Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-31.2 - CERTIFICATION - Enochian Biosciences Inc | f10k2016ex31ii_dandritbio.htm |
| EX-32.1 - CERTIFICATION - Enochian Biosciences Inc | f10k2016ex32i_dandritbio.htm |
| EX-31.1 - CERTIFICATION - Enochian Biosciences Inc | f10k2016ex31i_dandritbio.htm |
United states
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
☒ Annual report under section 13 Or 15( d ) of the securities exchange act of 1934
For the fiscal year ended June 30, 2016
☐ transition report under section 13 Or 15( d ) of the securities exchange act of 1934
For the transition period from
Commission file number 000-54478
| DANDRIT BIOTECH USA, INC. |
| (Name of registrant in its charter) |
| Delaware | 45-2559340 | |
| (State
or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) |
(I.R.S.
Employer Identification No.) | |
| Fruebjergvej 3 Box 62, 2100 Copenhagen, Denmark | 2100 | |
| (Address of principal executive offices) | (Zip Code) |
+45 391 79840
(Registrant’s telephone number, including area code)
DanDrit Biotech USA, Inc.
Fruebjergvej 3, Box 62
2100 Copenhagen, Denmark
+45 39179840
(Name, address, including zip code, and telephone number, including area code, of agent for service)
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| Title of Class | Name of Exchange | |
| Not applicable | Not applicable |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: Common Stock, $0.0001 par value
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. ☐ Yes ☒ No
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. ☐ Yes ☒ No
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Exchange Act during the last 12 months (or for such shorter period that -the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§ 232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer or a smaller reporting company.
| Large accelerated filer | ☐ | Accelerated filer | ☐ |
| Non-accelerated filer | ☐ | Smaller reporting company | ☒ |
| (Do not check if a smaller reporting company) | |||
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). ☐ Yes ☒ No
On December 31, 2015, the aggregate market value of the voting and non-voting common equity held by non-affiliates was $32,509,226.
Indicate the number of shares outstanding of each of the issuer’s classes of common stock, as of the latest practicable date.
As of September 25, 2016, the number of shares of the registrant’s classes of common stock outstanding was 9,533,290.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Not applicable.
CONTENTS
| i |
Cautionary Language Regarding Forward-Looking Statements and Industry Data
This Annual Report on Form 10-K contains “forward-looking statements” within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. Forward-looking statements can be identified by the fact that they do not relate strictly to historical or current facts. Forward-looking statements are based upon our current assumptions, expectations and beliefs concerning future developments and their potential effect on our business. In some cases, you can identify forward-looking statements by the following words: “may,” “could,” “would,” “should,” “expect,” “intend,” “plan,” “anticipate,” “believe,” “approximately,” “estimate,” “predict,” “project,” “potential” or the negative of these terms or other comparable terminology, although the absence of these words does not necessarily mean that a statement is not forward-looking. A forward-looking statement is neither a prediction nor a guarantee of future events or circumstances, and those future events or circumstances may not occur. You should not place undue reliance on forward-looking statements, which speak only as of the date of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. These forward-looking statements are all based on currently available operating, financial and competitive information and are subject to various risks and uncertainties. Our actual future results and trends may differ materially depending on a variety of factors, including, but not limited to, the risks and uncertainties discussed under "Risk Factors" and "Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations". Given these risks and uncertainties, you should not rely on forward-looking statements as a prediction of actual results. Any or all of the forward-looking statements contained in this Annual Report on Form 10-K and any other public statement made by us, including by our management, may turn out to be incorrect. We are including this cautionary note to make applicable and take advantage of the safe harbor provisions of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995 for forward-looking statements. We expressly disclaim any obligation to update or revise any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise.
Factors that may cause or contribute actual results to differ from these forward-looking statements include, but are not limited to, the following:
| ● | all the risks inherent in the establishment of any new or early stage company, particularly one in proteomics, biotechnology or other research and development-intensive business; | |
| ● | the Company’s absence of significant sales or sales revenues and its limited history of operations including limited manufacturing and sales operations to date, which make it difficult to predict future performance; | |
| ● | operations that have required and will continue to require significant financial resources and working capital, without offsetting revenues from sales of products and services; | |
| ● | the need to make multiple assumptions in preparing forecasts and projections of any kind, and significant difficulties in predicting and forecasting accurately the expenses likely to be incurred and the revenues likely to be generated in the Company’s attempt to commercialize and sell its present and potential future products and services specifically for use in protein research; | |
| ● | significant competition in biotechnology generally, including from companies that are larger, have greater financial resources, have larger research and development budgets and programs, are more established and have greater market acceptance in the relevant markets; | |
| ● | the high rate of technological change or advancement in the field of protein research and biotechnology, and the related risks that innovation by a competitor may render the Company’s products obsolete or less desirable and that obsolescence of a product or service might occur before the product or service can gain market acceptance, significant levels of sales and revenues, or profitability; | |
| ● | the risk that the Company will have difficulties executing its intended business plan; | |
| ● | the risk that the Company’s research and development efforts will not succeed, or will not succeed in sufficient time, to allow commercialization and sales at levels sufficient to generate revenues in excess of expenses; | |
| ● | the need to raise additional capital and/or obtain other additional funding; | |
| ● | risks and uncertainties related to intellectual property rights, including the potential for expensive litigation concerning intellectual property issues; |
| ii |
| ● | potential barriers, risks, uncertainties and obstacles to the Company’s plans to manufacture its own products; | |
| ● | potential barriers, risks, uncertainties and obstacles to the Company’s ability to develop, introduce, and gain market acceptance for its products and services for protein research, for example because of perceived issues relating to quality and safety, customers’ reluctance to invest in new technologies and/or widespread acceptance of other technologies; | |
| ● | potential problems and difficulties managing growth, including potential challenges in implementing appropriate operational and financial systems, developing and then expanding and scaling up production, attracting and/or retaining good to excellent employees in all phases of anticipated future operations, expanding sales and marketing infrastructure and capabilities, providing adequate training and supervision to maintain high quality standards; | |
| ● | risks associated with the tightening or other adverse changes in the overall capital and credit markets and decreased availability of investment capital and/or credit, bank financing or other debt financing as and when needed or at favorable terms including fixed and/or low interest rates; and | |
| ● | other risks over which we have no control. |
All forward-looking statements speak only as of the date of this report. We undertake no obligation to update any forward-looking statements or other information contained herein. Stockholders and potential investors should not place undue reliance on these forward-looking statements. Although we believe that our plans, intentions and expectations reflected in or suggested by the forward-looking statements in this report are reasonable, we cannot assure stockholders and potential investors that these plans, intentions or expectations will be achieved. These cautionary statements qualify all forward-looking statements attributable to us or persons acting on our behalf.
Information regarding market and industry statistics contained in this report is included based on information available to us that we believe is accurate. It is generally based on academic and other publications that are not produced for purposes of securities offerings or economic analysis. Forecasts and other forward-looking information obtained from these sources are subject to the same qualifications and the additional uncertainties accompanying any estimates of future market size, revenue and market acceptance of products and services. Except as required by U.S. federal securities laws, we have no obligation to update forward-looking information to reflect actual results or changes in assumptions or other factors that could affect those statements.
| iii |
Unless otherwise indicated or the context otherwise requires, all references in this prospectus to “DanDrit,” “we,” “us,” “our” or the “Company” are to DanDrit Biotech USA, Inc., a Delaware corporation (“DanDrit USA”), together with its wholly-owned subsidiary DanDrit Biotech A/S, a Danish limited company, organized under the Danish Act on Limited Companies of the Kingdom of Denmark (“DanDrit Denmark,” or the “Subsidiary”).
Overview of Our Business
DanDrit a biotechnology company seeking to develop what we believe could be the world’s first vaccine approved for the treatment of colorectal cancer. For more than a decade we have developed and patented vaccines successfully used in initial clinical trials in Europe and Asia including: (i) MelCancerVac™ (MCV) for treatment of cancer (one phase I/II trial in Denmark and two phase II trials in Denmark and Singapore), (ii) Tolerogenic (producing immunologic tolerance) dendritic cell (TDC) (pre-clinical stage in Denmark) and (iii) Melvaccine (MV) a melanoma cell lysate used as stand-alone vaccine (pre-clinical state in Denmark). We plan to continue our clinical development program in Europe and the United States. Springing from academic roots in Denmark, DanDrit has built upon its scientific and medical skills to advance candidate therapies, targeted initially at non-small-cell-lung-cancer (NSCLC) and colorectal cancer (sometimes referred to herein as CRC). In 2001, MCV was developed as a result of the combined efforts and research of DanDrit researchers and employees. On September 22, 2008, the Singapore government granted to DanDrit Denmark a named-patient compassionate use program of MCV. DanDrit’s dendritic cell vaccine, MCV, was evaluated in three single-arm Phase II clinical trials in cancer where MCV demonstrated potential efficacy. However, these three clinical trials generated data reported in published papers which indicated that the data needed to be confirmed in a larger, comparative randomized clinical trial. As a result, DanDrit, with the assistance of experienced practitioners in colorectal cancer treatment, designed a randomized trial with stage IV colorectal cancer patients and plans to conduct this randomized Phase III trial to assess the ability of MCV to prevent relapse of stage IV NED colorectal cancer patients with No Evidence of Disease (NED). Neither the US Federal Drug Administration (FDA) nor any other comparable governmental agency has reviewed MCV. Therefore, any assessment of its safety or efficacy only reflects the opinion of the Company. Furthermore, it does not indicate that MCV will achieve favorable results in any later stage trials or that the FDA or comparable agency will ultimately determine that MCV is safe and effective for purposes of granting marketing approval.
In June 2015, DanDrit’s Board of Directors approved a change to DanDrit’s fiscal year end from December 31 to June 30.
Our Biotechnology
We believe that DanDrit's next generation of dendritic cell vaccine technology may benefit of the following technological competitive advantages over other cancer vaccines, such as Dendreon’s FDA approved Provenge™ cancer vaccine :
| ● | The vaccine is generated within eight days from a patient’s peripheral blood draw. We are able to generate the vaccine quickly because only 250ml of blood is required to be drawn. Leukapheresis, a medical technology in which the blood of a patient is passed through a dialysis machine that separates out one particular constituent and returns the remainder to the patient’s circulation is not needed. |
| ● | The vaccine uses an allogenic (using cells, tissues, or organs, sourced from a genetically non-identical member of the same species as the recipient (“Allogenic”)) tumor lysate (a fluid containing the contents of lysed cells) as opposed to inconvenient autologous (from the patient) tumor lysate. Our cancer-specific antigens are off-the-shelf and therefore DanDrit does not need a patient’s tumor cells to manufacture the vaccine. |
| 1 |
| ● | The vaccine is polytopic (targets several cancer specific antigens). As a result, the risk of the tumor escaping is more limited and more T-cells can be activated than if the vaccine is targeting one antigen only. However, MCV has a focus on melanoma-associated antigen (“MAGE”)-A antigens that are only expressed by tumors and absent in normal tissues. |
MCV demonstrated efficacy in three separate Phase II clinical trials in colorectal and non-small cell lung cancer. Even if MCV can be used for various cancers, DanDrit has decided to focus MCV’s clinical development specifically on the treatment of advanced CRC.
History
DanDrit USA was originally incorporated in Delaware on January 18, 2011 under the name “Putnam Hills Corp.” as a vehicle to pursue a business combination through the acquisition of, or merger with, an operating business. We filed a Registration Statement on Form 10 with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”) on August 12, 2011.
On February 12, 2014, in accordance with the terms and conditions of a Share Exchange Agreement (the “Share Exchange Agreement”), we completed the acquisition of approximately 100% of the issued and outstanding capital stock of DanDrit Denmark (the “Share Exchange”) and as a result became DanDrit Denmark’s parent company (the “Parent”). In connection with the Share Exchange, each outstanding share of common stock of DanDrit Denmark was exchanged for 1.498842 shares of DanDrit USA’s common stock, par value $.0001 per share (the “Common Stock”) for an aggregate of 6,000,000 shares, including 185,053 shares of Common Stock reserved for issuance, in accordance with Section 70 of the Danish Companies Act and the Articles of Association of DanDrit Denmark, to the DanDrit Denmark shareholders who did not consent to the Share Exchange and deemed issued and outstanding for accounting purposes. In addition, in connection with the Share Exchange (1) the sole shareholder prior to the Share Exchange agreed to cancel 4,400,000 shares of outstanding Common Stock owned by it and (2) the board of directors and executive management of DanDrit Denmark was appointed to serve as the Board of Directors and executive management of DanDrit USA effective upon the resignation of the sole officer and director of DanDrit USA prior to the closing of the Share Exchange.
Emerging Growth Company
As a company with less than $1.0 billion in revenue during our last fiscal year, we qualify as an “emerging growth company” as defined in the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act, or JOBS Act, enacted in April 2012. An “emerging growth company” may take advantage of reduced reporting requirements that are otherwise applicable to public companies. These provisions include, but are not limited to:
| ● | Reduced disclosure about our executive compensation arrangements; |
| ● | No non-binding shareholder advisory votes on executive compensation or golden parachute arrangements; |
| ● | Exemption from the auditor attestation requirement in the assessment of our internal control over financial reporting; and |
| ● | Reduced disclosure of financial information in this prospectus, limited to two years of audited financial information and two years of selected financial information. |
As a smaller reporting company, each of the foregoing exemptions is currently available to us. We may take advantage of these exemptions until the last day of our fiscal year following the fifth anniversary of the date of the first sale of our common equity securities pursuant to an effective registration statement under the Securities Act, which such fifth anniversary will occur in 2018 or such earlier time that we are no longer an emerging growth company. We would cease to be an emerging growth company if we have more than $1.0 billion in annual revenues as of the end of a fiscal year, if we are deemed to be a large accelerated filer under the rules of the Securities and Exchange Commission, or if we issue more than $1.0 billion of non-convertible debt over a three-year-period. The JOBS Act permits an emerging growth company to take advantage of an extended transition period to comply with new or revised accounting standards applicable to public companies; provided, however, that an emerging growth company may elect to opt out of the extended transition period and comply with the requirements that apply to non-emerging growth companies but any such election to opt out is irrevocable. We have not elected to opt out of the transition period.
| 2 |
Because we have elected to take advantage of certain of the reduced disclosure obligations and may elect to take advantage of other reduced reporting requirements in future filings, the information that we provide to our stockholders may be different than you might receive from other public reporting companies in which you hold equity interests.
Our Business Strategy
Our clinical development strategy is focused on conducting a Phase III clinical trial in advanced colorectal cancer. DanDrit intends to conduct a randomized multicenter Phase III clinical trial to determine the ability of MCV to prevent recidivism in stage IV colorectal patients with no evidence of disease (NED) after resection of metastasis and chemotherapy. This randomized trial is planned to be enrolled within two years. We believe that positive clinical data will be the catalyst to unlock commercial revenues for DanDrit through either MCV acquisition by a pharmaceutical partner or licensing arrangements that would yield upfront and milestone payments as well as royalties.
Furthermore, parallel to the previously described clinical trial, DanDrit may pursue a registration trial to support potential approval of MCV in China. This trial would be conducted under China’s State Food and Drug Administration (the “SFDA”) regulations with a Chinese oncology pharmaceutical partner. China has recently put in place a drug approval system.
DanDrit is headquartered in the USA and also runs operations from its subsidiary in Denmark.
Our Proposed Clinical Trial
DanDrit intends to develop globally the use of MCV in the treatment of colorectal cancer, and to follow that expansion with the treatment of other types of cancer. DanDrit currently intends to focus its development program, a randomized multicenter Phase III clinical trial in stage IV colorectal cancer in Italy, known as VIVA (MelCancerVac vaccine in patients with stage IV colorectal cancer with no evidence of disease after standard of care, a randomized Phase III adjuvant study).
The VIVA clinical trial with an adaptive design plans to first enroll 174 stage IV colorectal cancer patients after resection of metastases and chemotherapy. These patients have no evidence of disease but are not cured of cancer. Their Relapse Free Survival (an endpoint used to analyze the results of the treatment for the cancer which renders the patient apparently disease free, such as surgery plus adjuvant therapy, where, in the Relapse-Free Survival, the event is relapse rather than death) is only 24 to 26 months. The objective of the VIVA Phase III clinical study is to lengthen the survival of these patients. Treatment will be randomized against reference therapy. Patients will be included after resection of their primary tumor and metastases and after appropriate peri-operative or post-operative chemotherapy by random assignment to a non-vaccine control group or a vaccine group receiving five vaccinations with 14-day administration intervals followed by ten vaccines with two-month intervals. Inclusion will take place ten weeks after finishing the last round of chemotherapy (FOLFOX or FOLFIRI) and after a negative tumor scan (head, thoracic and abdominal cavities) and normal carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) prior to inclusion in the vaccine or the control groups. The control group will receive standard therapy. In the event of disease progression, as verified by tumor scan and biomarker levels during the vaccination schedule, MCV vaccinations will be discontinued.
Products
DanDrit’s MCV demonstrated potential efficacy in three separate Phase II clinical trials in colorectal and non-small cell lung cancer. Even if MCV can be used for various cancers, DanDrit has decided to initiate MCV’s clinical development with advanced colorectal cancer. We believe that a maintenance therapy for advanced colorectal cancer represents a genuine commercial opportunity for MCV. A clear and unmet medical need for a safe maintenance therapy offers the opportunity to confirm the potential efficacy of MCV in a favorable setting.
| 3 |
The purpose of the VIVA trial will be to determine the ability of MCV to prevent recidivism in stage IV colorectal patients with no evidence of disease after resection of metastasis and chemotherapy. Using an Adaptive Design Clinical Study, which allows modification made to trial and/or statistical procedures of ongoing clinical trials based on accrued data, the VIVA trial will evaluate MCV with standard of care against standard of care alone in 174 colorectal cancer patients using as primary endpoints Relapse Free Survival (RFS) at 18 months and Overall Survival (OS). We anticipate that the first step of the VIVA trial can be completed within three years.
DanDrit has learned how to manufacture dendritic cells, immune cells forming part of the mammalian immune system with the main function of processing antigen material and presenting it on the surface to other cells of the immune system, functioning as antigen-presenting cells, in vitro from monocyte (a type of white blood cell) precursor cells taken from patients eligible for DanDrit’s therapies. The preparation of tumor lysate containing selections of cancer-specific non-self-antigens allows DanDrit to sensitize patients’ dendritic cells. The use of the patient’s own monocyte cells from peripheral blood (autologous cell therapy) overcomes the issues associated with non-self-allergic reactions to immune therapies.
DanDrit’s intellectual property is protected with patents and trademarks. DanDrit’s candidate vaccines are based on the MCV platform that is protected by a family of issued or submitted patents. DanDrit’s lead product has completed Phase II clinical trials in Denmark and Singapore. Following the results of DanDrit’s Singapore Phase II clinical trials, Singapore authorities allowed the use of MCV for CRC on a humanitarian named patient basis. Named patient programs provide controlled, pre-approval access to drugs in response to requests by physicians on behalf of specific, or “named”, patients before those medicines are licensed in the patient’s home country. Governments worldwide, such as Singapore’s government, have created provisions for granting access to drugs prior to approval for patients who have exhausted all alternative treatment options and do not match clinical trial entry criteria. Often grouped under the labels of compassionate use, expanded access, or named patient supply, these programs are governed by rules which vary by country defining access criteria, data collection, promotion, and control of drug distribution. Through these programs, patients are able to access drugs in late-stage clinical trials or approved in other countries for a genuine, unmet medical need, before those drugs have been licensed in the patient’s home country. In September 2008, DanDrit Denmark and the National Cancer Centre of Singapore (NCC) entered into a collaboration agreement regarding a clinical named patient program conducted in Singapore at NCC with the dendritic cell vaccine MCV. NCC has established a GMP approved laboratory in which the manufacturing of MCV takes place. NCC has received approval from the relevant governmental authorities for the import of lysate necessary for production of MCV. The clinical and research and development activities of the named patient program relate to the Company’s product, MCV. The purpose for the Singapore named patient program is to provide patients with advanced colorectal cancer or other forms of cancer(s) with the presence of MAGE antigen expression an alternative treatment for the vaccination with MCV, where there is no further indication for surgery or treatment with chemotherapy. Patients are recruited on named patient basis according to the patient inclusion and exclusion criteria stated in the phase II study protocol. However, there may be some exceptional cases where treatment will be made based on a doctor’s discretion regarding the patient’s quality of life.
To date, clinical trials of MCV have been targeted to patients in terminal stages of cancer with non-resectable bulky tumors who failed to respond to surgery and chemotherapy. Several patients showed extended overall survival with good quality of life. Several patients showed stable disease with no progression of tumors. There was evidence of tumor regression in some patients (see “Clinical Trials Data and Product Approvals”).
These achievements have been built on a carefully executed R&D program that generated practical solutions to scientific and medical challenges. Through this development program, DanDrit gained advanced understanding of the role of dendritic cells in immunoregulation and cancer.
We believe that non-core applications of dendritic cell technologies mastered by DanDrit have applications in infectious diseases and auto-immune diseases such as diabetes (seventh leading cause of death in the US). We believe that these other applications may represent opportunities for potential out-licensing and cooperation.
| 4 |
DENDRITIC CELLS, THE THERAPEUTIC PLATFORM
Summary
Early academic work at the Danish Cancer Society was spun-out into DanDrit Denmark. None of the personnel at the Danish Cancer Society, or any other third-party, retains any rights to the intellectual property underlying the Company’s business, technology or product candidates, including MCV. The fundamental scientific postulate of DanDrit is the fact that key cells in the immune system can be sensitized to cancer cells that carry foreign (or non-self) antigens. These key antigen-presenting cells are the dendritic cells. Dendritic cells encounter and recognize foreign antigens. Dendritic cells can assimilate and process the cells expressing these antigens. The key components of these antigens (known as epitopes and several epitopes are known as polytopes) are subsequently presented on the cell surface of the dendritic cell. Dendritic cells travel to lymph nodes and other lymphatic tissues where the epitopes are presented to other immune cells, including cell-killing T lymphocytes. T lymphocytes sensitized by dendritic cells can then recognize and kill tumor cells carrying tumor-specific antigens recognized by the dendritic cells. The main aim is to kill tumor cells without killing normal body tissues.
From DanDrit’s point of interest, this might represent a dendritic cell instructing a T-lymphocyte to kill tumor cells presents itself as a “Cancer Vaccine” company and its lead product, MelCancerVac® (MCV), a polytopic vaccine, targets colorectal cancer in the first instance. In addition, DanDrit has developed several technologies relevant to dendritic cell production, including:
| ● | Generation of fast track dendritic cells | |
| ● | Processing and presentation of protein antigen | |
| ● | Characterization of DanDrit dendritic cells | |
| ● | Analysis of lysate uptake by DanDrit dendritic cells | |
| ● | MicroRNA profiling of DanDrit dendritic cells | |
| ● | Effect of Resiquimod (a drug that acts as an immune response modifier, and has antiviral and anti-tumoral activity) on production of Interleukin 12 (Il-12), a secreted protein factor that is naturally produced by dendritic cells in response to antigenic stimulation and Interleukin 10 (IL-10), a protein that inhibits the synthesis of a number of other signaling proteins. |
| ● | Generation of tolerogenic dendritic cells | |
| ● | Development of Il-12 based potency assay |
DanDrit’s vaccine candidates are based on the MCV platform and are protected by a family of issued and submitted patents. DanDrit’s lead product has completed Phase II clinical trials in Denmark and Singapore.
To date, clinical trials of MCV have been targeted to patients in terminal stages of disease who failed to respond to surgical resection and chemotherapies. Some patients showed extended overall survival with good quality of life. Many patients showed stable disease with no progression of tumor. There was evidence of tumor regression in some patients. (see “Clinical Trials Data and Product Approvals”).
Some of this research in dendritic cells could have implications that reach beyond DanDrit’s cancer vaccine vision.
Dendritic Cells and the immune response
Dendritic cells were first recognized by Paul Langerhans in the late 19th century. For this reason such cells in the skin may still be referred to as Langerhans cells. The term “dendritic cell” was first used by Ralph Steinman and Zanvil Cohn in 1973. Steinman received the 2007 Lasker Award for this work and the 2011 Medicine Nobel Prize.
Like macrophages, cells whose role is to phagocytose, or engulf and then digest, cellular debris and pathogens, either as stationary or as mobile cells, dendritic cells are involved in the processing of antigens and their presentation to the cells that directly carry out the immune response through antibody generation (B lymphocytes) or cell killing activity (T- lymphocytes). Like macrophages, dendritic cells are mobile and once stimulated by an antigen, activated macrophages and dendritic cells move from their host tissue (usually skin or epithelial tissue such as gut, mucous membranes, lung etc.) to lymphatic tissues where they encounter and stimulate cells that mediate the immune response.
| 5 |
Unsurprisingly, macrophages and dendritic cells are closely related. Both are derived from circulating blood cells known as monocytes, a type of white blood cell which constitutes roughly 10% of all white blood cells. Monocytes, macrophages and immature dendritic cells are all phagocytic cells, that is, they engulf and process foreign antigens. On activation by the uptake of antigen, dendritic cells mature and become mobile. The mobile mature dendritic cells are capable of stimulating T-lymphocytes through the expression of T-cell stimulatory antigens on their cell surfaces.
It is possible to force monocytes to differentiate in vitro into immature dendritic cells. This is the basis of DanDrit’s proprietary dendritic cell production process. As in nature, DanDrit’s process involves a subtle communication between monocytes and cytokines (small proteins that important in the communication process that governs basic cellular activities and coordinates cell actions). Dendritic cells produced by DanDrit are functionally, morphologically and biochemically very similar – if not identical – to natural dendritic cells.
Figure 1 Principle of Dendritic Cell cancer vaccines
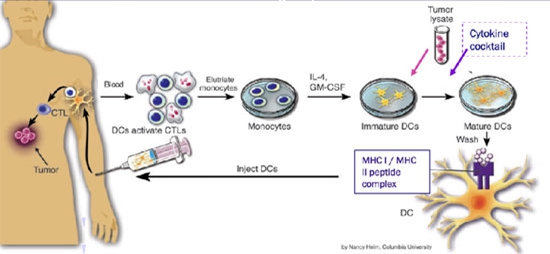
DanDrit’s platform technology is based on isolating patient monocytes and transforming them into immature dendritic cells in vitro. This is achieved by exposing monocytes to cytokines (interleukin 4, IL-4; and granulocyte macrophage colony stimulating factor, GM-CSF). Still in vitro these immature dendritic cells are activated by exposure to a cancer cell line lysate. This cancer cell lysate contains many “non-self” antigens of the cancer/testis family. Although coded by the human genome, these antigens are not normally expressed in tissues other than cancer or testis (note that testis and immune system are isolated from each other). Once sensitized in vitro, the immature dendritic cells are matured by exposure to a DanDrit proprietary cytokine cocktail. The now mature dendritic cells can be re-injected to the patient via a simple 0.2 ml intra-dermal injection and they will find their way to the lymphatic tissues. There, they will stimulate multiple cell killing (T) lymphocytes which will become sensitized to the cancer-specific antigens present in the lysate.
The Platform Technology, MelCancerVac®
MelCancerVac® (MCV) is a cellular immunotherapy for treatment of cancer. MCV has been studied in two cancers: Non-Small Cell Lung cancer (NSCLC) and colorectal cancer (CRC).
DanDrit’s platform technology comprises two arms:
| ● | autologous dendritic cells obtained by the activation of patient-derived monocytes; and | |
| ● | proprietary lysate from melanoma-derived cell line expressing a range of cancer/testis antigens, notably the MAGE-A family |
| 6 |
The melanoma lysate component of MCV is manufactured from a melanoma cell line established by DanDrit scientists. This cell line was isolated from a melanoma tumor that expressed antigens found in a wide range of tumors but not in normal tissues (other than the testis). These antigens belong to a family of cancer/testis antigens (including mostly MAGE-A antigens) found in many tumors.
Furthermore, by exposing DanDrit’s proprietary melanoma tumor cell to 5-aza-deoxycytadine (5-aza-CdR/Decitabine), which is an inhibitor of DNA methylation, DanDrit has shown that derived tumor lysates (MCV5AZA) express a far wider range of tumor-specific antigens.
Antigen characterization
For a patient to respond favorably to MCV, it is necessary that the antigens presented by the patient’s tumor show a significant match with the antigens in the lysate. The level of expression of antigens in each batch of lysate is determined by a procedure known as Reverse Transcriptase Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction or “RT-QPCR”. Clearly all patient cells will present many thousands of antigens, as will the lysate. MCV’s lysate component is isolated from a melanoma cell line that expresses a great many cancer/testis antigens at significant level. This broad spectrum of cancer/testis antigens is what makes MCV a good cancer vaccine. Figure 2 (below) shows how RT-QPCR can analyze levels of antigen expression as measured by messenger RNA.
Figure 2 Comparison of tumor antigen expression in MCV with two patient biopsies
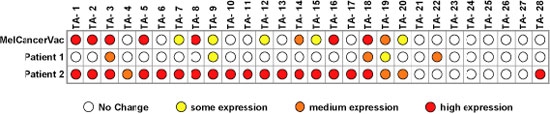
In this example, TA-1 to TA-28 are 28 known tumor antigens (antigens that are only expressed by cancer cells and not by normal cells). We can see that 14 of these antigens are present in MCV. Twenty-one cancer-specific antigens are expressed by the tumor in patient two, which indicates a good chance of promoting a cancer killing response. In patient one there is not a strong overlap of MCV antigens and the five patient’s tumor antigens. The chances of promoting a strong immune response are less but still significant (TA-3, TA-9, TA-18, and TA-19 are shared).
By analyzing patient’s tumors by RT-QPCR, it is possible to select patients that have the best chance of success with MCV. However, other uncharacterized antigens may also be present that might promote a response.
Clinical Trials Data and product approvals
Overall clinical results
No dendritic cell-based vaccination has to date demonstrated life-threatening side effects. The only potential adverse events associated with dendritic cell vaccines to date are a flu-like symptom with fevers (up to 39-40 degrees Celsius), chills, and headaches in some patients. The occurrence of these adverse events did not require additional treatment or hospitalization. Some patients may also develop a vitiligo, a skin condition in which there is a loss of brown color (pigment) from areas of skin, resulting in irregular white patches that feel like normal skin, when melanocyte differentiation antigens are used as targets in immunotherapy. However, this has not occurred, to DanDrit’s knowledge, with MCV in clinical trials that have been conducted to date.
MCV is produced according to the principles of Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) in facilities approved by the Danish Medicine Agency and EU regulation for the production of medicines from patient blood in aseptic conditions. No products of animal origin are used during vaccine preparation. Quality control is performed for each individual batch of the vaccine as well as for the lysate used in the loading of dendritic cells.
| 7 |
MCV was originally developed in 2001 as a result of the combined research efforts of DanDrit researchers and employees and has been tested in clinical trials for the treatment of colorectal cancer (CRC) and non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
CRC Clinical Trials
| ● | Phase I/II at Gentofte Hospital, Denmark (investigator-sponsored trial)– Completed, November 2004 – April 2006 | |
| ● | Phase II at the National Cancer Centre, Singapore (investigator-sponsored trial) – Completed, November 2005 – March 2007 |
NSCLC Clinical Trials
| ● | Phase II at Herlev Hospital, Denmark (Dandrit-sponsored trial) – Completed, January 2006 – September 2009 |
ColoRectal Cancer (CRC) in Denmark
The clinical trial using MCV at the University Hospital of Copenhagen, Gentofte, in Denmark was an investigator sponsored trial. The principal investigator and sponsor of the trial was Dr. Anders Fischer, a recognized specialist in surgical oncology in Demark and the department head of the Dept. of Surgical Gastroenterology at Copenhagen University Hospital in Gentofte, who received a grant to fund the trials provided by the Aase & Einar Danielsen Foundation. Dr. Jacob Rosenberg, a professor and surgeon, working in the Dept. of Surgical Gastroenterology at Copenhagen University and Dr. Mogen Claesson, a director of DanDrit designed the trial and proposed it to Dr. Fischer to act as sponsor and principal investigator. Enrollment of CRC patients started in October 2004 and the study ended in September 2006. Certain DanDrit staff, including Dr. Rosenberg and Dr. Claesson, as well as two other employees of DanDrit Denmark at the time of the study closely collaborated with the researchers at Gentofte Hospital responsible for the day to day work of the study with respect to the study design, analysis and interpretation of data obtained in the Denmark CRC Trial. In addition, the patents and proprietary knowledge of DanDrit and its employees were utilized in connection with the analysis and interpretation of the data that resulted from the study. The results and findings of the trial were published in established scientific journals (Phase I study: J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2006 Jun;25(2):201-6., Phase II study, clinical data: Oncol Rep. 2008 Dec;20(6):1305-11., Immunological data: Acta Oncol. 2009;48(8):1157-64.), which were co-authored by Dr. Rosenberg, Dr. Claesson and the two other DanDrit staff researchers.
The data described in this prospectus with respect to the Copenhagen CRC trial have been obtained from the published papers issued in connection with the study. Twenty patients with advanced colorectal cancer (Dukes D - not curable by resection and no further conventional therapy options available) were included in the study (six patients in phase I and 14 in phase II).
The purpose of this open phase I/II study was to study the tolerability and effect of MCV given as intradermal injections to patients with metastasizing colorectal cancer, where there was no indication for surgery or chemotherapy. The first part was a phase I study to investigate whether treatment with MCV is in any way toxic. No toxicity was observed and the study continued into phase II to study the effect and tolerability of MCV. At the completion of the study stable disease was observed in twenty percent of the enrolled patients. This data was achieved with DanDrit’s early MCV vaccine, which has since been replaced by an improved MCV. The MCV was improved subsequent to the completion of the clinical trials described in this prospectus, but included the addition of aza-cytidine to the DDM-1 culture to de-methylize the genome in order to optimize tumor specific antigen expression. The benefit was marginal and did not justify switching to a different product during the trials. As a result, all trials we will present to the FDA and EMEA will use the same cell line and the same manufacturing process.
| 8 |
Inclusion criteria:
| ● | Age 25-75 | |
| ● | No chemo or radiotherapy within six weeks prior to inclusion | |
| ● | Expected survival > four month |
| ● | Performance status two according to the performing status of WHO | |
| ● | Adequate hepatic and renal function | |
| ● | Adequate hematopoietic and coagulation capacity | |
| ● | Normal EKG or non-clinical significant abnormal EKG | |
| ● | Preserved pulmonary function |
Exclusion criteria for the trial:
| ● | Uncontrolled serious infection | |
| ● | Systemic corticosteroid treatment or other immune suppressive treatment in the last two months | |
| ● | Participation in other clinical trials over the former six weeks | |
| ● | For women, pregnancy or lactation |
Study design: dendritic cells were generated from autologous peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC). In order to increase the level of circulating leukocytes, patients exercised five minutes on a treadmill before 200 ml of blood was drawn. Patients were scheduled for ten vaccinations consisting of 3-5x106 dendritic cells. Vaccinations were given bi-weekly intra-dermally on the proximal thigh with two injections each thigh. Adverse events were monitored and classified according to the National Cancer Institute’s Common Toxicity Criteria (NCI’s CTC). Evaluation of responses was made according to the Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (“RECIST”) criteria and patients were CT scanned before entering the study, after five vaccinations and after ten vaccinations. Quality of life was monitored by questionnaires bi-weekly. The study was performed at the Department of Surgical Gastroenterology at Gentofte University Hospital, Copenhagen, Denmark according to ICH Guidelines for Good Clinical Practice (European Directive on GCP 2001/20/EC).
RECIST is a set of published rules that define when tumors in cancer patients improve ("respond"), stay the same ("stabilize"), or worsen ("progress") during treatments. The criteria were published in February 2000 by an international collaboration including the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (“EORTC”), National Cancer Institute of the United States, and the National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group. Today, the majority of clinical trials evaluating cancer treatments for objective response in solid tumors are using RECIST.
| 9 |
The aim of the phase II CRC study in Denmark was to evaluate the effect of treating patients with advanced colorectal cancer with a cancer vaccine based on dendritic cells pulsed with an allogenic tumor cell lysate. Twenty patients with advanced colorectal cancer were consecutively enrolled, with 17 completed the full study. Dendritic cells (DC) were generated from autologous peripheral blood mononuclear cells and pulsed with allogenic tumor cell lysate containing high levels of cancer-testis antigens. Vaccines were biweekly administered intra-dermally with a total of 10 vaccines per patient. CT scans were performed and responses were graded according to the RECIST criteria. Quality of life was monitored with the SF-36 questionnaire. Four patients of the 17 were graded with stable disease, two of whom remained stable throughout the entire study period. Analysis of changes in the patients’ quality of life revealed stability in the sub-groups: “physical function” (p=0.872), “physical role limitation” (p=0.965), “bodily pain” (p= 0.079), “social function” (p=0.649), “emotional role limitation” (p=0.252) and “mental health” (p=0.626). The median survival from inclusion was 5.3 months (range 0.2 - 29.2 months) with one patient still being alive almost 30 months after inclusion in the trial. Toxicity and adverse events were graded according to the National Cancer Institute’s common Toxicity Criteria. At the first evaluating CT scan, four patients were categorized with stable disease and at the second evaluating CT scan two of these patients still had stable disease and one of them received additional monthly vaccines because of the remaining stability in the disease. DanDrit determined that treatment with this DC-based cancer vaccine was safe and non-toxic. Stable disease was found in 24% (4/17) of the patients participating in the full study. The quality of life remained stable for most categories stable throughout the study period. Stable disease is defined as a tumor that is neither growing nor shrinking. Stable disease also means that no new tumors have developed and that the cancer has not spread to any new regions of the body (the cancer is not getting better or worse) and quality of life, measured using a global health score, was at the baseline with no or minimal variation. Variations in the patients' self-reported quality of life during the study period, assessed by the SF-36 questionnaire, were estimated using Freidman's statistical analysis. There were no significant variation in the patients' ‘physical function’ (p=0.872), ‘physical role limitation’ (p=0.965), ‘bodily pain’ (p=0.079), ‘social function’ (p=0.649), ‘emotional role limitation’ (p=0.252) and ‘mental health’ (p=0.626). There was a significant variation concerning ‘general health perception’ (p=0.006) and ‘vitality’ (p=0.011).
Primary endpoints of the study were tumor response according to RECIST criteria and quality of life (Burgdorf SK, Fischer A, Myschetzky PS, Munksgaard SB, Zocca MB, Claesson MH, Rosenberg J. Clinical responses in patients with advanced colorectal cancer to a dendritic cell based vaccine. Oncol Rep. 2008 Dec;20(6):1305-11. PubMed PMID:19020707) and secondary endpoints for the study were responses measured by immunological parameters (Burgdorf SK, Claesson MH, Nielsen HJ, Rosenberg J. Changes in cytokine and biomarker blood levels in patients with colorectal cancer during dendritic cell-based vaccination. Acta Oncol. 2009;48(8):1157-64. doi:10.3109/02841860903099964. PubMed PMID: 19863224).
A measure of quality of life for the colorectal cancer trial in Denmark, DanDrit used the SF-36 Global Health Score questionnaire to evaluate the patients' quality of life throughout the study period. At the time of the trial, this questionnaire from the Medical Outcome Study (MOS), conducted by the RAND Corporation, was both recommended and validated. All patients in the trial independently filled in the questionnaire every two weeks. The SF-36 Global Health Score questionnaire consists of eight scaled scores, which are the weighted sums of the questions in their section. Each scale is directly transformed into a 0-100 scale on the assumption that each question carries equal weight. The lower the score is the more disability is reported by the patient. Higher scores reflect less disability i.e. a score of zero is equivalent to maximum disability and a score of 100 is equivalent to no disability. The eight different aspects of quality of life reflecting different aspects of the patient’s self-reported quality of life are:
| ● | vitality | |
| ● | physical functioning |
| ● | bodily pain | |
| ● | general health perceptions | |
| ● | physical role functioning | |
| ● | emotional role functioning | |
| ● | social role functioning | |
| ● | mental health |
The fact that patients' SF-36 Global Health Score was high signifies that when entering the study the patients’ quality of life was comparable to the healthy background population. The fact that it remained stable signifies that there were no significant changes in the patients’ quality of life during treatment. This correlates with the fact that the treatment was well tolerated by all patients and that investigators did not observe severe adverse effects from the treatment.
| 10 |
A more in depth analysis of the components of the patients’ quality of life revealed a stability in certain parameters that measure quality of life. The “p” refers to the p-value. In a statistical test, the p-value is the probability of getting the same value for a model built around two hypotheses, one is the "neutral" hypothesis, and the other is the hypothesis under testing. In the Friedman analysis that was used for QOL testing in this study, a p-value below 0.05 means that the values varied throughout the observation period (but says nothing about increase or decrease). A p-value above 0.05 means that the QOL values were stable throughout the observation period.
The graph below indicates the specific p-values of “general health perception” and “vitality” throughout the study:

The Company does not believe that any significant information can be inferred from the variation observed, even if statistically significant, with respect to these two parameters as it would have been anticipated that these extremely sick patients with a progressive disease would have resulted in variations in QOL over the course of the study. For this same reason, it is, however, more significant that 6 of the 8 parameters showed stability as it can be inferred that the treatment had a positive impact on the QOL of patients.
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in Denmark
DanDrit sponsored and funded this MCV clinical trial conducted at Herlev Hospital, University of Copenhagen, in Denmark by Quintiles A/S (“Quintiles”) and ACRO Nordic A/S (“ACRO”) as contract research organizations (CROs). The title of the study is: “Vaccination with Autologous Dendritic Cells Pulsed with Allogeneic Tumor Lysate (MelCancerVac) for the Treatment of Patients with Advanced or Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer”. The principal investigator was Dr. Anders Mellemgaard, the head of the Department of Lung Medicine at Herlev Hospital. Dr. Claesson and three other DanDrit employees worked and collaborated with the researchers at the Herley Hospital with respect to study design and the analysis and interpretation of data obtained from the NSCLC Trial. The results of the trial were published in a recognized scientific journal (World Journal of Vaccines, 2013, 3, 68-76) in a paper that was co-authored by Dr. Claesson and the three other DanDrit employees that collaborated with the NSCLC Trial researchers.
The NSCLC trial was designed as an open-label, phase II clinical study. Enrolled patients had disseminated, inoperable NSCLC after chemotherapy; the patients did not want further chemotherapy: and no other systemic treatments could be offered to them.
| 11 |
The primary objective was to measure the antigen specific immunological reaction between vaccine antigens and the patients’ immune system in vivo and in vitro. The secondary objectives were to estimate the patients’ survival time, the tumor response according to RECIST criteria, and the patients’ quality of life during the study period. Primary endpoint was tumor response, assessed by clinical benefit rate, the percentage of patients with advanced or metastatic cancer who have achieved complete response, partial response and stable disease to a therapeutic intervention in clinical trials of anticancer agents (CBR), however the study also evaluated PFS and overall survival (OS) as secondary endpoints. Complete response (CR) is a figure representing the percentage of patients whose cancer disappears after treatment. Partial response (PR) is a figure representing the percentage of patients whose cancer shrinks after treatment. PR describes a tumor that has decreased in size by at least 30%. The term stable disease (SD) describes a tumor that is neither growing nor shrinking. SD also means that no new tumors have developed, and that the cancer has not spread to any new regions of the body (the cancer is not getting better or worse). The median overall survival was 7.4 months (95% confidence interval (CI), used to indicate the reliability of an estimate, 4.5-17.5 months). Two patients were still alive at the time of analysis. An exploratory analysis showed that patients with PR and SD had significantly better survival (median, 18.1 months) compared to those with progressive disease (median, 6.2 months; P = .007). Although the median time to tumor progression was short at 2.4 months (95% CI, 1.9-4.1 months), five patients experienced a prolonged PFS of more than 6 months; and two of them (reviewed below) continued to be progression-free at time of analysis (PFS >27 and >37 months).
The first patient was included in January 2007. A total of 28 patients were included in the trial. Treatments prior to DC vaccinations, tumor histology, smoking status, number of vaccinations, age and gender were recorded. The median age was 58.5 years (46-74 years). All patients received systemic anti-cancer treatment prior to inclusion. At the time of inclusion, 15 patients were in performance status (PS) 0 and seven patients were in PS 1. Fifteen months after termination of the trial, 4 patients (patient number 1, 2, 12 and 13) were still alive. These four patients who remained in stable disease after more than 10 vaccinations had different histology subtypes: one broncho-alveolar carcinoma, one squamous cell carcinoma and two adenocarcinoma. In this Phase II trial a 43% CBR (the percentage of patients with advanced or metastatic cancer who have achieved CR, PR and SD to a therapeutic intervention in clinical trials of anticancer agents) was observed, with six patients showing stable disease. Five of these patients were immunologically responding to the vaccine (ELISPOT –IFN Gamma positive) while eight of nine patients with no clinical response had no IFN gamma response. Sixteen patients received at minimum six vaccines and were evaluated by CT scans. Of those, nine patients showed progression on the 1st evaluation CT scan three months after initiation of treatment, and seven patients had stable disease, representing a 43% CBR. For these 7 patients remaining in stable disease (SD) for a variable period of time, the overall survival curve showed a plateau after two years.
In this NSCLC trial, quality of life was measured by self-administered questionnaire using EORTC Quality of Life Questionnaire (QLQ)-C30 version 3 and QLQ-LC13. The QLQ-C30 is composed of both multi-item scales and single-item measures. These include five functional scales, three symptom scales, a global health status/quality of life scale, and six single items. Each of the multi-item scales includes a different set of items - no item occurs in more than one scale. All of the scales and single-item measures range in score from 0 to 100. A high scale score represents a higher response level. Thus, a high score for a functional scale represents a high/healthy level of functioning, a high score for the global health status/quality of life represents a high quality of life, but a high score for a symptom scale/item represents a high level of symptomatology/problems. Version 3.0 is currently the standard version of the QLQ-C30, and should be used for all new studies. An essential component of the EORTC QLQ development strategy involves the use of cancer-specific supplementary questionnaire modules which, when employed in conjunction with the QLQ-C30, can provide more detailed information relevant to evaluating the quality of life in specific patient populations. The additional QLQ-LC13 questionnaire is specifically designed for lung cancer patients. The QLQ-LC13 includes questions assessing lung cancer-associated symptoms (cough, hemoptysis, dyspnea and site specific pain), treatment-related side effects (sore mouth, dysphagia, peripheral neuropathy and alopecia) and pain medication. The questionnaire was filled by the patients at baseline, and by the time of the 5th, 6th, 7th, 8th, 9th and 10th vaccinations. The data from the quality of life questionnaires was collected and coded according to EORTC. An overall evaluation of general quality of life-score for the global question of “How do you rate your overall quality of life during the past week” remained stable throughout the study period. More specific factors such as anxiety and lung specific symptoms also remained unchanged during the study-period.
The NSCLC trial in Denmark evaluated the clinical and immunological effects of dendritic cell (DC) vaccination in patients with NSCLC. Autologous DCs were pulsed with a MAGE containing allogenic melanoma cell lysate (MCV). Twenty-two patients initiated the vaccination program including a total of ten vaccinations. Seven patients remained in SD three months after the first vaccination. After 10 vaccinations, six months after vaccine initiation, four patients still showed SD and continued vaccinations on a monthly basis. These four patients received a total of 12, 16, 26 and 35 vaccinations, respectively. Five patients showed unexpectedly prolonged survival. The treatment was well tolerated and only minor adverse events were reported. Quality of life did not change during the study period. In four out of seven patients with SD, vaccine-specific T cells were detected by interferon gamma (IFNγ) (a small protein that plays a role in immunity against infections and for tumor control mostly by activating microphages) Elispot assays, whereas only one patient with progressive disease (PD) showed vaccine-specific responses. This DC-based vaccine trial has indicated a correlation between vaccine-specific immunity and sustained SD. The finding of a significant correlation between prolonged disease stabilization and vaccine-specific cellular responses may support the latter notion and support the hypothesis that immune responses may play a role in disease control even long time after the actual treatment. This is in sharp contrast to the rapid effect of anti-cancer treatments such as chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Furthermore, the trial demonstrated an unexpectedly prolonged survival in some patients, which may indicate delayed effect of DC vaccination after completion of the treatment. In addition, the investigators reported that this kind of vaccine treatment was feasible and the logistics were manageable in this patient group.
| 12 |
In conclusion, 7 out of 22 NSCLC patients vaccinated with autologous DC pulsed with an allogenic Clinical Trial Authorization (CTA) containing tumor cell lysate had prolonged disease stabilization. In the course of DC vaccination vaccine-specific IFNγ responses were detected in peripheral blood of four of patients with SD and one patient with progressive disease. However, from this study it is not possible to conclude whether the vaccine treatment and the subsequent IFNγ responses are involved in the clinical cause of these patients. To elucidate the full efficacy of vaccine treatment of patients with NSCLC, the investigators recommended that a randomized trial should be conducted.
Colorectal Cancer (CRC) in Singapore
A single arm phase II clinical study was also sponsored and funded by the Singapore National Cancer Centre (NCC) to investigate the efficacy of intradermal vaccination with MCV in patients with advanced colorectal cancer. The principal investigator of the Singapore CRC Trial was Dr. Han Chong Toh, a recognized specialist in medical oncology in Singapore. While Dandrit Denmark was not sponsor of the trial, it assisted in the design and proposal of the trial to the SNCC and Dr. Toh. Dr. Claesson and two other DanDrit employees collaborated with the researchers at the Singapore National Cancer Center, with respect to the study design and the analysis and interpretation of data obtained from the Singapore CRC Trial. The results and findings of the Singapore CRC trial were published in recognized scientific journals (Clinical results: Clin. Cancer Res. 2009 Dec 15;15(24):7726-7736., Immunological data: Vaccine. 2009 Dec 11;28(2):542-7.) that was co-authored by Dr. Claesson and the two other employees of DanDrit Denmark that collaborated with the researchers at the NCC in Singapore.
The study used DanDrit’s patented procedure for generating dendritic cells. All included patients had tumors which antigenically correlated with the vaccine, i.e. were MAGE-A positive. The purpose of the study was to investigate the objective efficacy and specific immunologic response of the MCV vaccination. The first patient was enrolled in June 2005, and by June 2007 a total of 20 patients had been treated and evaluated.
The vaccine was given to advanced colorectal cancer patients pre-treated with chemotherapy, where there was no further indication for surgery or treatment with chemotherapy.
Treatment with MCV did not appear to adversely affect the patient’s quality of life, measured based on a global health score of 68.3 prior to treatment with minimal variation through the course of the treatment. The health-related quality of life assessment quantifies how the individual's well-being may be affected over time by a disease, such as cancer. Health-related quality of life is assessed using patient questionnaires. These questionnaires are multidimensional and cover physical, social, emotional, cognitive, work- or role-related and spiritual aspects, as well as a wide variety of cancer related symptoms, therapy induced side effects, and the financial impact of cancer. The questionnaire from the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) is most commonly used to evaluate the impact of cancer on sufferers. MCV induced objective responses in seven of 20 patients (six responses were stable disease and one response was partial regression of tumor mass). Significant immunological and clinical correlation was observed. Results from the trial were presented orally at the AACR meeting in Singapore in November 2007.
The CRC trial in Singapore evaluated the efficacy and toxicity of MCV in advanced colorectal cancer patients expressing at least one of six MAGE-A antigens. Dendritic cells were cultured from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and pulsed with allogenic lysate and matured using cytokines to achieve high CD83 and CCR7 expressing dendritic cells. Each patient received up to 10 intradermal vaccinations (3-5 x 106 cells/dose) at biweekly intervals. Twenty patients received a total of 161 vaccinations. Treatment was well-tolerated with minimal adverse events. Quality of life measurement using global health score was high at baseline and did not change during the duration of the trial. In this study, statistical testing was done with repeated t-tests comparing baseline with each time point. A “t-test” is a statistical analysis used to determine whether there is a statistical difference between averages or means of a group with a small sample size. The “baseline” is a starting point from which a comparison can be made and is typically established prior to the beginning of a study as a point of comparison for monitoring and evaluating data at various point in a study. The term “ comparing baseline with each time point ” refers to the comparison of data at a defined point in time against the originally established “baseline”.
| 13 |
Since the p-values did not change during the duration of the trial, we believe that there were no statistical differences regarding quality of life in this study in any of the parameters at any time points.
The colorectal cancer patients who are eligible for the humanitarian program in Singapore must present a profile similar to the one of the patients who were recruited in the phase IIa clinical trial. However, there have been some exceptional cases where treatment has been based on a doctor’s discretion on the patient’s quality of life. Also, patients are monitored according to the previous phase II study protocol. To date we have not received a detailed report regarding the final outcomes for patients participating in the Singapore trials.
MAGE-A-expressing metastatic colorectal cancer patients with prior progressive disease treated with MCV achieved a competitive Clinical Benefit Rate of 40%. While patients with single metastatic sites in either lung or nodal regions tended to have more durable responses (see patients 1, 2 and 9 in table below), Stable Disease was also attained in patients with bulky multiple metastases (see patient 6 in table below). Five patients notably remained progression-free for over six months and two patients with significant tumor burden (see patients 1 and 9 in table below) were still progression-free for over 27 and 37 months respectively. We recognize that adopting the primary endpoint of Clinical Benefit Rate using RECIST criteria has limitations. This study protocol was designed in 2005 where objective response rate (ORR) and Clinical Benefit Rate evaluation as primary endpoints in Phase II cancer vaccine trials were not uncommon. Nevertheless, the investigators did evaluate Progression Free Survival and Overall Survival as secondary endpoints, which may better reflect true vaccine efficacy.
A meta-analysis of 32 cancer vaccine clinical studies in patients with advanced colorectal cancer reported a Clinical Benefit Rate in 11.2% of patients and an overall response rate (Complete Response and Partial Response) of 0.9%. The defined clinical benefit rate (Complete Response, Partial Response, Stable Disease) was observed in 17% (12/70) of colorectal cancer patients who received Dendritic Cell vaccines.
Patients’ Characteristics
| ID | Age
(years) |
Sex | PS | Site of disease | No.
of Chemo-regimens |
Disease at Accrual | No. of vaccinations | BOR | Time to Tumor response (months) | Duration of response (months) | TTP
(months) |
Survival Time (months) | ||||||||||||||
| 1 | 72 | F | 1 | LN | 1 | PD | 10 | SD | 2.7 | > 25.0 | * | > 27.7 | * | 39.7 | † | |||||||||||
| 2 | 67 | F | 1 | Lung | 0 | PD | 10 | SD | 2.9 | 4.2 | 7.1 | 35.6 | ||||||||||||||
| 3 | 53 | F | 2 | Lung, LN, Pelvic, Bone | 4 | PD | 10 | SD | 1.7 | 5.2 | 6.9 | 6.9 | ||||||||||||||
| 4 | 43 | F | 1 | Lung, Adrenal, LN | 4 | PD | 3 | PD | - | - | 2.6 | 5.9 | ||||||||||||||
| 5 | 54 | M | 1 | Liver, Lung, Ascites, LN | 3 | PD | 3 | ND‡ | - | - | > 3.8 | ‡ | 3.8 | ‡ | ||||||||||||
| 6 | 76 | M | 0 | Liver, Peritoneum, Pelvic, Lung, LN, Serosa | 3 | PD | 10 | SD | 1.8 | 2.4 | 4.1 | 7.6 | ||||||||||||||
| 7 | 33 | F | 1 | Bone | 2 | PD | 9 | PD | - | - | 2.0 | 6.5 | ||||||||||||||
| 8 | 75 | F | 0 | Lung | 0 | PD | 10 | PD | - | - | 1.9 | 13.1 | ||||||||||||||
| 9 | 62 | F | 1 | LN, Lung and Pelvic | 3 | PD | 10 | PR | 2.5 | > 35.4 | * | > 37.9 | * | 37.9 | † | |||||||||||
| 10 | 73 | M | 0 | Liver, LN | 2 | PD | 10 | PD | - | - | 2.1 | 19.6 | ||||||||||||||
| 11 | 64 | M | 0 | Liver | 1 | PD | 10 | PD | - | - | 2.1 | 6.4 | ||||||||||||||
| 12 | 57 | M | 1 | Lung, Liver, LN | 2 | PD | 10 | PD | - | - | 2.3 | 7.5 | ||||||||||||||
| 13 | 65 | F | 1 | LN, Pleural, Lung, Liver | 5 | PD | 5 | PD | - | - | 1.6 | 2.9 | ||||||||||||||
| 14 | 49 | M | 1 | Lung, Liver, Peritoneum | 5 | PD | 8 | SD | 2.3 | 1.2 | 3.5 | 7.2 | ||||||||||||||
| 15 | 72 | M | 0 | LN, Pleural, Liver, Lung | 2 | PD | 4 | PD | - | - | 1.8 | 3.2 | ||||||||||||||
| 16 | 77 | M | 1 | Liver, Bone, Lung | 4 | PD | 10 | SD | 1.6 | 1.9 | 3.5 | 13.0 | ||||||||||||||
| 17 | 75 | F | 0 | Lung, Liver | 1 | PD | 10 | PD | - | - | 1.9 | 17.5 | ||||||||||||||
| 18 | 54 | F | 0 | LN, Lung | 1 | PD | 10 | SD | 1.8 | 4.9 | 6.7 | 23.2 | ||||||||||||||
| 19 | 75 | M | 0 | Lung, Liver, | 2 | PD | 3 | PD | - | - | 2.0 | 2.9 | ||||||||||||||
| 20 | 41 | F | 1 | Lung, Skin, LN, Bone | 5 | PD | 6 | PD | - | - | 1.9 | 4.5 |
* Indicates that the patient has not progressed at the time of analysis.
† Patients who are alive at the time of analysis have their survival time censored at the time of last follow up.
‡ Patient withdrawn due to poor performance status; survival time was censored at last date in the study.
Abbreviations: PS, performance status according to Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group; CT, chemotherapy; RT, radiotherapy; BOR, best overall response; TTP, time to tumor progression; LN, lymph node; F, female; M, male; SD, stable disease of at least 4 weeks; PD, progressive disease; ND, CT scan not done; PR, partial response.
| 14 |
ECOG PERFORMANCE STATUS
| ||
| Grade | ECOG | |
| 0 | Fully active, able to carry on all pre-disease performance without restriction | |
| 1 | Restricted in physically strenuous activity but ambulatory and able to carry out work of a light or sedentary nature, e.g., light house work, office work | |
| 2 | Ambulatory and capable of all self-care but unable to carry out any work activities. Up and about more than 50% of waking hours | |
| 3 | Capable of only limited self-care, confined to bed or chair more than 50% of waking hours | |
| 4 | Completely disabled. Cannot carry on any self-care. Totally confined to bed or chair | |
| 5 | Dead | |
As of 2006, there were a total of eight clinical DC vaccination studies in patients with metastatic colon cancer, all with peptide-pulsed DC. To our knowledge, this study which adopted an allogenic tumor lysate-based DC vaccine achieves the highest Clinical Benefit Rate in advanced colorectal cancer patients compared to these previous Dendritic Cell vaccination clinical trials. The clinical activity of this present Dendritic Cell-based vaccine might reflect its polytopic nature, its allogenic adjuvant-like components, the quality of the Dendritic Cell preparation (i.e. high uniform expression of CD83, CD86, HLA class II, and CCR7), the intradermal route of vaccine injection securing optimal lymph drainage to regional lymph nodes, the presence of MAGE expression in both patients and vaccine and the increased frequency of delivery (ten injections).
Quality of life measurement using global health score was high at baseline and did not vary much across time. In this study, statistical testing was done with repeated t-tests comparing baseline with each time point., Since the p. values did not vary across time, we believe that there were no statistical differences regarding quality of life in this study in any of the parameters at any time points.
| 15 |
Treatment with MCV did not appear to adversely affect the patient’s quality of life, measured based on a global health score of 68.3 prior to treatment with minimal variation through the course of the treatment. The health-related quality of life assessment quantifies how the individual's well-being may be affected over time by a disease, such as cancer. Health-related quality of life is assessed using patient questionnaires. These questionnaires are multidimensional and cover physical, social, emotional, cognitive, work- or role-related and spiritual aspects, as well as a wide variety of cancer related symptoms, therapy induced side effects, and the financial impact of cancer. The questionnaire from the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) is most commonly used to evaluate the impact of cancer on sufferers. MCV induced objective responses in seven of 20 patients (six responses were stable disease and one response was partial regression of tumor mass). Significant immunological and clinical correlation was observed.
Compassionate Use/Named Patient Approval
Further to the data emerging from the Singapore CRC trial, the Singapore government requested and approved (22 September 2008) that named patients be offered MCV therapy at cost. This first compassionate use approval marked a significant milestone for the progress and acceptability of the MCV therapeutic model. This compassionate program could be used as a model to initiate sales of MCV in other countries of the ASEA such as Thailand or Malaysia. Outside the United States, named patient programs provide controlled, pre-approval access to drugs in response to requests by physicians on behalf of specific, or “named”, patients before those medicines are licensed in the patient’s home country. Governments worldwide, such as Singapore’s government, have created provisions for granting access to drugs prior to approval for patients who have exhausted all alternative treatment options and do not match clinical trial entry criteria. Often grouped under the labels of compassionate use, expanded access, or named patient supply, these programs are governed by rules which vary by country defining access criteria, data collection, promotion, and control of drug distribution. Through these programs, patients are able to access drugs in late-stage clinical trials or approved in other countries for a genuine, unmet medical need, before those drugs have been licensed in the patient’s home country. In September 2008, DanDrit Denmark and the National Cancer Centre of Singapore (NCC) entered a collaboration agreement regarding a clinical named patient program conducted in Singapore at NCC with the dendritic cell vaccine MCV. NCC has established a GMP approved laboratory in which the manufacturing of MCV takes place. NCC has received approval from the relevant governmental authorities for the import of lysate necessary for production of MCV. The clinical and research and development activities of the named patient program relate to the Company’s product, MCV. The purpose for the Singapore named patient program is to provide patients with advanced colorectal cancer or other forms of cancer(s) with the presence of MAGE antigen expression an alternative treatment for the vaccination with MCV, where there is no further indication for surgery or treatment with chemotherapy. Patients are recruited on named patient basis according to the patient inclusion and exclusion criteria stated in the phase II study protocol. However, there may be some exceptional cases where treatment will be made based on a doctor’s discretion regarding the patient’s quality of life.
100% Off-the-Shelve Vaccines
Autologous (from the patient) dendritic cells cancer vaccines are tailor made for each individual patient. This personalized medicine approach is appealing to the patients but may present several drawbacks to a pharmaceutical company. Creating a new, unique vaccine for each patient may be perceived as complex, time consuming, and expensive. Therefore, DanDrit developed MelVaxin™. This program presented below capitalizes on the knowledge and the expertise gained with DanDrit’s proprietary lysate used for MCV but is on hold now.
Melvaxin™
A second platform product, MelVaxin™ has been also evaluated. MelVaxin™ is similar to the lysate component of MCV. DanDrit proposed injecting MelVaxin™ into the skin to promote natural dendritic cell responses that will attack the tumor expressing cancer/testis antigens. It is necessary to inject MelVaxin™ with an immuno-stimulator such as GM-CSF, BCG or an adjuvant (such as 3M’s TLR7 and TLR8 agonists). A preclinical program could be performed in minipigs. These animals have immune response profiles, particularly of skin injection, that are very close to human. This program, currently on hold, can be reinitiated when staff is available to manage this program. This takes second place to the MCV2 program and illustrates DanDrit’s professional commitment to advancing lead clinical products.
| 16 |
Other Future Products
Other cancers
DanDrit has already made progress with clinical trials of NSCLC and CRC. DanDrit is now focusing its clinical development on advanced colorectal cancer, but DanDrit may if opportunity arises extend its range of cancer targets to answer the desperate need for effective new therapies. As an illustration, bladder cancers or esophageal cancers may be such opportunities. The two types of esophageal cancers the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (EC) and the esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC) expressed MAGE -A. Worldwide, EC is the most frequent malignant esophageal cancer accounting for at least 10,000 deaths per year. But in Western countries, EAC is the most rapidly increasing cancer compared with other malignancies. Surgical resection is currently the only potential cure with or without neo-adjuvant or adjuvant chemo-and/or radiotherapy, the five year survival rate is less than 20%. At first presentation, approximately 50-60% of patients with esophageal cancer are not eligible for surgery and have a very poor outcome.
Tolerogenic Dendritic Cells
Some dendritic cells seem to instruct cell-killing T cell clones to abandon their mission by self-destructing through an apoptotic pathway. This may offer the possibility of eliminating those T cells responsible for the manifestation of auto-immune disease. In MCV dendritic cells are derived in such a way that the resulting dendritic cells promote an immune reaction. However, dendritic cells may also be derived in such a way that they are tolerogenic, they promote immune tolerance. Promoting immune tolerance can be used to treat autoimmune diseases such as early stage type I diabetes (where insulin secreting cells are still present) or even to help prevent rejection of tissue transplantation. In this way the tolerogenic dendritic cells are used to turn off an undesirable immune reaction. DanDrit has established methods to derive tolerogenic dendritic cells from peripheral blood monocytes, similar to the approach used to generate immunogenic dendritic cells in MCV. Tolerogenic dendritic cells are easily distinguished by their function in vitro. DanDrit has filed patents to cover the generation of tolerogenic dendritic cells.
Non-Core Products – Out-licensing
Non-core patents are being developed for application in dendritic cell related applications that are not cancer-related. We believe that revenues from licensing such non-core products will support core product and core technology development.
The principal non-core intellectual property relates to tolerogenic dendritic cells, their production and application in auto-immune diseases to include type 1 diabetes. DanDrit’s fast track production methods for dendritic cells might be out-licensed for non-competitive applications in areas other than cancer.
Fast-track production of Dendritic Cells
The generation of mature immunogenic dendritic cells from peripheral blood monocytes requires eight days of growth in culture. The efficiency of producing MCV could be improved if the time required to generate dendritic cells could be significantly reduced. DanDrit has tested many protocols for generating dendritic cells quickly. Two promising methods have emerged from intensive research activities to generate dendritic cells in either two days or five days. The fast track methods for generating dendritic cells produce immunogenic dendritic cells that are comparable to cells generated using DanDrit’s standard technique. These fast track methods are covered by DanDrit’s existing dendritic cell technology patent.
This fast-track production technology could be of commercial interest for other companies working in non-competitive areas of dendritic cell technology.
MicroRNAs for dendritic cell quality control
DanDrit patented a method using microRNAs to characterize dendritic cells and establish a basis for quality control. To date there are few dendritic-cell specific antigens and those existing are covered by patents. DanDrit has patented its microRNA approach developed with Bioneer (note that patents are 100% owned by DanDrit).
| 17 |
Proposed Clinical Trial
The proposed Phase III study with an adaptive design plans to enroll 174 stage IV colorectal cancer patients after resection of metastases and chemotherapy. Regulatory authorities in the United States and Europe have published guidance documents on the use and implementation of adaptive design trials. These documents include descriptions of adaptive trials and a requirement for prospectively written standard operating procedures and working processes for executing adaptive trials.
The proposed patients in the trial will therefore have no evidence of disease. The clinical study is designed as a randomized, multicenter, Phase III clinical study. Patients will be included after resection of their primary tumor and metastases in liver and after appropriate peri- or post-operative chemotherapy by random assignment to a non-vaccine control group or a vaccine group receiving five vaccinations with 14-day administration intervals followed by ten vaccines with two-month intervals. Inclusion is planned to take place one month after finishing the last round of peri- or post-operative chemotherapy (FOLFOX or FOLFIRI) and after a negative tumor scan (head, thoracic and abdominal cavities) and normal CarcinoEmbryogenic Antigen (CEA) blood levels prior to inclusion in the vaccine or the control groups. In the event of disease progression, as verified by tumor scan during the vaccination schedule, MCV vaccinations will be discontinued. The table below summarizes the key features of the proposed clinical study.
Traditionally drug development has consisted of a sequence of independent trials organized in different phases. Full development typically involved (1) a learning phase II trial and (2) one or two confirmatory pivotal phase III trial(s). The new seamless phase II/III designs are aimed at interweaving the two phases of full development by combining them into one single, uninterrupted study conducted in two steps. Adaptive seamless clinical trial designs have proved to be effective in several clinical research areas, such as the development of Velcade™ intended for multiple myeloma and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma or a long-acting glucagon-like peptide-1 analog (dulaglutide) in a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study of overweight/obese patients with type 2 diabetes: the EGO study. Adaptive seamless phase II/III designs enable a clinical trial to be conducted in steps with the sample size calculation selected on the basis of data observed in the first step to continue along to the second step. The main statistical challenge in such a design is ensuring control of the type I error rate. Most methodology for such trials is based on the same endpoint being used for interim and final analyses. However, in some settings like our clinical trial, the primary endpoint, overall survival, can be observed only after long-term follow-up. In this case the design includes a shorter term endpoint data, in our case, relapse free survival at 18 months. If short-term data are available for some patients for whom the primary endpoint is not available, basing treatment selection on these data may lead to increase of the type I error rate (false positive).
Phase III Overview
| Purpose | To determine the safety and efficacy of our investigational vaccine in colorectal cancer and to determine its ability to prevent relapse in stage IV colorectal patients with no evidence of disease (after resection and chemotherapy) |
| Study Type | Interventional |
| Study design | |
| Endpoint (primary) | Efficacy : Relapse Free Survival at 18 months; Overall Survival |
| Endpoint (secondary) | Carcino-Embryonic Antigen (CEA); Quality of Life |
| Intervention Model | Parallel assignment 174 patients |
| Allocation | Randomized |
| Adaptive Design | Purpose: seamless Phase II/III clinical trial |
| Treatment | Five vaccines bi-weekly (intra-dermal administration) followed by ten vaccines every two months |
| Location | Italy (and USA) |
| Expected Duration | Three years |
| Eligibility | Stage IV colorectal cancer patients After resection and chemotherapy and no evidence of disease (CT scan and CEA back to normal)
●
Vaccine therapy given after FOLFOX or FOLFIRI (after completion of course of chemotherapy)
|
| Independent data Management Committee | Pr. Axel Grothey (Mayo Clinic, USA) |
| 18 |
Critical Success Factors
The points below are a specific, focused list of critical factors and challenges that need to be considered for the project, during the critical start-up phase and throughout the project life cycle. In addition to the sections noted below, during the course of the study, DanDrit will be pro-active in discussing the Critical Factors with the investigators.
Oncology studies by their nature have a degree of complexity not always encountered in other therapeutic areas. We believe success of the CRC study will be related to these Critical Success Factors. Our approach to each critical factor is detailed below. DanDrit identified the following key factors for success:
| ● | Patient accrual and site selection |
| ● | Assessment of patient response | |
| ● | Study design and collection of patient data | |
| ● | Vaccine supply | |
| ● | Patient safety | |
| ● | Multinational regulatory requirements | |
| ● | CRO previous experience | |
| ● | Adaptive trial design experience |
Patient accrual and site selection
The proposed VIVA clinical trial will enroll 174 patients at 35 GISCAD sites in Italy. Additional patients (number to be estimated based on interim data) will be enrolled from the US.
The selected patient population will be easier to work with than the patients in Phase II. It is reasonable to expect the response rate to be greater for MCV, or for any immunotherapy, in a patient population with minimal residual disease). Consequently, in this Phase III trial, patients will have to be NED, raising the likelihood that the immune system can generate a response against cancer as it re-occurs. We believe this may ultimately lead to better data from the Phase III trial. Careful selection of study sites using evidence based feasibility research, discussion with colorectal key opinion leaders (KOLs), contact with investigators at key sites and our past clinical experience in this indication and with cancer vaccines will be required. The GISCAD Foundation for Research on Cancer (GISCAD) in Italy (Pr. Sobrero) is recognized as among the world’s premier cancer research and treatment facilities and leaders in colorectal cancer research. As an illustration GISCAD conducted recently the TOSCA trial, a clinical trial evaluating FOLFOX-4 3 months vs. 6 Months and Bevacizumab as adjuvant therapy for patients with Stage II/III CRC. The network of Italian hospitals enrolled 3,800 patients in the recent Thiazolidinediones or Sulfonylureas and Cardiovascular Accidents (TOSCA) trial.
Accrual rates are estimates and can be further refined. Inadequate enrollment is one of the biggest drivers of wasted cost and time in clinical trials. Therefore, DanDrit has taken a very conservative position regarding site selection and patient enrollment.
| 19 |
Assessment of patient response
In general, in oncology vaccine studies, the relationship between clinical response, survival (and other measures of efficacy) and immune response may be unclear. Changes in patients’ immunological profiles during vaccination protocols, their response to the vaccine components as measured by delayed-type hypersensitivity (DTH), used as the primary measure of the ability to immunize a patient to a tumor cell or specific tumor antigen; the enzyme-linked immunosorbent spot (ELISPOT), a common method for monitoring immune responses In humans; cluster of differentiation (CD) antigen profiles, protocol used for the identification and investigation of cell surface molecules ; and other strategies to attempt to correlate treatment outcome with the results of vaccination are variable. The paper describing the Phase II study in CRC patients by Toh et al indicates that a plasma protein expression profile has been identified for responding patients. Continued evaluation of immunological profiles of the patients and the collection of these data and correlation with outcomes may be desirable but for this POC study will not be necessary.
In a guidance document by the FDA, “Clinical Considerations for Therapeutic Cancer Vaccines” (September 2009), the agency recognizes that immunological approaches to tumor control may require significant time to develop, and that careful clinical assessment of patients must be performed as well as the use of methods that rely on radiological measurement of tumor size (e.g. RECIST). The guidance indicates that for cancer vaccines, patients may be observed to develop indications of progressive disease based on radiological measurement, but that these indications may also be transient and that tumor regression is still a possibility as the immunological response develops. Methods to incorporate such an approach will help avoid premature termination of study treatment for some patients.
Tumor burden has also been a confounding problem for oncology vaccine development because of tumor-induced immune-suppression in some patients and because of progression prior to immune response. These issues may be obviated in this study of no-evident-disease subjects.
Patient safety
DanDrit believes that MCV appears to be safe and well tolerated in studies to date. Adverse events related to the vaccine appear to be Grade 1-2 and consist of mostly superficial toxicities as describe above. Patients in the proposed study will have recovered from previous treatments and will be apparently disease free: thus, at this time, only general safety precautions and observations related to the patient population are recommended.
Injection site reactions and other toxicities expected in the class of DC vaccines will be included in site training. Some volume of Severe Adverse Events can be anticipated in a population of advanced CRC patients. Discrimination of events related to vaccine against a background of underlying disease and prior chemo or and/or radiotherapy will be necessary.
In addition to reviewing assignment of causality, a independent Data and Safety management Co mittee will assist in the assessment for efficacy.
Regulatory
DanDrit will seek scientific advice from AIFA (Italian agency) and the the European Medicines Agency EMEA (ATMP) in connection with the Phase III trials in Italy. GISCAD provided preparation and assistance for the Scientific Advice process in EMEA including the following activities:
| ● | Regulatory review of pertinent data | |
| ● | Discussions/kick off meeting with DanDrit contact(s), for background, pertinent issues, proposed questions, strategic discussion etc. | |
| ● | Prepare a briefing package for Scientific Advice includes QC using the existing information in the Investigational Medicinal Product Dossier (IMPD)/Investigator Brochure (IB) as the basis for the package | |
| ● | Set up and attend meeting with EU regulatory agency and conduct all associated administrative tasks (letters, post meeting minutes, etc.) |
| 20 |
We are seeking a clinical trial authorization to commence a Phase III trial in Italy which we anticipate will run over a three year period. Ordinarily a drug requires two Phase III trials before it can apply for FDA approval. Consequently the first patient for Phase III could be considered commencement of ‘pivotal’ trials for MCV. Also, DanDrit intends to move to a pivotal trial in China with a Chinese partner. Currently, the China Food and Drug Administration offers a low-cost clinical development pathway for cancer drugs developed, manufactured and commercialized in China. DanDrit intends to file an investigational new drug (IND) application with the FDA to initiate the process to permit manufacturing capability of MCV in the U.S. and to include U.S. patients in the Phase III trials initiated in Italy. Once an IND application has been filed in the U.S., we believe that we will be able to expand the Phase III trials initiated in Europe to the U.S., however we cannot estimate at this time when we will be able to begin enrolling U.S. patients in the trial.
Our Competitive Strengths
We believe our following strengths position us to increase our revenue and profitability:
| ● | Cutting Edge Technology. We believe immunotherapy is one of the waves of the future in cancer treatment. | |
| ● | Colorectal Market Potential. Colorectal cancer is a large market with a well identified unmet medical need for safe maintenance therapy. The clinical data for MCV to date gives the potential for the vaccine to eventually become the standard of care for maintenance therapy. We believe that MCV has the potential to alter the treatment paradigm by prolonging periods of remission after response to chemotherapy. If MCV works as expected in colorectal cancer, we believe it would likely prove beneficial in other tumors that over-express MAGE-A including lung, breast and esophageal cancer. | |
| ● | Regulatory Precedent. Dendreon with Provenge™, its prostate cancer vaccine, pioneered the regulatory pathway for MCV. Dendreon worked with the FDA to develop the protocols allowing a cellular therapy such as MCV to be approved for clinical use. DanDrit could be the next generation of dendritic cell vaccine with several improvements over its competition: stimulate a cellular immune response rather than just an antibody response, no need for leukapheresis to produce the vaccine, intradermal administration, convenience of an allogenic vaccine, polytopic approach but with a focus on the MAGE-A antigen family and reliable manufacturing. | |
| ● | Successful Use in Singapore. The Singapore National Cancer Center have provided MCV to colorectal cancer patients within an on-going compassionate use program in Singapore. Based on that experience, DanDrit is seeking a potential collaboration with a Chinese oncology pharma partner that may speed up large scale commercialization of MCV. | |
| ● | Strong IP Protection. The technology is patented with a long patent life. DanDrit owns 100% of the technology, without intellectual property issues. |
Our Strategy
Our strategy is focused on conducting the VIVA clinical trial in advanced colorectal cancer that may trigger a partnership deal that, if successful, should bring a significant return on investment (based on analysis of past acquisitions of peer cancer vaccine companies).
DanDrit intends to conduct a randomized multicenter clinical trial to determine the ability of MCV to prevent recidivism in stage IV colorectal patients with no evidence of disease after surgical resection of metastasis and chemotherapy. The same need for a safe effective maintenance therapy exists for stage III colorectal cancer patients with no evidence of disease after resection.
| 21 |
This VIVA trial is planned to be completed within three years in Italy. DanDrit’s management is confident that upcoming clinical data will be the catalyst to unlock commercial revenues for DanDrit through either acquisition by pharmaceutical partner or licensing deals that would yield upfront and milestone payments as well as royalties.
We are also considering a registration trial to support potential approval of MCV in China. This trial would be conducted under China Food and Drug Administration regulations with a Chinese oncology pharmaceutical partner, such as the TASLY Group or 3S Bio. Contacts with 3S Bio and the TASLY Group have already been initiated. China has recently put in place a drug approval system that includes a low-cost first clinical approval pathway especially for Chinese biotechnology companies. The approval for local biotechnology players is advantageous, since costs for a pivotal clinical trial in China are estimated at one tenth of EU or U.S. costs. Therefore, we plan to collaborate with a Chinese company such as the TASLY Group to develop, manufacture and sell MCV in China. Several factors are also making a partnership with a Chinese pharmaceutical company attractive:
| ● | For registration, the clinical trial can only be performed in sites approved by the China Food and Drug Administration. | |
| ● | Screening for MAGE-A could be attractive to the China Food and Drug Administration, but tumor samples could not be shipped outside of China for genomic testing. Therefore a partner who can perform MAGE-A screening in China is valuable. |
In addition, the China Food and Drug Administration relies more than other agencies on risk benefit assessment. Risk benefit assessment in China remains the “heart” of determining the value of products and is a more favorable assessment approach to MCV as the vaccine is, thus far, well tolerated with what DanDrit believes to be a strong safety profile (due to dendritic cell technology).
Furthermore, due to high unmet medical need, the approval for cancer drugs is also more favorable than in other regions of the world. Because cancer is the first cause of mortality in China, the approval process for oncology drugs benefits from easier rules than those that govern drugs targeting other diseases. The State Food and Drug Administration (the predecessor of China Food and Drug Administration) granted 114 CTA approvals for oncology global/regional trials from 2005 to 2010. Generally, in order to approve a cancer drug in China:
| ● | Usually only one pivotal study is required | |
| ● | With only 100 to 800 patients (most likely 300 patients) | |
| ● | An open-label study design is accepted (without placebo control) | |
| ● | The statistical consideration are also attractive as relatively low statistical significance (P value 0.03~0.05) is required | |
| ● | Overall additional flexibility exists for oncology drugs, driven by the benefit/risk ratio |
Furthermore, a special review and approval procedure applies to oncology drugs. The review and approval procedure could shorten the review time and can enhance communication with the China Food and Drug Administration. By the end of 2010, 28 drugs obtained approval, and more than half were oncology drugs (ten chemical drugs, and five biologics).
We believe that it is important to take advantage of this development opportunity quickly as the paradigm for oncology drug development is changing rapidly in China:
| ● | There is an unprecedented number of anti-cancer therapies in development and the standard of care changes quickly | |
| ● | The complexity of information concerning tumor genetics and signaling pathways is growing and will bring greater opportunities for personalized medicine |
| 22 |
Industry
DanDrit’s lead products for NSCLC and CRC address about 40% of all cancer deaths. Other important cancers include Breast (8% of deaths), Prostate (6% of deaths) and Pancreas (6% of deaths). Together these top 5 cancers are responsible for 60% of all cancer deaths.
Cancers Incidence and MortalityWorld (source GLOBCAN 2012
| WORLD | Male | Female | Both sexes | |||||||||
| Population (thousands) | 3,557,717 | 3,496,728 | 7,054,446 | |||||||||
| Number of new cancer cases (thousands) | 7,410.4 | 6,657.5 | 14,067.9 | |||||||||
| Age-standardised rate (W) | 204.9 | 165.2 | 182.0 | |||||||||
| Risk of getting cancer before age 75 (%) | 21.0 | 16.4 | 18.5 | |||||||||
| Number of cancer deaths (thousands) | 4,653.4 | 3,548.2 | 8,201.6 | |||||||||
| Age-standardised rate (W) | 126.3 | 82.9 | 102.4 | |||||||||
| Risk of dying from cancer before age 75 (%) | 12.7 | 8.4 | 10.5 | |||||||||
| 5-year prevalent cases, adult population (thousands) | 15,296.1 | 17,159.1 | 32,455.2 | |||||||||
| Proportion (per 100,000) | 589.4 | 660.5 | 625.0 | |||||||||
| 5 most frequent cancers (ranking defined by total number of cases) | ||||||||||||
| Lung | Breast | Lung | ||||||||||
| Prostate | Colorectum | Breast | ||||||||||
| Colorectum | Lung | Colorectum | ||||||||||
| Stomach | Cervix uteri | Prostate | ||||||||||
| Liver | Stomach | Stomach | ||||||||||
There were 14.1 million new cancer cases, 8.2 million cancer deaths and 32.6 million people living with cancer (within 5 years of diagnosis) in 2012 worldwide.. Cancer is still the main cause of death in developed countries – accounting for ~33% of death and remains an area of huge unmet medical need. The cancer market has a high growth potential for the coming years with an expected 7% annual growth rate for the years 2011- 2018. The American Cancer Society disclosed that there were 1,638,910 new cancer cases in the US for 2012 with 577,190 associated deaths.
In Europe the number of new cancer cases for 2012 was estimated at 3.45 million with a 1.75 million deaths. The cancer market is the fastest growing pharmaceutical market with $83 billion expected growth of the cancer drug market by 2020.
The per-treatment price of chemotherapy for CRC is approximately $30,000. We expect that, if our vaccine is approved for use in CRC patients, the cost per-treatment will be approximately equal to the per-treatment cost of chemotherapy.
Due to its safety profile, MCV should fit easily into the treatment paradigm of most cancers. The initial label of adjuvant therapy for stage IV colorectal cancer with no evidence of disease after surgical resection of metastases could be a door opener for the larger colorectal cancer market. DanDrit’s pharmaceutical partner should be able to grow the label to the larger adjuvant for stage III colorectal cancer market.
| 23 |
Colorectal Cancer
The figure below presents the market opportunity for MCV in advanced colorectal treatment.
Despite numerous therapeutic advances, colorectal cancer continues to be associated with one of the worst survival rates of all cancers. Metastatic liver disease is found in 10% to 25% of patients having surgery for primary colorectal cancer instead of liver metastasis are detected in 40-50% of patients with diagnosed colon cancer . Then, standard of care “treatment” for colorectal cancer patients after resection surgery and chemotherapy is only observation. When surgical resections of liver metastases are possible, as in 20% of the affected patients, five years survival may approach 35%. According to the most recent papers, the median RFS in patients receiving combined surgery and chemotherapy with No Evidence of Disease is 24-26 months. The same need for a safe effective maintenance therapy exists for stage III colorectal cancer patients with no evidence of disease after surgical resection and chemotherapy.
We believe that it is of great importance for colorectal cancer patients receiving surgery alone or surgery combined with peri- or post-operative chemotherapy, that new and more effective therapies are developed and offered in the post-treatment period. The aim of the proposed trial is to study whether our lead vaccine can increase the progression-free survival for these patients.
Licensing Potential and Cooperation Agreements
The following discussion represents opportunities that we believe can expand the use of our technology.
Alliance with Chinese Company
In addition of the size of their national market, Chinese biotech firms currently benefit from a low cost first clinical development path. The Chinese approval process is favorable for local biotechnology companies. With a Chinese partner, we plan to conduct a Phase III trial in China for lower costs than in the U.S. and at a faster pace. A successful Phase III trial could result in large scale commercialization in China and Southeast Asia.
Furthermore, the domestic market in China for cancer therapies is expected to grow due to a large aging population, expanded insurance coverage, higher government healthcare spending, rising disposable incomes and the high incidence of cancer among the population. In spite of recent price cuts, we believe that the market for cancer therapies in China represents a long-term opportunity based on the factors set forth above.
It has been estimated that almost 4 million Chinese — out of a total population of 1.35 billion — develop cancer every year, and nearly 3 million die from the disease annually. In China, cancer is now the leading cause of mortality.
Although China has less than 20% of the world’s population, it accounts for more than 25% of global cancer deaths. The majority of cancers in China are now caused by unhealthy diets, increased alcohol consumption, sedentary lifestyles, obesity, smoking and environmental pollution. A rapidly aging population will further increase China’s cancer burden.
China’s population is becoming wealthier and more urbanized — meaning that more Chinese are looking for greater access to medical care and are demanding better quality medical products and services. By 2025, China’s urban middle class population is expected to represent almost 70% of the country’s total population.
| 24 |
Alliance Strategy
In addition to its lead compound MCV, DanDrit has built a pipeline of dendritic cell based cancer therapies, currently addressing 40% of all cancer-related deaths. MCV can be indicated to cancers over-expressing MAGE-A. Cancers over-expressing MAGE-A include among others, lung cancer, colorectal cancer, breast cancer, and esophageal cancers. DanDrit intends to work with strategic partners to strengthen the in-house pipeline.
We control key technologies with relevance outside our core business area and these we may out-license or co-develop with suitable partners.
MyTomorrows
In December 2013, DanDrit entered an agreement with MyTomorrows (“MT”), a Dutch company, regarding a Patient Name Use Program (PNU) for MCV. This program will allow DanDrit to sell MCV for one year of treatment (10 vaccines) to cancer patients through MT. MT offers a worldwide online platform providing access to non-registered medicines for patients with life threatening diseases.
MT is a turnkey solution and will be in charge of regulatory, recruitment, logistics, and pharmacovigilance. DanDrit’s potential liabilities are limited to quality control of cGMP manufacturing of MCV. DanDrit expects several benefits from this agreement. First,DanDrit anticipates minor short term revenue generation as MT will transfer payment as soon as a patient orders MCV. DanDrit also anticipates that this program may contribute to lowering the cost of manufacturing of the clinical lot through economy of scale. Finally, this program may also generate real life data for MCV.
Manufacturing
In 2012, DanDrit has out-sourced the GMP manufacturing of its lysate. We believe that proving that our technology transfer was possible was a key step in finding and working with a future pharmaceuticals partner. DanDrit evaluated several possible EU-based contract manufacturing organizations (CMOs) and selected Cellin Technologies, a CMO based in Tallin, Estonia. The collaboration with Cellin Technologies in Estonia demonstrated that GMP production of lysate could not only be transferred but that the production could be scaled up. We consider that the potential economy of scale that can be expected in the cost of lysate production could become a competitive advantage versus other cancer vaccine companies using recombinant production of cancer-specific antigens (i.e. Mage-A3 from GSK). Also, the collaboration with the Estonian CMO is based on a pure fee-for-services basis and can be discontinued at any time without notice.
DanDrit intends to establish a closed fully automatized manufacturing process. We learned from the Dendreon’s experience that an efficient manufacturing process should be in place before approval for commercialization. Cost saving should be expected from a fully automatized vaccine production. We also assume that a fully efficient manufacturing process may increase the value of a deal with a pharmaceutical partner.
Cell Banking
The melanoma cell lines used by DanDrit in the production of our lysate (MCL) are stored at ultra-low temperature in liquid nitrogen at Symbion Science Park, Copenhagen, Denmark. Both master- and working cell banks are stored this way and the contents of the cell banks (both master and working) are recorded in log books. Nitrogen levels are maintained by the staff of DanDrit Biotech at least once a week and any activity in regards to storage (shipment of cells, nitrogen levels etc.) are documented in the appropriate log book.
Furthermore, for security reasons, samples of the master cell banks are also stored at specialized cell storage facilities in England. In addition, samples of one working cell bank from the DDM1.7 cell line are stored at Cellin technologies in Estonia for production purposes.
Sales, Marketing and Distribution
The business model of DanDrit is to focus on early development of dendritic cell based vaccine. We have significantly reduced the fixed costs linked with our operation and do not intend to build an expensive marketing, sales and distribution organization. We will rely on pharmaceutical partners with demonstrated relevant experience in commercialization of cancer products to market, sell and distribute MCV. At completion of the comparative clinical trial, we plan to enter into a collaboration agreement with a pharmaceutical partner regarding the regulatory approval, marketing, sales and distribution of MCV.
| 25 |
Intellectual Property
As a company primarily focused on pharmaceutical research, we expect that our most valuable assets are our intellectual property. This includes U.S. and foreign patents, patent applications, common-law trademarks, trade secrets and know-how. We are pursuing an aggressive intellectual property strategy.
DanDrit intends to aggressively defend its patents through legal process if necessary. Where appropriate, DanDrit may in-license intellectual property that may add to the strength and defense of our core business. DanDrit’s intellectual property comprises patents, trademarks, copyright and secret know-how.
DanDrit’s core business is cancer therapy. Where DanDrit’s patents and secret know-how are applicable to non-core business areas we will consider out-licensing for relevant non-core applications.
DanDrit filed its first Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT) patent application on November 29, 2002 with priority claimed from 2001 with the Danish application, shortly after our formation.
DanDrit may continue to patent its innovations, such as novel dendritic cell production systems or dendritic cell quality control. To support potential income streams DanDrit may patent non-core applications of its dendritic cell technologies so as to secure future revenue streams from out-licensing activity.
Patents
| ● | Pharmaceutical composition for inducing an immune response in a human or animal (2001 Denmark (DK), 2002 PCT) | |
| This patent was first filed in November 2002. The patent covers and describes the usage of an allogenic melanoma cell lysate (MCL)-pulsed autologous DC vaccine expressing at least one of six MAGE-A antigens overexpressed by the cell line being the source of the lysate. The patent covers the antigen composition used in the generation of MelCancerVac and the claims for producing MelCancerVac. In this patent the antigens are specified to mainly belong to the cancer testis family. The family of antigens is expressed in a wide variety of cancer forms. In the International Preliminary Report on Patentability (IPRP) all claims were determined to be novel and inventive. The patent expiry date is November 29, 2022. This patent has been granted in: Europe, the USA, China, Australia, Singapore, Japan, Russia, Hong Kong. This patent is pending in: Israel and Norway. This patent is owned by the Company and was not licensed from third parties. The patent protection means that the cancer specific antigen-rich lysate obtained from our cell line cannot be commercially made, used, distributed or sold without DanDrit's consent. These patent rights can be usually enforced in a court, which, in most systems, holds the authority to stop patent infringement. | ||
| ● | Protocol for generating dendritic cells (2005 DK, 2008 PCT) | |
| This patent covers the generation of dendritic cells based on a blood sample of 200 ml. The patent differs from other DC generating patents by the utilization of reduced temperature and a single blood sample. DCs exposed to tumor antigens followed by treatment with T(h)1-polarizing differentiation signals have paved the way for the development of DC-based cancer vaccines. Critical parameters for generation of optimal functional clinical grade DCs are a very competitive area. DanDrit has developed a method that covers the generation of immature dendritic cells under reduced temperature settings which by further activation has been shown to give a high yield of homogeneous and fully matured DCs. This patent was filed on December 7, 2006. In the International Preliminary Report on Patentability (IPRP) a large majority of claims were found to be novel and inventive. The patent expiry date is 2032. This patent was granted in 2012 in China, Eurasia, Russia, Europe, Israel, Mexico, Malaysia, New Zealand. This patent is owned by DanDrit and was not licensed from third parties. The patent protection means that the method that DanDrit use to generate dendritic cells cannot be commercially used, distributed or sold without DanDrit's consent. These patent rights can be usually enforced in a court, which, in most systems, holds the authority to stop patent infringement. |
| 26 |
| ● | Method for generating tolerogenic dendritic cells employing decreased temperature (2007) | |
| DanDrit has expanded the method of development of mature dendritic cells to also include the generation of regulatory DCs. In addition to DCs used for cancer immunotherapy, DanDrit has developed an additional arm of DCs, namely regulatory/tolerogenic DCs to be used for treatment of various autoimmune diseases such as Type 1 diabetes and Multiple Sclerosis. This patent was filed on November 13, 2008. Patent pending: worldwide. 1st Office Action received in Europe August 25, 2010. This patent is owned by the Company and was not licensed from third parties. The patent protection means that the method that DanDrit use to produce tolerogenic dendritic cells cannot be commercially used, distributed or sold without DanDrit's consent. These patent rights can be usually enforced in a court, which, in most systems, holds the authority to stop patent infringement. |
| ● | Micro RNAs as markers of the functional state of a dendritic cell | |
| This patent covers and demonstrates that functionally different DCs carry unique microRNA signatures. By examining a handful of microRNA profiles one can analyze the function of DC vaccines. We believe this is a valuable addition to other vaccine quality control measures that are currently used in studies that involve DCs. Critical parameters for assessment of the optimal functional state of DCs and prediction of the vaccine potency of activated DCs have in the past been based on measurements of differentiation surface markers like HLA-DR, CD80, CD83, CD86, and CCR7 and the level of secreted cytokines like interleukin-12p70. However, the level of these markers does not provide a complete picture of the DC phenotype and may be insufficient for prediction of clinical outcome for DC-based therapy. We have identified additional biomarkers by investigating the differential expression of microRNAs (miRNAs) in mature DCs relative to immature DCs. The patent was filed on November 14, 2008. In the International Preliminary Report on Patentability, a large majority of claims were found to be novel and inventive. Patent pending: Europe and USA. 1st Office Action received in Europe on August 18, 2010. Follow up action on election restriction received in the USA on October 21, 2010. This patent is owned by the Company and was not licensed from third parties. The patent protection means that the method that DanDrit use to test and release its dendritic cells cannot be commercially used, distributed or sold without DanDrit's consent. These patent rights can be usually enforced in a court, which, in most systems, holds the authority to stop patent infringement. |
All of the above patents are protected by relevant international extensions.
Trademarks
A policy of product trademarking and branding has been adopted by DanDrit. Trademarks have been obtained for
MelCancerVac™
MelVaxin™
DanDrit™
Commercial Secrets
In addition to intellectual property protected by patents and copyrights, DanDrit has commercial secrets relating to its products, production processes, know-how and future strategies. Where it is expedient to share such secret information this will be done under the protection of a confidentiality (or secrecy) agreement. Such agreements require the signing parties to keep DanDrit’s commercial secrets confidential unless:
| ● | at the time of disclosure the confidential information was already known to the recipient as evidenced by written record pre-dating such disclosure; |
| 27 |
| ● | at the time of disclosure the confidential information is generally available to the public or subsequently becomes available to the public other than by an act of omission on the part of the recipient; or | |
| ● | the confidential information has been made available to the recipient (on a non-confidential basis) by a third party having the lawful right to do so. |
Governmental Regulation
Orphan Drug status for MCV
The United States and Europe may designate drugs for relatively small patient populations as orphan drugs. Orphan drug designation does not convey any advantage in, or shorten the duration of, the regulatory review and approval process, but does make the product eligible for orphan drug exclusivity, reduced filing fees and specific tax credits. Generally, if a company receives the first marketing approval for a product with an orphan drug designation in the clinical indication for which it has such designation, the product is entitled to orphan drug exclusivity. Orphan drug exclusivity means that the FDA will not approve another application to market the same drug for the same indication, except in limited circumstances, for a period of seven years in the United States. This exclusivity, however, could block the approval of our proposed product candidates if a competitor obtains marketing approval before us. We plan to apply for orphan drug status for MCV to treat stage IV CRC with NED after surgical resection and chemotherapy if we meet the eligibility criteria. However, note that, even if we obtain orphan drug exclusivity MCV, we may not be able to maintain the status. For example, if a competitive product is shown to be clinically superior to our product, any orphan drug exclusivity we have will not block the approval of such competitive product.
Fast Track designation for development of MCV
We intend to request Fast Track designation for MCV. If a drug is intended for the treatment of a serious or life-threatening condition and the drug demonstrates the potential to address unmet medical needs for this condition, the drug sponsor may apply for FDA Fast Track designation for a particular indication. Marketing applications filed by sponsors of products in Fast Track development may qualify for priority review under the policies and procedures offered by the FDA, but the Fast Track designation does not assure any such qualification or ultimate marketing approval by the FDA. Receipt of Fast Track designation may not result in a faster development process, review or approval compared to drugs considered for approval under conventional FDA procedures. In addition, the FDA may withdraw any Fast Track designation at any time. We may seek Fast Track designation for our vaccine product candidates or any other product candidates, but the FDA may not grant this status to any of our proposed product candidates.
Approval for Commercialization
MCV and any future product candidates that we will be developing will require approval of the FDA before they can be marketed in the U.S. Although our focus at this time is primarily on the U.S. market, in the future similar approvals will need to be obtained from foreign regulatory agencies before we can market our current and proposed product candidates in other countries.
The process for filing and obtaining FDA approval to market therapeutic products is both time-consuming and costly, with no certainty of a successful outcome. The historical failure rate for companies seeking to obtain FDA approval of therapeutic products is high and, with the exception of Dendreon Corp.’s dendritic cell vaccine for the treatment of prostate cancer, no cancer stem cell or dendritic cell-based cancer vaccine has to date been approved by the FDA. This process includes conducting extensive pre-clinical research and clinical testing, which may take longer and cost more than we initially anticipate due to numerous factors, including without limitation, difficulty in securing appropriate centers to conduct trials, difficulty in enrolling patients in conformity with required protocols in a timely manner, unexpected adverse reactions by patients in the trials to our proposed product candidates and changes in the FDA’s requirements for our testing during the course of that testing.
| 28 |
The time required to obtain FDA and other approvals is unpredictable but often can exceed five years following the commencement of clinical trials, depending upon the complexity of the product and other factors. Any analysis we perform of data from preclinical and clinical activities is subject to confirmation and interpretation by regulatory authorities, which could delay, limit or prevent regulatory approval. We may also encounter unexpected delays or increased costs due to a variety of reasons, including new government regulations from future legislation or administrative actions or from changes in FDA policy during the period of product development, clinical trials and FDA regulatory review.
Any delay or failure in our clinical trial program and in obtaining required approvals would have a material adverse effect on our ability to generate revenues from the particular product. Furthermore, any regulatory approval to market a product may be subject to limitations on the indicated uses for which we may market the product. These limitations may limit the size of the market for the product.
Environmental Matters
We are subject to a broad range of federal, state, local and foreign environmental laws and regulations which govern, among other things, air emissions, wastewater discharges and the handling, storage disposal and release of wastes and hazardous substances. It is our policy to comply with applicable environmental requirements at all of our facilities. We are also subject to laws, such as the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation and Liability Act (“CERCLA”), that may impose liability retroactively and without fault for releases or threatened releases of hazardous substances at on-site or off-site locations. We are subject to similar requirements in Denmark and other European countries.
Research and Development
Research and development costs are charged to operations as incurred and consist primarily of clinical trial costs for the Company’s VIVA Phase III clinical trial, related party manufacturing costs, consulting costs, contract research and development costs, and compensation costs.
Discovery and preclinical research and development expenses include costs for substantial external scientific personnel, technical and regulatory advisers, and others, costs of laboratory supplies used in our internal research and development projects, travel, regulatory compliance, and expenditures for preclinical and clinical trial operation and management when we are actively engaged in clinical trials. Because we are pre-revenue company, we do not allocate research and development costs on a project basis. We adopted this policy, in part, due to the unreasonable cost burden associated with accounting at such a level of detail and our limited number of financial and personnel resources.
Competition
There is extensive competition in the biopharmaceutical industry and the technology is developing rapidly. DanDrit is developing a vaccine for the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer, where competing products may be introduced. If these newly developed products are more efficient, cheaper, more patient-friendly, safer, or better placed than DanDrit’s vaccine candidates, or if DanDrit’s competitors develop drugs that reduce or eliminate the need for DanDrit’s vaccine candidates, such competition could reduce or eliminate DanDrit’s commercial opportunities. Many of DanDrit’s competitors have substantially greater financial, technical and human resources than DanDrit and significantly more experience than DanDrit with preclinical and clinical research and development and in obtaining regulatory approval of pharmaceutical products.
DanDrit’s drugs may face competition as a result of many factors, including the route of administration (e.g. oral administration vs. injection), the availability and cost of production, efficiency of DanDrit’s partners’ marketing and sales efforts as well as the price of DanDrit’s products. DanDrit has limited or no previous experience in these areas. DanDrit’s inability to compete effectively would have a material adverse effect on DanDrit’s business, financial condition, results of operations and future growth opportunities. At this time, DanDrit does not represent a significant presence in the biopharmaceutical industry.
Several companies are trying to capitalize on the growing interest for immunotherapy in the treatment of cancer.
| 29 |
Two Directly Competing Companies
The figure below outlines the competitive landscape for MCV. Note that colorectal cancer, while providing a large market opportunity (it is the second most killer cancer after lung cancer), offers a more robust competitive landscape than other cancers. In the colorectal cancer space DanDrit faces two main competitors:
| ● | Bavarian Nordic (“BN”): CV-301, BN’s second compound, is in clinical development with advanced colorectal cancer patients | |
| ● | Immatics: its second compound is in clinical development in early stage colorectal cancer patients |
Bavarian Nordic (BAVA.CO) and CV-301

With its lead vaccine Prostvac™ from Therion Biologics and NCI, Bavarian Nordic (BN) also acquired Panvac™ vaccine. This PANVAC™ vaccine failed to prove efficacy in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer who failed gemcitabine. BN is currently focusing its efforts on Prostvac™ for treatment of prostate cancer, currently in Phase III. However, in 2012, BN re-initiated the clinical development of Panvac™ (re-named CV-301).
CV-301 is a cancer immunotherapy product candidate incorporating two antigens, CEA and MUC-1, in a viral vector. CV-301 is an off-the-shelf immunotherapy product candidate for the treatment of multiple cancers. It originates from the same poxvirus technology platform as PROSTVAC™. Both PROSTVAC™ and CV-301 are prime-boost vaccines sequentially combining two different poxviruses (vaccinia and fowlpox).
CV-301 had been studied in different cancers in clinical trials led by the National Cancer Institute. One study was a randomized Phase II trial in patients with metastatic breast cancer. The study enrolled 48 patients to receive CV-301 in combination with docetaxel or docetaxel alone. The primary study endpoint was PFS, while secondary endpoints included overall survival and immunologic correlative studies. A preliminary analysis of the study showed PFS of 6.6 months in the CV-301 group versus 3.8 months among those receiving docetaxel alone. Final study data are pending results from five patients that remained on study at the time of the analysis. Because of its size the study was not designed to reach statistical significance.
More directly relevant to DanDrit was the colorectal Phase II study of CV-301 conducted by Morse at Duke University. The objective of the trial was to determine whether one of two vaccines based on dendritic cells and poxvectors encoding CEA and MUC1 would lengthen survival in patients with resected metastases of colorectal cancer. The studied patients were, disease-free after CRC metastasectomy and perioperative chemotherapy (n = 74). They were randomized to injections of autologous DCs modified with PANVAC (DC/PANVAC) or PANVAC with per injection GM-CSF (granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor). Endpoints were recurrence-free survival overall survival, and rate of CEA-specific immune responses. Clinical outcome was compared with that of an unvaccinated, contemporary group of patients who had undergone CRC metastasectomy, received similar perioperative therapy, and would have otherwise been eligible for the study.
| 30 |
The recurrence-free survival at two years was similar (47% and 55% for DC/PANVAC and PANVAC/GM-CSF, respectively). At a median follow-up of 35.7 months, there were two of 37 deaths in the DC/PANVAC arm and five of 37 deaths in the PANVAC/GM-CSF arm. The rate and magnitude of T-cell responses against CEA was statistically similar between study arms.
As a group, vaccinated patients had superior survival compared with the contemporary unvaccinated group. Both DC and pox-vector vaccines had similar activity. Survival was longer for vaccinated patients than for a contemporary unvaccinated group.
In 2013, Bavarian Nordic expanded its license with the National Cancer Institute (NCI) for CV-301 to include colon cancer. The original collaboration agreement executed in 2011, involved multiple cancers including breast, lung, ovarian and other cancers.
In 2016, BN announced that the future development of CV301 will focus on combination treatments with checkpoint inhibitors.
Immatics Biotechnologies

The second direct competitor is Immatics (previously known as Biomira), a German/ US biotech company who currently focuses its clinical efforts on a Phase III in Renal Cell Carinoma for its lead vaccine. However, Immatic also develops a vaccine in colorectal cancer (enter Phase I in 2012). Note that Immatic’s technology is peptide-based rather than a dendritic cell approach and that Immatics is targeting its vaccine toward early stage colorectal cancer rather than resected advanced colorectal cancer like Bavarian and DanDrit. This private German company only discovers and develops tumor-associated peptides for the immunotherapy of cancer. Immatics reported that they raised €53.8million in a Series C financing round to finance a Phase III pivotal trial of their lead product IMA901 which in data reported in June 2014 at ASCO demonstrated the potential to confer an overall survival benefit in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. In 2016, Immatics did not make any announcement regarding development in colorectal cancer patients.
Employees
The Company currently has 2 full-time employees.
Facilities and Offices
The Company’s corporate headquarters are located in Symbion Science Park, Fruebjergvej 3, 2100 Copenhagen, Denmark and 375 Park Avenue, Suite 2607, New York, NY, 10152. We lease approximately 1,108 square feet at our Symbion location which is used for work and storage of cells and biological material in freezers. The lease is for a term of three years. The office in New York is a virtual office space that can be terminated with one month’s notice.
Until May 31, 2015 we occupied approximately 1,620 square feet at Bredgade 75, 3rd Floor, 1263 Copenhagen K, Denmark, which was used for office space. The Company does not anticipate renting additional office space in the near future.
| 31 |
You should carefully consider and evaluate all of the information in the risk factors listed below. If any of these risks occur, our business, results of operations and financial condition could be harmed, the price of our common stock could decline, and future events and circumstances could differ significantly from those anticipated in the forward-looking statements contained in this report.
RISKS ASSOCIATED WITH DANDRIT’S BUSINESS AND INDUSTRY
We have had a history of losses and no or minimal revenues, which raise substantial doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern.
Since our inception through June 30, 2016, we have an accumulated deficit of $(26,300,694). We can offer no assurance that we will ever operate profitably or that we will generate positive cash flow in the future. There can be no assurance that our continuing efforts to execute our business plan will be successful and that we will be able to continue as a going concern. To date, we have generated minimal revenues from our operations. Our history of losses and minimal revenues raise substantial doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern. As a result, our management expects the business to continue to experience negative cash flow for the foreseeable future and cannot predict when, if ever, our business might become profitable. We will need to raise additional funds, and such funds may not be available on commercially acceptable terms, if at all. If we are unable to raise funds on acceptable terms, we may not be able to execute our business plan, take advantage of future opportunities, or respond to competitive pressures or unanticipated requirements. This may seriously harm our business, financial condition and results of operations. The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared in conformity with US GAAP, which contemplates our continuation as a going concern.
DanDrit lacks an established operating history on which to evaluate its business and determine if it will be able to execute its business plan. The Company can give no assurance that its operations will result in profits.
DanDrit USA was formed in January 2011 as a vehicle to pursue a business combination through the acquisition of, or merger with, an operating business. On February 12, 2014, pursuant to the Share Exchange Agreement, DanDrit USA completed the acquisition of 100% of the issued and outstanding capital stock of DanDrit Denmark, a Danish corporation formed in 2001, and as a result became DanDrit Denmark’s parent company. DanDrit USA has a limited operating history that makes it difficult to evaluate its business. DanDrit has not begun sales of its products, and cannot say with certainty when, if ever, it will begin to achieve profitability. No assurance can be made that DanDrit will ever become profitable.
DanDrit has incurred losses in prior periods and expects to incur losses in the foreseeable future. DanDrit may never be profitable.
DanDrit had net losses for the year ending June 30, 2016 of $1,735,239, the six months ended June 30, 2015 of $2,673,448, as well as net loss for the year ended December 31, 2014 of $2,370,833. DanDrit expects to continue to sustain losses for the foreseeable future.
As sales of DanDrit’s products have generated minimal operating revenues, DanDrit has relied on loans and on sales of its debt and equity securities to continue operations. If DanDrit is unable to raise funds through sales of its securities or otherwise, there can be no assurance that DanDrit will be able to implement its business plan, generate sustainable revenue or ever achieve profitable operations. DanDrit expects to have operating losses until such time as it develops a substantial and stable revenue base. DanDrit cannot assure its investors that it can achieve or sustain profitability on a quarterly or annual basis in the future.
DanDrit may not be able to develop its vaccines to yield satisfactory results and they may never be approved for use by regulatory authorities. If DanDrit is unable to successfully commercialize its vaccines, the Company’s prospects, financial position, results of operations and future opportunities will be materially adversely affected.
None of DanDrit’s vaccine candidates has completed full clinical development. Because DanDrit’s vaccine candidates generally belong to new classes of cell therapy, they will require extensive further development, testing and funding before the Company can seek regulatory approval for any of these vaccines.
DanDrit’s prospects in the short term, including DanDrit’s ability to generate revenue and make new strategic alliances, depend on DanDrit’s ability to develop, obtain regulatory approval for and commercialize its current vaccine candidates with satisfactory results. If DanDrit fails to develop the vaccines DanDrit has in its pipeline, it will have a material adverse effect on DanDrit’s business, financial condition, results of operations and future growth opportunities.
There can be no assurance that DanDrit will succeed in implementing its Phase III clinical trials for advanced colorectal cancer so that the results of these clinical trials will support further preclinical or clinical studies, or that DanDrit will be able to develop new vaccine candidates or successfully commercialize any of those cancer vaccine candidates at a later time. If DanDrit does not do this, it cannot achieve its growth potential and this will have a material adverse effect on DanDrit’s prospects, financial position, results of operations and future opportunities.
Results of our early clinical trials do not insure future success.
The results of early clinical trials may not necessarily be indicative of future results. Achieving positive results in preclinical testing and early clinical trials does not constitute any assurance that in future clinical trials sufficient data can be obtained to document a vaccine candidate’s efficacy and safety. The safety and efficacy of a vaccine candidate in development must be supported by extensive data from preclinical studies and clinical trials.
| 32 |
A number of companies in the pharmaceutical industry and in the biopharmaceutical industry, including companies that have greater resources and more experience than DanDrit, have achieved significant negative results in clinical phase IIb and III trials, even after obtaining promising results in preclinical and early clinical studies. Results that are considered acceptable in early clinical studies may not be confirmed or may be interpreted differently in subsequent studies. DanDrit cannot predict whether the clinical phase IIb and III and other clinical trials that may be implemented will demonstrate sufficient efficacy and safety to obtain regulatory approval to market any of DanDrit’s vaccine candidates.
Negative or non-satisfactory results of clinical trials involving DanDrit’s vaccine candidates could lead to DanDrit or its collaborators having to perform additional nonclinical and/or clinical trials, which could result in higher costs and significantly delay the marketing authorization application for such vaccine candidates by the regulatory authority, or could lead to an application for a more narrowly defined use, or another indication for the vaccine candidate than originally expected. Such results could also lead to the complete elimination of a vaccine candidate. If any of these risks materialize, it could have a material adverse effect on DanDrit’s business, financial condition, results of operations and future growth opportunities.
DanDrit is a clinical-stage biopharmaceutical company which makes it difficult to assess its future viability.
DanDrit is a clinical-stage biopharmaceutical company. It has not yet demonstrated an ability to successfully overcome many of the risks and uncertainties frequently encountered by companies in new and rapidly evolving fields, particularly in the biopharmaceutical area. For example, to execute its business plan, DanDrit will need to successfully:
| ● | execute on product (vaccine) candidate development activities; | |
| ● | obtain required regulatory approvals for the development and commercialization of its product candidates; | |
| ● | maintain, leverage and expand its intellectual property portfolio; | |
| ● | gain market acceptance for its products; | |
| ● | develop and maintain any strategic relationships it elects to enter into; and; | |
| ● | manage its spending as costs and expenses increase due to preclinical development, clinical trials, regulatory approvals and commercialization. |
Even if DanDrit is unsuccessful in accomplishing these objectives, it may not be able to develop product candidates, raise capital, expand its business or continue its operations.
DanDrit will be dependent on collaboration and licensing arrangements to develop and commercialize its products. These relationships may be unsuccessful and may not result in the development of vaccine candidates. In that case, our business, financial condition and growth opportunities will be materially adversely affected.
DanDrit expects to depend on collaboration and licensing agreements with third parties who we expect will provide additional personnel and other resources and funding required to develop and commercialize its products. Until these relationships are established, our plans for developing some of our vaccines may be uncertain. There can be no assurance that DanDrit will be able to enter into or maintain these agreements, that the results of these agreements will further the development of a vaccine, or that DanDrit will receive income from these agreements. Furthermore, collaborators that we anticipate may enter into agreements with us may change their priorities; make reallocation of resources; terminate the agreements; end or further delay the development of vaccine candidates; downgrade or change plans or strategies for regulatory approval or commercialization of the vaccine candidate; find it difficult to retain key employees; or be taken over by companies that are our competitors.
We expect that these collaboration and licensing agreements will entitle us to milestone payments and a percentage of sales related to the vaccine candidates that are commercialized. If a third party with which DanDrit has established a collaboration or licensing arrangement stops the development of a vaccine candidate, there can be no assurance that all rights in respect of the vaccine candidate will be reassigned to us. A transfer of these rights may be delayed for various reasons, which may result in the delay of all work performed for the vaccine candidate.
| 33 |
Since we are dependent on third parties to develop and commercialize our product candidates, any adverse change in these anticipated relationships will have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, and future growth opportunities.
Changes in regulatory requirements and regulations could have a material adverse effect on DanDrit.
DanDrit’s products are subject to extensive regulatory requirements, including public and/or regulatory limits set by the FDA and the European Medicines Agency (“EMA”). These laws and regulations, including those relating to reporting on safety, product safety and advertising and marketing of products are applicable to all aspects of DanDrit’s business.
DanDrit and/or any future third party with which it has an effective collaboration or licensing agreement may be subject to changes in applicable governmental regulations and/or regulatory framework and be subject to additional or more onerous restrictions, which may make it necessary to make changes to personnel, facilities or procedures that could result in increased costs and adversely affect DanDrit’s business activities, including the development and commercialization of DanDrit’s vaccine candidates.
If DanDrit or its affiliates do not comply with applicable regulatory requirements or comply with significant legislative changes. DanDrit or its affiliates can be fined or risk having regulatory approvals suspended or withdrawn, risking recall or seizure of products, restrictions on activities and/or civil or criminal prosecution, which could have a material adverse effect on DanDrit’s business, financial condition, results of operations and future growth opportunities. Furthermore, we cannot guarantee that our vaccine candidates will be approved by the regulating agencies.
As long as the relevant regulatory authorities have not considered and approved applications for DanDrit’s vaccine candidates (New Drug Application (NDA) or equivalent) DanDrit and its affiliates cannot commercialize DanDrit’s vaccine candidates. Production and marketing of DanDrit’s products and DanDrit’s ongoing research and development activities are subject to rules set by numerous public authorities throughout the world. The regulatory authorities of each country can set their own requirements and may refuse to approve a product or may require additional data before approving a product, even if the product is approved by another regulating agency. Approvals may include restrictions on the marketing or use of products, which could adversely affect the amount of DanDrit’s revenue from the sale of those products.
We may in the future conduct clinical trials for MCV or any future product candidates in sites outside the United States and the FDA may not accept data from trials conducted in such locations.
We have conducted, and may in the future choose to conduct, one or more of our clinical trials outside of the United States. Although the FDA may accept data from clinical trials conducted outside the United States, acceptance of this data is subject to certain conditions imposed by the FDA. For example, the clinical trial must be well designed and conducted and performed by qualified investigators in accordance with ethical principles. The study population must also adequately represent the U.S. population, and the data must be applicable to the U.S. population and U.S. medical practice in ways that the FDA deems clinically meaningful. Generally, the patient population for any clinical studies conducted outside of the United States must be representative of the population for whom DanDrit intends to label the product in the United States. In addition, while these clinical trials are subject to the applicable local laws, FDA acceptance of the data will be dependent upon its determination that the studies also complied with all applicable U.S. laws and regulations. There can be no assurance the FDA will accept data from trials conducted outside of the United States. If the FDA does not accept the data from our clinical trial conducted outside the United States, it would likely result in the need for additional trials within the United States, which would be costly and time-consuming and delay or permanently halt our development of MCV or any future vaccine candidates.
In connection with the anticipated filing of our IND application with the FDA, we plan to submit trial results for trials that we did not sponsor, which the FDA may refuse to consider.
DanDrit was only a sponsor of one of the clinical trials completed to date for MCV while DanDrit Denmark employees and certain affiliates were closely involved in the design of the studies and the analysis and interpretation of the resulting data of all three studies. As a result, DanDrit intends to present all applicable data with respect to the current trials that is available to it, regardless of DanDrit’s specific role in any one of the trials. There are no assurances that the FDA will accept any data that DanDrit submits in support of its IND application for any clinical trial in which it was not a sponsor or principal investigator.
| 34 |
There can be no assurance that regulators will complete their review process in a timely manner, or that DanDrit vaccine candidates will obtain regulatory approval.
If DanDrit or any third party with which we have an effective collaboration or licensing agreement experience difficulties or delays in obtaining regulatory approvals, the development and commercialization of our vaccine candidates may be significantly delayed or even discontinued. Such difficulties or delays could result in significantly increased development costs and/or a delay or elimination of payments to us from our collaborators. This would have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and future growth opportunities.
DanDrit will be dependent on external suppliers of certain services and technologies.
DanDrit will be dependent on a number of external parties such as contract laboratories and clinical research organizations, and in some cases our collaborators to:
| ● | Implement preclinical studies (pharmacology, toxicology testing and safety pharmacological evaluations). | |
| ● | Provide DanDrit with vaccine materials and support DanDrit’s activities related to preclinical and clinical studies. | |
| ● | Implement, inspect and/or monitor some or all aspects of the preclinical or clinical studies with DanDrit’s product candidates. | |
| ● | Ensure compliance with regulatory requirements such as Good Clinical Practice, Good Manufacturing Practice (“GMP”) and Good Laboratory Practices. | |
| ● | Deliver IT services. | |
| ● | Produce vaccine drugs and vaccines in accordance with GMP. |
The third parties DanDrit depends on may not be available when needed, or might not, if available, comply with all statutory and contractual requirements, and/or otherwise provide their services in a timely manner or in an acceptable manner.
DanDrit’s succes is dependent on its ability to recruit and retain qualified scientific and management personnel.
Recruiting and retaining qualified scientific and management personnel for the planning and execution of research and development; preparation of applications for intellectual property rights and regulatory approvals; and negotiating and maintaining cooperation with existing and new partners is essential for DanDrit.
There can be no assurance that DanDrit will be able to attract and retain such persons considering the demand for experienced employees from numerous pharmaceutical companies, chemical companies, specialized biopharmaceutical companies, universities and other research institutions. DanDrit’s employment contracts contain no limitation on competition that would prevent DanDrit’s current employees from being employed by DanDrit’s competitors or partners, if they choose to leave DanDrit.
DanDrit may in the future require additional expertise and manpower in areas such as preclinical trials, management of clinical trials, regulatory affairs, marketing, business development and management of partnerships. Inability to obtain or develop such expertise, or hire the employees it needs, on reasonable terms, could have a material adverse effect on DanDrit’s business, financial condition, results of operations and future growth opportunities.
| 35 |
If DanDrit’s employees commit fraud or other misconduct, including noncompliance with regulatory standards and requirements and insider trading, its business may experience serious adverse consequences.
DanDrit is exposed to the risk of employee fraud or other misconduct. Misconduct by employees could include intentional failures to comply with FDA regulations, to provide accurate information to the FDA, to comply with manufacturing standards the Company has established, to comply with federal and state health-care fraud and abuse laws and regulations, to report financial information or data accurately or to disclose unauthorized activities to DanDrit.
In particular, sales, marketing and business arrangements in the healthcare industry are subject to extensive laws and regulations intended to prevent fraud, kickbacks, self-dealing and other abusive practices. These laws and regulations may restrict or prohibit a wide range of pricing, discounting, marketing and promotion, sales commission, customer incentive programs and other business arrangements. Employee misconduct could also involve the improper use of information obtained in the course of clinical trials, which could result in regulatory sanctions and serious harm to our reputation. DanDrit has adopted a Code of Business Conduct and Ethics but it is not always possible to identify and deter employee misconduct, and the precautions DanDrit takes to detect and prevent this activity may not be effective in controlling unknown or unmanaged risks or losses or in protecting us from governmental investigations or other actions or lawsuits stemming from a failure to be in compliance with such laws or regulations. If any such actions are instituted against DanDrit, and DanDrit is not successful in defending itself or asserting its rights, those actions could have a significant impact on its business, including the imposition of significant fines or other sanctions.
DanDrit’s products may not achieve market acceptance. This would have a material adverse effect on the Company’s business, financial condition, results of operations and future growth opportunities.
The drugs DanDrit or its collaborators may develop may not gain market acceptance among physicians, patients, third-party payers and the medical community, even if they are approved by the applicable regulatory bodies for marketing. The degree of market acceptance of the products approved for sale depends on a number of factors, including:
| ● | The ability of DanDrit or its collaborators to demonstrate the clinical efficacy, safety and benefits of the products. | |
| ● | The ability of DanDrit or its collaborators to demonstrate that the product has advantages over existing therapies or new alternative treatments. | |
| ● | The frequency and severity of any adverse effects arising from the use of the products. | |
| ● | The price of the products. | |
| ● | The subsidies DanDrit receives. | |
| ● | Efficacy within the therapeutic range for the illnesses the products are directed towards. | |
| ● | Patient comfort and user administration. | |
| ● | Requirements for marketing. | |
| ● | The level of support for marketing and distribution. |
DanDrit has no control over most of these factors. Furthermore, it may be difficult for DanDrit, to the extent that competitors are able to commercialize competing products before its vaccine candidates obtain regulatory approval, to develop a market for a vaccine because doctors, patients or third-party payers may have become accustomed to using a competing, existing product or for other reasons, even though its drug may be more effective or has other advantages.
If any of the vaccines DanDrit develops fail to achieve market acceptance in the future, the Company may not be able to generate significant revenue, which would have a material adverse effect on its business, financial condition, results of operations and future growth opportunities.
| 36 |
The use of DanDrit’s drugs or vaccine candidates may lead to unforeseen side effects. If any of our drugs or vaccine candidates is deemed to be unsafe, our business, financial condition, results of operations and future growth opportunities could be materially adversely affected.
All drugs are associated with a risk of allergic, immunologic genes or hypersensitivities. The Company tests for allergic and immunological genes actions in preclinical and clinical studies, but if any of its products cause other allergic or immunological reactions than those considered acceptable by patients, doctors or regulatory authorities, the Company or its collaborators may be required to conduct additional clinical trials that will cause delays and increase costs for the development of a product, or development may have to be terminated or suspended on the grounds that participants will be exposed to unacceptable health risks.
Even in cases where pre-clinical or clinical studies have been successful, or received regulatory approval, a product can later prove to be unsafe. The incidence of adverse events may make it necessary for the Company and for its collaborators to carry out further investigations and studies. If a product is determined to be unsafe, the Company and its collaborators can be fined or risk having regulatory approvals suspended or withdrawn, be required to cease selling activities relating to the product, be required to recall the product, be subject to seizure of products, or be exposed to civil or criminal prosecution. Any of these results could have a material adverse effect on the Company’s business, financial condition, results of operations and future growth opportunities.
Third party reimbursement and reform measures on health care could have a material adverse effect on the commercial success of DanDrit’s vaccine candidates.
Market acceptance of DanDrit’s vaccine candidates depends in part on the extent to which the public and private health insurance and other third-party payers will subsidize DanDrit’s drugs.
Governments, insurance companies and health organizations are increasingly seeking to reduce healthcare costs by limiting coverage, price and reimbursement levels of new vaccine products as well as in some cases rejecting coverage. Reimbursement practices vary significantly from country to country, and some countries require that products undergo a lengthy review by the authorities before they meet the public support requirements.
In the United States, in Canada and in many other countries, pricing and/or profitability of some or all prescription pharmaceuticals and biopharmaceuticals are subject to varying degrees of government control. Healthcare reform and controls on healthcare spending may limit the price we charge for any products and the amounts thereof that we can sell. In particular, in the United States, the federal government and private insurers have changed and have considered ways to change, the manner in which healthcare services are provided. In March 2010, the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, as amended by the Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act, or collectively, PPACA, became law in the United States. PPACA substantially changes the way healthcare is financed by both governmental and private insurers and significantly affects the healthcare industry.
In addition, other legislative changes have been proposed and adopted since PPACA was enacted. These changes include aggregate reductions to Medicare payments to providers of up to 2% per fiscal year, which went into effect on April 1, 2013. In January 2013, President Obama signed into law the American Taxpayer Relief Act of 2012, which, among other things, further reduced Medicare payments to several types of providers and increased the statute of limitations period for the government to recover overpayments to providers from three to five years. These new laws may result in additional reductions in Medicare and other healthcare funding, which could have a material adverse effect on our customers and accordingly, our financial operations.
We anticipate that PPACA, as well as other healthcare reform measures that may be adopted in the future, may result in more rigorous coverage criteria and additional downward pressure on the reimbursement we may receive for any approved product. Moreover, payment methodologies may be subject to changes in healthcare legislation and regulatory initiatives. For example, the Middle Class Tax Relief and Job Creation Act of 2012 required the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, or CMS, to reduce the Medicare clinical laboratory fee schedule by 2% in 2013, which in turn serves as a base for 2014 and subsequent years. CMS also recently proposed to re-examine payment amounts for tests reimbursed under the Medicare clinical laboratory fee schedule due to changes in technology and, in addition, proposed to bundle the Medicare payments for certain laboratory tests ordered while a patient received services in a hospital outpatient setting. Such changes went into effect January 1, 2014. Levels of reimbursement may be impacted by current and future legislation, regulation or reimbursement policies of third-party payors in a manner that may harm the demand and reimbursement available for our products, which in turn could harm our future product pricing and sales. Any reduction in reimbursement from Medicare and other government programs may result in a similar reduction in payments from private payors. The implementation of cost containment measures or other healthcare reforms may prevent us from being able to generate revenue, attain profitability or commercialize our products.
| 37 |
There may be delays or difficulties in the recruitment and monitoring of patients in clinical trials. Any such delays could have a material adverse effect on DanDrit’s business, financial condition, results of operations and future growth opportunities.
All clinical development of new vaccine candidates depends on the recruitment of volunteer suitable patients for clinical trials. The ability to recruit patients depends on certain factors, including the prevalence of the disease in the population. It may be more difficult to find a sufficient number of patients to participate in clinical trials for drugs being developed for a disease that is common among the general population. Even if a disease is frequent among the population, there may be a number of other companies developing drugs that target the same disease who may eventually have more success in recruiting among the total group of potential patients for their clinical studies. If we or our collaborators find it difficult to recruit a sufficient number of patients to participate in clinical trials for one of its vaccine candidates DanDrit and/or its collaborators may have to postpone or discontinue ongoing clinical trials. Delays may also result in increased costs for clinical studies and may affect the implementation of studies required for a vaccine candidate’s approval. Delay or complete termination of a clinical trial program could have a material adverse effect on DanDrit’s business, financial condition, results of operations and future growth opportunities.
DanDrit may not be able to make, or cause others to conduct, animal testing in the future. This could have a material adverse effect on our research and development work.
Research into dendritic cell vaccines does not generally involve animals. But, certain aspects of DanDrit’s biotechnology research and development may be carried out on animals. Changes to laws and regulations, recognized clinical procedures, or experimental protocols may have a negative impact on this research and development. Pressure from society, which may lead to restrictions on the use of animals or result in actions against DanDrit, its affiliates or its clinical research organizations from groups of people or individuals who are against animal testing may also have a material adverse effect on research and development work.
DanDrit faces extensive competition. If its vaccine candidates cannot compete successfully, its business, financial condition, results of operations and future growth opportunities could be materially, adversely affected.
There is extensive competition in the biopharmaceutical industry and the technology is developing rapidly. DanDrit is developing a vaccine for the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer, where competing products may be introduced. If these newly developed products are more efficient, cheaper, more patient-friendly, safer, or better placed than DanDrit’s vaccine candidates, or if DanDrit’s competitors develop drugs that reduce or eliminate the need for DanDrit’s vaccine candidates, such competition could reduce or eliminate DanDrit’s commercial opportunities. Many of DanDrit’s competitors have substantially greater financial, technical and human resources than DanDrit and significantly more experience than DanDrit with preclinical and clinical research and development and in obtaining regulatory approval of pharmaceutical products.
DanDrit’s drugs may face competition as a result of many factors, including the route of administration (e.g. oral administration vs. injection), the availability and cost of production, efficiency of DanDrit’s partners’ marketing and sales efforts as well as the price of DanDrit’s products. DanDrit has limited or no previous experience in these areas. DanDrit’s inability to compete effectively would have a material adverse effect on DanDrit’s business, financial condition, results of operations and future growth opportunities.
DanDrit is likely to be exposed to product liability claims. If product liability lawsuits are successfully brought against the Company, its insurance may be inadequate. If a judgment were to exceed our insurance coverage, our business could be materially, adversely affected.
DanDrit will likely be exposed, by virtue of the nature of its business, to the risk of potential product liability claims, which is typical regarding the clinical development, manufacture and marketing of drugs. Even in cases where DanDrit has granted licenses to third parties to manufacture and sell its products, there can be no assurance that DanDrit will not be included in any product liability claims relating to these medicines, or claims by third parties, including DanDrit’s partners, for indemnity or other compensation from DanDrit in connection with any such claims.
| 38 |
DanDrit plans to obtain product liability insurance coverage once our clinical trials commence. However, the Company’s insurance coverage may not be sufficient to reimburse it for any expenses or losses it may suffer. Moreover, insurance coverage is becoming increasingly expensive, and, in the future, the Company may not be able to maintain insurance coverage at a reasonable cost or in sufficient amounts to protect it against losses due to liability. If and when the Company obtains marketing approval for its product candidates, it intends to expand its insurance coverage to include the sale of commercial products; however, the Company may be unable to obtain this product liability insurance on commercially reasonable terms. On occasion, large judgments have been awarded in class action lawsuits based on drugs that had unanticipated side effects. The cost of any product liability litigation or other proceedings, even if resolved in the Company’s favor, could be substantial. A successful product liability claim or series of claims brought against the Company could cause its share price to decline and, if judgments exceed its insurance coverage, could decrease the Company’s cash and adversely affect its business.
DanDrit has insufficient funds to develop its business, which may adversely affect its future growth. Future funding may not be available to it on acceptable terms, or at all, which would force DanDrit to terminate, delay, reduce or suspend its operations, research and development programs and other commercialization efforts.
DanDrit will need to raise substantial additional capital to fund its operations and to develop and commercialize its products. As of June 30, 2016 and 2015, respective, the Company had approximately $23,368 and $1,474,134 in cash and cash equivalents, respectively. The Company currently does not have cash to sustain its operations for the next 12 months. The Company will need to sell equity securities or borrow funds in order to develop these growth strategies and its inability to raise the additional capital and/or borrow the funds needed to implement these plans may adversely affect its business and future growth. These factors create an uncertainty as to the Company's ability to continue as a going concern. The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared in conformity with US GAAP, which contemplates our continuation as a going concern. Please see note 2 to the financials.
The Company’s future capital requirements may be substantial and will depend on many factors including:
| ● | The Company’s clinical trial results, rates of progress and costs; |
| ● | the cost, timing and outcomes of seeking FDA and other regulatory authority approval of its products; |
| ● | the cost of filing and prosecuting patent applications and the cost of defending its patents; |
| ● | the cost of prosecuting infringement actions against third parties; |
| ● | subject to receipt of marketing approval, revenue received from sales of approved products, if any, in the future; |
| ● | any product liability or other lawsuits related to its products; |
| ● | the expenses needed to attract and retain skilled personnel; and |
| ● | the costs associated with being a public company. |
DanDrit does not have any committed external source of funds or other support for its operational or development efforts. Until it can generate a sufficient amount of product revenue to finance its cash requirements, which it may never do, DanDrit expects to finance future cash needs through a combination of public or private equity offerings, debt financings, collaborations, strategic alliances, licensing arrangements and other marketing and distribution arrangements. Additional financing may not be available to the Company when it needs it or it may not be available on favorable terms. If the Company raises additional capital through marketing and distribution arrangements or other collaborations, strategic alliances or licensing arrangements with third parties, it may have to relinquish certain valuable rights to MCV or potential future product candidates, technologies, future revenue streams or research programs, or grant licenses on terms that may not be favorable to it. If the Company raises additional capital through public or private equity offerings, the ownership interest of its existing stockholders will be diluted, and the terms of these securities may include liquidation or other preferences that adversely affect its stockholders’ rights.
| 39 |
If the Company raises additional capital through debt financing, it may be subject to covenants limiting or restricting our ability to take specific actions, such as incurring additional debt, making capital expenditures or declaring dividends. If it is unable to obtain adequate financing when needed, the Company may have to delay, reduce the scope of, or suspend one or more of its clinical studies or research and development programs or its commercialization efforts.
Raising capital in the future could cause dilution to our existing shareholders, and may restrict our operations or require us to relinquish rights.
In the future, we may seek additional capital through a combination of private and public equity offerings, debt financings and collaborations and strategic and licensing arrangements. To the extent that we raise additional capital through the sale of equity or convertible debt securities, the ownership interests of our existing shareholders will be diluted, and the terms may include liquidation or other preferences that adversely affect the rights of our existing shareholders. Debt financing, if available, would result in increased fixed payment obligations and may involve agreements that include covenants limiting or restricting our ability to take specific actions such as incurring debt, making capital expenditures or declaring dividends. If we raise additional funds through collaboration, strategic alliance and licensing arrangements with third parties, we may have to relinquish valuable rights to our technologies, future revenue streams or product candidates, or grant licenses on terms that are not favorable to us.
We depend on intellectual property and the failure to protect our intellectual property could adversely affect our future growth and success. This would have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
We rely on patent, trademark and copyright law, trade secret protection, and confidentiality and other agreements with employees, customers, collaborators and others to protect our intellectual property. However, some of our intellectual property is not covered by any patent or patent application, and, despite precautions, it may be possible for third parties to obtain and use our intellectual property without authorization.
We do not know whether any patents will be issued from pending or future patent applications or whether the scope of the issued patents is sufficiently broad to protect our technologies or processes. The patent position of biotechnology companies is generally uncertain because it involves complex legal and factual considerations. The standards applied by the United States Patent and Trademark Office and foreign patent offices in granting patents are not always applied uniformly or predictably. For example, there is no uniform worldwide policy regarding patentable subject matter or the scope of claims allowable in biotechnology and pharmaceutical patents. Consequently, patents may not issue from our pending patent applications. As such, we do not know the degree of future protection that we will have on our proprietary products and technology.
| 40 |
We endeavor to aggressively protect our technologies through patents covering compositions of matter, drug targets and aspects of mechanism of action, drug product formulation, methods of use and methods of manufacture, and trade secrets. We have filed patent applications and in-licensed others with respect to our technology both domestically and internationally and anticipate filing multiple patent applications, in the future. While we believe that we will be able to secure adequate and enforceable patent protection for our products and technologies, there is no guarantee that patent protection can be obtained, and even if it is obtained that such patent protection will ultimately be deemed valid, sufficiently enforceable, sufficient to preclude competition or not infringe upon the rights of other parties. Furthermore, the laws of some foreign countries may not protect intellectual property rights to the same extent as do the laws of the United States and Denmark.
The patents protecting our proprietary technologies expire after a period of time. Currently, our patents have expiration dates ranging from 2021 through 2032. Although we have attempted to incorporate technology from our core patents into specific patented product applications, product designs and packaging to extend the lives of our patents, this approach may not be successful in protecting our proprietary technology. If we are not successful in protecting our proprietary technology, it could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
We may not be successful in protecting our proprietary rights. Any infringement upon our intellectual property rights could have an adverse effect on our ability to develop our products and sell them commercially.
Issued patents covering one or more of our product candidates could be found invalid or unenforceable if challenged in court. If that were to happen, our business would be adversely impacted.
If we were to initiate legal proceedings against a third party to enforce a patent covering one of our product candidates, the defendant could counterclaim that our patent is invalid and/or unenforceable. In patent litigation in the United States, defendant counterclaims alleging invalidity and/or unenforceability are commonplace. Grounds for a validity challenge could be an alleged failure to meet any of several statutory requirements, for example, lack of novelty, obviousness or non-enablement. Grounds for an unenforceability assertion could be an allegation that someone connected with prosecution of the patent withheld relevant information from the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office, or made a misleading statement, during prosecution. The outcome following legal assertions of invalidity and unenforceability during patent litigation is unpredictable. With respect to the validity question, for example, we cannot be certain that there is no invalidating prior art, of which we and the patent examiner were unaware during prosecution. If a defendant were to prevail on a legal assertion of invalidity and/or unenforceability, we would lose at least part, and perhaps all, of the patent protection on one or more of our product candidates or certain aspects of our platform technology. Such a loss of patent protection could have a material adverse impact on our business.
We may unintentionally infringe the intellectual property rights of others, which may prevent or delay our product development efforts and stop us from commercializing or increase the costs of commercializing our products.
Our commercial success depends significantly on our ability to operate without infringing the patents and other intellectual property rights of third parties. For example, there could be issued patents of which we are not aware that our products infringe. There also could be patents that we believe we do not infringe, but that we may ultimately be found to infringe. Moreover, patent applications are in some cases maintained in secrecy until patents are issued. The publication of discoveries in the scientific or patent literature frequently occurs substantially later than the date on which the underlying discoveries were made and patent applications were filed. Because patents can take many years to issue, there may be currently pending applications of which we are unaware that may later result in issued patents that our products infringe. For example, pending applications may exist that provide support or can be amended to provide support for a claim that results in an issued patent that our product infringes.
Third parties may assert that we are employing their proprietary technology without authorization. If a court held that any third-party patents are valid, enforceable and cover our products or their use, the holders of any of these patents may be able to block our ability to commercialize our products unless we obtained a license under the applicable patents, or until the patents expire. We may not be able to enter into licensing arrangements or make other arrangements at a reasonable cost or on reasonable terms. Any inability to secure licenses or alternative technology could result in delays in the introduction of our products or lead to prohibition of the manufacture or sale of products by us.
| 41 |
Unfavorable outcomes in intellectual property litigation could limit our research and development activities and/or our ability to commercialize certain products.
If third parties successfully assert intellectual property rights against us, we might be barred from using certain aspects of our technology, or barred from developing and commercializing certain products. Prohibitions against using certain technologies, or prohibitions against commercializing certain products, could be imposed by a court or by a settlement agreement between us and a plaintiff. In addition, if we are unsuccessful in defending against allegations of patent infringement or misappropriation of trade secrets, we may be forced to pay substantial damage awards to the plaintiff. There is inevitable uncertainty in any litigation, including intellectual property litigation. There can be no assurance that we would prevail in any intellectual property litigation, even if the case against us is weak or flawed. If litigation leads to an outcome unfavorable to us, we may be required to obtain a license from the patent owner in order to continue our research and development programs or to market our product(s). It is possible that the necessary license will not be available to us on commercially acceptable terms, or at all. This could limit our research and development activities, our ability to commercialize certain products, or both.
Most of our competitors are larger than we are and have substantially greater resources. They are, therefore, likely to be able to sustain the costs of complex patent litigation longer than we could. In addition, the uncertainties associated with litigation could have a material adverse effect on our ability to raise the funds necessary to continue our clinical trials, continue our internal research programs, in-license needed technology, or enter into strategic partnerships that would help us bring our product candidates to market.
In addition, any future patent litigation, interference or other administrative proceedings will result in additional expense and distraction of our personnel. An adverse outcome in such litigation or proceedings may expose us or any future collaborators to loss of our proprietary position, expose us to significant liabilities, or require us to seek licenses that may not be available on commercially acceptable terms, if at all.
Changes in U.S. patent law could diminish the value of patents in general, thereby impairing our ability to protect our products.
As is the case with other pharmaceutical companies, our success is heavily dependent on intellectual property, particularly patents. Obtaining and enforcing patents in the biopharmaceutical industry involves both technological and legal complexity. Therefore, obtaining and enforcing pharmaceutical patents is costly, time-consuming and inherently uncertain. In addition, the United States has recently enacted and is currently implementing wide-ranging patent reform legislation. The United States Supreme Court has ruled on several patent cases in recent years, either narrowing the scope of patent protection available in certain circumstances or weakening the rights of patent owners in certain situations. In addition to increasing uncertainty with regard to our ability to obtain patents in the future, this combination of events has created uncertainty with respect to the value of patents, once obtained. Depending on decisions by the U.S. Congress, the federal courts, and the U.S. PTO, the laws and regulations governing patents could change in unpredictable ways that would weaken our ability to obtain new patents or to enforce our existing patents and patents that we might obtain in the future.
Confidentiality agreements with employees and third parties may not prevent unauthorized disclosure of trade secrets and other proprietary information.
In addition to patents, we rely on other methods to protect our trade secrets, technical know-how, and proprietary information. In the course of our research and development activities and our business activities, we often rely on confidentiality agreements to protect our proprietary information. Such confidentiality agreements are used, for example, when we talk to vendors of laboratory or clinical development services or potential collaborators. We take steps to protect our proprietary information, and our confidentiality agreements are carefully drafted to protect our proprietary interests. Nevertheless, there can be no guarantee that an employee or an outside party will not make an unauthorized disclosure of our proprietary confidential information. This might happen intentionally or inadvertently. It is possible that a competitor will make use of such information in spite of any legal action we might take against persons making such unauthorized disclosures.
Trade secrets are difficult to protect. Although we use reasonable efforts to protect our trade secrets, our employees, consultants, contractors, or outside collaborators might intentionally or inadvertently disclose our trade secret information to competitors. Enforcing a claim that a third party illegally obtained and is using any of our trade secrets is expensive and time consuming, and the outcome is unpredictable. In addition, courts outside the United States sometimes are less willing than U.S. courts to protect trade secrets. Moreover, our competitors may independently develop equivalent knowledge, methods and know-how.
| 42 |
Foreign currency fluctuations could adversely impact financial performance.
Our reporting currency is the United States dollar. Because of our activities in Denmark, the United Kingdom and continental Europe, we are exposed to fluctuations in foreign currency rates. We may manage the risk to such exposure by entering into foreign currency futures and option contracts. Foreign currency fluctuations may have a significant effect on our operations in the future.
Assuming that our vaccine candidates receive regulatory approval and we begin sales of these products, our results may fluctuate due to certain regulatory, marketing and competitive factors over which we have little or no control.
Assuming that our vaccine candidates receive regulatory approval and we begin the sale of these products, the factors listed below, some of which we cannot control, may cause our revenue and results of operations to fluctuate significantly:
| ● | Actions taken by regulatory bodies relating to the verification, registration or health effects of our products; | |
| ● | The extent to which existing and newly developed products obtain market acceptance; |
| ● | The timing and size of customer purchases; | |
| ● | Customer concerns about the stability of our business, which could cause them to seek alternatives to our solutions and products; and | |
| ● | Increases in raw material costs. |
We will incur significant costs as a result of operating as a public company, and our management may be required to devote substantial time to compliance initiatives, which may have a material effect on our business.
As a public company, we incur significant legal, accounting and other expenses. In addition, the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, as well as rules subsequently implemented by the SEC, have imposed various requirements on public companies, including requiring establishment and maintenance of effective disclosure and financial controls as well as mandating certain corporate governance practices. Our management and other personnel devote a substantial amount of time and financial resources to these compliance initiatives
If we fail to staff our accounting and finance function adequately, or maintain internal control systems adequate to meet the demands that are placed upon us as a public company, we may be unable to report our financial results accurately or in a timely manner and our business and stock price may suffer. The costs of being a public company, as well as diversion of management’s time and attention, may have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
A significant portion of our assets and the majority of our officers and directors are located outside of the United States and therefore it may be difficult for an investor to enforce within the United States any judgments obtained against us or such officers and directors.
A significant portion of our assets are located outside of the United States. In addition, the majority of our officers and directors are nationals and/or residents of countries other than the United States, and all or a substantial portion of such persons’ assets are located outside the United States. As a result, it may be difficult for an investor to effect service of process or enforce within the United States any judgments obtained against us or such officers or directors, including judgments predicated upon the civil liability provisions of the securities laws of the United States or any state thereof. In addition, there is uncertainty as to whether the courts of other jurisdictions would recognize or enforce judgments of United States courts obtained against us or our directors and officers predicated upon the civil liability provisions of the securities laws of the United States or any state thereof, or be competent to hear original actions brought in other jurisdictions against us, or such officers and directors predicated upon the securities laws of the United States or any state thereof.
| 43 |
RISKS RELATED TO OWNERSHIP OF OUR COMMON STOCK
Our majority stockholders will control our Company for the foreseeable future, including the outcome of matters requiring stockholder approval.
Our officers, directors, and five percent stockholders collectively own more than 50% of our outstanding shares of common stock. In addition, these stockholders and previous stockholders of the Company’s subsidiary, DanDrit Denmark entered into a voting agreement in connection with the Merger, whereby they agreed to vote in favor of nominees for directors selected by the parties to the voting agreement as described therein. As a result, such entities and individuals will have the ability, acting together, to control the election of our directors and the outcome of corporate actions requiring stockholder approval, such as: (i) a merger or a sale of our Company, (ii) a sale of all or substantially all of our assets, and (iii) amendments to our articles of incorporation and bylaws. This concentration of voting power and control could have a significant effect in delaying, deferring or preventing an action that might otherwise be beneficial to our other stockholders and be disadvantageous to our controlling stockholders. Certain of these individuals also have significant control over our business, policies and affairs as officers or directors of the Company. Therefore, you should not rely on your ability to have any control over our Company.
An investment in our Company should be considered illiquid.
An investment in our Company requires a long-term commitment, with no certainty of return. Because we became a reporting company other than by the traditional means of conducting an initial public offering of our common stock, we may be unable to establish a liquid market for our common stock. In addition, investment banks may be less likely to agree to underwrite primary or secondary offerings on behalf of our Company or its stockholders in the future than they would if we had become a public reporting company by means of an initial public offering of common stock. If all or any of the foregoing risks occur, it would have a material adverse effect on our Company.
An active, liquid trading market for our common stock may not develop or be sustained.
Presently, our common stock is traded on the Over-the-Counter Markets, or OTC.QB, and we are in our early stages, therefore, an investment in the Company will require a long-term commitment, with no certainty of return. Presently there is limited trading in our stock and in the absence of an active trading market:
| ● | investors may have difficulty buying and selling or obtaining market quotations; |
| ● | market visibility for shares of our common stock may be limited; and |
| ● | a lack of visibility for shares of our common stock may have a depressive effect on the market price for shares of our common stock. |
The lack of an active market impairs your ability to sell your shares at the time you wish to sell them or at a price that you consider reasonable. The lack of an active market may also reduce the fair market value of your shares. An inactive market may also impair our ability to raise capital to continue to fund operations by selling shares and may impair our ability to acquire additional intellectual property assets by using our shares as consideration.
Even if an active trading market for our common stock develops, the market price of our common stock may be volatile.
Even if an active market for our common stock develops, of which no assurances can be given, the market price for our common stock may be volatile and subject to wide fluctuations in response to factors including the following:
| ● | actual or anticipated fluctuations in our quarterly or annual operating results; |
| ● | changes in financial or operational estimates or projections; |
| ● | conditions in markets generally; |
| ● | changes in the economic performance or market valuations of companies similar to ours; and |
| ● | general economic or political conditions in the United States or elsewhere. |
| 44 |
In particular, the market prices of biotechnology companies like ours have been highly volatile due to factors, including, but not limited to:
| ● | any delay or failure to conduct a clinical trial for our product or receive approval from the FDA and other regulatory agents; |
| ● | developments or disputes concerning our product’s intellectual property rights; |
| ● | our or our competitors’ technological innovations; |
| ● | changes in market valuations of similar companies; |
| ● | announcements by us or our competitors of significant contracts, acquisitions, strategic partnerships, joint ventures, capital commitments, new technologies, or patents; and |
| ● | failure to complete significant transactions or collaborate with vendors in manufacturing our product. |
The securities market has from time to time experienced significant price and volume fluctuations that are not related to the operating performance of particular companies. These market fluctuations may also materially and adversely affect the market price of shares of our common stock.
Penny stock regulations may impose certain restrictions on the marketability of our securities.
The SEC has adopted regulations which generally define “penny stock” to be any equity security that has a market price (as defined) less than $5 per share, subject to certain exceptions. Our common stock is presently subject to these regulations which impose additional sales practice requirements on broker-dealers who sell such securities to persons other than established customers and accredited investors (generally those with assets in excess of $1,000,000, excluding the net value of the person’s primary residence, or annual income exceeding $200,000, or $300,000 together with the investor’s spouse). For transactions covered by these rules, the broker-dealer must make a special suitability determination for the purchase of such securities and have received the purchaser’s written consent to the transaction prior to the purchase. Additionally, for any transaction involving a “penny stock”, unless exempt, the rules require the delivery, prior to the transaction, of a risk disclosure document mandated by the SEC relating to the “penny stock” market. The broker-dealer must also disclose the commission payable to both the broker-dealer and the registered representative, current quotations for the securities and, if the broker-dealer is the sole market maker, the broker-dealer must disclose this fact and the broker-dealer’s presumed control over the market. Finally, monthly statements must be sent disclosing recent price information for the “penny stock” held in the account and information on the limited market in “penny stocks”. Consequently, the “penny stock” rules may restrict the ability of broker-dealers to sell our securities and may negatively affect the ability of purchasers of our shares of common stock to sell such securities.
Investors may face significant restrictions on the resale of your shares due to state “blue sky” laws.
Each state has its own securities laws, often called “blue sky” laws, which (1) limit sales of securities to a state’s residents unless the securities are registered in that state or qualify for an exemption from registration, and (2) govern the reporting requirements for broker-dealers doing business directly or indirectly in the state. Before a security is sold in a state, there must be a registration in place to cover the transaction, or it must be exempt from registration. The applicable broker-dealer must also be registered in that state.
We do not know whether our securities will be registered or exempt from registration under the laws of any state. A determination regarding registration will be made by those broker-dealers who agree to serve as market makers for our common stock. There may be significant state blue sky law restrictions on the ability of investors to sell, and on purchasers to buy, our securities. Our investors should therefore consider the resale market for our common stock to be limited, as investors may be unable to resell their shares without the significant expense of state registration or qualification.
| 45 |
As an “emerging growth company” under the JOBS Act, we are permitted to rely on exemptions from certain disclosure requirements.
We qualify as an “emerging growth company” under the JOBS Act. As a result, we are permitted to and may rely on exemptions from certain disclosure requirements. For so long as we are an emerging growth company, we will not be required to:
| ● | have an auditor report on our internal controls over financial reporting pursuant to Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act; |
| ● | comply with any requirement that may be adopted by the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board regarding mandatory audit firm rotation or a supplement to the auditor’s report providing additional information about the audit and the financial statements (i.e., an auditor discussion and analysis); |
| ● | submit certain executive compensation matters to shareholder advisory votes, such as “say-on-pay”, “say-on-frequency” and “say-on-golden parachute;” and |
| ● | disclose certain executive compensation related items such as the correlation between executive compensation and performance and comparisons of the Chief Executive’s compensation to median employee compensation. |
In addition, Section 107 of the JOBS Act also provides that an emerging growth company can take advantage of the extended transition period provided in Section 7(a)(2)(B) of the Securities Act for complying with new or revised accounting standards. In other words, an emerging growth company can delay the adoption of certain accounting standards until those standards would otherwise apply to private companies. We are not choosing to “opt out” of this provision. Section 107 of the JOBS Act provides that our decision to opt out of the extended transition period for complying with new or revised accounting standards is irrevocable.
We will remain an “emerging growth company” until the last day of our fiscal year following the fifth anniversary of the date of our first sale of common equity securities pursuant to an effective registration under the Securities Act, or until the earliest of (i) the last day of the first fiscal year in which our total annual gross revenues exceed $1 billion, (ii) the date that we become a “large accelerated filer” as defined in Rule 12b-2 under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, which would occur if the market value of our ordinary shares that is held by non-affiliates exceeds $700 million as of the last business day of our most recently completed second fiscal quarter or (iii) the date on which we have issued more than $1 billion in non-convertible debt during the preceding three year period.
Until such time, however, we cannot predict if investors will find our common stock less attractive because we may rely on these exemptions. If some investors find our common stock less attractive as a result, there may be a less active trading market for our common stock and our stock price may be more volatile.
We have never paid dividends on our common stock.
We have never paid dividends on our common stock and do not presently intend to pay any dividends in the foreseeable future. We anticipate that any funds available for payment of dividends will be re-invested into the Company to further its business strategy. Because we do not anticipate paying dividends in the future, the only opportunity for our stockholders to realize the creation of value in our common stock will likely be through a sale of those shares.
We have the right to issue shares of preferred stock. If we were to issue preferred stock, it is likely to have rights, preferences and privileges that may adversely affect the common stock.
We are authorized to issue 10,000,000 shares of “blank check” preferred stock, with such rights, preferences and privileges as may be determined from time-to-time by our Board of Directors. Our Board of Directors is empowered, without stockholder approval, to issue preferred stock in one or more series, and to fix for any series the dividend rights, dissolution or liquidation preferences, redemption prices, conversion rights, voting rights, and other rights, preferences and privileges for the preferred stock. No shares of preferred stock are presently issued and outstanding and we have no immediate plans to issue shares of preferred stock. The issuance of shares of preferred stock, depending on the rights, preferences and privileges attributable to the preferred stock, could adversely reduce the voting rights and powers of the common stock and the portion of the Company’s assets allocated for distribution to common stockholders in a liquidation event, and could also result in dilution in the book value per share of the common stock being offered. The preferred stock could also be utilized, under certain circumstances, as a method for raising additional capital or discouraging, delaying or preventing a change in control of the Company, to the detriment of the investors in the common stock being offered. We cannot assure you that the Company will not, under certain circumstances, issue shares of its preferred stock.
| 46 |
1B. Unresolved Staff Comments
There are no unresolved staff comments.
Our corporate headquarters are located in Symbion Science Park, Fruebjergvej 3, 2100 Copenhagen, Denmark and 375 Park Avenue, Suite 2607, New York, NY, 10152, USA. The Company leases 2 locations as follows:
| Location | Use | Terms | ||
| Symbion Science Park, Fruebjergvej 3, 2100 Copenhagen, Denmark |
1,108 square feet used for work and storage of cells and biological material in freezers | The lease can be terminated by either party on three month’s notice. | ||
|
375 Park Avenue Suite 2607 New York, NY 10152 |
Virtual office space. | On March 25, 2015, the Company entered into an agreement for use of virtual office space at a rate of $375/month on a month-to-month basis, which can be terminated by either party on one month’s notice. | ||
| Bredgade 75, 3rd floor, DK-1263 Copenhagen K |
2,000 square feet used for office space | The lease was terminated on May 31, 2015. The Company does not anticipate renting additional office space in the near future. |
From time to time, we may be involved in litigation relating to claims arising out of our operations in the normal course of business. We are not currently a party to in any legal proceeding that we believe would have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition or operating results.
Item 4. Mine Safety Disclosures.
Not applicable.
| 47 |
Item 5. Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
Market Information
The Company's Common Stock is traded on the Over-The-Counter Bulletin Board. The following table sets forth the range of high and low bid quotations on the Common Stock for the quarterly periods indicated, as reported by the National Quotation Bureau, Inc. The quotations are inter-dealer prices without retail mark-ups, mark downs or commissions and may not represent actual transactions.
| Fiscal Year Ended June 30, 2017 | High | Low | ||||||
| Third Quarter (through September 22, 2016) | 3.00 | 0.75 | ||||||
| Fiscal Year Ended June 30, 2016 | High | Low | ||||||
| Third Quarter | 6.25 | 4.00 | ||||||
| Fourth Quarter | 5.00 | 3.00 | ||||||
| First Quarter | 3.90 | 1.50 | ||||||
| Second Quarter | 3.50 | 1.25 | ||||||
| Six Months Ended June 30, 2015 | High | Low | ||||||
| First Quarter | 6.17 | 6.00 | ||||||
| Second Quarter | 6.25 | 2.06 | ||||||
| Fiscal Year Ended December 31, 2014 | High | Low | ||||||
| First Quarter (1) | - | - | ||||||
| Second Quarter (1) | - | - | ||||||
| Third Quarter (1) | - | - | ||||||
| Fourth Quarter (2) | - | - |
(1) Not available for trading.
(2) The common stock was available to be traded on the Over-The-Counter Bulletin Board, but there were no trades during the quarter.
Holders of Common Stock
As of September 22, 2016 we had 9,533,290 shares of common stock issued and outstanding and approximately 46 stockholders of record.
Dividends
The Company has not declared or paid any cash dividends on its common stock and does not intend to declare or pay any cash dividend in the foreseeable future. The payment of dividends, if any, is within the discretion of the Board of Directors and will depend on the Company’s earnings, if any, its capital requirements and financial condition and such other factors as the Board of Directors may consider.
Sales of Unregistered Securities
Not applicable.
Securities Authorized for Issuance under Equity Compensation Plans
On February 6, 2014, the Board of Directors adopted and the Company’s sole stockholder approved the DanDrit Biotech USA, Inc. 2014 Equity Incentive Plan. We have reserved 1,206,000 shares of our common stock for issuance in accordance with the terms of the plan. As of the date of this report, no awards have been made from the plan.
| 48 |
Item 6. Selected Financial Data
The registrant is a smaller reporting company and is not required to provide this information.
Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
The following discussion of our financial condition and results of operations should be read in conjunction with our financial statements and the related notes to those statements included elsewhere in this report. In addition to the historical financial information, the following discussion and analysis contains forward-looking statements that involve risks and uncertainties. Our actual results may differ materially from those anticipated in these forward-looking statements.
We are a biotechnology company currently based in Copenhagen, Denmark. We are committed to developing what we believe could be the world’s first vaccine against colorectal cancer. For more than a decade, we have developed and patented compounds successfully used in initial clinical trials in Europe and Asia including: (i) MelCancerVac TM (MCV) for treatment of cancer (one phase I/II trial in Denmark and two phase II trials in Denmark and Singapore), (ii) Tolerogenic dendritic cell (TDC) (pre-clinical stage in Denmark) and (iii) Melvaccine (MV) a melanoma cell lysate used as stand-alone vaccine (pre-clinical state in Denmark). We expect to continue our clinical development program in the United States, Europe and Asia. Springing from academic roots in Denmark, we have built upon our scientific and medical skills to advance a number of candidate therapies, targeted initially at non-small-cell-lung-cancer (NSCLC) and colorectal-cancer (CRC). On September 22, 2008, the Singapore government authorized MCV for a named patient compassionate use for CRC. We have conducted three single-arm Phase II clinical trials in cancer where our dendritic cell vaccine, MCV demonstrated efficacy. The three clinical trials generated data indicating prospects in a larger and different clinical setting. More specifically, this efficacy data needed to be confirmed in a comparative randomized trial with advanced colorectal cancer patients.Neither the FDA nor or any other comparable governmental agency has reviewed MCV. Therefore, any assessment of its safety or efficacy only reflects the opinion of the Company. Furthermore, it does not indicate that MCV will achieve favorable results in any later stage trials or that the FDA or comparable agency will ultimately determine that MCV is safe and effective for purposes of granting marketing approval.
As a result, DanDrit Denmark, with the assistance of key opinion leaders in colorectal cancer treatment, has designed a randomized trial with 174 stage IV colorectal cancer patients after surgical resection and chemotherapy. Using an adaptive design clinical study that includes a prospectively planned opportunity for modification of one or more specified aspects of the study design and hypotheses based on analysis of data (usually interim data) from subjects in the study (an “Adaptive Design Clinical Study”), we significantly reduced the cost and duration of a Phase III study and we believe we can complete the study within three years. Regulatory authorities in the United States and Europe have both published guidance documents on the use and implementation of adaptive design trials. These documents both include description of adaptive trials and include a requirement for prospectively written standard operating procedures and working processes for executing adaptive trials and a recommendation that sponsor companies engage with CROs that have the necessary experience in running such trials.
To date, our operations have been funded by sales of our securities, loans and, to a lesser extent, by sales of our products. Sales of our products alone will not support our current operations and we expect this to be the case until our MCV vaccine is approved for marketing in the United States and European. Even if we are successful in having MCV approved for sale in the United States and European, we cannot guarantee that a market for the product will develop. We may never be profitable.
Change in Fiscal Year End
In June 2015, DanDrit’s Board of Directors approved a change to DanDrit’s fiscal year end from December 31 to June 30. In view of this change, this MD&A compares the financial statements as of and for the year ended June 30, 2016 with the unaudited financial statements as of and for the year ended June 30, 2015 (the transition period). We are also including a discussion and analysis of our financial statements for fiscal years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013.
| 49 |
Share Exchange
On February 12, 2014, the Company closed the Share Exchange in accordance with the terms and conditions of the Share Exchange Agreement and as a result became DanDrit Denmark’s parent company. In connection with the Share Exchange, each outstanding share of common stock of DanDrit Denmark was exchanged for 1.498842 shares of DanDrit USA’s Common Stock for an aggregate of 6,000,000 shares, including 185,053 shares of Common Stock reserved for issuance, in accordance with Section 70 of the Danish Companies Act and the Articles of Association of DanDrit Denmark, to the DanDrit Denmark shareholders who did not consent to the Share Exchange and deemed issued and outstanding for accounting purposes. In addition, in connection with the Share Exchange (1) the sole shareholder prior to the Share Exchange agreed to cancel 4,400,000 shares of outstanding Common Stock owned by it and (2) the board of directors and executive management of DanDrit Denmark was appointed to serve as the Board of Directors and executive management of DanDrit USA effective upon the resignation of the sole officer and director of DanDrit USA prior to the closing of the Share Exchange.
Recent Developments
DanDrit Biotech A/S signs contract for collaboration contract relating to VIVA Phase III adjuvant study
In March 2015, DanDrit Denmark signed a final contract of collaboration with the University Hospital IRCCS “San Martino” - IST - National Institute for Cancer Research, better known as San Martino Hospital of Genoa (IST). The collaboration relates to the VIVA Phase III adjuvant study of DanDrit vaccine in patients with no evidence of disease stage IV colorectal cancer (CRC). VIVA’s primary aim is to evaluate the efficacy of MCV in preventing relapse in stage IV CRC patients rendered Disease Free after completion of standard treatment according to local practices. IST is acting as Contract Research Organization for DanDrit. Prof. Alberto Sobrero is the Principal Investigator of this randomized multicenter study.
In March 2015, DanDrit Denmark also signed a contract of collaboration with the Fondazione Giscad per la Ricercasui Tumori (foundation for research on cancer) (GISCAD). GISCAD, the Gruppo Italiano per lo Studio dei Carcinoma dell’Apparato Digerente (Italian Group for the Study of Carcinoma of the Digestive Track) has conducted 46 phase II and III trials with the support and collaboration of AIFA (Italian Drug Agency) and involves 160 oncology centers in Italy. GISCAD will assist DanDrit in the identification, enrollment, compliance monitoring and management of the 30 clinical sites in Italy.
Trends, Events and Uncertainties
Research and development of new technologies is, by its nature, unpredictable. We cannot assure you that our technology will be adopted, that we will ever earn revenues sufficient to support our operations, or that we will ever be profitable. Furthermore, since we have no committed source of financing, we cannot assure you that we will be able to raise money as and when we need it to continue our operations. If we cannot raise funds as and when we need them, we may be required to severely curtail, or even to cease, our operations.
| 50 |
RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
Year ended June 30, 2016 compared to the year ended June 30, 2015 (unaudited); year ended December 31, 2014 compared to the year ended December 31, 2013
The following table sets forth our revenues, expenses and net income for the year ended June 30, 2016 and 2015 (unaudited) and for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013. The financial information below is derived from our audited consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this report.
| For the Year Ended | For the Year Ended | |||||||||||||||
| June 30, | December 31, | |||||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 (Unaudited) | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||||||
| Net Sales | $ | 42,769 | $ | 0 | $ | 0 | $ | 32,768 | ||||||||
| Cost of Goods Sold | 5,275 | 279,588 | 295,661 | 109,299 | ||||||||||||
| Gross Profit (Loss) | 37,494 | (279,588 | ) | (295,661 | ) | (76,531 | ) | |||||||||
| Operating Expenses: | ||||||||||||||||
| General and administrative expenses | 1,229,865 | 1,636,602 | 1,644,918 | 1,233,683 | ||||||||||||
| Research and Development expenses | 804,188 | 1,625,488 | - | - | ||||||||||||
| Depreciation and Amortization | 27,395 | 17,198 | 18,981 | 38,297 | ||||||||||||
| Consulting expenses | 96,976 | 624,707 | 469,666 | 390,437 | ||||||||||||
| Total Operating Expense | 2,158,424 | 3,903,995 | 2,133,565 | 1,662,417 | ||||||||||||
| Loss from Operations | (2,120,930 | ) | (4,183,583 | ) | (2,429,226 | ) | (1,738,948 | ) | ||||||||
| Other Income (Expense) | ||||||||||||||||
| Interest (expense) | (2,364 | ) | (45,685 | ) | (84,550 | ) | (652,703 | ) | ||||||||
| Gain on forgiveness of debt | - | - | 49,016 | |||||||||||||
| Gain (loss) on currency transactions | (74,732 | ) | (356,647 | ) | (40,583 | ) | 19,541 | |||||||||
| Gain on derivative liability | - | - | - | 175,732 | ||||||||||||
| Interest and other income | - | 5,689 | 5,937 | 1 | ||||||||||||
| Total Other Income (Expense) | (77,096 | ) | (396,643 | ) | (119,196 | ) | (408,413 | ) | ||||||||
| Loss Before Income Taxes | (2,198,026 | ) | (4,580,226 | ) | (2,548,422 | ) | (2,147,361 | ) | ||||||||
| Income Tax Expense (Benefit) | (462,787 | ) | (418,404 | ) | (177,539 | ) | - | |||||||||
| Net Loss | (1,735,239 | ) | (4,161,822 | ) | (2,370,883 | ) | (2,147,361 | ) | ||||||||
| BASIC AND DILUTED LOSS PER SHARE | $ | (0.18 | ) | $ | (0.44 | ) | $ | (0.32 | ) | $ | (0.40 | ) | ||||
| WEIGHTED AVERAGE NUMBER OF COMMON SHARES OUTSTANDING - BASIC AND DILUTED | 9,533,290 | 9,533,290 | 7,500,142 | 5,332,721 | ||||||||||||
| For the Year Ended | For the Years Ended | |||||||||||||||
| June 30, | December 31, | |||||||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 (Unaudited) | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||||||
| (Net Loss) | $ | (1,735,239 | ) | $ | (4,161,822 | ) | $ | (2,370,883 | ) | $ | (2,147,361 | ) | ||||
| (Currency Translation, Net of Taxes) | 20,701 | 559,701 | 306,439 | (219,470 | ) | |||||||||||
| (Other Comprehensive Loss) | $ | (1,714,538 | ) | $ | (3,602,121 | ) | $ | (2,064,444 | ) | $ | (2,366,831 | ) | ||||
Comparison of the Year ended June 30, 2016 and June 30, 2015 (Unaudited) and for the years ended December 31, 2014 and December 31, 2013
Revenues
Our net sales for the year ended June 30, 2016 were $42,769 as compared to June 30, 2015, net sales were $0 (unaudited). The increase was due to compassionate use sale to Singapore.
Our net sales for the year ended December 31, 2014 were $0 as compared to December 31,2013, net sales were $32,768, representing a year over year decrease in sales of $32,768 or 100%. This decrease was due to the decrease of the Singapore compassionate use sales.
| 51 |
Cost of Goods Sold
Our cost of goods sold for the year ended June 30, 2016 were $5,275 as compared to June 30, 2015, cost of goods sold were $279,588 (unaudited), representing a year over year decrease in cost of goods sold of $274,313 or 98%. The decrease was due to lysate manufacturing.
Our cost of goods sold increased by $186,362 or 171% during the year ended December 31, 2014, to $295,661, from $109,299 in cost of goods sold for the year ended December 31, 2013. The increase was due to additional costs of technology transfer of lysate manufacturing.
Gross Profit Loss
Gross profit for the years ended June 30, 2016 was $37,494 compared to a gross loss of $279,588 (unaudited) for same period in 2015, representing a decrease in the gross loss of $317,082. The change from a gross profit from a gross loss is a result of compassionate use sales in 2016.
Gross loss for the year ended December 31, 2014 was $295,661 compared to a loss of $76,531 for same period in 2013, representing an increase in the loss of $219,130, or 286%. The increase in gross loss was due to no sales and higher cost of goods sold for the year ended December 31, 2014.
Expenses
Our operating expense for the year ended June 30, 2016 totaled $2,158,424, representing a decrease of $1,745,571 or 45% compared to $3,903,995 (unaudited) for the year ended June 30, 2015. The largest contributor to the operating expenses for the year ended June 30, 2016 is the decrease in Research and development expenses of $821,300 attributable to delays in the initiation of VIVA phase III clinical trial.
Our operating expense for the year ended December 31, 2014 totaled $2,133,565, representing an increase of $471,148 or 28% compared to $1,662,417 for the year ended December 31, 2013. The largest contributors to the operating expenses for both years were the increase in legal expenses, consulting expenses, and salaries of $155,501, $135,854, and $100,549 respectively.
General and administrative expense for the year ended June 30, 2016 was $1,229,865, compared to $1,636,602 (unaudited) for the year ended June 30, 2015, representing a decrease of $406,737, or 25%. The net decrease was due primarily to a decrease in legal expenses and the resignation of the Company CFO.
General and administrative expense for the year ended December 31, 2014 was $1,644,918 compared to $1,233,683 for the year ended December 31, 2013, representing an increase of $411,235, or 33%. This increase was due primarily to costs associated with the audit and the costs associated with becoming publically traded in November of 2014. General and administrative expenses include office rental, website management, insurance, and salaries.
Depreciation and amortization expenses for the year ended June 30, 2016 and 2015 were $27,395 and $17,198 (unaudited), respectively, representing an increase of $10,197 or 59%.
Depreciation and amortization expenses for the year ended December 31, 2014 and 2013 were $18,981 and $38,297, respectively, representing a decrease of 50%. This decrease was due primarily to the decrease in depreciable assets.
Consulting expenses for the years, ended June 30, 2016 totaled $96,976 compared to $624,707 (unaudited) for the year ended June 30, 2015, representing a decrease of $527,731, or 85%. This decrease was primarily due to fees associated with raising funds through a private offering in December 2014.
Consulting expenses for the year ended December 31, 2014 totaled $469,666 compared to $390,437 for the year ended December 31, 2013, representing an increase of $79,229, or 21%. During 2014, we employed consultants to assist us with the valuation of DanDrit Denmark in preparation for the Share Exchange, the preparation of the S-1 registration statement that was effective on August 12, 2014, and consultants for our VIVA phase III clinical trial.
Other income (expense) net for the years ended June 30, 2016 and 2015 were ($77,096) and ($396,643) (unaudited), respectively, representing a decrease of 319,547 or 81%. This decrease was due primarily to the decrease in losses on currency transactions and interest expense.
| 52 |
Other income (expense) net for the year ended December 31, 2014 and 2013 were ($119,196) and ($408,413), respectively, representing an increase in other income of $289,217 or 70%. This increase was due primarily to decrease in interest expense of $568,153 for the year ended December 31, 2014.
Net Loss
Net loss for the years ended June 30, 2016 was $1,735,239 compared to $4,161,822 (unaudited) for the years ended June 30, 2015, representing a decrease of $2,426,583, or 58%. The decrease in the net loss for the year ended June 30, 2016 is primarily due to the decrease in the total operating expenses of $1,745,571 and other expense of $319,547.
Net loss for the year ended December 31, 2014 was $2,370,883 compared to $2,147,361 for the year ended December 31, 2013, representing an increase of $223,522, or 10%. The increase in the net loss for the year ended December 31, 2014 is primarily due to the increase in the general and administrative expenses of $411,235.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
We have historically satisfied our capital and liquidity requirements through funding from our largest shareholders, the issuance of convertible notes (which over time have been converted into shares of our common stock) and the sale of common stock. At June 30, 2016 and 2015, we had cash and cash held in escrow of $23,368 and $1,474,134 and working capital / (deficit) of $(775,750) and $910,522, respectively.
The accompanying unaudited consolidated financial statements have been prepared in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles of the United States of America, which contemplate continuation of the Company as a going concern. However, the Company has incurred significant losses, has not yet been successful in establishing profitable operations and has short-term obligations in excess of anticipated cash. These factors raise substantial doubt about the ability of the Company to continue as a going concern. In this regard, management plans to mitigate this doubt by raising additional funds through debt and/or equity offerings and by substantially increasing sales once approval for the Company’s product is obtained. The Company has subsequently received a commitment for a $500,000 investment, a commitment for a DKK 1,000,000 $153,750 1% convertible note, and DKK 3,400,000 approximately $507,000, in 1% convertible notes payable maturing December 31, 2017. The Company is attempting to raise $15,000,000 or more through a private placement offering and close the acquisition of the assets of OncoSynergy, Inc. The closing of the private placement is contingent on the closing of the acquisition of the assets of OncoSynergy, Inc.There is no assurance that the Company will be successful in raising additional funds through the debt or equity or achieving profitable operations. The consolidated financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of these uncertainties.
We may also need additional funds for possible future strategic acquisitions of businesses, products or technologies complementary to our business. If additional funds are required, we may raise such funds from time to time through public or private sales of equity or debt securities. Financing may not be available on acceptable terms, or at all, and our failure to raise capital when needed could materially adversely impact our growth plans and our financial condition and results of operations.
As of June 30, 2016 and 2015, the outstanding balance of $38,235 and $38,235 for professional fees paid by a shareholder and amounts advanced to the Company are reported as notes payable - related party. The $38,235 notes payable were acquired in the reverse acquisition. The amounts are unsecured, non-interest bearing and have no stipulated repayment terms.
A 6% promissory note payable to NLBDIT 2010 Enterprises, LLC, an entity controlled by a shareholder of the Company, was acquired by the Company in the reverse acquisition, payable on February 12, 2014 upon the completion date of the Share Exchange. As of June 30, 2016 and 2015, the outstanding balance on the note, including accrued interest, was $ 47,233 and $44,879. During the years ended June 30, 2016 and 2015 the Company recorded related party interest on the note of $2,354 and $2,126.
| 53 |
Cash Flows
Year ended June 30, 2016 compared to the year ended June 30, 2015 (unaudited) and year ended December 31, 2014 compared to the year ended December 31, 2013
Cash used from operating activities for the year ended June 30, 2016 was $1,472,289, representing a decrease in the loss of $3,750,989 compared to the cash used from operating activities of $5,223,278 (unaudited) for the year ended June 30, 2015. This decrease was primarily due to the decrease in the 2016 net loss versus 2015 and payment of accrued expenses in 2015 versus increases in accrued expenses in 2016.
Cash loss from operating activities for the year ended December 31, 2014 was $2,034,175, representing a decrease in the loss of $96,453 compared to the cash loss from operating activities of $2,130,628 for the year ended December 31, 2013. This decrease was primarily due to a decrease in total interest expenses and an increase of in research and development income tax credit.
Changes in assets and liabilities as of June 30, 2016 compared to June 30, 2015 included the following:
For the year ended June 30, 2016, other receivables increased $424,109 primarily for research and development tax credits, related party payables increased $153,597, accounts payable decreased $198,666 and accrued expenses decreased $717,521. For the year ended June 30, 2015 (unaudited) other receivables increased $59,870 and accounts payable and accrued expenses increased $120,365 and $156,114, respectively.
Changes in assets and liabilities as of December 31, 2014 compared to December 31, 2013 included the following:
For the year ended December 31, 2014, other receivables decreased $17,440 primarily for value added tax receivable, related party payables increased $212,438, accounts payable increased $162,950 and accrued expenses decreased $124,309. For the year ended December 31, 2013 other receivables decreased $56,346 and accounts payable and accrued expenses decreased $2,674 and $406,152, respectively.
Cash used in investing activities was ($1,052,989) for the year ended June 30, 2016, as compared to cash used in investing activities of $(905,881) (unaudited) for the year ended June 30, 2015. From time to time the Company attorney holds cash balance in escrow.
Cash used in investing activities was $1,952,034 for the year ended December 31, 2014, as compared to cash used in investing activities of $105,015 for the year ended December 31, 2013. Cash used for investing activities increased during the year ended December 31, 2014 primarily due to an increase in the amount of $1,952,034 of cash held in escrow.
Cash provided by financing activities was $0 for the year ended June 30, 2016 as compared to cash provided by financing activities of $5,811,042 (unaudited) for the year ended June 30, 2015 from the proceeds from the 2014 stock offerings offset by payments of notes payable and offering costs.
Cash provided by financing activities was $6,669,807 for the year ended December 31, 2014 as compared to cash provided by financing activities of $2,469,526 for the year ended December 31, 2013. The increase of approximately $4,200,281 in cash provided by financing activities in the year ended December 31, 2014, compared to the year ended December 31, 2013, was due to cash received in connection with sale of common stock of the Company.
Off Balance Sheet Arrangements
As of June 30, 2016, we had no off-balance sheet arrangements. We are not aware of any material transactions which are not disclosed in our consolidated financial statements.
| 54 |
Significant Accounting Policies and Critical Accounting Estimates
The methods, estimates, and judgments that we use in applying our accounting policies have a significant impact on the results that we report in our consolidated financial statements. Some of our accounting policies require us to make difficult and subjective judgments, often as a result of the need to make estimates regarding matters that are inherently uncertain. In addition, Section 107 of the JOBS Act provides that an emerging growth company can take advantage of the extended transition period provided in Section 7(a)(2)(B) of the Securities Act for complying with new or revised accounting standards. In other words, an emerging growth company can delay the adoption of certain accounting standards until those standards would otherwise apply to private companies. We are not choosing to “opt out” of this provision. Section 107 of the JOBS Act provides that our decision to opt out of the extended transition period for complying with new or revised accounting standards is irrevocable. As a result of our election, not to “opt out” of Section 107, DanDrit’s financial statements may not be comparable to companies that comply with public company effective dates.
Our most critical accounting estimates include:
Property and Equipment — Property and equipment are stated at cost. Expenditures for major renewals and betterments that extend the useful lives of property and equipment are capitalized, upon being placed in service. Expenditures for maintenance and repairs are charged to expense as incurred. Depreciation is computed for financial statement purposes on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful lives of the assets which range from four to six years.
Intangible Assets — Definite life intangible assets include patents. The Company accounts for definite life intangible assets in accordance with Financial Accounting Standards Board, (“FASB”) Accounting Standards Codification, (“ASC”) Topic 350, “Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets” and amortized the patents on a straight line basis over the estimated useful life of twenty years. Costs incurred in relation to patent applications are capitalized costs and amortized over the estimated useful life of the patent. If it is determined that a patent will not be issued, the related remaining patent application costs are charged to expense.
Revenue Recognition and Sales — The Company’s sales of its MelCancerVac colorectal cancer treatment have been limited to a compassionate use basis in Singapore after stage IIA trials and the vaccine is not currently approved for sale for any other use or location. The Company accounts for revenue recognition in accordance with Securities and Exchange Commission Staff Accounting Bulletin No. 101, “Revenue Recognition in Financial Statements” (SAB 101), FASB ASC 605 Revenue Recognition. The Company recognizes revenue when rights and risk of ownership have passed to the customer, when there is persuasive evidence of an arrangement, product has been shipped or delivered to the customer, the price and terms are finalized, and collection of the resulting receivable is reasonably assured. Products are primarily shipped FOB shipping point at which time title passes to the customer.
Value Added Tax - In Denmark, Value Added Tax (“VAT”) of 25% of the invoice amount is collected in respect of the sales of goods on behalf of tax authorities. The VAT collected is not revenue of the Company; instead, the amount is recorded as a liability on the balance sheet until such VAT is paid to the authorities. VAT of 25% is also paid to Danish and EU vendors on invoices. These amounts are refundable from the respective governmental authority and recorded as other receivables in the accompanying financial statements.
Accounting Estimates - The preparation of financial statements in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities, the disclosures of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amount of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ from those estimated.
Recently Enacted Accounting Standards
For a description of accounting changes and recent accounting standards, including the expected dates of adoption and estimated effects, if any, on our consolidated financial statements, see “Note 1: Recent Accounting Pronouncements” in the financial statements included elsewhere in this report.
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk
The registrant is a smaller reporting company and is not required to provide this information.
| 55 |
Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data
DANDRIT BIOTECH USA, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Index to Consolidated Financial Statements
| 56 |

4397 South Albright Drive, Salt Lake City, UT 84124
(801) 277-2763 Phone • (801) 277-6509 Fax
DANDRIT BIOTECH USA, INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
Fruebjergvej 3 Box 62
2100 Copenhagen, Denmark
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of DanDrit Biotech USA, Inc. and Subsidiary as of June 30, 2016 and 2015, and the related consolidated statements of operations, consolidated other comprehensive income, consolidated stockholders’ equity (deficit) and consolidated cash flows for the year ended December 31, 2016, six months ended June 30, 2015 and year ended December 31, 2014. These consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these consolidated financial statements based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the consolidated financial statements are free of material misstatement. The company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal controls over financial reporting for the year ended June 30, 2016, six months ended June 30, 2015 and year ended December 31, 2014. Our audit included consideration of internal controls over financial reporting as a basis for designing audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the company’s internal controls over financial reporting for the year ended June 30, 2016, six months ended June 30, 2015 and year ended December 31, 2014. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the consolidated financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall consolidated financial statement presentation. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, based on our audit, the consolidated financial statements audited by us present fairly, in all material respects, the consolidated financial position of DanDrit Biotech USA, Inc. and Subsidiary as of June 30, 2016 and 2015, and the consolidated results of their operations and their consolidated cash flows for the for the year ended June 30, 2016, six months ended June 30, 2015 and year ended December 31, 2014, in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States of America.
The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared assuming the Company will continue as a going concern. As discussed in Note 2 to the financial statements, the Company has incurred losses, an accumulated deficit and has a short-term obligations in excess of anticipated cash. These factors raise substantial doubt about the Company's ability to continue as a going concern. Management's plans in regards to these matters are also described in Note 2. The consolidated financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of these uncertainties.
/S/ Gregory & Associates, LLC
September 28, 2016
Salt Lake City, Utah
| F-1 |
DANDRIT BIOTECH USA INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
| Balance at | Balance at | |||||||
| June 30, 2016 | June 30, 2015 | |||||||
| ASSETS | ||||||||
| Current Assets: | ||||||||
| Cash (1) | $ | 23,368 | $ | 421,145 | ||||
| Cash held in escrow (2) | - | 1,052,989 | ||||||
| Other receivables | 695,418 | 432,125 | ||||||
| Prepaid expenses | 13,693 | - | ||||||
| Total Current Assets | 732,479 | 1,906,259 | ||||||
| Property and Equipment, net accumulated depreciation | - | - | ||||||
| OTHER ASSETS: | ||||||||
| Definite life intangible assets | 135,743 | 164,046 | ||||||
| Deposits | 2,609 | 2,572 | ||||||
| Total Other Assets | 138,352 | 166,618 | ||||||
| Total Assets | 870,831 | 2,072,877 | ||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
| F-2 |
DANDRIT BIOTECH USA INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
| Balance at | Balance at | |||||||
| June 30,
2016 | June 30,
2015 | |||||||
| LIABILITIES | ||||||||
| Current Liabilities: | ||||||||
| Notes payable - related party, current portion | 102,882 | 100,614 | ||||||
| Accounts payable - trade | 1,087,758 | 512,783 | ||||||
| Accounts payable - related party | 97,357 | 366,035 | ||||||
| Accrued expenses | 220,232 | 16,305 | ||||||
| Total Current Liabilities | 1,508,229 | 995,737 | ||||||
| Long Term Liabilities | ||||||||
| Notes payable - related Party | - | - | ||||||
| Total Long-Term Liabilities | - | - | ||||||
| Total Liabilities | 1,508,229 | 995,737 | ||||||
| STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY (DEFICIT): | ||||||||
| Common stock; par value 0.0001, 100,000,000 shares authorized, 9,533,290 issued and outstanding at June 30, 2016 and 2015 | 953 | 953 | ||||||
| Additional paid-in capital | 25,098,050 | 25,098,050 | ||||||
| Other comprehensive income, net | 564,293 | 543,592 | ||||||
| Accumulated Deficit | (26,300,694 | ) | (24,565,455 | ) | ||||
| Total Stockholders' Equity (Deficit) | (637,398 | ) | 1,077,140 | |||||
| Total Liabilities and Stockholders' (Deficit) | $ | 870,831 | $ | 2,072,877 | ||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
| F-3 |
DANDRIT BIOTECH USA INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENT OF OPERATIONS
| For the Year Ended | For the Six Months Ended | For the Year Ended | ||||||||||
| June 30, | June 30, | December 31, | ||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
| Net Sales | $ | 42,769 | $ | - | $ | - | ||||||
| Cost of Goods Sold | 5,275 | 65,932 | 295,661 | |||||||||
| Gross Profit (Loss) | 37,494 | (65,932 | ) | (295,661 | ) | |||||||
| Operating Expenses: | ||||||||||||
| General and administrative expenses | 1,229,865 | 739,189 | 1,644,918 | |||||||||
| Research and Development expenses | 804,188 | 1,625,488 | - | |||||||||
| Depreciation and Amortization | 27,395 | 7,973 | 18,981 | |||||||||
| Consulting expenses | 96,976 | 295,983 | 469,666 | |||||||||
| Total Operating Expense | 2,158,424 | 2,668,633 | 2,133,565 | |||||||||
| Loss from Operations | (2,120,930 | ) | (2,734,565 | ) | (2,429,226 | ) | ||||||
| Other Income (Expense) | ||||||||||||
| Interest (expense) | (2,364 | ) | 3,101 | (84,550 | ) | |||||||
| Gain (loss) on currency transactions | (74,732 | ) | (315,846 | ) | (40,583 | ) | ||||||
| Interest and other income | - | - | 5,937 | |||||||||
| Total Other Income (Expense) | (77,096 | ) | (312,745 | ) | (119,196 | ) | ||||||
| Loss Before Income Taxes | (2,198,026 | ) | (3,047,310 | ) | (2,548,422 | ) | ||||||
| Income Tax Expense (Benefit) | (462,787 | ) | (373,862 | ) | (177,539 | ) | ||||||
| Net Loss | (1,735,239 | ) | (2,673,448 | ) | (2,370,883 | ) | ||||||
| BASIC AND DILUTED LOSS PER SHARE | $ | (0.18 | ) | $ | (0.28 | ) | $ | (0.32 | ) | |||
| WEIGHTED AVERAGE NUMBER OF COMMON SHARES OUTSTANDING- BASIC AND DILUTED | 9,533,290 | 9,533,290 | 7,500,142 | |||||||||
| WEIGHTED AVERAGE BASIC AND DILUTED LOSS PER SHARE | $ | (0.18 | ) | $ | (0.28 | ) | $ | (0.32 | ) | |||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
| F-4 |
DANDRIT BIOTECH USA INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OTHER COMPREHENSIVE LOSS
| For the Year Ended | For the Six Months Ended | For the Year Ended | ||||||||||
| June 30, | June 30, | December 31, | ||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
| (Net Loss) | $ | (1,735,239 | ) | $ | (2,673,448 | ) | $ | (2,370,883 | ) | |||
| (Currency Translation, Net of Taxes) | 20,701 | 268,343 | 306,439 | |||||||||
| (Other Comprehensive Loss) | $ | (1,714,538 | ) | $ | (2,405,105 | ) | $ | (2,064,444 | ) | |||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
| F-5 |
DANDRIT BIOTECH USA INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENT OF STOCKHOLDERS' (DEFICIT)
For the Six Months Ended June 30, 2015 and Years Ended December 31, 2014 and 2013
| Additional | Accumulated | Other | ||||||||||||||||||
| Common Stock | Paid in | Earnings | Comprehensive | |||||||||||||||||
| Shares | Amount | Capital | (Deficit) | Income (loss) | ||||||||||||||||
| BALANCE, December 31, 2013 | 6,000,000 | $ | 600 | $ | 17,867,546 | $ | (19,521,126 | ) | $ | (31,190 | ) | |||||||||
| To record the recapitalization of Subsidiary in connection with the February 12, 2014 Share Exchange Agreement where in the Dandrit Biotech USA Inc. (“Parent”) issued 6,000,000 common shares to acquire Dandrit Biotech A/S (“Subsidiary”) Dandrit Biotech USA Inc, (Formerly Putnam Hills Corp), | 2,040,000 | 204 | (79,436 | ) | - | - | ||||||||||||||
| To record the issuance of 4,000 and 141,000 common shares on September 4, 2014 in connection Initial Public Offering valued at $5 per share or $4,000 and $141,000, respectfully. Net of stock offering cost of $67,000 | 145,000 | 14 | 657,985 | - | - | |||||||||||||||
| To record the issuance of 100 common shares on September 24, 2014 in connection Initial Public Offering valued at $5 per share or $500. | 100 | 0.01 | 500 | - | - | |||||||||||||||
| To record the issuance of 889,690 common shares in October, 2014 in connection Initial Public Offering valued at $5 per share or $4,358,879 net of stock offering cost of $89,360 | 889,690 | 89 | 4,359,001 | - | - | |||||||||||||||
| To record the issuance of 58,500 common shares on November 13, 2014 in connection Initial Public Offering valued at $5 per share or $292,500. | 58,500 | 6 | 292,494 | - | - | |||||||||||||||
| To record the issuance of 400,000 common shares on December 31, 2014 in connection private placement valued at $5 per share or $2,000,000. | 400,000 | 40 | 1,999,960 | - | - | |||||||||||||||
| Equity Adjustment for Foreign Currency Translation Year Ended December 31, 2014 | - | - | - | - | 306,439 | |||||||||||||||
| Rounding | - | - | - | 2 | - | |||||||||||||||
| Net Loss for the year Ended December 31, 2014 | - | - | - | (2,370,883 | ) | - | ||||||||||||||
| BALANCE, December 31, 2014 | 9,533,290 | $ | 953 | $ | 25,098,050 | $ | (21,892,007 | ) | $ | 275,249 | ||||||||||
| Equity Adjustment for Foreign Currency Translation for the six months ended June 30, 2015. | - | - | - | - | 268,343 | |||||||||||||||
| Net Loss for the Six Months Ended June 30, 2015 | - | - | - | (2,673,448 | ) | - | ||||||||||||||
| BALANCE, June 30, 2015 | 9,533,290 | $ | 953 | $ | 25,098,050 | $ | (24,565,455 | ) | $ | 543,592 | ||||||||||
| Equity Adjustment for Foreign Currency Translation for the year ended June 30, 2016. | - | - | - | - | 20,701 | |||||||||||||||
| Net Loss for the year Ended June 30, 2016 | - | - | - | (1,735,239 | ) | - | ||||||||||||||
| BALANCE, June 30, 2016 | 9,533,290 | $ | 953 | $ | 25,098,050 | $ | (26,300,694 | ) | $ | 564,293 | ||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
| F-6 |
DANDRIT BIOTECH USA INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS
| For the Year Ended | For the Six Months Ended | For the Year Ended | ||||||||||
| June 30, | June 30, | December 31, | ||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
| Cash Flows from Operating Activities: | ||||||||||||
| Net (Loss) | $ | (1,735,239 | ) | $ | (2,673,448 | ) | $ | (2,370,883 | ) | |||
| Adjustments to reconcile net (loss) to net cash provided (used) by operations: | ||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization | 27,395 | 22,368 | 45,201 | |||||||||
| Accrued Interest on Notes Payable – Related Party | 2,354 | 2,126 | ||||||||||
| Changes in assets and liabilities: | ||||||||||||
| (Increase) decrease in other receivable, | (263,293 | ) | (424,109 | ) | 17,440 | |||||||
| (Increase) decrease in prepaid expenses & deposits | (13,730 | ) | 4,574 | 22,988 | ||||||||
| Increase (decrease) in accounts payable | 574,975 | (198,666 | ) | 162,950 | ||||||||
| Increase (decrease) in accounts payable – related party | (268,678 | ) | 153,597 | 212,438 | ||||||||
| Increase (decrease) in accrued expenses | 203,927 | (717,521 | ) | (124,309 | ) | |||||||
| Total Adjustments | 262,950 | (1,157,631 | ) | 336,708 | ||||||||
| Net Cash (Used) by Operating Activities | (1,472,289 | ) | (3,831,079 | ) | (2,034,175 | ) | ||||||
| Cash Flows from Investing Activities: | ||||||||||||
| Net decrease (increase) in cash held in escrow | 1,052,989 | 976,513 | (1,952,034 | ) | ||||||||
| Net Cash Used by Investing Activities | 1,052,989 | 976,513 | (1,952,034 | ) | ||||||||
| Cash Flows from Financing Activities: | ||||||||||||
| Proceeds from notes payable - related party | - | - | 814,291 | |||||||||
| Proceeds from stock sales | - | - | 7,377,089 | |||||||||
| Payment of stock offering costs | - | - | (89,360 | ) | ||||||||
| Payments on notes payable - related party | - | - | (1,432,213 | ) | ||||||||
| Net Cash Provided by Financing Activities | - | - | 6,669,807 | |||||||||
| (Gain) loss on Currency Translation | 21,523 | 266,880 | 306,439 | |||||||||
| Net Increase (Decrease) in Cash and Cash Equivalents | (397,777 | ) | (2,587,686 | ) | 2,990,037 | |||||||
| Cash and Cash Equivalents at Beginning of Period | 421,145 | 3,008,831 | 18,794 | |||||||||
| Cash and Cash Equivalents at End of Period | 23,368 | 421,145 | 3,008,831 | |||||||||
| Supplemental Disclosures of Cash Flow Information: | ||||||||||||
| Cash paid during the year for | ||||||||||||
| Interest | - | 1,467 | 82,816 | |||||||||
| Income Taxes | - | - | - | |||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
| F-7 |
DANDRIT BIOTECH USA INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 1 — SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Business and Basis of Presentation - DanDrit Biotech USA, Inc. (“DanDrit USA”, the “Company”, “we”, “us”, “our”) (formerly Putnam Hills Corp) was originally incorporated in the state of Delaware on January 18, 2011 as a vehicle to pursue a business combination through the acquisition of, or merger with, an operating business.
DanDrit BioTech A/S, a Danish Corporation was incorporated on April 1, 2001 (“DanDrit Denmark”) a 96.92% owned subsidiary of the Company. The Company engages in the research and development, manufacturing and clinical trials of pharmaceutical and biological products for the human treatment of cancer using the dendritic cell technology.
Year End - In June 2015, DanDrit’s board of directors approved a change to DanDrit’s fiscal year end from December 31 to June 30.
Reverse Acquisition - On February 12, 2014, pursuant to the Share Exchange Agreement (the "Share Exchange Agreement"), DanDrit USA completed the acquisition of 100% of the issued and outstanding capital stock of DanDrit Denmark (the “Share Exchange”) and as a result became DanDrit Denmark’s parent company (the “Parent”). Prior to the Share Exchange there were 5,000,000 shares of the common stock, par value $.0001 per share (the “Common Stock”) of Parent outstanding. Parent and an existing shareholder agreed to cancel 4,400,000 shares of its Common Stock and issued 1,440,000 shares of Common Stock for legal and consulting services related to the Share Exchange and a future public offering. At the time of the Share Exchange each outstanding share of common stock of DanDrit Denmark was exchanged for 1.498842 shares of Parent’s Common Stock, for a total of 6,000,000 shares, resulting in 8,040,000 shares of the Parent’s Common Stock outstanding immediately following the Share Exchange, including 185,053 shares of Common Stock reserved for issuance in accordance with Section 70 of the Danish Companies Act and the Articles of Association of DanDrit Denmark to the DanDrit Denmark shareholders who have not consented to the Share Exchange (the “Non-Consenting Shareholders”) , and deemed issued and outstanding for accounting purposes.
Consolidation - For the year ended June 30, 2016, six months ended June 30, 2015 and year ended December 31, 2014, the consolidated financial statements include the accounts and operations of the DanDrit Denmark, and the accounts and operations of DanDrit USA. All material inter-company transactions and accounts have been eliminated in the consolidation.
Functional Currency / Foreign currency translation - The functional currency of DanDrit Biotech A/S is the Danish Kroner (“DKK”). The Company’s reporting currency is the U.S. Dollar for the purpose of these financial statements. The Company’s balance sheet accounts are translated into U.S. dollars at the period-end exchange rates and all revenue and expenses are translated into U.S. dollars at the average exchange rates prevailing during year ended June 30, 2016, six months ended June 30, 2015 and year ended December 31, 2014 Translation gains and losses are deferred and accumulated as a component of other comprehensive income in stockholders’ equity. Transaction gains and losses that arise from exchange rate fluctuations from transactions denominated in a currency other than the functional currency are included in the statement of operations as incurred.
Cash and Cash Equivalents - The Company considers all highly liquid debt instruments purchased with a maturity of three months or less to be cash equivalents. The Company had balances held in a financial institution in the United States in excess of federally insured States amounts at June 30, 2016 and 2015 of $0 and $0, respectively. In May 2015 mostly of the cash balances were transferred to a financial institution in Denmark and a trust account at the Lett Law firm. At June 30, 2016 and 2015 we had cash and cash held in escrow balances of $23,368 and $1,474,134, respectively.
Property and Equipment - Property and equipment are stated at cost. Expenditures for major renewals and betterments that extend the useful lives of property and equipment are capitalized upon being placed in service. Expenditures for maintenance and repairs are charged to expense as incurred. Depreciation is computed for financial statement purposes on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful lives of the assets which range from four to six years (See Note 3).
| F-8 |
DANDRIT BIOTECH USA INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 1 — SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (continued)
Intangible Assets - Definite life intangible assets include patents. The Company accounts for definite life intangible assets in accordance with Financial Accounting Standards Board, (“FASB”) Accounting Standards Codification, (“ASC”) Topic 350, “Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets” and amortized the patents on a straight line basis over the estimated useful life of twenty years. Costs incurred in relation to patent applications are capitalized cost and amortized over the estimated useful life of the patent. If it is determined that a patent will not be issued, the related remaining patent application costs are charged to expense.
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets - Long-lived assets, such as property, plant, and equipment and patents are reviewed for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable. Circumstances which could trigger a review include, but are not limited to: significant decreases in the market price of the asset; significant adverse changes in the business climate or legal factors; current period cash flow or operating losses combined with a history of losses or a forecast of continuing losses associated with the use of the asset; and current expectation that the asset will more likely than not be sold or disposed of significantly before the end of its estimated useful life.
Recoverability of assets to be held and used is measured by a comparison of the carrying amount of an asset to estimated undiscounted future cash flows expected to be generated by the asset. If the carrying amount of an asset exceeds its estimated undiscounted future cash flows, an impairment charge is recognized by the amount by which the carrying amount of the asset exceeds the fair value of the asset. Assets to be disposed of would be separately presented in the balance sheet and reported at the lower of the carrying amount or fair value less costs to sell, and would no longer be depreciated. The depreciable basis of assets that are impaired and continue in use is their respective fair values.
Revenue Recognition and Sales - The Company’s sales of its MelCancerVac colorectal cancer treatment have been limited to a compassionate use basis in Singapore after stage IIA trials and is not approved for current sale for any other use or location. The Company accounts for revenue recognition in accordance with the Securities and Exchange Commission Staff Accounting Bulletin No. 101, “Revenue Recognition in Financial Statements” (SAB 101), FASB ASC 605 Revenue Recognition. The Company recognizes revenue when rights and risk of ownership have passed to the customer, when there is persuasive evidence of an arrangement, product has been shipped or delivered to the customer, the price and terms are finalized, and collections of the resulting receivable is reasonably assured. Products are primarily shipped FOB shipping point at which time title passes to the customer.
Value Added Tax - In Denmark, Value Added Tax (“VAT”) of 25% of the invoice amount is collected in respect of the sales of goods on behalf of tax authorities. The VAT collected is not revenue of the Company; instead, the amount is recorded as a liability on the balance sheet until such VAT is paid to the authorities. VAT of 25% is also paid to Danish and EU vendors on invoices. These amounts are refundable from the respective governmental authority and recorded as other receivables in the accompanying financial statements.
Research and Development Expenses - The Company expenses research and development expenses incurred in formulating, improving, validating and creating alternative or modified processes related to and expanding the use of our MAGE –A dendrite cell cancer therapy. Research and development expenses were included in operating expenses for the year ended June 30, 2016, six months ended June 30, 2015 and year ended December 31, 2014 with the amount of $804,188 $1,625,488 and $0, respectably.
Our research and development expenses may fluctuate substantially from quarter to quarter depending on the clinical studies and the timing of samples supporting the clinical studies.
Income Taxes - The Company accounts for income taxes in accordance with FASB ASC Topic 740 Accounting for Income Taxes. This statement requires an asset and liability approach for accounting for income taxes.
| F-9 |
DANDRIT BIOTECH USA INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 1 — SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (continued)
Loss Per Share - The Company calculates earnings/(loss) per share in accordance with FASB ASC 260 Earnings Per Share. Basic earnings per common share (EPS) are based on the weighted average number of common shares outstanding during each period. Diluted earnings per common share are based on shares outstanding (computed as under basic EPS) and potentially dilutive common shares. Potential common shares included in the diluted earnings per share calculation include in-the-money stock options that have been granted but have not been exercised.
Derivatives - We generally do not use derivative financial instruments to hedge exposures to cash-flow, market or foreign-currency risks. However, we have entered into certain other financial instruments and contracts, such as debt financing arrangements with features that are either (i) not afforded equity classification, (ii) embody risks not clearly and closely related to host contracts, or (iii) may be net-cash settled by the counterparty. These instruments are required to be carried as derivative liabilities, at fair value.
We estimate fair values of all derivative instruments, such as embedded conversion features utilizing Level 3 inputs (defined below in Note 1: Fair Value of Financial Instruments). We use the Black-Scholes option valuation technique because it embodies all of the requisite assumptions (including trading volatility, estimated terms and risk free rates) necessary to fair value these instruments. Estimating fair values of derivative financial instruments requires the development of significant and subjective inputs that may, and are likely to, change over the duration of the instrument with related changes in internal and external market factors. In addition, option-based techniques are highly volatile and sensitive to changes in the market price of our common stock, which have historically had high volatility. Since derivative financial instruments are initially and subsequently carried at fair value, our income will reflect the volatility in these estimate and assumption changes.
We report our derivative liabilities at fair value on the balance sheets. As of June 30, 2016 and 2015, we had no derivative liabilities.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments - The Company accounts for fair value measurements for financial assets and financial liabilities in accordance with FASB ASC Topic 820. The authoritative guidance, which, among other things, defines fair value, establishes a consistent framework for measuring fair value and expands disclosure for each major asset and liability category measured at fair value on either a recurring or nonrecurring basis. Fair value is defined as the exit price, representing the amount that would either be received to sell an asset or be paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants. As such, fair value is a market-based measurement that should be determined based on assumptions that market participants would use in pricing an asset or liability. As a basis for considering such assumptions, the guidance establishes a three-tier fair value hierarchy, which prioritizes the inputs used in measuring fair value as follows:
| ● | Level 1. Observable inputs such as quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities; |
| ● | Level 2. Inputs, other than the quoted prices in active markets, that are observable either directly or indirectly; and |
| ● | Level 3. Unobservable inputs in which there is little or no market data, which require the reporting entity to develop its own assumptions. |
Unless otherwise disclosed, the fair value of the Company’s financial instruments including cash, accounts receivable, prepaid expenses, investments, accounts payable, accrued expenses, capital lease obligations and notes payable approximates their recorded values due to their short-term maturities.
Accounting Estimates - The preparation of financial statements in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities, the disclosures of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amount of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ from those estimated.
| F-10 |
DANDRIT BIOTECH USA INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 1 — SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (continued)
Recent Accounting Pronouncements - In May 2014, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) issued a new standard to achieve a consistent application of revenue recognition within the U.S., resulting in a single revenue model to be applied by reporting companies under U.S. generally accepted accounting principles. Under the new model, recognition of revenue occurs when a customer obtains control of promised goods or services in an amount that reflects the consideration to which the entity expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods or services. In addition, the new standard requires that reporting companies disclose the nature, amount, timing, and uncertainty of revenue and cash flows arising from contracts with customers. On July 9, 2015, the FASB agreed to delay the effective date by one year; accordingly, the new standard is effective for us beginning in the first quarter of 2018 and we expect to adopt it at that time. The new standard is required to be applied retrospectively to each prior reporting period presented or retrospectively with the cumulative effect of initially applying it recognized at the date of initial application. We have not yet selected a transition method, nor have we determined the impact of the new standard on our consolidated financial statements.
In 2015, the FASB issued an amended standard requiring that we classify all deferred tax assets and liabilities as non-current on the balance sheet instead of separating deferred taxes into current and non-current. The amended standard is effective for us beginning in the first quarter of 2017; early adoption is permitted and we are evaluating whether we will early adopt. The amended standard may be adopted on either a prospective or retrospective basis. We do not expect that the adoption of this standard will have a significant impact on our financial position or results of operations.
In February 2016, the FASB issued changes to the accounting for leases that primarily affect presentation and disclosure requirements. The new standard will require the recognition of a right to use asset and underlying lease liability for operating leases with an initial life in excess of one year. This standard is effective for us beginning in the first quarter of 2019. We have not yet determined the impact of the new standard on our consolidated financial statements.
Other recent accounting pronouncements issued by the FASB did not or are not believed by management to have a material impact on the Company's present or future financial statements.
Reclassification - The financial statements for the six months ended June 30, 2015 and year ended December 31, 2014 have been reclassified to conform to the headings and classifications used in the June 30, 2016 financial statements.
NOTE 2 — GOING CONCERN
The accompanying unaudited consolidated financial statements have been prepared in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles of the United States of America, which contemplate continuation of the Company as a going concern. However, the Company has incurred significant losses, has not yet been successful in establishing profitable operations and has short-term obligations in excess of anticipated cash. These factors raise substantial doubt about the ability of the Company to continue as a going concern. In this regard, management plans to mitigate this doubt by raising additional funds through debt and/or equity offerings and by substantially increasing sales once approval for the Company’s product is obtained. The Company is attempting to raise $15,000,000 or more through a private placement offering and close the acquisition of OncoSynergy, Inc. The Company has subsequently received a commitment for a $500,000 investment, a commitment for a DKK 1,000,000 $153,750 1% convertible note and DKK 3,400,000 approximately $511,275, in 1% convertible notes payable maturing December 31, 2017. The closing of the private placement is contingent on the closing of the acquisition of the assets of OncoSynergy, Inc.There is no assurance that the Company will be successful in raising additional funds through the debt or equity or achieving profitable operations. The consolidated financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of these uncertainties.
NOTE 3 — PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT
Property and equipment consisted of the following at June 30, 2016 and 2015:
| Useful Life | June 30,
2016 | June
30, 2015 | ||||||||
| Lab equipment and instruments | 4-6 | $ | 163,959 | $ | 164,778 | |||||
| Computer equipment | 4-6 | 56,155 | 56,436 | |||||||
| 220,114 | 221,214 | |||||||||
| Less Accumulated Depreciation | (220,114 | ) | (221,214 | ) | ||||||
| Net Property and Equipment | $ | - | $ | - | ||||||
Depreciation expense amounted to $0 for the year ended June 30, 2016, $0 for the six months ended June 30, 2015, and $0 for the year ended December 31, 2014. The Company’s property and equipment is held as collateral on the notes payable related party.
| F-11 |
DANDRIT BIOTECH USA INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 4 — DEFINITE-LIFE INTANGIBLE ASSETS
At June 30, 2016 and 2015, definite-life intangible assets, net of accumulated amortization, consist of patents on the Company’s products and processes of $135,743 and $164,046, respectively. The patents are recorded at cost and amortized over twenty years from the date of application. Amortization expense for the year ended June 30, 2016 was $27,395, including $12,048 in losses on abandoned assets. Amortization expense for the six months ended June 30, 2015 was $7,973. Amortization expense for the year ended December 31, 2014 was $18,981. Expected future amortization expense for the years ended are as follows:
| Year ending June 30, | ||||
| 2017 | $ | 14,794 | ||
| 2018 | 14,794 | |||
| 2019 | 14,794 | |||
| 2020 | 14,835 | |||
| 2021 | 14,794 | |||
| Thereafter | 61,732 | |||
| $ | 135,743 | |||
NOTE 5 — NOTES PAYABLE – RELATED PARTY
Notes payable to related parties consists of the following as of June 30, 2016 and 2015:
| June
30, 2016 | June
30, 2015 | |||||||
| Non-Interest Bearing Loan Payable Sunrise Financial Group Inc. | $ | 38,235 | $ | 38,235 | ||||
| Note Payable ML Group | 17,414 | 17,500 | ||||||
| 6% Promissory Note payable to NLBDIT 2010 Enterprises, LLC | 47,233 | 44,879 | ||||||
| Total Notes Payable – Related Party | 102,882 | 100,614 | ||||||
| Less Current Maturities | (102,882 | ) | (100,614 | ) | ||||
| Note Payables – Related Party Long Term | $ | - | $ | - | ||||
The following represents the future maturities of long-term debt as of June 30, 2016:
| Year ending June 30, | ||||
| 2017 | 102,882 | |||
| 2018 | - | |||
| 2019 | - | |||
| 2020 | - | |||
| 2021 | - | |||
| Thereafter | - | |||
| $ | 102,882 | |||
| F-12 |
DANDRIT BIOTECH USA INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 5 — NOTES PAYABLE – RELATED PARTY (continued)
As of June 30, 2015, the outstanding balance of $38,235 for professional fees paid by a shareholder and amounts advanced to the Parent are reported as notes payable - related party. The $38,235 notes payable were acquired in the reverse acquisition. The amounts are unsecured, non-interest bearing and have no stipulated repayment terms.
A 6% promissory note payable to NLBDIT 2010 Enterprises, LLC, an entity controlled by a shareholder of the Company, was acquired by the Company in the reverse acquisition, payable on February 12, 2014 upon the completion date of the Share Exchange. As of June 30, 2016, the outstanding balance on the note, including accrued interest, was $47,233. During the year ended June 30, 2016, six months ended June 30, 2015 and year ended December 31, 2014 the Company recorded related party interest on the note of $2,354, $1,164 and $2,126, respectively.
NOTE 6 — DERIVATIVE LIABILITIES
The Company does not use derivative financial instruments to hedge exposures to cash-flow, market or foreign-currency risks. However, the Company has entered into certain other financial instruments and contracts, such as debt financing arrangements with features that are either (i) not afforded equity classification, (ii) embody risks not clearly and closely related to host contracts, or (iii) may be net-cash settled by the counterparty. These instruments are required to be carried as derivative liabilities, at fair value.
The fair value of the shares to be issued upon conversion of the debt financing is recorded as a derivative liability, with the change in the fair value recorded as a gain or loss in the accompanying statement of operations As of June 30, 2016 and 2015 the Company did not have any convertible debt financing or derivative liabilities. The Company has subsequently entered into convertible debt financing agreements See Note 14.
NOTE 7 — LEASES
Operating Leases — The Company leases laboratory and production space under operating lease agreements which can be cancelled with 3 months’ notice. The lease calls for monthly payments of DKK 6,300 (approximately $937 at June 30, 2016).
On March 27, 2014, the Company entered into an operating lease agreement for office space from a related party. The Lease calls for monthly payments of DKK 10,000 (approximately $1,496), increasing to DKK 20,000 (approximately $2,992) on July 1, 2014. The lease was terminated on May 31, 2015.
On March 25, 2015, the Company entered into an agreement for use of virtual office space at a rate of $375/month on a month-to-month basis, which can be terminated by either party on one month’s notice.
Lease expense charged to operations was $15,744, $20,800 and $32,297 for the year ended June 30, 2016, six months ended June 30, 2015 and year ended December 31, 2014, respectively.
NOTE 8 — INCOME TAXES
The Company accounts for income taxes in accordance with FASB ASC Topic 740, Accounting for Income Taxes; which requires the Company to provide a net deferred tax asset or liability equal to the expected future tax benefit or expense of temporary reporting differences between book and tax accounting and any available operating loss or tax credit carry forwards. The amount of and ultimate realization of the benefits from the deferred tax assets for income tax purposes is dependent, in part, upon the tax laws in effect, the Company’s future earnings, and other future events, the effects of which cannot be determined.
As of June 30, 2016 and 2015, the Company had net operating loss carryforwards of approximately $10,136,400 and $10,311,877, respectively, giving rise to deferred tax assets of $2,230,008 and $2,268,613, respectively for Danish tax purposes which do not expire.
| F-13 |
DANDRIT BIOTECH USA INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 8 — INCOME TAXES (continued)
As of June 30, 2016 and 2015, the Company had net operating loss carryforwards of approximately $934,920 and $784,011, respectively, giving rise to deferred tax assets of $328,072 and $266,564, respectively for United States tax purposes which expire in 2036.
The Company files Danish and US income tax returns, and they are generally no longer subject to tax examinations for years prior to 2008 for their Danish tax returns and 2012 for their US tax returns.
The temporary differences, tax credits and carry forwards gave rise to the following deferred tax asset (liabilities) at June 30, 2016 and 2015:
| June 30, | ||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | |||||||
| Excess of Tax over book depreciation Fixed assets | $ | 7,660 | $ | 10,240 | ||||
| Excess of Tax over book depreciation Patents | 870 | 5,560 | ||||||
| Net Operating Loss Carryforward | 2,558,080 | 2,535,177 | ||||||
| Valuation Allowance | (2,566,610 | ) | (2,550,977 | ) | ||||
| Total Deferred Tax Asset (Liabilities) | $ | - | $ | - | ||||
In accordance with prevailing accounting guidance, the Company is required to recognize and disclose any income tax uncertainties. The guidance provides a two-step approach to recognize and disclose any income tax uncertainties. The guidance provides a two-step approach to recognizing and measuring tax benefits and liabilities when realization of the tax position is uncertain. The first step is to determine whether the tax position meets the more-likely-than-not condition for recognition and the second step is to determine the amount to be recognized based on the cumulative probability that exceeds 50%. The amount of and ultimate realization of the benefits from the deferred tax assets for income tax purposes is dependent, in part, upon the tax laws in effect, the Company’s future earnings, and other future events, the effects of which can be difficult to determine and can only be estimated. Management estimates that it is more likely than not that the Company will not generate adequate net profits to use the deferred tax assets; and consequently, a valuation allowance was recorded for all deferred tax assets.
A reconciliation of income tax expense at the federal statutory rate to income tax expense at the Company’s effective rate is as follows for the year ended June 30, 2016, six months ended June 30, 2015, and year ended December 31, 2014:
| June 30, | December 31, | |||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
| Computed Tax at Expected Statutory Rate | $ | (747,329 | ) | $ | (1,036,085 | ) | $ | (866,463 | ) | |||
| Non-US Income Taxed at Different Rates | 236,700 | 319,541 | 255,356 | |||||||||
| Non-Deductible expenses / other items | 32,209 | - | (3,063 | ) | ||||||||
| Valuation allowance | 15,633 | 342,683 | 436,631 | |||||||||
| Income Tax Expense | $ | (462,787 | ) | $ | (373,862 | ) | $ | (177,539 | ) | |||
The components of income tax expense (benefit) from continuing operations for the year ended June 30, 2016, six months ended June 30, 2015, and for the year ended December 31, 2014 consisted of the following:
| June 30, | December 31, | |||||||||||
| Current Tax Expense | 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | |||||||||
| Danish Income Tax (Credits) | $ | (462,787 | ) | $ | (373,862 | ) | $ | (177,539 | ) | |||
| Deferred Income Tax Expense (Benefit) | ||||||||||||
| Excess of Tax over Book Depreciation Fixed Assets | 2,580 | 2,471 | 19,259 | |||||||||
| Excess of Tax over Book Depreciation Patents | 4,690 | 5,470 | 67,488 | |||||||||
| Net Operating Loss Carryforwards | (22,903 | ) | (342,683 | ) | (523,378 | ) | ||||||
| Change in the Valuation allowance | 15,633 | 334,742 | 436,631 | |||||||||
| Total Deferred Tax Expense | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | ||||||
Deferred income tax expense/(benefit) results primarily from the reversal of temporary timing differences between tax and financial statement income.
| F-14 |
DANDRIT BIOTECH USA INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 9 — LOSS PER SHARE
The following data shows the amounts used in computing loss per share and the effect on income and the weighted average number of shares of potential dilutive common stock for the year ended June 30, 2016, six months ended June 30, 2015, and year ended December 31, 2014:
| For the Year Ended | For the Six Months Ended | For the Year Ended | ||||||||||
| June 30, | June 30, | December 31, | ||||||||||
| 2016 | 2015 | 2014 | ||||||||||
| Net (Loss) | $ | (1,735,239 | ) | $ | (2,673,448 | ) | $ | (2,370,883 | ) | |||
| Weighted average number of common shares used in basic earnings per share | 9,533,290 | 9,533,290 | 7,500,142 | |||||||||
| Effect of dilutive securities, stock options and warrants | - | - | - | |||||||||
| Weighted average number of common shares and potential dilutive common shares outstanding used in dilutive earnings per share | 9,533,290 | 9,533,290 | 7,500,142 | |||||||||
For the year ended June 30, 2016, six months ended June 30, 2015 and year ended December 31, 2014, the Company had no options outstanding to purchase common stock of the Parent.
The Company subsequently issued four convertible notes payable totaling $360,900 and a commitment for a $150,375 convertible note which are convertible into 255,637 common shares. The Company issued 900,000 stock options to purchase shares at $2.00 per share.
NOTE 10 — STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
Common Stock — The Company has 100,000,000 authorized shares of Common stock $0.0001. As of June 30, 2016 and 2015 there were 9,533,290 shares issued and outstanding.
Share Exchange Agreement / Reverse Acquisition - On February 12, 2014, in accordance with the terms and conditions of a Share Exchange Agreement (the "Share Exchange Agreement"), we completed the acquisition of approximately 100% of the issued and outstanding capital stock of DanDrit Denmark (the “Share Exchange”) and as a result became DanDrit Denmark’s parent company (the “Parent”). In connection with the Share Exchange, each outstanding share of common stock of DanDrit Denmark was exchanged for 1.498842 shares of DanDrit USA’s common stock, par value $.0001 per share (the “Common Stock”) for an aggregate of 6,000,000 shares, including 185,053 shares of Common Stock reserved for issuance, in accordance with Section 70 of the Danish Companies Act and the Articles of Association of DanDrit Denmark, to the DanDrit Denmark shareholders who did not consent to the Share Exchange and deemed issued and outstanding for accounting purposes. In addition, in connection with the Share Exchange (1) the sole shareholder prior to the Share Exchange agreed to cancel 4,400,000 shares of outstanding Common Stock owned by it and (2) the board of directors and executive management of DanDrit Denmark was appointed to serve as the Board of Directors and executive management of DanDrit USA effective upon the resignation of the sole officer and director of DanDrit USA prior to the closing of the Share Exchange.
| F-15 |
DANDRIT BIOTECH USA INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 10 — STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY (continued)
Common Stock Issuances – On December 31, 2014, the Company received $2,000,000 in connection with a private offering of 400,000 shares of common stock at an offering price of $5.00 per share.
During the year ended December 31, 2014, pursuant to the Company’s offering up to $12,000,000 (2,400,000 shares) of common stock at an offering price of $5.00 per share in an initial public offering pursuant to a registration statement effective on August 12, 2014, the Company sold 1,093,290 shares of common stock for gross proceeds of $5,466,450 less offering costs of $156,360.
Voting- Holders of the Company’s common stock are entitled to one vote for each share held of record on each matter submitted to a vote of stockholders, including the election of directors, and do not have any right to cumulate votes in the election of directors.
Dividends- Holders of the Company’s common stock are entitled to receive ratably such dividends as our Board of Directors from time to time may declare out of funds legally available.
Liquidation Rights- In the event of any liquidation, dissolution or winding-up of affairs of the Company, after payment of all of our debts and liabilities, the holders of the Company’s common stock will be entitled to share ratably in the distribution of any of our remaining assets.
NOTE 11 - COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
Shares held for non-consenting shareholders – In connection with the Share Exchange agreement certain shareholders of Dandrit Denmark had not been identified or did not consent to the exchange of shares. In accordance with Section 70 of the Danish Companies Act and the Articles of Association of DanDrit Denmark, the Non-Consenting Shareholders that did not exchange the DanDrit Denmark equity interests owned by such Non-Consenting Shareholders for shares of the Company, will be entitled to receive up to 185,053 shares of common stock of the Company that each such Non-Consenting Shareholder would have been entitled to receive if such shareholder had consented to the Share Exchange. The 185,053 shares have been reflected as issued and outstanding in the accompanying financial statements.
Clinical Trial Agreements – The Company’s subsidiary, DanDrit Biotech A/S signed a contract of collaboration with the University Hospital IRCCS “San Martino” - IST – National Institute for Cancer Research, known as the San Martino Hospital of Genoa. Dr. Alberto Sobrero, the Head of the Medical Oncology Unit at the San Martino Hospital, is principal investigator of the randomized multicenter study. The collaboration relates to a Phase III adjuvant study of DanDrit’s vaccine in patients with no evident disease (“NED”) stage IV colorectal cancer (“CRC”). The primary goal of the study is to evaluate the efficacy of DanDrit’sMelCancerVac® (“MCV”) in stage IV CRC patients rendered disease free after the completion of standard treatments in accordance with local practices.
On April 28, 2015 the Company entered into a service agreement with Fondazione Giscad per la Ricerca sui Tumori to support Dandrit in a clinical trial to be conducted in Italy
Patient Name Use Program Agreements - On December 16, 2013, DanDrit Denmark entered into an agreement with a Dutch company (the “MCV Partner”) regarding a Patient Name Use Program (PNU) for the Company’s MCV. This program will allow DanDrit Denmark to sell MCV for a year of treatment (10 vaccines) to cancer patients through the MCV Partner. The MCV Partner offers a worldwide online platform providing access to non-registered medicines for patients with life threatening diseases. The MCV Partner is a turnkey solution and will be in charge of regulatory, recruitment, logistics, and pharmaco vigilance. The Company will pay the MCV Partner a royalty on a country to country basis for 20 years on MCV sales sold under the agreement. Either party may terminate the agreement with 180 day written notice.
On April 23, 2015, the Company entered into a collaboration agreement with Riyadh Pharma in Saudi Arabia to promote cooperation in the manufacturing and marketing of DanDrit's dendritic cell cancer vaccine.
Manufacturing agreements - On January 28, 2014, the Company entered into an agreement with Cellin Technologies for the manufacture of the MCV Cancer vaccine.
| F-16 |
DANDRIT BIOTECH USA INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 11 — COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES (continued)
On August 8, 2014, the Company entered into an agreement with Cellin Technologies for the manufacture of the Melanoma Cell Lysate.
Food and Drug Administration (FDA) - The FDA has extensive regulatory authority over biopharmaceutical products (drugs and biological products), manufacturing protocols and procedures and the facilities in which they will be manufactured. Any new bio product intended for use in humans is subject to rigorous testing requirements imposed by the FDA with respect to product efficacy and safety, possible toxicity and side effects. FDA approval for the use of new bio products (which can never be assured) requires several rounds of extensive preclinical testing and clinical investigations conducted by the sponsoring pharmaceutical company prior to sale and use of the product. At each stage, the approvals granted by the FDA include the manufacturing process utilized to produce the product. Accordingly, the Company’s cell systems used for the production of therapeutic or bio therapeutic products are subject to significant regulation by the FDA under the Federal Food, Drug and Cosmetic Act, as amended.
Product liability - The contract production services for therapeutic products offered exposes an inherent risk of liability as bio therapeutic substances manufactured, at the request and to the specifications of customers, could foreseeably cause adverse effects. The Company seeks to obtain agreements from contract production customers indemnifying and defending the Company from any potential liability arising from such risk. There can be no assurance, however, that the Company will be successful in obtaining such agreements in the future or that such indemnification agreements will adequately protect the Company against potential claims relating to such contract production services. The Company may also be exposed to potential product liability claims by users of its products. A successful partial or completely uninsured claim against the Company could have a material adverse effect on the Company’s operations.
Employment Agreements - The Company and its Subsidiary have employment agreements with officers of the Company.
Contingencies - The Company is from time to time involved in routine legal and administrative proceedings and claims of various types. While any proceedings or claim contains an element of uncertainty, management does not expect a material impact on our results of operations or financial position.
Consulting Agreement — As of December 11, 2014, the Company entered into an agreement with Northern Biotech Fund SARL, an entity controlled by a shareholder of the Company. Northern Biotech Fund SARL provides consulting services to the Company in connection with planning and structuring a fund raising for the Company. In 2014 consultancy expenses were $148,395 and for the six month ended June 30, 2015 the consultancy expenses were $240,000.
NOTE 12 — RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
During the year ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, the Company entered into various notes payable with shareholders of the Company, the notes were repaid during 2014.
On March 27, 2014 the Company entered into an operating lease agreement for office space from a shareholder of the Company (See Note 7). During the six months ended June 30, 2015 the Company paid the related party $14,500. During the year ended December 31, 2014, the Company paid the related party $23,152. The lease was terminated on May 31, 2015.
During the six months ended June 30, 2015 and during the year ended December 31, 2014, JARO Holding ApS owned by a director of the Company, provided medical consultancy services to the Company. During year ended June 30, 2016, the six months ended June 30, 2015, and year ended December 31, 2014, the Company recorded medical consultancy expense of $44.620, $44,886, and $29,925, respectively.
| F-17 |
DANDRIT BIOTECH USA INC. AND SUBSIDIARY
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 12 — RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS (continued)
In June, 2015 the Company paid DKK50.000 ($7,499) to Paseco ApS for consultancy services provided in June 2015.
During the year ended June 30, 2016, six months ended June 30, 2015 and the year ended December 31, 2014, a law firm partially owned by the Company’s Chairman of the Board of Directors provided legal services to the Company and recorded legal expense of $105,107, $132,414 and 288,546, respectively. At June 30, 2016 and 2015, the Company had a payable to the firm in the amount of $97,357 and $366,035. At June 30, 2016 and 2015, the Company had an escrow account of $0 and $1,052,989 with the Lett Law Firm
NOTE 13 — ASSET PURCHASE AGREEMENT
During April 2016 the Company entered into an Asset Purchase Agreement (the “Purchase Agreement”) wherein the Company will acquire OncoSynergy, Inc. The purchase price for the acquisition consists of (i) a number of shares of Common Stock of the Company equal to the number of shares of Series A Common Stock and Common Stock outstanding of the OncoSynergy, Inc. immediately prior to the closing of the Transaction, and (ii) derivative securities (including any option, right, warrant, call, convertible security, right to subscribe, conversion right or other agreement or commitment immediately outstanding prior to the closing, if any), of like tenor, except as to timing of exercisability and maturity, exercisable or convertible into a like number of shares of Common Stock, and having rights, preferences, terms and conditions consistent in all other respects with such outstanding derivative security. Immediately following the closing it is estimated OncoSynergy, Inc. will hold between 33% and 40% of the capital stock of the Company on a fully diluted basis, assuming the exercise or conversion in full of all outstanding derivative securities of the Dandrit BioTech USA, Inc.
NOTE 14 — SUBSEQUENT EVENT
The Company’s management reviewed material events through September 28, 2016.
Convertible Notes Payable - On July 1, 2016, the Company entered into a 1% convertible notes for DKK400,000 (approximately $60,150), with a shareholder of the Company. The note matures December 31, 2017. The note is convertible into common shares at $2.00 per share. The Company will recorded a discount on the notes for the conversion feature and a derivative liability based on the fair value of the conversion feature using the Black Scholes Option Pricing Model. The discount will be amortized as interest expense over the term of the note using the effective interest method.
On July 19, 2016, the Company entered into a 1% convertible notes for DKK400,000 (approximately $60,150), with a shareholder of the Company The note matures December 31, 2017. The note is convertible into common shares at $2.00 per share. The Company will recorded a discount on the notes for the conversion feature and a derivative liability based on the fair value of the conversion feature using the Black Scholes Option Pricing Model. The discount will be amortized as interest expense over the term of the note using the effective interest method.
On August 24, 2016, the Company entered into a 1% convertible notes for DKK600,000 (approximately $90,225). The note matures December 31, 2017. The note is convertible into common shares at $2.00 per share. The Company will recorded a discount on the notes for the conversion feature and a derivative liability based on the fair value of the conversion feature using the Black Scholes Option Pricing Model. The discount will be amortized as interest expense over the term of the note using the effective interest method.
On September 21, 2016, the Company entered into a 1% convertible notes for DKK1,000,000 (approximately $150,375). The note matures December 31, 2017. The note is convertible into common shares at $2.00 per share. The Company will recorded a discount on the notes for the conversion feature and a derivative liability based on the fair value of the conversion feature using the Black Scholes Option Pricing Model. The discount will be amortized as interest expense over the term of the note using the effective interest method.
On September 28, 2016, the Company received a commitment for a 1% convertible notes for DKK1,000,000 (approximately $150,375). The note matures December 31, 2017. The note is convertible into common shares at $2.00 per share. The Company will record a discount on the notes for the conversion feature and a derivative liability based on the fair value of the conversion feature using the Black Scholes Option Pricing Model. The discount will be amortized as interest expense over the term of the note using the effective interest method.
On July 1, 2016, the Company entered into a financial service agreement with APE Invest AS (an entity owned by a director of the Company) for consultancy services related to the Company raising additional equity financing in the US and Danish Capital Markets. The agreement calls for monthly payment of $20,000 with a $100,000 retainer payment due November 1, 2016. The agreement can be terminated with 12 month notice.
On September 15, 2016, the Company granted options to the Company’s president, Chairman of the Board and a Board Member to each purchase 300,000 commons shares at $2.00 per share expiring December 31, 2019. The options vest immediately upon issuance and contain certain anti-dilution provisions.
| F-18 |
Item 9. Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure
Not applicable.
Item 9A. Controls and Procedures
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Our Chief Executive Officer (the “Certifying Officer”) is responsible for establishing and maintaining disclosure controls and procedures for the Company. The Certifying Officer has designed such disclosure controls and procedures to ensure that material information is made known to him, particularly during the period in which this Report was prepared.
The Certifying Officer is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting for the Company used the “Internal Control over Financial Reporting Integrated Framework” issued by Committee of Sponsoring Organizations (“COSO”) to conduct an extensive review of the Company’s “disclosure controls and procedures” (as defined in the Exchange Act, Rules 13a-15(e) and 15-d-15(e)) as of the end of each of the periods covered by this Report (the “Evaluation Date”). Based upon that evaluation, the Certifying Officer concluded that, as of June 30, 2016, our disclosure controls and procedures were not effective in ensuring that the information we were required to disclose in reports that we file or submit under the Securities and Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) rules and forms.
The Certifying Officer based his conclusion on the fact that the Company has identified material weaknesses in controls over financial reporting, detailed below. In order to reduce the impact of these weaknesses to an acceptable level, the Company has contracted with consultants with expertise in U.S. GAAP and SEC financial reporting standards to review and compile all financial information prior to filing that information with the SEC. However, even with the added expertise of these consultants, we still expect to be deficient in our internal controls over disclosure and procedures until sufficient capital is available to hire the appropriate internal accounting staff and individuals with requisite GAAP and SEC financial reporting knowledge. There have been no significant changes in internal controls or in other factors that could significantly affect internal controls subsequent to the date of their evaluation, including any corrective actions with regard to significant deficiencies and material weaknesses.
Management Annual Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting for the Company. Management used the “Internal Control over Financial Reporting Integrated Framework” issued by COSO to conduct an extensive review of the Company’s internal controls over financial reporting to make that evaluation. As of June 30, 2016, the Company had identified deficiencies in internal controls that constituted material weaknesses in internal controls. Due to these material weaknesses, management concluded that internal controls over financial reporting as of June 30, 2016 were not effective, based on COSO’s framework.
The deficiencies are attributed to the fact that the Company does not have adequate resources to address complex accounting issues, as well as an inadequate number of persons to whom it can segregate accounting tasks within the Company so as to ensure the segregation of duties between those persons who approve and issue payment from those persons who are responsible to record and reconcile such transactions within the Company’s accounting system. These control deficiencies will be monitored and attention will be given to the matter as we continue to accelerate through our current growth stage.
Management has concluded that these control deficiencies constitute a material weakness. In order to reduce the impact of these weaknesses to an acceptable level, we have contracted with consultants with expertise in U.S. GAAP and SEC financial reporting standards to review and compile all financial information prior to filing that information with the SEC. However, even with the added expertise of these consultants, we still expect to be deficient in our internal controls over disclosure and procedures until sufficient capital is available to hire the appropriate internal accounting staff and individuals with requisite GAAP and SEC financial reporting knowledge. There were no significant changes in our internal control over financial reporting or in other factors that occurred during our most recent fiscal year that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, internal control over financial reporting.
This Annual Report does not include attestation reports of the Company’s registered public accounting firms regarding internal controls over financial reporting. Management’s report was not subject to attestation by the Company’s registered public accounting firm pursuant to rules of the Securities and Exchange Commission that permit the Company to provide only management’s report in this Annual Report.
Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
On March 10, 2016, the board of directors (the “Board”) of DanDrit Biotech USA, Inc., a Delaware corporation (the “Company”), accepted the amicable resignation of Lone Degn from the Company as its Chief Financial Officer, effective March 10, 2016.
Except as set forth above, there were no changes in our internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the period covered by this report that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
| 57 |
None.
Item 10. Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance
The following table identifies our executive officers and directors, their ages, their respective offices and positions, and their respective dates of election or appointment.
| Name | Age | Position | Officer/Director Since | |||
| Dr. Eric Leire | 58 | Chief Executive Officer and Director (Principal Executive Officer) | February 2014 | |||
| Dr. Eric Leire | 58 | Chief Financial Officer and Director (Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) | April 2016 | |||
| N.E. Nielsen | 67 | Chairman of the Board | February 2014 | |||
| Aldo Michael Noes Petersen | 54 | Director | February 2014 |
Executive officers are appointed by and serve at the pleasure of the Board of Directors. Our certificate of incorporation provides for the annual election of directors. At each annual meeting of stockholders, our directors will be elected to serve until their respective successors have been elected and qualified.
There are no family relationships, as defined in subparagraph (d) of Item 401 of Regulation S-K, among any of our executive officers and directors. To the best of our knowledge, none of our directors or executive officers has, during the past ten years, been involved in any legal proceedings described in subparagraph (f) of Item 401 of Regulation S-K.
Background
The following is a brief summary of the background of each of our directors and executive officers.
Dr. Eric Patterson Leire, MD, MBA. Dr. Eric Leire has served as the Chief Executive Officer and a director of DanDrit Denmark since April 2011. Dr. Leire also served for two years as Chief Executive Officer and director of DKTI A/S, a listed Danish investment company from September 2012. Prior to these roles Dr. Leire was a partner at BioFund Venture Capital, a Finnish biotech venture fund, from August 2006 through September 2010 and a partner at Medwell Capital Corp., a Canadian venture fund, from April 2010 through May 2011. Dr. Leire has worked globally for many international pharmaceutical organizations, including Schering-Plough, Pfizer, Inc., Boots Pharmaceuticals Company PLC, Harvard AIDS Institute and bioStrategies Group. Dr. Leire also served as the CEO of US biotech companies APT Therapeutics and Paringenix and currently serves on the board of directors of Novicol Canada and DanDrit Biotech USA Inc. Dr. Leire received his medical degree from the University of Medicine of Grenoble in 1980 and his MBA from ISA-HEC and the Kellogg School of Management at Northwestern University in 1991. The Board of Directors believes that Dr. Leire’s significant global experience in the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries will be a significant asset to DanDrit as it carries out its business plan and for those reasons determined that he should serve on the Board of Directors.
| 58 |
NE Nielsen. Mr. Nielsen is a lawyer and has been a partner at the Lett Law Firm in Denmark since April 2011. His practice areas are capital market conditions, securities law, boards of directors, managerial, finance and acquisitions. He currently serves as the chairman and a board member of numerous companies, including as Chairman of DanDrit Biotech A/S since June 2013, director of the board of Charles Christensen A/S since 1983 and as Chairman since May 2010, Chairman of Charles GulveEngros A/S since June 2002, Chairman of InterMail A/S since January 1995, Chairman of Gammelrand Holding A/S since December 2009, Chairman of GammelrandSkærvefabrik A/S since May 1995, director of the board of EjendomsaktieselskabetMatr. 43 EiAvedøre since August 2000 and as Chairman since February 2009, Chairman of GammelrandBeton A/S since April 2001, director of P.O.A. Ejendomme A/S since July 1994 and Chairman since April 2007, and Chairman of KonveloutfabrikkenDanmakrs Fond and. Within the last five years Mr. Nielsen has served as a board member or chairman in the following companies: Brøndbyerns I.F. Fodbold A/S from June 2013 to April 2014, AmagerbankenAktieselskab from December 1999 to November 2010, Ambu A/S from February 1999 to December 2012, CarepointHaslev/Ringsted from June 2009 to August 2009, Cimber Sterling A/S from September 2000 to September 2010, Cimber Sterling Group A/S from September 2005 to September 2010, Danica-ElektronikApS from March 1993 to September 2012, GPV Industri A/S from December 1986 to June 2011, GPV International A/S from April 2009 to June 2009, Henrik Olsen Automobiler A/S from April 2010 to May 2010, Kirk &Thorsen Invest A/S from February 2013 to April 2013, Olsen BilerAdministraton A/S from April 2007 to May 2010, Olsen Biler Ringsted-Haslev A/S from April 2007 to May 2010, Satair A/S from November 1994 to October 2011, Satair Service A/S from May 1995 to May 2011, Torm A/S from September 2000 to January 2013 and Weibel Scientific A/S from January 1986 to September 2012. Mr. Nielsen’s significant global experience as a member of the board of directors or chairman of various entities led the Board of Directors to believe that Mr. Nielsen is qualified to serve as a director of the Company.
Aldo Petersen. Aldo Petersen has been chairman of LiqTech International, Inc. since August 2011. He has been the Chief Executive Officer of APE Invest A/S, a private Danish investment company, since 2006 when he sold Telepartner A/S, a formerly NASDAQ-listed company that he founded in 1986. Prior to Telepartner, he started and sold one of Denmark’s first hedge funds, Dansk Fromue Invest. Mr. Petersen was a major investor in Greentech Energy Systems A/S, a renewable energy company that builds wind farms in Denmark, Germany, Poland and Italy. He is a private investor in wind farms in Germany and France, and was also a major investor in Football Club Copenhagen (listed on the Copenhagen Stock Exchange). Mr. Petersen has a B.A. degree in Economics from Copenhagen Business School. The Board of Directors believes that Mr. Petersen’s experience as a businessman and his knowledge of the capital markets qualifies him to be a director.
Compliance with Section 16(a) of the Exchange Act
Section 16(a) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 requires executive officers, directors and persons who own more than 10% of a registered class of our equity securities to file reports of ownership with the Securities and Exchange Commission. Executive officers, directors and more than 10% shareholders are required by regulations to furnish us with copies of all Section 16(a) reports they file.
Based solely on the Company’s review of the copies of the forms received by it during the period ended June 30, 2016, the Company believes that the no person who, at any time during such fiscal year, was a director, officer or beneficial owner of more than 10% of the Company’s common stock, failed to comply with all Section 16(a) filing requirements during such fiscal years.
| 59 |
Code of Ethics
On July 12, 2012, the Company adopted a formal code of ethics statement for senior officers and directors (the “Code of Ethics”) that is designed to deter wrongdoing and to promote ethical conduct and full, fair, accurate, timely and understandable reports that the Company files or submits to the SEC and others. A form of the Code of Ethics is attached as an exhibit to this report. Requests for copies of the Code of Ethics should be sent in writing to DanDrit Biotech USA, Inc., 375 Park Avenue, Suite 2607, New York, NY, 10152.
Corporate Governance
Our Board of Directors has not adopted procedures by which security holders may recommend nominees to our Board of Directors and that has not changed.
Insider Participation Concerning Executive Compensation
The Company is a smaller reporting company and is not required to provide this information.
Director Independence
Our Board of Directors has determined that Messrs. Nielsen and Petersen are independent as that term is defined in the listing standards of the NYSE MKT. In making these determinations, our Board of Directors has concluded that none of our independent directors has an employment, business, family or other relationship which, in the opinion of our Board of Directors, would interfere with the exercise of independent judgment in carrying out the responsibilities of a director. Our other directors, Dr.Leire and Mr. Rosenberg, are not considered independent under these rules because Mr. Leire serve as executive officers and Mr. Rosenberg serves as a consultant.
Item 11. Executive Compensation
The following table sets forth certain information with respect to compensation for year ended June 30, 2016, the six months ended June 30, 2015 and the year ended December 31, 2014 earned by or paid to our chief executive officer, chief financial officer.
| Stock | Option | |||||||||||||||||
| Name and Principal Position | Year | Salary ($) | Awards($) | Awards ($) | Total ($)(1) | |||||||||||||
| Dr. Eric Leire, | 2016(2) | 360,029 | 360,029 | |||||||||||||||
| Chief Executive Officer and Director | 2015(3) | 157,101 | - | - | 157,101 | |||||||||||||
| 2014(4) | 341,275 | - | - | 341,275 | ||||||||||||||
| Lone Degn | 2016(2) | 95,665 | - | - | 95,665 | |||||||||||||
| Former Chief Financial Officer | 2015(3) | 35,854 | 35,854 | |||||||||||||||
| Robert Wolfe, | 2015(3) | 125,200 | - | - | 125,200 | |||||||||||||
| Former Chief Financial Officer | 2014(4) | 84,000 | - | - | 84,000 | |||||||||||||
| (1) | All values, except for compensation to Robert Wolfe, are reported on an as-converted basis from Danish Krone (DKK) to U.S. dollars ($) based on the average currency exchange rate of $1.00 = DKK 6,7234, for the year ended June 30, 2016. We do not make any representation that the Danish Krone amounts could have been, or could be, converted into U.S. dollars at such rate on June 30, 2015, or at any other rate. | |
| (2) | Represents the year ended June 30, 2016 | |
| (3) | Represents the six months ended June 30, 2015 | |
| (3) | Represents the year ended December 31, 2014 |
Employment Arrangements
Agreements with Named Executive Officers
We have employments agreement with Dr. Leire, Ms. Degn and Mr. Robert Wolfe.
| 60 |
Leire Employment Agreement
Effective March 1, 2012, DanDrit Denmark entered into an Employment Agreement with Dr. Eric Leire, to serve as its Managing Director. Pursuant to the terms and conditions of the Employment Agreement, Dr. Leire will be employed by DanDrit Denmark for an indefinite term unless the agreement is earlier terminated as described below. The Employment Agreement provides that the Dr. Leire will receive a salary of 2,100,000 DKK ($341,275 calculated on an as-converted basis from Danish Krone (DKK) to U.S. dollars ($) based on the currency exchange rate of $1.00 = DKK 6.1534, as of December 31, 2014) gross per year, to be paid in equal monthly installments on the last day of each month and subject to annual review and increases by our Board of Directors, as it deems appropriate.
In addition to his salary, Dr. Leire will be entitled to receive: (i) a company car at a value up of DKK 5,100 ($829) per month (monthly lease value) and DanDrit Denmark shall defray all expenses in connection with the maintenance and use of the car; (ii) coverage of all expenses relating to Dr. Leire’s mobile phone, home computer, Internet connection as well as his home phone; (iii) coverage of all the expenses relating to Dr. Leire’s subscription to a fitness club; (iv) a bonus of up to DKK 400,000 ($65,005) per year if Dr. Leire reaches certain conditions as specified in the Employment Agreement; and (v) coverage under DanDrit Denmark’s pension plan. In accordance with the pension plan, the Company pays a pension contribution of 10% of Dr. Leire’s salary, while Dr. Leire pays a contribution of 5% of his salary.
DanDrit Denmark may terminate Dr. Leire’s employment with 12 months’ notice to the end of a month. If DanDrit Denmark terminates Dr. Leire’s employment, he shall be entitled to be released from his duty to work (in Danish “fritstillet”) during the notice period. Dr. Leire may terminate the employment at 6 months’ notice to the end of a month. In case of material breach, the non-defaulting party can terminate the Employment Agreement without notice and can claim damages in accordance with the general Danish law of damages. If Dr. Leire suspends payments, or insolvency proceedings are commenced against his estate, DanDrit Denmark can terminate the employment without notice. The employment shall cease without notice to the end of the month in which Dr. Leire attains the age of 70. The Employment Agreement contains non-competition and non-solicitation clauses.
Degn Employment Agreement
Effective March 12, 2015, DanDrit Denmark entered into an Employment Agreement with Ms. Degn to serve as its Chief Financial Officer. Pursuant to the terms and conditions of the Employment Agreement, Ms. Degn will be employed by DanDrit Denmark for an indefinite term unless the agreement is earlier terminated as described below. The Employment Agreement provides that Ms. Degn will receive a salary of DKK 60,000 gross per month, to be paid monthly on the last business day of each month and subject to annual review and increases by the board of directors of DanDrit Denmark, as it deems appropriate.
In addition to her salary, Ms. Degn will be entitled to receive reimbursement of all reasonable costs and expenses incurred in connection with the performance of her duties in accordance with the terms of the Degn Employment Agreement In addition, DanDrit Denmark has agreed to contribute an amount equal to ten percent (10%) of Ms. Degn’s yearly salary to a pension fund or bank account established for such purpose.
On March 10, 2016, the Company accepted the amicable resignation of Lone Degn from the Company as its Chief Financial Officer, effective March 10, 2016.
Wolfe CFO Service Agreement
Effective January 1, 2014, DanDrit Denmark entered into a CFO Service Agreement with Robert Wolfe to serve as its Chief Financial Officer and Chief Financial Officer of DanDrit USA following the closing of the Share Exchange. Pursuant to the terms and conditions of the CFO Service Agreement, Mr. Wolfe was employed by DanDrit Denmark for an indefinite term. The CFO Service Agreement provided that Mr. Wolfe received a salary of $78,000 gross per year which was paid monthly and a one-time sign on fee of $6,000.
| 61 |
In addition to his salary, Mr. Wolfe was entitled to receive reimbursement of all reasonable costs relating to his work for the Company, including travel, accommodation and meal expenses incurred in connection with work outside the agreed premises.
On March 13, 2015, the Company, DanDrit Denmark and Mr. Wolfe entered into an agreement pursuant to which Mr. Wolfe ceased to be Chief Financial Officer of DanDrit Denmark effective as of April 28, 2015.
The foregoing description of the terms and conditions of the employment agreements provides only a brief summary and are qualified in their entirety by reference to the full text of the employment agreements, which are filed as exhibits to this report.
Outstanding Equity Awards as of June 30, 2016
As of June 30, 2016, there were no outstanding equity awards to our named executive officers.
Board Compensation
For the Year Ended June 30, 2016, Six Months Ended June 30, 2015 and Year Ended December 31, 2014, we did not compensate our directors, or issue any equity awards to our directors, for their services other than to reimburse them for out-of-pocket expenses incurred in connection with their attendance at meetings of the Board of Directors. In order to attract and retain qualified independent directors, we may in the future adopt a compensation plan for non-employee directors that includes cash as well as equity-based compensation.
Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters
The following table sets forth, as of September 8, 2016, certain information regarding the beneficial ownership of the shares in DanDrit USA, of (i) our executive officers, (ii) our directors and (iii) each person known to us who is known to be the beneficial owner of more than 5% of the shares in DanDrit USA. In accordance with the rules of the SEC, “beneficial ownership” includes voting or investment power with respect to securities. To our knowledge, except as indicated in the footnotes to this table and pursuant to applicable community property laws, the persons named in the table have sole voting and investment power with respect to all shares of common stock beneficially owned by them. Unless indicated otherwise, the address for the beneficial holders is c/o DanDrit Biotech USA, Inc., P.O. Box 189, Randolph, VT 05060.
Beneficial ownership of the common stock is determined in accordance with the rules of the Securities and Exchange Commission and includes any shares of common stock over which a person exercises sole or shared voting or investment power, or of which a person has a right to acquire ownership at any time within 60 days. Except as otherwise indicated, we believe that the persons named in this table have sole voting and investment power with respect to all shares of common stock held by them. Applicable percentage ownership in the following table is based on 9,533,290 shares of common stock outstanding as of September 8, 2016 plus, for each individual, any securities that individual has the right to acquire within 60 days of September 8, 2016.
| Dandrit Biotech USA Inc. | ||||||||
| Name of Beneficial Owner | Number of Shares | % Ownership | ||||||
| Directors/Officers: | ||||||||
| Eric Jean Marie Leire(1) | 8,615 | * | ||||||
| NE Nielsen | - | * | ||||||
| Aldo Petersen | - | * | ||||||
| Directors/Officers Total: | 8,615 | * | ||||||
| 5% Shareholders: | ||||||||
| Belle Invest ApS (2) | 486,677 | 5.11 | % | |||||
| Roas Holding ApS (2) | 55,078 | 0.58 | % | |||||
| Equine Invest ApS (3) | 900,000 | 9.44 | % | |||||
| Quint ApS (3) | 300,000 | 3.15 | % | |||||
| Paseco ApS(4) | 483,429 | 5.07 | % | |||||
| Po-Ma Invest ApS (5) | 1,171,364 | 12.29 | % | |||||
| Sune Olsen Holding ApS (6) | 908,650 | 9.53 | % | |||||
| RS Group ApS (7) | 1,070,869 | 11.23 | % | |||||
| Karsten Ree Holding B ApS (8) | 500,000 | 5.24 | % | |||||
| 5% Shareholders Total: | 5,876,067 | 61.64 | % | |||||
| Total: | 5,884,682 | 61.72 | % | |||||
* Indicates less than 1%.
| (1) | The holder has an address of 5084 Bunch Road Summerfield NC 27358 USA. |
| 62 |
| (2) | Shares are owned by Bele Invest ApS, a Danish entity and Roas Holding ApS, a Danish entity both with an address of Vermehrensvej 7, 2930 Klampenborg Denmark. The voting and disposition of the shares owned by the Bele Invest ApS and Roas Holding ApS are controlled by Mrs. Dina Rosenberg. |
| (3) | Equine Invest ApS - holding 900,000 shares - is a Danish entity which has an address of Praestemosevej 10, 3480 Fredensborg, Denmark. Equine Invest ApS is 100% owned and controlled by the company Quint ApS - holding 300,000 shares - is a Danish entity which has an address of Praestemosevej 10, 3480 Fredensborg, Denmark, which is 100% owned and controlled by Mark Szigethy of Praestemosevej 10, 3480 Fredensborg. The voting and disposition of the shares owned by Equine Invest ApS is controlled by Mark Szigethy. |
| (4) | Paseco ApS is a Danish entity which has an address of Naesset 26, Munkebo 5330 Denmark. Northern Biotech Fund Sarl is a Luxembourg entity and has an address of C/O Banque Havilland SA, 35A Avenue JF Kennedy, Luxembourg. The voting and disposition of the shares owned by Paseco and Northern Biotech are controlled by Ole Abildgaard. |
| (5) | Po-Ma Invest ApS - holding 1,171,364 shares - is a Danish entity which has an address of c/o Torben Bjørn Christensen, Oeveroedvej 36B, 2840 Holte, Denmark. Po-Ma Invest ApS is 100% owned by the company VICH 7826 ApS, c/o Torben Bjørn Christensen, Oeveroedvej 36B, 2840 Holte, Denmark. The voting and disposition of the shares owned by Po-Ma Invest ApS is controlled by Torben Bjørn Christensen. |
| (6) | Shares are owned by Sune Olsen Holding ApS, Biotech Invest ApS and Sardinian Solar Park ApS, all Danish entities with an address of Jagtvej 169 B 4, 2100 Copenhagen, Denmark. The voting and disposition of the shares owned by the companies are controlled by Mr. Olsen. |
| (7) |
RS Group ApS is a Danish entity which has an address of Stumpedyssevej 17, 2970 Horsholm. The voting and disposition of the shares owned by RS Group are controlled by Mr. Renè Sindlev.
|
| (8) |
Karsten Ree Holding B ApS is a Danish entity which has an address of Generatorvej 8 B, 2860 Soeborg, Denmark. The voting and disposition of the shares owned by Karsten Ree Holding B ApS is controlled by Karsten Ree. |
Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions and Director Independence
Described below are transactions or series of transactions that occurred from January 1, 2014 through the date of this report (the “Reporting Period”) between us and our executive officers, directors or the beneficial owners of 5% or more of our common stock, and certain persons affiliated with or related to these persons, including family members, in which they had or will have a direct or indirect material interest in an amount that exceeds the lesser of $120,000 or 1% of the average of our total assets as of year-end for the last two completed fiscal years, other than compensation arrangements that are otherwise required to be described under “Executive Compensation.”
On January 7 2015, professional fees of $317,613 were paid on behalf of the Company to the Lett Law Firm for services billed during the Reporting Period. The chairman of the board of the Company is a partner of the Lett Law Firm. On February 12, 2014, in connection with the closing of the Share Exchange, the Company and NLBDIT 2010 Services, LLC (“NLBDIT”) entered into a Share Cancellation Agreement pursuant to which NLBDIT agreed to the cancellation of an aggregate of 4,400,000 issued and outstanding shares of common stock of the Company owned by NLBDIT prior to the Share Exchange, effective upon the closing of the Share Exchange.
| 63 |
Subsequent to the conversion of the Sune Olsen Debt, DanDrit Denmark received a loan facility (the “Subsequent Sune Olsen Holding Loan”) from Sune Olsen Holding to ensure financing until new equity is raised. Under the Sune Olsen Holding Loan DanDrit Denmark has received the following amounts: on November 11, DKK 1,500,000 ($276,651), on November 20, 2013 DKK 405,000 ($74,696), on December 2, 2013 DKK 900,000 ($165,990), in total DKK 2,805,000 ($517,337). The Subsequent Sune Olsen Holding Loan is to be repaid the latest of 14 days after completion of the contemplated public offering of the Company or February 1, 2015.On November 26, 2014, the Company repaid the Subsequent Sune Olsen Holding Loan and interest thereon.
DanDrit Denmark received an additional loan (the “New Sune Olsen Loan”) from Sune Olsen, managing member of Sune Olsen Holding, to ensure financing until new equity is raised. The New Sune Olsen Loan in the amount of DKK 1,000,000 ($184,434) was issued on December 20, 2013. The New Sune Olsen Loan was to be repaid May 1, 2014 and carried an interest of 5% per year, or approximately DKK18,966 ($3,498) as of March 31, 2014. During March 2014, DanDrit Denmark extended the maturity date of the New Sune Olsen Loan from May 1, 2014 to the latest of 14 days after the completion of the contemplated stock offering of the Company or February 1, 2015.On November 26, 2014 the Company repaid the New Sune Olsen Loan and interest thereon.
On February 15, 2014 and March 18, 2014, DanDrit Denmark received loans (the “2014 Loans”) of DKK 2,500,000 and 2,300,000, respectively, equivalent to approximately $461,877 and $424,927, respectively (based on the currency exchange rate of $1.00 = DKK 5.4283). The 2014 Loans, evidenced by that certain Loan Agreement by and between DanDrit Denmark and PasecoApS, a shareholder of DanDrit USA (“Paseco”) dated March 21, 2014, carry an interest of 5% per year and are payable on February 1, 2015. On April 29, 2014, DanDrit Denmark and Paseco entered into an amendment whereby the terms of the 2014 Loans could be extended at the Company’s option for an additional year with an increase in the interest rate to 7.00%. As of October 17, 2014, the outstanding balance on the 2014 Loans including accrued interest was $836,830 based on the currency exchange rate of October 17, 2014. On October 17, 2014, the Company repaid the loan and interest in its entirety.
On March 27, 2014, the Company entered into an operating sublease agreement for office space with Paseco. The lease called for months payments of DKK 10,000 increasing to DKK 20,000 as of July 1, 2014 (approximately $1,496 and 2,992, respectively). The lease was terminated on May 31, 2015.
During the six months ended June 30, 2015 and during the year ended December 31, 2014, JARO Holding ApS owned by a director of the Company, provided medical consultancy services to the Company. During year ended June 30, 2016, the six months ended June 30, 2015, and year ended December 31, 2014, the Company recorded medical consultancy expense of $44.620, $44,886, and $29,925, respectively.
In June, 2015 the Company paid DKK50,000 ($7,499) to Paseco ApS for consultancy services provided in June 2015.
During the year ended June 30, 2016, six months ended June 30, 2015 and the year ended December 31, 2014, a law firm partially owned by the Company’s Chairman of the Board of Directors provided legal services to the Company and recorded legal expense of $105,107, $132,414 and 288,546, respectively. At June 30, 2016 and 2015, the Company had a payable to the firm in the amount of $97,357 And $366,035.
As of June 30, 2015, the Company had an escrow account of $1,052,989 with the Lett Law Firm.
As of June 30, 2015, the outstanding balance of $38,235 for professional fees paid by a shareholder and amounts advanced to the Parent are reported as loan payable - related party. The $38,235 loans payable were acquired in the reverse acquisition. The amounts are unsecured, non-interest bearing and have no stipulated repayment terms.
A 6% promissory note payable to NLBDIT 2010 Enterprises, LLC, an entity controlled by a shareholder of the Company, was acquired by the Company in the reverse acquisition, payable on February 12, 2014 upon the completion date of the Share Exchange. As of June 30, 2015, the outstanding balance on the note, including accrued interest, was $44,879. During the six months ended June 30, 2015 and 2014 and twelve months ended December 31, 2014 the Company recorded related party interest on the Note of $2,126, $1,521 (unaudited), and $619, respectively
Except as otherwise indicated herein, there have been no other related party transactions, or any other transactions or relationships required to be disclosed pursuant to Item 404 and Item 407(a) of Regulation S-K.
| 64 |
Approval of Related Party Transactions
The Company has not adopted written policies and procedures for the review and approval of any transaction required to be reported under Item 404(a) of Regulation S-K. In approving these transactions, the Company follows the guidance of section 144 of the Delaware General Corporation Law.
Item 14. Principal Accounting Fees and Services
The following information sets forth fees billed to us by RaichEndeMalter& Co. LLP (“Raich LLP”) during the six months ended June 30, 2015 and fiscal years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013 and Gregory & Associates, LLC (“Gregory & Associates”) during the six months ended June 30, 2015 and fiscal years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013 for: (i) services rendered for the audit of our annual financial statements and the review of our quarterly financial statements, (ii) services that were reasonably related to the performance of the audit or review of our financial statements and that are not reported as audit fees, (iii) services rendered in connection with tax compliance, tax advice and tax planning, and (iv) all other fees for services rendered.
Audit Fees
The aggregate fees billed by Gregory & Associates for such professional services were $55,800 for the year ended December 31, 2015, $46,625 for the six months ended June 30, 2015 and $67,835 for the year ended December 31, 2014.
Audit-Related Fees
There were no fees billed Gregory & Associates for assurance and related services that are reasonably related to the performance of the audit or review of the Company’s financial statements for the year ended June 30, 2016 and December 31, 2014 and six months ended June 30, 2015.
Tax Fees
There were no fees billed by Gregory & Associates for Tax services for the years ended June 30, 2016 and December 31, 2014 and the six months ended June 30, 2015.
All Other Fees
The aggregate fees billed by Gregory & Associates for such professional services, including reading, consents and comfort letters associated with the Company’s S1 offering, were $22,380 for the year ended December 31, 2014 and $0 for the years ended December 31, 2013. The aggregate fees billed by Raich LLP for other products and services were $0 for the six months ended June 30, 2015; and for the years ended December 31, 2014 and December 31, 2013 were $0 and $6,791, respectively.
Audit Committee’s Pre-Approval Process
The Company’s Board of Directors which acts as the audit committee approves all audit services.
| 65 |
Item 15. Exhibits, Financial Statement Schedules - update
Exhibit No. |
Description | |
| 1.1 | Placement Agency Agreement, dated August 12, 2014, by and among the Company and Sunrise Securities Corp.(1) | |
| 2.1 | Share Exchange Agreement dated February 12, 2014. (4) | |
| 2.2 | Share Cancellation Agreement dated February 12, 2014. (4) | |
| 3.1 | Certificate of Incorporation. (2) | |
| 3.2 | Bylaws.(2) | |
| 3.3 | Articles of Association of DanDrit Denmark, as amended, dated February 26, 2004. (4) | |
| 3.4 | Certificate of Ownership and Merger, dated February 12, 2014. (4) | |
| 4.1 | Form of Common Stock Certificate.(5) | |
| 10.1 | Intellectual Property Assignment by and between DanDrit Denmark and Alexei Kirkin dated June 5, 2002. (4) | |
| 10.2 | Collaboration Agreement by and between DanDrit Denmark and National Cancer Centre of Singapore Pte Ltd dated November 11, 2008. (4) | |
| 10.3 | Master Services Agreement by and between DanDrit Denmark and Aptiv Solutions (UK) Ltd dated October 11, 2011. (4) | |
| 10.4 | Employment Agreement by and between DanDrit Denmark and Dr. Eric Leire dated February 5, 2012.(4)+ | |
| 10.5 | Box Packing and Moving Agreement by and between DanDrit Denmark and Bryde&Sonner A/S dated May 23, 2012. (4) | |
| 10.6 | Debt Instrument by and between DanDrit Denmark and Sune Olsen Holding ApS dated March 31, 2013. (4) | |
| 10.7 | Lease Agreement by and between Symbion A/S and DanDrit Denmark dated July 8, 2013. (4) | |
| 10.8 | Lease Agreement by and between OrdnungApS and DanDrit Denmark. (4) | |
| 10.9 | Debt Instrument by and between DanDrit Denmark and Sune Olsen Holding ApS dated January 17, 2014. (4) | |
| 10.10 | Early Access Agreement by and between DanDrit Denmark and Impatients, N.V. dated December 20, 2013. (4) | |
| 10.11 | Consultancy Agreement by and between DanDrit Denmark and Dina Rosenberg dated February 4, 2014. (4) | |
| 10.12 | Consulting Agreement by and between DanDrit Denmark and Paseco ApS dated February 11, 2014. (4) | |
| 10.13 | DanDrit Biotech USA, Inc. 2014 Equity Incentive Plan (4) | |
| 10.14 | Loan Agreement by and between DanDrit Denmark and Paseco ApS dated April 29, 2014. (6) | |
| 10.15 | Letter of Support of Paseco ApS related to committed 2M DKK in additional financing, dated May 2, 2014. (6) |
| 66 |
| 10.16 | Form of Securities Purchase dated as of December 31, 2014. (7) | |
| 10.17 | CFO Service Agreement by and between DanDrit Denmark and Mr. Robert Wolfe dated February 10, 2014.(8) | |
| 10.18 | Loan Agreement by and between DanDrit Denmark and Paseco ApS dated March 21, 2014.(9) | |
| 10.19 | Loan Agreement by and between DanDrit Denmark and Paseco ApS dated March 27, 2014.(9) | |
| 14.1 | Code of Ethics. (3) | |
| 31.1* | Certification of Principal Executive Officer pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a) or Rule 15d-14(a) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. | |
| 31.2* | Certification of Chief Financial Officer pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a) or Rule 15d-14(a) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. | |
| 32.1** | Certification of Principal Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer pursuant to Rule 13a-14(b) or Rule 15d-14(b) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 and 18 U.S.C. Section 1350. | |
| 101.INS | XBRL Instance Document* | |
| 101.SCH | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema* | |
| 101.CAL | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase* | |
| 101.DEF | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase* | |
| 101.LAB | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase* | |
| 101.PRE | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase* |
| + | Agreement with management. | |
| * | Filed herewith. | |
| ** | Furnished herewith. | |
(1) |
Filed as an exhibit to the Company’s Form 8-K filed with the SEC on August 12, 2014 and incorporated herein by reference. | |
| (2) | Filed as an exhibit to the Company’s Form 10 filed with the SEC on August 12, 2011 and incorporated herein by reference. | |
| (3) | Filed as an exhibit to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K filed with the SEC on July 17, 2012 and incorporated herein by reference. | |
| (4) | Filed as an exhibit to the Company’s registration statement on Form S-1 filed with the SEC on February 14, 2014. | |
| (5) | Filed as an exhibit to the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K, as filed with the SEC on May 16, 2014, and incorporated herein by this reference. | |
| (6) | Filed as an exhibit to the Company's Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q, as filed with the SEC on May 14, 2014, and incorporated herein by this reference. | |
| (7) | Filed as an exhibit to the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K, as filed with the SEC on December 31, 2014, and incorporated herein by this reference. | |
| (8) | Filed as an exhibit to the Company’s Form S-1/A filed with the SEC on June 23, 2014 and incorporated herein by reference. | |
| (9) | Filed as an exhibit to the Company’s Form S-1/A filed with the SEC on March 31, 2014 and incorporated herein by reference. |
| 67 |
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| Date: September 28, 2016 | DANDRIT BIOTECH USA, INC. | |
| By: | /s/ Eric Leire | |
| Eric Leire | ||
| Chief Executive Officer | ||
| (Principal Executive Officer) | ||
| By: | /s/ Eric Leire | |
| Eric Leire | ||
| Chief Financial Officer | ||
| (Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) | ||
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| Signature | Title | Date | ||
| /s/ Dr. Eric Leire | Chief Executive Officer and Director | September 28, 2016 | ||
| Dr. Eric Leire | (Principal Executive Officer) | |||
| /s/ NE Nielsen | Chairman of the Board | September 28, 2016 | ||
| NE Nielsen | ||||
| /s/ Aldo Michael Noes Petersen | Director | September 28, 2016 | ||
| Aldo Michael Noes Petersen | ||||
68
