Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| 8-K - 8-K - Aldeyra Therapeutics, Inc. | d156982d8k.htm |

A Novel Pharmaceutical Platform Focused on Inflammation and Inborn Errors of Aldehyde Metabolism March 2016 Exhibit 99.1

Disclaimers and Forward-Looking Statements This presentation contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, including statements regarding Aldeyra’s possible or assumed future results of operations and expenses, business strategies and plans, research and development plans or expectations, trends, market sizing, competitive position, industry environment and potential growth opportunities, among other things.. Forward-looking statements include all statements that are not historical facts and, in some cases, can be identified by terms such as “may,” “might,” “will,” “objective,” “intend,” “should,” “could,” “can,” “would,” “expect,” “believe,” “anticipate,” “project,” “target,” “design,” “estimate,” “predict,” “potential,” “plan” or similar expressions and the negatives of those terms. Forward-looking statements involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors that may cause Aldeyra’s actual results, performance or achievements to be materially different from any future results, performance or achievements expressed or implied by the forward-looking statements. Aldeyra is at an early stage of development and may not ever have any products that generate significant revenue. Important factors that could cause actual results to differ materially from those reflected in Aldeyra's forward-looking statements include, among others, the timing of commencement, enrollment and completion of Aldeyra’s clinical trials; the timing and success of preclinical studies and clinical trials conducted by Aldeyra and its development partners; the ability to obtain and maintain regulatory approval to commercialize Aldeyra’s product candidates, and the labeling for any approved products; the scope, progress, expansion, and costs of developing and commercializing Aldeyra’s product candidates; the size and growth of the potential markets for Aldeyra’s product candidates and the ability to serve those markets; Aldeyra’s expectations regarding its expenses and revenue, the sufficiency or use of Aldeyra’s cash resources and needs for additional financing; the rate and degree of market acceptance of any of Aldeyra’s product candidates; Aldeyra’s expectations regarding competition; Aldeyra’s anticipated growth strategies; Aldeyra’s ability to attract or retain key personnel; Aldeyra’s ability to establish and maintain development partnerships; Aldeyra’s expectations regarding federal, state and foreign regulatory requirements; regulatory developments in the United States and foreign countries; Aldeyra’s ability to obtain and maintain intellectual property protection for its product candidates; the anticipated trends and challenges in Aldeyra’s business and the market in which it operates; the use or sufficiency of Aldeyra’s cash or cash equivalents; and other factors that are described in the “Risk Factors” and “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” sections of Aldeyra’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2014 and Aldeyra’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2015, which are on file with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and available on the SEC's website at www.sec.gov. Additional factors may also be set forth in those sections of Aldeyra’s quarterly annual report on form 10-Q K for the year ended December 31, 2015, which will be filed with the SEC in the first quarter of 2016 In addition to the risks described above and in Aldeyra's other filings with the SEC, other unknown or unpredictable factors also could affect Aldeyra's results. No forward-looking statements can be guaranteed and actual results may differ materially from such statements. The information in this presentation is provided only as of March 9, 2016, and Aldeyra undertakes no obligation to update any forward-looking statements contained in this presentation on account of new information, future events, or otherwise, except as required by law.
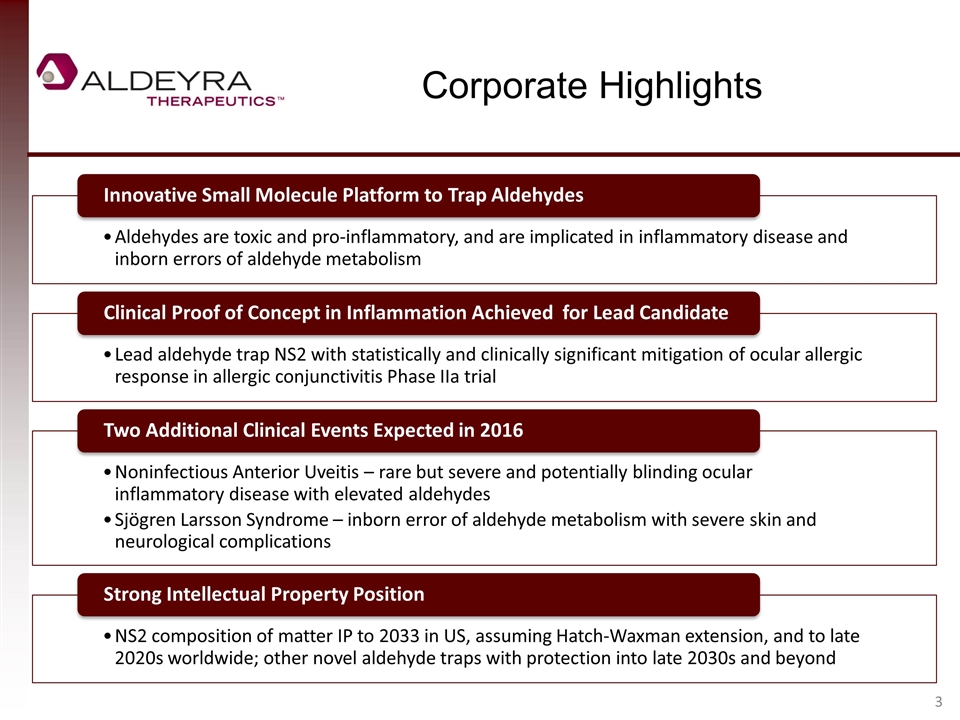
Corporate Highlights Clinical Proof of Concept in Inflammation Achieved for Lead Candidate Two Additional Clinical Events Expected in 2016 Aldehydes are toxic and pro-inflammatory, and are implicated in inflammatory disease and inborn errors of aldehyde metabolism Innovative Small Molecule Platform to Trap Aldehydes Noninfectious Anterior Uveitis – rare but severe and potentially blinding ocular inflammatory disease with elevated aldehydes NS2 composition of matter IP to 2033 in US, assuming Hatch-Waxman extension, and to late 2020s worldwide; other novel aldehyde traps with protection into late 2030s and beyond Strong Intellectual Property Position Lead aldehyde trap NS2 with statistically and clinically significant mitigation of ocular allergic response in allergic conjunctivitis Phase IIa trial Sjögren Larsson Syndrome – inborn error of aldehyde metabolism with severe skin and neurological complications

Management and Directors Todd Brady, M.D., Ph.D. – President, CEO, & Director 20 years of pharmaceutical business and clinical development Domain Associates, Phenome Sciences, (acquired by Xanthus/Antisoma), Aderis Pharmaceuticals (acquired by Schwarz/UCB) Steve Tulipano, CPA – Chief Financial Officer 28 years of financial experience Biogen, Javelin Pharmaceuticals David Clark, M.D. – Chief Medical Officer 18 years of clinical development experience Pfizer, GSK, Wilson Therapeutics Scott Young – Chief Operating Officer 30 years of pharmaceutical clinical development Genzyme, Genetics Institute, Oxigene, Repligen Board of Directors Boyd Clarke – Former CEO Aviron (acquired by MedImmune) Gary Phillips, M.D. – Chief Strategy Officer Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals Neal Walker, D.O. – CEO Aclaris Therapeutics Ben Bronstein, M.D. – Former CEO Peptimmune (acquired by Genzyme) Marty Joyce – Former CFO of Serono USA Jesse Treu, Ph.D. – Domain Associates Todd Brady – CEO Aldeyra Therapeutics

The Aldehyde Trap Platform
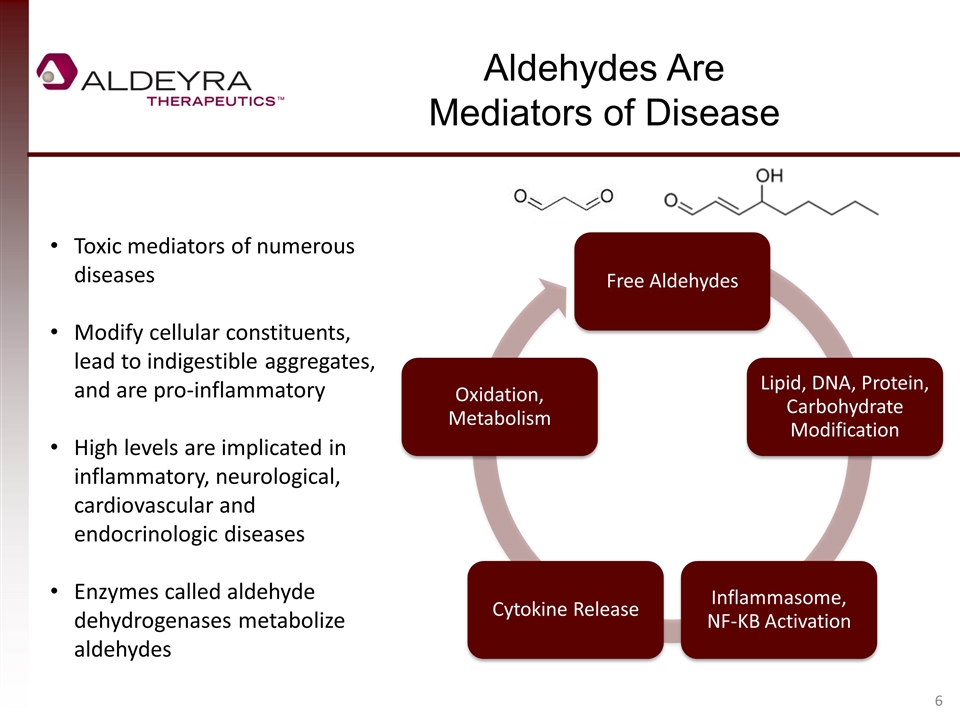
Aldehydes Are Mediators of Disease Toxic mediators of numerous diseases Modify cellular constituents, lead to indigestible aggregates, and are pro-inflammatory High levels are implicated in inflammatory, neurological, cardiovascular and endocrinologic diseases Enzymes called aldehyde dehydrogenases metabolize aldehydes Free Aldehydes Lipid, DNA, Protein, Carbohydrate Modification Inflammasome , NF-KB Activation Cytokine Release Oxidation, Metabolism
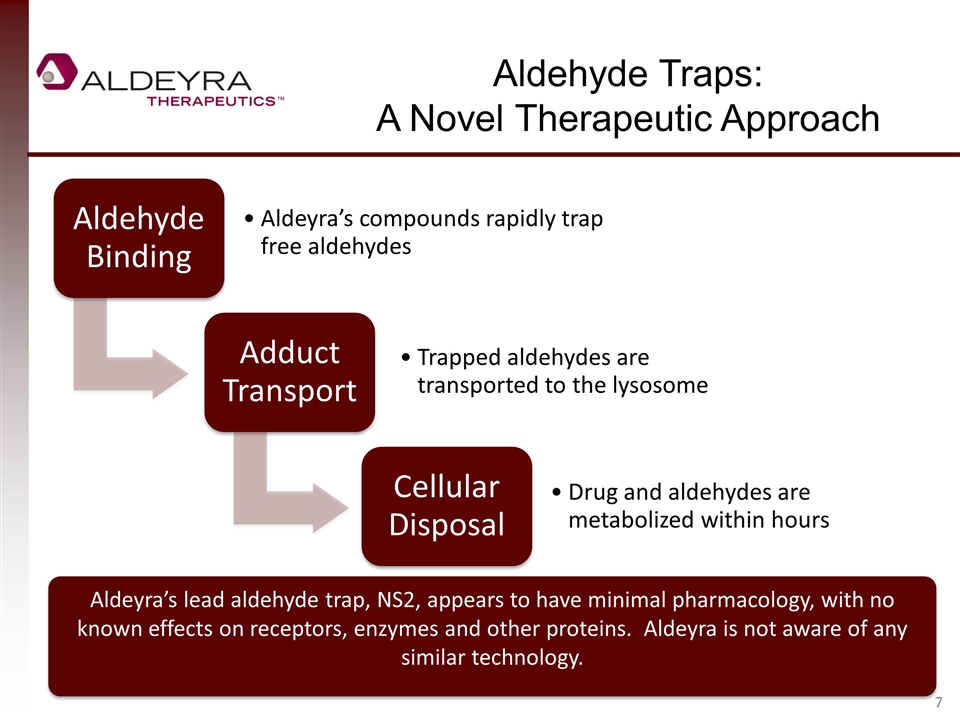
Aldehyde Traps: A Novel Therapeutic Approach Aldeyra’s lead aldehyde trap, NS2, appears to have minimal pharmacology, with no known effects on receptors, enzymes and other proteins. Aldeyra is not aware of any similar technology. Aldehyde Binding Aldeyra’s compounds rapidly trap free aldehydes Adduct Transport Trapped aldehydes are transported to the lysosome Cellular Disposal Drug and aldehydes are metabolized within hours

Overview of Clinical Programs
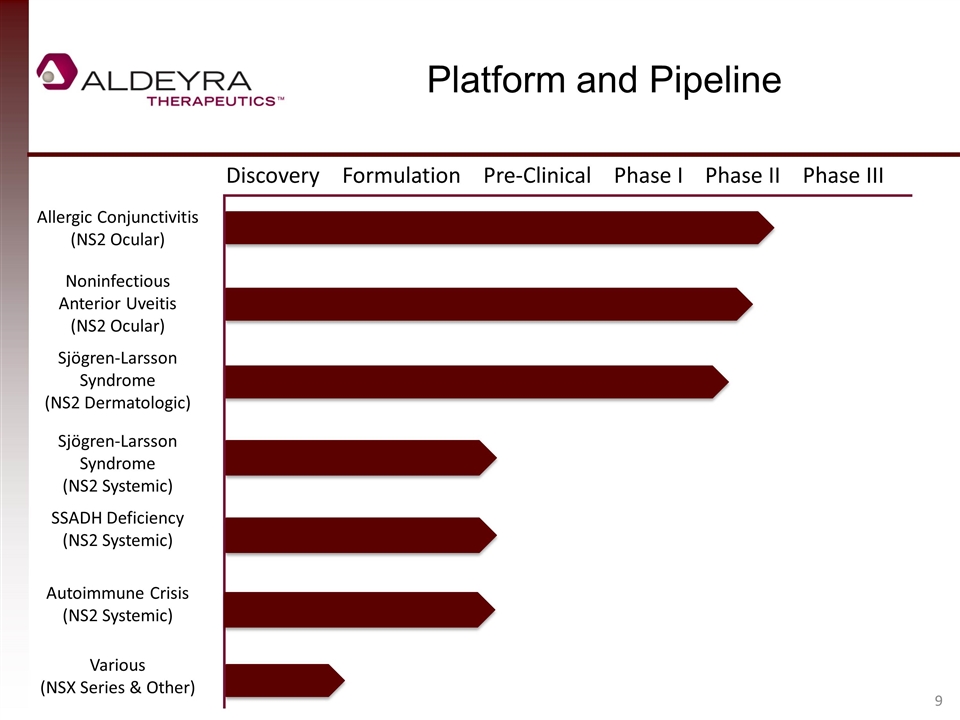
Platform and Pipeline Discovery Formulation Pre-Clinical Phase I Phase II Phase III Allergic Conjunctivitis (NS2 Ocular) Noninfectious Anterior Uveitis (NS2 Ocular) Sjögren-Larsson Syndrome (NS2 Dermatologic) Sjögren-Larsson Syndrome (NS2 Systemic) SSADH Deficiency (NS2 Systemic) Autoimmune Crisis (NS2 Systemic) Various (NSX Series & Other)

Allergic Conjunctivitis: A Common Unmet Medical Need Aldeyra’s lead aldehyde trap mitigated the ocular allergic response at levels that are statistically and clinically significant in a Phase IIa clinical trial Q1 2016. Allergic conjunctivitis affects 20% or more of worldwide population Symptoms include stinging, burning, tearing, pain, itching, redness Aldehydes may mediate IL-5 release and other pro-allergy cytokines Some patients are steroid-dependent, and adrenergic agonists not suitable for chronic use
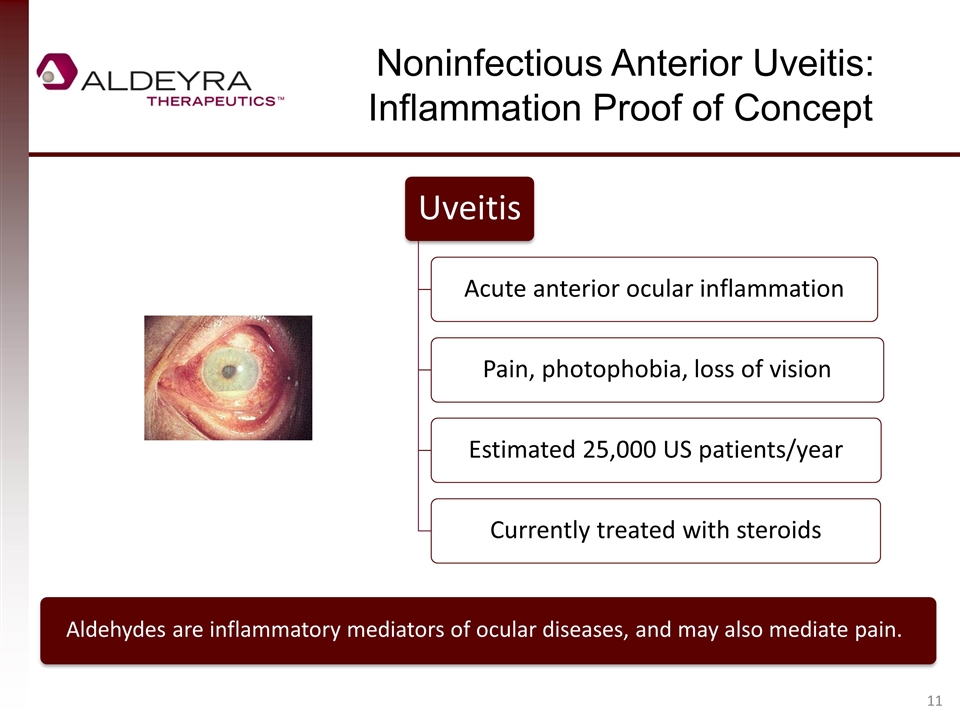
Noninfectious Anterior Uveitis: Inflammation Proof of Concept Aldehydes are inflammatory mediators of ocular diseases, and may also mediate pain. Uveitis Acute anterior ocular inflammation Pain, photophobia, loss of vision Estimated 25,000 US patients/year Currently treated with steroids
Sjögren-Larsson Syndrome (SLS): A Rare Disease with No Therapy An aldehyde trap could be analogous to enzyme replacement therapy (1) Extrapolating from a Swedish estimate, it is generally assumed that there are approximately 1,000 SLS patients in the United States and a greater number of SLS patients in Europe. Rare disease caused by mutation in Fatty Aldehyde Dehydrogenase, leading to high levels of toxic aldehydes Symptoms include severe skin thickening (ichthyosis), retinal disease, and neurological disorders Diagnosed at birth, but no approved therapy that addresses disease; patients survive into 50s Estimated 0.4 births/100,000 = about 1000 patients in US and a greater number in Europe (1)
Unmet Medical Need for Our Current Clinical Indications We believe that there is significant market demand for a novel therapy that is safe and effective in the indications that we intend to develop. For allergic conjunctivitis, long-term activity of anti-histamines and adrenergic agonists is variable. Therapies for noninfectious anterior uveitis are associated with significant side effects. There is no FDA-approved therapy for Sjögren-Larsson Syndrome.

Inflammatory Disease Allergic Conjunctivitis Noninfectious Anterior Uveitis
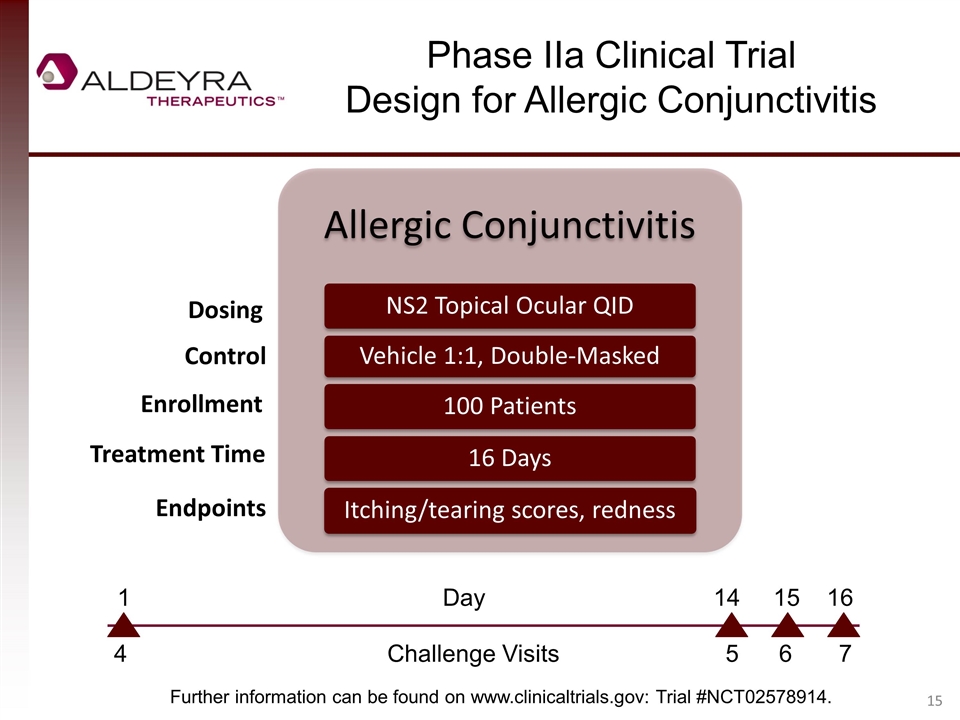
Phase IIa Clinical Trial Design for Allergic Conjunctivitis Dosing Control Enrollment Treatment Time Endpoints Further information can be found on www.clinicaltrials.gov: Trial #NCT02578914. 4 Challenge Visits 5 6 7 1 Day 14 15 16 Allergic Conjunctivitis NS2 Topical Ocular QID Vehicle 1:1, Double-Masked 100 Patients 16 Days Itching/tearing scores, redness
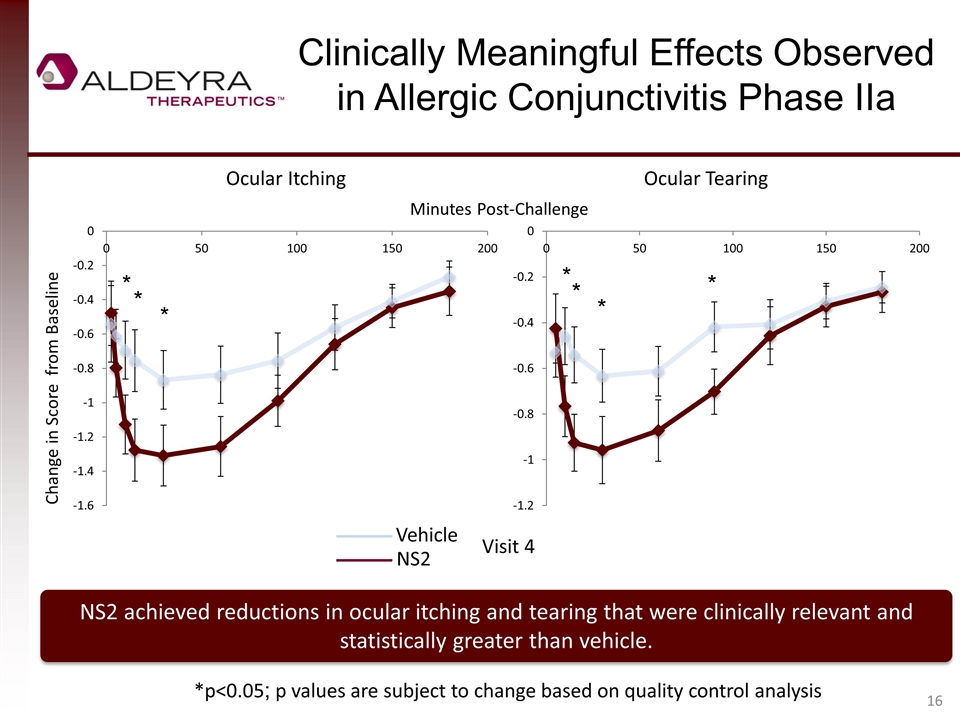
Clinically Meaningful Effects Observed in Allergic Conjunctivitis Phase IIa NS2 achieved reductions in ocular itching and tearing that were clinically relevant and statistically greater than vehicle. Change in Score from Baseline Ocular Itching Ocular Tearing Vehicle NS2 Visit 4 Minutes Post-Challenge * * * * * * * *p<0.05; p values are subject to change based on quality control analysis
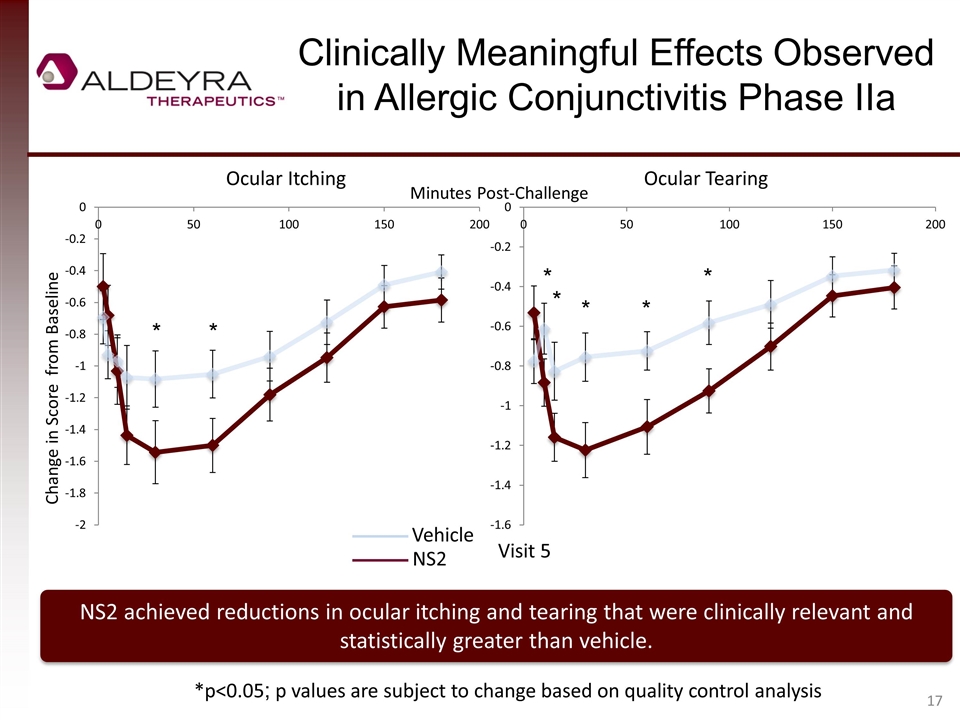
Clinically Meaningful Effects Observed in Allergic Conjunctivitis Phase IIa NS2 achieved reductions in ocular itching and tearing that were clinically relevant and statistically greater than vehicle. Change in Score from Baseline Ocular Itching Ocular Tearing Vehicle NS2 *p<0.05; p values are subject to change based on quality control analysis Visit 5 Minutes Post-Challenge * * * * * * *
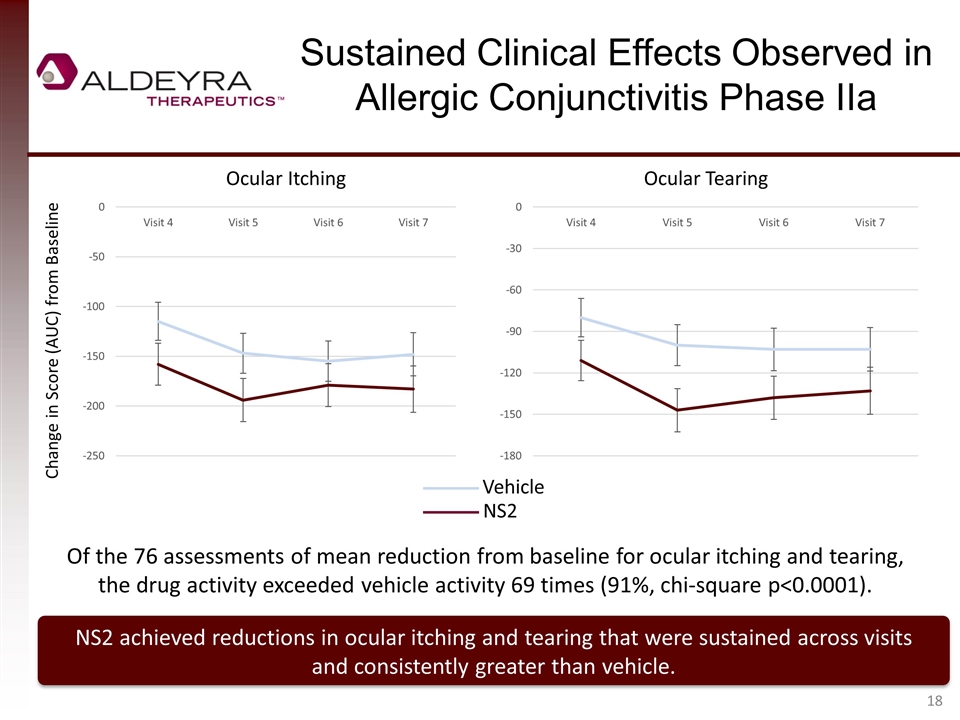
Sustained Clinical Effects Observed in Allergic Conjunctivitis Phase IIa NS2 achieved reductions in ocular itching and tearing that were sustained across visits and consistently greater than vehicle. Change in Score (AUC) from Baseline Ocular Itching Ocular Tearing Vehicle NS2 Of the 76 assessments of mean reduction from baseline for ocular itching and tearing, the drug activity exceeded vehicle activity 69 times (91%, chi-square p<0.0001).

Phase IIa Allergic Conjunctivitis Clinical Summary The current Phase II in noninfectious anterior uveitis is testing the same concentration of topical ocular NS2 at the same dosing frequency. Topical ocular NS2 generally well-tolerated with no safety issues Two drop-outs (4%) in the NS2 treatment arm Transient and primarily mild stinging Sustained clinically relevant reductions in baseline ocular itching and tearing scores, with peak changes exceeding one point on four-point scale Consistent statistical superiority over vehicle response Reduction in allergic response from baseline similar in magnitude to drugs marketed for allergic conjunctivitis Results suggest that aldehyde trapping is a novel anti-inflammatory mechanism that could potentially apply to other forms of ocular and non-ocular inflammation
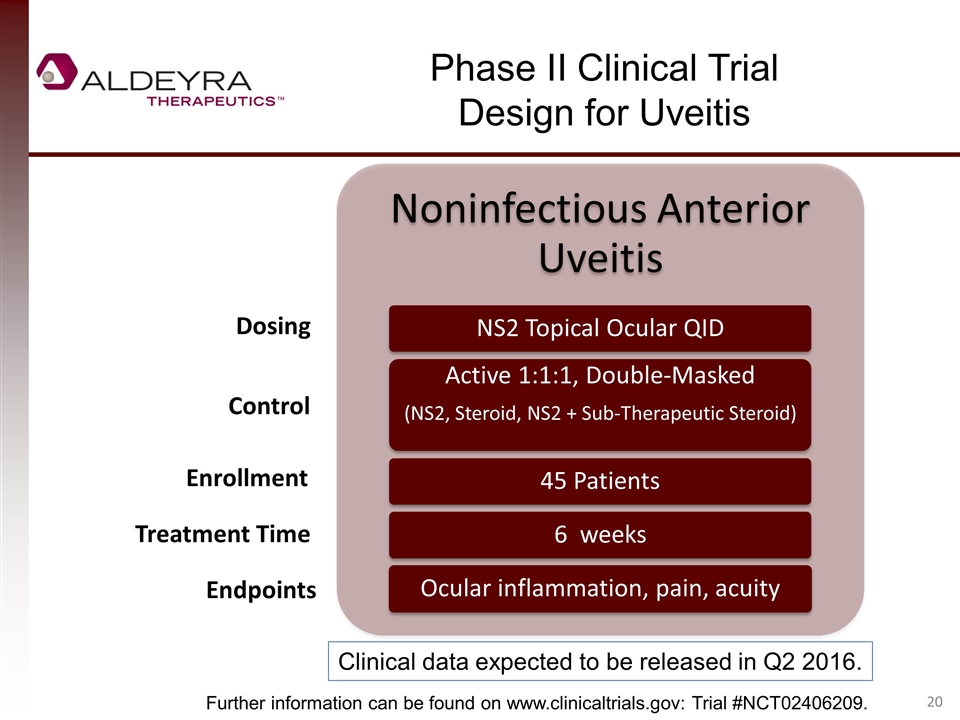
Phase II Clinical Trial Design for Uveitis Dosing Control Enrollment Treatment Time Endpoints Further information can be found on www.clinicaltrials.gov: Trial #NCT02406209. Clinical data expected to be released in Q2 2016. Noninfectious Anterior Uveitis NS2 Topical Ocular QID Active 1:1:1, Double-Masked (NS2, Steroid, NS2 + Sub-Therapeutic Steroid) 45 Patients 6 weeks Ocular inflammation, pain, acuity
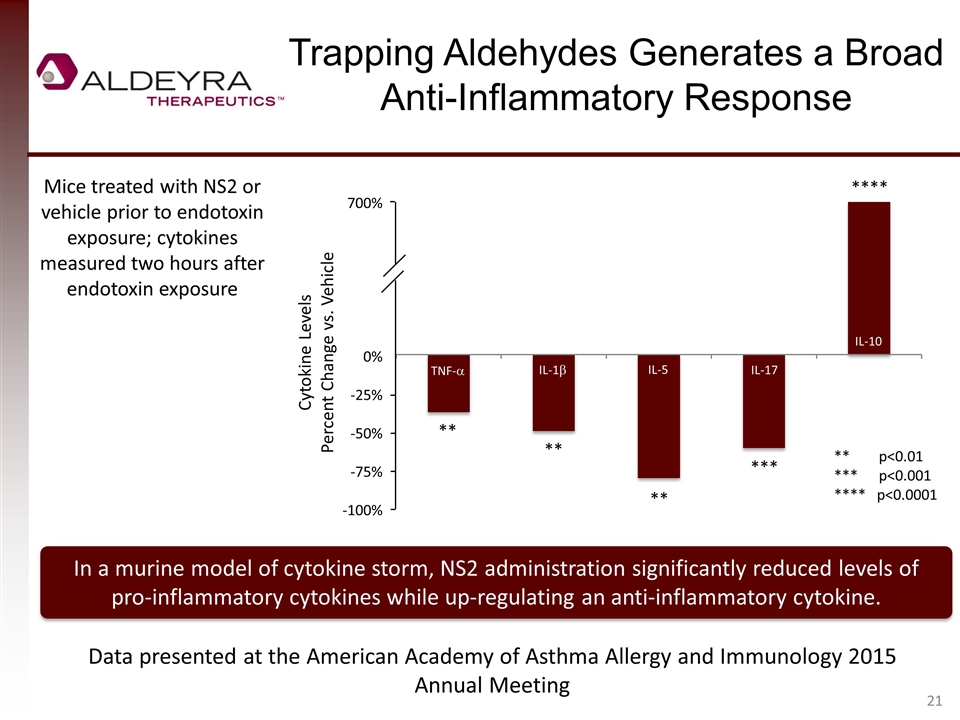
Trapping Aldehydes Generates a Broad Anti-Inflammatory Response In a murine model of cytokine storm, NS2 administration significantly reduced levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines while up-regulating an anti-inflammatory cytokine. Mice treated with NS2 or vehicle prior to endotoxin exposure; cytokines measured two hours after endotoxin exposure ** p<0.01 *** p<0.001 **** p<0.0001 ** ** *** ** Data presented at the American Academy of Asthma Allergy and Immunology 2015 Annual Meeting **** 700% 0% -25% -50% -75% -100% TNF-a IL-1b IL-5 IL-17 IL-10 Cytokine Levels Percent Change vs. Vehicle
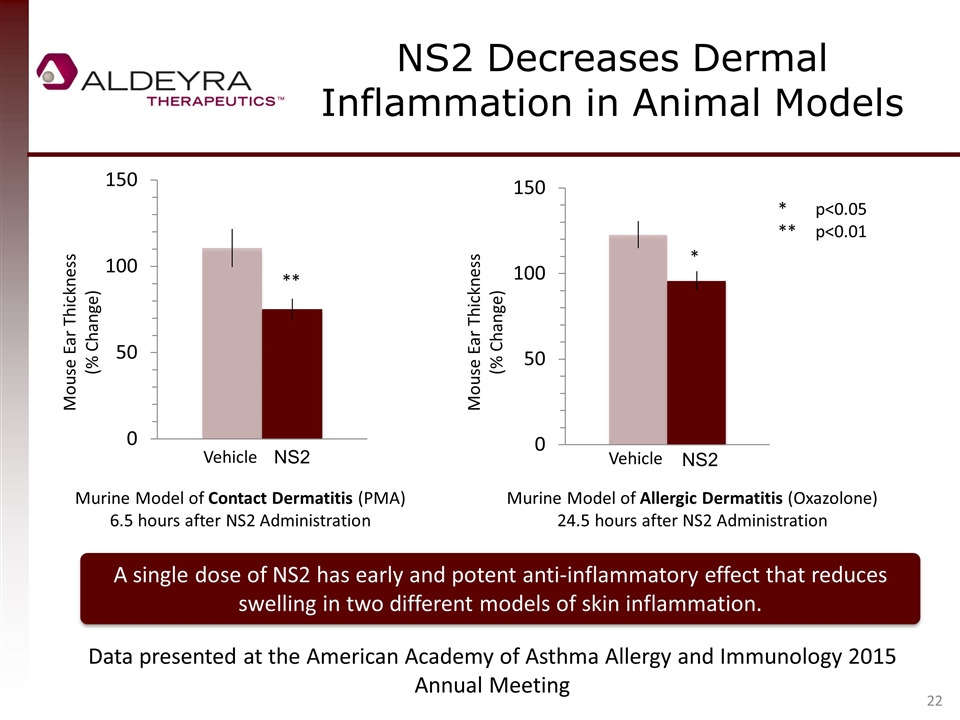
NS2 Decreases Dermal Inflammation in Animal Models Mouse Ear Thickness (% Change) ** Vehicle NS2 Vehicle NS2 * *p<0.05 **p<0.01 Murine Model of Contact Dermatitis (PMA) 6.5 hours after NS2 Administration Murine Model of Allergic Dermatitis (Oxazolone) 24.5 hours after NS2 Administration A single dose of NS2 has early and potent anti-inflammatory effect that reduces swelling in two different models of skin inflammation. Mouse Ear Thickness (% Change) Data presented at the American Academy of Asthma Allergy and Immunology 2015 Annual Meeting
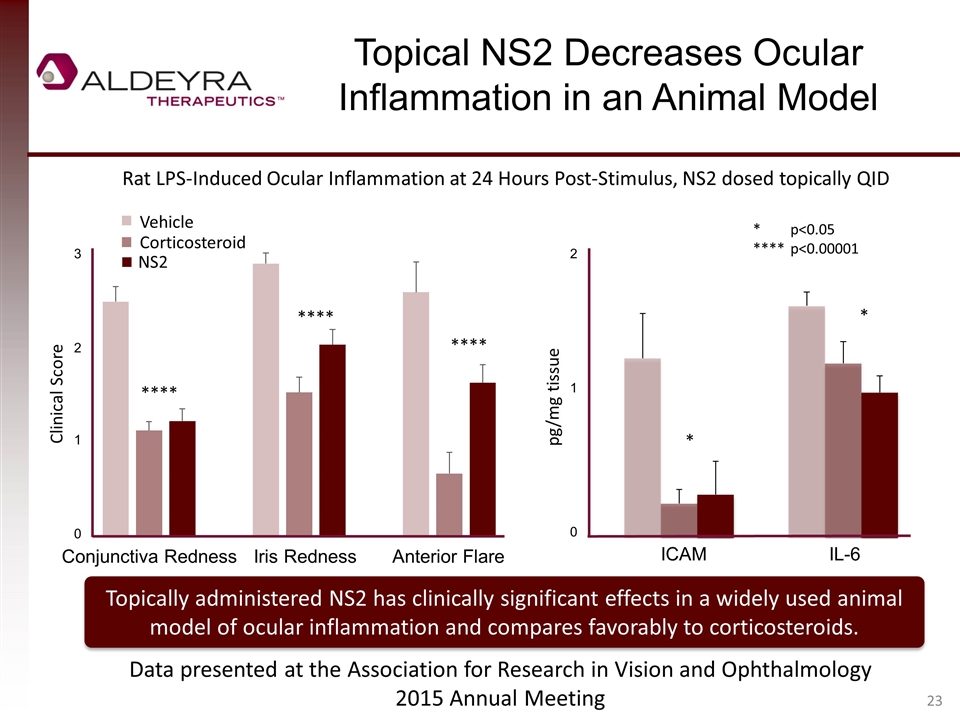
Topical NS2 Decreases Ocular Inflammation in an Animal Model pg/mg tissue * *p<0.05 ****p<0.00001 Rat LPS-Induced Ocular Inflammation at 24 Hours Post-Stimulus, NS2 dosed topically QID Topically administered NS2 has clinically significant effects in a widely used animal model of ocular inflammation and compares favorably to corticosteroids. Clinical Score Data presented at the Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology 2015 Annual Meeting * 3 2 1 0 Conjunctiva RednessIris Redness Anterior Flare 2 1 0 ICAM IL-6 **** **** **** NS2 Corticosteroid Vehicle

Inborn Errors of Aldehyde Metabolism Sjögren-Larsson Syndrome Succinic Semi-aldehyde Dehydrogenase Deficiency
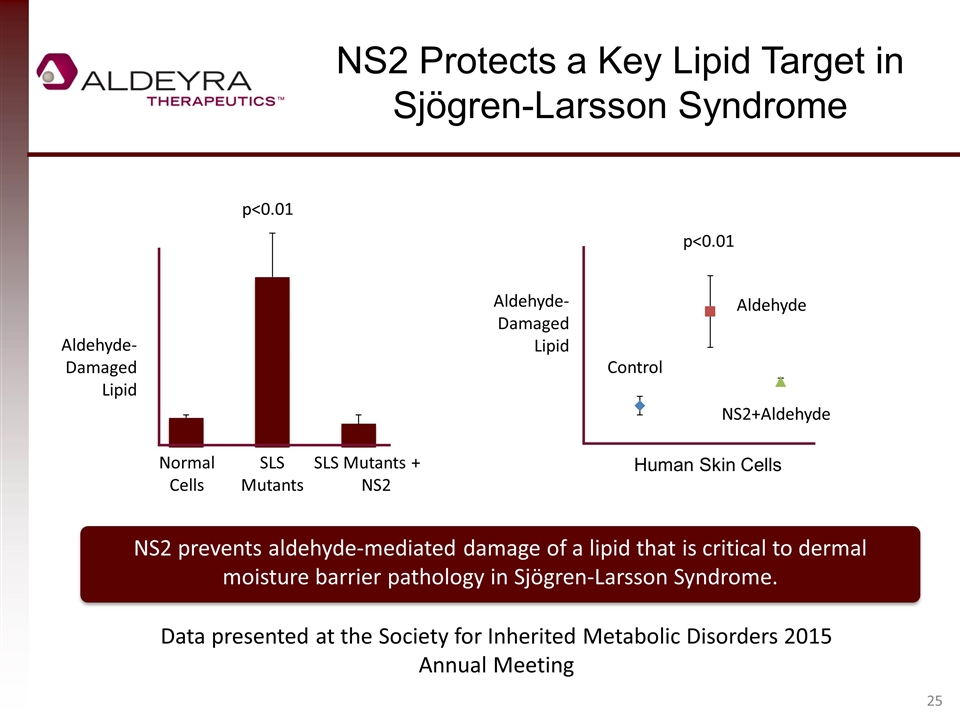
NS2 Protects a Key Lipid Target in Sjögren-Larsson Syndrome Aldehyde-Damaged Lipid Control Aldehyde NS2+Aldehyde Human Skin Cells Aldehyde-Damaged Lipid Normal Cells SLS Mutants SLS Mutants + NS2 NS2 prevents aldehyde-mediated damage of a lipid that is critical to dermal moisture barrier pathology in Sjögren-Larsson Syndrome. p<0.01 p<0.01 Data presented at the Society for Inherited Metabolic Disorders 2015 Annual Meeting
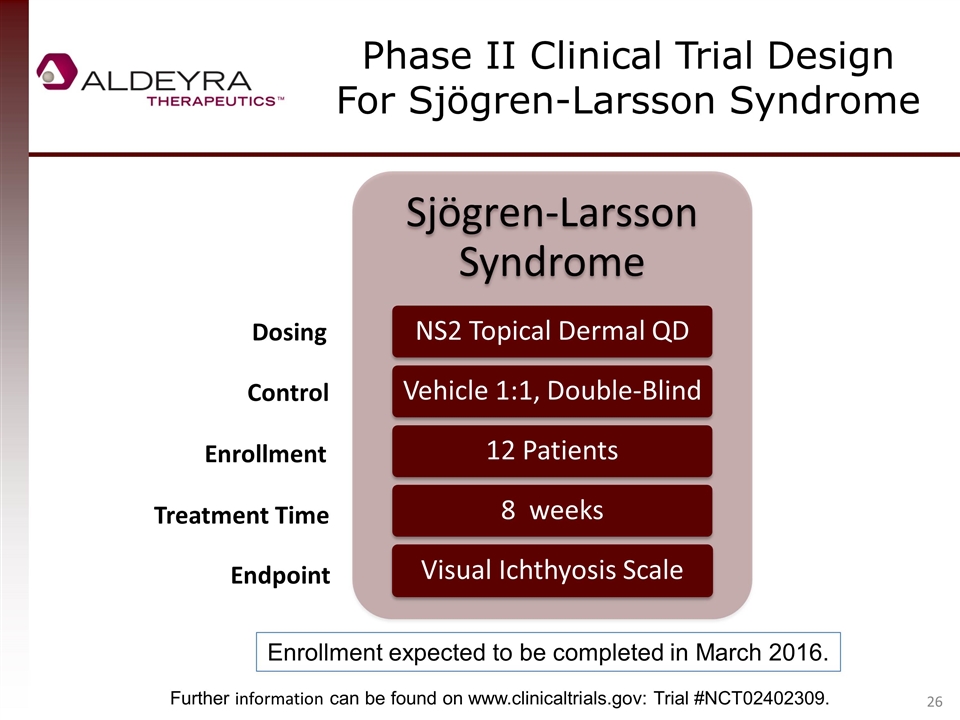
Phase II Clinical Trial Design For Sjögren-Larsson Syndrome Dosing Control Enrollment Treatment Time Endpoint Further information can be found on www.clinicaltrials.gov: Trial #NCT02402309. Enrollment expected to be completed in March 2016. Sjögren -Larsson Syndrome NS2 Topical Dermal QD Vehicle 1:1, Double-Blind 12 Patients 8 weeks Visual Ichthyosis Scale
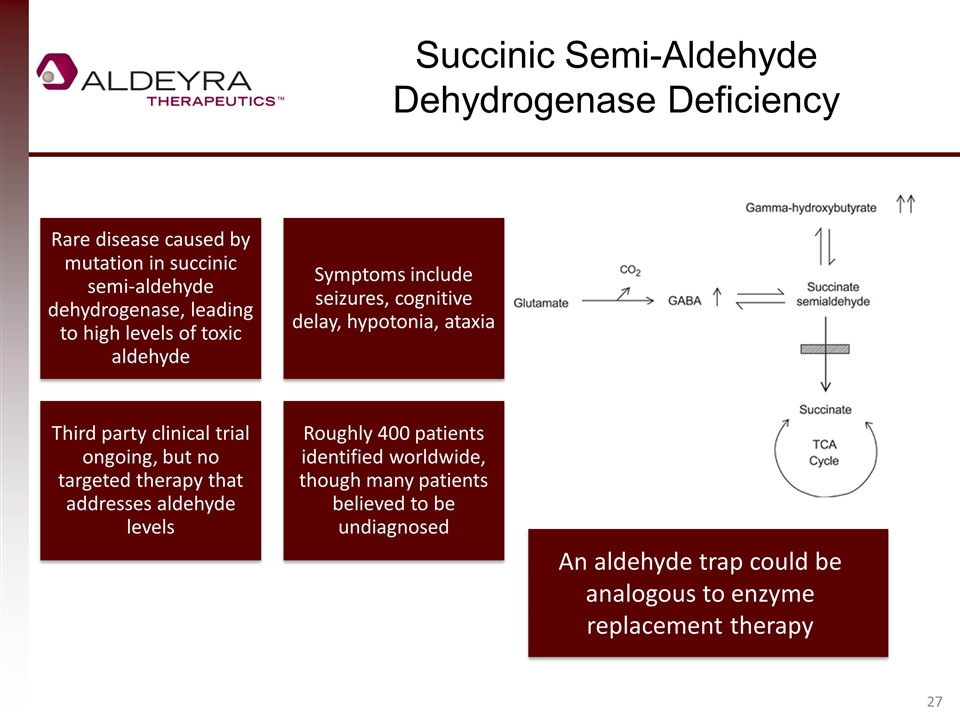
Succinic Semi-Aldehyde Dehydrogenase Deficiency An aldehyde trap could be analogous to enzyme replacement therapy Rare disease caused by mutation in succinic semi-aldehyde dehydrogenase, leading to high levels of toxic aldehyde Symptoms include seizures, cognitive delay, hypotonia , ataxia Third party clinical trial ongoing, but no targeted therapy that addresses aldehyde levels Roughly 400 patients identified worldwide, though many patients believed to be undiagnosed
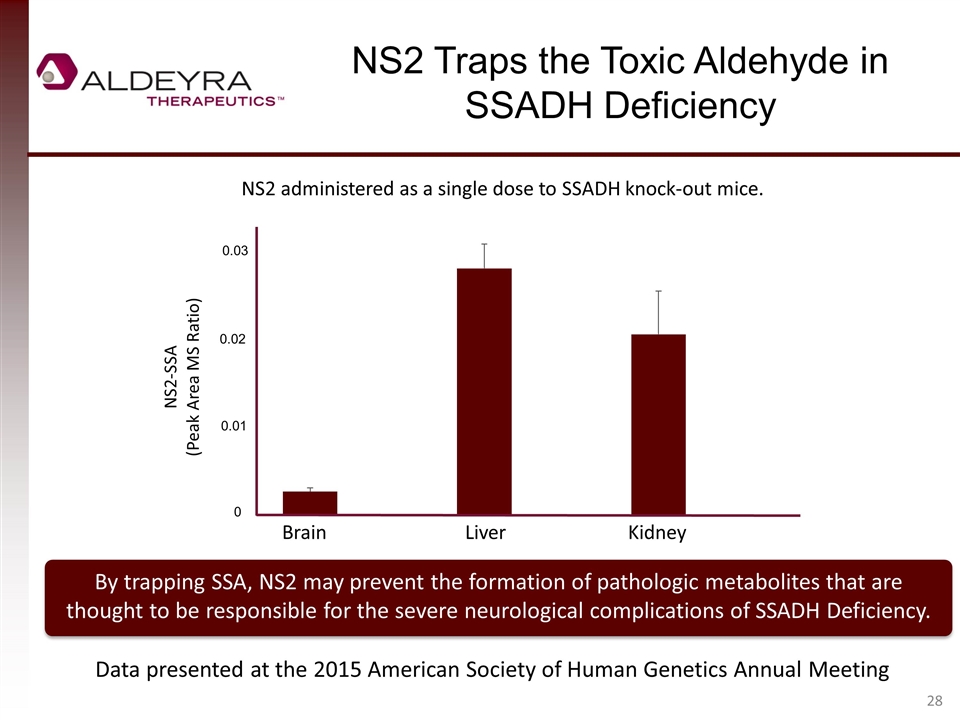
NS2 Traps the Toxic Aldehyde in SSADH Deficiency By trapping SSA, NS2 may prevent the formation of pathologic metabolites that are thought to be responsible for the severe neurological complications of SSADH Deficiency. NS2 administered as a single dose to SSADH knock-out mice. Brain Liver Kidney 0.03 0.02 0.01 0 NS2-SSA (Peak Area MS Ratio) Data presented at the 2015 American Society of Human Genetics Annual Meeting

IP and Investment Thesis
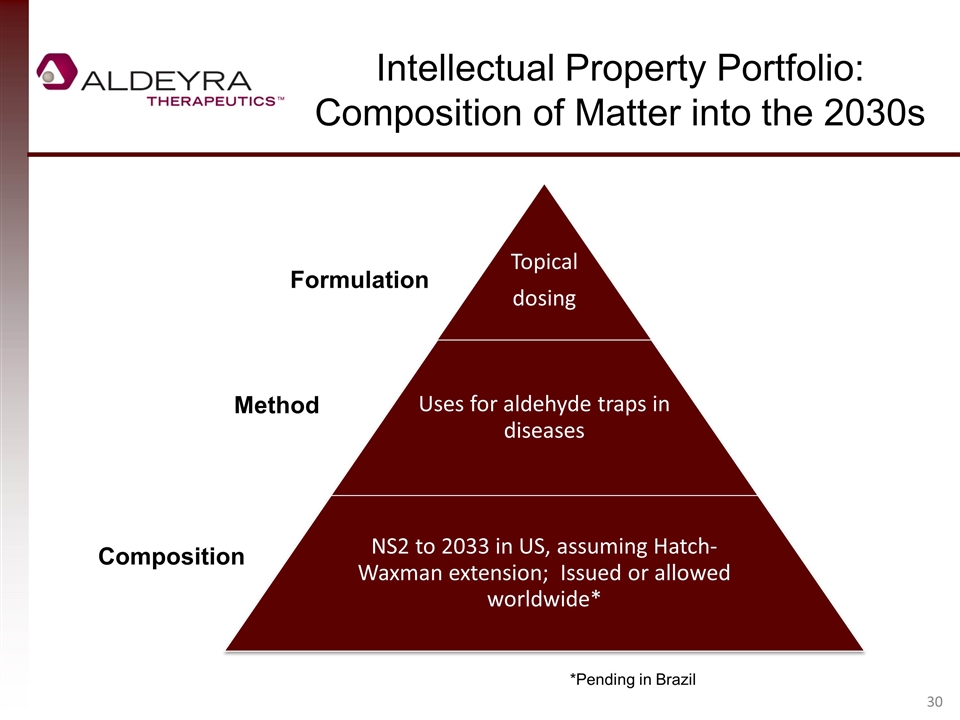
Intellectual Property Portfolio: Composition of Matter into the 2030s *Pending in Brazil Formulation Composition Method NS2 to 2033 in US, assuming Hatch-Waxman extension; Issued or allowed worldwide* Uses for aldehyde traps in diseases Topical dosing
Corporate Highlights Clinical Proof of Concept in Inflammation Achieved for Lead Candidate Two Additional Clinical Events Expected in 2016 Aldehydes are toxic and pro-inflammatory, and are implicated in inflammatory disease and inborn errors of aldehyde metabolism Innovative Small Molecule Platform to Trap Aldehydes Noninfectious Anterior Uveitis – rare but severe and potentially blinding ocular inflammatory disease with elevated aldehydes NS2 composition of matter IP to 2033 in US, assuming Hatch-Waxman extension, and to late 2020s worldwide; other novel aldehyde traps with protection into late 2030s and beyond Strong Intellectual Property Position Lead aldehyde trap NS2 with statistically and clinically significant mitigation of ocular allergic response in allergic conjunctivitis Phase IIa trial Sjögren Larsson Syndrome – inborn error of aldehyde metabolism with severe skin and neurological complications
