Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-31.1 - CERTIFICATE OF PRINCIPAL EXECUTIVE OFFICER PURSUANT TO SECTION 302 - Zeltiq Aesthetics Inc | exhibit311q415.htm |
| EX-21.1 - LIST OF SUBSIDIARIES - Zeltiq Aesthetics Inc | exhibit211q415.htm |
| EX-31.2 - CERTIFICATE OF PRINCIPAL FINANCIAL OFFICER PURSUANT TO SECTION 302 - Zeltiq Aesthetics Inc | exhibit312q415.htm |
| EX-12.1 - RATIO OF EARNINGS TO FIXED CHARGES - Zeltiq Aesthetics Inc | exhibit121q415.htm |
| EX-23.1 - CONSENT OF PRICEWATERHOUSECOOPERS LLP - Zeltiq Aesthetics Inc | exhibit231q415.htm |
| EX-10.49 - EMPLOYEE OFFER LETTER - Zeltiq Aesthetics Inc | exhibit1049q42015.htm |
| EX-32.1 - CERTIFICATE OF PEO AND PFO PURSUANT TO 18 U.S.C. SECTION 1350 - Zeltiq Aesthetics Inc | exhibit321q415.htm |
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
____________________________________________
FORM 10-K
____________________________________________
(Mark One)
ý | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
OR
¨ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
Commission file number: 001-35318
____________________________________________
ZELTIQ Aesthetics, Inc.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
____________________________________________
Delaware | 27-0119051 | |
(State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | (I.R.S. employer identification no.) | |
4698 Willow Road, Suite 100
Pleasanton, CA 94588
(Address of principal executive offices and Zip Code)
(925) 474-2500
(Registrant’s telephone number, including area code)
____________________________________________
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
Title of each class: Common Stock
Name of each exchange on which registered: The NASDAQ Global Select Market
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes x No ¨
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Exchange Act. Yes ¨ No x
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ý No ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes ý No ¨
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant's knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act (check one):
Large accelerated filer | ý | Accelerated filer | ¨ | |||
Non-accelerated filer | ¨ | Smaller reporting company | ¨ | |||
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.): Yes ¨ No ý
Aggregate market value of registrant's common stock held by non-affiliates of the registrant, based upon the closing price of a share of the registrant's common stock on June 30, 2015 (the last business day of the registrant's most recently completed second quarter) as reported by NASDAQ Global Select Market on that date: $953,437,429. Shares of the registrant's common stock held by each executive officer, director and person who owns 15% or more of the outstanding common stock of the registrant have been excluded in that such persons may be deemed to be affiliates. This determination of affiliate status is not necessarily a conclusive determination for other purposes.
As of March 10, 2016, there were 39,310,213 shares of the registrant’s common stock, par value $0.001 per share, outstanding.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Portions of the registrant's definitive Proxy Statement to be filed with Commission pursuant to Regulation 14A in connection with the registrant's 2015 Annual Meeting of Stockholders, to be filed on or before April 29, 2016, are incorporated by reference into Part III of this Form 10-K.
ZELTIQ Aesthetics, Inc.
FORM 10-K
For the Year Ended December 31, 2015
TABLE OF CONTENTS
PAGE NUMBER | ||
PART I | ||
Item 1. | ||
Item 1A. | ||
Item 1B. | ||
Item 2. | ||
Item 3. | ||
Item 4. | ||
PART II | ||
Item 5. | ||
Item 6. | ||
Item 7. | ||
Item 7A. | ||
Item 8. | ||
Item 9. | ||
Item 9A. | ||
Item 9B. | ||
PART III | ||
Item 10. | ||
Item 11. | ||
Item 12. | ||
Item 13. | ||
Item 14. | ||
PART IV | ||
Item 15. | ||
2
CAUTIONARY LANGUAGE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2015, or “Form 10-K,” contains forward-looking statements concerning our business, operations, and financial performance and condition as well as our plans, objectives, and expectations for business operations and financial performance and condition. Any statements contained herein that are not of historical facts may be deemed to be forward-looking statements. You can identify these statements by words such as “anticipate,” “believe,” “could,” “estimate,” “expect,” “goal,” “intend,” “may,” “objective,” “plan,” “potential,” “continue,” “should,” “project,” “will,” “would,” and other similar expressions that are predictions of or indicate future events and future trends. These forward-looking statements are based on current expectations, estimates, forecasts, and projections about our business and the industry in which we operate and management's beliefs and assumptions and are not guarantees of future performance or development and involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties, and other factors that are in some cases beyond our control. As a result, any or all of our forward-looking statements in this Form 10-K may turn out to be inaccurate. Factors that could materially affect our business operations and financial performance and condition include, but are not limited to, less than anticipated growth in the number of customers electing to purchase CoolSculpting systems, insufficient patient demand for CoolSculpting procedure, our failure to correctly estimate and control our future expenditures, the success of our sales and marketing, and our ability to protect and enforce our intellectual property relating to our technology, as well as those other risks and uncertainties described herein under “Risk Factors.” You are urged to consider these factors carefully in evaluating the forward- looking statements and are cautioned not to place undue reliance on the forward-looking statements. The forward-looking statements are based on information available to us as of the filing date of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Unless required by law, we do not intend to publicly update or revise any forward-looking statements to reflect new information or future events or otherwise. You should, however, review the factors and risks we describe in the reports we will file from time to time with the Securities and Exchange Commission, or SEC, after the date of this Form 10-K.
PART I
ITEM 1. | BUSINESS |
Overview
ZELTIQ Aesthetics, Inc. is a medical technology company focused on developing and commercializing products utilizing our proprietary controlled cooling technology platform. Our first commercial product, the CoolSculpting system, is designed to selectively reduce stubborn fat bulges. CoolSculpting is based on the scientific principle that fat cells are more sensitive to cold than the overlying skin and surrounding tissues. CoolSculpting utilizes precisely controlled cooling to reduce the temperature of fat cells in the treated area, which is intended to cause fat cell elimination through a natural biological process known as apoptosis, without causing scar tissue or damage to the skin, nerves, or surrounding tissue. We developed CoolSculpting to safely, noticeably, and measurably reduce the fat layer within a treated fat bulge without requiring the patient to diet or exercise. In our pivotal U.S. clinical trial involving 60 patients, physicians were able to accurately differentiate between pre- and post-treatment photographs in 88% of the patients, while unable to identify aesthetic benefits in the remaining 12%. We received clearance from the Food and Drug Administration, or FDA, in September 2010 to market CoolSculpting for the selective reduction of fat around the flanks, an area commonly referred to as the “love handles.” We received further FDA clearance in May 2012 to use CoolSculpting for the selective reduction of fat around the abdomen area. In April 2014, CoolSculpting was cleared by the FDA for treatment of the thigh area, and, in January 2015, CoolSculpting was cleared by the FDA for treatment at lower temperatures which will enable shorter treatment times. Most recently, in September 2015, the FDA cleared CoolSculpting for treatment of the submental area under the chin, an area that is consistently ranked as one of the top areas of concern both by consumers and physicians. We sell our CoolSculpting system primarily to dermatologists, plastic surgeons, aesthetic specialists and OBGYN physicians and generate revenue primarily from sales of our CoolSculpting system and from sales of consumables to our customers. Consumables are the CoolSculpting procedure packs we sell that are needed to perform procedures using our CoolSculpting system.
The global market for aesthetic procedures is significant. In the United States alone, the American Society of Aesthetic Plastic Surgery, or the ASAPS, estimates that consumers spent approximately $12 billion on aesthetic procedures in 2014. Invasive procedures (such as liposuction and tummy tucks, arm, buttock and thigh lifts) and minimally-invasive procedures (such as laser-assisted liposuction, laser lipolysis or injection lipolysis) effectively reduce fat but involve surgical procedures that require significant physician skill and resources, may involve pain, downtime, and expense for the patient, and carry the risks associated with any surgical procedure. Existing non-invasive procedures, which currently include those based on radio frequency, laser, or high intensity focused ultrasound, avoid the patient downtime and high costs of invasive and minimally-invasive procedures, but often are painful, produce limited or inconsistent results, and may require multiple treatments, and ongoing maintenance treatments. In addition, existing non-invasive procedures are not capable of selectively targeting fat cells, which can lead to damage to the surrounding tissues. Further, the treatment methods used by many existing invasive, minimally-invasive, and non-invasive procedures acutely injure fat cells in the treated area, which leads to fat cell elimination through a biological process known as
3
necrosis. Unlike apoptosis, necrosis triggers the body's wound-healing response and can result in scar tissue formation in the treated area. This scar tissue can lead to stiffening of the treated area and limits the number of times a patient can undergo these types of procedures in one area or the efficacy of any repeat treatments.
We developed CoolSculpting to provide patients with a safe, effective, non-invasive, and convenient procedure to reduce stubborn fat bulges that are not satisfactorily served by existing fat reduction and body contouring procedures. CoolSculpting is clinically proven to reduce fat bulges, allowing most patients to achieve noticeable and measurable aesthetic results without the pain, expense, downtime, and risks associated with invasive and minimally-invasive procedures. Further, these results are achieved without the pain, multiple procedures, and maintenance programs required with other non-invasive procedures. Because the fat layer in the treated area is reduced by eliminating fat cells that will not be replaced by the body, we believe the aesthetic benefits patients achieve through CoolSculpting will be durable. In addition, patients can elect to repeat the CoolSculpting procedure multiple times on the same treatment area if they desire further fat reduction. We offer training to our customers to better enable them to identify those patients whose aesthetic appearance will be noticeably improved by the reduction of their fat bulges through CoolSculpting. Due to these advantages, we believe CoolSculpting is appealing to both existing consumers who have previously had one or more aesthetic procedures, and to new consumers who have not previously elected to undergo an aesthetic procedure.
Our customers can market CoolSculpting as a premium, highly-differentiated, non-invasive fat reduction procedure. Based on our commercial data and customer experiences, we have seen attractive economic benefits for our customers. In addition, the CoolSculpting procedure does not require significant training or skill, as it is largely automated. Once the procedure is initiated, the CoolSculpting system is self-monitoring, allowing our customer to see and treat other patients or perform concurrent procedures (such as injections or other dermal treatments) on the same patient during the balance of the CoolSculpting procedure. Further, we believe CoolSculpting's appeal will allow our customers to target the aesthetic first-time user market and expand their aesthetic practices.
We market CoolSculpting to dermatologists, plastic surgeons, aesthetic specialists and OBGYN physicians. Aesthetic specialists are physicians who elect to offer aesthetic procedures as a significant part of their practices, but are not board-certified dermatologists or plastic surgeons. Some of the practices to which we sell have purchased or may elect to purchase more than one CoolSculpting system. We utilize our direct sales organization to market and sell CoolSculpting in our North American market which includes the United States and related territories, as well as Canada. In our markets located outside of North America, we market and sell CoolSculpting through both a direct sales force and a network of distributors. Our sales force and distributors also target dermatologists, plastic surgeons, aesthetic specialists and OBGYN physicians who have practices focused on aesthetic procedures and who express a willingness to position CoolSculpting as a premium, differentiated treatment and participate in our practice marketing and support programs. Our primary markets outside of North America are located in Asia-Pacific, Europe, the Middle East, Africa and Latin America. Revenue from markets outside of North America accounted for 24%, 23% and 20% of our total revenue for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively. We are driving growth in CoolSculpting procedures through our targeted marketing programs that provide our customers with practice development programs which include organization assessments and recommendations, sales training, practice marketing strategies, and metric analysis. After we establish a significant installed base of CoolSculpting systems in specific markets, we partner with our customers' practices on marketing, advertising, and promotional activities in their local markets to drive demand for CoolSculpting. To further enhance and expand our brand awareness, in 2015 we launched a direct-to-consumer advertising campaign, which includes television, radio and print media, throughout the U.S. and in selected target cities in North America and Europe. Direct-to-consumer advertising builds awareness in the marketplace by having consumers (a) go to existing local practices and request treatment and drive consumable revenue, or (b) go to their local physician who does not yet have consumable services, create the desire and drive system revenue.
We generate revenue from sales of our CoolSculpting system and from sales of cycles in the form of consumable procedure packs to our customers. As of December 31, 2015, we had an installed base of 4,634 CoolSculpting systems installed across 3,765 practices worldwide. As of December 31, 2015, 2.5 million CoolSculpting revenue cycles had been shipped to our customers and distributors. A cycle is an authorization to perform one procedure to one specific area on the body; customers can only perform a treatment if they have purchased a cycle. We generated revenue of $255.4 million, $174.5 million and $111.6 million for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively. System revenue represented 51%, 53% and 55% of our total revenue for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively. Consumable revenue accounted for 49%, 47% and 45% of our total revenue for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
Our business is dependent upon the success of CoolSculpting, and we cannot assure you that we will be successful in significantly expanding physician and patient demand for CoolSculpting. In addition, we will continue to incur significant expenses for the foreseeable future as we expand our commercialization and other business activities. Although, based upon our current plans and market conditions, we believe that our existing cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments will be sufficient to satisfy our anticipated cash requirements for the foreseeable future, we cannot assure you that we will be able to maintain profitability.
4
Market Overview
The global market for aesthetic procedures is significant. The ASAPS estimates that U.S. consumers spent approximately $12 billion on approximately ten million aesthetic procedures in 2014. According to the ASAPS, total aesthetic procedures in the United States have grown by 274% between 1997 and 2014, with non-invasive aesthetic procedures growing by 508% during this same period. According to the ASAPS, the top five aesthetic surgical procedures in 2014 were liposuction, breast augmentation, eyelid surgery, tummy tuck and nose reshaping, and the top five non-invasive procedures in 2014 were Botox, soft tissue fillers, laser hair removal, chemical peel and microdermabrasion. No one treatment procedure is offered by all physicians, and treatments vary in terms of the treatment goal and desired effect. As a result, the total aesthetic market as reported by the ASAPS does not represent the market potential for CoolSculpting or any other single product or treatment, but illustrates that each year patients elect to have millions of procedures to enhance their appearance.
We believe several factors are contributing to the ongoing growth in aesthetic procedures, including:
• | Continuing focus on body image and appearance. Both women and men continue to be concerned with their body image and appearance, fueled in part by popular culture's perpetuation of the ideal thin body type for women and the ideal lean and defined body type for men. We believe the size and wealth of the aging “baby boomer” demographic segment and its desire to retain a youthful appearance for professional and personal reasons have driven the growth in aesthetic procedures. |
• | Broader availability of safe non-invasive aesthetic procedures. Technological developments have resulted in the introduction of a broader range of safe, non-invasive aesthetic procedures. According to the ASAPS, non-invasive aesthetic treatments are growing faster than invasive surgical procedures. |
• | Increased physician focus on aesthetic procedures. We believe increased restrictions imposed by managed care and government agencies on reimbursement for medical treatments are motivating our customers to establish or expand their elective aesthetic practices, which generally consist of procedures paid for directly by patients. We expect this trend to continue as our customers look for ways to expand their practices and improve profitability. |
Limitations of Existing Fat Reduction and Body Contouring Procedures
Fat reduction and body contouring procedures, including invasive, minimally-invasive, and non-invasive procedures, have become increasingly popular. The following discussion outlines the benefits of these existing procedures, as well as our opinion of the inherent limitations of these procedures when compared to CoolSculpting. Many of the companies marketing these procedures have greater resources and brand recognition than we do. In addition, some of the procedures offered by our competitors have broad market acceptance with our target customers and their patients.
Invasive and Minimally-Invasive Procedures
Physicians currently perform a number of invasive surgical procedures for fat reduction and body contouring, including liposuction, abdominoplasty (tummy tucks), gluteoplasty (buttock lifts), brachioplasty (arm lift), thighplasty (thigh lift), lower rhytidectomy (neck lift) and mentoplasty (chin). Laser-assisted liposuction, laser lipolysis, ultrasound lipolysis and injection lipolysis are minimally-invasive alternatives for fat reduction and body contouring. These minimally-invasive procedures require the physician to surgically insert a cannula, or metal tube, into the area to be treated and to use heat or ultrasound energy from the cannula to damage fat cells. Patients who are obese and require significant fat reduction to achieve aesthetic results are candidates for invasive and minimally-invasive procedures. Although effective at reducing a significant amount of fat, these invasive and minimally-invasive procedures present the following limitations:
• | Surgical risks. All invasive and minimally-invasive procedures disrupt the skin's barrier function and therefore may increase risks of infection, local or widespread scarring, perforation, and hemorrhage. These procedures generally require a general or local anesthesia, which carries additional risks. |
• | Pain and downtime. Invasive procedures may involve pain and may require weeks of post-surgical recovery. As a result, patients may need to spend significant time away from work and take prescribed pain medications for extended periods of time post-surgery. In addition, body lifts may severely limit muscle movement in the treated area during recovery, which can limit a patient's mobility for a significant period of time. Minimally-invasive procedures require a surgical incision or multiple injections, and may cause patient pain. Patients generally require at least two days or more of recovery time after a minimally-invasive procedure, which may require the patient to miss work and necessitate prescribed pain medications post-surgery. |
• | Potentially undesired results. Invasive procedures may cause non-uniform fat reduction, dimpling, lumpiness, numbness, scarring, discoloration, or sagging skin in the treated area. Follow-up surgeries may be required to correct these problems. Minimally-invasive procedures can cause skin or tissue damage if, among other things, the physician does not carefully control the heat or ultrasound energy delivered in the treatment area. |
• | Physician skill and technique dependent. The aesthetic results achieved through invasive and minimally-invasive procedures are dependent upon a physician's skill and training, which can vary from physician to physician. In addition, these procedures require a significant amount of direct physician time to perform. |
5
• | High cost. Invasive and minimally-invasive procedures can be significantly more expensive for patients than non-invasive aesthetic procedures. In addition, there is an opportunity cost for physicians as these procedures require direct physician involvement and supervision. |
Non-Invasive Procedures
Patients who do not require significant fat reduction to achieve aesthetic results may explore non-invasive fat reduction and body contouring procedures to avoid the pain, expense, downtime, and surgical risks associated with invasive and minimally-invasive procedures. Existing non-invasive procedures used for body contouring or fat reduction, other than CoolSculpting, currently include those based on various forms of energy, including radiofrequency, laser, or ultrasound. Although these procedures are generally safer and less expensive than invasive and minimally-invasive procedures, these procedures have the following limitations when compared to CoolSculpting:
• | Limited, inconsistent, and unpredictable results. We believe existing non-invasive procedures have limited efficacy and produce inconsistent fat reduction results. In addition, these procedures are not capable of selectively targeting fat cells, which can lead to unpredictable results, including damage to surrounding tissue. |
• | Multiple steps required. Existing non-invasive procedures based on radio frequency or laser energy often require multiple steps spread over several weeks before the patient obtains noticeable aesthetic results, requiring the patient to schedule and coordinate multiple, time-consuming office visits. |
• | Maintenance requirements. Some existing non-invasive procedures have only a temporary treatment effect, and thus require periodic maintenance treatments to sustain the desired aesthetic results. |
• | Technique dependent. Existing non-invasive procedures often require highly trained personnel to conduct the treatment. Poor technique may lead to reduced efficacy and inconsistent aesthetic results. |
• | Pain. Energy based products that utilize heat to destroy fat cells are associated with significant procedural pain and discomfort. Patients may require pain medications to tolerate the procedure. Pain management considerations may complicate the procedure and impose additional risks associated with pain medications. |
Our Solution
CoolSculpting is a non-invasive fat reduction procedure that is clinically proven to be safe and effective and provides most patients with noticeable and measurable aesthetic results. CoolSculpting utilizes our proprietary controlled cooling technology to selectively reduce stubborn fat bulges. CoolSculpting is based on the scientific principle that fat cells are more sensitive to cold than the overlying skin and surrounding tissues. CoolSculpting precisely cools the targeted fat bulge, and is designed to eliminate fat cells through a natural biological process known as apoptosis, without causing scar tissue or damage to the skin, nerves, or surrounding tissues.
We believe that CoolSculpting provides the following benefits to our customers and their patients:
• | Clinically proven, consistent, and durable results. Clinical studies involving more than 300 patients demonstrate that a single CoolSculpting procedure can noticeably and measurably reduce the fat layer within a treated fat bulge without requiring diet or exercise. In our pivotal U.S. clinical trial involving 60 patients, physicians were able to accurately differentiate between pre- and post-treatment photographs in 88% of the patients. Patients typically notice results as soon as three weeks following the CoolSculpting procedure, with the most dramatic results occurring over a period of two to four months for most patients. Because the fat layer in the treated area is reduced by eliminating fat cells that will not be replaced by the body, we believe the aesthetic benefits patients achieve in the treated area will be durable. |
• | Safety profile. CoolSculpting selectively targets fat cells. Our proprietary treatment algorithms are designed to sufficiently cool the fat cells in the treated area to obtain the desired aesthetic results while preserving the skin and surrounding tissues. We designed the CoolSculpting system to constantly monitor the controlled cooling process and to automatically terminate the procedure if it detects any errors and warm the treated area if the detected temperature falls below our cooling algorithms. As of December 31, 2015, we have shipped 2.5 million revenue cycles. To date, approximately 3,500 clinical complaints have been reported to us, representing 0.14% of all cycles. The most common clinical complaints relate to pain associated with the procedure, as well as common side effects, such as redness and edema. Medical Device Reports were filed when we believed reporting requirements were met. |
• | Patient satisfaction. CoolSculpting allows most patients to achieve noticeable and measurable aesthetic results without the pain, expense, downtime, and risks associated with invasive and minimally-invasive procedures for fat reduction. In addition, unlike many other non-invasive procedures, patients are not required to undergo multiple treatment procedures or adopt special diet or exercise programs following the procedure to obtain aesthetic results. Patients have the flexibility to undergo a CoolSculpting procedure discreetly, scheduling an appointment for the procedure in the morning before work, during a lunch break, or in the evening. In our pivotal clinical study, 82% of the participating patients reported satisfaction with the |
6
CoolSculpting procedure. As a further indication of patient satisfaction, our customers reported that 45% of their patients returned for an additional CoolSculpting treatment, according to the market research study we commissioned through Easton Associates.
• | Repeatability enabled by natural biological process. CoolSculpting is designed to reduce the fat layer in the treated area through apoptosis, a natural biological process that leads to gradual elimination of the fat cells from the body. Unlike other treatment methods, we designed CoolSculpting to avoid triggering the body's wound-healing response, which can lead to the formation of scar tissue. As a result, patients can elect to have the CoolSculpting procedure repeated multiple times on the same treatment area if they desire further fat reduction. Because fat cells are gradually eliminated from the body following a CoolSculpting treatment over a three to 16 week period, we recommend that patients wait at least six weeks before repeating a CoolSculpting procedure on the same treatment area. |
• | Reproducible results. The CoolSculpting procedure requires limited training and skill to obtain successful aesthetic results. We designed the CoolSculpting system to be easy to operate and largely automated which results in a more consistent application and reproducible results. Once the procedure is started, the clinician is not required to monitor or make any adjustments to the CoolSculpting system during the balance of the procedure. |
• | Differentiated, high-value product for physician practices. Our selective distribution strategy is designed to enable our customers to market CoolSculpting as a premium, highly-differentiated, non-invasive fat reduction procedure. Based on our commercial data and customer experiences, we have seen attractive economic benefits for our customers. In addition, the clinician is not required to administer the procedure and can see and treat other patients or perform concurrent procedures, such as injections or other dermal treatments, on the same patient during the CoolSculpting procedure. |
• | Ability to expand the aesthetic market. Through market research we have confirmed there is strong consumer demand for a non-invasive procedure that can address the aesthetic concerns of individuals who have stubborn fat bulges. During the third quarter of 2013, we conducted an additional quantitative survey of 3,515 adults in the United States through Berglas Research, an independent marketing research company, and are able to project that more than 85 million consumers are considered aesthetically-oriented and qualify for CoolSculpting. Among this group and based on this study, we project that 22.4 million consumers would be interested in learning more about the CoolSculpting procedure after reading the product description. During the fourth quarter of 2015, we conducted a quantitative survey of 3,261 adults in the United States through Quintessent Marketing, an independent marketing research company, and are able to project that more than 106 million consumers are considered aesthetically-oriented and qualify for CoolSculpting. Among this group and based on this study, we project that 28.6 million consumers would be interested in learning more about the CoolSculpting procedure after reading the product description. The ASAPS reported 135,000 non-invasive fat reduction procedures in 2014. When we compare our potential audience to the number of procedures conducted we find that our market penetration is lower than 1%. Additionally, according to a separate market research study we commissioned through Easton Associates in 2011, our customers participating in the study reported that 30% of their CoolSculpting patients were aesthetic first-time users. Based on these results, we believe our customers will be able to target the aesthetic first-time user market and expand their aesthetic practice due to CoolSculpting's appeal. |
Our Strategy
Our goal is to become a leading medical technology company focused on developing and commercializing products utilizing our proprietary controlled cooling technology platform. To achieve this goal, we intend to:
• | Selectively market and sell our CoolSculpting system. With CoolSculpting established as a premium, highly-differentiated treatment we plan to continue to market and sell our CoolSculpting system to dermatologists, plastic surgeons, aesthetic specialists and OBGYN physicians. Some of our target practice sites have purchased or may elect to purchase more than one CoolSculpting system. Our sales force and distributors target dermatologists, plastic surgeons, aesthetic specialists and OBGYN physicians who have practices focused on aesthetic procedures and who express a willingness to position CoolSculpting as a premium, differentiated treatment and participate in our practice marketing and support programs. |
• | Deliver a Focused and Efficient Marketing Strategy. Our marketing strategy is designed to accelerate revenue while reducing overall sales and marketing spend through establishing co-operative customer partnerships and a direct-to-consumer program. This model has enabled our customers to leverage their local-market knowledge to create tailored, local patient marketing programs, with strong digital emphasis, to achieve greater awareness and demand. We intend to expand our co-operative customer partnership program in 2016. We also have a 5-step practice marketing program designed to help practices leverage established best practices relating to patient and staff treatments, front desk operations and internal and external marketing. At the core of this 5-step program is Treatment-to-Transformation, or T2T, a customized assessment and treatment protocol, which has revolutionized the way our customers use CoolSculpting to deliver improved outcomes and high patient satisfaction. We believe this clinical protocol has been instrumental in improving our system utilization and driving incremental system sales in existing practices. Its adoption was and continues to be a significant contributor to our current and long-term growth objectives. |
7
• | Leverage Data and Customer Insights. During 2013 and 2014, we launched our HIPAA compliant connectivity and data management tool, CoolConnect, across our installed base to collect real-time sales, demographic and marketing data that we believe can further optimize marketing strategies for both us and our customers. This information provides valuable trends and insights to our Practice Development Managers, or PDMs, showing both account-level treatment information and comparisons against peer-group counterparts within the same geographic area. We also leveraged our 2013 customer segmentation research to hone our messaging targeted towards consumers, and we have implemented a consistent creative strategy based on these insights. |
• | Highly Optimized, Experienced and Fully Trained Sales Force. Our North American sales force is a bifurcated organization that has produced stronger focus and results on system sales and high-margin consumable sales. This organization is split between Area Sales Managers (ASMs), who focus on system sales, and Practice Development Managers (PDMs), who focus on assisting practices to market CoolSculpting to patients, product training and driving system utilization. We have continued to hire high quality, experienced sales representatives and sales management personnel in both categories and train the sales organization to optimize performance in their respective roles. This initiative has resulted in improved system placements to both existing and new practices, as well as increased system utilization, contributing to our recent revenue growth. We believe our sales force will continue to generate increased customer adoption and patient awareness momentum in the marketplace. We also believe that our focus on driving system utilization will offer the opportunity to drive increased sales of our high gross margin procedure packs. |
• | Increase utilization of CoolSculpting through our marketing and customer support programs. We are driving demand for CoolSculpting procedures through our marketing and customer support programs. Through our PDMs we provide our customers with training on patient assessments, how to apply the CoolSculpting technology, practice development and marketing support to help our customers make CoolSculpting a key offering within their practices. We also intend to continue our co-operative marketing strategy with individual practices which is designed to encourage our customers to promote CoolSculpting to their aesthetic patients and those outside of their practices. To further support our customized marketing approach, we created the ZELTIQ Training Centers where we hold our training program, CoolSculpting University, or CSU. CSU is focused on customer training and education programs to optimize patient outcomes. In 2015, we hosted over 1,800 medical professionals from 865 offices worldwide at our CSU programs. This program invites practices to attend hands-on training where they learn the proper techniques for T2T, including a complete treatment assessment, applicator placement and patient consultation. Customers are also trained on a specific practice enhancement execution protocols designed to accelerate utilization and maximize the use of their CoolSculpting offering that includes branding, grassroots initiatives and digital marketing tactics. To address the demand for this training from our customers we currently have one training center in Pleasanton, California which we opened in 2013, and a second center in Reston, Virginia, which we opened in the second quarter of 2015. Our PDMs then visit customers in the field to further customize and optimize the program at a local level to ensure it is delivering improved patient flow. We believe this program is particularly well suited to the aesthetics industry. We also intend to continue to participate in industry trade shows, clinical workshops, and company-sponsored conferences with expert panelists. |
• | Increase our international presence. There is strong global demand for aesthetic procedures outside of North America, especially in Asia, Latin America, and Europe. We intend to increase our market penetration outside of North America and build global brand recognition. We have received regulatory approval or are otherwise free to market CoolSculpting in numerous international markets, where use of the product is generally not limited to specific treatment areas. Our customers in these markets commonly perform CoolSculpting procedures on the back and chest, in addition to the flanks, abdomen, thigh and submental area. We intend to seek regulatory approval to market CoolSculpting in additional international markets, as well as grow our international sales and marketing organization to focus on increasing sales and strengthening our customer relationships. As part of that strategy, we are and intend to continue to opportunistically deploy a direct sales force in select international markets. |
• | Expand our FDA-cleared indications for CoolSculpting. We currently have FDA clearance to market CoolSculpting in the United States for the selective reduction of fat in the flanks, an area commonly known as the “love handles,” the abdomen area, the thigh area and the submental area under the chin. We intend to continue to seek additional regulatory clearances from the FDA to expand our United States marketable indications for CoolSculpting to other areas on the body. |
• | Leverage our technology platform. We are exploring additional uses of our proprietary controlled cooling technology platform for the dermatology, plastic surgery, aesthetic and OBGYN markets. We are also exploring potential therapeutic uses for our platform technology, either directly or through collaborative arrangements with strategic partners. |
• | Streamlined R&D Focus and Capital Deployment. Our R&D efforts and associated capital deployment have been recently streamlined to focus on making the CoolSculpting procedure safer, more comfortable, faster and more efficacious. Our research is focused on optimizing the patient outcome and increasing practice efficiency by reducing treatment duration. In the long-term, we remain focused on leveraging our proprietary cooling technology into new applications and indications for CoolSculpting to treat acne and into areas with a smaller volume of fat on the body. |
8
The CoolSculpting Experience
Patient Consultation
The first step of the CoolSculpting process is a patient consultation. We designed our CoolSculpting system to address the aesthetic concerns of individuals who are not considered obese but have stubborn fat bulges. Utilizing our PDMs and CSU program, we train our customers to properly identify those patients who would be good candidates for CoolSculpting and educate their patients on the aesthetic results they should expect from a CoolSculpting procedure. We also instruct our customers to explain to their patients the natural process of fat cell elimination triggered by a CoolSculpting procedure, so that they understand the expected time period before they will notice the full aesthetic results as well as the potential to repeat the procedure for additional aesthetic results. While some patients may notice results as soon as three weeks following a CoolSculpting procedure, the full aesthetic results are generally achieved over a period of two to four months following treatment. Because we believe the consultation process is an important step in ensuring patients are pleased with their CoolSculpting procedure, we encourage our customers to personally conduct the patient consultation.
The CoolSculpting Procedure
CoolSculpting is a non-invasive procedure that is clinically proven to be safe and effective and provides most patients with noticeable and measurable aesthetic results. Once the desired treatment area has been identified, the clinician applies our consumable CoolGel to the skin surface of the treatment area to ensure consistent thermal contact and to protect the skin from freezing. The CoolSculpting applicator is then positioned on the treatment area over the CoolGel, and the fat bulge is drawn into the applicator and positioned between its cooling panels. In the case of our CoolSmooth applicator, a non-suction based applicator is secured by disposable securement accessories. Once the applicator is affixed on the treatment area, no further clinician intervention is required for the duration of the procedure. The rate of the controlled cooling is modulated by thermoelectric cooling elements and controlled by sensors in the applicator that monitor the cooling of the fat bulge. Just prior to the end of the procedure, the CoolSculpting system signals the clinician that the treatment is ending. When the procedure is completed, the CoolSculpting system automatically terminates the cooling, and the clinician then removes the CoolSculpting applicator from the treatment area.
Patient Experience
Our surveys indicate that most patients find the CoolSculpting procedure easy to tolerate. Generally, anesthesia and pain medications are not required before, during, or after a CoolSculpting procedure. Patients feel a tugging sensation from the suction created when the CoolSculpting applicator (other than our CoolSmooth applicator) is placed on the treatment area. At the onset of the procedure, patients also experience a chilling sensation in the treatment area that subsides after a few minutes, as the cooling produces an anesthetic effect. Patients can talk on their cell phones, read, listen to music, work on their laptop, relax, or sleep during the procedure.
After completion of a CoolSculpting procedure, patients may resume their normal activities, including work and exercise. CoolSculpting patients generally do not experience any significant adverse side effects.
Our CoolSculpting System
We generate revenue primarily from sales of our CoolSculpting system and from sales of consumables to our customers. Sales of systems can include sales of systems to new customers that include our entire suite of applicators, as well as multi-system sales to new customers or sales to existing customers which may not include the entire suite of applicators. Additionally, some practices may purchase additional applicators, or add-on applicators, for existing systems. We generate consumable revenue through sales of cycles in the form of consumable procedure packs, each of which includes our consumable CoolGels, CoolLiners, Geltraps and in the case of our CoolSmooth procedure packs, disposable securement accessories, all of which are used by our customer during treatments. In addition, each consumable procedure pack includes a disposable computer cartridge that we market as the CoolCard. The CoolCard contains enabling software that permits our customers to perform a fixed number of CoolSculpting procedures, or cycles.
We also announced the launch of a new CoolMini-only system, providing physicians with the option to purchase a system that only comes with the CoolMini applicator which was specifically designed to treat smaller pockets of fat, including the submental fat area, or "double chin". We began offering this new configuration in the first quarter of 2016, enabling us to target physicians that primarily or exclusively focus on facial aesthetic treatments. The system can be upgraded with the purchase of additional software and applicators. With these individually purchased upgrades, the system has the ability to treat other body areas.
CoolSculpting Control Unit
The CoolSculpting control unit is the base of the CoolSculpting system and contains the simple user interface, power management and control functions, and chiller unit that is responsible for the controlled cooling. Our CoolSculpting control unit also contains a Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996, or HIPAA, compliant connectivity and data management tool that
9
locally tracks and collects data about each procedure performed as well as any error messages that may be generated during the procedure. We can collect and analyze this information to help our customers better understand their usage patterns and improve their marketing plans, utilization, and profitability.
Additionally, the CoolSculpting control unit features: (1) a color touchscreen which provides operators with clear visual directions to initiate a CoolSculpting procedure, continuous status updates, and easy to follow notifications or corrective actions in the rare event of a procedure interruption; (2) vents which provide airflow and reduce heat build-up allowing our CoolSculpting system to be used in a standard physician treatment room without any special ventilation requirements or room modifications; (3) a drawer which provides storage space for our CoolSculpting CoolGels, CoolLiners, Geltraps and user documentation; and (4) the unit is mobile, allowing a physician to easily transfer the CoolSculpting unit between treatment rooms and reach different treatment areas on a patient.
CoolSculpting Applicators
The CoolSculpting applicator: (1) delivers vacuum suction and cooling to the fat bulge being treated; (2) can be used to start and stop a CoolSculpting procedure and to turn the vacuum suction on and off; and, (3) has a thermoelectric cooling panel with temperature and pressure sensors which provide precise thermal control and monitoring of the fat bulge being treated and will automatically stop the procedure if a problem is detected. In the case of our CoolSmooth applicator, which is a non-suction based applicator, the applicator is secured by disposable securement accessories.
With the launch of our CoolMini applicator in September 2015, we currently offer six CoolSculpting applicators for use with our CoolSculpting system. Each CoolSculpting applicator is designed to allow the physician to treat a different size and shape fat bulge.
1. | CoolCore - designed for use on small and medium fat bulges. |
2. | CoolMax - designed for use on larger fat bulges. |
3. | CoolCurve+ - designed to fit tightly curved contours. |
4. | CoolFit - designed for use on long, narrow fat bulges. |
5. | CoolSmooth Pro - designed for use on non-pinchable fat bulges. |
6. | CoolMini - designed to address smaller fat bulges, including the submental area under the chin. |
In addition to the above applicators that we include in our current system bundle, we recently announced the launch of a new family of applicators called CoolAdvantage. These applicators reduce treatment time by nearly half compared to our existing applicators due to lower temperatures. In Q2 2016 we expect to release our first applicator from this family, which will feature an adaptable 3-in-1 configuration and enhanced cup design. Additionally, in Q4 2016 we expect to launch the second applicator from this family, which will address larger fat bulges.
CoolSculpting Procedure Packs
A CoolCard is required to operate the CoolSculpting control unit and is programmed with enabling software that permits the CoolSculpting control unit to perform a fixed number of procedures, or cycles. In addition, each CoolCard is programmed with an encrypted security certificate that prevents the performance of a CoolSculpting procedure unless the CoolCard is recognized and authenticated by the specific CoolSculpting control unit and CoolSculpting applicator. The security certificate is designed to ensure that customers pay for each CoolSculpting procedure and prevent the use of counterfeit CoolCards. Our consumable CoolGels are cotton sheets saturated in a solution that protects the skin and ensures proper thermal coupling during a CoolSculpting procedure. One CoolGel is required for each treated area and is not reusable. Our consumable plastic CoolLiners and Geltraps protect the applicator from gel contact. One CoolLiner is recommended per patient for hygienic reasons. In the case of our CoolSmooth procedure packs, the applicator is secured by disposable securement accessories.
10
Our Technology
Our Technology Platform
Our controlled cooling technology platform is based on the scientific principle that cooling can be delivered safely and non-invasively to achieve specific biological outcomes, selectively affecting certain cells, tissues, or structures in and below the skin. The ability to predict and control the impact of cold exposure by developing algorithms to control the rate and period of the cooling is well established in the field of cryobiology and cryogenic medicine. Moderate cold has been demonstrated to trigger cellular apoptosis (programmed cell death), whereas more extreme cold causes uncontrolled cell death. Additionally, certain cells and tissue types exhibit particular sensitivity or resistance to cold injury. This principle enables the selective elimination of certain cells or tissues via a desired biologic pathway using precise cooling temperatures. In addition, the function of certain biological systems can be affected by cold exposure. Cold is known to reduce nerve conduction, and can produce either a transient or a prolonged interruption in nerve function depending on the specific thermal parameters applied. We believe the ability to control tissue effects by modulating the cooling algorithm with our technology platform enables multiple potential therapeutic applications in addition to our CoolSculpting fat reduction application.
Our CoolSculpting Technology
Our CoolSculpting technology utilizes the sensitivity of fat cells to cold injury to selectively eliminate subcutaneous fat tissue without affecting the skin or other surrounding tissues. Termed Cryolipolysis®, this technology enables a non-invasive alternative for subcutaneous fat reduction through cellular apoptosis. Cellular apoptosis is a normally occurring biological process whereby cells are eliminated as part of normal cell turnover. When injurious external stimuli (such as cold) are applied to a target cell, the apoptotic process may be triggered. If triggered, the injured cell consequently enters an orderly, regulated process of gradual degradation into smaller bodies which are absorbed by the body's immune system over time. This pathway to cellular elimination is in contrast to cellular necrosis, or uncontrolled cell death, in which an acute injury to the cell leads to lysis of the cell. Cellular necrosis triggers an aggressive inflammatory response leading to fibrotic scar tissue formation, which is not observed with cellular apoptosis. The cold treatment algorithm implemented by the CoolSculpting technology is designed to trigger apoptosis, eliminating fat cells without generating a wound healing reaction.
The CoolSculpting technology has been clinically demonstrated to cause reductions in fat layer thickness without impacting the skin or other tissues or structures in the treatment area. Fat cells are particularly sensitive to cold injury due to their composition; they contain a large lipid droplet within the cell membrane which constitutes the majority of the cell's volume. When cooled, lipids crystallize (undergo phase transition to an ordered molecular state) at a temperature well above the freezing point of water. Exposure of fat cells to these moderately cold temperatures causes the lipid droplets to crystallize, causing a subtle molecular injury which triggers the apoptotic sequence. However, the cooling does not affect cell types without high lipid content, preserving the health of the epidermis, dermis, and the underlying tissue. The interactions between cold and different cell and tissue types have been investigated extensively in scientific studies and are well documented in the literature.
A simplified description of the CoolSculpting process is as follows:
1. | Cooling applicator is applied and the fat bulge being treated is suctioned into the applicator head (unless our CoolSmooth applicator is being used, in which case it is secured by disposable securement accessories). |
2. | Subcutaneous fat in the treatment area is precisely cooled at a rate that does not cause scar tissue or damage to the skin, nerves, or surrounding tissues. |
3. | Maintained cooling causes lipid crystallization in the fat cells and triggers apoptosis of the fat cells. |
4. | Patient's natural immune response leads to gradual elimination of the fat cells, resulting in a reduction in the fat layer thickness and an improvement in the appearance of the treated fat bulge. |
Clinical History and Development of CoolSculpting
The founding principles of controlled cooling for the non-invasive and selective reduction of fat cells were originated at the Wellman Center for Photomedicine at the Massachusetts General Hospital, or MGH, a teaching affiliate of Harvard Medical School. CoolSculpting’s core technology was developed by Harvard scientists Dr. R. Rox Anderson and Dr. Deiter Manstein, two pioneers in the aesthetic industry. Researchers at MGH were prompted by published reports of cold-induced panniculitis, or inflammation of subcutaneous adipose tissue, in a syndrome frequent in young children called popsicle panniculitis, whereby inflammation of the fatty tissue in the lower cheek occurred after children sucked for a prolonged time on frozen treats. Clinical reports of popsicle panniculitis suggested that human adipose tissue may be preferentially damaged by exposure to cold. Based on these reports, research scientists at MGH conducted further research and patented certain aspects of Cryolipolysis technology. In May 2005, we secured an exclusive, worldwide license to the Cryolipolysis technology developed at MGH.
Following our licensing of the Cryolipolysis technology from MGH, we initiated animal and human clinical testing to support the development of the CoolSculpting procedure. These scientific studies used objective endpoints, including histologic and ultrasound assessments and outcome evaluation by blinded, independent panel review, and provided evidence of the safety and efficacy of the CoolSculpting procedure. As of December 31, 2015, there were over 60 peer-reviewed scientific journal articles and published
11
conference abstracts discussing the effects of our CoolSculpting technology, both by physicians affiliated with our company as clinical and scientific advisers, as well as by independent investigators.
Preclinical Studies
We conducted animal testing primarily in pig models. In the original MGH studies, Manstein et al. investigated the feasibility of Cryolipolysis, established correlations between cold treatment parameters (temperature, time) and fat reduction, and evaluated the impact on serum lipid levels in Yucatan pigs (see Manstein D, Laubach H, Watanabe K, et al: Selective cryolysis: A novel method of non-invasive fat removal. Lasers Surg Med 40:595-604, 2009). All sites treated with cold exposure less than -1°C developed panniculitis and fat layer reduction. No significant changes in the lipid profiles of the animals were noted immediately post-treatment or at any time point studied.
A subsequent study was performed by Zelickson et al. (see Zelickson B, Egbert BM, Preciado J, et al: Cryolipolysis for non-invasive fat cell destruction: Initial results from a pig model. Dermatol Surg 35:1462-1470, 2009). In this study, three pigs underwent a single Cryolipolysis treatment, while the fourth pig underwent seven treatments with the Cryolipolysis device at different time points before euthanasia. Histopathology demonstrated an approximate reduction of 50% in the thickness of the superficial fat layer. No adverse impact on the skin was observed and lipid panels revealed no significant variations in lipid profiles at any time in the study.
Clinical Studies
We have conducted multiple institutional review board-approved (IRB-approved), non-significant risk human clinical studies to assess the use of controlled cooling for selective fat reduction.
Pre-abdominoplasty study. An initial exploratory human clinical study of Cryolipolysis was performed at a single site in the United States on 180 patients. In this study, patients who were scheduled to undergo abdominoplasty were treated with our technology in the lower abdomen at different intervals up to 180 days prior to their scheduled surgery date. At the time of abdominoplasty, the treated tissue was excised and processed for histologic evaluation. There were no significant changes in the fat tissue at seven days post-treatment, relative to the untreated control. This supports that controlled cooling triggers an apoptotic mechanism of fat cell elimination, as this process occurs gradually and is not evident immediately after cold exposure. At 14 days post-treatment, infiltration of immune cells (macrophages) were observed in the fat layer, as indicated by intense nuclei staining. These cells are responsible for the removal of the apoptotic fat cells via phagocytosis. At 90 days post-treatment, the fibrous septae (connective tissue fibers) in the fat layer were condensed due to elimination of fat cells. There was no evidence of dermal, epidermal, nerve, or blood vessel inflammation, and there was no evidence of fibrosis (scar tissue formation).
Pivotal study. To support our 510(k) notification for the use of CoolSculpting for non-invasive fat reduction of the flanks, commonly referred to as the love handles, we completed a prospective, multi-center U.S. human clinical trial in 2007. A total of 60 patients were treated at 12 dermatology or plastic surgery centers in the United States. Follow-up periods for both safety and efficacy were at two and six months. An additional one-week assessment was performed via telephone interview to document potential side effects. The primary endpoint was assessed on the basis of blinded, independent panel review of photographs. Patients were treated with our technology for 30 to 60 minutes. Patients were treated on one flank only to aid in the assessment of the primary endpoint. Outcomes were assessed via photographs, ultrasound measurements, and patient satisfaction questionnaires.
Primary endpoint. The primary effectiveness endpoint was the correct identification of the series of pre-treatment images versus six-month post-treatment images by the three independent physician reviewers who specialize in dermatology or plastic surgery. High resolution digital photographs were made of the patients' abdomens at specific degrees of rotation. The physicians were blinded to the identification of which photograph corresponded to the baseline image. Each reviewer was then asked to determine which photograph corresponded to the baseline photograph series and record their selections onto individual data collection forms. Intra-rater consistency among reviewers was determined by the inclusion of repeat sets. The order in which the patients were presented to the reviewer was randomized; within each patient, the set presentation was also randomized (e.g., left or right side of the presentation slide). It was expected that the percentage of correct identification of the pre-treatment images would be at least 80% based on past identification rates.
For all patients, regardless of weight change during the study period, reviewers were able to correctly identify baseline photos in 88% of the cases. Because fluctuations in weight can confound photo identifications, the primary endpoint outcome was also calculated for the patients who maintained their weight within five pounds of their baseline weight, and found that the correct identification percentage rose to 92%. These results suggest that clinically-meaningful changes were produced in the vast majority of patients regardless of subsequent weight change.
Secondary endpoints. The study also evaluated the following secondary outcome measures: reduction in the fat layer thickness as demonstrated by comparison of pre-treatment and post-treatment ultrasound measurements and patient satisfaction as determined by the results of a patient satisfaction questionnaire at the six-month follow-up visit. Standardized techniques for obtaining
12
ultrasound images were developed and validated to ensure consistency throughout the study. A percent change in fat layer thickness was determined for an untreated area of the abdomen to account for patient weight variation during the study. A percent change in fat layer thickness was determined for the treated area to account for fat layer thickness reduction due to fat cell elimination through Cryolipolysis and patient weight variation during the study. Fat layer thickness changes were normalized for each patient by subtracting the percent change in fat layer thickness in the untreated area from the percent change in fat layer thickness in the treated area to remove the influence of weight variations.
Ultrasound results demonstrated a mean reduction in the fat layer of 19% for the entire study population. These fat layer reductions were statistically significant as compared to the control region. Since the pivotal study, we have continued to enhance and optimize the CoolSculpting procedure. The CoolSculpting algorithms used during the pivotal study used a lower CIF (Cooling Intensity Factor) and/or shorter treatment times than the algorithm currently in commercial use with our CoolSculpting system. As a result, we believe the average percentage fat layer reduction produced by our current commercial version of the CoolSculpting system may exceed the percentage fat layer reduction measured by ultrasound in our pivotal study. Patient surveys showed that 82% of the participants were satisfied with the CoolSculpting procedure, and 79% agreed that there was a noticeable improvement in the appearance of their treated fat bulge.
Safety results. Treatment sites were evaluated immediately after treatment and at subsequent follow-up visits. Evidence of local inflammation was anticipated after a CoolSculpting treatment based on the body's reaction to a cold stimulus, and resolved spontaneously in all cases. Erythema, in most cases minor or moderate, was seen immediately post-treatment in virtually all patients. However, this condition had resolved itself within one week in the large majority of cases (93%). Purpura/bruising occurred in 27% of patients after the procedure was performed, and by the one week assessment had resolved in all but 5% of the patients. Minor or moderate edema was reported in only 13% of patients immediately after the procedure, and had universally resolved within a week. Numbness was common immediately after the CoolSculpting procedure, occurring in 87%. A week later only approximately half of the patients still experienced some degree of numbness (in no case marked), and by two months only 7% still had numbness; in all cases it was mild. At the six-month follow-up visit, no patient complained of numbness or tingling.
Blood was drawn from a subset of patients (n=10) for evaluation of serum lipids and liver tests. The mean values in all patient groups show no trends over time and there were no clinically meaningful differences between baseline and post-treatment values.
A total of four adverse events were reported in our pivotal study. Two involved pain during the initial cooling exposure; in both cases treatment was discontinued. These events resolved without intervention approximately one week after treatment. One patient reported bruising in the treated area one-day post treatment. Resolution was documented at an optional follow-up conducted four weeks post treatment. The fourth adverse event involved a report of pain and muscle spasm in the treatment area rated as a one (minor in severity) occurring once a month for three months. In a follow-up visit three weeks after the complaint, the patient stated the muscle spasm had resolved and the patient did not feel that the spasms were related to the treatment. None of the adverse events reported during this study were considered serious.
Conclusions. The clinical findings of our pivotal study confirmed the safety and effectiveness of our CoolSculpting technology and procedure. Photographic review and ultrasound measurements demonstrated clinically significant and measurable reductions in the fat layer thickness in the treated area. Independent photo review of baseline and post-treatment images (the primary endpoint) yielded a correct identification percentage exceeding the 80% criteria, and a statistically significant achievement of the success criteria. No serious adverse events were reported. Side effects and adverse events were typically mild and transient and all resolved spontaneously without medical intervention. Post-treatment lipid profile and liver function test results exhibited only normal variations with no discernible difference from baseline. Patient survey results supported overall patient satisfaction with the treatment.
13
Research and Development
Our ongoing research and development activities are primarily focused on improving and enhancing our CoolSculpting system and the CoolSculpting procedure. Our research and development efforts related to CoolSculpting currently include:
• | Additional treatment indications. We intend to seek additional regulatory clearances from the FDA to expand our marketed indications for CoolSculpting in the United States to other areas of the body. |
• | Additional applicators. We are developing additional applicators for the CoolSculpting system to expand our range of available applicator sizes and configurations, which will provide our customers with additional flexibility in selecting the applicator that best fits the body contour to be treated. In 2015, with our recent FDA clearance for lower temperatures, we launched our CoolSmooth PRO applicator in the second quarter of 2015. In addition, in the fourth quarter of 2015, we introduced our CoolMini applicator for treatment of smaller areas, including under the chin. |
• | Enhanced algorithms. CoolSculpting utilizes our proprietary treatment algorithms to ensure the fat cells in the treated area are sufficiently cooled to obtain the desired aesthetic results while preserving the overlying skin and surrounding tissues. We are continuing to examine the interaction between controlled cooling and tissue response to enhance our proprietary treatment algorithms. |
• | Point of Sale information feature. Our CoolSculpting system currently records information locally at the unit level about each treatment procedure, including information regarding procedure and patient statistics. Our direct sales force and our distributors can collect this information for analysis. With CoolConnect, which is a HIPAA compliant connectivity and data management tool, we are able to accumulate and analyze treatment procedure information at the point of sale. These data points assist our sales force in discussions with customers regarding their marketing efforts and program effectiveness. CoolConnect continues to be used across our installed base to collect real-time sales, demographic and marketing data that we believe can further optimize marketing strategies for both us and our customers. This information provides valuable trends and insights to our PDMs showing both account-level treatment information and comparisons against peer-group counterparts within the same geographic area. |
• | Procedure tracking. To help ensure we capture each procedure performed with our CoolSculpting system, we are continuing to optimize the security encryption in our CoolCards to protect against third-party manipulation or the use of counterfeit CoolCards with our CoolSculpting system. |
• | Design improvements. We are continuing to optimize the design of our CoolSculpting system to improve reliability and to reduce our manufacturing and repair costs. |
In addition to these development activities related to CoolSculpting, we are exploring additional uses of our proprietary controlled cooling technology platform for the dermatology, plastic surgery, aesthetic and OBGYN markets. We are also exploring potential therapeutic uses for our platform technology, either directly or through collaborative arrangements with strategic partners. Although MGH cannot restrict our future product development efforts, the terms of our license agreement with MGH may require us to pay MGH a royalty on commercial sales of future products we develop or that may be developed by our strategic partners. Whether we are required to pay a royalty will depend on whether our future products incorporate the intellectual property we license from MGH. Any royalty we are required to pay will reduce our profits from sales of such future products and may make it more difficult for us to successfully commercialize these products directly or through a strategic partner.
As of December 31, 2015, we had 74 employees focused on research and development. In addition to our internal team, we retain third-party contractors from time to time to provide us with assistance on specialized projects. We also work closely with experts in the medical community to supplement our internal research and development resources. Research and development expenses for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013, were $22.9 million, $18.2 million and $17.1 million, respectively.
Sales and Marketing
Sales
In North America, we utilize a direct sales force to sell CoolSculpting. As of December 31, 2015, we had a North American sales force of 143 employees. To support the continued roll-out of CoolSculpting, we intend to continue to invest in our North American sales force.
In international markets, we sell CoolSculpting primarily through a network of distributors. As of December 31, 2015, we had an international sales team of 40 employees supporting approximately 50 independent distributors. Additionally, we utilize a separate direct sales force of 15 employees to sell into certain key markets in Europe. Our product currently has regulatory approval in 74 countries. We are increasing and intend to continue to increase penetration of our installed base in international markets in which CoolSculpting is currently sold and expand into attractive new international markets by identifying and training qualified distributors. We require our distributors to provide customer training, to invest in equipment and marketing, and to attend certain exhibitions and industry meetings. In addition, we are opportunistically pursuing direct sales and expanding our marketing campaigns in select international markets.
14
We enter into distribution agreements with our distributors outside of North America. Our distribution agreements generally provide the distributor with a right to distribute our product for a limited period of time and are renewable by written agreement and terminable upon a material breach by either party, insolvency of the distributor, or a change of control of the distributor. Following the expiration or termination of the agreement, the distributor has an obligation to continue servicing existing customers for a period ranging from two to three months, upon our written request. Our distribution agreements generally provide the exclusive right to distribute our products within a designated territory, with certain distributors only receiving non-exclusive rights within a designated territory. We require distributors to purchase a minimum number of CoolSculpting systems each calendar quarter over the term of the agreement. The agreement sets forth the minimum quarterly purchase obligations for the first calendar year of the term of the agreement, and the parties will agree each year on the minimum quarterly purchase obligations for the remaining quarters during the term of the agreement. If the distributor fails to meet one of its minimum quarterly purchase obligations, we can convert the distributor to a non-exclusive distributor during the remaining term or terminate the agreement. These agreements also provide customary indemnities to the distributor including claims of patent infringement in the designated territory, material product defects, and our negligence or willful misconduct.
Customers
As of December 31, 2015 and 2014, Ideal Image, which is a large aesthetic chain, along with its affiliated franchises, accounted for 10% and 24% of accounts receivable, respectively. Furthermore, Ideal Image and its affiliated franchises accounted for 10% of total revenue during the year ended December 31, 2015. No individual customer accounted for greater than 10% of total revenue during the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013.
Customer Marketing and Support Programs
We intend to drive CoolSculpting procedures through our targeted marketing and customer support programs. Since 2013, we have hired and trained a group of PDMs. Our PDMs train our customers on the use of the CoolSculpting system when the CoolSculpting system is first delivered to the customer's practice site. Following this initial training, our PDMs educate our customers on current CoolSculpting best practices and provide customers and their staff with sales and marketing training and support to help them increase patient demand for CoolSculpting procedures.
We also continue to offer a comprehensive practice certification program, originally launched in 2011. A customer's participation in this certification program and our other practice support programs, other than the initial training program, is voluntary. We have found that the most successful practices have the customer involved in every part of the training and marketing process. To become certified, customers must commit to engage in quarterly business strategy meetings with one of our PDMs, educate members of their office in our CoolSculpting best practices, and adopt our guidelines for before and after patient photographs. Once certified, customers receive distinction on our website. Furthermore, in late 2013 we launched the first of our customer training programs, CoolSculpting University. This program enables new and existing customers to successfully launch their CoolSculpting programs through a curriculum that includes hands-on education, live treatments and lecture-style presentations. In 2015, we hosted over 1,800 medical professionals from 865 offices worldwide at our CSU programs. To address the demand for this training from our customers we currently have one training center in Pleasanton, California which we opened in 2013, and a second center in Reston, Virginia, which we opened in the second quarter of 2015. Also, we hosted nine satellite CSU programs internationally for the year ended December 31, 2015.
In addition, with the launch of our HIPAA compliant connectivity and data management tool, CoolConnect, across our installed base, we are able to collect real-time sales, demographic and marketing data that we believe can further optimize marketing strategies for both us and our customers. This information provides valuable trends and insights to our PDMs, showing both account-level treatment information and comparisons against peer-group counterparts within the same geographic area. We also leveraged our 2013 customer segmentation research to hone our messaging targeted towards consumers, and we have implemented a consistent creative strategy based on these insights.
Direct-to-Consumer
In 2015, we launched a direct-to-consumer advertising program in selected markets to build awareness and interest in the marketplace. The national campaign leverages learnings from the successful direct-to-consumer pilot held in 11 U.S. cities: Atlanta, Dallas, Denver, Houston, San Diego, Miami / Ft. Lauderdale, Minneapolis, Philadelphia, Phoenix, Seattle, Washington, DC. CoolSculpting website traffic significantly increased in those markets, and local CoolSculpting providers experienced a significant increase in patient interest and treatments. The multiple channels ZELTIQ plans to leverage include television commercials, radio spots, digital advertising, social media, and public relations. As of December 31, 2015, our program is active nationally in the U.S. and we have an ongoing pilot in the United Kingdom.
15
Customer Support
We strive to provide our customers and authorized distributors with superior customer support. We maintain a staff of Customer Care personnel in our facilities in Pleasanton, California and Reston, Virginia, as well as in the United Kingdom, to support our customers worldwide. This staff is available by telephone and email to field inquiries, troubleshoot product issues, facilitate sales activities and support the commercial activities of our international distributors. In addition, we provide worldwide technical support to our customers and distributors year round. Our goal is to minimize the disruption caused by a service event, and we strive to repair our customer's CoolSculpting system or provide the customer with a replacement CoolSculpting system within one day after notifying us of a problem. In the event of a technical issue with a CoolSculpting system, one of our Customer Care personnel will call the customer and determine whether the technical issue may be resolved over the telephone or whether the issue requires intervention. If the issue cannot be resolved by telephone, our Customer Care personnel will request our third-party logistics provider to ship and setup a replacement CoolSculpting system, or the applicable module of the CoolSculpting system, at the customer's office. To reduce shipping times and costs, we ensure that a number of CoolSculpting systems and replacement modules are available in specific regions throughout North America and other international locations. Upon arrival at the customer site, our logistics provider will move the replacement CoolSculpting system or module into the customer's office, unpack it, set it up and then power on the CoolSculpting system to ensure it is working properly. Because of the modular design of our CoolSculpting system, our logistics provider is not required to have any specialized training or expertise, and a number of logistics providers are available to provide these services. Upon completion, our logistics provider calls our Customer Care personnel and confirms the successful delivery and setup, and then ships the defective CoolSculpting system or module to our headquarters for repair. We allow our customers to keep the newly delivered CoolSculpting system or the applicable module, and we repair and reuse the defective CoolSculpting system or module received from our customer for future service calls. In the direct markets outside of North America and our Europe direct markets, our CoolSculpting system is serviced and supported through our independent distributors. We pro-actively deploy replacement CoolSculpting systems, modules, and components to strategic hubs worldwide to facilitate quick response time to service events and to maximize customer “uptime.”
We provide a standard limited warranty on our products of one year for both control units and applicators for our direct customers. For indirect customers in international markets, we provide a standard limited warranty on our products of approximately three years for control units and one year for applicators. We also offer an extended warranty on both our CoolSculpting control units and CoolSculpting applicators.
Manufacturing
We occupy 34,176 square feet in our manufacturing facility in Dublin, California and 15,755 square feet of warehouse space in Livermore, California. We manufacture our CoolSculpting system and store raw materials at our Dublin facility. The Livermore facility is used for assembling our procedure packs and distribution of our CoolSculpting systems and procedure packs. Through 2012 and the beginning of 2013, we had utilized OnCore Manufacturing LLC, or OnCore, to manufacture and supply to us our CoolSculpting system. During the second quarter of 2013, we fully in-sourced the manufacturing of our CoolSculpting system.
We depend upon suppliers for some critical components of our manufacturing processes and for materials used in our manufacturing processes. Some of these components and materials are supplied by a single vendor, and some are subject to certain minimum order quantities. Generally, we rely on purchase orders rather than long-term contracts with our suppliers, which subjects us to risks, including price increases and component shortages. We continue to evaluate alternative sources of supply for these components and materials.
CoolGels, CoolLiners, pretreatment wipes and other consumables continue to be manufactured by third-party manufacturers. In addition, our CoolSculpting system contains two critical components, the integrated circuit contained in the CoolSculpting control unit and the CoolCard, which is supplied by a company in Japan, and the connector that attaches our applicators to the control unit, which is supplied by a separate company in the United States. We do not have supply agreements with the suppliers of these critical components beyond purchase orders. However, we maintain a safety stock inventory for these critical components equal to one year of forecasted part requirements of the integrated circuit and one month of connectors in finished assemblies, as well as at least a three month supply of connectors to support open sales orders.
Manufacturing facilities that produce finished medical devices intended for distribution in the United States and internationally are subject to regulation and periodic unannounced inspection by the FDA and other domestic and international regulatory agencies. In the United States, we are required to manufacture our products in compliance with the FDA's Quality System Regulation, or QSR, which cover the methods and documentation of the design, testing, control, manufacturing, labeling, quality assurance, packaging, storage, and shipping of our products. The FDA inspected our Pleasanton facility in April 2011 and April 2013, and had no findings or observations. In international markets, we are required to obtain and maintain various quality assurance and quality management certifications. We have obtained the following international certifications: EN ISO 13485:2012 Quality Management Systems Requirements for regulatory purposes, ISO 13485:2003 under CMDCAS (Canada), Ordinance 169
16
certification (Japan), 93/42/EEC MDD certification to Annex II Full Quality System (Europe). We have recently been audited by our Notified Body, TUV Rheinland, and all certifications have been extended to cover all of our facilities.
Neither our third-party contract manufacturers nor our suppliers are currently required to comply with the FDA's QSR, as these parties do not provide us with a finished medical device. However, we maintain a quality system designed to be compliant to QSR and have procedures in place designed to ensure that all products and materials purchased by us conform to specified requirements, including evaluation of suppliers, and where required, qualification of the components supplied.
In 2016, we plan to begin manufacturing certain products in Ireland. We are in the process of identifying a facility as well as qualifying our manufacturing line.
Our current facilities are adequate to support our near term operations; however, they may not be sufficient in the long term. Leases for our manufacturing and warehouse locations expire in May 2017. We are currently in the process of re-evaluating our lease terms for some of our facilities.
Our business typically has a short sales cycle, and to date we have not had a significant backlog of orders at the end of any given quarter. We define backlog as unshipped orders resulting from lack of available product to fulfill non-cancelable sales orders.
Competition
The medical technology and aesthetic product markets are highly competitive and dynamic, and are characterized by rapid and substantial technological development and product innovations. Demand for CoolSculpting could be limited by the products and technologies offered now or in the future by our competitors. We designed CoolSculpting to address the aesthetic concerns of individuals who have stubborn fat bulges. Patients who are significantly obese and who do not have specific fat bulges but require significant fat reduction to achieve aesthetic results are candidates for invasive and minimally-invasive procedures, such as liposuction, laser-assisted liposuction and injection lipolysis, in which a compound is administered into the fat under the skin to eliminate the fat cells. Although effective at reducing fat, these invasive and minimally-invasive procedures may involve patient pain, expense, downtime, and the risks typically associated with surgical procedures. As a result, patients who do not require significant fat reduction to achieve meaningful aesthetic results explore non-invasive fat reduction and body contouring procedures to avoid the pain, expense, downtime, and surgical risks associated with invasive and minimally-invasive procedures.
In addition to the above invasive and minimally invasive procedures, the FDA has also cleared the marketing of several noninvasive technologies for fat reduction, circumferential reduction, fat cell destruction or body contouring. These noninvasive procedures involve various energy forms, including radio frequency, laser, or high intensity focused ultrasound, applied through the skin to eliminate fat cells. These technologies vary in the number of treatments required to produce a noticeable effect. Additionally, the high temperatures involved in certain of these procedures may lead to the patient experiencing various degrees of pain.
We believe that the marketing of these products has extended the sales cycle for CoolSculpting and may continue to have an impact on our sales in the future.
Due to less stringent regulatory requirements, there are many more aesthetic products and procedures available for use in international markets than are cleared for use in the United States. There are also fewer limitations on the claims our competitors in international markets can make about the effectiveness of their products and the manner in which they can market them. As a result, we face more competition in these markets than in the United States.
We also generally compete against medical technology and aesthetic companies, including those offering products and technologies unrelated to fat reduction, for physician resources and mind share. Some of our competitors have a broad range of product offerings, large direct sales forces, and long-term customer relationships, which could inhibit our market penetration efforts. Our potential customers also may need to recoup the cost of expensive products that they have already purchased from our competitors, and thus they may decide to delay or not to purchase our CoolSculpting system.
We believe that CoolSculpting competes favorably, largely on the basis of the following competitive factors:
• | CoolSculpting only affects fat cells without endangering any other structures in the skin resulting in more consistent, more predictable and durable outcomes; |
• | CoolSculpting is able to achieve measurable results with minimal patient discomfort and high patient satisfaction; |
• | CoolSculpting does not require a person to administer the procedure after the procedure is started which creates favorable customer practice economics by freeing uptime for the practice to generate additional revenue with new patients or with the patient undergoing CoolSculpting; and |
• | Effectiveness of sales and marketing programs and initiatives along with product placement and distribution strategy. |
Patents and Proprietary Technology
17
To establish and protect our proprietary technologies and products, we rely on a combination of patent, copyright, trademark, and trade-secret laws, as well as confidentiality provisions in our contracts. We have implemented a patent strategy designed to protect our technology and facilitate commercialization of our current and future products. As of December 31, 2015, our patent portfolio comprised 122 issued patents and 87 pending patent applications, each of which we either own directly or for which we are the exclusive licensee. Our intellectual property portfolio for our core Cryolipolysis technology was built through the combination of licensing patents from third parties and the issuance of new patents to us as the result of our ongoing development activities. Many of our issued and pending patents were exclusively licensed from MGH and generally relate to our core technology relating to our CoolSculpting system. In general, patents have a term of 20 years from the application filing date or earliest claimed priority date. We expect our issued and exclusively licensed patents to expire in 2023 or later.
We also rely on trade secrets, technical know-how, contractual arrangements, and continuing innovation to protect our intellectual property and maintain our competitive position. We have a policy to enter into confidentiality agreements with third parties, employees, and consultants. We also have a policy that our employees and consultants sign agreements requiring that they assign to us their interests in intellectual property such as patents and copyrights arising from their work for us. It is our policy that all employees sign an agreement not to compete unfairly with us during their employment and upon termination of their employment through the misuse of confidential information, soliciting employees, and soliciting customers.
ZELTIQ®, CoolSculpting®, Cryolipolysis® and our logo are among our registered trademarks in the United States and in certain foreign countries.
Seasonal Fluctuations
Seasonal fluctuations in the number of patients seeking treatment and the availability of our customers are likely to continue to affect our business. Seasonal fluctuations occur in both system revenue and consumable revenue as well as by geographic region. Specifically, our customers often take vacation or are on holiday during the summer months and therefore tend to perform fewer procedures, particularly in certain international countries. These seasonal trends have caused and will likely continue to cause, fluctuations in our quarterly results, including fluctuations in sequential revenue growth rates.
Material Agreements
Massachusetts General Hospital License Agreement
In May 2005, we entered into an exclusive license agreement with the General Hospital Corporation, which owns and operates the Massachusetts General Hospital, or MGH, which was amended and restated in September 2011. Under this agreement, MGH granted to us an exclusive worldwide, royalty-bearing license to patent applications related to our controlled cooling platform technology, including the removal of cutaneous, subcutaneous or subdermal fat, treatment or removal of cellulite, and any therapy or procedures to the tissues and structures of the skin, subcutaneous tissue, and tumors, lesions and adipose tissue of the skin and of subdermal tissue. As consideration for the license granted to us by MGH, we agreed to pay to MGH (i) an upfront, non-refundable license issue fee of $0.3 million, (ii) a non-refundable minimum annual license maintenance payment of $75,000, $0.1 million, $0.2 million and $0.2 million upon the first, second, third and each subsequent anniversary of the effective date of the agreement following our first commercial sale, respectively, credited against royalty payments due to MGH on net income and distributor income in the same year, (iii) payments totaling approximately $8.1 million upon the successful achievement of regulatory and commercial milestones, including (a) $1.1 million due upon receipt of FDA clearance to market our CoolSculpting system for the selective reduction of fat, (b) $1 million due upon achieving cumulative net sales of $70 million, and (c) $6 million due upon the earlier to occur of achieving cumulative net sales of $200 million or the completion of a change of control as defined in the agreement, including a qualifying initial public offering and (iv) a 7% royalty on net sales (as defined in the agreement) of CoolSculpting. We have the option to buy down up to 25% of the future royalty payments, and the agreement has a provision that requires an equitable adjustment to a specified royalty rate triggered by certain market conditions. We also agreed to pay to MGH a percentage of sublicense royalties in certain circumstances and to reimburse MGH for all costs associated with the preparation, filing, prosecution, and maintenance of the patent rights under the agreement.
The agreement will remain in full force and effect for the later of (i) the life of any patents that issue from the underlying patent applications, which are expected to expire in 2023 or (ii) one year after the last commercial sale for which a royalty is due to MGH, unless terminated in accordance with its terms and conditions. MGH may terminate the agreement upon our insolvency, failure to maintain insurance, breach of the agreement, failure to satisfy our development progress obligations, or failure to make required payments. We may terminate the agreement for any reason upon 90 days' advance written notice to MGH.
In September 2015, we entered into a new agreement with MGH to obtain an exclusive license to develop and commercialize certain patents and technology for the treatment of acne and certain related skin conditions. We are obligated to pay a 3% royalty on net sales, as defined in such agreement, of products incorporating such technology.
18
As of December 31, 2015, we have completed all milestones associated with the license agreement with MGH and have made all required license fee and milestone payments to MGH, described above. We continue to pay the royalty on net sales as required by the agreement and currently have no additional obligations to MGH resulting from any sublicensing agreement.
Government Regulation
The design, development, manufacture, testing and sale of our products are subject to regulation by numerous governmental authorities, principally the FDA, and corresponding state and foreign regulatory agencies.
Regulation by the FDA
In the United States, the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, or FDCA, FDA regulations and other federal and state statutes and regulations govern, among other things, medical device design and development, pre-clinical and clinical testing, premarket clearance or approval, registration and listing, manufacturing, labeling, storage, advertising and promotion, sales and distribution, export and import, and post-market surveillance. The FDA regulates the design, manufacturing, servicing, sale, and distribution of medical devices, including aesthetic devices. Failure to comply with applicable U.S. requirements may subject a company to a variety of administrative or judicial sanctions, such as warning letters, product recalls, product seizures, total or partial suspension of production or distribution, injunctions, fines, civil penalties, and criminal prosecution. The FDA can also refuse to approve pending applications.
Each medical device we wish to distribute commercially in the United States will require marketing authorization from the FDA prior to distribution. The two primary types of FDA marketing authorization applicable to a device are premarket notification, also called 510(k) clearance, and premarket approval, also called PMA approval. The type of marketing authorization is generally linked to the classification of the device. The FDA classifies medical devices into one of three classes (Class I, II, or III) based on the degree of risk the FDA determines to be associated with a device and the level of regulatory control deemed necessary to ensure the device's safety and effectiveness. Devices requiring fewer controls because they are deemed to pose lower risk are placed in Class I or II. Class I devices are deemed to pose the least risk and are subject only to general controls applicable to all devices, such as requirements for device labeling, premarket notification, and adherence to the FDA's current Good Manufacturing Practices, or cGMP, and Quality System Regulation, or QSR. Class II devices are intermediate risk devices that are subject to general controls and may also be subject to special controls such as performance standards, product-specific guidance documents, special labeling requirements, patient registries, or post-market surveillance. Class III devices are those for which insufficient information exists to assure safety and effectiveness solely through general or special controls and include life-sustaining, life-supporting or implantable devices, devices of substantial importance in preventing impairment of human health, or which present a potential, unreasonable risk of illness or injury.
Most Class I devices and some Class II devices are exempted by regulation from the 510(k) clearance requirement and can be marketed without prior authorization from the FDA. Some Class I devices that have not been so exempted and Class II devices are eligible for marketing through the 510(k) clearance pathway. By contrast, devices placed in Class III generally require PMA approval or 510(k) de novo clearance prior to commercial marketing. The PMA approval process is more stringent, time-consuming, and expensive than the 510(k) clearance process; however, the 510(k) clearance process has also become increasingly stringent and expensive.
The CoolSculpting system originally received 510(k) clearance in 2008 as a skin cooling device to minimize pain and thermal injury during laser and dermatological treatments. An additional 510(k) notification was submitted to the FDA in 2008 for the indication of cold-assisted lipolysis and a reduction in the subcutaneous fat layer. That premarket notification was subsequently determined by the FDA to be not substantially equivalent to the predicates identified because the device had a new intended use that alters the therapeutic effect impacting safety and effectiveness; therefore, our device for cold-assisted lipolysis and a reduction in the subcutaneous fat layer was automatically classified as Class III. We petitioned the FDA that this classification should be Class II because it does not support or sustain human life, is not of substantial importance in preventing impairment of human health, and does not present a potential, unreasonable risk of illness or injury. In September 2010, the FDA approved our de novo petition for Class II reclassification and issued a clearance letter for non-invasive fat reduction of the flanks (love handles). Subsequently on May 2, 2012, we received FDA clearance for expansion of the CoolSculpting indication to include the abdomen area. In April 2014, CoolSculpting was cleared by the FDA for treatment of the thigh area, and most recently, in January 2015, CoolSculpting was cleared by the FDA for treatment at lower temperatures which will enable shorter treatment times. Most recently, in September 2015, the FDA cleared CoolSculpting for treatment of the submental area under the chin, an area that is consistently ranked as one of the top areas of concern both by consumers and physicians.
We are also seeking additional regulatory clearances from the FDA to expand our United States marketed indications for CoolSculpting to areas on the body other than the flanks, abdomen, thighs and the submental area. We have received regulatory approval or are otherwise free to market CoolSculpting in numerous international markets where use of the product is generally not limited to specific treatment areas.
19
510(k) clearance. To obtain 510(k) clearance for a medical device, an applicant must submit a premarket notification to the FDA demonstrating that the device is “substantially equivalent” to a device legally marketed in the United States that is not subject to PMA approval, commonly known as the “predicate device.” A device is substantially equivalent if, with respect to the predicate device, it has the same intended use and has either (i) the same technological characteristics or (ii) different technological characteristics and the information submitted demonstrates that the device is as safe and effective as a legally marketed device and does not raise different questions of safety or effectiveness. A showing of substantial equivalence sometimes, but not always, requires clinical data. Generally, the 510(k) clearance process can exceed 90 days and may extend to a year or more.
After a device has received 510(k) clearance for a specific intended use, any change or modification that significantly affects its safety or effectiveness, such as a significant change in the design, materials, method of manufacture or intended use, may require a new 510(k) clearance or PMA approval and payment of an FDA user fee. The determination as to whether or not a modification could significantly affect the device's safety or effectiveness is initially left to the manufacturer using available FDA guidance; however, the FDA may review this determination to evaluate the regulatory status of the modified product at any time and may require the manufacturer to cease marketing and recall the modified device until 510(k) clearance or PMA approval is obtained. The manufacturer may also be subject to significant regulatory fines or penalties.
Before we can submit a medical device for 510(k) clearance, we may have to perform a series of generally short studies over a period of months, including method comparison, reproducibility, interference and stability studies to ensure that users can use the device successfully. Some of these studies may take place in clinical environments, but are not usually considered clinical trials. For PMA submissions, we would generally be required to conduct a longer clinical trial over a period of years that supports the clinical utility of the device and how the device will be used.
PMA approval. A PMA application requires the payment of significant user fees to the FDA. PMA applications must be supported by valid scientific evidence, which typically requires extensive data, including technical, pre-clinical, clinical, and manufacturing data, to demonstrate to the FDA's satisfaction the safety and effectiveness of the device. A PMA application must also include, among other things, a complete description of the device and its components, a detailed description of the methods, facilities and controls used to manufacture the device, and proposed labeling.
The FDA has 45 days from its receipt of a PMA to determine whether the application will be accepted for filing based on the agency's threshold determination that it is sufficiently complete to permit substantive review. Once the submission is accepted for filing, the FDA begins an in-depth review. During this review period, the FDA may request additional information or clarification of information already provided. In addition, the FDA will conduct a pre-approval inspection of the manufacturing facility or facilities to ensure compliance with the QSR, which requires manufacturers to follow design, testing, control, documentation and other quality assurance procedures.
FDA review of an initial PMA application is required by statute to take between six to 10 months, although the process typically takes significantly longer, and may require several years to complete. The FDA can delay, limit, or deny approval of a PMA application for many reasons, including:
• | it is not demonstrated that there is reasonable assurance that the device is safe or effective under the conditions of use prescribed, recommended, or suggested in the proposed labeling; |
• | the data from pre-clinical studies and clinical trials may be insufficient; and |
• | the manufacturing process, methods, controls, or facilities used for the manufacture, processing, packing, or installation of the device do not meet applicable requirements. |
If the FDA evaluations of both the PMA application and the manufacturing facilities are favorable, the FDA will either issue an approval letter or an approvable letter, which usually contains a number of conditions that must be met to secure final approval of the PMA. If the FDA's evaluation of the PMA or manufacturing facilities is not favorable, the FDA will deny approval of the PMA or issue a not approvable letter. A not approvable letter will outline the deficiencies in the application and, where practical, will identify what is necessary to make the PMA approvable. The FDA may also determine that additional clinical trials are necessary, in which case the PMA approval may be delayed for several months or years while the trials are conducted and then the data is submitted in an amendment to the PMA. Once granted, PMA approval may be withdrawn by the FDA if compliance with post approval requirements, conditions of approval or other regulatory standards is not maintained or problems are identified following initial marketing.
Approval by the FDA of new PMA applications or PMA supplements may be required for modifications to the manufacturing process, labeling, device specifications, materials or design of a device that is approved through the PMA process. PMA supplements often require submission of the same type of information as an initial PMA application, except that the supplement is limited to information needed to support any changes from the device covered by the original PMA application and may not require as extensive clinical data or the convening of an advisory panel.
20
Regulation After FDA Clearance or Approval
Any devices we manufacture or distribute pursuant to clearance or approval by the FDA are subject to pervasive and continuing regulation by the FDA and certain state agencies, including establishment registration and device listing with the FDA. We are required to adhere to applicable regulations setting forth detailed cGMP requirements, as set forth in the QSR, which include, among other things, testing, control and documentation requirements. Non-compliance with these standards can result in, among other things, fines, injunctions, civil penalties, recalls or seizures of products, total or partial suspension of production, refusal of the government to grant 510(k) clearance or PMA approval of devices, withdrawal of marketing approvals and criminal prosecutions. We have designed and operate our manufacturing facilities under the FDA's cGMP requirements and are subject to periodic inspection by the FDA for compliance with regulatory requirements.
Because we are a manufacturer of medical devices, we must also comply with medical device reporting requirements by reviewing and reporting to the FDA whenever there is evidence that reasonably suggests that one of our products may have caused or contributed to a death or serious injury. We must also report any incident in which our product has malfunctioned if that malfunction would likely cause or contribute to a death or serious injury if it were to recur. Labeling and promotional activities are subject to scrutiny by the FDA and, in certain circumstances, by the Federal Trade Commission. Medical devices approved or cleared by the FDA may not be promoted for unapproved or uncleared uses, otherwise known as “off-label” promotion. The FDA and other agencies actively enforce the laws and regulations prohibiting the promotion of off-label uses, and a company that is found to have improperly promoted off-label uses may be subject to significant liability, including substantial monetary penalties and criminal prosecution.
Export of Our Products
Export of products subject to the 510(k) notification requirements, but not yet cleared to market, is permitted with FDA authorization provided certain requirements are met. Unapproved products subject to the PMA approval requirements may be exported if the exporting company and the device meet certain criteria, including, among other things, that the device complies with the laws of the receiving country and the company submits a “Simple Notification” to the FDA when the company begins to export. If the company or device does not comply with such criteria, FDA approval must be obtained for export. To obtain FDA export approval, if required, we must meet certain requirements, including, among other things and with some exceptions, documentation demonstrating that the product is approved for import into the country to which it is to be exported and, in some instances, safety data to demonstrate that export of the device will not be contrary to public health or safety.
Foreign Government Regulation
The regulatory review process for medical devices varies from country to country, and many countries also impose product standards, packaging requirements, environmental requirements, labeling requirements and import restrictions on devices. Each country has its own tariff regulations, duties, and tax requirements. Failure to comply with applicable foreign regulatory requirements may subject a company to fines, suspension or withdrawal of regulatory approvals, product recalls, seizure of products, operating restrictions, criminal prosecution, or other consequences.
Fraud and Abuse Regulations
We may be subject to numerous federal and state health care anti-fraud laws, including the federal anti-kickback statute and False Claims Act that are intended to reduce waste, fraud, and abuse in the health care industry. These laws are broad and subject to evolving interpretations. They prohibit many arrangements and practices that are lawful in industries other than health care, including certain payments for consulting and other personal services, some discounting arrangements, the provision of gifts and business courtesies, the furnishing of free supplies and services, and waivers of payments. In addition, many states have enacted or are considering laws that limit arrangements between medical device manufacturers and physicians and other health care providers and require significant public disclosure concerning permitted arrangements. These laws are vigorously enforced against medical device manufacturers and have resulted in manufacturers paying significant fines and penalties and being subject to stringent corrective action plans and reporting obligations. We must operate our business within the requirements of these laws and, if we were accused of violating them, could be forced to expend significant resources on investigation, remediation, and monetary penalties. Companies targeted in such prosecutions have paid substantial fines in the hundreds of millions of dollars or more, have been forced to implement extensive corrective action plans, can be excluded from federal health care programs and become subject to substantial civil and criminal penalties, and have often become subject to consent decrees severely restricting the manner in which they conduct their business.
Because we have commercial operations overseas, we are subject to the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act, or FCPA, and other countries' anti-corruption/anti-bribery regimes, such as the U.K. Bribery Act and Chinese anti-corruption laws. The FCPA prohibits improper payments or offers of payments to foreign governments and their officials for the purpose of obtaining or retaining business. Safeguards we implement to discourage improper payments or offers of payments by our employees, consultants, sales agents or distributors may be ineffective, and violations of the FCPA and similar laws may result in severe criminal or civil sanctions, or
21
other liabilities or proceedings against us, any of which would likely harm our reputation, business, financial condition and result of operations.
Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act
Our operations are impacted by the federal Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act of 2010, which, as amended is known as the ACA. Effective January 1, 2013, we began to incur a 2.3% excise tax on sales of medical devices in the United States. Medical device excise tax payments totaled $3.1 million, $2.2 million and $1.4 million during the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively. Such excise tax has been temporarily suspended effective January 1, 2016 through December 31, 2017. Compliance with the ACA has imposed administrative and financial burdens on us.
Environmental Regulation
We are subject to numerous foreign, federal, state, and local environmental, health and safety laws and regulations relating to, among other matters, safe working conditions, product stewardship and end-of-life handling or disposition of products, and environmental protection, including those governing the generation, storage, handling, use, transportation and disposal of hazardous or potentially hazardous materials. Some of these laws and regulations require us to obtain licenses or permits to conduct our operations. Environmental laws and regulations are complex, change frequently and have tended to become more stringent over time. Although the costs to comply with applicable laws and regulations, including requirements in the European Union relating to the restriction of use of hazardous substances in products, have not been material, we cannot predict the impact on our business of new or amended laws or regulations or any changes in the way existing and future laws and regulations are interpreted or enforced, nor can we ensure we will be able to obtain or maintain any required licenses or permits.
Employees
As of December 31, 2015, we had 535 employees, with 283 employees in sales and marketing, 74 in research and development, including clinical, regulatory and certain quality functions, 101 employees in operations, and 77 employees in general and administrative. We have never had a work stoppage and none of our employees are covered by collective bargaining agreements or represented by a labor union. We believe our employee relations are in good standing and we strive to foster a positive work environment.
Financial Information About Geographic Areas
Financial information regarding revenue and long-lived assets by geographic area is included in Note 14 “Segment Information” in “Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements” included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Financial information regarding revenue, profit and loss and total assets is included in the financial statements in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
General Information
We were originally incorporated in Delaware in March 2005 as Juniper Medical, Inc. In July 2007, we changed our name to ZELTIQ Aesthetics, Inc. Our principal corporate offices are located at 4698 Willow Road, Suite 100, Pleasanton, CA 94588 and our telephone number is (925) 474-2500. Our website is located at www.coolsculpting.com. The information contained on, or that can be accessed through, our website is not part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
We make available free of charge on our website our Annual Report on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, current reports on Form 8-K and amendments to those reports filed or furnished pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Exchange Act, as soon as reasonably practicable after we electronically file such material with, or furnish it to, the United State Securities and Exchange Commission, or SEC. You may obtain a free copy of these reports in the "investor relations, corporate governance" section of our website, www.coolsculpting.com. The reports filed with the SEC are also available at www.sec.gov.
ITEM 1A. RISK FACTORS
Our operations and financial results are subject to various risks and uncertainties, including those described below, which could adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations, cash flows, and the trading price of our common stock. The risks and uncertainties described below are not the only ones we face. Additional risks that we currently do not know about or that we currently believe to be immaterial may also impair our business operations.
22
Risks Related to Our Business
Patient demand for the procedures for which our products are used is particularly sensitive to economic trends. If there is the perception that economic trends are negative, patient demand for the procedures for which our products are used may decrease, which could cause practitioner demand for these systems to drop and our operating results could be harmed.
The decision to undergo a procedure from our systems are driven by consumer demand. If patient demand for procedures using our systems decreases, practitioner demand for our systems could drop. Procedures performed using our systems are elective procedures, the cost of which must be borne by the patient, and are not reimbursable through government or private health insurance. As a result, our revenues, and therefore our operating results, are particularly vulnerable to economic trends. If the economic conditions our customers' patients face worsen, or for other reasons demand from patients for procedures using our systems decreases, our business would be negatively impacted and our financial performance would be materially harmed.
We may not be able to correctly estimate or control our future operating expenses, which could lead to cash shortfalls.
Our operating expenses may fluctuate significantly in the future as a result of a variety of factors, many of which are outside of our control. These factors include:
• | our commercialization strategy; |
• | the time, resources, and expense required to develop and conduct clinical trials and seek additional regulatory clearances and approvals for additional treatment indications for CoolSculpting and for any additional products we may develop; |
• | the costs of preparing, filing, prosecuting, defending, and enforcing patent claims and other patent related costs, including litigation costs and the results of such litigation; |
• | any adverse events associated with CoolSculpting or product liability or other lawsuits related to our products and the costs associated with defending them or the results of such lawsuits; |
• | costs associated with obtaining components for manufacturing, including increases due to changes in foreign exchange rates or increased shipping costs; |
• | the costs to attract and retain personnel with the skills required for effective operations; and |
• | the costs associated with being a public company. |
Further, our budgeted expense levels are based in part on our expectations concerning future revenue from CoolSculpting. We may be unable to reduce our expenditures in a timely manner to compensate for any unexpected shortfalls in revenue. Accordingly, a significant shortfall in market acceptance or demand for CoolSculpting could have an immediate and material adverse impact on our business and financial condition.
Economic uncertainty has reduced and may continue to reduce patient demand for our products; if there is not sufficient patient demand for the procedures for which our products are used, practitioner demand for these systems could drop, resulting in unfavorable operating results.
The aesthetic industry in which we operate is particularly vulnerable to economic trends. The decision to undergo a procedure from our systems is driven by consumer demand. Procedures performed using our systems are elective procedures, the cost of which must be borne by the patient, and are not reimbursable through government or private health insurance. In times of economic uncertainty, individuals often reduce the amount of money that they spend on discretionary items, including aesthetic procedures. The general economic difficulties being experienced and the lack of availability of consumer credit for some of our customers' patients are adversely affecting certain markets in which we operate.
If the economic hardships our customers' patients face continue or worsen, our business would be negatively impacted and our financial performance would be materially harmed in the event that any of the above factors discourage patients from seeking the procedures for which our products are used.
Due to a number of factors outside of our direct control, our financial results may fluctuate unpredictably, which could adversely affect our stock price.
The rapid evolution of the markets for medical technologies and aesthetic products make it difficult for us to predict our future performance. In addition, a number of factors, many of which are outside of our control, may contribute to fluctuations in our financial results, such as:
• | quarter to quarter variation in customer demand for purchasing CoolSculpting systems; |
23
• | the inability for our customers to obtain necessary financing; |
• | changes in the length of the sales process; |
• | performance of our international distributors; |
• | media coverage of CoolSculpting and positive or negative patient experiences, the procedures or products of our competitors, or our industry; |
• | our ability to maintain our current or obtain further regulatory clearances or approvals; |
• | delays in, or failure of, product and component deliveries by our third-party contract manufacturers or suppliers, whether due to their inability to meet our demands or other forces, such as port strikes, labor shortages or other factors that could impact shipping costs or the ability of manufacturers to ship components to us; |
• | seasonal or other variations in patient demand for aesthetic procedures; |
• | introduction of new aesthetic procedures or products that compete with CoolSculpting; and |
• | adverse changes in the economy that reduce patient demand for elective aesthetic procedures. |
Fluctuations in our financial results could negatively affect our stock price.
We are dependent upon the success of CoolSculpting. If the market acceptance for CoolSculpting fails to grow significantly, our business and future prospects will be harmed.
We commenced commercial sales of CoolSculpting for the selective reduction of fat in the United States in late 2010, and expect that the revenue we generate from sales of our CoolSculpting system and CoolSculpting consumables will account for substantially all of our revenue for at least the next several years. Accordingly, our success depends on the continued and growing acceptance among customers and patients of CoolSculpting as a preferred aesthetic treatment for the selective reduction of fat. Although we have received FDA clearance to market CoolSculpting for the selective reduction of fat in the flanks, abdomen, thighs and the submental area in the United States and are approved or are otherwise free to market CoolSculpting in numerous international markets, increased acceptance among customers and patients of CoolSculpting may not occur. We cannot assure you that demand for CoolSculpting will continue or grow among customers and patients. Because we expect to derive substantially all of our revenue for the foreseeable future from sales of CoolSculpting systems and consumables associated with each CoolSculpting cycle, any failure of this product to satisfy customer or patient demand will harm our business and future prospects.
Any failure to build and manage our direct sales and marketing force effectively could have a material adverse effect on our business.
We rely on a direct sales force to sell CoolSculpting in the United States, Canada and certain markets in Europe. To meet our anticipated sales objectives, we intend to opportunistically build a direct sales and marketing force in certain international markets. There are significant risks involved in building and managing our sales and marketing organization, including risks related to our ability to:
• | hire qualified individuals as needed; |
• | generate sufficient leads within our target customer group for our sales force; |
• | provide adequate training for the effective sale and marketing of CoolSculpting; |
• | retain and motivate our direct sales and marketing professionals; and |
• | effectively oversee geographically dispersed sales and marketing teams. |
Our failure to adequately address these risks could have a material adverse effect on our ability to increase sales and use of our CoolSculpting systems, which would cause our revenue to be lower than expected and harm our results of operations. In addition, as we transition to direct sales in certain international markets, consistent with our sales strategy, the transition may result in a slow-down of growth or even a reduction in sales in those markets during the transition process as our distributors anticipate losing the ability to sell our products. Furthermore, our transition to direct sales in certain international markets could impact the performance of distributors in otherwise unaffected international markets as distributors may anticipate that their territories may be transitioned in the future.
Our ability to market CoolSculpting in the United States is limited to the non-invasive reduction of fat around the flanks, abdomen, thighs and submental area, and if we want to expand our marketing claims, we will need to obtain additional FDA clearances or approvals, which may not be granted.
We currently have FDA clearance to market CoolSculpting in the United States for the non-invasive reduction of fat around the flanks, an area commonly known as the “love handles,” the abdomen area, the thigh area and the submental area under the chin. This clearance restricts our ability to market or advertise CoolSculpting treatment for other specific body areas, which could limit customer and patient adoption of CoolSculpting. Developing and promoting new treatment indications and protocols and new
24
treatment applicators for our CoolSculpting system are elements of our growth strategy, but we cannot predict when or if we will receive the clearances required to so implement those elements. In addition, we will be required to conduct additional clinical trials or studies to support our applications, which may be time-consuming and expensive, and may produce results that do not result in FDA clearances. In the event that we do not obtain additional FDA clearances, our ability to promote CoolSculpting in the United States will be limited. Because we anticipate that sales in the United States will account for a substantial majority of our revenue for the foreseeable future, ongoing restrictions on our ability to market CoolSculpting in the United States could harm our business and limit our revenue growth.
Customers must make significant capital expenditures to purchase our CoolSculpting systems, which makes it difficult to increase our customer base, and if we are not able to convince customers to make this capital expenditure, our ability to grow our business will be harmed.
Customers must make significant capital expenditures to purchase our CoolSculpting systems, and our ability to increase the number of customers willing to make these significant capital expenditures and make CoolSculpting a significant part of their practices depends on the success of our sales and marketing programs. We must be able to demonstrate that the cost of our CoolSculpting system and the revenue that a customer can derive from performing CoolSculpting cycle are compelling when compared to the cost and revenue associated with alternative aesthetic treatments our customer may offer. In addition, alternative treatments may be invasive, minimally-invasive, or non-invasive and we must, in some cases, overcome a bias against non-invasive aesthetic procedures for fat reduction, principally from plastic surgeons. Further, we believe our marketing programs, including our co-operative marketing strategy with individual practices, will be critical in driving additional CoolSculpting procedures, but these programs require customers commitment and involvement to succeed. If we are unable to increase customer adoption and use of CoolSculpting, our financial performance will be adversely affected.
If there is not sufficient patient demand for CoolSculpting procedures, our financial results and future prospects will be harmed.
The CoolSculpting procedure is an elective procedure, the cost of which must be borne by the patient, and is not reimbursable through government or private health insurance. The decision to undergo a CoolSculpting procedure is thus driven by patient demand, which may be influenced by a number of factors, such as:
• | the success of our sales and marketing programs, including our co-operative marketing strategy with individual practices, as to which we have limited experience; |
• | the cost, safety, and effectiveness of CoolSculpting versus other aesthetic treatments; |
• | the price of CoolSculpting relative to other aesthetic products and alternative treatments; |
• | the willingness of patients to wait up to four months post-treatment to notice the aesthetic results of a CoolSculpting procedure; |
• | the ability to obtain regulatory clearance to market CoolSculpting for additional treatment indications in the United States; |
• | the adverse event profile of CoolSculpting, including warnings, side effects, and contraindications, which are subject to change; |
• | the extent to which our customers recommend CoolSculpting to their patients; |
• | our success in attracting consumers who have not previously purchased an aesthetic procedure; |
• | the extent to which our CoolSculpting procedure satisfies patient expectations; |
• | our ability to properly train our customers in the use of CoolSculpting such that their patients do not experience excessive discomfort during treatment or adverse side effects; |
• | consumer sentiment about the benefits and risks of aesthetic procedures generally and CoolSculpting in particular; |
• | the success of any direct-to-consumer marketing efforts we initiate to build awareness in the marketplace; and |
• | general consumer confidence, which may be impacted by economic and political conditions. |
Our success depends in part upon patient satisfaction with the effectiveness of CoolSculpting.
To generate repeat and referral business, patients must be satisfied with the effectiveness of CoolSculpting. Our clinical studies demonstrate that a single CoolSculpting procedure noticeably and measurably reduces the fat layer within a treated fat bulge without requiring diet or exercise. However, we designed CoolSculpting to address the aesthetic concerns of individuals who have stubborn fat bulges. Although there are no technical or regulatory restrictions on the use of CoolSculpting based on patient weight, we believe patients who are significantly obese and who do not have specific fat bulges but require significant fat reduction to achieve aesthetic results are better candidates for invasive and minimally-invasive procedures not offered by us. In addition, results obtained from a CoolSculpting procedure occur gradually over a period of two to four months after treatment and patient perception of their results may vary. Although we train our customers to select the appropriate patient candidates for a CoolSculpting procedure, explain to their patients the time period over which the results from a CoolSculpting procedure will occur, and take before and after photographs of a patient, our customers may not select appropriate patient candidates or CoolSculpting may produce results that may not meet patients' expectations. If patients are not satisfied with the long term aesthetic benefits or safety of CoolSculpting,
25
or feel that it is too expensive for the results obtained, our reputation and future sales will suffer. As market experience of CoolSculpting increases and more procedures are performed, we may learn more about the risk profile of the CoolSculpting system and receive reports of new side effects. For example, we have received reports of rare side effects, including late-onset pain, subcutaneous induration, which is hardening of normally soft tissue under the skin, hernia, and paradoxical hyperplasia, which is unusually enlarged tissue volume in the treatment area.
To market and sell CoolSculpting in markets outside of North America, we mainly depend on third-party distributors.
We currently depend on third-party distributors to sell, market, and service our CoolSculpting systems in certain markets outside of North America and to train our customers in these markets. We may need to engage additional third-party distributors to expand in new markets outside of North America. We are subject to a number of risks associated with our dependence on these third parties, including:
• | we lack day-to-day control over the activities of third-party distributors; |
• | third-party distributors may not commit the necessary resources to market, sell, and service our systems to the level of our expectations; |
• | third-party distributors may not be as selective as we would be in choosing customers to purchase CoolSculpting systems or as effective in training customers in marketing and patient selection; |
• | third-party distributors may terminate their arrangements with us on limited, or no, notice or may change the terms of these arrangements in a manner unfavorable to us; |
• | disagreements with our distributors could require or result in costly and time-consuming litigation or arbitration which we could be required to conduct in jurisdictions with which we are not familiar; and |
• | ability to collect amounts owed from third-party distributors, who may operate in currency controlled countries. |
If we fail to establish and maintain satisfactory relationships with our third-party distributors, our revenue and market share may not grow as anticipated, and we could be subject to unexpected costs, each of which would harm our results of operations and financial condition.
There are additional hurdles we must overcome in order to effectively market and sell CoolSculpting in markets outside of North America.
We believe that a significant percentage of our business will continue to come from sales in markets outside of North America through increased penetration in countries where we currently market and sell CoolSculpting directly and through our third-party distributor network, combined with expansion into new international markets. However, international sales are subject to a number of risks, including:
• | difficulties in staffing and managing our international operations; |
• | increased competition as a result of more products and procedures receiving regulatory approval or otherwise free to market in international markets; |
• | longer accounts receivable payment cycles and difficulties in collecting accounts receivable; |
• | reduced or varied protection for intellectual property rights in some countries; |
• | export restrictions, trade regulations, and foreign tax laws; |
• | fluctuations in currency exchange rates, which could increase the selling costs of, and therefore lower demand for, our products overseas; |
• | foreign certification and regulatory clearance or approval requirements; |
• | difficulties in developing effective marketing campaigns in unfamiliar foreign countries; |
• | customs clearance and shipping delays; |
• | political, social, and economic instability abroad, terrorist attacks, and security concerns in general; |
• | preference for locally produced products; |
• | potentially adverse tax consequences, including the complexities of foreign value-added tax systems, tax inefficiencies related to our corporate structure, and restrictions on the repatriation of earnings; |
• | the burdens of complying with a wide variety of foreign laws and different legal standards; and |
• | increased financial accounting and reporting burdens and complexities. |
The extent to which we encounter these additional obstacles could require us to dedicate significant financial and management resources which could negatively affect our financial results.
26
Our inability to effectively compete with our competitors may prevent us from achieving further market penetration or improving our operating results.
The medical technology and aesthetic product markets are highly competitive and dynamic, and are characterized by rapid and substantial technological development and product innovations. Demand for CoolSculpting could be limited by the products and technologies offered by our competitors, including newly announced products and technologies, whether or not effective. We designed CoolSculpting to address the aesthetic concerns of individuals who have stubborn fat bulges. Patients who are obese and who do not have specific fat bulges but require significant fat reduction to achieve aesthetic results are candidates for invasive and minimally-invasive procedures, such as liposuction, laser-assisted liposuction and injection lipolysis, in which a compound is administered into the fat under the skin to eliminate the fat cells. Patients who do not require significant fat reduction to achieve meaningful aesthetic results explore non-invasive fat reduction and body contouring procedures to avoid the pain, expense, downtime, and surgical risks associated with invasive and minimally-invasive procedures. In the United States, the FDA has cleared the marketing of several noninvasive technologies for fat reduction, circumferential reduction, fat cell destruction or body contouring. These noninvasive procedures involve various energy forms, including radio frequency, laser, or high intensity focused ultrasound, applied through the skin to eliminate fat cells. We believe that the marketing of these products has extended the sales cycle for CoolSculpting beginning in 2013 and may continue to have an impact on our sales in the future. The timing of, and publicity around, the introduction of such products or other technologies is outside our control, and may have an adverse impact on our sales and the rate at which practices purchase CoolSculpting systems and/or cycles in the form of consumable procedure packs.
Due to less stringent regulatory requirements, there are many more aesthetic products and procedures available for use in international markets than are approved for use in the United States. For example, multiple ultrasound based products have been cleared for marketing outside the United States. There are also fewer limitations on the claims our competitors in international markets can make about the effectiveness of their products and the manner in which they can market them. As a result, we face more competition in these markets than in the United States.
We also compete generally against medical technology and aesthetic companies, including those offering products and technologies unrelated to fat reduction, for customer resources and mind share. Some of our competitors have a broad range of product offerings, large direct sales forces, and long-term customer relationships with our target customers, which could inhibit our market penetration efforts. Our potential customers also may need to recoup the cost of expensive products that they have already purchased from our competitors, and thus they may decide to delay purchasing, or not to purchase, our CoolSculpting system.
Many of our competitors are large, experienced companies that have substantially greater resources and brand recognition than we do. Competing in the medical technology and aesthetic markets could result in price-cutting, reduced profit margins, and limited market share, any of which would harm our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
Third parties may attempt to produce counterfeit versions of our products and which may harm our ability to sell our CoolSculpting systems or consumables, negatively affect our reputation, or harm patients and subject us to product liability.
Third parties may seek to develop, manufacture, distribute and sell systems that we believe infringe our proprietary rights, which would compete against our CoolSculpting systems and impair our ability to sell our CoolSculpting systems in jurisdictions in which our proprietary rights are not upheld. In addition, counterfeit products may be promoted in a way that misleads consumers into believing they are affiliated with us. If counterfeit products are used with or in place of our products, we could be subject to product liability lawsuits resulting from the use of damaged or defective goods and suffer damage to our reputation.
For example, in January 2013, the Mercantile Court in Spain rendered its ruling on the merits of Massachusetts General Hospital's, or MGH, and our request for a permanent injunction against Clinipro's LipoCryo device based on Clinipro's infringement of two European patents owned by MGH and globally licensed exclusively to us. While the Mercantile Court had earlier granted in 2012 MGH's and our request for a preliminary injunction, the Court, in the January 2013 ruling, denied the request for a permanent injunction, and the Mercantile Court’s ruling has been upheld on appeal. The Mercantile Court's ruling affects only Clinipro's activities in Spain. Further, although we and MGH did prevail against Clinipro in a patent infringement case in France, holding that an MGH patent exclusively licensed to us is valid and enforceable and enjoining Clinipro and its distributors from selling LipoCryo in France, Clinipro appealed that ruling. The French court of appeal overturned a portion of the ruling related to sufficiency of disclosure, which has the potential to affect certain claims in MGH's patents. We are entitled to and intend to pursue an appeal. However, there is no assurance that we will prevail.
In addition, in May 2014, the United States District Court Eastern District of Wisconsin granted a mandatory injunction in our favor against a clinic using and promoting “Freeze Sculpting” treatments with a counterfeit device. Other counterfeit users are
27
present in the United States and although our enforcement strategy is aggressive, there is no assurance that we will be successful in our actions to enjoin them from using or promoting treatments with counterfeit devices.
If we are unable to manufacture our CoolSculpting system in high-quality commercial quantities successfully and consistently to meet demand, our growth will be limited and our reputation could be harmed.
Our CoolSculpting system consists of a CoolSculpting control unit and our CoolSculpting applicators. Our CoolSculpting procedure packs are composed of consumable CoolGels, CoolLiners, and in the case of our CoolSmooth procedure packs, disposable securement accessories, all of which are used by our customer during treatments. In addition, each consumable procedure pack includes a disposable computer cartridge that we market as the CoolCard. The CoolCard contains enabling software that permits our customer to perform a fixed number of CoolSculpting cycles. We manufacture our CoolSculpting system at our own facilities. During the second quarter of 2013, we fully in-sourced the manufacturing of our CoolSculpting system. CoolGels, CoolLiners and disposable securement accessories continue to be manufactured through third-party contract manufacturers. To manufacture our CoolSculpting system in the quantities that we believe will be required to meet anticipated increased market demand, we will need to increase manufacturing capacity, which will involve significant challenges and may require additional regulatory approvals. In addition, the development of these manufacturing capabilities will require us to invest substantial additional funds and hire and retain the technical personnel who have the necessary manufacturing experience. We may not successfully complete any required increase to existing manufacturing processes in a timely manner, or at all.
If there is a disruption to our manufacturing operations, we will have no other means of producing our CoolSculpting systems until we restore the affected facilities or develop alternative manufacturing facilities or methods, including potentially re-outsourcing our manufacturing operations. Additionally, any damage to or destruction of our facilities or equipment may significantly impair our ability to manufacture CoolSculpting systems on a timely basis.
If we are unable to produce CoolSculpting systems in sufficient quantities to meet anticipated customer demand, our revenue, business, and financial prospects would be harmed. In addition, if we experience any quality issues in the manufacturing of CoolSculpting systems, this could result in product recalls. Manufacturing delays related to quality control could negatively impact our ability to bring our CoolSculpting system and procedure packs to market, harm our reputation, and decrease our revenue. Any recall could be expensive and generate negative publicity, which could impair our ability to market our CoolSculpting system and further affect our results of operations.
We outsource the manufacturing of key components to third-party contract manufacturers.
Key components of our consumable procedure packs, including CoolGels, CoolLiners and securement accessories used with our CoolSmooth applicator, are manufactured by third-party contract manufacturers. If the operations of third-party contract manufacturers are interrupted or if they are unable to meet our delivery requirements due to capacity limitations, regulatory problems or other constraints, we may be limited in our ability to fulfill new customer orders or to repair equipment at current customer sites. Any change to another contract manufacturer would likely entail significant delay, require us to devote substantial time and resources, and could involve a period in which our products could not be produced in a timely or consistently high-quality manner, any of which could harm our reputation and results of operations.
Our manufacturing operations are dependent upon third-party suppliers, making us vulnerable to supply shortages and price fluctuations, which could harm our business.
Our CoolSculpting system contains a few critical components, the integrated circuit contained in the CoolSculpting control unit, the CoolSculpting applicators and the CoolCard, which is supplied by a company in Japan, and the connector that attaches our applicators to the control unit, which is supplied by a separate company in the United States. The single source suppliers of these critical components may not be replaced without significant effort and delay in production. We do not have supply agreements with the suppliers of these critical components beyond purchase orders. However, we attempt to maintain a safety stock inventory for these critical components equal to one year of forecasted part requirements of the integrated circuit and one month of connectors in finished assemblies, as well as at least three months' supply of connectors to support open purchase orders. Such forecasted amounts may be inaccurate and we may experience shortages as a result of serious supply problems or longer lead times with these suppliers as well as an increased demand for our products. In addition, several other non-critical components and materials that compose our CoolSculpting system are currently supplied by a single supplier or a limited number of suppliers. In many of these cases, we have not yet qualified alternate suppliers and rely upon purchase orders, rather than long-term supply agreements. A supply interruption or an increase in demand beyond our current suppliers' capabilities could harm our ability to manufacture our CoolSculpting system to meet demand until new sources of supply are identified and qualified, which could impact our sales and/or gross margins. Our reliance on these suppliers subjects us to a number of risks that could harm our business, including:
28
• | interruption of supply resulting from modifications to or discontinuation of a supplier's operations; |
• | interruption of supply, or increased shipping costs, resulting from port strikes, work stoppages or other unrest; |
• | delays in product shipments resulting from uncorrected defects, reliability issues, or a supplier's variation in a component; |
• | a lack of long-term supply arrangements for key components with our suppliers; |
• | inability to obtain adequate supply in a timely manner, or to obtain adequate supply on commercially reasonable terms; |
• | difficulty and cost associated with locating and qualifying alternative suppliers for our components in a timely manner; |
• | production delays related to the evaluation and testing of products from alternative suppliers, and corresponding regulatory qualifications; |
• | delay in delivery due to our suppliers prioritizing other customer orders over ours; |
• | damage to our brand reputation caused by defective components produced by our suppliers; |
• | increased cost of our warranty program due to product repair or replacement based upon defects in components produced by our suppliers; and |
• | fluctuation in delivery by our suppliers due to changes in demand from us or their other customers. |
Any interruption in the supply of components or materials, or our inability to obtain substitute components or materials from alternate sources at acceptable prices in a timely manner, could impair our ability to meet the demand of our customers, which would have an adverse effect on our business.
We forecast sales to determine requirements for components and materials used in our CoolSculpting system, and if our forecasts are incorrect, we may experience delays in shipments or increased inventory costs.
We keep limited materials, components, and finished products on hand. To manage our operations with our third-party contract manufacturers and suppliers, we forecast anticipated product orders and material requirements to predict our inventory needs and enter into purchase orders on the basis of these requirements. Several components of our CoolSculpting system require an order lead time of six months or more. If our business expands, and our demand for components and materials increases beyond our estimates, our contract manufacturers and suppliers may be unable to meet our demand. In addition, if we underestimate our component and material requirements, we may have inadequate inventory, which could interrupt, delay, or prevent delivery of our CoolSculpting system to our customers. In contrast, if we overestimate our component and material requirements, we may have excess inventory, which would increase our expenses. Further, outside forces, such as port strikes, could impact our ability to receive components necessary to meet demand. Any of these occurrences would negatively affect our financial performance and the level of satisfaction our customers have with our business.
There exists a potential for misuse of our CoolSculpting system, which could harm our reputation and our business.
Under state law in the United States, our customers can generally allow nurse practitioners, technicians, and other non-physicians to perform CoolSculpting procedures under their supervision. Similarly, in markets outside of the United States, our customers can allow non-physicians to perform CoolSculpting procedures under their supervision. Although we and our distributors provide training on the use of CoolSculpting systems, we do not supervise the procedures performed with our CoolSculpting system, nor can we be assured that direct physician supervision of procedures occurs according to our recommendations. The potential misuse of our CoolSculpting system by physicians and non-physicians may result in adverse treatment outcomes, which could harm our reputation and expose us to costly product liability litigation.
Product liability suits could be brought against us due to defective design, labeling, material, workmanship, or misuse of our CoolSculpting system, or unanticipated adverse events, and could result in expensive and time-consuming litigation, payment of substantial damages, an increase in our insurance rates and substantial harm to our reputation.
29
If our CoolSculpting system is defectively designed, manufactured, or labeled, contains defective components, or is misused, we may become subject to substantial and costly litigation by our customers or their patients. Misusing our CoolSculpting system or failing to adhere to operating guidelines can cause skin damage and underlying tissue damage and, if our operating guidelines are found to be inadequate, we may be subject to liability. Furthermore, if a patient is injured in an unexpected manner after undergoing a CoolSculpting procedure, even if the procedure was performed in accordance with our operating guidelines, we may be subject to product liability claims. We may also be subject to additional liability from claims related to known rare side effects such as late-onset pain, subcutaneous induration, hernia, and paradoxical hyperplasia. Product liability claims could divert management attention from our core business, be expensive to defend, and result in sizable damage awards against us. We currently have product liability insurance, but it may not be adequate to cover us against potential liability and it may be subject to material deductibles. In addition, we may not be able to maintain insurance in amounts or scope sufficient to provide us with adequate coverage against all potential liabilities. Any product liability claims brought against us, with or without merit, could increase our product liability insurance rates or prevent us from securing continuing coverage, could harm our reputation in the industry, and could reduce product sales. Product liability claims in excess of our insurance coverage, as well as deductibles under insurance policies, would be paid out of cash reserves, harming our financial condition and reducing our operating results.
Although we are currently exploring the use of our proprietary controlled cooling technology for other indications, such as for the treatment of acne and certain related skin conditions, there can be no guarantee that our research and development efforts in these additional indications will be successful.
We are currently exploring the use of our proprietary controlled cooling technology for other indications, and in September 2015 we entered into a new collaboration and patent license agreement with MGH to develop and commercialize a controlled cooling product for the treatment of acne and certain related skin conditions. However, there can be no guarantee that our research and development efforts will produce results that will enable us to pursue a regulatory submission to commercialize our proprietary controlled cooling technology for use in acne or any other indication, or that any submission that we make will receive regulatory approval. If our research and development efforts are not successful, we will have expended research and development efforts and capital in pursuing these indications without realizing any benefits from these efforts and expenses.
Security breaches and other disruptions could compromise our information and expose us to liability, which would cause our business and reputation to suffer.
We rely on networks, information management software and other technology, or information systems, including the Internet and third-party hosted services, to support a variety of business processes and activities, including procurement and supply chain, manufacturing, distribution, invoicing, order processing and collection of payments. We use information systems to process financial information and results of operations for internal reporting purposes and to comply with regulatory financial reporting, legal and tax requirements. In addition, we depend on information systems for digital marketing activities and electronic communications among our locations around the world and between company personnel as well as customers and suppliers. Because information systems are critical to many of our operating activities, our business processes may be impacted by system shutdowns or service disruptions. These disruptions may be caused by failures during routine operations such as system upgrades or user errors, as well as network or hardware failures, malicious or disruptive software, computer hackers, geopolitical events, natural disasters, failures or impairments of telecommunications networks, or other catastrophic events. These events could result in unauthorized disclosure of material confidential information. If our information systems suffer severe damage, disruption or shutdown and our business continuity plans do not effectively resolve the issues in a timely manner, we could experience delays in reporting our financial results and we may lose revenue and profits as a result of our inability to timely manufacture, distribute, invoice and collect payments. Misuse, leakage or falsification of information could result in a violation of data privacy laws and regulations and damage our reputation and credibility, and could expose us to liability. We may also be required to spend significant financial and other resources to remedy the damage caused by a security breach or to repair or replace networks and information systems.
Like most major corporations, our information systems are a target of attacks. Although the disruptions to our information systems that we have experienced to date have not had a material effect on our business, financial condition or results of operations, there can be no assurance that such disruptions will not have a material adverse effect on us in the future.
We may encounter issues with privacy and security of personal information.
CoolConnect allows us to obtain information directly from CoolSculpting systems deployed by our customers and, as a result, we expect to become subject to certain data privacy and security regulation by both the federal government and the states in which we conduct our business. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996, or HIPAA, and its implementing
30
regulations, established uniform federal standards for certain “covered entities,” which include certain health care providers, health care clearinghouses, and health plans. These standards govern the conduct of specified electronic health care transactions and govern the privacy and security of protected health information, or PHI. The Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act, or HITECH Act, makes HIPAA’s security standards directly applicable to “business associates,” which are independent contractors or agents of covered entities that create, receive, maintain, or transmit PHI in connection with providing a service for or on behalf of a covered entity. The HITECH Act increased the civil and criminal penalties that may be imposed against covered entities, business associates and certain other persons, and gave state attorneys general authority to enforce HIPAA’s requirements.
A portion of the data that we expect to obtain and handle for or on behalf of our customers is considered PHI. Under HIPAA and our contractual agreements with our covered entity customers, we expect to be considered a “business associate” to those customers, and be required to maintain the privacy and security of PHI in accordance with HIPAA and the terms of our business associate agreements with customers, including by implementing HIPAA-required administrative, technical and physical safeguards. We have incurred, and will continue to incur, significant costs to establish and maintain these safeguards and, if additional safeguards are required to comply with HIPAA regulations or our customers’ requirements, our costs could increase further, which would negatively affect our operating results. Furthermore, we cannot guarantee that such safeguards will be adequate. If we fail to maintain adequate safeguards, or we or our agents and subcontractors use or disclose PHI in a manner prohibited or not permitted by HIPAA or our business associate agreements, we could be subject to significant liabilities and consequences, including but not limited to contractual damages, government investigation, fines, private litigation, and/or negative publicity.
We have increased the size of our company significantly and over a short period, and difficulties managing our growth could adversely affect our business, operating results, and financial condition.
We have increased our headcount from 208 at January 1, 2013, to 535 at December 31, 2015, and plan to continue to hire additional employees as we increase our commercialization and sales activities for CoolSculpting. This growth has placed and may continue to place a strain on our management and our administrative, operational, and financial infrastructure. Our ability to manage our operations and growth requires the continued improvement of our operational, financial and management controls, reporting systems, and procedures, particularly to meet the reporting requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. If we are unable to manage our growth effectively or if we are unable to attract additional highly qualified personnel, our business, operating results, and financial condition may be harmed.
We depend on skilled and experienced personnel to operate our business effectively. If we are unable to recruit, hire, and retain these employees, our ability to manage and expand our business will be harmed, which would impair our future revenue and profitability.
Our success largely depends on the skills, experience, and efforts of our executive officers and other key employees. We do not have employment contracts with any of our executive officers or other key employees that require these officers to stay with us for any period of time. Any of our executive officers and other key employees may terminate their employment with us at any time. The loss of any of our executive officers and other key employees could weaken our management expertise and harm our business operations.
In addition, our ability to retain our skilled employees and our success in attracting and hiring new skilled employees will be a critical factor in determining whether we will be successful in the future. We may not be able to meet our future hiring needs or retain our existing employees. We will face significant challenges and risks in hiring, training, managing, and retaining sales and marketing, product development, financial reporting, and regulatory compliance employees, many of whom are geographically dispersed. Failure to attract and retain personnel, particularly our sales and marketing, product development, financial reporting, and regulatory compliance personnel, would materially harm our ability to compete effectively and grow our business.
We may need to raise additional funds in the future, and such funds may not be available on a timely basis, or at all.
The year 2015 is the first year in which we have generated positive cash flow from operations. Until such time, if ever, as we can achieve significant and sustained positive cash flows from sales of our CoolSculpting system and from sales of cycles in the form of consumable procedure packs, we will be required to finance our operations with our cash resources. We may need to raise additional funds in the future to support our operations. We cannot be certain that additional capital will be available as needed on acceptable terms, or at all. If we require additional capital at a time when investment in our company, in medical technology or aesthetic product companies or the marketplace in general is limited, we may not be able to raise such funds at the time that we desire, or at all. If we do raise additional funds through the issuance of equity or convertible securities, the percentage ownership of holders of our common stock could be significantly diluted and these newly issued securities may have rights, preferences, or privileges senior to those of holders of our common stock. If we obtain debt financing, a substantial portion of our operating cash
31
flow may be dedicated to the payment of principal and interest on such indebtedness, and the terms of the debt securities issued could impose significant restrictions on our operations. If we raise additional funds through collaborations and licensing arrangements, we could be required to relinquish significant rights to our technologies and products, or grant licenses on terms that are not favorable to us.
If we fail to manage our exposure to global financial and securities market risk successfully, our operating results and financial statements could be materially impacted.
The primary objective of most of our investment activities is to preserve principal. To achieve this objective, a majority of our marketable investments are investment grade, liquid, fixed-income securities and money market instruments denominated in U.S. dollars. If the carrying value of our investments exceeds the fair value, and the decline in fair value is deemed to be other-than-temporary, we will be required to write down the value of our investments, which could materially harm our results of operations and financial condition. Moreover, the performance of certain securities in our investment portfolio correlates with the credit condition of the U.S. financial sector. In our current unstable credit environment, we might incur significant realized, unrealized or impairment losses associated with these investments.
Our ability to use net operating losses and tax credit carryforwards to offset future tax liabilities may be limited.
We have substantial federal net operating loss carryforwards, or NOLs, and state and federal tax credit carryforwards. A lack of future taxable income would adversely affect our ability to utilize these NOLs and tax credit carryforwards. In addition, under Section 382 of the U.S. Internal Revenue Code, or the Code, a corporation that experiences a more-than 50% ownership change over a three-year testing period is subject to limitations on its ability to utilize its pre-change NOLs and tax credit carryforwards to offset future taxable income. Future changes in our stock ownership, many of the causes of which are outside of our control, could result in an ownership change under Section 382 of the Code. Our NOLs and tax credit carryforwards may also be impaired under state law. As a result of these limitations, we may not be able to utilize a material portion of the NOLs and tax credit carryforwards.
If taxing authorities challenge our recently implemented international tax structure, we may be required to pay more in taxes than we currently expect.
During fiscal 2015, we implemented an international tax structure that includes a research and development cost-sharing arrangement, certain licenses and other contractual arrangements between us and our wholly-owned foreign subsidiaries. As a result of these changes, we anticipate that our consolidated pre-tax income will be subject to foreign tax at relatively lower tax rates when compared to the United States federal statutory tax rate and, as a consequence, our effective income tax rate is expected to be lower than the United States federal statutory rate. Our future effective income tax rates could be adversely affected if tax authorities challenge our international tax structure or if the relative mix of United States and international income changes for any reason. Accordingly, there can be no assurance that our income tax rate will be less than the United States federal statutory rate in future periods.
Regulations related to conflict minerals could adversely impact our business.
Regulations promulgated by the United States Security and Exchange Commission, or SEC, prescribe annual disclosure and reporting requirements for public companies that use tin, tantalum, tungsten and gold, known as conflict minerals, mined from the Democratic Republic of Congo and adjoining countries, referred to as Covered Countries, in their products. These disclosure requirements require us to use diligent efforts to determine which conflict minerals we use and the source of those conflict minerals. We have determined that we use at least one of these conflict minerals in the manufacture of our CoolSculpting system, and so we are subject to these reporting requirements. We filed our most recent conflict minerals report on June 1, 2015, reporting that we could not yet determine whether the conflict minerals we source were, directly or indirectly, used to finance or benefit armed groups in the Covered Countries. There are and will continue to be costs associated with complying with these disclosure requirements. Further, these disclosure requirements could adversely affect the sourcing, supply and pricing of materials used in our CoolSculpting system and related consumables. In addition, our inability to conclude that we use conflict free minerals may damage our reputation. If we determine it is necessary to redesign our CoolSculpting system and/or related consumables to enable us to confirm that we do not use conflict minerals, we would incur costs associated with doing so.
32
Risks Related to Regulation
The regulatory clearance and approval process is expensive, time-consuming, and uncertain, and the failure to obtain and maintain required regulatory clearances and approvals could prevent us from commercializing our CoolSculpting system and any future products, such as for the treatment of cellulite, acne and certain related skin conditions, we develop.
We are investing in the research and development of new products and procedures based on our proprietary controlled cooling technology platform, such as for the treatment of cellulite, acne and certain related skin conditions. Our products are subject to 510(k) clearance by the FDA prior to their marketing for commercial use in the United States, and to any approvals required by foreign governmental entities prior to their marketing outside the United States. In addition, if we make any changes or modifications to our CoolSculpting system that could significantly affect its safety or effectiveness, or would constitute a change in its intended use, we may be required to submit a new notification for 510(k) clearance, premarketing approval or foreign regulatory approvals. For example, we will be required to submit new 510(k) notification to expand our ability to market CoolSculpting for use on other areas of the body beyond the flanks, abdomen, thighs and submental area, and for the treatment of cellulite, acne and certain related skin conditions.
The 510(k) clearance process, as well as the process for obtaining foreign approvals, can be expensive, time-consuming, and uncertain. We anticipate that the direct clinical costs to support a 510(k) notification for an additional indication for CoolSculpting will range from $0.25 million to $0.5 million. In addition to the time required to conduct clinical trials, it generally takes from four to twelve months from submission of a notification to obtain 510(k) clearance; however, it may take longer, and 510(k) clearance may never be obtained. Delays in receipt of, or failure to obtain, clearances or approvals for any product enhancements or new products we develop, and for the treatment of cellulite, acne and certain related skin conditions, would result in delayed, or no, realization of revenue from such product enhancements or new products and in substantial additional costs which could decrease our profitability.
In addition, we are required to continue to comply with applicable FDA and other regulatory requirements once we have obtained clearance or approval for a product. There can be no assurance that we will successfully maintain the clearances or approvals we have received or may receive in the future. Our clearances can be revoked if safety or effectiveness problems develop. Any failure to maintain compliance with FDA and applicable international regulatory requirements could harm our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
We will be subject to significant liability if we are found to have improperly promoted CoolSculpting for off-label uses.
The FDA strictly regulates the promotional claims that may be made about FDA-cleared products. In particular, a product may not generally be promoted for uses that are not cleared or approved by the FDA as reflected in the product's labeling. Our current FDA labeling only permits marketing CoolSculpting in the United States for use on the flanks, the abdomen, the thigh area and the submental fat area under the chin, and restricts us from promoting it for use on other parts of the body. The FDA does not regulate the practice of medicine however, and, we are aware that CoolSculpting is used by our customers on other parts of the body. If we are found to have inappropriately promoted such off-label uses, we may become subject to significant liability. The federal government has levied large civil and criminal fines against companies for alleged improper promotion and entered agreements with several companies that require cumbersome reporting and oversight of sales and marketing practices. The FDA has also requested that companies enter into consent decrees or permanent injunctions under which specified promotional conduct is changed or curtailed.
CoolSculpting may cause or contribute to adverse medical events that we are required to report to the FDA and if we fail to do so, we could be subject to sanctions that would materially harm our business.
Rare side effects have been reported after receiving CoolSculpting treatments, such as late-onset pain, subcutaneous induration, hernia, and paradoxical hyperplasia. There may be other new side effects that are reported to us as use of CoolSculpting increases. We may need to update our labeling, or take other regulatory action, in response to adverse event reports. In addition, FDA regulations require that we report certain information about adverse medical events if our medical devices may have caused or contributed to those adverse events, or if our device has malfunctioned. The timing of our obligation to report is triggered by the date we become aware of the adverse event as well as the nature of the event. We may fail to report adverse events we become aware of within the prescribed timeframe. We may also fail to appreciate that we have become aware of a reportable adverse event, especially if it is not reported to us as an adverse event or if it is an adverse event that is unexpected or removed in time from the use of our products. If we fail to comply with our reporting obligations, the FDA could take action including criminal prosecution, the imposition of civil monetary penalties, revocation of our device clearance or approval, seizure of our products, or delay in approval or clearance of future products.
33
We are currently, and in the future our contract manufacturers may be, subject to various governmental regulations related to the manufacturing of CoolSculpting, and we may incur significant expenses to comply with, experience delays in our product commercialization as a result of, and be subject to material sanctions if we or our contract manufacturers violate these regulations.
Our manufacturing processes and facilities are required to comply with the FDA's Quality System Regulation, or QSR, which covers the procedures and documentation of the design, testing, production, control, quality assurance, labeling, packaging, sterilization, storage, and shipping of our devices. Although we believe we are compliant with the QSRs, the FDA enforces the QSR through periodic announced or unannounced inspections of manufacturing facilities. We have been, and anticipate in the future being, subject to such inspections, as well as to inspections by other federal and state regulatory agencies.
Failure to comply with applicable FDA requirements, or later discovery of previously unknown problems with our products or manufacturing processes, including our failure or the failure of one of our third-party contract manufacturers to take satisfactory corrective action in response to an adverse QSR inspection, can result in, among other things:
• | administrative or judicially-imposed sanctions; |
• | injunctions or the imposition of civil penalties; |
• | recall or seizure of our products; |
• | total or partial suspension of production or distribution; |
• | the FDA's refusal to grant pending future clearance or pre-market approval for our products; |
• | withdrawal or suspension of marketing clearances or approvals; |
• | clinical holds; |
• | warning letters; |
• | refusal to permit the import or export of our products; and |
• | criminal prosecution of us or our employees. |
Any of these actions, in combination or alone, could prevent us from marketing, distributing, or selling our products and would likely harm our business.
We could have to issue a correction or removal to reduce a risk to health posed by our device or to remedy a violation which may present a risk to health. In addition, a product defect or regulatory violation could lead to a government-mandated or voluntary recall by us. The FDA could request that we initiate a voluntary recall if a product was defective or presented a risk of injury or gross deception. The FDA could order a recall if there is a reasonable probability that our product would cause serious adverse health consequences or death. Regulatory agencies in other countries have similar authority to recall devices because of material deficiencies or defects in design or manufacture that could endanger health. Any recall would divert management attention and financial resources, could cause the price of our shares of common stock to decline and expose us to product liability or other claims, including contractual claims from parties to whom we sold products and harm our reputation with customers. A recall involving our CoolSculpting system would be particularly harmful to our business and financial results and, even if we remedied a particular problem, would have a lasting negative effect on our reputation and demand for our products.
Legislative or regulatory healthcare reforms may make it more difficult and costly for us to obtain regulatory clearance or approval of our products and to produce, market, and distribute our products after clearance or approval is obtained.
From time to time, legislation is drafted and introduced in Congress that could significantly change the statutory provisions governing the regulatory clearance or approval, manufacture, and marketing of regulated products or the reimbursement thereof.
In addition, FDA regulations and guidance are often revised or reinterpreted by the FDA in ways that may significantly affect our business and our products. For example, in the future, the FDA may require more burdensome premarket approval of our procedures rather than the 510(k) clearance process we have used to date and anticipate primarily using in the future. Our CoolSculpting Platform is also subject to state regulations which are, in many instances, in flux. Any new regulations or revisions or reinterpretations of existing regulations may impose additional costs or lengthen review times of our products. We cannot determine what effect changes in regulations, statutes, legal interpretation or policies, when and if promulgated, enacted or adopted may have on our business in the future. Such changes could, among other things, require:
• | changes to manufacturing methods; |
• | recall, replacement, or discontinuance of certain products; |
• | additional record keeping; and |
• | additional warnings. |
34
Each of these would likely entail substantial time and cost and could materially harm our financial results. In addition, delays in receipt of or failure to receive regulatory clearances or approvals for our new products would harm our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
Federal and state governments in the United States are also undertaking efforts to control growing health care costs through legislation, regulation, and voluntary agreements with medical care providers, and third-party payers. In March 2010, Congress enacted comprehensive health care reform legislation known as the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act of 2010, which, as amended is known as the ACA. The ACA imposes a 2.3% excise tax on certain sales of medical devices by manufacturers in the United States. Although the excise tax has been temporarily suspended effective January 1, 2016 through December 31, 2017, there is no assurance that such suspension will continue. We expect compliance with the ACA to continue to impose significant administrative and financial burdens on us, which may harm our results of operations.
We may be subject to various federal and state laws pertaining to health care marketing and promotional practices and other business practices, and any violations by us of such laws could result in fines or other penalties.
State and federal authorities have targeted medical technology companies for alleged violations of laws and regulations, based on off-label marketing schemes and other improper promotional practices. Companies targeted in such prosecutions have paid substantial fines in the hundreds of millions of dollars or more, have been forced to implement extensive corrective action plans, and have often become subject to consent decrees severely restricting the manner in which they conduct their business. If we become the target of such an investigation or prosecution based on our marketing and promotional practices, we could face similar sanctions which would materially harm our business.
To our knowledge, the CoolSculpting Platform is not reimbursed by any third party payors, including federal health care programs such as Medicare and Medicaid. This helps to limit our possible exposure under certain U.S. health regulatory laws that have been at issue in some other medical technology enforcement. This also means we are not required to track and report marketing expenditures under the federal physician payment “sunshine” provisions enacted under the ACA. However, in the event third party reimbursement were available (or was caused to be paid inappropriately), our business could potentially be subject to a range of broad-reaching health regulatory laws, including, for example, the federal health care anti-kickback statute, the ACA’s “sunshine” provisions, and the federal civil false claims act. In addition, even without third party reimbursement for the CoolSculpting Platform, state “consumer protection” laws generally prohibit unfair and deceptive marketing practices directed at consumers, and such laws are generally broad enough to prohibit a range of marketing activities with respect to health care products and services that may be acceptable in other industries.
We may be exposed to liabilities under the FCPA and other anti-corruption laws, and any determination that we violated these laws could have a material adverse effect on our business.
We are subject to the Foreign Corrupt Practice Act of 1977, or FCPA, and other laws that prohibit improper payments or offers of payments to foreign governments and their officials and political parties by U.S. persons and issuers as defined by the statute, for the purpose of obtaining or retaining business. Also, similar worldwide anti-bribery laws, such as the U.K. Bribery Act and Chinese anti-corruption laws, generally prohibit companies and their intermediaries from making improper payments to non-U.S. officials for the purpose of obtaining or retaining business. Some of our distribution partners are located in parts of the world that have experienced governmental corruption to some degree and, in certain circumstances, strict compliance with anti-bribery laws may conflict with local customs and practices. Although we have implemented policies and procedures to discourage these practices by our employees, our existing safeguards and any future improvements may prove to be less than effective, and our employees, consultants, sales agents or distributors may engage in conduct for which we might be held responsible. Violations of the FCPA or international anti-corruption laws may result in severe criminal or civil sanctions, and we may be subject to other liabilities, which could negatively affect our business, operating results and financial condition. In addition, the U.S. government may seek to hold us liable for successor liability FCPA violations committed by companies in which we invest or that we acquire. We cannot assure you that our internal control policies and procedures will protect us from reckless or negligent acts committed by our employees, distributors, partners, consultants or agents.
We are subject to numerous environmental, health and safety laws and regulations, and must maintain licenses or permits, and non-compliance with these laws, regulations, licenses, or permits may expose us to significant costs or liabilities.
We are subject to numerous foreign, federal, state, and local environmental, health and safety laws and regulations relating to, among other matters, safe working conditions and environmental protection, including those governing the generation, storage, handling, use, transportation, and disposal of hazardous or potentially hazardous materials. Some of these laws and regulations require us to obtain licenses or permits to conduct our operations. Environmental laws and regulations are complex, change frequently and have tended to become more stringent over time. If we violate or fail to comply with these laws, regulations,
35
licenses, or permits, we could be fined or otherwise sanctioned by regulators. We cannot predict the impact on our business of new or amended laws or regulations or any changes in the way existing and future laws and regulations are interpreted or enforced, nor can we ensure we will be able to obtain or maintain any required licenses or permits.
Risks Related to Our Intellectual Property
If we are unable to obtain, maintain, and enforce intellectual property protection covering our CoolSculpting system and any future products we develop, others may be able to make, use, or sell products substantially the same as ours, which could adversely affect our ability to compete in the market.
Our commercial success is dependent in part on obtaining, maintaining, and enforcing our intellectual property rights, including our patents and the patents we exclusively license. If we are unable to obtain, maintain, and enforce intellectual property protection covering our CoolSculpting system and any other products we develop, others may be able to make, use, or sell products that are substantially the same as ours without incurring the sizable development and licensing costs that we have incurred, which would adversely affect our ability to compete in the market.
We seek to obtain and maintain patents and other intellectual property rights to restrict the ability of others to market products that compete with our products. As of December 31, 2015, our patent portfolio comprised 122 issued patents and 87 pending patent applications, each of which we own solely or license exclusively. However, patents may not be issued on any pending or future patent applications we file and, moreover, issued patents owned or licensed to us now or in the future may be found by a court to be invalid or otherwise unenforceable. Also, even if our patents are determined by a court to be valid and enforceable, they may not drafted or interpreted sufficiently broadly to prevent others from marketing products and services similar to ours or designing around our patents, and they may not provide us with freedom to operate unimpeded by the patent rights of others.
We have a number of foreign patents and applications, and expect to continue to pursue patent protection in the jurisdictions in which we do or intend to business. However, the laws of some foreign jurisdictions do not protect intellectual property rights to the same extent as laws in the United States, and many companies have encountered significant difficulties in obtaining, protecting, and defending such rights in foreign jurisdictions. If we encounter such difficulties or we are otherwise precluded from effectively protecting our intellectual property rights in foreign jurisdictions, our business prospects could be substantially harmed.
The patent positions of medical technology companies can be highly uncertain and involve complex legal and factual questions for which important legal principles remain unresolved. No consistent policy regarding the breadth of claims allowed in patents in these fields has emerged to date in the United States or in many foreign jurisdictions. Both the U.S. Supreme Court and the Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit have made, and will likely continue to make, changes in how the patent laws of the United States are interpreted. Similarly, foreign courts have made, and will likely continue to make, changes in how the patent laws in their respective jurisdictions are interpreted. In addition, the U.S. Congress is currently considering legislation that would change provisions of the patent law. We cannot predict future changes U.S. and foreign courts may make in the interpretation of patent laws or changes to patent laws which might be enacted into law by U.S. and foreign legislative bodies. Those changes may materially affect our patents, our ability to obtain patents or the patents and applications of our collaborators and licensors.
Future protection for our proprietary rights is uncertain because legal means afford only limited protection and may not adequately protect our rights or permit us to gain or keep our competitive advantage, which could adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations. For example:
• | others may be able to make systems or devices that are similar to ours but that are not covered by the claims of our patents; |
• | others may assert that our licensors or we were not the first to make the inventions covered by our issued patents or pending patent applications; |
• | our pending patent applications may not result in issued patents; |
• | our issued patents may not provide us with any competitive advantages or may be held invalid or unenforceable as a result of legal challenges by third parties; |
• | the claims of our issued patents or patent applications when issued may not cover our CoolSculpting system or the future products we develop; |
• | there may be dominating patents relevant to our controlled cooling technology of which we are not aware; |
• | there may be prior public disclosures that could invalidate our inventions or parts of our inventions of which we are not aware; |
• | the laws of foreign countries may not protect our proprietary rights to the same extent as the laws of the United States; and |
• | we may not develop additional proprietary technologies that are patentable. |
From time to time, we analyze our competitors' products and services, and may in the future seek to enforce our patents or other rights to counter perceived infringement. However, infringement claims can be expensive and time-consuming. In addition, in an
36
infringement proceeding, a court may decide that the patent we seek to enforce is invalid or unenforceable, or may refuse to stop the other party from using the technology at issue on the grounds that the patent in question does not cover the technology in question. An adverse result in any litigation could put one or more of our patents at risk of being invalidated or interpreted narrowly. Similarly, some of our competitors may be able to devote significantly more resources to intellectual property litigation, and may have significantly broader patent portfolios to assert against us if we assert our rights against them. Finally, because of the substantial discovery required in connection with intellectual property litigation, there is a risk that some of our confidential information could be disclosed or otherwise compromised during this type of litigation.
For example, in January 2013, the Mercantile Court in Spain rendered its ruling on the merits of Massachusetts General Hospital's, or MGH, and our request for a permanent injunction against Clinipro's LipoCryo device based on Clinipro's infringement of two European patents owned by MGH and globally licensed exclusively to us. While the Mercantile Court had earlier granted in 2012 MGH's and our request for a preliminary injunction, the Court, in the January 2013 ruling, denied the request for a permanent injunction, and the Mercantile Court’s ruling has been upheld on appeal. The Mercantile Court's ruling affects only Clinipro's activities in Spain. Further, although we and MGH did prevail against Clinipro in a patent infringement case in France, holding that an MGH patent exclusively licensed to us is valid and enforceable and enjoining Clinipro and its distributors from selling LipoCryo in France, Clinipro has appealed that ruling, and there is no assurance that Clinipro will not prevail.
We rely on a license relationship with Massachusetts General Hospital for much of our core intellectual property, and this arrangement could restrict the scope and enforcement of our intellectual property rights and limit our ability to successfully commercialize our products.
We have exclusively licensed certain intellectual property from the General Hospital Corporation, a not-for-profit Massachusetts Corporation, which owns and operates MGH related to our CoolSculpting system. We rely on MGH to file and prosecute patent applications and maintain patents and otherwise protect the intellectual property we license. We have not had and do not have primary control over these activities for certain of our patents or patent applications and other intellectual property rights we license, and therefore cannot guarantee that these patents and applications will be prosecuted or immediately enforced in a manner consistent with the best interests of our business. We cannot be certain that such activities by third parties have been or will be conducted in compliance with applicable laws and regulations or will result in valid and enforceable patents and other intellectual property rights. Additionally, we cannot control the publication or other disclosures of research carried out by MGH relating to technology that could otherwise prove patentable.
Pursuant to the terms of the license agreement with MGH, MGH has the right to control enforcement of our licensed patents or defense of any claims asserting the invalidity of these patents. Even if we are permitted to pursue such enforcement or defense, we will require the cooperation of MGH, and cannot guarantee that we would receive it. We cannot be certain that MGH will allocate sufficient resources or prioritize its or our enforcement of such patents or defense of such claims to protect our interests in the licensed patents. If we cannot obtain patent protection, or enforce existing or future patents against third parties, our competitive position and our financial condition could suffer.
We are exploring additional uses of our proprietary controlled cooling technology platform for the dermatology, plastic surgery, aesthetic and OBGYN markets. We also plan to explore potential therapeutic uses for our platform technology, either directly or through collaborative arrangements with strategic partners. Although MGH cannot restrict our future product development efforts, the terms of our license agreement with MGH may require us to pay MGH a royalty of up to 7% of net sales of future products we develop or that may be developed by our strategic partners. Whether we are required to pay a royalty will depend on whether our future products incorporate the intellectual property we licensed from MGH. Any royalty we are required to pay will reduce our income from sales of such future products and may make it more difficult for us to successfully commercialize these products directly or through a strategic partner.
37
If we are unable to protect the confidentiality of our proprietary information and know-how, the value of our technology and products could be adversely affected.
We rely on trade-secret protection to protect our interests in proprietary know-how and for processes for which patents are difficult or impossible to obtain or enforce. We may not be able to protect our trade secrets adequately. We have limited control over the protection of trade secrets used by our third-party contract manufacturers and suppliers. Although we use reasonable efforts to protect our trade secrets, our employees, consultants, contractors and outside scientific advisors may unintentionally or willfully disclose our information to competitors. Enforcing a claim that a third-party illegally obtained and is using any of our trade secrets is expensive and time consuming, and the outcome is unpredictable. In addition, courts outside the United States are sometimes less willing to protect trade secrets. We rely, in part, on non-disclosure and confidentiality agreements with our employees, consultants and other parties to protect our trade secrets and other proprietary technology. These agreements may be breached and we may not have adequate remedies for any breach. Moreover, others may independently develop equivalent proprietary information, and third parties may otherwise gain access to our trade secrets and proprietary knowledge. We may now or in the future incorporate open source software in our products' firmware. Open source software licenses can be ambiguous, and there is a risk that these licenses could be construed to require us to disclose or publish, in source code form, some or all of our proprietary firmware code. Any disclosure of confidential information into the public domain or to third parties could allow our competitors to learn our trade secrets and use the information in competition against us, which could adversely affect our competitive advantage.
Our CoolSculpting system and any future products or services we develop could be alleged to infringe patent rights of others, which may require costly litigation and, if we are not successful, could cause us to pay substantial damages or limit our ability to commercialize our products.
Our commercial success depends on our ability to develop, manufacture, and market our CoolSculpting system and use our proprietary controlled cooling technology without infringing the patents and other proprietary rights of third parties. As the medical technology and aesthetic product industries expand and more patents are issued, the risk increases that there may be patents issued to third parties that relate to our products and technology of which we are not aware or that we must challenge to continue our operations as currently contemplated. Our products may infringe or may be alleged to infringe these patents.
In addition, because patent applications in the United States and many foreign jurisdictions are typically not published until eighteen months after filing (or, in some cases, are not published until they issue as patents) and because publications in the scientific literature often lag behind actual discoveries, we cannot be certain that others have not filed patent applications for technology covered by our issued patents or our pending applications. Another party may have filed, and may in the future file, patent applications covering our products or technology similar to ours. Any such patent application may have priority over our patent applications or patents, which could further require us to obtain rights to issued patents covering such technologies. If another party has filed a U.S. patent application on inventions similar to ours, we may have to participate in an interference proceeding declared by the Patent and Trademark Office, or PTO, to determine priority of invention in the United States. The costs of these proceedings could be substantial, and it is possible that such efforts would be unsuccessful if the other party had independently arrived at the same or similar invention prior to our own invention, resulting in a loss of our U.S. patent position with respect to such inventions.
There is substantial litigation involving patent and other intellectual property rights in the medical technology and aesthetic industries generally. If a third party claims that we or any collaborator infringes its intellectual property rights, we may face a number of issues, including, but not limited to:
• | infringement and other intellectual property claims which, regardless of merit, may be expensive and time-consuming to litigate and may divert our management's attention from our core business; |
• | substantial damages for infringement, which we may have to pay if a court decides that the product at issue infringes on or violates the third party's rights, and if the court finds that the infringement was willful, we could be ordered to pay treble damages and the patent owner's attorneys' fees; |
• | a court prohibiting us from selling or licensing our products unless the third party licenses its product rights to us, which it is not required to do at a commercially reasonable price or at all; |
• | if a license is available from a third party, we may have to pay substantial royalties, upfront fees or grant cross-licenses to intellectual property rights for our products; and |
• | redesigning our products or processes so they do not infringe, which may not be possible at all or may require substantial monetary expenditures and time, during which our products may not be available for sale. |
Some of our competitors may be able to sustain the costs of complex patent litigation more effectively than we can because they have substantially greater resources. Even if resolved in our favor, litigation or other legal proceedings relating to intellectual property claims may cause us to incur significant expenses, and could distract our technical and management personnel from their
38
normal responsibilities. In addition, there could be public announcements of the results of hearings, motions or other interim proceedings or developments and if securities analysts or investors perceive these results to be negative, it could have a substantial adverse effect on the price of our common stock. Finally, any uncertainties resulting from the initiation and continuation of any litigation could have a material adverse effect on our ability to raise the funds necessary to continue our operations.
Our intellectual property rights will further be affected in ways that are difficult to anticipate by the provisions of the America Invents Act (2011).
Enacted in September 2011, the America Invents Act, or AIA, is the first major overhaul of the U.S. patent system since 1952, and includes a number of changes to established practices, which came into effect between September 2011 and March 2013. The most significant changes include the transition to a modified first-to-file system, the availability of new post-grant review for issued patents, various procedural changes including the third-party submission of prior art and the availability of derivation proceedings and supplemental examination, and an expanded prior commercial user rights defense to a claim of patent infringement. The scope of these changes and the lack of experience with their practical implementation, suggest a transitional period with some uncertainty over the next few years. Several provisions of the AIA will likely be tested in U.S. federal courts over time.
The changes to the U.S. patent system in the AIA will have an impact on our intellectual property rights and how business is conducted in general. For example, the recently implemented modified first-to-file system places a premium on filing as early as possible and appears to increase what is available as prior art, by changing the applicable definitions. In particular, the grace period in the year prior to the filing date is now limited to an inventor’s own publications, and third party publications occurring after a publication by the inventor. For patent applications filed on or after March 16, 2013, we may expect post-grant review challenges initiated up to nine months after the corresponding patent issues.
While the AIA was intended to make the resolution of intellectual property disputes easier and less expensive, we may in the future have to prove that we are not infringing patents or we may be required to obtain licenses to such patents. However, we do not know whether such licenses will be available on commercially reasonable terms, or at all. Prosecution of patent applications, post-grant opposition proceedings, and litigation to establish the validity and scope of patents, to assert patent infringement claims against others and to defend against patent infringement claims by others will be expensive and time-consuming. There can be no assurance that, in the event that claims of any of our owned or licensed patents are challenged by one or more third parties, any court or patent authority ruling on such challenge will determine that such patent claims are valid and enforceable. An adverse outcome in such litigation or post grant proceeding could cause us to lose exclusivity relating to the subject matter delineated by such patent claims and may have a material adverse effect on our business. If a third party is found to have rights covering products or processes used by us, we could be forced to cease using the products or processes covered by the disputed rights, be subject to significant liabilities to such third party and/or be required to license technologies from such third party.
Risks Related to Our Common Stock
Our stock price has been and will likely continue to be volatile.
Our stock price is volatile and from October 19, 2011, the first day of trading of our common stock, to March 10, 2016, our stock has had low and high sales prices per share in the range from $3.20 to $38.49 per share. Among the factors that may cause the market price of our common stock to fluctuate are the risks described in this “Risk Factors” section and other factors, including:
• | fluctuations in our operating results or the operating results of our competitors; |
• | changes in estimates of our financial results or recommendations or cessation of coverage by securities analysts; |
• | changes in the estimates of the future size and growth rate of our market opportunity; |
• | changes in accounting principles or changes in interpretations of existing principles, which could affect our financial results; |
• | conditions and trends in the markets we serve; |
• | changes in general economic, industry, and market conditions; |
• | success of competitive technologies and procedures; |
• | changes in our pricing policies; |
• | announcements of significant new technologies, procedures, or acquisitions by us or our competitors; |
• | changes in legislation or regulatory policies, practices or actions; |
• | the commencement or outcome of litigation involving our company, our general industry or both; |
• | recruitment or departure of our executives and other key employees; |
• | changes in our capital structure, such as future issuances of securities or the incurrence of debt; |
• | actual or expected sales of our common stock by the holders of our common stock; and |
• | the trading volume of our common stock. |
39
In addition, the stock market in general and the market for medical technology and aesthetic product companies in particular may experience a loss of investor confidence. The stock markets recently have experienced extreme price and volume fluctuations that have affected and continue to affect the market prices of equity securities of many companies. These fluctuations often have been unrelated or disproportionate to the operating performance of those companies. These broad market and industry fluctuations, as well as general economic, political and market conditions such as recessions, interest rate changes or international currency fluctuations, may negatively impact the market price of our common stock. In the past, companies that have experienced volatility in the market price of their stock have been subject to securities class-action litigation. Further, class-action litigation, even if unsuccessful, could be costly to defend and divert management's attention and resources, which could further materially harm our financial condition and results of operations.
The requirements of being a public company may strain our resources, divert management's attention, and affect our ability to attract and retain qualified board members.
As a public company, we are subject to the reporting requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, or the Exchange Act, the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, the Dodd-Frank Act, the listing requirements of the securities exchange on which we trade and other applicable federal and state securities rules and regulations. Compliance with these rules and regulations has legal and financial compliance costs, makes some activities difficult, time-consuming or costly and places demand on our business systems and resources. The Exchange Act requires, among other things, that we file annual, quarterly and current reports with respect to our business and operating results.
As a public company in the United States, we and our independent registered public accounting firm are required pursuant to Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, or Section 404, to furnish a report, among other things, on the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting, which we determined was not effective as of December 31, 2015. In the event that we are not able to demonstrate compliance with Section 404 in a timely manner, or are unable to produce timely or accurate financial statements, we may be subject to sanctions or investigations by regulatory authorities such as the SEC and the securities exchange on which we trade and investors may lose confidence in our operating results, which would have a material adverse effect on our business and on the price of our common stock and our ability to access the capital markets.
In addition, changing laws, regulations, and standards relating to corporate governance and public disclosure are creating uncertainty for public companies, increasing legal and financial compliance costs and making some activities more time-consuming. These laws, regulations, and standards are subject to varying interpretations, in many cases due to their lack of specificity, and, as a result, their application in practice may evolve over time as new guidance is provided by regulatory and governing bodies. This could result in continuing uncertainty regarding compliance matters and higher costs necessitated by ongoing revisions to disclosure and governance practices. We intend to invest resources to comply with evolving laws, regulations, and standards, and this investment may result in increased general and administrative expenses and a diversion of management's time and attention from revenue-generating activities to compliance activities. If our efforts to comply with new laws, regulations, and standards differ from the activities intended by regulatory or governing bodies due to ambiguities related to practice, regulatory authorities may initiate legal proceedings against us and our business may be harmed.
If we fail to maintain an effective system of internal controls, we may not be able to accurately report our financial results, which could lead to a loss of investor confidence in our financial statements and have an adverse effect on our stock price.
Effective internal controls are necessary for us to provide reliable and accurate financial statements and to effectively prevent fraud. We devote significant resources and time to comply with the internal control over financial reporting requirements of the Sarbanes Oxley Act of 2002. As further described in Part II Item 9A “Controls and Procedures,” management has concluded that, because of a material weakness in our risk assessment process, our disclosure controls and procedures were not effective as of December 31, 2015. Although we have begun the steps necessary to remediate the material weakness, we cannot assure you that the processes, procedures and controls we implement will result in full remediation of the material weakness. Failure to remediate the material weakness, or additional material weaknesses in our internal control over financial reporting, could result in material misstatements in our financial statements or cause us to fail to timely meet our reporting obligations. Inadequate internal controls could cause investors to lose confidence in our reported financial information, which could have a negative effect on investor confidence in our financial statements, the trading price of our stock and our access to capital.
Additionally, if we continue to fail to have effective controls and procedures for financial reporting in place, we could be unable to provide timely and accurate financial information and be subject to de-listing on the NASDAQ Global Select Market, SEC investigation, and civil or criminal sanctions and our stock price could decline.
40
We do not currently intend to pay dividends on our common stock.
We have never paid cash dividends on our common stock and do not anticipate paying cash dividends on our common stock in the foreseeable future. We currently intend to invest our future earnings, if any, to fund the development and growth of our business. The payment of dividends will be at the discretion of our Board of Directors and will depend on our results of operations, capital requirements, financial condition, future prospects, restrictions imposed by applicable law, any limitations on payments of dividends present in any debt agreements we may enter into and other factors our Board of Directors may deem relevant. If we do not pay dividends, your ability to achieve a return on our common stock will depend on any future appreciation in the market price of our common stock. There is no guarantee that our common stock will appreciate in value or even maintain the price at which our holders have purchased their common stock.
Our directors, executive officers, and entities with which they are affiliated hold a significant portion of our common stock, which may lead to conflicts of interest with other stockholders over corporate transactions and other corporate matters.
Our directors, executive officers, and entities with which they are affiliated beneficially own approximately 16% of our outstanding common stock as of March 10, 2016. This concentration of ownership may not be in the best interests of our other stockholders. We are not aware of any stockholder or voting agreements or understandings between or among our directors, officers, or holders of our outstanding common stock currently in place. However, these stockholders, acting together, would be able to exercise significant influence on all matters requiring stockholder approval, including the election of directors and significant corporate transactions such as mergers or other business combinations. This influence could delay, deter, or prevent a third party from acquiring or merging with us, which could adversely affect the market price of our common stock.
Anti-takeover provisions in our charter documents and under Delaware law could make an acquisition of us more difficult, limit attempts by our stockholders to replace or remove our current directors and management team, and limit the market price of our common stock.
Our amended and restated certificate of incorporation and amended and restated bylaws contain provisions that may delay or prevent a change of control, discourage bids at a premium over the market price of our common stock, and adversely affect the market price of our common stock and the voting and other rights of the holders of our common stock. These provisions include:
• | dividing our board into three classes, with each class serving a staggered three-year term; |
• | prohibiting our stockholders from calling a special meeting of stockholders or acting by written consent; |
• | permitting our board to issue additional shares of our preferred stock, with such rights, preferences and privileges as they may designate, including the right to approve an acquisition or other changes in control; |
• | establishing an advance notice procedure for stockholder proposals to be brought before an annual meeting, including proposed nominations of persons for election to our Board of Directors; |
• | providing that our directors may be removed only for cause; |
• | providing that vacancies on our Board of Directors may be filled only by a majority of directors then in office, even though less than a quorum; and |
• | requiring the approval of our Board of Directors or the holders of a super-majority of our outstanding shares of capital stock to amend our bylaws and certain provisions of our certificate of incorporation. |
Although we believe these provisions collectively provide for an opportunity to receive higher bids by requiring potential acquirers to negotiate with our board, they would apply even if the offer may be considered beneficial by some stockholders. In addition, these provisions may frustrate or prevent any attempts by our stockholders to replace or remove our current management team by making it more difficult for stockholders to replace members of our board, which is responsible for appointing the members of our management.
Moreover, because we are incorporated in Delaware, we are governed by the provisions of Section 203 of the Delaware General Corporation Law, which prohibits a person who owns in excess of 15% of our outstanding voting stock from merging or combining with us for a period of three years after the date of the transaction in which the person acquired in excess of 15% of our outstanding voting stock, unless the merger or combination is approved in a prescribed manner. The restrictions contained in Section 203 are not applicable to any of our existing stockholders that currently own 15% or more of our outstanding voting stock.
ITEM 1B. | UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS |
None.
ITEM 2. | PROPERTIES |
We occupy 45,858 square feet for our executive offices in Pleasanton, California, under a lease which extends through March 2019, 19,465 square feet in our manufacturing facility in Dublin, California, under a lease which extends through May 2017, and 15,755 square feet of warehouse space in Livermore, California, under a lease which extends through May 2017. We also occupy office and warehouse space near Gatwick, United Kingdom, under a lease which extends through December 2018, as well as office space in London, United Kingdom, under a lease which extends through April 2016, Taipei, Taiwan, under a lease which extends through August 2016, Seoul, South Korea, under a lease which extends through August 2016, Reston, Virginia, under a lease which extends through September 2020, and Galway, Ireland under two leases which extend through September 2016 and March 2016, respectively. We are currently in the process of reevaluating our lease terms for some of our facilities.
41
ITEM 3. | LEGAL PROCEEDINGS |
Not applicable.
ITEM 4. | MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES |
Not applicable.
42
PART II
ITEM 5. | MARKET FOR REGISTRANT'S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES |
Market Information for Common Stock
Our common stock has been traded on the NASDAQ Global Select Market under the symbol of “ZLTQ” since it began trading on October 19, 2011. The following table sets forth on a per share basis, for the periods indicated, the high and low sale prices of our common stock as reported by the NASDAQ Global Select Market.
2015 | High | Low | |||||
First Quarter | $ | 35.90 | $ | 26.15 | |||
Second Quarter | 34.32 | 25.79 | |||||
Third Quarter | 38.49 | 27.40 | |||||
Fourth Quarter | 36.25 | 26.55 | |||||
2014 | |||||||
First Quarter | $ | 24.79 | $ | 16.05 | |||
Second Quarter | 20.99 | 15.07 | |||||
Third Quarter | 27.04 | 13.30 | |||||
Fourth Quarter | 30.02 | 20.54 | |||||
As of March 10, 2016, there were approximately 21 holders of record of our common stock. In addition, we believe that a significant number of beneficial owners of our common stock held their shares in street name.
Dividend Policy
We have never declared or paid any cash dividends on our common stock. We currently intend to retain all future earnings, if any, for use in our business and do not anticipate paying any cash dividends on our common stock in the foreseeable future.
Performance Graph
The following graph shows the total stockholder return of an investment of $100 in cash on October 19, 2011 through December 31, 2015, for (1) our common stock, (2) the NASDAQ Composite index and (3) the NASDAQ Medical Equipment Index. All values assume reinvestment of the full amount of all dividends. No cash dividends have been declared on shares of our common stock. Stockholder returns over the indicated period are based on historical data and are not necessarily indicative of future stockholder returns.
43
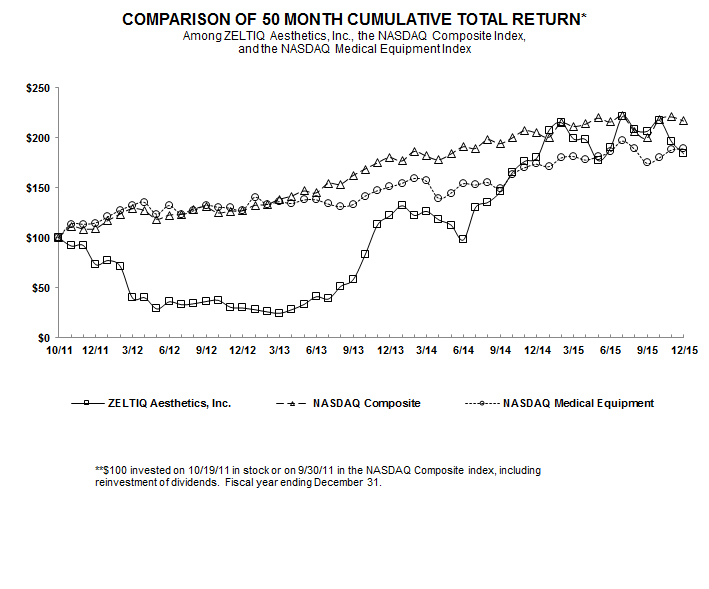
Cumulative Total Return as of | |||||||||||
December 31, 2013 | December 31, 2014 | December 31, 2015 | |||||||||
ZELTIQ Aesthetics, Inc. | $ | 122.00 | $ | 180.06 | $ | 184.06 | |||||
NASDAQ Composite | 181.10 | 205.86 | 217.11 | ||||||||
NASDAQ Medical Equipment | 146.27 | 165.10 | 189.52 | ||||||||
Repurchases of Equity Securities
Not applicable.
44
ITEM 6. | SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA |
The following tables set forth the selected consolidated financial data for each of the years in the five-year period ended December 31, 2015. The selected consolidated financial data is qualified in its entirety and should be read in conjunction with the Consolidated Financial Statements and related Notes thereto and Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations contained elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. We have derived the statement of operations data for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, and the balance sheet data as of December 31, 2015 and 2014, from the audited consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. The statement of operations data for the years ended December 31, 2012 and 2011, and the balance sheet data as of December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011, were derived from the audited consolidated financial statements that are not included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Selected Consolidated Financial Data | |||||||||||||||||||
(in thousands, except per share data) | |||||||||||||||||||
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||
2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | 2011 | |||||||||||||||
Revenue | $ | 255,416 | $ | 174,478 | $ | 111,626 | $ | 76,194 | $ | 68,144 | |||||||||
Cost of revenue (1) | 74,375 | 50,064 | 34,189 | 25,506 | 26,101 | ||||||||||||||
Gross profit | 181,041 | 124,414 | 77,437 | 50,688 | 42,043 | ||||||||||||||
Operating expenses: | |||||||||||||||||||
Research and development (1) | 22,909 | 18,196 | 17,090 | 12,693 | 10,488 | ||||||||||||||
Sales and marketing (1) | 125,458 | 83,579 | 63,185 | 51,167 | 28,953 | ||||||||||||||
General and administrative (1) | 28,980 | 20,515 | 16,510 | 16,867 | 11,299 | ||||||||||||||
Total operating expenses | 177,347 | 122,290 | 96,785 | 80,727 | 50,740 | ||||||||||||||
Income (loss) from operations | 3,694 | 2,124 | (19,348 | ) | (30,039 | ) | (8,697 | ) | |||||||||||
Interest income (expense), net | 58 | 63 | 80 | 129 | (93 | ) | |||||||||||||
Other income (expense), net | (420 | ) | (425 | ) | 103 | (92 | ) | (765 | ) | ||||||||||
Income (loss) before income taxes | 3,332 | 1,762 | (19,165 | ) | (30,002 | ) | (9,555 | ) | |||||||||||
Provision for (benefit from) income taxes | (38,470 | ) | 231 | 140 | 141 | 48 | |||||||||||||
Net income (loss) | 41,802 | 1,531 | (19,305 | ) | (30,143 | ) | (9,603 | ) | |||||||||||
Cumulative dividends on convertible preferred stock | — | — | — | — | (5,099 | ) | |||||||||||||
Net income (loss) attributable to common stockholders | $ | 41,802 | $ | 1,531 | $ | (19,305 | ) | $ | (30,143 | ) | $ | (14,702 | ) | ||||||
Net income (loss) per share attributable to common stockholders, basic (2) | $ | 1.08 | $ | 0.04 | $ | (0.53 | ) | $ | (0.87 | ) | $ | (1.96 | ) | ||||||
Net income (loss) per share attributable to common stockholders, diluted (2) | $ | 1.02 | $ | 0.04 | $ | (0.53 | ) | $ | (0.87 | ) | $ | (1.96 | ) | ||||||
As of December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||
2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | 2011 | |||||||||||||||
Balance Sheet Data: | |||||||||||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 35,710 | $ | 28,649 | $ | 25,798 | 22,876 | $ | 83,908 | ||||||||||
Restricted cash, short- and long-term investments | 16,809 | 21,651 | 30,613 | 36,173 | 255 | ||||||||||||||
Working capital | 68,402 | 56,540 | 42,430 | 49,590 | 84,086 | ||||||||||||||
Total assets | 178,827 | 103,905 | 88,054 | 90,269 | 105,999 | ||||||||||||||
Total capital lease obligations | 262 | 382 | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||
Total notes payable | — | — | — | — | 310 | ||||||||||||||
Total stockholders' equity | $ | 124,302 | $ | 70,519 | $ | 62,576 | $ | 72,580 | $ | 94,303 | |||||||||
45
(1) | The following table presents stock-based compensation related to stock based awards granted to employees and non-employees in each expense category or as a reduction in revenue. For further information, please see Note 9 to our audited consolidated financial statements set forth in Part II, Item 8 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. |
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||
2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | 2011 | |||||||||||||||
Revenue | $ | 205 | $ | 833 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | |||||||||
Cost of revenue | 744 | 443 | 248 | 131 | 54 | ||||||||||||||
Research and development | 1,619 | 1,073 | 1,645 | 894 | 542 | ||||||||||||||
Sales and marketing | 5,129 | 2,917 | 1,783 | 827 | 533 | ||||||||||||||
General and administrative | 5,522 | 4,117 | 2,984 | 3,137 | 1,150 | ||||||||||||||
Total stock-based compensation | $ | 13,219 | $ | 9,383 | $ | 6,660 | $ | 4,989 | $ | 2,279 | |||||||||
(2) | See Notes 2 and 12 to our audited consolidated financial statements for an explanation of the calculations of our basic and diluted net income (loss) per share of common stock attributable to common stockholders. |
ITEM 7. | MANAGEMENT'S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS |
You should read the following discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations in conjunction with “Selected Financial Data” and our consolidated financial statements and the notes thereto included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. In addition to historical information, the following discussion contains forward-looking statements that are subject to risks and uncertainties. Actual results may differ substantially from those referred to herein due to a number of factors, including but not limited to risks described in the section entitled Risk Factors in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Also see "Cautionary Language Regarding Forward-Looking Statements" immediately prior to Part I of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Overview
We are a medical technology company focused on developing and commercializing products utilizing our proprietary controlled cooling technology platform. Our first commercial product, the CoolSculpting system, is designed to selectively reduce stubborn fat bulges. We generate revenue primarily from sales of our CoolSculpting system, add-on applicators and from sales of cycles in the form of consumable procedure packs to our customers. Our CoolSculpting system comprises a CoolSculpting control unit and our CoolSculpting applicators which are designed to allow a physician to treat a different size and shape fat bulge. With the launch of our CoolMini applicator in September 2015, we currently offer six CoolSculpting applicators for use with our CoolSculpting system.
We received clearance from the Food and Drug Administration, or FDA, in September 2010 to market CoolSculpting for the selective reduction of fat around the flanks, an area commonly referred to as the “love handles.” In May 2012, CoolSculpting was cleared by the FDA for treatment of the abdomen area. In April 2014, CoolSculpting was cleared by the FDA for treatment of the thigh area, and, in January 2015, CoolSculpting was cleared by the FDA for treatment at lower temperatures which will enable shorter treatment times. Most recently, in September 2015, the FDA cleared CoolSculpting for treatment of the submental area under the chin, an area that is consistently ranked as one of the top areas of concern both by consumers and physicians. We may seek additional regulatory clearances from the FDA to expand our United States marketed indications for CoolSculpting to areas on the body other than the flanks, abdomen and thighs. We have received regulatory approval or are otherwise free to market CoolSculpting in numerous international markets where use of the product is generally not limited to specific treatment areas. Customers in these markets commonly perform CoolSculpting procedures on the back and chest, in addition to the flanks, abdomen and thighs.
In the United States and related territories, as well as Canada, we use our direct sales organization to selectively market CoolSculpting. In markets outside of North America, including Asia Pacific, Latin America and Europe, we sell CoolSculpting through both a direct sales organization as well as a network of distributors. We intend to continue developing our international sales and marketing organization to focus on increasing sales and strengthening our customer relationships. We also intend to seek regulatory approval to market CoolSculpting in key additional international markets, including markets in Asia and Europe. Revenue from markets outside of North America accounted for 24%, 23% and 20% of our total revenue for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
46
Our ongoing research and development activities are primarily focused on improving and enhancing our CoolSculpting system and CoolSculpting procedure. In addition to these development activities related to CoolSculpting, we are exploring additional uses of our proprietary controlled cooling technology platform for the dermatology, plastic surgery, aesthetic and OBGYN markets. We are also exploring potential therapeutic uses for our platform technology, either directly or through collaborative arrangements with strategic partners.
Revenue
We generate revenue primarily from sales of our CoolSculpting system and from sales of consumables to our customers. We generated revenue of $255.4 million, $174.5 million and $111.6 million for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
System revenue. Sales of our CoolSculpting system include the CoolSculpting control unit and our CoolSculpting applicators. Sales of systems can include sales of systems to new customers that include our entire suite of applicators, as well as multi-system sales to new customers or sales to existing customers which may not include the entire suite of applicators. Additionally, some practices may purchase additional applicators, or add-on applicators, for existing systems. Our standard terms do not allow for trial or evaluation periods, rights of return, or refund payments contingent upon the customer obtaining financing or other terms that could impact the customer’s obligation. System revenue represented 51%, 53% and 55% of our total revenue for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively. Our worldwide installed base grew by 46% from 3,176 units as of December 31, 2014, to 4,634 units as of December 31, 2015.
Consumable revenue. We generate consumable revenue through sales of cycles in the form of consumable procedure packs, each of which includes our consumable CoolGels, CoolLiners, and in the case of our CoolSmooth procedure packs, disposable securement accessories, all of which are used by our customer during treatments. In addition, each consumable procedure pack includes a disposable computer cartridge that we market as the CoolCard. The CoolCard contains enabling software that permits our customers to perform a fixed number of CoolSculpting procedures, or cycles. Consumable revenue accounted for 49%, 47% and 45% of our total revenue for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively. We shipped 980,339, 625,186 and 382,247 CoolSculpting revenue cycles to our customers during the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
Our business plan focuses on expanding our installed base of systems at customers, and increasing our consumable revenue by driving demand for CoolSculpting procedures through our targeted marketing programs. We anticipate that as we continue to implement our business plan and expand our installed base our consumable revenue will increase as a percentage of our total revenue.
Seasonality. Seasonal fluctuations in the number of patients seeking treatment and the availability of our customers are likely to continue to affect our business. Seasonal fluctuations occur in both system revenue and consumable revenue as well as by geographic region. Specifically, our customers often take vacation or are on holiday during the summer months and therefore tend to perform fewer procedures, particularly in certain international countries. These seasonal trends have caused and will likely continue to cause, fluctuations in our quarterly results, including fluctuations in sequential revenue growth rates.
Market in which we operate. The medical technology and aesthetic product markets are highly competitive and dynamic, and are characterized by rapid and substantial technological development and product innovations. We compete with many other technologies for consumer demand. Further, the aesthetic industry in which we operate is particularly vulnerable to economic trends. The decision to undergo a procedure from our systems is driven by consumer demand. Procedures performed using our systems are elective procedures, the cost of which must be borne by the patient, and are not reimbursable through government or private health insurance. In times of economic uncertainty or recession, individuals often reduce the amount of money that they spend on discretionary items, including aesthetic procedures. The general economic difficulties being experienced and the lack of availability of consumer credit for some of our customers' patients could adversely affect the markets in which we operate.
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
The preparation of our consolidated financial statements is in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States of America, or GAAP. The preparation of our consolidated financial statements requires management to make judgments and estimates that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities, the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements, and the reported amounts of revenue and expenses during the reporting period. Our management believes that we consistently apply these judgments and estimates and the consolidated financial statements and accompanying notes fairly represent all periods presented. However, any differences between these judgments and estimates and actual results could have a material impact on our consolidated statements of income and financial position.
47
Critical accounting estimates, as defined by the Securities and Exchange Commission, are those that are most important to the portrayal of our consolidated financial condition and results of operations and require our management’s most difficult and subjective judgments and estimates of matters that are inherently uncertain. Historically, our critical accounting estimates have not differed materially from actual results. However, if our assumptions change, we may need to revise our estimates, or take other corrective actions, either of which may also have a material adverse effect on our statements of operations, liquidity, and financial condition.
We believe the following critical accounting policies involve significant areas where management applies judgments and estimates in the preparation of our financial statements.
Revenue Recognition
We derive our revenue from the sales of the CoolSculpting system, consisting of a control unit and applicators, and, from time to time, related extended warranty arrangements, and from the sale of cycles in the form of consumable procedure packs, each of which includes our consumable CoolGels, CoolLiners, and in the case of our CoolSmooth procedure packs, disposable securement accessories, all of which are used by our customer during treatments. We earn revenue from the sale of these products to our customers and to distributors. We recognize revenue when persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists, transfer of title to the customer has occurred, the sales price is fixed or determinable, and collectability is probable. Revenue is deferred in the event that any of the revenue recognition criteria is not met. Each consumable procedure pack includes a disposable computer cartridge that we market as the CoolCard. The CoolCard contains enabling software that permits our customers to perform a fixed number of CoolSculpting procedures, or cycles. We do not market this software separately from the CoolSculpting system or from the CoolCard. Rather, the functionality that the software provides is part of the overall CoolCard product. We market the CoolSculpting system as a non-invasive aesthetic device for the selective reduction of fat, not for its embedded software attributes included in the CoolCard that enable its use. We do not provide rights to upgrades and enhancements or post contract customer support for the embedded software. In addition, we do not incur significant software development costs or capitalize our software development costs. Based on this assessment, we consider the embedded software in the CoolCard incidental to the CoolCard product as a whole and determined that revenue recognition should not be governed by the provisions of Topic 985 of the FASB Accounting Standards Codification, or ASC.
Persuasive Evidence of an Arrangement. We use contracts or customer purchase orders to determine the existence of an arrangement.
Delivery. Our standard terms specify that title transfers upon shipment to the customer. We use third party shipping documents to verify that title has transferred.
Sales Price Fixed or Determinable. We assess whether the sales price is fixed or determinable at the time of the transaction. Sales prices are documented in the executed sales contract or purchase order received prior to shipment. Our standard terms do not allow for trial or evaluation periods, rights of return or refund, payments contingent upon the customer obtaining financing or other terms that could impact the customer's obligation.
Collectability. We assess whether collection is reasonably assured based on a number of factors, including the customer's past transaction history and credit worthiness.
Multiple-Element Arrangements. Typically, all products sold to a customer are delivered at the same time. If a partial delivery occurs as authorized by the customer, we allocate revenue to the various products based on their vendor-specific objective evidence of fair value, or VSOE, if VSOE exists according to ASC 605-25 as the basis of determining the relative selling price of each element. If VSOE does not exist, we may use third party evidence of fair value, or TPE, to determine the relative selling price of each element. If neither VSOE nor TPE exists, we may use management's best estimate of the sales price, or ESP, of each element to determine the relative selling price. We base the relative selling prices for control units, applicators, CoolCards and extended warranty on established price lists and separate, stand-alone sales of these elements. We establish best estimates within a range of selling prices considering multiple factors including, but not limited to, factors such as size of transaction, pricing strategies and market conditions. We believe the use of the ESP allows revenue recognition in a manner consistent with the underlying economics of the transaction. Our products do not require maintenance or support. Additionally, from time to time there may be undelivered elements in a multiple element arrangement, such elements generally being training or extended warranty. We defer revenue on undelivered elements of an arrangement and recognize it once all revenue recognition criteria have been met.
48
Shipping and handling costs. We expense shipping and handling costs as incurred and include them in cost of revenue. In those cases where we bill shipping and handling costs to customers, we classify the amounts billed as revenue.
Customer Programs and Payments
We regularly evaluate the adequacy of our estimates for product returns, cooperative marketing arrangements, customer incentive programs and pricing programs. Future market conditions and product transitions may require us to take action to change such programs. In addition, when the variables used to estimate these costs change, or if actual costs differ significantly from the estimates, we would be required to record incremental increased or reductions to sales, cost of goods sold or operating expenses. If, at any future time, we become unable to reasonably estimate these costs, recognition of revenue might be deferred until products are sold to users, which would adversely impact sales in the period of transition.
Accruals for Customer Programs
We record an accrued liability for cooperative marketing arrangements and customer incentive programs. The estimated cost of these programs is recorded as a reduction of revenue or as an operating expense, if we receive a separately identifiable benefit from the customer and can reasonably estimate the fair value of that benefit. Significant management judgment and estimates must be used to determine the cost of these programs in any accounting period.
Cooperative Marketing Arrangements. We offer cooperative marketing programs to our North American customers, allowing the customers to receive partial reimbursement for qualifying advertising expenditures which promote the Company's product and brand. Customer participation, as well as reimbursement amounts, is predicated upon purchase levels of CoolCards. The objective of these arrangements is to encourage advertising and promotional events to increase sales of our products. Accruals for these marketing arrangements are recorded at the time of sale, or time of commitment, based on the related program parameters, review of related advertising and historical experience.
Customer Incentive Programs. Our customer incentive program consists of rebates for our distributors based on purchase levels. Estimated costs of customer rebates and similar incentives are recorded at the later of the time the incentive is offered, based on the specific terms and conditions of the program or the time the related revenue is recognized.
Customer incentive programs include performance-based incentives and consumer rebates. We offer performance-based incentives to our distribution customers, retail customers and indirect partners based on pre-determined performance criteria. Accruals for performance-based incentives are recognized as a reduction of the sale price at the later of the time the incentive is offered, based on the specific terms and conditions of the program or the time the related revenue is recognized. Estimates of required accruals are determined based on negotiated terms, consideration of historical experience, anticipated volume of future purchases, and inventory levels in the channel. Certain incentive programs require management to estimate the number of customers who will actually redeem the incentive based on historical experience and the specific terms and conditions of particular programs.
Accounting for Payments to Customers
We occasionally enter into transactions where we provide consideration to our customers in the forms of cash payments or stock-based awards in exchange for certain goods and services. We account for such payments to customers in accordance with ASC 605-50, Revenue Recognition: Customer Payments and Incentives, which requires management to characterize the payment as a reduction of revenue if we are unable to demonstrate the receipt of a benefit that is identifiable and sufficiently separable from the revenue transaction and reasonably estimate the fair value of the benefit identified. Significant management judgment and estimates must be used to determine the fair value of the benefit received in any period. For stock awards, we believe that the fair value of the awards is more reliably measured than the fair value of the benefit received. The fair value of the stock awards is measured as of the date at which either the commitment for performance by the customer to earn the award is reached or the date the customer’s performance is complete. Until that point is reached, the award is revalued at each reporting period with the true-up to fair value recorded in current period earnings.
49
Investments
We invest our excess cash balances primarily in certificates of deposit, commercial paper, corporate bonds, and U.S. Government agency securities. Investments with original maturities greater than 90 days that mature less than one year from the consolidated balance sheet date are classified as short-term investments. We classify all of our investments as available-for-sale and record such assets at estimated fair value in the consolidated balance sheets, with unrealized gains and losses, if any, reported as a component of accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) in stockholders' equity. We report realized gains and losses from maturities of all such securities in earnings and computed using the specific identification cost method. We report realized gains or losses and charges for other-than-temporary declines in value, if any, on available-for-sale securities in other income (expense), net as incurred. We periodically evaluate these investments for other-than-temporary impairment.
Product Warranties
We provide a standard limited warranty on our products of one year for both control units and applicators for our direct customers. For indirect customers in international markets, we provide a standard limited warranty on our products of approximately three years for control units and one year for applicators.
We estimate and provide for future costs for initial product warranties upon shipment. We base product warranty costs on related freight, material, technical support labor and overhead costs. We provide for the estimated product warranty costs by considering our historical costs and applying the experience rates to each product sold over the outstanding warranty period. We must exercise judgment in estimating our expected product warranty costs. If actual product failure rates, freight, material, technical support, labor, and overhead costs differ from our estimates, we will be required to revise our estimated warranty liability. We have recorded a liability of $0.5 million and $0.6 million as of December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively, for future warranty expense.
We offer an extended warranty on both our CoolSculpting control units and CoolSculpting applicators. We recognize the revenue from the sale of an extended warranty over the extended warranty coverage period. Our revenue from the sale of extended warranties for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013 were $3.5 million, $2.1 million and $1.0 million, respectively.
Stock-Based Compensation
We recognize stock-based compensation cost for only those shares ultimately expected to vest over the requisite service period of the award. We estimate the fair value of stock options using a Black-Scholes valuation model, which requires the input of highly subjective assumptions, including the option’s expected term and stock price volatility. In addition, judgment is also required in estimating the number of stock-based awards that we expect to be forfeited. Forfeitures are estimated based on historical experience at the time of grant and revised, if necessary, in subsequent periods if actual forfeitures differ from those estimates. The assumptions used in calculating the fair value of share-based payment awards represent management’s best estimates, but these estimates involve inherent uncertainties and the application of management’s judgment. As a result, if factors change and we use different assumptions, our stock-based compensation expense could be materially different in the future.
Income Taxes
We are subject to income taxes in multiple jurisdictions, including but not limited to the United States and United Kingdom, and we use estimates in determining our income taxes. We use the asset and liability method of accounting for income taxes. Under this method, we calculate deferred tax asset or liability account balances at the balance sheet date using current tax laws and rates in effect for the year in which the differences are expected to affect our taxable income.
Recognition of deferred tax assets is appropriate when realization of such assets is more likely than not. Since inception, we determined that a valuation allowance should be recorded against all of our domestic net deferred tax assets. We perform a quarterly assessment over the realizability of our deferred tax assets that requires us to exercise significant judgment and make estimates about our ability to generate revenue, gross profit, operating income and taxable income in future periods. Due to strong operating results in recent years, the expectation that we will continue to generate taxable income into the foreseeable future and our tax planning action of migrating and licensing certain intellectual property to our foreign entities, our assessment regarding whether it is more likely than not that we will realize our deferred tax assets has changed. We released $40.4 million of the valuation allowance on all domestic deferred tax assets except for California R&D credits as of December 31, 2015. We continue to apply a valuation allowance against our California R&D credit deferred tax assets. In reaching this conclusion we considered, among other things, our recent financial and operating results (three years of cumulative income, eight consecutive quarters of profitability and strong revenue growth). We gave the most significant weight in our evaluation to the objective, direct positive evidence related to our recent strong financial results, particularly our positive levels of pre-tax income.
50
We follow the accounting guidance for uncertainties in income taxes, which prescribes a recognition threshold and measurement process for recording uncertain tax positions taken, or expected to be taken in a tax return, in the consolidated financial statements. As of December 31, 2015 we have substantially released our valuation allowance and believe our currently unrecognized tax benefits would, if recognized, affect our effective income tax rate.
We assess all material positions taken in any income tax return, including all significant uncertain tax positions, in all tax years that are still subject to assessment or challenge by relevant taxing authorities. Assessing an uncertain tax position begins with the initial determination of the position's sustainability and is measured at the largest amount of benefit that is greater than 50% likely to be realized upon ultimate settlement. As of each balance sheet date, unresolved uncertain tax positions must be reassessed, and we will determine whether the factors underlying the sustainability assertion have changed and whether the amount of the recognized tax benefit is still appropriate. The recognition and measurement of tax benefits requires significant judgment. Our judgments concerning the recognition and measurement of a tax benefit might change as new information becomes available.
Utilization of net operating losses and tax credit carryforwards may be limited by “ownership change” rules, as defined in Section 382 of the Internal Revenue Code. Similar rules may apply under state tax laws. We have assessed the application of Internal Revenue Code Section 382, during the fourth quarter of 2015, and concluded no limitation currently applies, and we will continue to monitor activities in the future. In the event we experience any subsequent changes in ownership, the amount of net operating losses and research and development credit carryovers available in any taxable year could be limited and may expire unutilized.
Out of period adjustments
During the three months ended December 31, 2015, we recorded an out-of-period correcting adjustment of $0.3 million to increase cost of revenue to write-off certain inventory related to service parts. Of this adjustment, $0.2 million related to the three months ended September 30, 2015 and the remainder primarily in the other quarters of 2015. We do not believe that such amounts are material to any prior period consolidated financial statements, and the impact of correcting these errors in the three months ended December 31, 2015 is not material to the current consolidated financial statements.
During the three months ended June 30, 2015, we recorded an out-of-period correcting adjustment of $0.2 million to increase cost of revenue to write-off of certain inventory held by vendors. Of this adjustment, $0.1 million, $23,000 and $42,000 related to the fiscal years ended December 31, 2012, 2013 and 2014, respectively. We do not believe that such amounts are material to any prior period consolidated financial statements, and the impact of correcting these errors during the year ended December 31, 2015 is not material to the current consolidated financial statements.
During the three months ended December 31, 2014, we recorded an out-of-period correcting adjustment related to stock-based compensation that resulted in $0.7 million of revenue reduction. The adjustment to revenue resulted from an error in the application of generally accepted accounting principles related to payments to customers for services starting in the second quarter of 2013 through the third quarter of 2014. Of the total amount of this adjustment, $0.4 million related to the fiscal year ended December 31, 2013. The error caused the overstatement of revenue and sales and marketing expense in prior periods due to the misclassification of this stock-based compensation. This adjustment did not have any impact to our consolidated net income (loss) as reported in the consolidated statements of operations in any current or prior annual period. We do not believe that such amounts are material to the current and previously reported consolidated financial statements.
Results of Operations
Revenue (in thousands, except for percentages):
Year Ended | ||||||||||||||
December 31, | ||||||||||||||
2015 | 2014 | $ Change | % Change | |||||||||||
Revenue | ||||||||||||||
System revenue | $ | 130,698 | $ | 93,015 | $ | 37,683 | 41 | % | ||||||
Consumable revenue | 124,718 | 81,463 | 43,255 | 53 | % | |||||||||
Total revenue | $ | 255,416 | $ | 174,478 | $ | 80,938 | 46 | % | ||||||
51
Year Ended | ||||||||||||||
December 31, | ||||||||||||||
2014 | 2013 | $ Change | % Change | |||||||||||
Revenue | ||||||||||||||
System revenue | $ | 93,015 | $ | 61,359 | $ | 31,656 | 52 | % | ||||||
Consumable revenue | 81,463 | 50,267 | 31,196 | 62 | % | |||||||||
Total revenue | $ | 174,478 | $ | 111,626 | $ | 62,852 | 56 | % | ||||||
Overall, we experienced an increase in revenue driven primarily by the expansion of our sales force into new and existing key markets, an increase in our installed base of CoolSculpting systems along with the release of our CoolSmooth PRO and CoolMini applicator, and increased focus and prioritization of our business through our revamped sales team structure and training.
System revenue. We experienced incremental growth in system revenue for the year ended December 31, 2015, as compared to the year ended December 31, 2014, as a result of increased system sales in both North America, including a large volume sale to Ideal Image, a large aesthetic chain along with its affiliated franchises, and our International markets due to the reasons stated above. Overall, we sold 1,458 systems in the year ended December 31, 2015, as compared to 1,001 systems in the year ended December 31, 2014. We also experienced an increase in sales of add-on applicators to existing customers primarily related to our launch of our CoolSmooth Pro and CoolMini applicators during the year. Such total incremental add-on applicator revenue was $15.5 million in the year ended December 31, 2015, which substantially relates to our CoolMini applicator, whereas in the year ended December 31, 2014, our incremental add-on revenue, related primarily to our CoolSmooth applicators, totaled $9.6 million. Add-on applicators allow our customers to optimize their existing system to fit different body shapes and sizes, as well as different body parts or regions of the body.
We experienced incremental growth in system revenue for the year ended December 31, 2014, as compared to the year ended December 31, 2013, as a result of increased system sales in both North America and our International markets due to the reasons stated above. Overall, we sold 1,001 systems in the year ended December 31, 2014, as compared to 692 systems in the year ended December 31, 2013. Additionally, with the launch of our CoolSmooth applicator in April 2014, system bundles included five CoolSculpting applicators for use with our CoolSculpting system which resulted in an increase in average selling price per system bundle. We also experienced an increase in sales of add-on applicators to existing customers primarily related to the launch of our CoolSmooth applicator. Such total incremental add-on applicator revenue was $9.6 million in the year ended December 31, 2014, whereas in the in the year ended December 31, 2013, our incremental add-on revenue, related primarily to our CoolFit and CoolCurve+ applicators, totaled $4.8 million. Add-on applicators allow our customers to optimize their existing system to fit different body shapes and sizes, as well as different body parts or regions of the body.
Consumable revenue. The increase in consumable revenue for the year ended December 31, 2015, as compared to the year ended December 31, 2014, was primarily due to the significant growth of our worldwide installed base of CoolSculpting systems and an increased number of consumable procedure packs shipped to our customers driven by our targeted marketing programs in the year ended December 31, 2015, as compared to the year ended December 31, 2014, as well as due the release of our CoolMini applicator which requires a different consumable procedure pack and carries a higher average selling price than our other applicators. Overall, we shipped 980,339, 625,186 and 382,247 CoolSculpting revenue cycles to our customers during the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
The increase in consumable revenue for the year ended December 31, 2014, as compared to the year ended December 31, 2013, was primarily due to the significant growth of our worldwide installed base of CoolSculpting systems and the success of our targeted marketing programs in the year ended December 31, 2014, as compared to the year ended December 31, 2013, as well as due to the release of our CoolSmooth applicator which requires a different consumable procedure pack than our other applicators. Our consumable procedure packs carry two tiers of pricing, and the CoolSmooth consumable procedure pack is priced at the lower tier. With the introduction of the CoolSmooth applicator in April 2014, we saw a shift of sales to the lower tier pricing, which offset the increase in volume to a small extent. Additionally, during the first quarter of 2014, we discontinued our practice of providing rebates to our customers associated with the Crystal Rewards Program, our customer loyalty program related to consumable purchases. These rebates reduced consumable revenue in periods prior to this program change.
52
Cost of Revenue and Gross Profit (in thousands, except for percentages):
Year Ended | ||||||||||||||
December 31, | ||||||||||||||
2015 | 2014 | $ Change | % Change | |||||||||||
Cost of revenue | $ | 74,375 | $ | 50,064 | $ | 24,311 | 49 | % | ||||||
% of total revenue | 29 | % | 29 | % | ||||||||||
Gross profit | $ | 181,041 | $ | 124,414 | $ | 56,627 | 46 | % | ||||||
Gross profit % | 71 | % | 71 | % | ||||||||||
Year Ended | ||||||||||||||
December 31, | ||||||||||||||
2014 | 2013 | $ Change | % Change | |||||||||||
Cost of revenue | $ | 50,064 | $ | 34,189 | $ | 15,875 | 46 | % | ||||||
% of total revenue | 29 | % | 31 | % | ||||||||||
Gross profit | $ | 124,414 | $ | 77,437 | $ | 46,977 | 61 | % | ||||||
Gross profit % | 71 | % | 69 | % | ||||||||||
Gross profit as a percentage of revenue typically fluctuates with product and regional mix, selling prices, material costs and revenue levels. The gross profit as a percentage of revenue for the year ended December 31, 2015, as compared to the year ended December 31, 2014, remained relatively unchanged. The increases in consumable revenue on a fixed base of overhead costs as well as a change in overall mix that resulted in a shift of revenue to consumables as a percentage of overall sales year over year were partially offset by reductions in average selling prices on our systems in 2015 compared to the same period in 2014 driven by sales to international customers, discounts on certain multiple system deals and a large volume sale to Ideal Image as well as due to our CoolSmooth PRO exchange program in 2015 which carries a lower gross profit contribution based on the reduced selling price associated with the exchange and the introduction of the CoolMini applicator which currently carries a higher standard cost than the other applicators we offer.
The increase in gross profit as a percentage of revenue for the year ended December 31, 2014, as compared to the year ended December 31, 2013, was mainly attributable to increased sales volume, as higher production driven by the increase in sales led to better utilization on a relatively fixed base of overhead costs. Additionally, the increase in gross profit as a percentage of revenue is attributable to our growing system installed base which continues to drive higher consumable sales which carry higher margins. We continue to focus on cost reduction across our product portfolio, as well as experience the benefit of the completion of the in-sourced manufacturing structure during the second quarter of 2013 and as result experienced a full year benefit of in-sourced manufacturing during 2014, compared to only the second half of 2013. These increases were offset in part by the high volume of sales of our CoolSmooth applicator, which during 2014 carried a slightly lower standard margin than our other applicators. This applicator was launched in April 2014 with introductory pricing through both the second and third quarter of 2014. We also experienced a slight decline in margins as result of higher international system sales as a percentage of total system revenue during 2014, when compared to 2013, which carry a lower standard margin than our North America system sales.
53
Operating Expenses (in thousands, except for percentages):
Year Ended | ||||||||||||||
December 31, | ||||||||||||||
2015 | 2014 | $ Change | % Change | |||||||||||
Operating expenses: | ||||||||||||||
Research and development | $ | 22,909 | $ | 18,196 | $ | 4,713 | 26 | % | ||||||
% of total revenue | 9 | % | 10 | % | ||||||||||
Sales and marketing | $ | 125,458 | $ | 83,579 | $ | 41,879 | 50 | % | ||||||
% of total revenue | 49 | % | 48 | % | ||||||||||
General and administrative | $ | 28,980 | $ | 20,515 | $ | 8,465 | 41 | % | ||||||
% of total revenue | 11 | % | 12 | % | ||||||||||
Total operating expenses | $ | 177,347 | $ | 122,290 | $ | 55,057 | 45 | % | ||||||
Year Ended | ||||||||||||||
December 31, | ||||||||||||||
2014 | 2013 | $ Change | % Change | |||||||||||
Operating expenses: | ||||||||||||||
Research and development | $ | 18,196 | $ | 17,090 | $ | 1,106 | 6 | % | ||||||
% of total revenue | 10 | % | 15 | % | ||||||||||
Sales and marketing | $ | 83,579 | $ | 63,185 | $ | 20,394 | 32 | % | ||||||
% of total revenue | 48 | % | 57 | % | ||||||||||
General and administrative | $ | 20,515 | $ | 16,510 | $ | 4,005 | 24 | % | ||||||
% of total revenue | 12 | % | 15 | % | ||||||||||
Total operating expenses | $ | 122,290 | $ | 96,785 | $ | 25,505 | 26 | % | ||||||
Research and development. Research and development expenses increased for the year ended December 31, 2015, as compared to the year ended December 31, 2014, primarily due to an increase in payroll related costs of $2.1 million attributed to higher headcount and an increase in performance-based compensation. We also experienced an increase in materials, operations and clinical costs of $1.3 million as we continue to explore ways to leverage our proprietary cooling platform for additional applications and indications including our recently announced CoolSmooth PRO and CoolMini, which were launched in the second and third quarter of 2015, respectively. Facilities and other allocable costs such as costs related to administrative functions, also increased by $0.6 million resulting from increased headcount and operating costs related to the growth in our business. Additionally, stock-based compensation expense increased by $0.5 million attributed to grants associated with our higher headcount during the year ended December 31, 2015.
Research and development expenses increased for the year ended December 31, 2014, as compared to the year ended December 31, 2013, primarily due to an increase in payroll related costs of $1.1 million attributed to higher headcount and an increase in performance-based compensation. This increase was offset in part by a $0.5 million decrease in consulting, time and expense, and administrative expenses as result of a reduction in the number of consultants being utilized. We also experienced an increase in materials, operations and clinical costs of $0.5 million as we continue to explore ways to leverage our proprietary cooling platform for additional applications and indications including our recently announced CoolSmooth PRO, which we expect to launch in the second quarter of 2015. Facilities and other allocable costs also increased by $0.3 million resulting from increased headcount and operating costs related to the growth in our business. Additionally, stock-based compensation expense decreased by $0.6 million attributed to costs associated with non-recurring severance expenses during the year ended December 31, 2013, with no similar activity during the year ended December 31, 2014.
Sales and marketing. Sales and marketing expenses increased for the year ended December 31, 2015, as compared to the year ended December 31, 2014, primarily due to the significant increase in headcount attributable to our sales force, which increased by 30% to 283 employees, compared to 214 employees in 2014, as we continue to expand into new and existing markets. This
54
growth in headcount resulted in an increase in payroll related costs of $15.3 million, which includes an increase in variable compensation resulting from revenue growth. Stock-based compensation expense also increased by $2.2 million attributed to grants to existing and new employees, including certain performance-based award grants, and due to an increase in stock price. Travel and related expenses increased by $5.1 million associated with sales efforts in the normal course of business as well as the training of new and existing members of our sales force. We also experienced an increase in advertising, public relations and collateral production expenses of $12.7 million due to our direct to consumer advertising campaign, which was launched in the second quarter of 2015 and such program was not in place in 2014. We also incurred expenses related to cooperative marketing arrangements and customer incentive programs, which allow our customers to receive partial reimbursement for qualifying advertising expenditures which promote our product and brand. The expense incurred with respect to these programs is dependent on both the number of qualifying customers as well as the amount of advertising expenditures by our customers that is determined to be reimbursable. The expense for these cooperative marketing arrangements included in our customer incentive programs increased by $3.0 million due to an increase in our customer base and change in the program in the current year that increased the number of eligible participants compared to the prior year. Additionally, allocable costs related to rent and administrative functions increased by $2.2 million resulting from increased headcount and operating costs related to the growth in our business.
Sales and marketing expenses increased for the year ended December 31, 2014, as compared to the year ended December 31, 2013, primarily due to the significant increase in headcount attributable to our sales force, which increased by 52%, as we continue to expand into new and existing markets. This growth in headcount resulted in an increase in payroll related costs of $8.3 million, which includes an increase in performance-based compensation resulting from revenue growth. Stock-based compensation expense also increased by $1.1 million attributed to grants to existing and new employees and due to an increase in stock price. Travel and related expenses increased by $3.5 million associated with sales efforts in the normal course of business as well as the training of new and existing members of our sales force. We also experienced an increase in advertising, public relations and collateral production expenses of $6.3 million associated with costs incurred in conjunction with our sales and marketing initiatives. These costs were primarily related to brand and collateral development associated with our re-branding initiative, which was launched in the second quarter of 2014. We also incur expenses related to cooperative marketing arrangements and customer incentive programs, which allows our customers to receive partial reimbursement for qualifying advertising expenditures which promote our product and brand. The expense incurred with respect to these programs is dependent on both the number of qualifying customers as well as the amount of advertising expenditures by our customers that is determined to be reimbursable. The expense for these cooperative marketing arrangements included in our customer incentive programs decreased by $1.8 million due to a change in the program during the first quarter of 2014 whereby the amount of available reimbursement was reduced and fewer customers were able to qualify for partial reimbursement on qualifying advertising expenditures.
General and administrative. General and administrative expenses increased for the year ended December 31, 2015, as compared to the year ended December 31, 2014, primarily due to an increase in payroll and personnel related costs of $2.8 million resulting from higher headcount in certain functions to support growth in our business, including our international market. Stock-based compensation expense also increased by $1.4 million attributed to grants to existing and new employees and due to an increase in stock price. We experienced a $2.6 million increase in legal expenses mainly due to an increase in IP enforcement, both domestically and overseas, and settlements relating to patient claims. Additionally, facilities increased by $2.0 million resulting from increased headcount and operating costs related to the growth in our business.
General and administrative expenses increased for the year ended December 31, 2014, as compared to the year ended December 31, 2013, primarily due to an increase in payroll related costs of $1.6 million resulting from higher headcount in certain functions to support growth in our business. Stock-based compensation expense also increased by $1.1 million attributed to grants to existing and new employees and due to an increase in stock price. Professional service fees increased by $0.7 million associated with the growth of our business as well as our expansion into international markets. Additionally, we experienced a $0.7 million increase in legal expenses mainly due to an increase in IP enforcement, both domestically and overseas.
Interest Income (Expense) and Other Income (Expense), Net (in thousands, except for percentages):
Year Ended | ||||||||||||||
December 31, | ||||||||||||||
2015 | 2014 | $ Change | % Change | |||||||||||
Interest income, net | $ | 58 | $ | 63 | $ | (5 | ) | (8 | )% | |||||
% of total revenue | — | % | — | % | ||||||||||
Other expense, net | $ | (420 | ) | $ | (425 | ) | $ | 5 | (1 | )% | ||||
% of total revenue | — | % | — | % | ||||||||||
55
Year Ended | ||||||||||||||
December 31, | ||||||||||||||
2014 | 2013 | $ Change | % Change | |||||||||||
Interest income, net | $ | 63 | $ | 80 | $ | (17 | ) | (21 | )% | |||||
% of total revenue | — | % | — | % | ||||||||||
Other income (expense), net | $ | (425 | ) | $ | 103 | $ | (528 | ) | (513 | )% | ||||
% of total revenue | — | % | — | % | ||||||||||
Interest income, net. During the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, interest income was earned on our available-for-sale securities. The amount of income earned varies based on the type of investments held, market conditions and other factors. The decrease in interest income is attributable to a decrease in our investments.
Other income (expense), net. Other income (expense), net for the year ended December 31, 2015 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2014 showed a slight fluctuation, the result of steady foreign exchange rates.
The change in other income (expense), net for the year ended December 31, 2014, as compared to the year ended December 31, 2013, was the result of an unfavorable change in foreign exchange rates, primarily the British Pound.
Income Taxes
Net income was favorably impacted by a tax benefit of approximately $38.5 million, of which $40.4 million is a deferred tax benefit related primarily to the release of the Company's deferred tax asset valuation allowance against net operating loss carryforwards and other deferred tax assets, offset by current period tax expense of $1.9 million. In our conclusion to release the valuation allowance against our U.S. Federal and State deferred tax assets we determined that the positive evidence outweighed the negative evidence and that it was more likely than not that all of our federal and state deferred tax assets, except for deferred tax assets related to certain research and development credits, will be realized. We continue to apply a valuation allowance against our California research and development credit deferred tax assets based on the fact that we have concluded that such amounts are unlikely to be realized in future periods. Our provision for income taxes for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013 of $0.2 million and $0.1 million, respectively, was for certain state and corporate taxes in foreign jurisdictions and certain income tax uncertainties, including interest and penalties.
During fiscal 2015, we have implemented an international tax structure that includes a research and development cost-sharing arrangement, certain licenses and other contractual arrangements between us and our wholly-owned foreign subsidiaries. As a result of these changes, we anticipate that our consolidated pre-tax income will be subject to foreign tax at relatively lower tax rates when compared to the United States federal statutory tax rate and, as a consequence, our effective income tax rate is expected to be lower than the United States federal statutory rate. Our future effective income tax rates could be adversely affected if tax authorities challenge our international tax structure or if the relative mix of United States and international income changes for any reason.
56
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Since our inception, we have financed our operations to date primarily through private placements of convertible preferred stock, promissory notes, borrowings under a loan agreement, product sales and the proceeds from our initial public offering, or IPO.
The following table summarizes our working capital, cash and cash equivalents, short-term and long-term investments as of December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, as follows (in thousands):
December 31, | |||||||||||
2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 35,710 | $ | 28,649 | $ | 25,798 | |||||
Short-term investments | 12,867 | 16,286 | 18,840 | ||||||||
Long-term investments | 3,490 | 4,805 | 11,442 | ||||||||
Total | $ | 52,067 | $ | 49,740 | $ | 56,080 | |||||
Working capital | $ | 68,402 | $ | 56,540 | $ | 42,430 | |||||
Summary Statement of Cash Flows
The following table summarizes our cash flows for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013 (in thousands):
Year Ended | |||||||||||
December 31, | |||||||||||
2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||
Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities | $ | 7,743 | $ | (856 | ) | $ | (4,081 | ) | |||
Net cash provided by investing activities | 445 | 6,357 | 4,384 | ||||||||
Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities | (418 | ) | (2,188 | ) | 2,562 | ||||||
Effect of exchange rate on cash and cash equivalents | (709 | ) | (462 | ) | 57 | ||||||
Net increase in cash and cash equivalents | $ | 7,061 | $ | 2,851 | $ | 2,922 | |||||
57
Cash Flows for the Years Ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013
Operating activities.
Net cash provided by operating activities was $7.7 million during the year ended December 31, 2015, and consisted of a net income of $41.8 million and non-cash items of $23.5 million, offset by a net change in operating assets and liabilities of $10.5 million. Non-cash items for the year ended December 31, 2015, consisted primarily of a stock-based compensation expense of $13.2 million, depreciation and amortization expense of $2.4 million, offset by the deferred income tax benefit of $40.4 million resulting from the release of the deferred tax asset valuation allowance. The significant items in the change in operating assets and liabilities include cash used resulting from increases in inventory of $12.9 million, an increase in accounts receivable of $12.9 million, and an increase in prepaid expenses and other assets of $5.3 million. Theses uses of cash were offset in part by an increase in accounts payable, accrued and other non-current liabilities of $18.4 million and an increase of $2.3 million in deferred revenue. We experienced an increase in inventory as we continued to build inventory to support expected customer demand, as well as increases in purchases of materials to support demand for our recently launched CoolMini applicator. The increase in accounts receivable is a function of the increase in sales as well as timing of payment receipts from customers. The increase in prepaid expenses and other assets is primarily due to the release of the valuation allowance related to our deferred tax assets, as well as new contracts, timing of payments and receivables for credit card payments in transit. The increase in accounts payable, accrued and other non-current liabilities was driven by the timing of invoice receipt and payments to vendors, higher accrued royalty and sales tax payable as result of an increase in sales, an increase in marketing accruals in conjunction with our sales and marketing initiatives such as our recently launched direct-to-consumer advertising program, an increase in accrued payroll and employee related expenses as a result of an increase in headcount and variable compensation, an increase in taxes payable due to an increase in net income, and due to the increase in accrued legal expenses as we continue to enforce our intellectual property domestically and overseas. The increase in deferred revenue is primarily driven by our increase in sales volume, an increase in extended warranty sales and the deferral of revenue related to discounts on extended warranties offered in conjunction with customer incentive plans, as well as an increase in revenue deferral for customer training that has not yet occurred.
Net cash used in operating activities was $0.9 million during the year ended December 31, 2014, and consisted of a net income of $1.5 million and non-cash items of $12.6 million, offset by a net change in operating assets and liabilities of $15.0 million. Non-cash items for the year ended December 31, 2014, consisted primarily of a stock-based compensation expense of $9.4 million, depreciation and amortization expense of $1.8 million and an increase of $0.9 million in expense related to excess and obsolete inventory. The significant items in the change in operating assets and liabilities include cash used resulting from increases in inventory of $6.9 million, an increase in accounts receivable of $11.2 million, and an increase in prepaid expenses and other assets of $2.4 million. Theses uses of cash were offset in part by an increase in accounts payable, accrued and other non-current liabilities of $2.6 million and an increase of $2.9 million in deferred revenue. We experienced an increase in inventory as we continued to build inventory to support expected customer demand, increases in purchases of materials to support demand for our CoolSmooth applicator launched in 2014 as well as compliance requirements for products being sold in the European Union. The increase in accounts receivable is a function of the increase in sales as well as timing of payment receipts from customers. The increase in prepaid expenses and other assets is primarily due to timing of payments, as well as receivables for credit card payments in transit. The increase in accounts payable, accrued and other non-current liabilities was driven by the timing of invoice receipt and payments to vendors, higher accrued royalty as result of an increase in sales, an increase in advance payments primarily from international customers due to timing of payment receipt and related shipment and due to an increase in accrued payroll and employee related expenses as a result of an increase in headcount. The increase in deferred revenue is primarily a result of an increase in extended warranty sales and the deferral of revenue related to discounts on extended warranties offered in conjunction with customer incentive plans, as well as an increase in revenue deferral for customer attendance of the CoolSculpting University that has not yet occurred.
Net cash used in operating activities was $4.1 million during the year ended December 31, 2013, and consisted of a net loss of $19.3 million, offset by a net change in operating assets and liabilities of $6.2 million and non-cash items of $9.0 million. Non-cash items for the year ended December 31, 2013, consisted primarily of a stock-based compensation expense of $6.7 million and depreciation and amortization expense of $1.7 million. The significant items in the change in operating assets and liabilities include cash generated from decreases in inventory of $2.2 million and an increase in accounts payable, accrued and other non-current liabilities of $7.5 million, offset in part by an increase in accounts receivable of $3.1 million. The decrease in inventory was as result of our continued focus on the management of inventory levels and increased sales. The increase in accounts payable, accrued and other non-current liabilities was driven by the timing of invoice receipt and payments to vendors as well as higher accrued payroll related to performance-based compensation, while the increase in accounts receivable is driven by the increase in sales as well as timing of payment receipts from customers.
Investing activities.
58
Net cash provided by investing activities was $0.4 million, $6.4 million and $4.4 million for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively. In 2015, we received proceeds from the sale and maturity, net of purchases, of $4.6 million of short-term and long-term investments. Purchases of property and equipment amounted to $4.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2015, primarily as result of purchases of leasehold improvements, furniture and fixtures and certain software to support the growth and expansion of our business and related facilities. In 2014, we received proceeds from the sale and maturity, net of purchases, of $8.9 million of short-term and long-term investments, offset in part by $2.3 million related to purchases of property and equipment. In 2013, we received proceeds from the sale and maturity, net of purchases, of $5.1 million of short-term and long-term investments, offset in part by $0.8 million related to purchases of property and equipment.
Financing activities.
Net cash used in financing activities during the year ended December 31, 2015 of $0.4 million consisted of $8.3 million of tax payments related to shares withheld for vested restricted stock units, offset in part by proceeds received from the issuance of common stock upon the exercise of stock options of $6.6 million and by the tax effect of employee stock plans of $1.4 million. Net cash used in financing activities during the year ended December 31, 2014 of $2.2 million consisted of $6.6 million of tax payments related to shares withheld for vested restricted stock units, offset in part by proceeds received from the issuance of common stock upon the exercise of stock options of $4.3 million. Net cash provided by financing activities during the year ended December 31, 2013 of $2.6 million consisted of $3.4 million proceeds received from the issuance of common stock upon the exercise of stock options and the employee stock purchase plan, offset in part by $0.9 million of tax payments related to shares withheld for vested restricted stock units.
Our cash, cash equivalents and investments increased by $2.3 million from $49.7 million as of December 31, 2014, to $52.1 million as of December 31, 2015. We expect to continue to invest in our research and development efforts, as well as in our sales and marketing organization, to support our current and expected growth and initiatives. Based on our current plans and market conditions, we believe that our existing cash, cash equivalents and investments will be sufficient to satisfy our anticipated cash requirements for at least the next twelve months. However, we cannot be certain that our planned levels of revenue, costs and expenses will be achieved. If our operating results fail to meet our expectations or if we fail to manage our inventory, accounts receivable or other assets, we could be required to seek additional funding through public or private financings or other arrangements. In such event, adequate funds may not be available when needed or may not be available on favorable or commercially acceptable terms, which could have a negative effect on our business and results of operations.
Contractual Obligations and Commitments
We have certain fixed contractual obligations and commitments that include capital lease obligations, operating lease obligations and purchase commitments. Changes in our business needs, fluctuating interest rates, and other factors may result in actual payments differing from the estimates. We have presented below a summary of the most significant assumptions used in our determination of amounts presented in the table to assist in the review of this information within the context of our consolidated financial position and results of operations. The following table summarizes our fixed contractual obligations and commitments, as of December 31, 2015 (in thousands):
Payments due in Fiscal Year | |||||||||||||||||||
Total | 2016 | 2017-2018 | 2019-2020 | After 2020 | |||||||||||||||
Contractual Obligations: | |||||||||||||||||||
Capital lease obligations | $ | 273 | $ | 132 | $ | 141 | $ | — | $ | — | |||||||||
Operating lease obligations | 7,311 | 2,344 | 3,970 | 997 | — | ||||||||||||||
Non-cancellable purchase commitments | 5,933 | 5,933 | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 13,517 | $ | 8,409 | $ | 4,111 | $ | 997 | $ | — | |||||||||
This compares to our fixed contractual obligations and commitments, as of December 31, 2014, of $11.7 million.
Massachusetts General Hospital Royalty Payments
59
In May 2005, we entered into an agreement with Massachusetts General Hospital, or MGH, to obtain an exclusive license to develop and commercialize the patent and the core technology that underlies our CoolSculpting system. We are obligated to pay a 7% royalty on net sales, as defined in the agreement, of CoolSculpting systems, applicators and procedure packs.
In September 2015, we entered into a new agreement with MGH to obtain an exclusive license to develop and commercialize certain patents and technology for the treatment of acne and certain related skin conditions. We are obligated to pay a 3% royalty on net sales, as defined in such agreement, of products incorporating such technology.
Lease Commitments
We lease facilities under non-cancellable operating leases with various expiration dates through September 2020. Rent expense for non-cancellable operating leases with scheduled rent increases is recognized on a straight-line basis over the lease term. Rent expense for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, was $2.5 million, $1.5 million and $1.4 million, respectively.
Future minimum lease payments under our non-cancellable operating leases as of December 31, 2015, are as follows (in thousands):
Year Ending December 31, | Amount | ||
2016 | $ | 2,344 | |
2017 | 2,058 | ||
2018 | 1,912 | ||
2019 | 763 | ||
2020 | 234 | ||
Total future minimum lease payments | $ | 7,311 | |
Capital Lease Obligations
We have entered into certain capital lease obligations to purchase equipment for operations which includes a bargain purchase option. The underlying assets and related depreciation are included in the appropriate property and equipment category and related accumulated depreciation account.
Future minimum payments required under capital leases as of December 31, 2015, are as follows (in thousands):
Year Ending December 31, | Amount | ||
2016 | $ | 132 | |
2017 | 141 | ||
Total future payments | $ | 273 | |
Less: Amount representing interest | $ | 11 | |
Present value of future minimum payments | 262 | ||
Less: Current portion | 124 | ||
Long term portion | $ | 138 | |
Unrecognized Tax Benefits
The contractual obligations table above excludes our gross liability for unrecognized tax benefits which totaled $0.3 million, including estimated interest and penalties, as of December 31, 2015, and is classified in long-term income taxes payable. We are unable to make a reasonably reliable estimate of the timing of payments in individual years due to uncertainties in the timing of tax audits, if any, or their outcomes. Accordingly, we have excluded this obligation from the schedule summarizing our significant obligations to make future payments under contractual obligations as of December 31, 2015, presented above.
60
Product Warranties
The estimated product warranty accrual was as follows (in thousands):
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||
2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Balance at the beginning of the period | $ | 569 | $ | 676 | |||
Settlement of pre-existing warranties | (658 | ) | (772 | ) | |||
Provision | 616 | 665 | |||||
Balance at the end of the period | $ | 527 | $ | 569 | |||
Related Party Transactions
Brazilian Distribution Agreement
We entered into a distribution agreement with ADVANCE Medical, Inc. and its wholly owned subsidiaries, Immunotech and BIOGEN, or ADVANCE, dated March 18, 2011, as our exclusive distributor of CoolSculpting in Brazil and Mexico, as amended on August 29, 2011, February 27, 2012, and September 4, 2012. The distribution agreement was further amended on August 15, 2014, whereby ADVANCE is no longer a distributor in Mexico effective November 13, 2014. As the exclusive distributor in Brazil, ADVANCE is required to purchase a minimum quantity of our products each calendar quarter throughout the term of the distribution agreement which expires on December 31, 2018. Venrock, a principal stockholder of ZELTIQ, owns an equity interest in ADVANCE Medical, Ltd., the parent company of ADVANCE. Dr. Bryan E. Roberts, who is a member of our Board of Directors, is also a partner of Venrock Associates. ADVANCE purchases product with payment terms up to 180 days, and to date no amounts have been determined to be unrecoverable. The revenue recognized by us under this distribution agreement for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, was $3.6 million, $1.9 million and $1.6 million, respectively. The accounts receivable balance under this distribution agreement as of December 31, 2015 and 2014, was $1.7 million and $0.2 million, respectively.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
On May 28, 2014, the Financial Accounting Standards Board, or FASB, issued Accounting Standards Update No. 2014-09, Revenue from Contracts with Customers. On August 12, 2015, the FASB issued ASU 2015-14, Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606): Deferral of the Effective Date, which delays the effective date of ASU 2014-09 by one year. The objective of this update is to provide a single, comprehensive revenue recognition model for all contracts with customers to improve comparability within industries, across industries, and across capital markets. This standard update contains principles that we will apply to determine the measurement of revenue and timing of when it is recognized. This guidance allows for two methods of adoption: (a) full retrospective adoption, meaning the guidance is applied to all periods presented, or (b) modified retrospective adoption, meaning the cumulative effect of applying this guidance is recognized as an adjustment to the fiscal 2018 opening Accumulated deficit balance. We expect to adopt this guidance effective January 1, 2018, and we are currently evaluating the two adoption methods as well as the impact this new guidance will have on our consolidated financial statements and related disclosures.
In August 2014, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update No. 2014-15, Disclosure of Uncertainties About an Entity's Ability to Continue as a Going Concern. This standard update provides guidance around management's responsibility to evaluate whether there is substantial doubt about an entity's ability to continue as a going concern and to provide related footnote disclosures. The new guidance is effective for all annual and interim periods ending after December 15, 2016 and is not expected to have an impact on our consolidated financial statements and related disclosures.
In April 2015, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update No. 2015-05 regarding Subtopic 350-40, “Intangibles - Goodwill and Other - Internal-Use Software.” This standard provides guidance to customers about whether a cloud computing arrangement includes a software license. If a cloud computing arrangement includes a software license, the customer should account for the software license element of the arrangement consistent with other software licenses. If a cloud computing arrangement does not include a software license, the customer should account for the arrangement as a service contract. The amendments are effective for annual and interim periods beginning after December 15, 2015. Early adoption is permitted. The amendments may be applied either prospectively to all arrangements entered into or materially modified after the effective date or retrospectively. We are currently evaluating the impact this new guidance will have on our consolidated financial statements and related disclosures.
61
In June 2015, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update No. 2015-10, Technical Corrections and Improvements. The standard covers a wide range of Topics in the Codification. The amendments in this standard represent changes to clarify the Codification, correct unintended application of guidance, or make minor improvements to the Codification that are not expected to have a significant effect on current accounting practice or create a significant administrative cost on most entities. The amendments are effective for fiscal years and interim periods within those fiscal years, beginning after December 15, 2015. We are currently evaluating the impact this new guidance will have on our consolidated financial statements and related disclosures.
In July 2015, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update No. 2015-11 to amend ASC Topic 330, Inventory ("ASC 330") to simplify the measurement of inventory. The amendments require that an entity measure inventory at the lower of cost and net realizable value instead of the lower of cost and market. This guidance is effective for public companies for years, and interim periods within those years, beginning on or after December 15, 2016, with earlier application permitted as of the beginning of an interim or annual reporting period. This guidance will be effective beginning in the first quarter of fiscal 2017. We are currently evaluating the impact this new guidance will have on our consolidated financial statements and related disclosures.
In November 2015, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update No. 2015-17, Income Taxes - Balance Sheet Reclassification of Deferred Taxes (Topic 740). This ASU requires that deferred tax liabilities and assets be classified as noncurrent in a classified statement of financial position. The current requirement that deferred tax liabilities and assets of a tax-paying component of an entity be offset and presented as a single amount is not affected by the amendments in this update. The amendments in this update are effective for financial statements issued for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2016, and interim periods within those annual periods. We early adopted this ASU on a prospective basis in the fourth quarter of 2015 and, as a result, we reclassified $40.5 million of current deferred tax assets to long-term assets on the accompanying consolidated balance sheet as of December 31, 2015.
In February 2016, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update No. 2016-02, Leases. This ASU requires lease assets and lease liabilities arising from leases, including operating leases, to be recognized on the balance sheet. ASU 2016-02 will become effective on January 1, 2019, and requires adoption using a modified retrospective approach. We are currently evaluating the impact of this guidance on our consolidated financial statements and related disclosures.
Off-balance Sheet Arrangements
As of December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, we did not have any relationships with unconsolidated entities or financial partnerships, such as entities often referred to as structured finance or special purpose entities, established for the purpose of facilitating off-balance sheet arrangements or other contractually narrow or limited purposes.
ITEM 7A. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK
We are exposed to market risks in the ordinary course of our business. These risks primarily include interest rate fluctuations and inflation. Our exposure to foreign currency exchange risk has been insignificant because the majority of our revenue and our expenses are incurred and paid in U.S. dollars.
Interest Rate Fluctuations
We hold cash equivalents as well as short-term and long-term fixed income securities. All maturities are less than two years. Our holdings include fixed and floating rate securities. Changes in interest rates could impact our anticipated interest income. The fair market value of our holdings may be adversely impacted due to a rise in interest rates; as a result, our future investment income may fall short of expectations due to changes in interest rates or we may suffer losses in principal if forced to sell securities which have declined in market value due to changes in interest rates. As of December 31, 2015 and 2014, we had approximately $16.4 million and $21.1 million invested in available-for-sale short-term and long-term investments, respectively. An immediate 10% change in interest rates would not have a material adverse impact on our future operating results and cash flows.
We do not have interest bearing liabilities as of December 31, 2015, and therefore, we are not subject to risks from immediate interest rate decreases.
Inflation
We do not believe that inflation has had a material effect on our business, financial condition, or results of operations. If our costs were to become subject to significant inflationary pressures, we may not be able to fully offset such higher costs through price increases. Our inability or failure to do so could harm our business, financial condition, and results of operations.
62
Foreign Exchange
We use the U.S. dollar as the reporting currency for our consolidated financial statements. Any significant revaluation of the British Pound and Euro may materially and adversely affect our results of operations upon translation of our United Kingdom and Ireland subsidiaries' financial statements into U.S. dollars. We generate revenue in British Pounds and Euro and a portion of our labor and manufacturing overhead expenses are in British Pounds. Additionally, a portion of our operating expenses are in British Pounds and Euro. Therefore, a fluctuation in British Pounds and Euro against the U.S. dollar could impact our gross profit, gross profit margin and operating expenses upon translation to U.S. dollars. A 10% appreciation or depreciation in British Pounds and Euro against the U.S. dollar would have an immaterial impact on our results of operations for fiscal 2015, 2014 and 2013.
We expect our international revenues to continue to be denominated largely in U.S. dollars. We also believe that our international operations will likely expand in the future if our business continues to grow. As a result, we anticipate that we may experience increased exposure to the risks of fluctuating currencies and may choose to engage in currency hedging activities to reduce these risks. However, we cannot be certain that any such hedging activities will be effective, or available to us at commercially reasonable rates. To date, we have not entered into any hedging transactions or used any other derivative financial instruments.
63
ITEM 8. | FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA |
INDEX TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
PAGE NUMBER | |
Supplementary Financial Data | |
64
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders of ZELTIQ Aesthetics, Inc.:
In our opinion, the accompanying consolidated balance sheets and the related consolidated statements of operations, comprehensive income (loss), stockholders' equity, and cash flows present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of ZELTIQ Aesthetics, Inc. and its subsidiaries at December 31, 2015 and 2014, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2015 in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. Also in our opinion, the Company did not maintain, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2015, based on criteria established in Internal Control-Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO) because a material weakness in internal control over financial reporting related to the Company’s risk assessment process existed as of that date. A material weakness is a deficiency, or a combination of deficiencies, in internal control over financial reporting, such that there is a reasonable possibility that a material misstatement of the annual or interim financial statements will not be prevented or detected on a timely basis. The material weakness referred to above is described in the Management's Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting appearing under Item 9A. We considered this material weakness in determining the nature, timing, and extent of audit tests applied in our audit of the 2015 consolidated financial statements, and our opinion regarding the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting does not affect our opinion on those consolidated financial statements. The Company's management is responsible for these financial statements, for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in management's report referred to above. Our responsibility is to express opinions on these financial statements and on the Company's internal control over financial reporting based on our integrated audits. We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audits to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement and whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audits of the financial statements included examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, and evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audits also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinions.
As discussed in Note 2 to the consolidated financial statements, the Company changed the manner in which it classifies deferred income taxes in 2015.
A company's internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company's internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (i) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (ii) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (iii) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company's assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
/s/ PRICEWATERHOUSECOOPERS LLP
San Jose, California
March 14, 2016
65
ZELTIQ Aesthetics, Inc.
Consolidated Balance Sheets
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
December 31, 2015 | December 31, 2014 | ||||||
ASSETS | |||||||
CURRENT ASSETS: | |||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 35,710 | $ | 28,649 | |||
Short-term investments | 12,867 | 16,286 | |||||
Accounts receivable, net | 33,359 | 21,472 | |||||
Inventory | 28,095 | 15,536 | |||||
Prepaid expenses and other current assets | 11,771 | 7,060 | |||||
Total current assets | 121,802 | 89,003 | |||||
Long-term investments | 3,490 | 4,805 | |||||
Restricted cash | 452 | 560 | |||||
Property and equipment, net | 6,969 | 3,724 | |||||
Intangible asset, net | 5,092 | 5,780 | |||||
Long-term deferred tax assets | 40,475 | — | |||||
Other assets | 547 | 33 | |||||
Total assets | $ | 178,827 | $ | 103,905 | |||
LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | |||||||
CURRENT LIABILITIES: | |||||||
Accounts payable | $ | 10,903 | $ | 5,824 | |||
Accrued and other current liabilities | 34,691 | 21,450 | |||||
Deferred revenue | 7,682 | 5,069 | |||||
Current portion of capital lease obligations | 124 | 120 | |||||
Total current liabilities | 53,400 | 32,463 | |||||
Long-term deferred revenue | 226 | 622 | |||||
Long-term capital lease obligations, less current portion | 138 | 262 | |||||
Other non-current liabilities | 761 | 39 | |||||
Total liabilities | $ | 54,525 | $ | 33,386 | |||
Commitments and contingencies (Note 7) | |||||||
STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY: | |||||||
Preferred stock, $0.01 par value: 50,000,000 shares authorized and no shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2015, and December 31, 2014 | — | — | |||||
Common stock, $0.001 par value: 500,000,000 shares authorized at December 31, 2015, and December 31, 2014; 39,217,630 and 38,123,998 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2015 and December 31, 2014, respectively | 43 | 42 | |||||
Additional paid-in capital | 215,621 | 202,701 | |||||
Accumulated other comprehensive loss | (1,636 | ) | (696 | ) | |||
Accumulated deficit | (89,726 | ) | (131,528 | ) | |||
Total stockholders’ equity | 124,302 | 70,519 | |||||
Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity | $ | 178,827 | $ | 103,905 | |||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
66
ZELTIQ Aesthetics, Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Operations
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
Year Ended | |||||||||||
December 31, | |||||||||||
2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||
Revenue | $ | 255,416 | $ | 174,478 | $ | 111,626 | |||||
Cost of revenue | 74,375 | 50,064 | 34,189 | ||||||||
Gross profit | 181,041 | 124,414 | 77,437 | ||||||||
Operating expenses: | |||||||||||
Research and development | 22,909 | 18,196 | 17,090 | ||||||||
Sales and marketing | 125,458 | 83,579 | 63,185 | ||||||||
General and administrative | 28,980 | 20,515 | 16,510 | ||||||||
Total operating expenses | 177,347 | 122,290 | 96,785 | ||||||||
Income (loss) from operations | 3,694 | 2,124 | (19,348 | ) | |||||||
Interest income, net | 58 | 63 | 80 | ||||||||
Other income (expense), net | (420 | ) | (425 | ) | 103 | ||||||
Income (loss) before income taxes | 3,332 | 1,762 | (19,165 | ) | |||||||
Provision for (benefit from) income taxes | (38,470 | ) | 231 | 140 | |||||||
Net income (loss) | $ | 41,802 | $ | 1,531 | $ | (19,305 | ) | ||||
Basic net income (loss) per share: | |||||||||||
Net income (loss) per share, basic | $ | 1.08 | $ | 0.04 | $ | (0.53 | ) | ||||
Weighted average shares of common stock outstanding used in computing net income (loss) per share, basic | 38,754,643 | 37,563,590 | 36,209,051 | ||||||||
Diluted net income (loss) per share: | |||||||||||
Net income (loss) per share, diluted | $ | 1.02 | $ | 0.04 | $ | (0.53 | ) | ||||
Weighted average shares of common stock outstanding used in computing net income (loss) per share, diluted | 40,795,646 | 40,996,972 | 36,209,051 | ||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
67
ZELTIQ Aesthetics, Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income (Loss)
(In thousands)
Year Ended | ||||||||||||
December 31, | ||||||||||||
2015 | 2014 | 2013 | ||||||||||
Net income (loss) | $ | 41,802 | $ | 1,531 | $ | (19,305 | ) | |||||
Other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax: | ||||||||||||
Foreign currency translation adjustments | (925 | ) | (767 | ) | 77 | |||||||
Changes in unrealized gains (losses) on available-for-sale securities | (15 | ) | (16 | ) | 2 | |||||||
Other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax | (940 | ) | (783 | ) | 79 | |||||||
Comprehensive income (loss) | $ | 40,862 | $ | 748 | $ | (19,226 | ) | |||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
68
ZELTIQ Aesthetics, Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Stockholders' Equity
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
Common Stock | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Shares | Amount | Additional Paid-in Capital | Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) | Accumulated Deficit | Total Stockholders' Equity | ||||||||||||||||||
Balances at December 31, 2012 | 35,852,105 | $ | 39 | $ | 186,287 | $ | 8 | $ | (113,754 | ) | $ | 72,580 | |||||||||||
Issuance of common stock upon exercise of stock options | 791,198 | 2 | 2,645 | — | — | 2,647 | |||||||||||||||||
Issuance of common stock in connection with ESPP | 188,467 | — | 791 | — | — | 791 | |||||||||||||||||
Proceeds for repayment of notes receivable from a stockholder | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
Issuance of common stock upon vesting of RSUs | 292,265 | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
Tax payments related to shares withheld for vested restricted stock units | (85,661 | ) | — | (876 | ) | — | — | (876 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Stock-based compensation | — | — | 6,660 | — | — | 6,660 | |||||||||||||||||
Change in unrealized gain (loss) on marketable securities, net of tax | — | — | — | 2 | — | 2 | |||||||||||||||||
Currency translation adjustments, net of tax | — | — | — | 77 | — | 77 | |||||||||||||||||
Net loss | — | — | — | — | (19,305 | ) | (19,305 | ) | |||||||||||||||
Balances at December 31, 2013 | 37,038,374 | $ | 41 | $ | 195,507 | $ | 87 | $ | (133,059 | ) | $ | 62,576 | |||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
69
ZELTIQ Aesthetics, Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Stockholders' Equity
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
Common Stock | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Shares | Amount | Additional Paid-in Capital | Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) | Accumulated Deficit | Total Stockholders' Equity | ||||||||||||||||||
Balances at December 31, 2013 | 37,038,374 | $ | 41 | $ | 195,507 | $ | 87 | $ | (133,059 | ) | $ | 62,576 | |||||||||||
Issuance of common stock upon exercise of stock options | 569,283 | 1 | 2,786 | — | — | 2,787 | |||||||||||||||||
Issuance of common stock in connection with ESPP | 103,089 | — | 1,532 | — | — | 1,532 | |||||||||||||||||
Issuance of common stock upon vesting of RSUs | 724,400 | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
Tax payments related to shares withheld for vested restricted stock units | (311,148 | ) | — | (6,594 | ) | — | — | (6,594 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Stock-based compensation | — | — | 9,383 | — | — | 9,383 | |||||||||||||||||
Tax benefit from employee stock plans | — | — | 87 | — | — | 87 | |||||||||||||||||
Change in unrealized gain on marketable securities, net of tax | — | — | — | (16 | ) | — | (16 | ) | |||||||||||||||
Currency translation adjustments, net of tax | — | — | — | (767 | ) | — | (767 | ) | |||||||||||||||
Net income | — | — | — | — | 1,531 | 1,531 | |||||||||||||||||
Balances at December 31, 2014 | 38,123,998 | $ | 42 | $ | 202,701 | $ | (696 | ) | $ | (131,528 | ) | $ | 70,519 | ||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
70
ZELTIQ Aesthetics, Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Stockholders' Equity
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
Common Stock | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Shares | Amount | Additional Paid-in Capital | Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) | Accumulated Deficit | Total Stockholders' Equity | ||||||||||||||||||
Balances at December 31, 2014 | 38,123,998 | $ | 42 | $ | 202,701 | $ | (696 | ) | $ | (131,528 | ) | $ | 70,519 | ||||||||||
Issuance of common stock upon exercise of stock options | 608,931 | 1 | 4,135 | — | — | 4,136 | |||||||||||||||||
Issuance of common stock in connection with ESPP | 108,552 | — | 2,492 | — | — | 2,492 | |||||||||||||||||
Issuance of common stock upon vesting of RSUs | 635,256 | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
Tax payments related to shares withheld for vested restricted stock units | (259,107 | ) | — | (8,283 | ) | — | — | (8,283 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Stock-based compensation | — | — | 13,219 | — | — | 13,219 | |||||||||||||||||
Tax benefit from employee stock plans | — | — | 1,357 | — | — | 1,357 | |||||||||||||||||
Change in unrealized gain on marketable securities, net of tax | — | — | — | (15 | ) | — | (15 | ) | |||||||||||||||
Currency translation adjustments, net of tax | — | — | — | (925 | ) | — | (925 | ) | |||||||||||||||
Net income | — | — | — | — | 41,802 | 41,802 | |||||||||||||||||
Balances at December 31, 2015 | 39,217,630 | $ | 43 | $ | 215,621 | $ | (1,636 | ) | $ | (89,726 | ) | $ | 124,302 | ||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
71
ZELTIQ Aesthetics, Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
(In thousands)
Year Ended | |||||||||||
December 31, | |||||||||||
2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||
CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES: | |||||||||||
Net income (loss) | $ | 41,802 | $ | 1,531 | $ | (19,305 | ) | ||||
Adjustments to reconcile net income (loss) to net cash provided by (used in) operating activities: | |||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 2,423 | 1,824 | 1,729 | ||||||||
Stock-based compensation | 13,219 | 9,383 | 6,660 | ||||||||
Deferred income tax (benefit) expense | (40,405 | ) | (19 | ) | 19 | ||||||
Amortization of investment premium, net | 89 | 221 | 343 | ||||||||
Provision for (recovery of) doubtful accounts receivable | 859 | 324 | (12 | ) | |||||||
Provision for excess and obsolete inventory | 270 | 853 | 262 | ||||||||
Loss on disposal and write-off of property and equipment | 6 | 46 | 2 | ||||||||
Changes in operating assets and liabilities: | |||||||||||
Accounts receivable | (12,920 | ) | (11,219 | ) | (3,064 | ) | |||||
Inventory | (12,941 | ) | (6,898 | ) | 2,225 | ||||||
Prepaid expenses and other assets | (5,338 | ) | (2,419 | ) | (693 | ) | |||||
Deferred revenue | 2,254 | 2,908 | 267 | ||||||||
Accounts payable, accrued and other liabilities | 18,425 | 2,609 | 7,486 | ||||||||
Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities | 7,743 | (856 | ) | (4,081 | ) | ||||||
CASH FLOWS FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES: | |||||||||||
Purchase of investments | (16,024 | ) | (13,444 | ) | (31,591 | ) | |||||
Proceeds from sale of investments | — | 1,000 | 11,143 | ||||||||
Proceeds from maturity of investments | 20,654 | 21,393 | 25,528 | ||||||||
Purchase of property and equipment | (4,279 | ) | (2,340 | ) | (834 | ) | |||||
Change in restricted cash | 94 | (252 | ) | 138 | |||||||
Net cash provided by investing activities | 445 | 6,357 | 4,384 | ||||||||
CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES: | |||||||||||
Principal payments on capital leases | (120 | ) | — | — | |||||||
Proceeds from issuance of common stock upon exercise of stock options | 6,628 | 4,319 | 3,438 | ||||||||
Tax payments related to shares withheld for vested restricted stock units | (8,283 | ) | (6,594 | ) | (876 | ) | |||||
Tax effect of employee stock plans | 1,357 | 87 | — | ||||||||
Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities | (418 | ) | (2,188 | ) | 2,562 | ||||||
Effect of exchange rate on cash and cash equivalents | (709 | ) | (462 | ) | 57 | ||||||
NET INCREASE IN CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS | 7,061 | 2,851 | 2,922 | ||||||||
CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS—Beginning of period | 28,649 | 25,798 | 22,876 | ||||||||
CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS—End of period | $ | 35,710 | $ | 28,649 | $ | 25,798 | |||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
72
ZELTIQ Aesthetics, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
1. The Company and Basis of Presentation
ZELTIQ Aesthetics, Inc. (the “Company”) was incorporated in the state of Delaware on March 22, 2005. The Company was founded to develop and commercialize a non-invasive product for the selective reduction of fat. Its first commercial product, the CoolSculpting system, is designed to selectively reduce stubborn fat bulges. CoolSculpting is based on the scientific principle that fat cells are more sensitive to cold than the overlying skin and surrounding tissues. CoolSculpting utilizes precisely controlled cooling to reduce the temperature of fat cells in the treated area, which leads to fat cell elimination through a natural biological process known as apoptosis, without causing scar tissue or damage to the skin, nerves, or surrounding tissues. The Company generates revenue from sales of its CoolSculpting system and from sales of consumables to its customers.
In August 2011, the Company incorporated ZELTIQ Limited as a wholly-owned subsidiary in the United Kingdom to serve as its sales office for direct sales in Europe. In December 2014, the Company incorporated ZELTIQ Ireland Limited and ZELTIQ Ireland International Limited as wholly-owned subsidiaries in Ireland for additional office support in Europe. In December 2015, the Company also incorporated ZELTIQ Ireland International Holdings Unlimited Company.
Out of period adjustments
During the three months ended December 31, 2015, the Company recorded an out-of-period correcting adjustment of $0.3 million to increase cost of revenue to write-off certain inventory related to service parts. Of this adjustment, $0.2 million related to the three months ended September 30, 2015 and the remainder primarily in the other quarters of 2015. The Company does not believe that such amounts are material to any prior period consolidated financial statements, and the impact of correcting these errors in the three months ended December 31, 2015 is not material to the current consolidated financial statements.
During the three months ended June 30, 2015, the Company recorded an out-of-period correcting adjustment of $0.2 million to increase cost of revenue to write-off of certain inventory held by vendors. Of this adjustment, $0.1 million, $23,000 and $42,000 related to the fiscal years ended December 31, 2012, 2013 and 2014, respectively. The Company does not believe that such amounts are material to any prior period consolidated financial statements, and the impact of correcting these errors in the year ended December 31, 2015 is not material to the current consolidated financial statements.
During the three months ended December 31, 2014, the Company recorded an out-of-period correcting adjustment related to stock-based compensation that resulted in $0.7 million of revenue reduction. The adjustment to revenue resulted from an error in the application of generally accepted accounting principles related to payments to customers for services starting in the second quarter of 2013 through the third quarter of 2014. Of the total amount of this adjustment, $0.4 million related to the fiscal year ending December 31, 2013. The error caused the overstatement of revenue and sales and marketing expense in prior periods due to the misclassification of this stock-based compensation. This adjustment did not have any impact to the Company's consolidated net income (loss) as reported in the consolidated statements of operations in any current or prior interim or annual period. The Company does not believe that such amounts are material to current and previously reported consolidated financial statements.
Basis of Presentation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States of America, or GAAP. Certain amounts in the prior year's consolidated financial statements have been reclassified to conform to the current period's presentation. These reclassifications had no impact on previously reported consolidated statements of cash flows or statements of operations.
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Principles of Consolidation
The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company and its wholly-owned subsidiaries. All intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated.
73
Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make certain estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenue and expenses during the reported periods. The primary estimates underlying the Company's financial statements include the value of revenue elements, accruals for discretionary customer programs and payments, product warranties, inventory valuation, allowance for doubtful accounts receivable, assumptions regarding variables used in calculating the fair value of the Company's equity awards, fair value of investments, useful lives of intangibles, income taxes and contingent liabilities. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Significant Risks and Uncertainties
The Company's future results of operations involve a number of risks and uncertainties. Factors that could affect the Company's future operating results and cause actual results to vary materially from expectations include, but are not limited to, rapid technological change, continued acceptance of the Company's products, competition from substitute products and larger companies, ability to protect proprietary technology from copy-cat or counterfeit versions the Company's products, strategic relationships and dependence on key individuals. If the Company fails to adhere to ongoing Food and Drug Administration, or FDA, Quality System Regulation, the FDA may withdraw its market clearance or take other action. The Company relies on sole-source suppliers to manufacture some of the components used in its product. The Company's manufacturers and suppliers may encounter supply interruptions or problems during manufacturing due to a variety of reasons, including failure to comply with applicable regulations, including the FDA's Quality System Regulation, equipment malfunction and environmental factors, any of which could delay or impede the Company's ability to meet demand.
Concentration of Credit Risk
Financial instruments that potentially subject the Company to concentrations of credit risk consist primarily of cash equivalents, marketable securities and trade receivables. The Company's cash equivalents and marketable securities are held in safekeeping by large, credit worthy financial institutions. The Company invests its excess cash primarily in U.S. banks, government and agency bonds, money market funds and corporate obligations. The Company has established guidelines relative to credit ratings, diversification and maturities that seek to maintain safety and liquidity. Deposits in these banks may exceed the amounts of insurance provided on such deposits. To date, the Company has not experienced any losses on its deposits of cash and cash equivalents.
The Company controls credit risk through credit approvals, credit limits, and monitoring procedures. The Company performs periodic credit evaluations of its customers and generally does not require collateral. Accounts receivable are recorded net of an allowance for doubtful accounts. The allowance for doubtful accounts is based on management's assessment of the collectability of specific customer accounts and the aging of the related invoices, and represents the Company's best estimate of probable credit losses in its existing trade accounts receivable. At December 31, 2015 and 2014, the Company's allowance for doubtful accounts was $1.2 million and $0.3 million, respectively.
The allowance for doubtful accounts consisted of the following activity for fiscal years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013 (in thousands):
Description | Balance at Beginning of Year | Charge to expense | Write-offs, net of recoveries | Balance at End of Year | ||||||||||||
Year ended December 31, 2013 | $ | 330 | $ | 59 | $ | (389 | ) | $ | — | |||||||
Year ended December 31, 2014 | — | 469 | (145 | ) | 324 | |||||||||||
Year ended December 31, 2015 | $ | 324 | $ | 1,032 | $ | (173 | ) | $ | 1,183 | |||||||
As of December 31, 2015 and 2014, Ideal Image, which is a large aesthetic chain, along with its affiliated franchises, accounted for 10% and 24% of accounts receivable, respectively. Furthermore, Ideal Image and its affiliated franchises accounted for 10% of total revenue during the year ended December 31, 2015. No individual customer accounted for greater than 10% of total revenue during the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013.
74
Cash and Cash Equivalents
The Company considers all highly liquid investments with a maturity of three months or less when purchased to be cash equivalents.
Investments
The Company invests its excess cash balances primarily in certificates of deposit, commercial paper, corporate bonds, and U.S. Government agency securities. Investments with original maturities greater than 90 days that mature less than one year from the consolidated balance sheet date are classified as short-term investments. The Company classifies all of its investments as available-for-sale and records such assets at estimated fair value in the consolidated balance sheets, with unrealized gains and losses, if any, reported as a component of accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) in stockholders' equity. Realized gains and losses from maturities of all such securities are reported in earnings and computed using the specific identification cost method. Realized gains or losses and charges for other-than-temporary declines in value, if any, on available-for-sale securities are reported in other income (expense), net as incurred. The Company periodically evaluates these investments for other-than-temporary impairment.
Inventory
Inventory is stated at the lower of cost (which approximates actual cost on a first-in, first-out basis) or market. Inventory that is obsolete or in excess of forecasted usage is written down to its estimated net realizable value based on assumptions about future demand and market conditions. Inventory write-downs are charged to cost of revenue and establish a new cost basis for the inventory.
Property and Equipment
Property and equipment are stated at cost. Depreciation is computed using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the assets. Maintenance and repairs are charged to expense as incurred. Assets not yet placed in use are not depreciated.
The useful lives of the property and equipment are as follows:
Lab equipment, tooling, and molds | 5 years |
Computer equipment | 3 years |
Computer software | 3 years |
Furniture and fixtures | 5 years |
Vehicles | 5 years |
Leasehold improvements | Shorter of lease term or estimated useful life |
Capitalized Software
The Company capitalizes costs associated with customized internal-use software systems that have reached the application development stage and meet recoverability tests. Such capitalized costs mainly include external direct costs utilized in developing or obtaining the applications. Capitalization of such costs begins when the preliminary project stage is complete and ceases at the point in which the project is substantially complete and is ready for its intended purpose. The capitalized costs associated with internal-use software are depreciated on a straight-line basis over each asset's estimated useful life, which is generally three years.
Restricted Cash
At December 31, 2015 and 2014, cash of $0.5 million and $0.6 million, respectively, was restricted from withdrawal and held by banks in the form of certificates of deposit. At December 31, 2015 and 2014, the certificates of deposit were held as collateral for the facility lease agreement in Pleasanton, California, and for its United Kingdom banking facilities and credit card programs.
Intangible Asset
The intangible asset consists of an exclusive license agreement for commercializing patents and other technology. All milestone payments subsequent to the date of the FDA approval are capitalized as purchased technology when paid, and are subsequently amortized into cost of revenue using the straight-line method over the estimated remaining useful life of the technology, not to exceed the term of the agreement or the life of the patent.
75
Impairment of Long-lived Assets
The Company reviews property and equipment and the intangible asset for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable. Recoverability is measured by comparison of the carrying amount to the future undiscounted net cash flows which the assets are expected to generate. If such assets are considered to be impaired, the impairment to be recognized is measured by the amount by which the carrying amount of the assets exceeds the assets' fair value determined using the projected discounted future net cash flows arising from the asset.
Through December 31, 2015, there have been no such impairments.
Revenue Recognition
The Company’s revenue is derived from the sales of the CoolSculpting system, consisting of a control unit and applicators, and, from time to time, related extended warranty arrangements, and from the sale of cycles in the form of consumable procedure packs, each of which includes consumable CoolGels, CoolLiners, and in the case of the Company's CoolSmooth procedure packs, disposable securement accessories, all of which are used by the Company's customer during treatments. The Company earns revenue from the sale of these products to its customers and to distributors. The Company recognizes revenue when persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists, transfer of title to the customer has occurred, the sales price is fixed or determinable, and collectability is probable. Revenue is deferred in the event that any of the revenue recognition criteria is not met. Each consumable procedure pack includes a disposable computer cartridge that the Company markets as the CoolCard. The CoolCard contains enabling software that permits the Company's customers to perform a fixed number of CoolSculpting procedures, or cycles. This software is not marketed separately from the CoolSculpting system or from the CoolCard. Rather, the functionality that the software provides is part of the overall CoolCard product. The CoolSculpting system is marketed as a non-invasive aesthetic device for the selective reduction of fat, not for its embedded software attributes included in the CoolCard that enable its use. The Company does not provide rights to upgrades and enhancements or post-contract customer support for the embedded software. In addition, the Company does not incur significant software development costs or capitalize its software development costs. Based on this assessment, the Company considers the embedded software in the CoolCard incidental to the CoolCard product as a whole and determined that revenue recognition should not be governed by the provisions of Topic 985 of the FASB Accounting Standards Codification, or ASC.
Persuasive Evidence of an Arrangement. The Company uses contracts or customer purchase orders to determine the existence of an arrangement.
Delivery. The Company's standard terms specify that title transfers upon shipment to the customer. The Company uses third party shipping documents to verify that title has transferred.
Sales Price Fixed or Determinable. The Company assesses whether the sales price is fixed or determinable at the time of the transaction. Sales prices are documented in the executed sales contract or purchase order received prior to shipment. The Company’s standard terms do not allow for trial or evaluation periods, rights of return or refund, payments contingent upon the customer obtaining financing or other terms that could impact the customer’s obligation.
Collectability. The Company assesses whether collection is reasonably assured based on a number of factors, including the customer’s past transaction history and credit worthiness.
Multiple-Element Arrangements. Typically, all products sold to a customer are delivered at the same time. If a partial delivery occurs as authorized by the customer, the Company allocates revenue to the various products based on their vendor-specific objective evidence of fair value, or VSOE, if VSOE exists according to ASC 605-25 as the basis of determining the relative selling price of each element. If VSOE does not exist, the Company may use third party evidence of fair value, or TPE, to determine the relative selling price of each element. If neither VSOE nor TPE exists, the Company may use management’s best estimate of the sales price, or ESP, of each element to determine the relative selling price. The relative selling prices for control units, applicators, CoolCards and extended warranty are based on established price lists and separate, stand-alone sales of these elements. The Company establishes best estimates within a range of selling prices considering multiple factors including, but not limited to, factors such as size of transaction, pricing strategies and market conditions. The Company believes the use of the ESP allows revenue recognition in a manner consistent with the underlying economics of the transaction. The Company’s products do not require maintenance or support. Additionally, from time to time there may be undelivered elements in a multiple element arrangement, such elements generally being training or extended warranty. The Company defers revenue on undelivered elements of an arrangement and recognizes it once all revenue recognition criteria have been met.
76
Customer Programs and Payments
The Company regularly evaluates the adequacy of its estimates for product returns, cooperative marketing arrangements, customer incentive programs and pricing programs. Future market conditions and product transitions may require the Company to take action to change such programs. In addition, when the variables used to estimate these costs change, or if actual costs differ significantly from the estimates, the Company would be required to record incremental increased or reductions to sales, cost of goods sold or operating expenses. If, at any future time, the Company becomes unable to reasonably estimate these costs, recognition of revenue might be deferred until products are sold to users, which would adversely impact sales in the period of transition.
Accruals for Customer Programs
The Company records an accrued liability for cooperative marketing arrangements and customer incentive programs. The estimated cost of these programs is recorded as a reduction of revenue or as an operating expense, if the Company receives a separately identifiable benefit from the customer and can reasonably estimate the fair value of that benefit. Significant management judgment and estimates must be used to determine the cost of these programs in any accounting period.
Cooperative Marketing Arrangements. The Company offers cooperative marketing programs to its North American customers, allowing the customers to receive partial reimbursement for qualifying advertising expenditures which promote the Company's product and brand. Customer participation, as well as reimbursement amounts, is predicated upon purchase levels of CoolCards. The objective of these arrangements is to encourage advertising and promotional events to increase sales of the Company's products. Accruals for these marketing arrangements are recorded at the later of time of sale, or time of commitment, based on the related program parameters, review of related advertising and historical experience.
Customer Incentive Programs. The Company's customer incentive program consists of rebates for its distributors based on purchase levels. Estimated costs of customer rebates and similar incentives are recorded at the later of the time the incentive is offered, based on the specific terms and conditions of the program or the time the related revenue is recognized.
Customer incentive programs include performance-based incentives and consumer rebates. The Company offers performance-based incentives to its distributor customers, direct partners and indirect partners based on pre-determined performance criteria. Accruals for performance-based incentives are recognized as a reduction of the sale price at the later of the time the incentive is offered, based on the specific terms and conditions of the program or the time the related revenue is recognized. Estimates of required accruals are determined based on negotiated terms, consideration of historical experience, anticipated volume of future purchases, and inventory levels in the channel. Certain incentive programs require management to estimate the number of customers who will actually redeem the incentive based on historical experience and the specific terms and conditions of particular programs.
Accounting for Payments to Customers
The Company occasionally enters into transactions where it provides consideration to its customers in the forms of cash payments or stock-based awards in exchange for certain goods and services. The Company accounts for such payments to customers in accordance with ASC 605-50, Revenue Recognition: Customer Payments and Incentives, which requires management to characterize the payment as a reduction of revenue if it is unable to demonstrate the receipt of a benefit that is identifiable and sufficiently separable from the revenue transaction and reasonably estimate the fair value of the benefit identified. Significant management judgment and estimates must be used to determine the fair value of the benefit received in any period. For stock awards, the Company believes that the fair value of the awards is more reliably measured than the fair value of the benefit received. The fair value of the stock awards is measured as of the date at which either the commitment for performance by the customer to earn the award is reached or the date the customer’s performance is complete. Until that point is reached, the award is revalued at each reporting period with the true-up to fair value recorded in current period earnings.
Cost of Revenue
Cost of revenue consists primarily of cost of finished and semi-finished products purchased from the Company's third-party suppliers, labor, material, and overhead involved in its internal manufacturing processes, technology amortization and royalty fees and cost of product warranty. In the event that a revenue transaction is deferred, the corresponding cost associated with the transaction will also be deferred.
Shipping and Handling
Shipping and handling costs charged to customers are recorded as revenue. Shipping costs are included in cost of revenue.
77
Research and Development
Research and development costs primarily consist of salaries, benefits, incentive compensation, stock-based compensation, and allocated facilities costs for employees and contractors engaged in research, clinical studies, regulatory affairs, and development. The Company expenses all research and development costs in the periods in which they are incurred.
Advertising costs
The cost of advertising and media is expensed as incurred. For the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, advertising costs totaled $17.4 million, $7.9 million and $8.9 million, respectively.
Product Warranties
The Company provides a standard limited warranty on its products of one year for both control units and applicators for its direct customers. For indirect customers in international markets, the Company provides a standard limited warranty on its products of approximately three years for control units and one year for applicators.
The Company accrues for the estimated future costs of repair or replacement upon shipment. The warranty accrual is recorded to cost of revenue and is based upon historical and forecasted trends in the volume of product failures during the warranty period and the cost to repair or replace the equipment. The Company bases product warranty costs on related freight, material, technical support labor and overhead costs. The estimated product warranty costs are assessed by considering historical costs and applying the experienced failure rates to the outstanding warranty period for products sold. The Company exercises judgment in estimating the expected product warranty costs, using data such as the actual and projected product failure rates, and average repair costs, including freight, material, technical support labor, and overhead costs, for products returned under warranty.
The Company offers an extended warranty on both its CoolSculpting control units and CoolSculpting applicators. The Company recognizes the revenue from the sale of an extended warranty over the extended warranty coverage period. The Company's revenue recognized from the sale of extended warranties for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013 were $3.5 million, $2.1 million and $1.0 million, respectively.
Stock-Based Compensation
The Company maintains incentive plans under which incentive and nonqualified stock options are granted primarily to employees and non-employee consultants.
Stock-based compensation cost is measured at the grant date, based on the fair value of the award, and is recognized as expense over the requisite service period. The fair value of stock-based awards to employees is estimated using the Black-Scholes option pricing model. The Company estimates its forfeiture rate based on an analysis of its actual forfeitures and will continue to evaluate the adequacy of the forfeiture rate assumption based on actual forfeitures, analysis of employee turnover, and other related factors.
Stock-based compensation expense related to stock options granted to non-employees is recognized as the stock options are earned. The awards generally vest ratably over the time period the Company expects to receive services from the non-employee. The fair values attributable to these options are amortized over the service period and the unvested portion of these options is remeasured at each vesting date.
Income Taxes
The Company utilizes the asset and liability method of accounting for income taxes, under which deferred taxes are determined based on the temporary differences between the financial statement and tax basis of assets and liabilities using tax rates expected to be in effect during the years in which the basis differences reverse and for operating losses and tax credit carryforwards. The Company estimates its income taxes and amounts ultimately payable or recoverable in multiple tax jurisdictions around the world. Estimates involve interpretations of regulations and are inherently complex. Resolution of income tax treatments in individual jurisdictions may not be known for many years after completion of any fiscal year. The Company is required to evaluate the realizability of its deferred tax assets on an ongoing basis to determine whether there is a need for a valuation allowance with respect to such deferred tax assets. A valuation allowance is recorded when it is more likely than not that some or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized. Significant management judgment is required in determining any valuation allowance recorded against deferred tax assets. In evaluating the ability to recover deferred tax assets, the Company considers all available positive and negative evidence giving greater weight to its recent cumulative losses
78
and its ability to carryback losses against prior taxable income and, commensurate with objective verifiability, the forecast of future taxable income including the reversal of temporary differences and the implementation of feasible and prudent tax planning strategies.
The Company recognizes and measures uncertain tax positions taken or expected to be taken in a tax return if it is more likely than not that the tax position will be sustained on examination by the taxing authorities, based on the technical merits of the position. The tax benefits recognized in the consolidated financial statements from such positions are then measured based on the largest benefit that has a greater than 50 percent likelihood of being realized upon ultimate settlement. The Company reports a liability for unrecognized tax benefits resulting from uncertain tax positions taken or expected to be taken in a tax return. The Company adjusts these reserves in light of changing facts and circumstances, such as the closing of a tax audit or the refinement of an estimate. To the extent that the final tax outcome of these matters is different than the amounts recorded, such differences will impact the provision for income taxes in the period in which such determination is made. The provision for income taxes includes the impact of reserve provisions and changes to reserves that are considered appropriate, as well as the related net interest. The Company recognizes interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits within the income tax provision. Accrued interest and penalties are included within the related tax liability line in the consolidated balance sheet.
The Company files annual income tax returns in multiple taxing jurisdictions around the world. A number of years may elapse before an uncertain tax position is audited and finally resolved. While it is often difficult to predict the final outcome or the timing of resolution of any particular uncertain tax position, the Company believes that its reserves for income taxes reflect the most likely outcome. The Company adjusts these reserves, as well as the related interest, in light of changing facts and circumstances. Settlement of any particular position could require the use of cash or loss of tax attributes.
At December 31, 2015, based on the Company's evaluation of the positive and negative evidence described in Note 11-Income Taxes, the Company concluded that the positive evidence outweighed the negative evidence and that it was more likely than not that the Company will realize all of its U.S. federal and state deferred tax assets, except for deferred tax assets related to California R&D credits. Consequently, at December 31, 2015, the Company reduced its deferred tax asset valuation allowance to $2.5 million. At December 31, 2014, the Company had a full valuation allowance against its U.S. deferred tax assets, net of expected reversals of existing deferred tax liabilities.
Net Income (Loss) Per Share
Basic net income (loss) per share of common stock is calculated by dividing the net income (loss) by the weighted-average number of shares of common stock outstanding for the period. Diluted net income (loss) per share of common stock is computed by giving effect to all potentially dilutive securities outstanding during the period, including options, restricted stock units and common stock issuable pursuant to the ESPP.
Comprehensive Income (Loss)
Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) includes foreign currency translation adjustments and unrealized gains (losses) on available-for-sale securities net of tax, the impact of which has been excluded from earnings and reflected as components of stockholders' equity.
Components of accumulated other comprehensive loss was as follows (in thousands):
December 31, | |||||||
2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Cumulative translation adjustments | $ | (1,615 | ) | $ | (690 | ) | |
Unrealized loss on marketable securities, net of tax | (21 | ) | (6 | ) | |||
Accumulated other comprehensive loss | $ | (1,636 | ) | $ | (696 | ) | |
Foreign currency translation
Based on an evaluation of economic facts and circumstances together with the functional currency analysis prescribed in ASC 830, Foreign Currency Matters, on October 1, 2013, the Company changed the functional and reporting currency for its operations in the United Kingdom from the U.S. Dollar to the British Pound. Such change did not have a material impact on the consolidated financial statements of the Company. The functional and reporting currency is the Euro for the Company's operations in Ireland and the U.S. dollar for all of its other foreign operations.
79
All assets and liabilities of the Company's operations in the United Kingdom and Ireland are translated to U.S. Dollars at current period end exchange rates, and revenue and expenses are translated to U.S. Dollars using average exchange rates in effect during the period. The gains and losses from the foreign currency translation of the foreign subsidiaries' financial statements are included as a separate component of stockholders' equity under "Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss)." Gains or losses arising from currency exchange rate fluctuations on transactions denominated in a currency other than the local functional currency are included in other income (expense), net. For the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, such amount totaled $(0.3) million, $(0.3) million and $24,000, respectively.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
On May 28, 2014, the Financial Accounting Standards Board, or FASB, issued Accounting Standards Update No. 2014-09, Revenue from Contracts with Customers. On August 12, 2015, the FASB issued ASU 2015-14, Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606): Deferral of the Effective Date, which delays the effective date of ASU 2014-09 by one year. The objective of this update is to provide a single, comprehensive revenue recognition model for all contracts with customers to improve comparability within industries, across industries, and across capital markets. This standard update contains principles that the Company will apply to determine the measurement of revenue and timing of when it is recognized. This guidance allows for two methods of adoption: (a) full retrospective adoption, meaning the guidance is applied to all periods presented, or (b) modified retrospective adoption, meaning the cumulative effect of applying this guidance is recognized as an adjustment to the fiscal 2018 opening accumulated deficit balance. The Company expects to adopt this guidance effective January 1, 2018, and is currently evaluating the two adoption methods as well as the impact this new guidance will have on its consolidated financial statements and related disclosures.
In August 2014, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update No. 2014-15, Disclosure of Uncertainties About an Entity's Ability to Continue as a Going Concern. This standard update provides guidance around management's responsibility to evaluate whether there is substantial doubt about an entity's ability to continue as a going concern and to provide related footnote disclosures. The new guidance is effective for all annual and interim periods ending after December 15, 2016. The new guidance is not expected to have an impact on the Company's consolidated financial statements and related disclosures.
In April 2015, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update No. 2015-05 regarding Subtopic 350-40, “Intangibles - Goodwill and Other - Internal-Use Software.” This standard provides guidance to customers about whether a cloud computing arrangement includes a software license. If a cloud computing arrangement includes a software license, the customer should account for the software license element of the arrangement consistent with other software licenses. If a cloud computing arrangement does not include a software license, the customer should account for the arrangement as a service contract. The amendments are effective for annual and interim periods beginning after December 15, 2015. Early adoption is permitted. The amendments may be applied either prospectively to all arrangements entered into or materially modified after the effective date or retrospectively. The Company is currently evaluating the impact this new guidance will have on its consolidated financial statements and related disclosures.
In June 2015, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update No. 2015-10, Technical Corrections and Improvements. The standard covers a wide range of Topics in the Codification. The amendments in this standard represent changes to clarify the Codification, correct unintended application of guidance, or make minor improvements to the Codification that are not expected to have a significant effect on current accounting practice or create a significant administrative cost on most entities. The amendments are effective for fiscal years and interim periods within those fiscal years, beginning after December 15, 2015. The Company does not anticipate that the adoption of this standard will have a material impact on its consolidated financial statements and footnote disclosures. The Company is currently evaluating the impact this new guidance will have on its consolidated financial statements and related disclosures.
In July 2015, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update No. 2015-11 to amend ASC Topic 330, Inventory ("ASC 330") to simplify the measurement of inventory. The amendments require that an entity measure inventory at the lower of cost and net realizable value instead of the lower of cost and market. This guidance is effective for public companies for years, and interim periods within those years, beginning on or after December 15, 2016, with earlier application permitted as of the beginning of an interim or annual reporting period. This guidance will be effective for the Company beginning in its first quarter of fiscal 2017. The Company is currently evaluating the impact this new guidance will have on its consolidated financial statements and related disclosures.
In November 2015, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update No. 2015-17, Income Taxes - Balance Sheet Reclassification of Deferred Taxes (Topic 740). This ASU requires that deferred tax liabilities and assets be classified as noncurrent in a classified statement of financial position. The current requirement that deferred tax liabilities and assets of a tax-paying component of an entity be offset and presented as a single amount is not affected by the amendments in this update. The amendments in this update are effective for financial statements issued for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2016, and interim periods within
80
those annual periods. The Company early adopted this ASU on a prospective basis in the fourth quarter of 2015 and, as a result, reclassified $40.5 million of current deferred tax assets to long-term assets on the accompanying in consolidated balance sheet as of December 31, 2015.
In February 2016, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update No. 2016-02, Leases. This ASU requires lease assets and lease liabilities arising from leases, including operating leases, to be recognized on the balance sheet. ASU 2016-02 will become effective for the Company on January 1, 2019, and requires adoption using a modified retrospective approach. The Company is currently evaluating the impact of this guidance on its consolidated financial statements and related disclosures.
3. Fair Value of Financial Instruments
Fair value is defined as the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability (an exit price) in an orderly transaction between market participants at the reporting date. The accounting guidance establishes a three-tiered hierarchy, which prioritizes the inputs used in the valuation methodologies in measuring fair value:
•Level 1—Quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities.
• | Level 2—Inputs other than Level 1 that are observable, either directly or indirectly, such as quoted prices in markets that are not active, or other inputs that are observable or can be corroborated by observable market data for substantially the full term of the assets or liabilities. |
• | Level 3—Unobservable inputs that are supported by little or no market activity and that are significant to the fair value of the assets or liabilities. The Company did not hold any Level 3 assets or liabilities at December 31, 2015. |
The categorization of a financial instrument within the valuation hierarchy is based on the lowest level of input that is significant to the fair value measurement.
The Company classifies its cash equivalents and investments within Level 1 and Level 2, as it uses quoted market prices or alternative pricing sources and models utilizing market observable inputs. The following tables set forth the fair value of the Company’s financial assets and liabilities by level within the fair value hierarchy (in thousands):
As of December 31, 2015 | |||||||||||||||
Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Fair Value | ||||||||||||
Financial Assets | |||||||||||||||
Cash equivalents: | |||||||||||||||
Money market funds | $ | 1,342 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 1,342 | |||||||
Short-term investments: | |||||||||||||||
U.S. Agency securities | — | 1,549 | — | 1,549 | |||||||||||
U.S. Treasury | — | 500 | — | 500 | |||||||||||
Corporate bonds | — | 7,763 | — | 7,763 | |||||||||||
Commercial paper | — | 500 | — | 500 | |||||||||||
Certificates of deposit | 2,555 | — | — | 2,555 | |||||||||||
Long-term investments: | |||||||||||||||
U.S. Agency securities | — | 497 | — | 497 | |||||||||||
Corporate bonds | — | 874 | — | 874 | |||||||||||
Certificates of deposit | 2,119 | — | — | 2,119 | |||||||||||
Total | $ | 6,016 | $ | 11,683 | $ | — | $ | 17,699 | |||||||
81
As of December 31, 2014 | |||||||||||||||
Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Fair Value | ||||||||||||
Financial Assets | |||||||||||||||
Cash equivalents: | |||||||||||||||
Money market funds | $ | 6,062 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 6,062 | |||||||
Short-term investments: | |||||||||||||||
U.S. Agency securities | — | 5,240 | — | 5,240 | |||||||||||
U.S. Treasury | — | 1,004 | — | 1,004 | |||||||||||
Corporate bonds | — | 7,774 | — | 7,774 | |||||||||||
Commercial paper | — | 1,349 | — | 1,349 | |||||||||||
Certificates of deposit | 919 | — | — | 919 | |||||||||||
Long-term investments: | |||||||||||||||
U.S. Agency securities | — | 999 | — | 999 | |||||||||||
U.S. Treasury | — | 500 | — | 500 | |||||||||||
Corporate bonds | — | 750 | — | 750 | |||||||||||
Certificates of deposit | 2,556 | — | — | 2,556 | |||||||||||
Total | $ | 9,537 | $ | 17,616 | $ | — | $ | 27,153 | |||||||
During the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, the Company did not have any transfers of financial assets measured at fair value on a recurring basis to or from Level 1, Level 2 or Level 3. The Company did not hold any Level 3 assets or liabilities as of December 31, 2015 and December 31, 2014.
The carrying amounts of the Company’s cash equivalents, accounts receivable and accounts payable approximate fair value due to their relatively short maturities.
82
4. Balance Sheet Components
Investments
The Company's short-term and long-term investments as of December 31, 2015 are as follows (in thousands):
Short-term | |||||||||||||||
Amortized Cost | Gross Unrealized Gains | Gross Unrealized Losses | Fair Value | ||||||||||||
U.S. Agency securities | $ | 1,551 | $ | — | $ | (2 | ) | $ | 1,549 | ||||||
U.S. Treasury | 500 | — | — | 500 | |||||||||||
Corporate bonds | 7,776 | — | (13 | ) | 7,763 | ||||||||||
Commercial paper | 500 | — | — | 500 | |||||||||||
Certificates of deposit | 2,555 | — | — | 2,555 | |||||||||||
Total | $ | 12,882 | $ | — | $ | (15 | ) | $ | 12,867 | ||||||
Long-term | |||||||||||||||
Amortized Cost | Gross Unrealized Gains | Gross Unrealized Losses | Fair Value | ||||||||||||
U.S. Agency securities | $ | 499 | $ | — | $ | (2 | ) | $ | 497 | ||||||
U.S. Treasury | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||
Corporate bonds | 878 | — | (4 | ) | 874 | ||||||||||
Certificates of deposit | 2,119 | — | — | 2,119 | |||||||||||
Total | $ | 3,496 | $ | — | $ | (6 | ) | $ | 3,490 | ||||||
The Company's short-term and long-term investments as of December 31, 2014 are as follows (in thousands):
Short-term | |||||||||||||||
Amortized Cost | Gross Unrealized Gains | Gross Unrealized Losses | Fair Value | ||||||||||||
U.S. Agency securities | $ | 5,240 | $ | 1 | $ | (1 | ) | $ | 5,240 | ||||||
U.S. Treasury | 1,003 | 1 | — | 1,004 | |||||||||||
Corporate bonds | 7,778 | 2 | (6 | ) | 7,774 | ||||||||||
Commercial paper | 1,349 | — | — | 1,349 | |||||||||||
Certificates of deposit | 919 | — | — | 919 | |||||||||||
Total | $ | 16,289 | $ | 4 | $ | (7 | ) | $ | 16,286 | ||||||
Long-term | |||||||||||||||
Amortized Cost | Gross Unrealized Gains | Gross Unrealized Losses | Fair Value | ||||||||||||
U.S. Agency securities | $ | 1,000 | $ | — | $ | (1 | ) | $ | 999 | ||||||
U.S. Treasury | 500 | — | — | 500 | |||||||||||
Corporate bonds | 752 | — | (2 | ) | 750 | ||||||||||
Certificates of deposit | 2,556 | — | — | 2,556 | |||||||||||
Total | $ | 4,808 | $ | — | $ | (3 | ) | $ | 4,805 | ||||||
83
For the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, gains or losses realized on the sale of investments were insignificant.
The contractual maturities of the Company's short-term and long-term investments as of December 31, 2015 are as follows (in thousands):
December 31, 2015 | |||||||
Amortized Cost | Fair Value | ||||||
Due in one year or less | $ | 12,882 | $ | 12,867 | |||
Due in one year to five years | 3,496 | 3,490 | |||||
$ | 16,378 | $ | 16,357 | ||||
When evaluating the investments for other-than-temporary impairment, the Company reviews factors such as the length of time and extent to which fair value has been below the amortized cost basis, review of current market liquidity, interest rate risk, the financial condition of the issuer, as well as credit rating downgrades. The Company believes that the unrealized losses are not other-than-temporary. The Company does not have a foreseeable need to liquidate the portfolio and anticipates recovering the full cost of the securities either as market conditions improve, or as the securities mature.
Inventory
The components of inventory consist of the following (in thousands):
December 31, | |||||||
2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Raw materials | $ | 9,117 | $ | 7,692 | |||
Finished goods | 18,978 | 7,844 | |||||
Total inventory | $ | 28,095 | $ | 15,536 | |||
Property and equipment, net
Property and equipment, net comprised the following (in thousands):
December 31, | |||||||
2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Lab equipment, tooling and molds | $ | 3,228 | $ | 2,766 | |||
Computer software | 2,019 | 1,337 | |||||
Computer equipment (1) | 2,757 | 1,366 | |||||
Leasehold improvements (1) | 1,670 | 1,070 | |||||
Furniture and fixtures | 950 | 494 | |||||
Vehicles | 35 | 35 | |||||
Total property and equipment | 10,659 | 7,068 | |||||
Less: Accumulated depreciation and amortization | (5,635 | ) | (4,111 | ) | |||
Construction in progress | 1,945 | 767 | |||||
Property and equipment, net | $ | 6,969 | $ | 3,724 | |||
Depreciation and amortization expense related to property and equipment was $1.7 million, $1.1 million and $1.0 million for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
(1) | During fiscal year 2015, the Company determined that the 2014 leasehold improvements category incorrectly contained computer equipment of $0.4 million. The table above has been revised to correctly reflect these assets |
84
within the computer equipment category in the 2014 comparable numbers. The Company concluded that this adjustment was not material to the previously issued consolidated financial statements.
Accrued and Other Current Liabilities
The following table shows the components of accrued liabilities (in thousands):
December 31, | |||||||
2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Accrued payroll and employee related expenses | $ | 14,887 | $ | 8,386 | |||
Accrued marketing expenses | 5,554 | 2,959 | |||||
Accrued royalty | 5,453 | 3,612 | |||||
Sales and other taxes payable | 3,703 | 2,123 | |||||
Advance payments from customers | 1,585 | 1,908 | |||||
Accrued legal expenses | 1,465 | 592 | |||||
Accrued warranty | 527 | 569 | |||||
Other | 1,517 | 1,301 | |||||
Total accrued and other current liabilities | $ | 34,691 | $ | 21,450 | |||
Deferred Revenue
The following table shows the components of deferred revenue, including long-term deferred revenue (in thousands):
December 31, | |||||||
2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Deferred revenue | $ | 1,347 | $ | 573 | |||
Deferred extended warranty revenue | 2,902 | 3,272 | |||||
Deferred training revenue | 3,115 | 1,381 | |||||
Other deferred revenue | 544 | 465 | |||||
Total deferred revenue | $ | 7,908 | $ | 5,691 | |||
Deferred Extended Warranty Revenue
The Company offers standard extended warranties which allows customers to receive service and support which extend beyond the contractual term of the product warranty. The Company recognizes these contracts over the life of the service period. Changes in the Company's deferred revenue, including long-term deferred revenue, related to extended warranties were as follows (in thousands):
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||
2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Balance at the beginning of the period | $ | 3,272 | $ | 1,443 | |||
Extended warranties issued | 3,158 | 3,897 | |||||
Amortization | (3,528 | ) | (2,068 | ) | |||
Balance at the end of the period | $ | 2,902 | $ | 3,272 | |||
Product Warranties
85
The estimated product warranty accrual was as follows (in thousands):
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||
2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Balance at the beginning of the period | $ | 569 | $ | 676 | |||
Settlement of pre-existing warranties | (658 | ) | (772 | ) | |||
Provision | 616 | 665 | |||||
Balance at the end of the period | $ | 527 | $ | 569 | |||
5. License Agreement with Massachusetts General Hospital
In May 2005, the Company entered into an exclusive license agreement with the General Hospital Corporation, a not for profit Massachusetts corporation, which owns and operates the Massachusetts General Hospital, or MGH. This agreement was amended and restated in September 2011. Under this agreement, the Company obtained an exclusive license to develop and commercialize the patent and the core technology that underlies its CoolSculpting system. The Company conducted development from 2005 through 2009, and thereafter started commercialization of the products. The agreement will remain in full force and effect for the later of (i) the life of any patents that issue from the underlying patent applications, which are expected to expire in 2023 or (ii) one year after the last commercial sale for which a royalty is due to MGH, unless terminated in accordance with its terms and conditions. MGH may terminate the agreement upon the Company's insolvency, failure to maintain insurance, material breach of the agreement including failure to satisfy the Company's post-sales requirements, or failure to make required payments. The Company may terminate the agreement for any reason upon 90 days' advance written notice to MGH. The Company has complied with its contractual requirements to date.
The Company is obligated to make various payments to MGH, including (i) a 7% royalty on net sales (as defined in the agreement) of CoolSculpting and (ii) milestone payments. During the year ended December 31, 2010, the Company paid MGH a $1.1 million milestone payment upon receipt of Food and Drug Administration, or FDA, clearance to market its CoolSculpting system for the selective reduction of fat. The remaining milestone payments including (i) $1 million due upon achieving cumulative net sales (as defined in the agreement) of $70 million and (ii) $6 million due upon the earlier to occur of achieving cumulative net sales (as defined in the agreement) of $200 million, or the completion of a qualifying initial public offering were made during the quarter ended December 31, 2011. As of December 31, 2011, the Company had completed all the milestones associated with the license agreement with MGH and had no milestone payments to MGH outstanding.
All payments made to MGH prior to the FDA product clearance are expensed as incurred as research and development costs. All milestone payments payable by the Company pursuant to the terms of the agreement subsequent to the date of the FDA clearance were capitalized as purchased technology when paid, and are subsequently amortized into cost of revenue using the straight-line method over the estimated remaining useful life of the technology, not to exceed the term of the agreement or the life of the patent. Royalty payments are accrued as the Company recognizes revenue, and are included in cost of revenue.
In September 2015, the Company entered into a new agreement with MGH to obtain an exclusive license to develop and commercialize certain patents and technology for the treatment of acne and certain related skin conditions. The Company is obligated to pay a 3% royalty on net sales, as defined in such agreement, of products incorporating such technology.
The intangible asset, net comprised the following (in thousands):
December 31, 2015 | December 31, 2014 | ||||||
Purchased technology | $ | 8,050 | $ | 8,050 | |||
Less: Accumulated amortization | (2,958 | ) | (2,270 | ) | |||
Intangible asset, net | $ | 5,092 | $ | 5,780 | |||
86
The amortization expense of the intangible asset was $0.7 million for each of the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013.
The total estimated annual future amortization expense of this intangible asset as of December 31, 2015, is as follows (in thousands):
Year ending December 31, | |||
2016 | $ | 650 | |
2017 | 650 | ||
2018 | 650 | ||
2019 | 650 | ||
2020 | 650 | ||
Thereafter | 1,842 | ||
Total | $ | 5,092 | |
6. Related Party Transactions
Brazilian Distribution Agreement
The Company entered into a distribution agreement with ADVANCE Medical, Inc. and its wholly owned subsidiaries, Immunotech and BIOGEN, or ADVANCE, dated March 18, 2011, as the Company's exclusive distributor of CoolSculpting in Brazil and Mexico, as amended on August 29, 2011, February 27, 2012 and September 4, 2012. The distribution agreement was further amended on August 15, 2014, whereby ADVANCE is no longer a distributor in Mexico, effective November 13, 2014. As the exclusive distributor in Brazil, ADVANCE is required to purchase a minimum quantity of the Company’s products each calendar quarter throughout the term of the distribution agreement which expires on December 31, 2018. Venrock, a principal stockholder of the Company, owns an equity interest in ADVANCE Medical, Ltd., the parent company of ADVANCE. Dr. Bryan E. Roberts, who is a member of the Company's Board of Directors, is also a partner of Venrock Associates. ADVANCE purchases product with payment terms up to 180 days, and to date no amounts have been determined to be unrecoverable. The revenue recognized by the Company under this distribution agreement for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, was $3.6 million, $1.9 million and $1.6 million, respectively. The accounts receivable balance under this distribution agreement as of December 31, 2015 and 2014, was $1.7 million and $0.2 million, respectively.
During fiscal year 2015, the Company determined that the 2014 and 2013 related party revenue disclosures were overstated by $0.2 million and $0.7 million, respectively, due to the incorrect inclusion of revenue from a non-related party customer. The amounts above have been revised to correct for these errors. The Company concluded that these adjustments were not material to the previously issued consolidated financial statements.
7. Commitments and Contingencies
Operating Lease Obligations
The Company leases facilities under non-cancellable operating leases with various expiration dates. Specifically, the Company occupies a facility in Pleasanton, California, under a lease which extends through March 2019, a manufacturing facility in Dublin, California, under a lease which extends through May 2017, and a warehouse space in Livermore, California, under a lease which extends through May 2017. The Company also occupies office and warehouse space near Gatwick, United Kingdom, under a lease which extends through December 2018, as well as office space in London, United Kingdom, under a lease which extends through April 2016, Taipei, Taiwan, under a lease which extends through August 2016, Seoul, South Korea, under a lease which extends through August 2016, Reston, Virginia, under a lease which extends through September 2020, Galway, Ireland under two leases which extend through September 2016 and March 2016, respectively. Rent expense for non-cancellable operating leases with scheduled rent increases is recognized on a straight-line basis over the lease term. Rent expense for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, was $2.5 million, $1.5 million and $1.4 million, respectively.
87
Future minimum lease payments under the non-cancellable operating leases as of December 31, 2015, are as follows (in thousands):
Year Ending December 31, | Amount | ||
2016 | $ | 2,344 | |
2017 | 2,058 | ||
2018 | 1,912 | ||
2019 | 763 | ||
2020 | 234 | ||
Total future minimum lease payments | $ | 7,311 | |
Capital Lease Obligations
The Company has entered into certain capital lease obligations to purchase equipment for operations which include a bargain purchase option. The underlying assets and related depreciation are included in the appropriate property and equipment category and related accumulated depreciation account.
Property and equipment includes the following amounts under leases that have been capitalized as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 were as follows (in thousands):
Useful life (Years) | December 31, 2015 | December 31, 2014 | |||||||
Computer equipment | 3 | $ | 382 | $ | 382 | ||||
Total capital leased equipment | 382 | 382 | |||||||
Less: Accumulated depreciation and amortization | (149 | ) | (21 | ) | |||||
Capital leased equipment, net | $ | 233 | $ | 361 | |||||
Total depreciation of assets acquired under capital leases was $0.1 million and $21,000 for the years ended December 31, 2015 and December 31, 2014, respectively, which is included in total depreciation and amortization expense. There were no such arrangements during the years ended December 31, 2013.
Future minimum payments required under capital leases as of December 31, 2015, are as follows (in thousands):
Year Ending December 31, | Amount | ||
2016 | $ | 132 | |
2017 | 141 | ||
Total future payments | $ | 273 | |
Less: Amount representing interest | $ | 11 | |
Present value of future minimum payments | 262 | ||
Less: Current portion | 124 | ||
Long term portion | $ | 138 | |
Purchase Commitments
The Company had non-cancellable purchase obligations to contract manufacturers and suppliers for $5.9 million at December 31, 2015.
Unrecognized Tax Benefits
88
The Company's gross liability for unrecognized tax benefits totaled $0.3 million, including estimated interest and penalties, as of December 31, 2015, and is classified in long-term income taxes payable. The Company is unable to make a reasonably reliable estimate of the timing of payments in individual years due to uncertainties in the timing of tax audits, if any, or their outcomes.
Legal Matters
From time to time, the Company may be involved in legal and administrative proceedings and claims of various types. Additionally, the Company may be subject to insurance related claims resulting from matters associated with CoolSculpting treatments. The Company records a liability in its consolidated financial statements for these matters when a loss is known and considered probable and the amount can be reasonably estimated. Management reviews these estimates in each accounting period as additional information becomes known and adjusts the loss provision when appropriate. If the loss is not probable or cannot be reasonably estimated, a liability is not recorded in the consolidated financial statements. If a loss is probable but the amount of loss cannot be reasonably estimated, the Company discloses the loss contingency and an estimate of possible loss or range of loss (unless such an estimate cannot be made). The Company does not recognize gain contingencies until they are realized. Legal costs incurred in connection with loss contingencies are expensed as incurred.
Product Liability Contingencies
The Company has historically been and continues to be predominantly self-insured for any product liability losses related to its products. The Company obtains third-party insurance to limit its exposure to these claims, but this insurance is subject to a cap on reimbursement. Product liability losses are, by their nature, uncertain and are based upon complex judgments and probabilities. The Company accrues for reported claims and estimates for incurred, but not reported claims, to the extent that such losses can be reasonably estimated. The Company determines its accruals for probable product liability losses based on various factors, including historical claims and settlement experience. The total amount of self-insured product liability claims settled in the year ended December 31, 2015 was $0.7 million. The total amount of self-insured product liability claims settled during the year ended December 31, 2014 was not material. The amount of reported and estimated incurred but not known self-insured product liability claims pending was $1.1 million as of December 31, 2015, which is recorded as an accrual on the Company's consolidated balance sheet and expected to be paid within one year. Such estimated claims were insignificant as of December 31, 2014.
Indemnifications
In the normal course of business, the Company enters into contracts that contain a variety of representations and warranties and provide for general indemnifications. The Company's exposure under these agreements is unknown because it involves claims that may be made against the Company in the future, but have not yet been made. To date, the Company has not paid any claims, and the Company believes that the estimated fair value of these indemnification obligations is minimal and has not accrued any amounts for these obligations.
Severance and Separation Agreements
Effective December 3, 2013, the Company's Chief Scientific Officer and Senior Vice President of Clinical entered into a separation agreement with the Company. As a result of this separation agreement, the Company incurred $0.3 million in termination benefits and $0.7 million in costs related to the modification of the employee's stock-based compensation, which were recorded during the year ended December 31, 2013. As of December 31, 2014, all of the termination benefits incurred during December 31, 2013 had been paid.
No similar costs were incurred during the year ended December 31, 2015 and 2014.
89
8. Stockholders' Equity
Preferred Stock
The Company's Certificate of Incorporation, as amended in October 2011, authorizes the Company to issue 50,000,000 shares of preferred stock with a par value of $0.01 per share. At December 31, 2015 and 2014, the Company had no preferred stock issued or outstanding.
Common Stock
Each share of common stock has the right to one vote. The holders of common stock are also entitled to receive dividends whenever funds are legally available and when declared by the Board of Directors, subject to the prior rights of holders of all classes of stock outstanding having priority rights as to dividends. No dividends have been declared or paid as of December 31, 2015.
9. Stock-Based Compensation Plans
Equity Incentive Programs
In 2005, the Company established its 2005 Stock Option Plan (the “2005 Plan”), covering employees, directors and consultants of the Company. Under the terms of the 2005 Plan, incentive and nonqualified stock option and stock purchase rights could be granted. In September 2011, upon the adoption of the Company's 2011 Equity Incentive Plan (the "2011 Plan") the Company ceased granting options under the 2005 Plan.
The 2011 Plan serves as the successor equity incentive plan to the Company's 2005 Plan and started with 89,234 shares of common stock available for issuance plus any shares of common stock issued pursuant to the 2005 Plan or subject to awards granted under the 2005 Plan that are forfeited, repurchased, returned or otherwise become available for issuance in accordance with the terms of the 2005 Plan. In addition, this plan reserve automatically increases on January 1 and each subsequent anniversary through January 1, 2021, by an amount equal to the smaller of five percent of the number of shares of common stock issued and outstanding on the immediately preceding December 31, or an amount determined by the Company's Board of Directors. The 2011 Plan provides for granting awards in the form of options, stock appreciation rights, restricted stock purchase rights, restricted stock bonuses, restricted stock units, performance shares, performance units, cash-based awards and other stock-based awards. Options granted under the 2011 Plan may be either ISOs or NSOs. ISOs may be granted only to the Company's employees. Any person who is not an employee of the Company on the effective date of the grant of an option may be granted only a NSO. Options under the 2011 Plan may be granted for periods of up to ten years and generally vest over a period of four years. The exercise price of an ISO and NSO shall not be less than 100% of the fair value of the shares on the date of grant. The exercise price of an option granted to a 10% stockholder shall not be less than 110% of the fair value of the underlying stock on the date of grant.
In April 2012, the Company's Board of Directors approved the 2012 Stock Plan ("2012 Plan") that became effective upon approval by the stockholders of the Company on June 15, 2012. The purpose of the 2012 Plan is to advance the interests of the Company and its stockholders by providing an incentive to attract, retain and reward persons performing services for the Company and by motivating such persons to contribute to the growth and profitability of the Company. The 2012 Plan seeks to achieve this purpose by providing for awards in the form of options, stock appreciation rights, restricted stock purchase rights, restricted stock bonuses, restricted stock units, performance shares, performance units, cash-based awards, other stock-based awards, and deferred compensation awards.
The 2012 Plan started with 1,500,000 shares of common stock available for issuance and there are no provisions in the 2012 Plan to increase the shares available for issuance. Options granted under the 2012 Plan may be either ISOs or NSOs. ISOs may be granted only to the Company's employees. Any person who is not an employee of the Company on the effective date of the grant of an option may be granted only a NSO. Options under the 2012 Plan may be granted for periods of up to ten years and generally vest over a period of four years. The exercise price of an ISO and NSO shall not be less than 100% of the fair value of the shares on the date of grant. The exercise price of an option granted to a 10% stockholder shall not be less than 110% of the fair value of the underlying stock on the date of grant.
90
Share-Based Awards Available for Grant
A summary of share-based awards available for grant is as follows:
Years Ended | ||||||||
December 31, 2015 | December 31, 2014 | December 31, 2013 | ||||||
Balance at beginning of fiscal year | 2,685,209 | 1,086,737 | 1,103,836 | |||||
Additional shares reserved | 1,000,000 | 1,851,794 | 1,200,000 | |||||
Options granted | (45,622 | ) | (255,000 | ) | (568,987 | ) | ||
Restricted stock units granted | (593,003 | ) | (508,729 | ) | (1,205,200 | ) | ||
Options canceled | 37,520 | 41,681 | 307,738 | |||||
Restricted stock units canceled | 174,094 | 157,358 | 163,689 | |||||
Restricted stock unit withheld for tax | 259,107 | 311,368 | 85,661 | |||||
Balance at end of fiscal year | 3,517,305 | 2,685,209 | 1,086,737 | |||||
Stock Option Awards
A summary of the stock option activity is as follows:
Options Outstanding | ||||||||||||||
Number of Shares | Weighted- Average Exercise Price | Weighted-Average Remaining Contractual Life (in Years) | Aggregate Intrinsic Value | |||||||||||
(in thousands) | ||||||||||||||
Balance, December 31, 2012 | 4,128,334 | 4 | $ | 4.96 | ||||||||||
Options granted | 568,987 | 6.60 | ||||||||||||
Options exercised | (791,198 | ) | 3.34 | |||||||||||
Options canceled | (307,738 | ) | 7.36 | |||||||||||
Balance, December 31, 2013 | 3,598,385 | $ | 5.36 | |||||||||||
Options granted | 255,000 | 18.42 | ||||||||||||
Options exercised | (569,283 | ) | 4.89 | |||||||||||
Options canceled | (41,681 | ) | 5.50 | |||||||||||
Balance, December 31, 2014 | 3,242,421 | $ | 6.47 | |||||||||||
Options granted | 45,622 | 34.65 | ||||||||||||
Options exercised | (608,931 | ) | 6.79 | |||||||||||
Options canceled | (37,520 | ) | 8.55 | |||||||||||
Balance, December 31, 2015 | 2,641,592 | $ | 6.86 | 6.81 | $ | 57,532 | ||||||||
Vested and expected to vest, December 31, 2015 | 2,620,217 | $ | 6.80 | 6.81 | $ | 57,187 | ||||||||
Vested and Exercisable, December 31, 2015 | 2,127,228 | $ | 6.22 | 6.72 | $ | 47,457 | ||||||||
91
The following table summarizes information about stock options outstanding as of December 31, 2015:
Options Outstanding | ||||||||
Exercise Price | Stock Options Outstanding | Weighted-Average Remaining Contractual Life (in Years) | Options Exercisable | |||||
$0.55-4.60 | 278,755 | 6.6 | 185,111 | |||||
4.62-4.62 | 90,000 | 6.9 | 55,625 | |||||
5.04-5.04 | 1,431,092 | 6.6 | 1,252,213 | |||||
5.06-6.34 | 295,572 | 6.9 | 242,576 | |||||
6.38-10.20 | 287,135 | 6.5 | 240,224 | |||||
11.30-17.44 | 56,229 | 7.4 | 32,267 | |||||
17.48-17.48 | 90,000 | 8.4 | 90,000 | |||||
20.88-20.88 | 47,187 | 8.1 | 20,105 | |||||
21.00-21.00 | 20,000 | 8.2 | 9,167 | |||||
$34.65-34.65 | 45,622 | 9.1 | — | |||||
2,641,592 | 2,127,288 | |||||||
Restricted Stock Activity
Activity related to restricted stock units and awards is set forth below:
Number of Units and Awards | Weighted- Average Grant Date Fair Value | ||||||
Balance, December 31, 2012 | 1,157,450 | $ | 5.38 | ||||
Restricted stock units granted | 1,205,200 | 5.57 | |||||
Restricted stock units released | (292,265 | ) | 5.35 | ||||
Restricted stock units canceled | (163,689 | ) | 4.31 | ||||
Balance, December 31, 2013 | 1,906,696 | $ | 5.60 | ||||
Restricted stock units granted | 508,729 | 19.99 | |||||
Restricted stock units released | (724,986 | ) | 6.03 | ||||
Restricted stock units canceled | (157,358 | ) | 6.50 | ||||
Balance, December 31, 2014 | 1,533,081 | $ | 10.08 | ||||
Restricted stock units granted | 593,003 | 31.96 | |||||
Restricted stock units released | (639,339 | ) | 10.76 | ||||
Restricted stock units canceled | (174,094 | ) | 14.16 | ||||
Balance, December 31, 2015 | 1,312,651 | $ | 19.09 | ||||
During the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, the Company withheld 259,107, 311,368 and 85,661 shares, respectively, based upon the Company's closing stock price on the vesting date to settle the employee's minimum statutory obligation for the applicable income and other employment taxes.
2011 Employee Stock Purchase Plan
In September 2011, the Company's Board of Directors approved the 2011 Employee Stock Purchase Plan (“2011 ESPP”) that became effective upon the completion of the IPO. The 2011 ESPP is designed to enable eligible employees to purchase shares of the Company's common stock at a discount. Each offering period consists of one six-month purchase period. The purchase price for shares of common stock under the 2011 ESPP is 85% of the of lesser of the fair market value of the Company's common stock on the first day of the applicable offering period or the purchase date.
92
There were 470,018 shares of the Company's common stock initially reserved for future purchase under its 2011 ESPP. On the first day of each year, beginning January 1, 2012 and through and including January 1, 2021, the maximum aggregate number of shares of common stock that may be issued under the 2011 ESPP will be increased by a number of shares equal to the smallest of a) one percent of the number of shares of common stock issued and outstanding on the immediately preceding December 31, or b) an amount determined by the Company's Board of Directors. During 2014, the number of shares of the Company's common stock reserved for future purchase under the 2011 ESPP was increased by 370,358 shares. During 2015, there were no additional shares of the Company's common stock reserved for future purchase under the 2011 ESPP.
The employee stock purchase plan offering periods will commence on or about the first trading days of December and June of each year and end on or about the last trading days of the next May and November, respectively.
During the year ended December 31, 2015, employees purchased 108,552 shares under the 2011 ESPP at a weighted average exercise price of $22.96. As of December 31, 2015, there were 456,835 shares of the Company's common stock available for future purchase under its 2011 ESPP.
Stock-Based Compensation Expense
Stock-based compensation related to all of the Company's stock-based awards and employee stock purchases was recorded as an expense or a reduction to revenue and allocated as follows (in thousands):
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||
Revenue | $ | 205 | $ | 833 | $ | — | |||||
Cost of revenue | 744 | 443 | 248 | ||||||||
Research and development | 1,619 | 1,073 | 1,645 | ||||||||
Sales and marketing | 5,129 | 2,917 | 1,783 | ||||||||
General and administrative | 5,522 | 4,117 | 2,984 | ||||||||
Total stock-based compensation | $ | 13,219 | $ | 9,383 | $ | 6,660 | |||||
Stock-based compensation expense includes charges related to performance based stock options and restricted stock units granted to certain executives. Stock-based compensation expense related to performance based stock options and restricted stock units was $2.5 million, $1.6 million and $1.0 million for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
Stock-based compensation expense for the year ended December 31, 2013 includes $0.7 million in modification charges incurred in connection with the severance packages to the Company's former executives. There were no such charges for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014.
Stock-based compensation for the year ended December 31, 2015 and December 31, 2014 includes $0.2 million and $0.8 million, respectively, recorded as a reduction to revenue related to payments to customers for services. Of the total amount recorded as a reduction to revenue, $0.4 million is related to an out-of-period adjustment related to the fiscal year ended December 31, 2014.
As of December 31, 2015, the total unrecognized compensation cost related to outstanding stock options, awards and employee stock purchases was $19.4 million, which is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average remaining period of 2.6 years.
Stock-Based Compensation Associated with Awards to Employees
The Company uses the Black-Scholes option pricing model to determine the fair value of stock options. The valuation model for stock compensation expense requires the Company to make assumptions and judgments about the variables used in the calculation including the expected term (weighted-average period of time that the options granted are expected to be outstanding); volatility of the Company's common stock, an assumed-risk-free interest rate and the estimated forfeitures of unvested stock options. The fair value of employee stock options was estimated using the following weighted-average assumptions:
93
Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||
2015 | 2014 | 2013 | ||||||
Expected term (in years) | 4.8 | 4.4 | 4.8 | |||||
Expected volatility | 63 | % | 43 | % | 51 | % | ||
Risk-free interest rate | 1.29 | % | 1.25 | % | 1.02 | % | ||
Expected dividend yield | 0 | % | 0 | % | 0 | % | ||
Expected Term. Subsequent to the Company's initial public offering of its common stock, or IPO in 2011, and through 2014, the expected term used was based on expected term of a group of similar entities, referred to as its “peer group.” In evaluating similarity, the Company considered factors such as industry, stage of life cycle and size. In 2015, the Company modified its approach by including its own historical data along with the expected term of the identified peer group companies. The Company will continue to apply this methodology until a sufficient amount of historical information regarding its own expected term becomes available.
Volatility. Subsequent to the IPO and through 2014, the Company continued to estimate its volatility based on the volatility of a group of similar entities, referred to as its "peer group". In evaluating similarity, the Company considered factors such as industry, stage of life cycle and size. In 2015, the Company modified its approach by including its own common stock trading history along with the volatility of the identified peer group companies. The expected stock price volatility is estimated using a combination of historical and peer group volatility to derive the expected volatility assumption. The Company believes the blended volatility is more representative of future stock price trends over the expected life of the options rather than just using historical or peer group volatility. The Company will continue to apply this methodology until a sufficient amount of historical information regarding the volatility of its own stock price becomes available.
Risk-Free Interest Rate. The risk-free interest rate is based on U.S. Treasury zero-coupon issues with remaining terms similar to the expected term on the options.
Dividend Yield. The Company has never paid any dividends and does not plan to pay dividends in the foreseeable future, and, therefore, used an expected dividend yield of zero in the valuation model.
Forfeitures. The Company is required to estimate forfeitures at the time of grant, and revise those estimates in subsequent periods if actual forfeitures differ from those estimates. The Company uses historical data to estimate pre-vesting option forfeitures and record stock based compensation expense only for those awards that are expected to vest. To the extent actual forfeitures differ from the estimates, the difference will be recorded as a cumulative adjustment in the period that the estimates are revised.
During the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, the Company granted 45,622, 255,000 and 543,987 stock options, respectively, to employees with a weighted-average grant date fair value of $18.19, $6.77 and $6.75 per share, respectively. The aggregate intrinsic value of options exercised was $2.8 million, $3.2 million and $6.8 million for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, and 2013, respectively. The aggregate intrinsic value is calculated as the difference between the exercise price and the estimated fair value of the Company's common stock at the date of exercise. The total fair value of shares vested was $2.7 million, $4.3 million and $4.9 million for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
During the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, the Company granted 593,003, 508,729 and 1,180,200 restricted stock units and restricted awards, respectively, to employees. The weighted-average grant date fair value as of the respective grant date of restricted stock units and restricted stock awards was $32.05, $19.99 and $5.62 for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively. The fair value as of the respective vesting dates of restricted stock units and restricted stock awards was $6.4 million, $4.3 million and $1.4 million for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
There was no capitalized stock-based compensation cost during the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013. The Company recognized stock-based compensation tax benefits of $1.3 million and $0.1 million during the years ended December 31, 2015 and December 31, 2014, respectively. There was no recognized stock-based compensation tax benefits during the year ended December 31, 2013.
94
Stock-Based Compensation for Non-employees
Stock-based compensation expense related to stock-based awards to non-employees is recognized as the stock-based awards are earned, generally through the provision of services. The Company believes that the fair value of the stock-based awards is more reliably measurable than the fair value of the services received. The fair value of the granted stock-based awards is calculated at each reporting date using the Black-Scholes option pricing model. During each of the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, the Company granted stock-based awards to non-employees which vest over 0.5 to 2.0 years. Stock-based compensation expense related to non-employee grants was $0.4 million, $0.6 million and $0.5 million for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively, of which $0.2 million and $0.8 million for an arrangement with a non-employee customer has been recorded as a reduction of revenue in the statement of operations during the years ended December 31, 2015 and December 31, 2014, respectively. Included in the 2014 amount is $0.4 million of expense related to the year ended December 31, 2013.
Performance-Based Restricted Stock Units (PRSUs)
From time to time, the Company will issue performance-based stock options and restricted stock units to senior executives. During the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, the Company granted 64,938, 40,000 and 40,000 performance-based restricted stock units, respectively, to certain senior executives, which are accounted for as equity awards. The number of units that ultimately vest depends on achieving certain performance criteria and can range from 0% to 100% of the number of units granted. The performance criteria are specific to the roles of each of the executives and are set by the Compensation Committee of the Board of Directors. The performance-based restricted stock units have no dividend or voting rights during the performance period. Each of the performance-based restricted stock units represents the contingent right to receive one share of the Company's common stock if the vesting conditions are satisfied. Compensation expense related to these grants is based on the grant date fair value of the award. Total stock-based compensation related to performance-based restricted awards was $2.5 million, $0.8 million and $0.2 million in the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively. As of December 31, 2015, 34,938 PRSUs were outstanding.
10. Employee Benefit Plans
In 2005, the Company adopted a retirement savings plan under Section 401(k) of the Internal Revenue Code. This plan covers all employees in the United States who meet minimum age and service requirements and allows participants to defer a portion of their annual compensation on a pre-tax basis. Company contributions to the plan may be made at the discretion of the Board of Directors. Matching 401(k) contributions expensed were $1.8 million, $1.5 million and $1.1 million for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
11. Income Taxes
The domestic and foreign components of income (loss) before income taxes were as follows (in thousands):
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||
Domestic | $ | 14,065 | $ | 1,443 | $ | (19,535 | ) | ||||
Foreign | (10,733 | ) | 319 | 370 | |||||||
Income (loss) before income taxes | $ | 3,332 | $ | 1,762 | $ | (19,165 | ) | ||||
Provision for (benefit from) income taxes consisted of the following (in thousands):
95
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||
Current provision: | |||||||||||
Federal | $ | 654 | $ | — | $ | — | |||||
State | 1,098 | 156 | 60 | ||||||||
Foreign | 183 | 94 | 61 | ||||||||
Total current | 1,935 | 250 | 121 | ||||||||
Deferred provision (benefit): | |||||||||||
Federal | (34,835 | ) | — | — | |||||||
State | (5,576 | ) | — | — | |||||||
Foreign | 6 | (19 | ) | 19 | |||||||
Total deferred | (40,405 | ) | (19 | ) | 19 | ||||||
Total provision for (benefit from) income taxes | $ | (38,470 | ) | $ | 231 | $ | 140 | ||||
The following is a reconciliation of the statutory federal income tax rate to the Company's effective tax:
Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||
2015 | 2014 | 2013 | ||||||
Tax at federal statutory rate | 35 | % | 35 | % | 35 | % | ||
State income taxes, net of federal benefit | 5 | 6 | 2 | |||||
Non-deductible permanent difference | 16 | 22 | (1 | ) | ||||
Non-deductible executive compensation | 51 | 150 | — | |||||
Change in valuation allowance | (1,394 | ) | (157 | ) | (34 | ) | ||
Research and development credits | (36 | ) | (47 | ) | (2 | ) | ||
Stock-based compensation | 11 | 6 | (1 | ) | ||||
Impact of foreign operations | 153 | (2 | ) | — | ||||
Other tax adjustment | 4 | — | — | |||||
Effective tax rate | (1,155 | )% | 13 | % | (1 | )% | ||
The impact of foreign operations primarily relates to the differential between the United States federal statutory rate and lower foreign statutory rates, including a charge for a license payment made in one of our foreign subsidiaries which is incurred in a zero tax rate jurisdiction, due to the Company's tax planning action described below. Tax effects of temporary differences that give rise to significant portions of the deferred tax assets are presented below (in thousands):
December 31, | |||||||
2015 | 2014 | ||||||
Net operating loss carryforwards | $ | 19,829 | $ | 31,237 | |||
Income tax credits | 5,867 | 4,838 | |||||
Other Tax Credit | 851 | — | |||||
Depreciation and amortization | 4,855 | 5,615 | |||||
Accruals and reserves | 7,606 | 4,316 | |||||
Stock-based compensation | 3,950 | 2,790 | |||||
Total deferred tax assets | 42,958 | 48,796 | |||||
Valuation allowance | (2,483 | ) | (48,730 | ) | |||
Net deferred tax assets | $ | 40,475 | $ | 66 | |||
As of December 31, 2015, the Company had federal and state net operating loss carryforwards of $104.3 million and $96.3 million, respectively. The federal net operating losses begin expiring in 2025 and state net operating losses begin expiring in 2017. As of December 31, 2015, the Company had credit carryforwards of approximately $4.2 million and $4.8 million available to reduce future taxable income, if any, for federal and state income tax purposes, respectively. The federal research and development credit carryforwards expire beginning 2025, and state credits can be carried forward indefinitely.
96
The federal and state net operating losses include $57.2 million and $22.9 million of excess stock based compensation that will result in increases to additional paid in capital, when realized.
The valuation allowance for deferred tax assets consisted of the following activity for the fiscal years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013 (in thousands):
Description | Balance at Beginning of Year | Additions | Deductions | Balance at End of Year | |||||||||||
Year ended December 31, 2013 | $ | 44,926 | $ | 6,077 | $ | — | $ | 51,003 | |||||||
Year ended December 31, 2014 | 51,003 | 1,011 | (3,284 | ) | 48,730 | ||||||||||
Year ended December 31, 2015 | $ | 48,730 | $ | 673 | $ | (46,920 | ) | (1) | $ | 2,483 | |||||
(1) | Of this deduction, $40.4 million relates to the release in the valuation allowance, which was recorded as a deferred tax benefit during the year. |
Utilization of net operating losses and tax credit carryforwards may be limited by ownership change rules, as defined in Section 382 of the Internal Revenue Code. Similar rules may apply under state tax laws. The Company has assessed the application of Internal Revenue Code Section 382, during the fourth quarter of 2015, and concluded no limitation currently applies, and the Company will continue to monitor activities in the future. In the event the Company experiences any subsequent changes in ownership, the amount of net operating losses and research and development credit carryovers available in any taxable year could be limited and may expire unutilized.
During the year ended December 31, 2015, the amount of gross unrecognized tax benefits increased by $1.4 million. The total amount of unrecognized tax benefits was $2.9 million as of December 31, 2015. The Company recognizes interest and penalties related to uncertain tax positions as part of the income tax provision. To date, such interest and penalties have not been material.
A reconciliation of the beginning and ending amount of unrecognized tax benefits is as follows (in thousands):
Balance as of January 1, 2013 | $ | 902 | |
Gross increase on tax positions related to the prior year | 1,434 | ||
Gross increase on tax positions related to the current year | 589 | ||
Balance as of December 31, 2013 | 2,925 | ||
Gross decrease on tax positions related to the prior year | (1,746 | ) | |
Gross increase (decrease) on tax positions related to the current year | 274 | ||
Balance as of December 31, 2014 | 1,453 | ||
Gross increase on tax positions related to the prior year | 99 | ||
Gross increase on tax positions related to the current year | 1,341 | ||
Balance as of December 31, 2015 | $ | 2,893 | |
While it is often difficult to predict the final outcome of any particular uncertain tax position, management does not believe that it is reasonably possible that the estimates of unrecognized tax benefits will significantly change during the next twelve months.
Each quarter the Company assesses the recoverability of its deferred tax assets under ASC 740, Income Taxes. The Company is required to establish a valuation allowance for any portion of the assets that the Company concludes is not more likely than not realizable. The Company's assessment considers, among other things, the three year cumulative net income, positive pretax net income and taxable income, forecasts of its future taxable income, carryforward periods, and its utilization experience with operating loss and tax credit carryforwards and tax planning actions.
Management believes that, based on a number of factors, which include the Company's historical operating performance and cumulative U.S. taxable income during the three most recent years, the Company's tax planning action of migrating and licensing certain intellectual property to its foreign subsidiaries as well as its forecasted future taxable income, it is more-likely-than-not that it will realize a benefit from its Federal and certain State deferred tax assets within allowable net loss carryforward periods. As such, in fourth quarter of 2015, the Company released a valuation allowance of $40.4 million against its Federal and certain State deferred tax assets, with a corresponding deferred tax benefit during the quarter. Due to strong
97
results during recent years and increased confidence that the Company will continue to generate taxable income into the foreseeable future, the Company's assessment regarding the potential to realize its deferred tax assets changed.
With respect to California deferred tax assets, the Company believes that, except for California R&D credits, all other deferred tax assets would be realized in the future. Although the Company anticipates generating taxable income in California in future years, expected continued generation of California R&D credits along with existing net operating loss carryforwards of $73 million will be sufficient to offset California taxable income in the foreseeable future. As such, the Company's ability to utilize its current California R&D credit carryforwards is not more likely than not, and the Company continues to apply a valuation allowance against these deferred tax assets. For other states' deferred tax assets, the Company believes it is more likely than not that those deferred tax assets will be realized in the future and as a result does not apply a valuation allowance against those deferred tax assets.
As of December 31, 2015, U.S. income taxes and foreign withholding taxes associated with the repatriation of undistributed earnings of foreign subsidiaries were not provided for on a cumulative total of $0.6 million. The Company intends to reinvest these earnings indefinitely in our foreign subsidiaries. If these earnings were distributed in the form of dividends or otherwise, or if the shares of the relevant foreign subsidiaries were sold or otherwise transferred, the Company would be subject to additional U.S. income taxes and foreign withholding taxes, net of related foreign tax credits. Determination of the amount of any unrecognized deferred income tax liability related to these earnings is not practicable because of the complexities of the hypothetical calculation.
The Company files income tax returns in the U.S. federal and state jurisdictions, in the United Kingdom and Ireland and all returns since inception remain open to examination.
On December 18, 2015, the President signed into law the Protecting Americans from Tax Hikes Act of 2015, which retroactively extends several expired tax provisions. Among the extended provisions is the Section 41 research credit for qualified research expenditures incurred through the end of 2015. The benefit of the reinstated credit impacted the consolidated statement of operations in the period of enactment, which was the fourth quarter of 2015 due to the reversal of the valuation allowance on federal research and development credit carryforwards.
12. Net Income (Loss) per Share of Common Stock
Basic net income (loss) per share of common stock is calculated by dividing the net income (loss) by the weighted-average number of shares of common stock outstanding for the period. Diluted net income (loss) per share of common stock is computed by giving effect to all potentially dilutive securities outstanding during the period, including stock options, restricted stock units and common stock issuable pursuant to the ESPP.
A reconciliation of the numerator and denominator used in the calculation of the basic and diluted net income (loss) per share is as follows:
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||||
2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||
Numerator | |||||||||||
Net income (loss) (in thousands) | $ | 41,802 | $ | 1,531 | $ | (19,305 | ) | ||||
Denominator | |||||||||||
Weighted average shares of common stock outstanding used in computing net income (loss) per share, basic | 38,754,643 | 37,563,590 | 36,209,051 | ||||||||
Dilutive effect of incremental shares and share equivalents | 2,041,003 | 3,433,382 | — | ||||||||
Weighted average shares of common stock outstanding used in computing net income (loss) per share, diluted | 40,795,646 | 40,996,972 | 36,209,051 | ||||||||
Net income (loss) per share: | |||||||||||
Net income (loss) per share, basic | $ | 1.08 | $ | 0.04 | $ | (0.53 | ) | ||||
Net income (loss) per share, diluted | $ | 1.02 | $ | 0.04 | $ | (0.53 | ) | ||||
98
Basic net income per share is computed using the weighted average number of common shares outstanding during the period. Diluted net income per share is computed using the treasury stock method to calculate the weighted average number of common shares and, if dilutive, potential common shares outstanding during the period. Potential dilutive common shares include unvested restricted stock awards and units and incremental common shares issuable upon the exercise of stock options, less shares from assumed proceeds. The assumed proceeds calculation includes actual proceeds to be received from the employee upon exercise, the average unrecognized stock compensation cost during the period and any tax benefits that will be credited upon exercise to additional paid-in capital. The following outstanding potentially dilutive securities were excluded from the computation of diluted net income (loss) per share of common stock for the periods presented, because including them would have been anti-dilutive:
Year Ended | ||||||||
December 31, | ||||||||
2015 | 2014 | 2013 | ||||||
Options to purchase common stock | 39,497 | 220,712 | 3,598,385 | |||||
Restricted stock units | 26,290 | 12,723 | 1,906,696 | |||||
Common stock issuable pursuant to the ESPP | — | — | 86,026 | |||||
Total | 65,787 | 233,435 | 5,591,107 | |||||
13. Supplemental Cash Flow Information
The supplemental cash flow information consists of the following (in thousands):
Year Ended | |||||||||||
December 31, | |||||||||||
2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||
Cash paid for interest | $ | 13 | $ | — | $ | — | |||||
Cash paid for income taxes | $ | 38 | $ | 285 | $ | 188 | |||||
Non-cash investing and financing activities: | |||||||||||
Assets acquired under capital leases | $ | — | $ | (382 | ) | $ | — | ||||
Accounts payable and accrued liabilities related to property, plant and equipment purchases | $ | 843 | $ | 106 | $ | 14 | |||||
14. Segment Information
Operating segments are defined as components of an enterprise about which separate financial information is available that is evaluated regularly by the chief operating decision maker, or decision making group, in deciding how to allocate resources and in assessing performance. The Company’s chief operating decision maker is its Chief Executive Officer. The Company has one business activity and there are no segment managers who are held accountable for operations. Accordingly, the Company has a single reportable segment structure. All of the Company’s principal operations and decision-making functions are located in the United States.
The Company’s revenue by geographic region, based on the location to where the product was shipped, is summarized as follows (in thousands):
Year Ended | |||||||||||
December 31, | |||||||||||
2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||
North America | $ | 193,376 | $ | 134,434 | $ | 89,150 | |||||
International | 62,040 | 40,044 | 22,476 | ||||||||
Total | $ | 255,416 | $ | 174,478 | $ | 111,626 | |||||
99
North America includes the United States and related territories as well as Canada. International is the rest of the world. Revenue for the United States was $180.5 million, $125.0 million and $83.7 million for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
The following table sets forth revenue by product expressed as dollar amounts (in thousands):
Year Ended | |||||||||||
December 31, | |||||||||||
2015 | 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||
System revenue | $ | 130,698 | $ | 93,015 | $ | 61,359 | |||||
Consumable revenue | 124,718 | 81,463 | 50,267 | ||||||||
Total | $ | 255,416 | $ | 174,478 | $ | 111,626 | |||||
Substantially all of the Company’s long-lived assets are located in the United States of America.
15. Subsequent Events
On February 25, 2016, Patrick F. Williams, Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer and the Company mutually agreed that Mr. Williams would cease to be an officer and employee of the Company effective April 18, 2016.
100
Supplementary Financial Data (unaudited)
The following table presents selected unaudited consolidated financial data for each of the eight quarters in the two-year period ended December 31, 2015. The selected quarterly financial data should be read in conjunction with the Company's consolidated financial statements and the related notes and "Item 7: Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations." This information has been derived from the Company's unaudited consolidated financial statements that, in management's opinion, reflect all recurring adjustments necessary to fairly state this information when read in conjunction with the Company's consolidated financial statements and the related notes appearing in the section entitled "Consolidated Financial Statements," Net income (loss) per share-basic and diluted, for the four quarters of each fiscal year may not sum to the total for the fiscal year because of the different number of shares outstanding during each period. The results of operations for any quarter are not necessarily indicative of the results to be expected for any future period.
(In thousands, except share and per share data) | |||||||||||||||
Quarter | |||||||||||||||
First | Second | Third | Fourth (1) | ||||||||||||
Year Ended December 31, 2015 | |||||||||||||||
Total revenue | $ | 51,558 | $ | 64,431 | $ | 61,202 | $ | 78,225 | |||||||
Gross profit | $ | 37,180 | $ | 46,315 | $ | 45,161 | $ | 52,385 | |||||||
Net income (loss) | $ | (2,129 | ) | $ | 1,178 | $ | 2,147 | $ | 40,606 | ||||||
Net income (loss) per share, basic | $ | (0.06 | ) | $ | 0.03 | $ | 0.06 | $ | 1.04 | ||||||
Shares used in calculation-basic | 38,383,022 | 38,649,873 | 38,881,183 | 39,093,825 | |||||||||||
Net income (loss) per share, diluted | $ | (0.06 | ) | $ | 0.03 | $ | 0.05 | $ | 0.99 | ||||||
Shares used in calculation-diluted | 38,383,022 | 41,641,660 | 40,860,593 | 40,966,744 | |||||||||||
Quarter | |||||||||||||||
First | Second | Third | Fourth | ||||||||||||
Year Ended December 31, 2014 | |||||||||||||||
Total revenue | $ | 30,975 | $ | 47,061 | $ | 45,670 | $ | 50,772 | |||||||
Gross profit | $ | 21,959 | $ | 33,401 | $ | 33,115 | $ | 35,939 | |||||||
Net income (loss) | $ | (7,337 | ) | $ | 2,769 | $ | 4,782 | $ | 1,317 | ||||||
Net income (loss) per share, basic | $ | (0.20 | ) | $ | 0.07 | $ | 0.13 | $ | 0.03 | ||||||
Shares used in calculation-basic | 37,215,697 | 37,440,537 | 37,630,222 | 37,958,395 | |||||||||||
Net income (loss) per share, diluted | $ | (0.20 | ) | $ | 0.07 | $ | 0.12 | $ | 0.03 | ||||||
Shares used in calculation-diluted | 37,215,697 | 40,597,275 | 40,926,034 | 41,434,178 | |||||||||||
(1) | In the fourth quarter of fiscal 2015, the Company released $40.4 million of its deferred tax asset valuation allowance. See Note 11 to the Consolidated Financial Statements. |
101
ITEM 9. CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE
None.
ITEM 9A. CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Based on our management's evaluation (with the participation of our principal executive officer and principal financial officer), as of December 31, 2015, the end of the period covered by this report, our principal executive officer and principal financial officer have concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, (the "Exchange Act") were not effective due to a material weakness in internal control over financial reporting described below in Management's Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting.
Management's Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d 15(f) under the Exchange Act). Our management, with the participation of our principal executive officer and principal financial officer, conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2015. This evaluation was based on the framework established in Internal Control–Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. Based on our assessment under the framework in Internal Control–Integrated Framework (2013), our management concluded that a material weakness exists as described below. A material weakness is “a deficiency or a combination of deficiencies, in internal control over financial reporting, such that there is a reasonable possibility that a material misstatement of the company’s annual or interim financial statement will not be prevented or detected in a timely basis.”
We did not maintain effective controls in our risk assessment process. Rapid growth in the size and scale of the business has made certain existing controls inadequate, and the implementation of new controls and control enhancements has not been sufficient to address new and evolving sources of potential misstatement. The material weakness resulted in immaterial misstatements relating to the completeness and accuracy of accounts receivable, inventory, accrued liabilities and operating expenses and related disclosures, which were primarily the result of a lack of controls over the completeness and accuracy of data used in accounting calculations and a failure to execute controls in the period-end close process on a timely basis.
Additionally, the material weakness could result in further misstatements of account balances or disclosures that would result in a material misstatement to the annual or interim consolidated financial statements that would not be prevented or detected. Accordingly, our management has determined that this control deficiency constitutes a material weakness.
Because of the material weakness, management concluded that the Company did not maintain effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2015 based on criteria in Internal Control–Integrated Framework (2013) issued by COSO.
The effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2015 has been audited by PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, as stated in their report which appears in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Management’s Plan to Remediate the Material Weakness
In order to remediate the material weakness, management has initiated or will initiate the following steps:
• | We had previously engaged an outside consulting firm to review and suggest recommendations to improve our financial close process and intend to implement their findings as soon as practicable; |
• | We had previously created a Director of Controls and Processes role to improve the design, implementation, execution and supervision of internal controls within the organization, which we have been in the process of hiring; |
• | Management intends to perform a detailed financial reporting risk assessment to identify areas that require improvement, and design new and enhanced control activities to address these areas; and |
• | Management intends to evaluate the form and frequency of existing control activities and implement changes to improve the precision and timeliness of controls in the financial reporting process. |
Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
102
There was no changes in our internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) under the Exchange Act) during the last fiscal quarter of 2015 that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
Inherent Limitations on the Effectiveness of Controls
Control systems, no matter how well designed and operated, can provide only reasonable, not absolute, assurance that the control systems' objectives are being met. Further, the design of any control systems must reflect the fact that there are resource constraints, and the benefits of all controls must be considered relative to their costs. Because of the inherent limitations in all control systems, no evaluation of controls can provide absolute assurance that all control issues and instances of fraud, if any, within our company have been detected. These inherent limitations include the realities that judgments in decision making can be faulty and that breakdowns can occur because of simple error or mistake. Control systems can also be circumvented by the individual acts of some persons, by collusion of two or more people, or by management override of the controls. The design of any system of controls is based, in part, on certain assumptions about the likelihood of future events, and there can be no assurance that any design will succeed in achieving its stated goals under all potential future conditions. Over time, controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions or deterioration in the degree of compliance with policies or procedures.
103
ITEM 9B. OTHER INFORMATION
Not applicable
104
PART III
ITEM 10. | DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE |
The following information is included in our Notice of Annual Meeting of Stockholders and Proxy Statement to be filed within 120 days after our fiscal year end of December 31, 2015, or the Proxy Statement, and is incorporated herein by reference:
• | Information regarding our directors and any persons nominated to become a director, as well as with respect to some other required board matters, set forth under Proposal 1 entitled “Election of Directors” and under “Information Regarding the Board of Directors and Corporate Governance” in the Proxy Statement. |
• | Information regarding our executive officers is set forth under “Executive Officers” in the Proxy Statement. |
• | Information regarding our audit committee and our designated “audit committee financial expert” is set forth under the caption “Information Regarding the Board of Directors and Corporate Governance” in the Proxy Statement. |
• | Information on our code of business conduct and ethics for directors, officers and employees set forth under the caption “Code of Business Conduct” under “Information Regarding the Board of Directors and Corporate Governance - Information Regarding Committees of the Board of Directors” in the Proxy Statement. |
• | Information regarding Section 16(a) beneficial ownership reporting compliance set forth under the caption “Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance” in the Proxy Statement. |
• | Information regarding procedures by which stockholders may recommend nominees to our board of directors is set forth under the caption “Consideration and Qualifications of Director Nominees” under “Information Regarding the Board of Directors and Corporate Governance” in the Proxy Statement. |
ITEM 11. | EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION |
Information regarding compensation of our named executive officers is set forth under the caption “Executive Compensation” in the Proxy Statement, which information is incorporated herein by reference.
Information regarding compensation of our directors is set forth under the caption "Director Compensation" in the Proxy Statement, which information is incorporated herein by reference.
Information relating to compensation policies and practices as they relate to risk management is set forth under the caption “Information Regarding the Board of Directors and Corporate Governance - Information Regarding Committees of the Board of Directors - Compensation Committee” in the Proxy Statement, which information is incorporated herein by reference.
Information regarding compensation committee interlocks is set forth under the caption “Information Regarding the Board of Directors and Corporate Governance - Information Regarding Committees of the Board of Directors - Compensation Committee Interlocks and Insider Participation" in the Proxy Statement, which information is incorporated herein by reference.
The Compensation Committee Report is set forth under the caption "Compensation Committee Report" under “Information Regarding the Board of Directors and Corporate Governance - Information Regarding Committees of the Board of Directors” in the Proxy Statement, which report is incorporated herein by reference.
ITEM 12. | SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS |
Information regarding security ownership of certain beneficial owners and management is set forth under the caption “Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management” in the Proxy Statement, which information is incorporated herein by reference.
Information regarding securities authorized for issuance under our equity compensation plans is set forth under the caption “Securities Authorized for Issuance under Equity Compensation Plans” in the Proxy Statement, which information is incorporated herein by reference.
105
ITEM 13. | CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE |
Information regarding certain relationships and related transactions is set forth under the caption "Transactions With Related Persons" in the Proxy Statement, which information is incorporated herein by reference.'
Information regarding director independence is set forth under the caption “Information Regarding the Board of Directors and Corporate Governance - Independence of The Board of Directors” in the Proxy Statement, which information is incorporated herein by reference.
ITEM 14. | PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING FEES AND SERVICES |
Information regarding principal auditor fees and services is set forth under “Proposal 2 - Ratification of Selection of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm - Principal Accountant Fees and Services” in the Proxy Statement, which information is incorporated herein by reference.
106
PART IV
ITEM 15. EXHIBITS, FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES
(a) The following documents are filed as part of this Form 10-K
1. Consolidated Financial Statements and Supplementary Financial Data:
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
Consolidated Balance Sheets
Consolidated Statements of Operations
Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income (Loss)
Consolidated Statements of Stockholders' Equity
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Supplementary Financial Data
2. Financial Statements Schedules
All schedules have been omitted because they are not required, not applicable, or the required information is included in the consolidated financial statements or notes thereto.
3.Exhibits
The exhibits listed in the Exhibits Index, immediately following the signature page to this Form 10-K, are filed or incorporated by reference as part of this Form 10-K.
107
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the Registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
ZELTIQ Aesthetics, Inc. | |||
Date: | March 14, 2016 | By: | /s/ Patrick F. Williams |
Patrick F. Williams | |||
Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer | |||
(Duly Authorized Officer, Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) | |||
108
POWER OF ATTORNEY
KNOW ALL PERSONS BY THESE PRESENTS, that each person whose signature appears below constitutes and appoints Mark J. Foley, Sergio Garcia and Patrick F. Williams, and each of them, as his or her true and lawful attorneys-in-fact and agents, with full power of substitution and resubstitution for him or her and in his or her name, place, and stead, in any and all capacities, to sign any and all amendments to this Annual Report on Form 10-K, and to file the same, with exhibits thereto and other documents in connection therewith, with the Securities and Exchange Commission, granting unto said attorneys-in-fact and agents, and each of them, full power and authority to do and perform each and every act and thing requisite and necessary to be done therewith, as fully to all intents and purposes as he might or could do in person, hereby ratifying and confirming all that said attorneys-in-fact and agents, and any of them or their substitute or substitutes, may lawfully do or cause to be done by virtue hereof.
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
Signature | Title | Date | ||
/s/ Mark J. Foley | President, Chief Executive Officer | March 14, 2016 | ||
Mark J. Foley | and Director (Principal Executive Officer) | |||
/s/ Patrick F. Williams | Senior Vice President and Chief | March 14, 2016 | ||
Patrick F. Williams | Financial Officer (Duly Authorized Officer, Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) | |||
/s/ Mary M. Fisher | Director | March 14, 2016 | ||
Mary M. Fisher | ||||
/s/ D. Keith Grossman | Director | March 14, 2016 | ||
D. Keith Grossman | ||||
/s/ Kevin C. O'Boyle | Director | March 14, 2016 | ||
Kevin C. O'Boyle | ||||
/s/ Bryan E. Roberts, Ph.D | Director | March 14, 2016 | ||
Bryan E. Roberts, Ph.D. | ||||
/s/ Andrew N. Schiff, M.D. | Director | March 14, 2016 | ||
Andrew N. Schiff, M.D. | ||||
109
EXHIBIT INDEX
Listed and indexed below are all Exhibits filed as part of this report.
Incorporated by Reference | ||||||||||||||
Exhibit No. | Description | Filed Herewith | Form | File No. | Exhibit No. | Date Filed | ||||||||
3.1 | Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation of ZELTIQ Aesthetics, Inc. | 10-Q | 001-35318 | 3.1 | 4/26/2013 | |||||||||
3.2 | Amended and Restated Bylaws of ZELTIQ Aesthetics, Inc. | 8-K | 001-35318 | 3.1 | 2/20/2015 | |||||||||
4.1 | Reference is made to Exhibits 3.1 and 3.2. | |||||||||||||
4.2 | Form of Stock Certificate. | S-1/A | 333-175514 | 4.1 | 9/23/2011 | |||||||||
10.1 | # | Amended and Restated Exclusive License Agreement, dated September 21, 2011, by and between ZELTIQ Aesthetics, Inc. (as successor in interest to Juniper Medical, Inc.) and The General Hospital Corporation d/b/a Massachusetts General Hospital. | S-1/A | 333-175514 | 10.4 | 10/11/2011 | ||||||||
10.2 | Office Building Lease, dated December 22, 2006, by and between ZELTIQ Aesthetics, Inc. (as successor in interest to Juniper Medical, Inc.) and Hacienda Portfolio Venture LLC (as successor in interest to Crosstown Ventures II, LLC). | S-1/A | 333-175514 | 10.4 | 8/17/2011 | |||||||||
10.3 | First Amendment to Office Building Lease, dated December 22, 2006, by and between ZELTIQ Aesthetics, Inc. (as successor in interest to Juniper Medical, Inc.) and Hacienda Portfolio Venture LLC (as successor in interest to Crosstown Ventures II, LLC). | S-1/A | 333-175514 | 10.5 | 8/17/2011 | |||||||||
10.4 | Second Amendment to Office Building Lease, dated September 24, 2010, by and between ZELTIQ Aesthetics, Inc. (as successor in interest to Juniper Medical, Inc.) and Hacienda Portfolio Venture LLC (as successor in interest to Crosstown Ventures II, LLC). | S-1/A | 333-175514 | 10.6 | 8/17/2011 | |||||||||
10.5 | Third Amendment to Office Building Lease, dated August 7, 2012, by and between ZELTIQ Aesthetics, Inc. (as successor in interest to Juniper Medical, Inc.) and Hacienda Portfolio Venture LLC (as successor in interest to Crosstown Ventures II, LLC). | 10-K | 001-35318 | 10.5 | 2/26/2014 | |||||||||
10.6 | Fourth Amendment to Office Building Lease, dated April 22, 2013, by and between ZELTIQ Aesthetics, Inc. (as successor in interest to Juniper Medical, Inc.) and Hacienda Portfolio Venture LLC (as successor in interest to Crosstown Ventures II, LLC). | 10-K | 001-35318 | 10.6 | 2/26/2014 | |||||||||
10.7 | Fifth Amendment to Office Building Lease, dated June 19, 2014, by and between ZELTIQ Aesthetics, Inc. and Hacienda Portfolio Venture LLC. | 10-Q | 001-35318 | 10.1 | 7/29/2014 | |||||||||
10.8 | Building Lease, dated October 3, 2013, by and between ZELTIQ Aesthetics, Inc. and Westcore Greenville, LLC. | 10-K | 001-35318 | 10.7 | 2/26/2014 | |||||||||
10.9 | First Amendment to Building Lease, dated May 5, 2014, by and between ZELTIQ Aesthetics, Inc. and Westcore Greenville, LLC. | 10-Q | 001-35318 | 10.2 | 7/29/2014 | |||||||||
110
10.10 | Third Amended and Restated Investor Rights Agreement, dated May 26, 2010, by and among ZELTIQ Aesthetics, Inc. and the individuals and entities listed on Exhibit A attached thereto. | S-1 | 333-175514 | 10.23 | 7/13/2011 | |||||||||
10.11 | * | Form of Indemnification Agreement, by and between ZELTIQ Aesthetics, Inc. and each of its directors and officers. | S-1 | 333-175514 | 10.17 | 7/13/2011 | ||||||||
10.12 | * | 2005 Stock Incentive Plan. | S-1/A | 333-175514 | 10.11 | 8/17/2011 | ||||||||
10.13 | * | Form of Stock Option Agreement under 2005 Stock Incentive Plan. | S-1/A | 333-175514 | 10.12 | 8/17/2011 | ||||||||
10.14 | * | Amendment to 2005 Stock Incentive Plan. | S-1/A | 333-175514 | 10.13 | 8/17/2011 | ||||||||
10.15 | * | 2011 Equity Incentive Plan. | S-8 | 333-175514 | 99.1 | 3/13/2013 | ||||||||
10.16 | * | Form of Stock Option Agreement under 2011 Equity Incentive Plan. | S-1/A | 333-175514 | 10.15 | 9/23/2011 | ||||||||
10.17 | * | Form of Restricted Stock Unit Agreement under the 2011 Stock Incentive Plan. | S-1/A | 333-175514 | 10.16 | 9/23/2011 | ||||||||
10.18 | * | Form of Restricted Stock Agreement under the 2011 Stock Incentive Plan. | S-1/A | 333-175514 | 10.17 | 9/23/2011 | ||||||||
10.19 | * | Form of Notice of Grant of Restricted Stock Unit under the 2011 Stock Incentive Plan. | S-1/A | 333-175514 | 10.18 | 9/23/2011 | ||||||||
10.20 | * | Form of Notice of Grant of Restricted Stock under the 2011 Stock Incentive Plan. | S-1/A | 333-175514 | 10.19 | 9/23/2011 | ||||||||
10.21 | * | Form of Notice of Grant of Stock Option under the 2011 Stock Incentive Plan. | S-1/A | 333-175514 | 10.20 | 9/23/2011 | ||||||||
10.22 | * | 2011 Employee Stock Purchase Plan. | S-1/A | 333-175514 | 10.21 | 9/23/2011 | ||||||||
10.23 | Third Amendment to Office Building Lease dated August 7, 2012 by and between ZELTIQ Aesthetics, Inc. and Hacienda Portfolio Venture LLC. | 10-Q | 001-35318 | 10.15 | 11/8/2012 | |||||||||
10.24 | * | ZELTIQ Aesthetics, Inc. 2012 Stock Plan. | S-8 | 333-183131 | 99.1 | 8/7/2012 | ||||||||
10.25 | * | 2013 Bonus Plan for Executive Officers. | 10-Q | 001-35318 | 10.2 | 10/31/2013 | ||||||||
10.26 | * | Form of Stock Option Agreement Under 2012 Stock Plan. | 10-K | 001-35318 | 10.50 | 3/13/2013 | ||||||||
10.27 | * | Form of Restricted Stock Units Agreement Under 2012 Stock Plan. | 10-K | 001-35318 | 10.51 | 3/13/2013 | ||||||||
10.28 | * | Form of Restricted Stock Agreement Under 2012 Stock Plan. | 10-K | 001-35318 | 10.52 | 3/13/2013 | ||||||||
10.29 | * | Form of Notice of Grant of Stock Option Under 2012 Stock Plan. | 10-K | 001-35318 | 10.53 | 3/13/2013 | ||||||||
10.30 | * | Form of Notice of Grant of Restricted Stock Units Under 2012 Stock Plan. | 10-K | 001-35318 | 10.54 | 3/13/2013 | ||||||||
10.31 | * | Form of Notice of Grant of Restricted Stock Under 2012 Stock Plan. | 10-K | 001-35318 | 10.55 | 3/13/2013 | ||||||||
10.32 | * | 2015 Compensation Arrangements with Non-Employee Directors | 10-Q | 001-35318 | 10.5 | 5/5/2015 | ||||||||
10.33 | * | Amended and Restated Offer Letter, dated February 25, 2014, between Keith Sullivan and ZELTIQ Aesthetics, Inc. | 10-Q | 001-35318 | 10.1 | 4/30/14 | ||||||||
10.34 | * | Amended and Restated Offer Letter, dated February 25, 2014, between Sergio Garcia and ZELTIQ Aesthetics, Inc. | 10-Q | 001-35318 | 10.2 | 4/30/14 | ||||||||
10.35 | * | Amended and Restated Offer Letter, dated February 25, 2014, between Carl Lamm and ZELTIQ Aesthetics, Inc. | 10-Q | 001-35318 | 10.3 | 4/30/14 | ||||||||
10.36 | * | Amended and Restated Offer Letter, dated February 25, 2014, between Len DeBenedictis and ZELTIQ Aesthetics, Inc. | 10-Q | 001-35318 | 10.4 | 4/30/14 | ||||||||
111
10.37 | * | Amended and Restated Offer Letter, dated February 25, 2014, between Patrick Williams and ZELTIQ Aesthetics, Inc. | 10-Q | 001-35318 | 10.5 | 4/30/14 | ||||||||
10.38 | * | Amended and Restated Offer Letter, dated February 25, 2014, between Mark Foley and ZELTIQ Aesthetics, Inc. | 10-Q | 001-35318 | 10.6 | 4/30/14 | ||||||||
10.39 | * | 2014 Compensation Arrangements with Executive Officers | 10-Q | 001-35318 | 10.7 | 4/30/14 | ||||||||
10.40 | Amendment to Amended and Restated Offer Letter, dated November 10, 2014, between Keith Sullivan and ZELTIQ Aesthetics, Inc. | 10-Q | 001-35318 | 10.1 | 5/5/15 | |||||||||
10.41 | Relocation Agreement, dated February 19, 2015, between Keith Sullivan and ZELTIQ Aesthetics, Inc. | 10-Q | 001-35318 | 10.2 | 5/5/15 | |||||||||
10.42 | Amended Relocation Agreement, dated March 12, 2015, between Keith Sullivan and ZELTIQ Aesthetics, Inc. | 10-Q | 001-35318 | 10.3 | 5/5/15 | |||||||||
10.43 | 2015 Compensation Arrangements for Named Executive Officers | 10-Q | 001-35318 | 10.4 | 5/5/15 | |||||||||
10.44 | Second Amendment to Building Lease, dated April 28, 2015, by and between ZELTIQ Aesthetics, Inc. and Westcore Greenville, LLC. | 10-Q | 001-35318 | 10.1 | 7/30/15 | |||||||||
10.45 | Amended and Restated Offer Letter, dated July 1, 2015, between Leonard DeBenedictis and ZELTIQ Aesthetics, Inc. | 10-Q | 001-35318 | 10.2 | 7/30/15 | |||||||||
10.46 | Employee Offer Letter Amendment; Compensation Adjustment and Performance Stock Unit Grant dated August 19, 2015, by and between Carl Lamm and ZELTIQ Aesthetics. | 10-Q | 001-35318 | 10.2 | 10/28/15 | |||||||||
10.47 | Employee Offer Letter Amendment; Ireland Assignment Details, dated August 20, 2015, by and between Carl Lamm and ZELTIQ Aesthetics, Inc. | 10-Q | 001-35318 | 10.3 | 10/28/15 | |||||||||
10.48 | Exclusive License Agreement, dated September 8, 2015, by and between ZELTIQ Aesthetics, and Massachusetts General Hospital. | 10-Q | 001-35318 | 10.1 | 10/28/15 | |||||||||
10.49 | Employee Offer Letter, dated December 16, 2015, by and between Todd Zavodnick and ZELTIQ Aesthetics, Inc. | X | ||||||||||||
12.1 | Calculation of Ratio of Earnings to Fixed Charges. | X | ||||||||||||
21.1 | List of subsidiaries. | X | ||||||||||||
23.1 | Consent of PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP, Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm. | X | ||||||||||||
24.1 | Power of Attorney (see signature page to this Form 10-K). | X | ||||||||||||
31.1 | Certification of Principal Executive Officer pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | X | ||||||||||||
31.2 | Certification of Principal Financial Officer pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | X | ||||||||||||
32.1 | Certification of Principal Executive Officer and Principal Financial Officer pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350 as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | X | ||||||||||||
101.INS | XBRL Instance Document | X | ||||||||||||
101.SCH | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema | X | ||||||||||||
112
101.CAL | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase | X | ||||||||||||
101.DEF | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase | X | ||||||||||||
101.LAB | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase | X | ||||||||||||
101.PRE | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase | X | ||||||||||||
______________________
# | Portions of this exhibit have been omitted and filed separately with the Securities and Exchange Commission, pending a determination by the Securities and Exchange Commission as to whether these portions should be granted confidential treatment. |
* | Management Compensation Plan or Arrangement |
113
