Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| 8-K - FORM 8-K - AERIE PHARMACEUTICALS INC | d228816d8k.htm |
 Investor Day October 5, 2016 Exhibit 99.1 |
 Aerie
Investor Day Agenda TIME
TOPIC PRESENTER 12:00 PM – 12:01 PM Welcome Richard Rubino, CFO 12:01 PM – 12:05 PM Strategy & Path Forward Vicente Anido, Ph.D., CEO 12:05 PM – 12:15 PM Physician’s Perspective Rick Lewis, M.D. CMO 12:15 PM – 12:30 PM Market Opportunity and Positioning Tom Mitro, President & COO 12:30 PM – 1:10 PM Roclatan and Rhopressa Update Theresa Heah, M.D., VP Clinical 1:10 PM – 1:20 PM Q&A Session Tom Mitro Rick Lewis, M.D. Theresa Heah, M.D. Casey Kopczynski, Ph.D. Marv Garrett 1:20 PM – 1:30 PM Pipeline & Research Update Casey Kopczynski, Ph.D., CSO 1:30 PM – 1:40 PM Global Strategy Craig Skenes 1:40 PM – 1:55 PM Q&A Session All 1:55 PM – 2:00 PM Financial Summary and Close Richard Rubino, CFO 2 TM TM |
 3 Important Information Any discussion of the potential use or expected success of our product candidates is subject to our product candidates
being approved by regulatory authorities. In addition, any discussion of clinical trial
results for Rhopressa (netarsudil ophthalmic
solution) 0.02% relate to the results in its first Phase 3 registration trials, Rocket 1 and Rocket 2, and for Roclatan (netarsudil/latanoprost ophthalmic solution) 0.02%/0.005% relate to the results in its Phase 3 registration
trial. The information in this presentation is current only as of its date
and may have changed or may change in the future. We undertake no
obligation to update this information in light of new information, future events or otherwise. We are not making any representation or warranty that the information in this presentation is accurate or complete.
Certain statements in this presentation are “forward-looking statements”
within the meaning of the federal securities laws. Words such as
“may,” “will,” “should,” “would,” “could,” “believe,” “expects,” “anticipates,” “plans,” “intends,” “estimates,”
“targets,” “projects,” “potential” or similar expressions
are intended to identify these forward-looking statements. These
statements are based on the Company’s current plans and expectations. Known and
unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors could cause actual results
to differ materially from those contemplated by the statements. In evaluating these statements, you should specifically consider various factors that may cause our actual results to differ materially from any
forward-looking statements. In particular, the topline Mercury 1 data presented
herein is preliminary and based solely on information available to us as
of the date of this document. In addition, the preclinical research discussed in this presentation is preliminary and the outcome of such preclinical studies may not be predictive of the outcome of later trials.
Any future clinical trial results may not demonstrate safety and efficacy sufficient to
obtain regulatory approval related to the preclinical research findings
discussed in this presentation. These risks and uncertainties are described more fully in the quarterly and annual reports that we file with the SEC, particularly in the sections titled “Risk Factors” and
“Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of
Operations.” Such forward-looking statements only speak as of
the date they are made. We undertake no obligation to publicly update or revise any forward- looking statements, whether because of new information, future events or otherwise, except as otherwise required by law.
TM TM |
 Strategy and Path Forward
Vicente Anido, Jr., Ph.D.
CEO and Chairman 4 |
 5 Aerie Late Stage IOP–Lowering Products Pre-Clinical Research • Rhopressa™ • Potential for disease modification and neuroprotection • AR-13154 • Significant lesion size reduction in wet AMD • Drug Delivery - Front and back of the eye • Rhopressa™ (netarsudil ophthalmic solution) 0.02%
• Inhibits ROCK, NET, lowers EVP, targets diseased tissue • NDA filed Q3 2016; entering launch mode • Roclatan™ (netarsudil/latanoprost ophthalmic solution) 0.02%/0.005%
• Fixed combination of Rhopressa™ and latanoprost • Two P3’s in process; first P3 achieved primary efficacy endpoint Aerie – Building a Major Ophthalmic Pharmaceutical Company Data on file |
 6 Our Strategy: Investor Day (Aerie S-1, 2013) Advance the development of our product candidates to approval Establish internal capabilities to commercialize our product candidates in North America (and potentially Europe) Explore partnerships with leading pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies to maximize the value of our product candidates outside of North America Continue to leverage and strengthen our intellectual property portfolio Expand our product portfolio through internal discovery efforts and possible in-licensing or acquisitions of additional ophthalmic product candidates or products |
 7 Aerie Strategy and Path Forward (October 2016) • Key Clinical Priorities • Rhopressa™: NDA filing submitted Q3 2016
Rocket 4 in process (not required for NDA filing)
• Roclatan™: Mercury 1 and Mercury 2 completion Mercury 3 commencement 1H 2017 (EU) • Research Initiatives • Rhopressa™
disease modification, neuroprotection, sustained release
•
AR-13154 potential in wet AMD, etc.
• Evaluating Aerie’s 3,000+ proprietary molecules • Business Development and Expansion Opportunities • Drug delivery opportunities for front and back of the eye • EU/JP clinical path and commercialization strategy • Ireland Manufacturing Facility • Fully Financed |
 Rhopressa TM and Roclatan TM Key Milestones 8 Q3-2017: Roclatan™ P3 Mercury 1 Topline safety (12 mos) Near YE 2017: Roclatan™ NDA filing expected 1H-2017: Roclatan™ P3 Mercury 3 (EU) to be initiated Q1-2016: Rhopressa™ Rocket 2 Topline safety (12 mos) Q3-2016: Rhopressa™ NDA filed Q4-2016: Rhopressa™ Rocket 4 Topline efficacy (3 mos) Q3-2016: Roclatan™ P3 Mercury 1 Topline efficacy (3 mos) Q2-2017: Roclatan™ P3 Mercury 2 Topline efficacy (3 mos) Q1-2016: Roclatan™ P3 Mercury 2 initiated 2017 2016 |
 Physician’s Perspective Richard Lewis, M.D. Chief Medical Officer 9 |
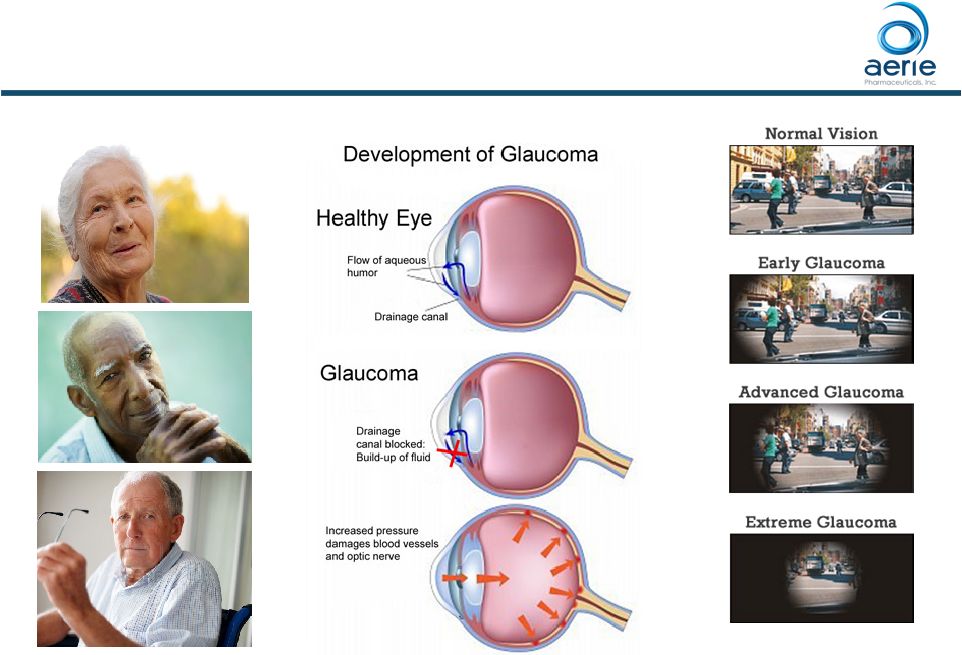 Glaucoma’s Common Pathway to Visual Loss
10 |
 How does
IOP cause visual loss? 11
60-year-old with initial IOP of 19 mmHg
* Sacramento Eye Consultants |
 ~75% of
U.S. Glaucoma Patients Have IOPs that are 25 mmHg at Time of
Diagnosis 12
Baseline IOP* 60% 20% 20% 5,308 Individuals Were Screened for the Prevalence of Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma (POAG) and the IOP at Time of Diagnosis 92% of Japanese Patients with POAG, IOPs Were 21 mmHg** The Baltimore Eye Survey * Sommer A, Tielsch JM, Katz J et al. Relationship between intraocular pressure and primary open angle glaucoma among
white and black Americans: The Baltimore eye survey. Arch Ophthalmol 1991;109:1090-1095 ** IWASE et al Tajimi study group. Japan Glaucoma Society. Ophthalmology, 2004 Sep, 111 (9): 1641-8. 25 - 34 mmHg 22 - 24 mmHg 21 mmHg (Normal Tension Glaucoma) |
 Therapy
of Glaucoma in 2016 Goal of treatment: Control IOP
• There is no direct correlation of the level of IOP at diagnosis with damage to optic nerve • Every 1 mmHg reduction lowers risk of visual field loss by 10%* • In general, the goal of therapy strives to get IOP to the low teens to prevent visual field loss from damage to the optic nerve 13 * EMGT, Arch Ophthalmol. 2003;121(1):48-56. Therapy options • Medications • Prostaglandins dominate – the first choice in almost all patients • 50% of these patients require second medication for sufficient IOP control • Surgery – SLT laser, MIGs, trabeculectomy, tubes |
 Latanoprost vs. Placebo: Time to Visual
Field Loss over 24 months
UKGTS* study: Recruited 516 newly diagnosed patients randomized
to latanoprost or placebo
• No limitation for low end of baseline IOP (excluded 30 mmHg) 14 Results: • Mean baseline IOP: 19.6 for latanoprost, 20.1 mmHg for placebo • 85% of patients had baseline IOP <25 mmHg • Latanoprost reduced glaucoma progression by 41%, however it did not stop glaucoma progression • Even at mean treated IOP of 15.8 mmHg, visual field deterioration continued in 15.2% of patients within 24 months of diagnosis *Garway-Heath et al for the UKGTS study group. Latanoprost for open-angle glaucoma (UKGTS): a randomised,
multicentre, placebo-controlled trial
Lancet 2015; 385: 1295–304.
|
 Challenges
in Treating Glaucoma 1.
Achieving target IOP lowering with existing medications
• The magnitude of initial IOP reduction was a major factor influencing outcome* • Current medications have poor additivity to PGAs • Current adjunctive medications all cause systemic, bothersome side effects 2. Like all chronic disease, adhering to treatment for glaucoma is poor • Non-compliance increases in patients taking drops more than once a day** 15 * Early Manifest Glaucoma Trial, Arch Ophthalmol. 2003;121(1):48-56. ** Data on file |
 Need for
New Medications •
Target the tissue causing IOP elevation
• Current medications either: • Lower inflow* – Beta Blockers such as timolol • Increase outflow* via the eye’s secondary drain, the uveoscleral pathway (prostaglandins such as latanoprost) – None target the primary drain of the eye, the trabecular meshwork – None have multiple mechanisms to maximize effect • Augment IOP lowering when combined with prostaglandins • Enhance compliance and adherence with less frequent dosing • Other goals** • Disease modifying • Neuroprotective 16 * Product package inserts. ** Donegan RK, Lieberman RL. J Med Chem.
2016;59(3):788-809. |
 Value of
Rhopressa TM ++
• Directed at site of pathology • The trabecular meshwork • Enhanced compliance • Once-a-day dosing • Efficacy • Achieves noninferiority to timolol where AA’s (Brimonidine) and CAI’s failed • Consistent IOP lowering across broad baseline range of Mercury 1 • Additive to prostaglandins • Safety • Lack of serious and systemic adverse events 17 ++ Data on file from Aerie Phase 3 clinical trials, Rocket 1, Rocket 2 and Mercury 1. |
 Roclatan Phase 3 Responder Analysis
Day 90: % of Patients
with IOP Reduced to 18 mmHg or Lower
*** *** *** 18 ***p<0.0001 vs Latanoprost and Rhopressa ### p<0.0001 vs Rhopressa , p<0.05 vs Latanoprost ++ Data on File Based on Mercury 1 Topline Interim 3-month 14% 23% 32% 42% 54% 15% 25% 39% 54% 69% 33% 44% 61% 71% 82% 0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100% IOP on Treatment Rhopressa™ (n=198) Latanoprost (n=223) Roclatan™ (n=200) ### ### TM TM TM |
 Roclatan ™ Hyperemia is Within the Range of the Three Leading PGA Medications * Parrish et al., American Journal of Ophthalmology, Vol. 135, No. 5 (2003); 3 month head to head study
of latanoprost, bimatoprost and travoprost
++ Data on File; Mean Mercury 1 rate of hyperemia
19 Includes all physician and patient reported hyperemia adverse events Incidence of Hyperemia Adverse Events* Bimatoprost 69% Latanoprost 47% Roclatan™ 53% ++ Travoprost 58% 40% 50% 60% 70% |
 Alphagan P Lumigan Travatan Z Combigan Simbrinza Conjunctival Hyperemia 10-20% 0.01% = 31% 0.03% = 45% 30-50% 5-15% Conjunctival Hemorrhage 1-4% 1-4% 1-4% Vision Blurred 1-4% 1-4% 1-4% 3-5% Lacrimation Increased Tearing 1-4% 1-4% Visual Acuity Reduced Visual disturbance 5-9% 1-4% 5-10% Visual disturbance 1-5% Eye Pruritus 10-20% 1-4% 5-10% 5-15% Erythema of Eyelid 1-4% 1-4% 1-5% Conjunctival Edema 1-4% 1-4% Other Allergic Conjunct 10-20%; Burning 5-9%; Conjunct folliculosis 5-9%; Ocular Allergy 5-9%; Allergic reaction 1-4%; Oral dryness 5-9%; Hypertension 5-9%; Blepharitis 1-4%; (40 additional AEs listed as 1-4%) Iris pigmentation, periorbital tissues and eyelashes; Changes in eyelashes; Intraocular inflammation Eye discomfort 5-10%; Foreign body 5-10%; Blepharitis 1-4%; Deeping eyelid sulcus; Ocular inflammation 1-4% Allergic conjunct 5-15%; Burning / Stinging 5-15%; Conj folliculosis 5-15%; Asthenia 1-5%; Blepharitis 1-5%; Corneal erosion 1-5%; Eyelid pruritus 1-5%; Eye pain 1-5%; Somnolence 1-5%; (11 additional AE 1-5%) Beta-Blocker & AA AE’s Ocular allergy 10-30%; Fatigue/drowsiness 10-30%; Eye irritation 3-5%; Dysgeusia 3-5%; Dry mouth3-5%; Eye allergy 3-5%; Sulfonamide Reactions; Blepharitis 1-5%; Dry eye 1-5%; Foreign Body 1-5%; Ocular discomfort 1-5% Safety Profile for Other Approved Products 20 Source: Package Inserts |
 Roclatan Will Change Treatment Paradigm
• Efficacy • Target IOP – there will be a “new low normal” • Percent of patients with IOP controlled using 1 med will increase • Step-wise changes to maximal therapy – why not go right at it? • Compliance • One medication, once a day vs. multiple medications, multiple times a day • Questions yet to be answered with investigator initiated studies • Roclatan in secondary glaucomas • Roclatan + other medications • Roclatan + other procedures (including SLT, MIGs, trabs, etc)
21 TM TM TM TM |
 Summary of
Physician’s Perspective •
Rhopressa and Roclatan represent major advances in treating glaucoma • Target the diseased trabecular meshwork • Once a day • Excellent efficacy • Additive to prostaglandins • Safe • It has been 20 years since the glaucoma community had a new medical therapy. It is long overdue and greatly anticipated. 22 TM TM |
 2016
Market Opportunity and Positioning Tom Mitro
President and Chief Operating Officer
23 |
 We Are in
Launch Mode •
Hired advertising agency
• Building our sales, marketing, medical affairs, regulatory and manufacturing teams that will support 100 sales representatives • Partnering with glaucoma thought leaders and organizations • Continuing research and message testing to the physician community • In dialogue with managed care decision makers 24 |
 US,
Europe and Japan 2015 IMS TRX* and TRX$
* (MM) Drug Class ($$ millions) US $ Europe $ Japan $ Total $ Prostaglandins (PGA and PGA FDC) $1,292 $866 $381 $2,539 Alpha Agonists (AA) $384 $54 $81 $519 Fixed Dose Combinations (FDC) $432 $277 $115 $824 Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors (CAI) $206 $156 $64 $426 Beta Blockers (BB) $160 $92 $81 $333 Total $$ $2,474 $1,445 $722 $4,641 Total TRx’s (millions) 33 87 27 147 • Totals exclude pilocarpine and epinephrine products as well as “other” in Japan (approximately 5% of total market); TRx
totals for Europe are for “big 5” markets. TRx’s may
under-represent US market compared with Europe and Japan due to use of
multiple-months of therapy per TRx in the US.
* Source: IMS data
25 |
 *Data on file Rhopressa ™ and Roclatan ™ Potential Market Positioning Rhopressa ™ Positioning Roclatan ™ Positioning Potential drug of choice as adjunctive therapy to PGAs when additional IOP lowering is desired Potential drug of choice for patients requiring maximal IOP lowering • Initial therapy for PGA non- responders and those with tolerability concerns • Normal-tension glaucoma • Patients using two or more glaucoma therapies • Patients at any IOP at risk of significant disease progression Also: Examples: 26 |
 Rhopressa and Roclatan Potential Product Advantages Rhopressa ™ Positioning Roclatan ™ Positioning Potential drug of choice as adjunctive therapy to PGAs when additional IOP lowering is desired Potential drug of choice for patients requiring maximal IOP lowering 27 TM TM Roclatan ™ Advantages • Efficacy vs. all other glaucoma
therapies • QD PM dose • Lack of serious and systemic AE’s Rhopressa ™ Advantages • Efficacy vs. other adjunctive therapies • QD PM dose • Lack of serious and systemic AE’s |
 Current Practices Characteristics of the Ideal Adjunct Rhopressa™ Clinical Profile Review Key Marketing Message Testing Rhopressa’s Place in Therapy and Sources of Use 28 From Current Practice to Rhopressa™ Availability Discussions with over 100 Ophthalmologists |
 Current
Physician Practices •
Ophthalmologists and optometrists strongly agree
with the following statement:
“Current adjunctive options for lowering IOP are a
compromise between efficacy, safety and ease of
use.” • Therefore there is strong interest in anything new that has the potential to improve patient care 29 Source: Data on File |
 Ranked
Characteristics of an Ideal Adjunctive Therapy
Confirmed Over Multiple Events and Methodologies
1. QD dosing (most others are BID or TID) 2. Clean safety profile 3. Better efficacy than most single agents 30 Source: Data on File |
 Rhopressa ™ Clinical Profile Review • Initial reaction to the profile has been overwhelmingly positive • Issues with current adjuncts are well recognized: • The lack of efficacy with current adjunctive options • Alpha Agonists and CAI’s (20% MS*) have inferior efficacy to beta-blockers (15% MS*) • The burden of eye drops that require instillation 2-3 times each day • The potential serious issues with systemic side effects 31 “I’ve been waiting for this, I’m very excited . . .it’s an exciting new
discovery, it offers more options, and more options are always good.”
“I’m glad for the glaucoma community, I can’t wait.”
* Market Share
Source: Data on File |
 Rhopressa ™ Could Replace a Significant Portion of Current Prescriptions 32 • All participants expressed interest in trying Rhopressa • Most participants anticipate using Rhopressa for ~50% of their adjunctive prescriptions • Rhopressa use would come from: • The TID adjuncts (Alphagan®, Azopt® and Trusopt®) to reduce treatment burden on patients • Beta blockers and fixed combinations containing a beta blocker to minimize systemic side effects (timolol, Combigan®,
Cosopt®) • First-line when PGA cosmetic side effects are a concern Source: Data on File TM TM TM |
 FirstWord
Market Research 9/23/16 •
Involved feedback from 106 ophthalmologists
• (36 in US and 70 in Europe) • “Assuming approval, to approximately what percentage of all glaucoma patients would you expect Rhopressa™ to be
prescribed after two years on the market?”
• 20% in US and 28% in Europe • “Assuming comparable efficacy data in a second Phase 3 study and an acceptable safety profile, how quickly would you expect adoption of Roclatan™ to occur?”
• 72% of US and 81% of Europe said “moderate to very quickly” 33 This marketing research was conducted independently from Aerie knowledge, input or influence Source: https://www.firstwordpharma.com/print/1418210?tsid=33 |
 Conclusions From the Physician
Market Research • Eye care professionals believe current adjunctive options are a compromise at best • The ideal product would be QD, effective and free of systemic side effects • Hyperemia is considered manageable and more than a fair trade for the dosing, efficacy and systemic safety benefits • Prescribers report that Rhopressa™ would become their adjunct of choice taking the place of other single-agent and timolol-containing products 34 Source: Data on File |
 Managed
Care Research •
Qualitative research with 10 managed care
organizations conducted this year
• Covered lives ranged from <250K to 50M+ per plan • Commercial, Medicare and managed Medicaid were represented • Tested Rhopressa™ and Roclatan™ for formulary acceptance on Commercial and Medicare Part D formularies • Second round of recent research 35 |
 Likelihood Of Formulary Approval
• Likelihood of formulary approval for Rhopressa and Roclatan scored high, 5.5 –
6.0 on a 7 point scale
36 Preferred Tier Non-Preferred Tier Not Covered Rhopressa™ 50% 50% 0% Roclatan™ 50% 50% 0% Medicare Part D: Percent of Formulary Tier Recommendations Without Contracting Consideration This was the second round of research where there were no “Not Covered” recommendations Source: Data on File TM TM |
 Managed
Care Research Summary •
Research results were very favorable and consistent with the previous round of
research •
Managed care decision makers see a need for
Rhopressa and Roclatan to be on formulary
• Novel MOA • Efficacy • Safety • QD dosing • Optimal formulary position and tier placement will require contracting • Glaucoma category is not heavily managed 37 Source: Data on File TM TM |
 Roclatan TM / Rhopressa TM Clinical Update Theresa Heah, MD MBA VP, Clinical Research and Medical Affairs 38 |
 Roclatan U.S. Registration Trial Design ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02558400, NCT02674854 “Mercury 1” One Year Safety (3 Mo. Interim Efficacy) Registration Trial U.S. “Mercury 2” 90-Day Efficacy Registration Trial U.S. and Canada Roclatan™ QD ~230 patients Rhopressa™ 0.02% QD ~230 patients latanoprost QD ~230 patients Roclatan™ QD ~230 patients Rhopressa™ 0.02% QD ~230 patients latanoprost QD ~230 patients 39 TM |
 Mercury 1
Trial Design Patients randomized
1:1:1 Primary endpoints: • Efficacy: Mean IOP at nine time points
(08:00, 10:00, and 16:00 at Week 2, Week 6, and Month 3) • Safety: Ocular and systemic safety during a 12-month treatment period ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02558400 Patients with open angle glaucoma (OAG) or ocular hypertension (OHT) with IOP >20 mmHg and < 36 mmHg at 8am N=718 subjects randomized at 58 US sites Roclatan PG324 (netarsudil/latanoprost) QD (PM) Rhopressa Netarsudil (AR-13324) 0.02% QD (PM) Latanoprost 0.005% QD (PM) 40 TM TM |
 Baseline
IOPs in Studies For Other Approved Glaucoma Drugs in Comparison to
Roclatan™ Inclusion criteria
(mmHg) at 8am Mean baseline IOPs (mmHg) Roclatan™ >20 and <36 23.7 Lumigan® 0.01% 22 and 34 23.5 Travatan Z® 24 and 36 25.7 Combigan® 22 and 34 21 and 32 Trial 1: 22.6 - 23.4 Trial 2: 23.3 - 23.6 Simbrinza® 24 and 36 Trial 1: 24.8 -25.0 Trial 2: 25.2 - 25.4 Alphagan® P 22 and 34 23.3 - 23.5 Azopt® 24 and 36 25.5 - 25.9 41 Sources: Data on File on Mercury 1 Topline Interim 3-month, Lumigan 0.01% SBA study #192024-008, Travatan Z SBA Study #C-97-71,
Combigan
SBA Study # 90342-013T and # 190342-019T, Simbrinza SBA Study #C-10-033 , AlphaganP™0.1% SBA study # 190342-021 and Azopt SBA Study #C-95-46 |
 Mercury 1
Baseline Demographics Roclatan
N = 238 Rhopressa TM N = 244 Latanoprost N = 236 Gender Male 104 (43.7%) 108(44.3%) 100 (42.4%) Female 134 (56.3%) 136 (55.7%) 136 (57.6%) Race, n (%) White 162 (68.1%) 167 (68.4%) 157 (66.5%) Black/African American 69 (29.0%) 70 (28.7%) 67 (28.4%) Asian 7 (2.9%) 6 (2.5%) 10 (4.2%) Multiple 0 (0%) 1 (0.4%) 2 (0.8%) Age (yrs) < 65 109 (45.8%) 107 (43.9%) 95 (40.3%) >65 129 (54.2%) 137 (56.1%) 141 (59.7%) Iris Color, n (%) Brown/Black 141 (59.2%) 137 (56.1%) 154 (65.3%) Blue/Grey/Green 68 (28.6%) 73 (29.9%) 62 (26.3%) Hazel 29 (12.2%) 34 (13.9%) 20 (8.5%) 42 ++ Data on File Based on Mercury 1 Topline Interim 3-month TM |
 Mercury 1
Patient Disposition Roclatan™
N = 238 Rhopressa™ N = 244 Latanoprost N = 236 Completed Month 3 201 (84.5%) 201 (82.4%) 223 (94.5%) Discontinued Prior to Month 3 37 (15.5%) 43 (17.6%) 13 (5.5%) Reasons for Discontinuation Adverse Event Withdrawal of Consent Non-Compliant Lost to Follow-up Lack of Efficacy Disallowed Concurrent Medication Investigator Decision Protocol Violation Other 25 (10.5%) 4 (1.7%) 0 1 (0.4%) 0 1 (0.4%) 2 (0.8%) 4 (1.7%) 0 23 (9.4%) 4 (1.6%) 1 (0.4%) 3 (1.2%) 5 (2.0%) 4 (1.6%) 0 1 (0.4%) 2 (0.8%) 0 4 (1.7%) 1 (0.4%) 1 (0.4%) 1 (0.4%) 1 (0.4%) 0 5 (2.1%) 0 43 ++ Data on File Based on Mercury 1 Topline Interim 3-month |
 Mercury 1
Discontinuation Rates Compare Favorably to Other Approved
Products Alphagan® 0.2%*
N = 221 Alphagan® P 0.1%** N =215 Latanoprost*** N=165 Completed Month 3 119 (53.8%) 183 (85.1%) 145 (87.9%) Early Discontinuation Prior to Month 3 102 (46.2%) 32 (14.9%) 20 (12.1%) Reasons for Discontinuation Adverse Event Protocol Violation Lack of Efficacy Discontinued/Other 54 0 17 35 19 1 10 2 0 4 1 15 *Alphagan™ 0.2% SBA, protocol # A342-103-7831** AlphaganP™0.1% SBA study # 190342-021*** Palmberg et al A 12-week, randomized, double-masked study of fixed combination latanoprost/timolol versus latanoprost or timolol monotherapy. Eur J Ophthalmol 2010; 20 (4 ): 708 – 718. Other included: withdrawal of consent, lost to follow up, non-compliant, disallowed concurrent medication
Early D/C rates for Alphagan® 0.2%, Alphagan® P 0.1% and Latanoprost :
46%, 15% and 12%
Mercury 1: D/C rate for the Roclatan™ was ~16%
44 |
 Mercury 1
Registration Trial Design •
Trial design follows FDA requirement for fixed dose combination
• Superiority of combination over each individual component • Statistically significant difference at each measured time point • Higher combo efficacy vs. components at ~1-3 mmHg, as previously accepted by FDA for product approval (i.e., Simbrinza ® )* 45 ++ Data on File Based on PG324 Pre-NDA meeting *Simbrinza® accessed on 29 Sept 2016 http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2013/204251Orig1s000MedR.pdf
th |
 Roclatan Achieved Statistical Superiority Over
Individual Components at All 9 Time Points
Mean IOP at Each Time Point (ITT)
***p<0.0001 vs Latanoprost and Rhopressa
46 ++ Data on File Based on Mercury 1 Topline Interim 3-month TM TM |
  Roclatan™ Phase 3, ITT
Roclatan™ superior to latanoprost by 1.3-2.5 mmHg (p<0.0001)
Roclatan™ superior to Rhopressa™ by 1.8-3.0 mmHg
(p<0.0001) 47
8:00 AM 24.8 24.8 24.6 10:00 AM 23.7 23.5 23.4 4:00 PM 22.6 22.6 22.4 Mean Diurnal 23.7 23.6 23.5 8:00 AM 15.6 18.6 17.8 -3.0 (-3.6, -2.5) -2.2 (-2.8, -1.7) 10:00 AM 14.9 17.8 17.4 -2.9 (-3.5, -2.3) -2.5 (-3.1, -1.9) 4:00 PM 14.8 17.2 17.2 -2.4 (-2.9, -1.9) -2.3 (-2.9, -1.8) Mean Diurnal 15.1 17.9 17.5 -2.8 (-3.3, -2.3) -2.4 (-2.9, -1.9) 8:00 AM 16.0 19.0 17.7 -3.0 (-3.6, -2.4) -1.7 (-2.3, -1.1) 10:00 AM 15.3 18.0 17.1 -2.7 (-3.3, -2.2) -1.9 (-2.5, -1.3) 4:00 PM 15.3 17.5 17.0 -2.2 (-2.7, -1.6) -1.7 (-2.2, -1.1) Mean Diurnal 15.5 18.2 17.3 -2.7 (-3.1, -2.2) -1.8 (-2.3, -1.3) 8:00 AM 16.2 18.9 17.6 -2.7 (-3.4, -2.1) -1.5 (-2.1, -0.9) 10:00 AM 15.3 18.2 16.9 -2.9 (-3.5, -2.3) -1.6 (-2.2, -1.0) 4:00 PM 15.4 17.2 16.7 -1.8 (-2.4, -1.2) -1.3 (-2.0, -0.7) Mean Diurnal 15.6 18.1 17.1 -2.5 (-3.0, -2.0) -1.5 (-2.0, -1.0) Day 90 Mean IOP mmHg Rhopressa™ Day 43 Day 15 Latanoprost Difference from Roclatan™ (95% CI) Roclatan™ N=238 Rhopressa™ N=244 Latanoprost N=236 Baseline ++ Data on File Based on Mercury 1 Topline Interim 3-month |
 Simbrinza ® Approval • The contribution of brinzolamide to the combination product ranges from 1.4 to 2.6 mmHg in study C-10-033 and from 1.6 to 2.6 mmHg in study C-10-039
• The contribution of brimonidine to the combination product ranges from 1.2 to 3.4 mmHg in study C-10-033 and from 0.9 to 3.7 mmHg in study C-10-039
FDA recommendation: • The clinically relevant information from Study C-10-039 and Study C-10-033
for the prescribing physician is that the IOP-lowering effect of Simbrinza was
greater (1-3 mmHg) than monotherapy with either 1% brinzolamide or
0.2% brimonidine tartrate throughout the duration of the trial (i.e. Week
2, Week 6, Month 3).
• Studies C-10-033 and C-10-039 demonstrate superiority of the combination
product, brinzolamide/brimonidine over each of the individual components by
a statistically and clinically significant amount.
Source; Simbrinza® accessed on 29 Sept 2016 2016 http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2013/204251Orig1s000MedR.pdf 48 th |
 Rhopressa™ Phase 3, 12
Month 8am IOP Efficacy Safety Population, Completed Patients (<27 mmHg) Difference in 8am mean IOP from Day 90 (Month 3) to Month 12: • Rhopressa™ QD: • Full population: +0.1 mmHg • Subset analyses: -0.3 to +0.3 mmHg Timolol BID: • Full population: +0.5 mmHg • Subset analyses: +0.1 to +1.4 mmHg Day 90 Month 12 Rhopressa™ QD (n=118) BL W2 W6 M3 M6 M9 M12 ++ Data on File Based on Rocket 2 Interim 12-month 49 |
 Latanoprost IOP Lowering Over Time
50 Source: Pfeiffer N. A comparison of the fixed combination of latanoprost and timolol with its individual
components. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol (2002) 240:893-899.
18 20 22 24 26 28 -4 0 2 13 26 Treatment Time (Weeks) Fixed Combination (n=140) Latanoprost (n=147) Timolol (n=149) |
 51 Source: Garway-Heath et al for the UKGTS study group. Latanoprost for open-angle glaucoma (UKGTS): a randomised, multicentre,
placebo-controlled trial
Lancet 2015; 385: 1295–304.
Latanoprost IOP Lowering Over Time |
 Mercury 1:
No Significant Effect of Discontinuations on Efficacy Results
• The primary statistical modeling of the primary efficacy analysis was agreed with the FDA using the intent-to-treat (ITT) population with imputation for any missing data • Statistical methods for imputation of missing data (such as LOCF, Monte Carlo Markov Chain) were used to test the robustness of the data • Efficacy results were similar for Per Protocol and imputation analyses 52 ++ Data on File Based on Mercury 1 Topline Interim 3-month |
 Roclatan™ Mercury 1, LOCF ITT
53 ++ Data on File Based on Mercury 1 Topline Interim 3-month ***p<0.0001 vs Latanoprost and Rhopressa™ *** *** *** *** *** *** *** *** *** |
  Roclatan™ Mercury 1, LOCF ITT
54 8:00 AM 24.8 24.8 24.6 10:00 AM 23.7 23.5 23.4 4:00 PM 22.6 22.6 22.4 Mean Diurnal 23.7 23.6 23.5 8:00 AM 15.9 18.7 17.9 -2.9 (-3.4, -2.3) -2.0 (-2.6, -1.4) 10:00 AM 15.0 18.1 17.5 -3.0 (-3.6, -2.4) -2.4 (-3.1, -1.8) 4:00 PM 15.1 17.4 17.3 -2.3 (-2.9, -1.8) -2.2 (-2.8, -1.7) Mean Diurnal 15.3 18.1 17.6 -2.7 (-3.3, -2.2) -2.2 (-2.8, -1.7) 8:00 AM 16.2 19.1 17.8 -2.9 (-3.6, -2.3) -1.6 (-2.2, -1.0) 10:00 AM 15.5 18.3 17.3 -2.8 (-3.4, -2.2) -1.8 (-2.4, -1.2) 4:00 PM 15.6 17.8 17.2 -2.2 (-2.7, -1.6) -1.6 (-2.1, -1.0) Mean Diurnal 15.8 18.4 17.4 -2.6 (-3.2, -2.1) -1.7 (-2.2, -1.1) 8:00 AM 16.4 19.5 17.7 -3.0 (-3.6, -2.4) -1.3 (-1.9, -0.7) 10:00 AM 15.4 18.6 17.1 -3.2 (-3.8, -2.5) -1.6 (-2.3, -1.0) 4:00 PM 15.6 17.7 16.9 -2.1 (-2.7, -1.5) -1.3 (-1.8, -0.7) Mean Diurnal 15.8 18.6 17.2 -2.8 (-3.3, -2.2) -1.4 (-2.0, -0.9) Day 90 Mean IOP mmHg Rhopressa™ Day 43 Day 15 Latanoprost Difference from Roclatan™ (95% CI) Roclatan™ N=238 Rhopressa™ N=244 Latanoprost N=236 Baseline ++ Data on File Based on Mercury 1 Topline Interim 3-month |
 Day 29:
% of Patients with IOP Reductions of 20%
Roclatan™ Phase 2b Responder Analysis
Source: Lewis RA, Levy B, Ramirez N, Kopczynski CC, Usner DW, Novack GD for the
PG324-CS201 Study Group. Fixed-dose combination of AR-13324
and latanoprost: a double-masked, 28-day, randomised, controlled study in patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension. Br J Ophthalmol 2015;0:1–6. doi:10.1136/bjophthalmol-2015-306778
55 9% 17% 23% 45% 67% 11% 28% 46% 65% 81% 32% 50% 63% 81% 93% 0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100% 40% 35% 30% 25% 20% Reduction 0.02% Rhopressa™ (n=78) 0.005% Latanoprost (n=73) 0.02% Roclatan™ (n=72) |
 Roclatan™ Phase 3 Responder Analysis:
Goal is to Achieve Lowest IOP Possible
Day 90: % of Patients with IOP Reductions of
20% ***p<0.0001 vs Latanoprost and Rhopressa™ ### p<0.0001 vs Rhopressa™, p<0.05 vs Latanoprost *** *** *** ### 56 ++ Data on File Based on Mercury 1 Topline Interim 3-month 7% 18% 29% 43% 56% 9% 21% 37% 61% 78% 35% 46% 65% 77% 88% 0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100% 40% 35% 30% 25% 20% Reduction Rhopressa™(n=198) Latanoprost (n=223) Roclatan™ (n=200) ### |
 Roclatan™ Phase 2b Responder Analysis
Day 29: % of Subjects with IOP Reduced to <
18 mmHg Source: Lewis RA, Levy B, Ramirez N, Kopczynski CC, Usner DW, Novack GD for the PG324-CS201 Study Group. Fixed-dose combination of
AR-13324 and latanoprost: a double-masked, 28-day,
randomised, controlled study in patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension. Br J Ophthalmol 2015;0:1–6. doi:10.1136/bjophthalmol-2015-306778
57 10% 21% 24% 39% 8% 18% 29% 47% 38% 46% 57% 69% 0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100% 15 mmHg 16 mmHg 17 mmHg 18 mmHg Reduction 0.02% Rhopressa™ (n=78) 0.005% Latanoprost (n=73) 0.02% Roclatan™ (n=72) |
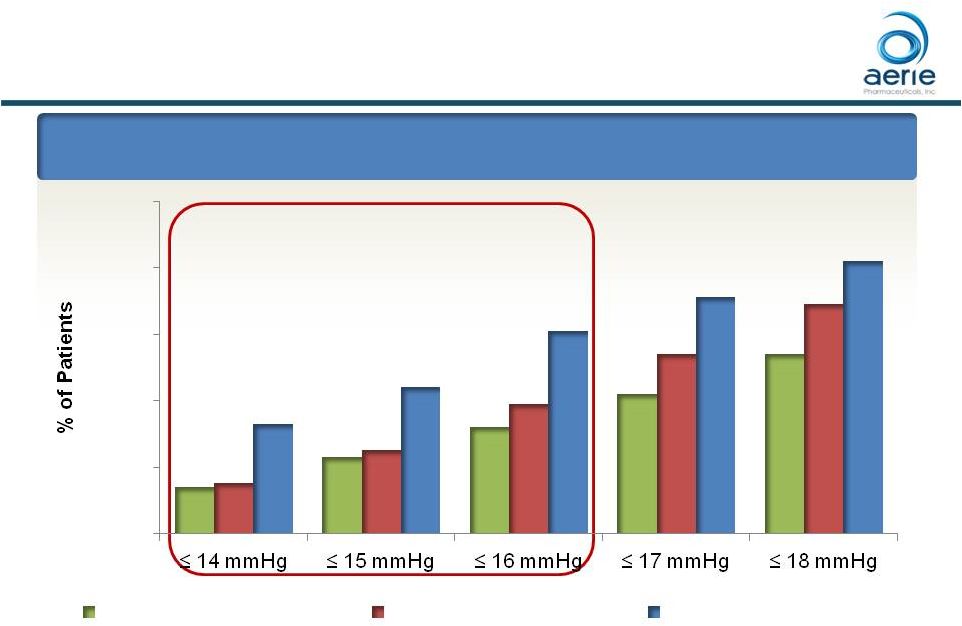
 Roclatan™ Phase 3 Responder Analysis:
Goal is to Achieve Lowest IOP Possible
Day 90: % of Patients
with IOP Reduced to 18 mmHg or Lower
*** *** *** 58 ***p<0.0001 vs Latanoprost and Rhopressa™ ### p<0.0001 vs Rhopressa™, p<0.05 vs Latanoprost ++ Data on File Based on Mercury 1 Topline Interim 3-month 14% 23% 32% 42% 54% 15% 25% 39% 54% 69% 33% 44% 61% 71% 82% 0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100% 14 mmHg 15 mmHg 16 mmHg 17 mmHg 18 mmHg IOP on Treatment Rhopressa™ (n=198) Latanoprost (n=223) Roclatan™ (n=200) ### ### |
 Xalacom®: % Subjects Reaching IOP Targets
• Xalacom® 16 mmHg: ~28% 15 mmHg: ~18% Source: Palmberg et al A 12-week, randomized, double-masked study of fixed combination latanoprost/timolol versus latanoprost or
timolol
monotherapy. Eur J Ophthalmol 2010; 20 (4 ): 708 – 718. *Lewis et al for the PG324-CS201 Study Group. Fixed-dose combination of AR-13324 and latanoprost: a double-masked, 28-day,
randomised, controlled study in patients with open-angle glaucoma or
ocular hypertension. Br J Ophthalmol 2015;0:1–6.
doi:10.1136/bjophthalmol-2015-306778
**Data on File based on Mercury 1 Topline Interim 3-month
• Roclatan™ Phase 3** Mercury 1 16 mmHg: 61% 15 mmHg: 44% 59 • Roclatan™ Phase 2* 16 mmHg: 46% 15 mmHg: 38% |
 • Roclatan™ met the criteria for demonstrating superiority over both latanoprost and Rhopressa™ for the primary efficacy analysis • statistical superiority of Roclatan™ was demonstrated at all 9 time points versus latanoprost and versus Rhopressa™ (p<0.0001) • IOP-lowering effect of Roclatan™ was greater (1-3 mmHg) than monotherapy with either latanoprost or Rhopressa™ throughout the duration of the study (i.e., Week 2, Week 6, Month 3) • Roclatan™ reduced mean diurnal IOPs to 16 mmHg or lower in 61 percent of patients, a significantly higher percentage than observed in the comparator arms Roclatan™ Performance Summary 60 ++ Data on File Based on Mercury 1 Topline Interim 3-month |
 Roclatan™ Safety Profile To Date • There were no drug-related serious adverse events (SAEs) • There was no evidence of treatment-related systemic effects (e.g., clinical laboratory or haematology values, heart rate or blood pressure) • The most common adverse event was conjunctival hyperemia with ~50% incidence, ~80% mild on biomicroscopy • Other ocular AEs • AEs occurring in ~5-11% of subjects receiving Roclatan™ included: conjunctival hemorrhage, eye pruritus, lacrimation increased and cornea verticillata ++ Data on File Based on Mercury 1 Topline Interim 3-month safety 61 |
 Roclatan™ Phase 3 Safety Profile Adverse Events
( 5.0% in any group) Roclatan™ n=238 Rhopressa™ n=244 Latanoprost n=236 Eye Disorders Conjunctival Hyperemia 126 (52.9%) 99 (40.6%) 33 (14.0%) Conjunctival Hemorrhage 25 (10.5%) 34 (13.9%) 1 ( 0.4%) Eye Pruritus 18 ( 7.6%) 17 ( 7.0%) 3 ( 1.3%) Lacrimation Increased 14 ( 5.9%) 15 ( 6.1%) 1 ( 0.4%) Cornea Verticillata 12 ( 5.0%) 9 ( 3.7%) 0 (0.0%) Administration Site Conditions Instillation site pain 46 (18.9%) 51 ( 20.9%) 15 ( 6.4%) Patients with known contraindications or hypersensitivity to latanoprost were excluded 62 ++ Data on File Based on Mercury 1 Topline Interim 3-month safety |
 When
Present, ~80% of Roclatan™ and
Rhopressa™ Hyperemia Graded as Mild For illustrative purposes only Grade Image Description 0 None/Normal 1 Mild 2 Moderate 3 Severe 63 ++ Data on File Based on Mercury 1 Topline Interim 3-month safety |
 No Change
in Mean Hyperemia Score Over Time (Interim Month 3)
• Hyperemia severity did not increase with continued dosing • Hyperemia was sporadic • Only ~18% of patients had hyperemia on each study visit day from week 2 to month 3 (similar to the rates seen for Rocket 1 and Rocket 2) • Only ~10% of Rhopressa™ patients had hyperemia on each study visit day from week 2 to month 12 (Rocket 2) Hyperemia severity 0 = none 1 = mild 2 = moderate 3 = severe 64 ++Data on File Based on Mercury 1 Topline Interim 3-month safety 0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 Baseline Week 2 Week 6 Month 3 Roclatan™ (N=238) Rhopressa™ (N=244) |
 Roclatan™ Adverse Events Summary • Conjunctival Hemorrhage • sporadic subconjunctival petechiae • Cornea Verticillata (corneal deposits*) • asymptomatic non-toxic lipid deposits • only visible via biomicroscopy evaluation • Instillation Site Pain • sporadic • transient ++ Data on File Based on Mercury 1 Topline Interim 3-month safety The updated term for these deposits based on MedDRA coding revisions* 65 |
 Rhopressa™ Update 66 |
 0.02%
Rhopressa™
Latanoprost 0.02% Rhopressa™ Latanoprost Rhopressa™ Phase 2b Results Phase 2b baseline IOP entry requirements: 24, 22, 22 mmHg (8am, 10am, 4pm) Baseline 22 – 26 mmHg (n=106) Baseline 22 – 26 mmHg (n=106) Baseline 22 – 36 mmHg (n=221) Baseline 22 – 36 mmHg (n=221) • Rhopressa™ and latanoprost clinically and statistically equivalent in patients with mean baseline IOPs of 22 - 26 mmHg (Day 28) ++ Data on File Bacharach J. et al for the AR-13324-CS202 Study Group. Double-masked, Randomized, Dose Response Study of AR-13324 versus
Latanoprost
in Patients with Elevated Intraocular Pressure. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ophtha.2014.08.022 67 |
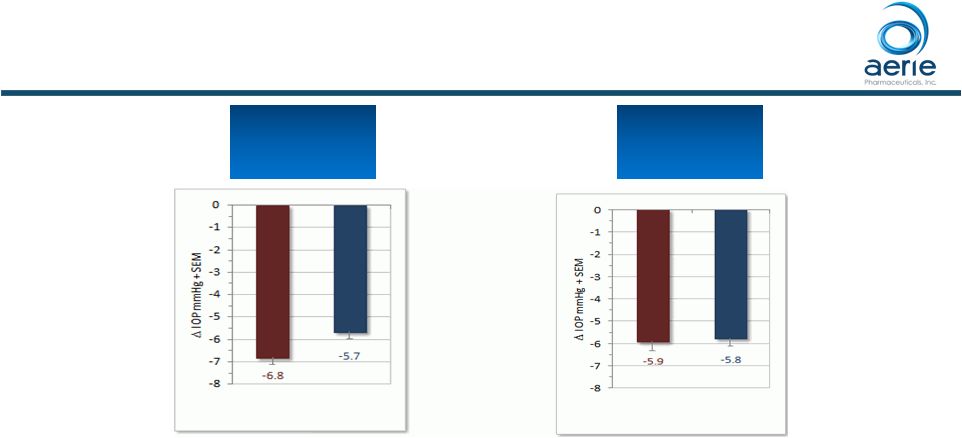
 Phase 3 Rhopressa™ Non-inferior to Latanoprost at Baseline IOP <25 mmHg 68 Mean IOP at Each Time Point (PP) ++ Data on File Based on Mercury 1 Topline Interim 3-month |
 Phase 3 Rhopressa™ Non-inferior to Latanoprost at Baseline IOP <25 mmHg Mean IOP at Each Time Point (ITT) 69 ++ Data on File Based on Mercury 1 Topline Interim 3-month |
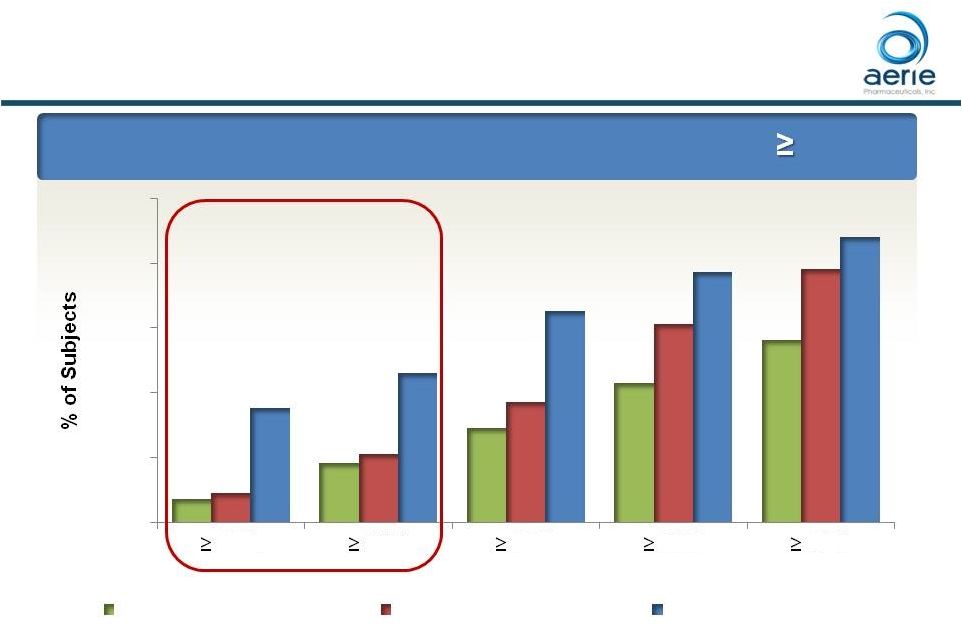
 Roclatan™ Phase 3 Responder Analysis Baseline IOP <25 mmHg 70 ++ Data on File Based on Mercury 1 Topline Interim 3-month *p<0.05 vs Latanoprost and Rhopressa™ # p<0.05 vs Rhopressa™ Day 90: % of Patients with IOP Reductions of 20% 9% 22% 34% 51% 65% 8% 17% 33% 55% 77% 26% 38% 59% 71% 84% 0% 20% 40% 60% 80% 100% 40% 35% 30% 25% 20% Reduction Rhopressa™ (n=103) Latanoprost (n=117) Roclatan™ (n=107) * * * # * |
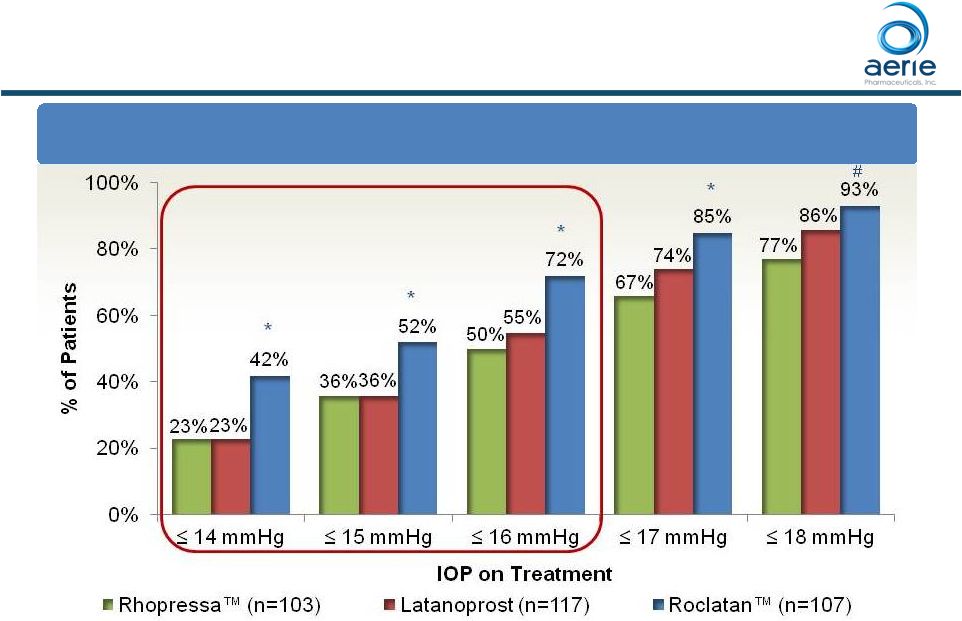 Roclatan TM Phase 3 Responder Analysis Baseline IOP <25 mmHg Day 90: % of Patients with IOP Reduced to 18 mmHg or Lower 71 ++ Data on File Based on Mercury 1 Topline Interim 3-month *p<0.05 vs Latanoprost and Rhopressa TM # p<0.05 vs Rhopressa TM |
 Roclatan TM Phase 3 Responder Analysis Baseline IOP 25 mmHg 72 ++ Data on File Based on Mercury 1 Topline Interim 3-month ***p<0.0001 vs Latanoprost and Rhopressa TM ; ### p<0.0001 vs Rhopressa TM , p<0.05 vs Latanoprost Confirms Rhopressa additive efficacy is maintained at high baseline IOPs Day 90: % of Patients with IOP Reductions of 20% |
 Roclatan TM Phase 3 Responder Analysis Baseline IOP 25 mmHg Day 90: % of Patients with IOP Reduced to 18 mmHg or Lower **p<0.01 vs Latanoprost and Rhopressa TM ++ Data on File Based on Mercury 1 Topline Interim 3-month Confirms Rhopressa additive efficacy is maintained at high baseline IOPs 73 |
 Rhopressa TM Performance Summary • Demonstrated non-inferiority to latanoprost in patients with baseline IOP < 25 mmHg • Efficacy relative to latanoprost improves as baseline IOP declines • Rhopressa TM maintained consistent IOP lowering across all baseline IOPs including 25 mmHg • Stable efficacy • Adverse event profile consistent with previous studies 74 ++ Data on File Based on Mercury 1 Topline Interim 3-month |
 Discussion Q & A 75 |
 Pipeline and Research Update
Casey Kopczynski, Ph.D.
Chief Scientific Officer
76 * * * * * * * * * * |
 • Rhopressa™ • Potential for disease modification and neuroprotection • AR-13154 • Significant lesion size reduction in wet AMD • Drug Delivery • Rhopressa™: Front of the eye • AR-13154: Back of the eye Advancing Earlier-Stage Pipeline Data on file |
 Beyond IOP: Rhopressa TM and Roclatan TM Have Potential to Improve Health of TM in Glaucoma Glaucoma, OHT PGA + Rhopressa™ PGA-Treated D C SC CB R Trabecular outflow Uveoscleral outflow D C SC CB R Trabecular outflow Uveoscleral outflow D C SC CB R Trabecular outflow Uveoscleral outflow IOP TM: Trabecular Meshwork, OHT: Ocular Hypertension, SC: Schlemm’s Canal, CB: Ciliary Body, IR: Iris
Rhopressa™ / Roclatan™ Potential to Increase Perfusion of TM Should
Provide More Nutrients and Antioxidants to the TM
78 |
 Rhopressa TM Live Imaging of Rhopressa TM -induced Increase in Trabecular Meshwork Outflow • Rhopressa TM -induced increase in trabecular outflow of aqueous humor visualized in real time using live-animal OCT imaging in mice • First study to show glaucoma drug affecting target tissue in real time SC SC TM TM Rhopressa TM Treatment Blue shading shows Schlemm’s Canal expanding due to enhanced fluid flow through TM
Li G. et al. Visualization of conventional outflow tissue responses to netarsudil in
living mouse eyes. Eur J Pharmacol. 2016 Apr 13. pii:
S0014-2999(16)30206-0 79 |
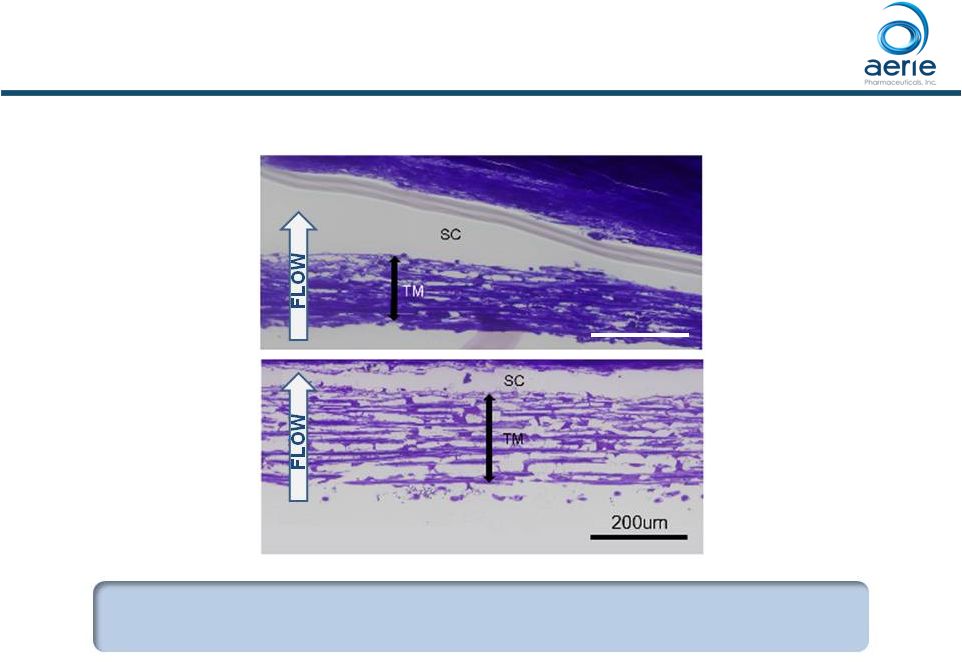 Rhopressa Causes Expansion of Human TM Tissue, Opening Spaces for Increased Outflow + Rhopressa Control Dan Stamer (Duke), Haiyan Gong (Boston University) TM: Trabecular Meshwork SC: Schlemm’s Canal Control = buffered saline solution Increasing Trabecular Outflow, Reducing Fibrosis Could Stop Degeneration of Outflow Tissues in Glaucoma 80 200um • Gong, H. et al., (2016 AGS Annual Meeting) “The Mechanisms of Increasing Outflow Facility by AR-13324M in Human Eyes”. TM TM |
 Rhopressa Blocks TGF-beta-Induced Expression of Fibrosis Proteins in Cultured Human TM Cells Control TGF 2 (8ng/ml) TGF 2 (8 ng/ml) + AR-13324* (500nM) P. Vasantha Rao, Duke University 81 TGF-beta Levels are Elevated in the Aqueous Humor of
Patients with Glaucoma TM * Active ingredient of Rhopressa™; TGF 2: Transforming growth factor 2; SMA: Smooth muscle actin; FSP1: Fibroblast-specific protein 1 • Pattabiraman, Padmanabhan P., et. Al., (2015 AOPT Meeting) “Effects of Rho Kinase inhibitor AR-13324 on actin cytoskeleton and TGF 2 and CTGF- induced fibrogenic activity in Human Trabecular Meshwork Cells”. |
 Evaluation of Steroid-induced Fibrosis in a 3D
Bioengineered Human Trabecular Meshwork
• Glauconix proprietary technology allows multi-layer growth of human TM cells on
scaffold to produce a 3D Bioengineered HTM (human trabecular meshwork)
• 3D HTM allows study drug effects on fluid dynamics across tissue • Provides tissue-based screening platform for drug development Steroid Treatment of Patients with Uveitis Can Damage TM, Cause Elevated IOP and Glaucoma 82 |
 Rhopressa Blocks and Reverses Steroid-Induced Expression of Fibrosis Proteins in Human TM Cells • Addition of Rhopressa 3 days after start of steroid treatment reverses the steroid-induced pro-fibrotic changes • AR: AR-13324 (active ingredient of Rhopressa ); PA: Prednisolone Acetate • Kopczynski, C.C. et al., (2016 ARVO Annual Meeting) “Anti-fibrotic Effects of AR-13324 in a 3D Bioengineered Human Trabecular
Meshwork Model of Steroid-induced Glaucoma”.
Secreted Protein Expression
83 TM TM TM |
 Products
in Development: Preclinical •
Netarsudil* sustained-release implant for Glaucoma
• Single injection to lower IOP for 3 – 6 months • Potential for increased efficacy, reduced ocular
side effects, neuroprotection
• Addresses problem of patient adherence to daily drops and gives control to the physician • AR-13154 implant for AMD, DR/DME • ROCK/PKC/PDGFR/JAK multi-kinase inhibitor • Addresses multiple drivers of disease - fibrosis, inflammation, vessel leakage and neovascularization • Efficacy demonstrated as monotherapy
and as adjunct to anti-VEGF therapy (preclinical) • Potential to improve long-term outcomes 84 * Active ingredient of Rhopressa TM |
 AR-13154 is ROCK Inhibitor with Additional
Activity Against PKC, PDGFR and JAK Kinases
• 182 Aerie compounds screened against 469 human kinases • AR-13154 identified as lead compound to address: • Vascular dysfunction ROCK, PKC, PDGFR • Fibrosis
ROCK, PKC, PDGFR
• Inflammation
ROCK, JAK Relationship tree of human kinases. TK, TKL, STE, CK1, AGC, CAMK, CMGC, Other: Kinase superfamilies
ROCK |
 AR-13154 vs. Eylea® in Preclinical AMD
Model 86 Laser-induced choroidal neovascularization (CNV) in rats Compounds delivered by intravitreal injection AR-13154 Numerically More Effective than Eylea ® in Rat Model of AMD Data on file; Effectiveness of AR-13154 Monotherapy and Combination Therapy in Animal Models of Wet Age-related Macular
Degeneration and Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy. Cheng-Wen Lin, Jill M.
Sturdivant, Mitchell A. deLong and Casey C. Kopczynski 20000
30000 40000 50000 60000 70000 80000 90000 100000 110000 Saline n=49 0.06 ug/mL AR-13154 n=28 0.6 ug/mL AR-13154 n=25 6 ug/mL AR-13154 n=25 800 ug/mL Eylea n=20 Total CNV Lesion Area (Day 21) * p<0.05 vs. Saline ** p<0.001 ® ** * |
 Topical
AR-13154(S) Provides Additive Efficacy to
Eylea ® in Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy Model 87 Oxygen-induced retinopathy model of PDR (mouse) 0.06% AR-13154(S) delivered topically from P12 to P17 Eylea ® delivered IP Confirms AR-13154(S) potential as monotherapy and as adjunct to anti-VEGF therapies Data on file; Effectiveness of AR-13154 Monotherapy and Combination Therapy in Animal Models of Wet Age-related Macular
Degeneration and Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy. Cheng-Wen Lin, Jill M.
Sturdivant, Mitchell A. deLong and Casey C. Kopczynski 0%
20% 40% 60% 80% 100% 120% Vehicle Control (n=55) AR-13154(S) topical (n=28) Eylea 1mg/kg IP (n=26) AR-13154(S) + Eylea (n=18) Total Neovascular Area -37% -34% -57% ** *** *** *** |
 AR-13154 Efficacy Driven Primarily by ROCK,
PKC Inhibition in Retina
88 Retinal tissue harvested from OIR mouse model AR-13154 effectively converted to active metabolite by esterases Active metabolite keeps ROCK, PKC activity, loses PDGFR, JAK activity Data on file; Effectiveness of AR-13154 Monotherapy and Combination Therapy in Animal Models of Wet Age-related Macular
Degeneration and Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy. Cheng-Wen Lin, Jill M.
Sturdivant, Mitchell A. deLong and Casey C. Kopczynski
Retinal Esterases X ROCK JAK PKC PDGFR AR-13154 Active Inactive ROCK PKC • • • |
 Preclinical Programs: Next Steps
• For both netarsudil* & AR-13154: – Pair with sustained delivery system Evaluating multiple technologies Bioerodable implant Targeting injection every 3-6 months – Establish long-term efficacy, PK in preclinical models – Initiate IND-enabling toxicology, CMC • Create next-generation netarsudil 89 * Active ingredient of Rhopressa™ • • • |
 Global Strategy Craig Skenes VP Business Development 90 |
 European
Strategy •
Aerie will complete the remaining development activities for
Rhopressa and Roclatan • Continue to engage with European authorities about regulatory requirements for both products • Addition of Rocket 4 (Rhopressa ) in the US and Mercury 3 (Roclatan ) in EU to other US registration trials is expected to be sufficient for approval • Plan to file Marketing Authorisation Application (MAA) for Rhopressa approximately mid-2017 • Targeting completion of European commercialization strategy by YE16 91 ™ ™ ™ ™ ™ |
 Japan
Strategy •
Aerie has adequate resources to complete the remaining
development activities for Rhopressa
and Roclatan • Ongoing discussions with PMDA for Rhopressa and Roclatan • Evaluating requirements for marketing approval of Rhopressa • Clinical studies in Japan will be required • Plan to finalize clinical strategy with PMDA by Q1’17 • Dialogue also ongoing with potential partners for development and commercialization of our products in Japan and Asia • Will advance the development of our products while partnering discussions continue • No requirement to complete transaction prior to receiving approval in Japan 92 TM TM TM TM TM |
 Discussion Q & A 93 |
 Financial Summary Richard Rubino CFO 94 |
 Financial
Summary •
Cash Balance as of June 30, 2016 = $112M
• 26.6M shares outstanding • Expected Cash Balance as of September 30, 2016 of ~$250M • ~33M shares outstanding • Expected Cash Balance as of December 31, 2016 of ~$230M • Updated Full-Year 2016 Cash Burn Guidance of ~$85M • Use of Proceeds from Recent Financings • General Corporate Purposes and Working Capital Requirements • Complete Funding of Rhopressa Commercialization Costs • Execution of Clinical Trials for Japan • Commencement of Construction of a Manufacturing Plant in Ireland 95 TM |
 Thank
You 96 |
