Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-99.1 - EX-99.1 - Ignyta, Inc. | d304283dex991.htm |
| 8-K - FORM 8-K - Ignyta, Inc. | d304283d8k.htm |

Overcoming drug resistance to TRK inhibition by rational combination of entrectinib and trametinib: from bench to bedside 28th EORTC-NCI-AACR symposium; November 2016 Exhibit 99.2
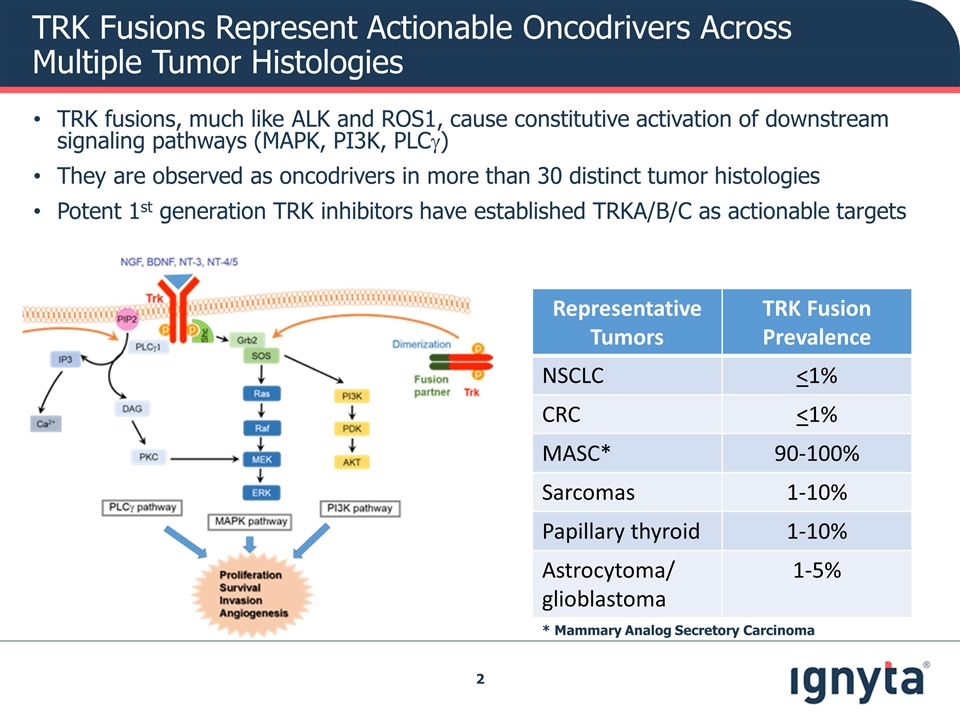
TRK Fusions Represent Actionable Oncodrivers Across Multiple Tumor Histologies TRK fusions, much like ALK and ROS1, cause constitutive activation of downstream signaling pathways (MAPK, PI3K, PLCg) They are observed as oncodrivers in more than 30 distinct tumor histologies Potent 1st generation TRK inhibitors have established TRKA/B/C as actionable targets * Mammary Analog Secretory Carcinoma Representative Tumors TRK Fusion Prevalence NSCLC <1% CRC <1% MASC* 90-100% Sarcomas 1-10% Papillary thyroid 1-10% Astrocytoma/ glioblastoma 1-5%
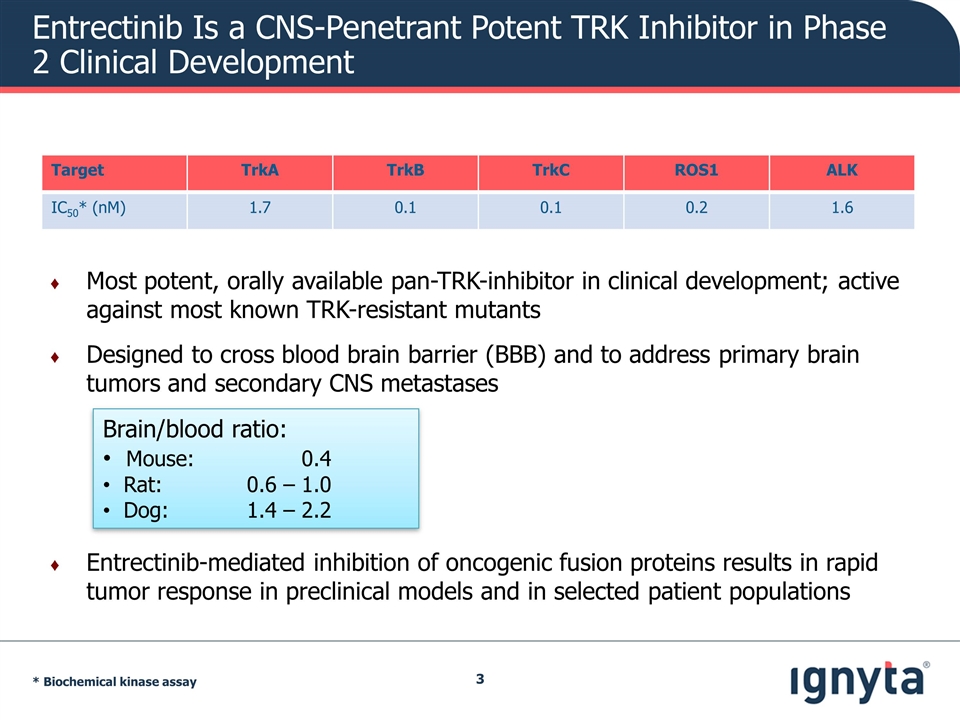
Entrectinib Is a CNS-Penetrant Potent TRK Inhibitor in Phase 2 Clinical Development Most potent, orally available pan-TRK-inhibitor in clinical development; active against most known TRK-resistant mutants Designed to cross blood brain barrier (BBB) and to address primary brain tumors and secondary CNS metastases Entrectinib-mediated inhibition of oncogenic fusion proteins results in rapid tumor response in preclinical models and in selected patient populations Target TrkA TrkB TrkC ROS1 ALK IC50* (nM) 1.7 0.1 0.1 0.2 1.6 * Biochemical kinase assay Brain/blood ratio: Mouse: 0.4 Rat: 0.6 – 1.0 Dog: 1.4 – 2.2
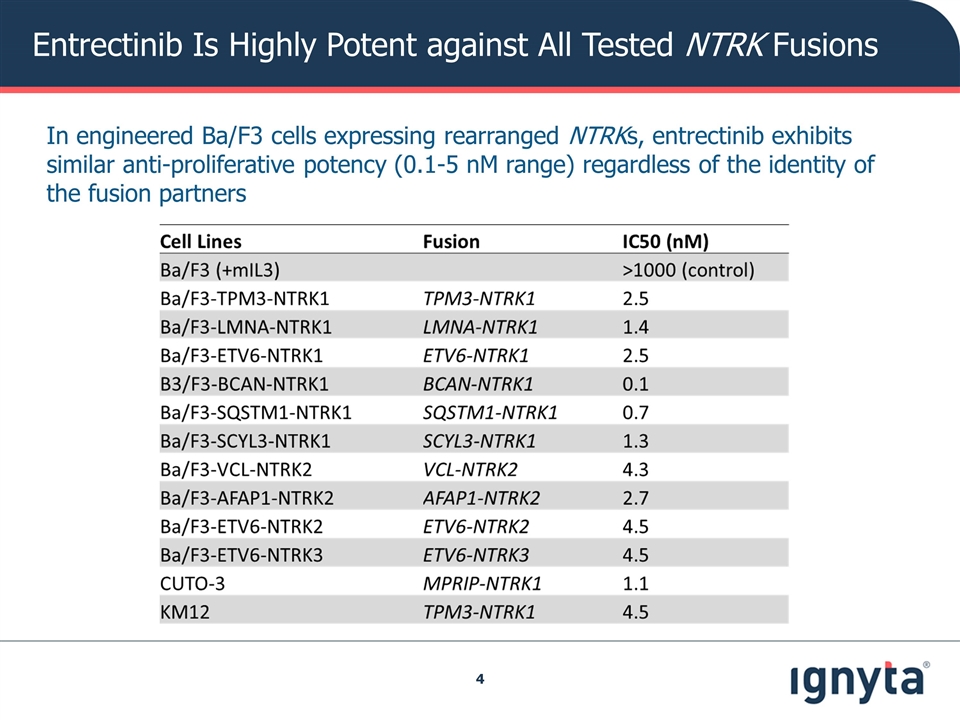
In engineered Ba/F3 cells expressing rearranged NTRKs, entrectinib exhibits similar anti-proliferative potency (0.1-5 nM range) regardless of the identity of the fusion partners Entrectinib Is Highly Potent against All Tested NTRK Fusions
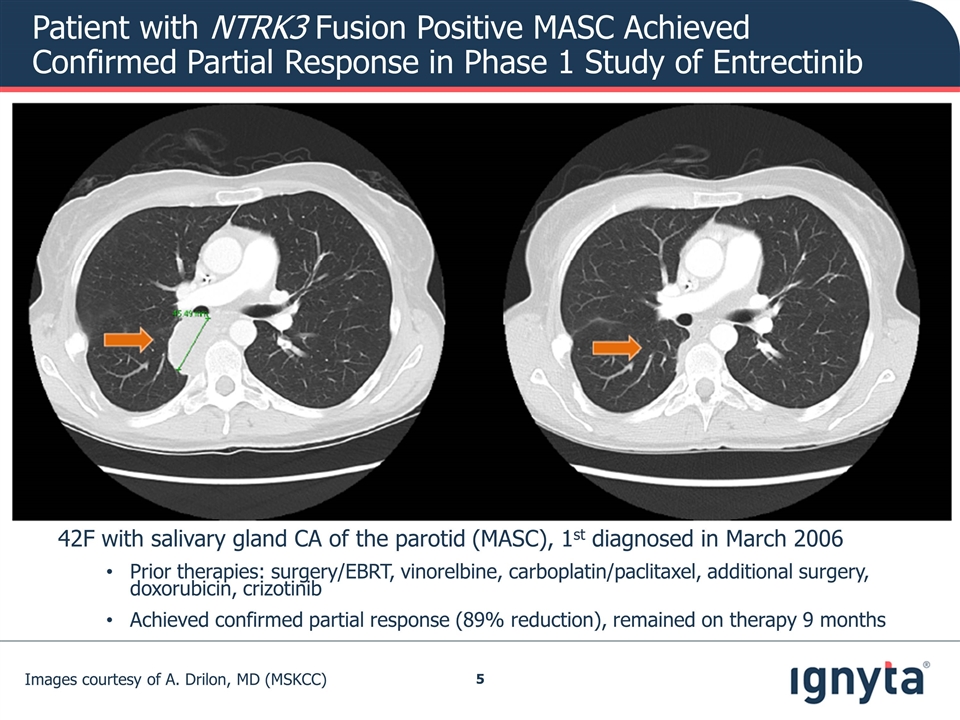
Images courtesy of A. Drilon, MD (MSKCC) 42F with salivary gland CA of the parotid (MASC), 1st diagnosed in March 2006 Prior therapies: surgery/EBRT, vinorelbine, carboplatin/paclitaxel, additional surgery, doxorubicin, crizotinib Achieved confirmed partial response (89% reduction), remained on therapy 9 months Patient with NTRK3 Fusion Positive MASC Achieved Confirmed Partial Response in Phase 1 Study of Entrectinib
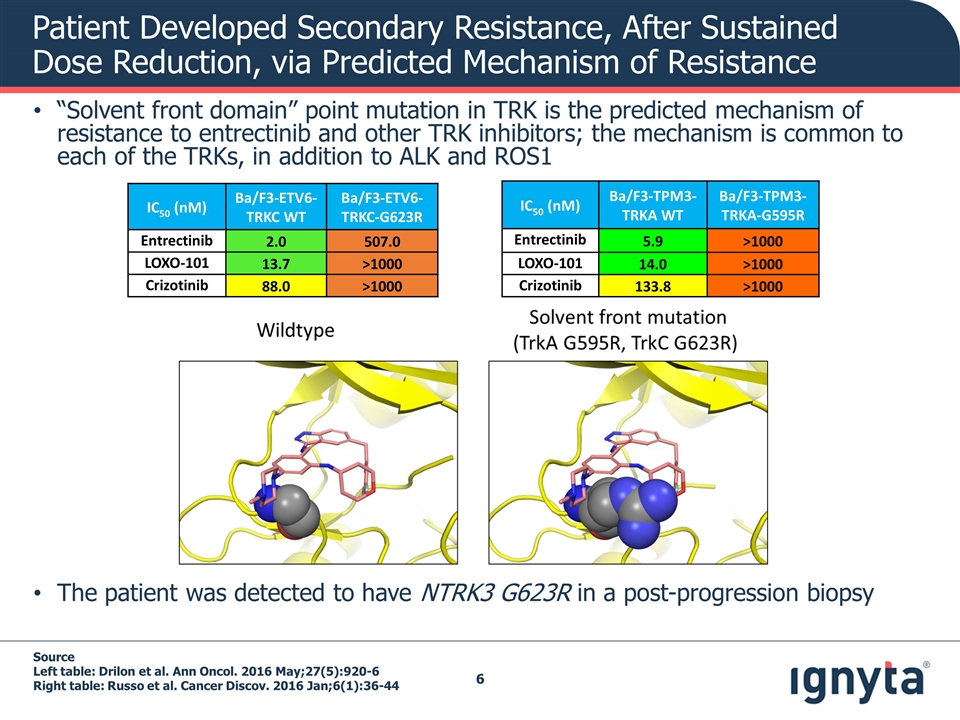
Patient Developed Secondary Resistance, After Sustained Dose Reduction, via Predicted Mechanism of Resistance “Solvent front domain” point mutation in TRK is the predicted mechanism of resistance to entrectinib and other TRK inhibitors; the mechanism is common to each of the TRKs, in addition to ALK and ROS1 The patient was detected to have NTRK3 G623R in a post-progression biopsy Source Left table: Drilon et al. Ann Oncol. 2016 May;27(5):920-6 Right table: Russo et al. Cancer Discov. 2016 Jan;6(1):36-44 IC50 (nM) Ba/F3-ETV6-TRKC WT Ba/F3-ETV6-TRKC-G623R Entrectinib 2.0 507.0 LOXO-101 13.7 >1000 Crizotinib 88.0 >1000 IC50 (nM) Ba/F3-TPM3-TRKA WT Ba/F3-TPM3-TRKA-G595R Entrectinib 5.9 >1000 LOXO-101 14.0 >1000 Crizotinib 133.8 >1000
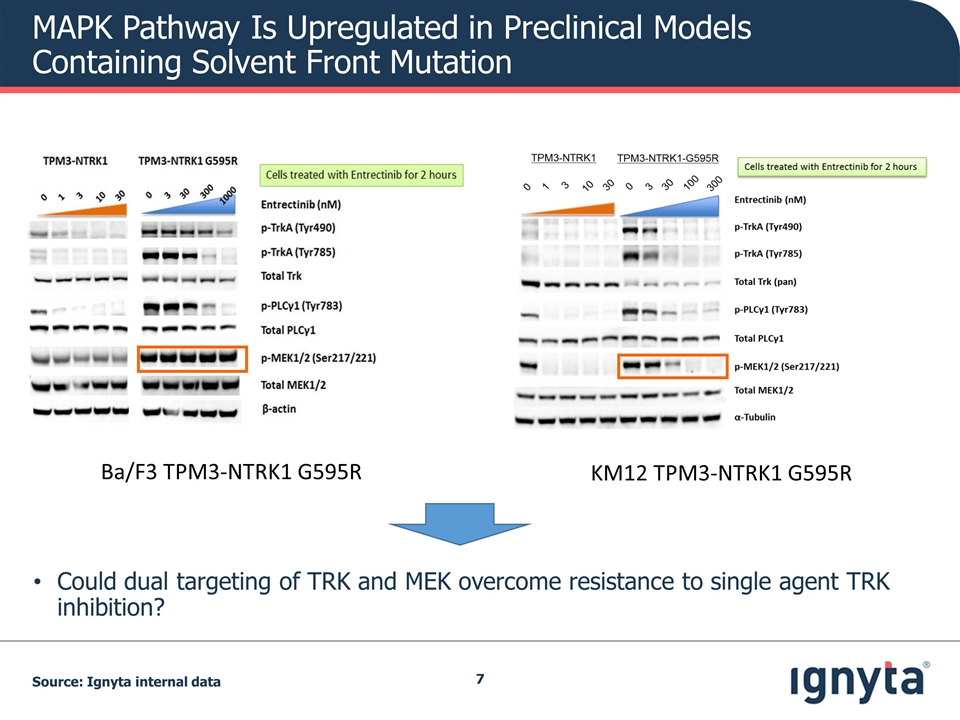
MAPK Pathway Is Upregulated in Preclinical Models Containing Solvent Front Mutation Source: Ignyta internal data Ba/F3 TPM3-NTRK1 G595R KM12 TPM3-NTRK1 G595R Could dual targeting of TRK and MEK overcome resistance to single agent TRK inhibition?
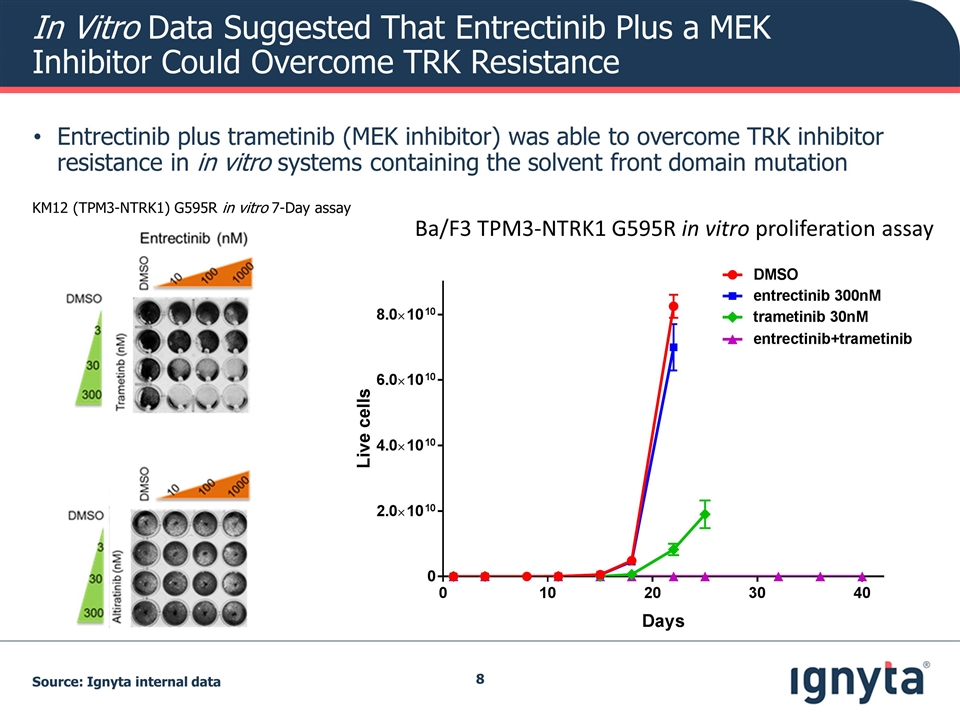
In Vitro Data Suggested That Entrectinib Plus a MEK Inhibitor Could Overcome TRK Resistance Entrectinib plus trametinib (MEK inhibitor) was able to overcome TRK inhibitor resistance in in vitro systems containing the solvent front domain mutation Ba/F3 TPM3-NTRK1 G595R in vitro proliferation assay KM12 (TPM3-NTRK1) G595R in vitro 7-Day assay Source: Ignyta internal data
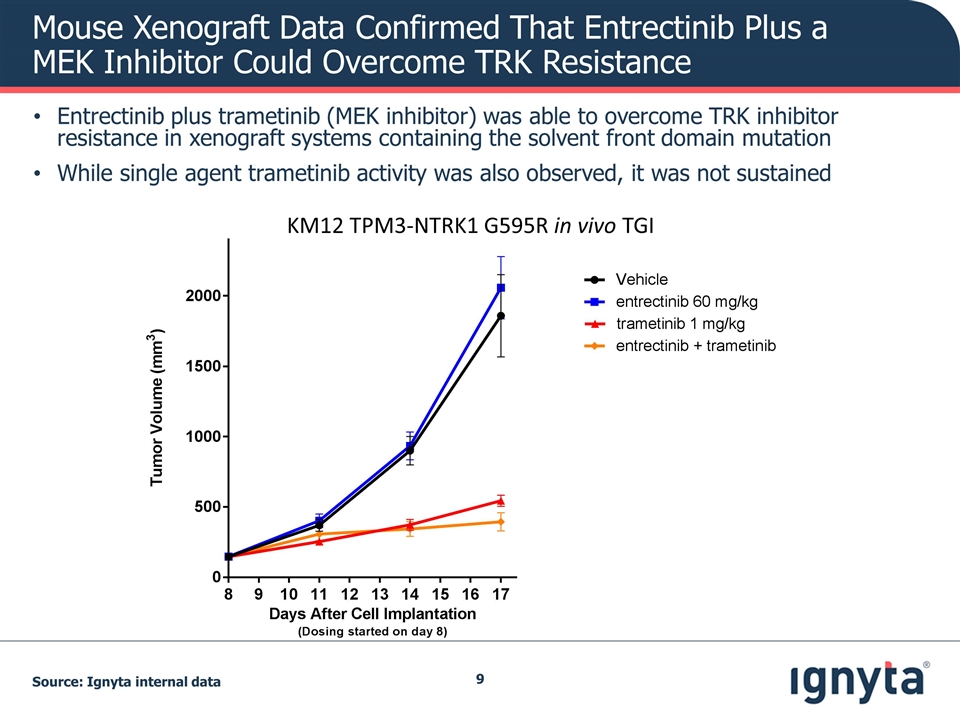
Mouse Xenograft Data Confirmed That Entrectinib Plus a MEK Inhibitor Could Overcome TRK Resistance Entrectinib plus trametinib (MEK inhibitor) was able to overcome TRK inhibitor resistance in xenograft systems containing the solvent front domain mutation While single agent trametinib activity was also observed, it was not sustained KM12 TPM3-NTRK1 G595R in vivo TGI Source: Ignyta internal data
NTRK3 Fusion MASC Patient Was Retreated with Entrectinib, in Combo with Trametinib Based on the preclinical data and lack of available therapy for the NTRK3 fusion MASC patient harboring the solvent front mechanism of resistance, a single patient protocol was submitted to FDA Patient began dose escalation study of entrectinib 400 mg and trametinib 0.5 mg on 7 Mar 2016 and reached a tolerable combination of entrectinib 200 mg and trametinib 2 mg. Combination therapy was tolerable as all drug-related adverse events were Grade 1 or 2; no new AEs specific to the combination were encountered. Patient achieved 22% reduction in tumor volume Patient remained on the combination regimen for 6.7 months. This single patient experience potentially confirms the preclinical observations, but more clinical experience is required to characterize both safety and potential efficacy of the combination regimen Source
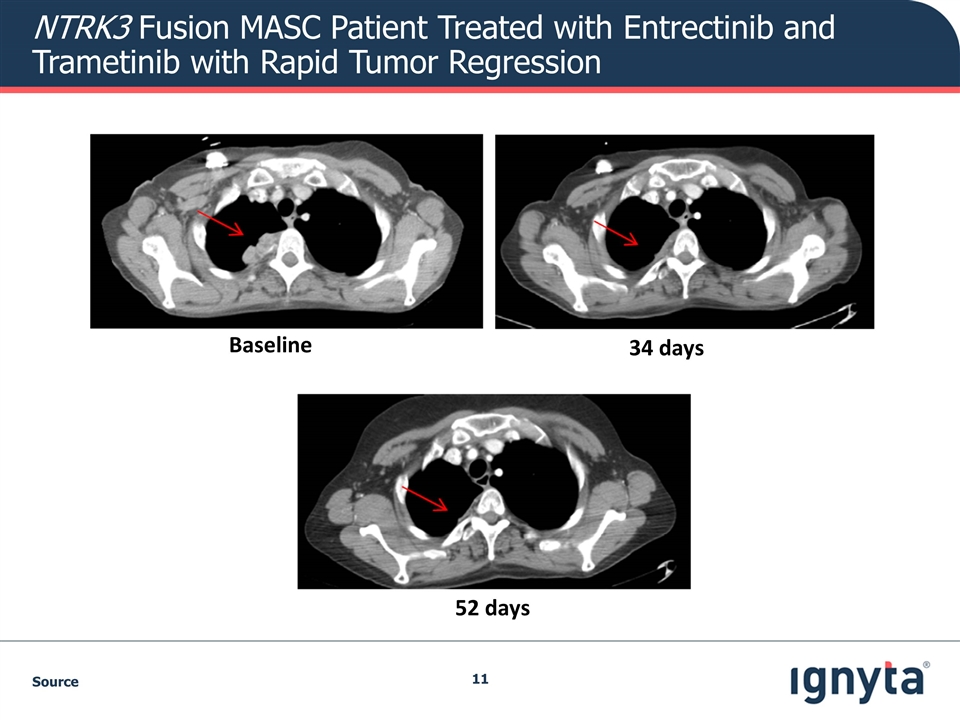
NTRK3 Fusion MASC Patient Treated with Entrectinib and Trametinib with Rapid Tumor Regression Source Baseline 34 days 52 days
A Phase 1/1b Study of Entrectinib in Combination with a MEK Inhibitor is Due to Initiate in 2017 Protocol currently being drafted Study anticipated to initiate in 2H:2017 Dose escalation of entrectinib in combination with a MEK inhibitor Patients with progression post-TRK, ROS1 or ALK inhibitors in any histology will be eligible for enrollment Entrectinib is also the subject of an ongoing global Phase 2 basket study open to patients with NTRK, ROS1, or ALK fusions in any tumor histology Source
