Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| 8-K - 8-K - PIPER JAFFRAY GLOBAL AGRICULTURE SYMPOSIUM (AUGUST 2016) - MOSAIC CO | a8-kpiperjaffrayglobalagri.htm |

1
State of the Fertilizer Industry
Piper Jaffray Global Agriculture Symposium
Minneapolis, MN
August 2, 2016
Andy Jung
Director, Market and Strategic Analysis
The Mosaic Company

2
Safe Harbor
This document contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. Such statements
include, but are not limited to, statements about the Wa’ad Al Shamal Phosphate Company (also known as MWSPC) and other proposed or
pending future transactions or strategic plans and other statements about future financial and operating results. Such statements are based upon
the current beliefs and expectations of The Mosaic Company’s management and are subject to significant risks and uncertainties. These risks
and uncertainties include but are not limited to risks and uncertainties arising from the ability of MWSPC to obtain additional planned funding in
acceptable amounts and upon acceptable terms, the timely development and commencement of operations of production facilities in the
Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, the future success of current plans for MWSPC and any future changes in those plans; difficulties with realization of
the benefits of our long term natural gas based pricing ammonia supply agreement with CF Industries, Inc., including the risk that the cost
savings initially anticipated from the agreement may not be fully realized over its term or that the price of natural gas or ammonia during the term
are at levels at which the pricing is disadvantageous to Mosaic; customer defaults; the effects of Mosaic’s decisions to exit business operations
or locations; the predictability and volatility of, and customer expectations about, agriculture, fertilizer, raw material, energy and transportation
markets that are subject to competitive and other pressures and economic and credit market conditions; the level of inventories in the distribution
channels for crop nutrients; the effect of future product innovations or development of new technologies on demand for our products; changes in
foreign currency and exchange rates; international trade risks and other risks associated with Mosaic’s international operations and those of joint
ventures in which Mosaic participates, including the risk that protests against natural resource companies in Peru extend to or impact the Miski
Mayo mine; changes in government policy; changes in environmental and other governmental regulation, including expansion of the types and
extent of water resources regulated under federal law, greenhouse gas regulation, implementation of numeric water quality standards for the
discharge of nutrients into Florida waterways or efforts to reduce the flow of excess nutrients into the Mississippi River basin, the Gulf of Mexico
or elsewhere; further developments in judicial or administrative proceedings, or complaints that Mosaic’s operations are adversely impacting
nearby farms, business operations or properties; difficulties or delays in receiving, increased costs of or challenges to necessary governmental
permits or approvals or increased financial assurance requirements; resolution of global tax audit activity; the effectiveness of Mosaic’s
processes for managing its strategic priorities; adverse weather conditions affecting operations in Central Florida, the Mississippi River basin, the
Gulf Coast of the United States or Canada, and including potential hurricanes, excess heat, cold, snow, rainfall or drought; actual costs of various
items differing from management’s current estimates, including, among others, asset retirement, environmental remediation, reclamation or other
environmental regulation, Canadian resources taxes and royalties, or the costs of the MWSPC, its existing or future funding and Mosaic’s
commitments in support of such funding; reduction of Mosaic’s available cash and liquidity, and increased leverage, due to its use of cash and/or
available debt capacity to fund financial assurance requirements and strategic investments; brine inflows at Mosaic’s Esterhazy, Saskatchewan,
potash mine or other potash shaft mines; other accidents and disruptions involving Mosaic’s operations, including potential mine fires, floods,
explosions, seismic events, sinkholes or releases of hazardous or volatile chemicals; and risks associated with cyber security, including
reputational loss, as well as other risks and uncertainties reported from time to time in The Mosaic Company’s reports filed with the Securities
and Exchange Commission. Actual results may differ from those set forth in the forward-looking statements.

3
Topics and Take-Aways
The Mosaic Company
Agricultural Observations and Outlook
- Near term: Pressure on grain prices in classic weather market
- But no crash expected and the long term food story remains
intact
Plant Nutrient Observations and Outlook
- Phosphate
• Cautious sentiment in 1H 2016, but positive demand
prospects
• Balanced S/D for the remainder of the decade
- Potash
• Potash supply adjustments taking place in response to prices
• Solid demand drivers and forecasts
• Relatively balanced supply/demand forecast

4
The Mosaic Company
5
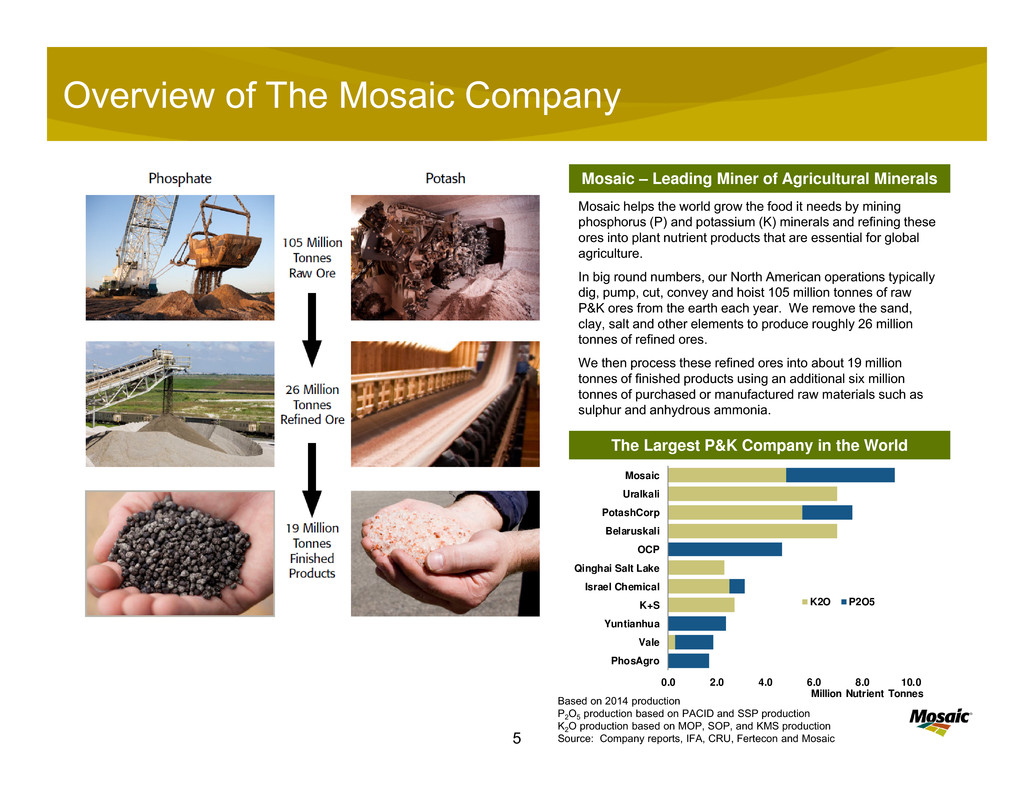
Overview of The Mosaic Company
Mosaic helps the world grow the food it needs by mining
phosphorus (P) and potassium (K) minerals and refining these
ores into plant nutrient products that are essential for global
agriculture.
In big round numbers, our North American operations typically
dig, pump, cut, convey and hoist 105 million tonnes of raw
P&K ores from the earth each year. We remove the sand,
clay, salt and other elements to produce roughly 26 million
tonnes of refined ores.
We then process these refined ores into about 19 million
tonnes of finished products using an additional six million
tonnes of purchased or manufactured raw materials such as
sulphur and anhydrous ammonia.
The Largest P&K Company in the World
Mosaic – Leading Miner of Agricultural Minerals
Based on 2014 production
P2O5 production based on PACID and SSP production
K2O production based on MOP, SOP, and KMS production
Source: Company reports, IFA, CRU, Fertecon and Mosaic
0.0 2.0 4.0 6.0 8.0 10.0
Mosaic
Uralkali
PotashCorp
Belaruskali
OCP
Qinghai Salt Lake
Israel Chemical
K+S
Yuntianhua
Vale
PhosAgro
Million Nutrient Tonnes
K2O P2O5

6
Phosphate Operations
U.S. Phosphate Operations
Offshore Phosphate Operations
35% equity stake in Bayovar phosphate rock mine in Peru
25% equity stake in Ma’aden II mine and chemical complex
under development in Saudi Arabia
53%47%
Phosphate Sales
2012-15
North
America Offshore

7
North American Potash Operations
46%
54%
Potash Sales
2012-15
North
America Offshore

8
Mosaic International Distribution
ADM Acquisition
ADM Acquisition
Strategic Rationale
• Mosaic is largest P&K producer and Brazil is the fastest
growing P&K market
• Provides downstream market access/pull through for our
North American P&K operations
• Accelerates our strategy to expand distribution in key
geographies (instant offense)
Assets Acquired
• Five blending plants and three tolling operations
• Total of 2.3 million tonnes of blending capacity

9
Agricultural Observations and Outlook

10
Wild swings in agricultural commodity markets…
Key crop prices declined rapidly
during the last six weeks
- World wheat supplies are ample
- Timely rainfall across U.S. Midwest
and non-threatening forecasts
pressure corn and soybean prices
• The 2016 Dec corn contract closed at $3.43
bu on July 29, off 24% or $1.06 per bu from its
peak on June 17
• The 2016 Nov soybean contract closed at
$10.03 bu on July 29, off 14% or $1.60 per bu
from its peak on June 10
But prices of some other
globally important crops – e.g.
sugar, coffee, cotton – remain
strong
- Sugar is up over 50% since the Feb low
3.20
3.40
3.60
3.80
4.00
4.20
4.40
4.60
US$
BU
New Crop Corn Price
Daily Close Dec '16 Contract
Source: CME
8.50
9.00
9.50
10.00
10.50
11.00
11.50
12.00
US$
BU
New Crop Soybean Price
Daily Close Nov '16 Contract
Source: CME
4.50
4.70
4.90
5.10
5.30
5.50
5.70
5.90
US$
BU
New Crop HRW Wheat Price
Daily Close Jul '17 Contract
Source: CME
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
Sep-15 Dec-15 Mar-16 Jun-16
US$
CWT
Source: NYMEX
Sugar Prices
Daily Close of Nearby Option
Data through July 29, 2016

11
… As managed funds switch their outlook
Funds built large net long positions
during the first half of 2016, following
a disappointing South American
harvest and fears of a La Niña
weather impact on North America.
- Corn net long was built to over 252,000
contracts on June 14.
- Soybean net long built to over 210,000
contracts on June 7.
But funds moved quickly from the
long side of the market during first
half of July as weather was largely
benign.
- In the case of corn, funds swung to a net
short position of nearly 66,000 contracts or
328 million bushels on July 26 – a 1.6 billion
bushel swing in just 6 weeks!
- In the case of soybeans, managers trimmed
their long position by 42% to about 122,000
contracts or 608 million bushels, as there
remains some weather premium in
-300
-200
-100
0
100
200
300
400
Jan '12 Jan '13 Jan '14 Jan '15 Jan '16
000's
Contracts
Source: CFTC
Net Position of Managed Funds
(Data through July 26, 2016)
Corn Soybeans

12
Phosphate and Potash Fertilizer Market
Observations & Outlook

13
NPKs remain affordable and generate high ROIs
Our plant nutrient affordability metric indicates that
plant nutrients are very affordable
The metric measured just .47 during the second
week of June, the lowest level seen in our records
dating to 2005
The metric registered .58 at the end of July, off
from .81 a year ago and well below the 2010-
present average of .73
Compared to a year ago, affordability has
improved due mostly to the drop in plant nutrient
costs
Nitrogen: continued strong demand, low raw
materials costs, large Chinese supplies, and new
capacity coming on stream
Phosphate: continued strong demand, lower raw
materials costs, moderate Chinese exports and
new capacity from Morocco and Saudi Arabia
Potash: continued strong demand, increased FSU
supplies, strong dollar lowers costs for all major
exporters, new capacity on the horizon
0.40
0.60
0.80
1.00
1.20
1.40
1.60
05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
Plant Nutrient Affordability
Plant Nutrient Price Index / Crop Price Index
Affordability Metric Average (2010-present)
Source: Weekly Price Publications, CME,
USDA, AAPFCO, Mosaic
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
500
Jan '13 Jul '13 Jan '14 Jul '14 Jan '15 Jul '15 Jan '16 Jul '16
$ ST
NPK Prices
fob NOLA Barge
DAP Potash Urea
Source: Green Markets and Argus FMB
Data through July 29, 2016

14
Demand Prospects, an example:
Strong Dollar ► Advantage Brazil
Despite the strengthening of the real (July MTD 3.28/US$ vs. 4.05 in January), local currency prices of
soybeans, sugar and coffee are at or near record levels today. This underpins recent upward revisions in
total plant nutrient shipments in 2016 and 2017.
50
75
100
125
150
175
200
225
250
275
300
05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
Index
Source: CME and CRB Forex
Prices in Brazilian Reais
Monthly Average of Front Month Contract
2005 = 100
Soybeans Sugar Coffee
Data through July 29, 2016

15
Phosphates: Cautious sentiment persists in 1H 2016, but
positive demand prospects in 2H and into 2017
Modest rebound in shipments
in 2016…
…before posting a more
pronounced recovery in 2017
- Moderate prices
- Strong uptake in India stemming
from current good monsoon and
above average reservoir storage
going into 2017
- Strong pull from Brazil continues
- Offsets destocking taking place in
2016
65-66
66-68
30
35
40
45
50
55
60
65
70
00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15E16F17F
Global Phosphate ShipmentsMMT Product
DAP/MAP/NPS*/TSP
Source: CRU and Mosaic
* NPS products containing 45 or more
combined units of N and P2O5

16
So Why Does the Market Feel ‘Loose’ in 2016?
Fewer Plant Closures and Unplanned Outages
Map of world with highlighted
countries describing facility
restart
GCT (Tunisia) rock production
disruptions (~250k)
Syrian war causes rock, and thus
TSP disruptions (~150k)
ICL (Israel) fire on superphos.
production line (~50k)
JPMC (Jordan) intermittent
technical issues (~100k)
Foskor (South Africa) technical fault
and labor strike (~100k)
Fertinal (Mexico) Rock production
disruptions (~75k)
MissPhos Closed (~500k)
PotashCorp Suwanee R. Closed (~425k)
Agrium Redwater extended turnaround in 1H,
Mosaic turnarounds, Simplot extended
turnaround in 1H (~275k)
(Total = ~1,200k)
ICS (Senegal) production
issues (~75k)
All tonnage values (high-analysis phosphate fertilizer equivalent) were
estimated by Mosaic based on facility capacity and market news
UralChem lower operating rate due to rock dispute in 1H (~150k)
Phosagro lower operating rate due to sulphur dispute in 2H (~50k)
We estimate that production was
reduced in 2015 (of high-analysis
phosphate fertilizer equivalent) versus
the prior year due to various issues –
closed, turnarounds, or supply
disruptions – by ~2.2 million tonnes
2015 Global Production Shortfalls:

17
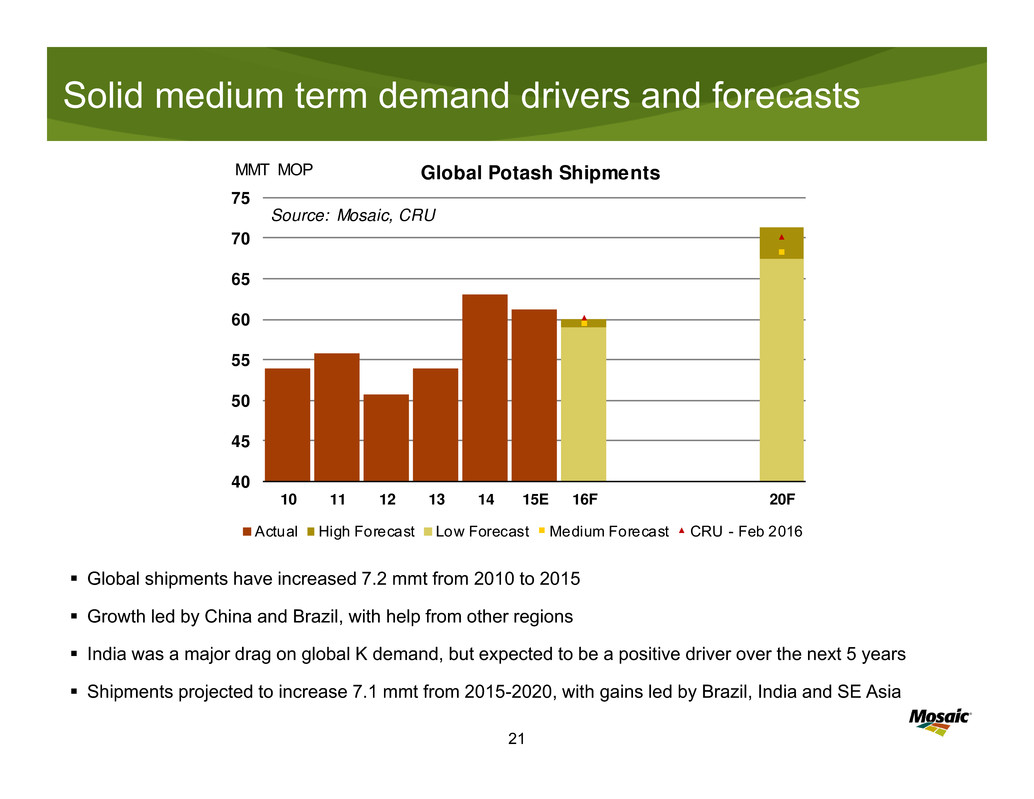
Solid medium term demand drivers and forecasts
Global shipments increased 3.9 mmt from 2010 to 2015 led by China, Brazil and SE Asia, but the growth was
front-loaded during this period
India was a major drag on global demand growth, but expected to be a major driver over the next 5 years
Shipments are projected to return to a more robust growth path from 2015 to 2020, rising 6.9 mmt with gains
led by India and Latin America (and despite a modest tick lower in Chinese demand)
45
50
55
60
65
70
75
10 11 12 13 14 15 16F 20F
Global Phosphate Shipments
Actual High Forecast Low Forecast Likely Forecast CRU - Apr 2016
MMT DAP/MAP/TSP
Source: Mosaic and CRU Phosphate Outlook April 2016

18
Stable (or perhaps a tightening) supply/demand balance
China accounted for all of the net increase in
phosphate supplies since 1995
China is embarking on permanent closure of some
uncompetitive capacity
- Possibility of a much more significant contraction in
capacity, with the latest ideas out of China* calling for
closure of ~3 million tonnes of P2O5 (which is not
included in our base case forecast at right)
Future demand growth will be met by supplies mostly
from Morocco and Saudi Arabia
54.1
58.8
3.1
1.6
0.9 0.8
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
2015 OCP Ma'aden Other China 2020F
MMT
P2O5
Source: CRU April 2016
Global Phosphoric Acid Capacity
We (as does CRU) project modest capacity and
moderate demand increases during the next five
years, but demand grows slightly faster than
capacity so operating rates trend upward
We expect more rapid demand growth and higher
and relatively stable global operating rates in the
mid-high 80% range
China capacity, production and exports remain
the biggest wild card
50%
55%
60%
65%
70%
75%
80%
85%
90%
95%
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
10 11 12 13 14 15E 16F 17F 18F 19F 20F
Global Capacity,
Production and Opr Rate
Effective Capacity Production Effective Acid Opr Rate
Mil Tonnes
DAP/MAP/NPS
Opr
Rate
Source: CRU and Mosaic
* Source: Ideas for Development of the Phosphate Fertilizer Industry in 2016-2020,
presented at the 23rd National Phosphate and Compound Fertilizer Industry Annual
Conference

19
Potash: Caution stoked by delays to the China contract
settlement, but demand rebound forecast in 2017
We have left unchanged our
shipment estimates for 2016 and
tabled preliminary forecasts for
moderate growth 2017
MOP shipments are forecast to
total 61 to 63 million tonnes next
year, led by a rebound in China
and continued growth in Brazil
25
30
35
40
45
50
55
60
65
00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16F 17F
Global Potash ShipmentsMil Tonnes KCl
Source: CRU and Mosaic 59-60
61-63

20
Acceleration of MOP imports expected in Brazil in 2H
0.0
1.0
2.0
3.0
4.0
5.0
6.0
7.0
8.0
9.0
10.0
00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 16F17F
Mil Tonnes Brazil MOP Import Demand
Source: CRU and Mosaic
DAP 264 300 -12% 325 -19%
MAP 1,228 1,149 7% 886 39%
TSP 314 370 -15% 426 -26%
Total 1,806 1,819 -1% 1,679 8%
SSP 320 282 13% 217 48%
MOP 3,811 3,712 3% 3,368 13%
Urea 1,616 1,411 14% 1,122 44%
Source: ANDA
Brazil Plant Nutrient Imports
% Chg
7-Yr
Avg1000 MT
7-Yr
Avg
YTD
2016
YTD
2015
Year-To-Date % Chg
Prior
Yr
Data through June
Potash shipments were up 16%, while imports were up only 3% or 100,000 tonnes
in the first half of this year. As a result, MOP inventories declined 180,000 tonnes
during the first half.
MOP imports are projected to total 8.5 million tonnes this year, with 3.9 million
tonnes in the first half and 4.6 million required during the second half of this year.
21
Solid medium term demand drivers and forecasts
Global shipments have increased 7.2 mmt from 2010 to 2015
Growth led by China and Brazil, with help from other regions
India was a major drag on global K demand, but expected to be a positive driver over the next 5 years
Shipments projected to increase 7.1 mmt from 2015-2020, with gains led by Brazil, India and SE Asia
40
45
50
55
60
65
70
75
10 11 12 13 14 15E 16F 20F
MMT MOP Global Potash Shipments
Actual High Forecast Low Forecast Medium Forecast CRU - Feb 2016
Source: Mosaic, CRU

22
Stable supply/demand balance going forward
2016 sees a contraction of global potash capacity
as the industry adjusts to new market conditions
New greenfield plants are still expected to come
on stream later in the decade, but few (if any)
projects not already under construction appear
likely to move forward in the near term
30
35
40
45
50
55
60
65
70
75
00 05 10 15 20F
MMT KCl
Source: Company Reports, Fertecon and Mosaic
Global Potash Capacity
Based on our assessment of operational capacity
(approximately 80 million tonnes in 2020), the
global operating rate is expected range from 85-
90% for the remainder of this decade
Further supply adjustments (or project delays)
could boost operating rates, given our demand
expectations
55%
60%
65%
70%
75%
80%
85%
90%
95%
100%
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
10 11 12 13 14 15 16F 17F 18F 19F 20F
Op RateMMT KCl
Source: Company Reports, CRU and Mosaic
Global Potash Capacity,
Production and Operating Rate
Capacity Production Op Rate

23
State of the Fertilizer Industry
Piper Jaffray Global Agriculture Symposium
Minneapolis, MN
August 2, 2016
Andy Jung
Director, Market and Strategic Analysis
The Mosaic Company
Thank You!
