature of such assets. When a triggering event occurs, the Company considers a wide range of available market data when assessing the estimated fair value. Such market data includes observations of the trading multiples of public companies considered comparable to the private companies being valued as well as publicly disclosed merger transactions involving comparable private companies. In addition, valuations are adjusted to account for company-specific issues, the lack of liquidity inherent in a non-public investment and the fact that comparable public companies are not identical to the companies being valued. Such valuation adjustments are necessary because in the absence of a committed buyer and completion of due diligence similar to that performed in an actual negotiated sale process, there may be company-specific issues that are not fully known that may affect value. Further, a variety of additional factors are reviewed by the Company, including, but not limited to, financing and sales transactions with third parties, current operating performance and future expectations of the particular investment, changes in market outlook and the third party financing environment. Because of the inherent uncertainty of valuations, estimated valuations may differ significantly from the values that would have been used had a ready market for the securities existed, and the differences could be material.
Goodwill—Goodwill represents the difference between the purchase price and the fair value of the identifiable tangible and intangible net assets resulting from business combinations. The Company performs a
105
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
qualitative analysis to determine whether it is more likely than not that the estimated fair value of a reporting unit is less than its book value. This includes a qualitative analysis of macroeconomic conditions, industry and market considerations, internal cost factors, financial performance, fair value history and other company specific events. If this qualitative analysis indicates that it is more likely than not that the estimated fair value is less than the book value for the respective reporting unit, the Company applies a two-step impairment test in which the Company determines whether the estimated fair value of the reporting unit is in excess of its carrying value. If the carrying value of the net assets assigned to the reporting unit exceeds the estimated fair value of the reporting unit, the Company performs the second step of the impairment test to determine the implied estimated fair value of the reporting unit’s goodwill. The Company determines the implied estimated fair value of goodwill by determining the present value of the estimated future cash flows for each reporting unit and comparing the reporting unit’s risk profile and growth prospects to selected, reasonably similar publicly traded companies. See Note 17 for additional information.
Definite-lived Intangible Assets—If a triggering event occurs, the Company determines the estimated fair value of definite-lived intangible assets by determining the present value of the expected cash flows. See Note 17 for additional information.
Indefinite-lived Intangible Asset—If a qualitative analysis indicates that it is more likely than not that the estimated fair value is less than the carrying value of an indefinite-lived intangible asset, the Company determines the estimated fair value of the indefinite-lived intangible asset (trade name) by determining the present value of the estimated royalty payments on an after-tax basis that it would be required to pay the owner for the right to use such trade name. If the carrying amount exceeds the estimated fair value, an impairment loss is recognized in an amount equal to the excess.
8. Property and Equipment
The major classes of property and equipment were as follows (in millions):
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Land, buildings and leasehold improvements |
$ | 333 | $ | 187 | ||||
| Equipment |
338 | 257 | ||||||
| Furniture and fixtures |
72 | 53 | ||||||
| Motor vehicles |
26 | 13 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Property and equipment, gross |
769 | 510 | ||||||
| Less accumulated depreciation |
(363 | ) | (322 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Property and equipment, net |
$ | 406 | $ | 188 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
9. Goodwill and Identifiable Intangible Assets
As of December 31, 2016, the Company has approximately $6,390 million of identifiable intangible assets, of which approximately $127 million, relating to trade names, is deemed to be indefinite-lived and, accordingly,
106
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
is not being amortized. Amortization expense associated with identifiable definite-lived intangible assets was as follows (in millions):
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
| Amortization expense |
$ | 210 | $ | 67 | $ | 58 | ||||||
Estimated amortization expense for existing identifiable intangible assets is expected to be approximately $837 million, $858 million, $844 million, $788 million and $567 million for the years ending December 31, 2017, 2018, 2019, 2020 and 2021, respectively. Estimated amortization expense can be affected by various factors, including future acquisitions or divestitures of service and/or licensing and distribution rights or impairments.
The following is a summary of identifiable intangible assets (in millions):
| As of December 31, 2016 | As of December 31, 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gross Amount |
Accumulated Amortization |
Net Amount |
Gross Amount |
Accumulated Amortization |
Net Amount | |||||||||||||||||||
| Definite-lived identifiable intangible assets: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Client relationships and backlog |
$ | 3,983 | $ | (125 | ) | $ | 3,858 | $ | 224 | $ | (76 | ) | $ | 148 | ||||||||||
| Trademarks, trade names and other |
384 | (15 | ) | 369 | 15 | (6 | ) | 9 | ||||||||||||||||
| Databases |
1,742 | (87 | ) | 1,655 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
| Software and related assets |
619 | (247 | ) | 372 | 279 | (196 | ) | 83 | ||||||||||||||||
| Non-compete agreements |
9 | — | 9 | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
| $ | 6,737 | $ | (474 | ) | $ | 6,263 | $ | 518 | $ | (278 | ) | $ | 240 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
| Indefinite-lived identifiable intangible assets: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
| Trade names |
$ | 127 | $ | — | $ | 127 | $ | 128 | $ | — | $ | 128 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
107
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
The following is a summary of goodwill by segment for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015 (in millions):
| Commercial Solutions |
Research & Development Solutions |
Integrated Engagement Services |
Consolidated | |||||||||||||
| Balance as of December 31, 2014 |
$ | 70 | $ | 346 | $ | 48 | $ | 464 | ||||||||
| Business combinations |
— | 262 | — | 262 | ||||||||||||
| Impact of foreign currency fluctuations and other |
— | (6 | ) | — | (6 | ) | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
| Balance as of December 31, 2015 |
70 | 602 | 48 | 720 | ||||||||||||
| Business combinations |
9,698 | 611 | 67 | 10,376 | ||||||||||||
| Impairment |
(23 | ) | — | — | (23 | ) | ||||||||||
| Impact of foreign currency fluctuations and other |
(330 | ) | (17 | ) | 1 | (346 | ) | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
| Balance as of December 31, 2016 |
$ | 9,415 | $ | 1,196 | $ | 116 | $ | 10,727 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
During the year ended December 31, 2016, the Company recorded impairment losses of $23 million. See Note 17 for additional information.
10. Accrued Expenses
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Compensation, including bonuses, fringe benefits and payroll taxes |
$ | 610 | $ | 401 | ||||
| Restructuring |
102 | 14 | ||||||
| Interest |
42 | 5 | ||||||
| Client contract related |
502 | 271 | ||||||
| Professional fees |
69 | 10 | ||||||
| Other |
168 | 60 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| $ | 1,493 | $ | 761 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
11. Credit Arrangements
The following is a summary of the Company’s revolving credit facilities at December 31, 2016:
| Facility |
Interest Rates | |
| $1,000 million (revolving credit facility) |
LIBOR in the relevant currency borrowed plus a margin (Margin of 2.00% at December 31, 2016) | |
| $25 million (receivables financing facility) |
LIBOR Market Index Rate (0.77% at December 31, 2016) plus 0.85% to 1.35% depending upon the Company’s debt rating | |
| £10 million (approximately $12 million) general banking facility with a European headquartered bank |
Bank’s base rate (0.25% at December 31, 2016) plus 1% |
108
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
At December 31, 2016, there were bank guarantees totaling approximately £5 million (approximately $6 million) issued against the availability of the general banking facility with a European headquartered bank through their operations in the United Kingdom.
The following table summarizes the Company’s debt at the dates indicated (dollars in millions):
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Senior Secured Credit Facilities: |
||||||||
| Senior Secured Term A Loan due 2021—U.S. Dollar LIBOR at average floating rates of 3.00% |
$ | 888 | $ | — | ||||
| Senior Secured Term A Loan due 2021—Euro LIBOR at average floating rates of 2.00% |
419 | — | ||||||
| Senior Secured Term B Loan due 2021—U.S. Dollar LIBOR at average floating rates of 3.50% |
1,700 | — | ||||||
| Senior Secured Term B Loan due 2021—Euro LIBOR at average floating rates of 3.75% |
765 | — | ||||||
| Term Loan A due 2020—LIBOR plus 1.75%, or 2.36% |
— | 829 | ||||||
| Term Loan B due 2022—the greater of LIBOR or 0.75% plus 2.50%, or 3.25% |
— | 597 | ||||||
| Revolving Credit Facility due 2021: |
||||||||
| U.S. Dollar denominated borrowings—U.S. Dollar LIBOR at average floating rates of 2.73% |
375 | — | ||||||
| 5.0% Senior Notes due 2026—U.S. Dollar denominated |
1,050 | — | ||||||
| 3.5% Senior Notes due 2024—Euro denominated |
658 | — | ||||||
| 4.125% Senior Notes due 2023—Euro denominated |
289 | — | ||||||
| 4.875% Senior Notes due 2023 |
800 | 800 | ||||||
| Receivables financing facility due 2018—LIBOR plus 0.85%, or 1.62% |
275 | 275 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Principal amount of debt |
7,219 | 2,501 | ||||||
| Less: unamortized discount |
(12 | ) | (24 | ) | ||||
| Less: unamortized debt issuance costs |
(7 | ) | (9 | ) | ||||
| Less: current portion |
(92 | ) | (49 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Long-term debt |
$ | 7,108 | $ | 2,419 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
109
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
Contractual maturities of long-term debt at December 31, 2016 are as follows (in millions):
| 2017 |
$ | 92 | ||
| 2018 |
367 | |||
| 2019 |
92 | |||
| 2020 |
92 | |||
| 2021 |
3,781 | |||
| Thereafter |
2,795 | |||
|
|
|
| ||
| $ | 7,219 | |||
|
|
|
|
Senior Secured Credit Agreement and Senior Notes
2016 Financing Transactions
At December 31, 2016, the Company’s senior secured credit facility provides financing of up to approximately $4,772 million, which consisted of $4,147 million principal amount of debt outstanding (as detailed in the table above) and $625 million of commitments that expire in 2021. The revolving credit facility is comprised of a $450 million senior secured revolving facility available in U.S. Dollars, a $400 million senior secured revolving facility available in U.S. Dollars, Euros, Swiss Francs and other foreign currencies and a $150 million senior secured revolving facility available in U.S. Dollars and Yen. The term A loans and revolving credit facility mature in October 2021, while the term B loans mature in March 2021. Under certain circumstances, the maturity date of the term A loans and the senior secured revolving facility may be accelerated to 2020. The Company is required to make scheduled quarterly payments on the term A loans equal to 1.25% of the original principal amount, with the remaining balance paid at maturity. The Company is required to make scheduled quarterly payments on the term B loans equal to approximately 0.25% of the original principal amount, with the remaining balance paid at maturity. In addition, beginning with fiscal year ending December 31, 2017, the Company is required to apply 50% of excess cash flow (as defined in the Company’s senior secured credit facility), subject to a reduction to 25% or 0% depending upon the Company’s senior secured first lien net leverage ratio, for prepayment of the Term Loans, with any such prepayment to be applied toward principal payments due in subsequent quarters. The Company is also required to pay an annual commitment fee that ranges from 0.30% to 0.40% in respect of any unused commitments under the revolving credit facility. The senior secured credit facility is collateralized by substantially all of the assets of the Company and the assets of the Company’s material domestic subsidiaries including 100% of the equity interests of substantially all of the Company’s material domestic subsidiaries and 66% of the equity interests of substantially all of the first-tier material foreign subsidiaries of the Company and its domestic subsidiaries.
On October 3, 2016, the Company refinanced the term A loans due 2019 (approximately $884 million) assumed in the Merger with a term A loan facility due in 2021 for an aggregate principal amount of approximately $1,350 million comprised of both U.S. Dollar denominated term A loans and Euro denominated term A loans. Additionally, the revolving credit facility was refinanced to an aggregate principal amount equal to $1,000 million. The additional proceeds were used, in part, to fund the redemption on November 1, 2016 of $500 million of 6% Senior Notes due 2020 assumed in the Merger, at a redemption price equal to 101.5% of the aggregate outstanding principal amount plus accrued interest to the redemption date. The Company incurred a loss on extinguishment of debt of approximately $8 million related to the aggregate payments for make-whole premiums.
On September 28, 2016, IMS Health issued senior unsecured notes totaling principal amount of $1,750 million, which consisted of (i) $1,050 million of 5% senior notes due October 2026 (the “5% Dollar Notes”) and
110
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
(ii) €625 million of 3.5% senior notes due October 2024 (the “3.5% Euro Notes” and, together with the 5% Dollar Notes, the “2016 Notes”). The proceeds of the 2016 Notes, which were assumed by the Company upon closing of the Merger, were used on October 3, 2016 to repay in full ($1,389 million) the term loans outstanding under the Quintiles Transnational senior secured credit facilities. Interest on the 2016 Notes is payable semi-annually, beginning on April 15, 2017. The notes are guaranteed on a senior unsecured basis by the Company’s wholly-owned domestic restricted subsidiaries (excluding IMS Japan K.K.) and, subject to certain exceptions, each of the Company’s future domestic subsidiaries that guarantees its other indebtedness or indebtedness of any of the guarantors. The 5% Dollar Notes and the 3.5% Euro Notes may be redeemed, either together or separately, prior to their final stated maturity, subject to a customary make-whole premium, at any time prior to October 15, 2021 with respect to the 5% Dollar Notes and October 15, 2019 with respect to the 3.5% Euro Notes (in each case subject to a customary “equity claw” redemption right) and thereafter subject to annually declining redemption premiums at any time prior to October 15, 2024 with respect to the 5% Dollar Notes and October 15, 2021 with respect to the 3.5% Euro Notes.
The Company also assumed in the Merger €275 million aggregate principal amount of 4.125% Senior Notes due in April 2023 (the “4.125% Senior Notes”). Interest on the 4.125% Senior Notes is payable semi-annually each year and commenced on October 1, 2015. The 4.125% Senior Notes are guaranteed on a senior unsecured basis by IMS Health’s wholly-owned domestic subsidiaries that are guarantors under the senior secured credit facilities. The Company may redeem the 4.125% Senior Notes, in whole or in part, at any time prior to April 1, 2018 at a price equal to 100% of the principal amount thereof, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to the date of redemption, plus a “make-whole” premium. On or after April 1, 2018, the Company may redeem all or a portion of the 4.125% Senior Notes at predetermined redemption prices set forth in the indenture governing the 4.125% Senior Notes plus accrued and unpaid interest to the date of redemption.
2015 Financing Transactions
On May 12, 2015, the Company through its wholly-owned subsidiary, Quintiles Transnational, entered into new senior secured credit facilities, which consisted of a $500 million revolving credit facility and $1.45 billion of term loans. In addition, Quintiles Transnational issued $800 million of 4.875% senior unsecured notes due 2023 (the “4.875% Senior Notes”) in a private placement. The term loans, in the amount of $1,389 million, were repaid in full on October 3, 2016 as discussed above. Interest on the 4.875% Senior Notes is paid semiannually on May 15 and November 15 of each year until maturity. The Senior Notes are unsecured senior obligations of QuintilesIMS and are effectively subordinated in right of payment to all secured obligations of QuintilesIMS, to the extent of the value of any collateral. Also on May 12, 2015, an outstanding term loan was repaid with proceeds from the new credit facilities entered into that day and the Company recognized an $8 million loss on extinguishment of debt, which included $1 million of unamortized debt issuance costs, $1 million of unamortized discount and $6 million of related fees and expenses.
Receivables Financing Facility
On December 5, 2014, the Company entered into a four-year arrangement to securitize certain of its accounts receivable. Under the receivables financing facility, certain of the Company’s accounts receivable are sold on a non-recourse basis by certain of its consolidated subsidiaries to another of its consolidated subsidiaries, a bankruptcy-remote special purpose entity (“SPE”). The SPE obtained a term loan and revolving loan commitment from a third party lender, secured by liens on the assets of the SPE, to finance the purchase of the accounts receivable, which included a $275 million term loan and a $25 million revolving loan commitment. The revolving loan commitment may be increased by an additional $35 million as amounts are repaid under the term loan. QuintilesIMS has guaranteed the performance of the obligations of existing and future subsidiaries that sell and service the accounts receivable under the receivables financing facility. The assets of the SPE are not
111
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
available to satisfy any of the Company’s obligations or any obligations of its subsidiaries. As of December 31, 2016, $25 million of revolving loans were available under the receivables financing facility.
The Company used the proceeds from the term loan under the receivables financing facility to repay in full the amount outstanding on the then outstanding revolving credit facility ($150 million), to repay $25 million of the then outstanding Term Loan B-3, to pay related fees and expenses and the remainder was used for general working capital purposes.
Restrictive Covenants
The Company’s debt agreements provide for certain covenants and events of default customary for similar instruments, including a covenant not to exceed a specified ratio of consolidated senior secured net indebtedness to Consolidated EBITDA, as defined in the Company’s senior secured credit facility and a covenant to maintain a specified minimum interest coverage ratio. If an event of default occurs under any of the Company’s or the Company’s subsidiaries’ financing arrangements, the creditors under such financing arrangements will be entitled to take various actions, including the acceleration of amounts due under such arrangements, and in the case of the lenders under the revolving credit facility and New Term Loans, other actions permitted to be taken by a secured creditor. Our long-term debt arrangements contain usual and customary restrictive covenants that, among other things, place limitations on our ability to declare dividends. For additional information regarding these restrictive covenants, see Part II, Item 5 “Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities—Dividend Policy” and Part II, Item 7 “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Liquidity and Capital Resources” included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. At December 31, 2016, the Company was in compliance with the financial covenants under the Company’s financing arrangements.
12. Leases
The Company leases facilities under operating leases, many of which contain renewal and escalation clauses. The Company also leases certain equipment under operating leases. The leases expire at various dates through 2029 with options to cancel certain leases at various intervals. Rental expenses under these agreements were $127 million, $109 million and $115 million in 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively.
The following is a summary of future minimum payments under operating leases that have initial or remaining non-cancelable lease terms in excess of one year at December 31, 2016 (in millions):
| Operating Leases | ||||
| 2017 |
$ | 171 | ||
| 2018 |
123 | |||
| 2019 |
94 | |||
| 2020 |
75 | |||
| 2021 |
56 | |||
| Thereafter |
159 | |||
|
|
|
| ||
| Total minimum lease payments |
$ | 678 | ||
|
|
|
| ||
13. Contingencies
The Company and its subsidiaries are involved in legal and tax proceedings, claims and litigation arising in the ordinary course of business. Management periodically assesses the Company’s liabilities and contingencies in
112
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
connection with these matters based upon the latest information available. For those matters where management currently believes it is probable that the Company will incur a loss and that the probable loss or range of loss can be reasonably estimated, the Company has recorded reserves in the consolidated financial statements based on its best estimates of such loss. In other instances, because of the uncertainties related to either the probable outcome or the amount or range of loss, management is unable to make a reasonable estimate of a liability, if any. However, even in many instances where the Company has recorded an estimated liability, the Company is unable to predict with certainty the final outcome of the matter or whether resolution of the matter will materially affect the Company’s results of operations, financial position or cash flows. As additional information becomes available, the Company adjusts its assessments and estimates of such liabilities accordingly.
The Company routinely enters into agreements with its suppliers to acquire data and with its clients to sell data, all in the normal course of business. In these agreements, the Company sometimes agrees to indemnify and hold harmless the other party for any damages such other party may suffer as a result of potential intellectual property infringement and other claims related to the use of the data. The Company has not accrued a liability with respect to these matters, as the exposure is considered remote.
Based on its review of the latest information available, management does not expect the impact of pending legal and tax proceedings, claims and litigation, either individually or in the aggregate, to have a material adverse effect on the Company’s results of operations, cash flows or financial position. However, one or more unfavorable outcomes in any claim or litigation against the Company could have a material adverse effect for the period in which it is resolved. The following is a summary of certain legal matters involving the Company.
The Company’s wholly-owned subsidiary, IMS Government Solutions Inc. (“IMS Government Solutions”), is primarily engaged in providing services under contracts with the United States government. United States government contracts are subject to extensive legal and regulatory requirements and, from time to time, agencies of the United States government have the ability to investigate whether contractors’ operations are being conducted in accordance with such requirements. IMS Government Solutions discovered potential noncompliance with various contract clauses and requirements under its General Services Administration Contract (the “GSA Contract”) which was awarded in 2002 to its predecessor company, Synchronous Knowledge Inc. (Synchronous Knowledge Inc. was acquired by IMS Health in May 2005). The potential noncompliance arose from two primary areas: first, at the direction of the government, work performed under one task order was invoiced under another task order without the appropriate modifications to the orders being made; and second, personnel who did not meet strict compliance with the labor categories component of the qualification requirements of the GSA Contract were assigned to contracts. The Company is currently unable to determine the outcome of all of these matters pending the resolution of the Voluntary Disclosure Program process and the ultimate liability arising from these matters could exceed the Company’s current reserves.
On February 13, 2014, a group of approximately 1,200 medical doctors and 900 private individuals filed a civil lawsuit with the Seoul Central District Court against IMS Korea and two other defendants, KPA and the Korean Pharmaceutical Information Center (“KPIC”). The civil lawsuit alleges KPA and KPIC collected their personal information in violation of applicable privacy laws without the necessary consent through a software system installed on pharmacy computer systems in Korea, and that personal information was transferred to IMS Korea and sold to pharmaceutical companies. The plaintiffs are claiming damages in the aggregate amount of approximately $6 million plus interest. The Company believes the lawsuit is without merit, rejects plaintiffs’ claims and intends to vigorously defend its position.
On July 23, 2015, indictments were issued by the Seoul Central District Prosecutors’ Office in South Korea against 24 individuals and companies alleging improper handling of sensitive health information in violation of, among others, South Korea’s Personal Information Protection Act. IMS Korea and two of its employees were among the individuals and organizations indicted. Although there is no assertion that IMS Korea used patient identified health information in any of its offerings, prosecutors allege that certain of IMS Korea’s data suppliers
113
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
should have obtained patient consent when they converted sensitive patient information into non-identified data and that IMS Korea had not taken adequate precautions to reduce the risk of re-identification. The Company believes the indictment is without merit, that it acted in compliance with all applicable laws at all times and intends to vigorously defend its position.
14. Stockholders’ Equity (Deficit)
Preferred Stock
The Company is authorized to issue 1.0 million shares of preferred stock, $0.01 per share par value. No shares of preferred stock were issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2016 or 2015.
Equity Repurchases
Equity Repurchase Program
On October 30, 2013, the Company’s Board of Directors (the “Board”) approved an equity repurchase program (the “Repurchase Program”) authorizing the repurchase of up to $125 million of either the Company’s common stock or vested in-the-money employee stock options, or a combination thereof. During 2015, the Board increased the stock repurchase authorization under the Repurchase Program by $600 million, which increased the total amount that has been authorized under the Repurchase Program to $725 million. On November 1, 2016, the Board increased the stock repurchase authorization under the Repurchase Program by $1.5 billion, which increased the total amount that has been authorized under the Repurchase Program to $2.225 billion. The Repurchase Program does not obligate the Company to repurchase any particular amount of common stock or vested in-the-money employee stock options, and it could be modified, extended, suspended or discontinued at any time. The timing and amount of repurchases are determined by the Company’s management based on a variety of factors such as the market price of the Company’s common stock, the Company’s corporate requirements, and overall market conditions. Purchases of the Company’s common stock may be made in open market transactions effected through a broker-dealer at prevailing market prices, in block trades, or in privately negotiated transactions. The Company may also repurchase shares of its common stock pursuant to a trading plan meeting the requirements of Rule 10b5-1 under the Exchange Act, which would permit shares of the Company’s common stock to be repurchased when the Company might otherwise be precluded from doing so by law. Repurchases of vested in-the-money employee stock options were made through transactions between the Company and its employees (other than its executive officers, who were not eligible to participate in the program), and this aspect of the Repurchase Program expired in November 2013. The Repurchase Program for common stock does not have an end date.
Below is a summary of the share repurchases made under the Repurchase Program (in millions, except per share data):
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
| Number of shares of common stock repurchased |
14.3 | 7.8 | — | |||||||||
| Aggregate purchase price |
$ | 1,098 | $ | 516 | $ | — | ||||||
| Average price per share |
$ | 76.57 | $ | 65.56 | $ | 47.51 | ||||||
From the plan’s inception in October 2013 through December 31, 2016, the Company has repurchased a total of $1,678 million of its securities under the Repurchase Program, consisting of $59 million of stock options and $1,619 million of common stock. As of December 31, 2016, the Company has remaining authorization to repurchase up to $547 million of its common stock under the Repurchase Program. In addition, from time to time, the Company has repurchased and may continue to repurchase common stock through private or other transactions outside of the Repurchase Program.
114
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
Other Equity Repurchases
On May 28, 2014, the Company completed the repurchase of 3.3 million shares of its common stock for $50.23 per share from TPG Quintiles Holdco, L.P., one of its existing stockholders, in a private transaction for an aggregate purchase price of approximately $165 million. The repurchase price per share of common stock was equal to 98% of the closing market price of the Company’s common stock on the New York Stock Exchange (“NYSE”) on May 27, 2014 (which was $51.26). This repurchase of shares from its existing stockholder was authorized in compliance with the Company’s related party transactions approval policy. The Company funded this private repurchase transaction with cash on hand. This private repurchase transaction was separate from and in addition to the Repurchase Program.
On November 10, 2014, the Company completed the repurchase of 4.3 million shares of its common stock for $58.09 per share, which was the price per share the underwriter paid to selling stockholders, for an aggregate purchase price of approximately $250 million. The Company funded this repurchase transaction with a combination of cash on hand and a $150 million draw on its revolving credit facility. This repurchase transaction was separate from and in addition to the Repurchase Program.
Non-controlling Interests
As discussed further in Note 15, the Company contributed businesses to a joint venture with Quest Diagnostics Incorporated (“Quest”) that was recorded at book value (carryover basis) because the Company owns 60% of the joint venture and maintains control of these businesses. As a result, Quest’s non-controlling interest in the joint venture, referred to as Q2 Solutions, is equal to 40%. Quest’s non-controlling interest was $227 million at December 31, 2016.
15. Business Combinations
IMS Health
On October 3, 2016, pursuant to the terms of the Merger Agreement, IMS Health merged with and into Quintiles, with Quintiles continuing as the Surviving Corporation. The combination of Quintiles and IMS Health capabilities and resources creates an information and technology enabled healthcare service provider with a full suite of end-to-end clinical and commercial offerings. The Merger was accounted for as a business combination with Quintiles considered the accounting and the legal acquirer. Immediately prior to the completion of the Merger, Quintiles reincorporated as a Delaware corporation. The Surviving Corporation changed its name to Quintiles IMS Holdings, Inc. At the effective time of the Merger, IMS Health common stock was automatically converted into 0.3840 of a share of the Company’s common stock. In addition, IMS Health equity awards held by current employees and certain members of the former IMS Health board of directors were converted into the Company’s equity awards after giving effect to the exchange ratio. The terms of these awards, including vesting provisions, are substantially consistent to those of the historical IMS Health equity awards. All of the Company’s and IMS Health’s performance units outstanding at the date of the Merger were converted into restricted stock units with service based vesting requirements. The merger consideration was approximately $10.4 billion (based on the closing price of the Company’s common stock on October 3, 2016), and consisted of the fair value of the Company’s common stock issued (approximately 126.6 million shares) in exchange for the IMS Health common stock as well as the fair value of the vested portion of the converted IMS Health equity awards. The Merger-date value of former IMS Health stock-based awards was valued using the Black-Scholes model and apportioned between Merger consideration (purchase price) and unearned compensation to be recognized in expense as earned in future periods based on remaining service periods. In connection with the IMS Health acquisition, the Company recorded goodwill, primarily attributable to the assembled workforce of IMS Health and the expected synergies, which was assigned to the Commercial Solutions segment ($9,688 million), the Research & Development Solutions segment ($533 million) and the Integrated Engagement Services segment ($67 million). The goodwill is not deductible for
115
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
income tax purposes. The Company’s assessment of fair value and the purchase price accounting are preliminary and subject to change upon completion. Further adjustments may be necessary as additional information related to the fair values of assets acquired and liabilities assumed is assessed during the measurement period (up to one year from the acquisition date).
Quest
On July 1, 2015, the Company and Quest closed on a joint venture transaction that resulted in the combination of their respective global clinical trials laboratory operations. The joint venture transaction was effected through the creation of two primary new legal entities that the Company controls. Both the Company’s and Quest’s clinical trials laboratory operations were contributed to these new legal entities. The Company accounted for the contribution of the Quest businesses as a business combination. Quest was issued a 40% equity interest in the legal entities, the fair value of which was $423 million on July 1, 2015 (40% of the fair value of all operations contributed by both parties) and represents the purchase price paid by the Company for the clinical trials laboratory operations that Quest contributed to the joint venture transaction. The resulting combined capabilities are designed to provide its clients with globally scaled end-to-end clinical trials laboratory services and the combined business is referred to and marketed as Q2 Solutions. The Company accounted for the contribution of the Quest businesses as a business combination and consolidated the related new legal entities in its financial statements with a non-controlling interest for the portion owned by Quest. The Company recorded goodwill, primarily attributable to assembled workforce and expected synergies. This business combination is part of the Research & Development Solutions segment and the resulting goodwill is not deductible for income tax purposes.
The following table summarizes the estimated fair value of the net assets acquired at the date of the acquisitions (in millions):
| IMS Health | Quest | |||||||
| Assets acquired: |
||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 2,031 | $ | 32 | ||||
| Accounts receivable and unbilled services |
528 | 6 | ||||||
| Prepaid expenses |
85 | 1 | ||||||
| Other current assets |
145 | 4 | ||||||
| Property and equipment |
247 | 16 | ||||||
| Goodwill |
10,288 | 262 | ||||||
| Other identifiable intangibles |
6,435 | 126 | ||||||
| Deferred income tax asset – long-term |
25 | — | ||||||
| Other long-term assets |
71 | — | ||||||
| Liabilities assumed: |
||||||||
| Accounts payable and accrued expenses |
(700 | ) | (13 | ) | ||||
| Unearned income |
(175 | ) | — | |||||
| Current portion of long-term debt |
(88 | ) | — | |||||
| Other current liabilities |
(45 | ) | — | |||||
| Long-term debt, less current portion |
(6,070 | ) | — | |||||
| Deferred income tax liability – long-term |
(2,104 | ) | (10 | ) | ||||
| Other long-term liabilities |
(248 | ) | (1 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Net assets acquired |
$ | 10,425 | $ | 423 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
116
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
The other identifiable intangible assets consisted of the following (in millions):
| IMS Health | Quest | |||||||
| Client relationships |
$ | 3,960 | $ | 74 | ||||
| Backlog |
— | 33 | ||||||
| Trade names |
385 | 19 | ||||||
| Databases |
1,820 | — | ||||||
| Software |
270 | — | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Total other identifiable intangibles |
$ | 6,435 | $ | 126 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Amortized over a weighted average useful life (in years) |
18 | 9 | ||||||
The acquired Quest trade name is an indefinite-lived intangible asset that is not amortized.
Acquisition Related Costs
Acquisition related costs include the direct and incremental costs associated with mergers and acquisitions such as investment banking, legal, accounting and consulting fees. The Company recognized approximately $36 million of acquisition related costs associated with the IMS Health merger during the year ended December 31, 2016, which are included with merger related costs on the consolidated statement of income. Acquisition related costs for all other acquisitions were immaterial and are not presented.
Unaudited Pro Forma Information
The following unaudited pro forma information presents the financial results as if the acquisition of IMS Health had occurred on January 1, 2015 with pro forma adjustments to give effect to (i) an increase in depreciation and amortization expense for fair value adjustments of property, plant and equipment and intangible assets, (ii) an increase in stock-based compensation expense resulting from the exchange of the vested IMS Health equity awards for the Company’s equity awards, (iii) to present transaction costs in the 2015 period, (iv) to reflect the effect on revenue from the deferred revenue fair value adjustment in the 2015 period, and (v) the related income tax effects. The pro forma results do not include any anticipated cost synergies, costs or other effects of the planned integration of IMS Health. Accordingly, such pro forma amounts are not necessarily indicative of the results that actually would have occurred for the periods presented below had the IMS Health acquisition been completed on January 1, 2015, nor are they indicative of the future operating results of the Company.
The following table summarizes the pro forma results (in millions, except earnings per share):
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||
|
|
2016 | 2015 | ||||||
| Revenues |
$ | 7,784 | $ | 7,180 | ||||
| Reimbursed expenses |
1,514 | 1,411 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Total revenues |
$ | 9,298 | $ | 8,591 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Net income attributable to Quintiles IMS Holdings, Inc. |
$ | 42 | $ | 450 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Earnings per share attributable to common stockholders: |
||||||||
| Basic |
$ | 0.17 | $ | 1.80 | ||||
| Diluted |
$ | 0.17 | $ | 1.76 | ||||
117
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
Pro forma information is not presented for any other acquisitions as the aggregate operations of the acquired businesses were not significant to the overall operations of the Company.
The Company’s consolidated statements of income for the year ended December 31, 2016 included $806 million of revenues related to the IMS Health acquisition. Following the closing of the IMS Health acquisition, the Company began integrating IMS Health’s operations. As a result, computing a separate measure of IMS Health’s stand-alone profitability for periods after the acquisition date is impracticable.
Other Acquisitions
In addition to the merger with IMS Health, the Company also completed three unrelated individually immaterial acquisitions during 2016, all of which occurred during December 2016. The purchase price allocations for some of these acquisitions will be finalized after the completion of the valuation of certain intangible assets and any adjustments to the preliminary purchase price allocation are not expected to have a material impact on the Company’s results of operations or financial position. During 2014, the Company completed one immaterial acquisition (Encore). In connection with the Encore acquisition in 2014, the Company recorded goodwill, primarily attributable to the assembled workforce of Encore and expected synergies, which was assigned to the Commercial Solutions segment and is deductible for income tax purposes. The accompanying consolidating financial statements include the results of the acquisitions subsequent to each respective closing date.
The following table provides certain financial information for these acquisitions, including the preliminary allocation of the purchase price to certain tangible and intangible assets acquired and goodwill (in millions):
|
|
Amortization Period |
2016 | 2014 | |||||||||
| Total purchase price, net of cash acquired(1) |
$ | 136 | $ | 92 | ||||||||
| Acquisition-related costs |
1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| Amounts recorded in the Consolidated Balance Sheets: |
||||||||||||
| Goodwill |
$ | 88 | $ | 63 | ||||||||
| Portion of goodwill deductible for income tax purposes |
— | 63 | ||||||||||
| Intangible assets: |
||||||||||||
| Client relationships |
6-10 years | $ | 31 | $ | 9 | |||||||
| Non-compete agreements |
2-5 years | 9 | — | |||||||||
| Backlog |
1-2 years | 7 | 1 | |||||||||
| Databases |
2 years | 1 | — | |||||||||
| Trade names |
2-4 years | — | 1 | |||||||||
| Software |
3 years | — | 3 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
| Total intangible assets |
$ | 48 | $ | 14 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
| (1) | Total purchase price, net of cash acquired, includes contingent consideration and deferred purchase payments. |
16. Restructuring
From time to time, the Company takes restructuring actions to adapt to changing market conditions. These actions include closing facilities, consolidating functional activities, eliminating redundant positions, aligning
118
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
resources with customer requirements and taking actions to improve process efficiencies. In 2016, the Company also acquired certain restructuring liabilities previously recorded by IMS Health.
During 2016, management approved restructuring plans to align its resources and reduce overcapacity. Also, in connection with the Merger, management approved a restructuring plan to reduce facility overcapacity and eliminate redundant roles. These actions are expected to continue throughout 2017 and are expected to consist of severance, facility closure and other exit-related costs. During 2016, the Company has recognized approximately $33 million of restructuring costs related to these restructuring plans.
During 2015, management approved a restructuring plan to align the Company’s resources and reduce overcapacity. These actions are expected to continue throughout 2017 and consist of severance, facility closure and other exit-related costs. Since the start of this plan in 2015, the Company has recognized approximately $23 million of restructuring costs related to this plan. Also during 2015, in connection with consummating the joint venture transaction with Quest, a restructuring plan was approved to reduce facility overcapacity and eliminate redundant roles. These actions are expected to continue throughout 2017, and since the start of this plan in 2015, the Company has recognized approximately $10 million of restructuring costs related to this plan.
In 2014, management approved restructuring plans to better align resources with the Company’s strategic direction. Since the start of these plans in 2014, the Company recognized approximately $11 million of restructuring costs related to these plans. All of the restructuring costs are related to severance and facility closure costs.
The following amounts were recorded for the restructuring plans (in millions):
| Severance and Related Costs |
Exit Costs | Total | ||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2014 |
$ | 5 | $ | 1 | $ | 6 | ||||||
| Expense, net of reversals |
30 | 1 | 31 | |||||||||
| Payments |
(23 | ) | (1 | ) | (24 | ) | ||||||
| Foreign currency translation |
— | 1 | 1 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| Balance at December 31, 2015 |
12 | 2 | 14 | |||||||||
| Expense, net of reversals |
60 | 3 | 63 | |||||||||
| Acquisitions |
80 | — | 80 | |||||||||
| Payments |
(48 | ) | (2 | ) | (50 | ) | ||||||
| Foreign currency translation and other |
(5 | ) | — | (5 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| Balance at December 31, 2016 |
$ | 99 | $ | 3 | $ | 102 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
The reversals were due to changes in estimates primarily resulting from the redeployment of staff and higher than expected voluntary terminations. Restructuring costs are not allocated to the Company’s reportable segments as they are not part of the segment performance measures regularly reviewed by management. The Company expects the majority of the restructuring accruals at December 31, 2016 will be paid in 2017 and 2018.
17. Impairment Charges
During the third quarter of 2016 as part of its annual impairment review, the Company determined that it was more likely than not that the fair value of its Encore reporting unit was less than its carrying amount due to certain strategic initiatives not performing as expected, resulting in a decline in revenues. The Company
119
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
performed a quantitative analysis using the present value of the estimated future cash flows, which confirmed that the Encore reporting unit’s goodwill was impaired. The Company proceeded to perform step two of its goodwill impairment assessment which resulted in the recognition of impairment losses of $23 million and $5 million for other-than-temporary declines in the fair value of goodwill and identifiable intangible assets, respectively.
18. Income Taxes
The components of income before income taxes and equity in earnings of unconsolidated affiliates are as follows (in millions):
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
| Domestic |
$ | (85 | ) | $ | 68 | $ | 96 | |||||
| Foreign |
564 | 471 | 405 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| $ | 479 | $ | 539 | $ | 501 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
The components of income tax expense attributable to continuing operations are as follows (in millions):
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
| Current expense: |
||||||||||||
| Federal and state |
$ | 64 | $ | 51 | $ | 62 | ||||||
| Foreign |
129 | 109 | 95 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| 193 | 160 | 157 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| Deferred (benefit) expense: |
||||||||||||
| Federal and state |
166 | 5 | (5 | ) | ||||||||
| Foreign |
(14 | ) | (6 | ) | (3 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| 152 | (1 | ) | (8 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| $ | 345 | $ | 159 | $ | 149 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
The differences between the Company’s consolidated income tax expense attributable to continuing operations and the expense computed at the 35% United States statutory income tax rate were as follows (in millions):
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
| Federal income tax expense at statutory rate |
$ | 167 | $ | 189 | $ | 175 | ||||||
| Research and development |
(11 | ) | (13 | ) | (17 | ) | ||||||
| Foreign nontaxable interest income |
(8 | ) | (9 | ) | (10 | ) | ||||||
| United States taxes recorded on foreign earnings |
252 | 38 | 19 | |||||||||
| Foreign rate differential |
(60 | ) | (49 | ) | (31 | ) | ||||||
| Other |
5 | 3 | 13 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| $ | 345 | $ | 159 | $ | 149 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
120
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
Due to the Merger, the Company reevaluated its indefinite reinvestment assertion based on the need for cash in the United States, including funding the Repurchase Program and potential acquisitions. Accordingly, the Company changed its assertion with respect to $2,801 million of foreign earnings, including $1,865 million of IMS Health’s previously undistributed historical foreign earnings. The Company intends to use these acquired foreign earnings to fund cash needs in the United States. Deferred income taxes of $625 million were recorded in 2016 related to non-indefinitely reinvested foreign earnings. Of that amount, $373 million was recorded through purchase accounting related to IMS Health’s historical foreign earnings and the remainder of $252 million was recorded through deferred income tax expense.
Undistributed earnings of the Company’s foreign subsidiaries amounted to approximately $3,564 million at December 31, 2016. Approximately $2,894 million of this total is not considered to be indefinitely reinvested and would be taxable upon repatriation. The Company has recorded a deferred income tax liability, net of foreign tax credits that would be generated upon repatriation, of $590 million as of December 31, 2016, associated with those earnings based upon the United States federal income tax rate. Upon distribution of those earnings in the form of dividends or otherwise, the Company would be subject to both United States income taxes (subject to an adjustment for foreign tax credits, if available) and withholding taxes payable to the various countries in which the Company’s foreign subsidiaries are located. If the approximately $670 million of indefinitely reinvested earnings were repatriated to the United States, it would generate an estimated $176 million of additional tax liability for the Company.
The income tax effects of temporary differences from continuing operations that give rise to significant portions of deferred income tax assets (liabilities) are presented below (in millions):
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Deferred income tax assets: |
||||||||
| Net operating loss and capital loss carryforwards |
$ | 242 | $ | 26 | ||||
| Tax credit carryforwards |
267 | 16 | ||||||
| Accrued expenses and unearned income |
75 | 23 | ||||||
| Employee benefits |
273 | 124 | ||||||
| Other |
32 | 13 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| 889 | 202 | |||||||
| Valuation allowance for deferred income tax assets |
(153 | ) | (22 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Total deferred income tax assets |
736 | 180 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Deferred income tax liabilities: |
||||||||
| Undistributed foreign earnings |
(590 | ) | (37 | ) | ||||
| Amortization and depreciation |
(2,026 | ) | (53 | ) | ||||
| Other |
(164 | ) | (12 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Total deferred income tax liabilities |
(2,780 | ) | (102 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Net deferred income tax (liabilities) assets |
$ | (2,044 | ) | $ | 78 | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
Due to the Merger, the Company recorded deferred tax liabilities related to intangible amortization recorded through purchase accounting in the amount of $2,308 million.
121
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
Additionally, due to the Merger, the Company had federal, state and local, and foreign tax credit and tax loss carryforwards, the tax effect of which was $528 million as of December 31, 2016. Of this amount, $29 million has an indefinite carryforward period, and the remaining $499 million expires at various times beginning in 2017. Some of these losses are subject to limitations under the Internal Revenue Code, however, management expects all losses to be utilized during the carryforward periods.
In 2016, the Company increased its valuation allowance by $131 million to $153 million at December 31, 2016 from $22 million at December 31, 2015. This increase is a result of the Merger as IMS Health had $129 million of valuation allowances recorded as of the date of the Merger. The valuation allowance is primarily related to loss carryforwards in various foreign and state jurisdictions.
A reconciliation of the beginning and ending amount of gross unrecognized income tax benefits is presented below (in millions):
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
| Balance at January 1 |
$ | 30 | $ | 41 | $ | 55 | ||||||
| IMS Health balance as of Merger |
37 | — | — | |||||||||
| Additions based on tax positions related to the current year |
3 | 2 | 3 | |||||||||
| Additions for income tax positions of prior years |
7 | 9 | 1 | |||||||||
| Impact of changes in exchange rates |
(3 | ) | (1 | ) | — | |||||||
| Reductions for income tax positions of prior years |
(1 | ) | (2 | ) | (6 | ) | ||||||
| Reductions due to the lapse of the applicable statute of limitations |
(9 | ) | (19 | ) | (12 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| Balance at December 31 |
$ | 64 | $ | 30 | $ | 41 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
As of December 31, 2016, the Company had total gross unrecognized income tax benefits of $64 million associated with over 100 jurisdictions in which the Company conducts business that, if recognized, would reduce the Company’s effective income tax rate.
The Company’s policy for recording interest and penalties relating to uncertain income tax positions is to record them as a component of income tax expense in the accompanying consolidated statements of income. In 2016, 2015 and 2014, the amount of interest and penalties recorded as an addition/(reduction) to income tax expense in the accompanying consolidated statements of income was $2 million, ($2) million and $1 million, respectively. As of December 31, 2016 and 2015, the Company had accrued approximately $11 million and $3 million, respectively, of interest and penalties.
The Company believes that it is reasonably possible that a decrease of up to $6 million in gross unrecognized income tax benefits for federal, state and foreign exposure items may be necessary within the next 12 months due to lapse of statutes of limitations or uncertain tax positions being effectively settled. The Company believes that it is reasonably possible that a decrease of up to $2 million in gross unrecognized income tax benefits for foreign items may be necessary within the next 12 months due to payments. For the remaining uncertain income tax positions, it is difficult at this time to estimate the timing of the resolution.
The Company conducts business globally and, as a result, files income tax returns in the United States federal jurisdiction and various state and foreign jurisdictions. In the normal course of business, the Company is subject to examination by taxing authorities throughout the world. The following table summarizes the tax years
122
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
that remain open for examination by tax authorities in the most significant jurisdictions in which the Company operates:
| United States |
2013-2015 | |
| India |
2006-2016 | |
| Japan |
2011-2015 | |
| United Kingdom |
2015 | |
| Switzerland |
2012-2015 |
In certain of the jurisdictions noted above, the Company operates through more than one legal entity, each of which has different open years subject to examination. The table above presents the open years subject to examination for the most material of the legal entities in each jurisdiction. Additionally, it is important to note that tax years are technically not closed until the statute of limitations in each jurisdiction expires. In the jurisdictions noted above, the statute of limitations can extend beyond the open years subject to examination.
Due to the geographic breadth of the Company’s operations, numerous tax audits may be ongoing throughout the world at any point in time. Income tax liabilities are recorded based on estimates of additional income taxes which may be due upon the conclusion of these audits. Estimates of these income tax liabilities are made based upon prior experience and are updated in light of changes in facts and circumstances. However, due to the uncertain and complex application of income tax regulations, it is possible that the ultimate resolution of audits may result in liabilities which could be materially different from these estimates. In such an event, the Company will record additional income tax expense or income tax benefit in the period in which such resolution occurs.
The Company had a tax holiday for Quintiles East Asia Pte. Ltd. in Singapore through June 2015. The income tax benefit of this holiday was approximately $2 million in both 2015 and 2014. The tax holiday increased earnings per share by approximately $0.02 in both 2015 and 2014.
19. Employee Benefit Plans
Pension and Postretirement Benefit Plans
The Company sponsors both funded and unfunded defined benefit pension plans. These plans provide benefits based on various criteria, including, but not limited to, years of service and salary. The Company also sponsors an unfunded postretirement benefit plan in the United States that provides health and prescription drug benefits to retirees who meet the eligibility requirements. The information presented herein includes the United States and Non-United States pension and postretirement benefit plans assumed in the merger with IMS Health on October 3, 2016. The Company uses a December 31 measurement date for all pension and postretirement benefit plans.
123
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
The following table summarizes changes in the benefit obligation, the plan assets and the funded status of the pension benefit plans (in millions):
| Pension Benefits | ||||||||||||
| United States Plans | Non-United States Plans | |||||||||||
| December 31 | ||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||
| Obligation and funded status: |
||||||||||||
| Change in benefit obligation |
||||||||||||
| Projected benefit obligation at beginning of year |
$ | — | $ | 154 | $ | 147 | ||||||
| Service costs |
4 | 18 | 15 | |||||||||
| Interest cost |
3 | 5 | 3 | |||||||||
| Expected return on plan assets |
— | — | (3 | ) | ||||||||
| Actuarial gains |
(30 | ) | (8 | ) | (2 | ) | ||||||
| Business combinations |
333 | 377 | 2 | |||||||||
| Benefits paid |
(2 | ) | (9 | ) | (6 | ) | ||||||
| Foreign currency fluctuations and other |
— | (29 | ) | (2 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| Projected benefit obligation at end of year |
308 | 508 | 154 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| Change in plan assets |
||||||||||||
| Fair value of plan assets at beginning of year |
— | 87 | 88 | |||||||||
| Actual return on plan assets |
5 | 4 | 1 | |||||||||
| Contributions |
1 | 9 | 6 | |||||||||
| Business combinations |
308 | 284 | 2 | |||||||||
| Benefits paid |
(2 | ) | (9 | ) | (6 | ) | ||||||
| Foreign currency fluctuations and other |
— | (27 | ) | (4 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| Fair value of plan assets at end of year |
312 | 348 | 87 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| Funded status |
$ | 4 | $ | (160 | ) | $ | (67 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
The following table summarizes the amounts recognized in the consolidated balance sheets related to the pension benefit plans (in millions):
| Pension Benefits | ||||||||||||
| United States Plans | Non-United States Plans | |||||||||||
| December 31 | ||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||
| Deposits and other assets |
$ | 45 | $ | 13 | $ | 19 | ||||||
| Accrued expenses |
1 | 9 | 5 | |||||||||
| Other long-term liabilities |
40 | 164 | 81 | |||||||||
| AOCI |
29 | (8 | ) | (14 | ) | |||||||
124
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
The following table summarizes the accumulated benefit obligation for all pension benefit plans (in millions):
| Pension Benefits | ||||||||||||
| United States Plans | Non-United States Plans | |||||||||||
| December 31 | ||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||
| Accumulated benefit obligation |
$ | 303 | $ | 469 | $ | 139 | ||||||
The Company recorded $4 million of benefit obligation for other postretirement benefits in connection with the Merger. At December 31, 2016, the liability remained $4 million, with $1 million recorded in accrued expenses and $3 million included with other long-term liabilities.
The following table provides the information for pension plans with an accumulated benefit obligation in excess of plan assets and projected benefit obligations in excess of plan assets (in millions):
| Pension Benefits | ||||||||||||
| United States Plans | Non-United States Plans | |||||||||||
| December 31 | ||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2016 | 2015 | ||||||||||
| Plans with accumulated benefit obligation in excess of plan assets: |
||||||||||||
| Accumulated benefit obligation |
$ | 43 | $ | 409 | $ | 83 | ||||||
| Fair value of plan assets |
2 | 271 | 8 | |||||||||
| Plans with projected benefit obligation in excess of plan assets: |
||||||||||||
| Projected benefit obligation |
44 | 444 | 95 | |||||||||
| Fair value of plan assets |
2 | 271 | 8 | |||||||||
125
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
The components of net periodic benefit cost changes in plan assets and benefit obligations recognized in other comprehensive loss were as follows (in millions):
| Pension Benefits | ||||||||||||||||
| United States Plans | Non-United States Plans | |||||||||||||||
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
| Service cost |
$ | 4 | $ | 18 | $ | 15 | $ | 13 | ||||||||
| Interest cost |
3 | 5 | 3 | 4 | ||||||||||||
| Expected return on plan assets |
(6 | ) | (6 | ) | (3 | ) | (4 | ) | ||||||||
| Amortization of actuarial losses |
— | 1 | 1 | — | ||||||||||||
| Amortization of prior service costs |
— | — | — | — | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
| Net periodic benefit cost |
1 | 18 | 16 | 13 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
| Other changes in plan assets and benefit obligations recognized in other comprehensive loss: |
||||||||||||||||
| Actuarial loss (gain) – current years |
(29 | ) | (5 | ) | — | — | ||||||||||
| Prior service (cost) credit – current years |
— | 0 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Amortization of actuarial losses |
— | (1 | ) | (1 | ) | — | ||||||||||
| Amortization of prior service costs |
— | — | — | — | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
| Total recognized in other comprehensive loss |
(29 | ) | (6 | ) | (1 | ) | — | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
| Total recognized in net periodic benefit cost and other comprehensive loss |
$ | (28 | ) | $ | 12 | $ | 15 | $ | 13 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
126
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
The components of other changes in plan assets and benefit obligations recognized in other comprehensive loss related to the other postretirement benefits plan are de minimis. In addition, the amounts in AOCI that are expected to be recognized as components of net periodic benefit cost (credit) during 2017 for pension and other postretirement benefit plans are de minimis.
Assumptions
The weighted average assumptions used to determine net periodic benefit cost were as follows for the years ended December 31:
| Pension Benefits | Other Postretirement Benefits | |||||||||||||||||||
| United States Plans | Non-United States Plans | |||||||||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | 2016 | ||||||||||||||||
| Discount rate |
3.62 | % | 1.88 | % | 2.46 | % | 3.01 | % | 2.40 | % | ||||||||||
| Rate of compensation increases |
3.00 | % | 5.27 | % | 4.32 | % | 4.36 | % | — | |||||||||||
| Expected return on plan assets |
7.94 | % | 4.26 | % | 4.05 | % | 5.21 | % | — | |||||||||||
The weighted average assumptions used to determine benefit obligations were as follows at December 31:
| Pension Benefits | Other Postretirement Benefits | |||||||||||||||
| United States Plans | Non-United States Plans | |||||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | |||||||||||||
| Discount rate |
4.17 | % | 1.68 | % | 2.50 | % | 2.90 | % | ||||||||
| Rate of compensation increases |
3.00 | % | 5.17 | % | 4.37 | % | — | |||||||||
The discount rate represents the interest rate used to determine the present value of the future cash flows currently expected to be required to settle the Company’s defined benefit plan obligations. The discount rates are derived using weighted average yield curves on AA-rated corporate bonds. The cash flows from the Company’s expected benefit obligation payments are then matched to the yield curve to derive the discount rates. At December 31, 2016, the discount rate ranged from 2.90% to 4.23% for our United States pension plan and postretirement benefit plan. The discount rate for our United Kingdom pension plans decreased to 2.35% to 2.60% at December 31, 2016 from 3.80% at December 31, 2015. The United States and United Kingdom plans represent approximately 76% of the consolidated benefit obligation as of December 31, 2016. The discount rates in other non-U.S. countries ranged from 0.30% to 11.60% at December 31, 2016, compared to 0.75% to 10.80% at December 31, 2015.
The Company’s assumption for the expected return on plan assets was determined by the weighted average of the long-term expected rate of return on each of the asset classes invested as of the balance sheet date. For plan assets invested in government bonds, the expected return was based on the yields on the relevant indices as of the balance sheet date. There is considerable uncertainty for the expected return on plan assets invested in equity and diversified growth funds. The expected rate of return on plan assets for the United States pension plans was 8.0%
127
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
at January 1, 2017. Outside the United States, the range of applicable expected rates of return was 0.8% to 9.0% as of January 1, 2017, compared to 4.2% to 9.0% as of January 1, 2016. The expected return on assets (“EROA”) was $13 million and $4 million and the actual return on assets was $10 million and $1 million for the years ended December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively.
Under the Company’s United States qualified retirement plan, participants have a notional retirement account that increases with pay and investment credits. The rate used to determine the investment credit (cash balance crediting rate) varies monthly and is equal to 1/12th of the yield on 30-year U.S. Government Treasury Bonds, with a minimum of 0.25%. At retirement, the account is converted to a monthly retirement benefit.
At December 31, 2016, the Company’s health care cost trend rate for the next seven years was assumed to be 7.0% and the assumed ultimate cost trend rate was 5%. The Company assumed that ultimate cost trend rate is reached in 2021.
Assumed health care cost trend rates could have a significant effect on the amounts reported for the health care plans. A one-percentage-point change in assumed health care cost trend rates at December 31, 2016 would have a de minimis effect on the total of service and interest cost and on the accumulated postretirement benefit obligation.
Plan Assets
The Company’s pension plan weighted average asset allocations, by asset category, were as follows:
| Plan Assets at December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||
| United States Plans | Non-United States Plans | Total | ||||||||||||||||||
| Asset Category |
2016 | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||
| Equity securities |
70.09 | % | 46.09 | % | 25.22 | % | 57.43 | % | 25.22 | % | ||||||||||
| Debt securities |
24.94 | 14.42 | 56.64 | 19.39 | 56.64 | |||||||||||||||
| Real estate |
4.97 | — | — | 2.35 | — | |||||||||||||||
| Other |
— | 39.49 | 18.14 | 20.83 | 18.14 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
| Total |
100.00 | % | 100.00 | % | 100.00 | % | 100.00 | % | 100.00 | % | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
The target asset allocation for the Company’s pension plans were as follows
| Asset Category |
United States Plans |
Non-United States Plans |
Total | |||||||||
| Equity securities |
60-80 | % | 35-50 | % | 45-65 | % | ||||||
| Debt securities |
20-30 | % | 10-20 | % | 10-30 | % | ||||||
| Real estate |
0-10 | % | — | % | 0-5 | % | ||||||
| Other |
— | % | 30-45 | % | 10-30 | % | ||||||
128
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
The following table summarizes United States plan assets measured at fair value (in millions):
| December 31, 2016 | December 31, 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Asset Category |
Level 1 | Level 2 | Total | Level 1 | Level 2 | Total | ||||||||||||||||||
| Domestic equities |
$ | 32 | $ | — | $ | 32 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||||||
| International equities |
20 | — | 20 | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| Corporate bonds |
46 | — | 46 | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| Real estate |
15 | — | 15 | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
| Total assets in the fair value heirarchy |
113 | — | 113 | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| Common/collective trusts measured at net asset value (“NAV”)(1) |
— | — | 199 | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
| Total |
$ | 113 | $ | — | $ | 312 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
The following table summarizes non-United States plan assets measured at fair value (in millions):
| December 31, 2016 | December 31, 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Asset Category |
Level 1 | Level 2 | Total | Level 1 | Level 2 | Total | ||||||||||||||||||
| International equities |
$ | — | $ | 57 | $ | 57 | $ | — | $ | 22 | $ | 22 | ||||||||||||
| Debt issued by national, state or local government |
2 | 48 | 50 | — | 49 | 49 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Diversified growth fund |
— | 14 | 14 | — | 15 | 15 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Investments funds |
— | 7 | 7 | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| Insurance contracts |
— | 133 | 133 | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other |
— | 6 | 6 | — | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
| Total assets in the fair value heirarchy |
2 | 265 | 267 | — | 87 | 87 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Assets measured at NAV (1) |
— | — | 81 | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
| Total |
$ | 2 | $ | 265 | $ | 348 | $ | — | $ | 87 | $ | 87 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
| (1) | Certain investments that are measured at fair value using the net asset value per share (or its equivalent) practical expedient have not been classified in the fair value hierarchy. The fair value amounts presented in the above plan asset tables are intended to permit reconciliation of the fair value of plan assets in the fair value hierarchy to the plan asset amounts presented in the above funded status table as of December 31, 2016 and 2015. |
Investments in mutual funds are valued at quoted market prices. Investments in common/collective trusts and pooled funds are valued at the NAV as reported by the trust. The NAV is based on the fair value of the underlying investments held by the fund less its liabilities. Insurance contracts are valued at the amount of the benefit liability. The Company has no Level 3 assets that rely on unobservable inputs to measure fair value.
Investment Policies and Strategies
The Company invests primarily in a diversified portfolio of equity and debt securities that provide for long-term growth within reasonable and prudent levels of risk. The asset allocation targets established by the Company are strategic and applicable to the plan’s long-term investing horizon. The portfolio is constructed and maintained to provide adequate liquidity to meet associated liabilities and minimize long-term expense and
129
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
provide prudent diversification among asset classes in accordance with the principles of modern portfolio theory. The plan employs a diversified mix of actively managed investments around a core of passively managed index exposures in each asset class. Within each asset class, rapid market shifts, changes in economic conditions or an individual fund manager’s outlook may cause the asset allocation to fall outside the prescribed targets. The majority of the Company’s plan assets are measured quarterly against benchmarks established by the Company’s investment advisors and the Company’s Asset Management Committee, who reviews actual plan performance and has the authority to recommend changes as deemed appropriate. Assets are rebalanced periodically to their strategic targets to maintain the plan’s strategic risk/reward characteristics. The Company periodically conducts asset liability modeling studies to ensure that the investment strategy is aligned with the obligations of the plans and that the assets will generate income and capital growth to meet the cost of current and future benefits that the plans provide. The pension plans do not have investments in Company stock at December 31, 2016 or 2015.
The portfolio for the Company’s United Kingdom pension plans seek to invest in a range of suitable assets of appropriate liquidity which will generate in the most effective manner possible, income and capital growth to ensure that there are sufficient assets to meet benefit payments when they fall due, while controlling the long-term costs of the plans and avoiding short-term volatility of investment returns. The plans seek to achieve these objectives by investing in a mixture of real (equities) and monetary (fixed interest) assets. It recognizes that the returns on real assets, while expected to be greater over the long-term than those on monetary assets, are likely to be more volatile. A mixture across asset classes should nevertheless provide the level of returns required by the plans. The trustee periodically conducts asset liability modeling exercises to ensure the investments are aligned with the appropriate benchmark to better reflect the plans’ liabilities. The trustee also undertakes to review this benchmark on a regular basis.
Cash Flows
Contributions
The Company expects to contribute approximately $23 million in required contributions to its pension and postretirement benefit plans during fiscal 2017. The Company may make additional contributions into its pension plans in fiscal 2017 depending on, among other factors, how the funded status of those plans changes and in order to meet minimum funding requirements as set forth in employee benefit and tax laws, plus additional amounts the Company may deem to be appropriate.
Estimated future benefit payments and subsidy receipts
The following benefit payments (net of expected participant contributions) for pension benefits are expected to be paid as follows (in millions):
| Pension Benefits | ||||
| 2017 |
$ | 29 | ||
| 2018 |
31 | |||
| 2019 |
34 | |||
| 2020 |
38 | |||
| 2021 |
42 | |||
| Years 2022 through 2026 |
210 | |||
|
|
|
| ||
| $ | 384 | |||
|
|
|
| ||
130
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
Benefit payments (net of expected participant contributions) for other postretirement benefits are expected to be de minimis over the periods presented.
Defined Contribution Plans
Defined contribution or profit sharing style plans are offered in Australia, Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Canada, the Czech Republic, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hong Kong, Hungary, India, Ireland, Israel, Japan, Malaysia, the Netherlands, New Zealand, Poland, Slovakia, South Africa, Sweden, Switzerland, Taiwan, Thailand, the United States and the United Kingdom. In some cases these plans are required by local laws or regulations.
In the United States, the Company has 401(k) plans under which the Company matches employee deferrals at varying percentages and specified limits of the employee’s salary. In 2016, 2015 and 2014, the Company expensed $39 million, $36 million and $31 million, respectively, related to matching contributions.
Certain key executives of the Company participate in an unfunded defined contribution executive retirement plan, assumed in the Merger, which was frozen to additional accruals for future service contributions in 2012. Participants continue to receive an annual investment credit based on the average of the annual yields at the end of each month on the AA-AAA rated 10 plus year maturity component of the Merrill Lynch United States Corporate Bond Master Index.
Other Plans
Plans accounted for as deferred compensation contracts
The Company provides certain executives with supplemental pension benefits in accordance with their individual employment arrangements. The above tables do not include the Company’s expense or obligation associate with providing these benefits. The obligation related to these benefits was approximately $1 million for the year ended December 31, 2016, and the Company’s expense for the year then ended was de minimis.
Plans accounted for as postretirement benefits
The Company provides certain executives with postretirement medical, dental and life insurance benefits. These benefits are individually negotiated arrangements in accordance with their individual employment arrangements. The above tables do not include the Company’s expense or obligation associate with providing these benefits. The obligation related to these benefits was approximately $12 million for the year ended December 31, 2016, and the Company’s expense for the year then ended was de minimis.
Stock Incentive Plans
Stock incentive plans provide incentives to eligible employees, officers and directors in the form of non-qualified stock options, incentive stock options, stock appreciation rights (“SARs”), restricted stock awards (“RSAs”), restricted stock units (“RSUs”), performance shares, performance units, covered annual incentive awards, cash-based awards and other stock-based awards, in each case subject to the terms of the stock incentive plans.
In addition, the Company assumed the equity incentive plans formerly related to IMS Health, the Quintiles IMS Holdings, Inc. 2014 Incentive and Stock Award Plan (the “2014 Equity Plan”) and the Quintiles IMS Holdings, Inc. 2010 Equity Plan (the “2010 Equity Plan”). The 2014 Equity Plan provides for the grant of stock options, SARs, restricted and deferred stock (including RSUs), dividend equivalents, other stock-based awards
131
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
and performance awards. The 2010 Equity Plan expired on April 4, 2014 and no new awards were granted under the 2010 Equity Plan.
As provided for in the Merger agreement, (i) each option to purchase IMS Health common stock outstanding immediately prior to the effective time of the Merger was converted into an option to acquire shares of the Company’s common stock, on substantially the same terms and conditions, adjusted by the 0.384 exchange ratio; and (ii) each stock-settled stock appreciation right of IMS Health outstanding immediately prior to the effective time of the Merger was converted into a stock-settled stock appreciation right corresponding to shares of Company common stock, on substantially the same terms and conditions, adjusted by the 0.384 exchange ratio. The fair value of those options and stock-settled stock appreciation rights was measured using the Black-Scholes model with the following assumptions: risk-free rate (0.87% – 1.49%); expected life (2.6 years – 7.6 years); dividend yield of zero; expected volatility (26% – 31%). Similarly, each IMS Health stock option, performance unit (assuming 100% of performance target), restricted stock award and restricted stock unit outstanding immediately prior to the effective time of the Merger was converted into a similar Company award, as appropriate, on substantially the same terms and conditions, at the 0.384 exchange ratio. The fair value of these awards was allocated to purchase price and unearned compensation, based on the past and future service conditions. The assumed awards related to the Merger have been identified as applicable, in the tables that follow.
The Company recognized stock-based compensation expense of $80 million, $38 million and $30 million in 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. Stock-based compensation expense is included in selling, general and administrative expenses on the accompanying consolidated statements of income. The associated future income tax benefit recognized was $24 million, $9 million and $8 million in 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. As of December 31, 2016, there was approximately $117 million of total unrecognized stock-based compensation expense related to outstanding non-vested stock-based compensation arrangements, which the Company expects to recognize over a weighted average period of 1.3 years.
As of December 31, 2016, there were 15.2 million shares available for future grants under all of the Company’s stock incentive plans.
The Company used the following assumptions when estimating the value of the stock-based compensation for stock options and SARs issued as follows:
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||
| Expected volatility |
20 – 30% | 26 – 41% | 26 – 43% | |||
| Weighted average expected volatility |
28% | 34% | 36% | |||
| Expected dividends |
0.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | |||
| Expected term (in years) |
0.3 – 6.6 | 3.7 – 6.7 | 1.5 – 6.7 | |||
| Risk-free interest rate |
0.32 – 2.19% | 1.06 – 2.04% | 0.28 – 2.21% | |||
Stock Options
The option price is determined by the Board at the date of grant and the options expire 10 years from the date of grant. The vesting schedule for options granted to employees is either (i) 20% per year beginning on the first anniversary of the date of grant; (ii) 25% per year beginning on the first anniversary of the date of grant; or (iii) 33% on the third anniversary of the date of grant and 67% on the fourth anniversary of the date of grant. Options granted
132
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
to our non-employee directors vest either (i) 100% on the first anniversary of the date of grant; or (ii) 34% on the anniversary of the date of grant and 33% on the second and third anniversaries of the date of grant.
The Company’s stock option activity in 2016 is as follows (in millions, except number of options and exercise price):
| Number of Options |
Weighted Average Exercise Price |
Aggregate Intrinsic Value | ||||||||||
| Outstanding at December 31, 2015 |
6,647,999 | $ | 38.04 | $ | 204 | |||||||
| Granted |
783,700 | $ | 64.66 | |||||||||
| Assumed – Merger |
3,563,037 | $ | 19.05 | |||||||||
| Exercised |
(3,385,720 | ) | $ | 29.69 | ||||||||
| Canceled |
(357,677 | ) | $ | 51.21 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
| Outstanding at December 31, 2016 |
7,251,339 | $ | 34.83 | $ | 299 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
The weighted average fair value per share of the options granted in 2016, 2015 and 2014 was $17.91, $21.96 and $18.72, respectively. The total intrinsic value of options exercised was approximately $155 million, $144 million and $77 million in 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. The Company received cash of approximately $101 million, $59 million and $33 million in 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively, from options exercised.
Selected information regarding the Company’s stock options as of December 31, 2016 is as follows:
| Options Outstanding |
Options Exercisable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Number of |
Exercise Price Range | Weighted Average Exercise Price |
Weighted Average Remaining Life (in Years) |
Number of Options |
Weighted Average Exercise Price | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1,160,999 |
$ | 8.34 | — | $ | 14.63 | $ | 9.19 | 3.55 | 1,160,999 | $ | 9.19 | |||||||||||||||||
| 1,167,220 |
$ | 15.11 | — | $ | 23.70 | $ | 18.18 | 3.86 | 1,128,911 | $ | 18.16 | |||||||||||||||||
| 1,216,960 |
$ | 24.59 | — | $ | 26.05 | $ | 25.65 | 4.13 | 1,216,960 | $ | 25.65 | |||||||||||||||||
| 1,299,632 |
$ | 28.13 | — | $ | 40.00 | $ | 34.47 | 5.88 | 831,112 | $ | 33.84 | |||||||||||||||||
| 1,620,603 |
$ | 42.74 | — | $ | 64.67 | $ | 57.71 | 8.06 | 648,436 | $ | 57.64 | |||||||||||||||||
| 785,925 |
$ | 64.86 | — | $ | 77.11 | $ | 65.10 | 8.07 | 364,350 | $ | 65.02 | |||||||||||||||||
The weighted average remaining contractual life of the options outstanding and exercisable as of December 31, 2016 is 5.6 years and 4.9 years, respectively. The total aggregate intrinsic value of the exercisable stock options and the stock options expected to vest as of December 31, 2016 was approximately $298 million.
Stock Appreciation Rights – Stock Settled
The exercise price of the stock-settled SARs (“SSRs”) is equal to the closing market price of the Company’s common stock as of the grant date and expire on the tenth anniversary of the date of grant. The SSRs are eligible to vest in equal increments of 25% on each of the first four anniversaries of the date of grant.
133
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
The Company’s SSR activity in 2016 is as follows (in millions, except number of SSRs and exercise price):
| Number of Options |
Weighted Average Exercise Price |
Aggregate Intrinsic Value | ||||||||||
| Outstanding at December 31, 2015 |
— | $ | — | $ | — | |||||||
| Assumed – Merger |
1,351,647 | $ | 62.13 | |||||||||
| Exercised |
(3,205 | ) | $ | 65.16 | ||||||||
| Canceled |
(35,120 | ) | $ | 61.72 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
| Outstanding at December 31, 2016 |
1,313,322 | $ | 62.13 | $ | 18 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
Prior to 2016, the Company did not have SSRs. The total intrinsic value of SSRs exercised was approximately $0.04 million in 2016.
The weighted average remaining contractual life of the SSRs outstanding and exercisable as of December 31, 2016 is 8.6 years and 7.9 years, respectively. The total aggregate intrinsic value of the exercisable SSRs and the SSRs expected to vest as of December 31, 2016 was approximately $18 million.
Stock Appreciation Rights – Cash Settled
The Company’s cash settled SARs (“CSRs”) require the Company to settle in cash an amount equal to the difference between the fair value of the Company’s common stock on the date of exercise and the grant price, multiplied by the number of CSRs being exercised. These awards either (i) vest 25% per year or (ii) vest 33% on the third anniversary of the date of grant and 67% on the fourth anniversary of the date of grant; or (iii) one-third per year beginning on the first anniversary of the date of grant.
The Company’s CSR activity in 2016 is as follows (in millions, except number of CSRs and grant price):
| Number of CSRs | Weighted Average Grant Price |
Aggregate Intrinsic Value | ||||||||||
| Outstanding at December 31, 2015 |
530,701 | $ | 50.46 | $ | 10 | |||||||
| Granted |
40,400 | $ | 70.34 | |||||||||
| Exercised |
(55,600 | ) | $ | 44.49 | ||||||||
| Canceled |
(36,325 | ) | $ | 55.78 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
| Outstanding at December 31, 2016 |
479,176 | $ | 52.42 | $ | 11 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
As of December 31, 2016, 2015 and 2014, the weighted average fair value per share of the CSRs granted was $34.25, $29.79 and $27.17, respectively. The Company paid approximately $2 million, $1 million and $0.4 million to settle exercised CSRs in 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively.
The weighted average remaining contractual life of the CSRs outstanding and exercisable as of December 31, 2016 is 7.2 years and 6.6 years, respectively. The total aggregate intrinsic value of the exercisable CSRs and the CSRs expected to vest as of December 31, 2016 was approximately $11 million.
134
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
Restricted Stock Units
The Company’s RSUs will settle in shares of the Company’s common stock within 45 days of the applicable vesting date. RSUs granted to employees vest either (i) 25% per year beginning on the first anniversary of the date of grant; (ii) one-third per year beginning on the first anniversary of the grant date; or (iii) 33% on the third anniversary of the date of grant and 67% on the fourth anniversary of the date of grant.
The Company’s RSU activity in 2016 is as follows:
| Number of RSUs | Weighted Average Grant- Date Fair Value | |||||||
| Outstanding at December 31, 2015 |
359,553 | $ | 60.60 | |||||
| Granted |
494,681 | $ | 68.65 | |||||
| Assumed – Merger |
1,054,567 | $ | 80.20 | |||||
| Performance units converted to RSUs |
144,239 | $ | 64.77 | |||||
| Vested |
(252,462 | ) | $ | 64.93 | ||||
| Canceled |
(79,761 | ) | $ | 65.80 | ||||
|
|
|
|
||||||
| Outstanding at December 31, 2016 |
1,720,817 | $ | 74.40 | |||||
|
|
|
|
||||||
As of December 31, 2016, there are 1.7 million RSUs outstanding with an intrinsic value of approximately $131 million.
Performance Units
The Company awarded performance units that contain both service and performance based vesting criteria. Vesting occurs if the recipient remains employed and depends on the degree to which the Company achieves certain cumulative adjusted diluted earnings per share goals during a three-year performance period (as defined in the award agreements). The fair value of these awards is equal to the closing price of the Company’s common stock on the grant date. All performance units outstanding at the date of the Merger were converted into time-based RSUs at 187% of target for performance units granted in 2015 and at 100% of target for performance units granted in 2016. Accordingly, as of December 31, 2016, there are no performance units outstanding.
The Company’s performance units activity in 2016 is as follows:
|
|
Number of Performance Units |
Weighted Average Grant- Date Fair Value | ||||||
| Non-vested at December 31, 2015 |
49,667 | $ | 64.93 | |||||
| Granted |
119,839 | $ | 64.67 | |||||
| Additional goal achievement shares |
12,727 | $ | 64.93 | |||||
| Vested |
(59,830 | ) | $ | 64.79 | ||||
| Canceled performance units converted to RSUs |
(122,403 | ) | $ | 64.74 | ||||
|
|
|
|
||||||
| Non-vested at December 31, 2016 |
— | $ | — | |||||
|
|
|
|
||||||
135
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
Restricted Stock Awards
The restricted stock awards (“RSAs”) issued during 2016 vest either (i) in equal increments of 50% on each of the second and fourth anniversaries of the grant date; or (ii) one-third per year beginning on the first anniversary of the date of grant.
The Company’s RSA activity in 2016 is as follows:
|
|
Number of RSAs | Weighted Average Grant-Date Fair Value | ||||||
| Outstanding at December 31, 2015 |
— | $ | — | |||||
| Granted |
86,356 | $ | 81.06 | |||||
| Assumed – Merger |
367,053 | $ | 80.20 | |||||
| Canceled |
(86,356 | ) | $ | 81.06 | ||||
|
|
|
|
||||||
| Outstanding at December 31, 2016 |
367,053 | $ | 80.20 | |||||
|
|
|
|
||||||
As of December 31, 2016, there are 0.4 million RSAs outstanding with an intrinsic value of approximately $28 million.
Employee Stock Purchase Plan
The Company sponsors an Employee Stock Purchase Plan (“ESPP”) which allows eligible employees to authorize payroll deductions of up to 10% of their base salary to be applied toward the purchase of full shares of the Company’s common stock on the last day of the offering period. Offering periods under the ESPP are six months in duration. Beginning April 1 and October 1 of each year. Participating employees purchase shares on the last day of each offering period at a discount of 15% of the closing price of the common stock on such date as reported on the NYSE. The aggregate number of shares of the Company’s common stock that may be issued under the ESPP may not exceed 2.5 million shares and no one employee may purchase any shares under the ESPP having a collective fair market value greater than $25,000 in any one calendar year. During 2016, 2015 and 2014, the Company issued 0.1 million shares, 0.1 million shares and 0.05 million shares, respectively, of common stock for purchases under the ESPP. Effective as of December 31, 2016, the ESPP was discontinued and participant contributions under the ESPP ceased. The final purchase of shares under the ESPP occurred on December 31, 2016.
Other
The Company sponsors a supplemental non-qualified deferred compensation plan, covering certain management employees, and maintains other statutory indemnity plans as required by local laws or regulations.
20. Related Party Transactions
The Company reimbursed its former Executive Chairman, who retired effective December 31, 2015 but remains a director of the Company, for business-related travel services he provided for himself and other Company employees with the use of his own airplane. In 2015 and 2014, the Company expensed approximately $1 million and $2 million, respectively, for such business-related travel expenses. The Company’s reimbursement obligations terminated effective December 31, 2015 in connection with its former Executive Chairman’s retirement.
136
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
In January 2010, the Company entered into a collaboration agreement with a related party, HUYA Bioscience International, LLC (“HUYA”), to fund up to $2 million of its research and development activity for a specific compound. Under the agreement, the Company had the potential to receive additional consideration which contractually would not exceed $17 million excluding interest if certain events had occurred. In February 2015, the Company and HUYA agreed to terminate the collaboration agreement. In connection with the termination, HUYA paid the Company $5 million to satisfy all of HUYA’s various payment obligations under the collaboration agreement.
During 2016, 2015 and 2014, the Company entered into a number of contracts with HUYA, primarily in Asia, in which the Company will provide up to approximately $(8 million) net cancellations, $32 million and $0.4 million, respectively, of services on a fee for services basis at arm’s length and at market rates. In 2016, 2015 and 2014, the Company provided approximately $6 million, $7 million and $2 million, respectively, of services under these agreements.
The Company has entered into other transactions with related parties including investments in and advances to unconsolidated affiliates which are discussed in Note 4.
21. Operations by Geographic Location
The table below presents the Company’s operations by geographical location. The Company attributes revenues to geographical locations based upon where the services are performed. The Company’s operations within each geographical region are further broken down to show each country which accounts for 10% or more of the totals (in millions):
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
| Revenues: |
||||||||||||
| Americas: |
||||||||||||
| United States |
$ | 2,145 | $ | 1,788 | $ | 1,589 | ||||||
| Other |
233 | 185 | 195 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| Americas |
2,378 | 1,973 | 1,784 | |||||||||
| Europe and Africa: |
||||||||||||
| United Kingdom |
461 | 410 | 402 | |||||||||
| Other |
1,594 | 1,237 | 1,275 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| Europe and Africa |
2,055 | 1,647 | 1,677 | |||||||||
| Asia-Pacific: |
||||||||||||
| Japan |
587 | 443 | 472 | |||||||||
| Other |
344 | 263 | 232 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| Asia-Pacific |
931 | 706 | 704 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| Revenues |
5,364 | 4,326 | 4,165 | |||||||||
| Reimbursed expenses |
1,514 | 1,411 | 1,295 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| Total revenues |
$ | 6,878 | $ | 5,737 | $ | 5,460 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
137
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
| As of December 31, | ||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Property, equipment and software, net: |
||||||||
| Americas: |
||||||||
| United States |
$ | 430 | $ | 170 | ||||
| Other |
25 | 1 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Americas |
455 | 171 | ||||||
| Europe and Africa: |
||||||||
| United Kingdom |
40 | 46 | ||||||
| Other |
214 | 32 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Europe and Africa |
254 | 78 | ||||||
| Asia-Pacific: |
||||||||
| Japan |
36 | 13 | ||||||
| Other |
34 | 9 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Asia-Pacific |
70 | 22 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Total property, equipment and software, net |
$ | 779 | $ | 271 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
22. Segments
The following table presents the Company’s operations by reportable segment. The Company is managed through three reportable segments, Commercial Solutions, Research & Development Solutions and Integrated Engagement Services. Commercial Solutions provides mission critical information, technology solutions and real-world insights and services to our life science clients. Research & Development Solutions, which primarily serves biopharmaceutical clients, is engaged in research and development and provides clinical research and clinical trial services. Integrated Engagement Services provides contract sales to both biopharmaceutical clients and the broader healthcare market.
Certain costs are not allocated to the Company’s segments and are reported as general corporate and unallocated expenses. These costs primarily consist of stock-based compensation and expenses for corporate overhead functions such as senior leadership, finance, human resources, information technology, facilities and legal. The Company does not allocate depreciation and amortization, restructuring costs, merger related costs or impairment charges to its segments. Revenues and costs for reimbursed expenses are not allocated to the Company’s segments. Asset
138
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
information by segment is not presented, as this measure is not used by the chief operating decision maker to assess the performance of the Company. Information presented below is in millions:
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
| Revenues |
||||||||||||
| Commercial Solutions |
$ | 1,096 | $ | 323 | $ | 230 | ||||||
| Research & Development Solutions |
3,472 | 3,159 | 3,050 | |||||||||
| Integrated Engagement Services |
796 | 844 | 885 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| Total revenues |
5,364 | 4,326 | 4,165 | |||||||||
| Costs of revenue |
||||||||||||
| Commercial Solutions |
644 | 239 | 174 | |||||||||
| Research & Development Solutions |
1,953 | 1,779 | 1,764 | |||||||||
| Integrated Engagement Services |
639 | 687 | 726 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| Total costs of revenue |
3,236 | 2,705 | 2,664 | |||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative expenses |
||||||||||||
| Commercial Solutions |
216 | 65 | 52 | |||||||||
| Research & Development Solutions |
577 | 556 | 542 | |||||||||
| Integrated Engagement Services |
82 | 79 | 81 | |||||||||
| General corporate and unallocated |
136 | 115 | 106 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| Total selling, general and administrative expenses |
1,011 | 815 | 781 | |||||||||
| Segment profit |
||||||||||||
| Commercial Solutions |
236 | 19 | 4 | |||||||||
| Research & Development Solutions |
942 | 824 | 744 | |||||||||
| Integrated Engagement Services |
75 | 78 | 78 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| Total segment profit |
1,253 | 921 | 826 | |||||||||
| General corporate and unallocated |
(136 | ) | (115 | ) | (106 | ) | ||||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
(289 | ) | (128 | ) | (121 | ) | ||||||
| Restructuring costs |
(71 | ) | (30 | ) | (9 | ) | ||||||
| Merger related costs |
(87 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
| Impairment charges |
(28 | ) | (2 | ) | — | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| Total income from operations |
$ | 642 | $ | 646 | $ | 590 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
23. Earnings Per Share
The following table reconciles the basic to diluted weighted average shares outstanding (in millions):
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
| Basic weighted average common shares outstanding |
149.1 | 123.0 | 128.0 | |||||||||
| Effect of dilutive stock options and share awards |
2.9 | 2.6 | 3.1 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| Diluted weighted average common shares outstanding |
152.0 | 125.6 | 131.1 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
139
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
The following table presents the weighted average number of outstanding stock-based awards not included in the computation of diluted earnings per share if they are subject to performance conditions or if the effect of including such stock-based awards in the computation would be anti-dilutive (in millions):
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
| Shares subject to performance conditions |
0.1 | 0.1 | — | |||||||||
| Shares subject to anti-dilutive stock-based awards |
1.1 | 1.0 | 1.2 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| Total shares excluded from diluted earnings per share |
1.2 | 1.1 | 1.2 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
The vesting of performance units is contingent upon the achievement of certain performance targets. The performance units are not included in diluted earnings per share until the performance targets have been met.
Stock-based awards will have a dilutive effect under the treasury method when the respective period’s average market value of the Company’s common stock exceeds the exercise proceeds.
24. Comprehensive Income
Below is a summary of the components of AOCI (in millions):
| Foreign Currency Translation |
Marketable Securities |
Derivative Instruments |
Defined Benefit Plans |
Income Taxes |
Total | |||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2013 |
$ | (6 | ) | $ | 6 | $ | (21 | ) | $ | (5 | ) | $ | 26 | $ | — | |||||||||
| Other comprehensive (loss) income before reclassifications |
(50 | ) | (1 | ) | (7 | ) | (10 | ) | 7 | (61 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Reclassification adjustments |
— | (5 | ) | 9 | — | (2 | ) | 2 | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2014 |
(56 | ) | — | (19 | ) | (15 | ) | 31 | (59 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive (loss) income before reclassifications |
(61 | ) | — | (13 | ) | — | 9 | (65 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Reclassification adjustments |
— | — | 18 | 1 | (6 | ) | 13 | |||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2015 |
(117 | ) | — | (14 | ) | (14 | ) | 34 | (111 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive (loss) income before reclassifications |
(506 | ) | — | (4 | ) | 34 | (5 | ) | (481 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Reclassification adjustments |
— | — | 28 | 1 | (7 | ) | 22 | |||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2016 |
$ | (623 | ) | $ | — | $ | 10 | $ | 21 | $ | 22 | $ | (570 | ) | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||||
140
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
Below is a summary of the (gains) losses reclassified from AOCI into the consolidated statements of income and the affected financial statement line item (in millions):
| Affected Financial Statement Line Item |
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||
| Reclassification Adjustments |
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||||
| Marketable securities |
Other expense (income), net | $ | — | $ | — | $ | (5 | ) | ||||||
| Income tax expense |
— | — | (2 | ) | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
| Total net of income taxes |
$ | — | $ | — | $ | (3 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
| Derivative instruments: |
||||||||||||||
| Interest rate swaps and caps |
Interest expense | 6 | $ | 12 | $ | 12 | ||||||||
| Foreign exchange forward contracts |
Revenues | 19 | 6 | (3 | ) | |||||||||
| Foreign exchange forward contracts |
Other expense (income), net | 3 | — | — | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
| Total before income taxes |
28 | 18 | 9 | |||||||||||
| Income tax benefit |
7 | 6 | 4 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
| Total net of income taxes |
$ | 21 | $ | 12 | $ | 5 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
| Defined benefit plans: |
||||||||||||||
| Amortization of actuarial losses |
See Note 19 | $ | 1 | $ | 1 | $ | — | |||||||
| Income tax benefit |
— | — | — | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
| Total net of income taxes |
$ | 1 | $ | 1 | — | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
25. Supplemental Cash Flow Information
The following table presents the Company’s supplemental cash flow information (in millions):
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
| Supplemental Cash Flow Information: |
||||||||||||
| Interest paid |
$ | 124 | $ | 82 | $ | 94 | ||||||
| Income taxes paid, net of refunds |
106 | 121 | 139 | |||||||||
| Non-cash Investing Activities: |
||||||||||||
| Fair value of consideration transferred in connection with business combinations |
$ | 10,425 | $ | 423 | $ | — | ||||||
141
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements - Continued
26. Quarterly Financial Data (Unaudited)
The following table summarizes the Company’s unaudited quarterly results of operations (in millions, except per share data):
| 2016 | ||||||||||||||||
| First Quarter | Second Quarter | Third Quarter | Fourth Quarter(2) | |||||||||||||
| Revenues |
$ | 1,108 | $ | 1,167 | $ | 1,136 | $ | 1,953 | ||||||||
| Income from operations |
179 | 151 | 168 | 144 | ||||||||||||
| Net income |
109 | 92 | 104 | (175 | ) | |||||||||||
| Net (income) loss attributable to non-controlling interests |
(2 | ) | (5 | ) | (5 | ) | (3 | ) | ||||||||
| Net income attributable to Quintiles IMS Holdings, Inc. |
$ | 107 | $ | 87 | $ | 99 | $ | (178 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
| Basic earnings per share(1) |
$ | 0.89 | $ | 0.73 | $ | 0.83 | $ | 0.74 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
| Diluted earnings per share(1) |
$ | 0.88 | $ | 0.71 | $ | 0.82 | $ | 0.74 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
| 2015 | ||||||||||||||||
| First Quarter | Second Quarter | Third Quarter | Fourth Quarter | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
| Revenues |
$ | 1,030 | $ | 1,074 | $ | 1,093 | $ | 1,129 | ||||||||
| Income from operations |
143 | 159 | 166 | 178 | ||||||||||||
| Net income |
87 | 85 | 108 | 108 | ||||||||||||
| Net (income) loss attributable to non-controlling interests |
— | — | 2 | (3 | ) | |||||||||||
| Net income attributable to Quintiles IMS Holdings, Inc. |
$ | 87 | $ | 85 | $ | 110 | $ | 105 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
| Basic earnings per share(1) |
$ | 0.69 | $ | 0.69 | $ | 0.91 | $ | 0.86 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
| Diluted earnings per share(1) |
$ | 0.68 | $ | 0.67 | $ | 0.89 | $ | 0.85 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
| (1) | The sum of the quarterly per share amounts may not equal per share amounts reported for year-to-date periods. This is due to changes in the number of weighted average shares outstanding and the effects of rounding for each period. |
| (2) | The fourth quarter of 2016 includes the results of operations of IMS Health since the date of the Merger on October 3, 2016. |
27. Subsequent Event
On February 12, 2017, the Board increased the stock repurchase authorization under the Repurchase Program by $1.0 billion with approximately $1.5 billion remaining available for repurchases under the program. See Note 14 for additional information regarding the Repurchase Program.
142
Table of Contents
Item 9. Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure
None.
Item 9A. Controls and Procedures
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
As required by Rule 13a-15 under the Exchange Act, as amended, we carried out an evaluation of the effectiveness of the design and operation of our disclosure controls and procedures under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including the Chief Executive Officer (“CEO”) and Chief Financial Officer (“CFO”). There are inherent limitations to the effectiveness of any system of disclosure controls and procedures, including the possibility of human error and the circumvention or overriding of the controls and procedures. Accordingly, even effective disclosure controls and procedures can only provide reasonable assurance of achieving their control objectives. Based upon our evaluation, our CEO and CFO concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures were effective to provide reasonable assurance that information required to be disclosed by us in the reports that we file or submit under the Exchange Act, as amended, is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the applicable rules and forms, and that it is accumulated and communicated to our management, including our CEO and CFO, as appropriate, to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Our management’s report on internal control over financial reporting is set forth in Part II, Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K and is incorporated herein by reference.
Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
There were no changes in our internal control over financial reporting during the quarter ended December 31, 2016 that materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
None.
143
Table of Contents
Item 10. Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance
The information required by this item is set forth under the headings “Election of Directors,” and “Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management – [Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance]” in our 2017 Proxy Statement to be filed with the SEC within 120 days after December 31, 2016 in connection with the solicitation of proxies for our 2017 annual meeting of stockholders (the “2017 Proxy Statement”) and is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 11. Executive Compensation
The information required by this item is set forth under the headings “Director Compensation,” “Compensation Discussion and Analysis,” “Compensation Committee Report,” “Compensation of Named Executive Officers,” and “Compensation Committee Interlocks and Insider Participation” in the 2017 Proxy Statement and is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters
The information required by this item is set forth under the headings “Securities Authorized for Issuance Under Equity Compensation Plan” and “Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management” in the 2017 Proxy Statement and is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions and Director Independence
The information required by this item is set forth under the headings “The Company’s Corporate Governance,” and “Ratification of the Appointment of the Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm” in the 2017 Proxy Statement and is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 14. Principal Accountant Fees and Services
The information required by this item is set forth under the headings “Proposal No. [5]: Ratification of the Appointment of the Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm—Fees Paid to Independent registered Public Accounting Firm” in the 2017 Proxy Statement and is incorporated herein by reference.
144
Table of Contents
Item 15. Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules
(a) The following documents are filed as part of this report:
| (1) Financial | Statements |
The following consolidated financial statements of Quintiles IMS Holdings, Inc. and its subsidiaries, and the independent registered public accounting firm’s report thereon, are included in Part II, Item 8 of this report:
| Page | ||||
| Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting |
81 | |||
| 82 | ||||
| 83 | ||||
| 84 | ||||
| 85 | ||||
| 86 | ||||
| 87 | ||||
| 88 | ||||
| (2) Financial | Statement Schedules |
| Schedule I—Condensed Financial Information of Registrant (Parent Company Only) |
148 | |||
| Schedule II—Valuation and Qualifying Accounts |
153 |
All other schedules are omitted, since the required information is not applicable or is not present in amounts sufficient to require submission of the schedule, or because the information required is included in the consolidated financial statements and notes thereto.
| (3) Exhibits |
The exhibits in the accompanying Exhibit Index following the signature page are filed or furnished as a part of this report and are incorporated herein by reference. The Company agrees to furnish to the SEC, upon request, copies of any long-term debt instruments that authorize an amount of securities constituting 10% or less of the total assets of Quintiles IMS Holdings, Inc. and its subsidiaries on a consolidated basis.
None.
145
Table of Contents
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. | ||
| By: |
/s/ Michael R. McDonnell | |
| Name: Michael R. McDonnell | ||
| Title: Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer | ||
Date: February 16, 2017
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| Signature |
Title |
Date | ||
| /S/ ARI BOUSBIB Ari Bousbib |
Chairman, Chief Executive Officer and President; Director (Principal Executive Officer) |
February 16, 2017 | ||
| /S/ MICHAEL R. MCDONNELL Michael R. McDonnell |
Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial Officer) |
February 16, 2017 | ||
| /S/ CHARLES E. WILLIAMS Charles E. Williams |
Senior Vice President, Corporate Controller (Principal Accounting Officer) |
February 16, 2017 | ||
| /S/ DR. DENNIS B. GILLINGS, CBE Dr. Dennis B. Gillings, CBE |
Lead Director | February 16, 2017 | ||
| /S/ JOHN P. CONNAUGHTON John P. Connaughton |
Director | February 16, 2017 | ||
| /S/ JONATHAN J. COSLET Jonathan J. Coslet |
Director | February 16, 2017 | ||
| /S/ JOHN G. DANHAKL John G. Danhakl |
Director | February 16, 2017 | ||
| /S/ MICHAEL J. EVANISKO Michael J. Evanisko |
Director | February 16, 2017 | ||
| /S/ JAMES A. FASANO James A. Fasano |
Director | February 16, 2017 | ||
146
Table of Contents
| Signature |
Title |
Date | ||
| /S/ JACK M. GREENBERG Jack M. Greenberg |
Director | February 16, 2017 | ||
| /S/ JOHN M. LEONARD, M.D. John M. Leonard, M.D. |
Director | February 16, 2017 | ||
| /S/ RONALD A. RITTENMEYER Ronald A. Rittenmeyer |
Director | February 16, 2017 | ||
| /S/ TODD B. SISITSKY Todd B. Sisitsky |
Director | February 16, 2017 | ||
147
Table of Contents
(2) Financial Statement Schedules
Schedule I—Condensed Financial Information of Registrant
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. (PARENT COMPANY ONLY)
CONDENSED STATEMENTS OF INCOME
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| (in millions) |
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative expenses |
$ | — | $ | 1 | $ | 2 | ||||||
| Merger related costs |
21 | — | — | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| Loss from operations |
(21 | ) | (1 | ) | (2 | ) | ||||||
| Interest income |
— | — | — | |||||||||
| Other expense, net |
— | — | — | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| Loss before income taxes and equity in earnings of subsidiary |
(21 | ) | (1 | ) | (2 | ) | ||||||
| Income tax benefit |
(4 | ) | (1 | ) | (1 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| Loss before equity in earnings of subsidiary |
(17 | ) | — | (1 | ) | |||||||
| Equity in earnings of subsidiary |
132 | 387 | 357 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| Net income |
$ | 115 | $ | 387 | $ | 356 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
148
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. (PARENT COMPANY ONLY)
CONDENSED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| (in millions) |
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
| Net income |
$ | 115 | $ | 387 | $ | 356 | ||||||
| Comprehensive income adjustments: |
||||||||||||
| Unrealized (losses) gains on available-for-sale securities, net of income taxes |
— | — | (1 | ) | ||||||||
| Unrealized (losses) gains on derivative instruments, net of income taxes of $3, ($4) and ($2) |
(7 | ) | (9 | ) | (5 | ) | ||||||
| Defined benefit plan adjustments, net of income taxes of $11, $— and ($3) |
23 | — | (7 | ) | ||||||||
| Foreign currency translation, net of income taxes of $(9), ($5) and ($2) |
(497 | ) | (56 | ) | (48 | ) | ||||||
| Reclassification adjustments: |
||||||||||||
| Gains on marketable securities included in net income, net of income taxes of $—, $— and ($2) |
— | — | (3 | ) | ||||||||
| Losses on derivative instruments included in net income, net of income taxes of $7, $6 and $4 |
21 | 12 | 5 | |||||||||
| Amortization of actuarial losses and prior service costs included in net income, net of income taxes |
1 | 1 | — | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| Comprehensive (loss) income |
$ | (344 | ) | $ | 335 | $ | 297 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
149
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. (PARENT COMPANY ONLY)
CONDENSED BALANCE SHEETS
| December 31, | ||||||||
| (in millions, except per share data) |
2016 | 2015 | ||||||
| ASSETS | ||||||||
| Current assets: |
||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 12 | $ | 5 | ||||
| Income taxes receivable |
4 | — | ||||||
| Other current assets and receivables |
— | — | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Total current assets |
16 | 5 | ||||||
| Investment in subsidiary |
8,631 | — | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Total assets |
$ | 8,647 | $ | 5 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY (DEFICIT) | ||||||||
| Current liabilities: |
||||||||
| Accounts payable |
$ | — | $ | — | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Total current liabilities |
— | — | ||||||
| Investment in subsidiary |
— | 569 | ||||||
| Payable to subsidiary |
14 | — | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Total liabilities |
14 | 569 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Commitments and contingencies |
||||||||
| Stockholders’ equity (deficit): |
||||||||
| Common stock and additional paid-in capital, 400.0 and 300.0 shares authorized at December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively, $0.01 par value, 248.3 and 119.4 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2016 and 2015, respectively |
10,602 | 9 | ||||||
| Accumulated deficit |
(399 | ) | (462 | ) | ||||
| Treasury stock, at cost, 12.9 shares at December 31, 2016 |
(1,000 | ) | — | |||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss |
(570 | ) | (111 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Total stockholders’ equity (deficit) |
8,633 | (564 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
| Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity (deficit) |
$ | 8,647 | $ | 5 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
150
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. (PARENT COMPANY ONLY)
CONDENSED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| (in millions) |
2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
| Operating activities: |
||||||||||||
| Net income |
$ | 115 | $ | 387 | $ | 356 | ||||||
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to cash provided by operating activities: |
||||||||||||
| Subsidiary loss (income) |
91 | 56 | (27 | ) | ||||||||
| Change in operating assets and liabilities: |
||||||||||||
| Accounts receivable and unbilled services |
— | — | 3 | |||||||||
| Income taxes payable and other liabilities |
(5 | ) | — | (1 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| Net cash provided by operating activities |
201 | 443 | 331 | |||||||||
| Investing activities: |
||||||||||||
| Investment in subsidiary, net of dividends received |
791 | — | — | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| Net cash provided by investing activities |
791 | — | — | |||||||||
| Financing activities: |
||||||||||||
| Stock issued under employee stock purchase and option plans |
97 | 64 | 35 | |||||||||
| Repurchase of common stock |
(1,097 | ) | (515 | ) | (415 | ) | ||||||
| Repurchase of stock options |
— | — | (8 | ) | ||||||||
| Intercompany with subsidiary |
15 | 1 | (3 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| Net cash (used in) provided by financing activities |
(985 | ) | (450 | ) | (391 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| (Decrease) increase in cash and cash equivalents |
7 | (7 | ) | (60 | ) | |||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of period |
5 | 12 | 72 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of period |
$ | 12 | $ | 5 | $ | 12 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
151
Table of Contents
QUINTILES IMS HOLDINGS, INC. (PARENT COMPANY ONLY)
NOTES TO CONDENSED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
The condensed parent company financial statements have been prepared in accordance with Rule 12-04, Schedule I of Regulation S-X as the restricted net assets of Quintiles IMS Holdings, Inc.’s (the “Company”) wholly-owned subsidiary, Quintiles IMS Incorporated exceed 25% of the consolidated net assets of the Company. The ability of Quintiles IMS Incorporated to pay dividends may be limited due to the restrictive covenants in the agreements governing its credit arrangements.
These condensed parent company financial statements include the accounts of Quintiles IMS Holdings, Inc. on a standalone basis (the “Parent”) and the equity method of accounting is used to reflect ownership interest in its subsidiary. Refer to the consolidated financial statements and notes presented elsewhere herein for additional information and disclosures with respect to these financial statements.
Since the Parent is part of a group that files a consolidated income tax return, in accordance with ASC 740, a portion of the consolidated amount of current and deferred income tax expense of the Company has been allocated to the Parent. The income tax benefit of $4 million, $1 million and $1 million in 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively, represents the income tax benefit that will be or were already utilized in the Company’s consolidated United States federal and state income tax returns. If the Parent was not part of these consolidated income tax returns, it would not be able to recognize any income tax benefit, as it generates no revenue against which the losses could be used on a separate filer basis.
Below is a summary of the dividends paid to the Parent by Quintiles IMS Incorporated in 2016, 2015 and 2014 (in millions):
| Amount | ||||
| Paid in December 2016 |
$ | 503 | ||
| Paid in November 2016 |
422 | |||
| Paid in June 2016 |
89 | |||
|
|
|
| ||
| Total paid in 2016 |
$ | 1,014 | ||
|
|
|
| ||
| Paid in December 2015 |
$ | 1 | ||
| Paid in November 2015 |
223 | |||
| Paid in May 2015 |
220 | |||
|
|
|
| ||
| Total paid in 2015 |
$ | 444 | ||
|
|
|
| ||
| Paid in November 2014 |
$ | 234 | ||
| Paid in May 2014 |
87 | |||
| Paid in January 2014 |
8 | |||
|
|
|
| ||
| Total paid in 2014 |
$ | 329 | ||
|
|
|
| ||
152
Table of Contents
Schedule II—Valuation and Qualifying Accounts
Deferred Tax Asset Valuation Allowance
Information presented below is in millions:
| Additions | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at Beginning of Year |
Charged to Expenses |
Charged to Other Accounts(a) |
Deductions(b) | Balance at End of Year | ||||||||||||||||
| December 31, 2016 |
$ | 22 | $ | 10 | $ | 129 | $ (8) | $ | 153 | |||||||||||
| December 31, 2015 |
$ | 25 | $ | 2 | $ | — | $ (5) | $ | 22 | |||||||||||
| December 31, 2014 |
$ | 30 | $ | 11 | $ | — | $ (16) | $ | 25 | |||||||||||
| (a) | Recorded through purchase accounting transaction. |
| (b) | Impact of reductions recorded to expense and translation adjustments. |
153
Table of Contents
| Incorporated by Reference | ||||||||||||||
| Exhibit Number |
Exhibit Description |
Filed Herewith |
Form | File No. | Exhibit | Filing Date | ||||||||
| 2.1* | Agreement and Plan of Merger, dated as of May 3, 2016, by and between Quintiles Transnational Holdings Inc. and IMS Health Holdings, Inc. (which includes the Plan of Conversion dated as of May 3, 2016 as Exhibit A thereto). | 8-K | 001-35907 | 2.1 | May 3, 2016 | |||||||||
| 3.1 | Second Amended and Restated Articles of Incorporation of Quintiles Transnational Holdings Inc. | S-1/A | 333-186708 | 3.1 | May 6, 2013 | |||||||||
| 3.2 | Third Amended and Restated Bylaws of Quintiles Transnational Holdings Inc. | S-3 | 333-199843 | 3.2 | November 4, 2014 | |||||||||
| 3.3 | Articles of Conversion, as filed with the North Carolina Secretary of State on October 3, 2016. | 8-K | 001-35907 | 3.1 | October 3, 2016 | |||||||||
| 3.4 | Certificate of Conversion, as filed with the Delaware Secretary of State on October 3, 2016. | 8-K | 001-35907 | 3.2 | October 3, 2016 | |||||||||
| 3.5 | Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation, as filed with the Delaware Secretary of State on October 3, 2016. | 8-K | 001-35907 | 3.3 | October 3, 2016 | |||||||||
| 3.6 | Amended and Restated Bylaws, effective October 3, 2016. | 8-K | 001-35907 | 3.4 | October 3, 2016 | |||||||||
| 4.1 | Specimen Common Stock Certificate of Quintiles Transnational Holdings Inc. | S-1/A | 333-186708 | 4.1 | April 26, 2013 | |||||||||
| 4.2 | Second Amended and Restated Registration Rights Agreement, dated May 14, 2013, among Quintiles Transnational Holdings Inc. and the stockholders identified therein. | 8-K | 001-35907 | 4.1 | May 15, 2013 | |||||||||
| 4.3 | Amendment No. 1, dated February 5, 2015, to Second Amended and Restated Registration Rights Agreement, dated May 14, 2013, among Quintiles Transnational Holdings Inc. and the stockholders identified therein. | 8-K | 001-35907 | 4.1 | February 6, 2015 | |||||||||
| 4.4 | Indenture dated as of May 12, 2015, among Quintiles Transnational Corp., the subsidiary guarantors listed therein and U.S. Bank National Association as trustee. | 8-K | 001-35907 | 4.1 | May 13, 2015 | |||||||||
| 4.5 | Form of 4.875% Rule 144A Senior Note due 2023 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit A to Exhibit 4.4). | 8-K | 001-35907 | 4.2 | May 13, 2015 | |||||||||
| 4.6 | Form of 4.875% Regulation S Senior Note due 2023 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit A to Exhibit 4.4). | 8-K | 001-35907 | 4.3 | May 13, 2015 | |||||||||
| 4.7 | Indenture, dated as of September 28, 2016, among Quintiles IMS Incorporated, the Guarantors listed therein and U.S. Bank National Association, as Trustee. | 8-K | 001-35907 | 4.1 | October 3, 2016 | |||||||||
| 4.8 | Senior Note Indenture, dated as of October 24, 2012, among IMS Health Incorporated, as Issuer, the Guarantors party thereto, and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as Trustee. | IMS Health S-1 |
333-193159 | 4.9 | January 2, 2014 | |||||||||
| 4.9 | Senior Note Indenture, dated as of March 30, 2015, among IMS Health Incorporated, as Issuer, the Guarantors party thereto, and Deutsche Trustee Company Limited, as Trustee. | IMS Health 10-Q |
001-36381 | 4.1 | May 15, 2015 | |||||||||
| 10.1 | Credit Agreement, dated June 8, 2011, among Quintiles Transnational Corp., as the Borrower, each lender from time to time party thereto, and JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., as Administrative Agent, Swing Line Lender and L/C Issuer. | S-1 | 333-186708 | 10.1 | February 15, 2013 | |||||||||
154
Table of Contents
| Incorporated by Reference | ||||||||||||||
| Exhibit Number |
Exhibit Description |
Filed Herewith |
Form | File No. | Exhibit | Filing Date | ||||||||
| 10.2 | Amendment No. 1, dated October 22, 2012, to Credit Agreement, dated June 8, 2011, among Quintiles Transnational Corp., as the Borrower, each lender from time to time party thereto, and JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., as Administrative Agent, Swing Line Lender and L/C Issuer. | S-1 | 333-186708 | 10.2 | February 15, 2013 | |||||||||
| 10.3 | Amendment No. 2, dated December 20, 2012, to Credit Agreement, dated June 8, 2011, among Quintiles Transnational Corp., as the Borrower, each lender from time to time party thereto, and JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., as Administrative Agent, Swing Line Lender and L/C Issuer. | S-1 | 333-186708 | 10.3 | February 15, 2013 | |||||||||
| 10.4 | Amendment No. 3, dated December 20, 2013, to Credit Agreement, dated June 8, 2011, among Quintiles Transnational Corp., as the Borrower, each lender from time to time party thereto, and JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., as Administrative Agent, Swing Line Lender and L/C Issuer. | 8-K | 001-35907 | 10.1 | December 20, 2013 | |||||||||
| 10.5 | Amendment No. 4, dated November 7, 2014, to Credit Agreement, dated June 8, 2011, among Quintiles Transnational Corp., as the Borrower, each lender from time to time party thereto, and JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., as Administrative Agent, Swing Line Lender and L/C Issuer. | 8-K | 001-35907 | 10.1 | November 10, 2014 | |||||||||
| 10.6 | Credit Agreement dated May 12, 2015, among Quintiles Transnational Corp., as the borrower, each lender from time to time party thereto, and JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., as Administrative Agent, a Swing Line Leader and an L/C Issuer | 8-K | 001-35907 | 10.1 | May 13, 2015 | |||||||||
| 10.7 | Third Amended and Restated Credit Agreement, dated as of March 17, 2014, among IMS Health Incorporated, as the Parent Borrower, IMS AG, as a Borrower, IMS Japan K.K., as a Borrower, Healthcare Technology Intermediate Holdings, Inc., as Holdings, Bank of America, N.A. as Administrative Agent, Swing Line Lender and L/C Issuer, and the other lenders party thereto. | IMS Health S-1/A |
333-193159 | 10.32 | March 24, 2014 | |||||||||
| 10.8 | Amendment No. 1, dated May 11, 2015, to Third Amended and Restated Credit and Guaranty Agreement, dated as of March 17, 2014, among IMS Health Incorporated, as the Parent Borrower, IMS AG, as a Borrower, IMS Japan K.K., as a Borrower, Healthcare Technology Intermediate Holdings, Inc., as Holdings, Bank of America, N.A. as Administrative Agent, Swing Line Lender and L/C Issuer, and the other lenders party thereto. | IMS Health 10-Q |
001-36381 | 10.1 | May 15, 2015 | |||||||||
| 10.9 | Amendment No. 2, dated January 15, 2016, to Third Amended and Restated Credit and Guaranty Agreement, dated as of March 17, 2014, among IMS Health Incorporated, as the Parent Borrower, IMS AG, as a Borrower, IMS Japan K.K., as a Borrower, Healthcare Technology Intermediate Holdings, Inc., as Holdings, Bank of America, N.A. as Administrative Agent, Swing Line Lender and L/C Issuer, and the other lenders party thereto. | IMS Health 8-K |
001-36381 | 10.1 | January 21, 2016 | |||||||||
| 10.10 | Amendment No. 3 to Third Amended and Restated Credit Agreement, dated as of October 3, 2016, among Quintiles IMS Incorporated, IMS AG, IMS Japan K.K., Quintiles IMS Holdings, Inc., the Guarantors party thereto, Bank of America N.A., as Administrative Agent and Collateral Agent, and the other Lenders party thereto, the Incremental Term A-3 Lenders party thereto and the Incremental Revolving Credit Lenders party thereto. | 8-K | 001-35907 | 10.9 | October 3, 2016 | |||||||||
155
Table of Contents
| Incorporated by Reference | ||||||||||||||
| Exhibit Number |
Exhibit Description |
Filed Herewith |
Form | File No. | Exhibit | Filing Date | ||||||||
| 10.11 | Senior Note Purchase Agreement, dated September 14, 2016, between IMS Health Incorporated, a wholly owned subsidiary of IMS Health Holdings, Inc., and the representative of the initial purchasers named therein. | 10-Q | 001-35907 | 10.10 | November 3, 2016 | |||||||||
| 10.12 | Amended and Restated Pledge and Security Agreement, dated as of March 17, 2014, among Healthcare Technology Intermediate Holdings, Inc., IMS Health Incorporated, each of the grantors party thereto, and Bank of America, N.A., as Administrative Agent. | IMS Health S-1/A |
333-193159 | 10.33 | March 24, 2014 | |||||||||
| 10.13 | U.S. Guaranty, dated as of March 17, 2014, among Healthcare Technology Intermediate Holdings, Inc., as Holdings, IMS Health Incorporated, as Parent Borrower, the other Guarantors party thereto from time to time, and Bank of America, N.A., as Administrative Agent. | IMS Health S-1/A |
333-193159 | 10.34 | March 24, 2014 | |||||||||
| 10.14 | Purchase and Sale Agreement, dated December 5, 2014, among Quintiles, Inc., as originator and initial servicer, Quintiles Laboratories, LLC, as originator, Quintiles Commercial US, Inc., as originator, and Quintiles Funding LLC, as buyer. | 8-K | 001-35907 | 10.1 | December 8, 2014 | |||||||||
| 10.15 | Receivables Financing Agreement, dated December 5, 2014, among Quintiles Funding LLC, as borrower, Quintiles, Inc., as initial servicer, PNC Bank, N.A., as administrative agent and lender, and the additional persons from time to time party thereto as lenders. | 8-K | 001-35907 | 10.2 | December 8, 2014 | |||||||||
| 10.16 | Assignment and Assumption Agreement, dated December 10, 2009, between Quintiles Transnational Corp. and Quintiles Transnational Holdings Inc. | S-1 | 333-186708 | 10.12 | February 15, 2013 | |||||||||
| 10.17 | Amended and Restated Stockholders Agreement, dated February 5, 2015, among Quintiles Transnational Holdings Inc. and the stockholders identified therein. | 8-K | 001-35907 | 10.1 | February 6, 2015 | |||||||||
| 10.18 | Stockholders Agreement, dated May 3, 2016, among Quintiles Transnational Holdings Inc. and the stockholders identified therein. | 8-K | 001-35907 | 10.4 | May 3, 2016 | |||||||||
| 10.19 | Voting Agreement, dated May 3, 2016, by and among Quintiles Transnational Holdings Inc. and affiliates of TPG Global, LLC. | 8-K | 001-35907 | 10.1 | May 3, 2016 | |||||||||
| 10.20 | Voting Agreement, dated May 3, 2016, by and between Quintiles Transnational Holdings Inc. and CPP Investment Board Private Holdings Inc. | 8-K | 001-35907 | 10.2 | May 3, 2016 | |||||||||
| 10.21 | Voting Agreement, dated May 3, 2016, by and between Quintiles Transnational Holdings Inc. and Leonard Green & Partners, L.P. | 8-K | 001-35907 | 10.3 | May 3, 2016 | |||||||||
| 10.22 | Share Repurchase Agreement, dated May 27, 2014, between Quintiles Transnational Holdings Inc. and TPG Quintiles Holdco, L.P. | 8-K | 001-35907 | 10.1 | May 28, 2014 | |||||||||
| 10.23† | Form of Director Indemnification Agreement. | S-1/A | 333-186708 | 10.13 | April 19, 2013 | |||||||||
| 10.24 | Form of Indemnification Agreement with each of the non-management directors of Quintiles IMS Holdings Inc. | 8-K | 001-35907 | 10.8 | October 3, 2016 | |||||||||
| 10.25† | Description of Independent Director Compensation, effective February 5, 2015. | 8-K | 001-35907 | 10.2 | February 6, 2015 | |||||||||
| 10.26† | Description of Independent Director Compensation, effective January 1, 2016. | 10-K | 001-35907 | 10.56 | February 11, 2016 | |||||||||
156
Table of Contents
| Incorporated by Reference | ||||||||||||||
| Exhibit Number |
Exhibit Description |
Filed Herewith |
Form | File No. | Exhibit | Filing Date | ||||||||
| 10.27 | Description of Non-Employee Director Compensation, effective as of January 1, 2017. | X | ||||||||||||
| 10.28† | Form of Non-Competition, Non-Solicitation, Confidentiality and IP Agreement. | 8-K | 001-35907 | 10.2 | October 19, 2015 | |||||||||
| 10.29† | Quintiles Transnational Holdings Inc. Annual Management Incentive Plan. | S-1/A | 333-186708 | 10.57 | April 19, 2013 | |||||||||
| 10.30† | Quintiles Transnational Holdings Inc. 2003 Stock Incentive Plan. | S-1 | 333-186708 | 10.14 | February 15, 2013 | |||||||||
| 10.31† | Form of Stock Option Award Agreement under the Quintiles Transnational Holdings Inc. 2003 Stock Incentive Plan. | S-1 | 333-186708 | 10.15 | February 15, 2013 | |||||||||
| 10.32† | Form of Restricted Stock Purchase Agreement under the Quintiles Transnational Holdings Inc. 2003 Stock Incentive Plan. | S-1 | 333-186708 | 10.16 | February 15, 2013 | |||||||||
| 10.33† | Quintiles Transnational Holdings Inc. 2008 Stock Incentive Plan. | S-1 | 333-186708 | 10.17 | February 15, 2013 | |||||||||
| 10.34† | Form of Stock Option Award Agreement for Senior Executives under the Quintiles Transnational Holdings Inc. 2008 Stock Incentive Plan. | S-1 | 333-186708 | 10.18 | February 15, 2013 | |||||||||
| 10.35† | Form of Stock Option Award Agreement for Non-Employee Directors under the Quintiles Transnational Holdings Inc. 2008 Stock Incentive Plan. | S-1 | 333-186708 | 10.19 | February 15, 2013 | |||||||||
| 10.36† | Quintiles Transnational Holdings Inc. 2013 Stock Incentive Plan. | S-1/A | 333-186708 | 10.22 | April 19, 2013 | |||||||||
| 10.37† | Form of Award Agreement Awarding Nonqualified Stock Options to Employees under the Quintiles Transnational Holdings Inc. 2013 Stock Incentive Plan. | S-1/A | 333-186708 | 10.23 | April 19, 2013 | |||||||||
| 10.38† | Form of Award Agreement Awarding Incentive Stock Options to Employees under the Quintiles Transnational Holdings Inc. 2013 Stock Incentive Plan. | 10-Q | 001-35907 | 10.2 | May 1, 2014 | |||||||||
| 10.39† | Form of Award Agreement Awarding Nonqualified Stock Options to Non-Employee Directors under the Quintiles Transnational Holdings Inc. 2013 Stock Incentive Plan. | S-1/A | 333-186708 | 10.24 | April 19, 2013 | |||||||||
| 10.40† | Form of Award Agreement Awarding Stock Appreciation Rights under the Quintiles Transnational Holdings Inc. 2013 Stock Incentive Plan. | S-1/A | 333-186708 | 10.56 | April 19, 2013 | |||||||||
| 10.41 | Form of Award Agreement Awarding Stock Appreciation Rights under the Quintiles IMS Holdings, Inc. 2013 Stock Incentive Plan effective February 2017. |
X | ||||||||||||
| 10.42† | Form of Award Agreement Awarding Restricted Stock Units under the Quintiles Transnational Holdings Inc. 2013 Stock Incentive Plan prior to February 2015. | 8-K | 001-35907 | 10.1 | November 26, 2013 | |||||||||
| 10.43† | Form of Award Agreement Awarding Restricted Stock Units under the Quintiles Transnational Holdings Inc. 2013 Stock Incentive Plan effective February 2015. | 10-K | 001-35907 | 10.34 | February 12, 2015 | |||||||||
| 10.44† | Form of Award Agreement Awarding Performance Units under the Quintiles Transnational Holdings Inc. 2013 Stock Incentive Plan. | 10-K | 001-35907 | 10.35 | February 12, 2015 | |||||||||
157
Table of Contents
| Incorporated by Reference | ||||||||||||||
| Exhibit Number |
Exhibit Description |
Filed Herewith |
Form | File No. | Exhibit | Filing Date | ||||||||
| 10.45 | Form of Award Agreement Awarding Performance Shares under the Quintiles IMS Holdings, Inc. 2013 Stock Incentive Plan effective February 2017. |
X | ||||||||||||
| 10.46 | Form of Restricted Stock Award Agreement under the Quintiles Transnational Holdings Inc. 2013 Stock Incentive Plan. | 10-Q | 001-35907 | 10.3 | November 3, 2016 | |||||||||
| 10.47 | Form of Award Agreement Awarding Restricted Stock Units under the Quintiles IMS Holdings, Inc. 2013 Stock Incentive Plan effective February 2017. |
X | ||||||||||||
| 10.48 | Quintiles IMS Holdings, Inc. Defined Contribution Executive Retirement Plan. | 8-K | 001-35907 | 10.7 | October 3, 2016 | |||||||||
| 10.49 | IMS Health Incorporated Defined Contribution Executive Retirement Plan, as amended and restated. | IMS Health S-1 |
333-193159 | 10.10 | January 2, 2014 | |||||||||
| 10.50 | First Amendment to the IMS Health Incorporated Retirement Excess Plan, dated March 17, 2009. | IMS Health S-1 |
333-193159 | 10.12 | January 2, 2014 | |||||||||
| 10.51 | Second Amendment to the IMS Health Incorporated Retirement Excess Plan, dated December 8, 2009. | IMS Health S-1 |
333-193159 | 10.13 | January 2, 2014 | |||||||||
| 10.52 | Third Amendment to the IMS Health Incorporated Retirement Excess Plan, dated April 5, 2011. | IMS Health S-1 |
333-193159 | 10.14 | January 2, 2014 | |||||||||
| 10.53 | Fourth Amendment to the IMS Health Incorporated Retirement Excess Plan (effective May 3, 2016). | IMS Health 10-Q |
001-36381 | 10.3 | July 28, 2016 | |||||||||
| 10.54 | Quintiles IMS Holdings, Inc. 2010 Equity Incentive Plan. | 8-K | 001-35907 | 10.5 | October 3, 2016 | |||||||||
| 10.55 | Healthcare Technology Holdings, Inc. 2010 Equity Incentive Plan, as amended and restated. | IMS Health S-1/A |
333-193159 | 10.16 | February 13, 2014 | |||||||||
| 10.56 | Form of IMS Time-and Performance-Based Stock Option Award Agreement under the 2010 Equity Incentive Plan. | IMS Health S-1 |
333-193159 | 10.17 | January 2, 2014 | |||||||||
| 10.57 | Form of IMS Time-Based Stock Option Award Agreement under the 2010 Equity Incentive Plan. | IMS Health S-1 |
333-193159 | 10.18 | January 2, 2014 | |||||||||
| 10.58 | Form of IMS Director Stock Option Award Agreement under the 2010 Equity Incentive Plan. | IMS Health S-1 |
333-193159 | 10.19 | January 2, 2014 | |||||||||
| 10.59 | Form of IMS Restricted Stock Unit Award Agreement under the 2010 Equity Incentive Plan. | IMS Health S-1 |
333-193159 | 10.20 | January 2, 2014 | |||||||||
| 10.60 | Form of IMS Director Restricted Stock Unit Award Agreement under the 2010 Equity Incentive Plan. | IMS Health S-1 |
333-193159 | 10.21 | January 2, 2014 | |||||||||
| 10.61 | Form of IMS Rollover Stock Appreciation Right Award Agreement under the 2010 Equity Incentive Plan. | IMS Health S-1 |
333-193159 | 10.22 | January 2, 2014 | |||||||||
158
Table of Contents
| Incorporated by Reference | ||||||||||||||
| Exhibit Number |
Exhibit Description |
Filed Herewith |
Form | File No. | Exhibit | Filing Date | ||||||||
| 10.62 | IMS Health Incorporated Savings Equalization Plan, as amended and restated effective as of January 1, 2011. | IMS Health S-1 |
333-193159 | 10.15 | January 2, 2014 | |||||||||
| 10.63 | 2013 IMS Health Annual Incentive Compensation Plan. | IMS Health S-1 |
333-193159 | 10.6 | January 2, 2014 | |||||||||
| 10.64 | Quintiles IMS Holdings, Inc. 2014 Incentive and Stock Award Plan. | 8-K | 001-35907 | 10.6 | October 3, 2016 | |||||||||
| 10.65 | Form of IMS Stock Appreciation Rights Agreement under the 2014 Incentive and Stock Award Plan. | IMS Health 8-K |
001-36381 | 10.1 | February 10, 2015 | |||||||||
| 10.66 | Form of IMS Performance Share Award Agreement under the 2014 Incentive and Stock Award Plan. | IMS Health 8-K |
001-36381 | 10.2 | February 10, 2015x | |||||||||
| 10.67 | 2014 IMS Health Annual Incentive Plan. | IMS Health S-1/A |
333-193159 | 10.30 | March 10, 2014 | |||||||||
| 10.68† | Quintiles Transnational Holdings Inc. Change of Control Severance Plan, which covers among others our executive officers. | 8-K | 001-35907 | 10.1 | November 6, 2015 | |||||||||
| 10.69 | Quintiles IMS Incorporated Employee Protection Plan, effective January 1, 2017. | X | ||||||||||||
| 10.70 | IMS Health Incorporated Employee Protection Plan and Summary Plan Description (as Amended and Restated effective January 1, 2014). | IMS Health 10-Q |
001-3681 | 10.1 | July 28, 2016 | |||||||||
| 10.71 | First Amendment to the IMS Health Incorporated Employee Protection Plan and Summary Plan Description (effective June 1, 2016). |
IMS Health 10-Q |
001-3681 | 10.2 | July 28, 2016 | |||||||||
| 10.72† | Quintiles Transnational Corp. 401(k) Restoration Plan, effective January 1, 2016 | 8-K | 001-35907 | 10.1 | December 18, 2015 | |||||||||
| 10.73† | Quintiles Transnational Holdings Inc. Employee Stock Purchase Plan. | S-8 | 333-193212 | 10.1 | January 6, 2014 | |||||||||
| 10.74† | First Amendment to Quintiles Transnational Holdings Inc. Employee Stock Purchase Plan. | 10-K | 001-35907 | 10.37 | February 12, 2015 | |||||||||
| 10.75† | Sub-Plan to the Employee Stock Purchase Plan, effective 2015. | 10-Q | 001-35907 | 10.1 | July 29, 2015 | |||||||||
| 10.76 | Quintiles IMS Incorporated Savings Equalization Plan, effective December 31, 2016. | X | ||||||||||||
| 10.77† | Quintiles Transnational Corp. Elective Deferred Compensation Plan, as amended and restated. | 10-Q | 001-35907 | 10.1 | October 28, 2015 | |||||||||
| 10.78 | Quintiles IMS Holdings Inc. Non-Employee Director Deferral Plan, effective January 1, 2017. | X | ||||||||||||
| 10.79 | Amended and Restated Employment Agreement among IMS Health Holdings, Inc., IMS Health Incorporated and Ari Bousbib, dated February 12, 2014. | IMS Health S-1/A |
333-193159 | 10.25 | March 10, 2014 | |||||||||
159
Table of Contents
| Incorporated by Reference | ||||||||||||||
| Exhibit Number |
Exhibit Description |
Filed Herewith |
Form | File No. | Exhibit | Filing Date | ||||||||
| 10.80 | Senior Management Nonstatutory Option Agreement between Healthcare Technology Holdings, Inc. and Ari Bousbib, dated December 1, 2010. | IMS Health S-1/A |
333-193159 | 10.23 | February 13, 2014 | |||||||||
| 10.81 | Senior Management Nonstatutory Option Agreement between Healthcare Technology Holdings, Inc. and Ari Bousbib, dated December 1, 2010. | IMS Health S-1/A |
333-193159 | 10.24 | February 13, 2014 | |||||||||
| 10.82 | Restricted Stock Unit Award Agreement between IMS Health Holdings, Inc. and Ari Bousbib dated February 12, 2014, incorporated herein by reference to Amendment 2 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 filed with the SEC on March 10, 2014. | IMS Health S-1/A |
333-193159 | 10.29 | March 10, 2014 | |||||||||
| 10.83 | Amendment No. 1, dated December 31, 2015, to Restricted Stock Unit Award Agreement between IMS Health Holdings, Inc. and Ari Bousbib dated February 12, 2014. | IMS Health 10-K |
001-36381 | 10.33 | February 19, 2016 | |||||||||
| 10.84 | Stock Appreciation Rights Agreement between IMS Health Holdings, Inc. and Ari Bousbib, dated February 10, 2015. | IMS Health 10-K |
001-36381 | 10.34 | February 19, 2016 | |||||||||
| 10.85 | Amendment No. 1, dated December 31, 2015, to Stock Appreciation Rights Agreement between IMS Health Holdings, Inc. and Ari Bousbib dated February 10, 2015. | IMS Health 10-K |
001-36381 | 10.35 | February 19, 2016 | |||||||||
| 10.86 | Restricted Stock Award Agreement between IMS Health Holdings, Inc. and Ari Bousbib dated December 31, 2015. | IMS Health 10-K |
001-36381 | 10.36 | February 19, 2016 | |||||||||
| 10.87 | Letter Agreement, dated May 3, 2016, between Quintiles Transnational Holdings Inc. and Ari Bousbib. | 8-K | 001-35907 | 10.6 | May 3, 2016 | |||||||||
| 10.88† | Executive Employment Agreement, dated September 25, 2003, among Dennis B. Gillings, Pharma Services Holding, Inc. and Quintiles Transnational Corp. | S-1 | 333-186708 | 10.26 | February 15, 2013 | |||||||||
| 10.89† | Assignment and Assumption Agreement, dated March 31, 2006, among Pharma Services Holding, Inc., Quintiles Transnational Corp., and Dennis B. Gillings. | S-1 | 333-186708 | 10.27 | February 15, 2013 | |||||||||
| 10.90† | Amendment, dated February 1, 2008, to Executive Employment Agreement, dated September 25, 2003, between Dennis B. Gillings and Quintiles Transnational Corp. | S-1 | 333-186708 | 10.28 | February 15, 2013 | |||||||||
| 10.91† | Agreement and Amendment, effective December 12, 2008, to Executive Employment Agreement, dated September 25, 2003, between Dennis B. Gillings and Quintiles Transnational Corp. | S-1 | 333-186708 | 10.29 | February 15, 2013 | |||||||||
| 10.92† | Third Amendment, dated December 31, 2008, to Executive Employment Agreement, dated September 25, 2003, between Dennis B. Gillings and Quintiles Transnational Corp. | S-1 | 333-186708 | 10.30 | February 15, 2013 | |||||||||
| 10.93† | Fourth Amendment, dated December 14, 2009, to Executive Employment Agreement, dated September 25, 2003, between Dennis B. Gillings and Quintiles Transnational Corp. | S-1 | 333-186708 | 10.31 | February 15, 2013 | |||||||||
| 10.94† | Fifth Amendment, dated April 18, 2013, to Executive Employment Agreement, dated September 25, 2003, between Dennis B. Gillings and Quintiles Transnational Corp. | S-1/A | 333-186708 | 10.32 | April 19, 2013 | |||||||||
160
Table of Contents
| Incorporated by Reference | ||||||||||||||
| Exhibit Number |
Exhibit Description |
Filed Herewith |
Form | File No. | Exhibit | Filing Date | ||||||||
| 10.95 | Rollover Agreement, dated August 28, 2003, among Pharma Services Holding, Inc., Dennis B. Gillings, Joan H. Gillings, Susan Ashley Gillings, the Gillings Family Foundation, the Gillings Limited Partnership and the GFEF Limited Partnership. | S-1 | 333-186708 | 10.33 | February 15, 2013 | |||||||||
| 10.96 | Amendment No. 1, dated September 23, 2003, to Rollover Agreement, dated August 28, 2003, among Pharma Services Holding, Inc., Dennis B. Gillings, Joan H. Gillings, Susan Ashley Gillings, the Gillings Family Foundation, the Gillings Limited Partnership and the GFEF Limited Partnership. | S-1 | 333-186708 | 10.34 | February 15, 2013 | |||||||||
| 10.97† | Stock Option Award Agreement, dated June 30, 2008, between Quintiles Transnational Corp. and Dennis B. Gillings. | S-1 | 333-186708 | 10.35 | February 15, 2013 | |||||||||
| 10.98 | Letter Agreement, dated May 3, 2016, between Quintiles Transnational Holdings Inc. and Dennis B. Gillings, CBE. | 8-K | 001-35907 | 10.5 | May 3, 2016 | |||||||||
| 10.99† | Letter Agreement, dated October 14, 2015, between Michael McDonnell and Quintiles Transnational Corp. | 8-K | 001-35907 | 10.3 | October 19, 2015 | |||||||||
| 10.100† | Initial Award Agreement Awarding Restricted Stock Units to Michael McDonnell under the Quintiles Transnational Holdings Inc. 2013 Stock Incentive Plan. | 10-K | 001-35907 | 10.29 | February 11, 2016 | |||||||||
| 10.101 | Letter agreement between the Company and Michael R. McDonnell effective on October 3, 2016. | 8-K | 001-35907 | 10.1 | October 3, 2016 | |||||||||
| 10.102† | Executive Employment Agreement, dated November 1, 2012, between James H. Erlinger III and Quintiles Transnational Corp. | 10-K | 001-35907 | 10.63 | February 12, 2015 | |||||||||
| 10.103 | Letter agreement between the Company and James H. Erlinger III effective on October 3, 2016. | 8-K | 001-35907 | 10.2 | October 3, 2016 | |||||||||
| 10.104 | Letter Agreement between the Company and W. Richard Staub, III, effective on December 1, 2016. | X | ||||||||||||
| 10.105† | Executive Employment Agreement, effective April 30, 2012, between Thomas H. Pike and Quintiles Transnational Corp. | S-1 | 333-186708 | 10.36 | February 15, 2013 | |||||||||
| 10.106† | Subscription Agreement, effective May 31, 2012, between Thomas H. Pike and Quintiles Transnational Holdings Inc. | S-1 | 333-186708 | 10.37 | February 15, 2013 | |||||||||
| 10.107† | Stock Option Award Agreement, dated May 10, 2012, between Quintiles Transnational Holdings Inc. and Thomas H. Pike. | S-1 | 333-186708 | 10.38 | February 15, 2013 | |||||||||
| 10.108† | Stock Option Award Agreement, dated May 31, 2012, between Quintiles Transnational Holdings Inc. and Thomas H. Pike. | S-1 | 333-186708 | 10.39 | February 15, 2013 | |||||||||
| 10.109† | First Amendment, dated May 3, 2016, to Executive Employment Agreement, dated April 12, 2012, between Thomas H. Pike and Quintiles Transnational Corp. | 8-K | 001-35907 | 10.7 | May 3, 2016 | |||||||||
| 10.110 | Second Amendment to Executive Employment Agreement, dated November 29, 2016, by and among Mr. Pike, Quintiles, Inc., and Quintiles IMS Holdings, Inc. | 8-K | 001-35907 | 10.1 | November 30, 2016 | |||||||||
| 10.111† | Executive Employment Agreement, effective July 30, 2010, between Kevin K. Gordon and Quintiles Transnational Corp. | S-1 | 333-186708 | 10.40 | February 15, 2013 | |||||||||
161
Table of Contents
| Incorporated by Reference | ||||||||||||||
| Exhibit Number |
Exhibit Description |
Filed Herewith |
Form | File No. | Exhibit | Filing Date | ||||||||
| 10.112† | First Amendment to Employment Agreement, dated November 22, 2010, to Executive Employment Agreement, effective July 30, 2010, between Kevin K. Gordon and Quintiles Transnational Corp. | S-1 | 333-186708 | 10.41 | February 15, 2013 | |||||||||
| 10.113† | Second Amendment, dated October 14, 2015, to Executive Employment Agreement, effective July 30, 2010, between Kevin K. Gordon and Quintiles Transnational Corp. | 8-K | 001-35907 | 10.1 | October 19, 2015 | |||||||||
| 21.1 | List of Subsidiaries of Quintiles IMS Holdings, Inc. | X | ||||||||||||
| 23.1 | Consent of PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP. | X | ||||||||||||
| 31.1 | Certification of Chief Executive Officer, pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a)/15d-14(a), as adopted pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | X | ||||||||||||
| 31.2 | Certification of Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer, pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a)/15d-14(a), as adopted pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | X | ||||||||||||
| 32.1 | Certification of Chief Executive Officer, pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | X | ||||||||||||
| 32.2 | Certification of Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer, pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | X | ||||||||||||
| 101 | Interactive Data Files Pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T: (i) Consolidated Statements of Income, (ii) Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income, (iii) Consolidated Balance Sheets, (iv) Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows, and (v) Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. | X | ||||||||||||
| † | Indicates management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement. |
| * | The Merger Agreement and the description thereof included herein have been included to provide investors and stockholders with information regarding the terms of the agreement. They are not intended to provide any other factual information about Quintiles or IMS Health or their respective subsidiaries or affiliates or stockholders. The representations, warranties and covenants contained in the Merger Agreement were made only for purposes of the Merger Agreement as of the specific dates therein, were solely for the benefit of the parties to the Merger Agreement, may be subject to limitations agreed upon by the contracting parties, including being qualified by confidential disclosures made for the purposes of allocating contractual risk among the parties to the Merger Agreement instead of establishing these matters as facts, and may be subject to standards of materiality applicable to the contracting parties that differ from those applicable to investors. Investors should not rely on the representations, warranties and covenants or any descriptions thereof as characterizations of the actual state of facts or condition of the parties thereto or any of their respective subsidiaries or affiliates. Moreover, information concerning the subject matter of representations and warranties may change after the date of the Merger Agreement, which subsequent information may or may not be fully reflected in public disclosures by Quintiles or IMS Health. Accordingly, investors should read the representations and warranties in the Merger Agreement not in isolation but only in conjunction with the other information about Quintiles or IMS Health and their respective subsidiaries that the respective companies include in reports, statements and other filings they make with the United States Securities and Exchange Commission. |
162
