Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-10.17 - EX-10.17 - TETRA TECH INC | a2230290zex-10_17.htm |
| EX-95 - EX-95 - TETRA TECH INC | a2230290zex-95.htm |
| EX-32.2 - EX-32.2 - TETRA TECH INC | a2230290zex-32_2.htm |
| EX-32.1 - EX-32.1 - TETRA TECH INC | a2230290zex-32_1.htm |
| EX-31.2 - EX-31.2 - TETRA TECH INC | a2230290zex-31_2.htm |
| EX-31.1 - EX-31.1 - TETRA TECH INC | a2230290zex-31_1.htm |
| EX-23 - EX-23 - TETRA TECH INC | a2230290zex-23.htm |
| EX-21 - EX-21 - TETRA TECH INC | a2230290zex-21.htm |
Use these links to rapidly review the document
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
| (Mark One) | ||
| ý | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
|
| For the Fiscal Year Ended October 2, 2016 | ||
| or | ||
| o | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 | |
| For the Transition Period from to | ||
Commission File Number 0-19655
TETRA TECH, INC.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| Delaware (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) |
95-4148514 (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
|
3475 East Foothill Boulevard, Pasadena, California 91107 (Address of principal executive offices) (Zip Code) |
||
(626) 351-4664 (Registrant's telephone number, including area code) |
||
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act: |
||
Common Stock, $.01 par value (Title of class) |
The NASDAQ Stock Market LLC (Name of exchange) |
|
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act:
None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ý No o
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes o No ý
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ý No o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Website, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes ý No o
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K (§229.405 of this chapter) is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant's knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of "large accelerated filer," "accelerated filer" and "smaller reporting company" in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. Large accelerated filer ý Accelerated filer o Non-accelerated filer (Do not check if a smaller reporting company) o Smaller reporting company o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). Yes o No ý
The aggregate market value of the registrant's common stock held by non-affiliates on March 24, 2016, was $1.4 billion (based upon the closing price of a share of registrant's common stock as reported by the Nasdaq National Market on that date).
On November 7, 2016, 57,060,803 shares of the registrant's common stock were outstanding.
DOCUMENT INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Portions of registrant's Proxy Statement for its 2017 Annual Meeting of Stockholders are incorporated by reference in Part III of this report where indicated.
2
3
This Annual Report on Form 10-K ("Report"), including the "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations," contains forward-looking statements regarding future events and our future results that are subject to the safe harbors created under the Securities Act of 1933 (the "Securities Act") and the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 (the "Exchange Act"). All statements other than statements of historical facts are statements that could be deemed forward-looking statements. These statements are based on current expectations, estimates, forecasts and projections about the industries in which we operate and the beliefs and assumptions of our management. Words such as "expects," "anticipates," "targets," "goals," "projects," "intends," "plans," "believes," "estimates," "seeks," "continues," "may," variations of such words, and similar expressions are intended to identify such forward-looking statements. In addition, statements that refer to projections of our future financial performance, our anticipated growth and trends in our businesses, and other characterizations of future events or circumstances are forward-looking statements. Readers are cautioned that these forward-looking statements are only predictions and are subject to risks, uncertainties and assumptions that are difficult to predict, including those identified below under "Risk Factors," and elsewhere herein. Therefore, actual results may differ materially and adversely from those expressed in any forward-looking statements. We undertake no obligation to revise or update publicly any forward-looking statements for any reason.
Tetra Tech, Inc. is a leading provider of consulting and engineering services that focuses on water, environment, infrastructure, resource management, energy, and international development. We are a global company that is renowned for our expertise in providing water-related services for public and private clients. We typically begin at the earliest stage of a project by identifying technical solutions and developing execution plans tailored to our clients' needs and resources. Our solutions may span the entire life cycle of consulting and engineering projects and include applied science, data analysis, research, engineering, design, construction management, and operations and maintenance.
Engineering News-Record ("ENR"), the leading trade journal for our industry, has ranked us the number one water services firm for the past 13 years, most recently in its May 2016 "Top 500 Design Firms" issue. In 2016, Tetra Tech was also ranked number one in water treatment/desalination, water treatment and supply, environmental management, dams and reservoirs, solid waste, and wind power. ENR ranks Tetra Tech among the largest 10 firms in numerous other service lines, including engineering/design, environmental science, chemical and soil remediation, site assessment and compliance, and hazardous waste.
Our reputation for high-end consulting and engineering services and our ability to apply our skills to develop solutions for water and environmental management has supported our growth over 50 years since the founding of our predecessor company. By combining ingenuity and practical experience, we have helped to advance solutions for managing water, protecting the environment, providing energy, and engineering the infrastructure for our cities and communities. Today, we are working on projects worldwide, and currently have approximately 16,000 staff, and over 400 offices.
4
Our mission is to be the premier worldwide consulting and engineering firm, focusing on water, environment, infrastructure, resource management, energy, and international development services. The following core principles form the underpinning of how we work together to serve our clients:
- •
- Service. We put our clients first. We listen closely to better understand
our clients' needs and deliver smart, cost-effective solutions that meet their needs.
- •
- Value. We solve our clients' problems as if they were our own. We develop
and implement real-world solutions that are innovative, efficient and practical.
- •
- Excellence. We bring superior technical capability, disciplined project
management, and excellence in safety and quality to all of our services.
- •
- Opportunity. Our people are our number one asset. Opportunity means new technical challenges that provide advancement within our company, encouraging a diverse workforce, and ensuring a safe workplace.
To continue our successful growth and our competitive position in the markets we serve, we have implemented the following strategy that is integral to our future success. Our approach is to lead with science and provide high-end solutions that are differentiated and of long-lasting sustainable benefit to our clients. Our approach encompasses five key aspects of differentiation:
Technical Differentiation. Since our inception, we have provided innovative consulting and engineering services, with a focus on providing cost-effective solutions for all aspects of water resource management. Adoption of emerging science and technology in the development of high-end consulting and engineering solutions is central to our approach to "lead with science" in the delivery of our services.
Relationships and Trust. We have achieved a broad client and contract base by understanding our clients' priorities and demonstrating a long track record of successful performance that results in repeat business and limits competition. We believe that proximity to our clients is also instrumental to integrating global experience and resources with an understanding of our local clients' needs. Over the past year, we worked in over 100 countries, helping government and private sector clients address complex water, environment, energy and related infrastructure needs.
Institutional Knowledge. Over our history, we have supported both public and private clients, many for multiple decades of continuous contracts and repeat business. Long-term relationships provide us with institutional knowledge of our clients' programs, past projects and internal resources. Institutional knowledge is often a significant factor in providing competitive proposals and cost-effective solutions tailored to our clients' needs.
One-of-a-Kind Solutions. We are often at the leading edge of new challenges where we are providing one-of-a-kind solutions. These might be a new water reuse technology, a unique solution to addressing new regulatory requirements, a new monitoring approach for assessing infrastructure assets or a computer model for real time management of water resources. We are constantly evolving our intellectual property, including a wide range of computer models, algorithms, analytical software, and environmental treatment approaches and instrumentation, often in collaboration with our forward-thinking clients. Bringing our one-of-a-kind solutions to real world problems is a differentiator in expanding our services and growing our business.
5
Smart Solutions and Innovation. Smart solutions often require taking the same pieces of the puzzle and putting them together in a different way for a better outcome. Complex projects for the public and private sectors, at the leading edge of policy and technology development, often require innovative solutions that combine multiple aspects of our interdisciplinary capabilities, technical resources and institutional knowledge.
Our strategy leverages our five differentiators to drive growth in our existing water, environment, infrastructure, resource management, energy, and international development markets. We are focused on continuing to expand our leadership position with long-term clients, while also investing in emerging growth areas. Our differentiated capabilities provide us a competitive advantage to address new opportunities in the marketplace and apply new technologies to the fastest growing areas of our business.
To support our growth plans, we actively attract, recruit and retain key hires. Our combination of high-end science and consulting with practical applications provides challenging and rewarding opportunities for our employees, thereby enhancing our ability to recruit and retain top quality talent. Our internal networking programs, leadership training, entrepreneurial environment, focus on technical excellence, and global project portfolio help to attract and retain highly qualified individuals.
We also maintain a strong emphasis on project management at all levels of the organization. Our client-focused project management is supported by strong fiscal management and financial tools. We take a disciplined approach to monitoring, managing and improving our return on investment in each of our business areas through our efforts to negotiate appropriate contract terms, manage our contract performance to minimize schedule delays and cost overruns, and promptly bill and collect accounts receivable.
Our strategic growth plans are augmented by our selective investment in acquisitions aligned with our business. Acquisitions enhance plans to broaden our service offerings, add contract capacity and extend our geographic presence. Our experience with acquisitions strengthens our ability to integrate and rapidly leverage the resources of the acquired companies post-acquisition.
In fiscal 2016, we managed our continuing operations under two reportable segments. We report our water resources, water and wastewater treatment, environment, and infrastructure engineering activities in the Water, Environment and Infrastructure ("WEI") reportable segment. Our Resource Management and Energy ("RME") reportable segment includes our oil and gas, energy, international development, waste management, remediation, and utilities services. In addition, we report the results of the wind-down of our non-core construction activities in the Remediation and Construction Management ("RCM") reportable segment. The following table presents the percentage of our revenue by reportable segment:
| |
Fiscal Year | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reportable Segment | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||
| WEI | 39.8 | % | 43.2 | % | 41.0 | % | ||||
| RME | 60.8 | 55.8 | 53.7 | |||||||
| RCM | 2.0 | 3.7 | 8.9 | |||||||
| Inter-segment elimination | (2.6 | ) | (2.7 | ) | (3.6 | ) | ||||
| 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | |||||
For additional information regarding our reportable segments, see Note 19, "Reportable Segments" of the "Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements" included in Item 8. For more information
6
on risks related to our business, segments and geographic regions, including risks related to foreign operations, see Item 1A, "Risk Factors" of this report.
Water, Environment and Infrastructure
WEI provides consulting and engineering services worldwide for a broad range of water, environment, and infrastructure-related needs in both developed and emerging economies. WEI supports both public and private clients including federal, state/provincial and local governments, and commercial clients. The primary WEI markets include water resources analysis and water management, environmental monitoring, data analytics, government consulting, and a broad range of civil infrastructure master planning and engineering design for facilities, transportation, and local development projects. WEI's services span from early data collection and monitoring, to data analysis and information technology, to science and engineering applied research, to engineering design, to construction management, and operations and maintenance.
WEI provides our clients with sustainable solutions that optimize their water management and environmental programs to address regulatory requirements, improve operational efficiencies, manage assets, and promote corporate responsibility. Our services advance sustainability through the "greening" of infrastructure, design of energy efficiency and resource conservation programs, innovation in the capture and sequestration of carbon, formulation of emergency preparedness and response plans, and improvement in water and land resource management practices. We provide climate change and energy management consulting, and greenhouse gas inventory assessment, certification, reduction, and management services.
Many government and commercial organizations face complex problems due to increased demand and competition for water and natural resources, newly understood threats to human health and the environment, aging infrastructure, and demand for new and more resilient infrastructure in emerging economies. Our integrated water management services support government agencies responsible for managing water supplies, wastewater treatment, storm water management, and flood protection. These services also support private sector clients that require water supply and treatment for industrial processes. We help our clients develop water supplies and manage water resources, while addressing a wide range of local and national government requirements and policies. Fluctuations in weather patterns and extreme events, such as prolonged droughts and more frequent flooding, are increasing concerns over the reliability of water supplies, the need to protect coastal areas, and flood mitigation and adaptation in metropolitan areas.
Examples of our services include the following:
- •
- Providing high-end water analysis services world-wide, including master planning; data analytics, modeling of surface and groundwater behavior,
particularly in the areas of water resources, watershed management, and climate adaptation analysis; drought mitigation and water supply development; and flood mitigation and management.
- •
- Supporting innovative software and system design services for a wide range of water resource, environmental and infrastructure data management
needs, including informational technology systems, portals, dashboards, data management, data analytics, and statistical analysis.
- •
- Providing smart water infrastructure solutions that integrate water modeling, instrumentation and controls, and real-time controls to create flexible water systems that respond to changing conditions, optimize use of infrastructure, and provide clients with the ability to more efficiently monitor and manage their water infrastructure.
7
- •
- Providing consulting and engineering design services that are applied to numerous aspects of water quality and quantity management, including
major water and wastewater treatment plants, combined sewer storage and separation, water reuse (indirect and potable reuse) programs, regional storm water management and green infrastructure design,
and drainage and flood control; supporting master planning, permitting, design, and construction of water-related redevelopment projects, and parks and river corridor restoration projects; and
providing water supply, water treatment, and water reuse services.
- •
- Providing comprehensive services for environmental planning, cleanup and reuse of sites contaminated with hazardous materials, toxic chemicals,
and oil and petroleum products, which cover all phases of the remedial planning process, starting with emergency response and initial site assessment through removal actions, remedial design and
implementation oversight; and supporting both commercial and government clients in planning and implementing remedial activities at numerous sites around the world, and providing a broad range of
environmental analysis and planning services.
- •
- Offering engineering design services for commercial clients; helping to renovate, upgrade, and modernize industrial water supplies, and address
water treatment and water reuse needs; and providing plant engineering, project execution, and program management services for industrial water treatment projects throughout the world.
- •
- Providing analytical, engineering, architecture, geotechnical, and construction management services for infrastructure projects, including
roadway monitoring and asset management services, collecting condition data, optimizing upgrades and long-term planning for expansion; providing multi-model design services for commuter railway
stations, airport expansions, bridges and major highways, and ports and harbors; and designing solutions to repair, replace, and upgrade older transportation infrastructure.
- •
- Providing infrastructure design services in extreme and remote areas by using specialized techniques that are adapted to local resources, while
minimizing environmental impacts, and considering potential climate change impacts. These include providing consulting, geotechnical, and design services to owners of transportation, natural
resources, energy and community infrastructure in the Arctic and areas of permafrost around the globe.
- •
- Providing planning, architectural, and engineering services for U.S. federal, state and local government, and commercial facilities and their
related infrastructure needs including military housing, and educational, institutional, corporate headquarters, healthcare, and research facilities; providing civil, electrical, mechanical,
structural, plumbing and fire protection engineering and design services for buildings and surrounding developments around the world; and providing engineering and construction management projects for
a wide range of clients with specialized needs, such as security systems, training and audiovisual facilities, clean rooms, laboratories, medical facilities and emergency preparedness facilities.
- •
- Providing technology systems to optimize the airspace system and related aviation systems integration for the U.S. and other countries. Our aviation airspace services include data management, data processing, communications and outreach, and systems development; and providing systems analysis and information management.
Resource Management and Energy
RME provides consulting and engineering services worldwide for a broad range of resource management and energy needs. RME supports both private and public clients, including global industrial
8
and commercial clients, major international development agencies, and U.S. federal agencies in large-scale remediation. The primary markets for RME's services include natural resources, energy, international development, remediation, waste management, and utilities. RME's services span from early data collection and monitoring, to data analysis and information technology, to feasibility studies and assessments, to science and engineering applied research, to engineering design, to construction management, and operations and maintenance. RME also supports engineering, procurement and construction management ("EPCM") for full service implementation of commercial projects.
RME supports our clients in addressing emerging policies, resource limitations and concern about climate change, including the design of energy conservation measures, retrofits to existing structures, upgrades to energy transmission infrastructure, and the development of renewable energy resources. We also support governments in deploying international development programs for developing nations to help them overcome numerous challenges, including access to potable water, agricultural programs, governance and infrastructure programs, education, and human health.
Examples of our services include the following:
- •
- Supporting oil and gas clients across North America, Australia, Papua New Guinea, and the Middle East in the upstream, midstream and downstream
market sectors. Our services include environmental permitting support, siting studies, strategic planning and analyses; design of well pads and surface impoundments for drilling sites; water
management for exploration activities; design of midstream pipelines and associated pumping stations and storage facilities; construction monitoring, design and construction management for downstream
sustaining capital projects; biological and cultural assessments, and site investigations; and hazardous waste site remediation.
- •
- Providing a full range of services to electric power utilities and independent power producers worldwide, ranging from macro-level planning and
management advisory services to project-specific environmental, engineering, construction management, and operational services, and advising on the design and implementation of a smart grid both in
the U.S. and internationally, including increasing utility automation, information and operational technologies, and critical infrastructure security. For utilities and governmental regulatory
agencies, services include policy and regulatory development, utility management, performance improvement, asset management and evaluation, and transaction support services. For developers and owners
of renewable energy resources such as solar grid and off-grid, on-shore and off-shore wind, biogas and biomass, tidal, and hydropower, and conventional power generation facilities, as well as
transmission and distribution assets, services include environmental, engineering, procurement, operations and maintenance, and regulatory support for all project phases.
- •
- Providing international development services to many donor agencies to develop safe and reliable water supplies and sanitation services,
support the eradication of poverty, improve livelihoods, promote democracy and increase economic growth; planning, designing, implementing, researching, and monitoring projects in the areas of climate
change, agriculture and rural development, governance and institutional development, natural resources and the environment, infrastructure, economic growth, energy, rule of law and justice systems,
land tenure and property rights, and training and consulting for public-private partnerships; and building capacity and strengthening institutions in areas such as global health, energy sector reform,
utility management, education, food security, and local governance.
- •
- Offering a wide range of consulting and engineering services for solid waste management, including landfill design and management, throughout the United States and Canada; providing design, construction management, and maintenance services to manage solid and hazardous
9
- •
- Providing environmental remediation and reconstruction services to evaluate and restore lands to beneficial use, including the identification, evaluation and destruction of unexploded ordinance, both domestically and internationally; investigating, remediating, and restoring contaminated facilities at military locations in the U.S. and around the world; managing large, complex sediment remediation programs that help restore rivers and coastal waters to beneficial use; constructing state-of-the-art water treatment plants for commercial clients; and supporting utilities in the U.S. in implementing infrastructure needs, including broadband, wired utilities, and natural gas distribution systems.
waste, for environmental, wastewater, energy, oil and gas containment, mining, utilities, aquaculture, and other industrial clients; designing and installing geosynthetic liners for large lining and capping projects, as well as innovative renewable energy projects such as solar energy-generating landfill caps; and providing full-service solutions for gas-to-energy facilities to efficiently use landfill methane gas.
Remediation and Construction Management
We report the results of the wind-down of our non-core construction activities in the RCM reportable segment. The remaining work to be performed in this segment will be substantially completed in fiscal 2017.
The following table presents brief examples of projects in our ongoing operations during fiscal 2016:
| Segment | Representative Projects | |
|---|---|---|
| WEI | • For the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency ("EPA") Office of Water and Office of Science and Technology, providing analysis of waterways in the U.S. and technical analysis of emerging monitoring and analytical techniques. |
|
|
• For the District of Columbia Department of the Environment, providing consulting and environmental analysis for the assessment and cleanup of contaminated sediments in a 12-mile portion of the Anacostia River and sites located within its watershed. |
|
|
• Providing emergency management and planning services for multiple state and local agencies, especially in coastal regions, such as response and recovery from wildfires in California, flooding in the Gulf Coast and West Virginia, and Hurricane Matthew along the U.S. Atlantic coast, and continued infrastructure recovery services following Superstorm Sandy in New York and New Jersey. |
|
|
• Providing EPA Superfund Technical Assessment and Response Team program support with emergency preparedness, environmental response, removal action, site assessment, community involvement, and other Superfund technical services at locations in 23 states. |
|
|
• For the Montana Department of Environmental Quality at the Carpenter-Snow Creek Mining District Superfund site, providing services including investigation, risk assessment, engineering study, design, cleanup oversight, and long-term monitoring services for an area that includes 70 abandoned mines and associated impacted lands. |
10
| Segment | Representative Projects | |
|---|---|---|
|
• Providing EPA climate change program support for implementing voluntary domestic and international programs to reduce emissions of methane (a significant greenhouse gas) from landfills, oil and gas operations, livestock farms, and wastewater treatment plants. |
|
|
• Providing smart water infrastructure solutions for stormwater capture and water quality management for municipalities in Los Angeles and San Diego, California. |
|
|
• Providing smart water solutions using real time control systems to reduce overflows, maximize use of retention in the system, and improve operational efficiency in cities in the U.S., Canada, and France. |
|
|
• Providing engineering services to the City of Clearwater, Florida for the design of the first potable water reuse project in Florida, using a combination of innovative groundwater recharge and treatment. |
|
|
• Providing program management for the City of Detroit for the broad implementation of community-based stormwater management and green infrastructure, effectively combining city revitalization initiatives and reduction of overflows. |
|
|
• Providing master planning services to Miami-Dade County, Florida in smart, energy efficient and resilient water infrastructure solutions for the most populous county in Florida. |
|
|
• Providing transportation planning, data collection and design services for the Province of Alberta, Canada, with specialized expertise in arctic region infrastructure. |
|
|
• Providing energy efficient, "net zero" project development and asset management services for the U.S. military, including the Army, Navy and Air Force. |
|
|
• Providing energy, environmental assessment and studies to mitigate the impact of military operations on sensitive flora and fauna at U.S. bases, such as the endangered desert tortoise on a Marine Corps base. |
|
|
• Providing master planning and engineering design services to the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers ("USACE") on U.S. bases and in international facilities through multiple district and program specific contracts. |
|
RME |
• For the U.S. Department of Energy ("DOE") – National Energy Technology Laboratory and the Electric Power Institute, utilizing gravity/magnetics techniques and geostatistical modeling to predict the potential for coal basins to become viable sources for rare earth elements. |
|
|
• For the Brazilian Samarco Mining Tailings Dam collapse, utilizing satellite images to assess dam breakage and perform virtual reality modeling. |
11
| Segment | Representative Projects | |
|---|---|---|
|
• For the U.S. Agency for International Development ("USAID"), implementing projects in Africa, Asia, the Middle East, Latin America, and Eastern Europe including the USAID Power Africa program with technical and capacity building expertise to accelerate clean energy project development; and for USAID and the government of Afghanistan, to empower women to increase gender diversity and engagement in civil society. |
|
|
• For USAID, designing and implementing climate change programs, including mitigation of global climate change impacts and strengthening of community resilience to withstand extreme weather events through programs in Southeast Asia, Latin America, and West Africa. |
|
|
• For the U.K. Department for International Development, designing and implementing projects in Africa, Asia, and the Middle East. |
|
|
• For the Australian Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade, implementing a range of development projects in the Asia Pacific region. |
|
|
• For DONG Energy, providing constraints analyses, siting studies, marine geophysical surveys, submarine cable routing analyses, specialty marine impact studies, permitting services, biological and cultural resource surveys, construction compliance, and support for U.S. east coast offshore energy projects. |
|
|
• For multiple oil & gas clients, providing engineering, detailed design, and construction monitoring for midstream pipeline companies; performing in-plant engineering and sustaining capital project work at downstream refineries; building a specialty insulated pipeline for the transport of hot bitumen in Alberta, Canada; and preparing the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission environmental permitting for the Mountain Valley gas pipeline project. |
|
|
• Using our proprietary Solar Thermal Aerobic Recirculation Treatment system to implement enhanced remediation of contaminated groundwater at multiple Caltex sites in Australia. |
|
|
• Designing the Puente Hills Intermodel Facility for the Los Angeles County Sanitation Districts. |
|
|
• Providing turn-key design, construction, dredging, and treatment services on the Lower Fox River in Wisconsin. |
|
|
• Treating water discharge from a closed mine site through the design-build of a state-of-the-art water treatment plant. |
|
|
• Working in the Marcellus Shale Play to transform a depleted natural gas field into the only commercial underground saltwater disposal injection well facility in Pennsylvania. |
|
|
• Preparing a third party environmental impact statement for Clean Line Energy and the DOE for a 720-mile overhead 600 kilovolt high voltage direct current electric transmission line across Oklahoma, Arkansas, and Tennessee. |
12
We provide services to a diverse base of international, U.S. commercial, U.S. federal, and U.S. state and local government clients. The following table presents the percentage of our revenue by client sector:
| |
Fiscal Year | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Client Sector | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||
International (1) |
28.1 | % | 24.6 | % | 25.9 | % | ||||
U.S. commercial |
29.5 | 32.0 | 28.9 | |||||||
U.S. federal government (2) |
30.4 | 30.9 | 30.9 | |||||||
U.S. state and local government |
12.0 | 12.5 | 14.3 | |||||||
|
100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
- (1)
- Includes revenue generated from foreign operations, primarily in Canada and Australia, and revenue generated from non-U.S. clients.
- (2)
- Includes revenue generated under U.S. federal government contracts performed outside the United States.
U.S. federal government agencies are significant clients. USAID accounted for 13.1%, 9.6% and 9.2% of our revenue in fiscal 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. The Department of Defense ("DoD") accounted for 8.2%, 10.4%, and 11.7% of our revenue in fiscal 2016, 2015, and 2014, respectively. We typically support multiple programs within a single U.S. federal government agency, both domestically and internationally. We also assist U.S. state and local government clients in a variety of jurisdictions across the United States. In Canada, we work for several provinces and a variety of local jurisdictions. Our commercial clients include companies in the chemical, energy, mining, pharmaceutical, retail, aerospace, automotive, petroleum, and communications industries. No single client, except for U.S. federal government clients, accounted for more than 10% of our revenue in fiscal 2016.
Our services are performed under three principal types of contracts with our clients: fixed-price, time-and-materials, and cost-plus. The following table presents the percentage of our revenue by contract type:
| |
Fiscal Year | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contract Type | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||
Fixed-price |
30.0 | % | 35.4 | % | 45.3 | % | ||||
Time-and-materials |
50.9 | 45.8 | 36.3 | |||||||
Cost-plus |
19.1 | 18.8 | 18.4 | |||||||
|
100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | ||||
Under a fixed-price contract, the client agrees to pay a specified price for our performance of the entire contract or a specified portion of the contract. Some fixed-price contracts can include date-certain and/or performance obligations. Fixed-price contracts carry certain inherent risks, including risks of losses from underestimating costs, delays in project completion, problems with new technologies, price increases for materials, and economic and other changes that may occur over the contract period. Consequently, the profitability of fixed-price contracts may vary substantially. Under our time-and-materials contracts, we are paid for labor at negotiated hourly billing rates and also paid for other expenses. Profitability on these contracts is driven by billable headcount and cost control. Many of our time-and-materials contracts are subject to maximum contract values and, accordingly, revenue related to these contracts is recognized as if
13
these contracts were fixed-price contracts. Under our cost-plus contracts, some of which are subject to a contract ceiling amount, we are reimbursed for allowable costs and fees, which may be fixed or performance-based. If our costs exceed the contract ceiling or are not allowable, we may not be able to obtain full reimbursement. Further, the amount of the fee received for a cost-plus award fee contract partially depends upon the client's discretionary periodic assessment of our performance on that contract.
Some contracts with the U.S. federal government are subject to annual funding approval. U.S. federal government agencies may impose spending restrictions that limit the continued funding of our existing contracts and may limit our ability to obtain additional contracts. These limitations, if significant, could have a material adverse effect on us. All contracts with the U.S. federal government may be terminated by the government at any time, with or without cause.
U.S. federal government agencies have formal policies against continuing or awarding contracts that would create actual or potential conflicts of interest with other activities of a contractor. These policies may prevent us from bidding for or performing government contracts resulting from or related to certain work we have performed. In addition, services performed for a commercial or government sector client may create conflicts of interest that preclude or limit our ability to obtain work for a private organization. We attempt to identify actual or potential conflicts of interest and to minimize the possibility that such conflicts could affect our work under current contracts or our ability to compete for future contracts. We have, on occasion, declined to bid on a project because of an existing or potential conflict of interest.
Some of our operating units have contracts with the U.S. federal government that are subject to audit by the government, primarily by the Defense Contract Audit Agency ("DCAA"). The DCAA generally seeks to (i) identify and evaluate all activities that contribute to, or have an impact on, proposed or incurred costs of government contracts; (ii) evaluate a contractor's policies, procedures, controls, and performance; and (iii) prevent or avoid wasteful, careless, and inefficient production or service. To accomplish this, the DCAA examines our internal control systems, management policies, and financial capability; evaluates the accuracy, reliability, and reasonableness of our cost representations and records; and assesses our compliance with Cost Accounting Standards ("CAS") and defective-pricing clauses found within the Federal Acquisition Regulation ("FAR"). The DCAA also performs an annual review of our overhead rates and assists in the establishment of our final rates. This review focuses on the allowability of cost items and the applicability of CAS. The DCAA also audits cost-based contracts, including the close-out of those contracts.
The DCAA reviews all types of U.S. federal government proposals, including those of award, administration, modification, and re-pricing. The DCAA considers our cost accounting system, estimating methods and procedures, and specific proposal requirements. Operational audits are also performed by the DCAA. A review of our operations at every major organizational level is conducted during the proposal review period. During the course of its audit, the U.S. federal government may disallow costs if it determines that we accounted for such costs in a manner inconsistent with CAS. Under a government contract, only those costs that are reasonable, allocable, and allowable are recoverable. A disallowance of costs by the U.S. federal government could have a material adverse effect on our financial results.
In accordance with our corporate policies, we maintain controls to minimize any occurrence of fraud or other unlawful activities that could result in severe legal remedies, including the payment of damages and/or penalties, criminal and civil sanctions, and debarment. In addition, we maintain preventative audit programs and mitigation measures to ensure that appropriate control systems are in place.
We provide our services under contracts, purchase orders, or retainer letters. Our policy requires that all contracts must be in writing. We bill our clients in accordance with the contract terms and periodically based on costs incurred, on either an hourly-fee basis or on a percentage-of-completion basis,
14
as the project progresses. Most of our agreements permit our clients to terminate the agreements without cause upon payment of fees and expenses through the date of the termination. Generally, our contracts do not require that we provide performance bonds. If required, a performance bond, issued by a surety company, guarantees a contractor's performance under the contract. If the contractor defaults under the contract, the surety will, at its discretion, complete the job or pay the client the amount of the bond. If the contractor does not have a performance bond and defaults in the performance of a contract, the contractor is responsible for all damages resulting from the breach of contract. These damages include the cost of completion, together with possible consequential damages such as lost profits.
Marketing and Business Development
Our management team establishes our overall business strategy. Our ongoing strategic planning defines and guides our investment in marketing and business development to leverage our differentiators and target priority programs and growth markets. We maintain centralized business development resources to develop our corporate branding and marketing materials, support proposal preparation and planning, conduct market research, and manage promotional and professional activities, including appearances at trade shows, direct mailings, advertising, and public relations.
We have established company-wide growth initiatives that reinforce internal coordination, track the development of new programs, identify and coordinate collective resources for major bids, and help us build interdisciplinary teams and provide innovative solutions for major pursuits. Our growth initiatives provide a forum for cross-sector collaboration and the development of interdisciplinary solutions. We continuously identify new markets that are consistent with our strategic plan and service offerings, and we leverage our full-service capabilities and internal coordination structure to develop and implement strategies to research, anticipate, and position us for future procurements and emerging programs.
Business development activities are implemented by our technical and professional management staff throughout the company with the support of company-wide resources and expertise. Our project managers and technical staff have the best understanding of a client's needs and the effect of local or client-specific issues, laws and regulations, and procurement procedures. Our professional staff members hold frequent meetings with existing and potential clients; give presentations to civic and professional organizations; and present seminars on research and technical applications. Essential to the effective development of business is each staff member's access to all of our service offerings through our internal technical and geographic networks. Our strong internal networking programs help our professional staff members to pursue new opportunities for both existing and new clients. These networks also facilitate our ability to provide services throughout the project life cycle from the early studies to operations and maintenance. Our enterprise-wide knowledge management systems include skills search tools, business development tracking, and collaboration tools.
Tetra Tech supports clients in more than 100 countries around the world, helping them to solve complex problems and achieve solutions that are technically, socially, and economically sustainable. Our high-end consulting and engineering services focus on using innovative technologies and creative solutions to minimize environmental impacts. Our greatest contribution toward sustainability is through the projects we perform every day for our clients. Sustainability is embedded in our projects – from recycling freshwater supplies to recycling waste products, reducing energy consumption, and reducing greenhouse gas emissions in developing countries.
Our Sustainability Program allows us to further expand our commitment to sustainability by encouraging, coordinating, and reporting on actions to minimize our collective impacts on the environment. Our Sustainability Program has three primary pillars: Projects – the solutions we provide for
15
our clients; Procurement – our procurement and subcontracting approaches; and Processes – the internal policies and processes that promote sustainable practices, reduce costs, and minimize environmental impacts. In addition, our program is based on the Global Reporting Initiative ("GRI") Sustainability Report Framework, the internationally predominant sustainability reporting protocol for corporate sustainability plans, which includes three fundamental areas: environmental, economic, and social sustainability.
Our Sustainability Program is led by our Chief Sustainability Officer, who has been appointed by executive management and is supported by other key corporate and operations representatives via our Sustainability Council. We have established a clear set of metrics to evaluate our progress toward our sustainability goals. Each metric corresponds with one or more performance indicators from GRI. These metrics include economic, health and safety, information technology, human resources, and real estate. We continuously implement sustainability-related policies and practices, and we assess the results of our efforts in order to improve upon them in the future. Our executive management team reviews and approves the Sustainability Program and evaluates our progress in achieving the goals and objectives outlined in our plan. We publish an annual sustainability report that documents our progress.
Acquisitions. We continuously evaluate the marketplace for acquisition opportunities to further our strategic growth plans. Due to our reputation, size, financial resources, geographic presence and range of services, we have numerous opportunities to acquire privately and publicly held companies or selected portions of such companies. We evaluate an acquisition opportunity based on its ability to strengthen our leadership in the markets we serve, add new geographies, and provide complementary skills. Also, during our evaluation, we examine an acquisition's ability to drive organic growth, its accretive effect on long-term earnings, and its ability to generate return on investment. Generally, we proceed with an acquisition if we believe that it could strategically expand our service offerings, improve our long-term financial performance, and increase shareholder returns.
We view acquisitions as a key component in the execution of our growth strategy, and we intend to use cash, debt or securities, as we deem appropriate, to fund acquisitions. We may acquire other businesses that we believe are synergistic and will ultimately increase our revenue and net income, strengthen our ability to achieve our strategic goals, provide critical mass with existing clients, and further expand our lines of service. We typically pay a purchase price that results in the recognition of goodwill, generally representing the intangible value of a successful business with an assembled workforce specialized in our areas of interest. Acquisitions are inherently risky, and no assurance can be given that our previous or future acquisitions will be successful or will not have a material adverse effect on our financial position, results of operations, or cash flow. All acquisitions require the approval of our Board of Directors.
On January 18, 2016, we acquired Coffey International Limited ("Coffey"), headquartered in Sydney, Australia. Coffey had approximately 3,300 staff delivering technical and engineering solutions in international development and geoscience. Coffey significantly expands our geographic presence, particularly in Australia and Asia Pacific, and is part of our RME segment. In addition to Australia, Coffey's international development business has operations supporting federal government agencies in the U.S. and the United Kingdom. In the second quarter of fiscal 2016, we also acquired INDUS Corporation ("INDUS"), headquartered in Vienna, Virginia. INDUS is a technology solutions firm focused on water data analytics, geospatial analysis, secure infrastructure, and software applications management for U.S. federal government customers, and is included in our WEI segment. In fiscal 2015, we acquired Cornerstone Environmental Group, LLC ("CEG"), headquartered in Middletown, New York. CEG is an environmental engineering and consulting firm focused on solid waste markets in the United States, and is included in our RME segment.
16
For detailed information regarding acquisitions, see Note 5, "Mergers and Acquisitions" of the "Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements" included in Item 8.
Divestitures. We regularly review and evaluate our existing operations to determine whether our business model should change through the divestiture of certain businesses. Accordingly, from time to time, we may divest certain non-core businesses and reallocate our resources to businesses that better align with our long-term strategic direction. We did not have any divestitures in fiscal 2016, 2015, or 2014.
The market for our services is generally competitive. We often compete with many other firms ranging from small regional firms to large international firms.
We perform a broad spectrum of consulting, engineering, and technical services across the water, environment, infrastructure, resource management, energy, and international development markets. Our client base includes U.S. federal government agencies such as the DoD, USAID, DOE, EPA and the Federal Aviation Administration; U.S. state and local government agencies; government and commercial clients in Canada and Australia; the U.S. commercial sector, which consists primarily of large industrial companies and utilities; and our international commercial clients. Our competition varies and is a function of the business areas in which, and the client sectors for which, we perform our services. The number of competitors for any procurement can vary widely, depending upon technical qualifications, the relative value of the project, geographic location, the financial terms and risks associated with the work, and any restrictions placed upon competition by the client. Historically, clients have chosen among competing firms by weighing the quality, innovation and timeliness of the firm's service versus its cost to determine which firm offers the best value. When less work becomes available in certain markets, price could become an increasingly important factor.
Our competitors vary depending on end markets and clients, and often we may only compete with a portion of a firm. We believe that our principal competitors include the following firms, in alphabetical order: AECOM Technology Corporation; AMEC Foster Wheeler; Arcadis NV; Black & Veatch Corporation; Brown & Caldwell; CDM Smith Inc.; CH2M HILL Companies, Ltd.; Chemonics International, Inc.; Exponent, Inc.; GHD; ICF International, Inc.; Jacobs Engineering Group Inc.; Leidos, Inc.; SNC-Lavalin Group Inc.; Stantec Inc.; TRC Companies, Inc.; Weston Solutions, Inc.; Willbros Group, Inc.; and WSP Global Inc.
We include in our backlog only those contracts for which funding has been provided and work authorization has been received. We estimate that approximately 70% of our backlog at the end of fiscal 2016 will be recognized as revenue in fiscal 2017, as work is being performed. However, we cannot guarantee that the revenue projected in our backlog will be realized or, if realized, will result in profits. In addition, project cancellations or scope adjustments may occur with respect to contracts reflected in our backlog. For example, certain of our contracts with the U.S. federal government and other clients are terminable at the discretion of the client, with or without cause. These types of backlog reductions could adversely affect our revenue and margins. Accordingly, our backlog as of any particular date is an uncertain indicator of our future earnings.
At fiscal 2016 year-end, our backlog was $2.4 billion, an increase of $477 million, or 25%, compared to fiscal 2015 year-end. Approximately $900 million and $1.5 billion of our backlog at the end of fiscal 2016 related to WEI and RME, respectively. The overall increase in our backlog was primarily due to the acquisition of Coffey in the second quarter of fiscal 2016.
17
We engage in various service activities that are subject to government oversight, including environmental laws and regulations, general government procurement laws and regulations, and other regulations and requirements imposed by the specific government agencies with which we conduct business.
Environmental. A significant portion of our business involves the planning, design, program management and construction management of pollution control facilities, as well as the assessment and management of remediation activities at hazardous waste sites, U.S. Superfund sites, and military bases. In addition, we contract with U.S. federal government entities to destroy hazardous materials, including weapons stockpiles. These activities require us to manage, handle, remove, treat, transport, and dispose of toxic or hazardous substances.
Some environmental laws, such as the U.S. Superfund law and similar state, provincial and local statutes, can impose liability for the entire cost of clean-up for contaminated facilities or sites upon present and former owners and operators, as well as generators, transporters, and persons arranging for the treatment or disposal of such substances. In addition, while we strive to handle hazardous and toxic substances with care and in accordance with safe methods, the possibility of accidents, leaks, spills, and events of force majeure always exist. Humans exposed to these materials, including workers or subcontractors engaged in the transportation and disposal of hazardous materials and persons in affected areas, may be injured or become ill. This could result in lawsuits that expose us to liability and substantial damage awards. Liabilities for contamination or human exposure to hazardous or toxic materials, or a failure to comply with applicable regulations, could result in substantial costs, including clean-up costs, fines, civil or criminal sanctions, third party claims for property damage or personal injury, or the cessation of remediation activities.
Certain of our business operations are covered by U.S. Public Law 85-804, which provides for government indemnification against claims and damages arising out of unusually hazardous activities performed at the request of the government. Due to changes in public policies and law, however, government indemnification may not be available in the case of any future claims or liabilities relating to other hazardous activities that we perform.
Government Procurement. The services we provide to the U.S. federal government are subject to the FAR and other rules and regulations applicable to government contracts. These rules and regulations:
- •
- require certification and disclosure of all cost and pricing data in connection with the contract negotiations under certain contract types;
- •
- impose accounting rules that define allowable and unallowable costs and otherwise govern our right to reimbursement under certain cost-based
government contracts; and
- •
- restrict the use and dissemination of information classified for national security purposes and the exportation of certain products and technical data.
In addition, services provided to the DoD are monitored by the Defense Contract Management Agency and audited by the DCAA. Our government clients can also terminate any of their contracts, and many of our government contracts are subject to renewal or extension annually. Further, the services we provide to state and local government clients are subject to various government rules and regulations.
18
We experience seasonal trends in our business. Our revenue and operating income are typically lower in the first half of our fiscal year, primarily due to the Thanksgiving (in the U.S.), Christmas and New Year's holidays. Many of our clients' employees, as well as our own employees, take vacations during these holiday periods. Further, seasonal inclement weather conditions occasionally cause some of our offices to close temporarily or may hamper our project field work in the northern hemisphere's temperate and arctic regions. These occurrences result in fewer billable hours worked on projects and, correspondingly, less revenue recognized.
Potential Liability and Insurance
Our business activities could expose us to potential liability under various laws and under workplace health and safety regulations. In addition, we occasionally assume liability by contract under indemnification agreements. We cannot predict the magnitude of such potential liabilities.
We maintain a comprehensive general liability insurance policy with an umbrella policy that covers losses beyond the general liability limits. We also maintain professional errors and omissions liability and contractor's pollution liability insurance policies. We believe that both policies provide adequate coverage for our business. When we perform higher-risk work, we obtain, if available, the necessary types of insurance coverage for such activities, as is typically required by our clients.
We obtain insurance coverage through a broker that is experienced in our industry. The broker and our risk manager regularly review the adequacy of our insurance coverage. Because there are various exclusions and retentions under our policies, or an insurance carrier may become insolvent, there can be no assurance that all potential liabilities will be covered by our insurance policies or paid by our carrier.
We evaluate the risk associated with insurance claims. If we determine that a loss is probable and reasonably estimable, we establish an appropriate reserve. A reserve is not established if we determine that a claim has no merit or is not probable or reasonably estimable. Our historic levels of insurance coverage and reserves have been adequate. However, partially or completely uninsured claims, if successful and of significant magnitude, could have a material adverse effect on our business.
At fiscal 2016 year-end, we had approximately 16,000 staff worldwide. A large percentage of our employees have technical and professional backgrounds and undergraduate and/or advanced degrees, including the employees of recently acquired companies. Our professional staff includes archaeologists, architects, biologists, chemical engineers, chemists, civil engineers, computer scientists, economists, electrical engineers, environmental engineers, environmental scientists, geologists, hydrogeologists, mechanical engineers, oceanographers, project managers and toxicologists. We consider the current relationships with our employees to be favorable. We are not aware of any employment circumstances that are likely to disrupt work at any of our facilities. See Part I, Item 1A, "Risk Factors" for a discussion of the risks related to the loss of key personnel or our inability to attract and retain qualified personnel.
19
Executive Officers of the Registrant
The following table shows the name, age and position of each of our executive officers at November 22, 2016:
| Name | Age | Position | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Dan L. Batrack |
58 | Chairman, Chief Executive Officer and President | ||
|
Mr. Batrack joined our predecessor in 1980 and was named Chairman in January 2008. He has served as our Chief Executive Officer and a director since November 2005, and as our President since October 2008. Mr. Batrack has served in numerous capacities over the last 30 years, including project scientist, project manager, operations manager, Senior Vice President and President of an operating unit. He has managed complex programs for many small and Fortune 500 clients, both in the United States and internationally. Mr. Batrack holds a B.A. degree in Business Administration from the University of Washington. |
|||
Steven M. Burdick |
52 |
Executive Vice President, Chief Financial Officer |
||
|
Mr. Burdick has served as our Executive Vice President, Chief Financial Officer since April 2011. He served as our Senior Vice President and Corporate Controller from January 2004 to March 2011. Mr. Burdick joined us in April 2003 as Vice President, Management Audit. Previously, Mr. Burdick served in financial executive management roles in private industry and with Ernst & Young LLP. Mr. Burdick holds a B.S. degree in Business Administration from Santa Clara University and is a Certified Public Accountant. |
|||
Ronald J. Chu |
59 |
Executive Vice President and President of Resource Management and Energy |
||
|
Mr. Chu has served as the President of RME since June 2007, and he has served as the Chief Executive Officer of Coffey since January 2016. He has more than 16 years of experience with us, and has served in various technical and management capacities, including project and program manager, office manager, regional manager and Chief Operating Officer of the predecessor to RME. Mr. Chu was named a Vice President in 2001, and has served as president of several subsidiary companies during his tenure with us. He began his career as a civil/sanitary engineer in 1981 and entered the environmental consulting field in 1984. His career has included management of major assessment, engineering and remediation programs for major oil and gas companies, Fortune 100 manufacturers, energy suppliers, and government agencies. Mr. Chu is a registered professional engineer in several states and has authored numerous technical articles. He holds a B.S. in Civil Engineering from Northeastern University and an M.S. in Environmental Engineering from the University of Southern California. |
20
| Name | Age | Position | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Leslie L. Shoemaker |
59 |
Executive Vice President and President of Water, Environment and Infrastructure |
||
|
Dr. Shoemaker was named President of WEI in April 2015. Dr. Shoemaker joined us in 1991, and has previously served in various management capacities, including project and program manager, water resources manager and infrastructure group president. From 2005 to 2015, she led our strategic planning, business development and company-wide collaboration programs. Her technical expertise is in the management of large-scale watershed and master planning studies, development of modeling tools and application of optimization tools for decision making. Dr. Shoemaker holds a B.A. degree in Mathematics from Hamilton College, a Master of Engineering from Cornell University and a Ph.D. in Agricultural Engineering from the University of Maryland. |
|||
William R. Brownlie |
63 |
Senior Vice President, Chief Engineer and Corporate Risk Management Officer |
||
|
Dr. Brownlie was named Senior Vice President and Chief Engineer in September 2009, and Corporate Risk Management Officer in November 2013. From December 2005 to September 2009, he served as a Group President. Dr. Brownlie joined our predecessor in 1981 and was named a Senior Vice President in December 1993. Dr. Brownlie has managed various operating units and programs focusing on water resources and environmental services, including work with USACE, the U.S. Air Force, U.S. Bureau of Reclamation and DOE. He is a registered professional engineer and has a strong technical background in water resources. Dr. Brownlie holds B.S. and M.S. degrees in Civil Engineering from the State University of New York at Buffalo and a Ph.D. in Civil Engineering from the California Institute of Technology. |
|||
Brian N. Carter |
49 |
Senior Vice President, Corporate Controller and Chief Accounting Officer |
||
|
Mr. Carter joined Tetra Tech as Vice President, Corporate Controller and Chief Accounting Officer in June 2011 and was appointed Senior Vice President in October 2012. Previously, Mr. Carter served in finance and auditing positions in private industry and with Ernst & Young LLP. Mr. Carter holds a B.S. in Business Administration from Miami University and is a Certified Public Accountant. |
|||
Craig L. Christensen |
63 |
Senior Vice President, Chief Information Officer |
||
|
Mr. Christensen joined us in 1998 through the acquisition of our Tetra Tech NUS, Inc. ("NUS") subsidiary. Mr. Christensen is responsible for our information services and technologies, including the implementation of our enterprise resource planning system. Previously, Mr. Christensen held positions at NUS, Brown and Root Services, and Landmark Graphics subsidiaries of Halliburton Company where his responsibilities included contracts administration, finance, and system development. Prior to his service at Halliburton, Mr. Christensen held positions at Burroughs Corporation and Apple Computer. Mr. Christensen holds B.A. and M.B.A. degrees from Brigham Young University. |
21
| Name | Age | Position | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Richard A. Lemmon |
57 |
Senior Vice President, Corporate Administration |
||
|
Mr. Lemmon joined our predecessor in 1981 in a technical capacity and became a member of its corporate staff in a management position in 1985. In 1988, at the time of our predecessor's divestiture from Honeywell, Inc., Mr. Lemmon structured and managed many of our corporate functions. He is currently responsible for insurance, risk management, human resources, safety and facilities. |
|||
Kevin P. McDonald |
57 |
Senior Vice President, Human Resources and Leadership Development |
||
|
Mr. McDonald joined us in 2003 through the acquisition of Foster Wheeler Environmental Corporation. He is responsible for all areas of human resources ("HR"), including executive compensation, employee benefits, succession planning, human resources information systems, and employment law compliance. Prior to leading our corporate HR organization, Mr. McDonald was the HR Director for one of our subsidiaries. He has more than 30 years' experience in the engineering and construction services industry. Mr. McDonald earned a B.S. degree in Management from the University of Scranton and an M.B.A from Fairleigh Dickinson University. |
|||
Janis B. Salin |
63 |
Senior Vice President, General Counsel and Secretary |
||
|
Ms. Salin joined us in February 2002. For the prior 18 years, Ms. Salin was a Principal with the law firm of Riordan & McKinzie in Los Angeles, and served as Managing Principal of that firm from 1990 to 1992. She served as our outside counsel from the time of our formation in 1988. Ms. Salin holds B.A. and J.D. degrees from the University of California at Los Angeles. |
All of our periodic report filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission ("SEC") pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the "Exchange Act"), are made available, free of charge, through our website located at www.tetratech.com, including our Annual Reports on Form 10-K, Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, Current Reports on Form 8-K and any amendments to these reports. These reports are available on our website as soon as reasonably practicable after we electronically file with or furnish the reports to the SEC. You may also request an electronic or paper copy of these filings at no cost by writing or telephoning us at the following: Tetra Tech, Inc., Attention: Investor Relations, 3475 East Foothill Boulevard, Pasadena, California 91107, (626) 351-4664.
We operate in a changing environment that involves numerous known and unknown risks and uncertainties that could materially adversely affect our operations. Set forth below and elsewhere in this report and in other documents we file with the SEC are descriptions of the risks and uncertainties that could cause our actual results to differ materially from the results contemplated by the forward-looking statements contained in this report. Additional risks we do not yet know of or that we currently think are immaterial may also affect our business operations. If any of the events or circumstances described in the following risks actually occurs, our business, financial condition or results of operations could be materially adversely affected.
22
Continuing worldwide political and economic uncertainties may adversely affect our revenue and profitability.
The last several years have been periodically marked by political and economic concerns, including decreased consumer confidence, the lingering effects of international conflicts, energy costs and inflation. Although certain indices and economic data have shown signs of stabilization in the United States and certain global markets, there can be no assurance that these improvements will be broad-based or sustainable. This instability can make it extremely difficult for our clients, our vendors and us to accurately forecast and plan future business activities, and could cause constrained spending on our services, delays and a lengthening of our business development efforts, the demand for more favorable pricing or other terms, and/or difficulty in collection of our accounts receivable. Our government clients may face budget deficits that prohibit them from funding proposed and existing projects. Further, ongoing economic instability in the global markets could limit our ability to access the capital markets at a time when we would like, or need, to raise capital, which could have an impact on our ability to react to changing business conditions or new opportunities. If economic conditions remain uncertain or weaken, or government spending is reduced, our revenue and profitability could be adversely affected.
Demand for our services is cyclical and vulnerable to economic downturns. If economic growth slows, government fiscal conditions worsen, or client spending declines further, then our revenue, profits and financial condition may deteriorate.
Demand for our services is cyclical, and vulnerable to economic downturns and reductions in government and private industry spending. Such downturns or reductions may result in clients delaying, curtailing or canceling proposed and existing projects. Our business traditionally lags the overall recovery in the economy; therefore, our business may not recover immediately when the economy improves. If economic growth slows, government fiscal conditions worsen, or client spending declines, then our revenue, profits and overall financial condition may deteriorate. Our government clients may face budget deficits that prohibit them from funding new or existing projects. In addition, our existing and potential clients may either postpone entering into new contracts or request price concessions. Difficult financing and economic conditions may cause some of our clients to demand better pricing terms or delay payments for services we perform, thereby increasing the average number of days our receivables are outstanding, and the potential of increased credit losses of uncollectible invoices. Further, these conditions may result in the inability of some of our clients to pay us for services that we have already performed. If we are not able to reduce our costs quickly enough to respond to the revenue decline from these clients, our operating results may be adversely affected. Accordingly, these factors affect our ability to forecast our future revenue and earnings from business areas that may be adversely impacted by market conditions.
Demand for our oil and gas, and mining services fluctuates and a decline in demand could adversely affect our revenue, profits and financial condition.
Demand for our oil and gas services fluctuates, and we depend on our customers' willingness to make future expenditures to explore for, develop, produce and transport oil and natural gas in the United States and Canada. Our customers' willingness to undertake these activities depends largely upon prevailing industry conditions that are influenced by numerous factors over which we have no control, including:
- •
- prices, and expectations about future prices, of oil and natural gas;
- •
- domestic and foreign supply of and demand for oil and natural gas;
- •
- the cost of exploring for, developing, producing and delivering oil and natural gas;
23
- •
- transportation capacity, including but not limited to train transportation capacity and its future regulation;
- •
- available pipeline, storage and other transportation capacity;
- •
- availability of qualified personnel and lead times associated with acquiring equipment and products;
- •
- federal, state, provincial and local regulation of oilfield activities;
- •
- environmental concerns regarding the methods our customers use to produce hydrocarbons;
- •
- the availability of water resources and the cost of disposal and recycling services; and
- •
- seasonal limitations on access to work locations.
Anticipated future prices for natural gas and crude oil are a primary factor affecting spending by our customers. Lower prices or volatility in prices for oil and natural gas typically decrease spending, which can cause rapid and material declines in demand for our services and in the prices we are able to charge for our services. Worldwide political, economic, military and terrorist events, as well as natural disasters and other factors beyond our control, contribute to oil and natural gas price levels and volatility and are likely to continue to do so in the future.
Further, the businesses of our global mining clients are, to varying degrees, cyclical and have experienced declines over the last three years due to lower global growth expectations and the associated decline in market prices. For example, depending on the market prices of uranium, precious metals, aluminum, copper, iron ore, and potash, our mining company clients may cancel or curtail their mining projects, which could result in a corresponding decline in the demand for our services among these clients. Accordingly, the cyclical nature of the mining industry could adversely affect our business, operating results or financial condition.
Our international operations expose us to legal, political, and economic risks in different countries as well as currency exchange rate fluctuations that could harm our business and financial results.
In fiscal 2016, we generated 28.1% of our revenue from our international operations, primarily in Canada and Australia, and from international clients for work that is performed by our domestic operations. International business is subject to a variety of risks, including:
- •
- imposition of governmental controls and changes in laws, regulations, or policies;
- •
- lack of developed legal systems to enforce contractual rights;
- •
- greater risk of uncollectible accounts and longer collection cycles;
- •
- currency exchange rate fluctuations, devaluations, and other conversion restrictions;
- •
- uncertain and changing tax rules, regulations, and rates;
- •
- the potential for civil unrest, acts of terrorism, force majeure, war or other armed conflict, and greater physical security risks, which may
cause us to leave a country quickly;
- •
- logistical and communication challenges;
24
- •
- changes in regulatory practices, including tariffs and taxes;
- •
- changes in labor conditions;
- •
- general economic, political, and financial conditions in foreign markets; and
- •
- exposure to civil or criminal liability under the U.S. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act ("FCPA"), the U.K. Bribery Act, the Canadian Corruption of Foreign Public Officials Act, the Brazilian Clean Companies Act, the anti-boycott rules, trade and export control regulations, as well as other international regulations.
For example, an ongoing government investigation into political corruption in Quebec contributed to the slow-down in procurements and business activity in that province, which adversely affected our business. The Province of Quebec has adopted legislation that requires businesses and individuals seeking contracts with governmental bodies be certified by a Quebec regulatory authority for contracts over a specified size. Our failure to maintain certification could adversely affect our business.
International risks and violations of international regulations may significantly reduce our revenue and profits, and subject us to criminal or civil enforcement actions, including fines, suspensions, or disqualification from future U.S. federal procurement contracting. Although we have policies and procedures to monitor legal and regulatory compliance, our employees, subcontractors, and agents could take actions that violate these requirements. As a result, our international risk exposure may be more or less than the percentage of revenue attributed to our international operations.
We derive a substantial amount of our revenue from U.S. federal, state and local government agencies, and any disruption in government funding or in our relationship with those agencies could adversely affect our business.
In fiscal 2016, we generated 42.4% of our revenue from contracts with U.S. federal, and state and local government agencies. A significant amount of this revenue is derived under multi-year contracts, many of which are appropriated on an annual basis. As a result, at the beginning of a project, the related contract may be only partially funded, and additional funding is normally committed only as appropriations are made in each subsequent year. These appropriations, and the timing of payment of appropriated amounts, may be influenced by numerous factors as noted below. Our backlog includes only the projects that have funding appropriated.
The demand for our U.S. government-related services is generally driven by the level of government program funding. Accordingly, the success and further development of our business depends, in large part, upon the continued funding of these U.S. government programs, and upon our ability to obtain contracts and perform well under these programs. Under the Budget Control Act of 2011, an automatic sequestration process, or across-the-board budget cuts (a large portion of which was defense-related), was triggered when the Joint Select Committee on Deficit Reduction, a committee of twelve members of Congress, failed to agree on a deficit reduction plan for the U.S. federal budget. The sequestration began on March 1, 2013. Although the Bipartisan Budget Act of 2013 provided some sequester relief through the end of fiscal year 2015, the sequestration requires reduced U.S. federal government spending from fiscal year 2016 through fiscal year 2021. A significant reduction in federal government spending or a change in budgetary priorities could reduce demand for our services, cancel or delay federal projects, and result in the closure of federal facilities and significant personnel reductions.
There are several additional factors that could materially affect our U.S. government contracting business, which could cause U.S. government agencies to delay or cancel programs, to reduce their orders under existing contracts, to exercise their rights to terminate contracts or not to exercise contract options
25
for renewals or extensions. Such factors, which include the following, could have a material adverse effect on our revenue or the timing of contract payments from U.S. government agencies:
- •
- the failure of the U.S. government to complete its budget and appropriations process before its fiscal year-end, which would result in the
funding of government operations by means of a continuing resolution that authorizes agencies to continue to operate but does not authorize new spending initiatives. As a result, U.S. government
agencies may delay the procurement of services;
- •
- changes in and delays or cancellations of government programs, requirements or appropriations;
- •
- budget constraints or policy changes resulting in delay or curtailment of expenditures related to the services we provide;
- •
- re-competes of government contracts;
- •
- the timing and amount of tax revenue received by federal, and state and local governments, and the overall level of government expenditures;
- •
- curtailment in the use of government contracting firms;
- •
- delays associated with insufficient numbers of government staff to oversee contracts;
- •
- the increasing preference by government agencies for contracting with small and disadvantaged businesses;
- •
- competing political priorities and changes in the political climate with regard to the funding or operation of the services we provide;
- •
- the adoption of new laws or regulations affecting our contracting relationships with the federal, state or local governments;
- •
- unsatisfactory performance on government contracts by us or one of our subcontractors, negative government audits or other events that may
impair our relationship with federal, state or local governments;
- •
- a dispute with or improper activity by any of our subcontractors; and
- •
- general economic or political conditions.
Our inability to win or renew U.S. government contracts during regulated procurement processes could harm our operations and significantly reduce or eliminate our profits.
U.S. government contracts are awarded through a regulated procurement process. The U.S. federal government has increasingly relied upon multi-year contracts with pre-established terms and conditions, such as indefinite delivery/indefinite quantity ("IDIQ") contracts, which generally require those contractors who have previously been awarded the IDIQ to engage in an additional competitive bidding process before a task order is issued. As a result, new work awards tend to be smaller and of shorter duration, since the orders represent individual tasks rather than large, programmatic assignments. In addition, we believe that there has been an increase in the award of federal contracts based on a low-price, technically acceptable criteria emphasizing price over qualitative factors, such as past
26
performance. As a result, pricing pressure may reduce our profit margins on future federal contracts. The increased competition and pricing pressure, in turn, may require us to make sustained efforts to reduce costs in order to realize revenue, and profits under government contracts. If we are not successful in reducing the amount of costs we incur, our profitability on government contracts will be negatively impacted. In addition, the U.S. federal government has scaled back outsourcing of services in favor of "insourcing" jobs to its employees, which could reduce our revenue. Moreover, even if we are qualified to work on a government contract, we may not be awarded the contract because of existing government policies designed to protect small businesses and under-represented minority contractors. Our inability to win or renew government contracts during regulated procurement processes could harm our operations and significantly reduce or eliminate our profits.
Each year, client funding for some of our U.S. government contracts may rely on government appropriations or public-supported financing. If adequate public funding is delayed or is not available, then our profits and revenue could decline.
Each year, client funding for some of our U.S. government contracts may directly or indirectly rely on government appropriations or public-supported financing. Legislatures may appropriate funds for a given project on a year-by-year basis, even though the project may take more than one year to perform. In addition, public-supported financing such as U.S. state and local municipal bonds may be only partially raised to support existing projects. Similarly, the impact of the economic downturn on U.S. state and local governments may make it more difficult for them to fund projects. In addition to the state of the economy and competing political priorities, public funds and the timing of payment of these funds may be influenced by, among other things, curtailments in the use of government contracting firms, increases in raw material costs, delays associated with insufficient numbers of government staff to oversee contracts, budget constraints, the timing and amount of tax receipts, and the overall level of government expenditures. If adequate public funding is not available or is delayed, then our profits and revenue could decline.
Our U.S. federal government contracts may give government agencies the right to modify, delay, curtail, renegotiate, or terminate existing contracts at their convenience at any time prior to their completion, which may result in a decline in our profits and revenue.
U.S. federal government projects in which we participate as a contractor or subcontractor may extend for several years. Generally, government contracts include the right to modify, delay, curtail, renegotiate, or terminate contracts and subcontracts at the government's convenience any time prior to their completion. Any decision by a U.S. federal government client to modify, delay, curtail, renegotiate, or terminate our contracts at their convenience may result in a decline in our profits and revenue.
As a U.S. government contractor, we must comply with various procurement laws and regulations and are subject to regular government audits; a violation of any of these laws and regulations or the failure to pass a government audit could result in sanctions, contract termination, forfeiture of profit, harm to our reputation or loss of our status as an eligible government contractor and could reduce our profits and revenue.
We must comply with and are affected by U.S. federal, state, local, and foreign laws and regulations relating to the formation, administration and performance of government contracts. For example, we must comply with FAR, the Truth in Negotiations Act, CAS, the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009, the Services Contract Act, and the DoD security regulations, as well as many other rules and regulations. In addition, we must also comply with other government regulations related to employment practices, environmental protection, health and safety, tax, accounting, and anti-fraud measures, as well as many others regulations in order to maintain our government contractor status. These laws and regulations affect how we do business with our clients and, in some instances, impose additional costs on our business operations. Although we take precautions to prevent and deter fraud, misconduct,
27
and non-compliance, we face the risk that our employees or outside partners may engage in misconduct, fraud, or other improper activities. U.S. government agencies, such as the DCAA, routinely audit and investigate government contractors. These government agencies review and audit a government contractor's performance under its contracts and cost structure, and evaluate compliance with applicable laws, regulations, and standards. In addition, during the course of its audits, the DCAA may question our incurred project costs. If the DCAA believes we have accounted for such costs in a manner inconsistent with the requirements for FAR or CAS, the DCAA auditor may recommend to our U.S. government corporate administrative contracting officer that such costs be disallowed. Historically, we have not experienced significant disallowed costs as a result of government audits. However, we can provide no assurance that the DCAA or other government audits will not result in material disallowances for incurred costs in the future. In addition, U.S. government contracts are subject to various other requirements relating to the formation, administration, performance, and accounting for these contracts. We may also be subject to qui tam litigation brought by private individuals on behalf of the U.S. government under the Federal Civil False Claims Act, which could include claims for treble damages. U.S. government contract violations could result in the imposition of civil and criminal penalties or sanctions, contract termination, forfeiture of profit, and/or suspension of payment, any of which could make us lose our status as an eligible government contractor. We could also suffer serious harm to our reputation. Any interruption or termination of our U.S. government contractor status could reduce our profits and revenue significantly.
If we extend a significant portion of our credit to clients in a specific geographic area or industry, we may experience disproportionately high levels of collection risk and nonpayment if those clients are adversely affected by factors particular to their geographic area or industry.
Our clients include public and private entities that have been, and may continue to be, negatively impacted by the changing landscape in the global economy. While outside of the U.S. federal government no one client accounted for over 10% of our revenue for fiscal 2016, we face collection risk as a normal part of our business where we perform services and subsequently bill our clients for such services. In the event that we have concentrated credit risk from clients in a specific geographic area or industry, continuing negative trends or a worsening in the financial condition of that specific geographic area or industry could make us susceptible to disproportionately high levels of default by those clients. Such defaults could materially adversely impact our revenues and our results of operations.
We have made and expect to continue to make acquisitions that could disrupt our operations and adversely impact our business and operating results. Our failure to conduct due diligence effectively, or our inability to successfully integrate acquisitions, could impede us from realizing all of the benefits of the acquisitions, which could weaken our results of operations.
A key part of our growth strategy is to acquire other companies that complement our lines of business or that broaden our technical capabilities and geographic presence. We expect to continue to acquire companies as an element of our growth strategy; however, our ability to make acquisitions is restricted under our credit agreement. Acquisitions involve certain known and unknown risks that could cause our actual growth or operating results to differ from our expectations or the expectations of securities analysts. For example:
- •
- we may not be able to identify suitable acquisition candidates or to acquire additional companies on acceptable terms;
- •
- we are pursuing international acquisitions, which inherently pose more risk than domestic acquisitions;
- •
- we compete with others to acquire companies, which may result in decreased availability of, or increased price for, suitable acquisition candidates;
28
- •
- we may not be able to obtain the necessary financing, on favorable terms or at all, to finance any of our potential acquisitions;
- •
- we may ultimately fail to consummate an acquisition even if we announce that we plan to acquire a company; and
- •
- acquired companies may not perform as we expect, and we may fail to realize anticipated revenue and profits.
In addition, our acquisition strategy may divert management's attention away from our existing businesses, resulting in the loss of key clients or key employees, and expose us to unanticipated problems or legal liabilities, including responsibility as a successor-in-interest for undisclosed or contingent liabilities of acquired businesses or assets.
If we fail to conduct due diligence on our potential targets effectively, we may, for example, not identify problems at target companies, or fail to recognize incompatibilities or other obstacles to successful integration. Our inability to successfully integrate future acquisitions could impede us from realizing all of the benefits of those acquisitions and could severely weaken our business operations. The integration process may disrupt our business and, if implemented ineffectively, may preclude realization of the full benefits expected by us and could harm our results of operations. In addition, the overall integration of the combining companies may result in unanticipated problems, expenses, liabilities, and competitive responses, and may cause our stock price to decline. The difficulties of integrating an acquisition include, among others:
- •
- issues in integrating information, communications, and other systems;
- •
- incompatibility of logistics, marketing, and administration methods;
- •
- maintaining employee morale and retaining key employees;
- •
- integrating the business cultures of both companies;
- •
- preserving important strategic client relationships;
- •
- consolidating corporate and administrative infrastructures, and eliminating duplicative operations; and
- •
- coordinating and integrating geographically separate organizations.
In addition, even if the operations of an acquisition are integrated successfully, we may not realize the full benefits of the acquisition, including the synergies, cost savings or growth opportunities that we expect. These benefits may not be achieved within the anticipated time frame, or at all.
Further, acquisitions may cause us to:
- •
- issue common stock that would dilute our current stockholders' ownership percentage;
- •
- use a substantial portion of our cash resources;
- •
- increase our interest expense, leverage, and debt service requirements (if we incur additional debt to pay for an acquisition);
29
- •
- assume liabilities, including environmental liabilities, for which we do not have indemnification from the former owners. Further,
indemnification obligations may be subject to dispute or concerns regarding the creditworthiness of the former owners;
- •
- record goodwill and non-amortizable intangible assets that are subject to impairment testing and potential impairment charges;
- •
- experience volatility in earnings due to changes in contingent consideration related to acquisition earn-out liability estimates;
- •
- incur amortization expenses related to certain intangible assets;
- •
- lose existing or potential contracts as a result of conflict of interest issues;
- •
- incur large and immediate write-offs; or
- •
- become subject to litigation.
Finally, acquired companies that derive a significant portion of their revenue from the U.S. federal government and do not follow the same cost accounting policies and billing practices that we follow may be subject to larger cost disallowances for greater periods than we typically encounter. If we fail to determine the existence of unallowable costs and do not establish appropriate reserves in advance of an acquisition, we may be exposed to material unanticipated liabilities, which could have a material adverse effect on our business.
If our goodwill or other intangible assets become impaired, then our profits may be significantly reduced.
Because we have historically acquired a significant number of companies, goodwill and other intangible assets represent a substantial portion of our assets. As of October 2, 2016, our goodwill was $718 million and other intangible assets were $49 million. We are required to perform a goodwill impairment test for potential impairment at least on an annual basis. We also assess the recoverability of the unamortized balance of our intangible assets when indications of impairment are present based on expected future profitability and undiscounted expected cash flows and their contribution to our overall operations. The goodwill impairment test requires us to determine the fair value of our reporting units, which are the components one level below our reportable segments. In determining fair value, we make significant judgments and estimates, including assumptions about our strategic plans with regard to our operations. We also analyze current economic indicators and market valuations to help determine fair value. To the extent economic conditions that would impact the future operations of our reporting units change, our goodwill may be deemed to be impaired, and we would be required to record a non-cash charge that could result in a material adverse effect on our financial position or results of operations.
For example, we wrote-off all of our Global Mining Practice's ("GMP") goodwill and identifiable intangible assets and recorded a related impairment charge of $60.8 million ($57.3 million after-tax) in the fourth quarter of fiscal 2015. We had no goodwill impairment in fiscal 2016.
We could be adversely affected by violations of the FCPA and similar worldwide anti-bribery laws.
The FCPA and similar anti-bribery laws generally prohibit companies and their intermediaries from making improper payments to foreign government officials for the purpose of obtaining or retaining business. The U.K. Bribery Act of 2010 prohibits both domestic and international bribery, as well as bribery across both private and public sectors. In addition, an organization that "fails to prevent bribery" by anyone associated with the organization can be charged under the U.K. Bribery Act unless the
30
organization can establish the defense of having implemented "adequate procedures" to prevent bribery. Improper payments are also prohibited under the Canadian Corruption of Foreign Public Officials Act and the Brazilian Clean Companies Act. Practices in the local business community of many countries outside the United States have a level of government corruption that is greater than that found in the developed world. Our policies mandate compliance with these anti-bribery laws, and we have established policies and procedures designed to monitor compliance with these anti-bribery law requirements; however, we cannot ensure that our policies and procedures will protect us from potential reckless or criminal acts committed by individual employees or agents. If we are found to be liable for anti-bribery law violations, we could suffer from criminal or civil penalties or other sanctions that could have a material adverse effect on our business.
We could be adversely impacted if we fail to comply with domestic and international export laws.
To the extent we export technical services, data and products outside of the United States, we are subject to U.S. and international laws and regulations governing international trade and exports, including but not limited to the International Traffic in Arms Regulations, the Export Administration Regulations, and trade sanctions against embargoed countries. A failure to comply with these laws and regulations could result in civil or criminal sanctions, including the imposition of fines, the denial of export privileges, and suspension or debarment from participation in U.S. government contracts, which could have a material adverse effect on our business.
If we fail to complete a project in a timely manner, miss a required performance standard, or otherwise fail to adequately perform on a project, then we may incur a loss on that project, which may reduce or eliminate our overall profitability.
Our engagements often involve large-scale, complex projects. The quality of our performance on such projects depends in large part upon our ability to manage the relationship with our clients and our ability to effectively manage the project and deploy appropriate resources, including third-party contractors and our own personnel, in a timely manner. We may commit to a client that we will complete a project by a scheduled date. We may also commit that a project, when completed, will achieve specified performance standards. If the project is not completed by the scheduled date or fails to meet required performance standards, we may either incur significant additional costs or be held responsible for the costs incurred by the client to rectify damages due to late completion or failure to achieve the required performance standards. The uncertainty of the timing of a project can present difficulties in planning the amount of personnel needed for the project. If the project is delayed or canceled, we may bear the cost of an underutilized workforce that was dedicated to fulfilling the project. In addition, performance of projects can be affected by a number of factors beyond our control, including unavoidable delays from government inaction, public opposition, inability to obtain financing, weather conditions, unavailability of vendor materials, changes in the project scope of services requested by our clients, industrial accidents, environmental hazards, and labor disruptions. To the extent these events occur, the total costs of the project could exceed our estimates, and we could experience reduced profits or, in some cases, incur a loss on a project, which may reduce or eliminate our overall profitability. Further, any defects or errors, or failures to meet our clients' expectations, could result in claims for damages against us. Failure to meet performance standards or complete performance on a timely basis could also adversely affect our reputation.
The loss of key personnel or our inability to attract and retain qualified personnel could impair our ability to provide services to our clients and otherwise conduct our business effectively.
As primarily a professional and technical services company, we are labor-intensive and, therefore, our ability to attract, retain, and expand our senior management and our professional and technical staff is an important factor in determining our future success. The market for qualified scientists and engineers is
31
competitive and, from time to time, it may be difficult to attract and retain qualified individuals with the required expertise within the timeframe demanded by our clients. For example, some of our U.S. government contracts may require us to employ only individuals who have particular government security clearance levels. In addition, we rely heavily upon the expertise and leadership of our senior management. If we are unable to retain executives and other key personnel, the roles and responsibilities of those employees will need to be filled, which may require that we devote time and resources to identify, hire, and integrate new employees. With limited exceptions, we do not have employment agreements with any of our key personnel. The loss of the services of any of these key personnel could adversely affect our business. Although we have obtained non-compete agreements from certain principals and stockholders of companies we have acquired, we generally do not have non-compete or employment agreements with key employees who were once equity holders of these companies. Further, many of our non-compete agreements have expired. We do not maintain key-man life insurance policies on any of our executive officers or senior managers. Our failure to attract and retain key individuals could impair our ability to provide services to our clients and conduct our business effectively.
Our revenue and growth prospects may be harmed if we or our employees are unable to obtain government granted eligibility or other qualifications we and they need to perform services for our customers.
A number of government programs require contractors to have certain kinds of government granted eligibility, such as security clearance credentials. Depending on the project, eligibility can be difficult and time-consuming to obtain. If we or our employees are unable to obtain or retain the necessary eligibility, we may not be able to win new business, and our existing customers could terminate their contracts with us or decide not to renew them. To the extent we cannot obtain or maintain the required security clearances for our employees working on a particular contract, we may not derive the revenue or profit anticipated from such contract.
Our actual business and financial results could differ from the estimates and assumptions that we use to prepare our financial statements, which may significantly reduce or eliminate our profits.
To prepare financial statements in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States of America ("GAAP"), management is required to make estimates and assumptions as of the date of the financial statements. These estimates and assumptions affect the reported values of assets, liabilities, revenue and expenses, as well as disclosures of contingent assets and liabilities. For example, we typically recognize revenue over the life of a contract based on the proportion of costs incurred to date compared to the total costs estimated to be incurred for the entire project. Areas requiring significant estimates by our management include:
- •
- the application of the percentage-of-completion method of accounting and revenue recognition on contracts, change orders, and contract claims,
including related unbilled accounts receivable;
- •
- unbilled accounts receivable, including amounts related to requests for equitable adjustment to contracts that provide for price
redetermination, primarily with the U.S. federal government. These amounts are recorded only when they can be reliably estimated and realization is probable;
- •
- provisions for uncollectible receivables, client claims, and recoveries of costs from subcontractors, vendors, and others;
- •
- provisions for income taxes, research and development tax credits, valuation allowances, and unrecognized tax benefits;
- •
- value of goodwill and recoverability of other intangible assets;
32
- •
- valuations of assets acquired and liabilities assumed in connection with business combinations;
- •
- valuation of contingent earn-out liabilities recorded in connection with business combinations;
- •
- valuation of employee benefit plans;
- •
- valuation of stock-based compensation expense; and
- •
- accruals for estimated liabilities, including litigation and insurance reserves.
Our actual business and financial results could differ from those estimates, which may significantly reduce or eliminate our profits.
Our profitability could suffer if we are not able to maintain adequate utilization of our workforce.
The cost of providing our services, including the extent to which we utilize our workforce, affects our profitability. The rate at which we utilize our workforce is affected by a number of factors, including:
- •
- our ability to transition employees from completed projects to new assignments and to hire and assimilate new employees;
- •
- our ability to forecast demand for our services and thereby maintain an appropriate headcount in each of our geographies and workforces;
- •
- our ability to manage attrition;
- •
- our need to devote time and resources to training, business development, professional development, and other non-chargeable activities; and
- •
- our ability to match the skill sets of our employees to the needs of the marketplace.
If we over-utilize our workforce, our employees may become disengaged, which could impact employee attrition. If we under-utilize our workforce, our profit margin and profitability could suffer.
Our use of the percentage-of-completion method of revenue recognition could result in a reduction or reversal of previously recorded revenue and profits.
We account for most of our contracts on the percentage-of-completion method of revenue recognition. Generally, our use of this method results in recognition of revenue and profit ratably over the life of the contract, based on the proportion of costs incurred to date to total costs expected to be incurred for the entire project. The effects of revisions to estimated revenue and costs, including the achievement of award fees and the impact of change orders and claims, are recorded when the amounts are known and can be reasonably estimated. Such revisions could occur in any period and their effects could be material. Although we have historically made reasonably reliable estimates of the progress towards completion of long-term contracts, the uncertainties inherent in the estimating process make it possible for actual costs to vary materially from estimates, including reductions or reversals of previously recorded revenue and profit.
33
If we are unable to accurately estimate and control our contract costs, then we may incur losses on our contracts, which could decrease our operating margins and reduce our profits. In particular, our fixed-price contracts could increase the unpredictability of our earnings.
It is important for us to accurately estimate and control our contract costs so that we can maintain positive operating margins and profitability. We generally enter into three principal types of contracts with our clients: fixed-price, time-and-materials and cost-plus.
The U.S. federal government and some clients have increased the use of fixed-priced contracts. Under fixed-price contracts, we receive a fixed price irrespective of the actual costs we incur and, consequently, we are exposed to a number of risks. We realize a profit on fixed-price contracts only if we can control our costs and prevent cost over-runs on our contracts. Fixed-price contracts require cost and scheduling estimates that are based on a number of assumptions, including those about future economic conditions, costs, and availability of labor, equipment and materials, and other exigencies. We could experience cost over-runs if these estimates are originally inaccurate as a result of errors or ambiguities in the contract specifications, or become inaccurate as a result of a change in circumstances following the submission of the estimate due to, among other things, unanticipated technical problems, difficulties in obtaining permits or approvals, changes in local laws or labor conditions, weather delays, changes in the costs of raw materials, or the inability of our vendors or subcontractors to perform. If cost overruns occur, we could experience reduced profits or, in some cases, a loss for that project. If a project is significant, or if there are one or more common issues that impact multiple projects, costs overruns could increase the unpredictability of our earnings, as well as have a material adverse impact on our business and earnings.
Under our time-and-materials contracts, we are paid for labor at negotiated hourly billing rates and also paid for other expenses. Profitability on these contracts is driven by billable headcount and cost control. Many of our time-and-materials contracts are subject to maximum contract values and, accordingly, revenue relating to these contracts is recognized as if these contracts were fixed-price contracts. Under our cost-plus contracts, some of which are subject to contract ceiling amounts, we are reimbursed for allowable costs and fees, which may be fixed or performance-based. If our costs exceed the contract ceiling or are not allowable under the provisions of the contract or any applicable regulations, we may not be able to obtain reimbursement for all of the costs we incur.
Profitability on our contracts is driven by billable headcount and our ability to manage our subcontractors, vendors, and material suppliers. If we are unable to accurately estimate and manage our costs, we may incur losses on our contracts, which could decrease our operating margins and significantly reduce or eliminate our profits. Certain of our contracts require us to satisfy specific design, engineering, procurement, or construction milestones in order to receive payment for the work completed or equipment or supplies procured prior to achievement of the applicable milestone. As a result, under these types of arrangements, we may incur significant costs or perform significant amounts of services prior to receipt of payment. If a client determines not to proceed with the completion of the project or if the client defaults on its payment obligations, we may face difficulties in collecting payment of amounts due to us for the costs previously incurred or for the amounts previously expended to purchase equipment or supplies.
Accounting for a contract requires judgments relative to assessing the contract's estimated risks, revenue, costs, and other technical issues. Due to the size and nature of many of our contracts, the estimation of overall risk, revenue, and cost at completion is complicated and subject to many variables. Changes in underlying assumptions, circumstances, or estimates may also adversely affect future period financial performance. If we are unable to accurately estimate the overall revenue or costs on a contract, then we may experience a lower profit or incur a loss on the contract.
34
Our failure to adequately recover on claims brought by us against clients for additional contract costs could have a negative impact on our liquidity and profitability.
We have brought claims against clients for additional costs exceeding the contract price or for amounts not included in the original contract price. These types of claims occur due to matters such as client-caused delays or changes from the initial project scope, both of which may result in additional cost. Often, these claims can be the subject of lengthy arbitration or litigation proceedings, and it is difficult to accurately predict when these claims will be fully resolved. When these types of events occur and unresolved claims are pending, we have used working capital in projects to cover cost overruns pending the resolution of the relevant claims. A failure to promptly recover on these types of claims could have a negative impact on our liquidity and profitability. Total accounts receivable at October 2, 2016 included approximately $45 million related to such claims.
Our failure to win new contracts and renew existing contracts with private and public sector clients could adversely affect our profitability.
Our business depends on our ability to win new contracts and renew existing contracts with private and public sector clients. Contract proposals and negotiations are complex and frequently involve a lengthy bidding and selection process, which is affected by a number of factors. These factors include market conditions, financing arrangements, and required governmental approvals. For example, a client may require us to provide a bond or letter of credit to protect the client should we fail to perform under the terms of the contract. If negative market conditions arise, or if we fail to secure adequate financial arrangements or the required government approval, we may not be able to pursue particular projects, which could adversely affect our profitability.
If we are not able to successfully manage our growth strategy, our business and results of operations may be adversely affected.
Our expected future growth presents numerous managerial, administrative, operational, and other challenges. Our ability to manage the growth of our operations will require us to continue to improve our management information systems and our other internal systems and controls. In addition, our growth will increase our need to attract, develop, motivate, and retain both our management and professional employees. The inability to effectively manage our growth or the inability of our employees to achieve anticipated performance could have a material adverse effect on our business.
Our backlog is subject to cancellation, unexpected adjustments and economic conditions, and is an uncertain indicator of future operating results.
Our backlog at October 2, 2016 was $2.4 billion, an increase of $477 million, or 25% compared to the end of fiscal 2015. We include in backlog only those contracts for which funding has been provided and work authorizations have been received. We cannot guarantee that the revenue projected in our backlog will be realized or, if realized, will result in profits. In addition, project cancellations or scope adjustments may occur, from time to time, with respect to contracts reflected in our backlog. For example, certain of our contracts with the U.S. federal government and other clients are terminable at the discretion of the client, with or without cause. These types of backlog reductions could adversely affect our revenue and margins. As a result of these factors, our backlog as of any particular date is an uncertain indicator of our future earnings.
35
Cyber security breaches of our systems and information technology could adversely impact our ability to operate.
We develop, install and maintain information technology systems for ourselves, as well as for customers. Client contracts for the performance of information technology services, as well as various privacy and securities laws, require us to manage and protect sensitive and confidential information, including federal and other government information, from disclosure. We also need to protect our own internal trade secrets and other business confidential information from disclosure. We face the threat to our computer systems of unauthorized access, computer hackers, computer viruses, malicious code, organized cyber-attacks and other security problems and system disruptions, including possible unauthorized access to our and our clients' proprietary or classified information. We rely on industry-accepted security measures and technology to securely maintain all confidential and proprietary information on our information systems. We have devoted and will continue to devote significant resources to the security of our computer systems, but they may still be vulnerable to these threats. A user who circumvents security measures could misappropriate confidential or proprietary information, including information regarding us, our personnel and/or our clients, or cause interruptions or malfunctions in operations. As a result, we may be required to expend significant resources to protect against the threat of these system disruptions and security breaches or to alleviate problems caused by these disruptions and breaches. Any of these events could damage our reputation and have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
If our business partners fail to perform their contractual obligations on a project, we could be exposed to legal liability, loss of reputation and profit reduction or loss on the project.
We routinely enter into subcontracts and, occasionally, joint ventures, teaming arrangements, and other contractual arrangements so that we can jointly bid and perform on a particular project. Success under these arrangements depends in large part on whether our business partners fulfill their contractual obligations satisfactorily. In addition, when we operate through a joint venture in which we are a minority holder, we have limited control over many project decisions, including decisions related to the joint venture's internal controls, which may not be subject to the same internal control procedures that we employ. If these unaffiliated third parties do not fulfill their contract obligations, the partnerships or joint ventures may be unable to adequately perform and deliver their contracted services. Under these circumstances, we may be obligated to pay financial penalties, provide additional services to ensure the adequate performance and delivery of the contracted services, and may be jointly and severally liable for the other's actions or contract performance. These additional obligations could result in reduced profits and revenues or, in some cases, significant losses for us with respect to the joint venture, which could also affect our reputation in the industries we serve.
If our contractors and subcontractors fail to satisfy their obligations to us or other parties, or if we are unable to maintain these relationships, our revenue, profitability, and growth prospects could be adversely affected.
We depend on contractors and subcontractors in conducting our business. There is a risk that we may have disputes with our subcontractors arising from, among other things, the quality and timeliness of work performed by the subcontractor, client concerns about the subcontractor, or our failure to extend existing task orders or issue new task orders under a subcontract. In addition, if a subcontractor fails to deliver on a timely basis the agreed-upon supplies, fails to perform the agreed-upon services, or goes out of business, then we may be required to purchase the services or supplies from another source at a higher price, and our ability to fulfill our obligations as a prime contractor may be jeopardized. This may reduce the profit to be realized or result in a loss on a project for which the services or supplies are needed.
36
We also rely on relationships with other contractors when we act as their subcontractor or joint venture partner. The absence of qualified subcontractors with which we have a satisfactory relationship could adversely affect the quality of our service and our ability to perform under some of our contracts. Our future revenue and growth prospects could be adversely affected if other contractors eliminate or reduce their subcontracts or teaming arrangement relationships with us, or if a government agency terminates or reduces these other contractors' programs, does not award them new contracts, or refuses to pay under a contract.
Our failure to meet contractual schedule or performance requirements that we have guaranteed could adversely affect our operating results.
In certain circumstances, we can incur liquidated or other damages if we do not achieve project completion by a scheduled date. If we or an entity for which we have provided a guarantee subsequently fails to complete the project as scheduled and the matter cannot be satisfactorily resolved with the client, we may be responsible for cost impacts to the client resulting from any delay or the cost to complete the project. Our costs generally increase from schedule delays and/or could exceed our projections for a particular project. In addition, project performance can be affected by a number of factors beyond our control, including unavoidable delays from governmental inaction, public opposition, inability to obtain financing, weather conditions, unavailability of vendor materials, changes in the project scope of services requested by our clients, industrial accidents, environmental hazards, labor disruptions and other factors. As a result, material performance problems for existing and future contracts could cause actual results of operations to differ from those anticipated by us and also could cause us to suffer damage to our reputation within our industry and client base.
New legal requirements could adversely affect our operating results.
Our business and results of operations could be adversely affected by U.S. health care reform, climate change, defense, environmental and infrastructure industry specific and other legislation and regulations. We are continually assessing the impact that health care reform could have on our employer-sponsored medical plans. Growing concerns about climate change may result in the imposition of additional environmental regulations. For example, legislation, international protocols, regulation or other restrictions on emissions could increase the costs of projects for our clients or, in some cases, prevent a project from going forward, thereby potentially reducing the need for our services. In addition, relaxation or repeal of laws and regulations, or changes in governmental policies regarding environmental, defense, infrastructure or other industries we serve could result in a decline in demand for our services, which could in turn negatively impact our revenues. We cannot predict when or whether any of these various proposals may be enacted or what their effect will be on us or on our customers.
Changes in resource management, environmental, or infrastructure industry laws, regulations, and programs could directly or indirectly reduce the demand for our services, which could in turn negatively impact our revenue.
Some of our services are directly or indirectly impacted by changes in U.S. federal, state, local or foreign laws and regulations pertaining to the resource management, environmental, and infrastructure industries. Accordingly, a relaxation or repeal of these laws and regulations, or changes in governmental policies regarding the funding, implementation or enforcement of these programs, could result in a decline in demand for our services, which could in turn negatively impact our revenue.
Changes in capital markets could adversely affect our access to capital and negatively impact our business.
Our results could be adversely affected by an inability to access the revolving credit facility under our credit agreement. Unfavorable financial or economic conditions could impact certain lenders'
37
willingness or ability to fund our revolving credit facility. In addition, increases in interest rates or credit spreads, volatility in financial markets or the interest rate environment, significant political or economic events, defaults of significant issuers, and other market and economic factors, may negatively impact the general level of debt issuance, the debt issuance plans of certain categories of borrowers, the types of credit-sensitive products being offered, and/or a sustained period of market decline or weakness could have a material adverse effect on us.
Restrictive covenants in our credit agreement may restrict our ability to pursue certain business strategies.
Our credit agreement limits or restricts our ability to, among other things:
- •
- incur additional indebtedness;
- •
- create liens securing debt or other encumbrances on our assets;
- •
- make loans or advances;
- •
- pay dividends or make distributions to our stockholders;
- •
- purchase or redeem our stock;
- •
- repay indebtedness that is junior to indebtedness under our credit agreement;
- •
- acquire the assets of, or merge or consolidate with, other companies; and
- •
- sell, lease, or otherwise dispose of assets.
Our credit agreement also requires that we maintain certain financial ratios, which we may not be able to achieve. The covenants may impair our ability to finance future operations or capital needs or to engage in other favorable business activities.
Our industry is highly competitive and we may be unable to compete effectively, which could result in reduced revenue, profitability and market share.
We are engaged in a highly competitive business. The markets we serve are highly fragmented and we compete with a large number of regional, national and international companies. Certain of these competitors have greater financial and other resources than we do. Others are smaller and more specialized, and concentrate their resources in particular areas of expertise. The extent of our competition varies according to the particular markets and geographic area. In addition, the technical and professional aspects of some of our services generally do not require large upfront capital expenditures and provide limited barriers against new competitors. The degree and type of competition we face is also influenced by the type and scope of a particular project. Our clients make competitive determinations based upon qualifications, experience, performance, reputation, technology, customer relationships and ability to provide the relevant services in a timely, safe and cost-efficient manner. This competitive environment could force us to make price concessions or otherwise reduce prices for our services. If we are unable to maintain our competitiveness and win bids for future projects, our market share, revenue, and profits will decline.
38
Legal proceedings, investigations, and disputes could result in substantial monetary penalties and damages, especially if such penalties and damages exceed or are excluded from existing insurance coverage.
We engage in consulting, engineering, program management, construction management, construction, and technical services that can result in substantial injury or damages that may expose us to legal proceedings, investigations, and disputes. For example, in the ordinary course of our business, we may be involved in legal disputes regarding personal injury claims, employee or labor disputes, professional liability claims, and general commercial disputes involving project cost overruns and liquidated damages, as well as other claims. In addition, in the ordinary course of our business, we frequently make professional judgments and recommendations about environmental and engineering conditions of project sites for our clients, and we may be deemed to be responsible for these judgments and recommendations if they are later determined to be inaccurate. Any unfavorable legal ruling against us could result in substantial monetary damages or even criminal violations. We maintain insurance coverage as part of our overall legal and risk management strategy to minimize our potential liabilities; however, insurance coverage contains exclusions and other limitations that may not cover our potential liabilities. Generally, our insurance program covers workers' compensation and employer's liability, general liability, automobile liability, professional errors and omissions liability, property, and contractor's pollution liability (in addition to other policies for specific projects). Our insurance program includes deductibles or self-insured retentions for each covered claim that may increase over time. In addition, our insurance policies contain exclusions that insurance providers may use to deny or restrict coverage. Excess liability and professional liability insurance policies provide for coverage on a "claims-made" basis, covering only claims actually made and reported during the policy period currently in effect. If we sustain liabilities that exceed or that are excluded from our insurance coverage, or for which we are not insured, it could have a material adverse impact on our results of operations and financial condition.
Unavailability or cancellation of third-party insurance coverage would increase our overall risk exposure as well as disrupt the management of our business operations.
We maintain insurance coverage from third-party insurers as part of our overall risk management strategy and because some of our contracts require us to maintain specific insurance coverage limits. If any of our third-party insurers fail, suddenly cancel our coverage, or otherwise are unable to provide us with adequate insurance coverage, then our overall risk exposure and our operational expenses would increase and the management of our business operations would be disrupted. In addition, there can be no assurance that any of our existing insurance coverage will be renewable upon the expiration of the coverage period or that future coverage will be affordable at the required limits.
Our inability to obtain adequate bonding could have a material adverse effect on our future revenue and business prospects.
Certain clients require bid bonds, and performance and payment bonds. These bonds indemnify the client should we fail to perform our obligations under a contract. If a bond is required for a particular project and we are unable to obtain an appropriate bond, we cannot pursue that project. In some instances, we are required to co-venture with a small or disadvantaged business to pursue certain U.S. federal or state government contracts. In connection with these ventures, we are sometimes required to utilize our bonding capacity to cover all of the payment and performance obligations under the contract with the client. We have a bonding facility but, as is typically the case, the issuance of bonds under that facility is at the surety's sole discretion. Moreover, due to events that can negatively affect the insurance and bonding markets, bonding may be more difficult to obtain or may only be available at significant additional cost. There can be no assurance that bonds will continue to be available to us on reasonable terms. Our inability to obtain adequate bonding and, as a result, to bid on new work could have a material adverse effect on our future revenue and business prospects.
39
Employee, agent, or partner misconduct, or our failure to comply with anti-bribery and other laws or regulations, could harm our reputation, reduce our revenue and profits, and subject us to criminal and civil enforcement actions.
Misconduct, fraud, non-compliance with applicable laws and regulations, or other improper activities by one of our employees, agents, or partners could have a significant negative impact on our business and reputation. Such misconduct could include the failure to comply with government procurement regulations, regulations regarding the protection of classified information, regulations prohibiting bribery and other foreign corrupt practices, regulations regarding the pricing of labor and other costs in government contracts, regulations on lobbying or similar activities, regulations pertaining to the internal controls over financial reporting, environmental laws, and any other applicable laws or regulations. For example, as previously noted, the FCPA and similar anti-bribery laws in other jurisdictions generally prohibit companies and their intermediaries from making improper payments to non-U.S. officials for the purpose of obtaining or retaining business. Our policies mandate compliance with these regulations and laws, and we take precautions to prevent and detect misconduct. However, since our internal controls are subject to inherent limitations, including human error, it is possible that these controls could be intentionally circumvented or become inadequate because of changed conditions. As a result, we cannot assure that our controls will protect us from reckless or criminal acts committed by our employees or agents. Our failure to comply with applicable laws or regulations, or acts of misconduct could subject us to fines and penalties, loss of security clearances, and suspension or debarment from contracting, any or all of which could harm our reputation, reduce our revenue and profits, and subject us to criminal and civil enforcement actions.
Our business activities may require our employees to travel to and work in countries where there are high security risks, which may result in employee death or injury, repatriation costs or other unforeseen costs.
Certain of our contracts may require our employees travel to and work in high-risk countries that are undergoing political, social, and economic upheavals resulting from war, civil unrest, criminal activity, acts of terrorism, or public health crises. For example, we currently have employees working in high security risk countries such as Afghanistan and Iraq. As a result, we risk loss of or injury to our employees and may be subject to costs related to employee death or injury, repatriation, or other unforeseen circumstances. We may choose or be forced to leave a country with little or no warning due to physical security risks.
Our failure to implement and comply with our safety program could adversely affect our operating results or financial condition.
Our project sites often put our employees and others in close proximity with mechanized equipment, moving vehicles, chemical and manufacturing processes, and highly regulated materials. On some project sites, we may be responsible for safety, and, accordingly, we have an obligation to implement effective safety procedures. Our safety program is a fundamental element of our overall approach to risk management, and the implementation of the safety program is a significant issue in our dealings with our clients. We maintain an enterprise-wide group of health and safety professionals to help ensure that the services we provide are delivered safely and in accordance with standard work processes. Unsafe job sites and office environments have the potential to increase employee turnover, increase the cost of a project to our clients, expose us to types and levels of risk that are fundamentally unacceptable, and raise our operating costs. The implementation of our safety processes and procedures are monitored by various agencies, including the U.S. Mine Safety and Health Administration, and rating bureaus, and may be evaluated by certain clients in cases in which safety requirements have been established in our contracts. Our failure to meet these requirements or our failure to properly implement and comply with our safety program could result in reduced profitability, the loss of projects or clients, or potential litigation, and could have a material adverse effect on our business, operating results, or financial condition.
40
We may be precluded from providing certain services due to conflict of interest issues.
Many of our clients are concerned about potential or actual conflicts of interest in retaining management consultants. U.S. federal government agencies have formal policies against continuing or awarding contracts that would create actual or potential conflicts of interest with other activities of a contractor. These policies, among other things, may prevent us from bidding for or performing government contracts resulting from or relating to certain work we have performed. In addition, services performed for a commercial or government client may create a conflict of interest that precludes or limits our ability to obtain work from other public or private organizations. We have, on occasion, declined to bid on projects due to conflict of interest issues.
If our reports and opinions are not in compliance with professional standards and other regulations, we could be subject to monetary damages and penalties.
We issue reports and opinions to clients based on our professional engineering expertise, as well as our other professional credentials. Our reports and opinions may need to comply with professional standards, licensing requirements, securities regulations, and other laws and rules governing the performance of professional services in the jurisdiction in which the services are performed. In addition, we could be liable to third parties who use or rely upon our reports or opinions even if we are not contractually bound to those third parties. For example, if we deliver an inaccurate report or one that is not in compliance with the relevant standards, and that report is made available to a third party, we could be subject to third-party liability, resulting in monetary damages and penalties.
We may be subject to liabilities under environmental laws and regulations.
Our services are subject to numerous U.S. and international environmental protection laws and regulations that are complex and stringent. For example, we must comply with a number of U.S. federal government laws that strictly regulate the handling, removal, treatment, transportation, and disposal of toxic and hazardous substances. Under the Comprehensive Environmental Response Compensation and Liability Act of 1980, as amended ("CERCLA"), and comparable state laws, we may be required to investigate and remediate regulated hazardous materials. CERCLA and comparable state laws typically impose strict, joint and several liabilities without regard to whether a company knew of or caused the release of hazardous substances. The liability for the entire cost of clean-up could be imposed upon any responsible party. Other principal U.S. federal environmental, health, and safety laws affecting us include, but are not limited to, the Resource Conversation and Recovery Act, National Environmental Policy Act, the Clean Air Act, the Occupational Safety and Health Act, the Federal Mine Safety and Health Act of 1977 (the "Mine Act"), the Toxic Substances Control Act, and the Superfund Amendments and Reauthorization Act. Our business operations may also be subject to similar state and international laws relating to environmental protection. Further, past business practices at companies that we have acquired may also expose us to future unknown environmental liabilities. Liabilities related to environmental contamination or human exposure to hazardous substances, or a failure to comply with applicable regulations, could result in substantial costs to us, including clean-up costs, fines, civil or criminal sanctions, and third-party claims for property damage or personal injury or cessation of remediation activities. Our continuing work in the areas governed by these laws and regulations exposes us to the risk of substantial liability.
Force majeure events, including natural disasters and terrorist actions, could negatively impact the economies in which we operate or disrupt our operations, which may affect our financial condition, results of operations, or cash flows.
Force majeure or extraordinary events beyond the control of the contracting parties, such as natural and man-made disasters, as well as terrorist actions, could negatively impact the economies in
41
which we operate by causing the closure of offices, interrupting projects, and forcing the relocation of employees. We typically remain obligated to perform our services after a terrorist action or natural disaster unless the contract contains a force majeure clause that relieves us of our contractual obligations in such an extraordinary event. If we are not able to react quickly to force majeure, our operations may be affected significantly, which would have a negative impact on our financial condition, results of operations, or cash flows.
We have only a limited ability to protect our intellectual property rights, and our failure to protect our intellectual property rights could adversely affect our competitive position.
Our success depends, in part, upon our ability to protect our proprietary information and other intellectual property. We rely principally on trade secrets to protect much of our intellectual property where we do not believe that patent or copyright protection is appropriate or obtainable. However, trade secrets are difficult to protect. Although our employees are subject to confidentiality obligations, this protection may be inadequate to deter or prevent misappropriation of our confidential information. In addition, we may be unable to detect unauthorized use of our intellectual property or otherwise take appropriate steps to enforce our rights. Failure to obtain or maintain trade secret protection could adversely affect our competitive business position. In addition, if we are unable to prevent third parties from infringing or misappropriating our trademarks or other proprietary information, our competitive position could be adversely affected.
Systems and information technology interruption could adversely impact our ability to operate.
We rely heavily on computer, information, and communications technology and systems to operate. From time to time, we experience system interruptions and delays. If we are unable to effectively deploy software and hardware, upgrade our systems and network infrastructure, and take steps to improve and protect our systems, systems operations could be interrupted or delayed.
Our computer and communications systems and operations could be damaged or interrupted by natural disasters, telecommunications failures, acts of war or terrorism, and similar events or disruptions. In addition, we face the threat of unauthorized system access, computer hackers, computer viruses, malicious code, organized cyber-attacks, and other security breaches and system disruptions. We devote significant resources to the security of our computer systems, but they may still be vulnerable to threats. Anyone who circumvents security measures could misappropriate proprietary information or cause interruptions or malfunctions in system operations. As a result, we may be required to expend significant resources to protect against the threat of system disruptions and security breaches, or to alleviate problems caused by disruptions and breaches.
Any of these or other events could cause system interruption, delays, and loss of critical data that could delay or prevent operations, and could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations, and cash flows, and could negatively impact our clients.
Our stock price could become more volatile and stockholders' investments could lose value.
In addition to the macroeconomic factors that have affected the prices of many securities generally, all of the factors discussed in this section could affect our stock price. Our common stock has previously experienced substantial price volatility. In addition, the stock market has experienced extreme price and volume fluctuations that have affected the market price of many companies, and that have often been unrelated to the operating performance of these companies. The overall market and the price of our
42
common stock may fluctuate greatly. The trading price of our common stock may be significantly affected by various factors, including:
- •
- quarter-to-quarter variations in our financial results, including revenue, profits, days sales outstanding, backlog, and other measures of
financial performance or financial condition, which may be affected by the following:
- •
- loss of key employees;
- •
- the number and significance of client contracts commenced and completed during a quarter;
- •
- creditworthiness and solvency of clients;
- •
- the ability of our clients to terminate contracts without penalties;
- •
- general economic or political conditions;
- •
- unanticipated changes in contract performance that may affect profitability, particularly with contracts that are fixed-price or have funding
limits;
- •
- contract negotiations on change orders, requests for equitable adjustment, and collections of related billed and unbilled accounts receivable;
- •
- seasonality of the spending cycle of our public sector clients, notably the U.S. federal government, the spending patterns of our commercial
sector clients, and weather conditions;
- •
- budget constraints experienced by our U.S. federal, and state and local government clients;
- •
- integration of acquired companies;
- •
- changes in contingent consideration related to acquisition earn-outs;
- •
- divestiture or discontinuance of operating units;
- •
- employee hiring, utilization and turnover rates;
- •
- delays incurred in connection with a contract;
- •
- the size, scope and payment terms of contracts;
- •
- the timing of expenses incurred for corporate initiatives;
- •
- reductions in the prices of services offered by our competitors;
- •
- threatened or pending litigation;
- •
- legislative and regulatory enforcement policy changes that may affect demand for our services;
- •
- the impairment of goodwill or identifiable intangible assets;
- •
- the fluctuation of a foreign currency exchange rate;
43
- •
- stock-based compensation expense;
- •
- actual events, circumstances, outcomes, and amounts differing from judgments, assumptions, and estimates used in determining the value of
certain assets (including the amounts of related valuation allowances), liabilities, and other items reflected in our consolidated financial statements;
- •
- success in executing our strategy and operating plans;
- •
- changes in tax laws or regulations or accounting rules;
- •
- results of income tax examinations;
- •
- the timing of announcements in the public markets regarding new services or potential problems with the performance of services by us or our
competitors, or any other material announcements;
- •
- speculation in the media and analyst community, changes in recommendations or earnings estimates by financial analysts, changes in investors'
or analysts' valuation measures for our stock, and market trends unrelated to our stock;
- •
- our announcements concerning the payment of dividends or the repurchase of our shares;
- •
- resolution of threatened or pending litigation;
- •
- changes in investors' and analysts' perceptions of our business or any of our competitors' businesses;
- •
- changes in environmental legislation;
- •
- broader market fluctuations; and
- •
- general economic or political conditions.
Volatility in the financial markets could cause a decline in our stock price, which could trigger an impairment of the goodwill of individual reporting units that could be material to our consolidated financial statements. A significant drop in the price of our stock could also expose us to the risk of securities class action lawsuits, which could result in substantial costs and divert management's attention and resources, which could adversely affect our business. Additionally, volatility or a lack of positive performance in our stock price may adversely affect our ability to retain key employees, many of whom are awarded equity securities, the value of which is dependent on the performance of our stock price.
Delaware law and our charter documents may impede or discourage a merger, takeover, or other business combination even if the business combination would have been in the best interests of our stockholders.
We are a Delaware corporation and the anti-takeover provisions of Delaware law impose various impediments to the ability of a third party to acquire control of us, even if a change in control would be beneficial to our stockholders. In addition, our Board of Directors has the power, without stockholder approval, to designate the terms of one or more series of preferred stock and issue shares of preferred stock, which could be used defensively if a takeover is threatened. Our incorporation under Delaware law, the ability of our Board of Directors to create and issue a new series of preferred stock, and provisions in our certificate of incorporation and bylaws, such as those relating to advance notice of certain stockholder
44
proposals and nominations, could impede a merger, takeover, or other business combination involving us, or discourage a potential acquirer from making a tender offer for our common stock, even if the business combination would have been in the best interests of our current stockholders.
Item 1B Unresolved Staff Comments
None.
At fiscal 2016 year-end, we owned three facilities located in the United States and leased approximately 350 operating facilities in domestic and foreign locations. Our significant lease agreements expire at various dates through 2025. We believe that our current facilities are adequate for the operation of our business, and that suitable additional space in various local markets is available to accommodate any needs that may arise.
The following table summarizes our ten most significant leased properties by location based on annual rental expenses (listed alphabetically):
| Location | Description | Reportable Segment | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pasadena, CA | Corporate Headquarters | Corporate | ||
| Adelaide, South Australia, Australia | Office Building | RME | ||
| Arlington, VA | Office Building | WEI | ||
| Bellevue, WA | Office Building | WEI | ||
| Fairfax, VA | Office Building | WEI | ||
| London, United Kingdom | Office Building | RME | ||
| New York, NY | Office Building | WEI / RME | ||
| Perth, Western Australia, Australia | Office Building | RME | ||
| Pittsburgh, PA | Office Building | WEI / RME | ||
| Sydney, New South Wales, Australia | Office Building | RME |
For a description of our material pending legal and regulatory proceedings and settlements, see Note 18, "Commitments and Contingencies" of the "Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements" included in Item 8.
Item 4. Mine Safety Disclosures
Section 1503 of the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act (the "Dodd-Frank Act") requires domestic mine operators to disclose violations and orders issued under the Mine Act by the U.S. Mine Safety and Health Administration. We do not act as the owner of any mines, but we may act as a mining operator as defined under the Mine Act where we may be an independent contractor performing services or construction at such mine. Information concerning mine safety violations or other regulatory matters required by Section 1503(a) of the Dodd-Frank Act and Item 104 of Regulation S-K is included in Exhibit 95.
45
Item 5. Market for Registrant's Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
Our common stock is traded on the NASDAQ Global Select Market under the symbol TTEK. There were 1,484 stockholders of record at November 7, 2016. The high and low sales prices per share for the common stock for the last two fiscal years, as reported by the NASDAQ Global Select Market, are set forth in the following tables.
| |
Prices | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
High | Low | |||||
| Fiscal 2016 | |
|
|||||
First quarter |
$ | 28.20 | $ | 23.80 | |||
Second quarter |
29.60 | 22.85 | |||||
Third quarter |
31.74 | 28.01 | |||||
Fourth quarter |
36.24 | 29.13 | |||||
Fiscal 2015 |
|||||||
First quarter |
$ | 27.84 | $ | 23.68 | |||
Second quarter |
27.25 | 22.98 | |||||
Third quarter |
27.48 | 23.87 | |||||
Fourth quarter |
27.52 | 24.12 | |||||
During fiscal 2016, we declared and paid dividends totaling $0.34 per share ($0.08 for the first and second quarters and $0.09 for the third and fourth quarters) of our common stock. In fiscal 2015, we paid dividends totaling $0.30 per share ($0.07 for the first and second quarters, and $0.08 for the third and fourth quarters) of our common stock. We currently intend to continue paying dividends on a quarterly basis, although the declaration of any future dividends will be determined by our Board of Directors and will depend on available cash, estimated cash needs, earnings, and capital requirements, as well as limitations in our long-term debt agreements.
Subsequent Event. On November 7, 2016, the Board of Directors declared a quarterly cash dividend of $0.09 per share payable on December 14, 2016 to stockholders of record as of the close of business on December 1, 2016.
For information regarding our stock-based compensation, see Note 11, "Stockholders' Equity and Stock Compensation Plans" of the "Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements" included in Item 8.
The following graph shows a comparison of our cumulative total returns with those of the NASDAQ Market Index and the S&P 1500 Construction and Engineering Index. The graph assumes that the value of an investment in our common stock and in each such index was $100 on October 2, 2011, and that all dividends have been reinvested. During fiscal 2016, we declared and paid dividends in the first and second quarters totaling $0.16 per share ($0.08 each quarter) on our common stock and paid dividends in
46
the third and fourth quarters totaling $0.18 per share ($0.09 each quarter) on our common stock. We declared and paid dividends totaling $0.30 and $0.14 per share in fiscal 2015 and 2014, respectively. We did not pay any dividends prior to fiscal 2014. Our self-selected Peer Group Index is the S&P 1500 Construction and Engineering Index. The comparison in the graph below is based on historical data and is not intended to forecast the possible future performance of our common stock.
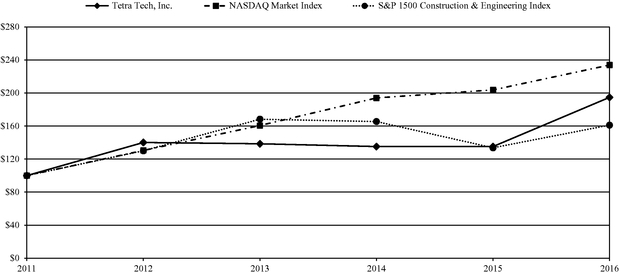
ASSUMES $100 INVESTED ON OCTOBER 02, 2011
ASSUMES DIVIDEND REINVESTED
FISCAL YEAR ENDED OCTOBER 02, 2016
| |
2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Tetra Tech, Inc. |
100.00 | 140.13 | 138.63 | 135.21 | 135.24 | 194.76 | |||||||||||||
NASDAQ Market Index |
100.00 | 130.53 | 160.67 | 194.05 | 203.86 | 234.02 | |||||||||||||
S&P 1500 C&E Index |
100.00 | 130.08 | 168.32 | 165.49 | 133.72 | 161.18 | |||||||||||||
The performance graph above and related text are being furnished solely to accompany this annual report on Form 10-K pursuant to Item 201(e) of Regulation S-K, and are not being filed for purposes of Section 18 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, and are not to be incorporated by reference into any of our filings with the SEC, whether made before or after the date hereof, regardless of any general incorporation language in such filing.
In June 2013, our Board of Directors authorized a stock repurchase program under which we could repurchase up to $100 million of our common stock. In February 2014, the Board amended this repurchase program to authorize the repurchase of up to $30 million in open market purchases through September 2014, revised the pricing parameters and extended the program through fiscal 2014. Stock repurchases could be made on the open market or in privately negotiated transactions with third parties. From the inception of this repurchase program through September 28, 2014, we repurchased through open market purchases a total of 3.9 million shares at an average price of $25.59 per share, for a total cost of $100 million. On November 10, 2014, the Board authorized a new stock repurchase program under which we could repurchase up to $200 million of our common stock over the next two years. As of October 2, 2016, we repurchased through open market purchases a total of 7.4 million shares at an average price of $26.91, for a total cost of $200 million under this repurchase program. These shares were repurchased
47
during the period from November 24, 2014 through October 2, 2016. A summary of the repurchase activity for the 3 months ended October 2, 2016 is as follows:
| Period | Total Number of Shares Purchased |
Average Price Paid per Share |
Total Number of Shares Purchased as Part of Publicly Announced Plans or Programs |
Maximum Dollar Value that May Yet be Purchased Under the Plans or Programs |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
|
||||||||||||
June 27, 2016 – July 24, 2016 |
196,503 | 30.86 | 196,503 | 18,436,974 | |||||||||
July 25, 2016 – August 28, 2016 |
282,930 | 33.48 | 282,930 | 8,964,214 | |||||||||
August 29, 2016 – October 2, 2016 |
253,045 | 35.43 | 253,045 | – | |||||||||
Subsequent Event. On November 7, 2016, our Board of Directors authorized a new stock repurchase program under which we could repurchase up to $200 million of our common stock.
Item 6. Selected Financial Data
The following selected financial data was derived from our audited consolidated financial statements. The selected financial data presented below should be read in conjunction with the information contained in Item 7, "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations," and our consolidated financial statements and the notes thereto contained in Item 8, "Financial Statements and Supplementary Data," of this report.
| |
Fiscal Year Ended | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
October 2, 2016 |
September 27, 2015 |
September 28, 2014 |
September 29, 2013 |
September 30, 2012 |
|||||||||||
| Statements of Operations Data | (in thousands, except per share data) |
|||||||||||||||
Revenue |
$ |
2,583,469 |
$ |
2,299,321 |
$ |
2,483,814 |
$ |
2,613,755 |
$ |
2,711,075 |
||||||
Operating income |
135,855 | 87,684 | 153,833 | 20,218 | 166,367 | |||||||||||
Net income (loss) attributable to Tetra Tech |
83,783 | 39,074 | 108,266 | (2,141 | ) | 104,380 | ||||||||||
Diluted net income (loss) attributable to Tetra Tech per share |
1.42 | 0.64 | 1.66 | (0.03 | ) | 1.63 | ||||||||||
Cash dividends paid per share |
0.34 | 0.30 | 0.14 | – | – | |||||||||||
Balance Sheet Data |
||||||||||||||||
Total assets |
$ |
1,800,779 |
$ |
1,559,242 |
$ |
1,776,404 |
$ |
1,799,092 |
$ |
1,671,030 |
||||||
Long-term debt, net of current portion |
331,501 | 180,972 | 192,842 | 203,438 | 81,047 | |||||||||||
Tetra Tech stockholders' equity |
869,259 | 856,325 | 1,012,079 | 997,763 | 1,018,970 | |||||||||||
Item 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
The following analysis of our financial condition and results of operations should be read in conjunction with Part I of this report, as well as our consolidated financial statements and accompanying notes in Item 8. The following analysis contains forward-looking statements about our future results of operations and expectations. Our actual results and the timing of events could differ materially from those described herein. See Part 1, Item 1A, "Risk Factors" for a discussion of the risks, assumptions, and uncertainties affecting these statements.
48
OVERVIEW OF RESULTS AND BUSINESS TRENDS
General. On an overall basis, our fiscal 2016 operating results reflected a significant improvement compared to fiscal 2015. Our revenue growth resulted from broad-based contract wins across our end markets, and was led by growth in U.S. federal government, U.S. state and local government, and U.S. commercial activities in waste management and environmental remediation. In fiscal 2016, we completed acquisitions that had a material impact on our financial results. On January 18, 2016, we acquired Coffey, headquartered in Sydney, Australia. Coffey had approximately 3,300 staff delivering technical and engineering solutions in international development and geoscience. Coffey significantly expands our geographic presence, particularly in Australia and Asia Pacific, and is part of our RME segment. In addition to Australia, Coffey's international development business has operations supporting federal government agencies in the U.S. and the United Kingdom. In the second quarter of fiscal 2016, we also acquired INDUS, headquartered in Vienna, Virginia. INDUS is a technology solutions firm focused on water data analytics, geospatial analysis, secure infrastructure, and software applications management for U.S. federal government customers, and is included in our WEI segment. We report results of operations based on 52 or 53-week periods ending on the Sunday nearest September 30. Fiscal years 2016, 2015 and 2014 contained 53, 52 and 52 weeks, respectively.
In fiscal 2016, our revenue increased 12.4% compared to fiscal 2015. The fiscal 2016 acquisitions contributed revenue of $320.6 million in fiscal 2016 since their respective acquisition dates. Excluding these contributions, our revenue decreased 1.6% in fiscal 2016 compared to last year. This decline primarily resulted from adverse foreign exchange rate fluctuations as the U.S. dollar was stronger on average in fiscal 2016 versus fiscal 2015 against most of the foreign currencies in which we conduct our international business, particularly the Canadian dollar. In addition, the revenue decline reflects a reduction in construction activities compared to last year, which resulted from our decision in fiscal 2014 to exit from select fixed-price construction markets in which RCM operated. On a constant currency basis, revenue from our ongoing business in fiscal 2016, excluding RCM and the fiscal 2016 acquisitions, increased 1.8% compared to fiscal 2015.
International. Our international business increased 28.3% in fiscal 2016 compared to the same period last year. This growth was primarily due to Coffey, which contributed international revenue of $211.6 million in fiscal 2016 from the acquisition date. Excluding this contribution but including the adverse impact of foreign exchange rate fluctuations, our international business decreased 9.2% in fiscal 2016 compared to last year. Excluding the impact of foreign exchange, our ongoing international business declined 2.1% compared to fiscal 2015, which reflects the commodity-driven slow-down in economic activity in Canada. We anticipate increased international revenue in fiscal 2017. However, if commodity prices remain low or decrease further, our international business could be negatively impacted.
U.S. Commercial. Our U.S. commercial business increased 3.7% in fiscal 2016 compared to fiscal 2015. This growth primarily reflects increased waste management and environmental remediation activities that were partially offset by reduced work for oil and gas clients. We expect our U.S. commercial revenue to be stable in fiscal 2017.
U.S. Federal Government. Our U.S. federal government business increased 10.5% in fiscal 2016 compared to fiscal 2015. Excluding the contributions from the fiscal 2016 acquisitions, our U.S. federal government business decreased 4.7% in fiscal 2016 compared to last year, partially due to the reduction in fixed-price construction activities in the RCM segment. Excluding these activities and the contributions from the fiscal 2016 acquisitions, our U.S. federal government revenue was flat in fiscal 2016 compared to last year. We experienced increased activity on civilian federal projects, which offset reduced activity on DoD projects. During periods of economic volatility, our U.S. federal government clients have historically been the most stable and predictable. We anticipate growth in U.S. federal revenue in fiscal 2017.
49
U.S. State and Local Government. Our U.S. state and local government business increased 7.9% in fiscal 2016 compared to fiscal 2015. We experienced this increase despite the impact of the aforementioned reduction in certain construction activities, especially those related to state transportation projects in the RCM segment. Excluding these activities, our U.S. state and local government revenue increased 10.8% in fiscal 2016 compared to last year. Many state and local government agencies are experiencing improved financial conditions that enable them to address major long-term infrastructure requirements, including the need for maintenance, repair, and upgrading of existing critical infrastructure and the need to build new facilities. As a result, we experienced broad-based growth in our U.S. state and local government project-related infrastructure revenue. We expect our U.S. state and local government business to show growth during fiscal 2017.
Fiscal 2016 Compared to Fiscal 2015
Consolidated Results of Operations
| |
Fiscal Year Ended | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
|
|
Change | ||||||||||
| |
October 2, 2016 |
September 27, 2015 |
|||||||||||
| |
$ | % | |||||||||||
| |
($ in thousands) |
||||||||||||
Revenue |
$ | 2,583,469 | $ | 2,299,321 | $ | 284,148 | 12.4 | % | |||||
Subcontractor costs |
(654,264 | ) | (580,606 | ) | (73,658 | ) | (12.7 | ) | |||||
Revenue, net of subcontractor costs (1) |
1,929,205 | 1,718,715 | 210,490 | 12.2 | |||||||||
Other costs of revenue |
(1,598,994 | ) | (1,402,925 | ) | (196,069 | ) | (14.0 | ) | |||||
Gross profit |
330,211 | 315,790 | 14,421 | 4.6 | |||||||||
Selling, general and administrative expenses |
(171,985 | ) | (170,456 | ) | (1,529 | ) | (0.9 | ) | |||||
Acquisition and integration expenses |
(19,548 | ) | – | (19,548 | ) | NM | |||||||
Contingent consideration – fair value adjustments |
(2,823 | ) | 3,113 | (5,936 | ) | (190.7 | ) | ||||||
Impairment of goodwill and other intangible assets |
– | (60,763 | ) | 60,763 | 100.0 | ||||||||
Operating income |
135,855 | 87,684 | 48,171 | 54.9 | |||||||||
Interest expense – net |
(11,389 | ) | (7,363 | ) | (4,026 | ) | (54.7 | ) | |||||
Income before income tax expense |
124,466 | 80,321 | 44,145 | 55.0 | |||||||||
Income tax expense |
(40,613 | ) | (41,093 | ) | 480 | 1.2 | |||||||
Net income including noncontrolling interests |
83,853 | 39,228 | 44,625 | 113.8 | |||||||||
Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests |
(70 | ) | (154 | ) | 84 | 54.5 | |||||||
Net income attributable to Tetra Tech |
83,783 | 39,074 | 44,709 | 114.4 | |||||||||
Diluted earnings per share |
$ | 1.42 | $ | 0.64 | $ | 0.78 | 121.9 | ||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
- (1)
- We believe that the presentation of "Revenue, net of subcontractor costs", which is a non-GAAP financial measure, enhances investors' ability to analyze our business trends and performance because it substantially measures the work performed by our employees. In the course of providing services, we routinely subcontract various services and, under certain USAID programs, issue grants. Generally, these subcontractor costs and grants are passed through to our clients and, in accordance with GAAP and industry practice, are included in our revenue when it is our contractual responsibility to procure or manage these activities. Because subcontractor services can vary significantly from project to project and period to period, changes in revenue may not necessarily be indicative of our business trends. Accordingly, we segregate subcontractor costs from revenue to promote a
50
better understanding of our business by evaluating revenue exclusive of costs associated with external service providers.
NM = not meaningful
The following table reconciles our reported results to non-GAAP ongoing results, which exclude the RCM results, certain purchase accounting-related adjustments, and the impact of changes in foreign exchange translation rates in fiscal 2016 compared to fiscal 2015. Ongoing results also exclude Coffey-related acquisition and integration expenses, and debt pre-payment fees in fiscal 2016. Additionally, ongoing diluted earnings per share ("EPS") for fiscal 2016 excludes the benefit of the retroactive extension of the research and development ("R&D") credits described below. The effective tax rate applied to the adjustments to EPS to arrive at ongoing EPS averaged 25% and 8% in fiscal 2016 and fiscal 2015, respectively. We apply the relevant marginal statutory tax rate based on the nature of the adjustments and the tax jurisdiction in which they occur. These average rates are lower than our overall effective tax rates due to certain acquisition and integration expenses incurred in fiscal 2016 and most of the impairment of goodwill and other intangible assets in fiscal 2015, which had no tax benefit. Both EPS and ongoing EPS were calculated using diluted weighted-average common shares outstanding for the respective periods as reflected in our consolidated statements of income.
| |
Fiscal Year Ended | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
|
|
Change | ||||||||||
| |
October 2, 2016 |
September 27, 2015 |
|||||||||||
| |
$ | % | |||||||||||
Revenue |
$ | 2,583,469 | $ | 2,299,321 | $ | 284,148 | 12.4 | % | |||||
Foreign exchange |
40,749 | – | 40,749 | – | |||||||||
RCM |
(52,150 | ) | (86,575 | ) | 34,425 | – | |||||||
Ongoing revenue |
$ | 2,572,068 | $ | 2,212,746 | $ | 359,322 | 16.2 | ||||||
Revenue, net of subcontractor costs |
$ | 1,929,205 | $ | 1,718,715 | $ | 210,490 | 12.2 | ||||||
Foreign exchange |
37,684 | – | 37,684 | – | |||||||||
RCM |
(17,267 | ) | (23,275 | ) | 6,008 | – | |||||||
Ongoing revenue, net of subcontractors costs |
$ | 1,949,622 | $ | 1,695,440 | $ | 254,182 | 15.0 | ||||||
Operating income |
$ | 135,855 | $ | 87,684 | $ | 48,170 | 54.9 | ||||||
Foreign exchange |
1,944 | – | 1,944 | – | |||||||||
Acquisition and integration expenses |
19,548 | – | 19,548 | – | |||||||||
Contingent consideration – fair value adjustments |
2,823 | (3,113 | ) | 5,936 | – | ||||||||
Impairment of goodwill and other intangible assets |
– | 60,763 | (60,763 | ) | – | ||||||||
Subtotal |
160,170 | 145,334 | 14,836 | 10.2 | |||||||||
RCM |
11,834 | 8,614 | 3,220 | – | |||||||||
Ongoing operating income |
$ | 172,004 | $ | 153,948 | $ | 18,056 | 11.7 | % | |||||
EPS |
$ | 1.42 | $ | 0.64 | $ | 0.78 | 121.9 | ||||||
Contingent consideration – fair value adjustments |
0.03 | (0.04 | ) | 0.07 | – | ||||||||
RCM |
0.14 | 0.10 | 0.04 | – | |||||||||
Acquisition and integration expenses |
0.29 | – | 0.29 | – | |||||||||
Coffey debt prepayment |
0.03 | – | 0.03 | – | |||||||||
Impairment of goodwill and other intangible assets |
– | 0.93 | (0.93 | ) | – | ||||||||
Retroactive R&D tax |
(0.03 | ) | (0.02 | ) | (0.01 | ) | – | ||||||
Ongoing EPS |
$ | 1.88 | $ | 1.61 | $ | 0.27 | 16.8 | ||||||
Foreign exchange |
0.03 | – | 0.03 | – | |||||||||
Ongoing EPS, net of foreign exchange |
$ | 1.91 | $ | 1.61 | $ | 0.30 | 18.6 | ||||||
51
In fiscal 2016, revenue and revenue, net of subcontractor costs, increased $284.1 million, or 12.4%, and $210.5 million, or 12.2%, respectively, compared to fiscal 2015. These results include the above-described fluctuation in foreign exchange rates and the reduction in certain construction activities compared to last year. Revenue declines caused by foreign exchange rate fluctuations resulted from a stronger U.S. dollar versus most of the foreign currencies in which we conduct our international business, particularly the Canadian dollar. These fluctuations negatively impacted revenue and revenue, net of subcontractor costs, by $40.7 million and $37.7 million, respectively, in fiscal 2016 compared to last year. Revenue and revenue, net of subcontractor costs, from the exited construction activities, which are reported in the RCM segment, declined $34.4 million and $6.0 million, respectively, in fiscal 2016 compared to fiscal 2015.
Our ongoing revenue and revenue, net of subcontractor costs, increased 16.2% and 15.0%, respectively, in fiscal 2016 compared to fiscal 2015. These increases reflect combined revenue and revenue, net of subcontractor costs, of $320.6 million and $233.1 million, respectively, in fiscal 2016 from the fiscal 2016 acquisitions since their respective acquisition dates in the second quarter of fiscal 2016. Excluding these contributions, our ongoing revenue and revenue, net of subcontractor costs, increased 1.8% and 1.2%, respectively, in fiscal 2016 compared to last year. These results reflect increased commercial and state and local government activity in our ongoing U.S. operations. On a combined basis, commercial and state and local government revenue and revenue, net of subcontractor costs in our ongoing U.S. operations increased $52.5 million and $34.1 million, respectively, in fiscal 2016 compared to fiscal 2015, primarily due to increased waste management, environmental remediation, and infrastructure activities. However, these increases were offset by a decline in our international activities that was caused primarily by the commodity-driven slowdown in economic activity in Canada.
Our operating income increased $48.2 million in fiscal 2016 compared to fiscal 2015. Our operating income in 2016 was reduced by Coffey-related acquisition and integration expenses of $19.5 million. For further detailed information regarding these expenses, see "Fiscal 2016 Acquisition and Integration Expenses" below. In addition, losses of $2.8 million resulting from changes in the estimated fair value of contingent earn-out liabilities reduced our operating income in fiscal 2016. These earn-out losses compare to a gain of $3.1 million in fiscal 2015 and are described below under "Fiscal 2016 and 2015 Earn-Out Adjustments." Further, we recognized a non-cash goodwill and other intangible asset impairment charge of $60.8 million in fiscal 2015 related to our GMP reporting unit, which is described below under "Fiscal 2015 Impairment of Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets." The aforementioned year-over-year foreign exchange rate fluctuations reduced operating income by $1.9 million in fiscal 2016 compared to fiscal 2015. The loss from exited construction activities in our RCM segment was $11.8 million in fiscal 2016 compared to $8.6 million last year. Our RCM results are described below under "Remediation and Construction Management." Excluding these non-operating items, ongoing operating income increased $18.1 million, or 11.7%, in fiscal 2016 compared to fiscal 2015.
The increase in our ongoing operating income in fiscal 2016 primarily reflects improved results in our RME segment compared to last year. On a constant currency basis, RME's ongoing operating income increased $21.1 million in fiscal 2016 compared to last year. This increase includes operating income of $12.5 million from Coffey since the acquisition date. Our RME results are described below under "Resource Management and Energy." The higher operating income in the RME segment was partially offset by intangible amortization, which increased by $1.9 million in fiscal 2016 compared to last year.
Interest expense, net was $11.4 million in fiscal 2016, compared to $7.4 million in the same period last year. Interest expense in fiscal 2016 includes Coffey-related debt pre-payment fees of $1.9 million that were incurred in the second quarter. The remaining increase in interest expense reflects additional borrowings to fund the Coffey acquisition.
52
Our effective tax rates for fiscal 2016 and 2015 were 32.6% and 51.2%, respectively. In fiscal 2016, we incurred $13.3 million of acquisition and integration expenses and debt pre-payment fees for which no tax benefit was recognized. Of this amount, $6.4 million resulted from acquisition expenses that were not tax deductible, and $6.9 million resulted from integration expenses and debt pre-payment fees incurred in jurisdictions with current and historical net operating losses where the related deferred tax asset was fully reserved. Additionally, during the first quarter of fiscal 2016, the Protecting Americans from Tax Hikes Act of 2015 was signed into law which permanently extended the federal R&D credits retroactive to January 1, 2015. Our income tax expense for fiscal 2016 included a tax benefit of $2.0 million attributable to operating income during the last nine months of fiscal 2015, primarily related to the retroactive recognition of the R&D credits. Our income tax expense for fiscal 2015 included a similar retroactive tax benefit of $1.2 million attributable to operating income during the last nine months of fiscal 2014. Our effective tax rate in fiscal 2015 also reflected the impact of the $60.8 million goodwill and intangible asset impairment charge, of which most was not tax deductible. Excluding these items, our effective tax rates for fiscal 2016 and 2015 were 30.9% and 32.5%, respectively. The lower tax rate this year primarily reflects a measurement change in tax positions taken in prior years relating in large part to developments in our ongoing IRS examination that reduced our effective tax rate by 2.0% in fiscal 2016.
EPS was $1.42 in fiscal 2016, compared to $0.64 in fiscal 2015. This comparison reflects the acquisition and integration expenses and debt pre-payment fees of $21.5 million ($19.0 million after tax) in fiscal 2016. These charges reduced EPS by $0.32 per share in fiscal 2016. Additionally, EPS in fiscal 2015 was lower due to the $60.8 million ($57.3 million after-tax) non-cash impairment charge for goodwill and other intangible assets, which reduced EPS by $0.93. The other non-operating items described above (foreign exchange, earn-out gains/losses, and RCM segment results) also adversely affected the year-over-year EPS comparisons. On the same basis as our ongoing operating income, EPS was $1.88 in fiscal 2016 compared to $1.61 last year.
Fiscal 2016 Acquisition and Integration Expenses
In fiscal 2016, we incurred Coffey-related acquisition and integration expenses of $19.5 million. The $7.9 million of acquisition expenses were primarily for professional services, such as legal and investment banking, to support the transaction. Throughout the remainder of fiscal 2016 subsequent to the acquisition date, we incurred costs of $11.6 million on integration activities, including the elimination of redundant general and administrative costs, real estate consolidation, and conversion of information technology platforms. As of October 2, 2016, these activities were substantially complete and all of the related costs had been paid.
Fiscal 2016 and 2015 Earn-Out Adjustments
In both fiscal 2016 and 2015, our operating income included significant non-cash adjustments related to our estimated contingent earn-out liabilities. We review and re-assess the estimated fair value of contingent consideration on a quarterly basis, and the updated fair value could differ materially from the initial estimates. During fiscal 2016, we increased our contingent earn-out liabilities and reported related losses in operating income of $2.8 million. These losses include a $1.8 million charge that reflected our updated valuation of the contingent consideration liability for CEG. This valuation included our updated projection of CEG's financial performance during the earn-out period, which exceeded our original estimate at the acquisition date. The remaining $1.0 million loss represented the final cash settlement of an earn-out liability that was valued at $0 at the end of fiscal 2015.
During fiscal 2015, we recorded a decrease in our contingent earn-out liabilities and reported a related gain in operating income of $3.1 million. This gain resulted from an updated valuation of the contingent consideration liability for Caber Engineering Inc. ("Caber"). Our assessment of the Caber liability included a review of the status of on-going projects in Caber's backlog and the inventory of
53
prospective new contract awards. We also considered the status of the upstream oil and gas industry in Western Canada, particularly in light of the recent decline in oil prices. As a result of this assessment, we concluded that Caber's operating income in the second year post-acquisition would be lower than our original estimate at the acquisition date and our subsequent estimates through fiscal 2014. We also concluded that Caber's operating income for the second earn-out period, which ended in the first quarter of fiscal 2015, would be lower than the minimum requirement of C$4.6 million to earn any contingent consideration. Accordingly, in fiscal 2015, we reduced the Caber contingent earn-out liability to $0, which resulted in a gain of $3.1 million. When we determined that Caber's operating income would be lower than our original estimate at the acquisition date, we also evaluated the related goodwill for potential impairment. We determined that the lower income projections were the result of temporary events, and did not negatively impact Caber's longer-term performance or result in a goodwill impairment.
Fiscal 2015 Impairment of Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets
In the fourth quarter of fiscal 2015, the mining sector continued to contract in response to lower global growth expectations driven in large part by China's actual and projected slower economic growth. Consistent with this trend, our mining customers continued their curtailment of capital spending for new mining projects. As a result, our GMP reporting unit experienced a 25% decline in revenue in the fourth quarter of fiscal 2015 compared to the same period of fiscal 2014. This negative trend was compared to the expected revenue growth of approximately 3% in the previous goodwill impairment test, performed as of June 30, 2014. Because of these results, we performed a strategic review of GMP in the fourth quarter of fiscal 2015, and determined that our mining activities would likely decline further in fiscal 2016, and that revenue and profits would not return to acceptable levels of performance in the foreseeable future. We also decided to redeploy our mining resources into other operational areas that have better growth and profitability prospects. Consequently, as of the first day of fiscal 2016, GMP was no longer a reporting unit. We considered GMP's financial performance and prospects in our goodwill impairment analysis in the fourth quarter of fiscal 2015 and determined that GMP's fair value had fallen significantly below its carrying value, including goodwill. As required, we performed further analysis to measure the amount of the impairment loss and, as a result, we wrote-off all of GMP's goodwill and identifiable intangible assets and recorded a related impairment charge of $60.8 million ($57.3 million after-tax) in the fourth quarter of fiscal 2015. The related goodwill and identifiable intangible assets that were determined not to be recoverable totaled $58.1 million and $2.7 million, respectively. We had no goodwill impairment in fiscal 2016.
Segment Results of Operations
In fiscal 2016, we managed our continuing operations under two reportable segments. We report our water resources, water and wastewater treatment, environment, and infrastructure engineering activities in the WEI reportable segment. Our RME reportable segment includes our oil and gas, energy, international development, waste management, remediation, and utilities services. In addition, we report the results of the wind-down of our non-core construction activities in the RCM reportable segment.
54
Water, Environment and Infrastructure
| |
Fiscal Year Ended | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
|
|
Change | ||||||||||
| |
October 2, 2016 |
September 27, 2015 |
|||||||||||
| |
$ | % | |||||||||||
| |
($ in thousands) |
||||||||||||
Revenue |
$ | 1,028,281 | $ | 993,631 | $ | 36,650 | 3.5 | % | |||||
Subcontractor costs |
(274,826 | ) | (230,355 | ) | (44,471 | ) | 19.3 | ||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Revenue, net of subcontractor costs |
$ | 753,455 | $ | 763,276 | $ | (9,821 | ) | (1.3 | ) | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Operating income |
$ | 95,996 | $ | 93,142 | $ | 2,854 | 3.1 | ||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Revenue increased 3.5% and revenue, net of subcontractor costs, decreased 1.3% in fiscal 2016 compared to fiscal 2015. On a constant currency basis, revenue and revenue, net of subcontractor costs, increased 5.0% and 0.5%, respectively, in fiscal 2016 compared to last year. As described above, foreign exchange rate fluctuations negatively impacted revenue and revenue, net of subcontractor costs, in the amounts of $15.3 million and $14.0 million, respectively, for fiscal 2016 compared to last year. The increases in revenue and revenue, net of subcontractor costs, resulted primarily from increased U.S. federal activity and additional work on infrastructure projects for U.S. state and local government clients.
Operating income increased $2.9 million in fiscal 2016 compared to fiscal 2015. Operating margin, based on revenue, net of subcontractor costs, improved to 12.7% in fiscal 2016 from 12.2% last year. This improved profitability primarily reflects the full-year benefit in fiscal 2016 of measures taken throughout last year to improve operational efficiency, primarily in our Canadian operations. These actions included the right-sizing of general and administrative staff and real estate consolidations.
Resource Management and Energy
| |
Fiscal Year Ended | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
|
|
Change | ||||||||||
| |
October 2, 2016 |
September 27, 2015 |
|||||||||||
| |
$ | % | |||||||||||
| |
($ in thousands) |
||||||||||||
Revenue |
$ | 1,569,702 | $ | 1,282,046 | $ | 287,656 | 22.4 | % | |||||
Subcontractor costs |
(411,219 | ) | (349,882 | ) | (61,337 | ) | 17.5 | ||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Revenue, net of subcontractor costs |
$ | 1,158,483 | $ | 932,164 | $ | 226,319 | 24.3 | ||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Operating income |
$ | 112,202 | $ | 93,359 | $ | 18,843 | 20.2 | ||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Revenue and revenue, net of subcontractor costs, increased 22.4% and 24.3%, respectively, in fiscal 2016 compared to fiscal 2015. On a constant currency basis, revenue and revenue, net of subcontractor costs, increased 24.5% and 26.8%, respectively, in fiscal 2016, compared to last year. As in the WEI segment, foreign exchange rate fluctuations negatively impacted revenue and revenue, net of subcontractor costs in the amounts of $26.4 million and $23.7 million, respectively, in fiscal 2016 compared to last year. The increases are primarily due to Coffey contributions of $302.9 million of revenue and $220.6 million of revenue, net of subcontractor costs in fiscal 2016 since the acquisition date. On a constant currency basis, excluding the Coffey contribution, our revenue and revenue, net of subcontractor costs,
55
increased 0.9% and 3.2%, respectively, in fiscal 2016 compared to fiscal 2015. The increases primarily reflect higher waste management and international development revenue.
Operating income increased $18.8 million ($21.1 million on a constant currency basis) in fiscal 2016 compared to fiscal 2015. Coffey contributed operating income of $12.5 million in fiscal 2016 since the acquisition date. The $6.3 million increase in operating income, excluding Coffey, in fiscal 2016 reflects the higher waste management and international development revenue.
Remediation and Construction Management
| |
Fiscal Year Ended | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
|
|
Change | ||||||||||
| |
October 2, 2016 |
September 27, 2015 |
|||||||||||
| |
$ | % | |||||||||||
| |
($ in thousands) |
||||||||||||
Revenue |
$ | 52,150 | $ | 86,575 | $ | (34,425 | ) | (39.8 | )% | ||||
Subcontractor costs |
(34,883 | ) | (63,300 | ) | 28,417 | (44.9 | ) | ||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Revenue, net of subcontractor costs |
$ | 17,267 | $ | 23,275 | $ | (6,008 | ) | (25.8 | ) | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Operating loss |
$ | (11,834 | ) | $ | (8,614 | ) | $ | (3,220 | ) | (37.4 | ) | ||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Revenue and revenue, net of subcontractor costs, decreased $34.4 million and $6.0 million, respectively, in fiscal 2016 compared to fiscal 2015. These decreases resulted from our decision to wind-down the RCM construction activities. The operating loss in fiscal 2016 resulted from adverse changes in the estimated costs to complete several of the remaining projects and legal expenses to resolve various outstanding project claims. In addition, the fiscal 2016 operating loss of $11.8 million includes $7.9 million of losses related to uncollectible accounts receivable, including claims. This loss was partially offset by a gain of $4.6 million from the settlement of a claim with a U.S. federal government client for work completed in fiscal 2013. The remaining RCM backlog at the end of fiscal 2016 was $26 million. The related work to be performed in this segment will be substantially completed in 2017.
56
Fiscal 2015 Compared to Fiscal 2014
Consolidated Results of Operations
| |
Fiscal Year Ended | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
|
|
Change | ||||||||||
| |
September 27, 2015 |
September 28, 2014 |
|||||||||||
| |
$ | % | |||||||||||
| |
($ in thousands) |
||||||||||||
Revenue |
$ | 2,299,321 | $ | 2,483,814 | $ | (184,493 | ) | (7.4 | )% | ||||
Subcontractor costs |
(580,606 | ) | (623,896 | ) | 43,290 | 6.9 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Revenue, net of subcontractor costs(1) |
1,718,715 | 1,859,918 | (141,203 | ) | (7.6 | ) | |||||||
Other costs of revenue |
(1,402,925 | ) | (1,577,481 | ) | 174,556 | 11.1 | |||||||
Selling, general and administrative expenses |
(170,456 | ) | (187,298 | ) | 16,842 | 9.0 | |||||||
Contingent consideration – fair value adjustments |
3,113 | 58,694 | (55,581 | ) | 94.7 | ||||||||
Impairment of goodwill and other intangible assets |
(60,763 | ) | – | (60,763 | ) | (100.0 | ) | ||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Operating income |
87,684 | 153,833 | (66,149 | ) | (43.0 | ) | |||||||
Interest expense – net |
(7,363 | ) | (9,490 | ) | 2,127 | 22.4 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Income before income tax expense |
80,321 | 144,343 | (64,022 | ) | (44.4 | ) | |||||||
Income tax expense |
(41,093 | ) | (35,668 | ) | (5,425 | ) | (15.2 | ) | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net income including noncontrolling interests |
39,228 | 108,675 | (69,447 | ) | (63.9 | ) | |||||||
Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests |
(154 | ) | (409 | ) | 255 | 62.3 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net income attributable to Tetra Tech |
$ | 39,074 | $ | 108,266 | $ | (69,192 | ) | (63.9 | ) | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
- (1)
- We believe that the presentation of "Revenue, net of subcontractor costs", which is a non-GAAP financial measure, enhances investors' ability to analyze our business trends and performance because it substantially measures the work performed by our employees. In the course of providing services, we routinely subcontract various services and, under certain USAID programs, issue grants. Generally, these subcontractor costs and grants are passed through to our clients and, in accordance with GAAP and industry practice, are included in our revenue when it is our contractual responsibility to procure or manage these activities. Because subcontractor services can vary significantly from project to project and period to period, changes in revenue may not necessarily be indicative of our business trends. Accordingly, we segregate subcontractor costs from revenue to promote a better understanding of our business by evaluating revenue exclusive of costs associated with external service providers.
In fiscal 2015, revenue and revenue, net of subcontractor costs, decreased $184.5 million, or 7.4%, and $141.2 million, or 7.6%, respectively, compared to fiscal 2014. These declines reflect the above-described reduction in construction activities and the fluctuation in foreign exchange rates. Revenue and revenue, net of subcontractor costs, from these construction activities, which are reported in the RCM segment, declined $134.5 million and $56.2 million, respectively, in fiscal 2015 compared to the previous year. Revenue declines caused by foreign exchange rate fluctuations resulted from a stronger U.S. dollar during fiscal 2015 versus most of the foreign currencies in which we conduct our international business, particularly the Canadian dollar. These fluctuations negatively impacted revenue and revenue, net of subcontractor costs, by $71.2 million and $64.4 million, respectively, in fiscal 2015 compared to fiscal 2014.
On a constant currency basis, our ongoing revenue and revenue, net of subcontractor costs, excluding the exited activities in the RCM segment increased 0.9% and decreased 1.2%, respectively, in fiscal 2015 compared to fiscal 2014. These results reflect increased state and local government and
57
commercial activity in our ongoing U.S. operations. On a combined basis, revenue and revenue, net of subcontractor costs, from these activities increased $78.3 million, or 8.6%, and $29.4 million, or 4.1%, respectively, in fiscal 2015 compared to the prior year, primarily due to increased environmental remediation, infrastructure, and energy-related activities. These increases were offset by a decline in our U.S. federal activity. Our ongoing U.S. federal revenue and revenue, net of subcontractor costs, decreased $46.4 million and $43.8 million, respectively, in fiscal 2015 compared to fiscal 2014, which primarily reflected less work for the DoD.
The following table reconciles our reported results to ongoing results, which exclude RCM results, purchase accounting adjustments, and the impact of foreign exchange translation:
| |
Fiscal Year Ended | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
|
|
Change | ||||||||||
| |
September 27, 2015 |
September 28, 2014 |
|||||||||||
| |
$ | % | |||||||||||
| |
($ in thousands) |
||||||||||||
Revenue |
$ | 2,299,321 | $ | 2,483,814 | $ | (184,493 | ) | (7.4 | )% | ||||
Foreign exchange |
71,227 | – | 71,227 | – | |||||||||
RCM |
(86,575 | ) | (221,109 | ) | 134,534 | – | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Ongoing revenue |
2,283,973 | 2,262,705 | 21,268 | 0.9 | |||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Revenue, net of subcontractor cost |
1,718,715 | 1,859,918 | (141,203 | ) | (7.6 | ) | |||||||
Foreign exchange |
64,421 | – | 64,421 | – | |||||||||
RCM |
(23,275 | ) | (79,498 | ) | 56,223 | – | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Ongoing revenue, net of subcontractor costs |
1,759,861 | 1,780,420 | (20,559 | ) | (1.2 | ) | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Operating income |
87,684 | 153,833 | (66,149 | ) | (43.0 | ) | |||||||
Foreign exchange |
3,122 | – | 3,122 | – | |||||||||
Contingent consideration – fair value adjustments |
(3,113 | ) | (58,694 | ) | 55,581 | – | |||||||
Impairment of goodwill and other intangible assets |
60,763 | – | 60,763 | – | |||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Subtotal |
148,456 | 95,139 | 53,317 | 56.0 | |||||||||
RCM |
8,614 | 45,151 | (36,537 | ) | – | ||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Ongoing operating income |
$ | 157,070 | $ | 140,290 | $ | 16,780 | 12.0 | ||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Our operating income decreased to $87.7 million in fiscal 2015 from $153.8 million in fiscal 2014. We recognized a non-cash goodwill and other intangible asset charge of $60.8 million in the fourth quarter of fiscal 2015 related to our GMP reporting unit. This item is described above under "Fiscal 2015 Impairment of Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets." The operating income decline also reflects the reduction in net gains related to changes in the estimated fair value of contingent earn-out liabilities. The earn-out net gains in fiscal 2015 are discussed above under "Fiscal 2016 and 2015 Earn-Out Adjustments." The earn-out net gains in fiscal 2014 are discussed below under "Fiscal 2014 Earn-Out Adjustments." In addition, the loss from the exited construction activities in our RCM segment was $8.6 million in fiscal 2015 compared to $45.2 million the previous year. The fiscal 2014 RCM results included project-related charges that are described below under "Remediation and Construction Management." Additionally, the aforementioned year-over-year foreign exchange rate fluctuations reduced operating income by $3.1 million in fiscal 2015 compared to fiscal 2014. Excluding these non-operating items, ongoing operating income increased $16.8 million, or 12.0%, compared to fiscal 2014.
The increase in ongoing operating income was primarily due to improved results in our RME segment. On a constant currency basis, operating income in RME increased $10.9 million, or 12.9%, in fiscal 2015 compared to fiscal 2015. This increase was primarily driven by improved results in our
58
midstream oil and gas operations, particularly in Western Canada. In addition, lower intangible asset amortization of $5.6 million, on a constant currency basis, contributed to the higher year-over-year ongoing operating income.
In fiscal 2015, we recorded income tax expense of $41.1 million, representing an effective tax rate of 51.2%. This tax rate is higher than the expected statutory tax rate primarily due to the $60.8 million goodwill and intangible assets impairment charge most of which was not tax deductible. In fiscal 2014, we recorded income tax expense of $35.7 million, representing an effective tax rate of 24.7%, which was lower than the expected rate due to the impact of gains from changes to contingent consideration liabilities, most of which were not taxable. Excluding these items in both years, our effective tax rate was 32.3% in fiscal 2015 compared to 36.2% in fiscal 2014. During the first quarter of fiscal 2015, the Tax Increase Prevention Act of 2014 was signed into law. This law retroactively extended the federal R&D credits for amounts incurred from January 1, 2014 through December 31, 2014. Our income tax expense for fiscal 2015 includes a tax benefit of $1.2 million attributable to operating income during the last nine months of fiscal 2014, primarily related to the retroactive recognition of these credits. The remainder of the decline in the effective tax rate was primarily due to a higher proportion of operating income from international operations, in fiscal 2015 compared to fiscal 2014, which have lower tax rates than the U.S.
Fiscal 2014 Earn-Out Adjustments
In fiscal 2014, our operating income included net gains of $3.1 million related to net decreases in our estimated contingent earn-out liabilities. The fiscal 2014 net gains primarily resulted from updated valuations of the contingent consideration liabilities for Parkland Pipeline ("Parkland"), which is part of our Oil, Gas and Energy reporting unit, and American Environmental Group ("AEG"), which is part of our Waste Management Group reporting unit. Both of these reporting units are in the RME segment.
We review and re-assess the estimated fair value of contingent consideration on a quarterly basis, and the updated fair value could differ materially from the initial estimates. In fiscal 2014, we recorded decreases in our contingent earn-out liability for Parkland and reported related gains in operating income of $44.6 million. These gains resulted from Parkland's actual and projected post-acquisition performance falling below our initial expectations concerning the likelihood and timing of achieving the relevant operating income thresholds in each of the three years subsequent to the acquisition. In the second quarter of fiscal 2014, we updated the estimated cost to complete a large fixed-price contract at Parkland and determined that the project would be break-even compared to the significant profit estimated the previous quarter when the project was initiated. As a result, during the second quarter of fiscal 2014 we reversed $5.3 million of profit previously recognized on the project. This variance, and our updated estimate that the revenue for the remainder of the project would produce no operating income, resulted in our conclusion that Parkland's operating income in the first and second earn-out periods would fall below the minimum operating income thresholds in each such year. As a result, we reduced the contingent earn-out liability for the first and second earn-out periods to $0, which resulted in gains totaling $24.7 million ($5.6 million and $19.1 million in the first and second quarters of fiscal 2014, respectively). The remaining fiscal 2014 gain of $19.9 million was recognized in the fourth quarter of fiscal 2014, which reduced the related liability to $0 at the end of fiscal 2014.
In fiscal 2014, we also recorded net decreases in our contingent earn-out liability for AEG and reported related net gains in operating income of $12.4 million. AEG's first earn-out period ended on the last day of the first quarter of fiscal 2014. As a result, during the first quarter of fiscal 2014, we performed a preliminary calculation of the contingent consideration for the first earn-out period and concluded that AEG's operating income in that period would be higher than both our original estimate at the acquisition date and our previous quarterly estimates. As a result, we increased the contingent earn-out liability for the first earn-out period, which resulted in additional expense of $1.0 million. The contingent consideration of $9.1 million for the first earn-out period was paid in the second quarter of fiscal 2014.
59
During calendar 2014, which corresponded to AEG's second earn-out period, adverse weather conditions hindered AEG's ability to complete its project field work. As a result, in the third quarter of fiscal 2014, we updated our projection of AEG's operating income for its second earn-out period. This assessment included a review of the status of on-going projects in AEG's backlog, and the inventory of prospective new contract awards. As a result of this assessment, we concluded that AEG's operating income in the second earn-out period would be significantly lower than our original estimate at the acquisition date, and would fall below the minimum operating income threshold, but would still exceed $9.0 million of operating income in order to earn the additional earn-out payment. As a result, we reduced the contingent earn-out liability, which resulted in a gain of $8.9 million.
During the fourth quarter of fiscal 2014, we performed an updated projection of AEG's operating income for its second earn-out period based on actual results and the forecast for the remainder of the second earn-out period. Based on this analysis, we concluded that AEG's operating income in the second earn-out period would be lower than the $9.0 million needed to receive the $4.5 million of contingent consideration that remained accrued for performance in both earn-out years. As a result, we reduced the contingent earn-out liability to $0, which resulted in a gain of $4.5 million in the fourth quarter of fiscal 2014, and net gains of $12.4 million for all of fiscal 2014.
Each time we determined that AEG's and Parkland's operating income would be lower than our original estimate at the acquisition date, we also evaluated the related goodwill for potential impairment. In each case, we determined that the lower income projections were the result of temporary events, and did not negatively impact the reporting unit's longer term performance or result in goodwill impairment.
Segment Results of Operations
Water, Environment and Infrastructure
| |
Fiscal Year Ended | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
|
|
Change | ||||||||||
| |
September 27, 2015 |
September 28, 2014 |
|||||||||||
| |
$ | % | |||||||||||
| |
($ in thousands) |
||||||||||||
Revenue |
$ | 993,631 | $ | 1,018,522 | $ | (24,891 | ) | (2.4 | )% | ||||
Subcontractor costs |
(230,355 | ) | (207,411 | ) | (22,944 | ) | 11.1 | ||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Revenue, net of subcontractor costs |
$ | 763,276 | $ | 811,111 | $ | (47,835 | ) | (5.9 | ) | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Operating income |
$ | 93,142 | $ | 93,853 | $ | (711 | ) | (0.8 | ) | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Revenue and revenue, net of subcontractor costs, decreased 24.9 million, or 2.4%, and $47.8 million, or 5.9%, respectively, compared to fiscal 2014. As described above, foreign exchange rate fluctuations negatively impacted revenue and revenue, net of subcontractor costs, in the amounts of $29.2 million and $27.3 million, respectively, in fiscal 2015. On a constant currency basis, our revenue increased $4.3 million, or 0.4%, in fiscal 2015 compared to the previous year. This growth reflects an increase in revenue from U.S. state and local government infrastructure projects across a broad range of government agencies.
Operating income decreased $0.7 million, or 0.8%, in fiscal 2015 compared to fiscal 2014. On a constant currency basis, our operating income increased $1.2 million, or 1.3%. These comparisons are consistent with the revenue trends as our relative profit margins were stable year-over-year at 12.2% in fiscal 2015 and 11.6% in fiscal 2014.
60
Resource Management and Energy
| |
Fiscal Year Ended | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
|
|
Change | ||||||||||
| |
September 27, 2015 |
September 28, 2014 |
|||||||||||
| |
$ | % | |||||||||||
| |
($ in thousands) |
||||||||||||
Revenue |
$ | 1,282,046 | $ | 1,333,127 | $ | (51,081 | ) | (3.8 | )% | ||||
Subcontractor costs |
(349,882 | ) | (363,817 | ) | 13,397 | (3.8 | ) | ||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Revenue, net of subcontractor costs |
$ | 932,164 | $ | 969,310 | $ | (37,146 | ) | (3.8 | ) | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Operating income |
$ | 93,359 | $ | 84,862 | $ | 8,497 | 10.0 | ||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Revenue and revenue, net of subcontractor costs, decreased $51.1 million, or 3.8%, and $37.1 million, or 3.8%, respectively, compared to fiscal 2014. Foreign exchange rate fluctuations had an adverse impact on revenue and revenue, net of subcontractor costs, during fiscal 2015 in the amounts of $43.2 million and $37.1 million, respectively. On a constant currency basis, revenue decreased $7.9 million, or 0.6% in fiscal 2015 compared to fiscal 2014. These decreases primarily reflect a decline in mining and upstream oil and gas revenue, particularly in Canada and Brazil, which were down $58.6 million year-over-year. These decreases were substantially offset by increased midstream oil and gas revenue in both the U.S. and Western Canada.
Operating income increased $8.5 million in fiscal 2015 compared to fiscal 2014. This increase primarily reflects improved profit in our midstream oil and gas business in Western Canada. Further, our fiscal 2014 results included a $5.3 million profit reversal on a fixed price construction management project. The operating income increase was partially offset by declines in our other commodity-based activities, including upstream oil and gas services and mining-related activities.
Remediation and Construction Management
| |
Fiscal Year Ended | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
|
|
Change | ||||||||||
| |
September 27, 2015 |
September 28, 2014 |
|||||||||||
| |
$ | % | |||||||||||
| |
($ in thousands) |
||||||||||||
Revenue |
$ | 86,575 | $ | 221,108 | $ | (134,533 | ) | (60.8 | )% | ||||
Subcontractor costs |
(63,300 | ) | (141,611 | ) | 78,311 | (55.3 | ) | ||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Revenue, net of subcontractor costs |
$ | 23,275 | $ | 79,497 | $ | (56,222 | ) | (70.7 | ) | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Operating loss |
$ | (8,614 | ) | $ | (45,151 | ) | $ | 36,537 | 80.9 | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Revenue and revenue, net of subcontractor costs, decreased $134.5 million and $56.2 million, respectively, compared to the previous year. These decreases resulted from our decision to wind-down the RCM construction activities. The operating loss in fiscal 2015 reflects our updated evaluation of the collectability of certain claims as well as related legal costs, and the costs required to complete the remaining projects in the RCM segment. The operating loss in fiscal 2014 reflects project-related charges principally from adjustments to estimated costs at completion that increased project costs.
61
In fiscal 2014, primarily in the fourth quarter, we recorded project-related charges principally from adjustments to estimated costs at completion that increased project costs. These charges included amounts primarily related to two lines of business in the RCM segment with U.S. federal and state and local government clients that we decided to exit or wind-down in the fourth quarter of fiscal 2014.
One of the businesses we decided to exit or wind-down related to fixed-price contracts for project management, construction management, and construction services, primarily for U.S. federal government clients. In the course of performing the required work, we encountered delays related to defective designs, permit issues and differing site conditions, among other factors, that slowed our progress. Due to these delays, we determined that the costs to complete the projects would exceed the contract values. As a result, we recorded related pre-tax project charges of $20.5 million on these projects in fiscal 2014. These projects were substantially completed in fiscal 2015.
The other business we decided to exit or wind-down related to fixed-price contracts for transportation projects with state government agencies. During the execution of these contracts, numerous issues and events disrupted our plans and progress, including weather delays, differing site conditions, drainage design changes, lane closure delays, and revised soil testing requirements. These issues caused us to incur costs in excess of the contract values and increase our estimates of the expected costs to complete. As a result, we recorded pre-tax charges to operating income of $9.1 million in the fourth quarter of fiscal 2014. These projects are expected to be completed in 2017, with total estimated costs to complete of approximately $22 million as of October 2, 2016. If our costs increase above this estimate, we could record further losses.
FINANCIAL CONDITION, LIQUIDITY AND CAPITAL RESOURCES
Capital Requirements. Our primary sources of liquidity are cash flows from operations and borrowings under our credit facilities. Our primary uses of cash are to fund working capital, capital expenditures, stock repurchases, cash dividends and repayment of debt, as well as to fund acquisitions and earn-out obligations from prior acquisitions. We believe that our existing cash and cash equivalents, operating cash flows and borrowing capacity under our credit agreement, as described below, will be sufficient to meet our capital requirements for at least the next 12 months. On November 10, 2014, the Board of Directors authorized a stock repurchase program under which we could repurchase up to $200 million of our common stock over the succeeding two years, of which $200 million has been repurchased as of October 2, 2016. During fiscal 2016, we declared and paid dividends totaling $0.34 per share ($0.08 for the first and second quarters and $0.09 for the third and fourth quarters) of our common stock. In fiscal 2015, we paid dividends totaling $0.30 per share ($0.07 for the first and second quarters, and $0.08 for the third and fourth quarters) of our common stock.
Subsequent Events. On November 7, 2016, the Board of Directors declared a quarterly cash dividend of $0.09 per share payable on December 14, 2016 to stockholders of record as of the close of business on December 1, 2016. On November 7, 2016, our Board of Directors also authorized a new stock repurchase program under which we could repurchase up to $200 million of our common stock.
We use a variety of tax planning and financing strategies to manage our worldwide cash and deploy funds to locations where they are needed. We also indefinitely reinvest our foreign earnings, and our current plans do not demonstrate a need to repatriate these earnings. Should we require additional capital in the United States, we may elect to repatriate these foreign funds or raise capital in the United States through debt or equity. If we were to repatriate these foreign funds, we would be required to accrue and pay additional U.S. taxes less applicable foreign tax credits.
As of October 2, 2016, cash and cash equivalents were $160.5 million, an increase of $25.1 million compared to the fiscal 2015 year-end. The increase was due to cash generated from operating activities and
62
net borrowing, partially offset by cash used for business acquisitions, share repurchases, capital expenditures and dividends.
Operating Activities. For fiscal 2016, net cash provided by operating activities was $142.0 million, a decrease of $20.8 million compared to fiscal 2015. This decrease was due primarily to $30.5 million in acquisition and integration expenses related to Coffey paid in fiscal 2016.
Investing Activities. Net cash used in investing activities was $94.0 million, an increase of $73.0 million in fiscal 2016 compared to fiscal 2015. The increase primarily resulted from cash used for the acquisitions of Coffey and INDUS in the second quarter of fiscal 2016, which totaled $81.3 million.
Financing Activities. For fiscal 2016, net cash used in financing activities was $25.4 million, a decrease of $98.2 million, compared to the prior year. The decrease primarily relates to increased net borrowings of $91.2 million for the fiscal 2016 acquisitions previously discussed.
Debt Financing. On May 7, 2013, we entered into a credit agreement that provided for a $205 million term loan facility and a $460 million revolving credit facility both maturing in May 2018. On May 29, 2015, we entered into a third amendment to our credit agreement (as amended, the "Credit Agreement") that extended the maturity date for the term loan and the revolving credit facility to May 2020. The Credit Agreement is a $654.8 million senior secured, five-year facility that provides for a $194.8 million term loan facility (the "Term Loan Facility") and a $460 million revolving credit facility (the "Revolving Credit Facility"). The Credit Agreement allows us to, among other things, finance certain permitted open market repurchases of our common stock, permitted acquisitions, and cash dividends and distributions. The Revolving Credit Facility includes a $150 million sublimit for the issuance of standby letters of credit, a $20 million sublimit for swingline loans, and a $150 million sublimit for multicurrency borrowings. The interest rate provisions of the term loan and the revolving credit facility did not materially change.
The Term Loan Facility is subject to quarterly amortization of principal, with $10.3 million payable in year 1, and $15.4 million payable in years 2 through 5. The Term Loan may be prepaid at any time without penalty. We may borrow on the Revolving Credit Facility, at our option, at either (a) a Eurocurrency rate plus a margin that ranges from 1.15% to 2.00% per annum, or (b) a base rate for loans in U.S. dollars (the highest of the U.S. federal funds rate plus 0.50% per annum, the bank's prime rate or the Eurocurrency rate plus 1.00%) plus a margin that ranges from 0.15% to 1.00% per annum. In each case, the applicable margin is based on our Consolidated Leverage Ratio, calculated quarterly. The Term Loan Facility is subject to the same interest rate provisions. The interest rate of the Term Loan Facility at the date of inception was 1.57%. The Credit Agreement expires on May 29, 2020, or earlier at our discretion, upon payment in full of loans and other obligations.
As of October 2, 2016, we had $346.8 million in outstanding borrowings under the Credit Agreement, which was comprised of $176.8 million under the Term Loan Facility and $170 million under the Revolving Credit Facility at a weighted-average interest rate of 1.92% per annum. In addition, we had $1.3 million in standby letters of credit under the Credit Agreement. Our average effective weighted-average interest rate on borrowings outstanding at October 2, 2016 under the Credit Agreement, including the effects of interest rate swap agreements described in Note 13, "Derivative Financial Instruments" of the "Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements", was 2.52%. At October 2, 2016, we had $288.7 million of available credit under the Revolving Credit Facility, of which $222.4 million could be borrowed without a violation of our debt covenants. In addition, we entered into agreements with three banks to issue up to $53 million in standby letters of credit. The aggregate amount of standby letters of credit outstanding under these additional facilities and other bank guarantees was $25.3 million, of which $6 million was issued in currencies other than the U.S. dollar.
63
The Credit Agreement contains certain affirmative and restrictive covenants, and customary events of default. The financial covenants provide for a maximum Consolidated Leverage Ratio of 3.00 to 1.00 (total funded debt/EBITDA, as defined in the Credit Agreement) and a minimum Consolidated Fixed Charge Coverage Ratio of 1.25 to 1.00 (EBITDA, as defined in the Credit Agreement minus capital expenditures/cash interest plus taxes plus principal payments of indebtedness including capital leases, notes and post-acquisition payments).
At October 2, 2016, we were in compliance with these covenants with a consolidated leverage ratio of 1.91x and a consolidated fixed charge coverage ratio of 2.82x. Our obligations under the Credit Agreement are guaranteed by certain of our subsidiaries and are secured by first priority liens on (i) the equity interests of certain of our subsidiaries, including those subsidiaries that are guarantors or borrowers under the Credit Agreement, and (ii) our accounts receivable, general intangibles and intercompany loans, and those of our subsidiaries that are guarantors or borrowers.
At the time of acquisition, Coffey had an existing secured credit facility with a bank, comprised of an overdraft facility, a term facility and a bank guaranty facility. This facility was amended in March 2016 to extend the term of the existing facility to April 8, 2016, and allow for the issuance of a parent guarantee and release of certain subsidiary guarantors. On April 8, 2016, the facility was amended again to provide for a secured AUD$30 million facility, which may be used by Coffey for bank overdrafts, short-term cash advances or bank guarantees. This facility expires in April 2017, is secured by the assets of certain Australian and New Zealand subsidiaries, and is supported by a parent guarantee. At October 2, 2016, the amount outstanding under this facility consisted solely of bank guarantees of $5.6 million.
Inflation. We believe our operations have not been, and, in the foreseeable future, are not expected to be, materially adversely affected by inflation or changing prices due to the average duration of our projects and our ability to negotiate prices as contracts end and new contracts begin.
Dividends. Our Board of Directors has authorized the following dividends:
| |
Dividend Per Share | Record Date | Total Maximum Payment |
Payment Date | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
(in thousands, except per share data) |
|||||||||
November 10, 2014 |
$ | 0.07 | November 26, 2014 | $ | 4,372 | December 15, 2014 | ||||
January 26, 2015 |
$ | 0.07 | February 11, 2015 | $ | 4,258 | February 26, 2015 | ||||
April 27, 2015 |
$ | 0.08 | May 14, 2015 | $ | 4,810 | May 29, 2015 | ||||
July 27, 2015 |
$ | 0.08 | August 17, 2015 | $ | 4,799 | September 4, 2015 | ||||
November 9, 2015 |
$ | 0.08 | November 30, 2015 | $ | 4,713 | December 11, 2015 | ||||
January 25, 2016 |
$ | 0.08 | February 12, 2016 | $ | 4,669 | February 26, 2016 | ||||
April 25, 2016 |
$ | 0.09 | May 13, 2016 | $ | 5,196 | May 27, 2016 | ||||
July 25, 2016 |
$ | 0.09 | August 12, 2016 | $ | 5,157 | August 31, 2016 | ||||
November 7, 2016 |
$ | 0.09 | December 1, 2016 | N/A | December 14, 2016 | |||||
64
Contractual Obligations. The following sets forth our contractual obligations at October 2, 2016:
| |
Total | Year 1 | Years 2 - 3 | Years 4 - 5 | Beyond | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
(in thousands) |
|||||||||||||||
Debt: |
||||||||||||||||
Credit facility |
$ | 346,813 | $ | 15,375 | $ | 30,750 | $ | 300,688 | $ | – | ||||||
Other debt |
50 | 50 | – | – | – | |||||||||||
Interest (1) |
14,292 | 5,185 | 7,255 | 1,852 | – | |||||||||||
Capital leases |
154 | 89 | 65 | – | – | |||||||||||
Operating leases (2) |
255,591 | 83,050 | 99,603 | 50,206 | 22,732 | |||||||||||
Contingent earn-outs (3) |
8,757 | 4,296 | 4,461 | – | – | |||||||||||
Deferred compensation liability |
20,824 | – | – | – | 20,824 | |||||||||||
Unrecognized tax benefits (4) |
18,787 | 10,814 | – | 7,973 | – | |||||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total |
$ | 665,268 | $ | 118,859 | $ | 142,134 | $ | 360,719 | $ | 43,556 | ||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
- (1)
- Interest primarily related to the Term Loan Facility is based on a weighted-average interest rate at October 2, 2016, on borrowings that are presently outstanding.
- (2)
- Predominantly represents real estate leases.
- (3)
- Represents the estimated fair value recorded for contingent earn-out obligations for acquisitions. The remaining maximum contingent earn-out obligations for these acquisitions total $15.5 million.
- (4)
- Represents liabilities for unrecognized tax benefits related to uncertain tax positions, excluding amounts related primarily to outstanding refund claims. We are unable to reasonably predict the timing of tax settlements, as tax audits can involve complex issues and the resolution of those issues may span multiple years, particularly if subject to negotiation or litigation. For more information, see Note 8, "Income Taxes" of the "Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements" included in Item 8.
We review the realizability of deferred tax assets on a quarterly basis by assessing the need for a valuation allowance. As of October 2, 2016, we performed our assessment of net deferred tax assets. Significant management judgment is required in determining the provision for income taxes and, in particular, any valuation allowance recorded against our deferred tax assets. Applying the applicable accounting guidance requires an assessment of all available evidence, positive and negative, regarding the realizability of the net deferred tax assets. Based upon recent results, we concluded that a cumulative loss in recent years exists in certain states and foreign jurisdictions. We have historically relied on the following factors in our assessment of the realizability of our net deferred tax assets:
- •
- taxable income in prior carryback years as permitted under the tax law;
- •
- future reversals of existing taxable temporary differences;
- •
- consideration of available tax planning strategies and actions that could be implemented, if necessary; and
- •
- estimates of future taxable income from our operations.
We considered these factors in our estimate of the timing and amount of the reversal of deferred tax assets, using assumptions that we believe are reasonable and consistent with operating results. However, as a result of cumulative pre-tax losses in certain foreign jurisdictions for the 36 months ended October 2, 2016, we concluded that our estimates of future taxable income and certain tax planning strategies did not constitute sufficient positive evidence to assert that it is more likely than not that certain deferred tax assets would be realizable before expiration. Based on our assessment, we concluded that it is
65
more likely than not that the assets will be realized except for the assets related to loss carry-forwards in foreign jurisdictions for which a valuation allowance of $23.8 million has been provided.
We are currently under examination by the Internal Revenue Service for fiscal years 2010 through 2013, and by the California Franchise Tax Board for fiscal years 2004 through 2009. We are also subject to various other state audits. With a few exceptions, we are no longer subject to U.S. federal, state and local, or non-U.S. income tax examinations for fiscal years before 2010.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
In the ordinary course of business, we may use off-balance sheet arrangements if we believe that such an arrangement would be an efficient way to lower our cost of capital or help us manage the overall risks of our business operations. We do not believe that such arrangements have had a material adverse effect on our financial position or our results of operations.
The following is a summary of our off-balance sheet arrangements:
- •
- Letters of credit and bank guarantees are used primarily to support project performance and insurance programs. We are required to reimburse
the issuers of letters of credit and bank guarantees for any payments they make under the outstanding letters of credit or bank guarantees. Our Credit Agreement and additional letter of credit
facilities cover the issuance of our standby letters of credit and bank guarantees and are critical for our normal operations. If we default on the Credit Agreement or additional credit facilities,
our inability to issue or renew standby letters of credit and bank guarantees would impair our ability to maintain normal operations. At October 2, 2016, we had $1.3 million in standby
letters of credit outstanding under our Credit Agreement, $25.3 million in standby letters of credit outstanding under our additional letter of credit facilities and $5.6 million of bank
guarantees under the existing Coffey facility.
- •
- From time to time, we provide guarantees and indemnifications related to our services. If our services under a guaranteed or indemnified
project are later determined to have resulted in a material defect or other material deficiency, then we may be responsible for monetary damages or other legal remedies. When sufficient information
about claims on guaranteed or indemnified projects is available and monetary damages or other costs or losses are determined to be probable, we recognize such guaranteed losses.
- •
- In the ordinary course of business, we enter into various agreements as part of certain unconsolidated subsidiaries, joint ventures, and other jointly executed contracts where we are jointly and severally liable. We enter into these agreements primarily to support the project execution commitments of these entities. The potential payment amount of an outstanding performance guarantee is typically the remaining cost of work to be performed by or on behalf of third parties under engineering and construction contracts. However, we are not able to estimate other amounts that may be required to be paid in excess of estimated costs to complete contracts and, accordingly, the total potential payment amount under our outstanding performance guarantees cannot be estimated. For cost-plus contracts, amounts that may become payable pursuant to guarantee provisions are normally recoverable from the client for work performed under the contract. For lump sum or fixed-price contracts, this amount is the cost to complete the contracted work less amounts remaining to be billed to the client under the contract. Remaining billable amounts could be greater or less than the cost to complete. In those cases where costs exceed the remaining amounts payable under the contract, we may have recourse to third parties, such as owners, co-venturers, subcontractors or vendors, for claims.
66
- •
- In the ordinary course of business, our clients may request that we obtain surety bonds in connection with contract performance obligations that are not required to be recorded in our consolidated balance sheets. We are obligated to reimburse the issuer of our surety bonds for any payments made thereunder. Each of our commitments under performance bonds generally ends concurrently with the expiration of our related contractual obligation.
CRITICAL ACCOUNTING POLICIES AND ESTIMATES
The preparation of our financial statements in conformity with U.S. GAAP requires us to make estimates and assumptions in the application of certain accounting policies that affect amounts reported in our consolidated financial statements and accompanying footnotes included in Item 8 of this report. In order to understand better the changes that may occur to our financial condition, results of operations and cash flows, readers should be aware of the critical accounting policies we apply and estimates we use in preparing our consolidated financial statements. Although such estimates and assumptions are based on management's best knowledge of current events and actions we may undertake in the future, actual results could differ materially from those estimates.
Our significant accounting policies are described in the "Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements" included in Item 8. Highlighted below are the accounting policies that management considers most critical to investors' understanding of our financial results and condition, and that require complex judgments by management.
Revenue Recognition and Contract Costs
We recognize revenue for most of our contracts using the percentage-of-completion method, primarily based on contract costs incurred to date compared to total estimated contract costs. We generally utilize the cost-to-cost approach to estimate the progress towards completion in order to determine the amount of revenue and profit to recognize. This method of revenue recognition requires us to prepare estimates of costs to complete contracts in progress. In making such estimates, judgments are required to evaluate contingencies such as potential variances in schedule; the cost of materials and labor productivity; and the impact of change orders, liability claims, contract disputes and achievement of contractual performance standards. Changes in total estimated contract cost and losses, if any, could materially impact our results of operations or financial position. Certain of our contracts are service-related contracts, such as providing operations and maintenance services or a variety of technical assistance services. Our service contracts are accounted for using the proportional performance method under which revenue is recognized in proportion to the number of service activities performed, in proportion to the direct costs of performing the service activities, or evenly across the period of performance depending upon the nature of the services provided.
We recognize revenue for work performed under three major types of contracts: fixed-price, time-and-materials and cost-plus.
Fixed-Price. We enter into two major types of fixed-price contracts: firm fixed-price ("FFP") and fixed-price per unit ("FPPU"). Under FFP contracts, our clients pay us an agreed fixed-amount negotiated in advance for a specified scope of work. We generally recognize revenue on FFP contracts using the percentage-of-completion method. If the nature or circumstances of the contract prevent us from preparing a reliable estimate at completion, we will delay profit recognition until adequate information about the contract's progress becomes available. Under our FPPU contracts, clients pay us a set fee for each service or production transaction that we complete. Accordingly, we recognize revenue under FPPU contracts as we complete the related service or production transactions, generally using the proportional performance method.
67
Time-and-Materials. Under time-and-materials contracts, we negotiate hourly billing rates and charge our clients based on the actual time that we spend on a project. In addition, clients reimburse us for our actual out-of-pocket costs of materials and other direct incidental expenditures that we incur in connection with our performance under the contract. The majority of our time-and-material contracts are subject to maximum contract values and, accordingly, revenue under these contracts is generally recognized under the percentage-of-completion method. However, time and materials contracts that are service-related contracts are accounted for utilizing the proportional performance method. Revenue on contracts that are not subject to maximum contract values is recognized based on the actual number of hours we spend on the projects plus any actual out-of-pocket costs of materials and other direct incidental expenditures that we incur on the projects. Our time-and-materials contracts also generally include annual billing rate adjustment provisions.
Cost-Plus. Under cost-plus contracts, we are reimbursed for allowable or otherwise defined costs incurred plus a negotiated fee. The contracts may also include incentives for various performance criteria, including quality, timeliness, ingenuity, safety and cost-effectiveness. In addition, our costs are generally subject to review by our clients and regulatory audit agencies, and such reviews could result in costs being disputed as non-reimbursable under the terms of the contract. Revenue for cost-plus contracts is recognized at the time services are performed. Revenue is not recognized for non-recoverable costs. Performance incentives are included in our estimates of revenue when their realization is reasonably assured.
If estimated total costs on any contract indicate a loss, we recognize the entire estimated loss in the period the loss becomes known. The cumulative effect of revisions to revenue, estimated costs to complete contracts, including penalties, incentive awards, change orders, claims, anticipated losses and others are recorded in the period in which the revisions are identified and the loss can be reasonably estimated. Such revisions could occur in any reporting period and the effects may be material depending on the size of the project or the adjustment.
Once contract performance is underway, we may experience changes in conditions, client requirements, specifications, designs, materials and expectations regarding the period of performance. Such changes are "change orders" and may be initiated by us or by our clients. In many cases, agreement with the client as to the terms of change orders is reached prior to work commencing; however, sometimes circumstances require that work progress without obtaining client agreement. Revenue related to change orders is recognized as costs are incurred. Change orders that are unapproved as to both price and scope are evaluated as claims.
Claims are amounts in excess of agreed contract prices that we seek to collect from our clients or other third parties for delays, errors in specifications and designs, contract terminations, change orders in dispute or unapproved as to both scope and price or other causes of unanticipated additional costs. Revenue on claims is recognized only to the extent that contract costs related to the claims have been incurred and when it is probable that the claim will result in a bona fide addition to contract value that can be reliably estimated. No profit is recognized on a claim until final settlement occurs. This can lead to a situation in which costs are recognized in one period and revenue is recognized in a subsequent period when a client agreement is obtained or a claim resolution occurs.
Insurance Matters, Litigation and Contingencies
In the normal course of business, we are subject to certain contractual guarantees and litigation. Generally, such guarantees relate to project schedules and performance. Most of the litigation involves us as a defendant in contractual disagreements, workers' compensation, personal injury and other similar lawsuits. We maintain insurance coverage for various aspects of our business and operations. However, we have elected to retain a portion of losses that may occur through the use of various deductibles, limits and
68
retentions under our insurance programs. This practice may subject us to some future liability for which we are only partially insured or are completely uninsured.
We record in our consolidated balance sheets amounts representing our estimated liability for self-insurance claims. We utilize actuarial analyses to assist in determining the level of accrued liabilities to establish for our employee medical and workers' compensation self-insurance claims that are known and have been asserted against us, as well as for self-insurance claims that are believed to have been incurred based on actuarial analyses but have not yet been reported to our claims administrators at the balance sheet date. We include any adjustments to such insurance reserves in our consolidated results of operations.
Except as described in Note 18, "Commitments and Contingencies" of the "Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements" included in Item 8, we do not have any litigation or other contingencies that have had, or are currently anticipated to have, a material impact on our results of operations or financial position. As additional information about current or future litigation or other contingencies becomes available, management will assess whether such information warrants the recording of additional expenses relating to those contingencies. Such additional expenses could potentially have a material impact on our results of operations and financial position.
Our stock-based compensation plans include stock options, restricted stock, restricted stock units ("RSUs"), performance share units ("PSUs"), and an employee stock purchase plan for our eligible employees and outside directors. Stock-based compensation cost is measured at the grant date based on the fair value of the award and is recognized as expense over the requisite service period. Determining the fair value of stock-based awards at the grant date requires management to make assumptions and apply judgment to determine the fair value of our awards. These assumptions and judgments include future employee turnover rates, along with estimating the future volatility of our stock price, future stock option exercise behaviors and, for performance-based awards, the achievement of company performance goals. Our stock-based compensation expense was $13.0 million, $10.9 million and $10.4 million for fiscal 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively.
The cost of an acquired company is assigned to the tangible and intangible assets purchased and the liabilities assumed on the basis of their fair values at the date of acquisition. The determination of fair values of assets and liabilities acquired requires us to make estimates and use valuation techniques when a market value is not readily available. Any excess of purchase price over the fair value of net tangible and intangible assets acquired is allocated to goodwill. Goodwill typically represents the value paid for the assembled workforce and enhancement of our service offerings.
Identifiable intangible assets include backlog, non-compete agreements, client relations, trade names, patents and other assets. The costs of these intangible assets are amortized over their contractual or economic lives, which range from one to ten years. We assess the recoverability of the unamortized balance of our intangible assets when indicators of impairment are present based on expected future profitability and undiscounted expected cash flows and their contribution to our overall operations. Should the review indicate that the carrying value is not fully recoverable, the excess of the carrying value over the fair value of the intangible assets would be recognized as an impairment loss.
We perform our annual goodwill impairment review at the beginning of our fiscal fourth quarter. In addition, we regularly evaluate whether events and circumstances have occurred that may indicate a potential change in recoverability of goodwill. We perform interim goodwill impairment reviews between
69
our annual reviews if certain events and circumstances have occurred, including a deterioration in general economic conditions, an increased competitive environment, a change in management, key personnel, strategy or customers, negative or declining cash flows, or a decline in actual or planned revenue or earnings compared with actual and projected results of relevant prior periods (see Note 6, "Goodwill and Intangible Assets" of the "Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements" in Item 8 for further discussion).
We believe the methodology that we use to review impairment of goodwill, which includes a significant amount of judgment and estimates, provides us with a reasonable basis to determine whether impairment has occurred. However, many of the factors employed in determining whether our goodwill is impaired are outside of our control and it is reasonably likely that assumptions and estimates will change in future periods. These changes could result in future impairments.
The goodwill impairment review involves the determination of the fair value of our reporting units, which for us are the components one level below our reportable segments. This process requires us to make significant judgments and estimates, including assumptions about our strategic plans with regard to our operations as well as the interpretation of current economic indicators and market valuations. Furthermore, the development of the present value of future cash flow projections includes assumptions and estimates derived from a review of our expected revenue growth rates, profit margins, business plans, cost of capital and tax rates. We also make certain assumptions about future market conditions, market prices, interest rates and changes in business strategies. Changes in assumptions or estimates could materially affect the determination of the fair value of a reporting unit. This could eliminate the excess of fair value over carrying value of a reporting unit entirely and, in some cases, result in impairment. Such changes in assumptions could be caused by a loss of one or more significant contracts, reductions in government or commercial client spending, or a decline in the demand for our services due to changing economic conditions. In the event that we determine that our goodwill is impaired, we would be required to record a non-cash charge that could result in a material adverse effect on our results of operations or financial position.
We use two methods to determine the fair value of our reporting units: (i) the Income Approach and (ii) the Market Approach. While each of these approaches is initially considered in the valuation of the business enterprises, the nature and characteristics of the reporting units indicate which approach is most applicable. The Income Approach utilizes the discounted cash flow method, which focuses on the expected cash flow of the reporting unit. In applying this approach, the cash flow available for distribution is calculated for a finite period of years. Cash flow available for distribution is defined, for purposes of this analysis, as the amount of cash that could be distributed as a dividend without impairing the future profitability or operations of the reporting unit. The cash flow available for distribution and the terminal value (the value of the reporting unit at the end of the estimation period) are then discounted to present value to derive an indication of the value of the business enterprise. The Market Approach is comprised of the guideline company method and the similar transactions method. The guideline company method focuses on comparing the reporting unit to select reasonably similar (or "guideline") publicly traded companies. Under this method, valuation multiples are (i) derived from the operating data of selected guideline companies; (ii) evaluated and adjusted based on the strengths and weaknesses of the reporting units relative to the selected guideline companies; and (iii) applied to the operating data of the reporting unit to arrive at an indication of value. In the similar transactions method, consideration is given to prices paid in recent transactions that have occurred in the reporting unit's industry or in related industries. For our annual impairment analysis, we weighted the Income Approach and the Market Approach at 70% and 30%, respectively. The Income Approach was given a higher weight because it has the most direct correlation to the specific economics of the reporting unit, as compared to the Market Approach, which is based on multiples of broad-based (i.e., less comparable) companies. Our last review at June 27, 2016 (i.e. the first day of our fourth quarter in fiscal 2016), indicated that we had no impairment of goodwill, and all of our reporting units had estimated fair values that were in excess of their carrying values, including
70
goodwill. We had no reporting units that had estimated fair values that exceeded their carrying values by less than 20%, excluding the impact of acquisitions completed within the last two fiscal years.
Contingent Consideration. Certain of our acquisition agreements include contingent earn-out arrangements, which are generally based on the achievement of future operating income thresholds. The contingent earn-out arrangements are based upon our valuations of the acquired companies and reduce the risk of overpaying for acquisitions if the projected financial results are not achieved.
The fair values of these earn-out arrangements are included as part of the purchase price of the acquired companies on their respective acquisition dates. For each transaction, we estimate the fair value of contingent earn-out payments as part of the initial purchase price and record the estimated fair value of contingent consideration as a liability in "Estimated contingent earn-out liabilities" and "Long-term estimated contingent earn-out liabilities" on the consolidated balance sheets. We consider several factors when determining that contingent earn-out liabilities are part of the purchase price, including the following: (1) the valuation of our acquisitions is not supported solely by the initial consideration paid, and the contingent earn-out formula is a critical and material component of the valuation approach to determining the purchase price; and (2) the former shareholders of acquired companies that remain as key employees receive compensation other than contingent earn-out payments at a reasonable level compared with the compensation of our other key employees. The contingent earn-out payments are not affected by employment termination.
We measure our contingent earn-out liabilities at fair value on a recurring basis using significant unobservable inputs classified within Level 3 of the fair value hierarchy (See Note 2, "Basis of Presentation and Preparation – Fair Value of Financial Instruments" of the "Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements" included in Item 8). We use a probability weighted discounted income approach as a valuation technique to convert future estimated cash flows to a single present value amount. The significant unobservable inputs used in the fair value measurements are operating income projections over the earn-out period (generally two or three years), and the probability outcome percentages we assign to each scenario. Significant increases or decreases to either of these inputs in isolation would result in a significantly higher or lower liability with a higher liability capped by the contractual maximum of the contingent earn-out obligation. Ultimately, the liability will be equivalent to the amount paid, and the difference between the fair value estimate and amount paid will be recorded in earnings. The amount paid that is less than or equal to the liability on the acquisition date is reflected as cash used in financing activities in our consolidated statements of cash flows. Any amount paid in excess of the liability on the acquisition date is reflected as cash used in operating activities.
We review and re-assess the estimated fair value of contingent consideration on a quarterly basis, and the updated fair value could differ materially from the initial estimates. Changes in the estimated fair value of our contingent earn-out liabilities related to the time component of the present value calculation are reported in interest expense. Adjustments to the estimated fair value related to changes in all other unobservable inputs are reported in operating income.
We file a consolidated U.S. federal income tax return and a combined California franchise tax return. In addition, we file other returns that are required in the states, foreign jurisdictions and other jurisdictions in which we do business. We account for certain income and expense items differently for financial reporting and income tax purposes. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are computed for the differences between the financial statement and tax bases of assets and liabilities that will result in taxable or deductible amounts in the future based on enacted tax laws and rates applicable to the periods in which the differences are expected to reverse. In determining the need for a valuation allowance on deferred tax assets, management reviews both positive and negative evidence, including current and historical results of
71
operations, future income projections and potential tax planning strategies. Based on our assessment, we have concluded that a portion of the deferred tax assets at October 2, 2016, primarily net operating losses and certain foreign intangibles, will not be realized, and we have reserved accordingly.
According to the authoritative guidance on accounting for uncertainty in income taxes, we may recognize the tax benefit from an uncertain tax position only if it is more likely than not that the tax position will be sustained on examination by the taxing authorities based on the technical merits of the position. The tax benefits recognized in the financial statements from such a position should be measured based on the largest benefit that has a greater than 50% likelihood of being realized upon ultimate settlement. For more information related to our unrecognized tax benefits, see Note 8, "Income Taxes" of the "Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements" included in Item 8.
RECENT ACCOUNTING PRONOUNCEMENTS
For a discussion of recent accounting standards and the effect they could have on the consolidated financial statements, see Note 2, "Basis of Presentation and Preparation" of the "Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements" included in Item 8.
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk
We do not enter into derivative financial instruments for trading or speculation purposes. In the normal course of business, we have exposure to both interest rate risk and foreign currency transaction and translation risk, primarily related to the Canadian and Australian dollar.
We are exposed to interest rate risk under our Credit Agreement. We can borrow, at our option, under both the Term Loan Facility and Revolving Credit Facility. We may borrow on the Revolving Credit Facility, at our option, at either (a) a Eurocurrency rate plus a margin that ranges from 1.15% to 2.00% per annum, or (b) a base rate for loans in U.S. dollars (the highest of the U.S. federal funds rate plus 0.50% per annum, the bank's prime rate or the Eurocurrency rate plus 1.00%) plus a margin that ranges from 0.15% to 1.00% per annum. Borrowings at the base rate have no designated term and may be repaid without penalty any time prior to the Facility's maturity date. Borrowings at a Eurodollar rate have a term no less than 30 days and no greater than 90 days. Typically, at the end of such term, such borrowings may be rolled over at our discretion into either a borrowing at the base rate or a borrowing at a Eurodollar rate with similar terms, not to exceed the maturity date of the Facility. The Facility matures on May 29, 2020. At October 2, 2016 we had borrowings outstanding under the Credit Agreement of $346.8 million at a weighted-average interest rate of 1.92% per annum.
In fiscal 2013, we entered into three interest rate swap agreements with three banks to fix the variable interest rate on $153.8 million of our Term Loan Facility. In fiscal 2014, we entered into two interest rate swap agreements with two banks to fix the variable interest rate on $51.3 million of our Term Loan Facility. The objective of these interest rate swaps was to eliminate the variability of our cash flows on the amount of interest expense we pay under our Credit Agreement. Our average effective interest rate on borrowings outstanding under the Credit Agreement, including the effects of interest rate swap agreements, at October 2, 2016 was 2.52%. For more information, see Note 14, "Derivative Financial Instruments" of the "Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements" in Item 8.
Most of our transactions are in U.S. dollars; however, some of our subsidiaries conduct business in foreign currencies, primarily the Canadian and Australian dollar. Therefore, we are subject to currency exposure and volatility because of currency fluctuations. We attempt to minimize our exposure to these fluctuations by matching revenue and expenses in the same currency for our contracts. Foreign currency gains and losses were immaterial for both fiscal 2016 and 2015. Foreign currency gains and losses are
72
reported as part of "Selling, general and administrative expenses" in our consolidated statements of income.
We have foreign currency exchange rate exposure in our results of operations and equity primarily as a result of the currency translation related to our foreign subsidiaries where the local currency is the functional currency. To the extent the U.S. dollar strengthens against foreign currencies, the translation of these foreign currency denominated transactions will result in reduced revenue, operating expenses, assets and liabilities. Similarly, our revenue, operating expenses, assets and liabilities will increase if the U.S. dollar weakens against foreign currencies. For 2016 and 2015, 28.1% and 24.6% of our consolidated revenue, respectively, was generated by our international business. For fiscal 2016, the effect of foreign exchange rate translation on the consolidated balance sheets was an increase in equity of $15.2 million compared to a reduction in equity of $100.8 million in fiscal 2015. These amounts were recognized as an adjustment to equity through other comprehensive income.
73
Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data
INDEX TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULE
74
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Stockholders of Tetra Tech, Inc.:
In our opinion, the accompanying consolidated balance sheets and the related consolidated statements of income, comprehensive income (loss), equity and cash flows present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of Tetra Tech, Inc. and its subsidiaries at October 2, 2016 and September 27, 2015, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended October 2, 2016 in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. In addition, in our opinion, the financial statement schedule listed in the accompanying index presents fairly, in all material respects, the information set forth therein when read in conjunction with the related consolidated financial statements. Also in our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of October 2, 2016, based on criteria established in Internal Control – Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission ("COSO"). The Company's management is responsible for these financial statements and financial statement schedule, for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in Management's Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting, appearing under Item 9A of this Form 10-K. Our responsibility is to express opinions on these financial statements, on the financial statement schedule, and on the Company's internal control over financial reporting based on our integrated audits. We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audits to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement and whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audits of the financial statements included examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, and evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audits also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinions.
A company's internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company's internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (i) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (ii) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (iii) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company's assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
75
As described in Management's Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting, management has excluded Coffey International Limited ("Coffey") and INDUS Corporation ("INDUS") from its assessment of internal control over financial reporting as of October 2, 2016 because they were acquired by the Company in purchase business combinations during 2016. We have also excluded Coffey and INDUS from our audit of internal control over financial reporting. Coffey and INDUS are wholly-owned subsidiaries of Tetra Tech, Inc. whose combined total assets and total revenues represent 5.8% and 12.4%, respectively, of the related consolidated financial statement amounts as of and for the year ended October 2, 2016.
/s/ PRICEWATERHOUSECOOPERS LLP
Los
Angeles, California
November 22, 2016
76
TETRA TECH, INC.
Consolidated Balance Sheets
(in thousands, except par value)
| ASSETS |
October 2, 2016 |
September 27, 2015 |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Current assets: |
|||||||
Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 160,459 | $ | 135,326 | |||
Accounts receivable – net |
714,336 | 636,030 | |||||
Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
46,262 | 42,125 | |||||
Income taxes receivable |
14,371 | 10,294 | |||||
| | | | | | | | |
Total current assets |
935,428 | 823,775 | |||||
| | | | | | | | |
Property and equipment – net |
67,827 | 64,906 | |||||
Investments in and advances to unconsolidated joint ventures |
2,064 | 1,886 | |||||
Goodwill |
717,988 | 601,379 | |||||
Intangible assets – net |
48,962 | 40,332 | |||||
Deferred income taxes |
630 | – | |||||
Other long-term assets |
27,880 | 26,964 | |||||
| | | | | | | | |
Total assets |
$ | 1,800,779 | $ | 1,559,242 | |||
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
LIABILITIES AND EQUITY |
|||||||
Current liabilities: |
|||||||
Accounts payable |
$ | 158,773 | $ | 150,284 | |||
Accrued compensation |
129,184 | 103,866 | |||||
Billings in excess of costs on uncompleted contracts |
88,223 | 93,989 | |||||
Deferred income taxes |
– | 20,787 | |||||
Current portion of long-term debt |
15,510 | 11,904 | |||||
Current contingent earn-out liabilities |
4,296 | 609 | |||||
Other current liabilities |
85,100 | 69,003 | |||||
| | | | | | | | |
Total current liabilities |
481,086 | 450,442 | |||||
| | | | | | | | |
Deferred income taxes |
60,348 |
34,759 |
|||||
Long-term debt |
331,501 | 180,972 | |||||
Long-term contingent earn-out liabilities |
4,461 | 3,560 | |||||
Other long-term liabilities |
53,980 | 32,711 | |||||
Commitments and contingencies (Note 18) |
|||||||
Equity: |
|||||||
Preferred stock – Authorized, 2,000 shares of $0.01 par value; no shares issued and outstanding at October 2, 2016 and September 27, 2015 |
– | – | |||||
Common stock – Authorized, 150,000 shares of $0.01 par value; issued and outstanding, 57,042 and 59,381 shares at October 2, 2016 and September 27, 2015, respectively |
570 | 594 | |||||
Additional paid-in capital |
260,340 | 326,593 | |||||
Accumulated other comprehensive loss |
(128,008 | ) | (143,171 | ) | |||
Retained earnings |
736,357 | 672,309 | |||||
| | | | | | | | |
Tetra Tech stockholders' equity |
869,259 | 856,325 | |||||
Noncontrolling interests |
144 | 473 | |||||
| | | | | | | | |
Total equity |
869,403 | 856,798 | |||||
| | | | | | | | |
Total liabilities and equity |
$ | 1,800,779 | $ | 1,559,242 | |||
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
See accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
77
TETRA TECH, INC.
Consolidated Statements of Income
(in thousands, except per share data)
| |
Fiscal Year Ended | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
October 2, 2016 |
September 27, 2015 |
September 28, 2014 |
||||||||
| |
|
||||||||||
Revenue |
$ | 2,583,469 | $ | 2,299,321 | $ | 2,483,814 | |||||
Subcontractor costs |
(654,264 | ) | (580,606 | ) | (623,896 | ) | |||||
Other costs of revenue |
(1,598,994 | ) | (1,402,925 | ) | (1,577,481 | ) | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Gross profit |
330,211 | 315,790 | 282,437 | ||||||||
Selling, general and administrative expenses |
(171,985 | ) | (170,456 | ) | (187,298 | ) | |||||
Acquisition and integration expenses |
(19,548 | ) | – | – | |||||||
Contingent consideration – fair value adjustments |
(2,823 | ) | 3,113 | 58,694 | |||||||
Impairment of goodwill and other intangible assets |
– | (60,763 | ) | – | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Operating income |
135,855 | 87,684 | 153,833 | ||||||||
Interest income |
996 |
680 |
804 |
||||||||
Interest expense |
(12,385 | ) | (8,043 | ) | (10,294 | ) | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Income before income tax expense |
124,466 | 80,321 | 144,343 | ||||||||
Income tax expense |
(40,613 |
) |
(41,093 |
) |
(35,668 |
) |
|||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net income including noncontrolling interests |
83,853 | 39,228 | 108,675 | ||||||||
Net income from noncontrolling interests |
(70 | ) | (154 | ) | (409 | ) | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net income attributable to Tetra Tech |
$ |
83,783 |
$ |
39,074 |
$ |
108,266 |
|||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Earnings per share attributable to Tetra Tech: |
|||||||||||
Basic |
$ | 1.44 | $ | 0.64 | $ | 1.68 | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Diluted |
$ | 1.42 | $ | 0.64 | $ | 1.66 | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Weighted-average common shares outstanding: |
|||||||||||
Basic |
58,186 | 60,913 | 64,379 | ||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Diluted |
58,966 | 61,532 | 65,146 | ||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash dividends paid per share |
$ |
0.34 |
$ |
0.30 |
$ |
0.14 |
|||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
See accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
78
TETRA TECH, INC.
Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income (Loss)
(in thousands)
| |
Fiscal Year Ended | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
October 2, 2016 |
September 27, 2015 |
September 28, 2014 |
|||||||
| |
|
|||||||||
Net income including noncontrolling interests |
$ | 83,853 | $ | 39,228 | $ | 108,675 | ||||
Other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax: |
||||||||||
Foreign currency translation adjustments |
14,392 | (98,287 | ) | (45,480 | ) | |||||
Gain (loss) on cash flow hedge valuations |
774 | (2,489 | ) | 1,029 | ||||||
Other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax |
15,166 | (100,776 | ) | (44,451 | ) | |||||
|
||||||||||
Comprehensive income (loss) including noncontrolling interests |
99,019 | (61,548 | ) | 64,224 | ||||||
Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests |
(70 |
) |
(154 |
) |
(409 |
) |
||||
Foreign currency translation adjustments, net of tax |
(3 | ) | 143 | 55 | ||||||
Comprehensive income attributable to noncontrolling interests |
(73 | ) | (11 | ) | (354 | ) | ||||
Comprehensive income (loss) attributable to Tetra Tech |
$ |
98,946 |
$ |
(61,559 |
) |
$ |
63,870 |
|||
See accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
79
TETRA TECH, INC.
Consolidated Statements of Equity
Fiscal Years Ended September 28, 2014, September 27, 2015, and October 2, 2016
(in thousands)
| |
Common Stock | |
Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) |
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
Additional Paid-in Capital |
Retained Earnings |
Total Tetra Tech Equity |
Non-Controlling Interests |
Total Equity |
||||||||||||||||||||
| |
Shares | Amount | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
BALANCE AT SEPTEMBER 29, 2013 |
64,134 | $ | 641 | $ | 443,099 | $ | 1,858 | $ | 552,165 | $ | 997,763 | $ | 1,040 | $ | 998,803 | ||||||||||
Comprehensive income, net of tax: |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net income |
108,266 | 108,266 | 409 | 108,675 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Foreign currency translation adjustments |
(45,425 | ) | (45,425 | ) | (55 | ) | (45,480 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
Gain on cash flow hedge valuations |
1,029 | 1,029 | 1,029 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Comprehensive income, net of tax |
63,870 | 354 | 64,224 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Distributions paid to noncontrolling interests |
(417 | ) | (417 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
Cash dividend of $0.14 per common share |
(8,956 | ) | (8,956 | ) | (8,956 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
Stock-based compensation |
10,374 | 10,374 | 10,374 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Stock options exercised |
1,263 | 13 | 22,956 | 22,969 | 22,969 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Shares issued for Employee Stock Purchase Plan |
246 | 2 | 5,597 | 5,599 | 5,599 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Stock repurchases |
(3,052 | ) | (30 | ) | (79,970 | ) | (80,000 | ) | (80,000 | ) | |||||||||||||||
Tax expense for stock options |
460 | 460 | 460 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
BALANCE AT SEPTEMBER 28, 2014 |
62,591 | 626 | 402,516 | (42,538 | ) | 651,475 | 1,012,079 | 977 | 1,013,056 | ||||||||||||||||
Comprehensive income, net of tax: |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net income |
39,074 | 39,074 | 154 | 39,228 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Foreign currency translation adjustments |
(98,144 | ) | (98,144 | ) | (143 | ) | (98,287 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
Loss on cash flow hedge valuations |
(2,489 | ) | (2,489 | ) | (2,489 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Comprehensive income (loss), net of tax |
(61,559 | ) | 11 | (61,548 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Distributions paid to noncontrolling interests |
(515 | ) | (515 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
Cash dividends of $0.30 per common share |
(18,240 | ) | (18,240 | ) | (18,240 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
Stock-based compensation |
10,926 | 10,926 | 10,926 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Stock options exercised |
510 | 5 | 8,985 | 8,990 | 8,990 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Shares issued for Employee Stock Purchase Plan |
243 | 3 | 5,200 | 5,203 | 5,203 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Stock repurchases |
(3,963 | ) | (40 | ) | (100,460 | ) | (100,500 | ) | (100,500 | ) | |||||||||||||||
Tax benefit for stock options |
(574 | ) | (574 | ) | (574 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
BALANCE AT SEPTEMBER 27, 2015 |
59,381 | 594 | 326,593 | (143,171 | ) | 672,309 | 856,325 | 473 | 856,798 | ||||||||||||||||
Comprehensive income, net of tax: |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net income |
83,783 | 83,783 | 70 | 83,853 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Foreign currency translation adjustments |
14,389 | 14,389 | 3 | 14,392 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Gain on cash flow hedge valuations |
774 | 774 | 774 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Comprehensive income, net of tax |
98,946 | 73 | 99,019 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Distributions paid to noncontrolling interests |
(402 | ) | (402 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
Cash dividends of $0.34 per common share |
(19,735 | ) | (19,735 | ) | (19,735 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
Stock-based compensation |
12,964 | 12,964 | 12,964 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Stock options exercised |
920 | 9 | 15,814 | 15,823 | 15,823 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Shares issued for Employee Stock Purchase Plan |
209 | 2 | 4,705 | 4,707 | 4,707 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Stock repurchases |
(3,468 | ) | (35 | ) | (99,465 | ) | (99,500 | ) | (99,500 | ) | |||||||||||||||
Tax benefit for stock options |
(271 | ) | (271 | ) | (271 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
BALANCE AT OCTOBER 2, 2016 |
57,042 | $ | 570 | $ | 260,340 | $ | (128,008 | ) | $ | 736,357 | $ | 869,259 | $ | 144 | $ | 869,403 | |||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
See accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
80
TETRA TECH, INC.
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
(in thousands)
| |
Fiscal Year Ended | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
October 2, 2016 |
September 27, 2015 |
September 28, 2014 |
|||||||
Cash flows from operating activities: |
||||||||||
Net income including noncontrolling interests |
$ |
83,853 |
$ |
39,228 |
$ |
108,675 |
||||
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash from operating activities: |
||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization |
45,588 | 44,201 | 54,540 | |||||||
Equity in income of unconsolidated joint ventures |
(1,652 | ) | (5,131 | ) | (2,804 | ) | ||||
Distributions of earnings from unconsolidated joint ventures |
2,796 | 5,252 | 2,724 | |||||||
Stock-based compensation |
12,964 | 10,926 | 10,374 | |||||||
Excess tax benefits from stock-based compensation |
(918 | ) | (172 | ) | (904 | ) | ||||
Deferred income taxes |
6,051 | 8,412 | (145 | ) | ||||||
Provision for doubtful accounts |
8,082 | (1,034 | ) | 1,467 | ||||||
Impairment of goodwill and other intangible assets |
– | 60,763 | – | |||||||
Fair value adjustments to contingent consideration |
2,823 | (3,113 | ) | (58,694 | ) | |||||
Lease termination costs and related asset impairment |
2,946 | 342 | 2,416 | |||||||
(Gain) loss on disposal of property and equipment |
(537 | ) | (6,014 | ) | 58 | |||||
Changes in operating assets and liabilities, net of effects of business acquisitions: |
||||||||||
Accounts receivable |
9,062 | 40,345 | (32,020 | ) | ||||||
Prepaid expenses and other assets |
3,720 | 12,970 | (4,481 | ) | ||||||
Accounts payable |
(3,002 | ) | (26,901 | ) | 31,772 | |||||
Accrued compensation |
8,434 | (7,676 | ) | (4,728 | ) | |||||
Billings in excess of costs on uncompleted contracts |
(13,874 | ) | (10,319 | ) | 23,833 | |||||
Other liabilities |
(19,321 | ) | (7,143 | ) | (9,419 | ) | ||||
Income taxes receivable/payable |
(4,995 | ) | 7,911 | 4,712 | ||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Net cash provided by operating activities |
142,020 | 162,847 | 127,376 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash flows from investing activities: |
||||||||||
Capital expenditures |
(11,945 | ) | (24,296 | ) | (19,404 | ) | ||||
Payments for business acquisitions, net of cash acquired |
(81,259 | ) | (11,680 | ) | (30,251 | ) | ||||
Changes in restricted cash |
(2,519 | ) | 4,530 | – | ||||||
Proceeds from sale of property and equipment |
3,076 | 10,426 | 4,594 | |||||||
Payment received on note from sale of operation |
– | – | 3,900 | |||||||
Investments in unconsolidated joint ventures |
(1,368 | ) | – | – | ||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Net cash used in investing activities |
(94,015 | ) | (21,020 | ) | (41,161 | ) | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash flows from financing activities: |
||||||||||
Payments on long-term debt |
(148,485 | ) | (75,459 | ) | (4,379 | ) | ||||
Proceeds from borrowings |
229,049 | 64,794 | – | |||||||
Payments of contingent earn-out liabilities |
(3,251 | ) | (3,199 | ) | (18,663 | ) | ||||
Debt pre-payment costs |
(1,935 | ) | (1,457 | ) | – | |||||
Distributions paid to noncontrolling interests |
(402 | ) | (515 | ) | (417 | ) | ||||
Excess tax benefits from stock-based compensation |
918 | 172 | 904 | |||||||
Repurchases of common stock |
(99,500 | ) | (100,500 | ) | (80,000 | ) | ||||
Net proceeds from issuance of common stock |
17,953 | 10,825 | 23,834 | |||||||
Dividends paid |
(19,735 | ) | (18,240 | ) | (8,956 | ) | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Net cash used in financing activities |
(25,388 | ) | (123,579 | ) | (87,677 | ) | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Effect of foreign exchange rate changes on cash |
2,516 | (5,301 | ) | (5,464 | ) | |||||
Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents |
25,133 |
12,947 |
(6,926 |
) |
||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of year |
135,326 | 122,379 | 129,305 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash and cash equivalents at end of year |
$ | 160,459 | $ | 135,326 | $ | 122,379 | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Supplemental information: |
||||||||||
Cash paid during the year for: |
||||||||||
Interest |
$ | 12,575 | $ | 7,323 | $ | 8,293 | ||||
Income taxes, net of refunds of $3.2 million, $5.4 million and $14.7 million |
$ | 35,273 | $ | 23,268 | $ | 28,092 | ||||
See accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
81
TETRA TECH, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
1. Description of Business
We are a leading provider of consulting and engineering services that focuses on water, environment, infrastructure, resource management, energy, and international development. We are a global company that is renowned for our expertise in providing water-related services for public and private clients. We typically begin at the earliest stage of a project by identifying technical solutions and developing execution plans tailored to our clients' needs and resources. Our solutions may span the entire life cycle of consulting and engineering projects and include applied science, data analysis, research, engineering, design, construction management, and operations and maintenance.
In fiscal 2016, we managed our continuing operations under two reportable segments. We report our water resources, water and wastewater treatment, environment, and infrastructure engineering activities in the Water, Environment and Infrastructure ("WEI") reportable segment. Our Resource Management and Energy ("RME") reportable segment includes our oil and gas, energy, international development, waste management, remediation, and utilities services. In addition, we report the results of the wind-down of our non-core construction activities in the Remediation and Construction Management ("RCM") reportable segment.
2. Basis of Presentation and Preparation
Principles of Consolidation and Presentation. The consolidated financial statements include our accounts and those of joint ventures of which we are the primary beneficiary. All significant intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation. Certain prior year amounts have been revised to conform to the current year presentation.
Fiscal Year. We report results of operations based on 52 or 53-week periods ending on the Sunday nearest September 30. Fiscal years 2016, 2015 and 2014 contained 53, 52 and 52 weeks, respectively.
Use of Estimates. The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America ("U.S. GAAP") requires us to make estimates and assumptions. These estimates and assumptions affect the amounts reported in our consolidated financial statements and accompanying notes. Although such estimates and assumptions are based on management's best knowledge of current events and actions we may take in the future, actual results could differ materially from those estimates.
Revenue Recognition and Contract Costs. We recognize revenue for most of our contracts using the percentage-of-completion method, primarily based on contract costs incurred to date compared to total estimated contract costs. We generally utilize the cost-to-cost approach to estimate the progress towards completion in order to determine the amount of revenue and profit to recognize. Revenue and cost estimates for each significant contract are reviewed and reassessed quarterly. Changes in those estimates could result in recognition of cumulative catch-up adjustments to the contract's inception-to-date revenue, costs, and profit in the period in which such changes are made. Changes in revenue and cost estimates could also result in a projected loss that would be recorded immediately in earnings. For fiscal years 2016, 2015 and 2014, we recognized net unfavorable operating income adjustments of $2.3 million, $8.9 million and $35.9 million, respectively, due to changes in estimates. As of October 2, 2016 and September 27, 2015, we recorded a liability for anticipated losses of $6.7 million and $10.5 million, respectively. The estimated cost to complete the related contracts as of October 2, 2016 was $23.6 million.
82
TETRA TECH, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
2. Basis of Presentation and Preparation (Continued)
Certain of our contracts are service-related contracts, such as providing operations and maintenance services or a variety of technical assistance services. Our service contracts are accounted for using the proportional performance method under which revenue is recognized in proportion to the number of service activities performed, in proportion to the direct costs of performing the service activities, or evenly across the period of performance depending upon the nature of the services provided.
We recognize revenue for work performed under three major types of contracts: fixed-price, time-and-materials and cost-plus.
Fixed-Price. We enter into two major types of fixed-price contracts: firm fixed-price ("FFP") and fixed-price per unit ("FPPU"). Under FFP contracts, our clients pay us an agreed fixed-amount negotiated in advance for a specified scope of work. We generally recognize revenue on FFP contracts using the percentage-of-completion method. If the nature or circumstances of the contract prevent us from preparing a reliable estimate at completion, we will delay profit recognition until adequate information about the contract's progress becomes available. Under our FPPU contracts, clients pay us a set fee for each service or production transaction that we complete. Accordingly, we recognize revenue under FPPU contracts as we complete the related service or production transactions, generally using the proportional performance method.
Time-and-Materials. Under time-and-materials contracts, we negotiate hourly billing rates and charge our clients based on the actual time that we spend on a project. In addition, clients reimburse us for our actual out-of-pocket costs for materials and other direct incidental expenditures that we incur in connection with our performance under the contract. The majority of our time-and-material contracts are subject to maximum contract values and, accordingly, revenue under these contracts is generally recognized under the percentage-of-completion method. However, time and materials contracts that are service-related contracts are accounted for utilizing the proportional performance method. Revenue on contracts that are not subject to maximum contract values is recognized based on the actual number of hours we spend on the projects plus any actual out-of-pocket costs of materials and other direct incidental expenditures that we incur on the projects. Our time-and-materials contracts also generally include annual billing rate adjustment provisions.
Cost-Plus. Under cost-plus contracts, we are reimbursed for allowable or otherwise defined costs incurred plus a negotiated fee. The contracts may also include incentives for various performance criteria, including quality, timeliness, ingenuity, safety and cost-effectiveness. In addition, our costs are generally subject to review by our clients and regulatory audit agencies, and such reviews could result in costs being disputed as non-reimbursable under the terms of the contract. Revenue for cost-plus contracts is recognized at the time services are performed. Revenue is not recognized for non-recoverable costs. Performance incentives are included in our estimates of revenue when their realization is reasonably assured.
If estimated total costs on any contract indicate a loss, we recognize the entire estimated loss in the period the loss becomes known. The cumulative effect of revisions to revenue, estimated costs to complete contracts, including penalties, incentive awards, change orders, claims, liquidated damages, anticipated losses, and other revisions are recorded in the period in which the revisions are identified and the loss can be reasonably estimated. Such revisions could occur in any reporting period and the effects may be material depending on the size of the project or the adjustment.
83
TETRA TECH, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
2. Basis of Presentation and Preparation (Continued)
Once contract performance is underway, we may experience changes in conditions, client requirements, specifications, designs, materials, and expectations regarding the period of performance. Such changes are "change orders" and may be initiated by us or by our clients. In many cases, agreement with the client as to the terms of change orders is reached prior to work commencing; however, sometimes circumstances require that work progress without obtaining client agreement. Revenue related to change orders is recognized as costs are incurred. Change orders that are unapproved as to both price and scope are evaluated as claims.
Claims are amounts in excess of agreed contract prices that we seek to collect from our clients or other third parties for delays, errors in specifications and designs, contract terminations, change orders in dispute or unapproved as to both scope and price, or other causes of unanticipated additional costs. Revenue on claims is recognized only to the extent that contract costs related to the claims have been incurred and when it is probable that the claim will result in a bona fide addition to contract value that can be reliably estimated. No profit is recognized on a claim until final settlement occurs. This can lead to a situation in which costs are recognized in one period and revenue is recognized in a subsequent period when a client agreement is obtained or a claims resolution occurs.
Cash and Cash Equivalents. Cash and cash equivalents include all highly liquid investments with maturities of 90 days or less at the date of purchase. Restricted cash of $2.5 million was included in "Prepaid expenses and other current assets" on the consolidated balance sheet at fiscal 2016 year-end. For cash held by our consolidated joint ventures, see Note 17, "Joint Ventures."
Insurance Matters, Litigation and Contingencies. In the normal course of business, we are subject to certain contractual guarantees and litigation. In addition, we maintain insurance coverage for various aspects of our business and operations. We record in our consolidated balance sheets amounts representing our estimated liability for these legal and insurance obligations. We include any adjustments to these liabilities in our consolidated results of operations.
Accounts Receivable – Net. Net accounts receivable is primarily comprised of billed and unbilled accounts receivable, contract retentions and allowances for doubtful accounts. Billed accounts receivable represent amounts billed to clients that have not been collected. Unbilled accounts receivable represent revenue recognized but not yet billed pursuant to contract terms or billed after the period end date. Most of our unbilled receivables at October 2, 2016 are expected to be billed and collected within 12 months. Unbilled accounts receivable also include amounts related to requests for equitable adjustment to contracts that provide for price redetermination. These amounts are recorded only when they can be reliably estimated and realization is probable. Contract retentions represent amounts withheld by clients until certain conditions are met or the project is completed, which may be several months or years. Allowances for doubtful accounts represent the amounts that may become uncollectible or unrealizable in the future. We determine an estimated allowance for uncollectible accounts based on management's consideration of trends in the actual and forecasted credit quality of our clients, including delinquency and payment history; type of client, such as a government agency or a commercial sector client; and general economic and particular industry conditions that may affect a client's ability to pay. Billings in excess of costs on uncompleted contracts represent the amount of cash collected from clients and billings to clients on contracts in advance of work performed and revenue recognized. The majority of these amounts will be earned within 12 months.
84
TETRA TECH, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
2. Basis of Presentation and Preparation (Continued)
Property and Equipment. Property and equipment are recorded at cost and are depreciated over their estimated useful lives using the straight-line method. When property and equipment are retired or otherwise disposed of, the cost and accumulated depreciation are removed from our consolidated balance sheets and any resulting gain or loss is reflected in our consolidated statements of income. Expenditures for maintenance and repairs are expensed as incurred. Generally, estimated useful lives range from three to ten years for equipment, furniture and fixtures. Buildings are depreciated over periods not exceeding 40 years. Leasehold improvements are amortized on a straight-line basis over the shorter of their estimated useful lives or the length of the lease.
Long-Lived Assets. Our policy regarding long-lived assets is to evaluate the recoverability of our assets when the facts and circumstances suggest that the assets may be impaired. This assessment is performed based on the estimated undiscounted cash flows compared to the carrying value of the assets. If the future cash flows (undiscounted and without interest charges) are less than the carrying value, a write-down would be recorded to reduce the related asset to its estimated fair value.
We recognize a liability for contract termination costs associated with an exit activity for costs that will continue to be incurred under a lease for its remaining term without economic benefit to us, initially measured at its fair value at the cease-use date. The fair value is determined based on the remaining lease rentals, adjusted for the effects of any prepaid or deferred items recognized under the lease, and reduced by estimated sublease rentals.
Business Combinations. The cost of an acquired company is assigned to the tangible and intangible assets purchased and the liabilities assumed on the basis of their fair values at the date of acquisition. The determination of fair values of assets and liabilities acquired requires us to make estimates and use valuation techniques when a market value is not readily available. Any excess of purchase price over the fair value of net tangible and intangible assets acquired is allocated to goodwill. Goodwill typically represents the value paid for the assembled workforce and enhancement of our service offerings. Transaction costs associated with business combinations are expensed as they are incurred.
Goodwill and Intangible Assets. Goodwill represents the excess of the aggregate purchase price over the fair value of the net assets acquired in a business acquisition. Following an acquisition, we perform an analysis to value the acquired company's tangible and identifiable intangible assets and liabilities. With respect to identifiable intangible assets, we consider backlog, non-compete agreements, client relations, trade names, patents and other assets. We amortize our intangible assets based on the period over which the contractual or economic benefits of the intangible assets are expected to be realized. We assess the recoverability of the unamortized balance of our intangible assets when indicators of impairment are present based on expected future profitability and undiscounted expected cash flows and their contribution to our overall operations. Should the review indicate that the carrying value is not fully recoverable, the excess of the carrying value over the fair value of the intangible assets would be recognized as an impairment loss.
We test our goodwill for impairment on an annual basis, and more frequently when an event occurs or circumstances indicate that the carrying value of the asset may not be recoverable. We believe the methodology that we use to review impairment of goodwill, which includes a significant amount of judgment and estimates, provides us with a reasonable basis to determine whether impairment has occurred. However, many of the factors employed in determining whether our goodwill is impaired are
85
TETRA TECH, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
2. Basis of Presentation and Preparation (Continued)
outside of our control and it is reasonably likely that assumptions and estimates will change in future periods. These changes could result in future impairments.
We perform our annual goodwill impairment review at the beginning of our fiscal fourth quarter. Our last annual review was performed at June 27, 2016 (i.e., the first day of our fiscal fourth quarter). In addition, we regularly evaluate whether events and circumstances have occurred that may indicate a potential change in recoverability of goodwill. We perform interim goodwill impairment reviews between our annual reviews if certain events and circumstances have occurred, including a deterioration in general economic conditions, an increased competitive environment, a change in management, key personnel, strategy or customers, negative or declining cash flows, or a decline in actual or planned revenue or earnings compared with actual and projected results of relevant prior periods (See Note 6, "Goodwill and Intangible Assets" for further discussion). We assess goodwill for impairment at the reporting unit level, which is defined as an operating segment or one level below an operating segment, referred to as a component. Our operating segments are the same as our reportable segments and our reporting units for goodwill impairment testing are the components one level below our reportable segments. These components constitute a business for which discrete financial information is available and where segment management regularly reviews the operating results of that component. We aggregate components within an operating segment that have similar economic characteristics.
The impairment test for goodwill is a two-step process involving the comparison of the estimated fair value of each reporting unit to the reporting unit's carrying value, including goodwill. We estimate the fair value of reporting units based on a comparison and weighting of the income approach, specifically the discounted cash flow method and the market approach, which estimates the fair value of our reporting units based upon comparable market prices and recent transactions and also validates the reasonableness of the multiples from the income approach. If the fair value of a reporting unit exceeds its carrying amount, the goodwill of the reporting unit is not considered impaired; therefore, the second step of the impairment test is unnecessary. If the carrying amount of a reporting unit exceeds its fair value, we perform the second step of the goodwill impairment test to measure the amount of impairment loss to be recorded. If our goodwill is impaired, we are required to record a non-cash charge that could have a material adverse effect on our consolidated financial statements.
Contingent Consideration. Most of our acquisition agreements include contingent earn-out arrangements, which are generally based on the achievement of future operating income thresholds. The contingent earn-out arrangements are based upon our valuations of the acquired companies and reduce the risk of overpaying for acquisitions if the projected financial results are not achieved.
The fair values of these earn-out arrangements are included as part of the purchase price of the acquired companies on their respective acquisition dates. For each transaction, we estimate the fair value of contingent earn-out payments as part of the initial purchase price and record the estimated fair value of contingent consideration as a liability in "Current contingent earn-out liabilities" and "Long-term contingent earn-out liabilities" on the consolidated balance sheets. We consider several factors when determining that contingent earn-out liabilities are part of the purchase price, including the following: (1) the valuation of our acquisitions is not supported solely by the initial consideration paid, and the contingent earn-out formula is a critical and material component of the valuation approach to determining the purchase price; and (2) the former owners of acquired companies that remain as key employees receive compensation other than contingent earn-out payments at a reasonable level compared with the
86
TETRA TECH, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
2. Basis of Presentation and Preparation (Continued)
compensation of our other key employees. The contingent earn-out payments are not affected by employment termination.
We measure our contingent earn-out liabilities at fair value on a recurring basis using significant unobservable inputs classified within Level 3 of the fair value hierarchy. We use a probability weighted discounted income approach as a valuation technique to convert future estimated cash flows to a single present value amount. The significant unobservable inputs used in the fair value measurements are operating income projections over the earn-out period (generally two or three years), and the probability outcome percentages we assign to each scenario. Significant increases or decreases to either of these inputs in isolation would result in a significantly higher or lower liability with a higher liability capped by the contractual maximum of the contingent earn-out obligation. Ultimately, the liability will be equivalent to the amount paid, and the difference between the fair value estimate and amount paid will be recorded in earnings. The amount paid that is less than or equal to the liability on the acquisition date is reflected as cash used in financing activities in our consolidated statements of cash flows. Any amount paid in excess of the liability on the acquisition date is reflected as cash used in operating activities.
We review and re-assess the estimated fair value of contingent consideration on a quarterly basis, and the updated fair value could differ materially from the initial estimates. Changes in the estimated fair value of our contingent earn-out liabilities related to the time component of the present value calculation are reported in interest expense. Adjustments to the estimated fair value related to changes in all other unobservable inputs are reported in operating income.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments. We determine the fair values of our financial instruments, including short-term investments, debt instruments and derivative instruments based on inputs or assumptions that market participants would use in pricing an asset or a liability. We categorize our instruments using a valuation hierarchy for disclosure of the inputs used to measure fair value. This hierarchy prioritizes the inputs into three broad levels as follows: Level 1 inputs are quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical assets or liabilities; Level 2 inputs are quoted prices for similar assets and liabilities in active markets or inputs that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly through market corroboration, for substantially the full term of the financial instrument; and Level 3 inputs are unobservable inputs based on our own assumptions used to measure assets and liabilities at fair value. The classification of a financial asset or liability within the hierarchy is determined based on the lowest level input that is significant to the fair value measurement.
The carrying amounts of cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable and accounts payable approximate fair values based on their short-term nature. The carrying amounts of our revolving credit facility approximates fair value because the interest rates are based upon variable reference rates (see Note 9, "Long-Term Debt" and Note 14, "Derivative Financial Instruments" for additional disclosure). Certain other assets and liabilities, such as contingent earn-out liabilities, assets held for sale and amounts related to cash-flow hedges, are required to be carried in our consolidated financial statements at fair value.
Our fair value measurement methods may produce a fair value calculation that may not be indicative of net realizable value or reflective of future fair values. Although we believe our valuation methods are appropriate and consistent with those used by other market participants, the use of different
87
TETRA TECH, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
2. Basis of Presentation and Preparation (Continued)
methodologies or assumptions to determine fair value could result in a different fair value measurement at the reporting date.
Derivative Financial Instruments. We account for our derivative instruments as either assets or liabilities and carry them at fair value. For derivative instruments that hedge the exposure to variability in expected future cash flows that are designated as cash flow hedges, the effective portion of the gain or loss on the derivative instrument is reported as a component of accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) in stockholders' equity and reclassified into income in the same period or periods during which the hedged transaction affects earnings. The ineffective portion of the gain or loss on the derivative instrument, if any, is recognized in current income. To receive hedge accounting treatment, cash flow hedges must be highly effective in offsetting changes to expected future cash flows on hedged transactions.
The net gain or loss on the effective portion of a derivative instrument that is designated as an economic hedge of the foreign currency translation exposure generated by the re-measurement of certain assets and liabilities denominated in a non-functional currency in a foreign operation is reported in the same manner as a foreign currency translation adjustment. Accordingly, any gains or losses related to these derivative instruments are recognized in current income. Derivatives that do not qualify as hedges are adjusted to fair value through current income.
Deferred Compensation. We maintain a non-qualified defined contribution supplemental retirement plan for certain key employees and non-employee directors that is accounted for in accordance with applicable authoritative guidance on accounting for deferred compensation arrangements where amounts earned are held in a rabbi trust and invested. Employee deferrals and our match are deposited into a rabbi trust, and the funds are generally invested in individual variable life insurance contracts that we own and are specifically designed to informally fund savings plans of this nature. Our consolidated balance sheets reflect our investment in variable life insurance contracts in "Other long-term assets." Our obligation to participating employees is reflected in "Other long-term liabilities." All income and expenses related to the rabbi trust are reflected in our consolidated statements of income.
Income Taxes. We file a consolidated U.S. federal income tax return and a combined California franchise tax return. In addition, we file other returns that are required in the states, foreign jurisdictions and other jurisdictions in which we do business. We account for certain income and expense items differently for financial reporting and income tax purposes. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are computed for the difference between the financial statement and tax bases of assets and liabilities that will result in taxable or deductible amounts in the future based on enacted tax laws and rates applicable to the periods in which the differences are expected to reverse. In determining the need for a valuation allowance, management reviews both positive and negative evidence, including current and historical results of operations, future income projections and potential tax planning strategies. Based on our assessment, we have concluded that a portion of the deferred tax assets at October 2, 2016 will not be realized.
According to the authoritative guidance on accounting for uncertainty in income taxes, we may recognize the tax benefit from an uncertain tax position only if it is more likely than not that the tax position will be sustained on examination by the taxing authorities based on the technical merits of the position. The tax benefits recognized in the financial statements from such a position should be measured based on the largest benefit that has a greater than 50% likelihood of being realized upon ultimate
88
TETRA TECH, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
2. Basis of Presentation and Preparation (Continued)
settlement. This guidance also addresses de-recognition, classification, interest and penalties on income taxes, accounting in interim periods and disclosure requirements for uncertain tax positions.
Concentration of Credit Risk. Financial instruments that subject us to credit risk consist primarily of cash and cash equivalents and net accounts receivable. In the event that we have surplus cash, we place our temporary cash investments with lower risk financial institutions and, by policy, limit the amount of investment exposure to any one financial institution. Approximately 22% of accounts receivable were due from various agencies of the U.S. federal government at fiscal 2016 year-end. The remaining accounts receivable are generally diversified due to the large number of organizations comprising our client base and their geographic dispersion. We perform ongoing credit evaluations of our clients and maintain an allowance for potential credit losses. Approximately 42.4%, 29.5% and 28.1% of our fiscal 2016 revenue was generated from our U.S government, U.S. commercial and international clients, respectively (see Note 19, "Reportable Segments" for more information).
Foreign Currency Translation. We determine the functional currency of our foreign operating units based upon the primary currency in which they operate. These operating units maintain their accounting records in their local currency, primarily Canadian and Australian dollars. Where the functional currency is not the U.S. dollar, translation of assets and liabilities to U.S. dollars is based on exchange rates at the balance sheet date. Translation of revenue and expenses to U.S. dollars is based on the average rate during the period. Translation gains or losses are reported as a component of other comprehensive income (loss). Gains or losses from foreign currency transactions are included in results of operations, with the exception of intercompany foreign transactions that are considered long-term investments, which are recorded in "Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss)" on the consolidated balance sheets.
Recently Adopted and Pending Accounting Guidance. In November 2015, the Financial Accounting Standards Board ("FASB") issued updated guidance as a part of its ongoing Simplification Initiative, with the objective of reducing complexity in accounting standards. The updated guidance requires that all deferred tax assets and liabilities, along with any related valuation allowance, be classified as noncurrent on the balance sheet. This guidance does not change the offsetting requirements for deferred tax liabilities and assets, which results in the presentation of one amount on the balance sheet. We adopted this guidance prospectively as of October 2, 2016, and our consolidated balance sheet reflects the new guidance for classification of deferred taxes.
In February 2015, the FASB issued updated guidance which changes the analysis that a reporting entity must perform to determine whether it should consolidate certain types of legal entities. The updated guidance is effective for interim and annual reporting periods in years beginning after December 15, 2015, with early adoption permitted. We adopted this guidance, which did not have an impact on our consolidated financial statements.
In April 2015, the FASB issued updated guidance intended to simplify, and provide consistency to, the presentation of debt issuance costs. The new standard requires that debt issuance costs be presented in the balance sheet as a direct deduction from the carrying amount of the debt liability, consistent with debt discounts. The updated guidance is effective for interim and annual reporting periods in years beginning after December 15, 2015, with early adoption permitted. We adopted this guidance, which did not have a material impact on our consolidated financial statements. We had $2.6 million of unamortized debt issuance costs at October 2, 2016.
89
TETRA TECH, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
2. Basis of Presentation and Preparation (Continued)
In August 2015, the FASB issued updated guidance relating to the SEC Staff Announcement at the June 18, 2015 Emerging Issues Task Force meeting on the presentation and subsequent measurement of debt issuance costs associated with line-of-credit arrangements. The updated guidance allows for the deferral and presentation of debt issuance costs as an asset which may be amortized ratably over the term of the line-of-credit arrangement, regardless of whether there are any related outstanding borrowings. The updated guidance is effective for interim and annual reporting periods in years beginning after December 15, 2015, with early adoption permitted. We adopted this guidance, which did not have a material impact on our consolidated financial statements.
In September 2015, the FASB issued updated guidance to simplify measurement-period adjustments in business combinations. The updated guidance eliminated the requirement that an acquirer in a business combination account for measurement-period adjustments retrospectively. Instead, an acquirer will recognize a measurement-period adjustment during the period in which it determines the amount of the adjustment. The updated guidance was effective for interim and annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2015, with early adoption permitted. We adopted this guidance, which did not have a material impact on our consolidated financial statements.
In May 2014, the FASB issued an accounting standard that will supersede existing revenue recognition guidance under current U.S. GAAP. The new standard is a comprehensive new revenue recognition model that requires a company to recognize revenue to depict the transfer of goods or services to a customer at an amount that reflects the consideration it expects to receive in exchange for those goods and services. The accounting standard is effective for us in the first quarter of fiscal 2019. Companies may use either a full retrospective or a modified retrospective approach to adopt this standard. We are currently evaluating the impact and method of the adoption of this guidance on our consolidated financial statements.
In January 2015, the FASB issued an amendment to the accounting guidance related to the income statement presentation of extraordinary and unusual items. The amendment eliminates from U.S. GAAP the concept of extraordinary items. The guidance is effective for us in the first quarter of fiscal 2017. We do not expect the adoption of this guidance to have an impact on our consolidated financial statements.
In January 2016, the FASB issued guidance that generally requires companies to measure investments in other entities, except those accounted for under the equity method, at fair value and recognize any changes in fair value in net income. The guidance is effective for annual and interim reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2017. We do not expect the adoption of this guidance to have a significant impact on our consolidated financial statements.
In February 2016, the FASB issued guidance that primarily requires lessees to recognize most leases on their balance sheets but record expenses on their income statements in a manner similar to current accounting. For lessors, the guidance modifies the classification criteria and the accounting for sales-type and direct financing leases. The guidance is effective for annual and interim periods beginning after December 15, 2018, with early adoption permitted. We are currently evaluating the impact that this guidance will have on our consolidated financial statements.
In March 2016, the FASB issued updated guidance which requires excess tax benefits and deficiencies on share-based payments to be recorded as income tax expense or benefit in the income
90
TETRA TECH, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
2. Basis of Presentation and Preparation (Continued)
statement rather than being recorded in additional paid-in capital. This guidance is effective for annual and interim periods beginning after December 15, 2016, with early adoption permitted. We do not expect the adoption of this guidance to have a material impact on our consolidated financial statements.
In June 2016, the FASB issued updated guidance which requires entities to estimate all expected credit losses for certain types of financial instruments, including trade receivables, held at the reporting date based on historical experience, current conditions, and reasonable and supportable forecasts. The updated guidance also expands the disclosure requirements to enable users of financial statements to understand the entity's assumptions, models and methods for estimating expected credit losses. This guidance is effective for annual and interim periods beginning after December 15, 2019, with early adoption permitted. We are currently evaluating the impact that this guidance will have on our consolidated financial statements.
In August 2016, the FASB issued guidance to address eight specific cash flow issues to reduce the existing diversity in practice in how certain cash receipts and cash payments are presented and classified in the statement of cash flows. This guidance is effective for annual and interim periods beginning after December 15, 2017, with early adoption permitted. We are currently evaluating the impact that this guidance will have on our consolidated financial statements.
In October 2016, the FASB issued updated guidance which requires entities to recognize the income tax consequences of an intra-entity transfer of an asset other than inventory when the transfer occurs. The updated guidance also requires entities to disclose a comparison of income tax expense or benefit with statutory expectations and disclose the types of temporary differences and carryforwards that give rise to a significant portion of deferred income taxes. This guidance is effective for annual and interim periods beginning after December 15, 2017, with early adoption permitted. We are currently evaluating the impact that this guidance will have on our consolidated financial statements.
3. Stock Repurchase and Dividends
On November 10, 2014, the Board of Directors authorized a stock repurchase program under which we could repurchase up to $200 million of our common stock over the succeeding two years. In fiscal 2016, we repurchased through open market purchases under this program a total of 3,468,062 shares at an average price of $28.69, for a total cost of $99.5 million.
On November 9, 2015, the Board of Directors declared a quarterly cash dividend of $0.08 per share payable on December 11, 2015 to stockholders of record as of the close of business on November 30, 2015. On January 25, 2016, the Board of Directors declared a quarterly cash dividend of $0.08 per share payable on February 26, 2016 to stockholders of record as of the close of business on February 12, 2016. On April 25, 2016, the Board of Directors declared a quarterly cash dividend of $0.09 per share payable on May 27, 2016 to stockholders of record as of the close of business on May 13, 2016. On July 25, 2016, the Board of Directors declared a quarterly cash dividend of $0.09 per share payable on August 31, 2016 to stockholders of record as of the close of business on August 12, 2016. Dividends totaling $19.7 million and $18.2 million were paid in fiscal 2016 and fiscal 2015, respectively.
Subsequent Events. On November 7, 2016, the Board of Directors declared a quarterly cash dividend of $0.09 per share payable on December 14, 2016 to stockholders of record as of the close of business on December 1, 2016. The Board also authorized a new stock repurchase program under which we could repurchase up to $200 million of our common stock.
91
TETRA TECH, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
4. Accounts Receivable – Net and Revenue Recognition
Net accounts receivable and billings in excess of costs on uncompleted contracts consisted of the following at October 2, 2016 and September 27, 2015:
| |
October 2, 2016 |
September 27, 2015 |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
(in thousands) |
||||||
Billed |
$ | 364,287 | $ | 331,364 | |||
Unbilled |
356,147 | 311,823 | |||||
Contract retentions |
29,135 | 24,333 | |||||
Total accounts receivable – gross |
749,569 | 667,520 | |||||
Allowance for doubtful accounts |
(35,233 |
) |
(31,490 |
) |
|||
Total accounts receivable – net |
$ | 714,336 | $ | 636,030 | |||
Billings in excess of costs on uncompleted contracts |
$ |
88,223 |
$ |
93,989 |
|||
Billed accounts receivable represent amounts billed to clients that have not been collected. Unbilled accounts receivable represent revenue recognized but not yet billed pursuant to contract terms or billed after the period end date. Except for amounts related to claims as discussed below, most of our unbilled receivables at October 2, 2016 are expected to be billed and collected within 12 months. Contract retentions represent amounts withheld by clients until certain conditions are met or the project is completed, which may be several months or years. The allowance for doubtful accounts represents amounts that are expected to become uncollectible or unrealizable in the future. We determine an estimated allowance for uncollectible accounts based on management's consideration of trends in the actual and forecasted credit quality of our clients, including delinquency and payment history; type of client, such as a government agency or a commercial sector client; and general economic and particular industry conditions that may affect a client's ability to pay. Billings in excess of costs on uncompleted contracts represent the amount of cash collected from clients and billings to clients on contracts in advance of revenue recognized. The majority of billings in excess of costs on uncompleted contracts will be earned within 12 months.
Once contract performance is underway, we may experience changes in conditions, client requirements, specifications, designs, materials and expectations regarding the period of performance. Such changes result in "change orders" and may be initiated by us or by our clients. In many cases, agreement with the client as to the terms of change orders is reached prior to work commencing; however, sometimes circumstances require that work progress without a definitive client agreement. Unapproved change orders constitute claims in excess of agreed contract prices that we seek to collect from our clients (or other third parties) for delays, errors in specifications and designs, contract terminations, or other causes of unanticipated additional costs. Revenue on claims is recognized when contract costs related to claims have been incurred and when their addition to contract value can be reliably estimated. This can lead to a situation in which costs are recognized in one period and revenue is recognized in a subsequent period, such as when client agreement is obtained or a claims resolution occurs.
92
TETRA TECH, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
4. Accounts Receivable – Net and Revenue Recognition (Continued)
Total accounts receivable at October 2, 2016 and September 27, 2015 included $45 million and $53 million, respectively, related to claims, including requests for equitable adjustment, on contracts that provide for price redetermination. During fiscal 2016, we collected $13.4 million to settle claims of $8.8 million, which resulted in gains in operating income of $4.6 million in the RCM reportable segment. We regularly evaluate all unsettled claim amounts and record appropriate adjustments to operating earnings when it is probable that the claim will result in a different contract value than the amount previously estimated. In fiscal 2016, we also recognized reductions to operating income in our RCM segment and a related increase in the allowance for doubtful accounts of $7.9 million as a result of our updated assessment of the collectability of certain accounts receivable, of which $4.6 million related to unsettled claims. In fiscal 2015, we settled two claims related to completed transportation projects in the RCM segment totaling $31 million for cash proceeds of $29 million and, as a result, recognized reduced revenue and operating income of $2.0 million.
Billed accounts receivable related to U.S. federal government contracts were $47.4 million and $61.9 million at October 2, 2016 and September 27, 2015, respectively. U.S. federal government unbilled receivables were $92.2 million and $74.2 million at October 2, 2016 and September 27, 2015, respectively. Other than the U.S. federal government, no single client accounted for more than 10% of our accounts receivable at October 2, 2016 and September 27, 2015.
5. Mergers and Acquisitions
In fiscal 2014, we made immaterial acquisitions that enhanced our service offerings and expanded our geographic presence in our WEI and RME segments.
In fiscal 2015, we acquired Cornerstone Environmental Group, LLC ("CEG"), headquartered in Middletown, New York. CEG is an environmental engineering and consulting firm focused on solid waste markets in the United States, and is included in our RME segment. The fair value of the purchase price for CEG was $15.9 million. Of this amount, $11.8 million was paid to the former owners and $4.1 million was the estimated fair value of contingent earn-out obligations, with a maximum of $9.8 million, based upon the achievement of specified financial objectives. The results of this acquisition were included in the consolidated financial statements from the closing date. The acquisition was not considered material to our consolidated financial statements. As a result, no pro forma information has been provided.
On January 18, 2016, we acquired control of Coffey International Limited ("Coffey"), headquartered in Sydney, Australia. Coffey had approximately 3,300 staff delivering technical and engineering solutions in international development and geoscience. Coffey significantly expands our geographic presence, particularly in Australia and Asia Pacific, and is part of our RME segment. In addition to Australia, Coffey's international development business has operations supporting federal government agencies in the U.S. and the United Kingdom. The fair value of the purchase price for Coffey was $76.1 million, in addition to $65.1 million of assumed debt, which consisted of secured bank term debt of $37.1 million and unsecured corporate bond obligations of $28.0 million. All of this debt was paid in full in the second quarter of fiscal 2016 subsequent to the acquisition.
In the second quarter of fiscal 2016, we also acquired INDUS Corporation ("INDUS"), headquartered in Vienna, Virginia. INDUS is an information technology solutions firm focused on water data analytics, geospatial analysis, secure infrastructure, and software applications management for U.S.
93
TETRA TECH, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
5. Mergers and Acquisitions (Continued)
federal government customers, and is included in our WEI segment. The fair value of the purchase price for INDUS was $18.7 million. Of this amount, $14.0 million was paid to the sellers and $4.7 million was the estimated fair value of contingent earn-out obligations, with a maximum of $8.0 million, based upon the achievement of specified operating income targets in each of the two years following the acquisition.
The following table summarizes the estimated fair values of assets acquired and liabilities assumed as of the respective acquisition dates for our acquisitions completed in fiscal 2016 (in thousands):
Accounts receivable |
$ | 71,515 | ||
Other current assets |
18,869 | |||
Property and equipment |
14,218 | |||
Goodwill |
107,618 | |||
Backlog and trade name intangible assets |
29,445 | |||
Other assets |
747 | |||
Current liabilities |
(77,606 | ) | ||
Borrowings |
(65,086 | ) | ||
Other long-term liabilities |
(4,885 | ) | ||
Net assets acquired |
$ | 94,835 | ||
Goodwill additions resulting from the above business combinations are primarily attributable to the existing workforce of the acquired companies and the synergies expected to arise after the acquisitions. Specifically, goodwill additions related to the fiscal 2016 acquisitions primarily represent the value of workforces with distinct expertise in the international development, geoscience, and software applications management markets. The goodwill addition related to the fiscal 2015 acquisition primarily represents the value of the workforce with distinct expertise in the solid waste market. In addition, these acquired capabilities, when combined with our existing global consulting and engineering business, result in opportunities that allow us to provide services under contracts that could not have been pursued individually by either us or the acquired companies. The results of these acquisitions were included in the consolidated financial statements from their respective closing dates.
Backlog and trade name intangible assets include the fair value of existing contracts and the underlying customer relationships with lives ranging from 1 to 5 years (weighted average of approximately 3 years) and the fair value of trade names with lives ranging from 3 to 5 years. The purchase price allocation is preliminary and subject to adjustment based upon the final determination of the net assets acquired and information necessary to perform the final valuation. We have not yet completed our final assessment of the fair values of purchased receivables, intangible assets, tax balances, contingent liabilities or acquired contracts. The final purchase price allocations may result in adjustments to certain assets and liabilities, including the residual amount allocated to goodwill. Goodwill recognized largely results from a substantial and technically qualified assembled workforce, which does not qualify for separate recognition, as well as expected future synergies from combining operations.
The table below presents summarized unaudited consolidated pro forma operating results including the related acquisition, integration and debt pre-payment charges, assuming we had acquired Coffey and INDUS at the beginning of fiscal 2015. These pro-forma operating results are presented for
94
TETRA TECH, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
5. Mergers and Acquisitions (Continued)
illustrative purposes only and are not indicative of the operating results that would have been achieved had the related events occurred at the beginning of fiscal 2015.
| |
Pro-Forma | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
Fiscal Year Ended | ||||||
| |
October 2, 2016 |
September 27, 2015 |
|||||
| |
(in thousands, except per share data) |
||||||
Revenue |
$ | 2,714,658 | $ | 2,749,653 | |||
Operating income |
152,676 | 73,209 | |||||
Net income attributable to Tetra Tech |
98,871 | 20,689 | |||||
Earnings per share attributable to Tetra Tech |
|||||||
Basic |
$ | 1.70 | $ | 0.33 | |||
Diluted |
$ | 1.68 | $ | 0.33 | |||
Since their respective acquisition dates, Coffey and INDUS combined contributed $320.6 million in revenue and $13.6 million in operating income for fiscal 2016. Amortization of intangible assets since their respective acquisition dates was $6.7 million for 2016.
Acquisition and integration expenses in the accompanying consolidated statements of income are comprised of the following:
| |
Fiscal Year Ended October 2, 2016 |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
(in thousands) |
|||
Severance including change in control payments |
$ | 10,917 | ||
Professional services |
5,685 | |||
Real estate-related |
2,946 | |||
Total |
$ | 19,548 | ||
As of October 2, 2016, all of the acquisition and integration expenses incurred to date have been paid. All acquisition and integration expenses are included in our Corporate reportable segment, as presented in Note 19. In addition, in the second quarter of fiscal 2016, we repaid Coffey's bank loans and corporate bonds in full, including $1.9 million in pre-payment charges that are included in interest expense.
Most of our acquisition agreements include contingent earn-out agreements, which are generally based on the achievement of future operating income thresholds. The contingent earn-out arrangements are based on our valuations of the acquired companies, and reduce the risk of overpaying for acquisitions if the projected financial results are not achieved. The fair values of any earn-out arrangements are included as part of the purchase price of the acquired companies on their respective acquisition dates. For each transaction, we estimate the fair value of contingent earn-out payments as part of the initial purchase price and record the estimated fair value of contingent consideration as a liability in "Current contingent earn-out liabilities" and "Long-term contingent earn-out liabilities" on the consolidated balance sheets. We consider several factors when determining that contingent earn-out liabilities are part of the purchase
95
TETRA TECH, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
5. Mergers and Acquisitions (Continued)
price, including the following: (1) the valuation of our acquisitions is not supported solely by the initial consideration paid, and the contingent earn-out formula is a critical and material component of the valuation approach to determining the purchase price; and (2) the former owners of acquired companies that remain as key employees receive compensation other than contingent earn-out payments at a reasonable level compared with the compensation of our other key employees. The contingent earn-out payments are not affected by employment termination.
We measure our contingent earn-out liabilities at fair value on a recurring basis using significant unobservable inputs classified within Level 3 of the fair value hierarchy. We use a probability-weighted discounted income approach as a valuation technique to convert future estimated cash flows to a single present value amount. The significant unobservable inputs used in the fair value measurements are operating income projections over the earn-out period (generally two or three years), and the probability outcome percentages we assign to each scenario. Significant increases or decreases to either of these inputs in isolation would result in a significantly higher or lower liability, with a higher liability capped by the contractual maximum of the contingent earn-out obligation. Ultimately, the liability will be equivalent to the amount paid, and the difference between the fair value estimate and amount paid will be recorded in earnings. The amount paid that is less than or equal to the contingent earn-out liability on the acquisition date is reflected as cash used in financing activities in our consolidated statements of cash flows. Any amount paid in excess of the contingent earn-out liability on the acquisition date is reflected as cash used in operating activities.
We review and re-assess the estimated fair value of contingent consideration on a quarterly basis, and the updated fair value could differ materially from the initial estimates. Changes in the estimated fair value of our contingent earn-out liabilities related to the time component of the present value calculation are reported in interest expense. Adjustments to the estimated fair value related to changes in all other unobservable inputs are reported in operating income. During fiscal 2016, we increased our contingent earn-out liabilities and reported related losses in operating income of $2.8 million. These losses include a $1.8 million charge that reflected our updated valuation of the contingent consideration liability for CEG. This valuation included our updated projection of CEG's financial performance during the earn-out period, which exceeded our original estimate at the acquisition date. The remaining $1.0 million loss represented the final cash settlement of an earn-out liability that was valued at $0 at the end of fiscal 2015.
During fiscal 2015, we decreased our contingent earn-out liabilities and reported a related gain in operating income of $3.1 million. This gain resulted from an updated valuation of the contingent consideration liability for Caber Engineering Inc. ("Caber"), which is part of our RME segment.
The acquisition agreement for Caber included a contingent earn-out agreement based on the achievement of operating income thresholds (in Canadian dollars) in each of the first two years beginning on the acquisition date, which was in the first quarter of fiscal 2014. The maximum earn-out obligation over the two-year earn-out period was C$8.0 million (C$4.0 million in each year). These amounts could be earned on a pro-rata basis for operating income within a predetermined range in each year. Caber was required to meet a minimum operating income threshold in each year to earn any contingent consideration. These thresholds were C$4.0 million and C$4.6 million in years one and two, respectively. In order to earn the maximum contingent consideration, Caber needed to generate operating income of C$4.4 million in year one and C$5.1 million in year two.
96
TETRA TECH, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
5. Mergers and Acquisitions (Continued)
The determination of the fair value of the purchase price for Caber on the acquisition date included our estimate of the fair value of the related contingent earn-out obligation. This initial valuation was primarily based on probability-weighted internal estimates of Caber's operating income during each earn-out period. As a result of these estimates, we calculated an initial fair value at the acquisition date of Caber's contingent earn-out liability of C$6.5 million in the first quarter of fiscal 2014. In determining that Caber would earn 81% of the maximum potential earn-out, we considered several factors including Caber's recent historical revenue and operating income levels and growth rates. We also considered the recent trend in Caber's backlog level and the prospects for the oil and gas industry in Western Canada.
Caber's actual financial performance in the first earn-out period exceeded our original estimate at the acquisition date. As a result, in the fourth quarter of fiscal 2014, we increased the related contingent consideration liability and recognized a loss of $1.0 million. This updated valuation included our assumption that Caber would earn the maximum amount of contingent consideration of $4.0 million in the first earn-out period. In the second quarter of fiscal 2015, we completed our final calculation of the contingent consideration for the first earn-out period and paid contingent consideration of C$4.0 million (USD$3.2 million). At that time we also evaluated our estimate of Caber's contingent consideration liability for the second earn-out period. This assessment included a review of the status of ongoing projects in Caber's backlog, and the inventory of prospective new contract awards. We also considered the status of the oil and gas industry in Western Canada, particularly in light of the decline in oil prices at the time. As a result of this assessment, we concluded that Caber's operating income in the second earn-out period would be lower than our original estimate at the acquisition date and our subsequent estimates through the first quarter of fiscal 2015. We also concluded that Caber's operating income for the second earn-out period would be lower than the minimum requirement of C$4.6 million to earn any contingent consideration. Accordingly, in the second quarter of fiscal 2015, we reduced the Caber contingent earn-out liability to $0, which resulted in a gain of $3.1 million. The second earn-out period ended in the first quarter of fiscal 2016 with no further adjustments.
The fiscal 2014 net gains primarily resulted from updated valuations of the contingent consideration liabilities for Parkland Pipeline ("Parkland") and American Environmental Group ("AEG"), which are both part of our RME segment.
The acquisition agreement for Parkland included a contingent earn-out agreement based on the achievement of operating income thresholds (in Canadian dollars) in each of the first three years beginning on the acquisition date, which was in the second quarter of fiscal 2013. The maximum earn-out obligation over the three-year earn-out period was C$56.0 million (C$12.0 million, C$22.0 million and C$22.0 million in earn-out years one, two and three, respectively). These amounts could be earned primarily on a pro-rata basis for operating income within a predetermined range in each year. To a lesser extent, additional earn-out consideration could be earned for operating income above the high-end of the range up to the contractual maximum of C$56.0 million. Parkland was required to meet a minimum operating income threshold in each year in order to earn any contingent consideration. These thresholds were C$34.7 million, C$38.2 million and C$41.9 million in years one, two and three, respectively. In order to earn the maximum contingent consideration, Parkland would need to generate operating income of C$42.5 million in year one, C$46.4 million in year two, and C$50.6 million in year three.
The determination of the fair value of the purchase price for Parkland on the acquisition date included our estimate of the fair value of the related contingent earn-out obligation. This initial valuation
97
TETRA TECH, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
5. Mergers and Acquisitions (Continued)
was primarily based on probability-weighted internal estimates of Parkland's operating income during each earn-out period. As a result of these estimates, we calculated an initial fair value at the acquisition date of Parkland's contingent earn-out liability of C$46.8 million in the second quarter of fiscal 2013. In determining that Parkland would attain 84% of the maximum potential earn-out, we considered several factors including Parkland's recent historical revenue and operating income levels and growth rates, the recent trend in Parkland's backlog, and the prospects for the midstream oil and gas industry in Western Canada.
As discussed below, in fiscal 2014, we recorded decreases in our contingent earn-out liability for Parkland and reported related net gains in operating income of $44.6 million. These gains resulted from Parkland's actual and projected post-acquisition performance falling below our initial expectations concerning the likelihood and timing of achieving the relevant operating income thresholds. The remaining difference compared to the initial value was due to currency translation, and the related liability was $0 at the end of fiscal 2014.
In the second quarter of fiscal 2014, we updated the estimated cost to complete a large fixed-price contract at Parkland, and determined that the project would be break-even compared to the significant profit estimated the previous quarter when the project was initiated. As a result, during the second quarter of fiscal 2014 we reversed $5.3 million of profit previously recognized on the project. This variance, and our updated estimate that the revenue for the remainder of the project would produce no operating income, resulted in our conclusion that Parkland's operating income in the first and second earn-out periods would fall below the minimum operating income thresholds in each such year. As a result, we reduced the contingent earn-out liability for the first and second earn-out periods to $0, which resulted in gains totaling $24.7 million ($5.6 million and $19.1 million in the first and second quarters of fiscal 2014, respectively).
In the fourth quarter of fiscal 2014, we updated our projection of Parkland's operating income for the third earn-out period. This assessment included a review of the projects in Parkland's backlog, the inventory of prospective new contract awards, and the forecast for economic activity in the Western Canada oil and gas sector. As a result of this assessment, we concluded that Parkland's operating income in the third earn-out period would be lower than our original estimate at the acquisition date and would fall below the minimum operating income threshold. As a result, we reduced the remaining contingent earn-out liability balance for the third earn-out period to $0, which resulted in a gain of $19.9 million.
The acquisition agreement for AEG included a contingent earn-out agreement based on the achievement of operating income thresholds in each of the first two years beginning on the acquisition date. The maximum earn-out obligation over the two-year earn-out period was $27.1 million ($11.3 million annually plus a $4.5 million one-time payment based on minimum operating income in each year). The annual amounts could be earned primarily on a pro-rata basis for operating income within a predetermined range in each year. To a lesser extent, additional earn-out consideration could be earned for operating income above the high-end of the range up to the contractual maximum of $27.1 million. AEG was required to meet a minimum operating income threshold in each year in order to earn any contingent consideration. These minimum thresholds were $10.0 million and $11.0 million in years one and two, respectively. In order to earn the maximum contingent consideration, AEG would need to achieve operating income of $17.5 million in year one and $18.5 million in year two. In addition, if AEG achieved
98
TETRA TECH, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
5. Mergers and Acquisitions (Continued)
operating income of at least $9.0 million during both earn-out periods, AEG would receive $4.5 million at the end of the second earn-out period.
The determination of the fair value of the purchase price for AEG on the acquisition date included our estimate of the fair value of the related contingent earn-out obligation. This initial valuation was primarily based on probability-weighted internal estimates of AEG's operating income during each earn-out period. As a result of these estimates, we calculated an initial fair value at the acquisition date of AEG's contingent earn-out liability of $21.5 million in the second quarter of fiscal 2013. In determining that AEG would attain 79% of the maximum potential earn-out we considered several factors including AEG's recent historical revenue and operating income levels and growth rates. We also considered the recent trend in AEG's backlog level and the prospects for the solid waste industry in the United States.
AEG's first earn-out period ended on the last day of the first quarter of fiscal 2014. As a result, during the first quarter of fiscal 2014, we performed a preliminary calculation of the contingent consideration for the first earn-out period and concluded that AEG's operating income in that period would be higher than both our original estimate at the acquisition date and our previous quarterly estimates. As a result, we increased the contingent earn-out liability for the first earn-out period, which resulted in an additional expense of $1.0 million. The contingent consideration of $9.1 million for the first earn-out period was paid in the second quarter of fiscal 2014.
During calendar 2014, which corresponds to AEG's second earn-out period, adverse weather conditions hindered AEG's ability to complete its project field work. As a result, in the third quarter of fiscal 2014, we updated our projection of AEG's operating income for its second earn-out period. This assessment included a review of the status of on-going projects in AEG's backlog, and the inventory of prospective new contract awards. As a result of this assessment, we concluded that AEG's operating income in the second earn-out period would be significantly lower than our original estimate at the acquisition date, would fall below the minimum operating income threshold, but would still exceed $9.0 million of operating income in order to earn the additional tranche. As a result, we reduced the contingent earn-out liability, which resulted in a gain of $8.9 million in the third quarter of fiscal 2014.
During the fourth quarter of fiscal 2014, we performed an updated projection of AEG's operating income for its second earn-out period based on actual results and the forecast for the remainder of the second earn-out period. Based on this analysis, we concluded that AEG's operating income in the second earn-out period would be lower than the $9.0 million needed to receive the $4.5 million of contingent consideration that remained accrued for performance in both earn-out years. As a result, we reduced the contingent earn-out liability to $0, which resulted in a gain of $4.5 million in the fourth quarter of fiscal 2014, and net gains of $13.2 million for all of fiscal 2014.
Each time we determined that Caber's, AEG's and Parkland's operating income would be lower than our original estimate at the acquisition date, we also evaluated the related goodwill for potential impairment. In each case, we determined that the lower income projections were the result of temporary events, and did not negatively impact the reporting unit's longer term performance or result in a goodwill impairment.
99
TETRA TECH, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
5. Mergers and Acquisitions (Continued)
At October 2, 2016, there was a total maximum of $15.5 million of outstanding contingent consideration related to acquisitions. Of this amount, $8.8 million was estimated as the fair value and accrued on our consolidated balance sheet.
The following table summarizes the changes in the carrying value of estimated contingent earn-out liabilities:
| |
Fiscal Year Ended | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
October 2, 2016 |
September 27, 2015 |
September 28, 2014 |
|||||||
| |
(in thousands) |
|||||||||
Beginning balance (at fair value) |
$ | 4,169 | $ | 7,030 | $ | 81,789 | ||||
Estimated earn-out liabilities for acquisitions during the fiscal year |
4,745 | 4,100 | 6,242 | |||||||
Increases due to re-measurement of fair value reported in interest expense |
271 | 136 | 1,846 | |||||||
Net increase (decrease) due to re-measurement of fair value reported as losses (gains) in operating income |
2,823 | (3,113 | ) | (58,694 | ) | |||||
Foreign exchange impact |
– | (785 | ) | (3,507 | ) | |||||
Earn-out payments: |
||||||||||
Reported as cash used in operating activities |
– | – | (1,984 | ) | ||||||
Reported as cash used in financing activities |
(3,251 | ) | (3,199 | ) | (18,662 | ) | ||||
Ending balance (at fair value) |
$ | 8,757 | $ | 4,169 | $ | 7,030 | ||||
6. Goodwill and Intangible Assets
The following table summarizes the changes in the carrying value of goodwill:
| |
WEI | RME | Total | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
(in thousands) |
|||||||||
Balance at September 28, 2014 |
$ | 281,930 | $ | 432,260 | $ | 714,190 | ||||
Goodwill additions |
– | 6,272 | 6,272 | |||||||
Foreign exchange translation |
(27,479 | ) | (33,486 | ) | (60,965 | ) | ||||
Goodwill impairment |
(43,703 | ) | (14,415 | ) | (58,118 | ) | ||||
Balance at September 27, 2015 |
210,748 | 390,631 | 601,379 | |||||||
Goodwill additions |
9,080 | 98,538 | 107,618 | |||||||
Goodwill adjustment |
– | 1,687 | 1,687 | |||||||
Foreign exchange translation |
2,125 | 5,179 | 7,304 | |||||||
Balance at October 2, 2016 |
$ | 221,953 | $ | 496,035 | $ | 717,988 | ||||
We perform our annual goodwill impairment review at the beginning of our fiscal fourth quarter. Our last review at June 27, 2016 (i.e. the first day of our fourth quarter in fiscal 2016), indicated that we had no impairment of goodwill, and all of our reporting units had estimated fair values that were in excess of their carrying values, including goodwill. We had no reporting units that had estimated fair values that
100
TETRA TECH, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
6. Goodwill and Intangible Assets (Continued)
exceeded their carrying values by less than 20%, excluding the impact of acquisitions completed within the last two fiscal years. In addition, we regularly evaluate whether events and circumstances have occurred that may indicate a potential change in the recoverability of goodwill. We perform interim goodwill impairment reviews between our annual reviews if certain events and circumstances have occurred, such as a deterioration in general economic conditions; an increase in the competitive environment; a change in management, key personnel, strategy or customers; negative or declining cash flows; or a decline in actual or planned revenue or earnings compared with actual and projected results of relevant prior periods.
In the fourth quarter of fiscal 2015, the mining sector continued to contract in response to lower global growth expectations driven in large part by China's actual and projected slower economic growth. Consistent with this trend, our mining customers continued their curtailment of capital spending for new mining projects. As a result, our Global Mining Practice ("GMP") reporting unit experienced a 25% decline in revenue in the fourth quarter of fiscal 2015 compared to the same period of fiscal 2014. This negative trend was compared to the expected revenue growth of approximately 3% in the previous goodwill impairment test, performed as of June 30, 2014. In response to these results, we performed a strategic review of GMP in the fourth quarter of fiscal 2015, and determined that our mining activities would likely decline further in fiscal 2016, and that revenue and profits would not return to acceptable levels of performance in the foreseeable future. We also decided to redeploy a significant portion of our mining resources into other operational areas that have better growth and profitability prospects. Consequently, as of the first day of fiscal 2016, GMP was no longer a reporting unit. We considered GMP's financial performance and prospects in our goodwill impairment analysis in the fourth quarter of fiscal 2015 and determined that GMP's fair value had fallen significantly below its carrying value, including goodwill. As required, we performed further analysis to measure the amount of the impairment loss and, as a result, we wrote-off all of GMP's goodwill and identifiable intangible assets and recorded a related impairment charge of $60.8 million ($57.3 million after-tax) in the fourth quarter of fiscal 2015. The related goodwill and identifiable intangible assets that were determined not to be recoverable totaled $58.1 million and $2.7 million, respectively.
Our fourth quarter 2016 and 2015 goodwill impairment reviews indicated that we had no other impairment of goodwill, and all of our other reporting units had estimated fair values that were in excess of their carrying values, including goodwill. Although we believe that our estimates of fair value for these reporting units are reasonable, if financial performance for these reporting units falls significantly below our expectations or market prices for similar business decline, the goodwill for these reporting units could become impaired.
Foreign exchange impact relates to our foreign subsidiaries with functional currencies that are different than our reporting currency. The gross amounts of goodwill for WEI were $304.4 million and $293.1 million at October 2, 2016 and September 27, 2015, respectively, excluding $82.4 million of accumulated impairment. The gross amounts of goodwill for RME were $529.2 million and $423.8 million at October 2, 2016 and September 27, 2015, respectively, excluding $33.2 million of accumulated impairment.
101
TETRA TECH, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
6. Goodwill and Intangible Assets (Continued)
The gross amount and accumulated amortization of our acquired identifiable intangible assets with finite useful lives included in "Intangible assets – net" on the consolidated balance sheets, were as follows:
| |
Fiscal Year Ended | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
October 2, 2016 | September 27, 2015 | ||||||||||||||
| |
Weighted- Average Remaining Life (in years) |
Gross Amount |
Accumulated Amortization |
Gross Amount |
Accumulated Amortization |
|||||||||||
| |
($ in thousands) |
|||||||||||||||
Non-compete agreements |
0.6 | $ | 881 | $ | (840 | ) | $ | 819 | $ | (587 | ) | |||||
Client relations |
3.0 | 112,367 | (83,514 | ) | 106,676 | (67,726 | ) | |||||||||
Backlog |
2.2 | 23,018 | (7,536 | ) | 2,115 | (1,444 | ) | |||||||||
Technology and trade names |
4.0 | 7,778 | (3,192 | ) | 2,506 | (2,027 | ) | |||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total |
$ | 144,044 | $ | (95,082 | ) | $ | 112,116 | $ | (71,784 | ) | ||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Foreign currency translation adjustments reduced net identifiable intangible assets by $1.1 million in fiscal 2016. Amortization expense for the identifiable intangible assets for fiscal 2016, 2015 and 2014 was $22.1 million, $20.2 million and $27.3 million, respectively.
Estimated amortization expense for the succeeding five years and beyond is as follows:
| |
Amount | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
(in thousands) |
|||
2017 |
$ | 22,617 | ||
2018 |
14,295 | |||
2019 |
6,989 | |||
2020 |
3,755 | |||
2021 |
666 | |||
Beyond |
640 | |||
Total |
$ | 48,962 | ||
102
TETRA TECH, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
7. Property and Equipment
Property and equipment consisted of the following:
| |
Fiscal Year Ended | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
October 2, 2016 |
September 27, 2015 |
|||||
| |
(in thousands) |
||||||
Land and buildings |
$ | 3,683 | $ | 3,661 | |||
Equipment, furniture and fixtures |
180,750 | 176,883 | |||||
Leasehold improvements |
30,261 | 21,582 | |||||
Total property and equipment |
214,694 | 202,126 | |||||
Accumulated depreciation |
(146,867 | ) | (137,220 | ) | |||
Property and equipment, net |
$ | 67,827 | $ | 64,906 | |||
The depreciation expense related to property and equipment, including assets under capital leases, was $22.8 million, $23.1 million and $26.5 million for fiscal 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. In fiscal 2015, we sold assets with a net book value of $4.4 million for net proceeds of $10.4 million, and recognized a corresponding net gain of $6.0 million, which is included in "Other costs of revenue" in our consolidated statements of income. This equipment was primarily related to our RCM segment.
8. Income Taxes
The income before income taxes, by geographic area, was as follows:
| |
Fiscal Year Ended | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
October 2, 2016 |
September 27, 2015 |
September 28, 2014 |
|||||||
| |
(in thousands) |
|||||||||
Income (loss) before income taxes: |
||||||||||
United States |
$ | 113,576 | $ | 118,822 | $ | 118,900 | ||||
Foreign |
10,890 | (38,501 | ) | 25,443 | ||||||
Total income before income taxes |
$ | 124,466 | $ | 80,321 | $ | 144,343 | ||||
103
TETRA TECH, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
8. Income Taxes (Continued)
Income tax expense consisted of the following:
| |
Fiscal Year Ended | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
October 2, 2016 |
September 27, 2015 |
September 28, 2014 |
|||||||
| |
|
(in thousands) |
|
|||||||
Current: |
||||||||||
Federal |
$ | 22,277 | $ | 23,836 | $ | 26,503 | ||||
State |
5,634 | 5,072 | 7,551 | |||||||
Foreign |
6,651 | 3,773 | 1,759 | |||||||
Total current income tax expense |
34,562 | 32,681 | 35,813 | |||||||
Deferred: |
||||||||||
Federal |
6,231 | 7,218 | 5,957 | |||||||
State |
(16 | ) | 2,335 | 434 | ||||||
Foreign |
(164 | ) | (1,141 | ) | (6,536 | ) | ||||
Total deferred income tax expense (benefit) |
6,051 | 8,412 | (145 | ) | ||||||
Total income tax expense |
$ |
40,613 |
$ |
41,093 |
$ |
35,668 |
||||
Total income tax expense was different from the amount computed by applying the U.S. federal statutory rate to pre-tax income as follows:
| |
Fiscal Year Ended | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
October 2, 2016 |
September 27, 2015 |
September 28, 2014 |
|||||||
Tax at federal statutory rate |
35.0 | % | 35.0 | % | 35.0 | % | ||||
State taxes, net of federal benefit |
3.1 | 5.0 | 3.4 | |||||||
Research and Development ("R&D") credits |
(3.4 | ) | (3.8 | ) | (0.6 | ) | ||||
Domestic production deduction |
(0.7 | ) | (0.8 | ) | (0.7 | ) | ||||
Tax differential on foreign earnings |
(5.5 | ) | (2.5 | ) | (5.5 | ) | ||||
Non-deductible executive compensation |
2.0 | – | – | |||||||
Goodwill and contingent consideration |
– | 12.0 | (8.2 | ) | ||||||
Stock compensation |
0.3 | 0.5 | 0.2 | |||||||
Valuation allowance |
2.4 | 5.7 | 0.3 | |||||||
Change in uncertain tax positions |
(2.0 | ) | – | – | ||||||
Other |
1.4 | 0.1 | 0.8 | |||||||
Total income tax expense |
32.6 |
% |
51.2 |
% |
24.7 |
% |
||||
Our effective tax rates for fiscal 2016 and 2015 were 32.6% and 51.2%, respectively. In fiscal 2016, we incurred $13.3 million of acquisition and integration expenses and debt pre-payment fees for which no tax benefit was recognized. Of this amount, $6.4 million resulted from acquisition expenses that were not tax deductible, and $6.9 million resulted from integration expenses and debt pre-payment fees incurred in jurisdictions with current and historical net operating losses where the related deferred tax asset was fully reserved. Additionally, during the first quarter of fiscal 2016, the Protecting Americans from Tax Hikes Act
104
TETRA TECH, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
8. Income Taxes (Continued)
of 2015 was signed into law which permanently extended the federal R&D credits retroactive to January 1, 2015. Our income tax expense for fiscal 2016 included a tax benefit of $2.0 million attributable to operating income during the last nine months of fiscal 2015, primarily related to the retroactive recognition of the R&D credits. Our income tax expense for fiscal 2015 included a similar retroactive tax benefit of $1.2 million attributable to operating income during the last nine months of fiscal 2014. Our effective tax rate in fiscal 2015 also reflected the impact of the $60.8 million goodwill and intangible asset impairment charge, of which most was not tax deductible. Excluding these items, our effective tax rates for fiscal 2016 and 2015 were 30.9% and 32.5%, respectively. The lower tax rate this year primarily reflects a measurement change in tax positions taken in prior years relating primarily to developments in our ongoing IRS examination that reduced our effective tax rate by 2.0% in fiscal 2016.
We are currently under examination by the Internal Revenue Service for fiscal years 2010 through 2013, and by the California Franchise Tax Board for fiscal years 2004 through 2009. We are also subject to various other state audits. With a few exceptions, we are no longer subject to U.S. federal, state and local, or non-U.S. income tax examinations for fiscal years before 2010.
Temporary differences comprising the net deferred income tax liability shown on the accompanying consolidated balance sheets were as follows:
| |
Fiscal Year Ended | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
October 2, 2016 |
September 27, 2015 |
|||||
| |
(in thousands) |
||||||
Deferred Tax Asset: |
|||||||
State taxes |
$ | 697 | $ | 1,746 | |||
Reserves and contingent liabilities |
2,539 | 3,842 | |||||
Allowance for doubtful accounts |
3,817 | 4,115 | |||||
Accrued liabilities |
24,663 | 19,404 | |||||
Stock-based compensation |
10,684 | 10,516 | |||||
Intangibles |
– | 2,910 | |||||
Loss carry-forwards |
23,514 | 5,512 | |||||
Valuation allowance |
(25,447 | ) | (7,791 | ) | |||
Total deferred tax asset |
40,467 | 40,254 | |||||
|
|||||||
Unbilled revenue |
(54,638 | ) | (46,513 | ) | |||
Prepaid expense |
(2,921 | ) | (5,506 | ) | |||
Intangibles |
(33,268 | ) | (33,068 | ) | |||
Property and equipment |
(9,358 | ) | (10,713 | ) | |||
Total deferred tax liability |
(100,185 | ) | (95,800 | ) | |||
Net deferred tax liability |
$ |
(59,718 |
) |
$ |
(55,546 |
) |
|
At October 2, 2016, undistributed earnings of our foreign subsidiaries, primarily in Canada, amounting to approximately $65.9 million are expected to be permanently reinvested. Accordingly, no provision for U.S. income taxes or foreign withholding taxes has been made. Upon distribution of those earnings, we would be subject to U.S. income taxes and foreign withholding taxes. Assuming the
105
TETRA TECH, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
8. Income Taxes (Continued)
permanently reinvested foreign earnings were repatriated under the laws and rates applicable at October 2, 2016, the incremental federal tax applicable to those earnings would be approximately $5.9 million.
At October 2, 2016, we had available unused state net operating loss ("NOL") carry forwards of $43.7 million that expire at various dates from 2022 to 2036; and available foreign NOL carry forwards of $74.2 million, of which $15.0 million expire at various dates from 2022 to 2036, and $59.2 million have no expiration date. We have performed an assessment of positive and negative evidence regarding the realization of the deferred tax assets. This assessment included the evaluation of scheduled reversals of deferred tax liabilities, availability of carrybacks, cumulative losses in recent years, and estimates of projected future taxable income. Although realization is not assured, based on our assessment, we have concluded that it is more likely than not that the assets will be realized except for the assets related to the loss carry-forwards and certain foreign intangibles for which a valuation allowance of $25.4 million has been provided.
At October 2, 2016, we had $22.8 million of unrecognized tax benefits. Included in the balance of unrecognized tax benefits at the end of fiscal year 2016 were $22.8 million of tax benefits that, if recognized, would affect our effective tax rate. It is not expected that there will be a significant change in the unrecognized tax benefits in the next 12 months. A reconciliation of the beginning and ending amount of unrecognized tax benefits is as follows:
| |
Fiscal Year Ended | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
October 2, 2016 |
September 27, 2015 |
September 28, 2014 |
|||||||
| |
(in thousands) |
|||||||||
Beginning balance |
$ | 21,618 | $ | 21,717 | $ | 25,886 | ||||
Additions for current year tax positions |
2,802 | 1,147 | 1,243 | |||||||
Additions for prior year tax positions |
1,466 | 2,309 | 1,416 | |||||||
Reductions for prior year tax positions |
(3,100 | ) | (23 | ) | – | |||||
Settlements |
– | (3,532 | ) | (6,828 | ) | |||||
Ending balance |
$ | 22,786 | $ | 21,618 | $ | 21,717 | ||||
We recognize potential interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits in income tax expense. During fiscal years 2016 and 2015, we accrued additional interest income of $0.2 million and interest expense of $0.4 million, respectively, and recorded reductions in accrued interest of $0 million and $0.5 million, respectively, as a result of audit settlements and other prior-year adjustments. The amount of interest and penalties accrued at October 2, 2016 and September 27, 2015 was $1.0 million and $1.2 million, respectively.
106
TETRA TECH, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
9. Long-Term Debt
Long-term debt consisted of the following:
| |
Fiscal Year Ended | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
October 2, 2016 |
September 27, 2015 |
|||||
| |
(in thousands) |
||||||
Credit facilities |
$ | 346,813 | $ | 192,203 | |||
Other |
198 | 673 | |||||
Total long-term debt |
347,011 | 192,876 | |||||
Less: Current portion of long-term debt |
(15,510 |
) |
(11,904 |
) |
|||
Long-term debt, less current portion |
$ |
331,501 |
$ |
180,972 |
|||
On May 7, 2013, we entered into a credit agreement that provided for a $205 million term loan facility and a $460 million revolving credit facility both maturing in May 2018. On May 29, 2015, we entered into a third amendment to our credit agreement (as amended, the "Credit Agreement") that extended the maturity date for the term loan and the revolving credit facility to May 2020. The Credit Agreement is a $654.8 million senior secured, five-year facility that provides for a $194.8 million term loan facility ( the "Term Loan Facility") and a $460 million revolving credit facility (the "Revolving Credit Facility"). The Credit Agreement allows us to, among other things, finance certain permitted open market repurchases of our common stock, permitted acquisitions, and cash dividends and distributions. The Revolving Credit Facility includes a $150 million sublimit for the issuance of standby letters of credit, a $20 million sublimit for swingline loans, and a $150 million sublimit for multicurrency borrowings. The interest rate provisions of the term loan and the revolving credit facility did not materially change.
The Term Loan Facility is subject to quarterly amortization of principal, with $10.3 million payable in year 1, and $15.4 million payable in years 2 through 5. The Term Loan may be prepaid at any time without penalty. We may borrow on the Revolving Credit Facility, at our option, at either (a) a Eurocurrency rate plus a margin that ranges from 1.15% to 2.00% per annum, or (b) a base rate for loans in U.S. dollars (the highest of the U.S. federal funds rate plus 0.50% per annum, the bank's prime rate or the Eurocurrency rate plus 1.00%) plus a margin that ranges from 0.15% to 1.00% per annum. In each case, the applicable margin is based on our Consolidated Leverage Ratio, calculated quarterly. The Term Loan Facility is subject to the same interest rate provisions. The interest rate of the Term Loan Facility at the date of inception was 1.57%. The Credit Agreement expires on May 29, 2020, or earlier at our discretion upon payment in full of loans and other obligations.
As of October 2, 2016, we had $346.8 million in outstanding borrowings under the Credit Agreement, which was comprised of $176.8 million under the Term Loan Facility and $170 million under the Revolving Credit Facility at a weighted-average interest rate of 1.92% per annum. In addition, we had $1.3 million in standby letters of credit under the Credit Agreement. Our effective weighted-average interest rate on borrowings outstanding at October 2, 2016 under the Credit Agreement, including the effects of interest rate swap agreements described in Note 14, "Derivative Financial Instruments", was 2.52%. At October 2, 2016, we had $288.7 million of available credit under the Revolving Credit Facility, of which $222.4 million could be borrowed without a violation of our debt covenants. In addition, we entered into agreements with three banks to issue up to $53 million in standby letters of credit. The aggregate
107
TETRA TECH, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
9. Long-Term Debt (Continued)
amount of standby letters of credit outstanding under these additional facilities and other bank guarantees was $25.3 million, of which $6.0 million was issued in currencies other than the U.S. dollar.
The Credit Agreement contains certain affirmative and restrictive covenants, and customary events of default. The financial covenants provide for a maximum Consolidated Leverage Ratio of 3.00 to 1.00 (total funded debt/EBITDA, as defined in the Credit Agreement) and a minimum Consolidated Fixed Charge Coverage Ratio of 1.25 to 1.00 (EBITDA, as defined in the Credit Agreement minus capital expenditures, cash interest plus taxes plus principal payments of indebtedness including capital leases, notes and post-acquisition payments).
At October 2, 2016, we were in compliance with these covenants with a consolidated leverage ratio of 1.91x and a consolidated fixed charge coverage ratio of 2.82x. Our obligations under the Credit Agreement are guaranteed by certain of our subsidiaries and are secured by first priority liens on (i) the equity interests of certain of our subsidiaries, including those subsidiaries that are guarantors or borrowers under the Credit Agreement, and (ii) our accounts receivable, general intangibles and intercompany loans, and those of our subsidiaries that are guarantors or borrowers.
At the time of the acquisition, Coffey had an existing secured credit facility with a bank, comprised of an overdraft facility, a term facility and a bank guaranty facility. This facility was amended in March 2016 to extend the term of the existing facility to April 8, 2016, and allow for the issuance of a parent guarantee and release of certain subsidiary guarantors. On April 8, 2016, the facility was amended again to provide for a secured AUD$30 million facility, which may be used by Coffey for bank overdrafts, short-term cash advances or bank guarantees. This facility expires in April 2017, is secured by assets of certain Australian and New Zealand subsidiaries, and is supported by a parent guarantee. At October 2, 2016, amounts outstanding under this facility consisted solely of bank guarantees of $5.6 million.
The following table presents scheduled maturities of our long-term debt:
| |
Amount | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
(in thousands) |
|||
2017 |
$ | 15,510 | ||
2018 |
15,425 | |||
2019 |
15,388 | |||
2020 |
300,688 | |||
2021 and beyond |
– | |||
Total |
$ | 347,011 | ||
10. Leases
We lease office and field equipment, vehicles and buildings under various operating leases. In fiscal 2016, 2015 and 2014, we recognized $75.0 million, $66.4 million and $70.0 million of expense
108
TETRA TECH, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
10. Leases (Continued)
associated with operating leases, respectively. The following are amounts payable under non-cancelable operating and capital lease commitments for the next five fiscal years and beyond:
| |
Operating | Capital | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
(in thousands) |
||||||
| 2017 | $ | 83,050 | $ | 89 | |||
| 2018 | 56,687 | 52 | |||||
| 2019 | 42,916 | 13 | |||||
| 2020 | 31,533 | – | |||||
| 2021 | 18,673 | – | |||||
| Beyond | 22,732 | – | |||||
Total |
$ | 255,591 | 154 | ||||
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
Less: Amounts representing interest |
6 |
||||||
| | | | | | | | |
Net present value |
$ | 148 | |||||
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
We vacated certain facilities under long-term non-cancelable leases and recorded contract termination costs of $2.9 million in fiscal 2016 and $0 million in fiscal 2015. These amounts were initially measured at the fair value of the portion of the lease payments associated with the vacated facilities, reduced by estimated sublease rentals, less the write off of a prorated portion of existing deferred items previously recognized on these leases. We expect the remaining lease payments to be paid through the various lease expiration dates that continue until 2025.
We initially measured the lease contract termination liability at the fair value of the prorated portion of the lease payments associated with the vacated facilities, reduced by estimated sublease rentals and other costs. If the actual timing and potential termination costs or realization of sublease income differ from our estimates, the resulting liabilities could vary from recorded amounts. These liabilities are reviewed periodically and adjusted when necessary.
The following is a reconciliation of the beginning and ending balances of these liabilities related to lease contract termination costs:
| |
WEI | RME | RCM | Total | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
(in thousands) |
||||||||||||
| Balance at September 28, 2014 | $ | 900 | $ | 5,046 | $ | 423 | $ | 6,369 | |||||
Adjustments (1) |
(369 | ) | (2,585 | ) | (246 | ) | (3,200 | ) | |||||
| Balance at September 27, 2015 | 531 | 2,461 | 177 | $ | 3,169 | ||||||||
Cost transfer between groups |
637 | (637 | ) | – | – | ||||||||
Cost incurred and charged to expense |
1,418 | 749 | – | 2,167 | |||||||||
Adjustments (1) |
(1,034 | ) | (1,060 | ) | (138 | ) | (2,232 | ) | |||||
| Balance as October 2, 2016 | $ | 1,552 | $ | 1,513 | $ | 39 | $ | 3,104 | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
- (1)
- Adjustments of the actual timing and potential termination costs or realization of sublease income.
109
TETRA TECH, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
11. Stockholders' Equity and Stock Compensation Plans
At October 2, 2016, we had the following stock-based compensation plans:
- •
- Employee Stock Purchase Plan ("ESPP"). Purchase rights to purchase common
stock are granted to our eligible full and part-time employees, and shares of common stock are issued upon exercise of the purchase rights. An aggregate of 2,373,290 shares may be issued pursuant to
such exercise. The maximum amount that an employee can contribute during a purchase right period is $5,000. The exercise price of a purchase right is the lesser of 100% of the fair market value of a
share of common stock on the first day of the purchase right period or 85% of the fair market value on the last day of the purchase right period (December 15, or the business day preceding
December 15 if December 15 is not a business day).
- •
- 2005 Equity Incentive Plan ("2005 EIP"). Key employees and non-employee
directors may be granted equity awards, including stock options and restricted stock and restricted stock units ("RSUs"). Options granted before March 6, 2006 vest at 25% on the first
anniversary of the grant date, and the balance vests monthly thereafter, such that these options become fully vested no later than four years from the date of grant. These options expire no later than
ten years from the date of grant. Options granted on and after March 6, 2006 vest at 25% on each anniversary of the grant date. These options expire no later than eight years from the grant
date. RSUs granted to date vest at 25% on each anniversary of the grant date.
Our Compensation Committee has also awarded restricted stock to executive officers and non-employee directors under the 2005 EIP. Restricted stock grants generally vest over a minimum three-year period, and may be performance-based, determined by EPS growth, or service-based. No further awards will be made under the 2005 EIP.
- •
- 2015 Equity Incentive Plan ("2015 EIP"). Key employees and non-employee directors may be granted equity awards, including stock options, performance share units ("PSUs") and RSUs. Shares issued with respect to awards granted under the 2015 EIP other than stock options or stock appreciation rights, which are referred to as "full value awards", are counted against the 2015 EIP's aggregate share limit as three shares for every share or unit actually issued. At October 2, 2016, there were 3.7 million shares available for future awards pursuant to the 2015 EIP.
The stock-based compensation and related income tax benefits were as follows:
| |
Fiscal Year Ended | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
October 2, 2016 |
September 27, 2015 |
September 28, 2014 |
|||||||
| |
(in thousands) |
|||||||||
Total stock-based compensation |
$ | 12,964 | $ | 10,926 | $ | 10,374 | ||||
Income tax benefit related to stock-based compensation |
(4,656 | ) | (3,811 | ) | (3,696 | ) | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Stock-based compensation, net of tax benefit |
$ | 8,308 | $ | 7,115 | $ | 6,678 | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
110
TETRA TECH, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
11. Stockholders' Equity and Stock Compensation Plans (Continued)
Stock option activity for the fiscal year ended October 2, 2016 was as follows:
| |
Number of Options (in thousands) |
Weighted- Average Exercise Price per Share |
Weighted- Average Remaining Contractual Term (in years) |
Aggregate Intrinsic Value (in thousands) |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
|
|
|||||||||||
Outstanding on September 27, 2015 |
2,985 | $ | 23.71 | ||||||||||
Granted |
242 | 27.16 | |||||||||||
Exercised |
(839 | ) | 30.04 | ||||||||||
Forfeited |
(21 | ) | 23.59 | ||||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Outstanding at October 2, 2016 |
2,367 | $ | 24.88 | 4.04 | $ | 25,068 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Vested or expected to vest at October 2, 2016 |
2,320 | $ | 24.88 | 3.99 | $ | 24,579 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Exercisable on October 2, 2016 |
1,776 | $ | 24.10 | 3.04 | $ | 20,197 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
The aggregate intrinsic value in the table above represents the total intrinsic value (the difference between our closing stock price on the last trading day of fiscal 2016 and the exercise price, times the number of shares) that would have been received by the in-the-money option holders if they had exercised their options on October 2, 2016. This amount will change based on the fair market value of our stock. At October 2, 2016, we expect to recognize $3.5 million of unrecognized compensation cost related to stock option grants over a weighted-average period of 4 years.
The weighted-average fair value of stock options granted during fiscal 2016, 2015 and 2014 was $8.05, $8.20 and $9.36, respectively. The aggregate intrinsic value of options exercised during fiscal 2016, 2015 and 2014 was $7.3 million, $2.3 million and $9.3 million, respectively.
The fair value of our stock options was estimated on the date of grant using the Black-Scholes option pricing model. The following assumptions were used in the calculation:
| |
Fiscal Year Ended | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
October 2, 2016 |
September 27, 2015 |
September 28, 2014 |
|||
| Dividend yield | 1.2% | 1.0% | – | |||
| Expected stock price volatility | 36.1% – 38.8% | 36.2% – 38.8% | 36.1% – 38.8% | |||
| Risk-free rate of return, annual | 1.6% – 1.8% | 1.5% – 1.7% | 1.3% – 1.5% | |||
For purposes of the Black-Scholes model, forfeitures were estimated based on historical experience. For the fiscal 2016, 2015 and 2014 year-ends, we based our expected stock price volatility on historical volatility behavior and current implied volatility behavior. Our risk-free rate of return was based
111
TETRA TECH, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
11. Stockholders' Equity and Stock Compensation Plans (Continued)
on constant maturity rates provided by the U.S. Treasury. The expected life was based on historical experience.
Net cash proceeds from the exercise of stock options were $18.0 million, $10.8 million and $23.8 million for fiscal 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. Our policy is to issue shares from our authorized shares upon the exercise of stock options. The actual income tax benefit realized from exercises of nonqualified stock options and disqualifying dispositions of qualified options for fiscal 2016, 2015 and 2014 was $5.3 million, $3.0 million and $4.6 million, respectively.
Restricted Stock, PSUs and RSUs
The fair value of the total compensation cost of each restricted stock award was determined at the date of grant using the market price of the underlying common stock as of the date of grant. For performance-based awards, our expected performance is reviewed to estimate the percentage of shares that will vest. The total compensation cost of the awards is then amortized over their applicable vesting period on a straight-line basis.
Restricted stock activity for the fiscal year ended October 2, 2016 was as follows:
| |
Number of Shares (in thousands) |
Weighted- Average Grant Date Fair Value |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
|
||||||
| Nonvested balance at September 27, 2015 | 104 | $ | 27.15 | ||||
Granted |
14 | 28.58 | |||||
Vested |
(49 | ) | 28.58 | ||||
Forfeited |
(34 | ) | 24.26 | ||||
| | | | | | | | |
Nonvested balance at October 2, 2016 |
35 |
$ |
28.58 |
||||
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
Vested or expected to vest at October 2, 2016 |
35 |
$ |
28.58 |
||||
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
In fiscal 2016, 2015 and 2014, we awarded 0 shares, 0 shares and 117,067 shares, respectively, of restricted stock to certain of our executive officers and non-employee directors. Vesting is performance-based, such that the percentage of awarded shares that ultimately vests, from 0% to 140%, is dependent on fiscal year EPS growth rates for the three fiscal years that end after the award date. In fiscal 2016 and 2015, an additional 13,932 shares and 15,605 shares, respectively, were awarded for performance-based adjustments in excess of 100% vesting. Restricted stock forfeitures resulted from performance-based vesting of less than 100%. Forfeited shares return to the pool of authorized shares available for award.
112
TETRA TECH, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
11. Stockholders' Equity and Stock Compensation Plans (Continued)
PSU activity for the fiscal year ended October 2, 2016 was as follows:
| |
Number of Shares (in thousands) |
Weighted- Average Grant Date Fair Value |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
|
||||||
| Nonvested balance at September 27, 2015 | 139 | $ | 31.66 | ||||
Granted |
138 | 31.63 | |||||
| | | | | | | | |
Nonvested balance at October 2, 2016 |
277 |
$ |
31.65 |
||||
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
In fiscal 2016, we awarded 137,777 PSUs to our executive officers and non-employee directors at the weighted-average fair value of $31.63 per share on the award date. All of the PSUs are performance-based and vest, if at all, after the conclusion of the three-year performance period. The number of PSUs that ultimately vest is based 50% on the growth in our EPS and 50% on our relative total shareholder return over the vesting period.
RSU activity for the fiscal year ended October 2, 2016 was as follows:
| |
Number of Shares (in thousands) |
Weighted- Average Grant Date Fair Value |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
|
||||||
| Nonvested balance at September 27, 2015 | 483 | $ | 26.75 | ||||
Granted |
217 | 27.14 | |||||
Vested |
(180 | ) | 26.03 | ||||
Forfeited |
(21 | ) | 27.11 | ||||
| | | | | | | | |
Nonvested balance at October 2, 2016 |
499 |
$ |
27.16 |
||||
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
In fiscal 2016, we also awarded 216,539 RSUs to our employees at a weighted average fair value of $27.14 per share on the award date. All of the RSUs have time-based vesting over a four-year period, except that RSUs awarded to directors vest after one year. At October 2, 2016, there were 499,021 RSUs outstanding. RSU forfeitures result from employment terminations prior to vesting. Forfeited shares return to the pool of authorized shares available for award.
In fiscal 2015, we awarded 234,685 RSUs to our employees at the weighted average fair value of $27.21 per share on the award date. All of the RSUs have time-based vesting over a four-year period, except that RSUs awarded to directors vest after one year. At September 27, 2015, there were 483,111 RSUs outstanding. RSU forfeitures result from employment terminations prior to vesting. Forfeited shares return to the pool of authorized shares available for award.
The stock-based compensation expense related to restricted stock, PSUs and RSUs for fiscal years 2016, 2015 and 2014 was $10.3 million, $7.5 million and $4.6 million, respectively, and was included in the total stock-based compensation expense. At October 2, 2016, there was $13.5 million of unrecognized
113
TETRA TECH, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
11. Stockholders' Equity and Stock Compensation Plans (Continued)
compensation costs related to restricted stock, PSUs and RSUs that will be substantially recognized by the end of fiscal 2019.
The following table summarizes shares purchased, weighted-average purchase price, cash received and the aggregate intrinsic value for shares purchased under the ESPP:
| |
Fiscal Year Ended | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
October 2, 2016 |
September 27, 2015 |
September 28, 2014 |
|||||||
| |
(in thousands, except for purchase price) |
|||||||||
Shares purchased |
209 | 243 | 245 | |||||||
Weighted-average purchase price |
$ | 22.54 | $ | 21.44 | $ | 22.99 | ||||
Cash received from exercise of purchase rights |
$ | 4,707 | $ | 5,204 | $ | 5,604 | ||||
Aggregate intrinsic value |
$ | 710 | $ | 1,277 | $ | 1,221 | ||||
The grant date fair value of each award granted under the ESPP was estimated using the Black-Scholes option pricing model with the following assumptions:
| |
Fiscal Year Ended | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
October 2, 2016 |
September 27, 2015 |
September 28, 2014 |
|||||||
Dividend yield |
1.3 | % | 1.1 | % | – | |||||
Expected stock price volatility |
23.7 | % | 23.7 | % | 29.2 | % | ||||
Risk-free rate of return, annual |
0.2 | % | 0.2 | % | 0.1 | % | ||||
Expected life (in years) |
1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||
For fiscal 2016, 2015 and 2014, we based our expected stock price volatility on historical volatility behavior and current implied volatility behavior. The risk-free rate of return was based on constant maturity rates provided by the U.S. Treasury. The expected life was based on the ESPP terms and conditions.
Included in stock-based compensation expense for fiscal 2016, 2015 and 2014 was $0.4 million, $0.6 million and $0.7 million, respectively, related to the ESPP. The unrecognized stock-based compensation costs for awards granted under the ESPP at October 2, 2016 and September 27, 2015 were $0.1 million. At October 2, 2016, ESPP participants had accumulated $2.8 million to purchase our common stock.
12. Retirement Plans
We have established defined contribution plans including 401(k) plans. Generally, employees are eligible to participate in the defined contribution plans upon completion of one year of service and in the 401(k) plans upon commencement of employment. For fiscal 2016, 2015 and 2014, employer contributions to the plans were $10.7 million, $9.8 million and $9.6 million, respectively.
114
TETRA TECH, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
12. Retirement Plans (Continued)
We have established a non-qualified deferred compensation plan for certain key employees and non-employee directors. Eligible employees and non-employee directors may elect to defer the receipt of salary, incentive payments, restricted stock, PSU and RSU awards, and non-employee director fees, which are generally invested by us in individual variable life insurance contracts we own that are designed to informally fund savings plans of this nature. At October 2, 2016 and September 27, 2015, the consolidated balance sheets reflect assets of $20.9 million and $19.5 million, respectively, related to the deferred compensation plan in "Other long-term assets," and liabilities of $20.8 million and $19.3 million, respectively, related to the deferred compensation plan in "Other long-term liabilities."
13. Earnings Per Share
The following table sets forth the number of weighted-average shares used to compute basic and diluted EPS:
| |
Fiscal Year Ended | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
October 2, 2016 |
September 27, 2015 |
September 28, 2014 |
|||||||
| |
(in thousands, except per share data) |
|||||||||
Net income attributable to Tetra Tech |
$ | 83,783 | $ | 39,074 | $ | 108,266 | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Weighted-average common shares outstanding – basic |
58,186 | 60,913 | 64,379 | |||||||
Effect of diluted stock options and unvested restricted stock |
780 | 619 | 767 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Weighted-average common stock outstanding – diluted |
58,966 | 61,532 | 65,146 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Earnings per share attributable to Tetra Tech: |
||||||||||
Basic |
$ | 1.44 | $ | 0.64 | $ | 1.68 | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Diluted |
$ | 1.42 | $ | 0.64 | $ | 1.66 | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
For 2016, 2015 and 2014, 0, 1.0 million and 0 options were excluded from the calculation of dilutive potential common shares, respectively. These options were not included in the computation of dilutive potential common shares because the assumed proceeds per share exceeded the average market price per share for that period. Therefore, their inclusion would have been anti-dilutive.
14. Derivative Financial Instruments
We use certain interest rate derivative contracts to hedge interest rate exposures on our variable rate debt. We enter into foreign currency derivative contracts with financial institutions to reduce the risk that cash flows and earnings will be adversely affected by foreign currency exchange rate fluctuations. Our hedging program is not designated for trading or speculative purposes.
We recognize derivative instruments as either assets or liabilities on the accompanying consolidated balance sheets at fair value. We record changes in the fair value (i.e., gains or losses) of the derivatives that have been designated as accounting hedges in our consolidated balance sheets as accumulated other comprehensive income (loss).
115
TETRA TECH, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
14. Derivative Financial Instruments (Continued)
In fiscal 2013, we entered into three interest rate swap agreements that we have designated as cash flow hedges to fix the variable interest rates on a portion of borrowings under our term loan facility. In the first quarter of fiscal 2014, we entered into two interest rate swap agreements that we designated as cash flow hedges to fix the variable interest rates on the borrowings under our term loan facility. At October 2, 2016 and September 27, 2015, the effective portion of our interest rate swap agreements designated as cash flow hedges before tax effect was $1.6 million and $2.3 million, respectively, all of which we expect to be reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) to interest expense within the next 12 months.
As of October 2, 2016, the notional principal, fixed rates and related expiration dates of our outstanding interest rate swap agreements are as follows:
| Notional Amount (in thousands) |
Fixed Rate |
Expiration Date |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
|
|
||||||||
$ |
44,203 | 1.36 | % | May 2018 | ||||||
|
44,203 | 1.34 | % | May 2018 | ||||||
|
44,203 | 1.35 | % | May 2018 | ||||||
|
22,102 | 1.23 | % | May 2018 | ||||||
|
22,102 | 1.24 | % | May 2018 | ||||||
The fair values of our outstanding derivatives designated as hedging instruments were as follows:
| |
|
Fair Value of Derivative Instruments as of |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
Balance Sheet Location | October 2, 2016 |
September 27, 2015 |
||||||
| |
|
(in thousands) |
|||||||
| |
|
||||||||
Interest rate swap agreements |
Other current liabilities | $ | 1,572 | $ | 2,518 | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
The impact of the effective portions of derivative instruments in cash flow hedging relationships on income and other comprehensive income from our interest rate swap agreements was immaterial for the fiscal years ended October 2, 2016 and September 27, 2015. Additionally, there were no ineffective portions of derivative instruments. Accordingly, no amounts were excluded from effectiveness testing for our foreign currency forward contracts and interest rate swap agreements. We had no derivative instruments that were not designated as hedging instruments for fiscal 2016, 2015 and 2014.
116
TETRA TECH, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
15. Reclassifications Out of Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss)
The accumulated balances and reporting period activities for fiscal 2016 and 2015 related to reclassifications out of accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) are summarized as follows:
| |
Foreign Currency Translation Adjustments |
Gain (Loss) on Derivative Instruments |
Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
(in thousands) |
|||||||||
Balances at September 28, 2014 |
$ | (43,085 | ) | $ | 547 | $ | (42,538 | ) | ||
Other comprehensive loss before reclassifications |
(98,144 |
) |
(203 |
) |
(98,347 |
) |
||||
Amounts reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive income |
||||||||||
Interest rate contracts, net of tax (1) |
– | (2,286 | ) | (2,286 | ) | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Net current-period other comprehensive loss |
(98,144 | ) | (2,489 | ) | (100,633 | ) | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Balances at September 27, 2015 |
$ | (141,229 | ) | $ | (1,942 | ) | $ | (143,171 | ) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Other comprehensive loss before reclassifications |
14,385 | 2,722 | 17,107 | |||||||
Amounts reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive income |
||||||||||
Interest rate contracts, net of tax (1) |
– | (1,944 | ) | (1,944 | ) | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Net current-period other comprehensive loss |
14,385 | 778 | 15,163 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Balances at October 2, 2016 |
$ | (126,844 | ) | $ | (1,164 | ) | $ | (128,008 | ) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
- (1)
- This accumulated other comprehensive component is reclassified in "Interest expense" in our consolidated statements of operations. See Note 14, "Derivative Financial Instruments", for more information.
16. Fair Value Measurements
Derivative Instruments. For additional information about our derivative financial instruments (see Note 2, "Basis of Presentation and Preparation" and Note 14, "Derivative Financial Instruments").
Contingent Consideration. We measure our contingent earn-out liabilities at fair value on a recurring basis (see Note 2, "Basis of Presentation and Preparation" and Note 5, "Mergers and Acquisitions" for further information).
Debt. The fair value of long-term debt was determined using the present value of future cash flows based on the borrowing rates currently available for debt with similar terms and maturities (Level 2 measurement, as described in Note 2, "Basis of Presentation and Preparation – Fair Value of Financial Instruments"). The carrying value of our long-term debt approximated fair value at October 2, 2016 and September 27, 2015. At October 2, 2016, we had borrowings of $346.8 million outstanding under our Credit Agreement, which were used to fund our business acquisitions, working capital needs, share repurchases, dividends, capital expenditures and contingent earn-outs (see Note 9, "Long-Term Debt" for more information).
117
TETRA TECH, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
17. Joint Ventures
Consolidated Joint Ventures
The aggregate revenue of the consolidated joint ventures was $3.7 million, $7.5 million and $12.3 million for fiscal 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. The assets and liabilities of these consolidated joint ventures were immaterial at fiscal 2016, 2015 and 2014 year-ends. These assets are restricted for use only by those joint ventures and are not available for our general operations. Cash and cash equivalents maintained by the consolidated joint ventures at October 2, 2016 and September 27, 2015 were $0.2 million and $0.7 million, respectively.
Unconsolidated Joint Ventures
We account for our unconsolidated joint ventures using the equity method of accounting. Under this method, we recognize our proportionate share of the net earnings of these joint ventures within "Other costs of revenue" in our consolidated statements of income. For fiscal 2016, 2015 and 2014, we reported $1.7 million, $5.1 million and $2.8 million of equity in earnings of unconsolidated joint ventures, respectively. Our maximum exposure to loss as a result of our investments in unconsolidated variable interest entities is typically limited to the aggregate of the carrying value of the investment. Future funding commitments for the unconsolidated joint ventures are immaterial. The unconsolidated joint ventures are, individually and in aggregate, immaterial to our consolidated financial statements.
The aggregate carrying values of the assets and liabilities of the unconsolidated joint ventures were $15.6 million and $13.5 million, respectively, at October 2, 2016, and $17.1 million and $15.2 million, respectively, at September 27, 2015.
18. Commitments and Contingencies
We are subject to certain claims and lawsuits typically filed against the engineering, consulting and construction profession, alleging primarily professional errors or omissions. We carry professional liability insurance, subject to certain deductibles and policy limits, against such claims. However, in some actions, parties are seeking damages that exceed our insurance coverage or for which we are not insured. While management does not believe that the resolution of these claims will have a material adverse effect, individually or in aggregate, on our financial position, results of operations or cash flows, management acknowledges the uncertainty surrounding the ultimate resolution of these matters.
19. Reportable Segments
Our reportable segments are described as follows:
WEI: WEI provides consulting and engineering services worldwide for a broad range of water and infrastructure-related needs in both developed and emerging economies. WEI supports both public and private clients including federal, state/provincial, and local governments, and global and local commercial clients. The primary markets for WEI's services include water resources analysis and water management, environmental restoration, government consulting, and a broad range of civil infrastructure master planning and engineering design for facilities, transportation, and regional and local development. WEI's services span from early data collection and monitoring, to data analysis and information
118
TETRA TECH, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
19. Reportable Segments (Continued)
technology, to science and engineering applied research, to engineering design, to construction management and operations and maintenance.
RME: RME provides consulting and engineering services worldwide for a broad range of resource management and energy needs. RME supports both private and public clients, including global industrial and commercial clients, U.S. federal agencies in large scale remediation, and major international development agencies. The primary markets for RME's services include natural resources, energy, international development, remediation, waste management and utilities. RME's services span from early data collection and monitoring, to data analysis and information technology, to science and engineering applied research, to engineering design, to construction management and operations and maintenance. RME also supports EPCM for full service implementation of commercial projects.
RCM: We report the results of the wind-down of our non-core construction activities in the RCM reportable segment. The remaining work to be performed in this segment will be substantially completed in fiscal 2017.
Management evaluates the performance of these reportable segments based upon their respective segment operating income before the effect of amortization expense related to acquisitions, and other unallocated corporate expenses. We account for inter-segment sales and transfers as if the sales and transfers were to third parties; that is, by applying a negotiated fee onto the costs of the services performed. All significant intercompany balances and transactions are eliminated in consolidation. In fiscal 2016, the Corporate segment operating losses included $19.5 million of acquisition and integration expenses, as described in Note 5, "Mergers and Acquisitions".
119
TETRA TECH, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
19. Reportable Segments (Continued)
The following tables set forth summarized financial information concerning our reportable segments:
Reportable Segments
| |
Fiscal Year Ended | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
October 2, 2016 |
September 27, 2015 |
September 28, 2014 |
|||||||
| |
(in thousands) |
|||||||||
Revenue |
||||||||||
WEI |
$ | 1,028,281 | $ | 993,631 | $ | 1,018,522 | ||||
RME |
1,569,702 | 1,282,046 | 1,333,127 | |||||||
RCM |
52,150 | 86,575 | 221,108 | |||||||
Elimination of inter-segment revenue |
(66,664 | ) | (62,931 | ) | (88,943 | ) | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Total revenue |
$ | 2,583,469 | $ | 2,299,321 | $ | 2,483,814 | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Operating Income |
||||||||||
WEI |
$ | 95,996 | $ | 93,142 | $ | 93,853 | ||||
RME |
112,202 | 93,359 | 84,862 | |||||||
RCM |
(11,834 | ) | (8,614 | ) | (45,151 | ) | ||||
Corporate (1) |
(60,509 | ) | (90,203 | ) | 20,269 | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Total operating income |
$ | 135,855 | $ | 87,684 | $ | 153,833 | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Depreciation |
||||||||||
WEI |
$ | 4,797 | $ | 5,335 | $ | 6,302 | ||||
RME |
15,703 | 13,342 | 14,089 | |||||||
RCM |
736 | 1,801 | 2,958 | |||||||
Corporate |
1,520 | 2,632 | 3,103 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Total depreciation |
$ | 22,756 | $ | 23,110 | $ | 26,452 | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
- (1)
- Includes goodwill and other intangible assets impairment charges, amortization of intangibles, other costs and other income not allocable to segments. The impairment charges of $60.8 million for fiscal 2015 was recorded at Corporate. The intangible asset amortization expense for fiscal 2016, 2015 and 2014 was $22.1 million, $20.2 million and $27.3 million, respectively. Corporate results also included income (loss) for fair value adjustments to contingent consideration liabilities of $(2.8) million, $3.1 million and $58.7 million for fiscal 2016, 2015 and 2014, respectively. Fiscal 2016 also included $19.5 million of acquisition and integration related expenses recorded at Corporate.
120
TETRA TECH, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
19. Reportable Segments (Continued)
| |
October 2, 2016 |
September 27, 2015 |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
(in thousands) |
||||||
Total Assets |
|||||||
WEI |
$ | 308,438 | $ | 287,112 | |||
RME |
522,895 | 422,133 | |||||
RCM |
39,107 | 57,612 | |||||
Corporate (1) |
930,339 | 792,385 | |||||
| | | | | | | | |
Total assets |
$ | 1,800,779 | $ | 1,559,242 | |||
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
- (1)
- Corporate assets consist of intercompany eliminations and assets not allocated to segments including goodwill, intangible assets, deferred income taxes and certain other assets.
Geographic Information
| |
Fiscal Year Ended | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
October 2, 2016 | September 27, 2015 | September 28, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||
| |
Revenue | Long-Lived Assets (2) |
Revenue | Long-Lived Assets (2) |
Revenue | Long-Lived Assets (2) |
|||||||||||||
| |
|
|
(in thousands) |
|
|
||||||||||||||
United States |
$ | 1,858,551 | $ | 59,334 | $ | 1,734,439 | $ | 61,526 | $ | 1,840,129 | $ | 61,940 | |||||||
Foreign countries (1) |
724,918 | 39,067 | 564,882 | 32,230 | 643,685 | 38,576 | |||||||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
- (1)
- Includes revenue generated from our foreign operations, primarily in Canada and Australia, and revenue generated from non-U.S. clients. Long-lived assets consist primarily of amounts from our Canadian operations.
- (2)
- Excludes goodwill and other intangible assets.
Major Clients
Other than the U.S. federal government, we had no single client that accounted for more than 10% of our revenue. All of our segments generated revenue from all client sectors.
121
TETRA TECH, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
19. Reportable Segments (Continued)
The following table presents our revenue by client sector:
| |
Fiscal Year Ended | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
October 2, 2016 |
September 27, 2015 |
September 28, 2014 |
|||||||
| |
(in thousands) |
|||||||||
Client Sector |
||||||||||
International (1) |
$ | 724,918 | $ | 564,882 | $ | 643,649 | ||||
U.S commercial |
763,443 | 736,815 | 713,266 | |||||||
U.S. federal government (2) |
784,368 | 709,600 | 772,290 | |||||||
U.S. state and local government |
310,740 | 288,024 | 354,609 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Total |
$ | 2,583,469 | $ | 2,299,321 | $ | 2,483,814 | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
- (1)
- Includes revenue generated from foreign operations, primarily in Canada and Australia, and revenue generated from non-U.S. clients.
- (2)
- Includes revenue generated under U.S. federal government contracts performed outside the United States.
20. Quarterly Financial Information – Unaudited
In the opinion of management, the following unaudited quarterly data for the fiscal years ended October 2, 2016 and September 27, 2015 reflect all adjustments necessary for a fair statement of the results of operations.
In fiscal 2016, we incurred Coffey-related acquisition and integration expenses totaling $19.5 million. These costs were recognized in the second, third, and fourth quarters of fiscal 2016 in the amounts of $15.9 million, $1.0 million, and $2.6 million, respectively. In addition, interest expense in fiscal 2016 includes Coffey-related debt pre-payment fees of $1.9 million that were incurred in the second quarter. As a result of GMP's financial performance and prospects, we wrote-off all of GMP's goodwill
122
TETRA TECH, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (Continued)
20. Quarterly Financial Information – Unaudited (Continued)
and intangible assets and recorded a related impairment charge of $60.8 million ($57.3 million after-tax) in the fourth quarter of fiscal 2015.
| |
First Quarter |
Second Quarter |
Third Quarter |
Fourth Quarter |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
(in thousands, except per share data) |
||||||||||||
Fiscal Year 2016 |
|||||||||||||
Revenue |
$ | 560,708 | $ | 627,384 | $ | 666,869 | $ | 728,508 | |||||
Operating income |
32,930 | 16,650 | 39,085 | 47,190 | |||||||||
Net income attributable to Tetra Tech |
23,239 | 3,744 | 25,694 | 31,106 | |||||||||
Earnings per share attributable to Tetra Tech (1): |
|||||||||||||
Basic |
$ | 0.39 | $ | 0.06 | $ | 0.44 | $ | 0.54 | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Diluted |
$ | 0.39 | $ | 0.06 | $ | 0.44 | $ | 0.53 | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Weighted-average common shares outstanding: |
|||||||||||||
Basic |
59,058 | 58,451 | 57,796 | 57,309 | |||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Diluted |
59,793 | 59,131 | 58,616 | 58,192 | |||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Fiscal Year 2015 |
|||||||||||||
Revenue |
$ | 581,056 | $ | 564,763 | $ | 575,108 | $ | 578,394 | |||||
Operating income (loss) |
36,612 | 30,398 | 40,721 | (20,047 | ) | ||||||||
Net income (loss) attributable to Tetra Tech |
25,575 | 19,017 | 26,206 | (31,724 | ) | ||||||||
Earnings (loss) per share attributable to Tetra Tech (1): |
|||||||||||||
Basic |
$ | 0.41 | $ | 0.31 | $ | 0.44 | $ | (0.53 | ) | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Diluted |
$ | 0.41 | $ | 0.31 | $ | 0.43 | $ | (0.53 | ) | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Weighted-average common shares outstanding: |
|||||||||||||
Basic |
62,452 | 61,153 | 60,207 | 59,963 | |||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Diluted |
63,112 | 61,723 | 60,792 | 59,963 | |||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
- (1)
- The sum of the quarterly EPS may not add up to the full-year EPS due to rounding.
123
Item 9. Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure
None.
Item 9A. Controls and Procedures
Evaluation of disclosure controls and procedures and changes in internal control over financial reporting
At October 2, 2016, we carried out an evaluation of the effectiveness of the design and operation of our disclosure controls and procedures. Based on our management's evaluation (with the participation of our principal executive officer and principal financial officer), our principal executive officer and principal financial officer have concluded that, as of the end of the period covered by this report, our disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Exchange Act), were effective.
Consistent with guidance issued by the Securities and Exchange Commission that an assessment of internal controls over financial reporting of a recently acquired business may be omitted from management's evaluation of disclosure controls and procedures, management is excluding an assessment of such internal controls of Coffey and INDUS, which we acquired January 18, 2016 and March 11, 2016, respectively, from its evaluation of the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures. The total assets and revenue related to Coffey and INDUS combined are approximately 5.8% and 12.4%, respectively, of the related consolidated financial statement amounts as of and for the fiscal year ended October 2, 2016.
Management's Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting. As defined in Exchange Act Rule 13a-15(f), internal control over financial reporting is a process designed by, or under the supervision of, our principal executive and principal financial officer and effected by our Board of Directors, management and other personnel to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of consolidated financial statements for external purposes in accordance with U.S. GAAP. Internal controls include those policies and procedures that (i) pertain to the maintenance of records that in reasonable detail accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of our assets; (ii) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with U.S. GAAP and that our receipts and expenditures are being made only in accordance with authorizations of our management and directors; and (iii) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of our assets that could have a material effect on our consolidated financial statements. Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate. Accordingly, even effective internal control over financial reporting can only provide reasonable assurance of achieving their control objectives.
Under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, we assessed the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting at October 2, 2016, based on the criteria in Internal Control – Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the COSO. Based upon this assessment, management has concluded that our internal control over financial reporting was effective at October 2, 2016, at a reasonable assurance level.
124
PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP, the independent registered public accounting firm that audited the consolidated financial statements included in this Form 10-K, has issued a report on our internal control over financial reporting. This report, dated November 22, 2016, appears on page 75 of this Form 10-K.
Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
There were no changes in our internal control over financial reporting during the three months ended October 2, 2016 that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
None.
Item 10. Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance
The information required by this item relating to our directors and nominees, regarding compliance with Section 16(a) of the Exchange Act, and regarding our Audit Committee is included under the captions "Item No. 1 – Election of Directors and Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance" in our Proxy Statement related to the 2017 Annual Meeting of Stockholders and is incorporated by reference.
Pursuant to General Instruction G(3) of Form 10-K, the information required by this item relating to our executive officers is included under the caption "Executive Officers of the Registrant" in Part I of this Report.
We have adopted a code of ethics that applies to our principal executive officer and all members of our finance department, including our principal financial officer and principal accounting officer. This code of ethics, entitled "Finance Code of Professional Conduct," is posted on our website. The Internet address for our website is www.tetratech.com, and the code of ethics may be found through a link to the Investor Relations section of our website.
We intend to satisfy the disclosure requirement under Item 5.05 of Form 8-K for any amendment to, or waiver from, a provision of this code of ethics by posting any such information on our website, at the address and location specified above.
Item 11. Executive Compensation
The information required by this item is included under the captions "Item No. 1 – Election of Directors" and "Executive Compensation Tables" in our Proxy Statement related to the 2017 Annual Meeting of Stockholders and is incorporated by reference.
Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters
The information required by this item relating to security ownership of certain beneficial owners and management, and securities authorized for issuance under equity compensation plans, is included under the caption "Security Ownership of Management and Significant Stockholders" in our Proxy Statement related to the 2017 Annual Meeting of Stockholders and is incorporated by reference.
125
Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence
The information required by this item relating to review, approval or ratification of transactions with related persons is included under the caption "Related Person Transactions," and the information required by this item relating to director independence is included under the caption "Item No. 1 – Election of Directors," in each case in our Proxy Statement related to the 2017 Annual Meeting of Stockholders and is incorporated by reference.
Item 14. Principal Accounting Fees and Services
The information required by this item is included under the captions "Item No. 4 – Ratification of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm" in our Proxy Statement related to the 2017 Annual Meeting of Stockholders and is incorporated by reference.
Item 15. Exhibits, Financial Statement Schedules
| (a.) | 1. | Financial Statements | |||
| The Index to Financial Statements and Financial Statement Schedule on page 74 is incorporated by reference as the list of financial statements required as part of this Report. | |||||
2. |
Financial Statement Schedule |
||||
| The Index to Financial Statements and Financial Statement Schedule on page 74 is incorporated by reference as the list of financial statement schedules required as part of this Report. | |||||
3. |
Exhibits |
||||
| The exhibit list in the Index to Exhibits on pages 130 – 131 is incorporated by reference as the list of exhibits required as part of this Report. |
126
TETRA TECH, INC.
SCHEDULE II – VALUATION AND QUALIFYING ACCOUNTS AND RESERVES
For the Fiscal Years Ended
September 28, 2014, September 27, 2015 and October 2, 2016
(in thousands)
| |
Balance at Beginning of Period |
Charged to Costs, Expenses and Revenue |
Deductions (1) | Other (2) | Balance at End of Period |
|||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allowance for doubtful accounts: | |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
Fiscal 2014 |
$ |
44,623 |
$ |
1,467 |
$ |
(4,855 |
) |
$ |
(1,455 |
) |
$ |
39,780 |
||||
Fiscal 2015 |
39,780 |
(1,034 |
) |
(5,965 |
) |
(1,291 |
) |
31,490 |
||||||||
Fiscal 2016 |
31,490 |
8,082 |
(12,191 |
) |
7,852 |
35,233 |
||||||||||
Income tax valuation allowance: |
||||||||||||||||
Fiscal 2014 |
$ |
7,459 |
$ |
396 |
$ |
– |
$ |
(279 |
) |
$ |
7,576 |
|||||
Fiscal 2015 |
7,576 |
4,609 |
– |
(4,394 |
) |
7,791 |
||||||||||
Fiscal 2016 |
7,791 |
3,856 |
– |
13,800 |
25,447 |
|||||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
- (1)
- Primarily represents uncollectible accounts written off, net of recoveries.
- (2)
- Includes allowances from new business acquisitions, loss in foreign jurisdictions, currency adjustments, and valuation allowance adjustments related to net operating loss carry-forwards.
127
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this Report on Form 10-K to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| TETRA TECH, INC. | ||||
By: |
/s/ DAN L. BATRACK |
|||
| Dated: November 16, 2016 | Dan L. Batrack Chairman, Chief Executive Officer and President |
|||
KNOW ALL PERSONS BY THESE PRESENTS, that each person whose signature appears below constitutes and appoints Dan L. Batrack and Steven M. Burdick, jointly and severally, his attorney-in-fact, each with the full power of substitution, for such person, in any and all capacities, to sign any and all amendments to this Annual Report on Form 10-K, and to file the same, with all exhibits thereto and other documents in connection therewith, with the Securities and Exchange Commission, granting unto said attorney-in-fact and agent full power and authority to do and perform each and every act and thing requisite and necessary to be done in connection therewith, as fully to all intents and purposes as he might do or could do in person, hereby ratifying and confirming all that each of said attorneys-in-fact and agents, or his substitute, may do or cause to be done by virtue hereof.
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this Report on Form 10-K has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| Signature | Title | Date | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
/s/ DAN L. BATRACK |
Chairman, Chief Executive Officer and President | November 16, 2016 | ||
|
Dan L. Batrack |
(Principal Executive Officer) | |||
/s/ STEVEN M. BURDICK |
Chief Financial Officer |
November 16, 2016 |
||
|
Steven M. Burdick |
(Principal Financial Officer) | |||
/s/ BRIAN N. CARTER |
Senior Vice President, Corporate Controller |
November 16, 2016 |
||
|
Brian N. Carter |
(Principal Accounting Officer) | |||
/s/ ALBERT E. SMITH |
Director |
November 16, 2016 |
||
|
Albert E. Smith |
||||
/s/ HUGH M. GRANT |
Director |
November 16, 2016 |
||
|
Hugh M. Grant |
128
| Signature | Title | Date | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| /s/ PATRICK C. HADEN | Director | November 16, 2016 | ||
|
Patrick C. Haden |
||||
/s/ J. CHRISTOPHER LEWIS |
Director |
November 16, 2016 |
||
|
J. Christopher Lewis |
||||
/s/ JOANNE M. MAGUIRE |
Director |
November 16, 2016 |
||
|
Joanne M. Maguire |
||||
/s/ J. KENNETH THOMPSON |
Director |
November 16, 2016 |
||
|
J. Kenneth Thompson |
||||
/s/ RICHARD H. TRULY |
Director |
November 16, 2016 |
||
|
Richard H. Truly |
||||
/s/ KIRSTEN M. VOLPI |
Director |
November 16, 2016 |
||
|
Kirsten M. Volpi |
||||
/s/ KIMBERLY E. RITRIEVI |
Director |
November 16, 2016 |
||
|
Kimberly E. Ritrievi |
129
| 3.1 | Restated Certificate of Incorporation of the Company (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K dated February 26, 2009). | |
3.2 |
Bylaws of the Company (amended and restated as of April 2009) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K dated April 24, 2009), and amended as of November 7, 2016 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K dated November 9, 2016). |
|
10.1 |
Amended and Restated Credit Agreement dated as of May 7, 2013 among Tetra Tech, Inc., Tetra Tech Canada Holding Corporation, the lenders party thereto and Bank of America, N.A., as Administrative Agent (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K dated May 9, 2013). |
|
10.2 |
Amendment No. 1 dated as of September 27, 2013 to the Amended and Restated Credit Agreement dated as of May 7, 2013 among Tetra Tech, Inc., Tetra Tech Canada Holding Corporation, the lenders party thereto and Bank of America, N.A., as Administrative Agent (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K dated September 27, 2013). |
|
10.3 |
Amendment No. 2 dated as of June 23, 2014 to the Amended and Restated Credit Agreement dated as of May 7, 2013 among Tetra Tech, Inc., Tetra Tech Canada Holding Corporation, the lenders party thereto and Bank of America, N.A., as Administrative Agent (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K dated June 23, 2014). |
|
10.4 |
Amendment No. 3 dated as of May 29, 2015 to the Amended and Restated Credit Agreement dated as of May 7, 2013 (as amended by Amendment No. 1 dated as of September 27, 2013 and Amendment No. 2 dated as of June 23, 2014) among Tetra Tech, Inc., Tetra Tech Canada Holding Corporation, Bank of America, N.A., as Administrative Agent, L/C Issuer and a Lender, U.S. Bank National Association, as L/C Issuer and a Lender, and the other Lenders party thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K dated June 2, 2015). |
|
10.5 |
Amendment No. 4 dated as of July 14, 2016 to the Amended and Restated Credit Agreement dated as of May 7, 2013 (as amended by Amendment No. 1 dated as of September 27, 2013, Amendment No. 2 dated as of June 23, 2014 and Amendment No. 3 dated as of May 29, 2015) among Tetra Tech, Inc., Tetra Tech Canada Holding Corporation, Bank of America, N.A., as Administrative Agent, L/C Issuer and a Lender, U.S. Bank National Association, as L/C Issuer and a Lender, and the other Lenders party thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company's Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 26, 2016). |
|
10.6 |
Amended and Restated Security Agreement dated as of May 7, 2013 made by Tetra Tech, Inc. and certain of its subsidiaries in favor of Bank of America, N.A., as Administrative Agent (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K dated May 9, 2013). |
|
10.7 |
Security Agreement dated as of May 7, 2013 made by Tetra Tech Canada Holding Corporation and certain of its subsidiaries in favor of Bank of America, N.A., as Administrative Agent (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K dated May 9, 2013). |
|
10.8 |
Amended and Restated Pledge Agreement dated as of May 7, 2013 made by Tetra Tech, Inc. and certain of its subsidiaries in favor of Bank of America, N.A., as Administrative Agent (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K dated May 9, 2013). |
130
| 10.9 | Pledge Agreement dated as of May 7, 2013 made by Tetra Tech Canada Holding Corporation and certain of its subsidiaries in favor of Bank of America, N.A., as Administrative Agent (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 to the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K dated May 9, 2013). | |
10.10 |
Employee Stock Purchase Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended September 30, 2012). |
|
10.11 |
2005 Equity Incentive Plan (as amended through November 7, 2011) (incorporated by reference to the Company's Proxy Statement for its 2012 Annual Meeting of Stockholders held on February 28, 2012).* |
|
10.12 |
First Amendment to the 2005 Equity Incentive Plan (as amended through November 7, 2011) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.9 to the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended September 29, 2013).* |
|
10.13 |
2015 Equity Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to the Company's Proxy Statement for its 2015 Annual Meeting of Stockholders held on March 5, 2015).* |
|
10.14 |
Form of Indemnity Agreement entered into between the Company and each of its directors and executive officers (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.20 to the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended October 3, 2004).* |
|
10.15 |
Deferred Compensation Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.17 to the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended September 30, 2007).* |
|
10.16 |
Amendment to Deferred Compensation Plan dated November 14, 2013 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.20 to the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended September 29, 2013).* |
|
10.17 |
Amended and Restated Change of Control Agreement with Dan L. Batrack dated November 7, 2016.+* |
|
10.18 |
Form of Amended and Restated Change of Control Agreement for executive vice presidents (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.22 to the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended September 28, 2014).* |
|
10.19 |
Executive Compensation Plan (as amended and restated November 14, 2013) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.23 to the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended September 29, 2013).* |
|
21. |
Subsidiaries of the Company.+ |
|
23. |
Consent of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm (PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP).+ |
|
24. |
Power of Attorney (included on page 128 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K). |
|
31.1 |
Chief Executive Officer Certification pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a)/15d-14(a).+ |
|
31.2 |
Chief Financial Officer Certification pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a)/15d-14(a).+ |
|
32.1 |
Certification of Chief Executive Officer pursuant to Section 1350.+ |
|
32.2 |
Certification of Chief Financial Officer pursuant to Section 1350.+ |
|
95. |
Mine Safety Disclosures.+ |
131
| 101 | The following financial information from our Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K, for the period ended October 2, 2016, formatted in eXtensible Business Reporting Language: (i) Consolidated Balance Sheets, (ii) Consolidated Statements of Operations, (iii) Consolidated Statement of Comprehensive Income (Loss), (iv) Consolidated Statements of Equity, (v) Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows, (vi) Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.+(1) |
- *
- Indicates a management contract or compensatory arrangement.
- +
- Filed herewith.
- (1)
- Pursuant to Rule 406T of Regulation S-T, the XBRL related information in Exhibit 101 to this Annual Report on Form 10-K shall not be deemed to be "filed" for purposes of Section 18 of the Exchange Act or otherwise subject to the liability of the section, and shall not be deemed part of a registration statement, prospectus or other document filed under the Securities Act or the Exchange Act, except as shall be expressly set forth by specific reference in such filings.
132
